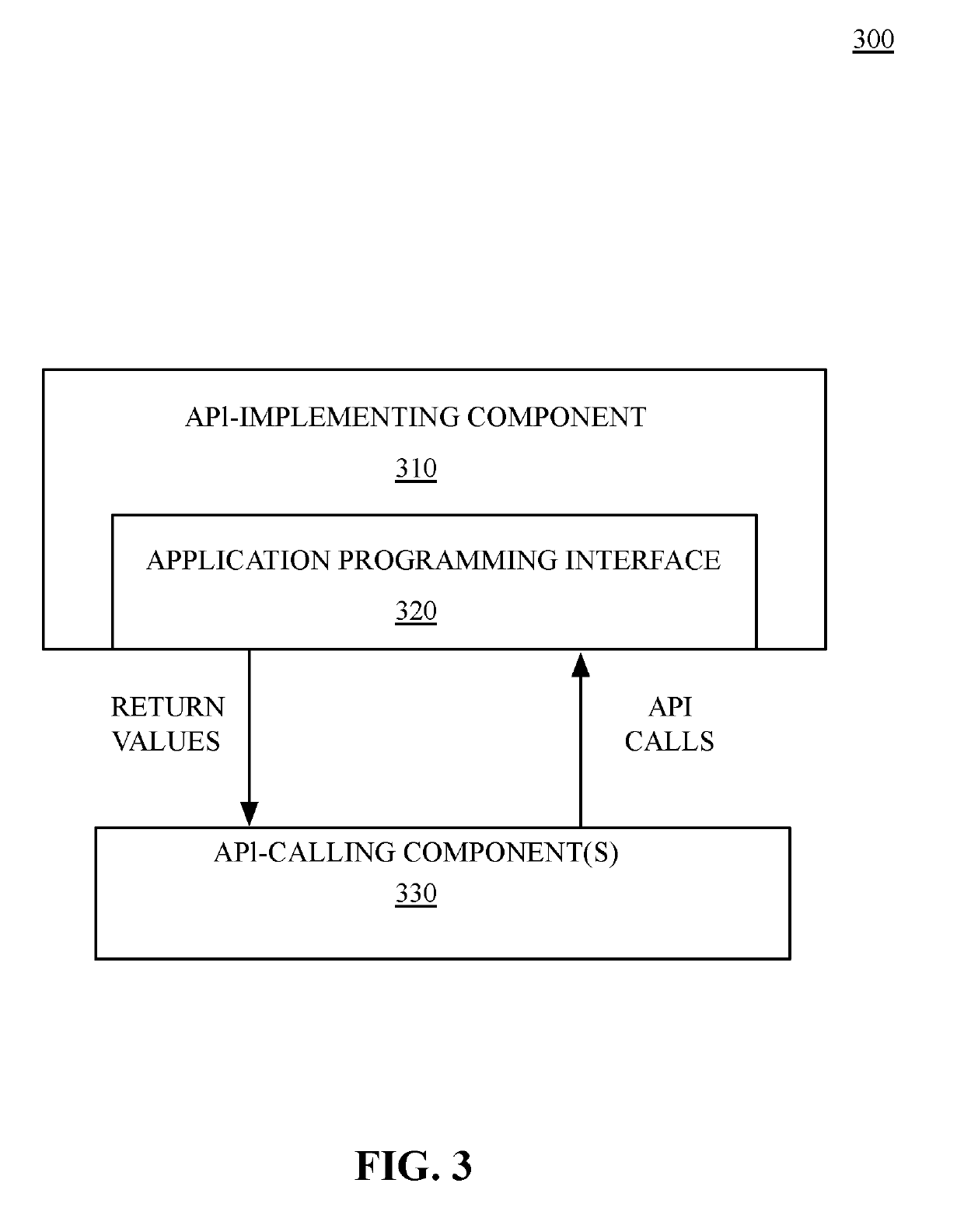
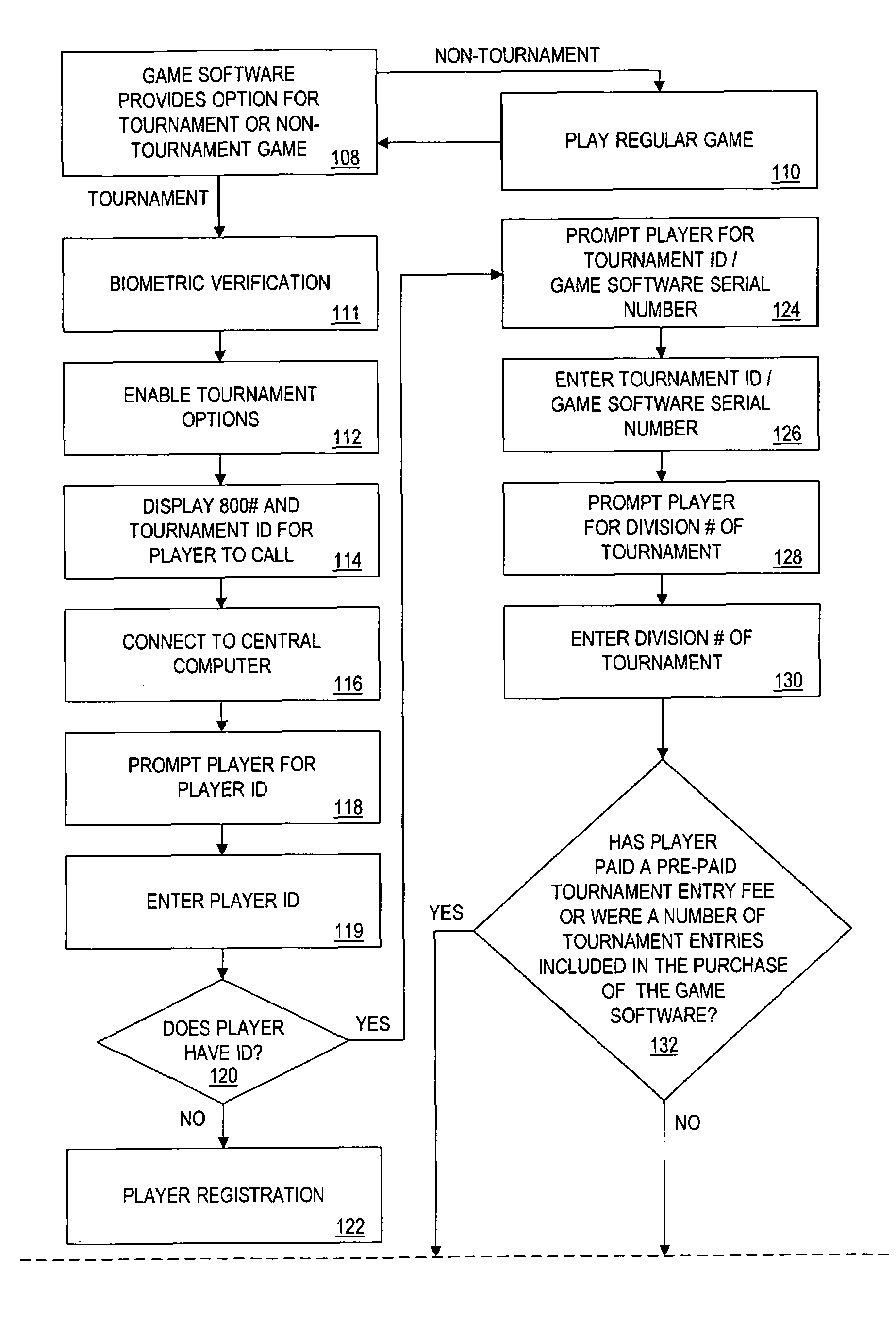
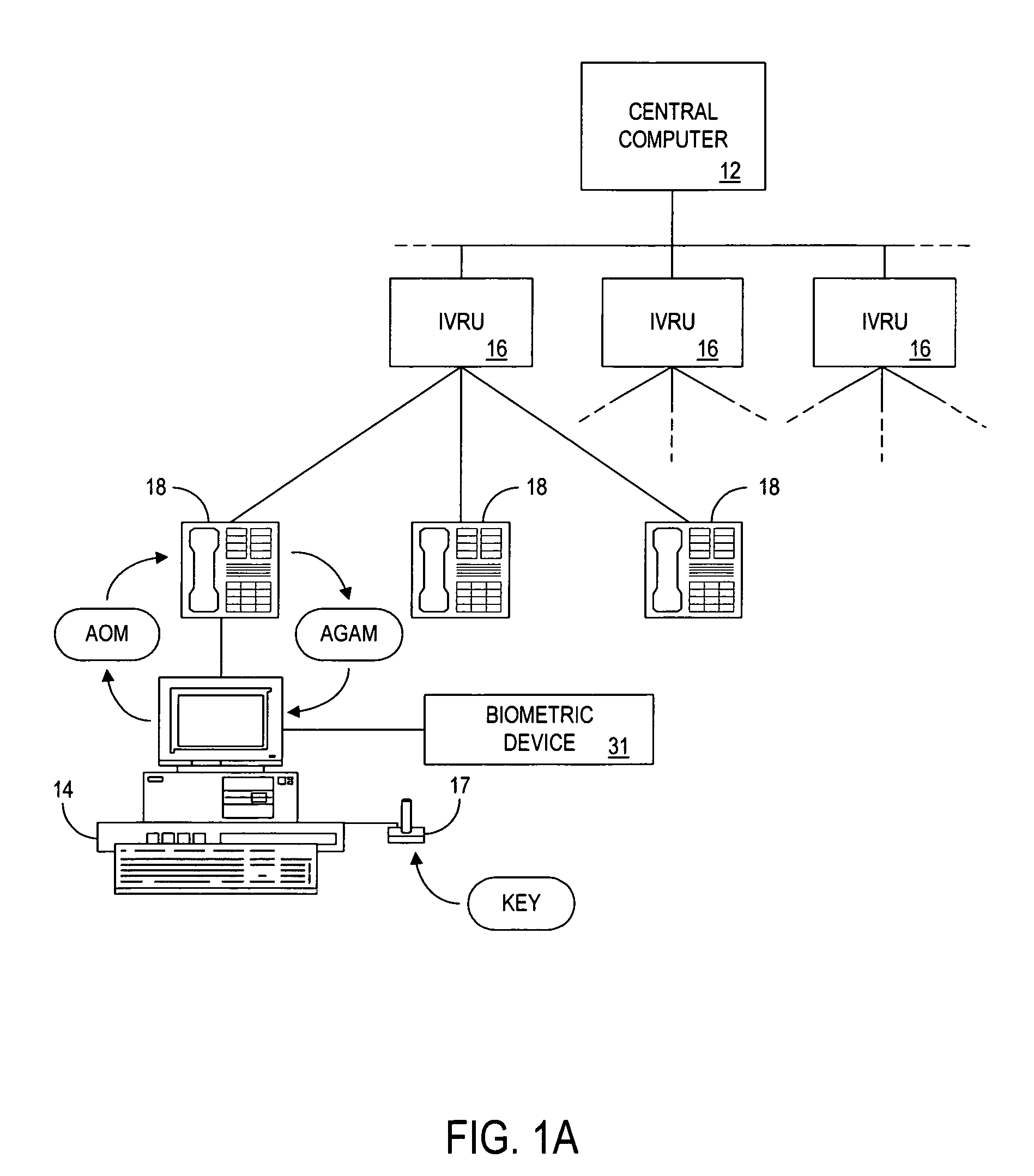
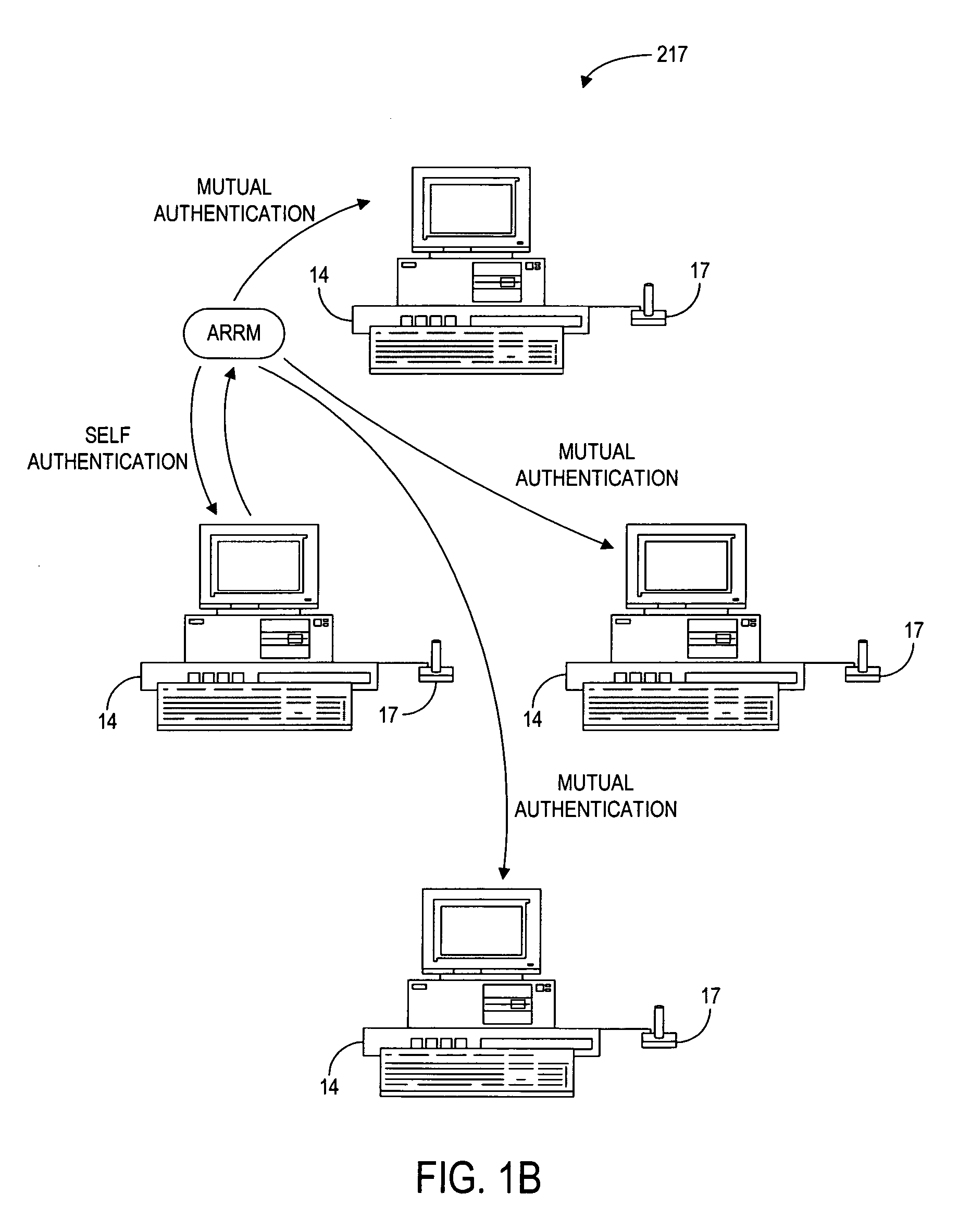
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97 results about "Central authority" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Central Authority is an agency or organization that is designated to play a key facilitating role in the implementation and operation of an international treaty in public and private international law.. Prior to the Hague Evidence Convention and the Hague Service Convention's of 1965 and 1970, most treaties would designate two separate agencies to, respectively, transmit and receive treaty ...
Methods and apparatus for awarding prizes based on authentication of computer generated outcomes using coupons
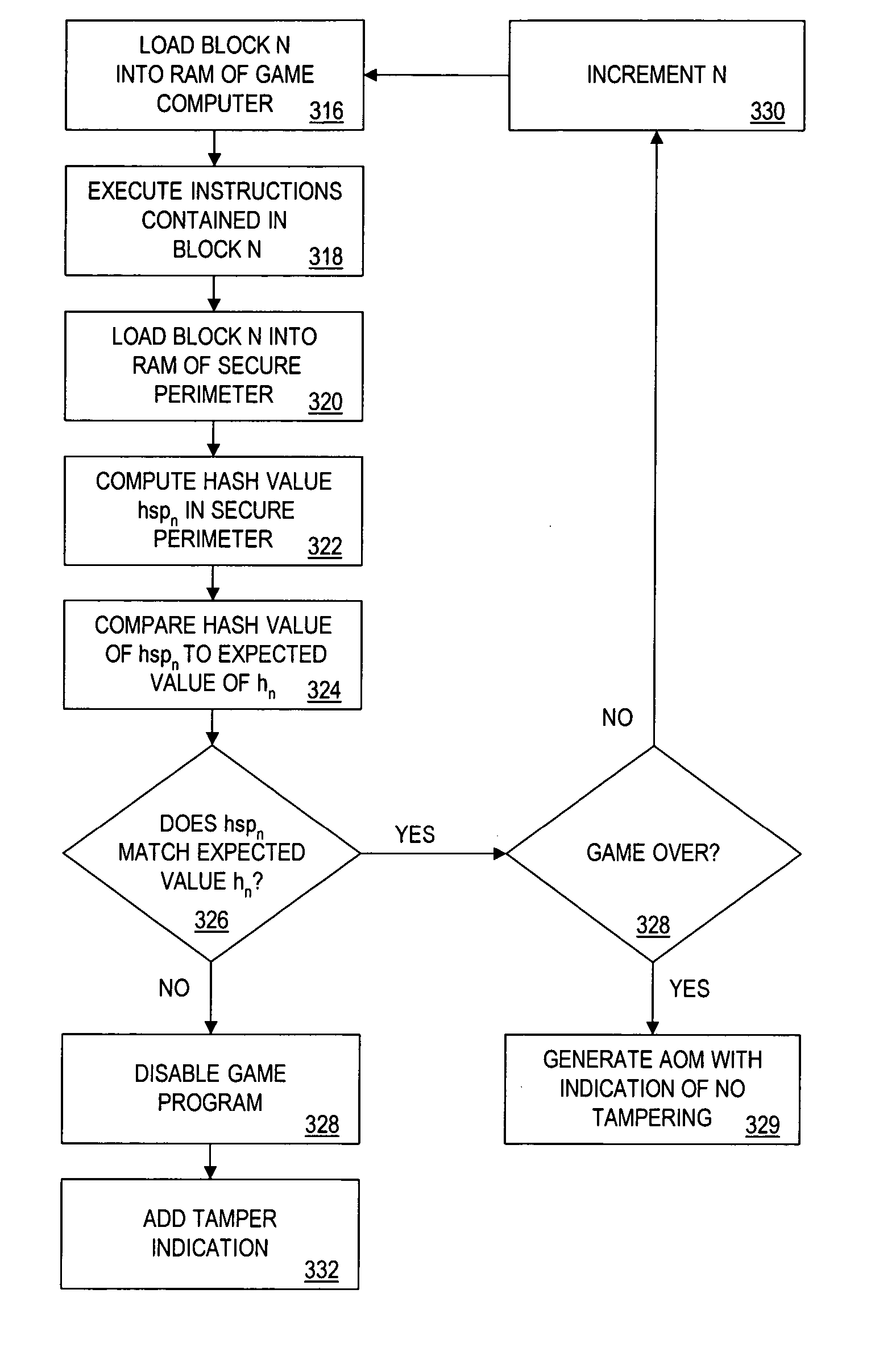
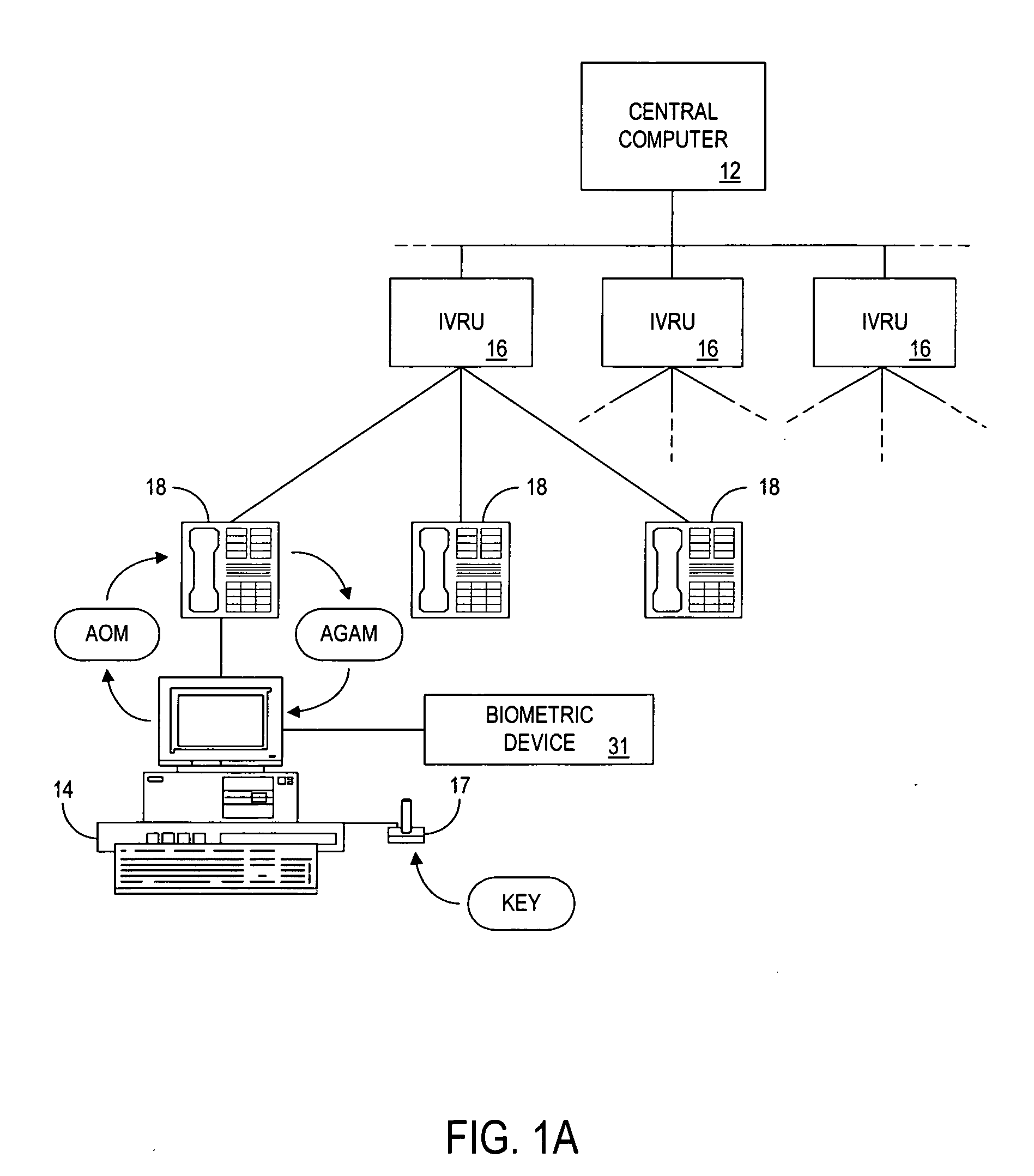
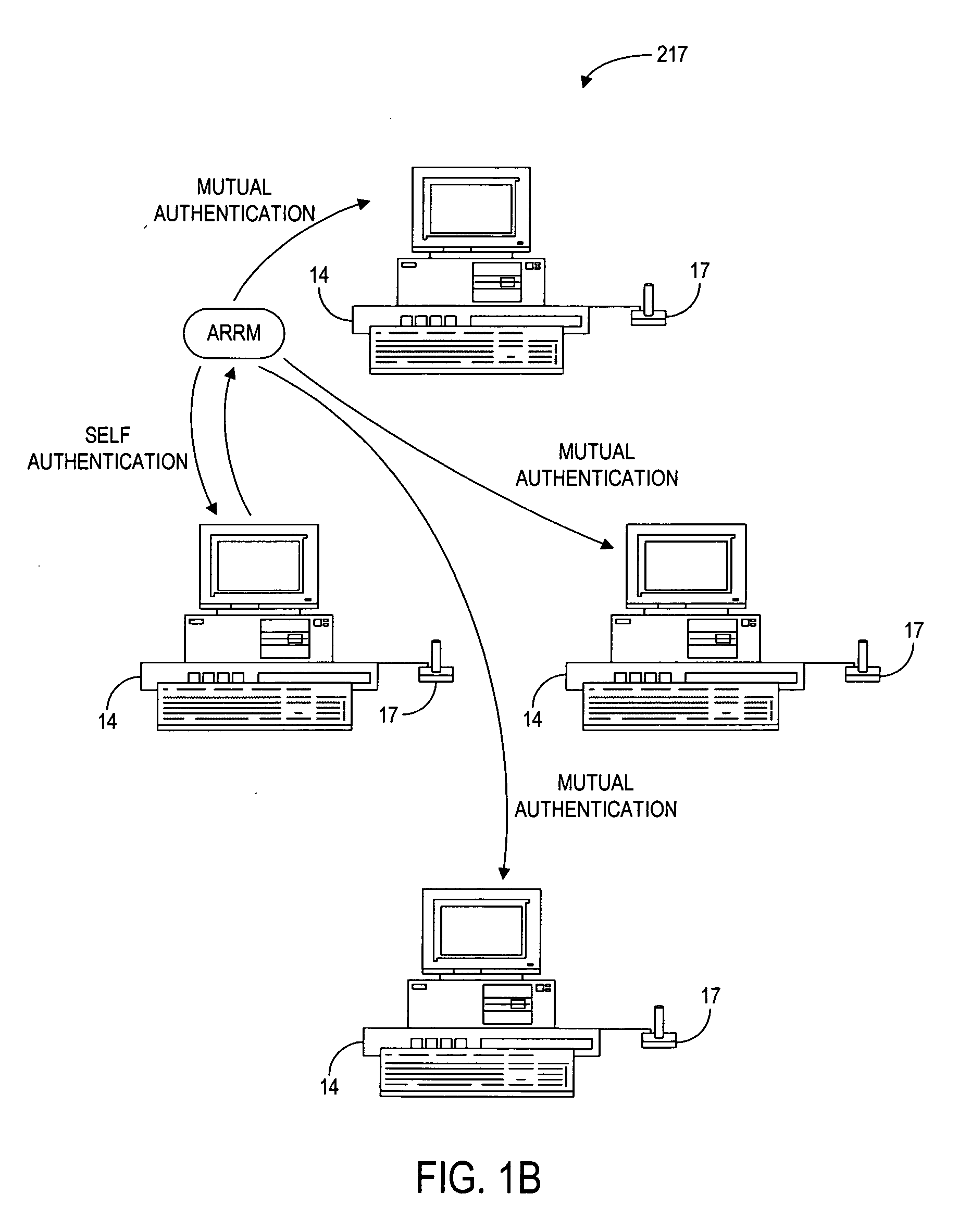
The present invention provides authentication of computer generated game or test results (“outcomes”), and a system by which persons who play games or take tests on a game or testing computer, respectively, may submit the outcomes of the games or tests to a central authority having at least one central computer, and have the central computer “certify” those outcomes as being accurately reported and fairly achieved. This certification of the computer generated result constitutes a “remote-auditing” of the activity taking place on the game computer. In one application, the system enables computer generated game tournaments in which players play the games on game computers and compete against each other by submitting the outcomes for those tournament games to the central computer, which certifies the outcomes and rates and ranks the players. In another application, the system provides for players of computer games to obtain a certified ranking and rating without participation in a tournament. In other embodiments, the system provides for self-authentication and certification of outcomes for games played on the game computer itself, or for mutual-authentication and certification of such outcomes on any other game computer in the system.
Owner:INVENTOR HLDG
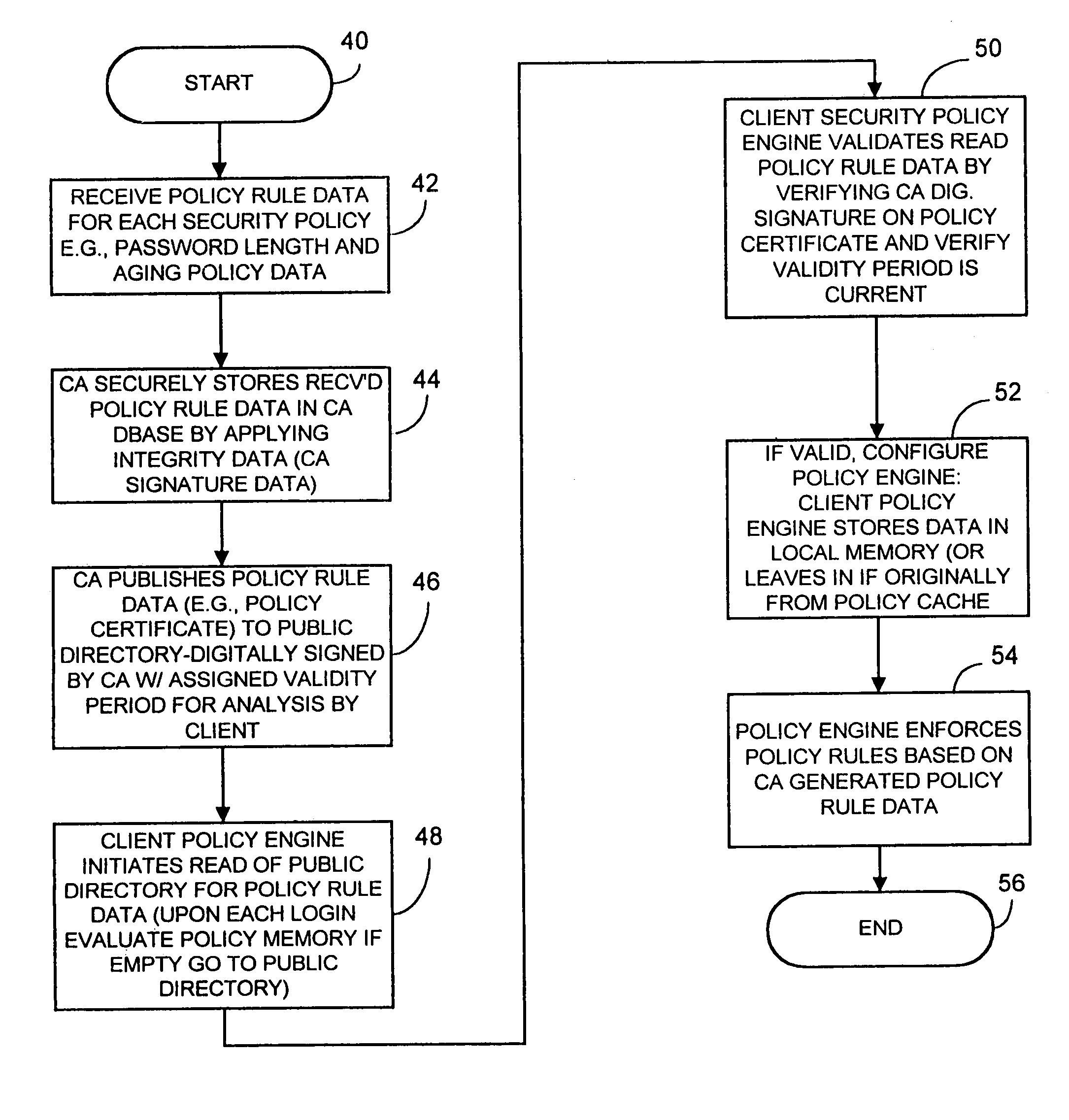
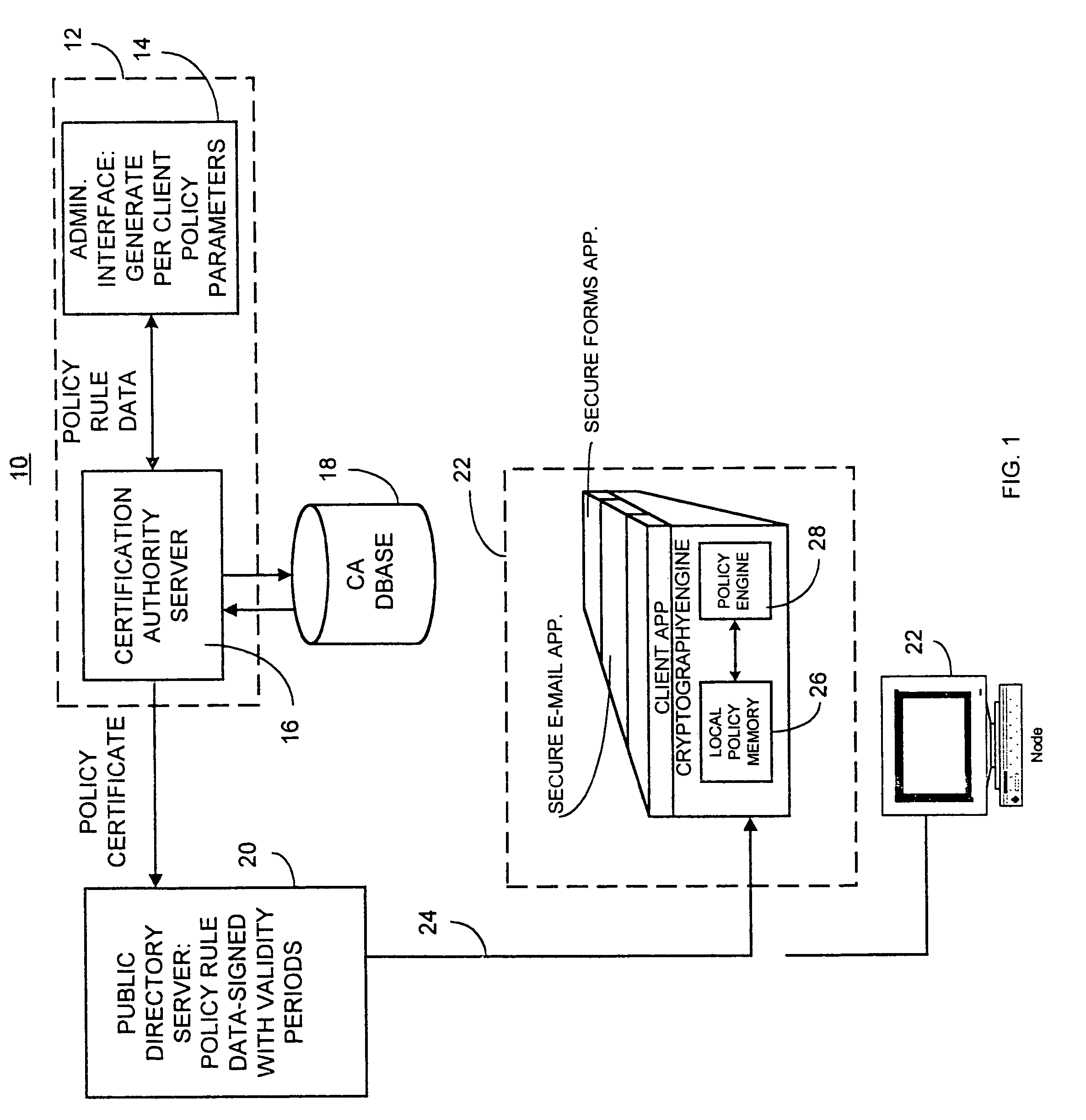
Computer network security system and method having unilateral enforceable security policy provision
InactiveUS7174563B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signaturePassword
A computer network security system and method utilizes digitally signed and centrally assigned policy data, such as password length rules, that is unilaterally enforced at network nodes by node policy enforcement engines. The policy data may be variable on a per client or network node basis through a centralized authority, such as a certification authority. The computer network security system provides variable security policy rule data for distribution to at least one network node through a central security policy rule data distribution source, such as the certification authority. The central security policy rule data distribution source associates a digital signature to the variable security policy rule data to ensure the integrity of the policies in the system. Each network node uses a policy rule data engine and policy rule table to decode policy rule data and enforce the policy rules as selectively determined through the central authority.
Owner:ENTRUST
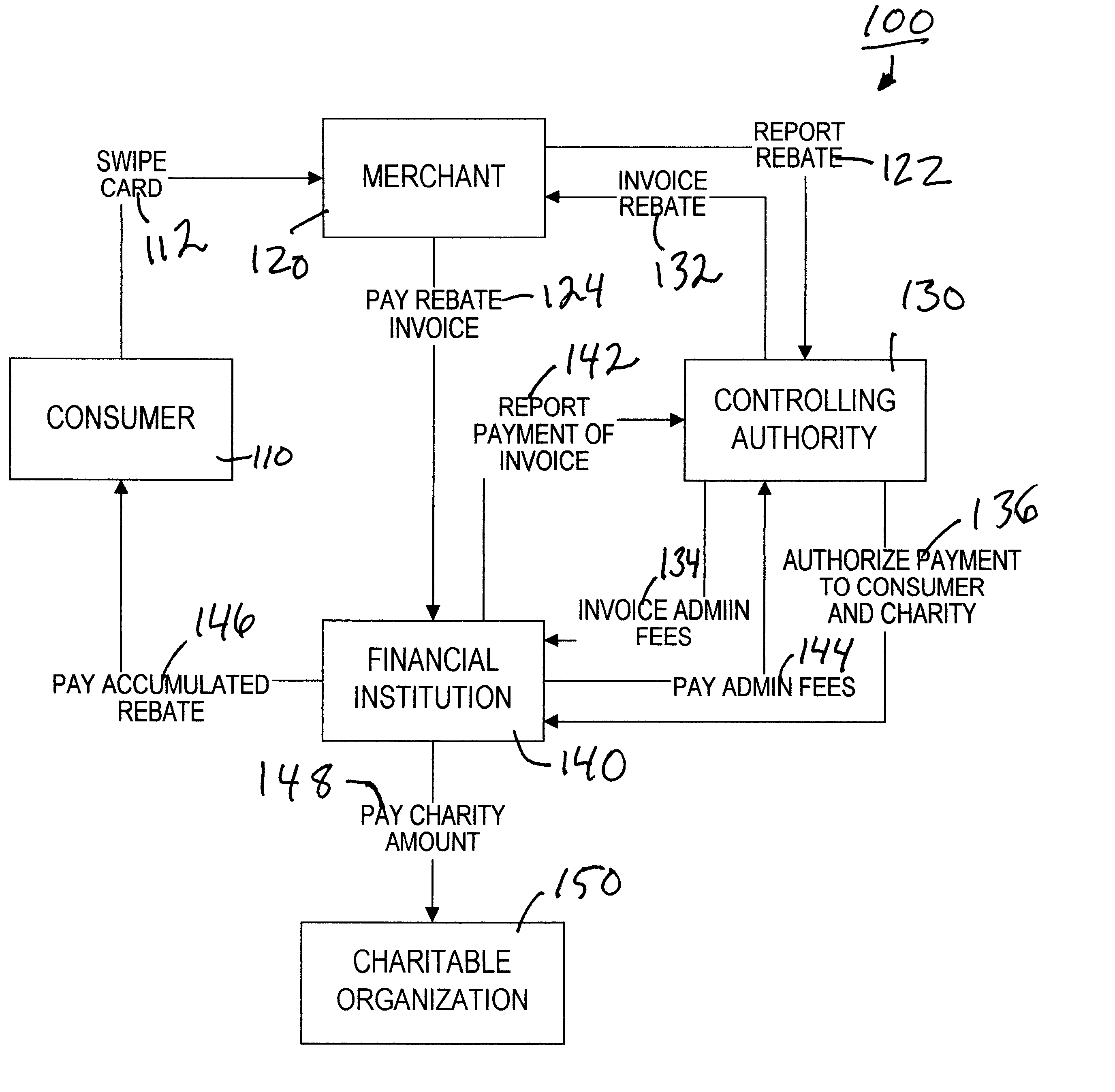
Method of administering a rebate system
In a method of administering a rebate system, rebate-related information is electronically transmitted from a rebate issuing entity and is received by a central processing authority. The rebate-related information includes information identifying a consumer and information relating to a purchase made by the consumer from the rebate issuing entity. The central authority determines an amount of a rebate that is to be credited to the consumer, based on information previously provided by the rebate issuing entity. The rebate issuing entity is invoiced for the amount of the rebate, wherein the amount is payable to an omnibus trust account, wherein a trustee has exclusive control over the omnibus trust account and the trustee is authorized to transfer a credit from the omnibus trust account to the consumer.
Owner:SOURCE
Blockchain systems and methods
InactiveUS20180276626A1Cryptography processingUser identity/authority verificationCentral authorityData bank
Systems and methods for micro-transactions using virtual currency via a blockchain. A central authority server provides a shadow ledger to track verified but unposted transactions with respect to users of the virtual currency economy. New proposed transactions are checked against both the master records in the blockchain database and the shadow ledger to confirm that, when posted to the blockchain, they will be valid. Confirmed transactions are authenticated via tokens provided to users, who then remit the tokens to participants in exchange for access to content (e.g., paywall content, ad-free content, etc.). Users may acquire virtual currency through similar micro-transactions conducted in reverse. The unposted, cached transactions are then posted to the blockchain in bulk.
Owner:DAPPSTERS LLC
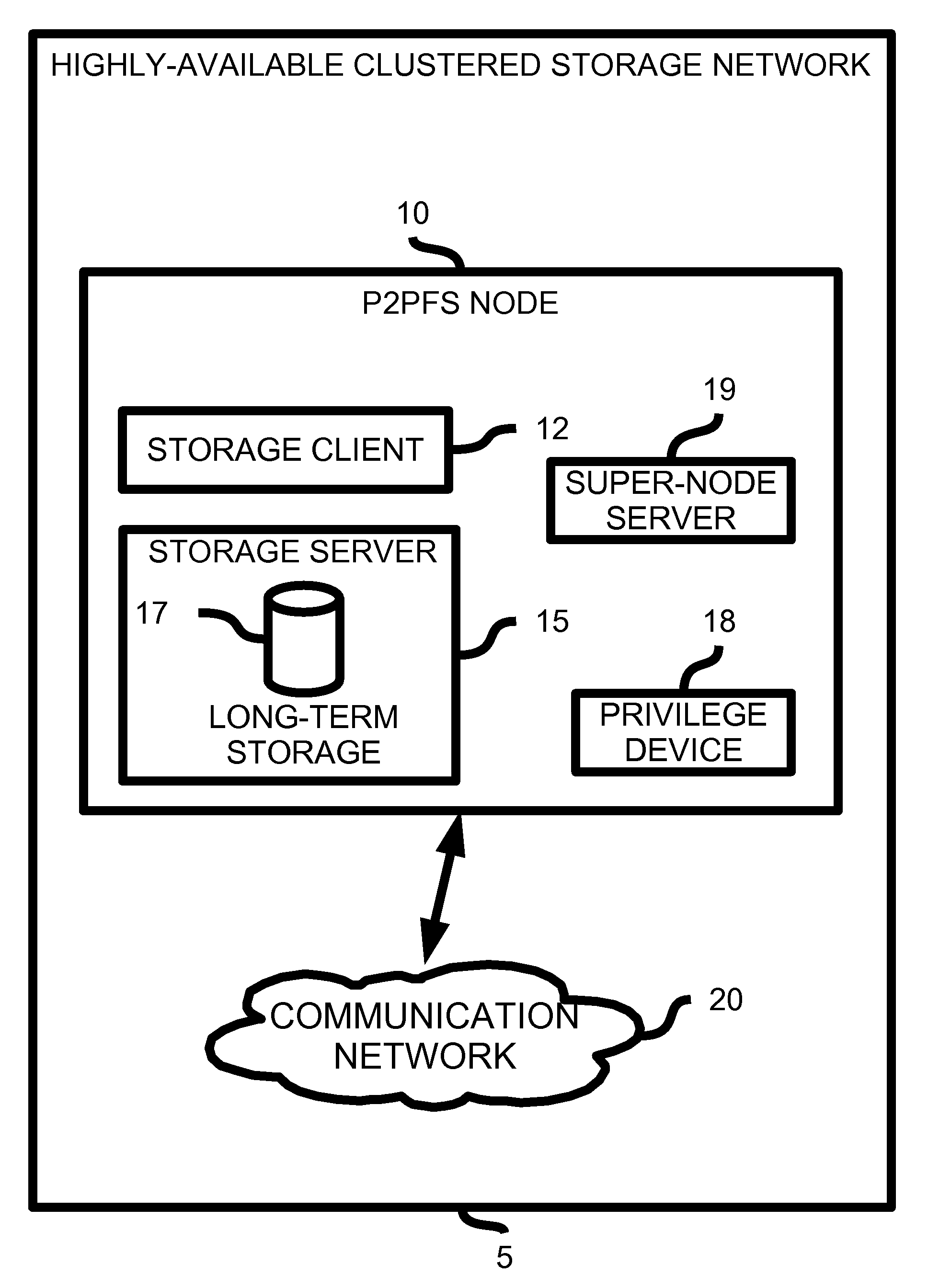
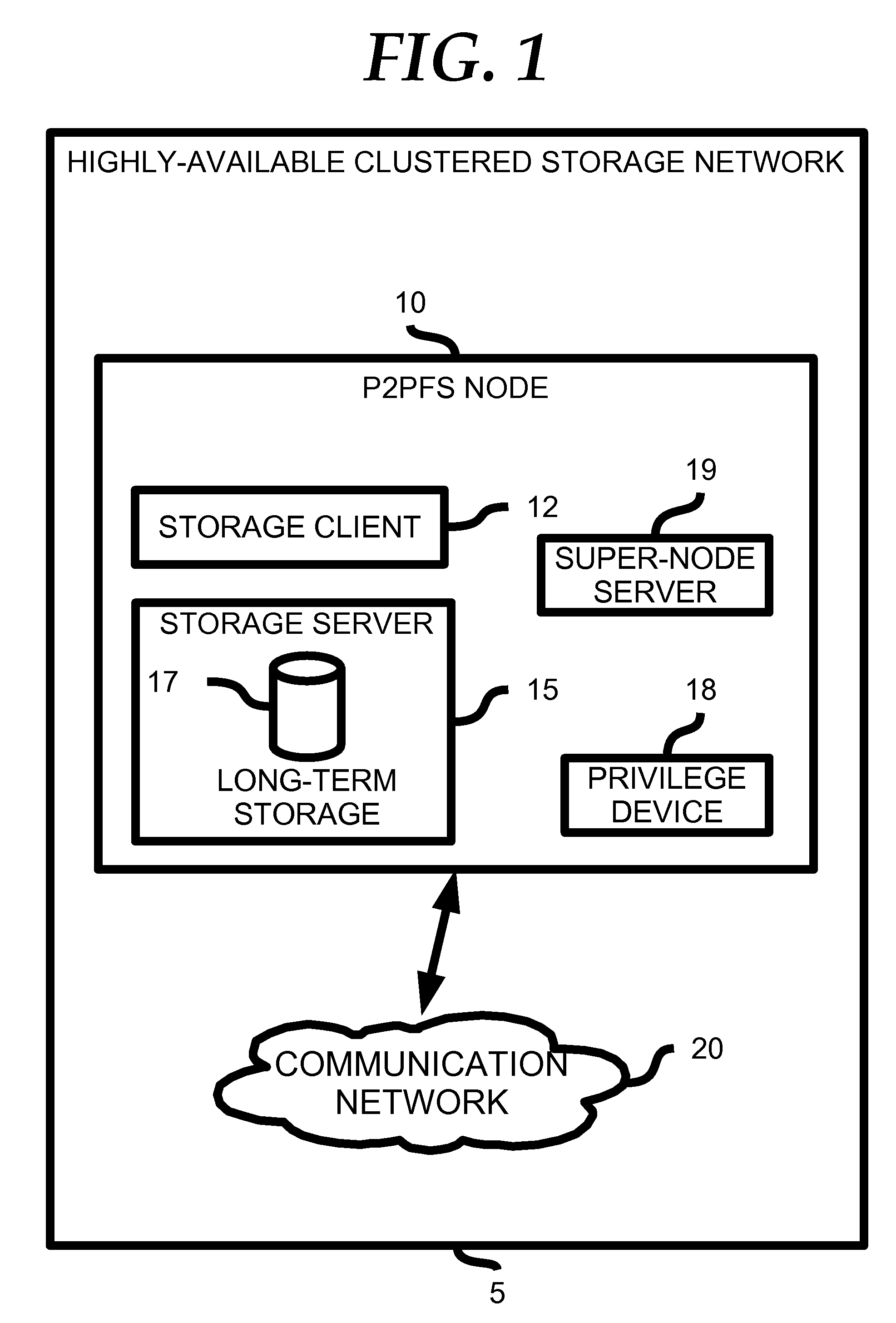
Highly Available Clustered Storage Network
InactiveUS20080077635A1Highly auto-configuringImprove scalabilityDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFault toleranceClustered file system
A computing method and system is presented that allows multiple heterogeneous computing systems containing file storage mechanisms to work together in a peer-to-peer fashion to provide a fault-tolerant decentralized highly available clustered file system. The file system can be used by multiple heterogeneous systems to store and retrieve files. The system automatically ensures fault tolerance by storing files in multiple locations and requires hardly any configuration for a computing device to join the clustered file system. Most importantly, there is no central authority regarding meta-data storage, ensuring no single point of failure.
Owner:DIGITAL BAZAR
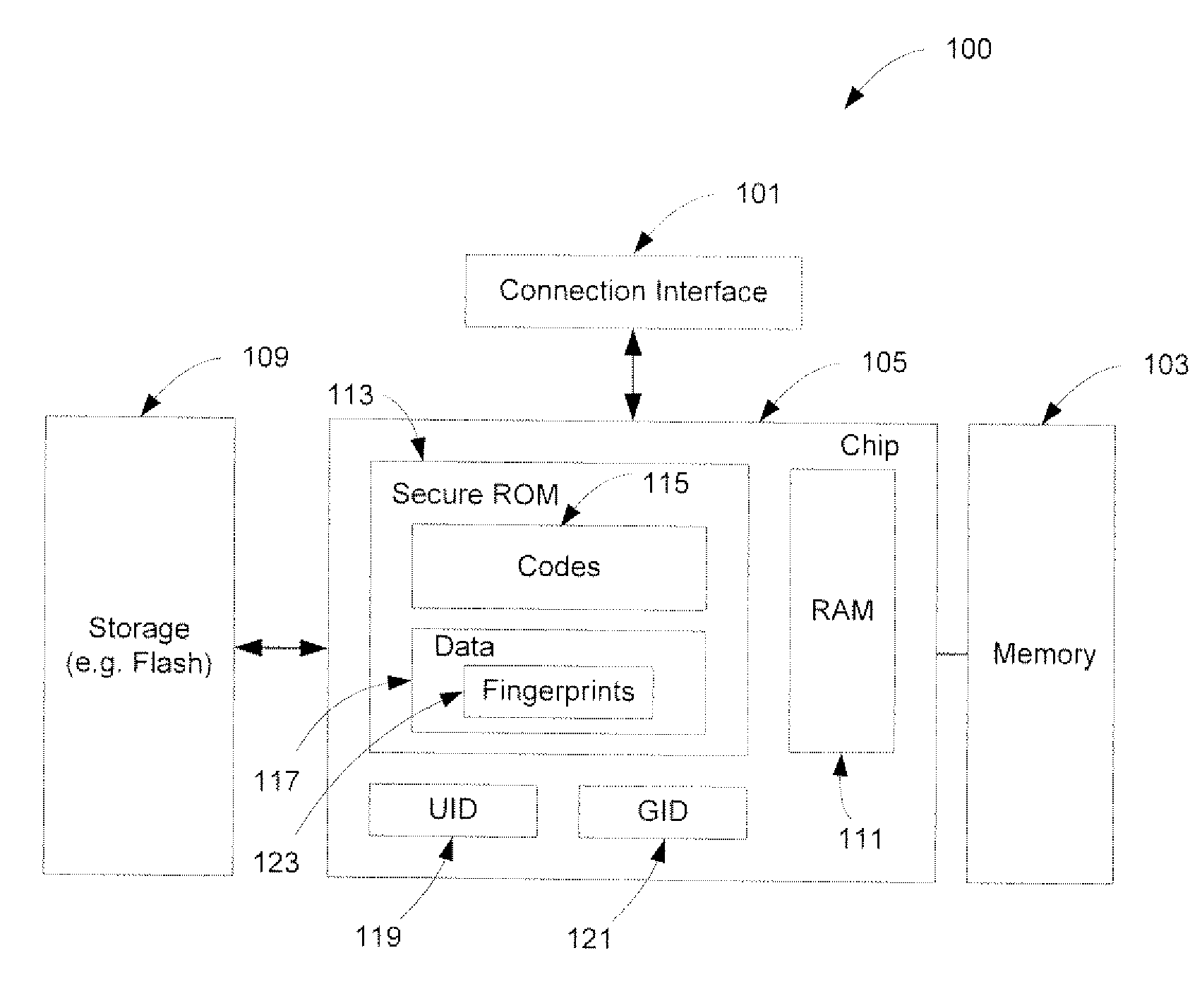
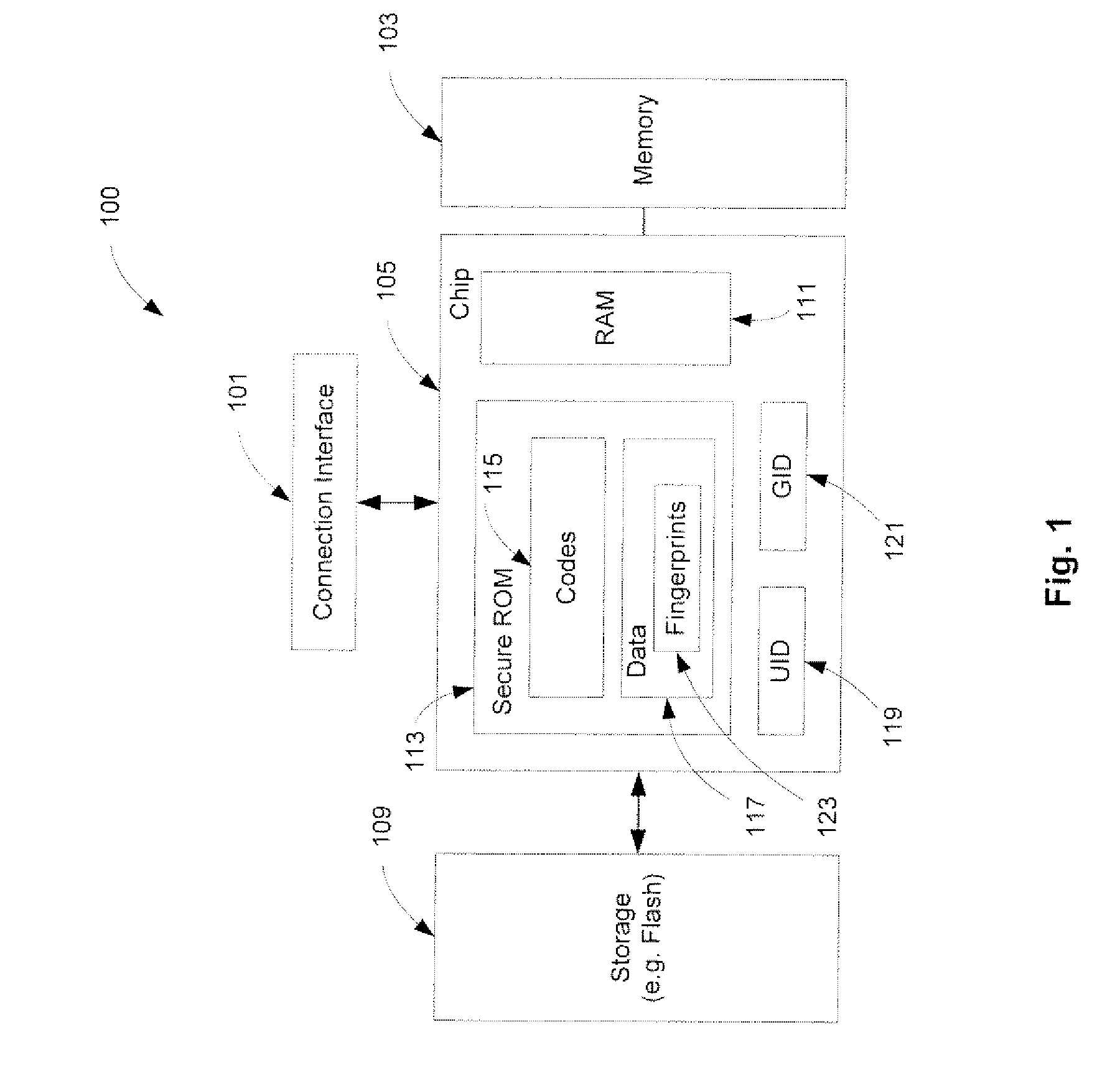
Securely Recovering a Computing Device
ActiveUS20080168275A1Multiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationTelecommunications linkDigital signature
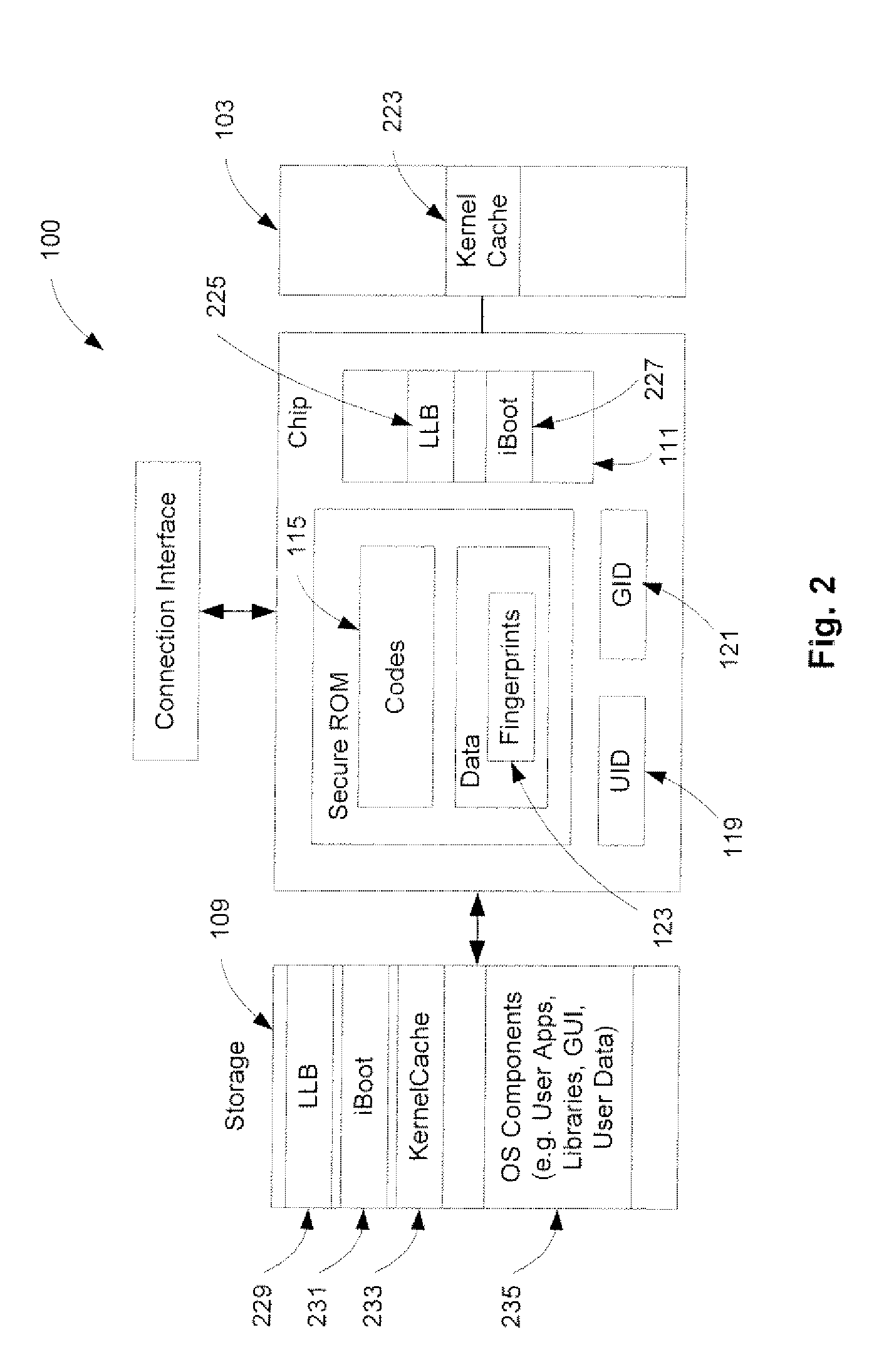
A method and an apparatus for establishing an operating environment by certifying a code image received from a host over a communication link are described. The code image may be digitally signed through a central authority server. Certification of the code image may be determined by a fingerprint embedded within a secure storage area such as a ROM (read only memory) of the portable device based on a public key certification process. A certified code image may be assigned a hash signature to be stored in a storage of the portable device. An operating environment of the portable device may be established after executing the certified code.
Owner:APPLE INC
Hardware trust anchors in sp-enabled processors
ActiveUS20100042824A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsOperational systemConfidentiality
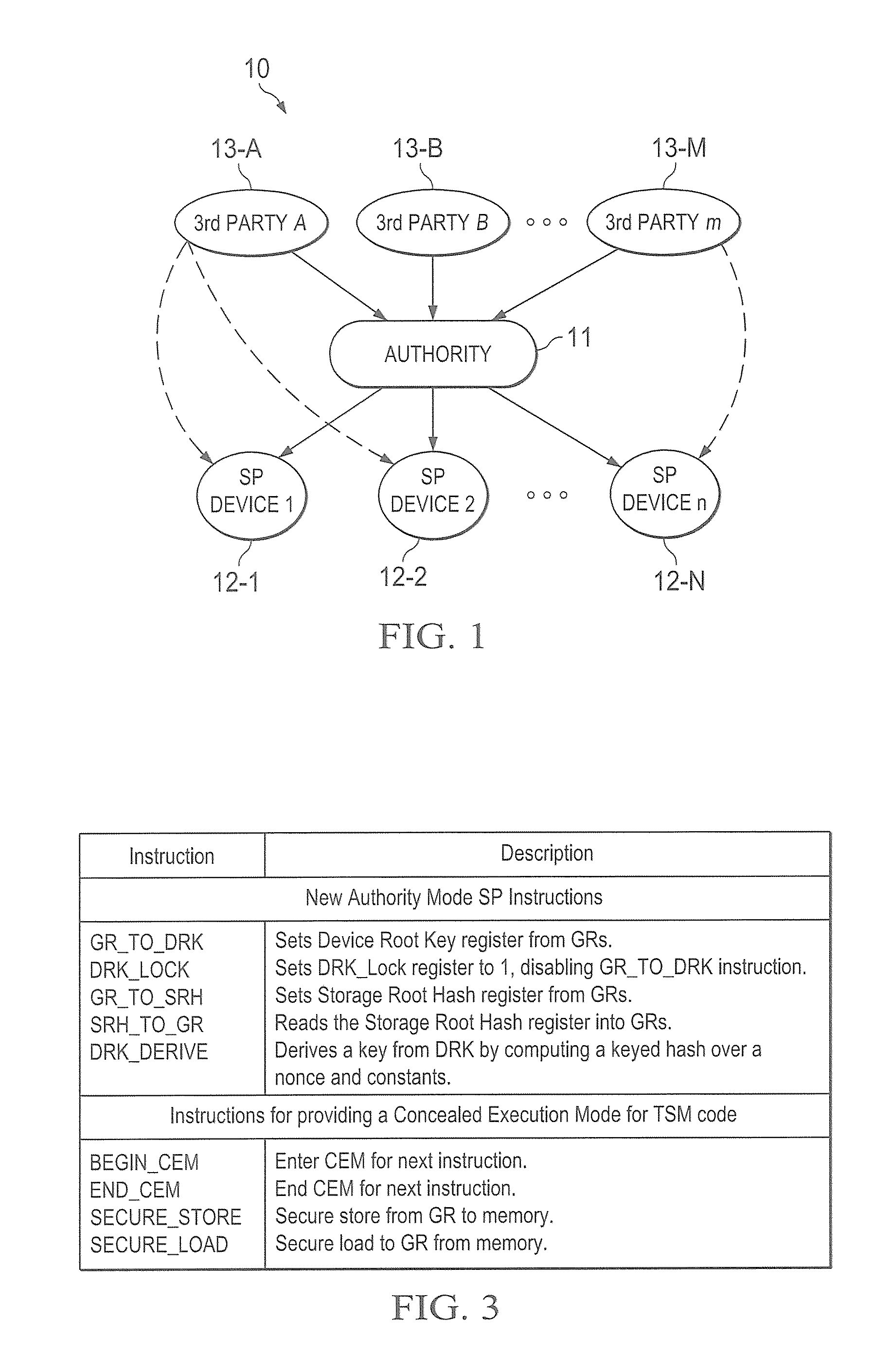
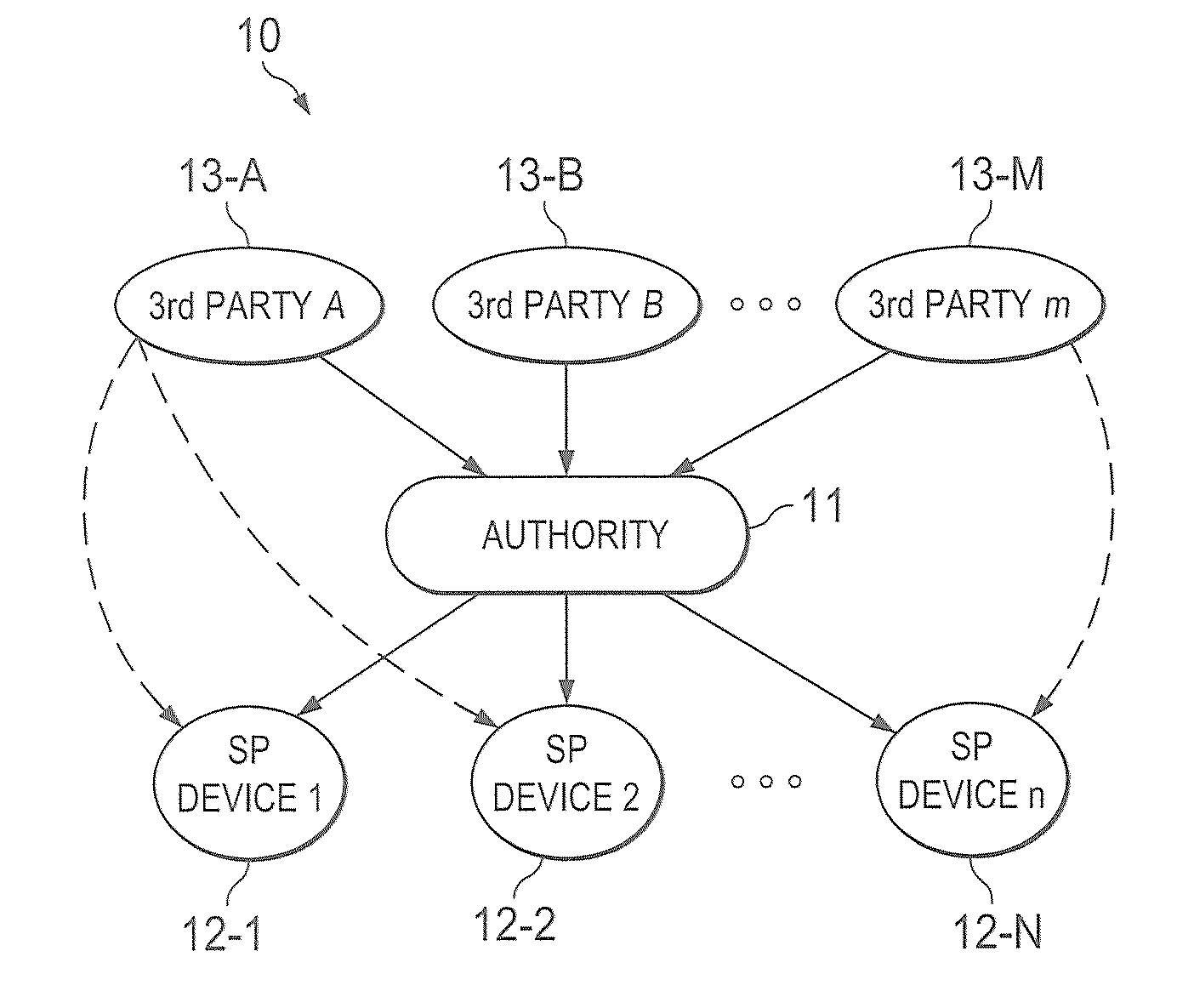
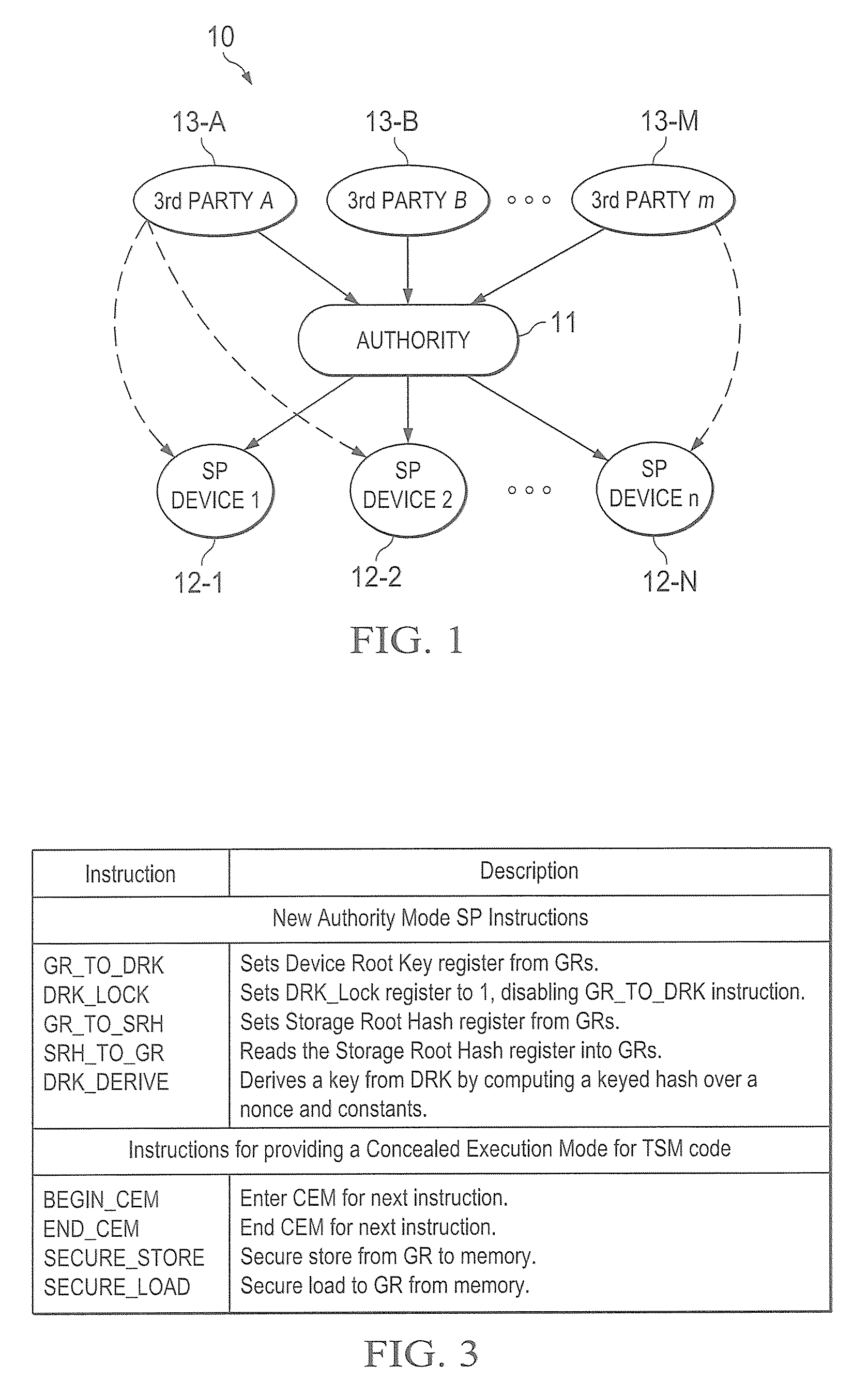
A trust system and method is disclosed for use in computing devices, particularly portable devices, in which a central Authority shares secrets and sensitive data with users of the respective devices. The central Authority maintains control over how and when shared secrets and data are used. In one embodiment, the secrets and data are protected by hardware-rooted encryption and cryptographic hashing, and can be stored securely in untrusted storage. The problem of transient trust and revocation of data is reduced to that of secure key management and keeping a runtime check of the integrity of the secure storage areas containing these keys (and other secrets). These hardware-protected keys and other secrets can further protect the confidentiality and / or integrity of any amount of other information of arbitrary size (e.g., files, programs, data) by the use of strong encryption and / or keyed-hashing, respectively. In addition to secrets the Authority owns, the system provides access to third party secrets from the computing devices. In one embodiment, the hardware-rooted encryption and hashing each use a single hardware register fabricated as part of the computing device's processor or System-on-Chip (SoC) and protected from external probing. The secret data is protected while in the device even during operating system malfunctions and becomes non-accessible from storage according to various rules, one of the rules being the passage of a certain time period. The use of the keys (or other secrets) can be bound to security policies that cannot be separated from the keys (or other secrets). The Authority is also able to establish remote trust and secure communications to the devices after deployment in the field using a special tamper-resistant hardware register in the device, to enable, disable or update the keys or secrets stored securely by the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
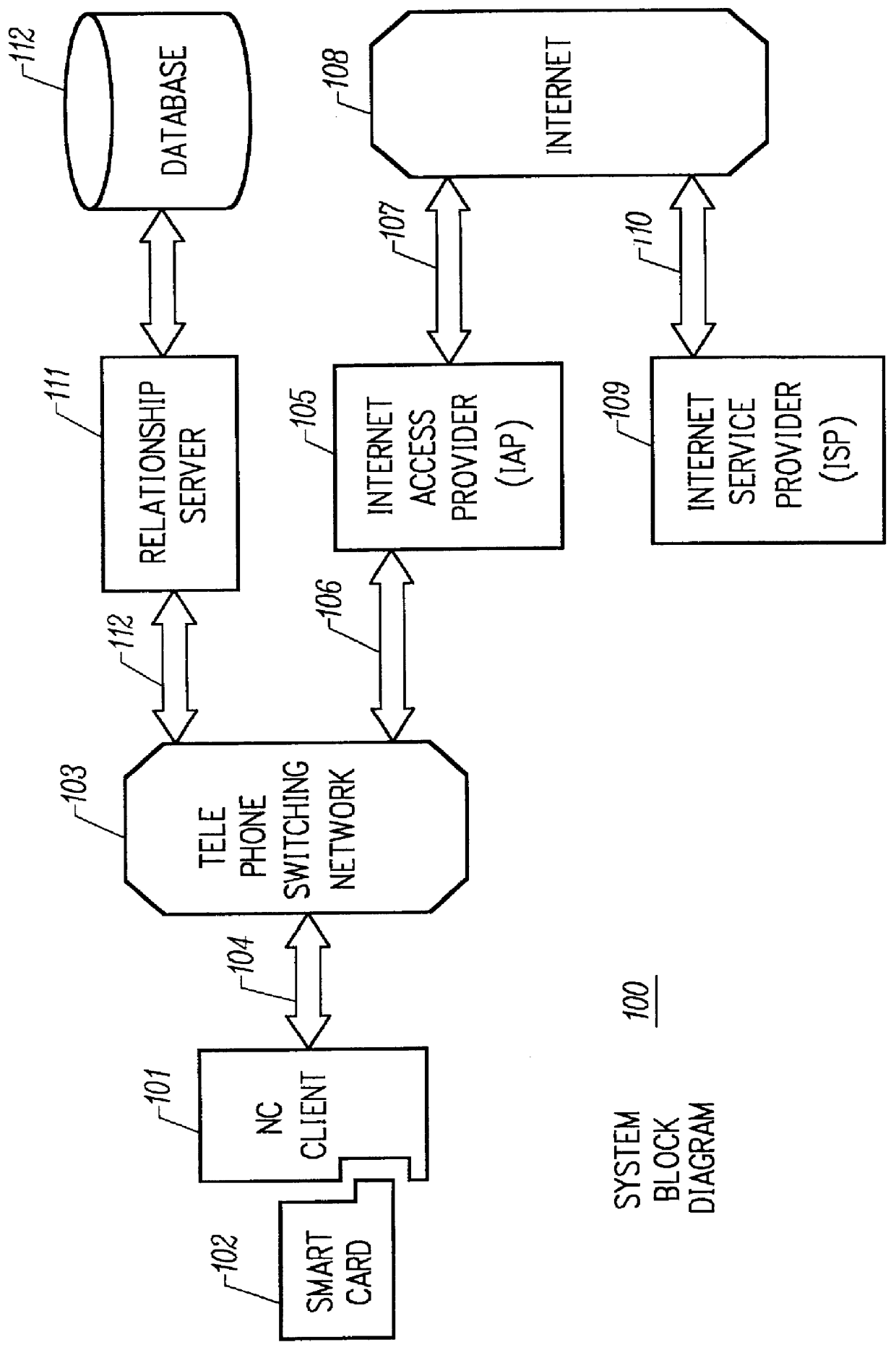
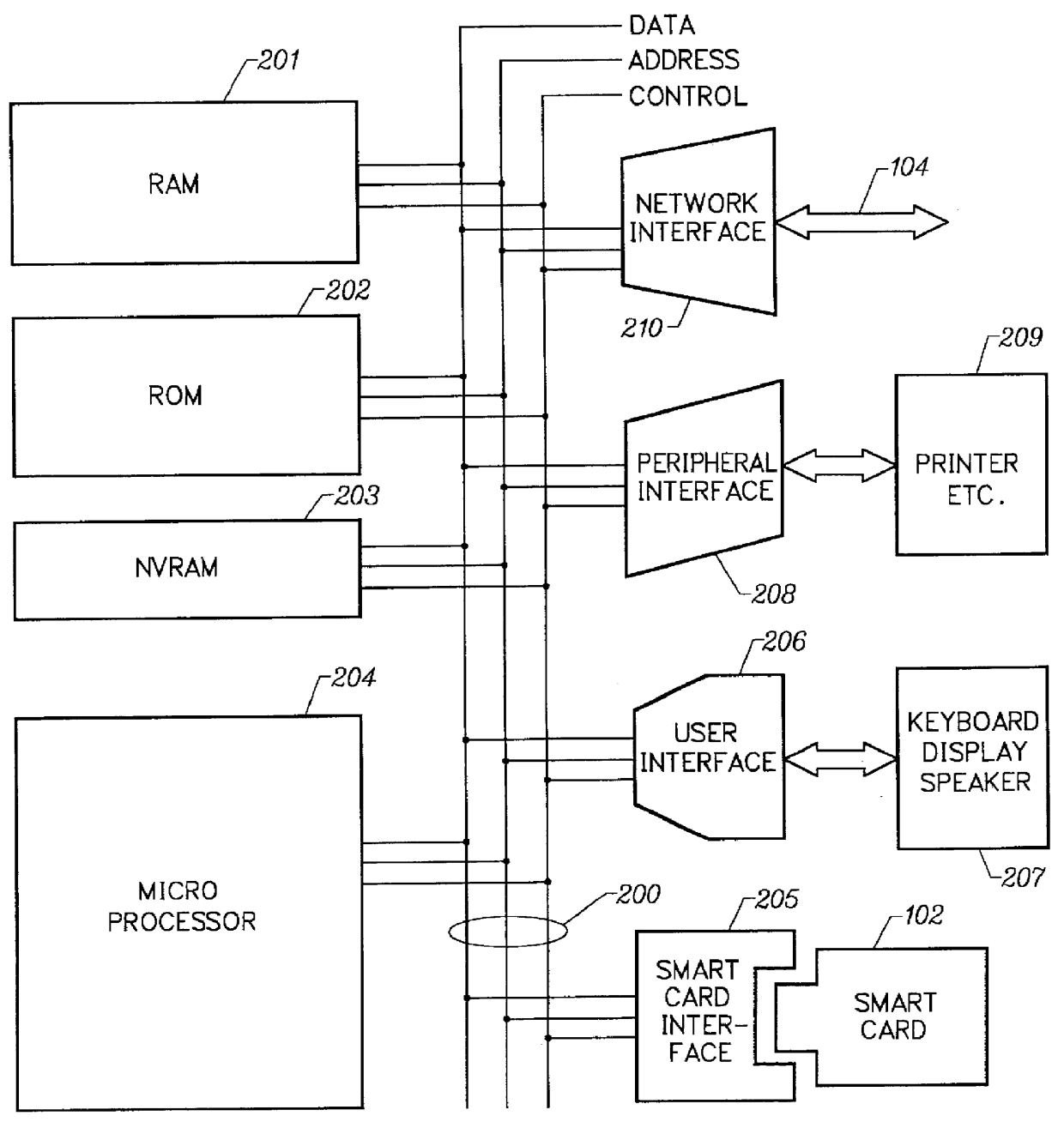
Mechanism for users with internet service provider smart cards to roam among geographically disparate authorized network computer client devices without mediation of a central authority
InactiveUS6108789ADigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureServer allocation
User specific internet service provider (ISP) account information is stored on the user's smart card, but the ISP specific connection information is stored within a network computer client device (NC). When the NC is first powered on and used, it calls the relationship server to receive connection information corresponding to the ISP that is either specified on the first user's smart card or is otherwise chosen by the first user. This connection information is preferably stored in non-volatile memory within the NC, so that even if the NC is powered down, it maintains the ability to connect to the ISP designated by its previous user. Each ISP is designated by a unique enterprise identification number assigned by the relationship server. When a subsequent user inserts his smart card into an NC, the NC compares the enterprise identification number on the smart card to the enterprise identification number within the NC. If the enterprise identification numbers match, the NC connects to the IAP already stored in the NC without dialing the relationship server. Only if the enterprise identification numbers do not match must the NC then dial the relationship server to download connection information for the ISP designated by the smart card enterprise identification number. In the preferred embodiment, the ISP contents of the smart card are digitally signed by the ISP. If the enterprise identification numbers match, then the ISP contents of the smart card are cryptographically authenticated using the public key within the authorized usage certificate for the ISP. If the cryptographic authentication fails, then the NC reprograms the smart card.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
Blockchain digital currency: systems and methods for use in enterprise blockchain banking
PendingUS20180268382A1Enhance security and traceability and authenticityPayment protocolsPayment circuitsDigital currencyFinancial transaction
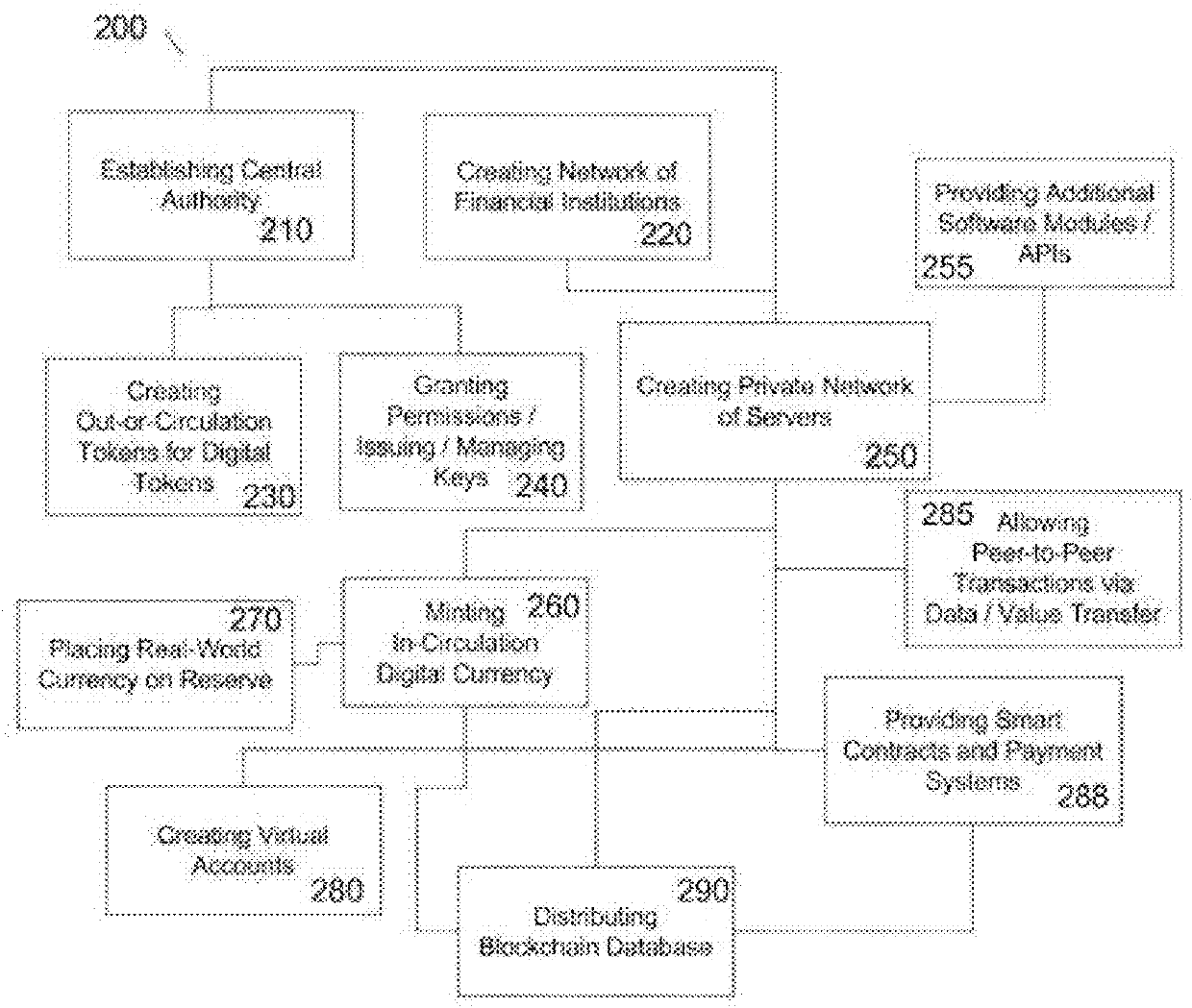
Methods and systems for using blockchain digital currency are provided herein. The methods and systems comprise a blockchain digital currency that is created and utilized on a permission-based network of financial institutions. The blockchain digital currency is created by a central authority and minted into circulation by banks within the network, and is backed by reserves of real world currency of any country. The digital currency can be used for any type of financial transaction, and the system provides security, trust, traceability and a detailed audit trail for all transactions.
Owner:WASSERMAN STEVEN VICTOR
Method and apparatus for providing cross-benefits via a central authority
InactiveUS7818284B1Easy to optimizeFacilitating commercePayment architectureMarketingCredit cardEngineering
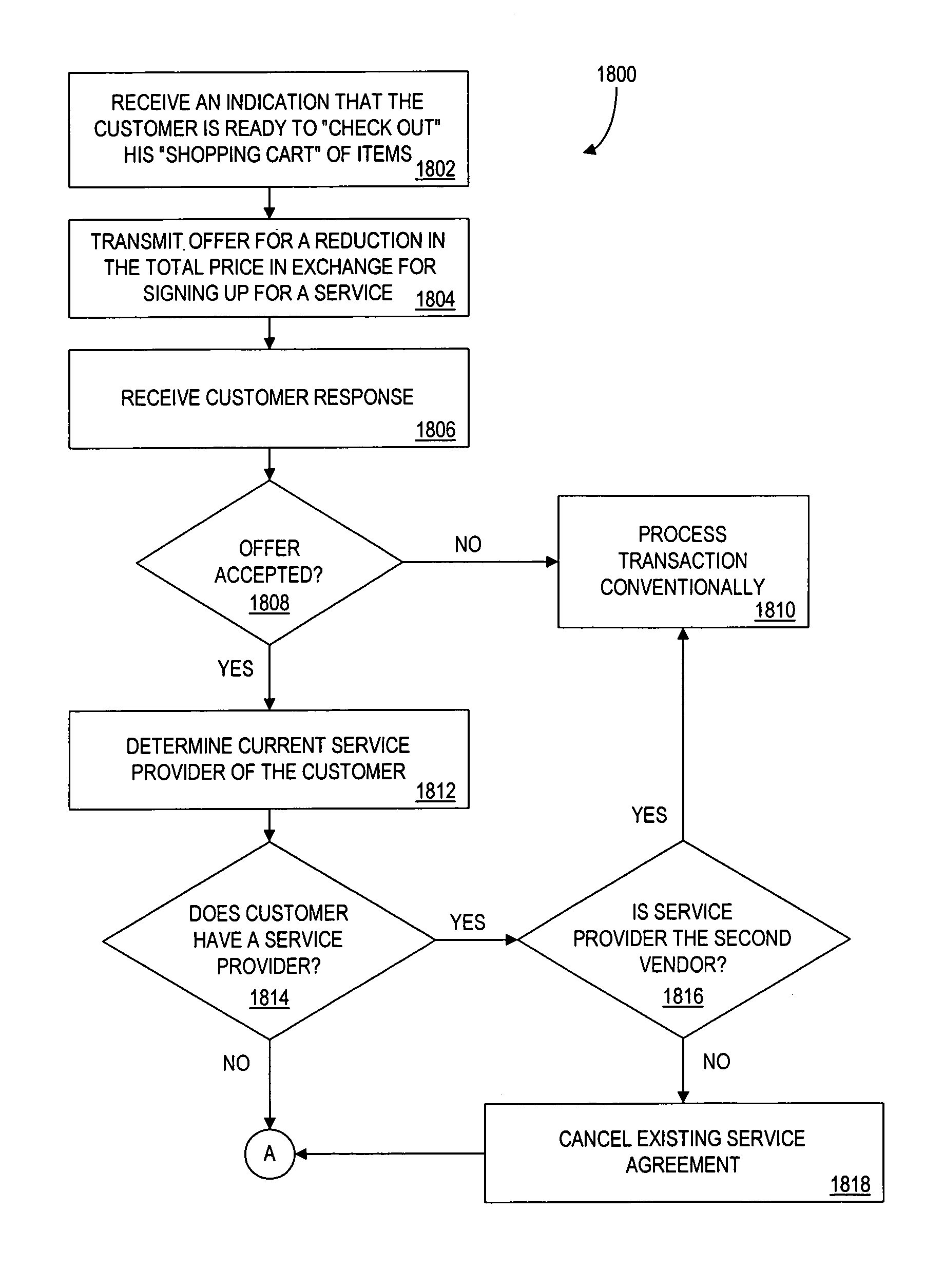
A controller is in communication with a plurality of vendors that are servicing customers, as well as with a plurality of “subsidizing” vendors seeking access to those customers. The controller receives from a first vendor an indication of one or more items that a customer is to purchase. In response, the controller transmits, on behalf of a subsidizing vendor, an indication of an offer for a subsidy such as a reduction in the customer's purchase price. If the customer accepts the offer, the controller provides an amount of funds from the subsidizing vendor to the first vendor. The controller may also retain a portion of the amount as payment. The controller also facilitates a transaction between the customer and the subsidizing vendor. For example, the customer may be required to sign up for a service (e.g. credit card account service) that is provided by the subsidizing vendor. By having the controller manage such a system by acting between subsidizing vendors and vendors that are servicing customers, a vendor need only communicate with the controller, rather than a plurality of other vendors.
Owner:PAYPAL INC
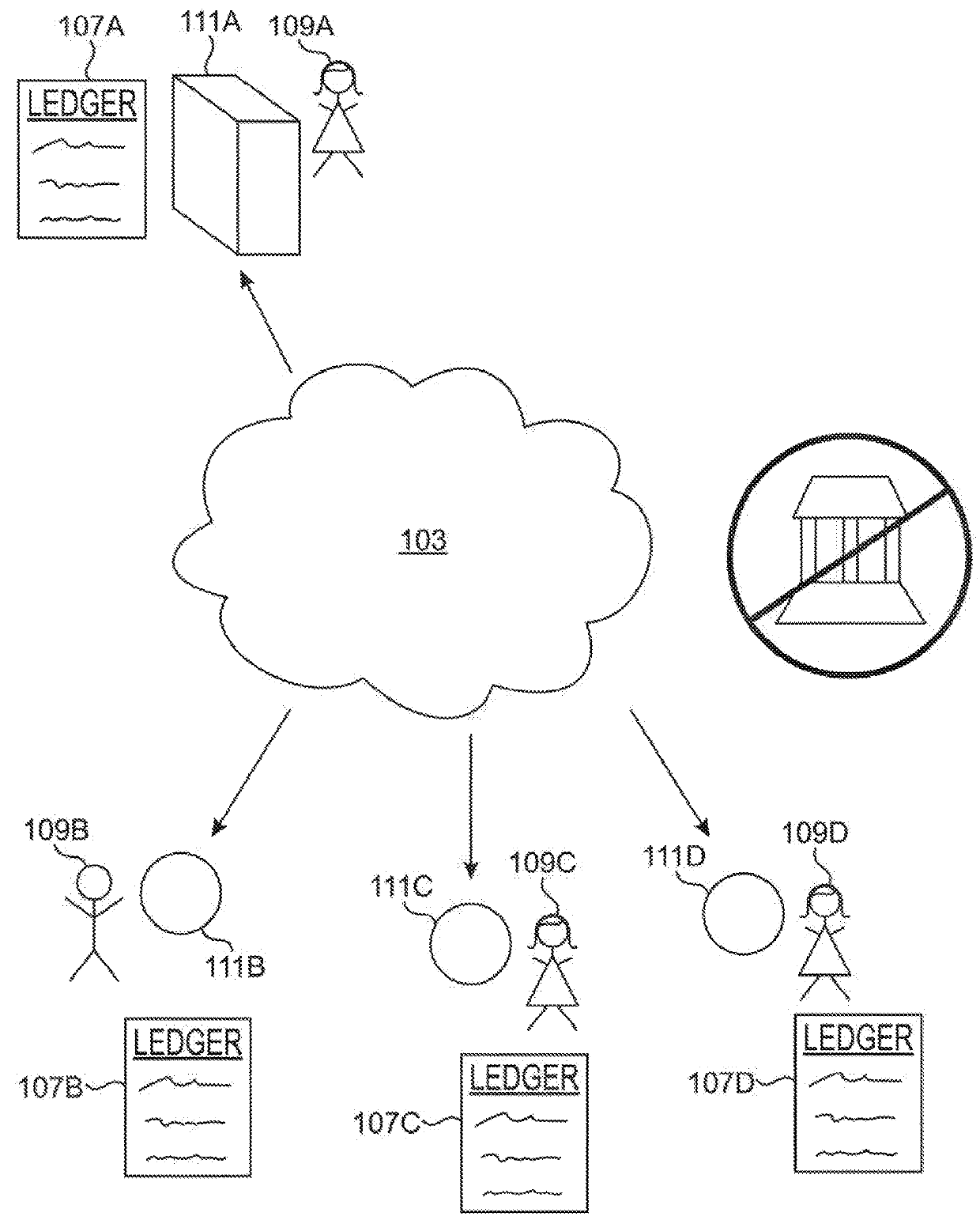
Transference tracking
PendingUS20190188706A1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationCentralized databaseCentral authority
Systems and methods are disclosed that provide for a blockchain-based transference tracking system to authenticate and register electronic transaction records. The transference tracking system, in one embodiment, is a permissioned, peer-to-peer, decentralized network containing an authorized, verifiable ledger of electronic transaction records that can be shared amongst authenticated actors. The decentralized ledger can be used as a substitute for a centralized database and enables automated tracking and reporting of electronic transaction records to an authoritative, but non-central authority using the blockchain of the transference tracking system.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and apparatus for awarding prizes based on authentication of computer generated outcomes using coupons
InactiveUS7362862B2Secret communicationApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingAWARDS PRIZESRanking
The present invention provides authentication of computer generated game or test results (“outcomes”), and a system by which persons who play games or take tests on a game or testing computer, respectively, may submit the outcomes of the games or tests to a central authority having at least one central computer, and have the central computer “certify” those outcomes as being accurately reported and fairly achieved. This certification of the computer generated result constitutes a “remote-auditing” of the activity taking place on the game computer. In one application, the system enables computer generated game tournaments in which players play the games on game computers and compete against each other by submitting the outcomes for those tournament games to the central computer, which certifies the outcomes and rates and ranks the players. In another application, the system provides for players of computer games to obtain a certified ranking and rating without participation in a tournament. In other embodiments, the system provides for self-authentication and certification of outcomes for games played on the game computer itself, or for mutual-authentication and certification of such outcomes on any other game computer in the system.
Owner:INVENTOR HLDG
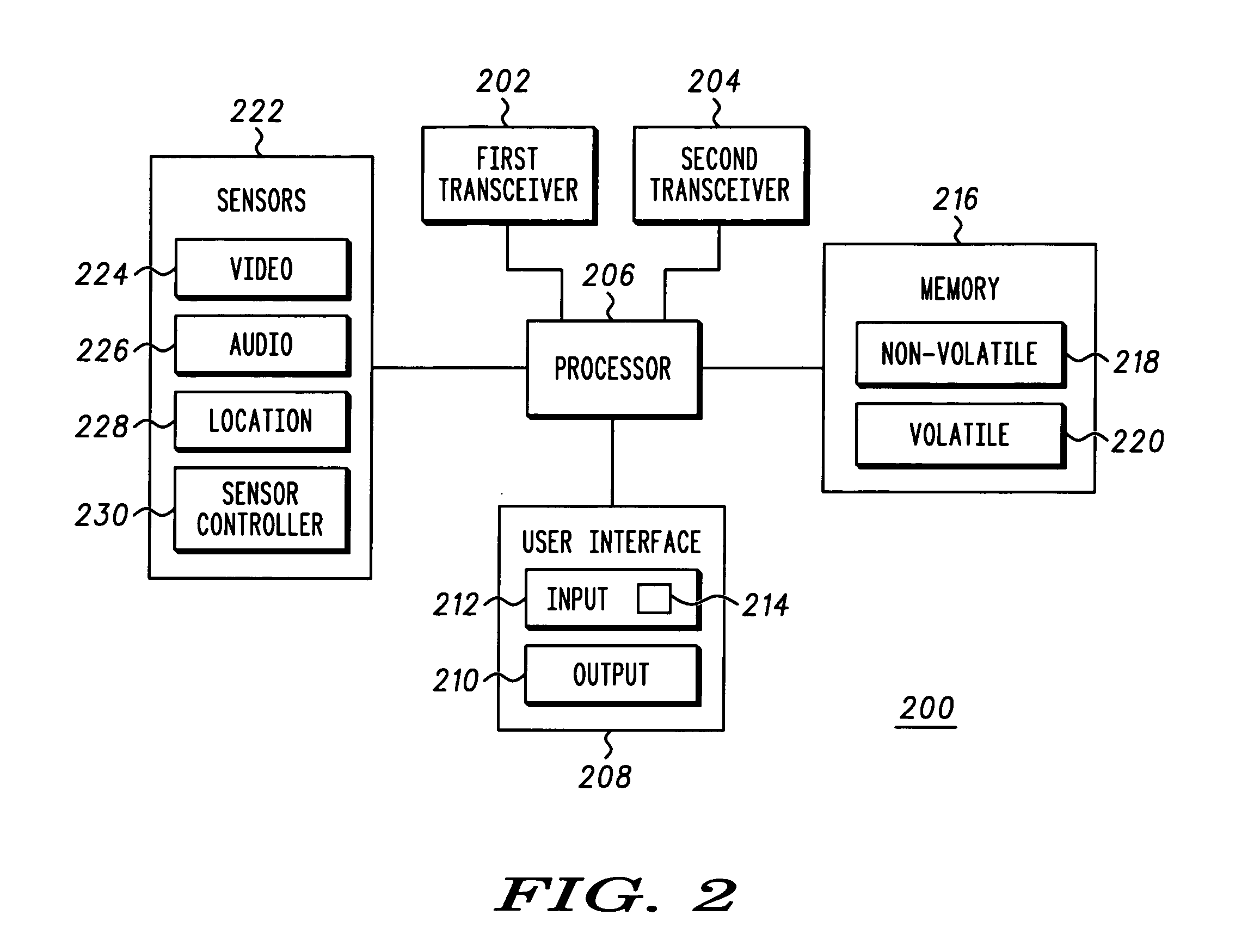
System and method for incident reporting, information gathering, reconstructing and alerting
InactiveUS20050101334A1Telemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBiological activationProcess information
A system and method for processing information about an incident is provided. The system comprises two or more communication devices (104, 112-126) in communication with each other and a central authority (128) capable of receiving data from the communication devices. Each communication device (104, 112-126) includes a media sensor (222) to collect data relating to an incident event (102). One communication device (104), in response to a user activation input, transmits a request signal to one or more other communication devices (112-126). Any communication device (112-126) that receives the request signal may collect data relating to the incident event (102) in response to the request signal. The central authority (128), after receiving the data collected by the wireless communication devices (104, 112-126), performs an action in response to receiving the data.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
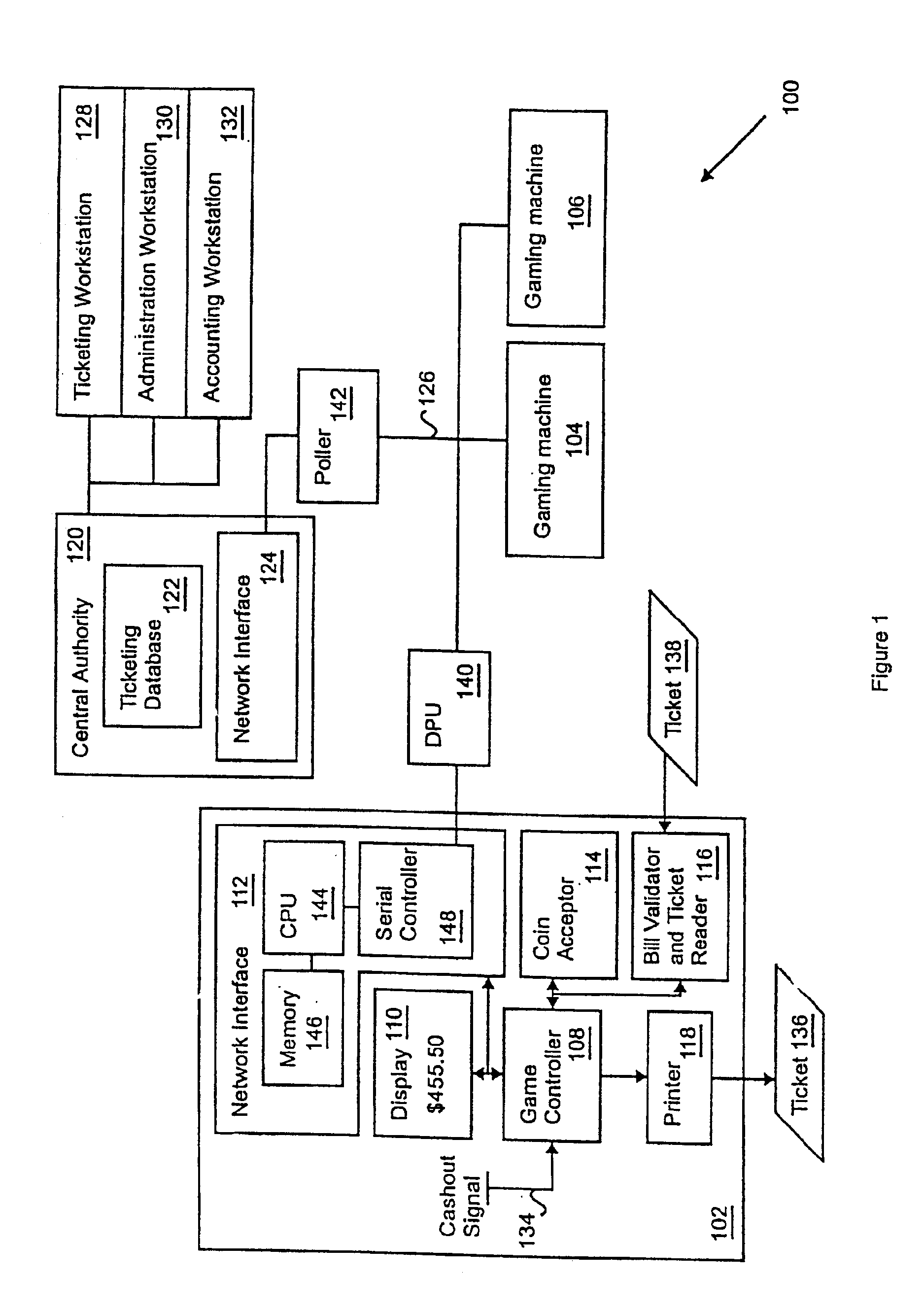
Apparatus and method for a cashless actuated gaming system
A gaming machine adapted to print validated tickets for a game player includes a microprocessor for controlling game operation (e.g., slot machine operation) and including a cashout signal input, a network interface coupled to the microprocessor for communicating with a central authority, and a memory in the network interface that stores a pre-loaded ticket validation number received from the central authority. In addition, a ticket printer is coupled to the microprocessor for printing a ticket that includes pending credit indicia and pre-loaded ticket validation indicia in response to a cashout signal on the cashout signal input. After the ticket is printed, the gaming machine obtains a new pre-loaded validation number in preparation for the next ticket printing event.
Owner:ARISTOCRAT TECH INC
Dynamic security authentication for wireless communication networks
ActiveUS20040179690A1Minimize exchangeMinimization of wasted bandwidthKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSystemic approachAuthentication server
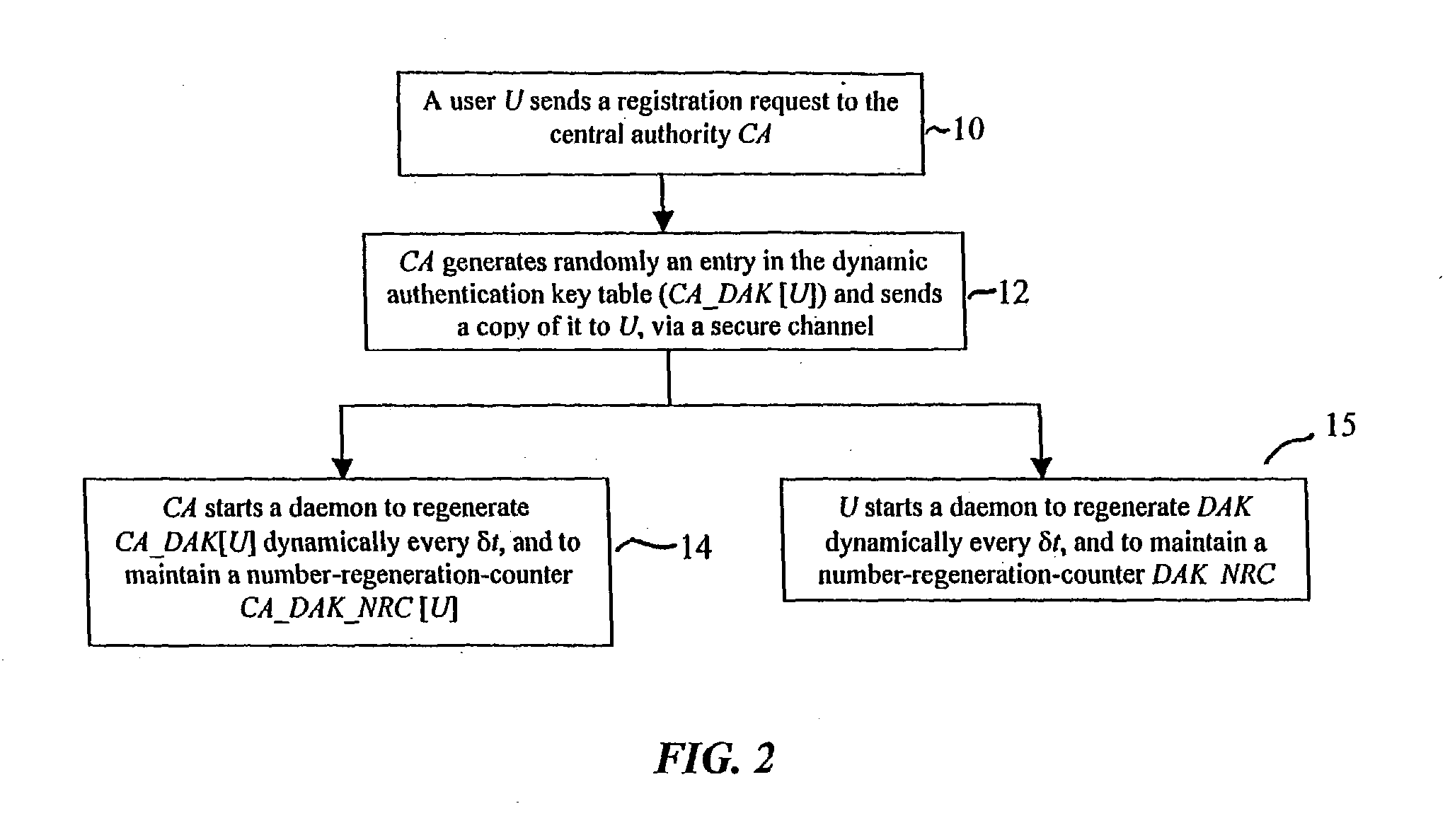
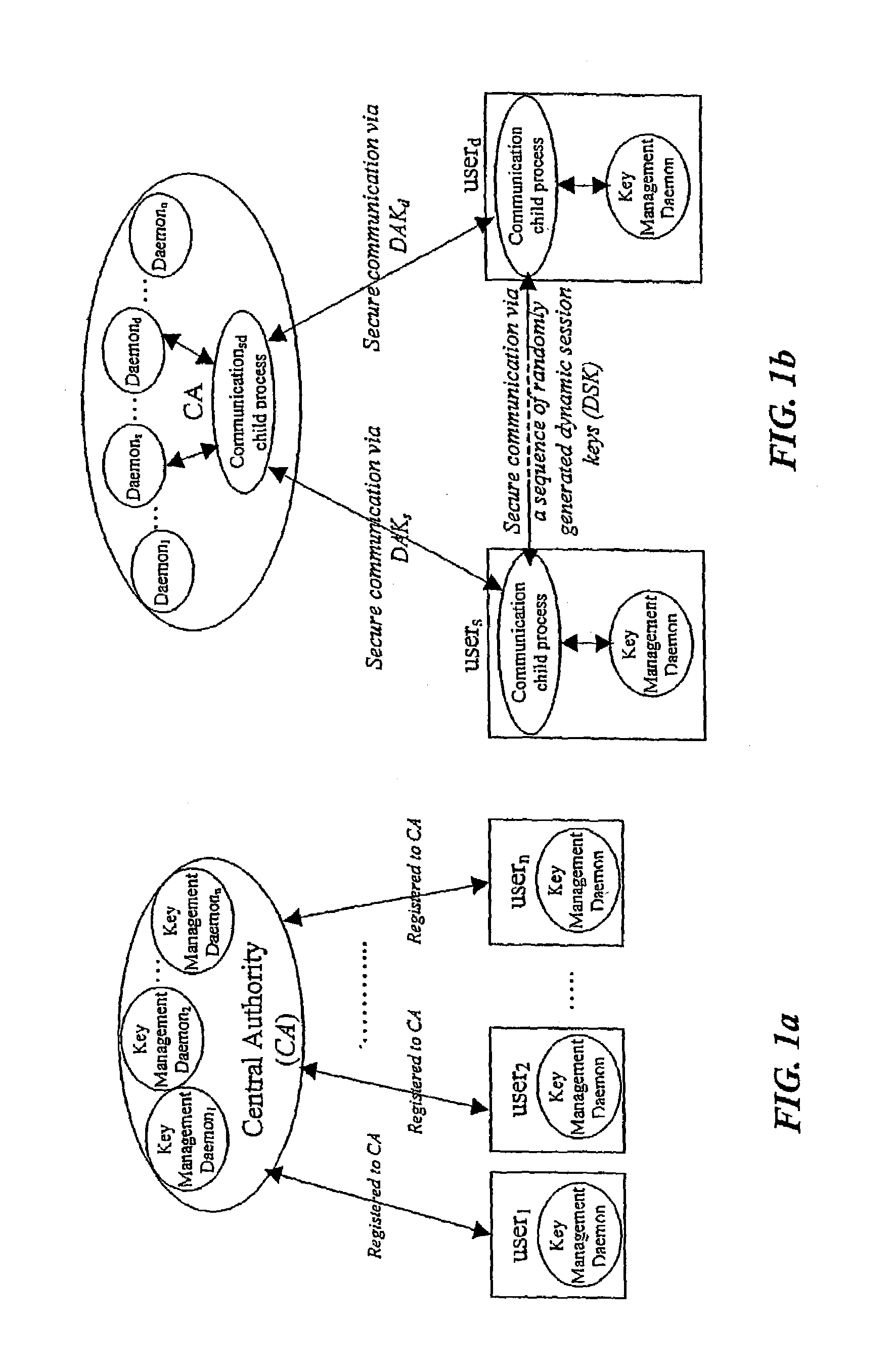
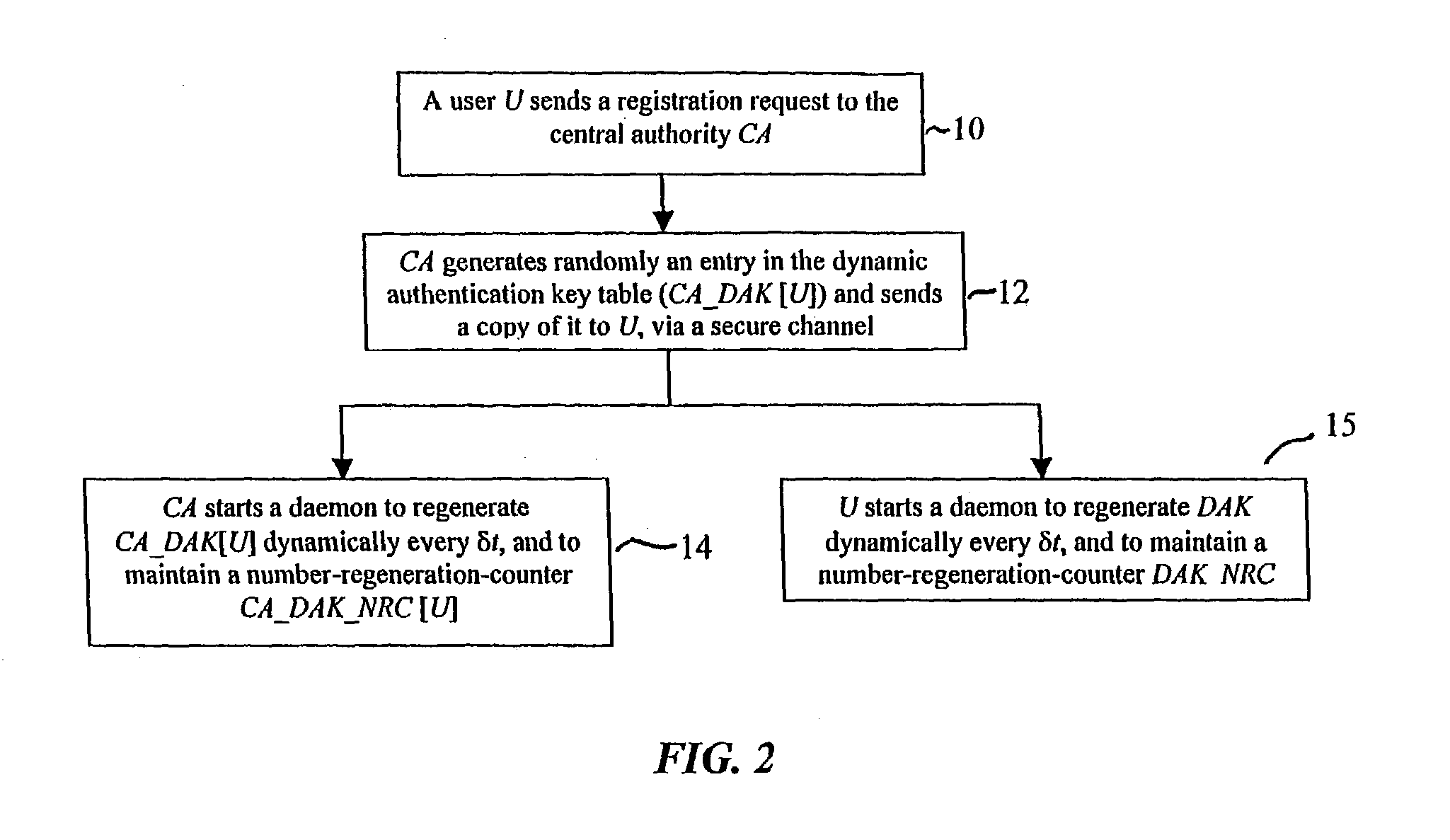
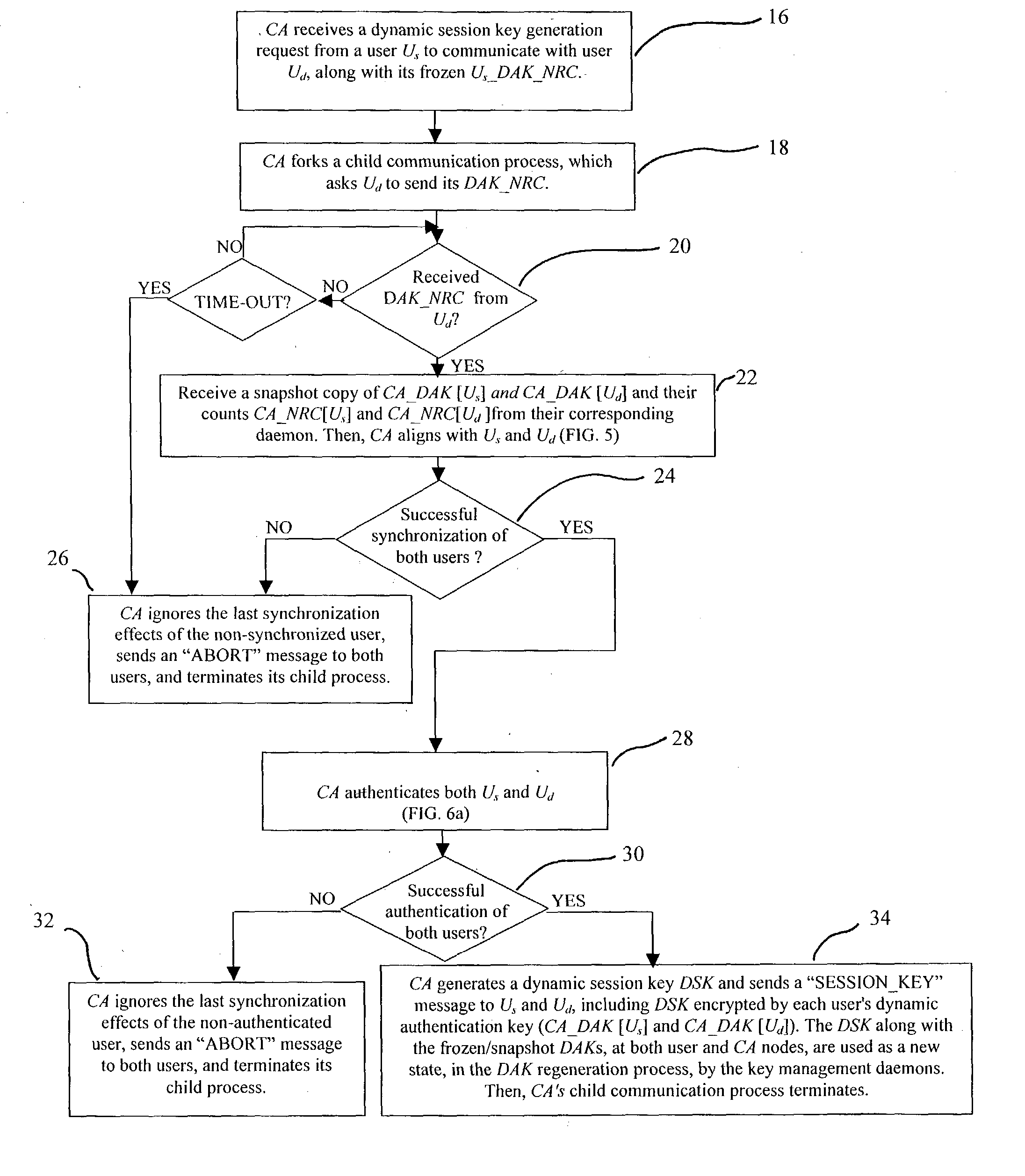
In a first embodiment, a dynamic computer system security method and system using dynamic encryption and full synchronization between system nodes. A data record created by a source user is encrypted with an initial dynamic session key. A new dynamic session key is generated based upon a data record and a previous dynamic session key. A central authority is used to synchronize and authenticate both source and destination users with constantly regenerated dynamic authentication keys. In a second embodiment, a method of providing dynamic security authentication between wireless communication network nodes. An initial authentication key and an address are assigned to certain of the nodes. The address along with information encrypted by the initial authentication key is sent to an authentication server. The authentication server and node or nodes synchronously regenerate authentication keys based upon the initial authentication key. Secure handovers occur between nodes via an authentication key.
Owner:MOXCHANGE LLC
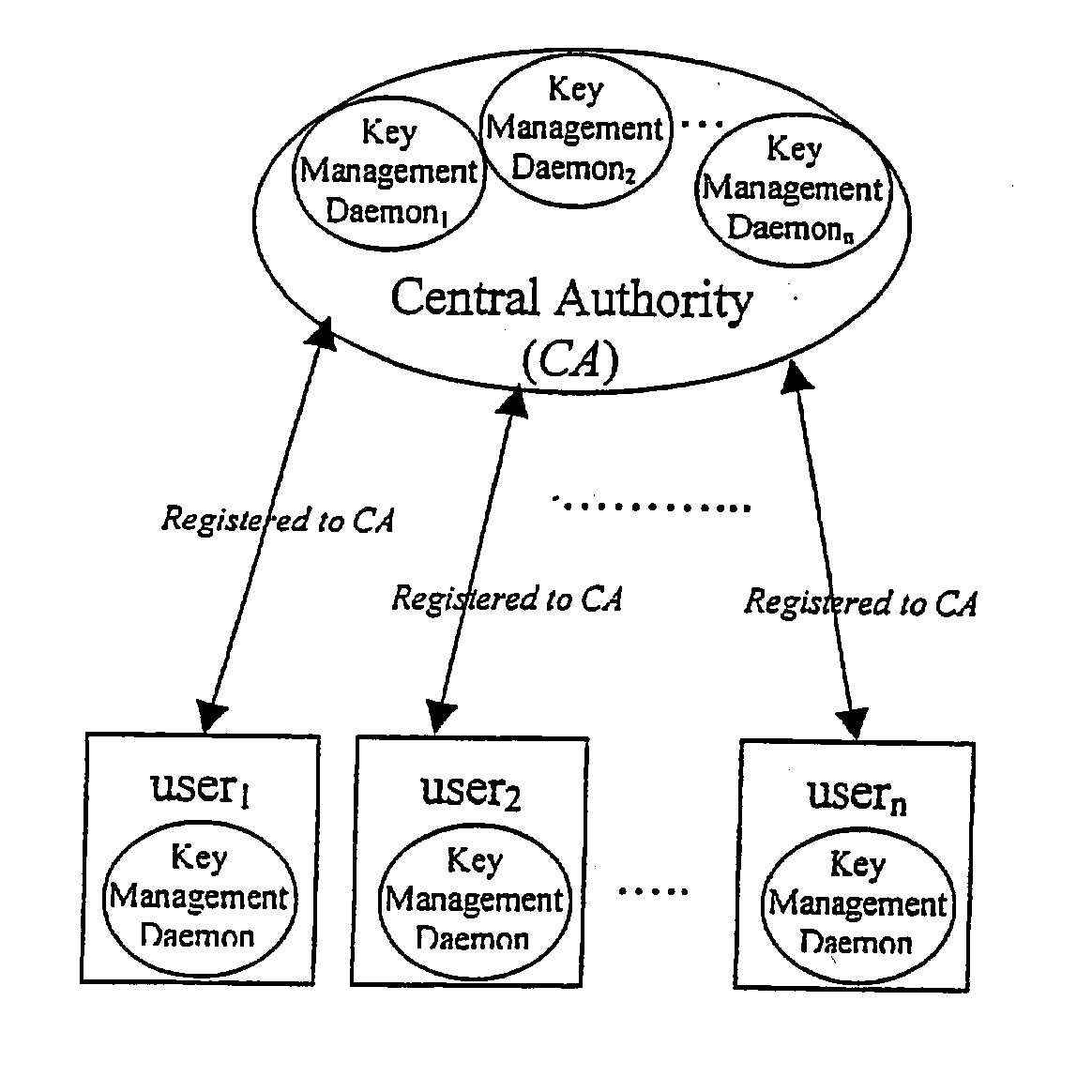
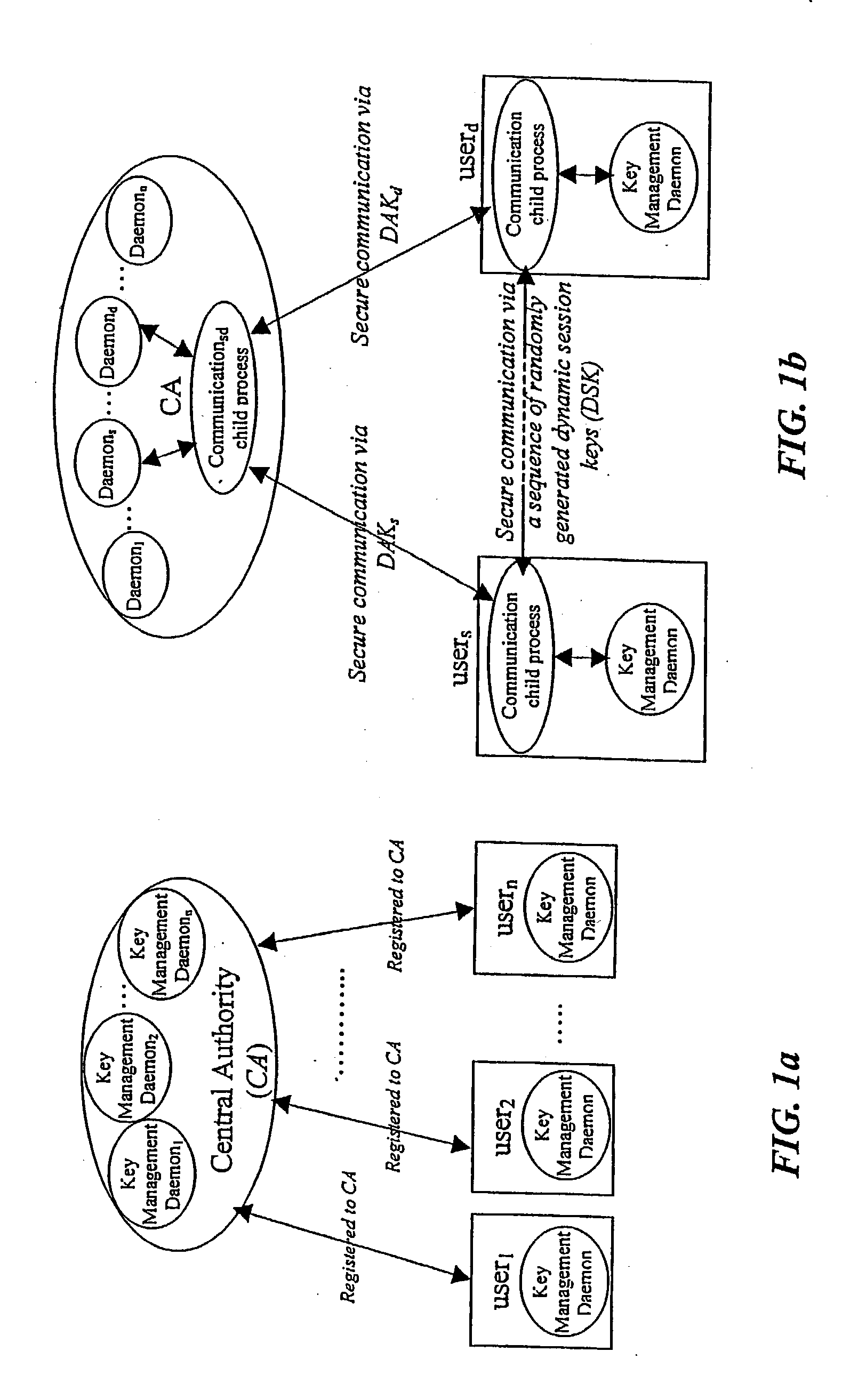
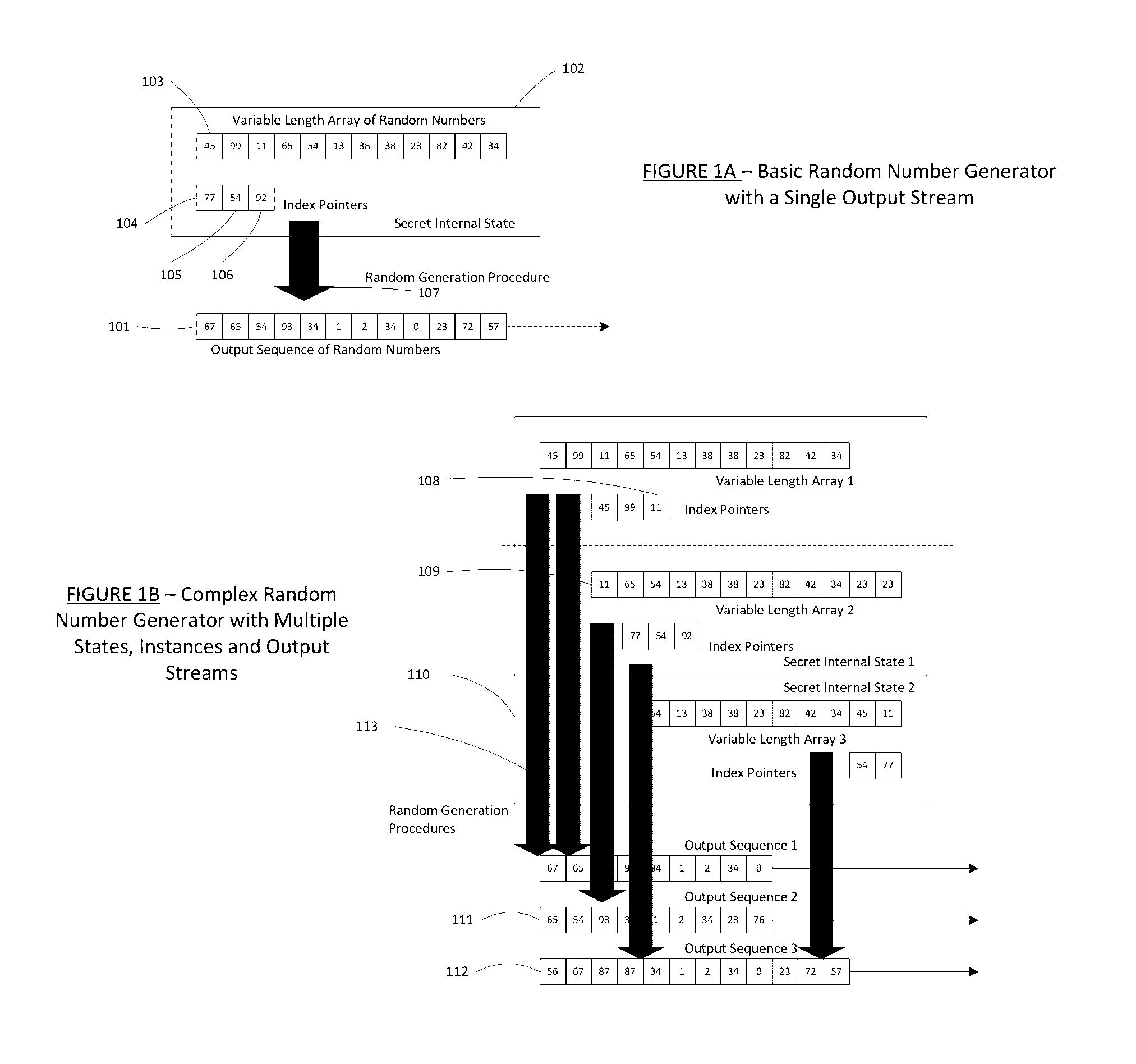
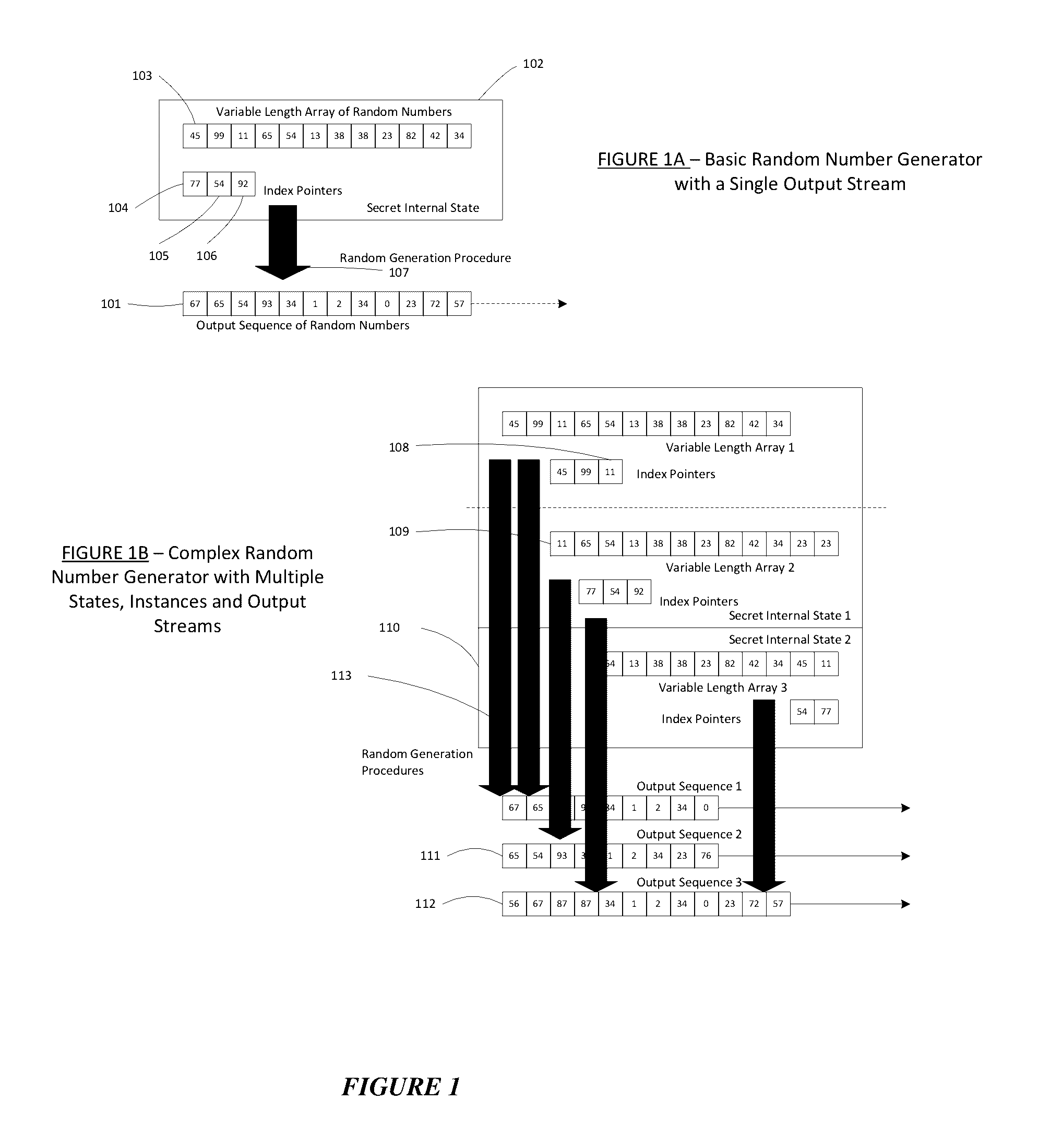
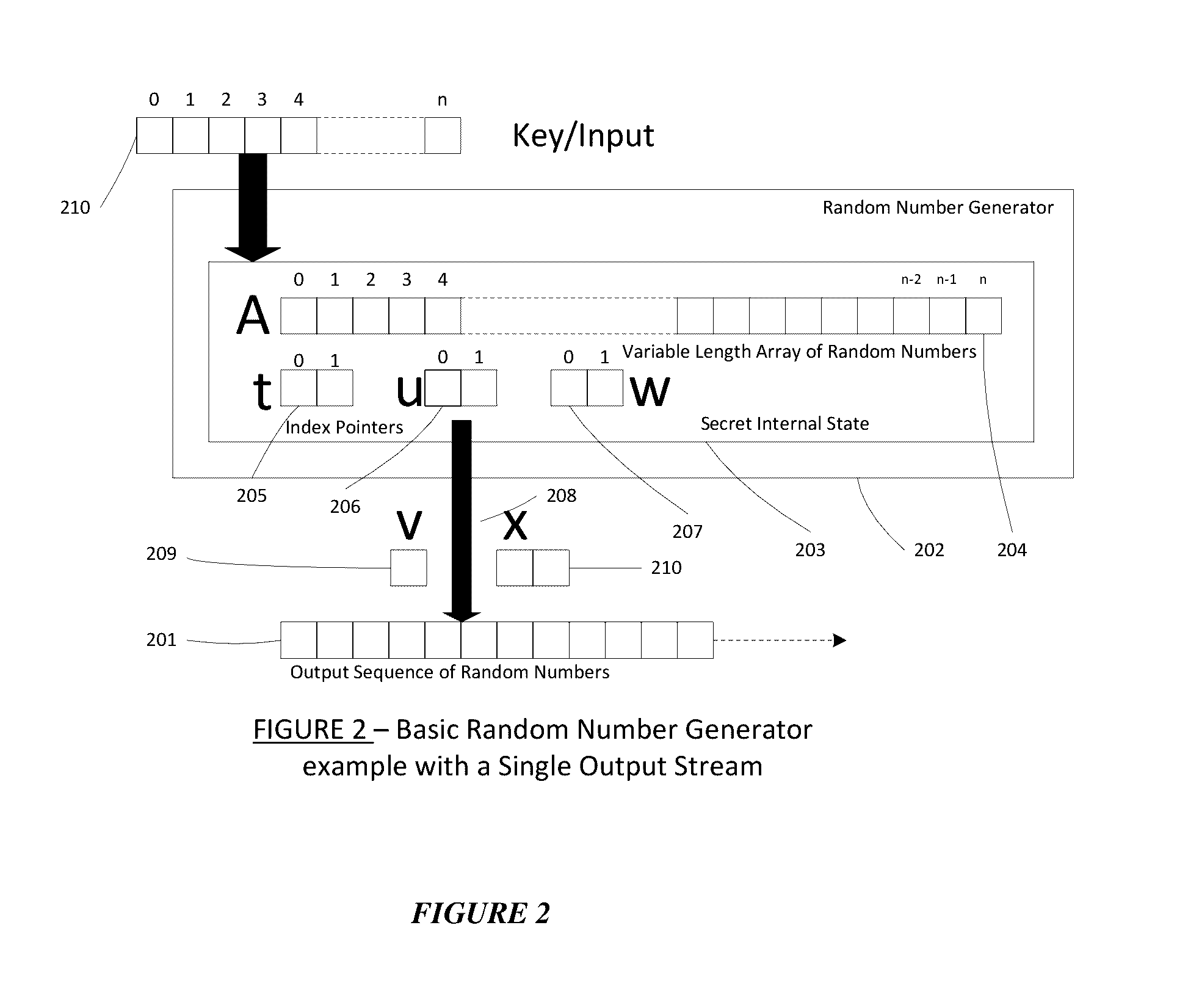
Method for a Dynamic Perpetual Encryption Cryptosystem
A dynamic computer communication security encryption method or system using an initial seed key and multiple random number generators of a specific design, whereby a sequence of independent random entropy values is produced by one set of random number generators and encrypted along with the message stream using the initial seed key, or the output of a second set of random number generators initialized with the initial seed key, and following the subsequent transmission of the variable encrypted entropy / message block, the entropy values are used to symmetrically or identically augment or increase the current uncertainty or entropy of the cryptosystem at both the sender and the receiver, prior to the next encryption block operation. The encryption process effectively entailing the use of multiple encryption ciphers, and the entropy augmentation process entailing the encryption or application of various logical mathematical operations on the already dynamic but deterministic internal state values of the second set of random number generators, effectively altering their deterministic outputs in a random probabilistic manner.Random length message value sequences from one or more data sources is combined with one or more random length entropy value sequences from an independent source, following which the entropy “updates” may also be used to alter, or change any cryptosystem variable, value or component in a randomly determined manner. In addition, whilst ensuring synchronization, the random entropy sequences also serve to “pollute” the cipher-stream and thereby hinder most current forms of cryptanalysis, whilst simultaneously injecting additional entropy into the cryptographic system and allowing for its propagation to affect any connected system nodes, and thereby introducing unpredictable entropy into the system pseudorandom number generator outputs, and thereby ensuring the perpetual generation of unpredictable random numbers.Super-encryption mechanics are independent of the user data, simple, fast and efficient, and can incorporate compression, error correction and asymmetric encryption authentication routines. But most importantly, super-encryption ensures resistance to brute force attacks (not possible to verify if a message was even sent), an ability to exceed “perfect secrecy” requirements, and an improvement on previous super-encipherment design, since overhead can be dramatically reduced from 100% overhead.Communication links previously established by system nodes with central authorities may be used for secure node authentication and registration, whilst allowing the central authority to broker and synchronize communication channels and providing mutual authentication and other security functions between the system nodes.
Owner:FIGUEIRA HELDER SILVESTRE PAIVA
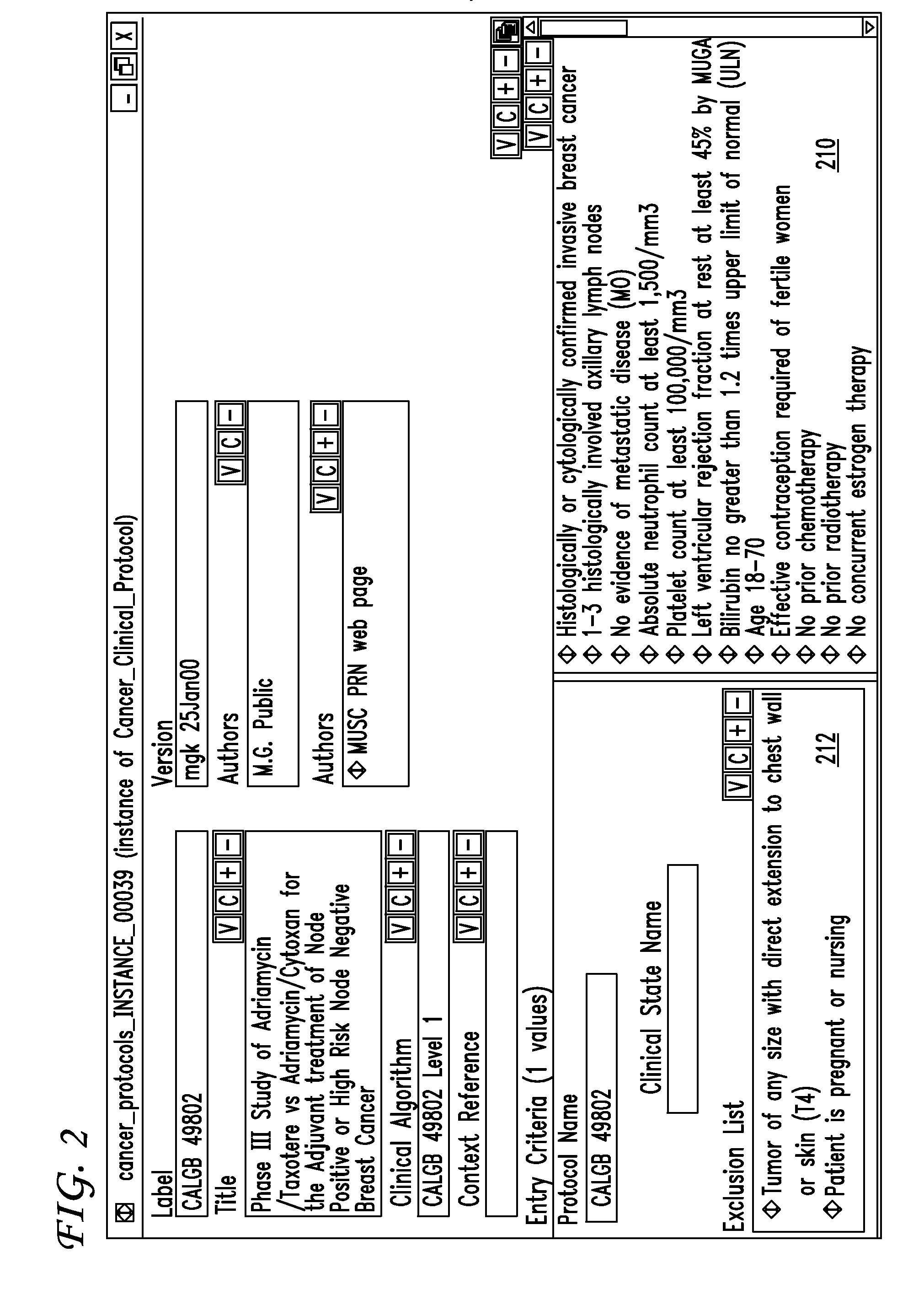
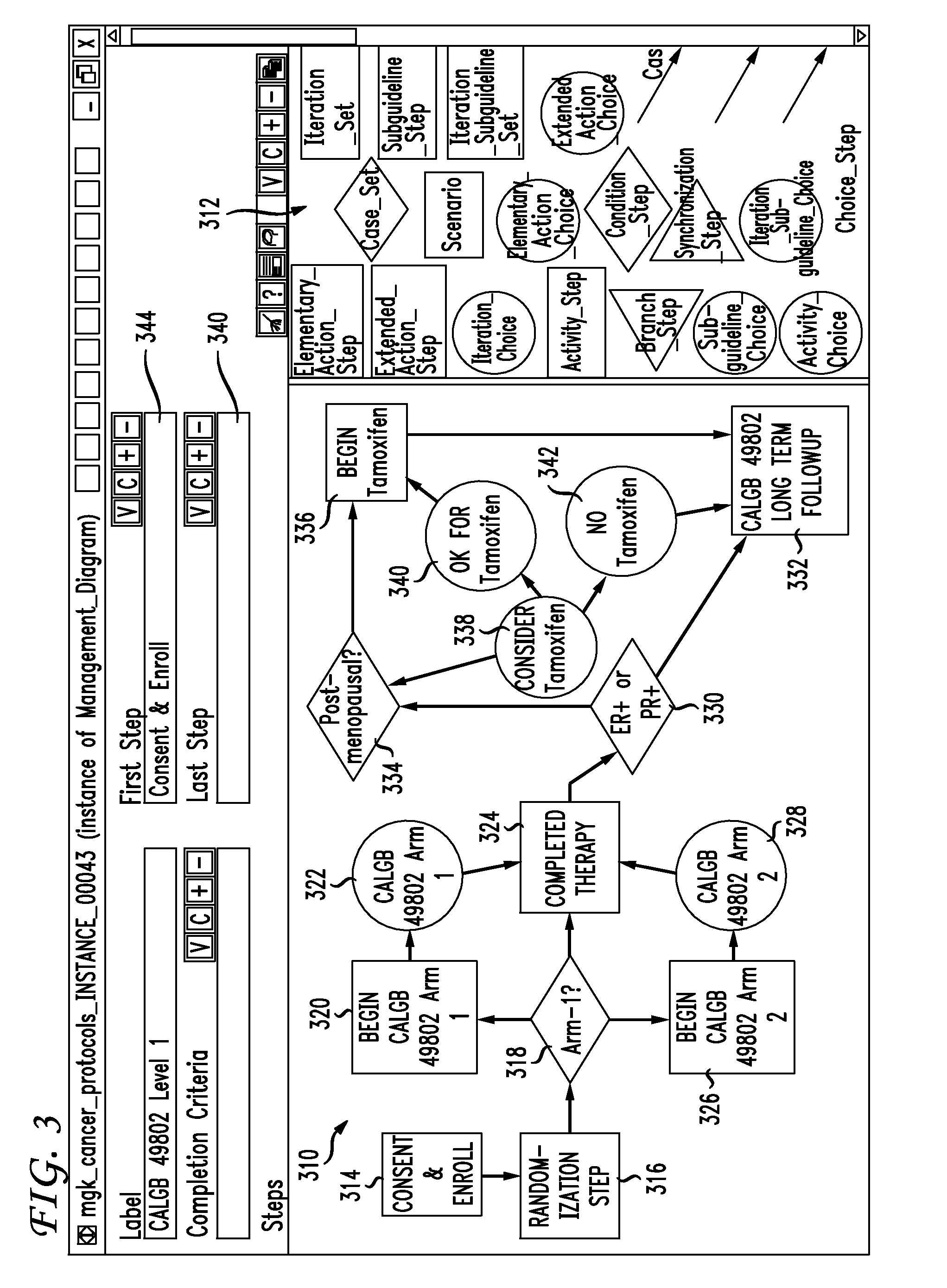
Clinical trials management system and method
InactiveUS20090313048A1Digital data processing detailsDrug and medicationsPatient managementEnd to end system
Clinical trials are defined, managed and evaluated according to an overall end-to-end system. The central authority creates protocol meta-models and makes them available to clinical trial protocol designers. Each meta-model includes a short list of preliminary patient eligibility attributes which are appropriate for a particular disease category. The protocol designer chooses the appropriate meta-model, and encodes the clinical trial protocol, including eligibility and patient workflow, within the selected meta-model. The resulting protocol database is stored together with databases of other protocols in a library of protocol databases. Sponsors and individual clinical sites have controlled access to the protocols. Study sites make reference to the pertinent protocol databases to which they have access in the protocol database library in order to perform patient eligibility screening. Once a patient is enrolled into a study, the protocol database indicates to the clinician what tasks are to be performed at each patient visit. These tasks can include both patient management tasks and data management tasks. The workflow graph advantageously also instructs the proper time for the clinician to obtain a patient's informed consent. The system reports patient progress to study sponsors, who can then monitor the progress of the trial, and to a central authority which can then generate performance metrics. Advantageously, a common controlled medical terminology database is used by all components of the system.
Owner:MEDIDATA SOLUTIONS
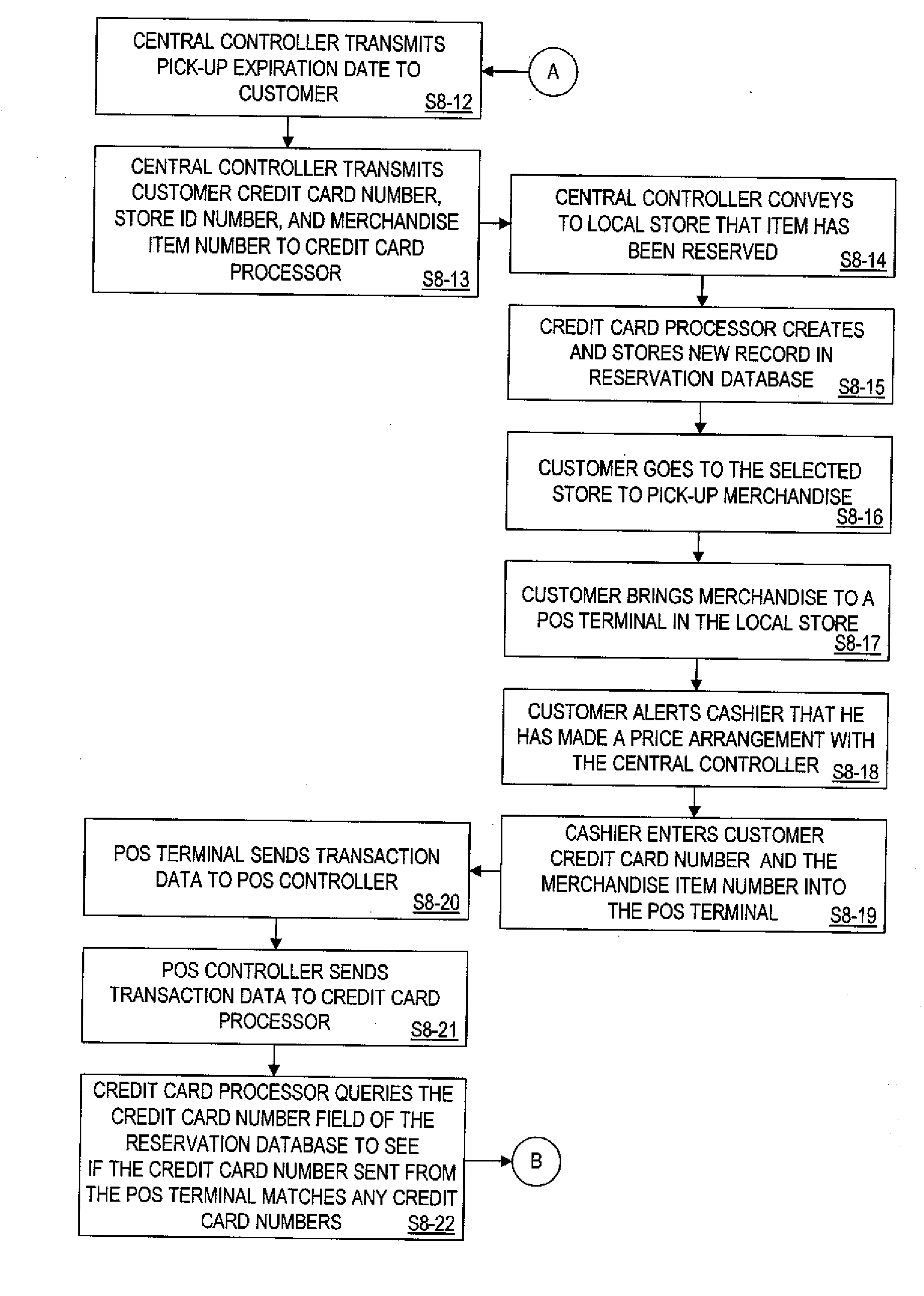
System and process for local acquisition of products priced online
InactiveUS20060224467A1Preserving profitabilityWithout upsetting either the normal pricing structure or profit margin of the retailerAcutation objectsCash registersCredit cardComputer terminal
A system and process for establishing prices for products on line and for allowing acquisition of those products from retailers that honor such prices. The system and process involve a customer having a credit card account, a computer terminal configured to access a network, and a central authority coupled to the computer terminal via the network. The central authority maintains information about a product and a corresponding price. The price is established by the central authority and the central authority is configured to communicate the information about the product and the price to the customer via the network. Also involved is a credit card processor that is coupled to the central authority. The credit card processor is configured to query the information maintained by the central authority and to receive the price from the central authority. A retailer is involved and includes a point-of-sale system coupled to the central authority and to the credit card processor. The retailer is configured to deliver the product to the customer after the customer purchases the product from the retailer via his credit card account or other form of payment at the price established by the central authority and provided to the retailer and the point-of-sale system by the credit card processor.
Owner:GROUPON INC
Simple installation of devices on a network
One embodiment of the invention employs techniques for the self-installation of network devices using fire-and-forget principles. These devices modify their own network configuration data, but do not modify the network configuration data of other devices. Utilizing fire-and-forget principles, the need for a central database and central authority on the network is not required but may still be used.
Owner:ECHELON CORP
System for central authority-permissioned transfer of blockchain tokens
InactiveUS20190340607A1Cryptography processingSecuring communicationTransfer systemCentral authority
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system for central authority-permissioned transfer of blockchain tokens. In particular, the a request is received to transfer a set of blockchain tokens that represent an ownership share in a physical asset from a first user to a second user. Information about the first user and second user is compared to a central authority repository that comprises a listing of vetted users permitted to perform transactions with blockchain tokens associated with the physical asset to determine that the first and second users are verified. In response to determining that the first and second users are verified a transaction function is built for the transfer of the set of blockchain tokens from a digital wallet of the first user to a digital wallet of the second user. Finally, the transaction function is published to a blockchain network associated with the set of blockchain tokens.
Owner:MASTERWORKS IO LLC
Dynamic security authentication for wireless communication networks
ActiveUS7233664B2Minimize exchangeMinimize wasteKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSystemic approachAuthentication server
In a first embodiment, a dynamic computer system security method and system using dynamic encryption and full synchronization between system nodes. A data record created by a source user is encrypted with an initial dynamic session key. A new dynamic session key is generated based upon a data record and a previous dynamic session key. A central authority is used to synchronize and authenticate both source and destination users with constantly regenerated dynamic authentication keys. In a second embodiment, a method of providing dynamic security authentication between wireless communication network nodes. An initial authentication key and an address are assigned to certain of the nodes. The address along with information encrypted by the initial authentication key is sent to an authentication server. The authentication server and node or nodes synchronously regenerate authentication keys based upon the initial authentication key. Secure handovers occur between nodes via an authentication key.
Owner:MOXCHANGE LLC
Computer system security via dynamic encryption
InactiveUS20040179682A1Minimize exchangeThe process is simple and fastKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSecure communicationSystemic approach
A dynamic computer system security method and system using dynamic encryption and full synchronization between system nodes. A data record from a data stream created by a source user is encrypted with an initial dynamic session key. A new dynamic session key is generated based upon a data record and a previous dynamic session key. The new dynamic session key is then used to encrypt the next data record. A central authority is used to synchronize and authenticate both source and destination users with dynamic authentication keys. The central authority and users constantly regenerate new dynamic authentication keys. A child process is forked to ensure synchronization and authentication of dynamic authentication keys of each node upon a request for a secure communication establishment from a user. The central authority generates the initial dynamic session key with the current dynamic authentication key to begin a secure communication session.
Owner:MOXCHANGE LLC
Ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption system and method
ActiveCN101807991AEnsure safetyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextAttribute-based encryption
The invention provides a ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption system and a ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption method, which comprise ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption systems with a central mechanism and without the central mechanism and a ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption method. The ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption system with the central mechanism comprises a plurality of attribute mechanisms of the central mechanism, an encrypting component and a client. The plurality of attribute mechanisms of the central mechanism initialize the system together, publish a system public key, and generate a system private key, a local private keys of an attribute mechanism and local public keys; the encrypting component encrypts a cleartext based on the system public key, each local public key and a universal access tree; and the client inputs a client identifier, client attribute sets and the like so as to generate client private key used for decrypting the encrypted ciphertext. Due to the implementing mode of the invention, a multi-mechanism ciphertext policy attribute-based encryption system is designed. The scheme is based on the ciphertext policy, so the scheme better meets the access control requirement in an actual information safety system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Revocation of cryptographic keys in the absence of a trusted central authority
ActiveUS20160254910A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationTrusted authorityCryptographic nonce
A method and apparatus is presented for revoking cryptographic keys within a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, consisting of sending a key revocation message by a network connected device to other network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network for inclusion in a ledger. In one embodiment the revocation message is signed using a private key of a public / private key pair to be revoked. In another embodiment an authorization for future revocation of the public / private key pair by a plurality of other public / private keys is sent for inclusion in the ledger, and subsequently the key revocation message is signed with one of the private keys of the plurality of public / private key pairs before sending the key revocation message. Once a valid key revocation message is included in the ledger, any future request to include a message signed by the revoked cryptographic key is rejected.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
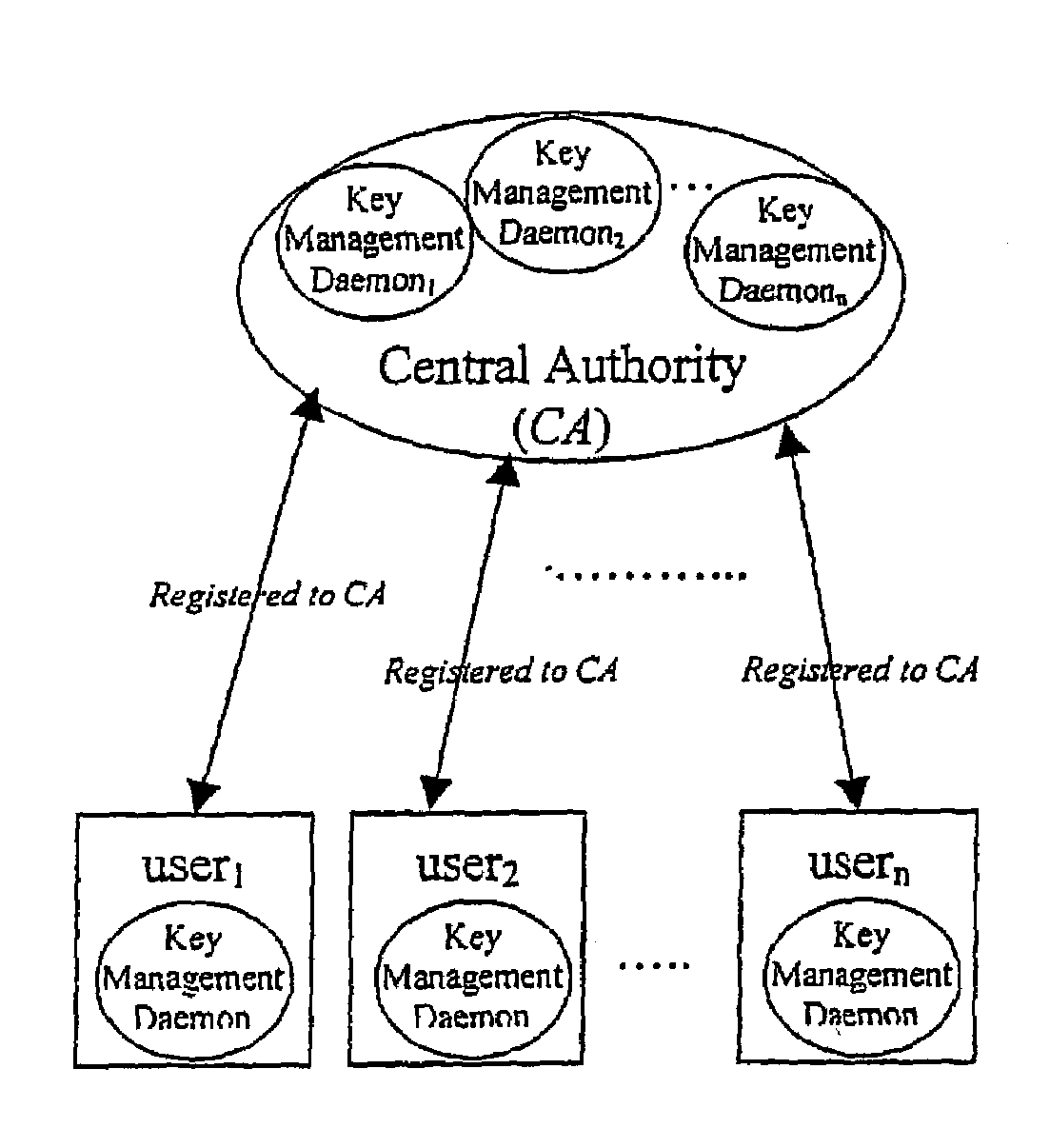
Computer implemented frameworks and methodologies for enabling identification verification in an online environment
InactiveUS20150319170A1Facilitate communicationDigital data authenticationTransmissionInternet usersLibrary science
Described herein are computer implemented frameworks and methodologies for enabling identification verification in an online environment. Embodiments of the invention have been particularly developed to enable Internet users to have their identities verified by a central authority, and use that verification in the context of later online interactions.
Owner:INVIGOR GRP LTD
Hardware trust anchors in SP-enabled processors
ActiveUS9317708B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationOperational systemConfidentiality
A trust system and method is disclosed for use in computing devices, particularly portable devices, in which a central Authority shares secrets and sensitive data with users of the respective devices. The central Authority maintains control over how and when shared secrets and data are used. In one embodiment, the secrets and data are protected by hardware-rooted encryption and cryptographic hashing, and can be stored securely in untrusted storage. The problem of transient trust and revocation of data is reduced to that of secure key management and keeping a runtime check of the integrity of the secure storage areas containing these keys (and other secrets). These hardware-protected keys and other secrets can further protect the confidentiality and / or integrity of any amount of other information of arbitrary size (e.g., files, programs, data) by the use of strong encryption and / or keyed-hashing, respectively. In addition to secrets the Authority owns, the system provides access to third party secrets from the computing devices. In one embodiment, the hardware-rooted encryption and hashing each use a single hardware register fabricated as part of the computing device's processor or System-on-Chip (SoC) and protected from external probing. The secret data is protected while in the device even during operating system malfunctions and becomes non-accessible from storage according to various rules, one of the rules being the passage of a certain time period. The use of the keys (or other secrets) can be bound to security policies that cannot be separated from the keys (or other secrets). The Authority is also able to establish remote trust and secure communications to the devices after deployment in the field using a special tamper-resistant hardware register in the device, to enable, disable or update the keys or secrets stored securely by the device.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +1
System and method for secure facsimile transmission
A system and method for the secure transmission of a facsimile, which verifies that a selected user transmitted the document and only allows for the designated recipient or recipients to receive the facsimile is provided. A sending user scans a document, which is then encrypted and digitally signed using the sender's private key, which is retrieved from a central authority or server. The digitally signed document is then encrypted using the recipient's public key. The encrypted digitally signed document is then faxed to the recipient. The device receiving the facsimile transmission then notifies the designated recipient of the receipt of the encrypted fax job. The recipient then logs onto the receiving device, which retrieves the sender's public key and the recipient's private key from the server. The retrieved keys are then used to decrypt the document and verify the identities of both the sender and the user.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Creation of database and structured information
InactiveUS20040267574A1Reduce the burden onSave their careerMedical data miningData processing applicationsHand heldVisual perception
A system through which verbal information can be utilized to create structured data with tags or inserted codes such as an XML code or the like provides hand held capability for easy adoption via CE, cell telephone, or other data entry devices. A visual display at the time of dictation can provide checklists, prompts or otherwise shape the entry to comport to a selected data context. The visual display can also be part of a transcriptionist system. By providing data in a coded fashion, analysis can be easily conducted such that alerts, bioterror alerts (e.g. evolving symptom or trend information for anthrax or the like) can be rapidly and perhaps automatically identified, and acted upon such as in providing health care alerts or locationally oriented statistical analysis information. A central database reporting function to a central authority (e.g., to the CDC or law enforcement) can be included for terrorist and other event management.
Owner:VERBAL WORLD
Reliable message distribution in an ad hoc mesh network
InactiveUS20050174972A1Traffic minimizationReasonable level of reliabilityNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexCentral authorityNetwork topology
A Data Distribution Service (DDS) transfers information between nodes in an ad hoc mobile mesh network. The DDS includes many different novel features including techniques for coalescing retransmit requests to minimize traffic, providing a reasonable level of reliability for event oriented communications, multicasting retransmissions for use by many nodes, and providing other optimizations for multicast traffic. The DDS uses UDP datagrams for communications. Communications operate in a truly peer-to-peer fashion without requiring central authority or storage, and can be purely ad hoc and not depend on any central server. The protocol is NACK-based, which is more suited to a mesh network than a traditional approach like TCP, which uses positive acknowledgements of all data. The DDS is amenable to very long recovery intervals, matching well with nodes on wireless networks that lose coverage for significant periods of time and also works well with constantly changing network topologies. Reliability can also be handled over a span of time that might correspond to losing wireless coverage.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System for the creation of database and structured information from verbal input
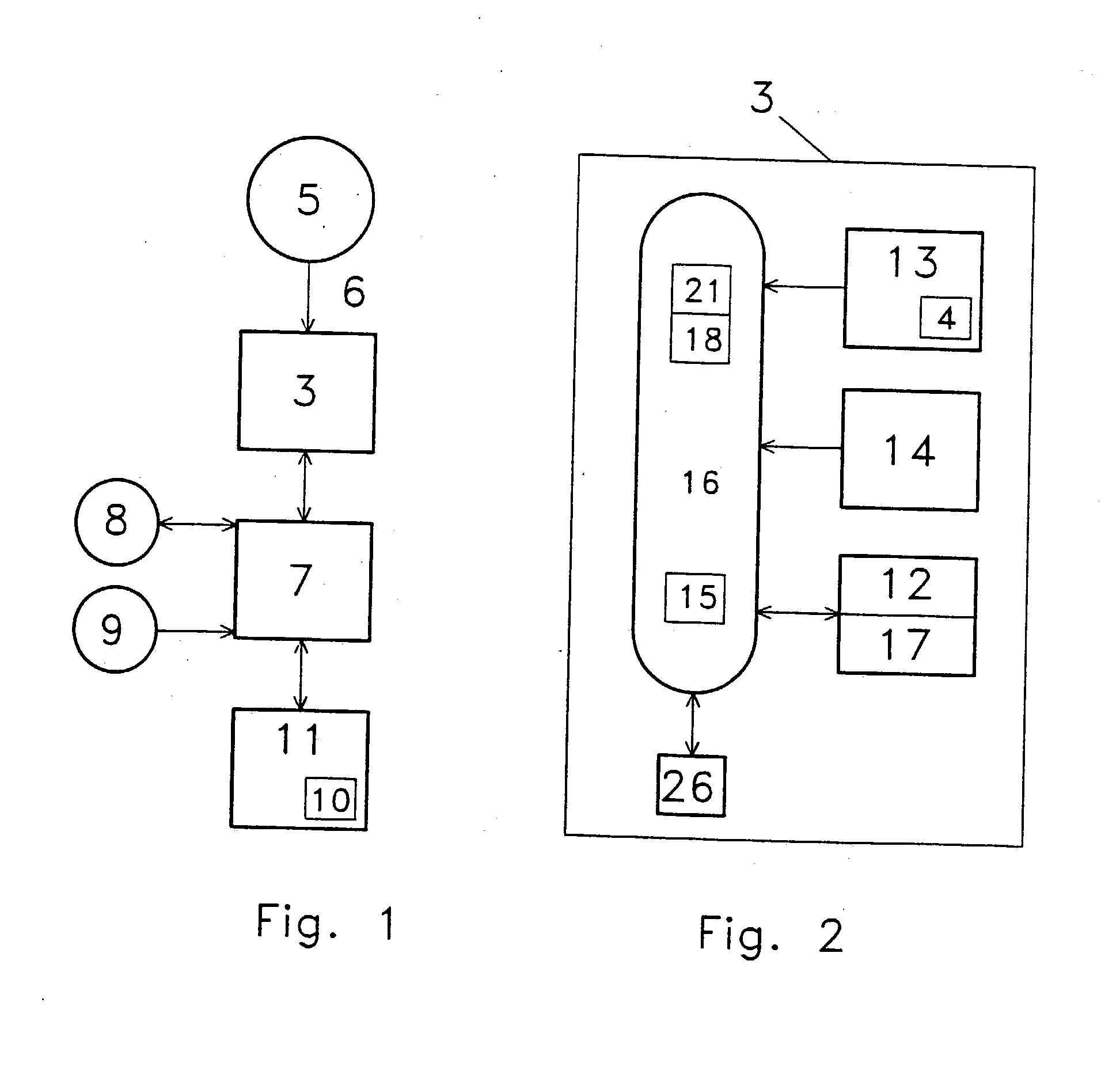
InactiveUS20040030704A1Save their careerReduce the burden onMedical data miningData processing applicationsHand heldVisual perception
A system through which verbal information can be utilized to create structured data with tags (2) or inserted codes such as an XML code or the like provides hand held capability for easy adoption. A visual display (13) at the time of dictation can provide checklists, prompts or otherwise shape the entry to comport to a selected data context. The visual display can also be part of a transcriptionist system (7). By providing data in a coded fashion, analysis can be easily conducted such that alerts, bioterror alerts (e.g. evolving symptom or trend information for anthrax or the like) can be rapidly and perhaps automatically identified, and acted upon such as in providing health care alerts or locationally oriented statistical analysis information. A central database (1) reporting function to a central authority (11) (e.g., to the CDC or law enforcement) can be included for terrorist and other event management.
Owner:ANTAEUS HEALTHCOM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com