Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104results about "Error coding/decoding sychronisation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
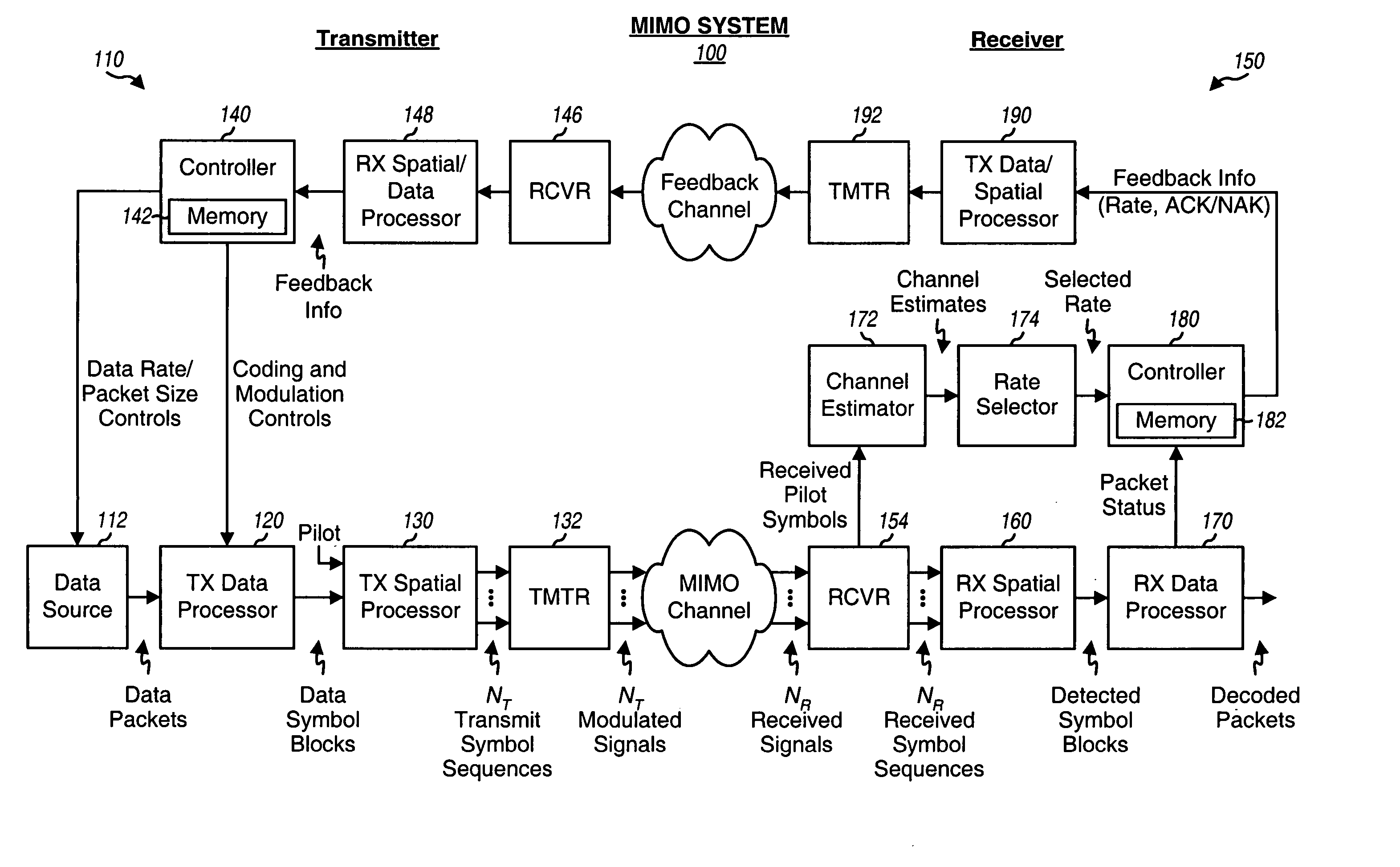
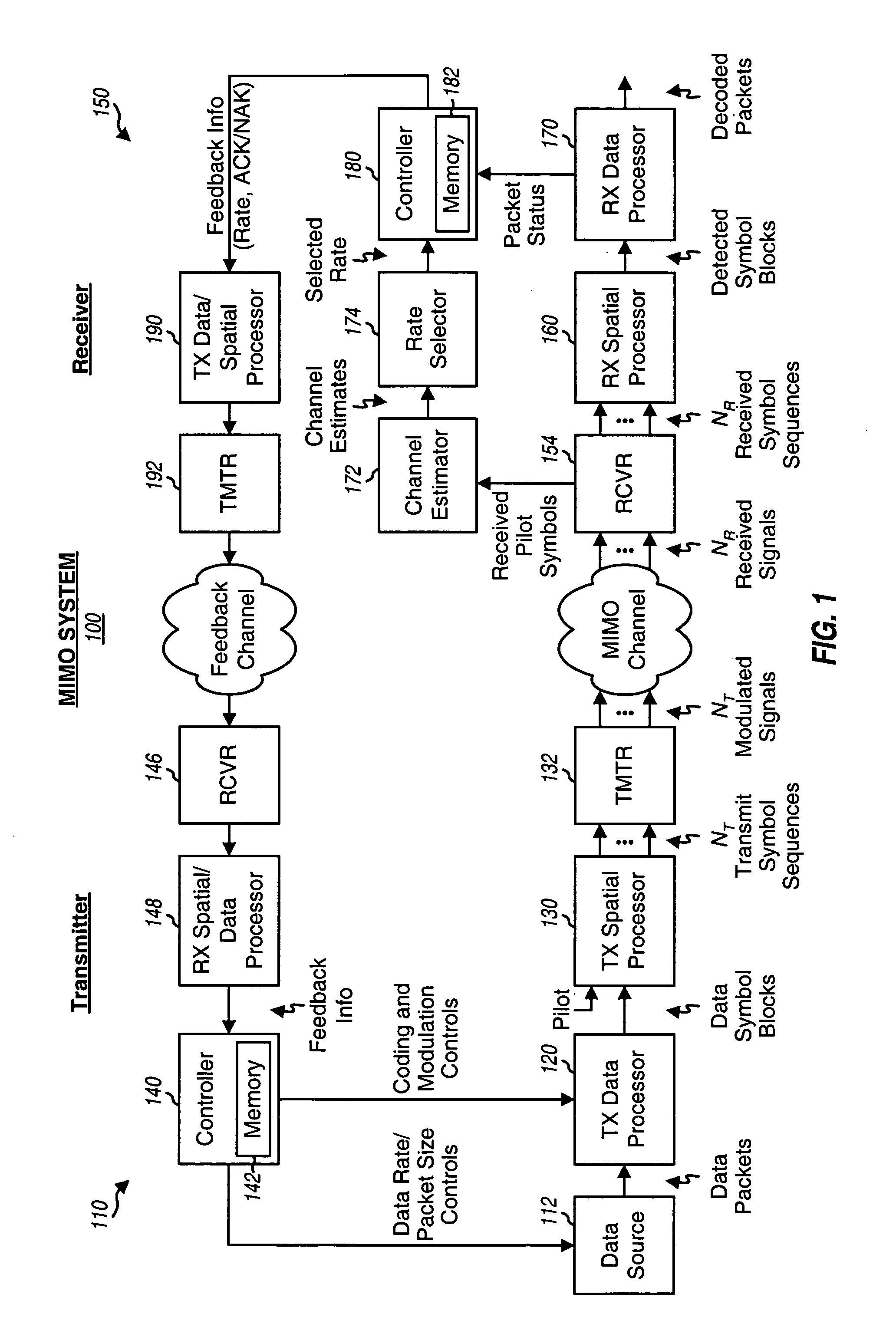
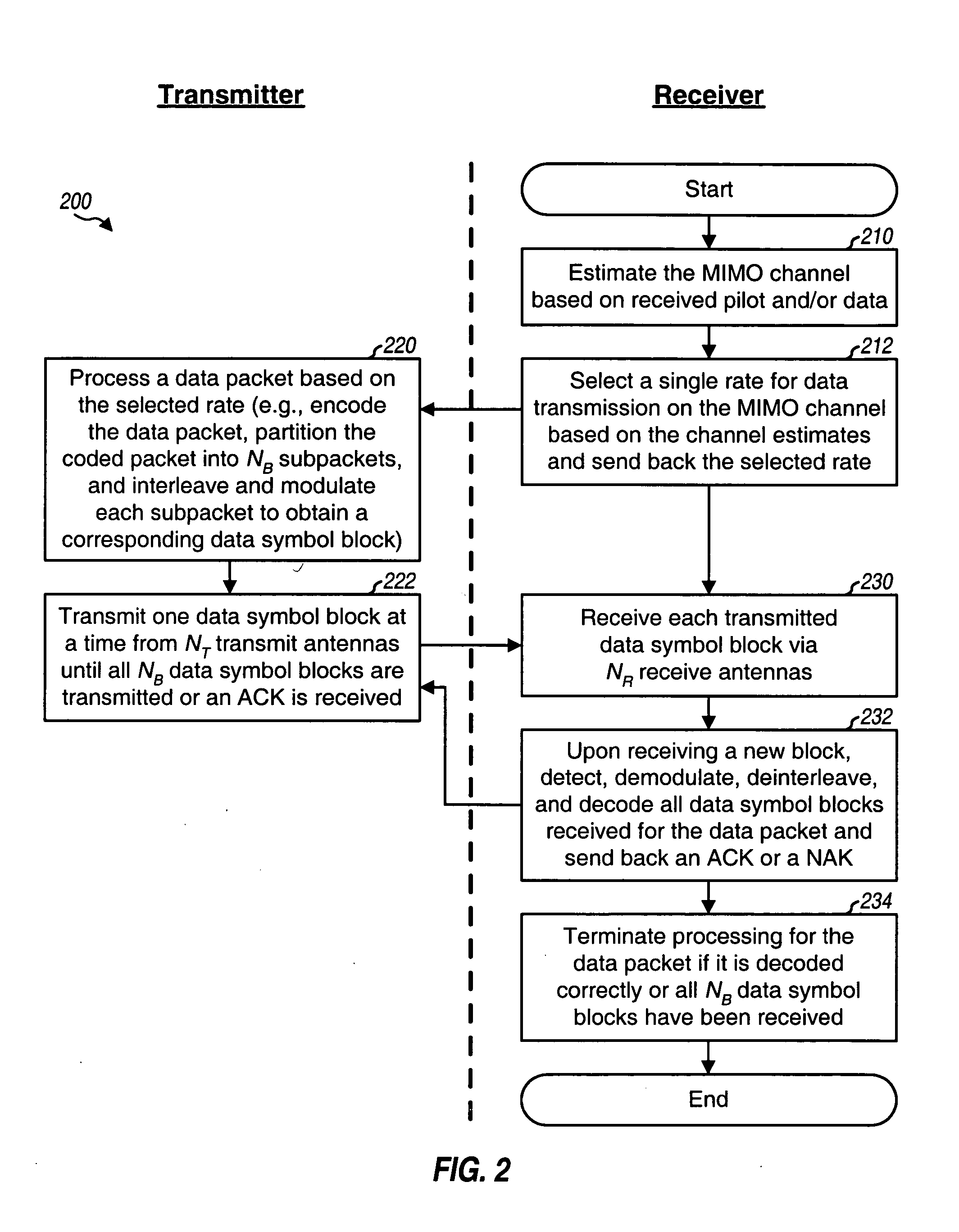
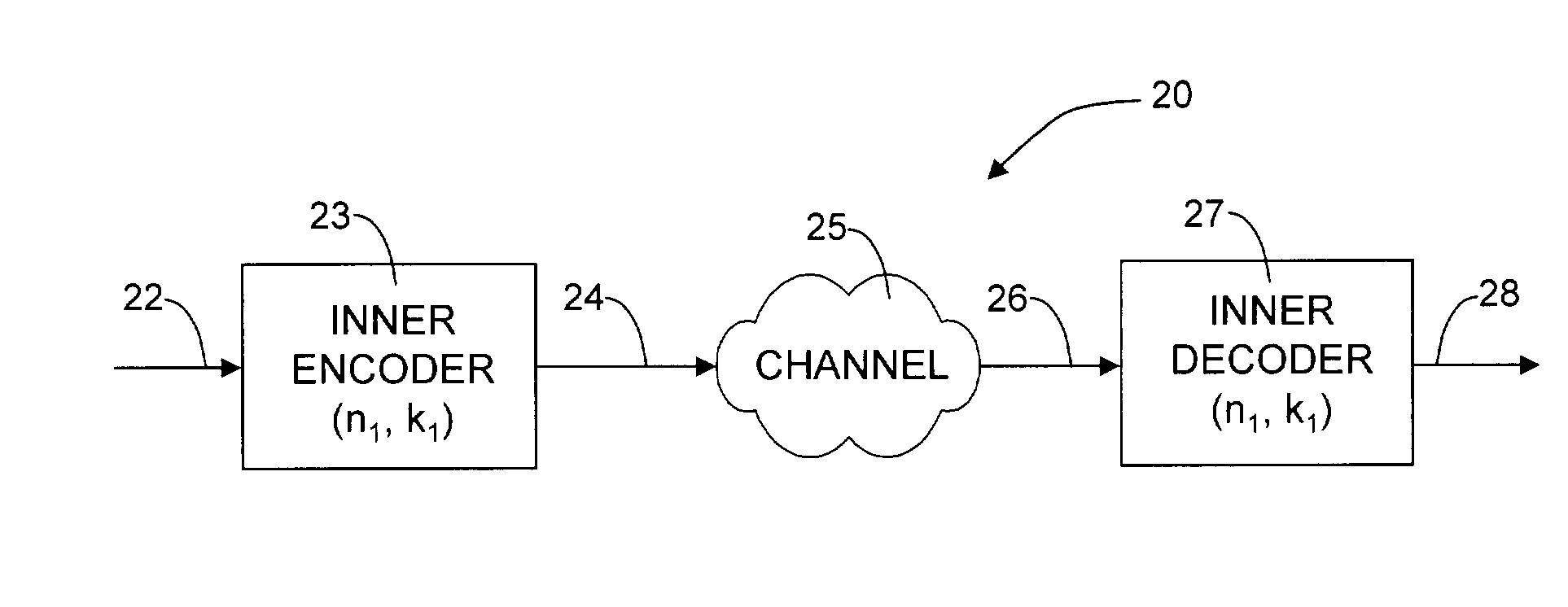
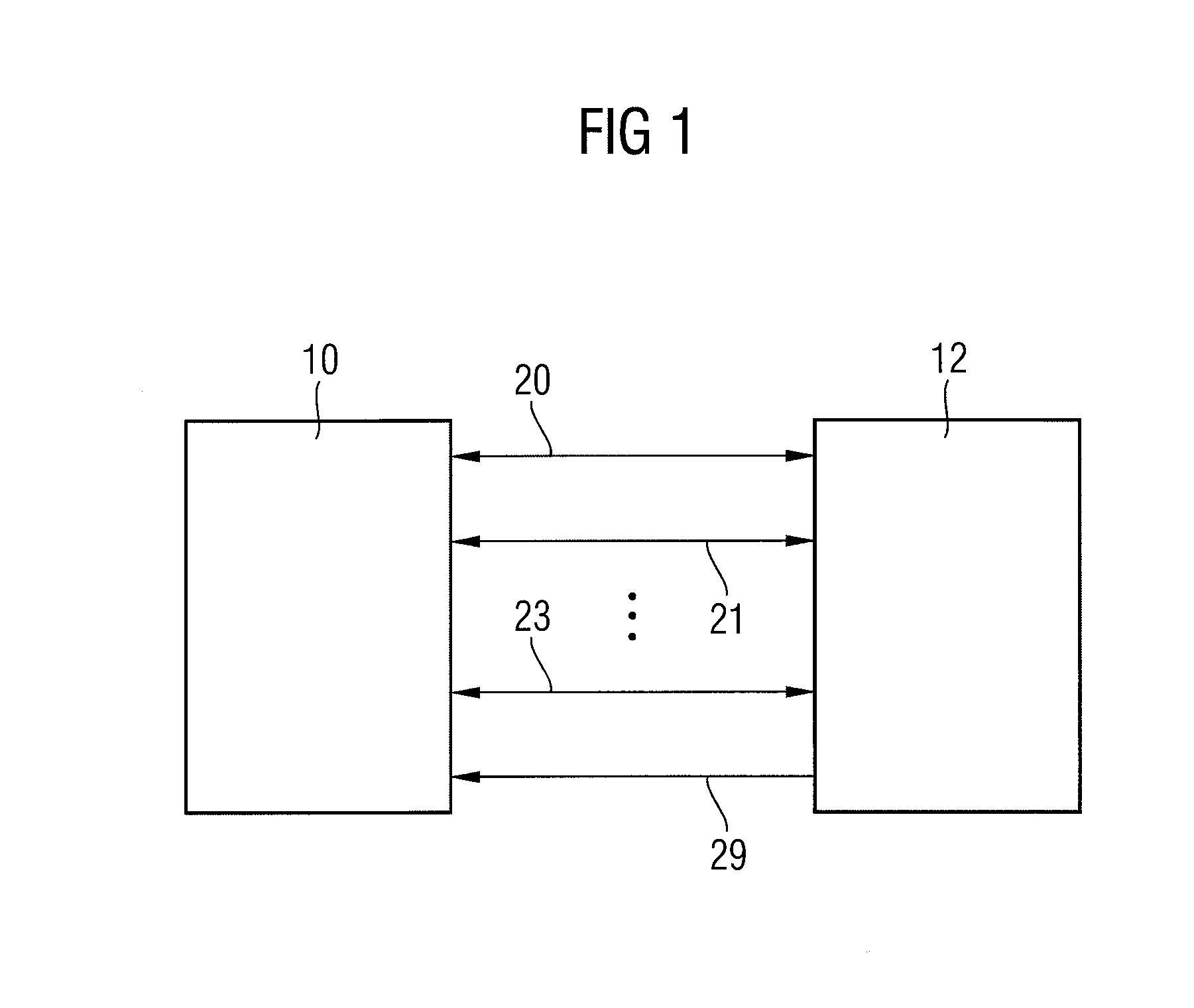
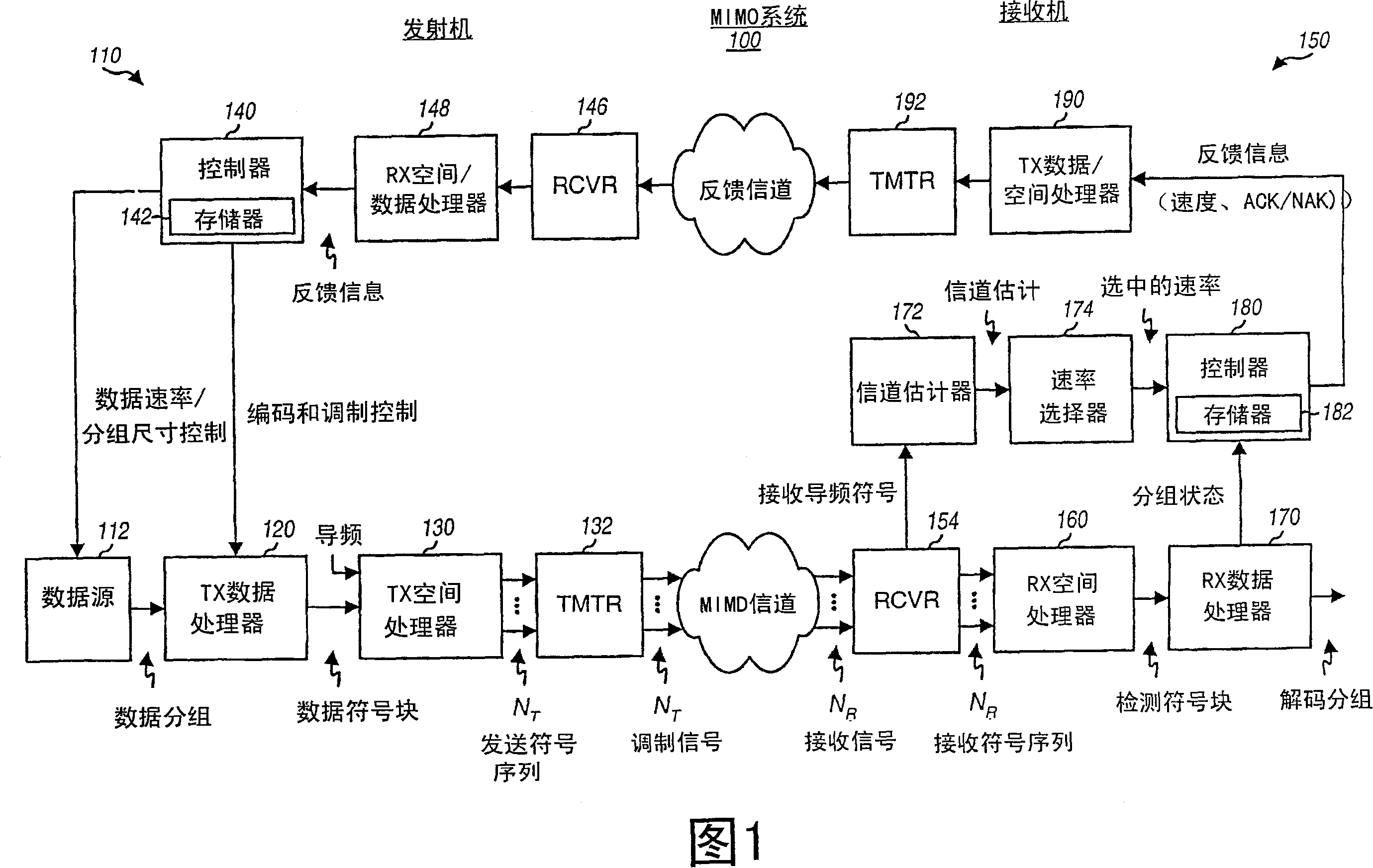
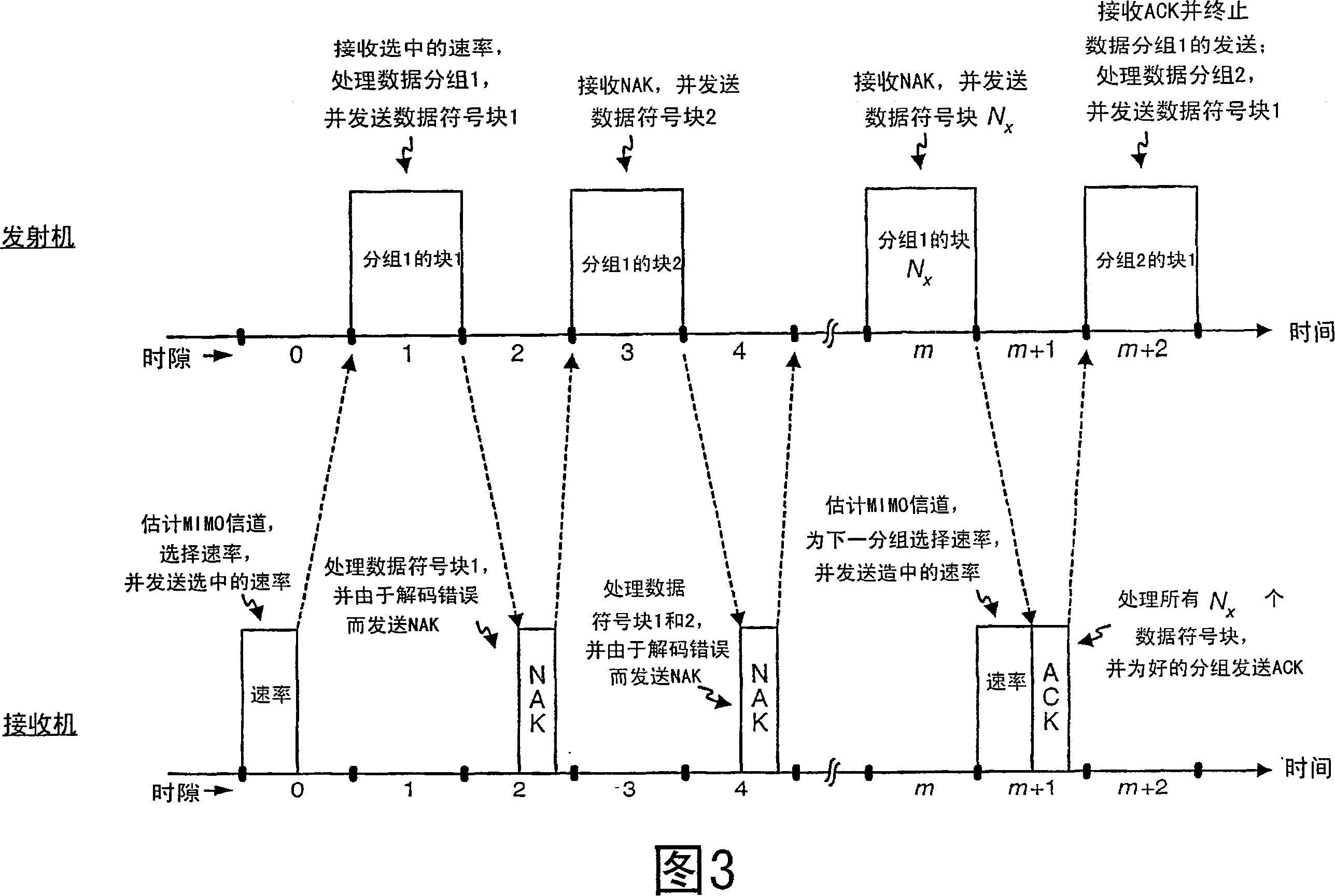
Incremental redundancy transmission in a MIMO communication system
ActiveUS20050052991A1Sufficient informationError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetComputer science
For an incremental redundancy (IR) transmission in a MIMO system, a transmitter processes (e.g., encodes, partitions, interleaves, and modulates) a data packet based on a selected rate to obtain multiple data symbol blocks. The transmitter transmits one data symbol block at a time until a receiver correctly recovers the data packet or all blocks are transmitted. Whenever a data symbol block is received from the transmitter, the receiver detects a received symbol block to obtain a detected symbol block, processes (e.g., demodulates, deinterleaves, re-assembles, and decodes) all detected symbol blocks obtained for the data packet, and provides a decoded packet. If the decoded packet is in error, then the receiver repeats the processing when another data symbol block is received for the data packet. The receiver may also perform iterative detection and decoding on the received symbol blocks for the data packet multiple times to obtain the decoded packet.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
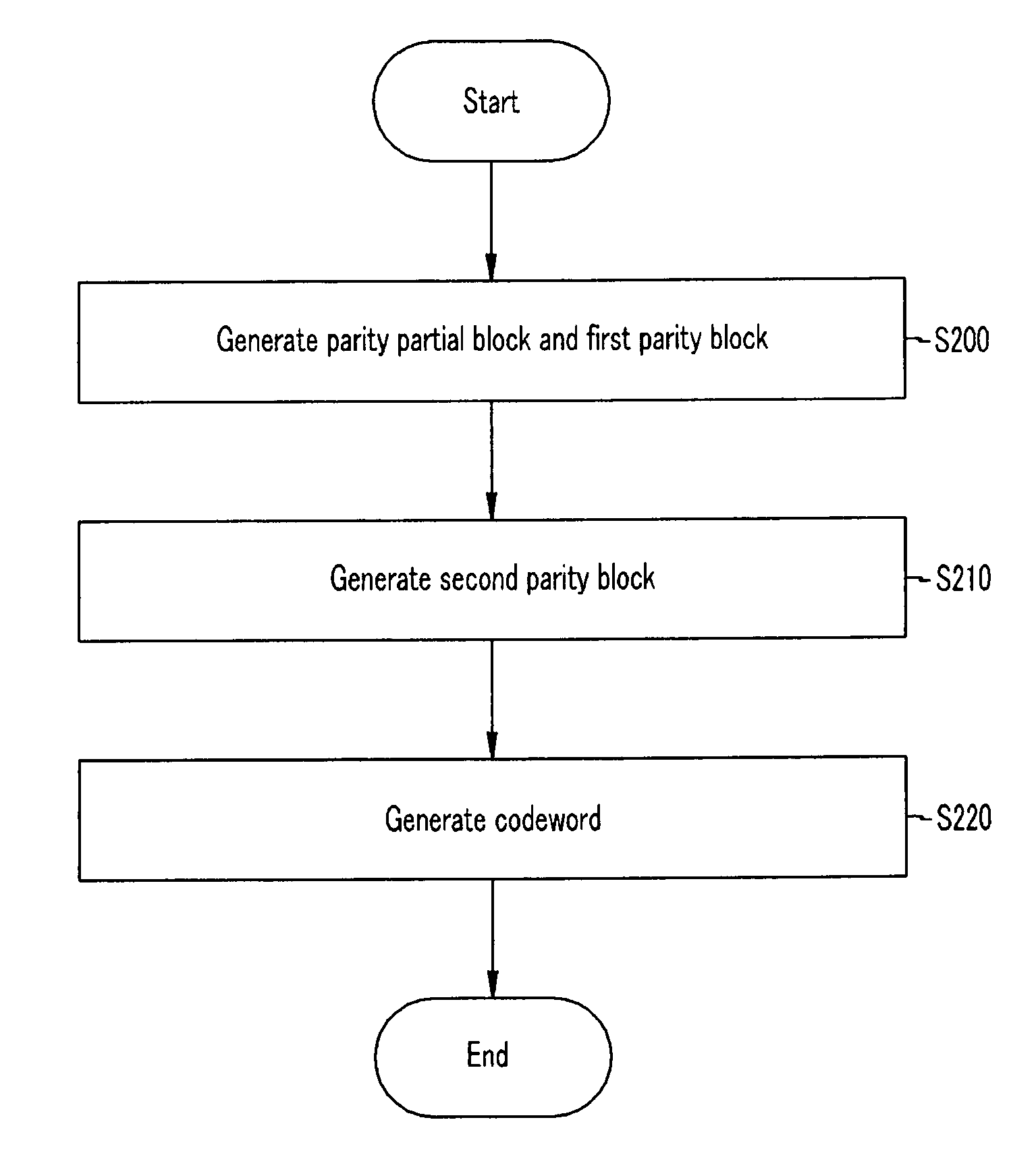
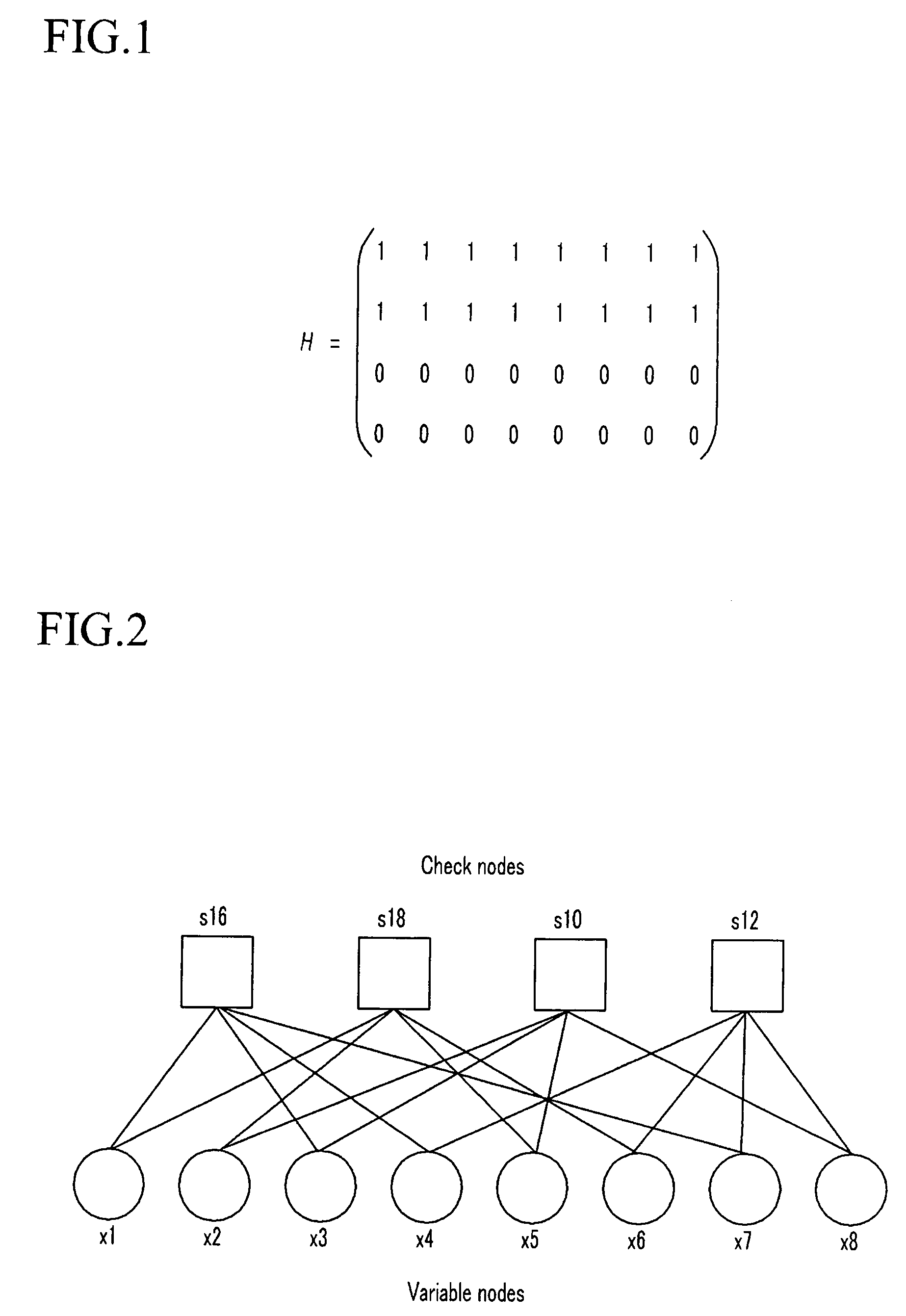
Parity check matrix storing method, block LDPC coding method, and apparatus using parity check matrix storing method
ActiveUS8190967B2Low density parity check (LDPC)Minimize complexityError detection/correctionError coding/decoding sychronisationParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a low density parity check (LDPC) encoding method and an apparatus thereof. In the LDPC encoding method, a matrix multiplication corresponding to ET−1 and T−1 is eliminated according to a structural characteristic in an encoding process. Accordingly, shift weights that are not −1 among shift weights corresponding to partial blocks A, B, and C of a parity check matrix are used to perform an encoding operation, and a cyclic shift operation of an information unit block is performed in parallel so that a first parity block and a second parity block may be simultaneously generated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
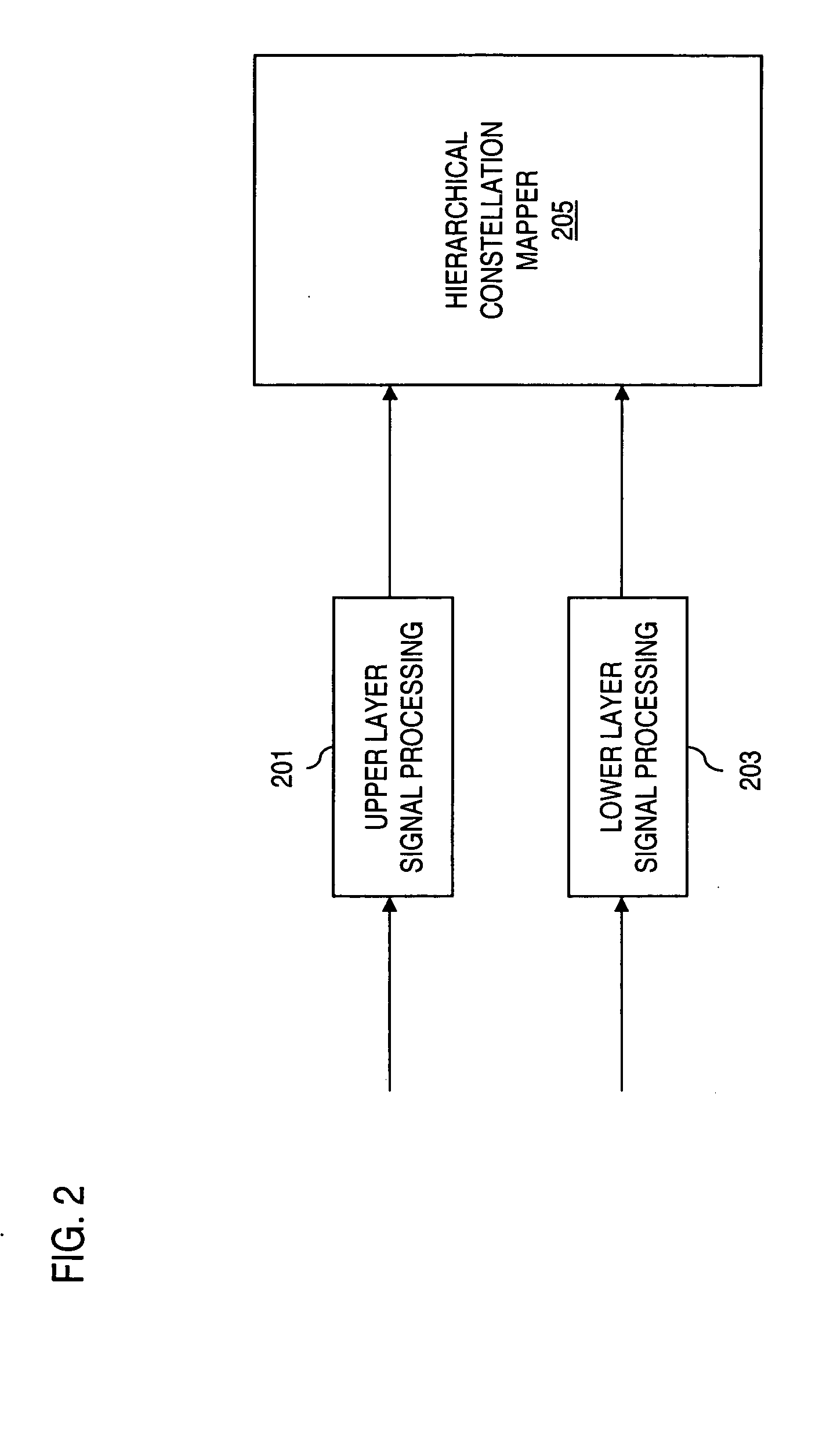
Method and apparatus for providing signal acquisition and frame synchronization in a hierarchical modulation scheme
ActiveUS20050089068A1Rapid and reliable frame acquisition without additional overheadError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesSignal onCode rate
An approach is provided for supporting signal acquisition and frame synchronization in a digital broadcast system utilizing Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. Hierarchical modulation is utilized to provide backward compatibility, whereby the lower layer signal is encoded using LDPC coding. A signal is received, whereby the signal is modulated according to the hierarchical modulation scheme including an upper layer and a lower layer. The signal includes a data pattern and a coded frame. The dependency of the received signal on the upper layer modulation is removed. The modulation removed signal is correlated with multiple predetermined data patterns to determine the data pattern of the signal. The code rate of the coded frame is derived based on the determined data pattern. The above arrangement is particularly suited to a digital satellite broadcast system.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
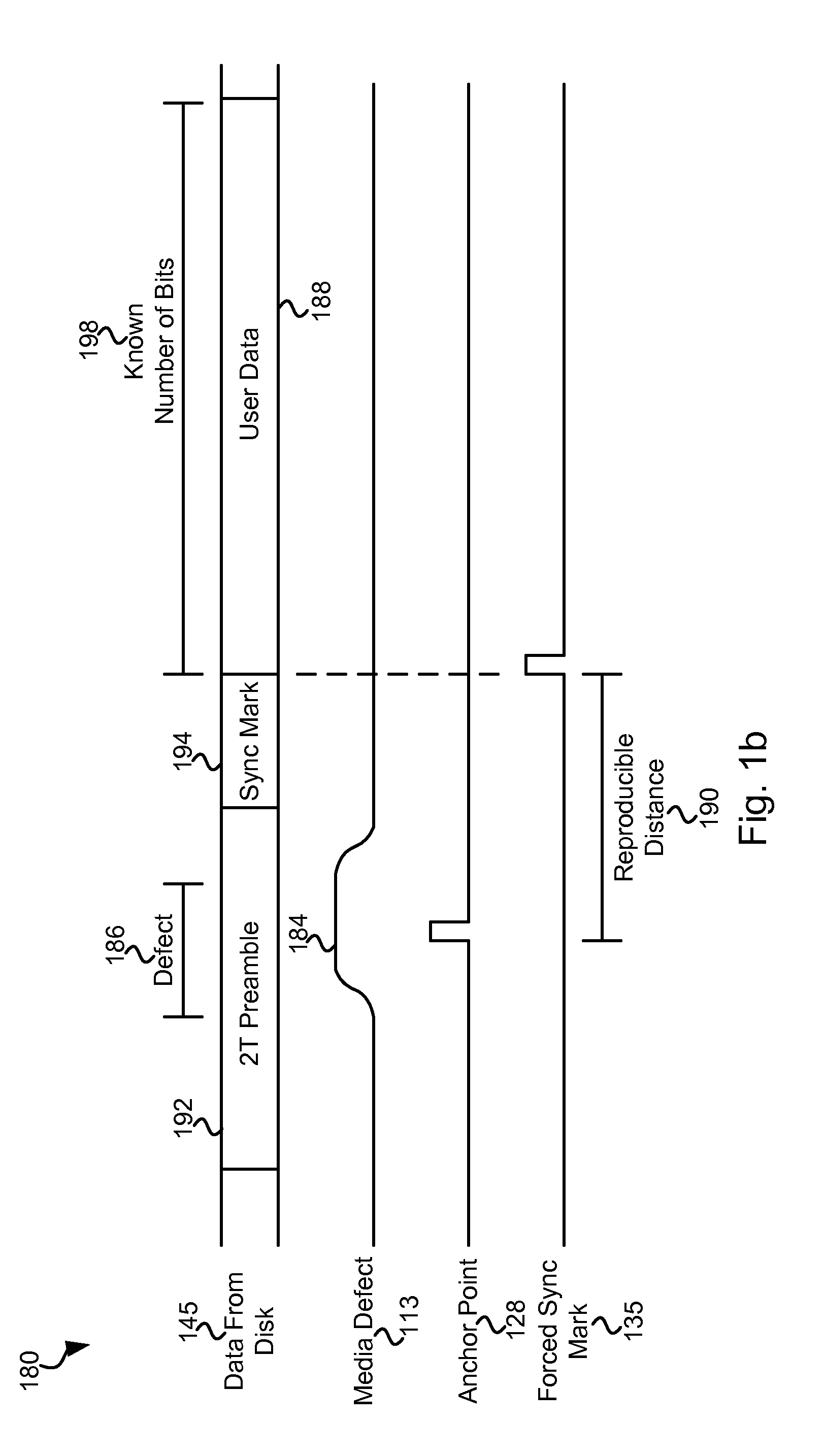
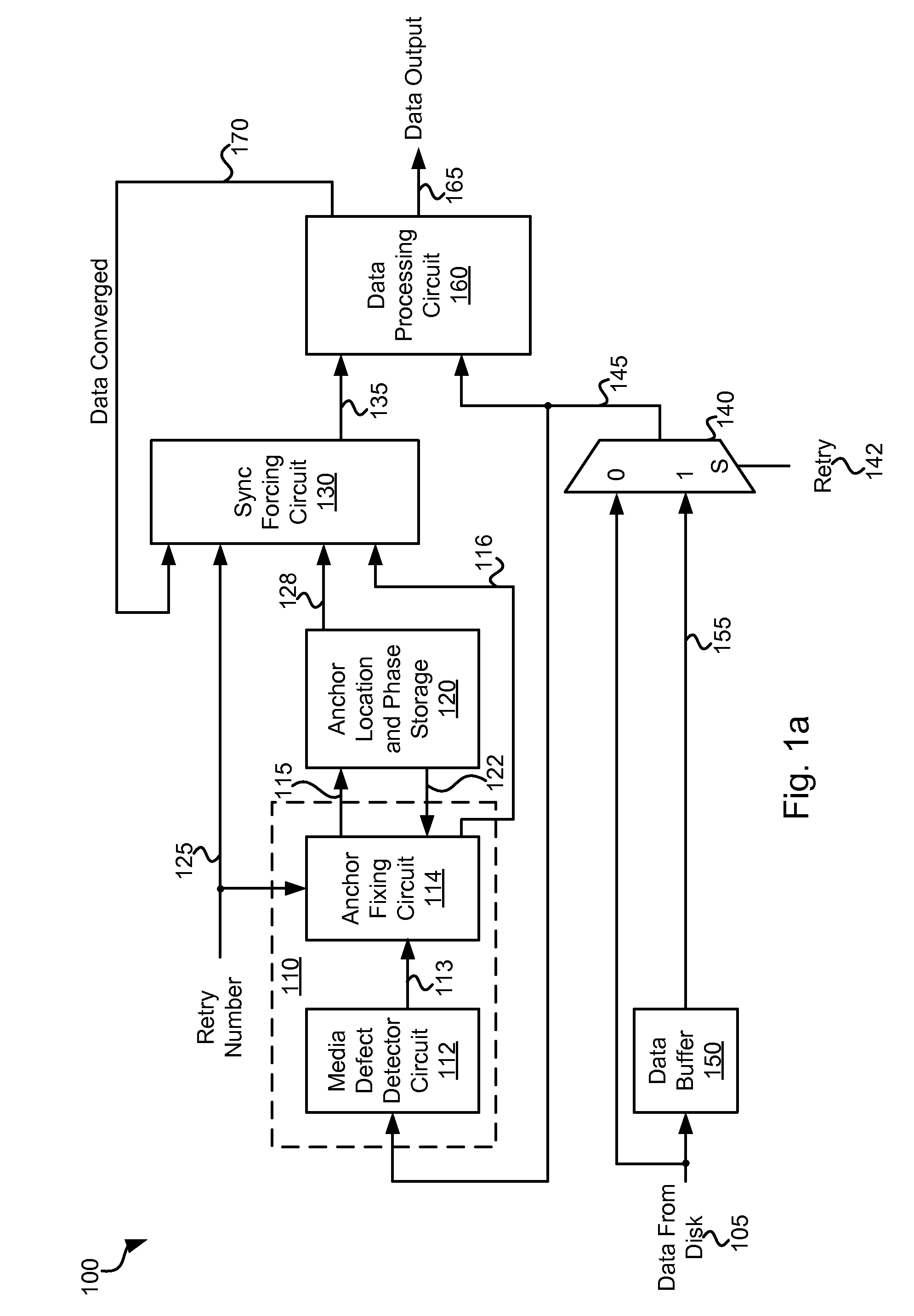
Systems and Methods for Data Recovery Using Enhanced Sync Mark Location
ActiveUS20110209026A1Digital data processing detailsError coding/decoding sychronisationAlgorithmDegree of similarity
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for identifying a reproducible location on a storage medium. As an example, a circuit is discussed that includes a data storage circuit, a pattern comparison circuit, and a threshold comparison circuit. The data storage circuit is operable to store a first set of data samples corresponding to a region of interest. The pattern comparison circuit is operable to compare a subset of the first set of data samples with a subset of a second set of data samples corresponding to the region of interest. The pattern comparison circuit is operable to yield a match value corresponding to a degree of similarity between the first set of data samples with the subset of a second set of data samples. The threshold comparison circuit is operable to indicate an anchor point based at least in part on the magnitude of the match value relative to a threshold value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Error correction improvement for concatenated codes
ActiveUS7146553B2Improve the correction effectMore capabilityError coding/decoding sychronisationCode conversionComputer hardwareForward error correction
An enhanced forward error correction system is disclosed. Transmitted data is encoded into codewords in multiple dimensions. The decoding of received data by a decoder is performed in multiple passes in each dimension, with corrected data provided as an output from each pass into another decoder for the next decode pass. The encoder in one embodiment comprises a parallel inner RS(247,239) encoder or encoders and parallel outer BCH(255,247) encoder or encoders. Additional steps are added for error multiplication reduction. The system provides an approach to detect generally uncorrectable patterns for concatenated codes and provides a correction mechanism for improving error correction performance.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Synchronization code methods
ActiveUS20060020433A1Improve robustnessQuality improvementError preventionError detection/correctionEncoding algorithmSubject matter
A system, method and computer software product are provided. One embodiment of the present invention provides a method for generating and employing numerical sequences that may be used for synchronization codes. In one embodiment of the present invention, the derivation of numerical sequences, or codes is based on an encoding algorithm. These codes enable synchronization between communicating devices, and may also be used for channelization. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HOLDING 81 LLC
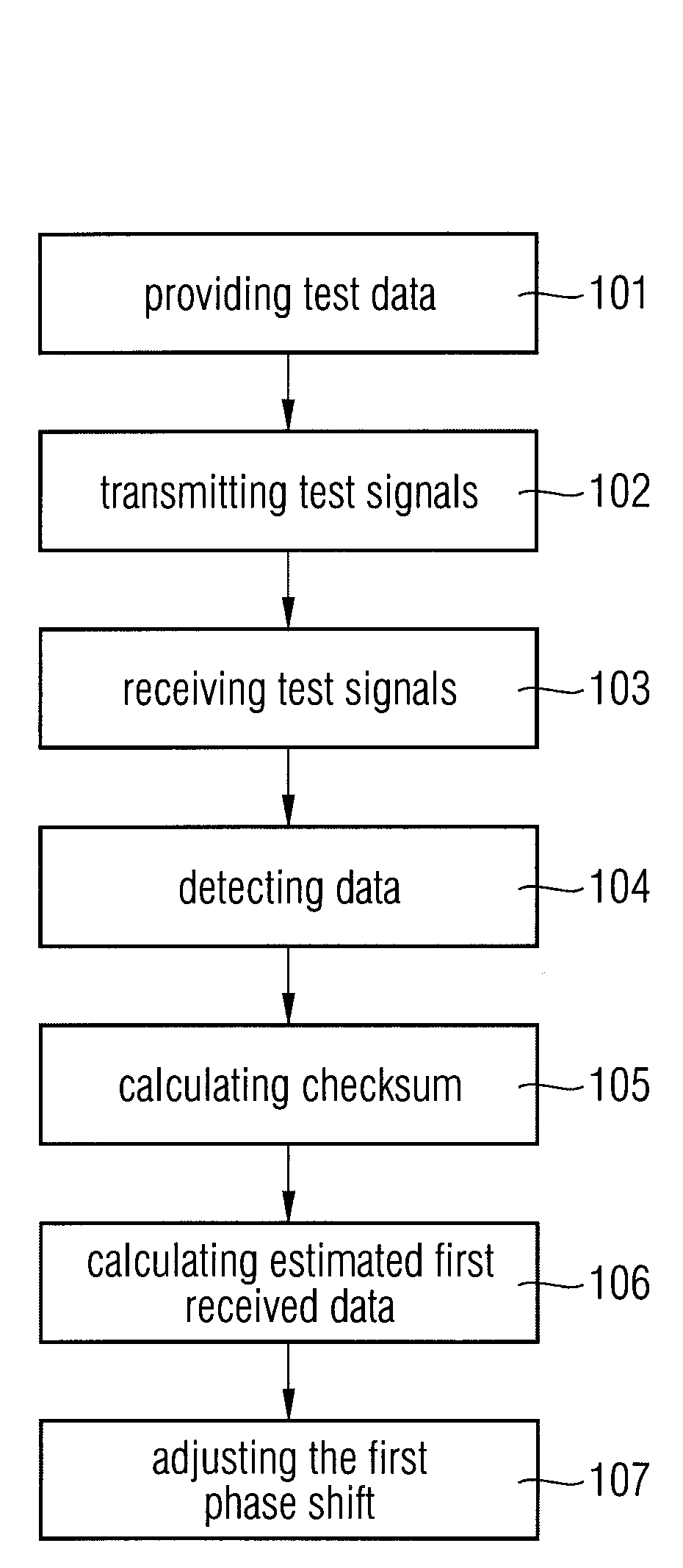
Phase shift adjusting method and circuit
InactiveUS7836386B2Improved memory controllerImproved memory deviceError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationPhase shiftedData signal
Method and system of adjusting a first phase shift between a first data signal and a clock signal at a sending device. First and second test signals representing first and second test data, respectively, are transmitted to a receiving device. The test signals have respective phase shifts relative to the clock signal. An error detection code is calculated from first and second received data carried by the transmitted signals. The error detection code is transmitted from the receiving device to the sending device. An estimated first received data is calculated from the error detection code, wherein the estimated first received data are calculated under the assumption that the second received data are identical to the second test data. The first phase shift is adjusted on the basis of a comparison of the estimated first received data and the first test data.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
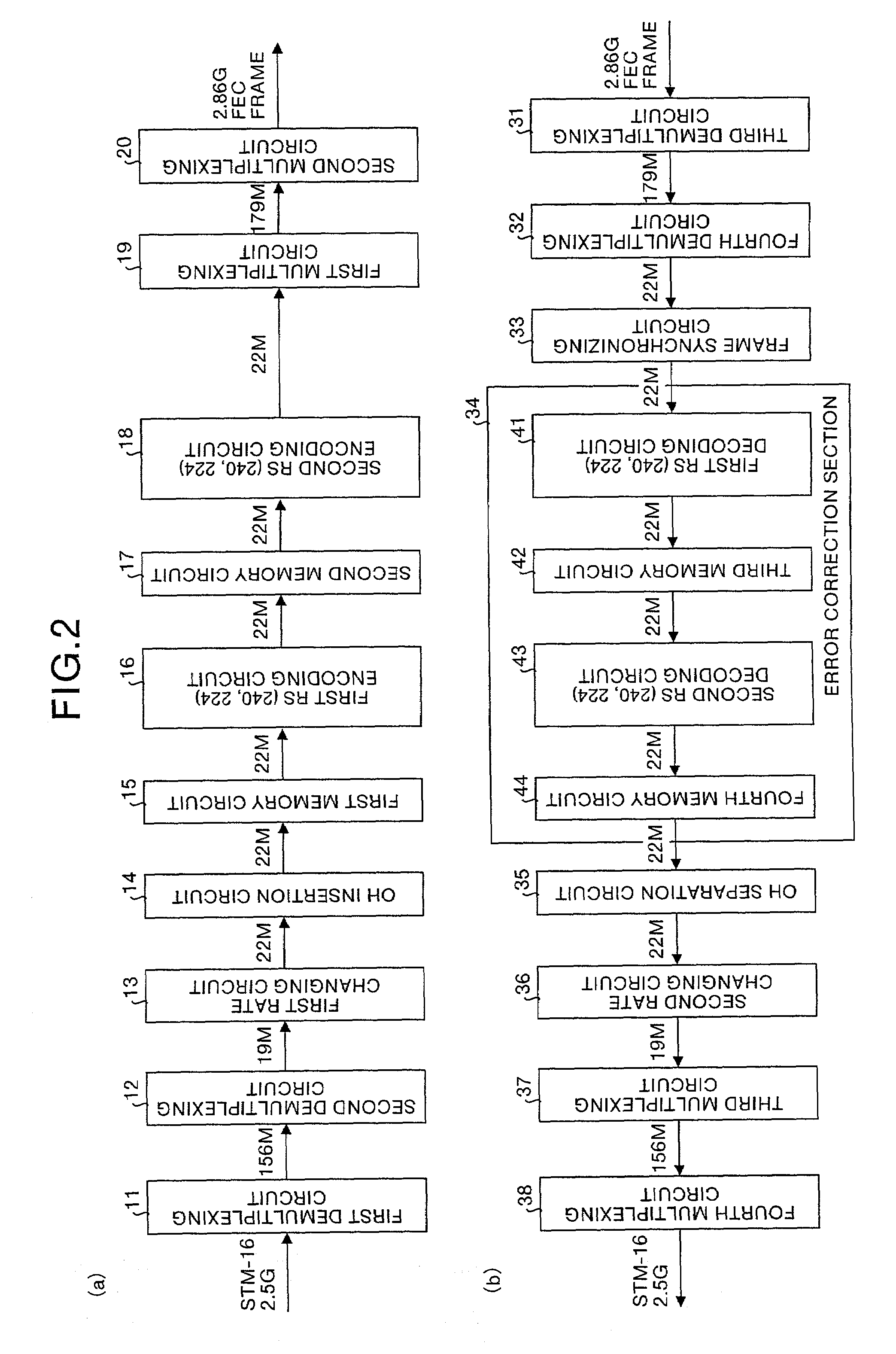
Optical transmission system, fec multiplexer, fec multiplexer/separator, and error correction method
An FEC multiplexing circuit (2) has a configuration in which a first memory circuit (15) is arranged on the input stage of a first RS encoding circuit (16), a second memory circuit (17) is arranged on the input stage of a second RS encoding circuit (18), error correction encoding is performed by a combination of different data having two directions, and thereafter, error correction codes are multiplexed to generate an FEC frame. On the other hand, an FEC demultiplexing circuit (6) has a configuration in which a third memory circuit (42) is arranged on the output stage of a first RS decoding circuit (41), a fourth memory circuit (44) is arranged on the output stage of a second RS decoding circuit (43), error correction is performed by a combination of different data having two directions, and, thereafter, parallel data read from the fourth memory circuit (44) are multiplexed to reproduce original information data.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Coding system and decoding system
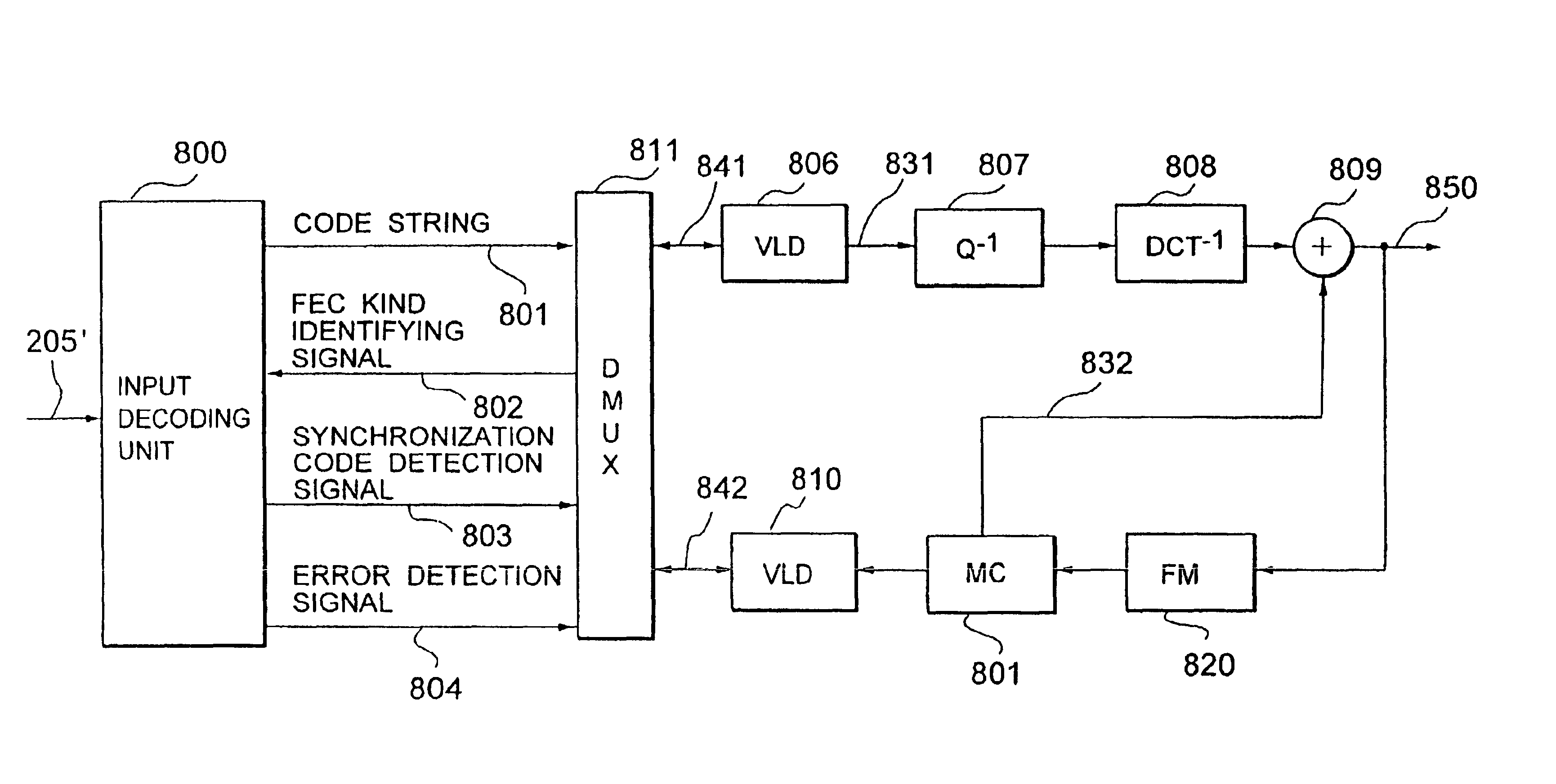
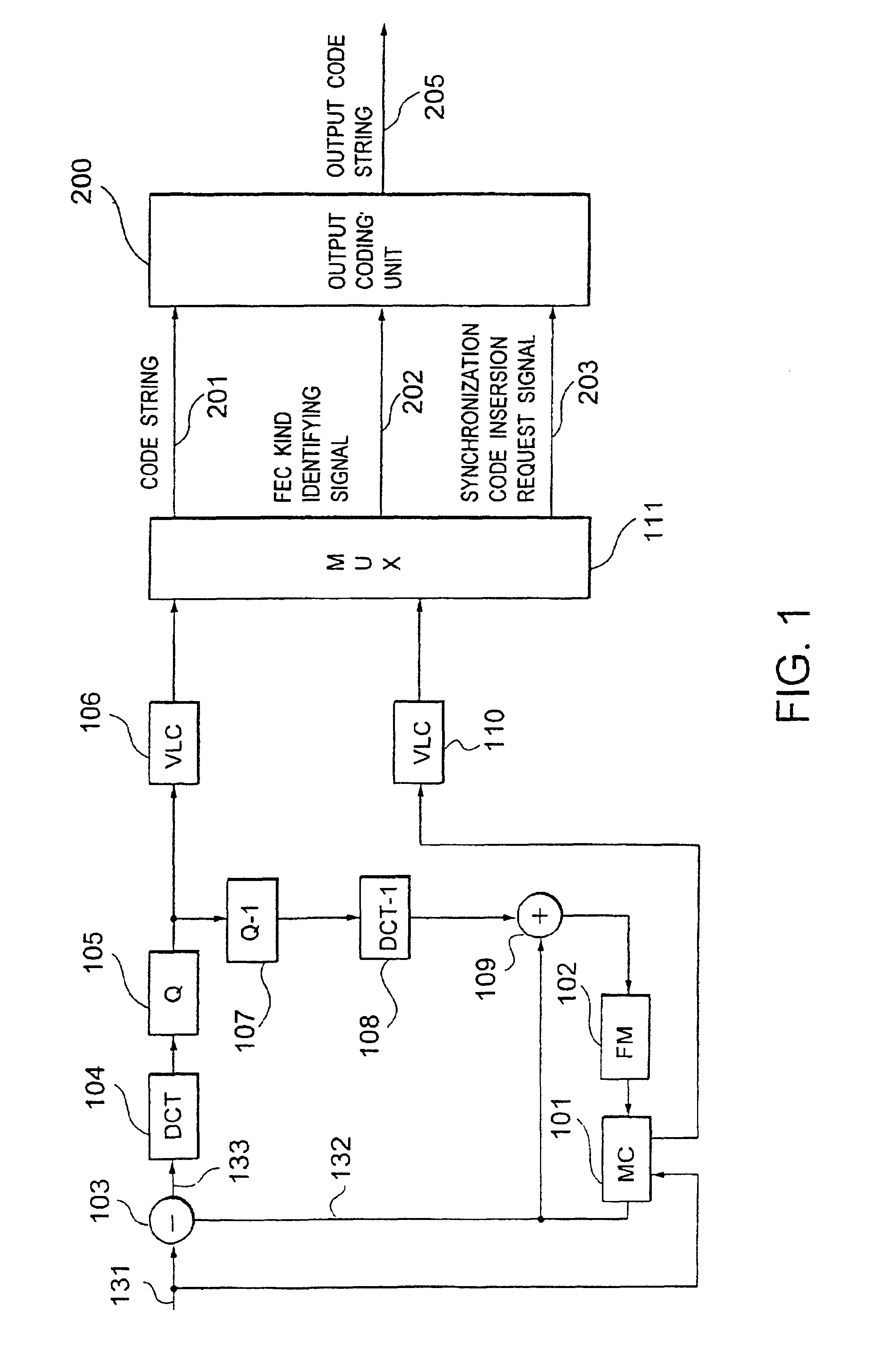
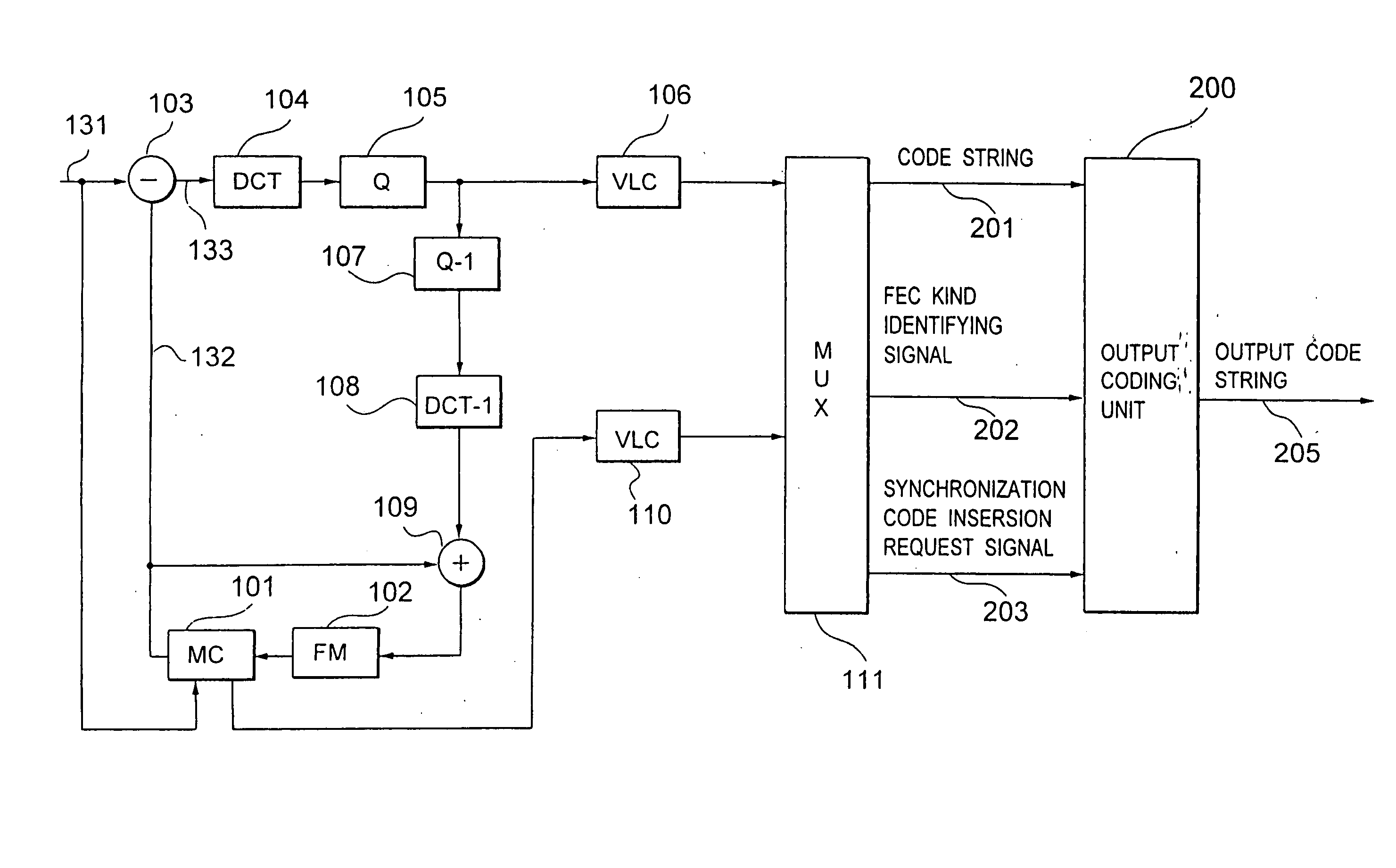
InactiveUS6918080B2Reduce in quantityImprove coding efficiencyPulse modulation television signal transmissionError correction/detection using convolutional codesMultiplexingProgramming language
In a coding system wherein an error correction / detect-ion coding is combined with a synchronization recovering technique using a synchronization code, the problems of a pseudo synchronization and a step out due to error detect-ion are solved. There is provided a coding part 212 for coding an input multiplexed code string 201 to an error correcting- / detecting code comprising an information bit and a check bit, and code string assembling part 213 for inserting a synchronization code into any one of a plurality of periodically predetermined synchronization code inserting positions in the code string 201, for arranging the information bit at an optional position in the code string, and for arranging the check bit at a position other than the synchronization code inserting positions in the code string 201 to assemble an output code string 205.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Synchronization loss resilient digital communication system using forward erasure correction
ActiveUS8046667B2Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareCommunications system
There is provided an apparatus for enabling recovery of missing information in a digital communication system. The apparatus includes a Forward Erasure Correction (FXC) encoder for computing FXC parity superpackets across information superpackets for subsequent recovery of any entire ones of the information superpackets that have been at least partially comprised due to synchronization loss.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Information carrying synchronization code and method for frame timing synchronization
ActiveUS20090116470A1Reduce complexitySimple procedureSynchronisation arrangementError coding/decoding sychronisationComputer hardwareRound complexity
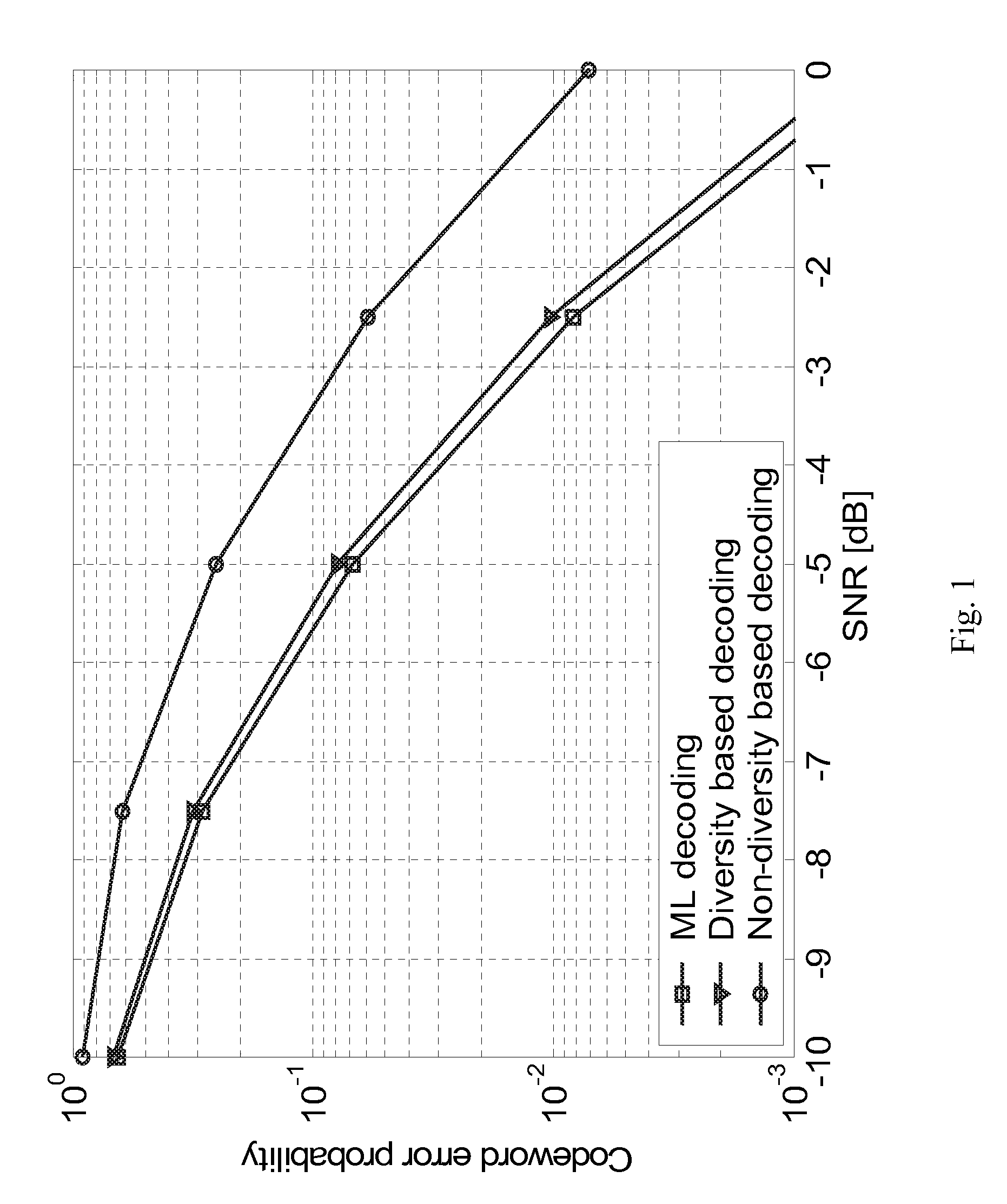
An improved method for conveying data and synchronization information in a telecommunication system is disclosed. The method uses a cyclically permutable code, to which a repetitive structure has been imposed, for carrying the data and synchronization information. The decoding procedure at the receiver then uses this repetitive structure of the code to reduce complexity by first evaluating, by use of hypotheses Hx, the repetitive codeword structure of received codewords and choosing a hypothesis corresponding to the repetitive codeword structure. Then the decoding procedure performs diversity combining of codeword elements of the codewords in accordance with the chosen hypothesis. The received codewords are further detected by comparing the diversity combined codeword elements to all possible codewords fulfilling the hypothesis.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
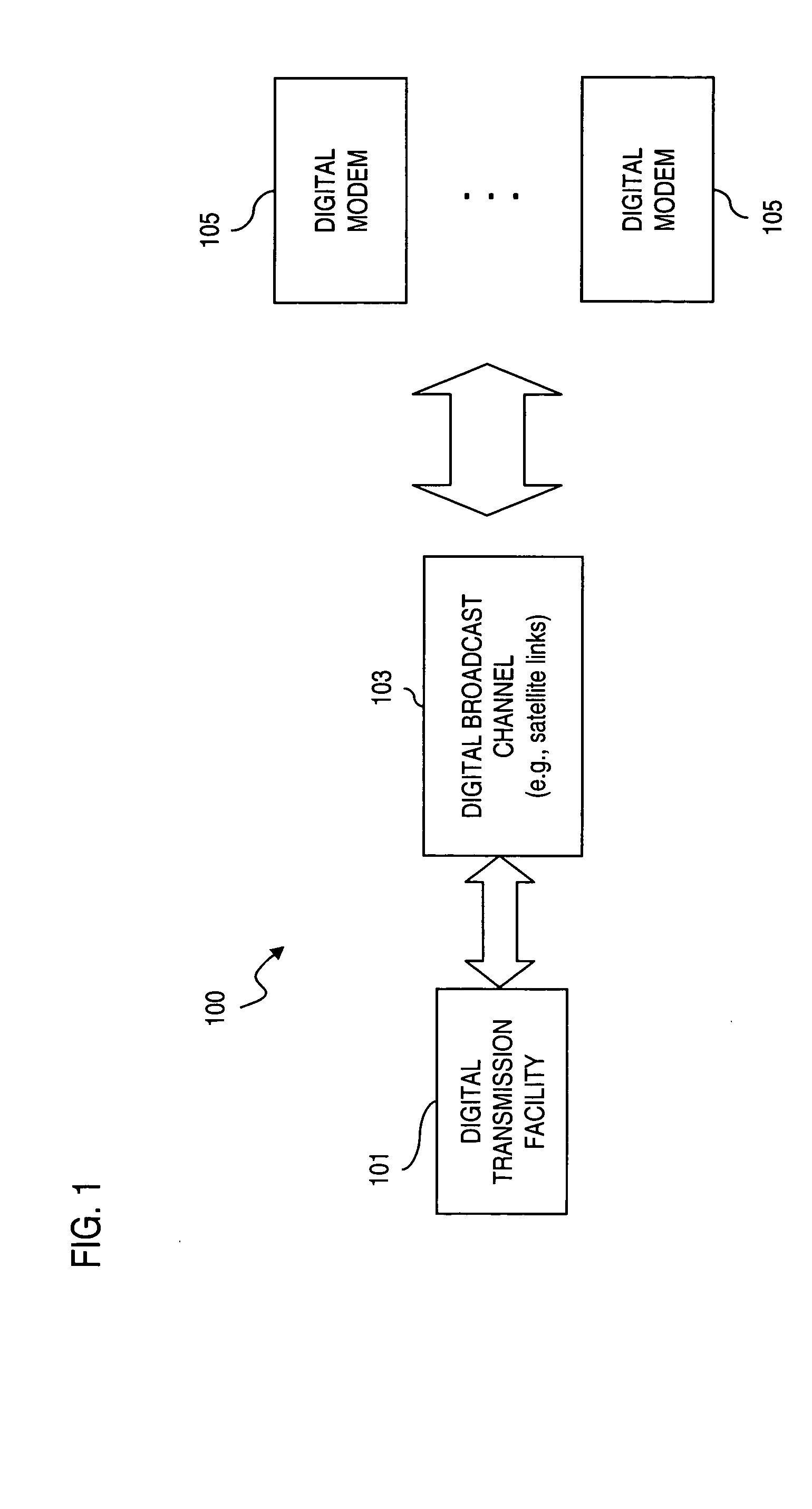
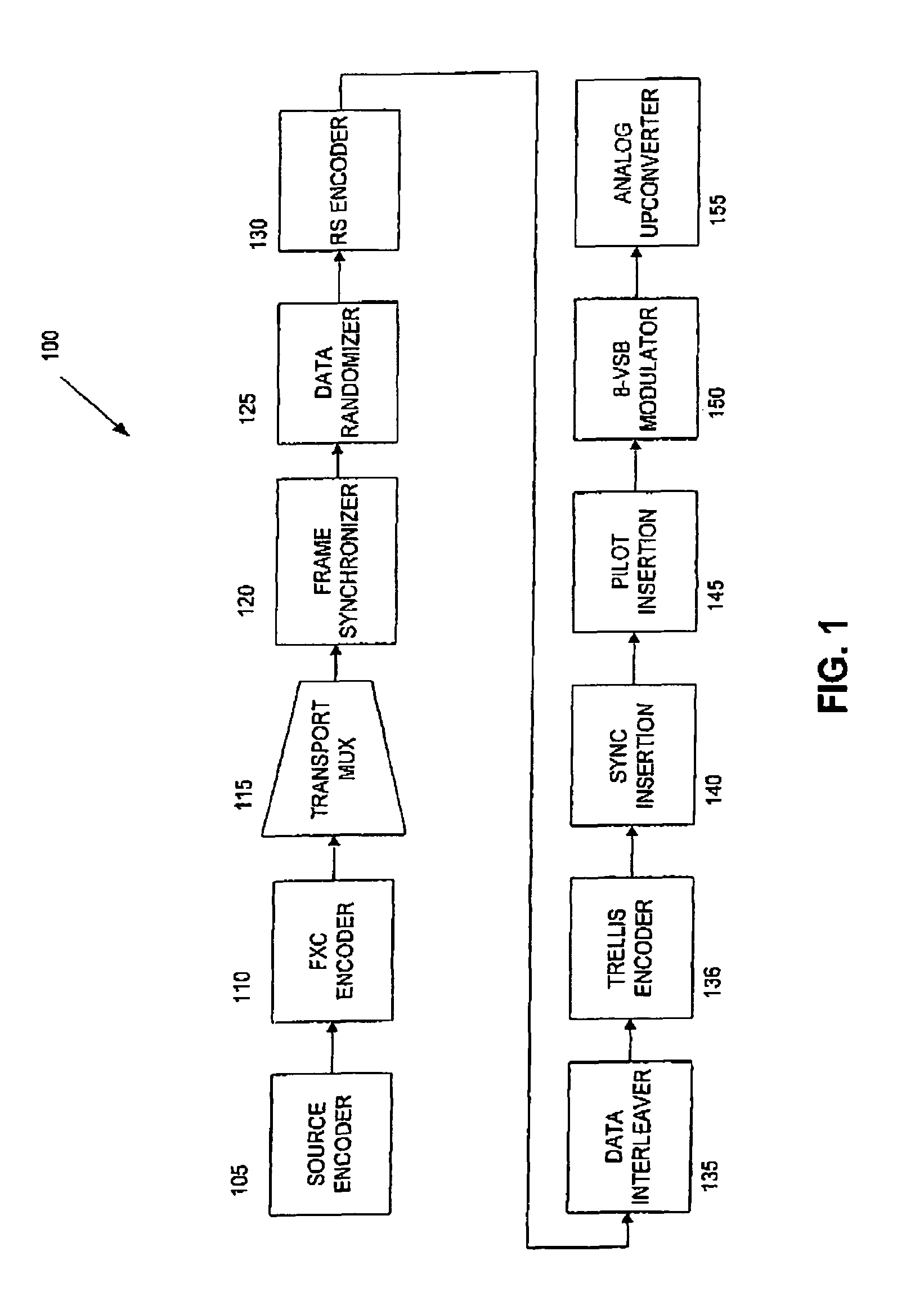
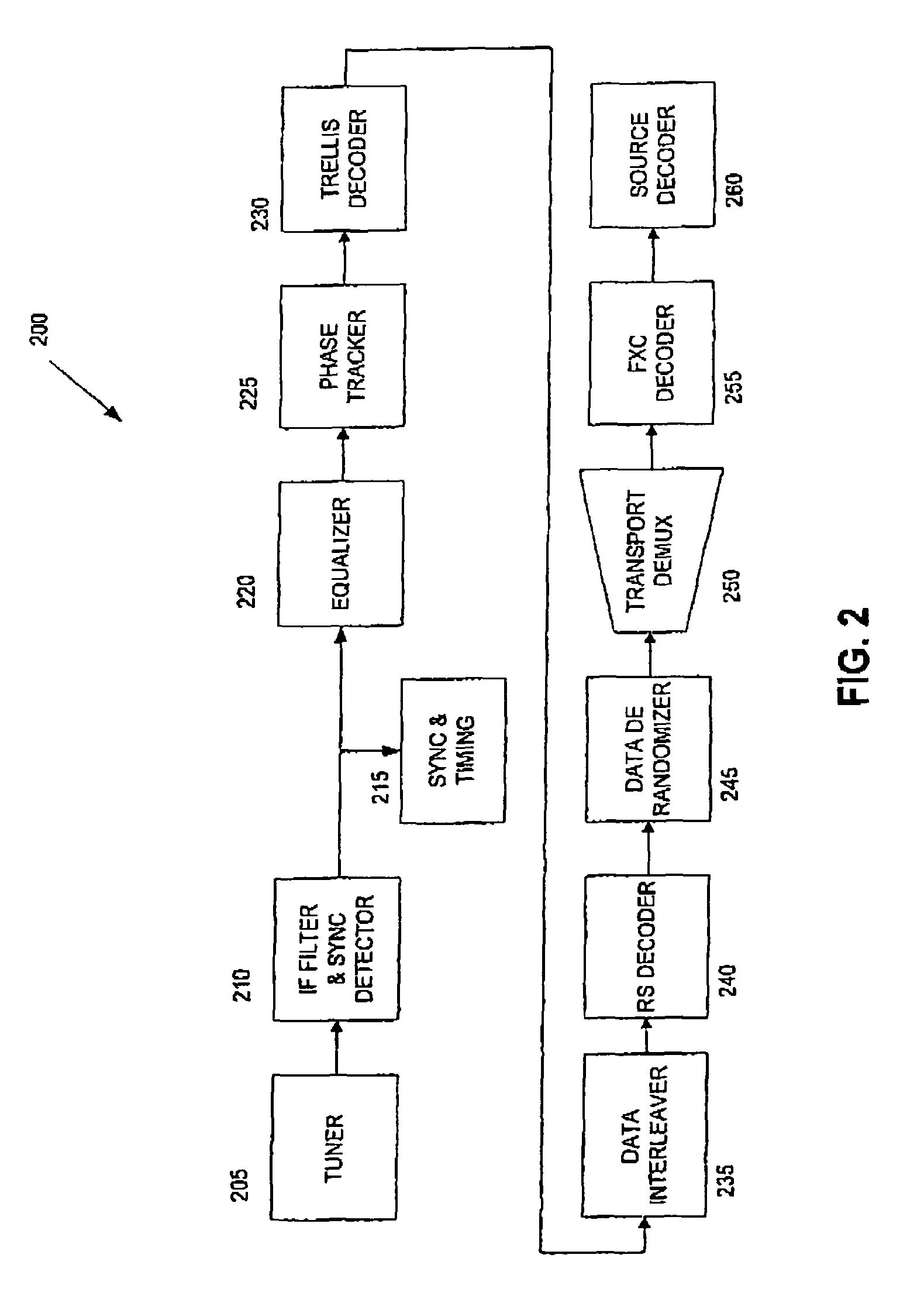
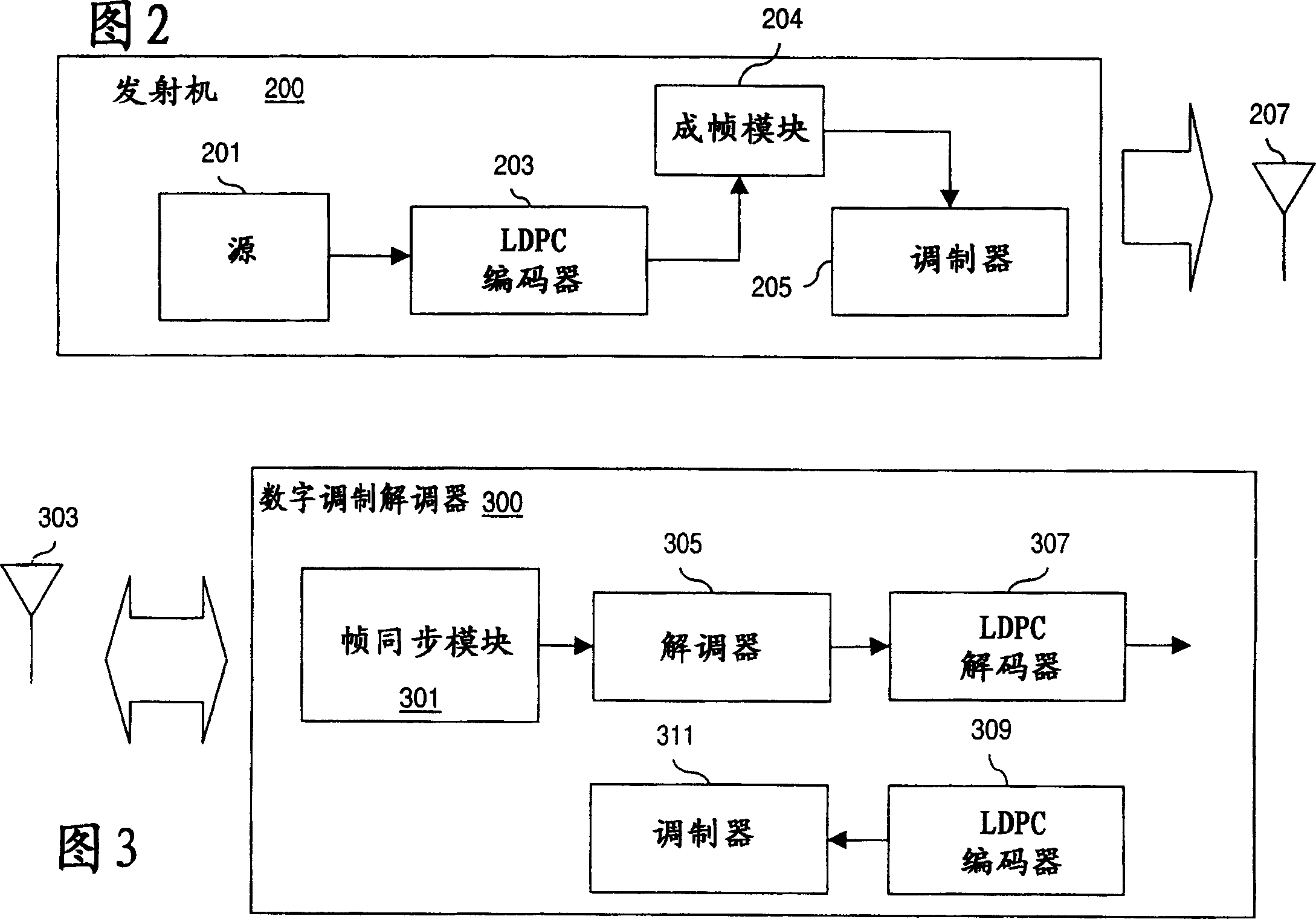
Framing structure for digital broadcasting and interactive services
ActiveCN1630281AError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationDigital audio broadcastingPhysical layer
An approach is provided for supporting frame synchronization in a digital broadcast and interactive system. A transmitter (200) includes an encoder (203, 309) that outputs a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codeword. The transmitter (200) also includes a framing module generates a LDPC coded frame in response to the LDPC codeword, and appends a physical layer signaling field to the LDPC codeword for specifying modulation and coding information associated with the LDPC coded frame. The physical layer signaling field is encoded with a Forward Error Correction (FEC) code and has an embedded framing structure to assist with frame synchronization. The above arrangement is particularly suited to a digital satellite broadcast system (100).
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
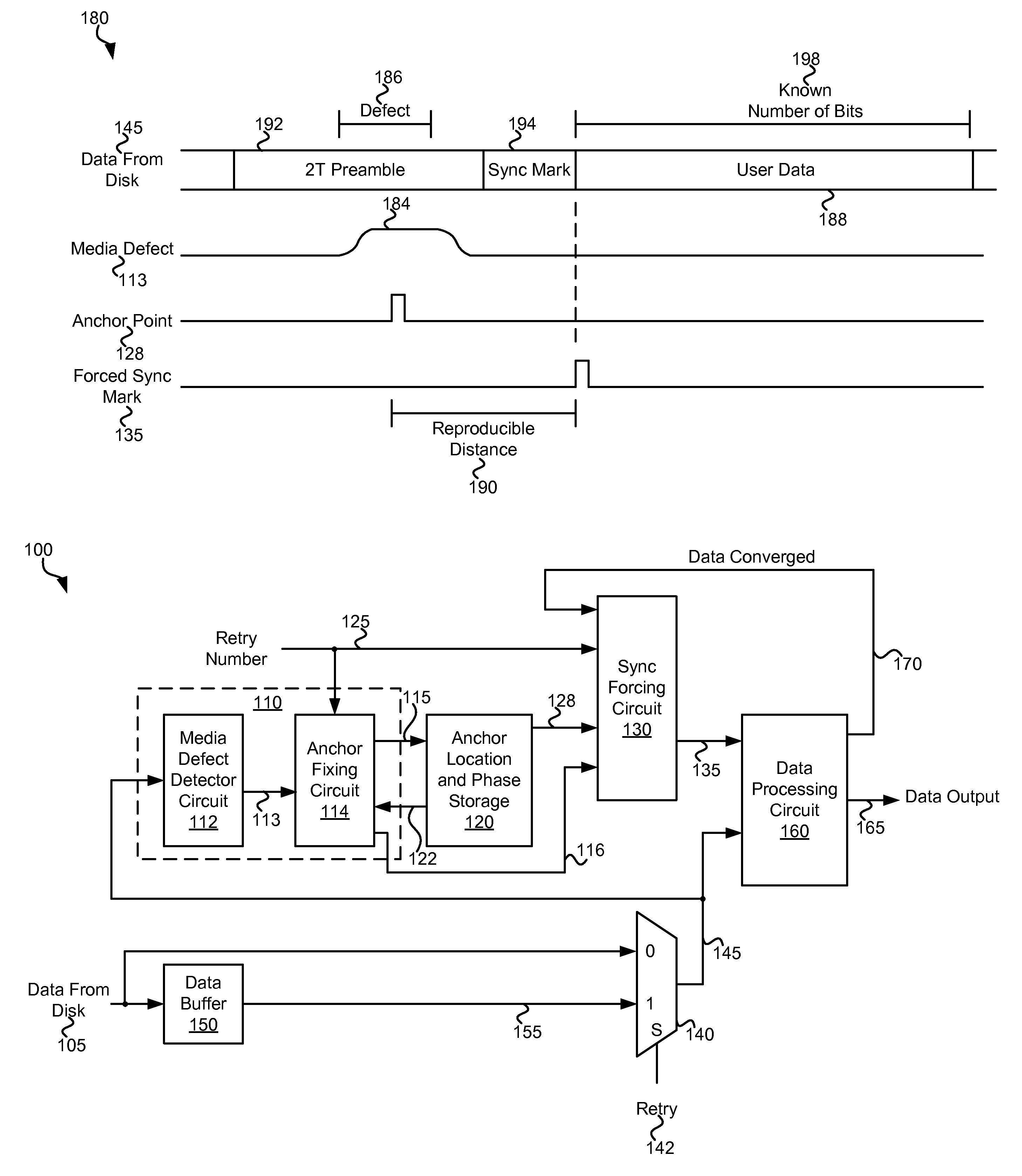
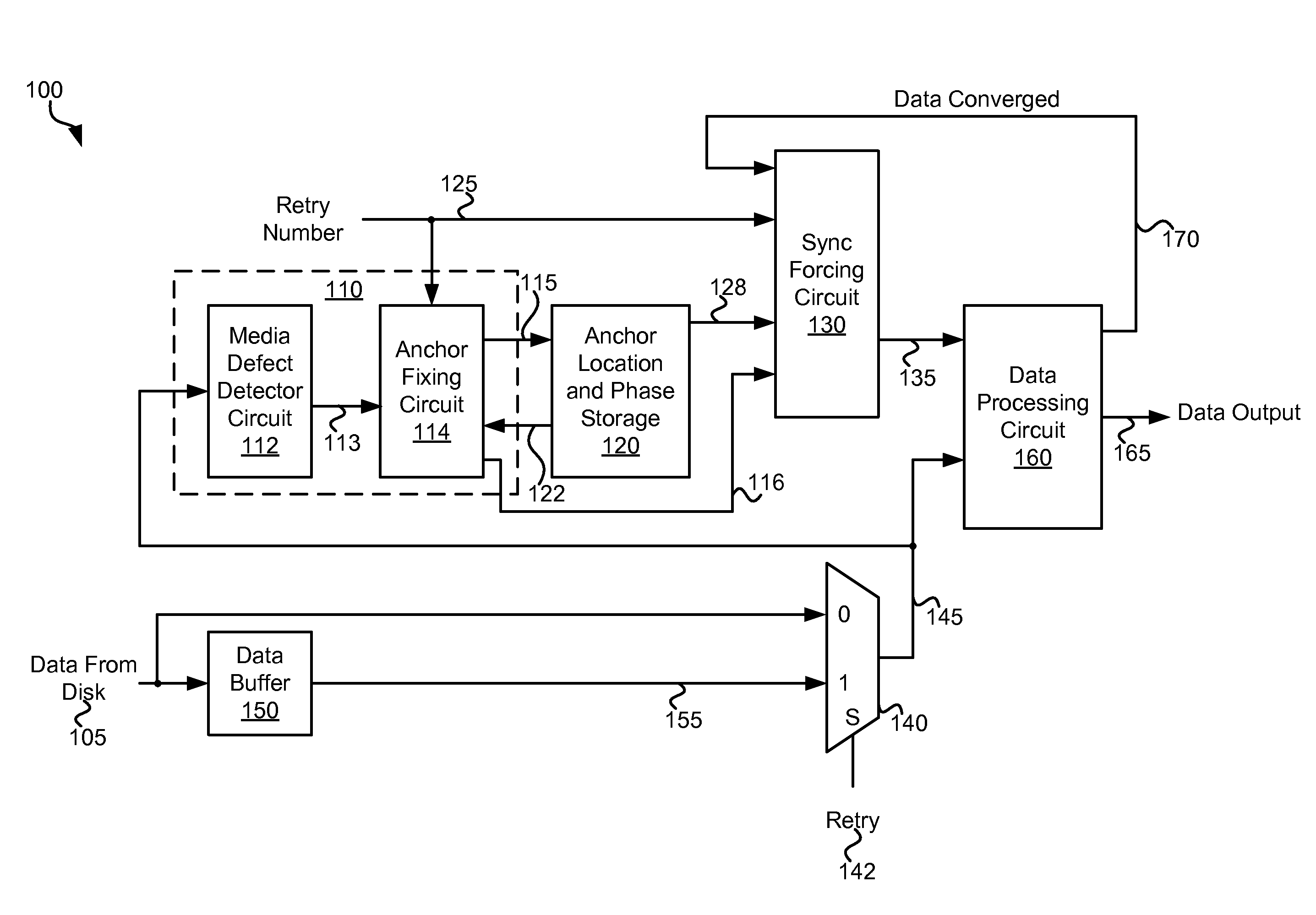
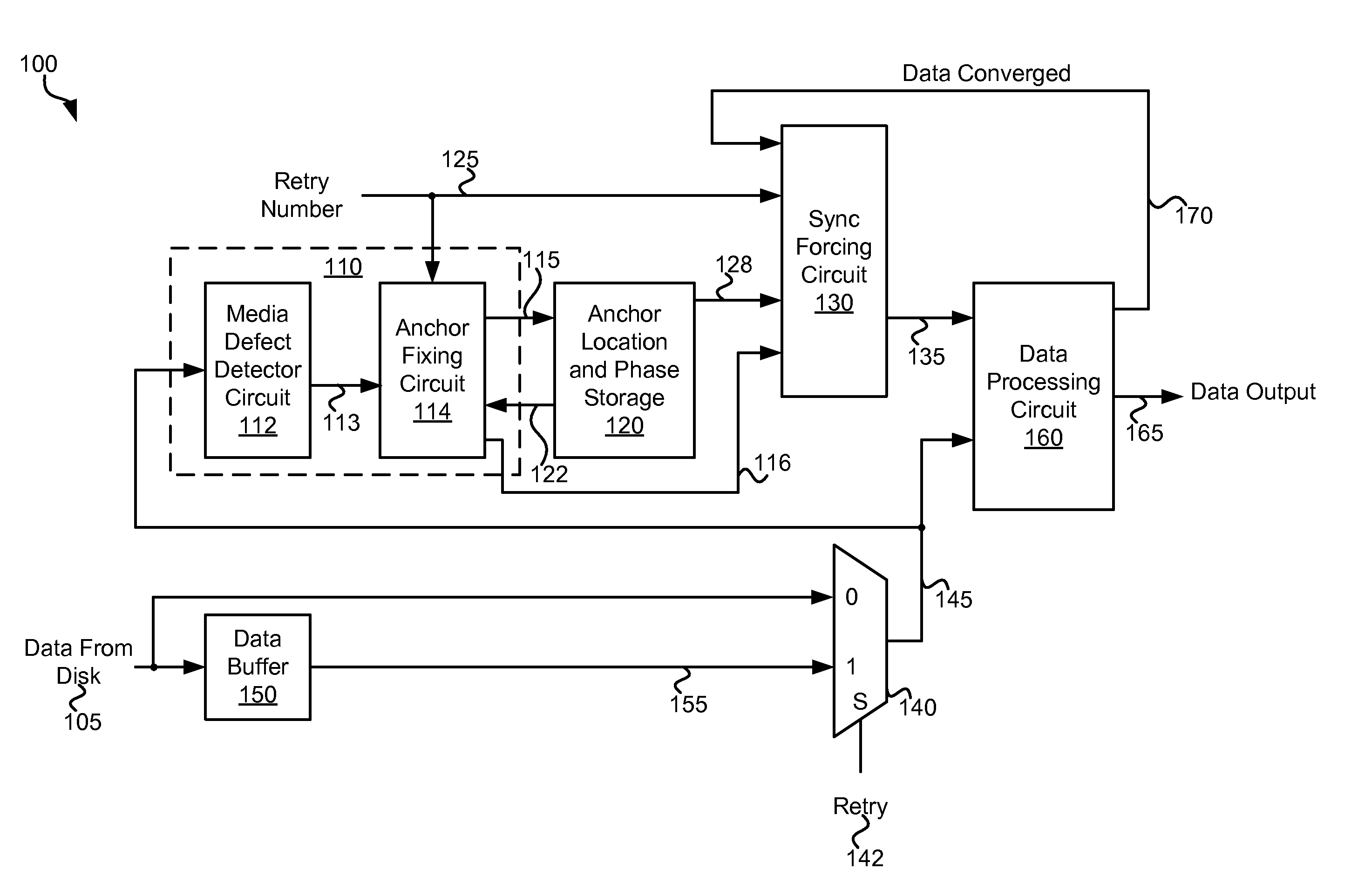
Systems and Methods for Data Recovery
InactiveUS20110205653A1Error coding/decoding sychronisationRecord information storageData recoveryComputer engineering
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for identifying a reproducible location on a storage medium. As an example, a circuit is described that include a media defect detector and an anchor fixing circuit. The media defect detector is operable to identify a media defect, and the anchor fixing circuit is operable to identify a location relative to the media defect. The location is reproducible.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for providing signal acquisition and frame synchronization in a hierarchical modulation scheme
ActiveUS7907641B2Rapid and reliable frame acquisition without additional overheadError preventionError correction/detection using LDPC codesData synchronizationSignal on
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
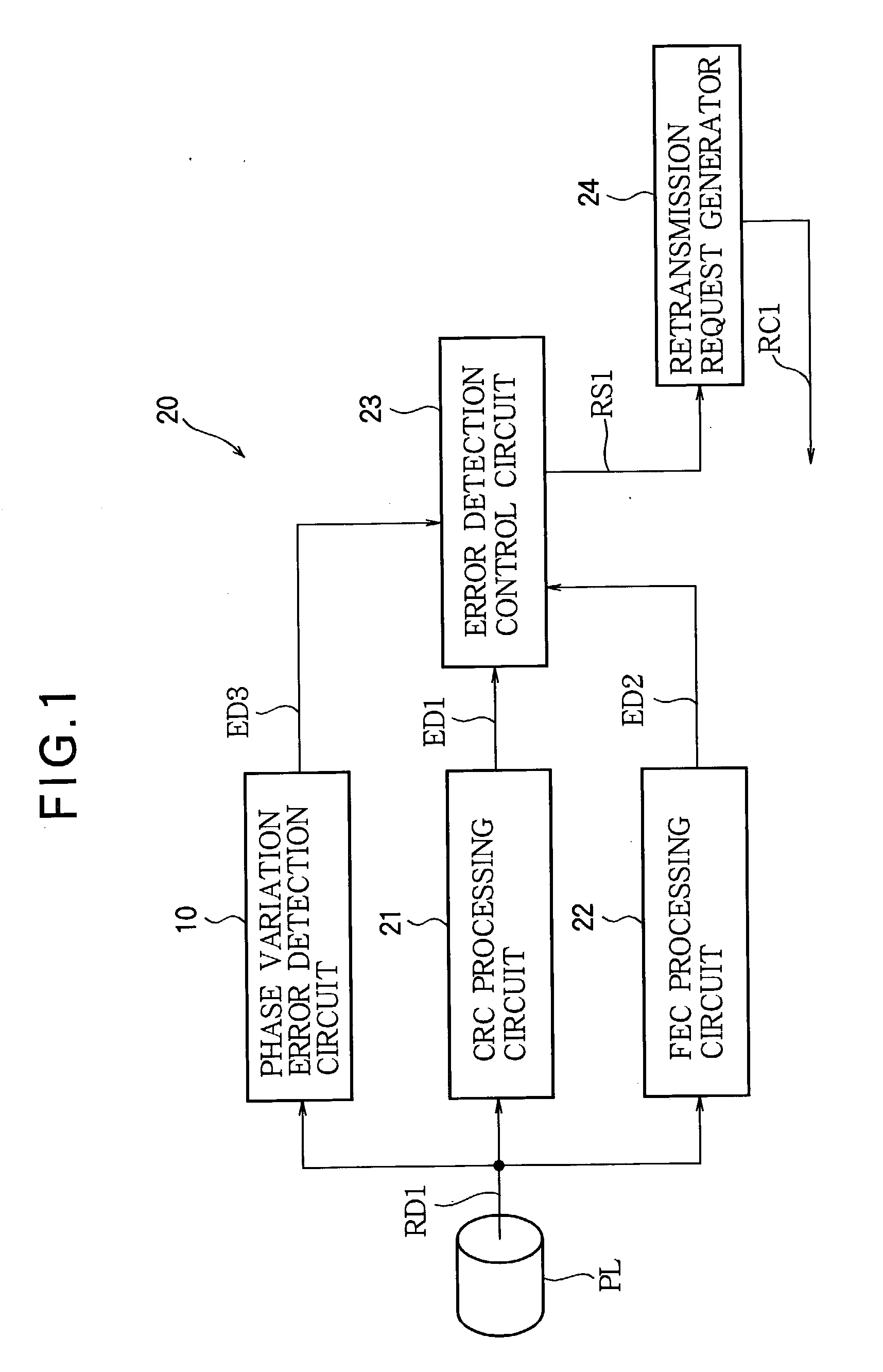
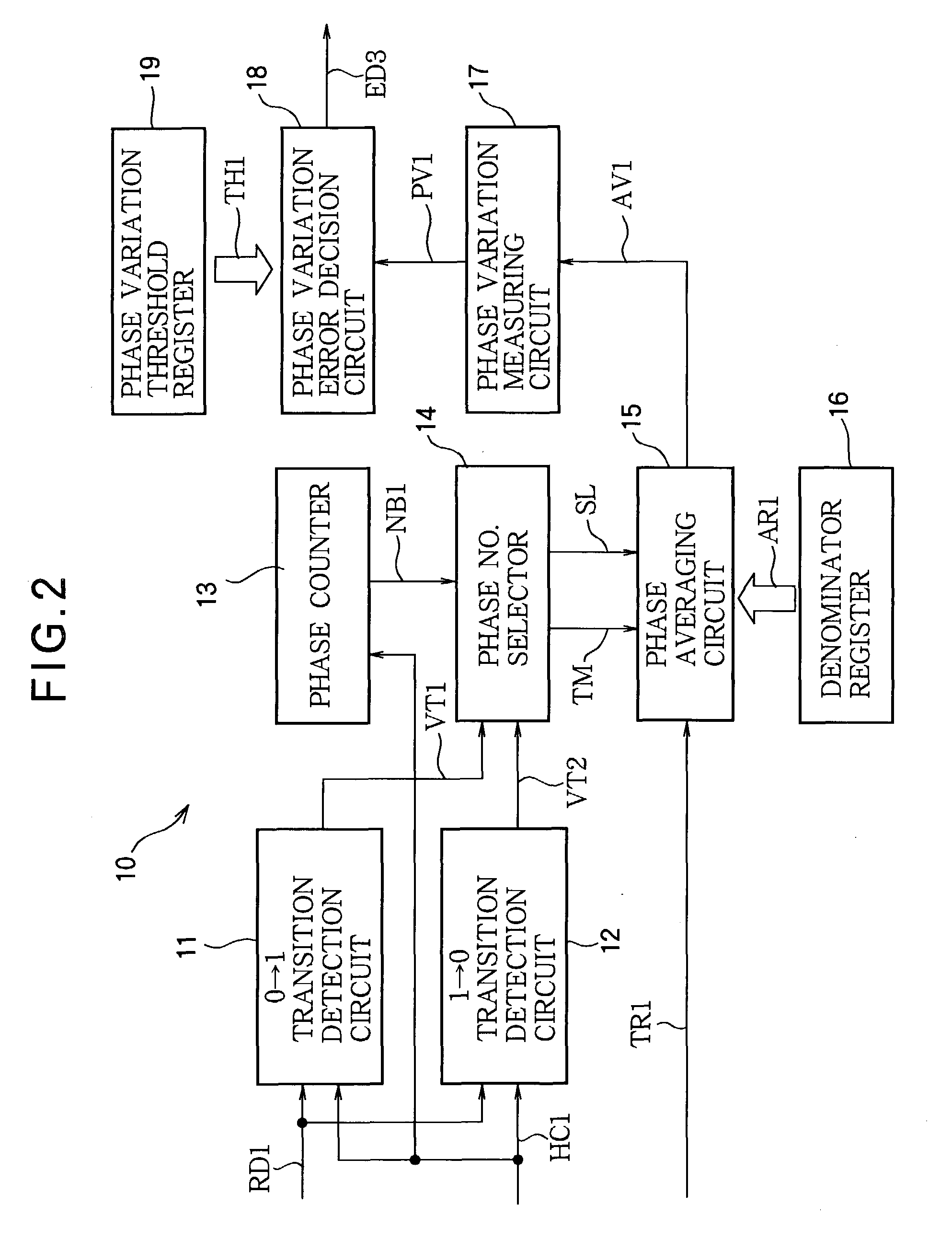
Synchronization error detection circuit
InactiveUS20040078737A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsEngineeringForward error correction
Synchronization errors in a received pulse train are detected by detecting rising or falling transitions in the pulse train, generating numbers in a repeating cycle having a length corresponding to the pulse rate, selecting the number generated when each transition is detected, and performing a predetermined operation on the selected numbers. The predetermined operation may include, for example, comparing the average values of the selected numbers in successive groups of transitions. Alternatively, the predetermined operation may include taking a difference between consecutively selected numbers to measure pulse widths in the pulse train. Synchronization error detection can be used to supplement data error detection and correction methods such as forward error correction and cyclic redundancy checks.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Coding system and decoding system
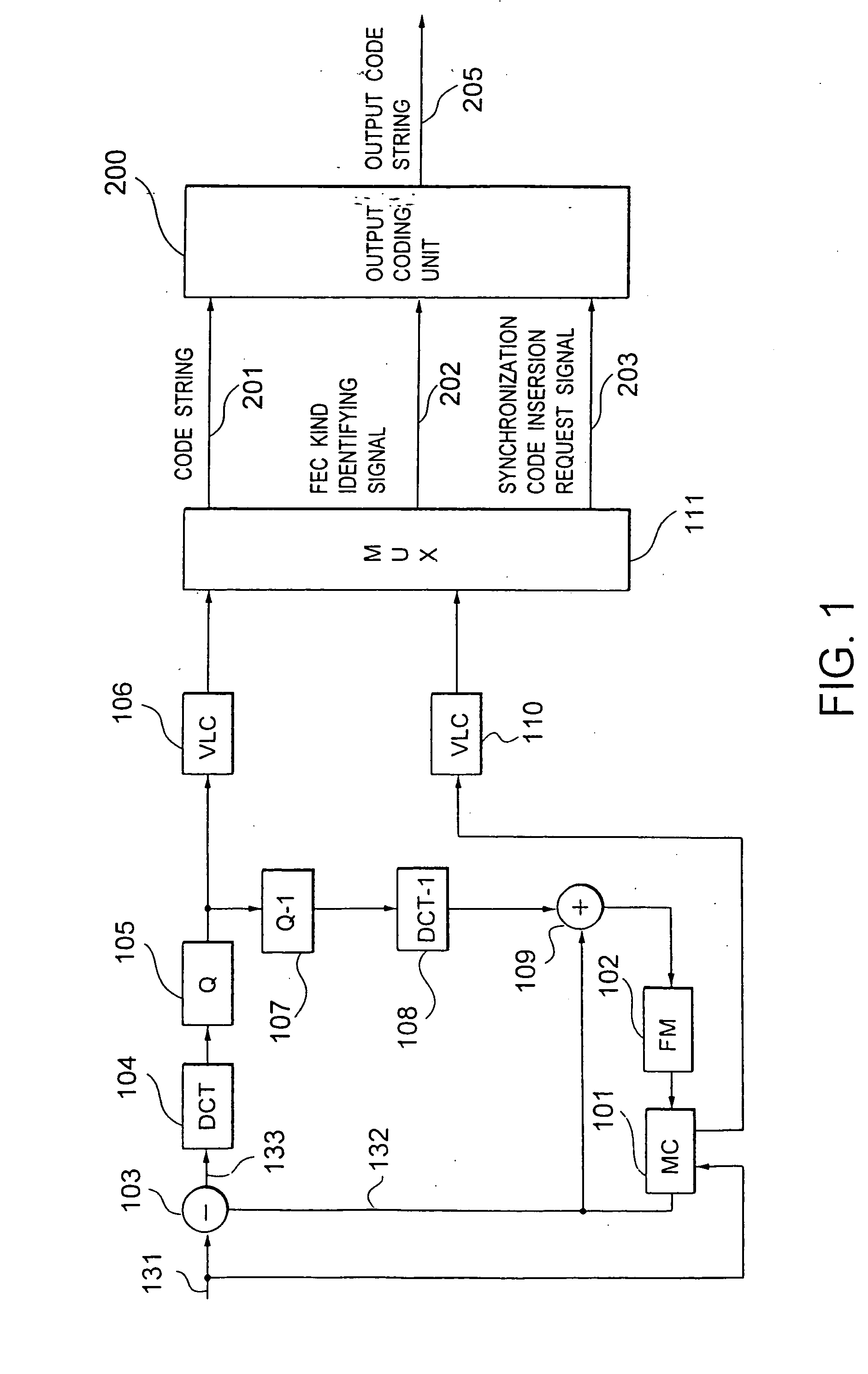
InactiveUS20050229078A1Reduce in quantityPulse modulation television signal transmissionError correction/detection using convolutional codesMultiplexingProgramming language
In a coding system wherein an error correction / detect-ion coding is combined with a synchronization recovering technique using a synchronization code, the problems of a pseudo synchronization and a step out due to error detect-ion are solved. There is provided a coding part 212 for coding an input multiplexed code string 201 to an error correcting- / detecting code comprising an information bit and a check bit, and code string assembling part 213 for inserting a synchronization code into any one of a plurality of periodically predetermined synchronization code inserting positions in the code string 201, for arranging the information bit at an optional position in the code string, and for arranging the check bit at a position other than the synchronization code inserting positions in the code string 201 to assemble an output code string 205.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Synchronization loss resilient digital communication system using forward erasure correction
ActiveUS20050213499A1Transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareCommunications system
There is provided an apparatus for enabling recovery of missing information in a digital communication system. The apparatus includes a Forward Erasure Correction (FXC) encoder for computing FXC parity superpackets across information superpackets for subsequent recovery of any entire ones of the information superpackets that have been at least partially comprised due to synchronization loss.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Phase shift adjusting method and circuit
InactiveUS20080075156A1Improved memory controllerImproved memory deviceError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationPhase shiftedData signal
Method and system of adjusting a first phase shift between a first data signal and a clock signal at a sending device. First and second test signals representing firs and second test data, respectively, are transmitted to a receiving device. The test signals have respective phase shifts relative to the clock signal. An error detection code is calculated from first and second received data carried by the transmitted signals. The error detection code is transmitted from the receiving device to the sending device. An estimated first received data is calculated from the error detection code, wherein the estimated first received data are calculated under the assumption that the second received data are identical to the second test data. The first phase shift is adjusted on the basis of a comparison of the estimated first received data and the first test data.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
Incremental redundancy transmission in a mimo communication system
ActiveCN101142774AError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsComputer scienceTransmitter
For an incremental redundancy (IR) transmission in a MIMO system, a transmitter processes (e.g., encodes, partitions, interleaves, and modulates) a data packet based on a selected rate to obtain multiple data symbol blocks. The transmitter transmits one data symbol block at a time until a receiver correctly recovers the data packet or all blocks are transmitted. Whenever a data symbol block is received from the transmitter, the receiver detects a received symbol block to obtain a detected symbol block, processes (e.g., demodulates, deinterleaves, re-assembles, and decodes) all detected symbol blocks obtained for the data packet, and provides a decoded packet. If the decoded packet is in error, then the receiver repeats the processing when another data symbol block is received for the data packet. The receiver may also perform iterative detection and decoding on the received symbol blocks for the data packet multiple times to obtain the decoded packet.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
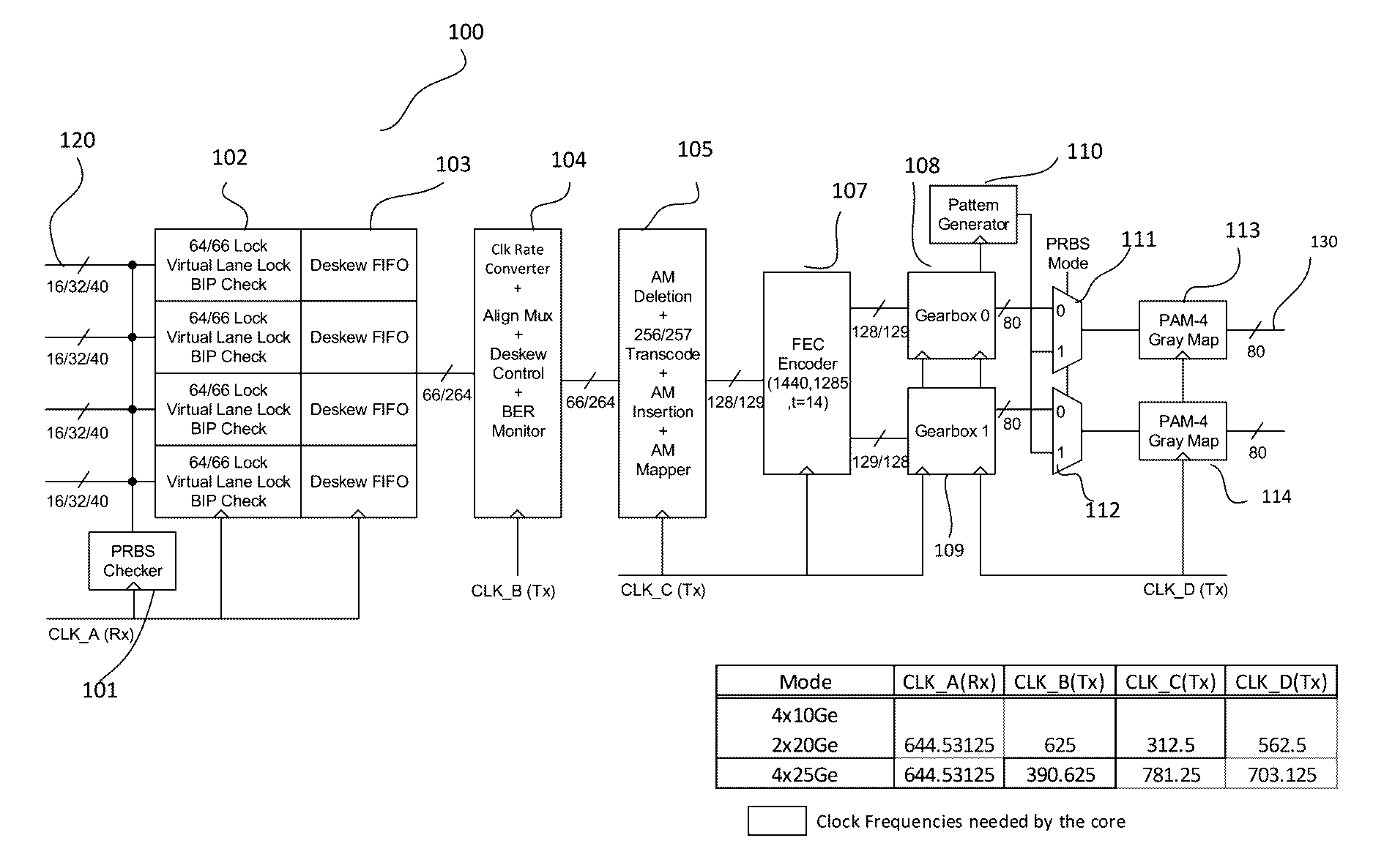
Pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) data communication with forward error correction
The present invention is directed to data communication system and methods. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention provide an apparatus that receives data from multiple lanes, which are then synchronized for transcoding and encoding. A pseudo random bit sequence checker may be coupled to each of the plurality of lanes, which is configured to a first clock signal A. Additionally, an apparatus may include a plurality of skew compensator modules. Each of the skew compensator modules may be coupled to at least one of the plurality of lanes. The skew-compensator modules are configured to synchronize data from the plurality of lanes. The apparatus additionally includes a plurality of de-skew FIFO modules. Each of the de-skew compensator modules may be coupled to at least one of the plurality of skew compensator modules.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
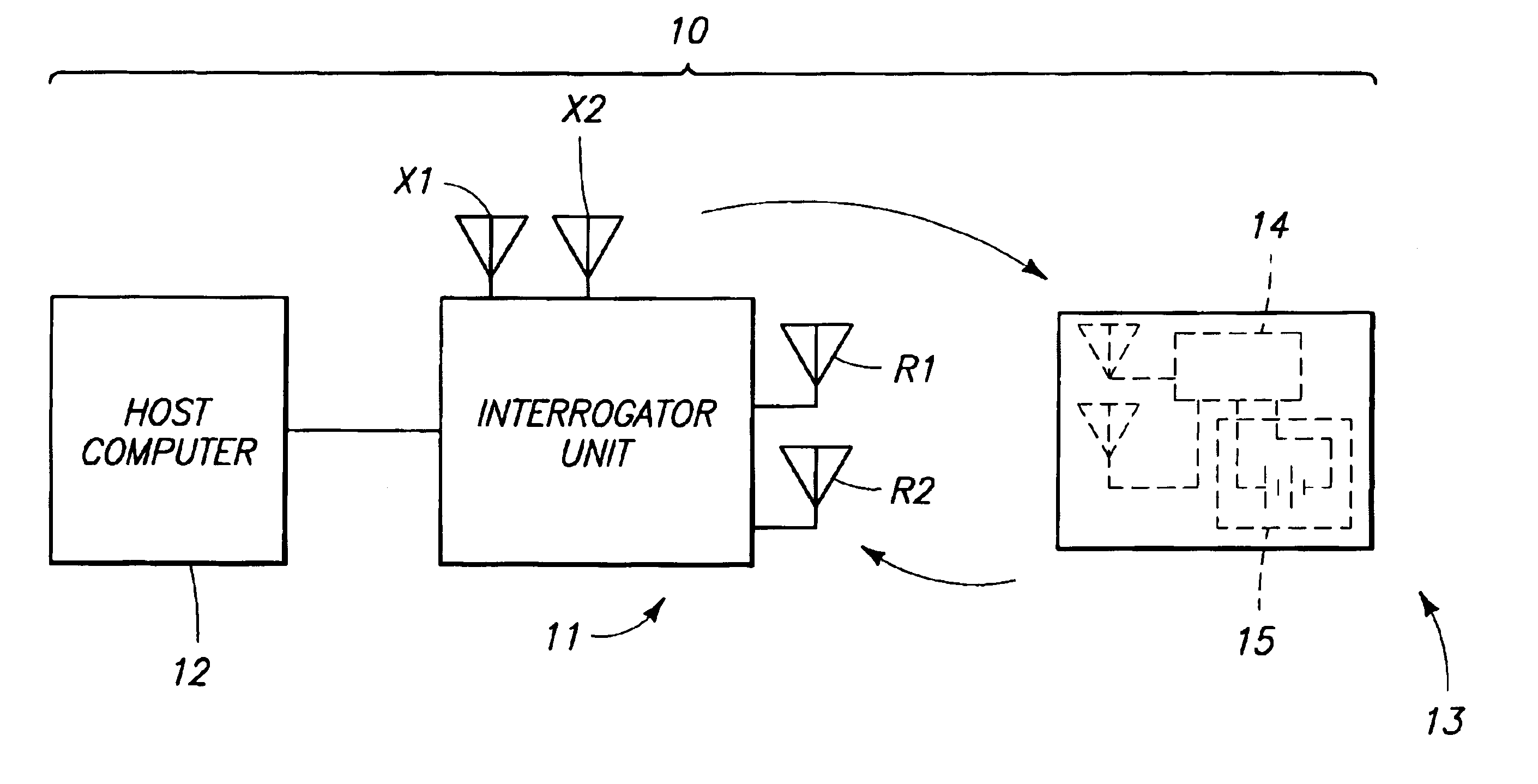
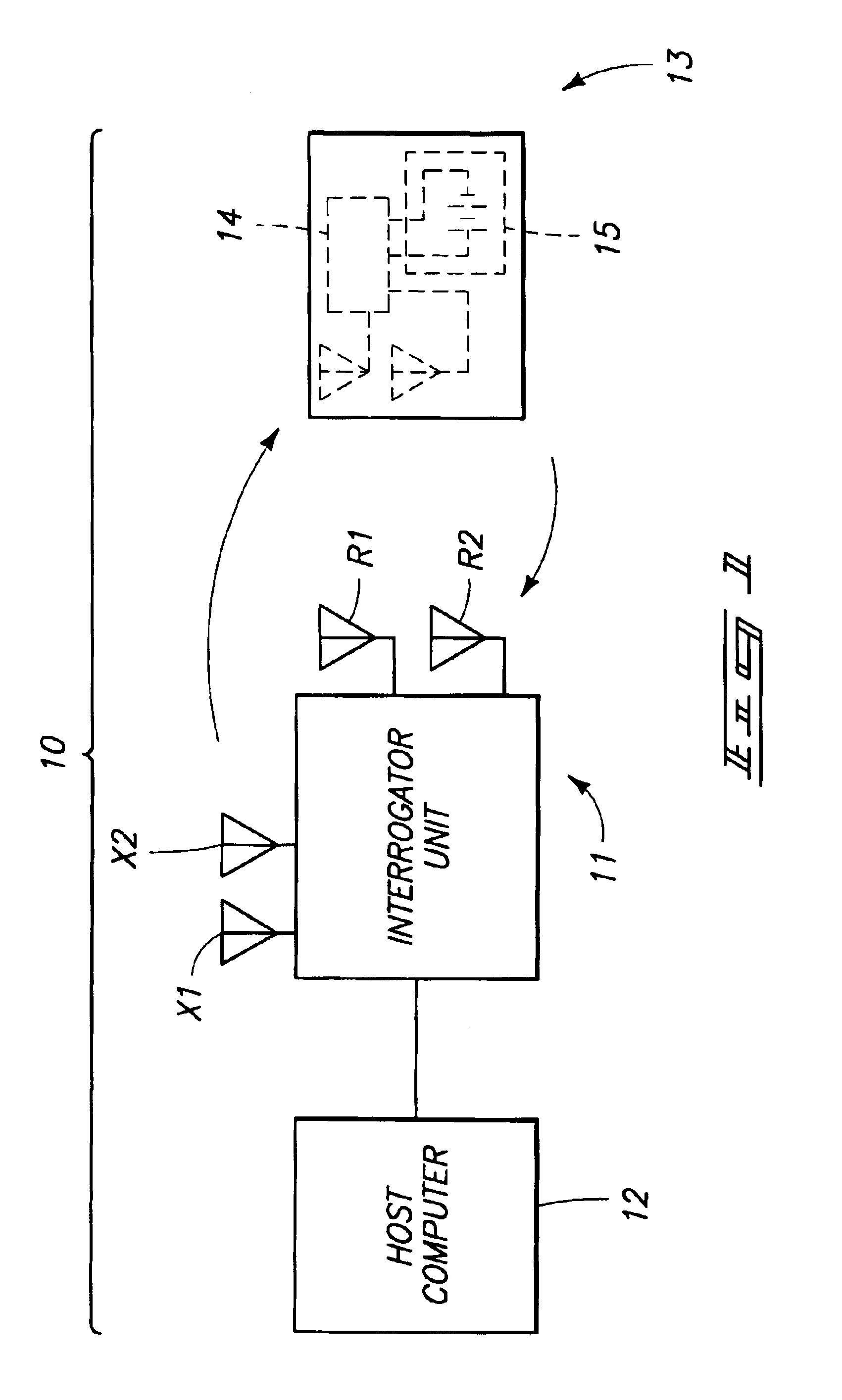
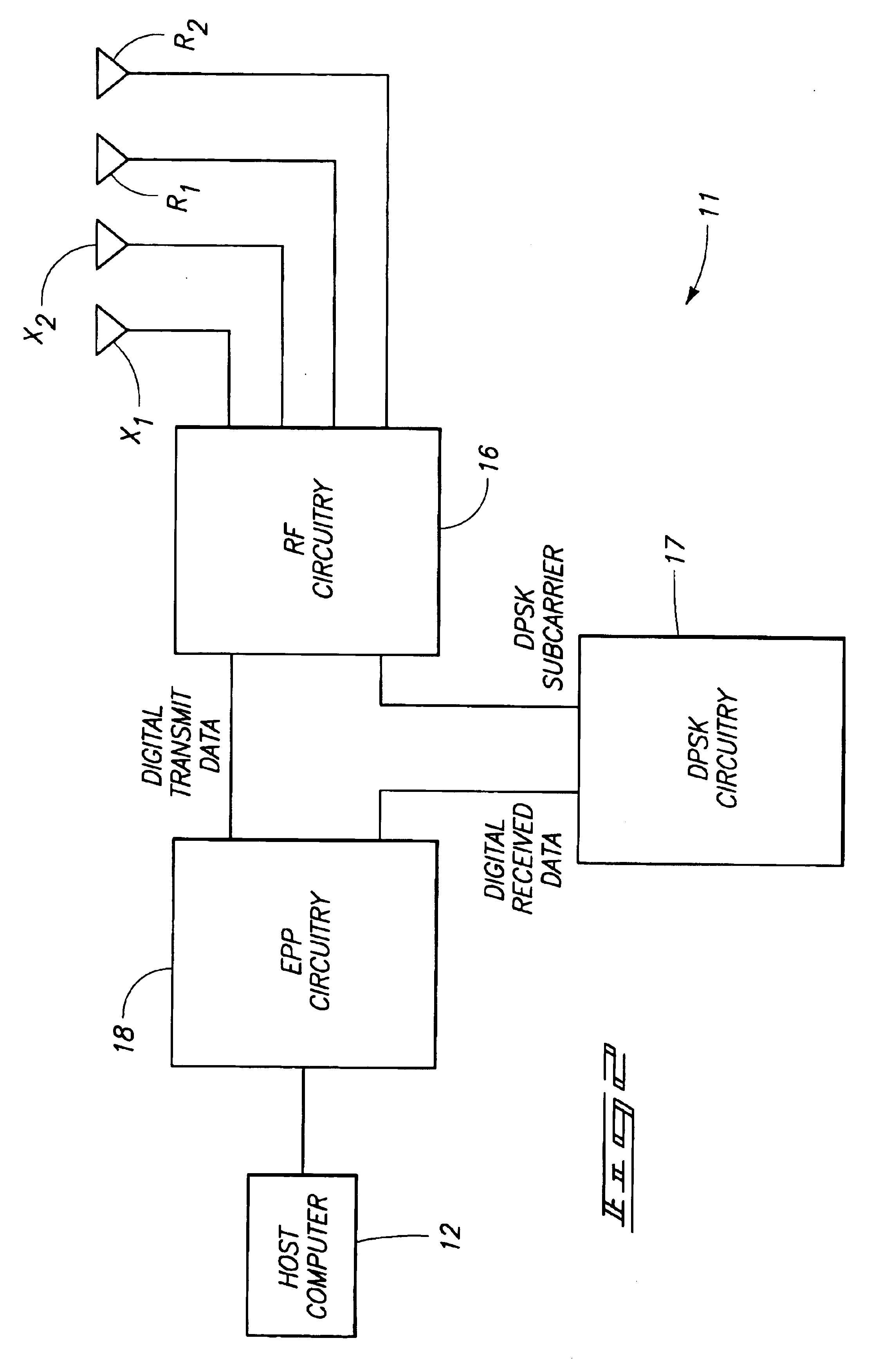
Transponder interrogators, radio frequency identification device communication systems, transponder interrogator communication methods, and radio frequency identification device communication methods
InactiveUS6938200B2Electronic circuit testingError detection/correctionCommunications systemData signal
The present invention includes bit synchronizers and methods of synchronizing and calculating error. One method of synchronizing with a data signal in accordance with the present invention includes providing a data signal having a first portion and a second portion, generating a timing signal, first adjusting the timing signal during the first portion of the data signal, accumulating a history value during the first portion of the data signal, and second adjusting the timing signal during a second portion of the data signal using the history.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Synchronization code methods
InactiveUS20080043779A1Improve robustnessQuality improvementError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationEncoding algorithmSubject matter
A system, method and computer software product are provided. One embodiment of the present invention provides a method for generating and employing numerical sequences that may be used for synchronization codes. In one embodiment of the present invention, the derivation of numerical sequences, or codes is based on an encoding algorithm. These codes enable synchronization between communicating devices, and may also be used for channelization. This Abstract is provided for the sole purpose of complying with the Abstract requirement rules that allow a reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure contained herein. This Abstract is submitted with the explicit understanding that it will not be used to interpret or to limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 73
Systems and methods for data recovery using enhanced sync mark location
ActiveUS8345369B2Digital data processing detailsError coding/decoding sychronisationTheoretical computer scienceDegree of similarity
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for identifying a reproducible location on a storage medium. As an example, a circuit is discussed that includes a data storage circuit, a pattern comparison circuit, and a threshold comparison circuit. The data storage circuit is operable to store a first set of data samples corresponding to a region of interest. The pattern comparison circuit is operable to compare a subset of the first set of data samples with a subset of a second set of data samples corresponding to the region of interest. The pattern comparison circuit is operable to yield a match value corresponding to a degree of similarity between the first set of data samples with the subset of a second set of data samples. The threshold comparison circuit is operable to indicate an anchor point based at least in part on the magnitude of the match value relative to a threshold value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
BCH forward error correction decoder
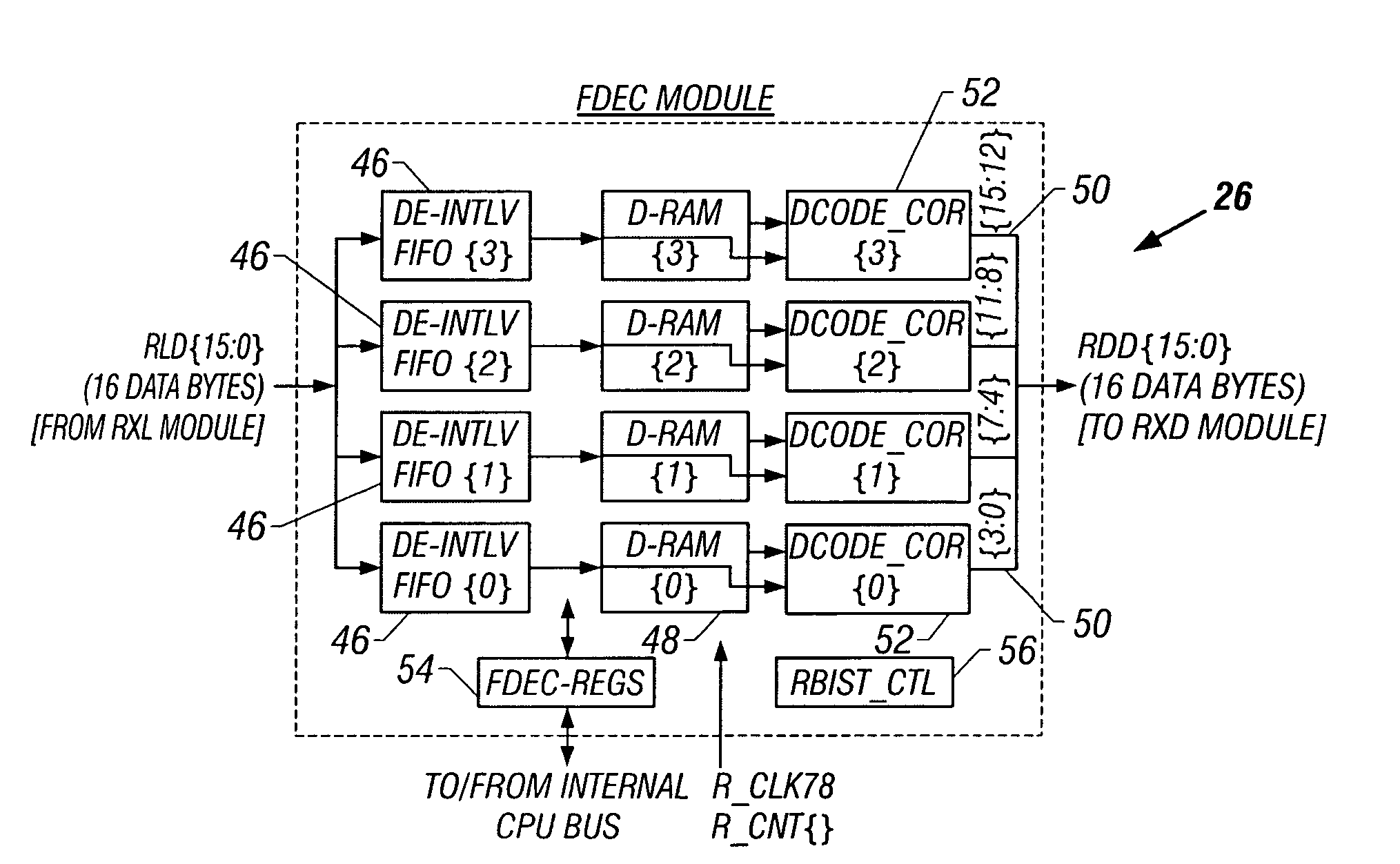
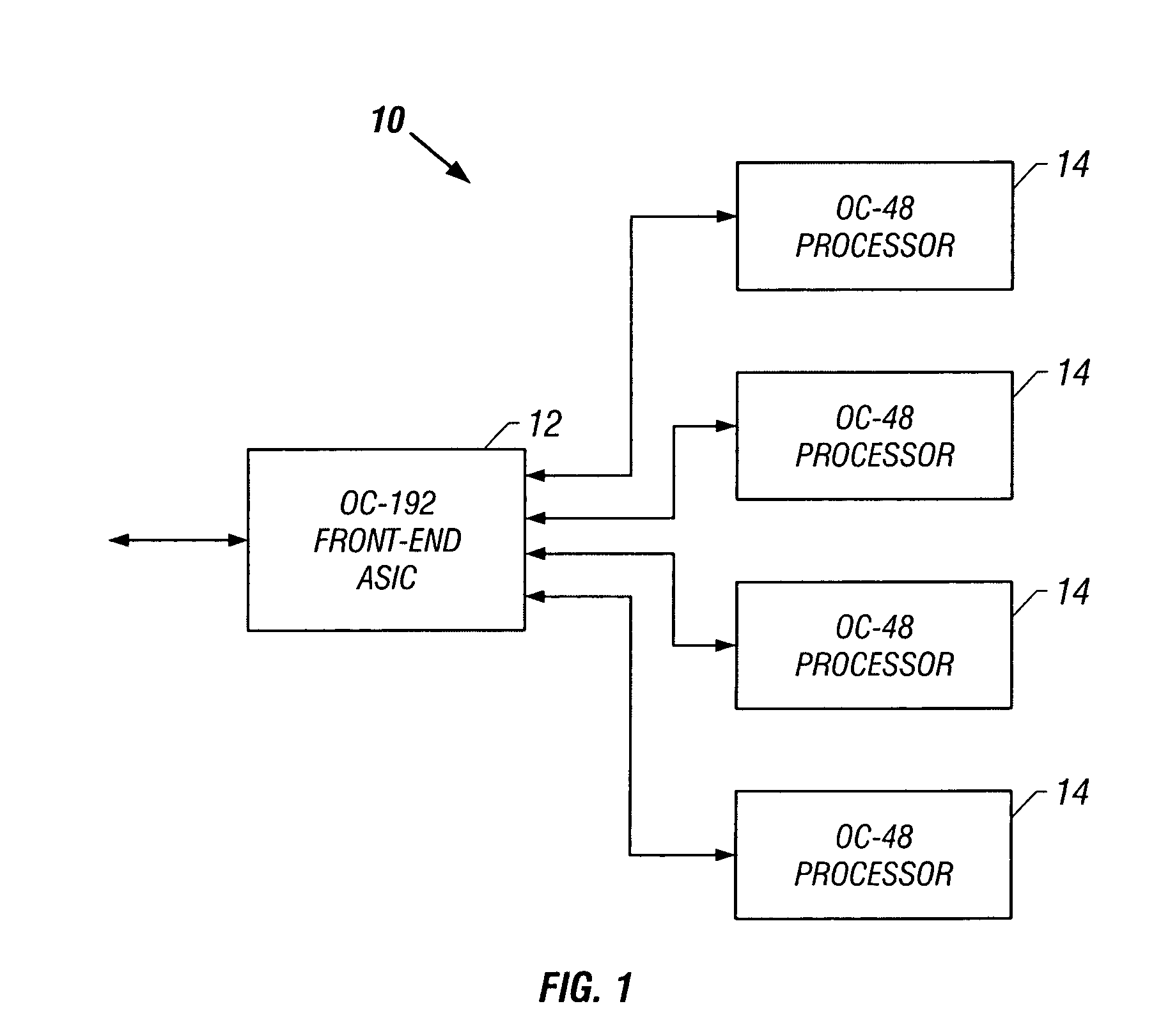
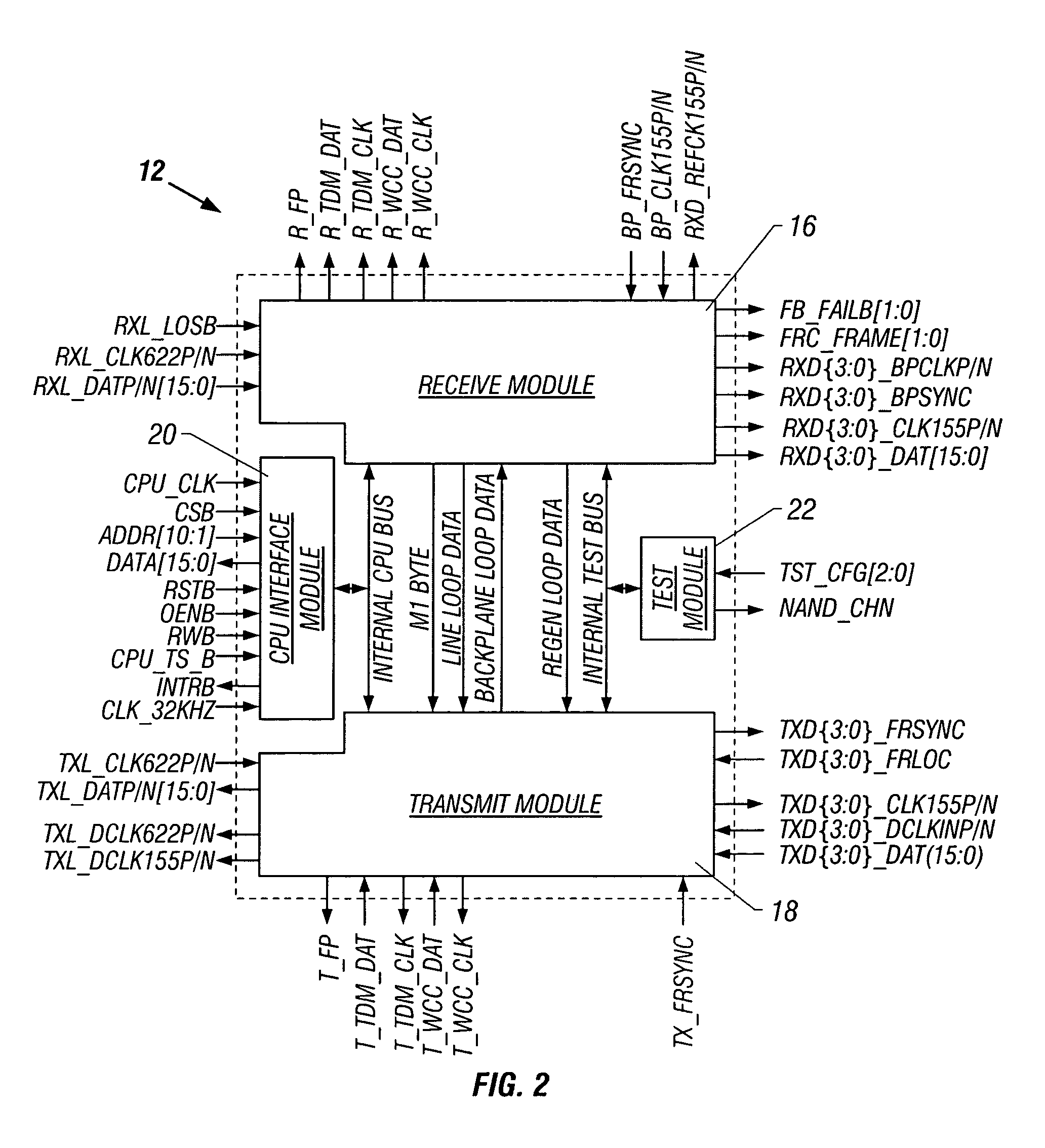
ActiveUS7447982B1Error coding/decoding sychronisationCode conversionForward error correctionApplication-specific integrated circuit
An OC-192 front-end application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) de-interleaves an OC-192 signal to create four OC-48 signals, and decodes error-correction codes embedded in each of the four OC-48 signals. The decoder generates a Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghem (BCH) error polynomial in no more than 12 clock cycles. The decoder includes several Galois field multiply accumulators, and a state machine which controls the Galois field units. If the error-correction code is a BCH triple error-correcting code, four Galois field units are used to carry out only six equations to solve the error polynomial. The Galois field units are advantageously designed to complete a Galois field multiply / accumulate operation in a single clock cycle. The Galois field units may operate in multiply or addition pass-through modes.
Owner:ICONVERSE +1
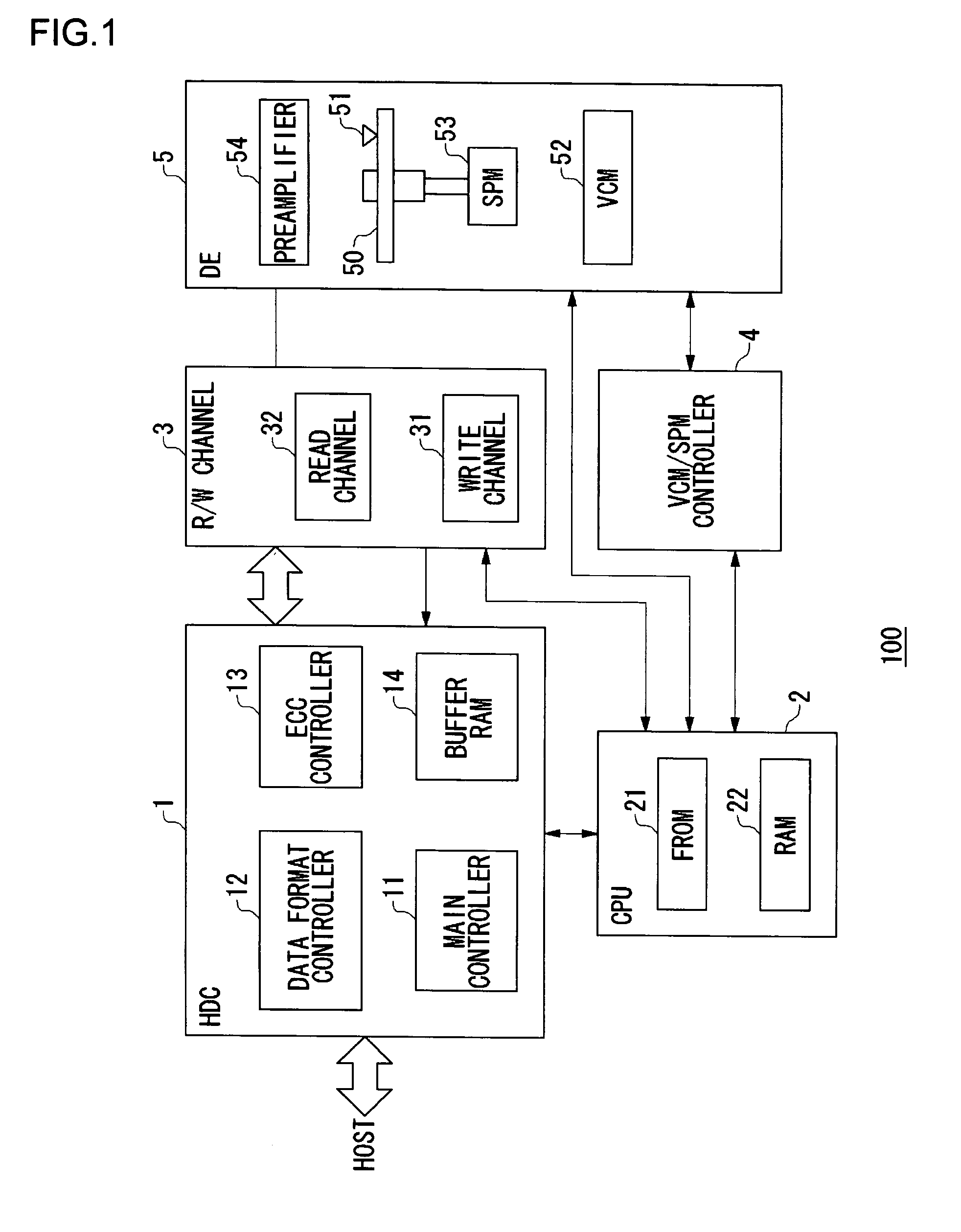
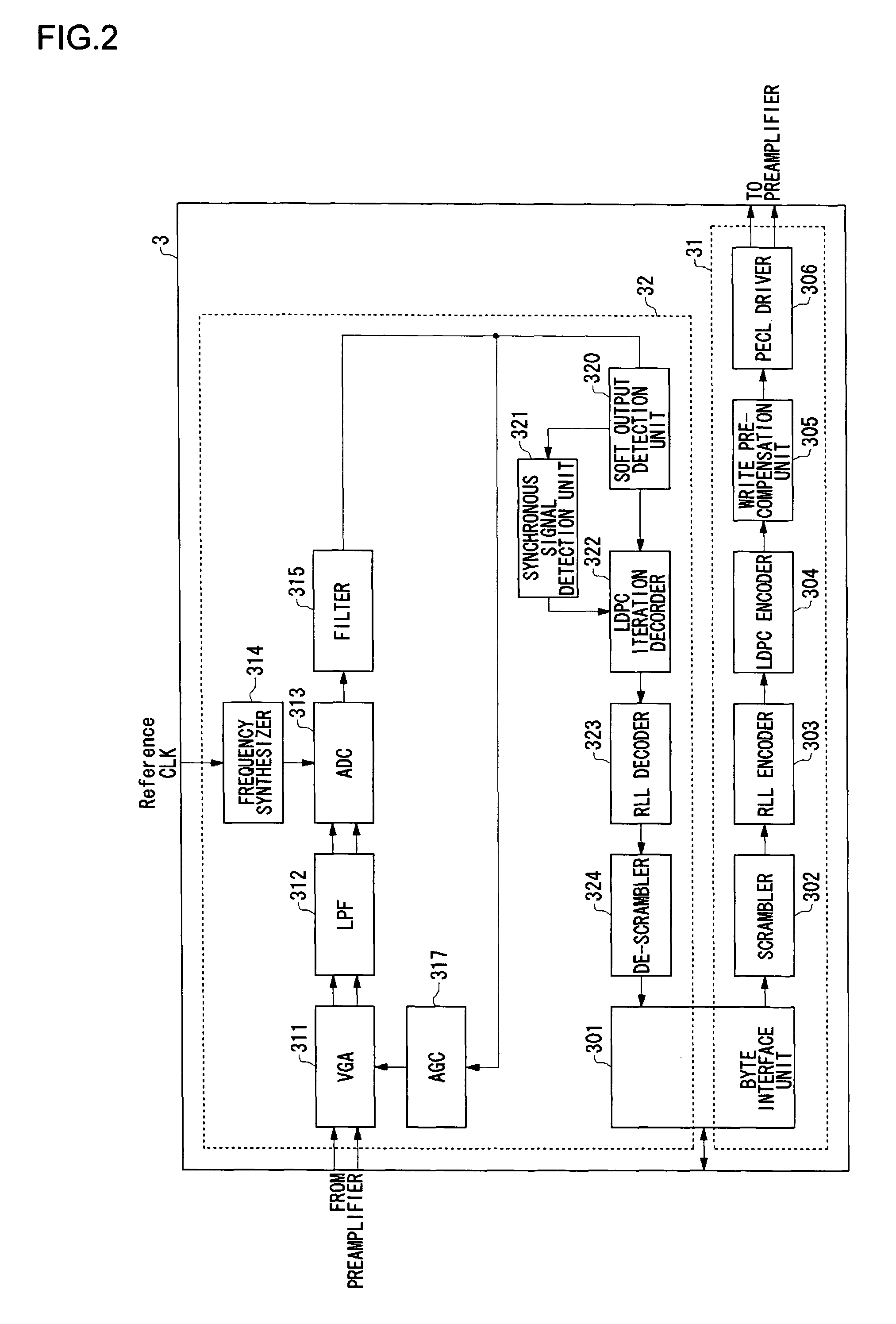
Data writing apparatus and a storage system
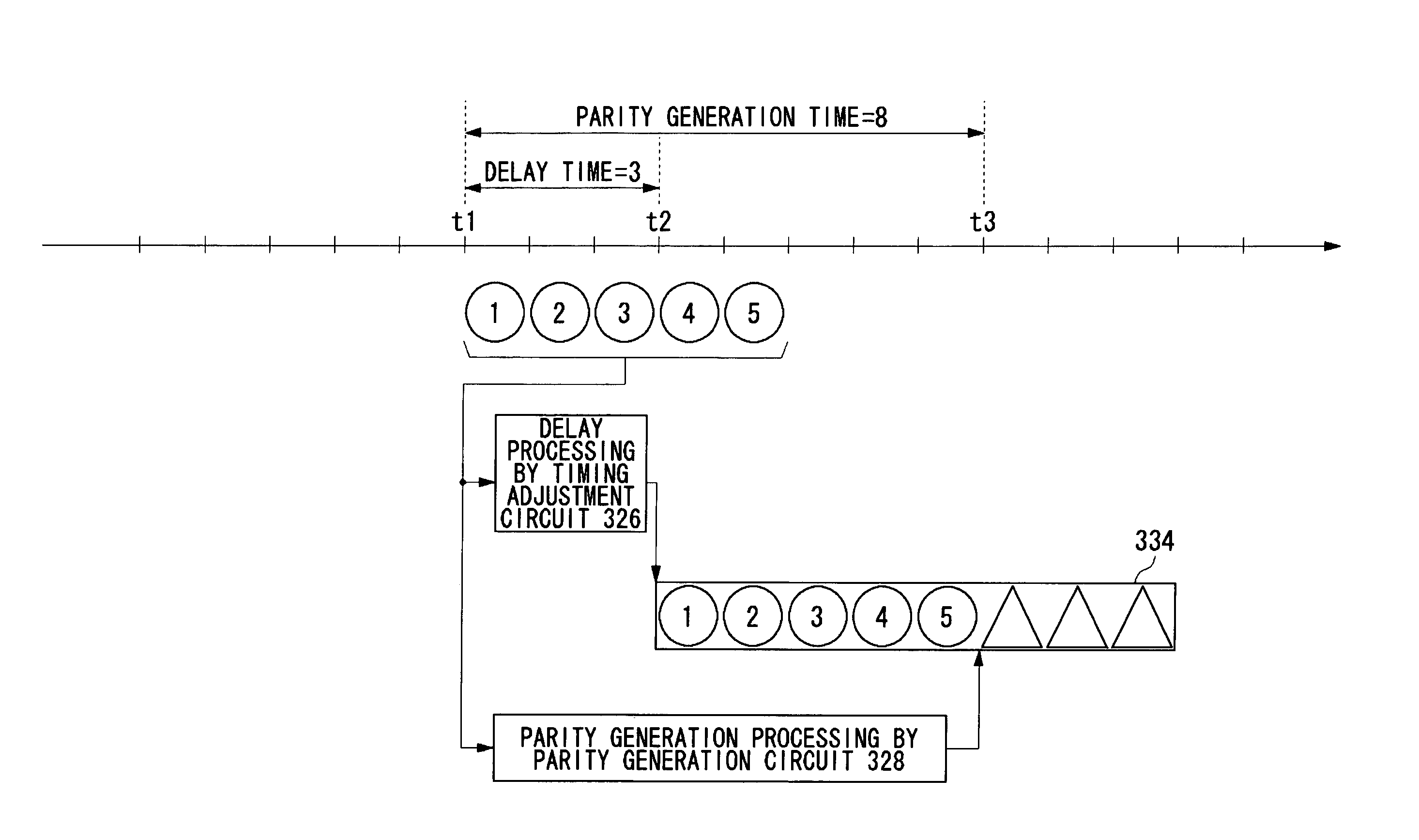
InactiveUS7783950B2Cancel out delay timeReduce hardware sizeError detection/correctionError coding/decoding sychronisationEmbedded systemEncoder
An LDPC encoder (304) includes a timing adjustment circuit (326) for performing timing adjustment on main data and outputting to a writing circuit (334), a parity generation circuit (328) for performing LDPC encoding on input signal series, generating the parity data, and outputting to the writing circuit (334), and the writing circuit (334) for sequentially receiving the main data and the parity data, and outputting to the storage apparatus via a write pre-compensation unit (305), a driver (306), and the like.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
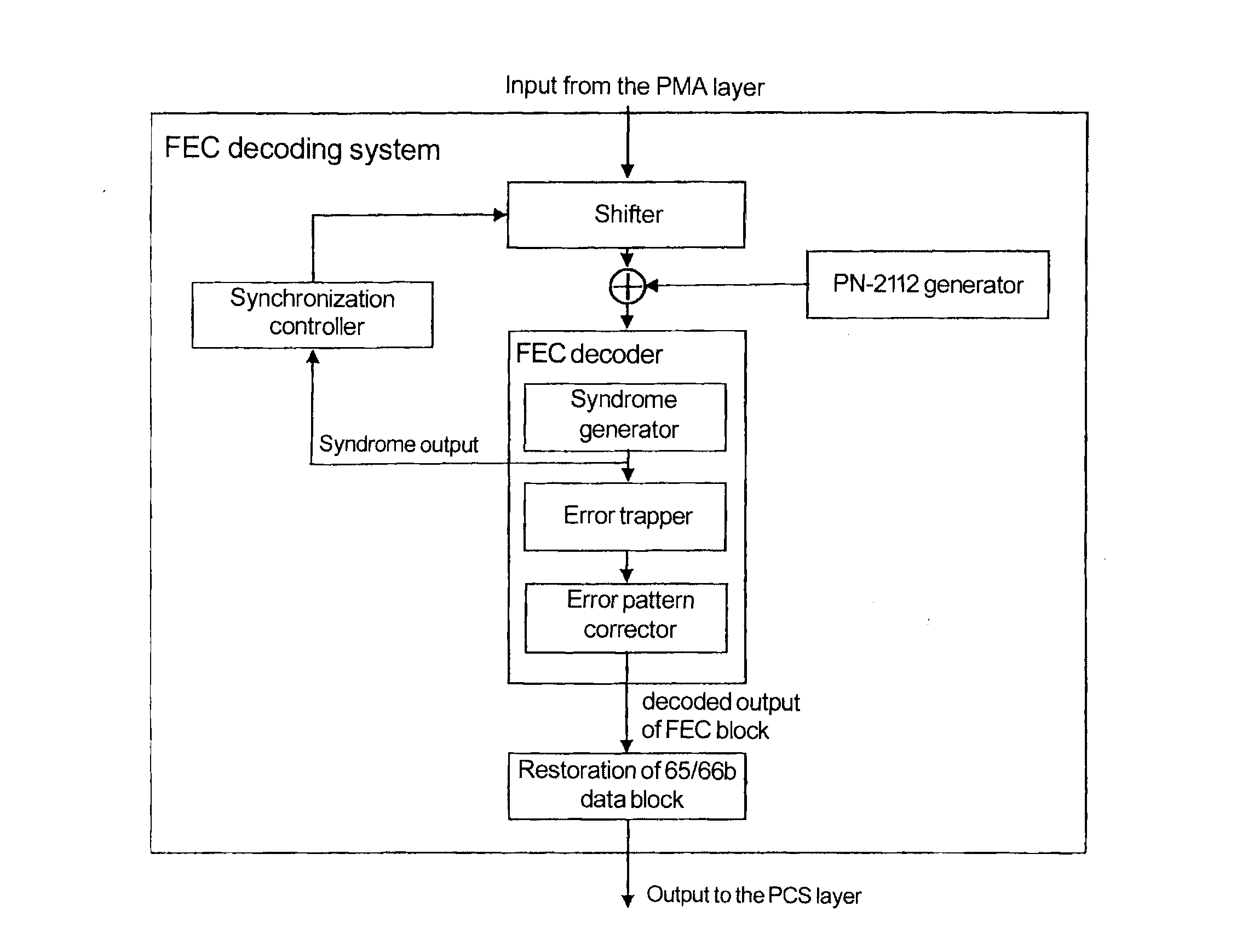
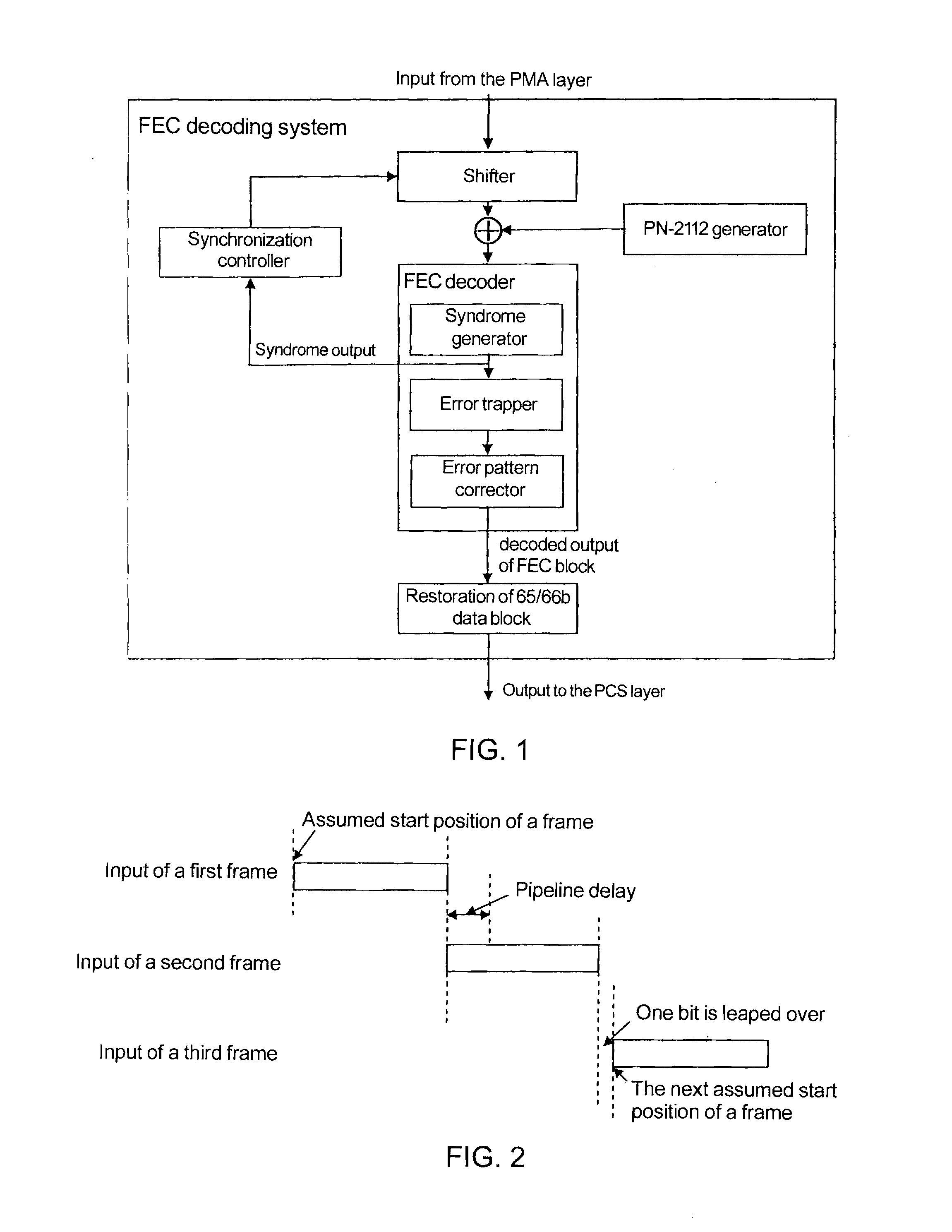
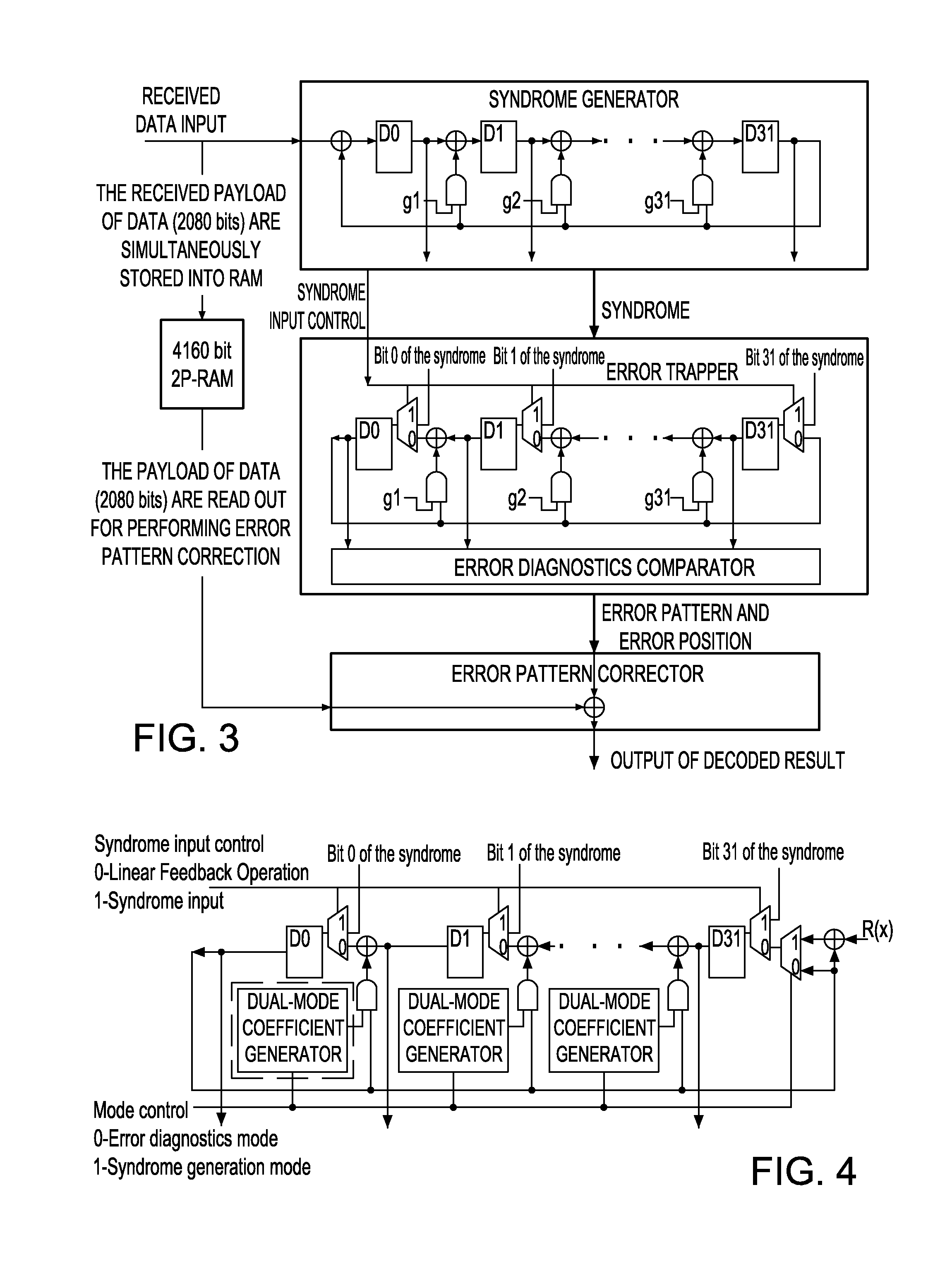
Frame Boundary Detection and Synchronization System for Data Stream Received by Ethernet Forward Error Correction Layer
InactiveUS20110078545A1Improvement of frame boundary detection speedFast frame synchronizationError preventionError coding/decoding sychronisationData streamForward error correction
The present invention discloses a frame boundary detection system and a synchronization system for a data stream received by an Ethernet Forward Error Correction layer. The frame boundary detection system includes a shifter, two descramblers, a syndrome generator and trapper. The error trapper includes a big-little endian mode controller for controlling the big-little endian conversion of the error trapper. If the error trapper operates in the big endian mode, the error trapper implements the function of the syndrome generator, operates at the same time with the syndrome generator, and performs a second FEC check, wherein when the shifter performs the FEC check by intercepting data with a length of one frame plus A bits, two start positions of the frame can be verified, where A is a positive integer less than a length of one frame. The invention can improve the frame boundary detection speed and the frame synchronization speed, and increase only a few hardware overheads.
Owner:IBM CORP
Bit interleaver for low-density parity check codeword having length of 64800 and code rate of 2/15 and 256-symbol mapping, and bit interleaving method using same
ActiveUS9577681B2Efficiently distributedError correction/detection using LDPC codesError coding/decoding sychronisationComputer hardwareSymbol mapping
A bit interleaver, a bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) device and a bit interleaving method are disclosed herein. The bit interleaver includes a first memory, a processor, and a second memory. The first memory stores a low-density parity check (LDPC) codeword having a length of 64800 and a code rate of 2 / 15. The processor generates an interleaved codeword by interleaving the LDPC codeword on a bit group basis. The size of the bit group corresponds to a parallel factor of the LDPC codeword. The second memory provides the interleaved codeword to a modulator for 256-symbol mapping.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Using broadcast for parallelized and rapid slice replication in a dispersed storage network
InactiveUS20170006099A1Error detection/correctionError coding/decoding sychronisationData segmentResult set
Methods for use in a dispersed storage network (DSN) to enable rapid replication of data slices. Following dispersed storage error encoding of a data segment by a device of the DSN, slice naming information is generated for the resulting set of data slices. The slice naming information includes slice names and indicates a naming convention utilized for uniquely identifying replicated data slices. A set of write slice requests, including the slice naming information and the set of data slices, is then generated and broadcast or multicast to multiple sets of storage units of the DSN. Upon receipt of a write slice request, the recipient storage unit generates an updated slice name according to the naming convention and stores both the data slice and updated slice name in local memory. The data slice may be subsequently read from the storage unit by identifying the updated slice name in a read request.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
Common broadcast receiver and method for processing a received signal thereof
InactiveUS20100220779A1Television system detailsMultiple-port networksSignal detectorPublic broadcasting
A common broadcast receiver that receives cable broadcast, terrestrial broadcast, and mobile broadcast signals is provided. The common broadcast receiver includes a synchronizer for receiving any one of a cable broadcast signal, a terrestrial broadcast signal, and a mobile broadcast signal including a training signal generated by a Deterministic Trellis Reset (DTR) and inserted in a data region, and synchronizing the received broadcast signal; and a signal detector for detecting any one of the cable broadcast signal, the terrestrial broadcast signal, and the mobile broadcast signal from the synchronized broadcast signal. Hence, the mobile broadcast signal can be received and processed in addition to the cable broadcast signal and the terrestrial broadcast signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Encoder signal processing device, encoder, and signal processing method and recording medium
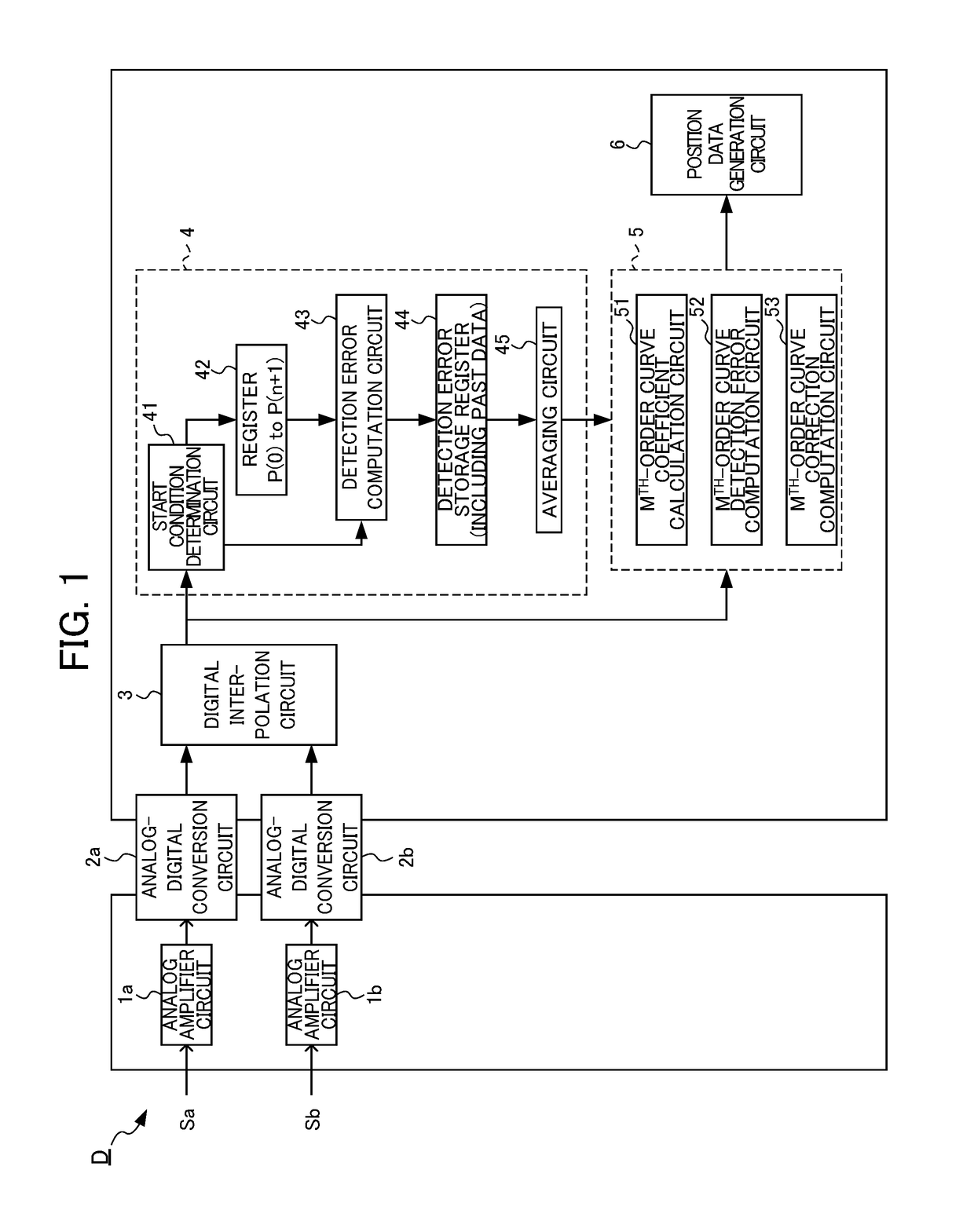
ActiveUS20180041231A1Suppress mutationError coding/decoding sychronisationCode conversionSignal onErrors and residuals
An encoder signal processing device detects position data at every predetermined time interval from an original signal which is an analog amount generated in an encoder according to movement of a measurement target. The encoder signal processing device includes: an approximate curve calculation unit that calculates an approximate curve of a detection error included in the original signal on the basis of the detection error of the position data at at least three or more points; an approximate error computation unit that computes an approximate value of the detection error of the position data at an arbitrary time point on the basis of the approximate curve of the detection error; and a position data correction unit that corrects the detection error of the position data at the arbitrary time point on the basis of the approximate value of the detection error of the position data.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com