Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
77 results about "Active fixation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
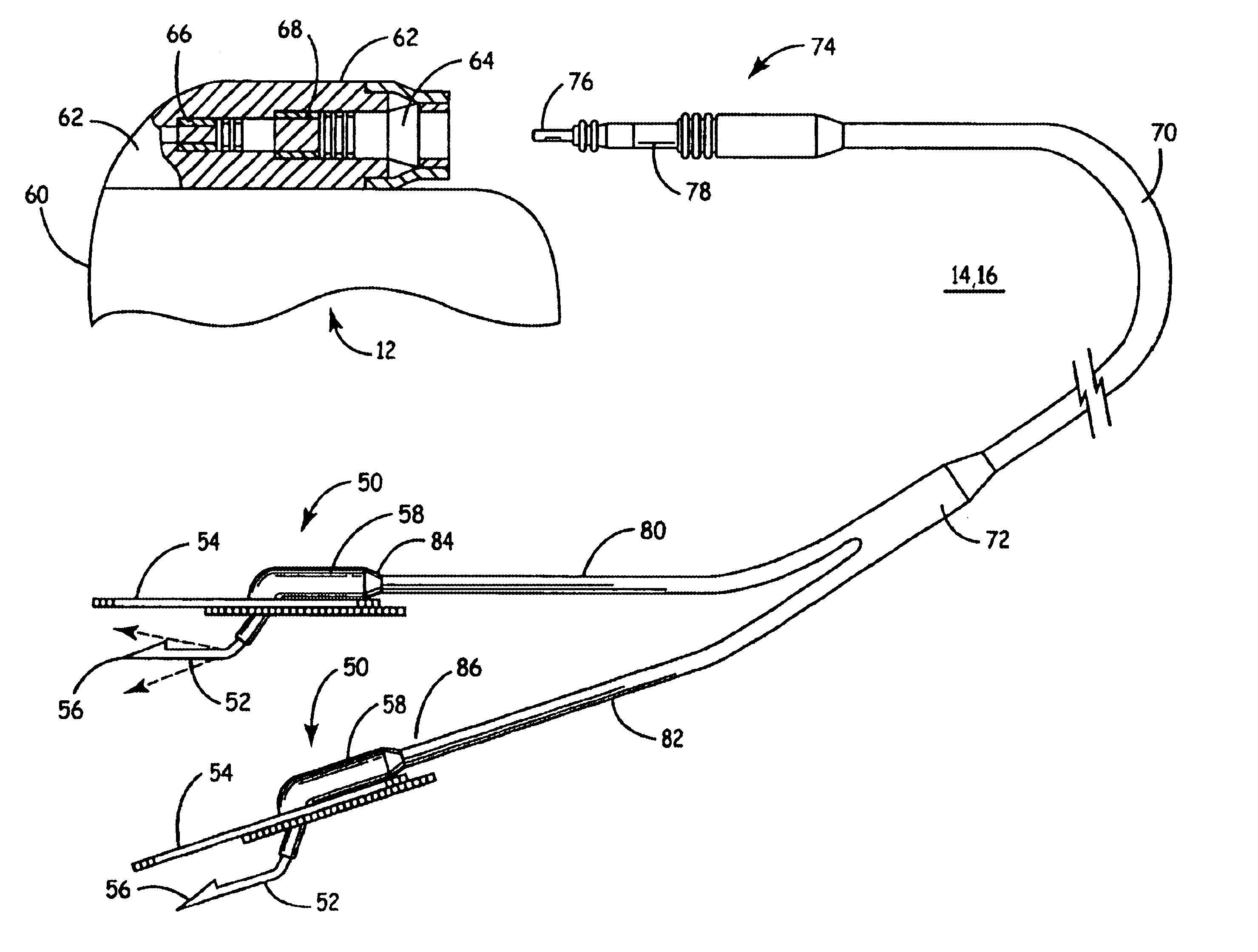
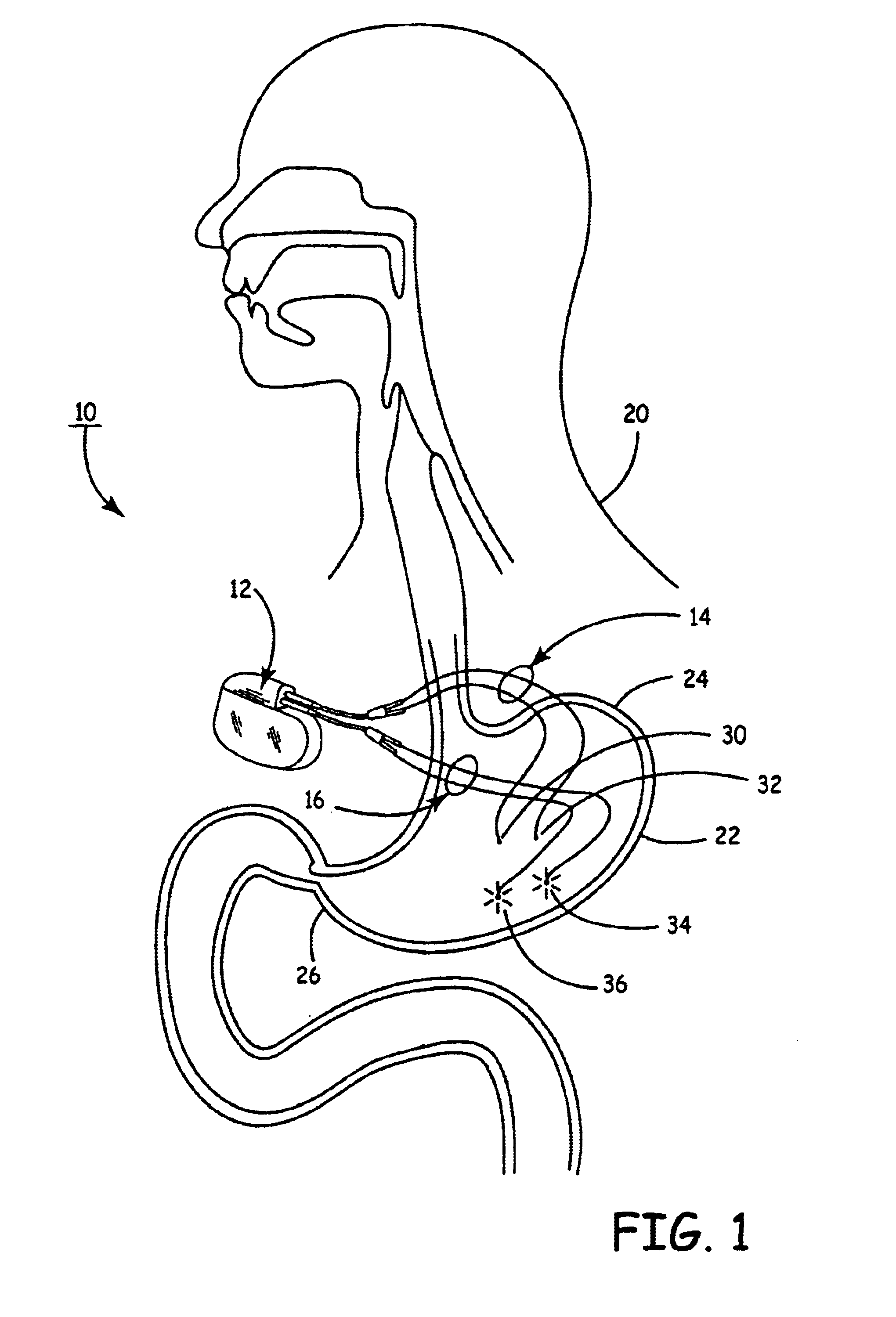
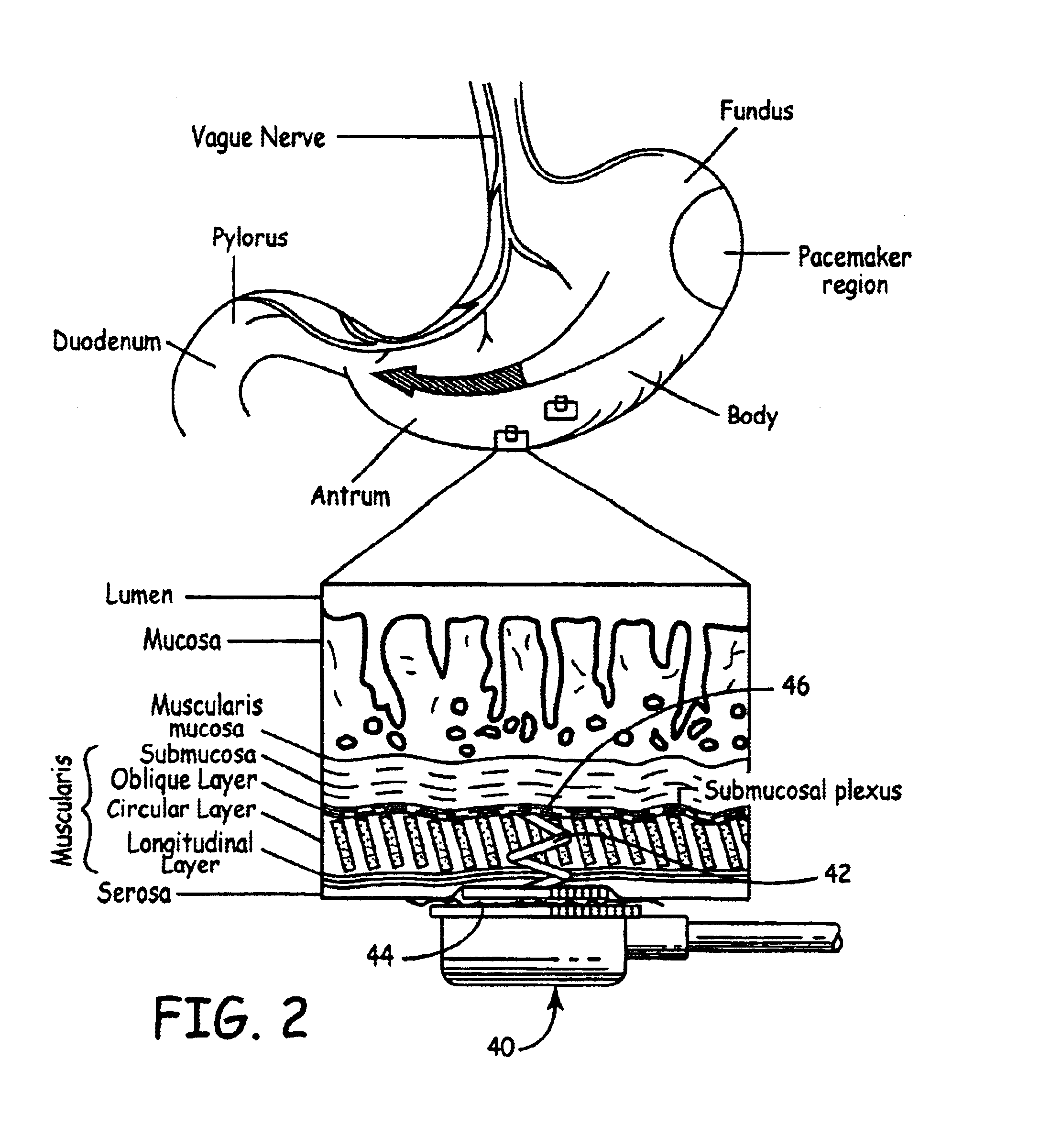
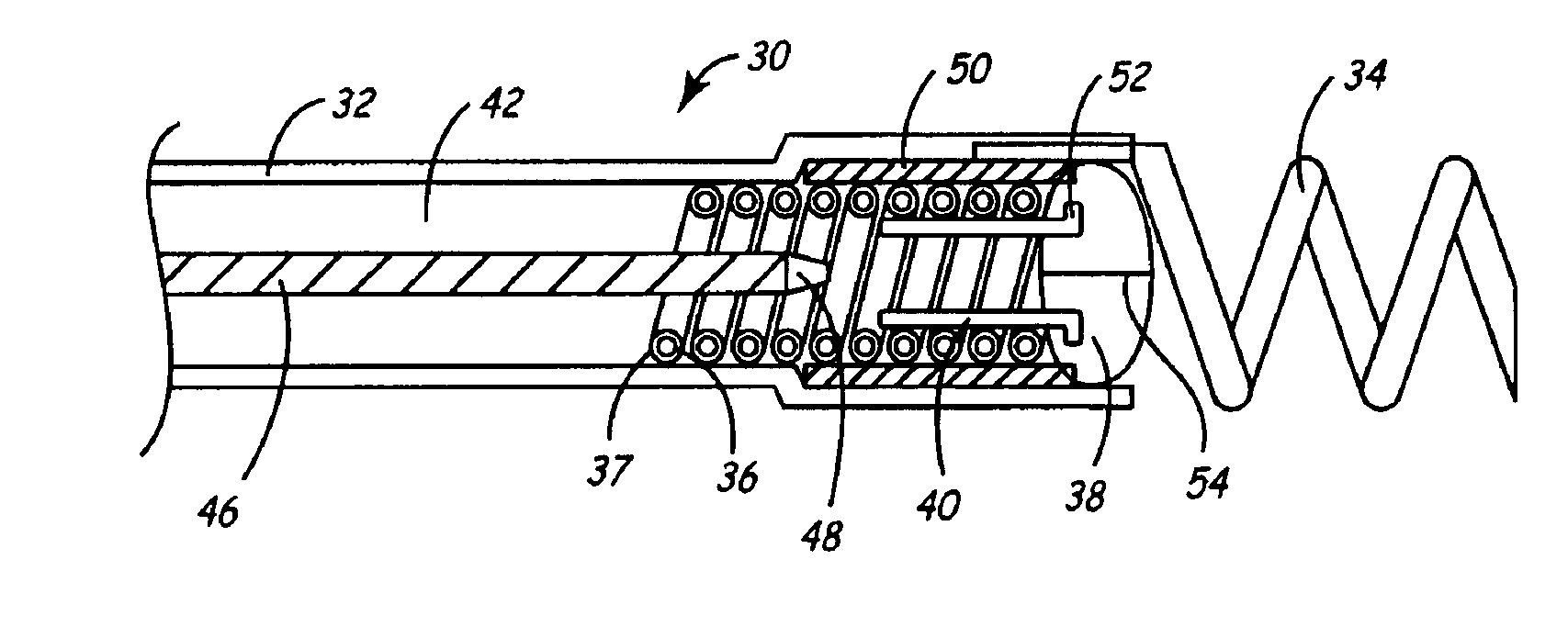
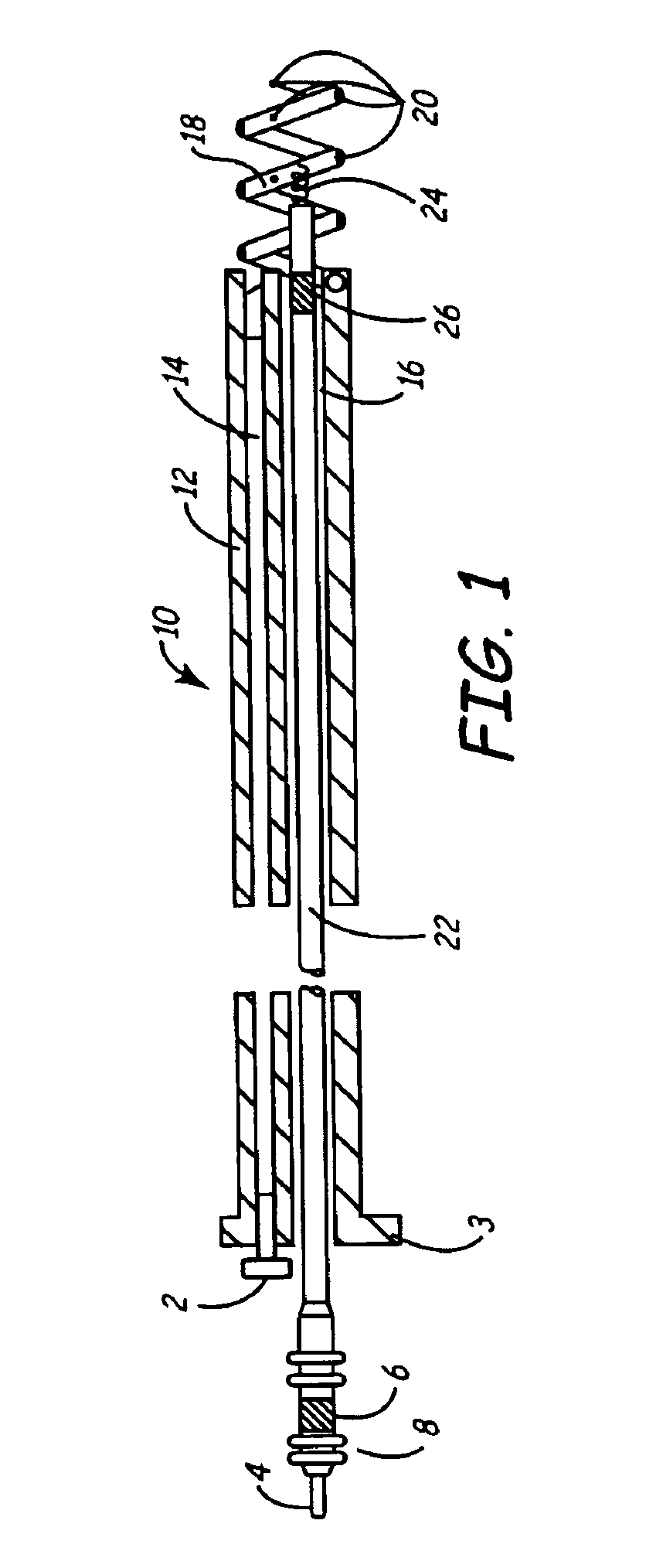
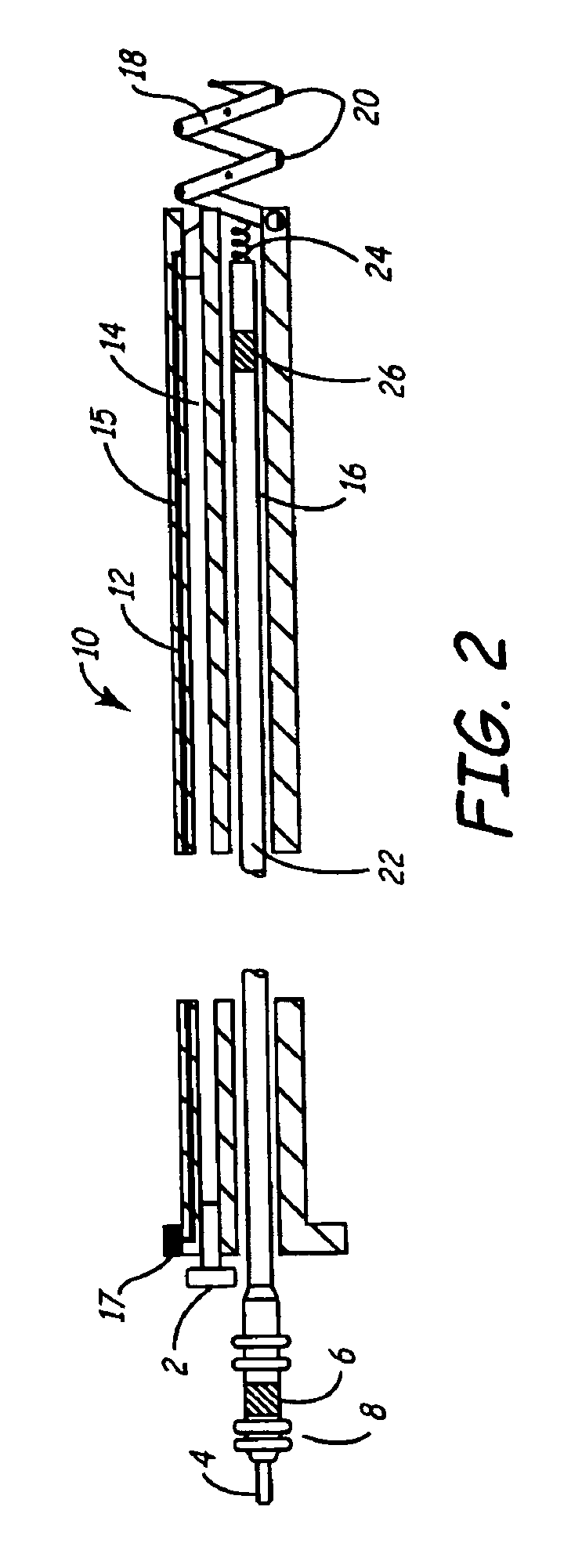
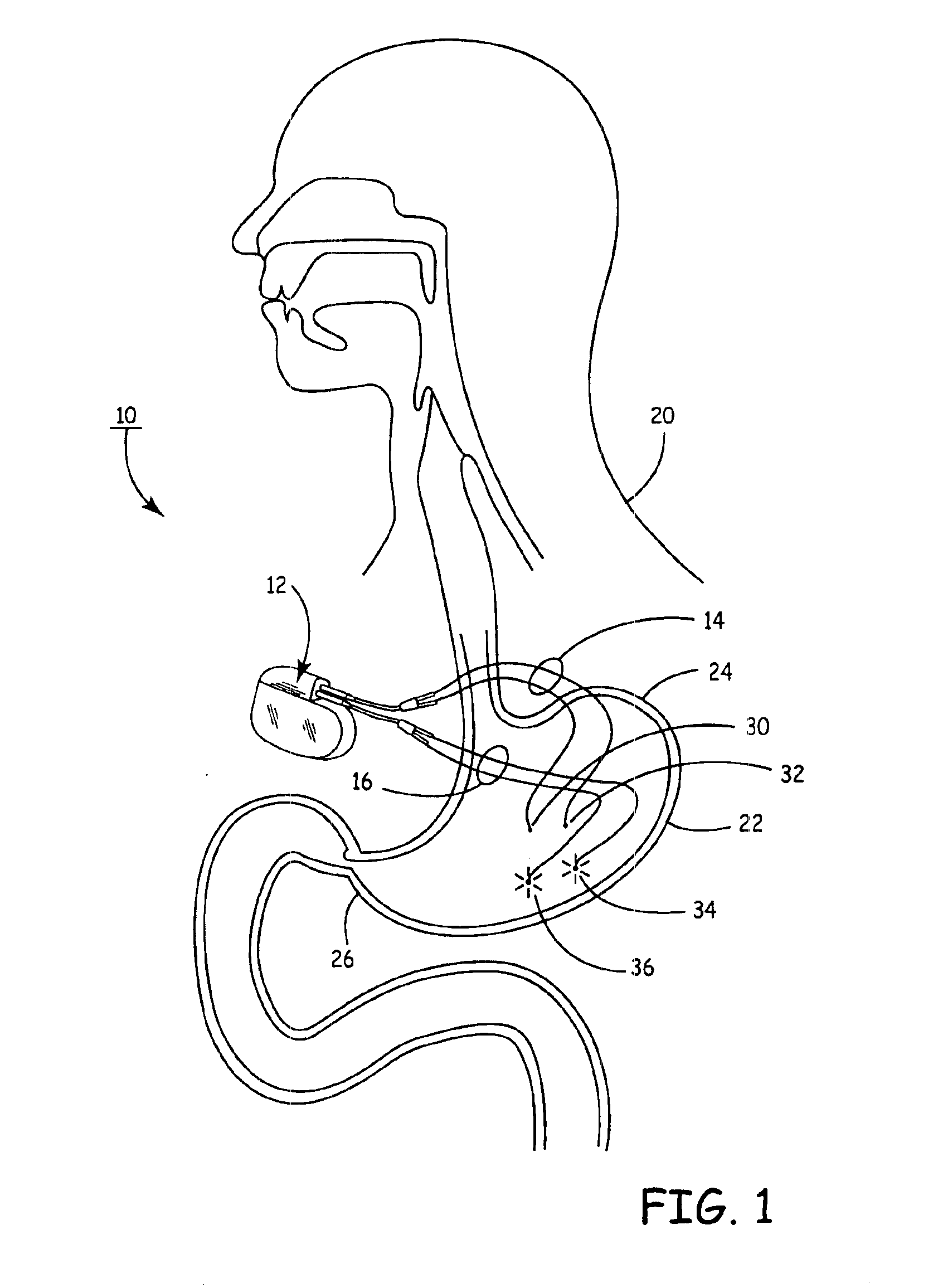
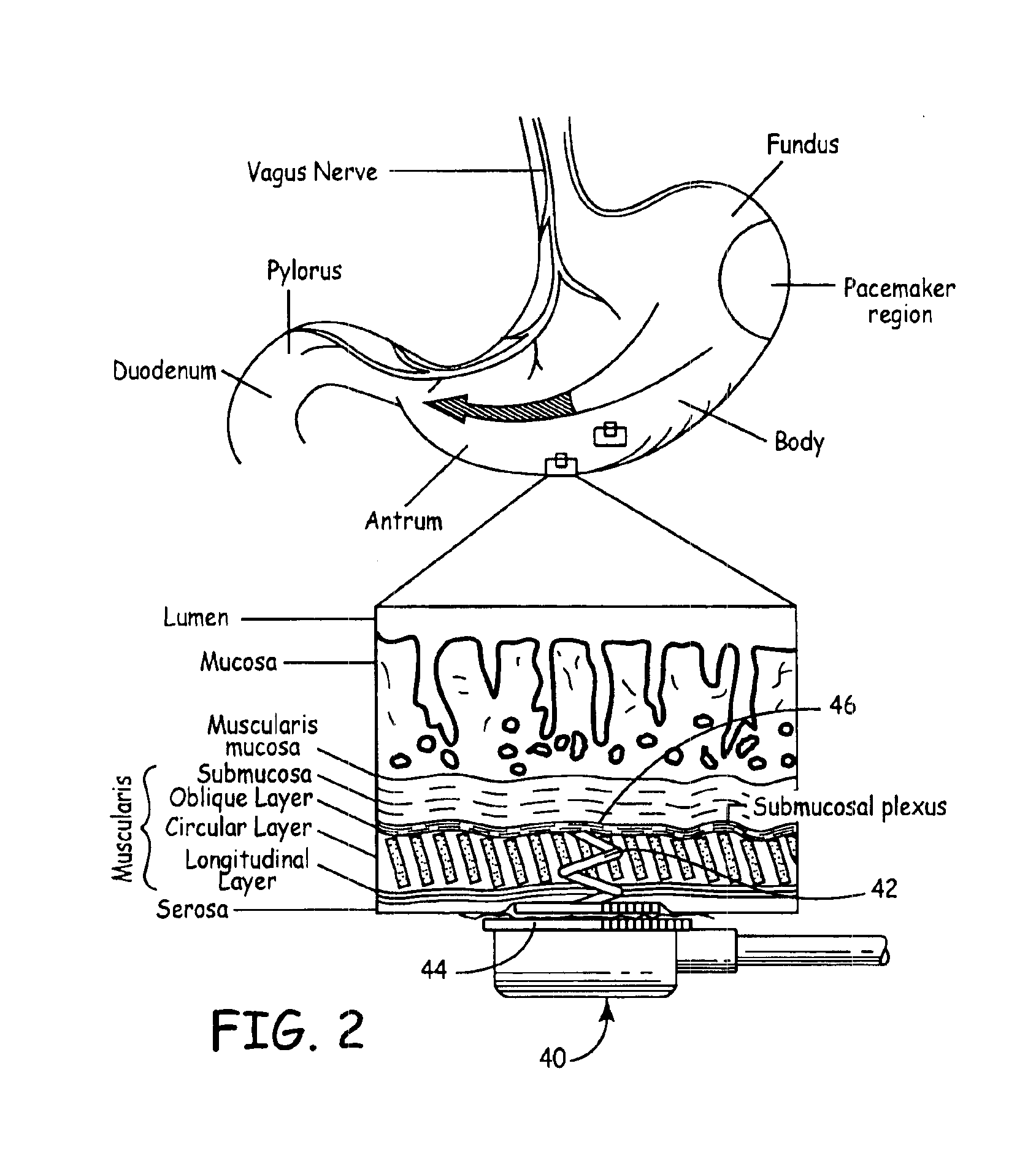
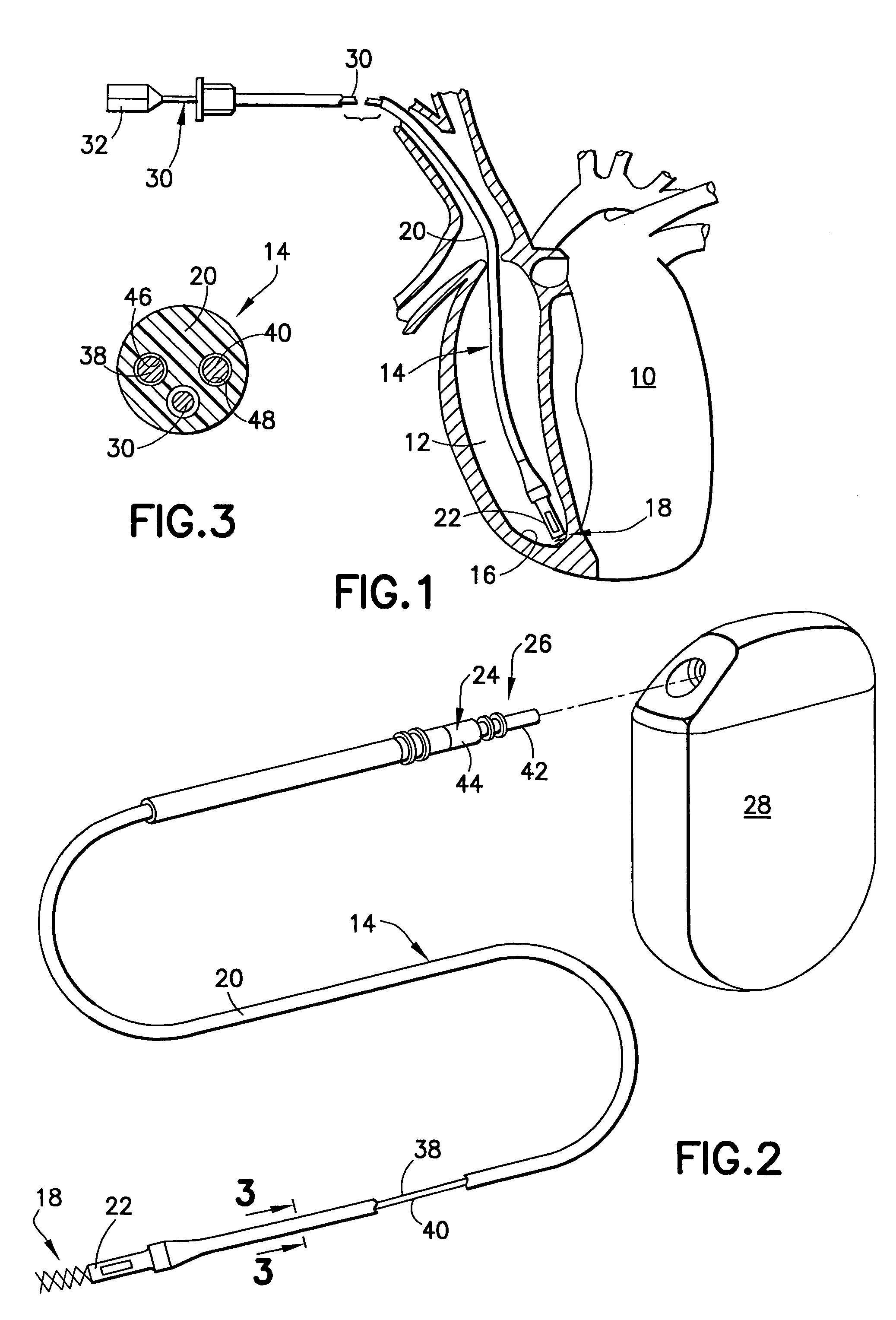
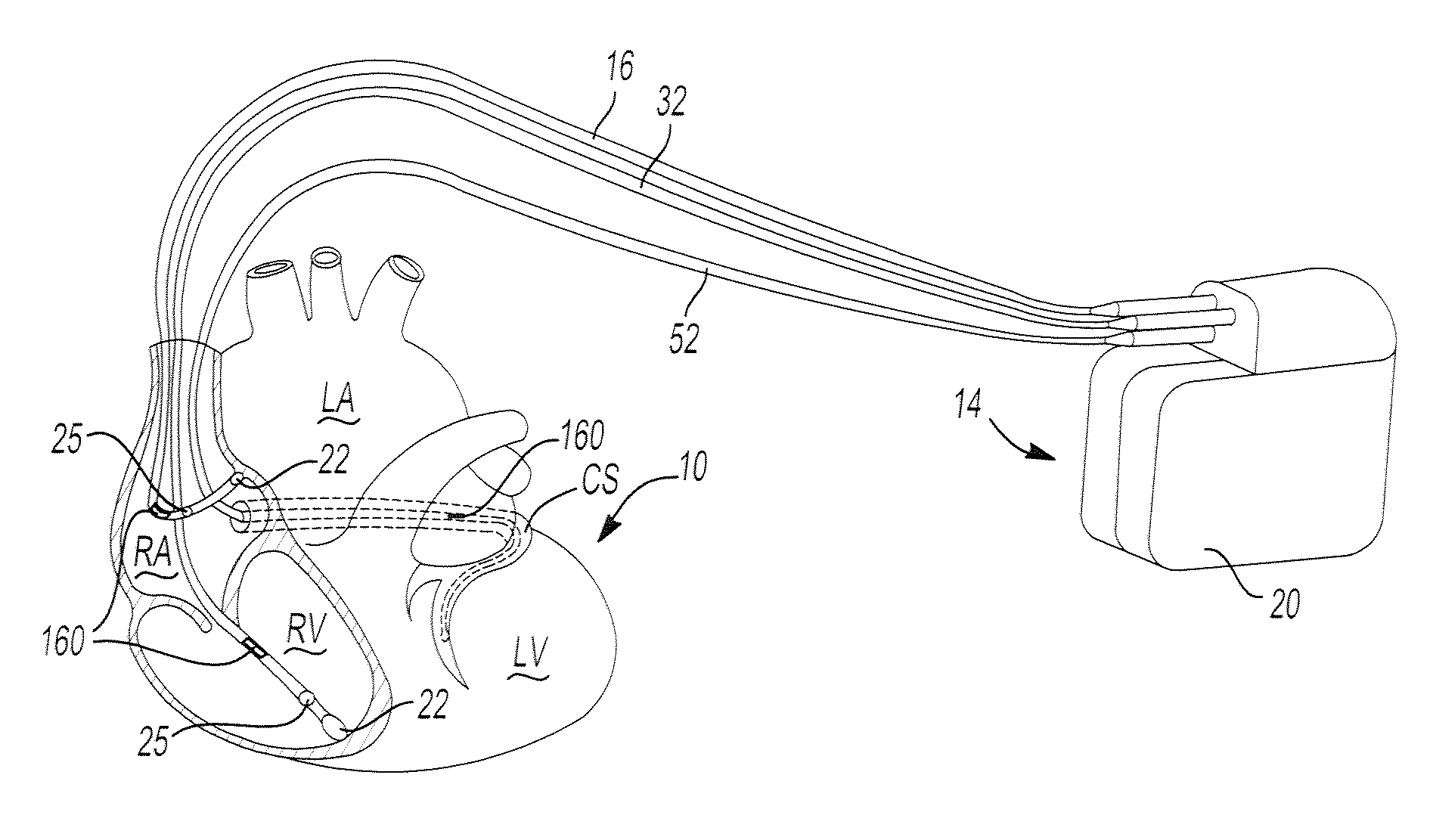
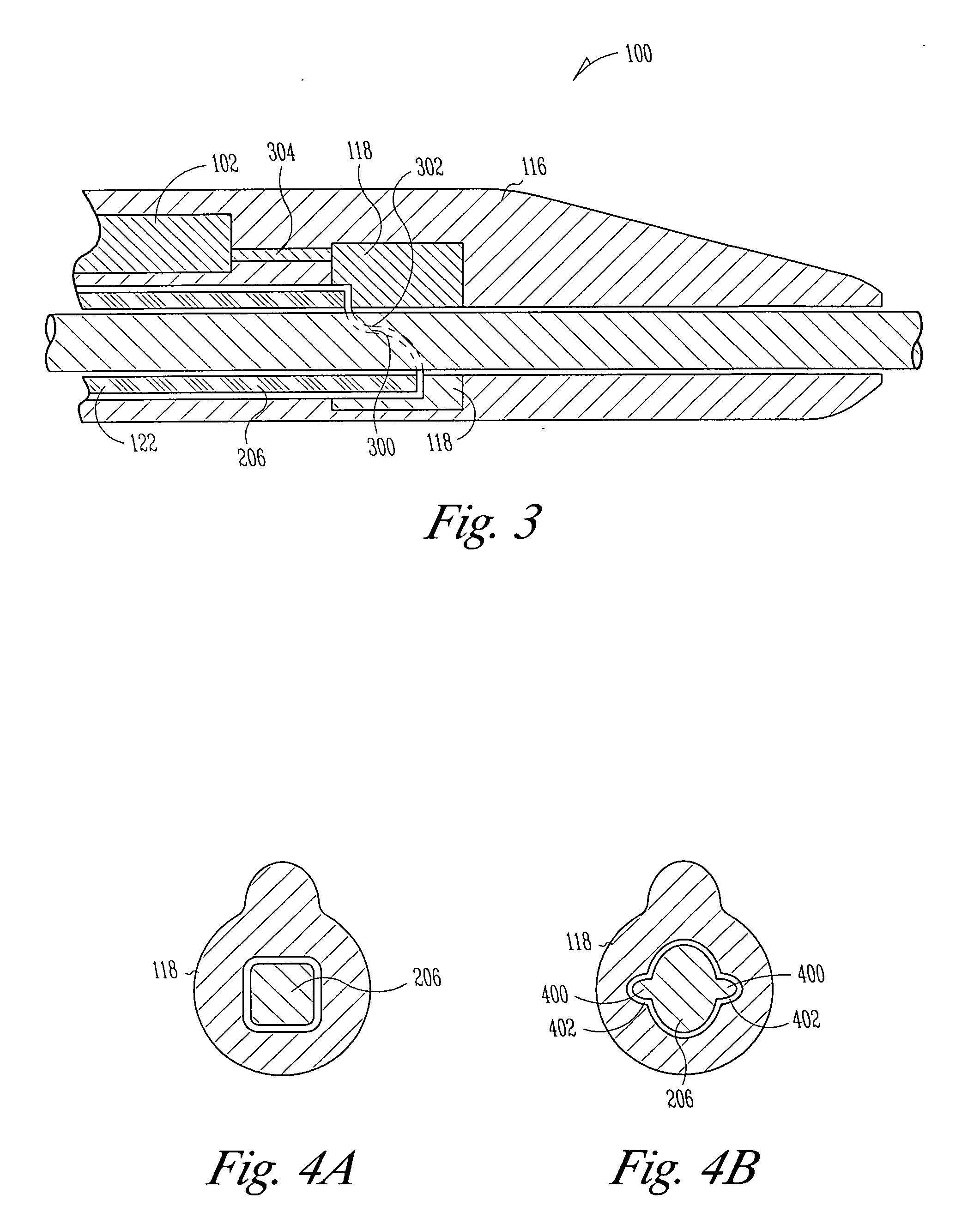
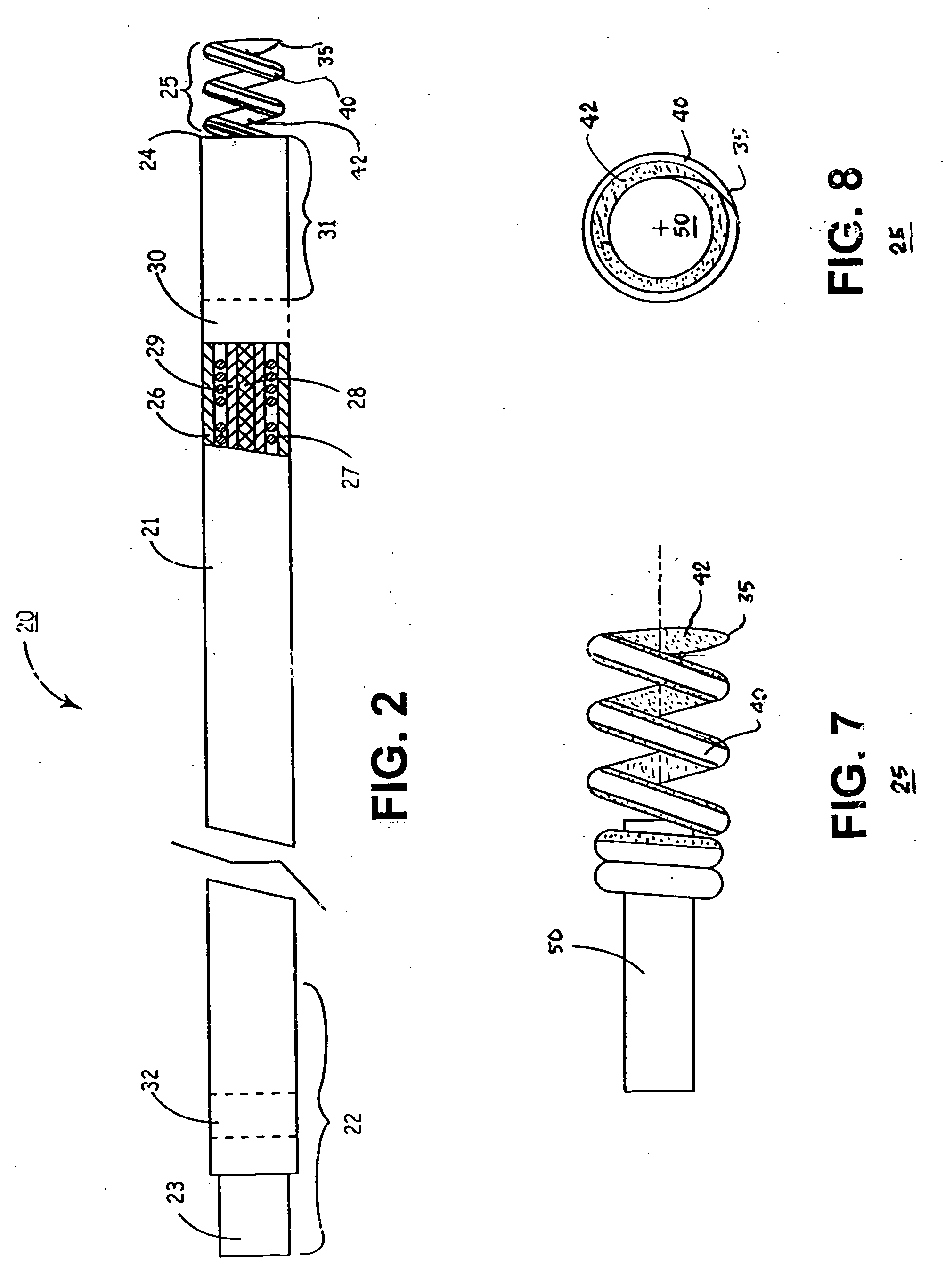
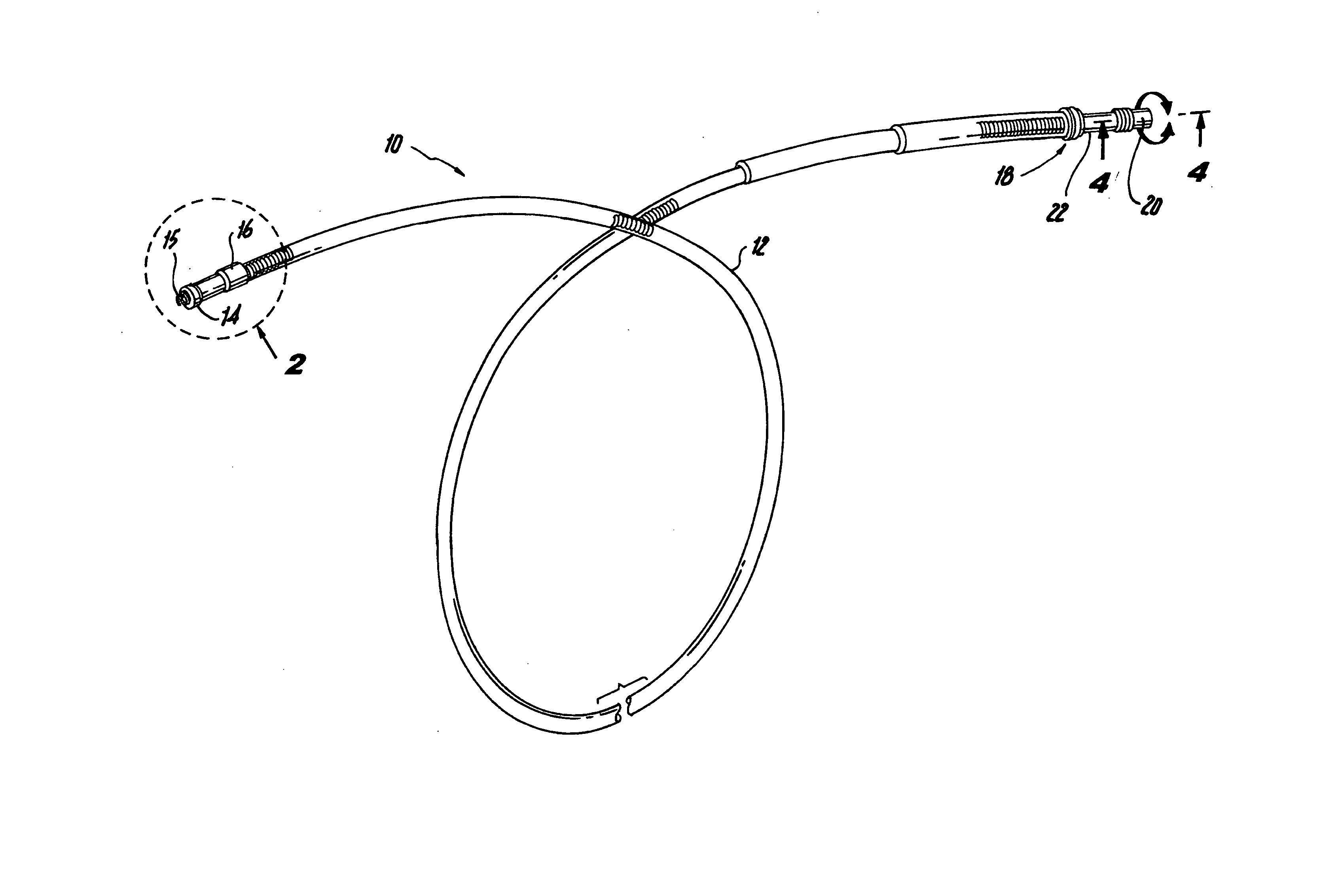
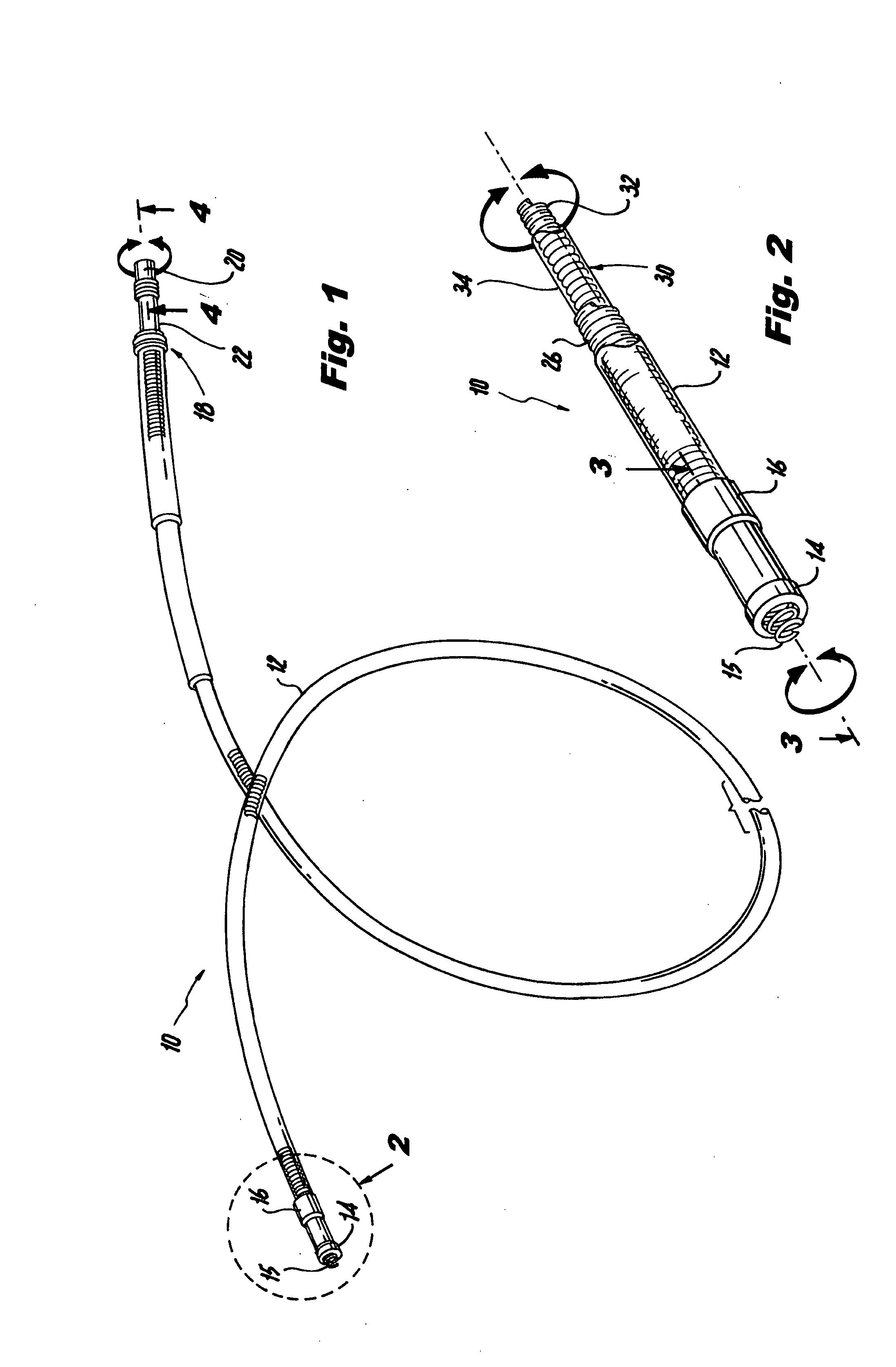
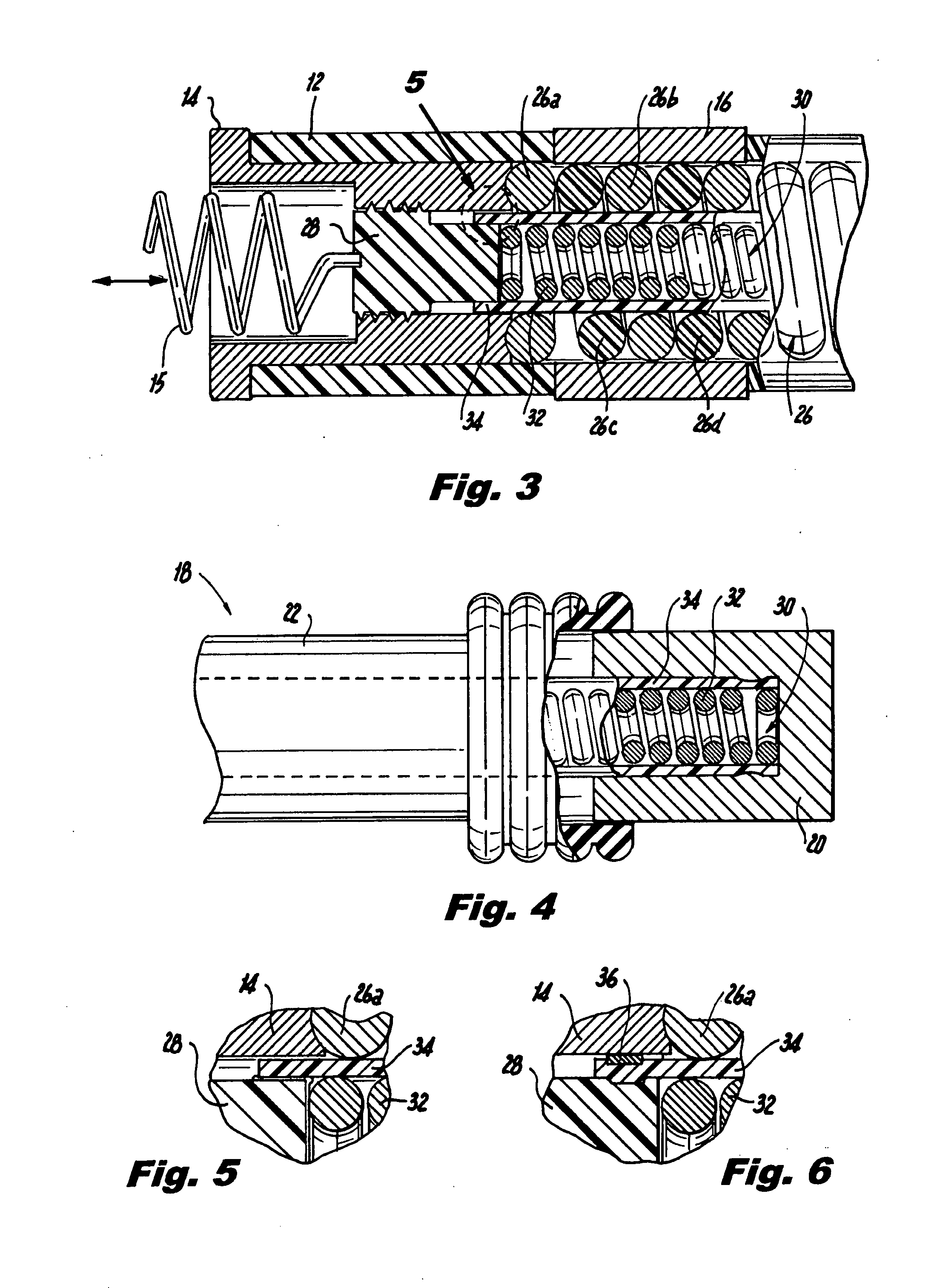
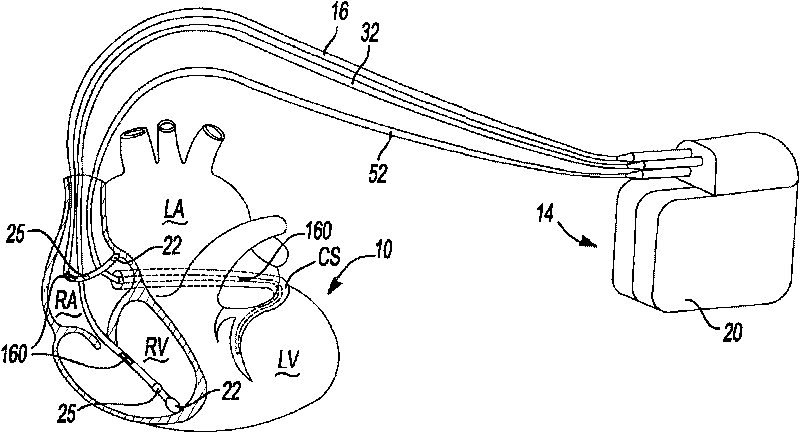
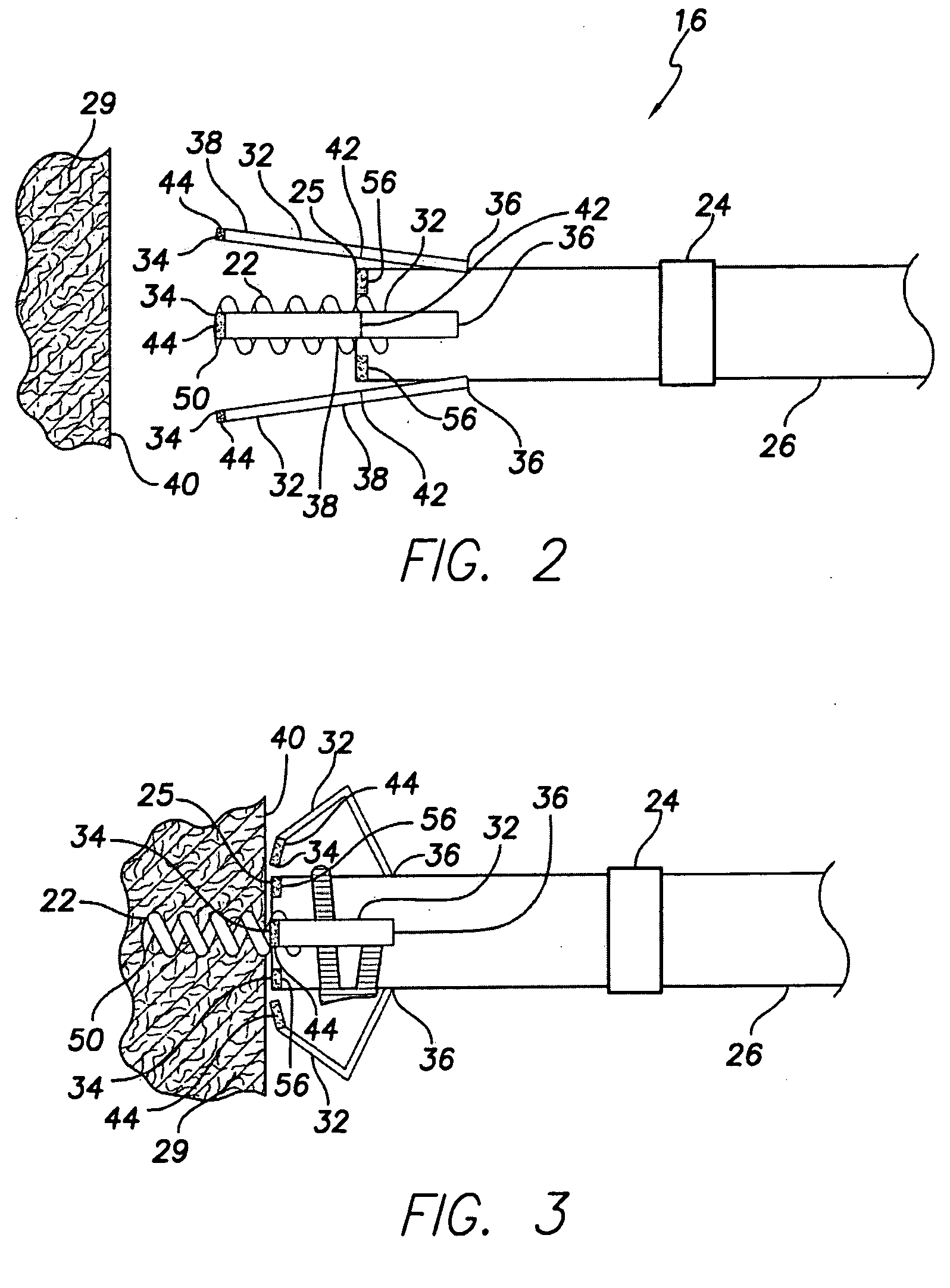
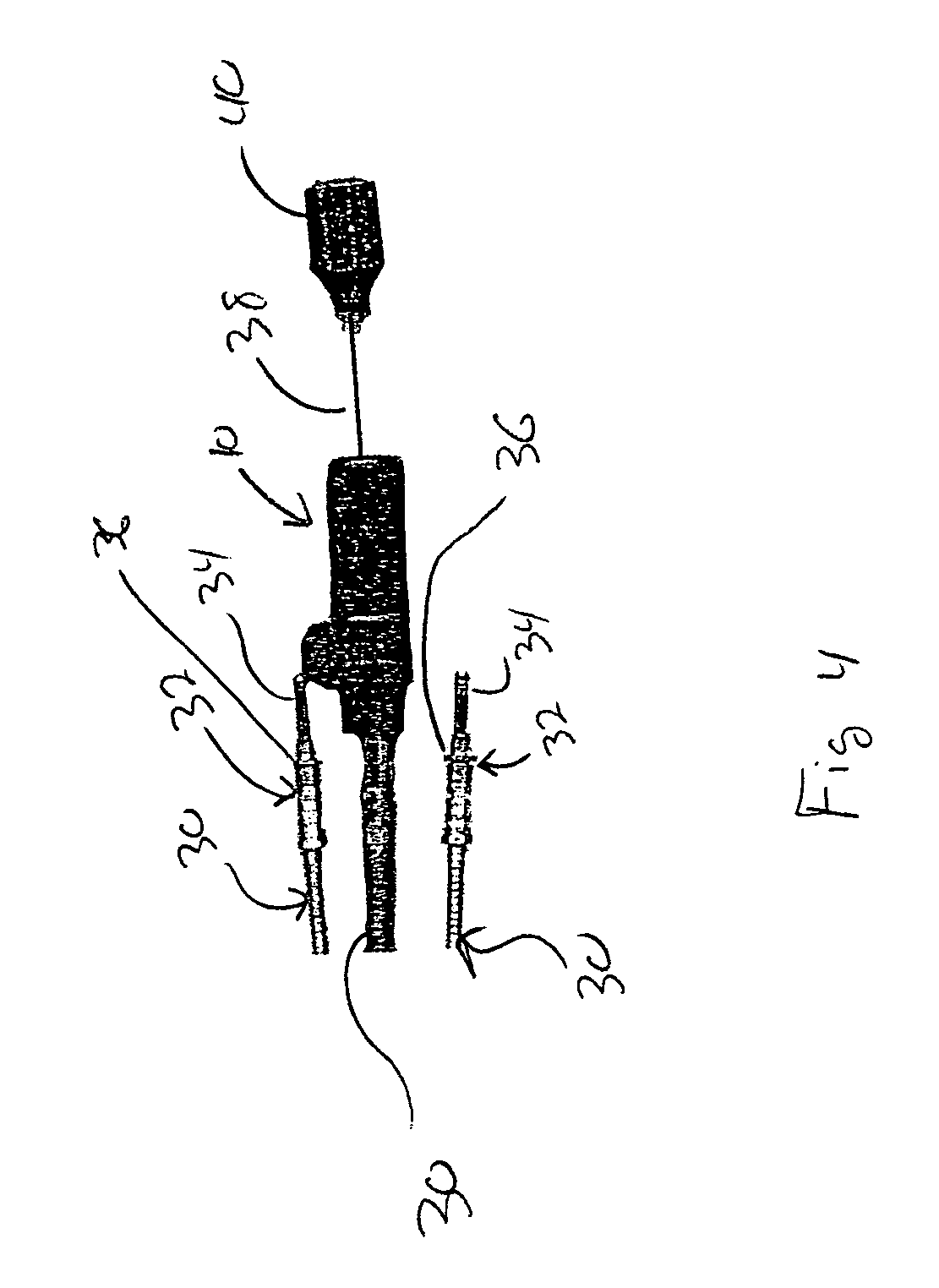
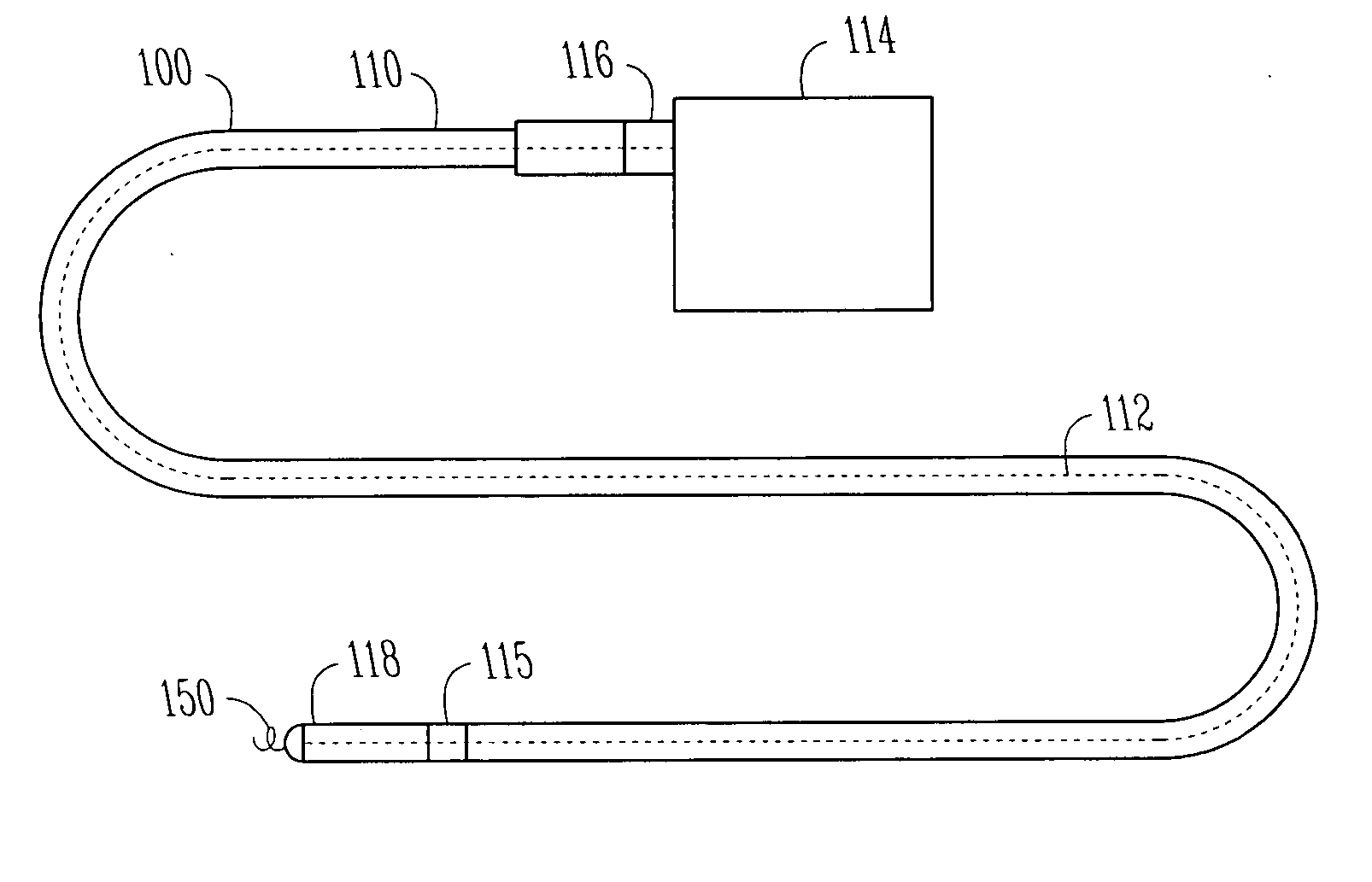
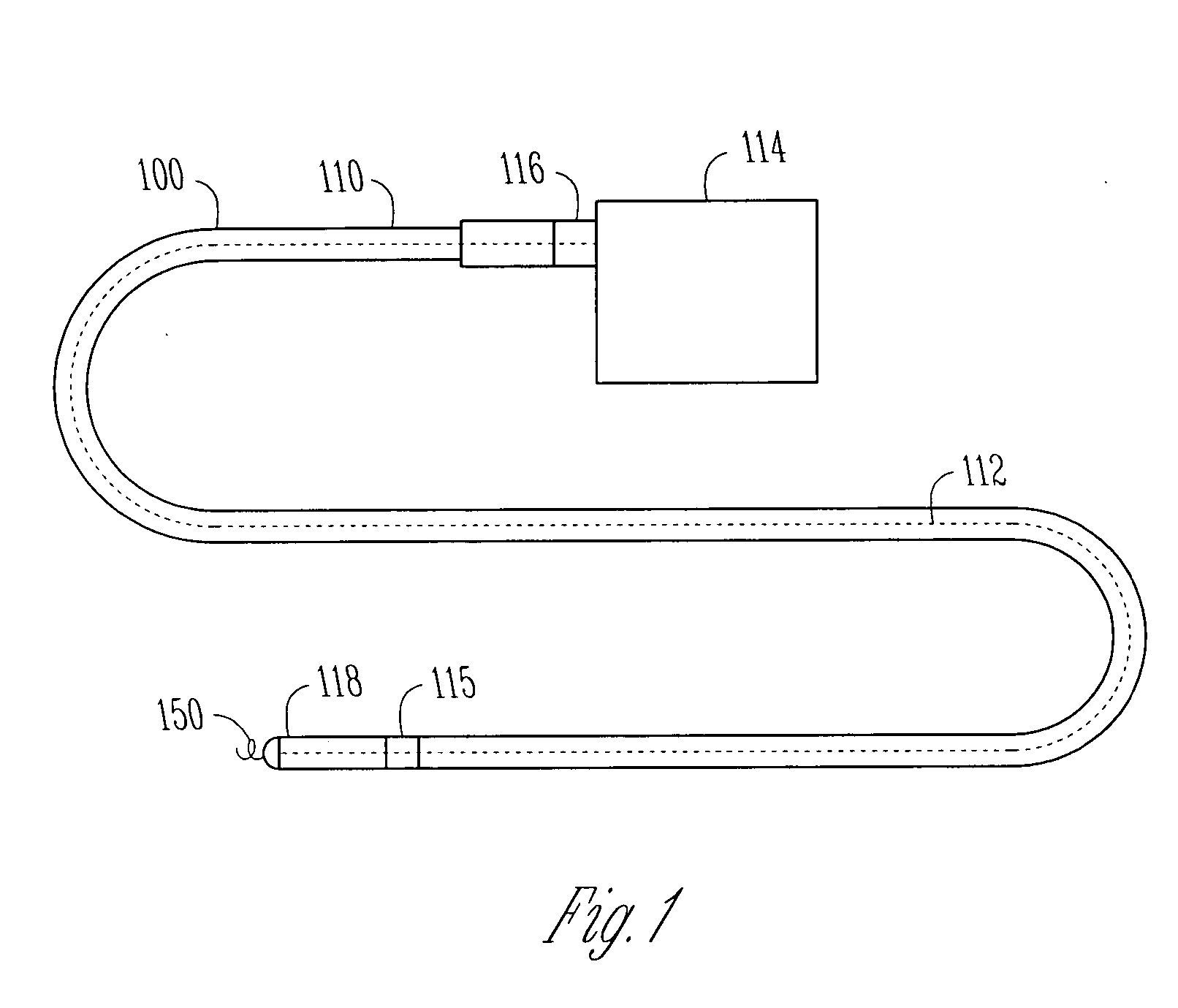
Implantable bifurcated gastrointestinal lead with active fixation
InactiveUS6876885B2Maximizing numberSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesTherapeutic DevicesActive fixation
Bifurcated, active fixation, gastrointestinal leads adapted to be implanted within the body at a site of the GI tract to conduct electrical stimulation and electrical signals of the GI tract between the gastrointestinal stimulator and the site are disclosed. The GI tract lead has a lead body comprising a common lead body trunk extending from a lead body trunk proximal end to a junction with a first plurality of lead body legs that extend from the junction to a like first plurality of lead body leg distal ends. An electrode head is formed at each lead body leg distal end having a plate and supporting at least one stimulation / sense electrode and an active fixation mechanism, whereby a plurality of active fixation attachment mechanisms are supported by a like plurality of electrode heads. The plurality of electrode heads can be affixed by the fixation mechanism at a plurality of spaced apart locations of the GI tract. The plurality of electrode heads can be affixed spaced apart an optimal distance for efficacious sensing and / or stimulation accommodating the physiology and any defects or surgical interventions of the physiology or other therapeutic equipment or IMDs that restrict full access to the GI tract.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
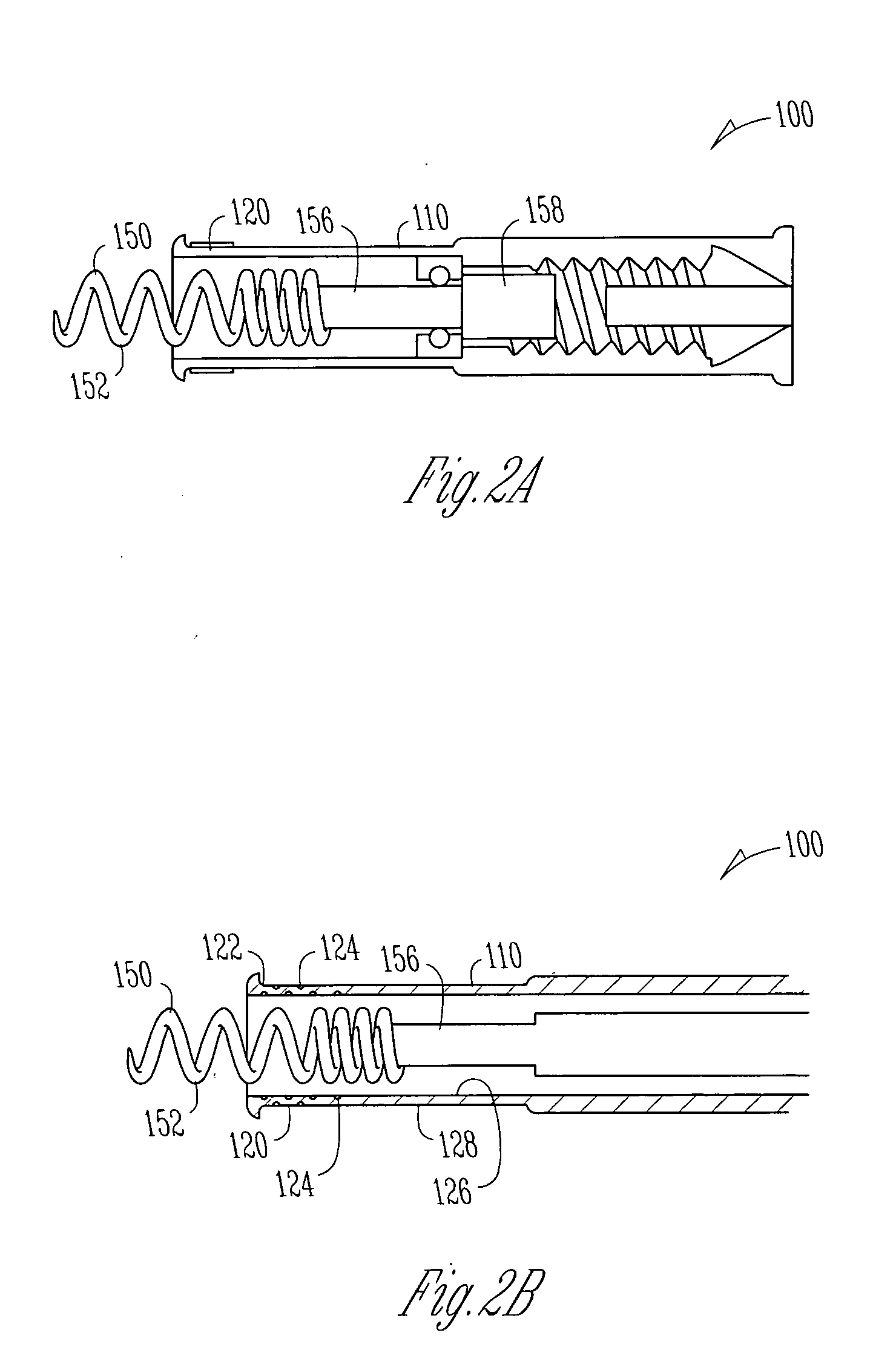
Delivery of active fixation implatable lead systems
An implantable lead system includes an elongated device slideably engaged within a lumen of a lead body. A distal portion of the elongated device is slidable through a helix tip coupled to a distal end of the lead body by passing through a pierceable fluid-tight seal disposed in proximity to the distal end of the lead body; the seal prevents ingress of bodily fluid into the lumen of the lead body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable gastrointestinal lead with active fixation
InactiveUS6952613B2Avoid displacementReduce polarizationSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesActive fixationCatheter
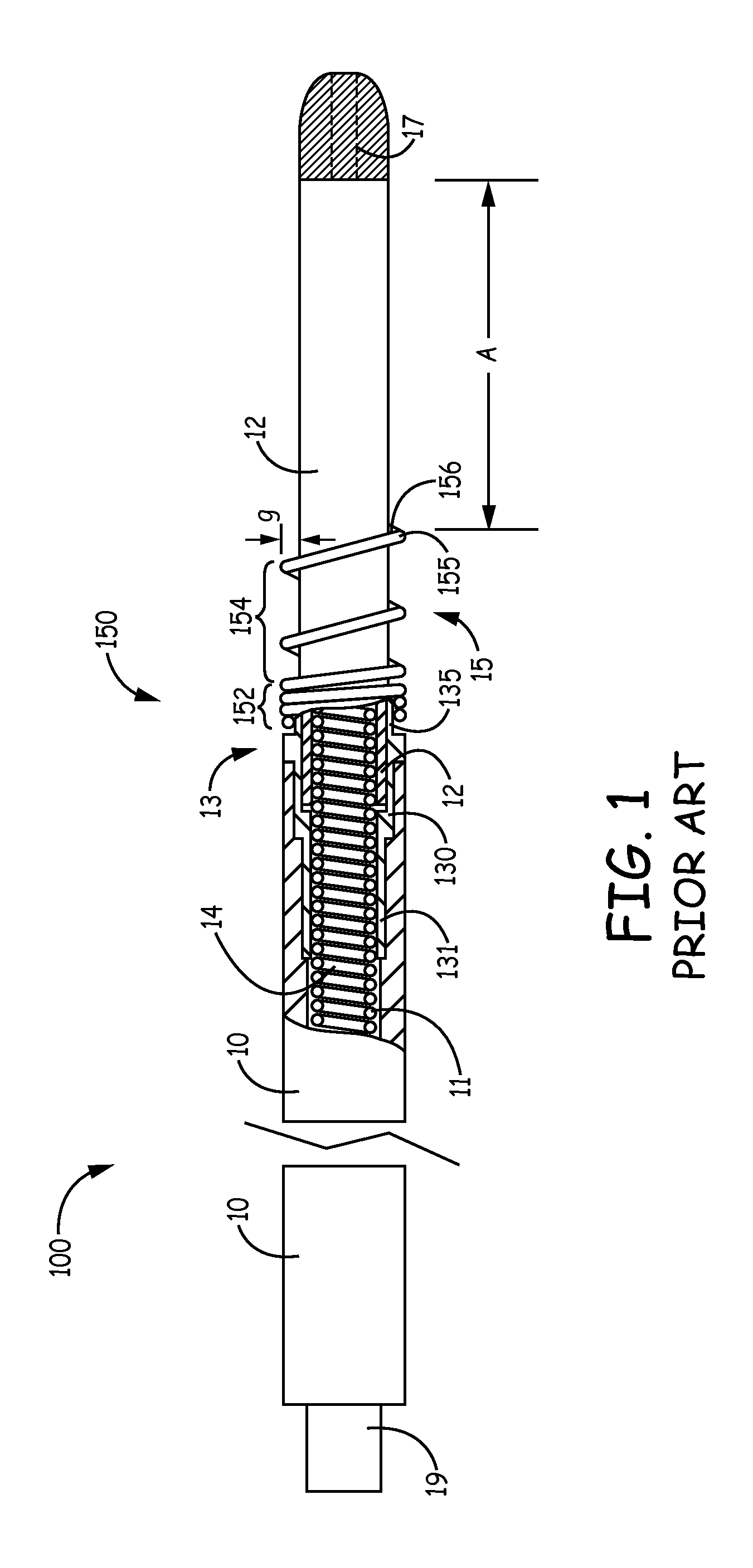
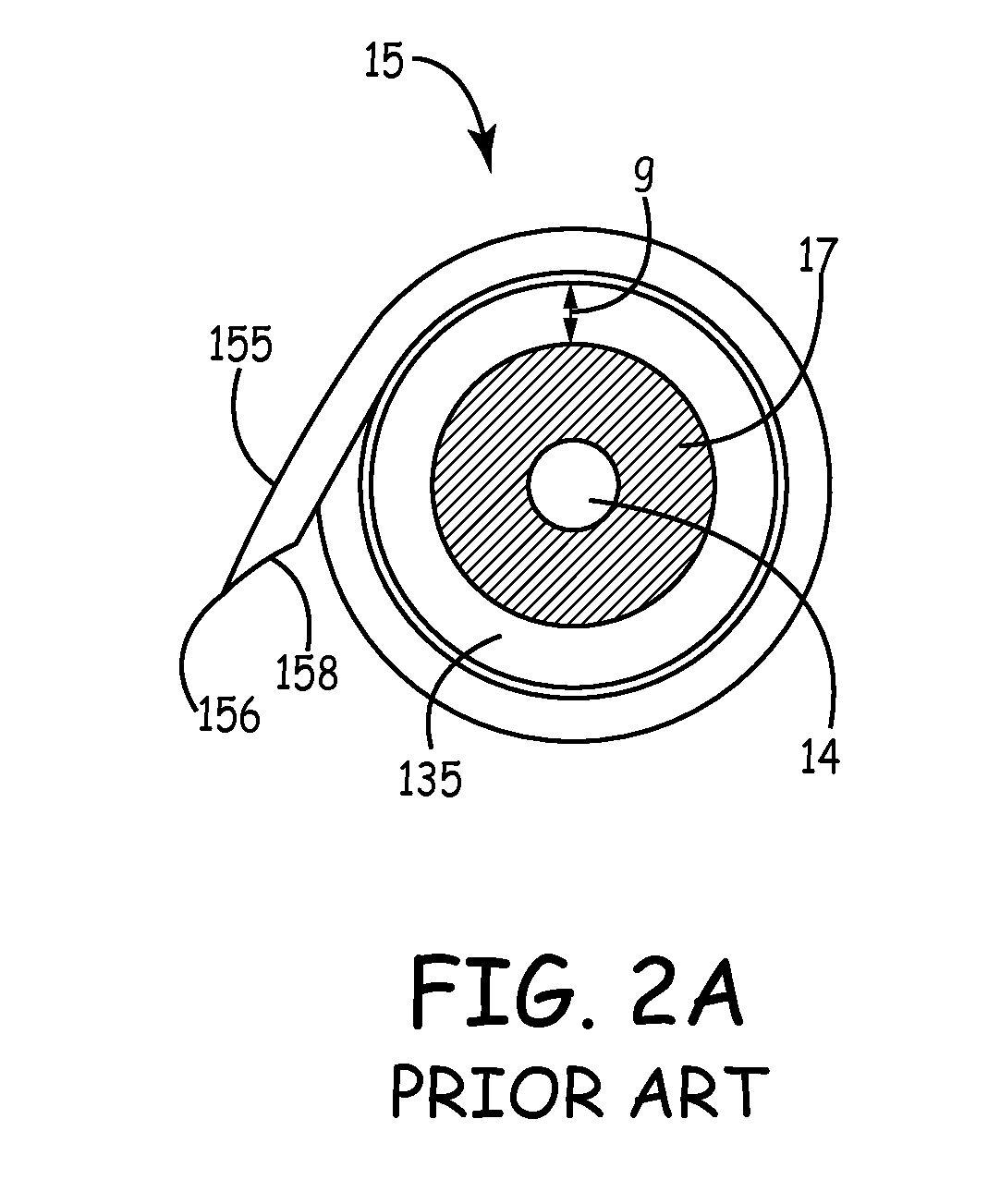
Active fixation, gastrointestinal leads adapted to be implanted within the body at a site of the GI tract to conduct electrical stimulation from an implantable or external gastrointestinal stimulator to the site and to conduct electrical signals of the GI tract from the site to the implantable or external gastrointestinal stimulator are disclosed. Disclosed active fixation mechanisms include one or more of hooks, and helixes extending from stops, e.g. plates, of an electrode head and functioning as stimulation / sense electrodes in unipolar and bipolar configurations or simply as fixation mechanisms. The active fixation mechanisms are coated to reduce inflammation and polarization effects.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
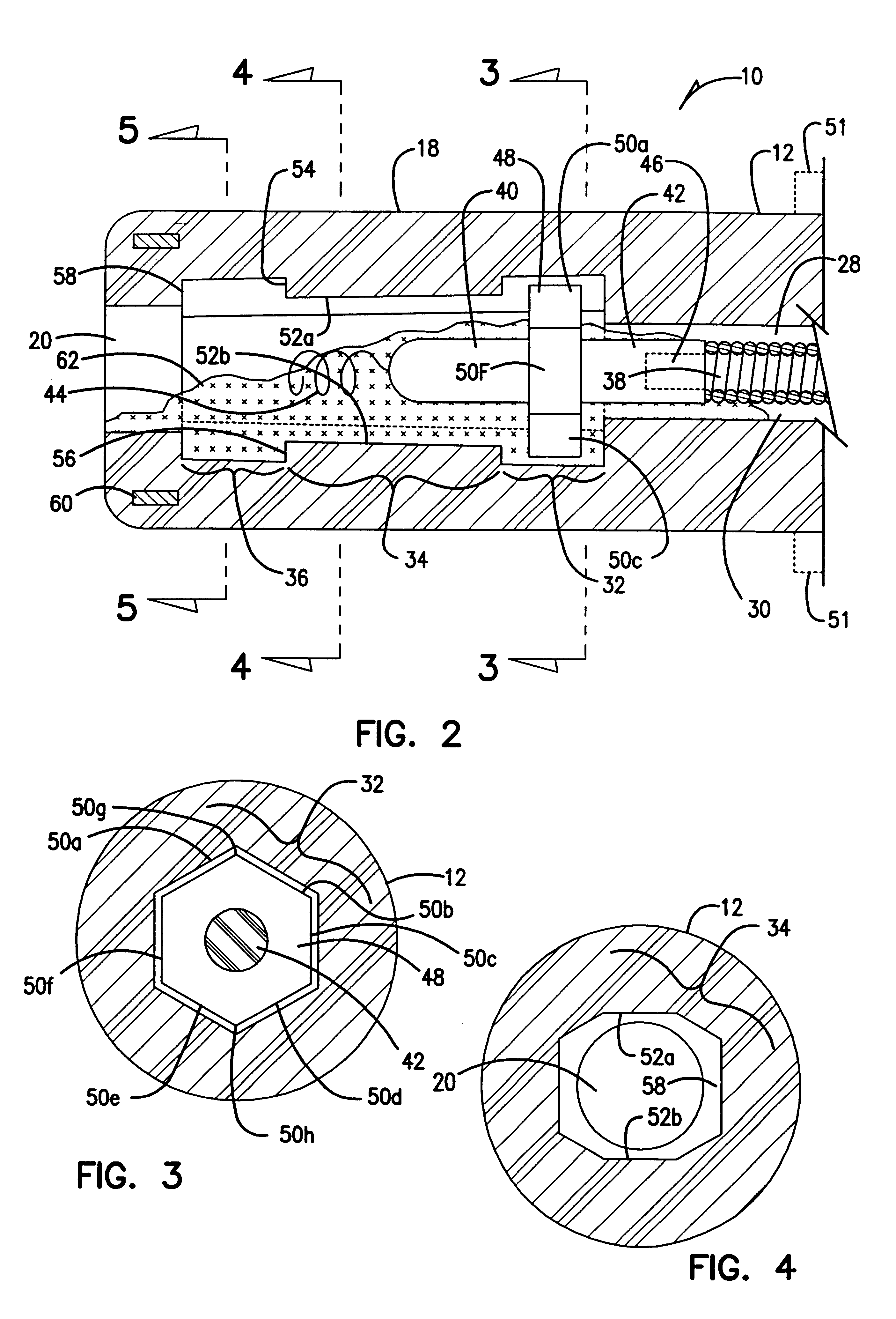
Active fixation lead with multiple density
An implantable lead adapted to transmit electrical signals between a connector assembly on a proximal end of the lead and at least one electrode carried by a distal end of the lead comprises a helical fixation element extendable and retractable from the distal end of the lead, the header comprising (a) an inner header part comprising an electrically conductive material that is substantially transparent fluoroscopically, the inner header part having a distal end, (b) an outer header part comprising an electrically insulating material, and (c) a collar attached to the distal end of the inner header part. The collar comprises a material that is substantially opaque fluoroscopically. The collar may be electrically conductive, and electrically and mechanically connected, preferably by means of an overlap joint, to the distal end of the inner header part. The conductive collar thus may be electrically connected to an electrical contact on the connector assembly via the electrically conductive inner header part, whereby the collar may be used for mapping the electrical activity of local body tissue. Alternatively, the collar may be electrically isolated by, for example, covering the outer surface of the collar with an electrically insulating layer.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Helical fixation elements for subcutaneous electrodes
Subcutaneous leads that incorporate active fixation elements including, for example, helical coils, provide for fixation of cardiac lead components within a patient. An implantable lead includes a lead body with a supported electrode configured for subcutaneous non-intrathoracic placement within a patient. A fixation element is provided on the implantable lead and configured to actively secure one or both of the subcutaneous electrode and the lead body in tissue. A delivery apparatus comprising a sheath may be employed that is configured to introduce the lead to a desired subcutaneous non-intrathoracic location. Lead delivery typically involves introducing a sheath into a subcutaneous non-intrathoracic body location of a patient, providing a lead supporting an electrode, advancing the lead through the sheath, actively fixing the lead to tissue, and thereafter removing the sheath from the patient.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
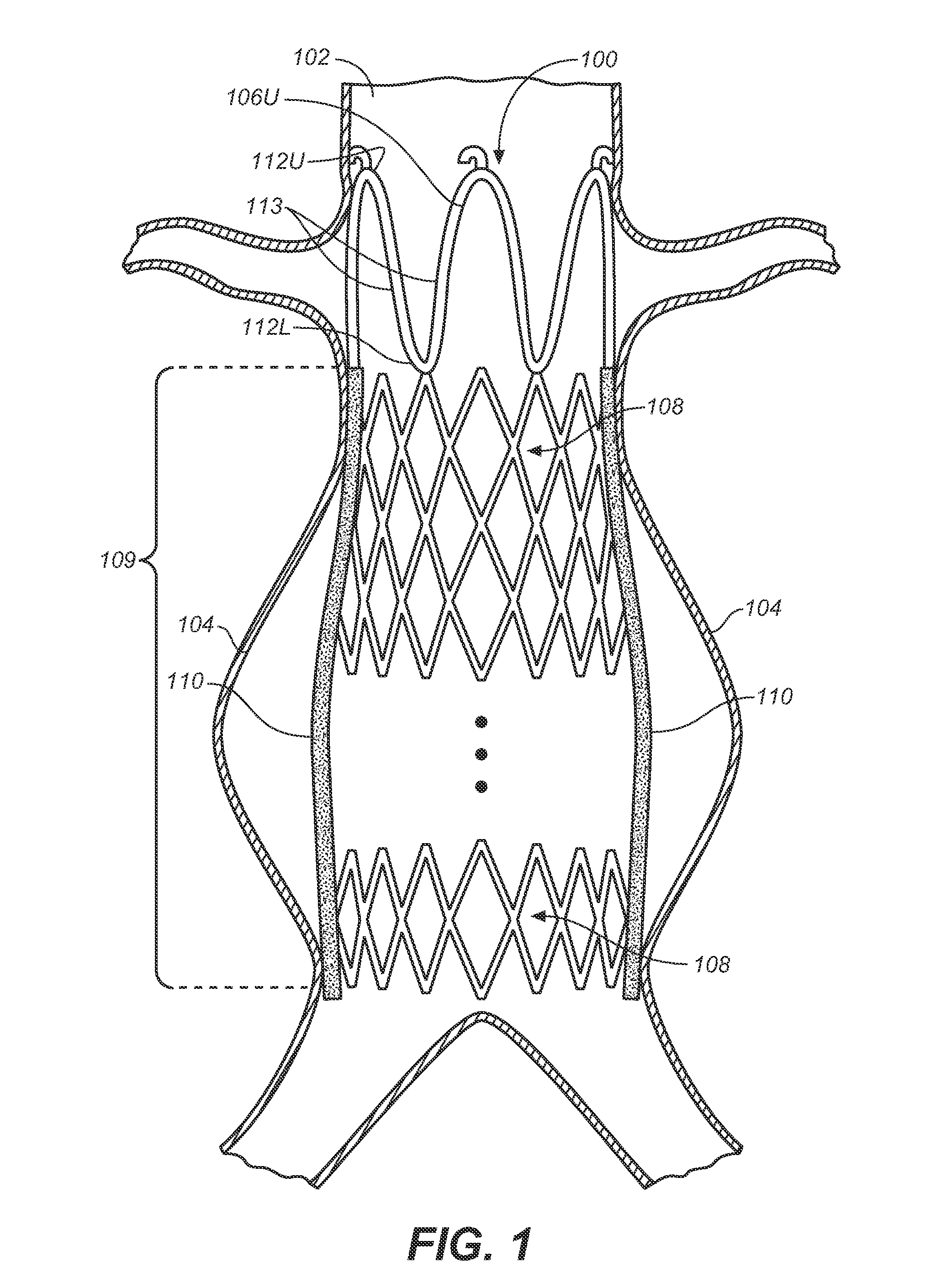
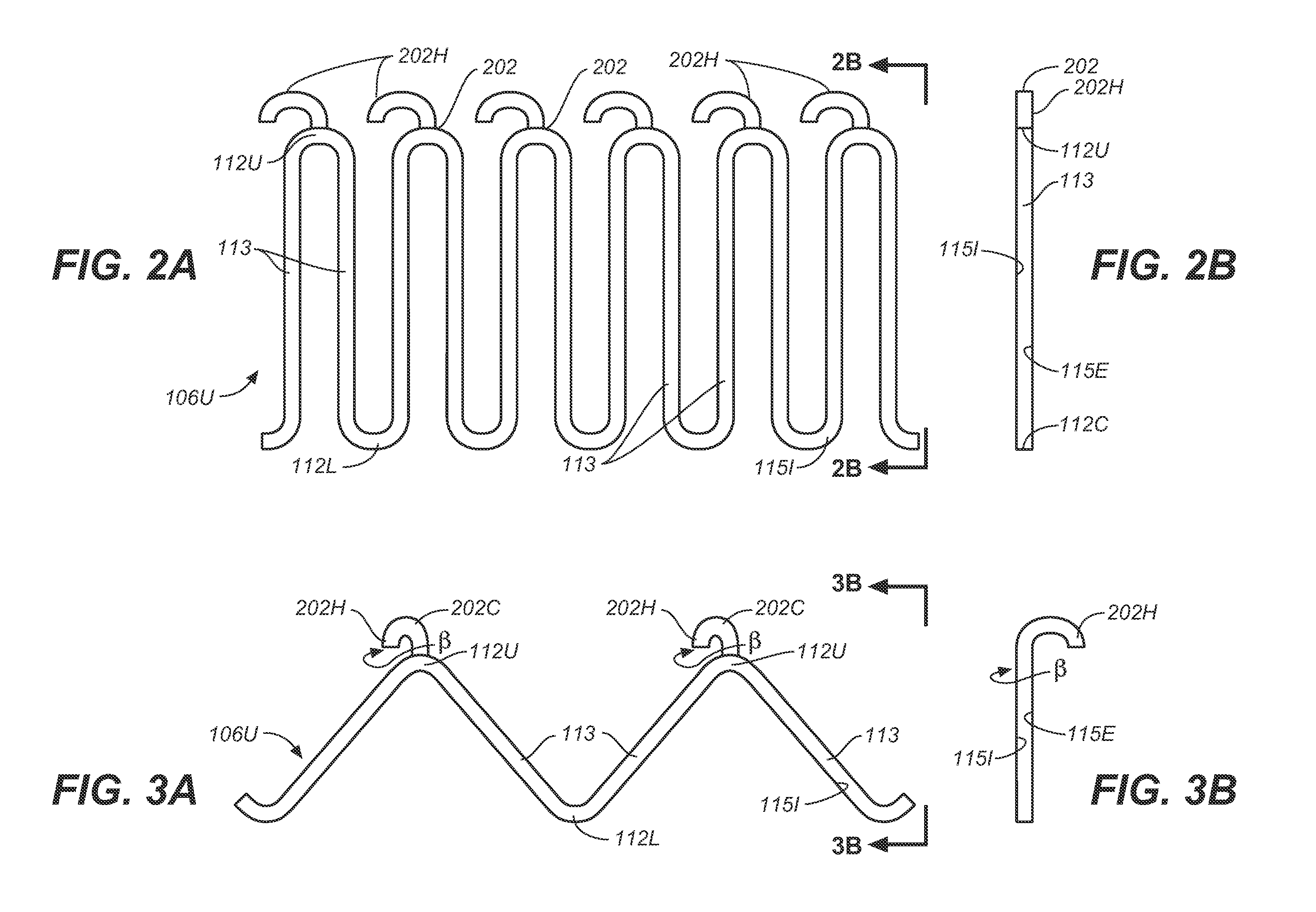
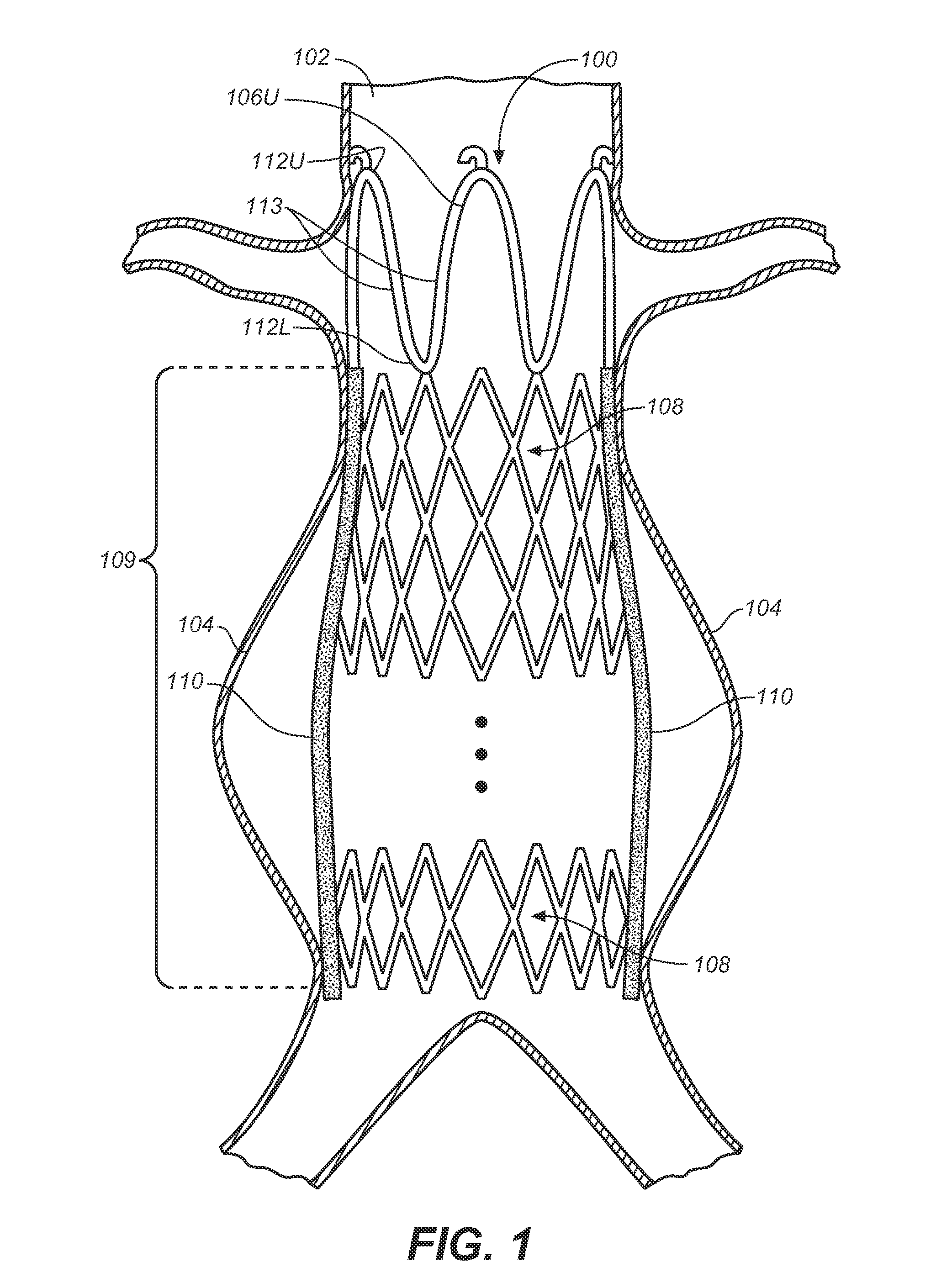
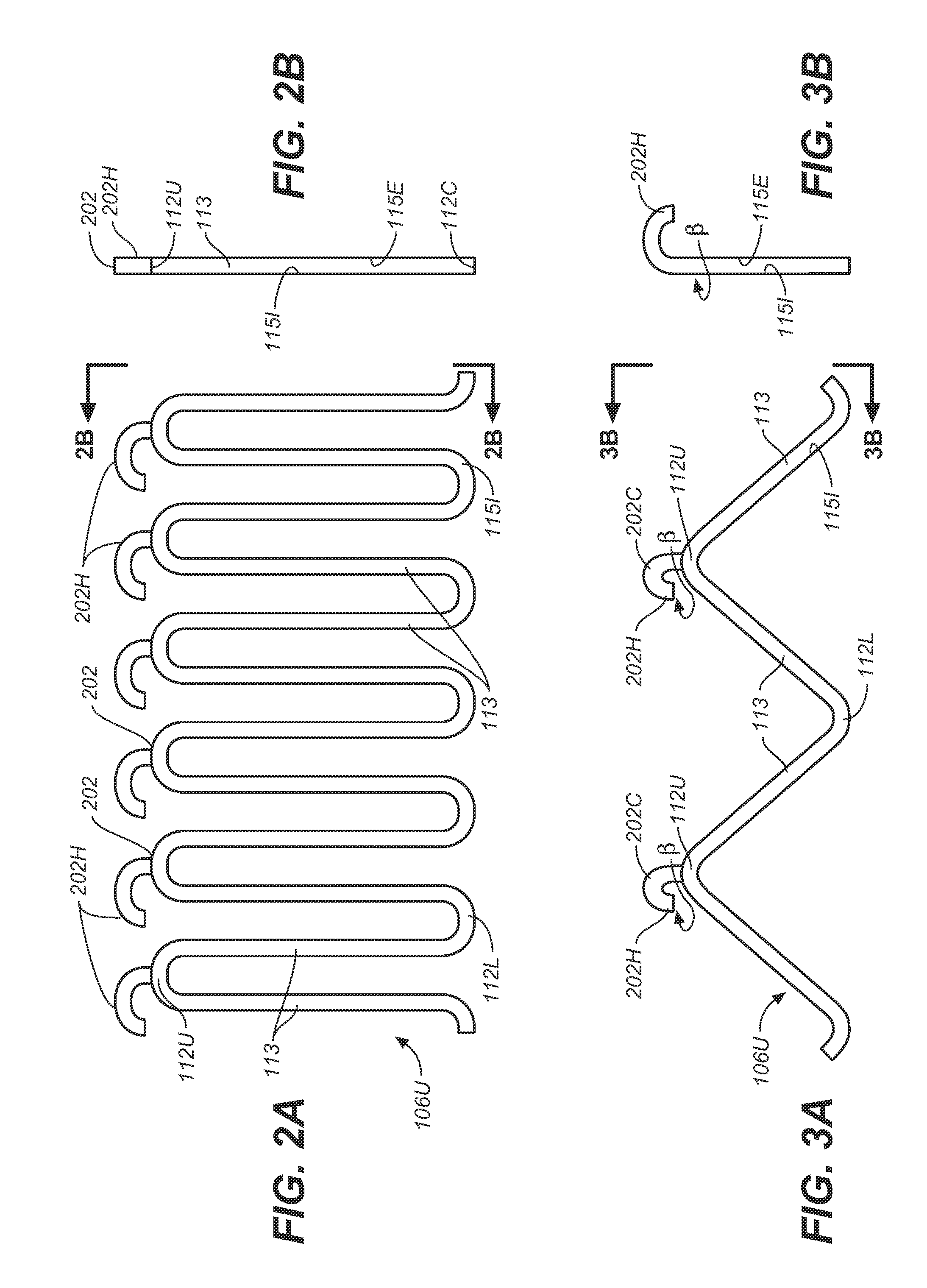
Self-Flaring Active Fixation Element for a Stent Graft
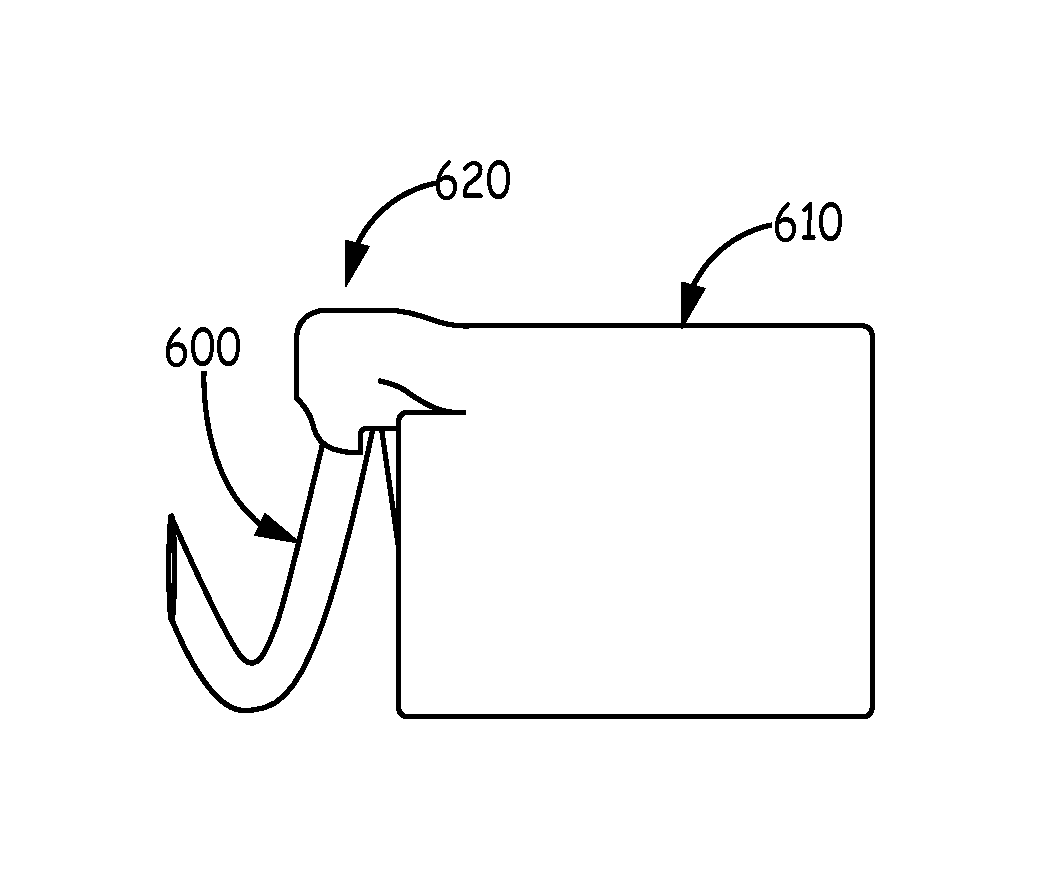
A stent graft includes a stent graft material of tubular shape and annular shaped stent elements coupled to the stent graft material. The stent graft further includes hooked fixation elements, having hook-end portions and coupling-end, circumferentially spaced about an annular shaped spring attachment element, and coupled to the stent graft at apexes of the spring attachment element. Before deployment the hook-end portions of the apexes of the attachment element and the hooked fixation elements attached thereto are compressed within the space bounded by the interior and exterior sides of the spring attachment element and angled laser cut strut inner surfaces under each apex of the spring attachment element are cut at an angle to cause apex and hook rotation at expansion and deployment. At deployment, the apex and hook-end portions rotate outwardly from the stent graft, partially penetrating the body vessel walls in which the stent graft is deployed and actively fixing the stent graft at the position of deployment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
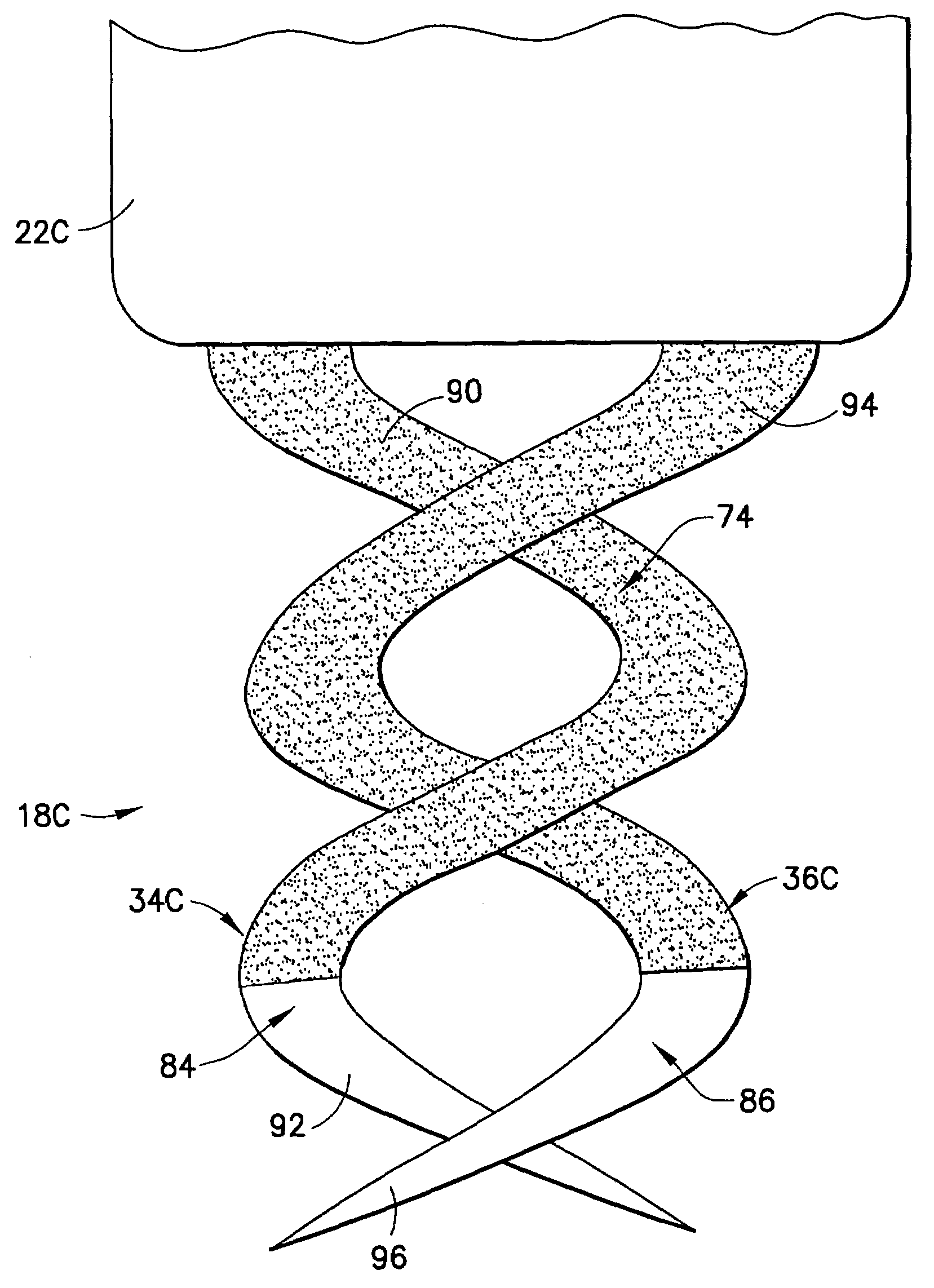
Dual helix active fixation stimulation lead
ActiveUS7212870B1Improve electricity efficiencyImproved and uniform sensingExternal electrodesElectrical conductorActive fixation
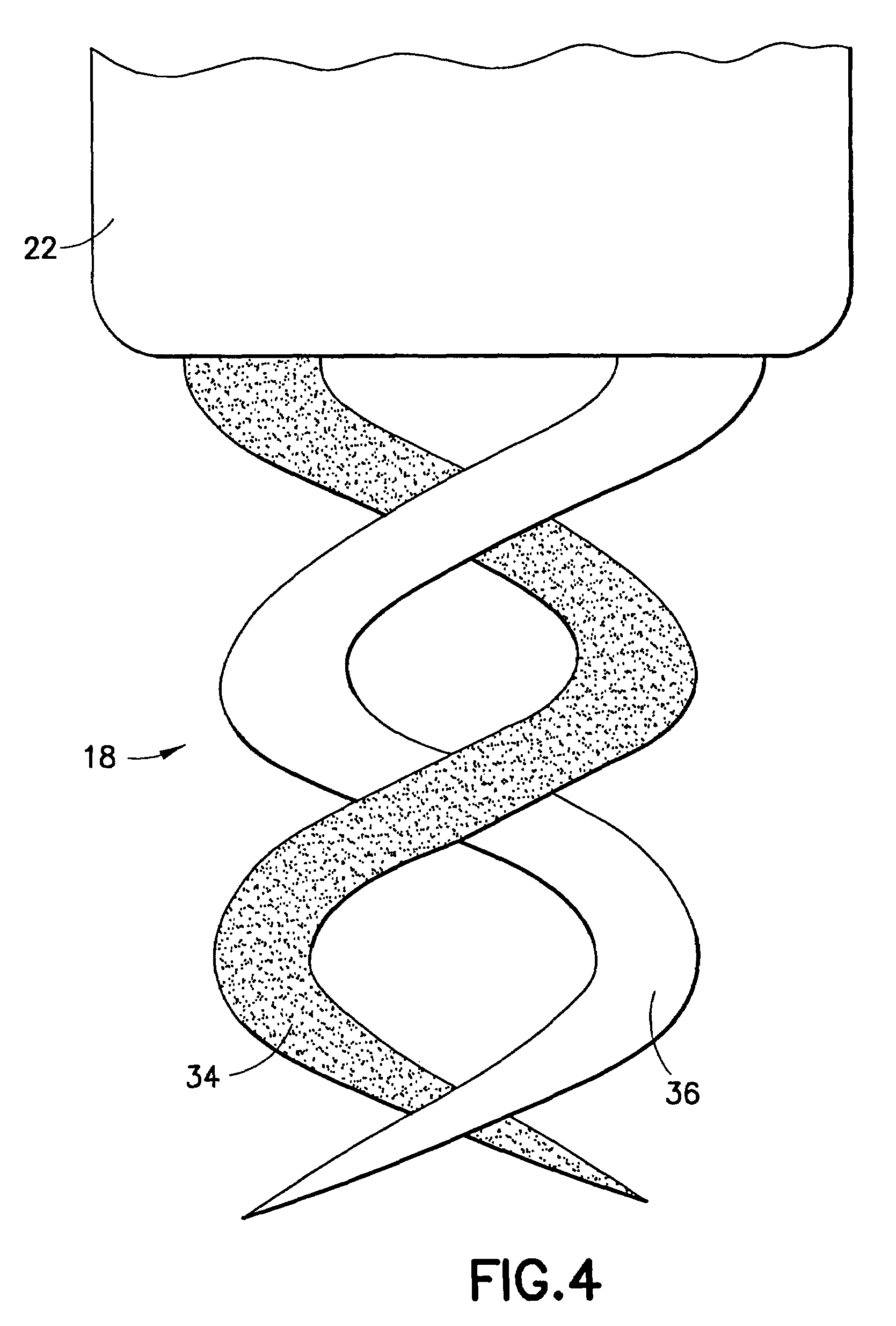
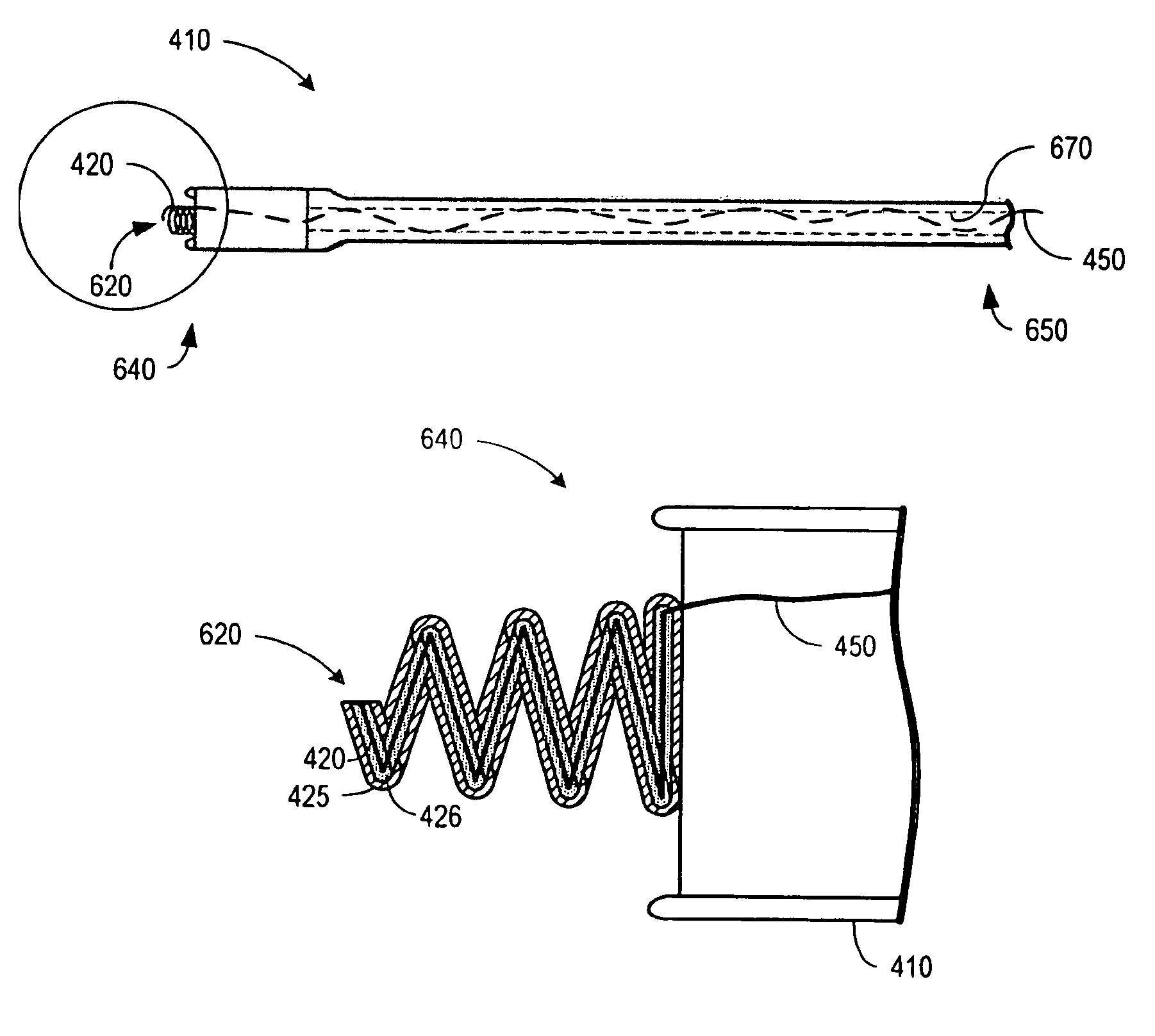
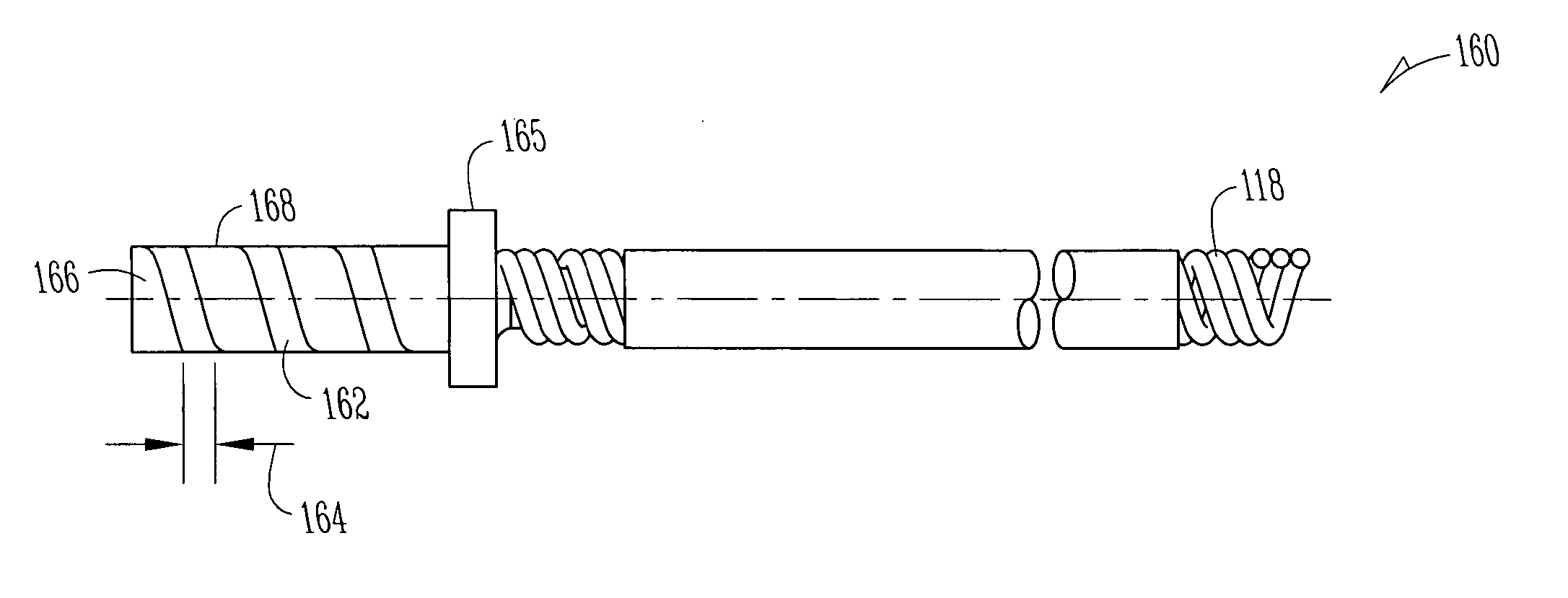
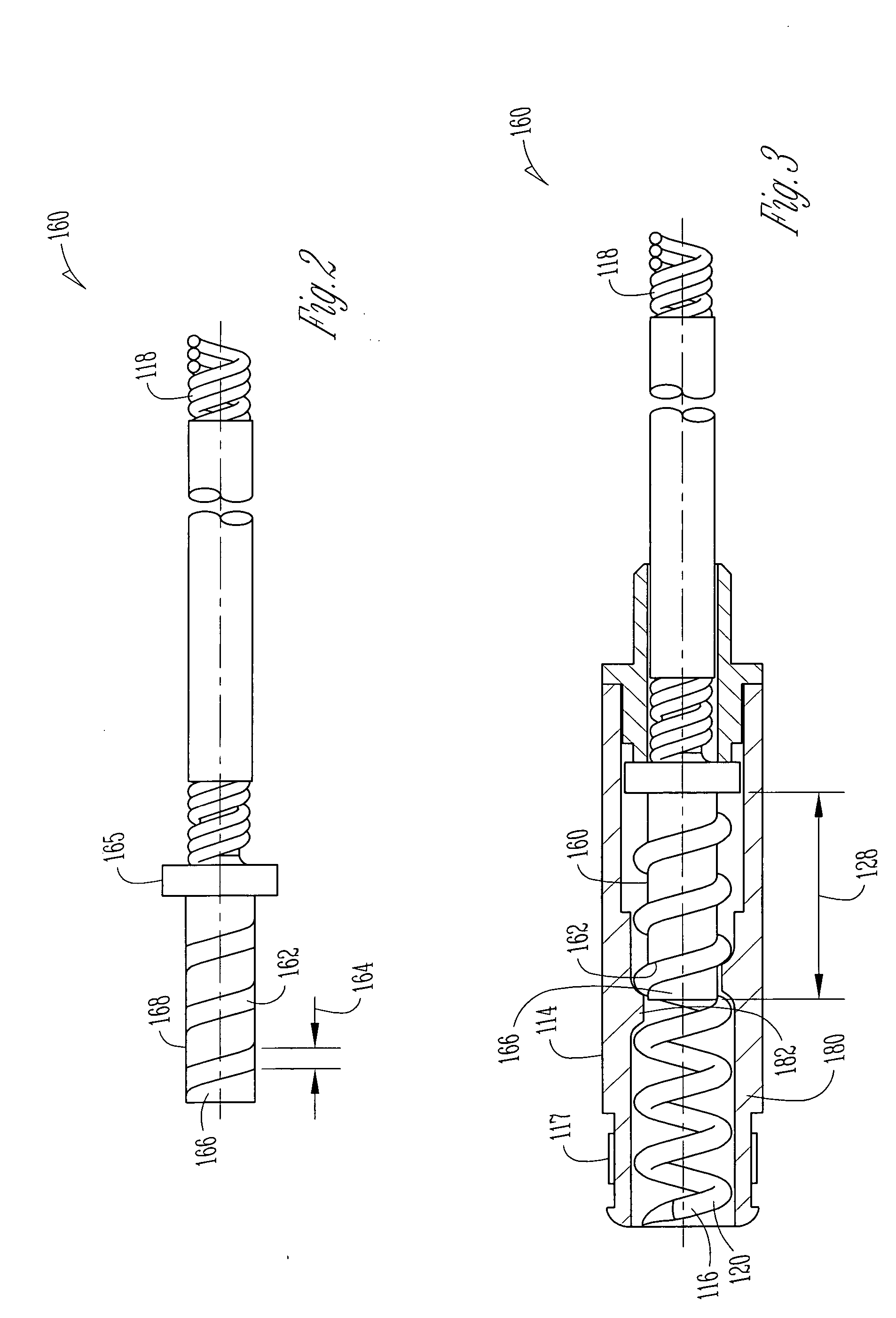
An implantable lead for use with an implantable medical device includes a lead body with first and second electrical conductors extending between its proximal and distal ends. An electrical connector at the proximal end of the lead body includes terminals electrically connected to the first and second conductors. First and second coaxial active fixation helices are coupled to the lead body's distal end, one being an anode, the other an electrically isolated cathode. Each helix has an outer peripheral surface with alternating insulated and un-insulated portions along its length with about a half of the surface area being insulated. The un-insulated portions of the helices may be formed as a plurality of islands in the insulated portions, or as rings spaced by insulative rings, or as longitudinally extending strips spaced by longitudinally extending insulative strips.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
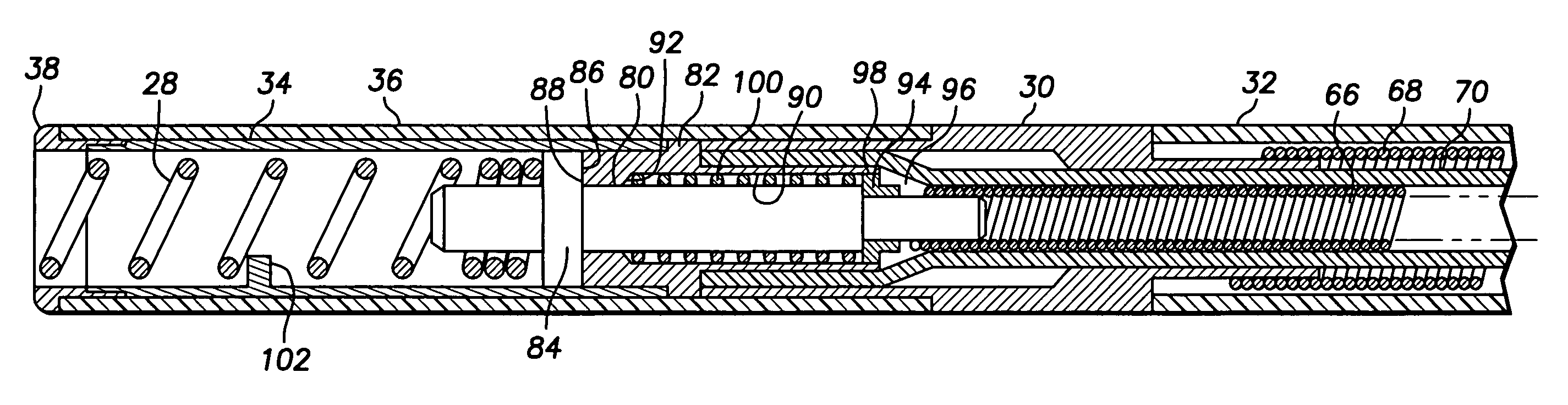
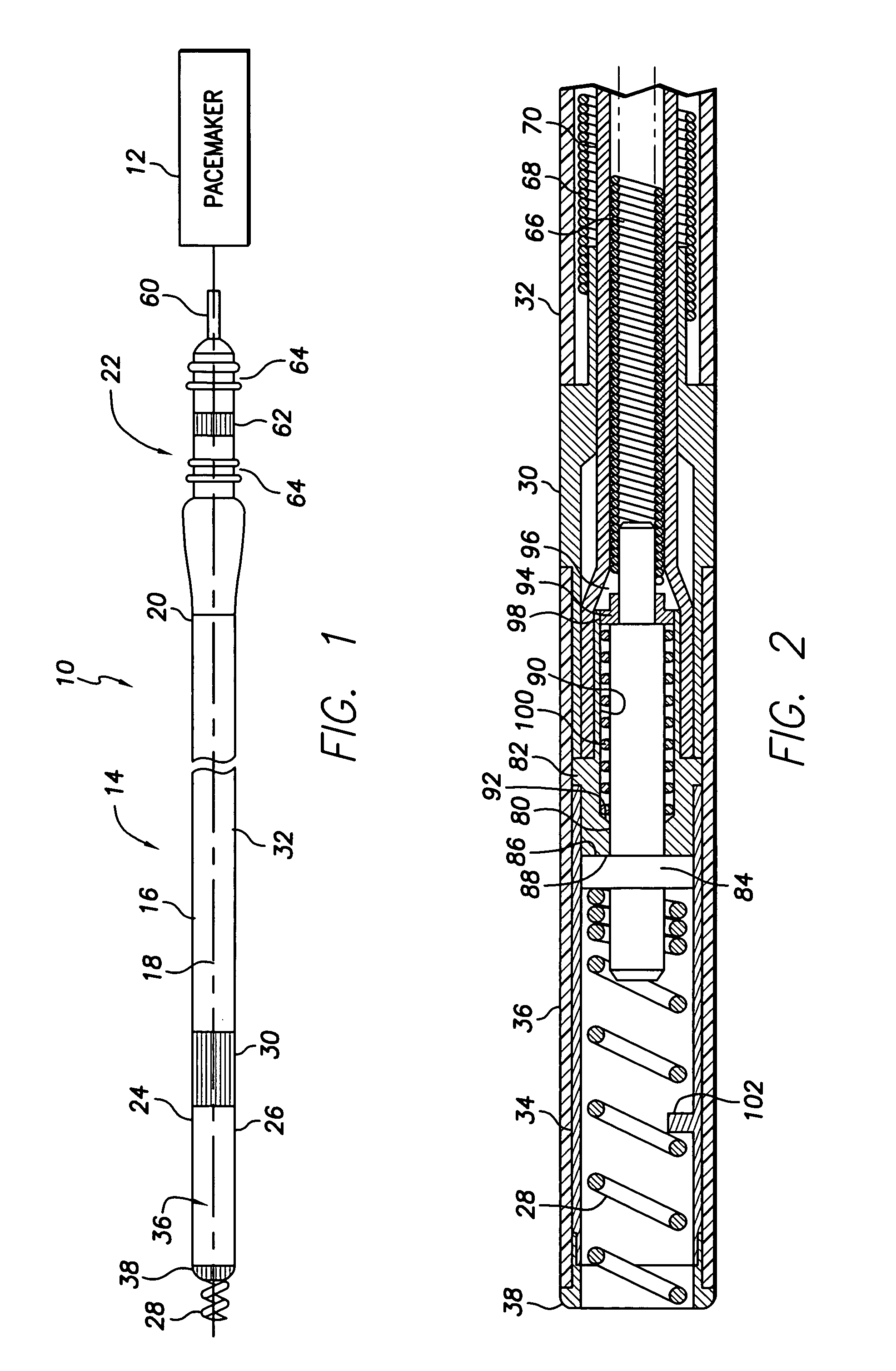
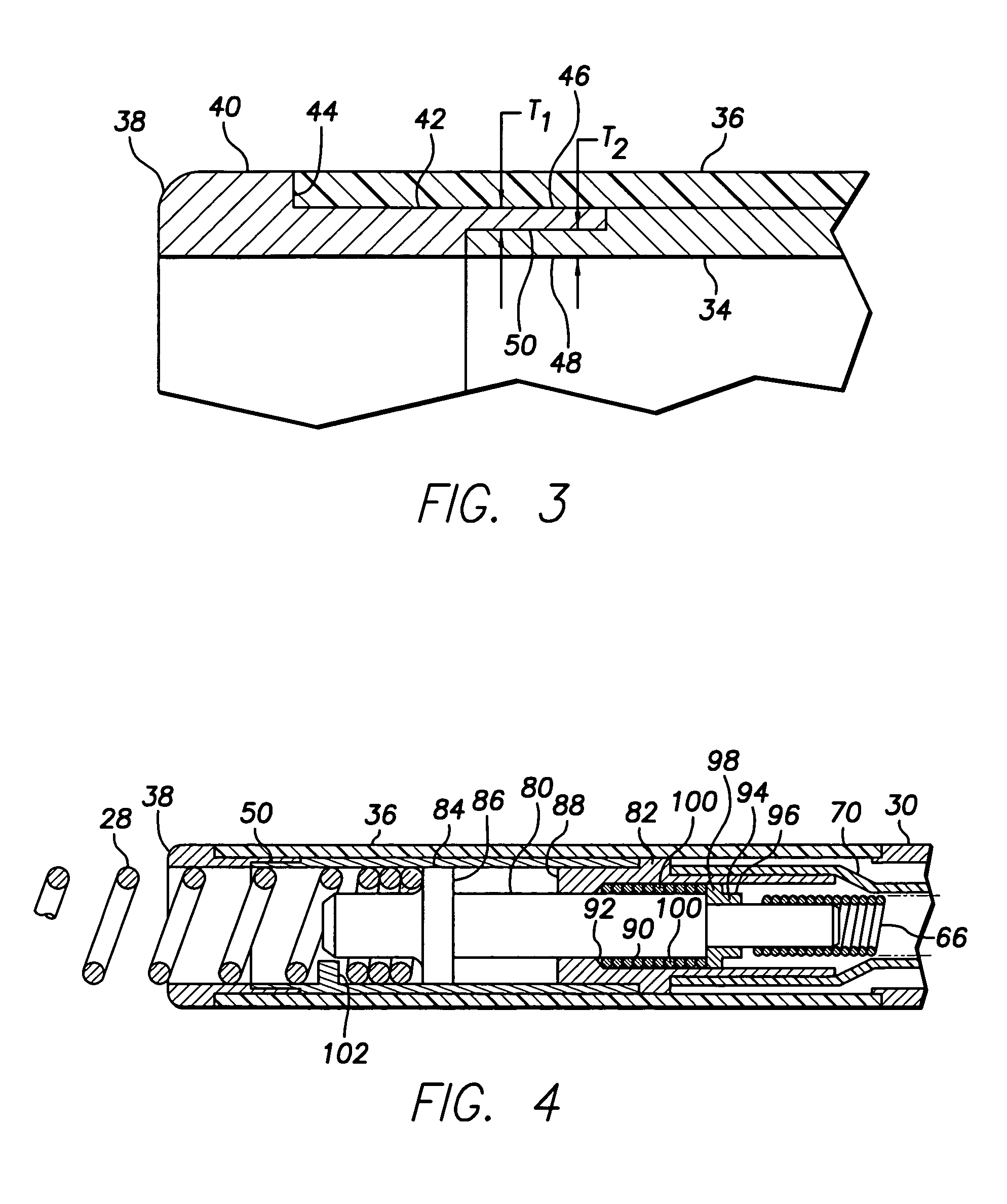
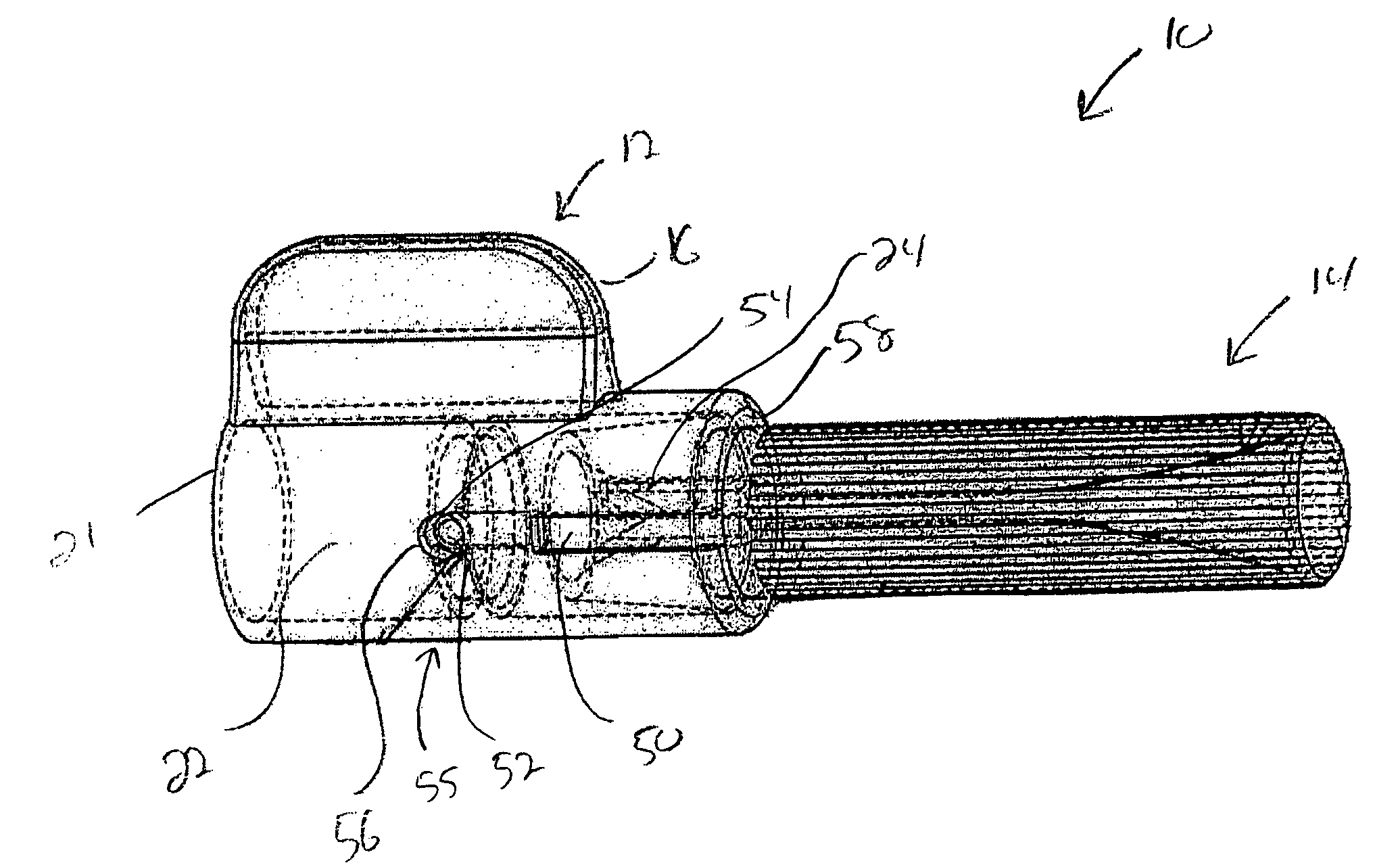
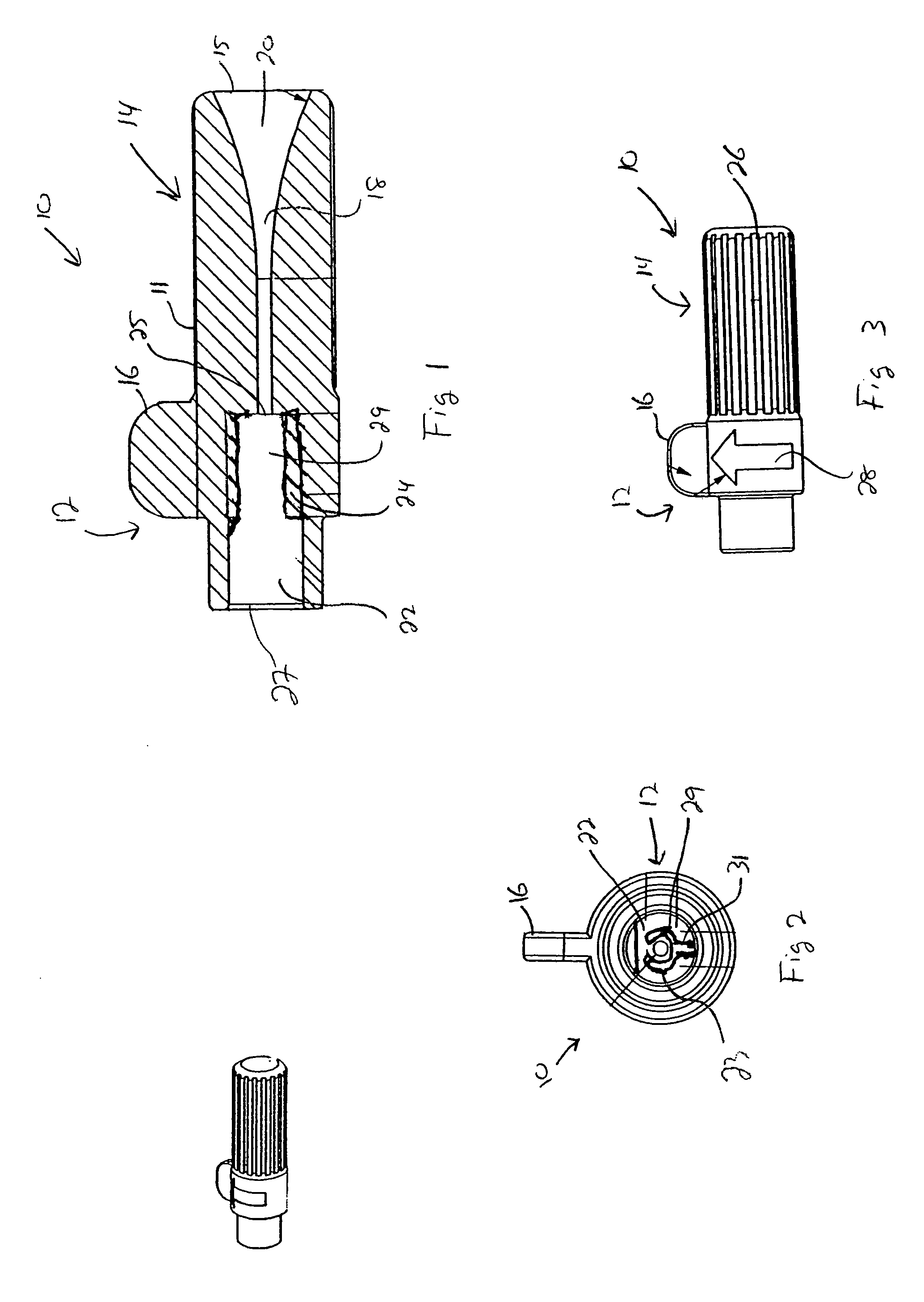
Bipolar screw-in lead
ActiveUS7840283B1Shorten the timeIncrease frictionInternal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineActive fixation
An implantable active fixation lead includes an outer sheath, a protector member having a peripheral surface extending between its distal and proximal end surfaces with a helical groove formed in the peripheral surface, and a fixation helix integral with the outer sheath. The fixation helix includes a tip end engageable with body tissue and slidably engaged with the helical groove for relative translation and rotation. A longitudinal force on the lead firmly engages the protector member's distal end surface with the body tissue. With the fixation helix initially retracted proximally of the protector member's distal end surface and disengaged from the body tissue, upon application of torque to the outer sheath, the distal end surface of the protector member is moved proximally with respect to the fixation helix which, simultaneously, is extended distally beyond the distal end surface of the protector member to an extended position into engagement with the body tissue.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
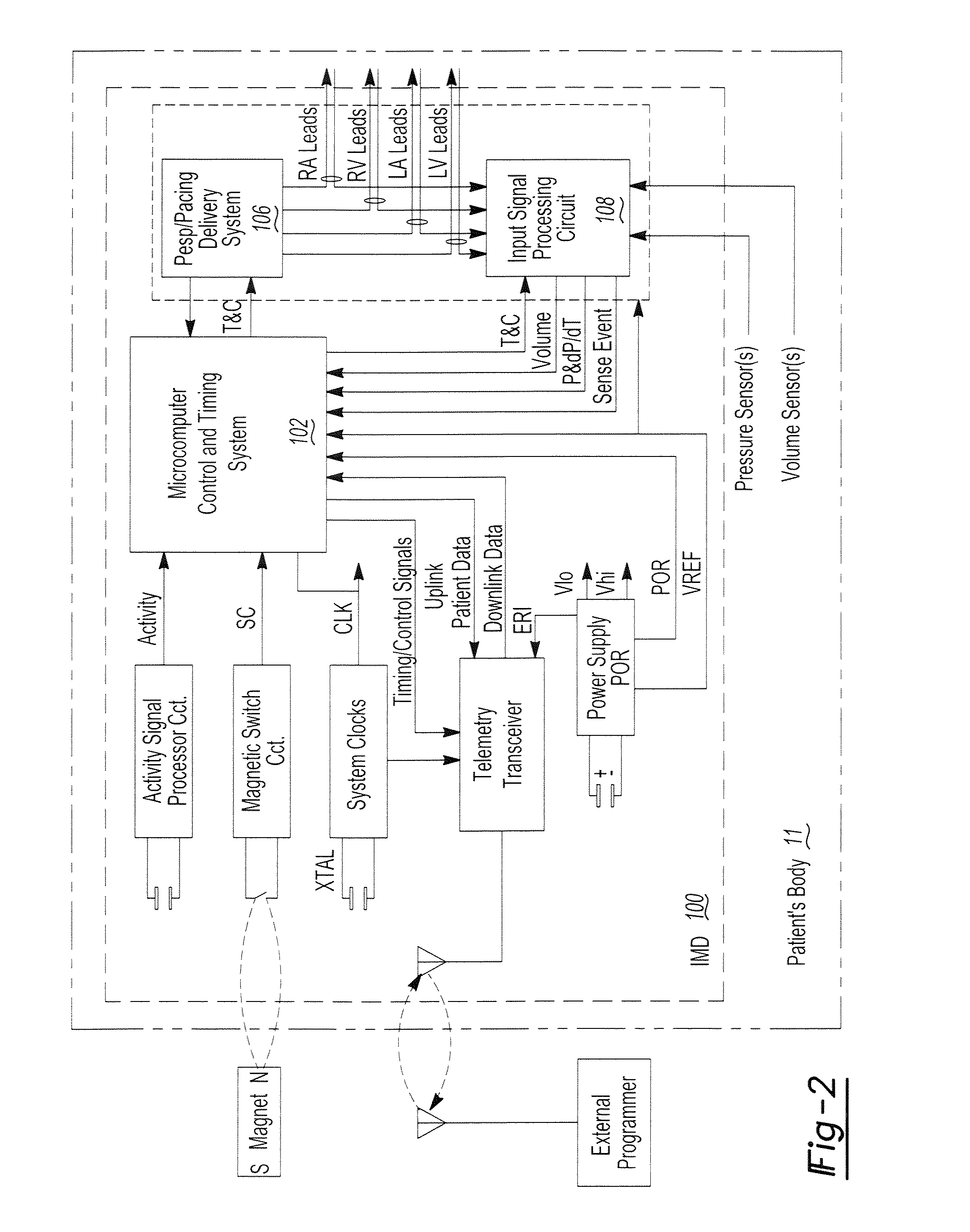
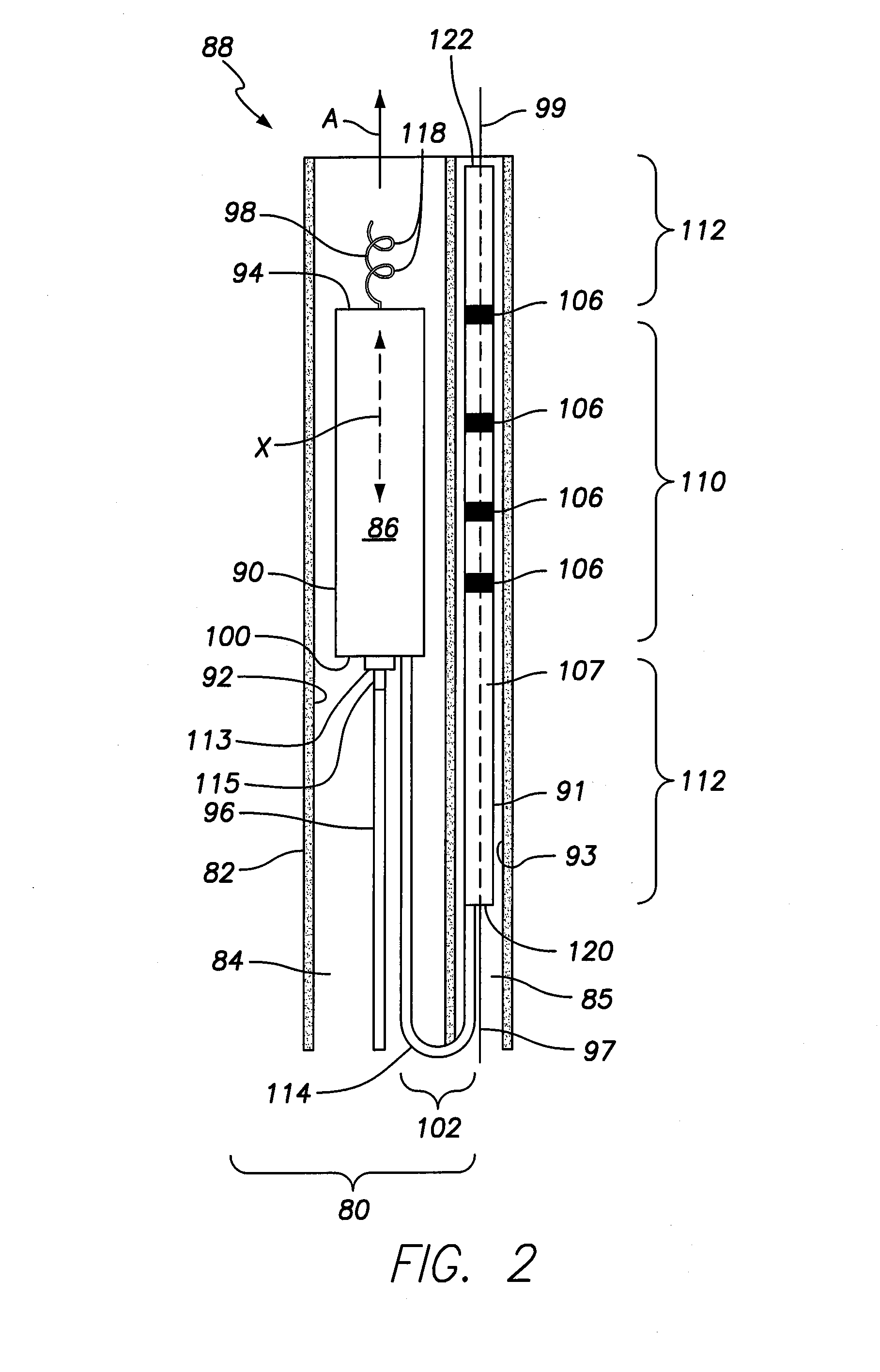
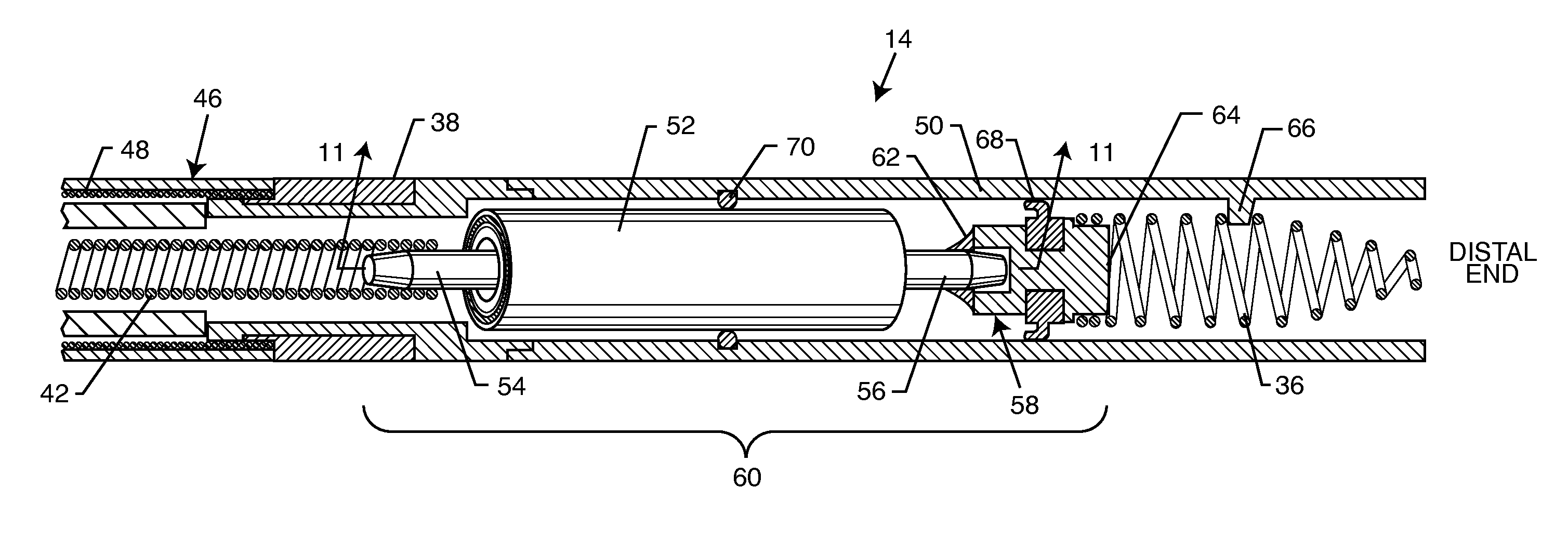
Chronically-implantable active fixation medical electrical leads and related methods for non-fluoroscopic implantation
Bio-impedance may be used for navigation systems to chronically implant pacing and defibrillation leads in the heart using a non-fluoroscopic position sensing unit (PSU). Such a system requires that a conductive material, such as a retractable helical tip-electrode, be exposed during implantation. Since the tip is retracted during implantation, this disclosure provides a modified distal portion employing at least one aperture (or “window”) for fluid exposure of the helix-electrode and a deployable internal sleeve for covering the aperture(s) when the helix-electrode is extended.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Lead assembly and methods including a push tube
InactiveUS20060036307A1Easy to browseSmall sectionTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
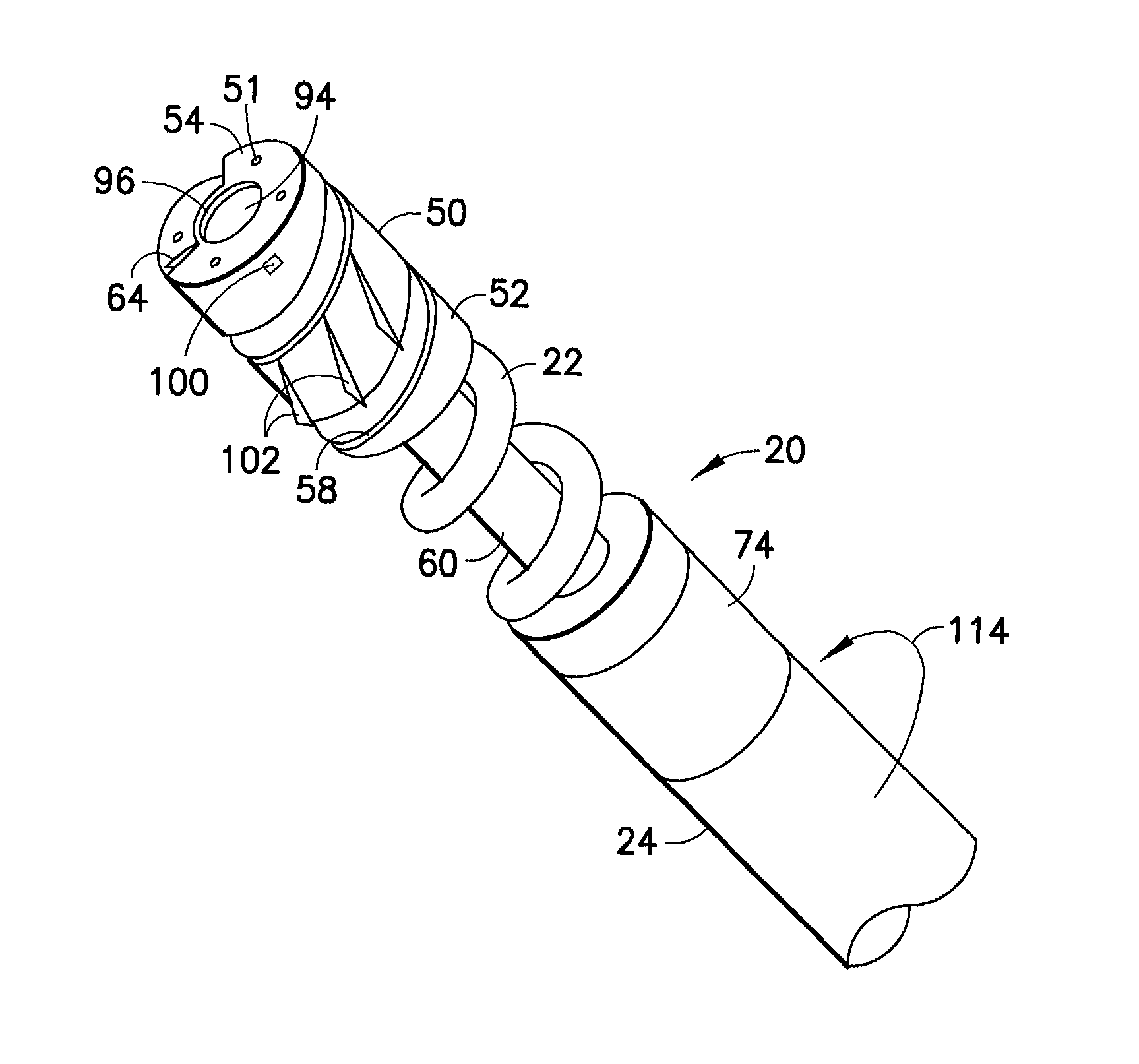
A lead assembly includes an elongate body having a conductor electrically coupled with an electrode coupled to the elongate body. The lead assembly includes a push tube extending along at least a portion of the elongate body. A distal tip is coupled to the elongate body substantially adjacent to the distal end of the elongate body. The distal tip is sized and shaped to couple with a push tube distal end. In one option, the distal tip includes a seat to receive the push tube distal end. In another option, the seat is a side rail seat and a guide wire extends along the elongate body and is slidably coupled with the side rail seat. The lead assembly includes, optionally, an active fixation device slidably coupled with a portion of the elongate body, and the active fixation device is sized and shaped to couple with the push tube.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Active fixation implantable medical lead configured to indicate via fluoroscopy embedment of helical anchor in cardiac tissue
An implantable medical lead for active fixation to cardiac tissue is disclosed herein. The lead may include a lead body distal end, a tissue fixation helical anchor and a structure. The tissue fixation helical anchor may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a distal tip. The structure may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a structure distal end including a first radiopaque marker. The structure may be biased to project the structure distal end near the distal tip. When the tissue fixation helical anchor is progressively embedded in the cardiac tissue, the cardiac tissue progressively displaces the structure distal end proximally.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Active fixation coronary sinus lead apparatus
InactiveUS20050070981A1Loss of efficacyReduce distortion problemsTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesCoronary sinusActive fixation
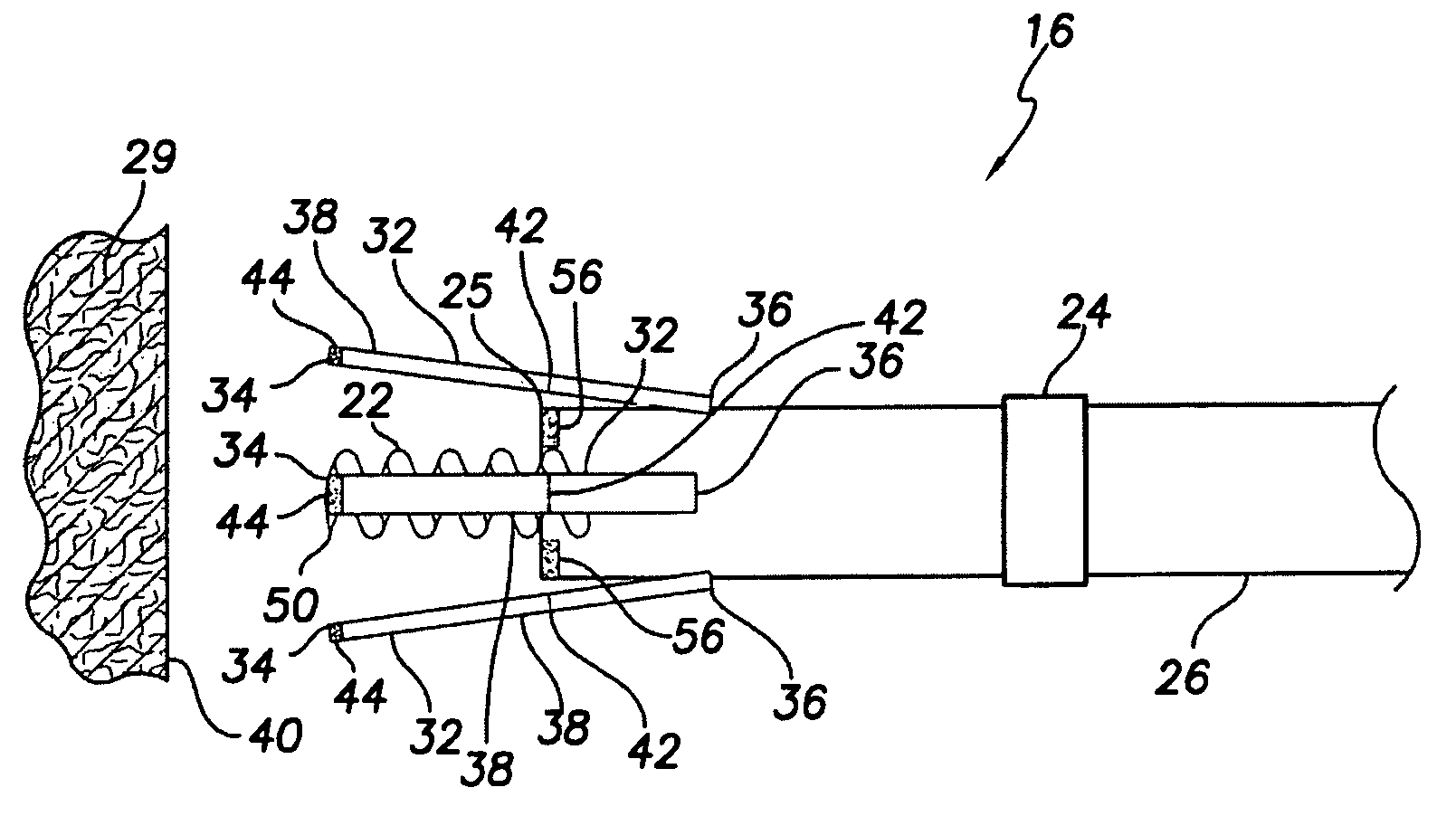
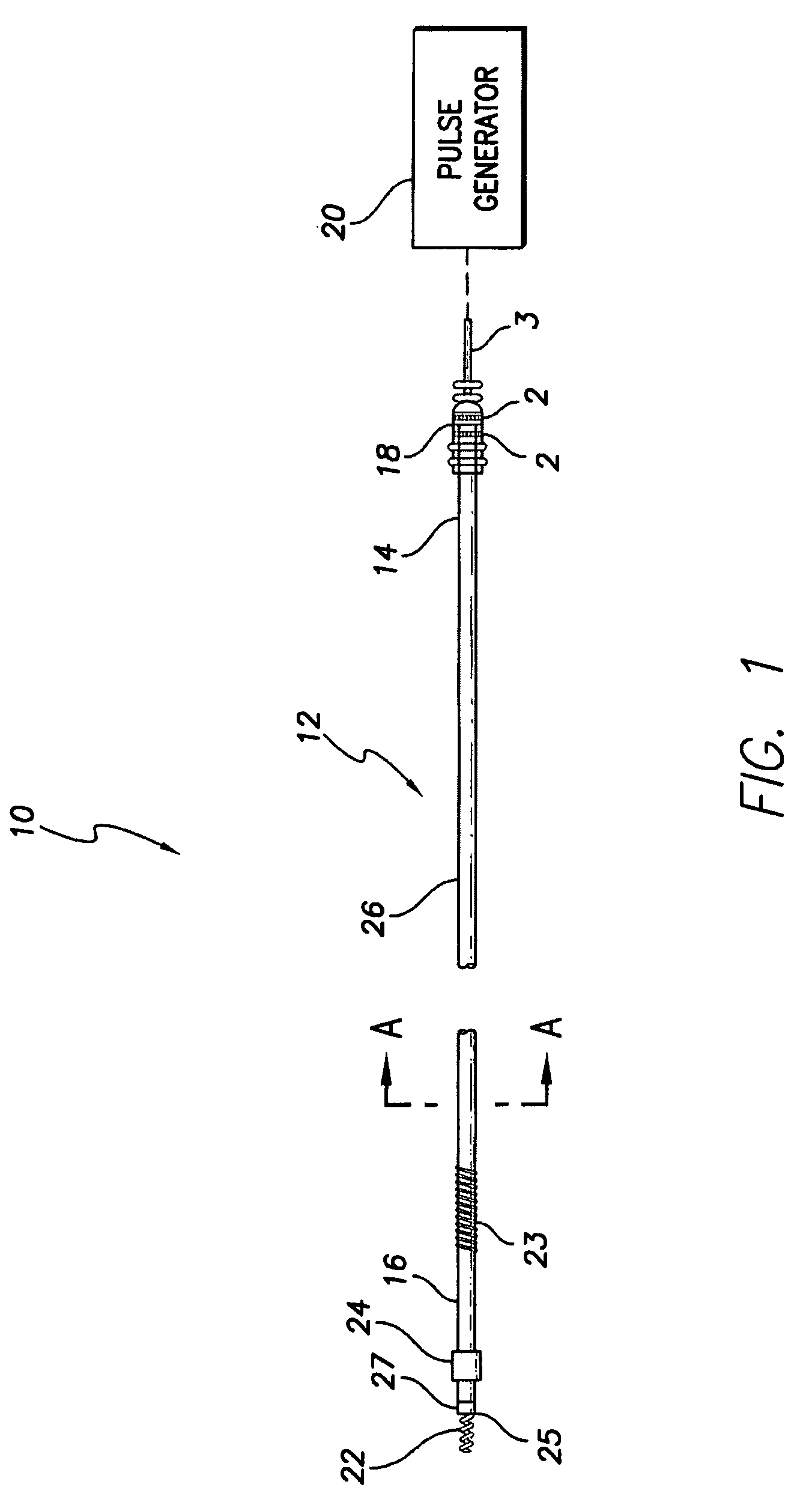
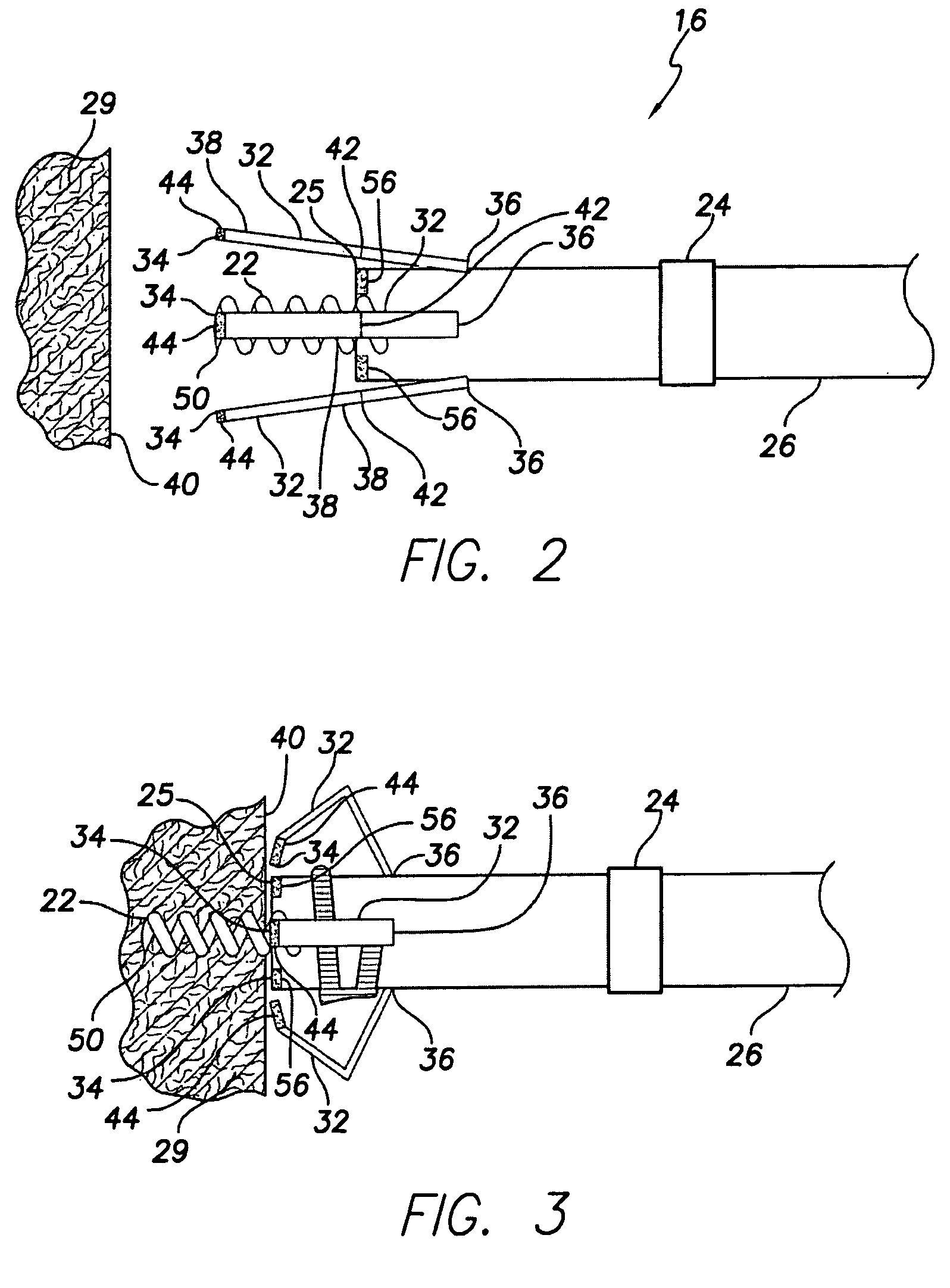
An active fixation coronary sinus lead apparatus includes electrode support means which include an electrode support longitudinal axis. A plurality of electrode segments are supported by the electrode support means and are arrayed around the electrode support longitudinal axis. A plurality of insulation segments are supported by the electrode support means and are arrayed around the electrode support longitudinal axis at positions opposite to the electrode segments. In this respect, the insulation segments are interspersed between the electrode segments. Electrode segment orientation means are connected to the electrode support means for selectively orienting the electrode segments and the insulation segments around the electrode support longitudinal axis. Vessel anchoring means, which can include three flexible anchor wing portions, are connected to the electrode support means for anchoring the apparatus to an interior wall of a blood vessel. A pressure monitoring system can be connected to the vessel anchoring means for monitoring pressure inside the anchoring means.
Owner:VERMA SUMIT
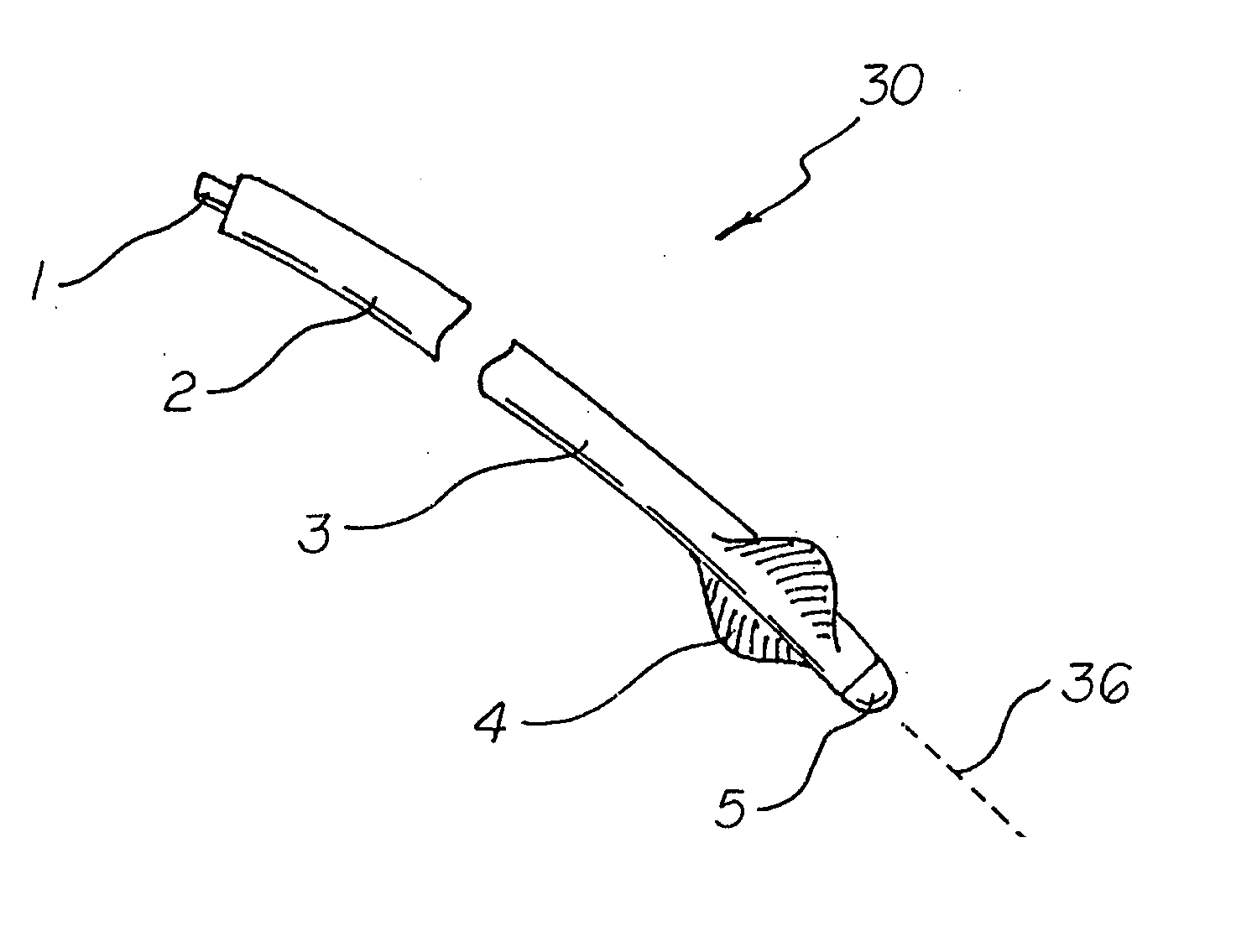
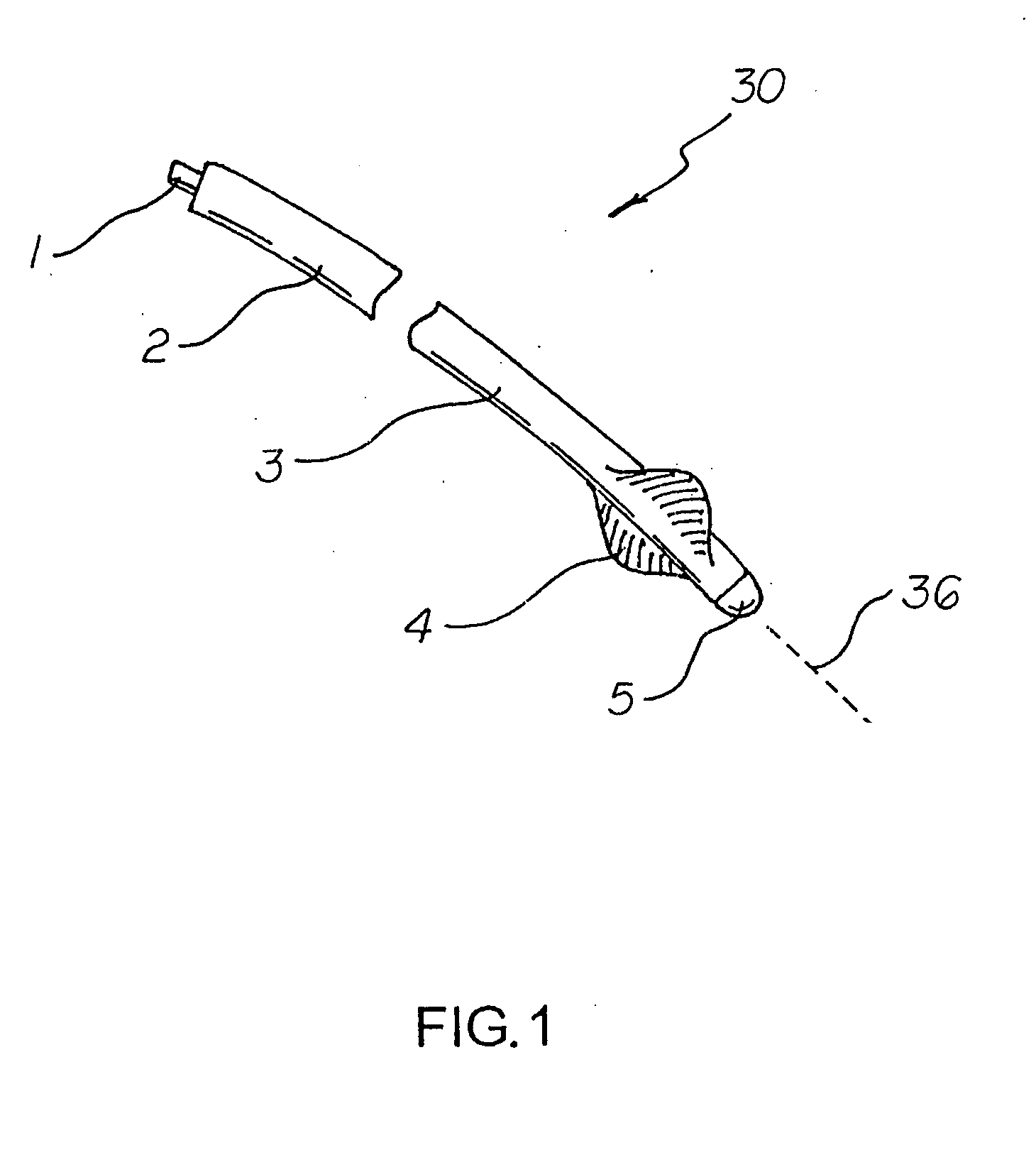
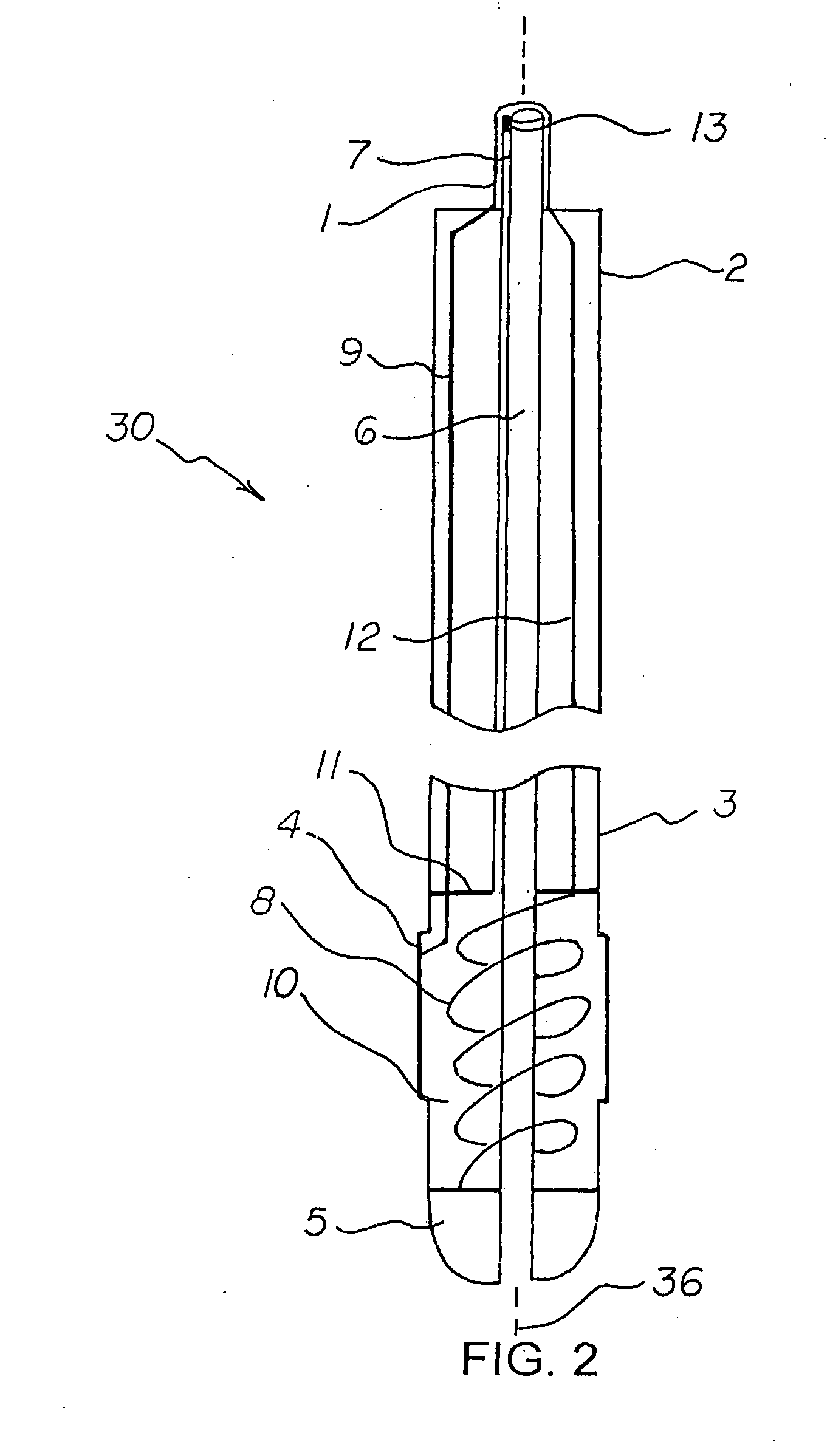
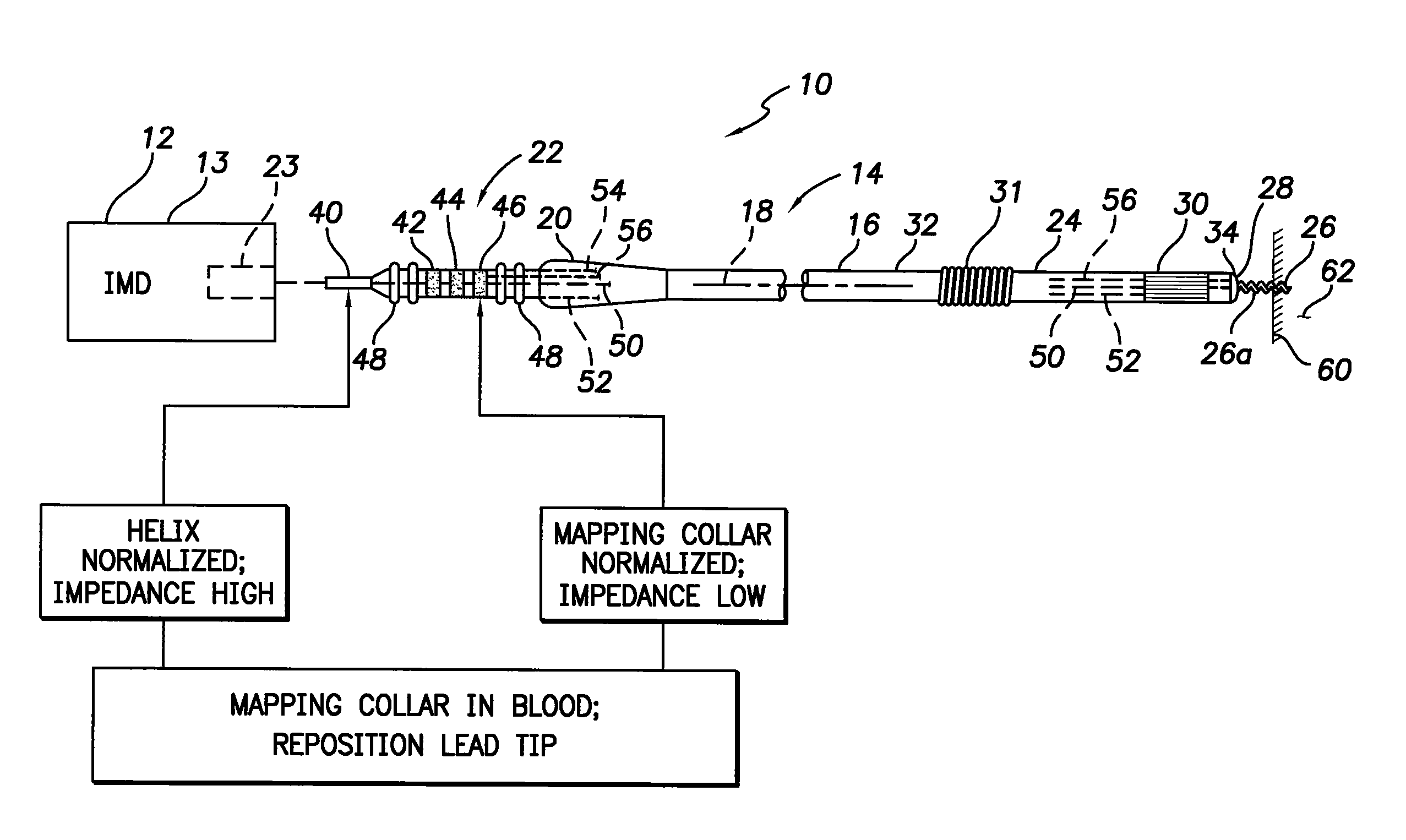
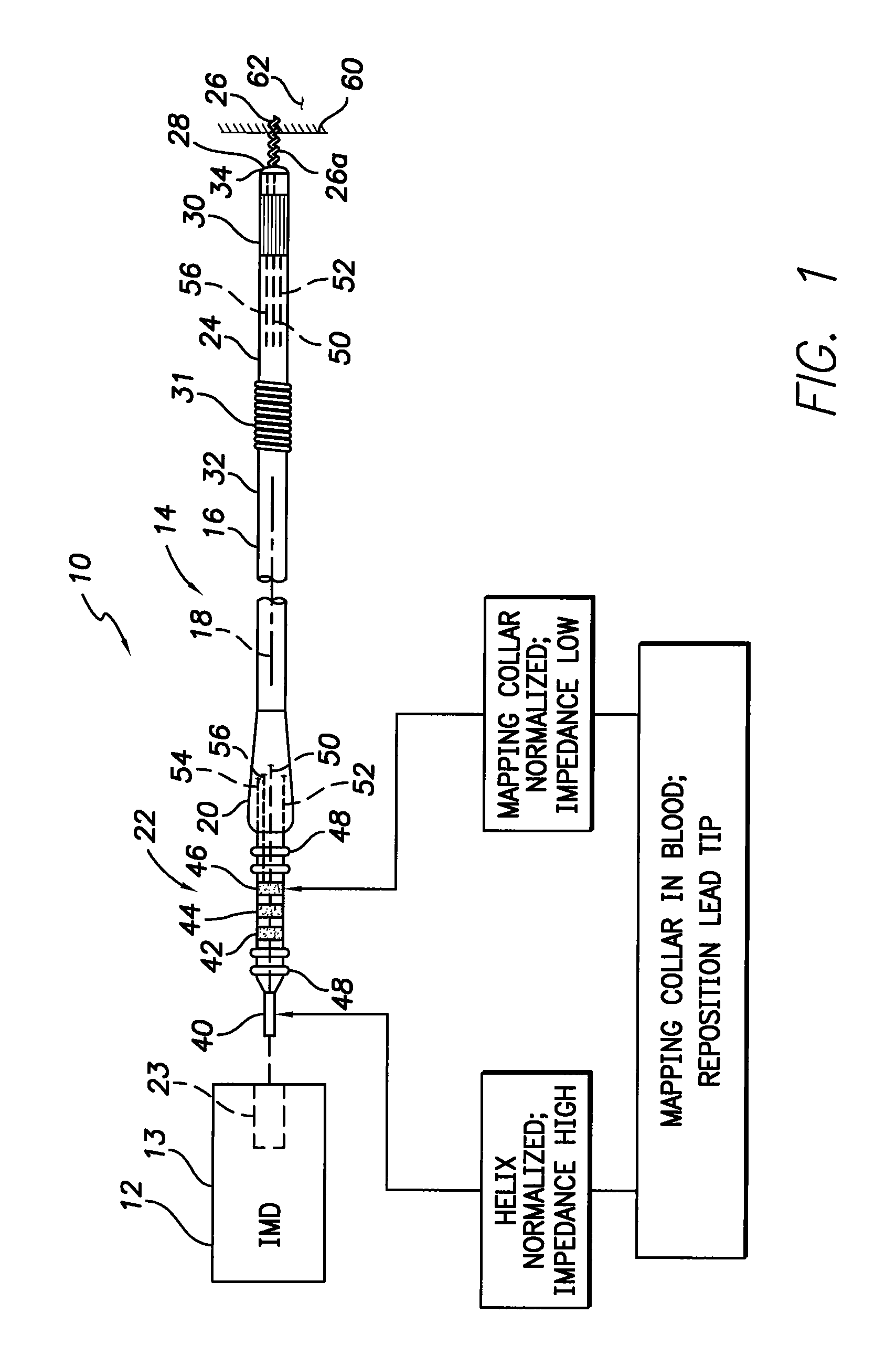
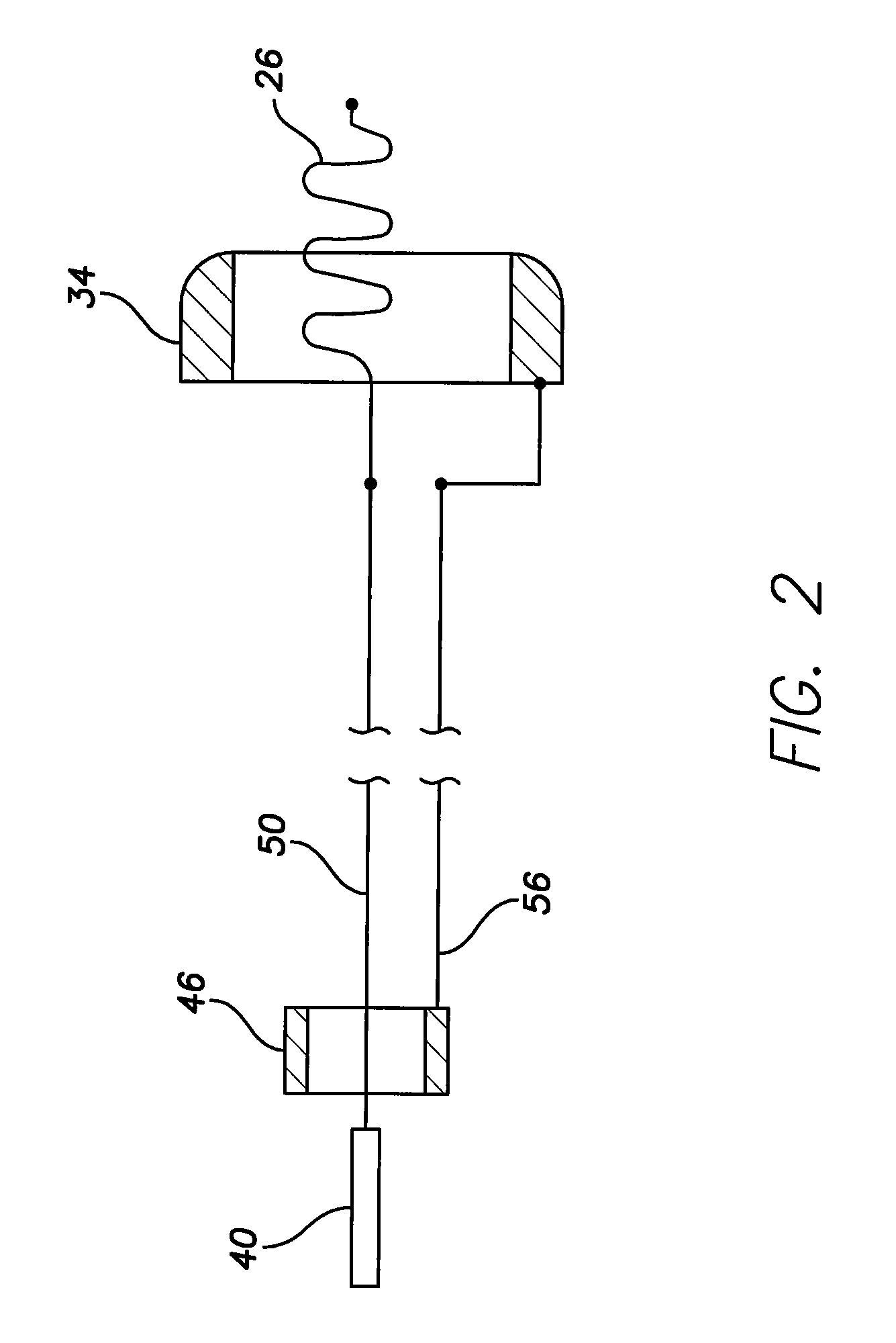
Active fixation medical lead and related method and system
An implantable medical lead of the invention comprises an electrically active helix electrode extendable and retractable relative to a distal tip of the lead, an electrically conductive mapping collar disposed at the lead's distal tip and a proximal end carrying an electrical connector assembly. The electrical connector assembly comprises a first terminal connected to the helix electrode and a second terminal separately connected to the mapping collar. An advantage of the independent helix electrode and mapping collar circuits is that the implanting physician can confirm from separate electrode impedance readings that the helix is in fact extended and fully embedded within the myocardium. Further, the independent mapping collar and helix electrode circuits may be used, in conjunction with a configurable or programmable switch network, to provide the implanting physician with a choice of electrode impedances.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Intra-cardiac implantable medical device with IC device extension for lv pacing/sensing
InactiveUS20140172034A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsActive fixationMedical device
An assembly is provided for introducing a device within a heart of a patient. The assembly is comprised of a sheath having at least one internal passage. An intra-cardiac implantable medical device (IIMD) is retained within the at least one internal passage, wherein the IIMD is configured to be discharged from a distal end of the sheath. The IIMD has a housing with a first active fixation member configured to anchor the IIMD at a first implant location within a local chamber of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
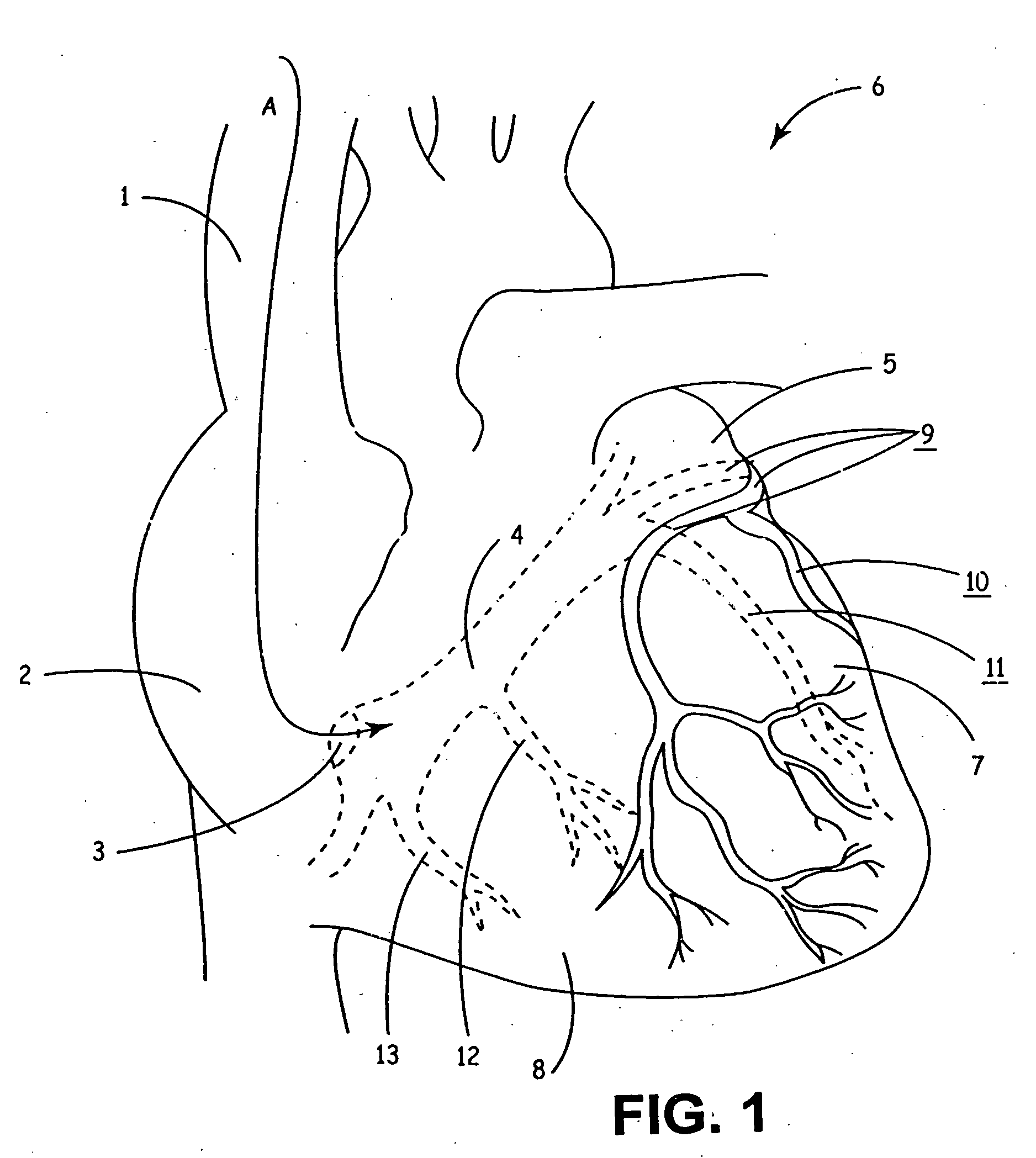
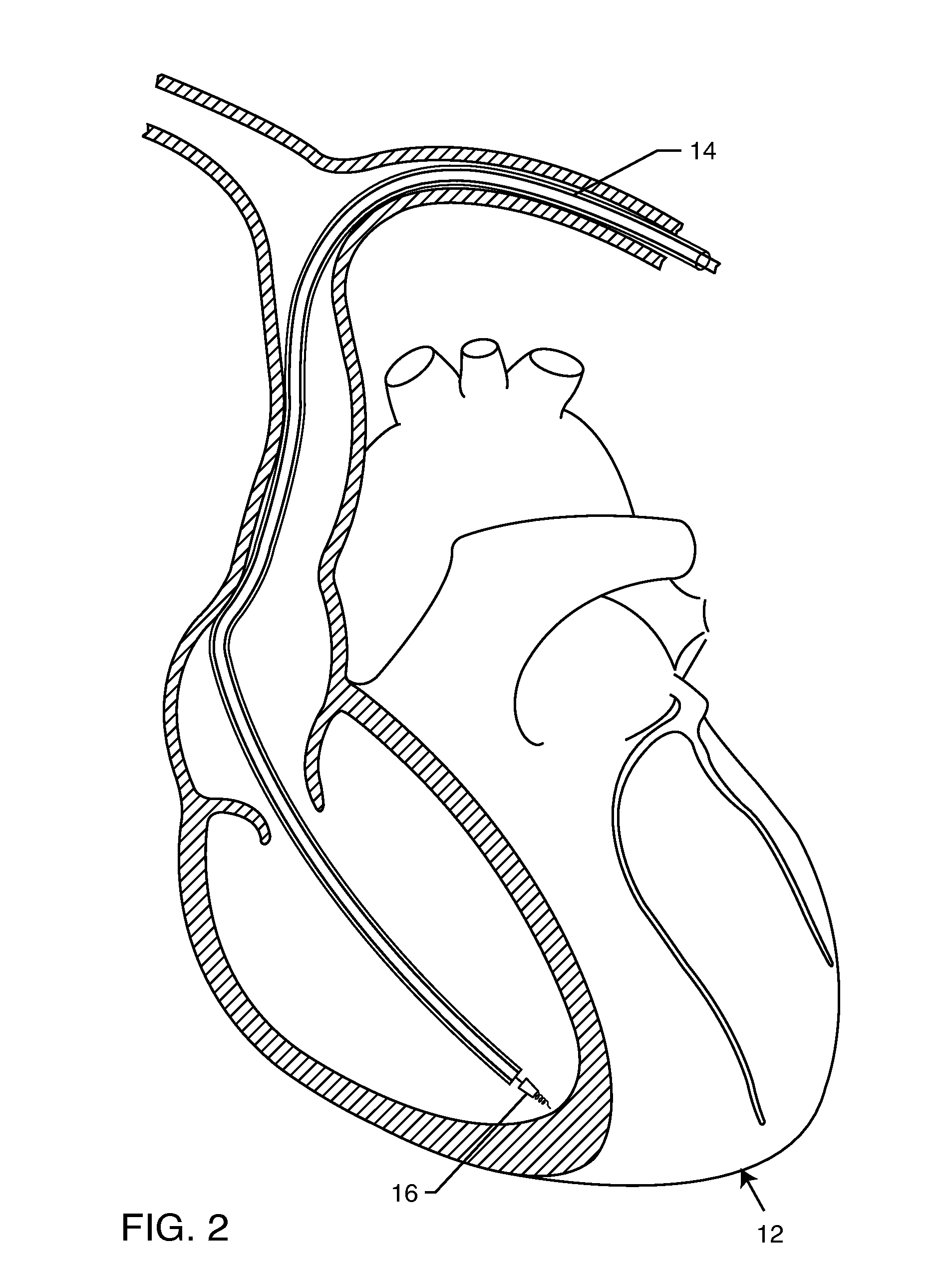
Intramyocardial lead implantation system and method
InactiveUS20050080470A1Facilitates slideable advancementEasy to implantEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesHelical coilCardiac monitoring
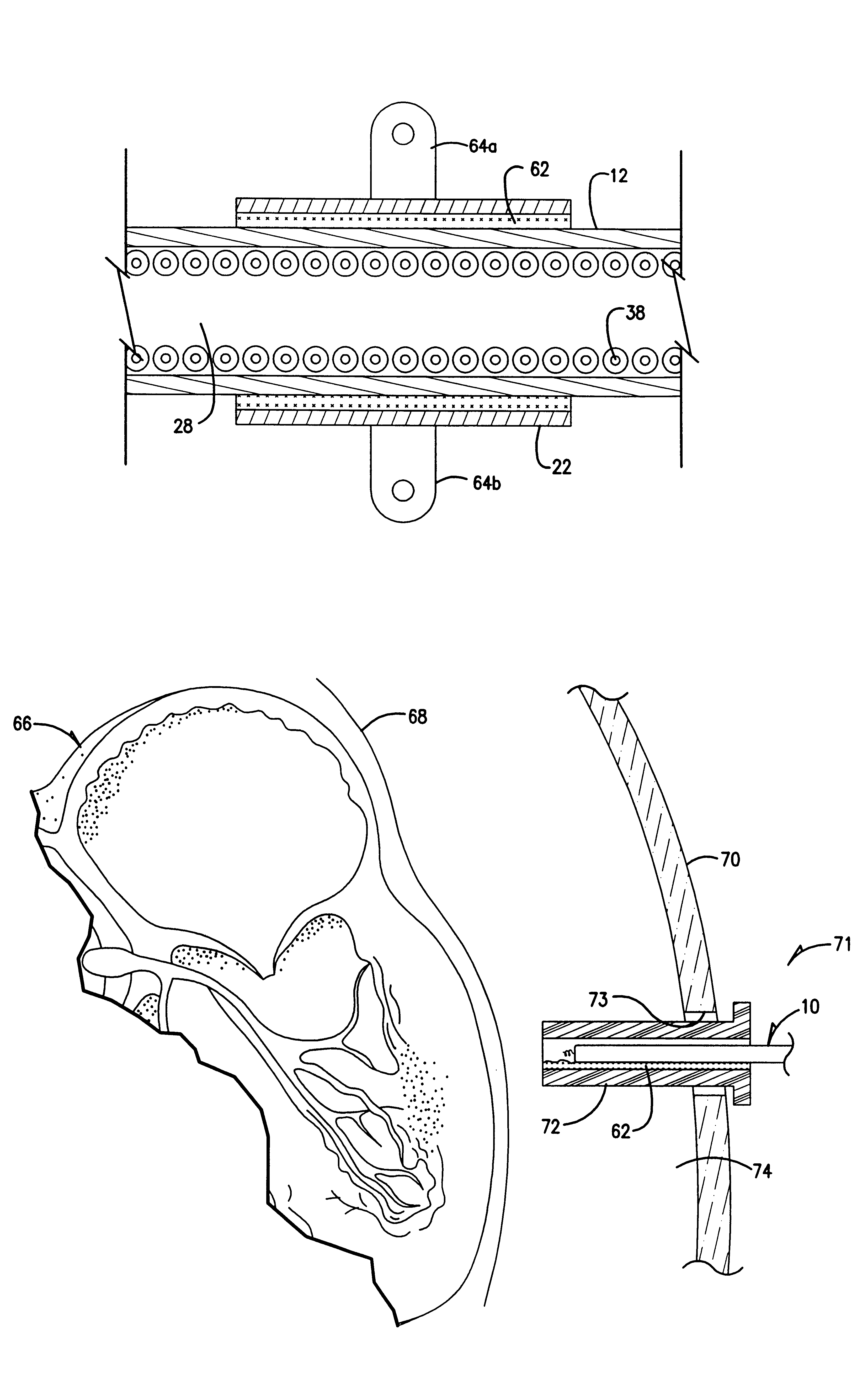
A system and method for placement of cardiac monitoring and stimulation leads. A lead is advanced into a myocardium of the patient's heart through a lead introducing system, and an electrode is implanted within the myocardium. The method may include gaining access with a cannula from an outer chest wall to the myocardium. Space is created in the myocardium using the lead introduction system. Aspects include eluting a steroid from the lead and into the myocardium, affixing the lead into myocardial tissue using an active fixation mechanism, such as a helical coil, and stabilizing the lead by suturing, clipping, stapling, or other method. A dilating sheath may be used to create a space within the myocardium sufficient in size to accommodate an implantable myocardial electrode. The system may include an implantation depth indicator such as a shoulder, a cuff, or a skirt on the lead.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
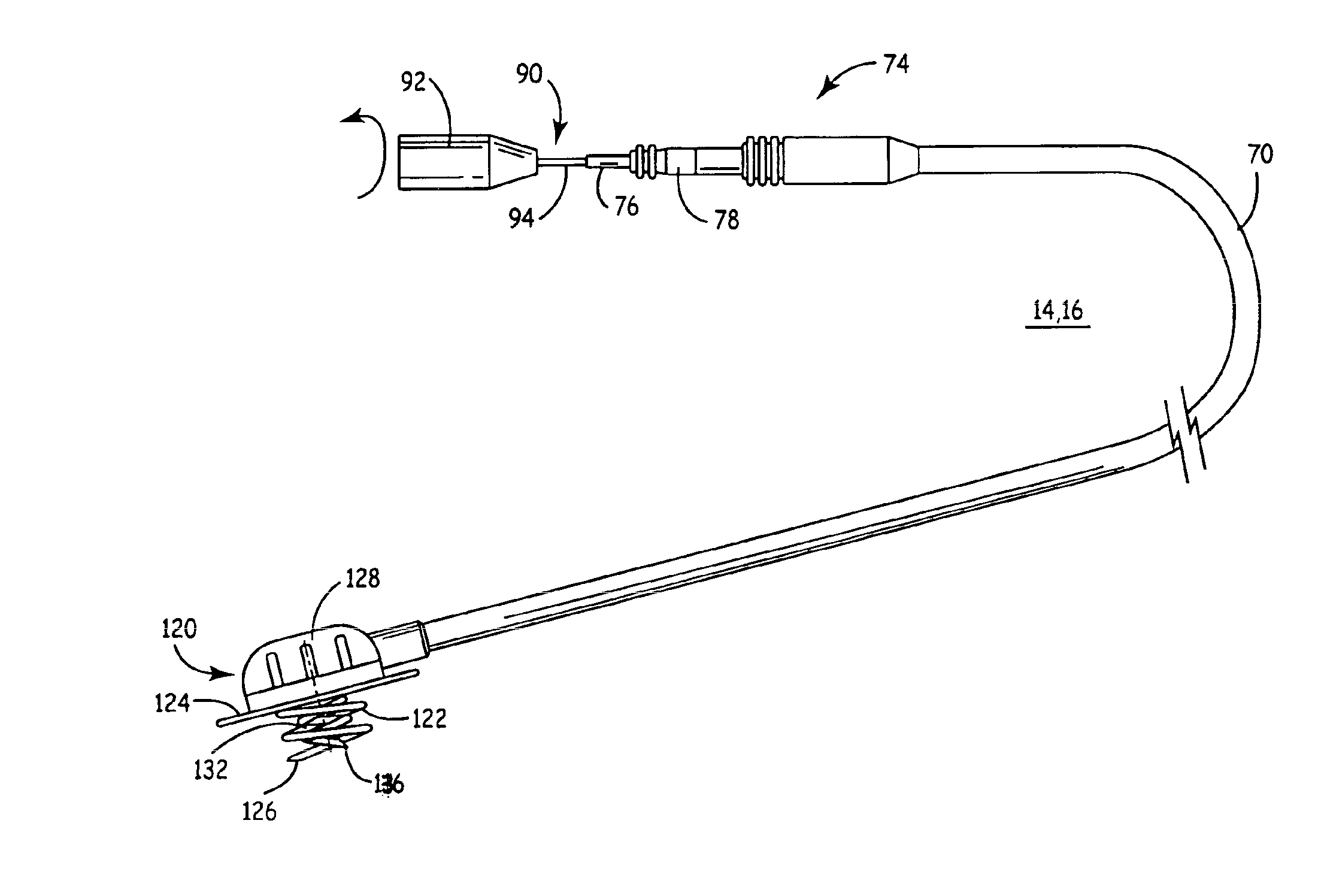
Device and method for the implantation of active fixation medical leads
A lead implantation tool is disclosed herein. The tool may be configured to operably couple to a lead connector end of an implantable cardiac electrotherapy lead including an active fixation helix tip and wherein the lead connector end includes a contact pin proximally extending from the lead connector end. The tool may include a feature configured to couple to the contact pin and a first mechanism configured to convert linear movement into rotational movement of the contact pin relative to the lead connector end. The tool may further include a second mechanism that causes a stylet extending through the tool and into the contact pin to at least one of distally and proximally displace within the contact pin.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Self-flaring active fixation element for a stent graft
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
High impedance active fixation electrode of an electrical medical lead
ActiveUS20060122682A1Improving impedanceSave battery powerAntipyreticAnalgesicsElectricityActive fixation
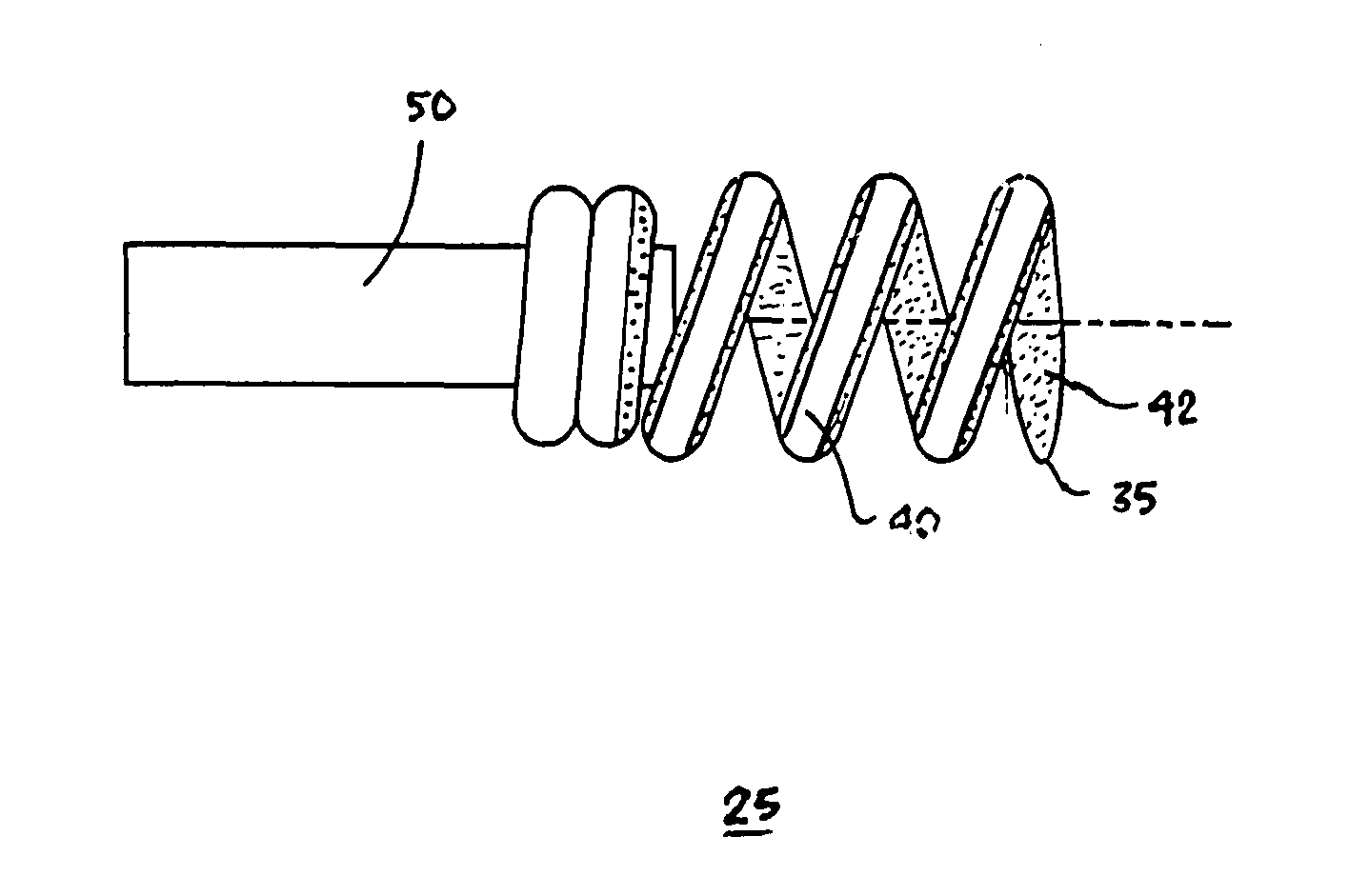
Electrical medical leads having active fixation electrodes, particularly helix electrodes intended to be screwed into body tissue, e.g., the heart, are disclosed having selectively applied insulation to optimize exposed electrode surface area and dispose the exposed electrode surface area toward tissue that is less traumatized by injury caused by screwing in the fixation helix. In a preferred fabrication method, an outer helical surface is masked by contact with a masking tube while a dielectric coating is applied to the inner helical surface of the coil turns of the helix, and the masking tube is removed when the dielectric coating has set. In one variation, at least one aperture is formed through the masking tube sidewall exposing an area of the outer helical surface thereby interrupting the uninsulated outer helical electrode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
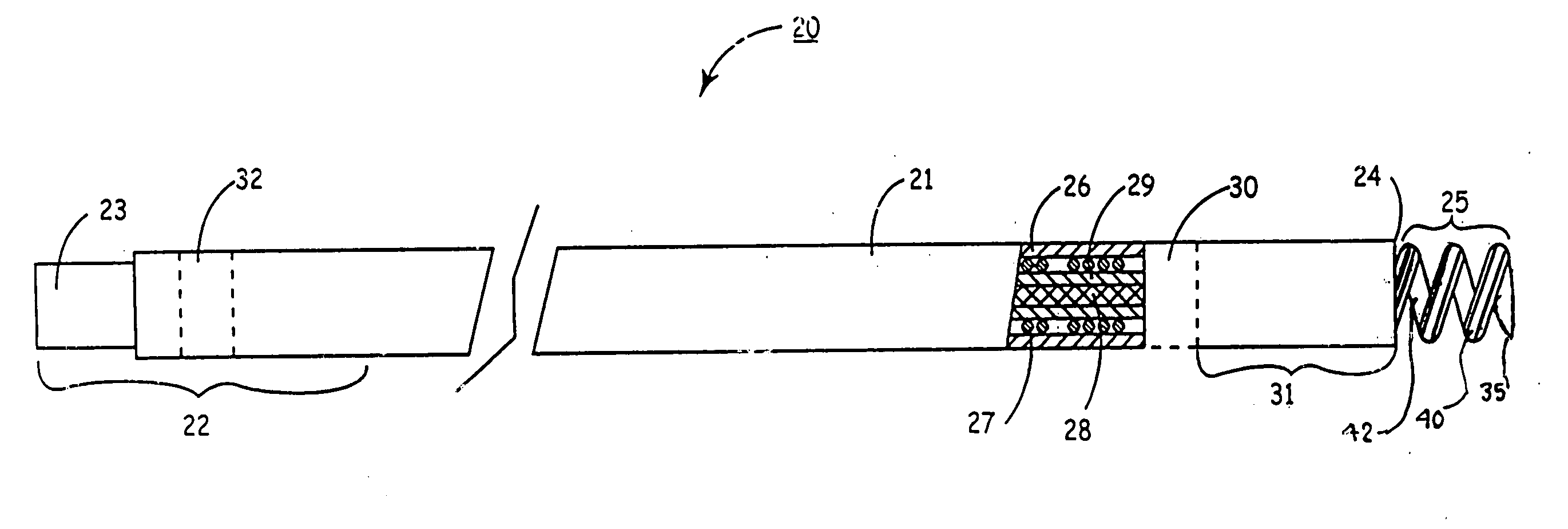
Low profile active fixation cardiac lead having torque transmitting means
An active fixation cardiac lead is disclosed that includes an elongated lead body having opposed proximal and distal end portions and an interior lumen that extends therethrough. A rotatable fixation element is operatively associated with the distal end portion of the lead body and a tubular torque-transmitting member extends through the interior lumen of the lead body. The tubular torque-transmitting member has a distal end connected to the fixation element and a proximal end connected to a rotatable actuator operatively associated with the proximal end portion of the lead body. Preferably, the rotatable actuator is part of a connector assembly that is operatively associated with the proximal end portion of the lead body.
Owner:OSCOR
Active fixation medical electrical lead
ActiveUS8755909B2Prevents wedgingGood removal effectEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesActive fixationEngineering
A medical electrical lead having an elongated lead body and a fixation helix extending along a generally helical axis, mounted around the outer circumference of the lead body. The fixation helix has a free end spaced from and extending from the lead body for less than the circumference of the lead body. The lead body includes an additional component which provides a rotation stop extending from the outer circumference of the lead body and provides stop surface generally perpendicular to the axis of the helix.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac lead with active fixation and biocompatible lubricant
InactiveUS6259953B1DiagnosticsTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical conductorActive fixation
A cardiac stimulator lead is provided that includes a connector for connecting to a cardiac stimulator and an insulating sleeve that has a first end coupled to the connector and a second end. The second end has an opening therein. An electrode is positioned in the insulating sleeve and has a piercing member. The electrode is moveable axially from a retracted position to an extended position wherein the piercing member projects from the opening. A conductor wire is disposed in the sleeve and coupled between the connector and the electrode for transmitting electric signals between the cardiac stimulator and the electrode. A lubricant is provided inside the insulating sleeve for lubricating the movement of the electrode. The lubricant reduces the potential for sticking, particularly for silicone lead sleeves.
Owner:INTERMEDICS
Electrically isolating electrical components in a medical electrical lead with an active fixation electrode
ActiveUS20100324640A1Obstruct passageAvoid flowSpinal electrodesMultiple-port networksElectricityElectrical conductor
A lead body adapted for in-vivo implantation in a living subject includes a proximal end configured for electrical and mechanical connection to a therapy or a monitoring device, and a distal end. A collar is disposed at the distal end of the lead body, and a casing is disposed within the collar and is translatable along a central longitudinal axis of the collar. At least one electrical conductor extends substantially the length of the lead body, and an electronic component is disposed within the casing and conductively coupled to the electrical conductor. An electrode is mechanically connected to the casing and conductively coupled to the electronic component. A seal is disposed between the casing assembly and the collar to prevent passage of ionic fluid into the lead body through its distal end.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Chronically-implantable active fixation medical electrical leads and related methods for non-fluoroscopic implantation
InactiveCN101711125ATransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringConductive materialsNavigation system
Bio-impedance may be used for navigation systems to chronically implant pacing and defibrillation leads in the heart using a non-fluoroscopic position sensing unit (PSU), such as a modified LocaLisa TM system from Medtronic Inc., which allows for variable frequency sampling of the position of electrode of a catheter. The PSU injects small AC signals via surface electrodes in three orthogonal axes, each on a slightly different frequency (e.g., near 30 KHz). Indwelling electrodes electrically connected to the PSU resolves the magnitude of induced voltage for each of the three frequencies, thus measuring voltage for each of the three axes. Voltages are divided by induced current to yield impedance in each axis for each electrode. Impedance is proportional to position within the body. Such a system requires that a conductive material, such as a retractable helical tip-electrode, be exposed during implantation. Since the tip is retracted during implantation, this disclosure provides a modified distal portion employing at least one aperture (or 'window') for fluid exposure of the helix-electrode and a deployable internal sleeve for covering the aperture(s) when the helix-electrode is extended.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Active Fixation Implantable Medical Lead Configured to Indicate via Fluoroscopy Embedment of Helical Anchor in Cardiac Tissue
An implantable medical lead for active fixation to cardiac tissue is disclosed herein. The lead may include a lead body distal end, a tissue fixation helical anchor and a structure. The tissue fixation helical anchor may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a distal tip. The structure may be coupled to the lead body distal end and include a structure distal end including a first radiopaque marker. The structure may be biased to project the structure distal end near the distal tip. When the tissue fixation helical anchor is progressively embedded in the cardiac tissue, the cardiac tissue progressively displaces the structure distal end proximally.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Lead fixation tool
A lead fixation tool includes a tapered opening for receiving and guiding a stylet into a lead. The fixation tool also includes an engagement mechanism for gripping a portion of the lead connector so that rotation of the tool causes rotation of an active fixation tip, such as a helical tip, coupled with the lead.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac lead having coated fixation arrangement
ActiveUS7197362B2Reduces exit blockReduced responseEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesFiberElectrical conductor
Implantable cardiac monitoring and stimulation devices and methods using cardiac leads employ coated fixation arrangements. The coating, such as an expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, reduces exit block by reducing the tissue response to the fixation arrangement, decreasing the amount of fibrotic tissue, and reducing exit block. An epicardial lead may include a lead body with one or more electrical conductors with associated insulators and an electrode assembly situated at the distal end. The electrode assembly includes an electrode having an active fixation arrangement such as a helical fixation element. The fixation arrangement is completely or partially coated with a fluoropolymer or has a sleeve on some or all of the active fixation arrangement. The coating or sleeve may include a steroid or other pharmacological eluting arrangement disposed on the active fixation arrangement.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Active fixation medical electrical lead
ActiveUS20130325094A1Prevents wedgingGood removal effectEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesActive fixationEngineering
A medical electrical lead having an elongated lead body and a fixation helix extending along a generally helical axis, mounted around the outer circumference of the lead body. The fixation helix has a free end spaced from and extending from the lead body for less than the circumference of the lead body. The lead body includes an additional component which provides a rotation stop extending from the outer circumference of the lead body and provides stop surface generally perpendicular to the axis of the helix.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
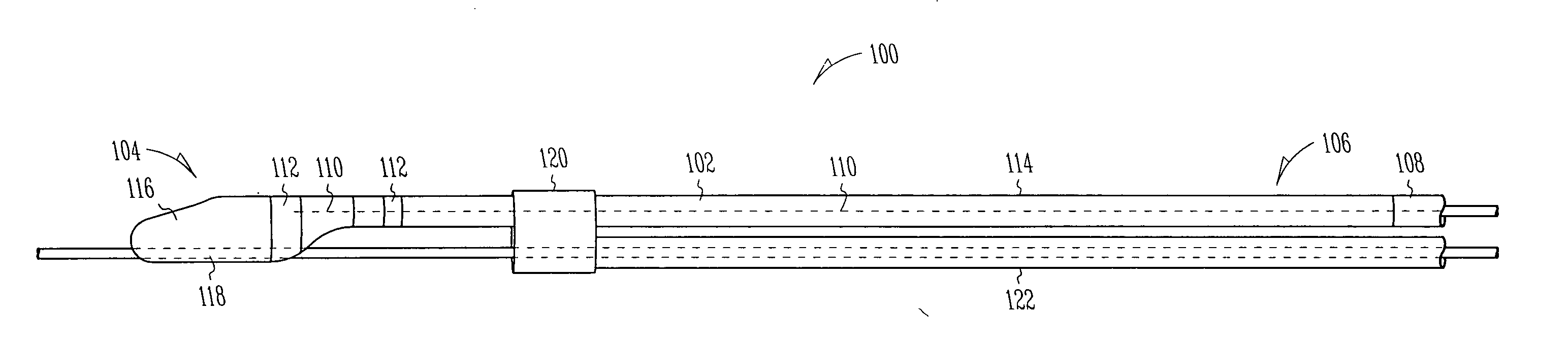
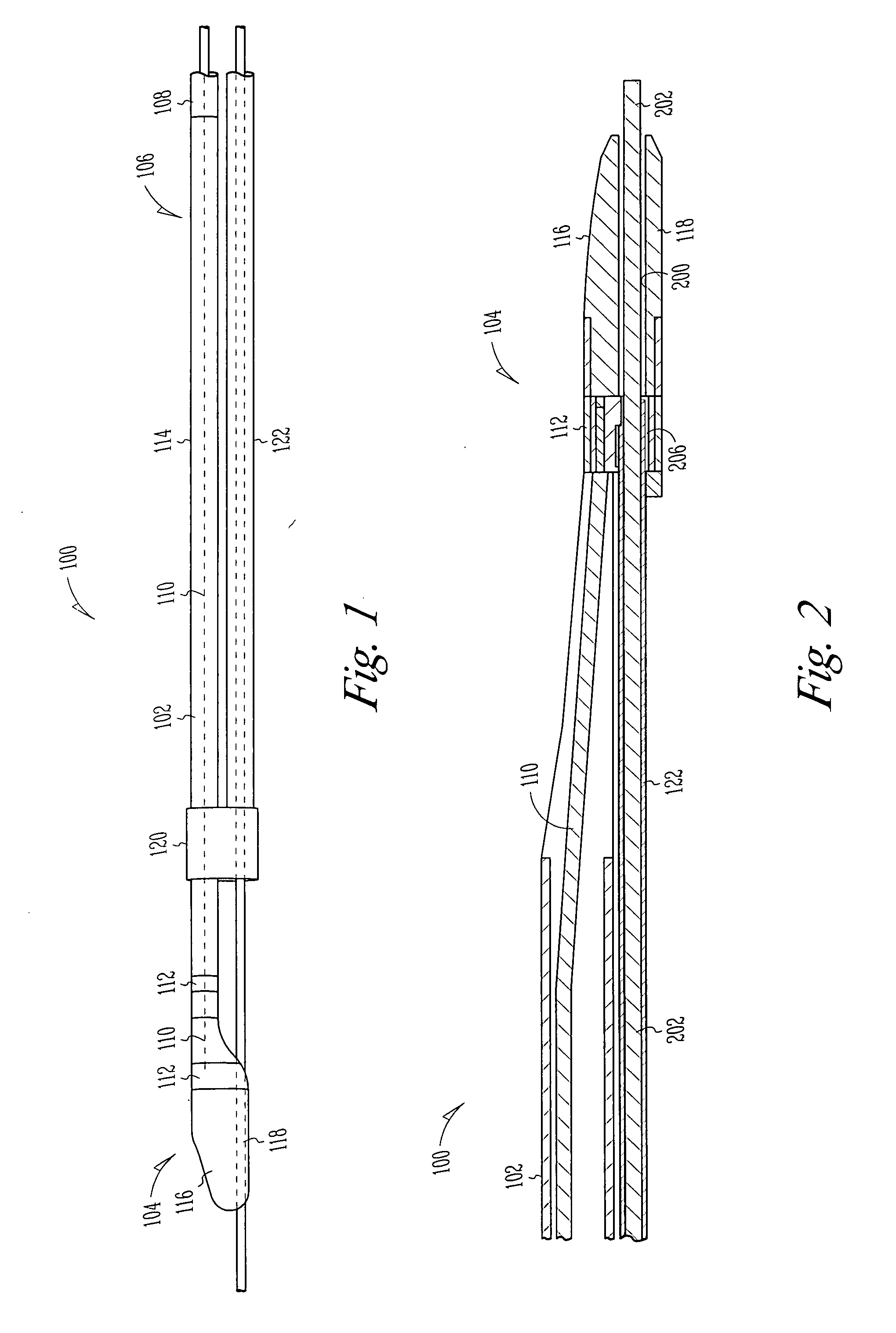
Extendable and retractable lead with an active fixation assembly
InactiveUS20050070984A1Transvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorEngineering
An extendable and retractable lead includes a lead body which extends from a distal end to a proximal end, where a conductor is disposed within the lead body. The lead assembly further includes a piston that is movably disposed within the lead body. A fixation helix is supported by the piston at a first portion of the fixation helix, where the first portion of the fixation helix forms a drive mechanism that advances and / or retracts the fixation helix.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
High impedance active fixation electrode of an electrical medical lead
ActiveUS7720550B2Reduce polarizationReduce inflammationAntipyreticAnalgesicsElectricityActive fixation
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Active fixation assembly for an implantable device
An implantable device such as a lead is adapted for implantation on or about the heart and for connection to a system for monitoring or stimulating cardiac activity. The implantable device includes an active fixation assembly for securing the device to tissue. The active fixation assembly includes one or more recessed portions therein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com