Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "Atrial wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
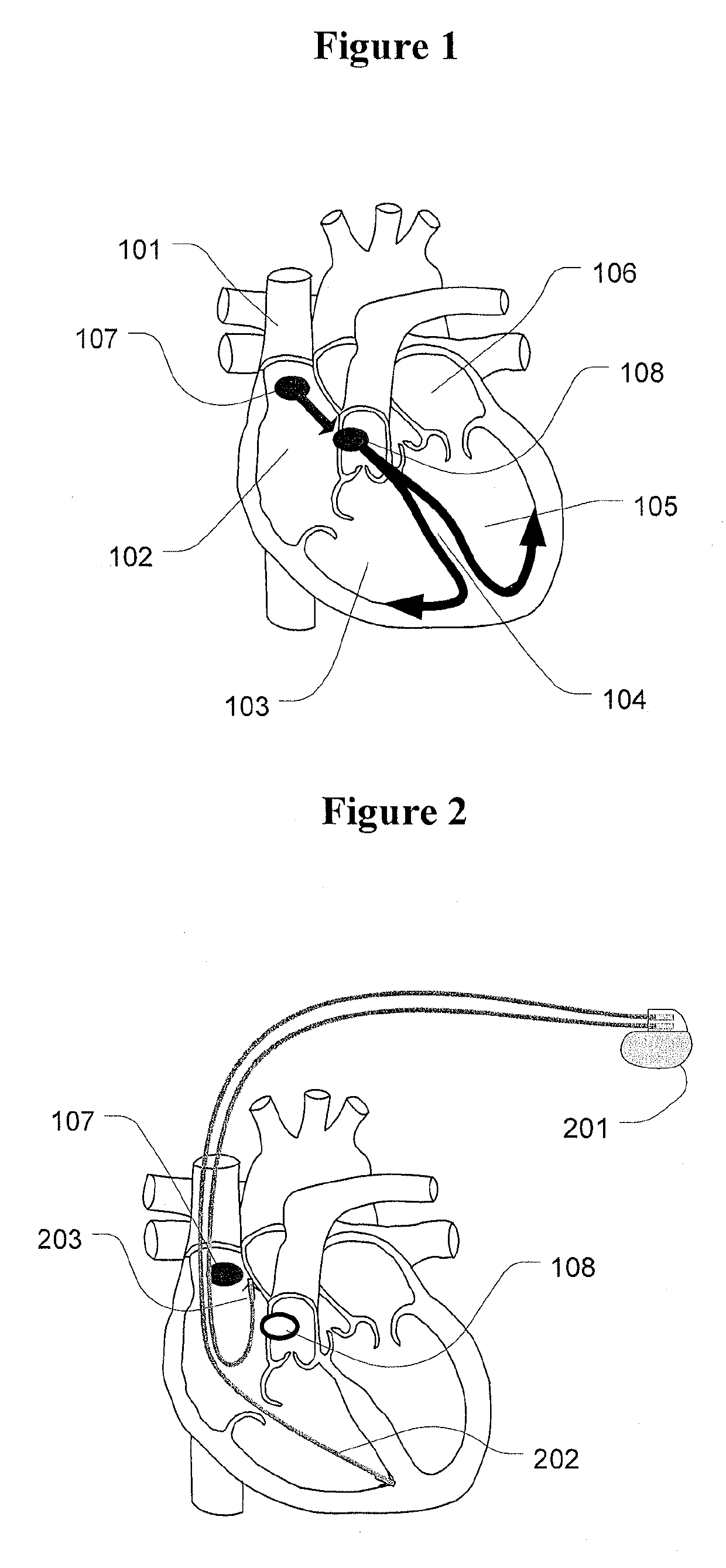
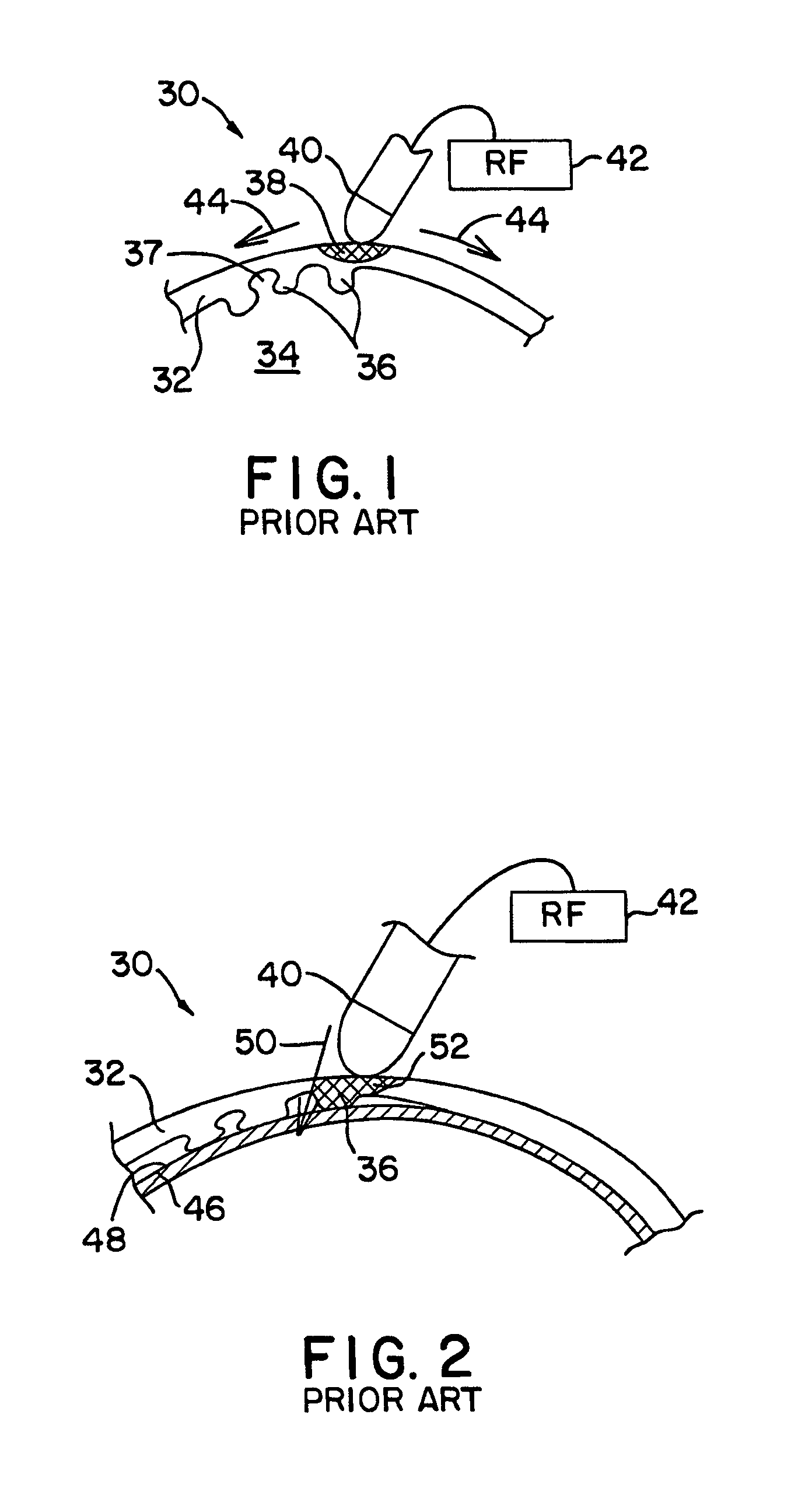
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the “wall” (called the septum) that separates the heart’s two upper chambers (the atria). ASDs are the second most common type of congenital heart defect. A hole in the atrial wall (patent foramen ovale, or PFO) is normal before and immediately after birth.
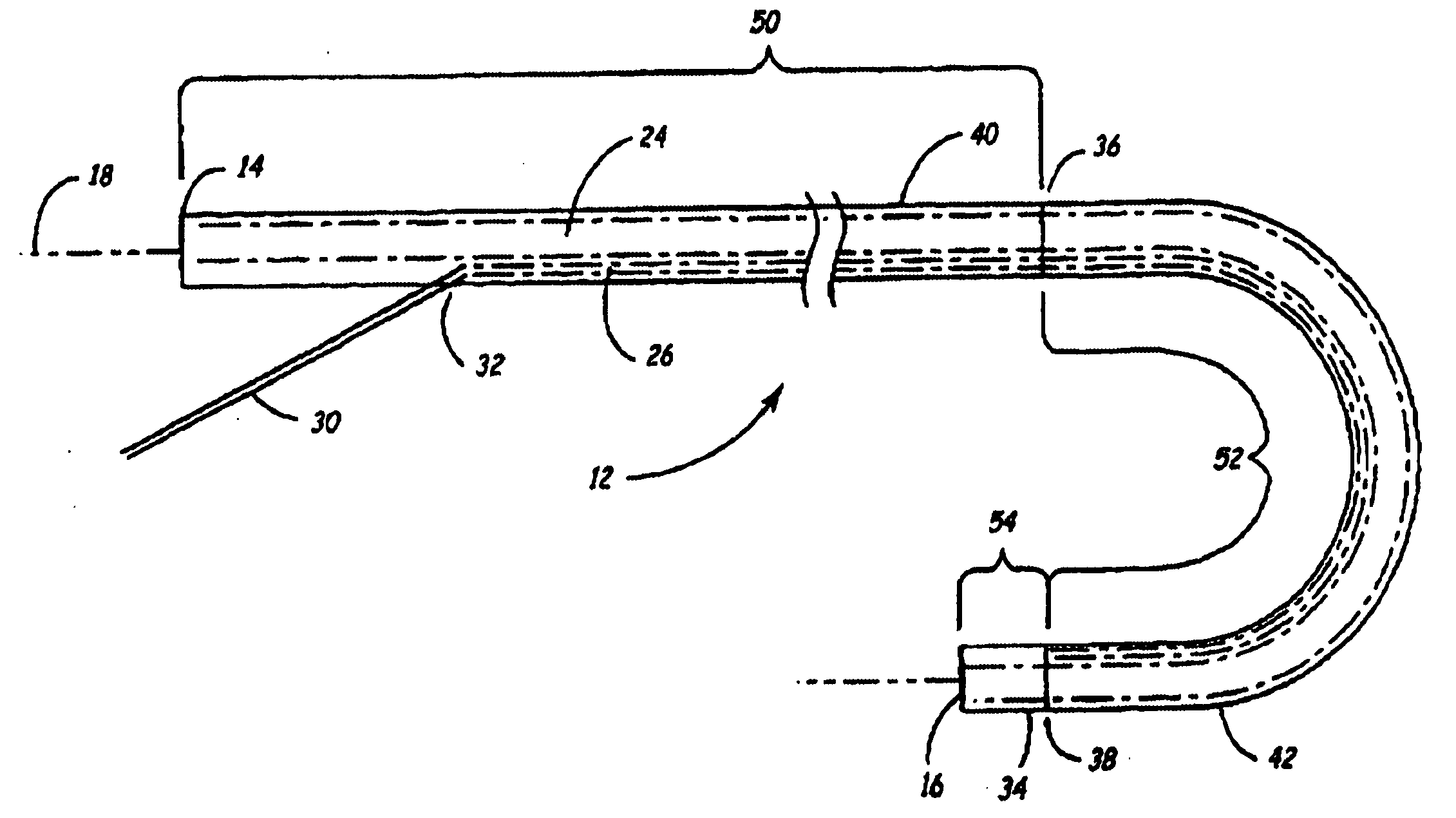
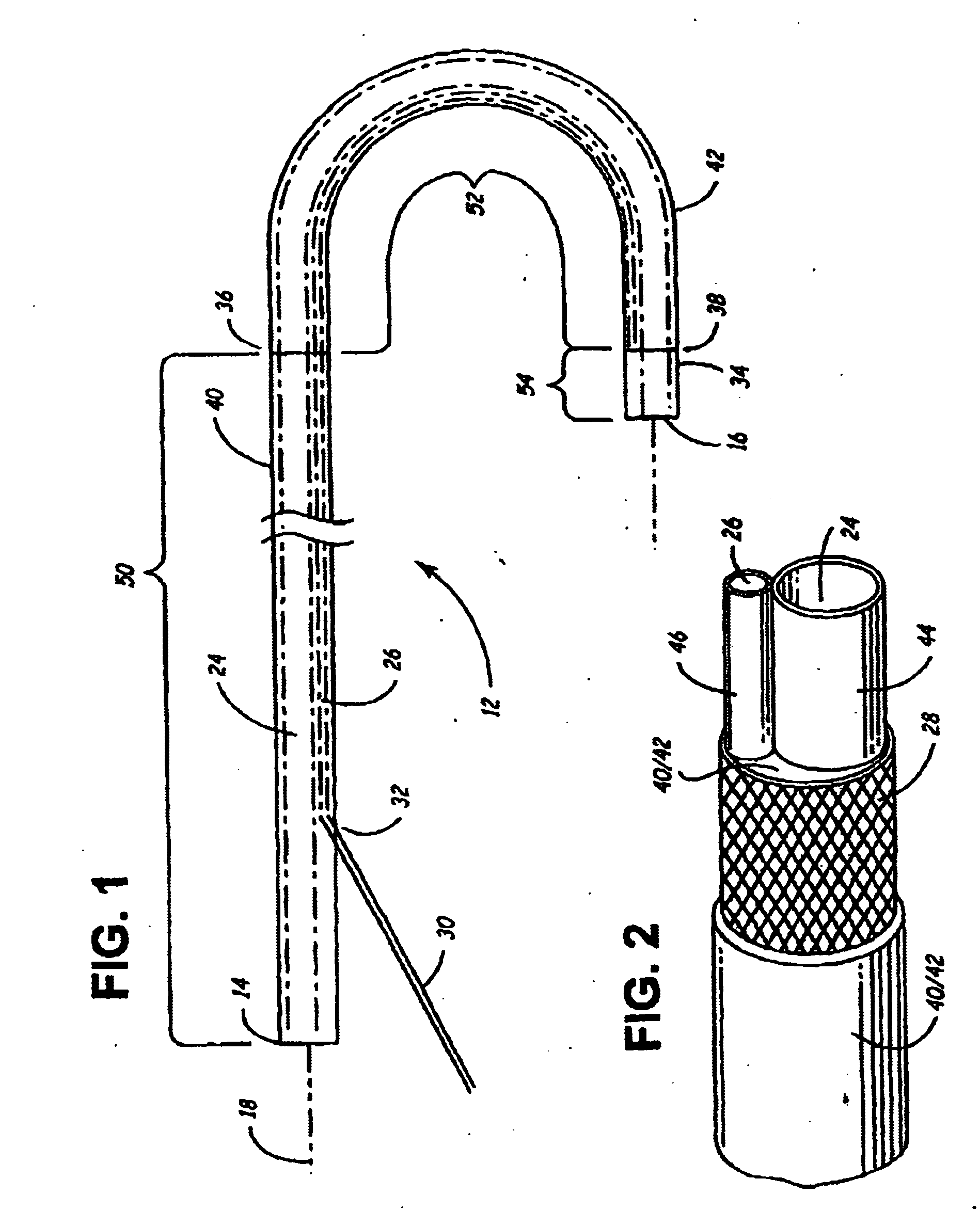
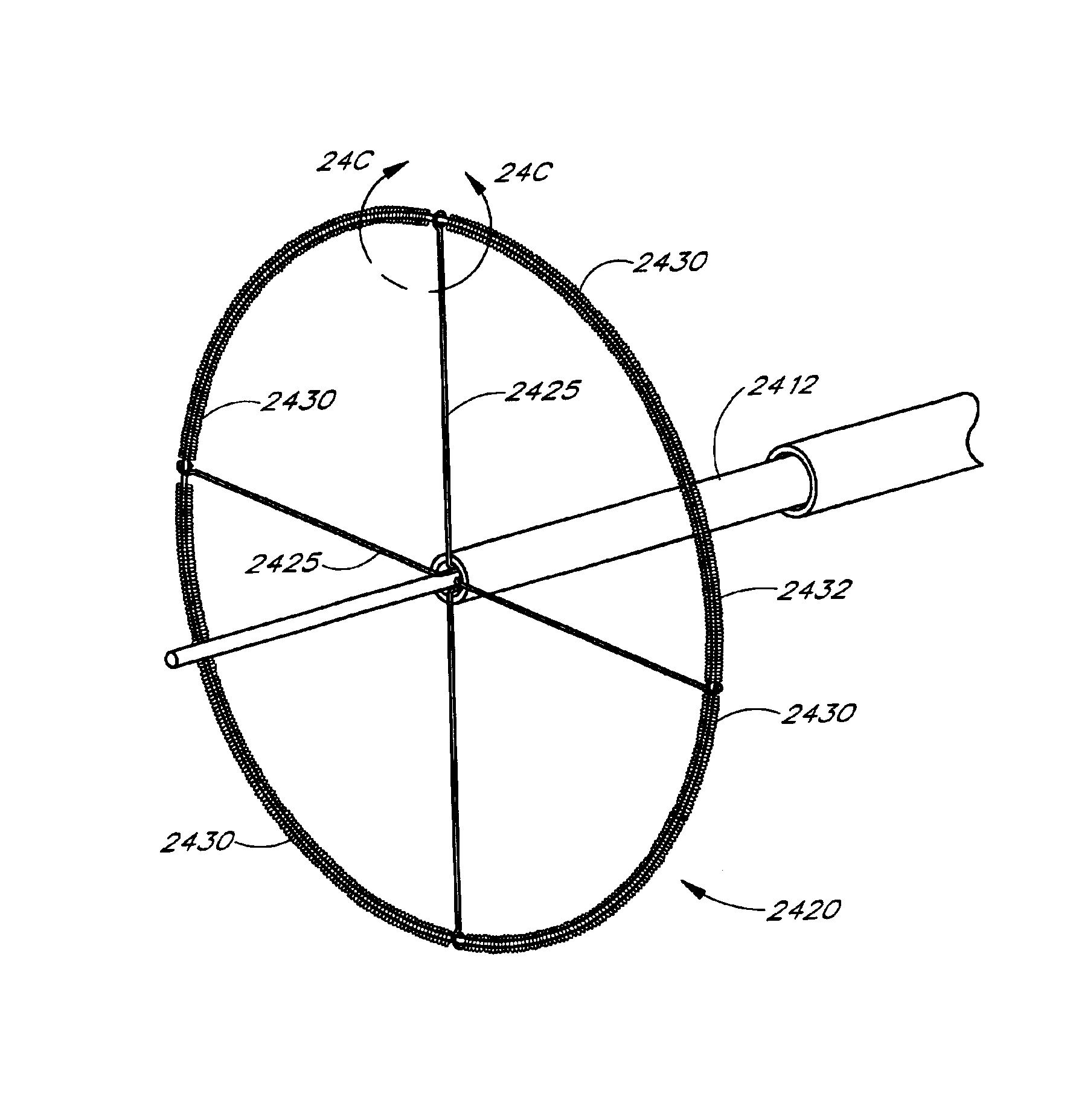
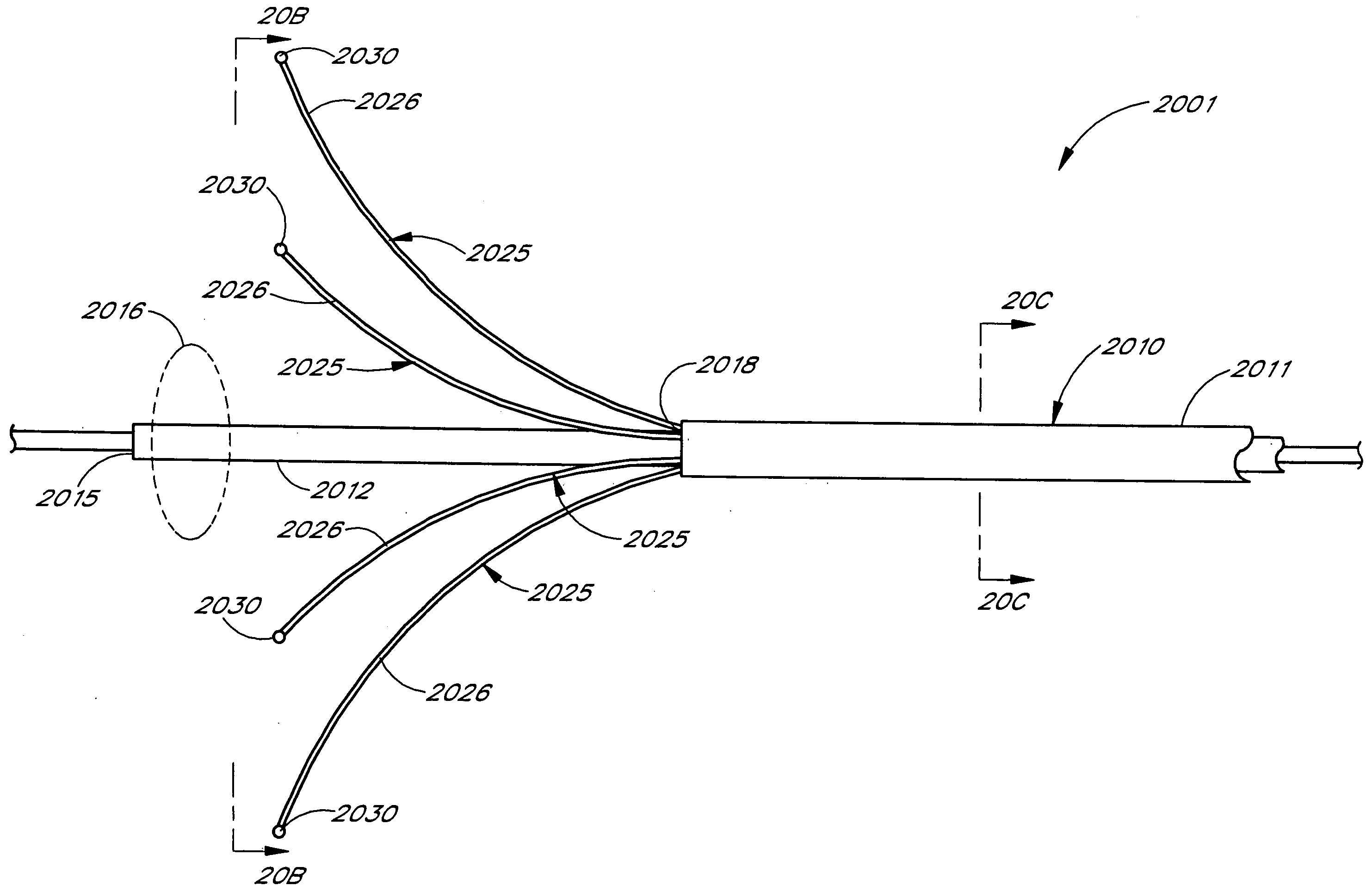
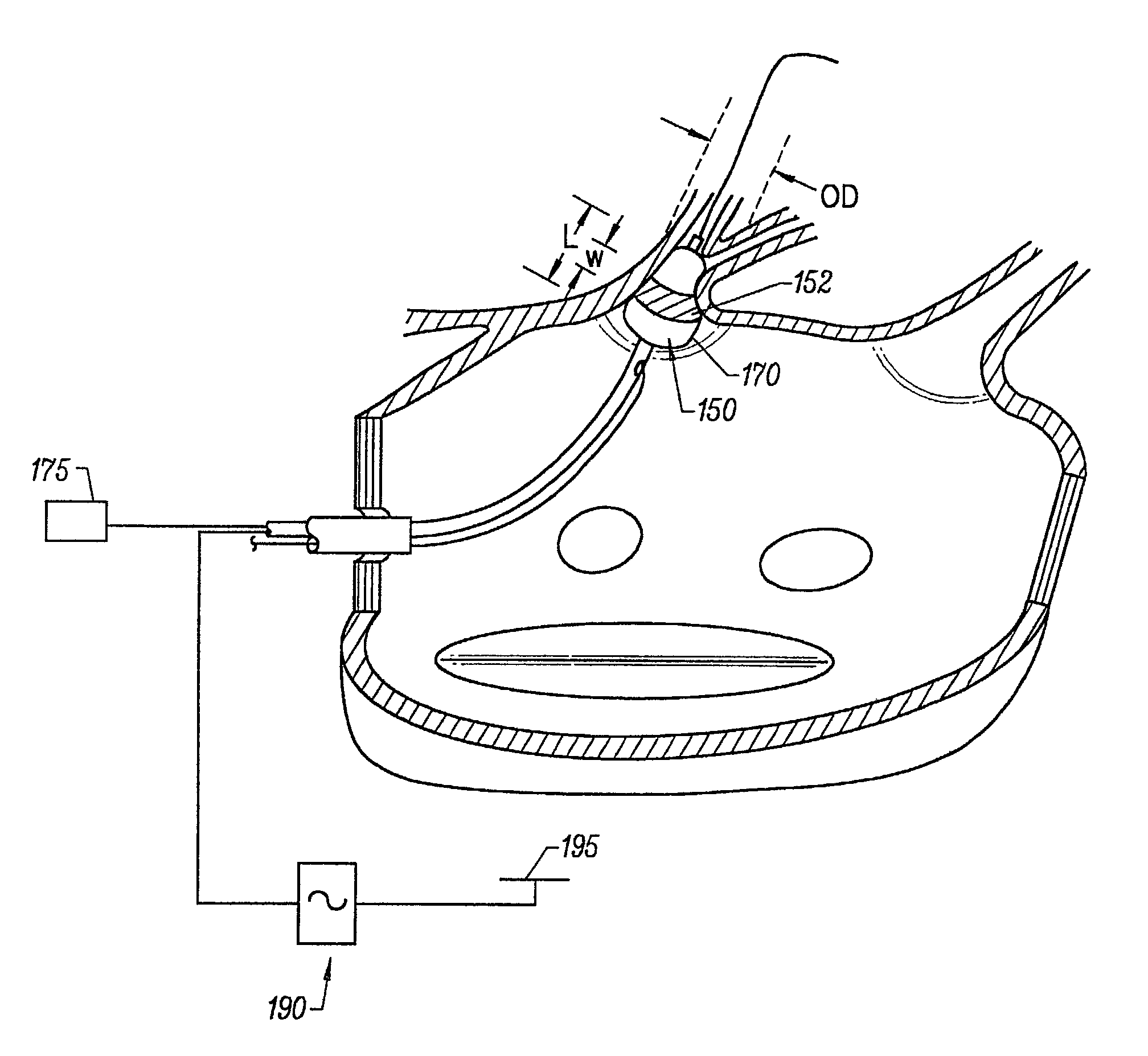
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
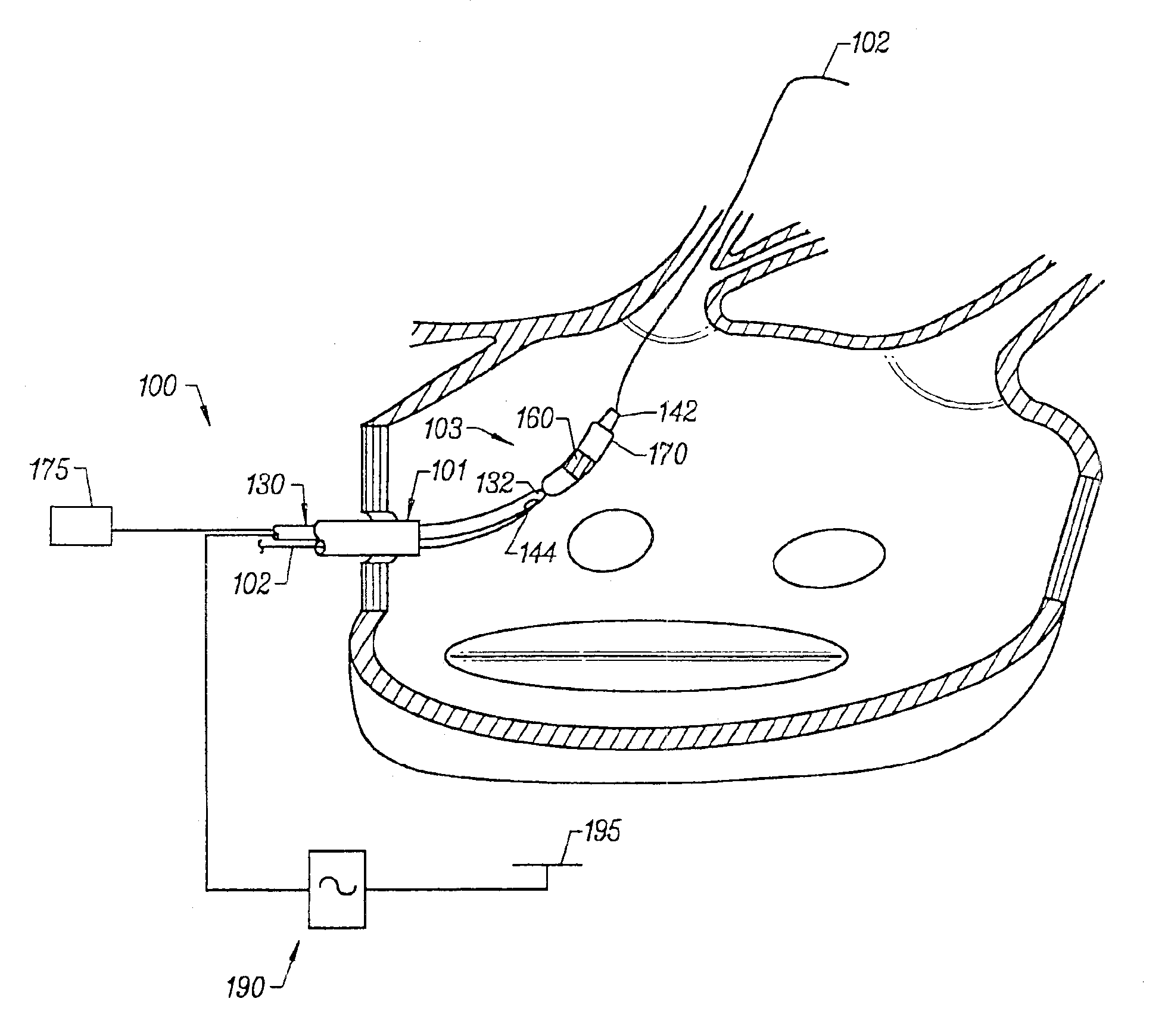
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
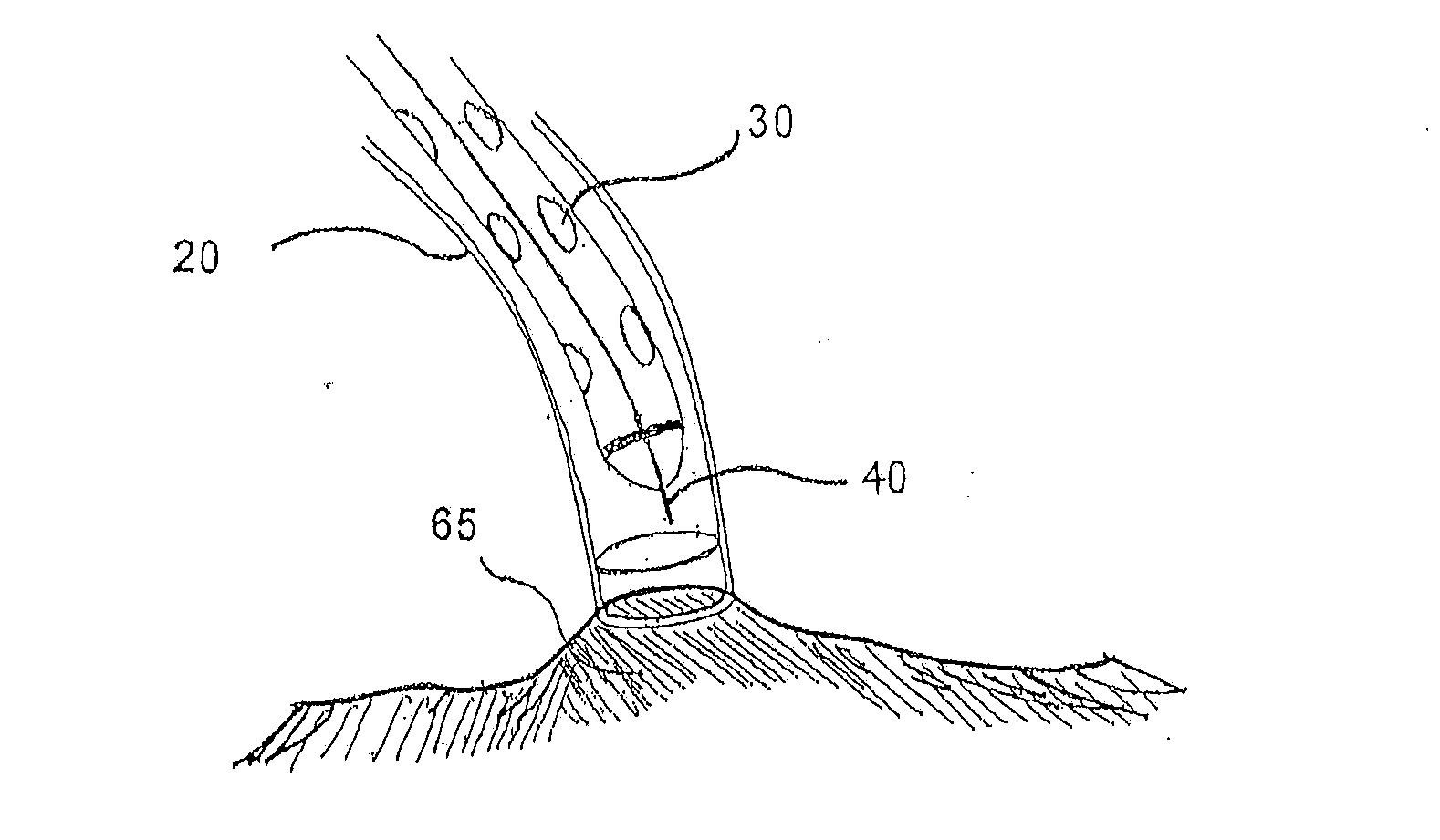
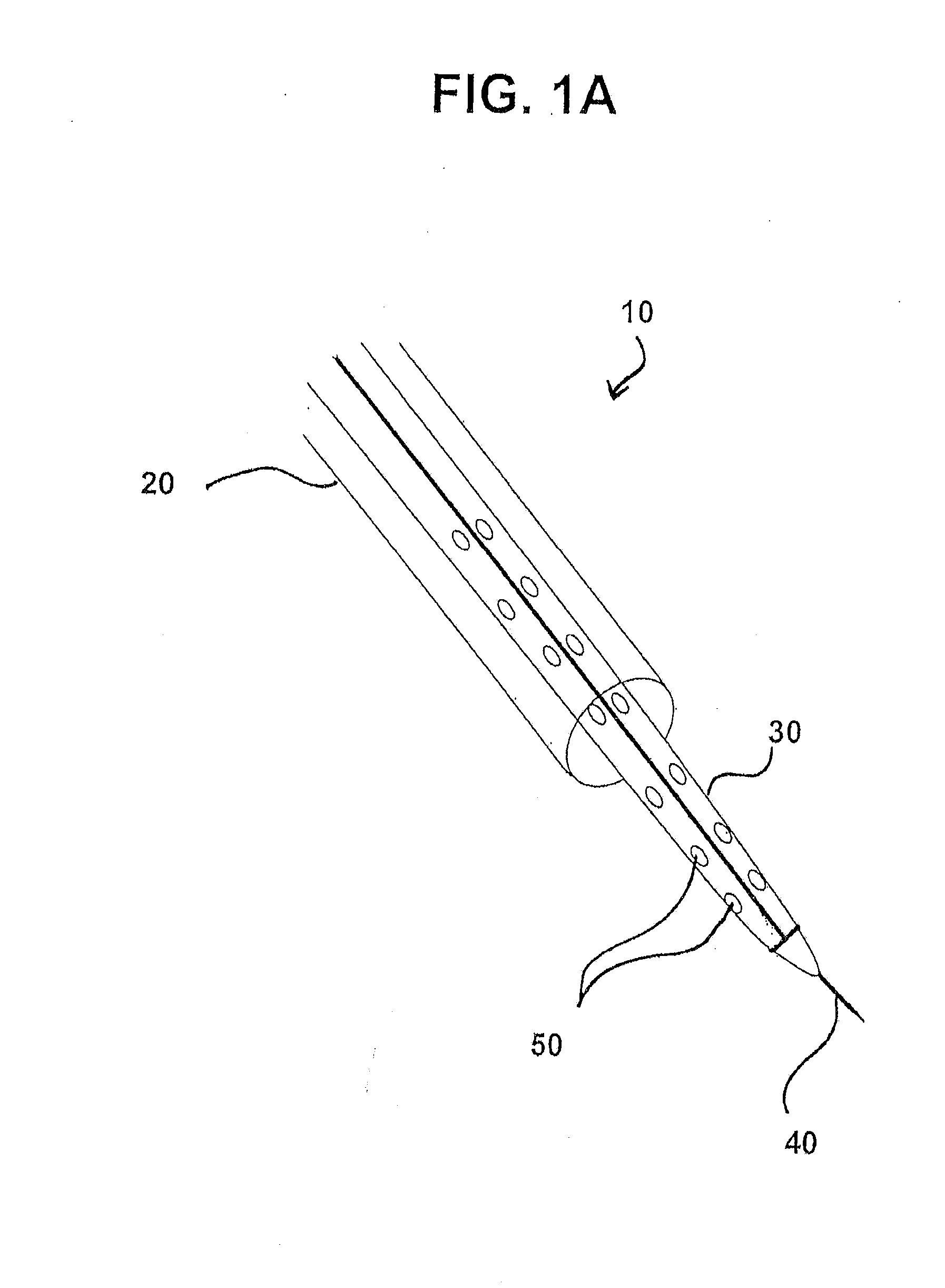
Methods and systems for accessing the pericardial space
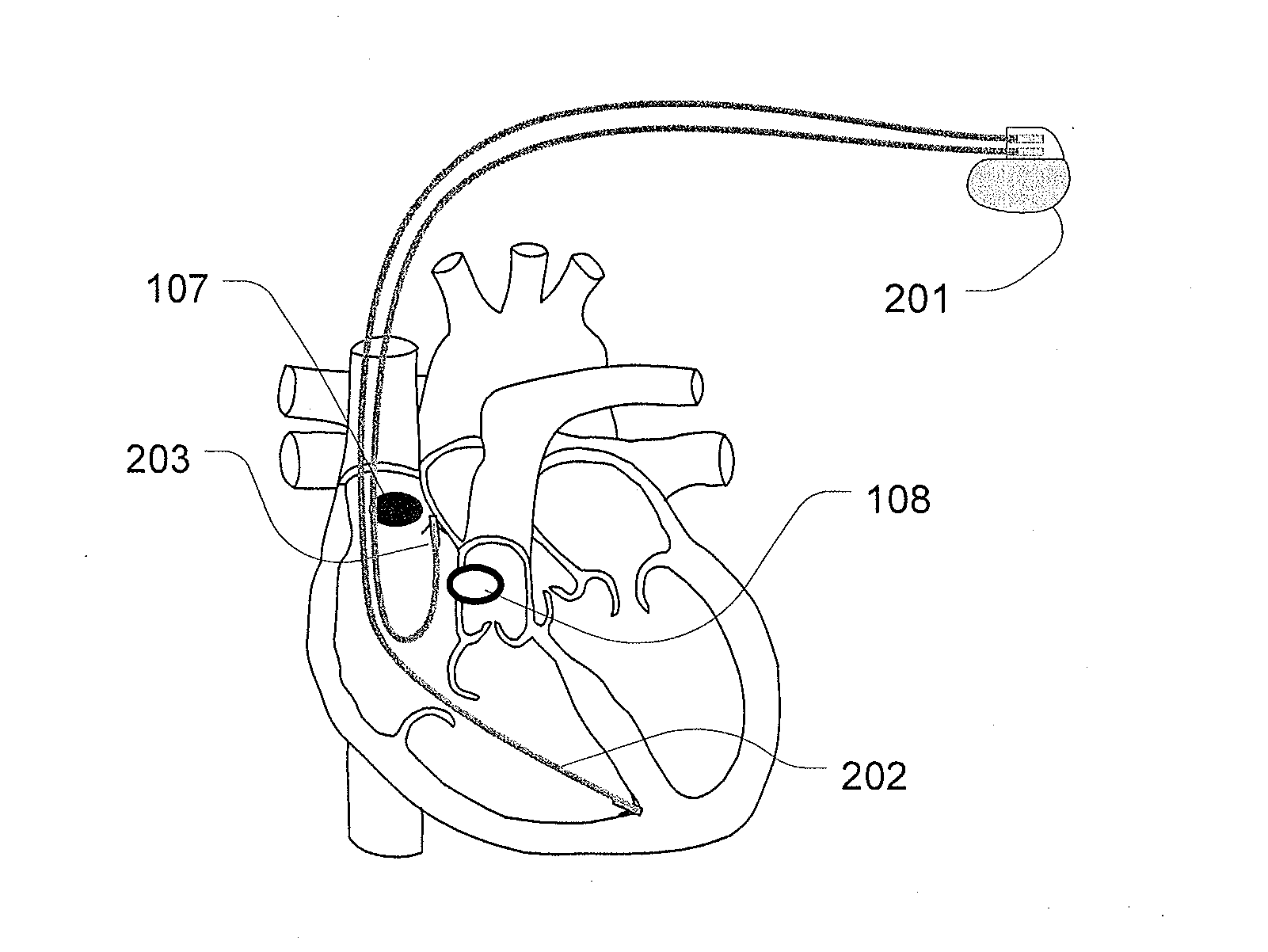
Methods and systems for transvenously accessing the pericardial space via the vascular system and atrial wall, particularly through the superior vena cava and right atrial wall, to deliver treatment in the pericardial space are disclosed. A steerable instrument is advanced transvenously into the right atrium of the heart, and a distal segment is deflected into the right atrial appendage. A fixation catheter is advanced employing the steerable instrument to affix a distal fixation mechanism to the atrial wall. A distal segment of an elongated medical device, e.g., a therapeutic catheter or an electrical medical lead, is advanced through the fixation catheter lumen, through the atrial wall, and into the pericardial space. The steerable guide catheter is removed, and the elongated medical device is coupled to an implantable medical device subcutaneously implanted in the thoracic region. The fixation catheter may be left in place.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tissue ablation device assembly and method of electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
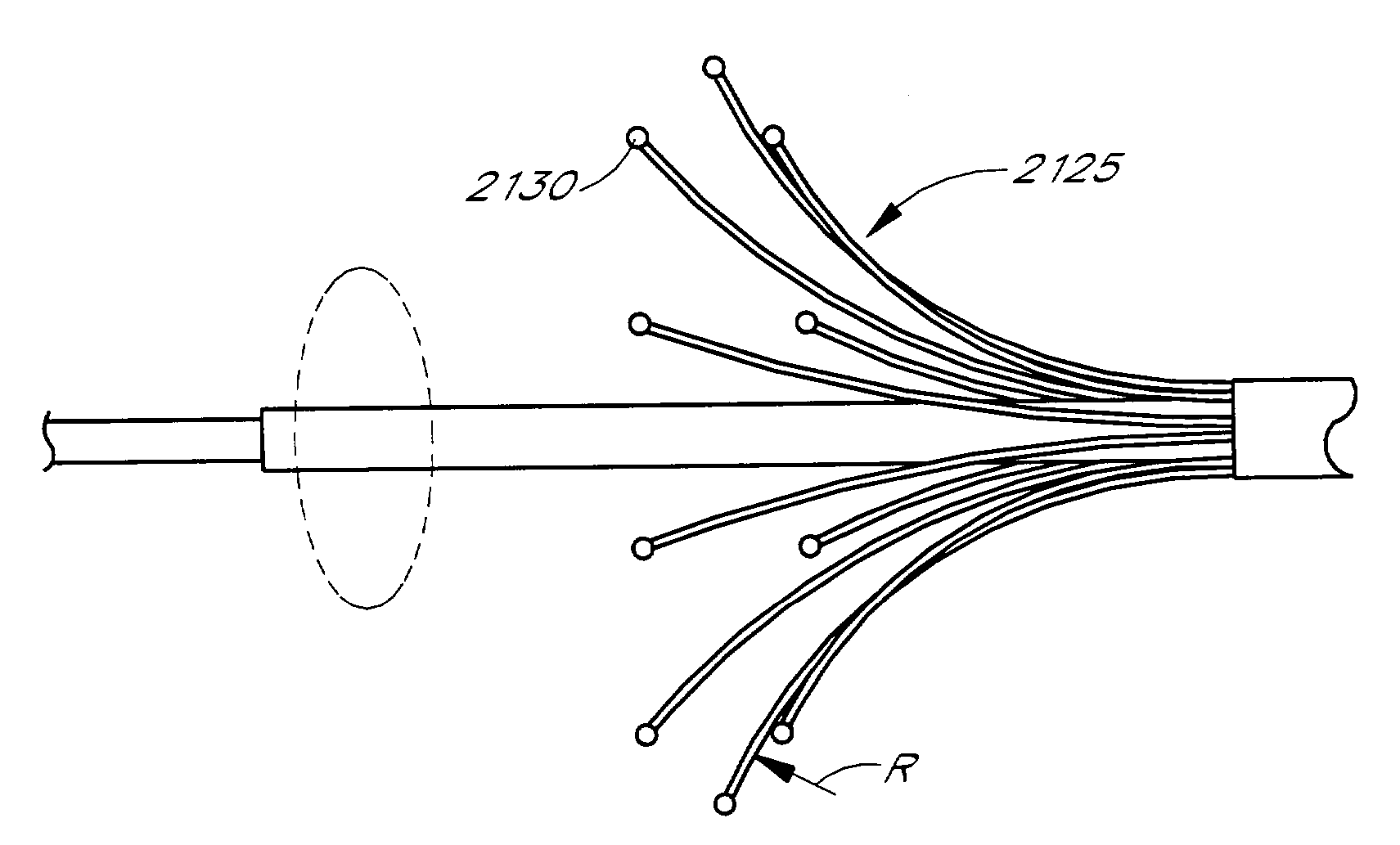
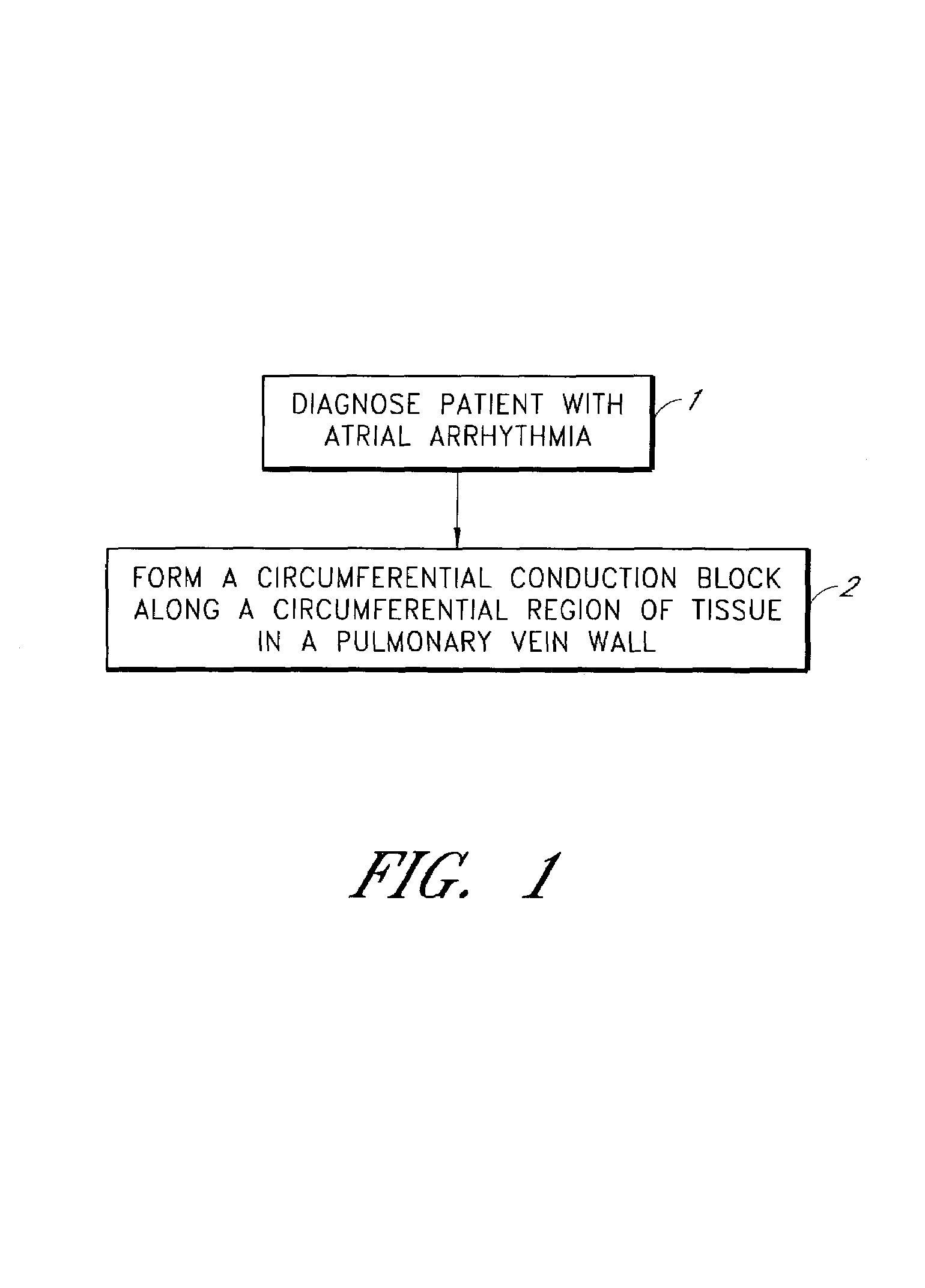
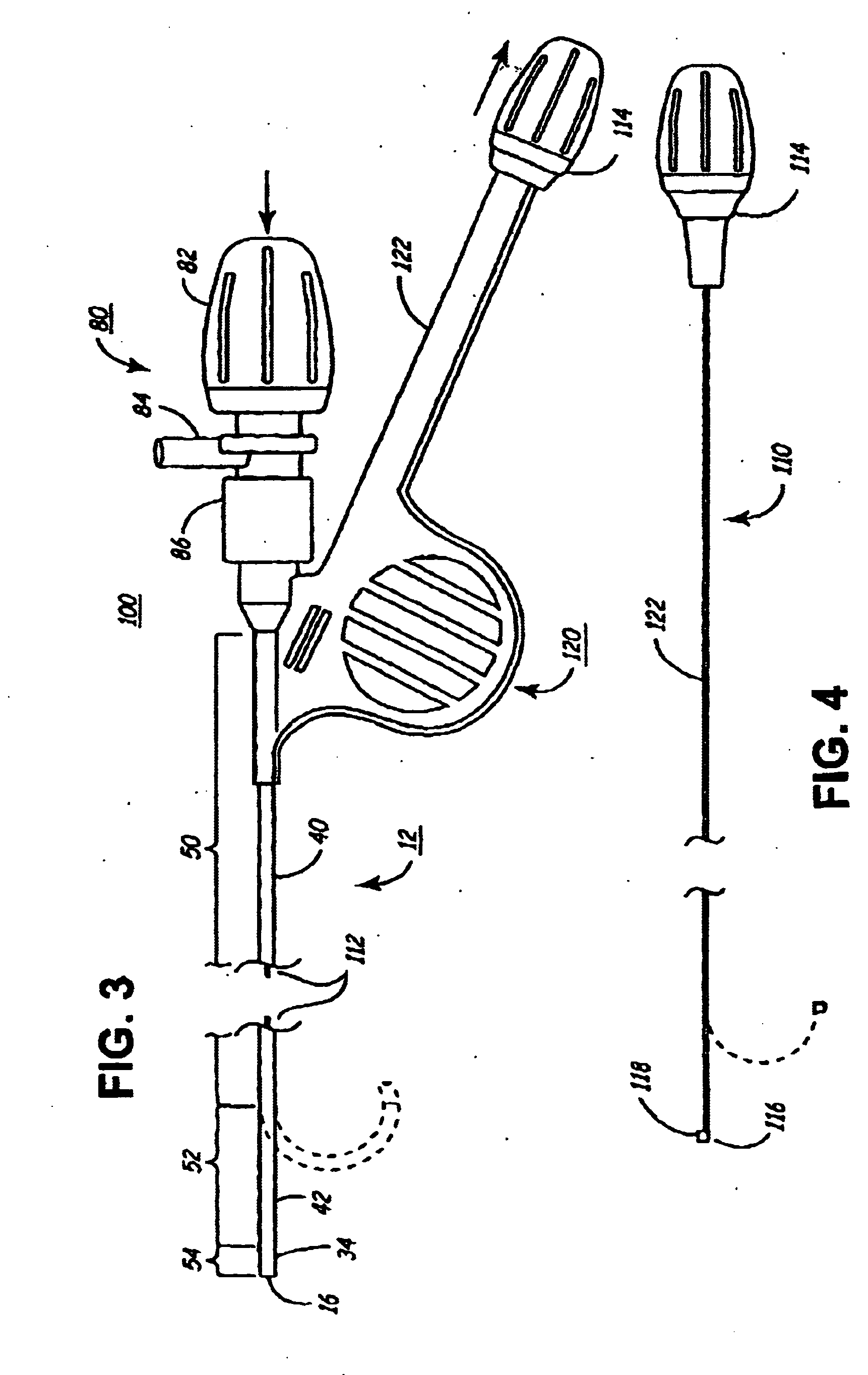
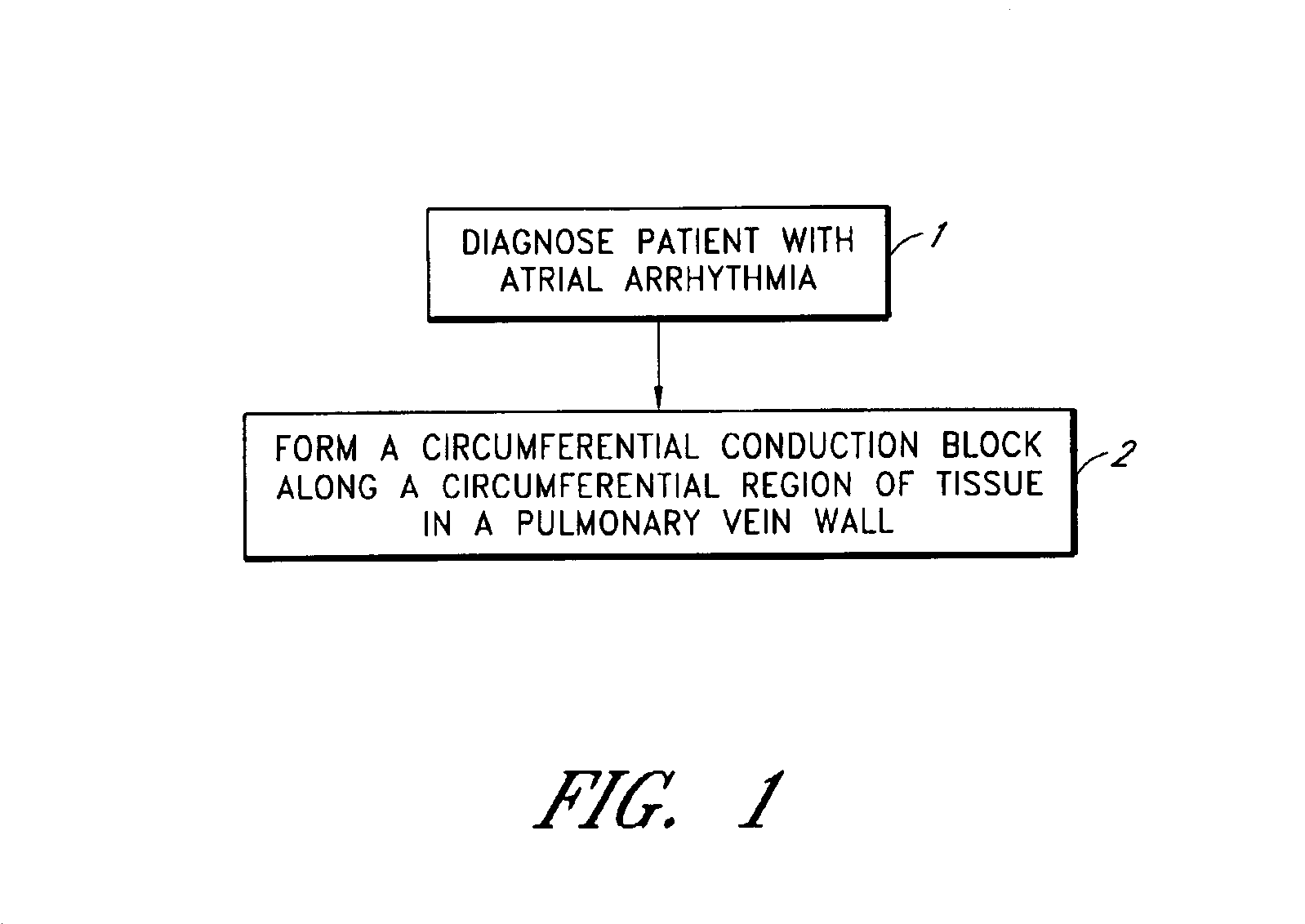
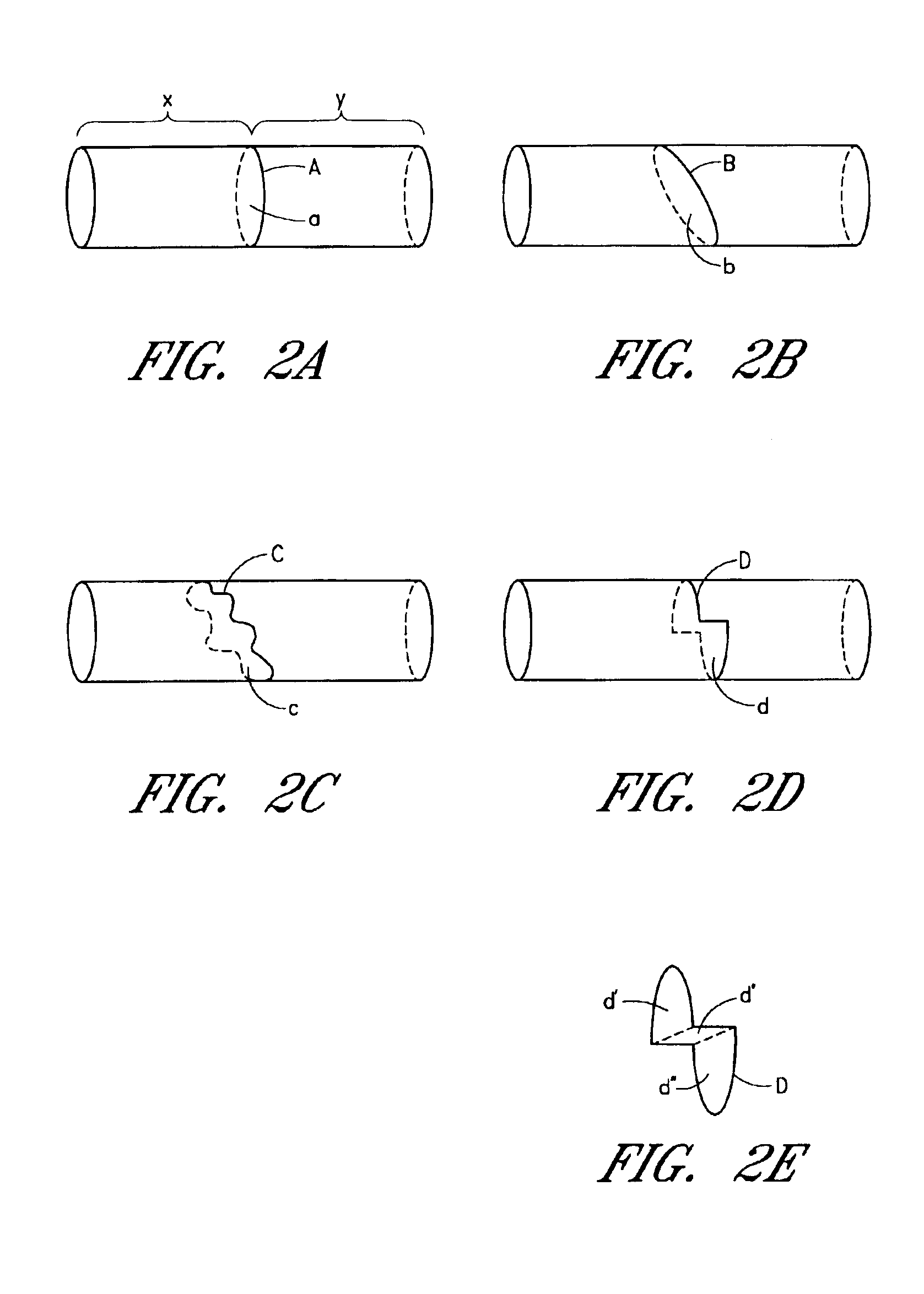
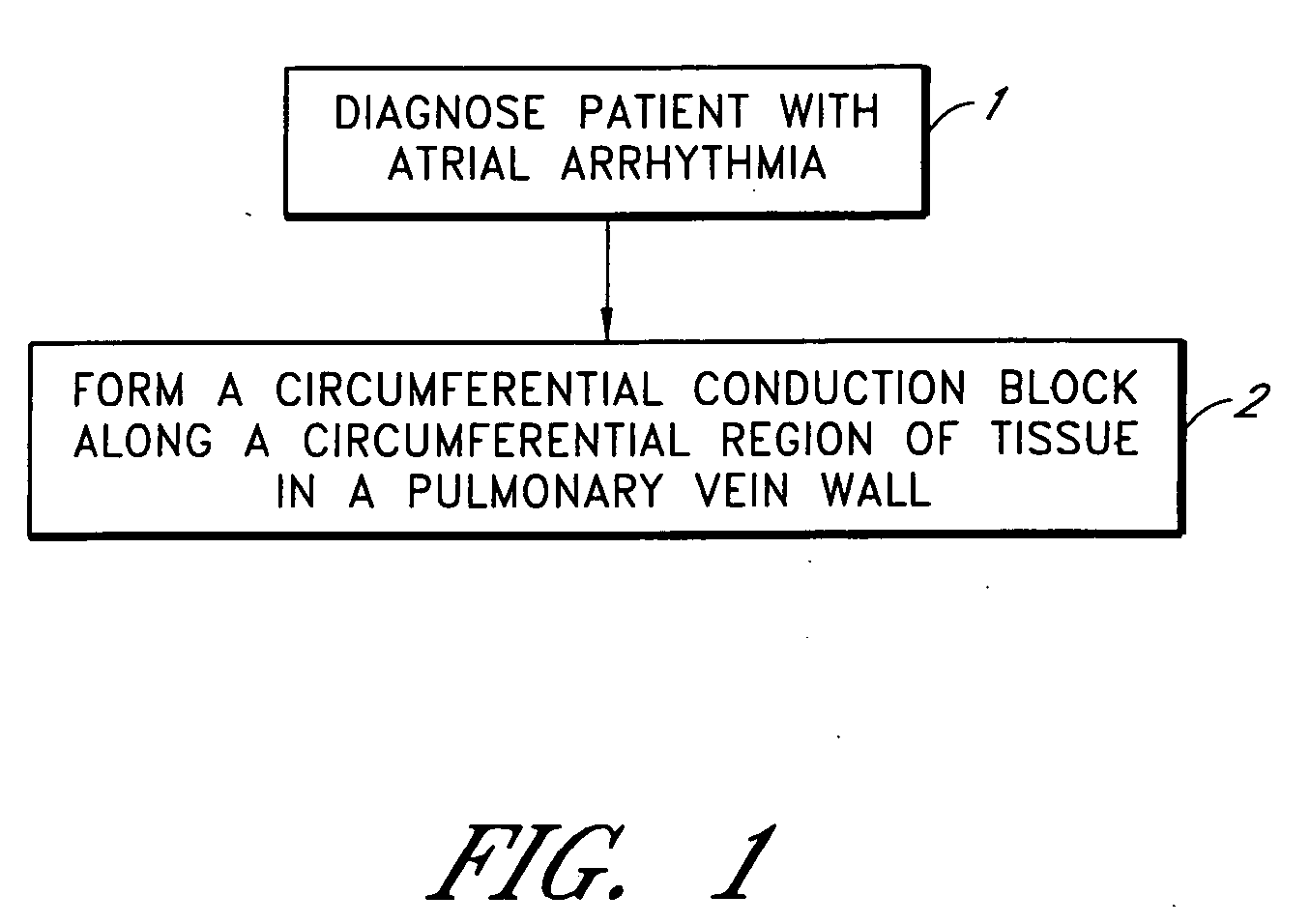
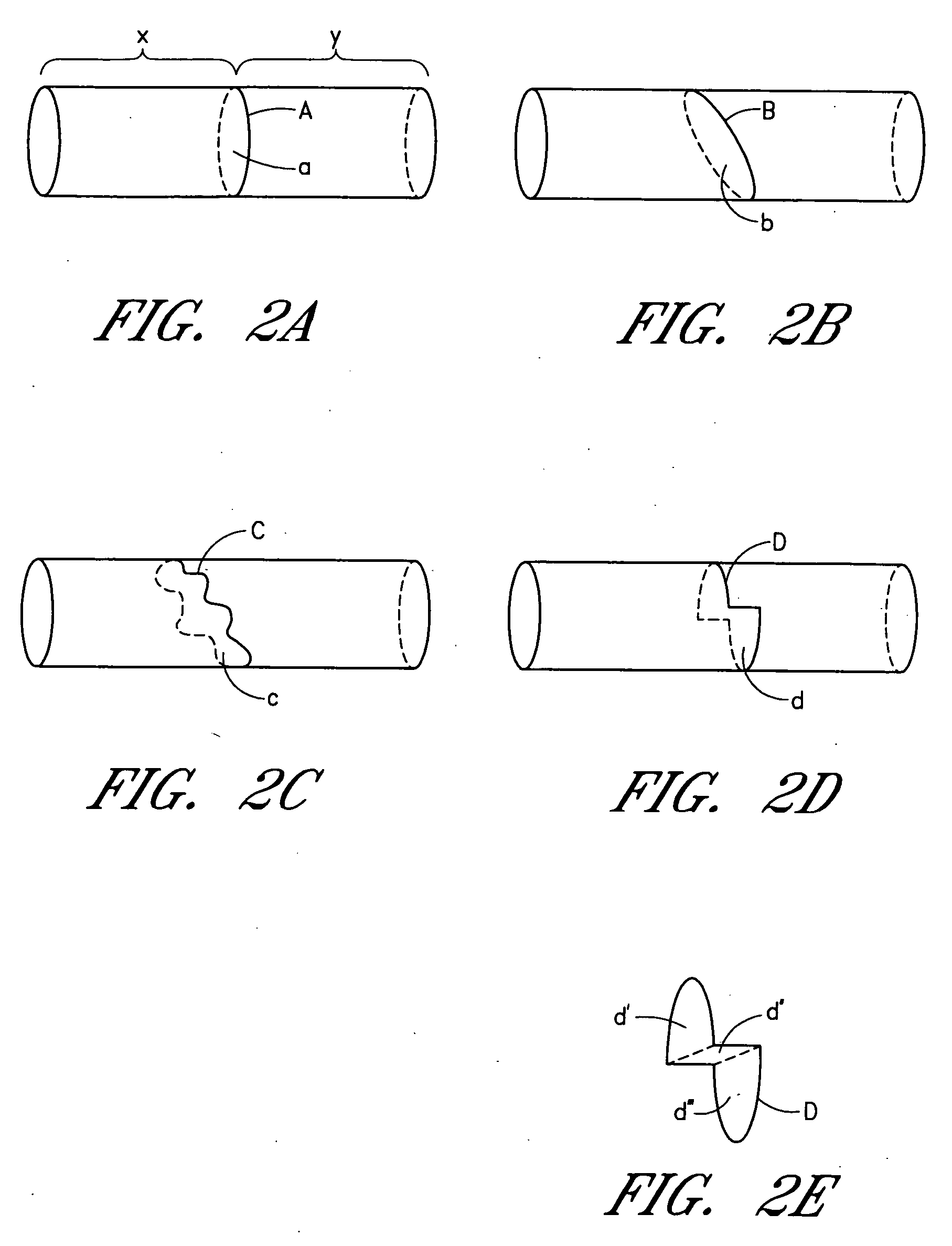
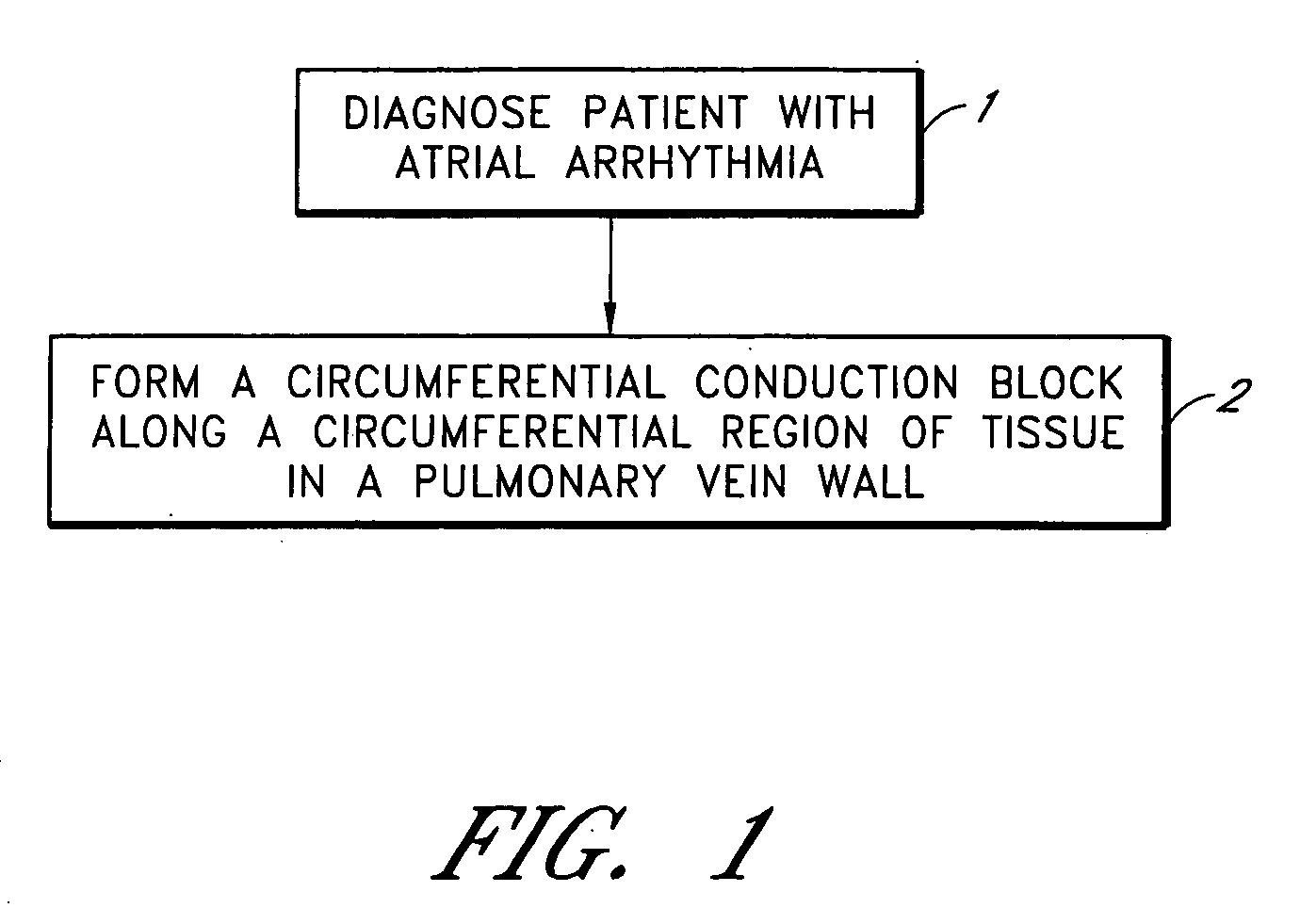
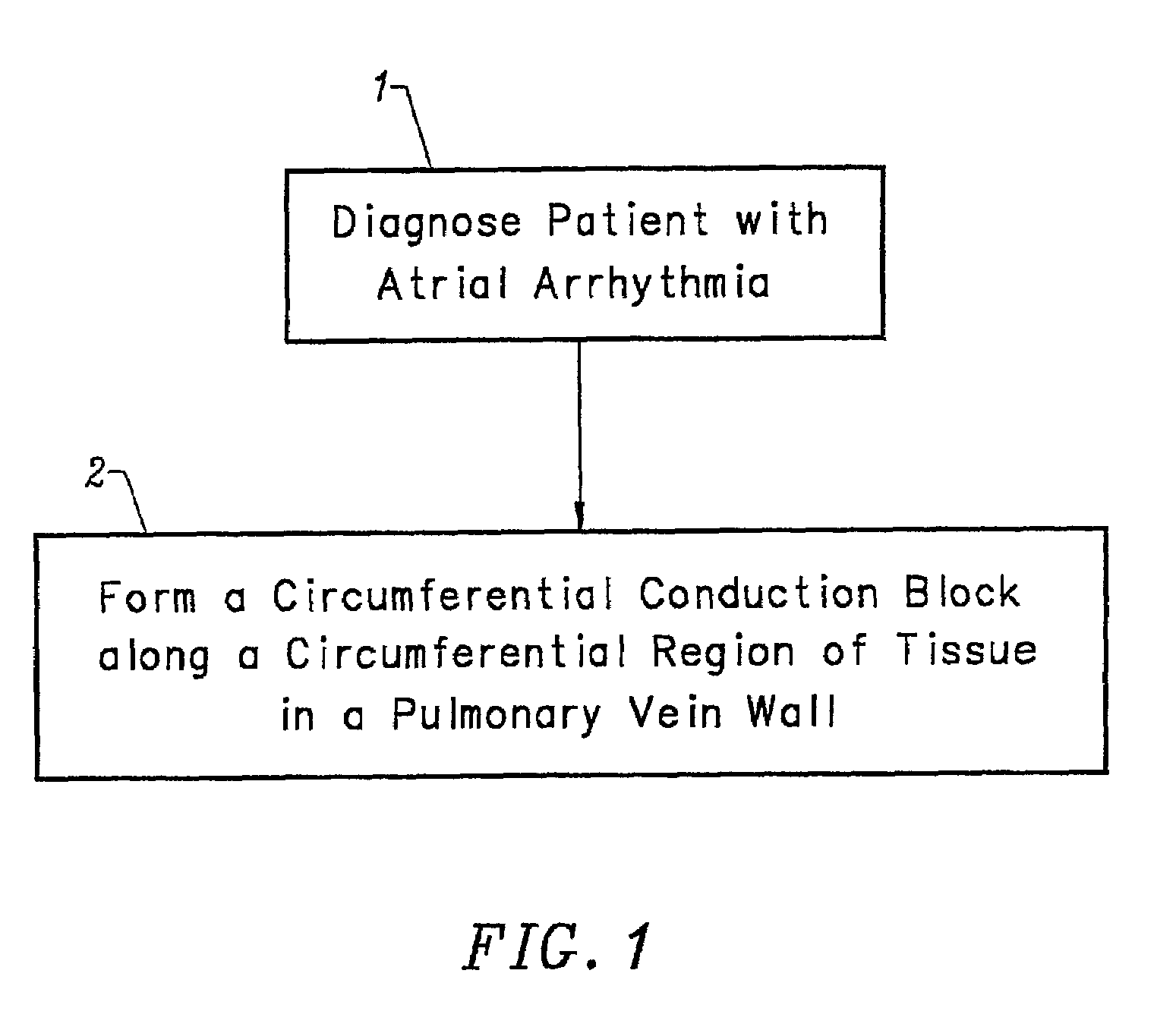
Device and method for forming a circumferential conduction block in a pulmonary vein
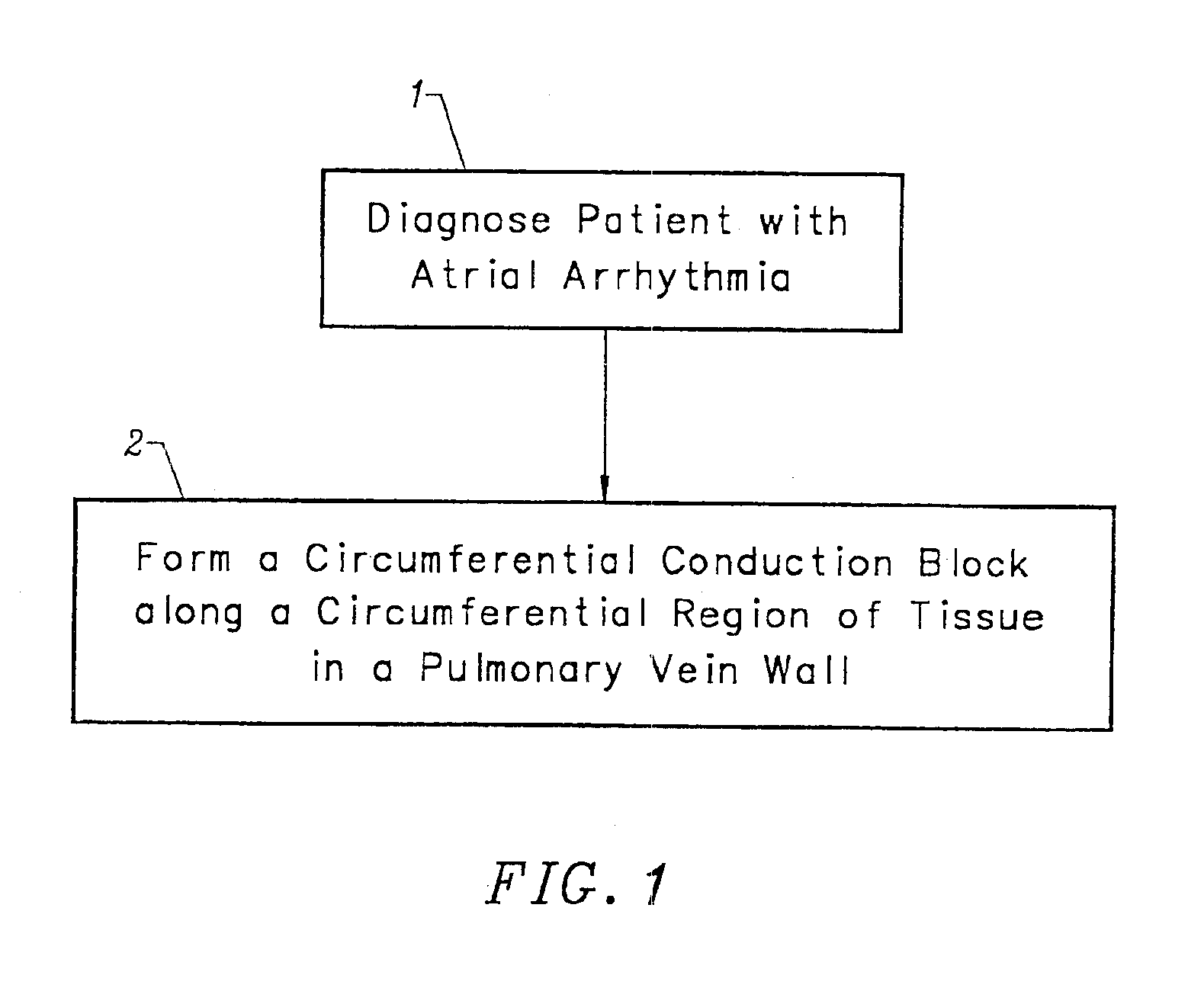
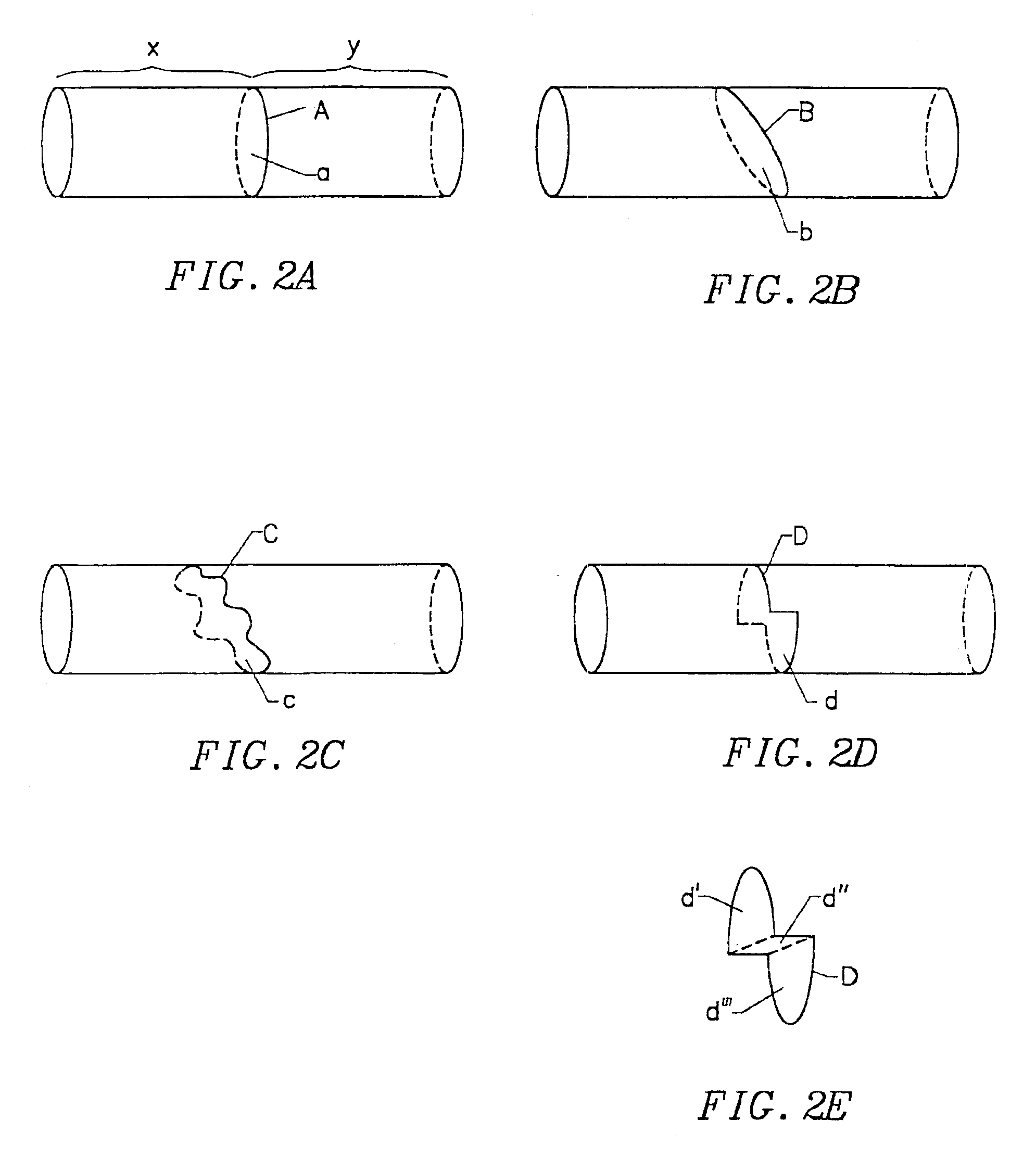
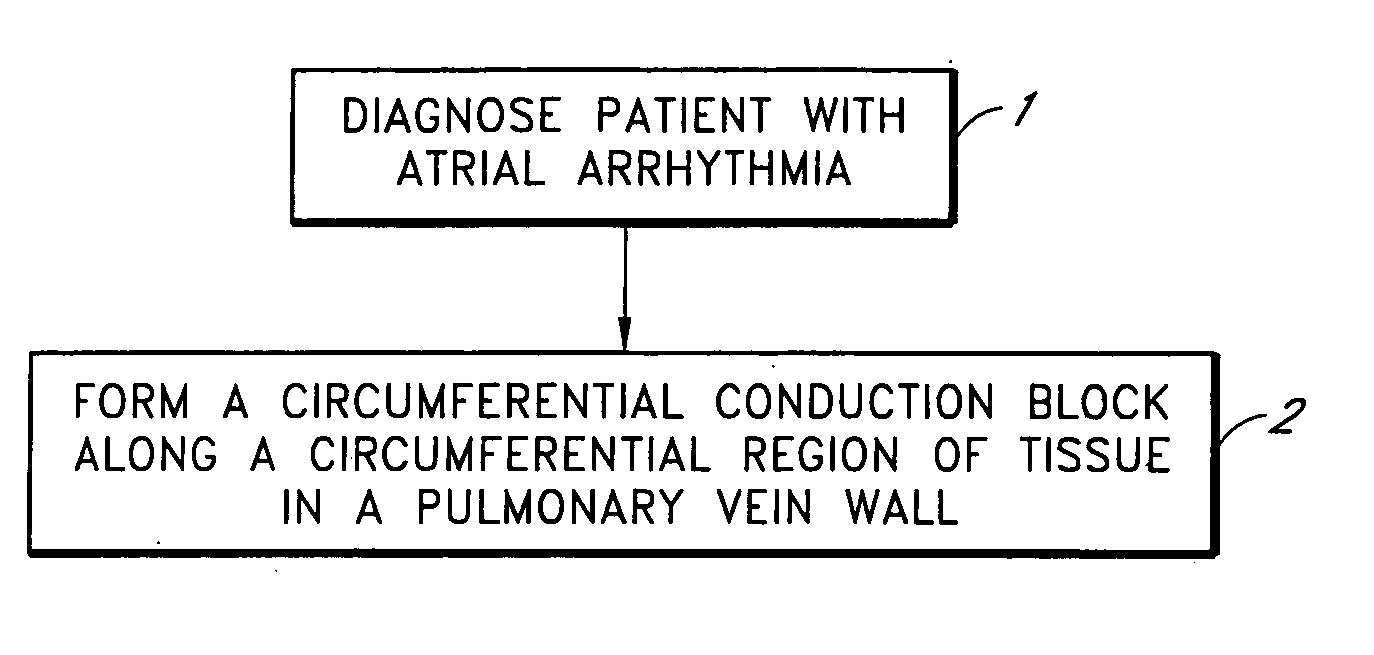
This invention is a method for treating a patient diagnosed with atrial arrhythmia by forming a circumferential conduction block along a circumferential path of tissue in a pulmonary vein wall that circumscribes the pulmonary vein lumen and transects the electrical conductivity of the pulmonary vein such that conduction is blocked along the longitudinal axis of the vein wall and into the left atrial wall. The method is performed to treat a patient with a focal arrythmogenic origin along the pulmonary vein wall by either ablating the focal origin or by isolating the focal origin from the atrial wall with the circumferential conduction block. The circumferential conduction block is also formed in a pulmonary vein in order to bridge the adjacent ends of two linear lesions, wherein each linear lesion is formed to extend between the pulmonary vein and another adjacent pulmonary vein in a less-invasive “maze”-type procedure. A circumferential ablation element in a circumferential ablation device assembly is used in a percutaneous translumenal catheter technique in order to form the circumferential conduction block in the pulmonary vein wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tissue ablation device assembly and method for electrically isolating a pulmonary vein ostium from an atrial wall
This invention is related to a tissue ablation system and method that treats atrial arrhythmia by ablating a circumferential region of tissue at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium. The system includes a circumferential ablation member with an ablation element and also includes a delivery assembly for delivering the ablation member to the location. The circumferential ablation member is generally adjustable between different configurations to allow both the delivery through a delivery sheath into the atrium and the ablative coupling between the ablation element and the circumferential region of tissue.
Owner:ATRIONIX
Device and method for forming a circumferential conduction block in a pulmonary vein
This invention is a method for treating a patient diagnosed with atrial arrhythmia by forming a circumferential conduction block along a circumferential path of tissue in a pulmonary vein wall that circumscribes the pulmonary vein lumen and transects the electrical conductivity of the pulmonary vein such that conduction is blocked along the longitudinal axis of the vein wall and into the left atrial wall. The method is performed to treat a patient with a focal arrythmogenic origin along the pulmonary vein wall by either ablating the focal origin or by isolating the focal origin from the atrial wall with the circumferential conduction block. The circumferential conduction block is also formed in a pulmonary vein in order to bridge the adjacent ends of two linear lesions, wherein each linear lesion is formed to extend between the pulmonary vein and another adjacent pulmonary vein in a less-invasive “maze”-type procedure. A circumferential ablation element in a circumferential ablation device assembly is used in a percutaneous translumenal catheter technique in order to form the circumferential conduction block in the pulmonary vein wall.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for accessing the pericardial space
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
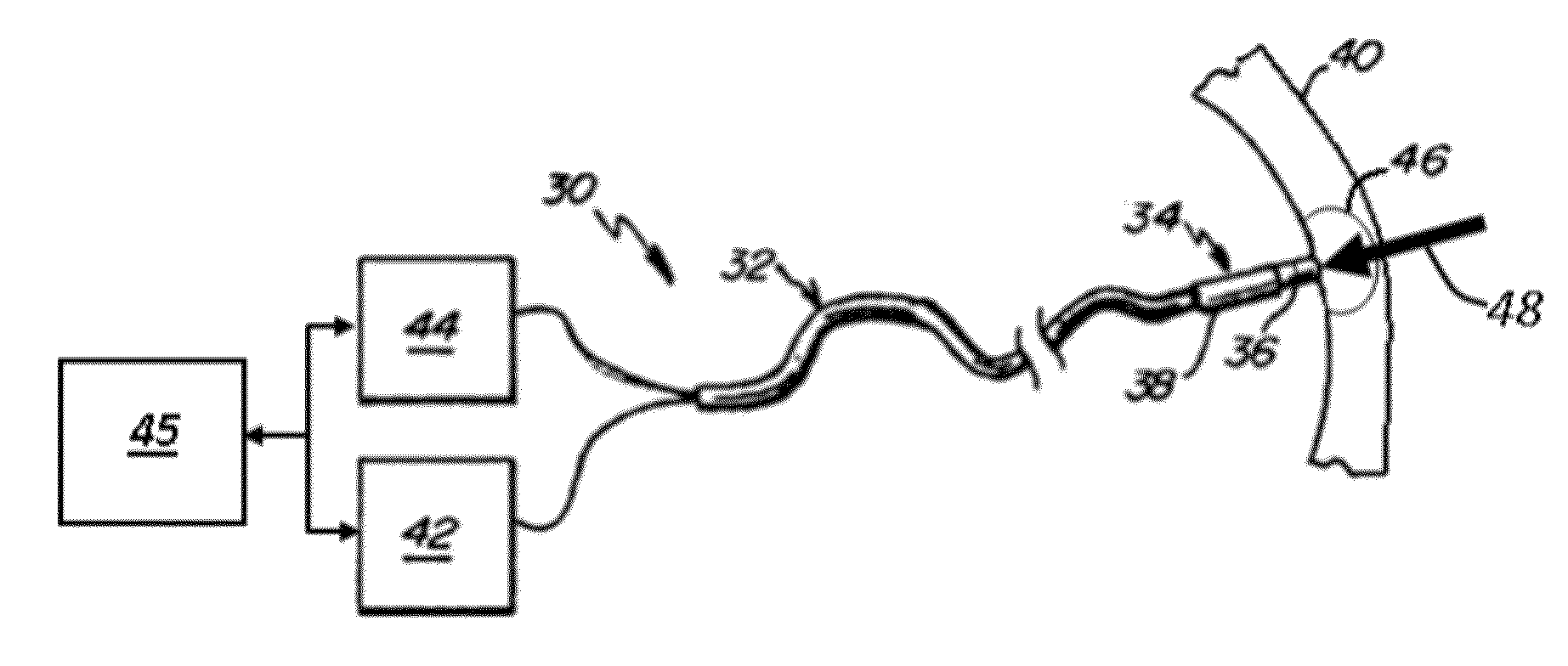
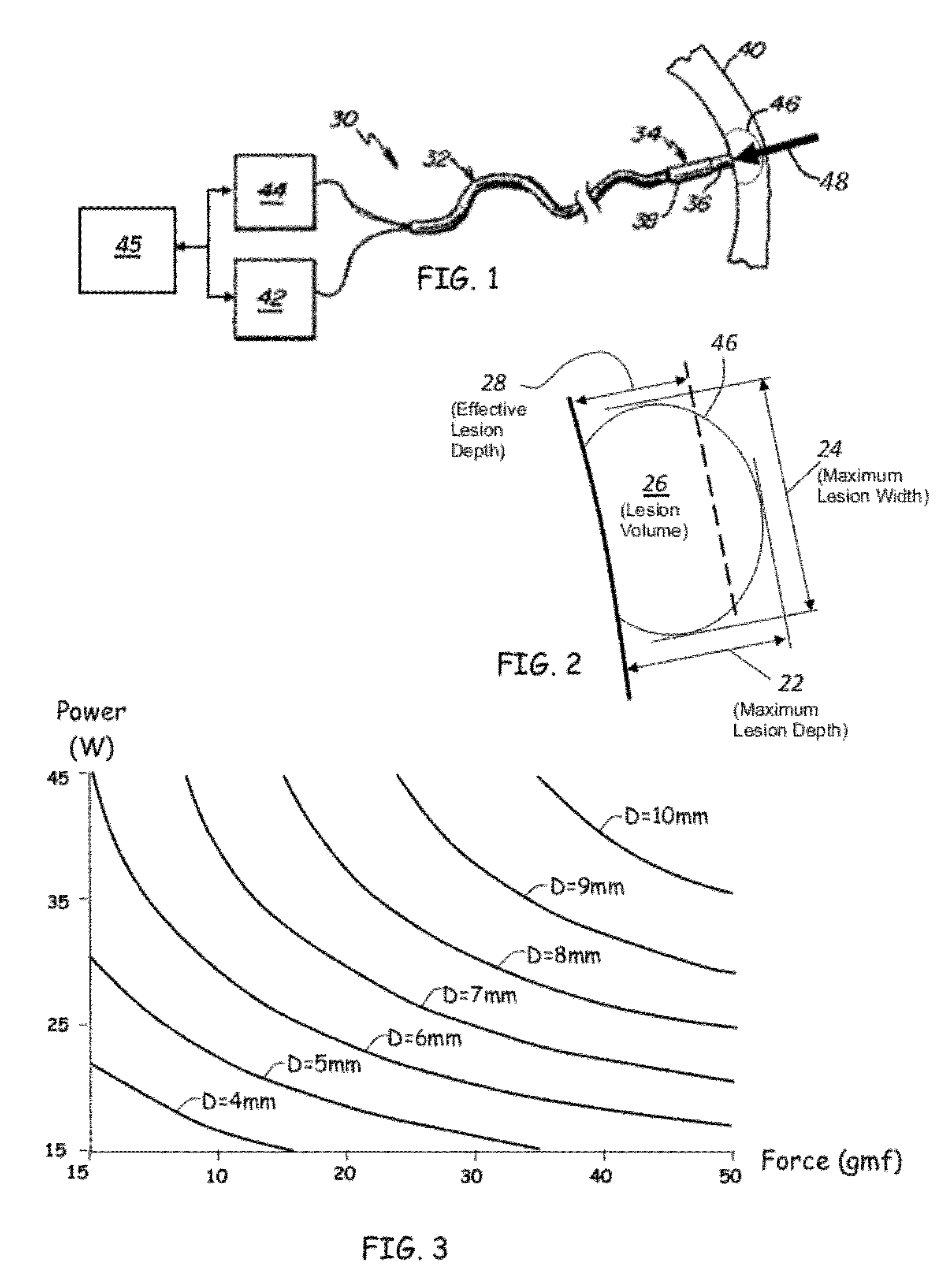
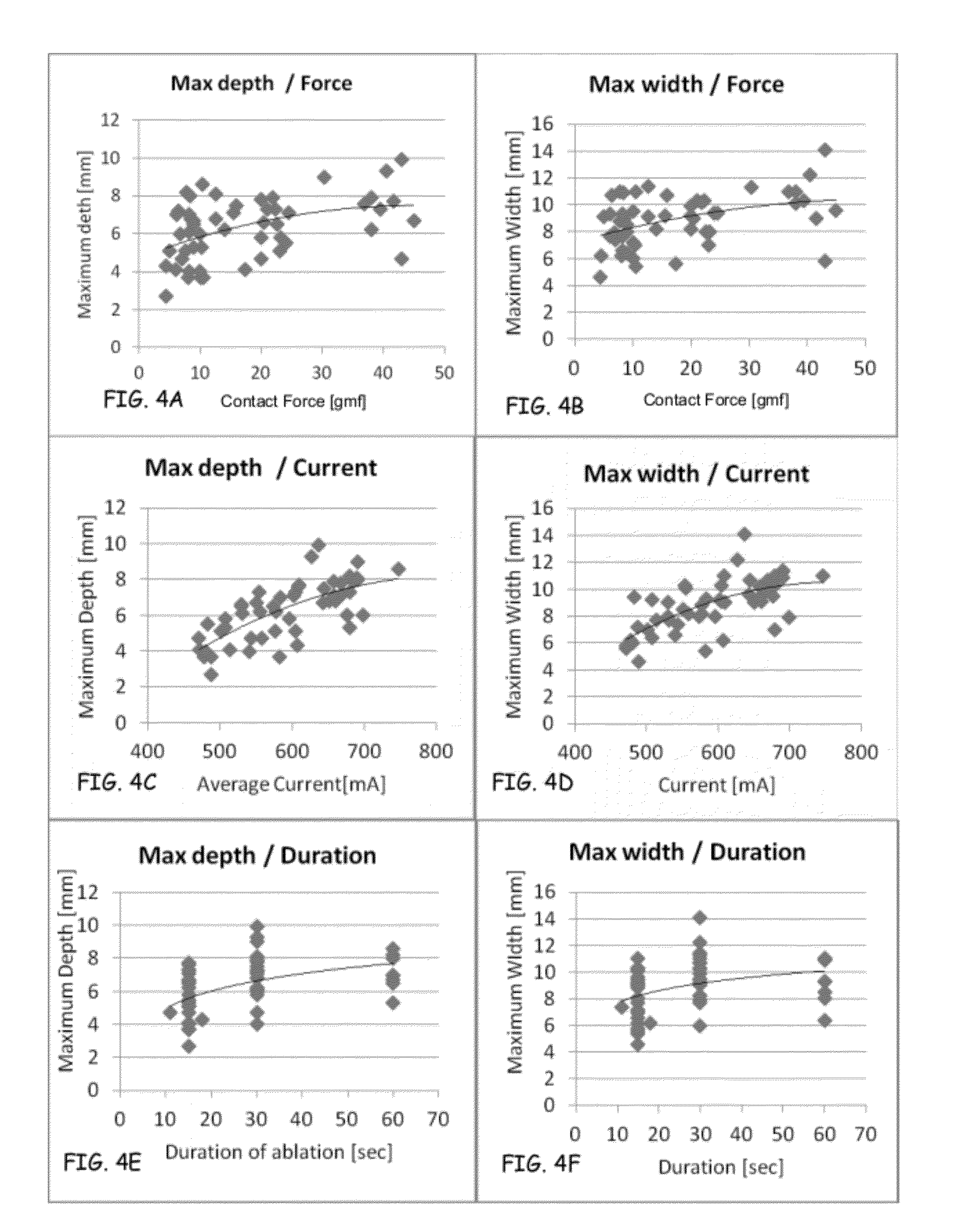
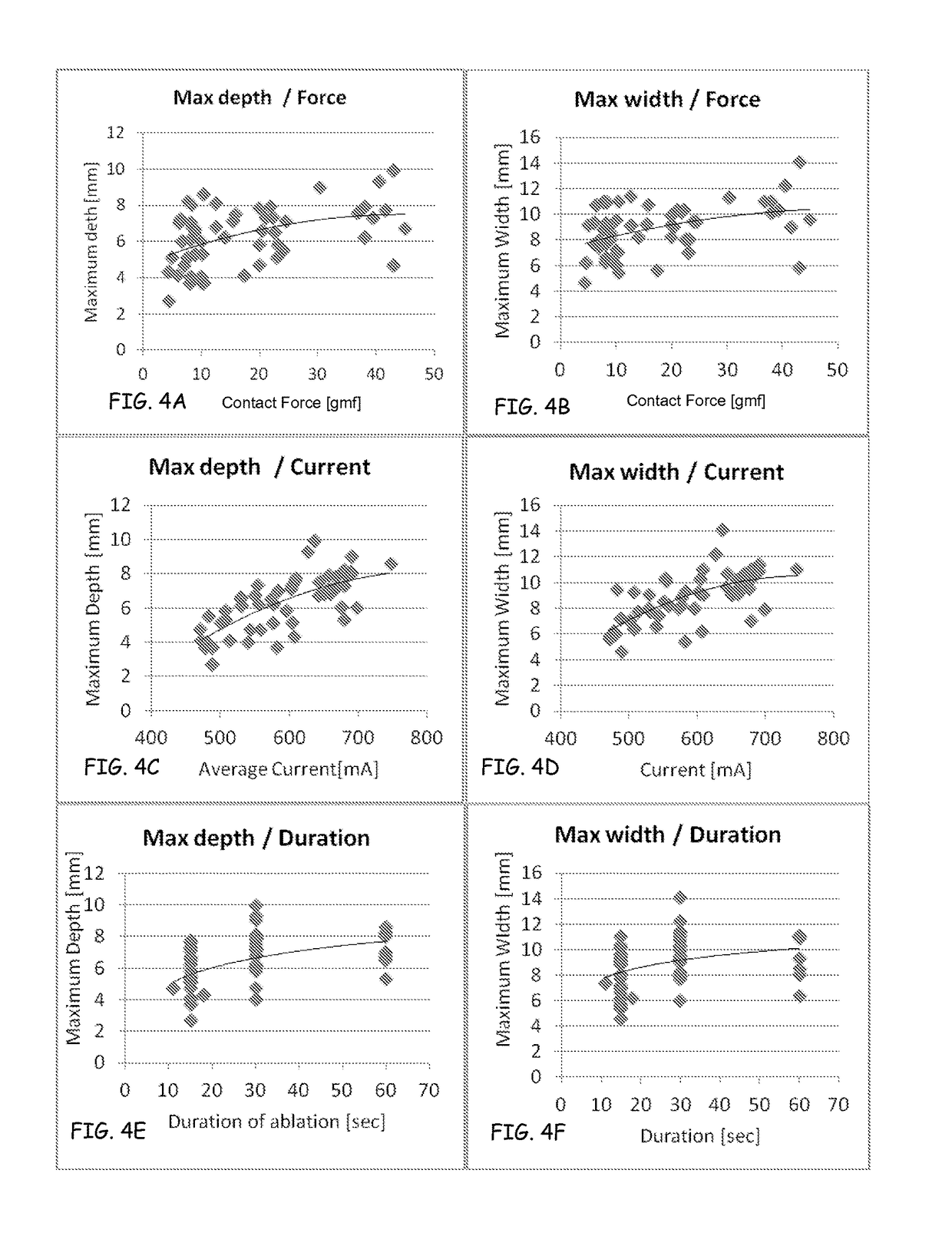
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
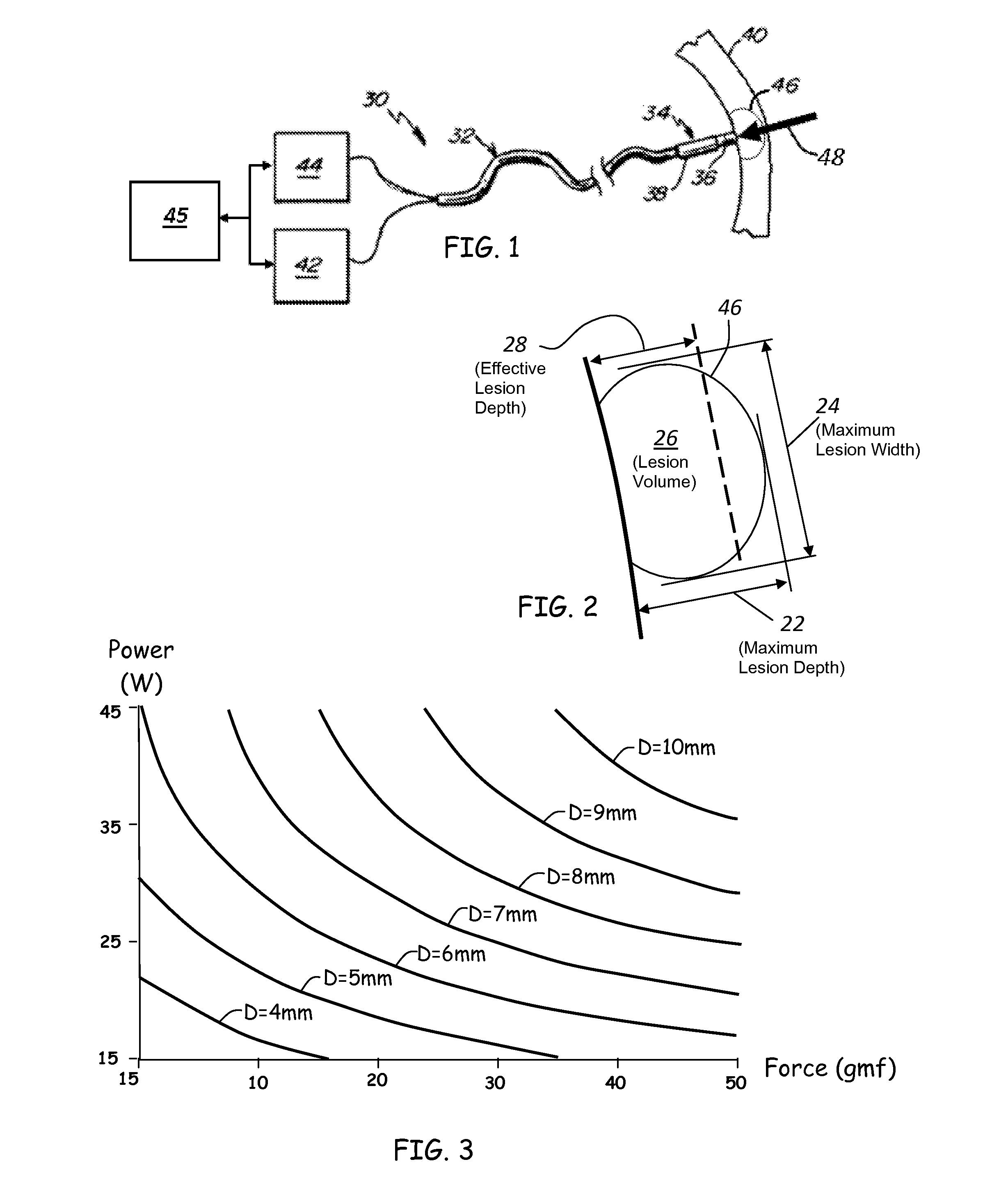
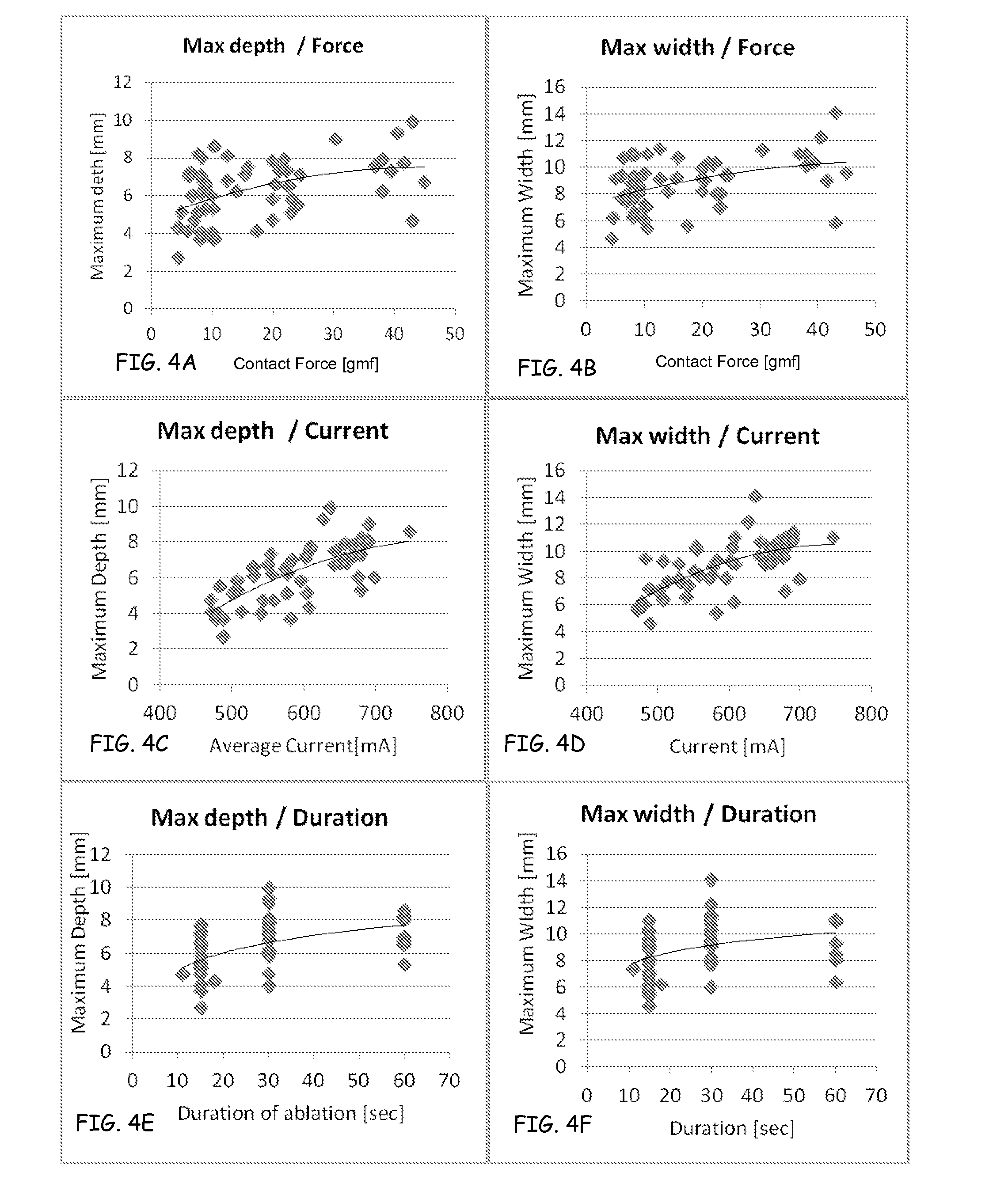
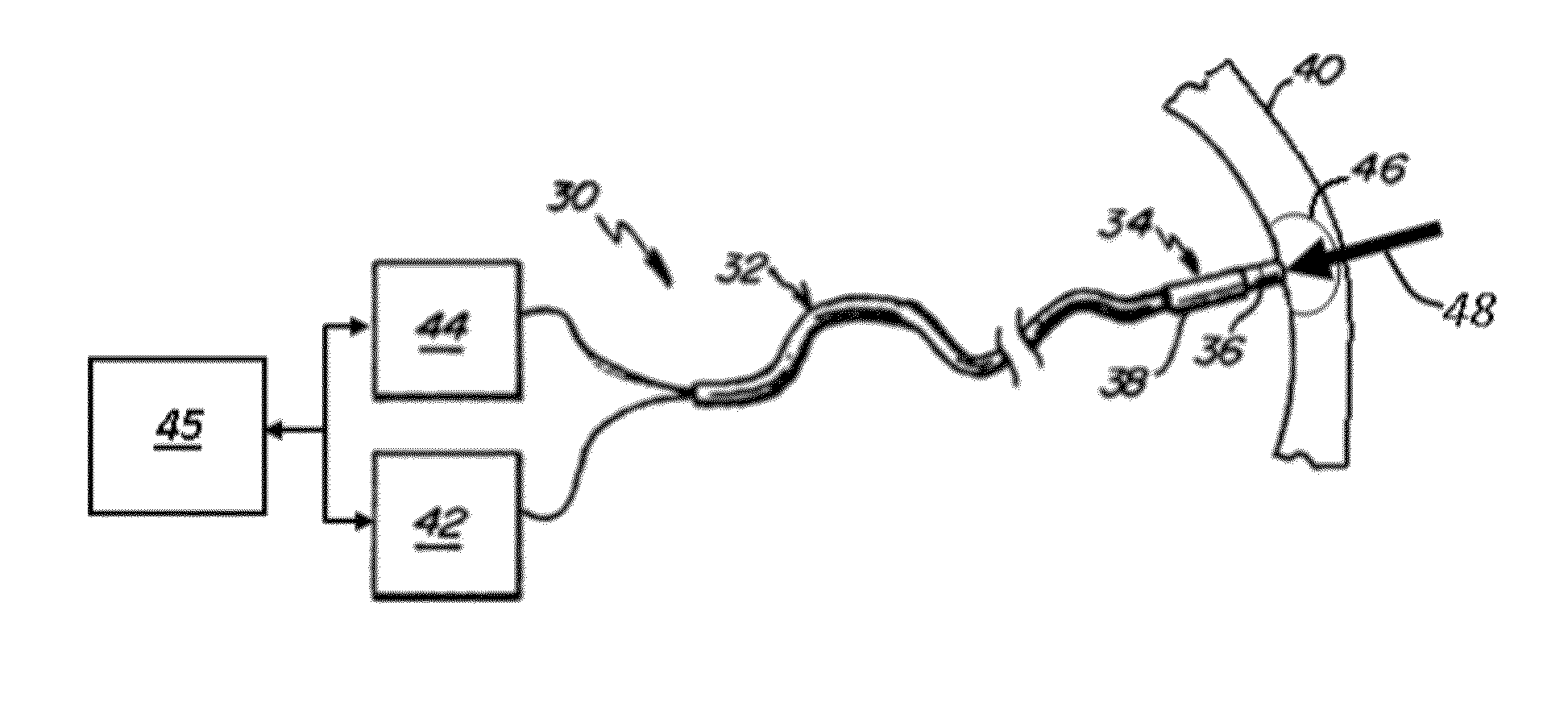
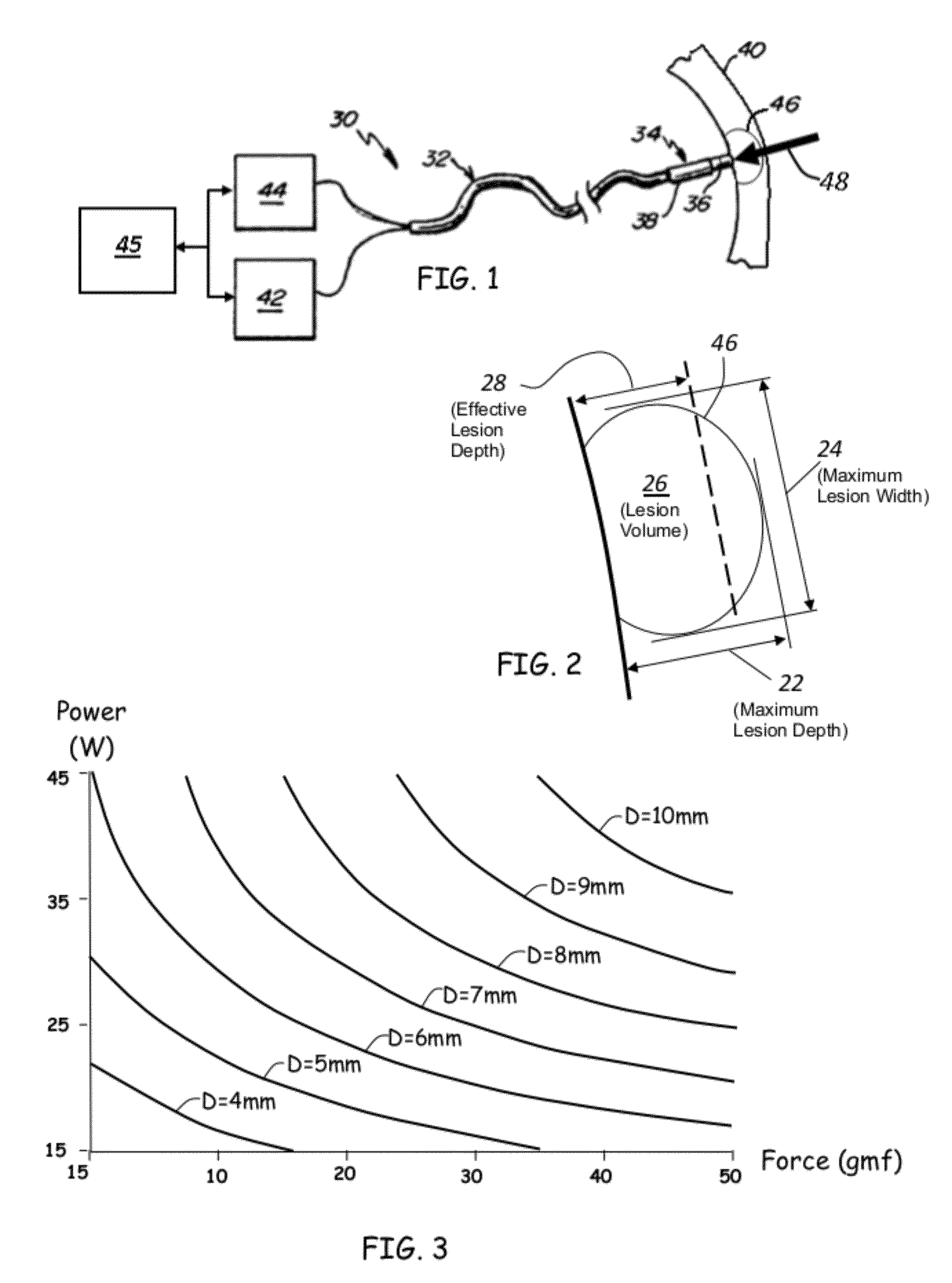
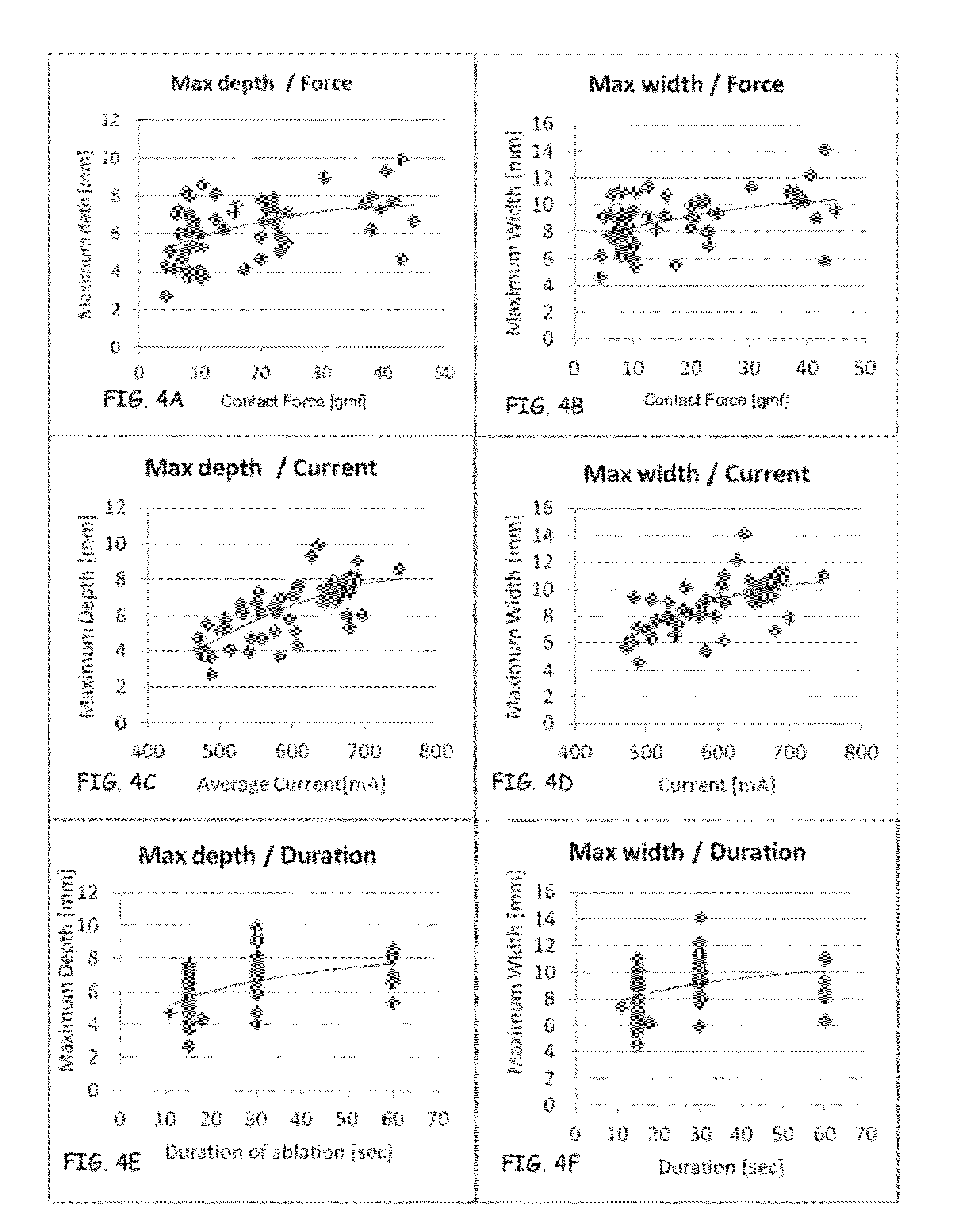
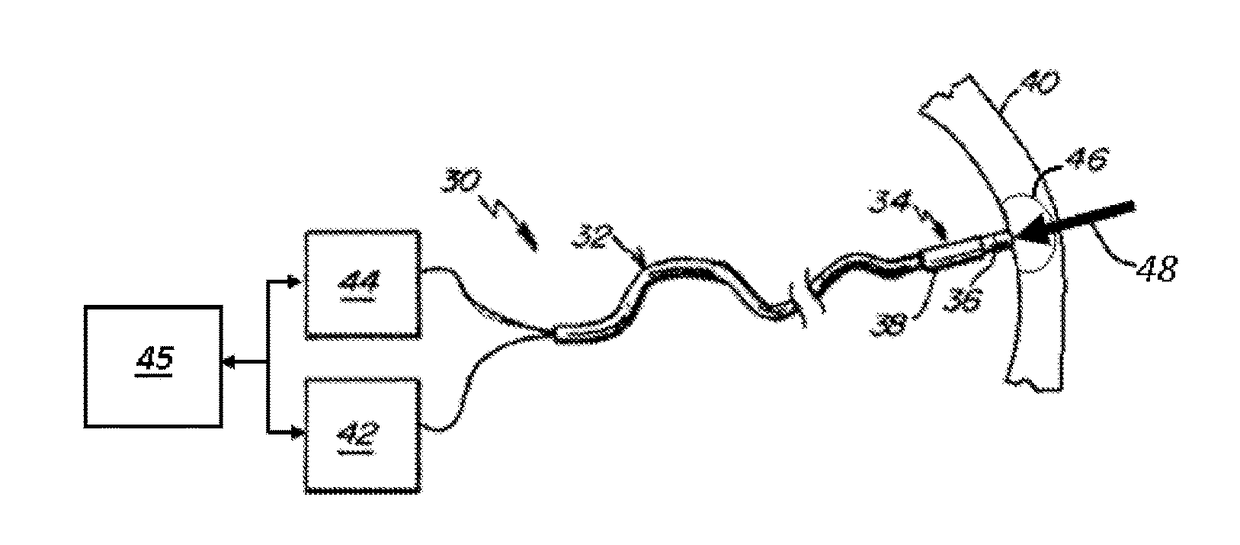
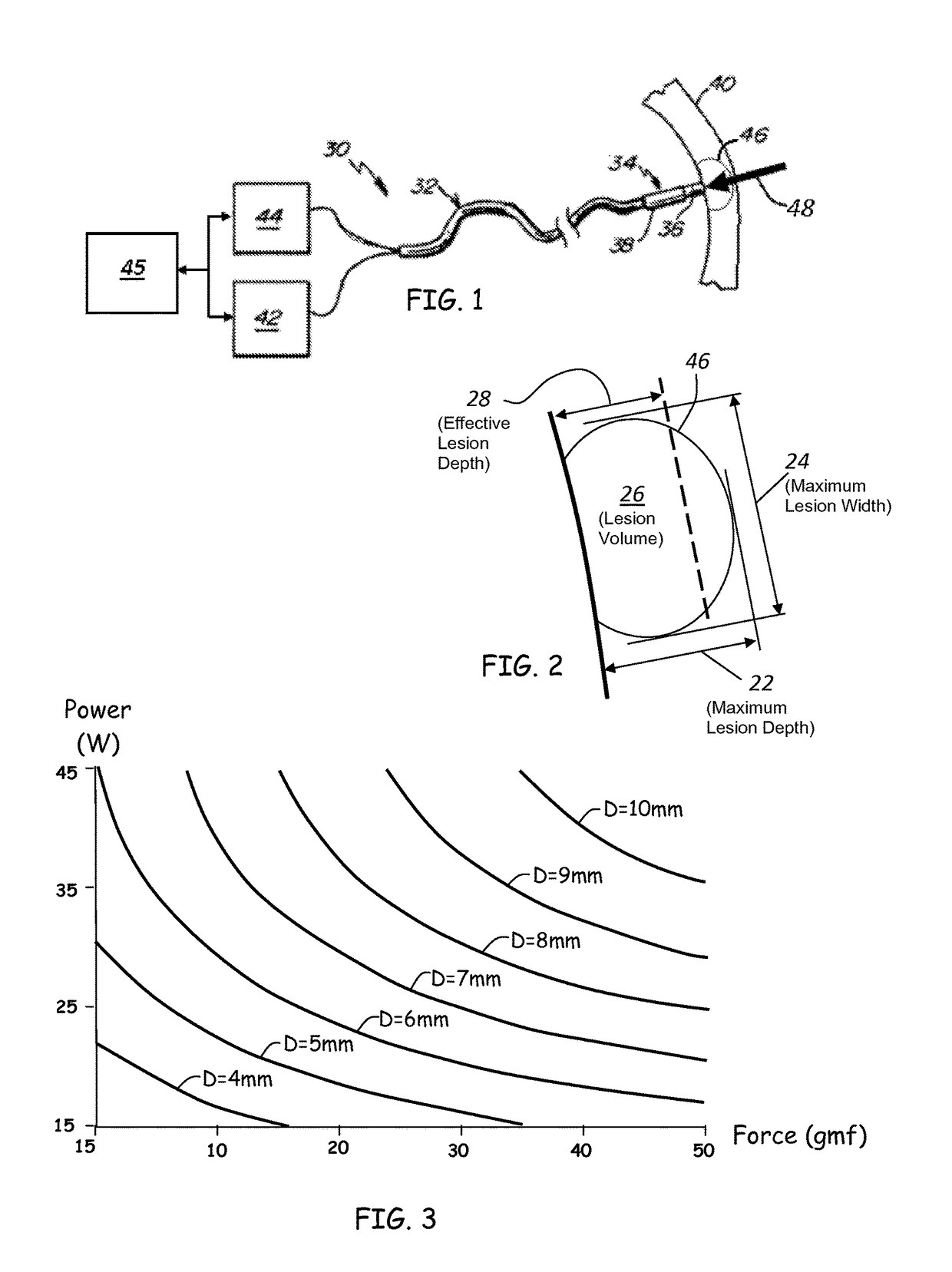
ActiveUS20120209260A1Easy to predictEffective isolation lineDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationAtrial wall
A method and device for determining the transmuriality and / or continuity of an isolation line formed by a plurality of point contact ablations. In one embodiment, a method for determining the size of a lesion (width, depth and / or volume) is disclosed, based on contact force of the ablation head with the target tissue, and an energization parameter that quantifies the energy delivered to the target tissue during the duration time of the lesion formation. In another embodiment, the sequential nature (sequence in time and space) of the ablation line formation is tracked and quantified in a quantity herein referred to as the “jump index,” and used in conjunction with the lesion size information to determine the probability of a gap later forming in the isolation line.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
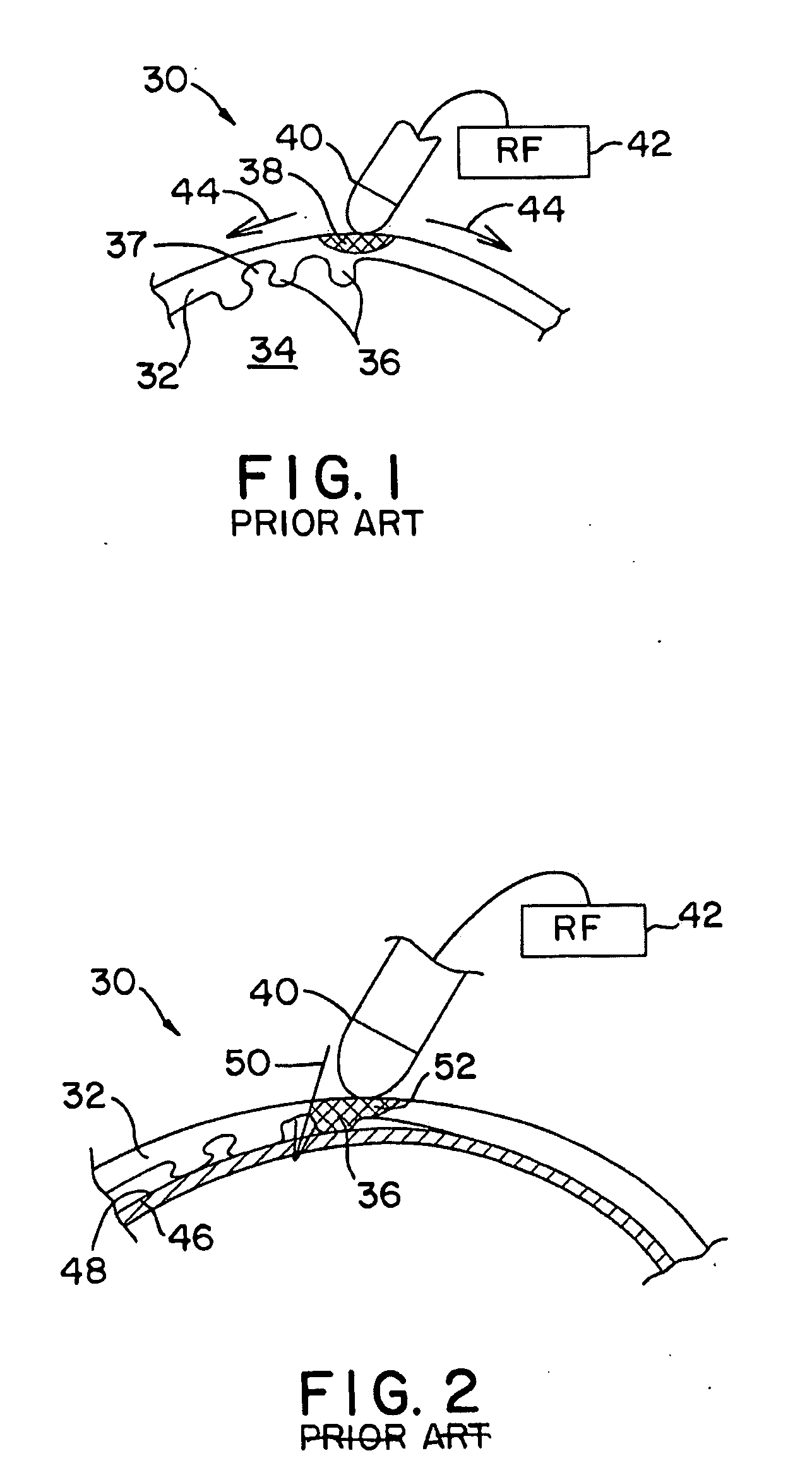
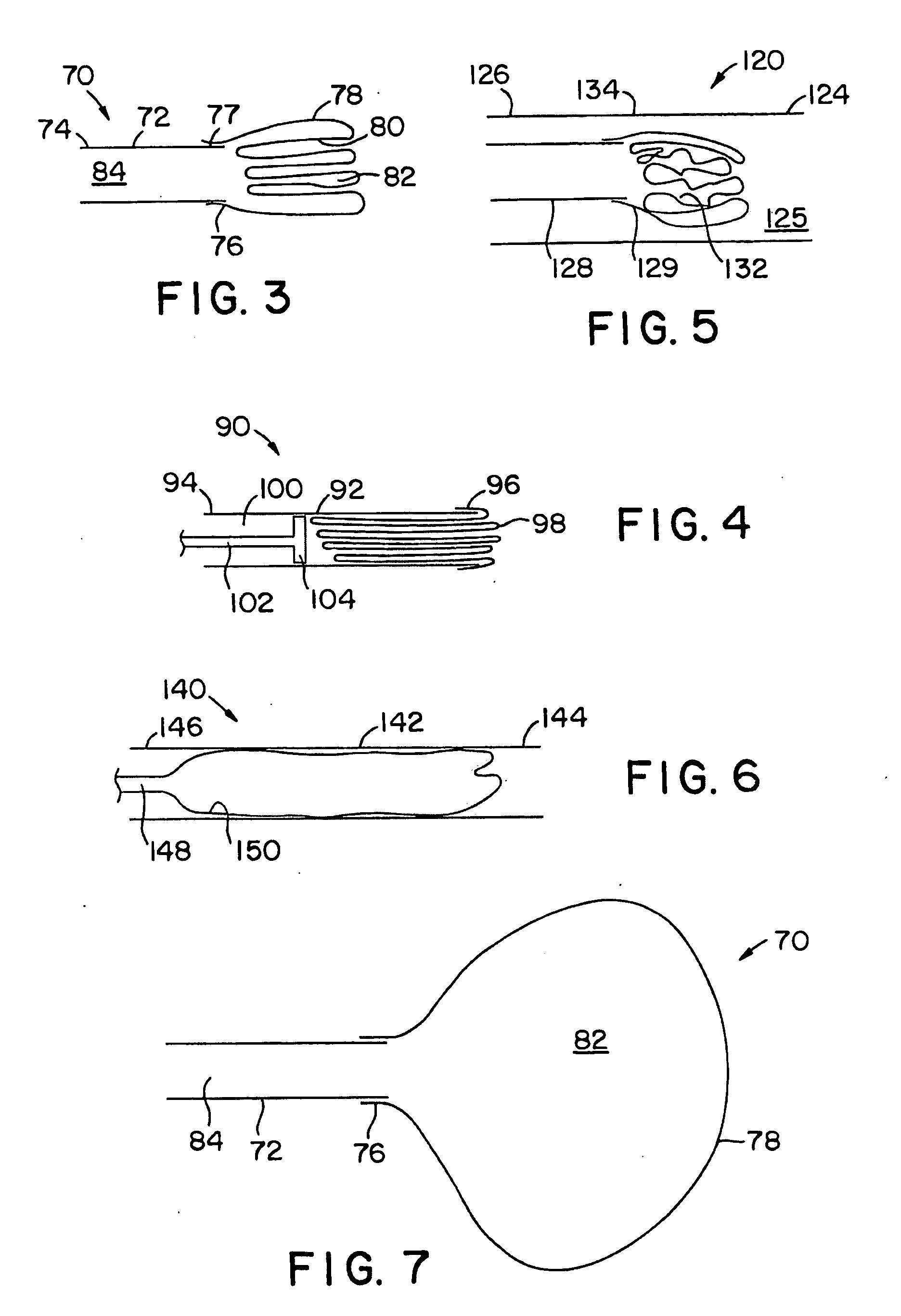
Composite structures and methods for ablating tissue to form complex lesion patterns in the treatment of cardiac conditions and the like
InactiveUS7115122B1Avoiding costly and intrusiveElectrotherapyDiagnosticsFibrillationElectrical impulse
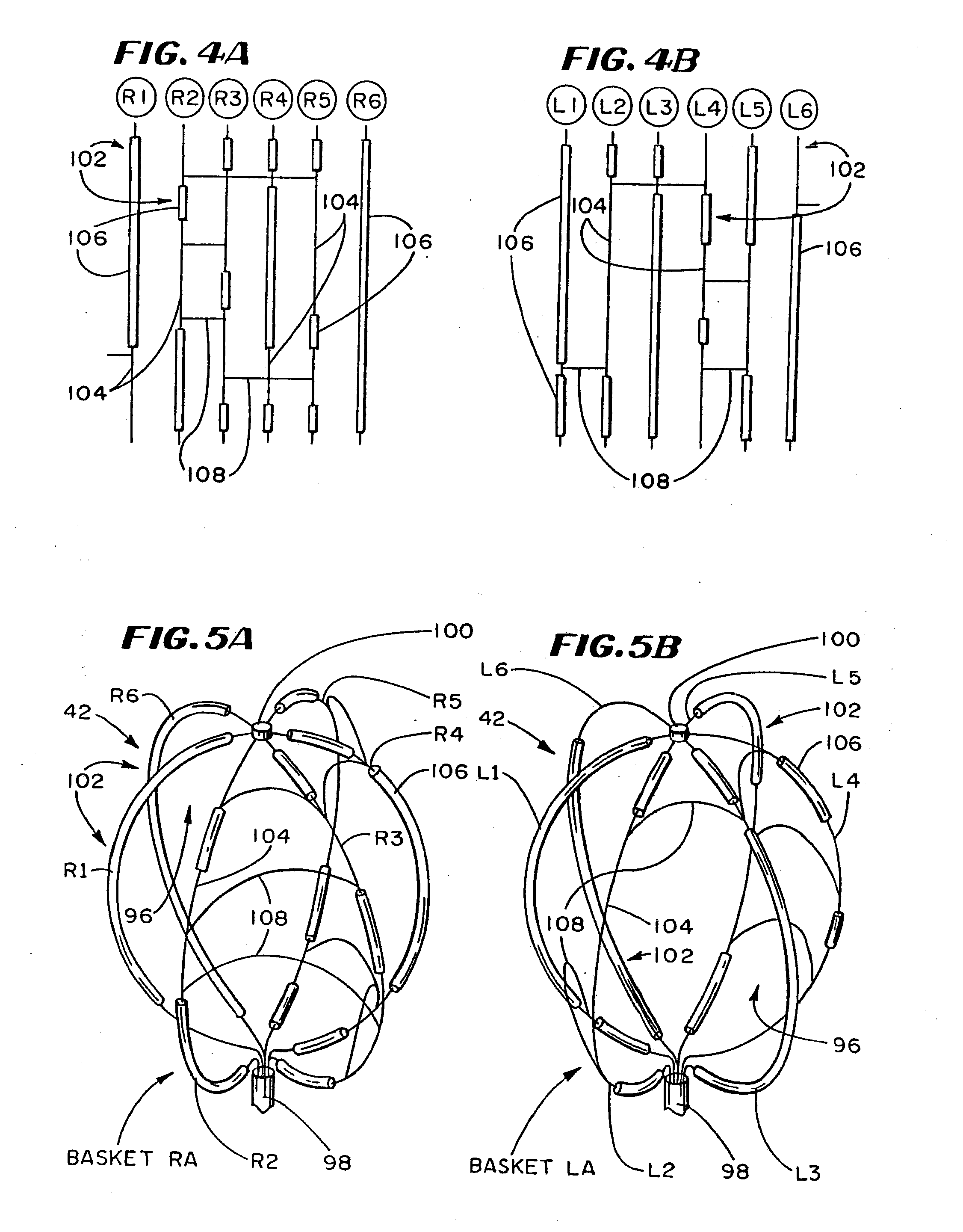
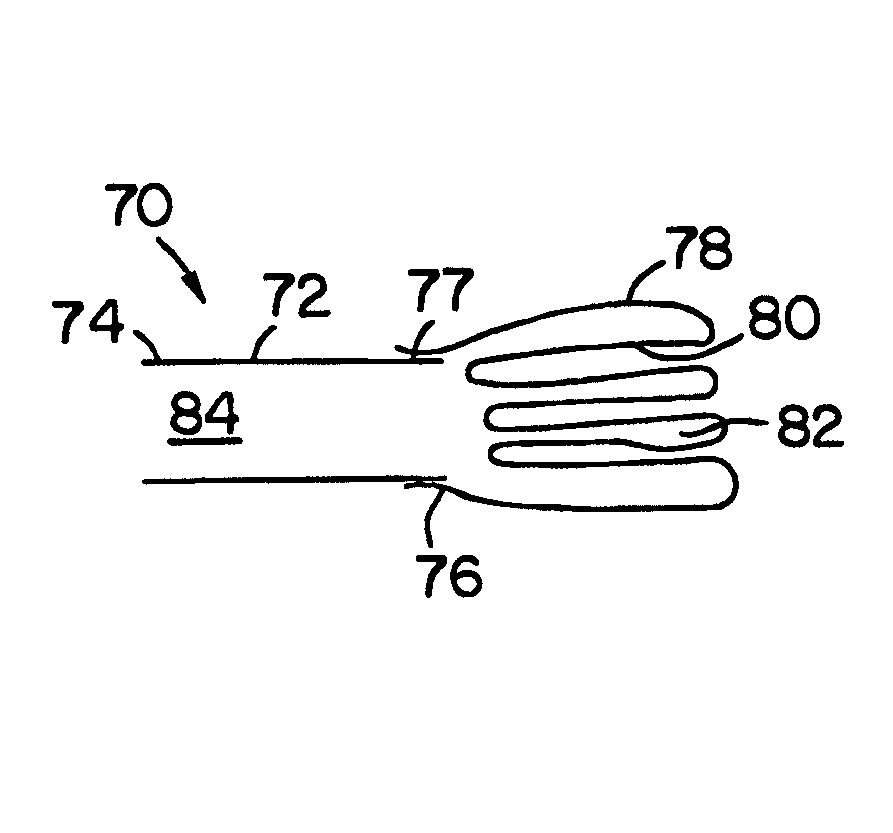
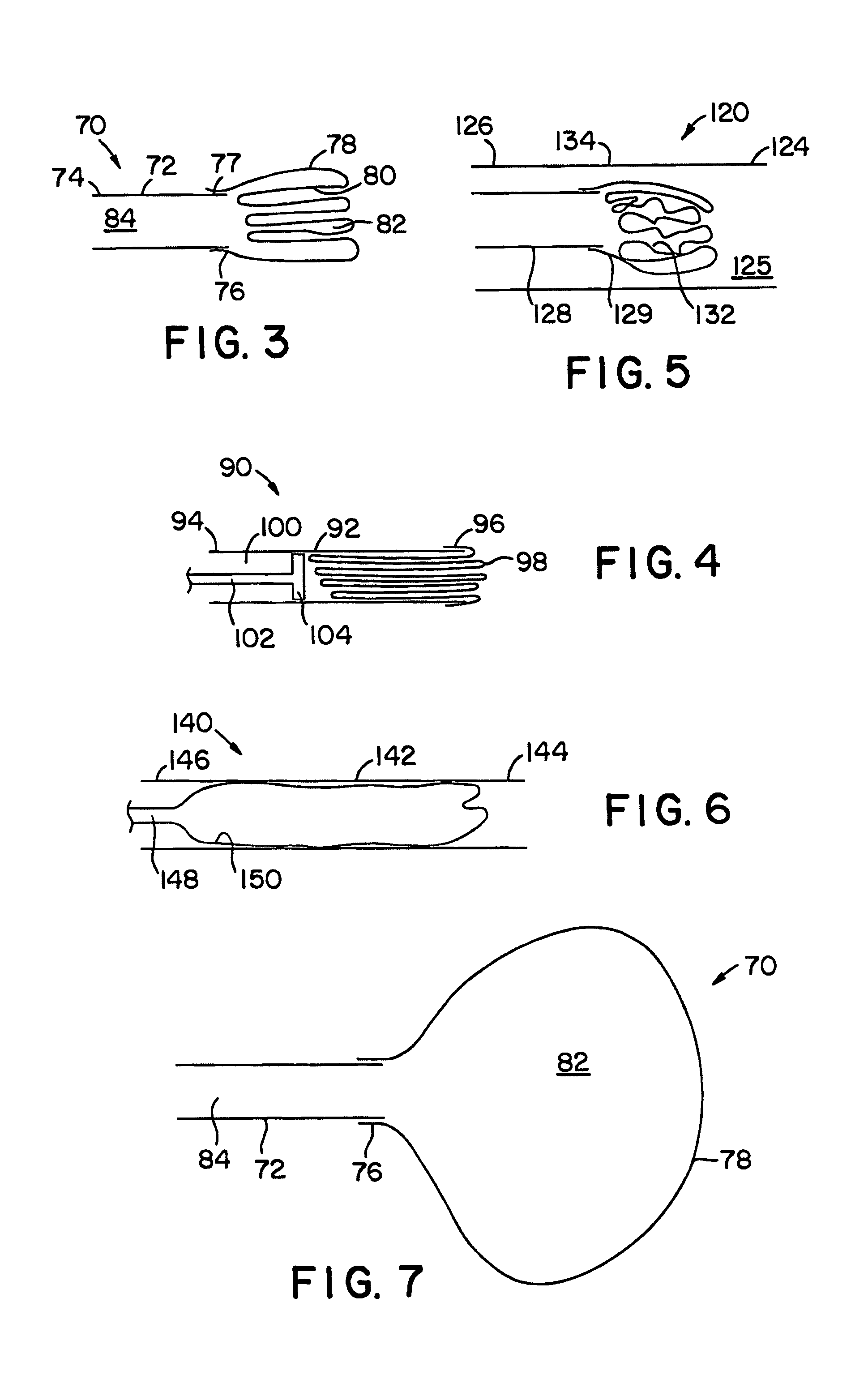
A method of ablating tissue in the heart to treat atrial fibrillation introduces into a selected atrium an energy emitting element. The method exposes the element to a region of the atrial wall and applies ablating energy to the element to thermally destroy tissue. The method forms a convoluted lesion pattern comprising elongated straight lesions and elongated curvilinear lesions. The lesion pattern directs electrical impulses within the atrial myocardium along a path that activates the atrial myocardium while interrupting reentry circuits that, if not interrupted, would cause fibrillation. The method emulates the surgical maze procedure, but lends itself to catheter-based procedures that do not require open heart surgical techniques. A composite structure for performing the method is formed using a template that displays in planar view a desired lesion pattern for the tissue. An array of spaced apart element is laid on the template. Guided by the template, energy emitting and non-energy emitting zones are formed on the elements. By overlaying the elements, the composite structure is formed, which can be introduced into the body to ablate tissue using catheter-based, vascular access techniques.
Owner:EP TECH
Intra-Atrial parasympathetic stimulation
InactiveUS20090005845A1Decreased heart rateReduce riskSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesAtrial wallAnesthesia
A method is provided, including implanting in an atrial wall of a subject, from within an atrium, a first electrode contact in a vicinity of a parasympathetic epicardial fat pad of the subject, and implanting a second electrode contact in a body of the subject outside of a heart and a circulatory system. A current is driven between the first and second electrode contacts, and configured to cause parasympathetic activation of the fat pad. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
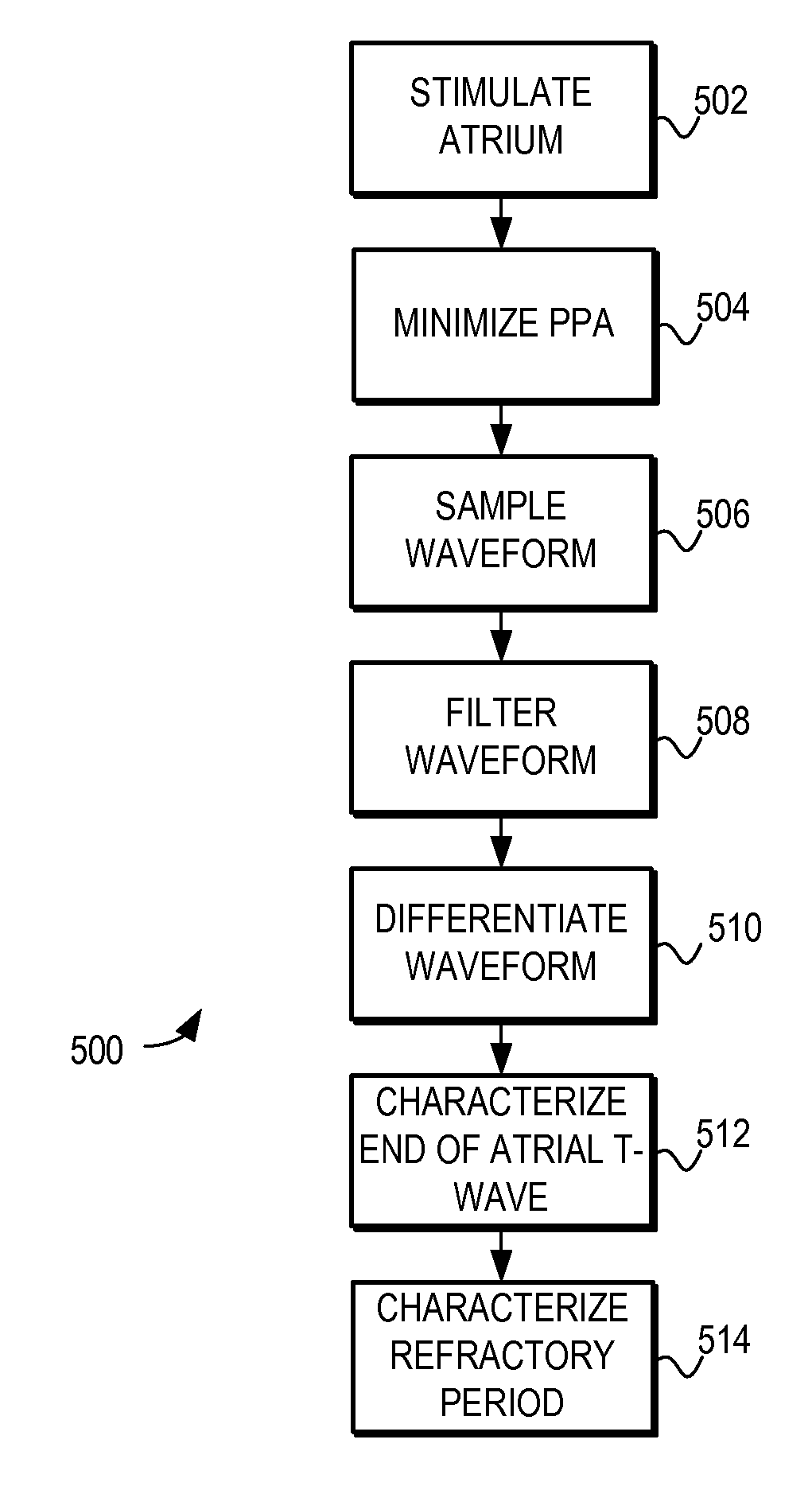
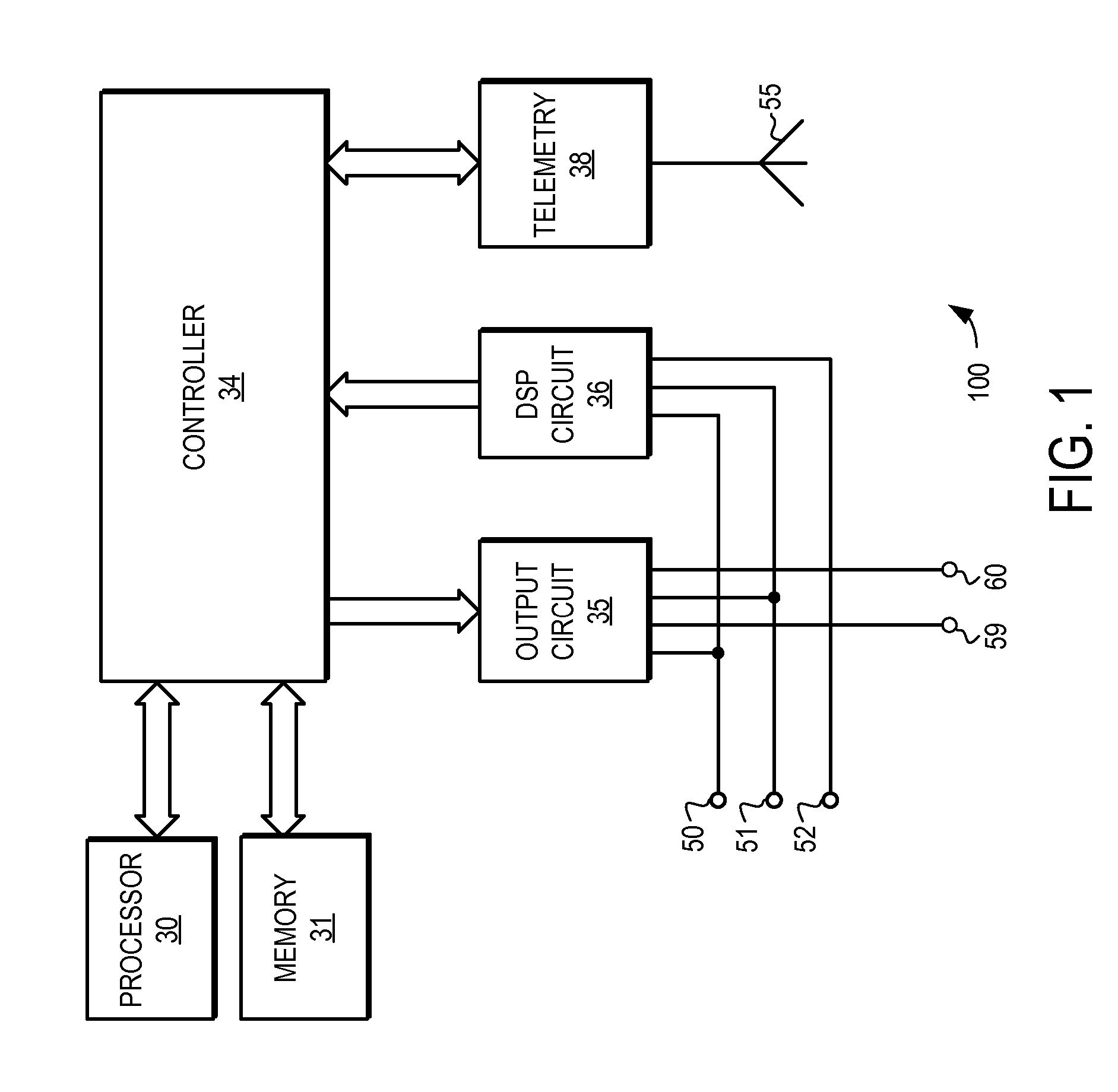
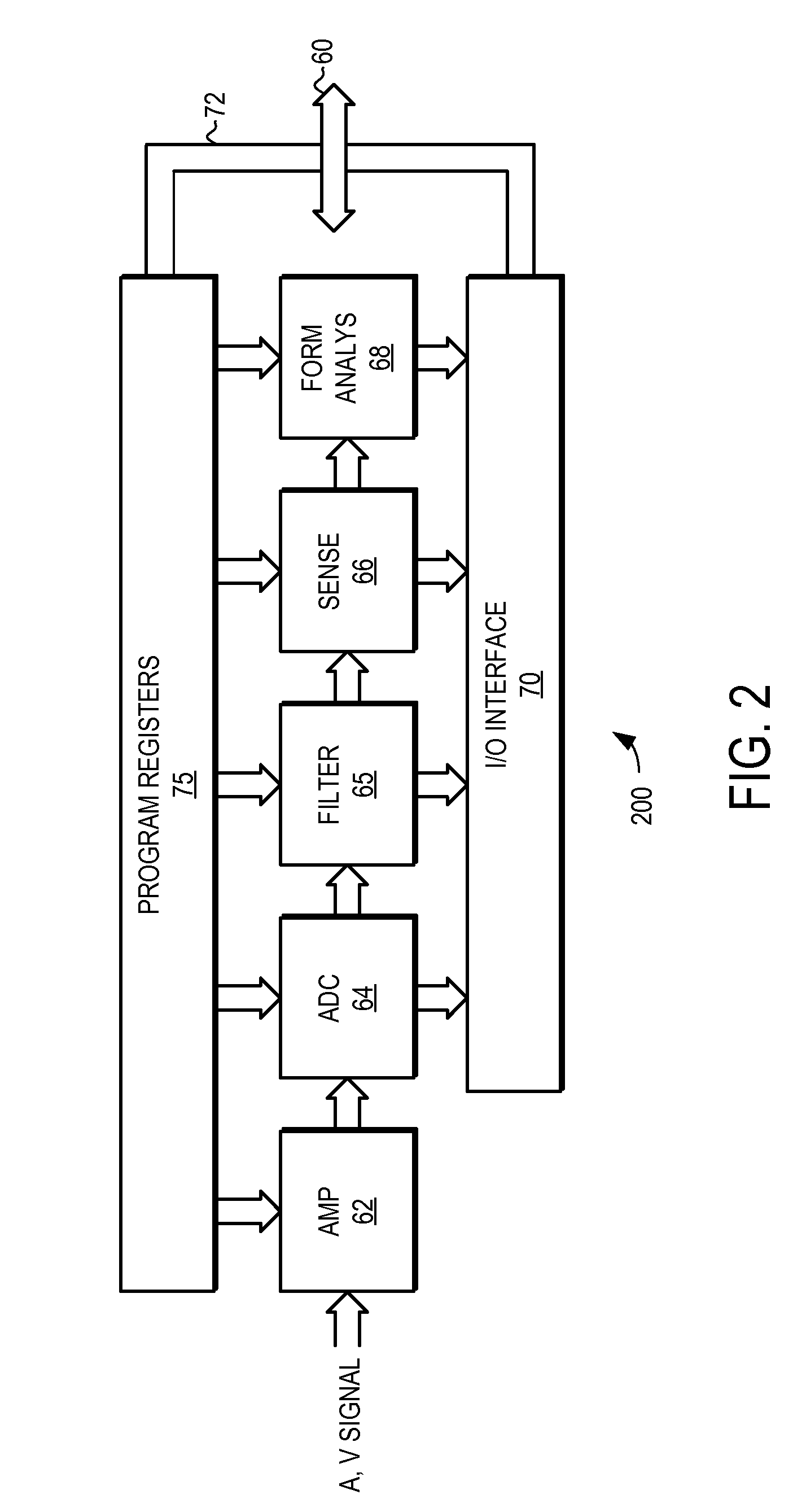
System and method for characterization of atrial wall using digital signal processing
A system and method for characterizing the atrial wall of the heart is provided. The characterization of the atrial wall can be used for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. For example, it can be used to detect precursors to various types of hear disease, such as atrial fibrillation. In one embodiment, the system and method is used to determine a likelihood of fibrosis in the atrial wall. Furthermore, the system and method can detect changes in atrial wall fibrosis that can indicate a continuing degradation in the atrial wall health and an increasing likelihood of atrial fibrillation. In another embodiment, the system and method is used to determine if electrical instability exists in the atrial wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
InactiveUS20160095653A1Easy to predictEffective isolation lineDiagnosticsCatheterRf ablationAtrial wall
A method and device for determining the transmurality and / or continuity of an isolation line formed by a plurality of point contact ablations. In one embodiment, a method for determining the size of a lesion (width, depth and / or volume) is disclosed, based on contact force of the ablation head with the target tissue, and an energization parameter that quantifies the energy delivered to the target tissue during the duration time of the lesion formation. In another embodiment, the sequential nature (sequence in time and space) of the ablation line formation is tracked and quantified in a quantity herein referred to as the “jump index,” and used in conjunction with the lesion size information to determine the probability of a gap later forming in the isolation line.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
System and method for characterization of atrial wall using digital signal processing
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for localization of a puncture site relative to a mammalian tissue of interest
InactiveUS20120191181A1Short operating timeLow costMulti-lumen catheterCannulasAtrial wallMammalian tissue
Systems and methods for localization of a puncture site on an atrial wall relative to a mammalian tissue of interest. In at least one embodiment, such a system includes a bodily access system, having an engagement catheter with an open distal end, a first lumen therethrough, and configured to reversibly attach to a first tissue using suction, a puncture device, configured to fit at least partially within the first lumen, and a scanner configured to identify at least a portion of the bodily access system when positioned within the luminal organ and further configured to identify a distance between a second tissue and a portion of the bodily access system. When such a system is used in connection with a therapeutic procedure, the distance between the second tissue and the portion of the bodily access system is used to facilitate a puncture of the first tissue at a desired location.
Owner:CVDEVICES
Methods and Apparatus to Stimulate the Heart
ActiveUS20160263383A1Inhibit renin-angiotensinLimiting of sodium retentionHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationAtrial wallVentricular contraction
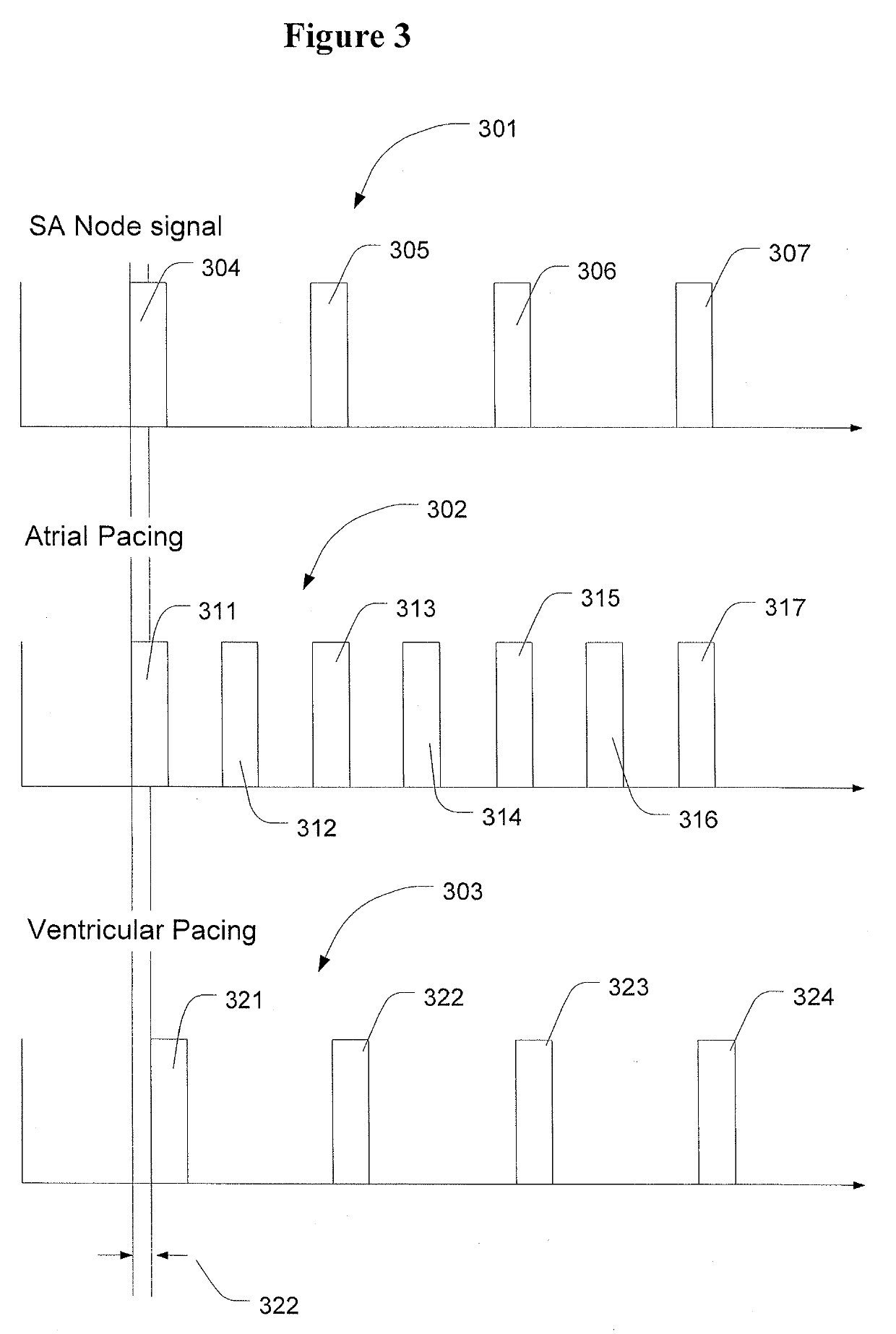
A method and apparatus for treatment of hypertension and heart failure by increasing secretion of endogenous atrial hormones by pacing of the heart. Pacing is done during the ventricular refractory period resulting in premature atrial contraction that does not result in ventricular contraction. Pacing results in the atrial wall stress, peripheral vasodilation, ANP secretion. Concomitant reduction of the heart rate is monitored and controlled as needed with backup pacing.
Owner:BACKBEAT MEDICAL
Closure system for atrial wall
ActiveUS20150039023A1Easy disposalSuccessive dispositionOcculdersSurgical veterinaryAtrial wallEngineering
A closure system, assembly and attended method for closing and opening in the tissue of the patient includes first and second closure members each including a biased construction operative for disposition of the closure members into an out of retracted and expanded orientations. A connector is disposed in interconnecting relation with the closure members and structured to establish at least a partial spacing there between. The biased construction and the interconnection of the closure members facilitate con current disposition of the closure members with one another into and through an introductory instrument as well as independent and successive disposition of the first and second closure members into a closing relation to the tissue opening upon exiting the introductory instrument.
Owner:CORQUEST MEDICAL
Catheter with coronary sinus ostium anchor
A method of treating cardiac tissue is provided, including positioning a first chamber of a medical device adjacent an atrial wall; directing a cryogenic coolant into the first chamber; anchoring the first chamber to the atrial wall through cryoadhesion; directing a distal portion of the medical device into the coronary sinus; and positioning a cardiac lead through at least a portion of the coronary sinus with the distal portion. The method may include measuring a temperature of the first chamber; removing the first chamber from the atrial wall once a predetermined threshold temperature of the first chamber is reached; anchoring a second chamber of the medical device to a portion of the coronary sinus; and / or perfusing blood flow through at least a portion of the second chamber.
Owner:MEDTRONIC ABLATION FRONTIERS
Methods and Apparatus to Stimulate the Heart
ActiveUS20190275336A1Lower blood pressureMaximize the affect of the atrial contractionHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationAtrial wallVentricular contraction
A method and apparatus for treatment of hypertension and heart failure by increasing secretion of endogenous atrial hormones by pacing of the heart. Pacing is done during the ventricular refractory period resulting in premature atrial contraction that does not result in ventricular contraction. Pacing results in the atrial wall stress, peripheral vasodilation, ANP secretion. Concomitant reduction of the heart rate is monitored and controlled as needed with backup pacing.
Owner:BACKBEAT MEDICAL
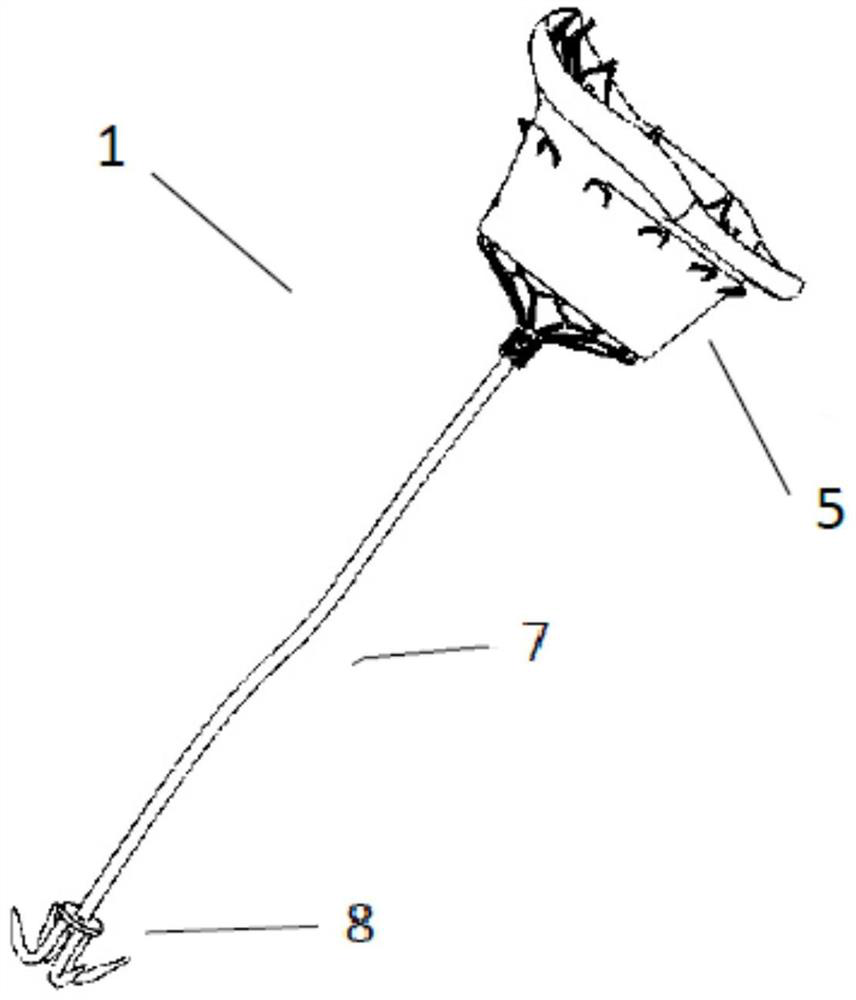
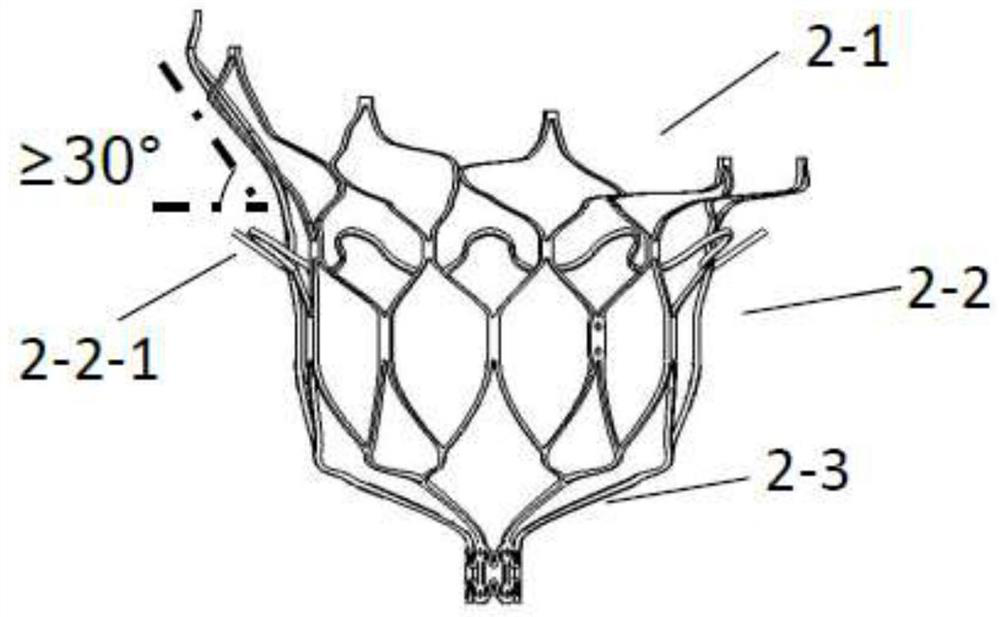
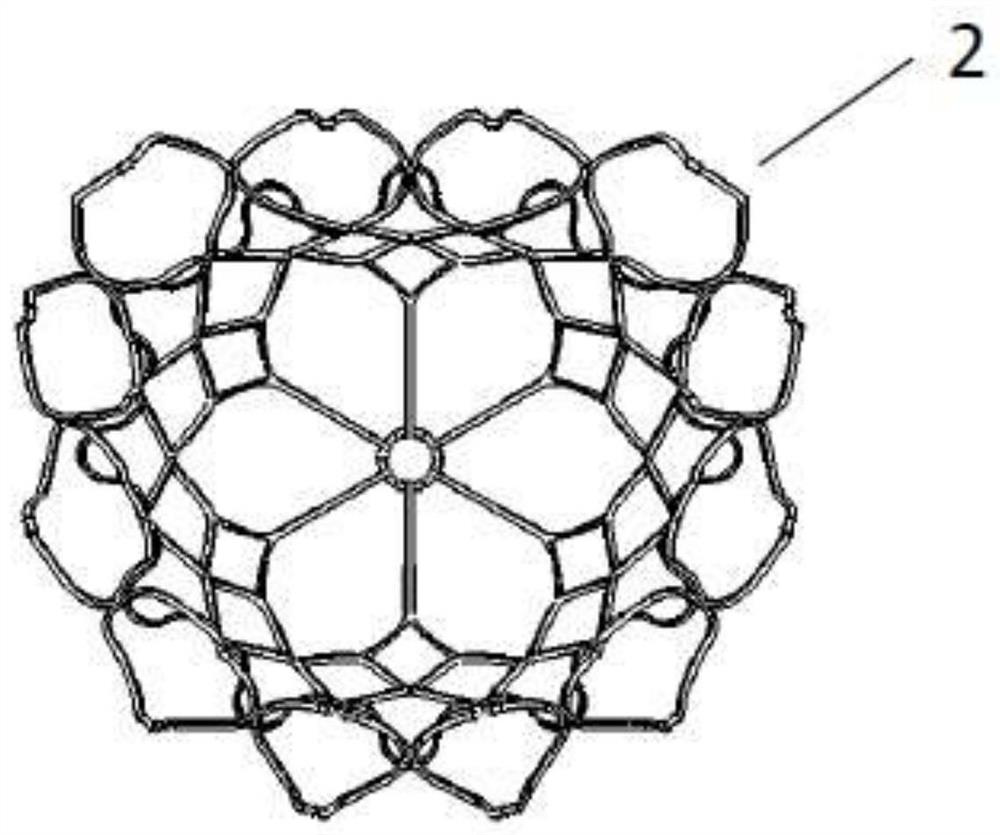
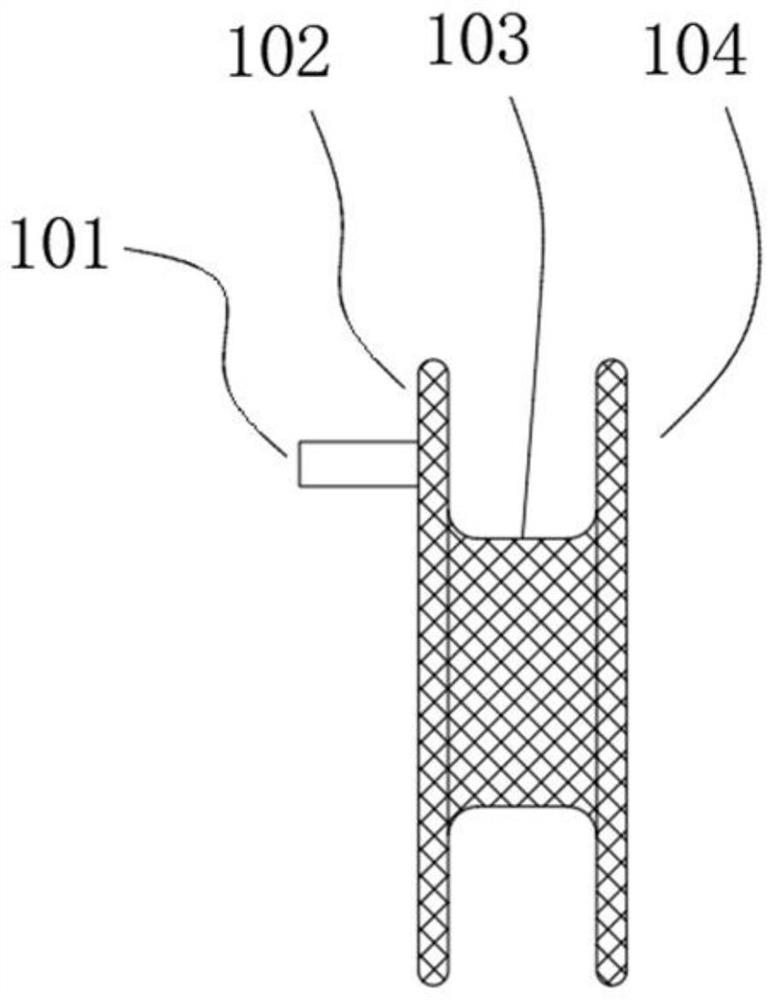
Prosthesis for preventing valve regurgitation
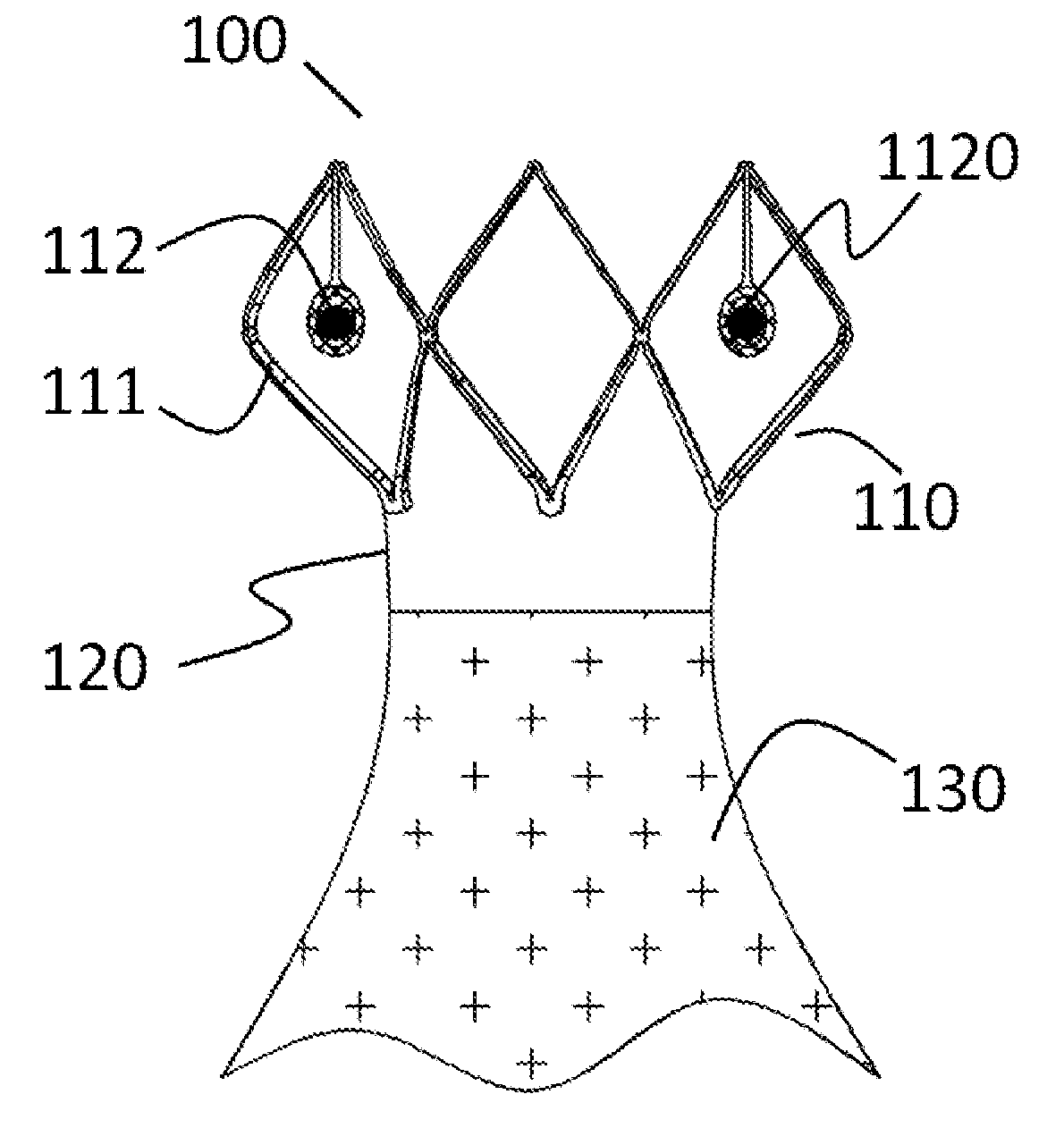
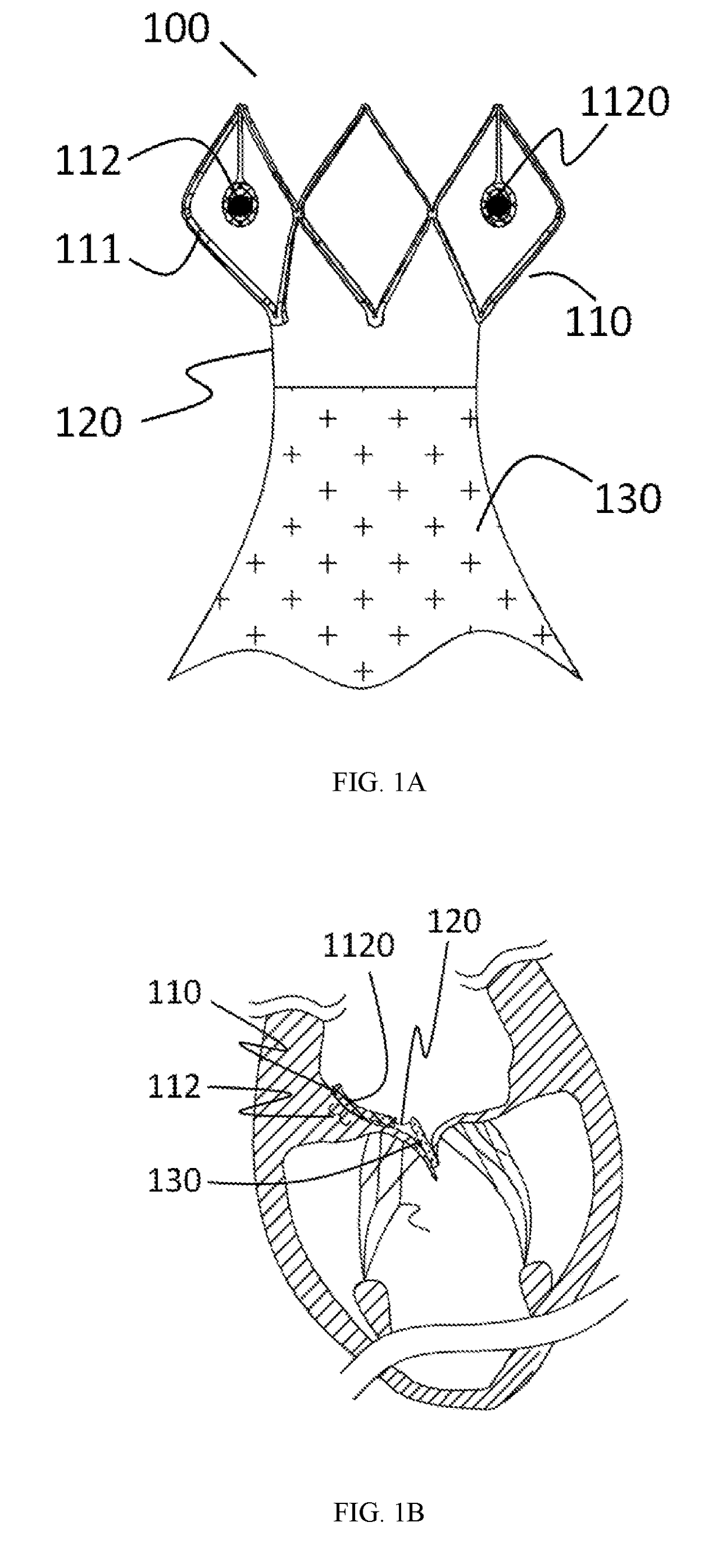
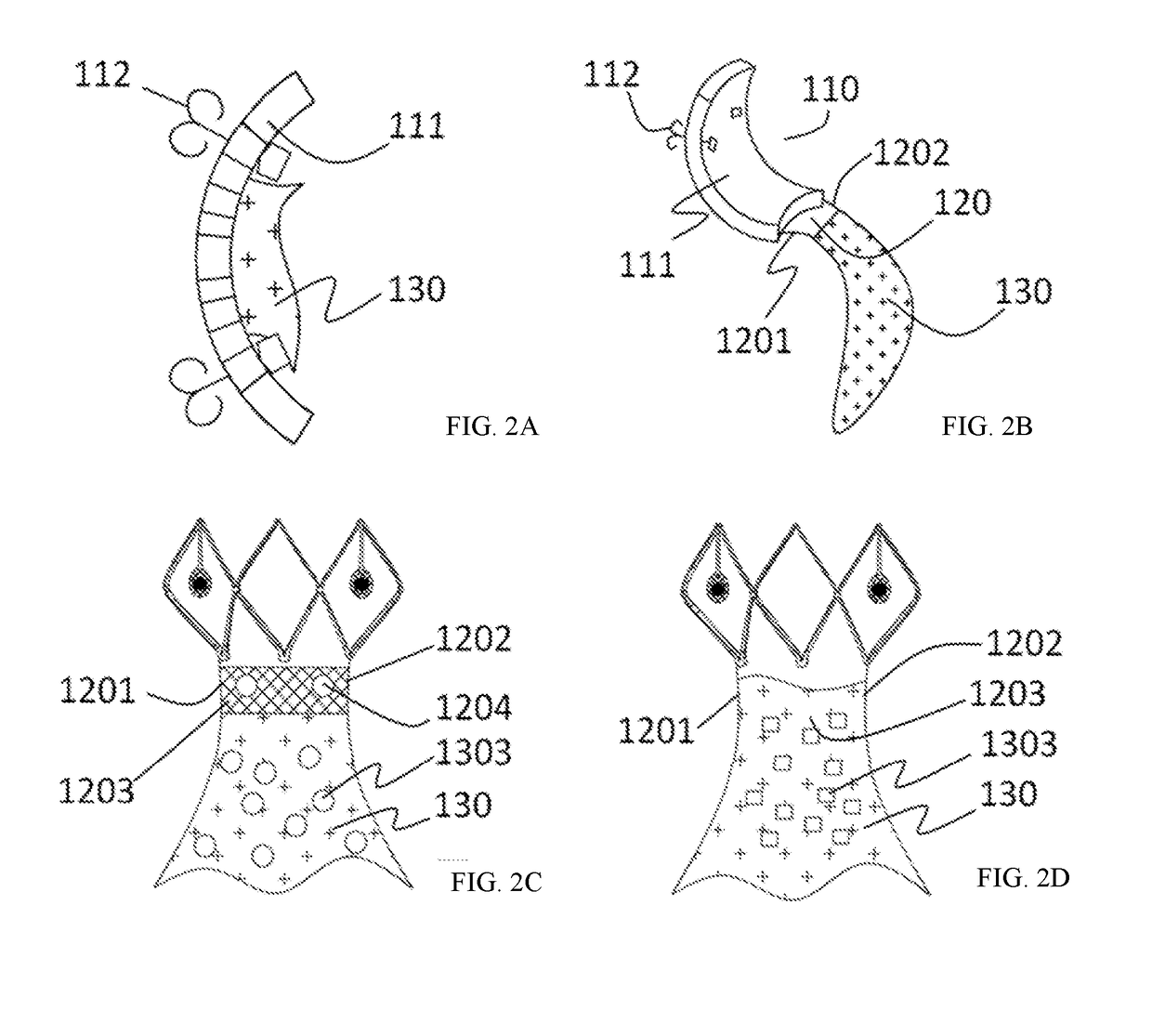
A prosthesis (100) for preventing a valve regurgitation, comprising a fixation unit (110), a connection piece (120) and a closure assisting piece (130); the fixation unit (110) comprises a fixation piece (111) and an anchor (112); the connection piece (120) is flexible, and a distal section thereof is connected to a proximal section of the fixation piece (111), and a proximal section thereof is connected to a distal section of the closure assisting piece (130); the fixation piece (111) is fixed on the atrial wall or a valve ring of a patient via the anchor (112); the deployed width of the fixation piece (111) is less than two-thirds of the circumference of a valve tissue annulus; the closure assisting piece (130) is located between autologous valve leaflets of the patient when in a free state; the maximum width of the closure assisting piece (130) is less than the maximum deployed width of a single autologous valve leaflet; and the proximal end of the anchor (112) is provided with an anti-disengagement end (1120). The position of the prosthesis (100) can be adjusted, and the prosthesis (100) is accurately positioned and firmly anchored, and does not readily adhere to tissue adjacent to the valve annulus of the patient.
Owner:NINGBO JENSCARE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Composite Structures and Methods for Ablating Tissue to Form Complex Lesion Patterns in the Treatment of Cardiac Conditions and the Like
InactiveUS20080161802A1Avoiding costly and intrusiveElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingFibrillationElectrical impulse
A method of ablating tissue in the heart to treat atrial fibrillation introduces into a selected atrium an energy emitting element. The method exposes the element to a region of the atrial wall and applies ablating energy to the element to thermally destroy tissue. The method forms a convoluted lesion pattern comprising elongated straight lesions and elongated curvilinear lesions. The lesion pattern directs electrical impulses within the atrial myocardium along a path that activates the atrial myocardium while interrupting reentry circuits that, if not interrupted, would cause fibrillation. The method emulates the surgical maze procedure, but lends itself to catheter-based procedures that do not require open heart surgical techniques. A composite structure for performing the method is formed using a template that displays in planar view a desired lesion pattern for the tissue. An array of spaced apart element is laid on the template. Guided by the template, energy emitting and non-energy emitting zones are formed on the elements. By overlaying the elements, the composite structure is formed, which can be introduced into the body to ablate tissue using catheter-based, vascular access techniques.
Owner:EP TECH
Endocardial dispersive electrode for use with a monopolar RF ablation pen
InactiveUS7497857B2Narrow lesionSmall incisionSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsRf ablationDirect path
Methods and devices for forming a lesion in a target tissue having a cavity within. A first RF electrode and a second RF electrode can be coupled to opposite poles of an RF current source. The second electrode can be inserted into the tissue cavity and expanded to contact the target tissue from within. The first electrode can be externally disposed against the target tissue while applying RF current between the first and second electrodes to ablate the target tissue. Some methods are directed to ablating tribiculated atrial wall tissue to treat atrial fibrillation. The second electrode can contact the tribiculated tissue directly from within to provide a direct path between the two electrodes. In some methods, the second electrode is inserted through an incision made to remove an atrial appendage. The methods can provide deeper, narrower lesions relative to those made using remote, indifferent electrodes. Atrial fibrillation ablation procedures can be performed using the invention, requiring fewer incisions than conventional methods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
ActiveUS9149327B2Easy to predictImprove integrityDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingRf ablationAtrial wall
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Endocardial Dispersive Electrode for Use with a Monopolar RF Ablation Pen
Methods and devices for forming a lesion in a target tissue having a cavity within a first RF electrode and a second RF electrode can be coupled to opposite poles of an RF current source. The second electrode can be inserted into the tissue cavity and expanded to contact the target tissue from within. The first electrode can be externally disposed against the target tissue while applying RF current between the first and second electrodes to ablate the target tissue. Some methods are directed to ablating tribiculated atrial wall tissue to treat atrial fibrillation. The second electrode can contact the tribiculated tissue directly from within to provide a direct path between the two electrodes. In some methods, the second electrode is inserted through an incision made to remove an atrial appendage. The methods can provide deeper, narrower lesions relative to those made using remote, indifferent electrodes. Atrial fibrillation ablation procedures can be performed using the invention, requiring fewer incisions than conventional methods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prediction of atrial wall electrical reconnection based on contact force measured during RF ablation
A method and device for determining the transmurality and / or continuity of an isolation line formed by a plurality of point contact ablations. In one embodiment, a method for determining the size of a lesion (width, depth and / or volume) is disclosed, based on contact force of the ablation head with the target tissue, and an energization parameter that quantifies the energy delivered to the target tissue during the duration time of the lesion formation. In another embodiment, the sequential nature (sequence in time and space) of the ablation line formation is tracked and quantified in a quantity herein referred to as the “jump index,” and used in conjunction with the lesion size information to determine the probability of a gap later forming in the isolation line.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Methods and Devices for Creation of Communication Between Aorta and Left Atrium
Methods and devices are disclosed for the formation of a communication between the aorta and left atrium. The method includes introducing a puncturing device, positioning the device at a location along the aorta, and advancing the puncturing device to create a pathway. The method may include: a. via an inferior artery, advancing a perforating tip of the puncturing device towards the aorta; b. positioning the perforating tip adjacent a wall of the aorta, proximate the left atrium; and c. advancing the perforating tip to perforate through the wall of the aorta and then through a wall of the left atrium, to create a pathway between the aorta and the left atrium, wherein the creation of the pathway can be confirmed with at least one of fluoroscopy, electro-anatomical mapping, pressure measurement, contrast injection, and echocardiograph.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Mitral valve device and use method
PendingCN112438827AEasy to fixReduce flow resistanceAnnuloplasty ringsAnatomical structuresAtrial wall
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to a mitral valve device and a use method. The mitral valve device comprises a support and a valve leaflet, wherein the support comprises an outer support and an inner support and is flexibly connected with the outer support through a suture membrane in a suture mode; the outer support comprises an outerexpansion frame and a lower barrel-shaped frame; the upper end of the outer expansion frame is used for being placed at the atrium end; the lower barrel-shaped frame is connected with the upper end and used for extending from the atrium end to the atrium through a valve ring; a highly-protruding atrium wall fitting face is arranged on one side of the outer expansion frame; a plurality of protruding structures are arranged at the position, close to the valve ring, of the peripheral side of the barrel-shaped frame; the inner support is cylindrical, and the valve leaflet is sutured in the inner support through a clamping piece; and a tightening structure is arranged at the tail end of the support and connected with an anchoring part through a pull rope. According to the mitral valve device and the use method, the mitral valve device can better adapt to the anatomical structure of the heart through the double-layer support structure and the asymmetric outer support, the influence of heartmovement on the inner support and the valve leaflet is reduced, the device plays the efficacy, and the service life of the device is prolonged.
Owner:QICHEN (SHANGHAI) MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Device for shunting and decompressing atrium
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, and particularly relates to a device for shunting and decompressing an atrium. The shunting and decompressing device is connected with a conveyor, and comprises a wire harness collector, a left atrium wall fixing structure, a middle connecting channel and a right atrium wall fixing structure, wherein the left atrium wall fixing structure communicates with the right atrium wall fixing structure through the middle connecting channel; one end of the wire harness collector is connected with the left atrium wall fixing structure,and the other end of the wire harness collector is connected with the conveyor; and the left atrium wall fixing structure and the right atrium wall fixing structure are pressed against the two sides of an atrium wall respectively, and are connected with the atrium through the middle connecting channel to shunt and decompress the atrium. By adopting the device, the pressure of the atrium can be lowered, the service life of the atrium is prolonged, heart failure is relieved, and the surgical success rate and surgical operation convenience are increased.
Owner:QICHEN (SHANGHAI) MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
Self-sealing cannula
The present invention discloses a self-sealing cannula and methods of its use. The self-sealing cannula can be minimally invasively placed into the heart for drawing and / or returning blood with a self-sealing function at the interface of the blood access site. The disclosed cannula can be implemented as a single lumen cannula or a double lumen cannula, which can be used with ventricular assist devices for heart support or pump-oxygenators for ECMO and respiratory support. Through a self-sealing mechanism fixed on the ventricular wall or atrial wall, a cannula body is attached to the self-sealing fixture and blood is drawn into the lumen via an external pump and returned to the circulation system through a separate cannula. In the case of the double lumen cannula embodiment, the blood will be drawn into the drainage lumen of the double lumen cannula and returned through an infusion lumen at the desired location. The present invention achieves minimally invasive insertion without surgical sutures to the heart, and allows for optimal drainage of the blood from the heart. With use of the double lumen cannula, it prevents need for multiple cannulation sites, and greatly reduces the blood recirculation. Removal of the cannula is simplified without need for suturing or insertion of a plugging member.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Mitral valve repair stent
ActiveCN113476181AReduced Risk of ComplicationsExtended service lifeHeart valvesAtrial wallEngineering
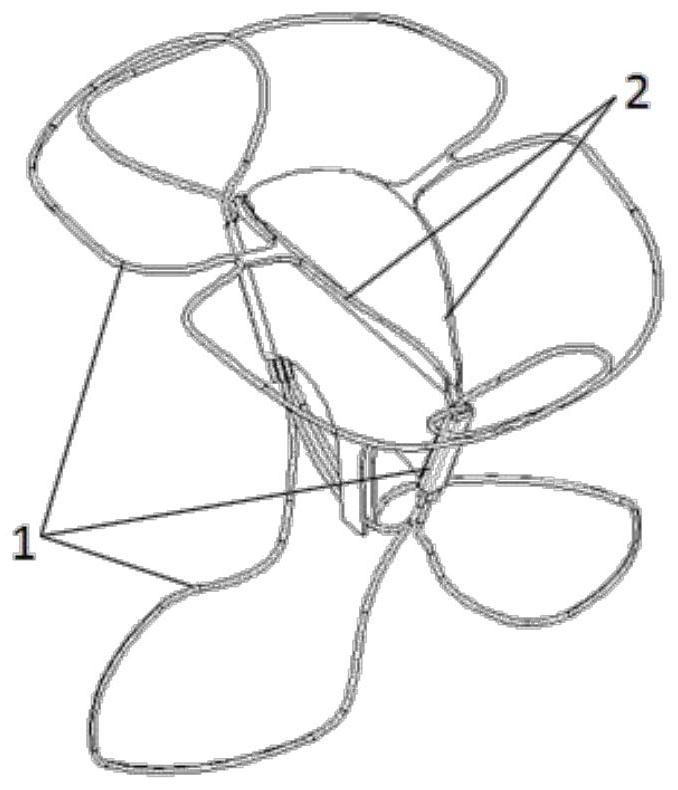
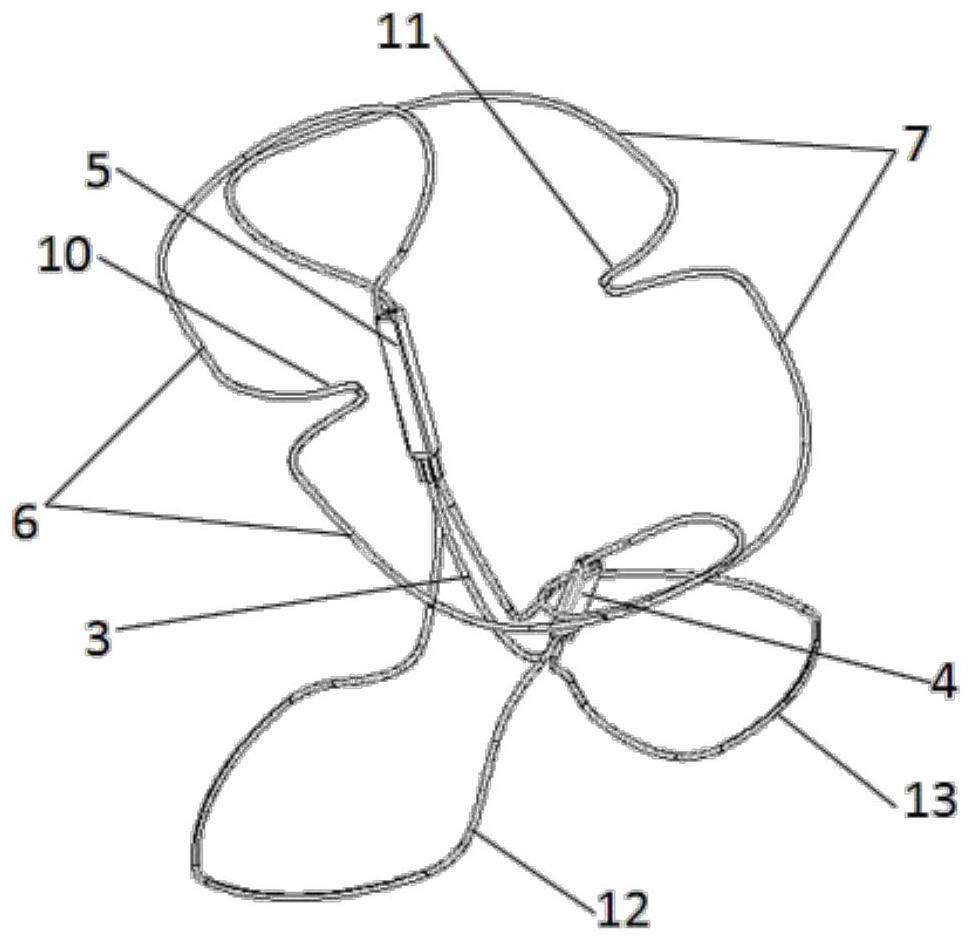
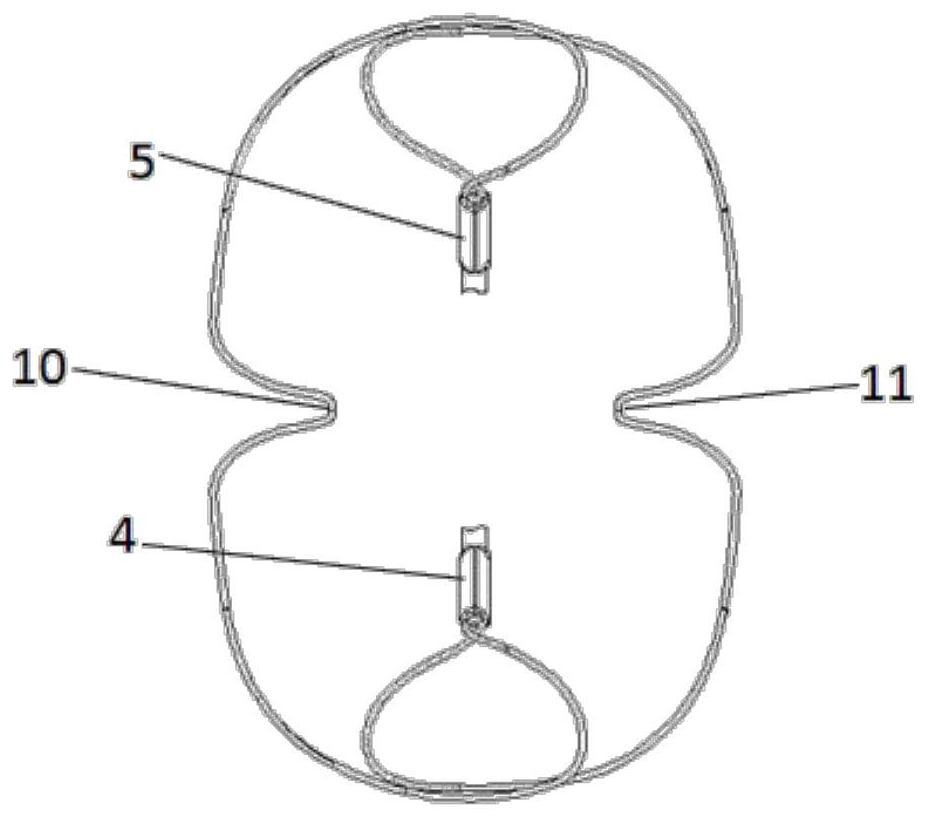
The invention relates to a mitral valve repair stent which comprises a skeleton and a valve assembly, the skeleton comprises an upper limiting piece, a middle fixing piece and a lower limiting piece, the middle fixing piece comprises a V-shaped supporting section, a first sleeve and a second sleeve, the V-shaped supporting section is connected with the lower end of the first sleeve and the lower end of the second sleeve; a front wing and a rear wing are correspondingly arranged on the front side and the rear side of the top of the valve assembly, the upper limiting piece comprises a first limiting curve section located above the front side and a second limiting curve section located above the rear side, the first limiting curve section and the second limiting curve section are connected with the upper ends of the first sleeve and the second sleeve on the left side and the right side respectively, and the middle parts of the first limiting curve section and the second limiting curve section are respectively concave inwards to form a front V-shaped connecting section and a rear V-shaped connecting section which are correspondingly connected with the front wing and the rear wing. The mitral valve repair stent has the advantages that after the stent is improved, the action on the atrial wall is small, the self-adaptive attaching and anchoring effect at the valve ring is good, the improved valve assembly is good in compliance and is matched with the improved stent, better closing performance is achieved, the complication probability is low, and the postoperative effect is good.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOMED MEDICAL DEVICE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com