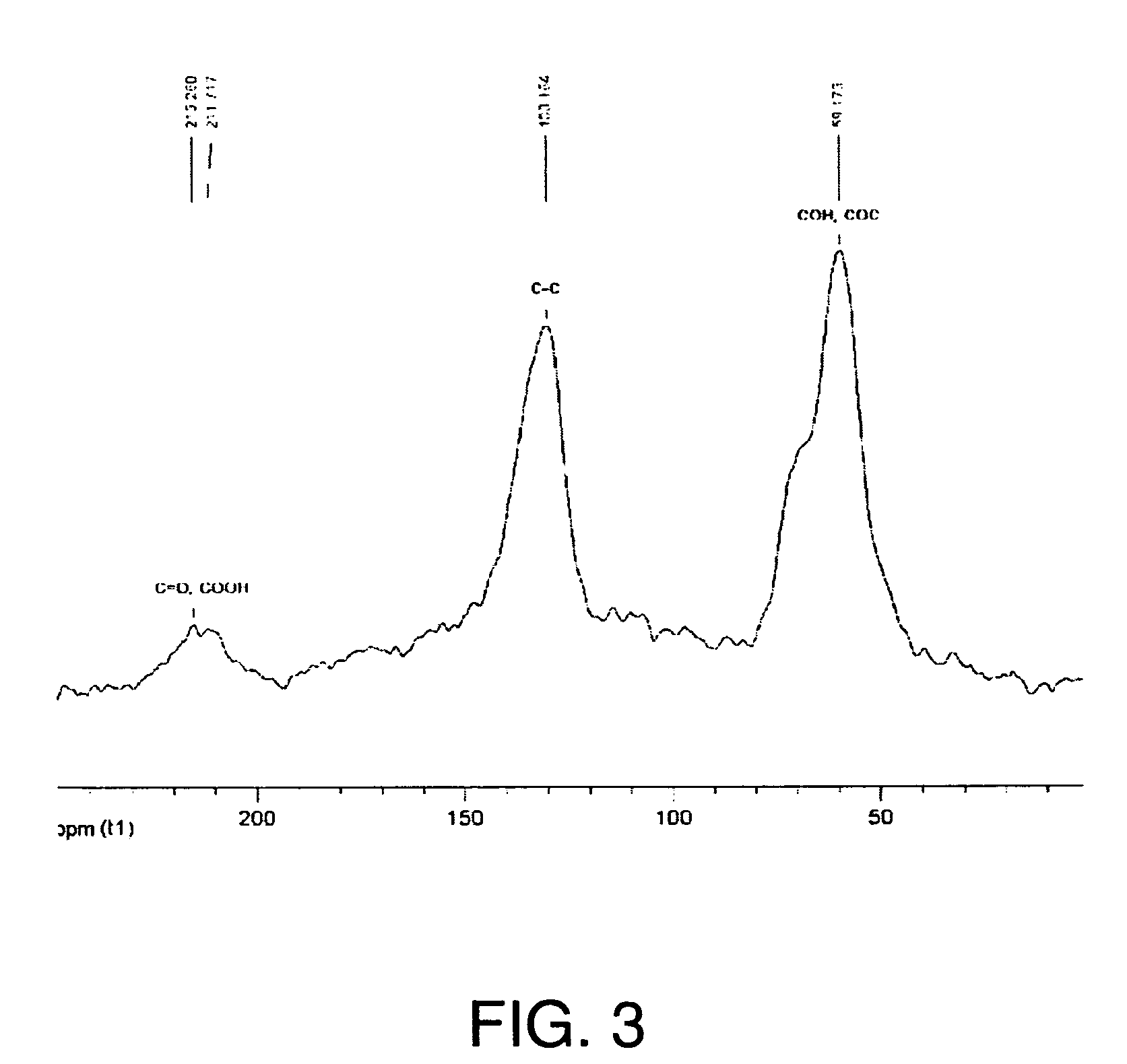
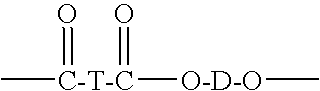
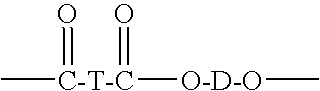
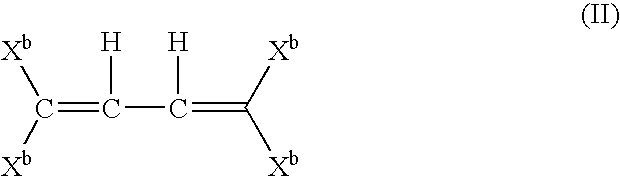
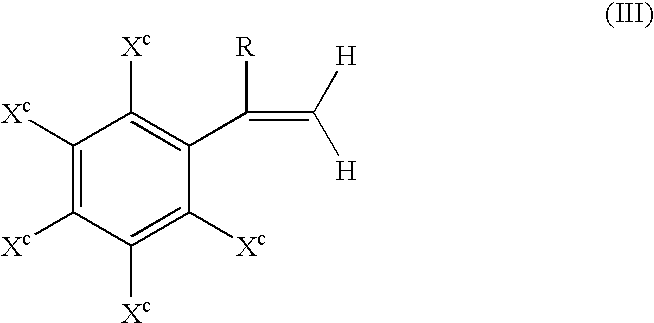
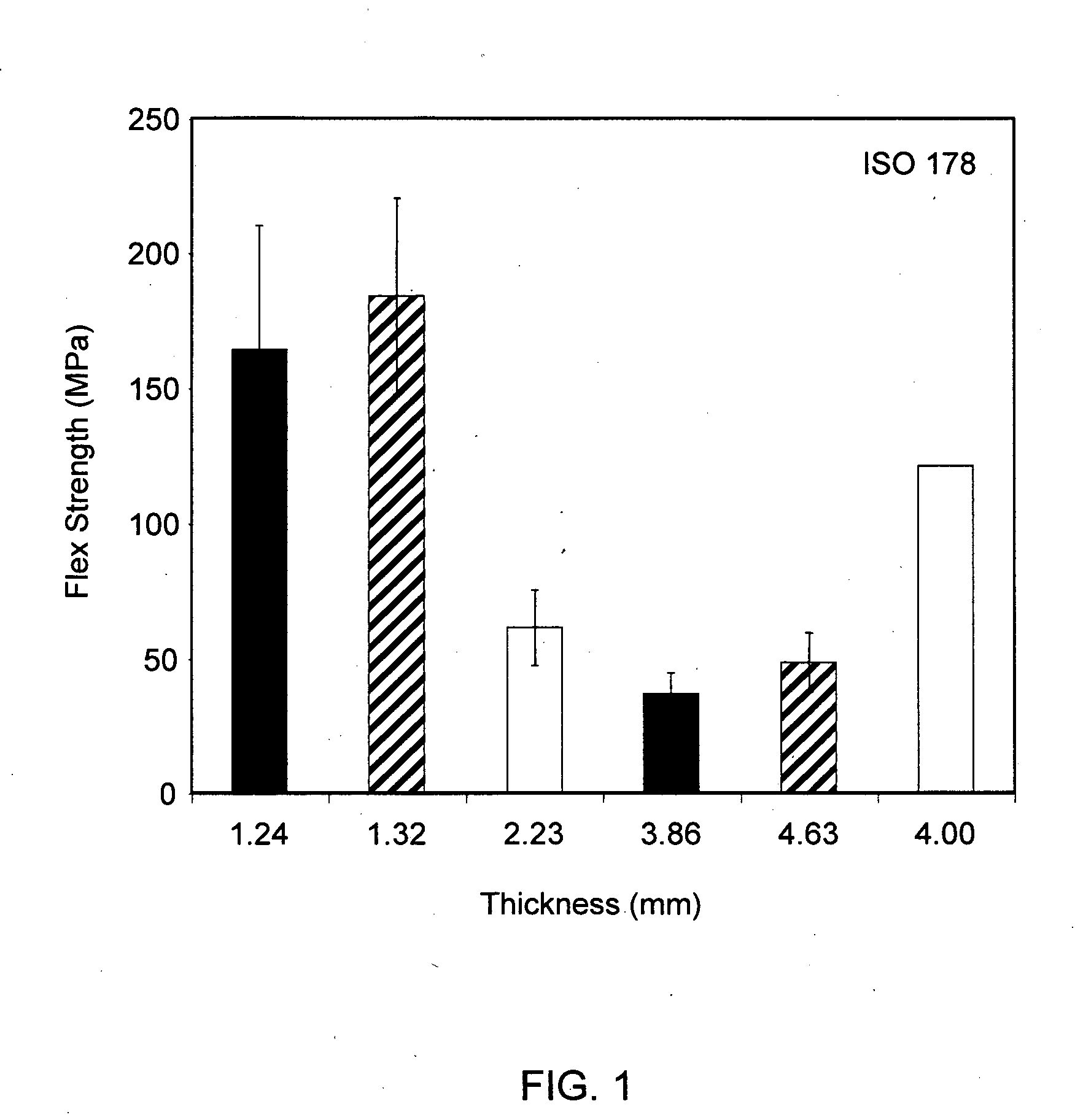
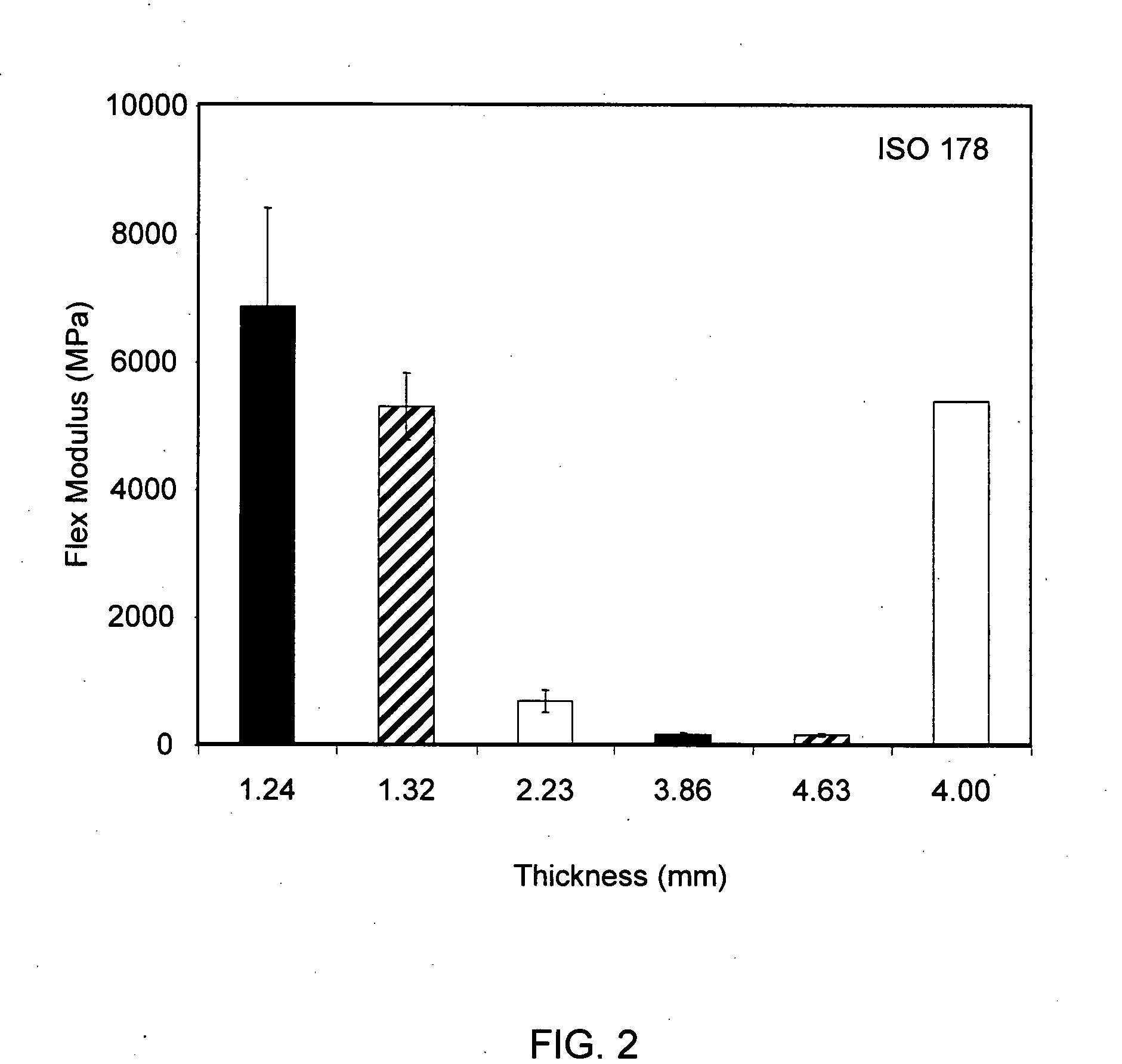
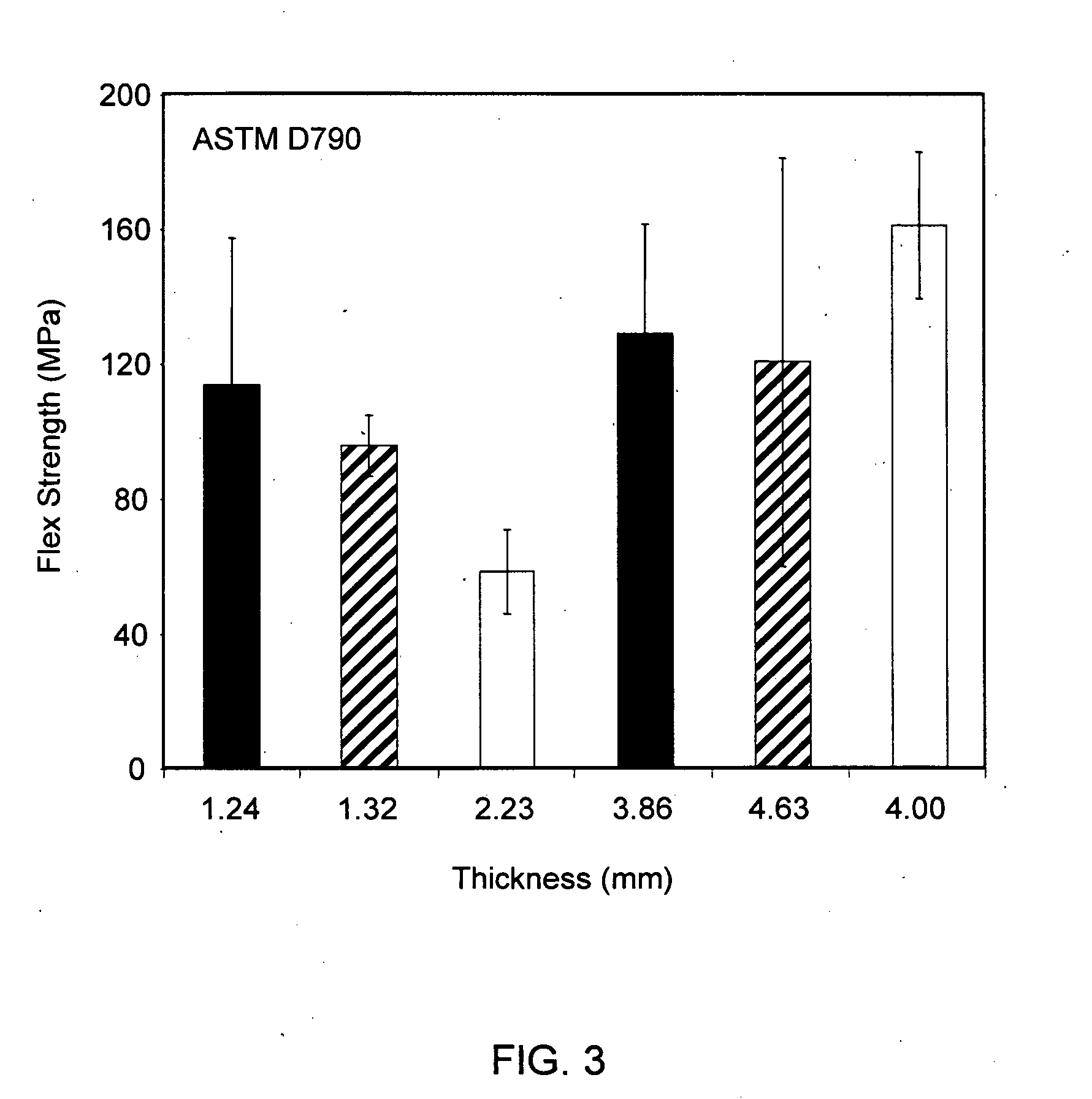
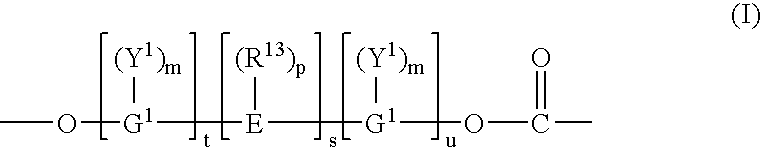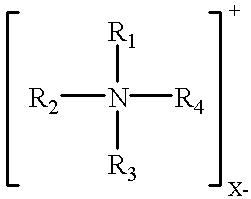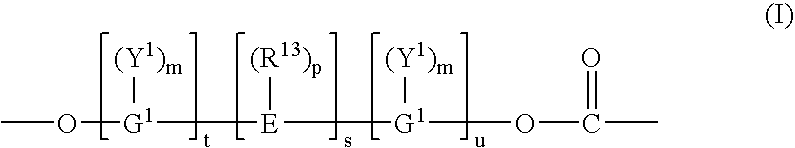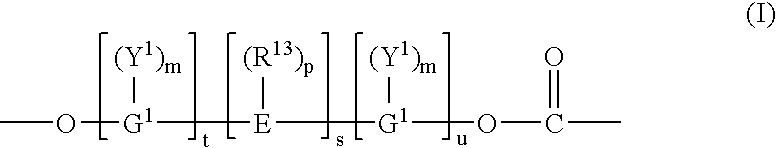Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
434results about How to "Increase modulus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasma curing process for porous low-k materials
InactiveUS6913796B2Improving elastic modulusImproving material hardnessSilicaLayered productsHardnessMaterials science
Low dielectric constant porous materials with improved elastic modulus and hardness. The process of making such porous materials involves providing a porous dielectric material and plasma curing the porous dielectric material to produce a plasma cured porous dielectric material. Plasma curing of the porous dielectric material yields a material with improved modulus and hardness. The improvement in elastic modulus is typically greater than or about 50%, more typically greater than or about 100%, and more typically greater than or about 200%. The improvement in hardness is typically greater than or about 50%. The plasma cured porous dielectric material can optionally be post-plasma treated. The post-plasma treatment of the plasma cured porous dielectric material reduces the dielectric constant of the material while maintaining an improved elastic modulus and hardness as compared to the plasma cured porous dielectric material. The post-plasma treated, plasma cured porous dielectric material has a dielectric constant between about 1.1 and about 3.5 and an improved elastic modulus and hardness.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
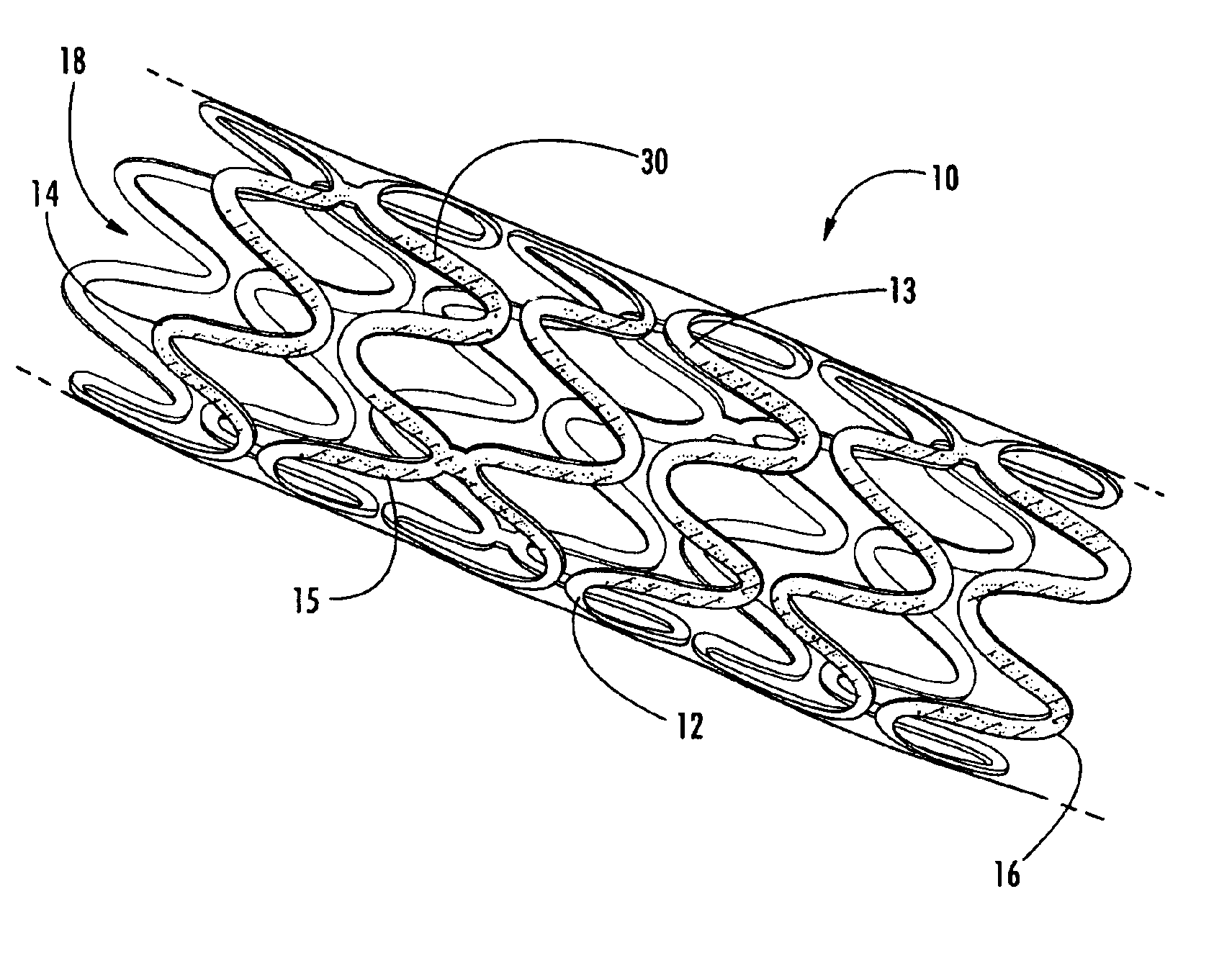
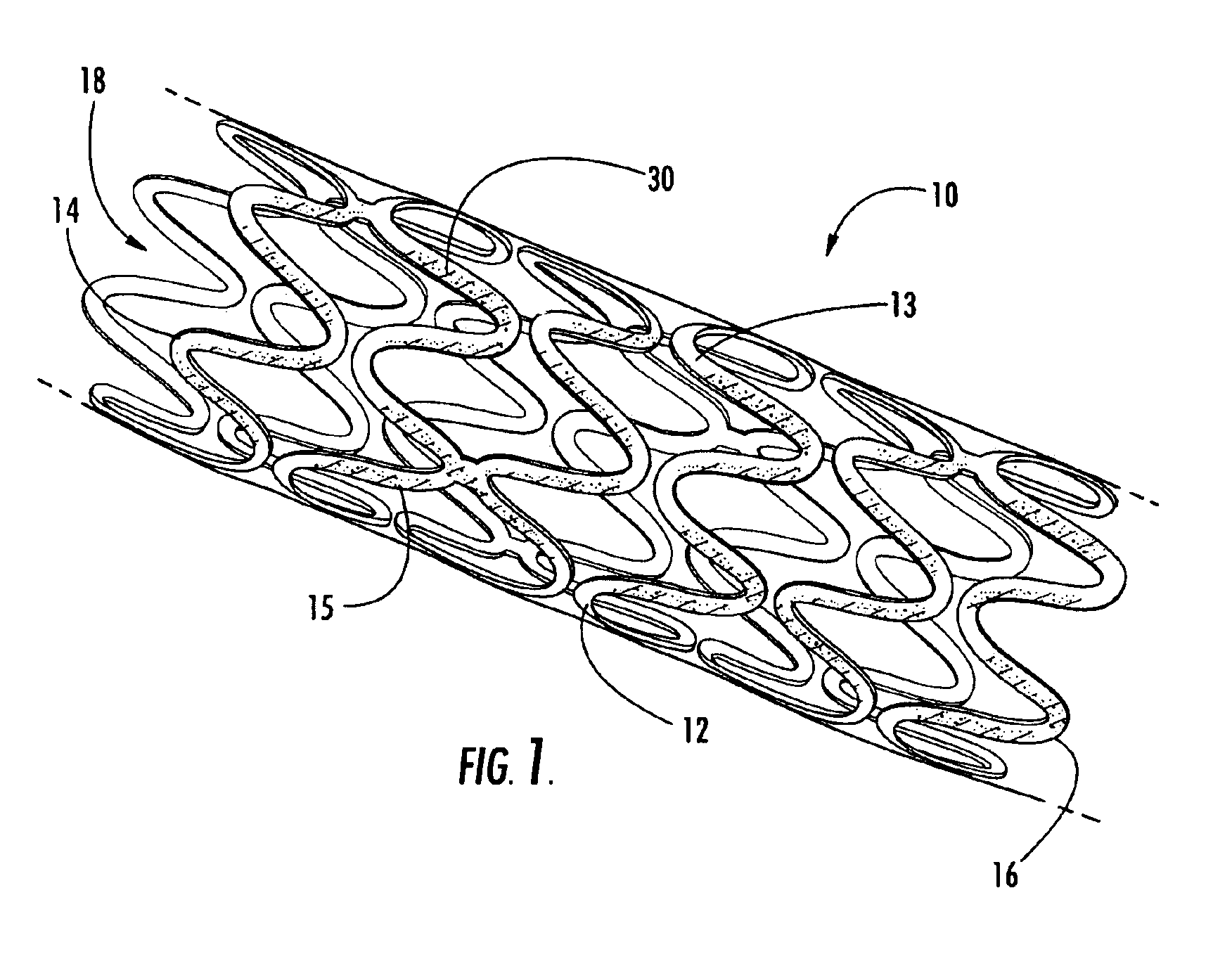
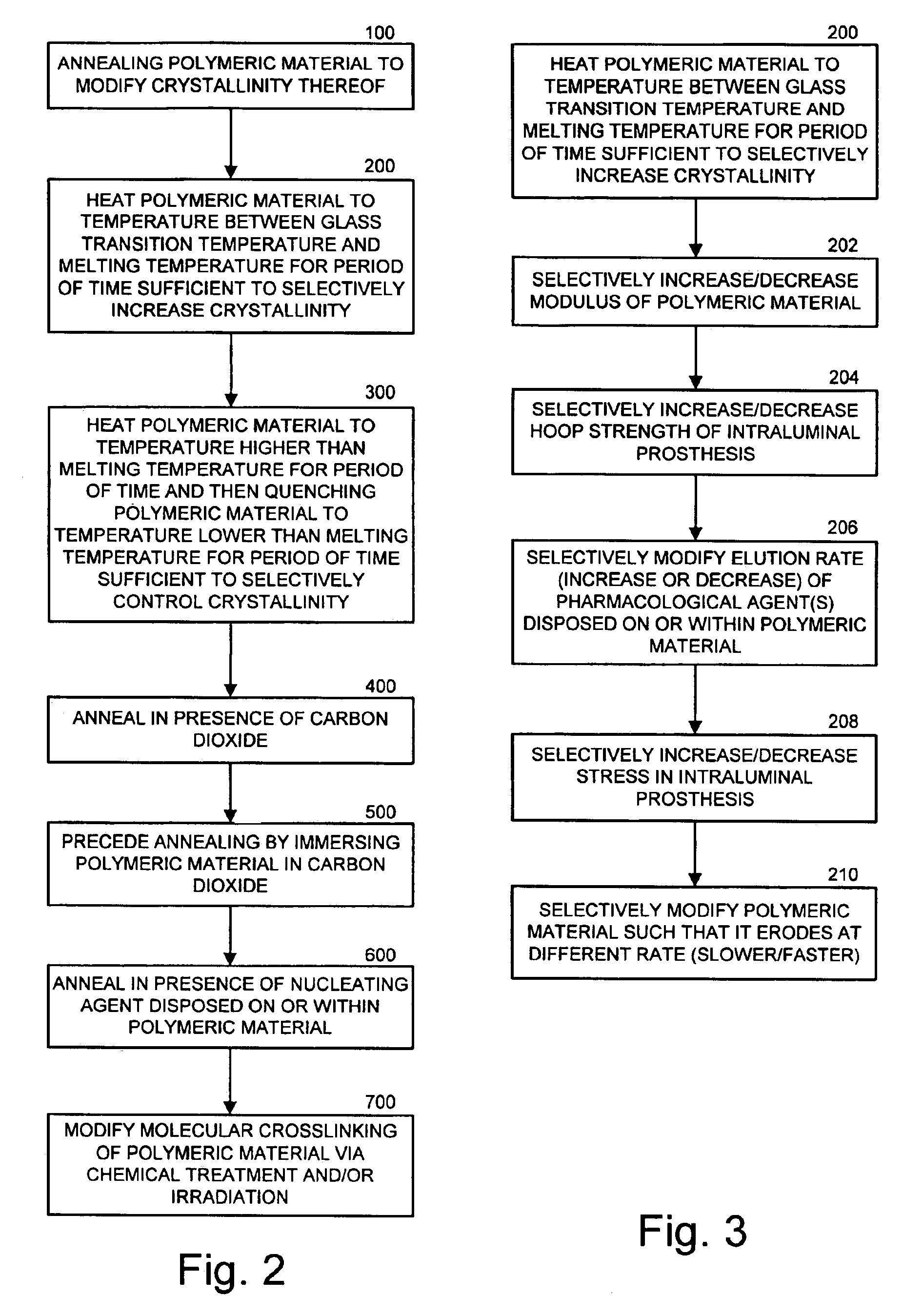
Intraluminal prostheses having polymeric material with selectively modified crystallinity and methods of making same
Methods of manufacturing polymeric intraluminal prostheses include annealing the polymeric material to selectively modify the crystallinity thereof. Annealing may be utilized to selectively modify various properties of the polymeric material of an intraluminal prosthesis, including: selectively increasing the modulus of the polymeric material; selectively increasing the hoop strength of the intraluminal prosthesis; selectively modifying the elution rate (increase or decrease) of a pharmacological agent subsequently disposed on or within the annealed polymeric material; selectively increasing / decreasing stress in the intraluminal prosthesis; and selectively modifying the polymeric material such that it erodes at a different rate.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
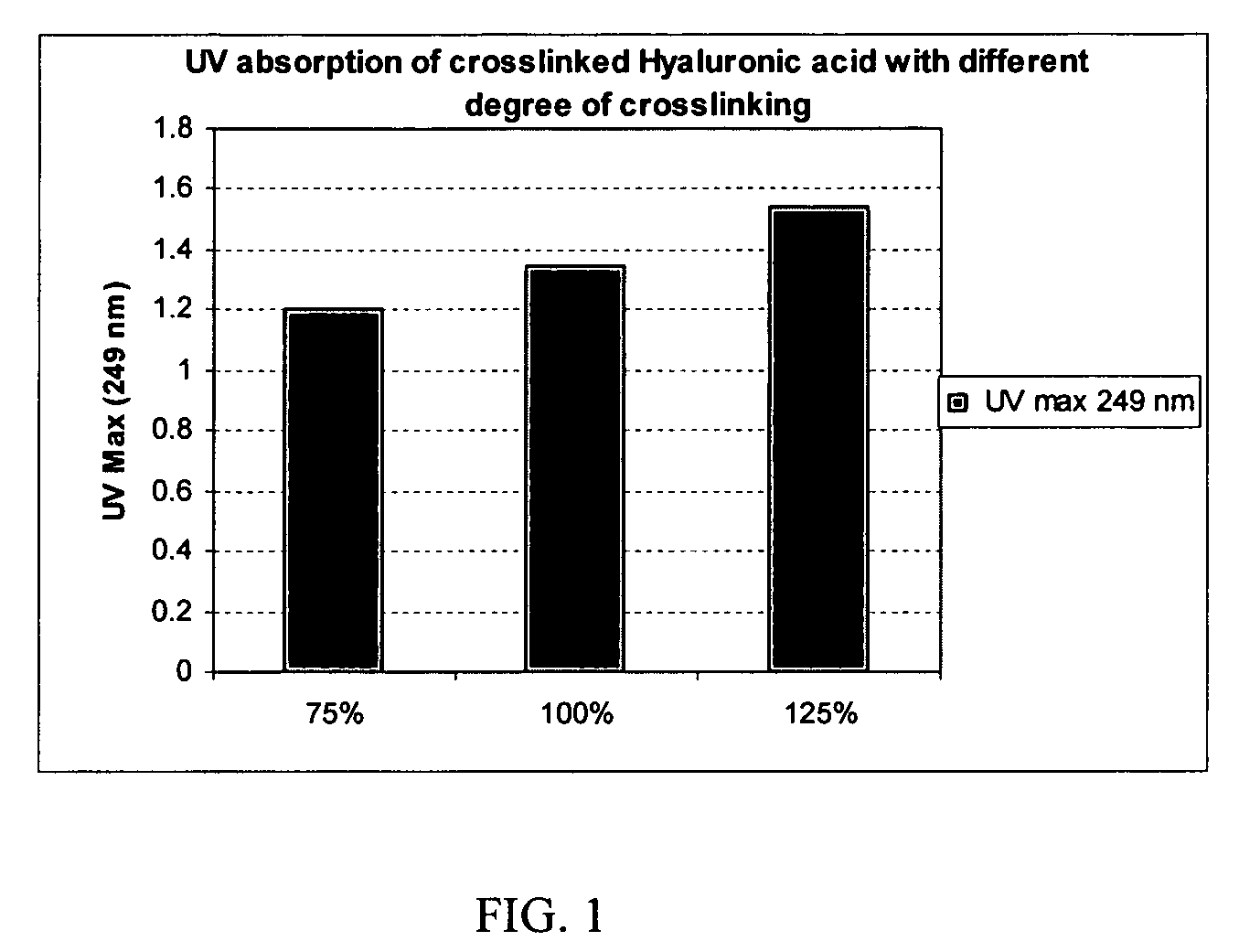
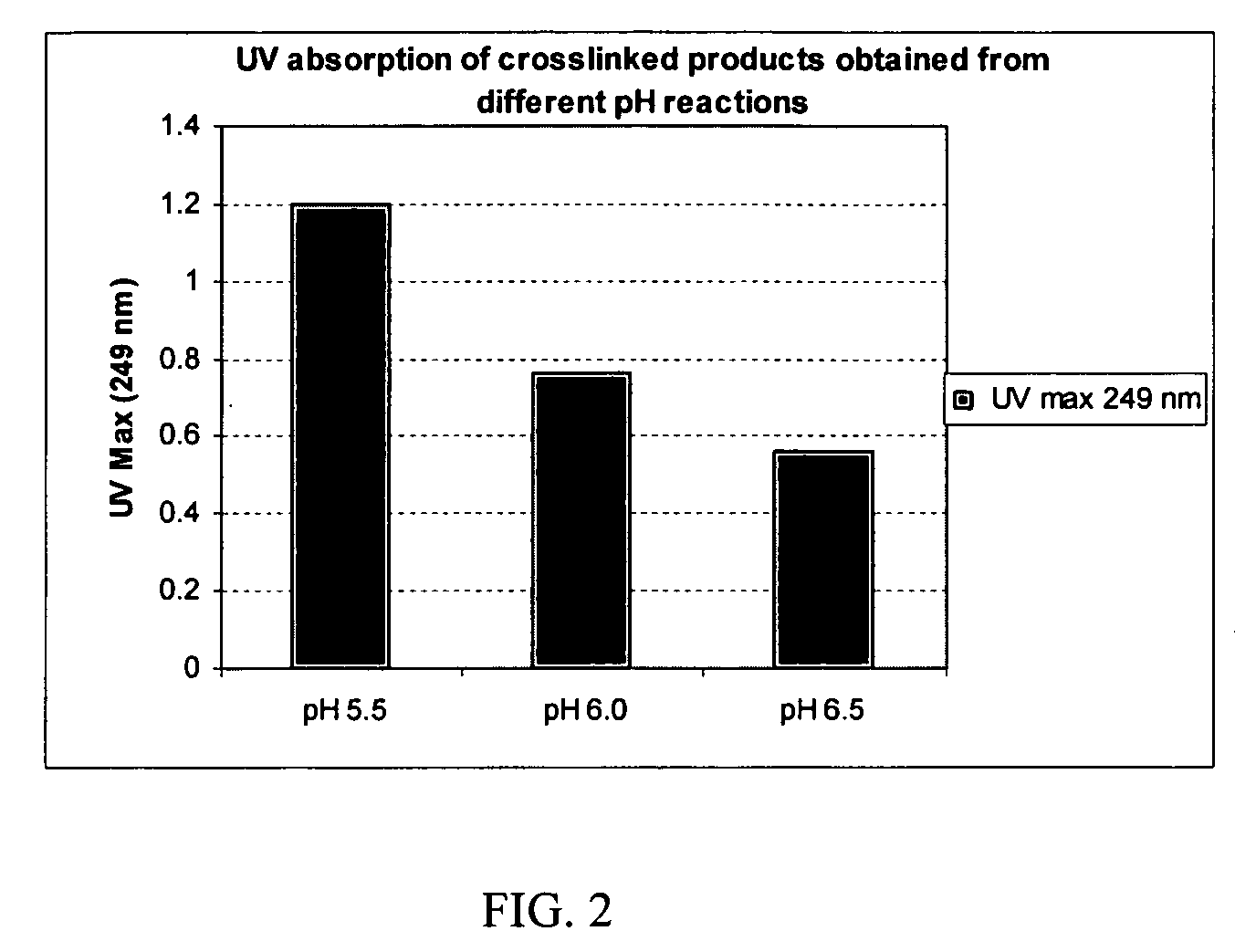
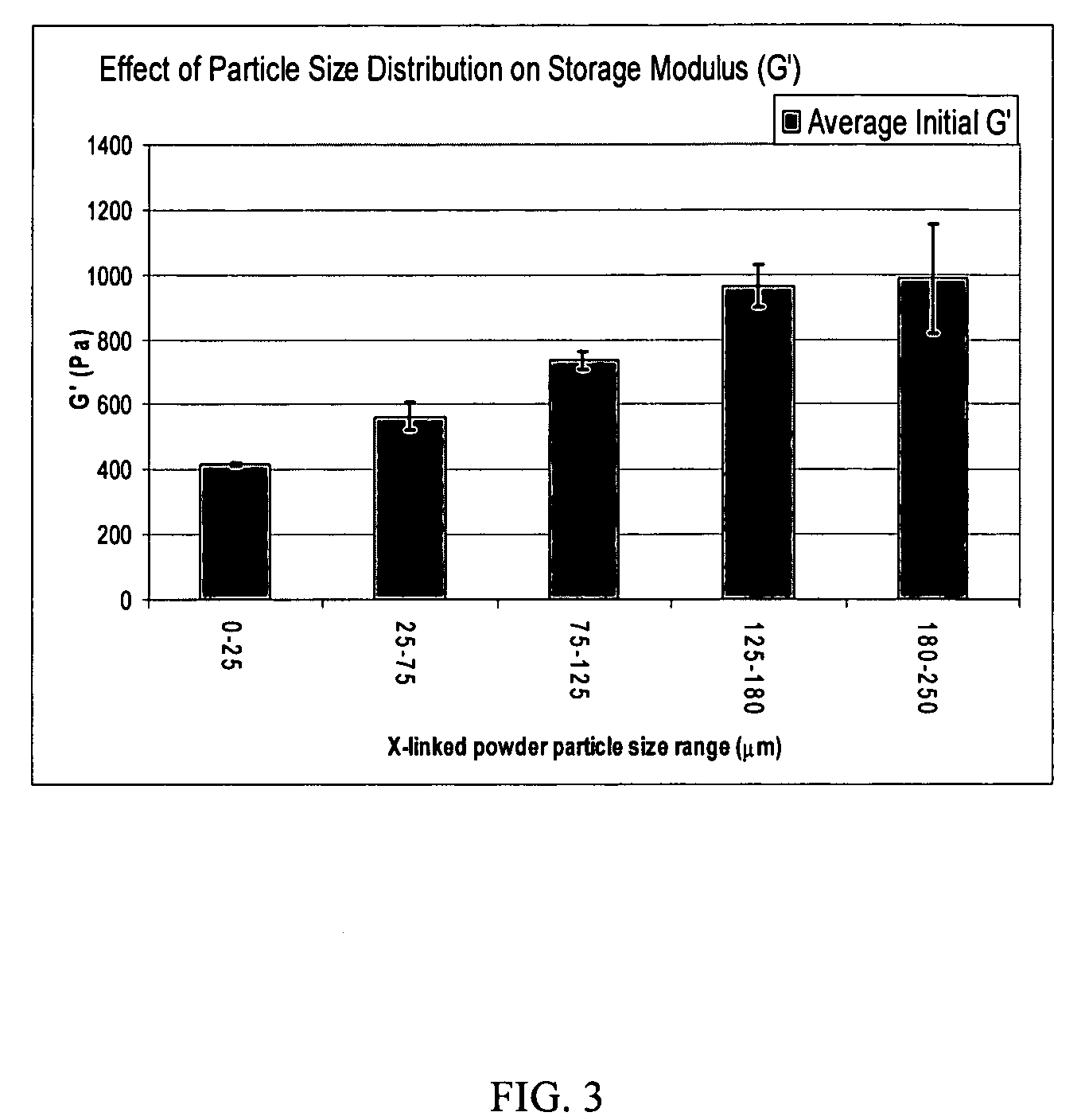
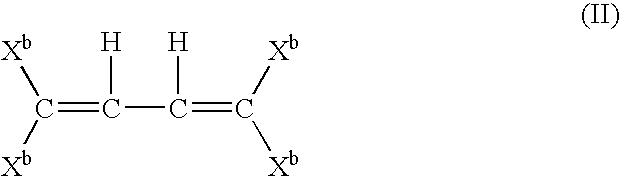
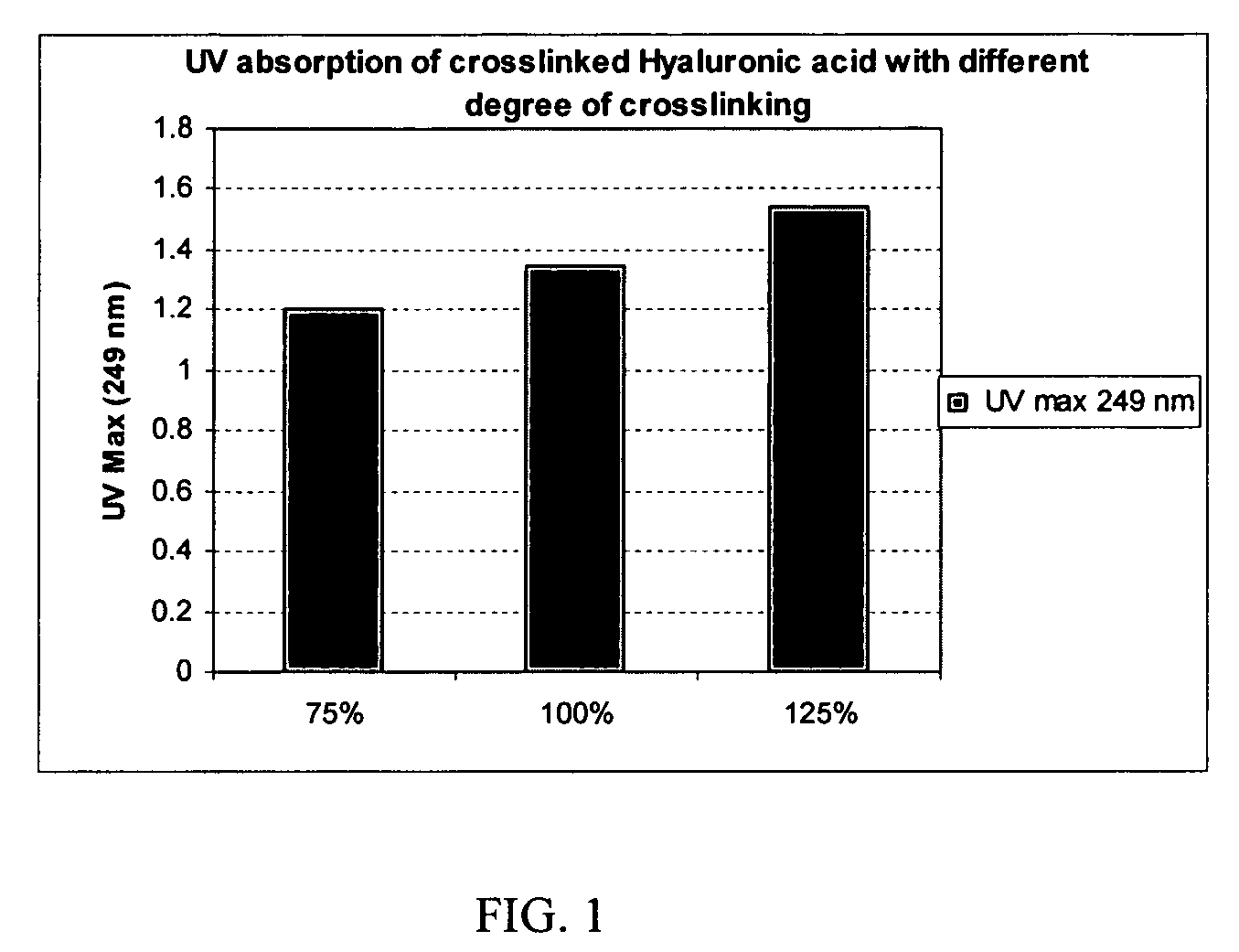
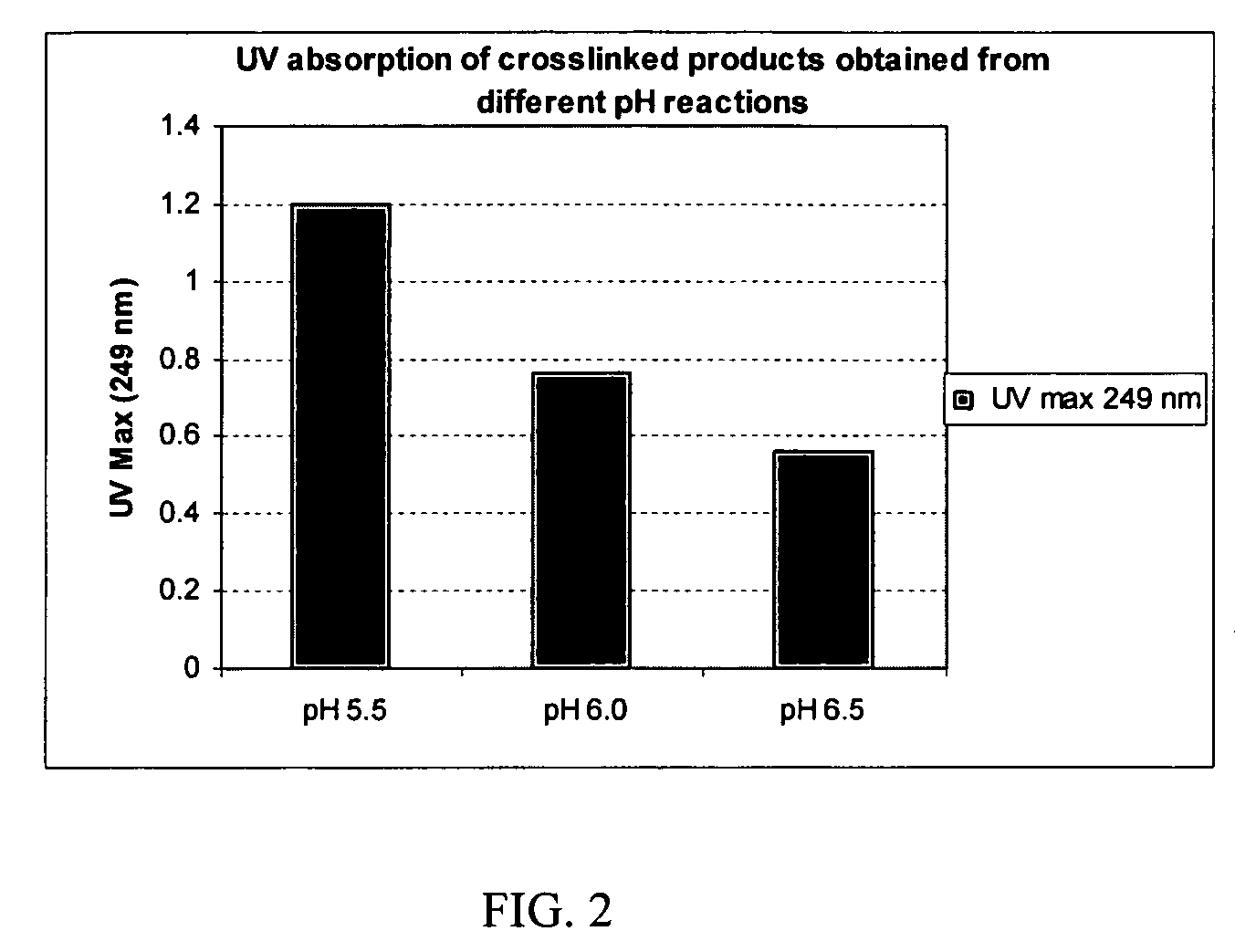
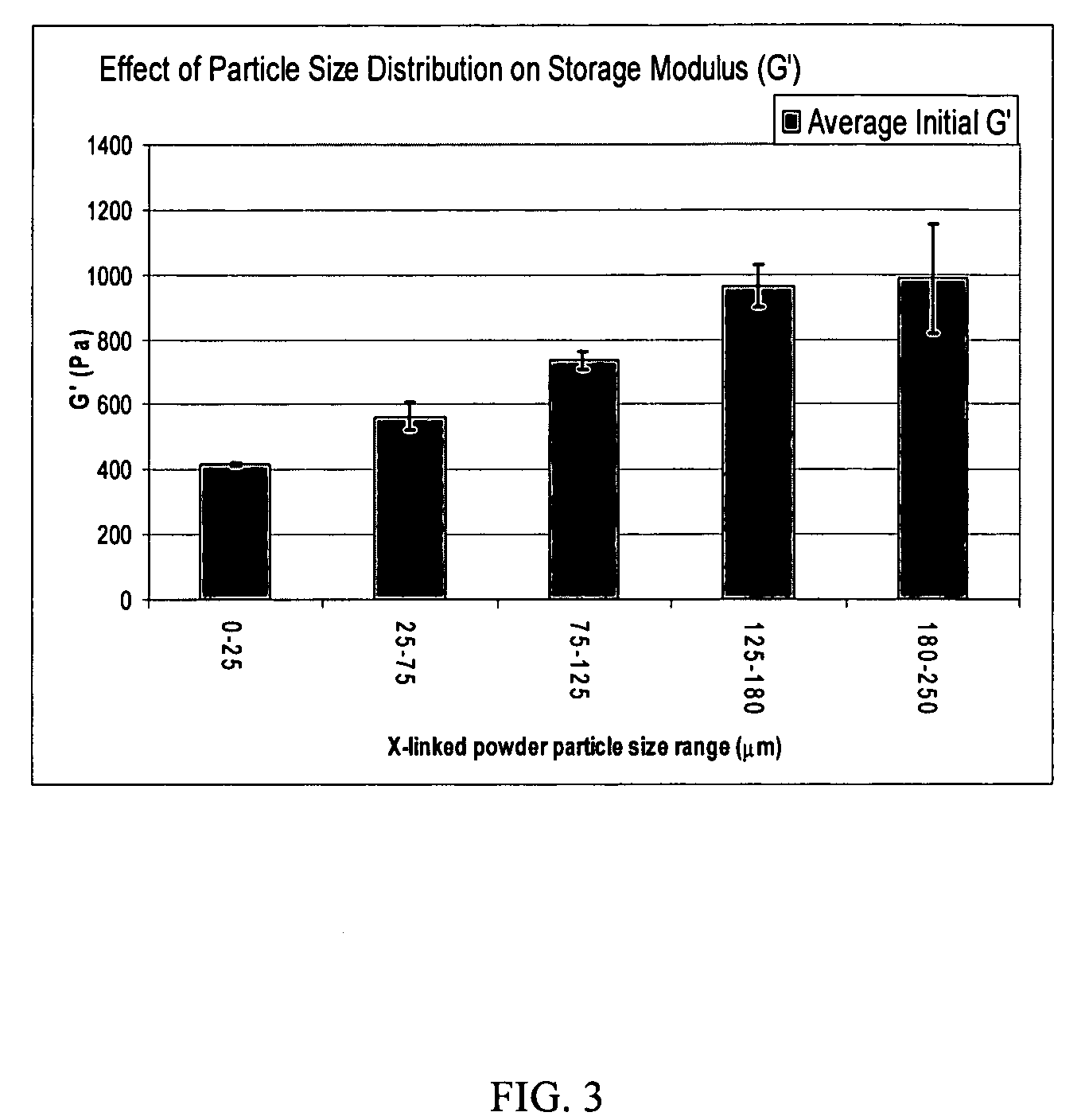
Crosslinked hyaluronic acid compositions for tissue augmentation
ActiveUS20050136122A1Improve drug deliveryReduce frequencyAntibacterial agentsBiocideAqueous solutionAverage diameter
A hyaluronic acid (HA) composition includes crosslinked, water-insoluble, hydrated HA gel particles. The HA includes crosslinks represented by the following structural formula: HA—U—R2—U—HA The variables are defined herein. A method of augmenting tissue in a subject includes inserting a needle into a subject at a location in the subject that is in need of tissue augmentation, wherein the needle is coupled to a syringe loaded with the HA composition, and applying force to the syringe, to deliver the HA composition into the subject. A method of preparing the HA composition, includes forming water-insoluble, dehydrated crosslinked HA particles, separating the water-insoluble, dehydrated particles by average diameter, selecting a subset of particles by average diameter, and hydrating the subset of dehydrated particles with a physiologically compatible aqueous solution. Another method of preparing the crosslinked HA composition includes crosslinking a precursor of the crosslinked HA with a biscarbodiimide in the presence of a pH buffer and dehydrating the crosslinked HA. Also included is a method of augmenting tissue in a subject that is in need of tissue augmentation. A method of stabilizing crosslinked HA includes hydrating water-insoluble, dehydrated crosslinked HA with a physiologically compatible aqueous solution that includes a local anesthetic, wherein the value of storage modulus G′ for the stabilized composition is at least about 110% of the value of G′ for a non-stabilized composition,. Also included is the stabilized HA composition.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS INC
Polymer compositions, method of manufacture, and articles formed therefrom
ActiveUS20060142455A1High tensile modulusImprove ductilityPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceFluoropolymer
A polymer composition is disclosed, which comprises a matrix polymer, a fluoropolymer that may be at least partially encapsulated by an encapsulating polymer, and a filler. Methods for making the polymer compositions and articles made of such compositions are also disclosed. The compositions and article can have improved tensile modulus, ductility, and / or impact properties.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Methods for the manufacture of sheets having a highly inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more inorganic aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form a sheet which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are formed into sheets by first extruding the mixtures and the passing the extruded materials between a set of rollers. The rolled sheets are dried in an accelerated manner to form a substantially hardened sheet, such as by heated rollers and / or a drying chamber. The inorganically filled sheets may have properties substantially similar to sheets presently made from traditional materials like paper, cardboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. Such sheets can be rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Compositions used in manufacturing articles having an inorganically filled organic polymer matrix
InactiveUS6090195AReadily and inexpensively mass producedHigh strengthClosure lidsWrappersFiberPolymer science
Compositions, methods, and systems for manufacturing articles, particularly containers and packaging materials, having a highly inorganically filled matrix. Suitable inorganically filled mixtures are prepared by mixing together an organic polymer binder, water, one or more aggregate materials, fibers, and optional admixtures in the correct proportions in order to form an article which has the desired performance criteria. The inorganically filled mixtures are molded to fashion a portion of the mixture into a form stable shape for the desired article. Once the article has obtained form stability, such as by heating to remove water by evaporation, the article is removed from the mold and allowed to harden to gain strength. The articles may have properties substantially similar to articles presently made from traditional materials like paper, paperboard, polystyrene, plastic, or metal. They have especial utility in the mass production of containers, particularly food and beverage containers.
Owner:EARTHSHELL SPE
Functional graphene-rubber nanocomposites
ActiveUS7745528B2Increase modulusImprove toughnessMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentElastomerX-ray
A polymer composition, containing a polymer matrix which contains an elastomer; and a functional graphene which displays no signature of graphite and / or graphite oxide, as determined by X-ray diffraction, exhibits excellent strength, toughness, modulus, thermal stability and electrical conductivity.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Orthopedic implant system
InactiveUS6066176AStrong interlocking fixationEasy to fixSurgical adhesivesBone implantPolymethyl methacrylateFemoral stem
It is an object of the present invention to provide an improved orthopedic implant system with satisfied biological, mechanical and morphological compatibilities. Solid metal femoral stem (entirely or partially) and solid metal acetabular head (entirely or partially) are covered with diffusion-bonded foamed-shaped sheet made of commercially pure titanium or titanium alloy(s). The open-cells in said foamed metal sheet are impregnated with biocompatible polymethyl methacrylate resin cement, which is reinforced with selected oxides (e.g., alumina, magnesia, zirconia, or a combination of these oxides) along with an application of a small amount of a metal primer agent.
Owner:OSHIDA YOSHIKI
Preparation method of completely peeled oxidation graphene/ rubber nanometer composite material
A preparation method of completely peeled oxidation graphene / rubber nanometer composite material adopts combination of emulsion compounding and flocculation processes or combination of emulsion compounding and spraying drying processes. The preparation method retains the phase state structure of the oxidation grapheme / rubber composite emulation in the liquid state and obtains the phase-state structure which is highly dispersed, highly peeled and dispersed in nanometer scale dispersion. Simultaneously, substances capable of acting with generating ionic bond effect or chemical bond effect with an oxidation graphene surface functional group are added into the oxidation graphene / hydrosol to serve as an interface agent, thereby improving interface combination effect of oxidation graphene and rubber. Vulcanized rubber prepared by the composite material of the preparation method through follow-up mixing and vulcanizing has mechanical property such as high tensile strength, stretching stress and tearing strength and is capable of greatly improving abrasion resistance and gas separation performance of the vulcanized rubber. The preparation method is simple, easy, low in cost, apt to industrialization and wide in suitable aspect, saves energy and has better economical and social benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU LVYUAN RUBBER RESOURCE RECYCLING INNOVATION CENT CO LTD
Crosslinked hyaluronic acid compositions for tissue augmentation
ActiveUS8124120B2Improve drug deliveryReduce frequencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineWater insoluble
Disclosed are hyaluronic acid (HA) compositions including crosslinked, water-insoluble, hydrated HA gel particles. Also disclosed are methods of making the HA compositions, and methods of using the HA composition to augment tissue in a subject.
Owner:ANIKA THERAPEUTICS INC
Macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes and acrylonitrile-based polymer and process for making the same
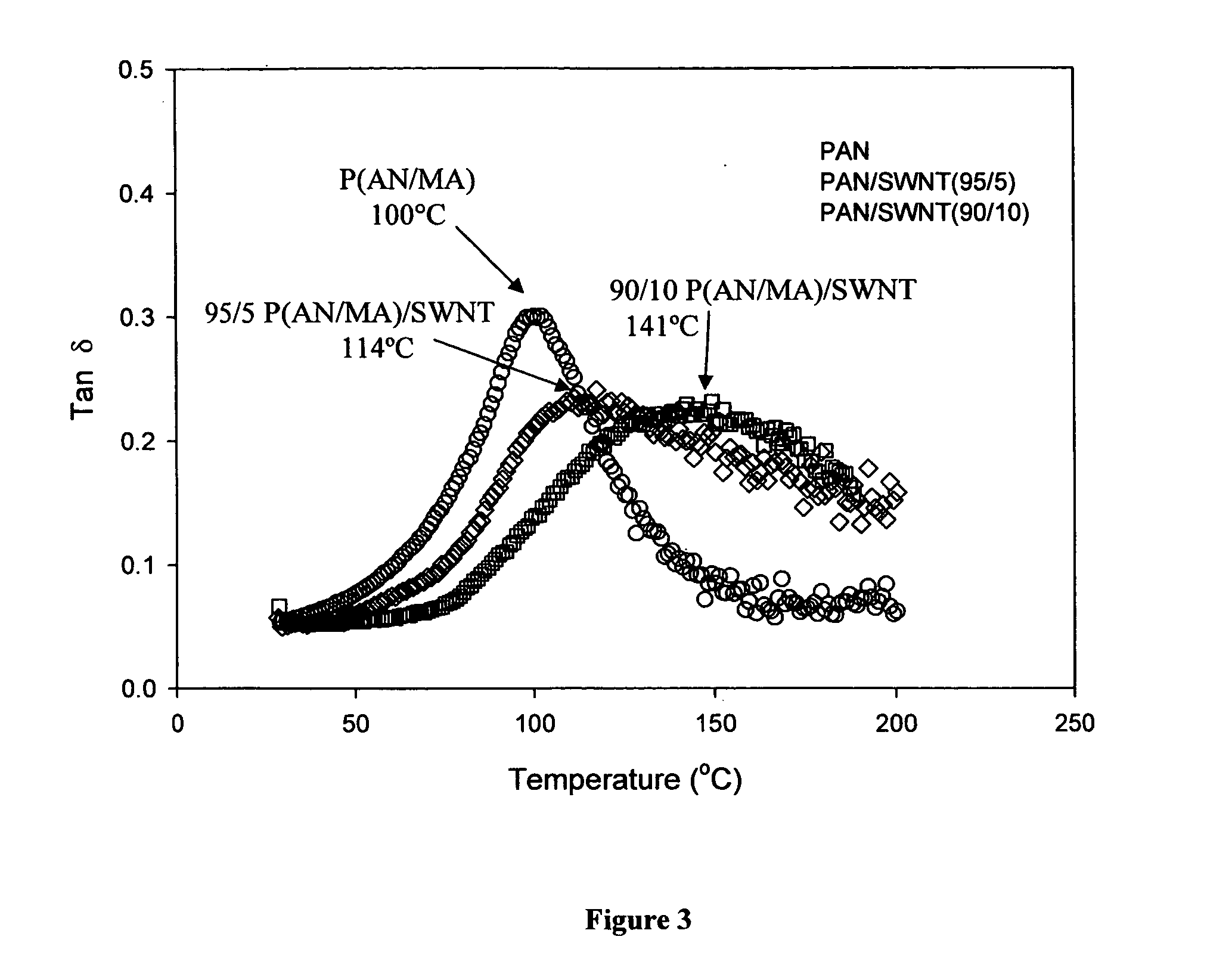
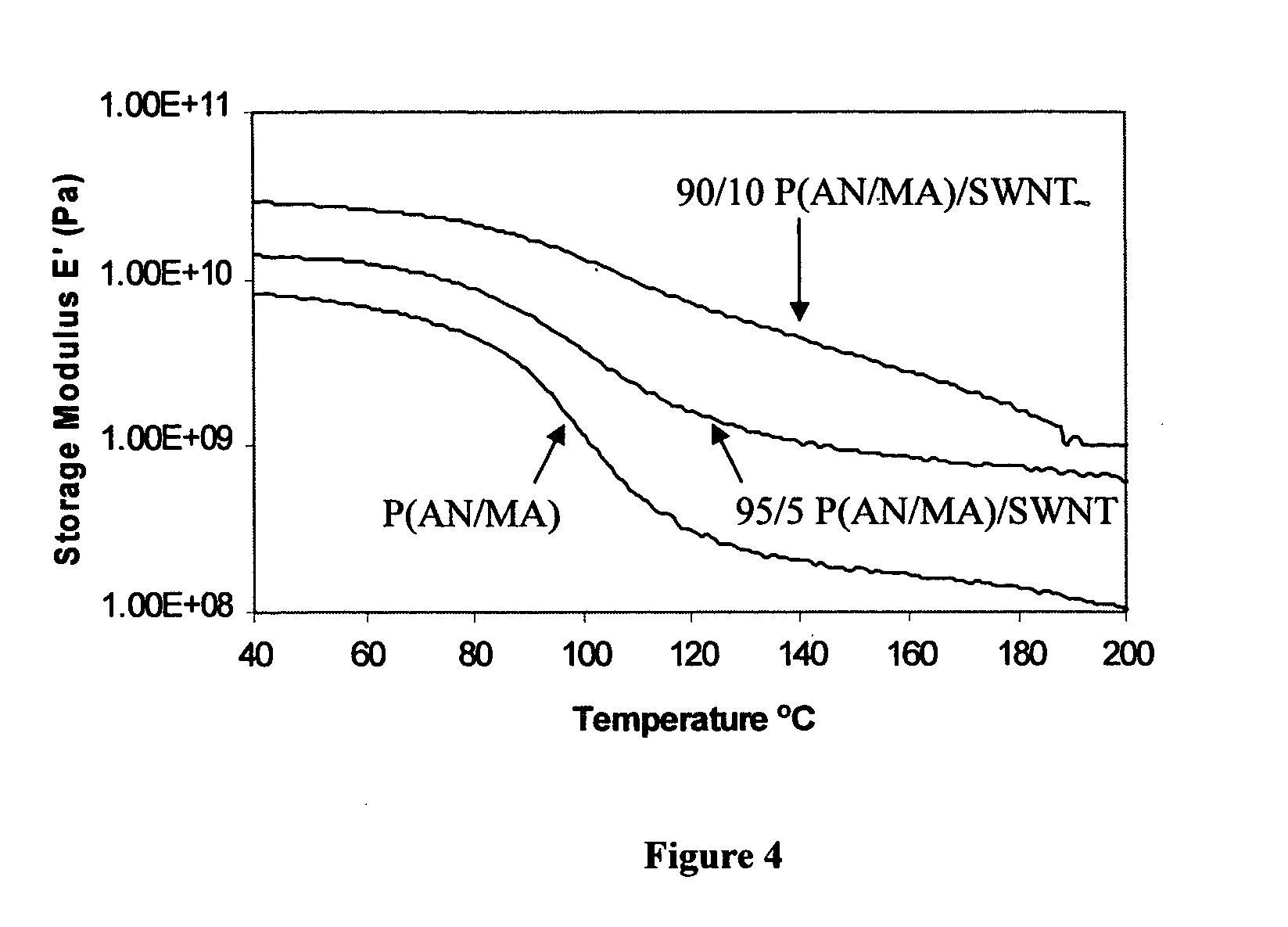
InactiveUS20050100501A1Good orientationIncrease modulusMaterial nanotechnologyElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureVitrificationPolymer science
The present invention relates to a high modulus macroscopic fiber comprising single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNT) and an acrylonitrile-containing polymer. In one embodiment, the macroscopic fiber is a drawn fiber having a cross-sectional dimension of at least 1 micron. In another embodiment, the acrylonitrile polymer-SWNT composite fiber is made by dispersing SWNT in a solvent, such as dimethyl formamide or dimethyl acetamide, admixing an acrylonitrile-based polymer to form a generally optically homogeneous polyacrylonitrile polymer-SWNT dope, spinning the dope into a fiber, drawing and drying the fiber. Polyacrylonitrile / SWNT composite macroscopic fibers have substantially higher modulus and reduced shrinkage versus a polymer fiber without SWNT. A polyacrylonitrile / SWNT fiber containing 10 wt % SWNT showed over 100% increase in tensile modulus and significantly reduced thermal shrinkage compared to a control fiber without SWNT. With 10 wt % SWNT, the glass transition temperature of the polymer increased by more than 40° C.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
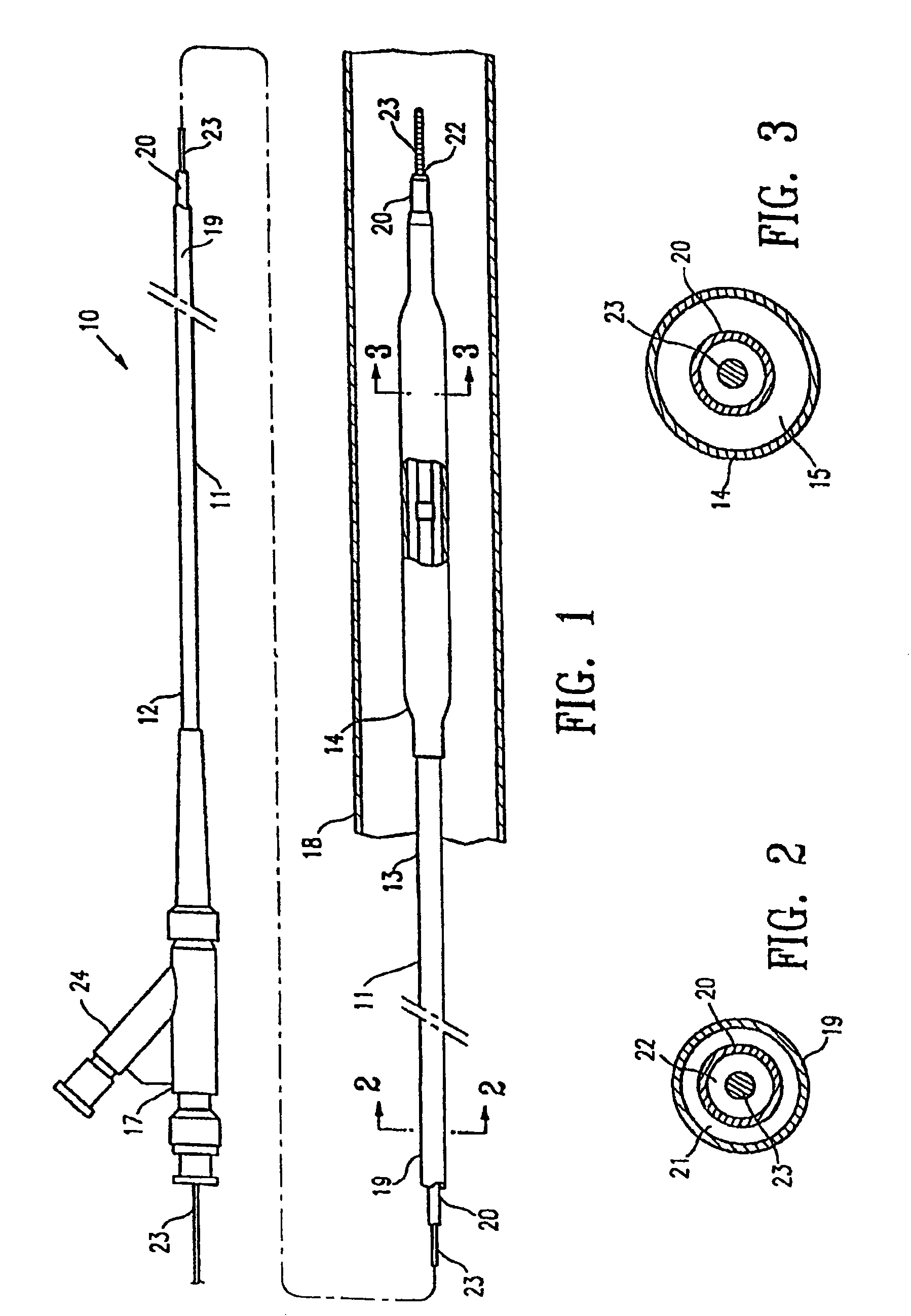
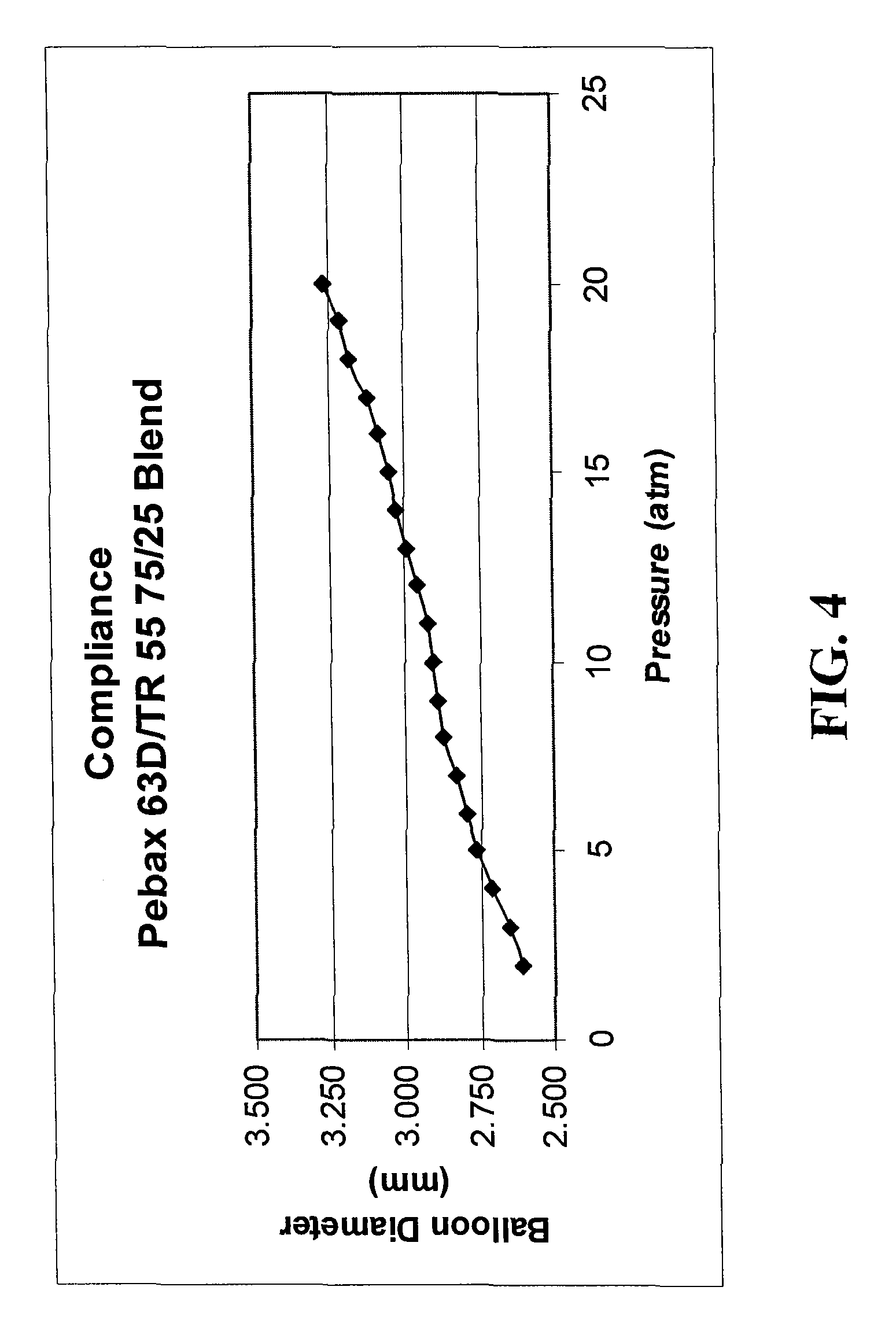
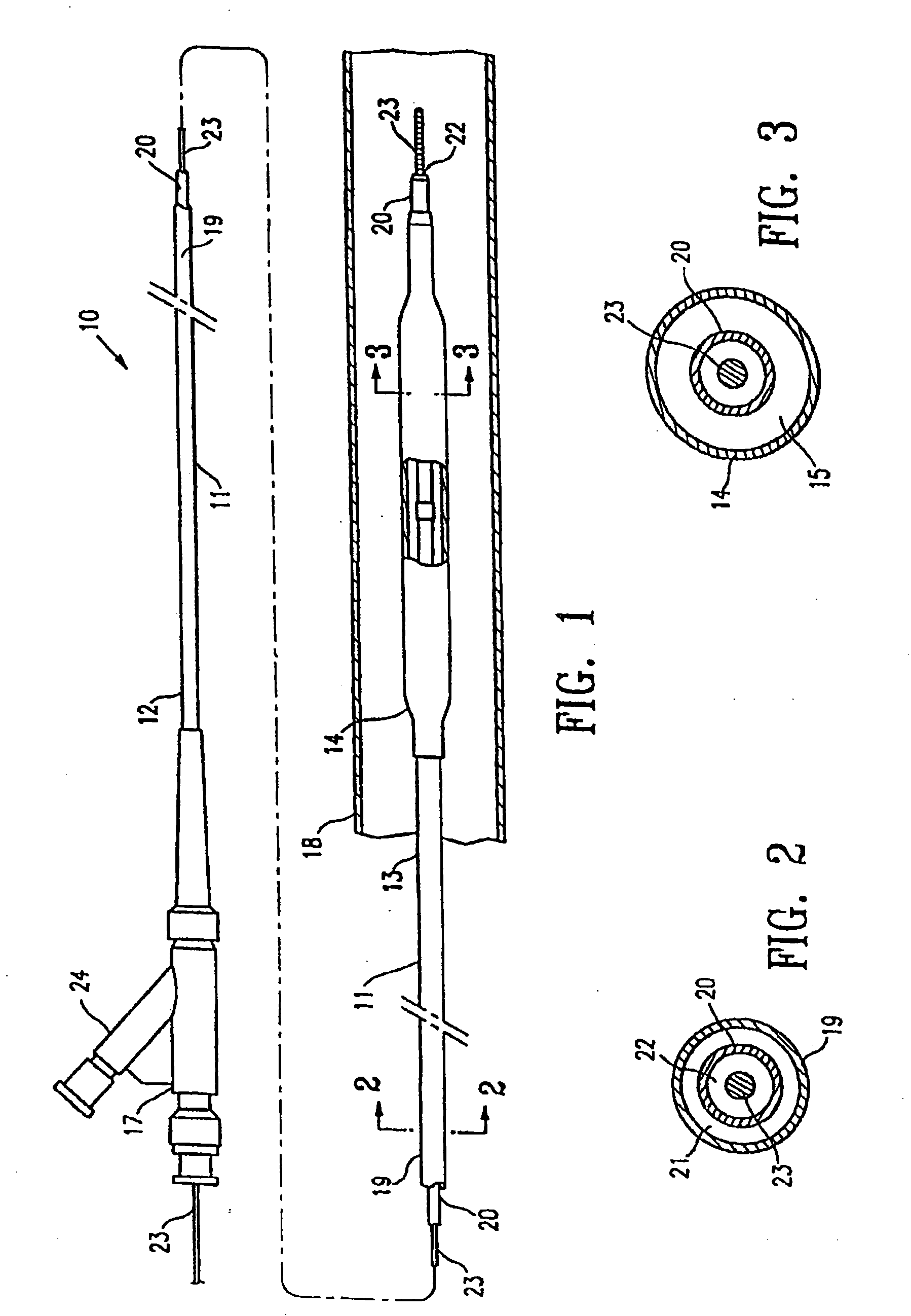
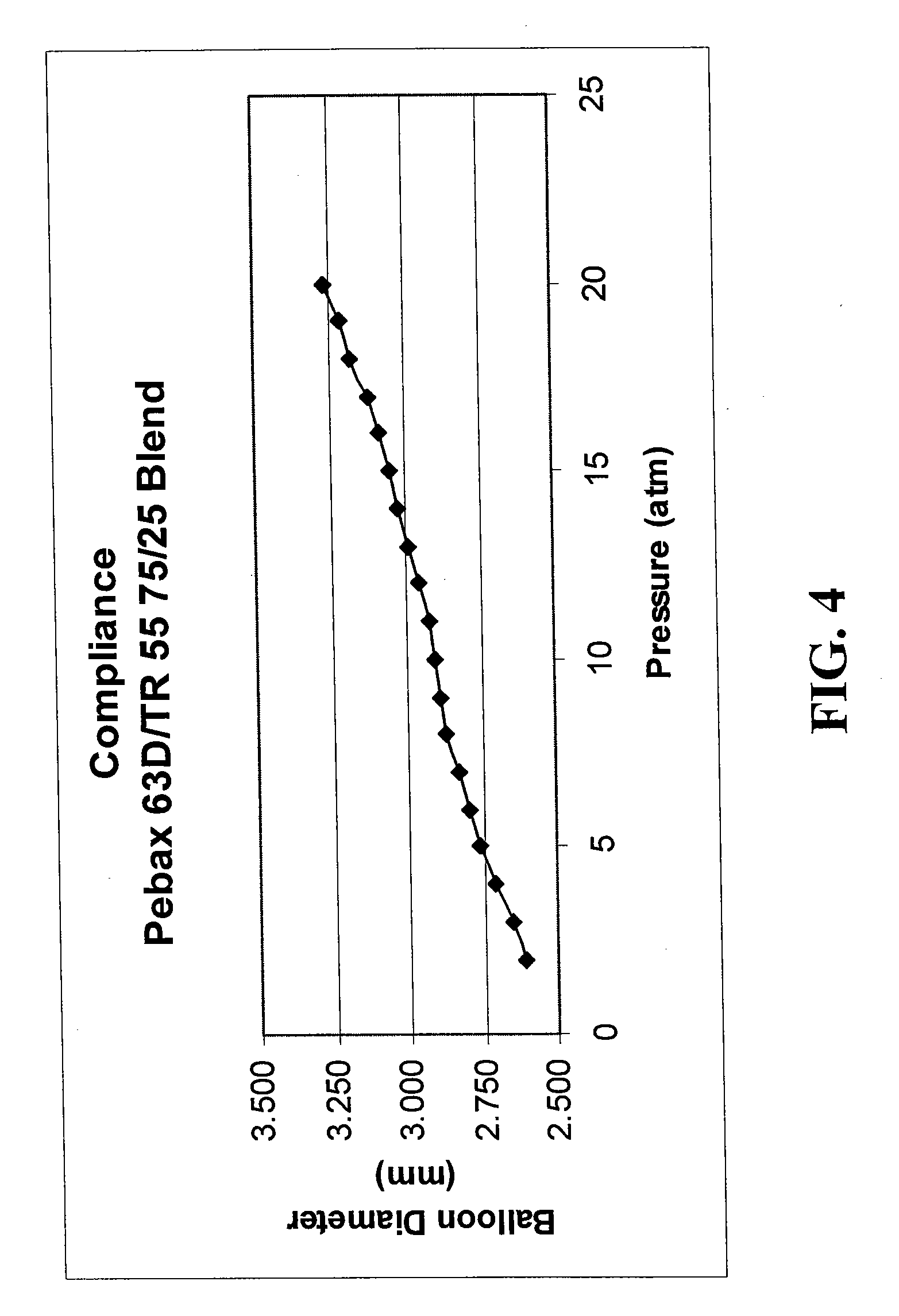
Robust multi-layer balloon
A multilayer balloon catheter is formed to have an inner layer and an outer layer, where the outer layer is adapted to resist shredding and premature rupture. The outer layer is formed of a material having a glass transition temperature that is lower than the transition or melting temperature of the inner layer. By forming the balloon on a mold at a temperature between the glass transition temperature of the outer layer and the glass transition or melting temperature of the inner layer, the outer layer will undergo a thermal relaxation that will alleviate some of the axial orientation of the polymer chains that develop during the formation of the multilayer balloon. This relaxation leads to a resistance to shredding when the balloon is expanded during operation.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
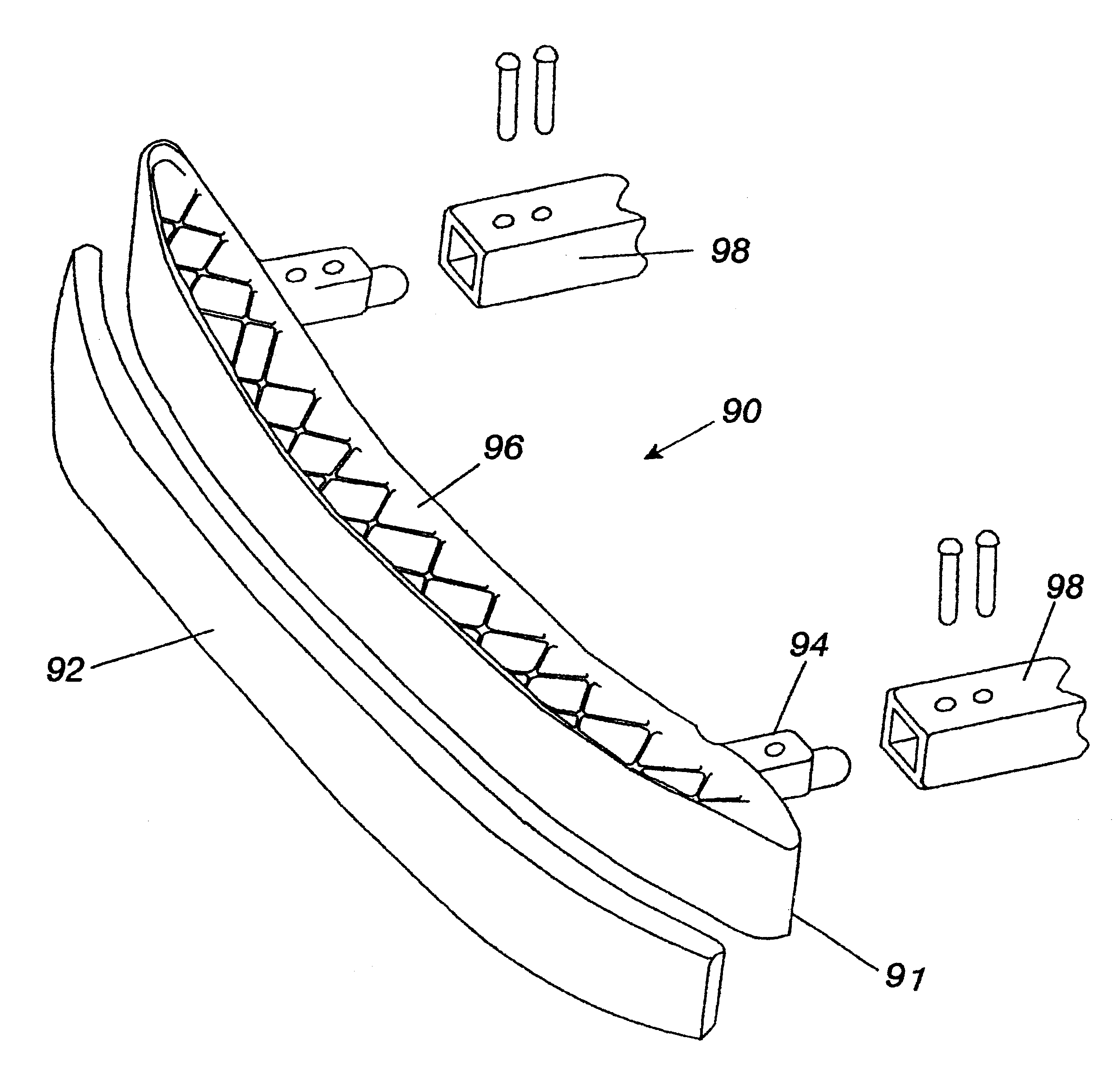
I-Section automotive bumper formed from mineral-filled glass mat thermoplastic (GMT) composite
InactiveUS6286879B1Improve flow characteristicsIncrease modulusBumpersCompression moldingShell molding
The invention is a fiber reinforced thermoplastic automotive bumper wherein the reduced fiber additions consist of a long, chopped glass mat with the addition of mineral fillers such as mica, talc or clay. The modified thermoplastic is used to produce I-section bumpers. The improved reinforced thermoplastic material has favorable flow characteristics which enable the material to substantially fill the deep ribs and mounting stay structures used in I-section bumpers during compression molding while improving the modulus or cross-face stiffness of the finished part. For the first time, improved flow characteristics during molding permit the material to flow evenly into small ribs, bosses and other features. The invention makes it possible to increase part integration, molding pencil braces, fascia supports, mounting holes and mounting stays. The front surface of the bumper may be covered with a conformal energy absorber made of plastic foarn. Moreover, the absorber serves to mount appearance fascia. The result is a cost-reduced, weight-reduced bumper with improved impact resistance.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Clay/organic chemical compositions useful as additives to polymer, plastic and resin matrices to produce nanocomposites and nanocomposites containing such compositions
InactiveUS6380295B1Good dispersionImprove structural strengthCoatingsSilicon compoundsAmmonium compoundsWater dispersible
This invention is of a hybrid organoclay that consists of an organic chemical / phyllosilicate clay intercalate that has been ion-exchanged with quaternary ammonium compounds. Since this hybrid organoclay is hydrophobic, it can be washed in water to remove reaction salts and excess water soluble or water dispersible polymers to give a clean product via inexpensive means such as filtration. This allows a better dispersing composition to be prepared without the difficulties of isolation presented by prior art which uses energy intensive means to remove the bulk of the water from the final product and cannot be easily washed. In one aspect, the present invention provides a solid clay / chemical composition that comprises: (a) one or more smectite clays, (b) a quaternary ammonium compound which reacts via an ion exchange mechanism with the smectite clay, and (c) one or more non-anionic organic materials that intercalate with the clay. The invention is useful both as an ingredient to form nanocomposites and as a rheological additive.
Owner:ELEMENTIS SPECIALTIES INC
Carbon nanofiber-dispersed resin fiber-reinforced composite material
ActiveUS7151129B2Improve balanceHigh strengthMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsSingle fiberNanofiber
The resin in a fiber-reinforced resin material that uses a single fiber reinforcing ply or a number of fiber reinforcing plies for reinforcing the resin material is reinforced by dispersing carbon nanofibers therein, whereby a fiber-reinforced composite resin material having improved strength such as compressive strength is provided. In a carbon nanofiber-dispersed resin fiber-reinforced composite material 1, an uncured resin 4 having carbon nanofibers 5 dispersed therein is impregnated into a number of fiber reinforcing plies 2a laid one upon another. Upon curing the resin 4, the strength of the matrix 3 itself is increased through the carbon nanofibers 5 dispersed in the resin 4. Moreover, the fiber reinforcement 2 and the resin 4 are joined together strongly by the carbon nanofibers 5, and hence the strength of the composite material, for example the compressive strength, which hitherto has been dependent on the strength of the resin 4 only, is improved.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY +1
Polymer Compositions, Method of Manufacture, and Articles Formed Therefrom
ActiveUS20080242789A1Improve ductilityIncrease modulusPigmenting treatmentCeramic shaping apparatusHeat deflection temperaturePolyester
A composition comprises, based on the total weight of the composition, from 10 to 80 wt. % of a polyester; from 10 to 80 wt. % of a polycarbonate; from 0 to 20 wt. % of an impact modifier; from 1 to less than 25 wt. % of a reinforcing filler; from 0.1 to less than 2.5 wt. % of a fibrillated fluoropolymer; from 0 to 5 wt. % of an additive selected from the group consisting of antioxidants, mold release agents, colorants, quenchers, stabilizers, and combinations thereof, wherein the composition has a heat deflection temperature of at least 110° C., measured in accordance with to ASTM D648 on 3.2 mm thick molded bars at 0.455 MPa.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Method of stimulating oil and gas wells using deformable proppants
ActiveUS20060151170A1Minimizing proppant pack damageImproves retained proppant pack permeabilityFluid removalDrilling compositionFracturing fluidUltimate tensile strength
A method of fracturing using deformable proppants minimizes proppant pack damage, without compromising the fracturing fluid's proppant transport properties during pumping, by use of deformable proppants. Selection of proppant is dependent upon the mechanical properties of the formation rock. The strength of the deformable proppant is dependent upon the modulus of the formation rock being treated such that the proppant is capable of providing, at the very least, a minimum level of conductivity in in-situ stress environments. The maximum elastic modulus of the deformable proppant is less than the minimum modulus of the formation rock which is being treated. The method is particularly applicable in fracturing operations of subterranean reservoirs such as those comprised primarily of coal, chalk, limestone, dolomite, shale, siltstone, diatomite, etc.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
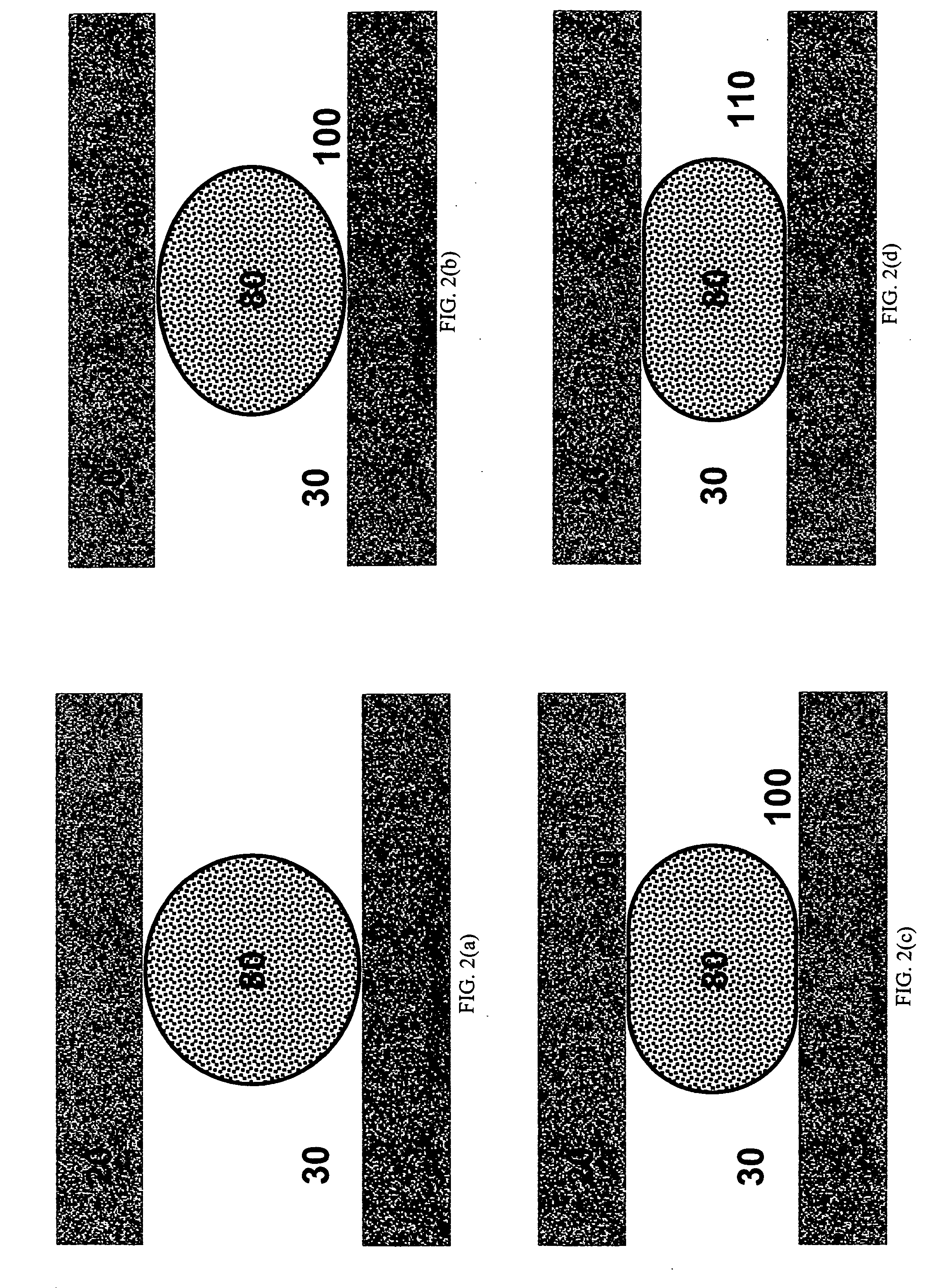
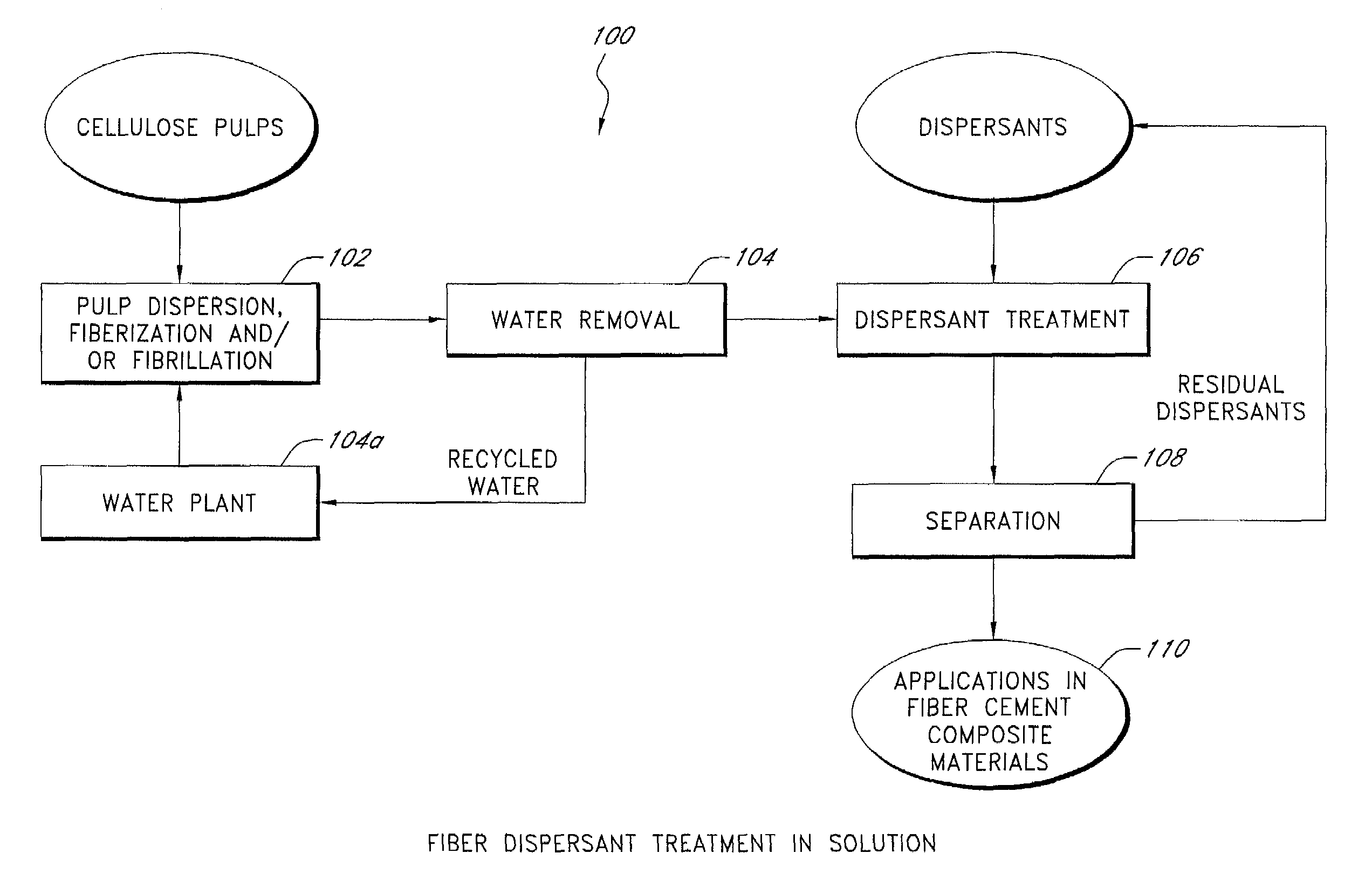
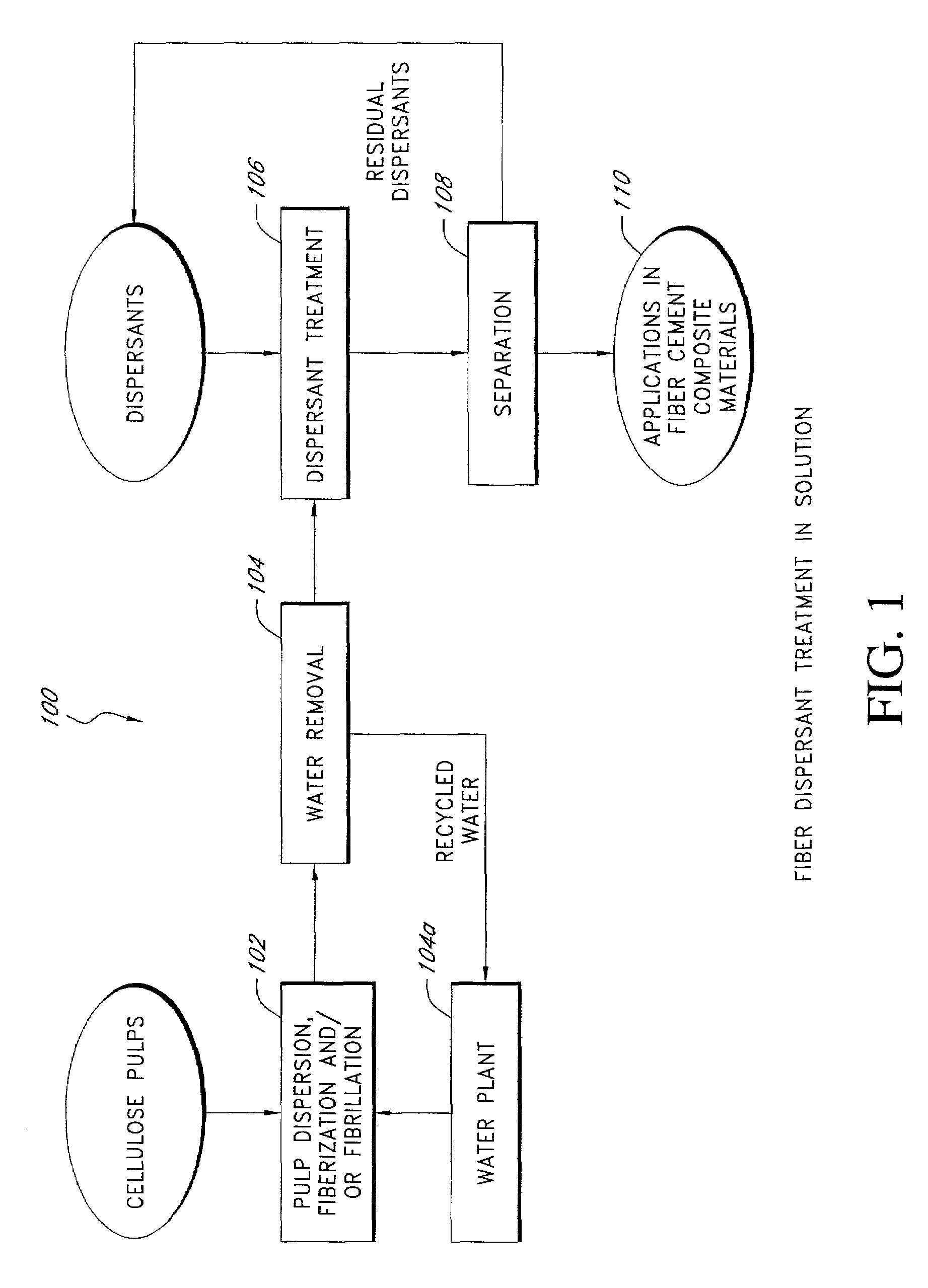
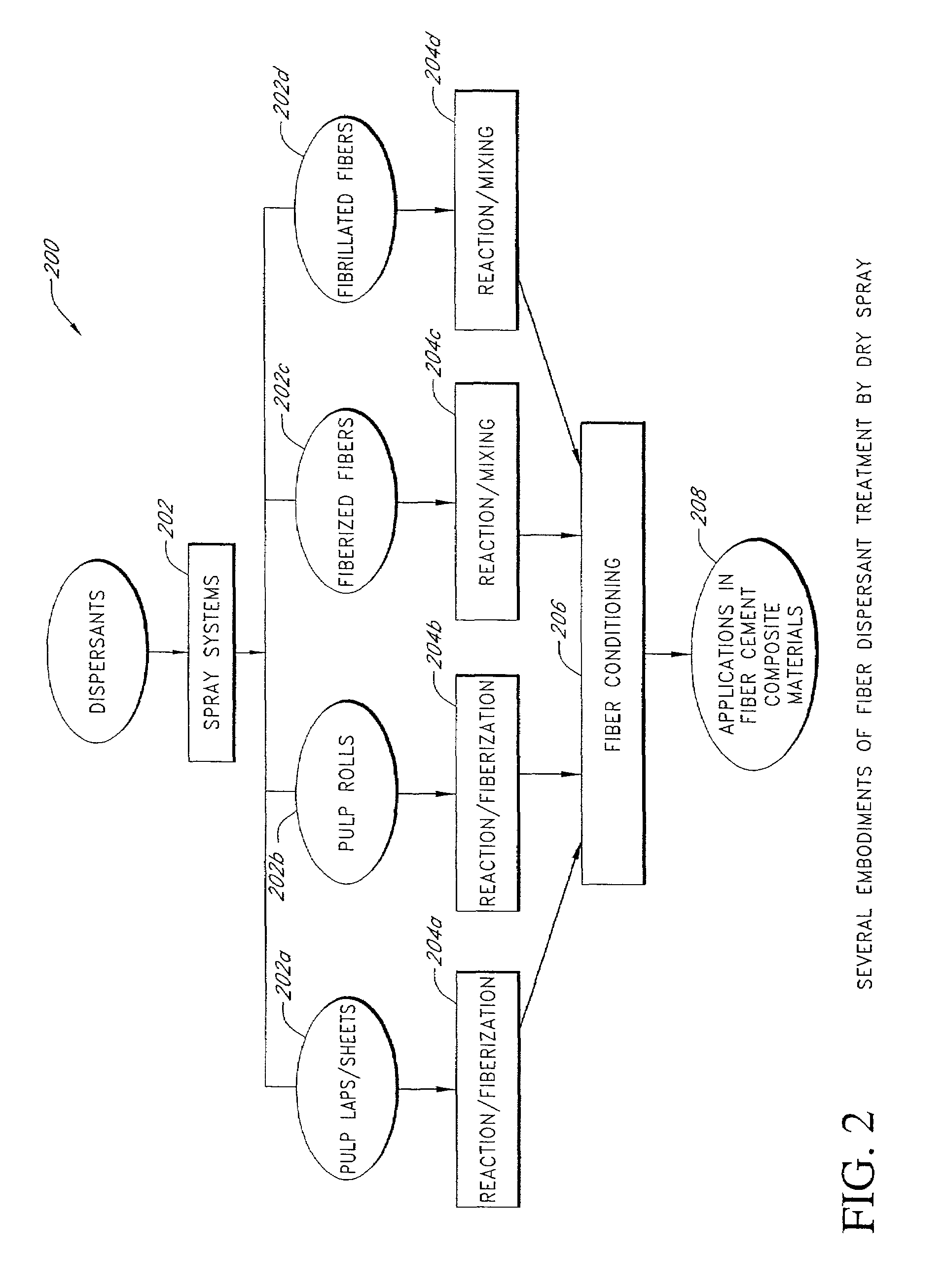
Fiber reinforced cement composite materials using chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility
InactiveUS7344593B2Improve material propertyIncrease modulusPulp properties modificationSolid waste managementBuilding materialFibre reinforcement
A fiber-reinforced building material in one embodiment incorporates cellulose fibers that are chemically treated with a dispersant to impart improved dispersibility to the fibers. The fibers are treated with a dispersant which deactivates the hydroxyl sites of the fiber surfaces and in some cases, making the fiber surface more hydrophobic. The dispersant inhibits the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose fiber surface from bonding with hydroxyl groups of other fibers and from bonding with hydroxyl groups of the same fiber, thereby significantly reducing inter-fiber and intra-fiber hydrogen bonding. The treated fibers can be readily dispersed and uniformly distributed throughout a mixture without re-clustering or reclumping once the mechanical mixing action stops. The chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility improve the fiber distribution and reinforcing efficiency, which in turn improves key physical and mechanical properties of the material such as the modulus of rupture, z-direction tensile strength, and toughness, and surface finishes. With improved fiber reinforcing efficiency, less dosage of fiber is needed to achieve the required physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH
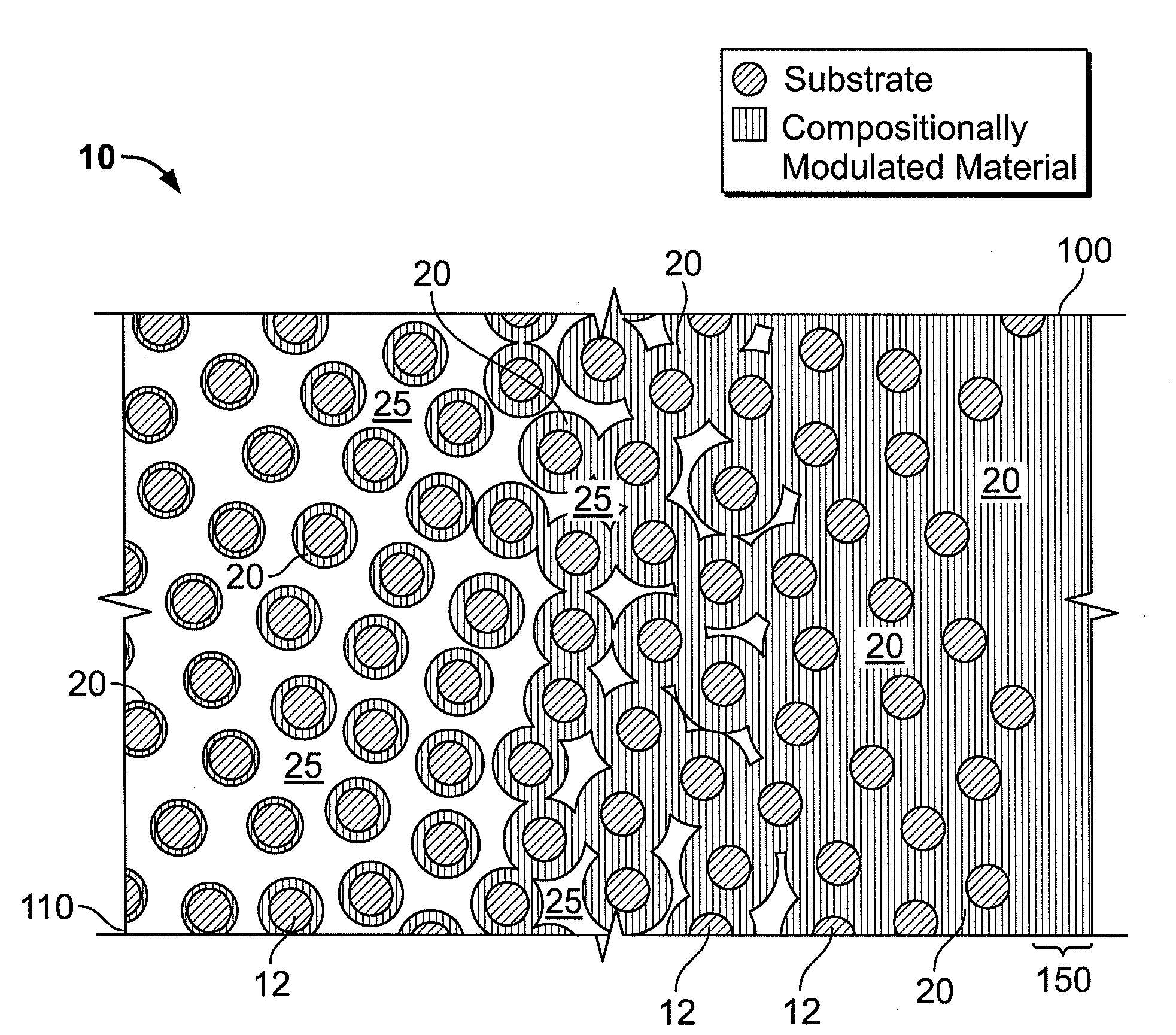
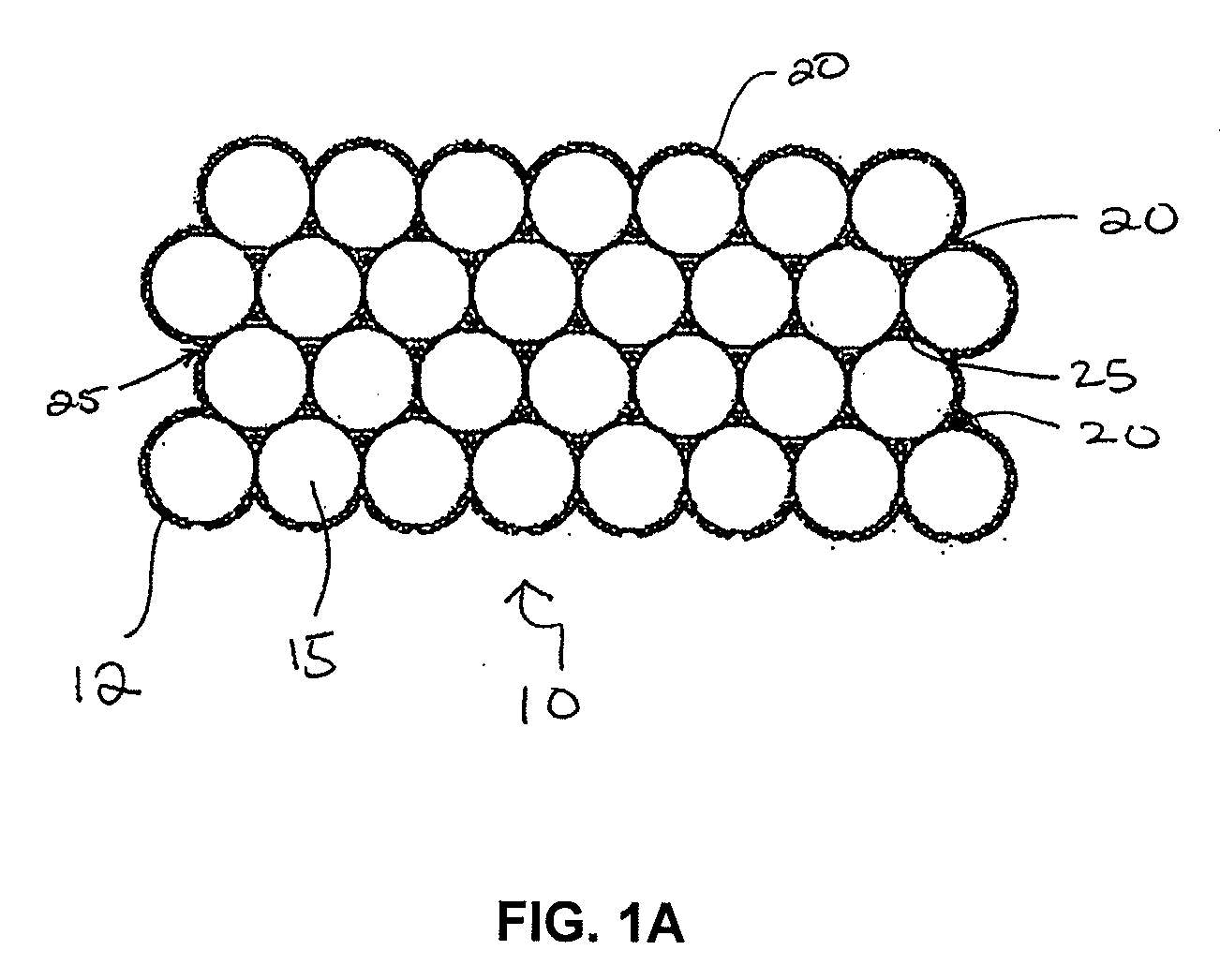
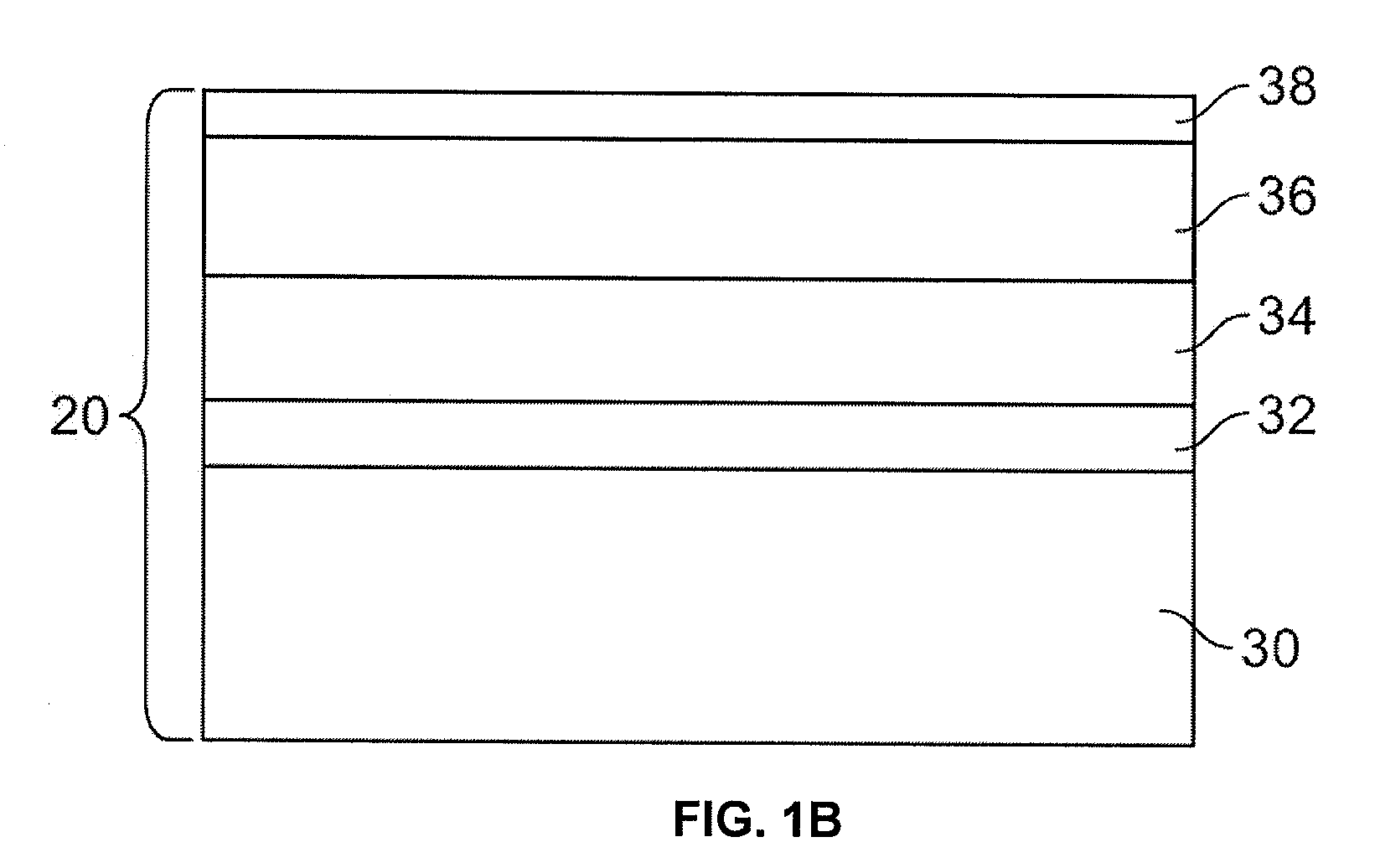
Compositionally modulated composite materials and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20090130425A1Easy to depositImprove material performanceArmourElectrolytic coatingsPorous substrateSports equipment
A light-weight composite material with enhanced structural characteristics includes, in one embodiment, a compositionally modulated nanolaminate coating electrically deposited into an open, accessible void structure of a porous substrate. As a result of including a nanolaminate within the void structure, the composite can include a greater amount of nanolaminate material per unit volume than can be achieved by depositing a nanolaminate material solely on a two-dimensional surface. In addition, the nanolaminate material as well as other material electrodeposited to form the composite is compositionally modulated so that discontinuities between layers are minimized and potentially eliminated. The light-weight but structurally enhanced composite material can be used in a number of different applications including, but not limited to, ballistic applications (e.g., armor panels or tank panels), automotive protection applications (e.g., car door panels, racing shells) and sporting equipment applications (e.g., golf club shafts and tennis racket frames).
Owner:MODUMETAL LLC
Bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material and a method for manufacturing the composite
InactiveUS20100121463A1Increase strength valueIncrease toughness valueSurgeryProsthesisFiberPolymer chemistry
The present invention relates to a bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material for surgical musculoskeletal applications comprising a bioabsorbable polymeric matrix material which is reinforced with bioabsorbable polymeric fibers and bioabsorbable ceramic fibers. The surgical bioabsorbable polymeric matrix material is reinforced with the bioabsorbable polymeric fibers and the bioabsorbable ceramic fibers from which at least a portion is longer than 150 μm. The invention also relates to a method for manufacturing a bioabsorbable and bioactive composite material.
Owner:BIORETEC
High-strength discontinuously-reinforced titanium matrix composites and method for manufacturing the same
The invention relates to manufacturing the flat or shaped titanium matrix composite articles having improved mechanical properties such as lightweight plates, sheets for aircraft and automotive applications, heat-sinking lightweight electronic substrates, armor plates, etc. High-strength discontinuously-reinforced titanium metal matrix composite (TMMC) comprises (a) titanium matrix or titanium alloy as a major component, (b) ceramic and / or ≦50 vol. % intermetallic hard particles dispersed in matrix, (c) complex carbide- and / or boride particles at least partially soluble in matrix at sintering or forging temperatures such as ≦50 vol. % AlV2C, AlTi2Si3, AlTi6Si3, VB2, TiVSi2, TiVB4, Ti2AlC, AlCr2C, TiAlV2, V2C, VSi2, Ta3B4, NbTiB4, Al3U2C3 dispersed in matrix. Method for manufacturing these TMMC materials is disclosed. Sintered TMMC density exceeds 98% and closed discontinuous porosity allows performing hot deformation in air without encapsulating. Near-full density near-net shape TMMC parts with acceptable mechanical properties were manufactured without hot deformation.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Polymer Compositions, Method of Manufacture, and Articles Formed Therefrom
ActiveUS20080246181A1Improve ductilityIncrease modulusMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPolytetramethylene terephthalateHeat deflection temperature
A composition comprises, based on the total weight of the composition: from 10 to 80 wt. % of a modified polybutylene terephthalate copolymer that (1) is derived from polyethylene terephthalate component selected from the group consisting of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate copolymers and (2) has at least one residue derived from the polyethylene terephthalate component; from 10 to 80 wt. % of a polycarbonate; from 0 to 20 wt. % of an impact modifier; from 1 to less than 25 wt. % of a reinforcing filler; from 0.1 to less than 2.5 wt. % of a fibrillated fluoropolymer; from 0 to 5 wt. % of an additive selected from the group consisting of antioxidants, mold release agents, colorants, quenchers, stabilizers, and combinations thereof. The composition has a heat deflection temperature of at least 110° C., measured in accordance with to ASTM D648 on 3.2 mm thick molded bars at 0.455 MPa.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Lightweight glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic material
InactiveUS20090011210A1Improve flexural and tensile strength and modulus propertyReduce basis weightLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentFlexural strengthFiber
A glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic sheet material is provided in which certain properties, or combinations of properties, are improved relative to similar comparative sheet materials. The sheet material generally comprises a glass mat or glass fabric fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin in which the thermoplastic resin at least partially impregnates the glass mat or fabric. The thermoplastic sheet material contains about 15 wt. % to about 65 wt. % of the glass mat or fabric based on the weight of the thermoplastic sheet material and has a thickness in the range of about 0.4 mm to about 3.0 mm. By including glass mat or fabric and maintaining the sheet thickness in the aforementioned range, the present invention thermoplastic sheet material exhibits improved flexural and / or tensile strength and modulus properties at reduced basis weight compared to a comparative thermoplastic sheet materials. A method of providing the glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic sheet material having an improved combination of flexural strength and modulus and / or tensile strength and modulus properties is also described, in which a first layer of a first thermoplastic resin, a second layer of a second thermoplastic resin, and a layer of glass mat or glass fabric are provided; the first thermoplastic resin layer, the second thermoplastic resin layer and the glass mat or glass fabric layer are arranged such that the glass mat or glass fabric layer is interposed between the first and second thermoplastic resin layers; and heat and pressure are applied to substantially melt and compress the first thermoplastic resin and / or the second thermoplastic resin and to at least partially impregnate the glass mat or glass fabric layer with the molten first thermoplastic resin and / or the molten second thermoplastic resin.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Composite electrode and electrolytes comprising nanoparticles and resulting devices
ActiveUS8593714B2Reduce power consumptionImprove mechanical propertiesNon-linear opticsComposite electrodeNanoparticle
This invention discloses novel electrochromic devices and polymer actuator materials where nanoparticles are used to make composites. In particular, the said nanoparticles are wire shaped and disc shaped. These composites allow EC devices to be made with improved performance, particularly display devices could be made that consume low power and can be manufactured at low cost.
Owner:AJJER
Composition and process for the sealing of microcups in roll-to-roll display manufacturing
InactiveUS8361356B2Improve adhesionQuality improvementSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCrystallographyElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a novel sealing composition for the manufacture of an electrophoretic or liquid crystal display, and a sealing process using the composition. The composition allows electrophoretic or liquid crystal cells to be seamlessly sealed and the sealing layer free of any defects.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Ultrasound assisted continuous process for dispersion of nanofibers and nanotubes in polymers
InactiveUS20090275689A1High performanceReduce pressureSpecial tyresAuxillary shaping apparatusNanometreHigh performance polymer
The present invention relates to processes for producing high performance polymer composites via ultrasonic treatment after initial mixing. These high performance polymer composites made from a combination of polymer and nanofibers and / or nanotubes. The ultrasonic treating method of the disclosed allows a more highly dispersed polymer composite mixture which provides increased thermal, mechanical and electrical properties.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Robust catheter tubing
ActiveUS20100130926A1Great cohesionImprove complianceStentsBalloon catheterTransition temperatureMelting temperature
A multilayer balloon catheter is formed to have an inner layer and an outer layer, where the outer layer is adapted to resist shredding and premature rupture. The outer layer is formed of a material having a glass transition temperature that is lower than the transition or melting temperature of the inner layer. By forming the balloon on a mold at a temperature between the glass transition temperature of the outer layer and the glass transition or melting temperature of the inner layer, the outer layer will undergo a thermal relaxation that will alleviate some of the axial orientation of the polymer chains that develop during the formation of the multilayer balloon. This relaxation leads to a resistance to shredding when the balloon is expanded during operation.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Self-Assembling Biomimetic Hydrogels Having Bioadhesive Properties
ActiveUS20140056806A1Good biocompatibilityImprove hydrophilicityBiocideIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInjection siteBioadhesive
The disclosure relates to a composition that is liquid at a temperature below the body temperature of a mammal and that solidifies at or above the body temperature of the mammal. The composition includes a thermally-desolubilizable polymer interspersed with a polymeric component of extracellular matrix and an encapsulated form of an amine compound (preferably an aminated component of extracellular matrix) that is de-encapsulated in the body of the mammal. The polymeric component is able to form covalent bonds with amine moieties in the aminated component, in one or more tissues in the body of the mammal, or both. Upon injection of a liquid suspension of these components into the body of the mammal, the thermally-desolubilizable polymer condenses, entrapping the polymeric component. The polymeric component binds covalently with a tissue in the body, and the aminated component end-caps the remaining reactive moieties of the polymeric component, forming a matrix at the site of injection. The disclosure also relates to uses of such compositions for forming a matrix on or within the body of a mammal. The compositions have a variety of uses, such as as bioadhesives, as sealants for ruptured tissues, as drug or imaging agent depots, or as mechanical cushions.
Owner:ROWAN UNIVERSITY
Cook-in package with tight appearance
InactiveUS6562443B1Increase modulusImprove toughnessWrappers shrinkageLamination ancillary operationsPolyesterPolyamide
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
Interlayers Comprising Modified Fumed Silica
InactiveUS20070287786A1Improve adhesionGood effectPigmenting treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsPlasticizerMoisture resistance
The present invention includes polymer interlayers that are used in multiple layer glazing panels. Interlayers of the present invention comprise a thermoplastic polymer, a plasticizer, and a fumed silica that has been modified to impart hydrophobic character. Interlayers incorporating such components have improved tensile modulus, moisture resistance, creep performance, anticorrosion effect, glass adhesion, and are well suited to a variety of applications, including, but not limited to, acoustic applications.
Owner:SOLUTIA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com