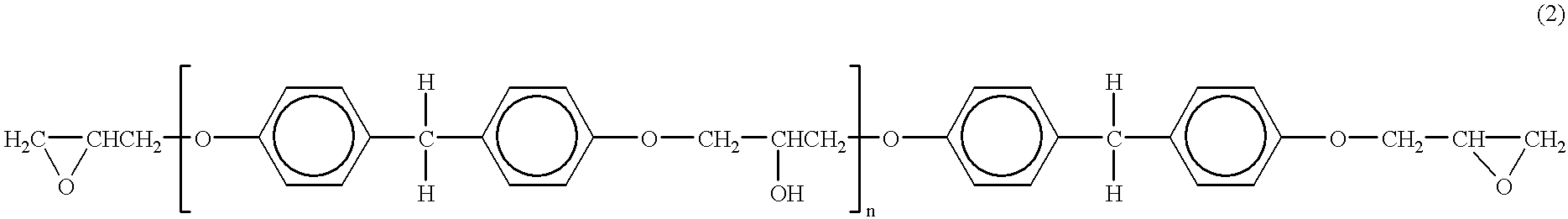
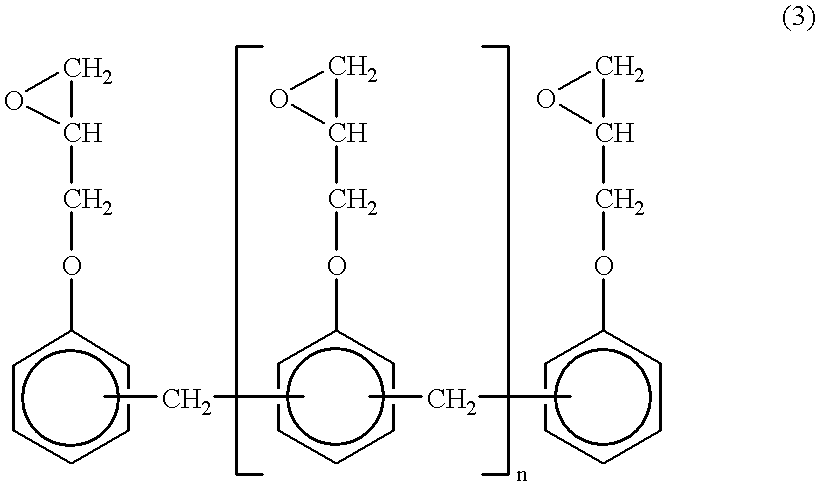
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2687 results about "Fibre reinforcement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
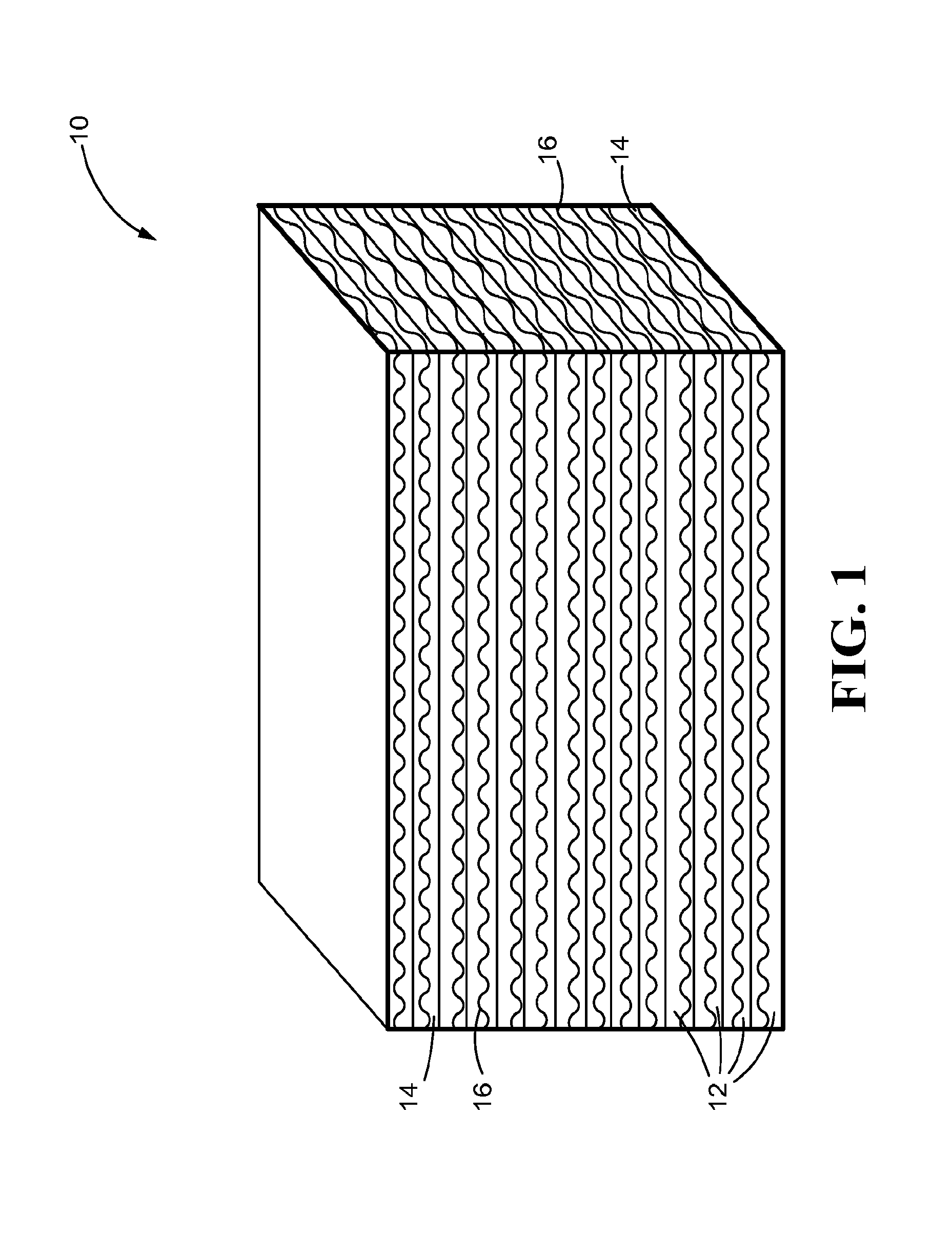
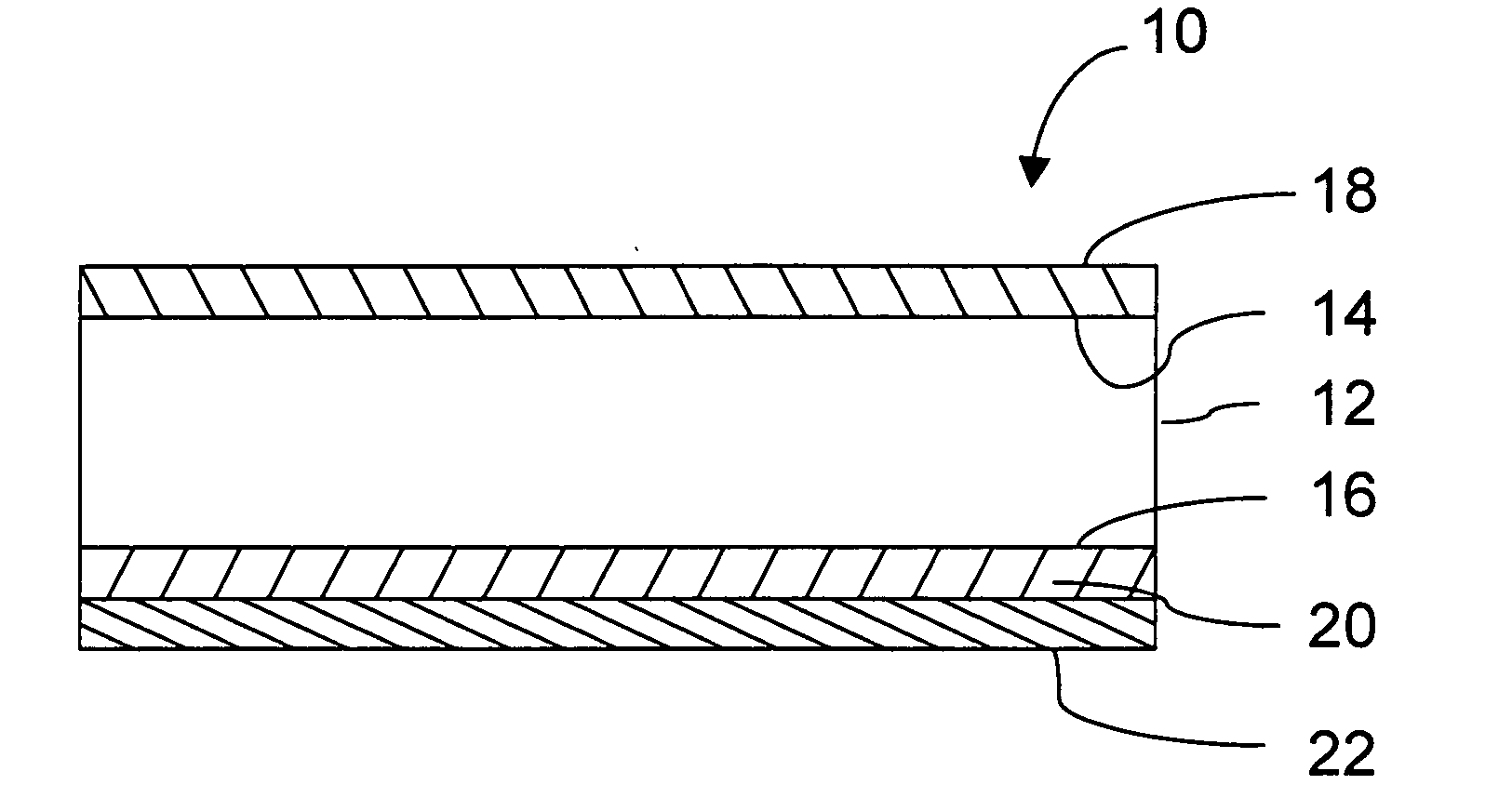
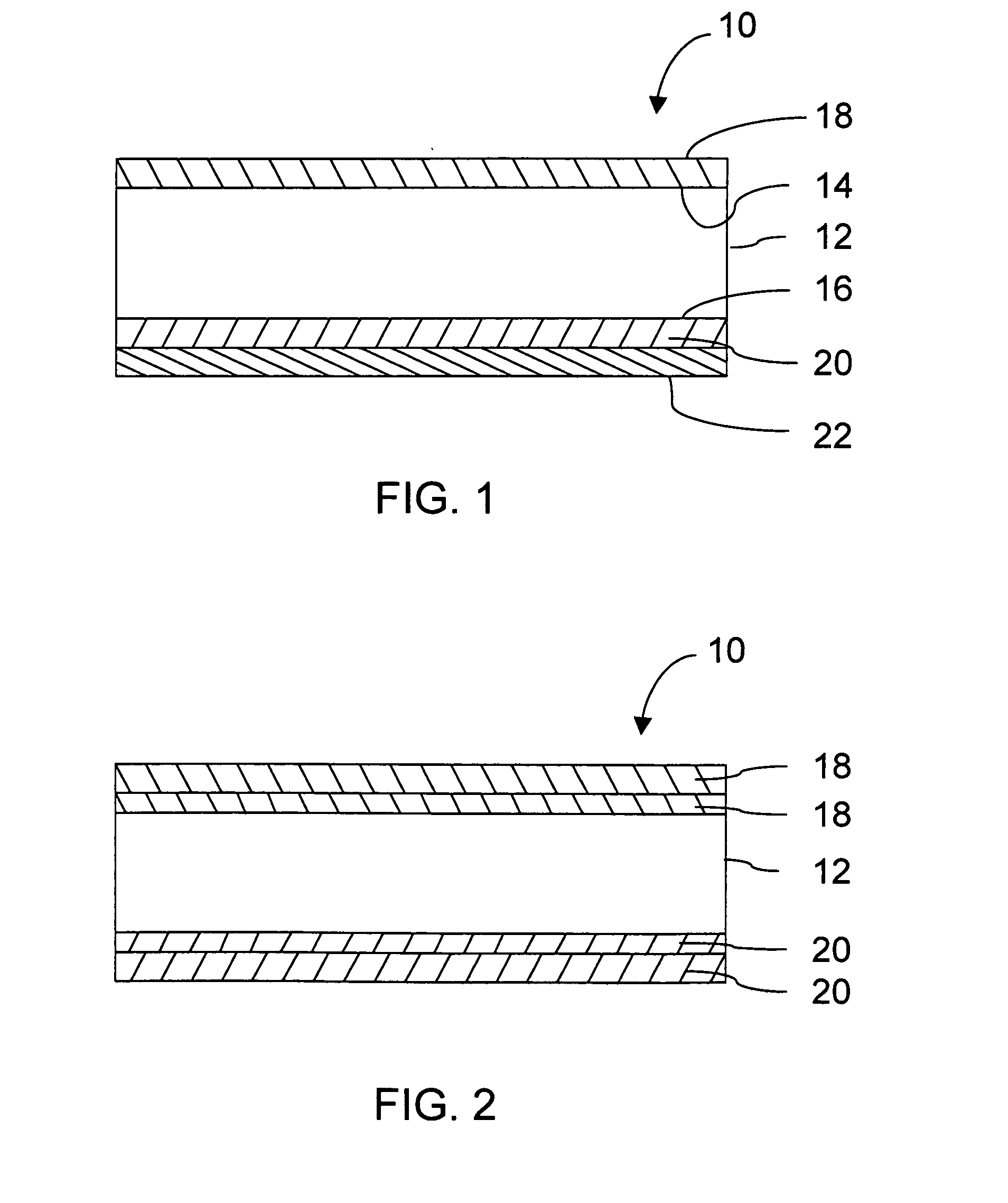
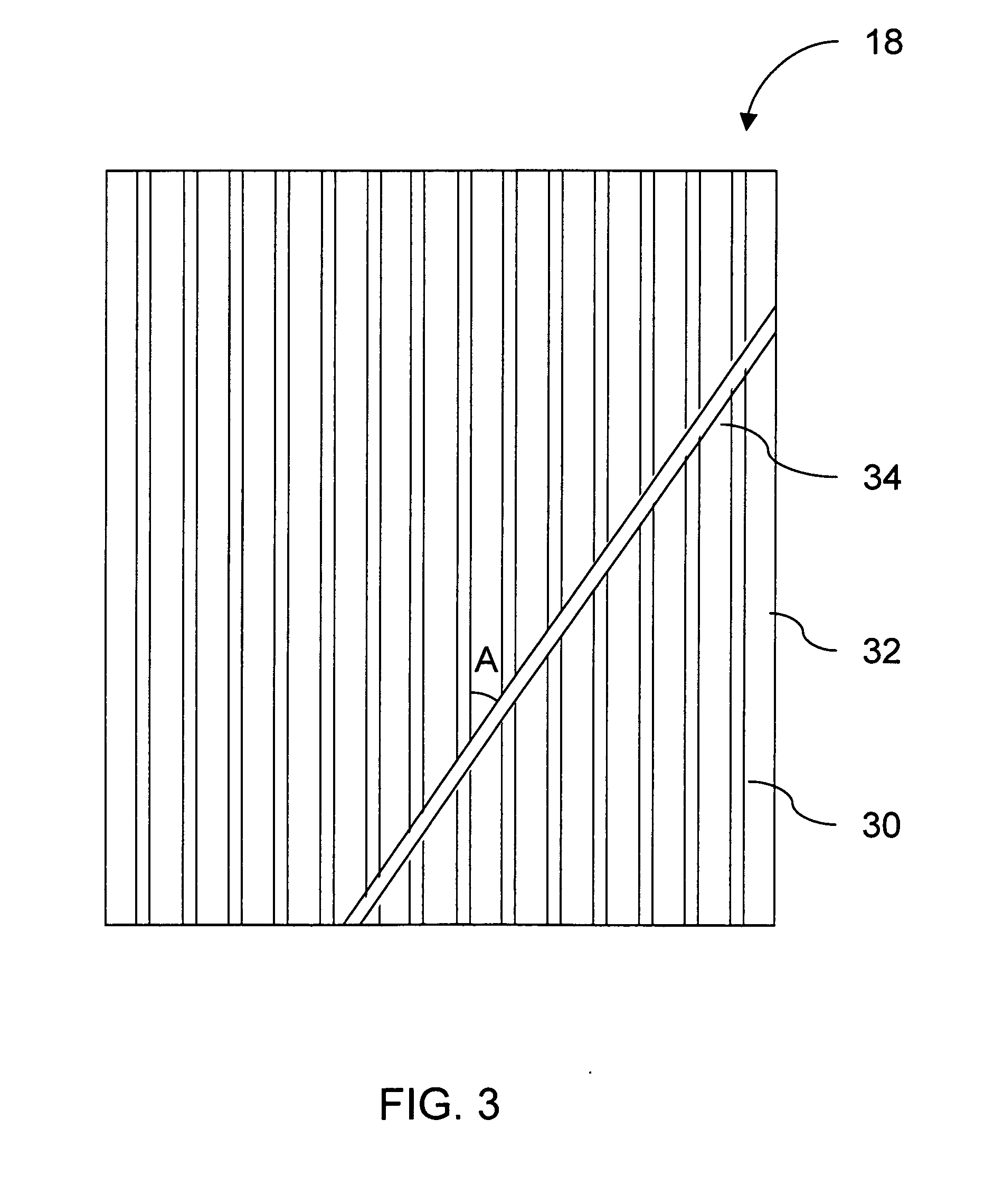
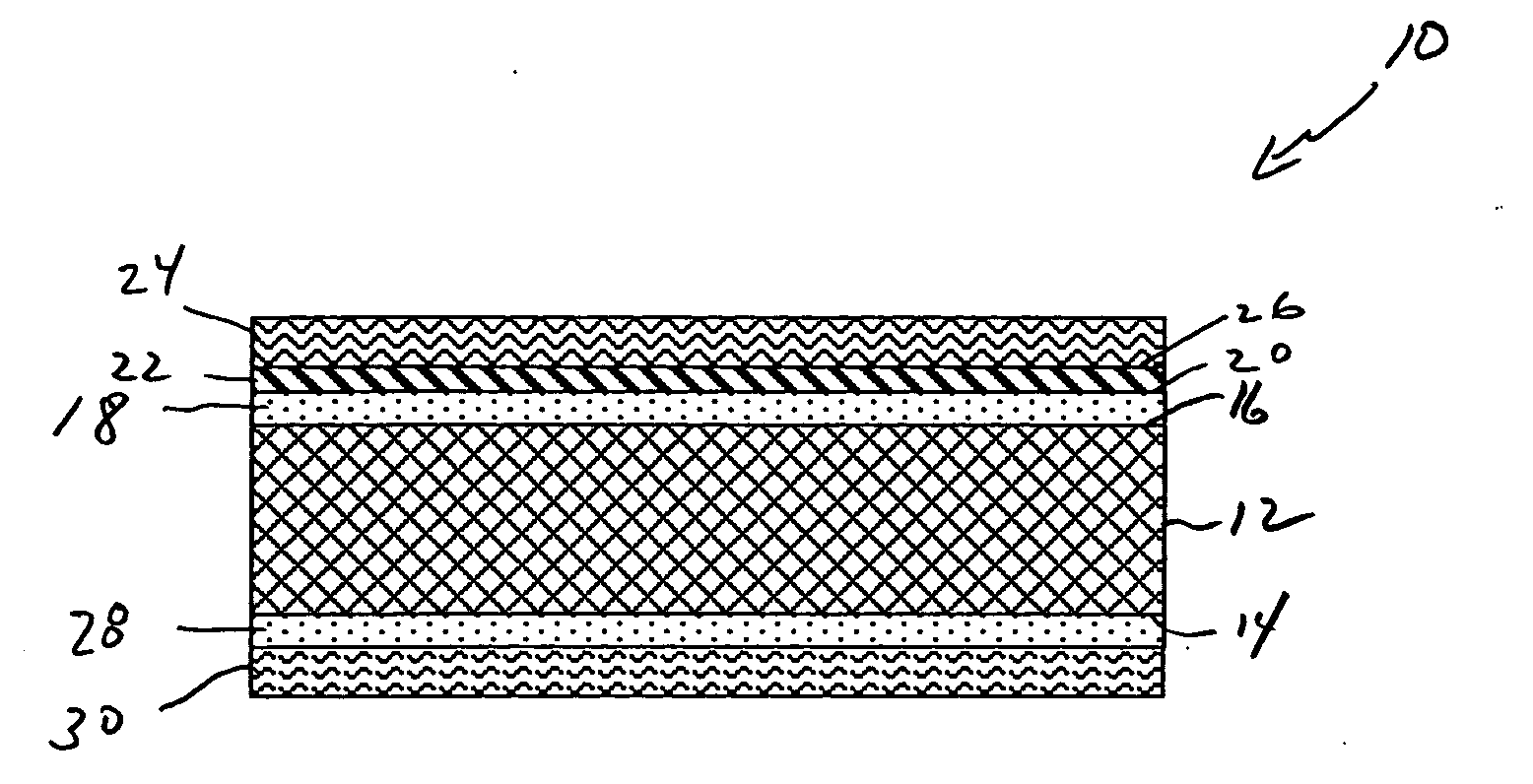
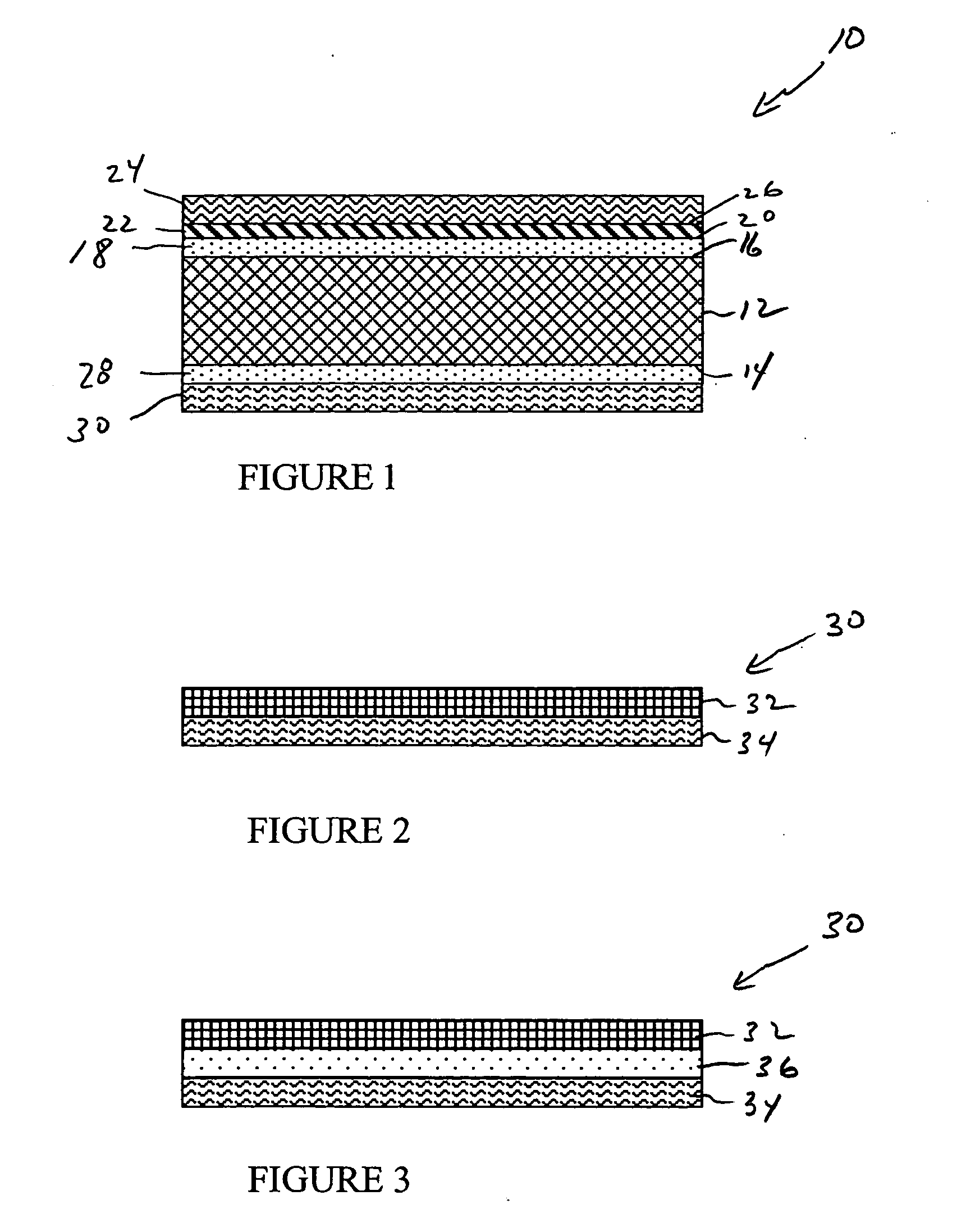
Reinforcement fibers are designed for specific and unique applications, ranging from micro synthetic fibers to reduce shrinkage and settlement cracking formed when concrete is still in the plastic state, to macro synthetic fibers as an alternative to traditional steel reinforcement for secondary reinforcement applicarions.
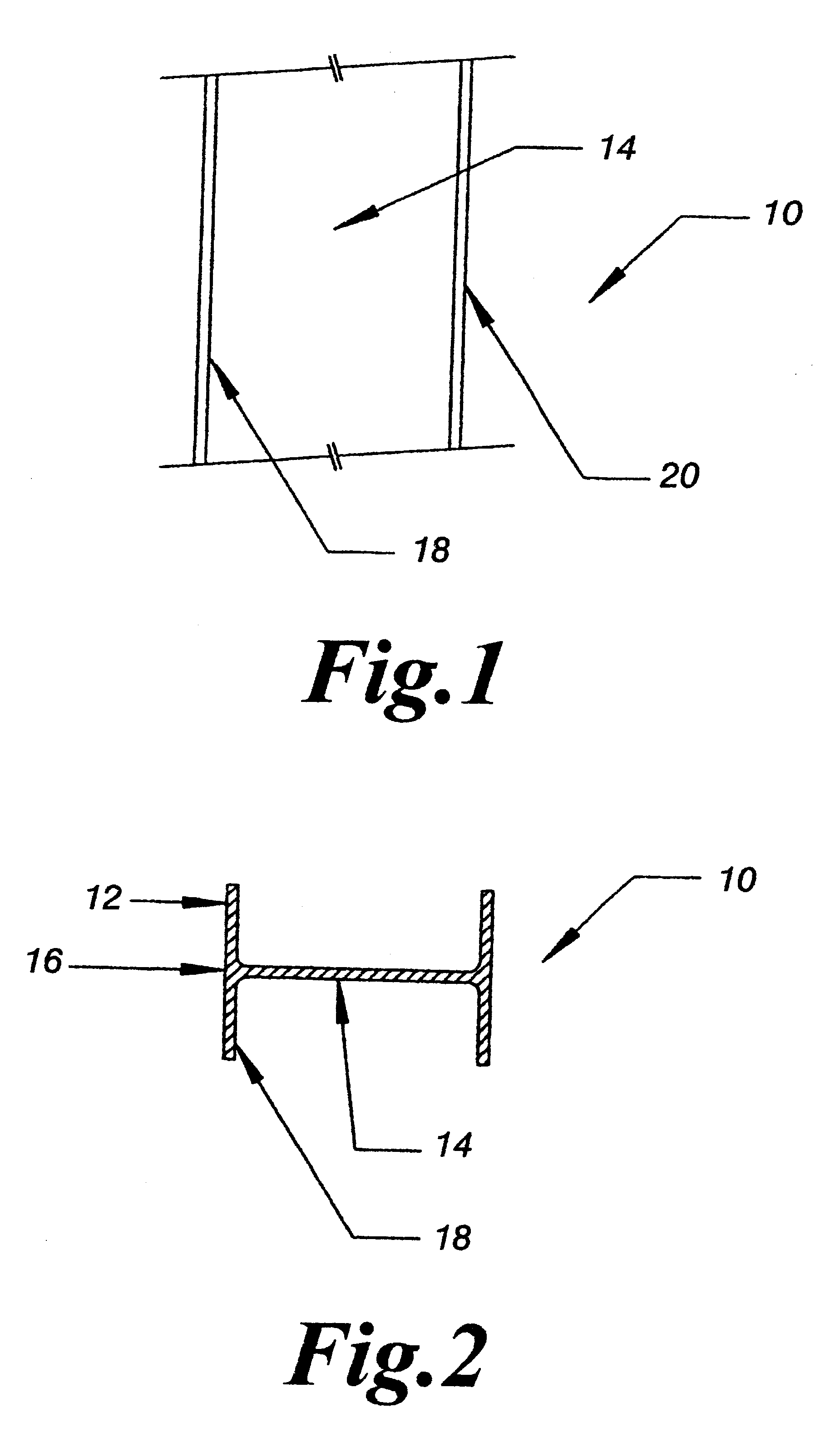
Proppants with fiber reinforced resin coatings
InactiveUS6528157B1High compressive strengthWithstanding stressCeramic layered productsDrilling compositionParticulatesResin coating
Coated particles made of particulate substrates having a coating of resin and fibrous material are provided for use in subterranean formations. The coated substrate particles are proppants useful to prop open subterranean formation fractures. The coated substrate particles are also useful for sand control, that is, acting as a filter or screen to prevent backwards flow of sand, other proppants or subterranean formation particles. Methods of making the coated particles are also disclosed.
Owner:HEXION INC
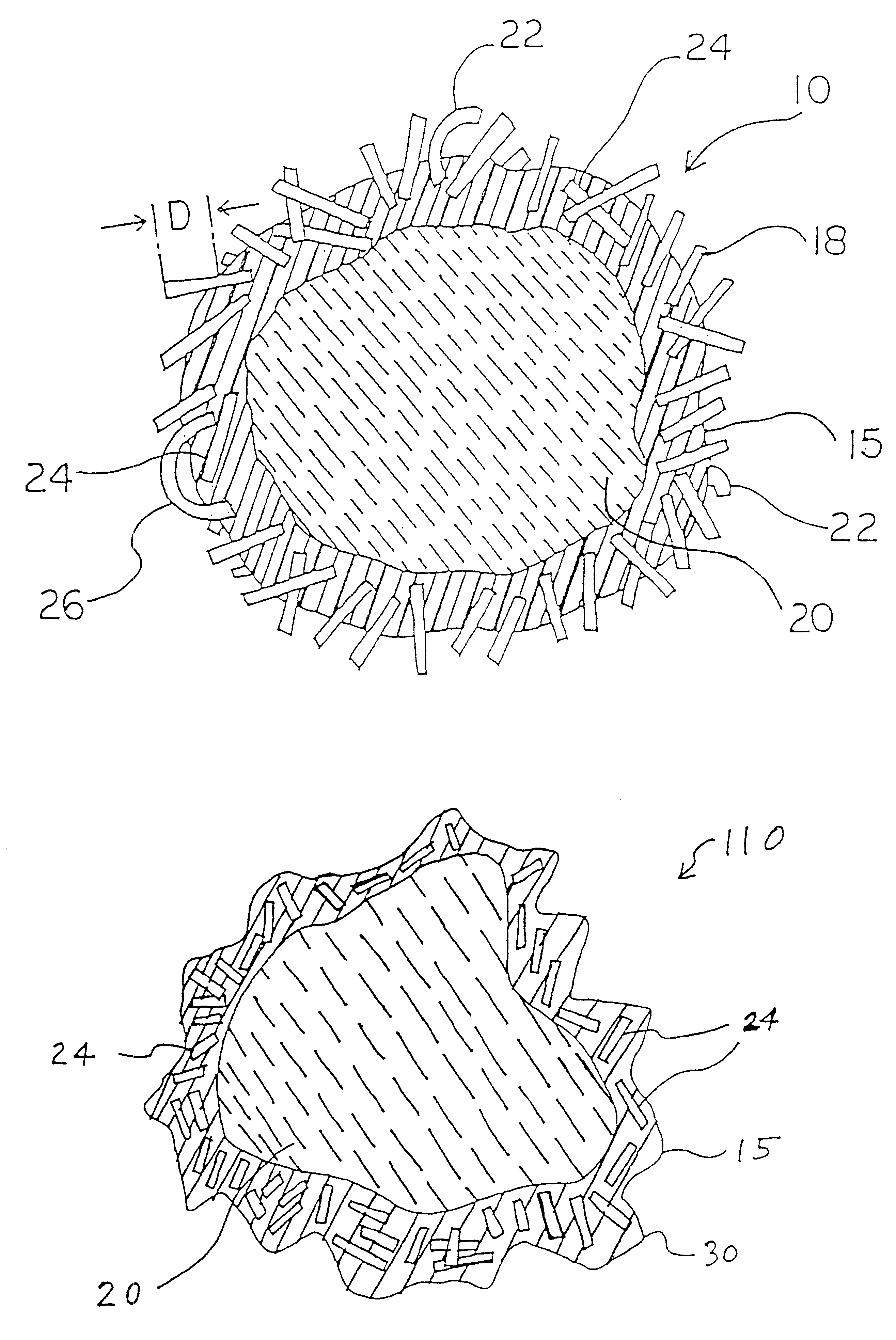
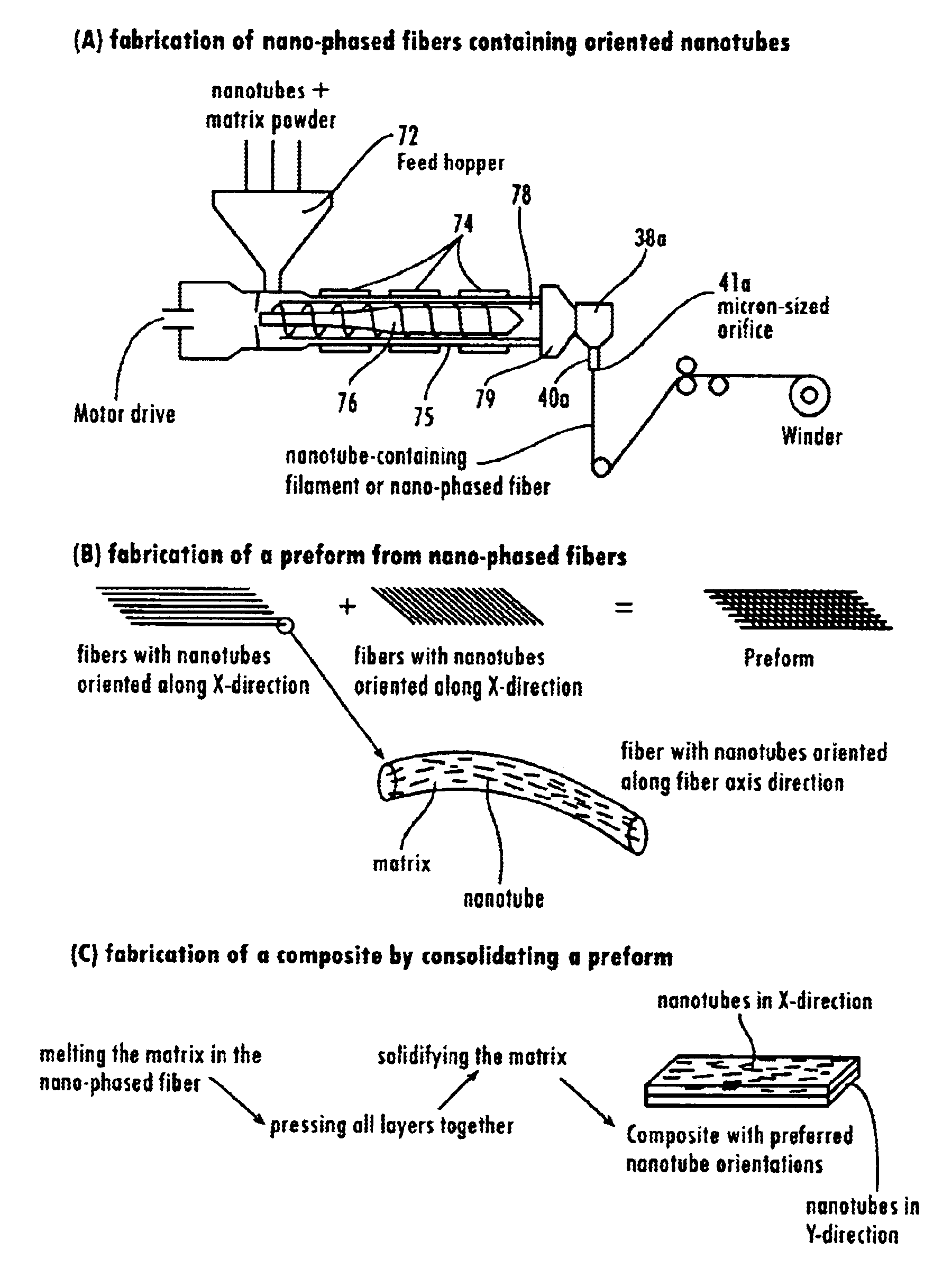
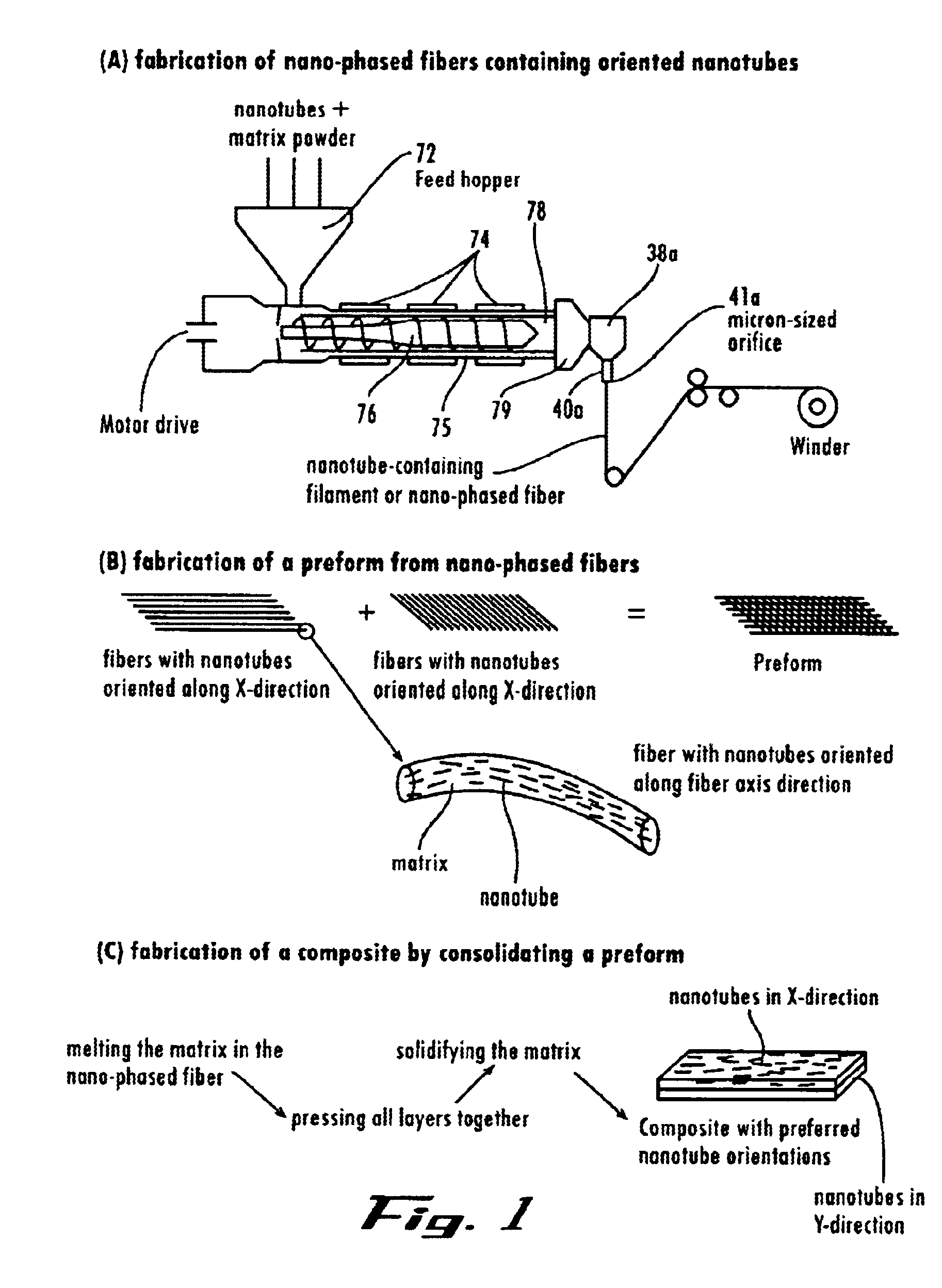
Nanotube fiber reinforced composite materials and method of producing fiber reinforced composites
InactiveUS6934600B2Requires minimizationGenerate efficientlyMaterial nanotechnologyAdditive manufacturing apparatusFiber-reinforced compositeMotion controller
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based compositions
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
Sheets having a starch-based binding matrix
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix, optionally reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, a cellulosic ether, optionally fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the cellulosic ether to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and cellulosic ether form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
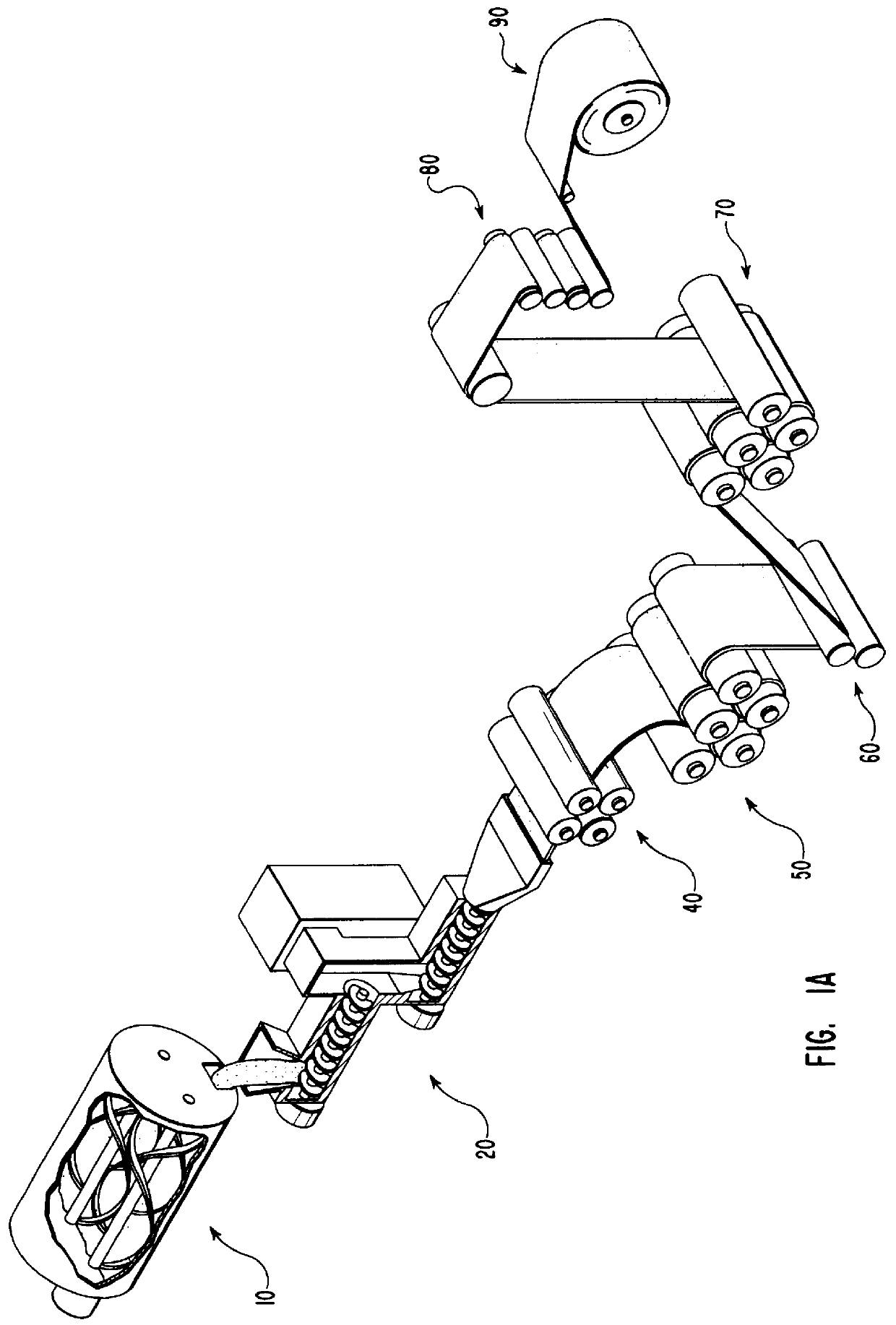
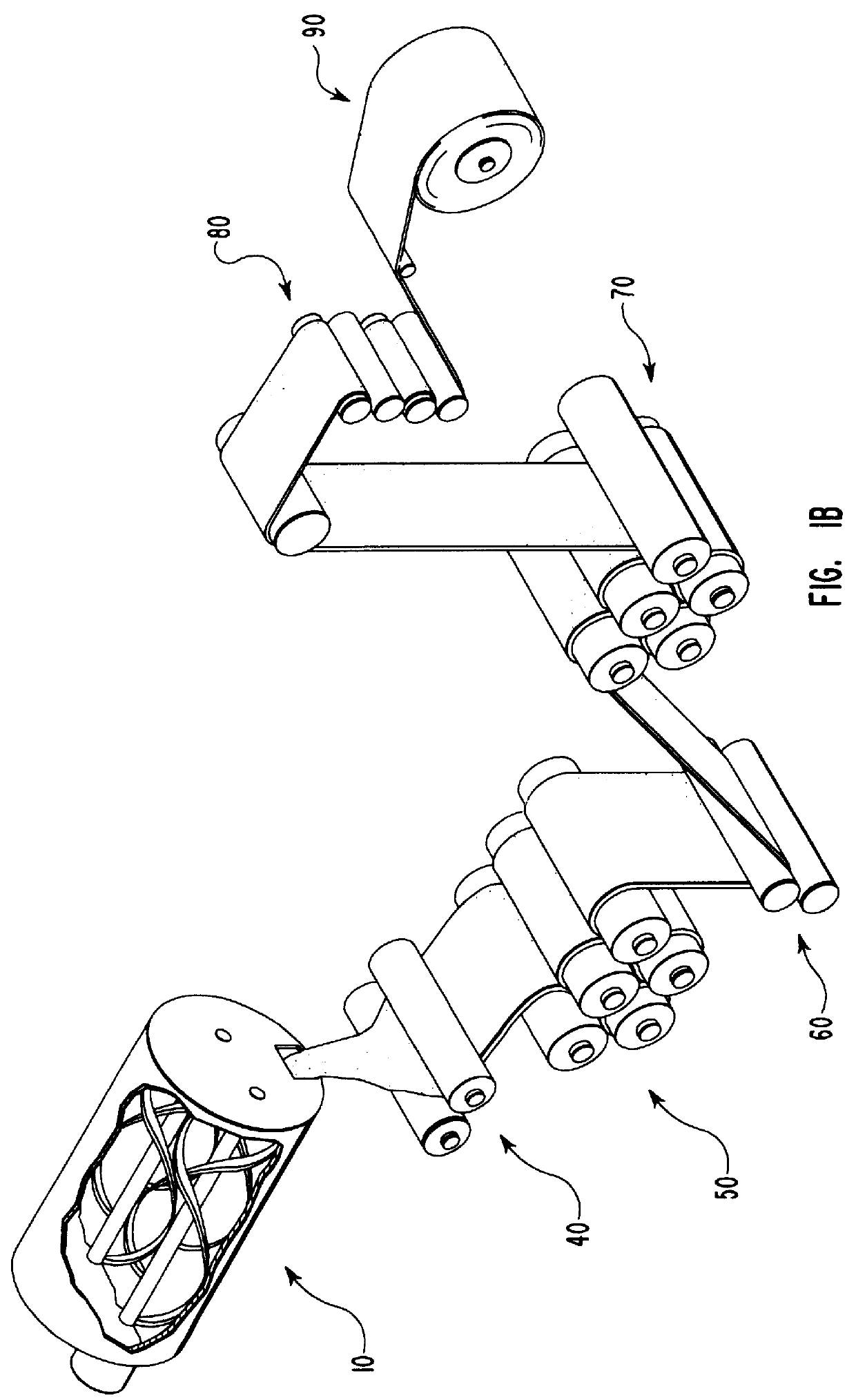
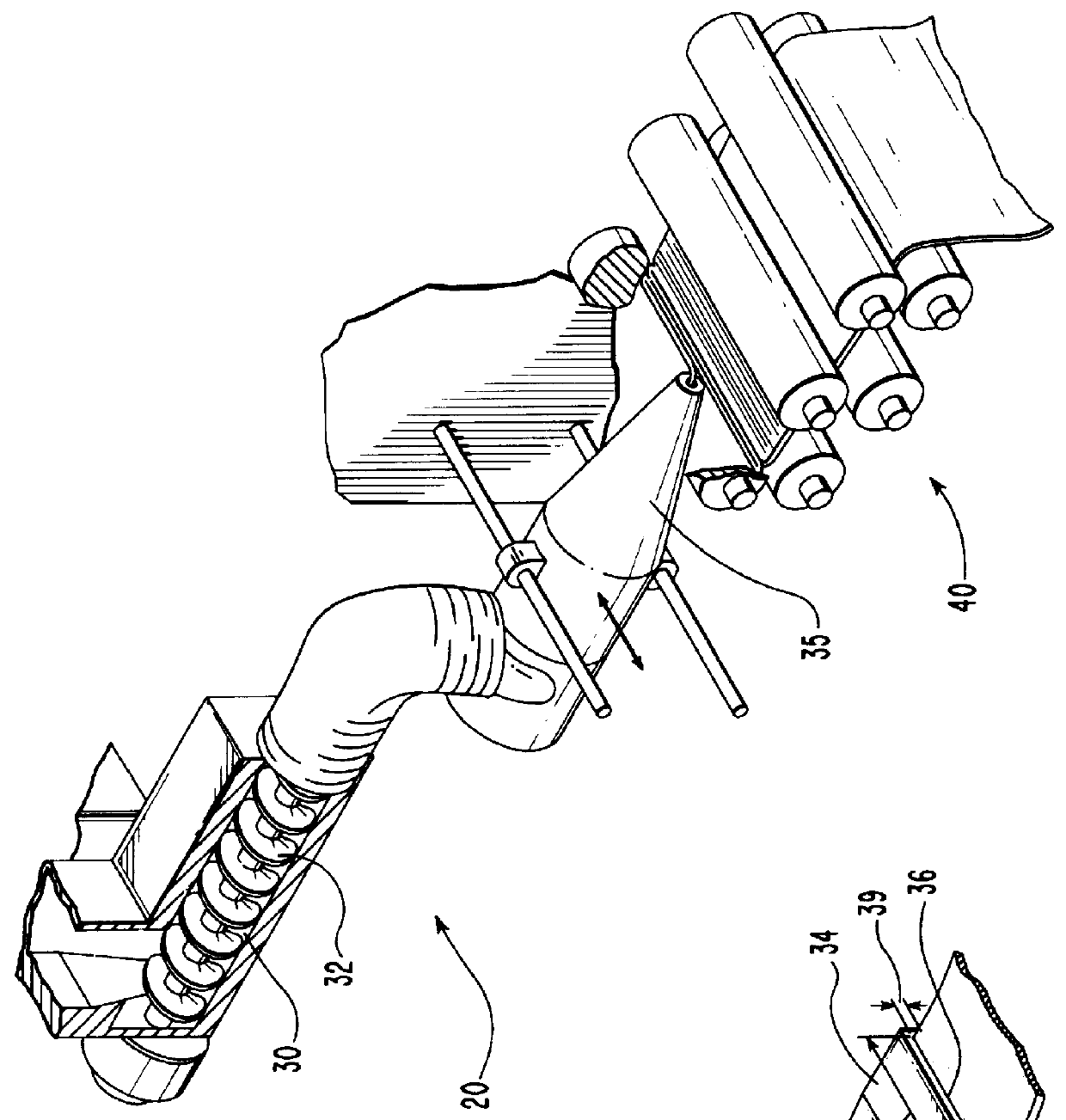
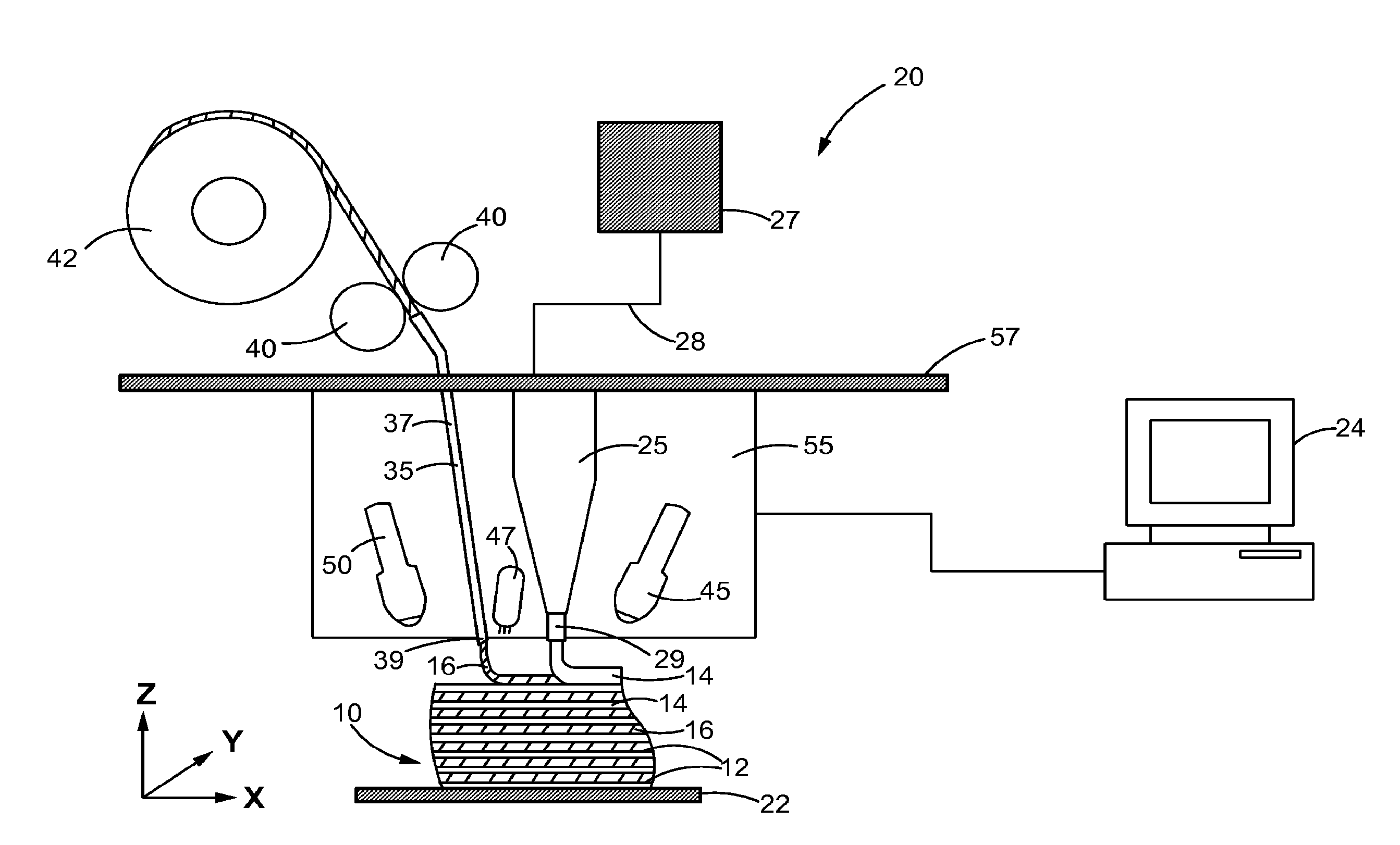
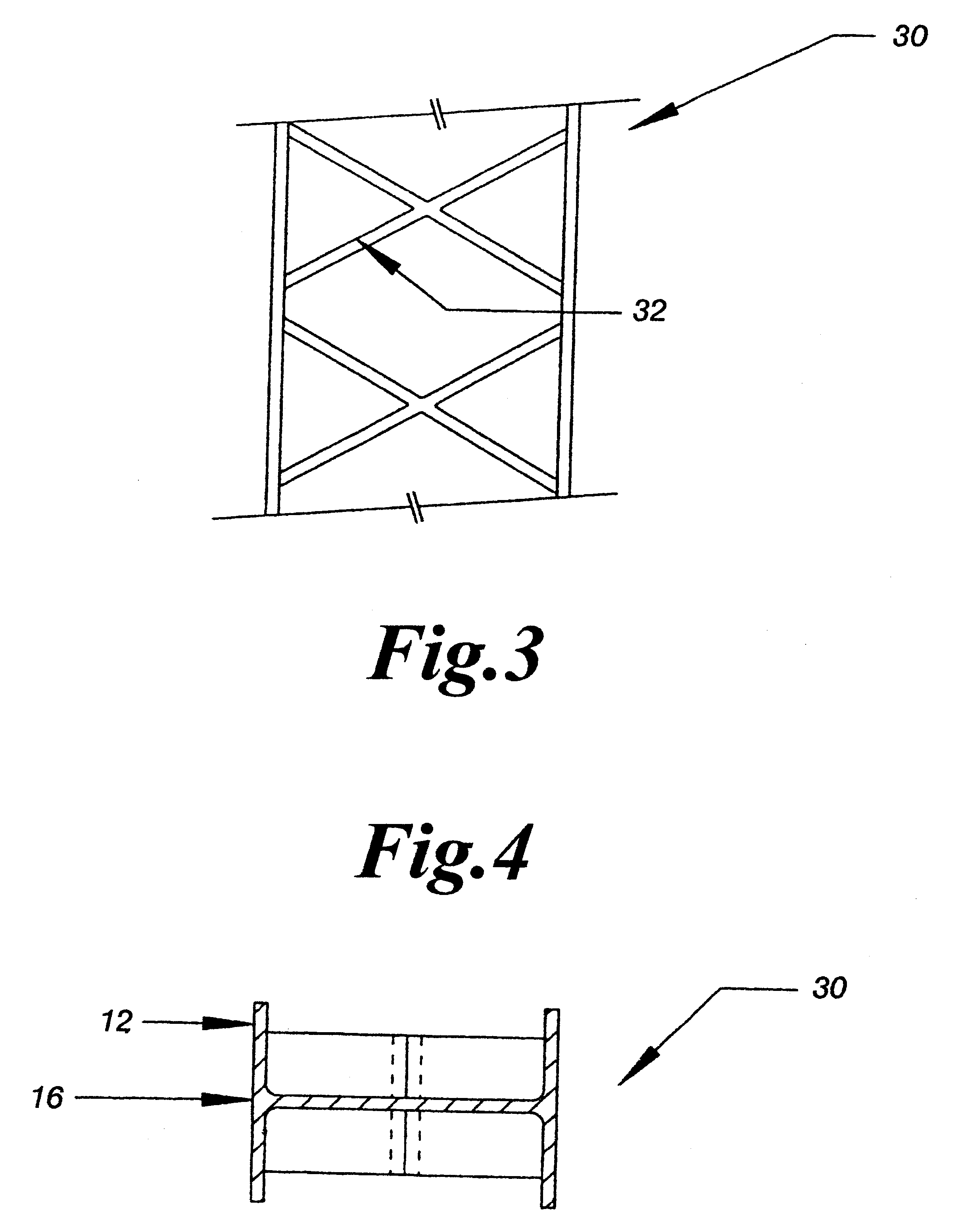
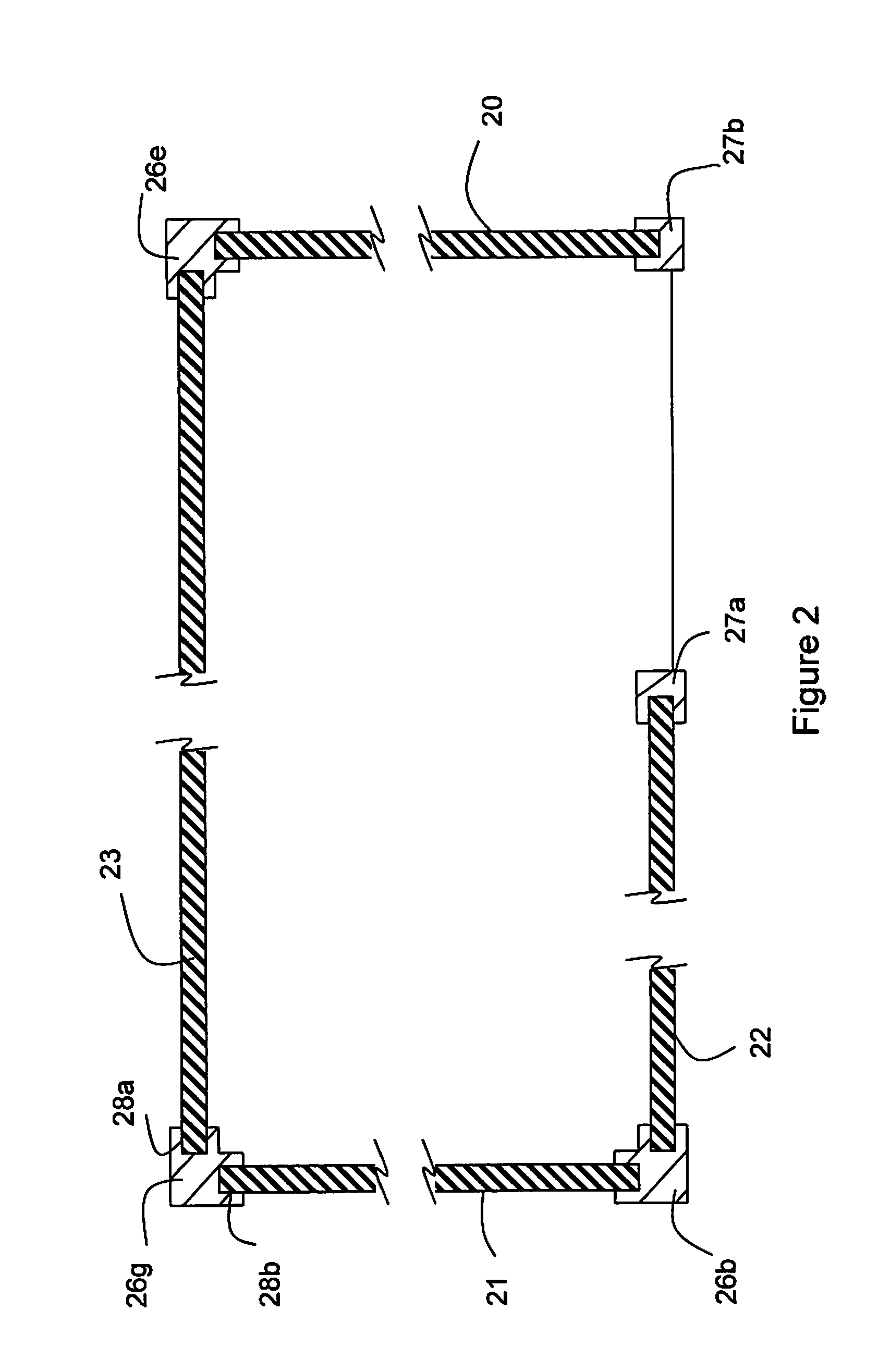
Continuous fiber-reinforced component fabrication
ActiveUS20160114532A1Additive manufacturing apparatusTailstocks/centresAdditive layer manufacturingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A machine for fabricating a fiber-reinforced component by additive manufacturing is disclosed. The machine may have a surface, a matrix feed configured to deposit a plurality of matrix layers on the surface, and a fiber feed configured to deposit a fiber layer on at least one of the plurality of matrix layers. The deposition of the plurality of matrix layers and the fiber layer may be controlled by a computer.
Owner:RTX CORP
Compositions and methods for manufacturing starch-based sheets
Compositions and methods for manufacturing sheets having a starch-bound matrix reinforced with fibers and optionally including an inorganic mineral filler. Suitable mixtures for forming the sheets are prepared by mixing together water, unmodified and ungelatinized starch granules, an auxiliary water-dispersible organic polymer, fibers, and optionally an inorganic mineral filler in the correct proportions to form a sheet having desired properties. The mixtures are formed into sheets by passing them between one or more sets of heated rollers to form green sheets. The heated rollers cause the auxiliary polymer to form a skin on the outer surfaces of the sheet that prevents the starch granules from causing the sheet to adhere to the rollers upon gelation of the starch. The green sheets are passed between heated rollers to gelatinize the starch granules, and then to dry the sheet by removing a substantial portion of the water by evaporation. The starch and auxiliary polymer form the binding matrix of the sheets with the fibers and optional inorganic filler dispersed throughout the binding matrix. The starch-bound sheets can be cut, rolled, pressed, scored, perforated, folded, and glued to fashion articles from the sheets much like paper or paperboard. The sheets are particularly useful in the mass production of containers, such as food and beverage containers.
Owner:E KHASHOGGI INDS
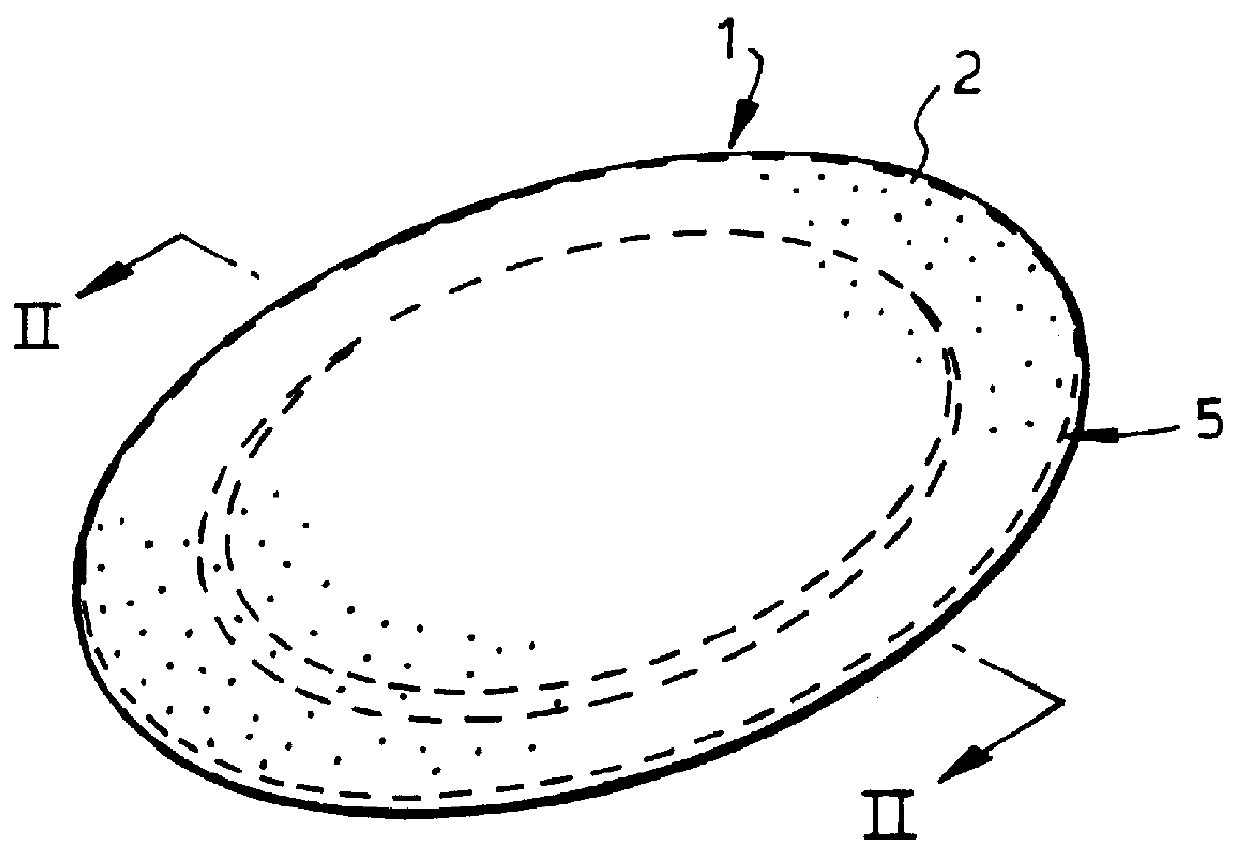
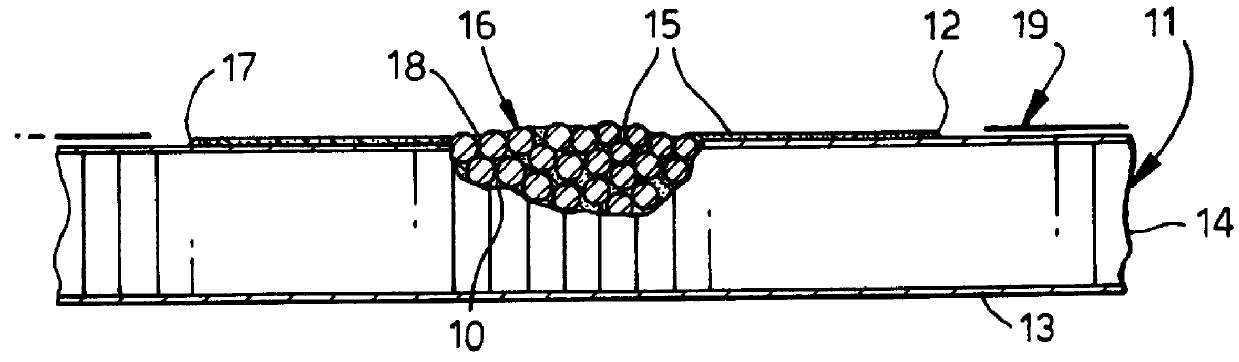
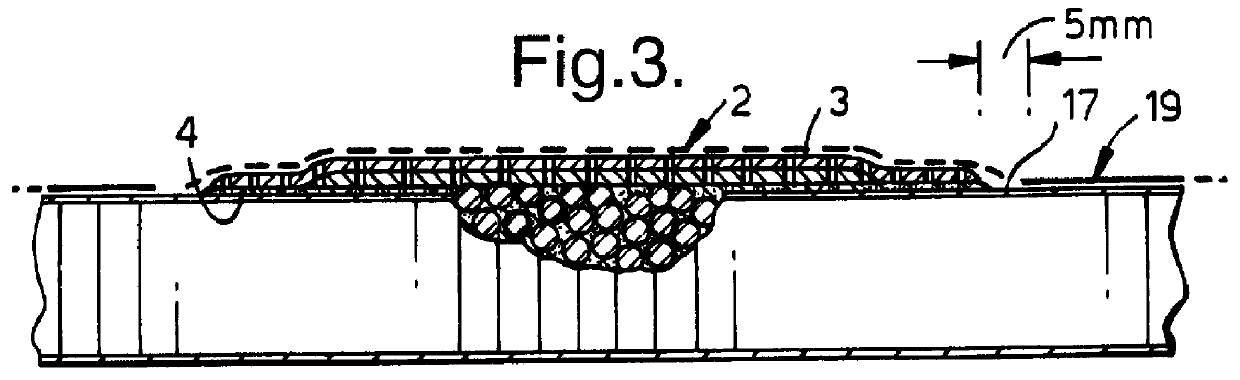
Repair of composite laminates
A patch of fibre reinforced plastics composite material, a repair kit including such a patch and a method of using such a patch and repair kit are provided. The patch (1) is for attachment to a surface (17) of a fibre reinforced plastics composite structure (11) over an area of damage (10) to the structure. The patch defines an outer surface (3), a bonding surface (4) opposed thereto and a peripheral edge. The patch includes fibre reinforcement and plastics matrix material with the latter being in a final state of hardness. The patch defines a series of small apertures (6) therethrough to allow the passage of gases and other matter through the patch to prevent entrapped air weakening the repair.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Thermoplastic composite material with improved smoke generation, heat release, and mechanical properties
InactiveUS20100021718A1Reduce fiber contentSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationAviationVolumetric Mass Density
A fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composite material having an advantageous combination of smoke generation, heat release, and mechanical property characteristics. The composite generally comprises a fiber-reinforced thermoplastic core containing discontinuous reinforcing fibers bonded together with one or more thermoplastic resins. The core material may further comprise at least one first skin material applied to a first surface of the core and / or one or more second skin material applied to a second surface of the core material. The thermoplastic core material has a maximum smoke density Ds (4 minutes) of less than 200 as measured in accordance with ASTM E662, a maximum heat release (5 minutes) of less than 65 kW / m2 as measured in accordance with FAA Heat release test FAR 25.853 (a) Appendix F, Part IV (OSU 65 / 65), and an average total heat release (2 minutes) of less than 65 kW / m2 as measured in accordance with FAA Heat release test FAR 25.853 (a) Appendix F, Part IV (OSU 65 / 65). The invention is useful in the manufacture of articles for aircraft, automotive, railcar, locomotive, bus, marine, aerospace and construction in which the certain advantages may be provided over other materials utilized for such applications.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Decorative interior sound absorbing panel
A multi-layered fiber reinforced thermoplastic sound absorbing panel includes a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface, and includes a thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent fibers, a tie layer covering the second surface of the core layer and including a thermoplastic material, and a barrier layer covering the tie layer. The barrier layer includes a thermoplastic material having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the core layer thermoplastic material. The tie layer bonds the barrier layer to the core layer. The panel also includes a non-woven layer including a fabric bonded to the barrier layer. The non-woven layer forms an outer surface of the panel.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Composite articles reinforced with highly oriented microfibers
InactiveUS6630231B2Improve toughnessHigh strengthLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentMaterial typePolymer science
A composite formed of a polymer matrix phase having a reinforcement phase including polymeric microfibers. The microfibers are preferably formed of a highly oriented polymer, having a high modulus value and a large surface area. The large surface area can serve to tightly bind the microfibers to the polymer matrix phase. The microfibers can be provided as a fully- or partially-microfibrillated film, as a non-woven web of entangled microfibers, or as a pulp having free fibers. The microfibers can be embedded in, or impregnated with, a polymer or polymer precursor. Some composite articles are formed from thermoset resins cured about a highly oriented polypropylene microfiber reinforcement phase, providing a strong, tough, moisture resistant article. One composite includes a matrix and reinforcement formed of the same material type and having substantially equal refractive indices, allowing the composite to be optically clear.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Expandable packer
InactiveUS7363970B2Improve scalabilityHigh strengthFluid removalSealing/packingNanoparticleNanofiber
An integral bodied composite packer is constructed entirely of a composite material. It can include an expandable middle portion with an elastomeric cover to engage an exterior surface of a well bore. The expandable portion can include continuous strands of polymeric fibers to reinforce the body and prevent extrusion. The packer body can have longitudinal cuts or slats to provide rigidity of the body after expansion. The slats can overlap. The packer can include an elastomeric cover or layer therein to engage the well bore. The expandable portion can include a reinforcement member in a laminar portion of the body made from high strength alloys, fiber-reinforced polymers and / or elastomers, nanofiber, nanoparticle, and nanotube reinforced polymers and / or elastomers.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
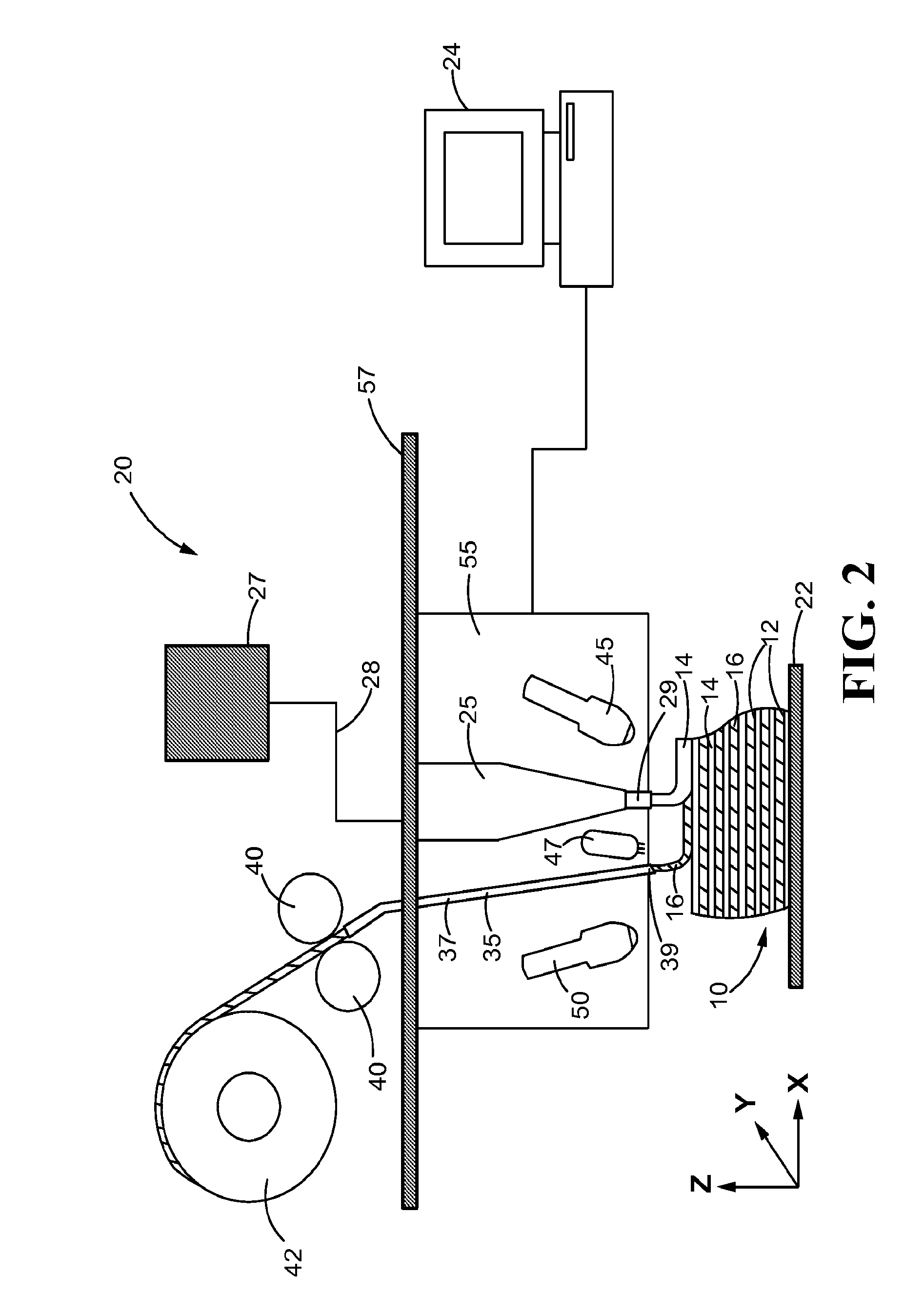
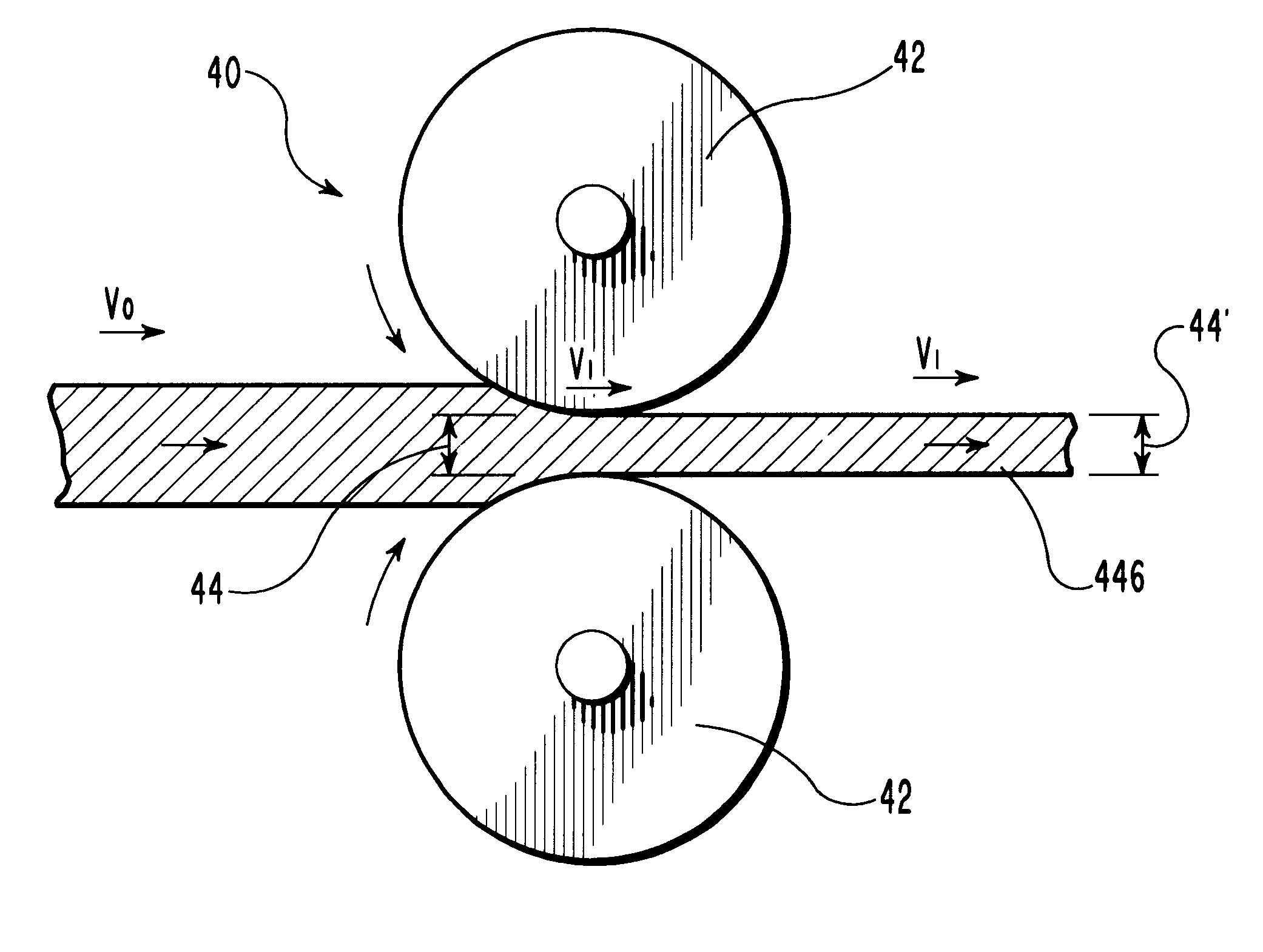
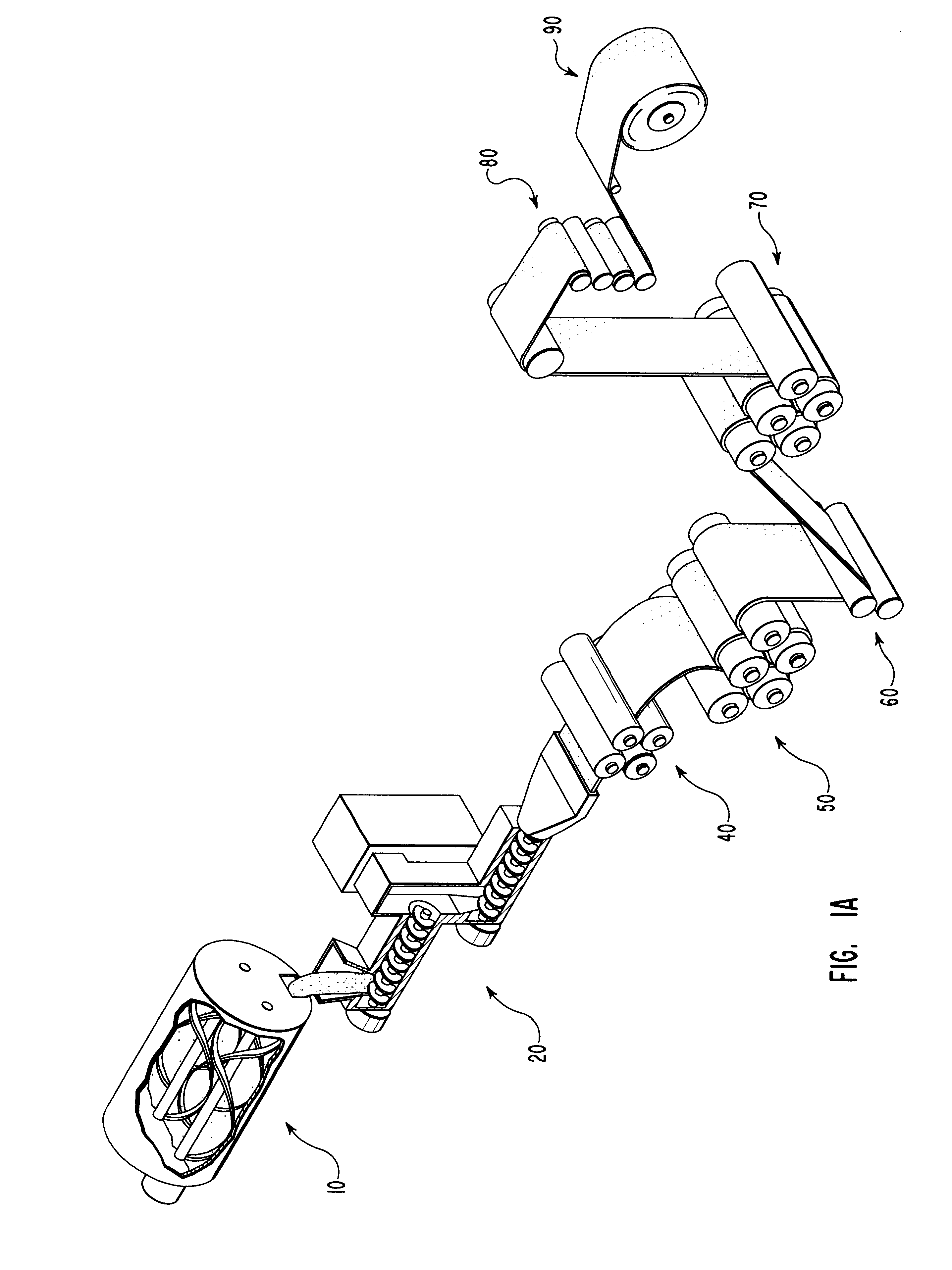
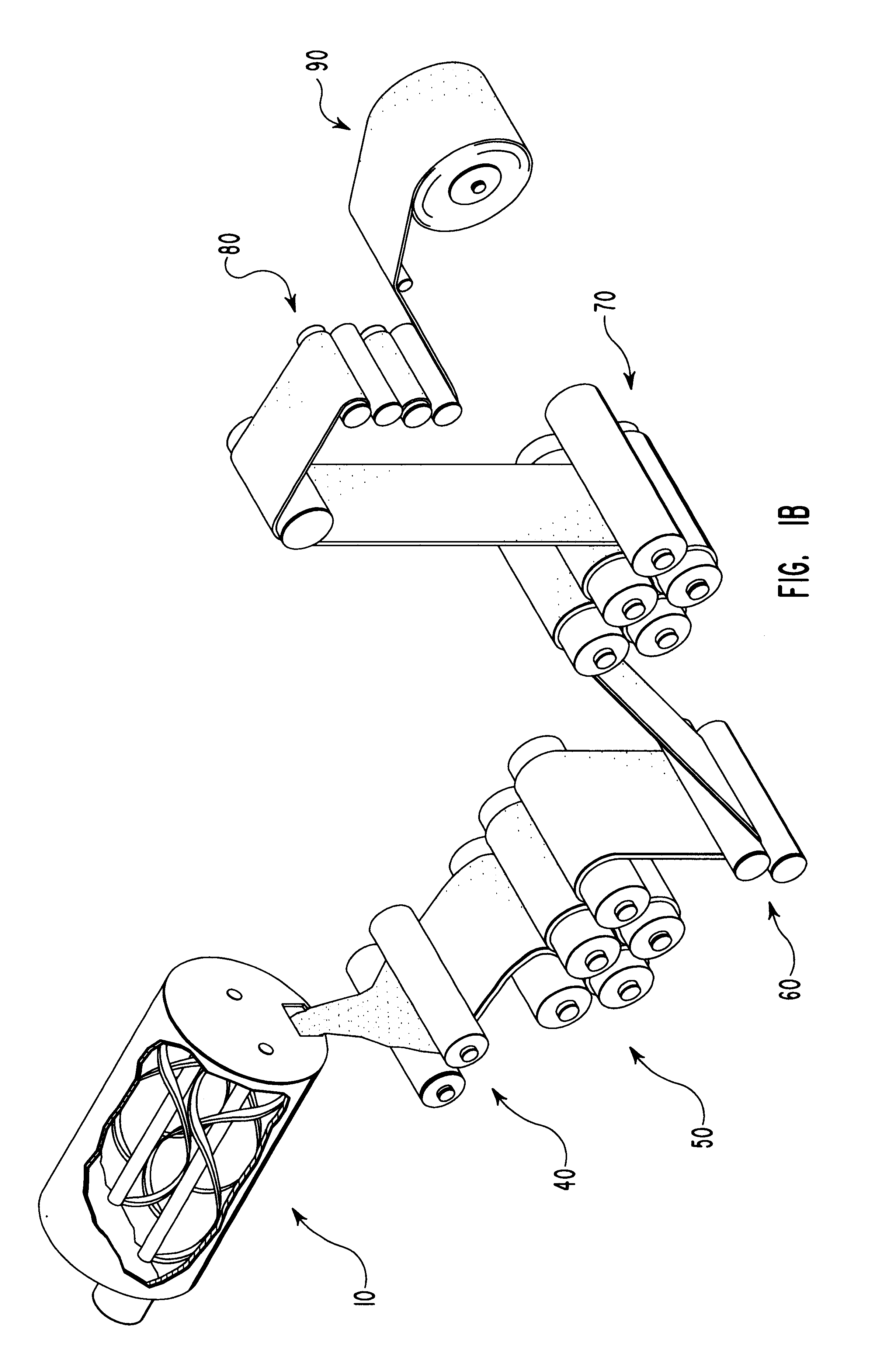
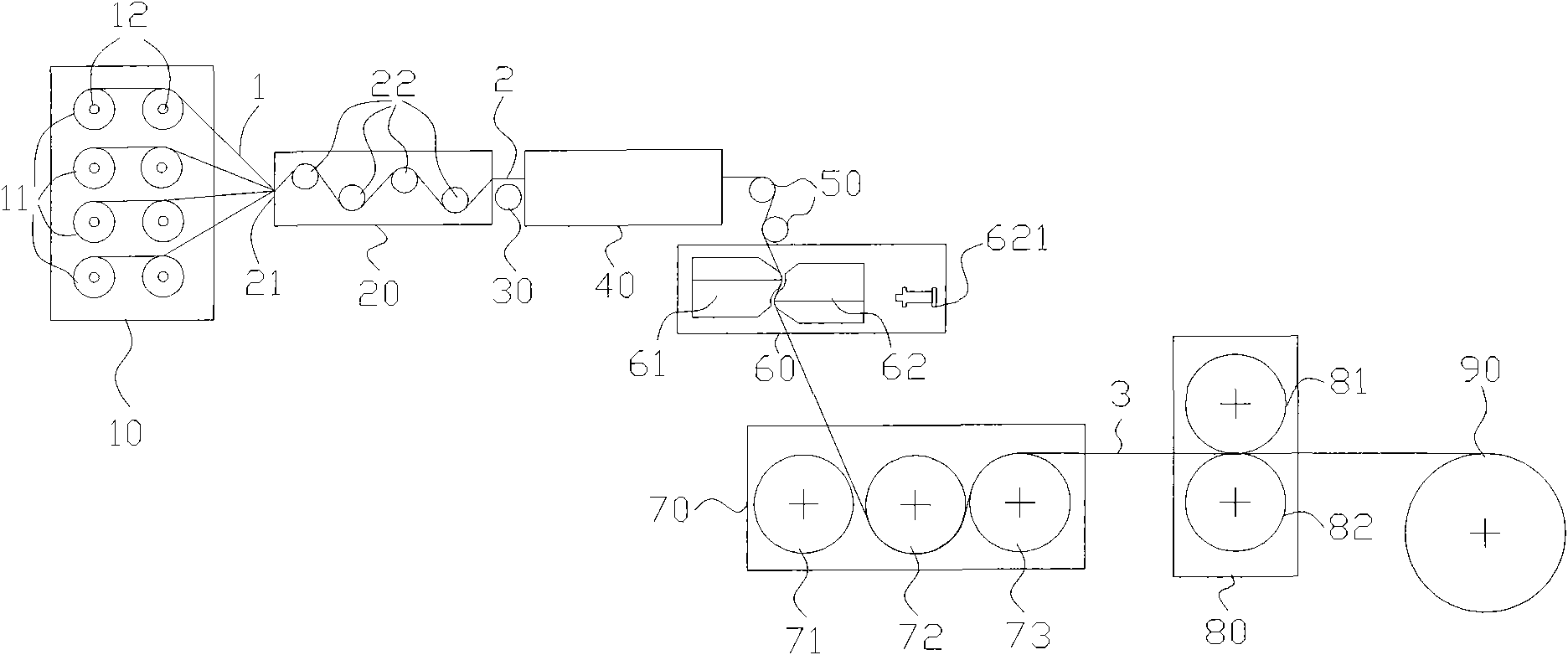
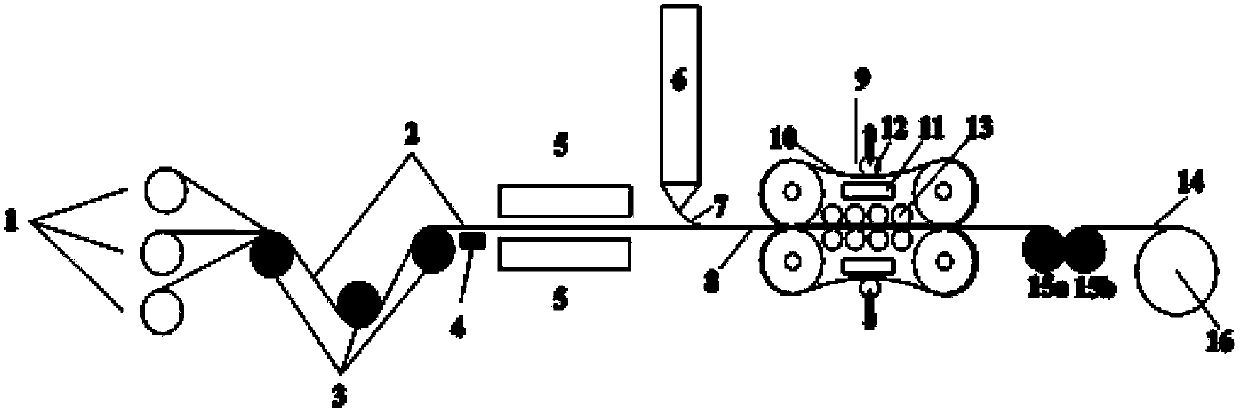
Preparation method of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite material prepreg and equipment thereof
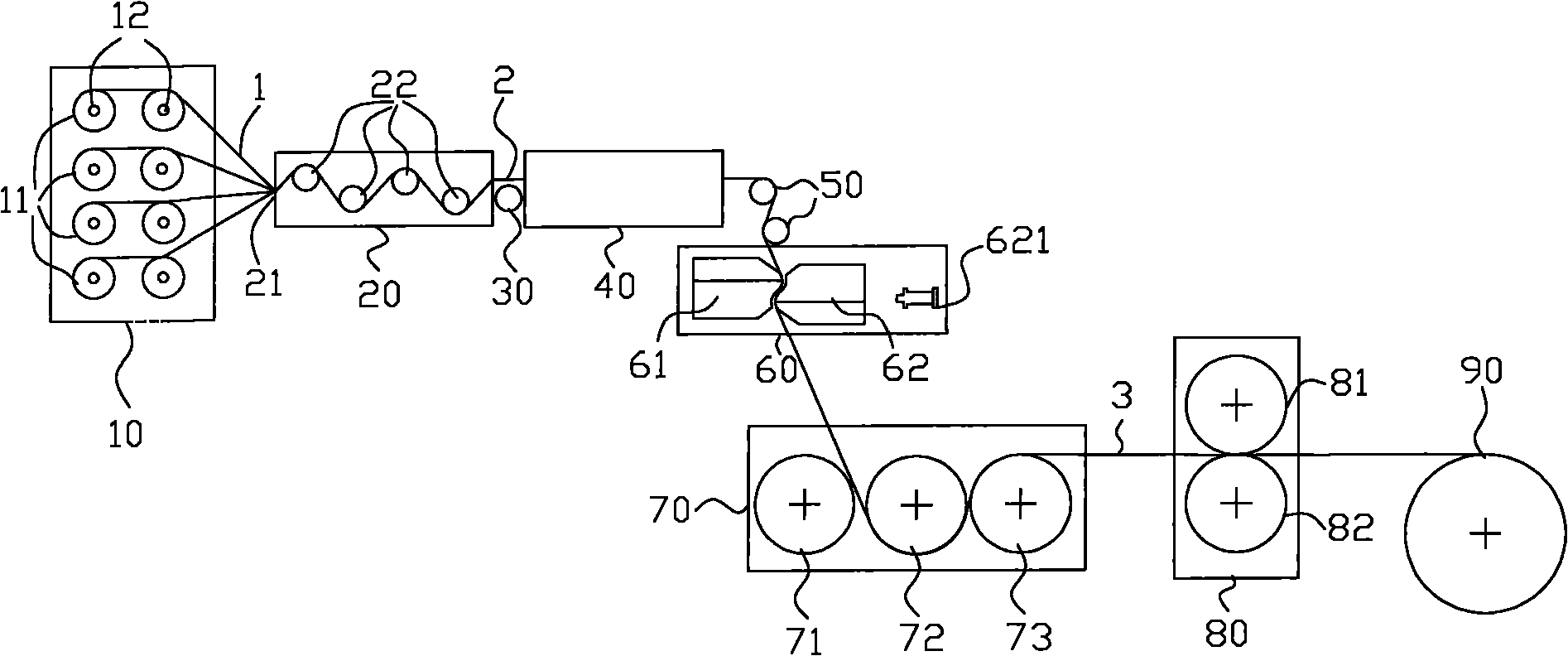
The invention relates to a preparation method of a continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite material prepreg and equipment thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (a) leading out and unfolding continuous fiber from a creel (10) to pass a tension adjusting device (20) and a static elimination device (30) in sequence, sending the fiber to a preheating oven (40) to preheat, and then passing a tension adjusting device (50); (b) leading a preheated continuous fiber band into a dual-extrusion die head set which can be opened and closed in a staggered manner to presoak; and (c) leading the presoaked continuous fiber band into a soaked rolling roll set (70) to soak, then cooling by a cooling roll-in device (80), and finally leading into a traction rolling device (90) for shaping by winding to obtain the product. Compared with the prior art, the invention significantly improve the dispersion, infiltrating property and operability of the fiber, and obtains the continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite material prepreg which has uniformly dispersed and completely soaked fiber.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Composite internal fixators
ActiveUS20120059376A1Desired performanceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsModel selectionElement analysis
A multi-layer, fiber-reinforced composite orthopaedic fixation device having a design selected based on a desired characteristic of the orthopaedic fixation device. The design may be selected according to a model of the device, the model defining design constraints, and the design may comprise a pattern of the fiber angle for each layer. The selection of a design may be analyzed using finite element analysis to determine whether the design will comprise the desired characteristic.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Catalytically enhanced filtration apparatus
A hot gas filtration apparatus includes a vessel, a plurality of filter elements mounted within the vessel and positioned such that hot gas flows through said filter elements, with each of said filter elements having a porous body, and a catalytic layer on surfaces of the porous body. The porous body of the filter element may include one of: a porous ceramic monolithic matrix, a continuous fiber reinforced ceramic composite (CFCC) matrix, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, and a metal-ceramic composite matrix. When the porous body is a nonoxide ceramic, a metallic matrix, an intermetallic matrix, a superalloy, or a metal-ceramic composite matrix, the invention further includes an oxidative resistant layer coating surfaces within the porous body, and the catalytic layer is on the oxidative resistant layer. A porous particulate removal membrane can be positioned on one or more surfaces of the filter element. The porous membrane can also provide a surface for one or more catalysts. The catalysts on the porous surface of the membrane(s) can be the same as or different from the catalysts on surfaces within the porous body.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method of molding complex composite parts using pre-plied multi-directional continuous fiber laminate
ActiveUS20110064908A1Simple processLayered productsEfficient propulsion technologiesShell moldingFiber-reinforced composite
Layers of unidirectional (UD) fiber prepreg are formed into a pre-plied, multi-directional, continuous fiber laminate that is used as a molding compound to form three dimensional structures. Cut-outs from the laminate are slotted and folded along fold lines to provide near-net-shaped preforms that may be compression molded to form fiber-reinforced composite structures having complex shapes.
Owner:HEXCEL
Sandwich structure and integrated formed article using the same
InactiveUS20090117366A1Improve mechanical propertiesGood thinnessSynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingAir bubbleFibre reinforcement
A sandwich structure (III) which has a core material (I) and, arranged on the both surfaces of said core material (I), a fiber-reinforced material (II) composed of a continuous reinforcing fiber (A) and a matrix resin (B), wherein the above core material (I) comprises a void. The void is formed by bubbles of a foamed material or, the core is composed of a discontinuous reinforcing fiber and a thermoplastic resin and the void is formed by interstices formed at crossings of filaments of said reinforcing fiber.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Fiber-reinforced ceramic composite material comprising a matrix with a nanolayered microstructure
InactiveUS20050181192A1Improve the immunityHigh strengthSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsCeramic compositeToughening
A fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composite material exhibiting increased matrix cracking strength and fracture toughness is produced by sequentially depositing a plurality of 5-500 nanometer-thick layers of a primary ceramic matrix material phase periodically separated by 1-100 nanometer-thick intermediate layers of a secondary matrix material phase onto the reinforcing fibers upon their consolidation. The resultant nanolayered matrix enhances the resistance to the onset of matrix cracking, thus increasing the useful design strength of the ceramic matrix composite material. The nanolayered microstructure of the matrix constituent also provides a unique resistance to matrix crack propagation. Through extensive inter-layer matrix fracture, debonding and slip, internal matrix microcracks are effectively diverted and / or blunted prior to their approach towards the reinforcing fiber, thus increasing the apparent toughness of the matrix constituent. This unique toughening mechanism serves to dampen energetic co-planar macrocrack propagation typically observed in conventionally manufactured ceramic matrix composites wherein matrix cracks are usually deflected at the fiber / matrix interphase region.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE HIGH TEMPERATURE COMPOSITES INC
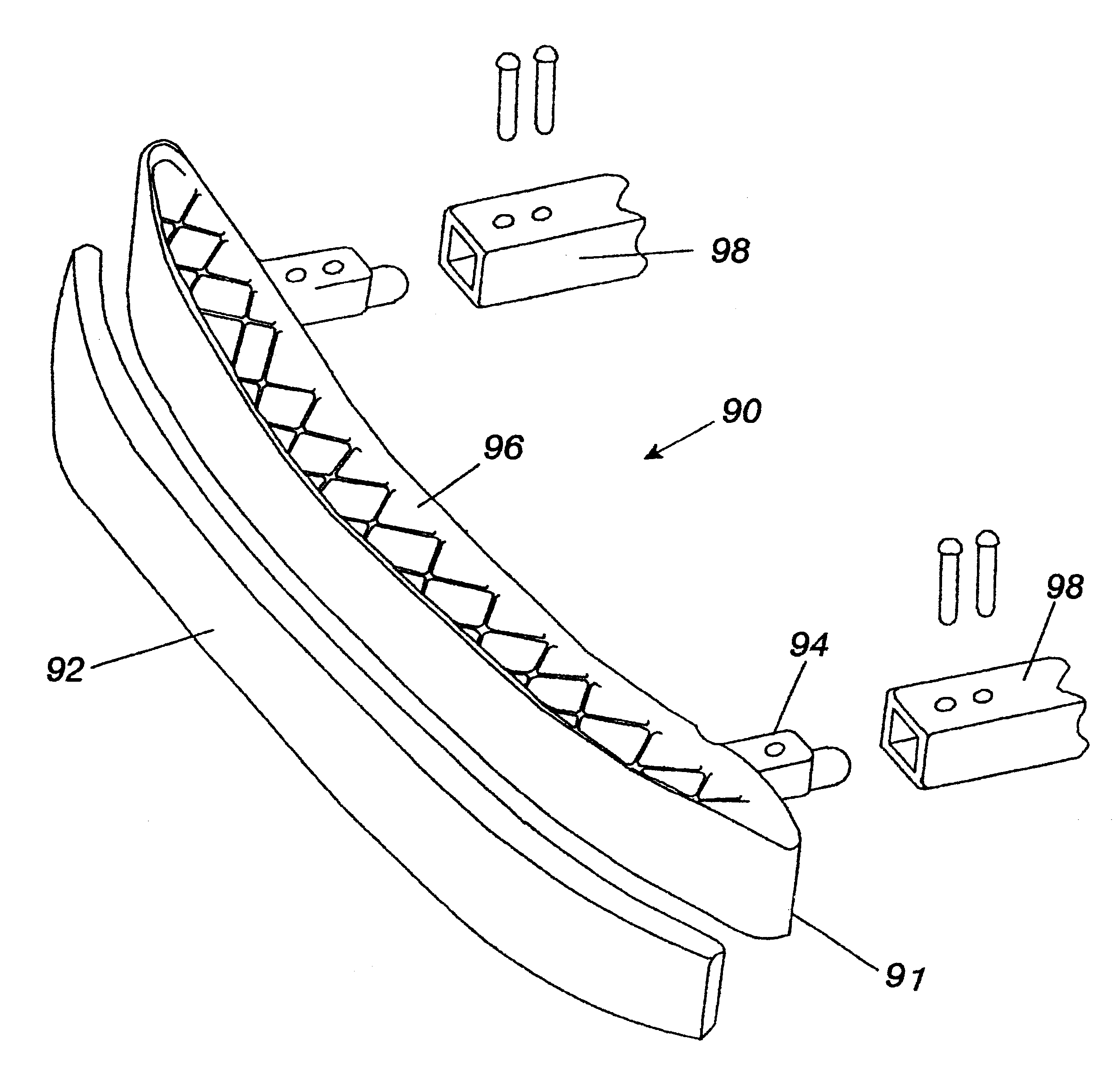
I-Section automotive bumper formed from mineral-filled glass mat thermoplastic (GMT) composite
InactiveUS6286879B1Improve flow characteristicsIncrease modulusBumpersCompression moldingShell molding
The invention is a fiber reinforced thermoplastic automotive bumper wherein the reduced fiber additions consist of a long, chopped glass mat with the addition of mineral fillers such as mica, talc or clay. The modified thermoplastic is used to produce I-section bumpers. The improved reinforced thermoplastic material has favorable flow characteristics which enable the material to substantially fill the deep ribs and mounting stay structures used in I-section bumpers during compression molding while improving the modulus or cross-face stiffness of the finished part. For the first time, improved flow characteristics during molding permit the material to flow evenly into small ribs, bosses and other features. The invention makes it possible to increase part integration, molding pencil braces, fascia supports, mounting holes and mounting stays. The front surface of the bumper may be covered with a conformal energy absorber made of plastic foarn. Moreover, the absorber serves to mount appearance fascia. The result is a cost-reduced, weight-reduced bumper with improved impact resistance.
Owner:AZDEL INC
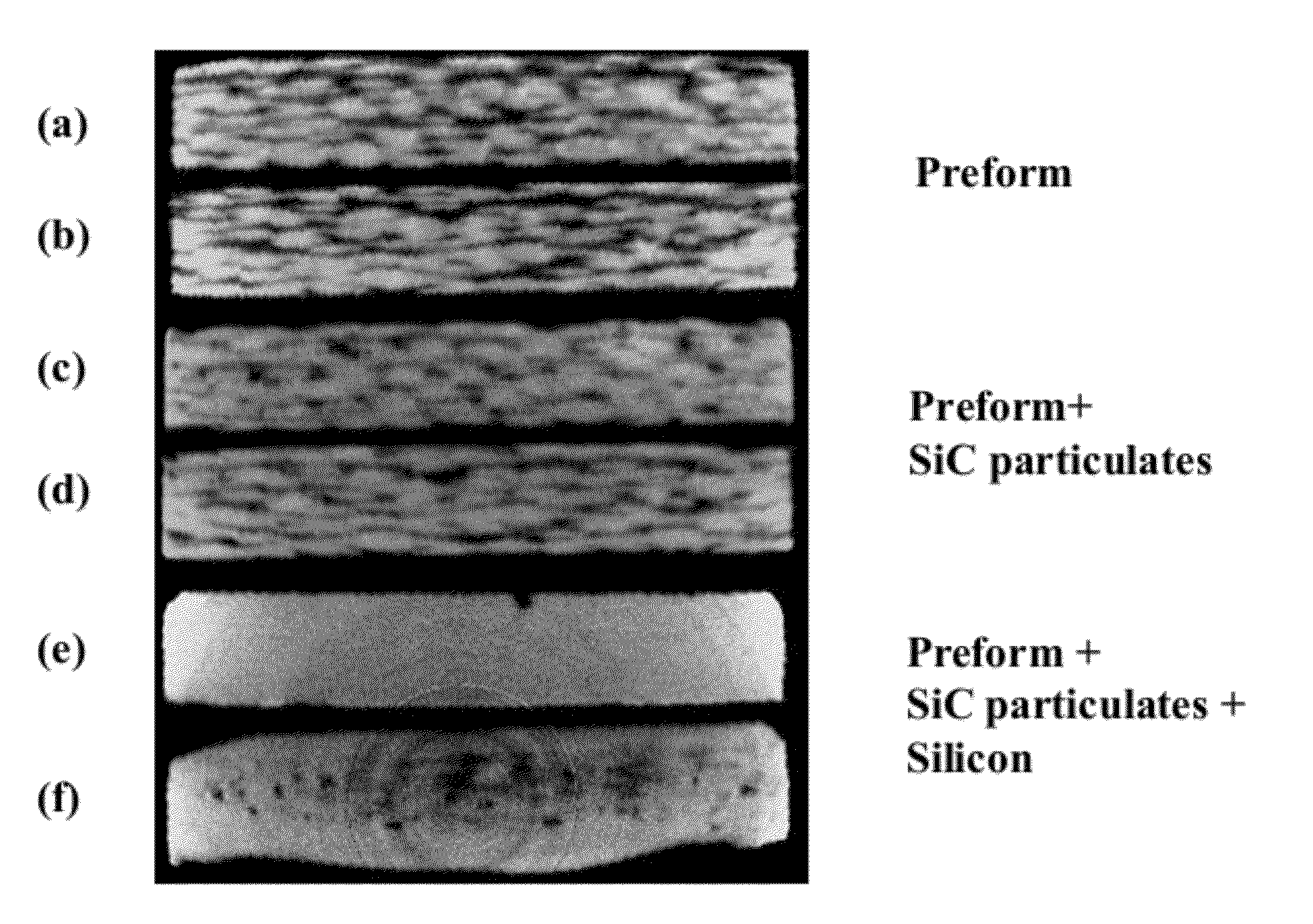
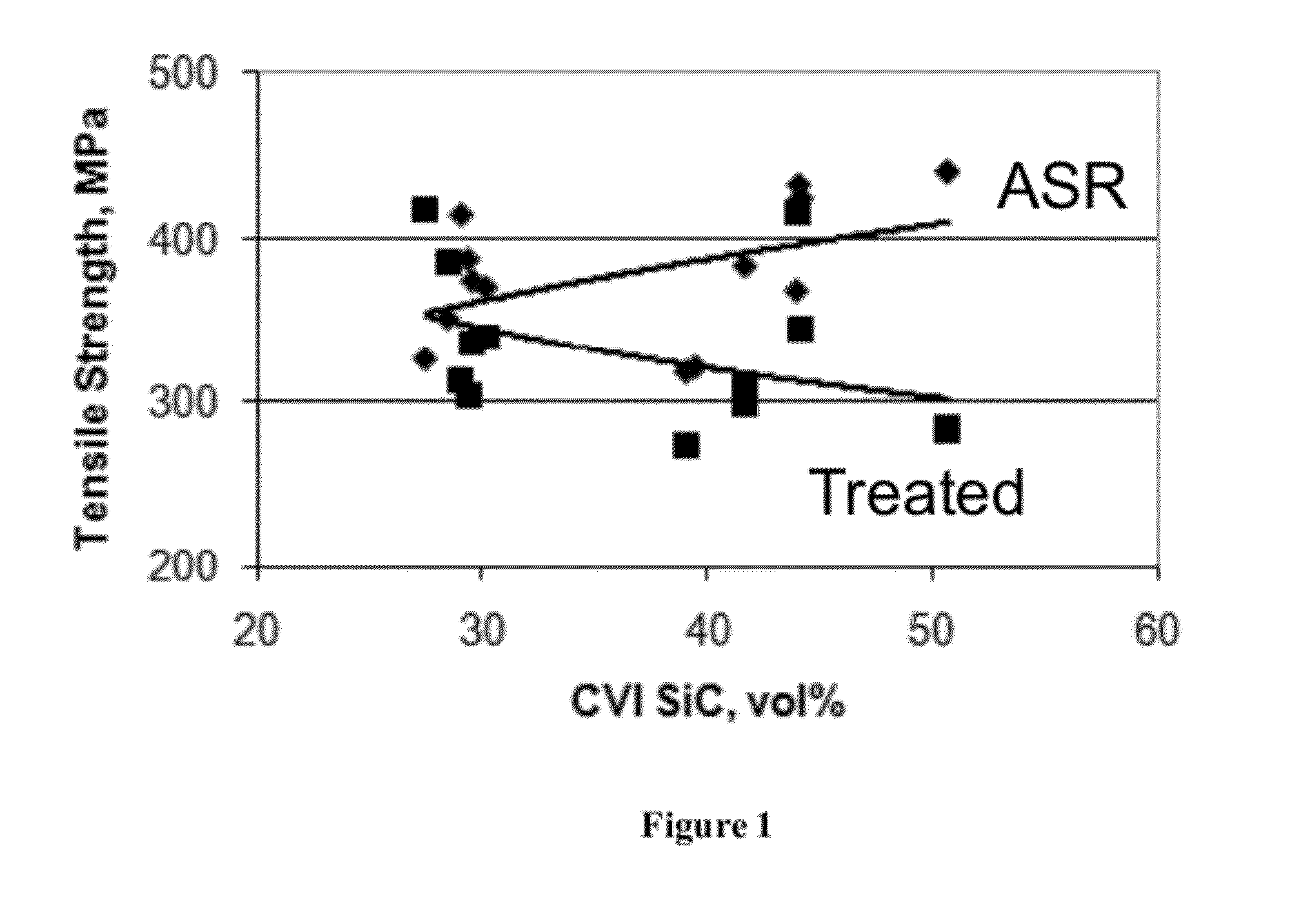
Method of improving the thermo-mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced silicon carbide matrix composites
InactiveUS20120076927A1Improve featuresImprove propertiesCeramic shaping apparatusCoatingsParticulatesGas phase
A thermal treatment process for improving thermo-mechanical properties of ceramic matrix composite materials such as silicon carbide (SiC) matrix composites is described. The treatment process removes excess silicon and / or other process-related defects from the SiC-based matrix as well as the fiber interfacial coating. This invention can be practiced with minimal strength loss for as-fabricated composites formed from high-strength continuous-length ceramic and carbon-based fibers that are functionally stable to 1600° C. and above. The invention provides a method for significantly improving composite thermal conductivity and creep resistance, and for reducing composite porosity. It has been demonstrated using state-of-the-art 2D woven SiC / SiC composites containing Sylramic-iBN SiC fibers, boron-nitride-based interfacial coatings, and hybrid matrices that are based on SIC formed by chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) and by a combination of CNI, SiC particulate infiltration, polymer infiltration and pyrolysis, and melt infiltration of silicon, silicon-based alloys, and silicides.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Fiber reinforced cement composite concrete precast construction member and production method thereof
InactiveCN102561584ARealize industrialized prefabrication productionImprove product qualityMouldsClimate change adaptationCement compositesArchitectural engineering
The invention relates to a fiber reinforced cement composite concrete precast construction member (PC-FRC) and a production method thereof, which are suitable for engineering of building exterior wall decoration, building structure containment, and energy conservation and heat preservation, are particularly suitable for prefabricated housing industrialization projects and are suitable for the fields of people's livelihood such as natural disaster prevention and post-disaster reconstruction. The fiber reinforced cement composite concrete precast construction member comprises a decorative finish layer, a fiber reinforced cement layer, a concrete structure layer, a heat preservation layer and a steel reinforcement framework, wherein the fiber reinforced cement layer is composited on the decorative finish layer and is connected with the concrete structure layer; the heat preservation layer is laid in the concrete structure layer and is completely coated by the concrete structure layer; the steel reinforcement framework is laid in the concrete structure layer; and the fiber reinforced cement layer, the heat preservation layer and the concrete structure layer are composited and molded in molds with models. According to the fiber reinforced cement composite concrete precast construction member, the connecting part of the surface of the precast construction member is provided with exposed steel reinforced bars, and the exposed steel reinforced bars are used for connecting precast pieces with building structures during building assembly; and suspension embedded pieces are laid in the concrete structure layer.
Owner:NANJING BEILIDA NEW MATERIAL SYST ENG
Resin composition for a fiber reinforced composite, a prepreg and a fiber reinforced composite
InactiveUS6287696B1Good tackinessGood drapabilitySynthetic resin layered productsYarnFiber-reinforced compositeMaterials science
The invention provides a resin composition for a fiber reinforced composite which can be used to produce a prepreg excellent in tackiness, drapability and windability around a mandrel, and also provides a prepreg in which reinforcing fibers are impregnated with a resin composition, and a fiber reinforced composite obtained from them. The resin composition includes a thermosetting resin and a thermoplastic resin with a weight average molecular weight of 200,000 to 5,000,000.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
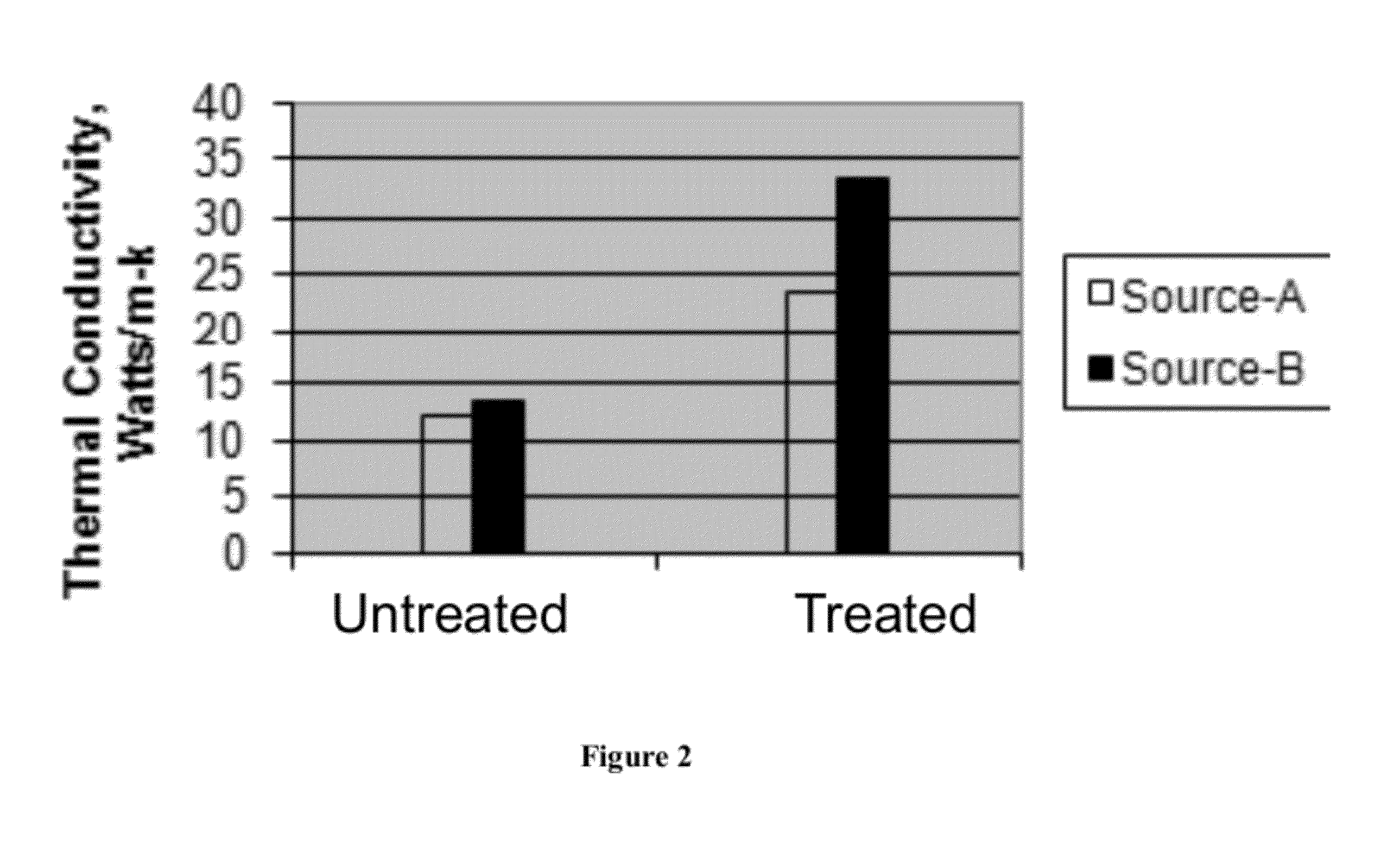
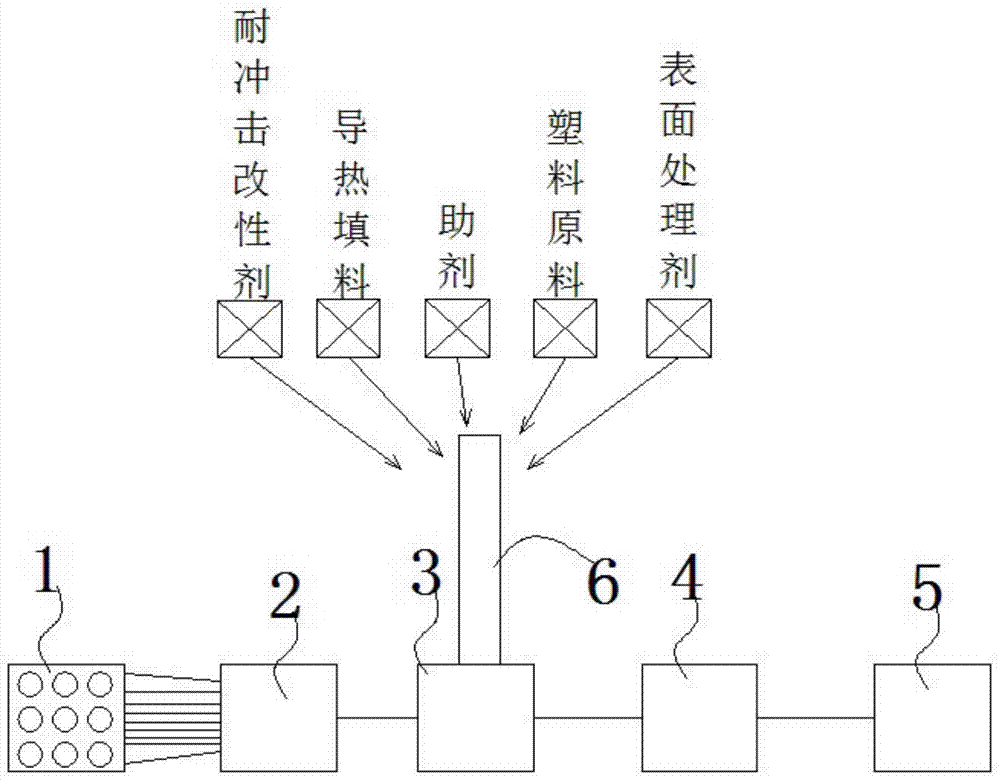
Continuous fiber composite high thermal conductive material and processing technology thereof
The invention discloses a continuous fiber composite high thermal conductive material and a processing technology thereof. When the continuous fiber is non-thermal conductive fiber, the high thermal conductive material comprises, by weight, 20%-60% of the continuous fiber, 0%-5% of a surface-treating agent, 5%-30% of a plastic raw material, 0%-5% of auxiliary agents, 20%-75% of thermal conductive filler and 0%-15% of an impact-resistant modifier; and when the continuous fiber is thermal conductive fiber, the high thermal conductive material comprises, by weight, 20%-70% of the continuous fiber, 0%-5% of the surface-treating agent, 10%-60% of the plastic raw material, 0%-5% of the auxiliary agents, 0%-50% of the thermal conductive filler and 0%-15% of the impact-resistant modifier. The processing technology is shown in the description. Continuous fiber-reinforced high thermal conductive plastic blend with high strength, low temperature resistance and good impact resistance can be prepared by a continuous fiber production device. The continuous fiber-reinforced high thermal conductive plastic blend contains relatively long fiber; and the length of the fiber is the same as that of particles. By adding the thermal conductive fiber, a thermal conductive coefficient can be controlled at 2-120 w / (m.k) and even higher.
Owner:上海智高贸易有限公司
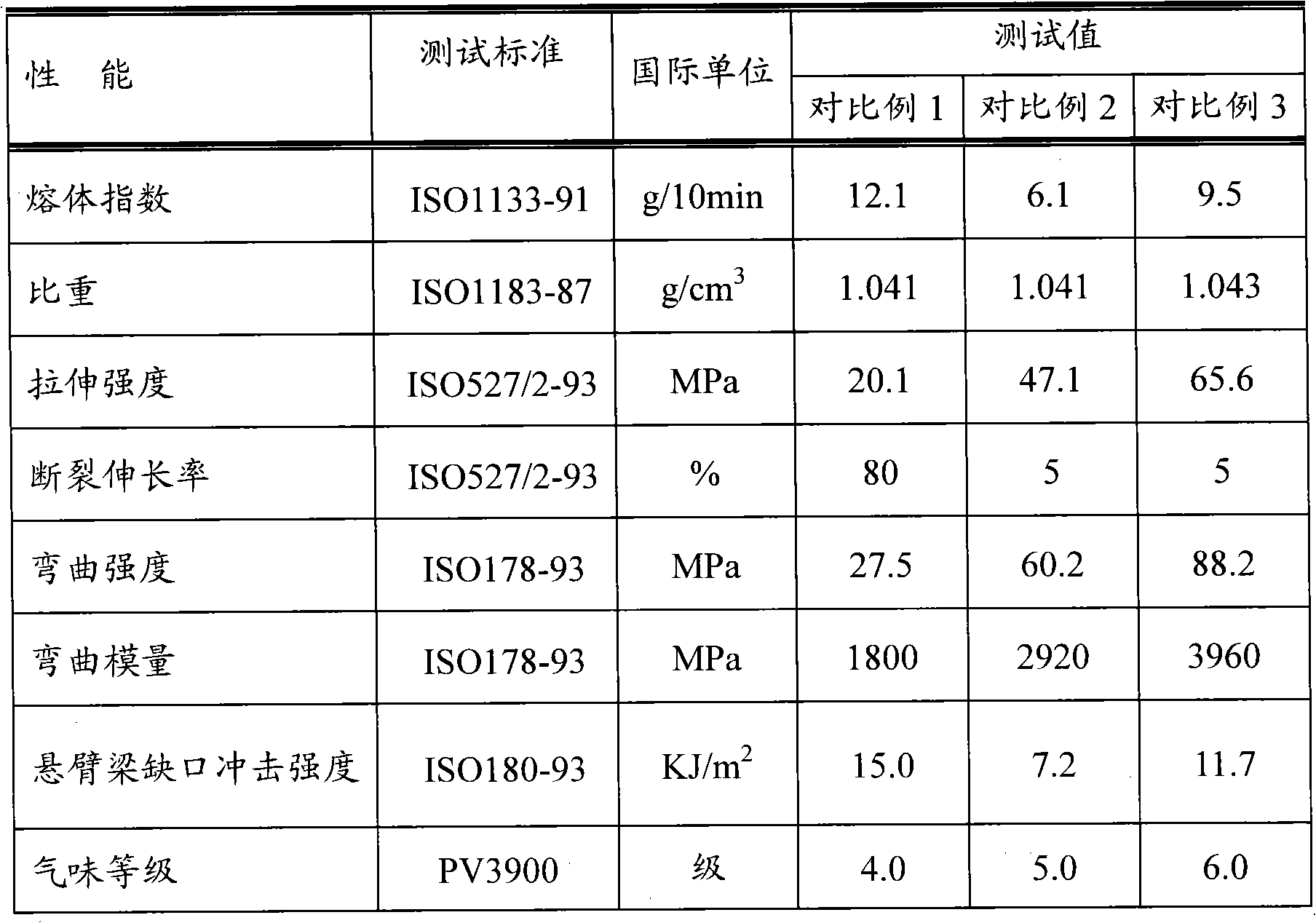
Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material with low odor and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material with low odor and a preparation method thereof. The glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material comprises the following components: 32-91% of polypropylene resin, 5-50% of glass fiber, 2-8% of compatilizer, 1-6% of odor inhibitor and 1-4% of other auxiliary agent. The reinforced polypropylene material with low odor is prepared by fusing, extruding and granulating the components through a double screw extruder under the temperature control condition of 220-240 DEG C. The odor inhibitor comprises 30-50% of ricinoleic acid zinc, 20-40% of metal oxide and 10-30% of a clay mineral system. The odor of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material can be inhibited through combining a physical method and a chemical method. The glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material prepared by the method has excellent odor performance; the odor level can be reduced below level 3; the physical property of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite material per se is not influenced after the odor inhibitor is added; and the application field of the glass fiber reinforced polypropylene material in vehicle interior trim parts and a part of home appliance parts can be widened.
Owner:CHENGDU KINGFA SCI & TECH ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD +3
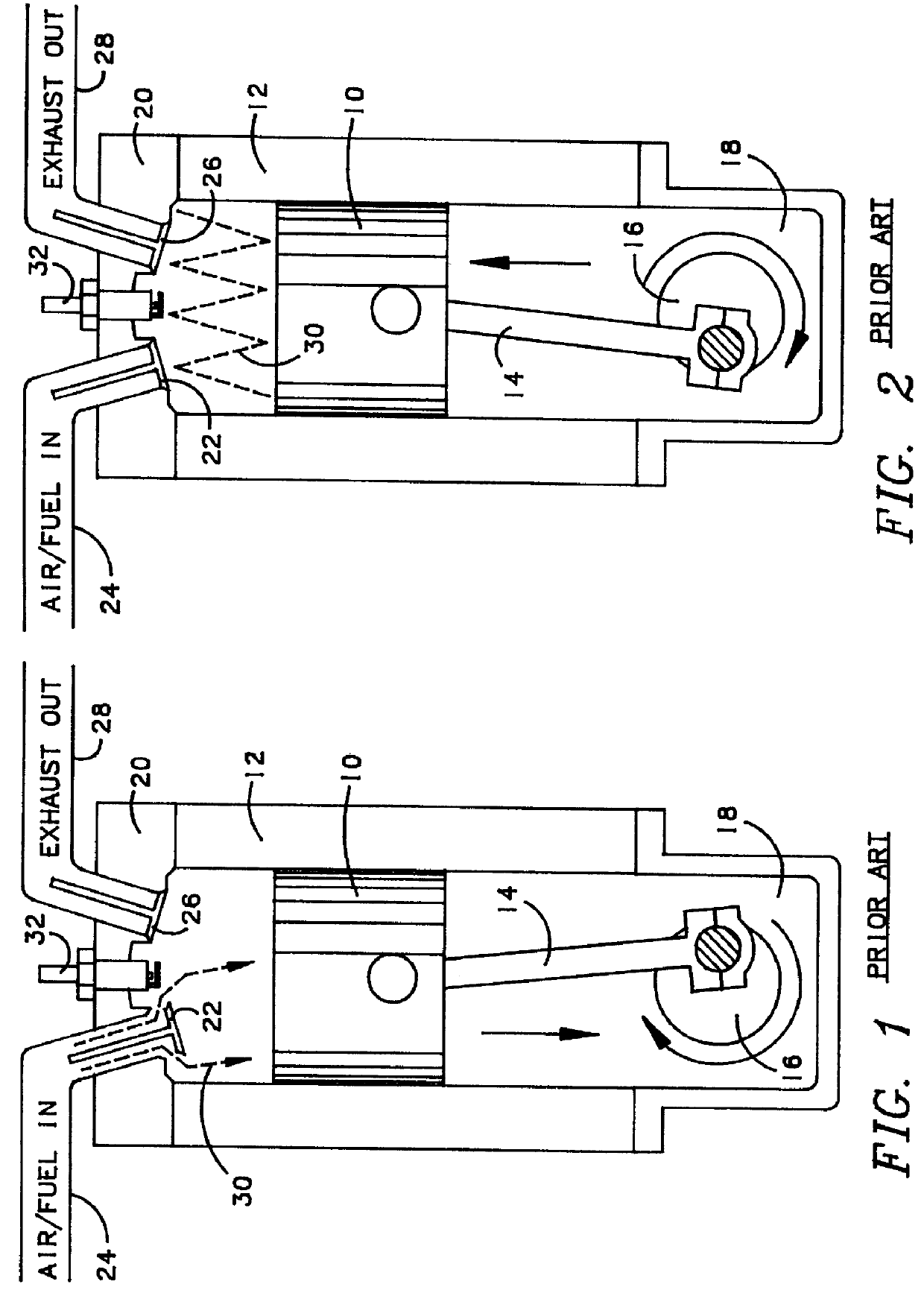
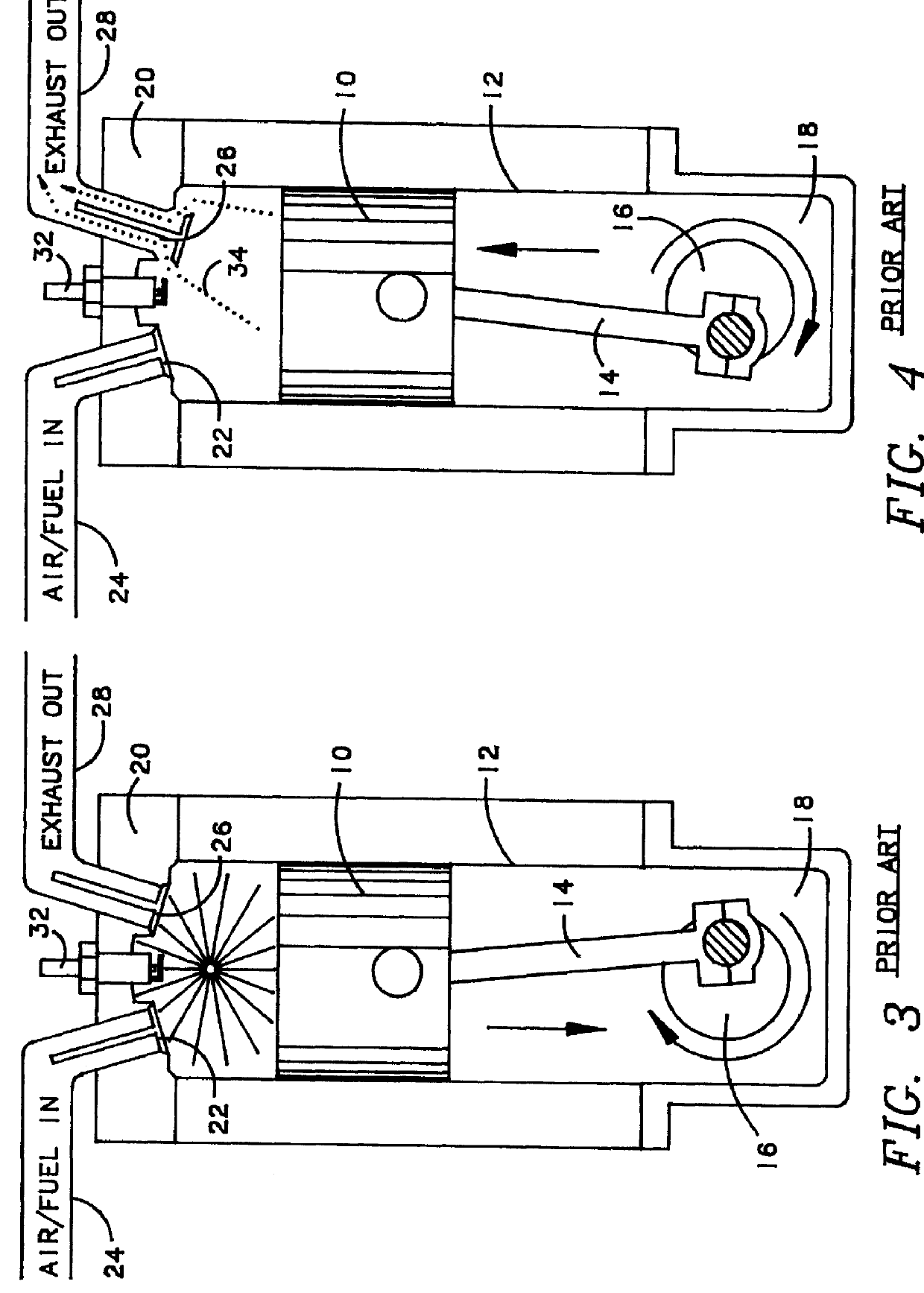
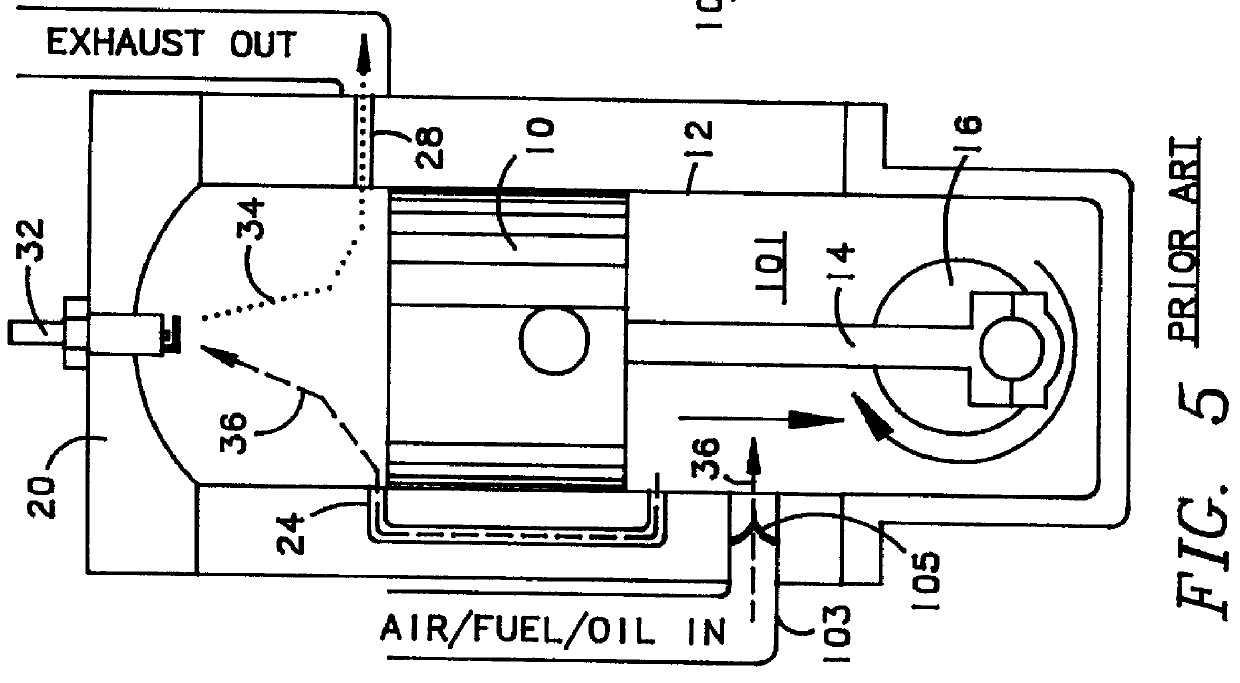
High efficiency low-pollution engine
InactiveUS6026568AEliminate needCasingsInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineCylinder head
An internal combustion engine of either two-cycle or four-cycle construction including a block having at least one cylinder bore therein having sidewalls carrying a liner of a structural fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite material disposed in sealed fiber reinforced sliding relationship within the cylinder bore, and a cylinder head sealing atop end of the cylinder bore to form a closed combustion chamber in combination with the piston. The cylinder head also has the structural fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite material disposed on an inner surface thereof facing the combustion chamber. The preferred engine is a two-cycle engine having an externally scavenged intake system and an oil sump lubricating system thereby eliminating the need to separately mix or inject lubricating oil. Higher operating temperatures and closer tolerances allow higher fuel efficiency and less pollutant production. A preferred structural fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite material and the method of making same is also disclosed.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Flame retardant antistatic high intension and tough composite tube made from polyvinyl chloride and preparation method
A flame-retarding antistatic composite PVC pipe with high strength and toughness is composed of internal layer, reinforcing fibre or fabric layer and external antistatic layer. It can be made up by coextruding out method or layer-by-layer coating method.
Owner:孙建宁 +1
Process for the manufacture of composite structures
The invention is a process for making a composite structure having a honeycomb core and face sheets using vacuum bagging techniques without the use of an autoclave. In detail, the process includes the following steps: 1) forming a preform sandwich assembly having previously de-bulked cover sheets impregnated with a fiber-reinforced resin having a first curing temperature, a honeycomb core and sheets of adhesive between the cover sheets and core, the first layer of adhesive having a second curing temperature less than the first curing temperature; 2) vacuum bagging the preform and drawing a vacuum; 3) initially heating the vacuum bagged preform at a heating rate of between 0.5 degree and 2 degrees per minute until the gel temperature of said adhesive is reached; 4) holding the temperature at the gel temperature until the layer of adhesive has cured; 5) raising the temperature to the first curing temperature of the fiber-reinforced resin; and 6) maintaining the temperature at the first curing temperature until the fiber-reinforced resin has cured.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Lightweight unit load device
InactiveUS20110247958A1Reduce weightRaise the ratioSynthetic resin layered productsLarge containersUnit load deviceUnit device
A unit load device constructed from fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite materials is described. Individual panels of the unit load device may be customized with composite materials and patterns. The joints are adapted to receive the ends of the panels of the unit load device and may further be customized with fiber reinforced composite materials to strengthen the joint. Some embodiments provide for construction of a unit load device from a variety of fiber reinforcing materials utilizing a matrix of thermoplastic polymers with similar softening temperatures. Each component part within the container was designed and / or created to address the specific needs of the particular part. The unit load devices described herein provide for all composite containers with a significant weight savings from conventional unit load devices.
Owner:COMPOSITE TRANSPORT TECH
Continuous fiber fabric reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material and production method thereof
The invention relates to a continuous fiber fabric reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material and a production method thereof. The composite material is produced from continuous fiber through thermoplastic resin melting and impregnating, cooling and molding, with the thickness of 0.20mm-0.35mm, wherein the content of the continuous fiber reinforced fabric is 40wt%-65wt%, the continuous fiber fabric is uniformly spread out and subjected to tension adjustment and static electricity elimination, then enters thermoplastic resin for melting and impregnating, and finally is cooled in a cooling unit and wound and formed to obtain the continuous fiber fabric reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material. Compared with the prior art, the continuous fiber fabric reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material and the production method solve a series of problems caused by too high resin viscosity in the existing thermoplastic resin and fiber reinforcing process, such as complex equipment process, too high equipment cost, not environment-friendly technological operation process, dry gauze easily caused by poor impregnation and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENIUS ADVANCED MATERIAL (GRP) CO LTD
Method for recovering carbon-fiber enhanced epoxy resin composite material
The invention relates to a method for recovering a carbon-fiber enhanced epoxy resin composite material. In the existing method, the requirement for equipment is high and the recovery cost is large. The method comprises the following steps of: cutting materials needing to be decomposed into blocks with the volume being 5cm<3>, putting the blocks in a backflow device containing acid liquor, heating for 5-20 minutes at the temperature of boiling point, cleaning and carrying out vacuum drying; then putting the obtained mixture into a reaction kettle, adding an organic solvent and an oxidizing agent, firstly heating, then cooling to normal temperature, and obtaining a primary product; and after cleaning, putting a solid product in the primary product into industrial acetone solution for dipping, obtaining recovered carbon fiber and carrying out pressure-reduced distillation on a liquid product to obtain phenol and derivatives thereof. In the method, reaction under low temperature and low pressure is realized and has the advantages of moderate reaction condition, easy control of reaction, fewer side products, no pollution basically and no corrosion to equipment and the like, so that the method is a green recovering method.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recycled carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material and preparation method thereof
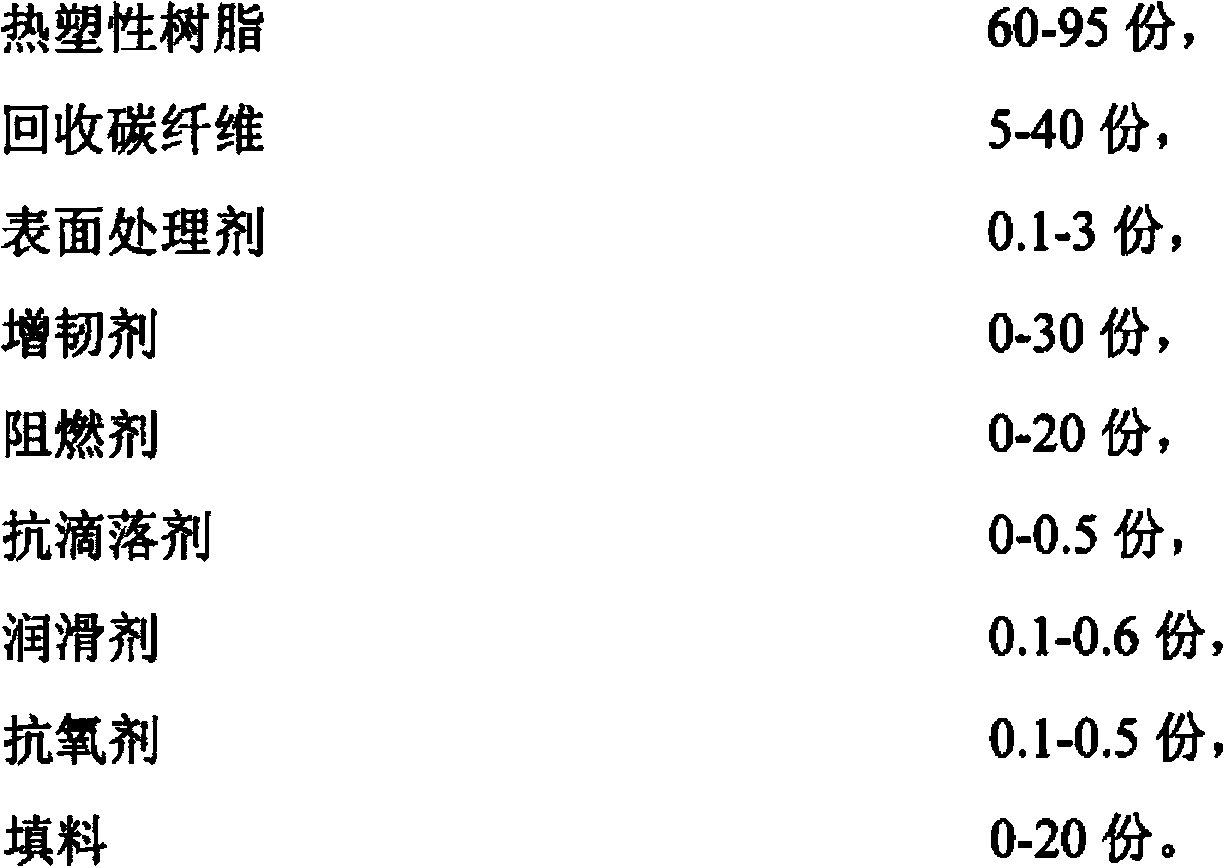
The invention relates to a recycled carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) weighing 5-40 parts of recycled carbon fiber according to a proportion, adding the recycled carbon fiber into a high-speed mixer, adding 0.1-3 parts of surface treating agent, and performing surface treatment on the recycled carbon fiber; (2) weighing 60-95 parts of thermoplastic resin, 0-30 parts of flexibilizer, 0-20 parts of fire retardant, 0-0.5 part of anti-drip agent, 0.1-0.6 part of lubricant, 0.1-0.5 part of antioxidant and 0-20 parts of filler according to the proportion, adding the raw materials into the high-speed mixer, and uniformly mixing the raw materials; (3) adding the uniformly mixed raw materials into a double-screw machine, and performing melt blending, extrusion, water cooling and strand pelletizing to obtain the recycled carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material. Compared with the prior art, the recycled carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin composite material has the advantages of low density, excellent mechanical performance, low cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com