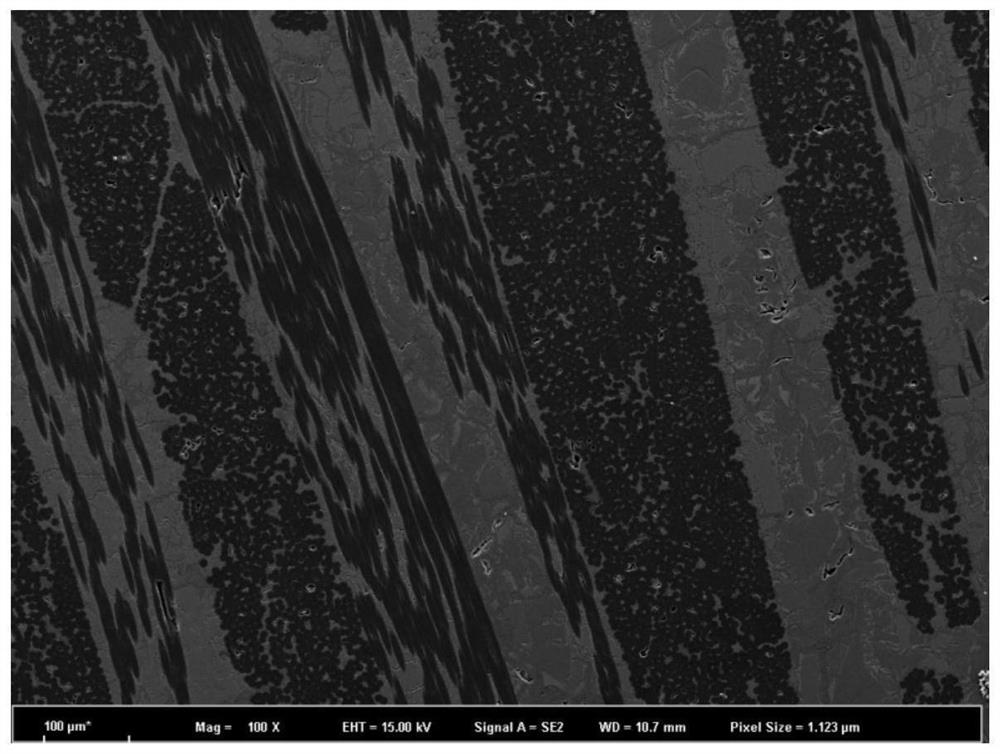
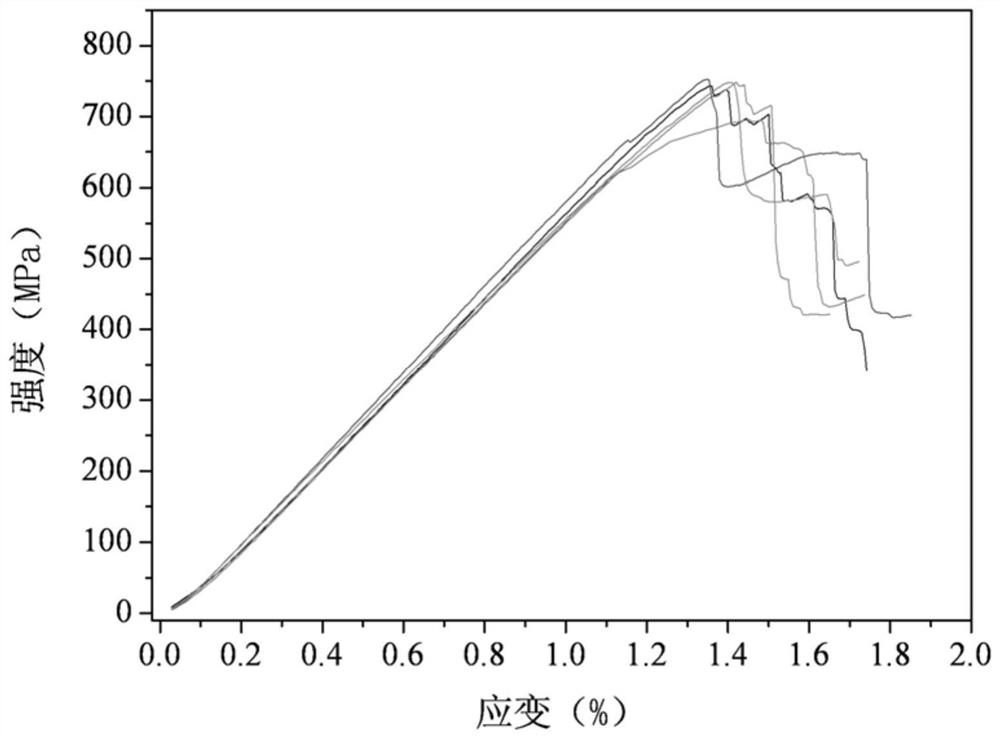
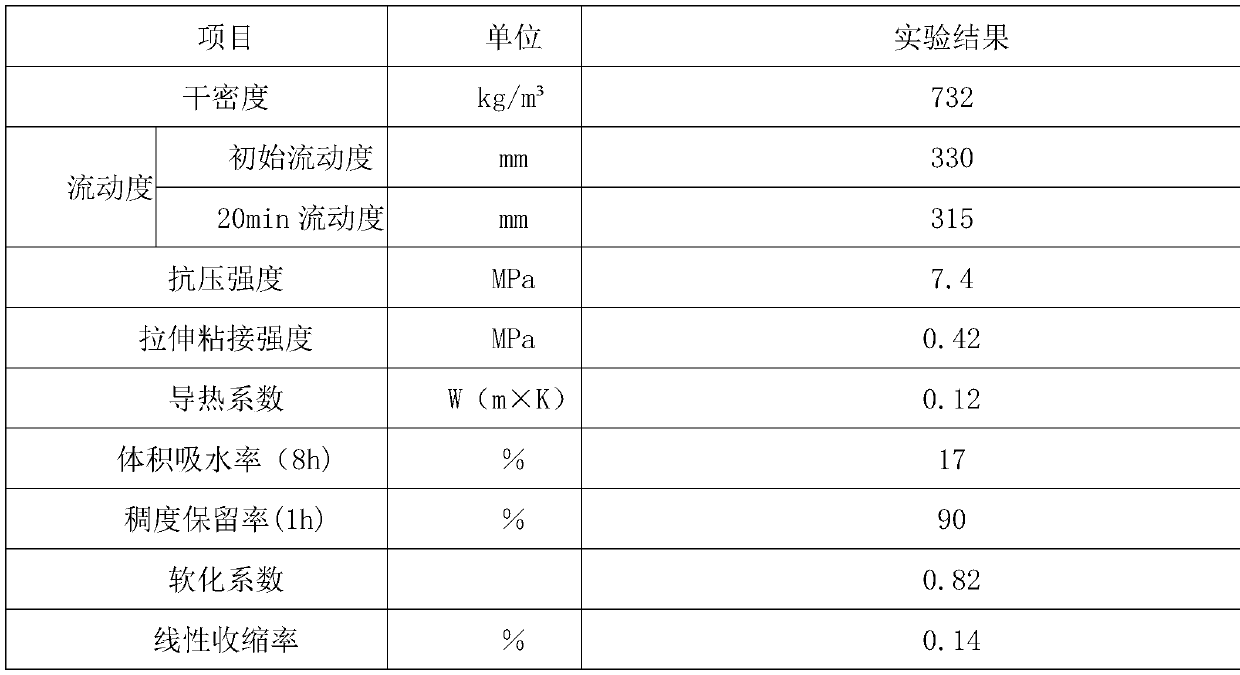
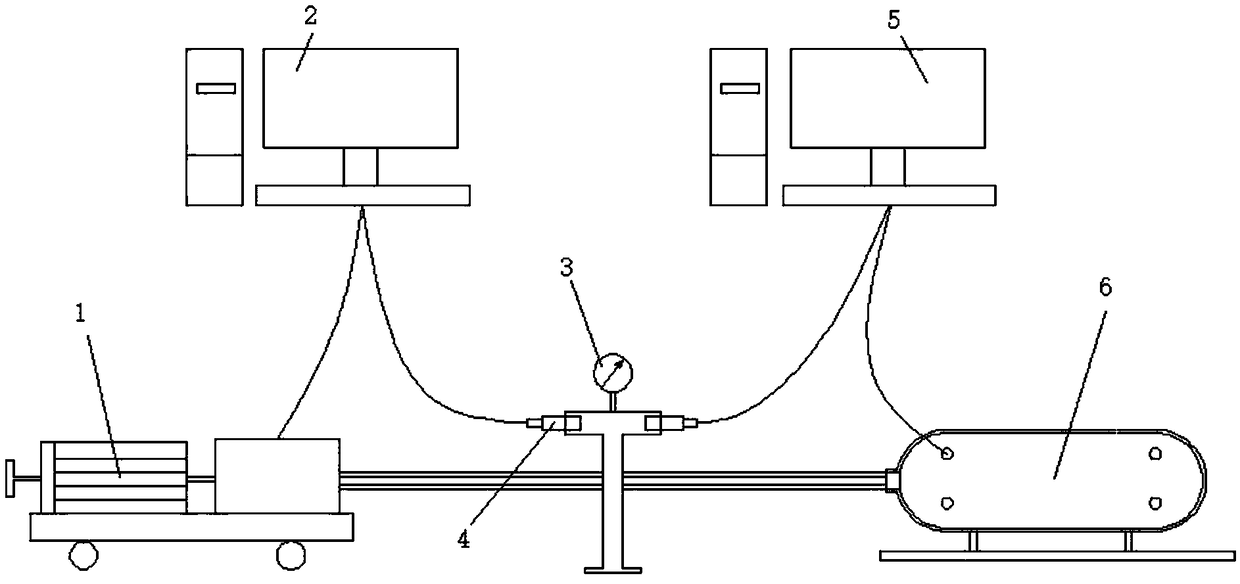
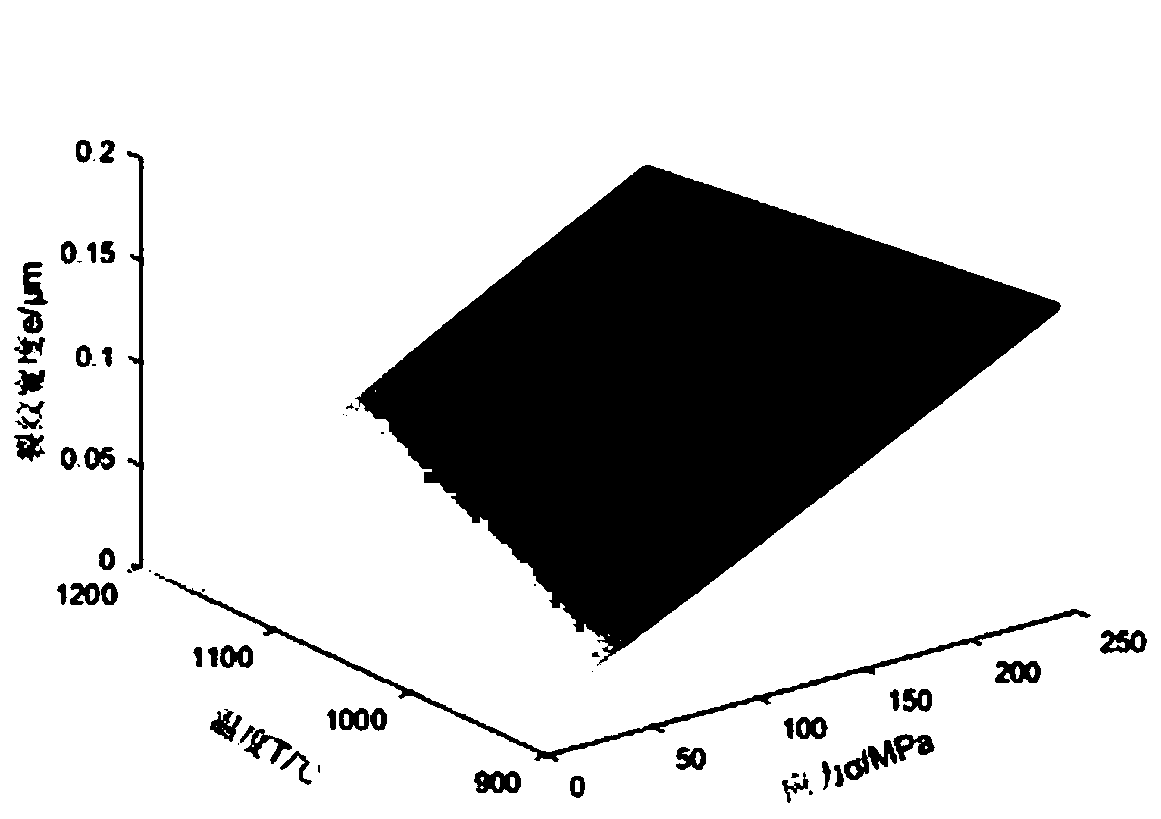
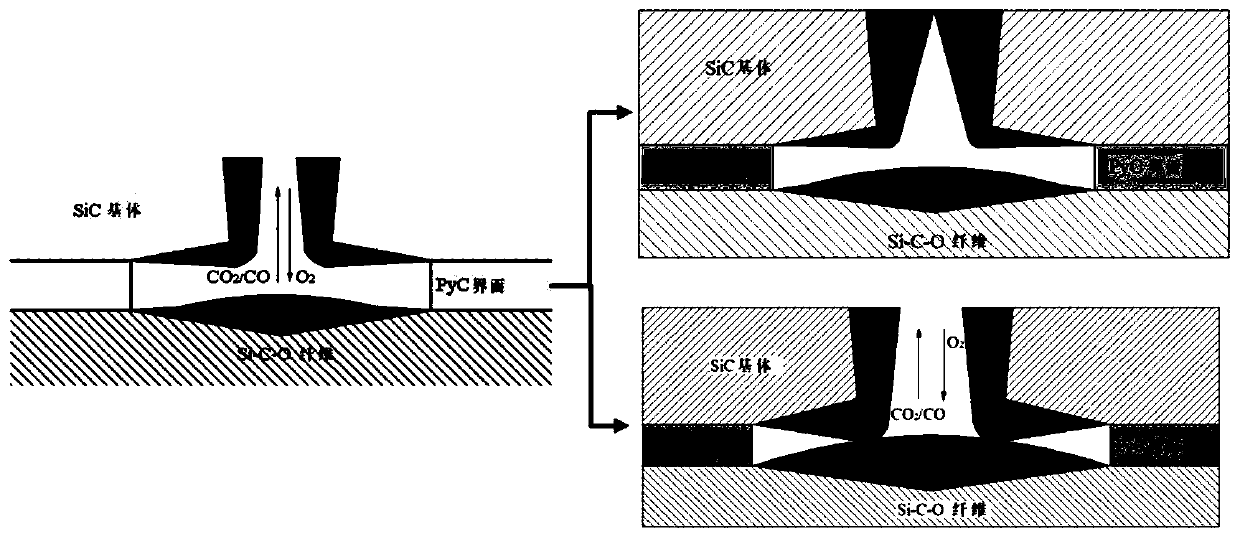
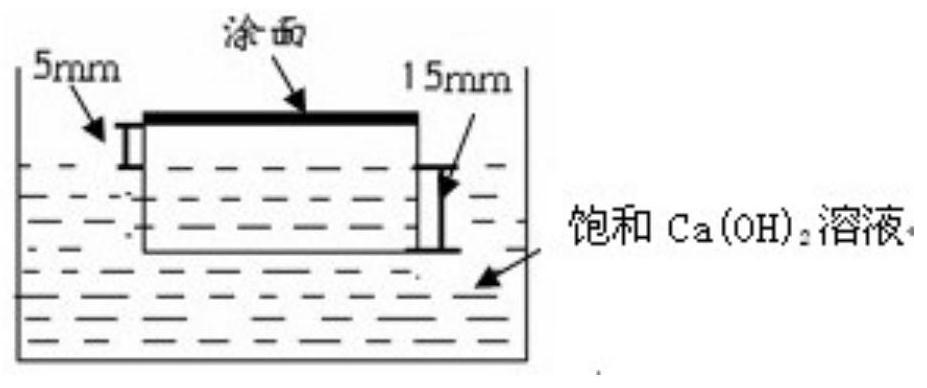
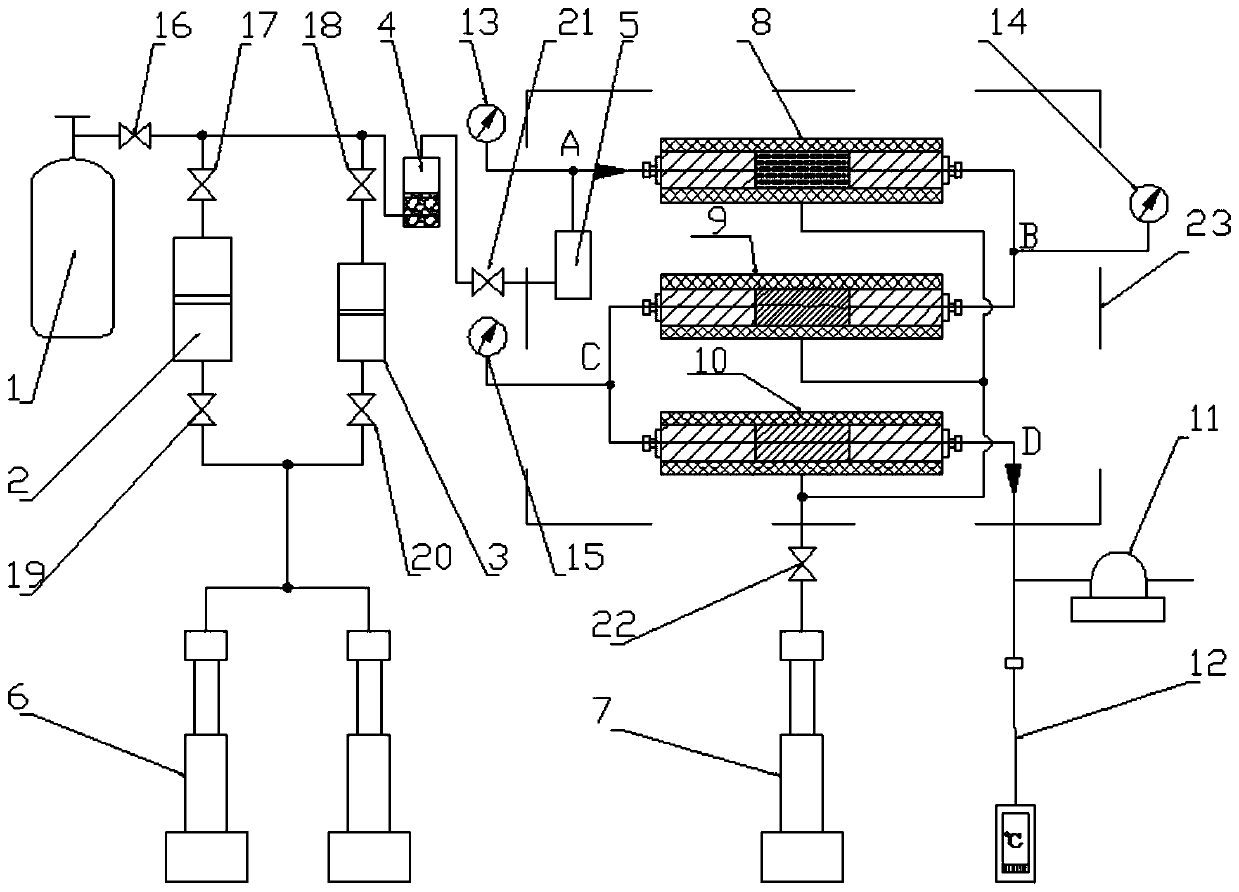
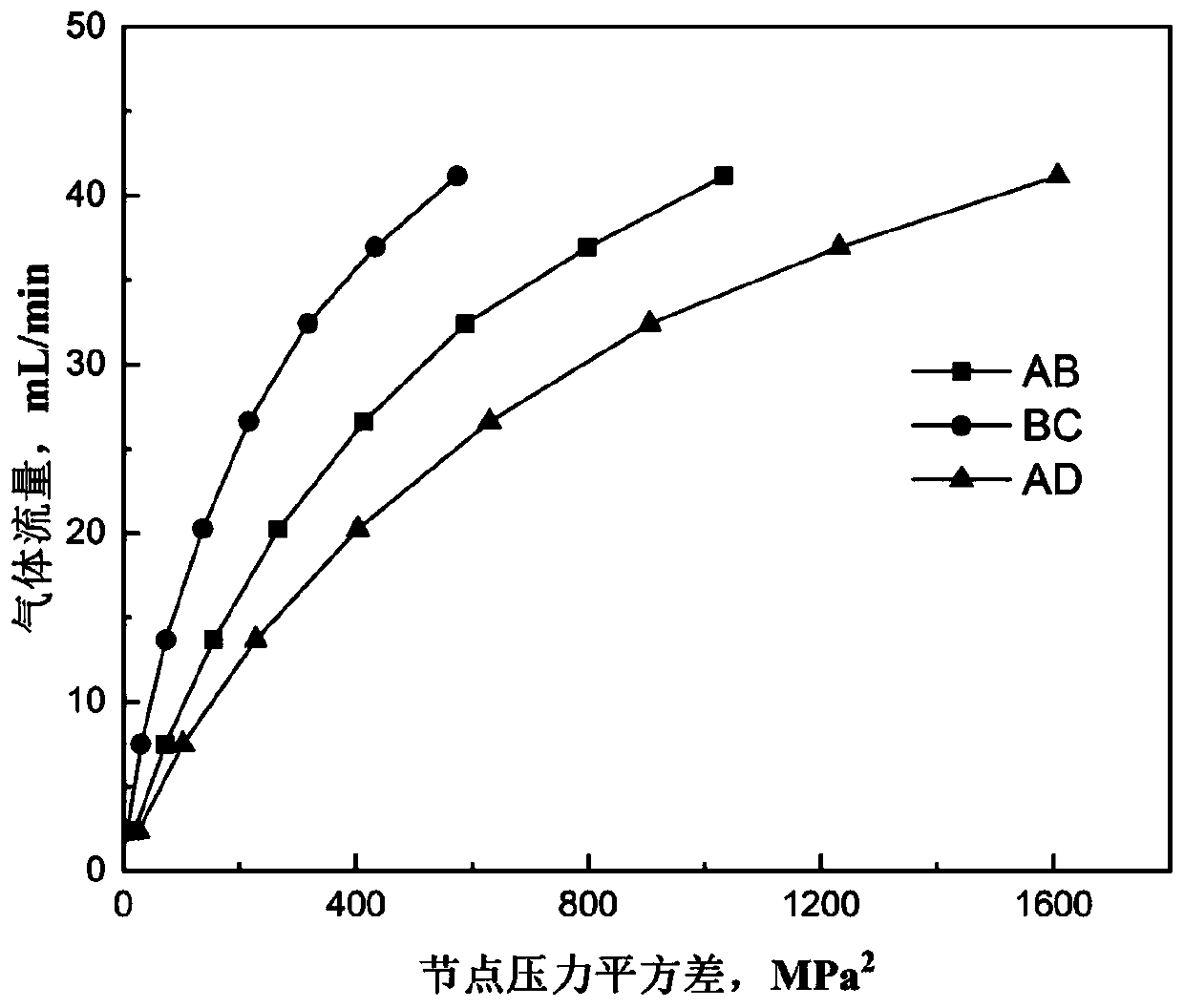
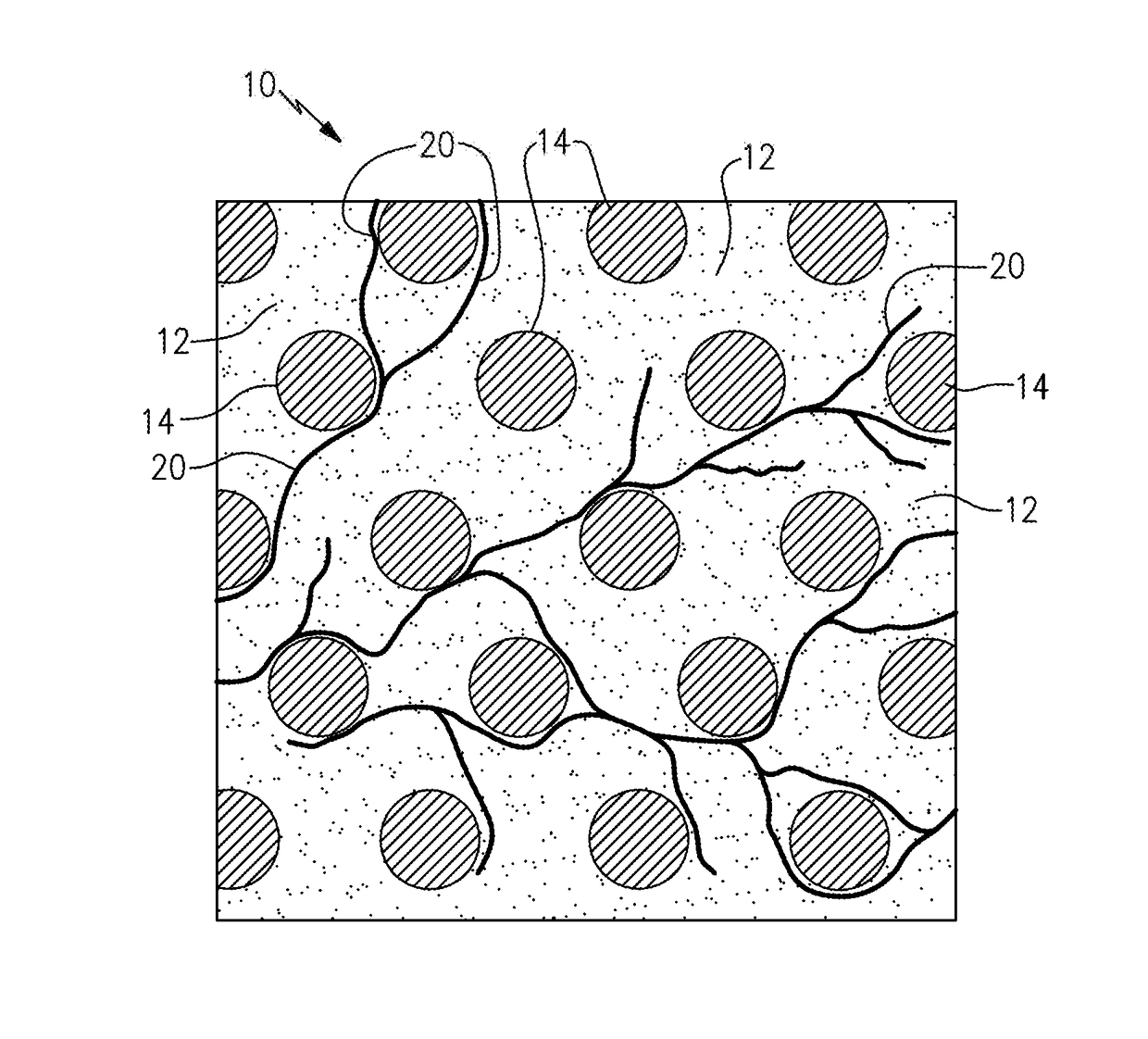
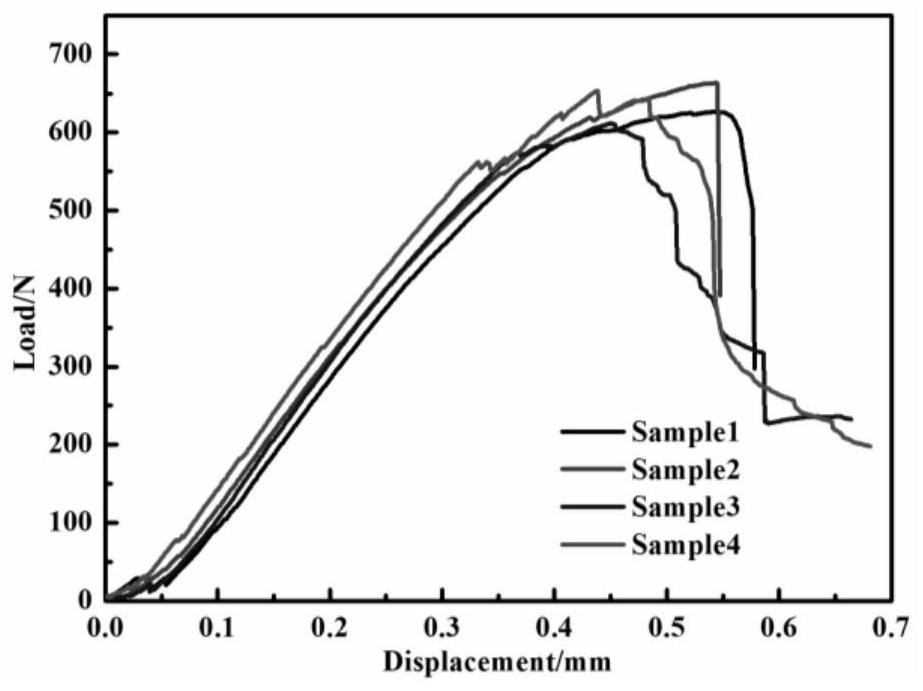
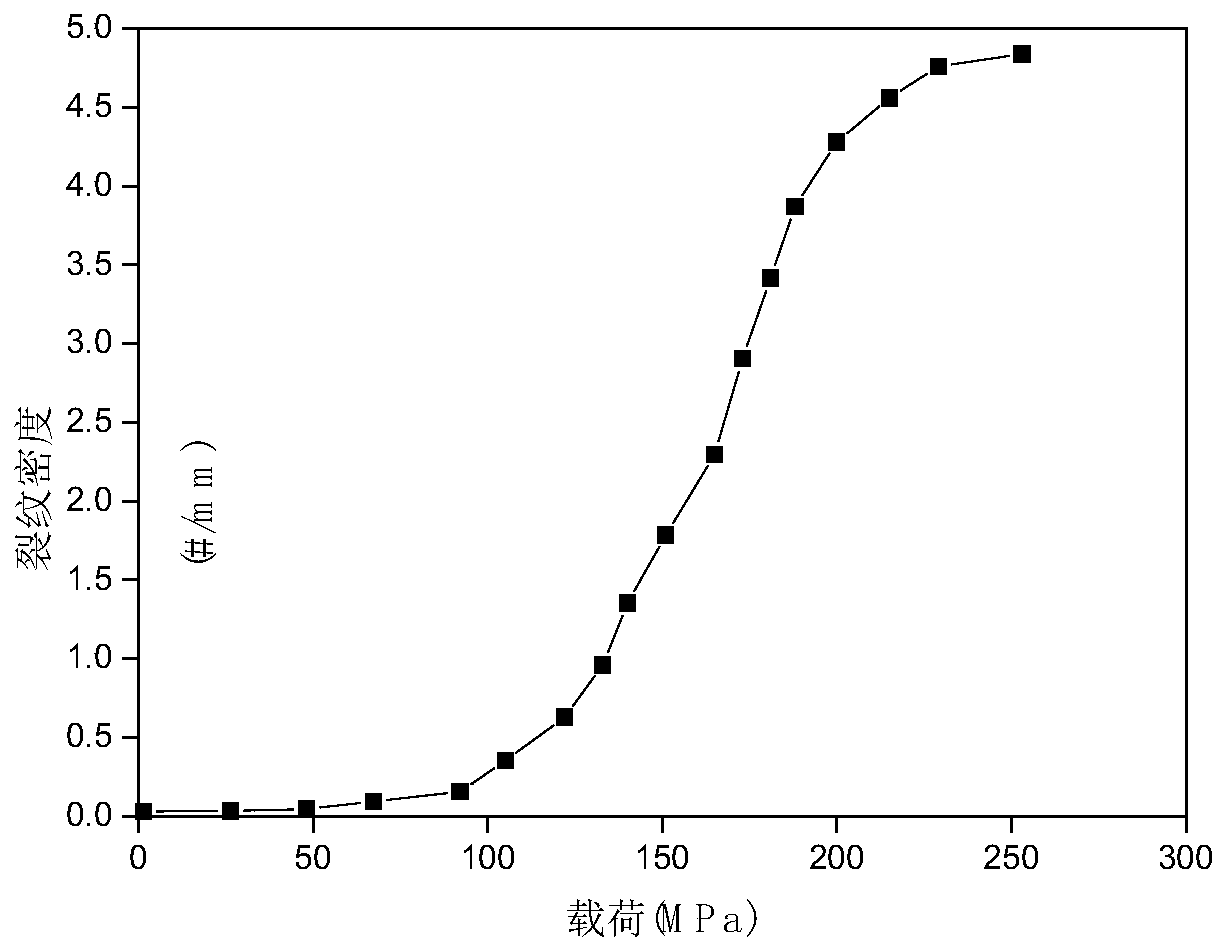
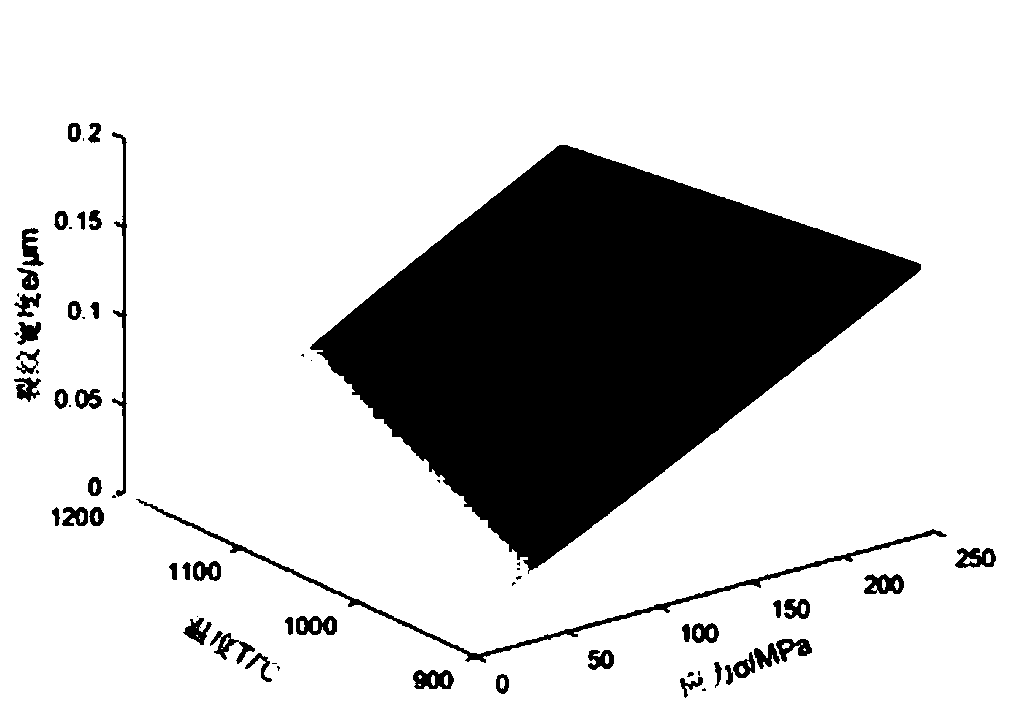
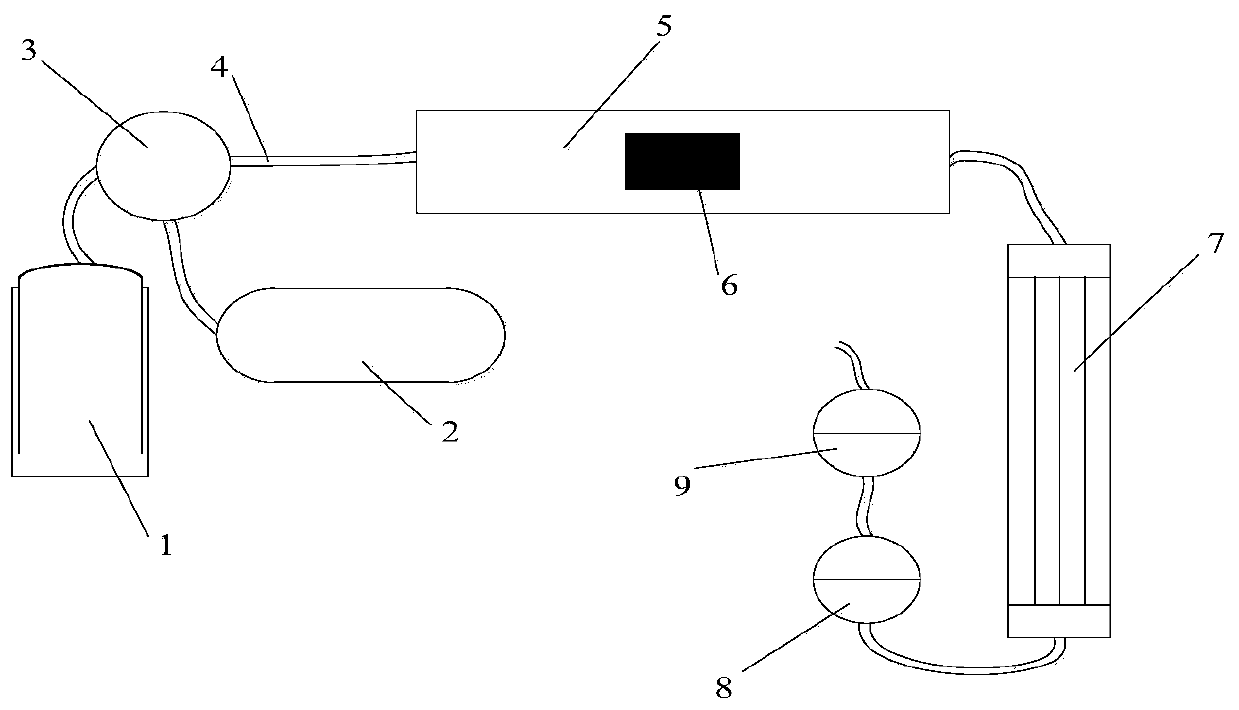
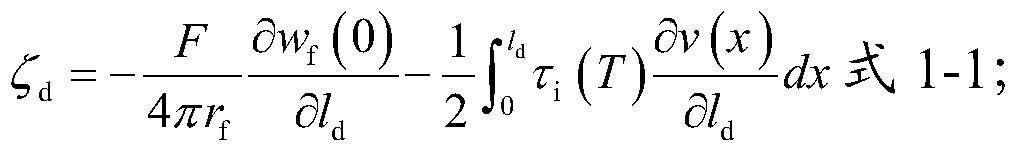Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
86 results about "Matrix cracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fiber-reinforced ceramic composite material comprising a matrix with a nanolayered microstructure
InactiveUS20050181192A1Improve the immunityHigh strengthSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsCeramic compositeToughening
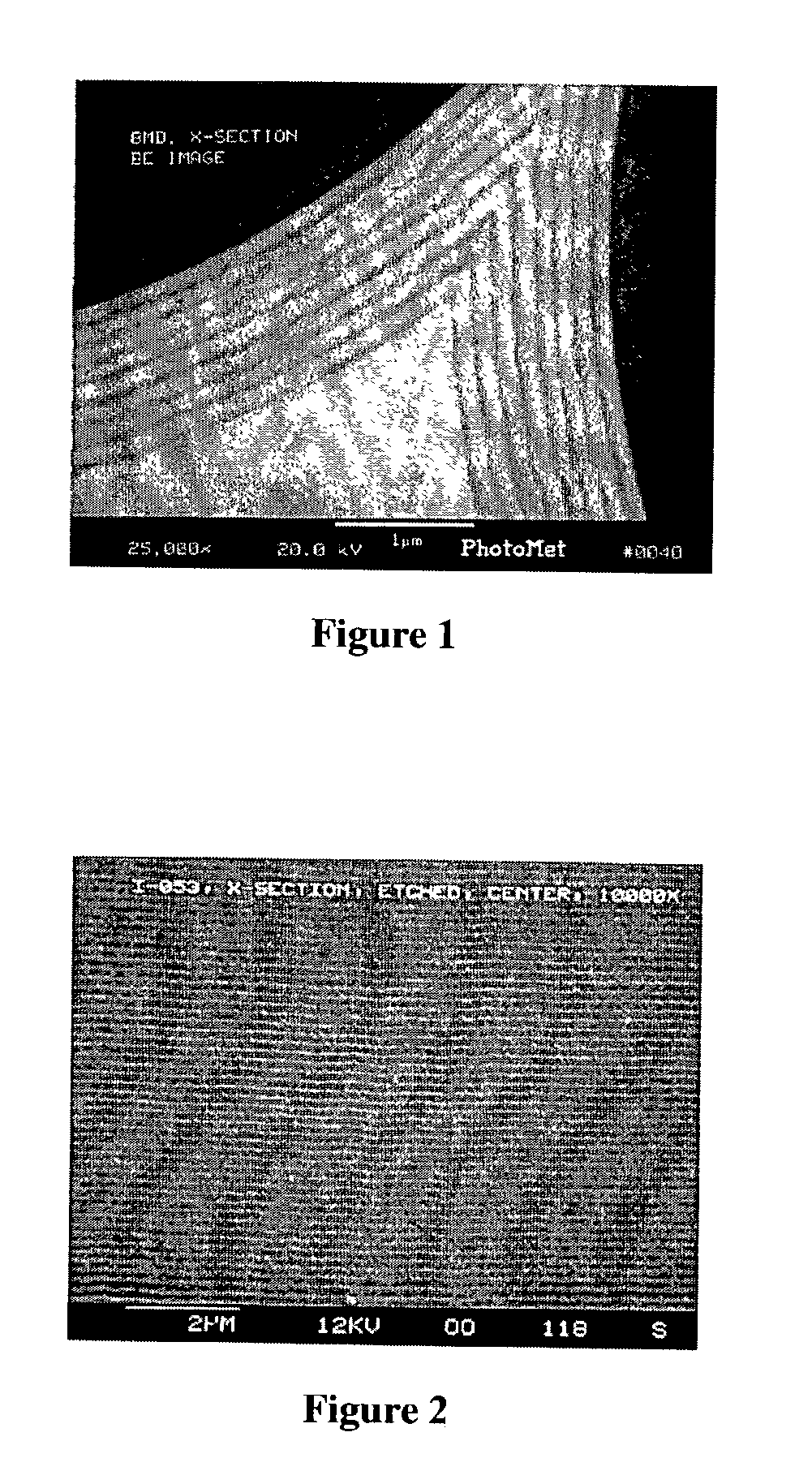
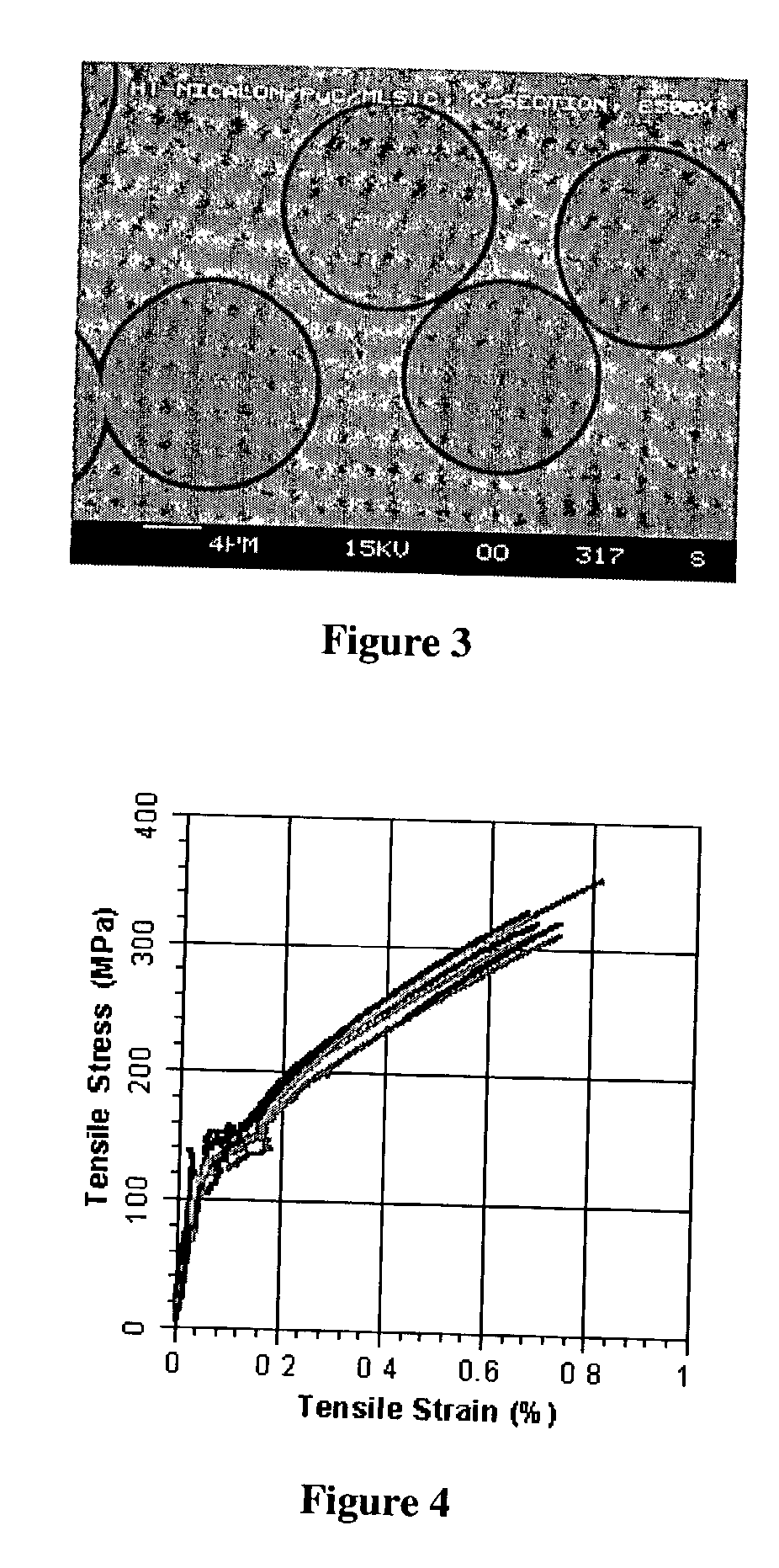
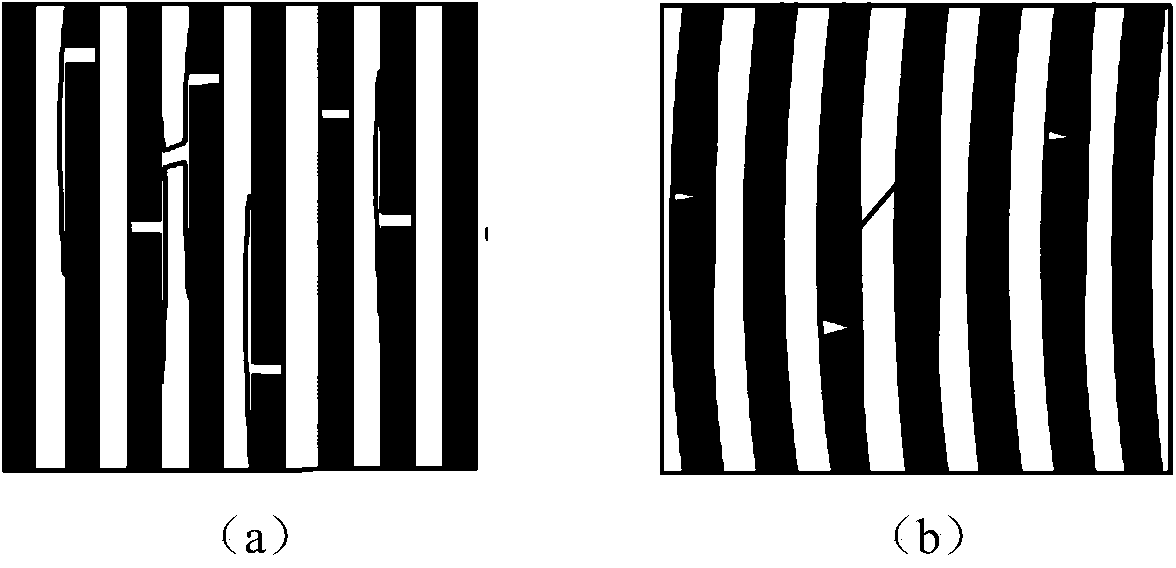
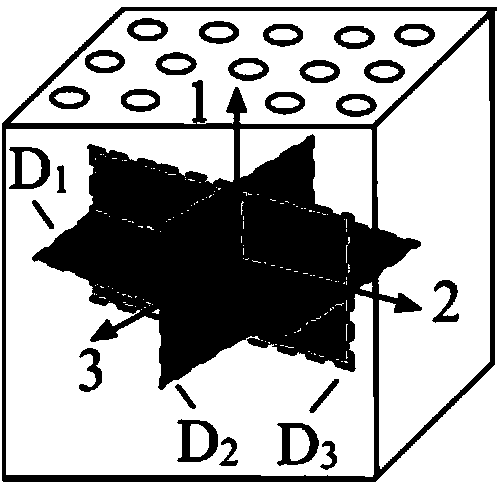
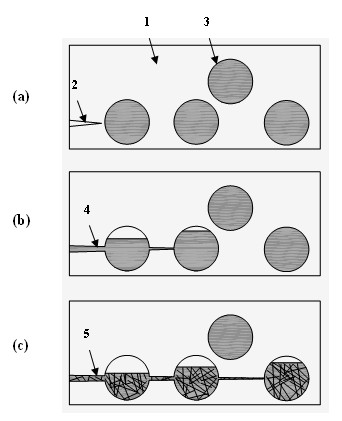
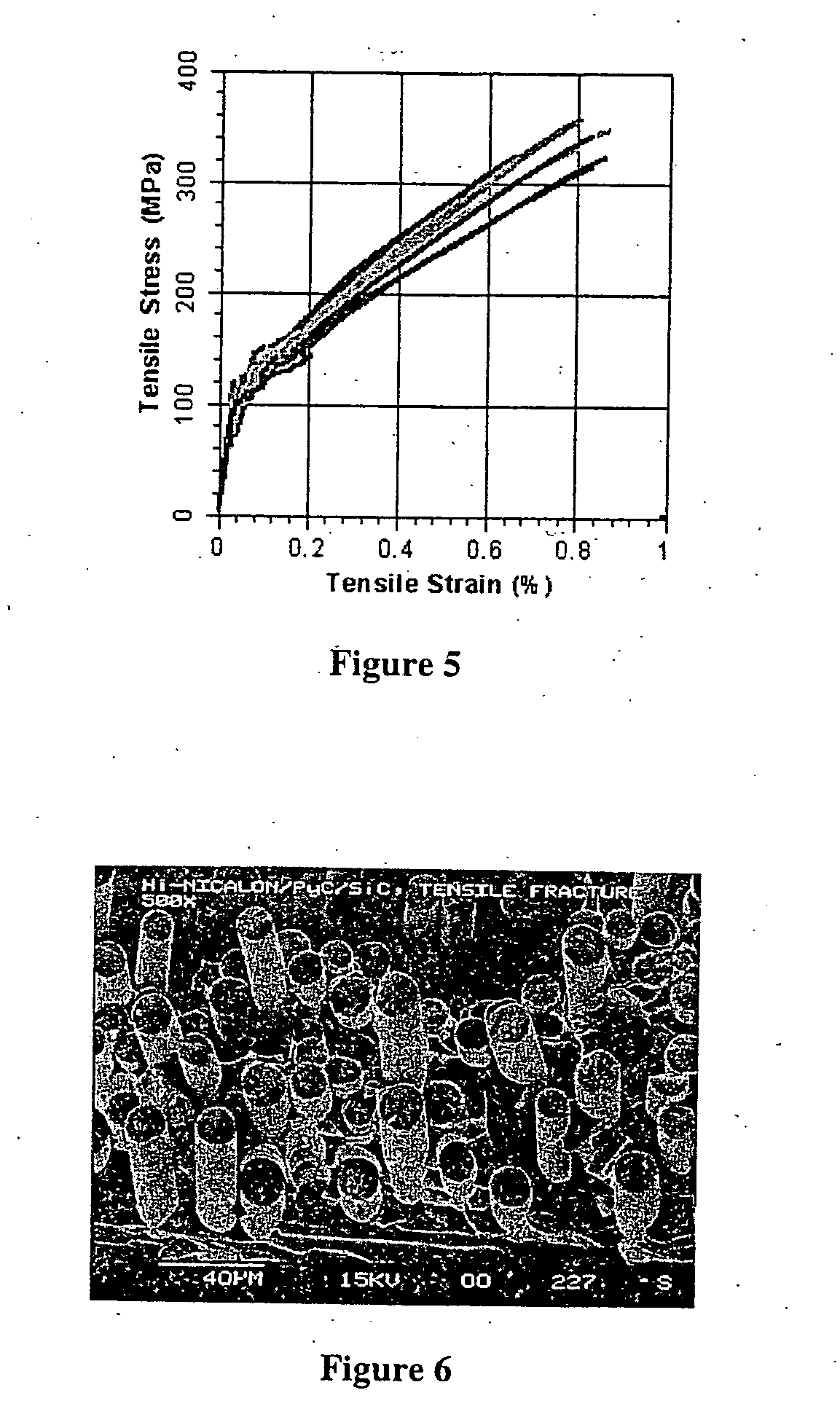
A fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composite material exhibiting increased matrix cracking strength and fracture toughness is produced by sequentially depositing a plurality of 5-500 nanometer-thick layers of a primary ceramic matrix material phase periodically separated by 1-100 nanometer-thick intermediate layers of a secondary matrix material phase onto the reinforcing fibers upon their consolidation. The resultant nanolayered matrix enhances the resistance to the onset of matrix cracking, thus increasing the useful design strength of the ceramic matrix composite material. The nanolayered microstructure of the matrix constituent also provides a unique resistance to matrix crack propagation. Through extensive inter-layer matrix fracture, debonding and slip, internal matrix microcracks are effectively diverted and / or blunted prior to their approach towards the reinforcing fiber, thus increasing the apparent toughness of the matrix constituent. This unique toughening mechanism serves to dampen energetic co-planar macrocrack propagation typically observed in conventionally manufactured ceramic matrix composites wherein matrix cracks are usually deflected at the fiber / matrix interphase region.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE HIGH TEMPERATURE COMPOSITES INC
Composite material structure failure analysis method based on continuum damage mechanics degradation model
InactiveCN103592175AComputing performanceAccurate calculationStrength propertiesMatrix damageContinuum damage mechanics
The invention relates to a composite material structure failure analysis method based on a continuum damage mechanics degradation model. According to the method, a three-dimensional continuum damage mechanics degradation model of a unidirectional fiber enhanced composite material is constructed, two types of damage forms such as fiber cracks and matrix cracks and the orientation of damages are considered, and meanwhile, the crack closure effect caused by coupling of the fiber damage and the matrix damage and reverse loading of load in a fiber stretching and compressing damage process is considered; three damage variables are respectively used for representing the fiber crack damage and two mutually-perpendicular matrix crack damages respectively, so that the continuum damage mechanics degradation model for failure analysis of a composite material structure is obtained. Compared with the conventional anti-climax degradation model, the continuum damage mechanics degradation model has the advantages that the behavior characteristics of the damaged composite material under different load states are considered, and the performance of the damaged material can be accurately represented; the composite material structure failure analysis method is suitable for simulation of a composite material structure damage process and forecasting of the intensity under a condition that the load state and a constraint situation are more complicated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for predicating stress-strain behavior under arbitrary loading and unloading of one-way ceramic matrix composite
ActiveCN104866690APrediction of stress-strain behaviorSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionFailure mechanism
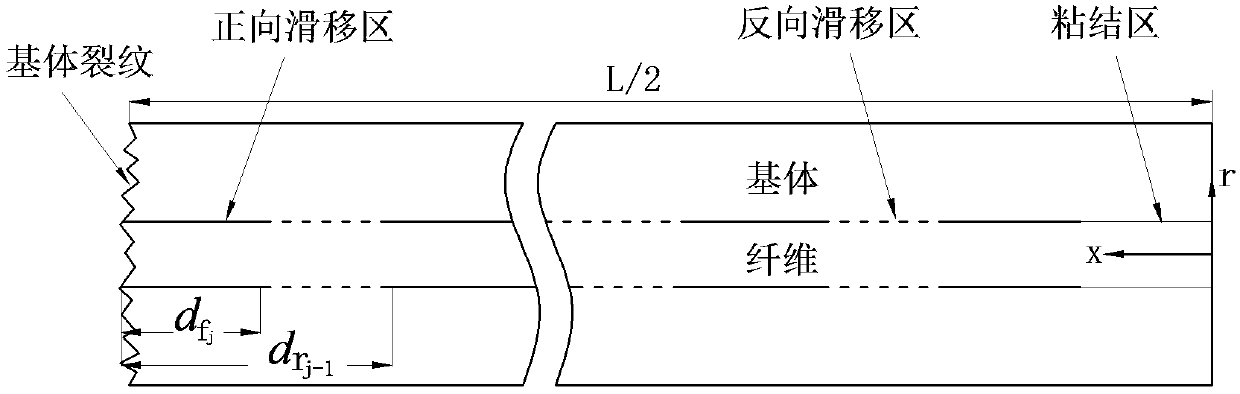
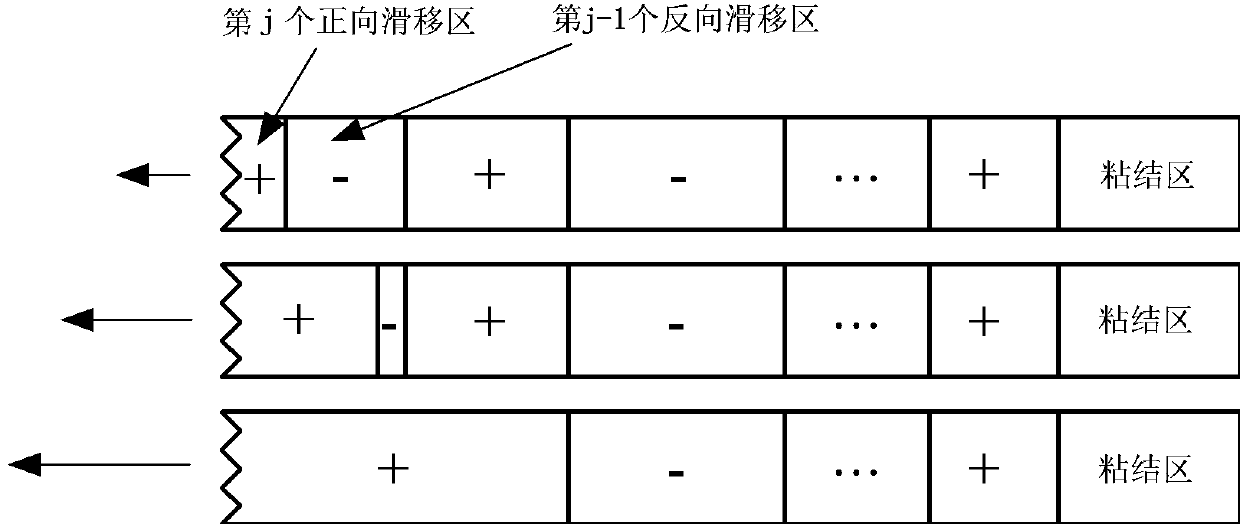
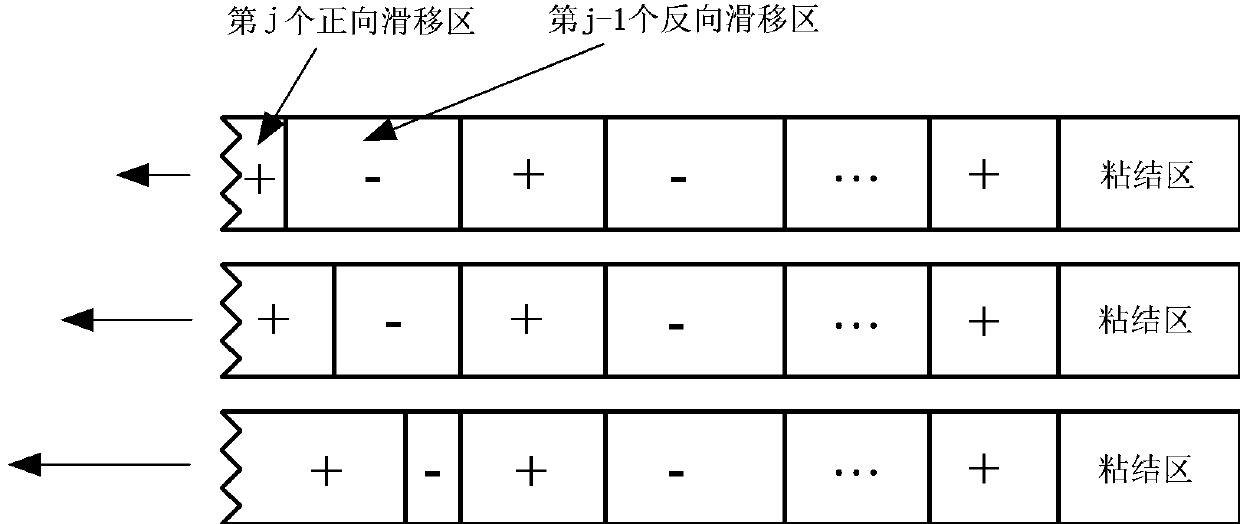
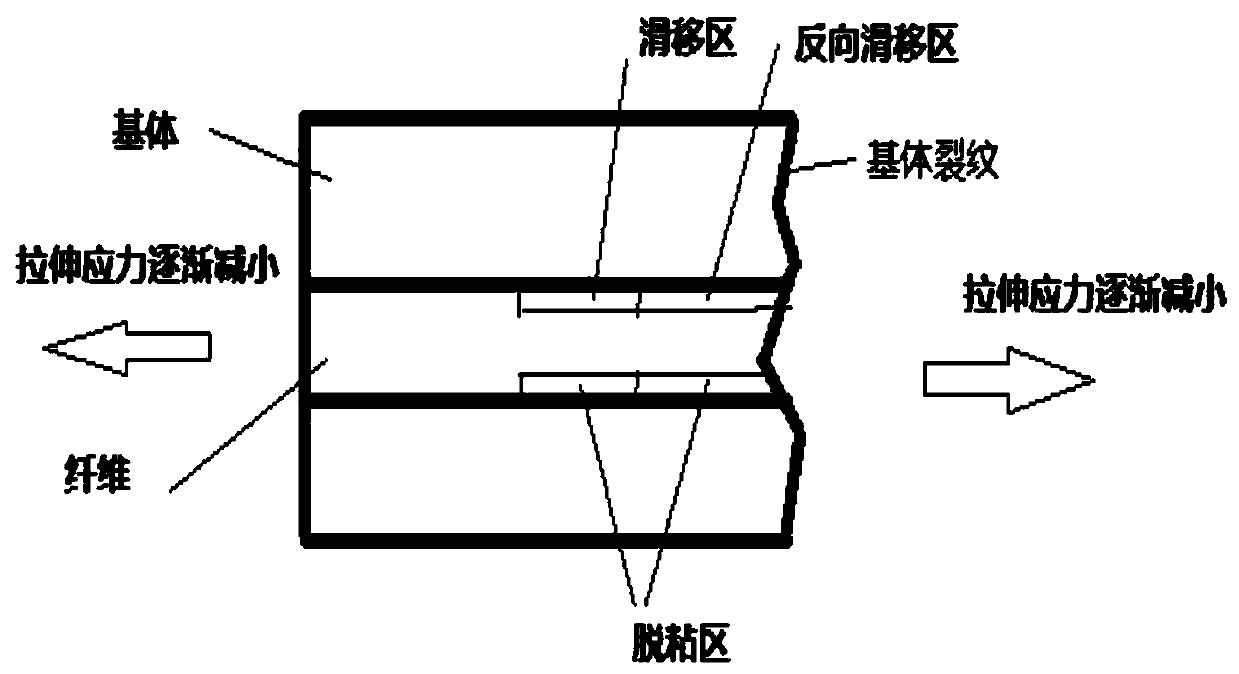
The invention relates to a method for predicating a stress-strain behavior of a composite, in particular to a method for predicating the stress-strain behavior under arbitrary loading and unloading of a one-way ceramic matrix composite. The invention aims at overcoming the defects of the prior art to provide the method capable of quickly predicating the stress-strain behavior under arbitrary loading and unloading of the one-way ceramic matrix composite. The invention provides the method for predicating the stress-strain behavior under arbitrary loading and unloading of the one-way ceramic matrix composite, and considers failure mechanisms, such as matrix cracking, fiber breakage, interface slip and interface abrasion. Generation and coverage rules for forward and reverse slip regions are provided, and the stress distribution and the strain are given in the presence of any number of forward and reverse slip regions. Most of formulas given by the method have analytical solutions, so that the stress-strain behavior under arbitrary loading and unloading of the one-way ceramic matrix composite can be quickly predicated.
Owner:南京长工智航科技有限公司
Room temperature self-repair thermoplastic polymer material
The invention relates to the technical field of self-repair materials, and discloses a room temperature self-repair thermoplastic polymer material. The material consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 77 to 94 percent of monomers for preparing thermoplastic resin matrix, 0.6 to 1.5 percent of initiator for preparing the thermoplastic resin matrix, 0.2 to 2.6 percent of chain transfer agent for preparing the thermoplastic resin matrix, and 2.5 to 20 percent of microcapsules containing vinyl monomers. According to the room temperature self-repair thermoplastic polymer material, when micro cracks are generated due to the action of an external force in use, the microcapsules embedded into the matrix crack to release a repair agent, and the repair agent and the matrix can undergo reversible addition-fragmentation transfer free radical polymerization, so that the fractured surfaces are stuck together, the cracks are prevented from being further expanded, and self-repair of the material is realized. The prepared self-repair thermoplastic polymer material is simple to prepare, and can automatically complete repair of the cracks at room temperature.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fiber-reinforced ceramic composite material comprising a matrix with a nanolayered microstructure
InactiveUS20050233127A1Improve the immunityHigh strengthSynthetic resin layered productsCeramic layered productsCeramic compositeToughening
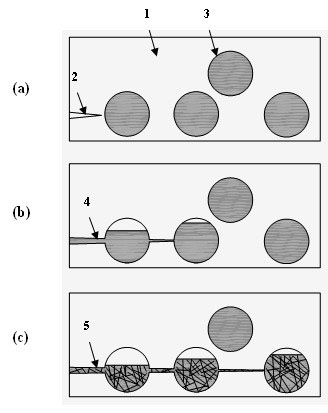
A fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composite material exhibiting increased matrix cracking strength and fracture toughness is produced by sequentially depositing a plurality of 5-500 nanometer-thick layers of a primary ceramic matrix material phase periodically separated by 1-100 nanometer-thick intermediate layers of a secondary matrix material phase onto the reinforcing fibers upon their consolidation. The resultant nanolayered matrix enhances the resistance to the onset of matrix cracking, thus. increasing the useful design strength of the ceramic matrix composite material. The nanolayered microstructure of the matrix constituent also provides a unique resistance to matrix crack propagation. Through extensive inter-layer matrix fracture, debonding and slip, internal matrix microcracks are effectively diverted and / or blunted prior to their approach towards the reinforcing fiber, thus increasing the apparent toughness of the matrix constituent. This unique toughening mechanism serves to dampen energetic co-planar macrocrack propagation typically observed in conventionally manufactured ceramic matrix composites wherein matrix cracks are usually deflected at the fiber / matrix interphase region.
Owner:STEFFIER WAYNE S
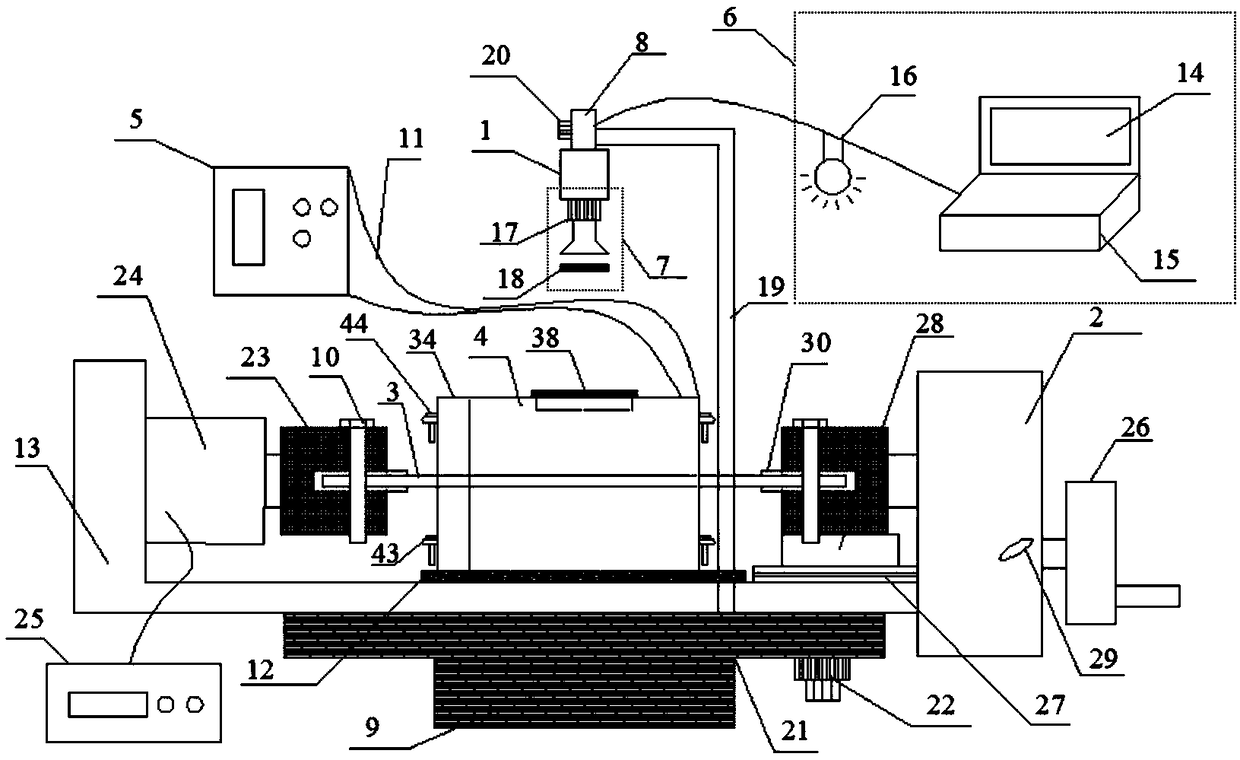
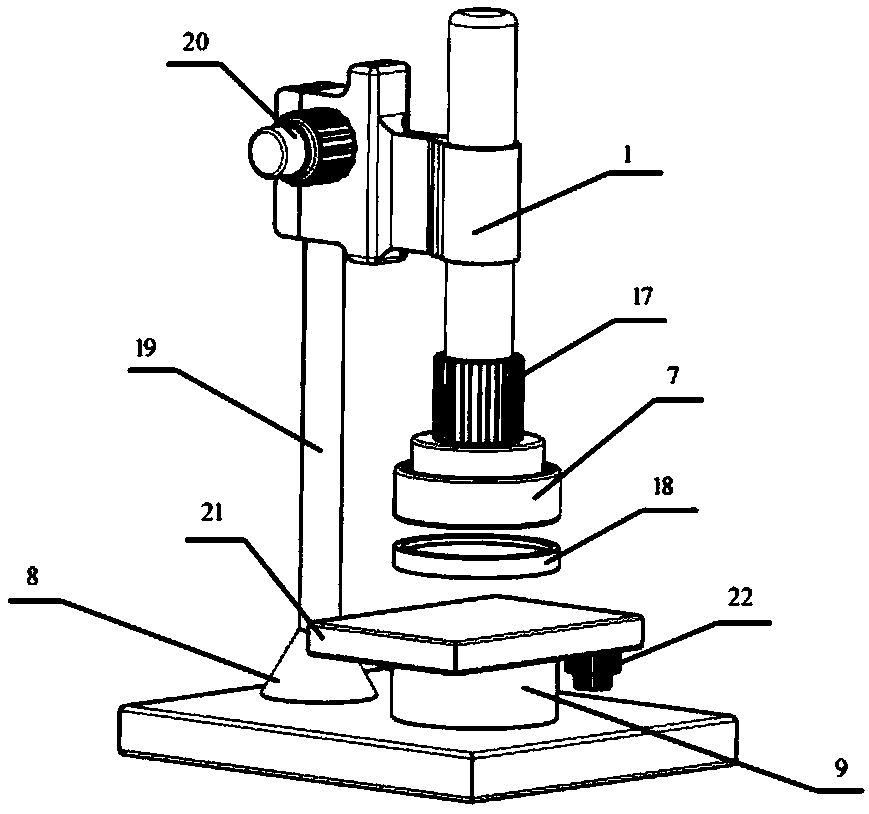
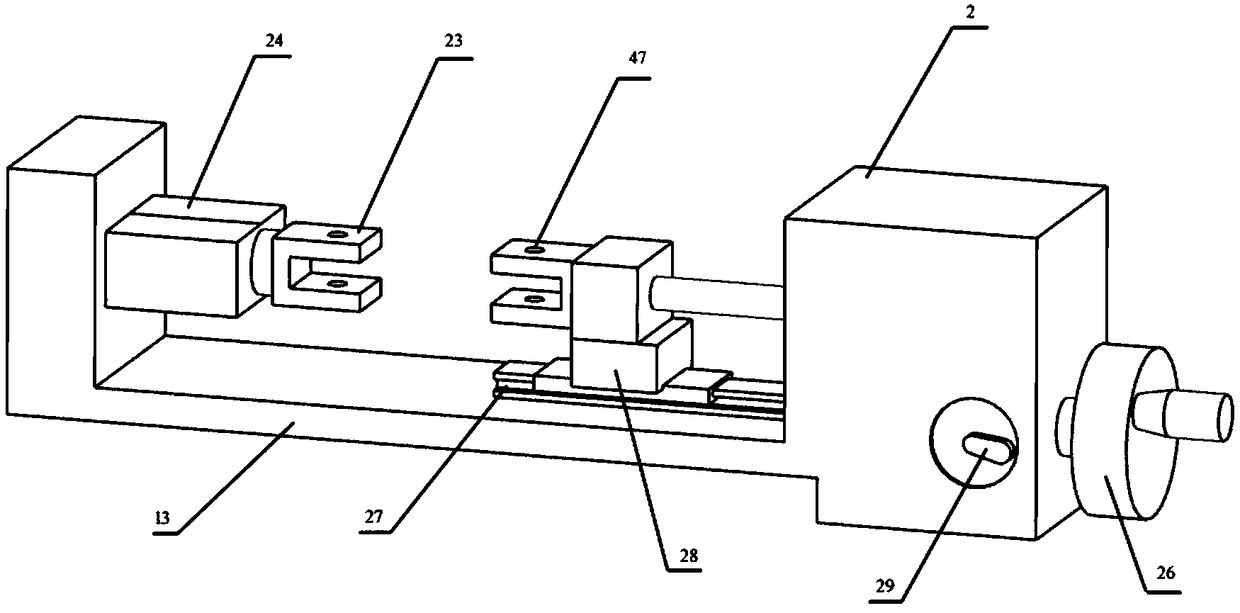
Ceramic matrix composite material high-temperature air environment substrate crack observation system and observation method
PendingCN108760526ARealize the observation of cracksAchieve observationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesObservation systemGlass sheet
The invention discloses a ceramic matrix composite material high-temperature air environment substrate crack observation system and an observation method. The system comprises a digital microscope, atension testing device, a test sample, a heating device and a temperature controller, wherein the digital microscope comprises a platform main control system, a zoom lens, a lens base and a two-dimensional moving device; the test sample is horizontally mounted on the tension testing device; the tension testing device is horizontally arranged on the two-dimensional moving device; a rectangular transparent quartz glass plate is embedded above the heating device and is horizontally placed on a thermal insulating pad of the base of the tension testing device; the zoom lens is aligned to the centerof the test sample through the transparent quartz glass plate; the heating device is connected with the temperature controller. The tension testing device, the split type micro heating device and thedigital microscope are all independent individuals and are convenient to mount and dismount, and in an atmospheric environment, matrix cracks of the ceramic matrix composite material can be conveniently observed under the action of high-temperature air and stress loads.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Self-healing microcapsule and preparation method thereof, paint, coating and epoxy resin composite material
Owner:河北京津冀再制造产业技术研究有限公司 +2
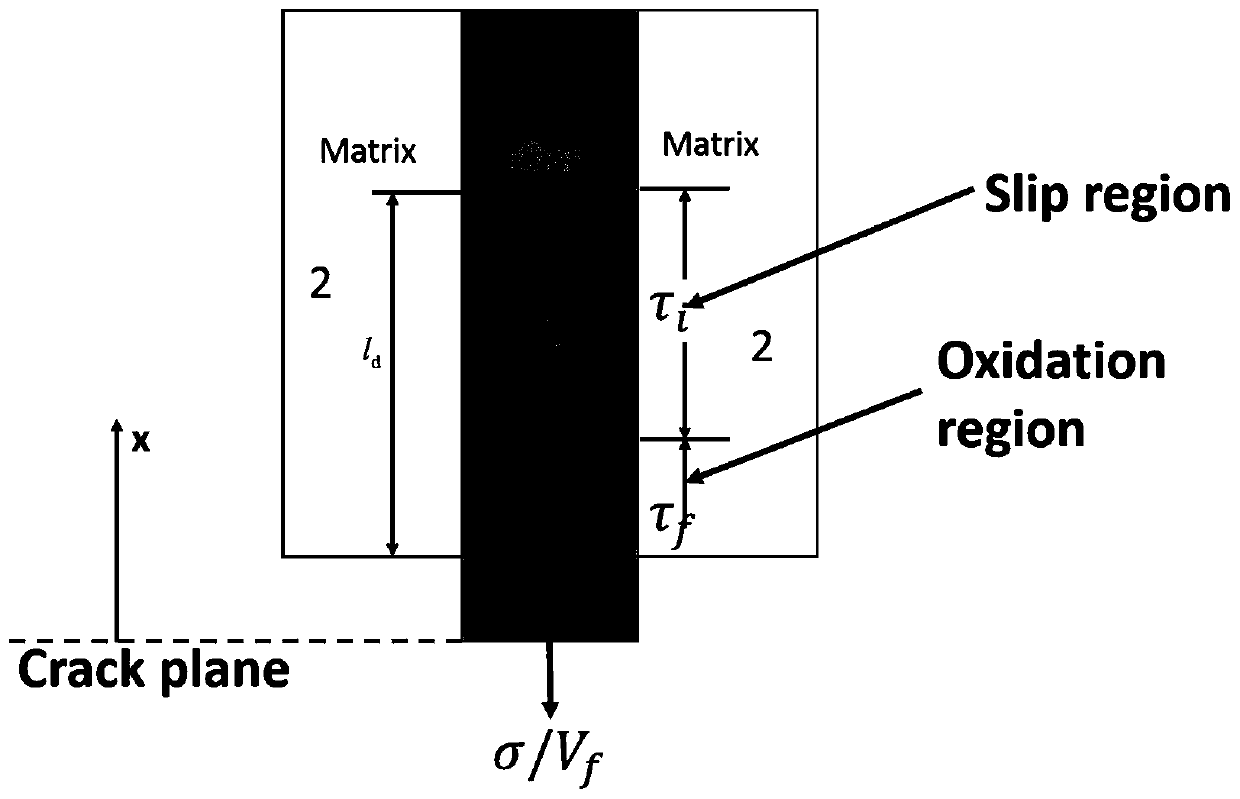
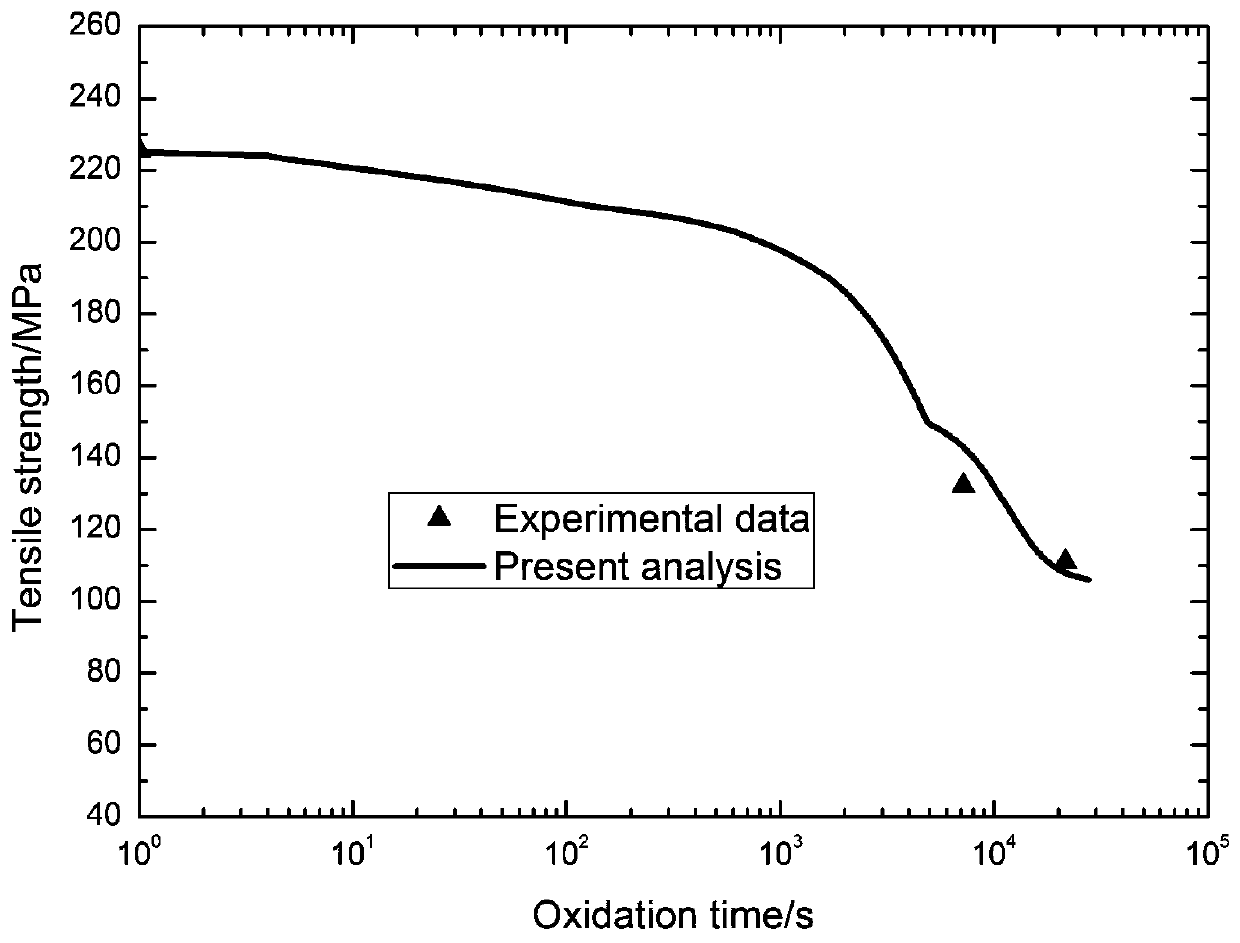
Method for predicting residual tensile strength of ceramic-based composite material in stress oxidation environment
ActiveCN109992850AAccurate Prediction of Tensile StrengthAccurate prediction of residual tensile strengthDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsBreakage probabilityResidual strength
The invention discloses a method for predicting the residual tensile strength of a ceramic-based composite material in a stress oxidation environment. The method comprises the following steps: determining a change rule of a one-way SiC / SiC composite material SiC matrix saturated crack spacing and a SiC matrix crack average spacing along with stress; determining the change rule of the SiC matrix crack width along with the stress and the temperature; acquiring oxygen concentrations at different positions in the material at different moments and solving the change rule of the interface consumption length and the thickness of the surface oxide layer of the SiC fiber at the crack along with stress, temperature and time; obtaining the axial stress distribution of the SiC fiber; determining the size of oxidation defects on the surface of the SiC fiber; deducing a SiC fiber characteristic strength distribution expression; deducing a SiC fiber breakage probability expression; acquiring the maximum stress in the bridging SiC fiber; solving the SiC fiber fracture probability under certain temperature, stress and oxidation time; obtaining the residual strength of the material. According to themethod, the residual tensile strength of the unidirectional SiC / SiC composite material at each moment, each temperature and the tensile stress level can be accurately predicted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
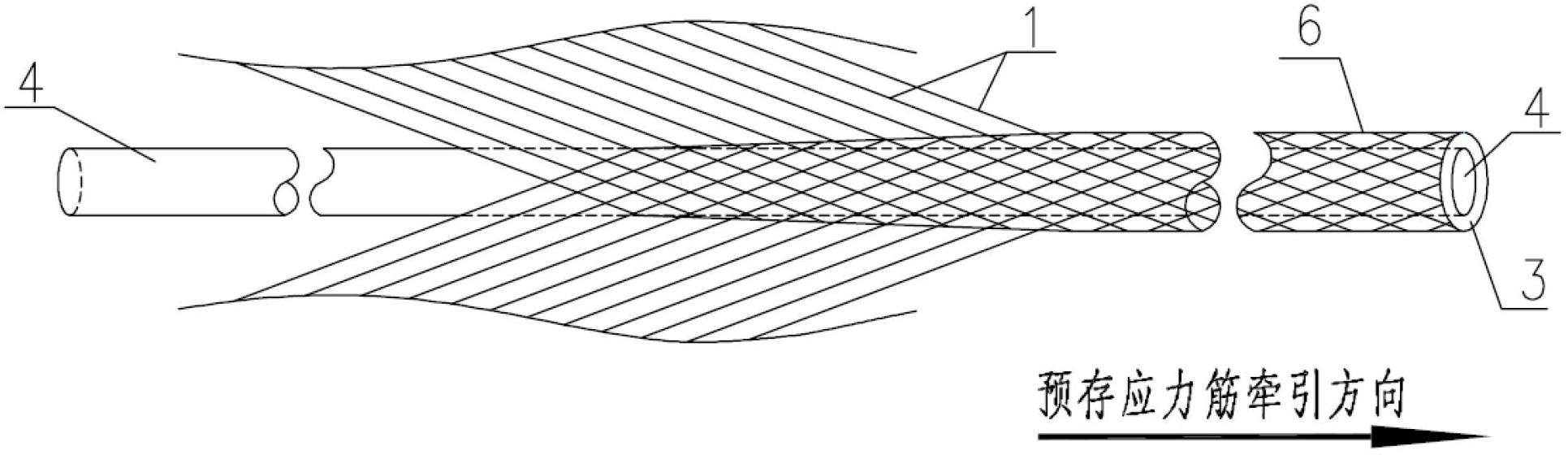
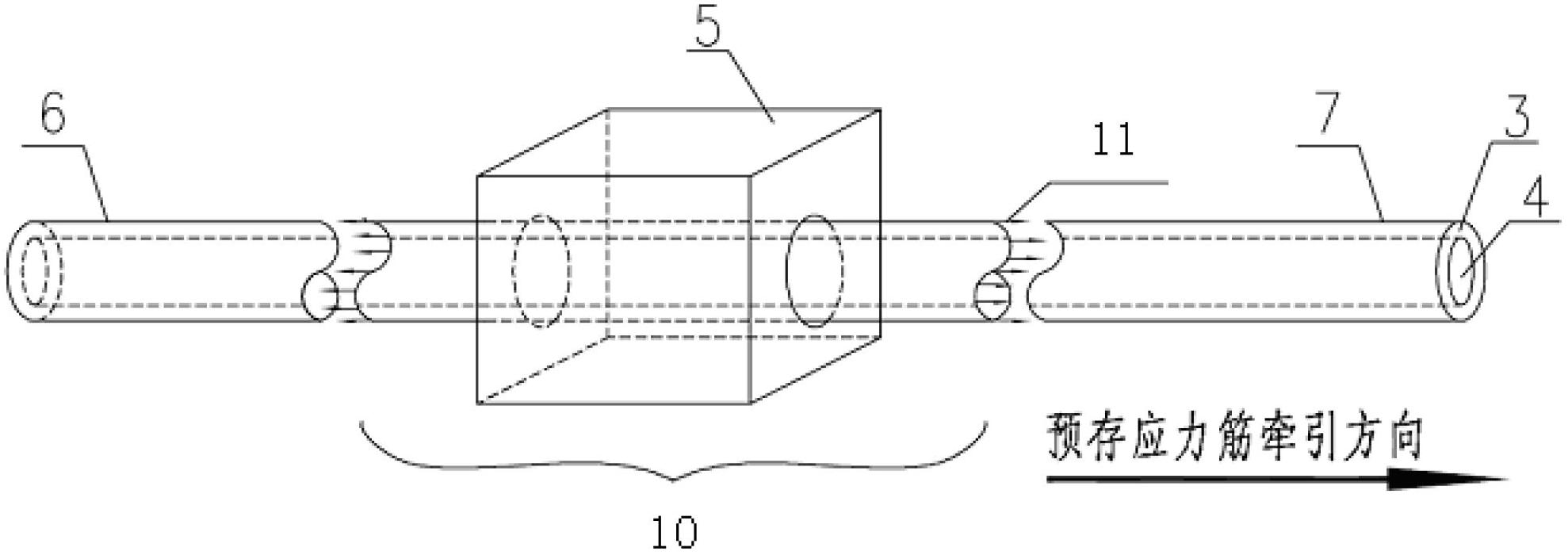
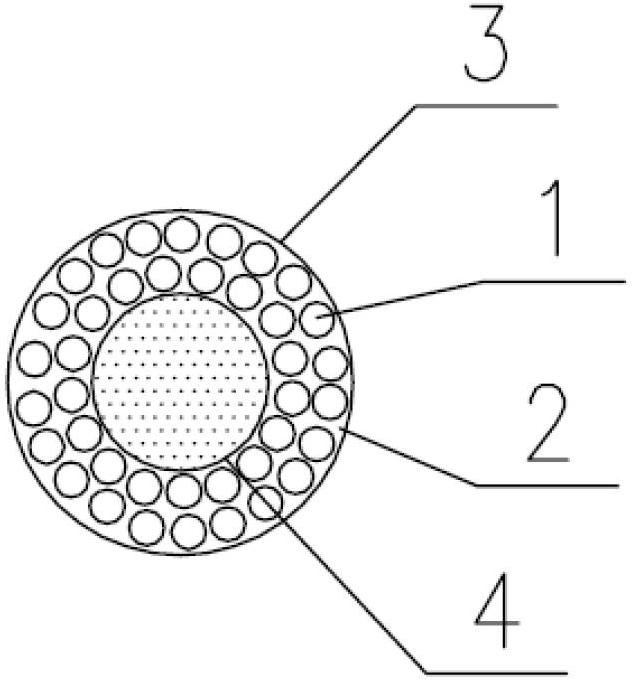
Prestressing tendon reinforced composite material and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a prestressing tendon reinforced composite material and a manufacturing method of the prestressing tendon reinforced composite material. comprising the following steps of: arranging prestressing tendons according to stress condition of a composite material; weaving the prestressing tendons and fibers to form a prefabricated body or using the prestressing tendons individually to form the prefabricated body; preparing the composite material by chemical vapor infiltration method (CVI); heating up to Tm temperature of a core body to soften the core body; and releasing prestress when an outer pipe retracts elastically to compress a combined base body. According to the invention, due to the arrangement flexibility and convenience of the prestressing tendons, the tendons are arranged according to the principal tensile stress trace, so that the stress performance of the structure ceramics or carbon base is improved better, the toughness and strength of the ceramic or carbon-based composite material are strengthened, and the problem that the continuous fiber reinforced ceramic or carbon-based composite material matrix cracks too early is solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-performance C/SiBCN composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a high-performance C / SiBCN composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a C interface layer,a SiC interface layer and / or a (C / SiC)n alternate interface layer, which is formed by alternate deposition of the C interface layer and the SiC interface layer, on the surface of a carbon fiber preform to obtain a modified carbon fiber preform; and with a liquid SiBCN precursor as an impregnation liquid, carrying out SiBCN matrix densification on the modified carbon fiber preform through a vacuumimpregnation / in-situ curing / medium-pressure cracking PIP process to obtain the high-performance C / SiBCN composite material. According to the invention, the proper interface layers are prepared, so atoughening function is achieved; an in-situ curing process is adopted, so outflow of the precursor in the curing process is avoided, and impregnation depth and impregnation efficiency are improved; and meanwhile, a medium-pressure cracking process is adopted, so SiBCN matrix cracks are reduced, the porosity of the material is reduced, and the mechanical property of the composite material is improved.
Owner:AEROSPACE INST OF ADVANCED MATERIALS & PROCESSING TECH
Method for preparing high-performance phosphogypsum-based self-leveling mortar
InactiveCN110436874AImprove interface pore structureReduce and suppress expansionCelluloseHigh fracture
The invention relates to the technical field of building materials, and discloses a method for preparing a high-performance phosphogypsum-based self-leveling mortar. The method comprises the followingsteps: S1, obtaining raw materials comprising 40-60 parts of phosphorus building gypsum, 15-22 parts of cement, 10-24 parts of fly ash, 3-10 parts of stone powder, 1.5-4 parts of a redispersible latex powder, 0.05-0.15 part of cellulose ether, 0.02-0.06 part of a nano-carbon fiber, 0.3-0.8 part of a water retaining agent, 0.1-1.3 parts of a water reducer, 0.1-0.4 part of an anti-settling agent, 0.01-0.08 part of a defoaming agent and 30-42 parts of fine sand aggregates; and S2, mixing the materials obtained in step S1, stirring the obtained mixture until uniformity, and adding water accounting for 13-15% of the total weight of the mixture and performing stirring until uniformity when the mortar is used. The reinforcement of a phosphogypsum-based self-leveling material and the high fracture toughness of the carbon fiber effectively reduce and inhibit the expansion of matrix cracks, and greatly improve the interfacial pore structure of the self-leveling material. The method of the invention improves the bonding degree of the interface of the phosphogypsum matrix, increases the toughness of the phosphogypsum matrix and increases the overall strength.
Owner:DEQING YANGTAI BUILDING MATERIAL
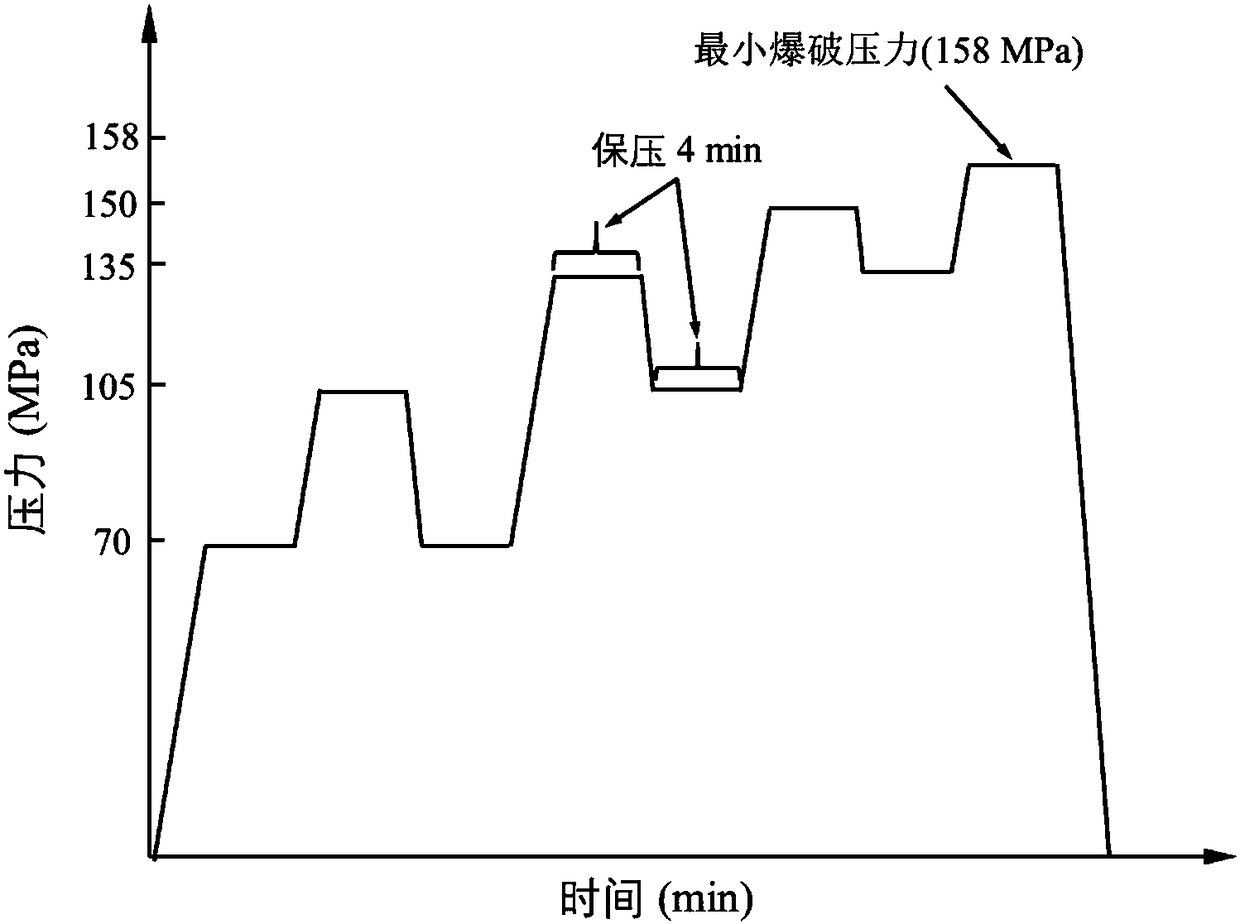
Device and method for monitoring hydraulic blasting of composite gas cylinder on basis of acoustic emission technique
InactiveCN108333258AEfficient assessment of injury statusMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesAcoustic emissionGas cylinder
The invention relates to the field of damage detection of composite gas cylinders and aims to provide a device and a method for monitoring hydraulic blasting of a composite gas cylinder on the basis of an acoustic emission technique. The device comprises a water pump connected to the composite gas cylinder through a pipe, wherein a pressure gauge and a pressure sensor are arranged on the pipe, anda water pump adjusting system is connected with the pressure sensor and the water pump respectively through signal lines; the composite gas cylinder is placed horizontally, and eight broadband sensors connected with an acoustic emission detection system through signal lines are arranged on the surface of the cylinder body; the acoustic emission detection system acquires acoustic emission signalsfrom the broadband sensors and pressure change data from the pressure sensor simultaneously. With adoption of the device and the method, acoustic emission amplitudes and change trend of energy signalparameters with pressure in a blasting process of the composite gas cylinder can be obtained, so that change conditions of fiber breaking and matrix cracking distinguished by acoustic emission signalfrequency under different pressure can be analyzed, and damage state of the gas cylinder can be evaluated effectively.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for predicting tensile strength of woven ceramic-based composite material
ActiveCN109781546APrediction is accurateMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress distributionFracture mechanics
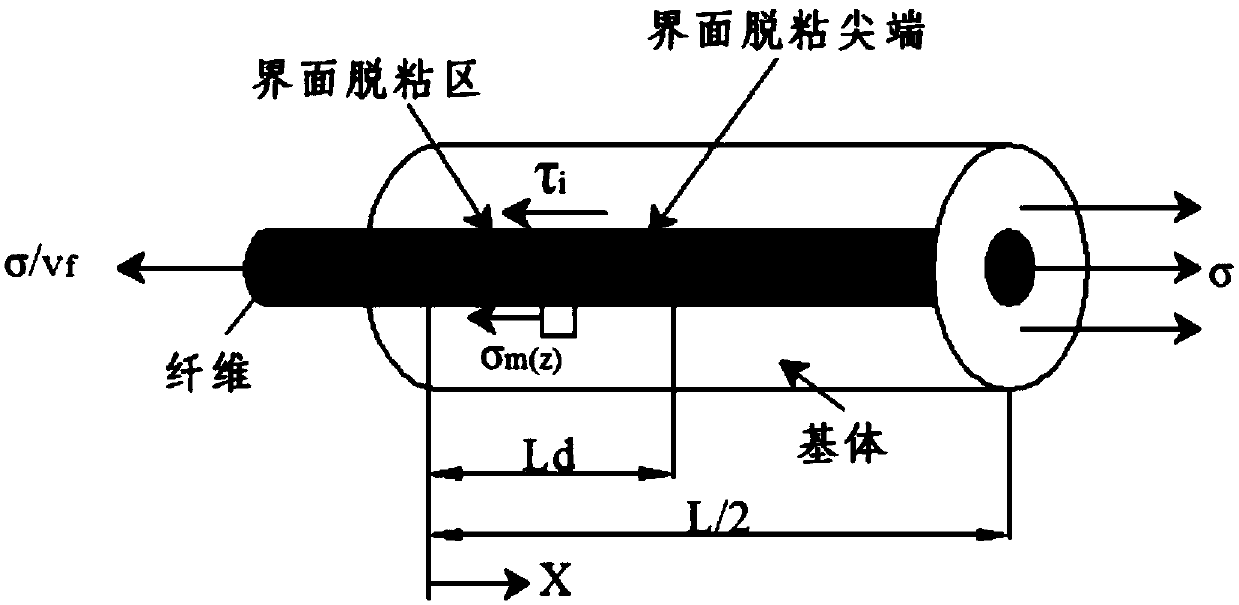
The invention belongs to the technical field of composite material tensile strength prediction, and particularly relates to a method for predicting the tensile strength of a woven ceramic matrix composite material. On the basis of considering the temperature and oxidation influence, a fiber / matrix interface debonding length equation and a fiber slippage length equation are established by adoptinga fracture mechanics method, and a stress distribution equation after matrix cracking and interface debonding damage of the woven ceramic matrix composite is considered; on the basis of total load bearing criterion, by combining the equations, a fiber / matrix interface oxidation area fiber fracture probability equation, a fiber / matrix interface debonding area fiber fracture probability equation anda fiber / matrix interface bonding area fiber fracture probability equation are established respectively, to obtain a fiber fracture probability and stress relation equation. The method is used for predicting the tensile strength of the woven ceramic matrix composite material, and the prediction result is higher in accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Prediction Method of Stress-Strain Behavior of Unidirectional Ceramic Matrix Composites under Arbitrary Loading and Unloading
ActiveCN104866690BPrediction of stress-strain behaviorSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionMetallurgy
The invention relates to a method for predicting the stress-strain behavior of a composite material, in particular to a method for predicting the stress-strain behavior of a unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material under arbitrary loading and unloading. The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the defects of the prior art and provide a method for quickly predicting the stress-strain behavior of the unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material during random loading and unloading. The invention provides a method for predicting the stress-strain behavior of a unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material under arbitrary loading and unloading, which considers failure mechanisms such as matrix cracking, fiber breakage, interface slippage, and interface wear. The generation and coverage rules of forward and reverse slip zones are proposed, and the stress distribution and strain when there are any number of forward and reverse slip zones are given. Most of the formulas provided by the invention have analytical solutions, so the stress-strain behavior of the unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material under arbitrary loading and unloading can be quickly predicted.
Owner:南京长工智航科技有限公司
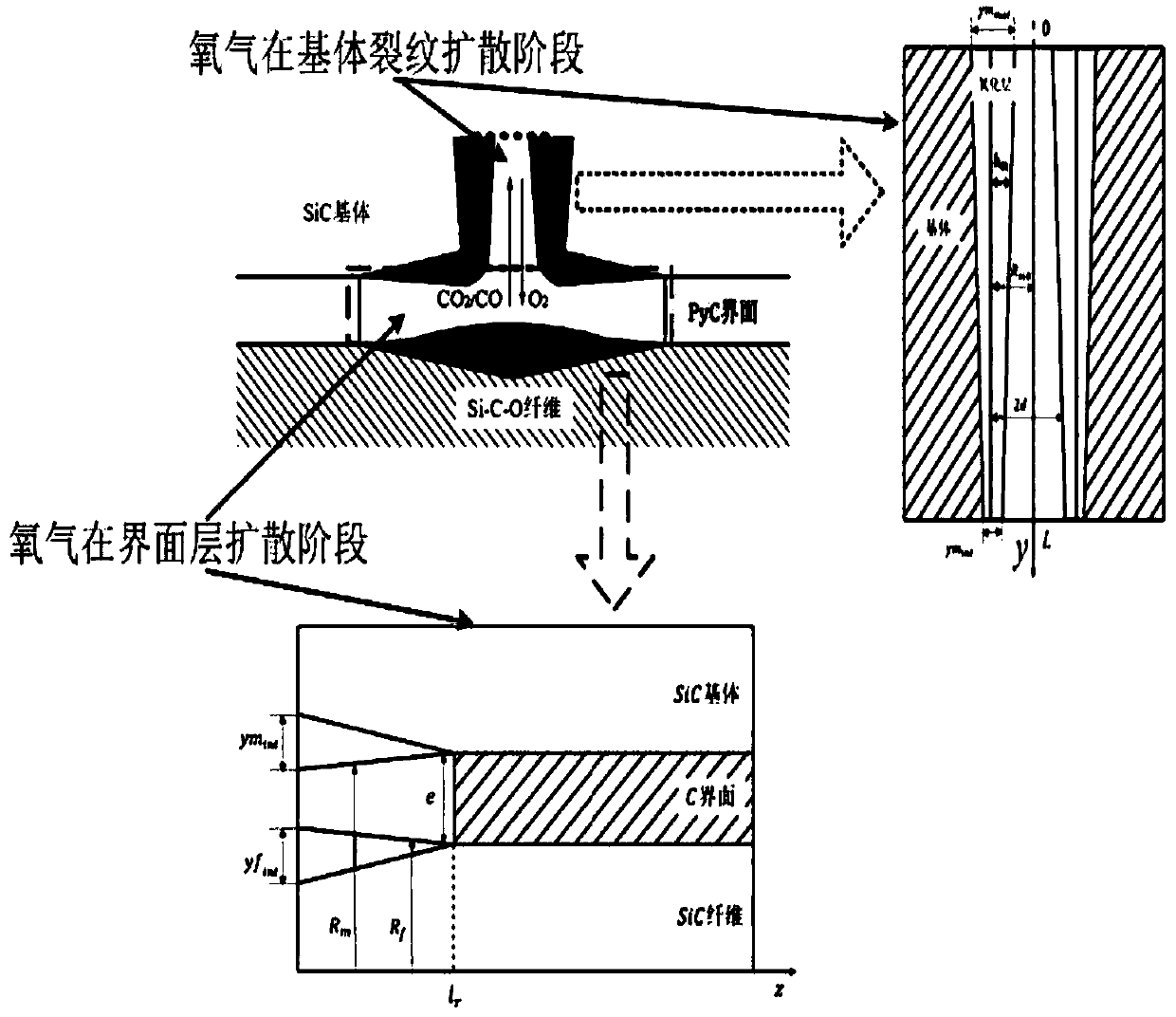
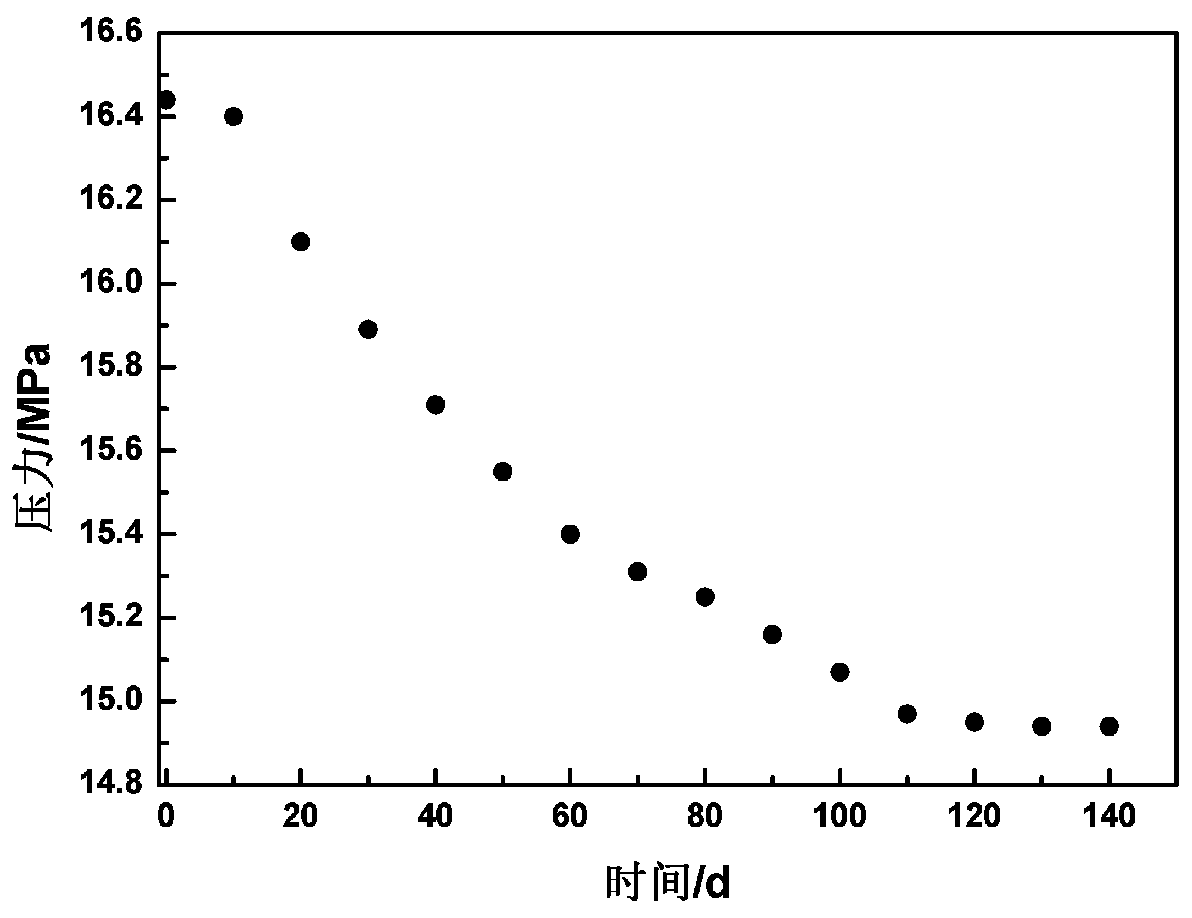
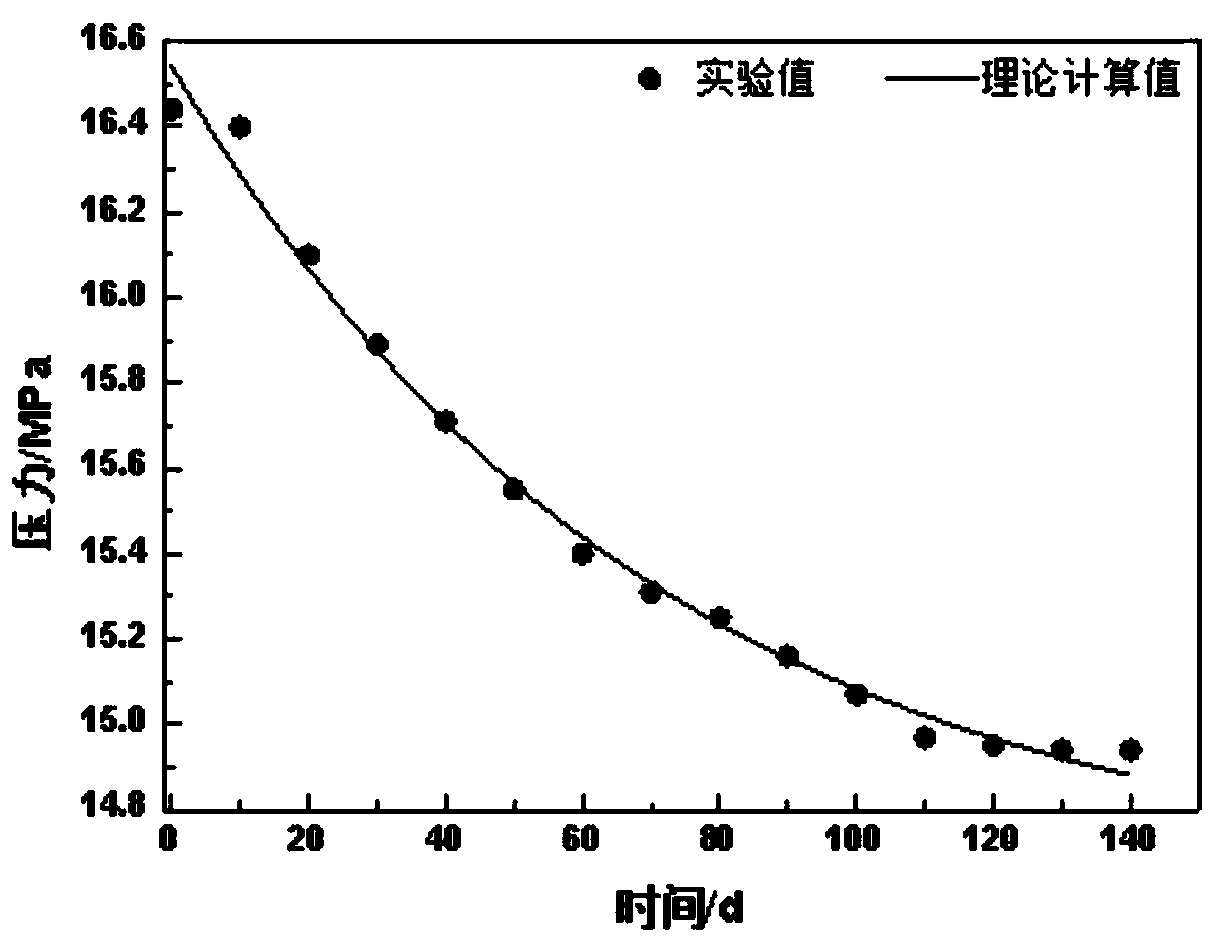
Experimental device for simulating CO2 in dense matrix-crack diffusion and front edge prediction method of experimental device
ActiveCN109883889AExperimental determination is accurateSimple structureSurface/boundary effectDiffusionEngineering
The invention discloses an experimental device for simulating CO2 in dense matrix-crack diffusion and a front edge prediction method of the experimental device. On the basis of the prior art, the experimental device is improved, cracks are simulated by a fracturing proppant compacting strip, and a transverse injection mode (if the injection is vertical, the pressure in the injection process may impact the matrix section, crude oil near the matrix section is caused to be squeezed into the deep part of the matrix, so that the diffusion experiment precision is affected) is adopted, the latent period effect caused by the pressure impact effect during gas injection is reduced, and the experimental determination of a diffusion coefficient is enabled to be more accurate. The improved device is easy to operate and can simulate the real environment better; and meanwhile, a experimental model is used for predicting the CO2 concentration field and diffusion front edge, the interference to the system balance caused by direct sampling to obtain CO2 concentration in the diffusion process is avoided, and the experimental accuracy is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
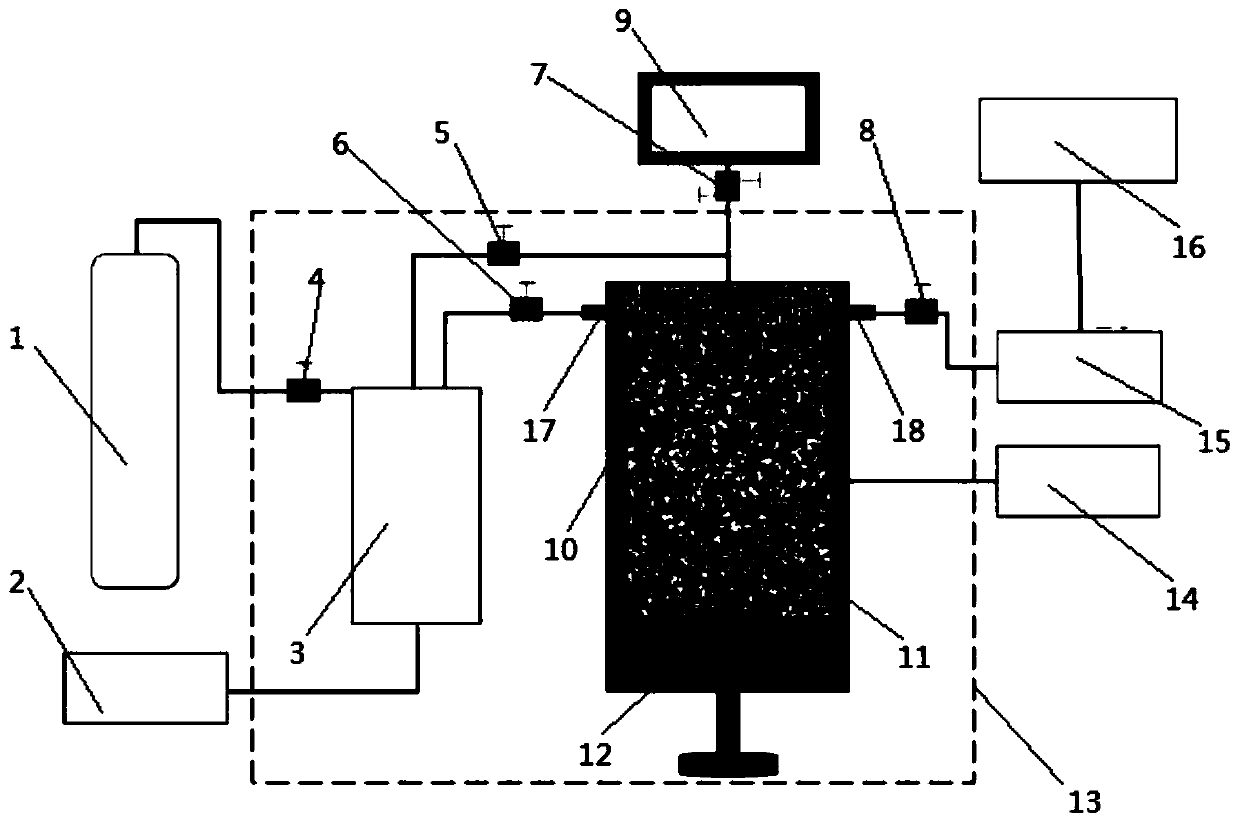
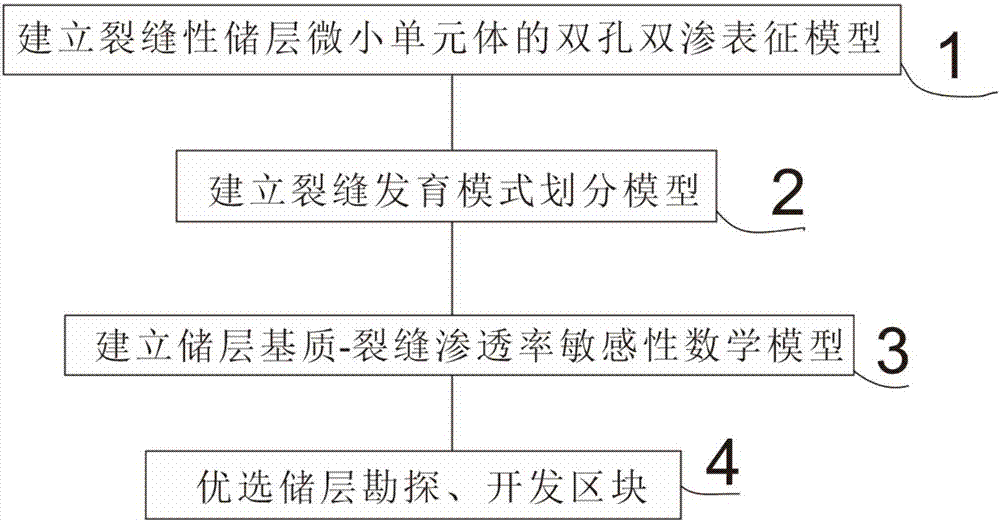
Crack development pattern and reservoir matrix-crack permeability sensitivity prediction method
InactiveCN108008117AHigh utility valueReduce forecasting costsEarth material testingSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelOperability
The invention relates to the field of oil and gas field exploration and development, in particular to a crack development pattern and reservoir matrix-crack permeability sensitivity prediction method.The method comprises the steps of on the basis of establishing a dual-hole dual-permeability indication model of a crack reservoir microelement, conducting simulation to obtain pore permeability parameter distribution of cracks, conducting crack multi-parameter simulation through a fine small block geologic model, and dividing development patterns of the cracks in different areas; utilizing porepermeability parameter distribution of a matrix to establish a reservoir matrix-crack permeability sensitivity math model; finally, preferentially selecting a reservoir exploration and development block. The crack development pattern and reservoir matrix-crack permeability sensitivity prediction method has high practical value to multi-value development pattern and reservoir matrix-crack permeability sensitivity prediction; meanwhile, the prediction cost is low, the operability is high, and a prediction result has practical significance for crack reservoir exploration and development.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
One-way ceramic matrix composite creep behavior prediction method
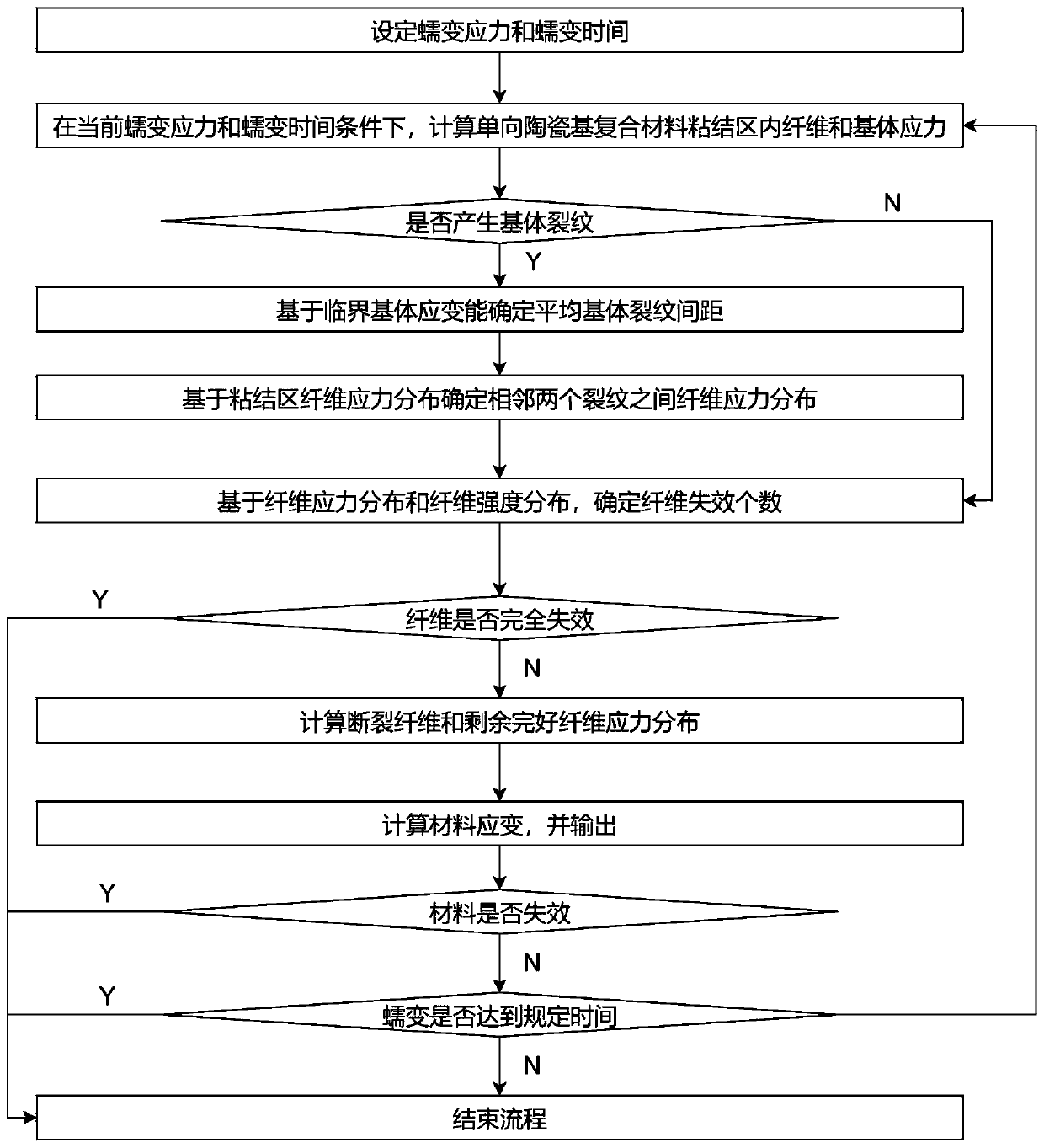
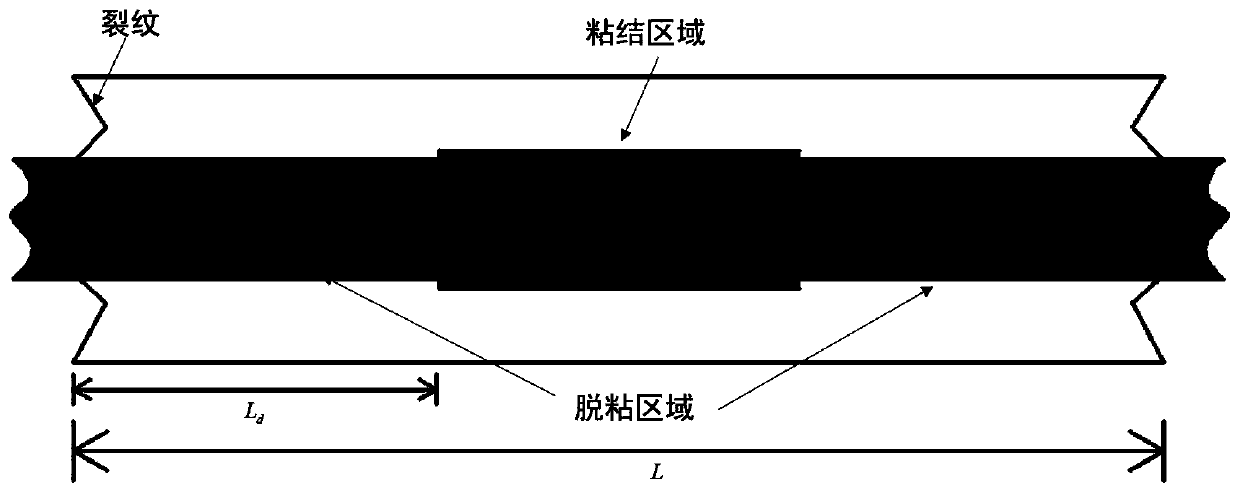
ActiveCN111024486AAccurately predict creep curvesRevealing Mesoscopic Failure MechanismsComputational materials scienceStrength propertiesCreep stressFailure mechanism
The invention discloses a one-way ceramic matrix composite creep behavior prediction method, which comprises the following steps: based on the same strain of bonding region fibers and a matrix, obtaining the stress of the bonding region fibers and the matrix under different creep stresses and times, and further obtaining the change of the matrix crack density. A shear-lag model is combined to obtain fiber stress change in the creep process, fiber failure and load borne by the failure fiber are considered, and finally a one-way ceramic matrix composite creep curve is calculated. According to the method, one-way ceramic matrix composite creep curves at different temperatures and creep stress levels can be accurately predicted, and the microscopic failure mechanism of material internal components is disclosed. On the other hand, the whole calculation process is concise and efficient, and the defects of high cost and long time consumption of an experimental method are overcome.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Non-rivet riveting device and method for carbon fiber composite material and aluminum alloy
ActiveCN108380765AAvoid damageGuaranteed forming qualityWeight reductionSelf lockingFibrous composites
The invention discloses a non-rivet riveting device and method for a carbon fiber composite material and an aluminum alloy and belongs to the technical field of composite material riveting. The technical problems that in the prior art, fiber breakage, matrix cracking and interface degumming and layering are likely to occur and the joint performance is low are solved. The device comprises a blank holder, a punch and a concave mold. The concave mold comprises a first spring cushion block, a second spring cushion block, a first spring, a second spring and a lower mold body. The non-rivet rivetingprocess of the carbon fiber composite material and the aluminum alloy is achieved through the device. By means of the process, an aluminum alloy plate forms a self-locking structure at a through holeof a carbon fiber composite material plate, the anti-tension, anti-shear and anti-fatigue properties of a joint are improved, riveting elements like rivets are not needed, and the mass is reduced.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for predicting mass change of ceramic-based composite material in stress oxidation environment
ActiveCN110096731AQuality improvementThe calculation process is simple and effectiveDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsOxygen
The invention discloses a method for predicting the mass change of a ceramic matrix composite material in a stress oxidation environment. The method comprises the following steps of determining the change rule of the number of matrix cracks of the material under the action of stress and high temperature; determining the change rule of the matrix crack width of the material under the action of stress and high temperature; determining a diffusion coefficient of oxygen in a crack channel; respectively determining the oxidation rate of each component; determining the volume change of the SiC fiberbefore and after the matrix reaction; determining an oxidation dynamics model of the material in a stress and high-temperature oxidation environment; determining the oxidation dynamics models at a crack diffusion stage and an interface layer expansion stage, and determining an oxide layer change rule and an interface consumption rule; determining a mass change rule of the material in the stress and high-temperature environment. According to the method, the combined action of stress and high-temperature oxidation on the oxidation mechanism of the unidirectional SiC / SiC composite material is considered, and the related theoretical support is provided for the mechanical property analysis of the ceramic-based composite material in the stress oxidation environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Basalt fiber/polypropylene composite material based on surface roughening and interface enhancement and preparation method of basalt fiber/polypropylene composite material
The invention discloses a basalt fiber / polypropylene composite material based on surface roughening interface enhancement and a preparation method of the basalt fiber / polypropylene composite material, and belongs to the technical field of new composite materials. The preparation method comprises basalt fiber surface roughening treatment and composite material preparation. The basalt fiber surface roughening treatment comprises the following steps: (1) acrylic acid dipping treatment; (2) electron beam irradiation treatment; and (3) in-situ growth of nano silicon dioxide on the surface of the basalt fiber. The surface of the short-cut basalt fiber is roughened, and part of alkyl is grafted on the surface of the short-cut basalt fiber, so that the contact area and interaction force between the basalt fiber and a polypropylene matrix are greatly increased, interface mechanical interlocking is enhanced, epiphytic crystallization of the polypropylene matrix on the fiber surface is promoted, stress conduction of the interface of the composite material is enhanced, the inhibition capability of the fibers on the development of matrix cracks in the deformation process is improved, and thus the mechanical property of the composite material is remarkably improved.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
Coating system with reinforced concrete pursuit performance, and anti-corrosion application of coating system
ActiveCN111794548AIncreased rift followabilityStrong crack followingBuilding repairsAnti-corrosive paintsMatrix crackingCoating system
The invention relates to the technical field of buildings, in particular to a coating system with reinforced concrete pursuit performance, and anti-corrosion application of the coating system, and more particularly relates to coating protection application of a concrete structure of ocean engineering. A coating sequentially comprises permeable epoxy resin seal primer, solvent-free epoxy resin putty, polyether-modified epoxy resin high-tenacity intermediate coat and elastic polyurethane top coat. The anti-corrosion application of the coating with the reinforced concrete surface pursuit performance is completed through six processes; and the coating with the reinforced concrete pursuit performance not only has excellent mechanical properties such as the good pursuit performance, high tensilestrength and matrix cracking prevention, but also has excellent protection properties of alkali resistance, aging resistance and chloride ion penetration resistance, the characteristics of short period and easy operation are achieved in the construction process, and a method is an effective method convenient to implement on site and capable of prolonging the life of the concrete structure.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for simulating gas flowing of matrix-crack system
ActiveCN110018105AFlow simulation implementationEfficient developmentPermeability/surface area analysisTemperature controlRock core
The invention discloses a device and method for simulating gas flowing of a matrix-crack system. The device comprises a gas pressurizing injection system, a model system, a constant temperature control system and a metering system which are sequentially connected, and the gas pressurizing injection system comprises a gas source tank and a pressurizing mechanism for pressurizing gas flowing out ofthe gas source tank; the model system comprises three stages of rock core gripper connected in series, a confining pressure pump for providing the confining pressure for each stage of rock core gripper, and pressure gauges arranged at the inlet ends of the rock core grippers correspondingly; the three stages of rock core grippers are sequentially filled with matrix rock cores, natural crack rock cores and manual crack rock cores; and the constant temperature control system is arranged outside the model system and used for simulating the formation temperature; and the metering system comprisesa flow meter arranged at the outlet end of the last stage of rock core gripper, and a temperature sensor. Flowing of the gas in the reservoir matrix-crack system can be simulated under high temperature and high pressure conditions.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
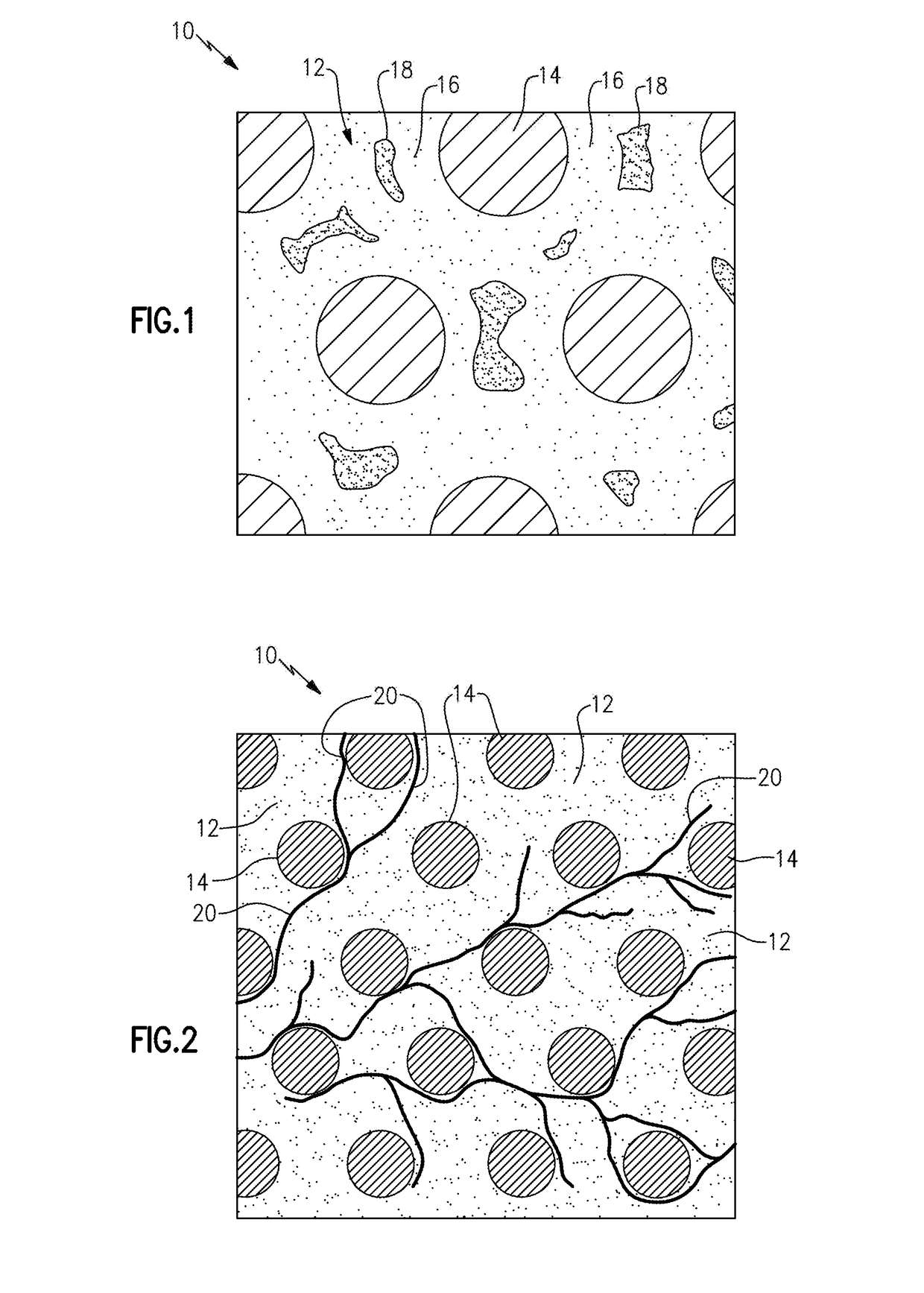
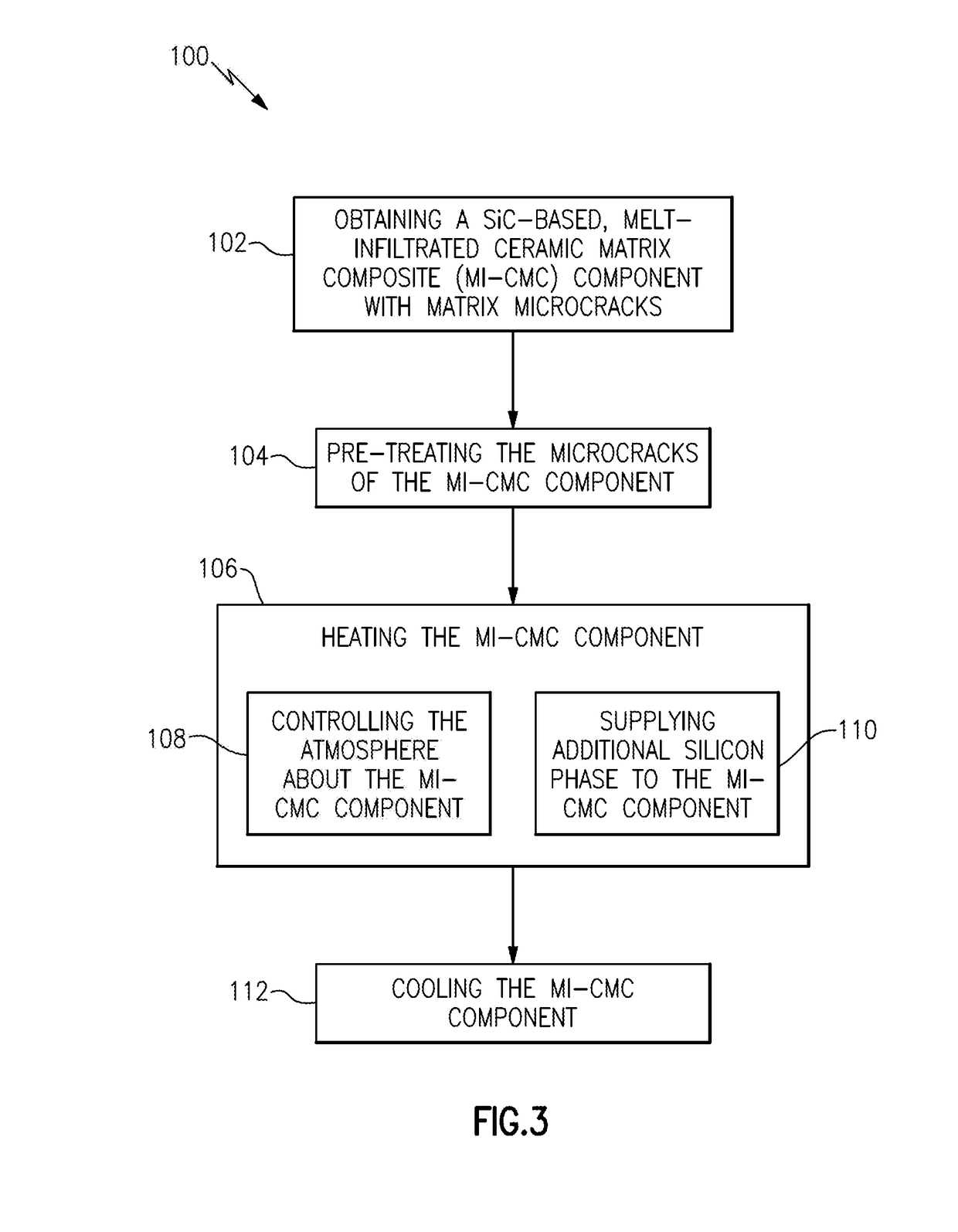
Methods of repairing matrix cracks in melt infiltrated ceramic matrix composites
A method of repairing matrix microcracks in MI-CMC components includes heating “free” silicon phase present within the cracked matrix portion of the component to a temperature above the melting point of the silicon phase. During heating of the component an additional source of silicon phase is supplied to the component. The atmosphere about the component is controlled during the heating of the component. The MI-CMC component is cooled below the melting point of the silicon phase to cool and solidify the silicon phase that has migrated into the microcracks to thereby bond the crack faces together.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for predicting tension-compression fatigue hysteresis loop of metal matrix composite material
ActiveCN110196996AStress-strain relationship predictionEfficient and convenient processForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationHysteresisTitanium matrix composites
The invention discloses a method for predicting a tension-compression fatigue hysteresis loop of a metal matrix composite material. The method specifically comprises the following steps of determiningthe fiber, matrix and shear stress distribution of a one-way silicon carbide fiber reinforced titanium matrix composite material debonding section and a non-debonding section according to a BHE shearhysteresis model; determining the length of the debonding area, the initial debonding stress of the interface and the complete debonding stress of the interface; determining the length of a reverse sliding area and the critical stress of reverse sliding; determining the stress-strain relationship between the stretching loading and unloading stages of the composite material; determining a stress-strain relationship between the compression loading stage and the unloading stage of the composite material; determining a change rule of the crack spacing and the interface shear stress along with thecycle number; determining a fiber breakage fraction of a given cycle number; and giving a cycle number N, and combining the above steps to obtain the fatigue hysteresis loop of the composite materialchanging with the cycle number. According to the method, the stress-strain relationship of the composite material under different matrix crack intervals, different sliding interface shear stresses, different fiber breakage volume fractions and different cycle numbers can be accurately predicted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for predicting arbitrary loading and unloading stress-strain curve of ceramic-based composite material in high-temperature oxidation environment
ActiveCN111241686ASave manpower and material resourcesGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCrazingMaterial resources
The invention discloses a method for predicting an arbitrary loading and unloading stress-strain curve of a ceramic-based composite material in a high-temperature oxidation environment. The method caneffectively simulate the arbitrary loading and unloading stress-strain curve of a unidirectional SiC / SiC composite material in a high-temperature oxidation environment; according to the method, the influences of the matrix crack density and width, the interface oxidation consumption length and the fiber tensile strength on the length and distribution of an interface slip region during loading ona stress-strain curve of the composite material in a high-temperature oxidation environment are considered; according to the method, a theoretical basis can be provided for the calculation of the fatigue life of the unidirectional SiC / SiC composite material under spectral load loading in the high-temperature oxidation environment; the method overcomes the defects of high test cost and high manpower and material resource consumption in the oxidation test of the arbitrary loading and unloading of the unidirectional ceramic-based composite material, and can save a large amount of manpower and material resources.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
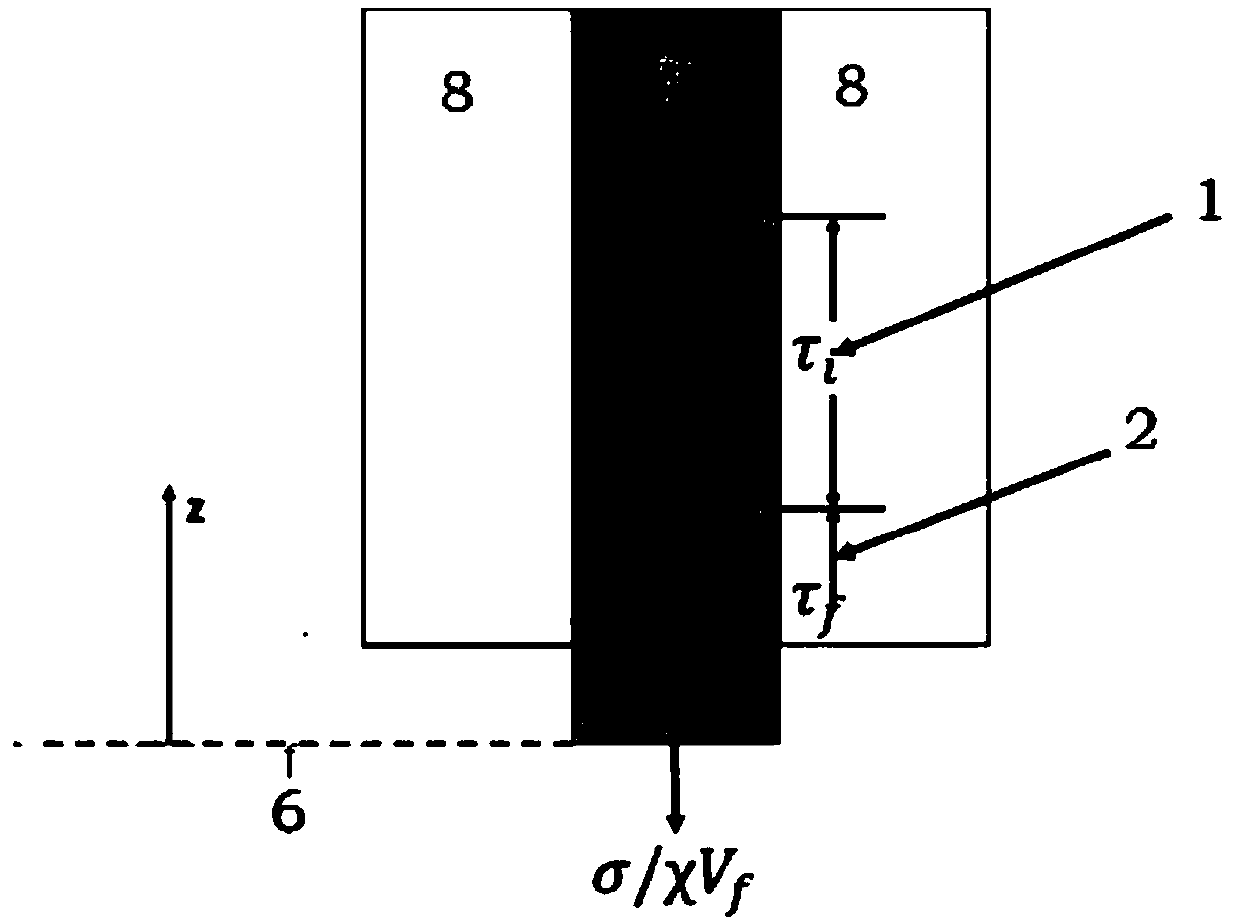
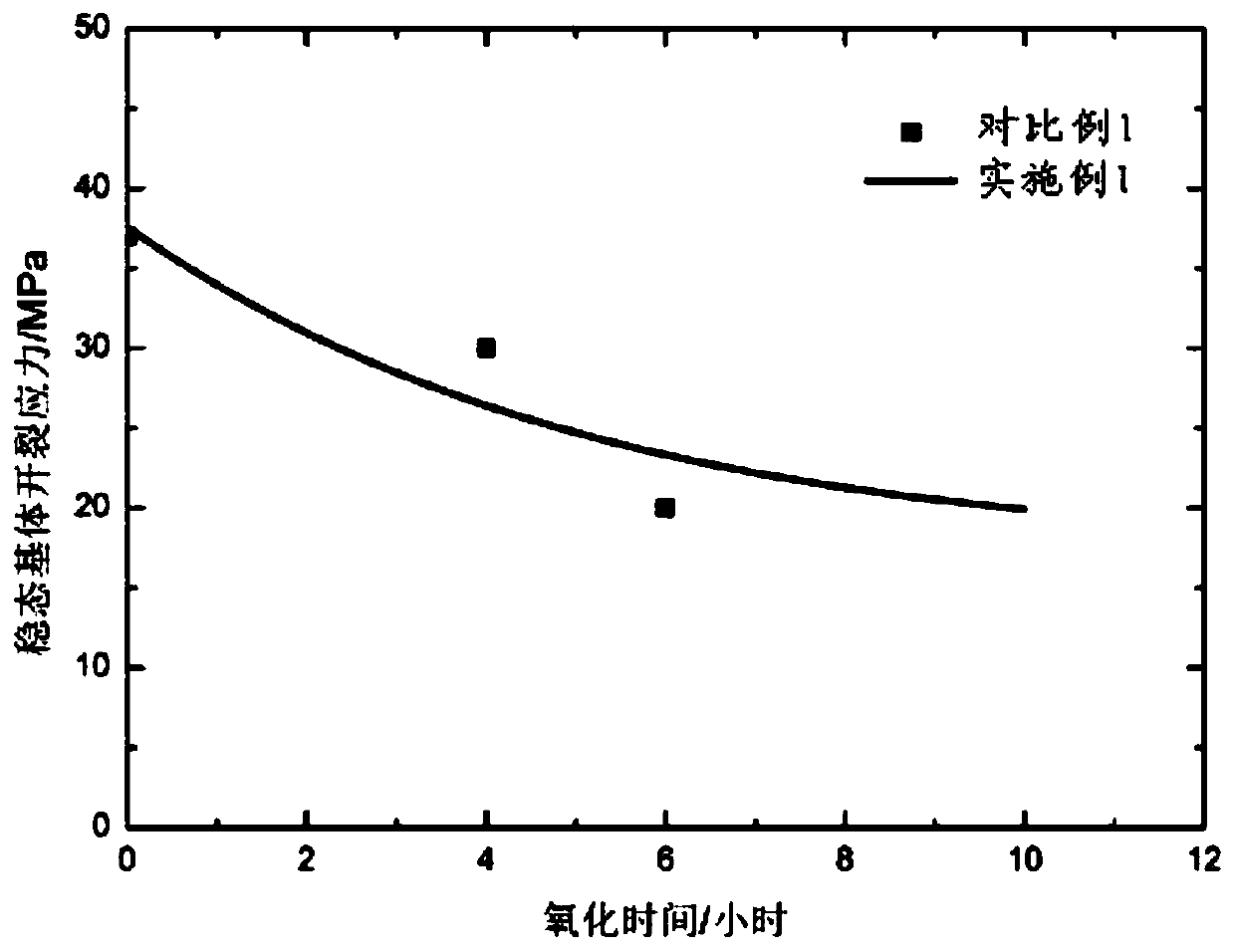
A method for predicting the cracking stress of a steady-state matrix of a woven ceramic-based composite material by considering the environmental influence
PendingCN109598098ACracking Stress PredictionForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationStress distributionEnvironment effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic matrix composite steady-state matrix cracking stress prediction, and particularly relates to a method for predicting the cracking stress of a steady-state matrix of a woven ceramic-based composite material by considering the environmental influence. The invention provides a steady-state matrix cracking stress distribution equation, which is constructed and obtained by utilizing the length of a fiber / matrix interface oxidation area, and the fiber / matrix interface oxidation zone friction shear stress under the temperature condition and thefiber / matrix interface debonding zone friction shear stress under the temperature condition are constructed, so that the temperature and oxidation factors are included into a steady-state matrix cracking stress equation, and a basis is provided for accurately predicting the cracking stress of the steady-state matrix of the woven ceramic matrix composite material. Results of the embodiment show that the prediction method provided by the invention can predict the cracking stress of the woven ceramic-based composite material at different use temperatures.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
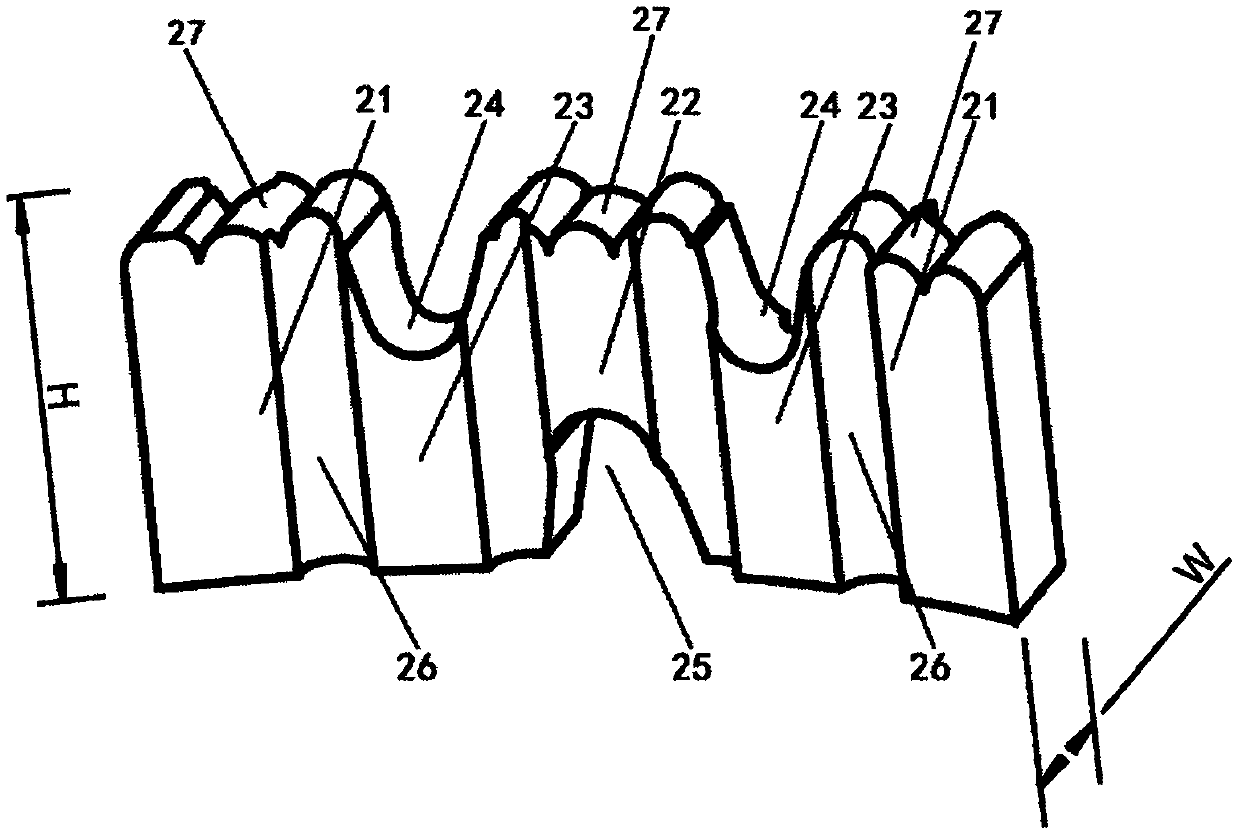
Drill bit and diamond thin-wall drill
ActiveCN109624097ASharpness does not fadeImprove impact resistanceStone-like material working toolsAlloySharpening
The invention relates to a drill bit and a diamond thin-wall drill, and belongs to the technical field of drilling tools. A sharpening structure is arranged on the drill bit, the sharpening structurecomprises shallow grooves which are formed in two side surfaces at an interval, and the shallow grooves extend from the working surface of the drill bit to the bottom surface; and according to the drill bit, a matrix structure is formed by diamond particles and metallic bond through cold pressing and sintering, and the metallic bond is prepared from the compositions in percentage by weight: 15-25wt% of electrolytic copper powder, 3-5wt% of atomized tin powder, 3-8wt% of nickel tetracarbonyl powder, 5-12wt% of FeCoCu superfine alloy powder, 10-20wt% of FeCuNiSn superfine alloy powder, 1-10wt% high-chromium iron powder and the balance of electrolytic iron powder. The drill bit is provided with a weakening structure, the sharpness can be maintained not to be decreased under a condition of drilling at circulation break, an anti-impact property and an anti-corrosion property of the drill bit are good, and a phenomenon of matrix cracking or tooth breaking under a high-speed drilling at circulation break condition can be significantly reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU FENGTAI TOOLS
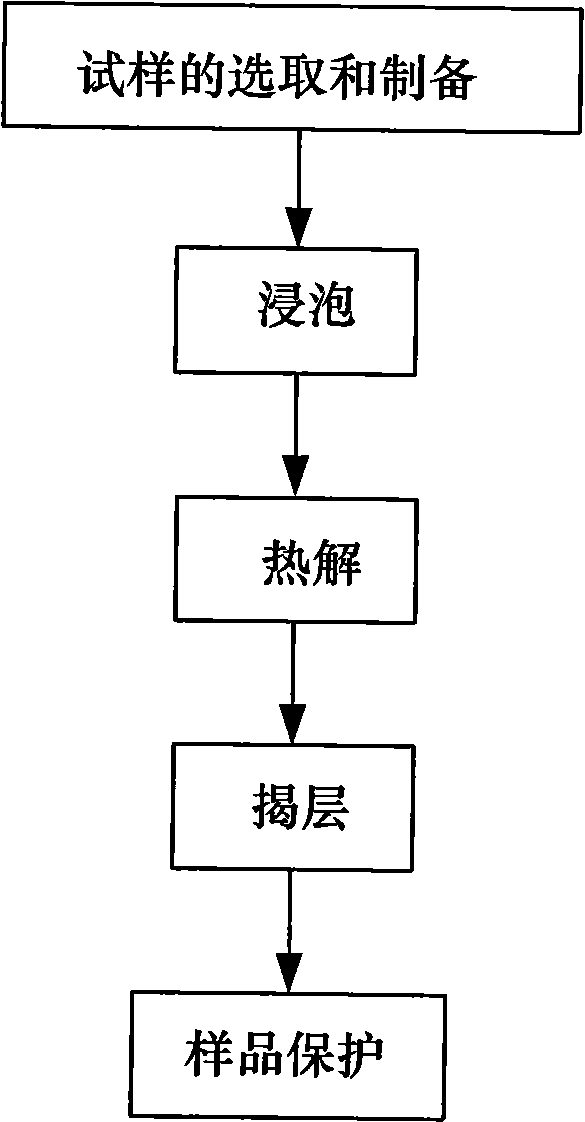
Defect hot-deply method of carbon fiber-reinforced modified bismaleimide laminates
InactiveCN101650272AUnique soaking methodNovel soaking methodPreparing sample for investigationNon destructiveLipid formation
The invention discloses a defect hot-deply method of carbon fiber-reinforced modified bismaleimide laminates. The method comprises the following steps: determining defects of a sample by non-destructive testing, preparing a label solution, soaking, pyrolyzing, deplying and protecting the sample. After being deplied, the sample keeps morphology features of a defect area, makes out the types, the sizes and the positions of the defects such as gap, delamination, poor (rich) lipid, matrix cracking and fiber bending (fracture), and provides the realest and most direct evidence for the further defect (breakage) forming mechanism analysis and the structural part failure analysis.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
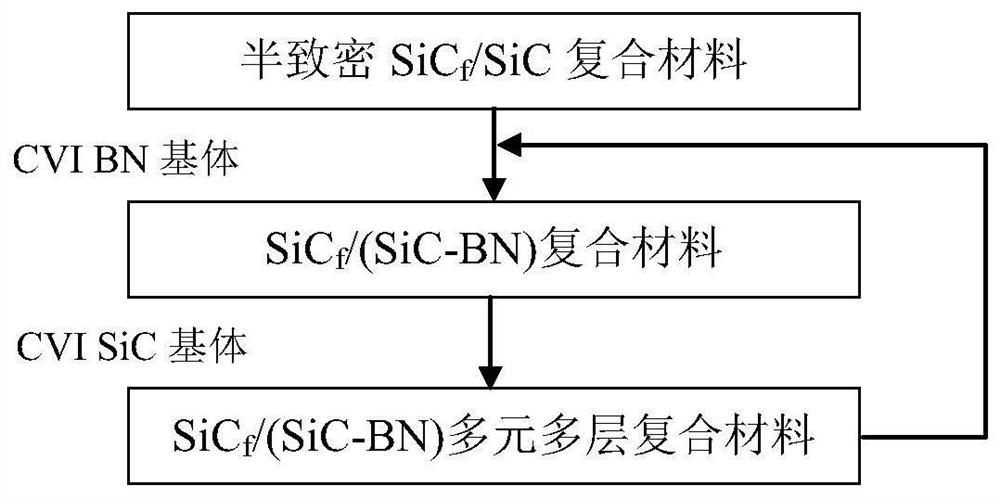
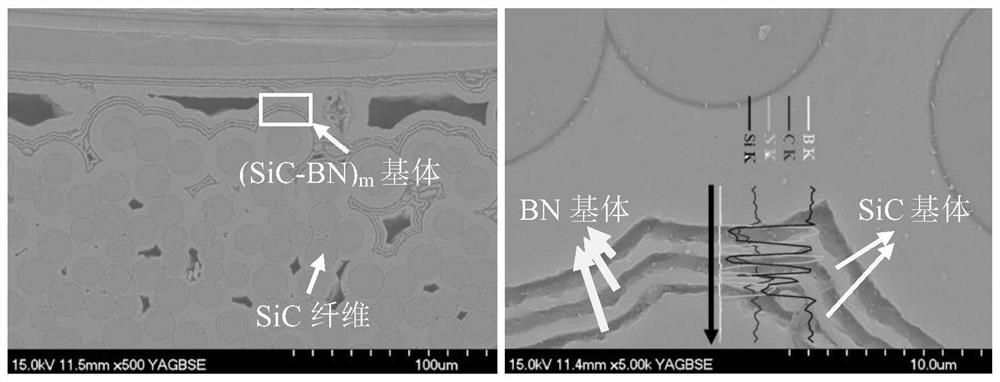
SiC fiber reinforced and toughened (SiC-BN)m multi-element multilayer self-healing ceramic matrix composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a SiC fiber reinforced and toughened (SiC-BN)m multi-element multi-layer self-healing ceramic matrix composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, a pyrolytic carbon interface is prepared in a SiC fiber preform, then a certain volume fraction of SiC matrix is introduced, and a semi-compact SiC / SiC composite material is obtained; and SiC and BN matrixes are alternatively deposited in the semi-compact SiC / SiC composite material to form a SiC-BN multi-element multi-layer matrix ((SiC-BN) m), so as to obtain the SiCf / (SiC-BN) m self-healing composite material. The SiC matrix mainly plays a role in bearing, and the BN matrix plays a role in crack deflection and self-healing. On one hand, the crystallinity of the BN determines the oxidation resistance and the crack deflection capacity of the BN, so that the BN with high crystallinity is obtained through process regulation and control, and meanwhile, as an oxygen diffusion path, a matrix crack also has a deep influence on the self-healing performance of the material. Therefore, the core of the invention is to obtain the multi-element multi-layer SiCf / (SiC-BN)m with the target layer thickness ratio and the n value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method for predicting inner oxidation morphology of unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material in stress water vapor environment
ActiveCN110246548AAccurate oxidation morphologyChemical processes analysis/designDesign optimisation/simulationWater vaporMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for predicting inner oxidation morphology of a unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material in a stress water vapor environment. The method comprises the following steps of determining a matrix crack number of the unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material; determining a crack width change rule; calculating a diffusion coefficient of water vapor in CO and H2 mixed gas; measuring a specific ratio of CO and H2 which are generated in actual oxidation reaction; and determining the inner oxidation morphology of the ceramic matrix composite material, namely calculating a water vapor concentration field, and determining the inner oxidation morphology of the ceramic matrix composite material at anytime. The method predicates the inner oxidation morphology of the ceramic matrix composite material in the stress water vapor environment and accurately acquires the inner crack wall oxidation of the material after stress oxidation, and oxidation morphology of fibers, an interface and a matrix after the water vapor enters the crack bottom, thereby supplying a theoretical support and an experiment basis for an oxidation problem of the unidirectional ceramic matrix composite material in the stress water oxygen coupling environment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com