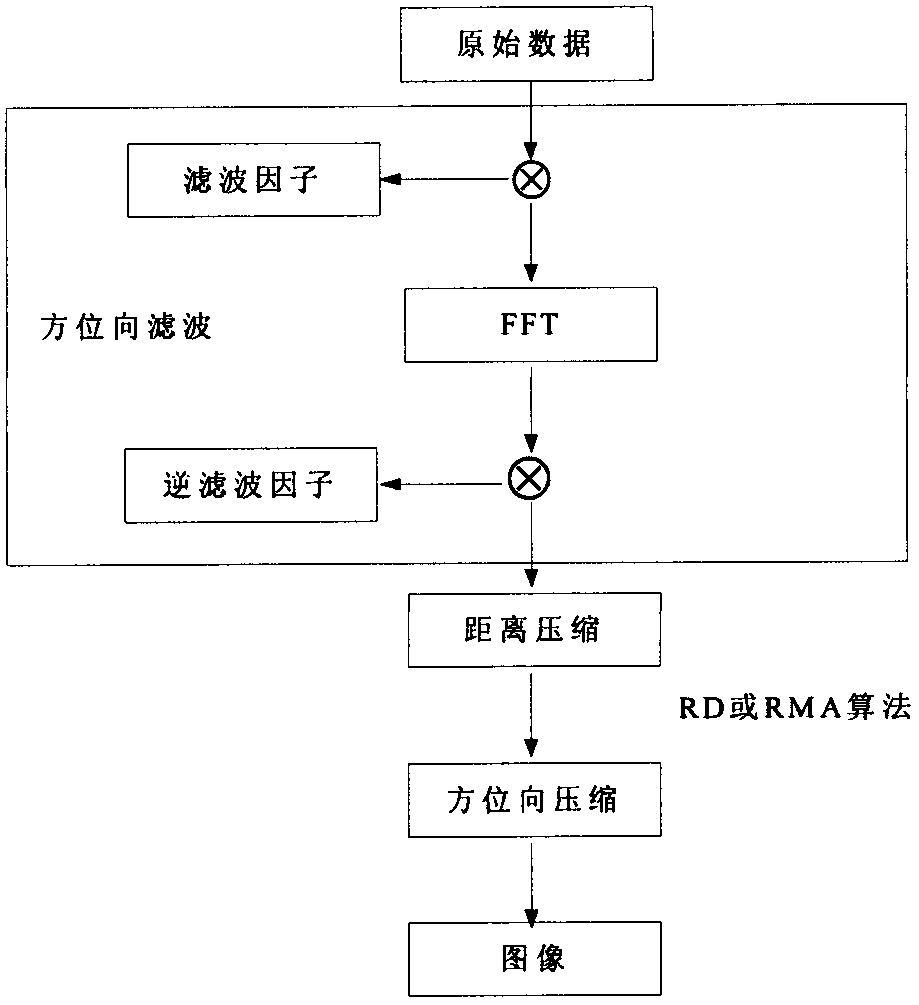
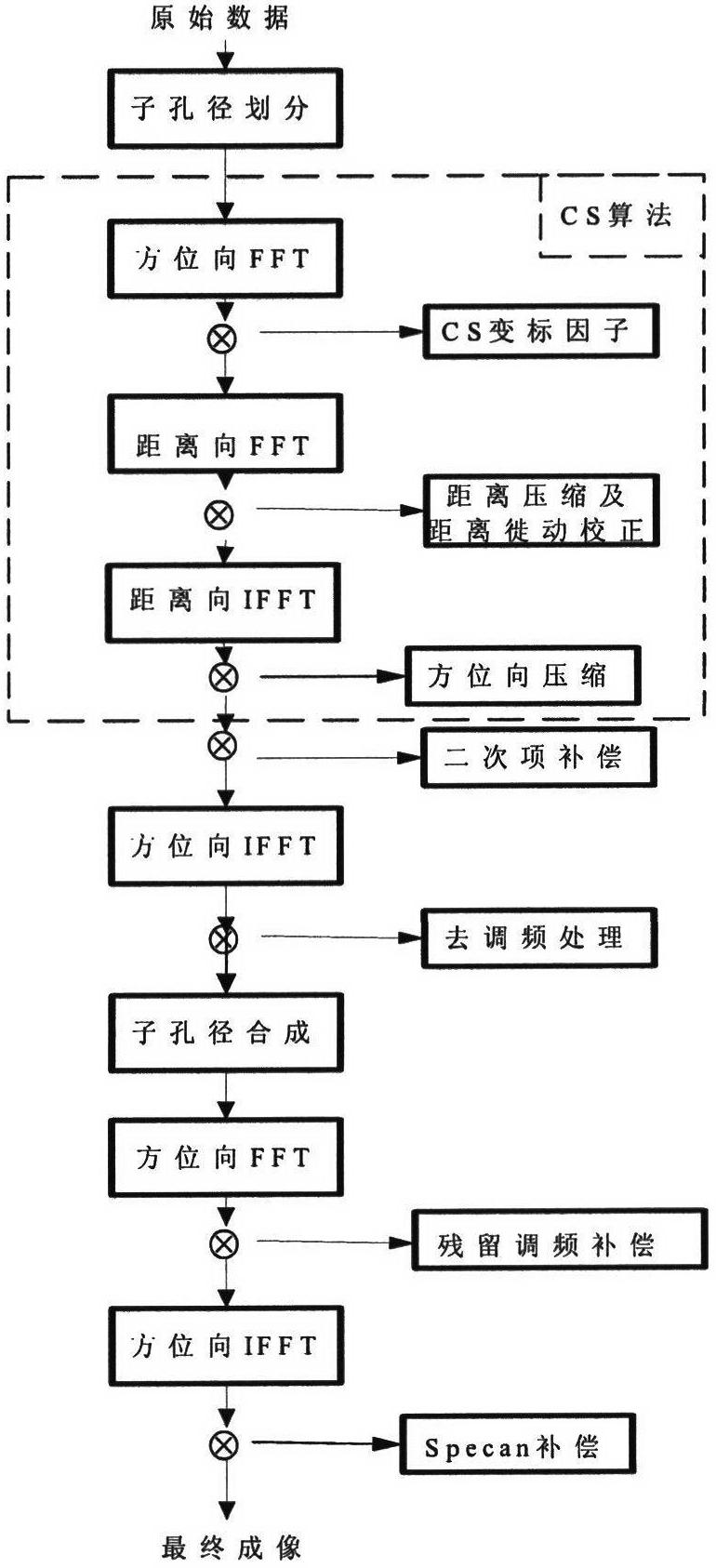
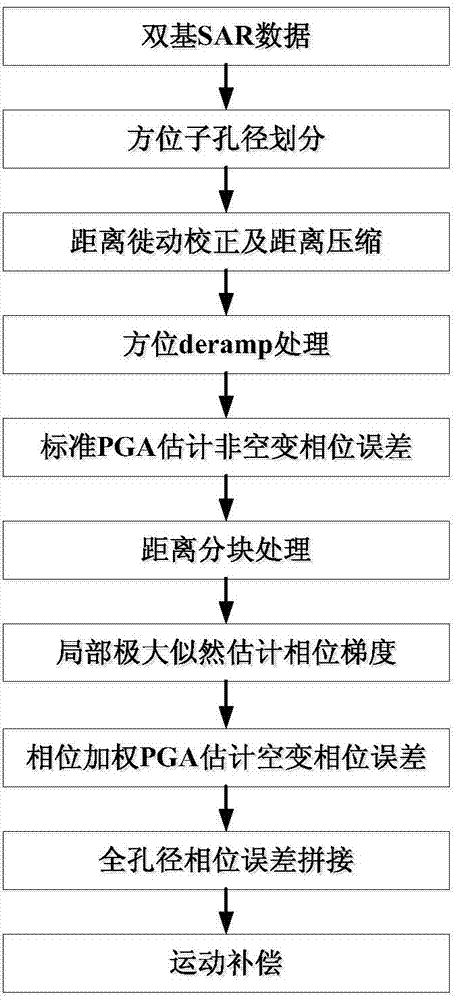
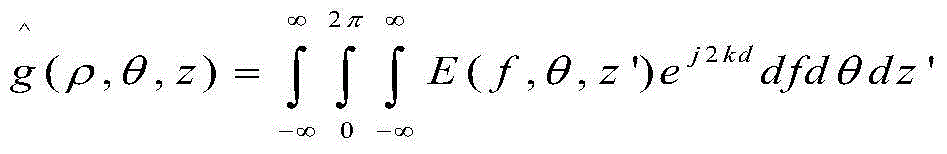Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
255 results about "Range migration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
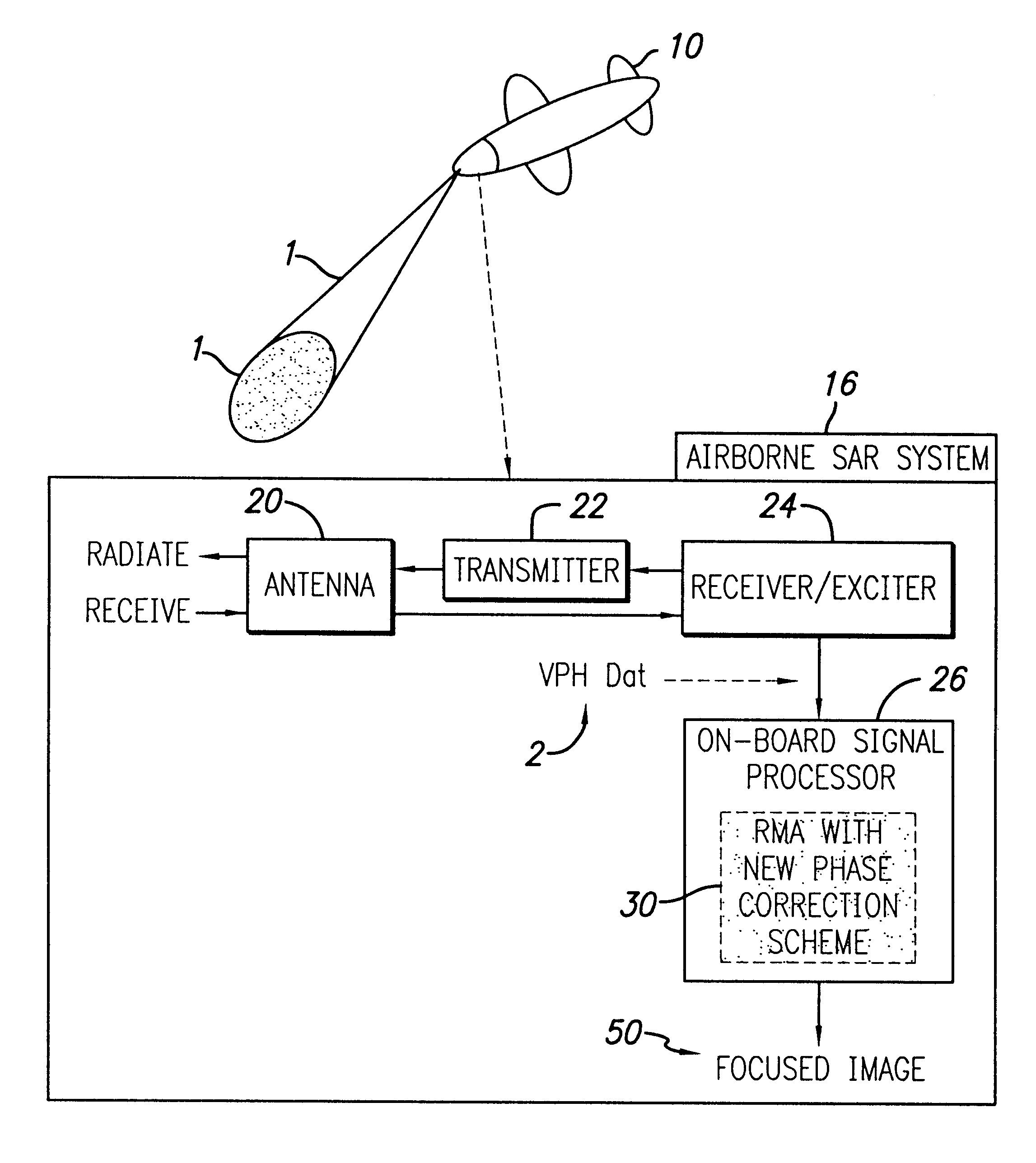
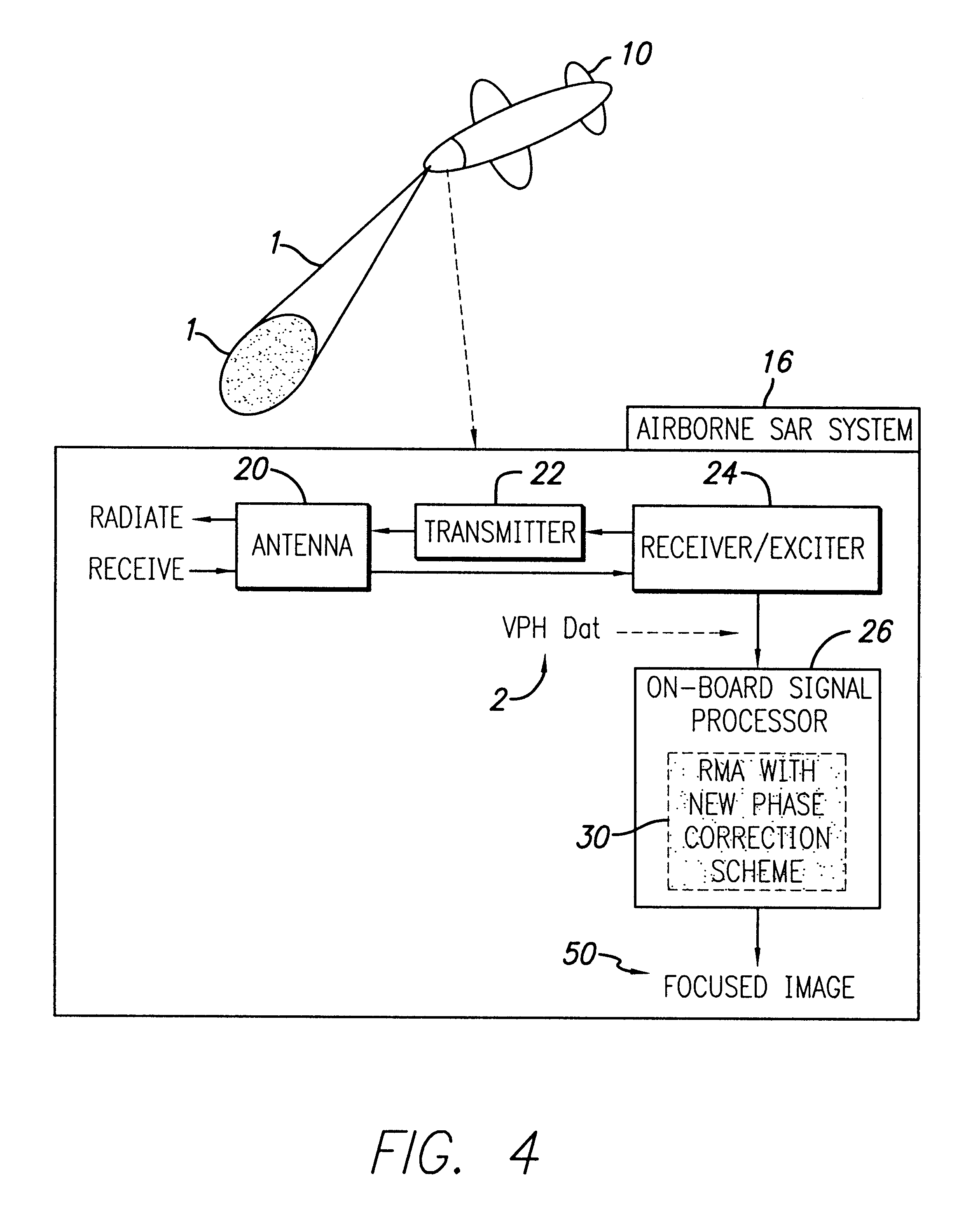
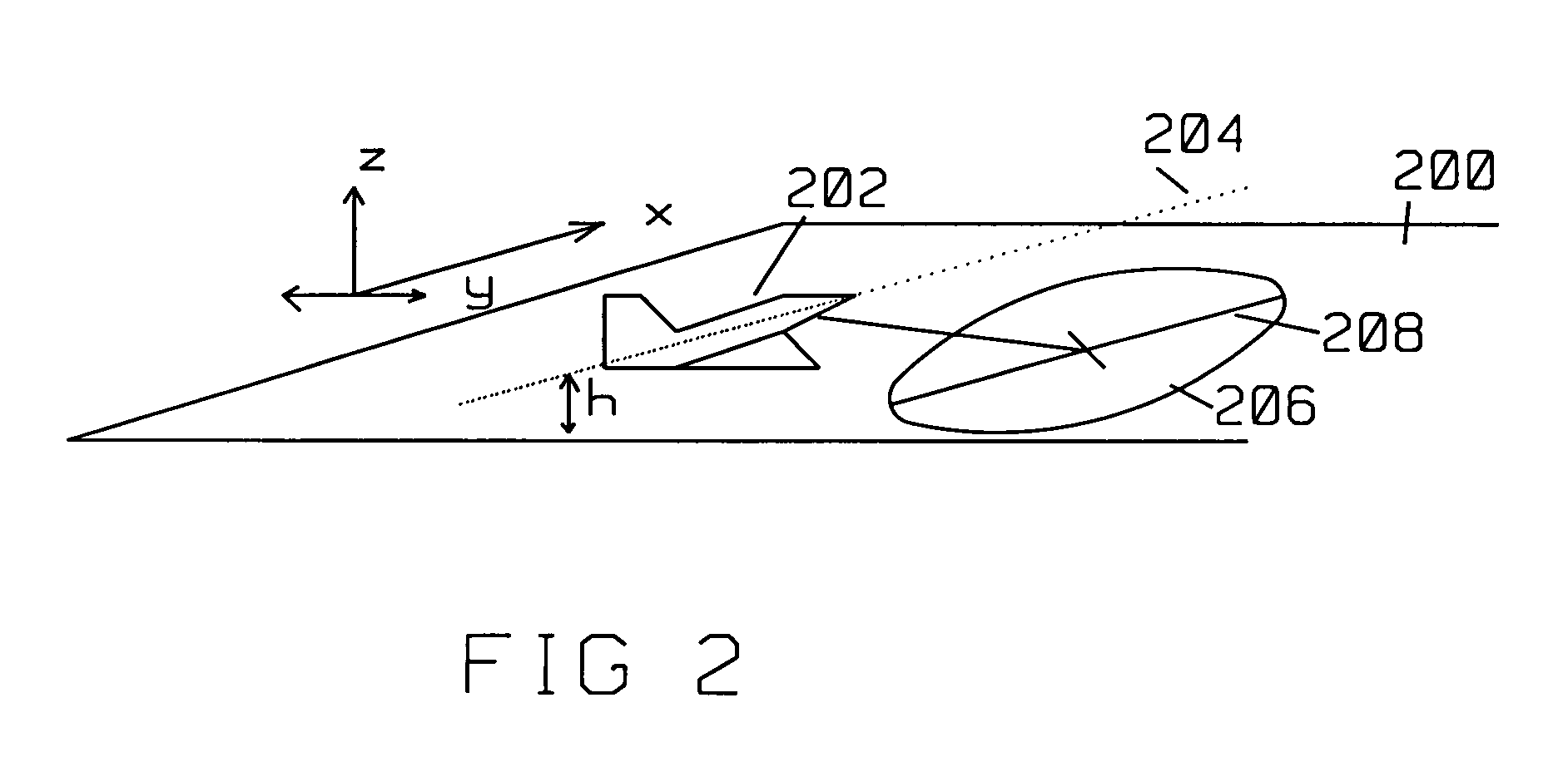
Method and system for forming very low noise imagery using pixel classification
InactiveUS20110012778A1High contrast imageReduce false alarm rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseRange migration
A method and system for generating images from projection data comprising inputting from at least one data receiving element first values representing correlated positional and recorded data; each of said first values forming a point in an array of k data points; forming an image by processing the projection data utilizing a pixel characterization imaging subsystem that combines the positional and recorded data to form the SAR imagery utilizing one of a back-projection algorithm or range migration algorithm; integrating positional and recorded data from many aperture positions, comprising: forming the complete aperture A0 for SAR image formation comprising collecting the return radar data, the coordinates of the receiver, and the coordinates of the transmitter for each position k along the aperture of N positions; forming an imaging grid comprising M image pixels wherein each pixel Pi in the imaging grid is located at coordinate (xP(i),yP(i), zP(i)); selecting and removing a substantial number of aperture positions to form a sparse aperture Ai; repeating the selecting and removing step for L iterations for each Ai; classifying each pixel in the image into either target class based on the statistical distribution of its amplitude across L iterations (1≦i≦L); whereby if an image pixel is classified so as to be associated with a physical object, its value is computed from its statistics; otherwise, the pixel is assumed to come from a non-physical object and is given the value of zero.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE +1
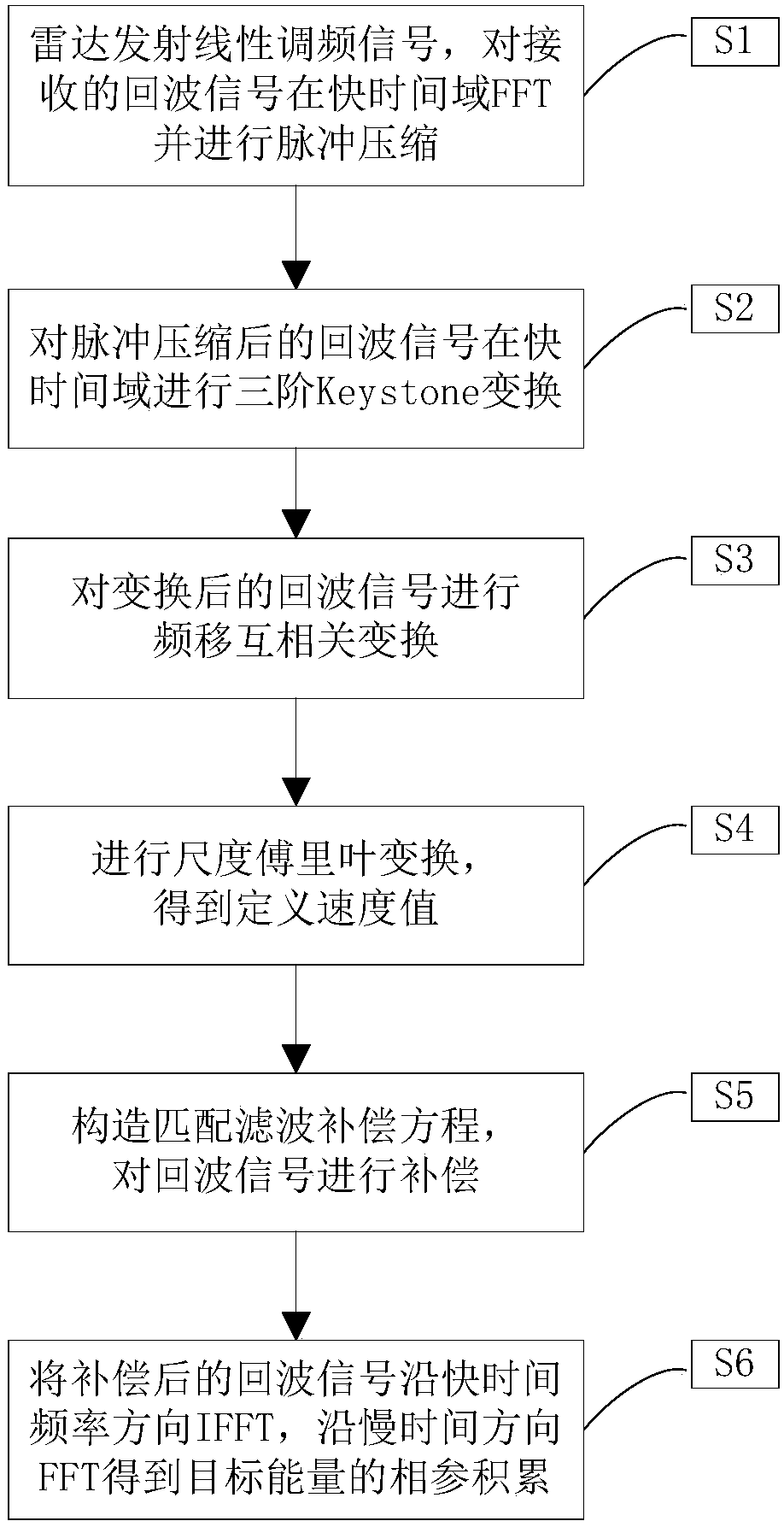
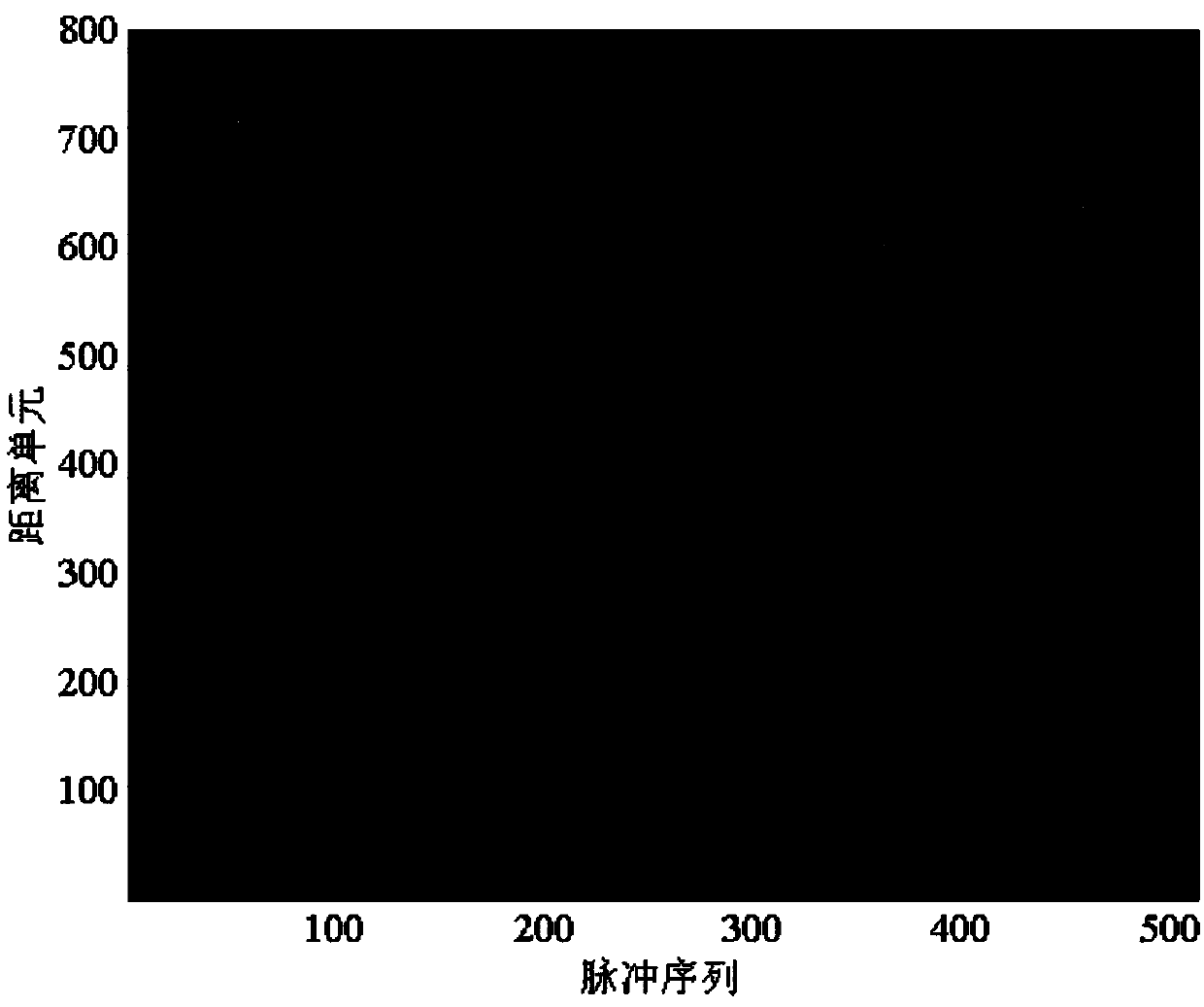
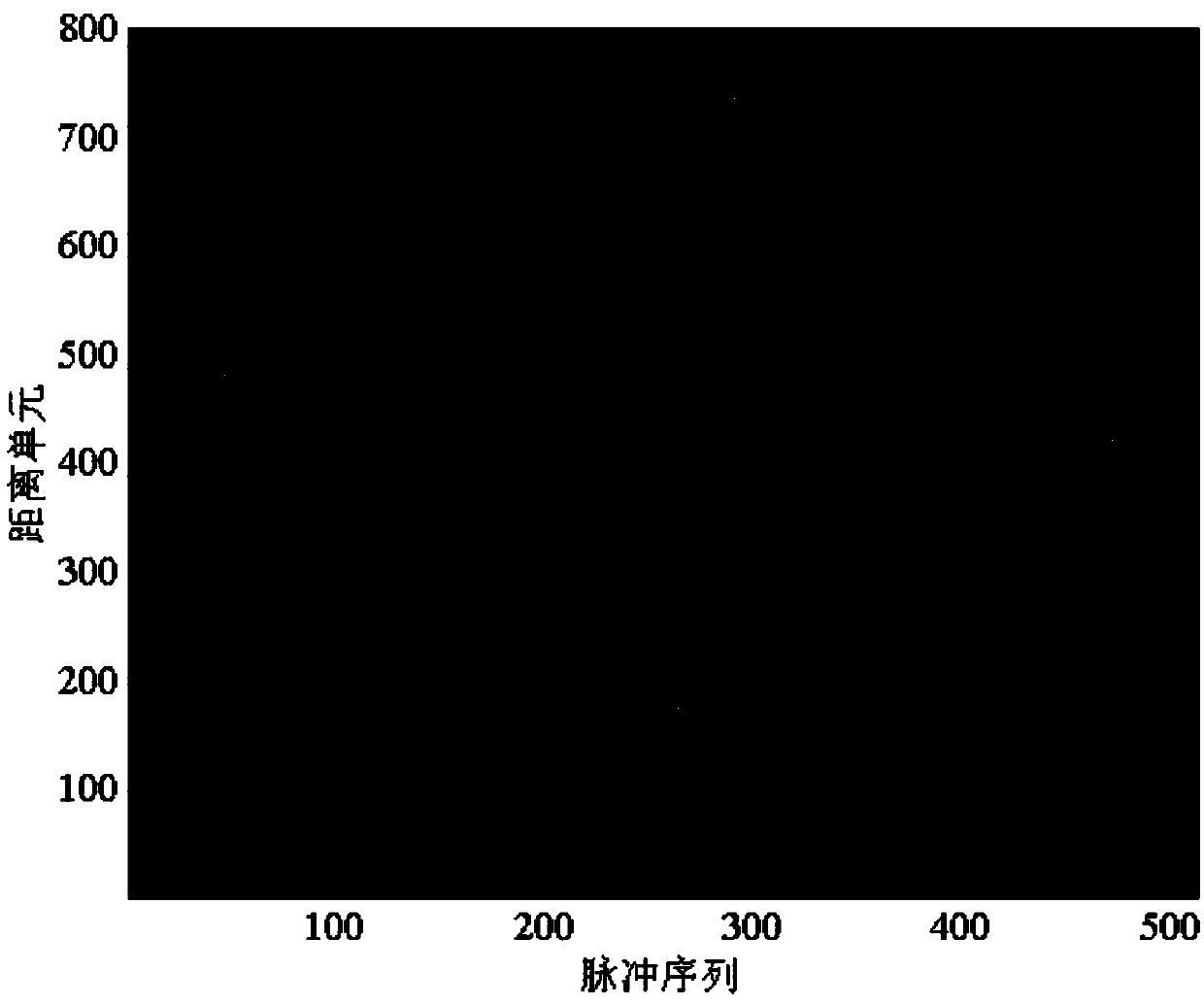
Target detection method based on Keystone and matched filtering
ActiveCN106970371AImprove the echo signal-to-noise ratioEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsPeak valueChirp
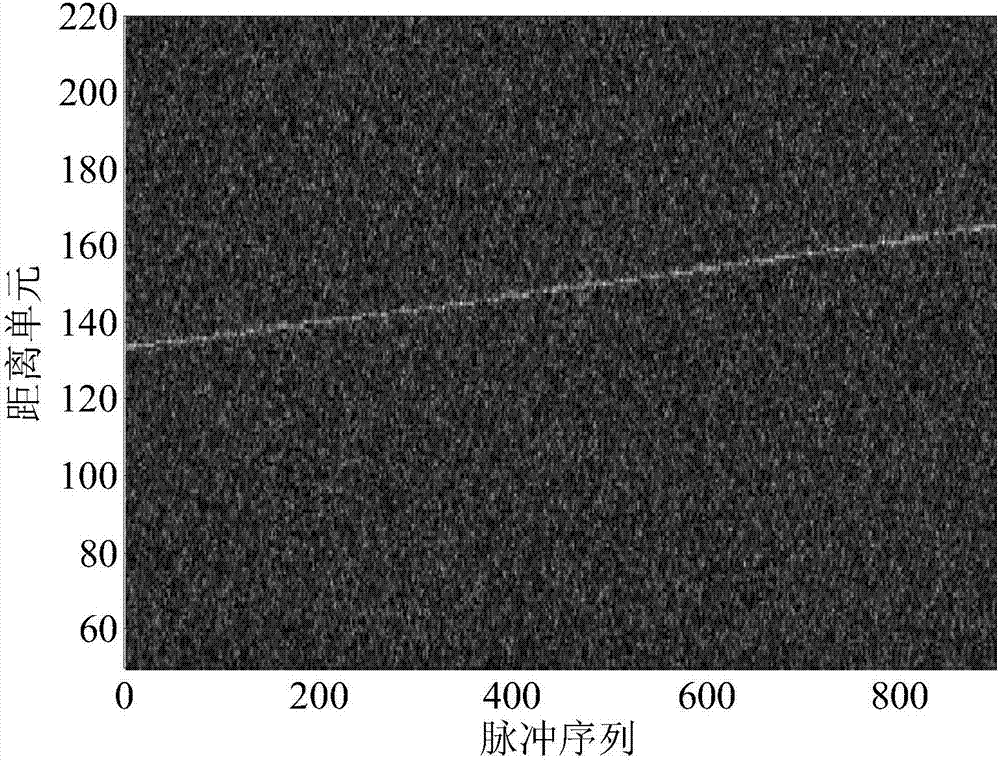
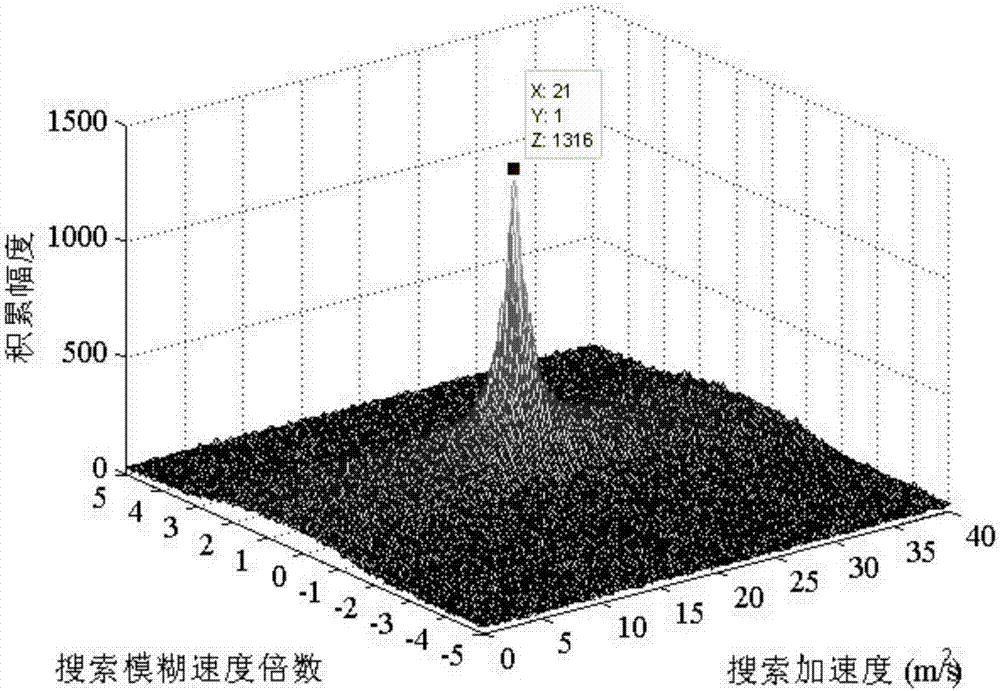
The invention discloses a target detection method based on Keystone and matched filtering and belongs to the radar weak signal detection technology field. The method comprises steps that firstly, a radar is utilized to emit a chirp signal, pulse compression for a received target echo signal is carried out, and first-order range migration caused by no fuzzy speed of a target is corrected through utilizing Keystone transformation; secondly, a fuzzy speed multiple and acceleration of the target are estimated through utilizing combined two-dimensional matched filtering processing of a distance frequency domain, and first-order range migration caused by the fuzzy speed of the target and second-order range bending and Doppler migration caused by acceleration are corrected and compensated; and lastly, phase-coherent accumulation of target energy is realized through fast Fourier transform, and a peak value of phase-coherent accumulation is utilized to carry out target detection. The method is advantaged in that amplitude and the phase information of target echoes are utilized to carry out long time phase-coherent accumulation, so a radar echo signal-to-noise ratio can be effectively improved, and target detection performance of the radar can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Imaging method for bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
InactiveCN102147469AAchieve precise focusImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler centroidFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses an imaging method for a bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Aiming at the defect existing when the existing method is used for the imaging process of the bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar, the imaging method adopts a bistatic forward-looking SAR point target response two-dimensional frequency spectrum based on the least square polynomial fitting; the frequency spectrum is the least square approximation of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum with the accurate theory. According to the characteristics of bistatic forward-looking invariant SAR direction, variant range and nonlinear and variant Doppler centroid range of range cell migration in an RD (radar domain) domain, bistatic forward-looking SAR range migration correction, secondary-range compression and high-order phase compensation are realized by the frequency spectrum so as to accurately focus the bistatic forward-looking SAR. Compared with the traditional SAR imaging method and the bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging method, the method disclosed by the invention has higher imaging precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for processing squint mapped synthetic aperture radar data
A method for processing squint-mapped synthetic aperture radar data of the present invention. The inventive method includes the steps of effecting range compression of the data; deskewing the data; performing a Fourier transform with respect to the deskewed data; providing a range migration interpolation of the transformed data; effecting a frequency remapping of the range interpolated data; and performing an inverse Fourier transform with respect to the deskewed data.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
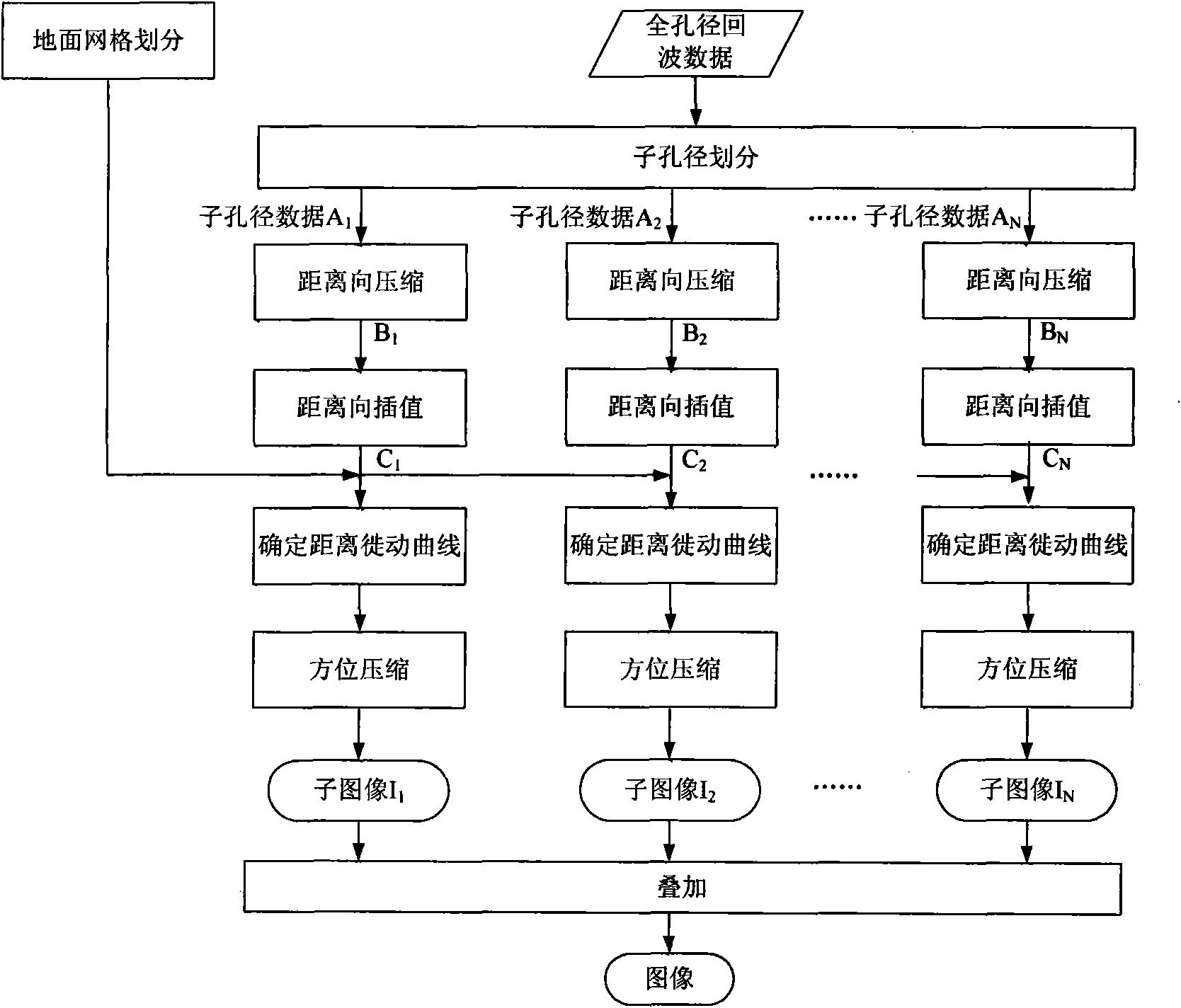
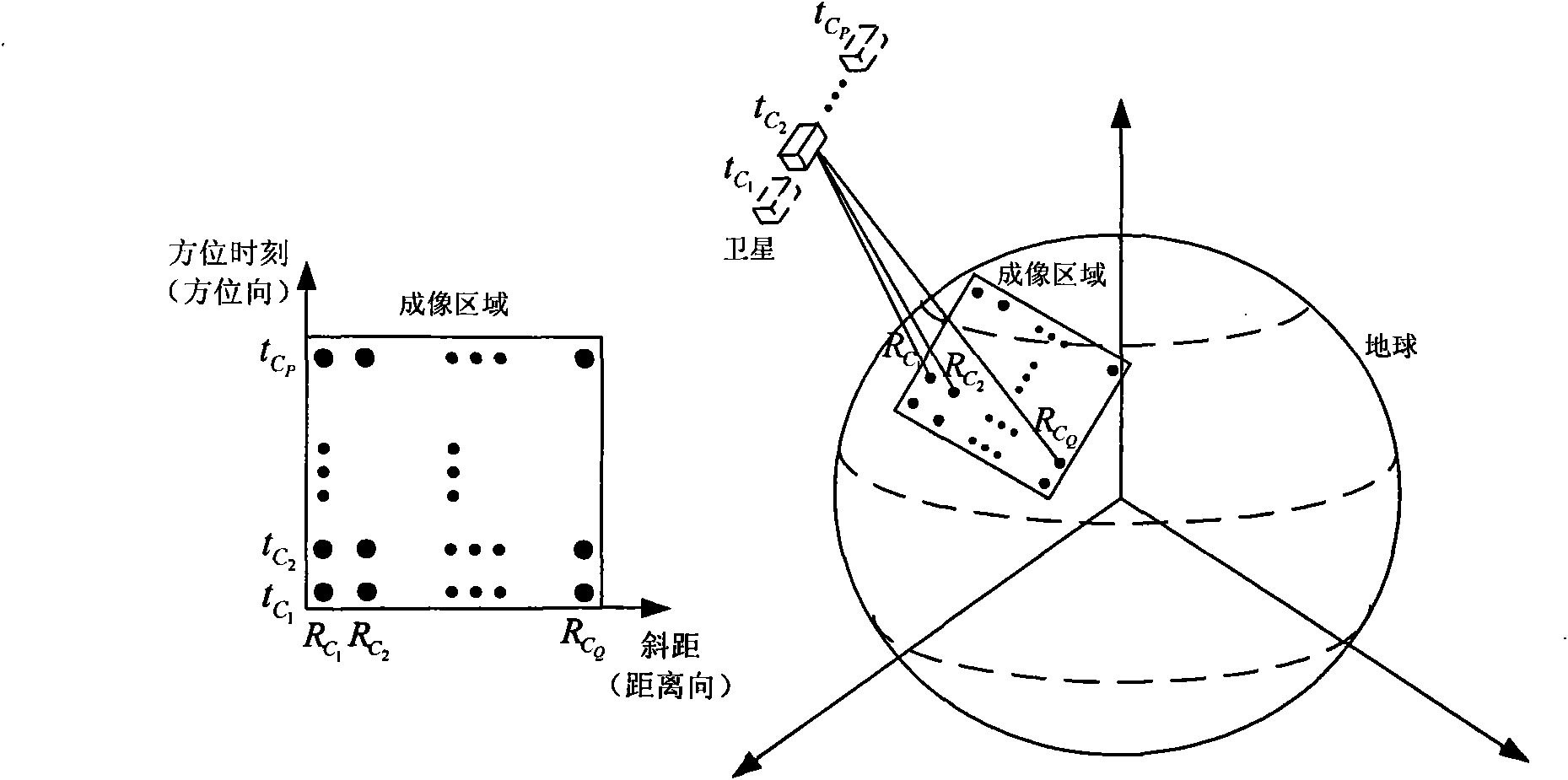
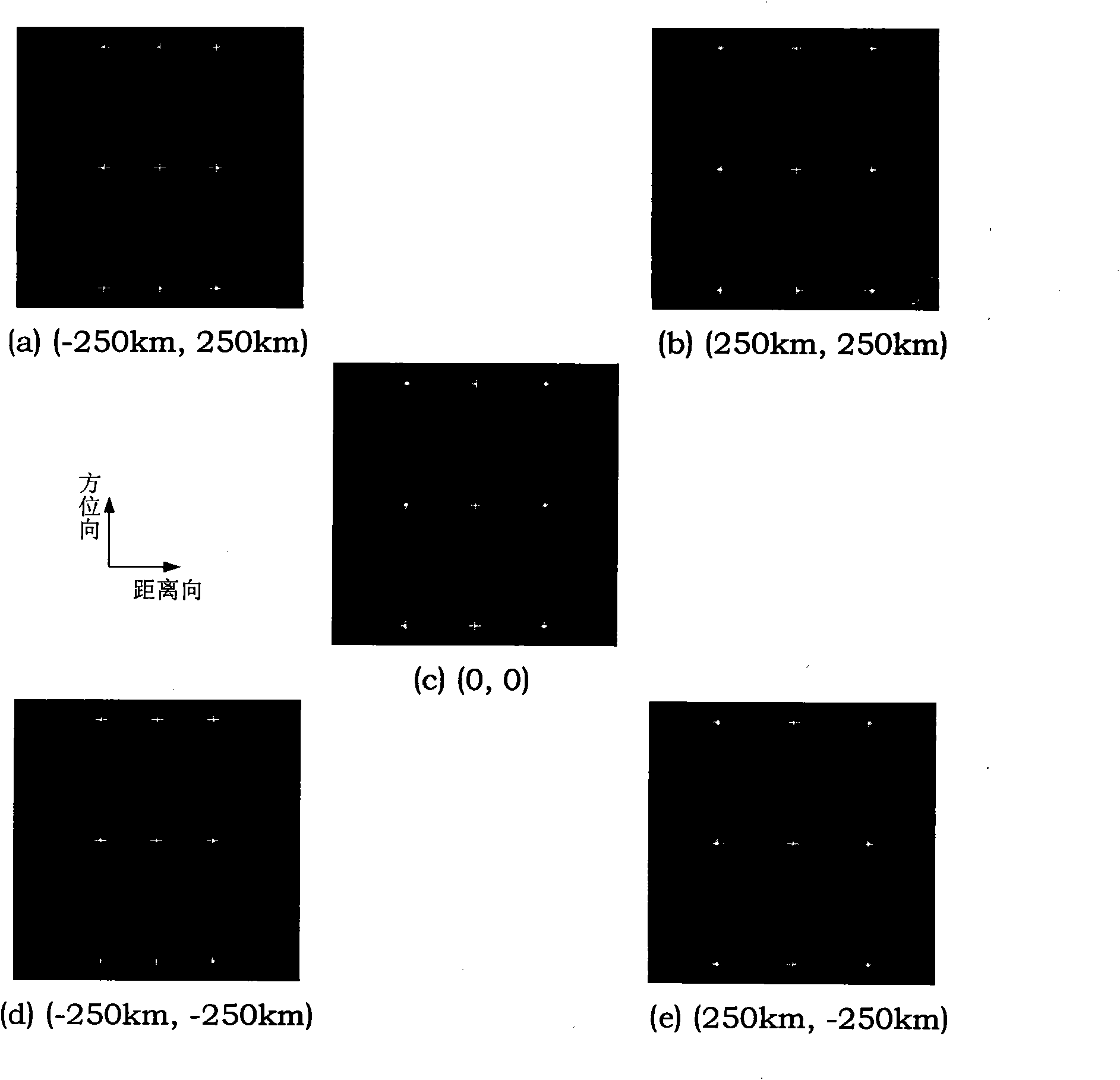
High-resolution imaging method for earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite
InactiveCN101915920AExcellent azimuth resolutionRealize multi-point target imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWide areaGrounding grid
The invention discloses a high-resolution imaging method for an earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, dividing a sub-aperture; 2, performing range compression on the sub-aperture data; 3, performing range interpolation on the sub-aperture data; 4, dividing a ground grid; 5, determining a range migration curve; 6, performing azimuth compression processing; and 7, superposing sub-aperture images to obtain the final image. By the imaging method provided by the invention, high-resolution imaging can be realized by processing the full-aperture echo data of the earth synchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar satellite, multi-point target imaging can be realized, namely azimuth compression can be performed on different range migration curves of different range and azimuth targets, and imaging in a wide-area scene range can be realized and the method has the characteristic of free imaging area, namely imaging can be performed on scenes at different positions as required.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
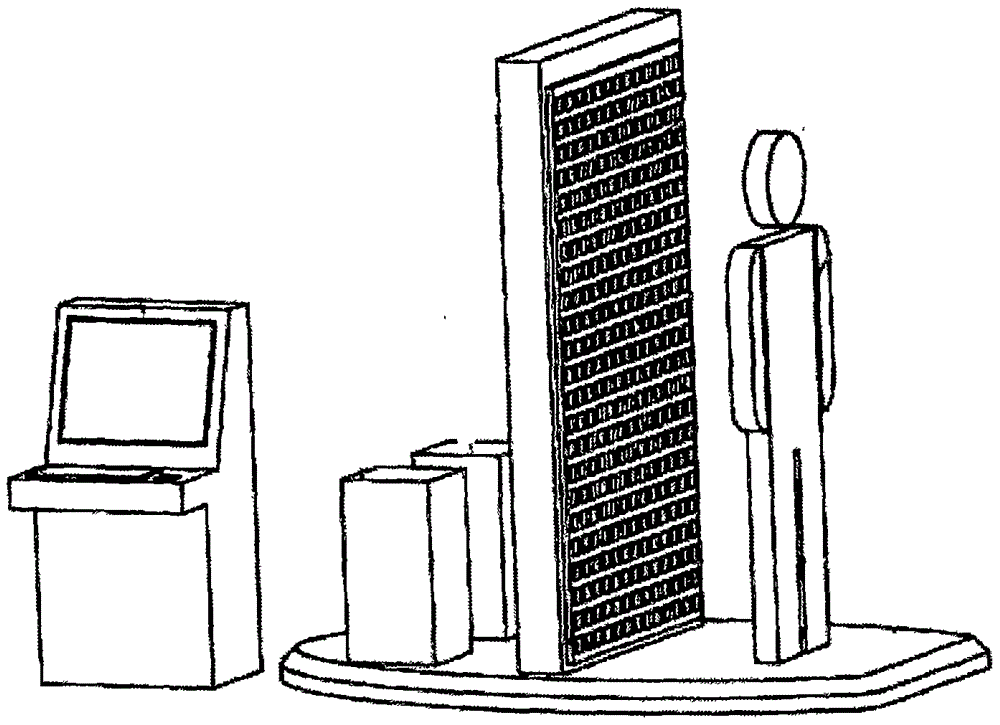
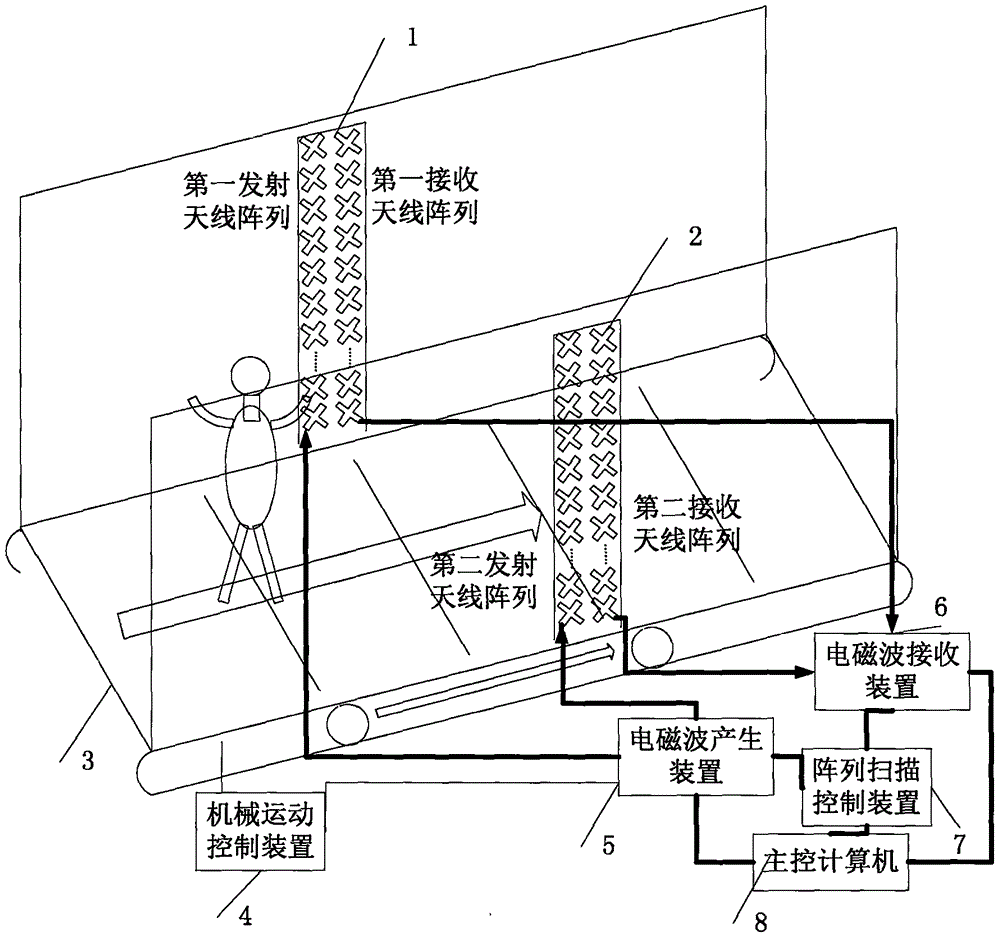
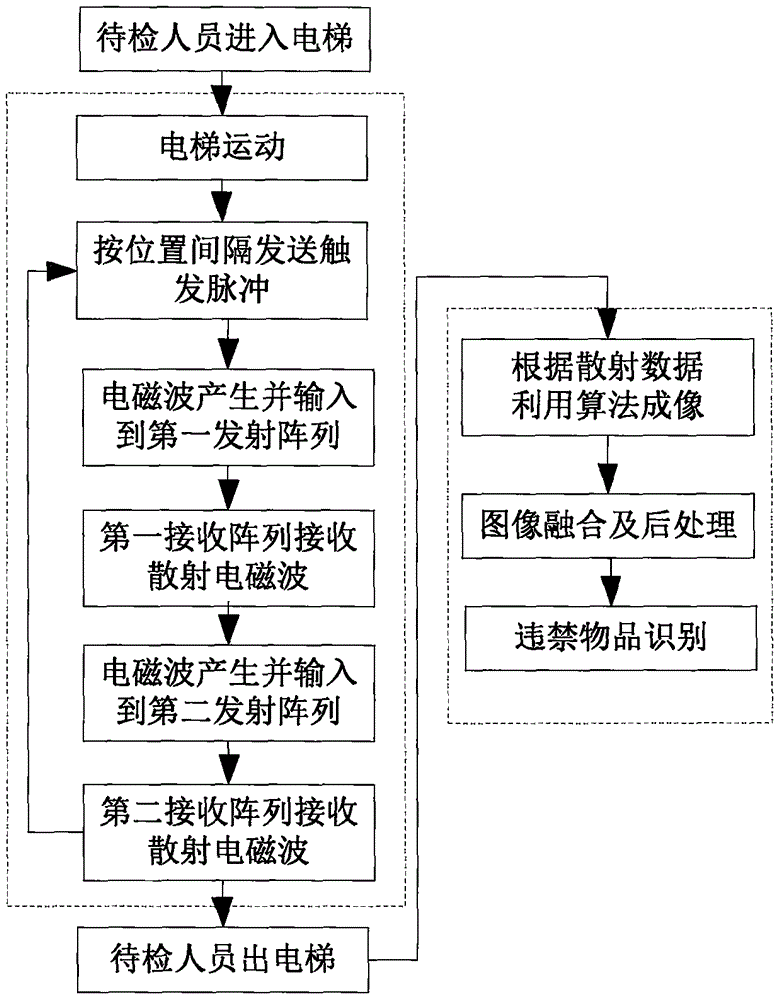
Microwave and millimeter wave human body safety check system and method
InactiveCN106093937AAvoid detection blind spotsImprove imaging effectDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrowaveRange migration
The invention provides a microwave and millimeter wave human body safety check system, including a first transmit-receive array, a second transmit-receive array, a translation elevator, a mechanical motion control device, an electromagnetic wave generation device, an electromagnetic wave reception device, an array scanning control device and a master control computer. The master control computer is responsible for coordination control of a whole system and for imagery processing of three-dimension scattering information. In the safety check system, a one-dimension antenna array can complete vertical scanning, the translation elevator can complete horizontal scanning, and scanning in a range direction is performed with the combination of broadband electromagnetic waves, and thus the three-dimension scattering information can be obtained. Three-dimension imaging of a target area can be completed using algorithms of back scattering or range migration, etc. The invention utilizes the travelling translation elevator, so that the to-be-checked people stagnation condition of a rotary-type imaging system is prevented, and safety check can be completed without influencing the travelling speed.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Radar slightly-moving target detection method based on Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function
ActiveCN103344949AEfficient accumulationFlexible matchingWave based measurement systemsTarget signalPulse pressure
The invention relates to a radar slightly-moving target detection method based on a Radon-linear canonical ambiguity function (RLCAF) and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing and detection. The radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF comprises the following steps that (1) demodulation and pulse pressure are conducted on a radar echo in the distance direction so that in-pulse accumulation can be completed; (2) the type of a target to be detected is predicted, and parameters are initialized; (3) the distance and Doppler migration are compensated through the RLCAF and signal energy of a slightly-moving target is accumulated; (4) the parameters are traversed and searched, an RLCAF domain detection unit figure is established, and constant false-alarm detection is conducted; (5) target moving parameters are estimated and moving trace points are output. According to the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF, the advantages of an ambiguity function and the advantages of linear canonical transformation are combined, non-uniform velocity translational motion target signals or turning target signals can be flexibly matched and accumulated in a clutter background, the signal-to-clutter ratio is improved, range migration can be compensated through the extraction of a target observation value in a distance-slow-time plane, phase-coherent accumulation for a long time is completed, the detection capacity of radar to the slightly-moving target is improved, and therefore the radar slightly-moving target detection method based on the RLCAF is wide in applicability.
Owner:NAVAL AVIATION UNIV
Implementation method of high resolution and wide swath spaceborne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) system
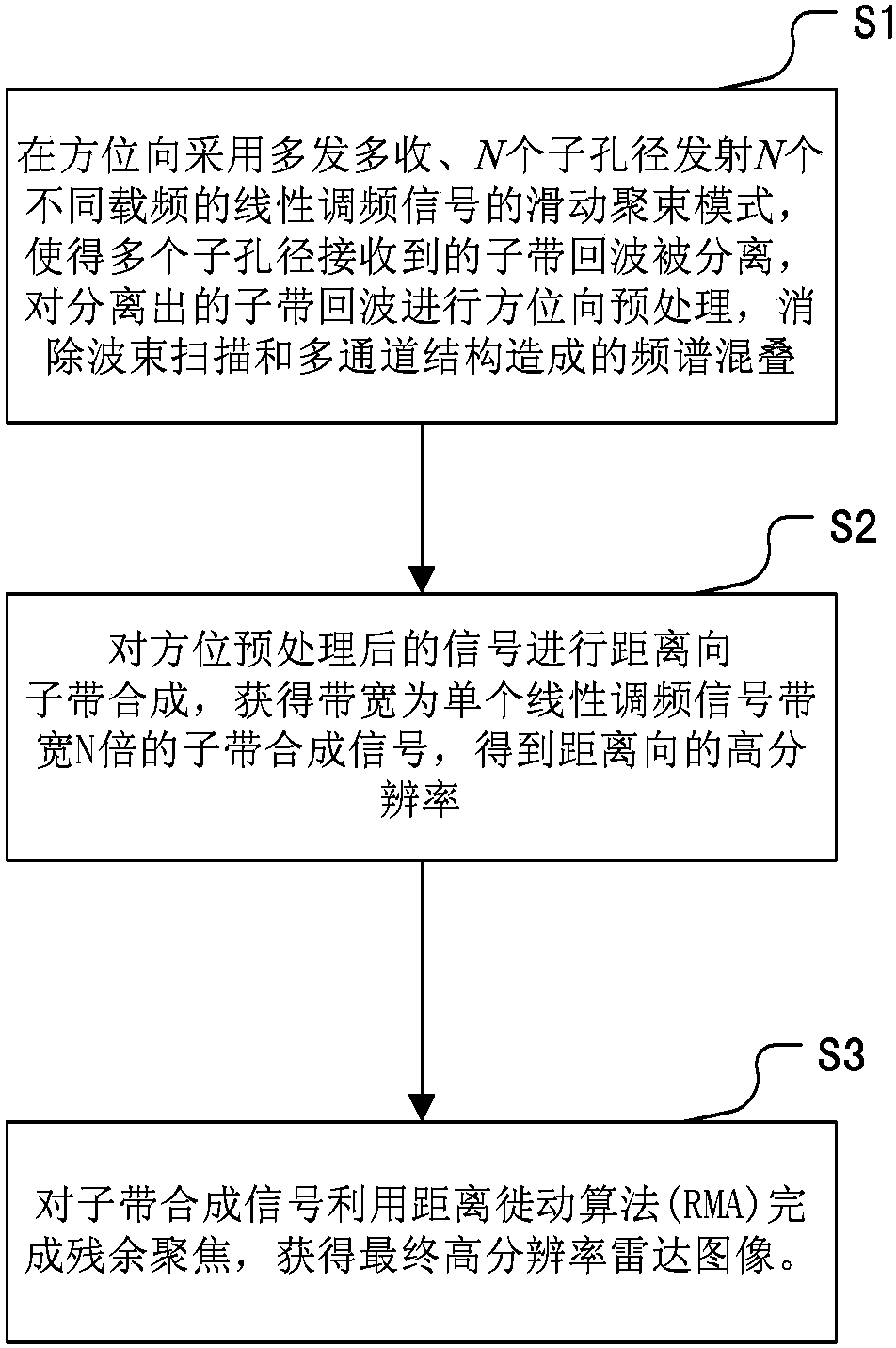
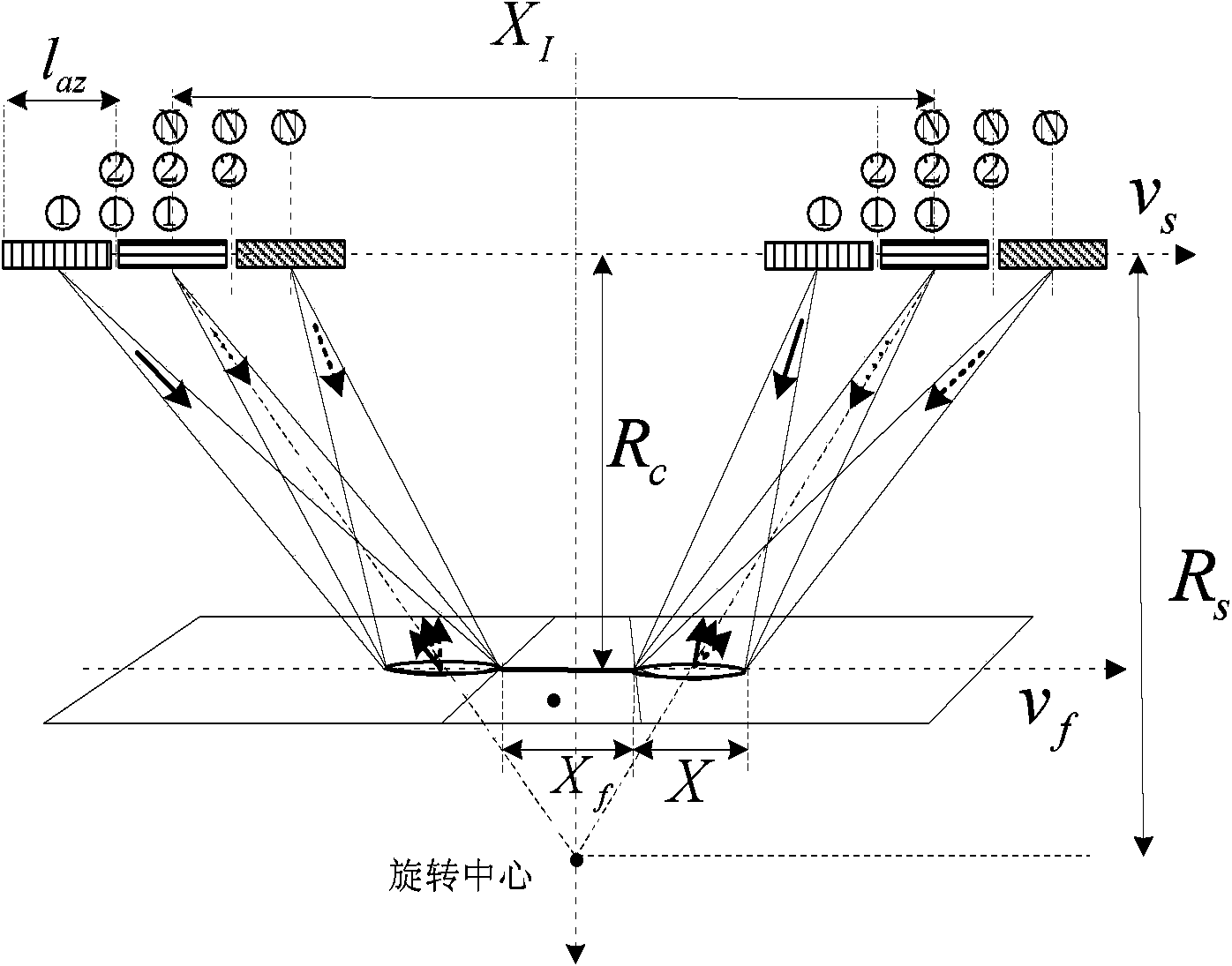
ActiveCN103728618AHigh-resolutionAvoid crosstalkRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumSynthetic aperture sonar
The invention discloses an implementation method of a high resolution and wide swath spaceborne SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) system. The implementation method comprises adopting the sliding bunching mode that multiple-input and multiple-output are performed and N different carrier frequencies of linear frequency modulation signals are transmitted from N sub-apertures in the azimuth direction of a spaceborne SAR to enable sub-band echoes which are received by the plurality of sub-apertures to be separated, performing azimuth pretreatment on the separated sub-band echoes and eliminating the spectrum overlapping caused by the beam scanning and the antenna multi-channel structure; performing range sub-band composition on signals after the azimuth pretreatment to obtain a sub-band composition signal and obtain the range high resolution, wherein the bandwidth of the sub-band composition signal is N times of the bandwidth of the single linear frequency modulation signal; achieving residual focusing of the sub-band composition signal through an RMA (Range Migration Algorithm) to obtain a final high resolution radar image.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
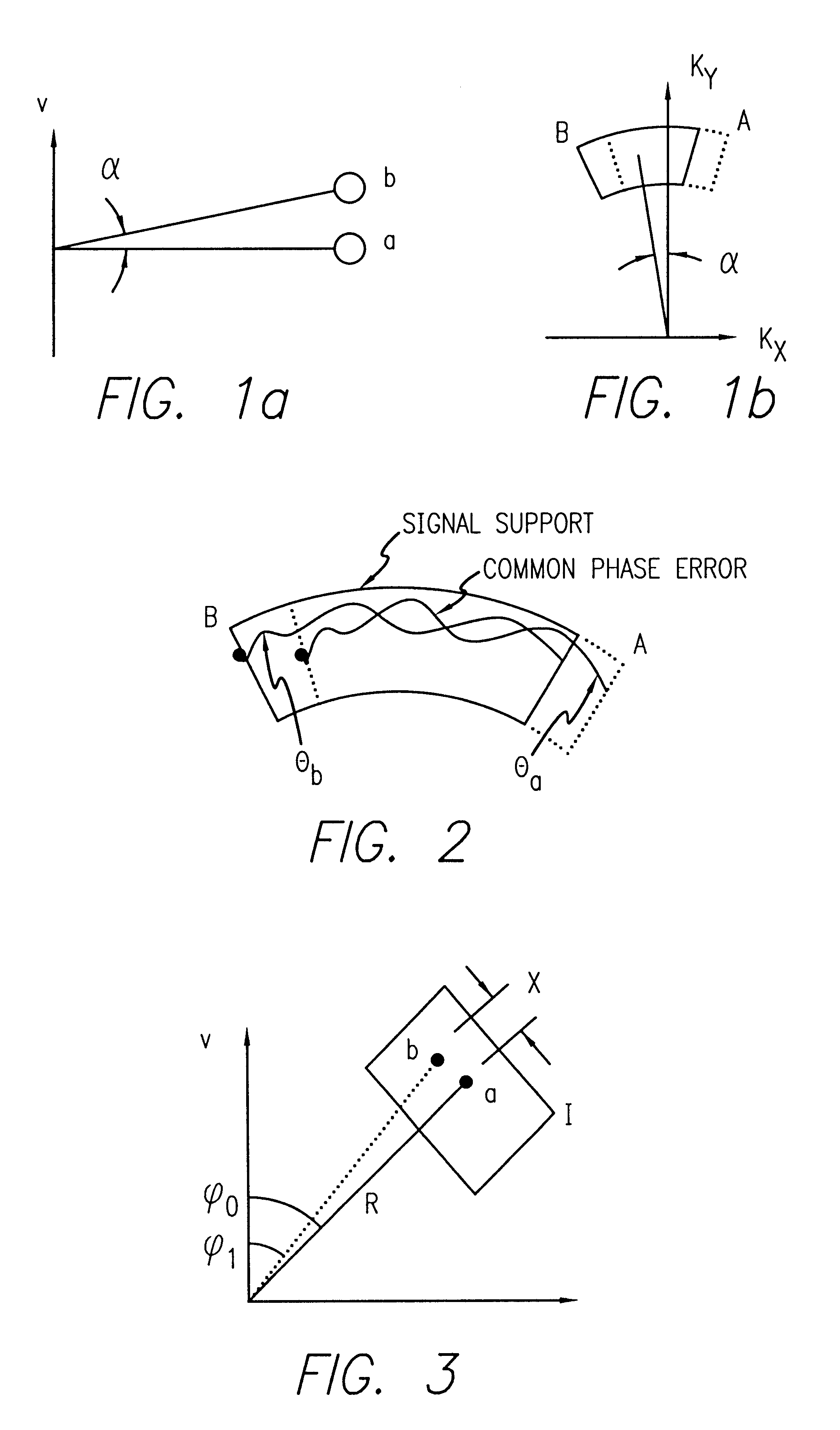
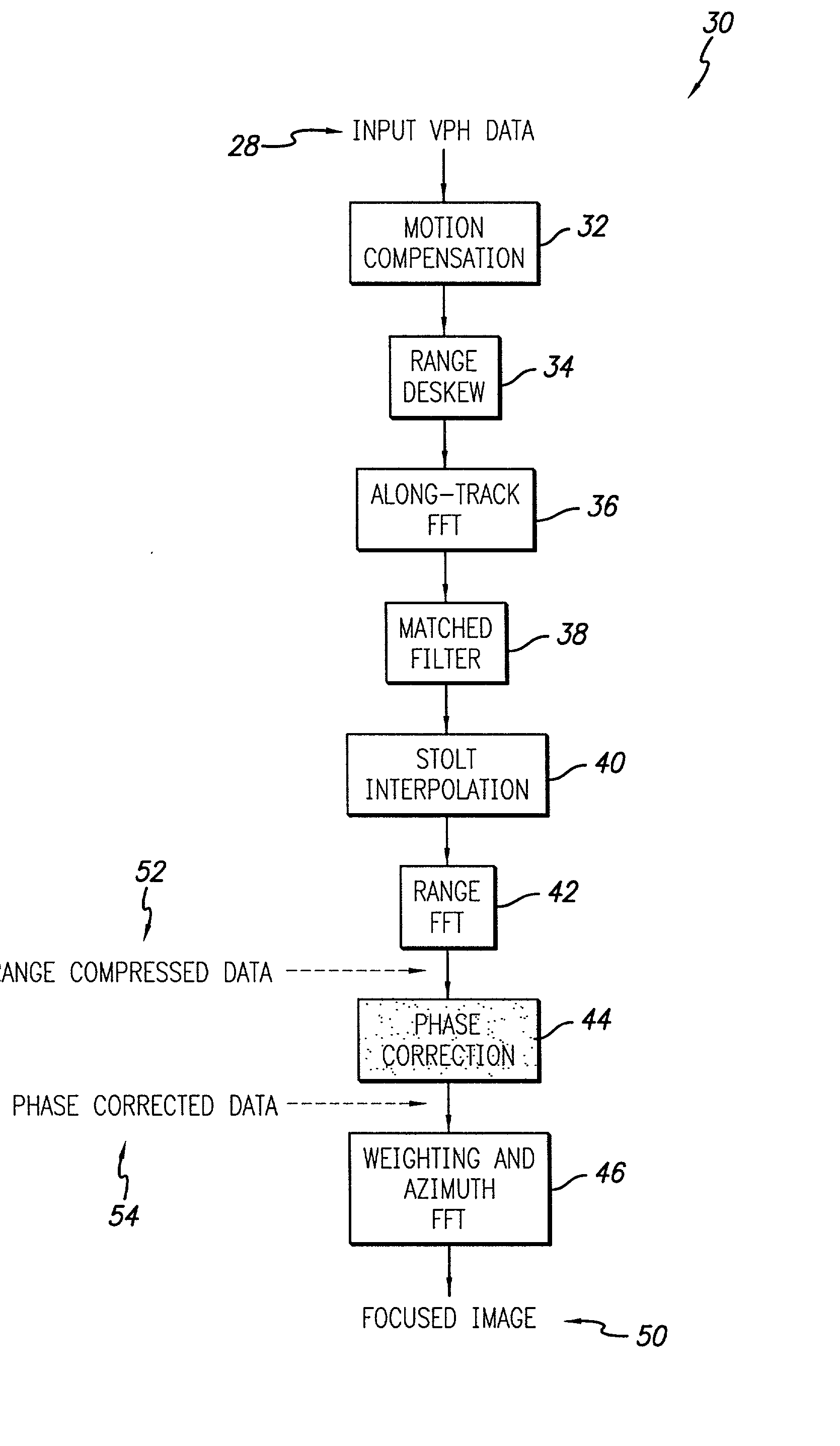
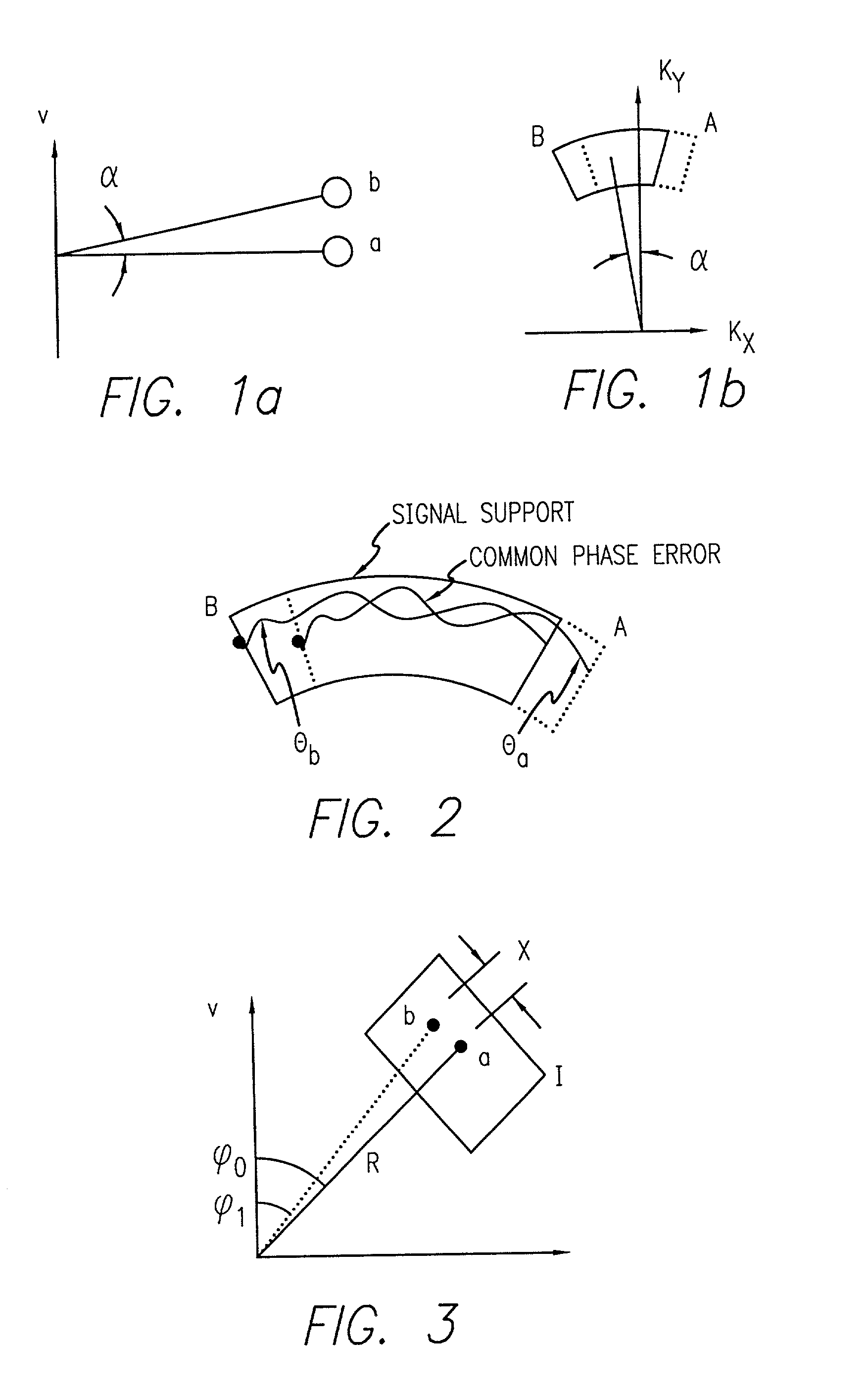
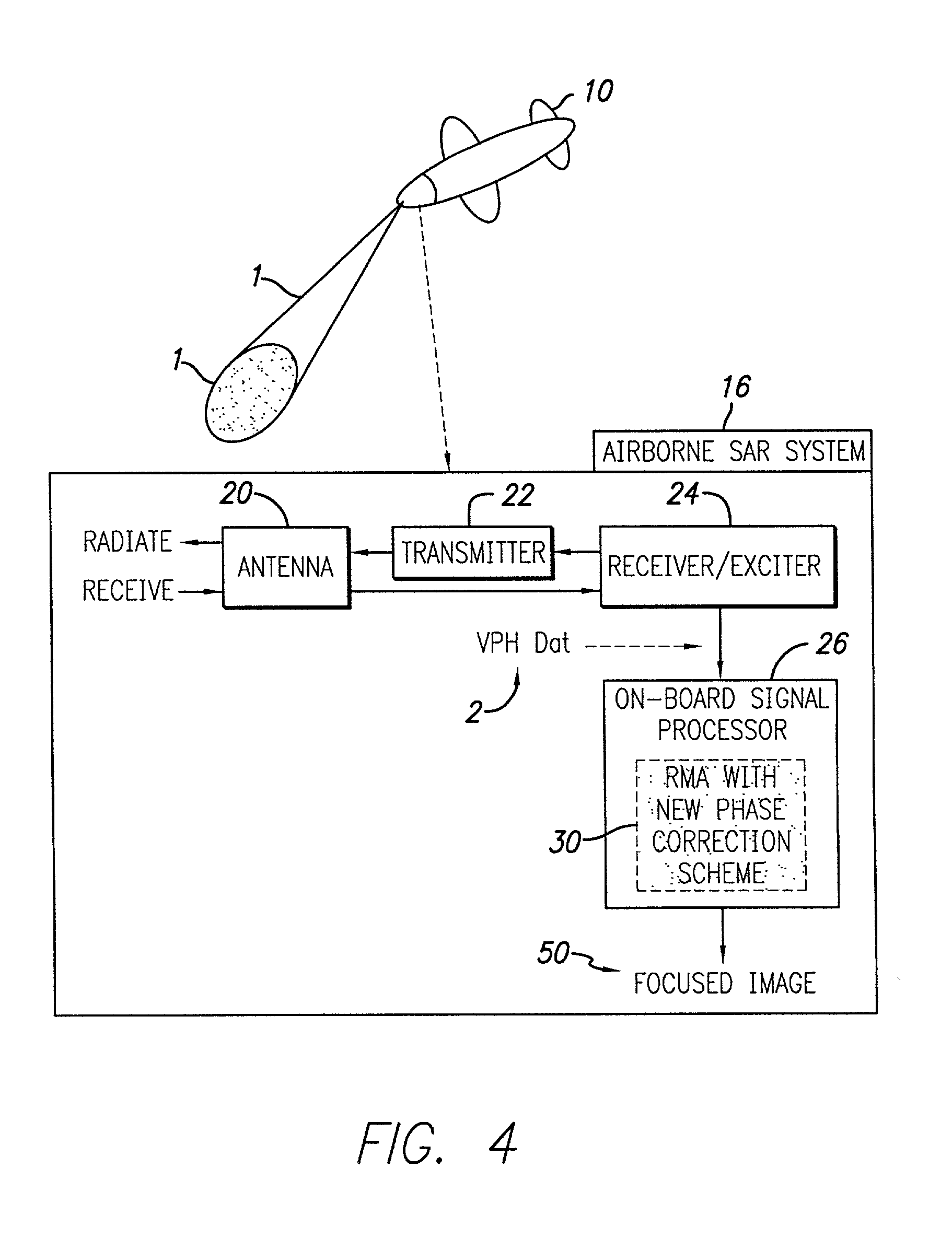
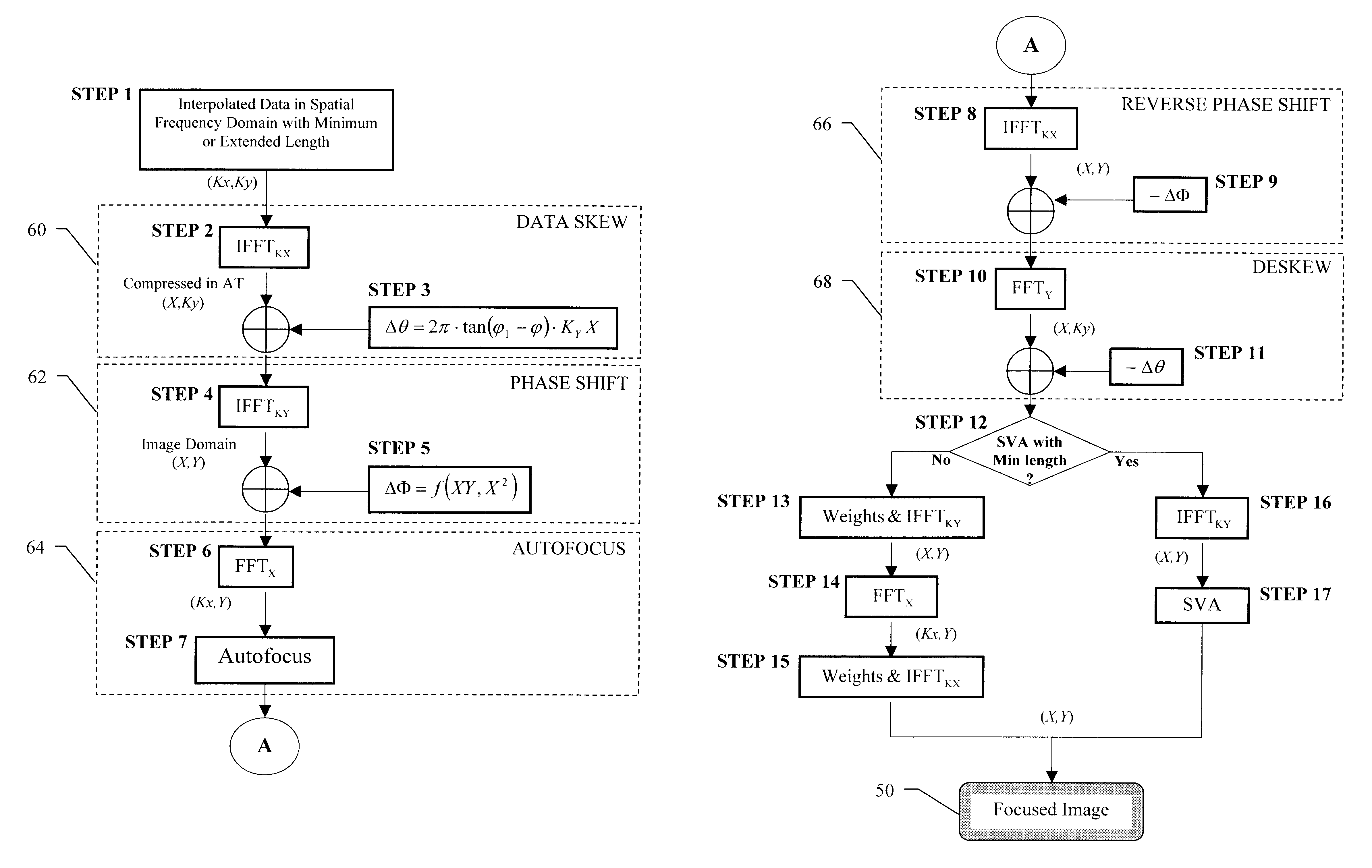
Efficient phase correction scheme for range migration algorithm
InactiveUS6670907B2Convenient lengthExemption stepsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBatch processingCommon phase error
A system and method for efficient phase error correction in range migration algorithm (RMA) for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems implemented by making proper shifts for each position dependent phase history so that phase correction can readily be performed using the aligned phase history data during batch processing. In its simplest form, the invention (44) is comprised of two main parts. First (60), alignment of the phase error profile is achieved by proper phase adjustment in the spatial (or image) domain using a quadratic phase function. Second (62), the common phase error can be corrected using autofocus algorithms. Two alternative embodiments of the invention are described. The first embodiment (44a) adds padded zeros to the range compressed data in order to avoid the wrap around effect introduced by the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform). This embodiment requires a third step (64): the target dependent signal support needs to be shifted back to the initial position after phase correction. The second embodiment (44b) uses the range compressed data without padded zeros. Instead, an aperture of greater length needs to be generated by the Stolt interpolation. In this embodiment, the third step (64) of shifting the signal support back can be eliminated.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Range migration correction method for pulse Doppler (PD) radar in feeble signal detection process
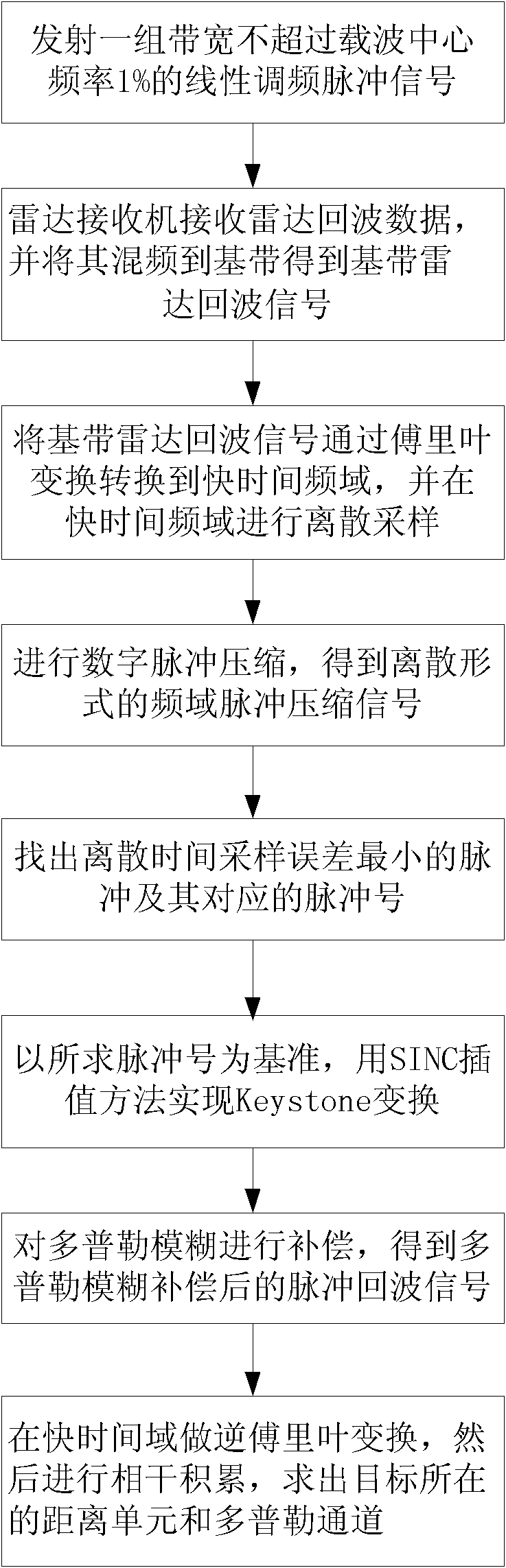
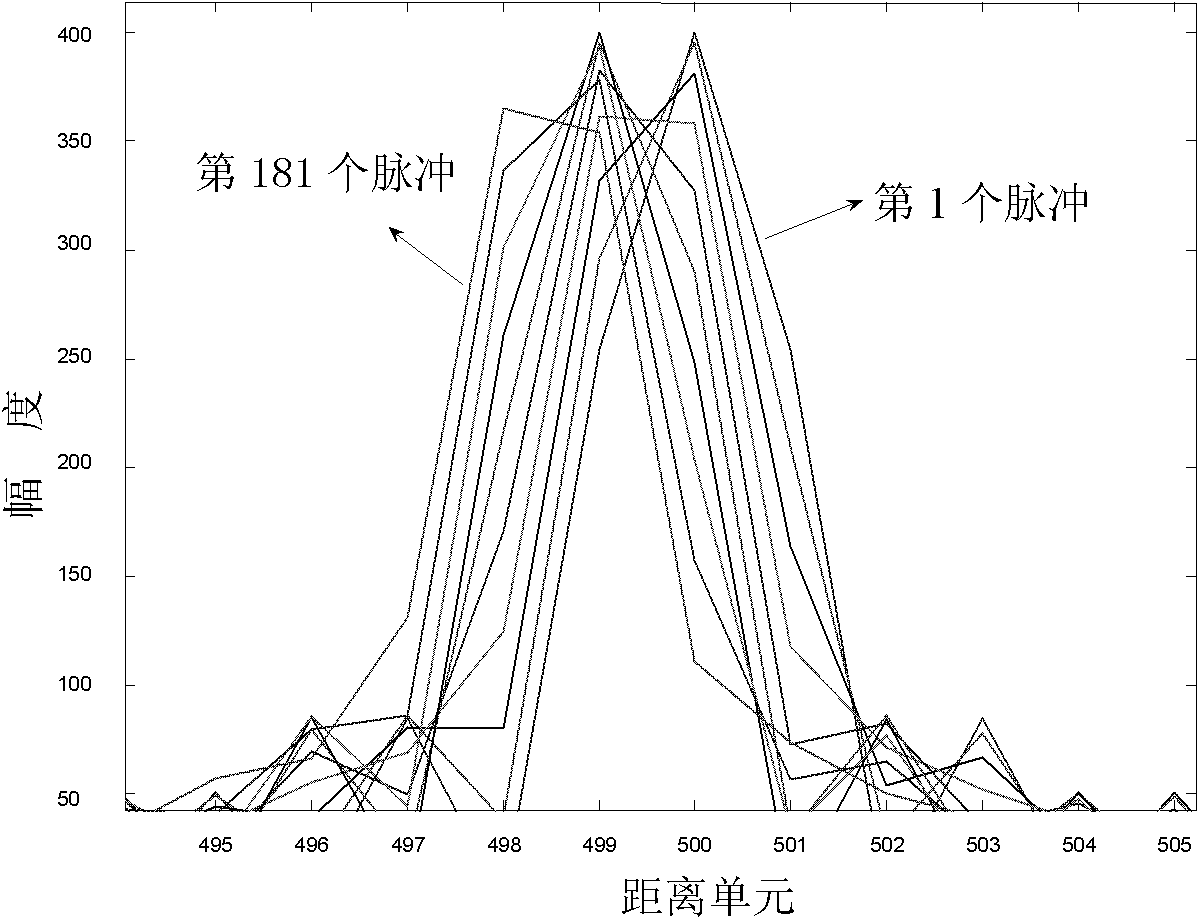
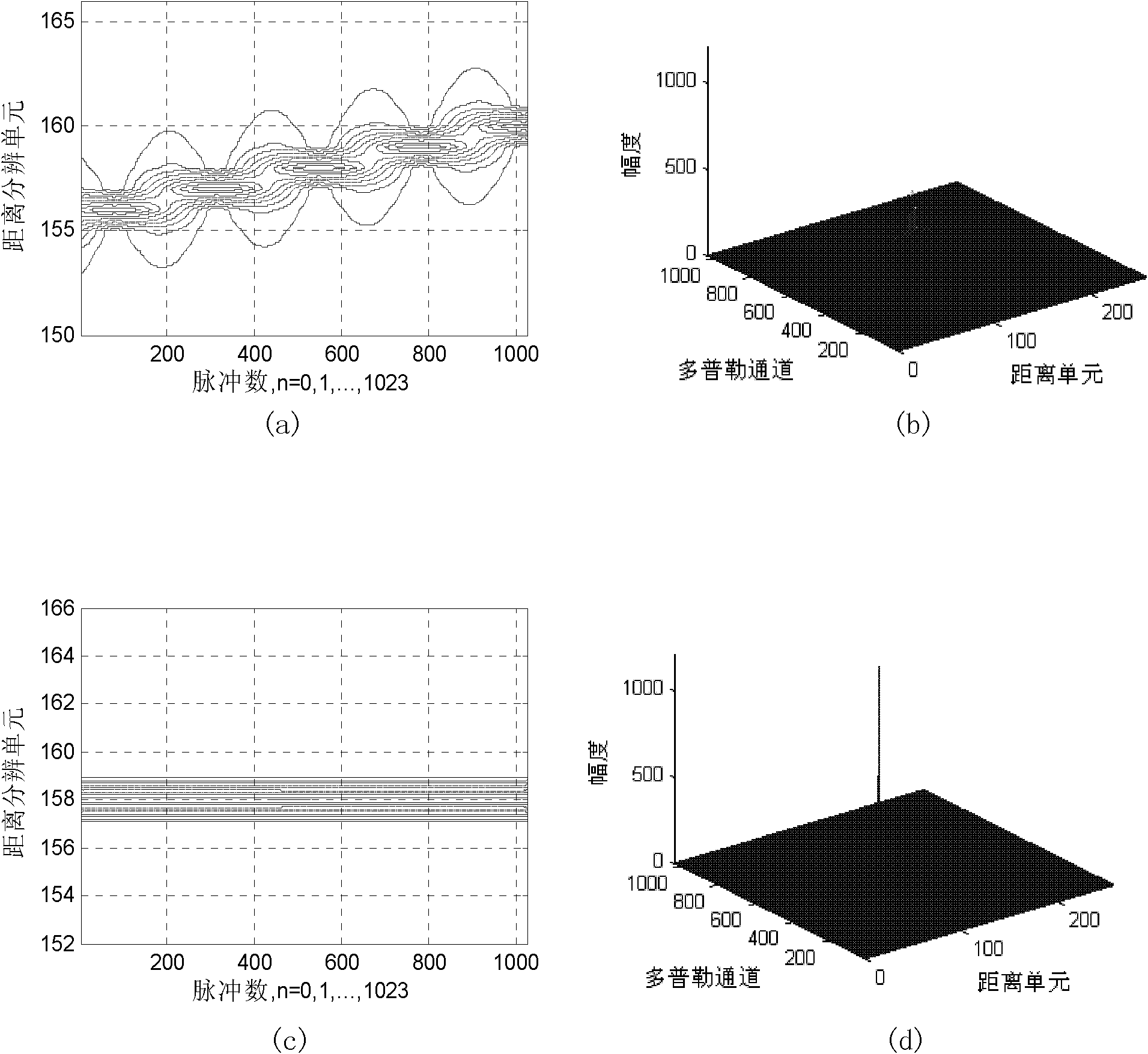
InactiveCN102323575ALow impact on detection performanceEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsTime errorRadar systems
The invention discloses a range migration correction method for a pulse Doppler (PD) radar in a feeble signal detection process, which mainly solves the problems that the discrete time sampling error is not considered, and the detection performance is low in the prior art, and is realized by the steps as follows: transmitting a set of linear frequency-modulation pulse signals of which the bandwidth does not exceed 1 percent of a centre carrier frequency by the radar; carrying out mixing on echo data to obtain a base band radar echo signal; carrying out Fourier transformation on the base band radar echo signal in a fast time domain; carrying out digital pulse compression on a signal obtained by carrying out the Fourier transformation through the fast time domain in the fast time domain, and finding out a corresponding pulse signal when the discrete time error is minimum; by taking the pulse signal as an alignment reference, realizing Keystone transformation by using an SINC interpolation method, and carrying out Doppler fuzzy compensation; and carrying out the Fourier transformation in the fast time domain, and carrying out coherent accumulation to work out a range cell in which the target is located and a Doppler channel. Compared with similar methods, the range migration correction method for PD radar in the feeble signal detection process is capable of reducing the influenceof the discrete time sampling error to minimum, and is capable of improving the detection performance of a radar system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for forming very low noise imagery using pixel classification
InactiveUS8193967B2High contrast imageReduce false alarm rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseRange migration
A method and system for generating images from projection data comprising inputting first values representing correlated positional and recorded data; forming an image by processing the projection data utilizing a pixel characterization imaging subsystem to form the SAR imagery utilizing one of a back-projection algorithm or range migration algorithm; integrating positional and recorded data from many aperture positions, comprising: forming the complete aperture A0 comprising collecting the return radar data, the coordinates of the receiver, and the coordinates of the transmitter for each position k along the aperture of N positions; forming an imaging grid comprising M image pixels; selecting and removing a substantial number of aperture positions to form a sparse aperture Aifor L iterations; classifying each pixel in the image into target class based on the statistical distribution of its amplitude across L iterations; otherwise, the pixel is given the value of zero.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE +1
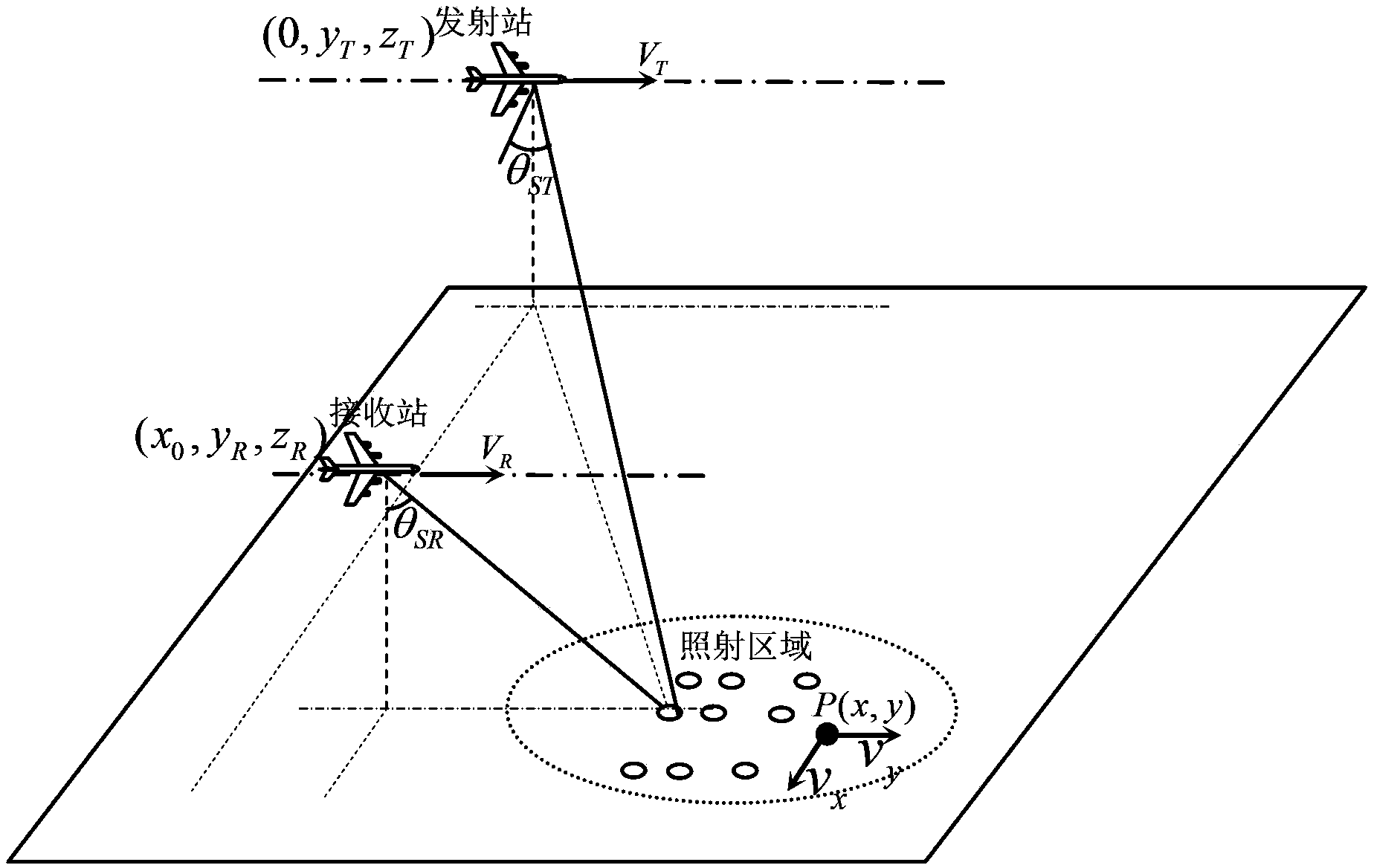
Bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar ground moving target detecting method and imaging method
ActiveCN103412310AReduce space changeSolve detection difficultiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationForward looking
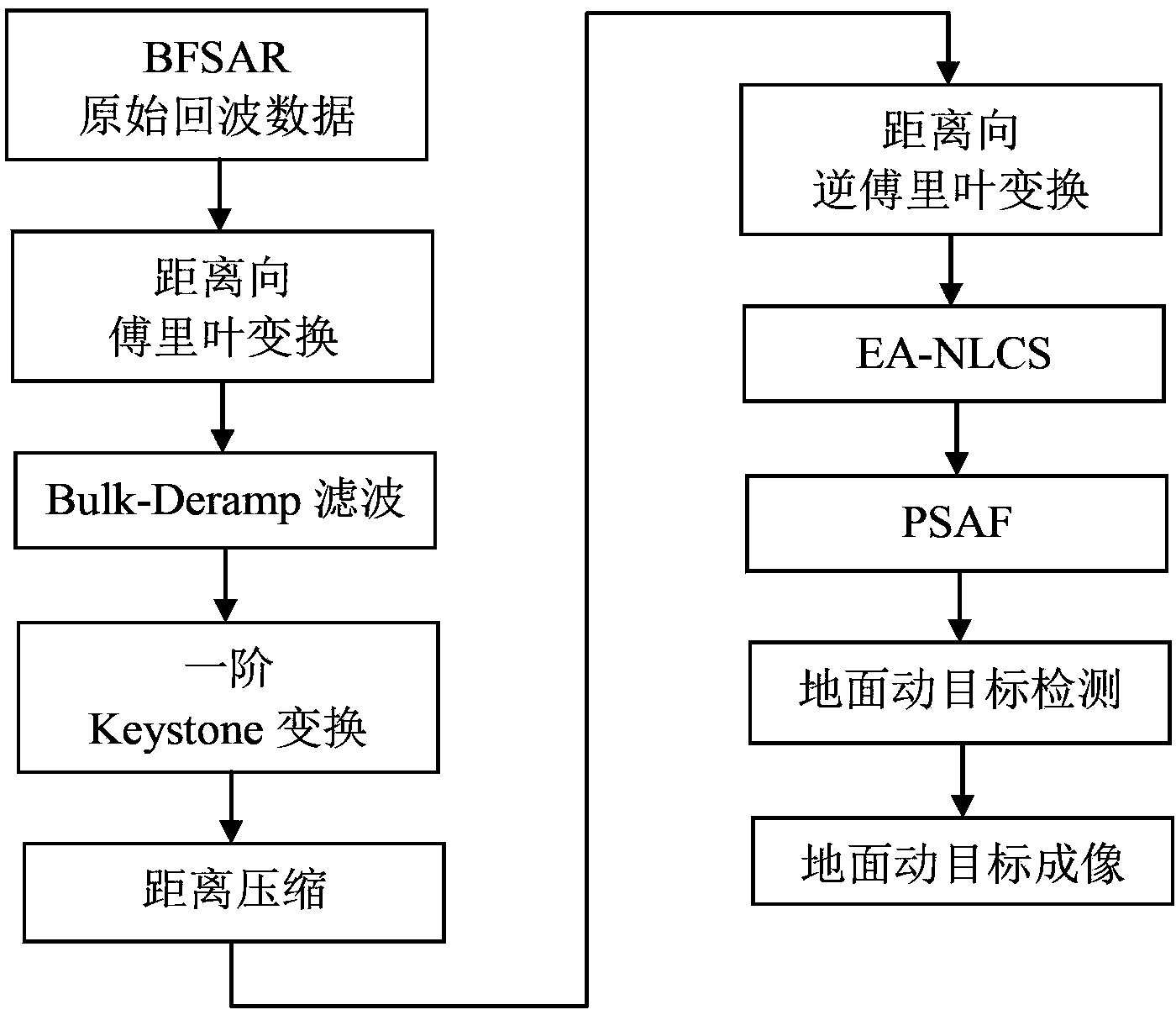
The invention discloses a bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar ground moving target detecting method and imaging method. The detecting method includes the steps of firstly, utilizing Bulk-Deramp filtering to eliminate Doppler blurs and reducing space variations of the Doppler rate; secondly, utilizing first-order Keystone conversion to complete range migration correction of a static target and a ground moving target; then, utilizing extended orientation nonlinear frequency modulation and frequency scaling operation to equilibrate the Doppler rate of the static target; meanwhile, enabling the Doppler rate of the ground moving target to be different from the Doppler rate of the static target; finally, building a second-order fuzzy function product, completing detection on the ground moving target and estimating the Doppler rate of the ground moving target. The problem that the moving target and the static target are hard to distinguish when BFSAR is under a background with strong clutter is solved. According to the imaging method, after the detection on the ground moving target is completed, an echo of the moving target is focused by using the estimated Doppler rate of the ground moving target, and then imaging the ground moving target is completed.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
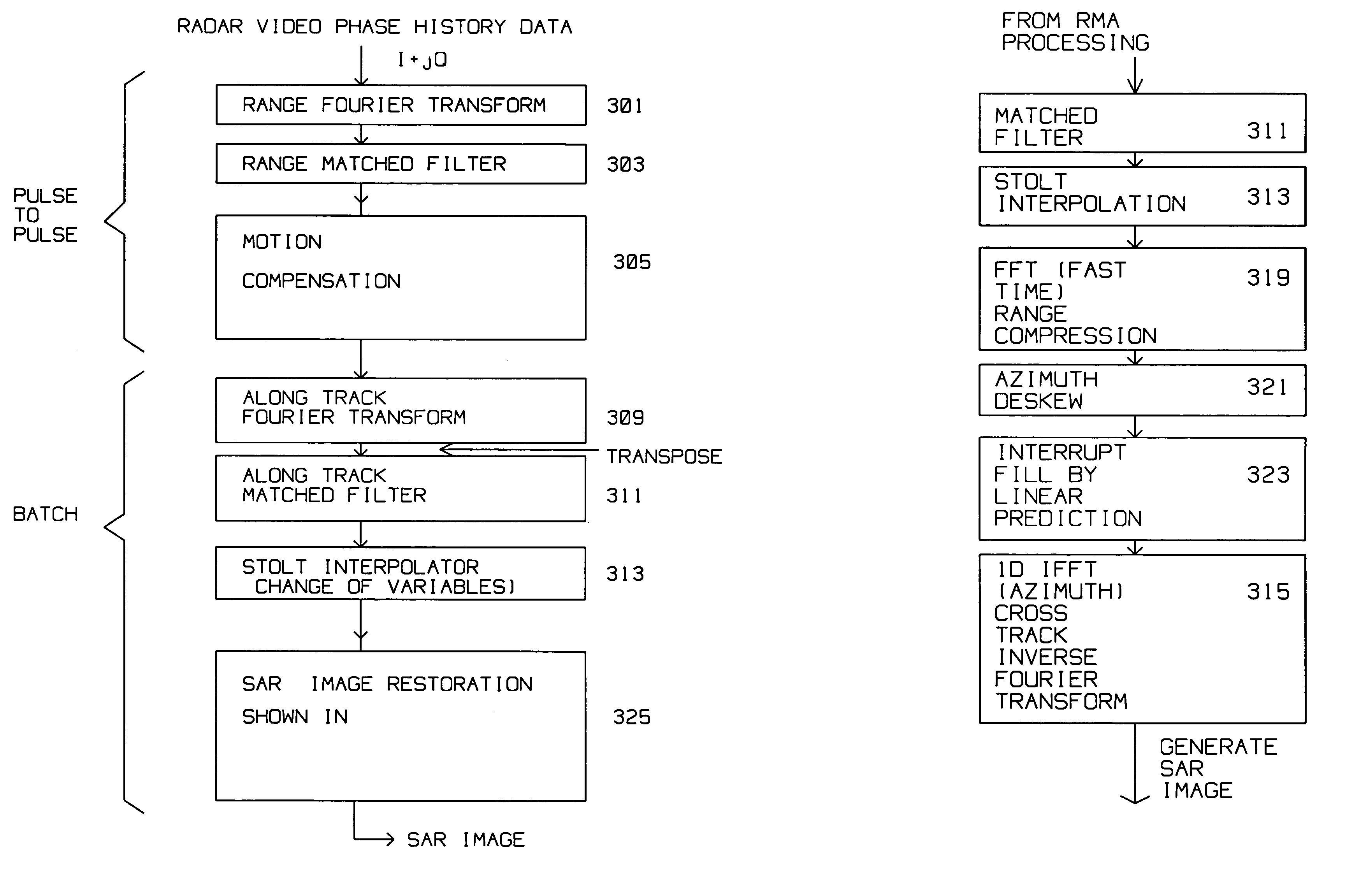
Interrupt SAR image restoration using linear prediction and Range Migration Algorithm (RMA) processing
SAR images are improved by a method for acquiring a synthetic aperture image from a sequence of periodic pulse returns where the sequence of periodic pulse returns is interspersed with interrupts, i.e. missing pulses. The interrupts mark the start and end of one or more segments, where the segments contain the periodic pulse returns form the SAR image. The method comprises the steps of:converting said pulse returns into a digital stream;performing an azimuth deskew on said digital stream to obtain a deskewed digital stream;forming a forward-backward data matrix from the deskewed digital stream for one or more segments;forming an average segment covariance from the forward-backward data matrix;computing a model order for the average segment covariance;computing one or more linear prediction coefficients using data contained in the forward backward data matrix, and model order;using the linear prediction coefficients to compute missing pulse returns belonging within the interrupts.The computation for extrapolating the missing pulse returns is introduced after the Stolt interpolator in RMA processing. In computing the model order, eigenvalues are found and compared to a threshold. Roots of a linear prediction polynomial are computed, then stabilized to obtain stabilized roots. Linear prediction coefficients are reconstituted using the stabilized roots. Sub-bands are used to decrease computing time for the missing pulse returns.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Phase-coherent accumulation detection method applied to three-order maneuvering target
ActiveCN108549067AEasy to detectImprove real-time performanceWave based measurement systemsFrequency shiftFourier transform
The invention provides a phase-coherent accumulation detection method applied to a three-order maneuvering target, belonging to the technical field of radar signals. The method comprises the followingsteps: carrying out fast-time frequency domain pulse compression on an echo signal, and carrying out three-order Keystone conversion so as to correct three-order range migration of a target; carryingout frequency shift mutual correlation and scale Fourier transform, so as to obtain a defined speed value; eliminating first-order range walk by virtue of the cooperation of a fast-time frequency domain matched filtering equation constructed by the defined speed, combining an accelerated speed with a jerk of the searched target by virtue of a two-dimensional matched filtering equation, and compensating and eliminating second-order range walk and Doppler spreading effect of the target; and detecting the phase-coherent accumulation of the energy of the target by virtue of slow time fast Fouriertransform. According to the method, phase-coherent accumulation is realized by virtue of the range and phase information of the target echo to eliminate the range migration and the Doppler migrationeffect of the three-order maneuvering target, so that the detection performance of radar can be remarkably improved, and the practicability is strong.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
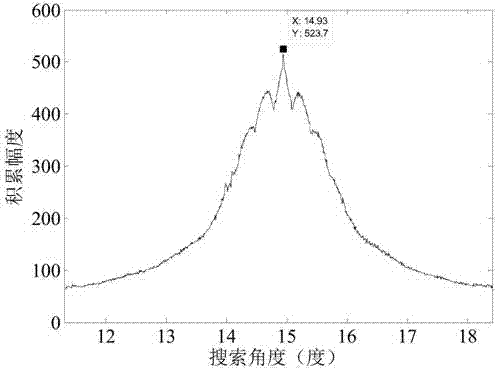
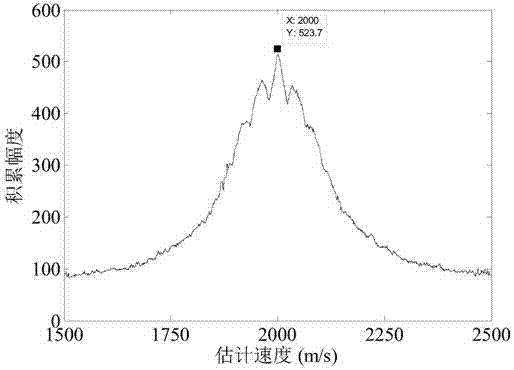
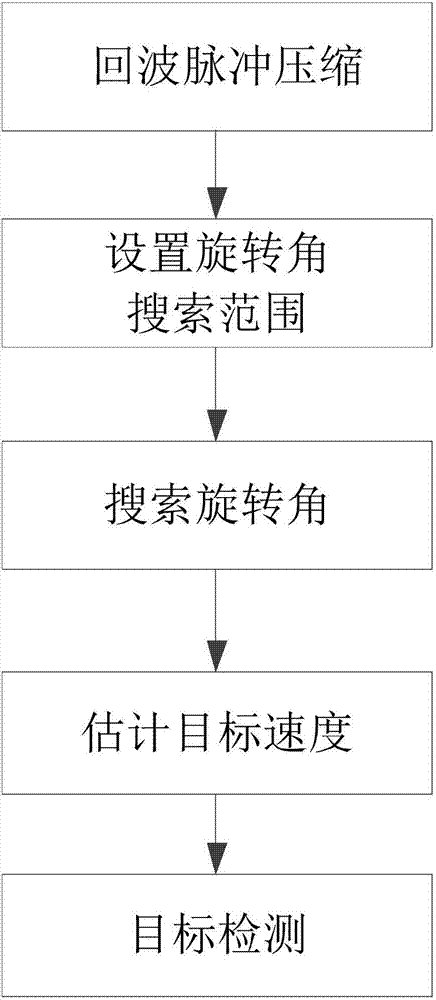
Position rotation transformation-based high-speed target phase-coherent accumulation detection method
InactiveCN106896358AEasy to detectEasy to implementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformRange migration
The present invention discloses a position rotation transformation-based high-speed target phase-coherent accumulation detection method and belongs to the technical field of radar weak signal detection. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, subjecting a received echo signal of a target to pulse compression through sending out a linear frequency modulation signal by using a radar; secondly, searching the rotation angle of echo data positions after pulse compression, and estimating the speed through the position rotation transformation traversal; thirdly, based on the searched rotation angle, subjecting all echo data positions to integral rotation to correct the first-order range migration; finally, realizing the phase-coherent accumulation of the target energy through the quick Fourier transformation process, and enabling the target detection based on an accumulated peak value. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the echo amplitude and the phase information of a moving target are subjected to phase-coherent accumulation, so that the radar echo signal-to-noise ratio is effectively improved. Therefore, the detection performance of the radar on the target is improved. All operations can be realized based on the quick Fourier transformation process, so that the engineering realization is facilitated. The method has popularization and application value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Interrupt SAR implementation for range migration (RMA) processing
ActiveUS20070159376A1Reduce restrictionsEnhance the imageRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationComplete sequence
A moving radar (405) generates a synthetic aperture image from an incomplete sequence of periodic pulse returns. The incomplete sequence of periodic pulse returns has one or more missing pulses. The radar converts the incomplete sequence of pulse returns into a digital stream. A computer (403) processes the digital stream by computing an along track Fourier transform (402), a range compression (408), an azimuth deskew (410) and an image restoration and auto focus (412). The image restoration and autofocus (412) utilizes a low order autofocus (501), a gap interpolation using a Burg algorithm (503), and a high order autofocus (505) for generating an interpolated sequence. The interpolated sequence contains a complete sequence of periodic pulse returns with uniform spacing for generating the synthetic aperture image. The image restoration and autofocus (412) computes a linear prediction coefficients estimate using the Burg Algorithm (606). The linear prediction coefficients estimate (606) is used to compute a weighted forward-backward interpolation to generate the complete sequence of periodic pulse returns (608).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Efficient phase correction scheme for range migration algorithm
InactiveUS20030142000A1Convenient lengthExemption stepsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBatch processingCommon phase error
A system and method for efficient phase error correction in range migration algorithm (RMA) for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems implemented by making proper shifts for each position dependent phase history so that phase correction can readily be performed using the aligned phase history data during batch processing. In its simplest form, the invention (44) is comprised of two main parts. First (60), alignment of the phase error profile is achieved by proper phase adjustment in the spatial (or image) domain using a quadratic phase function. Second (62), the common phase error can be corrected using autofocus algorithms. Two alternative embodiments of the invention are described. The first embodiment (44a) adds padded zeros to the range compressed data in order to avoid the wrap around effect introduced by the FFT (Fast Fourier Transform). This embodiment requires a third step (64): the target dependent signal support needs to be shifted back to the initial position after phase correction. The second embodiment (44b) uses the range compressed data without padded zeros. Instead, an aperture of greater length needs to be generated by the Stolt interpolation. In this embodiment, the third step (64) of shifting the signal support back can be eliminated.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Bistatic MIMO radar high-speed target across-range-gate speed measuring and positioning method
ActiveCN106443615AImprove estimation accuracyExact closed-form solutionWave based measurement systemsRange migrationRadar signal processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing, and discloses a bistatic MIMO radar high-speed target across-range-gate speed measuring and positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring L baseband echo pulse signals; compressing the pulse of the L baseband echo pulse signals to get pulse output signals, and estimating the rough estimated values of the launch azimuth angle, launch pitch angle and reception pitch angle of a target; determining the number of range gates spanned by the target based on the rough estimated values of the angles of the target; estimating the angle information and Doppler frequency of the target based on the number of range gates spanned by the target; and determining the coordinate information of the target based on the angle information of the target, and determining the speed of the target based on the Doppler frequency of the target. Under the condition that a radar target has range migration, the angle information and Doppler frequency of the radar target can be estimated accurately, and the radar target can be positioned accurately.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
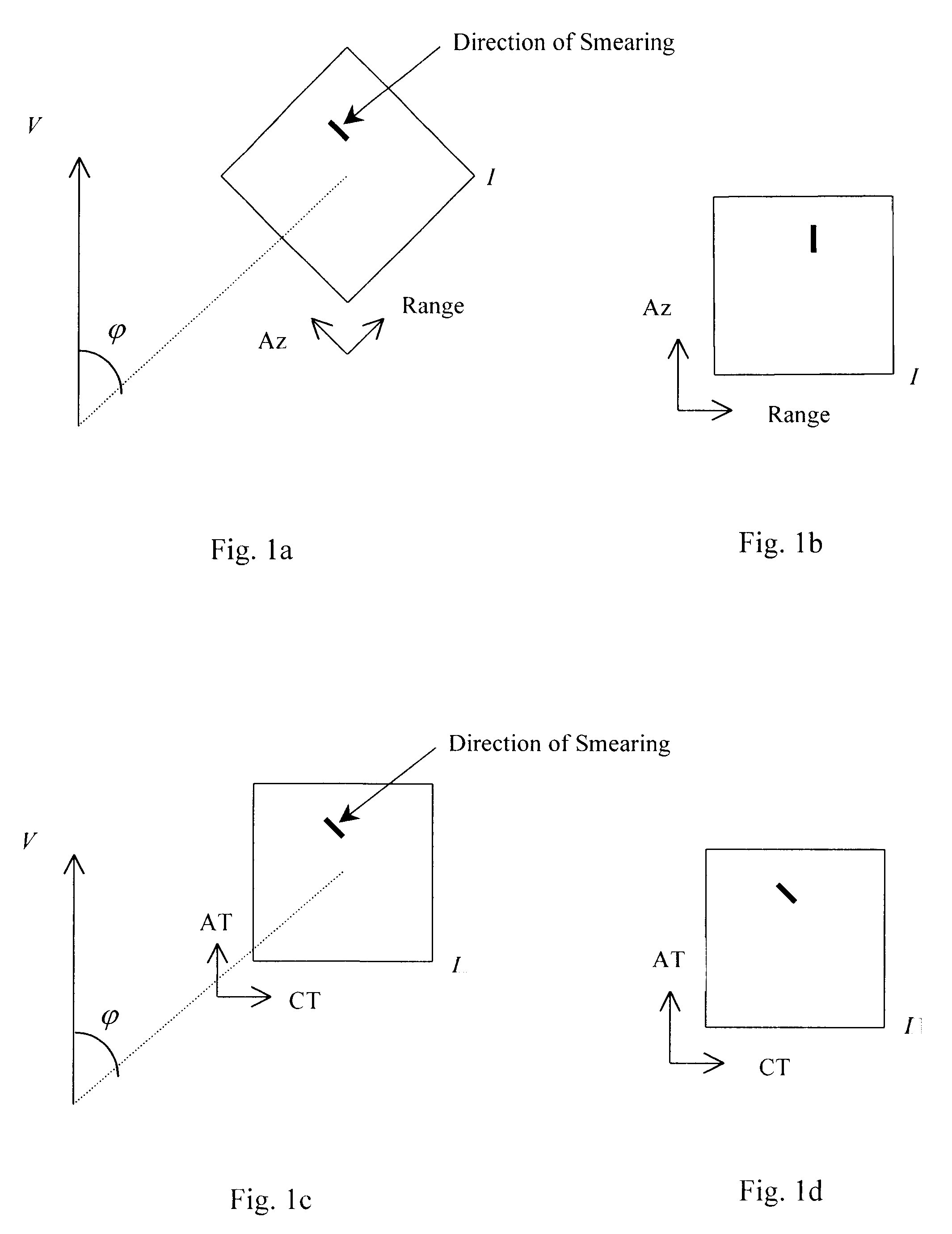
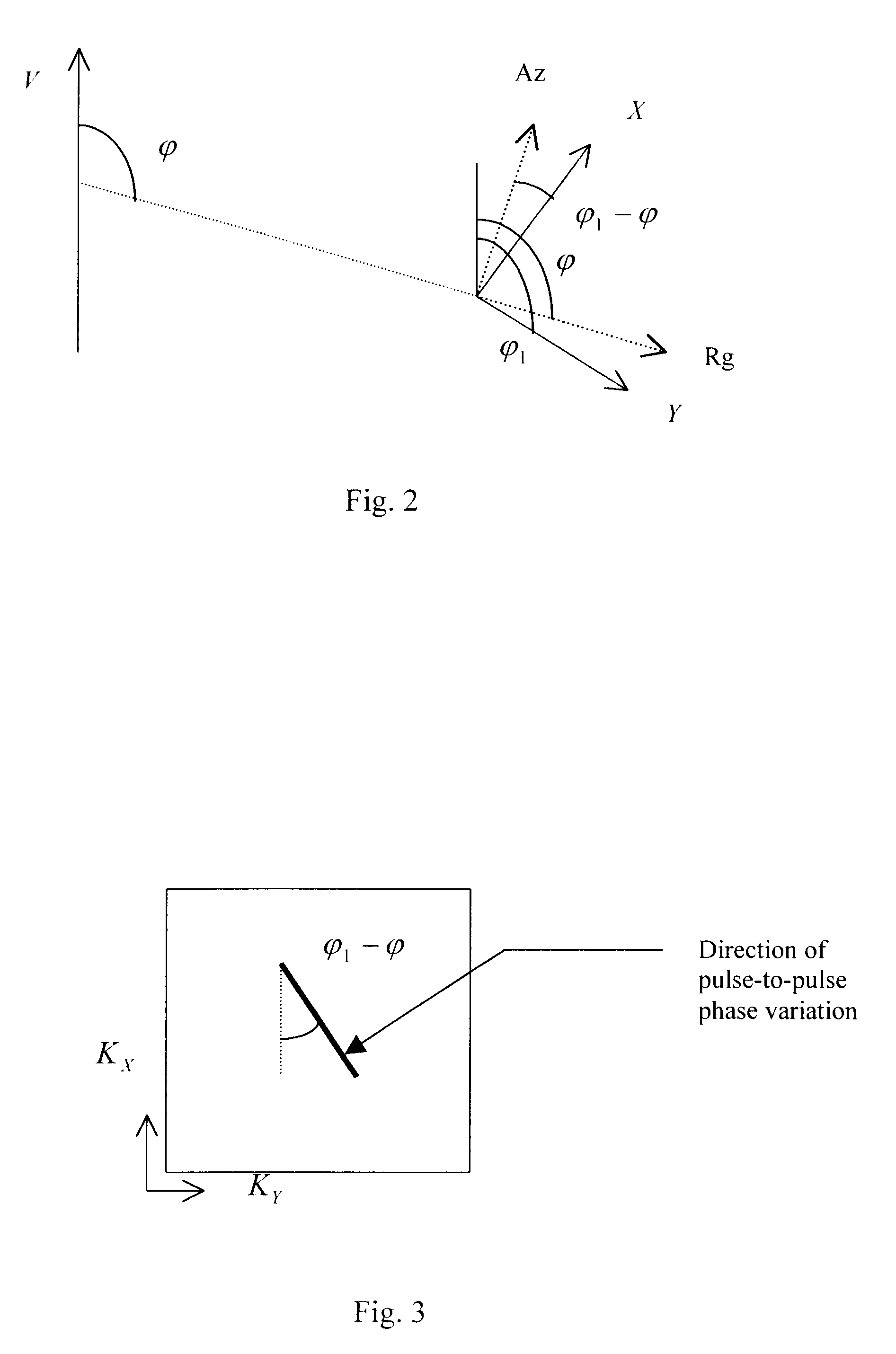
Focusing SAR images formed by RMA with arbitrary orientation
A system and method (44) for focusing an image oriented in an arbitrary direction when the collected synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data is processed using range migration algorithm (RMA). In accordance with the teachings of the present invention, first (60) the data is skewed so that the direction of smearing in the image is aligned with one of the spatial frequency axes of the image. In the illustrative embodiment, the smearing is aligned in the vertical direction. This is done through a phase adjustment that was derived from the requirements for proper shift in the spatial frequency domain. Next (62), the signal support areas from all targets are aligned by proper phase adjustment in the spatial (or image) domain. Finally (64), the common phase error can be corrected using autofocus algorithms.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Unified imaging method for synthetic aperture radar (SAR) in four modes
ActiveCN102879784AOvercome limitationsIncrease test costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationImage resolution
The invention discloses a unified imaging method for a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) in four modes aiming at the strip SAR, bunching SAR, sliding bunching SAR and TOPS SAR. The problem that the prior art is limited by the modes of the SAR is mainly solved. The method comprises the implementation processes of (1) receiving echo data of the original SAR of a platform, and performing range Fourier transform on an echo signal; (2) performing fractional order Fourier transform twice on the echo signal, and performing direction scaling processing; (3) performing range migration correction on the echo signal, and compensating a phase curve into a straight line through a hyperbolic curve; and (4) performing the fractional order Fourier transform twice, realizing focusing imaging, and removing the residual phase. The SAR imaging in the four modes can be finished through simple parameter setting, different scene and resolution requirements can be met, and the imaging method is wide in application range and can be applied to the fields of ground mapping, target identification and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Cylindrical surface near-field three-dimensional RCS imaging method combined with RM algorithm and BP algorithm
ActiveCN104133213AFast imagingImprove test effectivenessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationImaging algorithm
The invention provides a cylindrical surface near-field three-dimensional RCS imaging method combined with an RM algorithm and a BP algorithm. The range migration RM algorithm and the convolution-back projection BP algorithm are combined to design a new cylindrical surface near-field three-dimensional RCS imaging algorithm, and in the testing process, testing data of all the angles of a rotary table are imaged in real time by adopting the RM algorithm to obtain two-dimensional range azimuth direction images. After tests are finished, the two-dimensional range azimuth direction images are processed by adopting the BP algorithm so that final three-dimensional images can be obtained fast. According to the imaging algorithm, the time for the testing process is used, multiple integration of all points in a traditional algorithm is avoided, imaging speed is increased, longitudinal two-dimensional range azimuth direction imaging results can be monitored in real time in the testing process by using the imaging method, the invalid testing process can be avoided to a certain degree, and effectiveness of the tests can be improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Signal processing method of satellite-bone sliding spotlight synthetic aperture radar
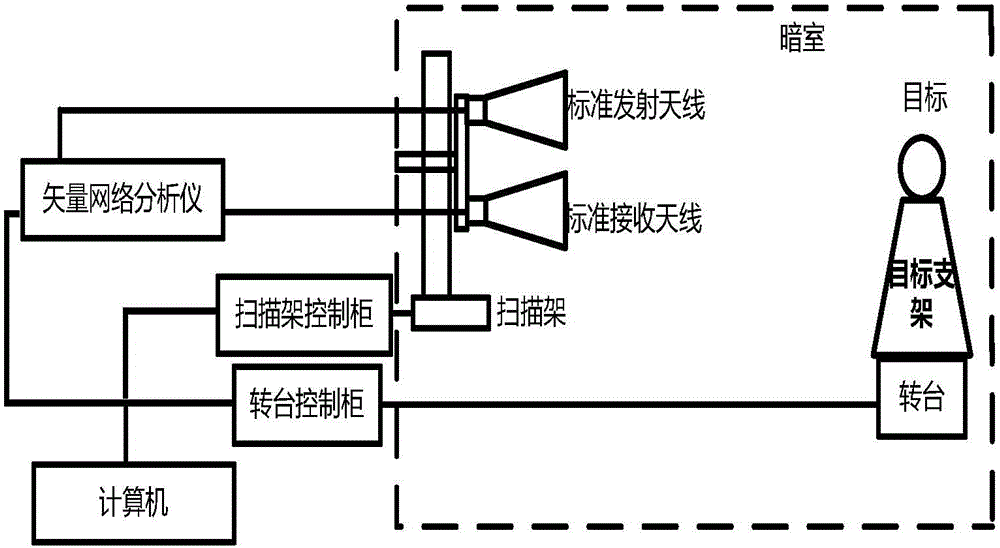
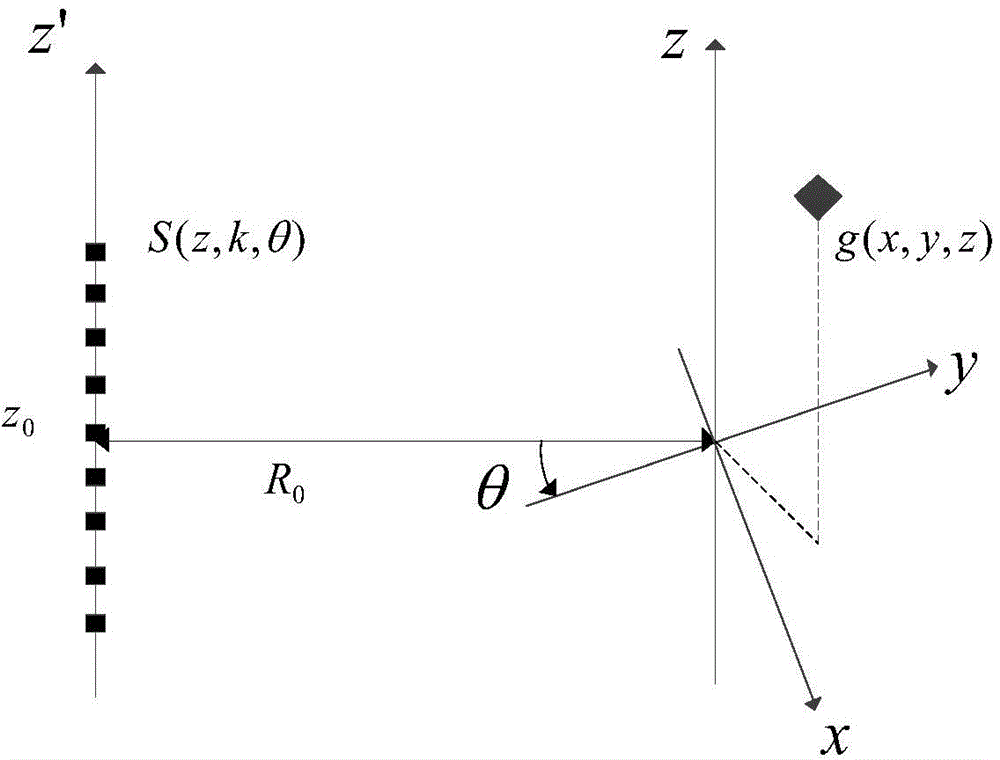
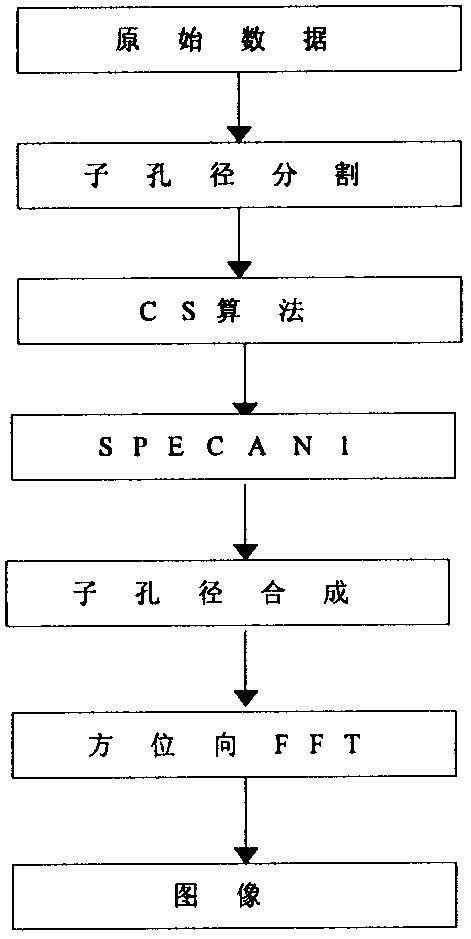
The invention discloses a signal processing method of a satellite-bone sliding spotlight synthetic aperture radar. The method includes: performing molecule aperture processing on original echo data of the sliding spotlight synthetic aperture radar (SAR); performing range compression and range migration correction through a chirp scaling (CS) algorithm; introducing squint angle compensation in theCS algorithm; compensating scene space-variant performance; adjusting range migration amount of all sub-apertures to be identical with Doppler parameters of full apertures in CS scalar variable factors as the standard; performing azimuth compression and quadratic term compensation in the frequency domain, and performing frequency modulation processing in the time domain; splicing data of all the sub-apertures and restoring resolution ratio of the full apertures; and enabling signals to have phase preservation performance through spectrum analyzer (SPECAN) processing. By adopting the signal processing method, imaging quality can be improved under the condition of large scene squinting.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Bistatic SAR motion compensation method based on phase gradient autofocus improvement
The invention discloses a bistatic SAR motion compensation method based on phase gradient autofocus improvement. The method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, motion compensation cannot be carried out under the condition of large motion errors. The method comprises the complementation steps that 1) range migration correction, range compression and deramp processing are carried out on sub-aperture data; 2) non-empty variable phase error estimation is carried out on signals through a PGA method, rough compensation is carried out on the data through the error estimation result, and residual phase errors are obtained; 3) the residual phase errors are unfolded to be a second-order polynomial of the range, and a constant term coefficient and linear and quadratic term coefficients are obtained; 4) the minimum mean square gradient estimation of the three coefficients is obtained through a phase weighting PGA, and the sub-aperture phase errors are obtained through the gradient estimation result; 5) the phase errors of the sub-aperture data are spliced to obtain full-aperture phase errors; 6) motion compensation and bistatic SAR imaging are carried out through the full-aperture phase errors. The method can be used for processing the bistatic SAR data under the condition of the large motion errors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
One-station fixed frequency-modulated continuous wave double-base SAR imaging method
ActiveCN103454632ALow efficiencyNo increase in computationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainRange migration
The invention discloses a one-station fixed frequency-modulated continuous wave double-base SAR imaging method. The one-station fixed frequency-modulated continuous wave double-base SAR imaging method mainly solves the problems that azimuth range migration spatial-variant properties and orientation frequency-modulated spatial-variant properties can not be corrected at the same time according to an existing method. The method is achieved according to the steps that (1) a two-dimension time domain echo signal of a target is acquired, and a distance frequency domain azimuth time domain echo signal of the target is calculated; (2) azimuth range migration spatial-variant properties and orientation frequency-modulated spatial-variant properties are corrected according to the distance frequency domain azimuth time domain echo signal; (3) residue phase compensation is conducted on the corrected signal, and range-direction range migration spatial-variant properties are corrected; (4) azimuth pulse compression is conducted on the signal after range-direction range migration spatial-variant property correction, and azimuth inverse Fourier transform is carried out to acquire a target time domain image. The one-station fixed frequency-modulated continuous wave double-base SAR imaging method has the advantages of being capable of correcting azimuth range migration spatial-variant properties and orientation frequency-modulated spatial-variant properties at the same time, high in achieving efficiency and capable of being used for one-station fixed frequency-modulated continuous wave double-base SAR imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
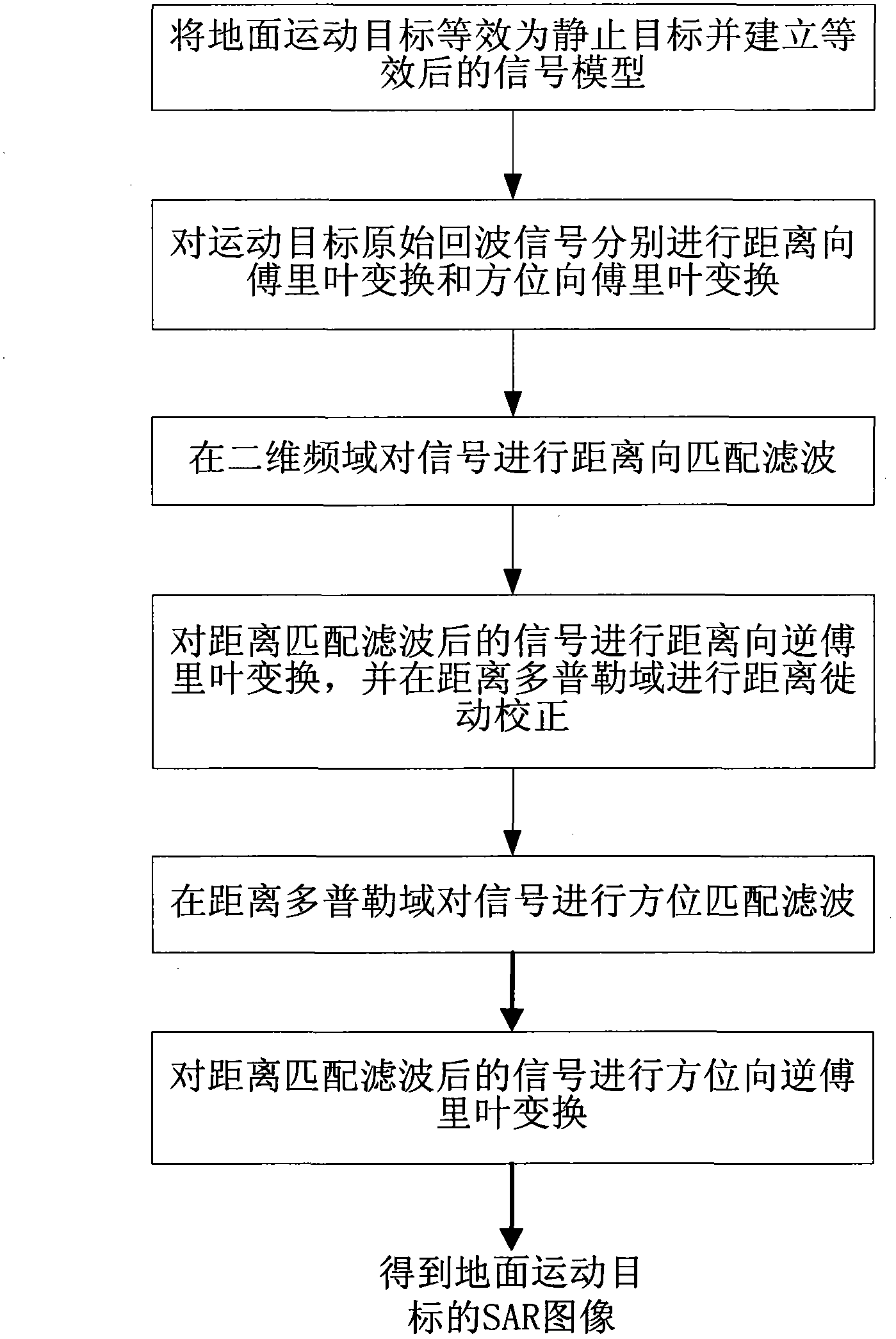
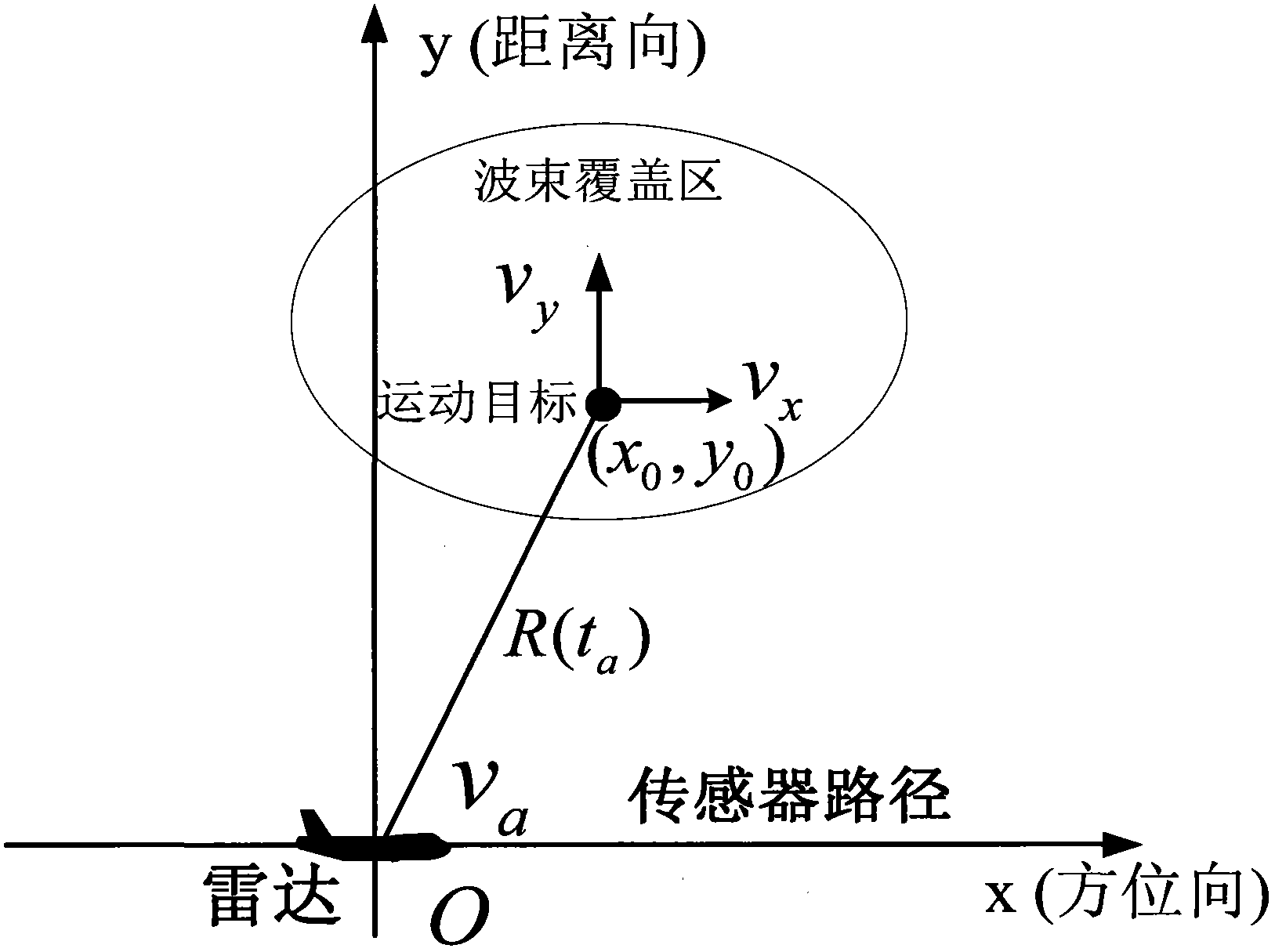
Equivalent range equation based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) ground motion target imaging method
InactiveCN103293520AQuality improvementSimplify the imaging processRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarTransformer
The invention discloses an equivalent range equation based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) ground motion target imaging method. The equivalent range equation based SAR ground motion target imaging method includes: subjecting a ground motion target to being equivalent to a static target by means of the equivalent range equation and building an equivalent signal model; subjecting target signals to Fourier transform in range and direction and transforming the signals to a two-dimensional field; matching filter in range of the two-dimensional field; performing inverse Fourier transform in range and correcting range migration; matching filter in direction; performing inverse Fourier transformer in direction and completing motion target imaging. The motion target is equivalent to the static target, the motion target is imaged by means of a static target imaging method, the problems that target direction is defocused and direction sidelobe is asymmetric in the prior art are solved, and the target can be imaged in high quality. The motion target can be imaged by the static target imaging technology, imaging of the motion target is simplified, and the equivalent range equation based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) ground motion target imaging method is easy to implement on engineering and can be used for an onboard SAR-GMTI (ground motion target imaging) to image the ground motion target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
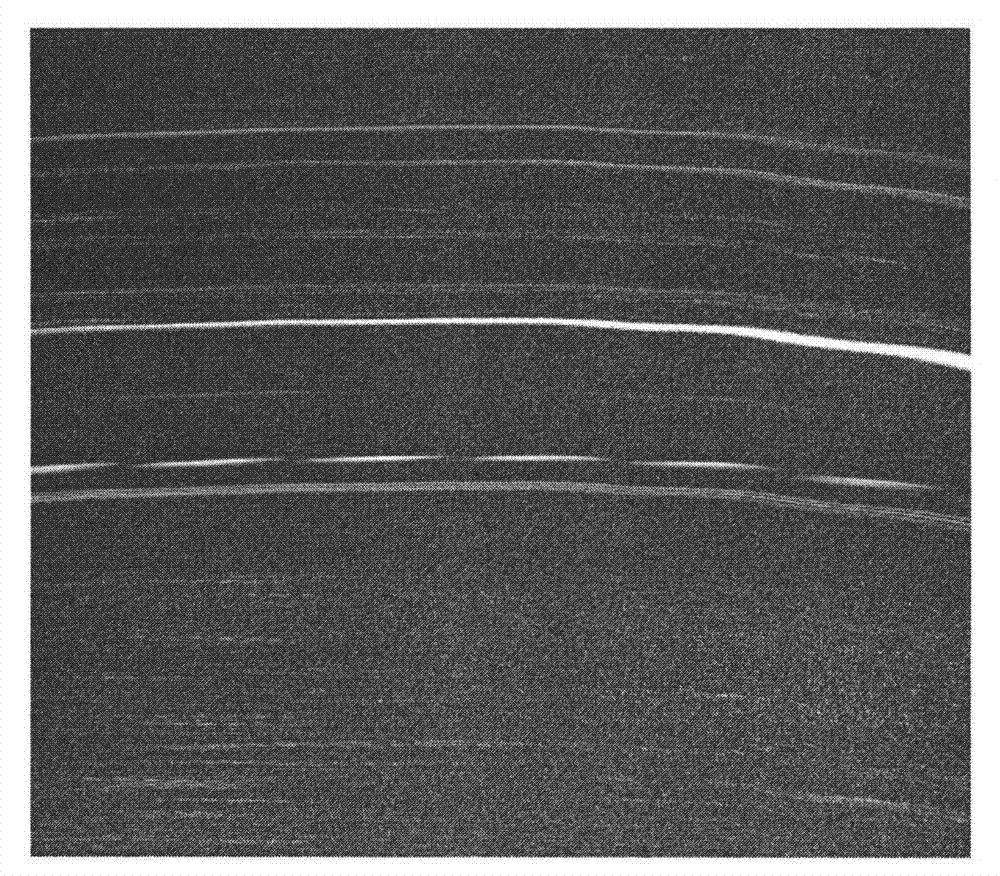
Self-focusing method suitable for ultra-high-resolution SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging
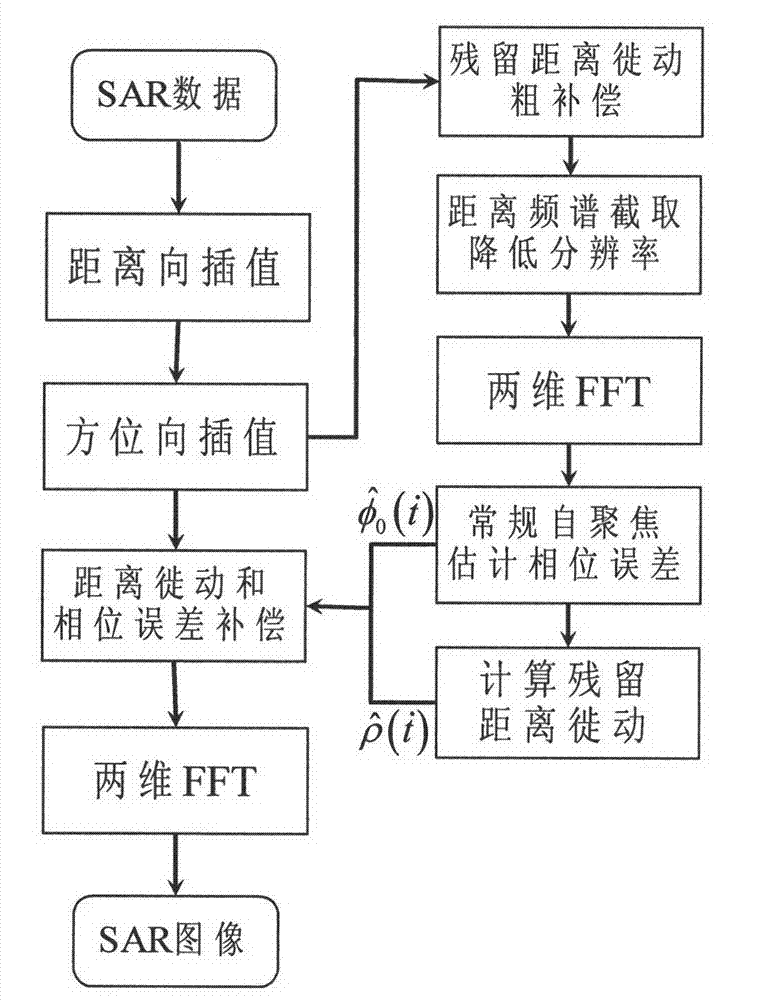
InactiveCN102788972AHigh compensation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationImage resolution
The invention relates to a self-focusing of method suitable for the ultra-high-resolution SAR (synthetic aperture radar) imaging, comprising the following steps: (1) subjecting the two-dimensional echo data to polar coordinate format conversion; (2) reducing the resolution of the distance vector; (3) carrying out coarse-resolution imaging to the distance vector; (4) estimating the azimuth phase error; (5) calculating the residual range migration; (6) compensating the residual error; and (7) carrying out two-dimensional Fourier transform for imaging.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Scanning radar angular super-resolution imaging method based on maximum posterior
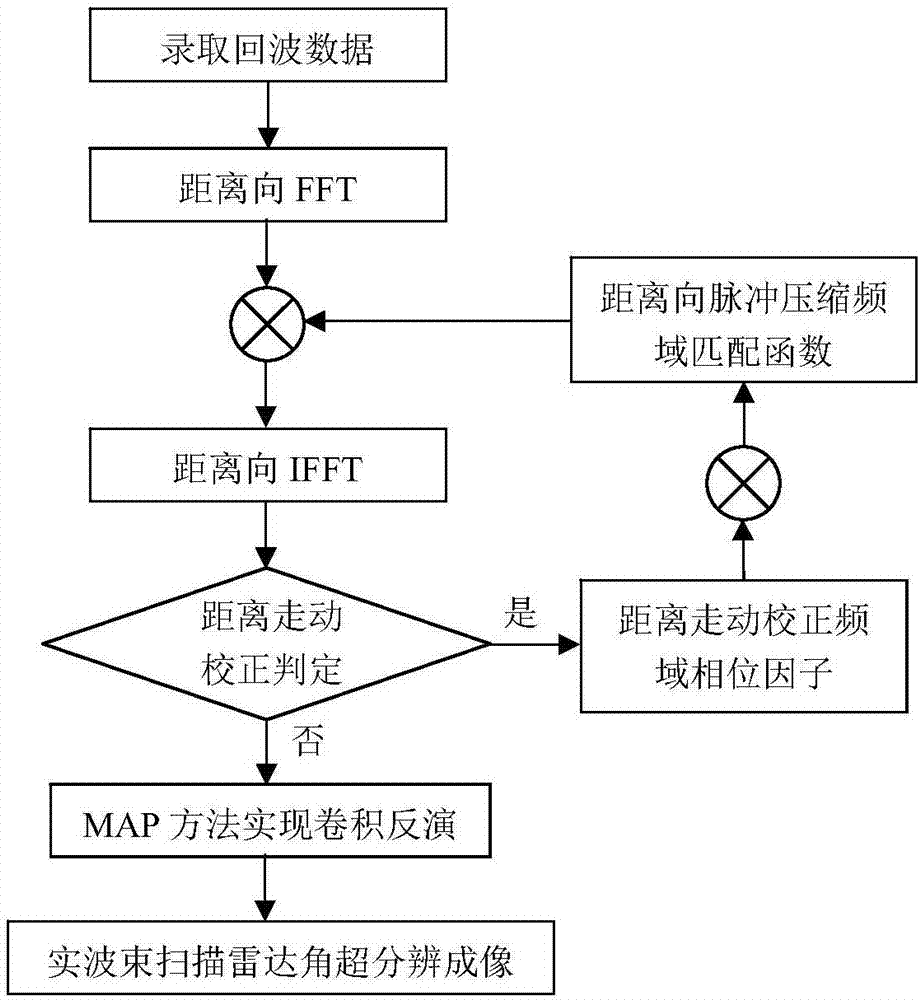
ActiveCN107271993AImprove resolutionRealization of super-resolution imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMaximum a posteriori estimationBeam scanning
The invention discloses a scanning radar angular super-resolution imaging method based on maximum posterior, which is applied to the fields of radar imaging technology and signal processing. The method includes the following steps: a linear frequency modulation signal is emitted by a real beam scanning radar, a two-dimensional echo signal of an irradiated region is acquired, and range high-resolution is implemented through a pulse compression technology and a range migration correction technology; the azimuth echo of the scanning radar is modeled as a convolution form of a radar antenna pattern and a target scattering coefficient according to an azimuth echo model of the scanning radar; and on the basis, radar angular super-resolution imaging is implemented using a convolution inversion method based on Maximum A Posteriori (MAP).
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
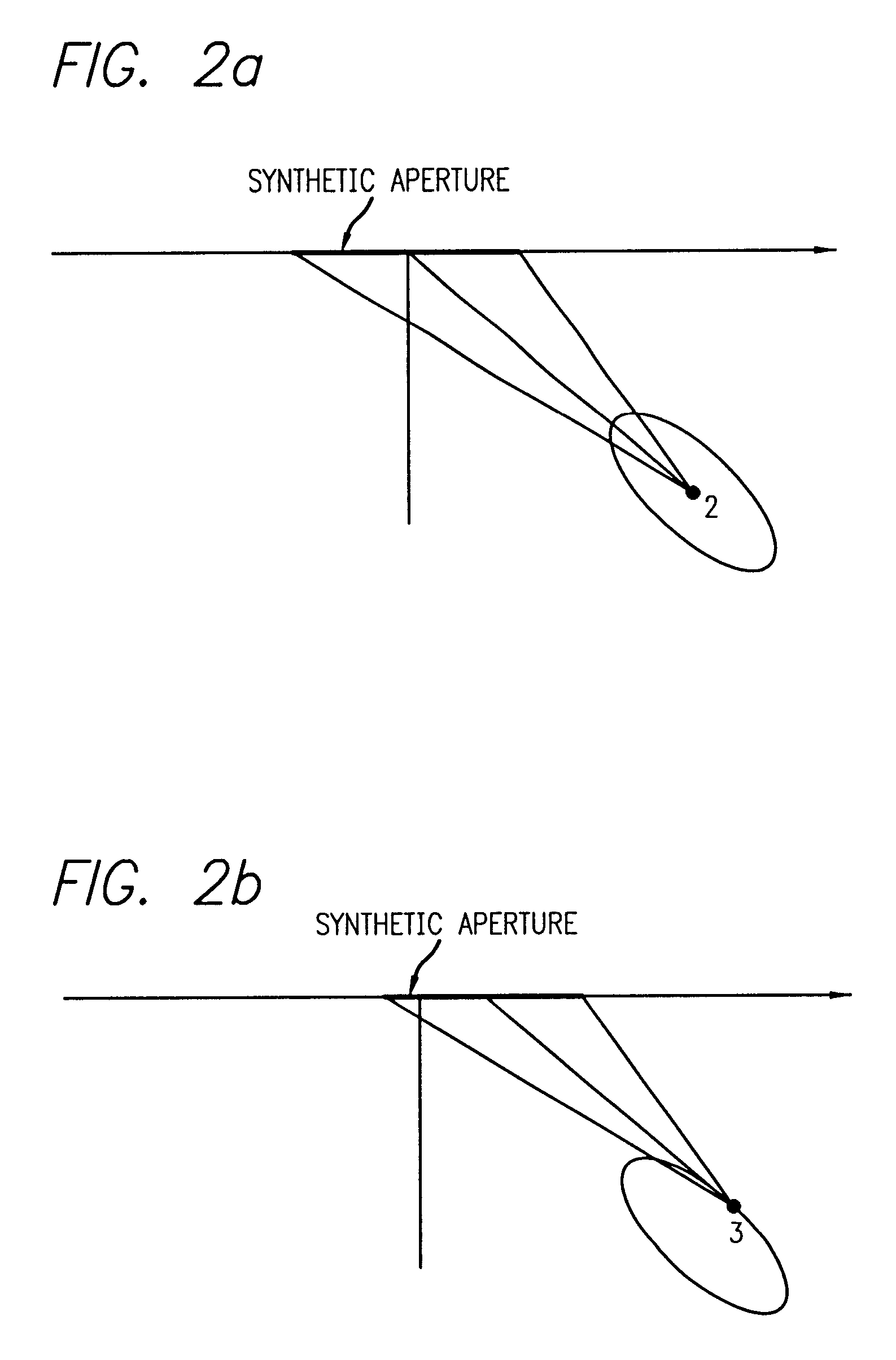
Conformal range migration algorithm (CRMA) "KARMA"
ActiveUS6987479B1Clearer SAR imageIncrease relative motionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRange migrationClassical mechanics
Motion compensation for coherent combination of pulses facilitates a SAR image of a scene on earth's surface. A great circle (406) is centered with respect to the earth's center, The great circle (406) has an axis (412) perpendicular to a first plane. Axis (412) passes through the earth's center. The first plane contains great circle (406) and includes the earth's center. Great circle (406) has a first center defined by an intersection of the first plane and axis (412). The scene has one or more radar scatterers and is located on a surface (402). The radar system is mounted on a moving platform (400) moving with a component of motion in a direction along great circle (406). The radar comprises a radar receiver for digitizing the radar returns having a phase from scatterers on surface (402), and a computer for focusing the phase of said radar returns from the scatterers on surface (402). The surface (402) is located on a local scene centerline circle (408), the local scene centerline circle (408) defining a second plane. This second plane is parallel to the first plane. The local scene centerline circle (408) is centered on the axis at a second center, where the second center is displaced with respect to the first center along the axis by a distance (414). The phase of the radar returns received from the scene is compensated for the motion of the moving platform (400) using a cylindrical coordinate system referenced with respect to the second center to yield a SAR image.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
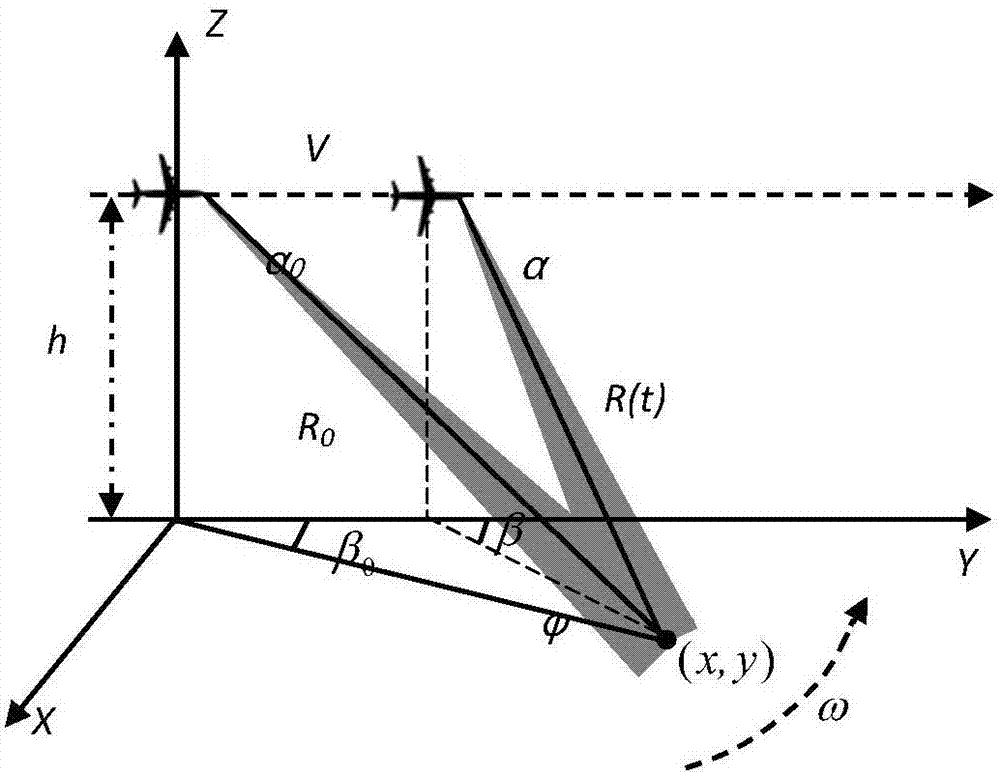
High squint synthetic aperture radar imaging processing method
InactiveCN105093224AAchieve precise focusImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler centroidRange migration
The invention discloses a high squint synthetic aperture radar imaging processing method, which comprises the steps of S1, calculating high squint synthetic aperture radar echo signals; S2, carrying out range fast Fourier transformation (FFT) and spatial-variant range walk correction on the echo signals, and removing range spatial-variant range walk; S3, carrying out range pulse compression and high-order range migration correction on the echo signals, and removing residual range migration; S4, carrying out azimuth spatial-variant property fitting of Doppler parameters on the echo signals; S5, balancing the Doppler centroid and the slope of frequency modulation of target points of the same range cell by adopting an extended azimuth nonlinear frequency modulation scaling algorithm; and S6, carrying out azimuth focusing so as to acquire an imaging result. The high squint synthetic aperture radar imaging processing method solves a range spatial-variant property and an azimuth spatial-variant property of the Doppler parameters, can realize precise focusing of monostatic SAR echo signals under a high-squint-angle condition, and can be widely applied to the fields of earth remote sensing, resource exploration, geological mapping, military reconnaissance and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Partitioning processing-based SAR real-time imaging method and system thereof
ActiveCN104020471AReduce memory requirementsTroubleshoot poor image qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionKinematicsImaging quality
The invention relates to a partitioning processing-based SAR real-time imaging method and a system thereof. A distance echo pulse compression module is used for carrying out pulse compression on each received distance echo datum; an azimuth dimension partitioning processing module is used for carrying out range migration correction and Doppler parameter and kinematic parameter estimation on azimuth subaperture data; a full-aperture parameter estimation module is used for carrying out conjoint analysis and estimation on each azimuth subaperture parameter to obtain full-aperture Doppler parameters and kinematic errors; an envelope compensation module is used for carrying out envelop compensation on the azimuth subaperture data; and a distance dimension partitioning processing module is used for carrying out phase compensation, azimuth pulse compression, multi-look processing and quantization output on data which has undergone envelope compensation. Then, partitioning processing-based SAR real-time imaging processing is finished. The method has low requirements on system memory, can be adopted to effectively solve the problem that range variance leads to poor image quality, and is especially suitable for a SAR real-time imaging system which has high requirements on real-time performance.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO MEASUREMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com