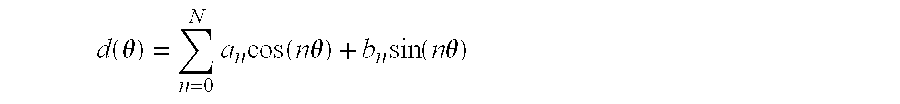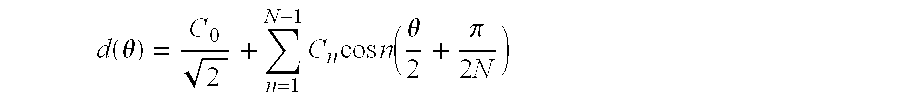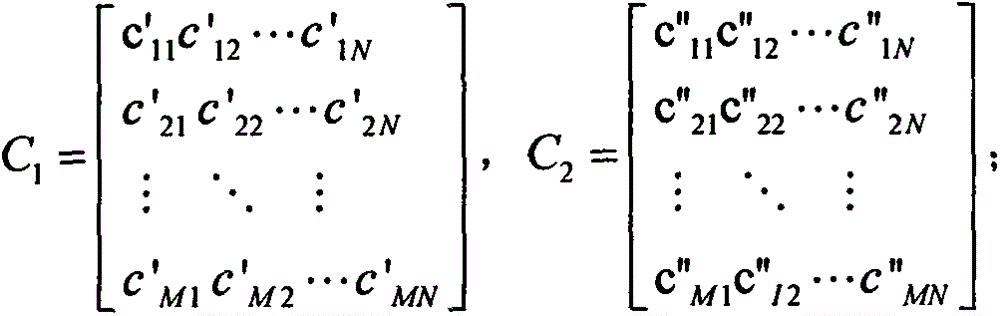Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Least square approximation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Least squares method, also called least squares approximation, in statistics, a method for estimating the true value of some quantity based on a consideration of errors in observations or measurements.
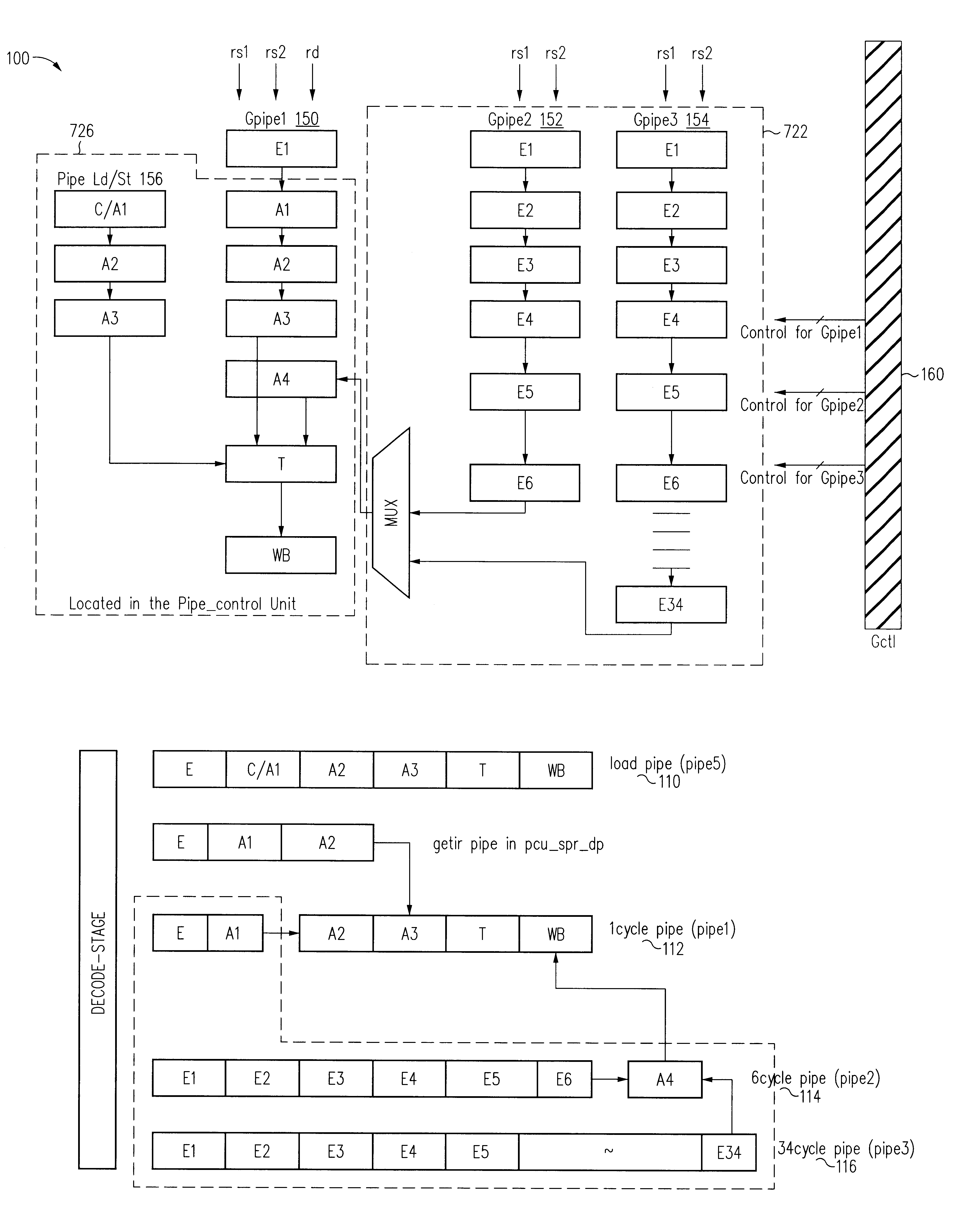
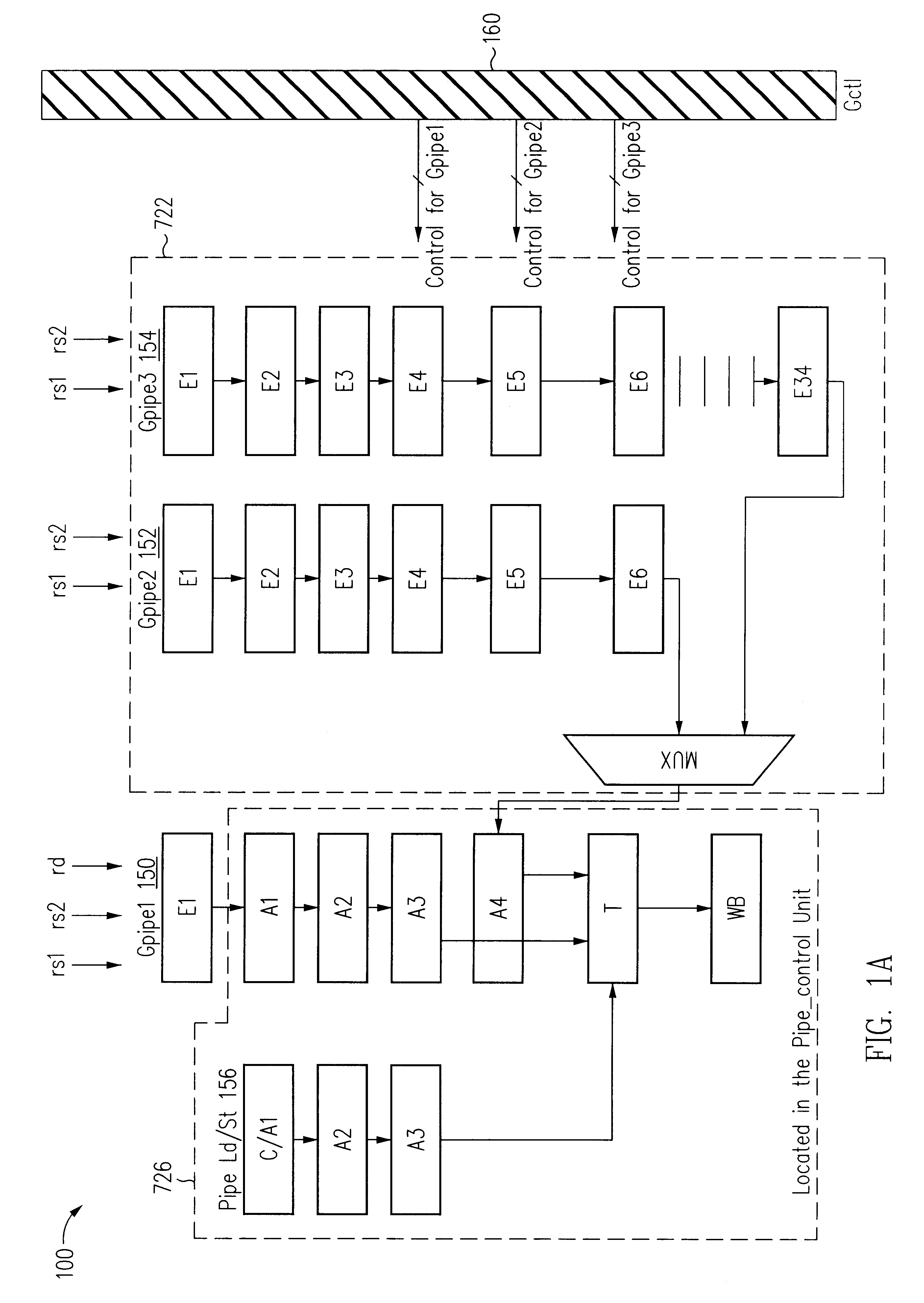
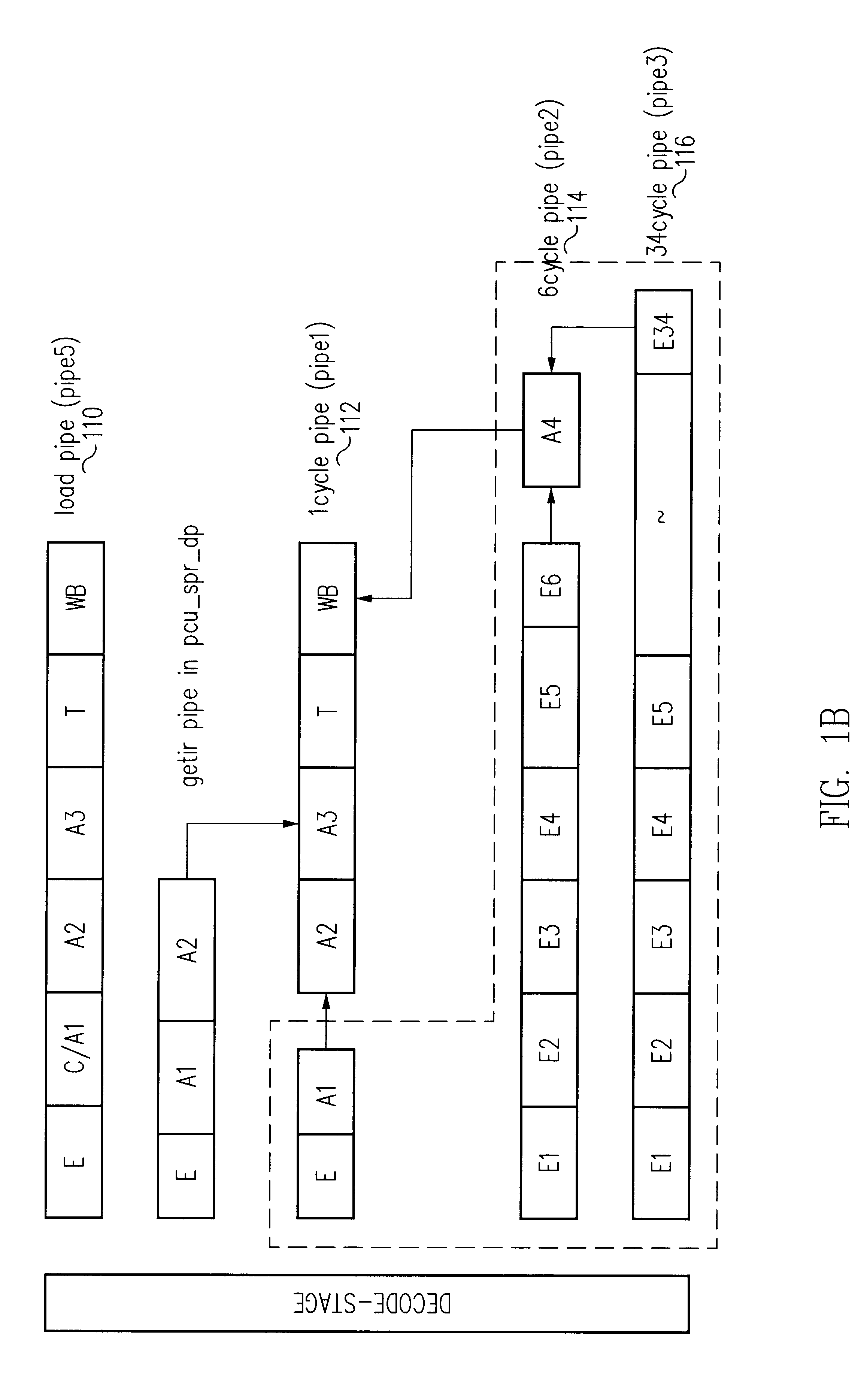
Floating point square root and reciprocal square root computation unit in a processor
InactiveUS6349319B1Computation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlFloating pointLeast mean square error
A method of computing a square root or a reciprocal square root of a number in a computing device uses a piece-wise quadratic approximation of the number. The square root computation uses the piece-wise quadratic approximation in the form:in each interval i. The reciprocal square root computation uses the piece-wise quadratic approximation in the form:in each interval i. The coefficients {overscore (A)}i, {overscore (B)}i, and {overscore (C)}i, and Ai, Bi, and Ci are derived for the square root operation and for the reciprocal square root operation to reduce the least mean square error using a least squares approximation of a plurality of equally-spaced points within an interval. In one embodiment, 256 equally-spaced intervals are defined to represent the 23 bits of the mantissa. The coefficients are stored in a storage and accessed during execution of the square root or reciprocal square root computation instruction.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
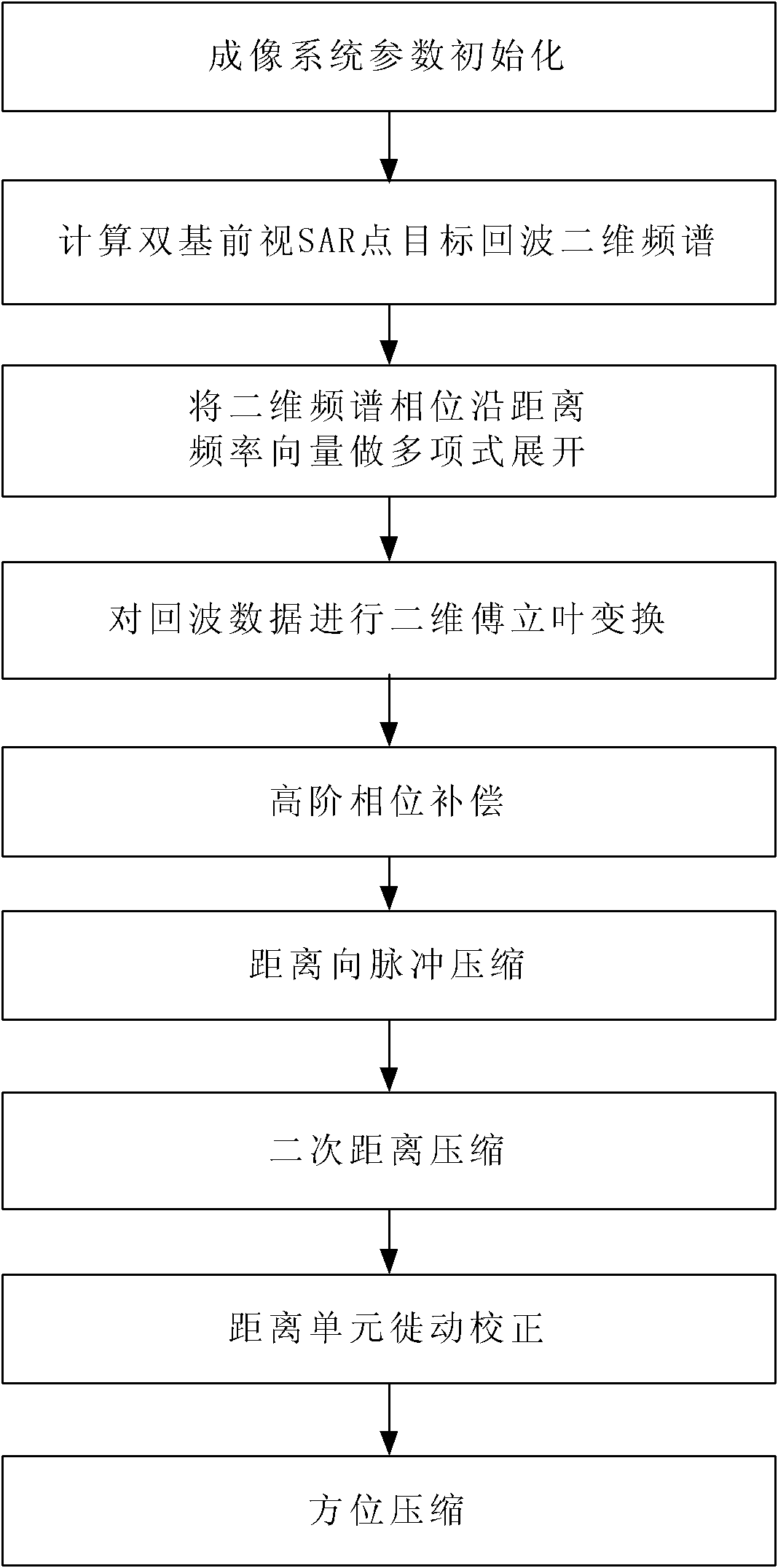
Imaging method for bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR)
InactiveCN102147469AAchieve precise focusImproving Imaging AccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler centroidFrequency spectrum
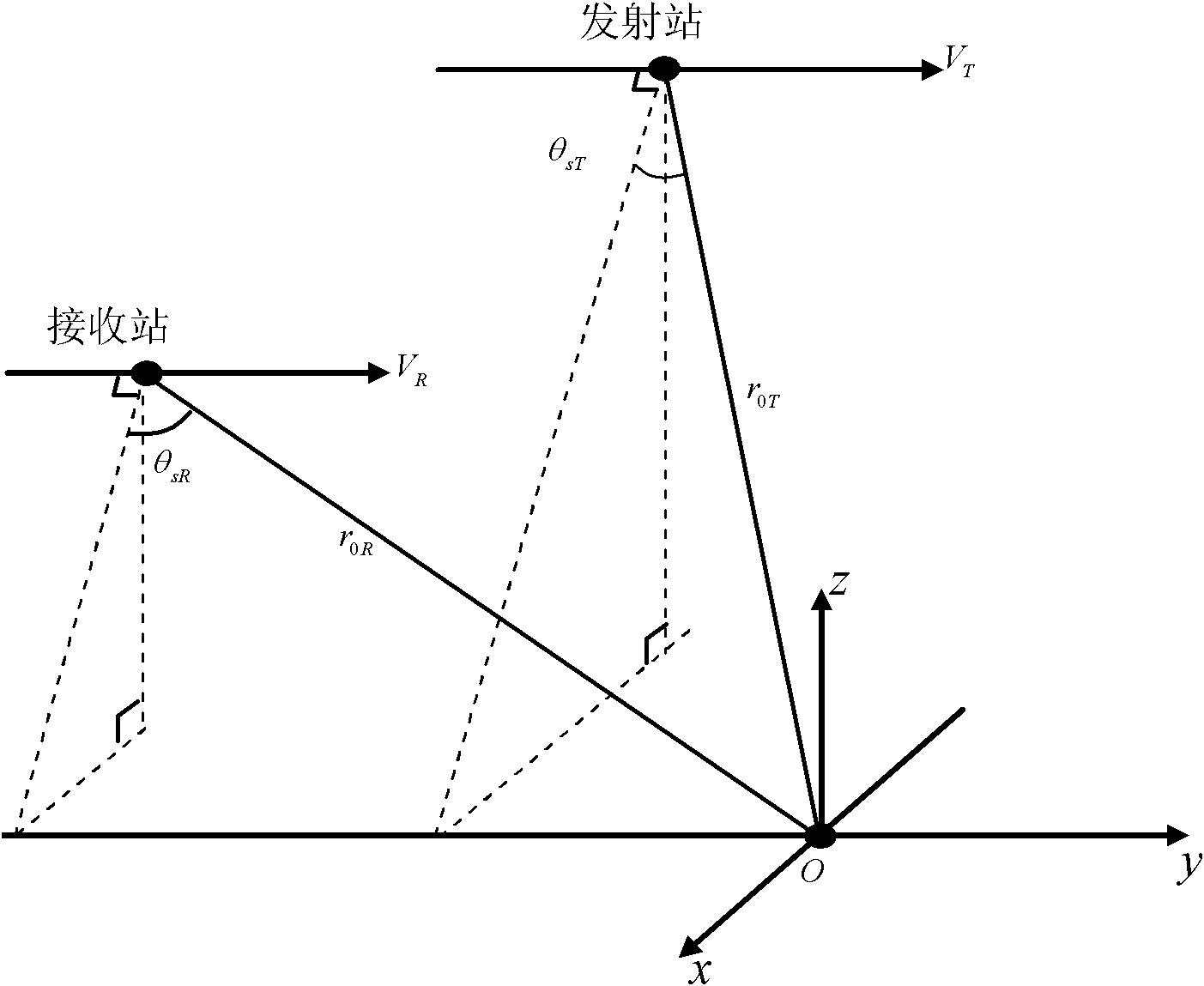
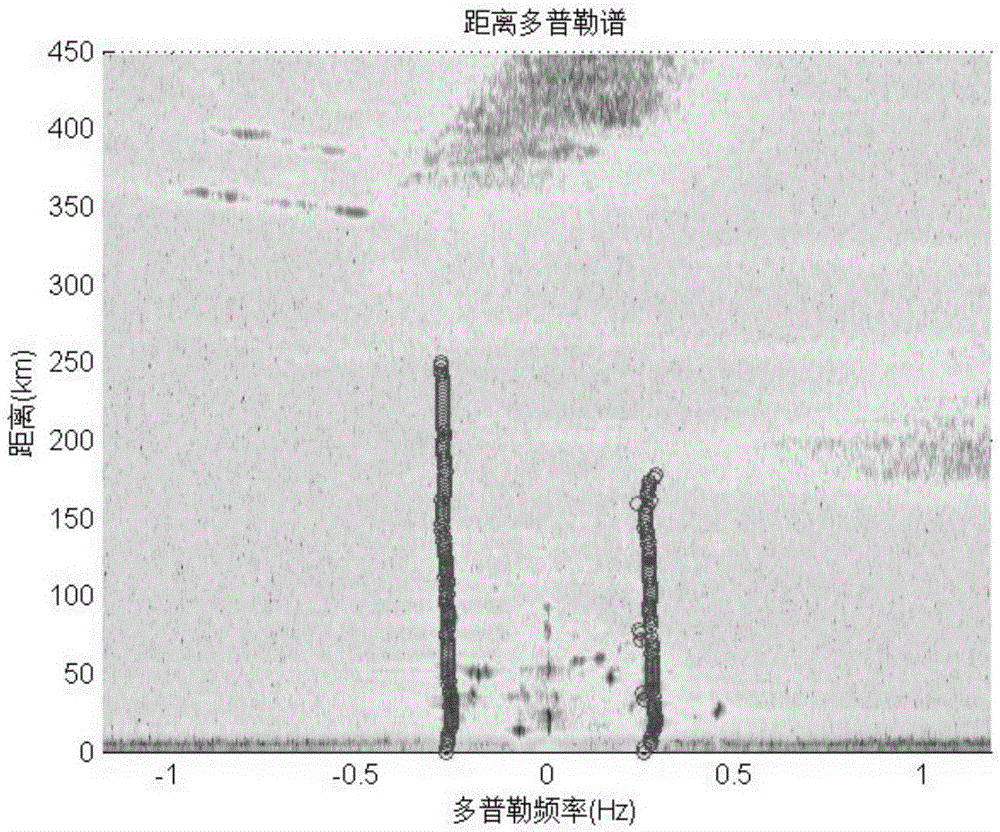
The invention discloses an imaging method for a bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (SAR). Aiming at the defect existing when the existing method is used for the imaging process of the bistatic forward-looking synthetic aperture radar, the imaging method adopts a bistatic forward-looking SAR point target response two-dimensional frequency spectrum based on the least square polynomial fitting; the frequency spectrum is the least square approximation of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum with the accurate theory. According to the characteristics of bistatic forward-looking invariant SAR direction, variant range and nonlinear and variant Doppler centroid range of range cell migration in an RD (radar domain) domain, bistatic forward-looking SAR range migration correction, secondary-range compression and high-order phase compensation are realized by the frequency spectrum so as to accurately focus the bistatic forward-looking SAR. Compared with the traditional SAR imaging method and the bistatic forward-looking SAR imaging method, the method disclosed by the invention has higher imaging precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
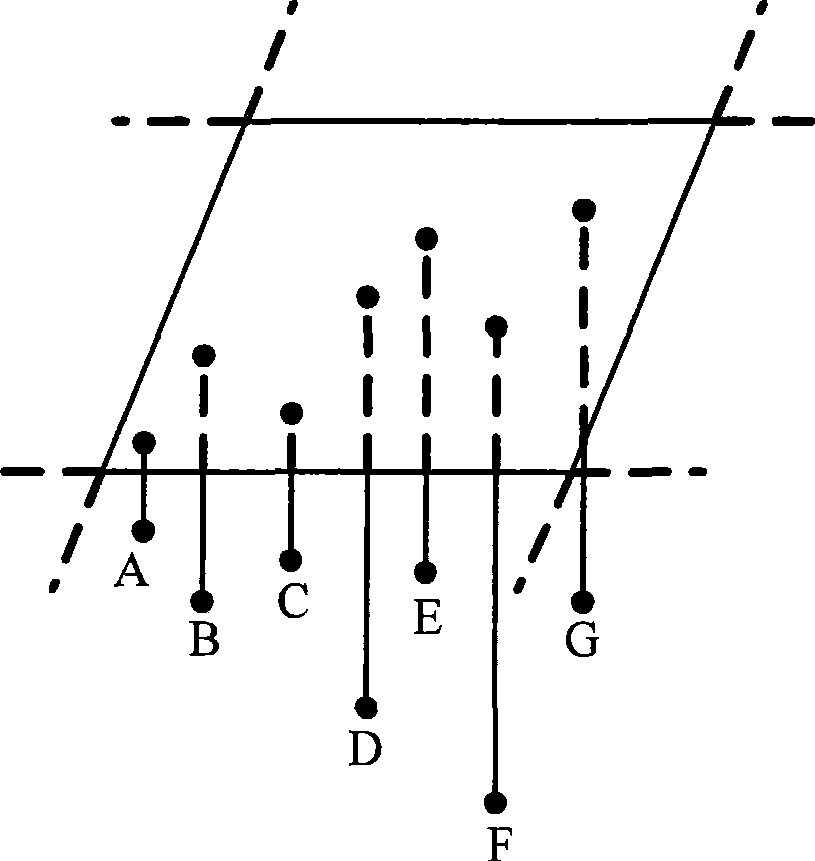
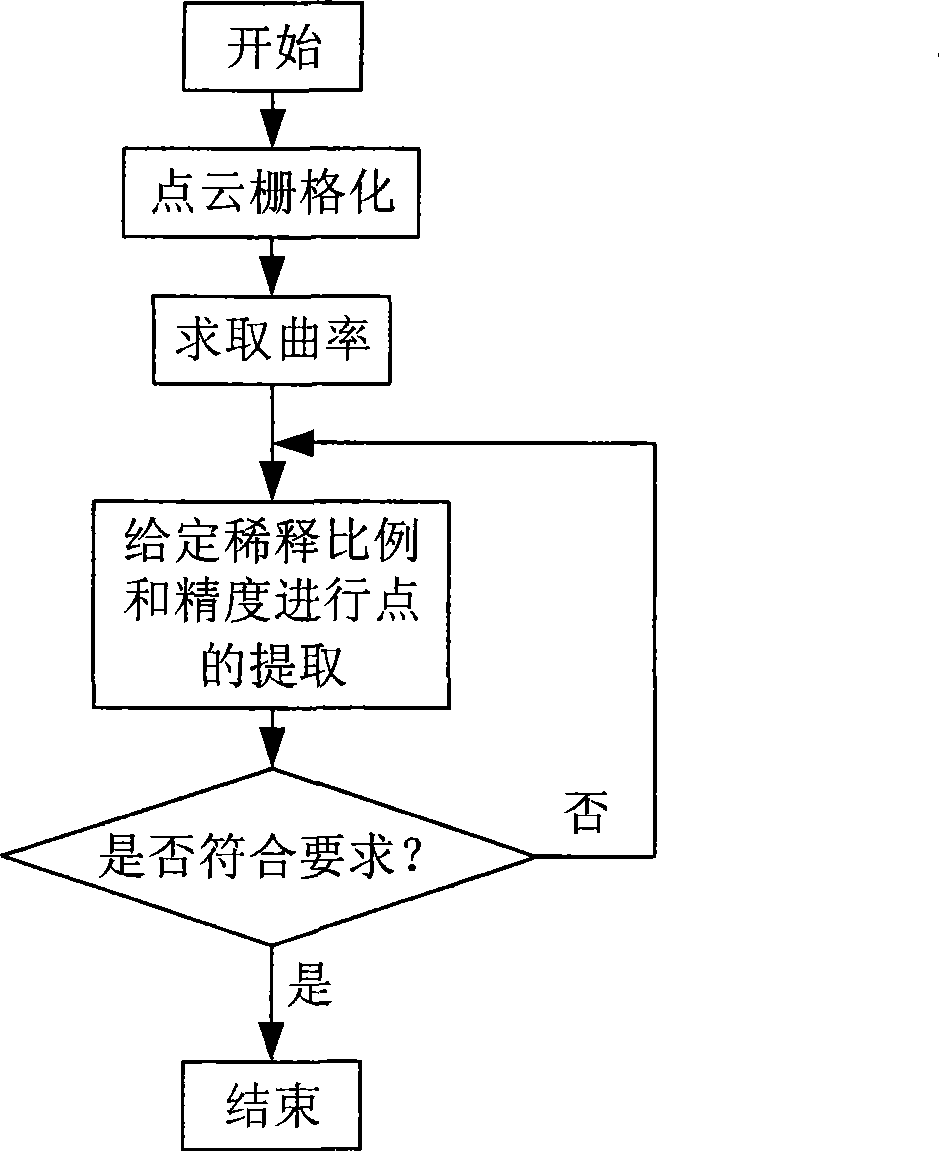
Three-dimensional scanning point cloud compressing method
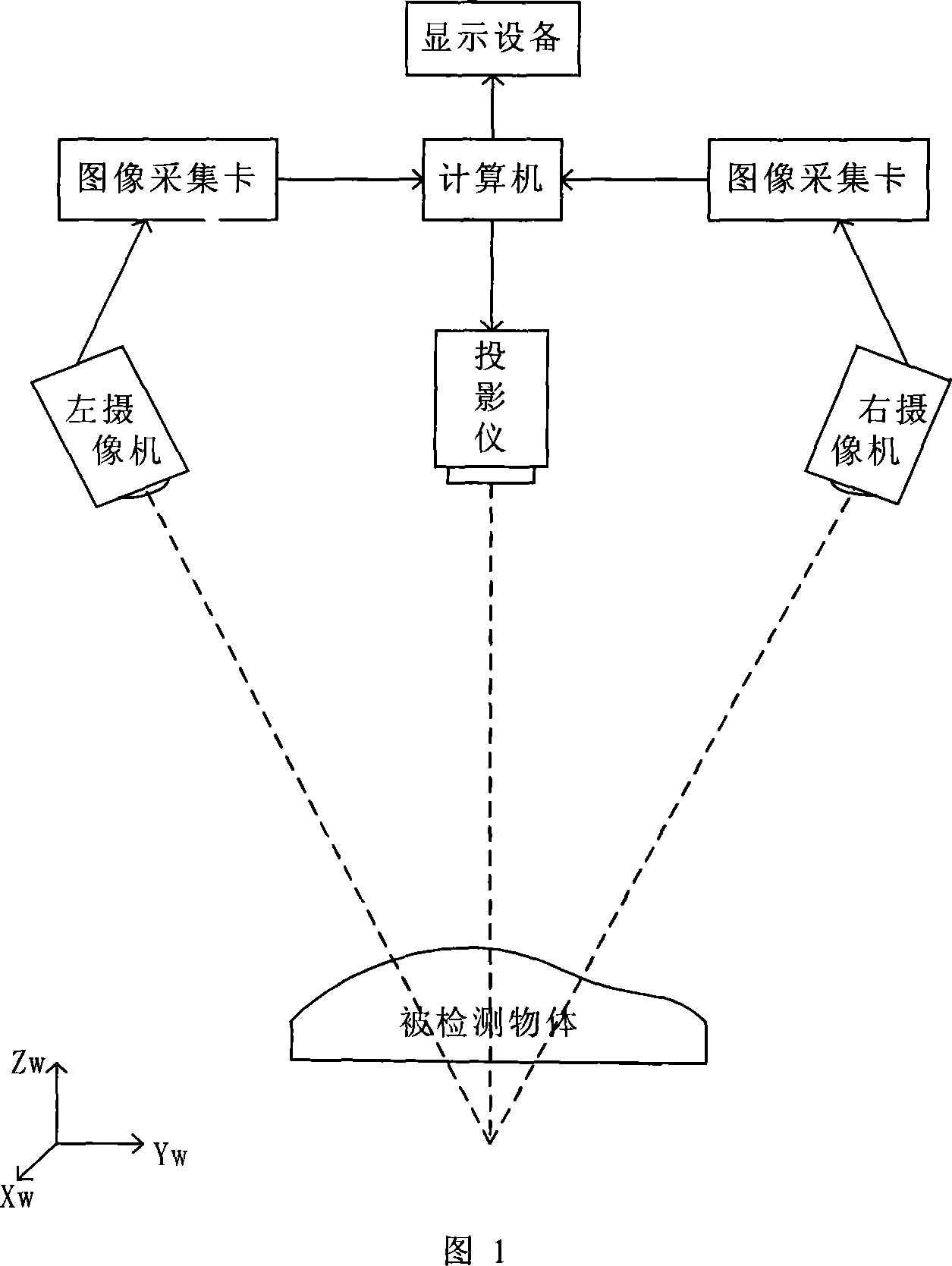
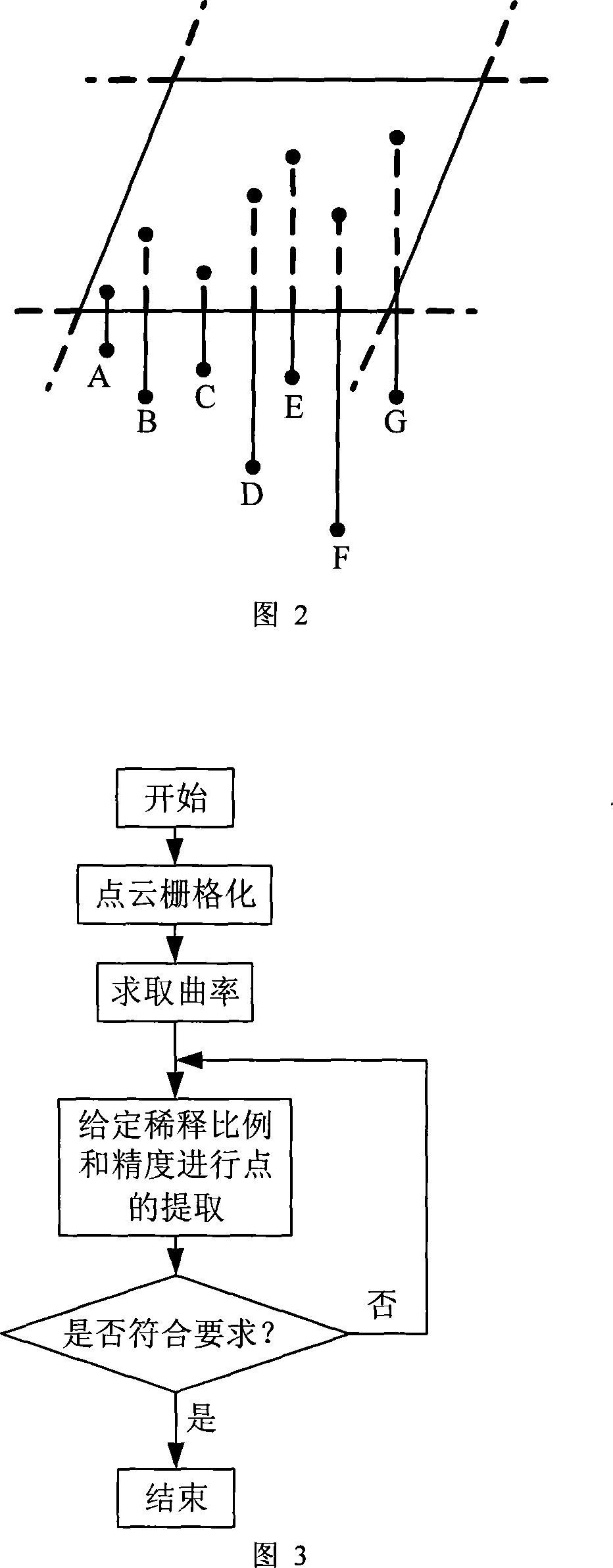
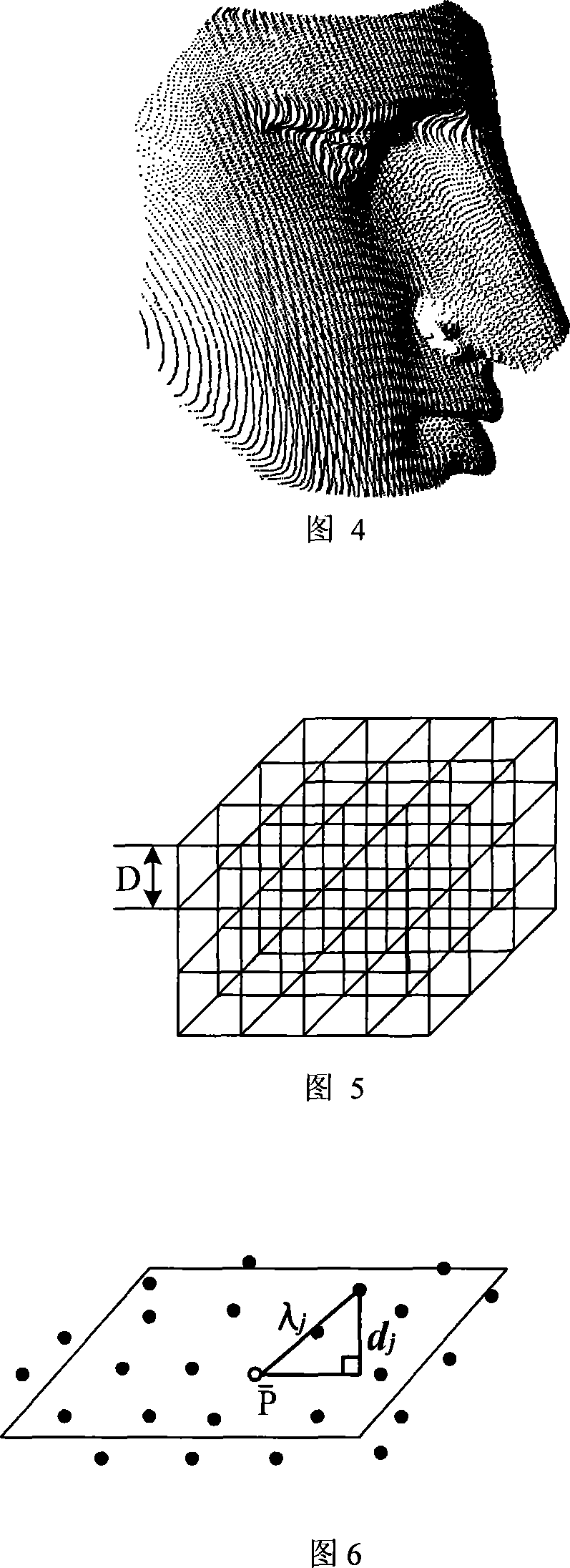
This invention relates to a method for reducing dot clouds of 3-D scanning, which carries out grid division to the dot-clouds, and the grid is the smallest exterior square body of a dot-cloud, the side length is L, then divides it into sub-grids with the side length of DalphaL3 / n along the directions of three coordinate axises, and alpha is the dilution ratio decided by the design, n is the dot number of the cloud, then dot set of the neighbour domain of Pi in the adjacent sub-grid of each dot KNB9Pi)={X1, X2apostrophe, Xn} is taken,takes the least square approximation plane of KNB9Pi) as the micro-cut plane S(Pi), takes Pi as the core of KNB(Pi), sets the distance from jth adjacent point of Pi to S(Pi) dj, and the distance to Pi lambdaj, then the function is fj(Pi)=dj / lambdaj, the curvature function of Pi is f(pi)=1 / kSigmafj(Pi) so as to obtain the curvature of every data point Pi, finally acquires the mean curvature in every small grid and gets the difference of the curvature of a point and the mean curvature and points smaller than the needed accuracy are selected as the points of the grid and others are deleted.
Owner:HAIAN COUNTY SHENLING ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE MFG +1
Composite material II type crack growth rate measuring method capable of acquiring crack growth S-N curve
InactiveCN103439194ASimplified Determination Method of Cracking ThresholdReduce testing costsMaterial strength using steady bending forcesFiberCrack growth resistance curve
A composite material II type crack growth rate measuring method capable of acquiring a crack growth S-N curve comprises five steps: 1, a single end-notched flexure (ENF) composite material sample is selected and formed through molding fiber cloth and resin; 2, the sample is tested through a three-point bending manner; 3, a triaxial movable high power digital measurement system is adopted to observe and measure the crack growth length, and the test load, the cycle index and the corresponding crack growth length are recorded; 4, the constant interface shear stress of a neutral surface of the composite material is worked out according to the engineering beam theory, and a three-parameter power function is adopted to fit the crack growth interface shear stress and the corresponding cycle index so as to obtain the crack growth S-N curve; 5, a dual-growth exponent function is utilized to fit the test load cycle index and the a-N curve of a corresponding crack growth length, and the crack growth rate is obtained after derivation; a Paris model and an energy release rate formula are adopted, and a crack growth rate curve is obtained through least-squares approximation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
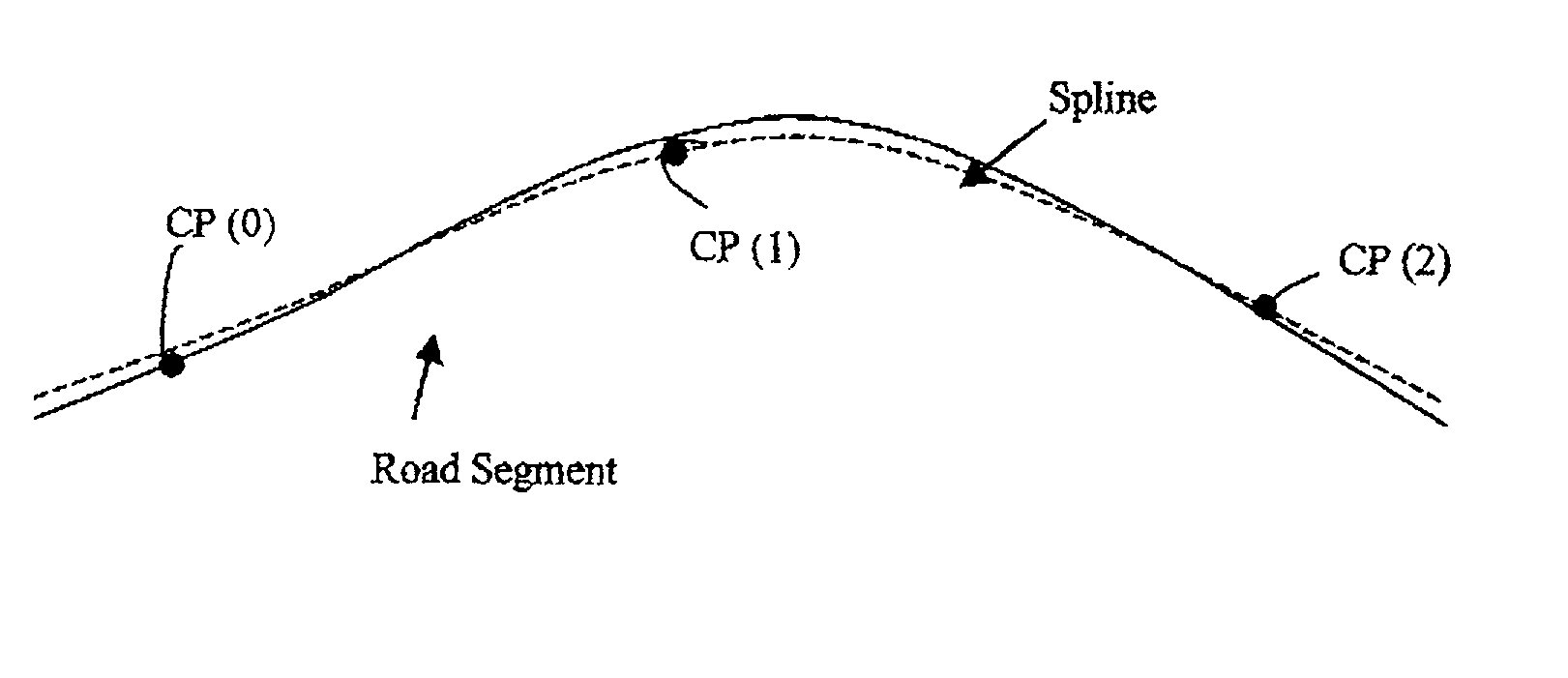
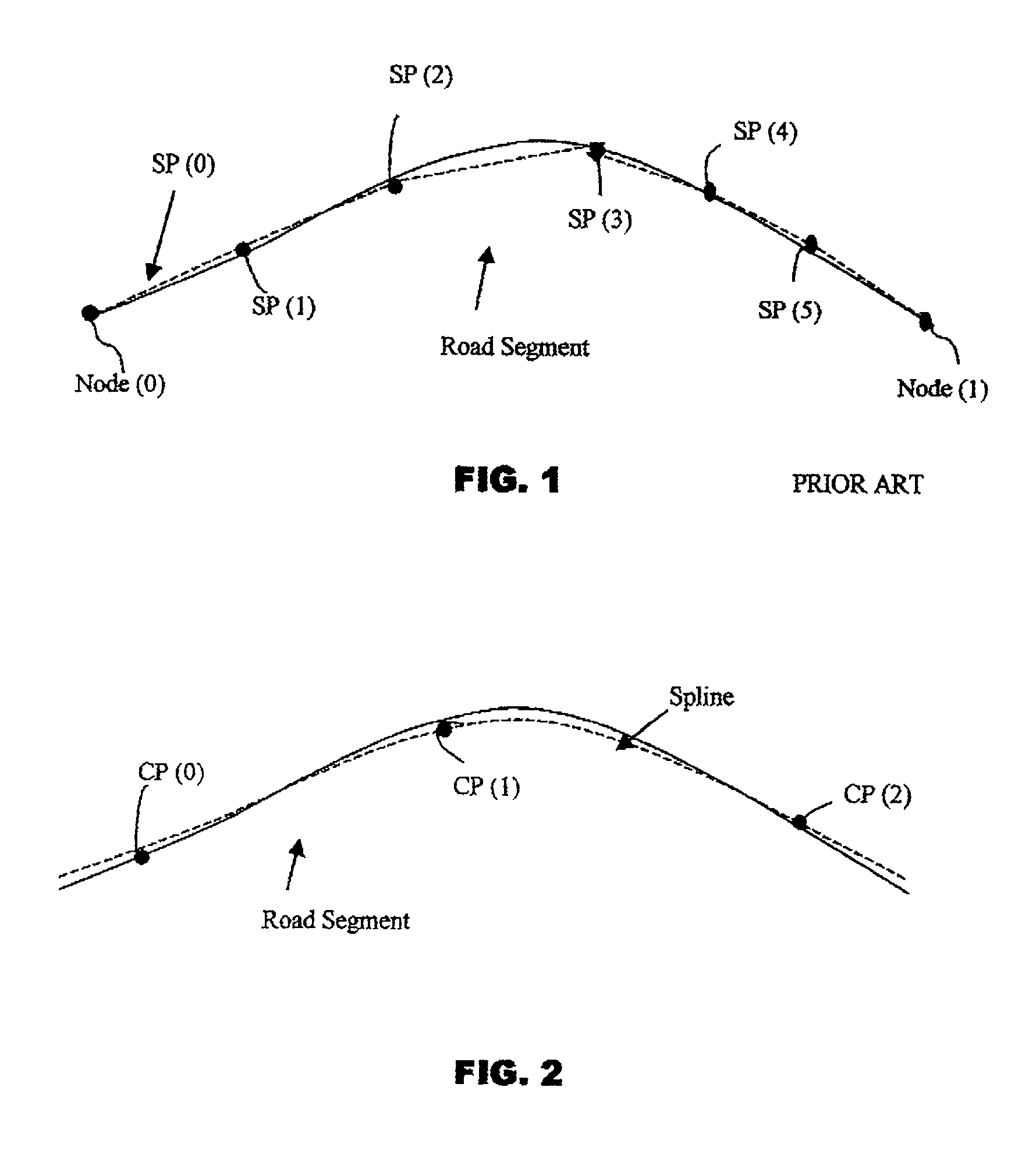
Method and system for representation of geographical features in a computer-based system
ActiveUS7805442B1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsGeographic featureComputer science
Cartographic data is represented using polynomial splines. To improve representation accuracy and reduce storage requirements, a database storing data points (shape points and nodes) is converted into a database of spline control points. The spline control points are computed by fitting a polynomial spline to the geographic features using a least squares approximation. The control points associated with each geographic feature are stored in a computer-usable database. The geographic features can be displayed by computing the spline functions using the stored control points.
Owner:HERE GLOBAL BV
Imperfect interface contact state nonlinear ultrasonic evaluation method based on micro texture
ActiveCN101666780ARealize contact status evaluationHigh sensitivityAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalSonificationNonlinear ultrasound
The invention relates to an interface contact state nonlinear ultrasonic testing method which belongs to the nondestructive testing filed. The method comprises the following steps: determining the frequency and the periodicity of detection signals according to the size and the material performance of a test piece forming a contact interface; by applying different pressures to a rough interface, changing the contact state, and carrying out ultrasonic transmission detection test on the rough interface; by carrying out nonlinear least-squares approximation processing on testing data of the test,determining micro characteristic composite parameters of the interface, computing a first-order rigidity coefficient and a second-order rigidity coefficient which are used for expressing the characteristics of the rough interface, and realizing ultrasonic expression of the contact characteristics of different rough interfaces. In the invention, the nonlinear ultrasonic coefficients are adopted toexpress the contact characteristics of the interface, the nonlinear ultrasonic detection has higher sensitivity comparing with the linear ultrasonic; by combining the micro texture and the rigidity relation of the interface, the method enables the macroscopic property of the interaction of the ultrasonic and the contact interface to be associated with the microcosmic property of the contact surface, thereby evaluating contact states of different microcosmic interfaces.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Mobile assembly for pencil beam XCT (X-ray Computed Tomography) system and a method for carrying out image reconstruction and coordinate system origin calibration by using same
InactiveCN101832954AUsing wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationGraphicsImaging processing
The invention discloses a mobile assembly suitable for a pencil beam XCT (X-ray computed tomography) system and a method for carrying out image reconstruction and coordinate system origin calibration by using the same, mainly aiming at the calibration of a projective coordinate origin of a round track scanning and imaging system based on an FDK (Feldlamp-Davis-Dress) algorithm. Because the accurate space positions of a ray source focus and a detector imaging plane cannot be directly measured, the projective coordinate origin cannot be exactly measured. The method comprises the following steps of: reconstructing an over-determined set based on an image, an image processing method and a least-squares approximation technology by utilizing a DR (Digital Radiograph) image sequence obtained by imaging a single ball target for multiple times at different positions of a pencil beam field; then solving for a projective coordinate point of the ray source focus on the imaging plane; and carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction by utilizing parameter values obtained by using the method to obtain an exact reconstruction result.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Shape representation using fourier transforms
ActiveUS20080170760A1Promote resultsGood localisationAcquiring/recognising eyesGraphicsFast Fourier transform
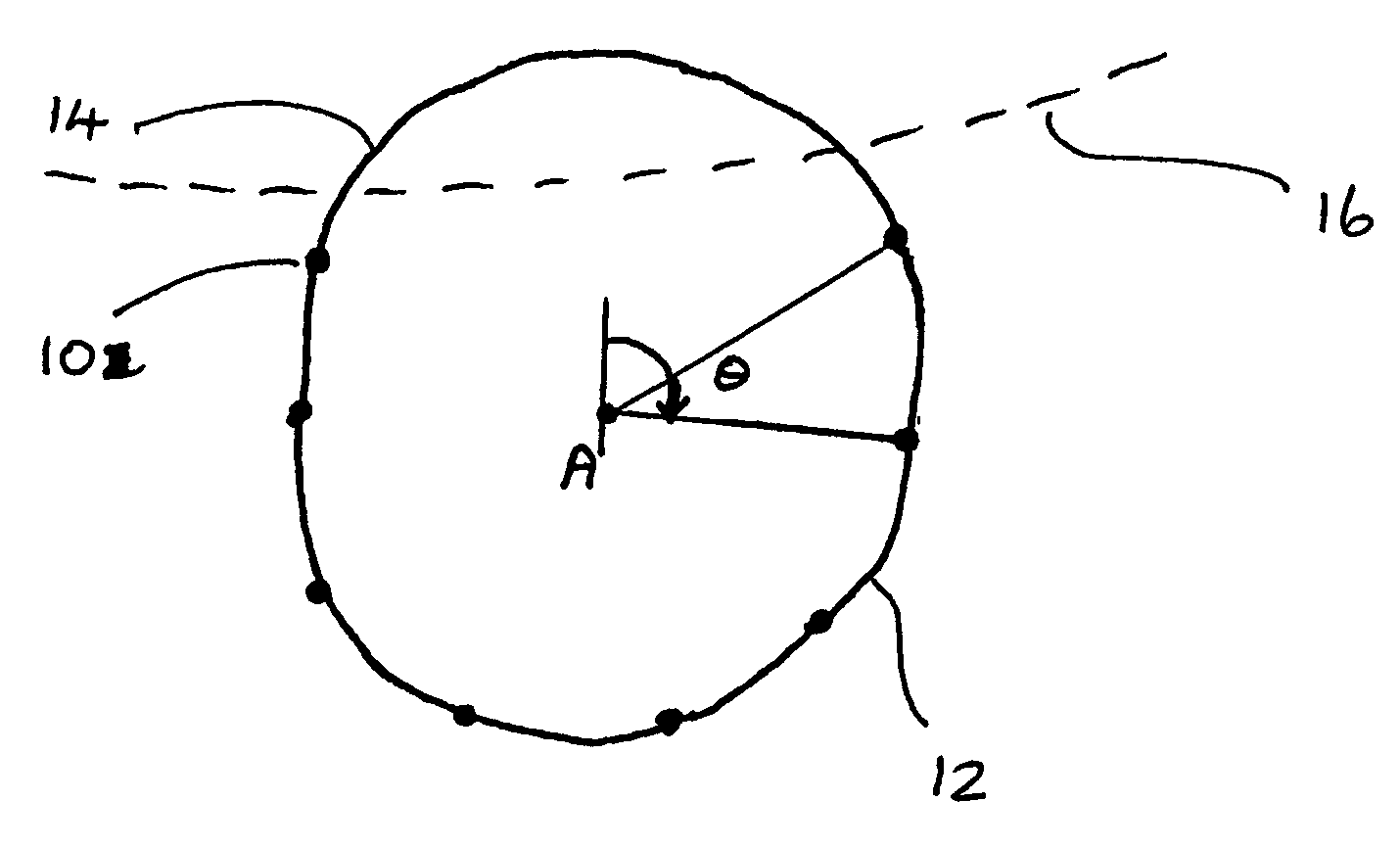
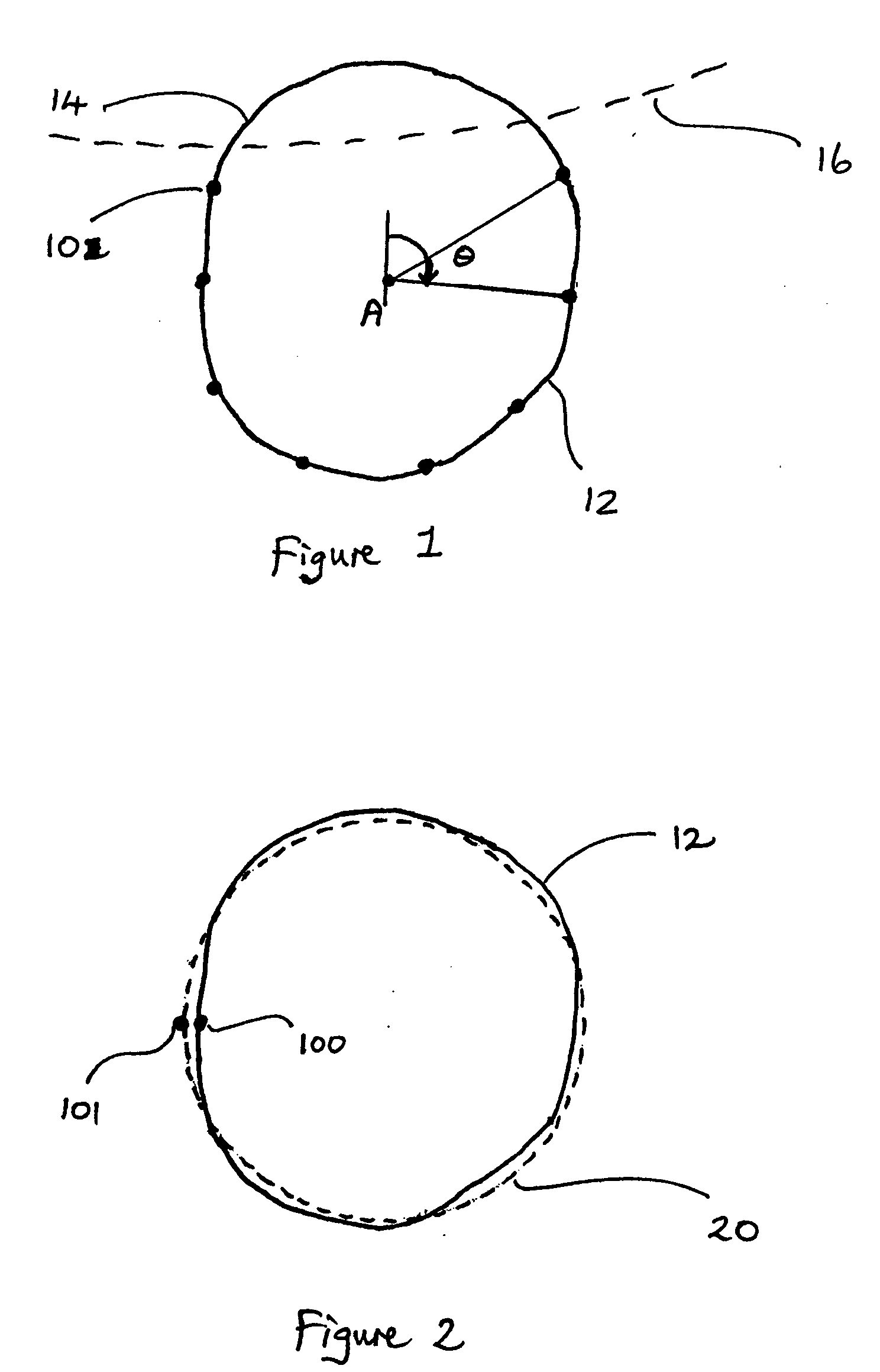
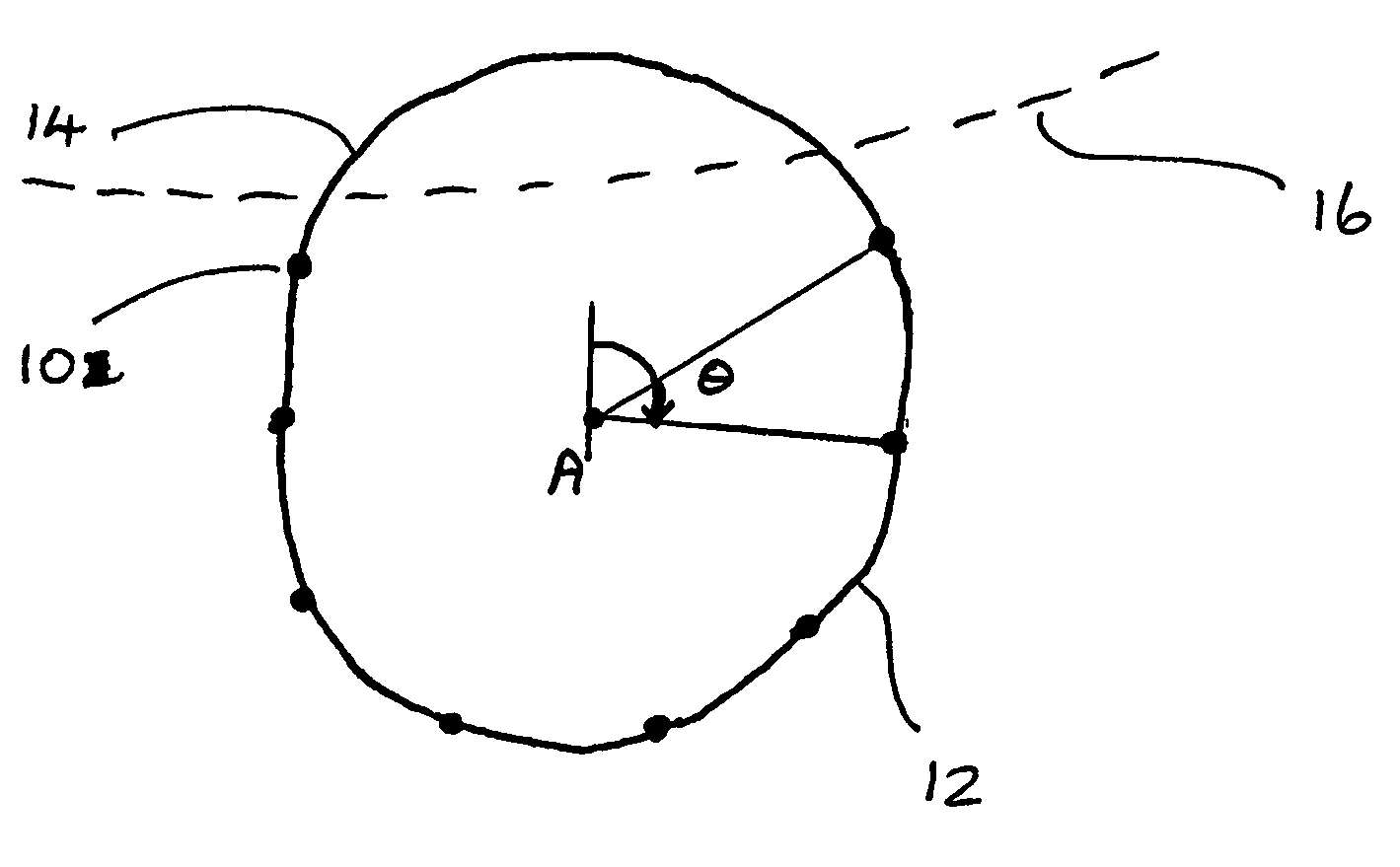
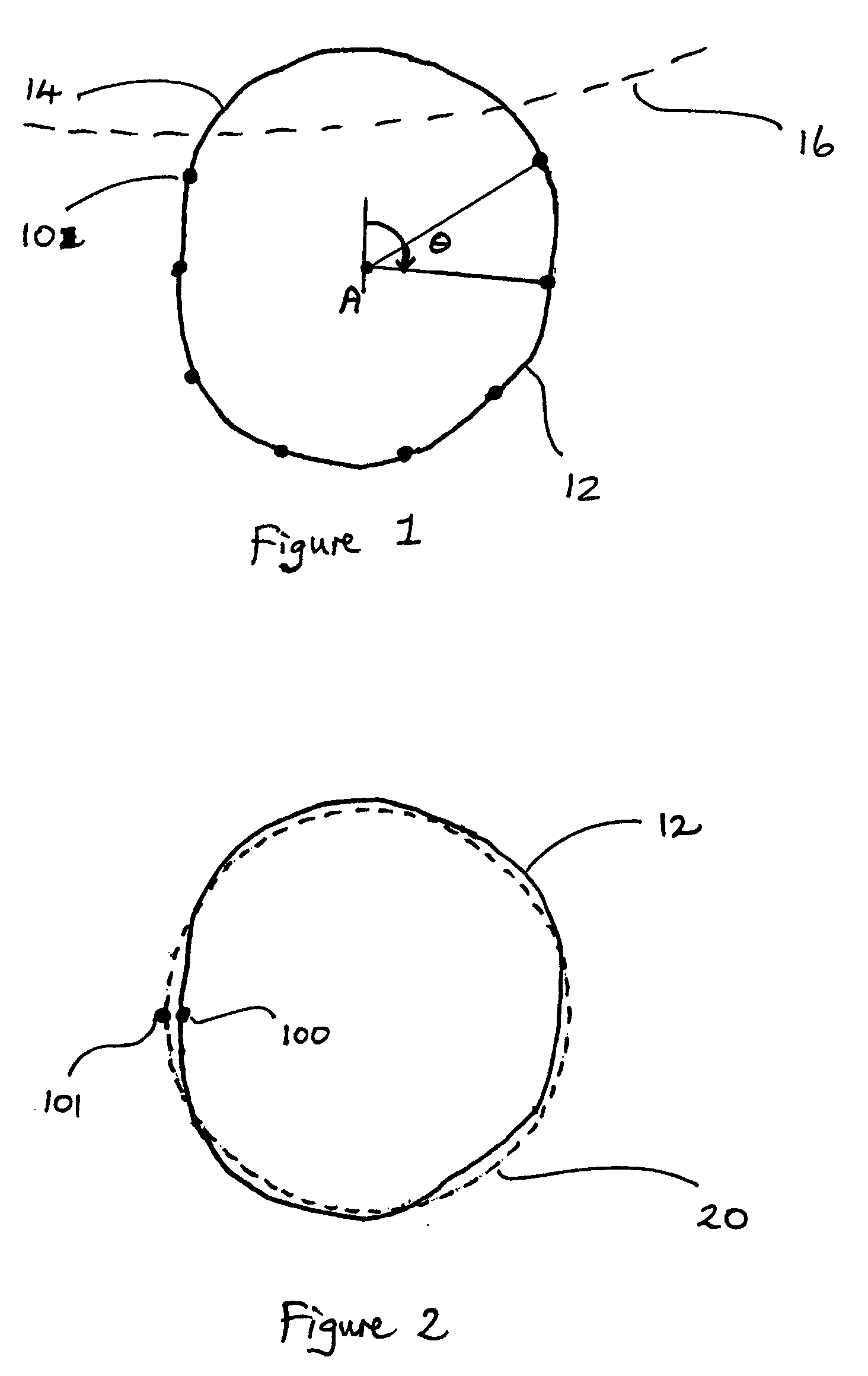
A method of approximating the inner or outer boundary of an iris comprises generating an approximate boundary representation (20) comprising a least squares approximation by a Fourier Series of a function of the angle (θ) about a fixed point (A) of the distance of measured points (10) on the boundary from the fixed point (A). More broadly, the method may be used to approximate the shape of any two-dimensional curve or figure.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
Shape representation using Cosine Transforms
ActiveUS20080170759A1Promote resultsGood localisationCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsLinear approximation
A method of approximating the inner or outer boundary of an iris comprises generating an approximate boundary representation (20) comprising a least squares approximation by a cosine transform series of a function of the angle (θ) about a fixed point (A) of the distance of measured points (10) on the boundary from the fixed point (A). More broadly, the method may be used to approximate the shape of any two-dimensional curve or figure.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
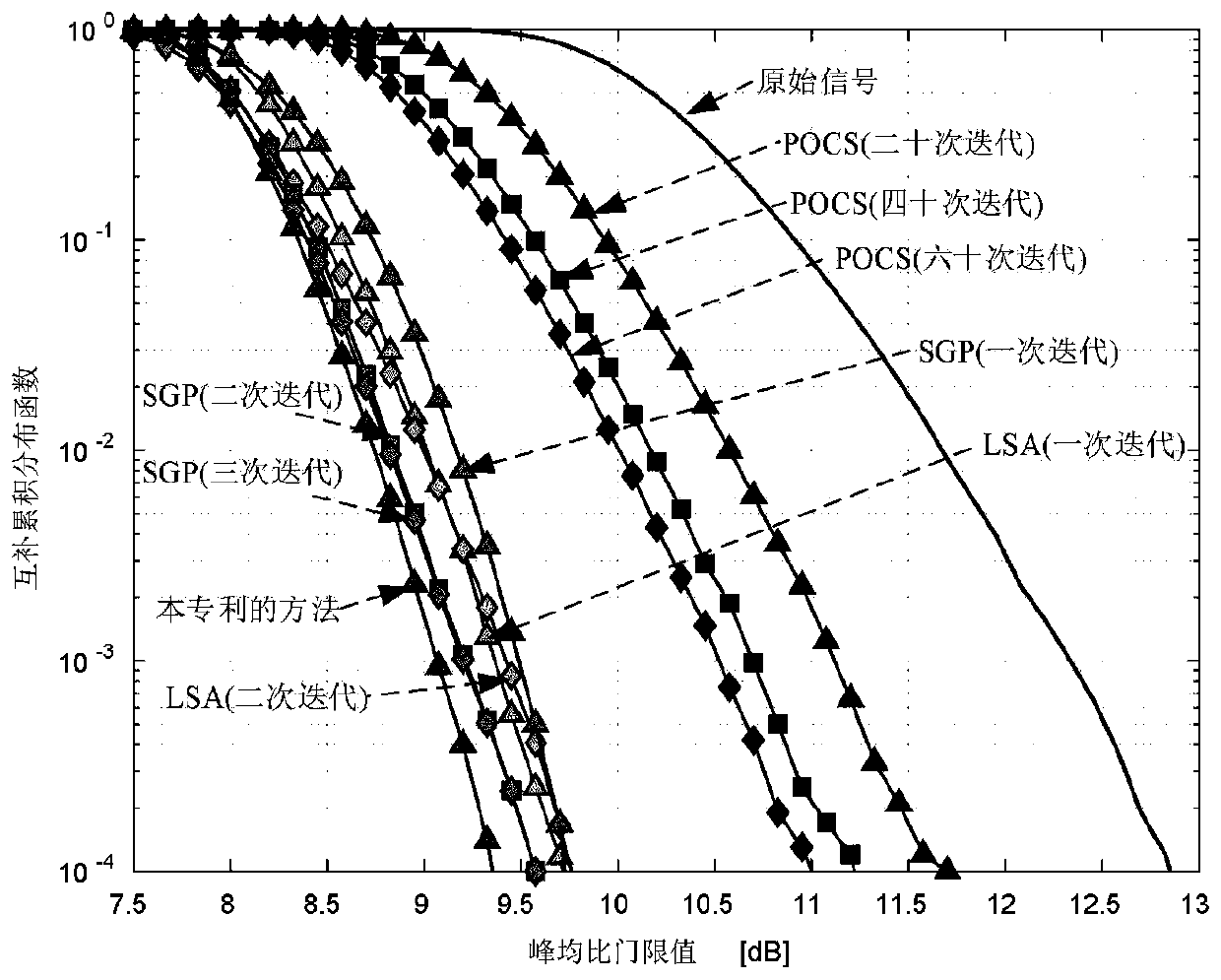
Method and system for suppressing ACE of peak-to-average ratio of high-order modulation OFDM signal
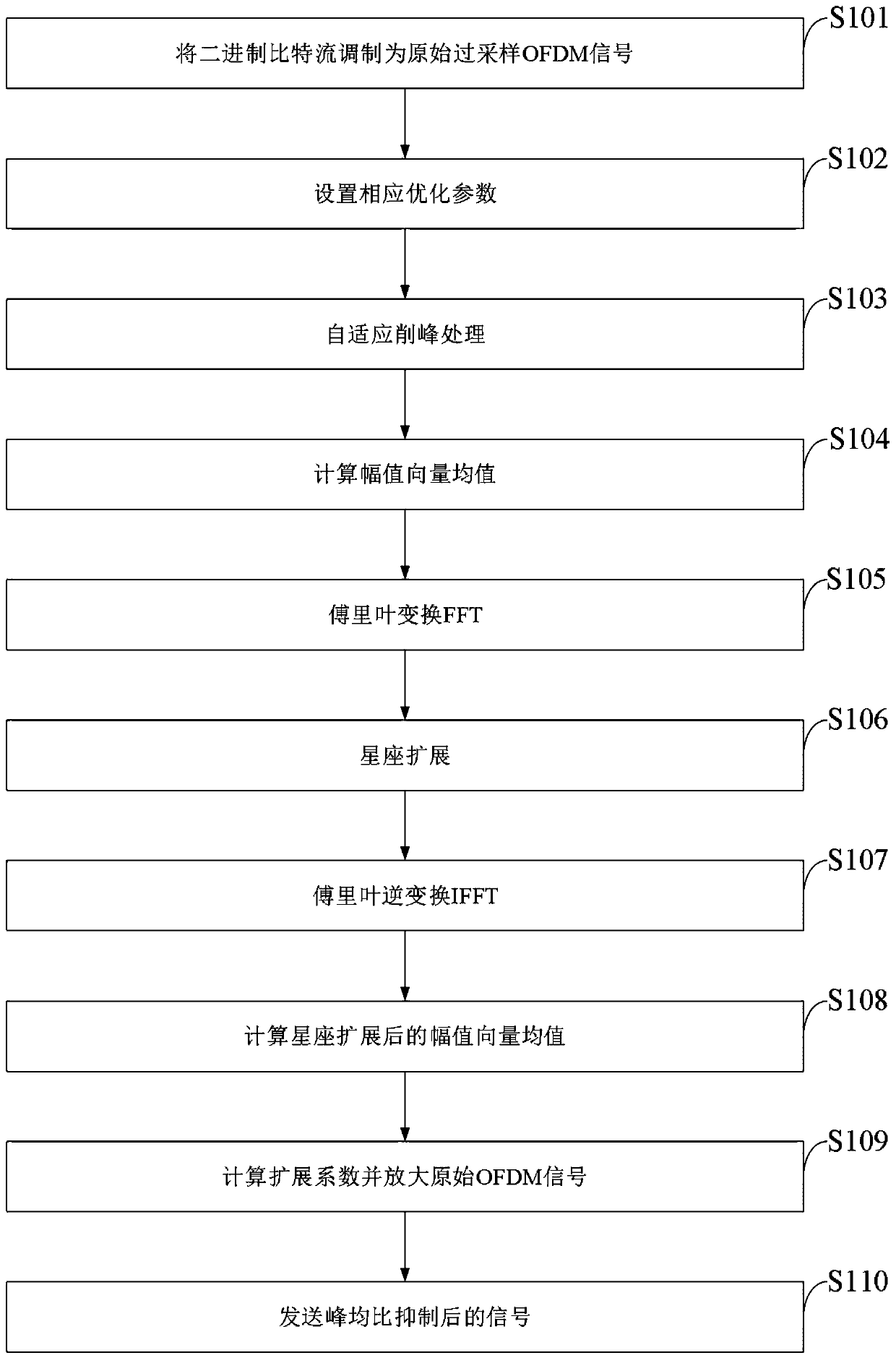
ActiveCN110336763AGuaranteed lossFast convergenceMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainExpansion factor
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronic communication, and discloses a method and a system for suppressing ACE of a peak-to-average ratio of a high-order modulation OFDM signal. Themethod comprises steps of redefining expansion rules of constellation in frequency domain; dynamically adjusting a peak clipping threshold according to the peak-to-average ratio of the current signalto obtain an effective peak-to-average ratio suppression gain, and enabling the bit error rate of the system not to be seriously deteriorated; after the effective peak-to-average ratio suppression gain is obtained, obtaining a proper expansion factor by correcting a least square approximation formula, amplifying an original time domain signal, and enhancing the signal peak-to-average ratio suppression effect. Based on the optimization strategy, the peak-to-average ratio of OFDM transmission signals is remarkably reduced under the condition that only one iteration is needed, the implementationcomplexity of the system is greatly reduced, meanwhile, it is guaranteed that the bit error rate and the loss of the out-of-band power spectrum performance are within an acceptable range, and the overall performance of the OFDM system is effectively improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
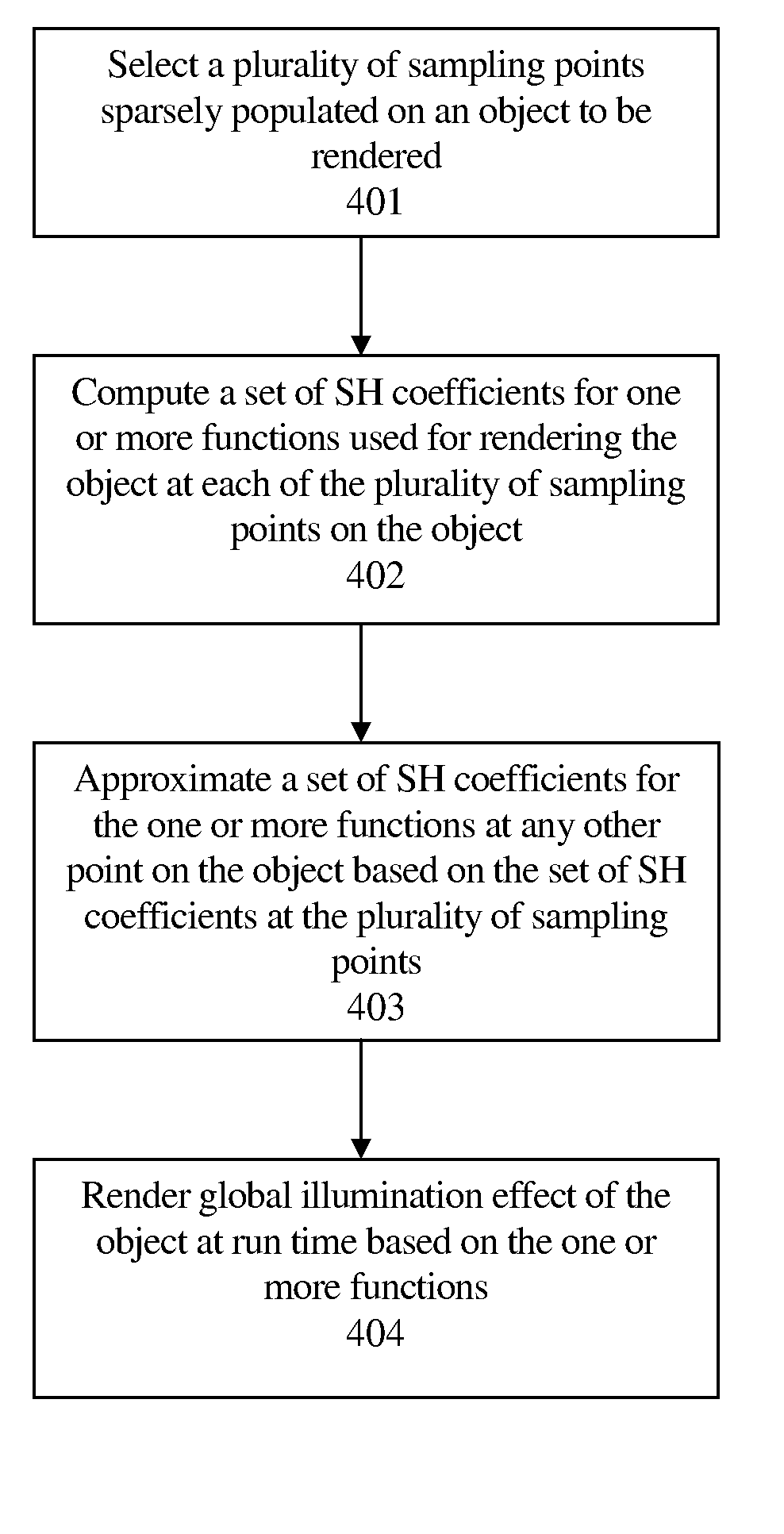
Method and system for scattered spherical harmonic approximation
A scattered spherical harmonic (SH) approximation method is proposed for pre-computation of SH coefficients at sampling vertices of an object to be rendered. The approach sparsely populates the object with a plurality of SH sampling vertices and uses the least squares approximation to calculate the SH coefficients at any (other) arbitrary point of the object by extrapolating from the computed SH coefficients at the SH sampling vertices.
Owner:DIGITAL DOMAIN PRODN
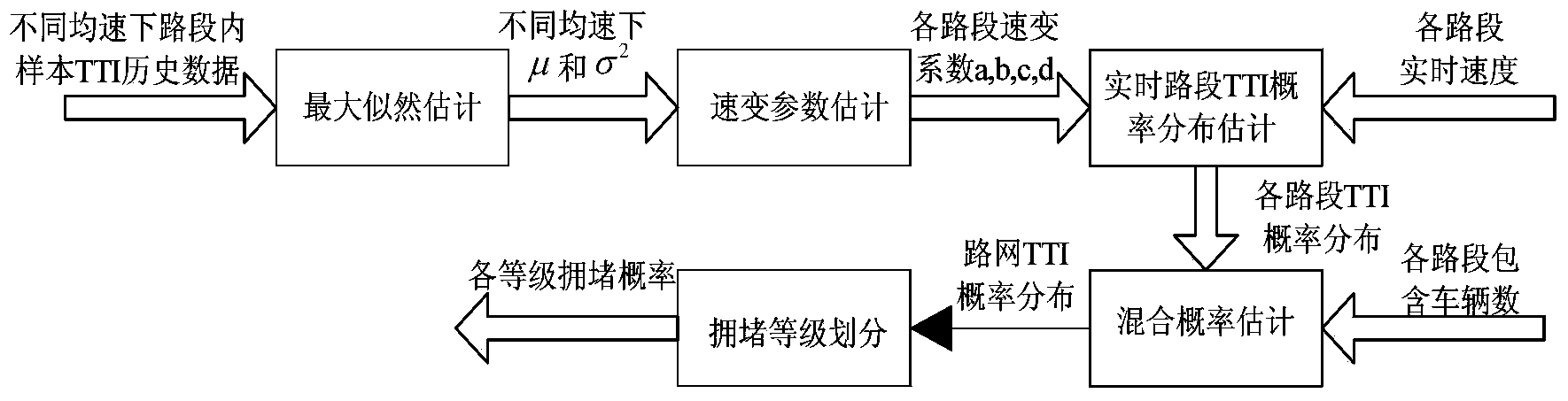
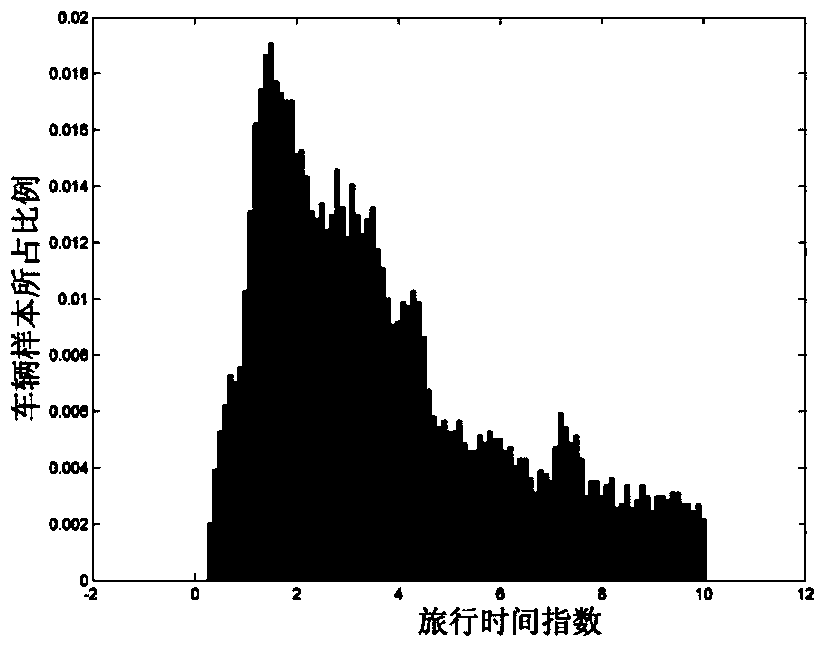
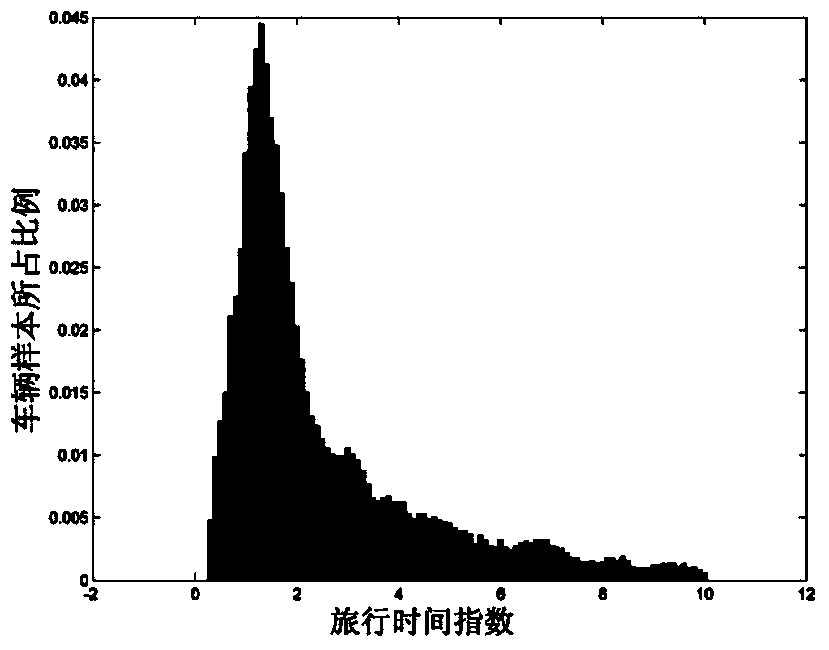
Travel congestion probability estimation method
ActiveCN104268415AReveal hidden orderSpecial data processing applicationsNormal densityProbability estimation
The invention discloses a travel congestion probability estimation method which includes the following steps of: counting the probability distribution of vehicle travel time indexes of each road section in the same target road network at different uniform velocity conditions; obtaining the probability distribution parameters mu m and sigma 2 at different uniform velocity conditions through maximum likelihood estimation; determining the speed variable coefficient of travel time index probability distribution in all road sections through least-squares approximation; calculating the corresponding probability distribution parameters mu m and sigma 2 according to the uniform velocity at each road section at given time so as to obtain the probability density of the vehicle travel time indexes at all road sections, then weighting the probability density of the vehicle travel time indexes at all road sections with the number of vehicles at road sections as the weight to obtain a probability density function p (z) of the vehicle travel time indexes in the road network, and obtaining the probability of three congestion conditions of the target road network according to a cumulative probability distribution function P (z) corresponding to the p (z). The travel congestion probability estimation method can escape from the influence of the road section lengths on the estimation result.
Owner:北京交通发展研究院
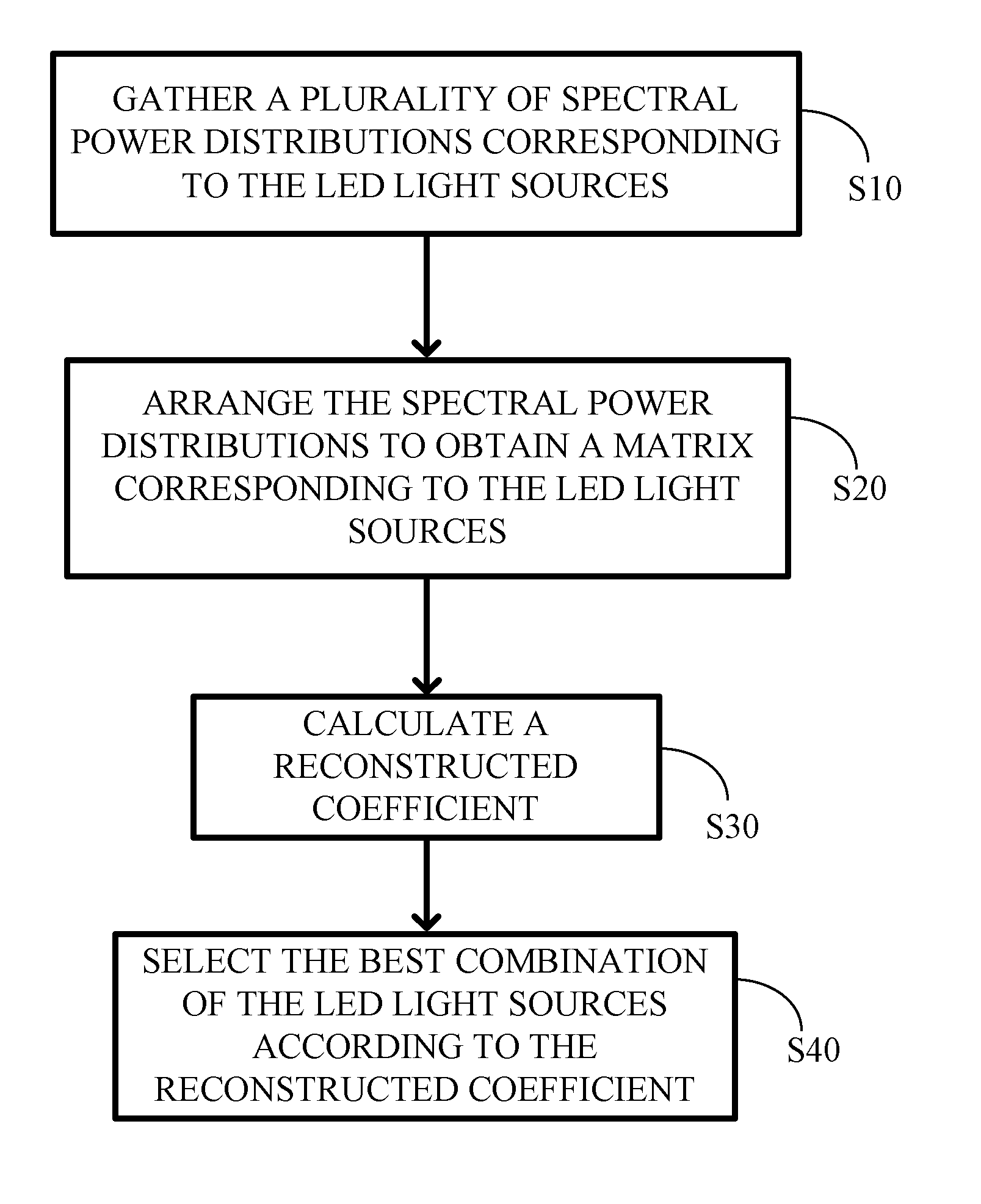
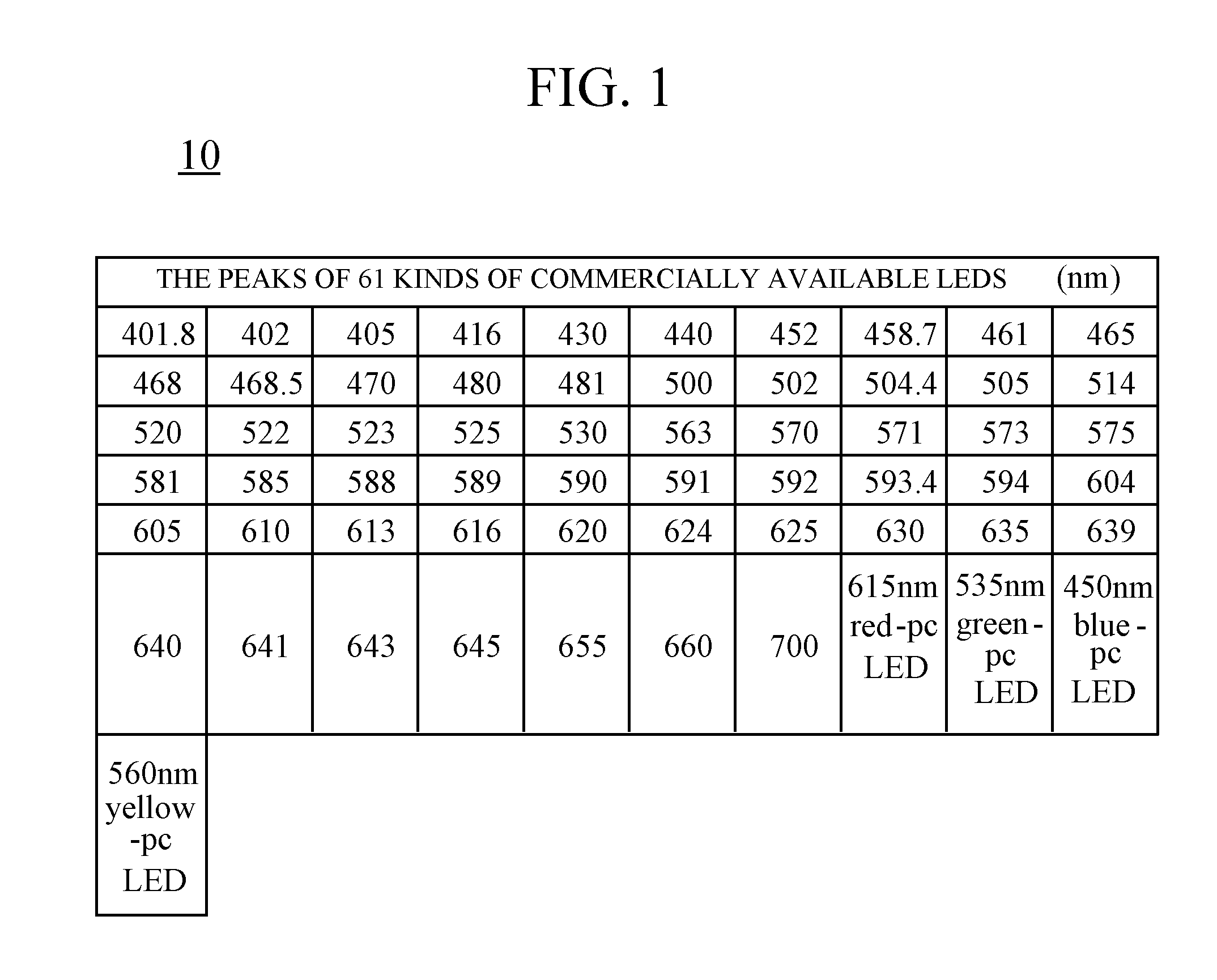
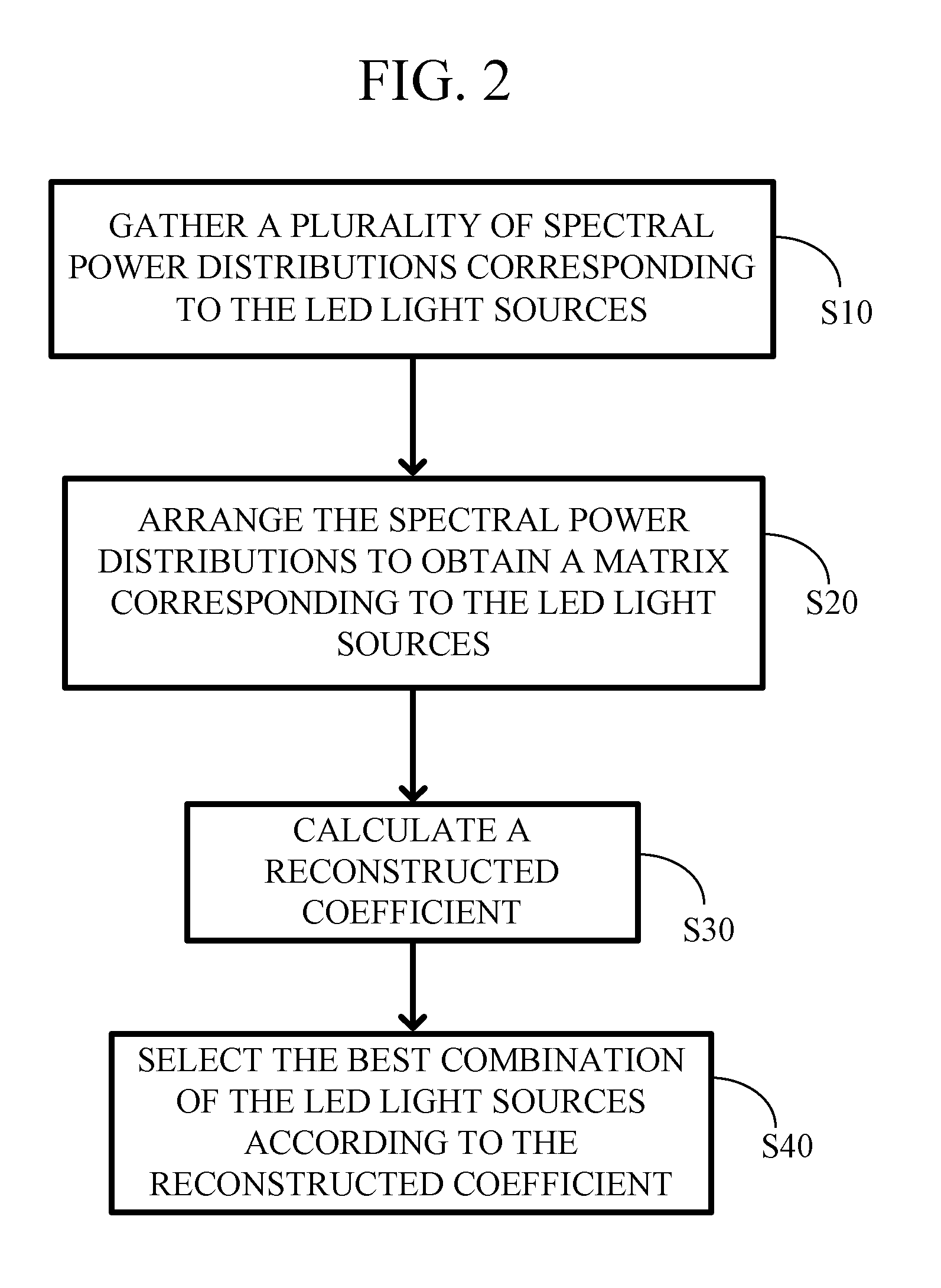
Method for optimal selecting LED light sources and implementing full spectrum light
InactiveUS20120010861A1Simple methodHigh indexPlanar light sourcesLight source combinationsFull-spectrum lightFull-Spectrum Lighting
A method for optimal selecting light-emitting diode (LED) light sources for full spectrum lighting is disclosed. The optimal selecting method includes the following steps: gathering a plurality of spectral power distributions corresponding to LED light sources; arranging the spectral power distributions to obtain a matrix A corresponding to the LED light sources; calculating a reconstructed coefficient, which is a least-square approximation of the matrix with respect to a spectral power distribution of a CIE standard illuminant; and selecting a best combination of the LED light sources according to the reconstructed coefficient. An LED light source assembly is also disclosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
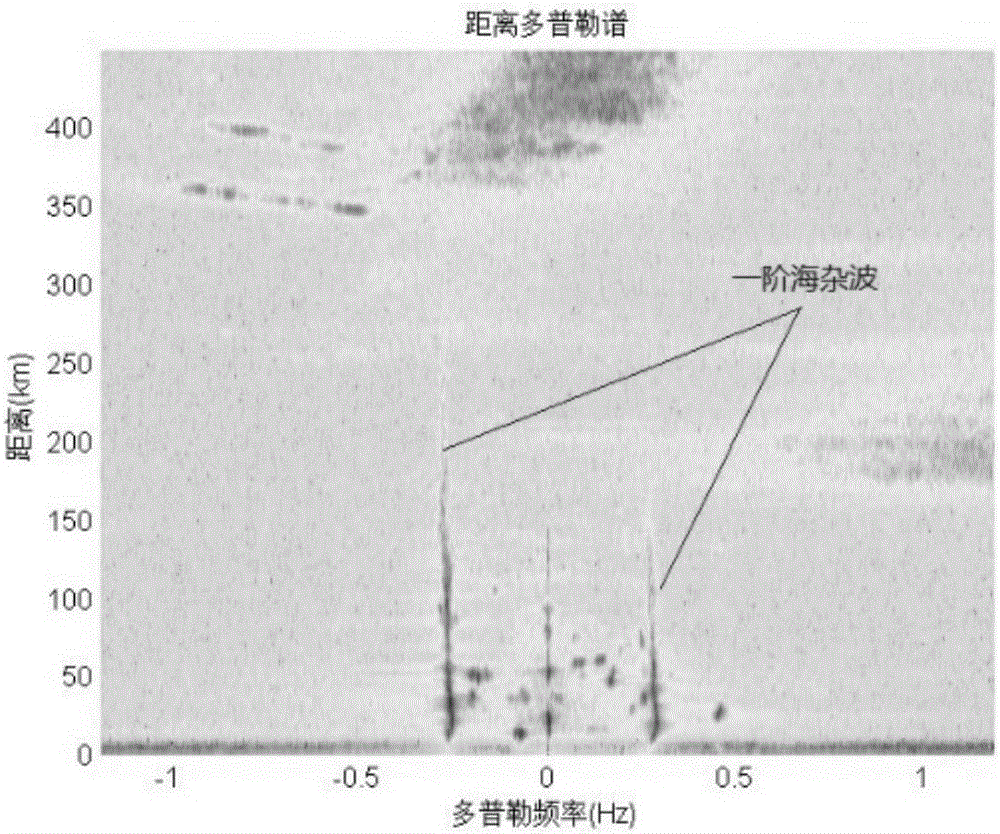
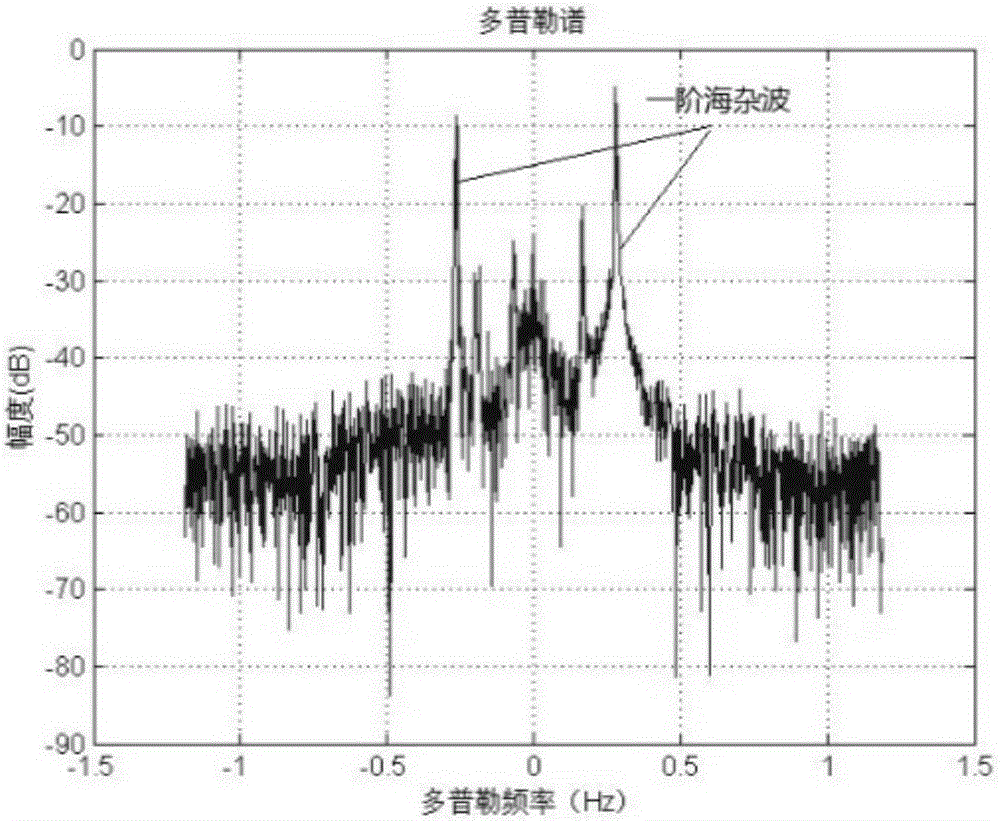
First-order sea clutter detection method based on least squares approximation
ActiveCN105891787AImprove accuracyReduce distractionsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBragg peakPeak value
Disclosed is a first-order sea clutter detection method based on least squares approximation. The invention relates to a first-order sea clutter detection method, and aims to solve the problem that the found Bragg peak position is inaccurate and the false alarm rate is high in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: calculating the theoretical Bragg frequency fB based on the working frequency f0 of radar, defining a noise zone on each sea element, and calculating the threshold of each sea element; detecting sea area sea state data according to the radar, determining the maximum radial velocity Vm of ocean current, and calculating the maximum Bragg frequency offset Delta fm; determining a search scope according to Delta fm and fB, determining a suspected point of the Bragg peak, confirming the threshold of the amplitude of the suspected point, and judging whether the current sea element is effective; for the effective sea elements, taking the neighboring points of an appropriate number of suspected points to form a point set, and acquiring the approximation function of the point set using a least squares approximation method; and finally, taking the peak point of the approximation function as a Bragg peak. The first-order sea clutter detection method is applied to the field of high-frequency ground wave radar detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for optimizing reliability of structural noise based on dimension-by-dimension analysis strategy
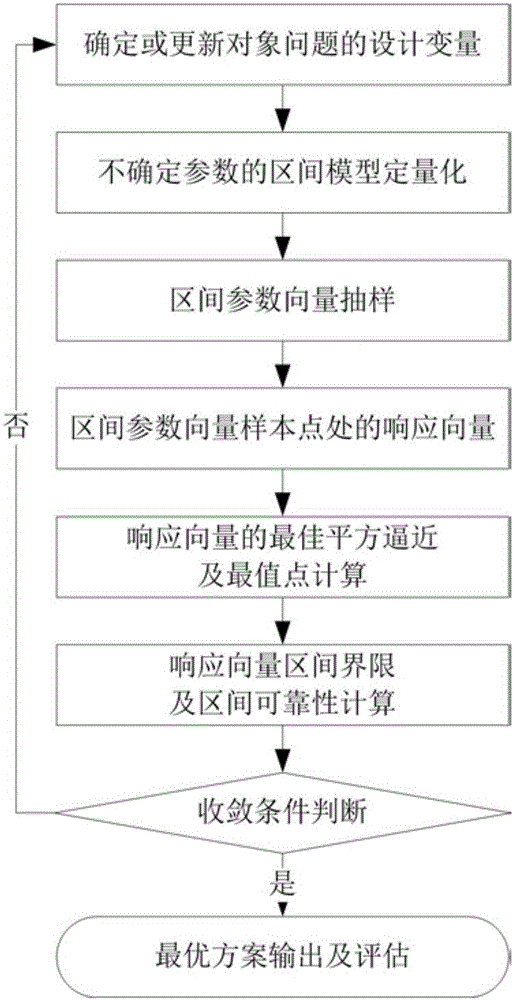
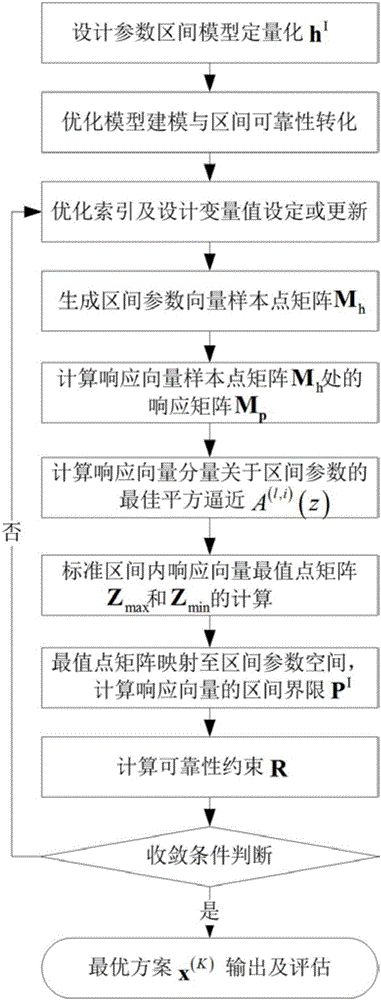
ActiveCN105912839AWide applicabilityAvoid conservatismInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsQuantitative modelAnalytical strategy
The invention discloses a method for optimizing reliability of structural noise based on a dimension-by-dimension analysis strategy. The method comprises following steps: firstly, establishing a structural noise optimizing model based on an interval reliability analysis model by using a quantitative structure for a model of interval value and environment and other uncertainties, determining orders and gauss integral points based on least-squares approximation responding to interval parameters by utilizing structural acoustics to response to nonlinearity degree related to interval parameters; secondly, utilizing gauss integral points and a quantitative model for interval numbers to sample parameter vectors of intervals, calculating response vector value at interval parameter sample points, establishing the best square approximation in order to determine the max-minimum point matrix such that response interval vectors can be calculated; and finally, utilizing response interval vectors and safety requirement to calculate reliability in intervals and finishing structural optimization under drive of the optimizing algorithm. The method for optimizing reliability of structural noise based on the dimension-by-dimension analysis strategy has following beneficial effects: by replacing classic safety factor with interval reliability, the method echoes the fine development trend of optimizing structural noise; conservativeness of a conventional optimizing method is effectively avoided; and the method has a broad application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
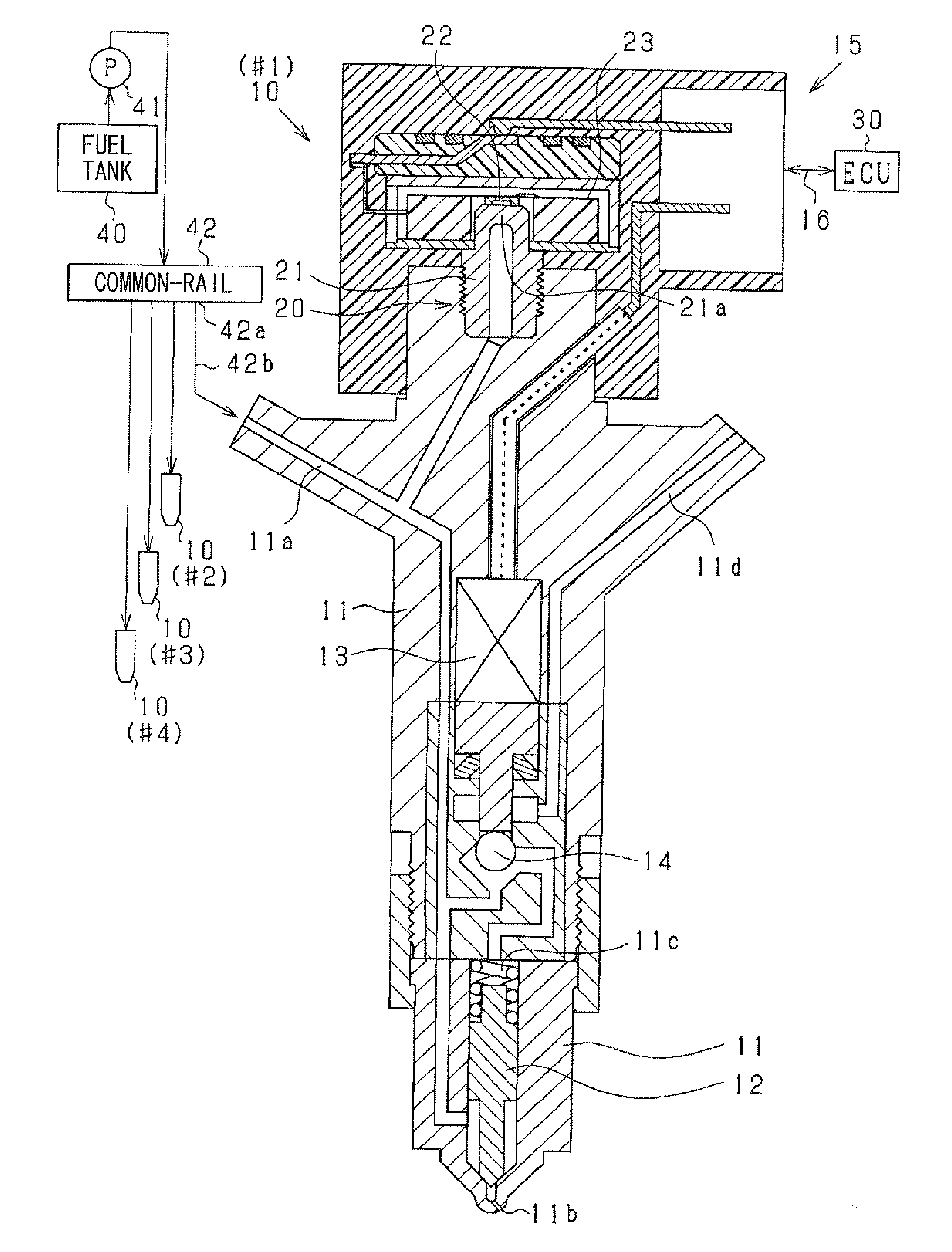
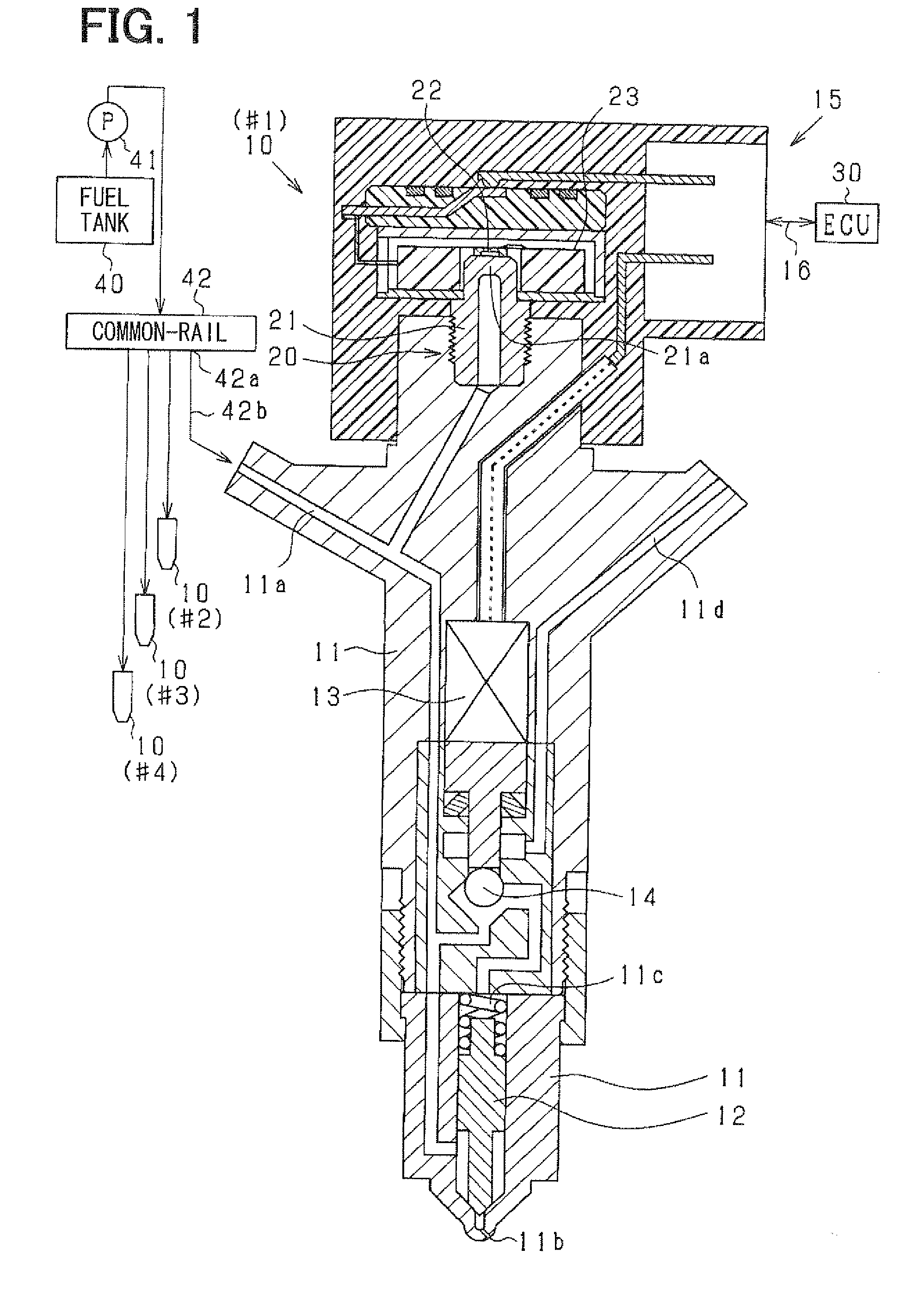
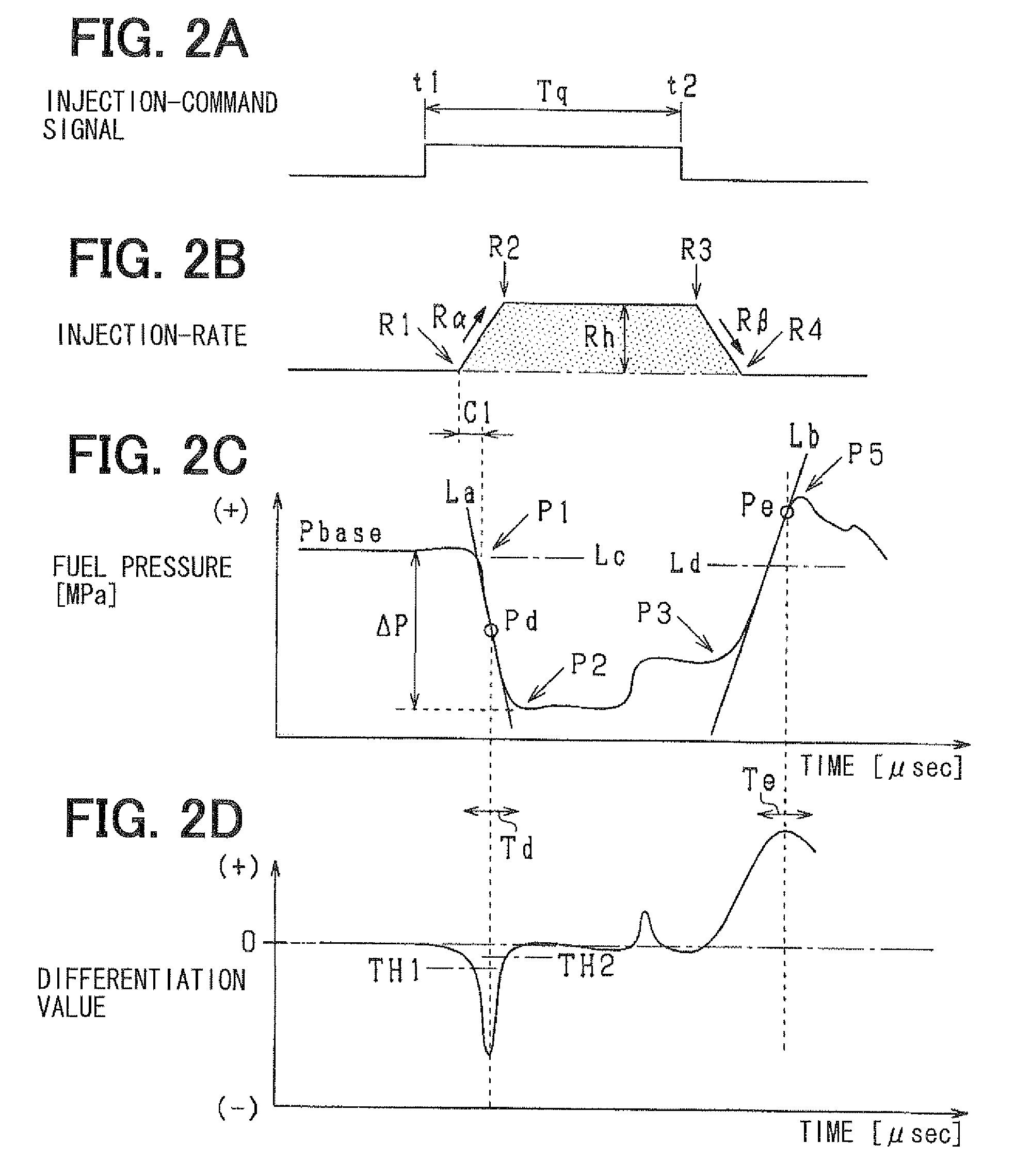
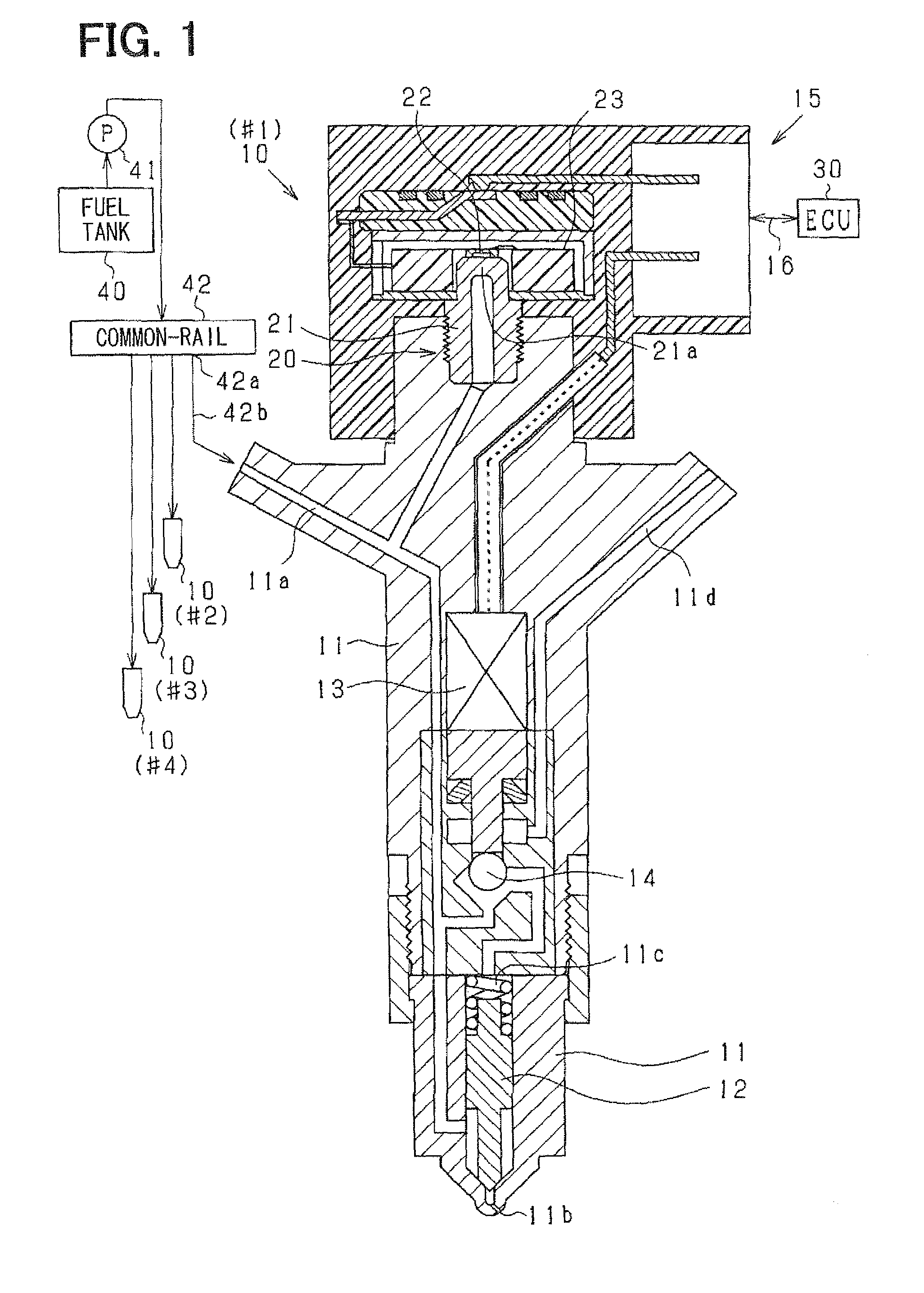
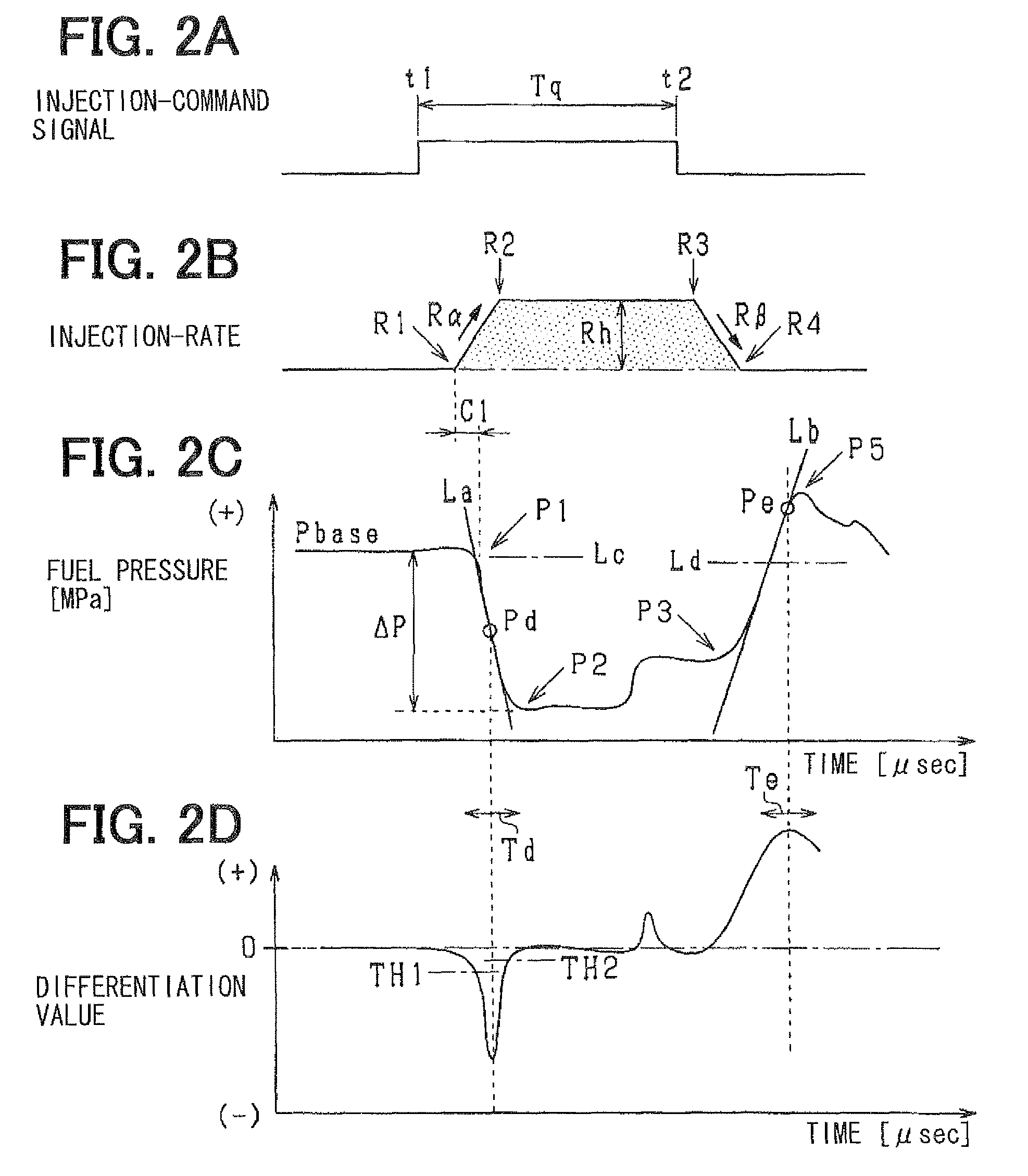
Fuel-injection condition detector
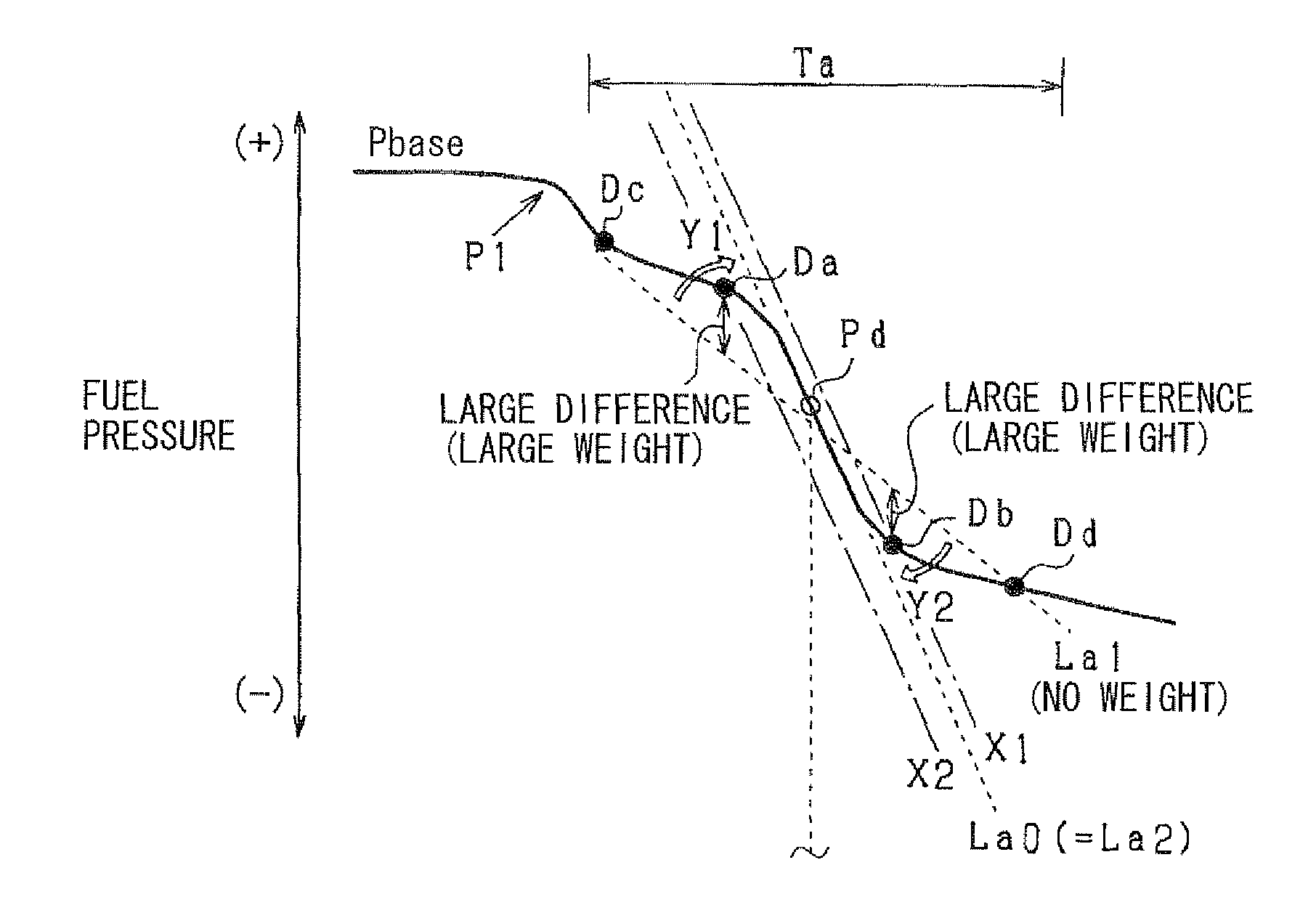
ActiveUS20120072134A1High correlationImprove accuracyInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlEngineeringFuel injection
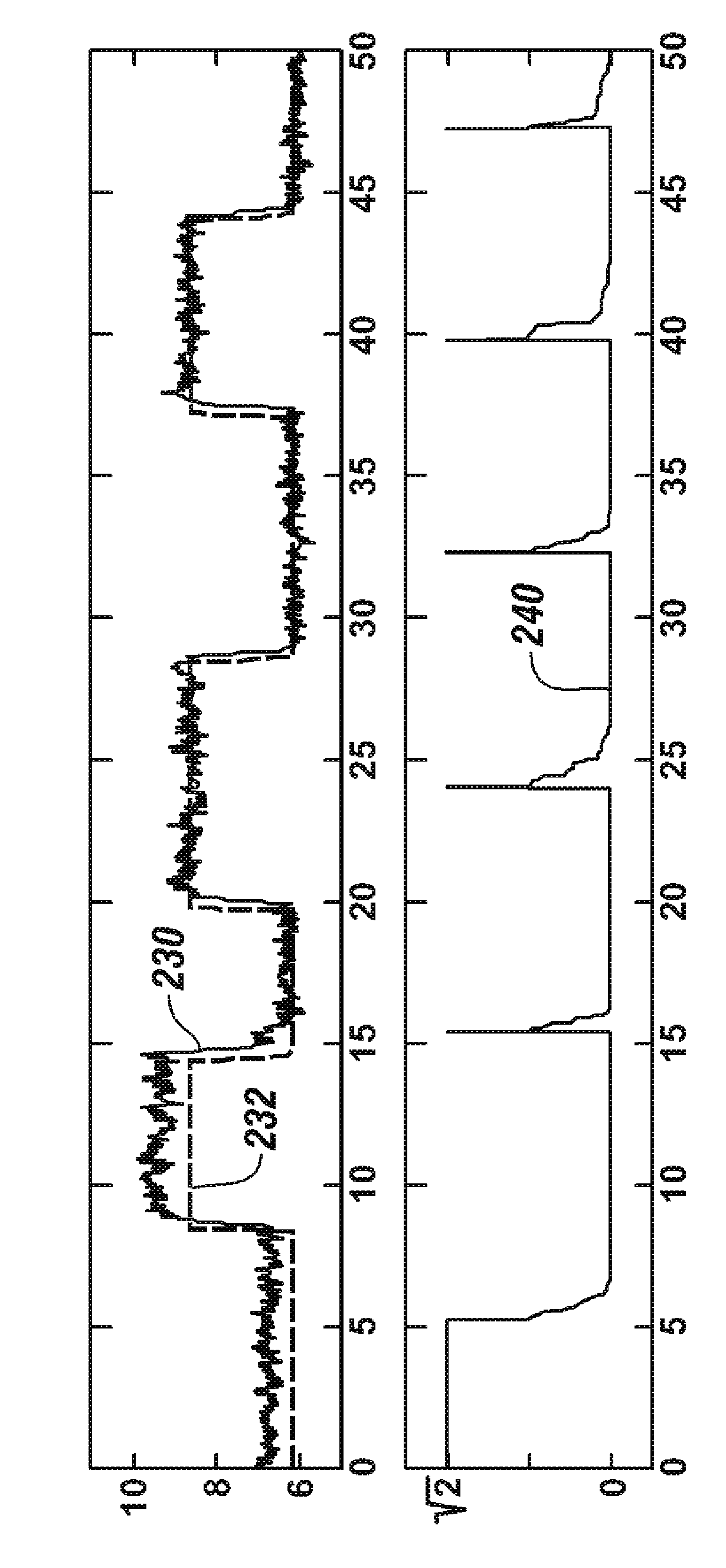
A fuel-injection condition detector includes a first approximate portion which approximates a plurality of fuel pressure values representing the descent pressure waveform or the ascent pressure waveform into a least-squares approximate line by least-squares method; and a weighting portion which applies a weight to the fuel pressure value. The weight is set greater as a difference between the fuel pressure and the least-squares approximate line is larger. Then, the weighted values are approximated into a weighted approximate line by the least-squares method.
Owner:DENSO CORP
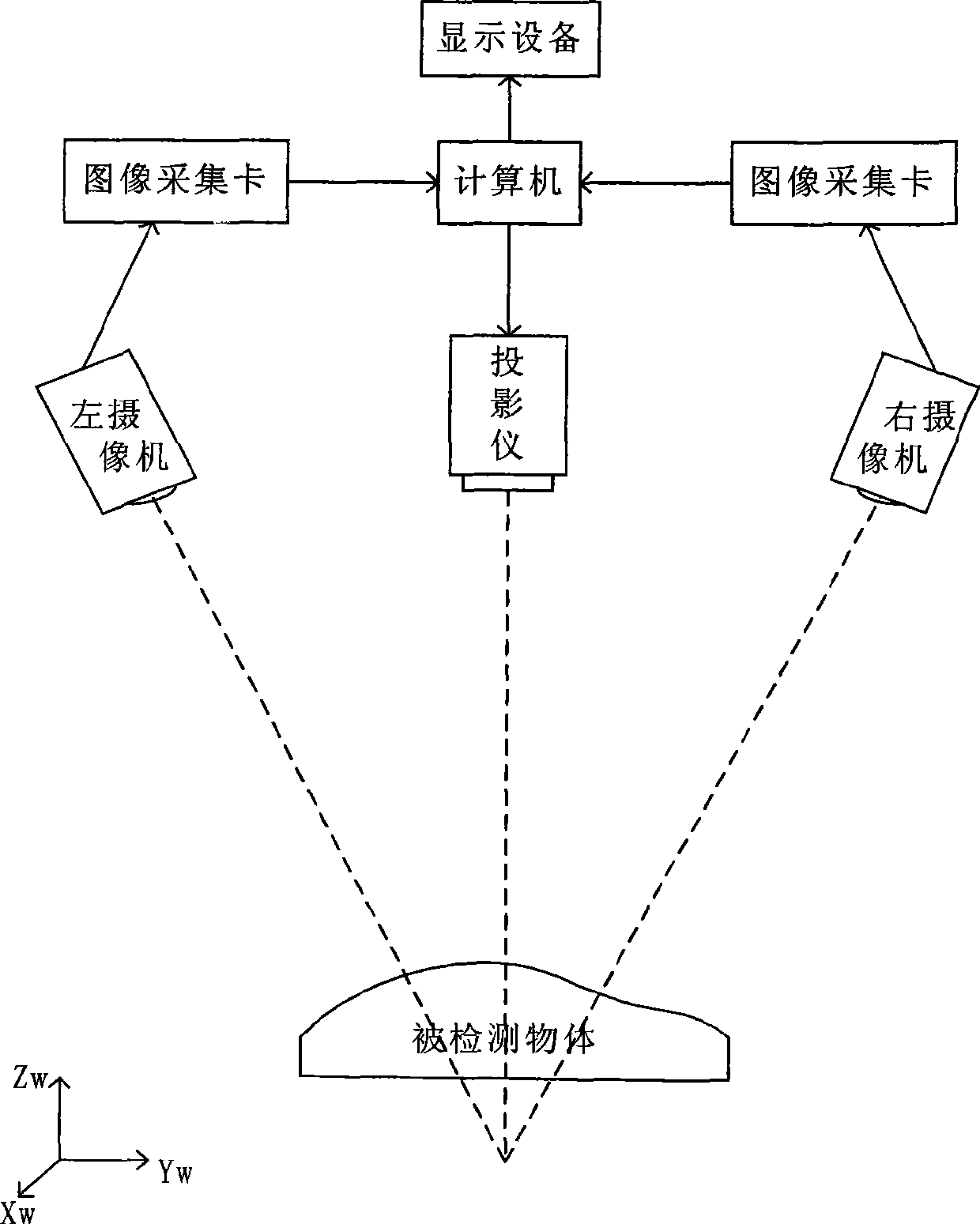
Phase nonlinear error compensation method in surface structured light three-dimensional imaging technology
InactiveCN113607087AProjection depth of field is smallGood projection brightnessUsing optical meansComputational physicsPhase shifting algorithm
The invention discloses a phase nonlinear error compensation method in a surface structured light three-dimensional imaging technology. The method comprises the following steps that: a four-step phase shift algorithm is employed to obtain phase information, and the phase information is substituted into a ratio of second harmonic to first harmonic, and a higher harmonic component ratio containing a gamma value is obtained; a harmonic component is obtained according to discrete Fourier transform, the gamma value is generally between 0 and 3, the gamma value which is not equal to 1 is pre-coded into a fringe image, a modulated harmonic component is obtained, and the pre-modulated gamma value of each pixel in the fringe image projected by a projector is calculated; and the pre-modulated gamma value obtained by calculation and the reflectivity are loaded into a projection fringe algorithm of the projector, and a camera and projector gray value modeling and least square approximation technology are utilized to obtain the accurate gamma value of each pixel in the fringe image projected by the projector, and the original fringe image of the projector is corrected through the accurate gamma value. According to the method of the invention, the error of the image collected by a camera can be greatly reduced.
Owner:苏州瑞威盛科技有限公司
Information processing apparatus and system using pixel data
InactiveUS7409074B2Television system detailsImage enhancementInformation processingImaging processing
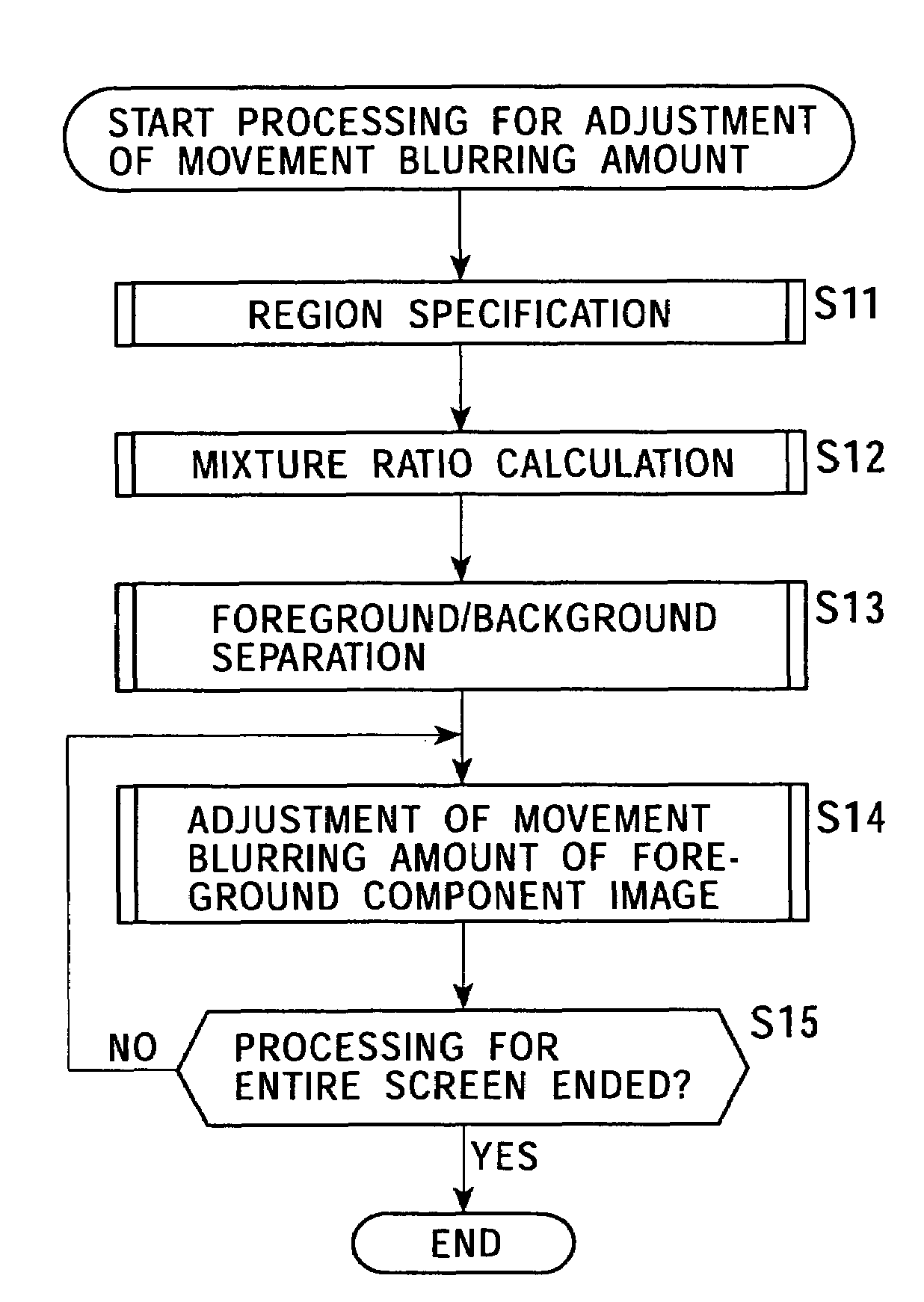
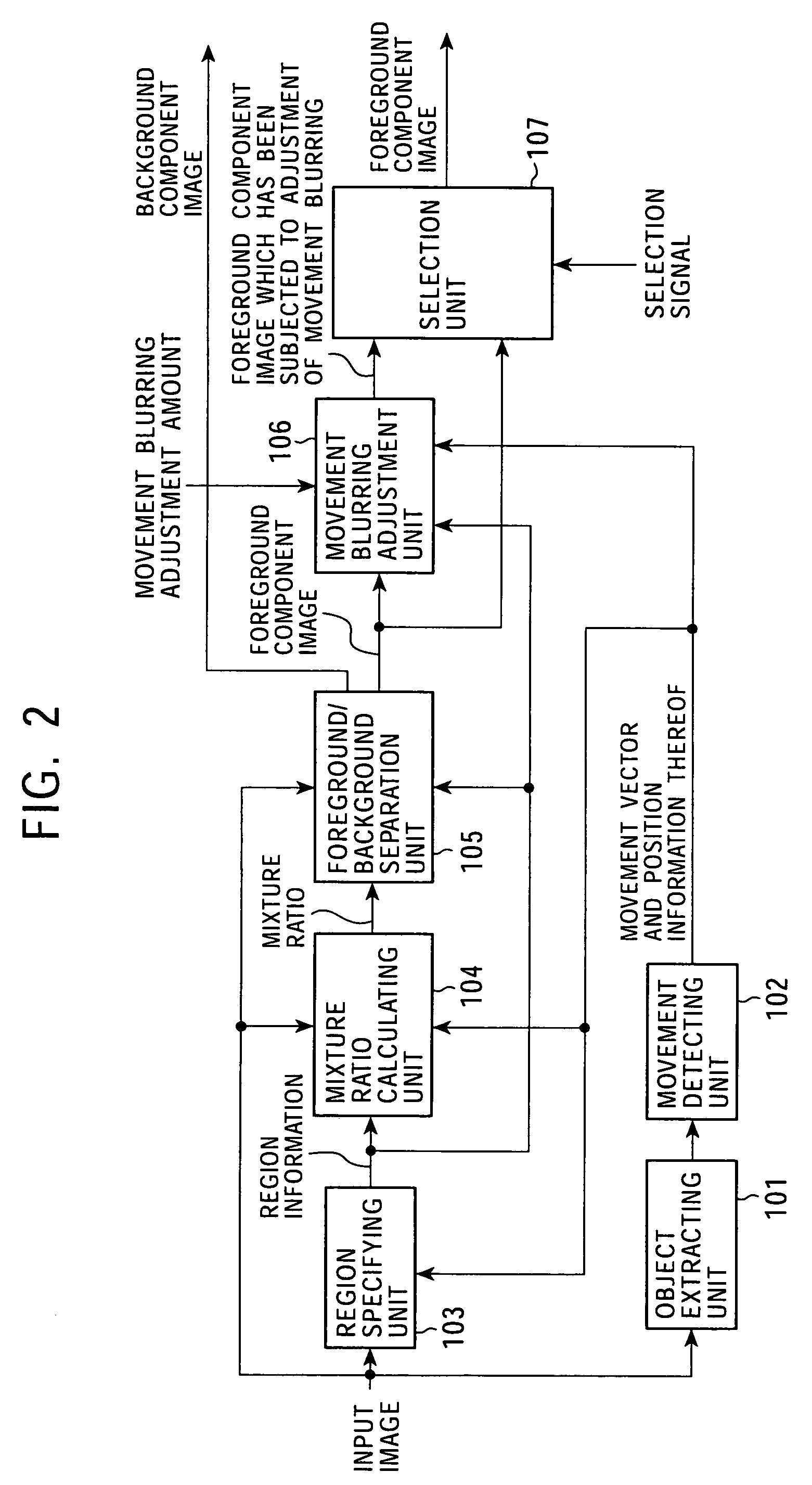
The present invention relates to an image processing device enabling detection of a mixture ratio indicating the state of mixture between multiple objects. A contour region information generating unit 421 and a normal equation generating unit 422 extracts contour region pixel data within a frame of interest positioned at a contour region with approximately a same mixture ratio, extracts corresponding pixel data from a frame different to the frame of interest, extracting background pixel data corresponding to the contour region pixel data or the corresponding pixel data, and generating an equation wherein the mixture ratio is an unknown number, based on region specifying information specifying a non-mixed region made up of a foreground region and background region and a mixed region. A least square approximation unit 423 detects the mixture ratio by solving the equation. The present invention can be applied to signals processing devices for processing image signals.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fuel-injection condition detector
ActiveUS8849592B2Improve accuracyHigh precision estimationElectrical controlFlow propertiesEngineeringFuel injection
A fuel-injection condition detector includes a first approximate portion which approximates a plurality of fuel pressure values representing the descent pressure waveform or the ascent pressure waveform into a least-squares approximate line by least-squares method; and a weighting portion which applies a weight to the fuel pressure value. The weight is set greater as a difference between the fuel pressure and the least-squares approximate line is larger. Then, the weighted values are approximated into a weighted approximate line by the least-squares method.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Full-automatic lensmeter
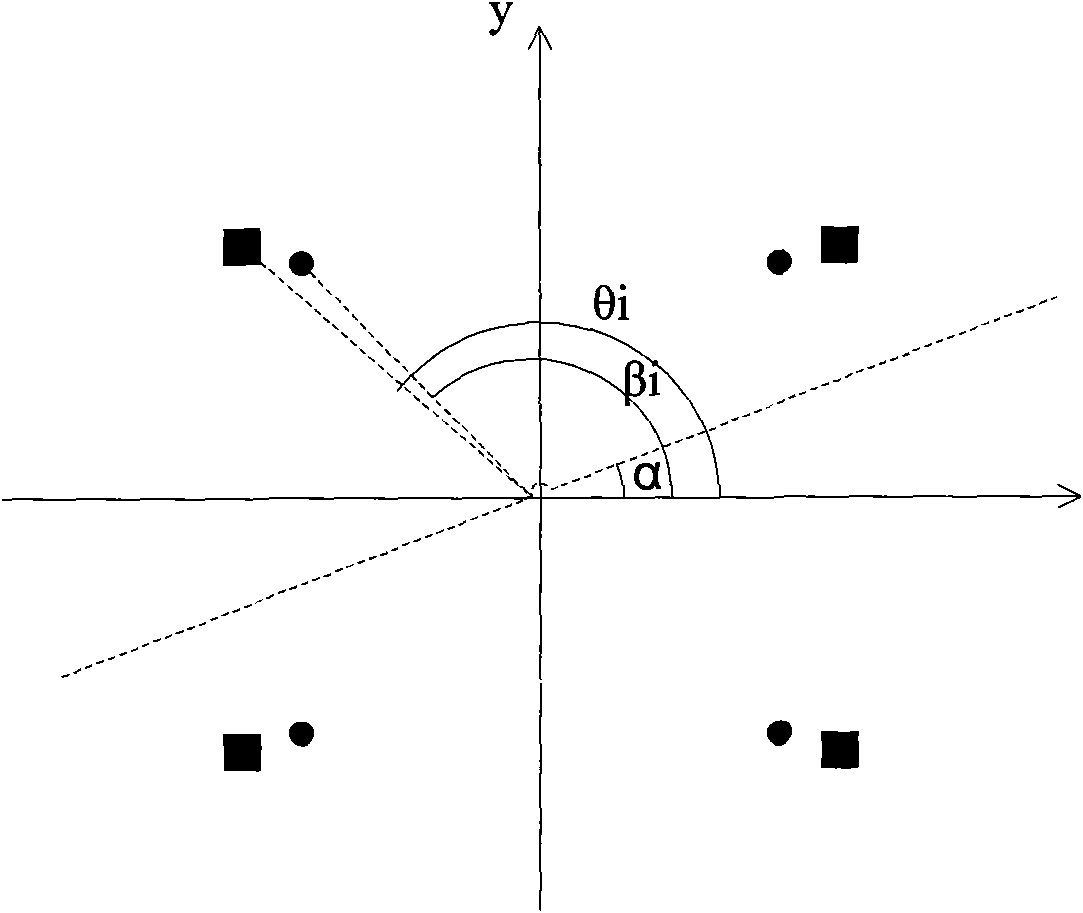
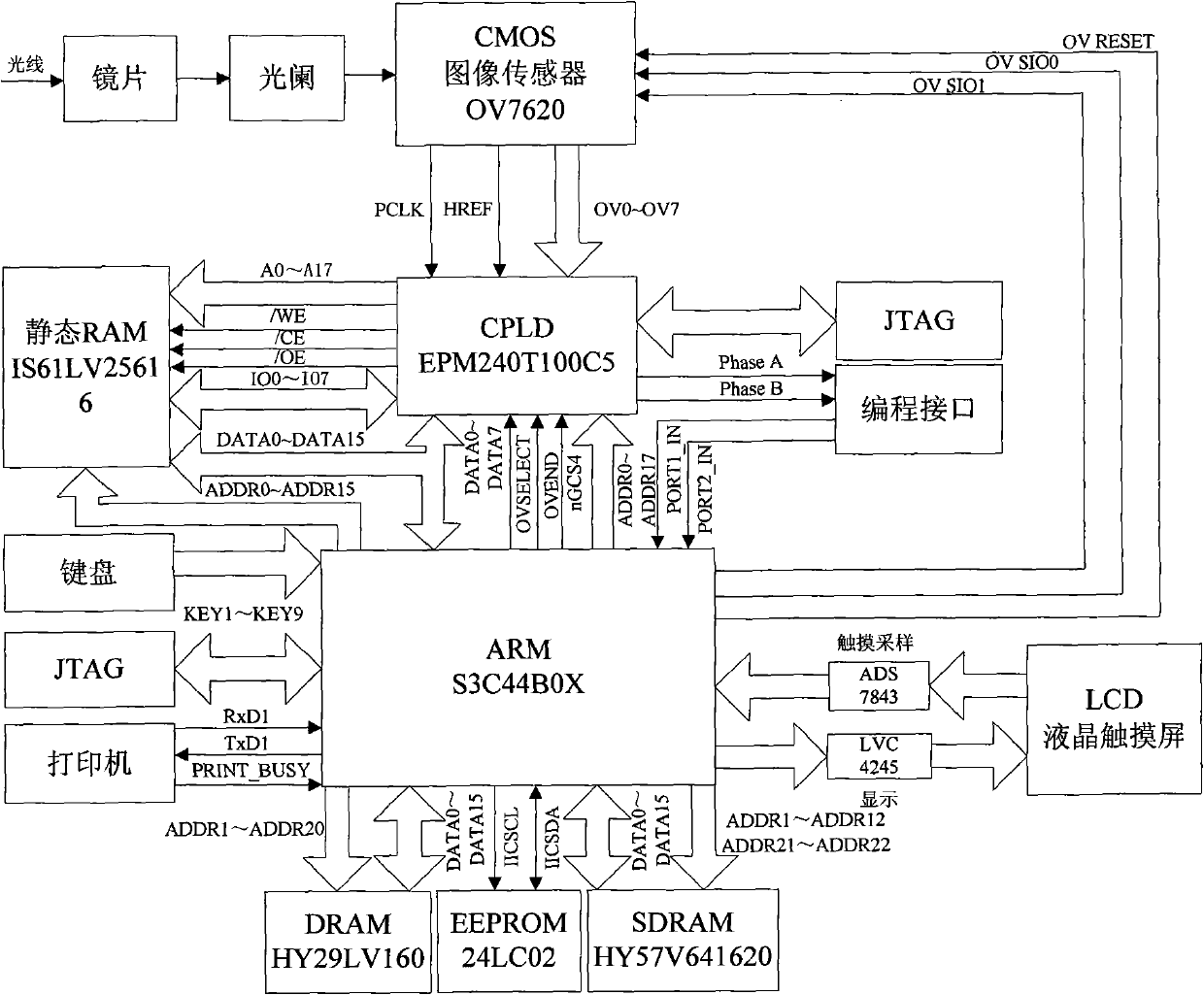
InactiveCN101639399AEasy to operateHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesLight spotAngular degrees
The invention relates to a full-automatic lensmeter which comprises an image sensor, a CPLD module and an ARM module, wherein the image sensor is used for collecting optical signals passing through alens to be detected, and the CPLD module and the ARM module are used for processing and controlling data. Coordinates of an initial light spot position are set to be (xi, yi), a distance to the centerof a circle is R, and an included angle formed by a connection line with the origin of the coordinates and the x axis is beta; after a lens is put, the coordinates of the light spot position is(*i, *i), the distance to the center of the circle is r, and the included angle formed by the connection line with the origin of the coordinates and the x axis is theta. The included angle of abase line of a dispersing lens and the x axis is alpha, and after the coordinates of the two pairs of the coordinates shifted into a coordinate system which uses the base line as the x axis are respectively (xi', yi') and (*i', *i'), wherein the subscripts i of the variables respectively represent four light spots, and all the four light spots or two light spots with the furthest distances are selected to carry out least-squares approximation so as to obtain the concave-sphere degree, the concave-cylinder degree and a base line angle. A distance x1 from the rear vertex of the lens to a diaphragm and a distance x2 from the diaphragm to an area array of the CCD image sensor are substituted into a lens vertex dioptrie expression calculated by the definitions of an index path and vertex dioptrie so as to obtain a vertex dioptrie value. The invention has convenient operation and high measuring precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Distributed batch estimation data fusion method of polynomial parameterized likelihood function
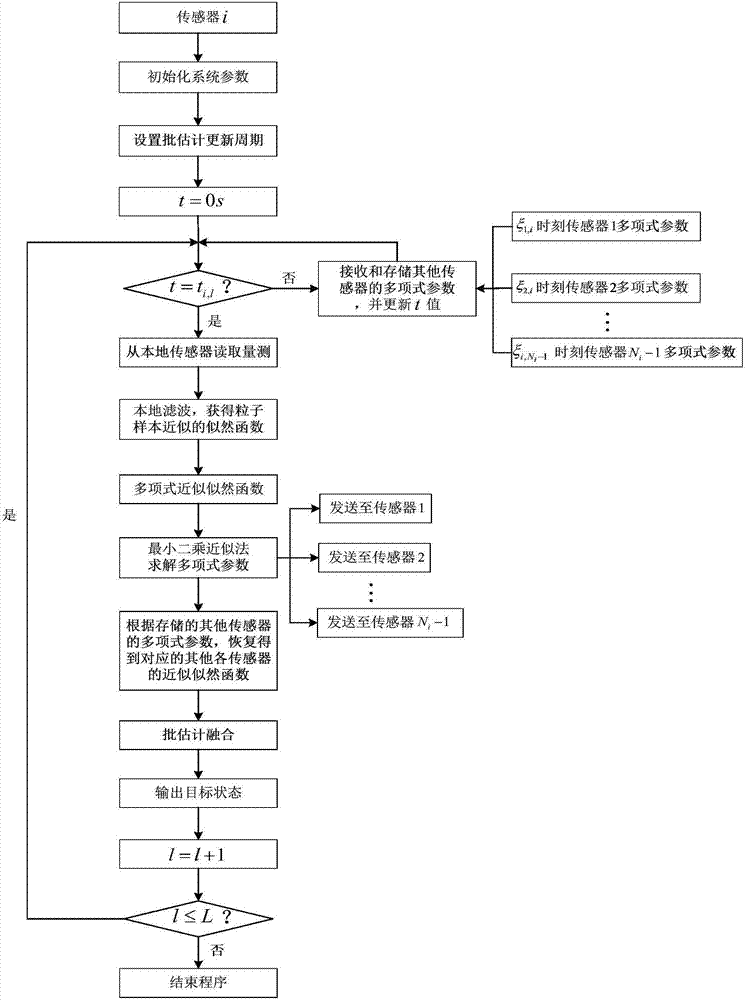
ActiveCN106973364ASolve problems that are difficult to integrateEasy to operateParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesNODALRadar
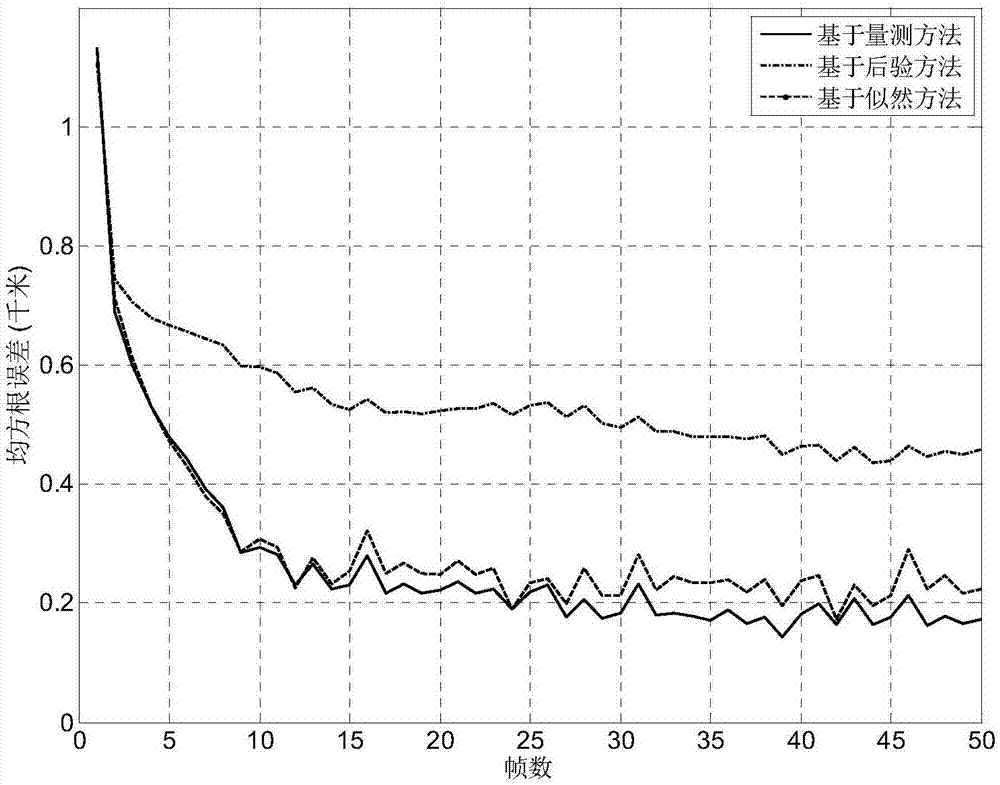
The invention discloses a distributed batch estimation data fusion method of polynomial parameterized likelihood functions. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, setting a batch estimation update cycle according to the local radar sampling rate or the actual demands for data update, obtaining approximate local likelihood functions of particle samples in multiple sensors by using a particle filter algorithm, and then solving to obtain polynomial parameters of the local sensor through a least square approximation method, implementing communication interaction on the polynomial parameters between the multiple sensors, finally recovering to obtain the approximate likelihood functions of the multiple sensors approximate to the particle samples by using the polynomial parameters, and fusing the approximate likelihood functions of the multiple sensors by adopting a batch estimation fusion method. By adopting the distributed batch estimation data fusion method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the asynchronous data is difficult to fuse due to different sampling rate and initial deviation in an asynchronous sensor network can be effectively solved; compared with a method for directly transmitting the primary measurement data between multiple sensor nodes, the communication traffic for transmitting the polynomial parameters can be lower; and the application has a higher accuracy than that of a posterior method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method to complete a learning cycle of a recursive least squares approximation
A method to control a non-linear system includes operating a learning cycle to approximate characteristics of the system and, once the learning cycle is complete, operating the system based upon the characteristics. The learning cycle includes monitoring operation of the system, approximating the characteristics of the system with a recursive least squares approximation based upon the monitored operation, comparing variance of the operation to a threshold variance, and completing the learning cycle based upon the variance exceeding the threshold variance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
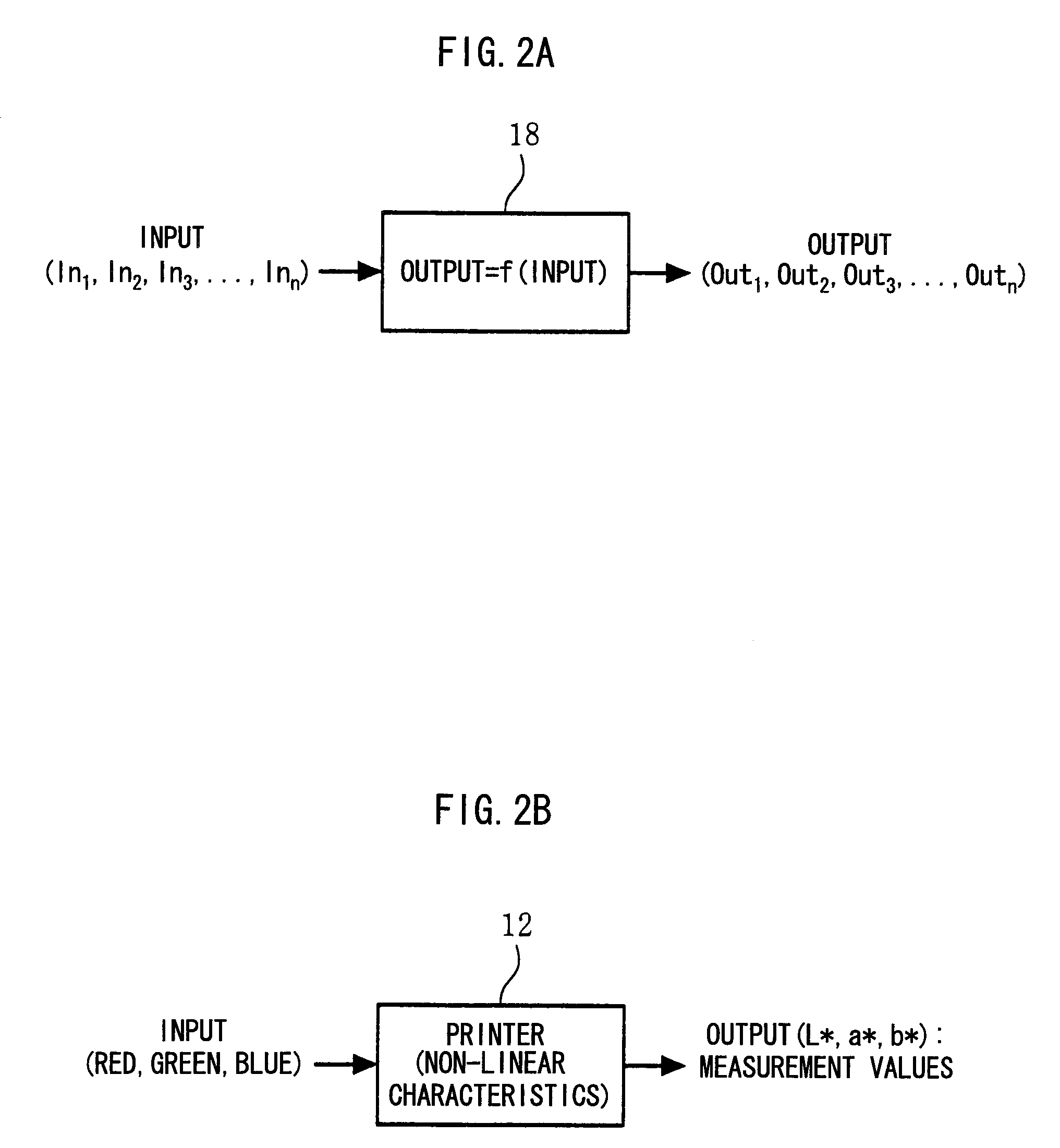
Color reproduction method
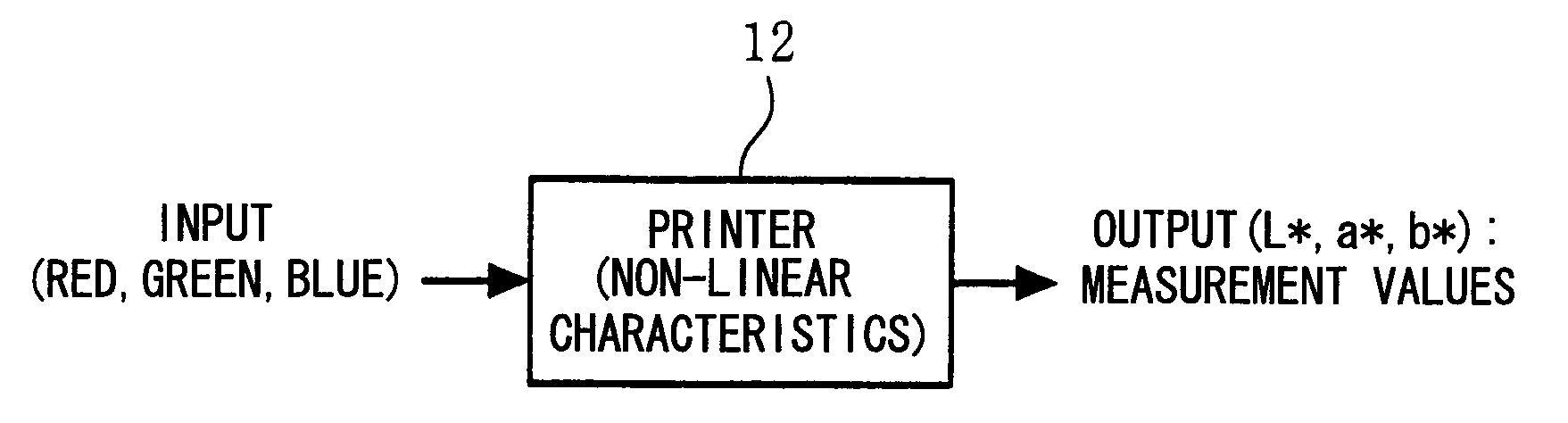
ActiveUS20100171968A1Improve accuracyShort durationDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationPoint sequencePartition of unity
A units of red {u1-uA}, B units of green {v1-vB} and C units of blue {w1-wC} are sampled and measurements are performed, and an interpolation equation is found from the A×B×C units of data in three-dimensions (L*, a*, b*) that are obtained. Firstly, A units of point sequence data in 3×B×C dimensions are least squares approximated for the parameters u, and Mu control points in 3×B×C dimensions are found. Then, B units of point sequence data in 3×C×Mu dimensions are least squares approximated for the parameters v, and My control points in 3×C×Mu dimensions are found. Next, C units of point sequence data in 3×Mu×Mv dimensions are least squares approximated for the parameters w, and Mw control points in 3×Mu×Mv dimensions are found. Then, output values (L*,a*,b*) corresponding to arbitrary input values (Red,Green,Blue) can be obtained by an interpolation equation according to Mu×Mv×Mw final control points in three dimensions and basis functions used in the least squares approximations.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Statistical analysis system applying linear regression method
The invention discloses a statistical analysis system applying a linear regression method. The statistical analysis system is characterized by comprising a sample receiving system, a system for processing samples to be analyzable, a system for further calculating all parameters needed by a linear regression model according to the content of the samples, and a system for manufacturing the linear regression model according to the calculation result of the step three. The conditional mean of y with a given X value is an affine function, under unusual conditions, the linear regression model can be a linear function representation with a median or other quantiles of conditional distribution of y under the condition of the given X serving as X, and like regression analysis in all forms, the focus of linear regression is put on conditional probability distribution of y with the given X value to achieve analysis. The linear regression model uses least square approximation for fitting. Estimated statistical properties generated by linear regression are easy to determine, and therefore the efficiency of statistical analysis is improved.
Owner:大连东方之星信息技术有限公司
Applying data regression and pattern mining to predict future demand
ActiveUS8700607B2Digital data processing detailsKnowledge representationData processing systemExpected value of sample information
Owner:VERSATA DEV GROUP
Three-dimensional scanning point cloud compressing method
InactiveCN100495442CReduce data volumeNo loss of detail features3D modellingPoint cloudComputational physics
Owner:HAIAN COUNTY SHENLING ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE MFG +1
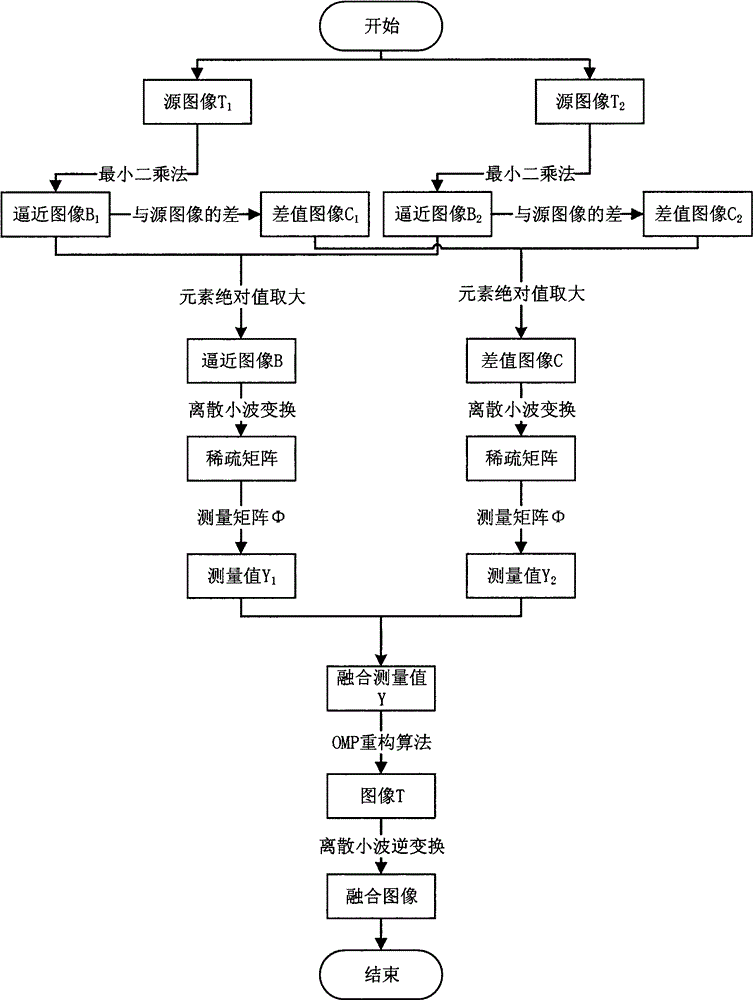
Secondary image fusion method combined with compressed sensing
The invention provides a secondary image fusion method combined with compressed sensing. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a least square approximation method is adopted to obtain an approximate image of a source image, and the difference between the source image and the approximate image is calculated to obtain a difference image; secondly, the approximate image and the difference image are fused in a spatial domain; based on fusion, a compressed sensing method is used for obtaining measured values of the approximate image and the difference image which are fused, and the measured values of the two images are fused again according to weight fusion rules to obtain a fused measured value; lastly, the fused measured value is subjected to reconstruction and inverse transformation through an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm to obtain an image subjected to secondary fusion. By means of the secondary image fusion method combined with compressed sensing, outline information and feature information of the image can be extracted, more useful information of the source image can be reserved, and therefore the definition of the image is enhanced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method and system for scattered spherical harmonic approximation
A scattered spherical harmonic (SH) approximation method is proposed for pre-computation of SH coefficients at sampling vertices of an object to be rendered. The approach sparsely populates the object with a plurality of SH sampling vertices and uses the least squares approximation to calculate the SH coefficients at any (other) arbitrary point of the object by extrapolating from the computed SH coefficients at the SH sampling vertices.
Owner:DIGITAL DOMAIN PRODN
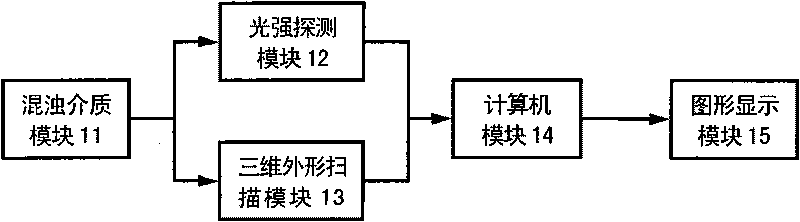
Method and device for transmitting photons in turbid medium
ActiveCN101738253AConvenient and accurate descriptionResolve transmissionPhotometryLuminous fluxDiffusion equation
The invention relates to a method and a device for transmitting photons in a turbid medium. The method comprises the following steps: arranging a plurality of discrete field nodes in the turbid medium, and solving a movable least square shape function on each field node in the turbid medium; correcting the movable least square shape function by a full transformation method to make the movable least square shape function have the property of a Dirac function; and performing interpolation by using the corrected least square shape function to acquire similar luminous flux density of the turbid medium, acquiring a diffusion equation and a weak form of a third boundary condition by a Galerkin method, acquiring and solving a matrix equation, acquiring the luminous flux density on the field node in the turbid medium, and further acquiring the luminous flux density of any point in the turbid medium by an interpolation method. The method and the device only arrange the field nodes, and do not need any field node connecting information and unit information so as to avoid a complex grid subdivision process; and by correcting the movable least square similar shape function, the shape function has the property of the Dirac function, and any boundary condition can be directly added.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
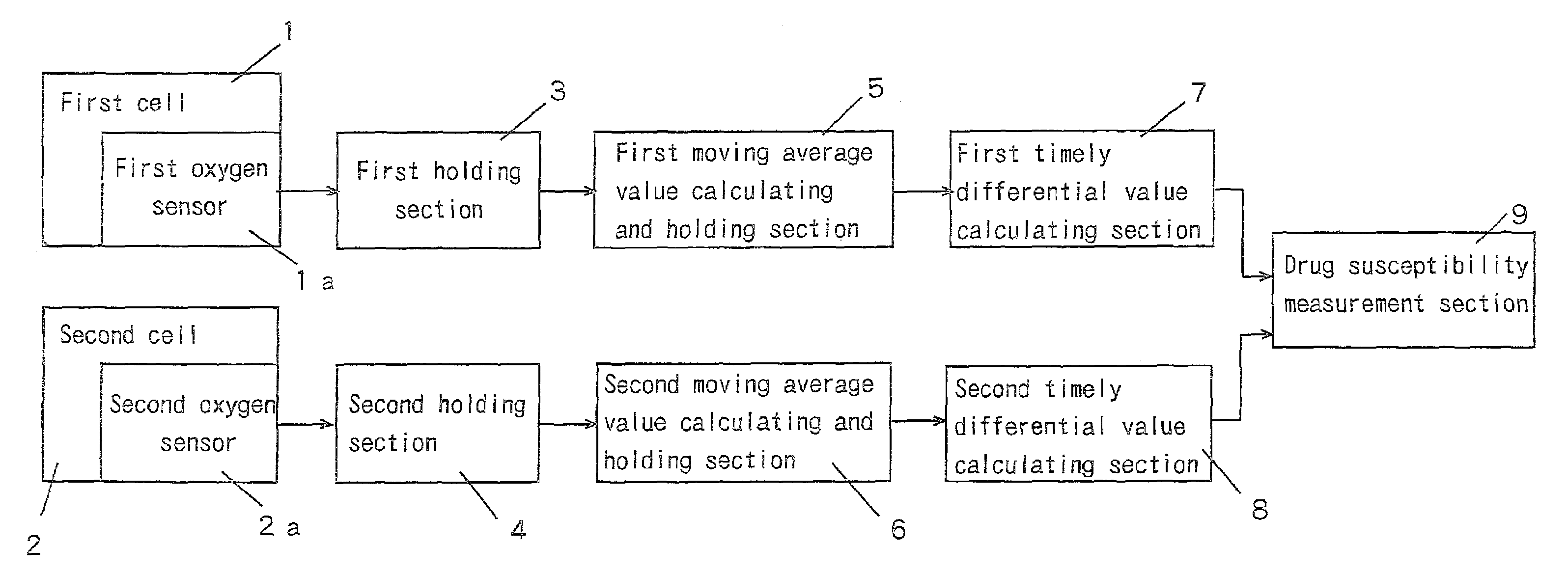
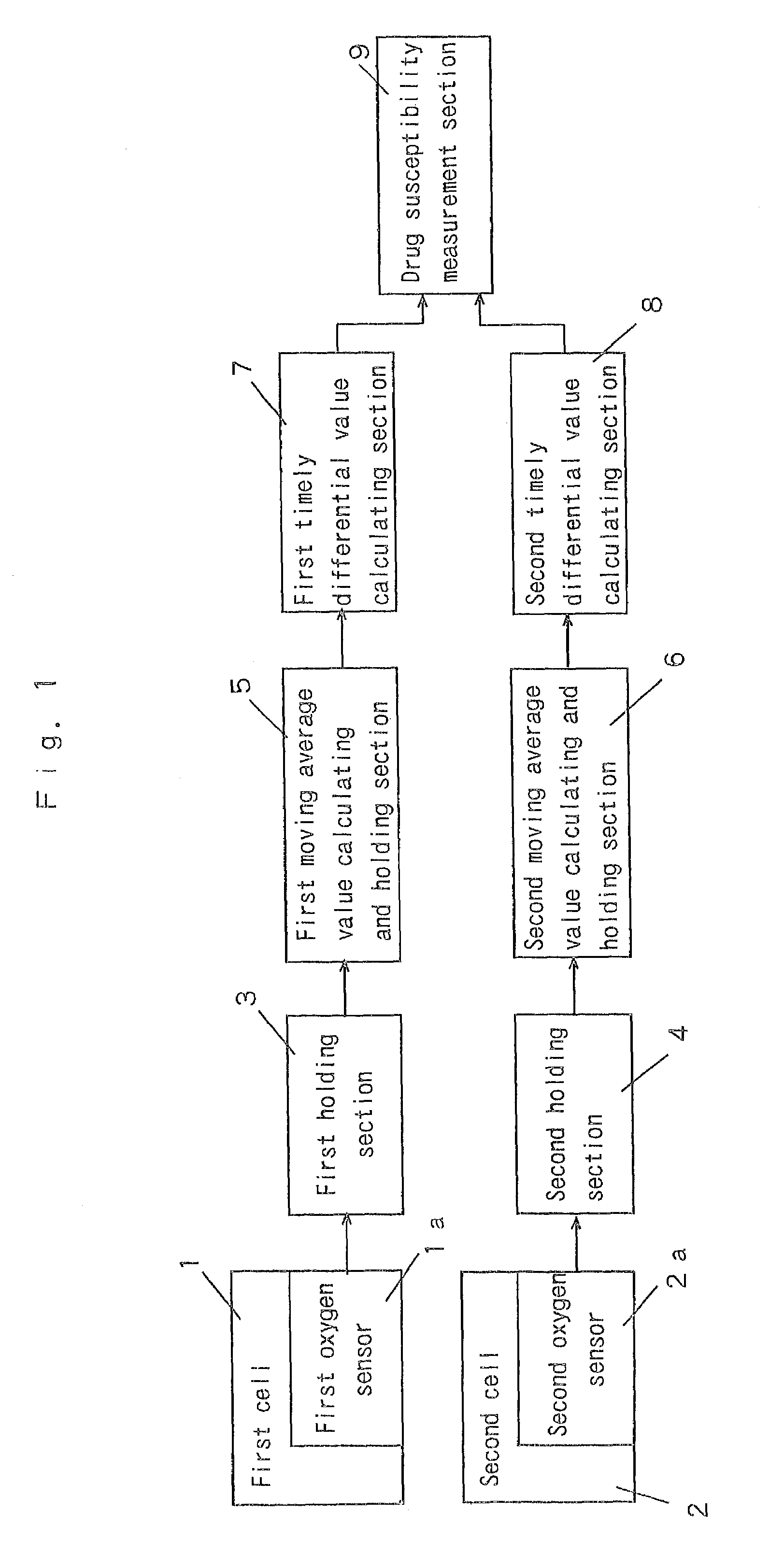
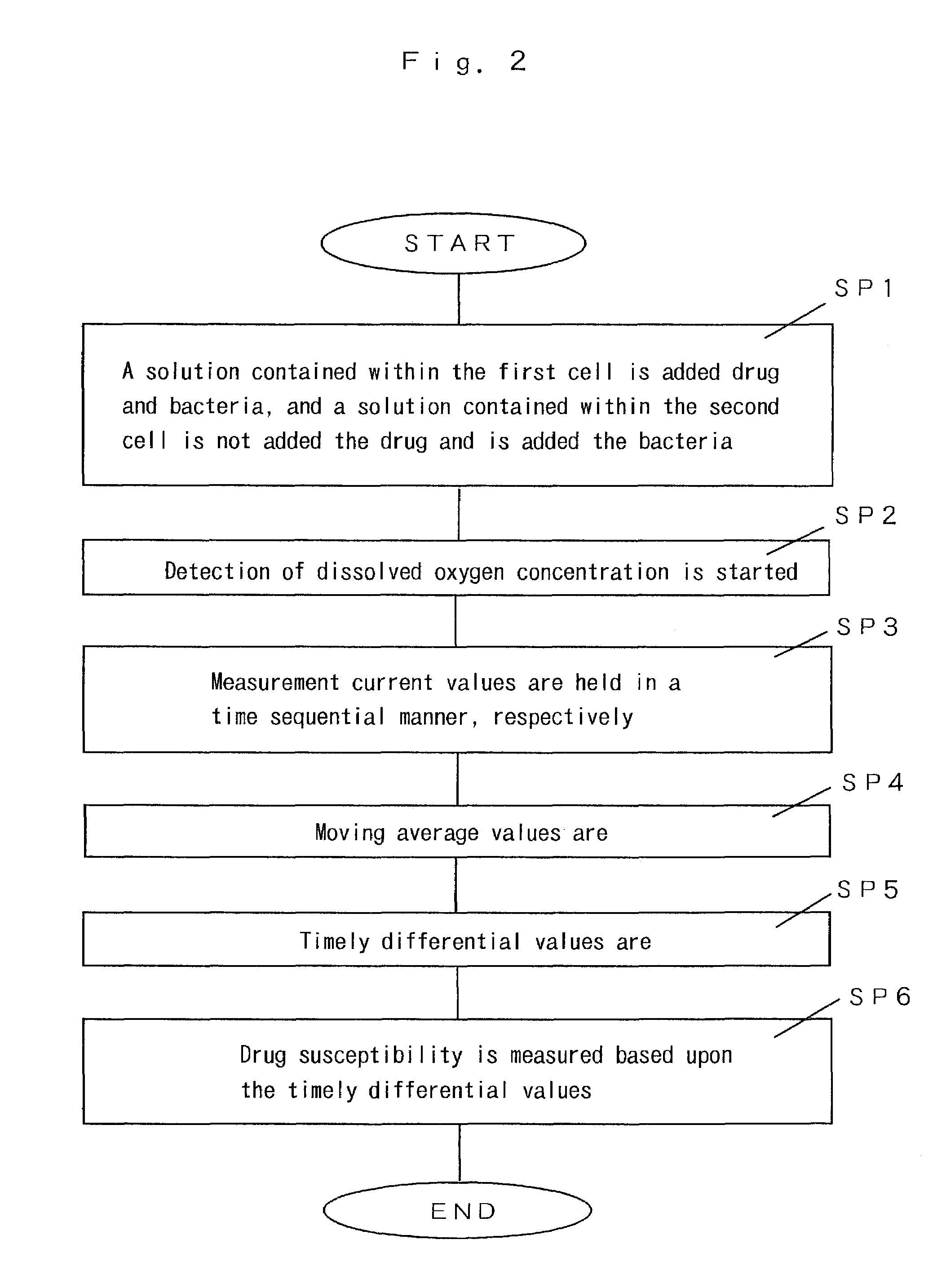
Drug susceptibility measurement method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7081353B2High measurement accuracyShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMoving averageMedicine
A method and apparatus wherein measurement current values output from a first oxygen sensor and a second oxygen sensor are time sequentially measured. Each moving average value is calculated from each sequential measurement current value. Each time differential value is calculated from the pair of each calculated moving average values, by least squares approximation. Then, drug susceptibility is measured based upon each calculated time differential value, so that drug the susceptibility measurement is performed quickly or accurately.
Owner:JIKEI UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com