First-order sea clutter detection method based on least squares approximation
A least squares and detection method technology, applied in the field of high-frequency ground wave radar detection, can solve the problems of inaccurate Bragg peak position and high false alarm rate, reduce interference such as spectrum splitting and high-frequency noise, improve accuracy, Solve the effect of inaccurate recognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0025] Specific implementation mode one: as Figure 8 As shown, the first-order sea clutter detection method based on the least squares approximation includes the following steps:
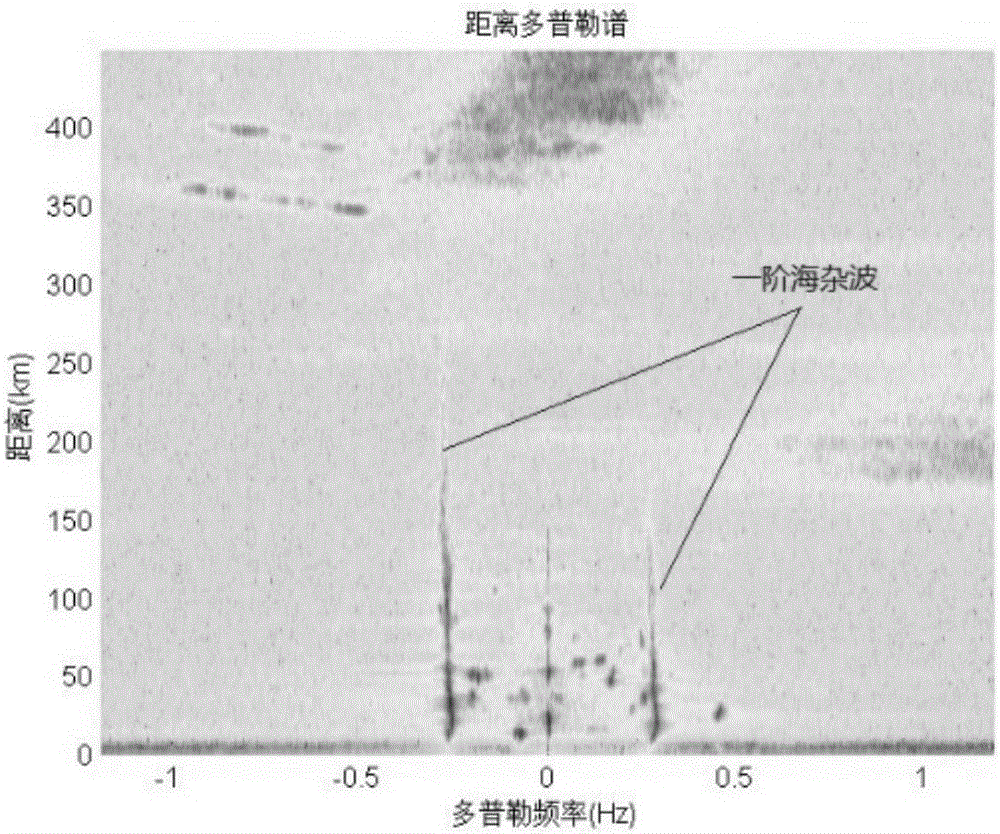
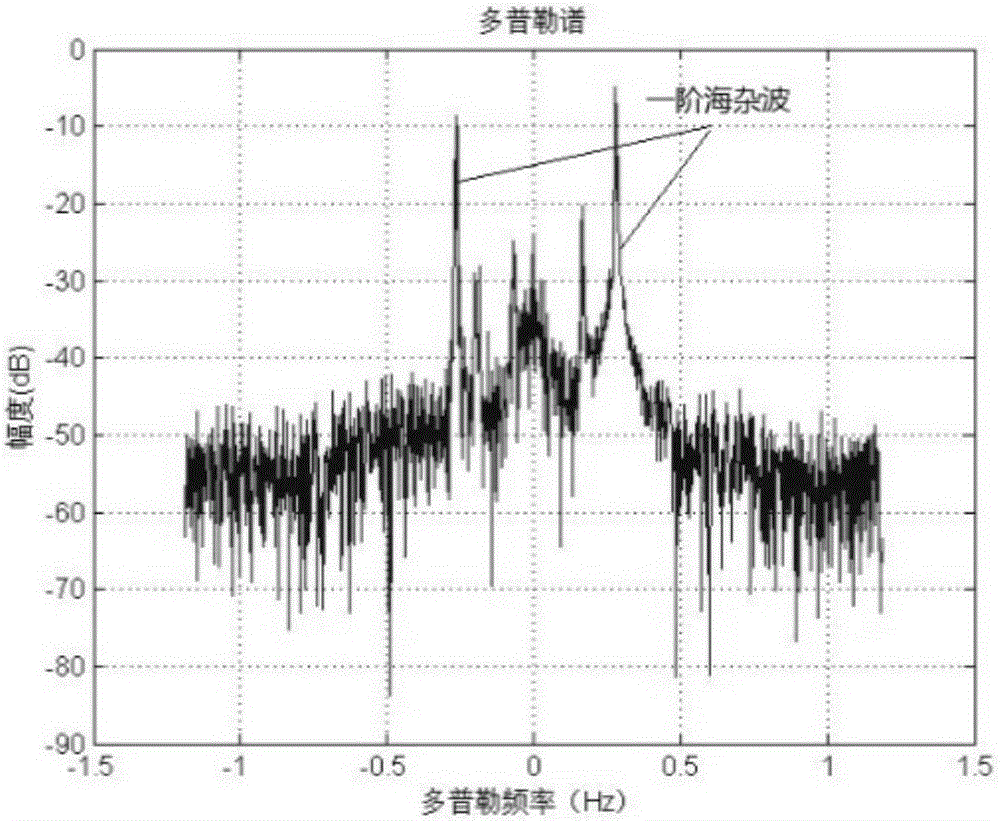
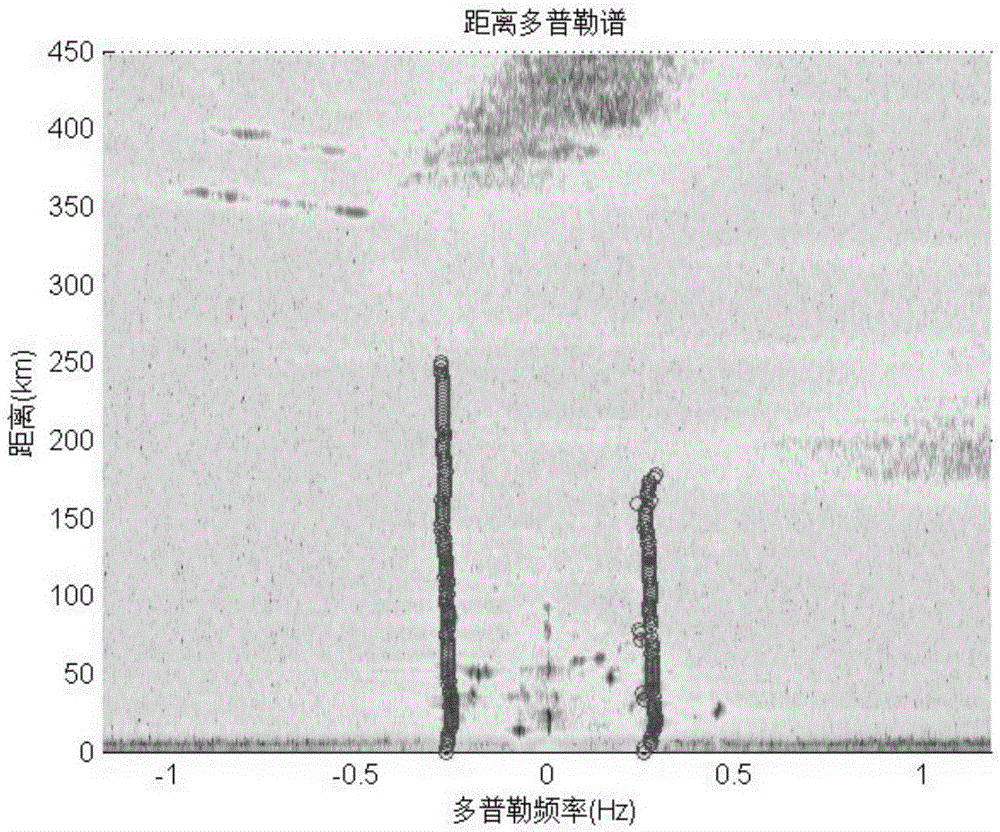
[0026] The original radar echo data undergoes two FFT operations and one DBF operation to obtain the azimuth-range-Doppler spectrum (ARD spectrum) of the echo data. The identification of the first-order sea clutter is to identify the position of the first-order Bragg peak on the ARD spectrum.
[0027] Step 1: From the operating frequency f of the radar 0 , get the theoretical Bragg frequency f B ;
[0028] Step 2: According to f obtained in step 1 B Delineate the noise area on each sea element, and obtain the threshold value of each sea element;
[0029] Step 3: According to the sea state data in the sea area detected by the radar, determine the maximum value V of the radial flow velocity of the ocean current m , and find the maximum value of the Bragg frequency offset Δf m ;
[0030] Step ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: obtain theoretical Bragg frequency f in the described step one B The formula is:
[0049] f B = ± 0.102 f 0 - - - ( 6 ) .
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0050] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is that: the threshold value obtained for each sea element in the step two is specifically:
[0051] The threshold for each sea element is N p and the sum of SNR, the N p is the base noise, and SNR (given according to the actual situation) is the set minimum signal-to-noise ratio.
[0052] In this algorithm, the Doppler frequency is in [-2f B ,2f B ] area is divided into noise area (the range of noise area can be adjusted according to the actual situation).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com