Equivalent range equation based SAR (synthetic aperture radar) ground motion target imaging method
A ground moving target and equivalent distance technology, applied in the field of radar, can solve problems such as azimuth defocusing, inaccurate focusing of moving targets, and affecting the recognition and classification of moving targets by the system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The airborne SAR-GMTI system is an advanced earth observation equipment, which has been widely used in both civil and military fields. Among them, ground moving target detection and ground moving target imaging play an important role in traffic monitoring and battlefield reconnaissance. Traditional imaging algorithms for moving targets usually make second-order approximation to the range equation of the target, but this approximation will lead to target azimuth defocus and asymmetry of azimuth side lobes. In order to solve the above problems, the present invention proposes a new imaging method for ground moving targets.
[0040]The invention is a SAR ground moving target imaging method based on the equivalent distance equation, which can be used in the airborne SAR-GMTI system working in the side-view mode. In this system, according to the motion characteristics of the radar and the target, a Observation geometry of slant range plane SAR. In this example, the carrier ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The SAR ground moving target imaging method based on the equivalent distance equation is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
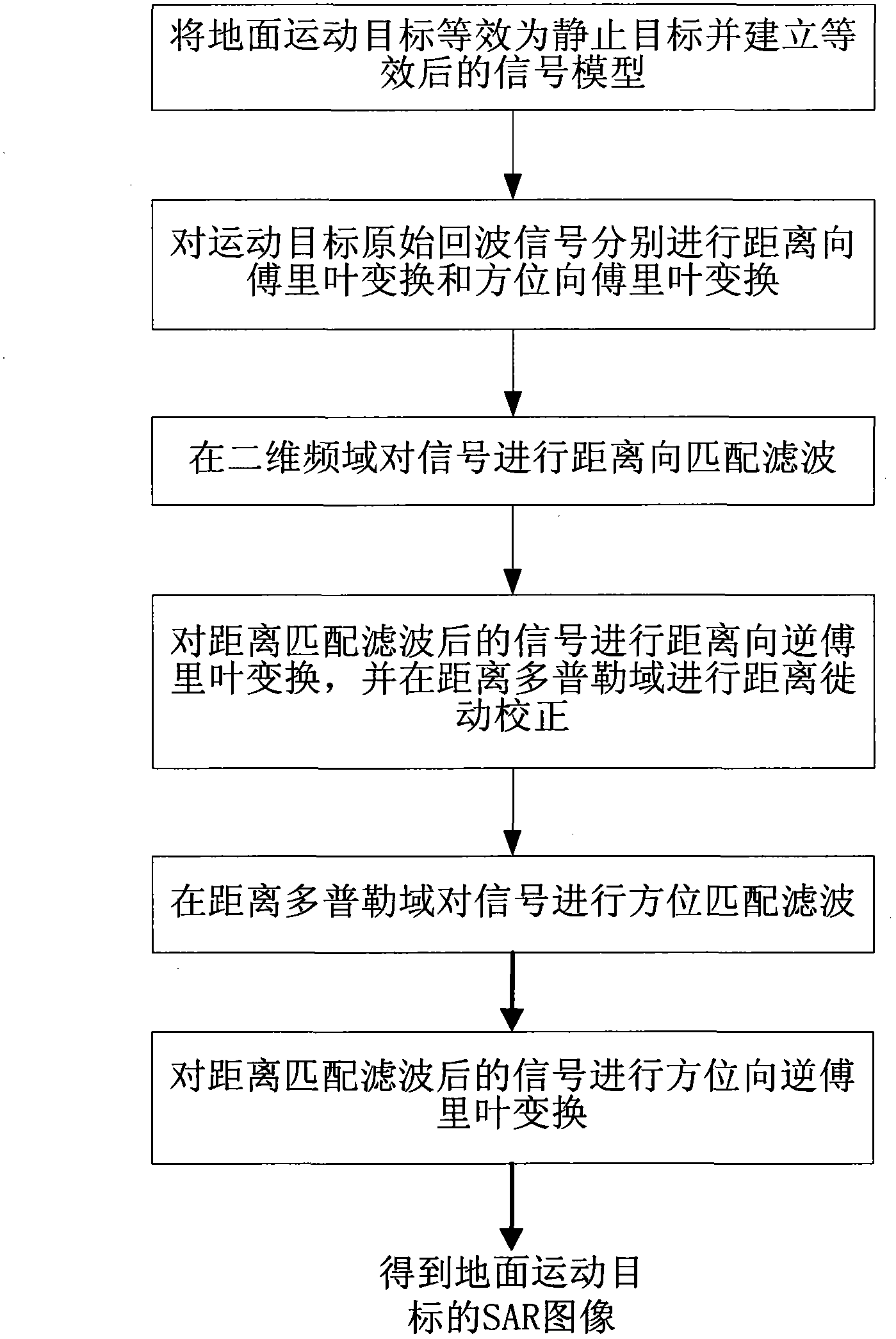
[0066] refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are further described in detail as follows:
[0067] Step 1, the ground moving target is equivalent to a stationary target and the equivalent signal model is established.
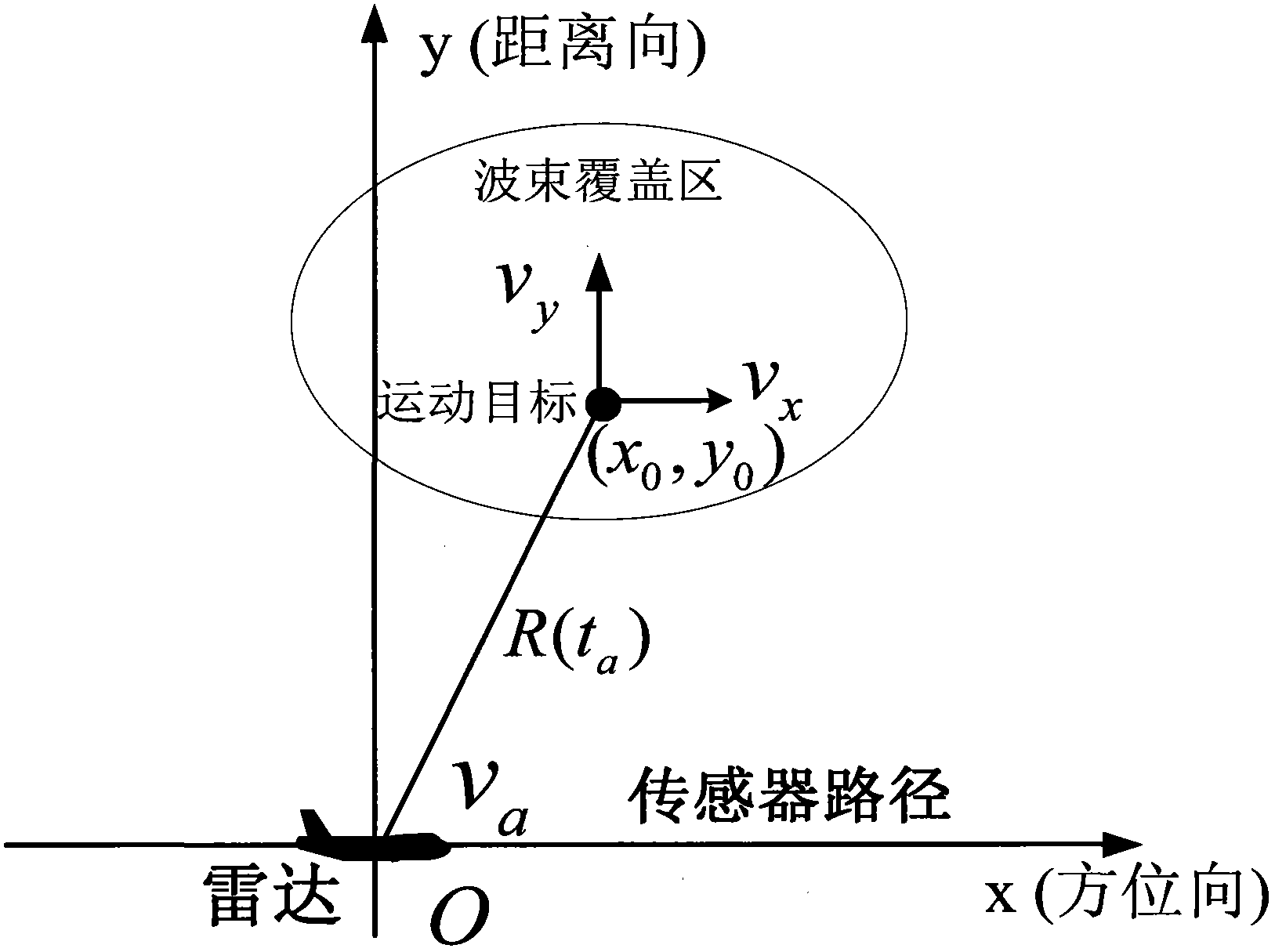
[0068] The observation geometry of slant range plane airborne SAR system is as follows: figure 2 shown. The radar works in the front and side view mode, and the speed of the radar platform is v a , the azimuth velocity of the ground moving target is v x , the range velocity projected onto the slant distance plane is v y , regardless of the target acceleration, set at t a = 0 moment, the radar is at the coordinate origin, and the target is at (x 0 ,y 0 ).
[0069] Therefore, t a The instantaneous distance from the target to the radar at any time can be expressed as:
[0070] R ...
Embodiment 3
[0116] The SAR ground moving target imaging method based on the equivalent distance equation is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2.
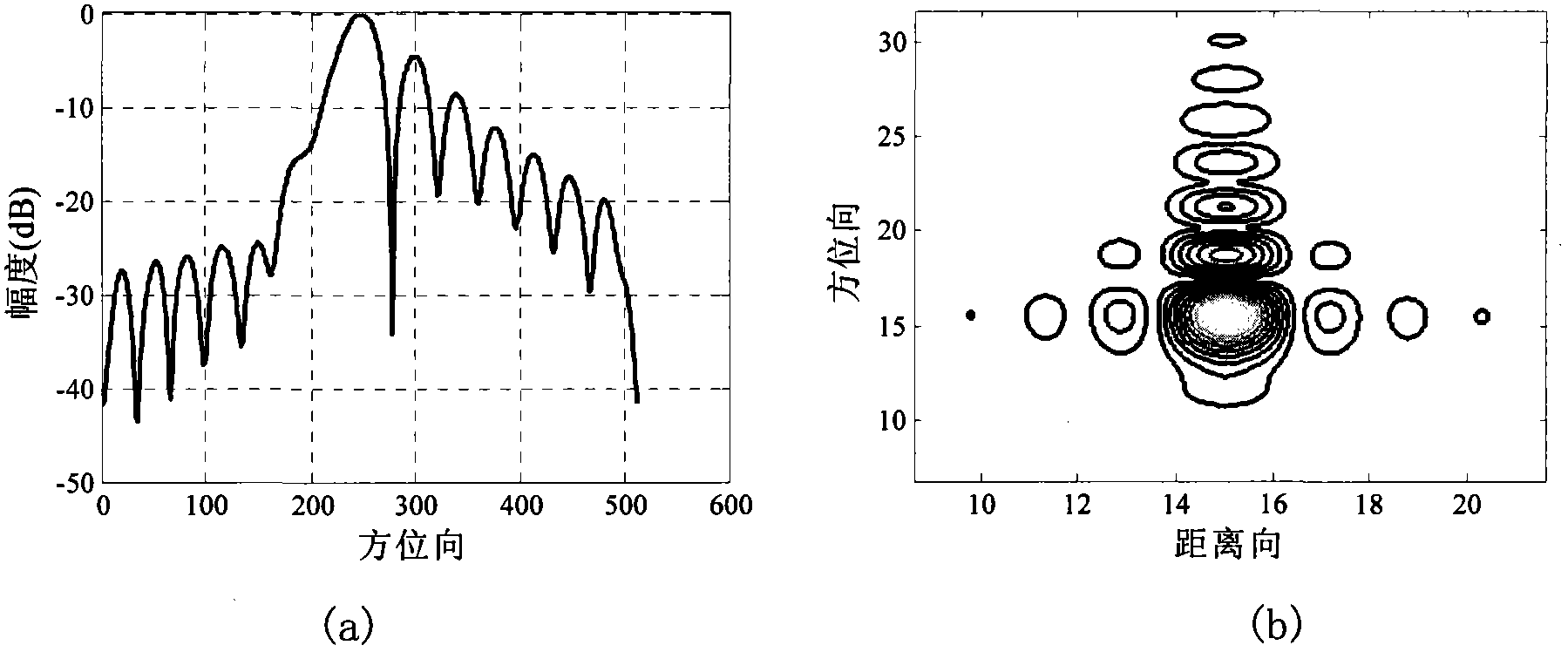
[0117] Simulation 1, the imaging simulation of ground moving targets based on the second-order Taylor approximation in the prior art.
[0118] The parameters of the SAR system are shown in Table 1, the target is located in the center of the scene, v x =5m / s, v y = 2m / s. The simulation considers that the target motion parameters are known. image 3 The literature [S.Q.Zhu, G.S.Liao, Y.Qu, Z.G.Zhou, and X.Y.Liu, "Ground moving targets imaging algorithm for synthetic aperture radar", IEEE Trans.Geosci.Remote Sens., vol.49, no.1 , pp.462-477, Jan.2011.] is a simulation result diagram of the ground moving target imaging method based on the second-order Taylor approximation, where: image 3 (a) is an azimuth plan view, image 3 (b) is the enlarged target contour map. In order to further analyze the focusing performance, Table 2 gives the image...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com