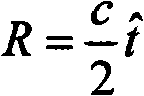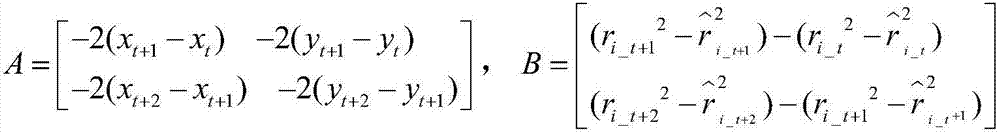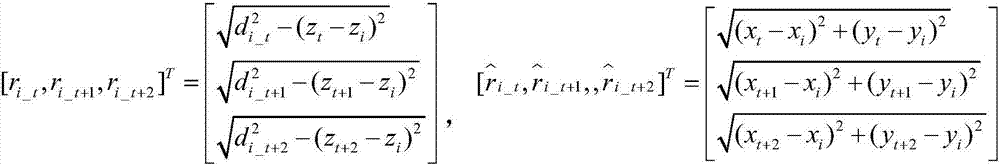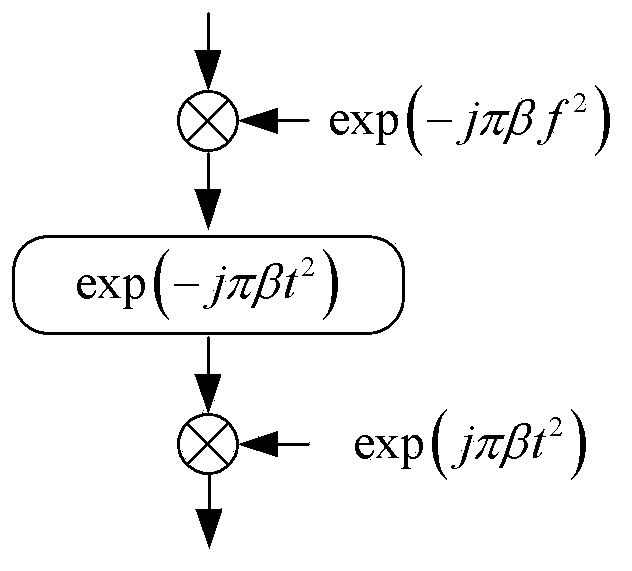Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
163 results about "Slant range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
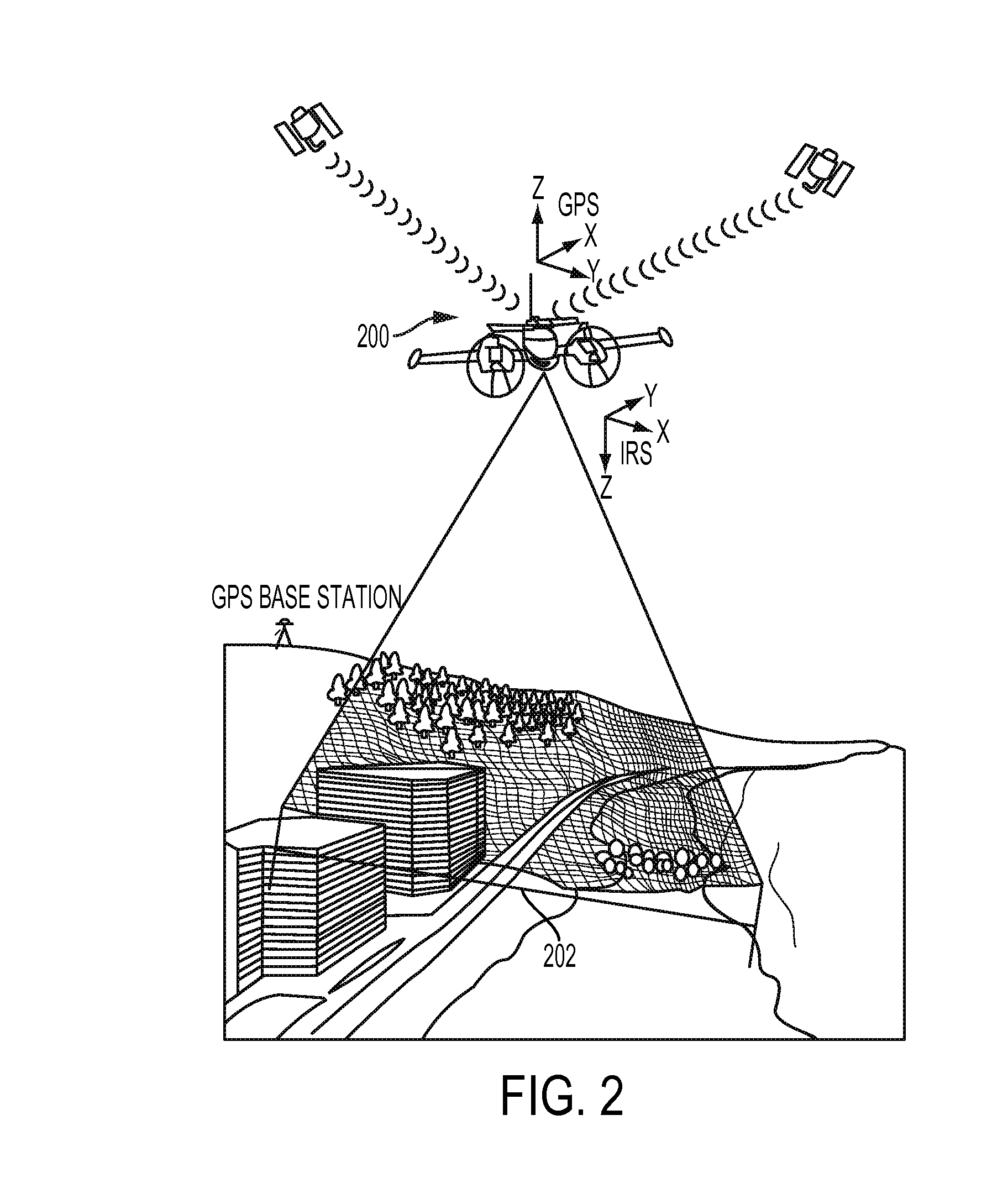
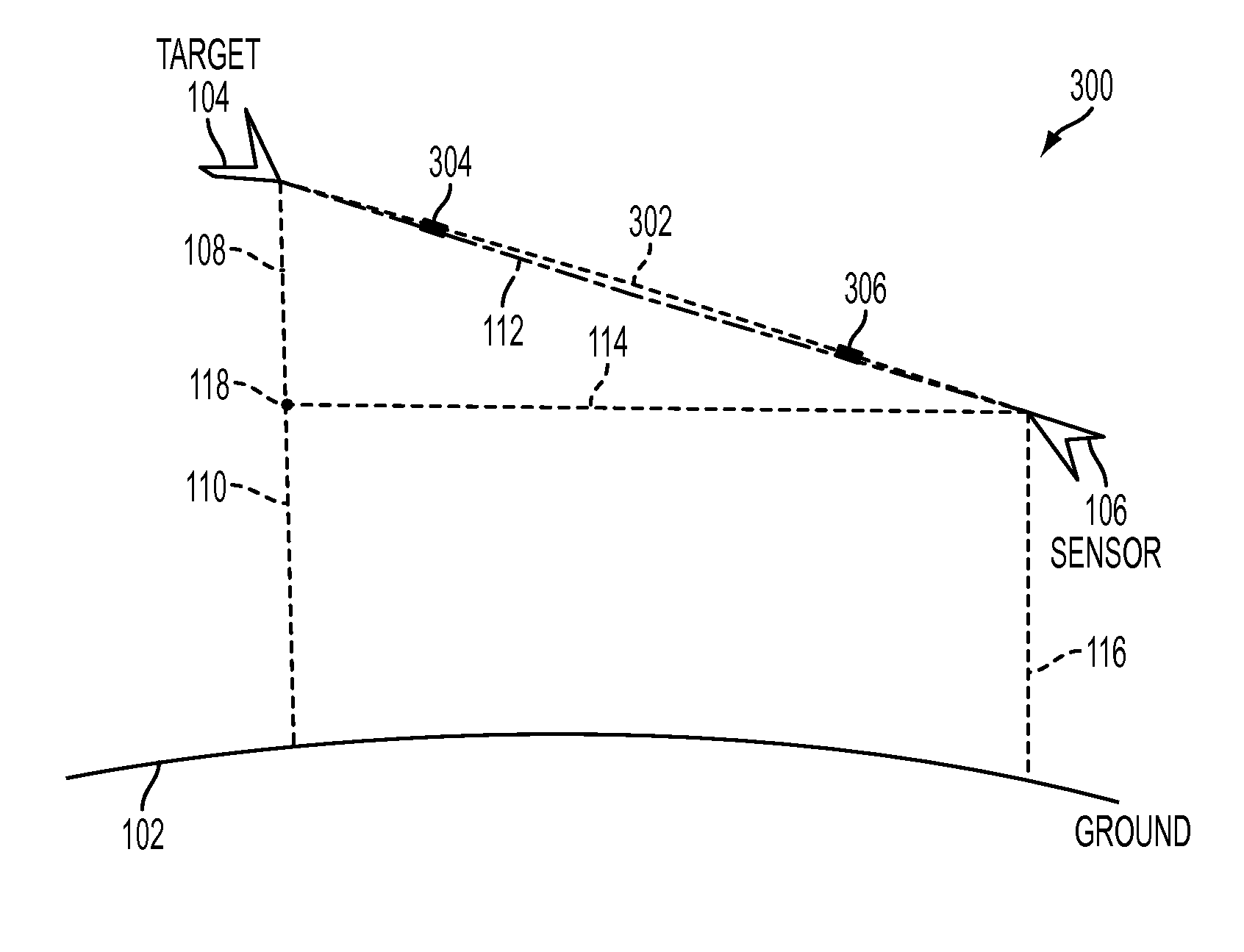
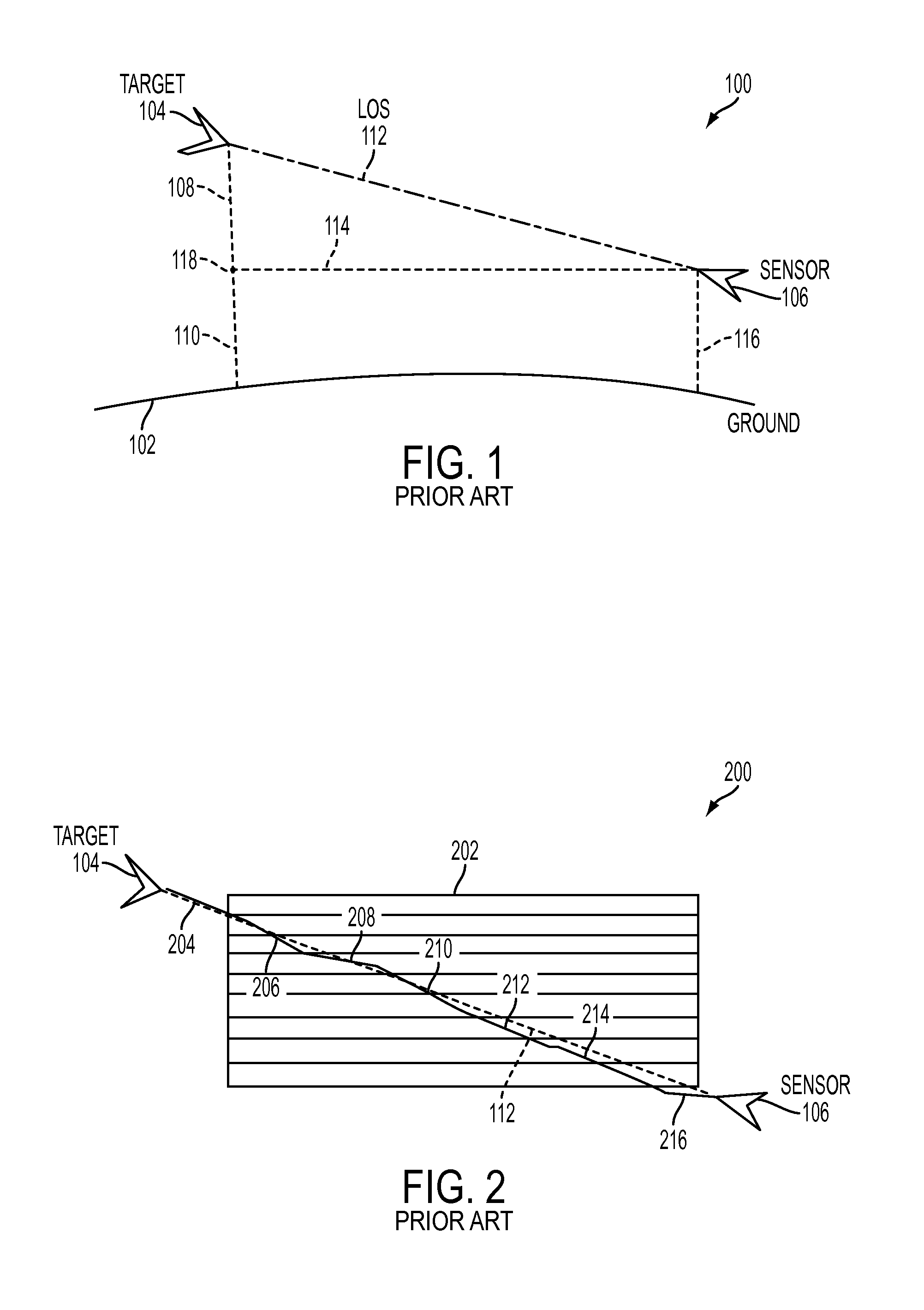
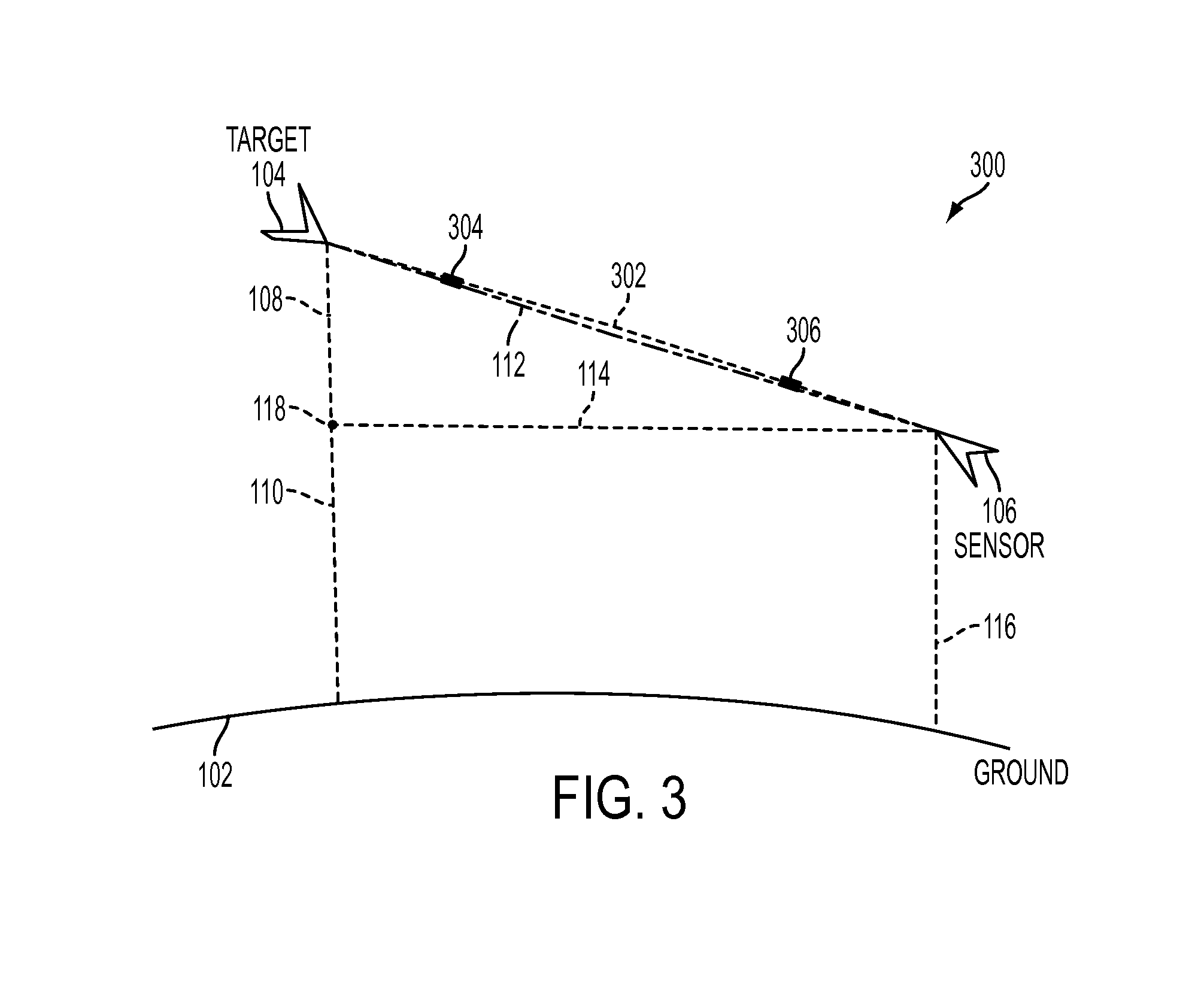
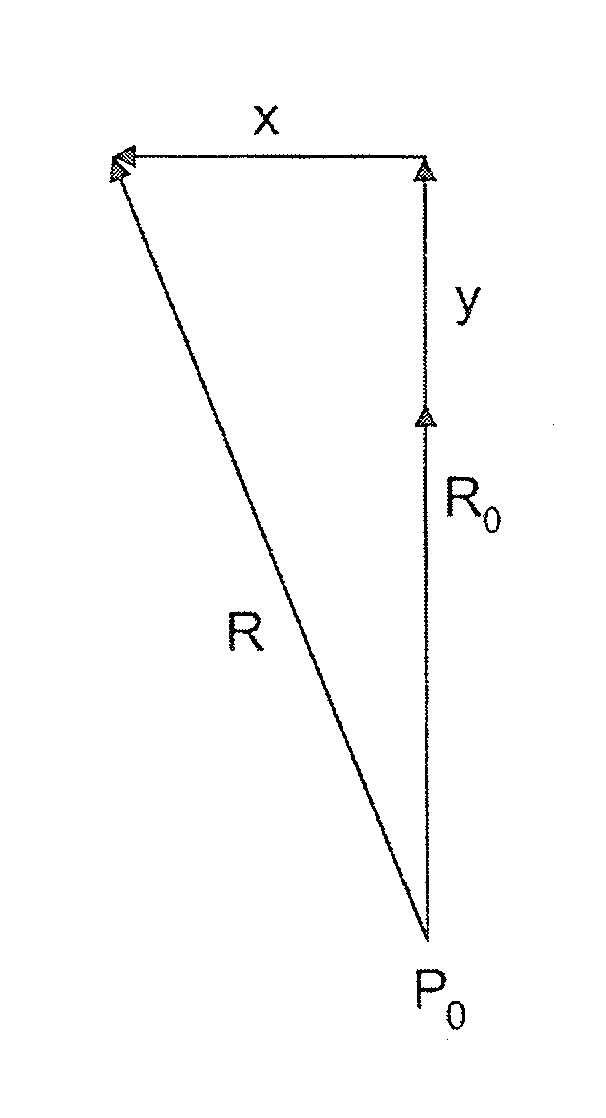
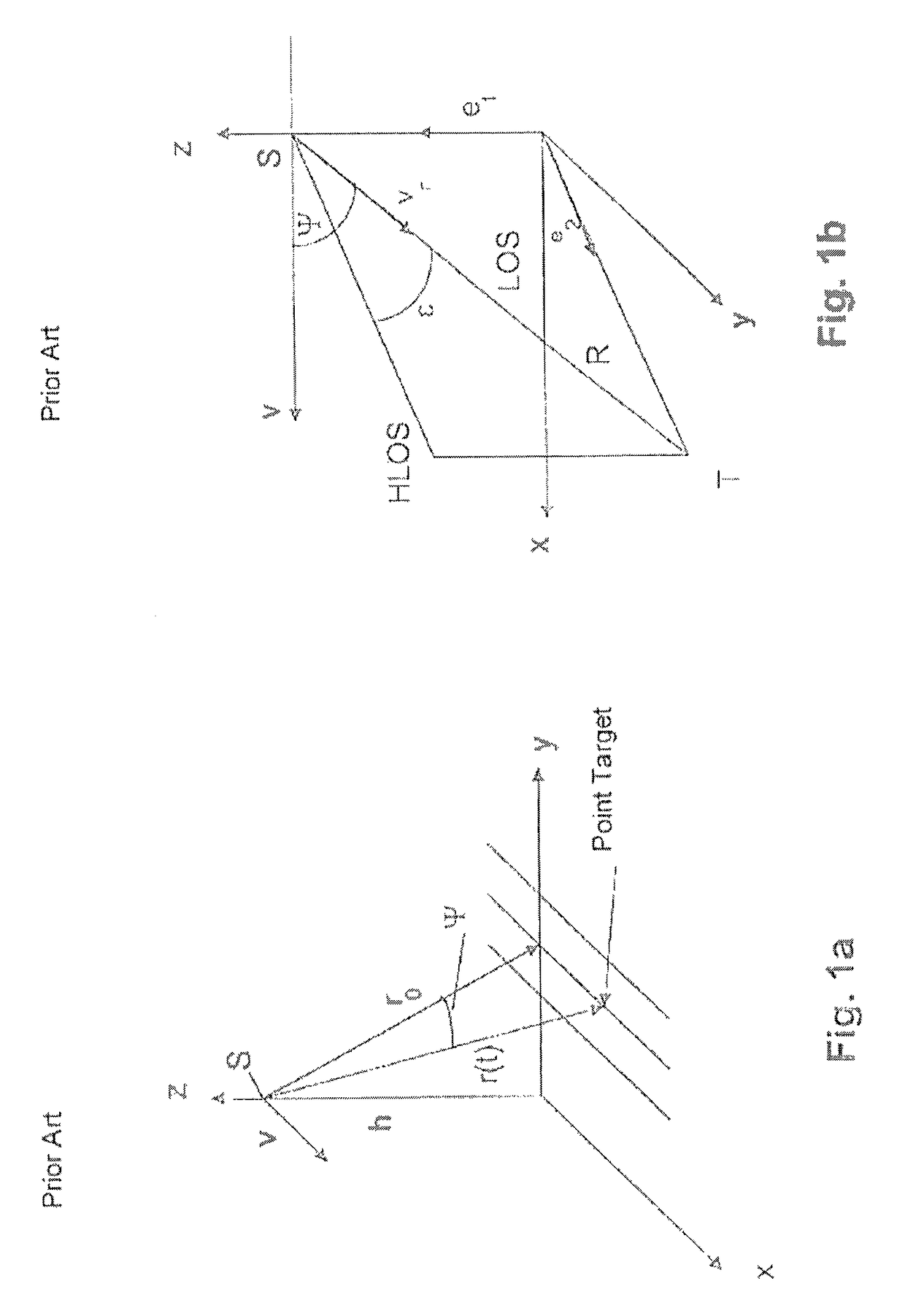
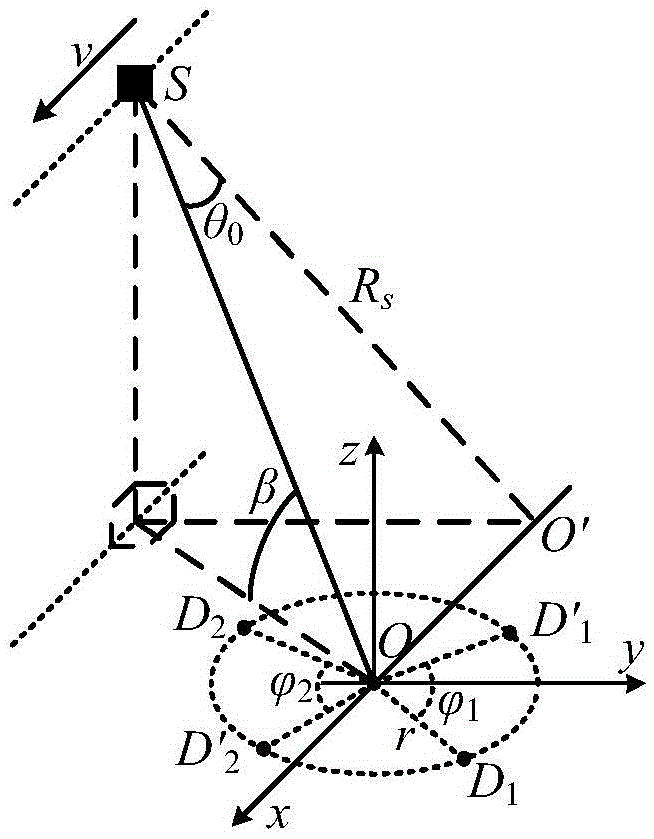
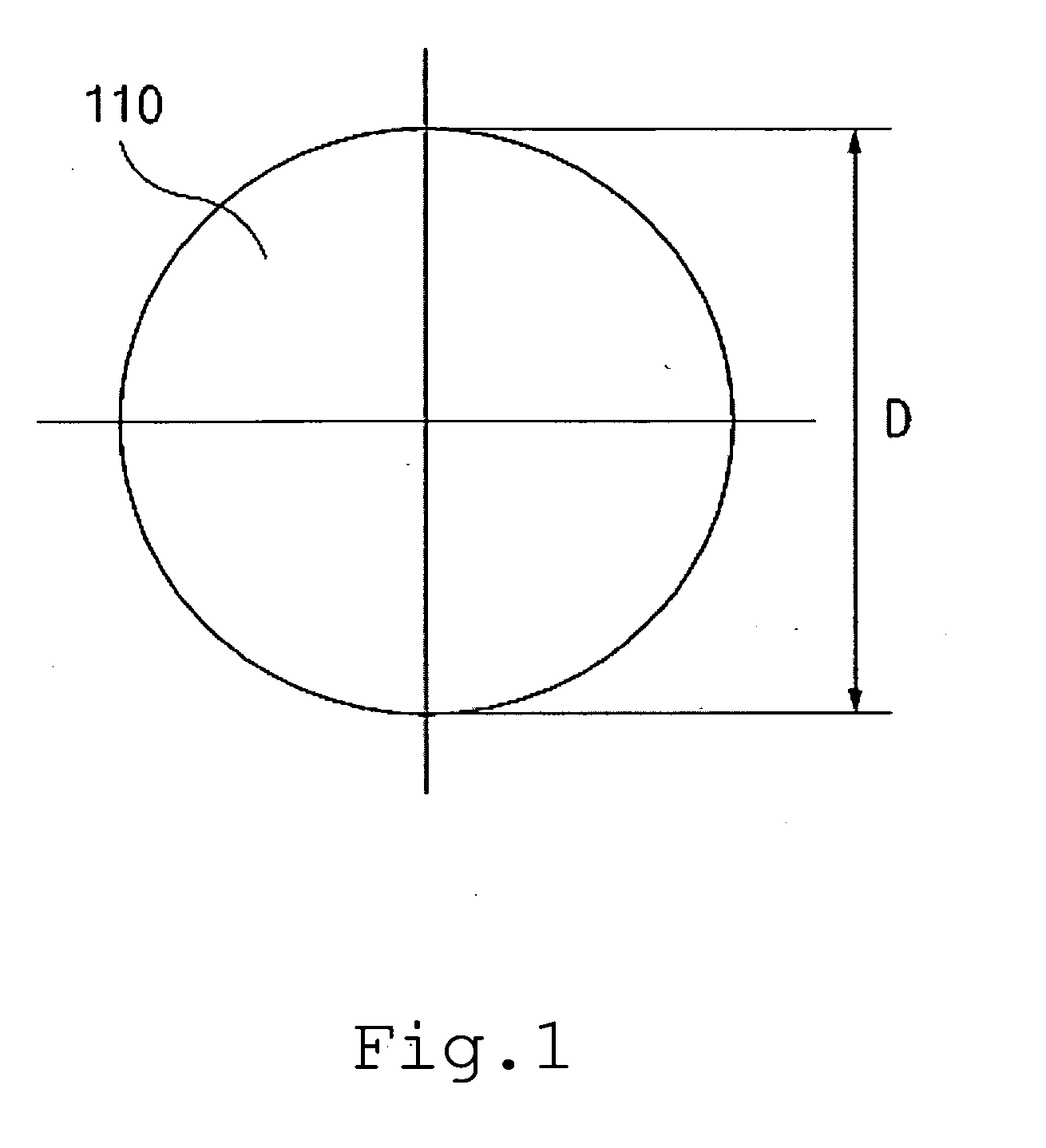
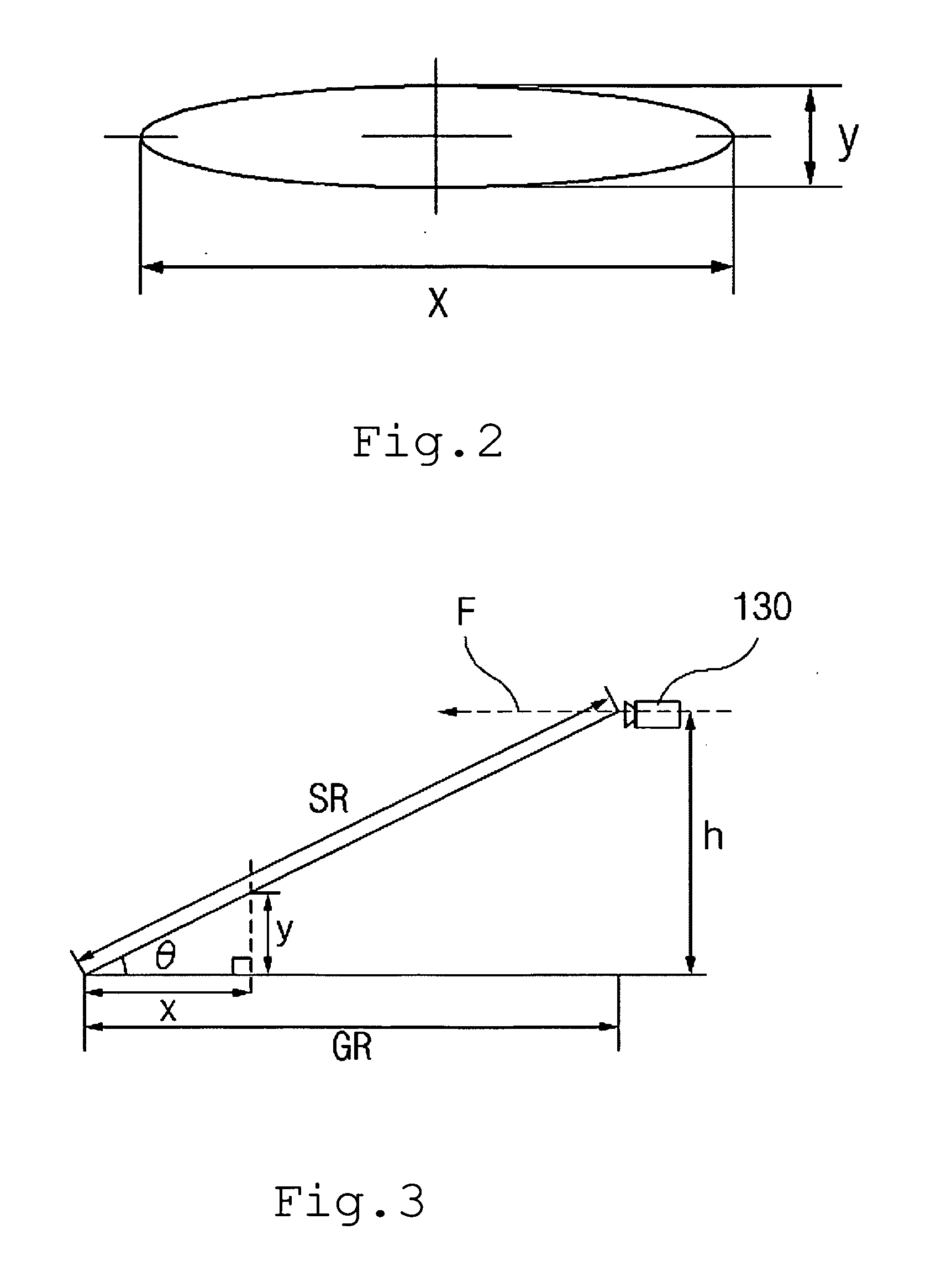
In radio electronics, especially radar terminology, slant range is the line-of-sight distance along a slant direction between two points which are not at the same level relative to a specific datum. An example of slant range is the distance to an aircraft flying at high altitude with respect to that of the radar antenna. The slant range (1) is the hypotenuse of the triangle represented by the altitude of the aircraft and the distance between the radar antenna and the aircraft's ground track (point (3) on the earth directly below the aircraft). In the absence of altitude information, for example from a height finder, the aircraft location would be plotted farther (2) from the antenna than its actual ground track.
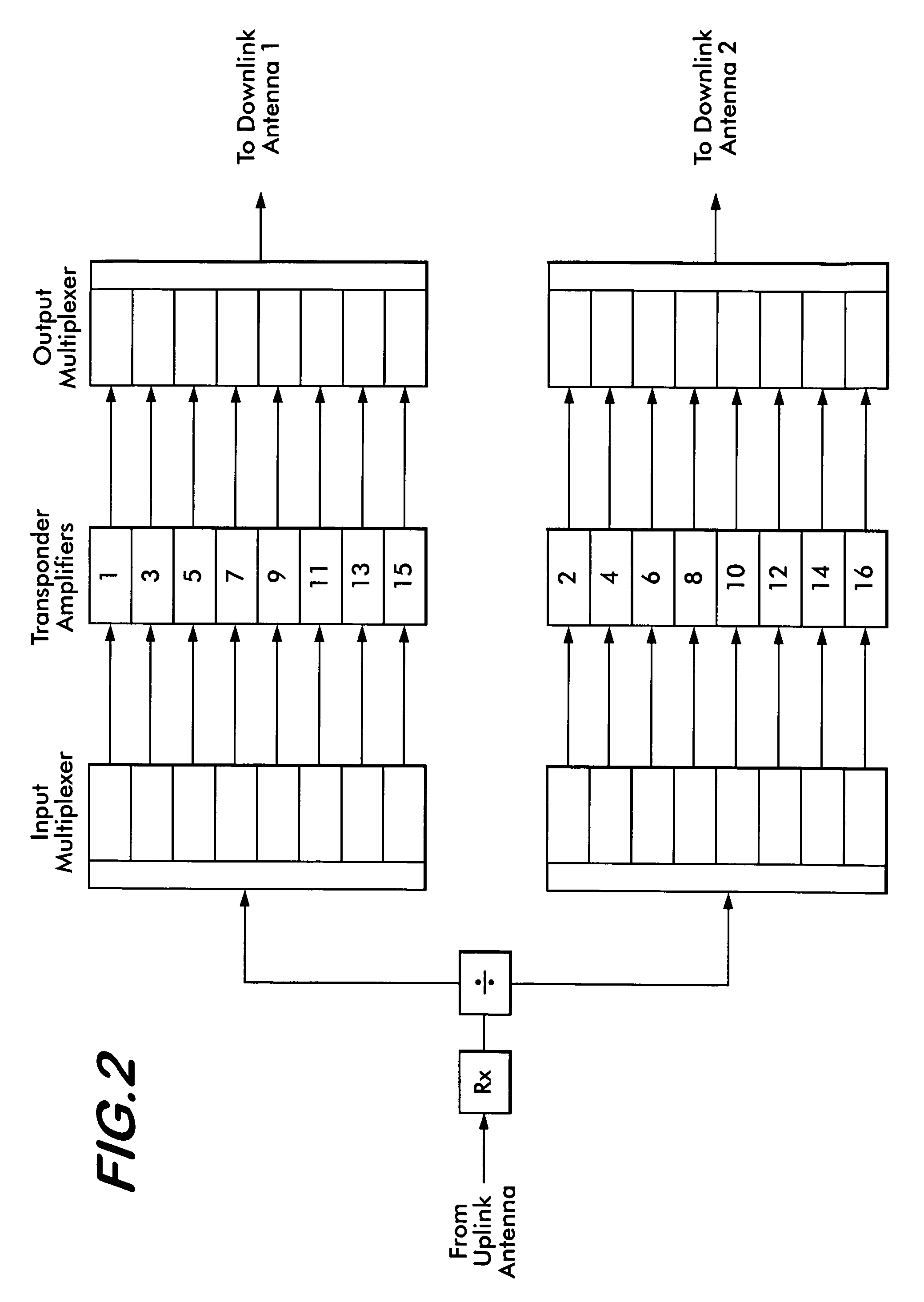
Wideband dual polarized base station antenna offering optimized horizontal beam radiation patterns and variable vertical beam tilt
ActiveUS6924776B2Improved radiation patternImprove front-to-back ratioLogperiodic antennasAntenna supports/mountingsRadiation patternPhysics
A dual polarized variable beam tilt antenna (10) having a plurality of offset element trays (12) each supporting pairs of dipole elements (14) to orient the dipole element pattern boresight at a downtilt. The maximum squint level of the antenna is a consistent downtilt off of boresight and which is at the midpoint of the antenna tilt range. The antenna provides a high roll-off radiation pattern through the use of Yagi dipole elements configured in this arrangement, having a beam front-to-side ratio exceeding 20 dB, a horizontal beam front-to-back ratio exceeding 40 dB, and is operable over an expanded frequency range.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Precision Approach Control
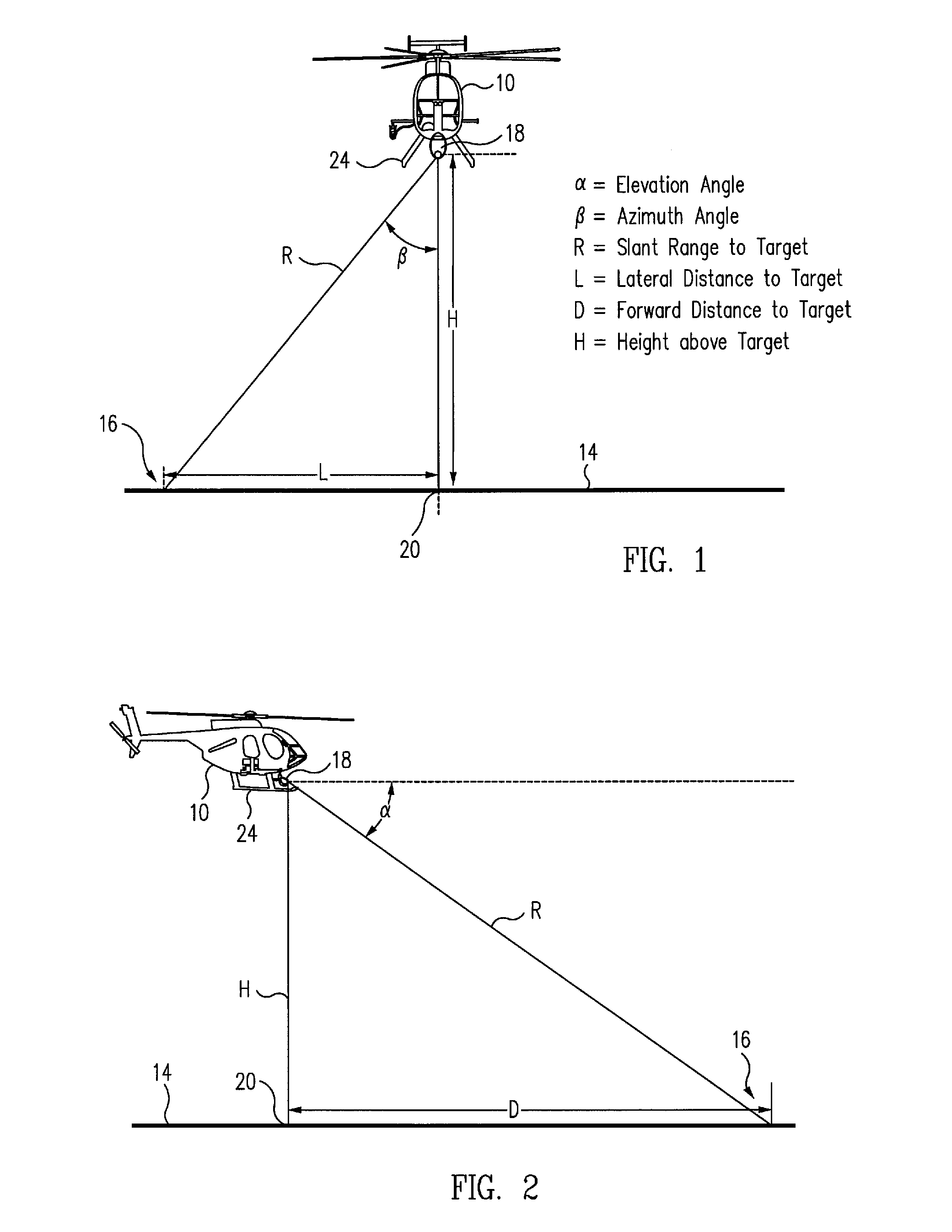
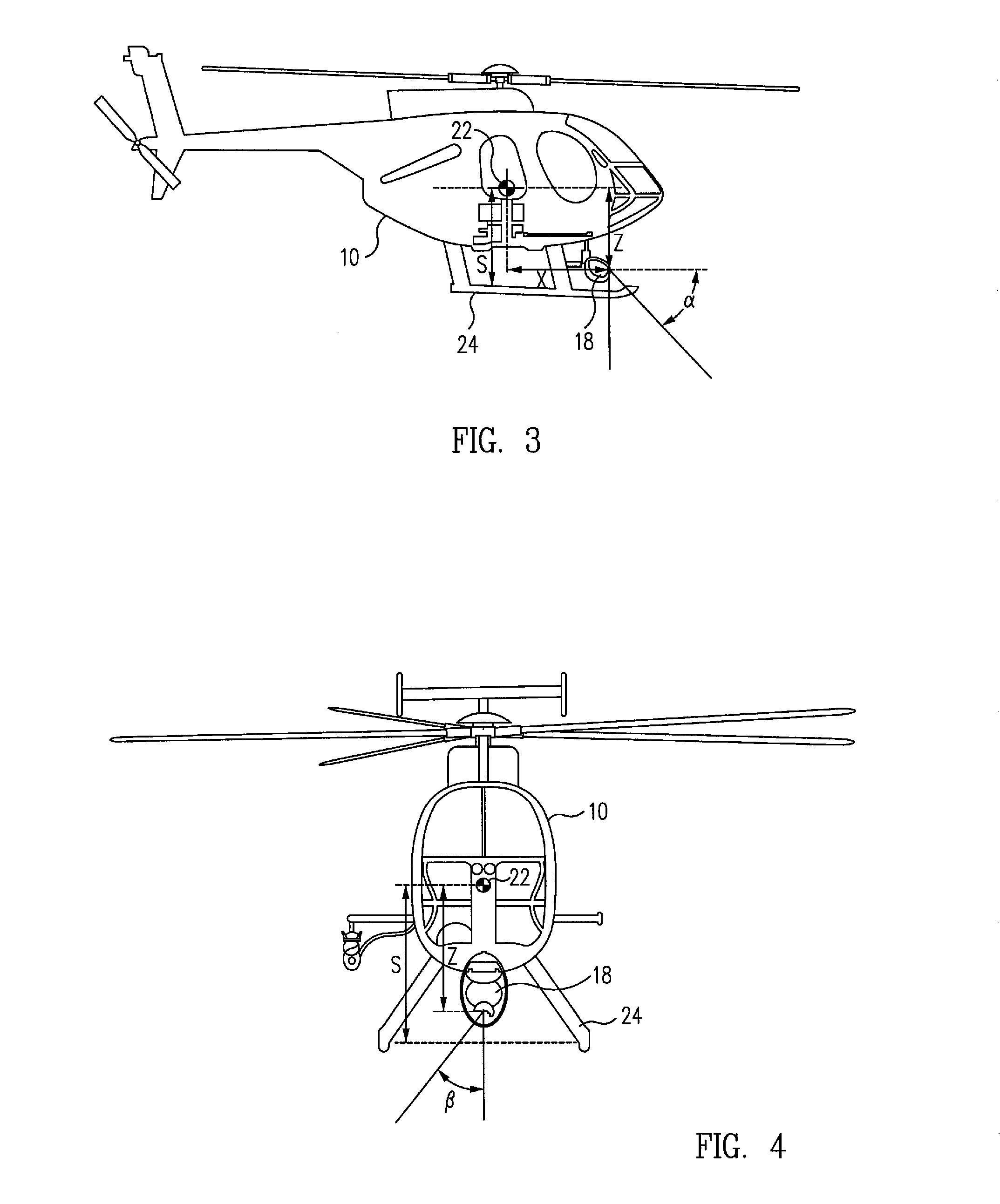
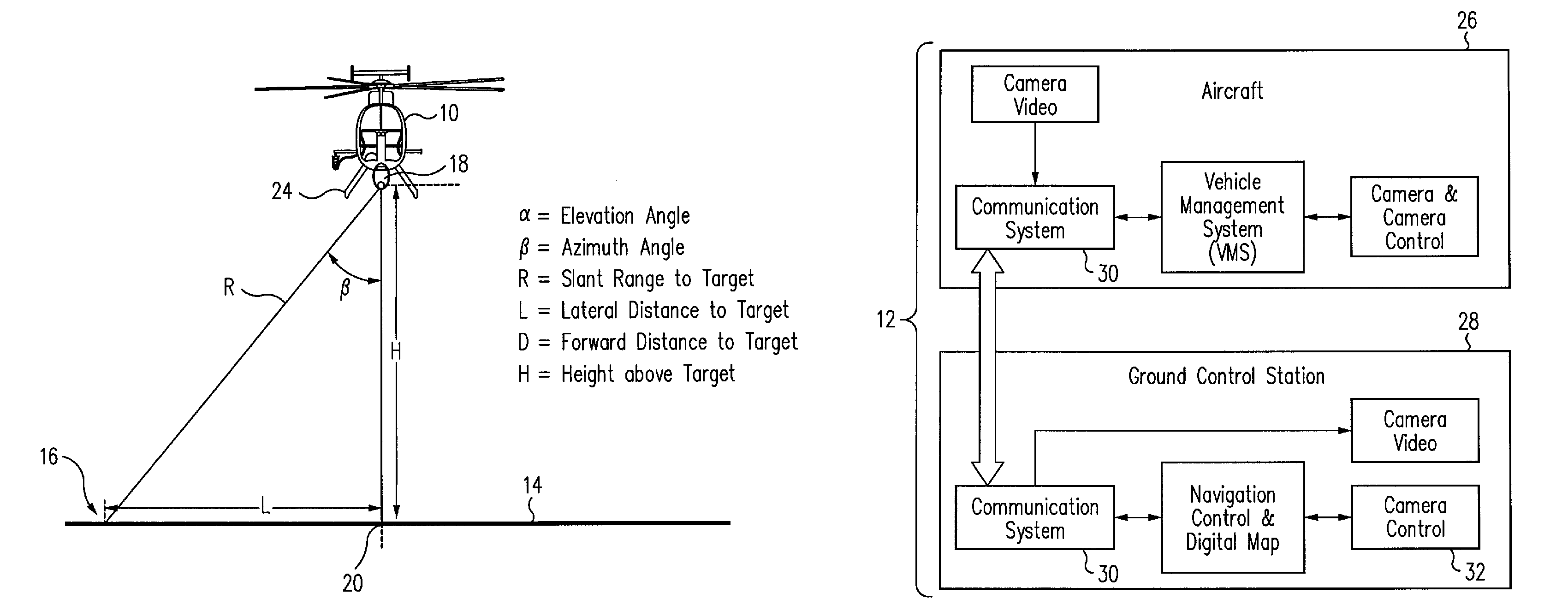
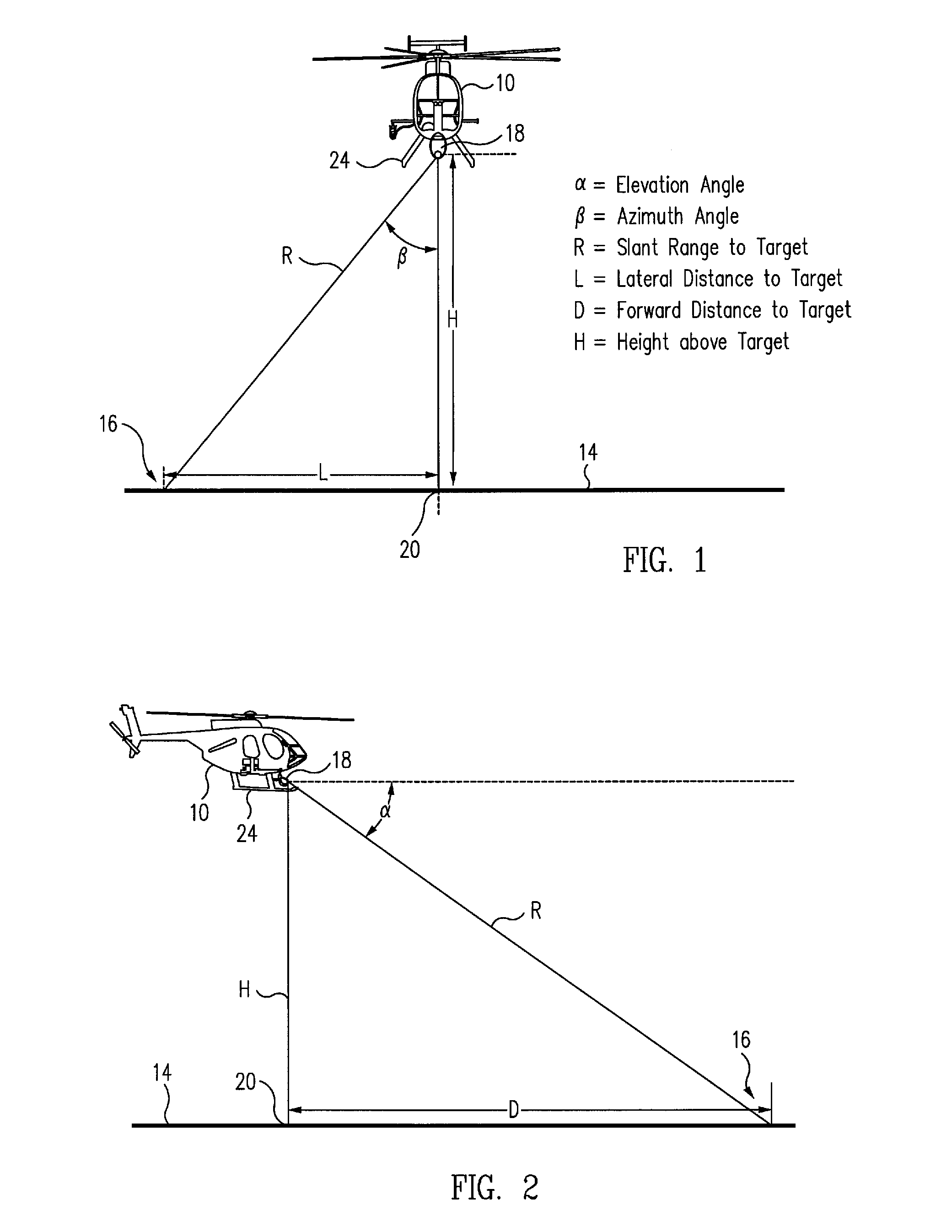
ActiveUS20080071431A1Great and easy controlSimple and inexpensive solutionVessels for aircraftDigital data processing detailsFixation pointControl system
An aircraft control system for operations close to the ground includes a camera having a rangefinder for measuring the azimuth, elevation and slant range from a fixed point on the aircraft relative to a selected target point on a surface below the aircraft, a navigation system for measuring the latitude and longitude of the aircraft on the surface, a computer for computing the position of the fixed point on the aircraft relative to the target point from the respective measurements of the camera and the navigation system, and a controller for controlling the movement of the aircraft such that the fixed point is positioned at a selected position above the selected target point on the surface. The controller may also include an automatic tracking mechanism for maintaining the position of the fixed point on the aircraft at the selected position above a moving object.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Laser scanning apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160259058A1Avoid it happening againEliminate negative effectsUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationBlind zoneLaser scanning
The disclosed embodiments include an apparatus and method of using a laser to scan the ground or a target from an airborne or ground-based platform. In certain embodiments, the apparatus and method produces a 3-D elevation model of the terrain. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes a pulsed laser, a receiver to detect and amplify the pulse after being reflected by objects on the ground (or the ground itself), and electronics which measures the time of flight of the optical pulse from which the slant range to the target is calculated. Technical advantages of the disclosed embodiments include avoiding blind zones to ensure that no laser shots are wasted. In certain embodiments for airborne applications, the apparatus may also be configured to maintain a constant swath width or constant spot spacing independent of aircraft altitude or ground terrain elevation.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
System for automatically landing aircraft using image signals and method of controlling the same
Disclosed herein are a system for automatically landing an aircraft using image signals and a method of controlling the system. The system includes an altimeter installed on the aircraft; a landing mark placed at a landing location on a landing runway; a camera installed on the aircraft, oriented toward the front of the aircraft, and configured to detect the shape of the landing mark in image information form; and a FCC configured to calculate the angle between the aircraft and the ground, the ground range and the slant range between the aircraft and the landing location using the altitude information measured by the altimeter, the image information of the landing mark captured by the camera, angle information composed of the pitch, roll and yaw angles of the aircraft, and the angle of entry into the landing runway, and configured to control the automatic landing of the aircraft.
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
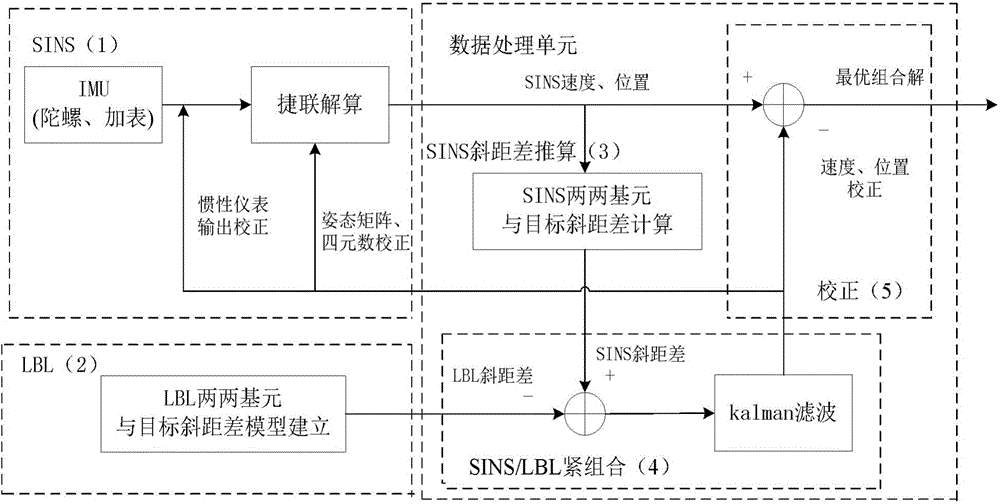
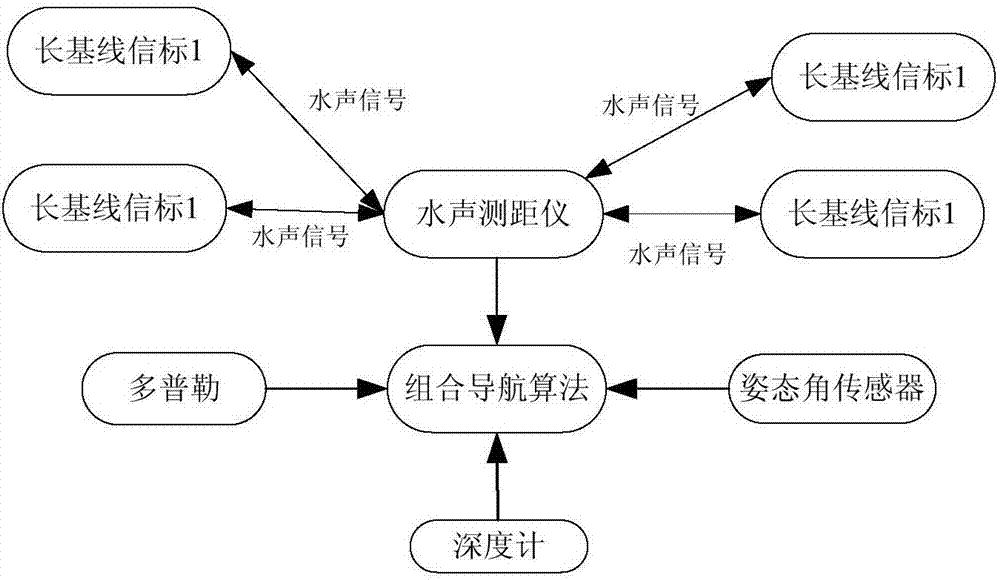
SINS/LBL (strapdown inertial navigation systems/long base line) tight combination based AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) underwater navigation positioning method
ActiveCN104457754ASolve the problem of error accumulation over timeReduce usageNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomRectangular coordinates
The invention provides an SINS / LBL (strapdown inertial navigation systems / long base line) tight combination based AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) underwater navigation positioning method. The SINS / LBL tight combination based AUV underwater navigation positioning method is characterized by comprising three major parts, namely an SINS mounted on an AUV, an LBL underwater sound positioning system laid on the seabed, and a data processing unit. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly performing a strapdown algorithm on IMU (inertial measurement unit) data to obtain AUV position information, and representing the position information by using earth rectangular coordinates; secondly reckoning an SINS slant-range difference according to the AUV position information provided by the SINS and hydrophone array position coordinates; and thirdly establishing an LBL slant-range difference model according to LBL positioning characteristics, and correcting SINS navigation positioning information according to filter estimation compensation by taking the difference value between the SINS slant-distance difference and the LBL slant-distance difference as an observed quantity of a kalman filter. According to the SINS / LBL tight combination based AUV underwater navigation positioning method, the use of GPS and other radio positioning systems is avoided at the same, and the AUV underwater operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for evaluating simulation imaging of multi-mode synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN101907704AAvoid modificationAvoid debuggingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSystems designWork pattern
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the simulation imaging of a multi-mode SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), which mainly solves the problems of poor adaptability to different operating modes, complex experiment process and long experiment time in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting an operating mode, inputting the parameters of a radar and the motion parameters of a carrier, loading a simulation scene and setting coordinates; secondly, setting a simulation radar echo signal according to a system environment; thirdly, imaging the radar echo signal to obtain a slant-range image; fourthly, geometrically correcting the slant-range image by using a three-dimensional geometric correction method to obtain a ground-range image; and finally, evaluating the quality of the ground-range image, and feeding back and correcting system parameters according the evaluation results so as to provide a feasible basis for a latter semi-physical simulation experiment. The method is applicable to three operating modes including a side looking mode, a slant looking mode and a scanning mode; only a plurality of parameters need to be input during operation, so that the experiment process can be simplified, the experiment time is saved, and the method can be used in a ground simulation experiment of SAR system design.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Aircraft precision approach control
ActiveUS7693617B2Great and easy controlSimple and inexpensive solutionVessels for aircraftDigital data processing detailsControl systemFlight vehicle
An aircraft control system for operations close to the ground includes a camera having a rangefinder for measuring the azimuth, elevation and slant range from a fixed point on the aircraft relative to a selected target point on a surface below the aircraft, a navigation system for measuring the latitude and longitude of the aircraft on the surface, a computer for computing the position of the fixed point on the aircraft relative to the target point from the respective measurements of the camera and the navigation system, and a controller for controlling the movement of the aircraft such that the fixed point is positioned at a selected position above the selected target point on the surface. The controller may also include an automatic tracking mechanism for maintaining the position of the fixed point on the aircraft at the selected position above a moving object.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Double-base foresight high-mobility platform SAR imaging method based on echo simulation
InactiveCN104898120AImprove computing efficiencyEffectively obtain high-precision echo dataRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a double-base foresight high-mobility platform SAR imaging method based on echo simulation, and the method mainly comprises the following steps: sequentially carrying out range-direction FFT and linear walking momentum correction of an obtained SAR time domain echo signal of a point target firstly, and sequentially obtaining a corrected echo signal and a corrected slant-range course; secondly enabling the corrected slant-range course to be equivalent to a single-base SAR slant-range form, and obtaining a three-order precise approximate expression of the corrected slant-range course; thirdly carrying out the range-direction FFT of the corrected echo signal, and sequentially obtaining a two-dimensional frequency spectrum of the time domain echo signal and the two-dimensional frequency spectrum phase term of the time domain echo signal; employing high-order polynomial-fitting to eliminate the spatial-variant property of the phase term of the two-dimensional frequency spectrum of the time domain echo signal, and obtaining the high-precision two-dimensional frequency spectrum of the time domain echo signal; and finally enabling the high-precision two-dimensional frequency spectrum to sequentially pass through a distance spatial-variant matching filter and a range-direction IFFT and range-Doppler domain matching filter, thereby obtaining an SAR image after focusing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Synthetic aperture radar imaging method and device based on non-linear frequency-modulated signals
ActiveCN105259552AFocusImprove performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMotion errorReference distance
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging method based on non-linear frequency-modulated signals. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out range pulse compression on echo data according to emitted non-linear frequency-modulated signals; compensating a motion error at a reference distance according to determined slant range error; then adopting Stolt mapping; and finally compensating a residual motion error and carrying out azimuth focusing. In this way, the imaging o the non-linear frequency-modulated signals is completed. The invention further discloses an SAR imaging device based on the non-linear frequency-modulated signals.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and Method for Atmospheric Correction of Information
ActiveUS20130006534A1Electromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDigital computer detailsAtmospheric correctionAtmospheric sciences
An atmospheric correction system (ACS) is proposed, which accounts for the errors resulting from the in-homogeneities in the operational atmosphere along the slant path by constructing atmospheric profiles from the data along the actual target to sensor slant-range path. The ACS generates a slant-range path based on the arbitrary geometry that models the sensor to target relationship. This path takes the atmosphere and obstructions between the two endpoints into account when determining the atmospheric profile. The ACS uses assimilation to incorporate weather data from multiple sources and constructs an atmospheric profile from the best available data. The ACS allows the user to take advantage of variable weather and information along the path that can lead to increased accuracy in the derived atmospheric compensation value.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for Determining the Geographic Coordinates of Pixels in SAR Images
ActiveUS20120133550A1Error in position determinationReduce errorsMaps/plans/chartsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionImage resolutionRange gate
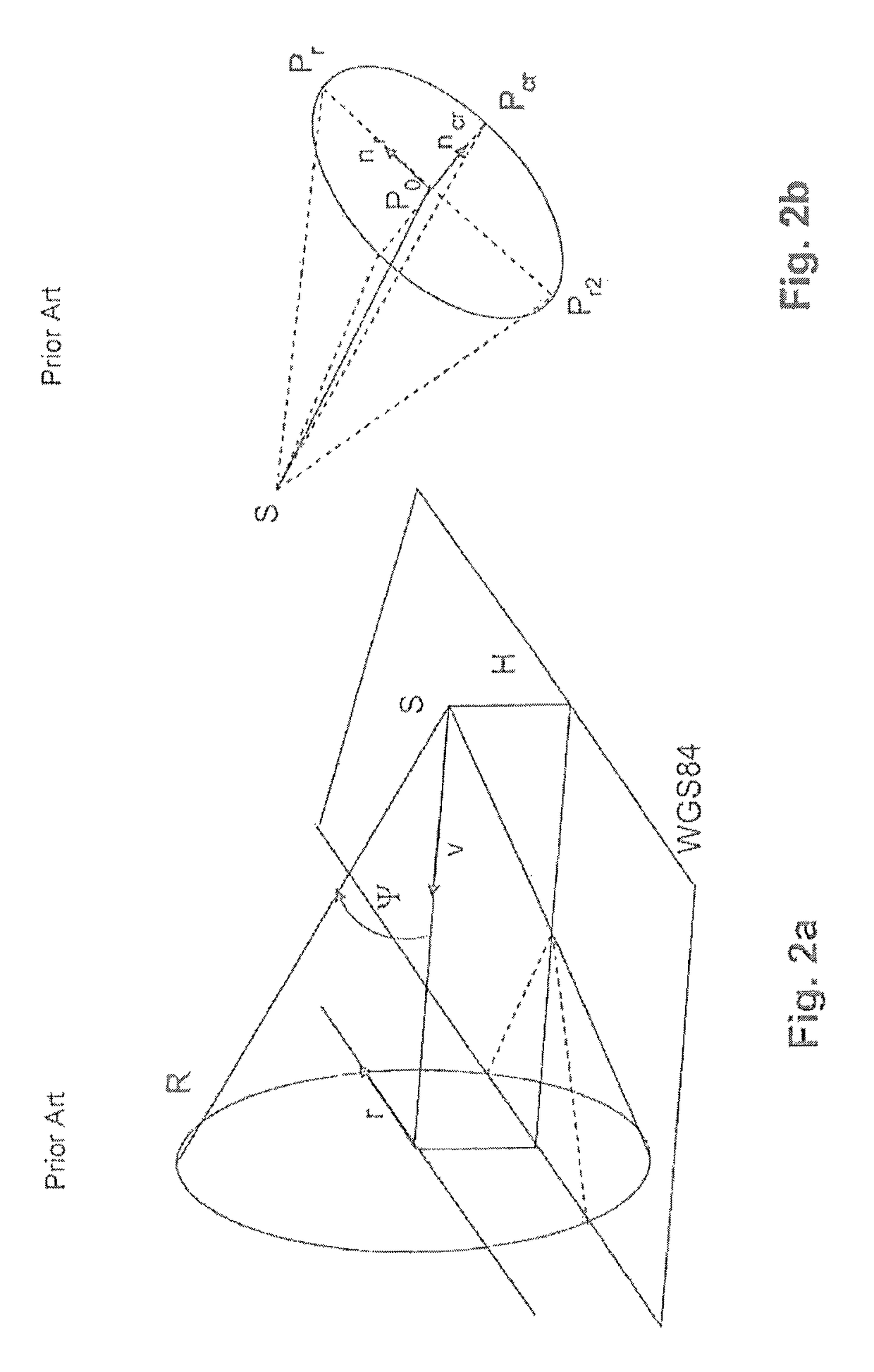
A method for effecting the airborne determination of geographic coordinates of corresponding pixels from digital synthetic aperture radar images, where the SAR images are available in the form of slant range images and the recording position of the respective SAR image is known. The coordinates of the corresponding pixels in the SAR images and the corresponding range gates are used in each case to determine the distance between a corresponding resolution cell on the ground and the respective recording position of the respective SAR image. The determined distances and associated recording positions of the SAR images are used to determine the geographic coordinates of the corresponding pixels in the SAR images by employing a WGS84 ellipsoid.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Imaging method for remote sensing satellite irradiation source forward-looking synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101975948ASolve the problem of two-dimensional nonlinear space variation compensationEasy to solveRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture sonarFrequency spectrum
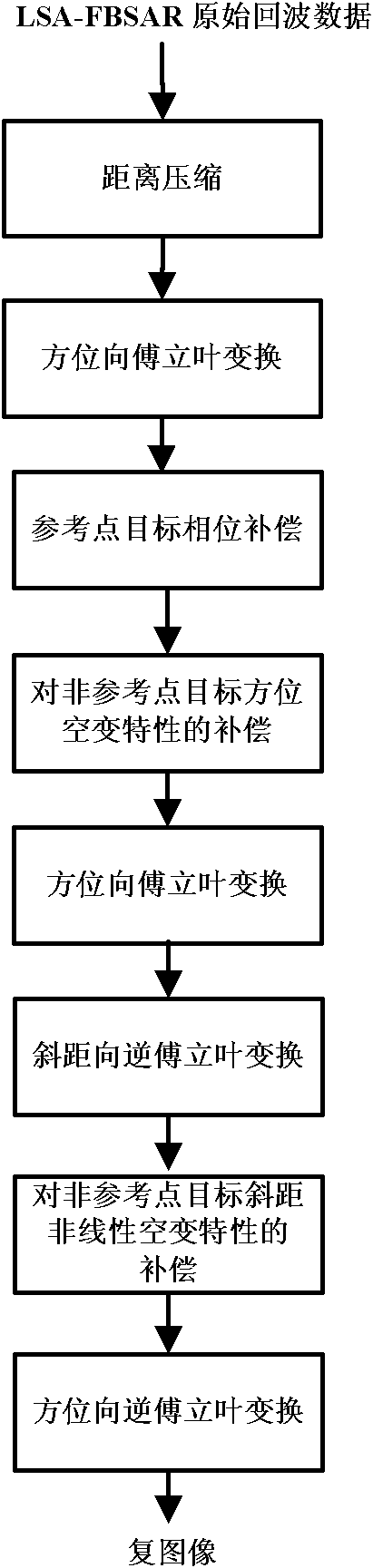
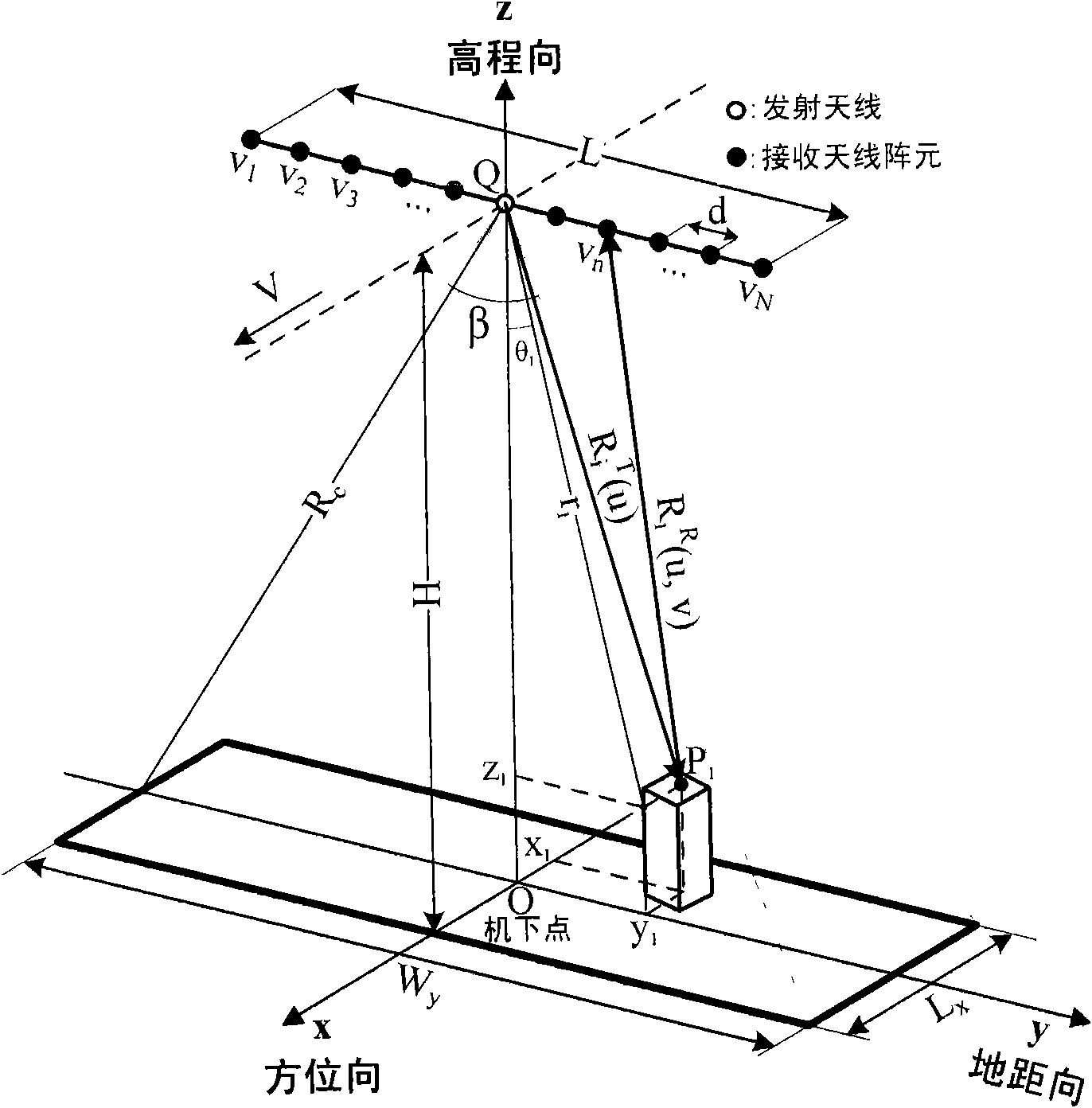
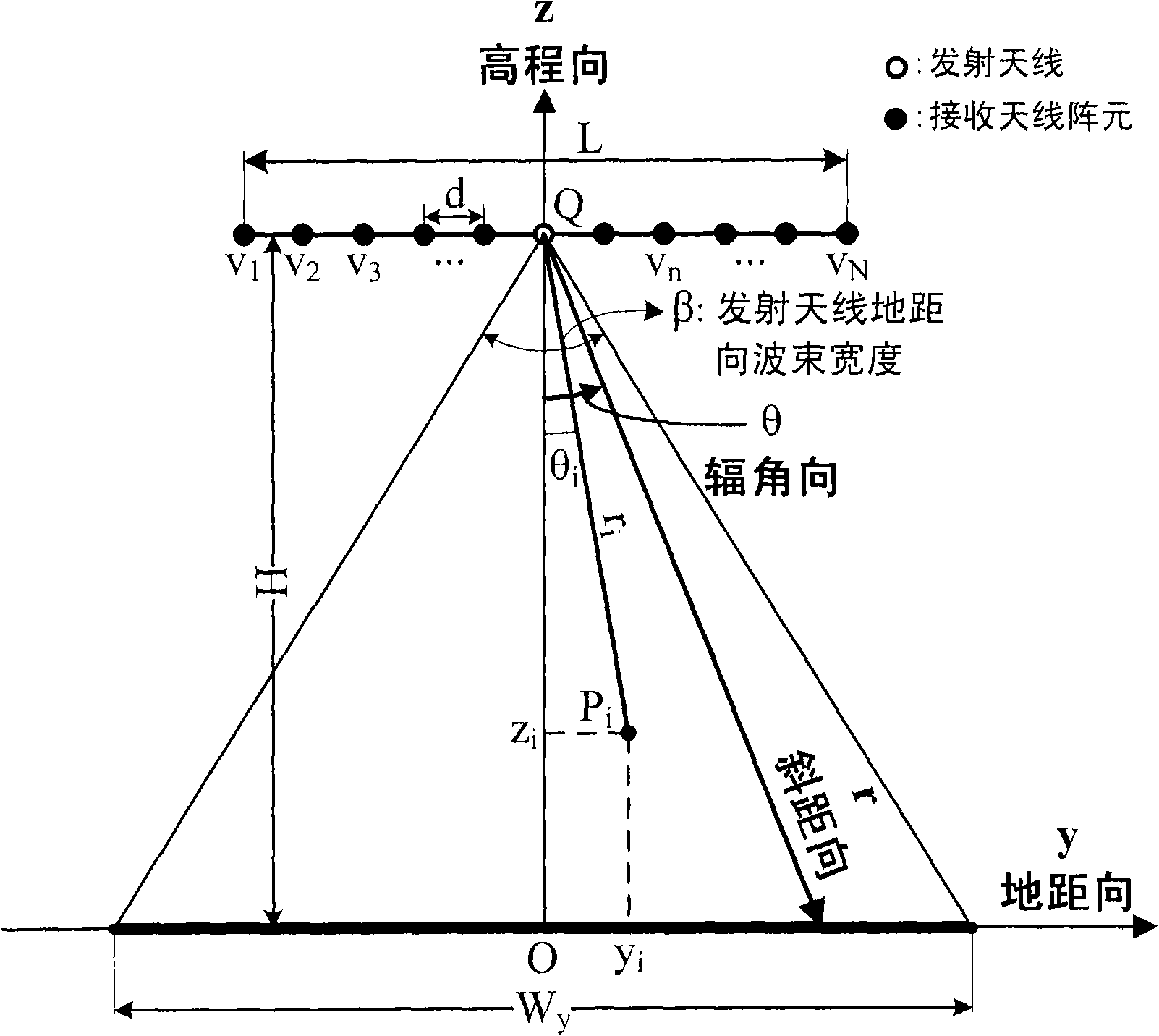
The invention provides a frequency domain imaging method for a remote sensing satellite irradiation source forward-looking synthetic aperture radar (LSA-FBSAR). In the method, a nonlinear mapping relationship between range dimension space-variant range cell migration (RCM) and azimuth dimension space-variant RCM is acquired from the complex coupling relationship of a two-dimensional frequency spectrum by the resolution representation of the frequency spectrum of an LSA-FBSAR system and the characteristic of forward-looking work of a receiving platform. The conventional two-dimensional space-variant RCM compensation processing procedure is improved; the compensation of the target azimuth of a non-reference point and slant-range two-dimensional space-variant RCM is realized by scaled Fourier transform-phase multiplication technology and interpolation-phase multiplication technology; the problem of severe geometric distortion such as bending, distortion and the like of an imaging result caused by two-dimensional nonlinear space-variant RCM is effectively solved; and the method is suitable for realizing the high-resolution imaging of the LSA-FBSAR.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
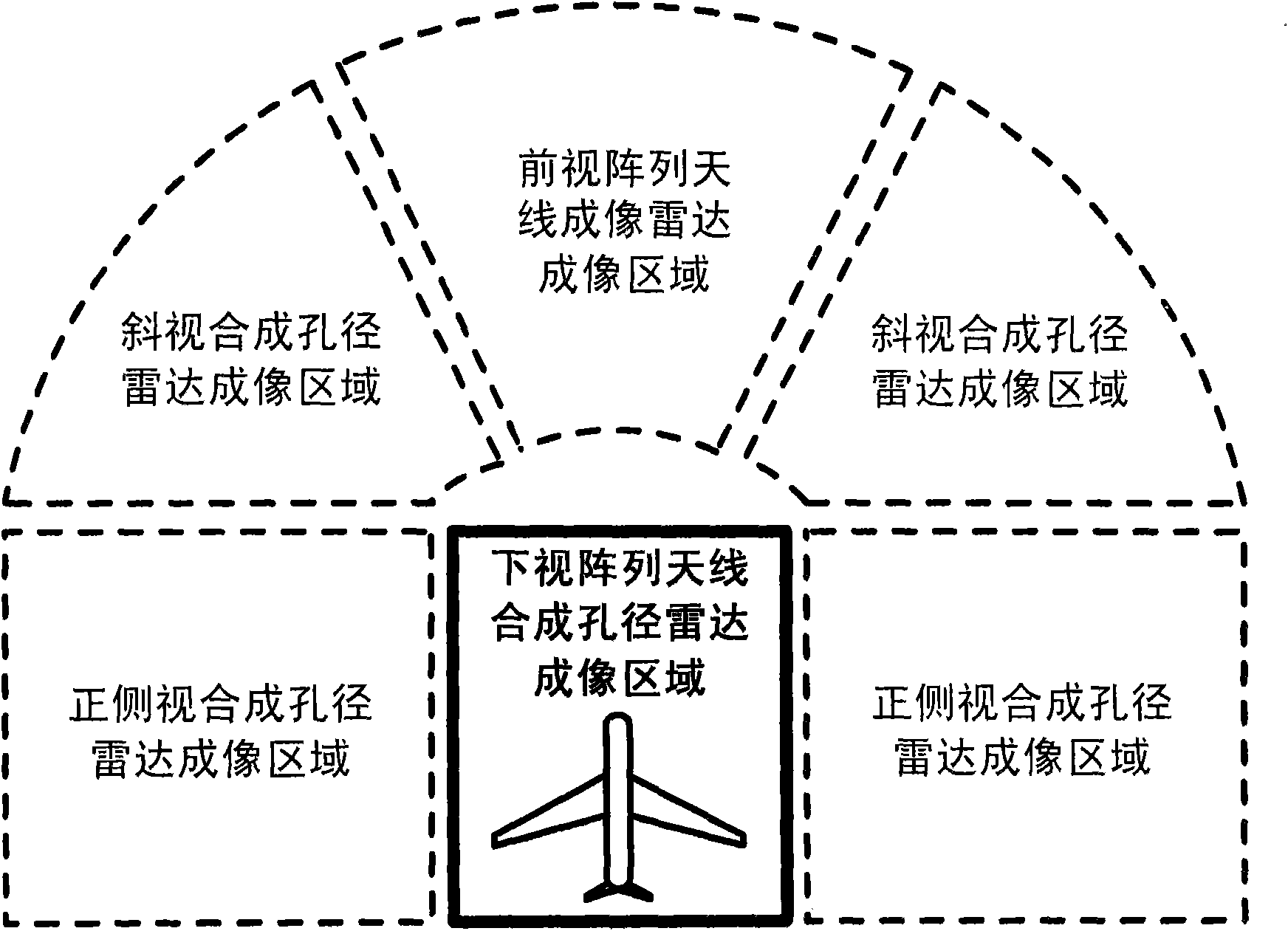
Three-dimensional focal imaging method of look-down array antenna synthetic aperture radar
InactiveCN101866001AImprove universalityShorten the timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFast Fourier transformAzimuth compression
The invention discloses a three-dimensional focal imaging method of a look-down array antenna synthetic aperture radar, which relates to radar technology. The method comprises: A) performing slant-range compression of collected original echo data of the look-down array antenna synthetic aperture radar; B) performing azimuth range migration correction of a signal obtained by the step A); C) performing the azimuth compression of a signal obtained by the step B); E) performing the ground-range range migration correction of the signal which is subjected to slant-range compression and azimuth compression; and F) performing the ground-range slant removal and ground-range Fourier transform of the signal obtained by the step E), and reestablishing the three-dimensional radar image of an imaged area in a cylindrical coordinate system. In the method of the invention, fewer antenna array elements are used for reestablishing the three-dimensional radar image of the imaged area, the range migration correction problem, which is not solved in the conventional three-dimensional imaging method, is solved, the ground-range wave beam forming calculation performed in the conventional three-dimension imaging method is converted into one time of complex multiplication and the Fourier transform, and a three-dimensional resolution image is thus acquired, and the required imaging time is reduced.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater robot integrated navigation method based on long baseline and online calibration of beacons
ActiveCN107990891AEffectively filter interferenceSuppression of accumulated navigation errorsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationKaiman filterUnderwater navigation
The invention relates to an integrated navigation method based on long baseline acoustic positioning and online calibration of beacons to realize underwater navigation and positioning of an underwaterrobot. The method comprises the following steps: the position of each long-baseline beacon is calibrated online on the basis of measured slant range value of single beacon of an AUV (autonomous underwater vehicle) at different moments; a Kalman filter based on long baseline acoustic positioning and inertial navigation data fusion is built, and position estimation for integrated navigation is calculated. The method can effectively realize fusion of long baseline positioning and inertial navigation data, has higher navigation and positioning precision, is convenient to transplant and can be applied to underwater navigation and positioning of various AUVs.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-dimensional spatial-variant correction method for airborne double base forward looking SAR azimuth phase
ActiveCN108710111AMake up for the defect of changing standard mismatchMake up for the lack of matchingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase filterRange migration
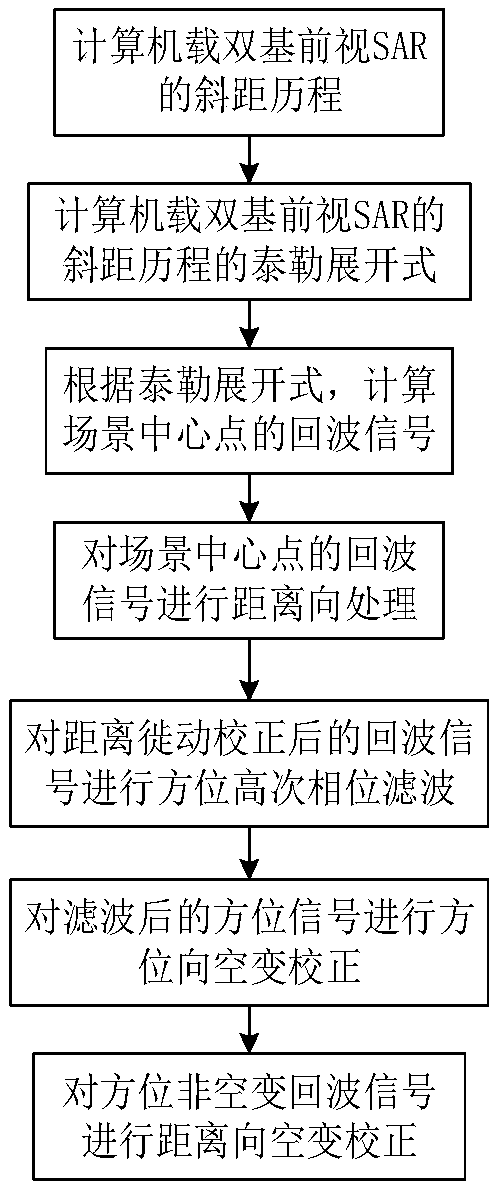
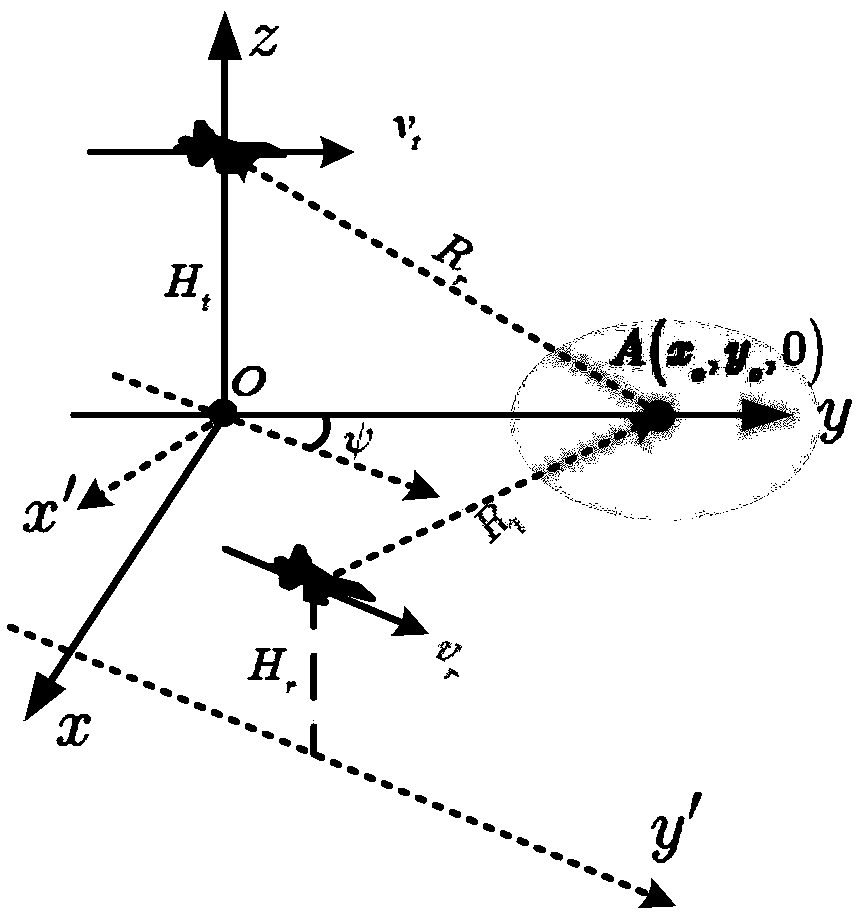
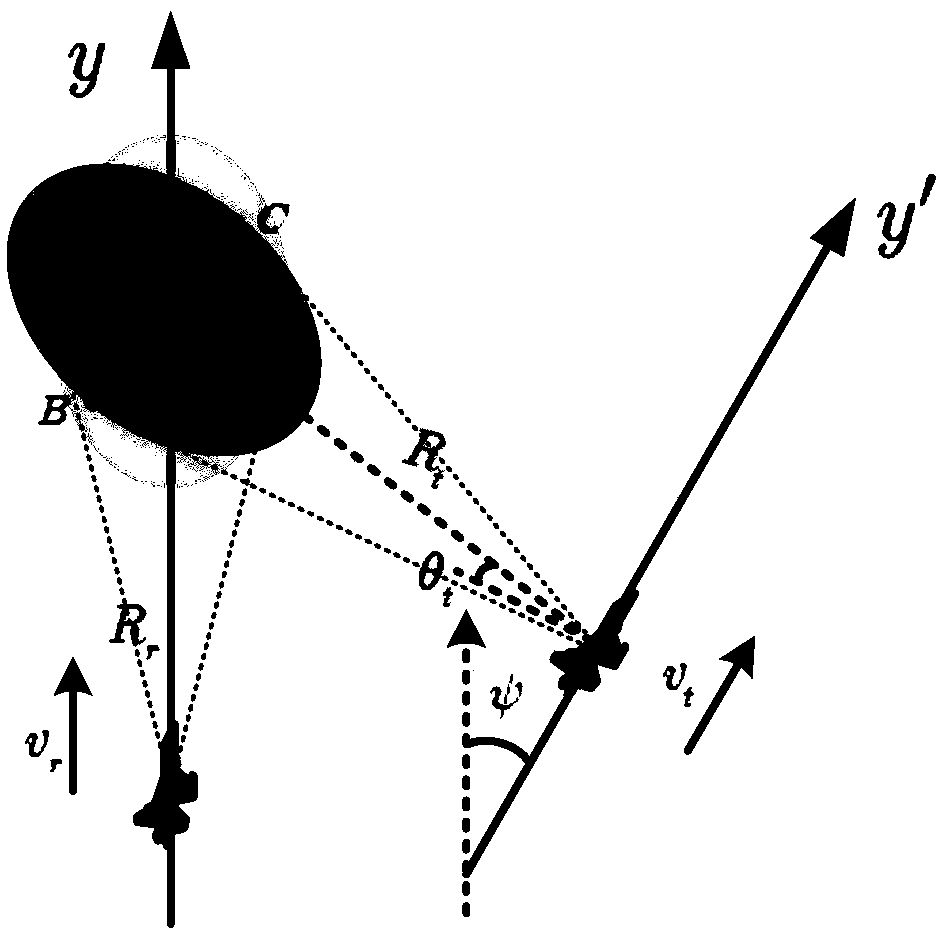
The invention provides a two-dimensional spatial-variant correction method for an airborne double base forward looking SAR azimuth phase. The technical problems in the prior art of poor azimuth phasefocusing effects under large wide scene imaging can be solved. The method includes the following steps: calculating the slant range of an airborne double base forward looking SAR; calculating the Taylor expansion of the slant range of the airborne double base forward looking SAR; calculating echo signals of a scene center point according to the Taylor expansion; performing range processing on theecho signals of the scene center point; performing azimuth high-order phase filtering on the echo signals after range migration correction; performing azimuth spatial-variant correction on filtered azimuth signals; and performing range spatial-variant correction on azimuth non spatial-variant echo signals. The method can effectively enhance the focusing precision of SAR echo data so that high quality SAR images can be obtained, and therefore, SAR image detection and discriminating performance can be enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Imaging method of synthetic aperture radar in large squint angle mode
InactiveCN103576147AImprove computing efficiencyEfficient resultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumSynthetic aperture sonar
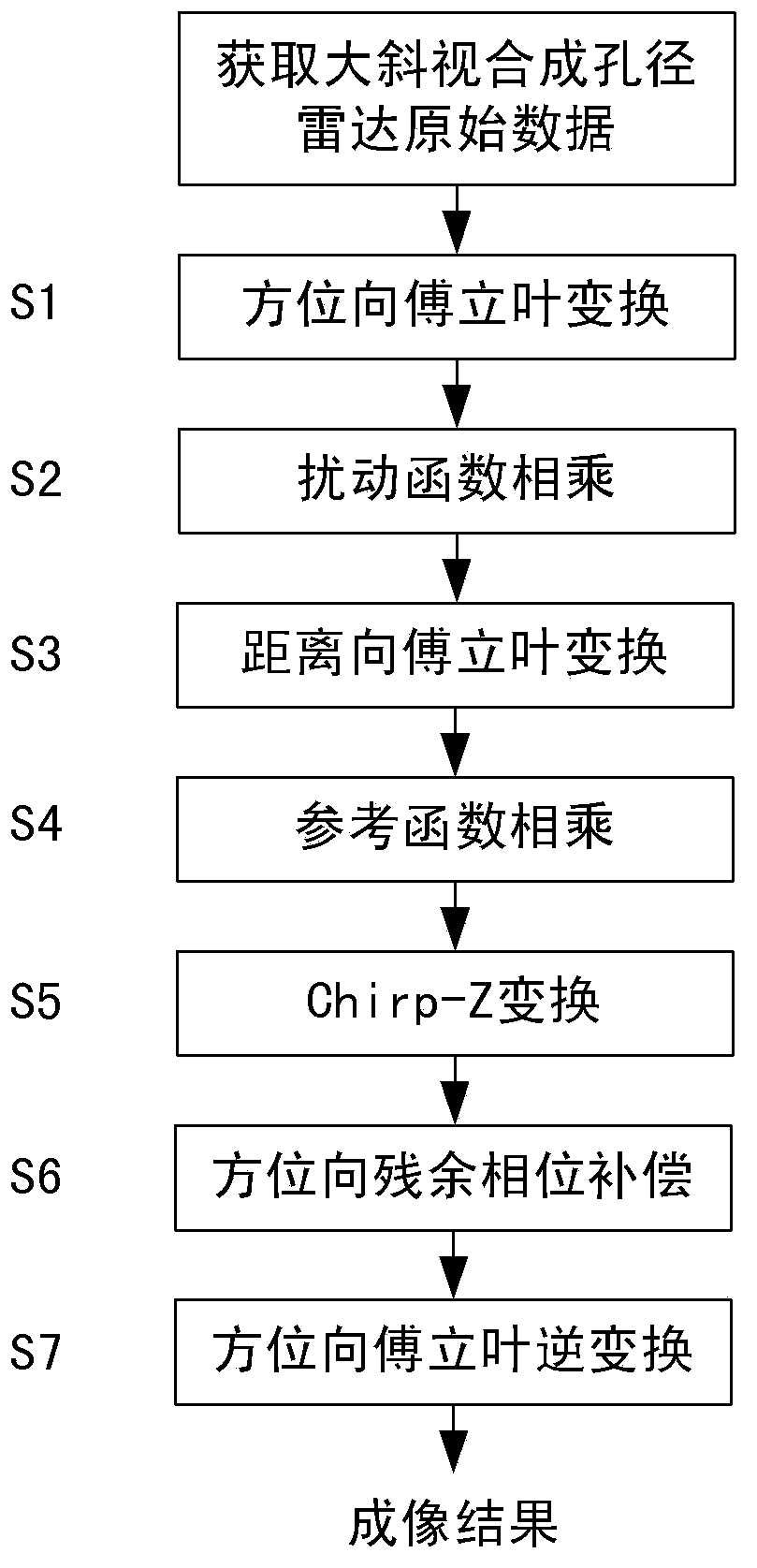
The present disclosure provides an imaging method for a Synthetic-Aperture Radar (SAR) in a high squint mode. The method includes: perform perturbation function multiplication for an echo signal in the azimuth Doppler domain-range time domain to eliminate the dependence of an echo signal quadratic azimuth-range coupling factor on the change of a target slant range; perform reference function multiplication in the two-dimensional frequency domain, wherein the reference function is a conjugate function of a point target echo spectrum at a reference slant range; complete compensation of all phases, which do not vary with the range, of a two-dimensional spectrum through the multiplication of the two-dimensional spectrum and the reference function; rectify the differential range migration factor of the echo signal in the two-dimensional frequency domain by utilizing Chirp-Z transform, complete range migration rectification by performing convolution once and phase multiplication twice; compensate an azimuth residual phase through the azimuth phase multiplication, and perform azimuth compression to obtain a focused SAR image. The method of the present disclosure can perform highly efficient and precise imaging for high squint SAR data.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
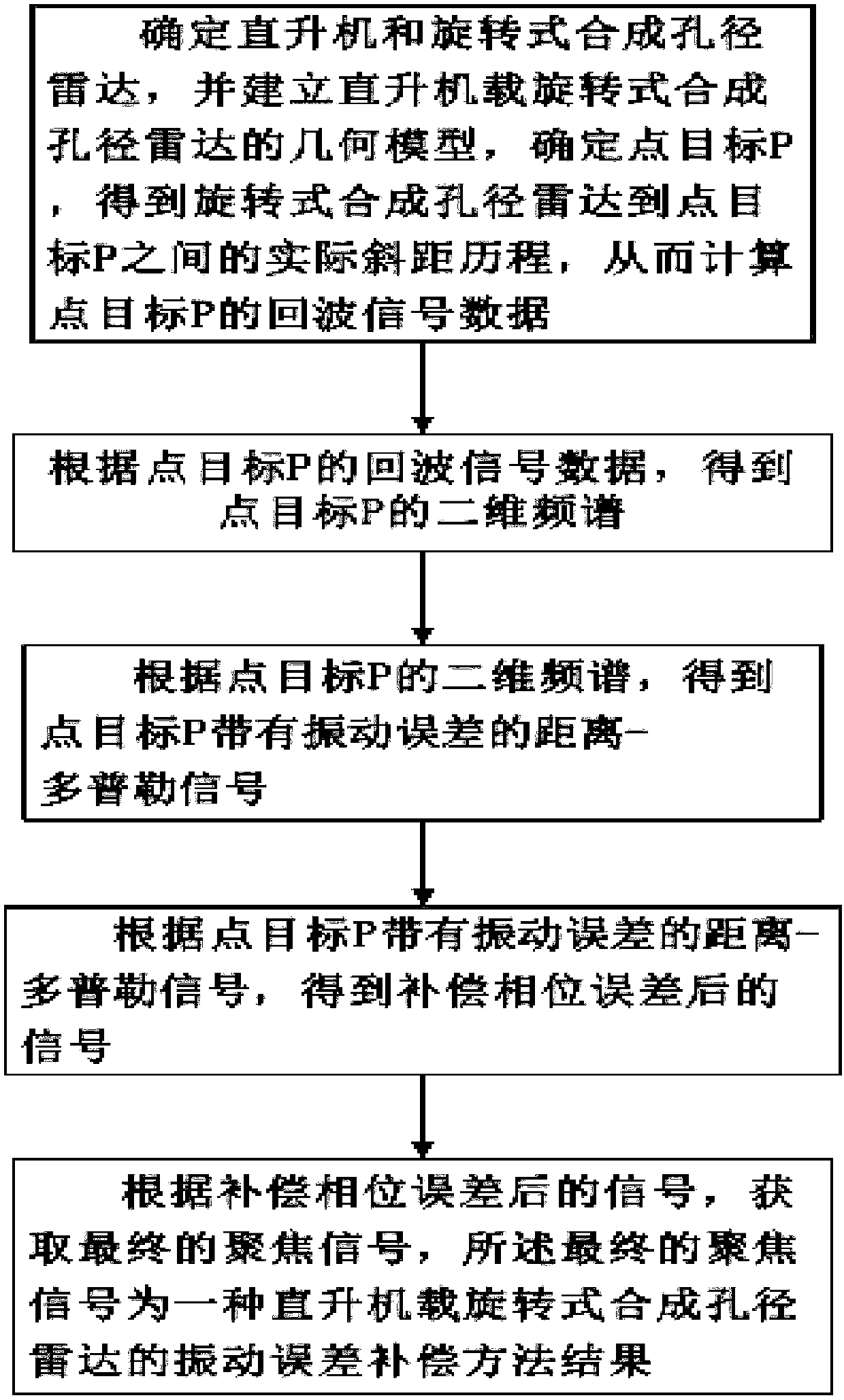
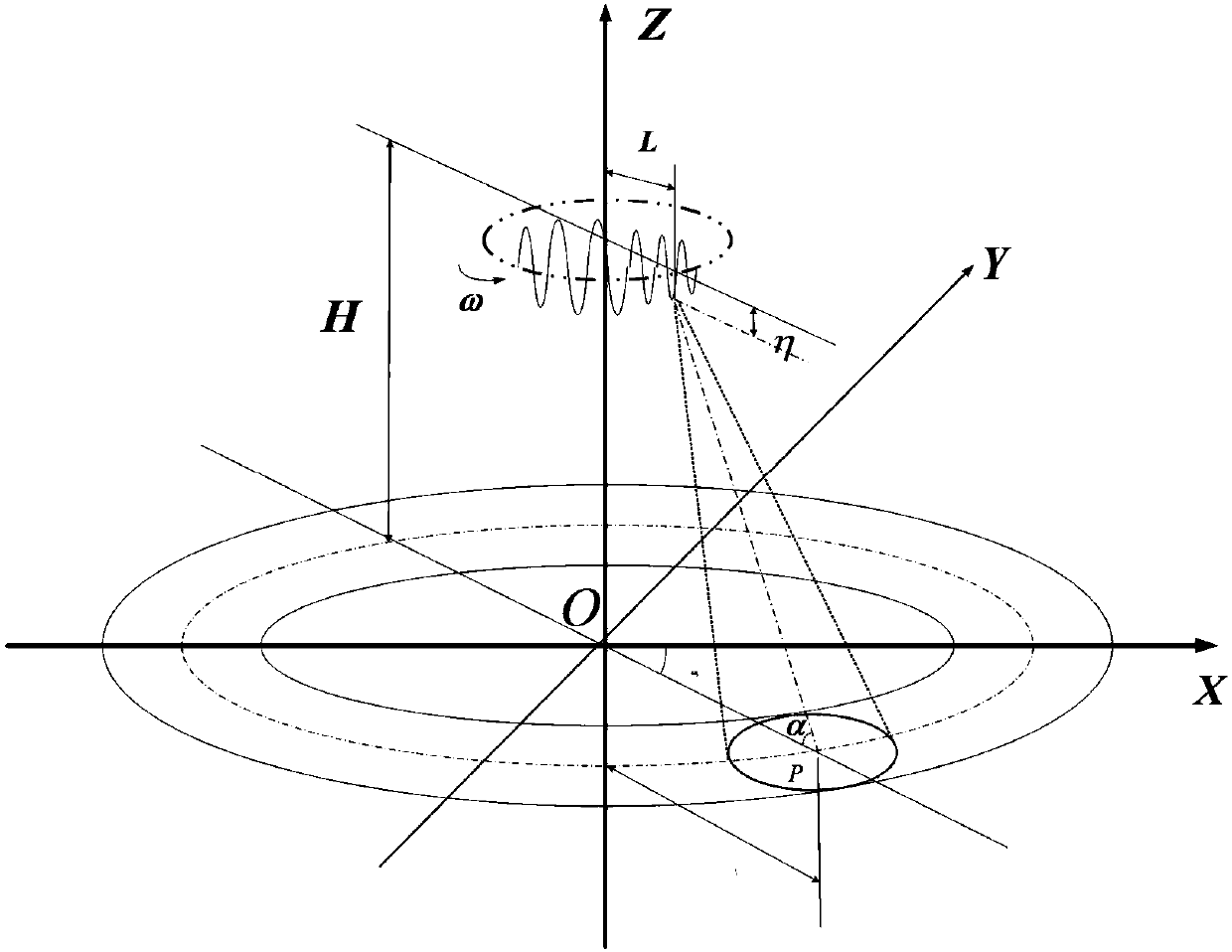
Vibration error compensation method for helicopter-borne rotation type synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a vibration error compensation method for helicopter-borne rotation type synthetic aperture radar, and belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing. The method mainly comprises the steps that a helicopter and rotation type synthetic aperture radar are determined, a geometric model of the helicopter-borne rotation type synthetic aperture radar is built, a pointtarget P is determined, the actual slant range course between the rotation type synthetic aperture radar and the point target P is obtained, and then echo signal data of the point target P is calculated; according to the echo signal data of the point target P, a two-dimensional spectrum of the point target P is obtained; according to the two-dimensional spectrum of the point target P, a point target P with vibration error distance-Doppler signal is obtained; according to the point target P with vibration error distance-Doppler signal, a signal obtained after phase error compensation is obtained; according to the signal obtained after phase error compensation, a final focusing signal is obtained, wherein the final focusing signal is the vibration error compensation method result of the helicopter-borne rotation type synthetic aperture radar.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Terminal guidance forward-looking radar echo simulation method based on missile motion parameter
The invention discloses a terminal guidance forward-looking radar echo simulation method based on a missile motion parameter. The method comprises the steps: changing a sampling period of a missile motion parameter into a pulse repetition period through interpolation according to a missile-borne radar parameter; setting a ground scattering point within a ground area irradiated by missile-borne radar, and obtaining the slant-range history of the scattering point according to the position information of the scattering point and the missile motion parameter; obtaining phase information of a scattering point echo distance range time domain filter and phase information of the scattering point according to the slant-range history of the scattering point and the pulse width of the radar, and constructing a scattering point echo azimuth time domain filter according to the azimuth information of the scattering point and a radar antenna direction map; obtaining echo information of the scattering point according to the scattering coefficient of the scattering point, the phase information of the scattering point, the scattering point echo distance range time domain filter and the scattering point echo azimuth time domain filter, and obtaining echo information of a whole radar irradiation scene by means of a time domain coherent superposition method.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Legendre-orthogonal-decomposition-baesd curve motion trajectory SAR wave-number domain imaging method
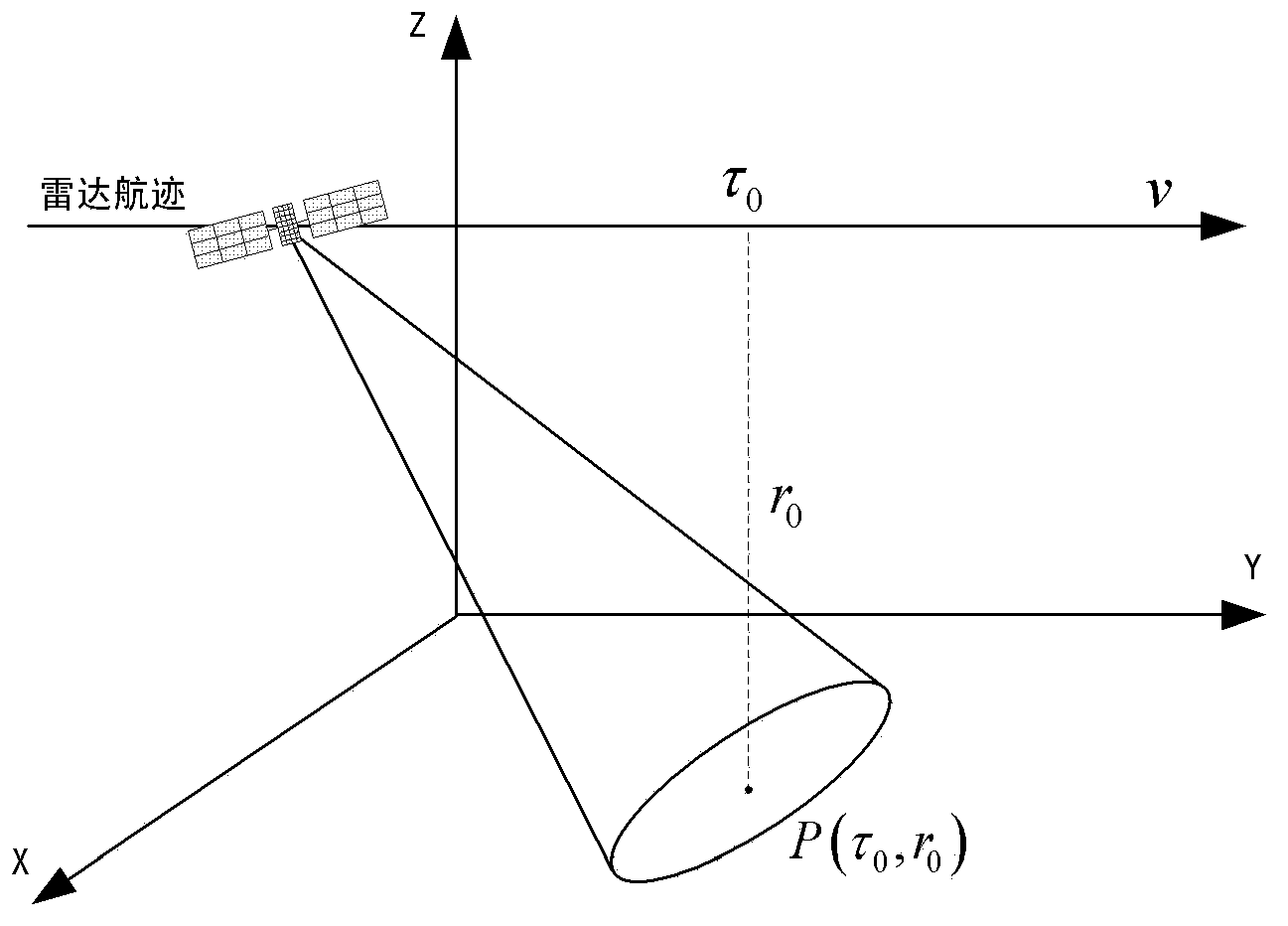
ActiveCN110208799AExact slope distance history expressionReduce phase errorRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAzimuth compressionTime domain
The invention relates to a Legendre-orthogonal-decomposition-baesd curve motion trajectory SAR wave-number domain imaging method. The method comprises: constructing a slant range history expression ina curved motion trajectory mode by using a three-dimensional speed and a three-dimensional acceleration; carrying out polynomial expansion on the constructed slant range history expression and carrying out keeping to the fourth order; transforming an SAR echo signal corresponding to the slant range into a two-dimensional frequency domain to obtain a two-dimensional frequency spectrum; with a Legendre orthogonal polynomial, spreading the two-dimensional frequency spectrum for a distance range frequency and carrying out keeping to a third order; carrying out phase compensation based on a two-dimensional frequency spectrum developed based on Legendre and completing distance migration correction and distance range focusing; and carrying out azimuth compression in a distance-Doppler domain andcarrying out transformation in a two-dimensional time domain to obtain a focusing image. Therefore, a target imaging blurring problem at the scene edge is solved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
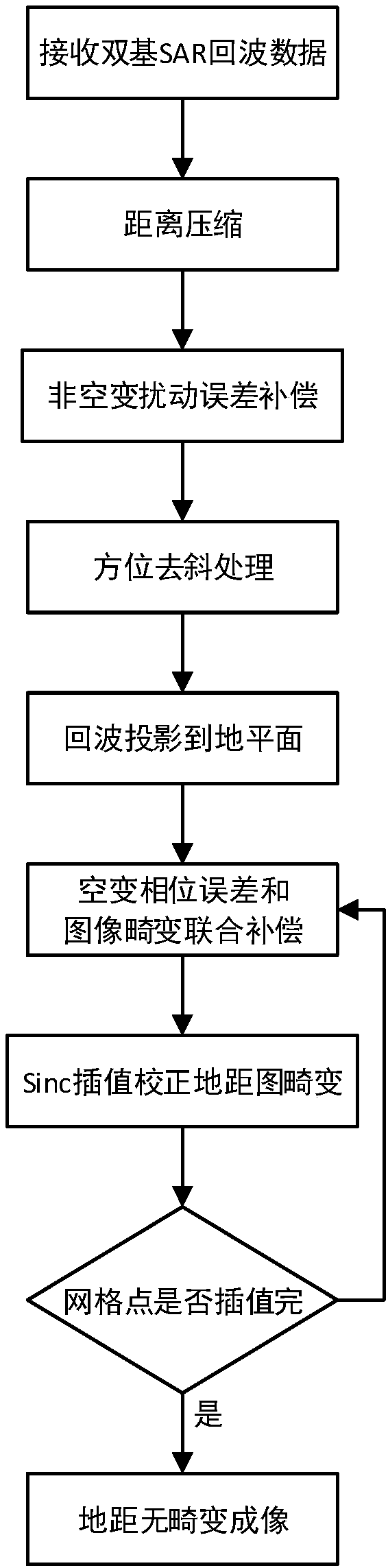
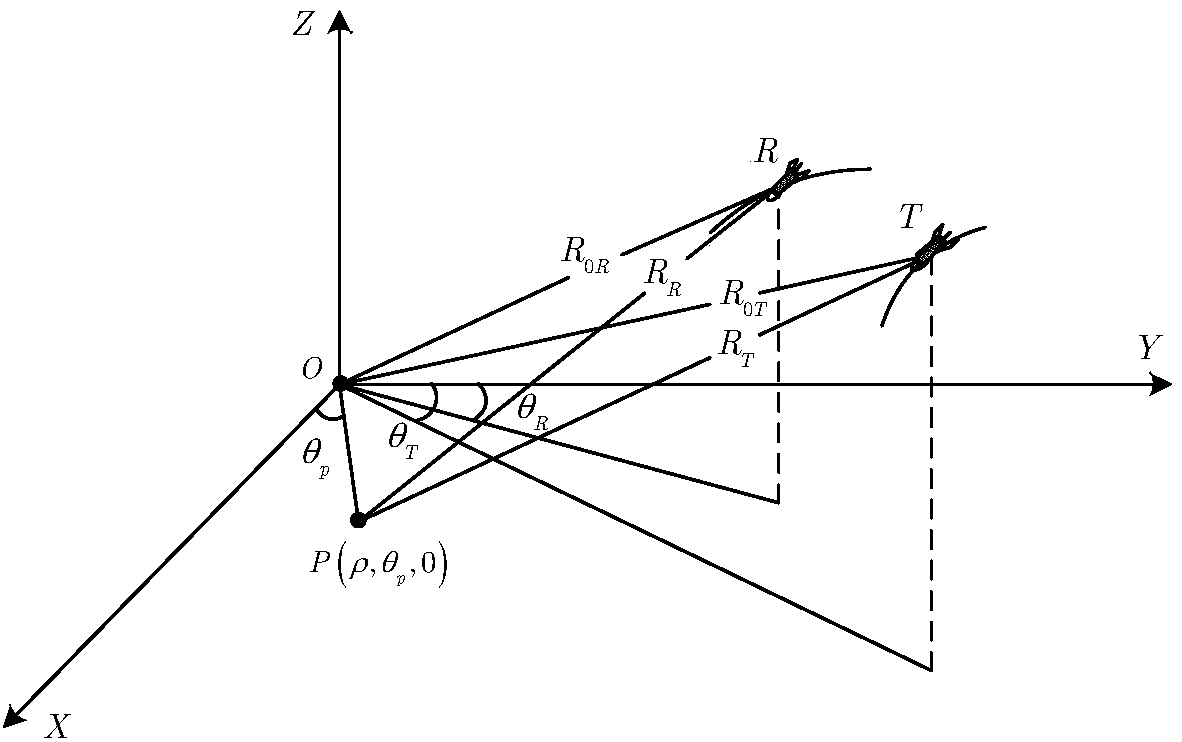
Bistatic arbitrary configuration SAR imaging method based on equivalent slant range
InactiveCN108490439AImproving Imaging AccuracyHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputer sciencePerformed Imaging
The invention discloses a bistatic arbitrary configuration SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) imaging method based on equivalent slant range. The bistatic arbitrary configuration SAR imaging method basedon equivalent slant range includes the steps: 1) constructing a bistatic equivalent slant range model; 2) performing range compression and non space variant error disturbance compensation; 3) performing azimuth de-sloping processing; 4) performing imaging on the ground range with distortion; 5) performing combined compensation of space variant phase error and image distortion on the imaging result; and 6) performing distortion correction on the ground range imaging with distortion. The bistatic arbitrary configuration SAR imaging method based on equivalent slant range can realize accurate phase and motion compensation for bistatic SAR imaging and obtain a bistatic SAR imaging result with higher focusing quality when three axles of a transmitting-receiving platform have velocity and acceleration.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
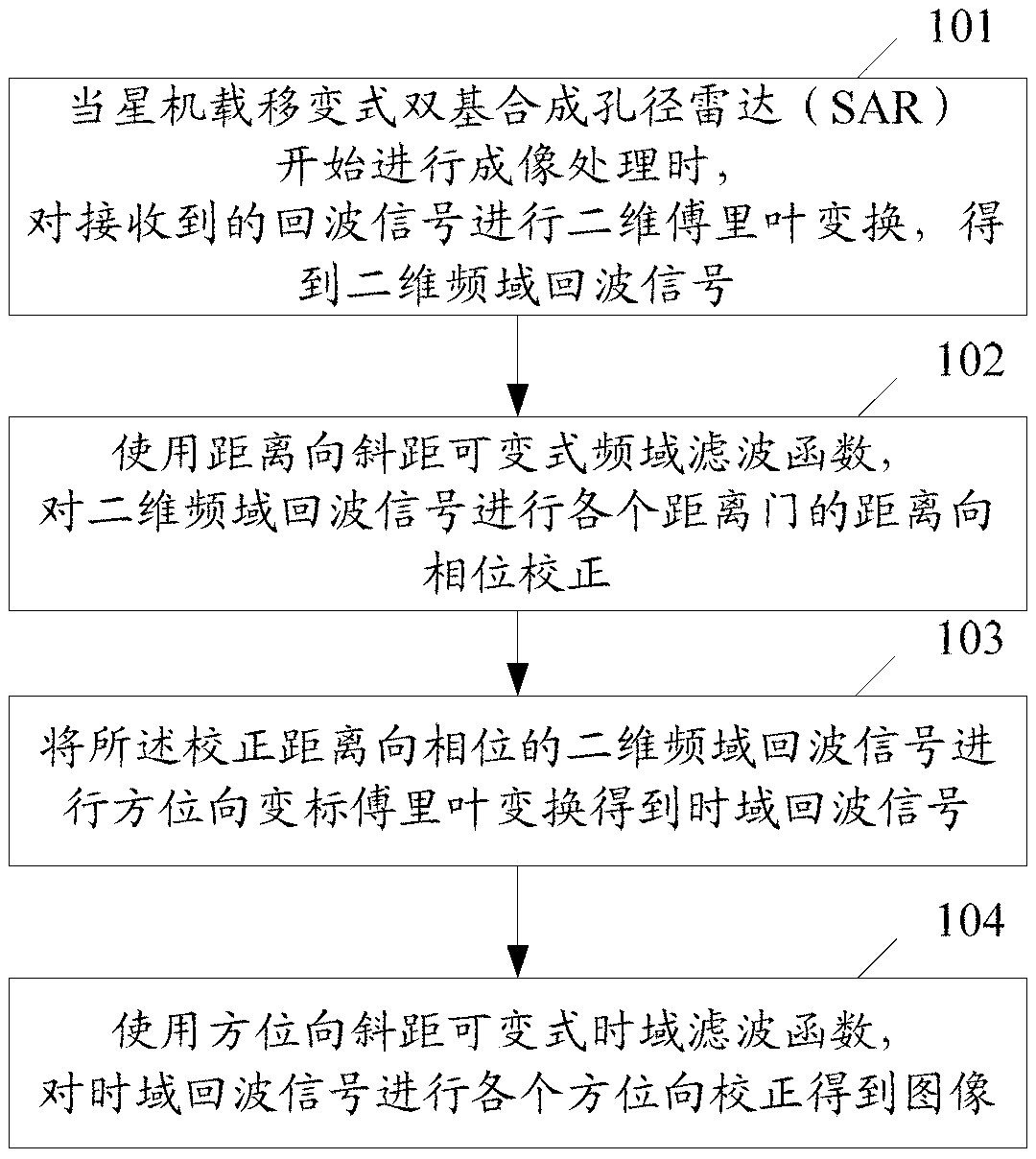
Method and device for imaging in satellite-borne and airborne double-base synthetic aperture radar
ActiveCN103323841ACompensation dependenceAccurate imagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInverse synthetic aperture radarRange gate
The invention discloses a method and device for imaging in satellite-borne and airborne double-base synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The method includes the steps that when the satellite-borne and airborne double-base synthetic aperture radar (SAR) performs the imaging process, the two-dimensional Fourier transform is performed on a received echo signal, and a two-dimensional frequency domain echo signal is obtained; by the utilization of a range slant-range variable frequency domain filtering function, range phase correction of all range gates is performed on the two-dimensional frequency domain echo signal; azimuth scaling Fourier conversion is performed on the two-dimensional frequency domain echo signal after the range phase correction, and a time-domain echo signal is obtained; by the utilization of an azimuth slant-range variable time-domain filtering function, correction in each azimuth is performed on the time-domain echo signal, and an image is obtained. The invention further discloses a device for the imaging in the satellite-borne and airborne double-base SAR. By the adoption of the method and the device, dependency, on slant ranges, of a target can be compensated, and then the imaging is more accurate.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for calibrating amplitude consistency of a plurality of ground receivers with radar satellite
ActiveCN103257340AIdeal far field effectThe signal propagation path is exactly the sameRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWorking environmentOrbit
The invention discloses a method for calibrating amplitude consistency of a plurality of ground receivers with a radar satellite, and relates to the microwave remote sensing calibrating technology. A satellite-based SAR in orbit is used as an emission source, the ground receivers are distributed within a certain range of a calibrating field, compensation processing is carried out on data received by all the ground receivers to reduce detecting error amount of level signals with same power by the ground receivers, and receiving amplitudes of the ground receivers are consistent. The ground receivers receive signals transmitted by the satellite-based SAR, a series of ground receivers are distributed inwards in a swath range, thus fitting of an SAR transmitting range antenna pattern can be achieved, a single ground receiver is arranged in a swath azimuth, and therefore an SAR transmitting azimuth antenna pattern can be measured. According to the method, the mode that the satellite-based SAR is used for transmitting signals, and the ground receivers receive the signals simultaneously in the same place is adopted, the working environment and the working condition are high in consistency, and accuracy and reliability of calibrated results of the amplitude consistency are ensured.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining the geographic coordinates of pixels in SAR images
A method for effecting the airborne determination of geographic coordinates of corresponding pixels from digital synthetic aperture radar images, where the SAR images are available in the form of slant range images and the recording position of the respective SAR image is known. The coordinates of the corresponding pixels in the SAR images and the corresponding range gates are used in each case to determine the distance between a corresponding resolution cell on the ground and the respective recording position of the respective SAR image. The determined distances and associated recording positions of the SAR images are used to determine the geographic coordinates of the corresponding pixels in the SAR images by employing a WGS84 ellipsoid.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Multi-receiver equidistant rectangular distribution-based SAR deception jamming method and system
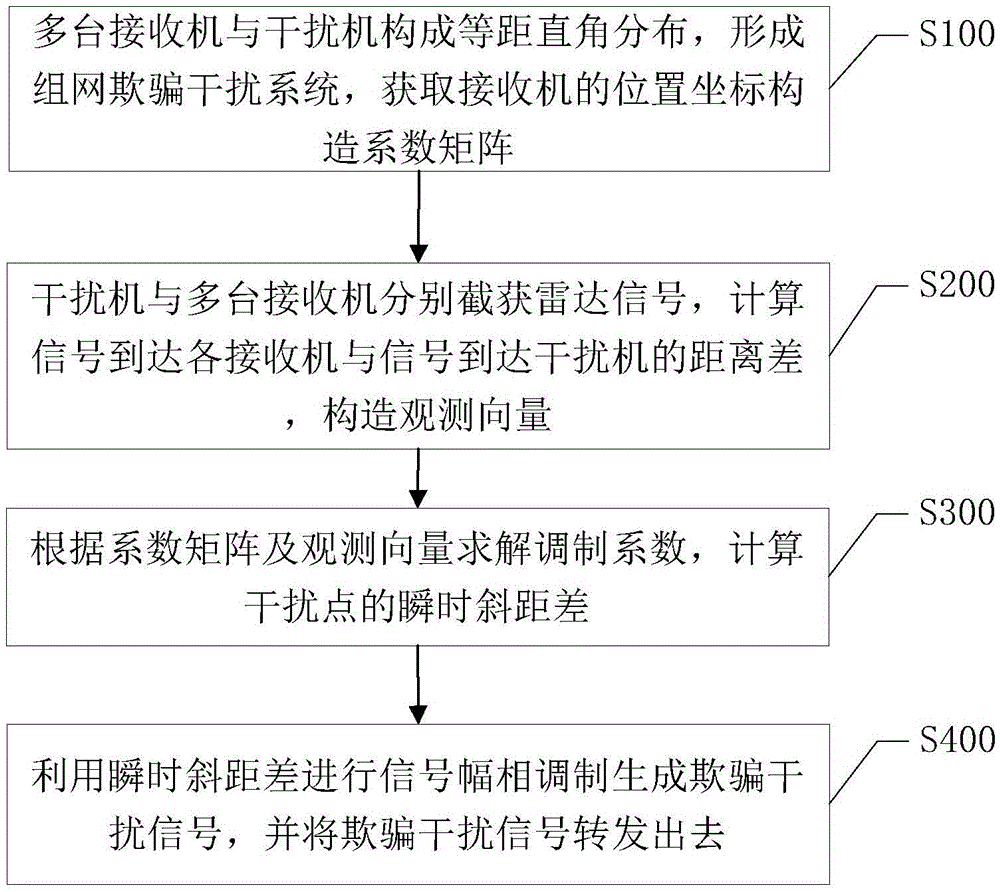
ActiveCN105467368AGood deception jamming effectQuality improvementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringEuclidean vector
The invention discloses a multi-receiver equidistant rectangular distribution-based SAR deception jamming method and system. The method includes the following steps that: a plurality of receivers and a jammer are in equidistant rectangular distribution, so as form a networking deception jamming system, and the position coordinates of the receivers are obtained to construct a coefficient matrix; the jammer and the plurality of receivers respectively intercept radar signals, and the difference of a distance by which the signals arrive at the receivers and a distance by which the signals arrive at the jammer is calculated, and an observation vector is constructed; a modulation coefficient is solved according to the coefficient matrix and the observation vector, the instantaneous slant range difference of interference points is calculated; and the instantaneous slant range difference is utilized to carry out signal amplitude and phase modulation, so that deception jamming signals are generated, and the deception jamming signals are forwarded. According to the method, the plurality of receivers are in equidistant rectangular expansion layout, and when a large error exists in investigation parameters, the optimal expansion layout of 2N receivers is set according to the magnitude of the error, so that the magnitude of the error can be decreased to 1 / 2N of that of the original error, and therefore, the precision of deception jamming modulation can be improved, and an interference image with higher quality can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
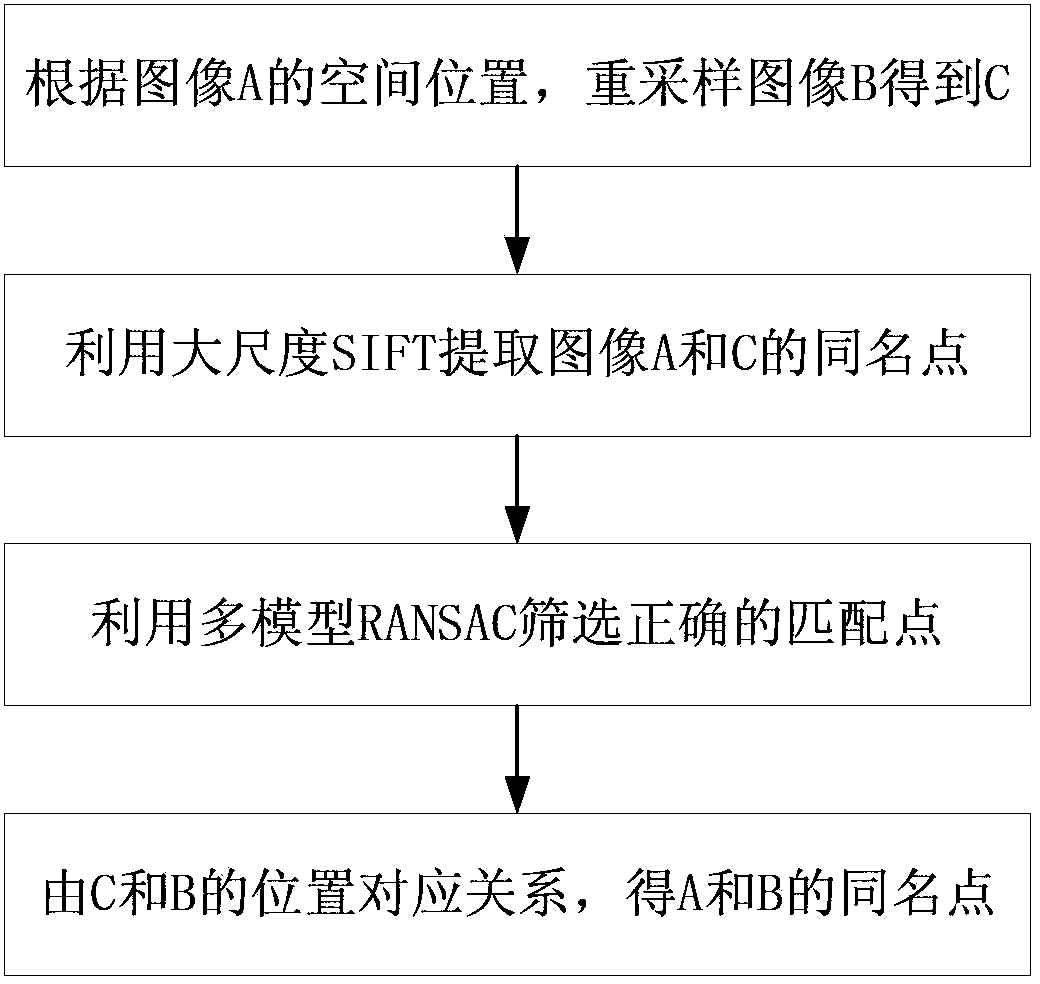
SAR slant range image match automatic extraction method based on geometric model
InactiveCN103646389AOvercome the problem of not extracting enough repetitive featuresIncrease the number of correct pointsImage analysisScale-invariant feature transformComputer vision
The invention provides a SAR slant range image match automatic extraction method based on a geometric model. According to the method, the problem that enough repeated characteristics cannot be extracted by a SIFT when large geometric distortion exists between slant range images can be overcome, and correct matching points can be effectively screened out based on the improved RANSAC algorithm. At first, the imaging geometrical relationship between two images is established through the carrier aircraft track and DEM so as to transform one image A onto coordinates of another image B to obtain an image C; then, matches between the image B and the image C are extracted by adopting scale invariant feature transform method (SIFT) on a sampled image; and finally, correct matches are screened out by adopting random sample consensus method (RANSAC), and match coordinates on the image C are transformed onto the image A to obtain matches of the image A and the image B.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
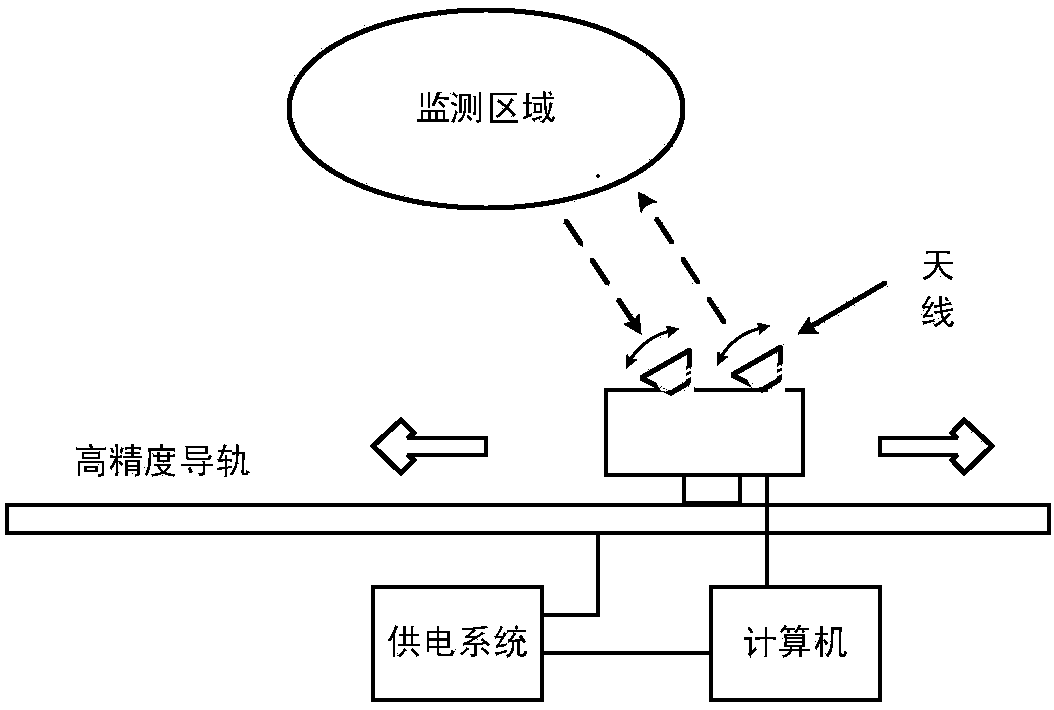
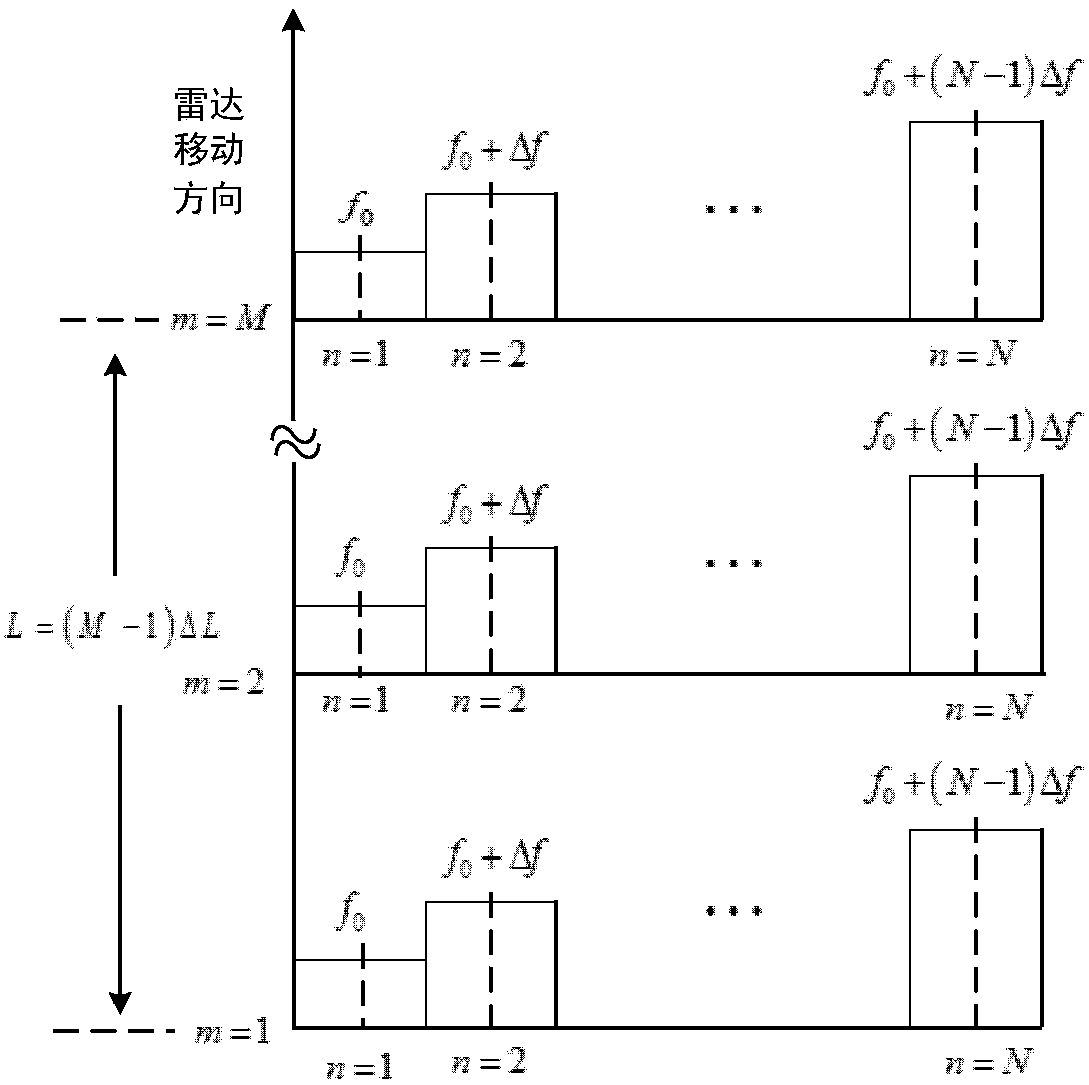
GB-SAR deformation monitoring method based on triple stepping
InactiveCN105180852AHigh range resolutionExpand the scope of monitoringUsing wave/particle radiation meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverDeformation monitoring
The invention provides a GB-SAR deformation monitoring method based on triple stepping. According to radar system design, GB-SAR based on triple stepping is utilized for deformation measurement; for first stepping, stepped frequency continuous wave (SFCW) signals are employed to synthesize large signal bandwidth, isolation is improved through transceiver antenna separation; for second stepping, a radar device is mounted on a linear guide rail and does stepping motion in a stop-go-stop mode, orientation resolution is improved through relatively large aperture synthesis, signals are emitted and received by the radar device in stop periods, so a phase error caused by signal transceiving in motion periods is avoided; for third stepping, radar device antennas do stepping motion sequentially along the orientation, a relatively wide monitoring area is covered, and data at different antenna positions are spliced and are used for imaging processing. Imaging processing on acquired data is carried out based on echo signal characteristics of the GB-SAR system, compensation for an instantaneous slant range difference between pulses is not necessary, computational complexity is relatively low, and timeliness requirement of the GB-SAR system can be satisfied.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System for automatically landing aircraft using image signals and method of controlling the same
Disclosed herein are a system for automatically landing an aircraft using image signals and a method of controlling the system. The system includes an altimeter installed on the aircraft; a landing mark placed at a landing location on a landing runway; a camera installed on the aircraft, oriented toward the front of the aircraft, and configured to detect the shape of the landing mark in image information form; and a FCC configured to calculate the angle between the aircraft and the ground, the ground range and the slant range between the aircraft and the landing location using the altitude information measured by the altimeter, the image information of the landing mark captured by the camera, angle information composed of the pitch, roll and yaw angles of the aircraft, and the angle of entry into the landing runway, and configured to control the automatic landing of the aircraft.
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
Satellite broadcast communication method and system
InactiveUS7643827B1Compensation effectImprove reliabilityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesSignificant differenceElectric power
The invention provides for the design of a single beam communication satellite system covering a single service area, either uplink, downlink or both, by which rain fade effects are totally compensated. The rain fades, characterized by fixed margins, are not exceeded for a certain percentages of time. The service area must be large enough so that the statistical rain fades (in decibels) vary significantly over the service area. The single beam antenna must be electrically large enough and must have a beam forming network capable of multiple component beams so that a gain profile can be established for the antenna which compensates for the fixed margins established over the service area. Since no subscriber has excess fixed margin this results in a minimum power system. Other significant effects such as differences in slant range and other systemic variations over the service area also can be compensated.
Owner:KIESLING JOHN D
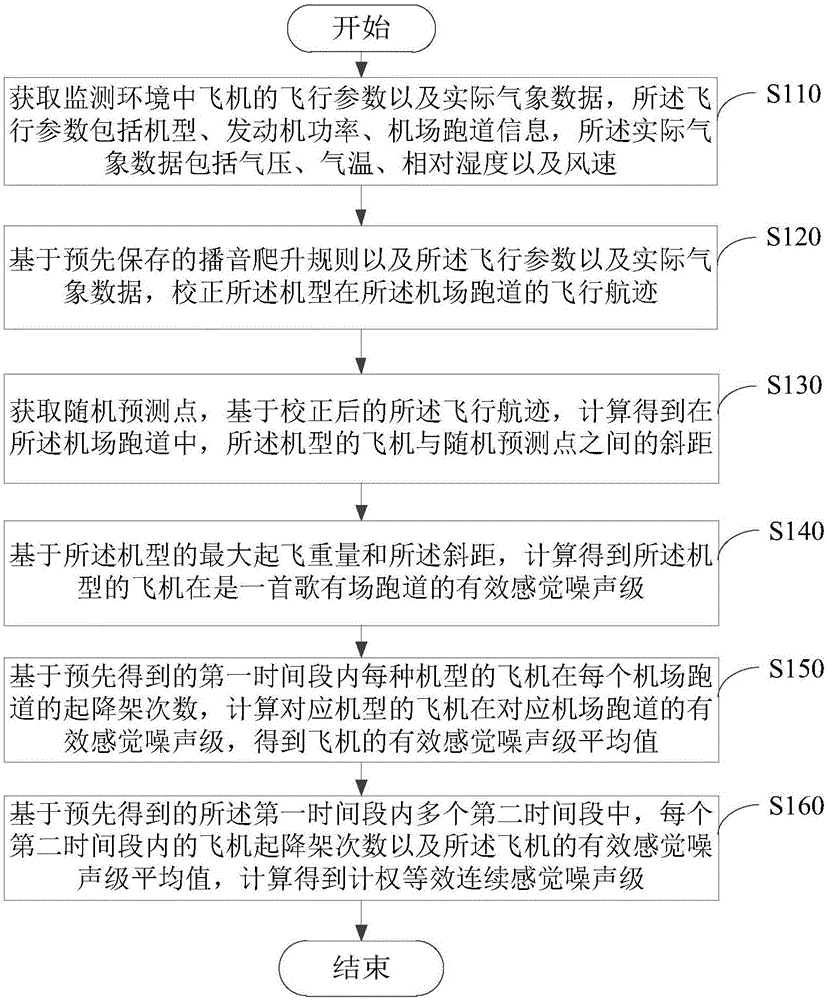
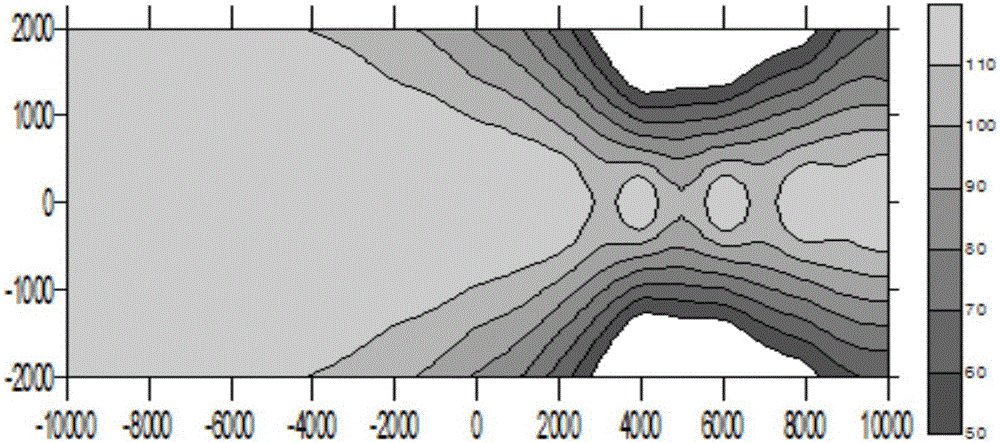
Aircraft noise monitoring method and device thereof
The invention provides an aircraft noise monitoring method and device. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring flight parameters and actual meteorological data of an aircraft in the monitoring environment, correcting a flight path of the aircraft at an airfield runway, acquiring a random predicted point, calculating a slant range between the aircraft and the random predicted point, calculating and obtaining effective perceived noise levels of the aircraft based on the maximum takeoff weight and the slant range of the aircraft, based on takeoff and landing aircraft times of each type aircraft obtained in advance at each airfield runway in a first period, calculating average values of the effective perceived noise levels of the aircraft, calculating and obtaining weighted equivalent continuous perceive noise levels based on takeoff and landing aircraft times of the aircraft in each second period and the average values of the effective perceived noise levels, a plurality of second periods are obtained in advance in the first period. By adopting the method, the problems that a traditional aircraft program noise monitoring method is accidental and can not evaluate the noise impact caused by aircraft noise objectively and accurately can be alleviated.
Owner:INST OF RADAR & ELECTRONICS CONFRONTATION ARMY AIR FORCE EQUIP RES INST OF PLA +1
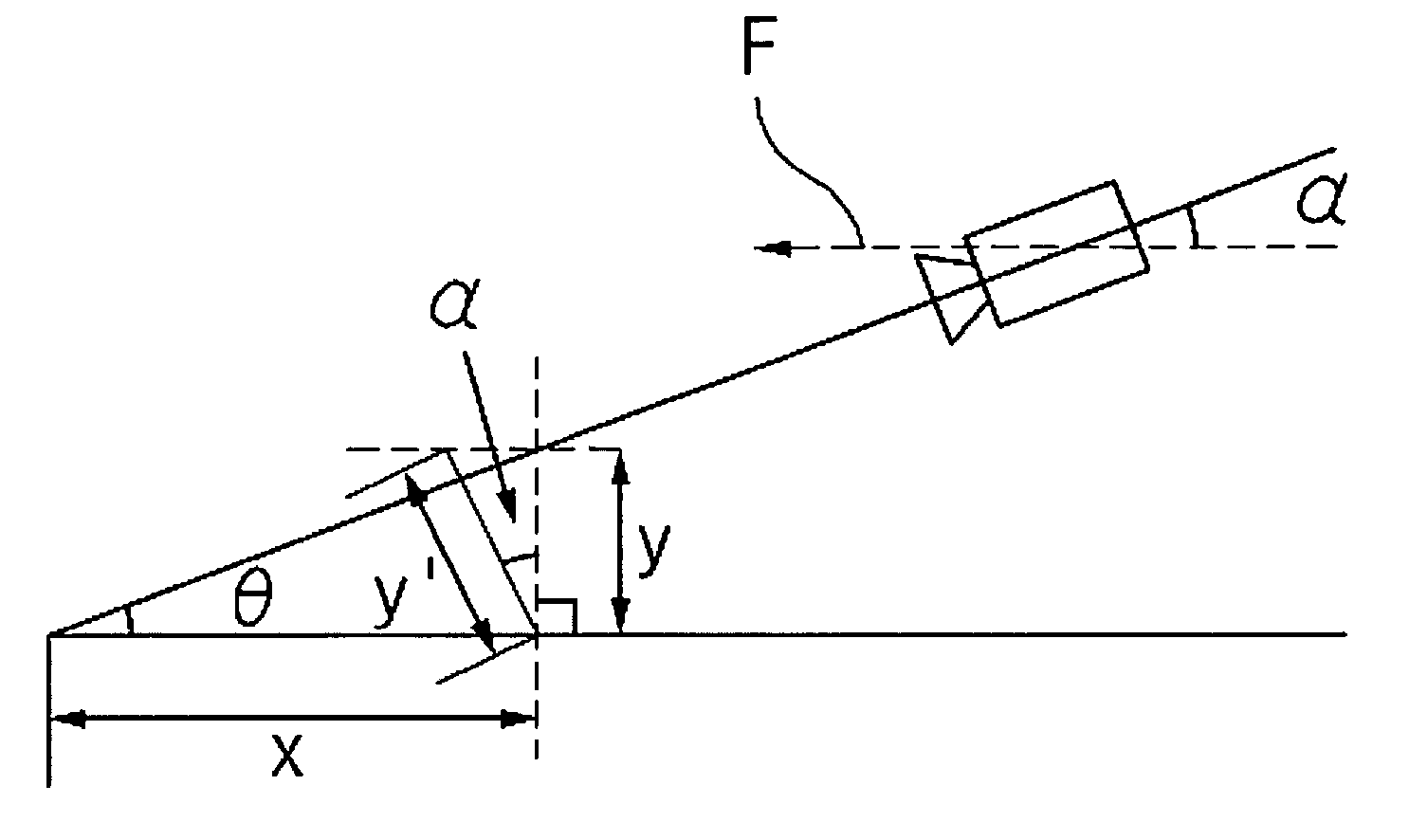
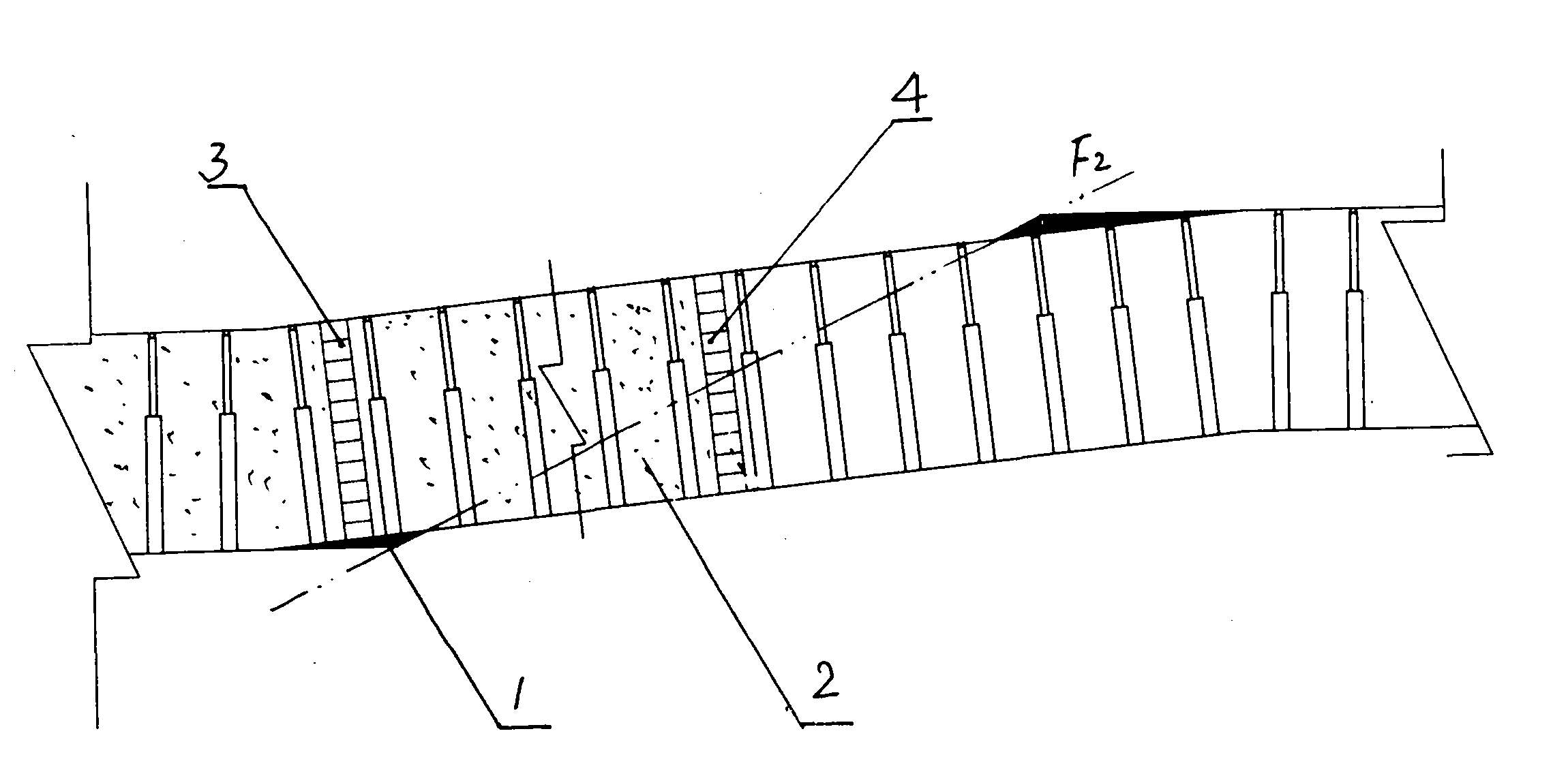
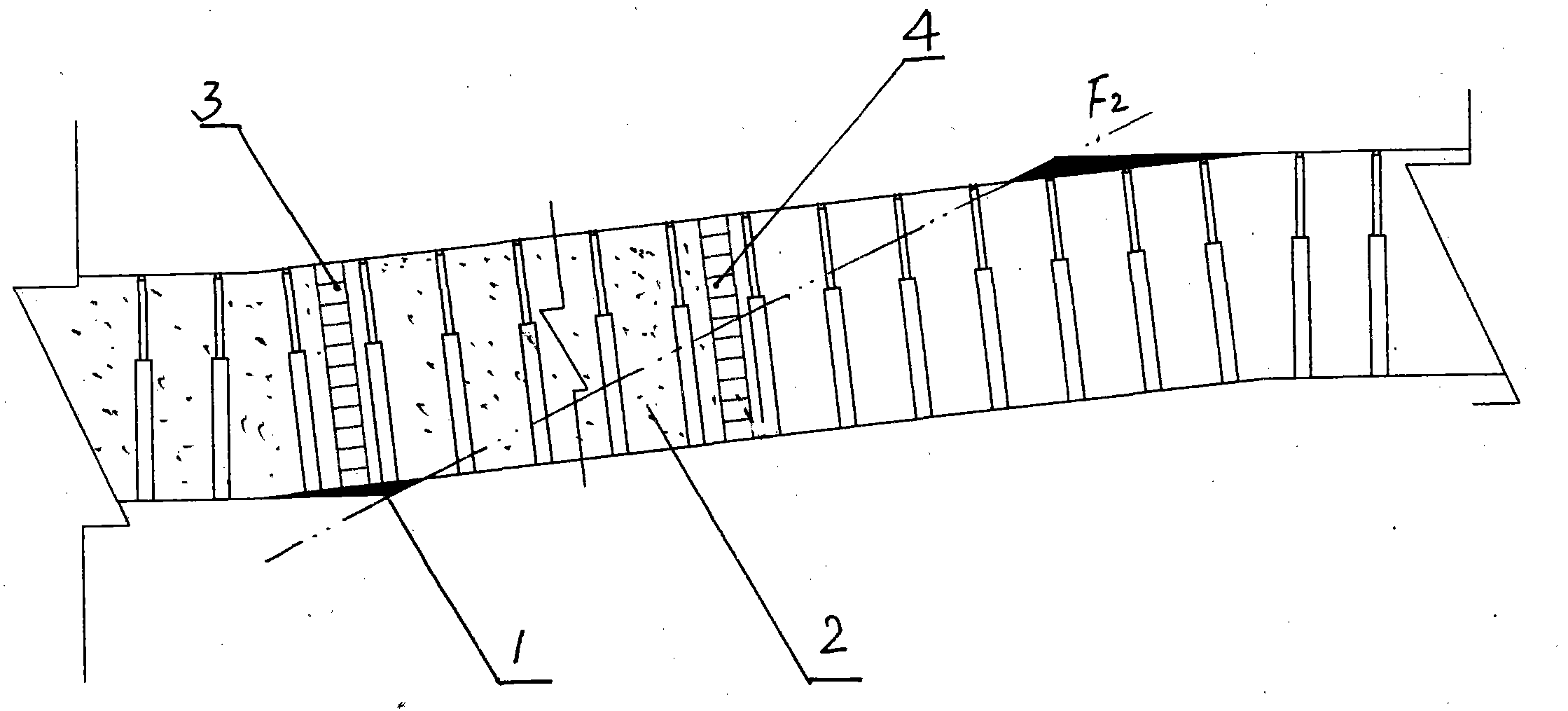
Coal mine up-dip working face slant range paste-like filling method
InactiveCN101881179ADense fillingImprove filling capacityMaterial fill-upEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a coal mine up-dip working face slant range paste-like filling method. The method comprises the following steps: during the up-dip mining process of the working face, a group of dam walls are arranged on a step with larger drop height, each dam wall is formed by filling floor mud in woven bags and stacking the woven bags side by side along the advancing direction of the working face, the roof is 18-22cm higher than the dam walls, the woven bags are stacked while the push-gather of the working face is performed forward; and when the push-gather of the working face reaches a filling interval, the filling pipeline extends to the worked-out section from the working face, and the paste-like is filled in each subsection divided by the dam walls in turn so that each subsection reaches the specified filling height. By adopting the step type filling technology of the invention, the paste filling height of each place on the working face is increased, the filling effect of the worked-out section is increased and the sinking amount of the overlying roadway on the working face is reduced.
Owner:新汶矿业集团有限责任公司孙村煤矿
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com