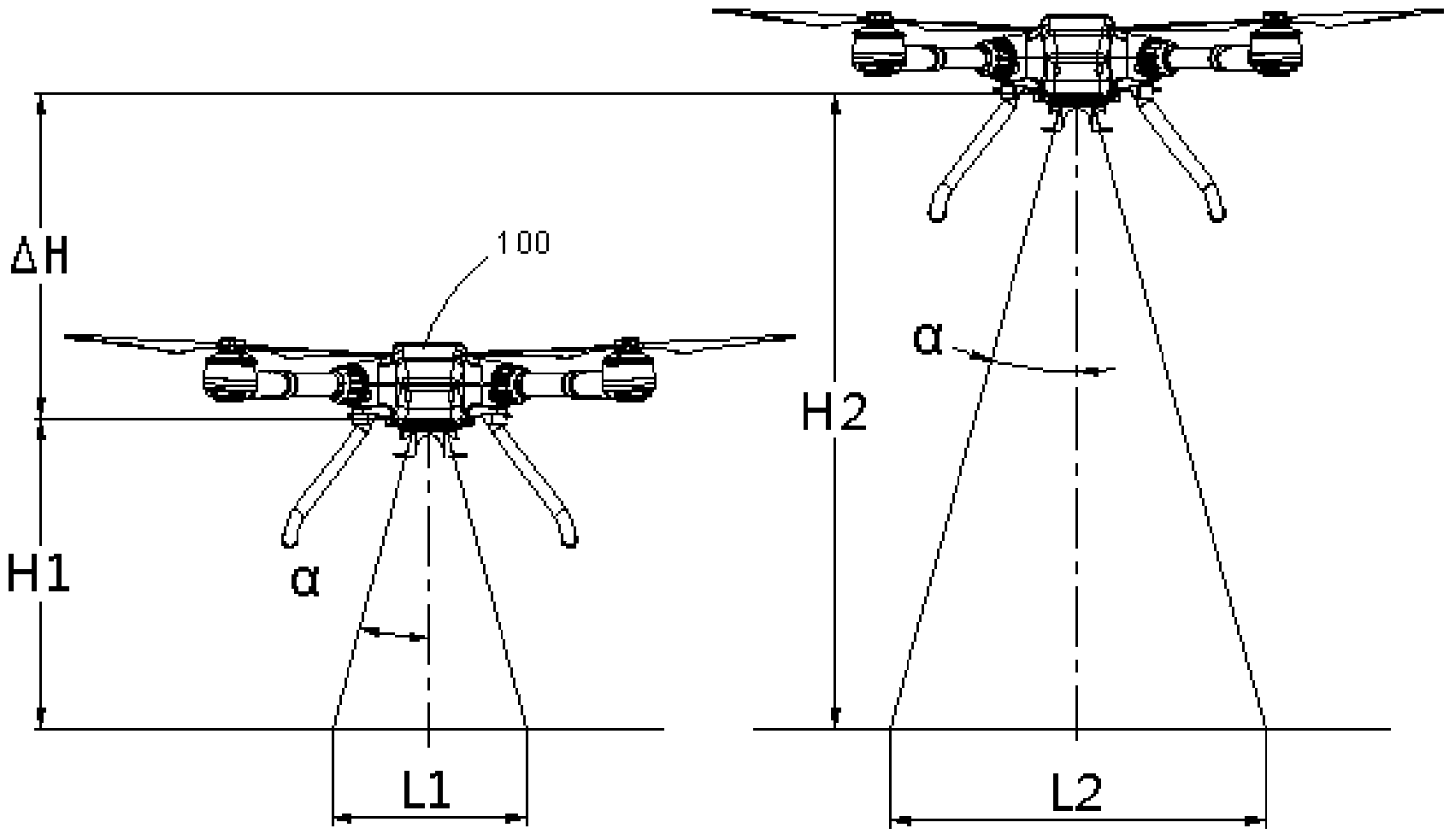
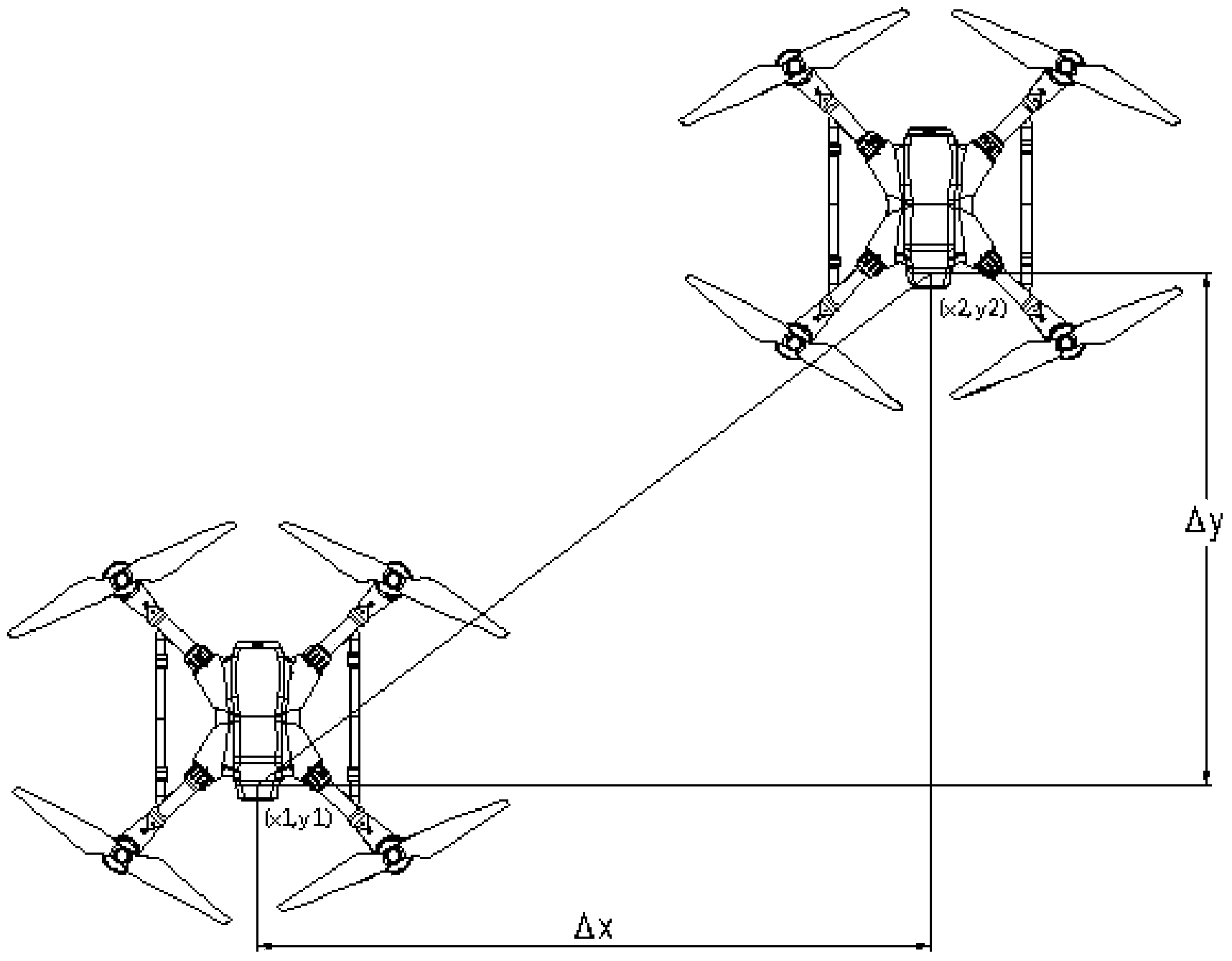
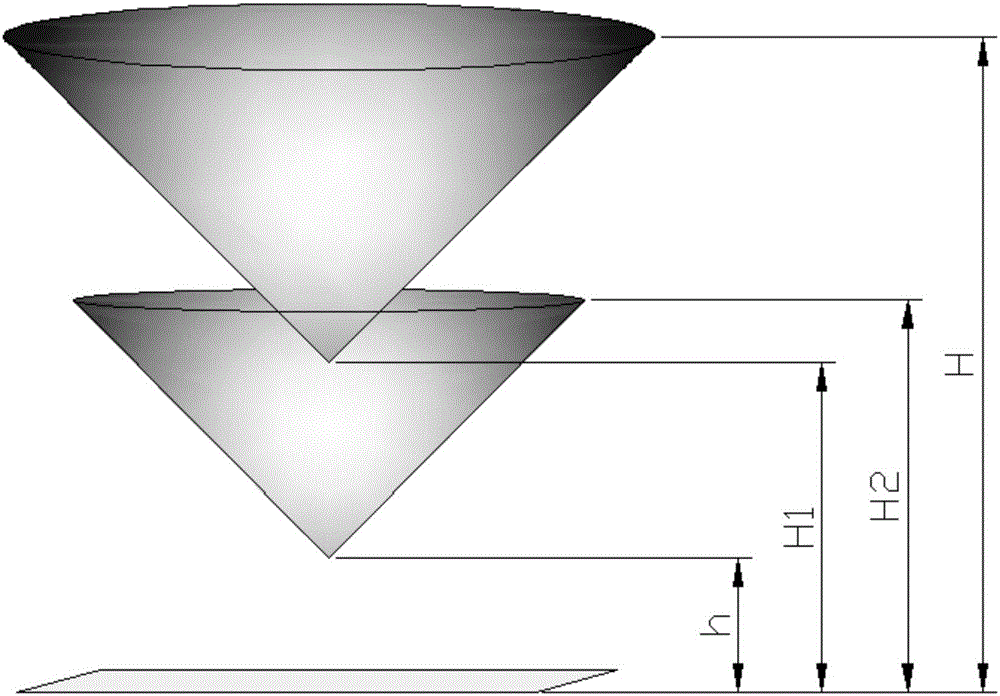
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199 results about "Automatic landing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
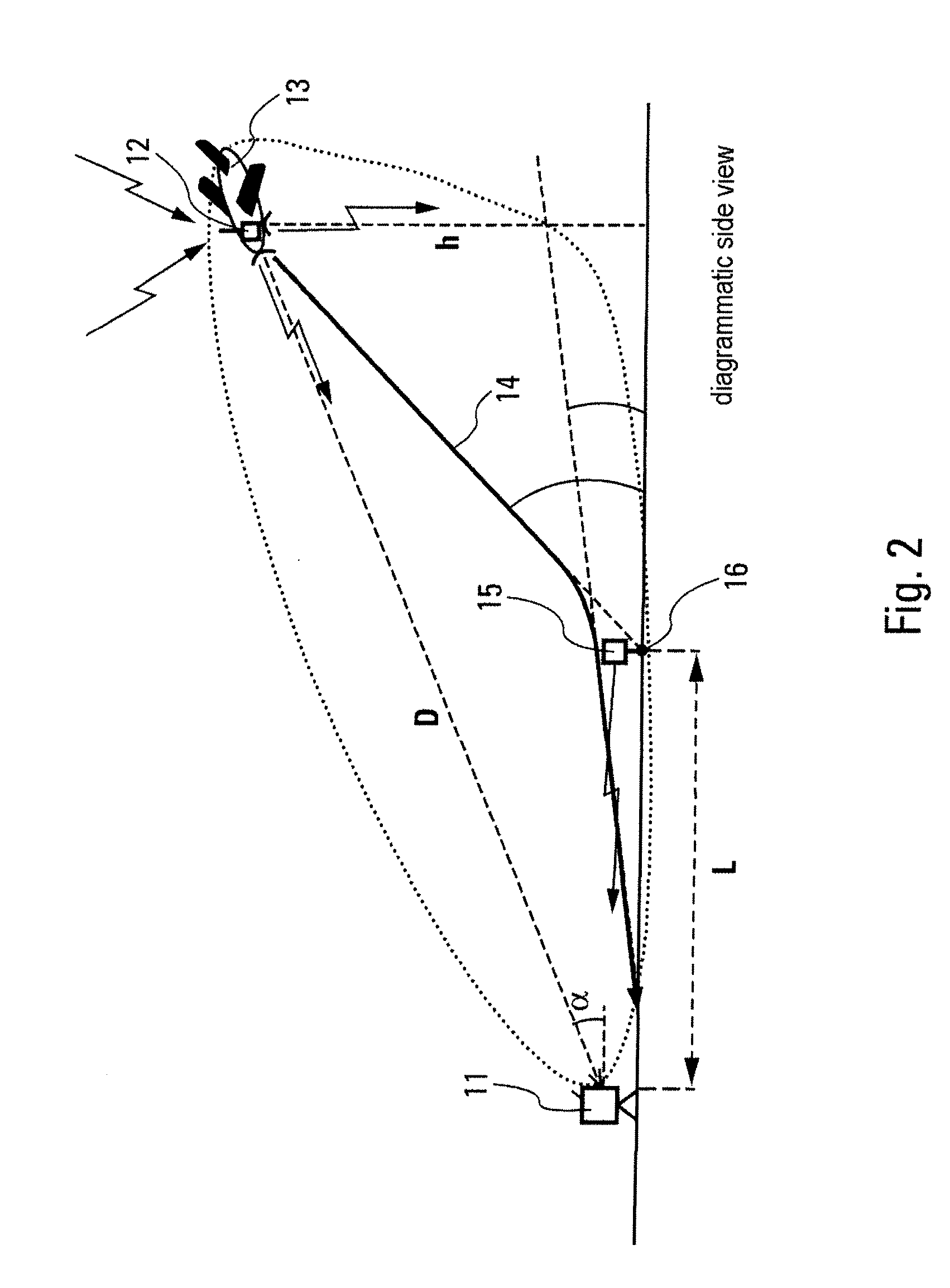
The first "commercial development" automatic landings (as opposed to pure experimentation) were achieved through realising that the vertical and lateral paths had different rules. Although the localiser signal would be present throughout the landing, the glide slope had to be disregarded before touchdown in any event.
Helicopter
ActiveUS20110301784A1Reduce problem sizeEasy to flyPropellersUnmanned aerial vehiclesMission planGround station
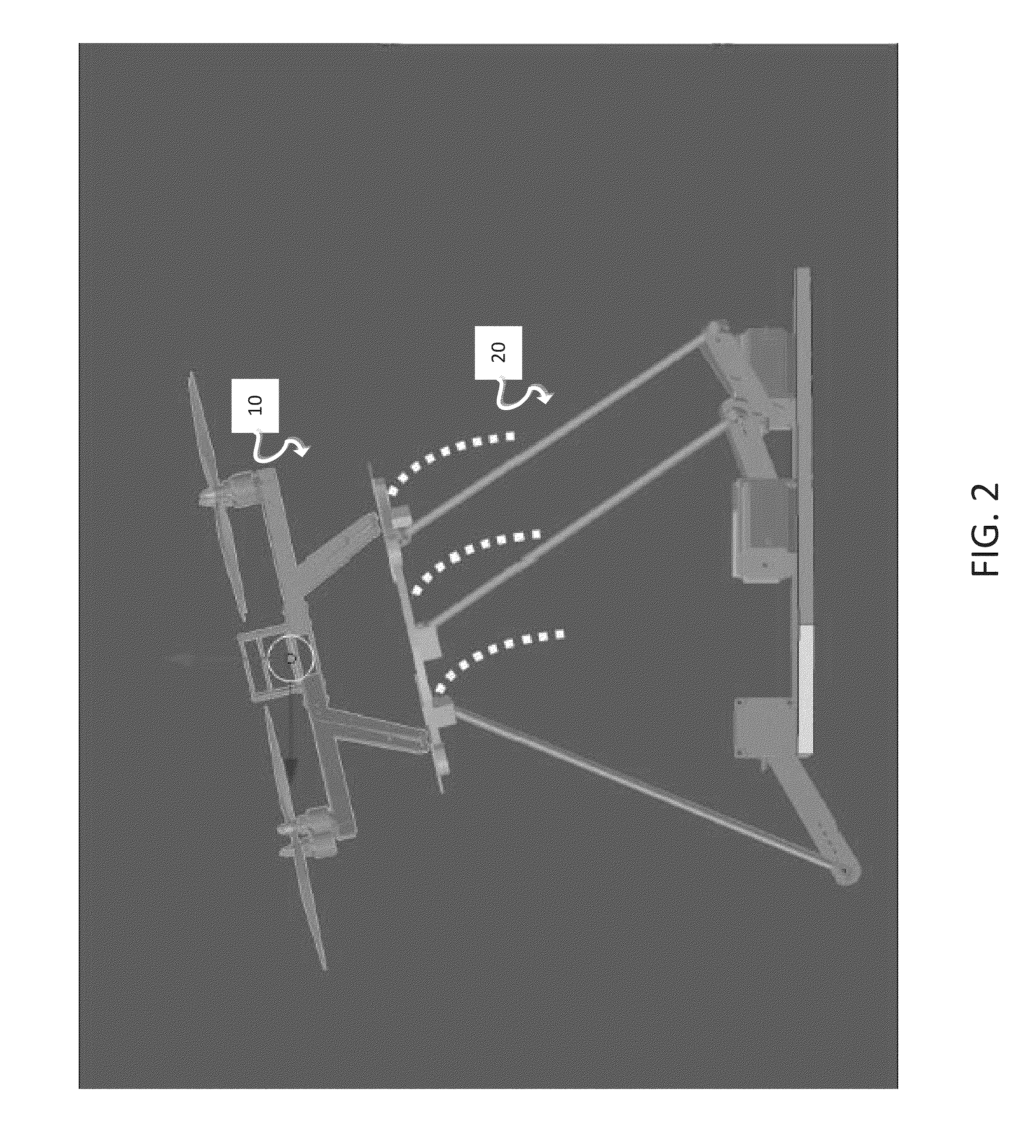
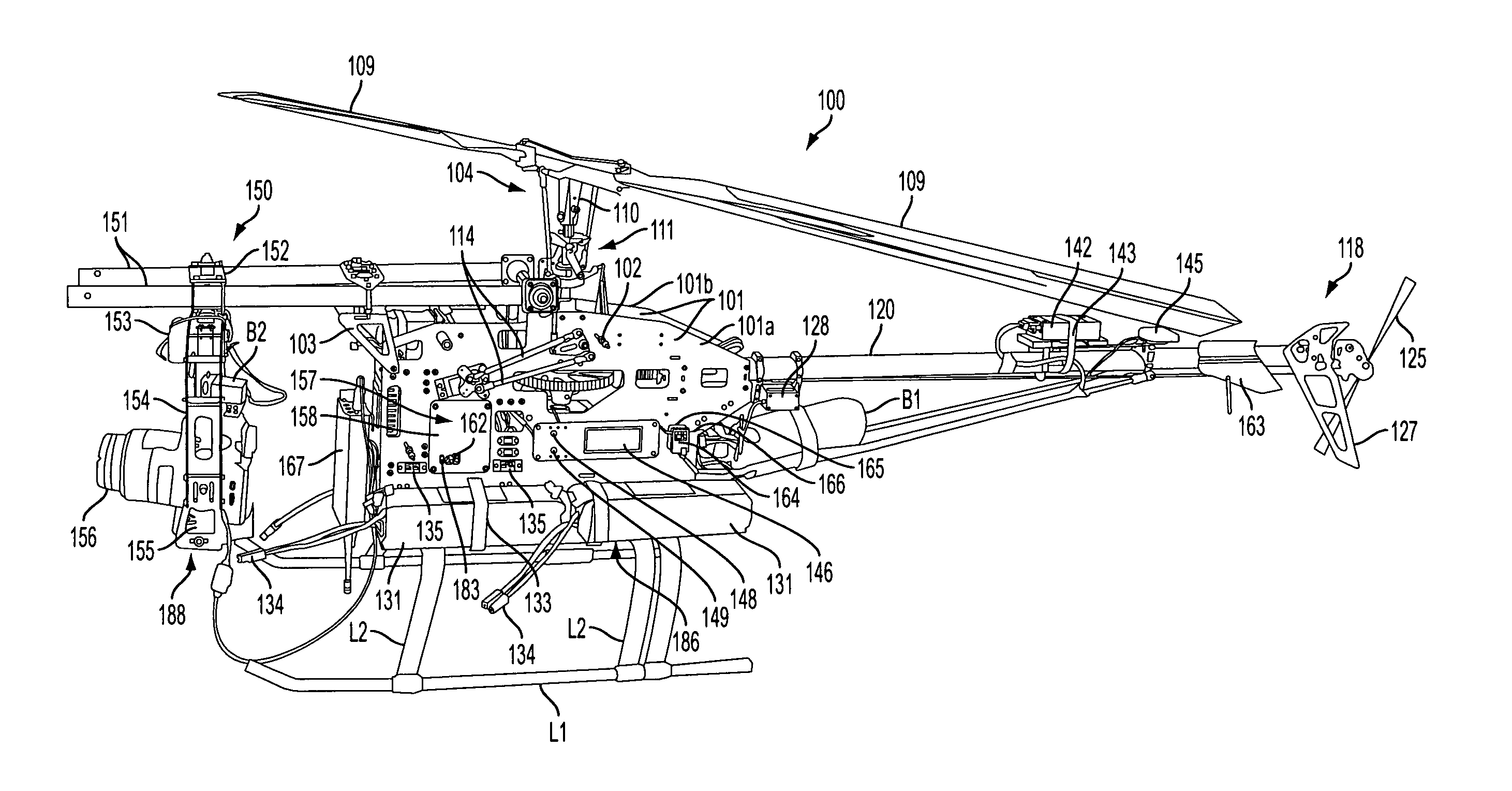
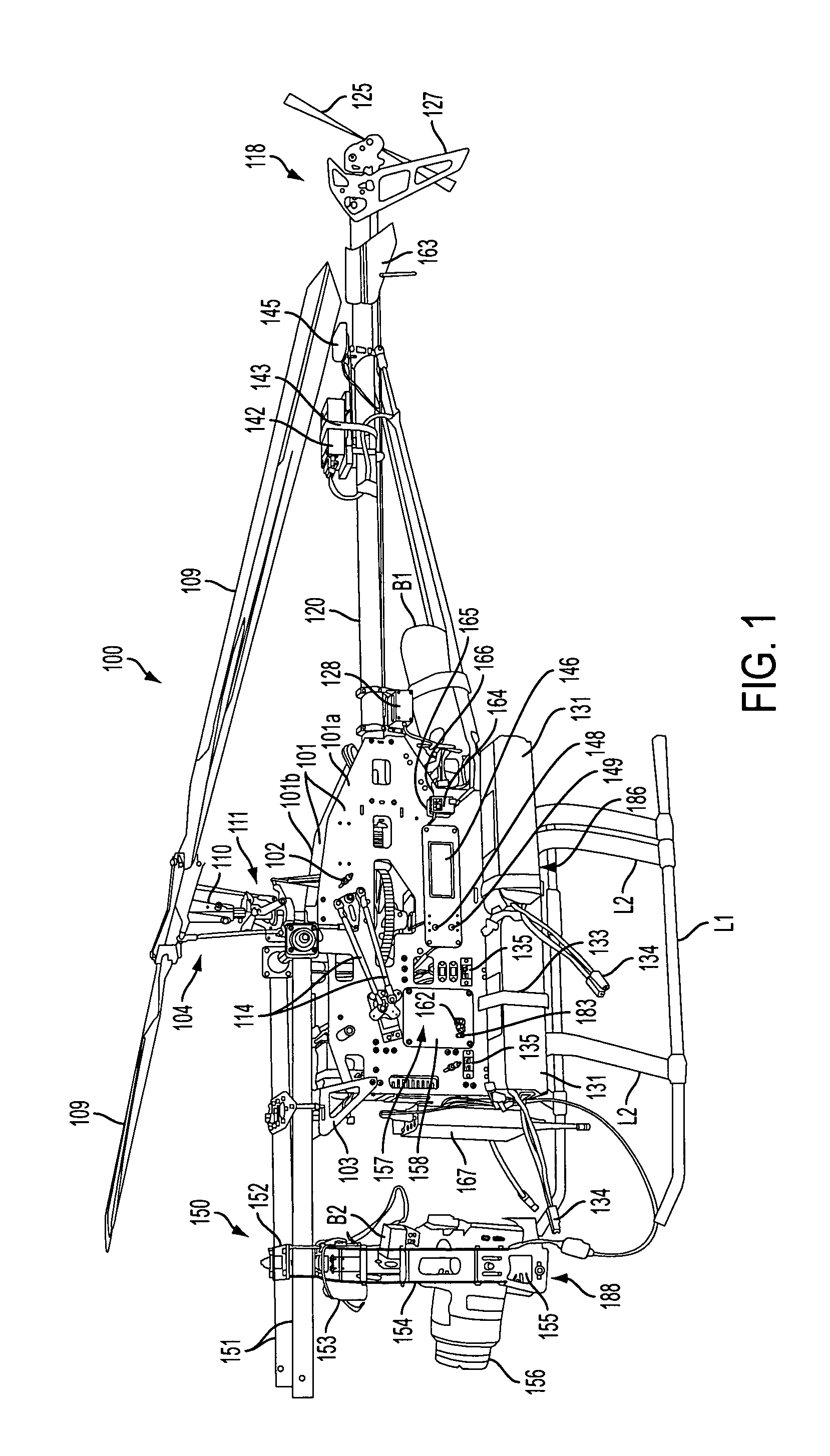
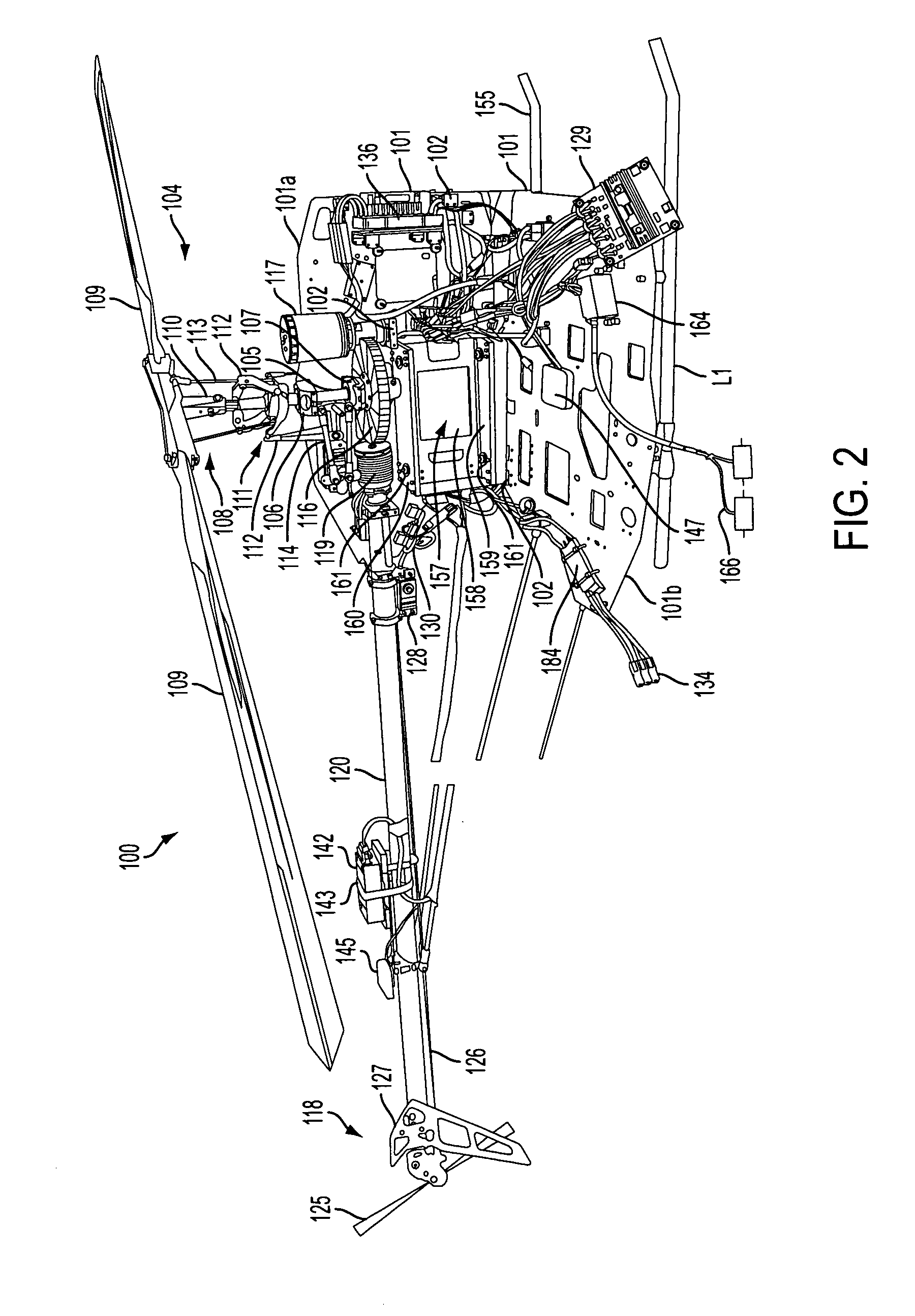
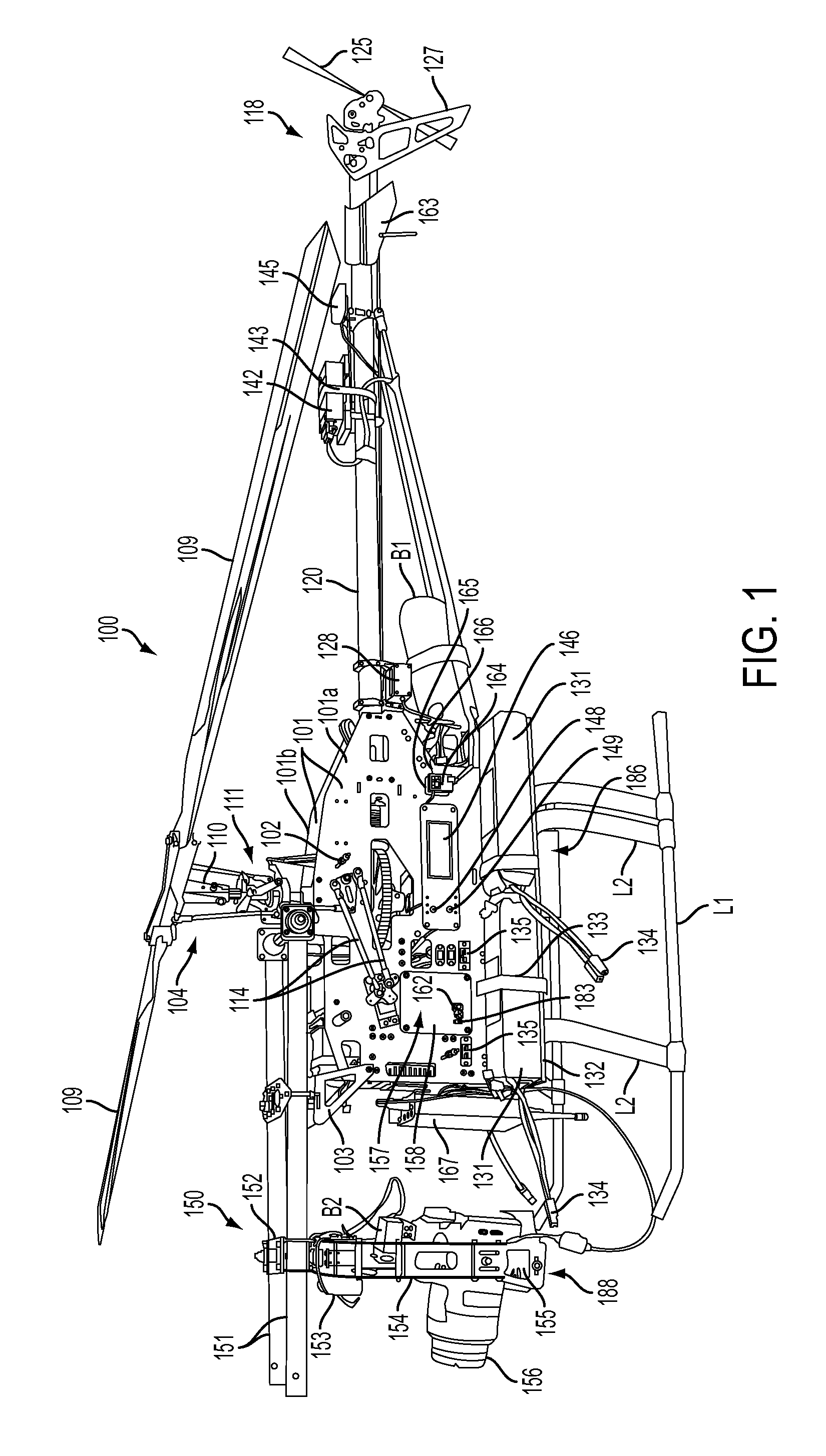
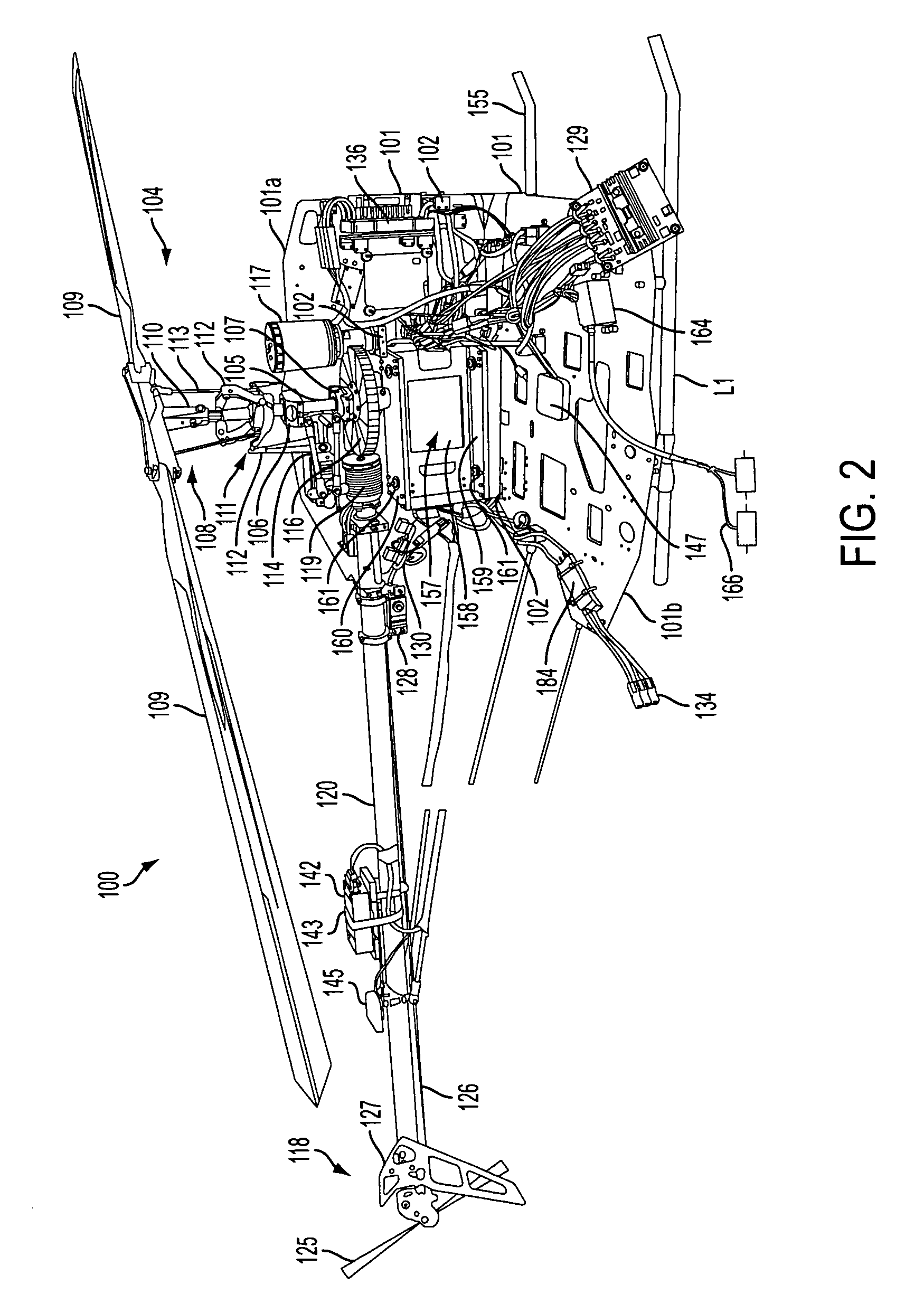
The present invention relates to a reduced scale industrial helicopter, with an integrated automatic flight control system, that includes core autopilot functions, GPS management, and full-function navigation systems. The autopilot technology includes rapid launch capability, real-time in-flight switching between one or more of a) remote control, b) autopilot-directed, c) ground station controlled, and d) home modes, and is upgradeable. The helicopter is used for high or low altitude surveillance, and can handle various payloads, including photographic missions. The helicopter may include onboard batteries and / or a unique battery unit disposed beneath the helicopter, and includes autonomous features such as automatic takeoff, automatic landing, safety return to home base, and predetermined mission plans.
Owner:GEOTECH ENVIRONMENTAL EQUIP
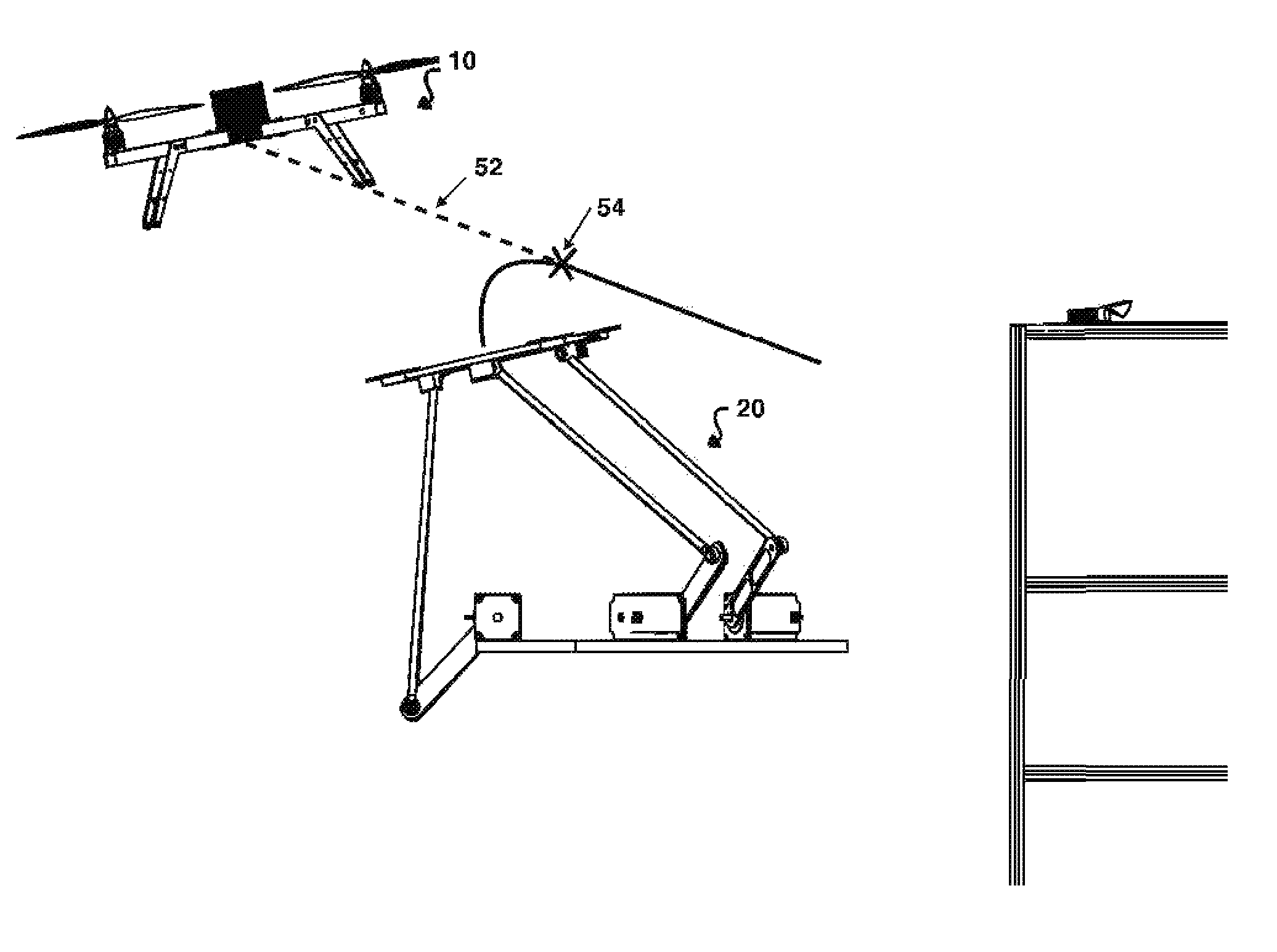
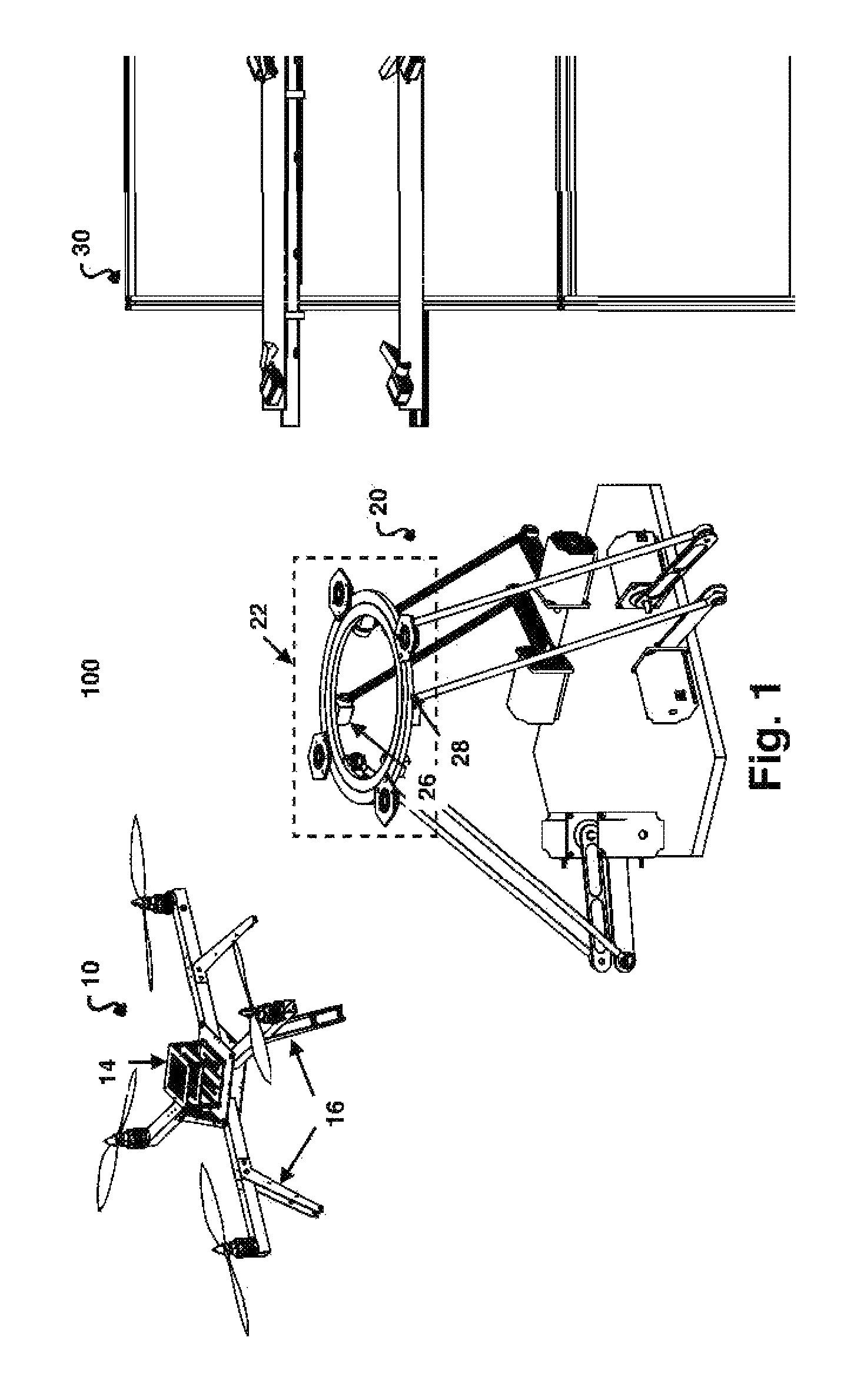
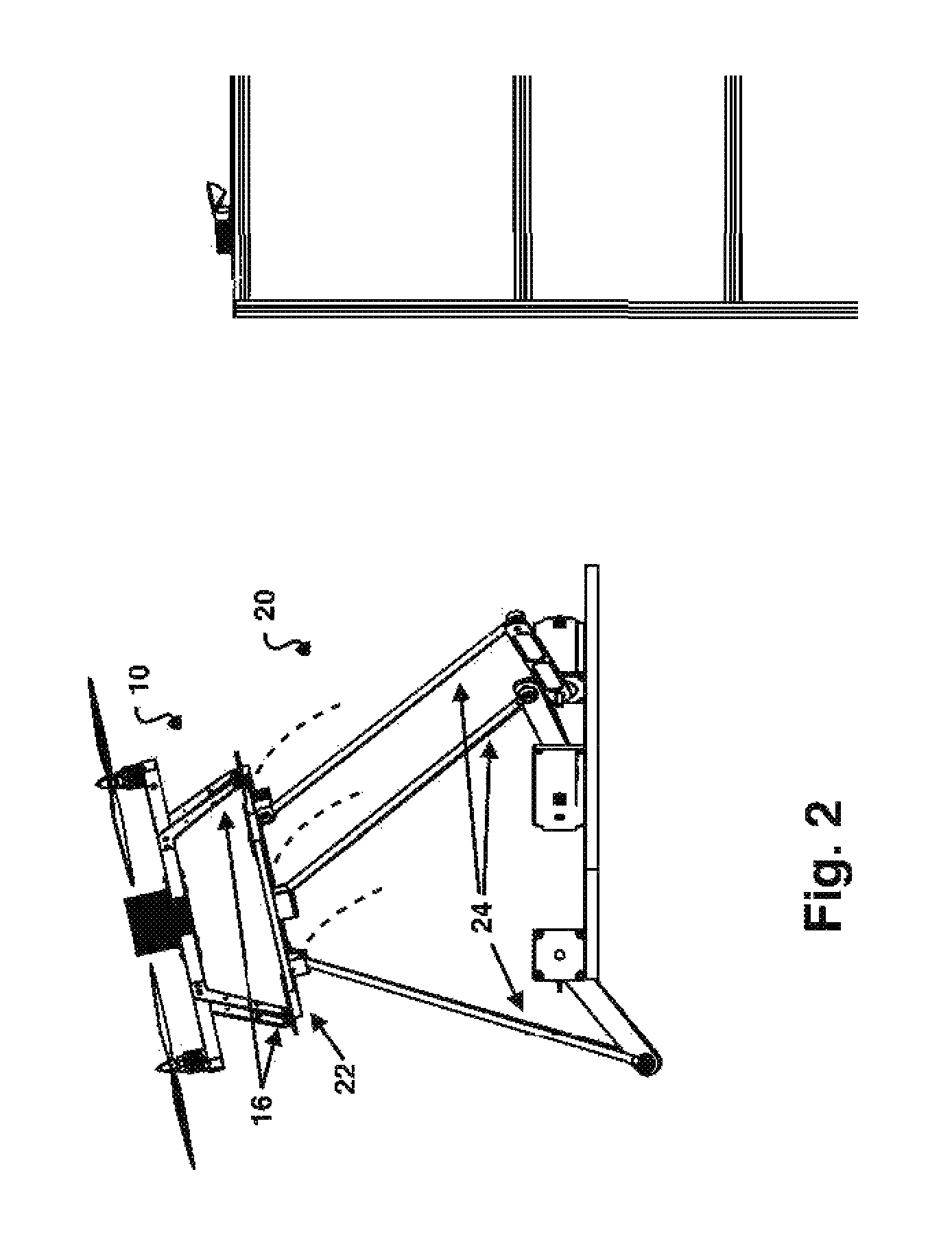
System for automatic takeoff and landing by interception of small uavs
ActiveUS20150266575A1Facilitate automatic capture and launchPrecise positioningArrester hooksArresting gearLifting capacityFlight vehicle
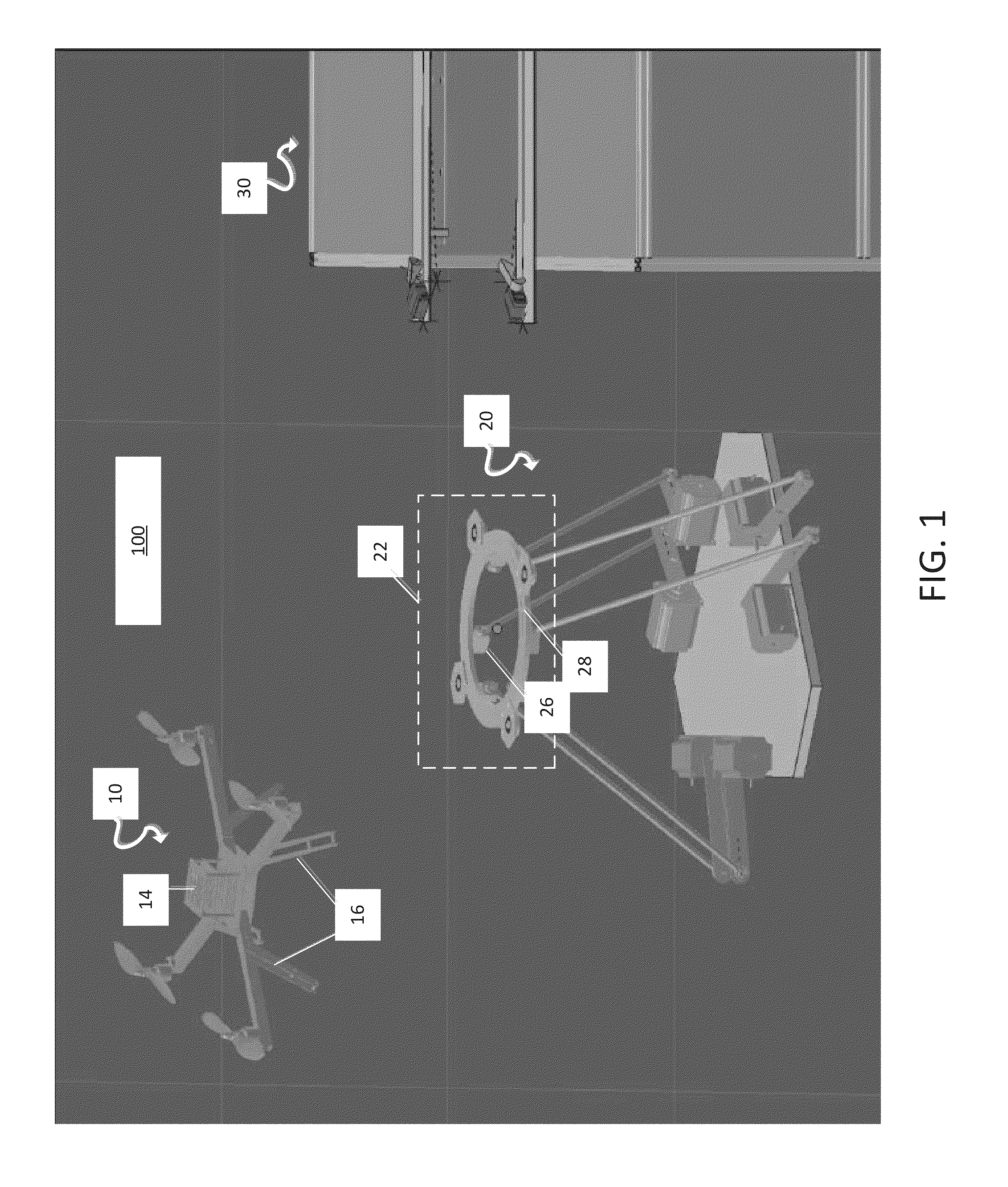
A system for facilitating automated landing and takeoff of an autonomous or pilot controlled hovering air vehicle with a cooperative underbody at a stationary or mobile landing place and an automated storage system used in conjunction with the landing and takeoff mechanism that stores and services a plurality of UAVs is described. The system is primarily characterized in that the landing mechanism is settable with 6 axes in roll, pitch, yaw, and x, y and z and becomes aligned with and intercepts the air vehicle in flight and decelerates the vehicle with respect to vehicle's inertial limits. The air vehicle and capture mechanism are provided with a transmitter and receiver to coordinate vehicle priority and distance and angles between landing mechanism and air vehicle. The landing and takeoff system has means of tracking the position and orientation of the UAV in real time. The landing mechanism will be substantially aligned to the base of the air vehicle. With small UAVs, their lifting capacity is limited. Reducing sensing and computation requirements by having the landing plate perform the precision adjustments for the landing operation allows for increased flight time and / or payload capacity.
Owner:BORKO BRANDON
Automatic landing method and device and air vehicle
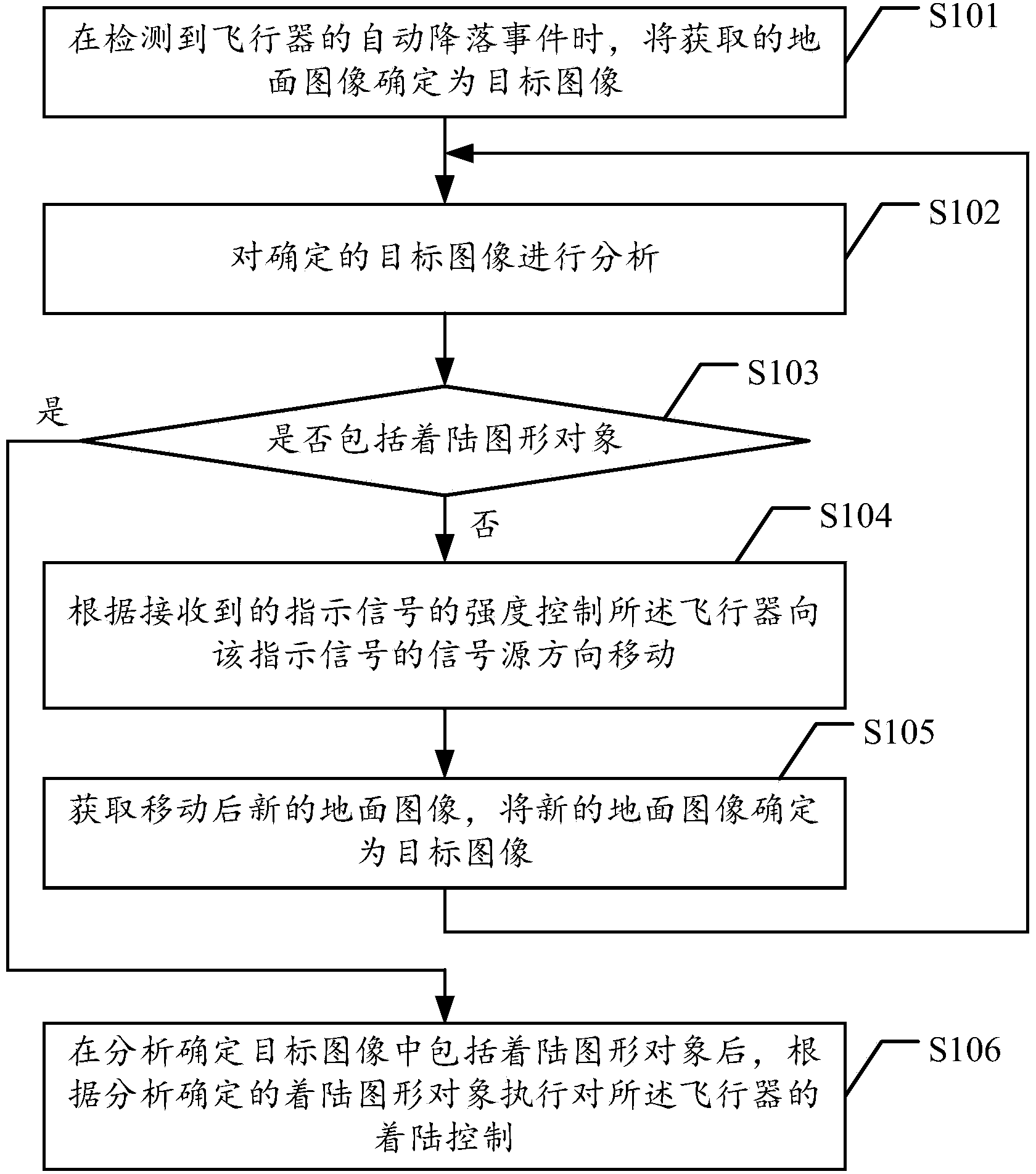
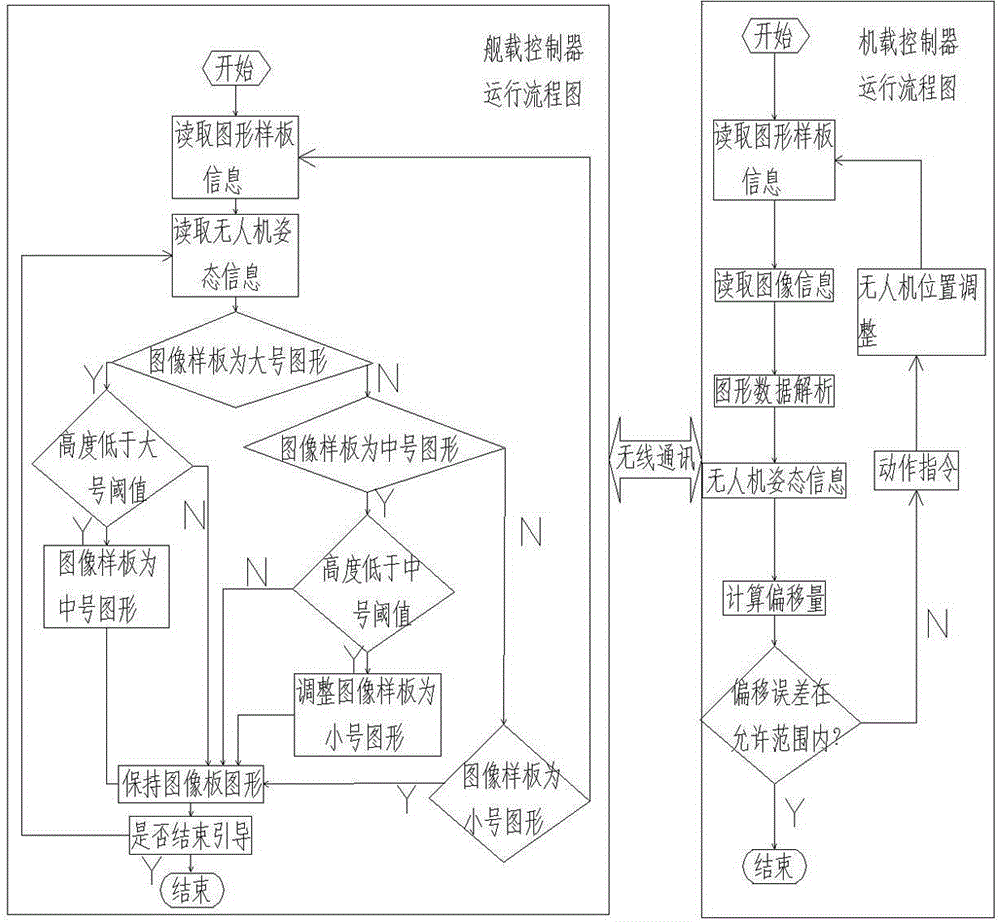
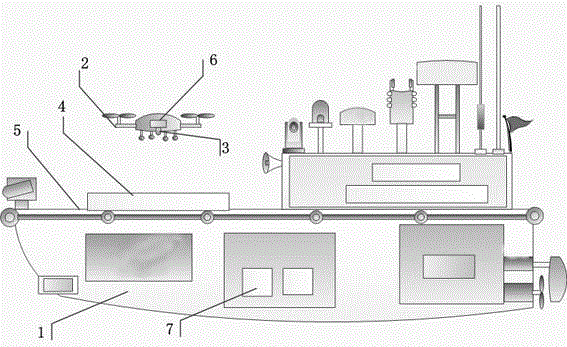
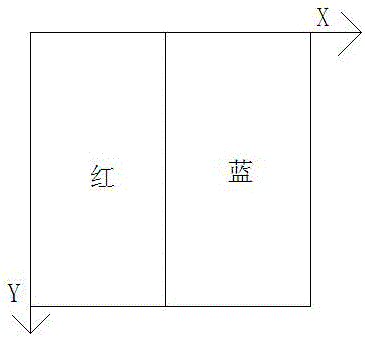
An embodiment of the invention provides an automatic landing method and device and an air vehicle. The automatic landing method comprises the steps of determining the acquired ground image to be a target image when an automatic landing event of the air vehicle is detected; analyzing the determined target image, when the fact that no landing graphic object is included in the target image is determined after analysis, controlling the air vehicle to move in the direction of a signal source of an indication signal according to strength of the received indication signal, acquiring a new ground image after movement of the air vehicle, and after the new ground image is determined to be the target image, executing the step repeatedly until the fact that the target image includes the landing graphic object is determined after analysis; after the fact that the target image includes the landing graphic object is determined after analysis, executing landing control over the air vehicle according to the landing graphic object determined by analysis. By means of the automatic landing method and device, the air vehicle can be guided to land automatically, conveniently, quickly and accurately under the conditions of weak GPS signals, and demands on automatic and intelligent control over the air vehicle of an air vehicle user are met well.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Autonomous and automatic landing system for drones
ActiveUS20090055038A1Improve robustnessSimple designAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlGuidance systemFlight vehicle
The invention relates to an automatic aircraft landing guidance system having an electromagnetic detecting and locating device, positioned on the ground and a first multifunction transmitting / receiving radiofrequency beacon, on board each guided aircraft and transmitting in particular a continuous wave. The detecting and locating device uses the continuous wave transmitted by the beacon to perform a passive locating intended to improve the accuracy of the measurement of the angular position of the aircraft. It also comprises means for generating and periodically transmitting to the aircraft, via the beacon, information enabling said aircraft to rejoin an optimum landing path from its position. The invention applies more particularly to the guidance of autonomous and automatic aircraft such as drones in the approach and landing phase.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and system for facilitating autonomous landing of aerial vehicles on a surface
ActiveUS20120130566A1Automatically determineAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlFlight vehicleLight beam
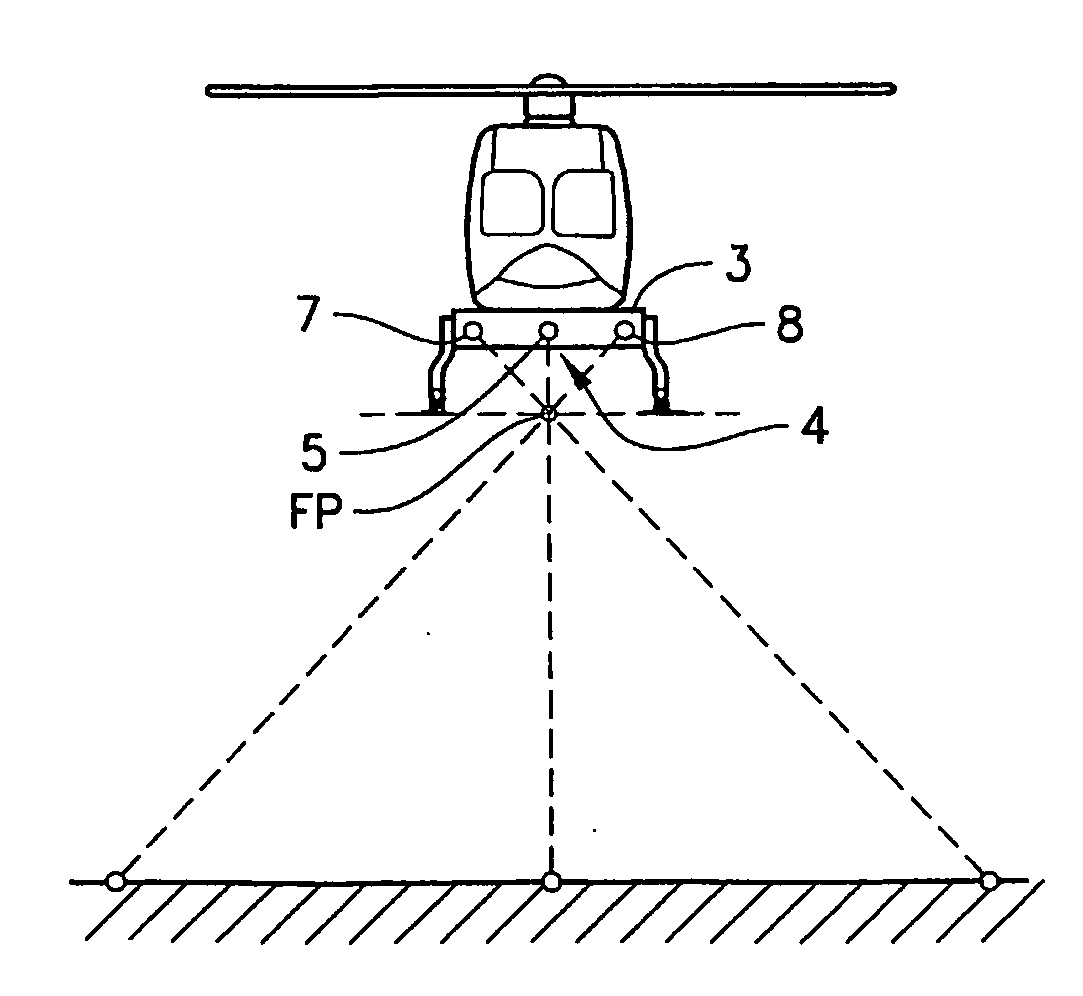
A system for facilitating autonomous landing of aerial vehicles on a surface. A beam emitter is directed downwards. A control module is configured to govern the vehicle. A processor processes image data. The beam emitter is arranged to emit simultaneously at least four beams directed towards the surface in order to project a pattern thereon. One beam emitter of the at least four beam emitters is placed in the center. An image capturing module captures subsequent images of the pattern.
Owner:SAAB AB
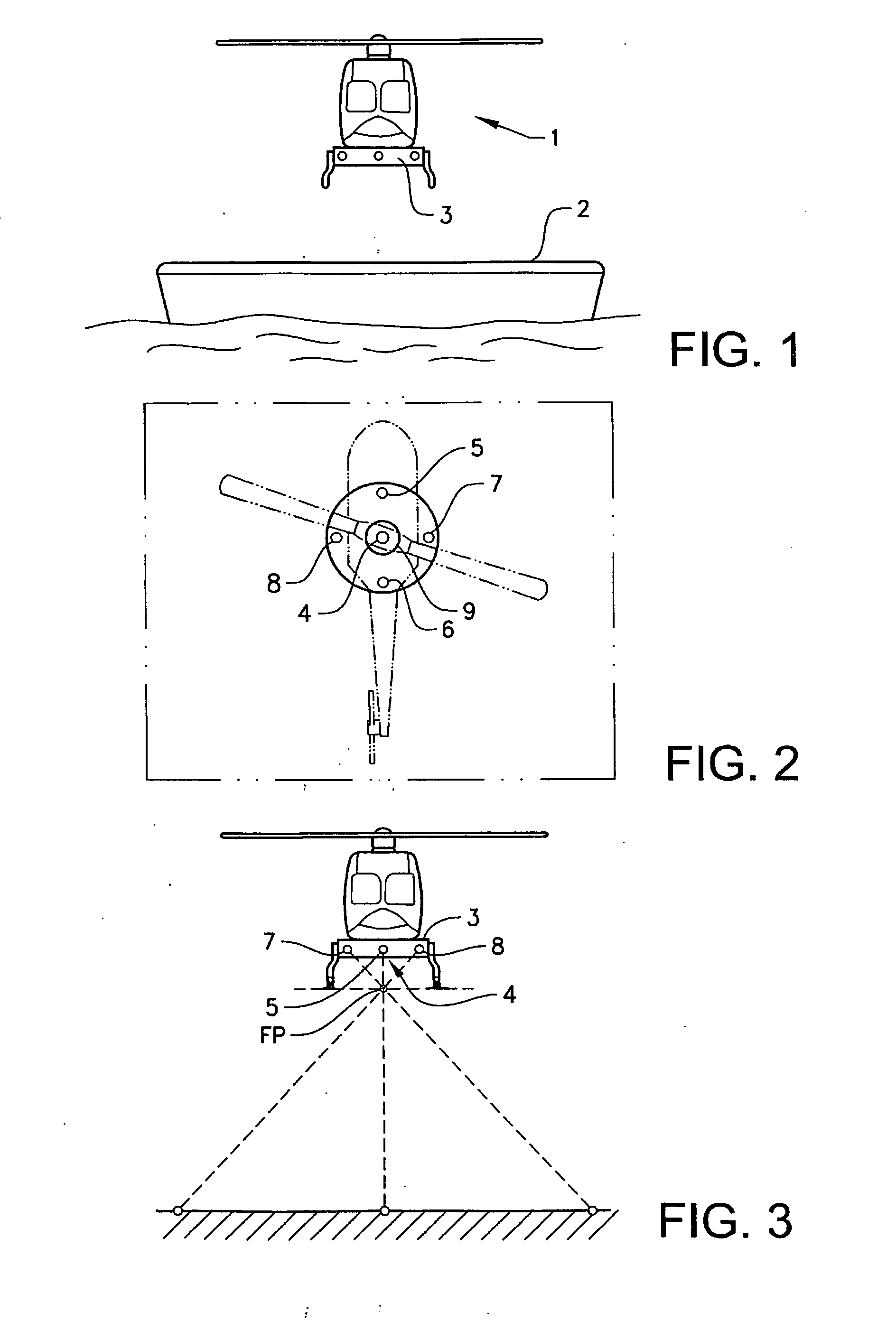
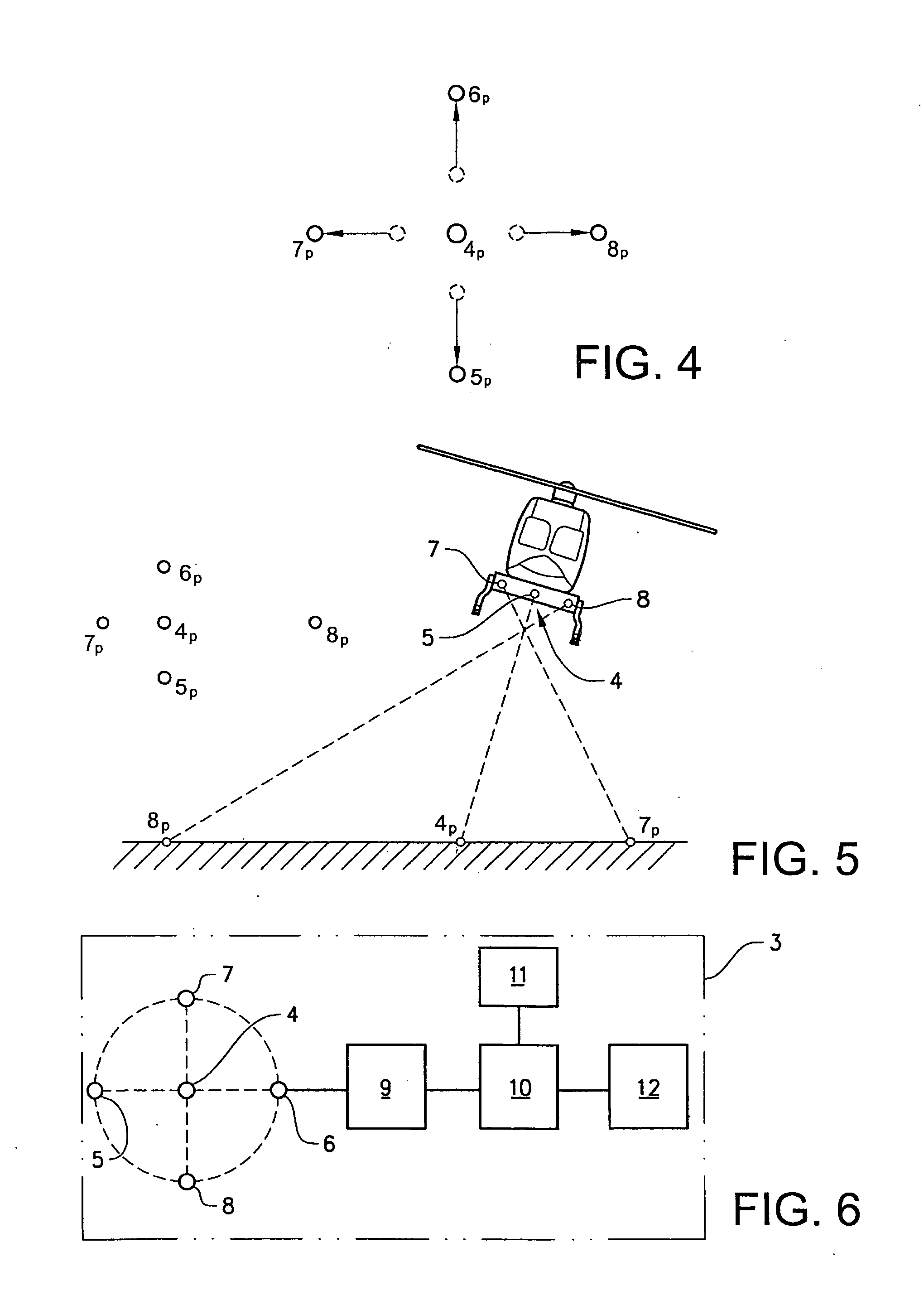
Autonomously landing an unmanned aerial vehicle
The present disclosure is directed toward systems and methods for enabling autonomous landing of an unmanned aerial vehicle. For example, systems and methods described herein enable autonomous landing of the unmanned aerial vehicle by providing an unmanned aerial vehicle ground station with various guidance systems for guiding the autonomous landing. In some embodiments, the guidance systems enable autonomous landing by providing one or more LEDs. In other embodiments, the guidance systems enable autonomous landing by providing various types of transmitted energy waves. In at least one embodiment, the guidance systems enable autonomous landing by providing a two-stage landing system that includes two or more types of transmitted energy.
Owner:SKYCATCH
Helicopter
ActiveUS9456185B2Reduce problem sizeEasy to flyAircraft componentsUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlMission plan
The present invention relates to a reduced scale industrial helicopter, with an integrated automatic flight control system, that includes core autopilot functions, GPS management, and full-function navigation systems. The autopilot technology includes rapid launch capability, real-time in-flight switching between one or more of a) remote control, b) autopilot-directed, c) ground station controlled, and d) home modes, and is upgradeable. The helicopter is used for high or low altitude surveillance, and can handle various payloads, including photographic missions. The helicopter may include onboard batteries and / or a unique battery unit disposed beneath the helicopter, and includes autonomous features such as automatic takeoff, automatic landing, safety return to home base, and predetermined mission plans.
Owner:GEOTECH ENVIRONMENTAL EQUIP
System for automatically landing aircraft using image signals and method of controlling the same
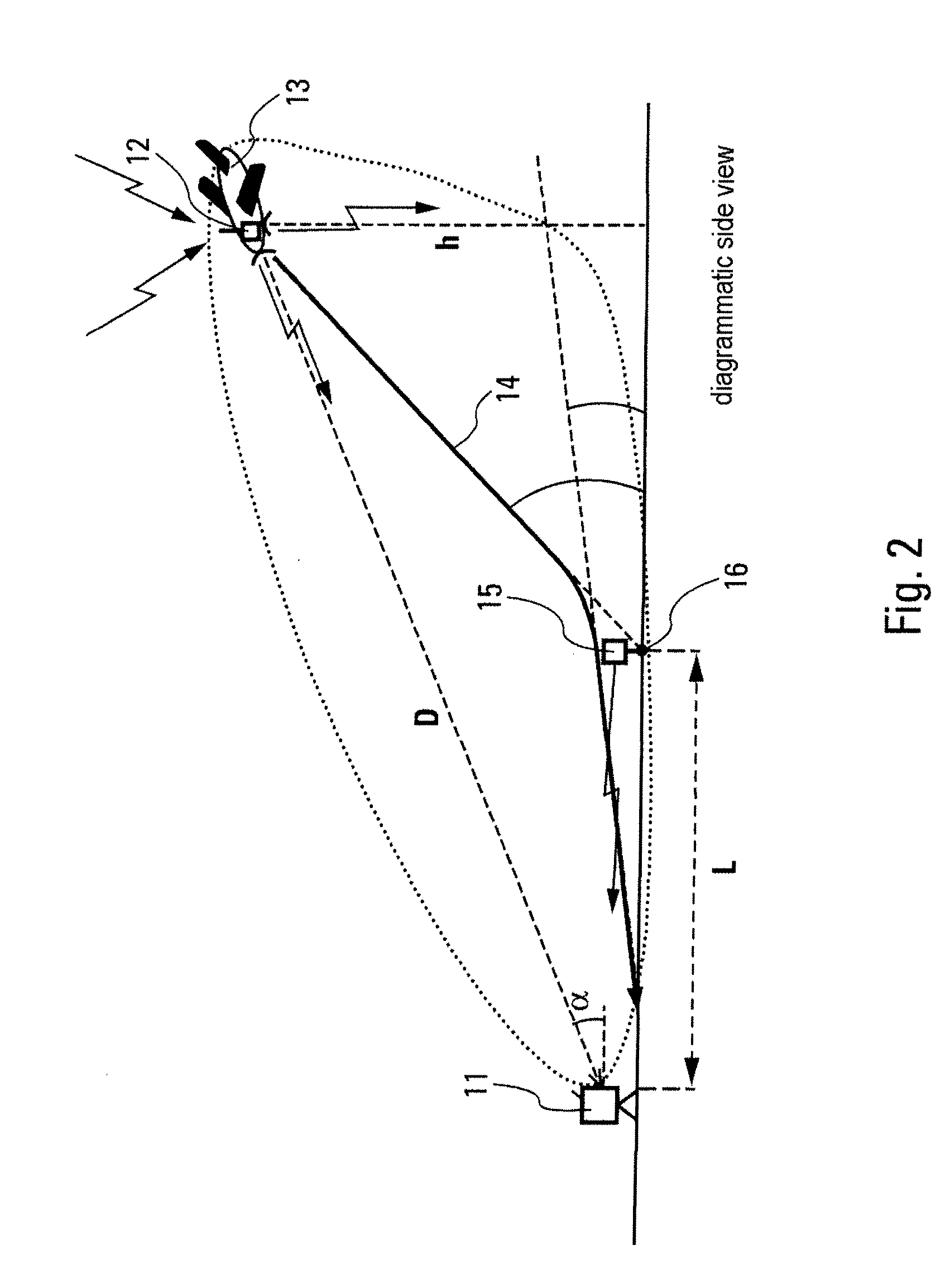
Disclosed herein are a system for automatically landing an aircraft using image signals and a method of controlling the system. The system includes an altimeter installed on the aircraft; a landing mark placed at a landing location on a landing runway; a camera installed on the aircraft, oriented toward the front of the aircraft, and configured to detect the shape of the landing mark in image information form; and a FCC configured to calculate the angle between the aircraft and the ground, the ground range and the slant range between the aircraft and the landing location using the altitude information measured by the altimeter, the image information of the landing mark captured by the camera, angle information composed of the pitch, roll and yaw angles of the aircraft, and the angle of entry into the landing runway, and configured to control the automatic landing of the aircraft.
Owner:KOREA AEROSPACE RES INST
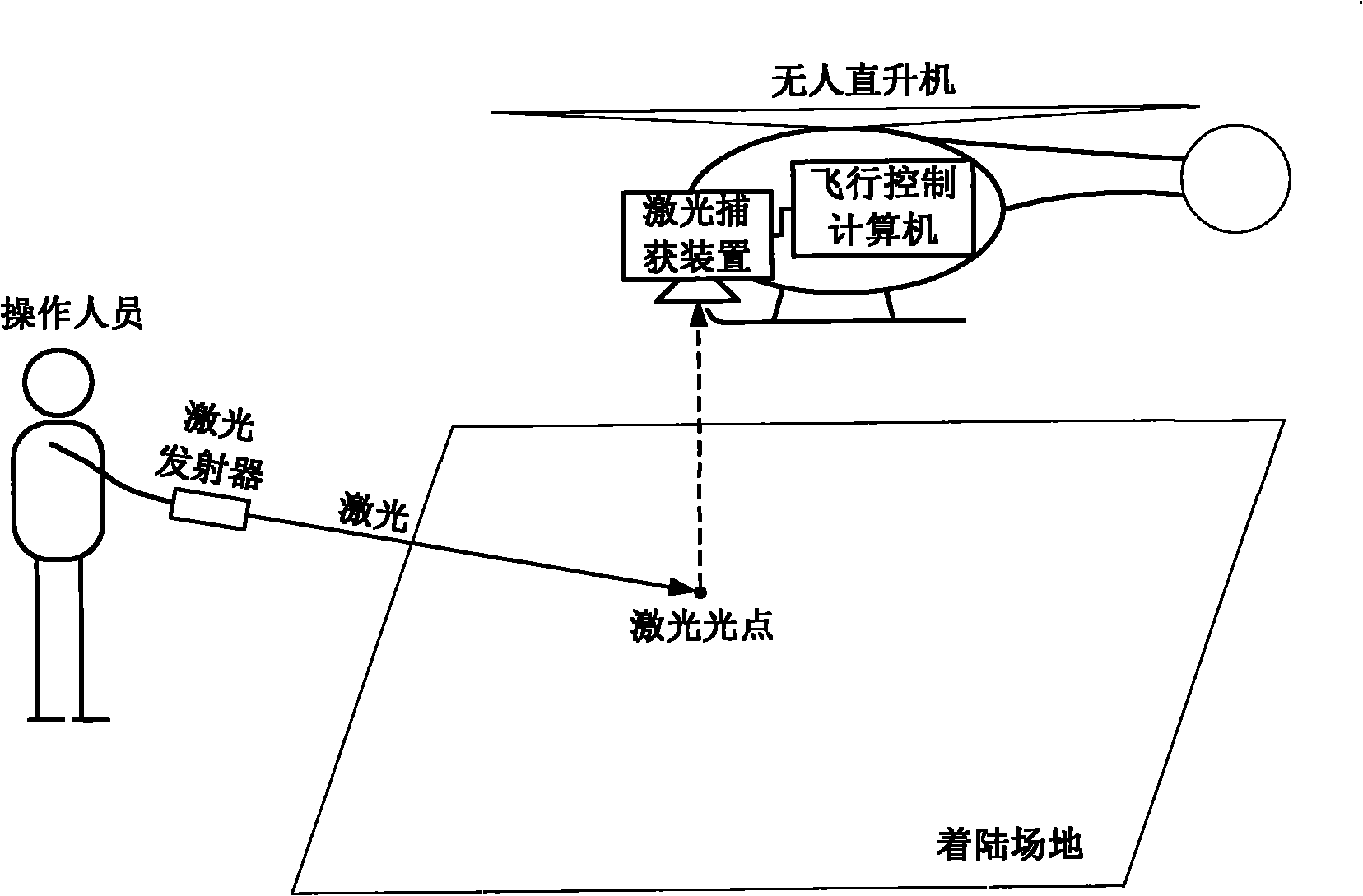
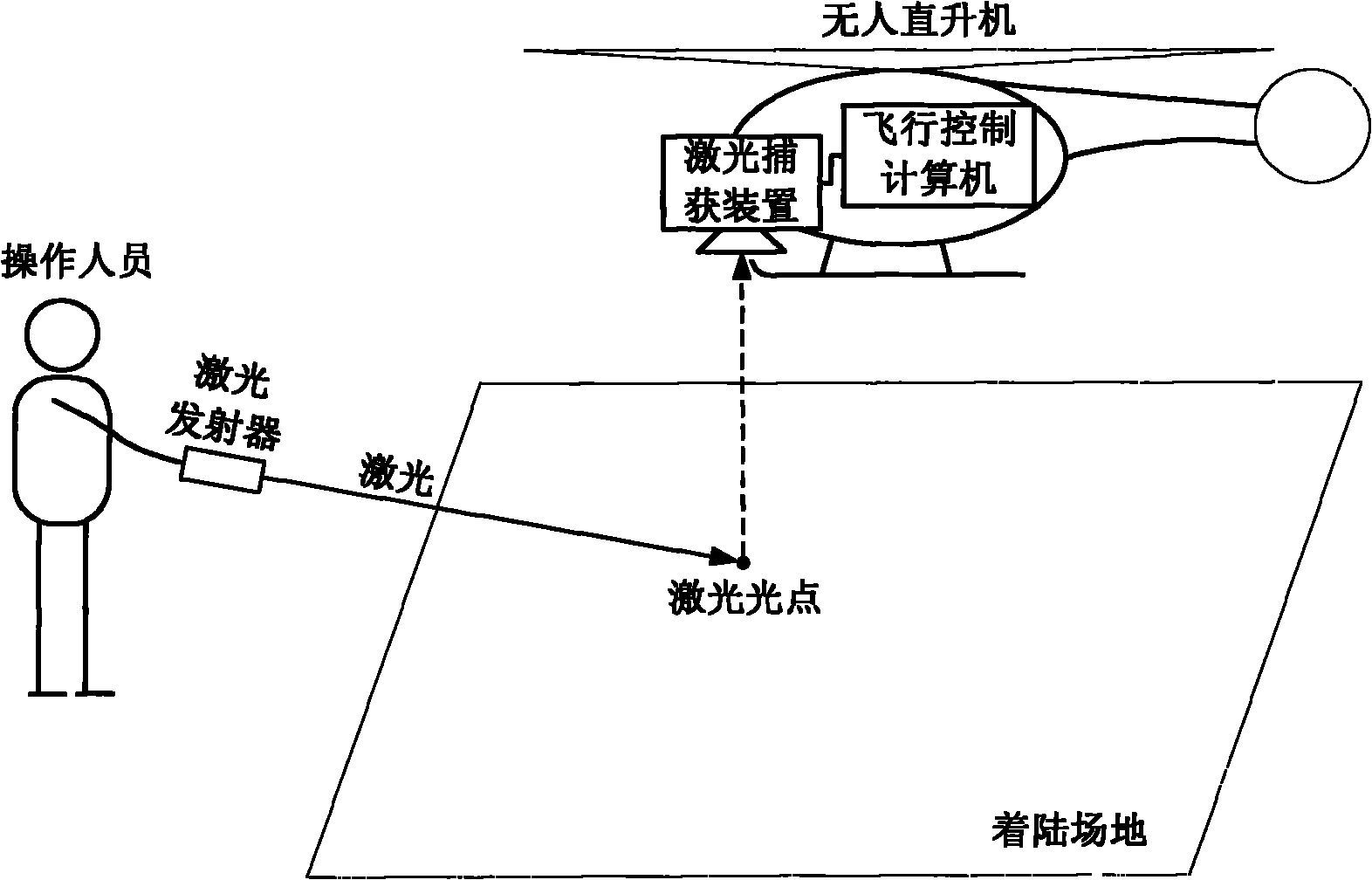
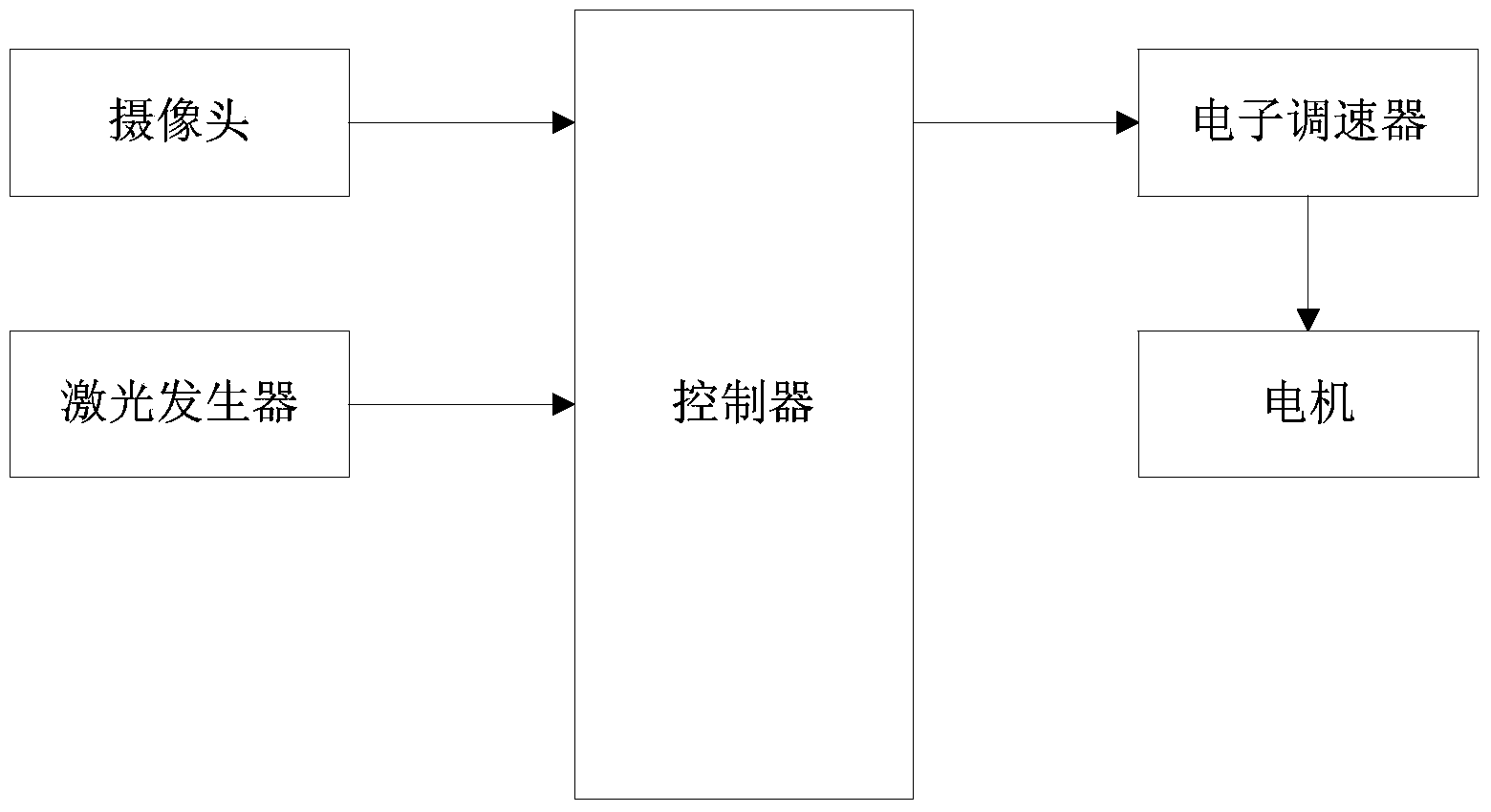
Unmanned helicopter automatic landing method based on laser guidance
InactiveCN101976078AStrong reliabilityEasy to changeVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlLaser transmitterAircraft flight control system
The invention relates to an unmanned helicopter automatic landing method based on laser guidance, belonging to the field of unmanned plane flight control. The method is characterized in that a laser transmitter, an airborne laser acquisition device and a flight control system are provided, wherein the laser transmitter is used for landing instructions, the air-borne laser acquisition device is used for acquiring laser spots projected to the ground by the laser transmitter, the flight control system is used for controlling helicopter tracing laser spots according to output signals of the laser acquisition device, so that the unmanned helicopter can gradually approach to the laser spots on the ground according to the instructions and guidance of the laser transmitter and descend to lower height at the same time until automatic landing is completed. According to the method, instructive accuracy of laser can be employed to accurately and conveniently guide the unmanned helicopter to automatically land.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System for automatic takeoff and landing by interception of small UAVs
ActiveUS9505493B2Facilitate automatic capture and launchPrecise positioningArresting gearLaunching/towing gearLifting capacityFlight vehicle
Owner:BORKO BRANDON
Autonomous and automatic landing system for drones
ActiveUS8265808B2High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlGuidance systemFlight vehicle
The invention relates to an automatic aircraft landing guidance system having an electromagnetic detecting and locating device, positioned on the ground and a first multifunction transmitting / receiving radiofrequency beacon, on board each guided aircraft and transmitting in particular a continuous wave. The detecting and locating device uses the continuous wave transmitted by the beacon to perform a passive locating intended to improve the accuracy of the measurement of the angular position of the aircraft. It also comprises means for generating and periodically transmitting to the aircraft, via the beacon, information enabling said aircraft to rejoin an optimum landing path from its position. The invention applies more particularly to the guidance of autonomous and automatic aircraft such as drones in the approach and landing phase.
Owner:THALES SA
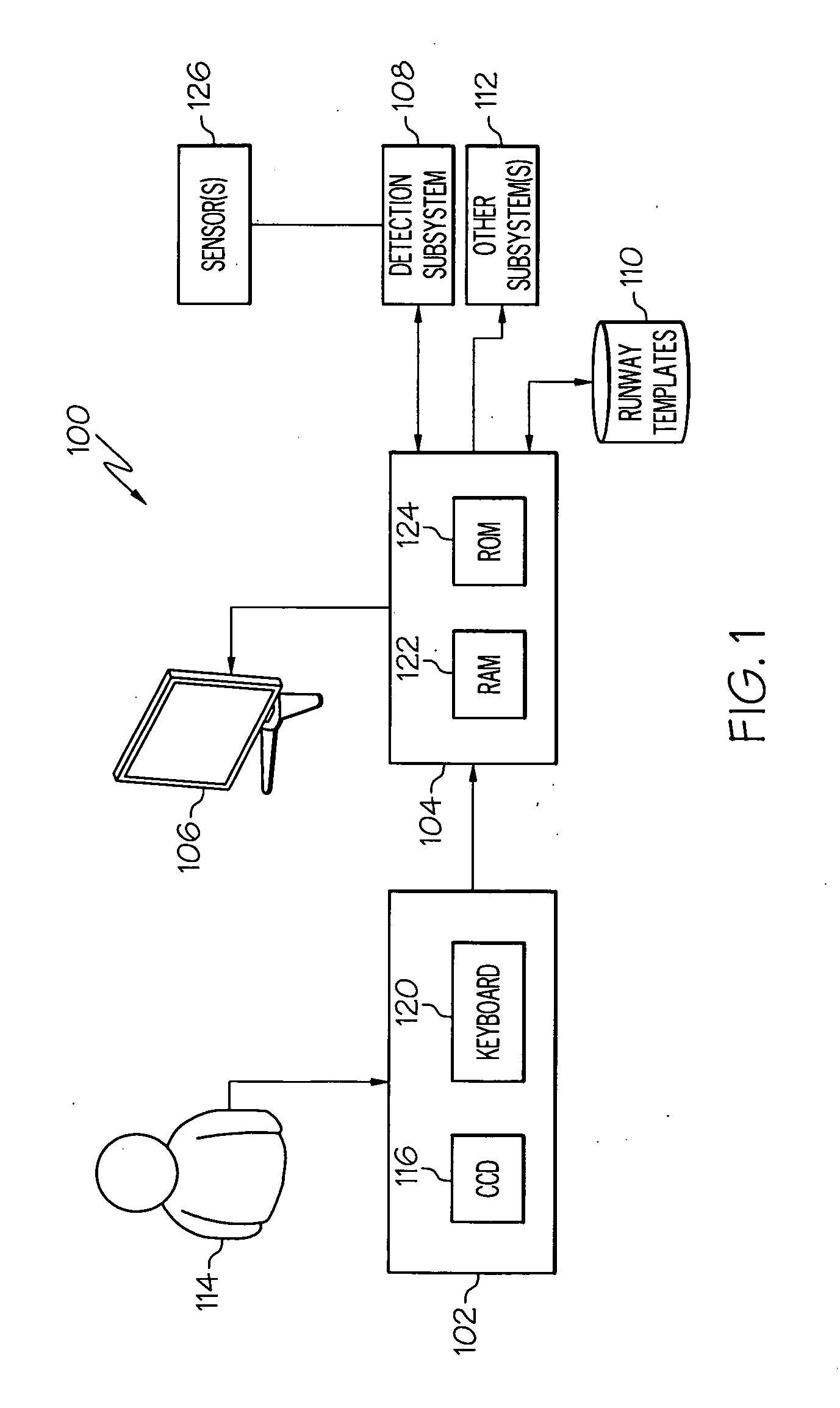
Automated landing area detection for aircraft
InactiveUS20100039294A1Well formedWave based measurement systemsScene recognitionFlight vehicleEngineering
A system for detecting a landing area or runway for an aircraft includes a detection subsystem, a processor architecture, flight deck instrumentation, and a runway feature template database. The system is operated to perform an automated method for visually confirming the presence of a runway on approach. The method obtains sensor data indicative of an approach area of the aircraft, and extracts visually distinguishable features of the approach area from the sensor data. The method also accesses the runway feature template corresponding to the intended approach runway for the aircraft, fits the visually distinguishable features to the runway feature template, and provides flight crew feedback in response to the fitting step.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
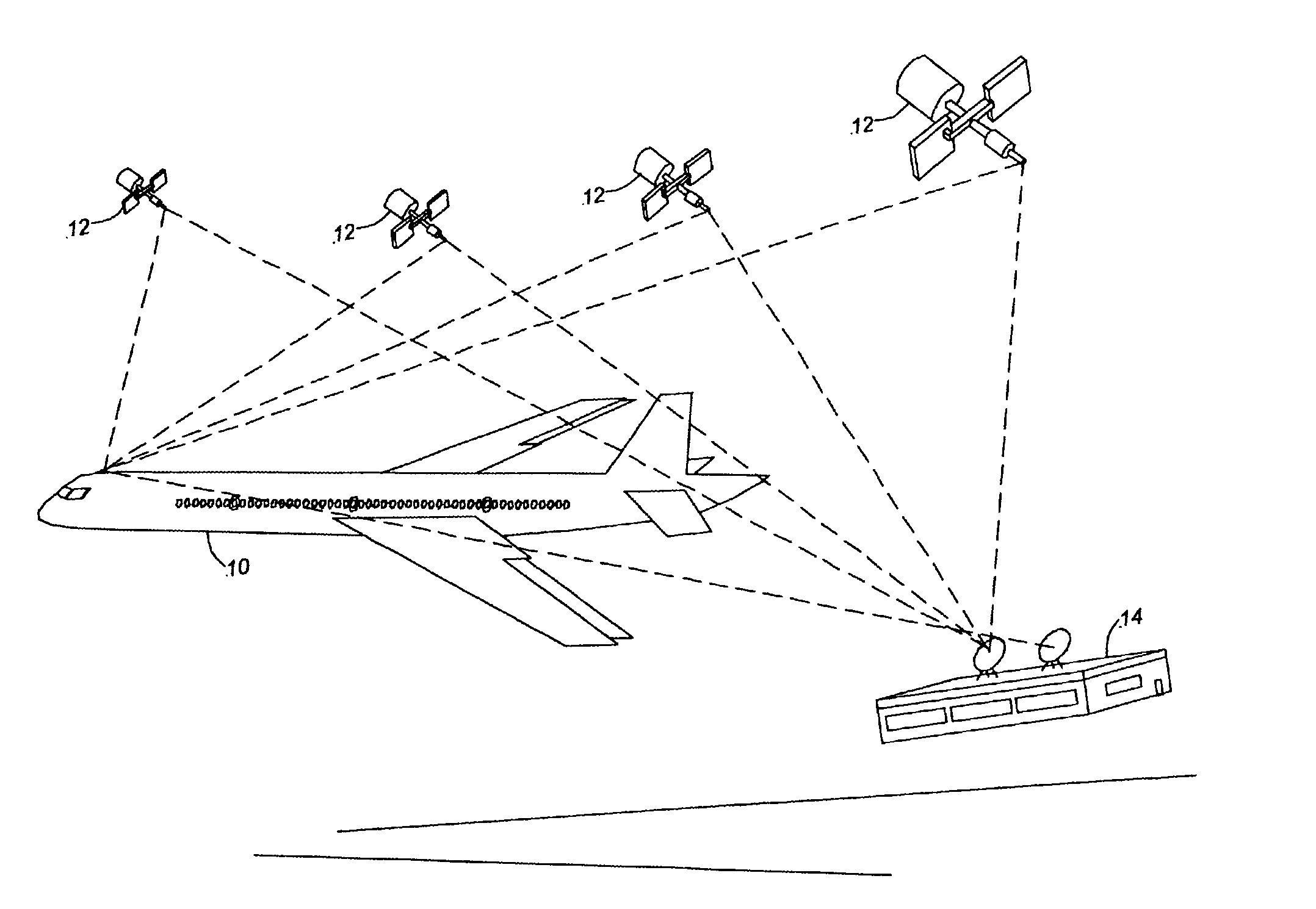
Procedure for Automatically Landing an Aircraft
ActiveUS20110066307A1Simple methodFacilitates holdingAnalogue computers for vehiclesVehicle position/course/altitude controlJet aeroplaneMarine navigation
A procedure and system are provided for automatically landing an aircraft, particularly an unmanned aircraft on a moving, particularly floating landing platform, for example, on an aircraft carrier, the aircraft being equipped with an automatic navigation device and an automatic landing control device. The procedure includes detecting the position of an intended landing spot, detecting motion data of the landing platform, determining at least one imminent point in time at which the landing spot takes up a reference position, transmitting the point in time and the reference position of the landing spot to the landing control device of the aircraft, and controlling the aircraft such that it reaches the landing spot at the point in time.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
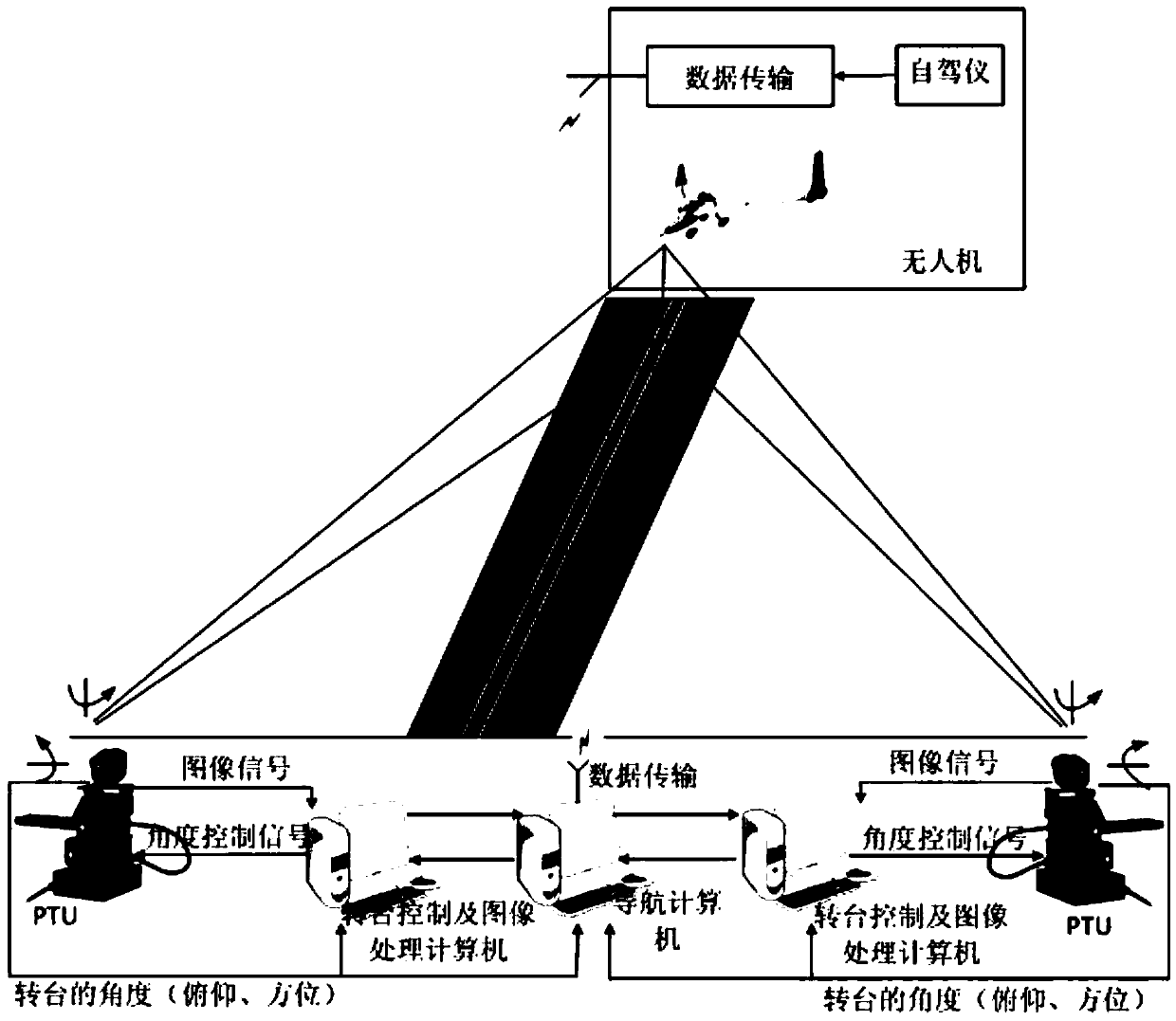
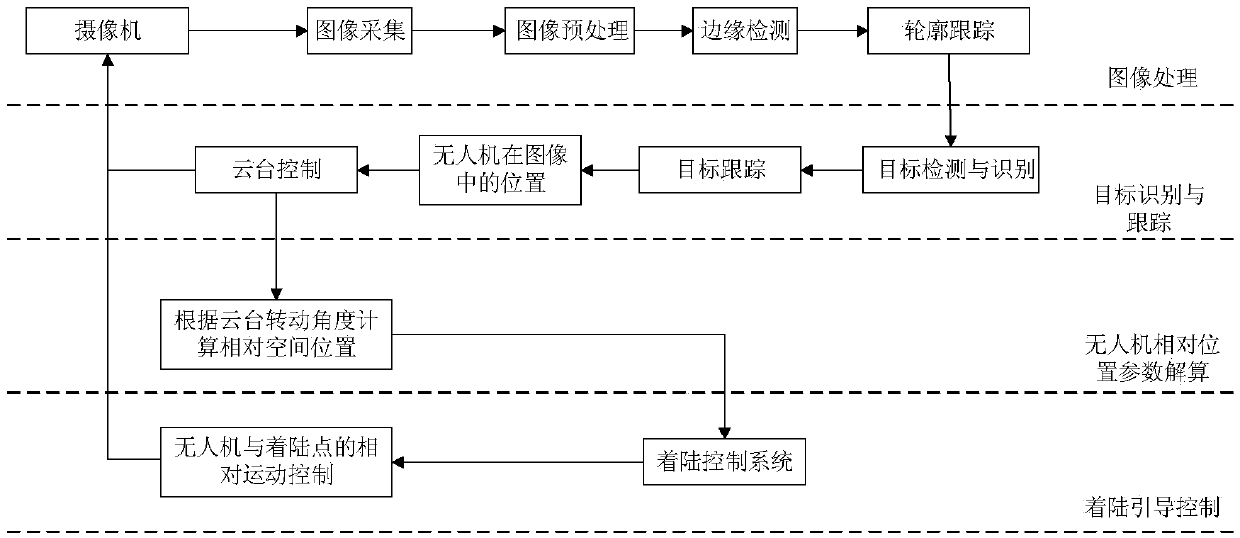
Infrared vision based automatic landing guidance method and system applied to fixed-wing UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle)
InactiveCN105501457AHigh precisionEnhanced target featuresAircraft landing aidsAutomatic aircraft landing aidsGuidance systemFixed wing
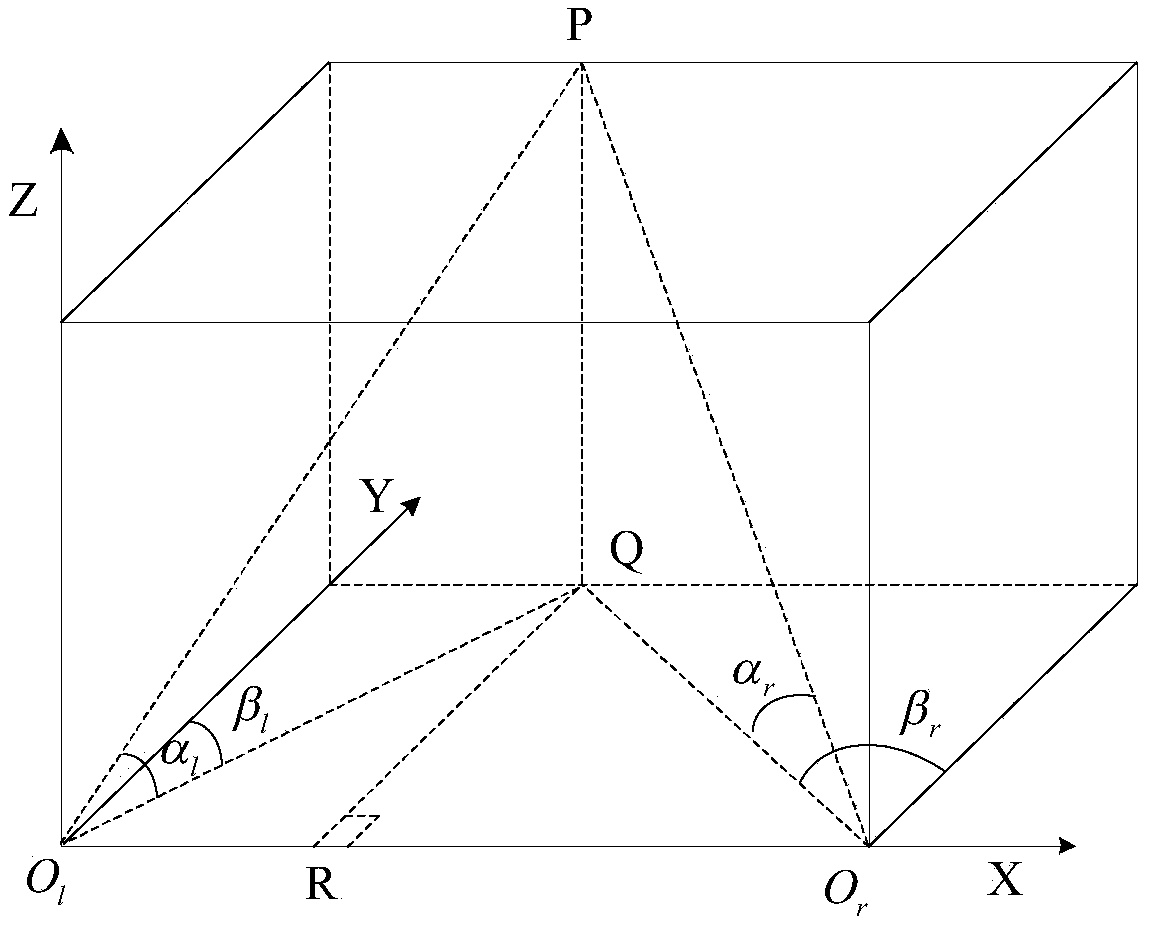
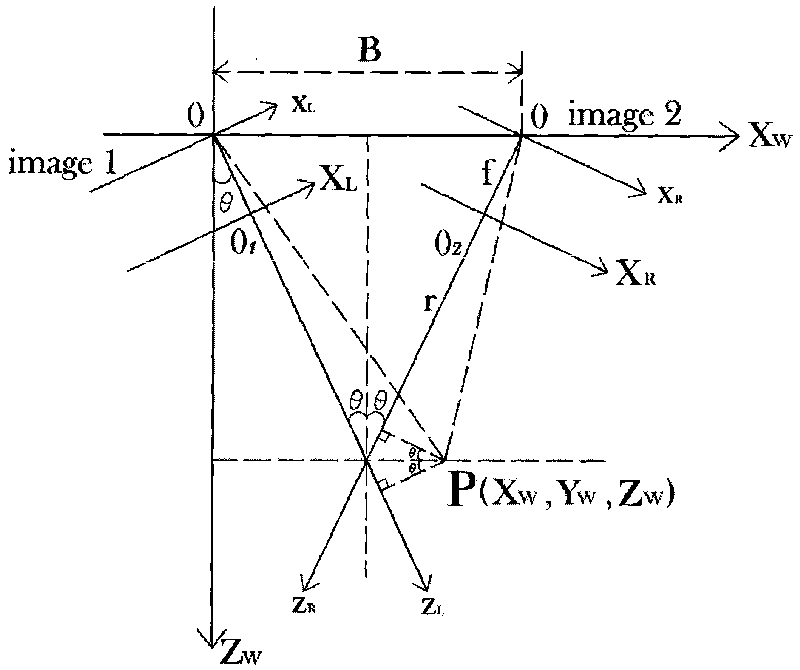
The invention discloses an infrared vision based automatic landing guidance method and system applied to a fixed-wing UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle). The system comprises two identical image tracking modules, an image processing module, a control module and a wireless transmission module, wherein each image tracking module comprises a camera and biaxial pan-tilt units. According to the method, the UAV is detected, identified and tracked in images with an image tracking technology, and deflecting angles of the pan-tilt units are accurately recorded; the relative space position of the UAV can be determined through geometric relationship analysis and trigonometric calculation of pitch heading angles of the two pan-tilt units and the distance between the pan-tilt units, and position information of the UAV is sent to the UAV through the wireless transmission module, so that the UAV is guided to accurately land. The infrared vision based automatic landing guidance system is constructed on two sides of a landing runway of the UAV, complicated image processing is performed based on powerful computing capacity of a ground-based computer, each guidance device is utilized to the greatest extent, the accuracy of the system is improved, the control is simple, and real-time performance and stability are good.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for on-line self-calibration of external parameters of cameras of bionic landing system of unmanned gyroplane
InactiveCN101692283ASolving Online Calibration ProblemsGet altitude information in real timeImage analysisBlind zoneOptical axis
The invention relates to a method for the on-line self-calibration of external parameters of cameras of a bionic landing system of an unmanned gyroplane. The method can solve the problem of a blind zone of stereoscopic vision in a descending process of a gyroplane and improve the landing precision of the unmanned gyroplane. The actual operating steps comprise: (1) calibration of internal parameters; (2) calibration of external parameters; and (3) on-line self-calibration of the external parameters. The method can realize the on-line self-calibration of the external parameters of double cameras carried in the unmanned gyroplane, obtain optical axis included angle information and height information of the cameras in real time, and effectively solve the problem of the blind zone of binocular stereoscopic vision, so that the automatic landing of the unmanned gyroplane is ensured, and the security of the system is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
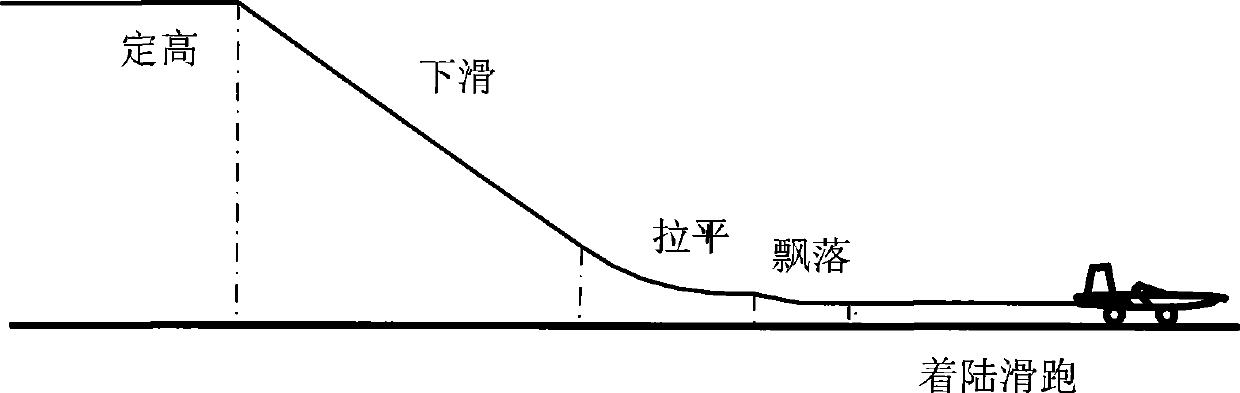
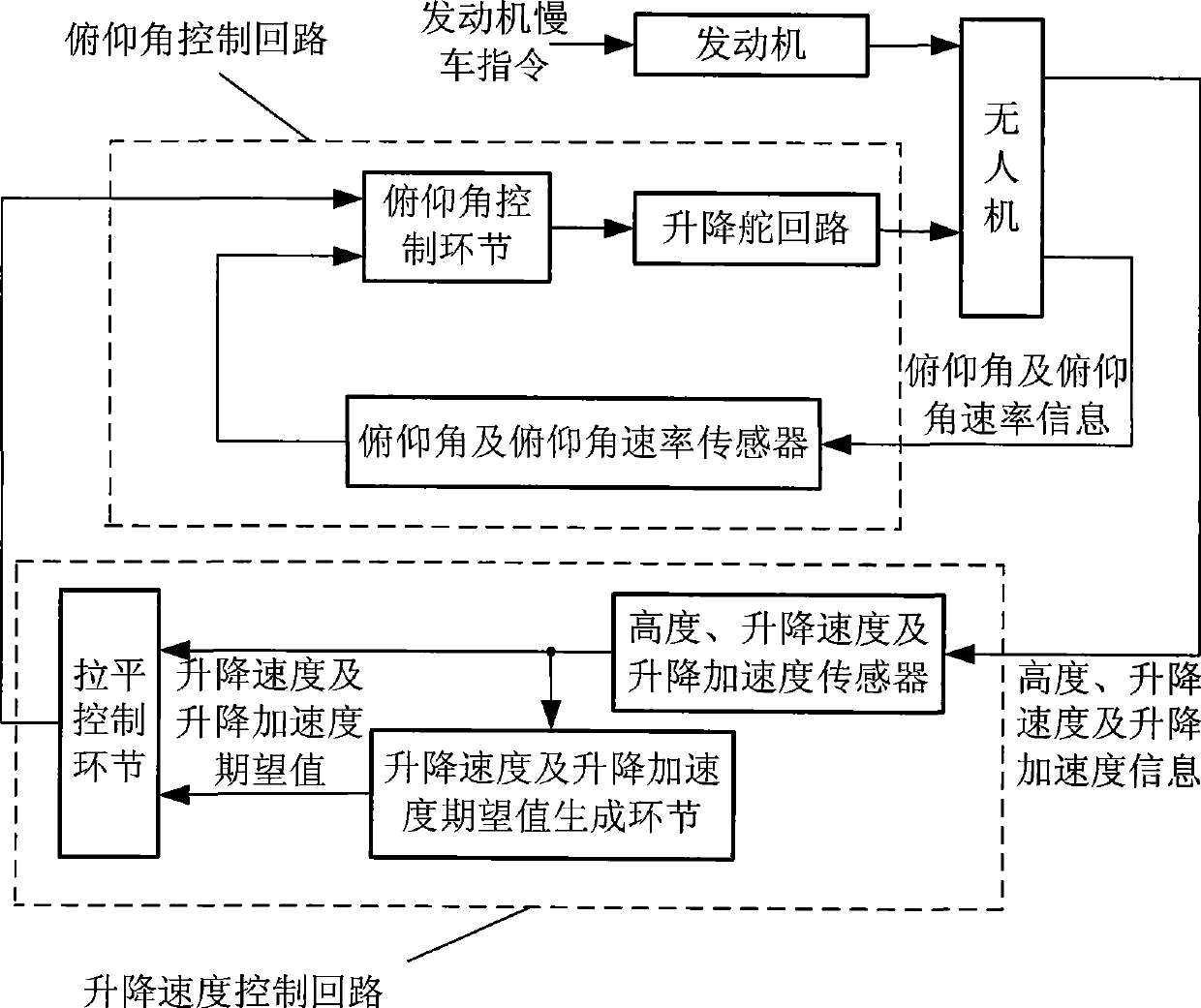
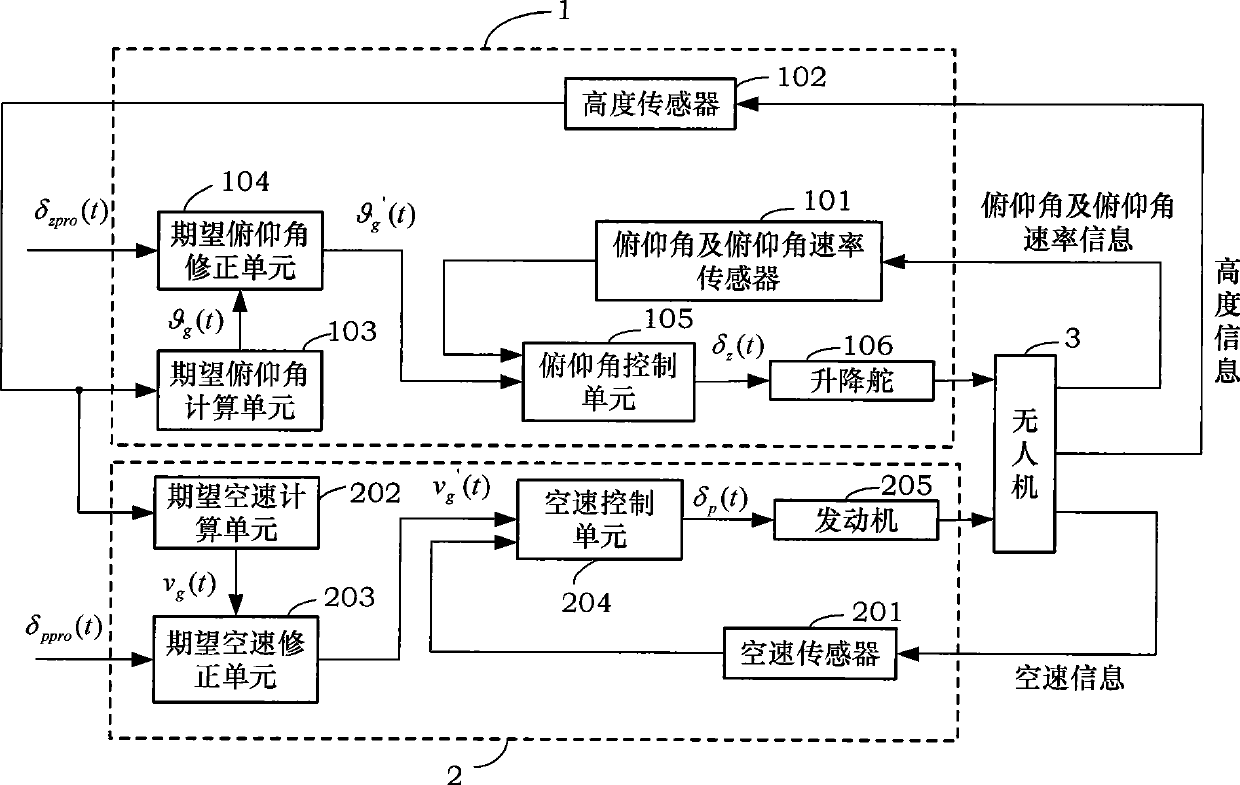
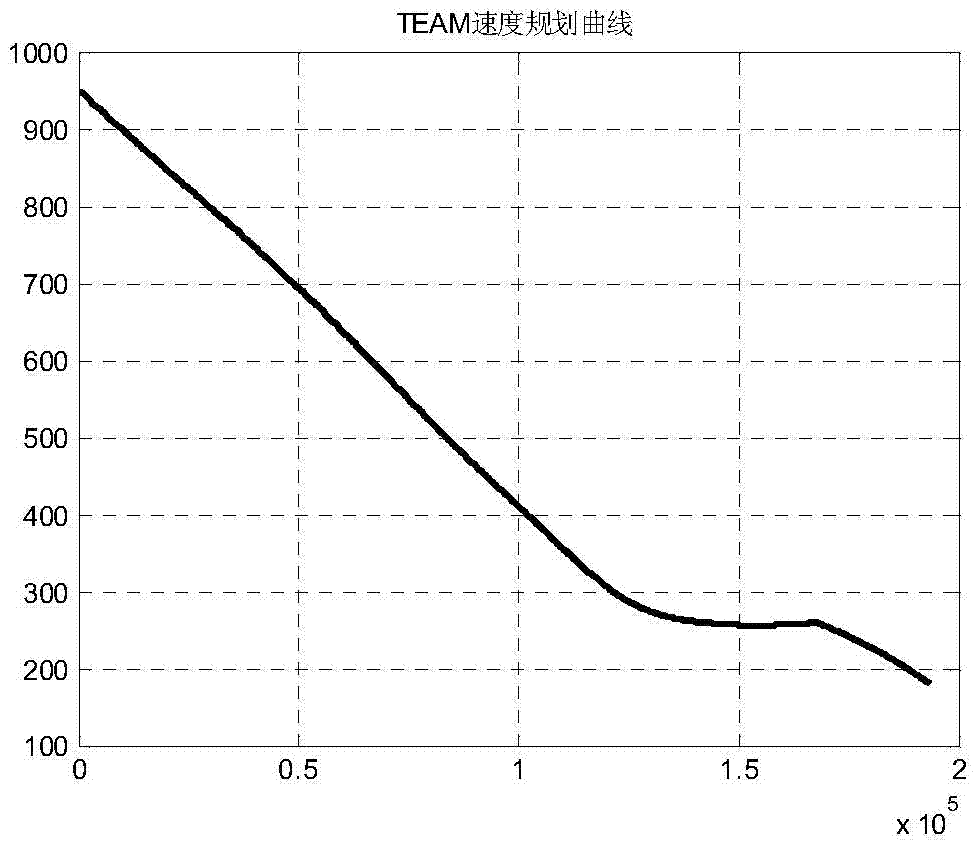
Small-sized unmanned aerial vehicle automatic landing leveling control method and apparatus
InactiveCN101441478AHigh longitudinal landing accuracy requirementsGood control effectVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlJet aeroplaneAttitude control
The invention discloses a method and a device for automatic landing leveling control of a small unmanned aerial vehicle. The landing leveling control device consists of a pitch attitude control circuit and an airspeed control circuit. Aiming at the problem that unmanned air vehicle with a simple sensor can not acquire vertical speed information and vertical acceleration speed information with required precision, the method and the device make full use of an available sensor information and calculate an expected pitch attitude g(t), an expected pitch attitude g'(t) containing correction, an expected airspeed vg(t), an expected airspeed vg'(t) containing correction, elevator control command delta Z(t), an engine chock valve command delta(t) and so on to realize control procedures in the control circuits and achieve the aim of automatic landing leveling control. Meanwhile, remote control operating personnel can operate an operating lever of an elevator and an operating lever of a chock valve in a leveling process according practical situation and carry out correction control of automatic leveling, thereby effectively improves the anti-interference capacity and landing precision of an airplane.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
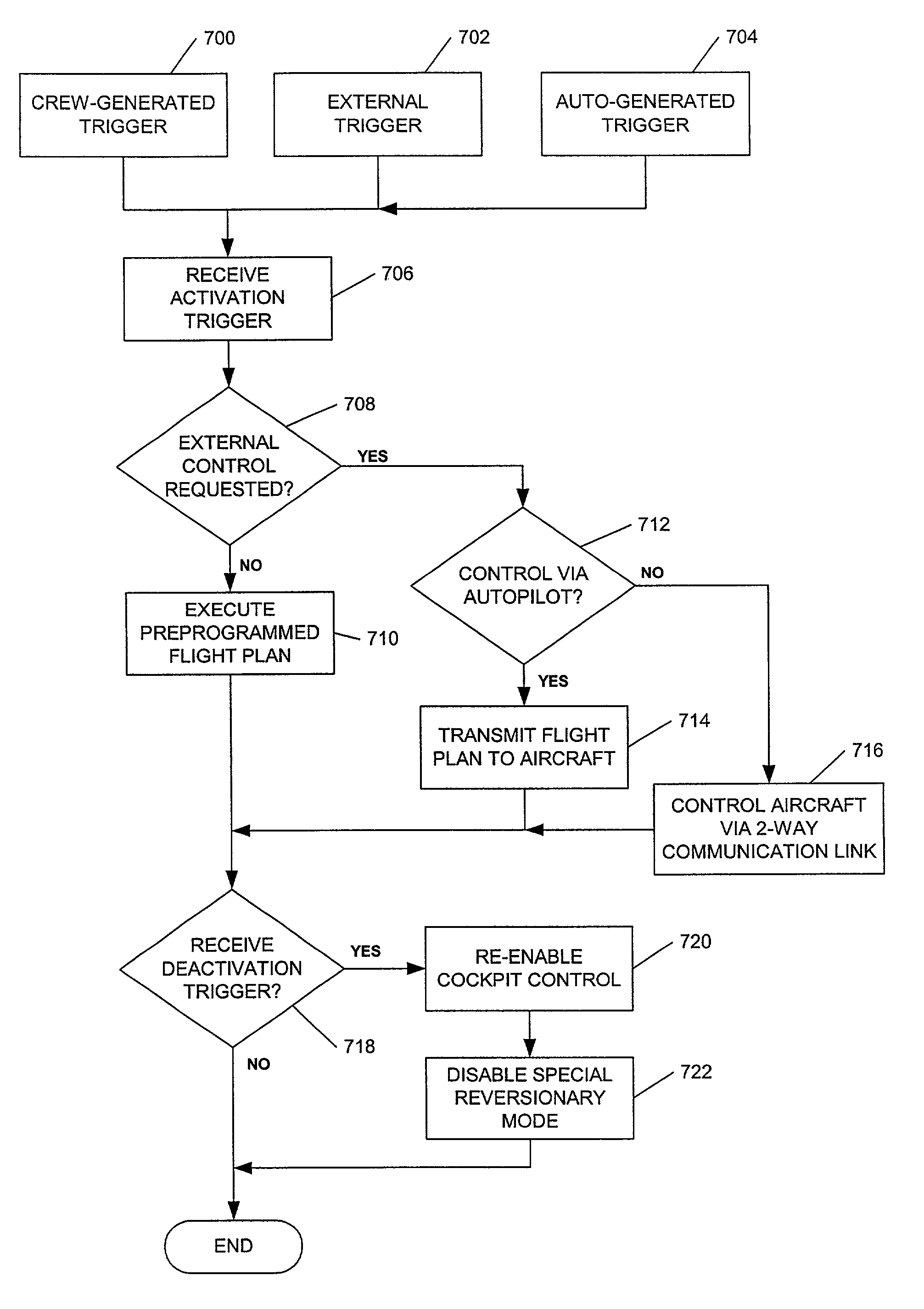
Emergency flight control system
ActiveUS20090179114A1Avoid controlAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAir traffic controlPopulated area
A method and system for preventing the control of an aircraft from the cockpit. In an exemplary embodiment, the system could be triggered externally. For example, an air traffic control (ATC) station could determine that the aircraft has deviated from its planned flight path. If personnel at the ATC station decide that the deviation is not attributable to the actions of the authorized flight crew, the personnel can transmit a signal to the aircraft that disables all normal cockpit control of the aircraft. Once normal flight controls are disabled, the aircraft may execute a preprogrammed emergency flight plan via its autopilot system, with or without the use of a flight management system (FMS). The emergency flight plan could cause the aircraft to fly to a sparsely populated area and enter a holding pattern, or it could cause the aircraft to land in a sparsely populated area or at an airport using an autoland system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Unmanned plane automatic landing system
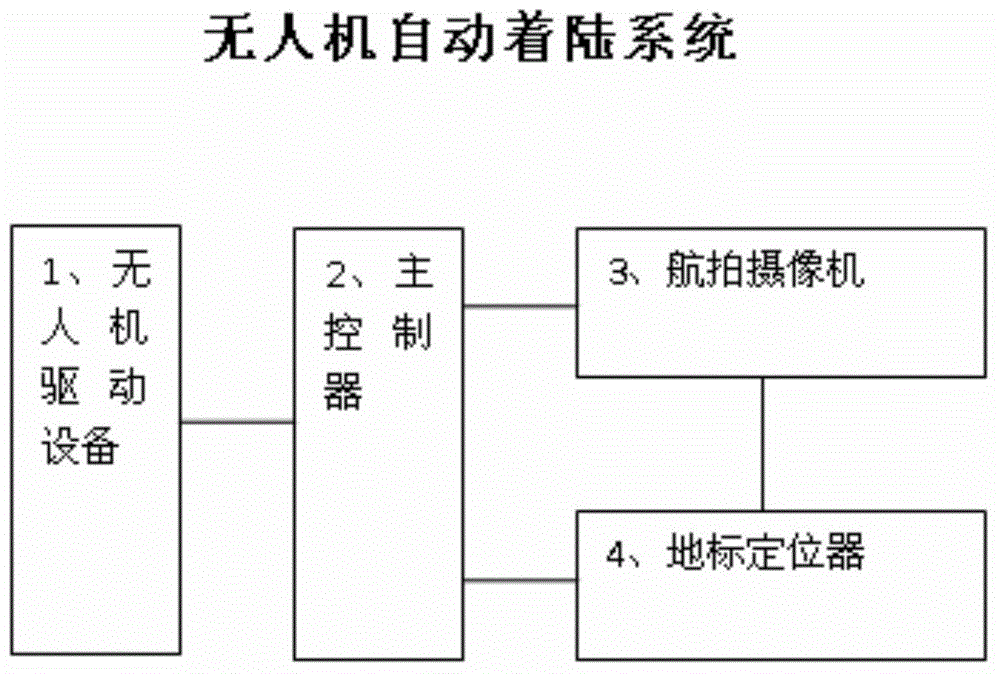
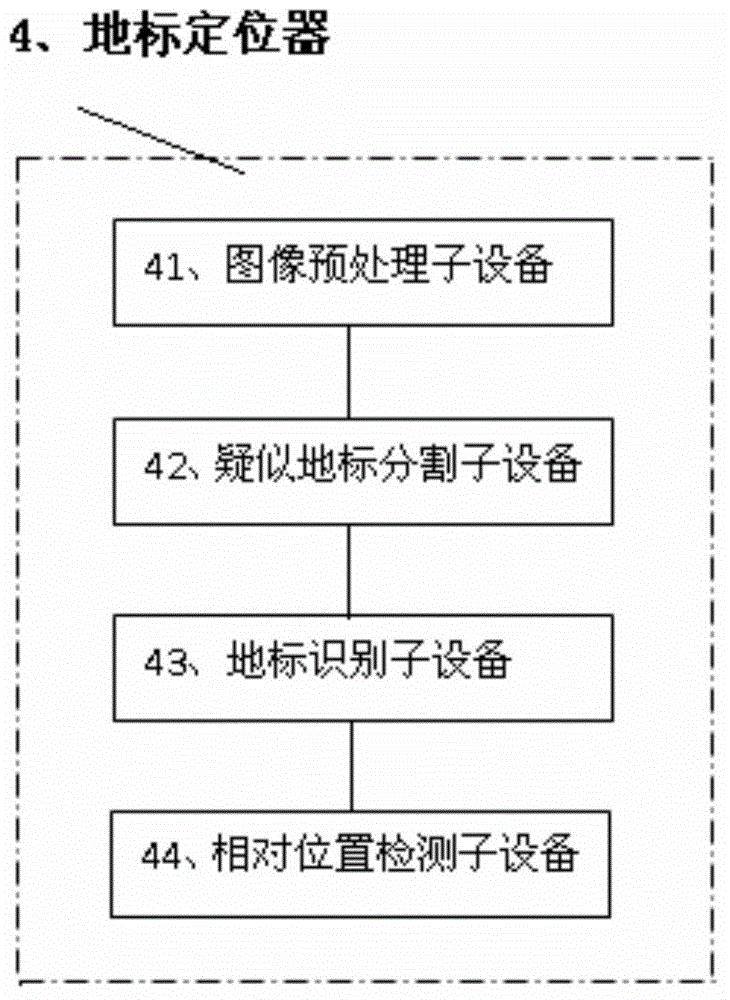
InactiveCN104679013AImplement searchNo outside interventionPosition/course control in three dimensionsImaging processingAerial photography
The invention relates to an unmanned plane automatic landing system. The system comprises an aerial photography camera, a landmark positioner, unmanned plane driving equipment and a main controller, wherein the aerial photography camera shoots suspected landmark region under an unmanned plane, so as to obtain a suspected landmark image; the landmark positioner performs image processing on the suspected landmark image, so as to obtain the relative height and the relative positioning distance from the unmanned plane to a landmark when the fact that the landmark exists in the suspected landmark image is determined; the main controller is respectively connected with the landmark positioner and the unmanned plane driving equipment, and controls the unmanned plane driving equipment to drive the unmanned plane to be landed on the landmark according to the relative height and the relative positioning distance. The unmanned plane automatic landing system can accomplish automatic and accurate landing of the unmanned plane in various different landforms, and improves the intelligence level of the unmanned plane.
Owner:WUXI SANGNIAN TECH
Emergency flight control system
ActiveUS7568662B1Analogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAir traffic controlEngineering
A method and system for preventing the control of an aircraft from the cockpit. In an exemplary embodiment, the system could be triggered externally. For example, an air traffic control (ATC) station could determine that the aircraft has deviated from its planned flight path. If personnel at the ATC station decide that the deviation is not attributable to the actions of the authorized flight crew, the personnel can transmit a signal to the aircraft that disables all normal cockpit control of the aircraft. Once normal flight controls are disabled, the aircraft may execute a preprogrammed emergency flight plan via its autopilot system, with or without the use of a flight management system (FMS). The emergency flight plan could cause the aircraft to fly to a sparsely populated area and enter a holding pattern, or it could cause the aircraft to land in a sparsely populated area or at an airport using an autoland system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Automatic landing system and method of rotor aircraft
ActiveCN104309803ALow costRealize the effect of automatic landingAircraft power plantsAircraft landing aidsAcute angleFlight vehicle
Owner:GUANGZHOU XAIRCRAFT TECH CO LTD
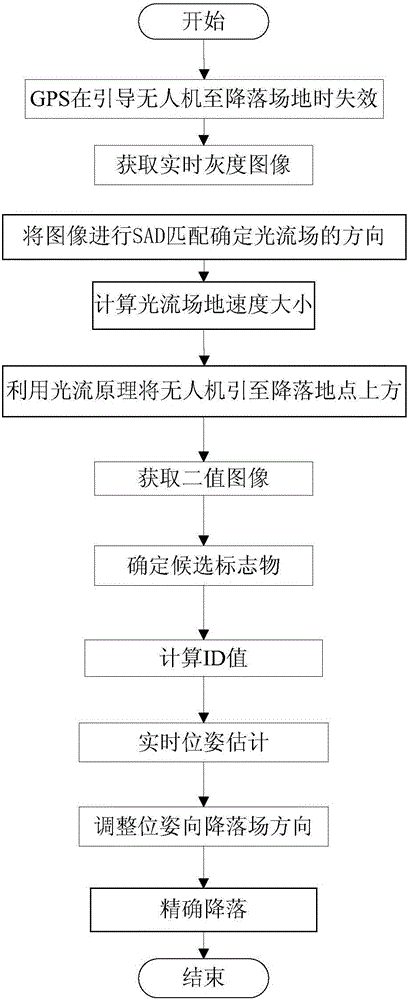
Unmanned plane automatic landing guiding method based on optical flow
ActiveCN106054929AFully autonomous landingImprove reliabilityTarget-seeking controlAttitude controlOptical flowSelf positioning
The invention provides an unmanned plane automatic landing guiding method based on an optical flow. In the process of landing, a marker is determined by processing the real-time image shot by the camera of an optical flow module, the position and attitude of the marker relative to an unmanned plane are estimated, the relative position and attitude information are sent to a flight controller to control the unmanned plane to gradually approach the landing target, and the full-autonomous landing of the unmanned plane can be ultimately achieved. Because the unmanned plane realizes the self-positioning in the autonomous flight and landing process by a downward viewing optical flow sensor, the visual positioning of itself can be completed without a GPS. And in the case of GPS failure, the auxiliary positioning can be carried out by means of the optical flow module, so that the unmanned plane can accurately find the landing site, and the reliability of the unmanned plane landing can be improved. The method is reasonable in design, can achieve accurate landing under different conditions, and is wide in applicability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Inverted-landing aircraft
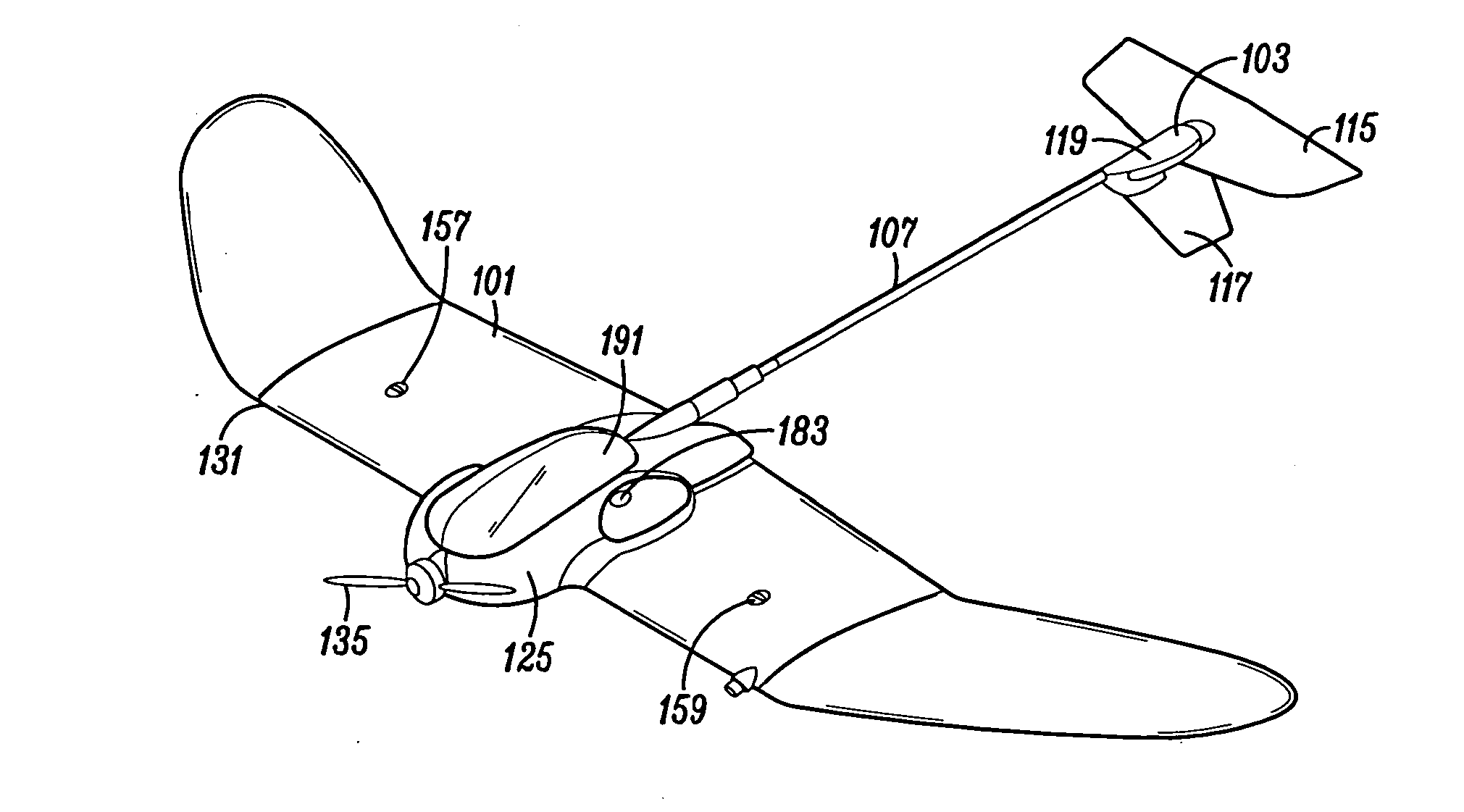
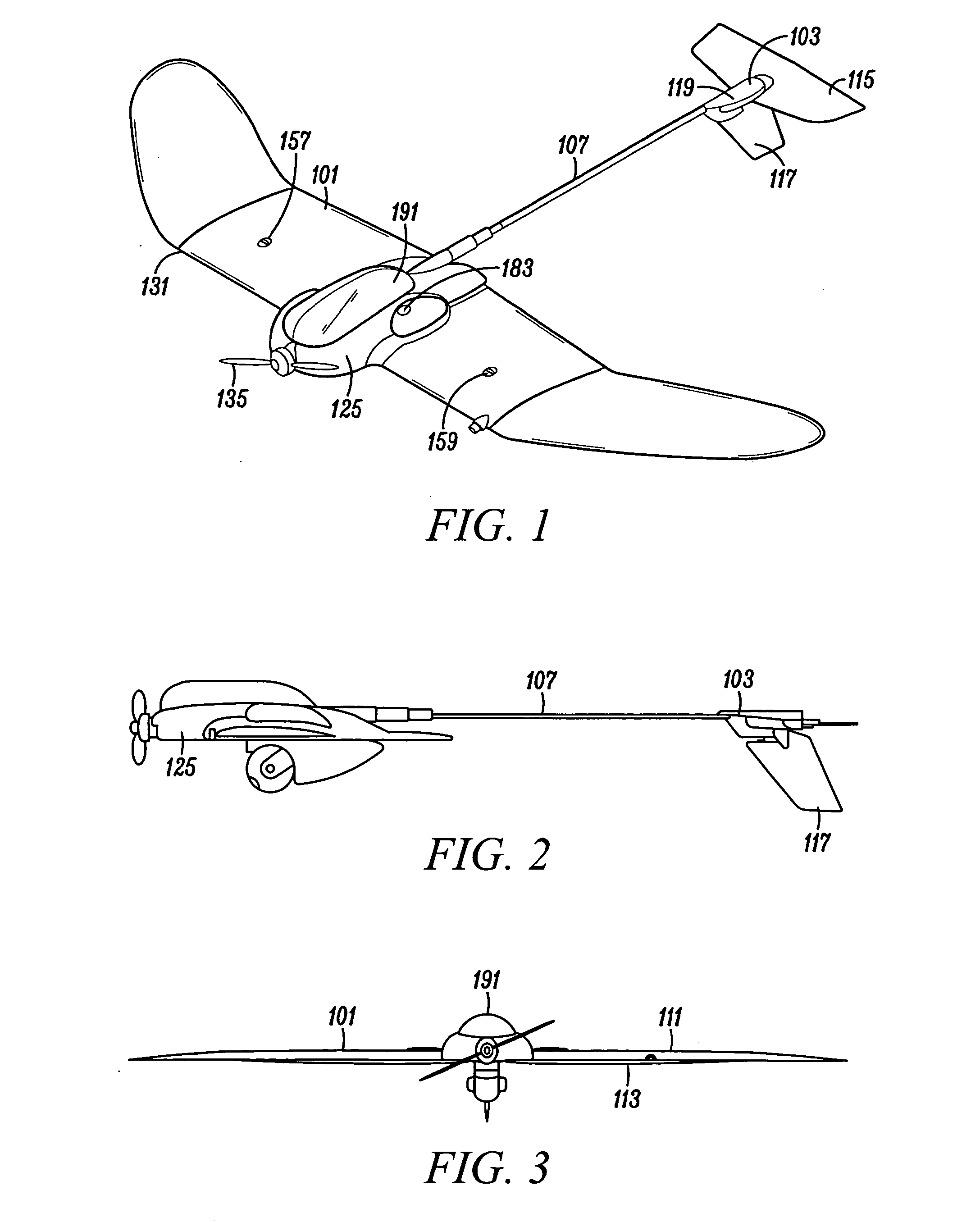
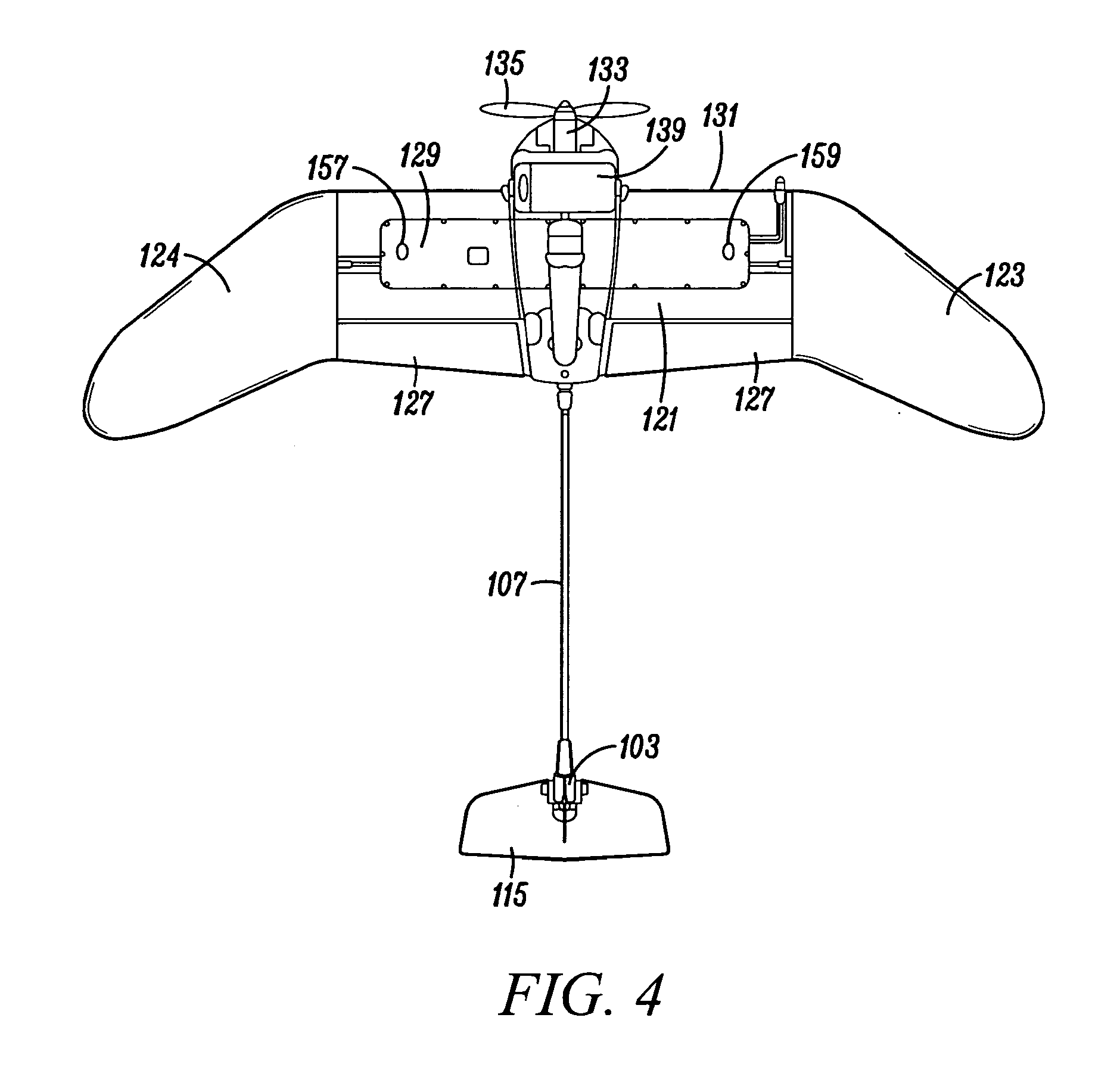
ActiveUS20140350748A1Free from damageAircraft componentsAnalogue computers for vehiclesJet aeroplaneControl system
An aircraft defining an upright orientation and an inverted orientation, a ground station; and a control system for remotely controlling the flight of the aircraft. The ground station has an auto-land function that causes the aircraft to invert, stall, and controllably land in the inverted orientation to protect a payload and a rudder extending down from the aircraft. In the upright orientation, the ground station depicts the view from a first aircraft camera. When switching to the inverted orientation: (1) the ground station depicts the view from a second aircraft camera, (2) the aircraft switches the colors of red and green wing lights, extends the ailerons to act as inverted flaps, and (3) the control system adapts a ground station controller for the inverted orientation. The aircraft landing gear is an expanded polypropylene pad located above the wing when the aircraft is in the upright orientation.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Methods and system for autonomous landing
ActiveUS20190187724A1Shorten the horizontal distanceUnmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftField of viewImage capture
A computer-implemented method for controlling an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) includes detecting a target marker based on a plurality of images captured by an imaging device carried by the UAV, determining a spatial relationship between the UAV and the target marker based at least in part on the plurality of images, and controlling the UAV to approach the target marker based at least in part on the spatial relationship while controlling the imaging device to track the target marker such that the target marker remains within a field of view of the imaging device.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
Geometric-programming-based gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method
ActiveCN104714553AReduced mobility requirementsQuick planningPosition/course control in three dimensionsGeometric programmingTrajectory planning
The invention discloses a geometric-programming-based gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method which is used for solving the technical problem that an existing gliding aircraft terminal area energy management trajectory planning method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, on the basis of the state of an aircraft entering a TAEM section, a geometric programming method is utilized for rapidly planning a reasonable and feasible TAEM plane trajectory; on the basis of the TAEM plane trajectory planning, height deduction is performed, and therefore a complete trajectory planning strategy is given. Due to the fact that the aircraft enters an entry of an automatic landing section in a spiral-line mode in the geographic planning process, the sudden overload change phenomenon is effectively avoided, and therefore the requirement for the aircraft maneuverability is lowered; meanwhile, during trajectory planning, the state of the aircraft at the TAEM section at the initial moment is considered, corresponding flight paths are planned in a classified mode for the entering state of the aircraft, the reasonable trajectory can be rapidly planned, the requirements for different entering directions are met, and the planning speed is high through simulation verification.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method of and system for deriving inertial-aided deviations for autoland systems during GPS signal interruptions
InactiveUS6845304B1Analogue computers for vehiclesPosition fixationTerrainInertial frame of reference
Deriving inertial-aided deviations for autoland systems during GPS signal interruptions involving an inertial reference system and a GPS landing system can include converting position coordinates of an aircraft from the inertial reference system to runway, lateral, and vertical coordinates. After this conversion, the method calibrates runway distance and lateral distance based on the converted position coordinates from the inertial reference system using runway distance and lateral distance from the GPS landing system with a third-order calibration filter when the aircraft is below a first height above terrain and calibrates vertical distance based on the converted position coordinates from the inertial reference system using vertical distance from the GPS landing system with a second-order calibration filter when the aircraft is below the first height above terrain. The method uses the calibrated runway, lateral, and vertical distances for deviation computations when GPS signals are interrupted below a second height above terrain.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
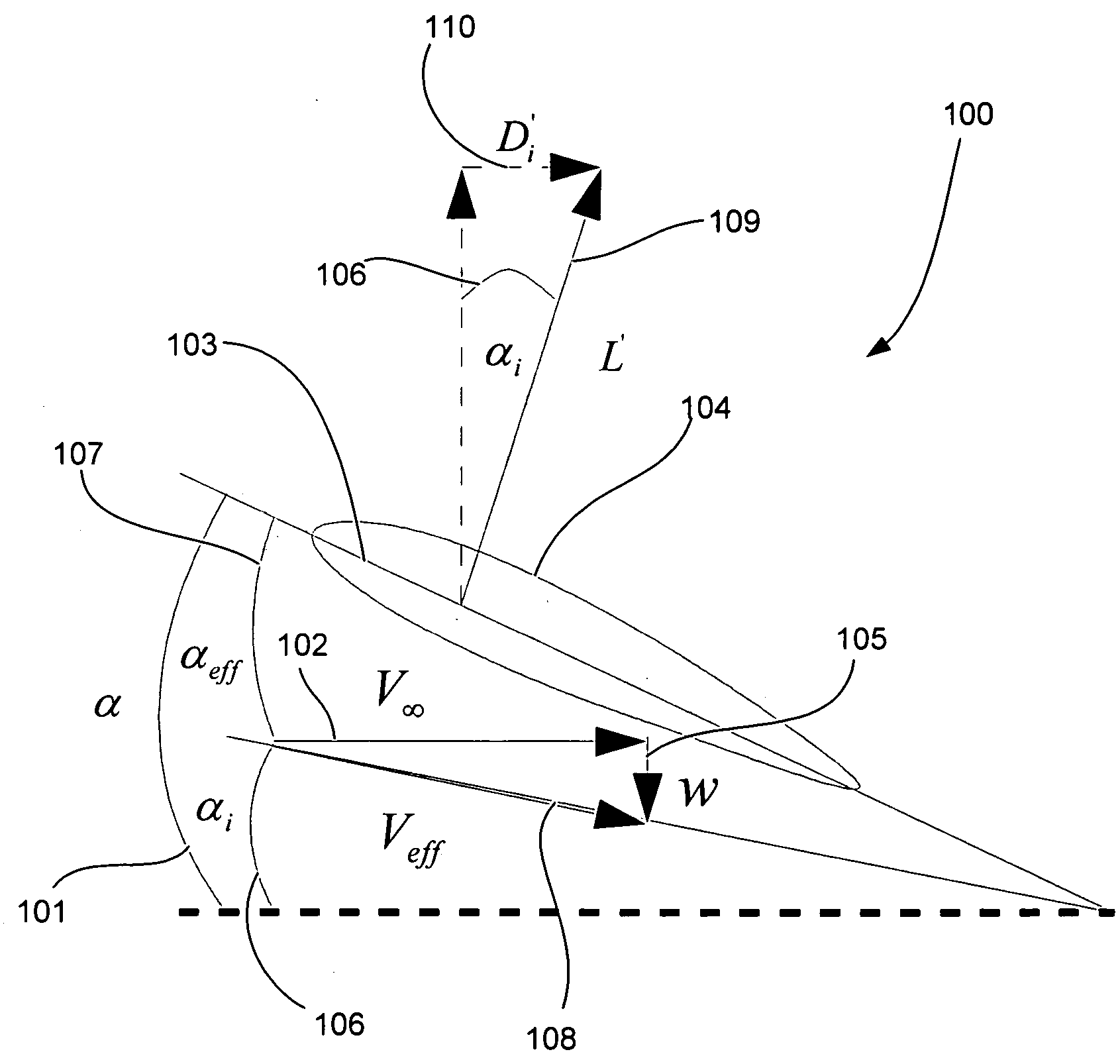
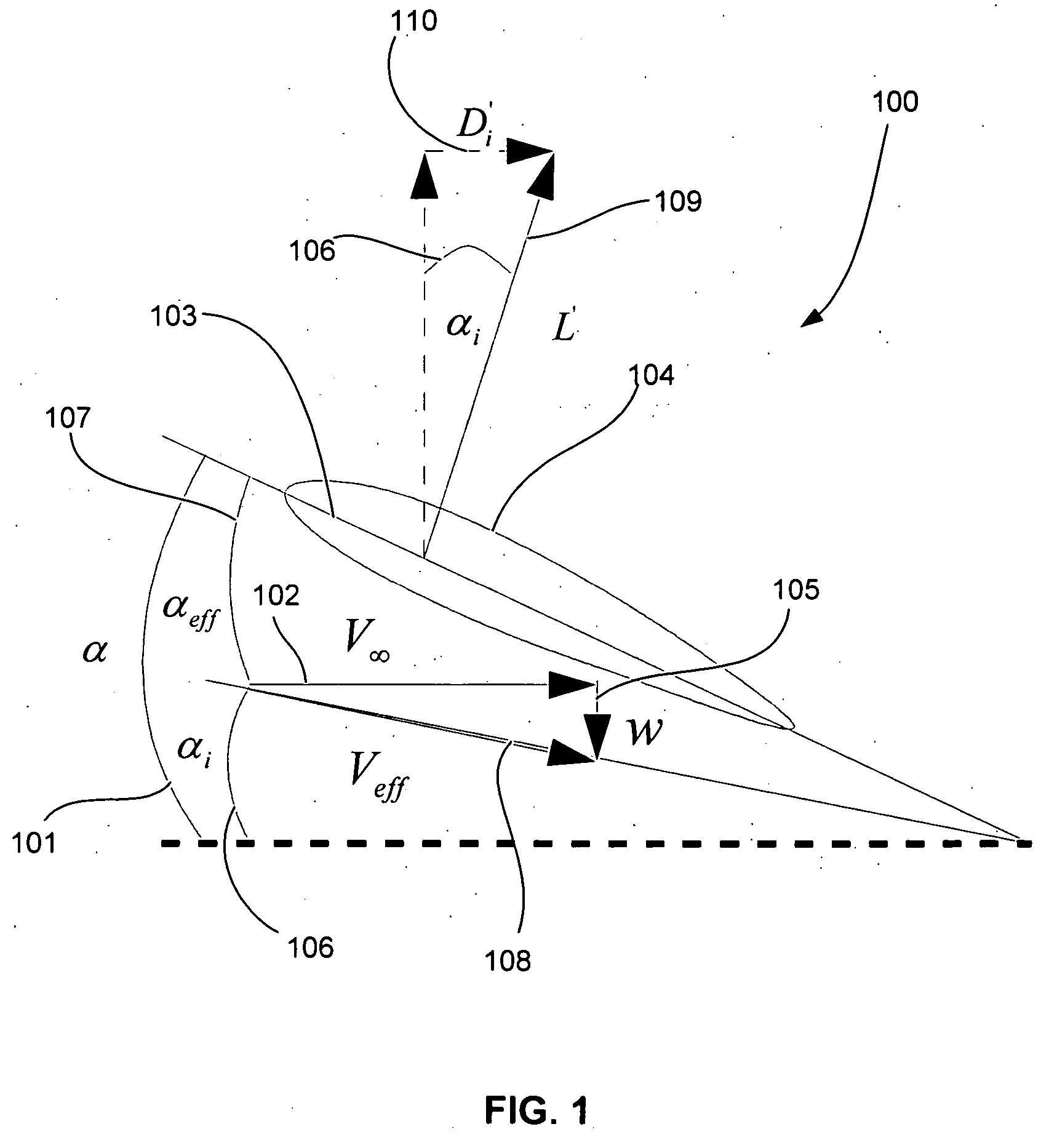
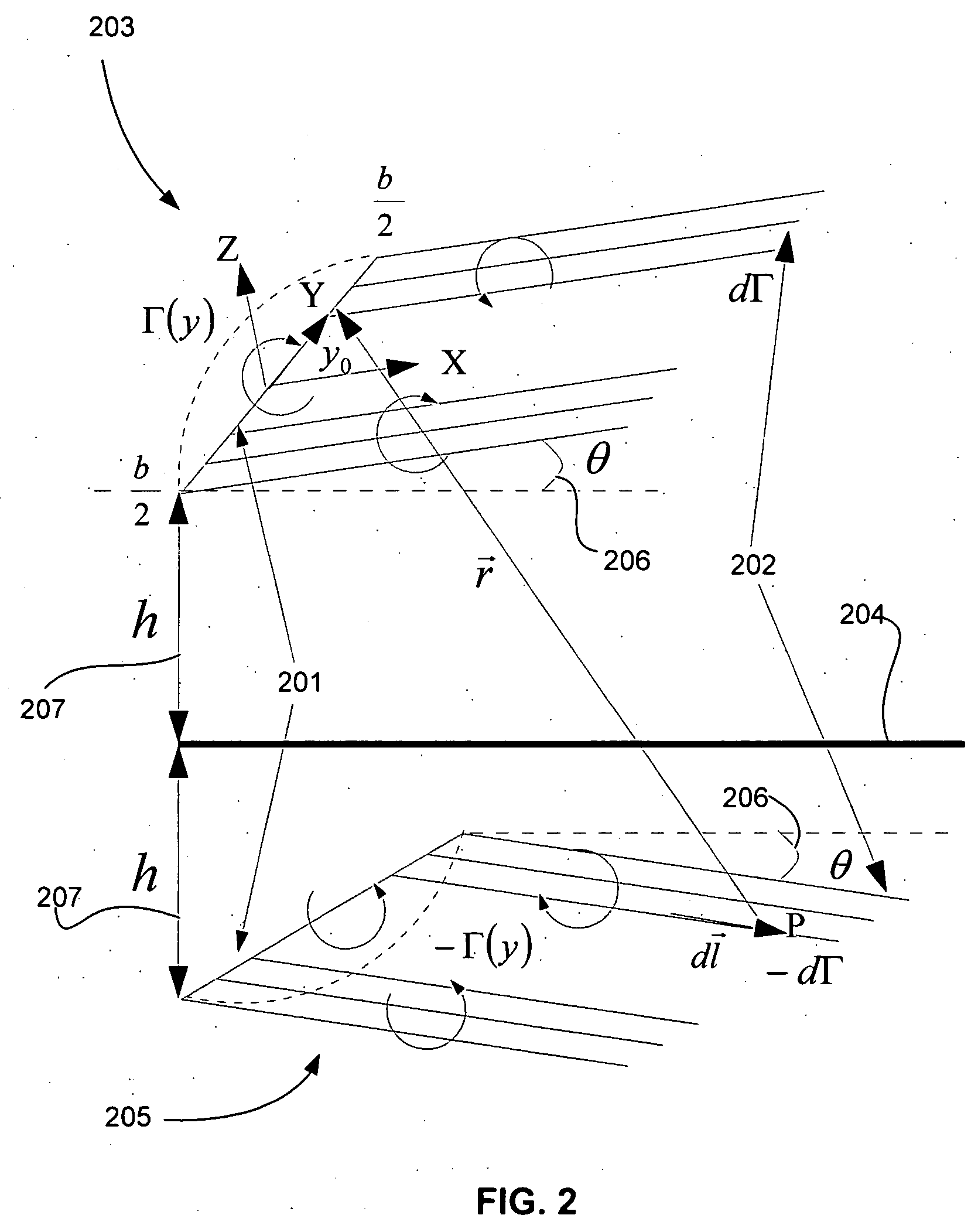
Prediction of dynamic ground effect forces for fixed wing aircraft
InactiveUS20050197811A1Design optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringLift line
Embodiments of the present invention relate to methods for calculating the aerodynamic forces and moments on fixed wing aircraft experiencing dynamic ground effects in subsonic flight. An airfoil and its trailing vortices are modeled as a lifting line with trailing vortex sheets and an image lifting line with trailing vortex sheets. The lifting line is located at a certain height above the ground and its image is located at an equal height below the ground, in order to satisfy a boundary condition of zero normal velocity at the ground. A downwash velocity at the airfoil is expressed as the sum of the downwash velocities from the lifting line and its image and is dependent on the height above the ground. The angle of attack of the airfoil is then expressed as a function its downwash velocity, the geometry of the airfoil, and a series representation of its vorticity distribution. The vorticity distribution is calculated from the angle of attack by numerical substitution. Aerodynamic forces and moments on the airfoil are calculated from the vorticity distribution. In another method, a lifting surface and image lifting surface are used to model an airfoil. These methods have particular use in autoland systems, autopilot systems and computer simulations.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
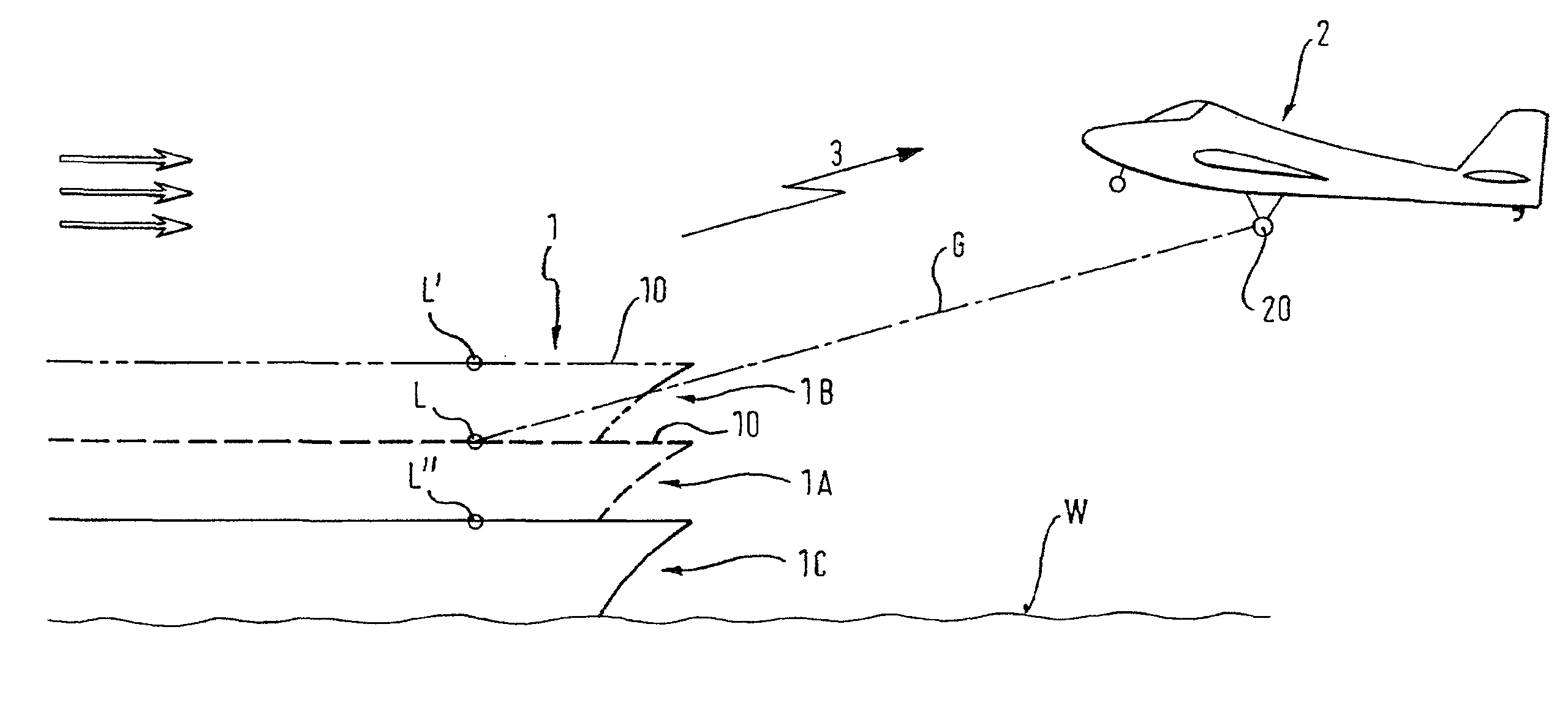
Autonomous and automatic landing method and system
A system and method are disclosed for automatic landing of an aircraft on a landing runway, including an on-board video camera intended to take images of the ground, image processor to extract from these images visual features of the landing runway, guidance system determining guidance commands of the aircraft to bring it into a nominal approach plane and to align it with the axis of the landing runway, from the respective positions of the visual features of the landing runway, in at least one of the images, where the guidance commands are supplied to a flight control computer.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
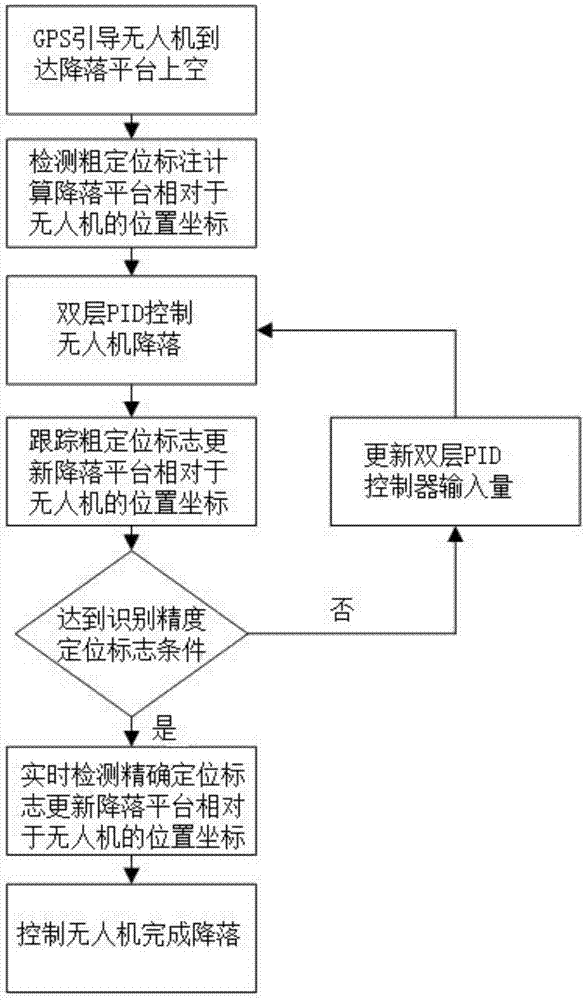
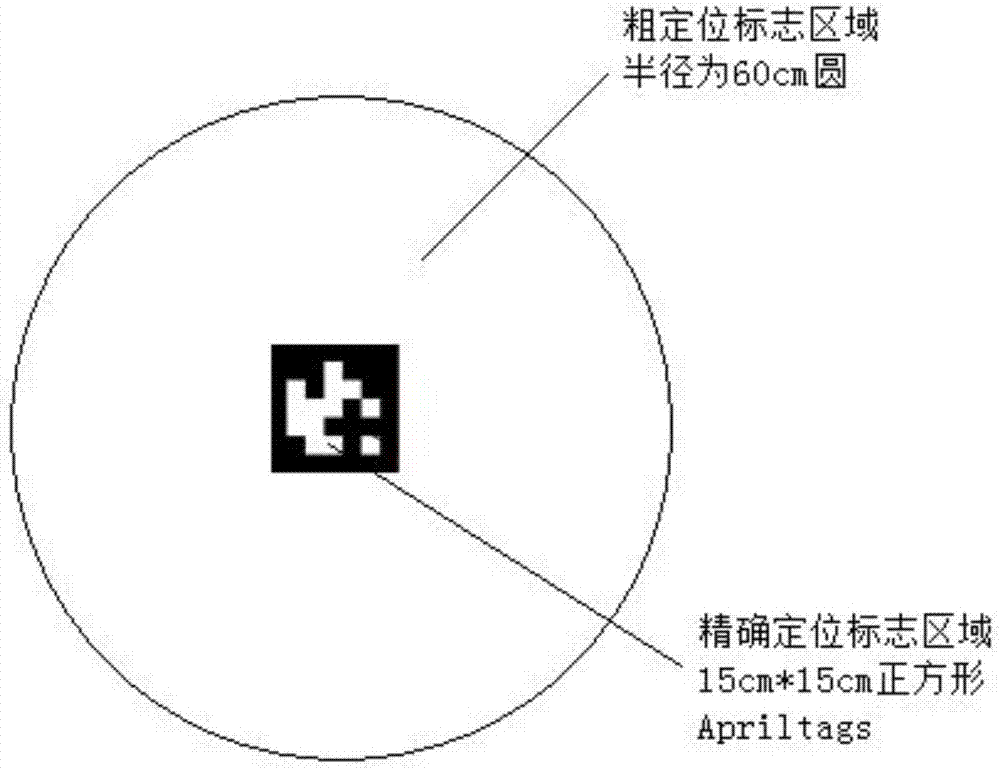
Automatic landing method of unmanned aerial vehicle based on visual guidance
ActiveCN107544550AAchieve autonomous landingHigh intelligenceTarget-seeking controlSkyUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an automatic landing method of an unmanned aerial vehicle based on visual guidance. The implementation scheme comprises the steps that 1, the unmanned aerial vehicle is guidedby GPS navigation to get to the sky above a landing platform; 2, a coarse positioning mark is detected according to an image shot by an airborne camera, and position coordinates of the landing platform relative to the unmanned aerial vehicle are calculated; 3, the unmanned aerial vehicle is controlled by an unmanned aerial vehicle double-layer PID controller to start descending; 4, the position coordinates of the landing platform relative to the unmanned aerial vehicle are updated, and thus the input of the double-layer PID controller is updated; and 5, when the unmanned aerial vehicle descends to reach a condition of recognizing an accurate positioning mark, real-time detection is performed by using an Apriltags technology to obtain new center coordinates of the landing platform, the input of the double-layer PID controller is updated, and accurate landing of the unmanned aerial vehicle is completed. The automatic landing method solves a problem of low GPS guided unmanned aerial vehicle landing accuracy and can be applied to accurate autonomous landing of the unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
UAV image-guided landing method of unmanned ship shipborne platform
ActiveCN105843242AEasy to scan at different heightsImprove securityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsMarine engineeringUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to a UAV image-guided landing method of an unmanned ship shipborne platform. An UAV is provided with an airborne controller and an image scanner which are connected with each other, the image scanner is arranged at the bottom part of the UAV, an unmanned ship is provided with a shipborne controller and an image display screen which are connected with each other, the image display screen is arranged on the shipborne platform, the airborne controller and the shipborne controller can exchange information, and when the airborne controller receives an automatic landing instruction, accurate landing of the UAV on the unmanned ship shipborne platform is achieved through adopting the image-guided landing method. The UAV image-guided landing method can overcome waggle of the unmanned ship shipborne platform, and guide the UAV to land in a target region safely and reliably.
Owner:SIFANG JIBAO WUHAN SOFTWARE CO LTD +2
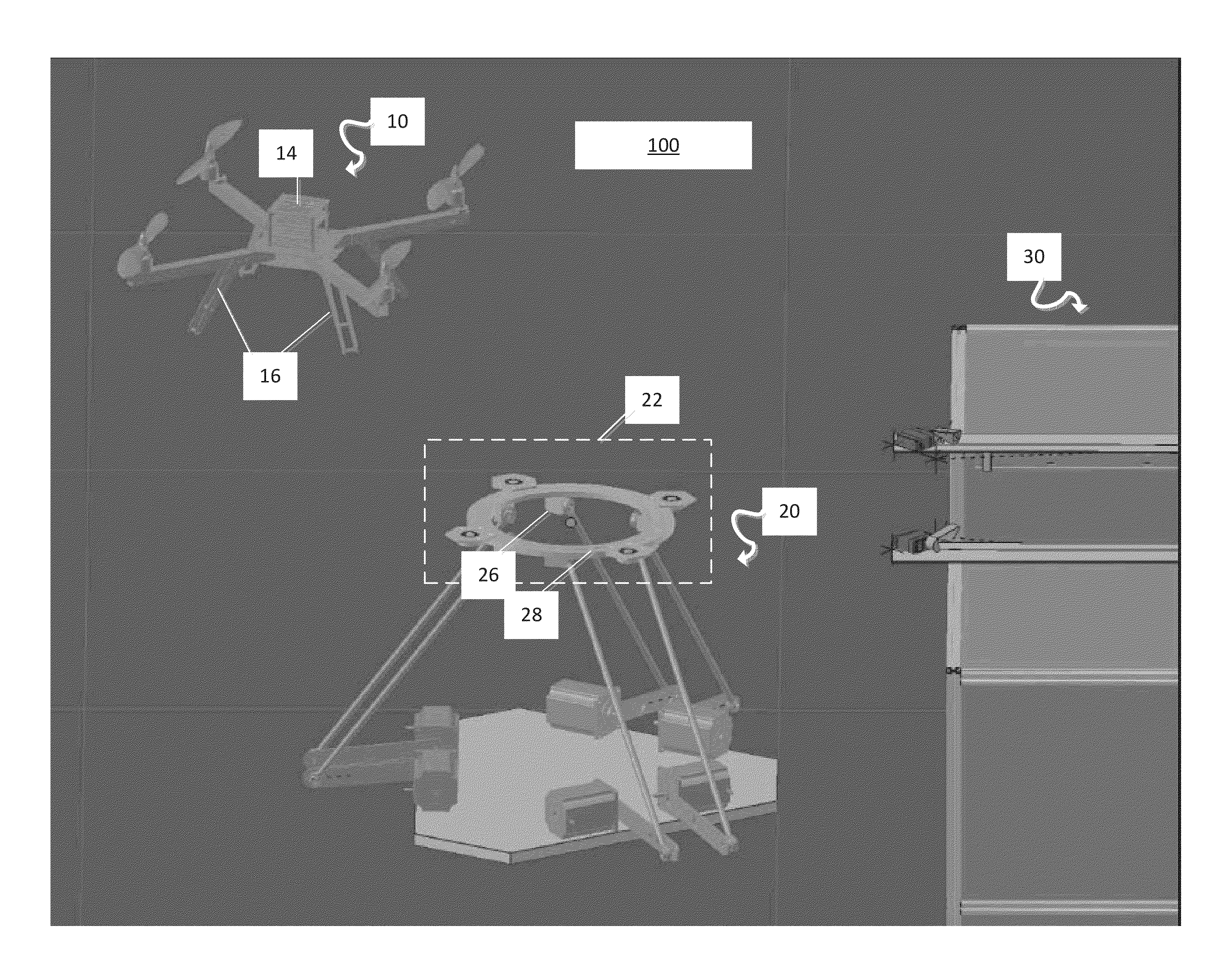
Systems and methods for charging unmanned aerial vehicles on a moving platform
ActiveUS20180364740A1Improve efficiencyReduce riskAutonomous decision making processUnmanned aerial vehiclesComputer moduleComputer science
Disclosed herein are system and method for automatically recharging a unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) on a moving platform, comprising: a software module identifying the moving platform; a software module estimating a real-time state of the moving platform; a software module controlling automatic landing of the UAV on the moving platform based on the real-time state estimation of the moving platform and data collected from the one or more sensors; a software module controlling automatic connection of the UAV to a charging station of the moving platform with a pre-determined orientation; and a software module controlling automatic taking off of the UAV from the moving platform after charging.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com