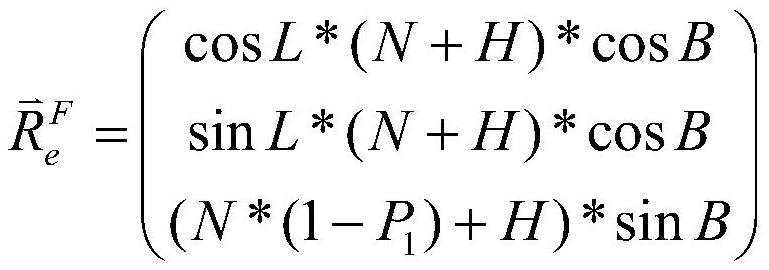Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54results about "Electromagnetic finder monitoring/testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
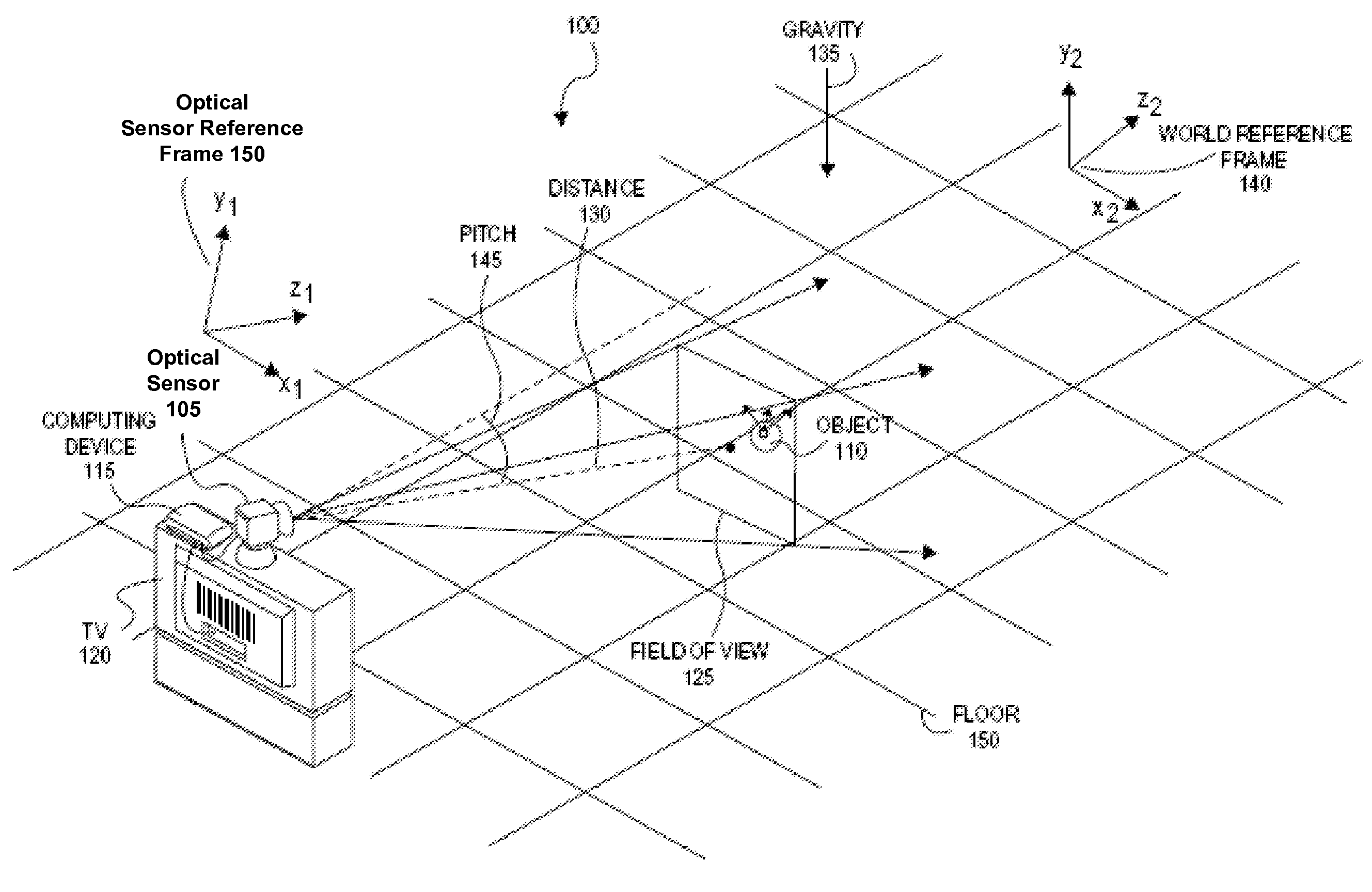
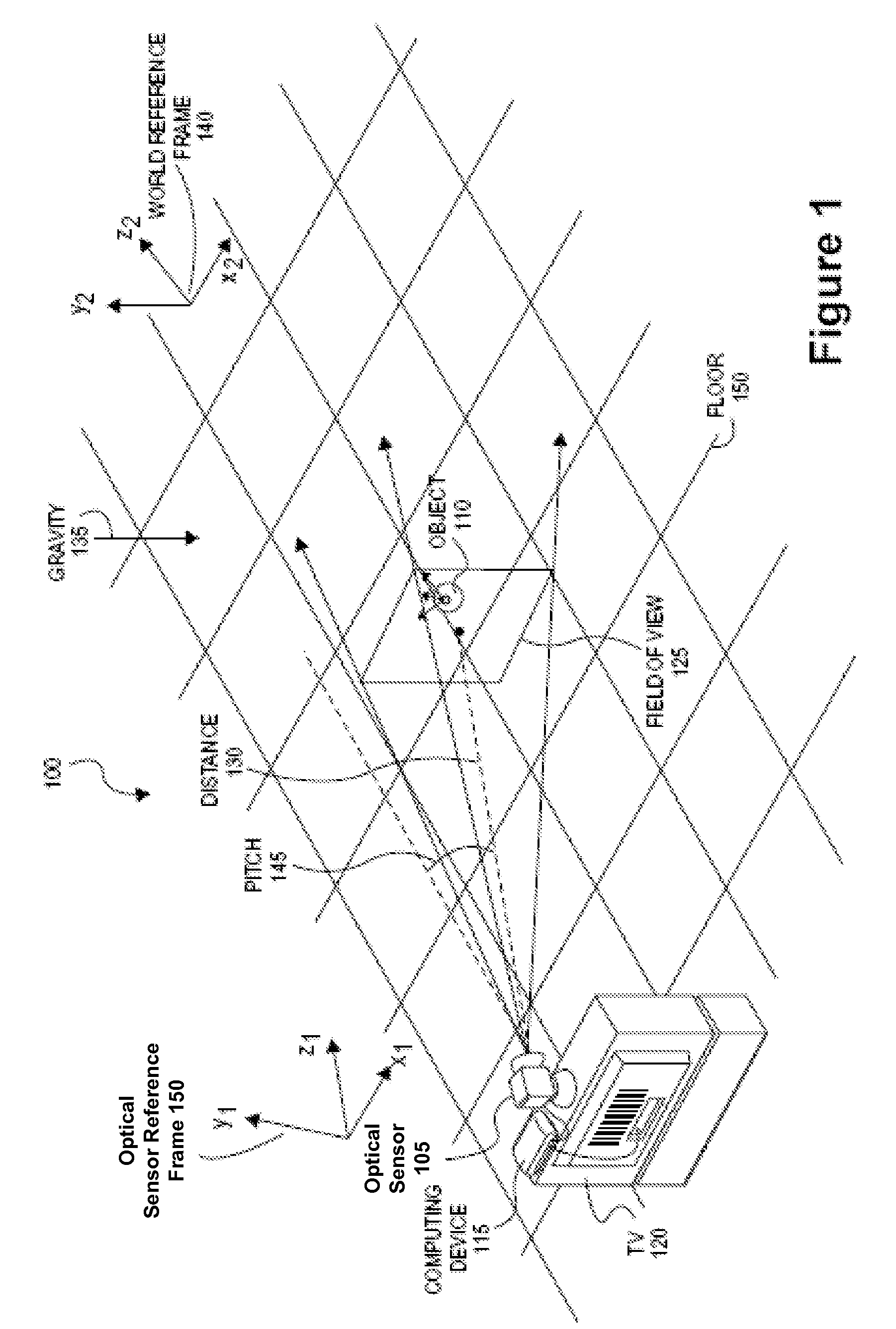
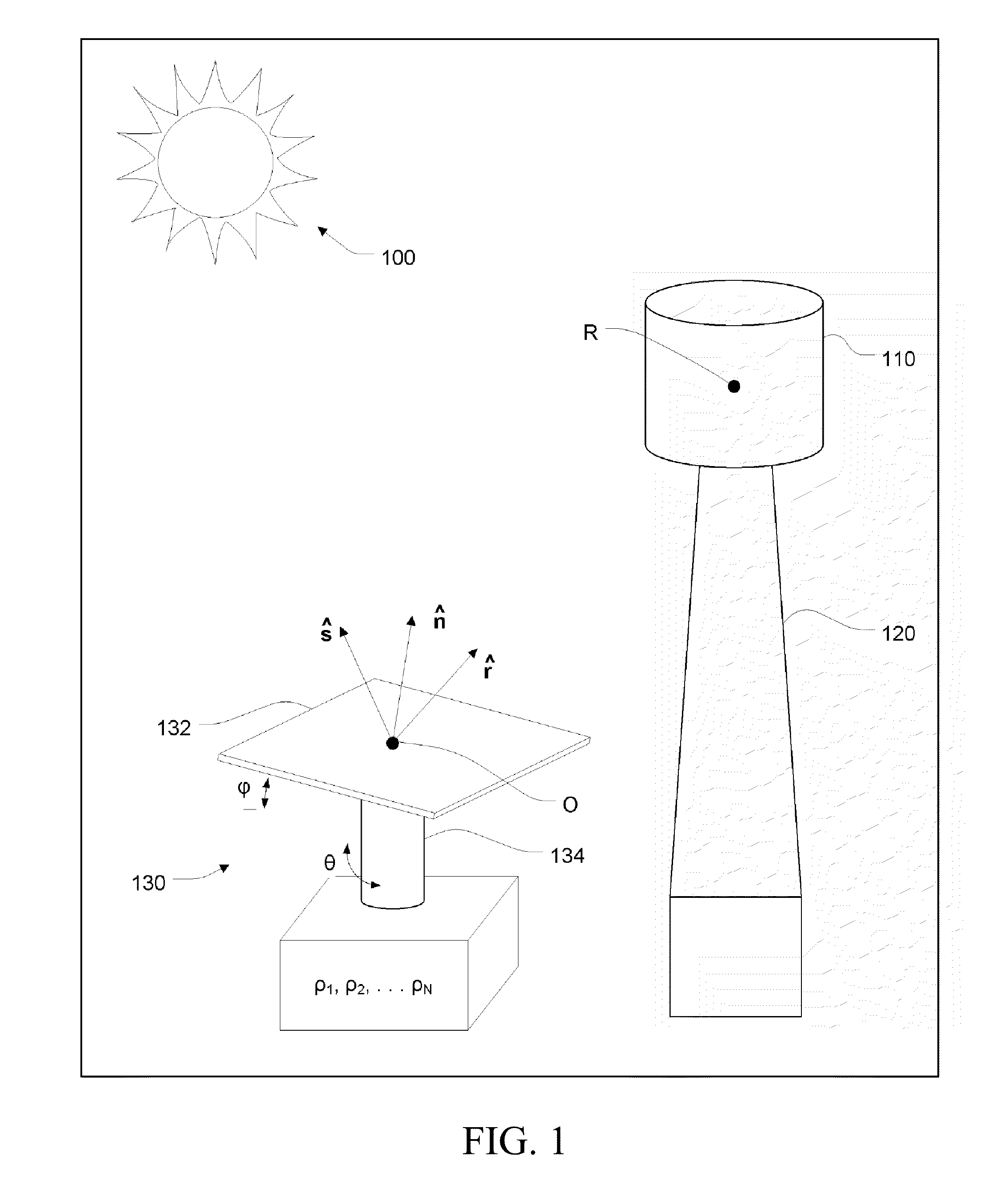
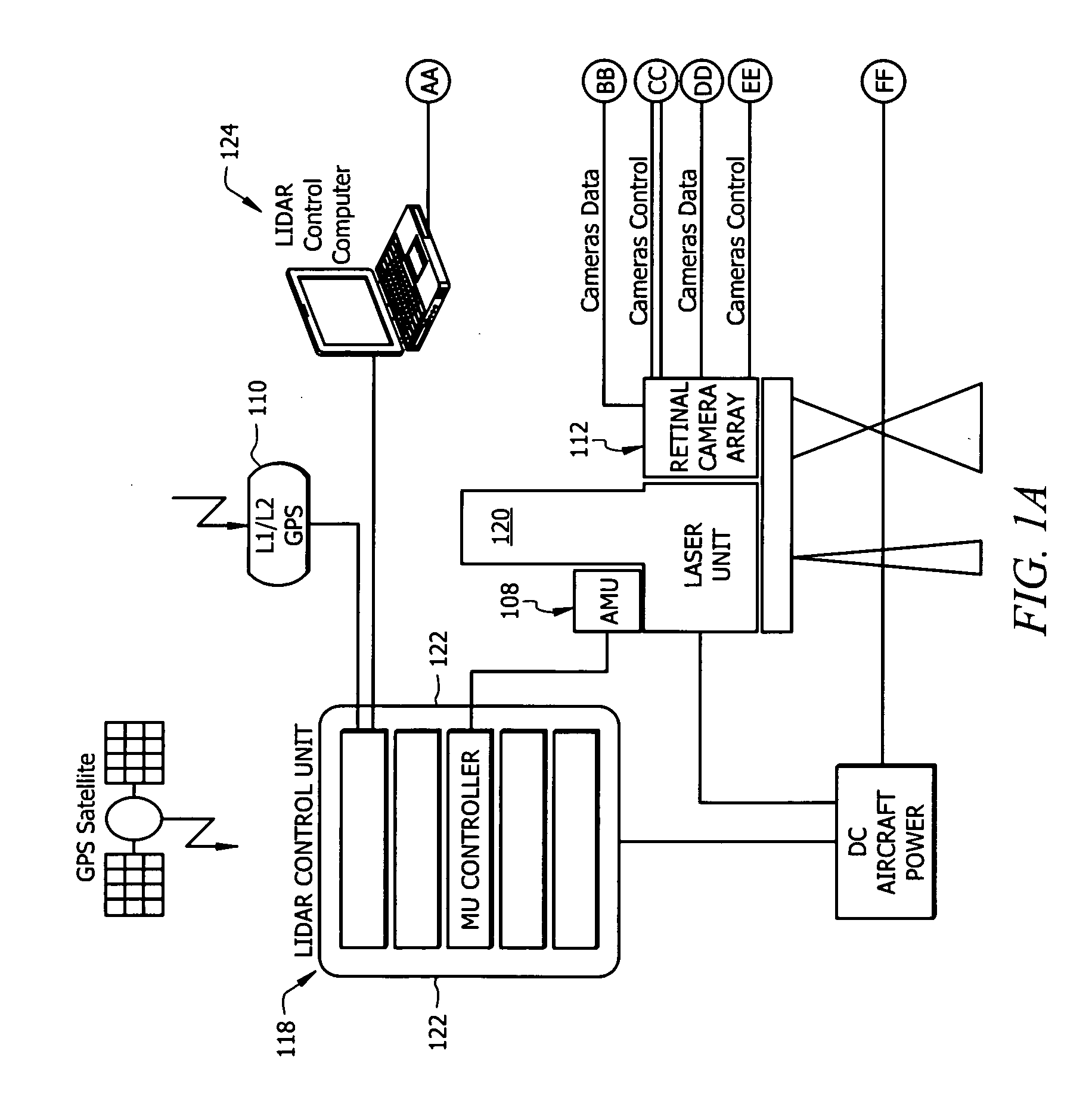
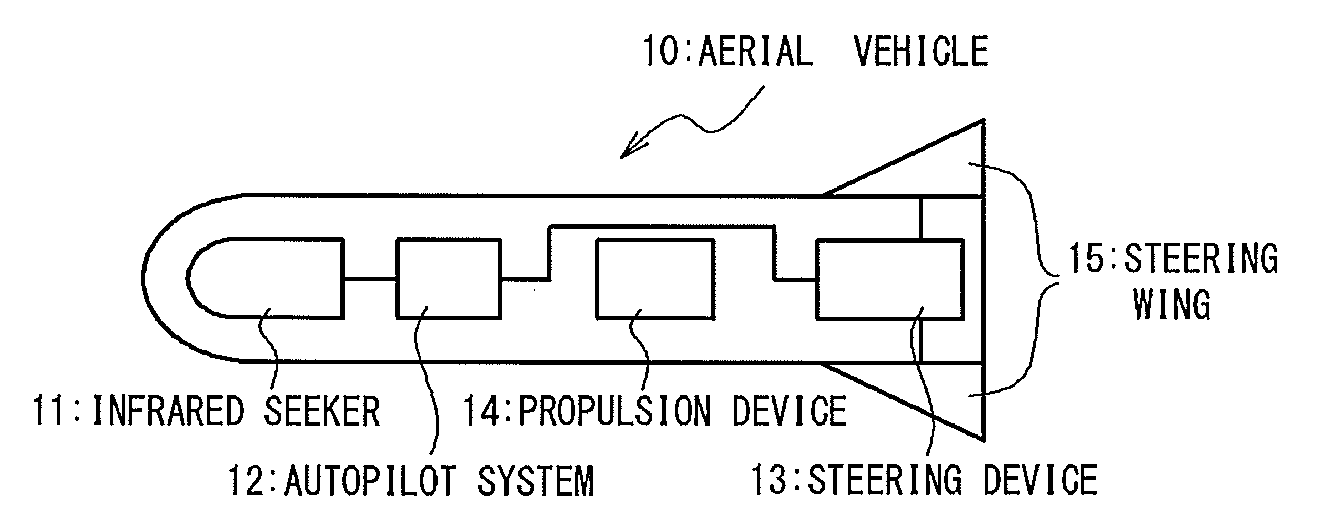
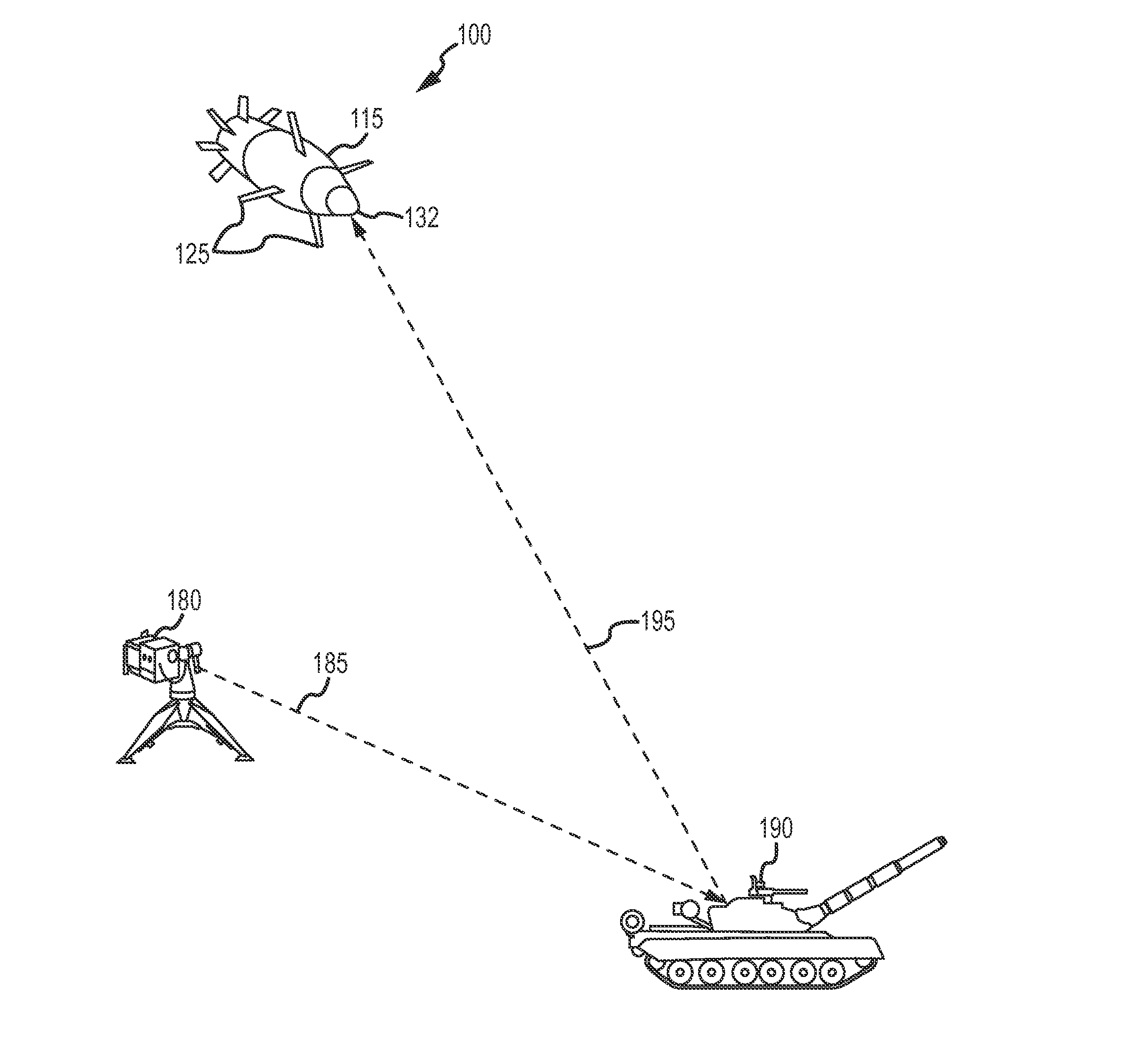
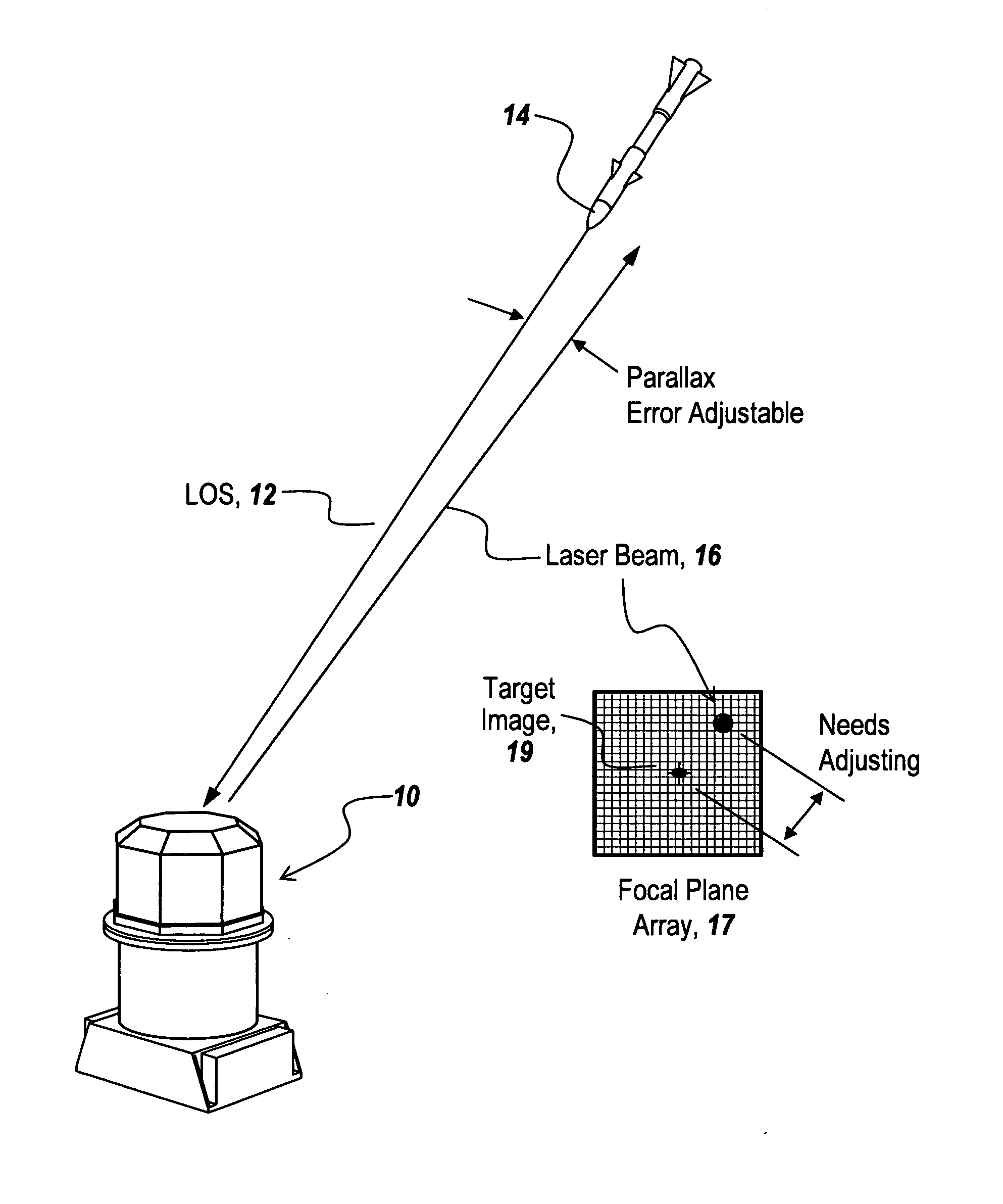
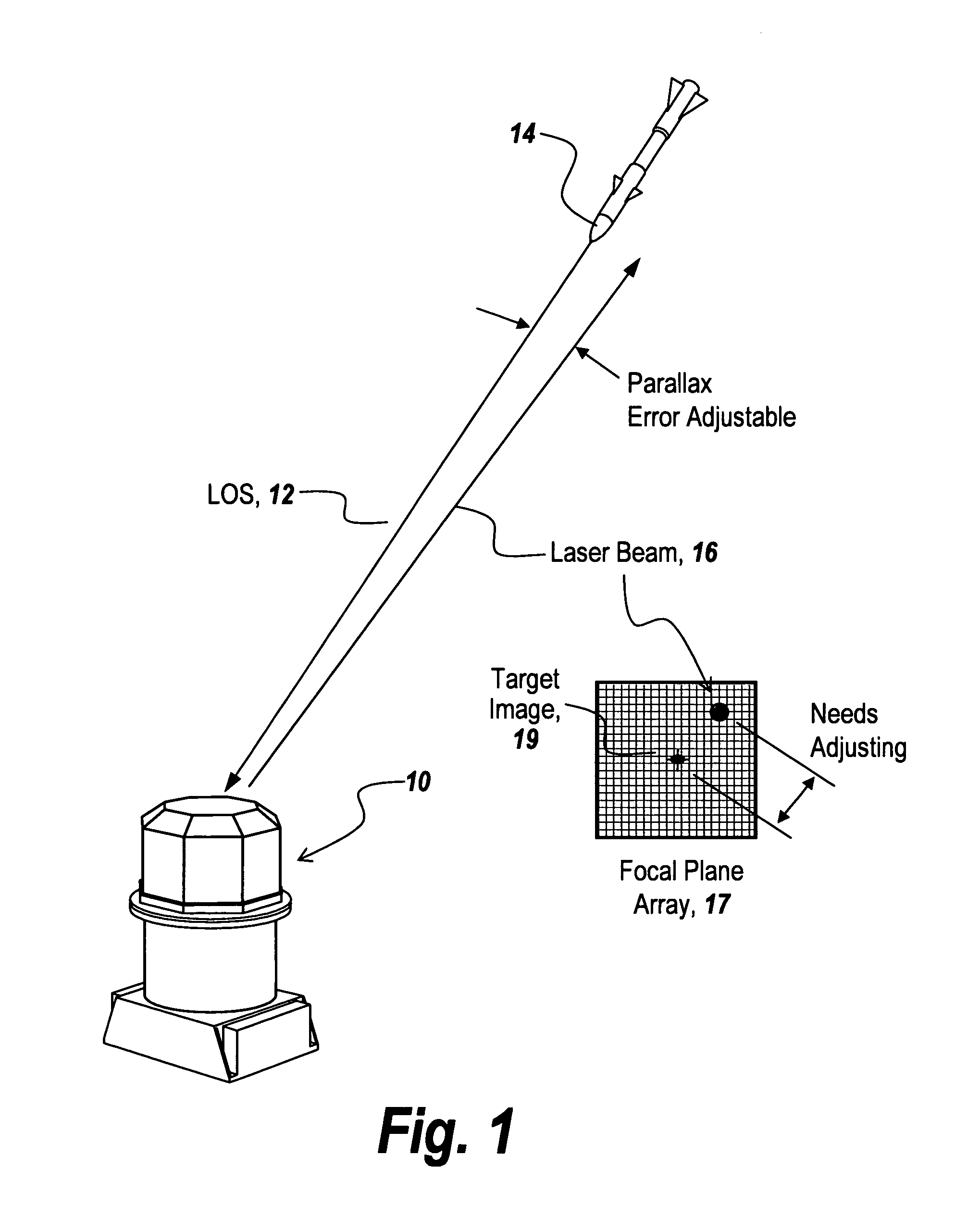
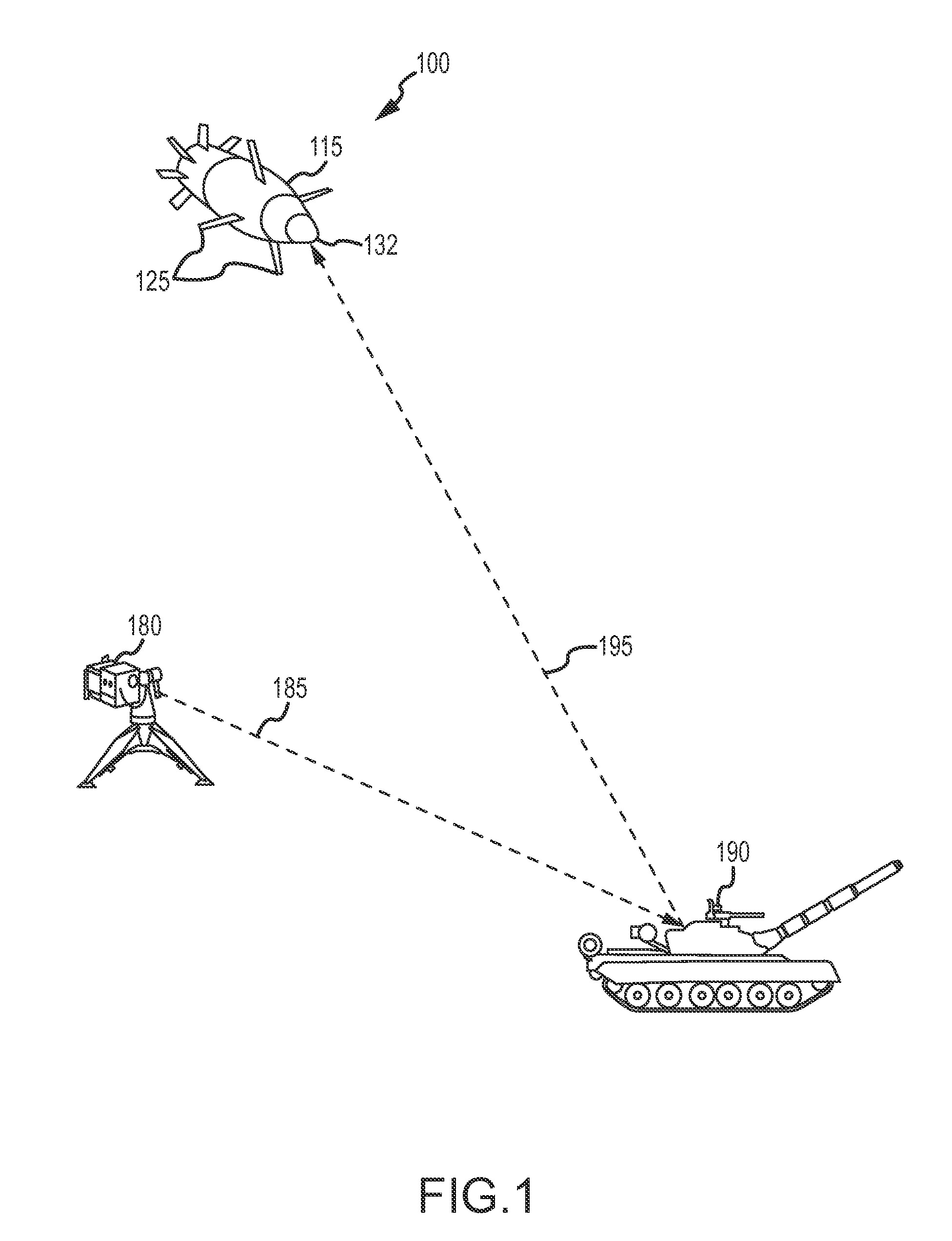
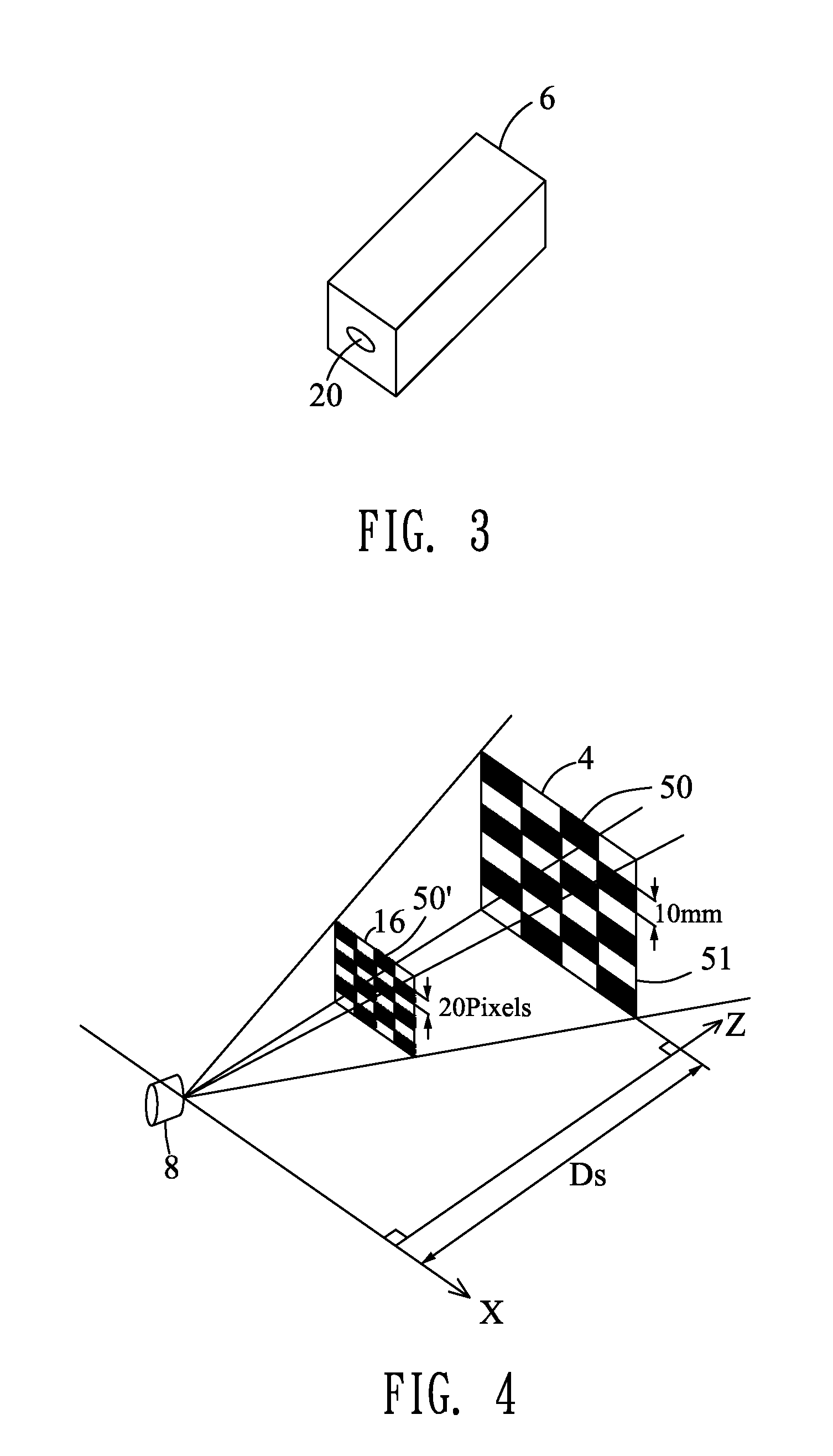
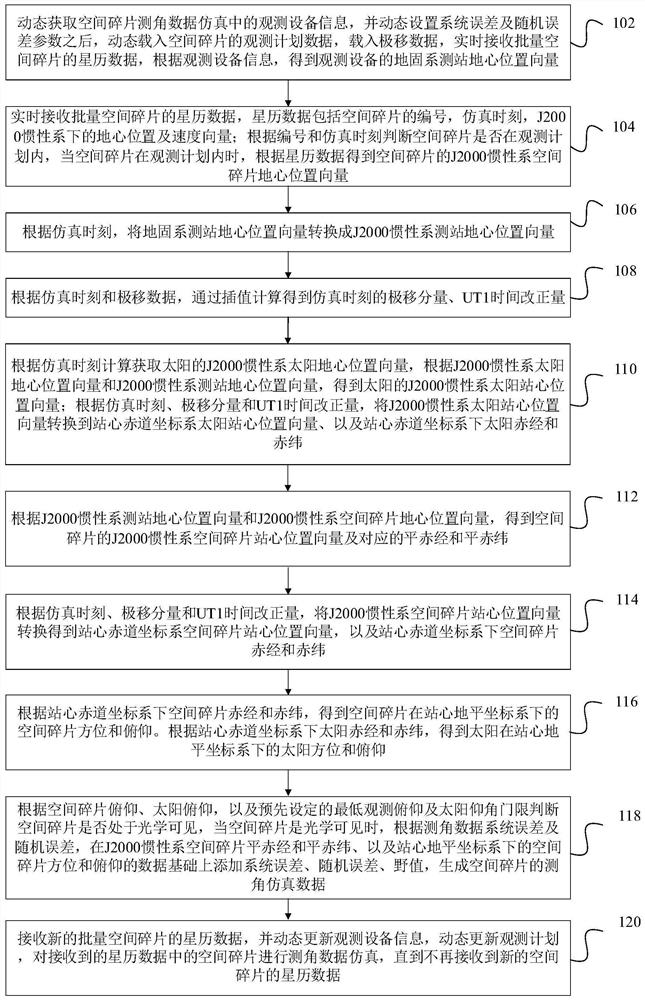
Tracking system calibration using object position and orientation
ActiveUS20100302378A1Television system detailsElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingOptical axisOptical transducers
To calibrate a tracking system, a computing device receives positional data of a tracked object from an optical sensor as the object is pointed approximately toward the optical sensor. The computing device computes a first angle of the object with respect to an optical axis of the optical sensor using the received positional data. The computing device receives inertial data corresponding to the object, wherein a second angle of the object with respect to a plane normal to gravity can be computed from the inertial data. The computing device determines a pitch of the optical sensor using the first angle and the second angle.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Camera-based heliostat calibration with artificial light sources
ActiveUS20100031952A1Error minimizationReduce search timeSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueHeliostatLight source
Systems and methods of calibrating heliostat parameters for subsequent open-loop sun-tracking, the calibration based on driving artificial light source reflections from one or more heliostats into one or more image sensors.
Owner:SEPCOIII ELECTRIC POWER CONSTR CO LTD
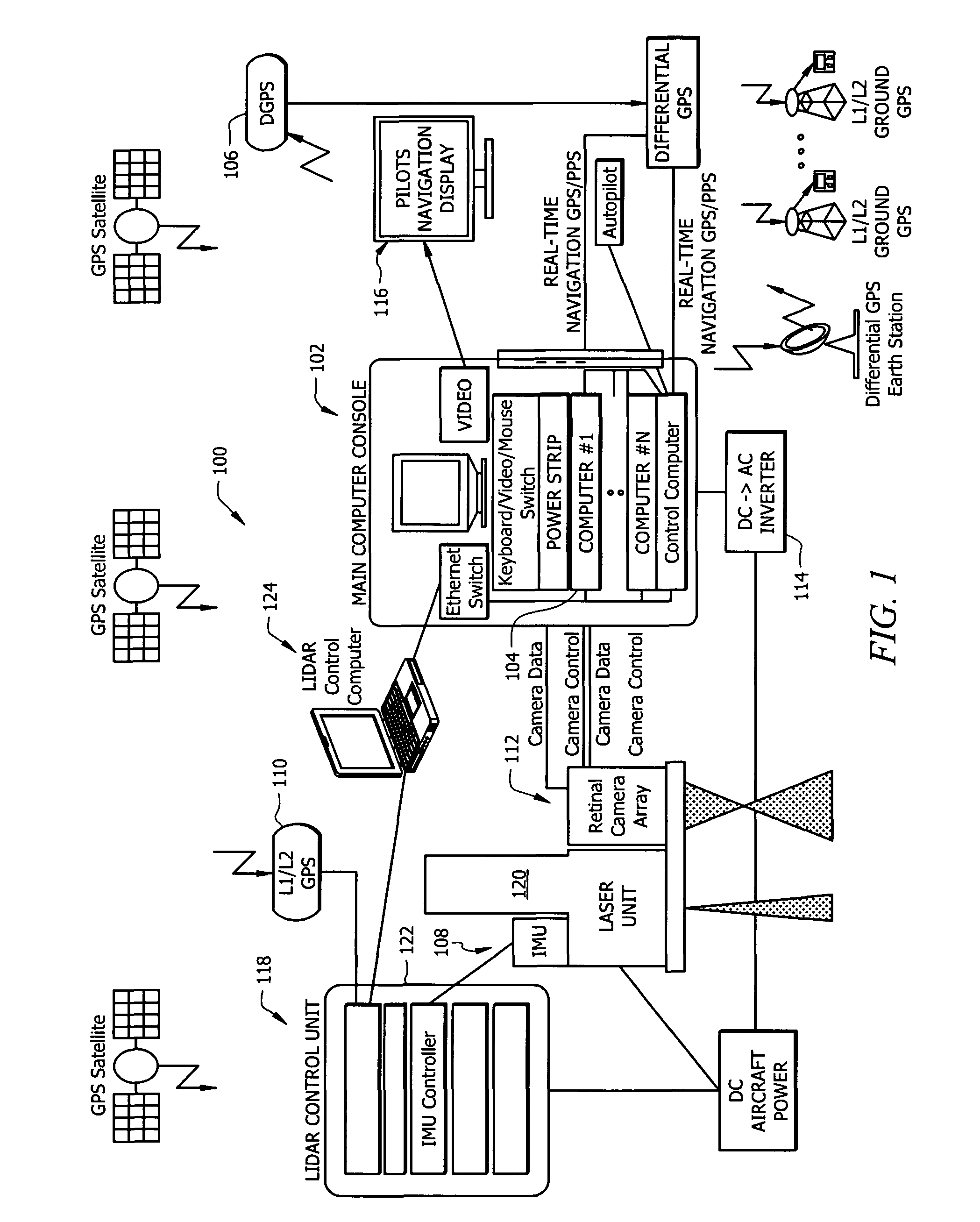
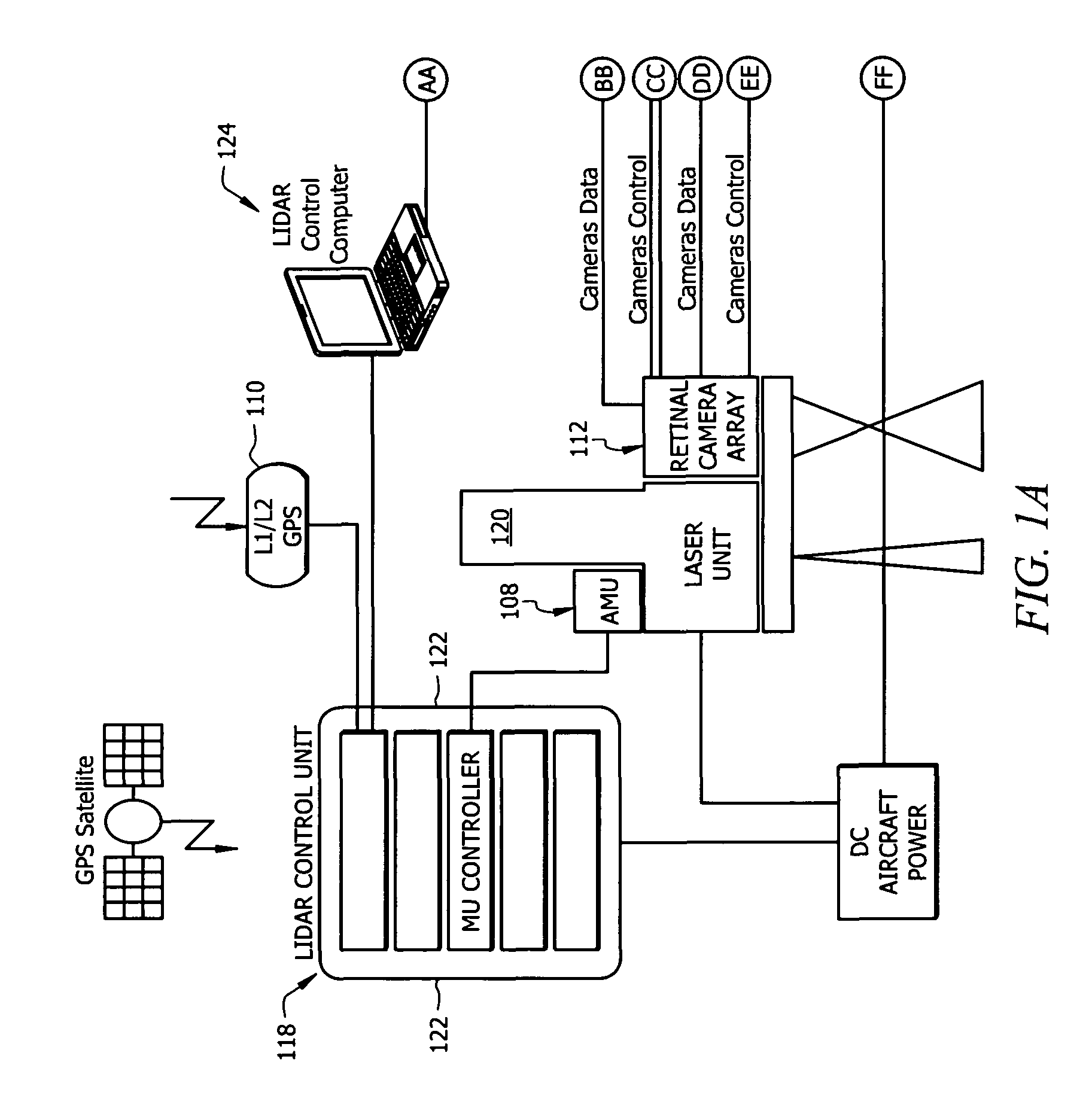
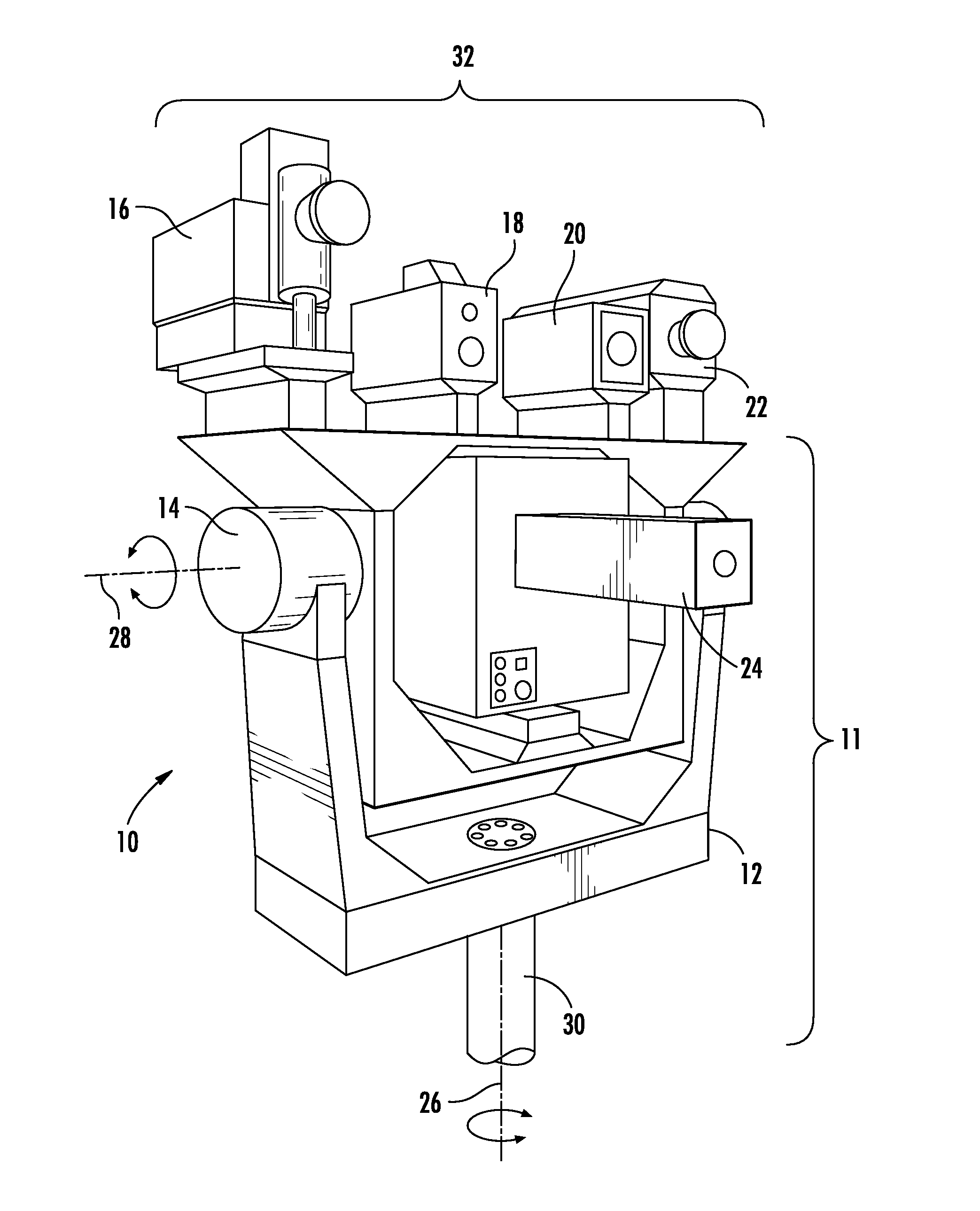
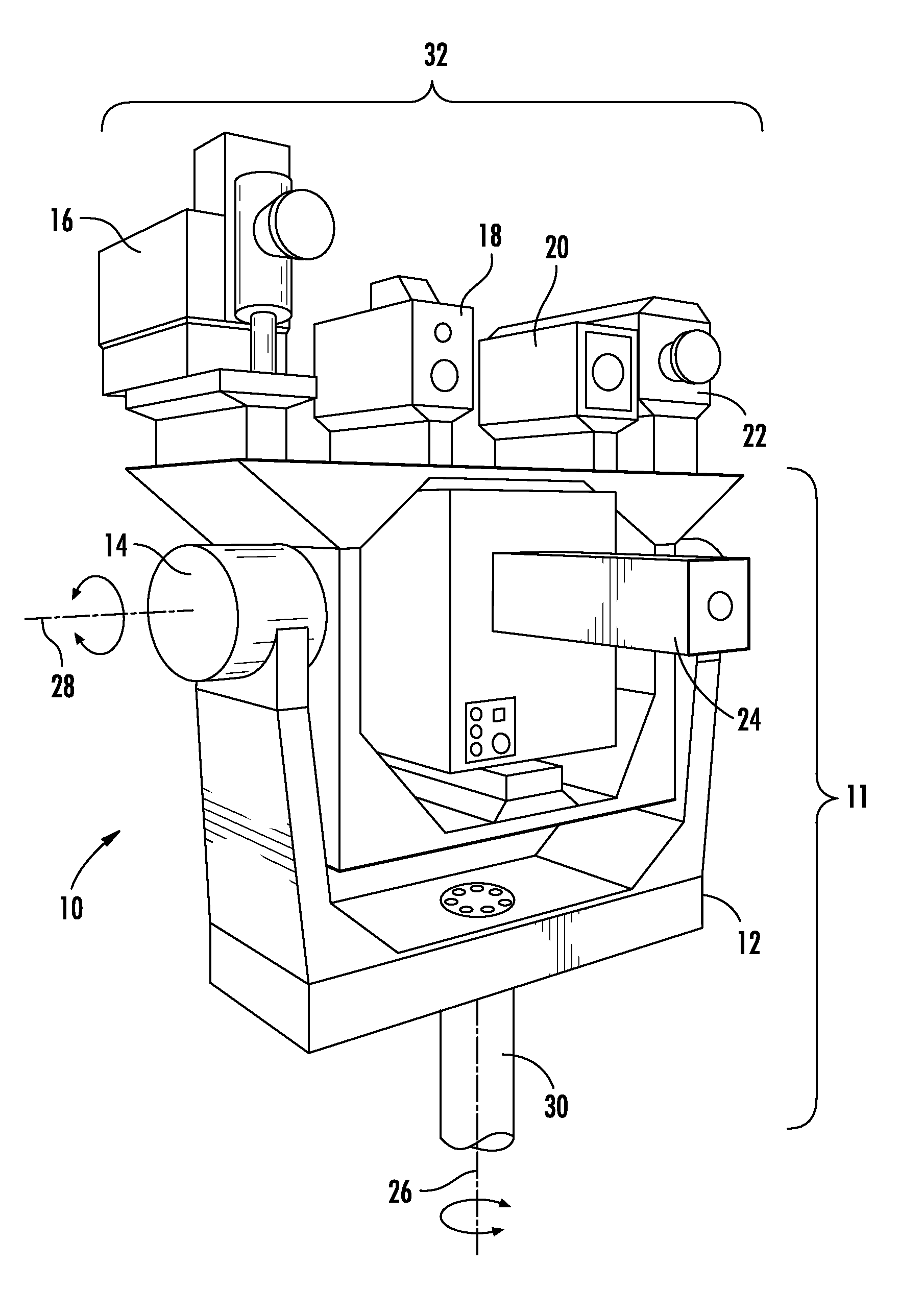
Self-calibrated, remote imaging and data processing system
ActiveUS20100235095A1Improve output qualityLimited resolutionNavigational calculation instrumentsRoad vehicles traffic controlData processing systemEngineering
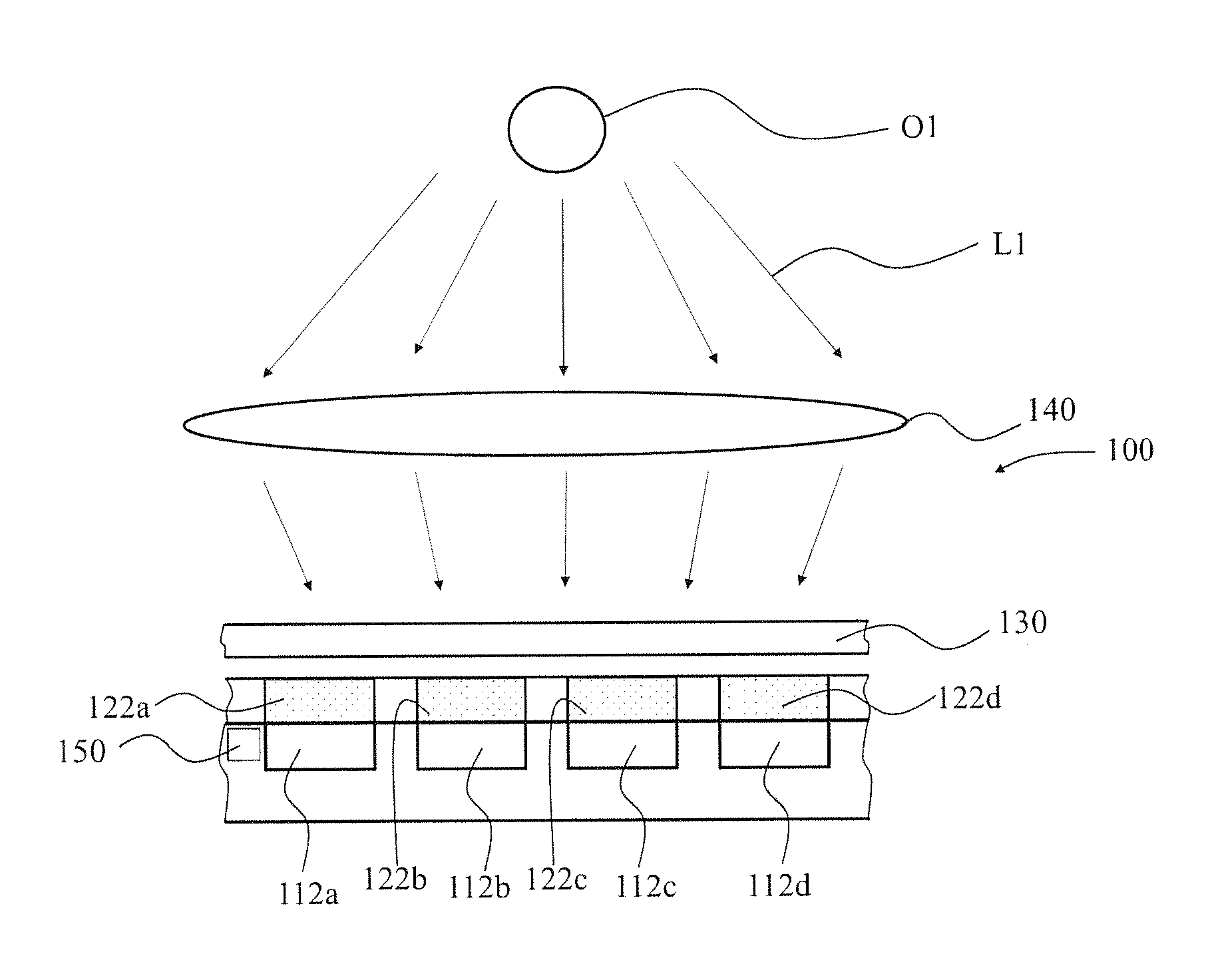
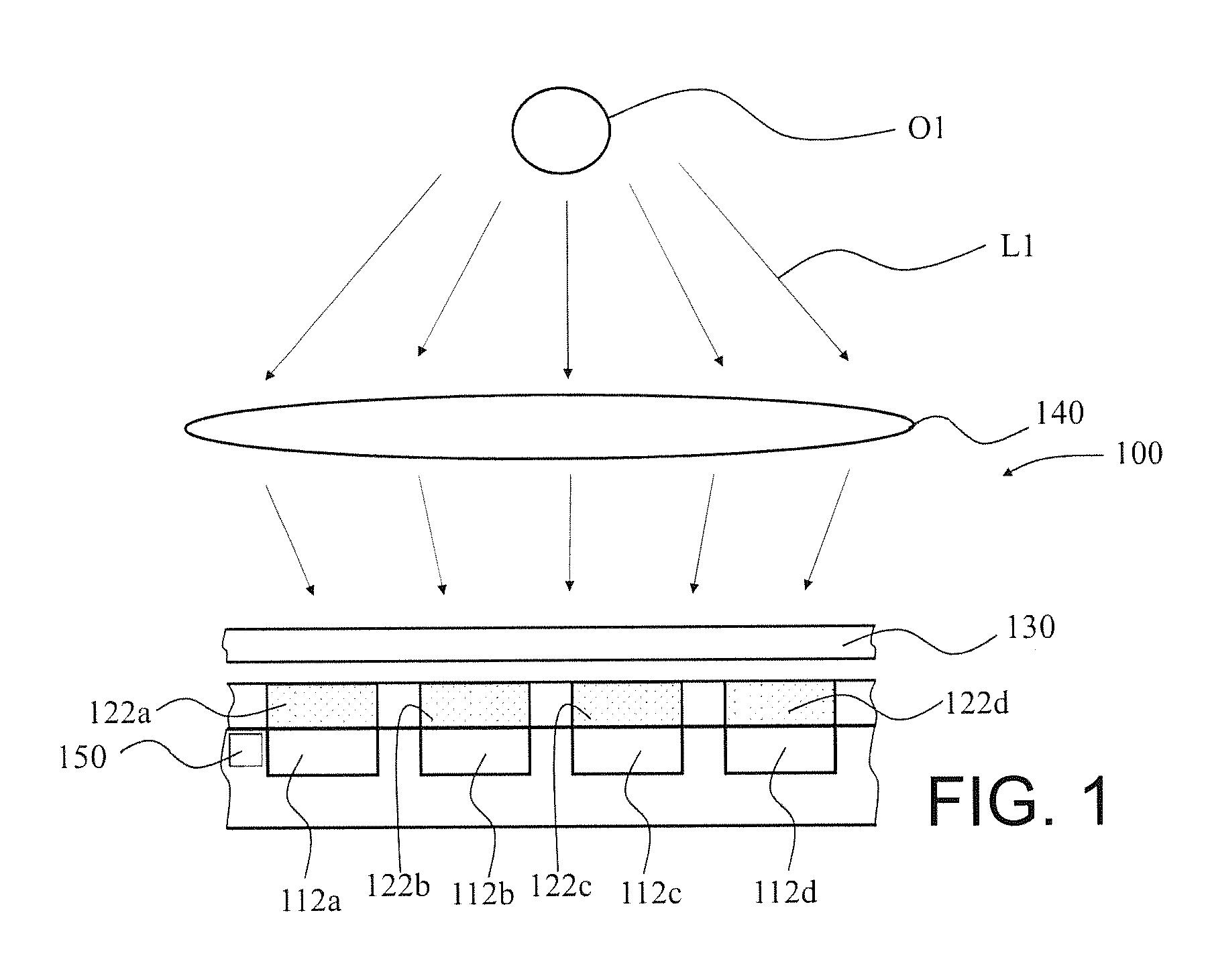
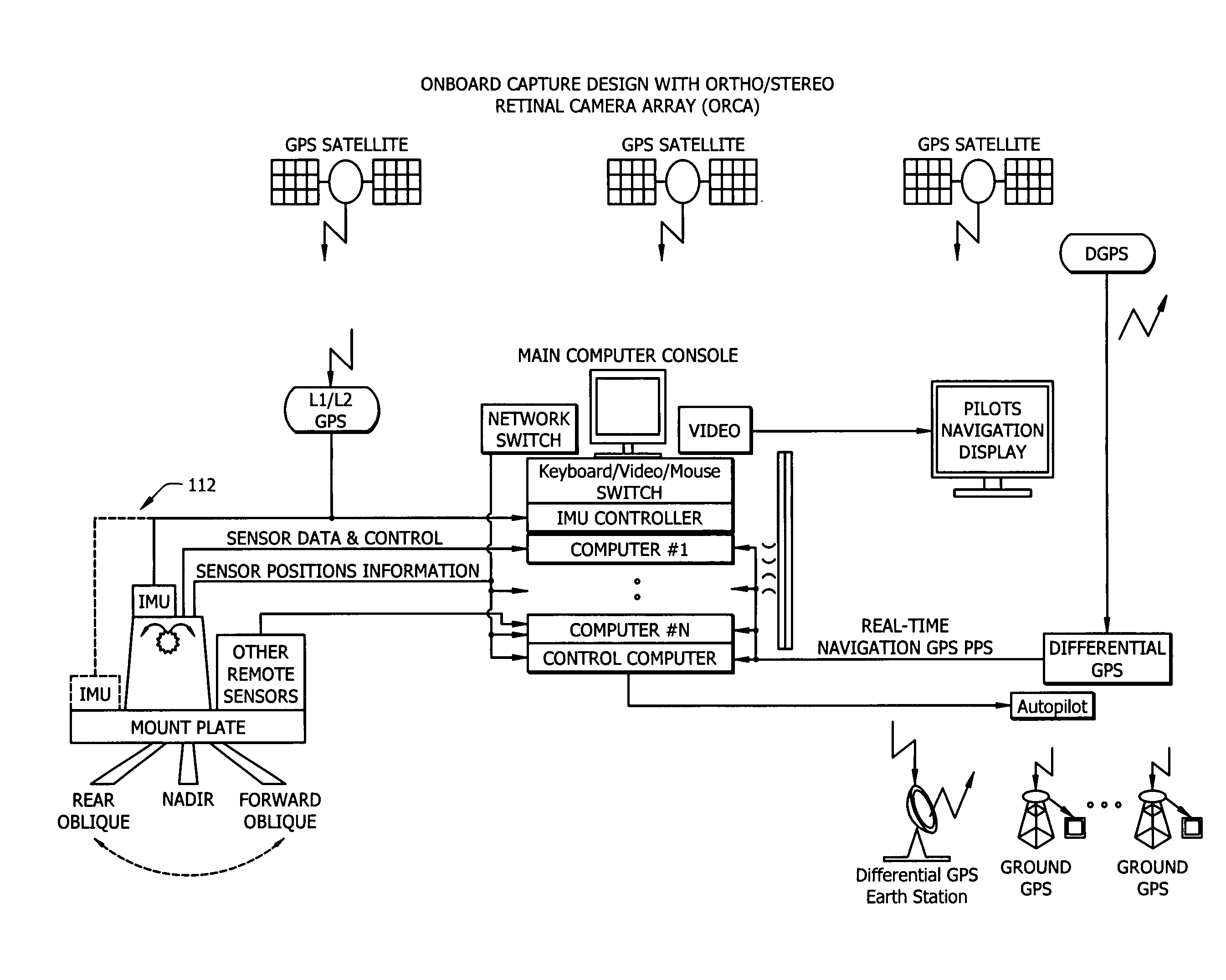
An imaging sensor system comprising: a rigid mount plate affixed to a vehicle; a first rigid mount unit affixed to the mount plate and having at least two imaging sensors disposed within the first mount unit, wherein a first imaging and a second imaging sensor each has a focal axis passing through an aperture in the first mount unit and the mount plate, wherein the first and second imaging sensor each generates a first array of pixels, wherein each array of pixels is at least two dimensional, wherein the first and second imaging sensors are offset to have a first image overlap area in the target area, wherein the first sensors image data bisects the second sensors image data in the first image overlap area.
Owner:VI TECH LLC
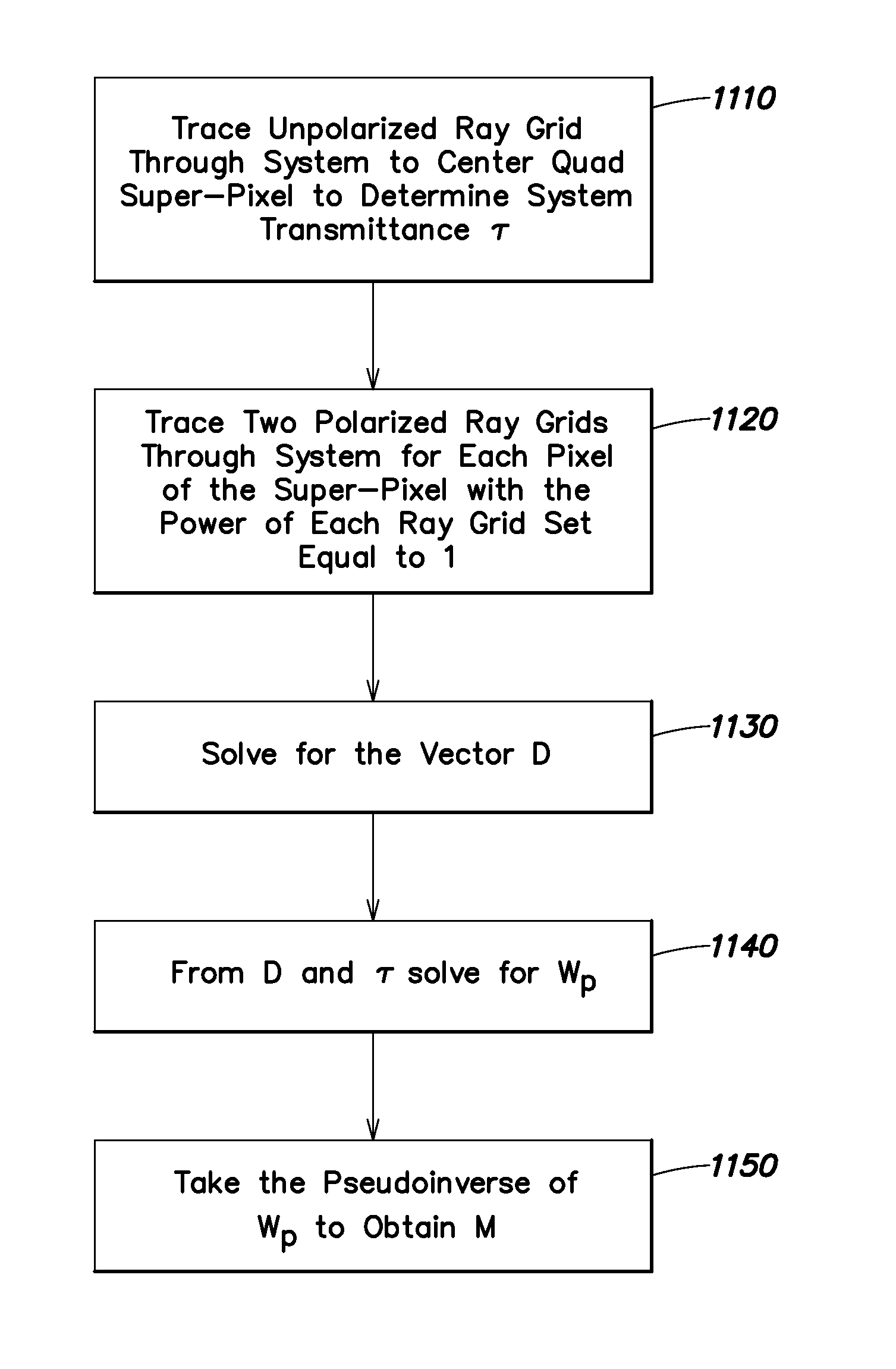
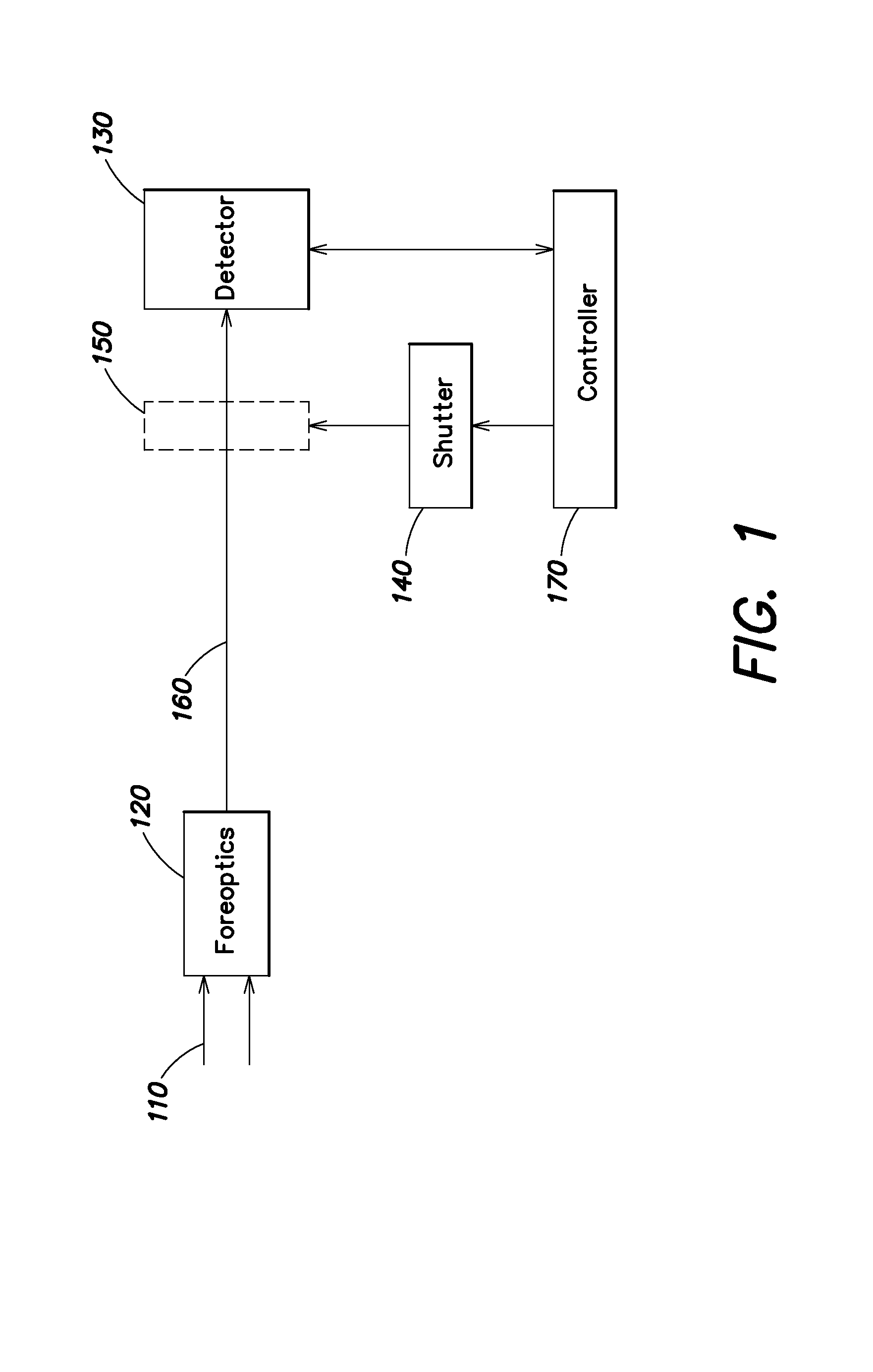
Movable pixelated filter array
ActiveUS20140063299A1Reduce system transmittanceEasy to addTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWavefrontDetector array
An optical imaging system and method including a movable pixelated filter array, a shutter mechanism to which the pixelated filter array is attached, and a controller configured to implement a data reduction algorithm. The shutter mechanism is configured to move the pixelated filter array into and out of the optical path, and the data reduction algorithm allows the controller to account for axial and / or lateral misalignment of the filter array relative to the imaging detector array or its conjugate. In certain examples, the controller is further configured to use the data reduction algorithms also to perform wavefront sensing, for example to estimate wavefront error.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Closed loop tracking system using signal beam
ActiveUS9010317B1Avoid problemsImprove efficiencySolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueSolar lightControl system
The invention is a system and method for heliostat mirror control. Here, each heliostat mirror generates a low intensity “signal beam”, directed at an angle off from the heliostat mirror's high intensity and sensor blinding “main beam” of reflected solar energy. The low intensity signal beams may be created by reflecting a small portion of the incident solar light at an angle from the main beam, by reflected artificial light, or from lasers shinning onto mirrors from known locations. The signal beams are detected by optical sensors mounted way from the main heliostat receiver focus, and can be used in a closed loop control system to efficiently ensure that individual heliostat mirrors in a heliostat array accurately track sunlight and direct the sunlight to a central receiver. Because heliostat mirrors need not be taken “off sun” for positioning, the system allows heliostat arrays to be run at high efficiency.
Owner:HELIOGEN HLDG INC
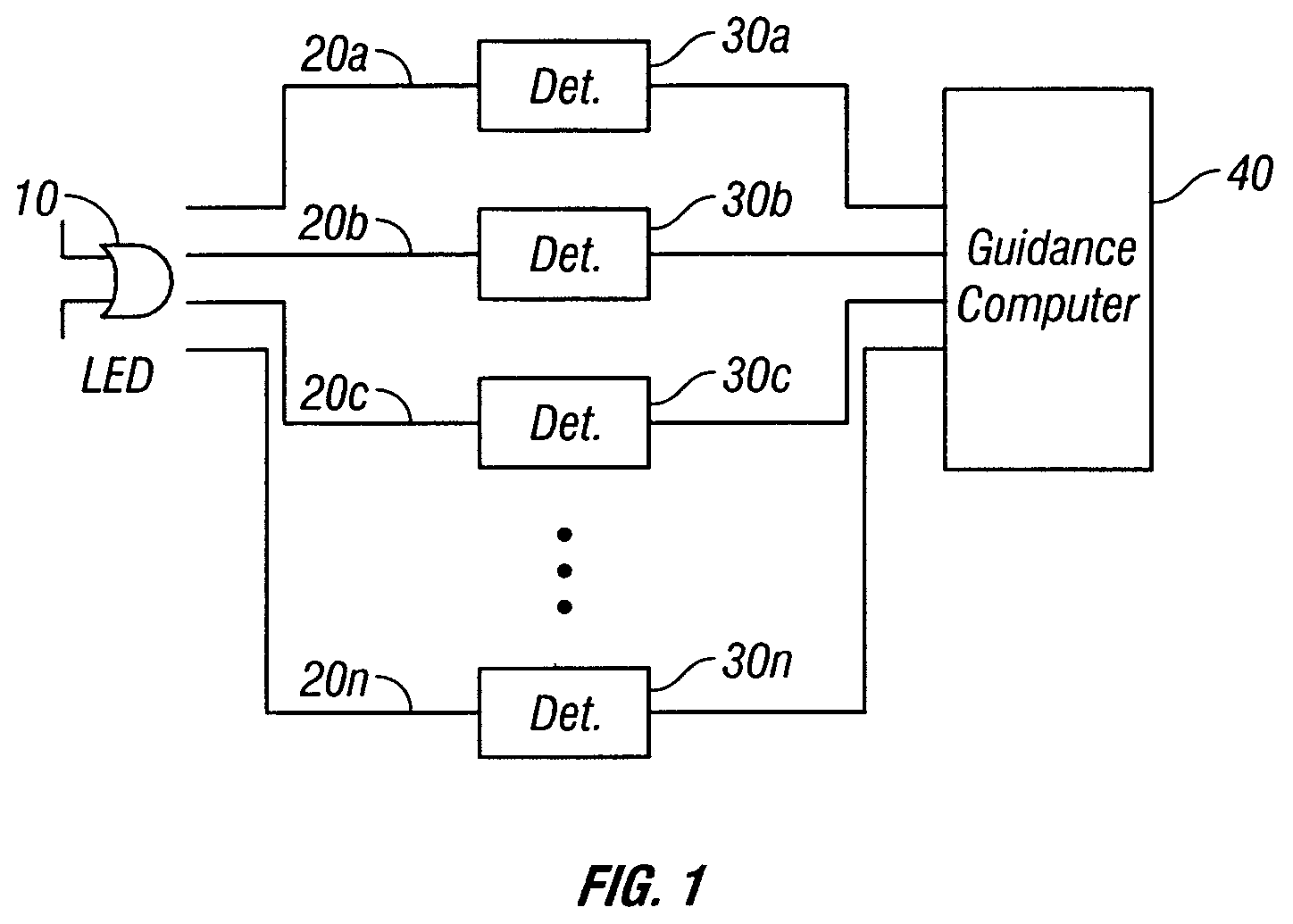
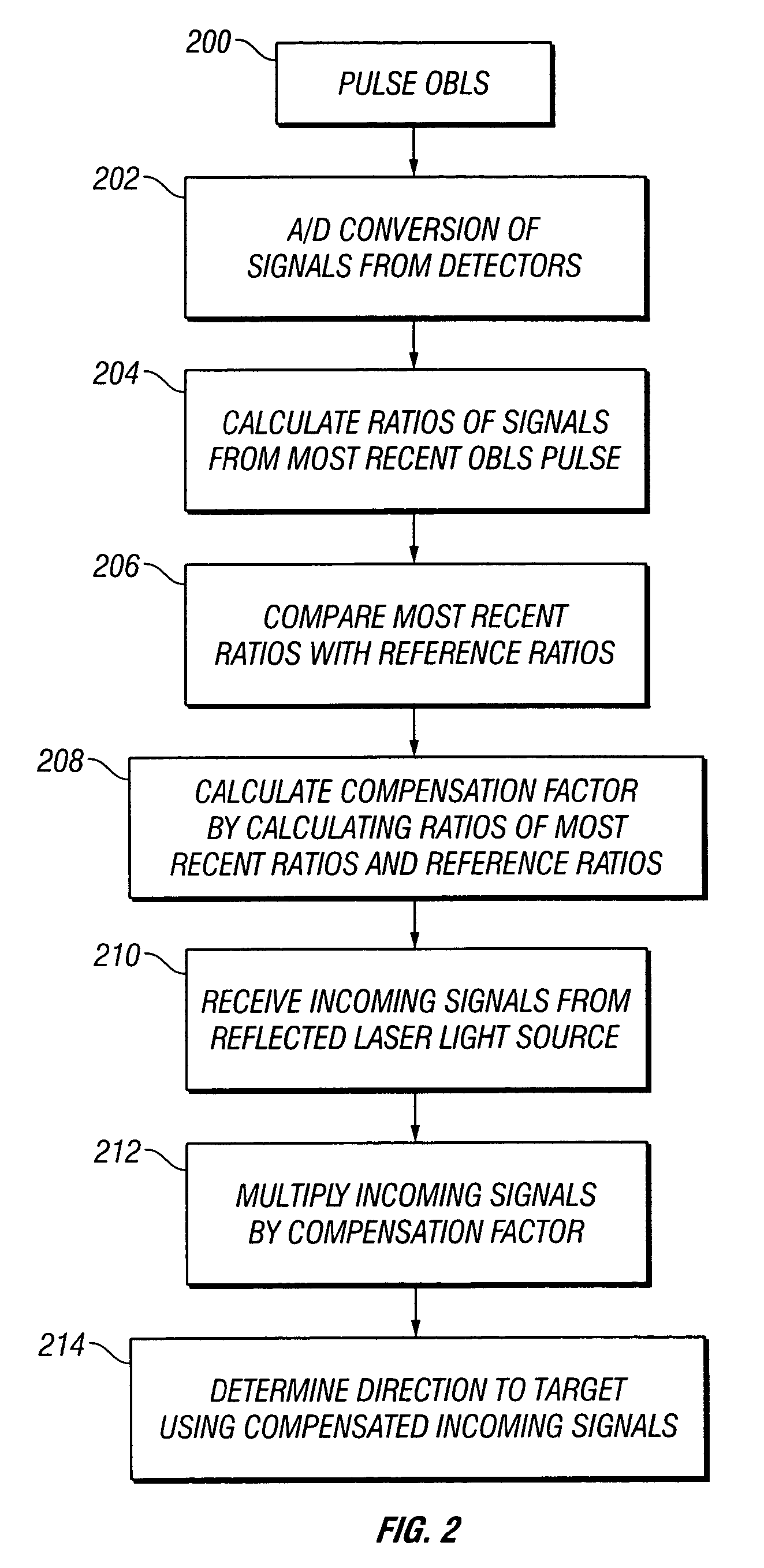
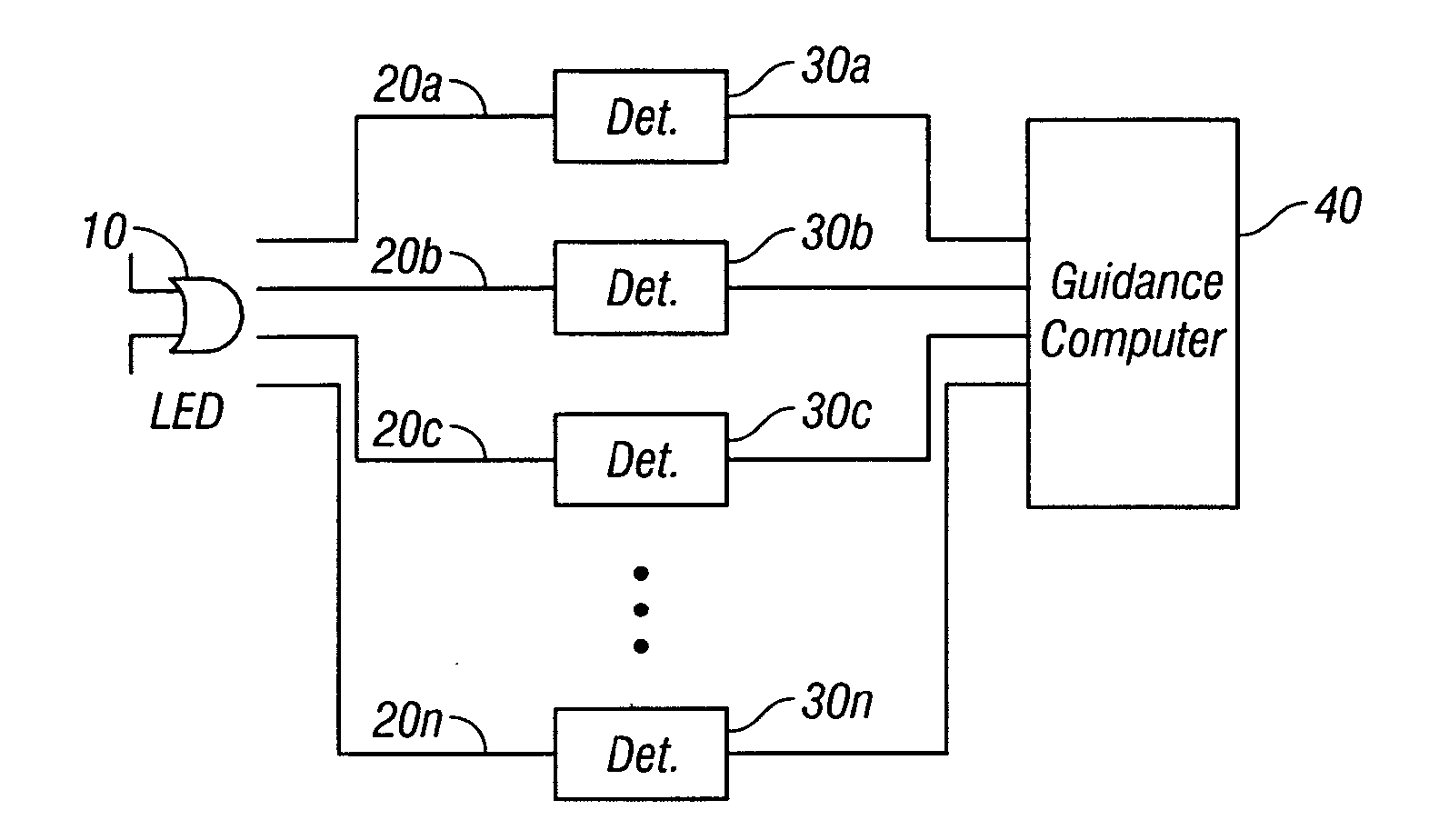
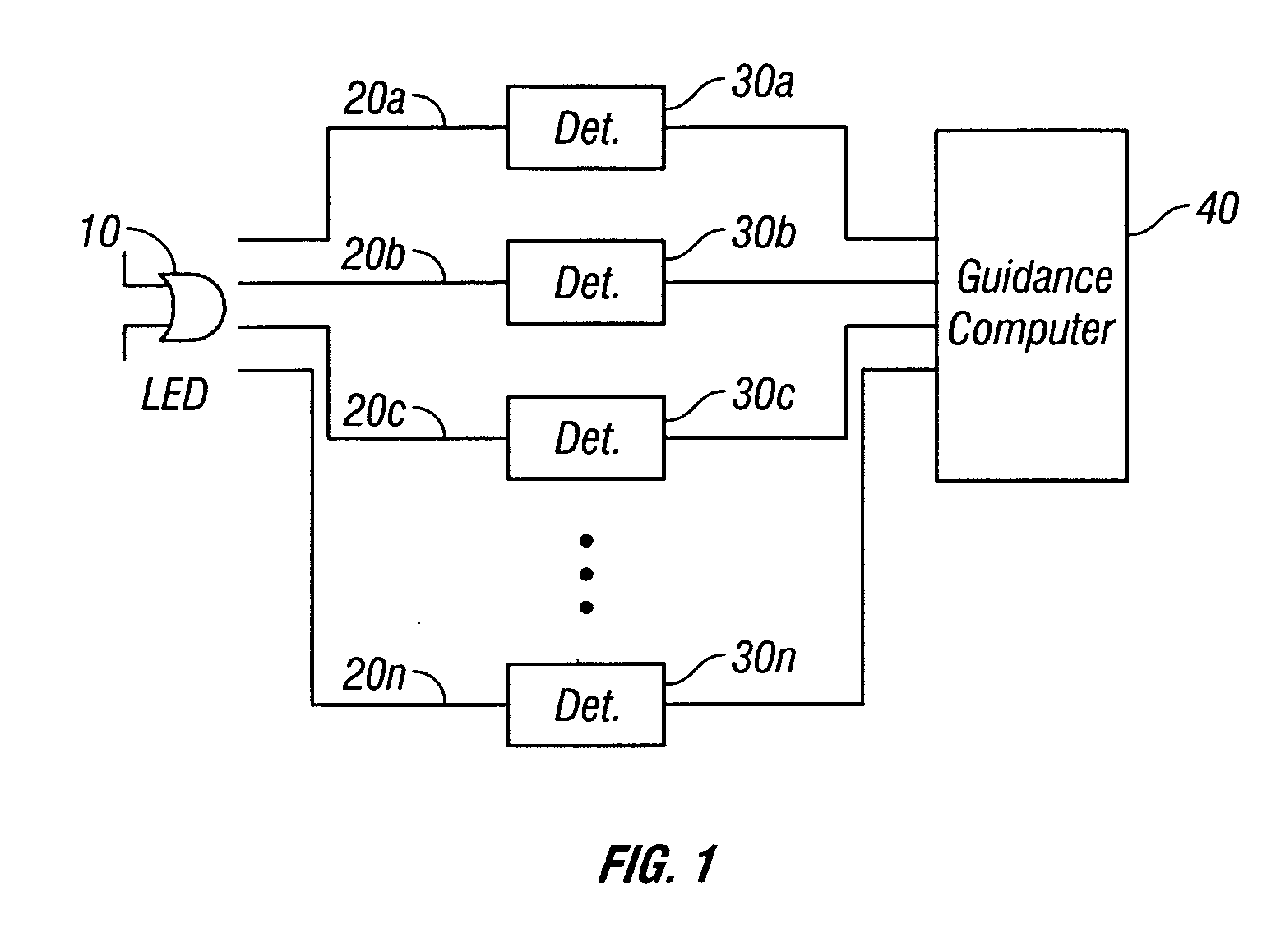
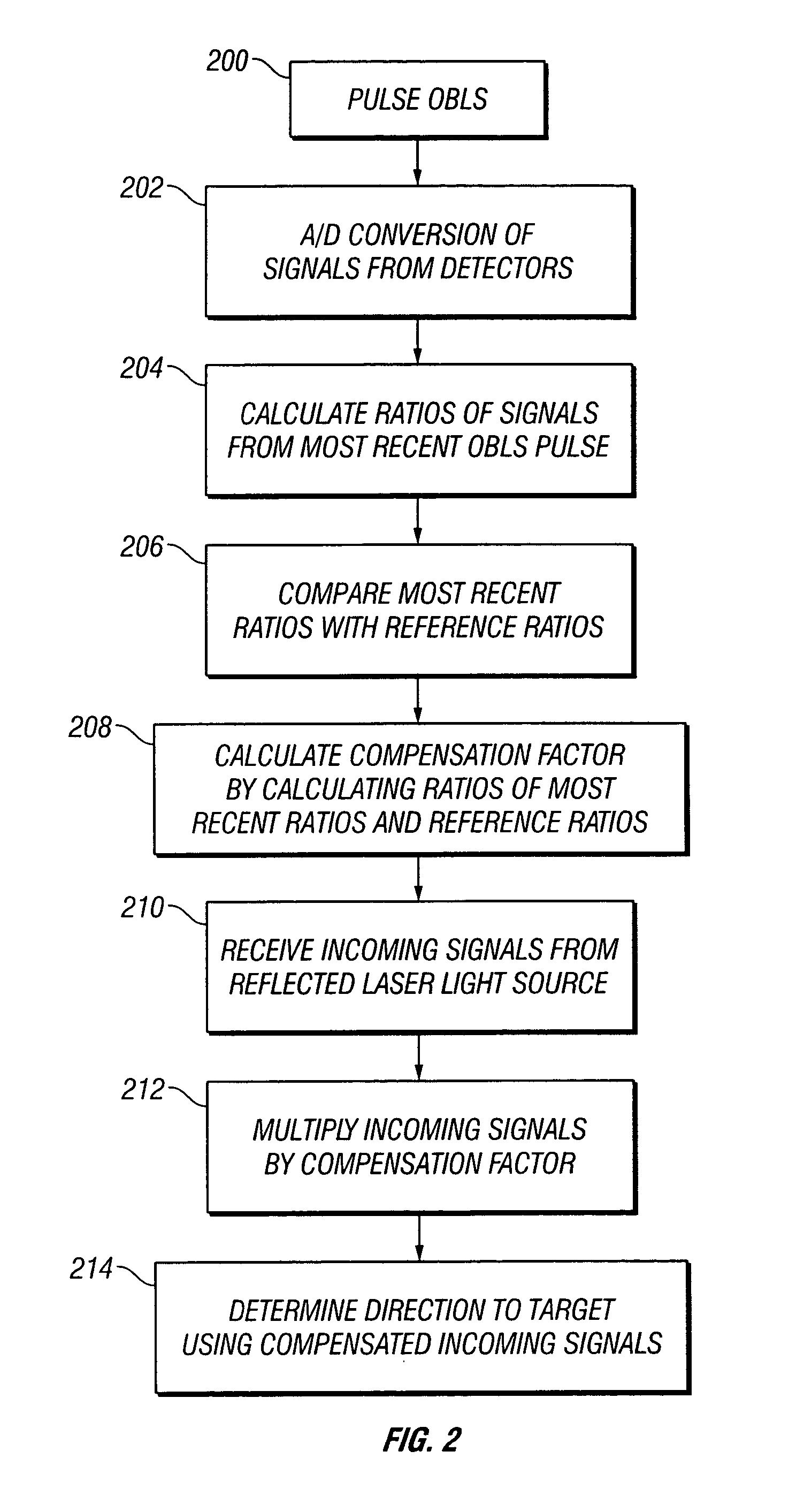
On-board light source based gain correction for semi-active laser seekers
ActiveUS7276681B2Accurate locationAccuracy of inadequatePhotometry using reference valueDirection controllersSemi activeOn board
The invention provides a method and apparatus for correcting for gain changes in detectors in a guided vehicle. In one version of the invention, an on board light source is used to generate a reference set of detector gains, which are stored in computer memory. The on board light source is then pulsed at subsequent times and the signals generated by the detectors are compared to the reference set of detector gains to determine whether any gains have changed.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and apparatus for spectrally-corrected ambient light sensor
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving outputs from multiple photodetectors, calculating a first ratio between first and second such outputs, calculating a second ratio between the first output and a difference corresponding to a flicker noise component obtained from the second output, and determining a contribution from multiple illumination types based at least in part on the first and second ratios. The method may also include obtaining multiple correction coefficients based at least in part on the determined contribution, and in turn determining an ambient light type present in proximity to the photodetectors using the correction coefficients and the first and second outputs.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
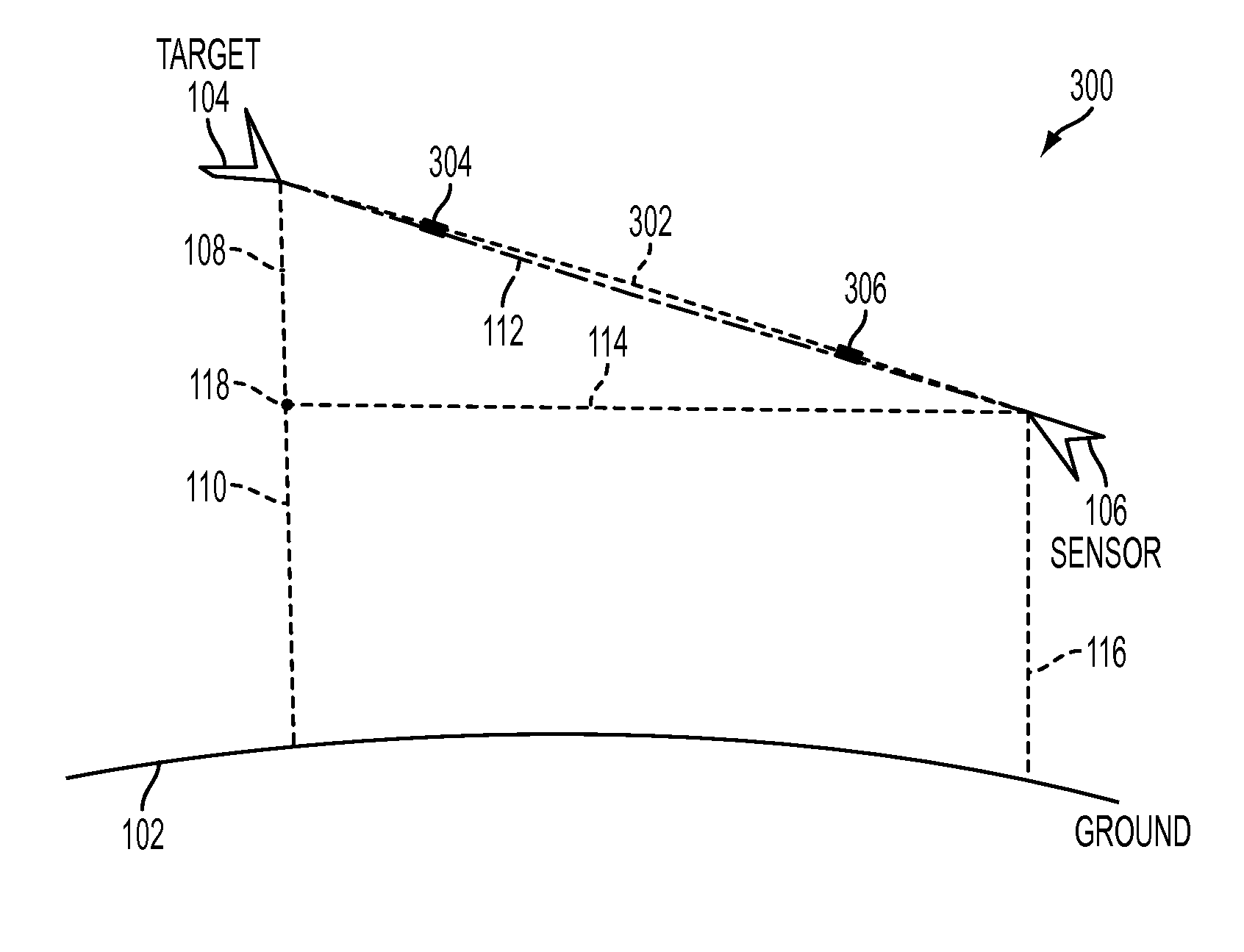
System and Method for Atmospheric Correction of Information
ActiveUS20130006534A1Electromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDigital computer detailsAtmospheric correctionAtmospheric sciences
An atmospheric correction system (ACS) is proposed, which accounts for the errors resulting from the in-homogeneities in the operational atmosphere along the slant path by constructing atmospheric profiles from the data along the actual target to sensor slant-range path. The ACS generates a slant-range path based on the arbitrary geometry that models the sensor to target relationship. This path takes the atmosphere and obstructions between the two endpoints into account when determining the atmospheric profile. The ACS uses assimilation to incorporate weather data from multiple sources and constructs an atmospheric profile from the best available data. The ACS allows the user to take advantage of variable weather and information along the path that can lead to increased accuracy in the derived atmospheric compensation value.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Camera-based heliostat calibration with artificial light sources
ActiveUS7994459B2Reduce search timeMaximize contrastSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueHeliostatSource system
Systems and methods of calibrating heliostat parameters for subsequent open-loop sun-tracking, the calibration based on driving artificial light source reflections from one or more heliostats into one or more image sensors.
Owner:SEPCOIII ELECTRIC POWER CONSTR CO LTD
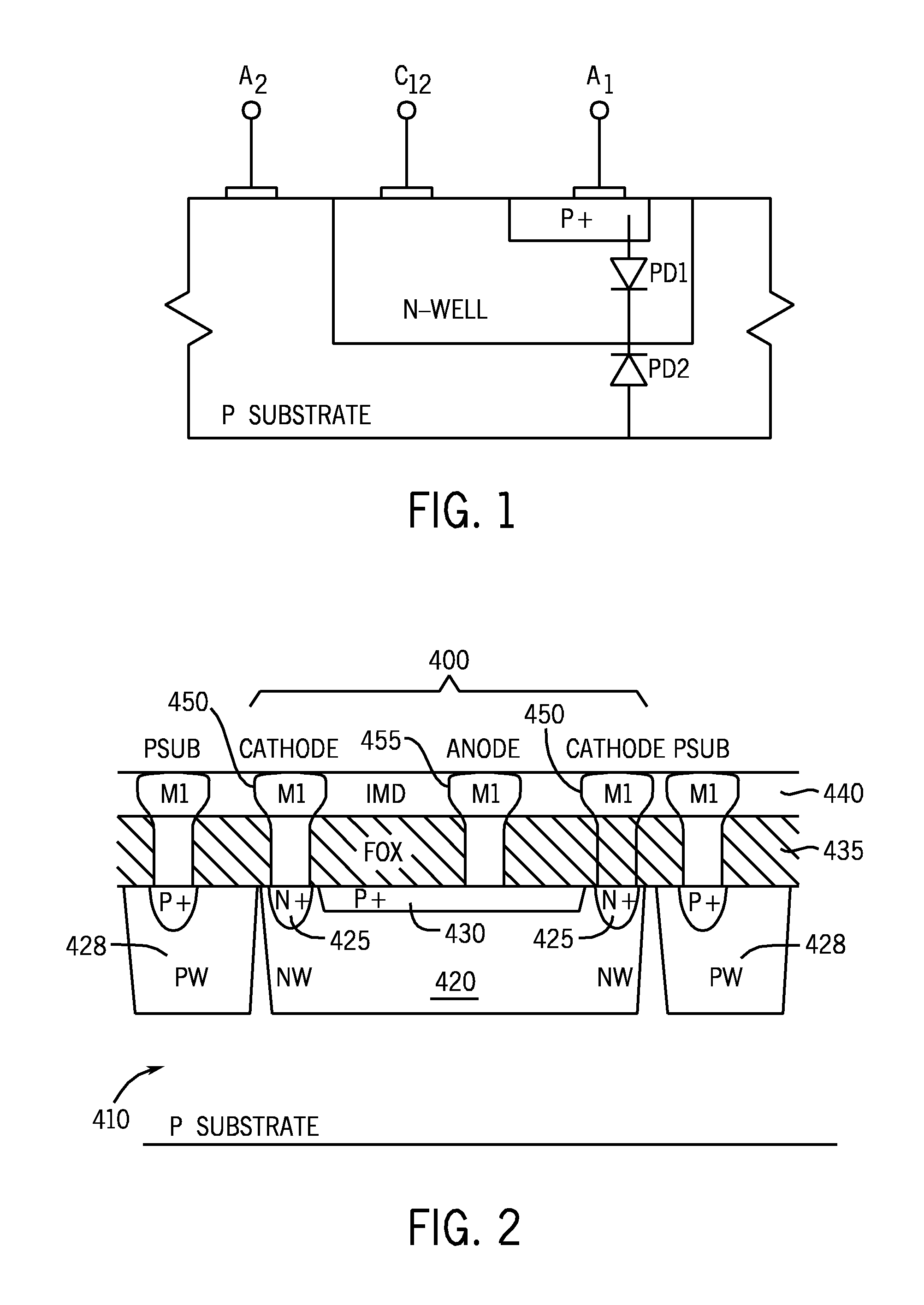
Optical sensor and optical sensor system
ActiveUS20160084650A1Low costSmall sizeOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingGratingOptical sensing
An optical sensor includes at least two optical sensing pixels and at least two different grating elements. These grating elements are disposed above these optical sensing pixels correspondingly.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Self-calibrated, remote imaging and data processing system
ActiveUS8483960B2Navigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationData processing systemEngineering
An imaging sensor system comprising: a rigid mount plate affixed to a vehicle; a first rigid mount unit affixed to the mount plate and having at least two imaging sensors disposed within the first mount unit, wherein a first imaging and a second imaging sensor each has a focal axis passing through an aperture in the first mount unit and the mount plate, wherein the first and second imaging sensor each generates a first array of pixels, wherein each array of pixels is at least two dimensional, wherein the first and second imaging sensors are offset to have a first image overlap area in the target area, wherein the first sensors image data bisects the second sensors image data in the first image overlap area.
Owner:VI TECH LLC
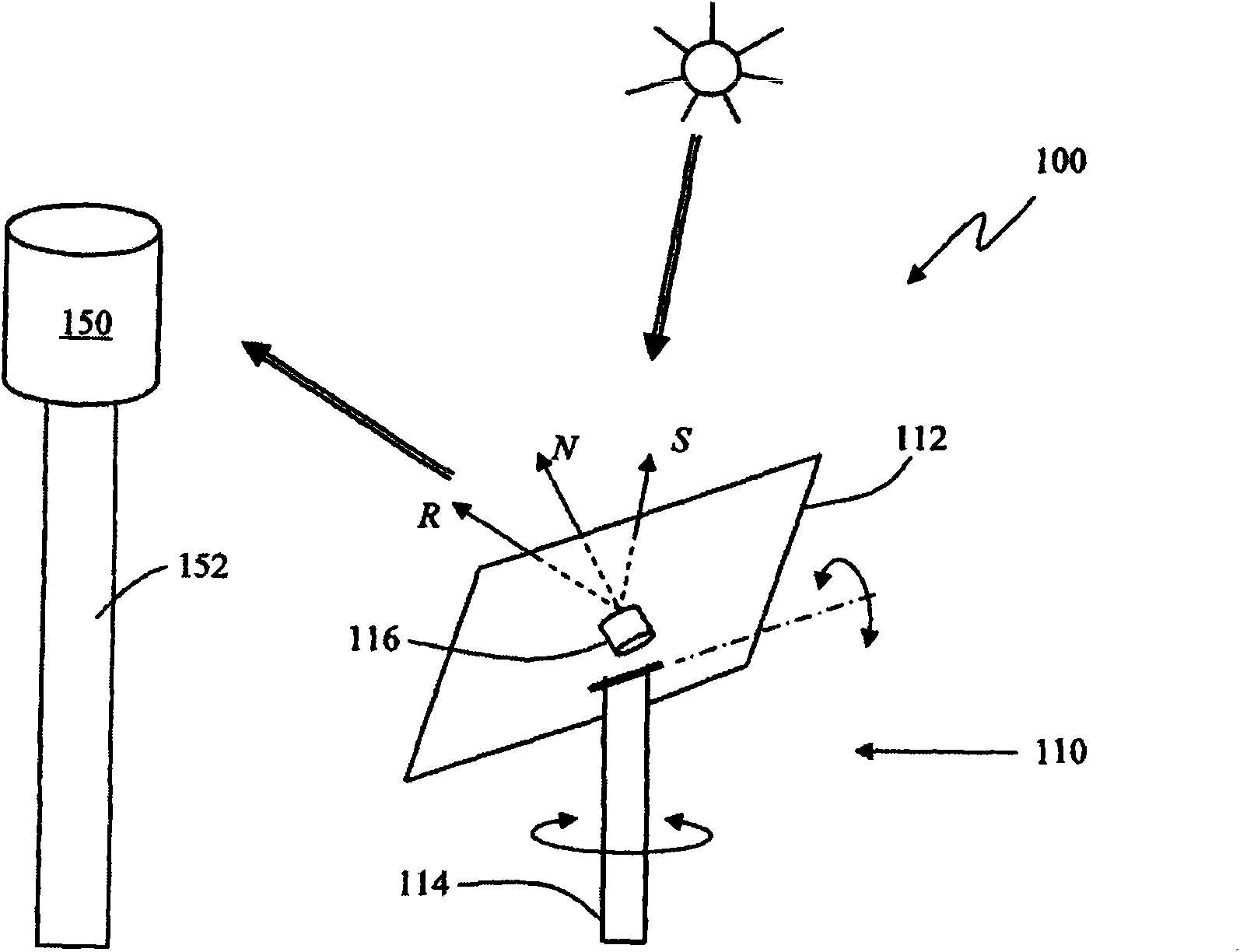
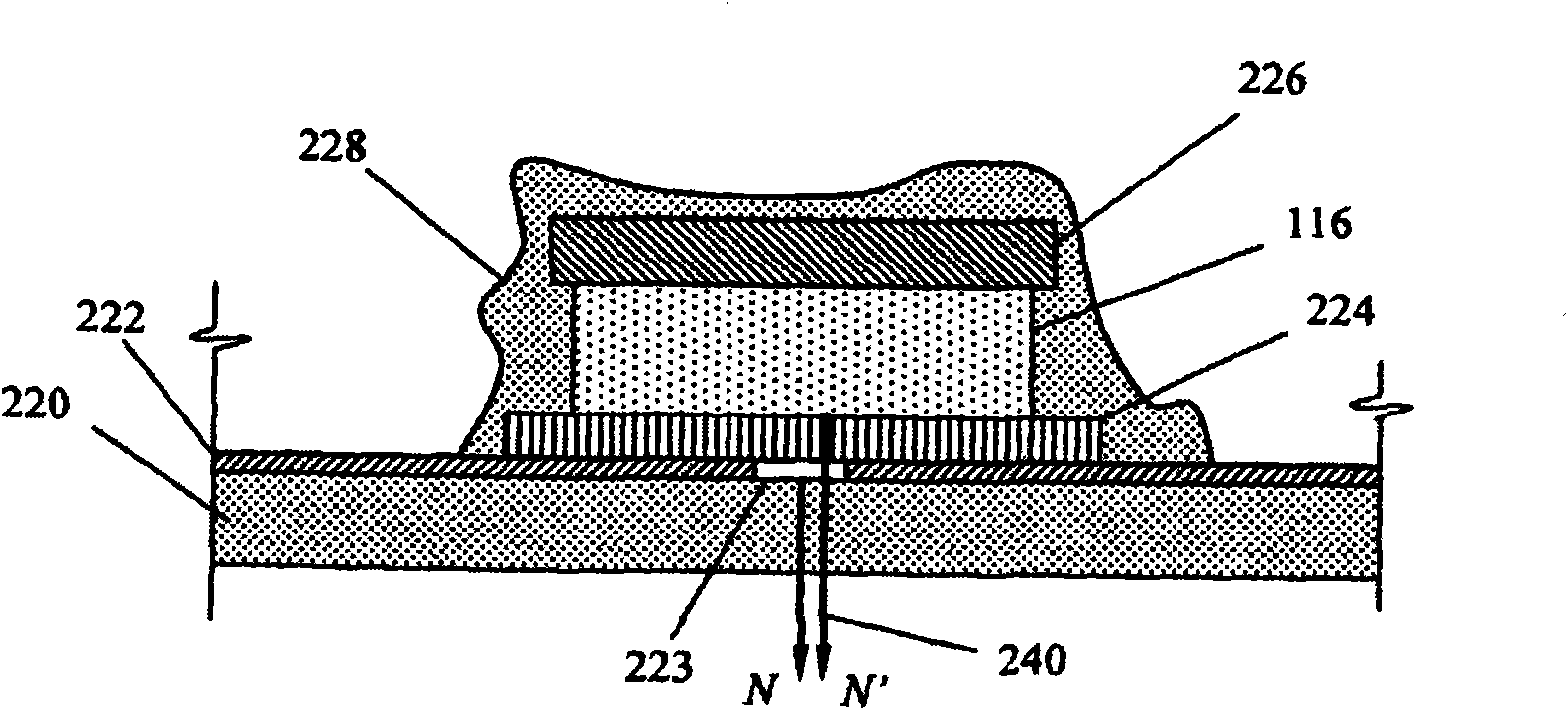
Heliostat with integrated image-based tracking controller
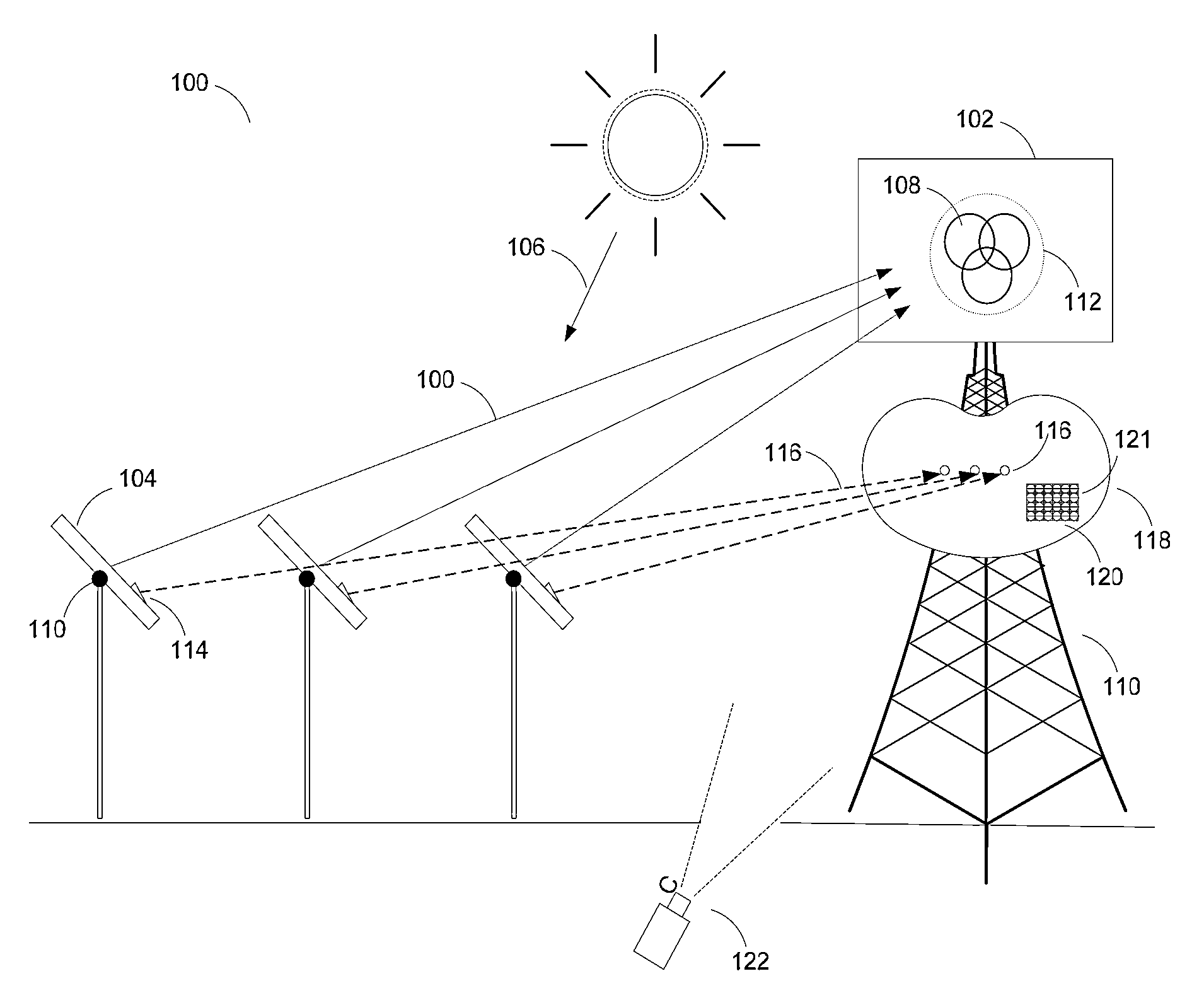
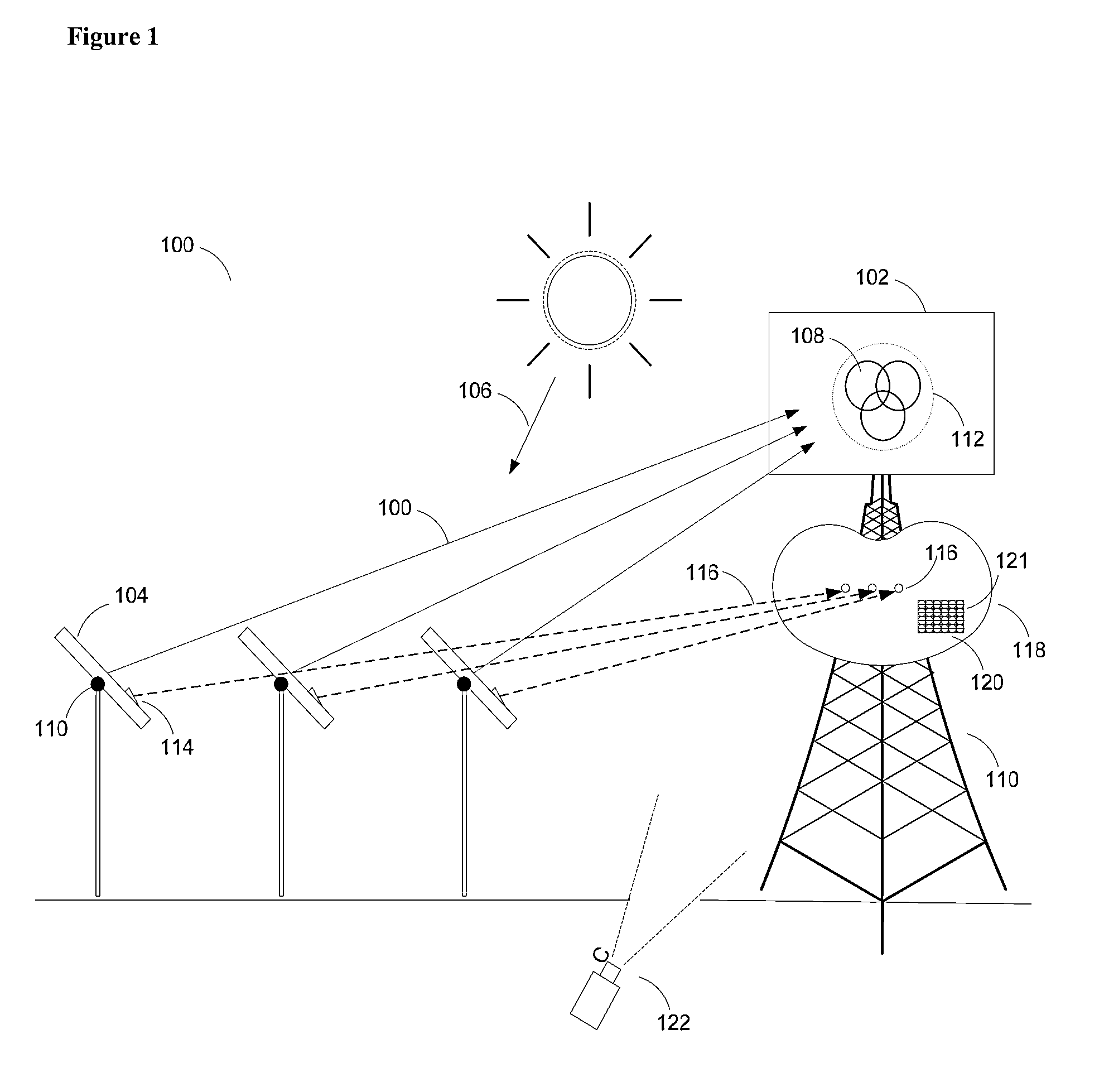
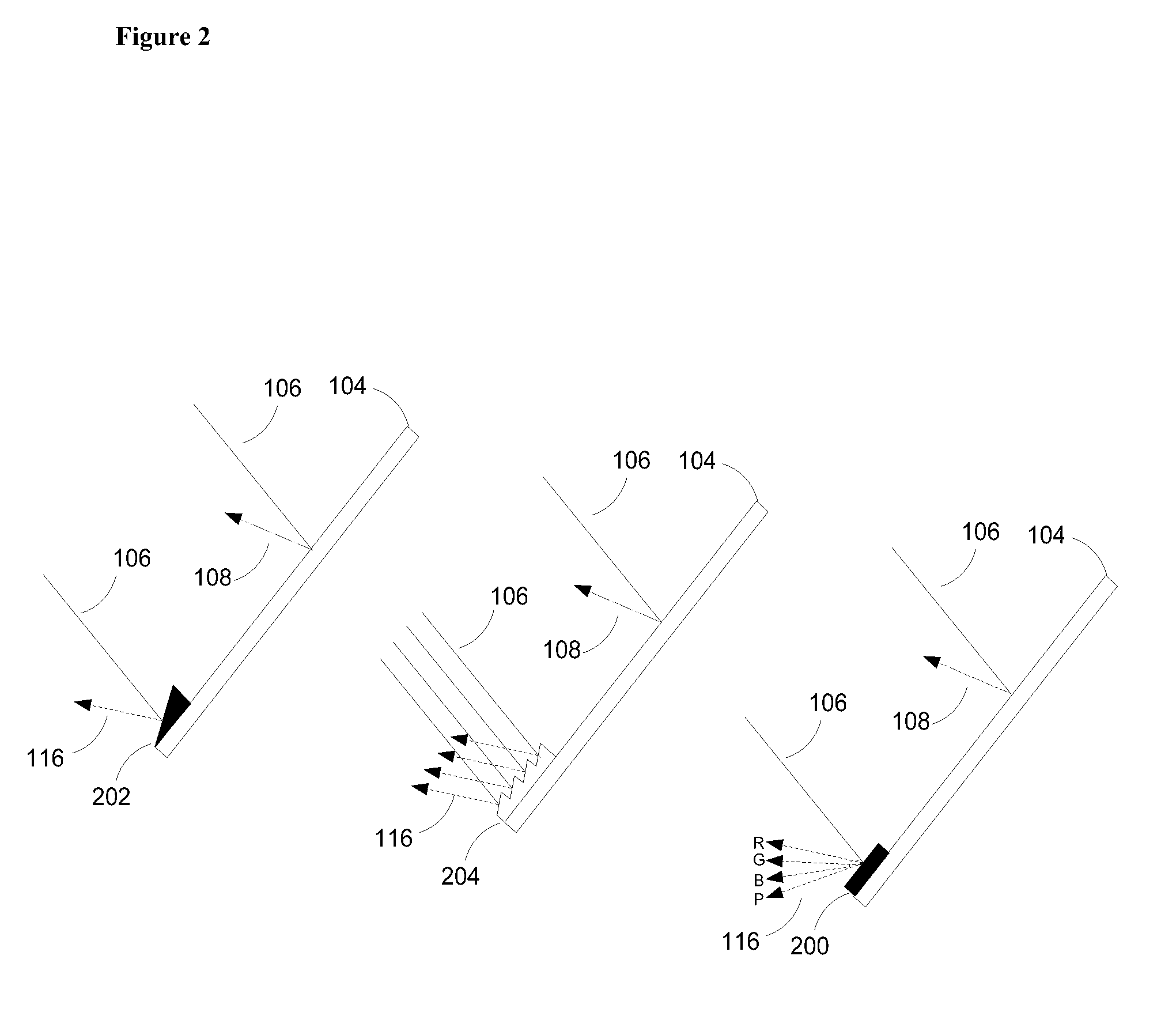
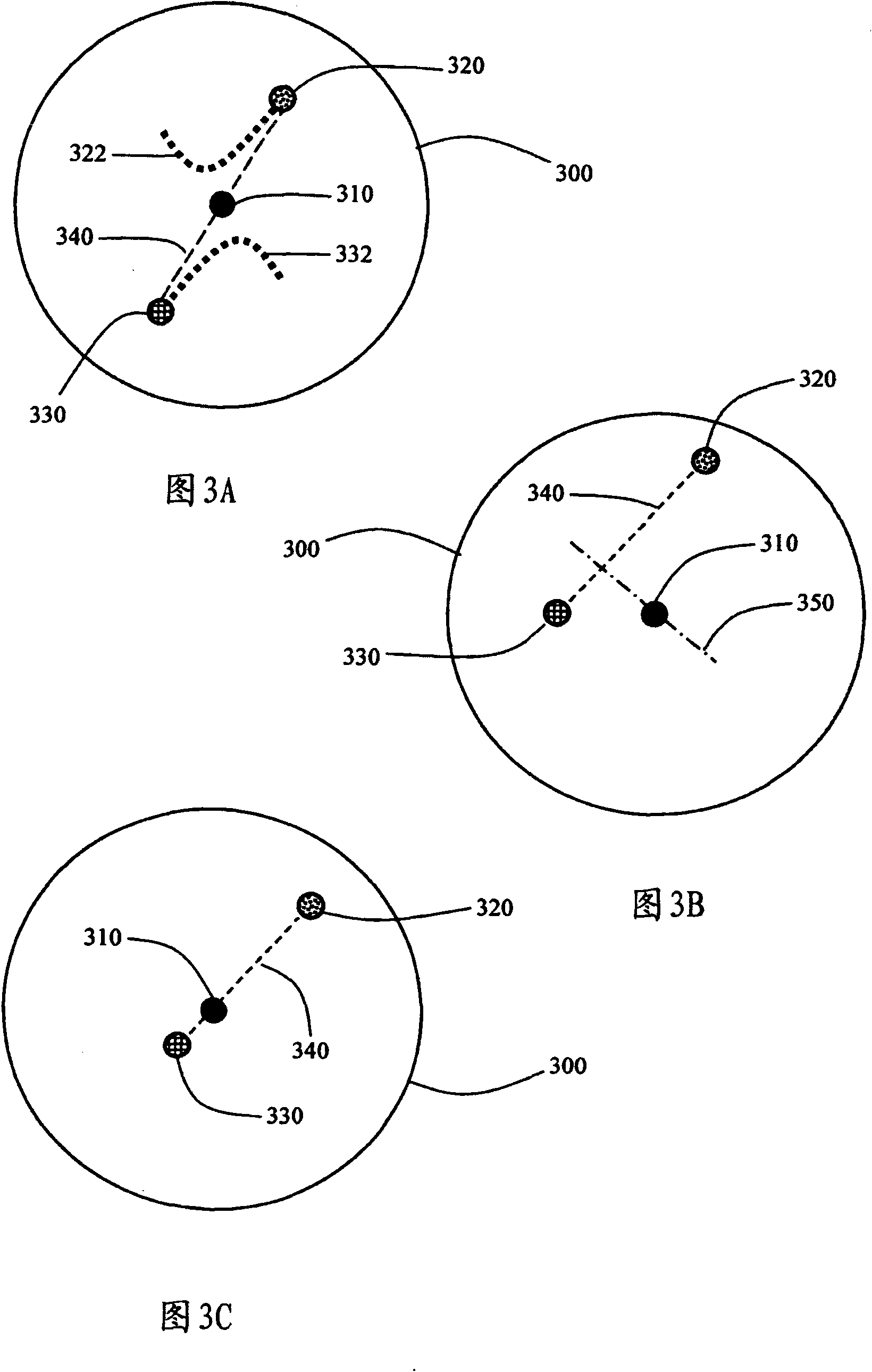
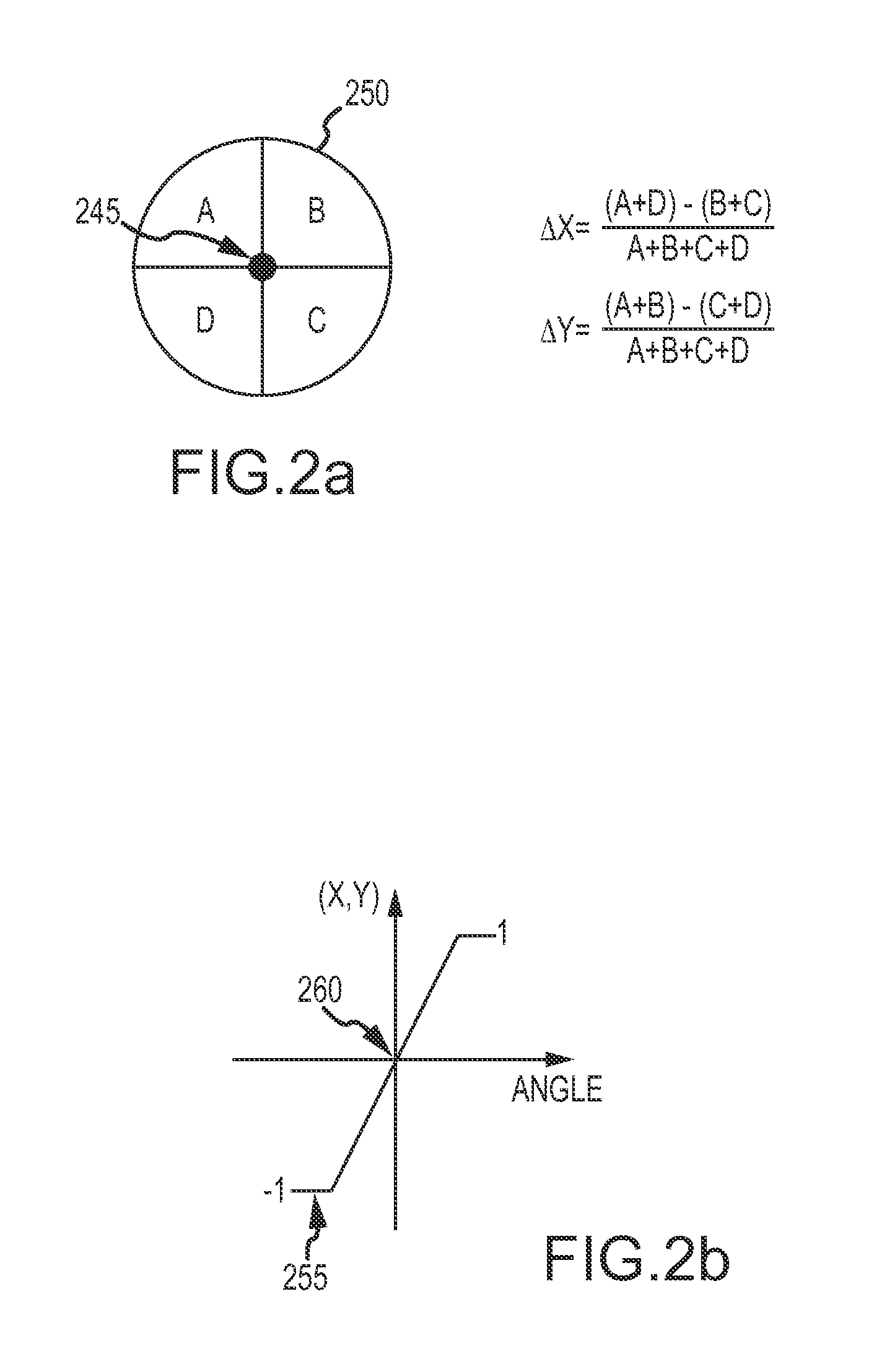
A system (100) for directing incident sun light to a receiver (150) based on an integral imager (116) is disclosed. The system includes an imager (116) mounted to a reflector (112); a tracking controller (226) coupled to the imager; and one or more actuators (114) connected to the reflector and tracking controller. The tracking controller (226) is configured to receive and process image data fromthe imager (116); determine angular positions of a radiation source and target relative to the mirror normal vector (N) based on the image data; and orient the reflector with the axis bisecting the angular positions of the sun and receiver (150). When the optical axis of the imager is precisely aligned with the vector normal to the reflector, the source and target will be detected as antipodal spots (320, 330) with respect to the center of the imager's field of view, which may be used to effectively track the sun or like object.
Owner:亿索乐公司
Optical test apparatus
ActiveUS20150276364A1Easy to handleSimple configurationTelevision system detailsAmmunition testingOptical testComputer science
An optical test apparatus includes a three-dimensional dome, light sources and a control unit. The three-dimensional dome covers a field of view of an image acquisition device. The image acquisition device is a test target device. The light sources are dispersedly arranged on the three-dimensional dome and generate a predetermined image on the three-dimensional dome. The first control unit controls the light sources.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Image processing system and method for removing or compensating for diffraction spots
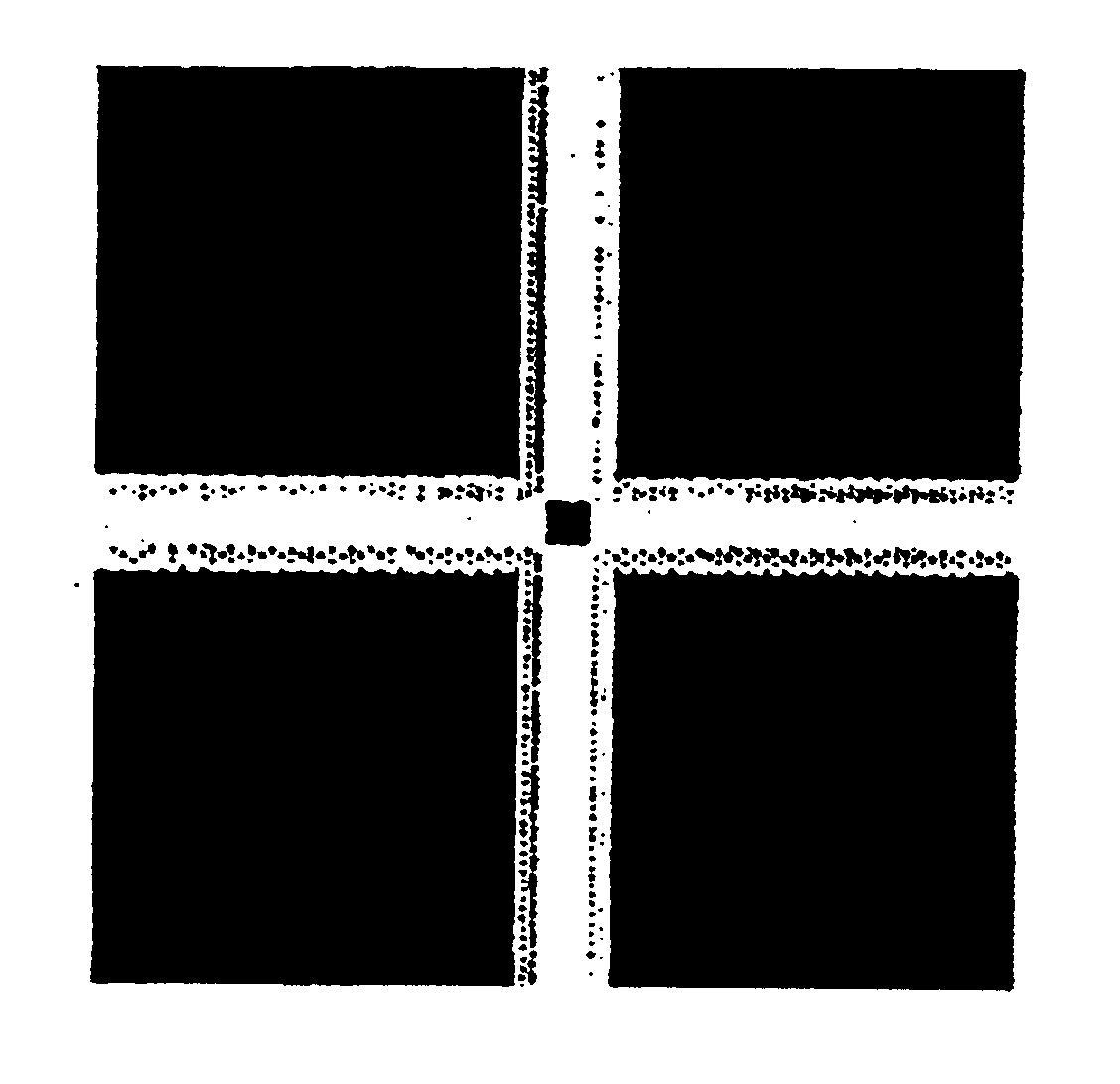
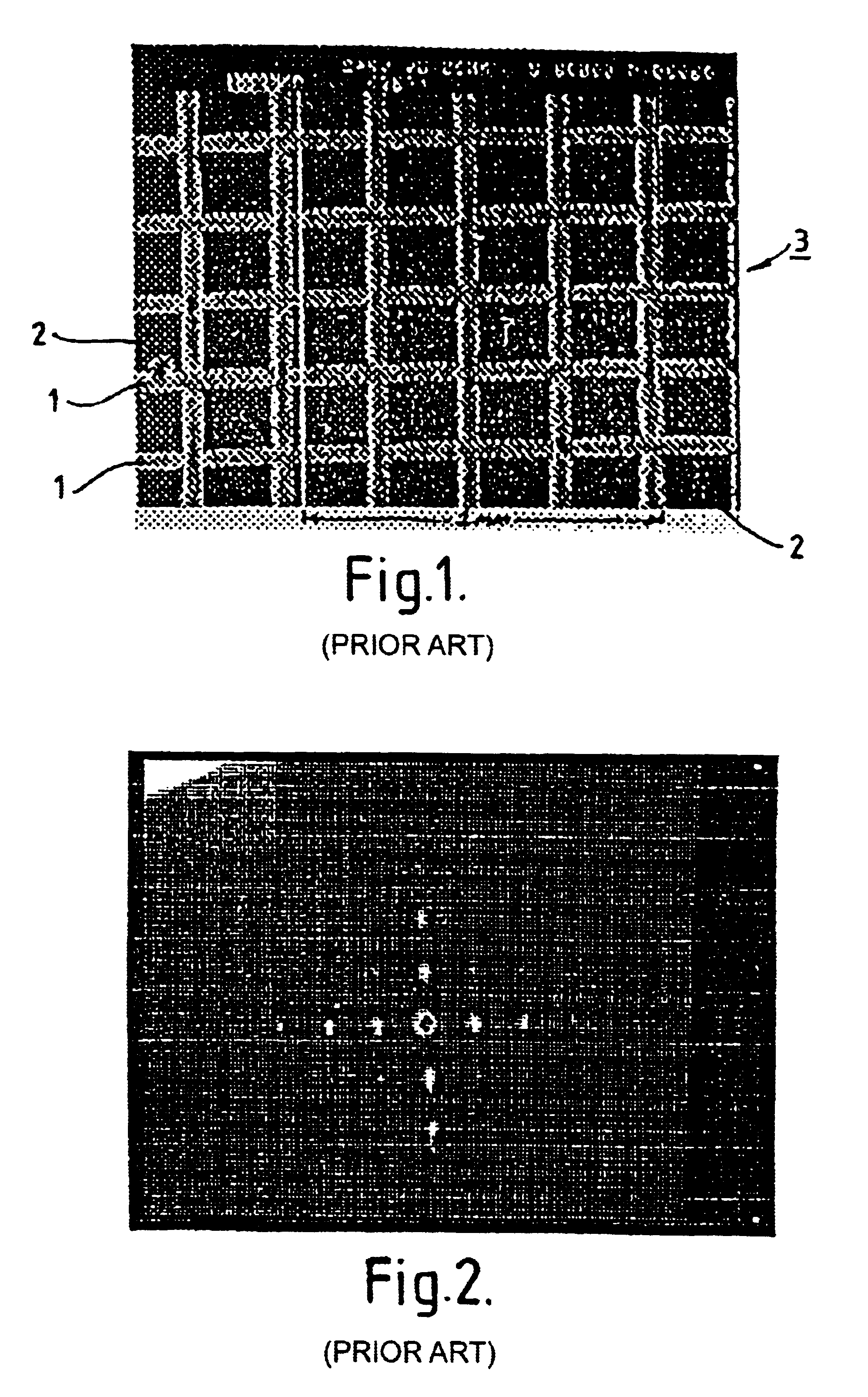
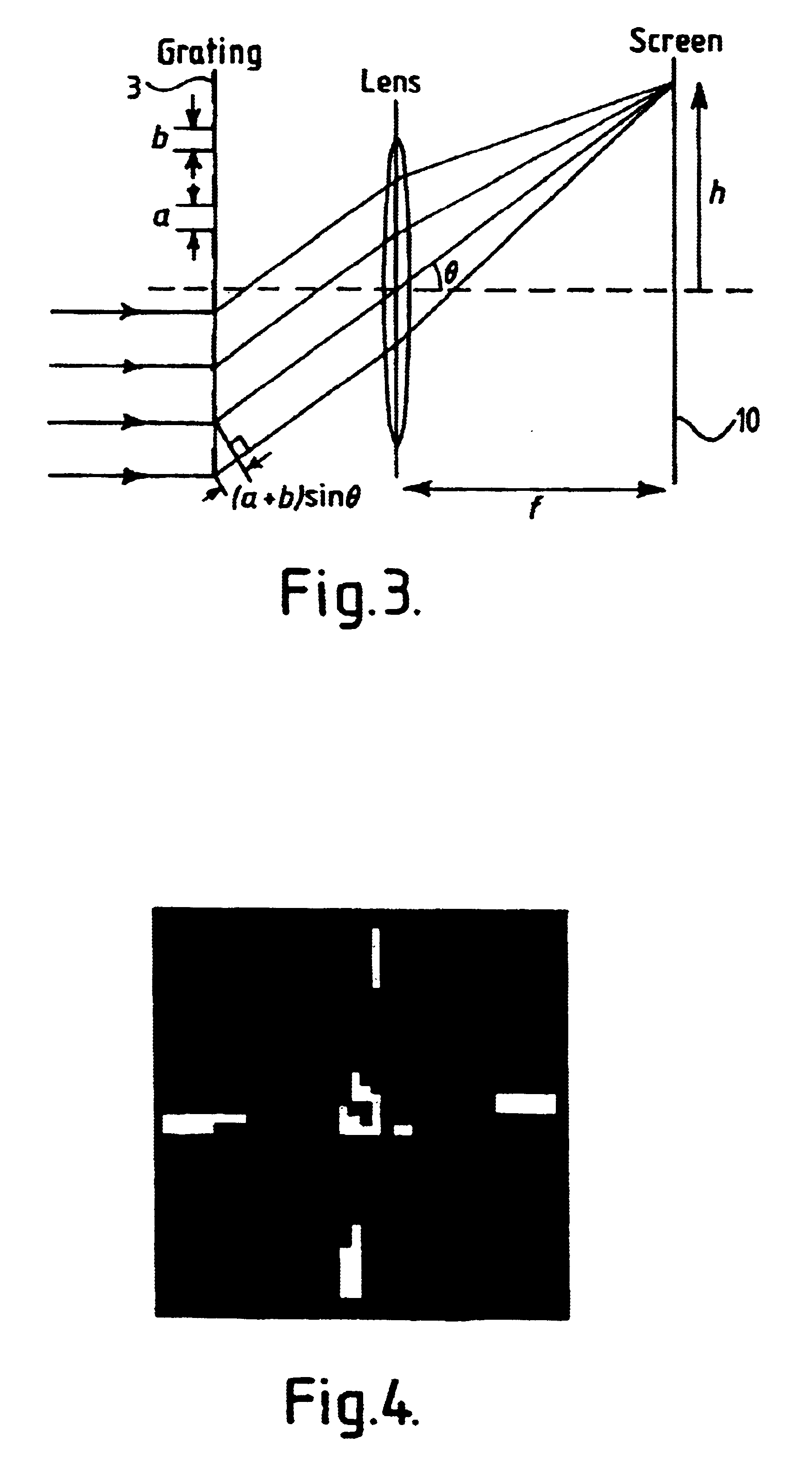
InactiveUS6630660B1Fast processingThe result is accurateElectric discharge tubesElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDiffraction effectImaging processing
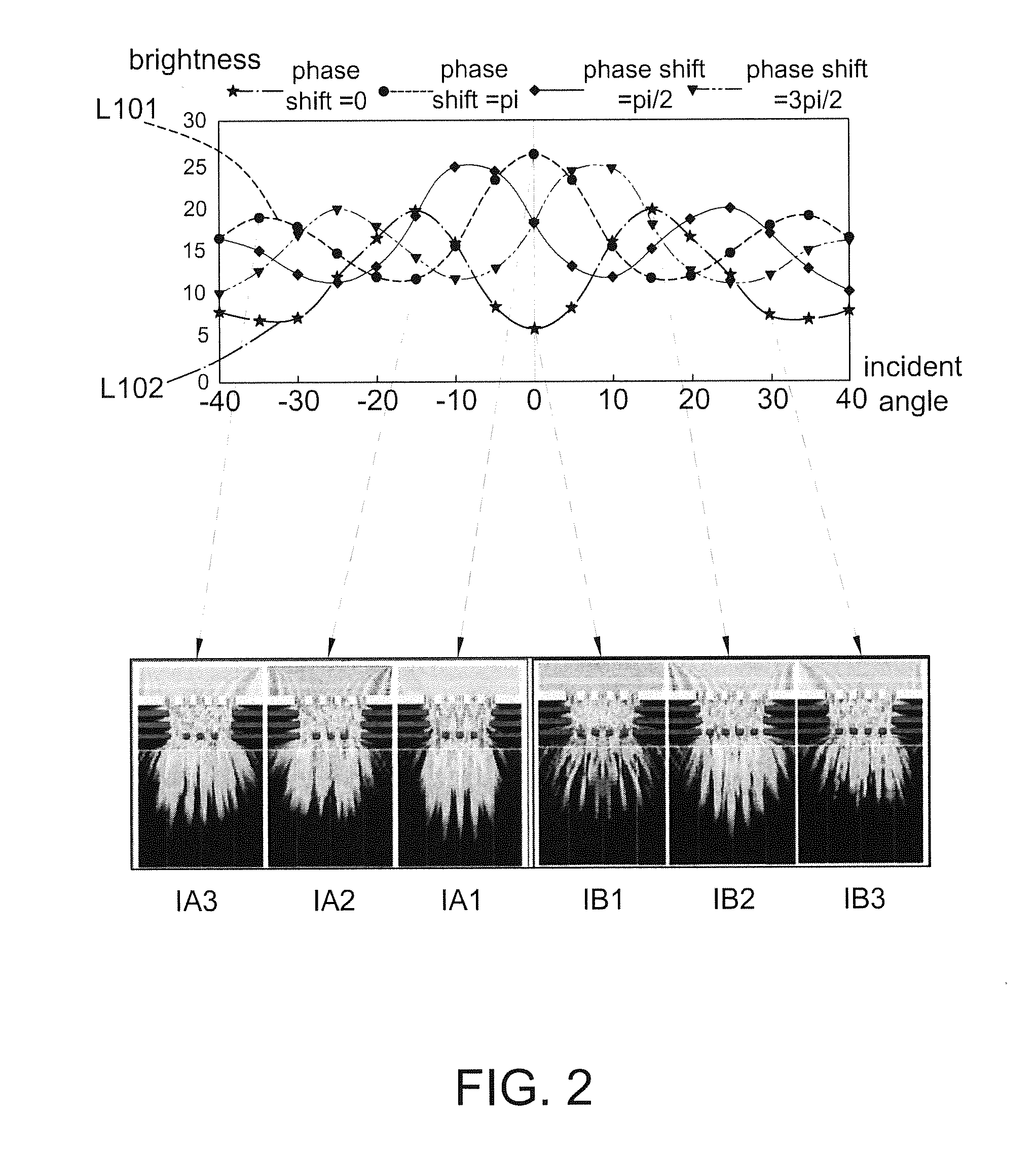
Method and apparatus for determining the location at which radiation is incident on the sensor system which includes an EMI screening mesh by comparing the actual image detected, which includes the higher order diffraction effects, with a search or sample image applied sequentially at different locations and determing the location of the sample image which gives the closest match. The sample image corresponds to an expected pattern or image from a point source incident at a particular location on a particular window / sensor system, and may be generated from a real source of known location and properties incident on the system, or may be a generated image, such as a standard image such as a cross pattern or determined mathematically, for example using Fourier transforms. Preferably, once the location of the point of incidence of the radiation has been determined, image processing techniques are applied to remove the diffraction spots.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
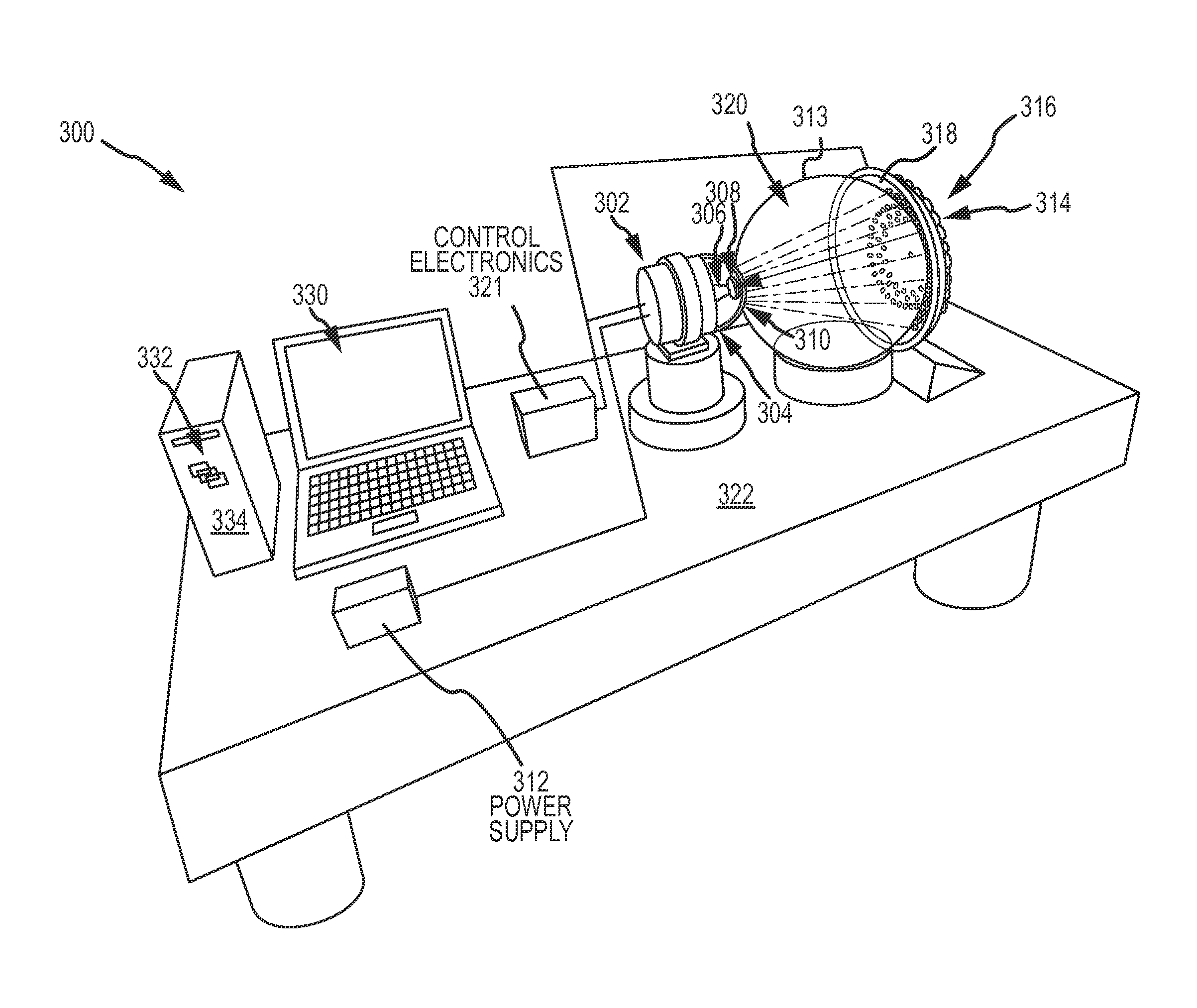
Compact fixed-source array test station for calibration of a semi-active laser (SAL) seeker
ActiveUS20130110440A1Reduce problem sizeReduce distanceTesting/calibration apparatusDirection controllersSemi activeLight beam
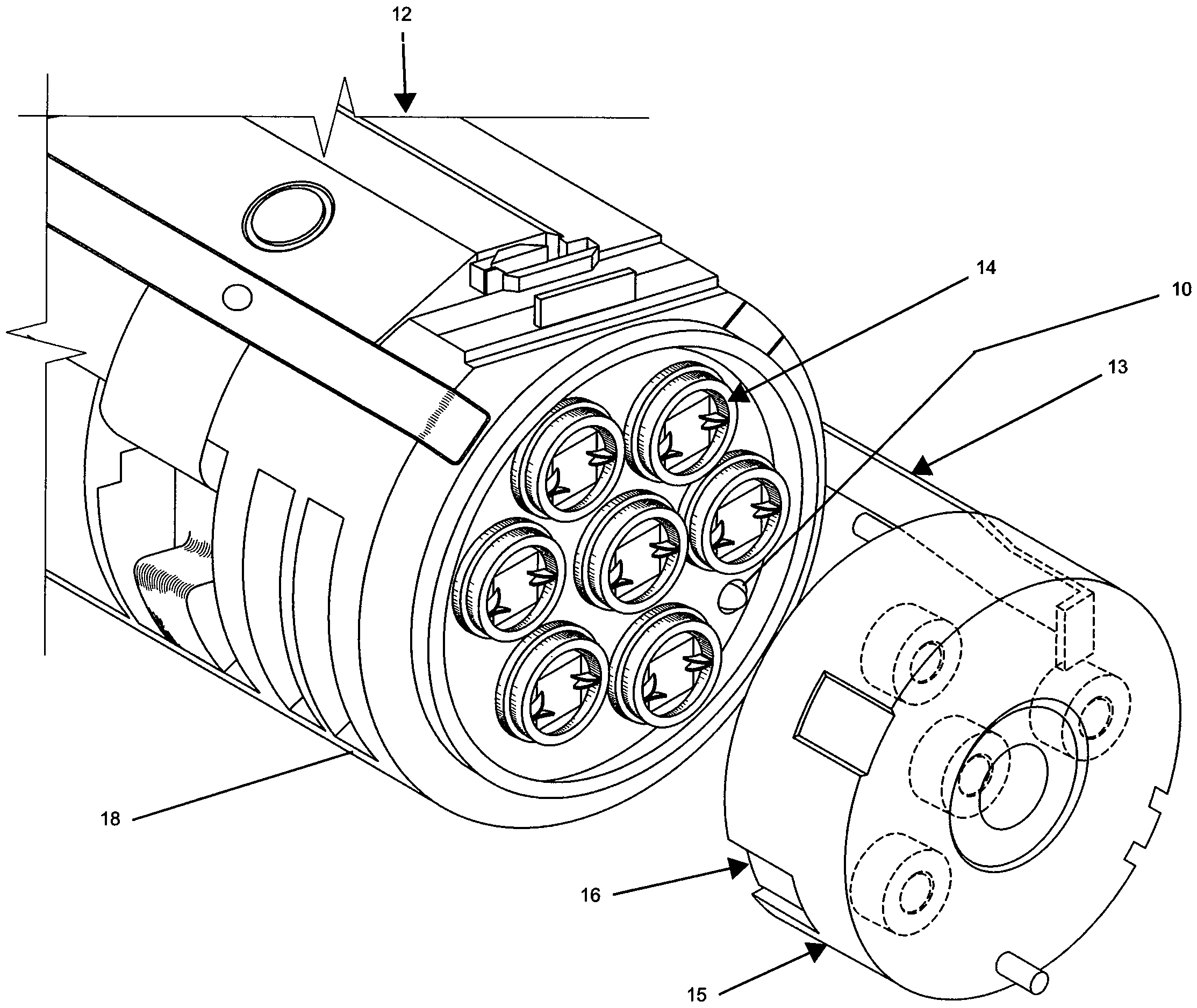
A fixed-source array test station provides a compact cost-effective high-throughput test bed for testing optical sensors that require stimulus at fixed angular positions. An array of fixed collimated sources at different angular positions in the sensor's FOV are positioned on a surface of a focal sphere at the effective focal length of a spherical lens and aligned along respective radial lines to the center of the spherical lens so that each said divergent optical beam is collimated by the spherical lens to form a collimated optical beam that overlaps the entire entrance pupil of the optical seeker. The sources are activated in accordance with an activation profile in order to calibrate or otherwise test the sensor.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Movable pixelated filter array
ActiveUS8842216B2Easy to addIncrease signal strengthTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationWavefrontDetector array
An optical imaging system and method including a movable pixelated filter array, a shutter mechanism to which the pixelated filter array is attached, and a controller configured to implement a data reduction algorithm. The shutter mechanism is configured to move the pixelated filter array into and out of the optical path, and the data reduction algorithm allows the controller to account for axial and / or lateral misalignment of the filter array relative to the imaging detector array or its conjugate. In certain examples, the controller is further configured to use the data reduction algorithms also to perform wavefront sensing, for example to estimate wavefront error.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
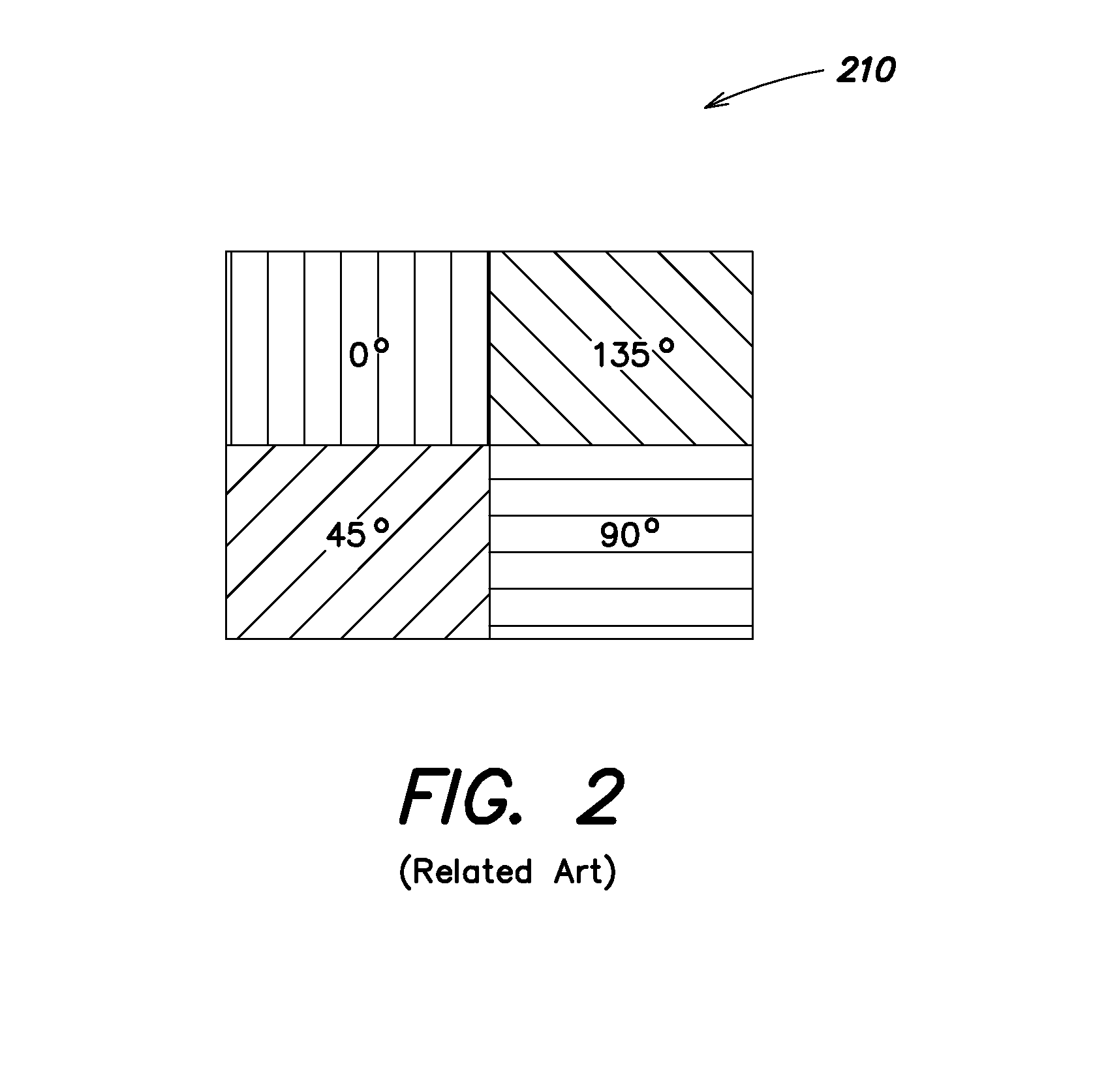
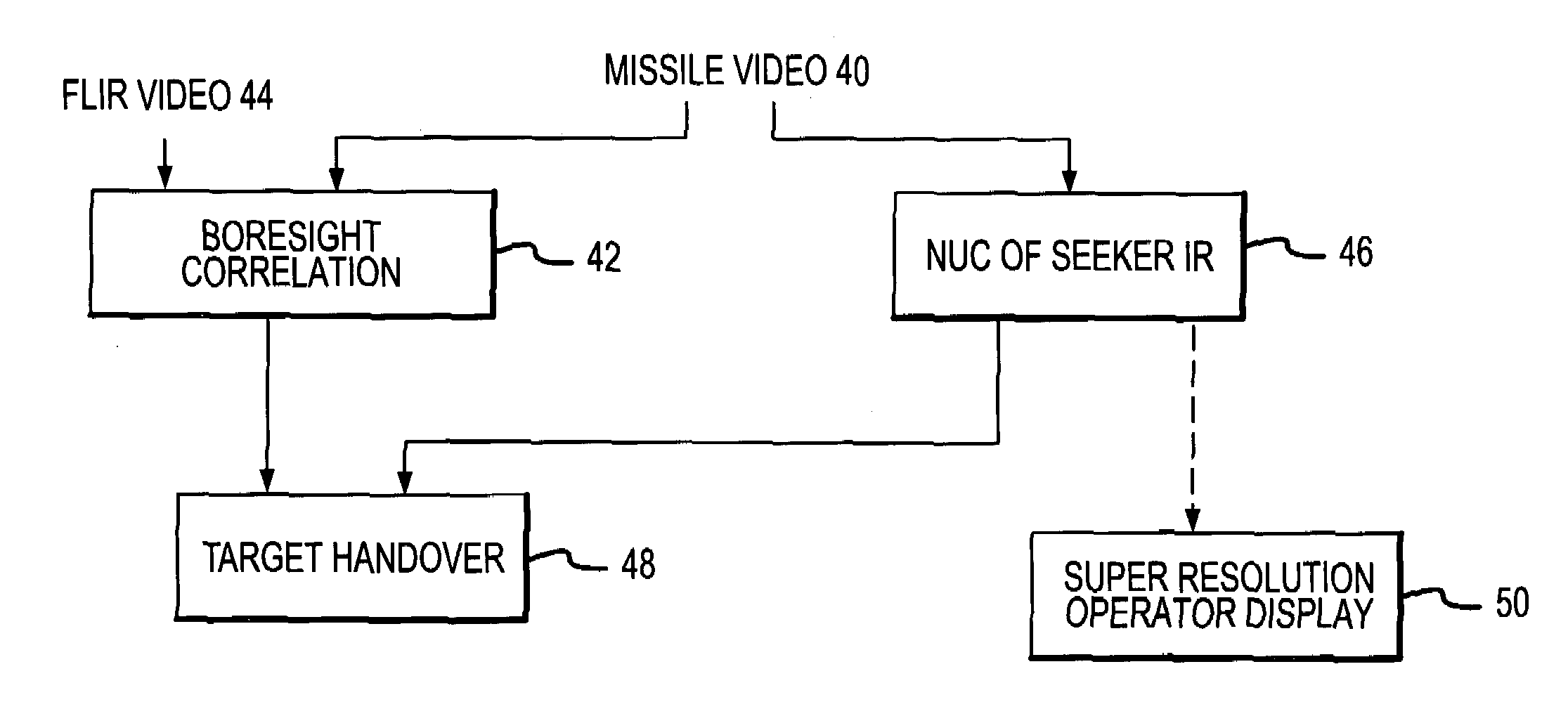
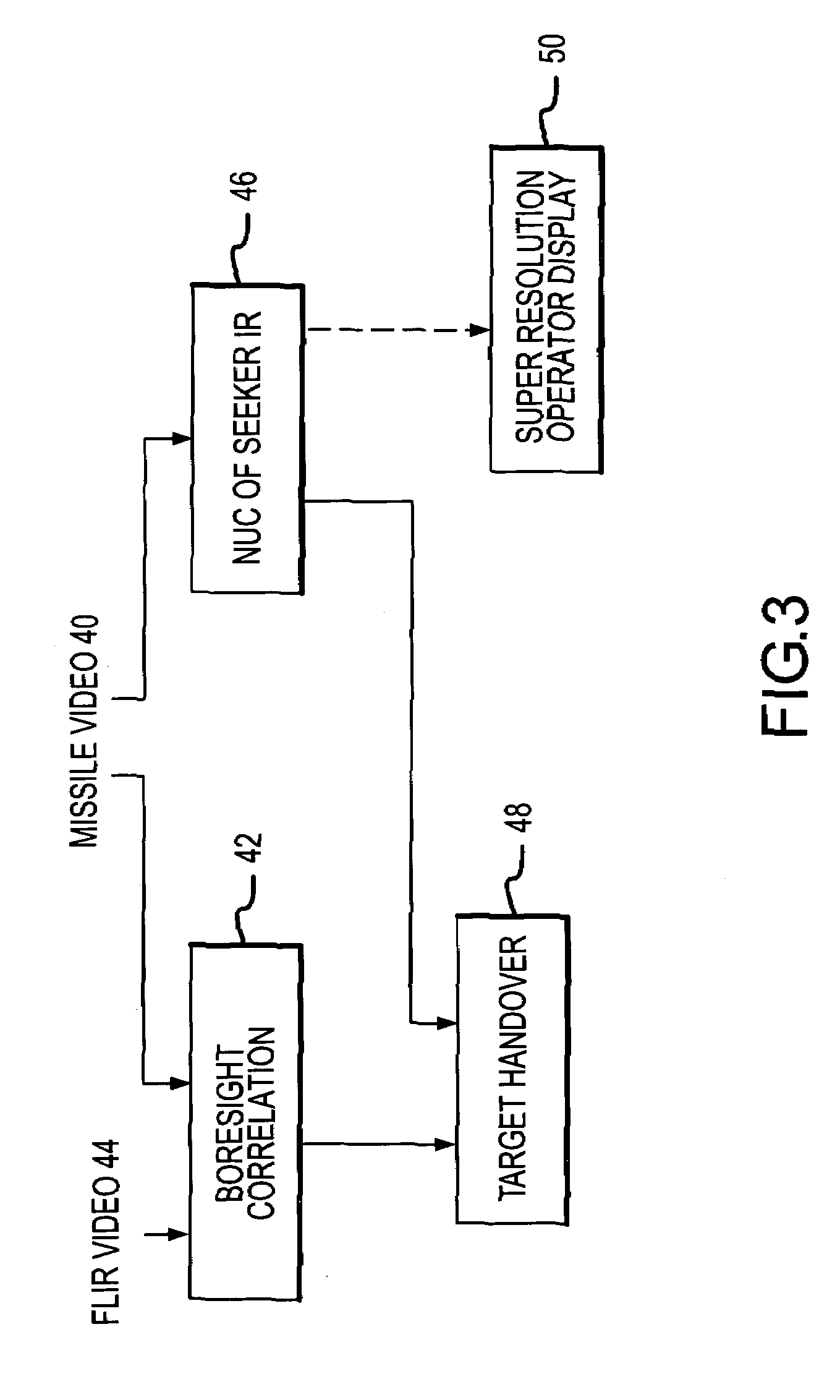
FLIR-to-missile boresight correlation and non-uniformity compensation of the missile seeker
ActiveUS7463753B2Simple and streamlined boresightEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsMangetographic processImage resolutionComputer science
The present invention provides for simple and streamlined boresight correlation of FLIR-to-missile video. Boresight correlation is performed with un-NUCed missile video, which allows boresight correlation and NUC to be performed simultaneously thereby reducing the time required to acquire a target and fire the missile. The current approach uses the motion of the missile seeker for NUCing to produce spatial gradient filtering in the missile image by differencing images as the seeker moves. This compensates DC non-uniformities in the image. A FLIR image is processed with a matching displace and subtract spatial filter constructed based on the tracked scene motion. The FLIR image is resampled to match the missile image resolution, and the two images are preprocessed and correlated using conventional methods. Improved NUC is provided by cross-referencing multiple measurements of each area of the scene as viewed by different pixels in the imager. This approach is based on the simple yet novel premise that every pixel in the array that looks at the same thing should see the same thing. As a result, the NUC terms adapt to non-uniformities in the imager and not the scene.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
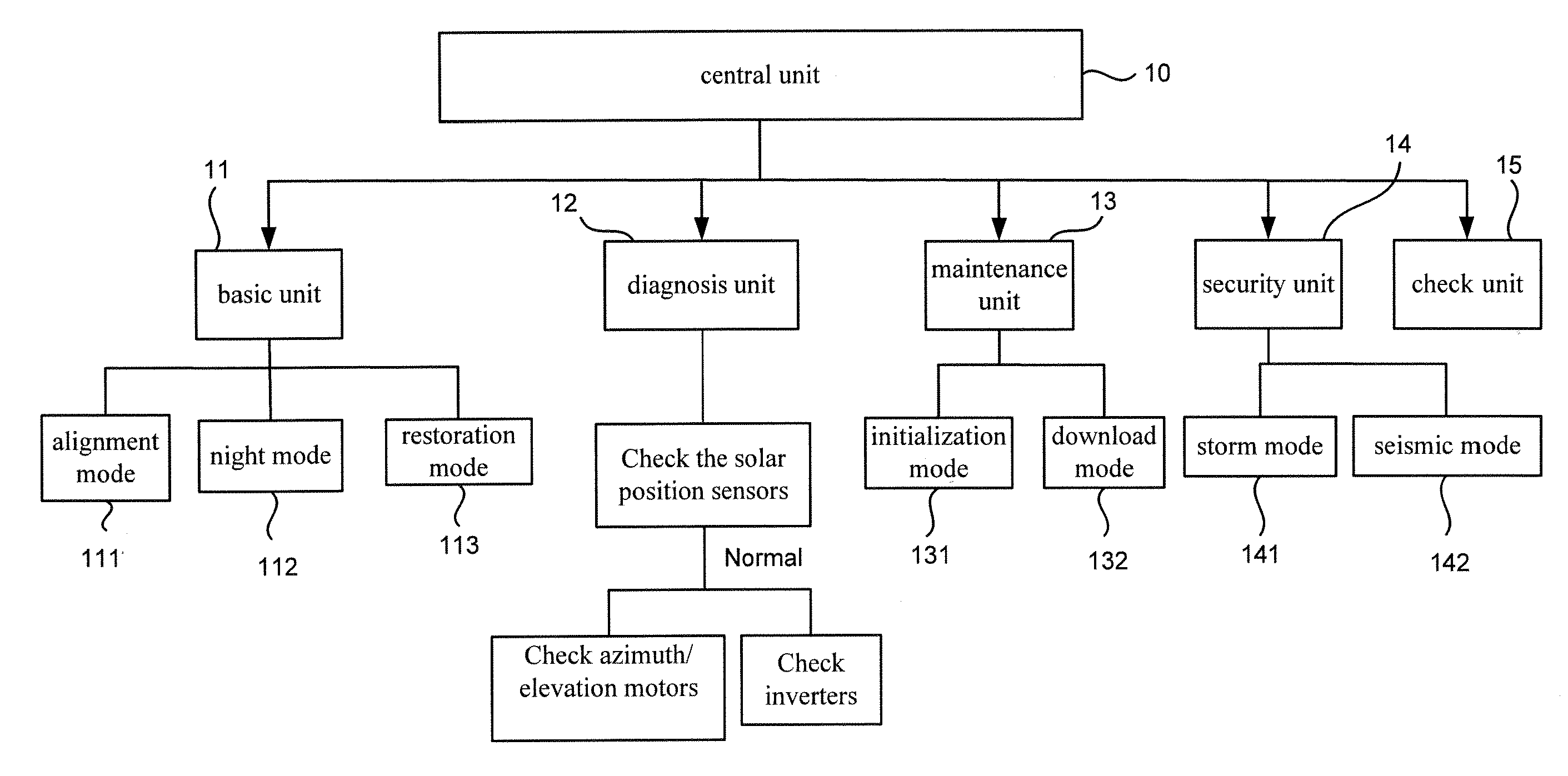
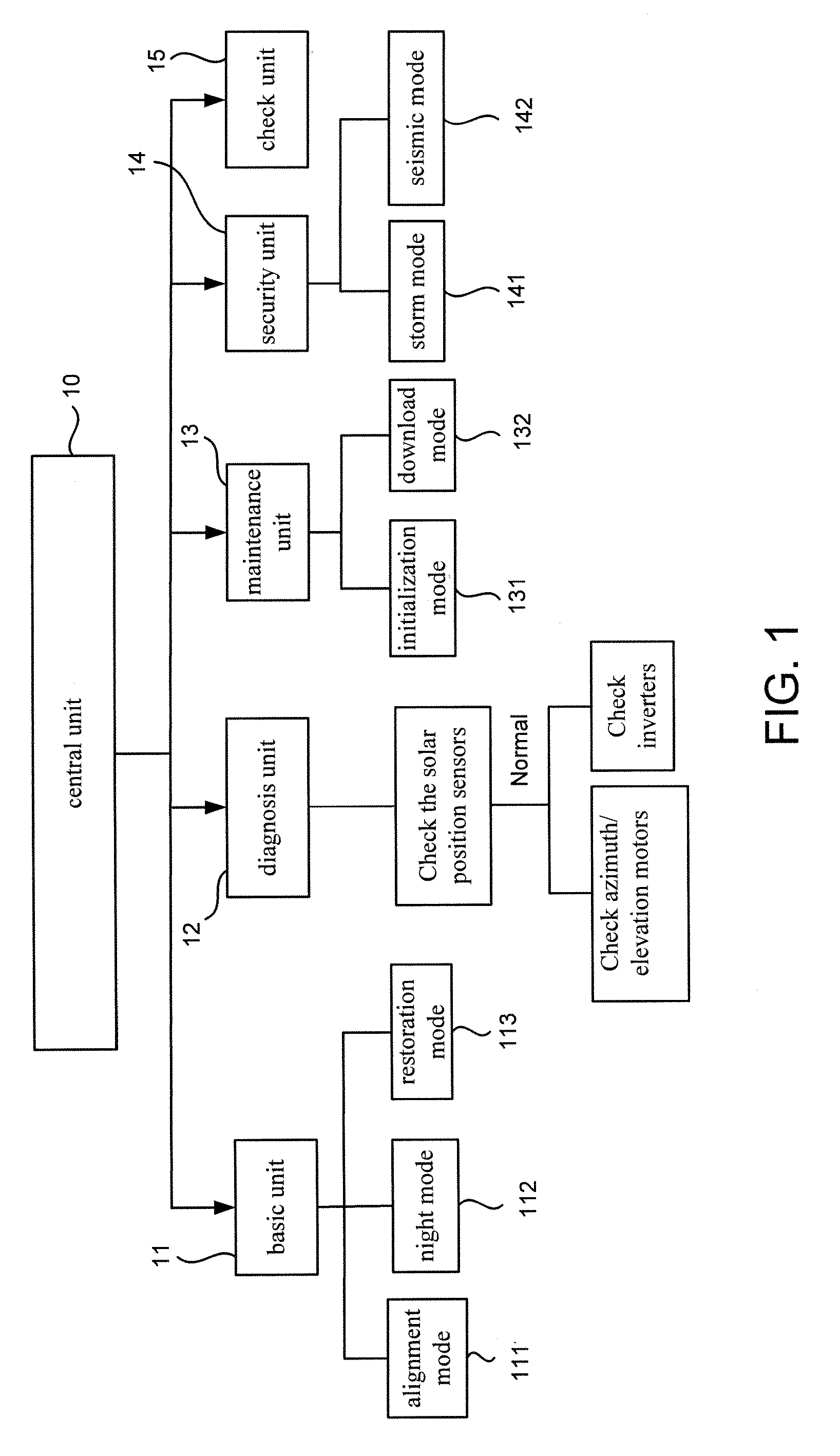
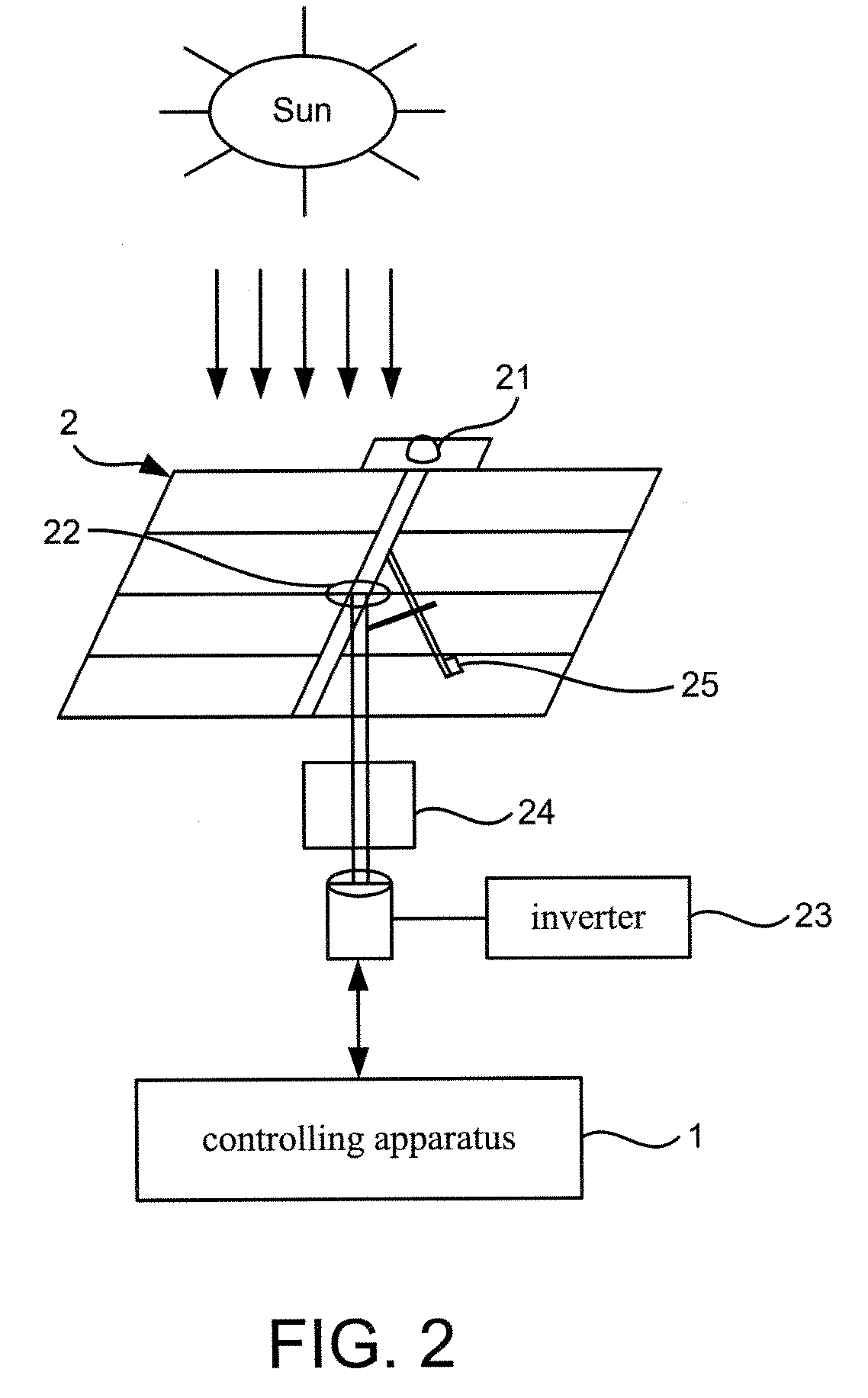
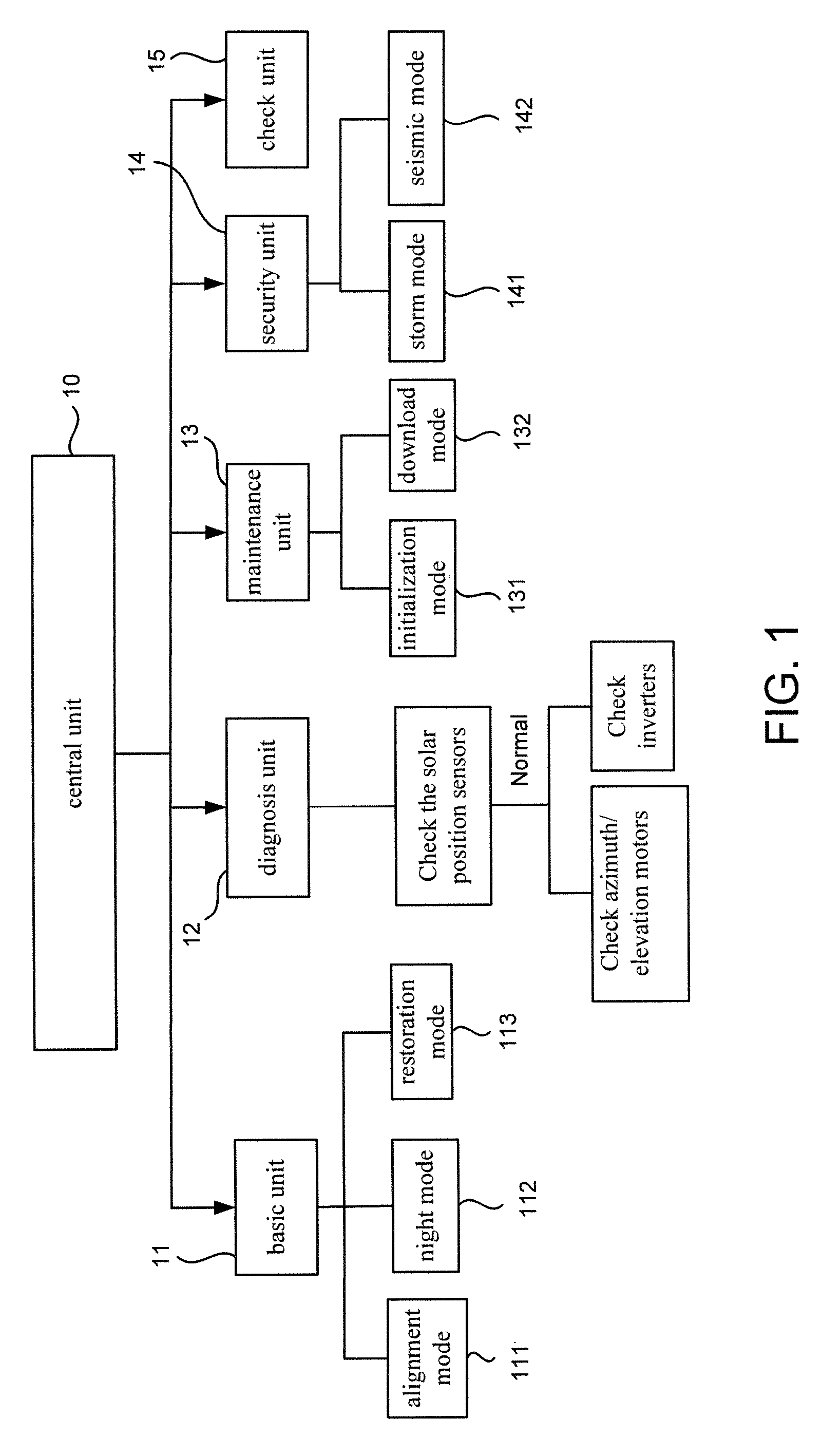
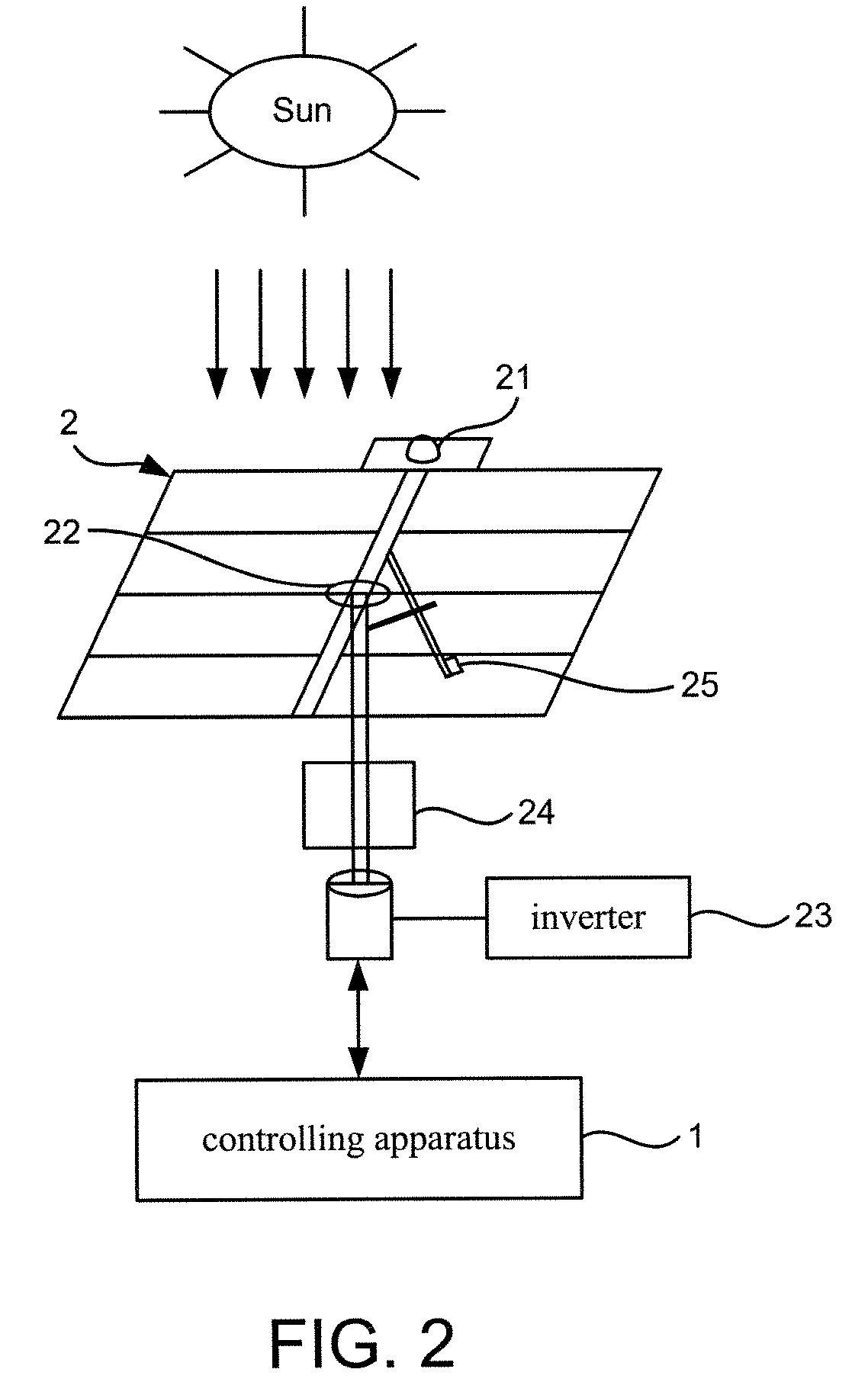
Controlling Apparatus for a Concentration Photovoltaic System
Disclosed is a controlling apparatus for use in a photovoltaic system. The photovoltaic system includes a solar cell array, an inverter and a solar tracker. The solar tracker includes a solar position sensor, a controller connected to the solar position sensor, a first motor connected to the controller for rotating the solar cell array according to the azimuth of the sun and a second motor connected to the controller for tilting the solar cell array according to the elevation of the sun. The controlling apparatus includes a central unit, a basic unit, a diagnosis unit, a maintenance unit, a security unit and a check unit.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
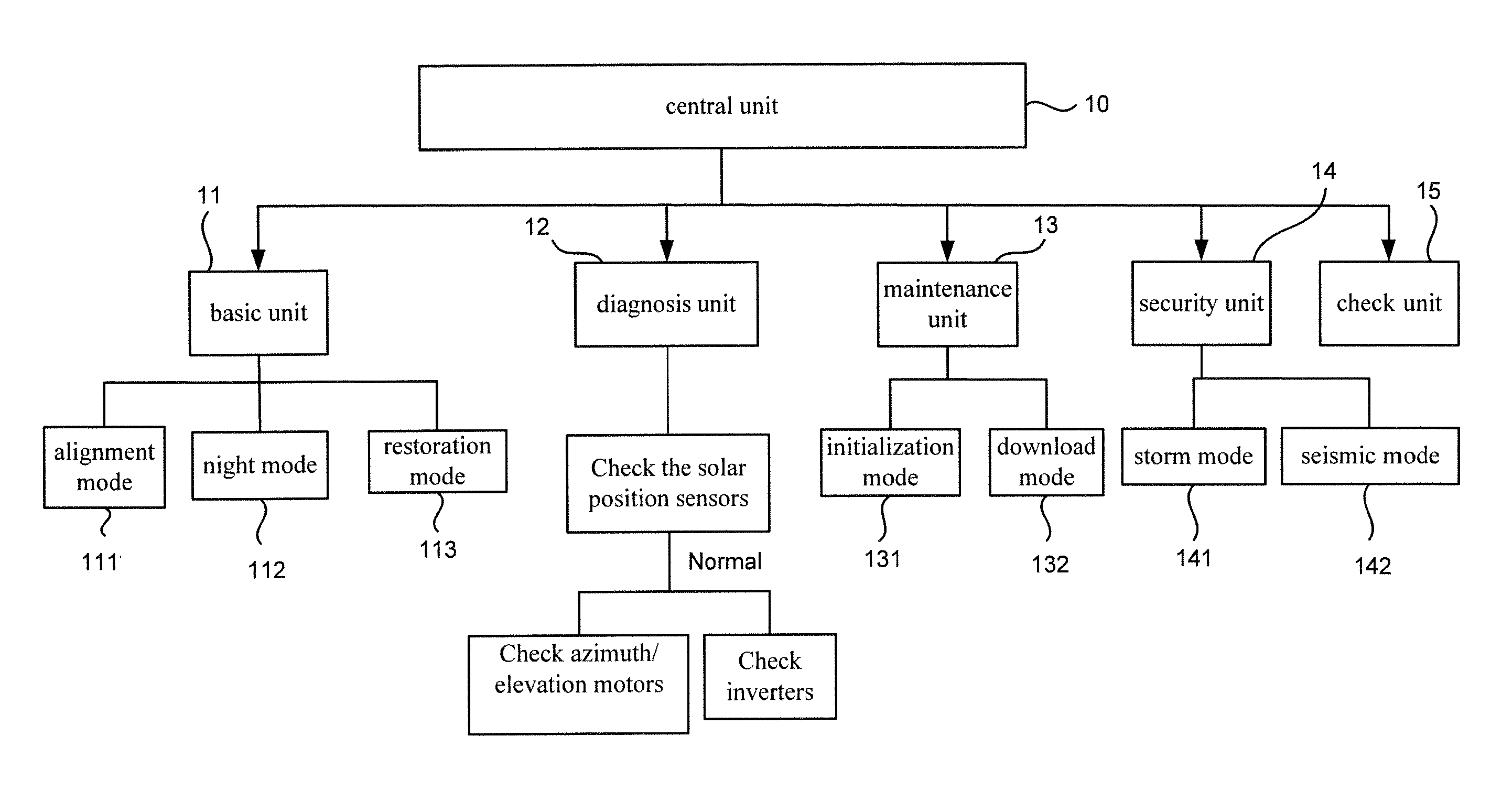
Controlling apparatus for a concentration photovoltaic system
Disclosed is a controlling apparatus for use in a photovoltaic system. The photovoltaic system includes a solar cell array, an inverter and a solar tracker. The solar tracker includes a solar position sensor, a controller connected to the solar position sensor, a first motor connected to the controller for rotating the solar cell array according to the azimuth of the sun and a second motor connected to the controller for tilting the solar cell array according to the elevation of the sun. The controlling apparatus includes a central unit, a basic unit, a diagnosis unit, a maintenance unit, a security unit and a check unit.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
On-board light source based gain correction for semi-active laser seekers
ActiveUS20060266919A1Accurate locationAccuracy of inadequatePhotometry using reference valueDirection controllersSemi activeOn board
The invention provides a method and apparatus for correcting for gain changes in detectors in a guided vehicle. In one version of the invention, an on board light source is used to generate a reference set of detector gains, which are stored in computer memory. The on board light source is then pulsed at subsequent times and the signals generated by the detectors are compared to the reference set of detector gains to determine whether any gains have changed.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
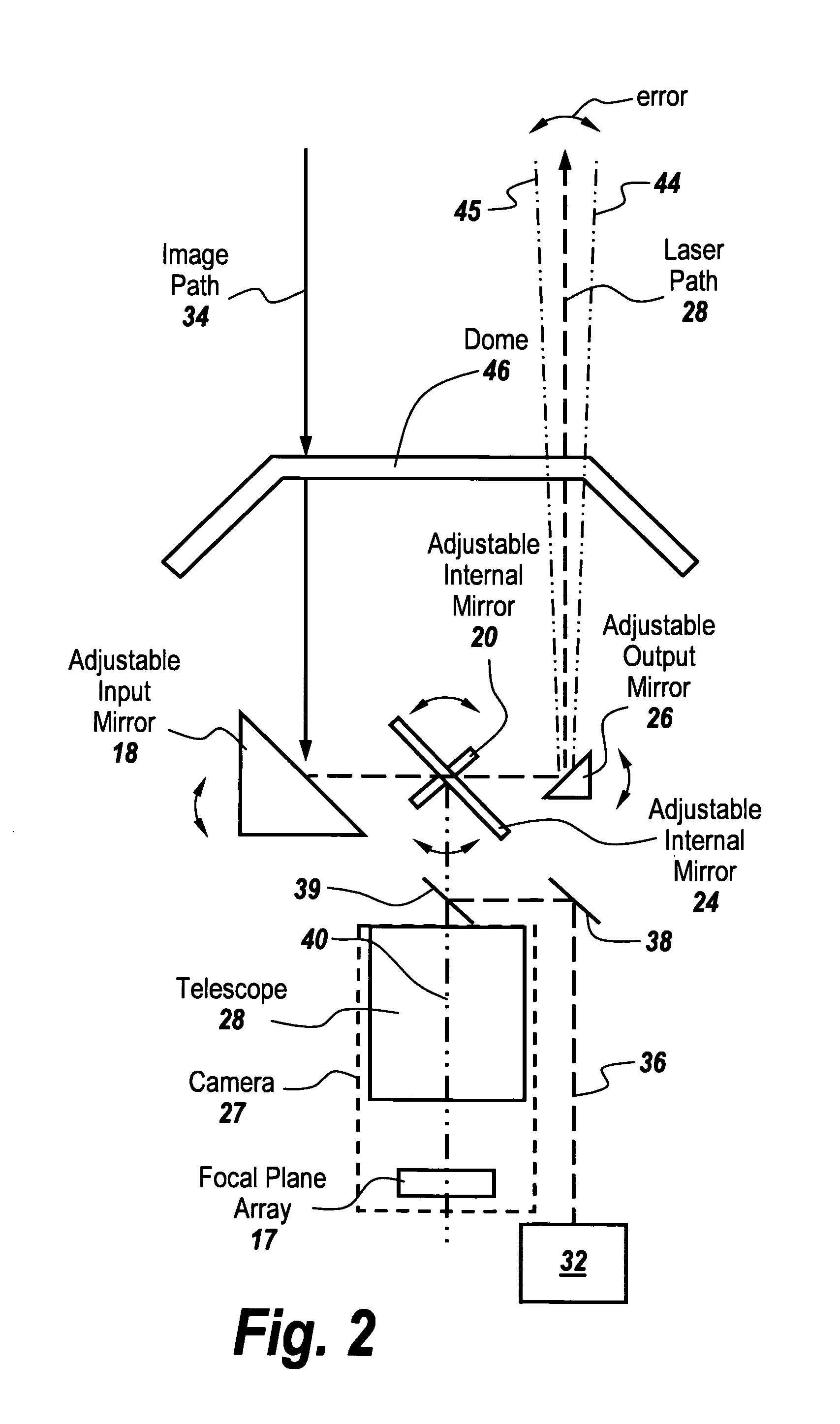
Non-Adjustable Pointer-Tracker Gimbal Used For Directed Infrared Countermeasures Systems
InactiveUS20160187126A1Large energyImprove accuracyAngle measurementDirection controllersCountermeasureLight beam
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Method and Apparatus for Acquiring Accurate Background Infrared Signature Data on Moving Targets
ActiveUS20110142284A1Radiation pyrometryElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingInfrared signatureTracking system
A method for measuring an infrared signature of a moving target includes: tracking the moving target with a tracking system along a path from a start position to an end position, measuring infrared radiation data of the moving target along the path, repositioning the tracking system to the start position, retracing the path to measure the infrared radiation data of the background, and determining the infrared signature of the moving target by comparing the infrared radiation data of the moving object with the infrared radiation data of the background without the moving object.
Owner:TEXTRON INNOVATIONS
Self-calibrated, remote imaging and data processing system
InactiveUS20130169811A1Navigational calculation instrumentsElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingData processing systemImaging data
An imaging sensor system, adaptably mountable to a vehicle having a view of a target area comprising: a rigid mount unit having at least two imaging sensors disposed within the mount unit, wherein a first imaging and a second imaging sensor each has a focal axis passing through an aperture in the mount unit, wherein the first imaging sensor generates a first image area comprising a first data array of pixels and the second imaging sensor generates a second image area comprising a second data array of pixels, wherein the first and second imaging sensors are offset to have a first image overlap area in the target area, wherein the first sensors image data bisects the second sensors image data in the first image overlap area.
Owner:VI TECH LLC
Amplitude comparison direction finding method and system
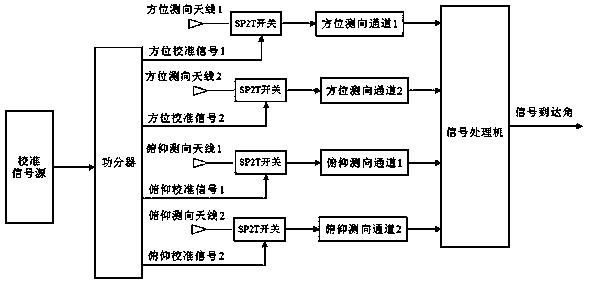
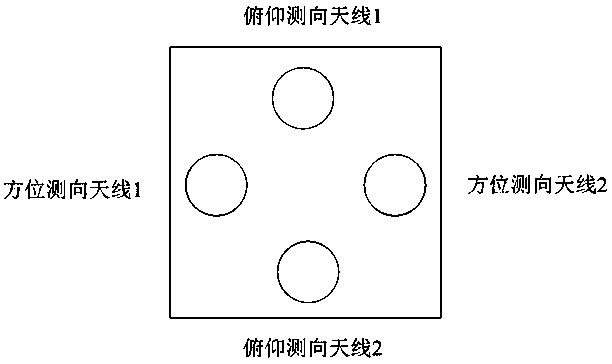
InactiveCN109507638AReduced Amplitude Consistency RequirementsEasy to implementElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingFindings methodsSoftware
The invention discloses an amplitude comparison direction finding method and system. The method comprises the following steps of generating calibrating signals according to designated frequency and power; according to the calibrating signals, calculating a real-time channel amplitude ratio; collecting interception signals and calculating the measurement amplitude ratio of the interception signals;according to the real-time channel amplitude ratio and the measurement amplitude ratio of the interception signals, calculating the actual amplitude ratio of the interception signals; according to the actual amplitude ratio, searching for a preestablished amplitude comparison form to acquire an angle of arrival corresponding to the actual amplitude ratio. The amplitude comparison direction finding method greatly reduces requirements on consistency of amplitude comparison channels, and by controlling calibrating processes through software, is simple in operation.
Owner:NANJING CHANGFENG AEROSPACE ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH
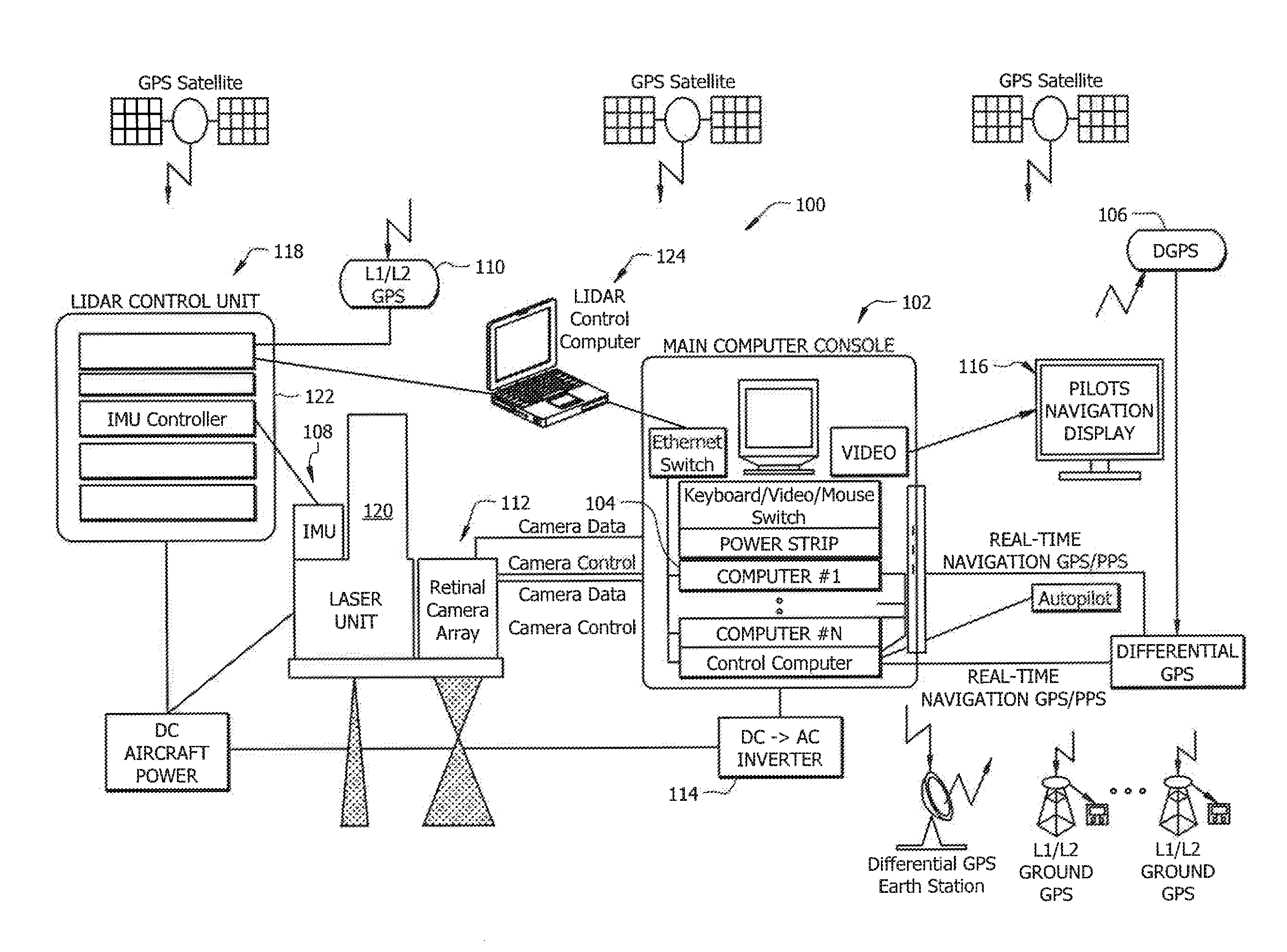
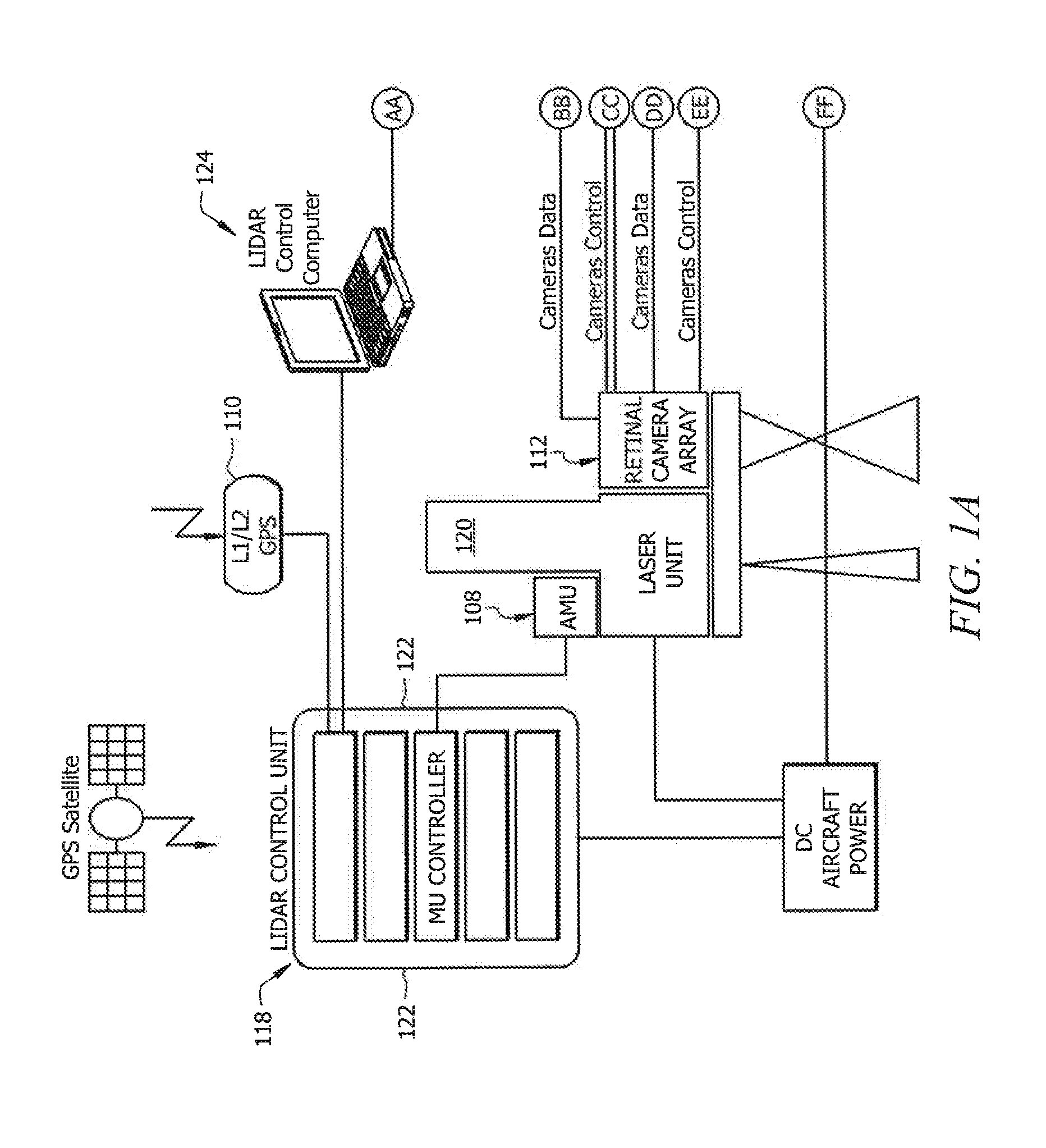
Doped fiber scene projection system and method
This invention pertains to a scene projection system and a method for projecting a scene that can simulate light temperature of above 2000 K. The system comprises of a light source part for generating light at a lower wavelength; a means part for individually controlling dynamic range, contrast, brightness, temporal characteristics and temporal dynamics of the light; a rare earth doped fiber part that re-emits the output light at a higher wavelength; and a means part for conveying light between its parts. The method comprises steps of generating light at a lower wavelength wavelength; individually controlling temporal characteristics, temporal dynamics, brightness and contrast of the light; passing the light through a rare earth-doped fiber; and re-emitting the light at a higher wavelength.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Non-Adjustable Pointer-Tracker Gimbal Used For Directed Infrared Countermeasures Systems
ActiveUS20160187125A1Large energyImprove accuracyAngle measurementDirection controllersCountermeasureLight beam
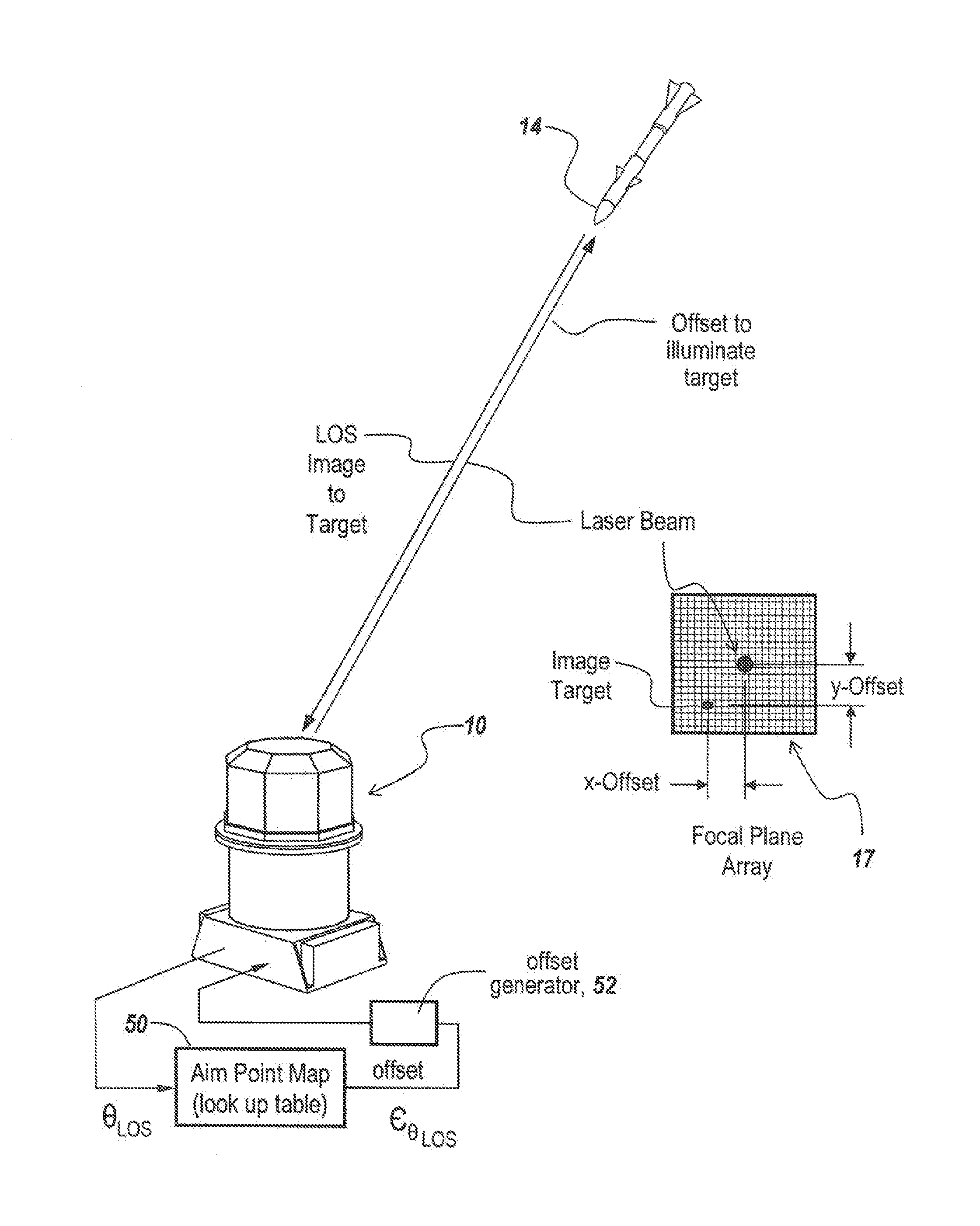
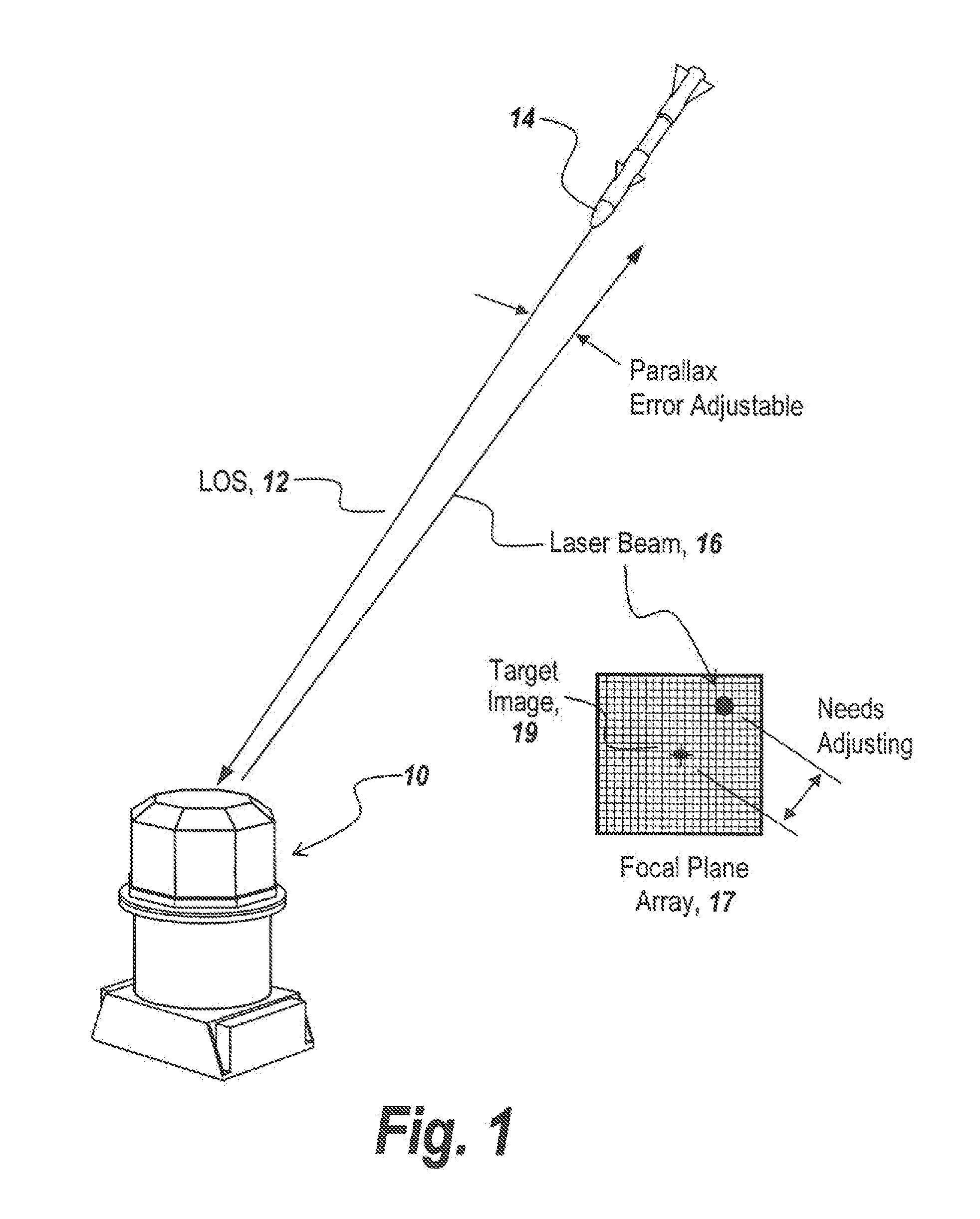
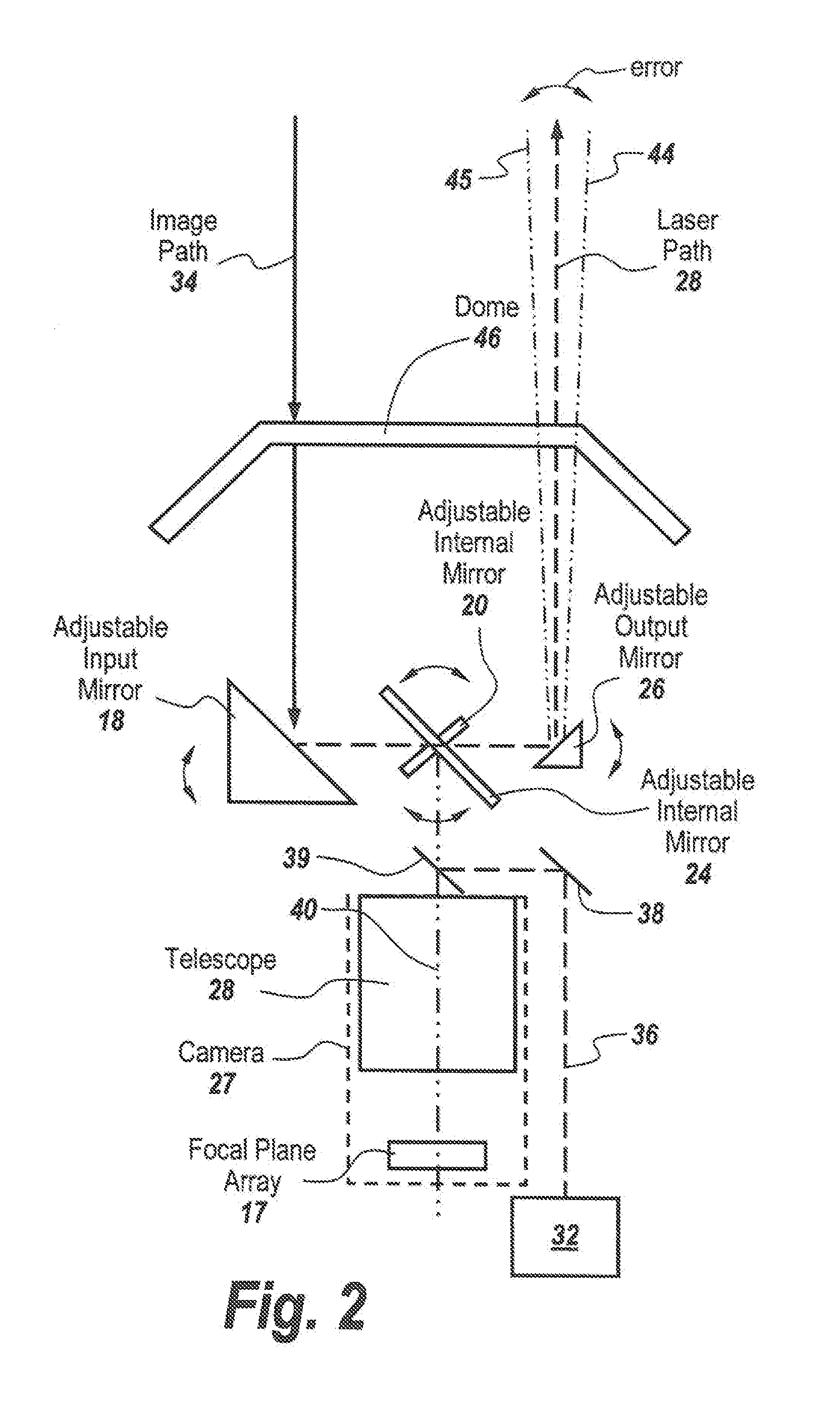
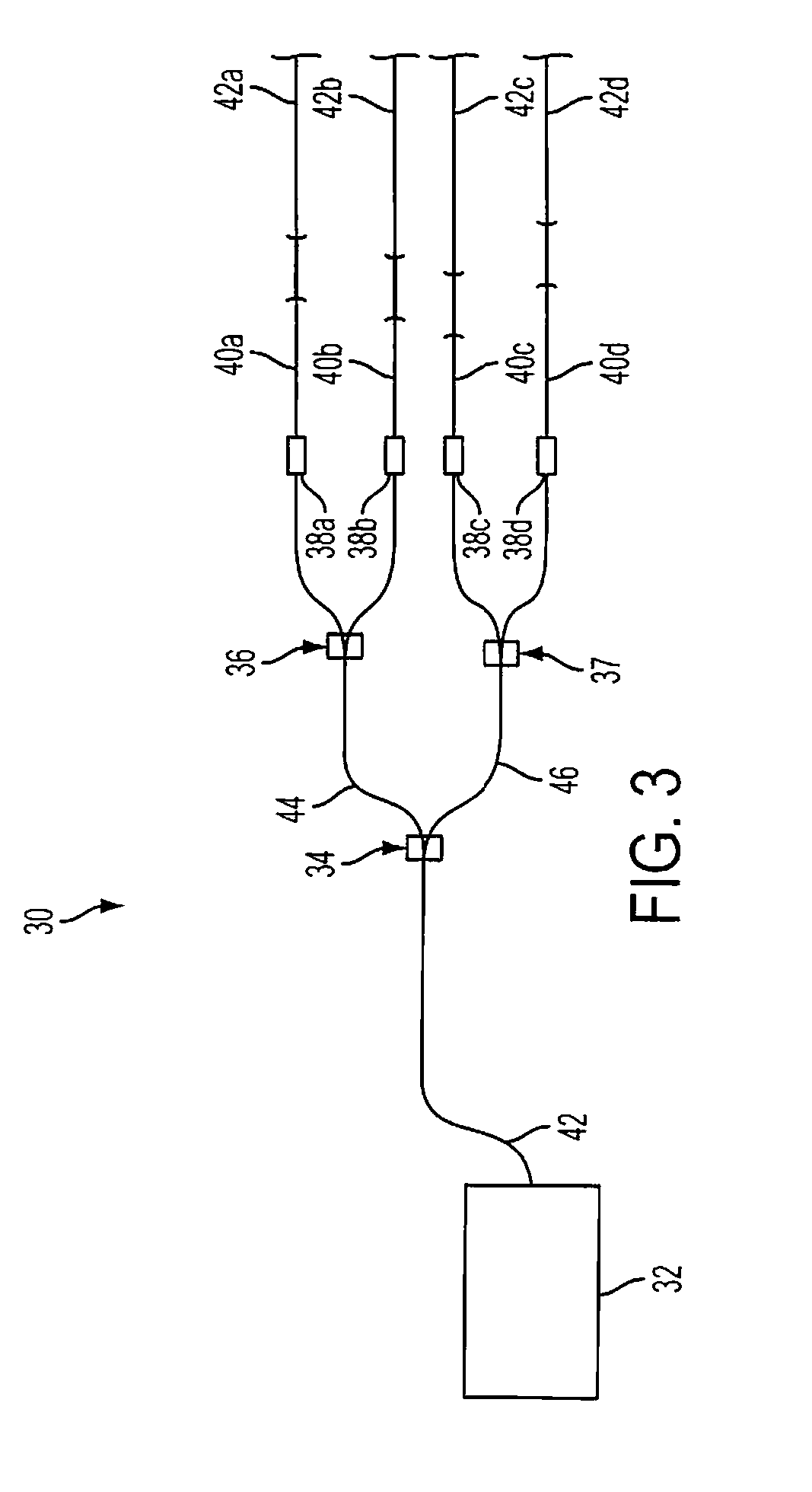
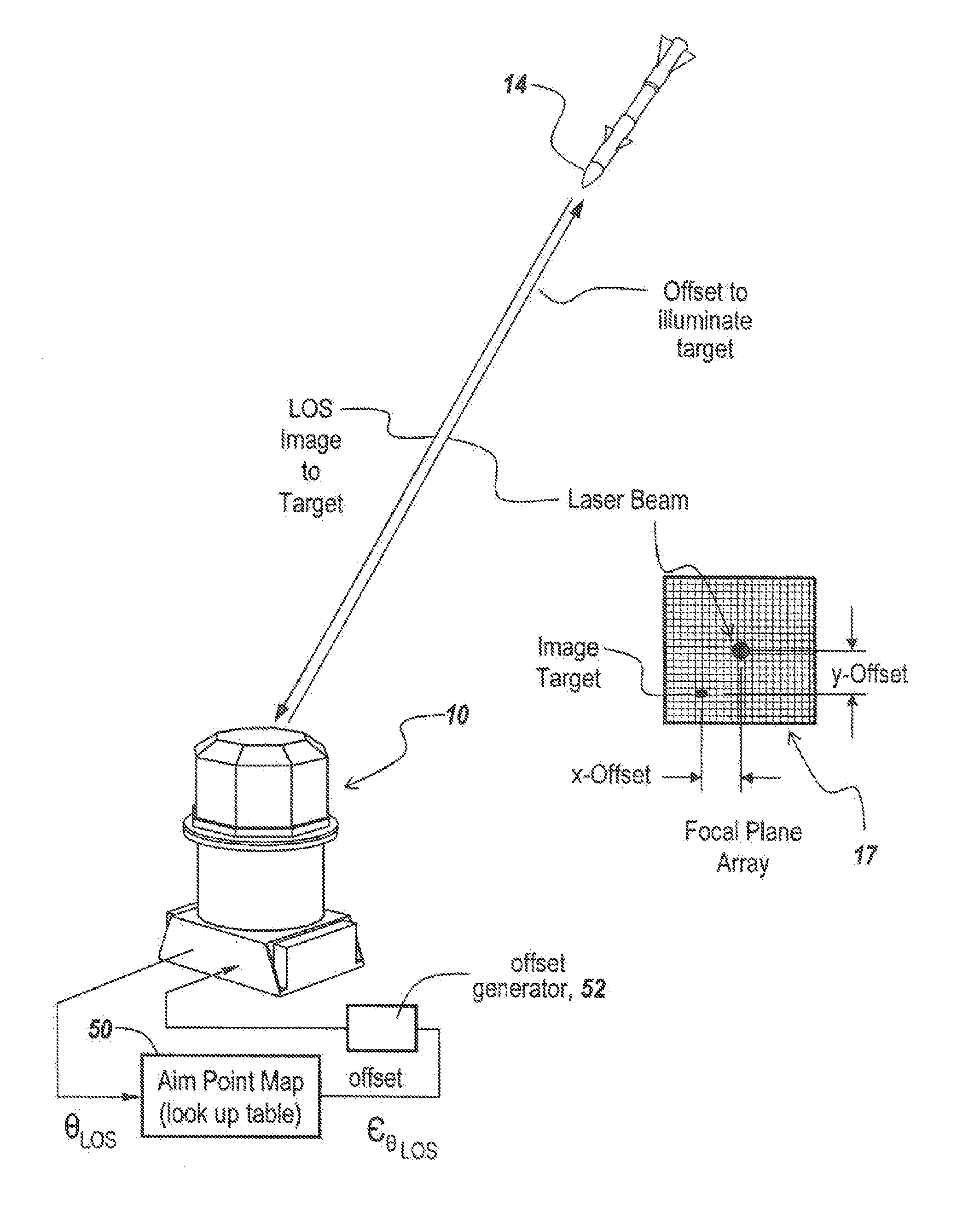
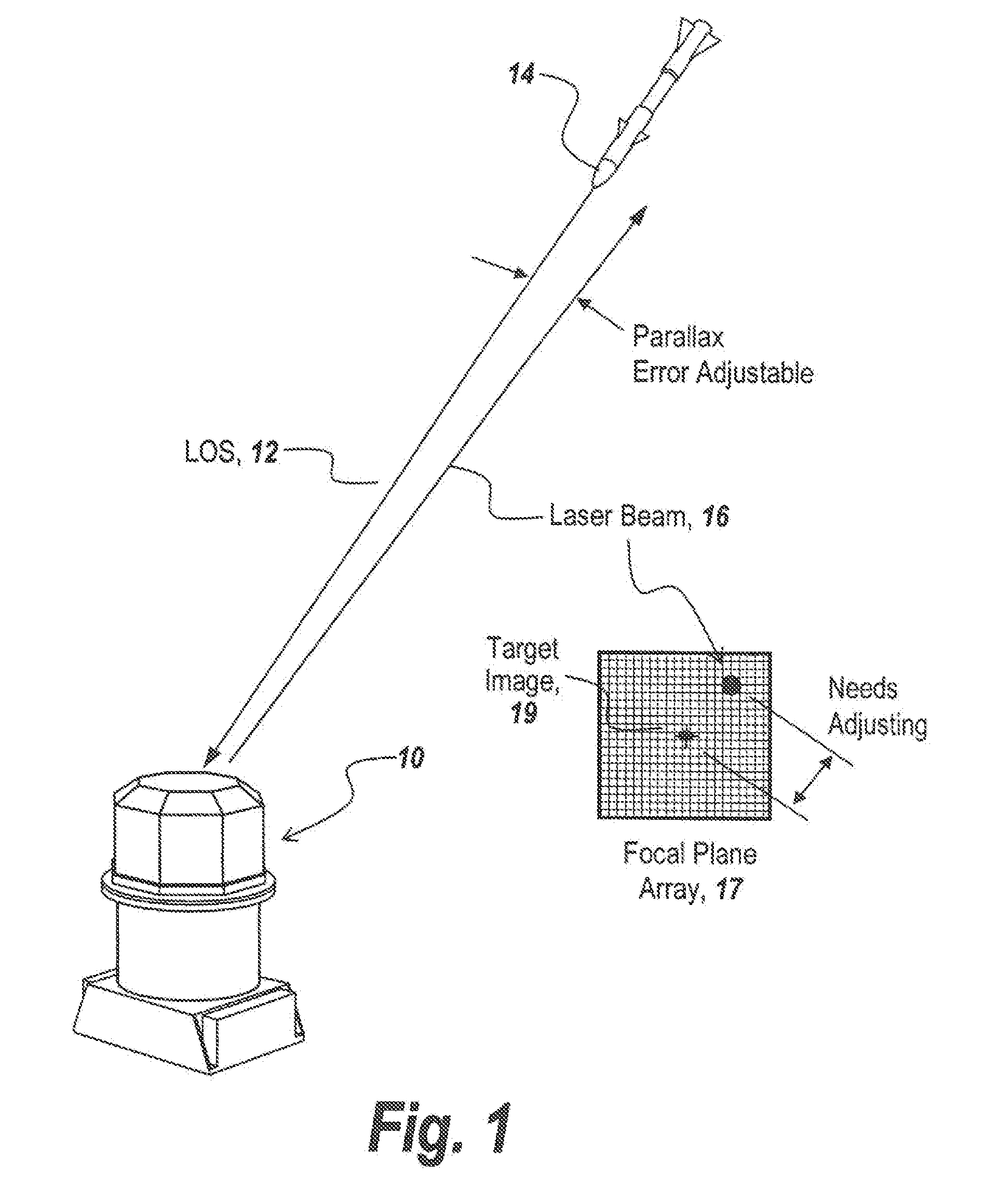
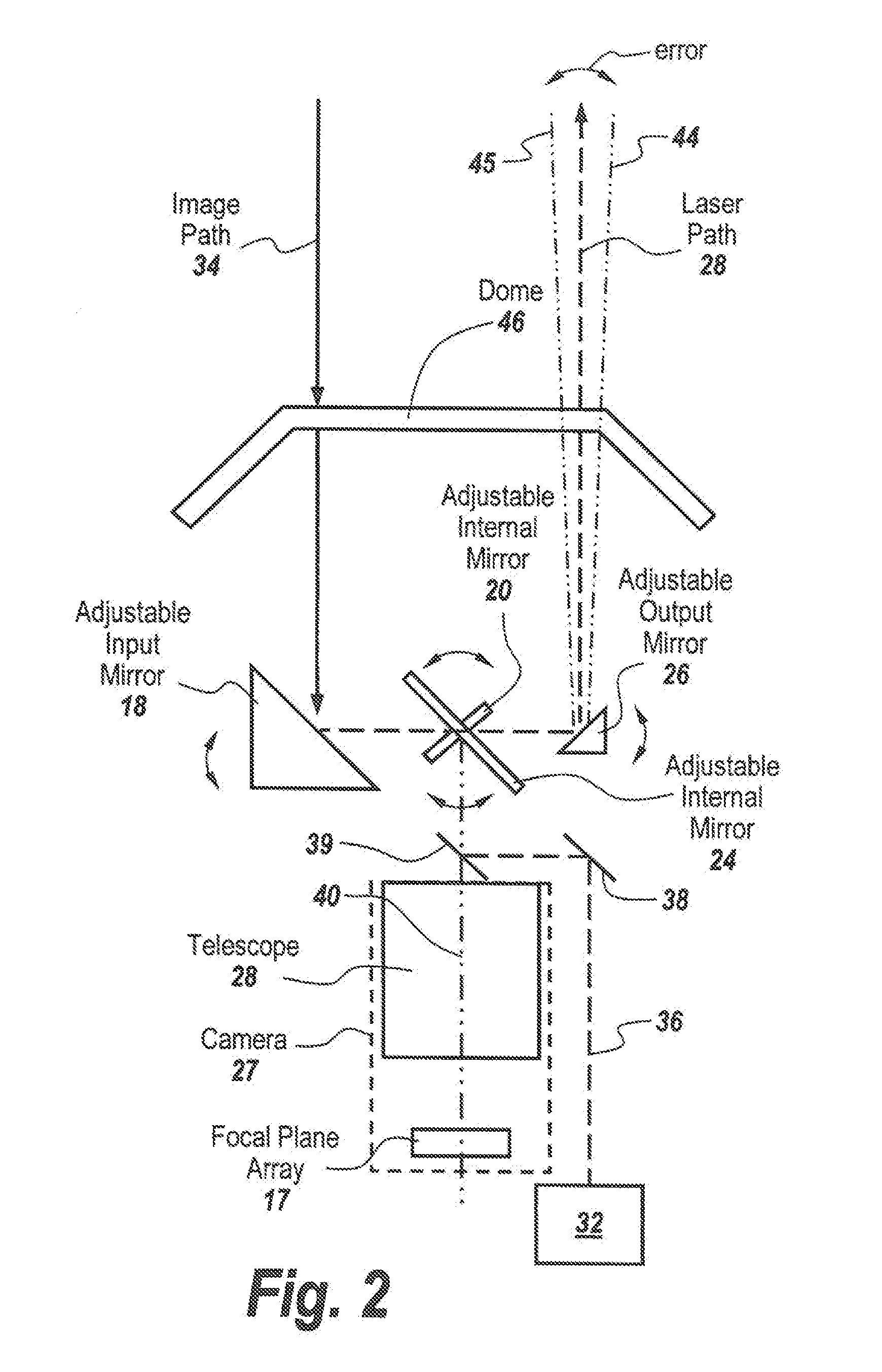
In a directed infrared countermeasure system, to assure parallelism between the line-of-sight to a target and the output beam, the input and output mirrors are fixedly attached to a uni-construction arm mounted to a rotatable azimuth platter to which internal mirrors are also fixedly attached. A system is provided for zeroing out alignment errors by developing an aim-point map for the gimbal that records initial alignment errors induced by manufacturing tolerances and uses the aim-point map error values to correct the output mirror orientation. The system also corrects for alignment errors induced by thermal gradients.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Non-adjustable pointer-tracker gimbal used for directed infrared countermeasures systems
ActiveUS9310191B1Expensive partLarge energyDirection controllersElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingCountermeasureLight beam
In a directed infrared countermeasure system, to assure parallelism between the line-of-sight to a target and the output beam, the input and output mirrors are fixedly attached to a uni-construction arm mounted to a rotatable azimuth platter to which internal mirrors are also fixedly attached. A system is provided for zeroing out alignment errors by developing an aim-point map for the gimbal that records initial alignment errors induced by manufacturing tolerances and uses the aim-point map error values to correct the output mirror orientation. The system also corrects for alignment errors induced by thermal gradients.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Compact fixed-source array test station for calibration of a semi-active laser (SAL) seeker
ActiveUS8447550B1Reduce problem sizeReduce distanceTesting/calibration apparatusDirection controllersSemi activeHigh flux
A fixed-source array test station provides a compact cost-effective high-throughput test bed for testing optical sensors that require stimulus at fixed angular positions. An array of fixed collimated sources at different angular positions in the sensor's FOV are positioned on a surface of a focal sphere at the effective focal length of a spherical lens and aligned along respective radial lines to the center of the spherical lens so that each said divergent optical beam is collimated by the spherical lens to form a collimated optical beam that overlaps the entire entrance pupil of the optical seeker. The sources are activated in accordance with an activation profile in order to calibrate or otherwise test the sensor.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
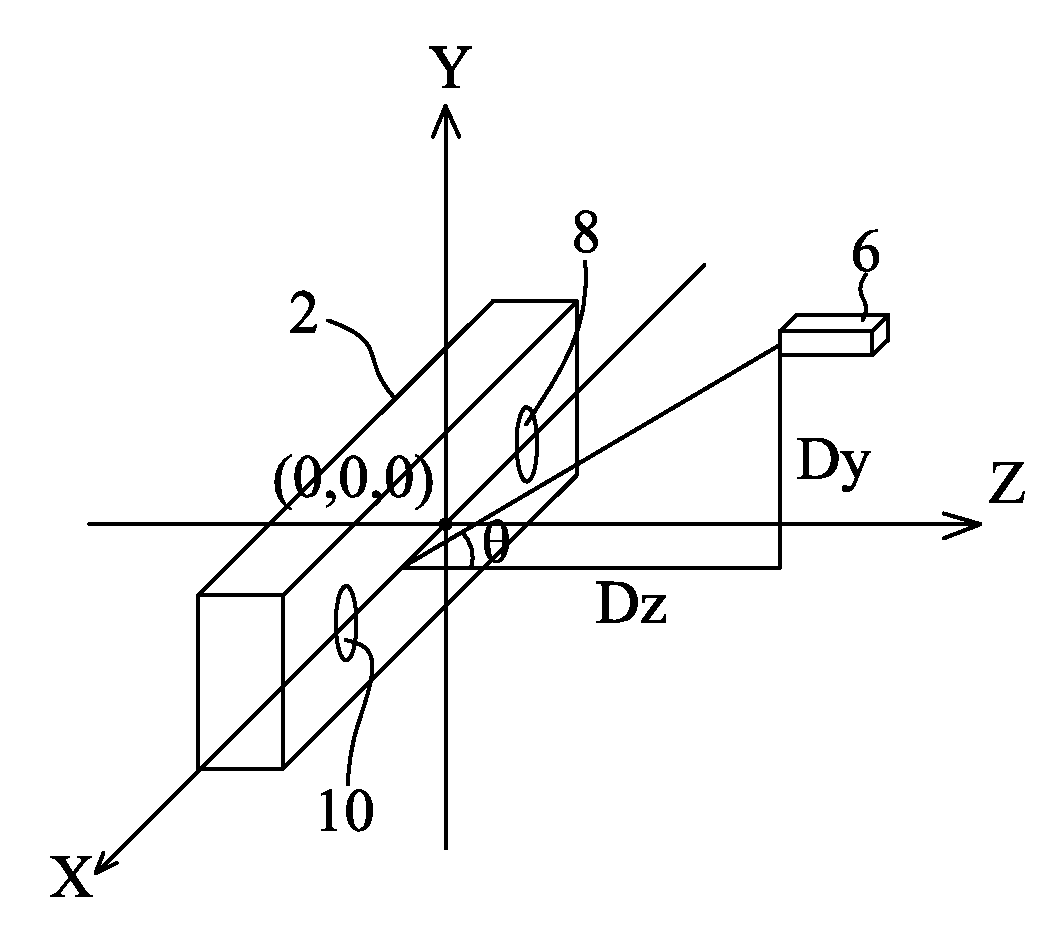
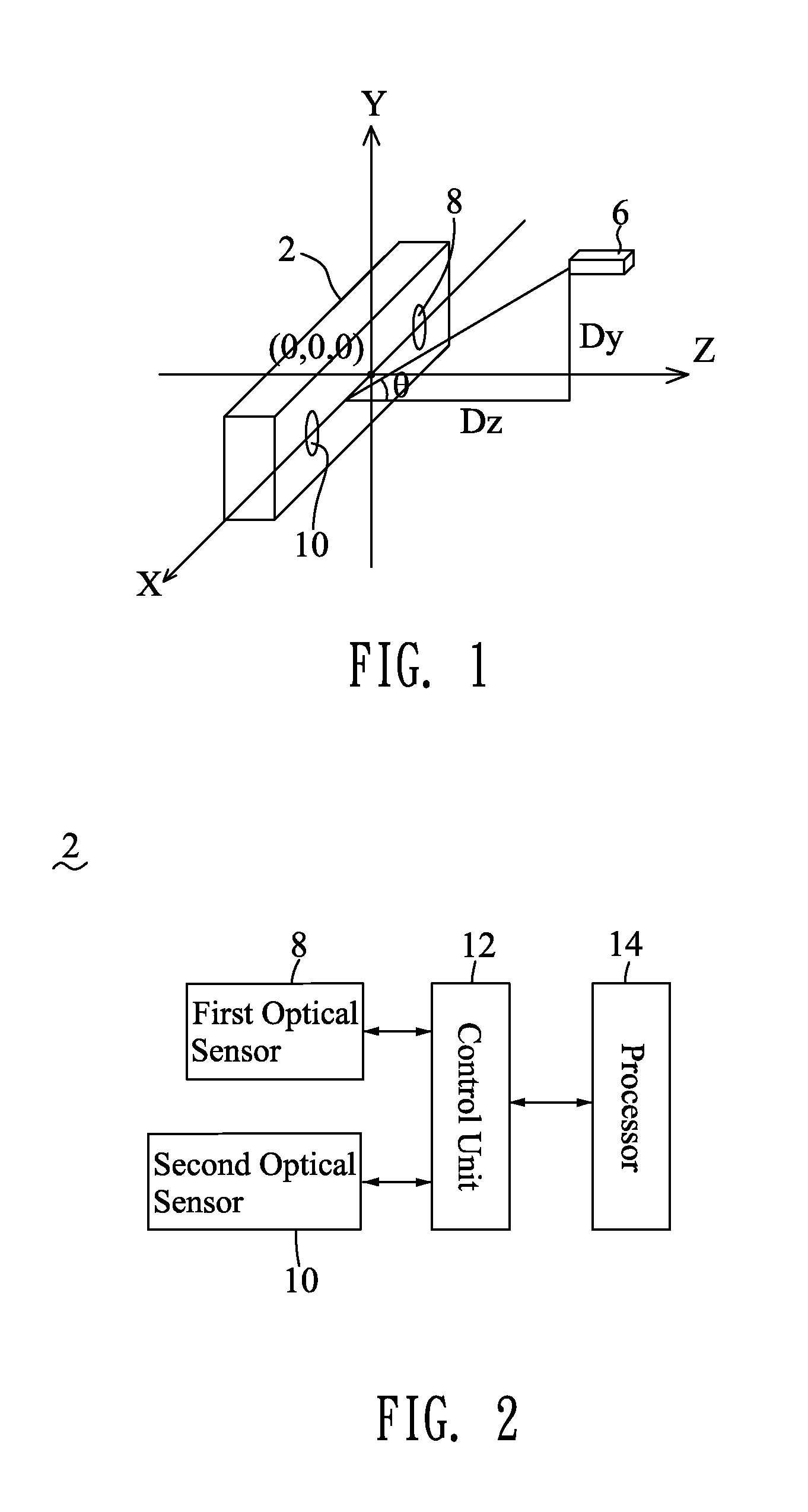
Optical Positioning Apparatus And Positioning Method Thereof
InactiveUS20110110559A1Optimize layoutEasy to useImage enhancementPhotometry using reference valueElectro-optical sensorLocation Equipment
An optical positioning apparatus and method are adapted for determining a position of an object in a three-dimensional coordinate system which has a first axis, a second axis and a third axis perpendicular to one another. The optical positioning apparatus includes a host device which has a first optical sensor and a second optical sensor located along the first axis with a first distance therebetween, and a processor connected with the optical sensors, and a calibrating device placed in the sensitivity range of the optical sensors with a second distance between an origin of the second axis and a coordinate of the calibrating device projected in the second axis. The optical sensors sense the calibrating device to make the processor execute a calibrating procedure, and then sense the object to make the processor execute a positioning procedure for determining the position of the object in the three-dimensional coordinate system.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
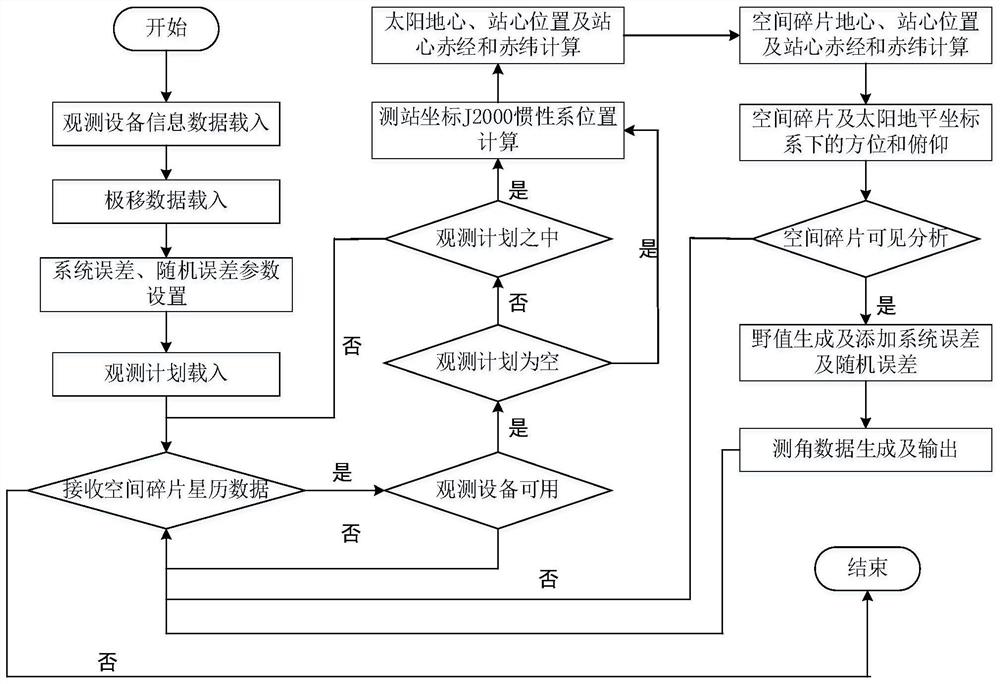
Space debris angle measurement data simulation method
ActiveCN112731281AImprove Simulation EfficiencyEnsure consistencyElectromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDesign optimisation/simulationData simulationSimulation
The invention relates to a space debris angle measurement data simulation method. The method comprises the steps of dynamically receiving and loading observation plan data of observation equipment by loading polar shift data, dynamically loaded observation equipment information data and dynamically inputting system errors and random errors of the equipment, according to information such as the spatial debris position and speed in a J2000 inertial coordinate system received in real time, converting into a space debris station center position under the J2000 inertial system to obtain a horizontal right ascension and a horizontal declination of the space debris under the J2000 inertial system and a right ascension and a declination of the space debris under a station center equator coordinate system, further converting into an azimuth and a pitch under a horizon coordinate, and adding a system error, a random error and a wild value to generate space debris angle measurement simulation data. According to the method, by loading the observation plan data, the space debris can be observed in a planned manner, the consistency of the simulation environment and the real observation environment is ensured in the simulation process, and the simulation efficiency of the angle measurement data is improved.
Owner:NO 63921 UNIT OF PLA
Popular searches
Color television details Direction/deviation determining electromagnetic systems Input/output processes for data processing Video games Instruments for comonautical navigation Solar heat devices Material analysis by optical means Navigation by astronomical means Solar heat collector for particular environment Solar-rays concentration
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com