Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
230 results about "Gobio gobio obtusirostris" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
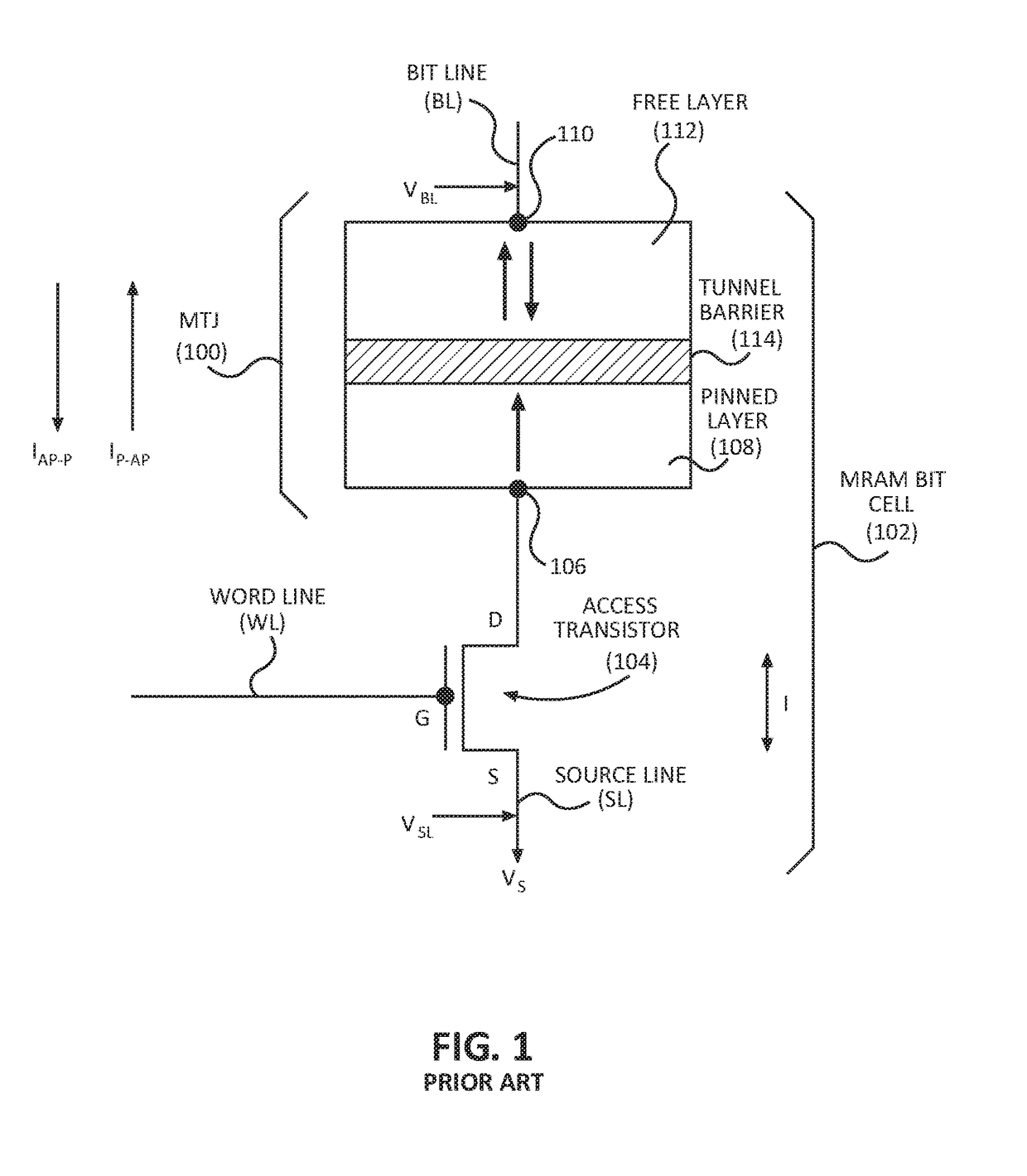
Magnetic tunneling junction configuration and a method for making the same
InactiveUS6897532B1Reduce the temperatureAvoid depositionTransistorNanomagnetismEngineeringGobio gobio obtusirostris
A method for forming a magnetic tunneling junction (MJT) is provided. In some embodiments, the method may include patterning one or more magnetic layers to form an upper portion of a MTJ. The method may further include patterning one or more additional layers to form a lower portion of the MTJ. In some cases, the lower portion may include a tunneling layer of the MTJ having a width greater than the upper portion. In addition, in some embodiments the method may further include patterning an electrode below the lower portion. In some cases, the electrode may include a lowermost layer with a thickness equal to or less than approximately 100 angstroms. In addition or alternatively, the electrode may have a width greater than the width of the tunneling layer. In yet other embodiments, the method may include forming spacers along the sidewalls of the upper and / or lower portions.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
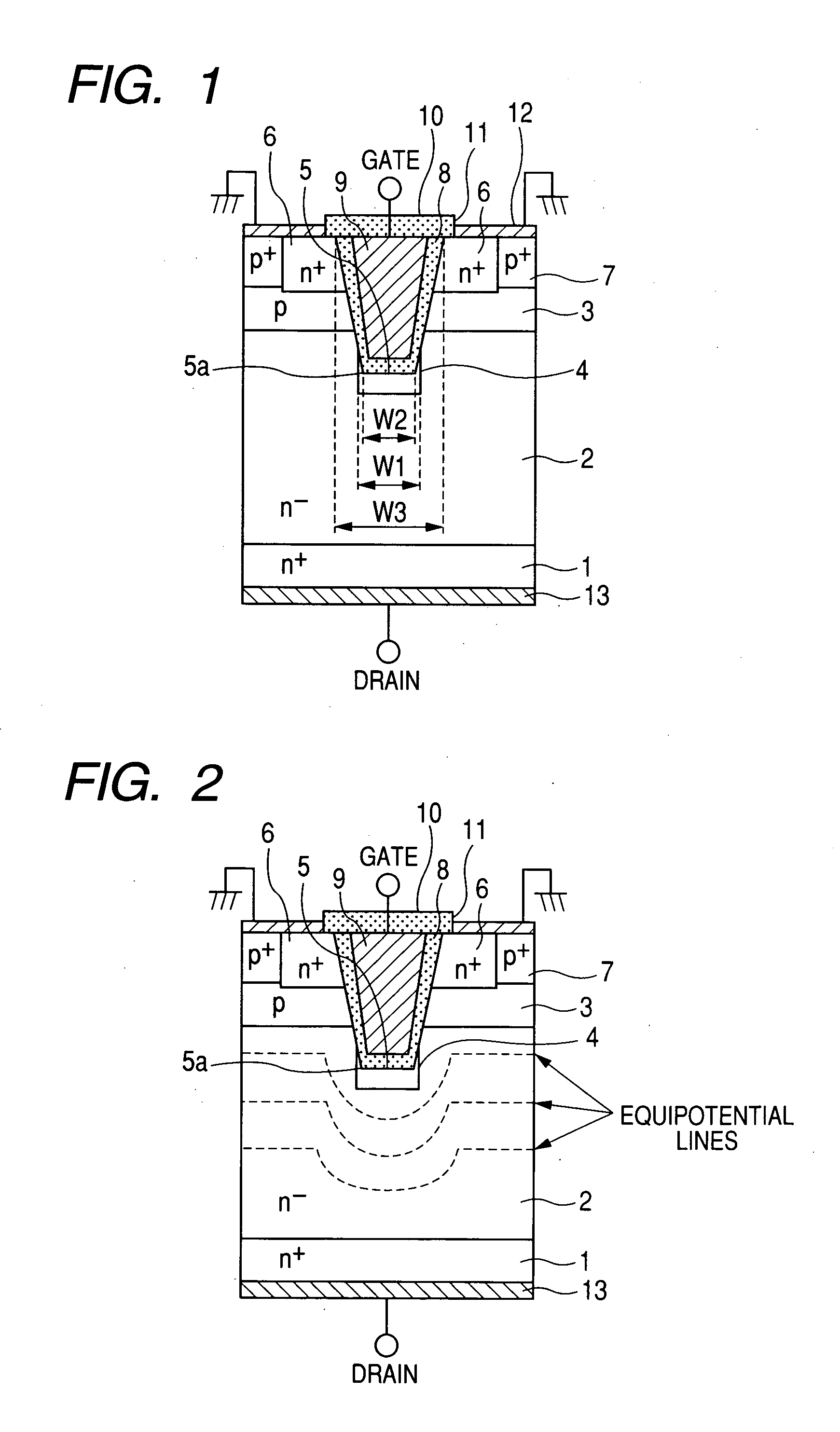
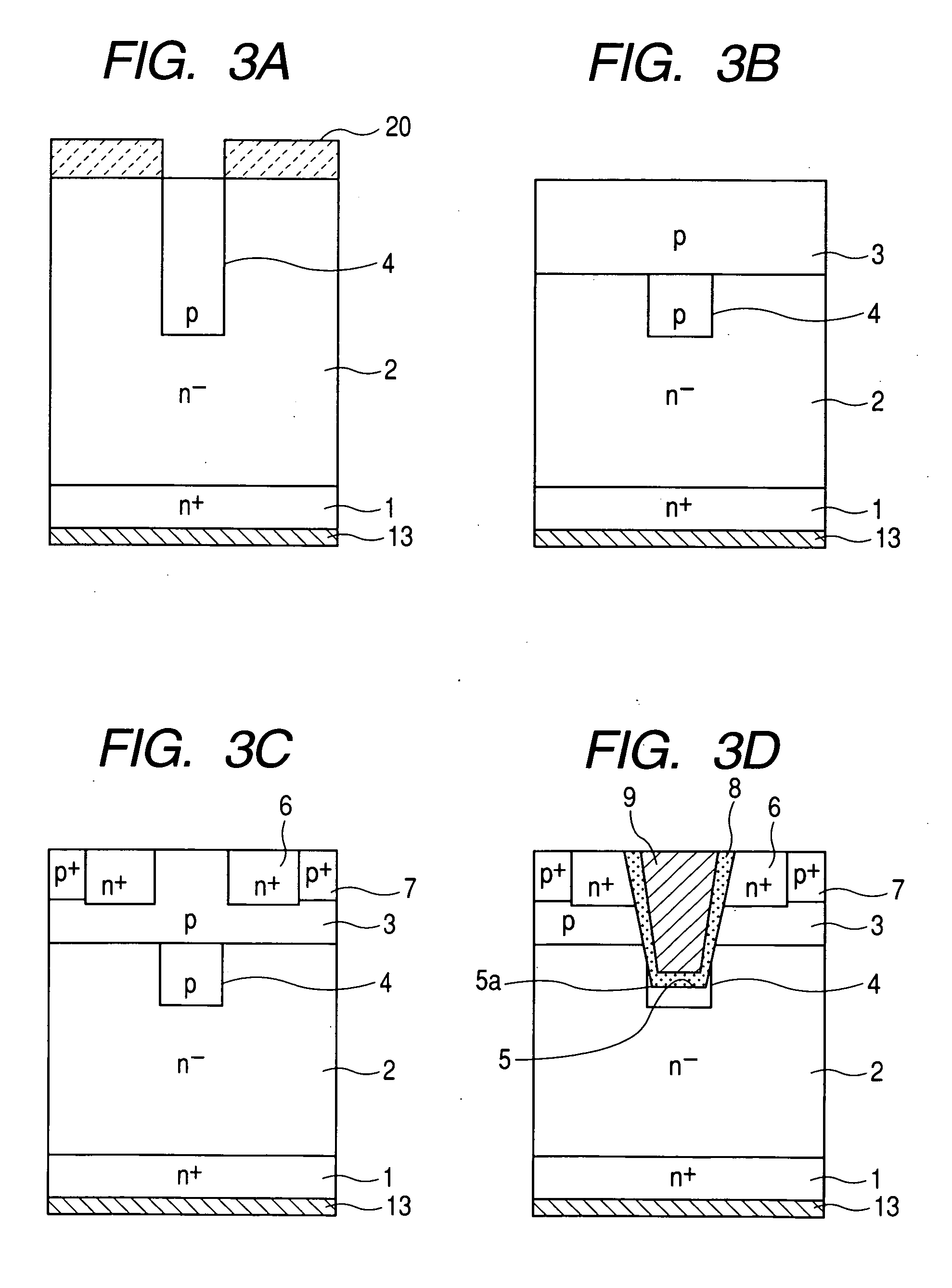
Silicon carbide semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080230787A1Avoid breakingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGobio gobio obtusirostrisSemiconductor
The silicon carbide semiconductor device includes a trench formed from a surface of a drift layer of a first conductivity type formed on a substrate of the first conductivity type, and a deep layer of a second conductivity type located at a position in the drift layer beneath the bottom portion of the trench. The deep layer is formed at a certain distance from base regions of the second conductivity type formed on the drift layer so as to have a width wider than the width of the bottom portion of the trench, and surround both the corner portions of the bottom portion of the trench.
Owner:DENSO CORP
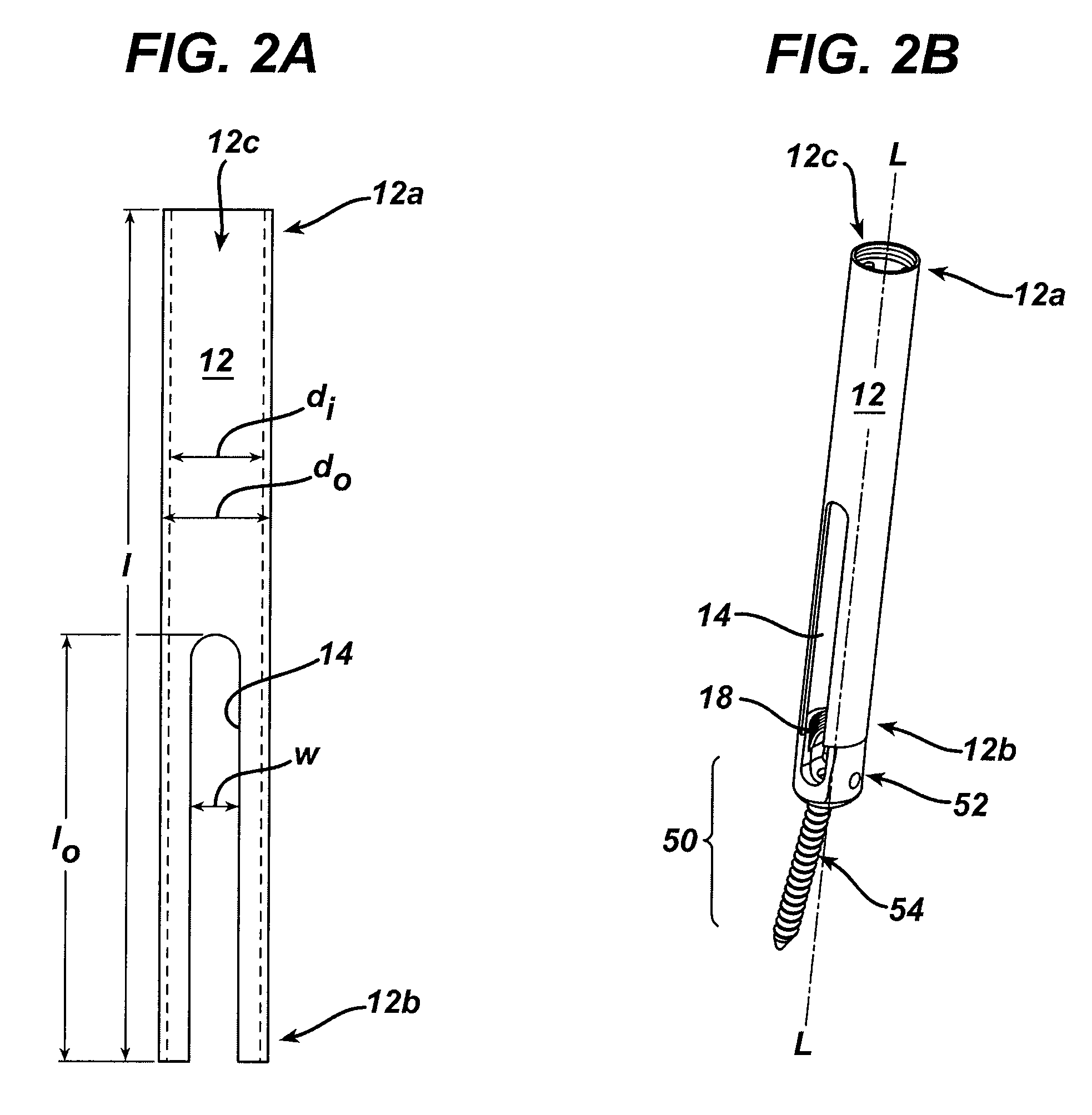
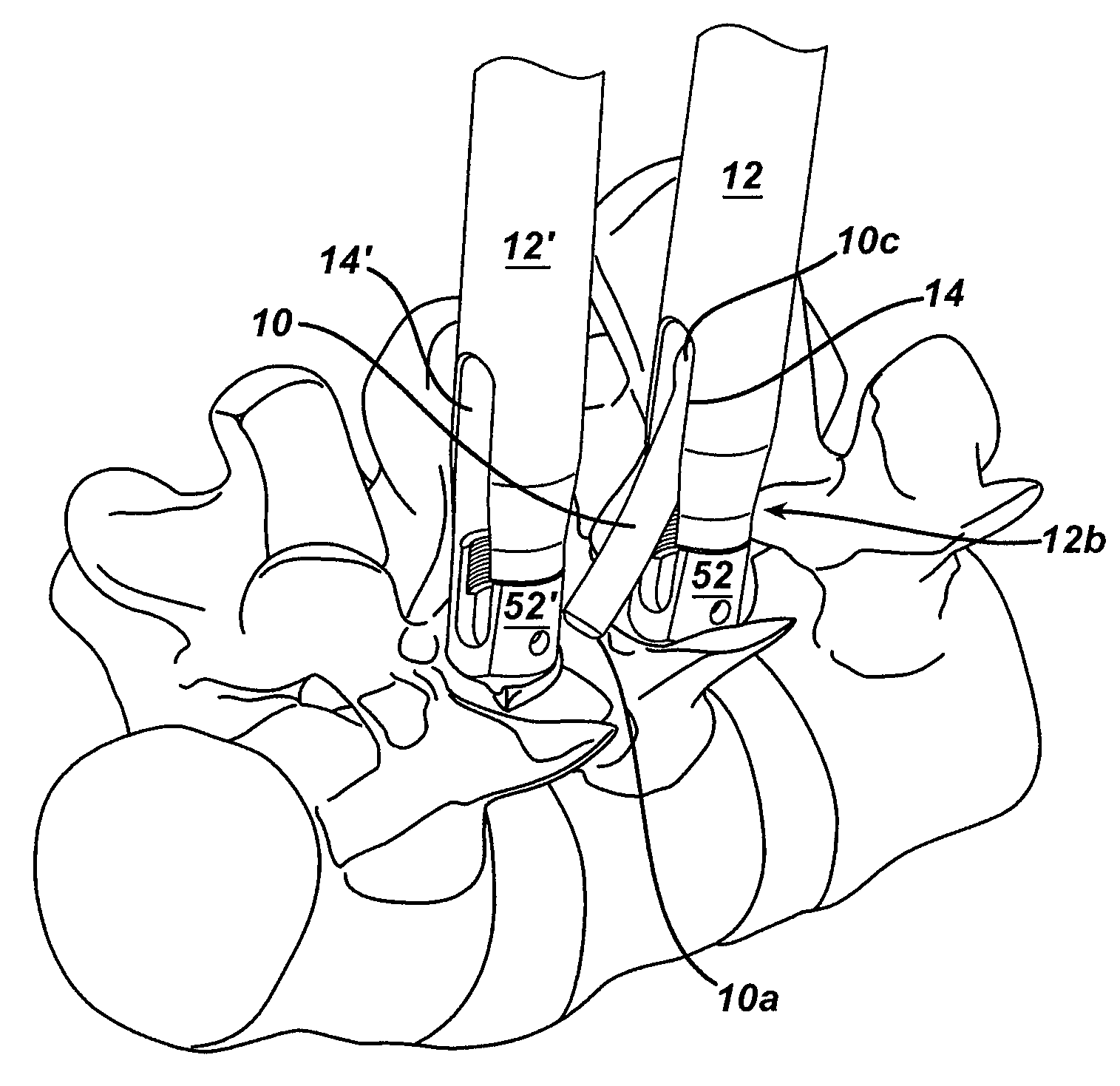
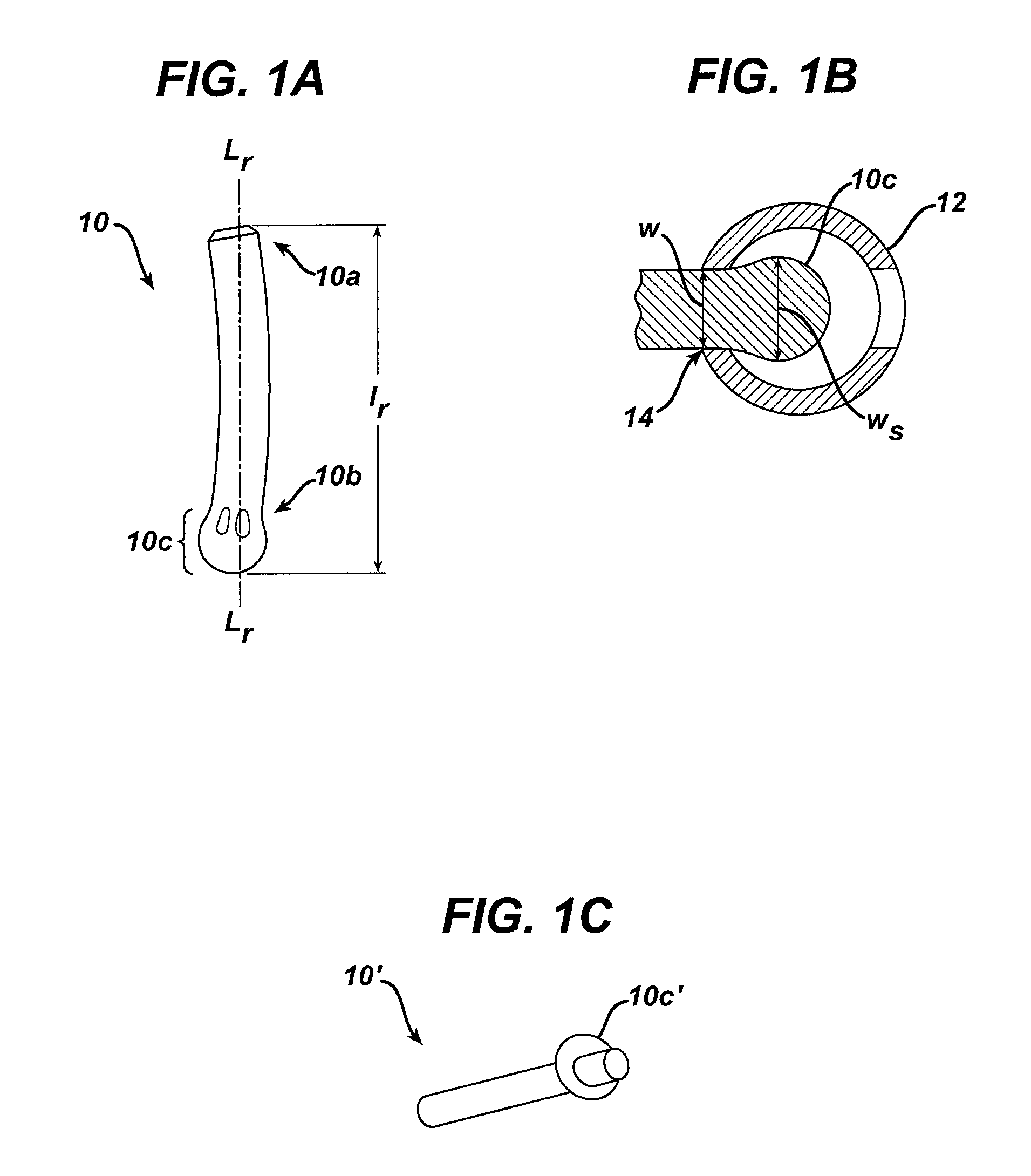
Spinal fixation element and methods
ActiveUS7547318B2Help positioningInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnGobio gobio obtusirostris
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
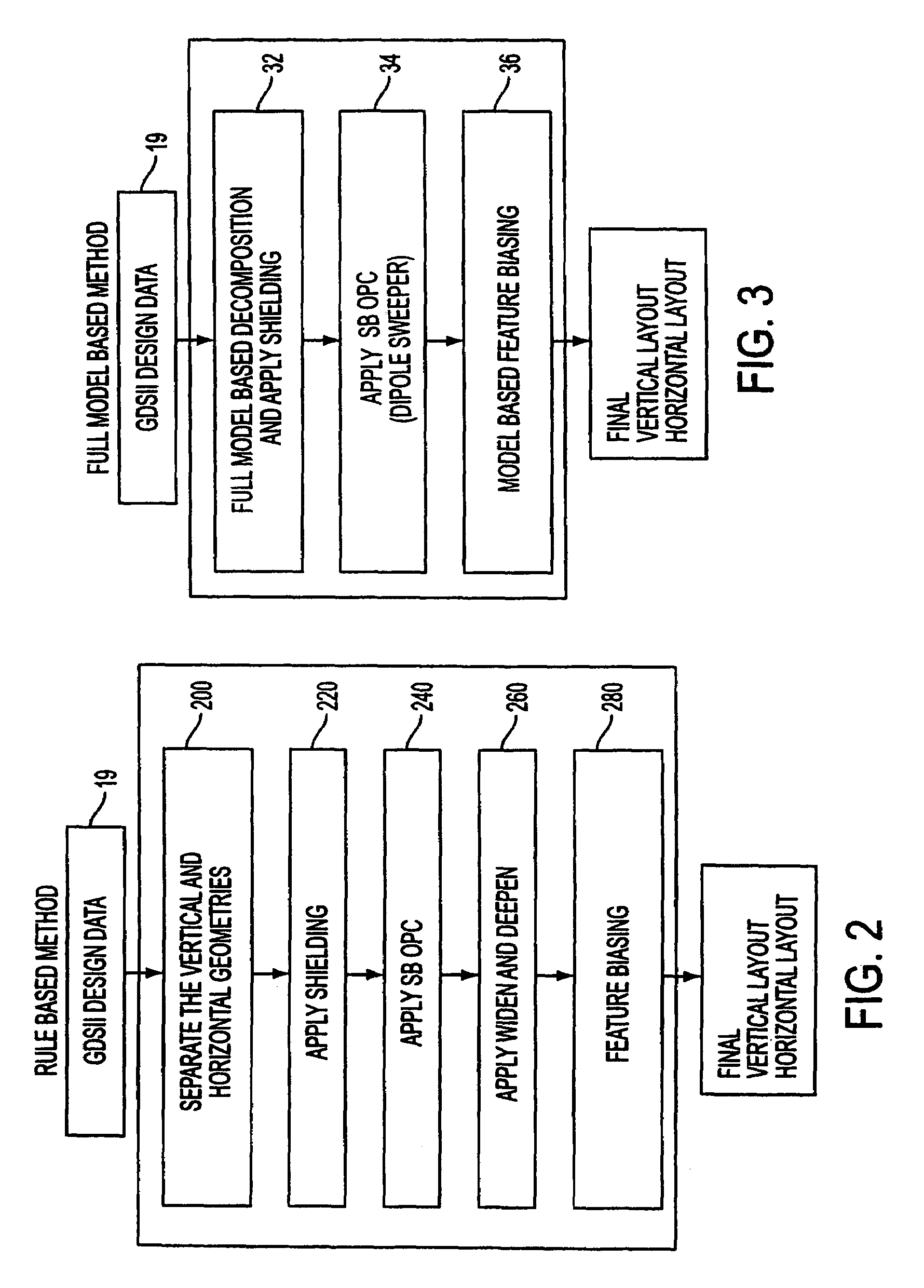
Method, program product and apparatus for performing double exposure lithography
InactiveUS20060277521A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistPhase shifted
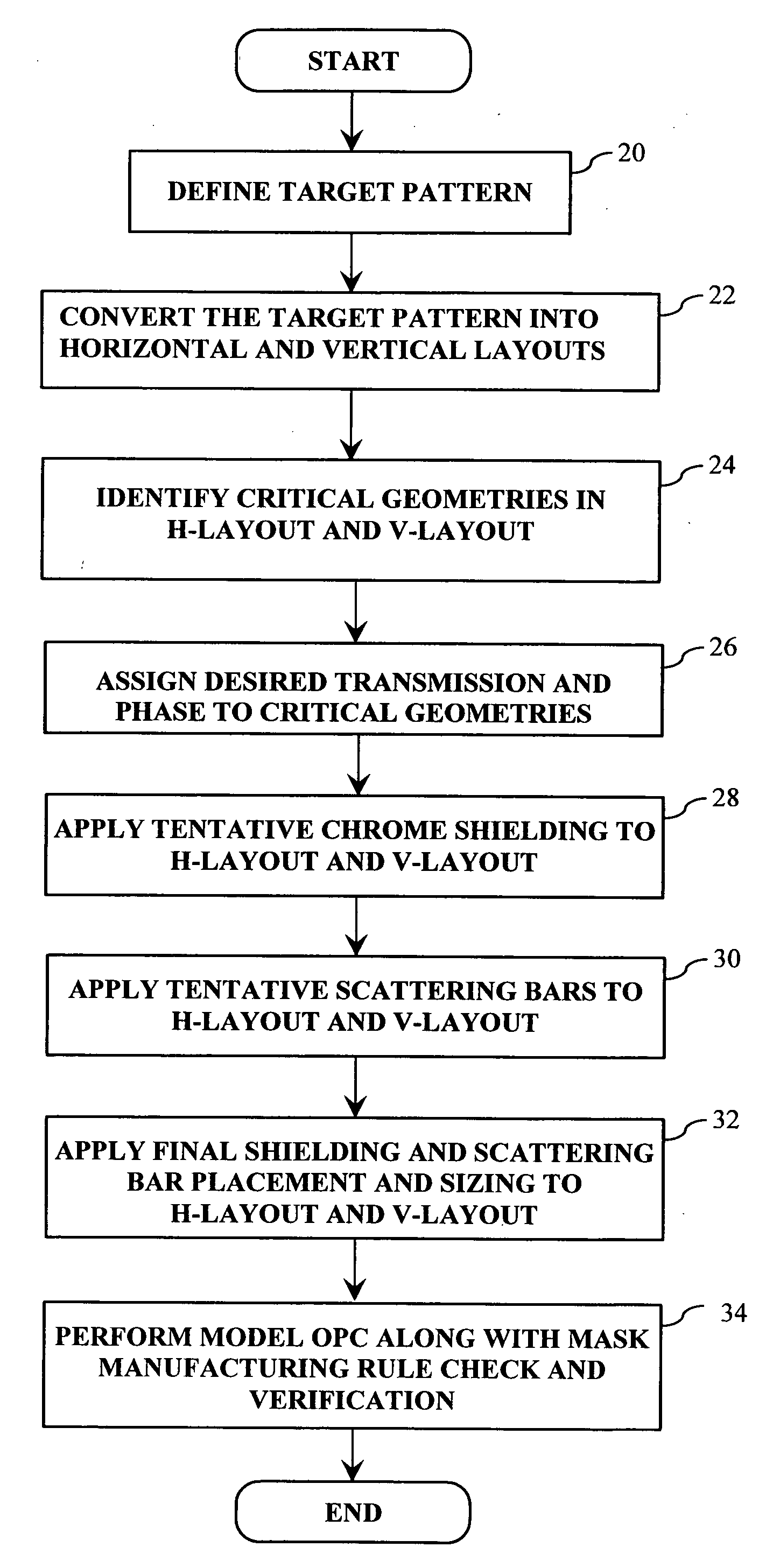
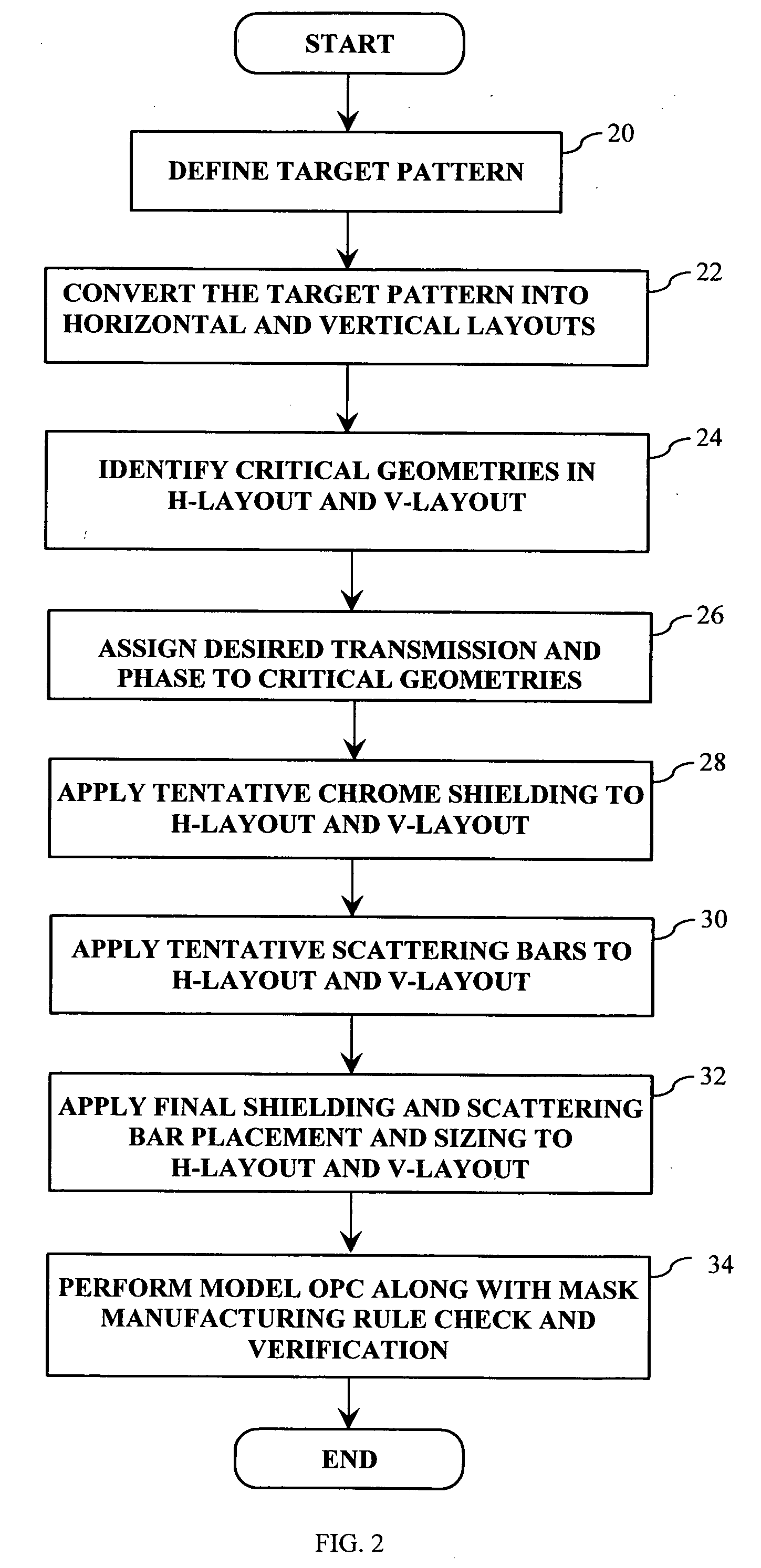
A method of generating complementary masks based on a target pattern having features to be imaged on a substrate for use in a multiple-exposure lithographic imaging process. The method includes the steps of: defining an initial H-mask corresponding to the target pattern; defining an initial V-mask corresponding to the target pattern; identifying horizontal critical features in the H-mask having a width which is less than a predetermined critical width; identifying vertical critical features in the V-mask having a width which is less than a predetermined critical width; assigning a first phase shift and a first percentage transmission to the horizontal critical features, which are to be formed in the H-mask; and assigning a second phase shift and a second percentage transmission to the vertical critical features, which are to be formed in the V-mask. The method further includes the step of assigning chrome to all non-critical features in the H-mask and the V-mask. The non-critical features are those features having a width which is greater than or equal to the predetermined critical width. The non-critical features are formed in the H-mask and the V-mask utilizing chrome. The target pattern is then imaged on the substrate by imaging both the H-mask and V-mask.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
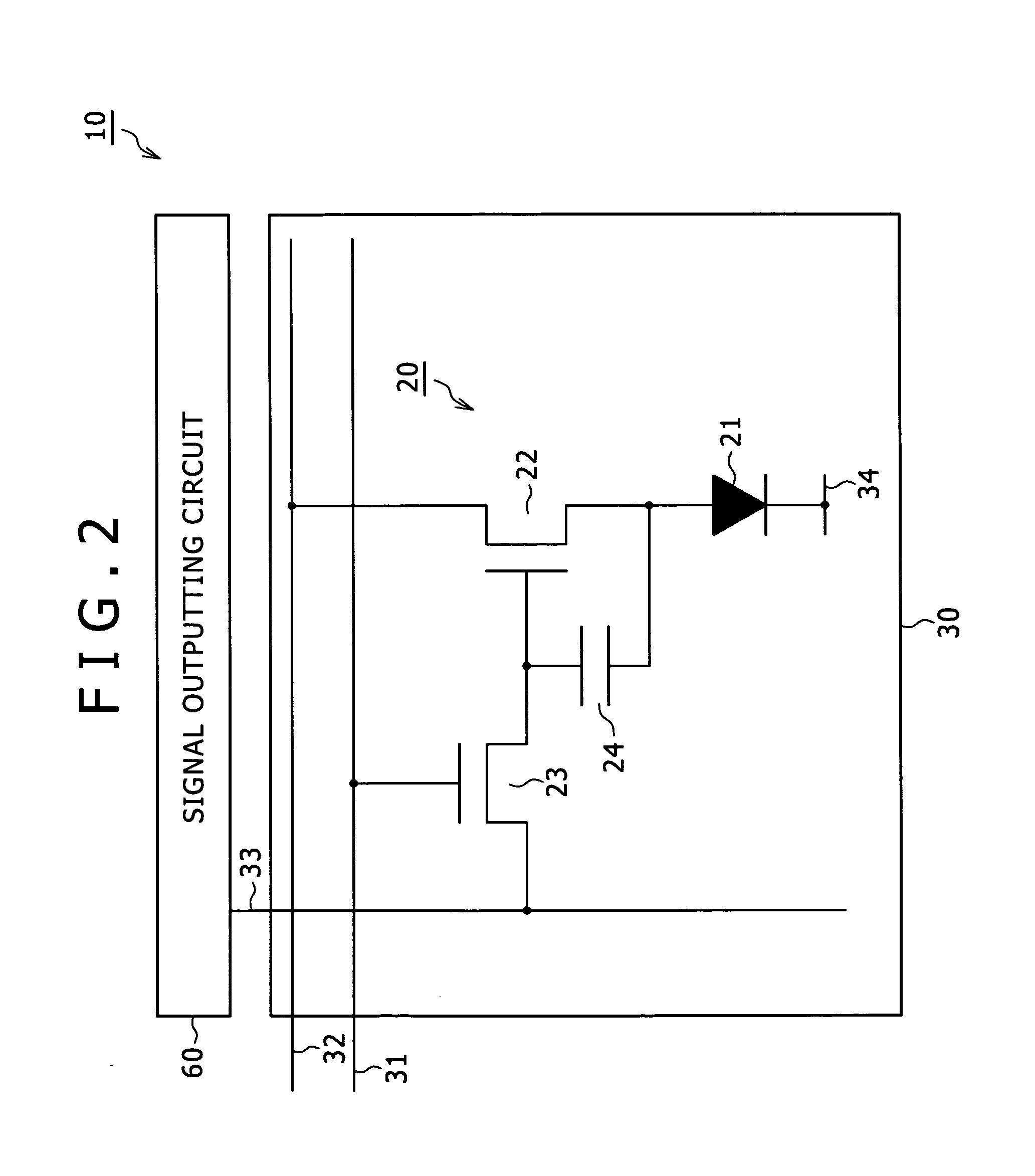
Liquid jet head and a liquid jet apparatus
ActiveUS20090284568A1Preventing piezoelectric elements from being brokenAvoid layeringPrintingLiquid jetPressure generation
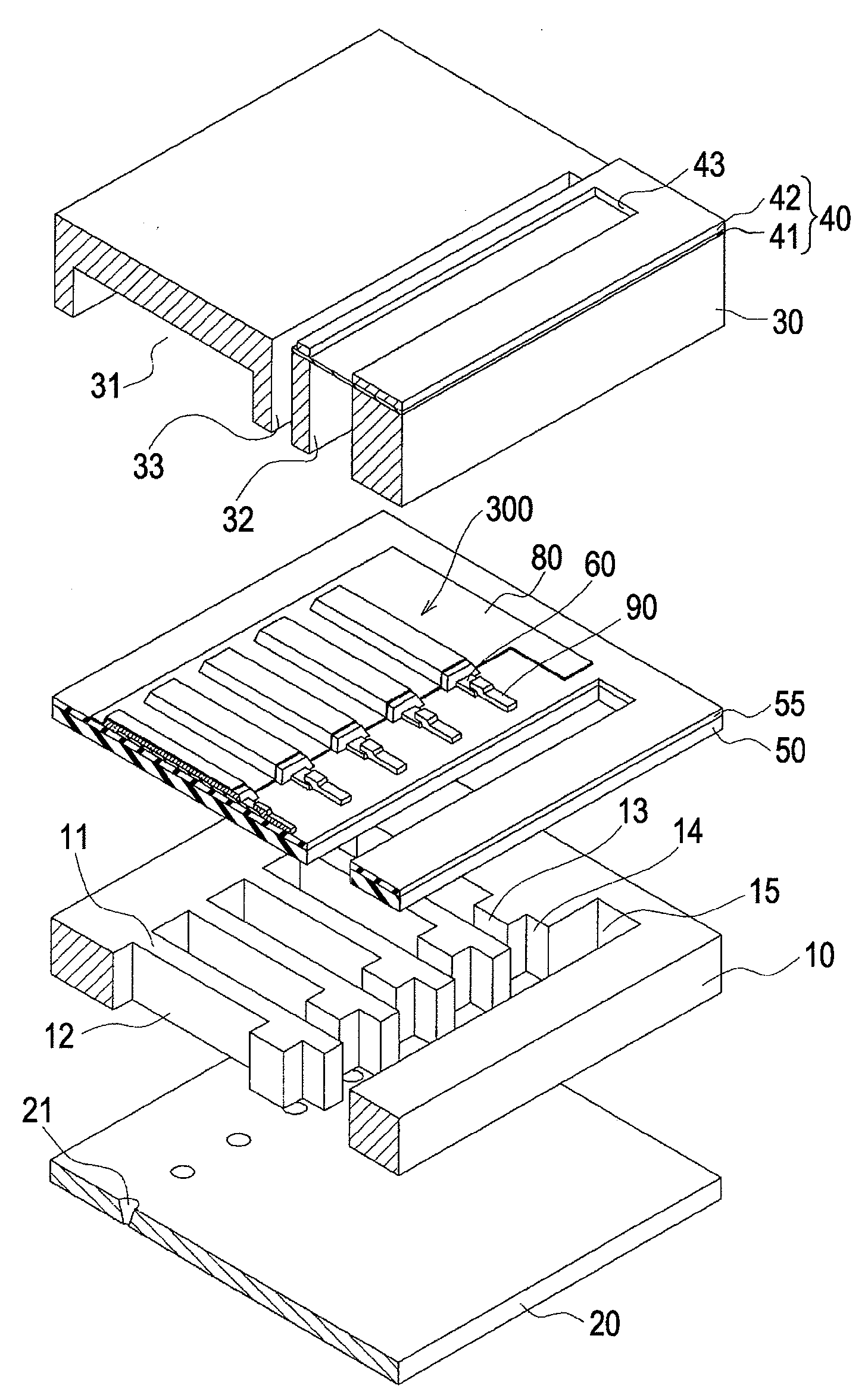
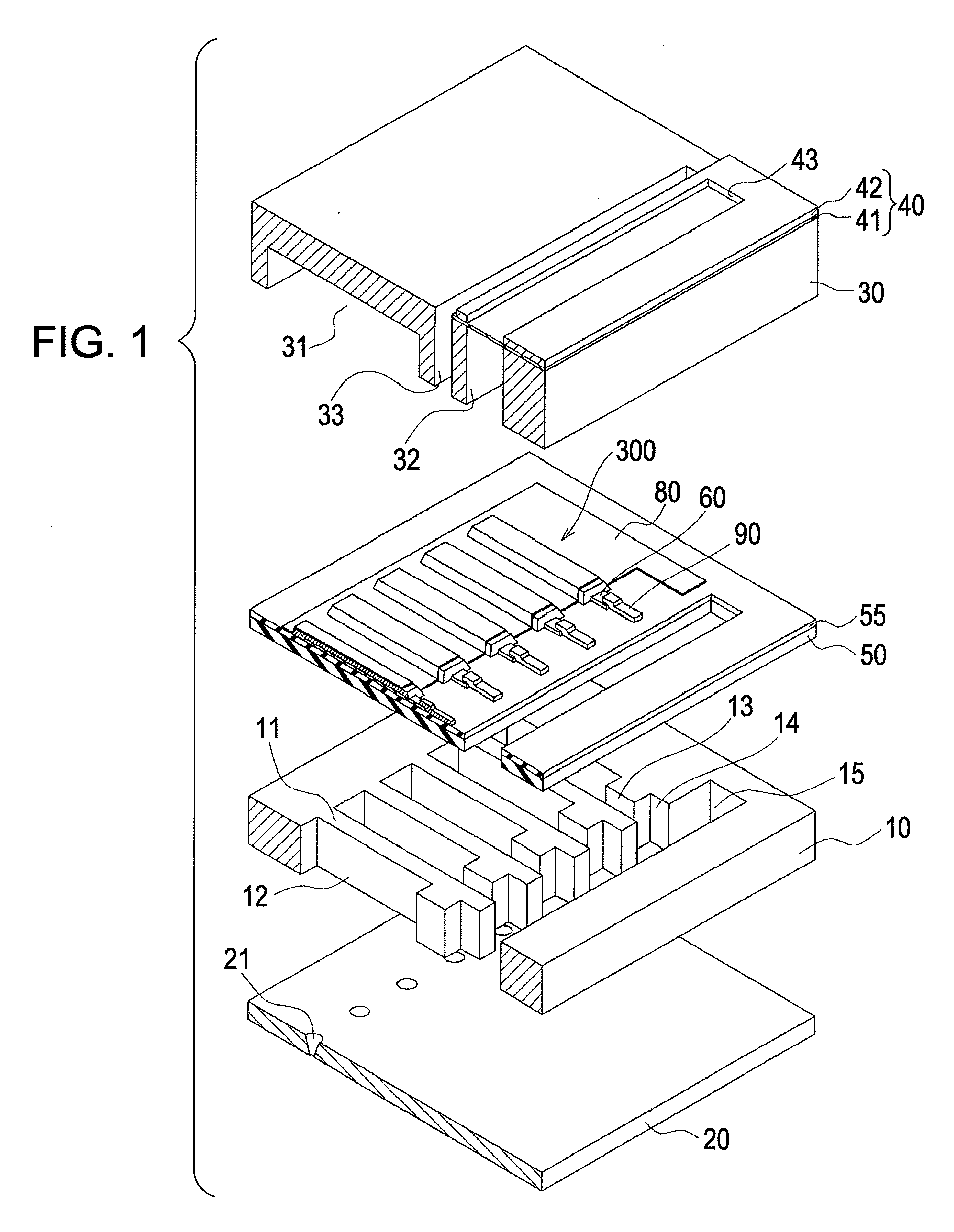
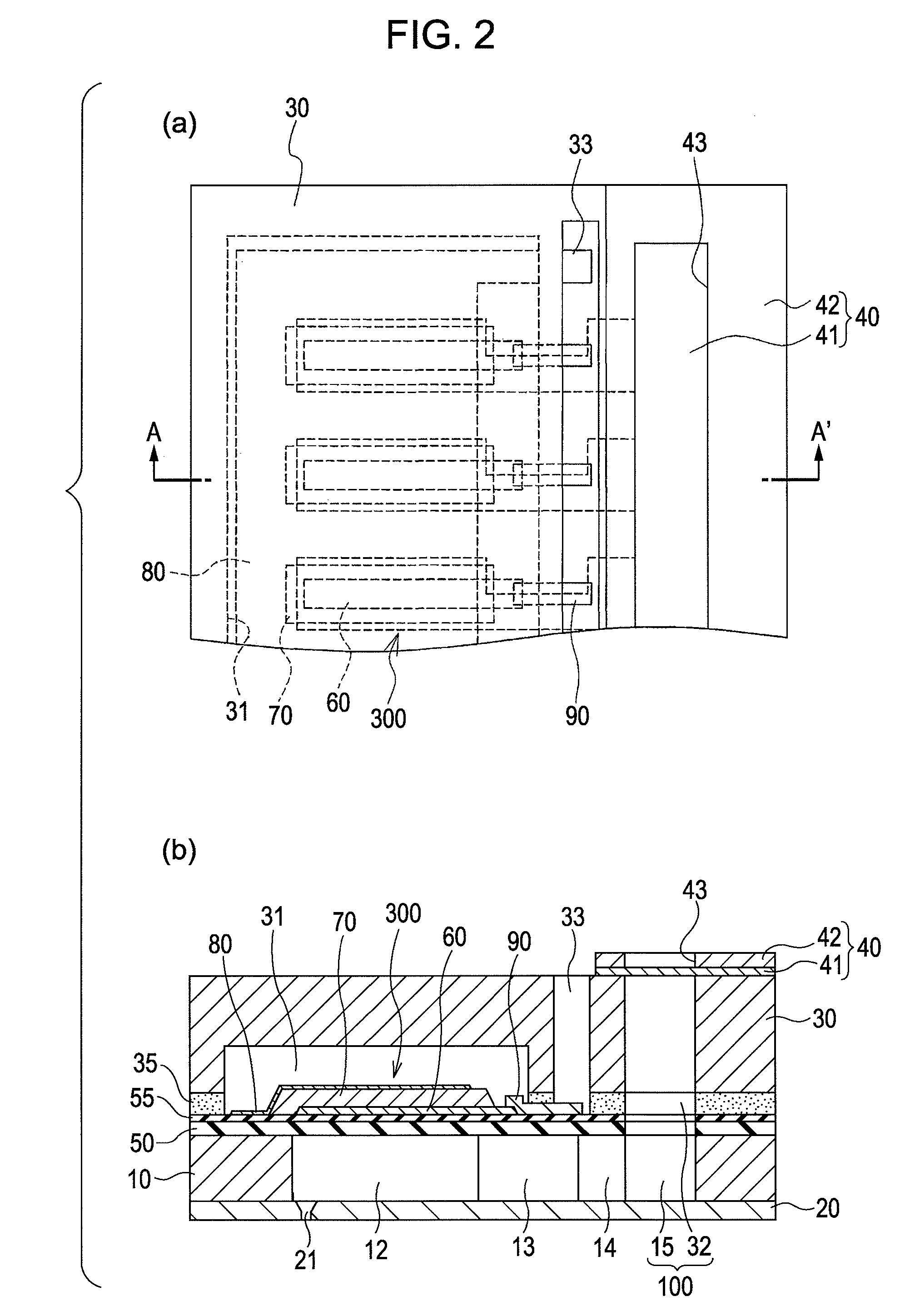
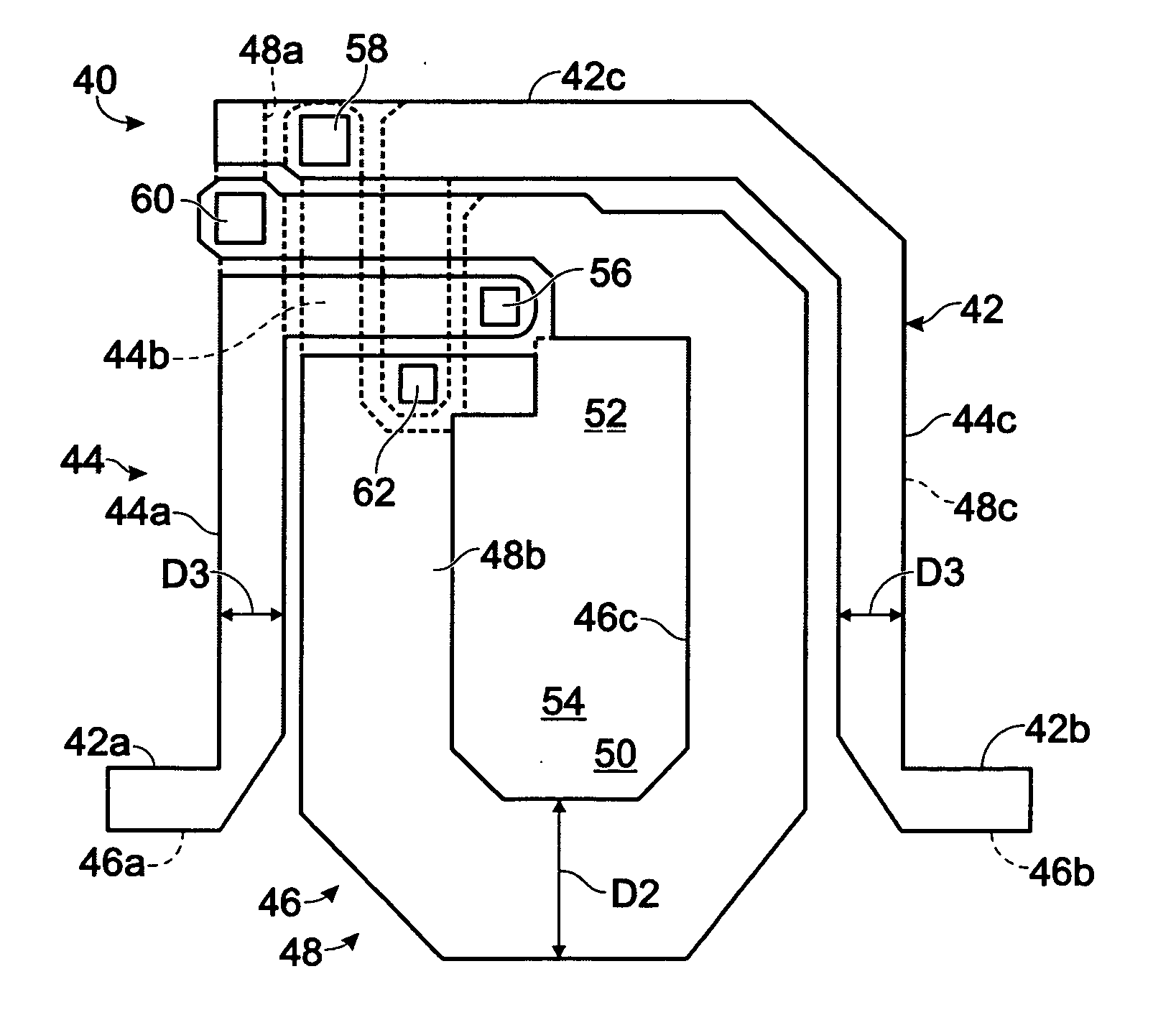
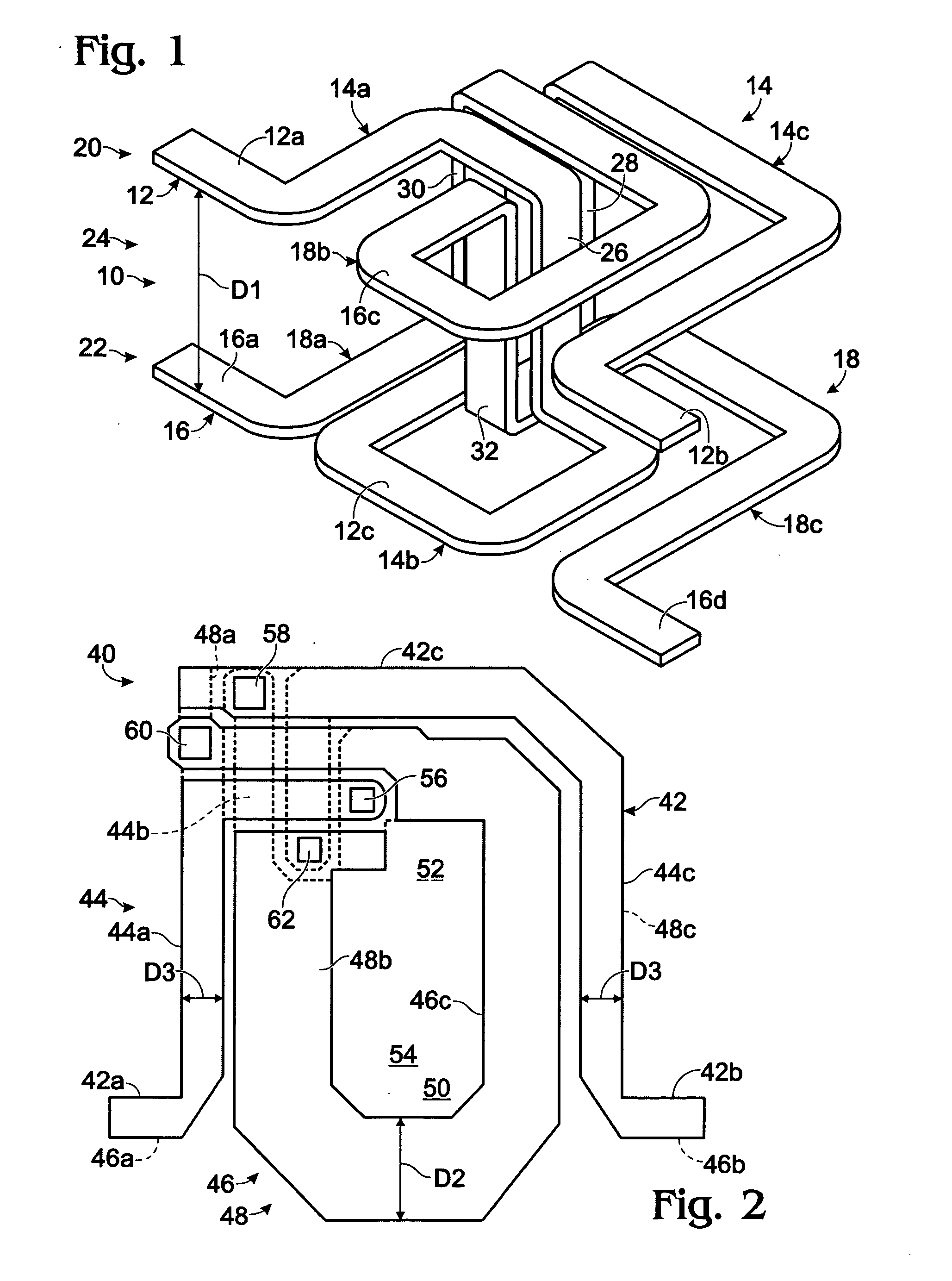
A lower electrode 60 in a region opposite each of pressure generation chambers 12 is formed to have a width smaller than the width of the corresponding pressure generation chamber 12, and an upper surface and an end surface of the lower electrode 60 in a region corresponding to each of the pressure generation chambers 12 is covered with a piezoelectric material layer 70. An end surface of the piezoelectric material layer 70 forms a slope surface sloping downward toward the outside, an upper surface and an end surface of the piezoelectric material layer 70 in the region opposite each of the pressure generation chambers 12 are covered with an upper electrode 80, and a distance D1 between the upper surface of the lower electrode 60 and the upper surface of the piezoelectric material layer 70 and a distance D2 between the end surface of the lower electrode and the end surface of the piezoelectric material layer 70 satisfy the relationship D2≧D1.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
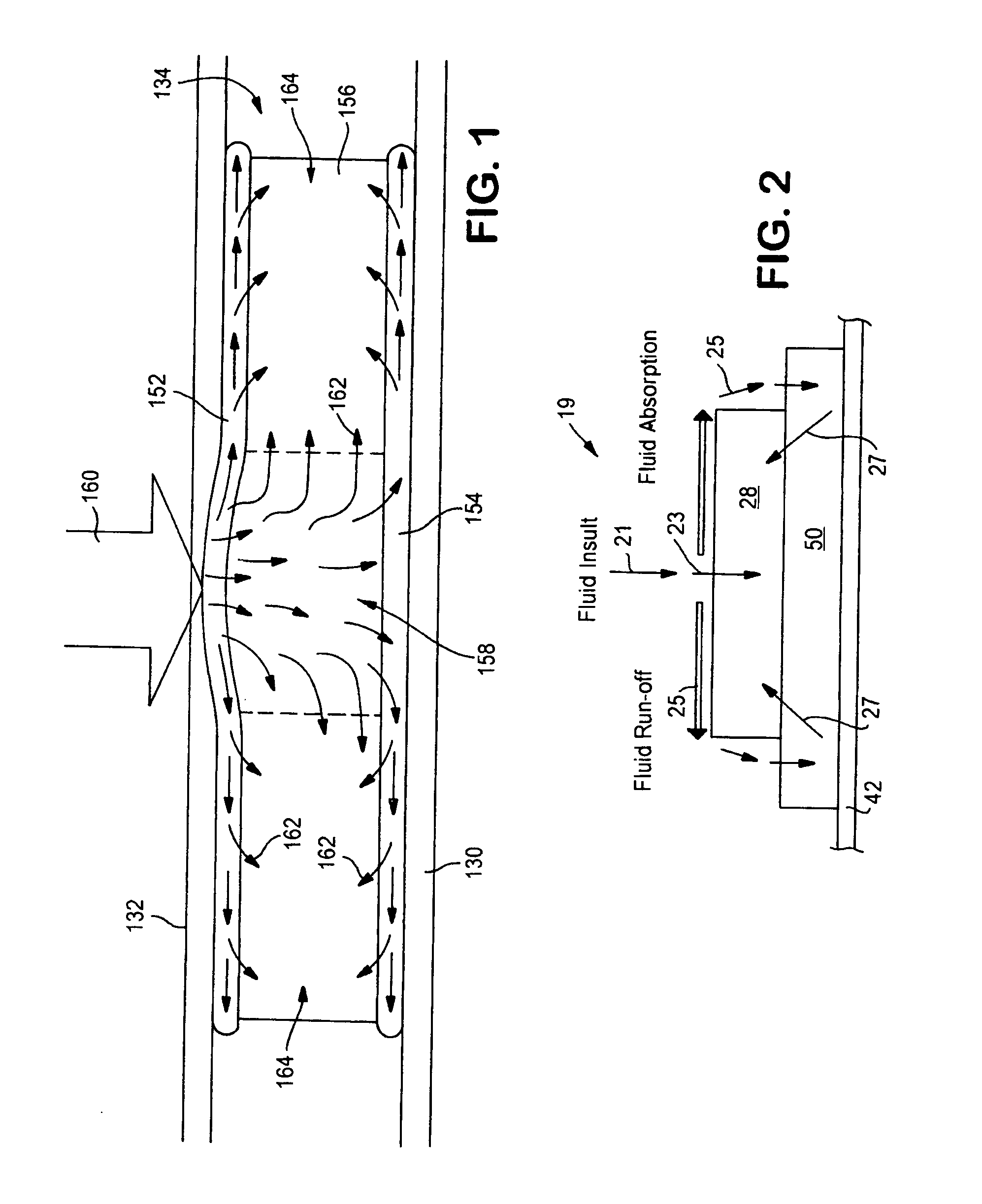
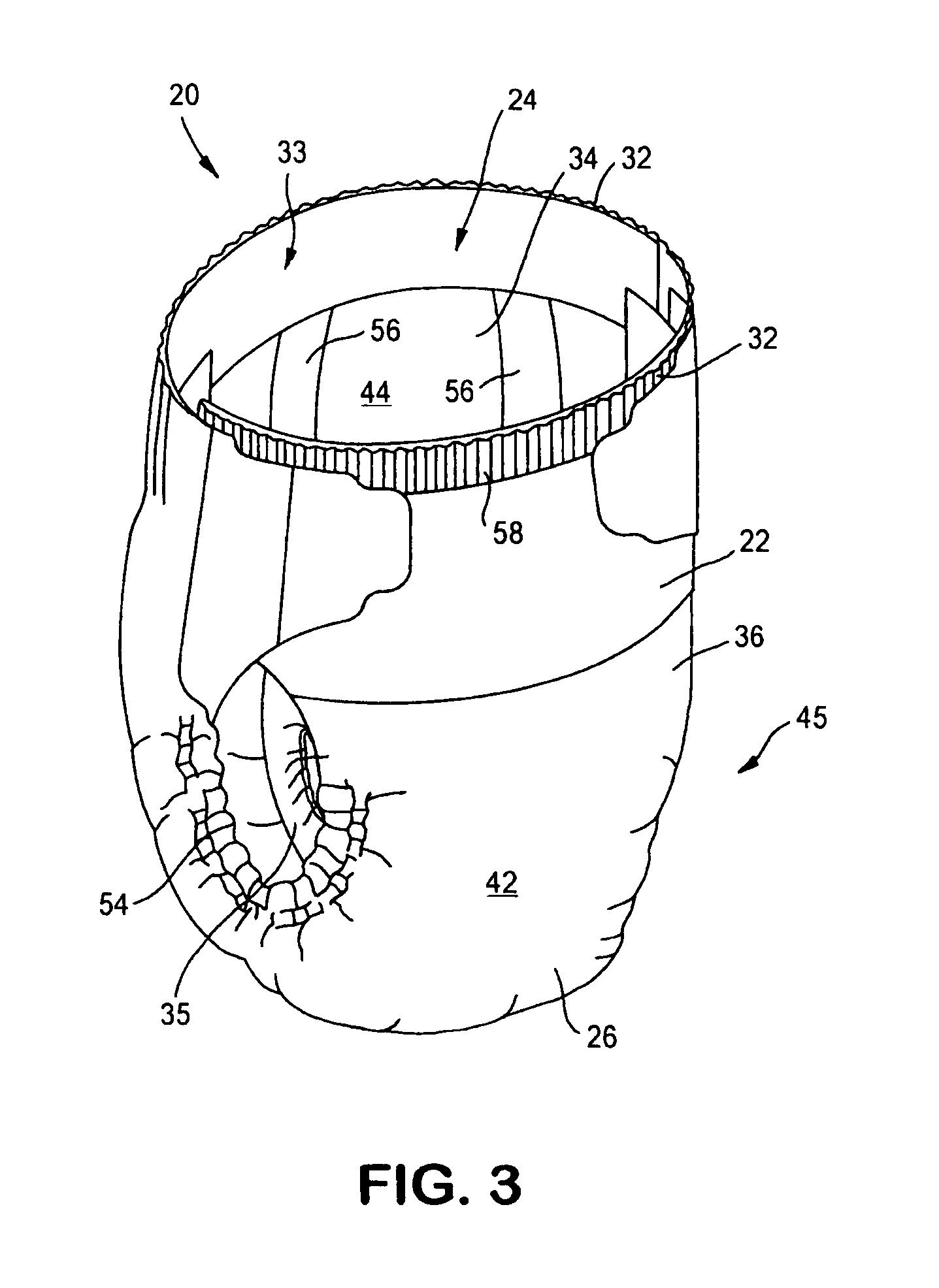
Absorbent article with improved fit and free liquid intake
InactiveUS20050027267A1Take advantage ofTake advantageBaby linensTamponsGobio gobio obtusirostrisCrotch
A disposable absorbent diaper has an outer cover, a bodyside liner, and an absorbent core positioned between the outer cover and the bodyside liner. A lofty, resilient, liquid permeable lofty spacer layer is positioned between the absorbent core and the outer cover and in liquid communication with the absorbent core. The absorbent core can be made from standard airformed materials which may have a combination of reduced surface area, narrow crotch width and a permeability level which may permit free liquid run off during insult to the garment. The lofty spacer layer has a high void volume and is also made of economical materials and desirably has a width in the crotch region greater than a width of the absorbent core in the crotch region to provide distribution of the free liquid run off underneath the absorbent core, allowing for reduction of the width of the absorbent core in the crotch region to provide an economical diaper with improved fit and leakage while reducing reliance on a gasketing system. The lofty resilient spacer layer will desorb into the absorbent core between insults thereby retaining its spacer layer function for use with breathable outer covers.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Spinal fixation element and methods
ActiveUS20090216328A1Help positioningInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnGobio gobio obtusirostris
A spinal fixation element is provided having a feature formed thereon that facilitates placement of the spinal fixation element through an access device, thus allowing the spinal fixation element to be positioned in relation to a spinal anchor that is coupled to the access device and that is implanted in a vertebra in a patient's spine. The feature also optionally facilitates placement of the spinal fixation element in relation to spinal anchors implanted in adjacent vertebrae. In particular, the spinal fixation element is adapted for use with an access device that has at least one slot or opening formed therein and having a width that is less than a width of the feature, thus preventing the feature from passing therethrough. The spinal fixation element can therefore be inserted through the access device, and a portion of the fixation element can be passed through the slot or opening in the access device while the feature is retained in the access device. As a result, the feature is seated within a spinal anchor that is coupled to the access device, and the remaining portion of the spinal fixation element can extend through the slot, preferably to be positioned within a spinal anchor disposed within an adjacent vertebra.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Solar cell
ActiveUS20120138141A1Reduce lossesFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringAuxiliary electrode
A solar cell includes a photoelectric conversion layer and a front electrode on the photoelectric conversion layer. The front electrode includes a bus bar electrode; at least one first finger electrode directly connected to the bus bar electrode; a plurality of connecting electrodes extending from the bus bar electrode and having a width smaller than a width of the bus bar electrode, wherein the plurality of connecting electrodes includes portions that are spaced apart from each other to form a space therebetween; at least one second finger electrode connected to at least one of the plurality of connecting electrodes; and an auxiliary electrode formed at the space between the portions of the plurality of connecting electrodes.
Owner:SHANGRAO JINKO SOLAR TECH DEV CO LTD
Grapho-epitaxy DSA process with dimension control of template pattern
InactiveUS8853085B1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistGobio gobio obtusirostris
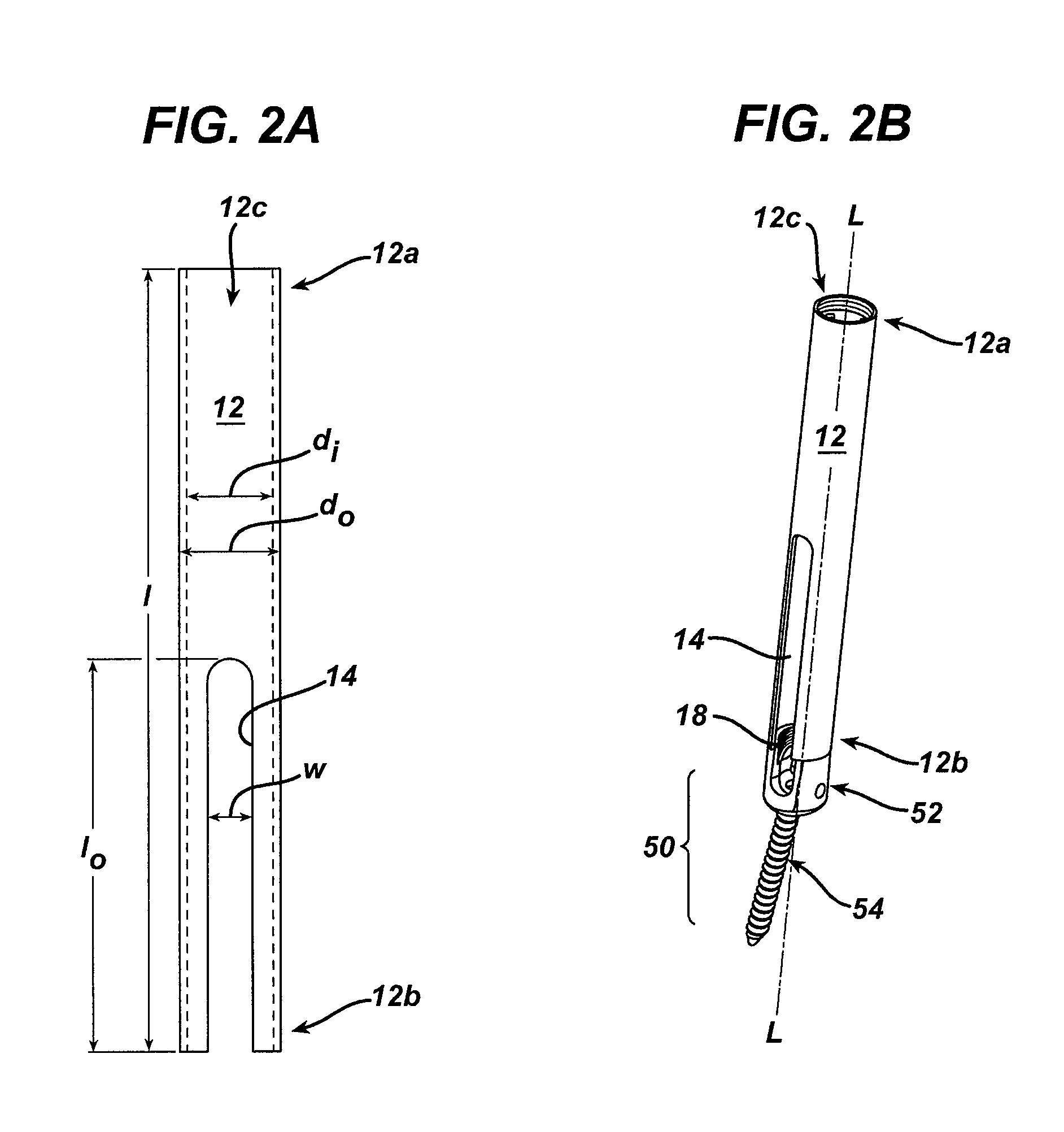
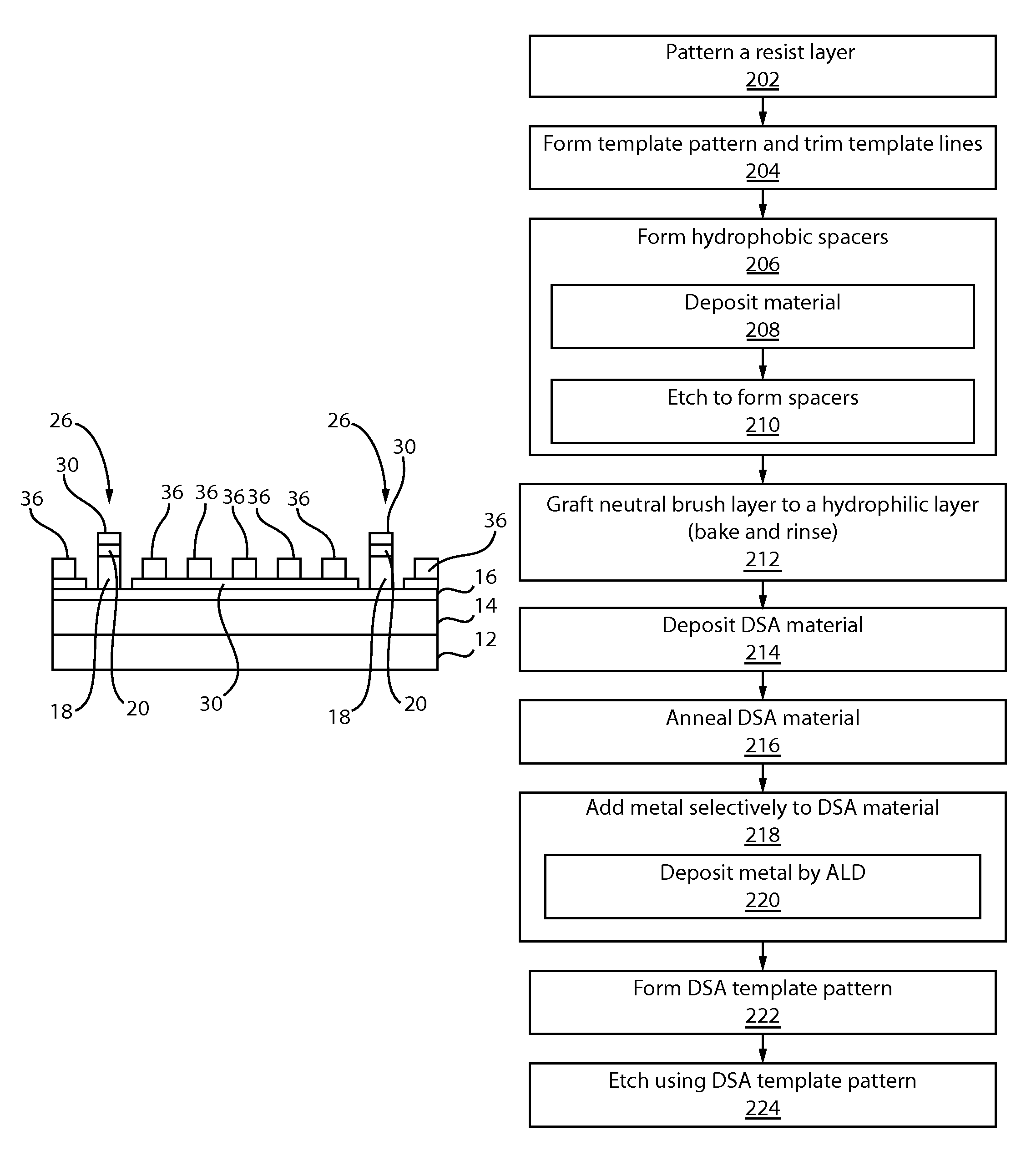
A method for defining a template for directed self-assembly (DSA) materials includes patterning a resist on a stack including an ARC and a mask formed over a hydrophilic layer. A pattern is formed by etching the ARC and the mask to form template lines which are trimmed to less than a minimum feature size (L). Hydrophobic spacers are formed on the template lines and include a fractional width of L. A neutral brush layer is grafted to the hydrophilic layer. A DSA material is deposited between the spacers and annealed to form material domains in a form of alternating lines of a first and a second material wherein the first material in contact with the spacers includes a width less than a width of the lines. A metal is added to the domains forming an etch resistant second material. The first material and the spacers are removed to form a DSA template pattern.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
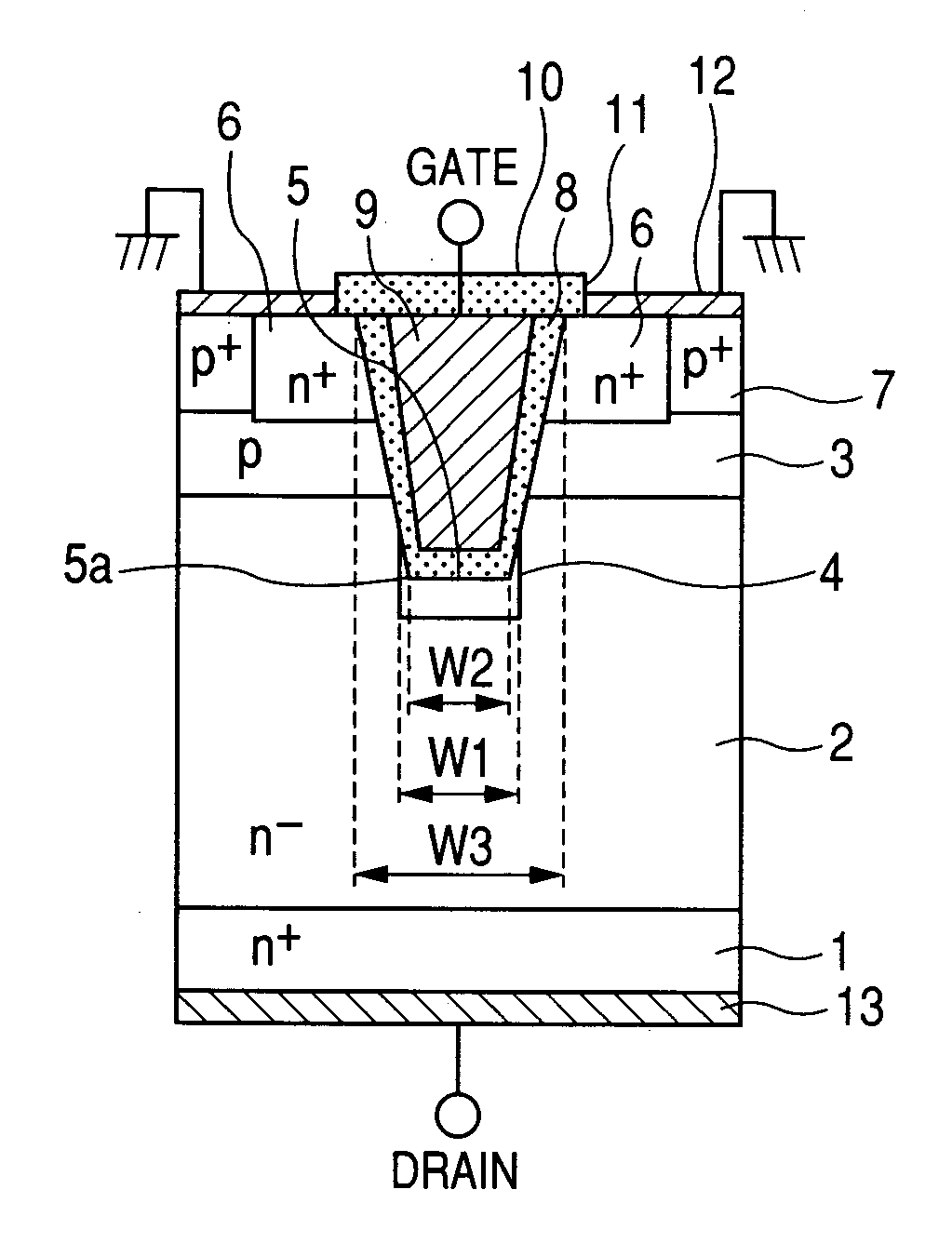
MOS transistor having a recessed gate electrode and fabrication method thereof
A metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistor having a recessed gate electrode and a fabrication method thereof are provided. The MOS transistor includes a semiconductor substrate and an isolation layer formed in a predetermined region of the semiconductor substrate to define an active region. A channel trench region is disposed within the active region to cross the active region. A gate insulating layer is disposed to cover sidewalls and a bottom of the channel trench region. The MOS transistor has a gate pattern that fills the channel trench region and crosses above the active region. A portion of the sidewall of the gate pattern is recessed at an upper corner of the channel trench region and has a width smaller than the width of the top of the gate pattern and smaller than the width of the channel trench region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flexible clamp
InactiveUS20080250614A1Small separationFixed securitySnap fastenersPhotovoltaic supportsGobio gobio obtusirostrisEngineering
A flexible clamp for clamping and spacing solar panel modules, including a captive flange forming a top portion, which includes a top face, a bottom face, a right side, a left side, a front side, a back side, a substantially planar underside to engage the modules upper surface. It also includes a longitudinal axis and an aperture disposed generally along that axis. First, second, and third horizontal members are disposed under the captive flange and include substantially planar surfaces generally parallel to the underside of the captive flange. Each horizontal member includes a right side, a left side, a front side, a back side, a width slightly less than the width of the captive flange, and an aperture coaxial with the aperture in the captive flange. A first vertical member connects the right side of the first horizontal member with the captive flange at a point slight right of the longitudinal axis and left of the right side, thus forming a right overhang for engaging a first solar panel. A second vertical member connects the left sides of the second and third horizontal members in such manner that a left overhang is formed, and this is adapted for engaging a second solar panel adjacent to the first panel. A third vertical member coplanar with the first vertical member connects the right sides of the second and third horizontal members. When a bolt is passed through the coaxial apertures and tightened, the clamp flexes and bows slightly outwardly.
Owner:ZANTE ANTHONY A
Apparatus for treating atherosclerosis
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Semiconductor device for preventing defective filling of interconnection and cracking of insulating film
InactiveUS7301241B2Prevent defective fillingDefective filling is preventedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInter layerElectrical conductor
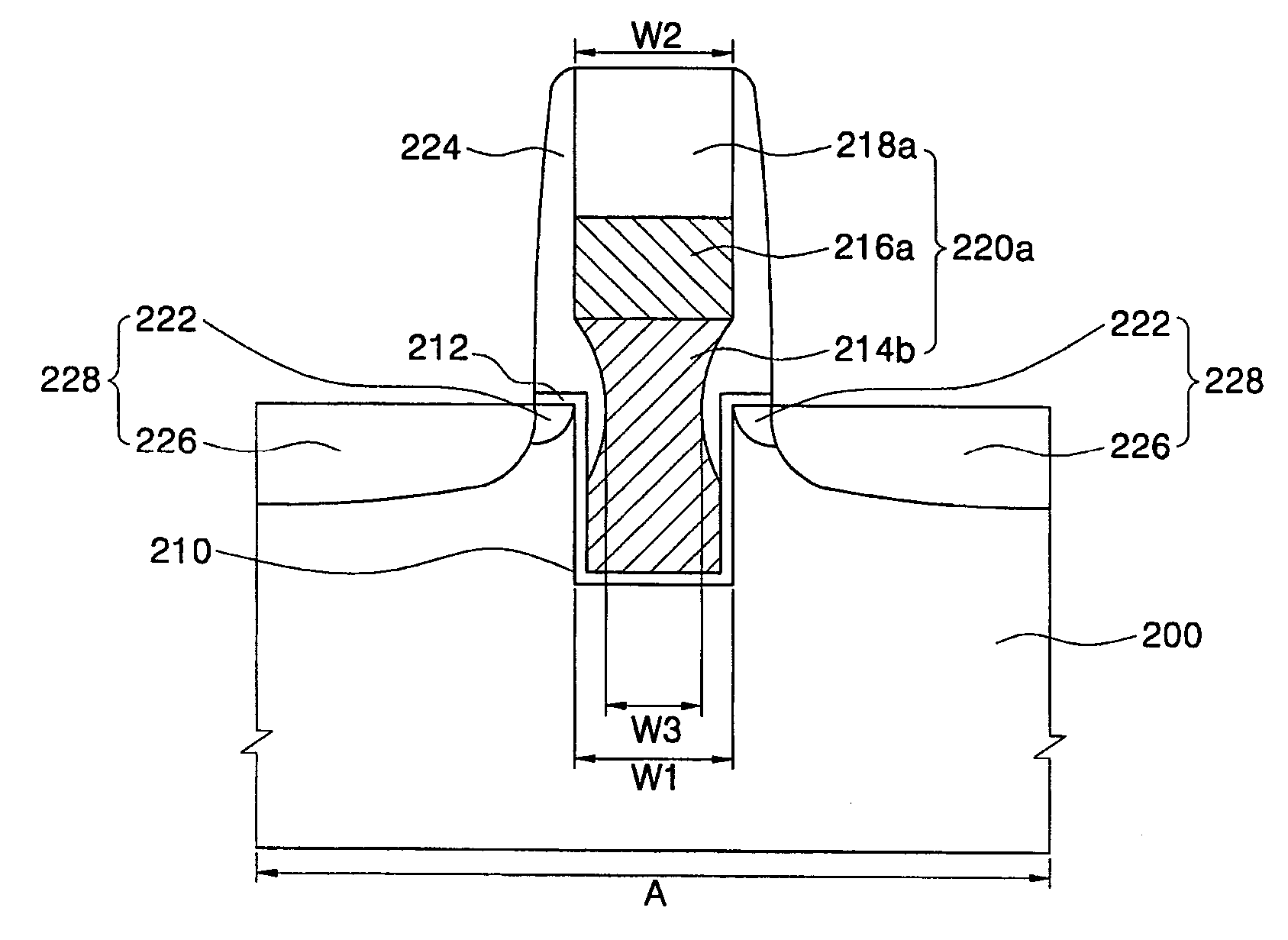
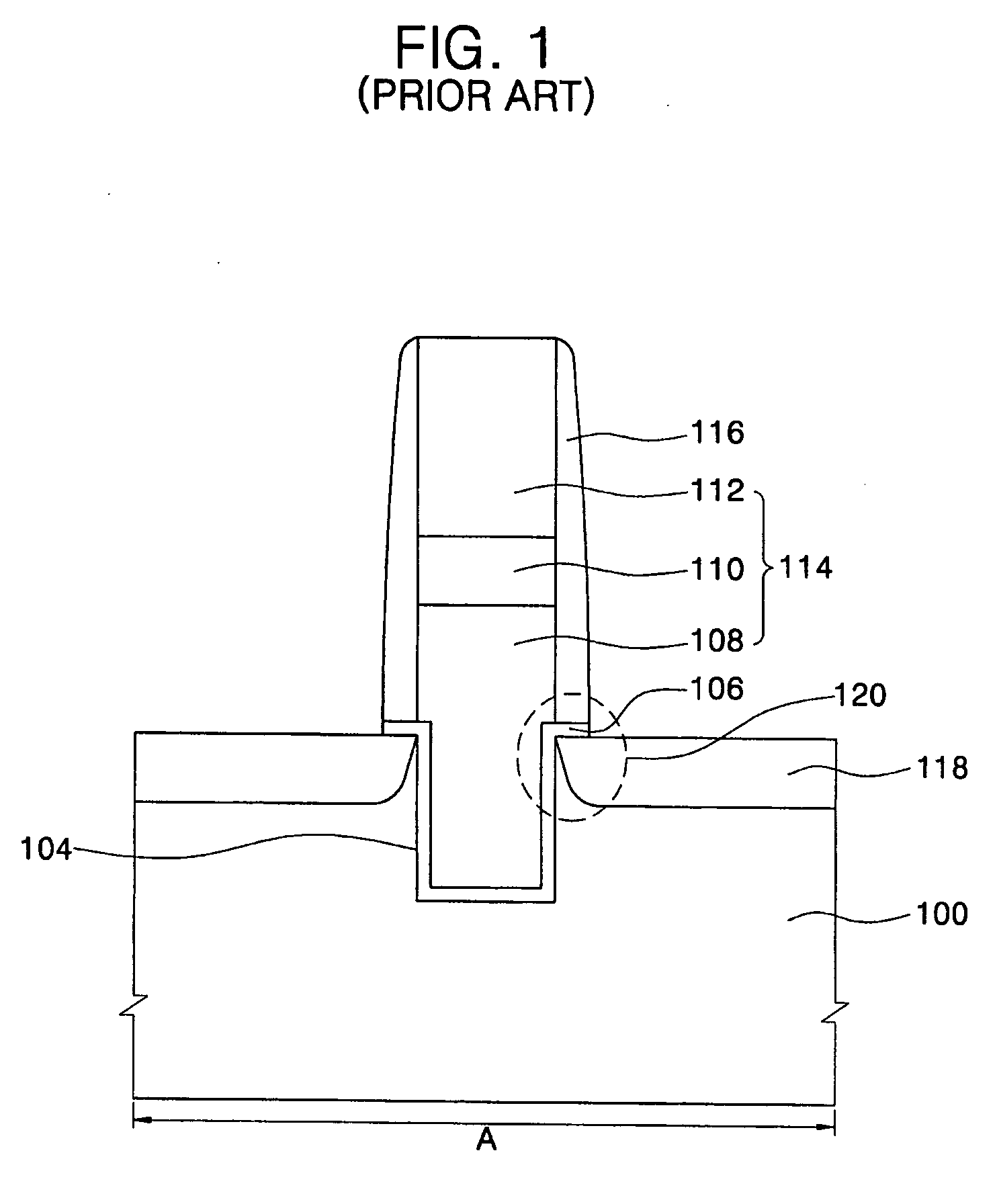
The semiconductor device has insulating films 40, 42 formed over a substrate 10; an interconnection 58 buried in at least a surface side of the insulating films 40, 42; insulating films 60, 62 formed on the insulating film 42 and including a hole-shaped via-hole 60 and a groove-shaped via-hole 66a having a pattern bent at a right angle; and buried conductors 70, 72a buried in the hole-shaped via-hole 60 and the groove-shaped via-hole 66a . A groove-shaped via-hole 66a is formed to have a width which is smaller than a width of the hole-shaped via-hole 66. Defective filling of the buried conductor and the cracking of the inter-layer insulating film can be prevented. Steps on the conductor plug can be reduced. Accordingly, defective contact with the upper interconnection layer and the problems taking place in forming films can be prevented.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
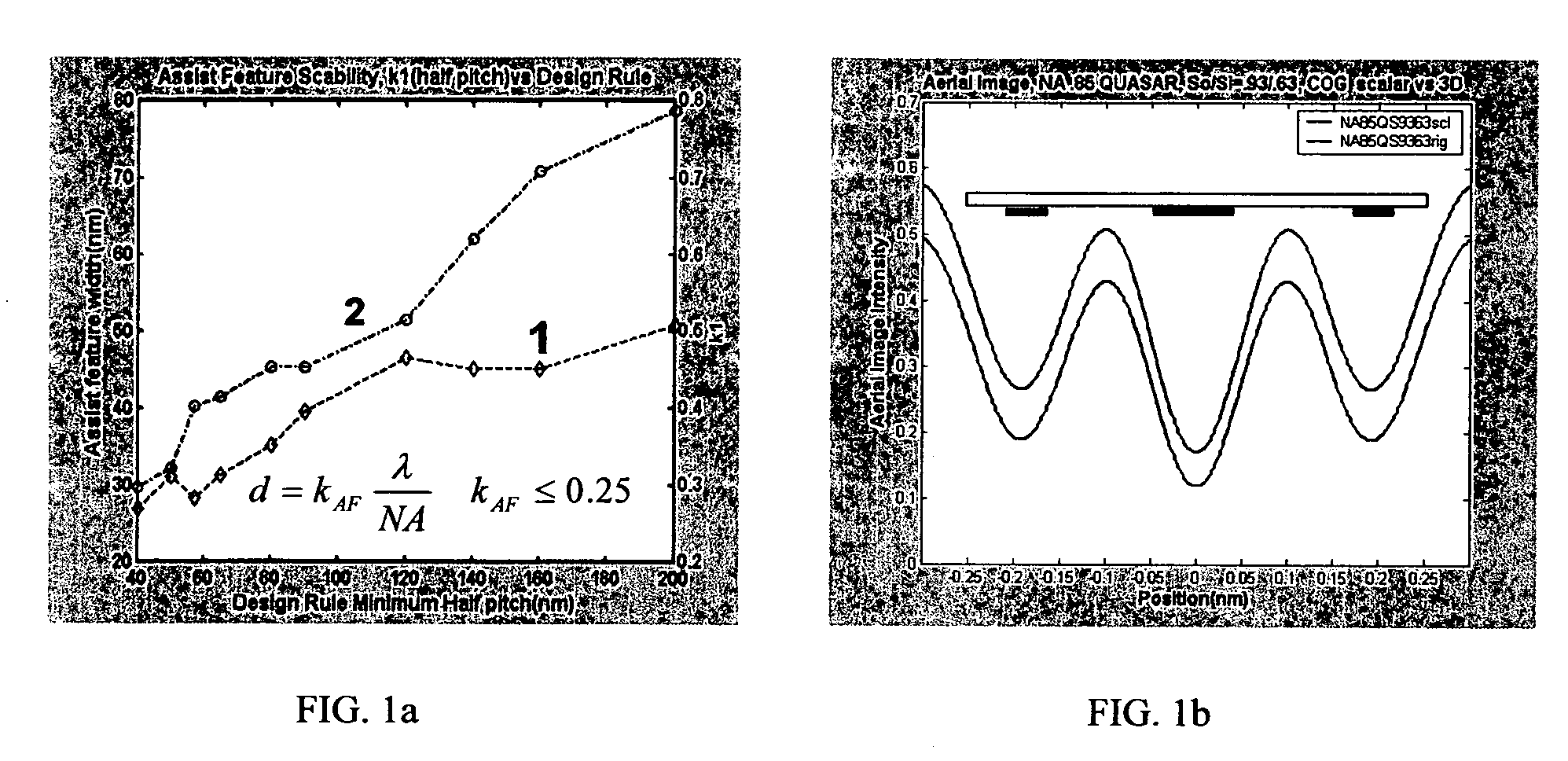
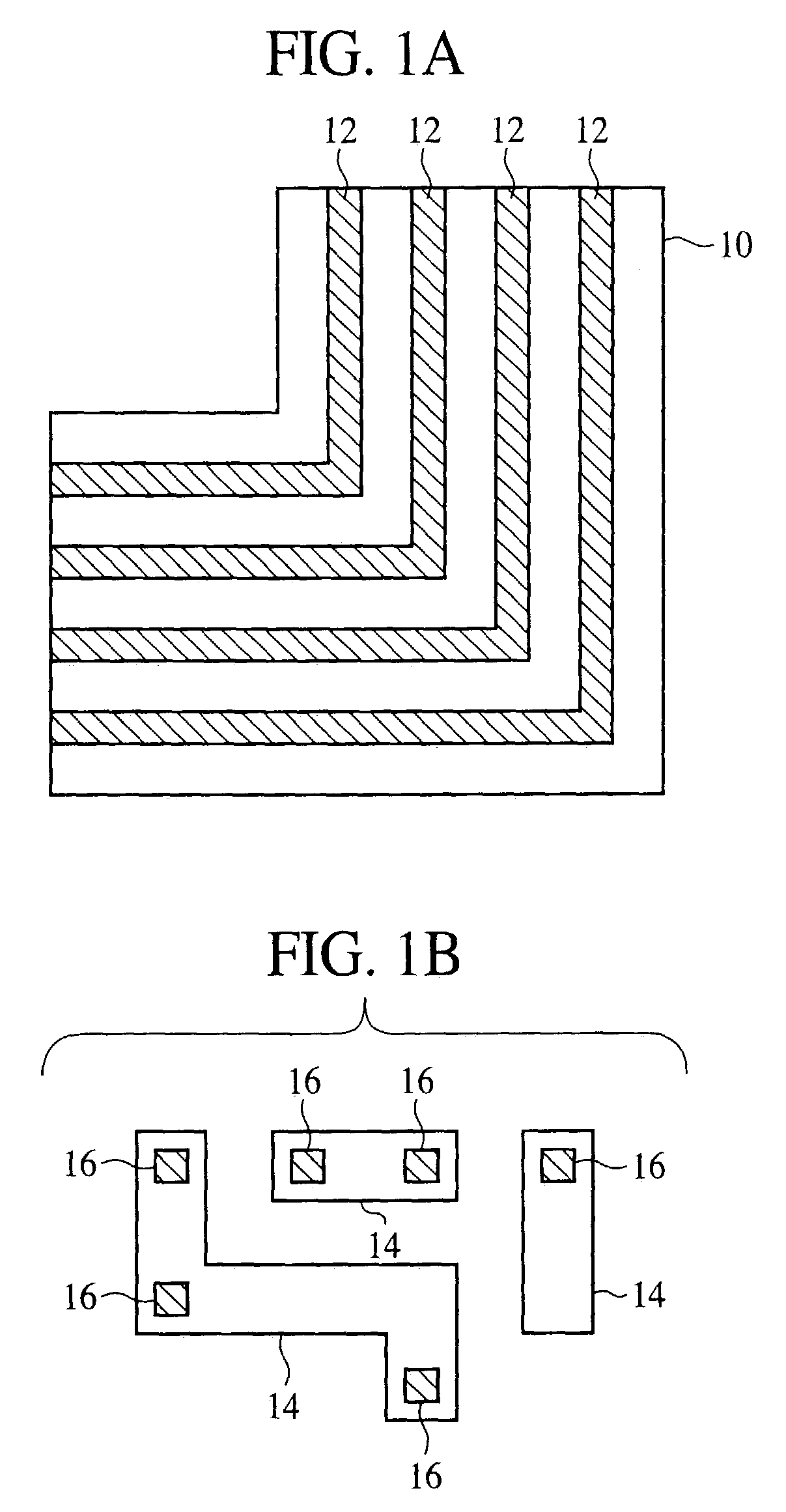
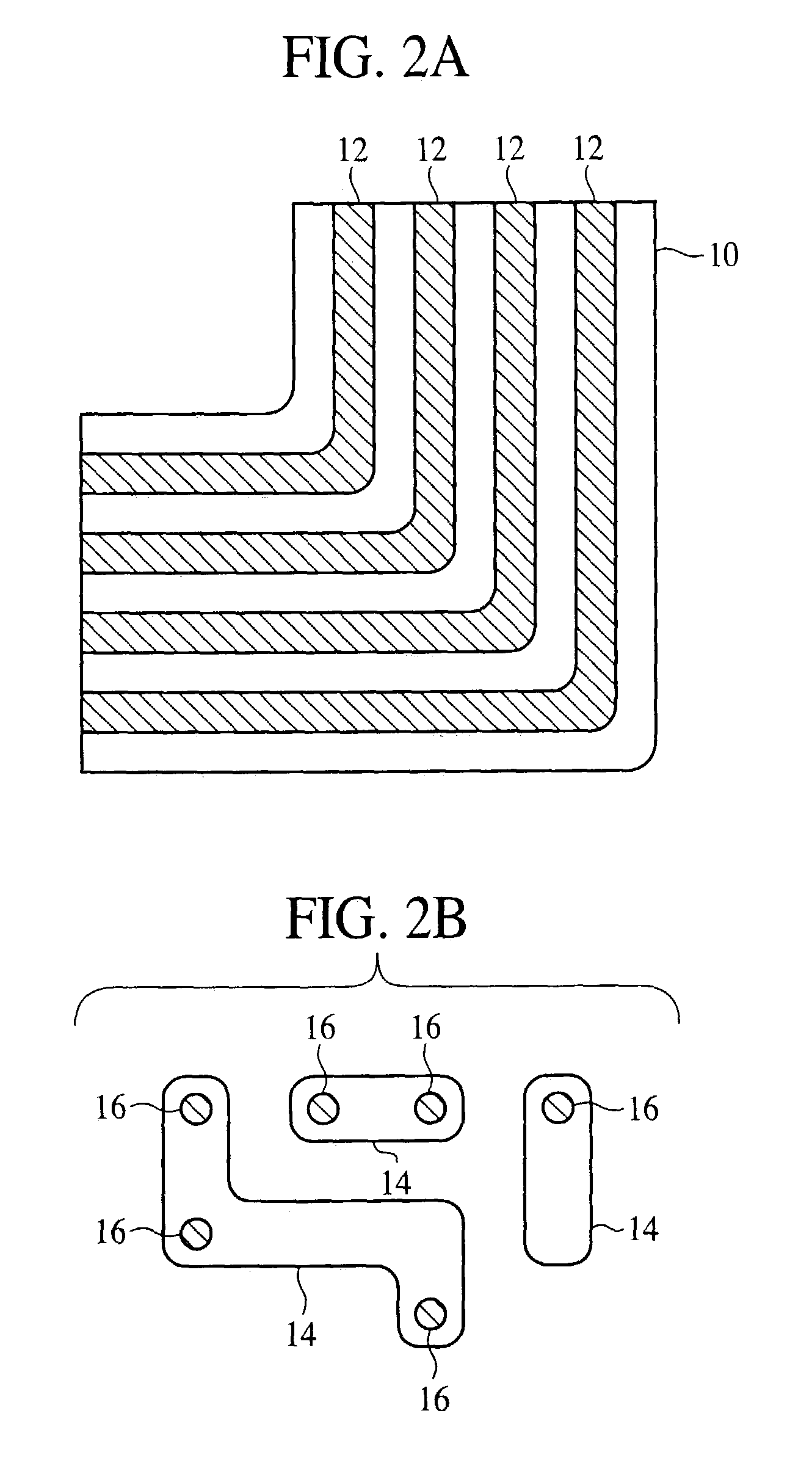
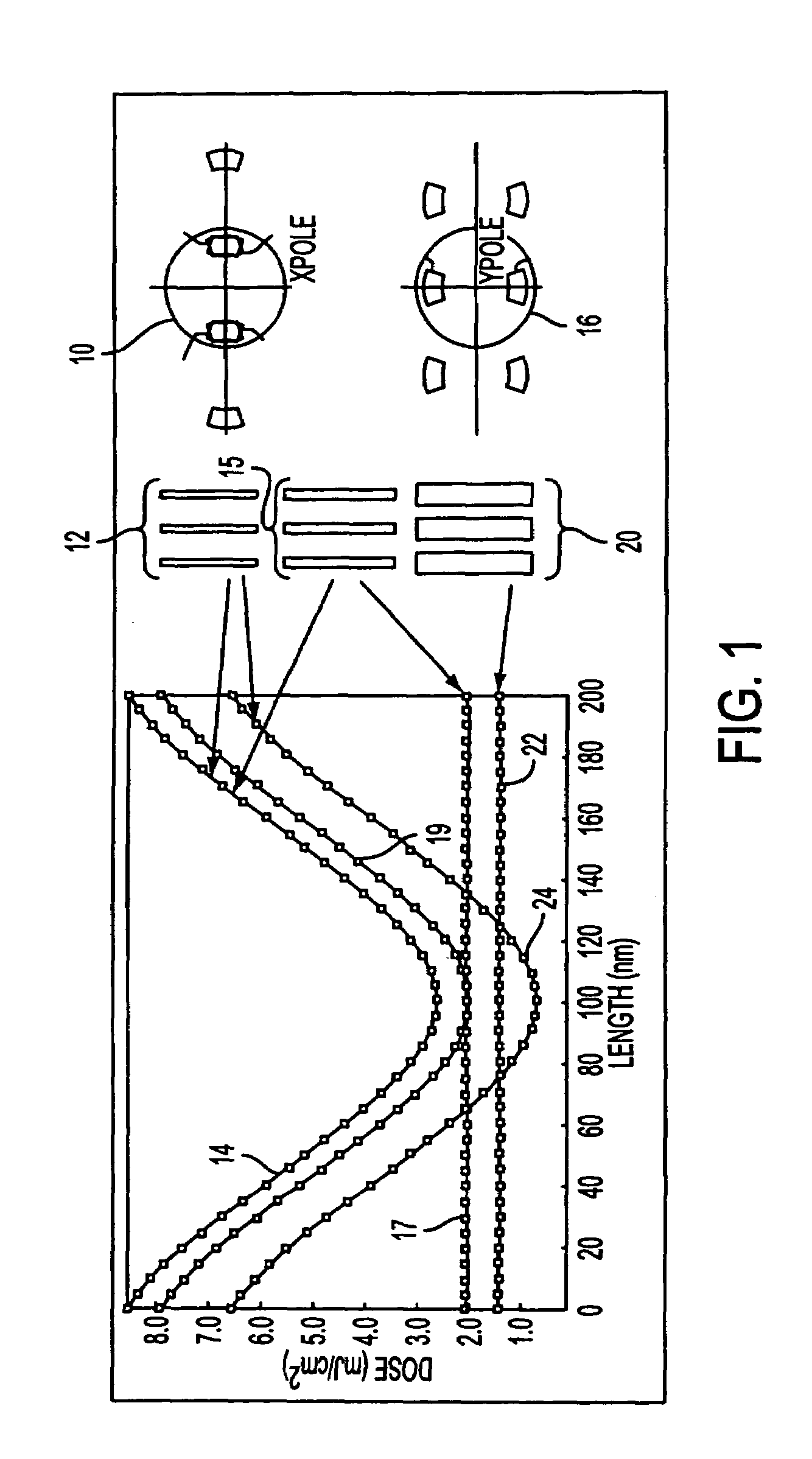
Method and apparatus for performing model-based layout conversion for use with dipole illumination
InactiveUS7138212B2Simple processExact reproductionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusVertical edgeGobio gobio obtusirostris
A method of generating complementary masks for use in a multiple-exposure lithographic imaging process. The method includes the steps of: identifying a target pattern having a plurality of features comprising horizontal and vertical edges; generating a horizontal mask based on the target pattern; generating a vertical mask based on the target pattern; performing a shielding step in which at least one of the vertical edges of the plurality of features in the target pattern is replaced by a shield in the horizontal mask, and in which at least one of the horizontal edges of the plurality of features in the target pattern is replaced by a shield in the vertical mask, where the shields have a width which is greater that the width of the corresponding feature in the target pattern; performing an assist feature placement step in which sub-resolution assist features are disposed parallel to at least one of the horizontal edges of the plurality of features in the horizontal mask, and are disposed parallel to at least one of the vertical edges of the plurality of features in the vertical mask, and performing a feature biasing step in which at least one of the horizontal edges of the plurality of features in the horizontal mask are adjusted such that the resulting feature accurately reproduces the target pattern, and at least one of the vertical edges of the plurality of features in the vertical mask are adjusted such that the resulting feature accurately reproduces the target pattern.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Extensible and stretch laminates with comparably low cross-machine direction tension and methods of making same
InactiveUS20060148354A1Reduce cross-machine direction tension valueReduce tensionPersonal careSynthetic resin layered productsAdhesiveGobio gobio obtusirostris
A method of producing a laminate material includes the steps of providing a first flexible sheet material; providing a second flexible sheet material having a first surface and a second surface, and also having a first width of 1X; stretching the second flexible sheet material in a cross-machine direction to a second width of between about 1.2X and 3 X when in a flattened state; necking the second flexible sheet material to produce an accordion shape, thereby reducing the second width of the sheet material to a third width, less than the width of the first width, such that the third width is between 0.65 X to 0.975 X when in an accordion shape; applying adhesive to the first surface of the second flexible sheet material with a slot coat adhesive process; and joining the first flexible sheet material to the first surface of the second flexible sheet material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Processor architecture for executing transfers between wide operand memories
InactiveUS20090089540A1Improve performanceEnhancing processor flexibilityInstruction analysisProgram control using wired connectionsMemory addressGeneral purpose
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
Display substrate, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20040108977A1Improve the display effectExcellent luminescent gray scale characteristicStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentGobio gobio obtusirostris
To provide an electro-optical device and an electronic apparatus capable of maintaining the display quality by preventing brightness unevenness without widening a frame. In a mounting terminal portion 102 connection portions (not shown) connecting to a fourth power source bus line 20 are provided in twoplaces. Driving current is supplied from the connection portions to the fourth power source bus line 20. The width of the fourth power source bus line is smaller than that of the width of a power source bus line supplying driving current from one place of the mounting terminal portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Image forming device having paper dust removing units
InactiveUS20030049043A1Efficient removalHigh quality imagingBrushesWork treatment devicesPaper dustImage formation
An image forming device capable of sufficiently removing paper dusts on a sheet thereby providing high quality image. A sheet transport path 38 is defined between a sheet supply section 7 provided with a separation pad 13 and a sheet supply roller 12 and an image forming section 5. Along the sheet supply section 7, at least a first paper dust removing roller 9b having a width slightly greater than the width of the separation pad 13 and a second paper dust removing roller 10b having a width slightly greater than the sheet width are disposed. Paper dusts generated upon friction against the separation pad 13 are removed by the first paper dust removing roller 9b, and paper dusts spreading over entire surface of the sheet are removed by the second paper dust removing roller 10b.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Bi-level coupler
ActiveUS20050122185A1Multiple-port networksSnap-action arrangementsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
A coupler is disclosed that includes first and second mutually coupled spirals disposed On opposite sides of a dielectric substrate. The substrate may be formed of one or more layers and the coils may have a number of turns appropriate for a given application. Conductors forming the spirals may be opposite each other on the substrate and each spiral may include one or more portions on each side of the substrate. Each conductor of the coupler may include an intermediate portion having a width that is more than the width of end portions. An extension may extend from each respective intermediate portion, with the two extensions extending in non-overlapping relationship.
Owner:WERLATONE INC
Machine for measuring outline dimension of vehicle
InactiveCN101685005AHigh measurement accuracyStrengthen supervisionUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUsing optical meansVehicle frameGobio gobio obtusirostris
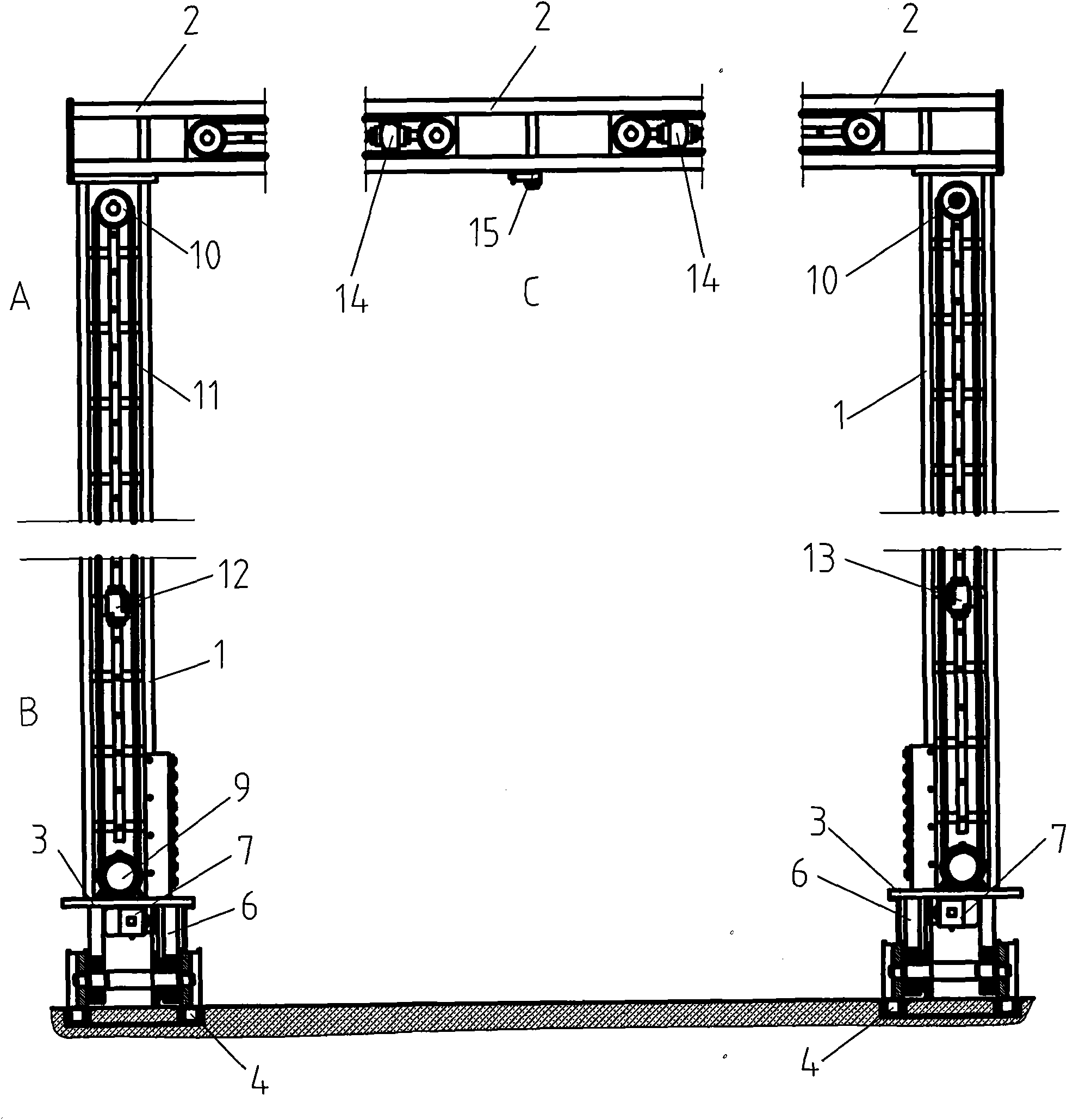
The invention discloses a device for detecting three-dimensional dimensions of a vehicle, which has the advantages of accurate measurement and high measurement efficiency. The device comprises symmetric portal frames, a control circuit and an operation panel, wherein an vehicle frame (3) which can drive the frames to move and a track (4) which is matched with a wheel (5) are arranged at the lowerend of each of the frames; especially, a length measuring device for measuring the length of the vehicle and a height measuring device for measuring the height of the vehicle are arranged on an upright post (1) of each of the frames, and a width measuring device for measuring the width of the vehicle is arranged on a transverse beam (2) of each of the frames; and the control circuit and the operation panel are connected with each measuring device. The invention has high measurement accuracy and high measurement speed, and can quickly complete the measurement of the three-dimensional dimensionsof the vehicle.
Owner:廊坊市威达科技发展有限公司 +1
Continuously variable transmissions, systems and methods
ActiveUS20170268638A1Large operating rangeLight weightGearing controlFriction gearingsGobio gobio obtusirostrisEngineering
Owner:FALLBROOK INTPROP COMPANY
Processor for executing switch and translate instructions requiring wide operands
InactiveUS20080189512A1Improve performanceEnhancing processor flexibilityInstruction analysisMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressGeneral purpose
A programmable processor and method for improving the performance of processors by expanding at least two source operands, or a source and a result operand, to a width greater than the width of either the general purpose register or the data path width. The present invention provides operands which are substantially larger than the data path width of the processor by using the contents of a general purpose register to specify a memory address at which a plurality of data path widths of data can be read or written, as well as the size and shape of the operand. In addition, several instructions and apparatus for implementing these instructions are described which obtain performance advantages if the operands are not limited to the width and accessible number of general purpose registers.
Owner:MICROUNITY
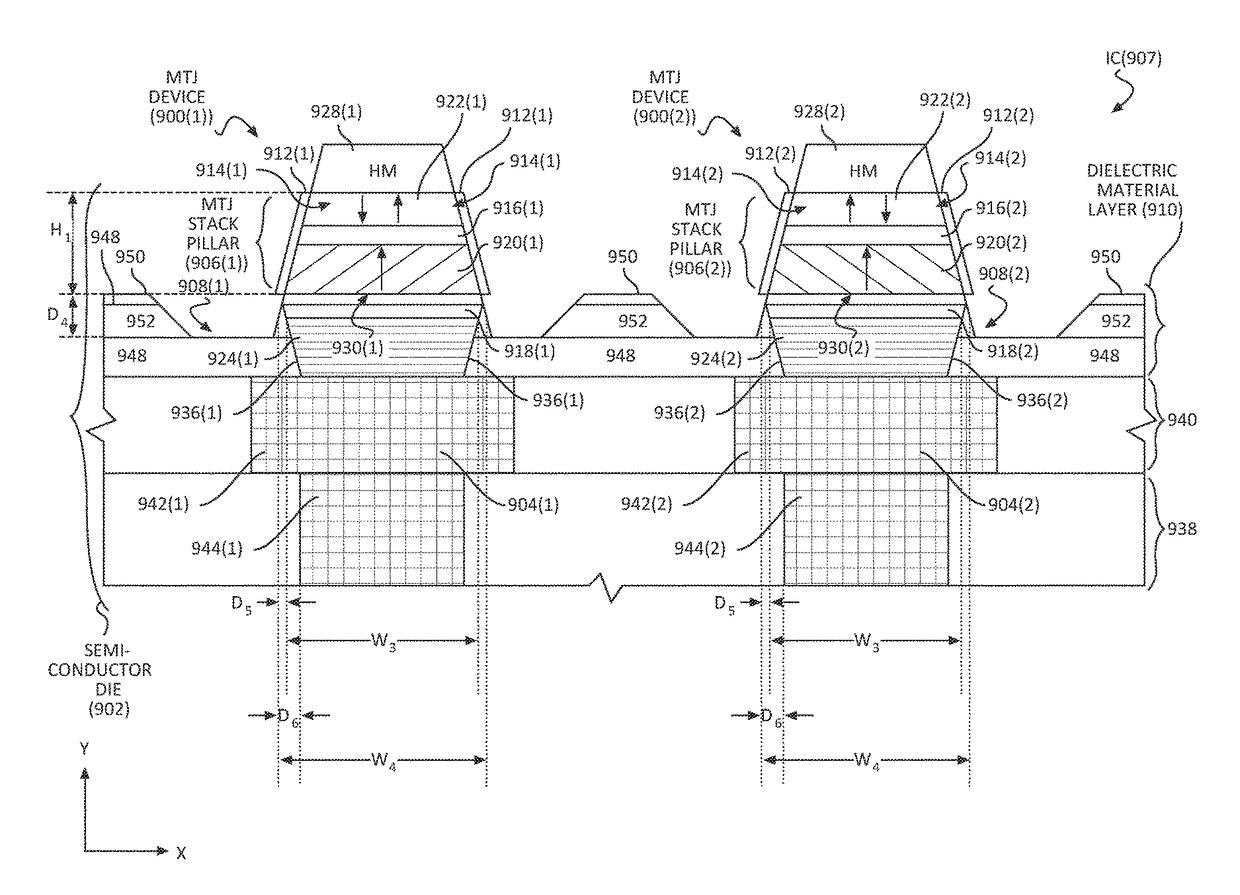
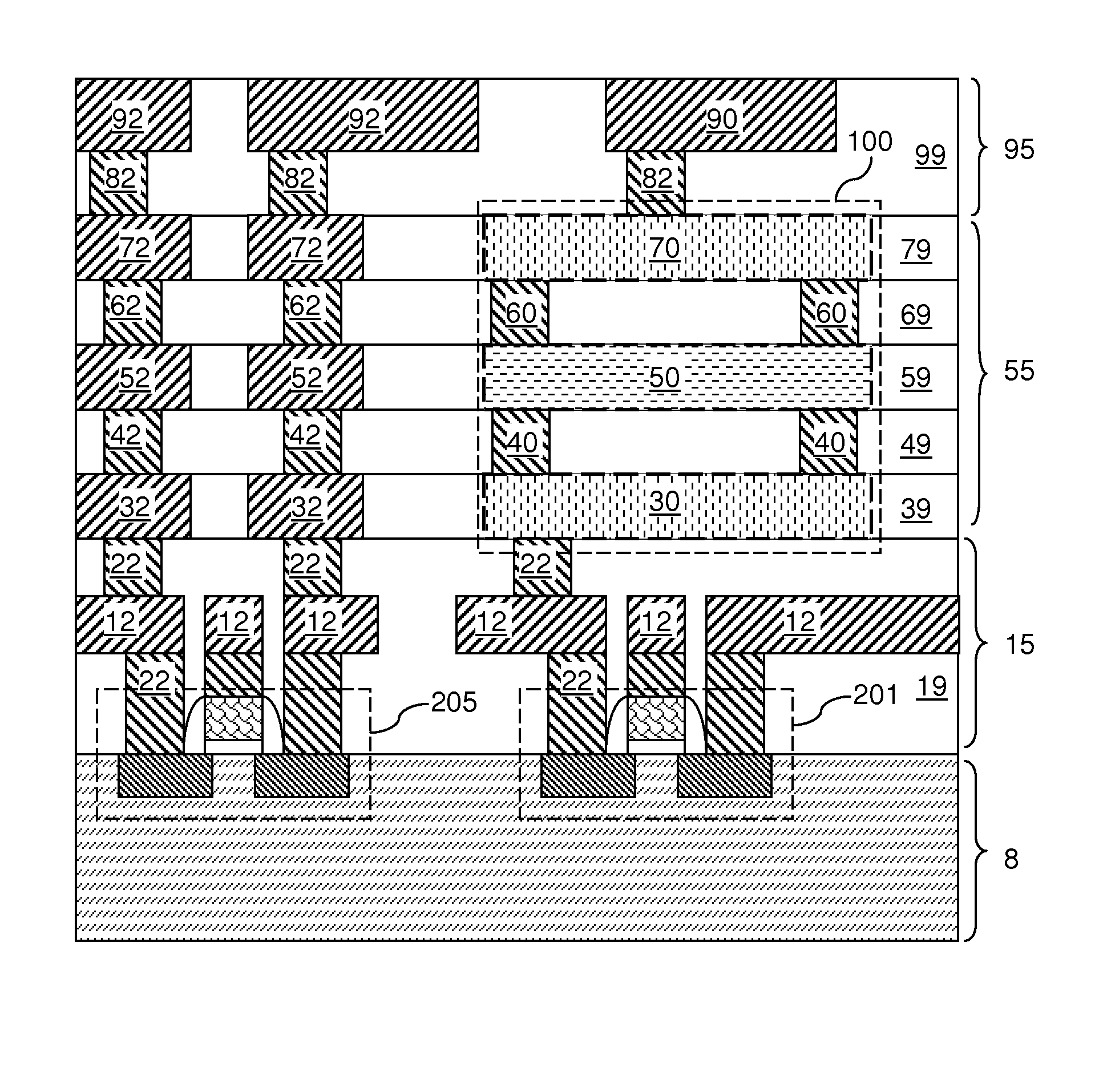
Reducing or avoiding metal deposition from etching magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) devices, including magnetic random access memory (MRAM) devices
ActiveUS20180040668A1Reducing and avoiding metal depositionReduce and avoid metal redepositionMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryRandom access memory
Aspects disclosed include reducing or avoiding metal deposition from etching magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) devices. In one example, a width of a bottom electrode of an MTJ device is provided to be less than a width of the MTJ stack of the MTJ device. In this manner, etching of the bottom electrode may be reduced or avoided to reduce or avoid metal redeposition as a result of over-etching the MTJ device to avoid horizontal shorts between an adjacent device(s). In another example, a seed layer is embedded in a bottom electrode of the MTJ device. In this manner, the MTJ stack is reduced in height to reduce or avoid metal redeposition as a result of over-etching the MTJ device. In another example, an MTJ device includes an embedded seed layer in a bottom electrode which also has a width less than a width of the MTJ stack.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Grapho-epitaxy dsa process with dimension control of template pattern
InactiveUS20140315390A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistGobio gobio obtusirostris
A method for defining a template for directed self-assembly (DSA) materials includes patterning a resist on a stack including an ARC and a mask formed over a hydrophilic layer. A pattern is formed by etching the ARC and the mask to form template lines which are trimmed to less than a minimum feature size (L). Hydrophobic spacers are formed on the template lines and include a fractional width of L. A neutral brush layer is grafted to the hydrophilic layer. A DSA material is deposited between the spacers and annealed to form material domains in a form of alternating lines of a first and a second material wherein the first material in contact with the spacers includes a width less than a width of the lines. A metal is added to the domains forming an etch resistant second material. The first material and the spacers are removed to form a DSA template pattern.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
Display apparatus and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20100156860A1Luminance unevenness can be suppressedCharacteristic of to shiftSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsColor imageGobio gobio obtusirostris
Disclosed herein is a display apparatus, including: a plurality of subpixels disposed adjacent each other and forming one pixel which forms a unit for formation of a color image; the plurality of subpixels including a first subpixel which emits light of the shortest wavelength and a second subpixel disposed adjacent the first subpixel; the second subpixel having a light blocking member disposed between the second subpixel and the first subpixel and having a width greater than a channel length or a channel width of a transistor which forms the second subpixel.
Owner:SONY CORP
Laminated structure, production method of the same, multilayer circuit board, active matrix substrate, and electronic display
ActiveUS20080029766A1High surface energyLower surface energyTransistorLiquid surface applicatorsActive matrixDisplay device
A disclosed laminated structure includes a wettability-variable layer containing a wettability-variable material whose surface energy changes when energy is applied thereto and including at least a high-surface-energy area having high surface energy and a low-surface-energy area having low surface energy; and a conductive layer formed on the high-surface-energy area. The high-surface-energy area includes a first area and a second area extending from the first area and having a width smaller than that of the first area.
Owner:RICOH KK
Modular hose reel
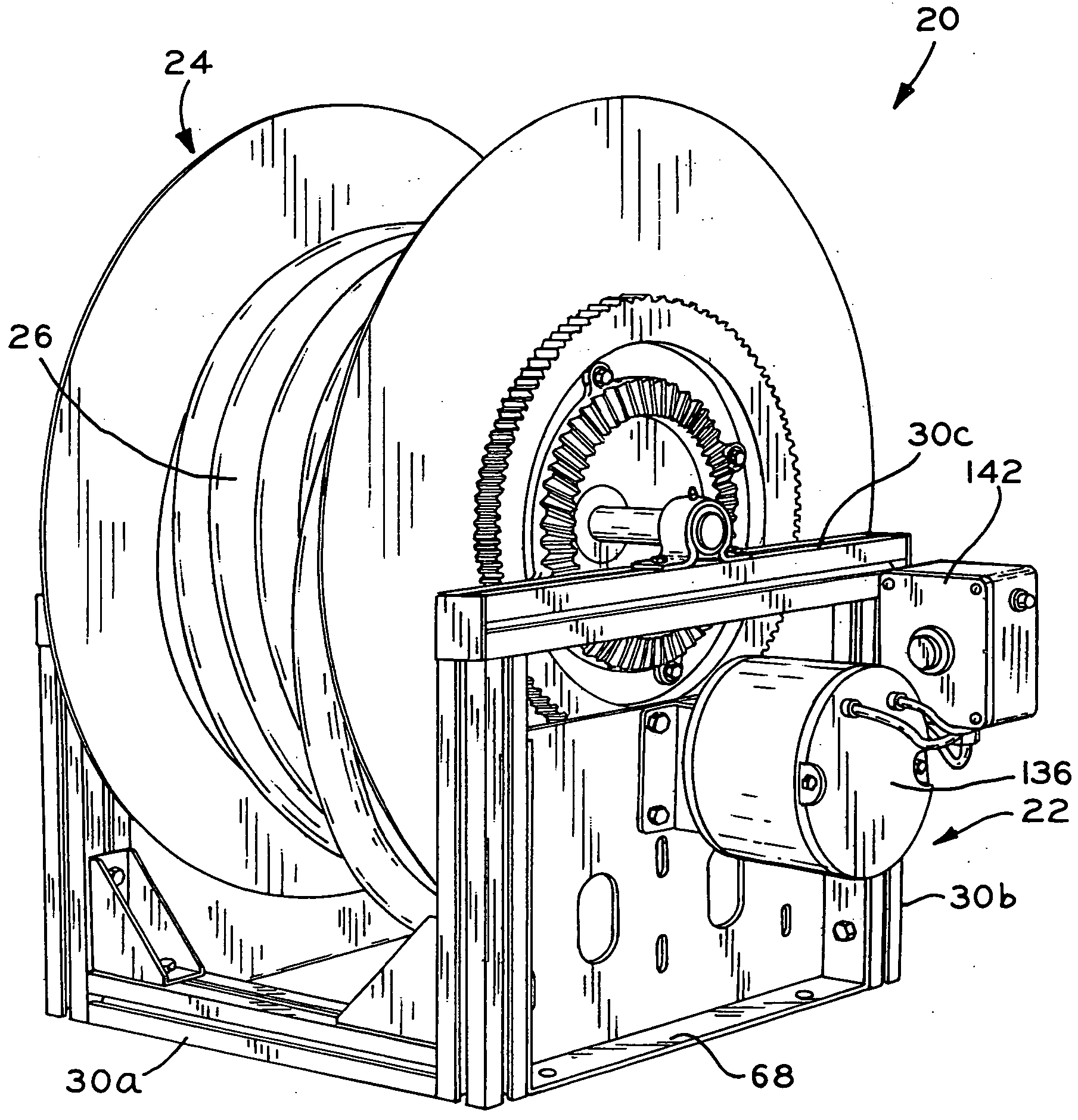
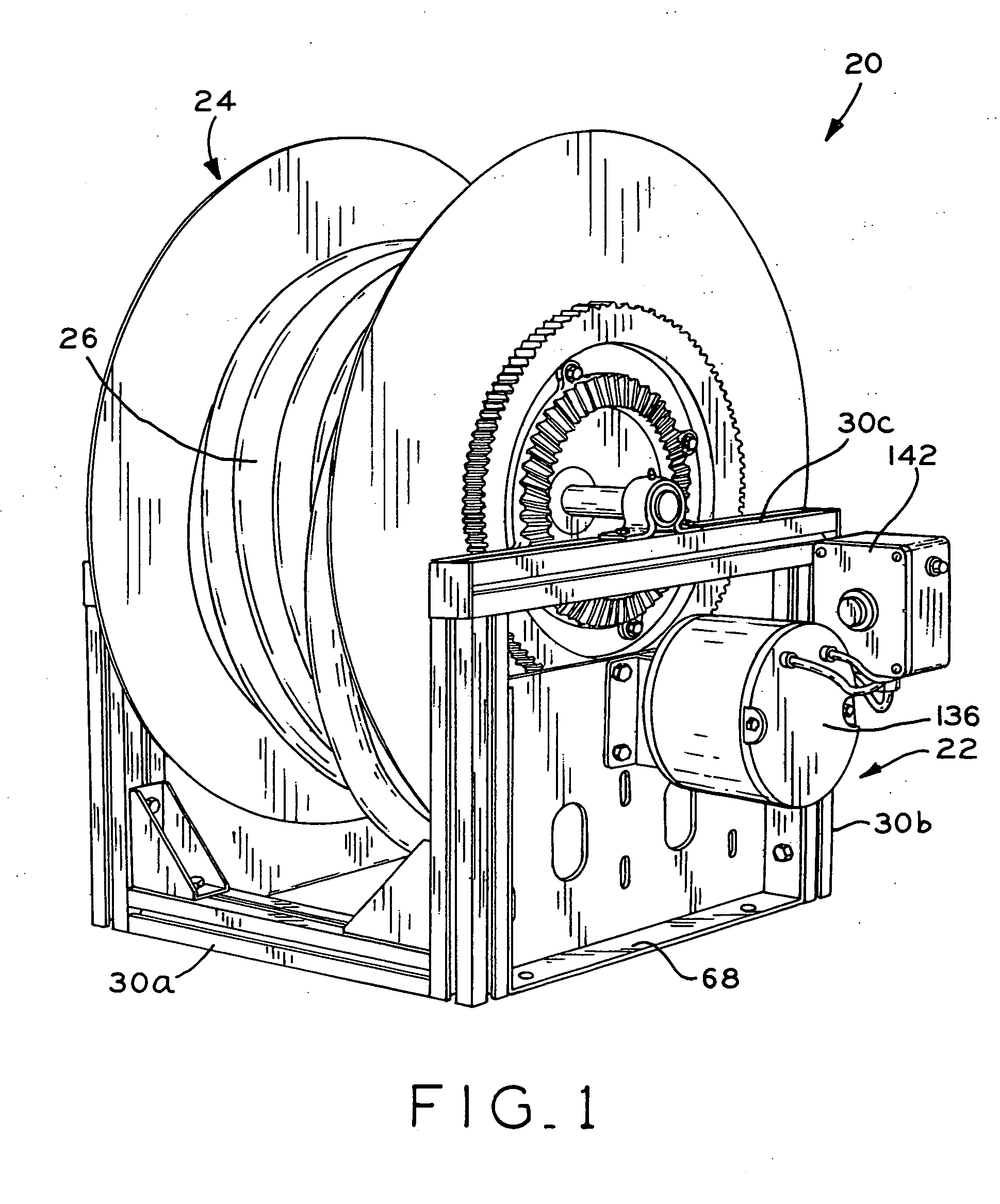
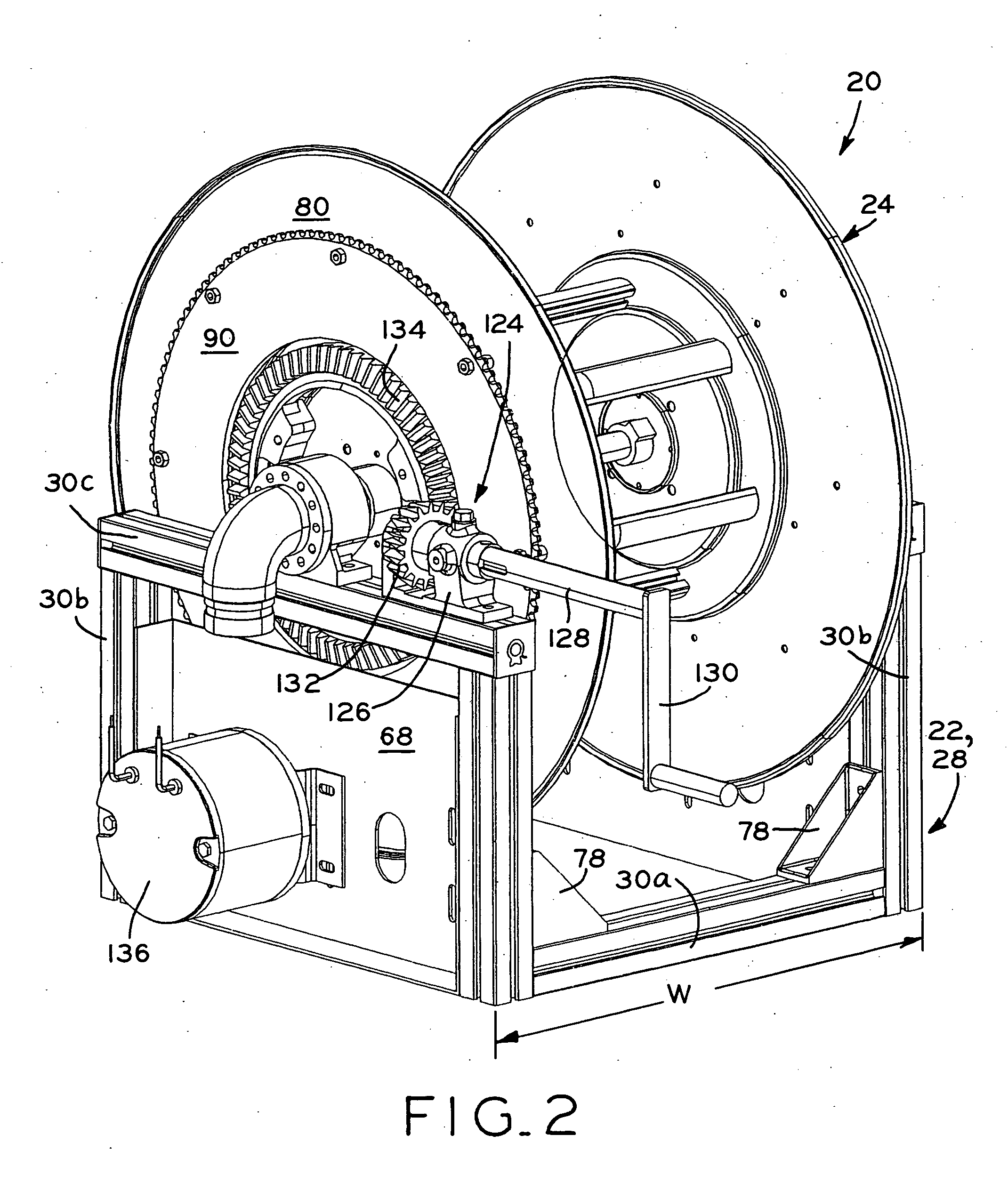
InactiveUS20050103918A1Easily custom manufactureConvenient lengthModularityGobio gobio obtusirostris
A reel, such as a hose reel, which includes a modular base assembly and a modular spool assembly. The base assembly includes a frame which is formed by a plurality of extruded frame components joined to one another by connecting members. The lengths of the frame components may be easily varied in order to in turn vary the overall width, depth, and height dimensions of the frame of the base assembly. The spool assembly includes a pair of side walls joined to one another by a plurality of spacer members. The length of the spacer members may be varied to in turn vary the width of the spool assembly. In one embodiment, the base assembly frame components and the spacer members are aluminum extrusions which are each cut to a selected length. In this manner, the width, depth, and height of the frame of the base assembly and the width of the spool assembly may be selectively varied to easily custom manufacture different reels having different overall sizes.
Owner:REELCRAFT INDS
Electrically programmable metal fuse
ActiveUS8421186B2Reduce the required powerPrevent thermal crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityMetal strips
A metal electrically programmable fuse (“eFuse”) includes a metal strip, having a strip width, of a metal line adjoined to wide metal line portions, having widths greater than the metal strip width, at both ends of the metal strip. The strip width can be a lithographic minimum dimension, and the ratio of the length of the metal strip to the strip width is greater than 5 to localize heating around the center of the metal strip during programming. Localization of heating reduces required power for programming the metal eFuse. Further, a gradual temperature gradient is formed during the programming within a portion of the metal strip that is longer than the Blech length so that electromigration of metal gradually occurs reliably at the center portion of the metal strip. Metal line portions are provides at the same level as the metal eFuse to physically block debris generated during programming.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Outsole with anti-slip tread
Owner:CHINOOK TRADING
Multi-nozzle organic vapor jet printing
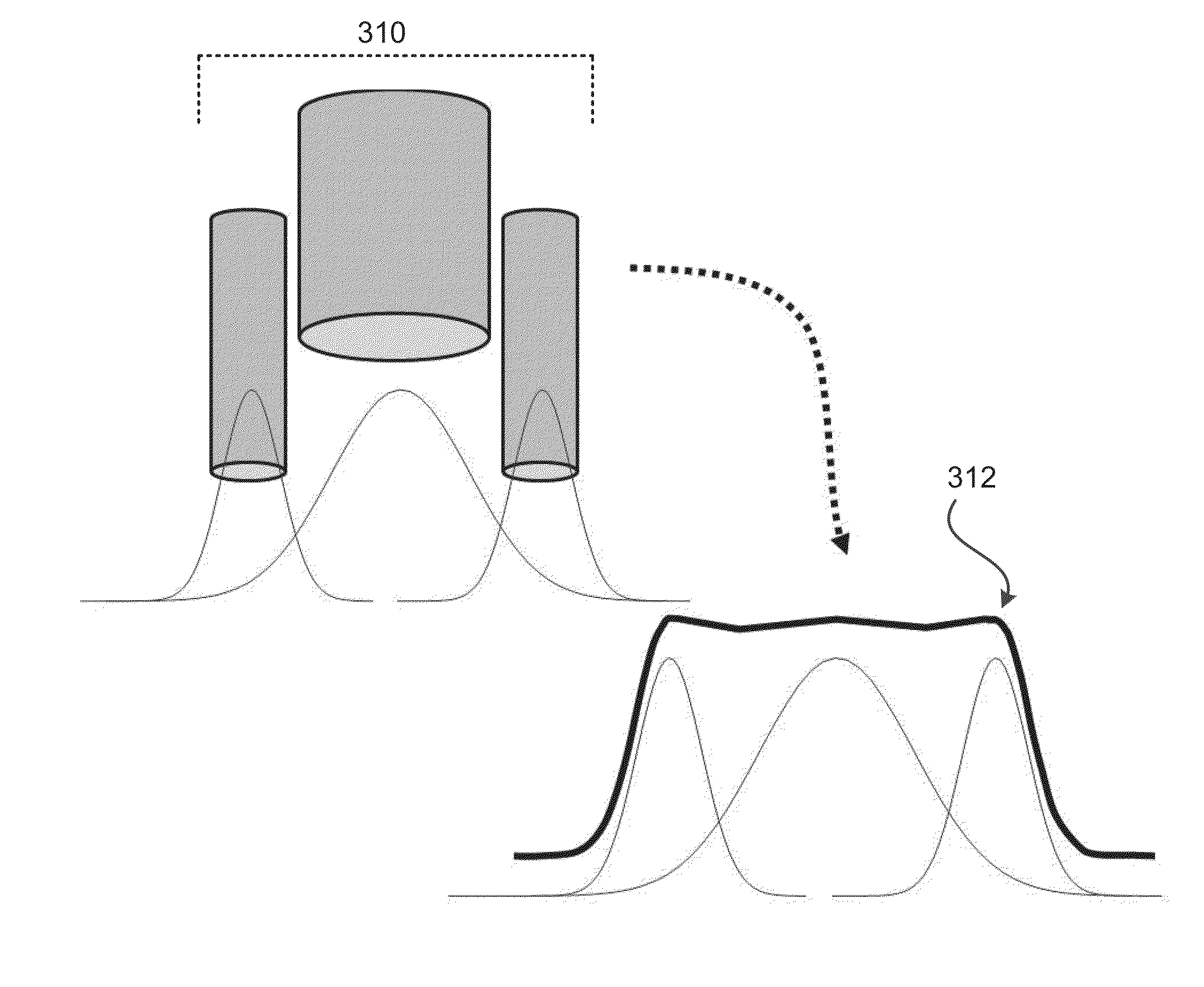
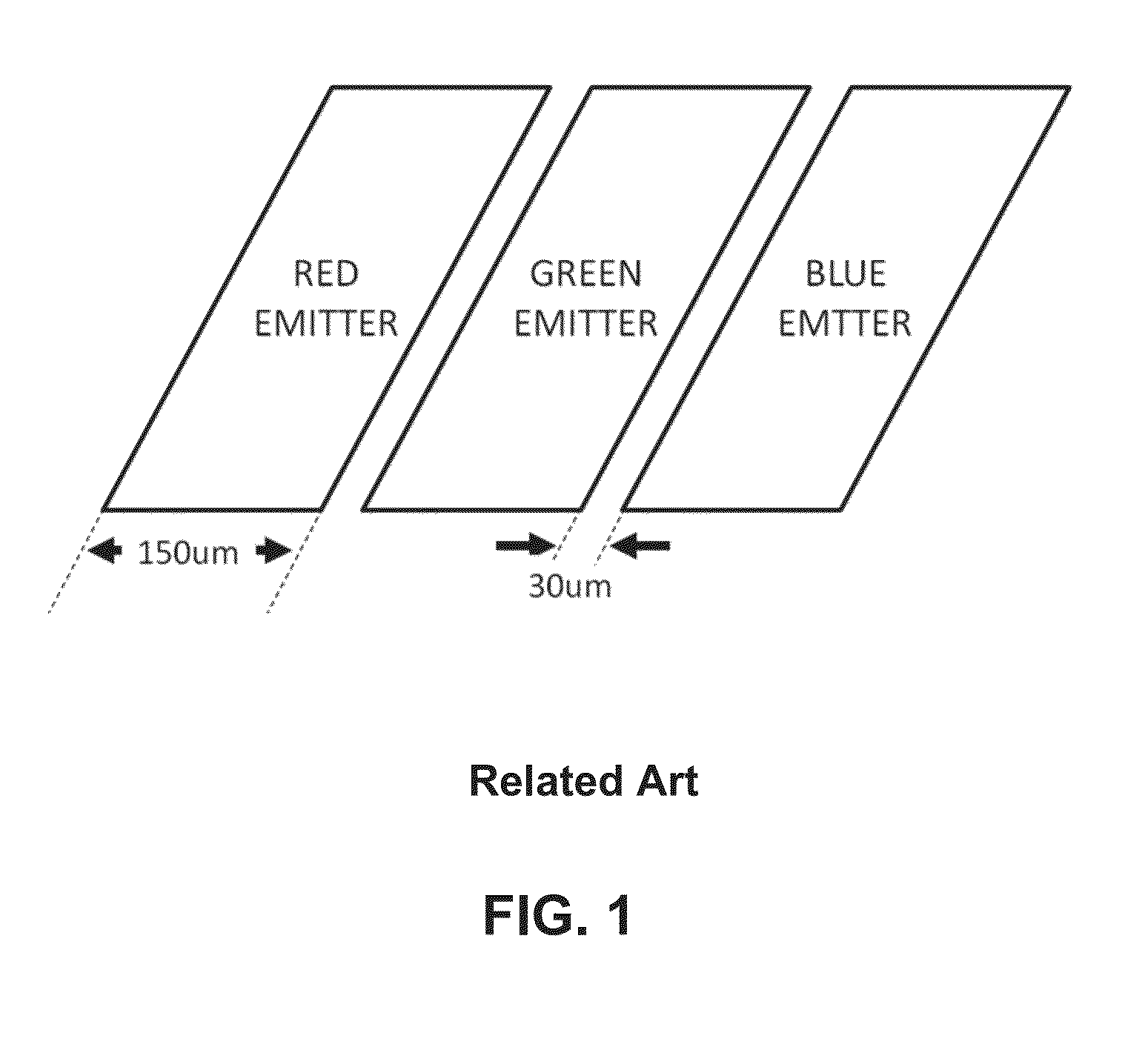
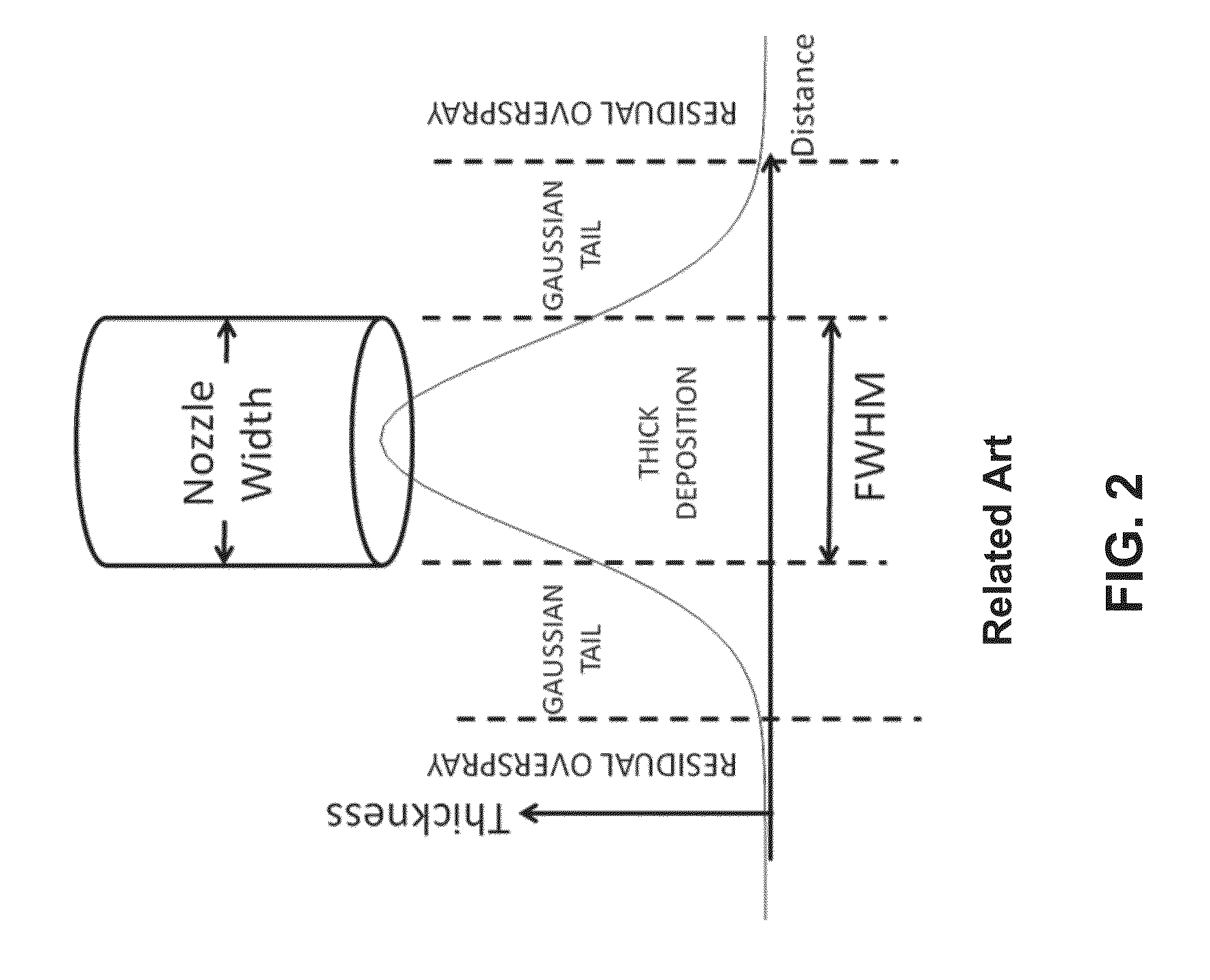
ActiveUS8728858B2High resolutionReducing undesirable “overspray”Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLeading edgeSpray nozzle
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com