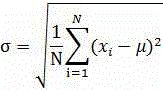Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
616 results about "Coefficient of variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
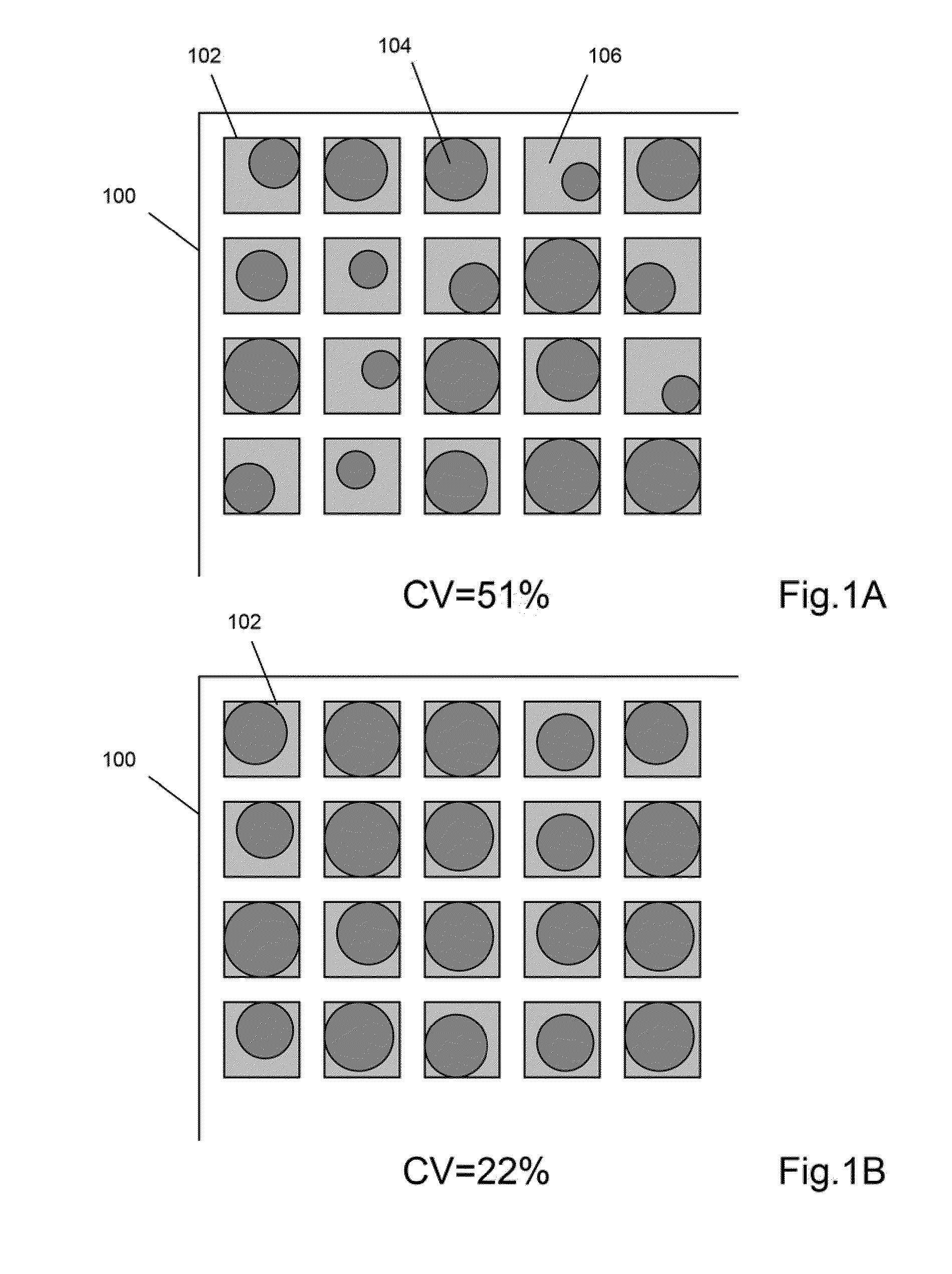
In probability theory and statistics, the coefficient of variation (CV), also known as relative standard deviation (RSD), is a standardized measure of dispersion of a probability distribution or frequency distribution. It is often expressed as a percentage, and is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation σ to the mean μ (or its absolute value, |μ|). The CV or RSD is widely used in analytical chemistry to express the precision and repeatability of an assay.
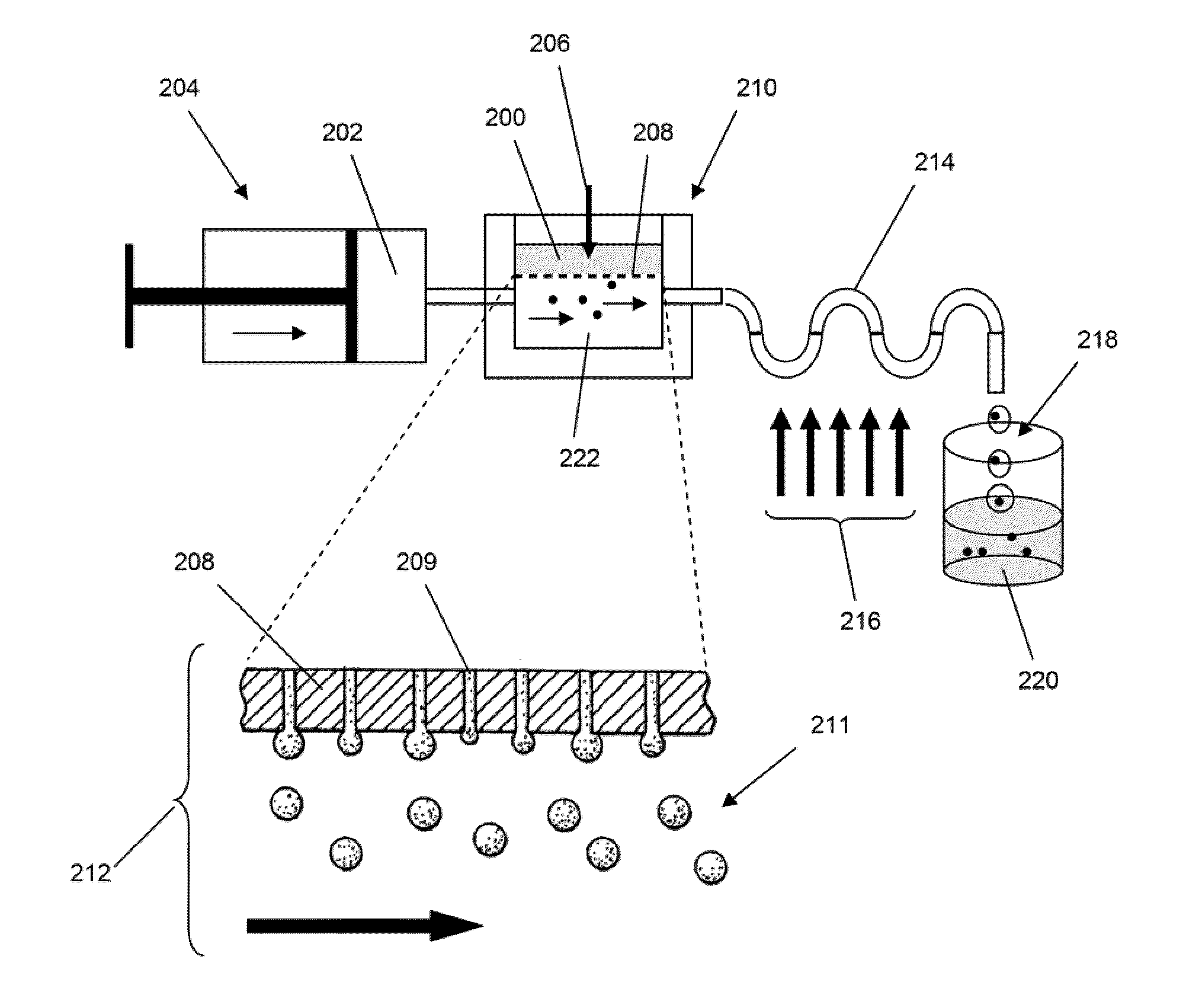
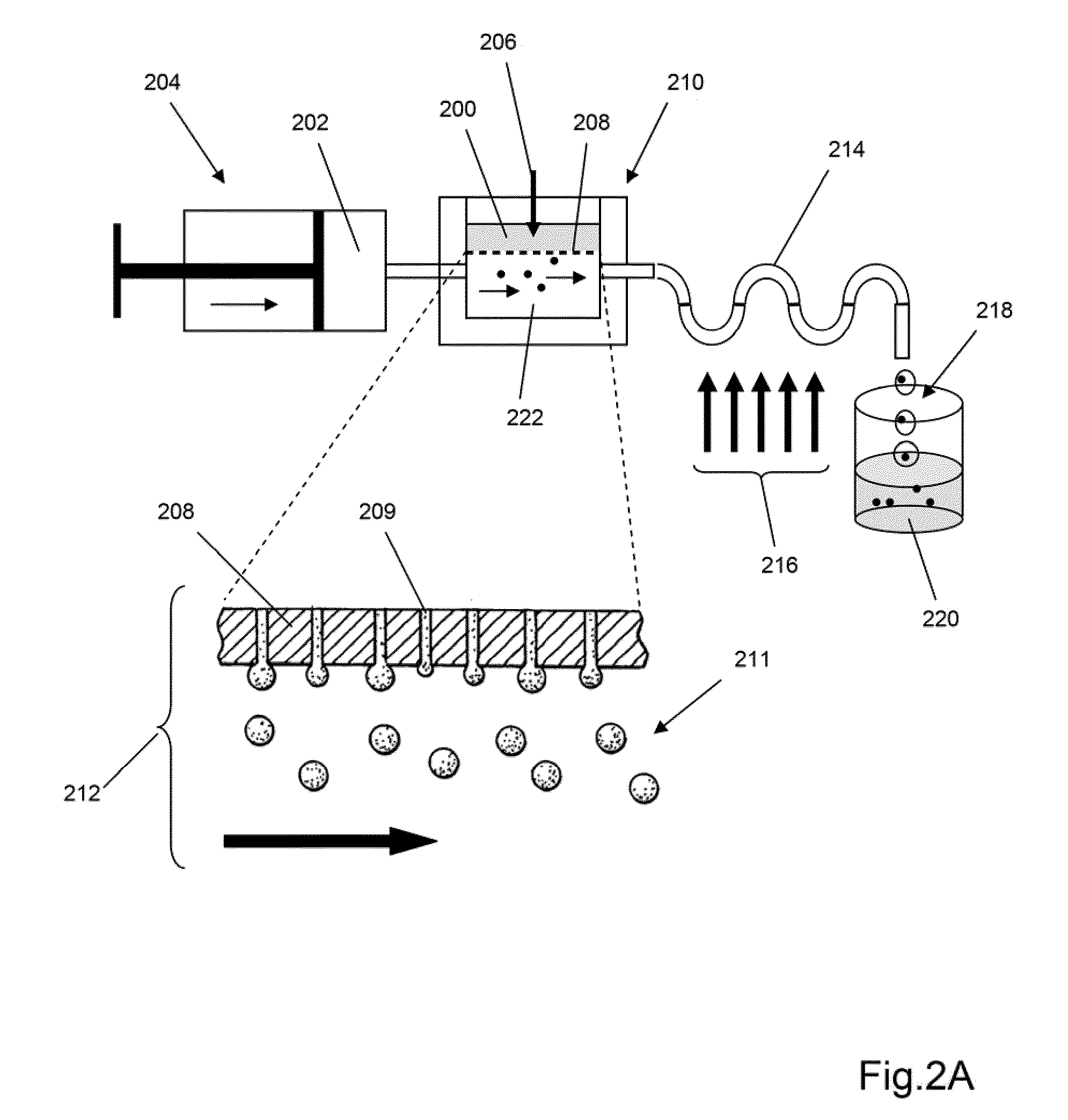
Scaffolded nucleic acid polymer particles and methods of making and using
ActiveUS20100304982A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsParticle compositionPolynucleotide
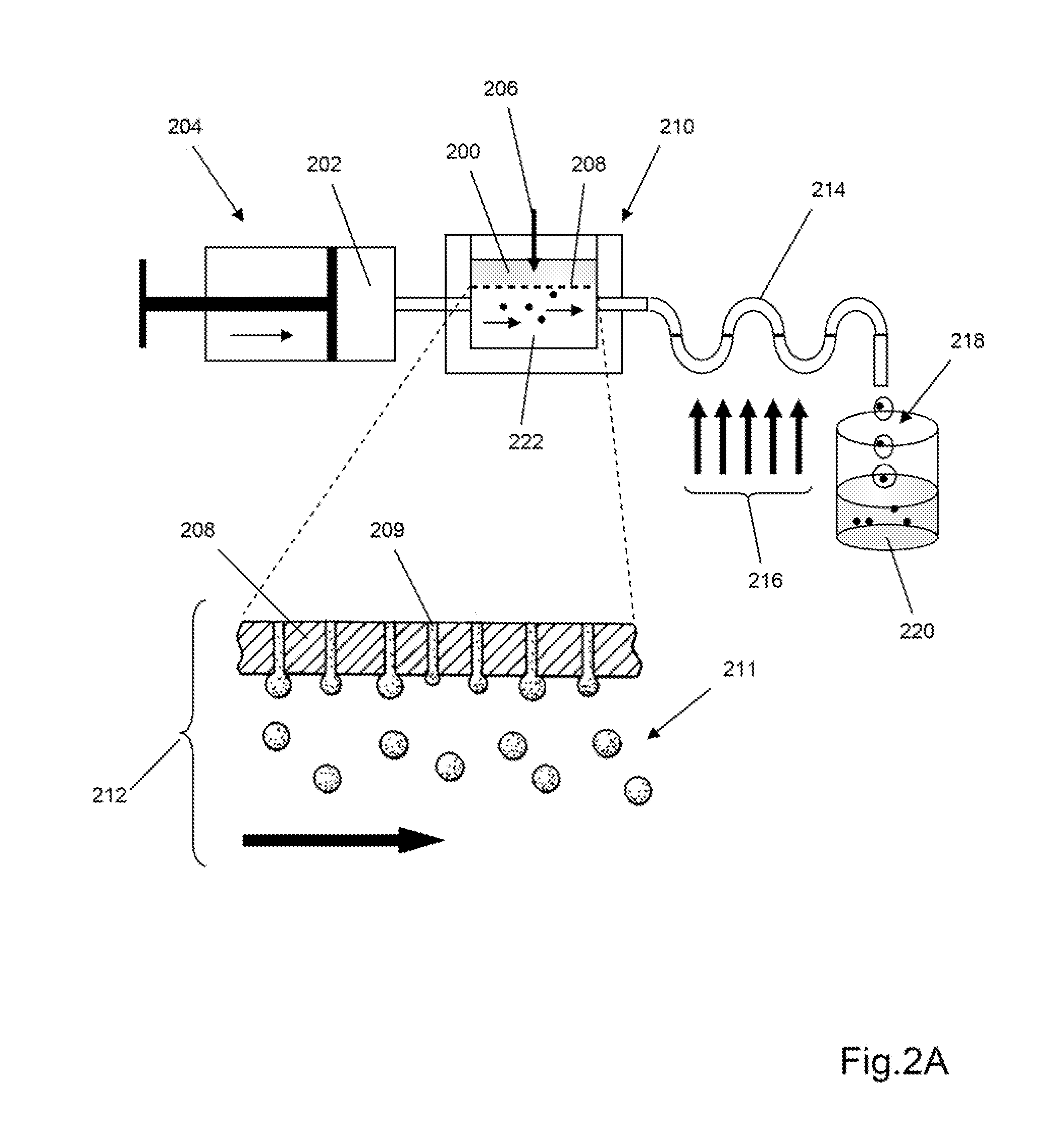
The invention provides particle compositions having applications in nucleic acid analysis. Nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention allow polynucleotides to be attached throughout their volumes for higher loading capacities than those achievable solely with surface attachment. In one aspect, nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention comprise polyacrylamide particles with uniform size distributions having low coefficients of variations, which result in reduced particle-to-particle variation in analytical assays. Such particle compositions are used in various amplification reactions to make amplicon libraries from nucleic acid fragment libraries.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Magnetic recording medium and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8535817B2Excellent characteristicsIncreased durabilityMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMetallurgyNon magnetic
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic recording medium comprising a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder and a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder in this order on a nonmagnetic support, whereinthe magnetic layer comprises a nonmagnetic powder of which coefficient of variation CV of a particle size distribution as denoted by the following formula (1):CV(%)=σ / φ×100 (1)is less than 20 percent, andthe magnetic layer has a thickness being equal to or less than 0.1 μm and falling within a range of 1.1≦φ / t≦8.0, wherein σ denotes a standard deviation of a particle diameter, φ denotes an average particle diameter of the nonmagnetic powder comprised in the magnetic layer being expressed in μm, and t denotes a thickness of the magnetic layer being expressed in μm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
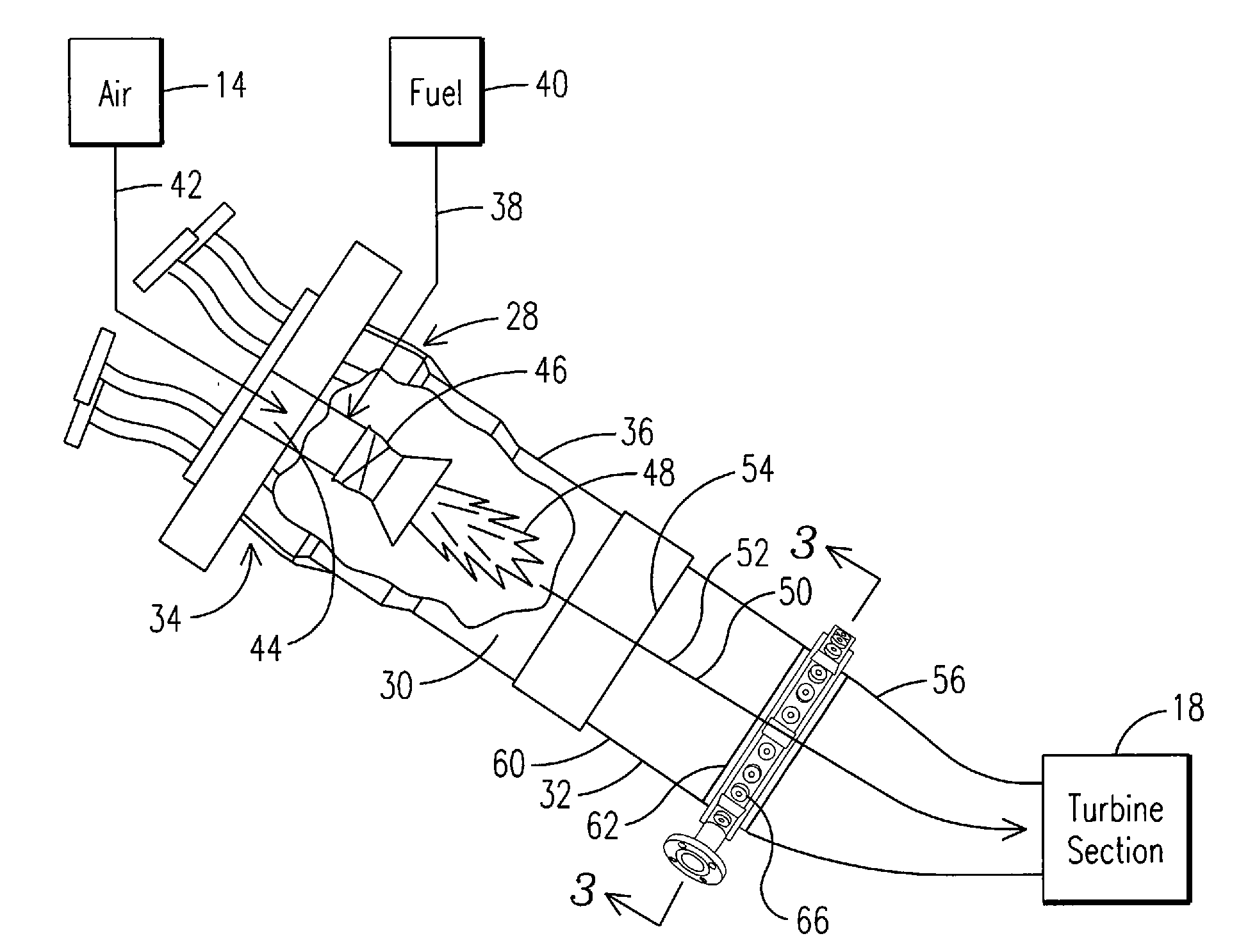
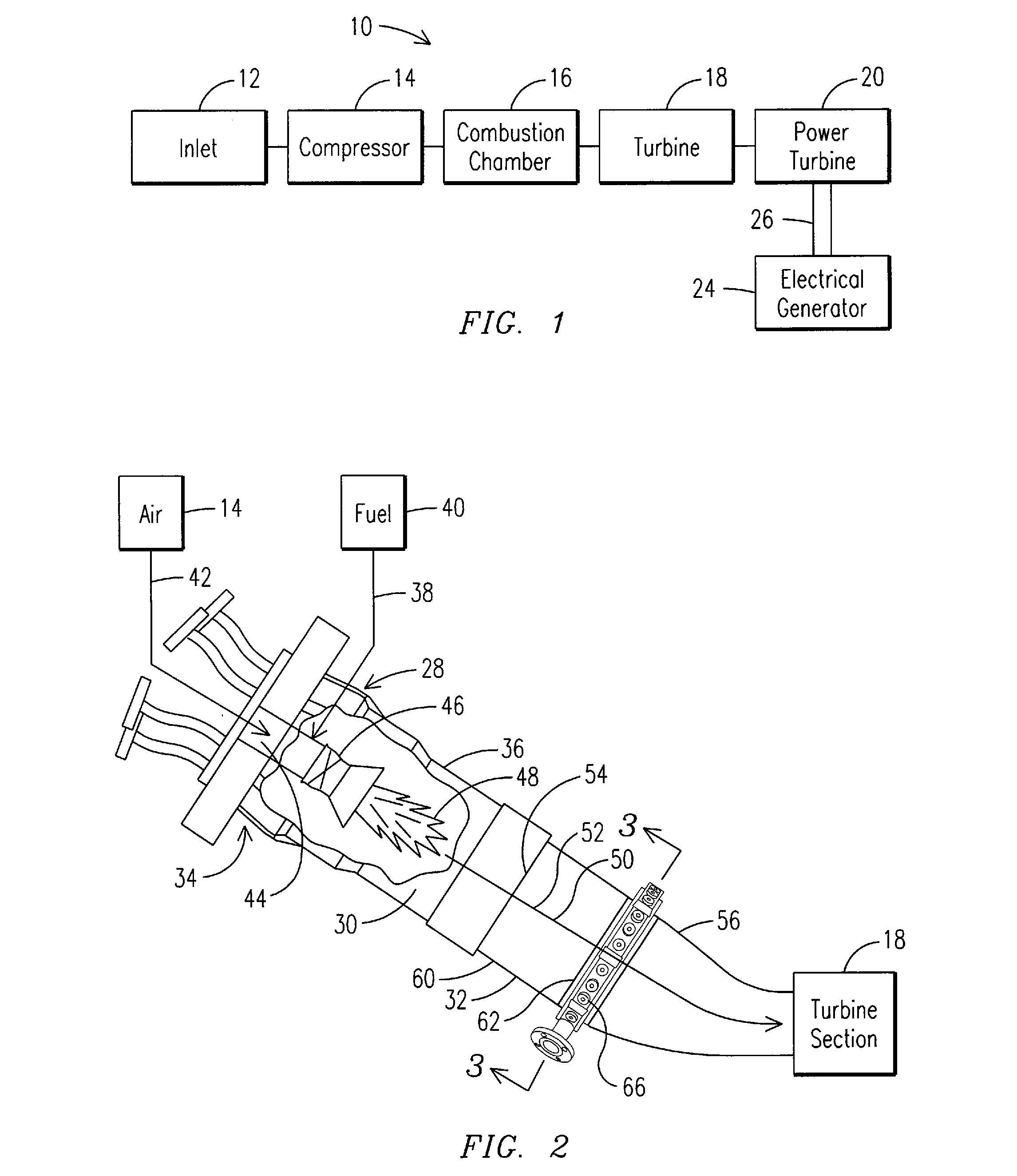
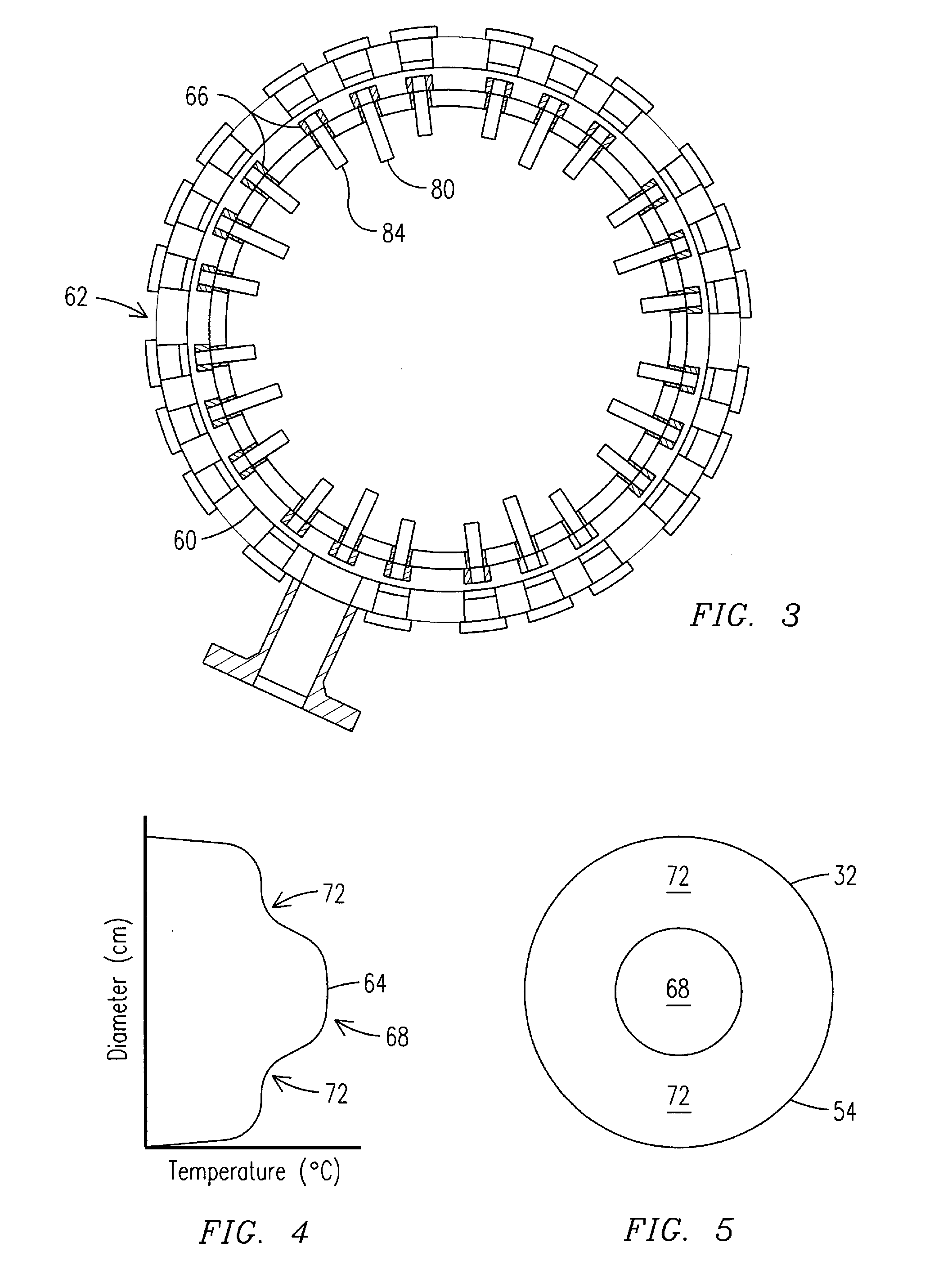
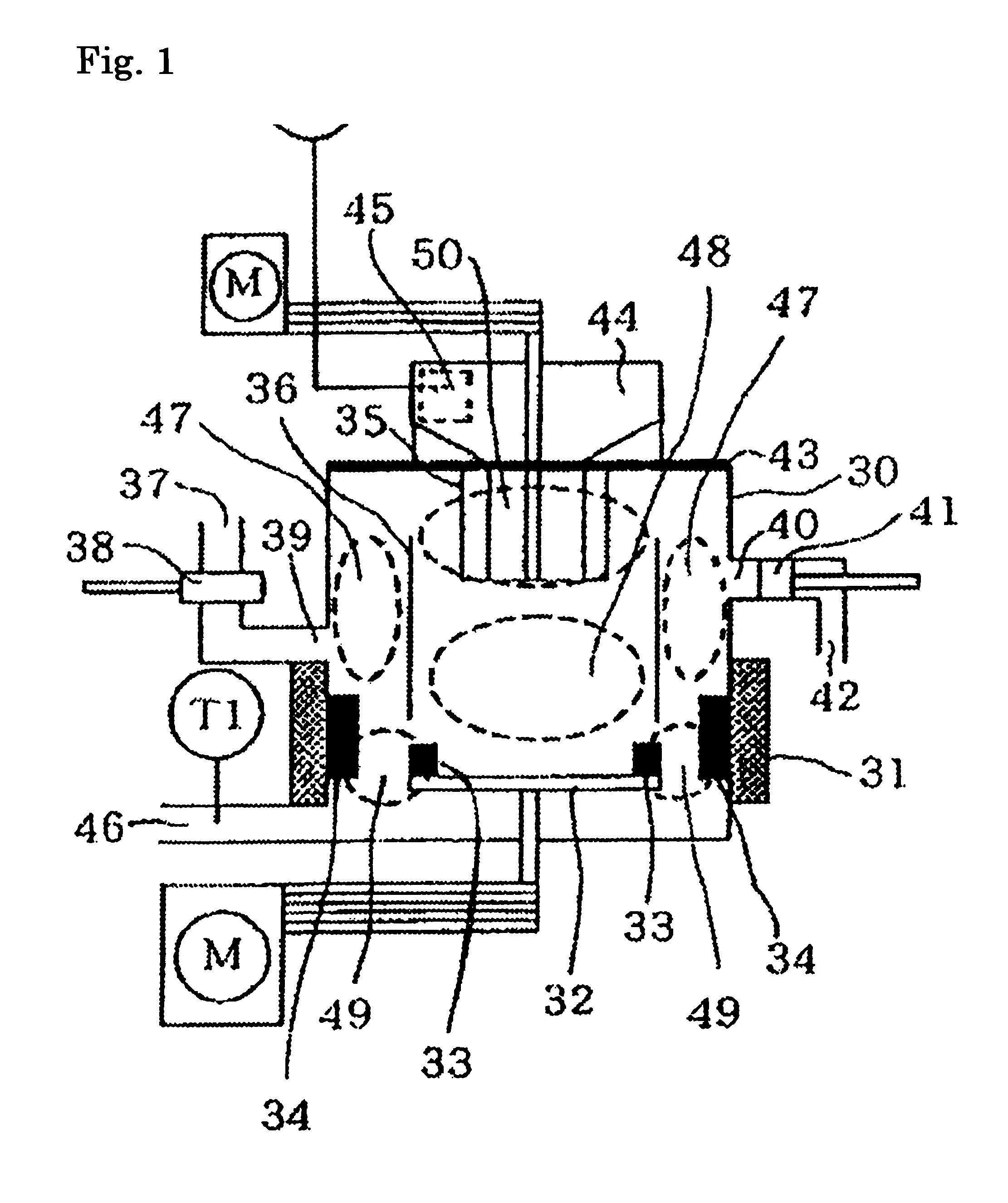
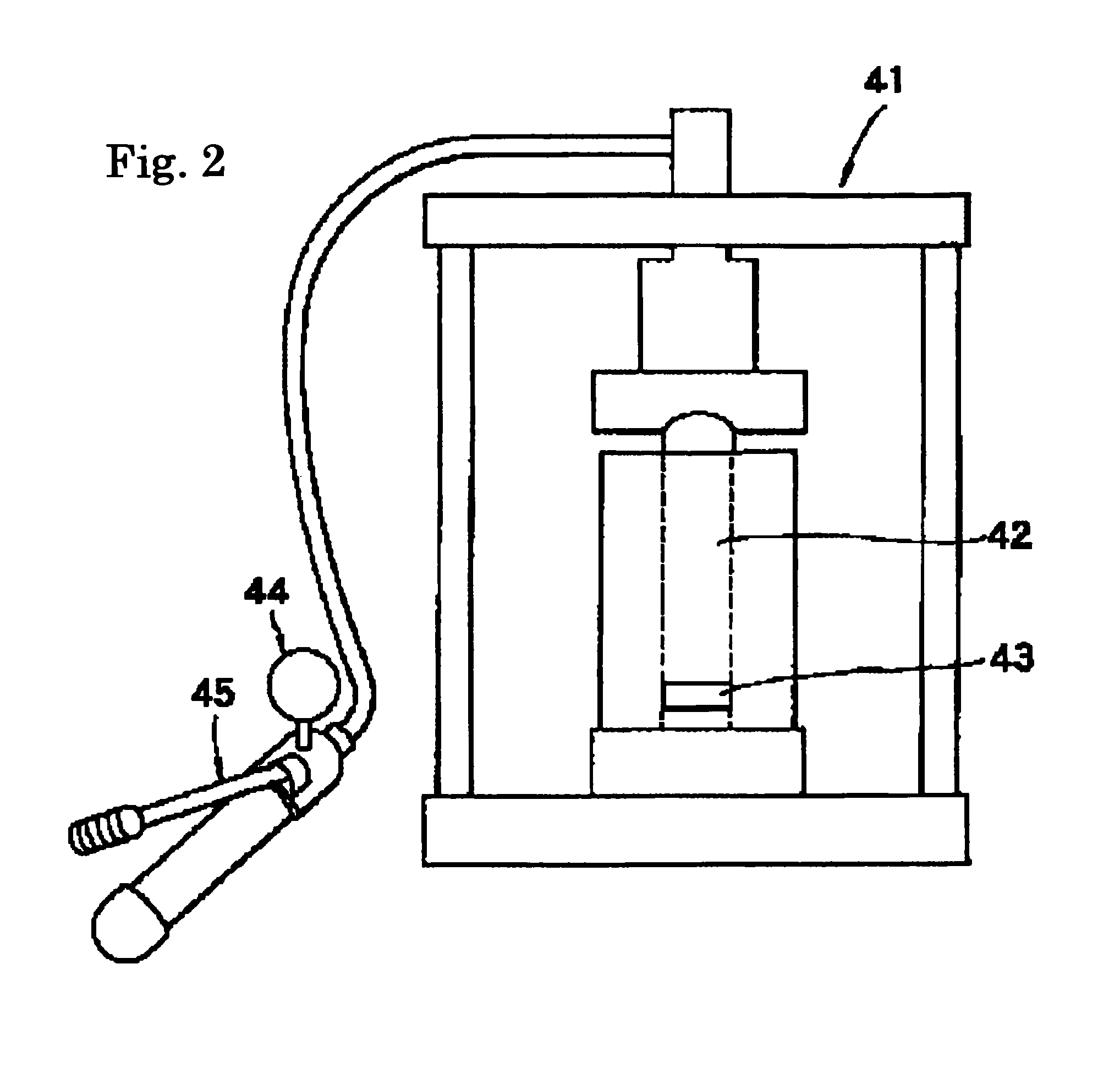
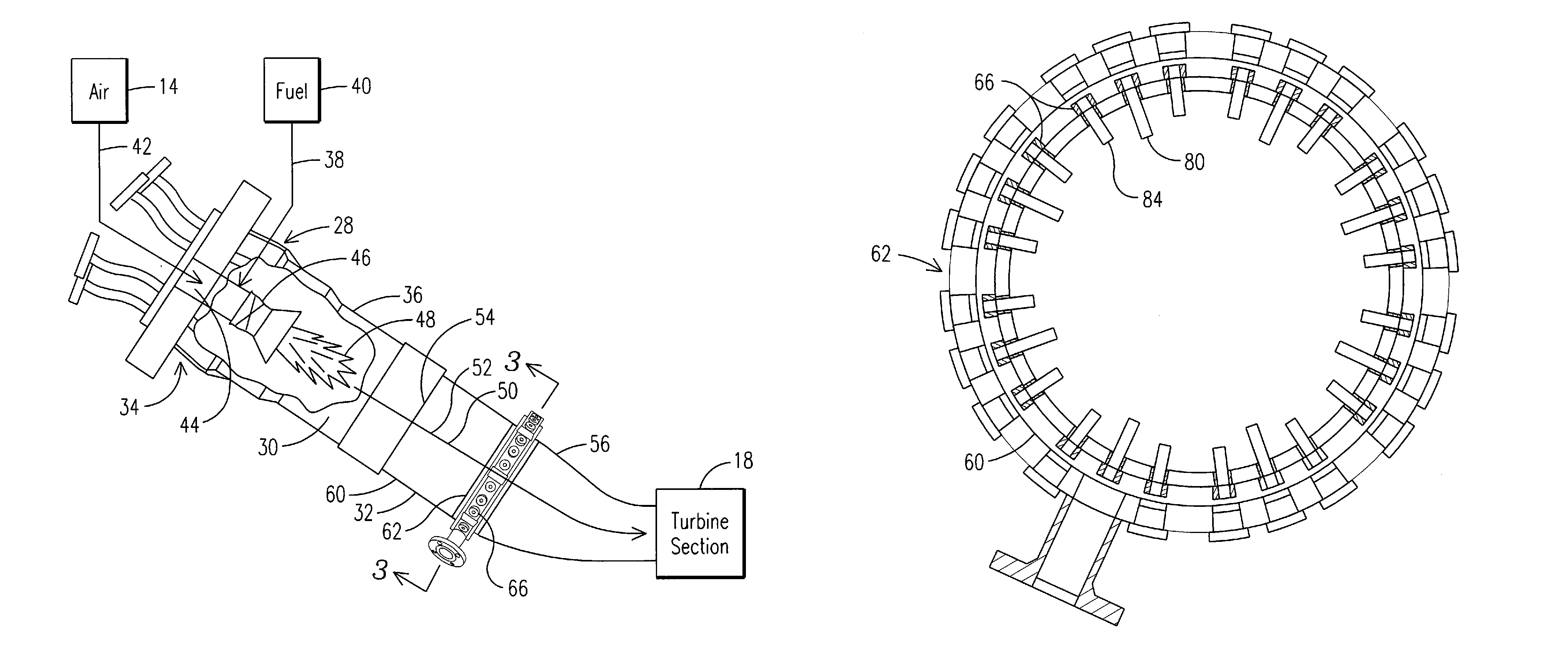
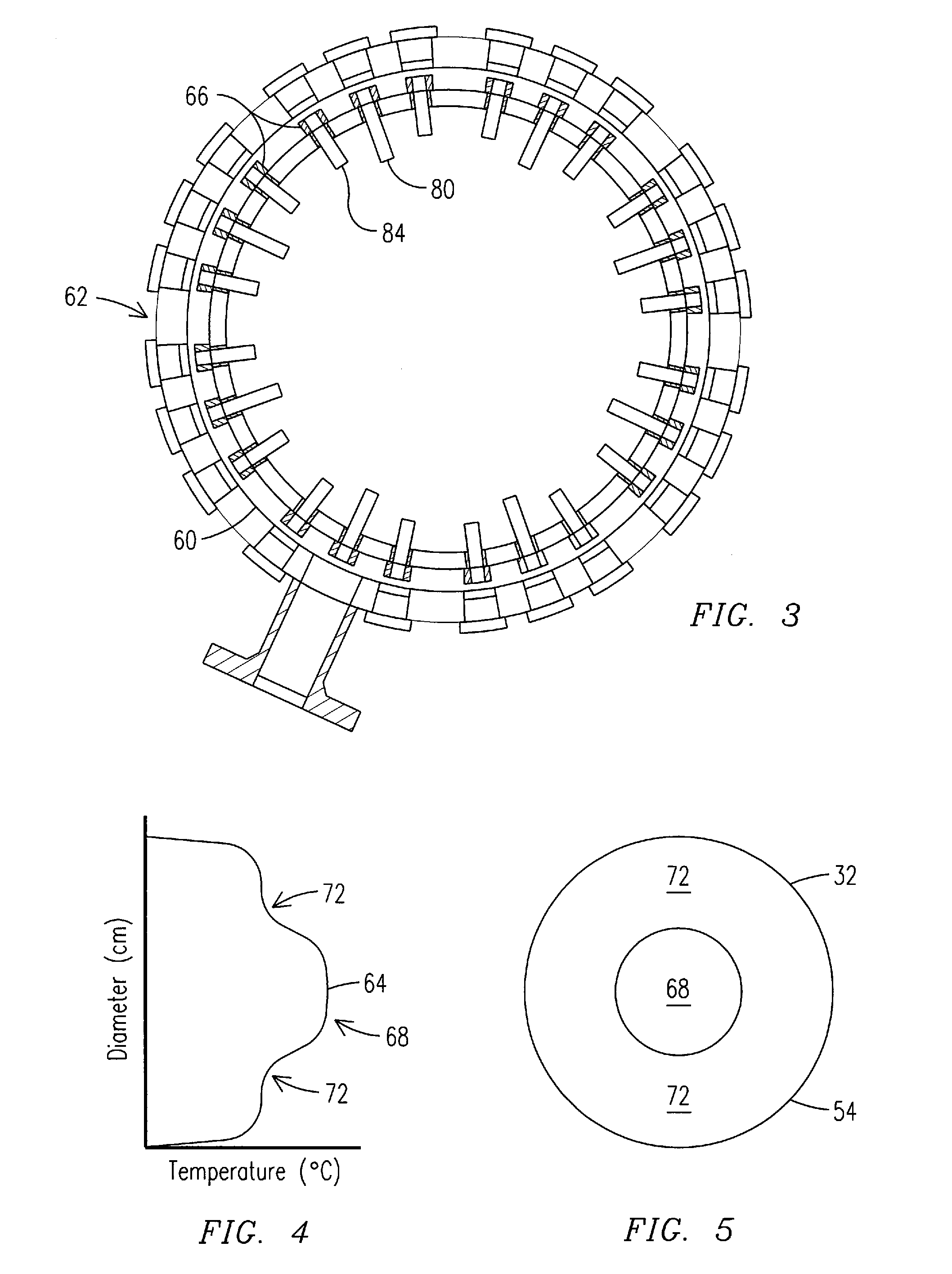
Apparatus and Method for Controlling the Secondary Injection of Fuel
In one embodiment, a combustor (28) for a gas turbine engine is provided comprising a primary combustion chamber (30) for combusting a first fuel to form a combustion flow stream (50) and a transition piece (32) located downstream from the primary combustion chamber (30). The transition piece (32) comprises a plurality of injectors (66) located around a circumference of the transition piece (32) for injecting a second fuel into the combustion flow stream (50). The injectors (66) are effective to create a radial temperature profile (74) at an exit (58) of the transition piece (32) having a reduced coefficient of variation relative to a radial temperature profile (64) at an inlet (54) of the transition piece (32). Methods for controlling the temperature profile of a secondary injection are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method for fast and accurate evaluation of periodic review inventory policy
InactiveUS6144945AThe process is fast and accurateLogisticsSpecial data processing applicationsRegular distributionComputational problem
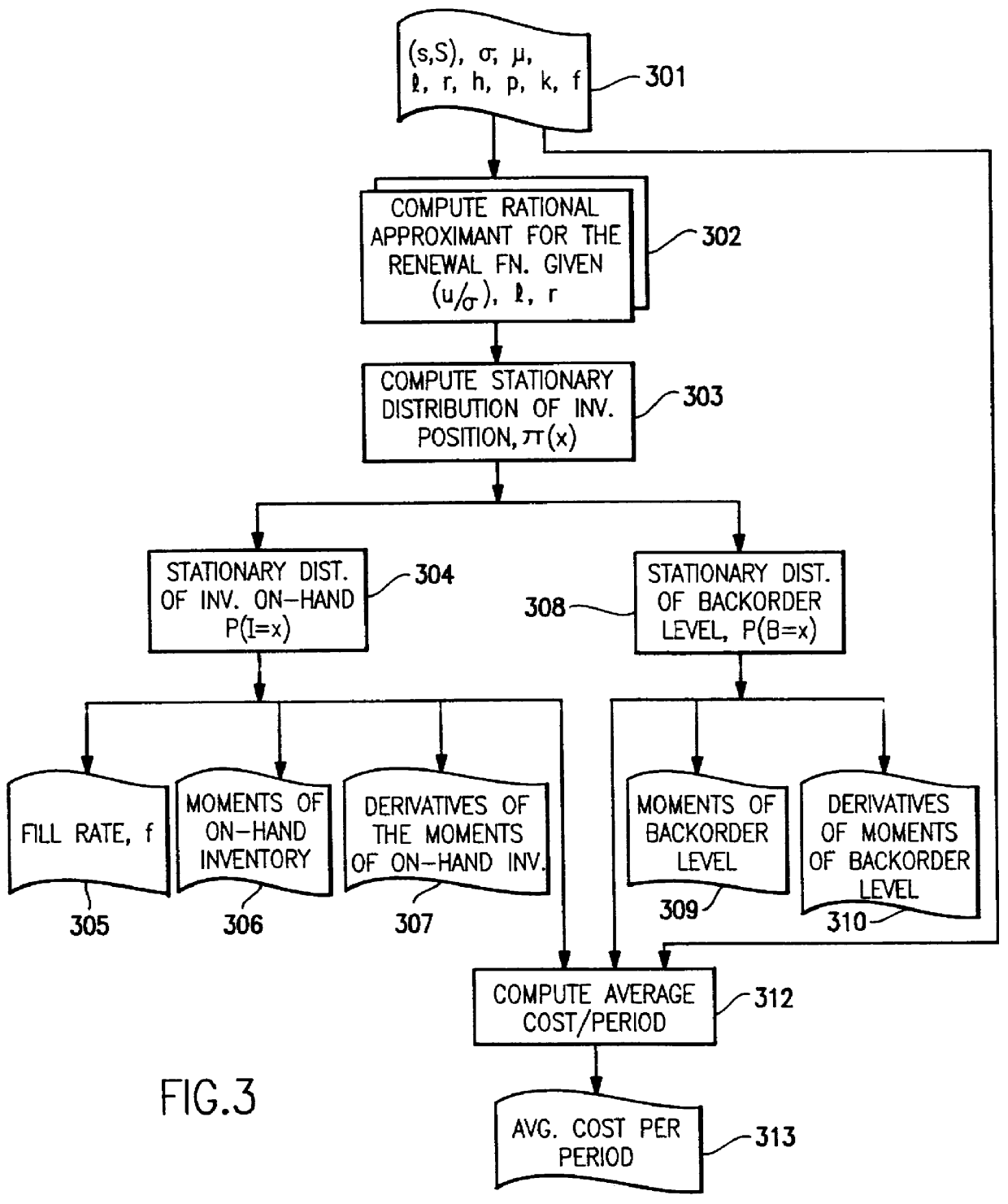
A computer implemented process is provided for fast and accurate evaluation of the performance characteristics of the periodic-review (s,S) inventory policy with complete back ordering. This policy has an underlying stochastic process that is a renewal process. The method provides a novel computer implementation of a fast and accurate way to compute approximations of the renewal function. In order to overcome the computational problems in evaluating renewal functions numerically, an approximation scheme has been devised whereby the renewal function of the truncated normal distribution can be characterized by two parameters: (1) its coefficient of variation, and (2) the point at which the function needs to be evaluated. This approximation is derived in two stages. In the first stage, a class of rational polynomial approximations are developed to the renewal function, called Pad+E,acu e+EE approximants. In the second stage, polynomial expressions are derived for each coefficient of the Pad+E,acu e+EE approximants in terms of the coefficient of variation of the distribution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Scaffolded Nucleic Acid Polymer Particles and Methods of Making and Using
InactiveUS20110195253A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementParticle compositionPolynucleotide
The invention provides particle compositions having applications in nucleic acid analysis. Nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention allow polynucleotides to be attached throughout their volumes for higher loading capacities than those achievable solely with surface attachment. In one aspect, nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention comprise polyacrylamide particles with uniform size distributions having low coefficients of variations, which result in reduced particle-to-particle variation in analytical assays. Such particle compositions are used in various amplification reactions to make amplicon libraries from nucleic acid fragment libraries.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Preparation of polysaccharide beads
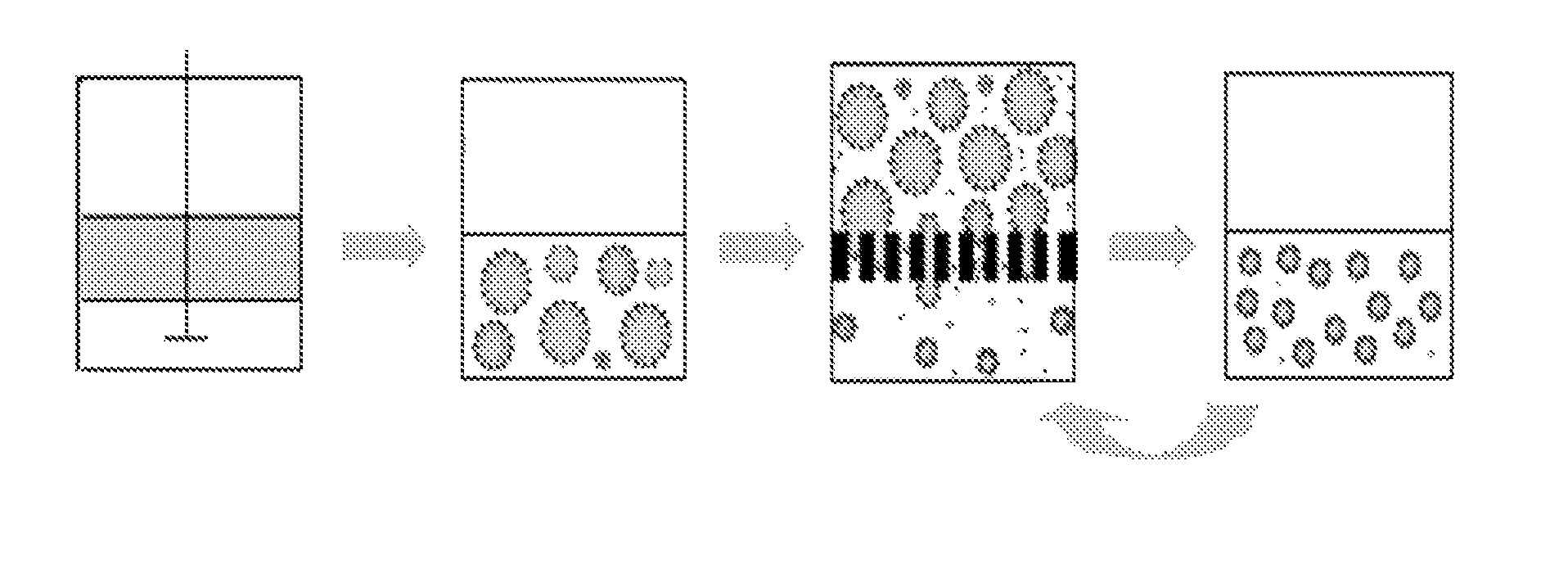
The present invention relates a method of preparing agarose beads, which method results in a population of beads which are of relatively uniform particle size. In an advantageous embodiment, the beads are of a particle size less than 10 μm, and the coefficient of variation C.V. of the population is less than 15%. The beads according to the invention are advantageously used in biological separation methods, such as in the production of chromatographic packing materials; drug carriers; or in any method of biological engineering.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
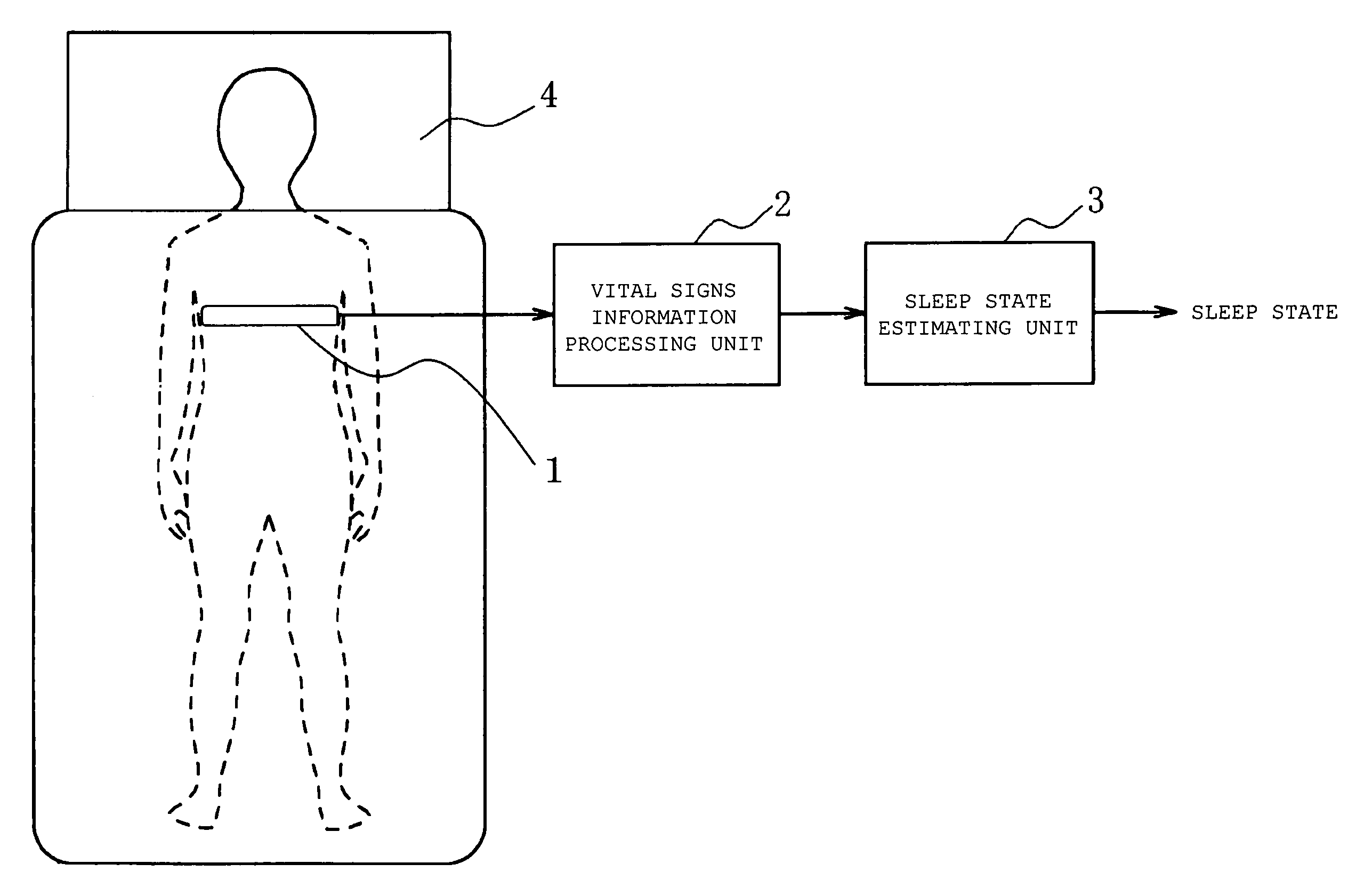
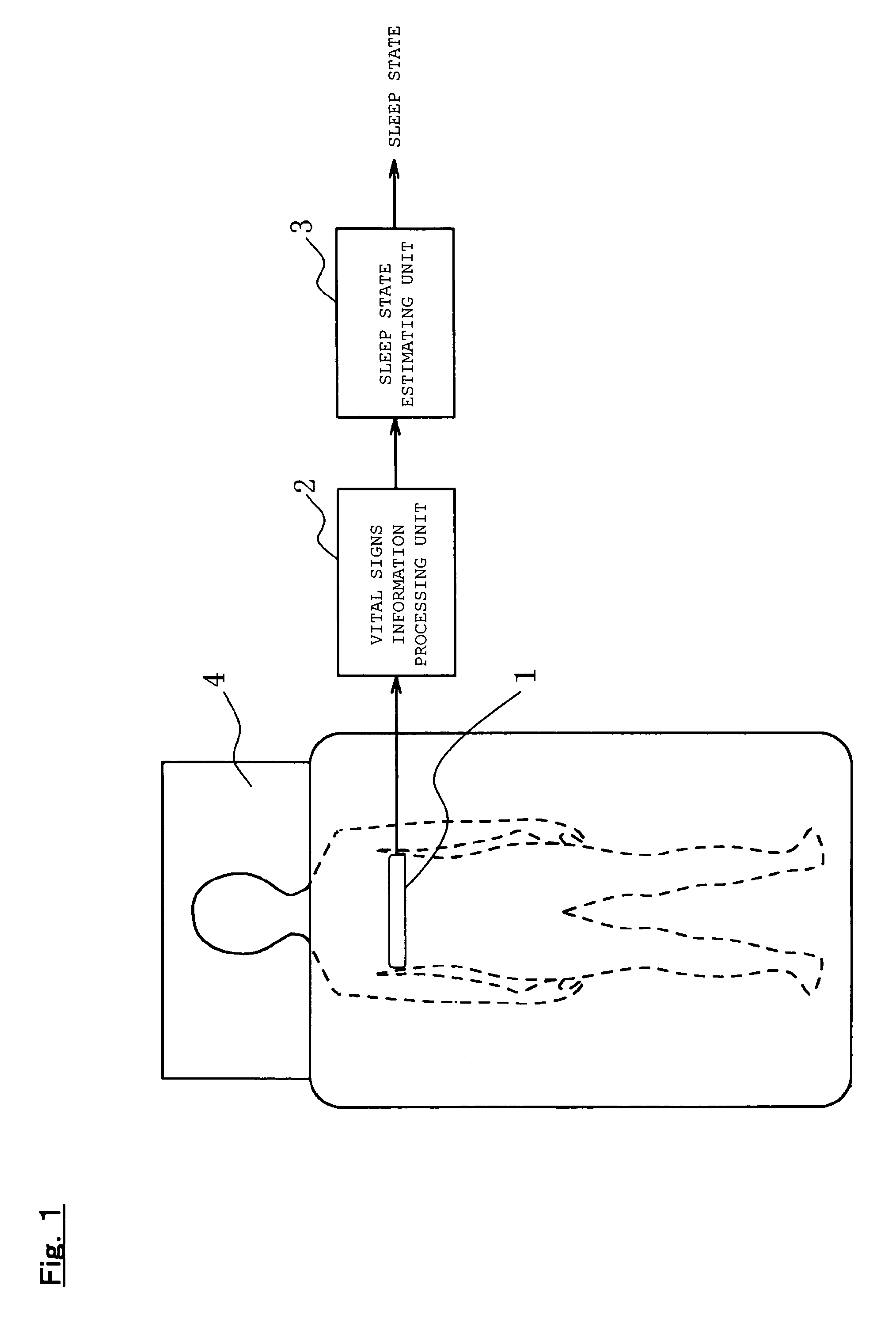
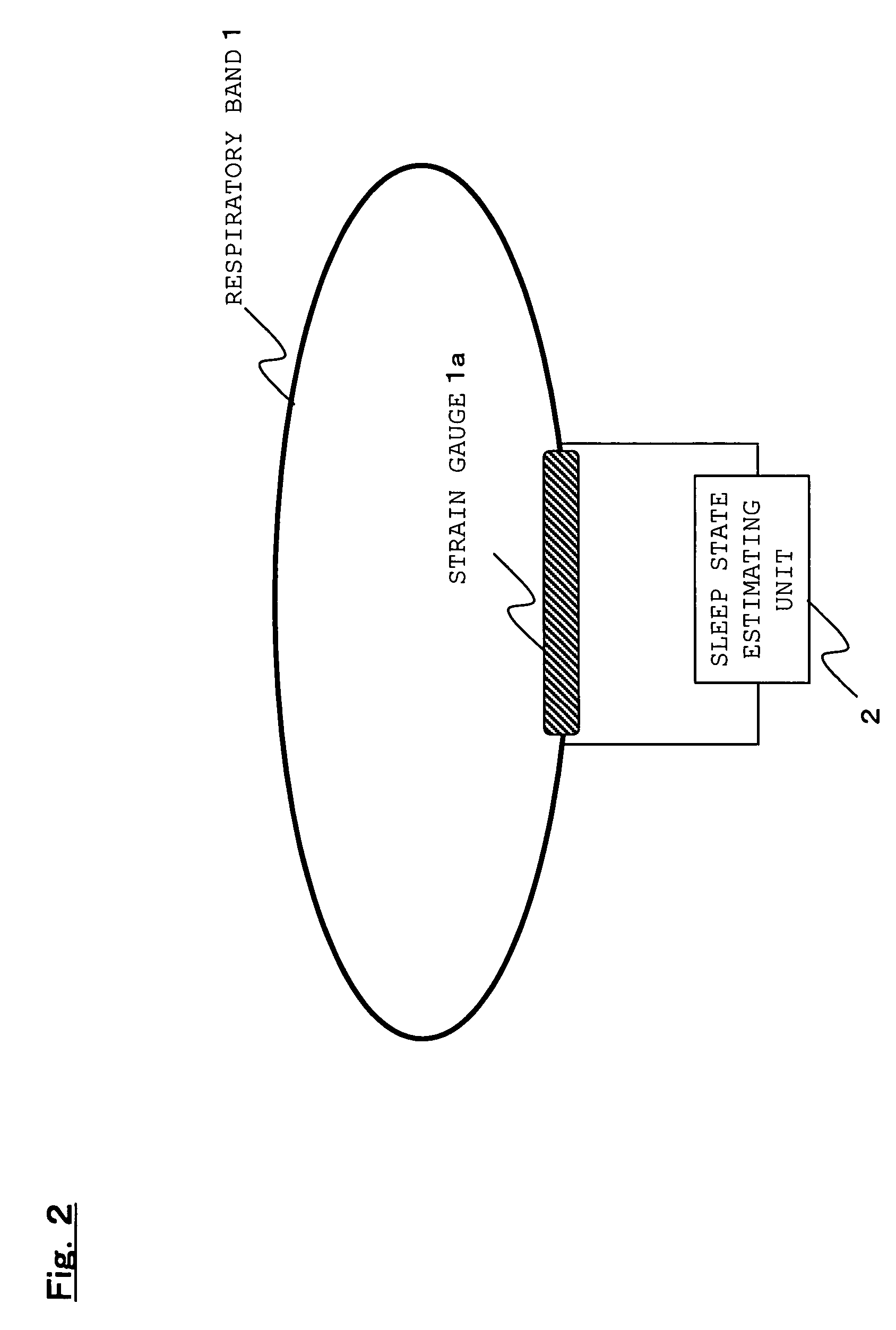
Sleep state estimation device and program product for providing a computer with a sleep state estimation function
InactiveUS7150718B2Simple processGood estimateStrain gaugeRespiratory organ evaluationSleep stateLight sleep
An object of the present invention is to provide a sleep state estimation device capable of estimating a sleep state (deep sleep, light sleep) in real time with relative simplicity. Voltage variations resulting from human respiratory movement are measured for each given period to calculate from the measurement results positive voltage peak values and time intervals between adjacent peaks. The obtained peak values and peak intervals are used to calculate a mean peak interval value A, a coefficient of variation B based on dispersion of the peak intervals, and a coefficient of variation C based on the peak values. The sleep state in this period is estimated from the calculation results. More specifically, referring to FIG. 5, the sleep state is estimated as a “wakeful state” or a “hypnagogic state” by checking whether the mean value A is larger or smaller than a threshold a and whether the coefficient of variation C is larger or smaller than a threshold c (S105) whereas the sleep state is estimated as the “hypnagogic state”, “light sleep” or “deep sleep” by checking whether the coefficient of variation B is larger or smaller than a threshold b and whether the coefficient of variation C is larger or smaller than the threshold c (S109, S113, S116, S117).
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
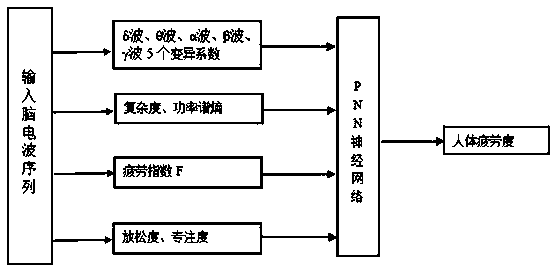
Human body fatigue evaluation method based on brain waves
The invention discloses a human body fatigue evaluation method based on brain waves. According to the method, a ThinkGearAM electroencephalogram chip is used for acquiring original brain wave signals, an built-in algorithm is used for analyzing and processing the original brain wave signals, and four kinds of parameters are given through calculation according to processed brain wave data; the four kinds of parameters include variable coefficients of five brain wave signals of original delta waves, original theta waves, original alpha waves, original beta waves and original gamma waves, two nonlinear parameters of complexity and power spectral entropy, a fatigue index F worked out through energy of four basic rhythms of the delta waves, the theta waves, the alpha waves and the beta waves in the brain waves, and two parameters of relaxation degree and attention degree extracted through the brain wave signals, and the four kinds of parameters serve as input of a probabilistic neural network (PPN), the output of the PNN serves as a human body fatigue evaluation basis, and therefore the human body fatigue can be judged according to the brain waves of people.
Owner:朱晓斐 +3
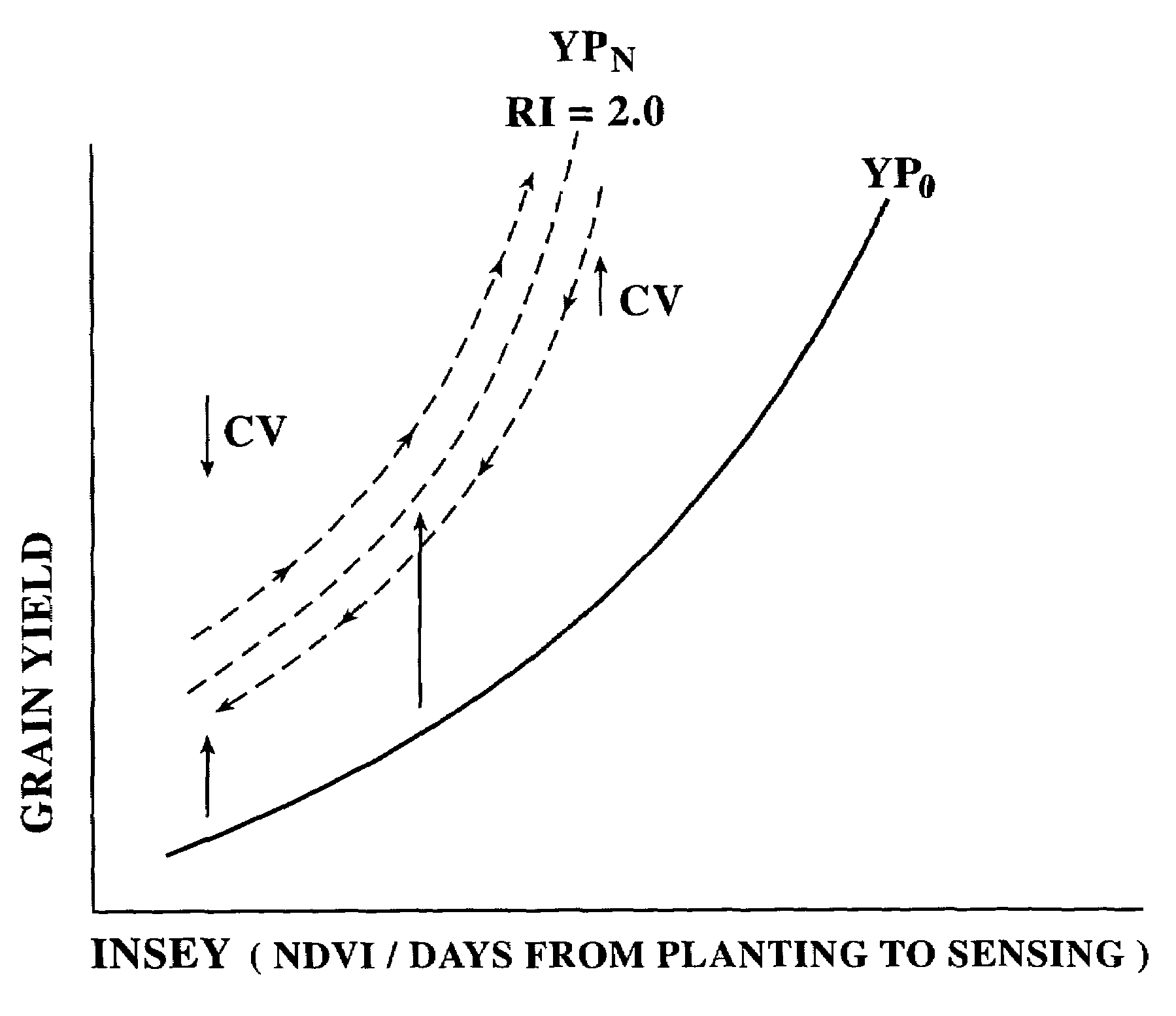
Use of within-field-element-size CV for improved nutrient fertilization in crop production
InactiveUS7188450B2Production be limitedPoor conditioningAnalogue computers for trafficFertilising methodsVegetation IndexMacro and micronutrients
A method for in-season macro and micronutrient application based on predicted yield potential, coefficient of variation, and a nutrient response index. The inventive method includes the steps of: determining a nutrient response index for a field; determining the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) of an area to fertilize; determining the coefficient of variation of NDVI over a plot; determining a predicted crop yield for the area without additional nutrient; determining an attainable crop yield for the area with additional nutrient; determining the nutrient requirement for the area as the difference between the nutrient removal at the attainable yield minus the nutrient removal at the predicted yield, adjusted by the efficiency of nutrient utilization in the particular crop as indicated by the coefficient of variation.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Developer for replenishment and image forming method
ActiveUS8142972B2Small sizeSimple processDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternEngineeringCoefficient of variation
Provided is a developer for replenishment capable of forming a high-quality image even upon duration. The developer for replenishment includes at least a toner and a magnetic carrier, and in the developer for replenishment, 1 part by mass of the magnetic carrier is blended with 2 to 50 parts by mass of the toner, and the magnetic carrier contains a ferrite core and a resin component, has a true specific gravity of 2.5 to 4.2 g / cm3, has a 50% particle diameter on a volume basis (D50) of 15 to 70 μm, and has an average circularity of 0.850 to 0.950, the average circularity having a coefficient of variation of 1.0 to 10.0%.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for producing structure
InactiveUS20060234396A1Shorten the timeReduce surface roughnessMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsPore diameterAluminum substrate
Disclosed is a method for producing a structure having: a stripping step in which an aluminum member including an aluminum substrate and an anodized layer present on the aluminum substrate, which layer contains micropores having an average pore diameter of 10 to 500 nm and a coefficient of variation in pore diameter of less than 30%, is electrolyzed in an aqueous acid solution by using the aluminum member for a cathode to thereby strip the anodized layer off the aluminum substrate so as to produce a structure composed of the anodized layer with a plurality of recesses. The method can produce a structure having regularly arranged recesses in a reduced time.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
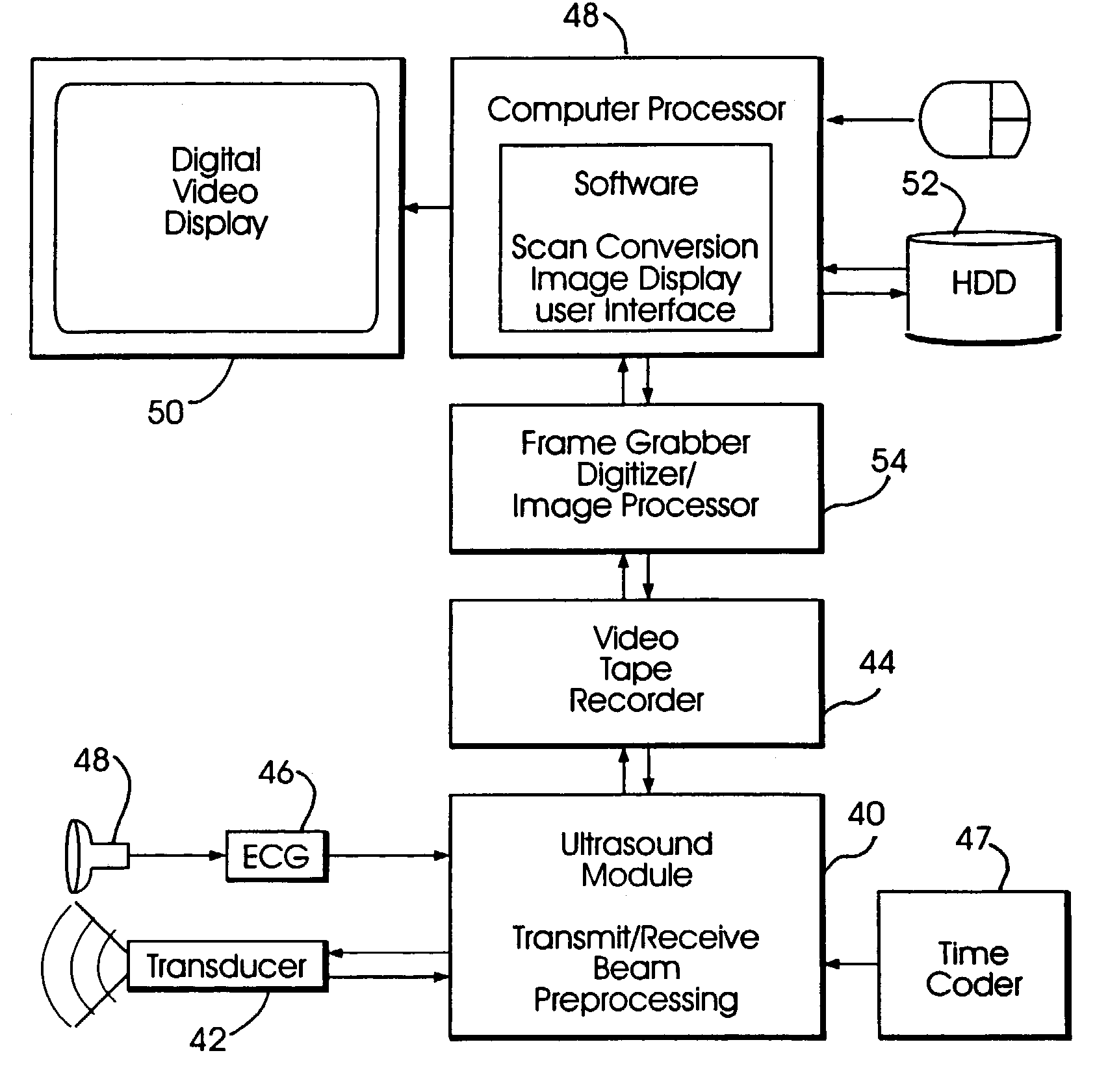
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS20040116812A1ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time "live" ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Method for quantitatively evaluating uniformity of cigarette density distribution
InactiveCN104165822AQuantitative evaluation of uniformitySimple methodSpecific gravity measurementDensity distributionComputer science
The invention discloses a method for quantitatively evaluating the uniformity of the cigarette density distribution. The method comprises the following steps: firstly making a cigarette density distribution curve according to the characteristic that the cigarette density is generally distributed in a way that two ends are dense, removing a dense end of a cigarette by utilizing an inflexion method, and then quantitatively evaluating the uniformity of the cigarette density distribution by utilizing a coefficient of variation method. The method is simple and feasible and capable of quantitatively evaluating the uniformity of the cigarette density distribution. By adopting the method, the mass stability of the cigarette after being rolled can be objectively reflected, and reference can be further provided for the improvement and optimized control of the cigarette quality.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Fine structural body and method of producing the same
Described is a structural body including at least partially an aluminum member having on a surface an anodized film with micropores present, in which: the micropores have a coefficient of variation in pore size of 5 to 50%; and the micropores are each sealed with a metal. The structural body can generate localized plasmon resonance having a sufficiently large intensity and be produced at low cost through a simple production process, and having a large surface area.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Apparatus and method for controlling the secondary injection of fuel
A combustor (28) for a gas turbine engine is provided comprising a primary combustion chamber (30) for combusting a first fuel to form a combustion flow stream (50) and a transition piece (32) located downstream from the primary combustion chamber (30). The transition piece (32) comprises a plurality of injectors (66) located around a circumference of the transition piece (32) for injecting a second fuel into the combustion flow stream (50). The injectors (66) are effective to create a radial temperature profile (74) at an exit (58) of the transition piece (32) having a reduced coefficient of variation relative to a radial temperature profile (64) at an inlet (54) of the transition piece (32). Methods for controlling the temperature profile of a secondary injection are also provided.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Polymeric articles having embedded phases
InactiveUS6447875B1Uniform widthIncrease widthSynthetic resin layered productsPlastersCoefficient of variationMechanical engineering
A die apparatus, a method of using the die apparatus to produce co-extruded polymeric articles, and co-extruded polymeric articles produced using the die apparatus and method are disclosed. The die apparatus includes a hollow vane configured to extrude a material into a chamber within the die, thereby producing a co-extruded web. The co-extruded web has a plurality of distinct, discontinuous phases in the cross-web direction, the phases having a uniform width as shown by a coefficient of variation of less than 8 percent for any three consecutive phases. The phases are substantially continuous down-web and are surrounded by a matrix having two or more layers.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
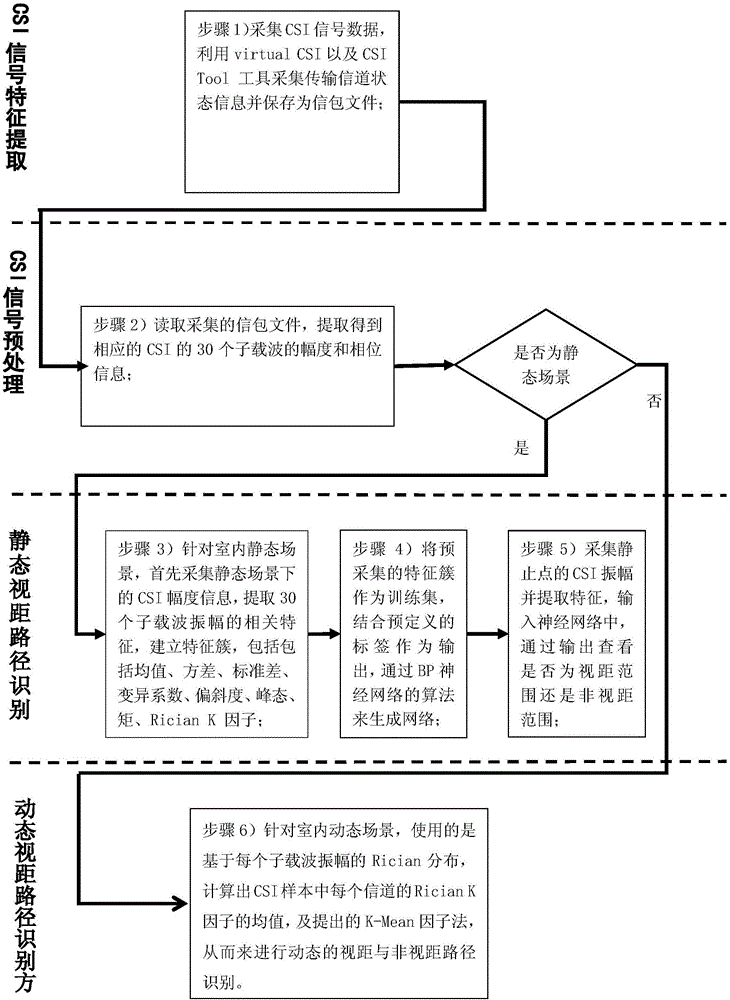
Line-of-sight path identification method in indoor environment based on channel state information
InactiveCN106792808AReduce overheadOvercome stabilityNetwork topologiesTransmission monitoringChannel state informationRician k factor
The invention discloses a line-of-sight path identification method in an indoor environment based on channel state information (CSI). The method comprises the following steps: at a CSI signal collection stage, extracting amplitude information of CSI from a signal packet; dividing indoor scenes into a static scene and a dynamic scene; in the static scene, extracting a mean, a variance, a standard deviation, a variation coefficient, a degree of skewness, a kurtosis, a moment and Rician K factors to form a characteristic cluster, then using the characteristic cluster as a training set of a BP neural network, generating the corresponding BP neural network through a pre-defined label, directly extracting the corresponding characteristic cluster from a newly collected static point, inputting the characteristic cluster into a network, and realizing static line-of-sight path identification; and in the dynamic scene, calculating the mean of the Rician K factors of each channel in a CSI sample by using Rician distribution based on the amplitude of each subcarrier, and performing dynamic line-of-sight and non-line-of-sight path identification. By adoption of the line-of-sight path identification method disclosed by the invention, the accuracy of static and dynamic line-of-sight path identification in the indoor environment can be improved, and indoor comprehensive identification of the line-of-sight range can be realized at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
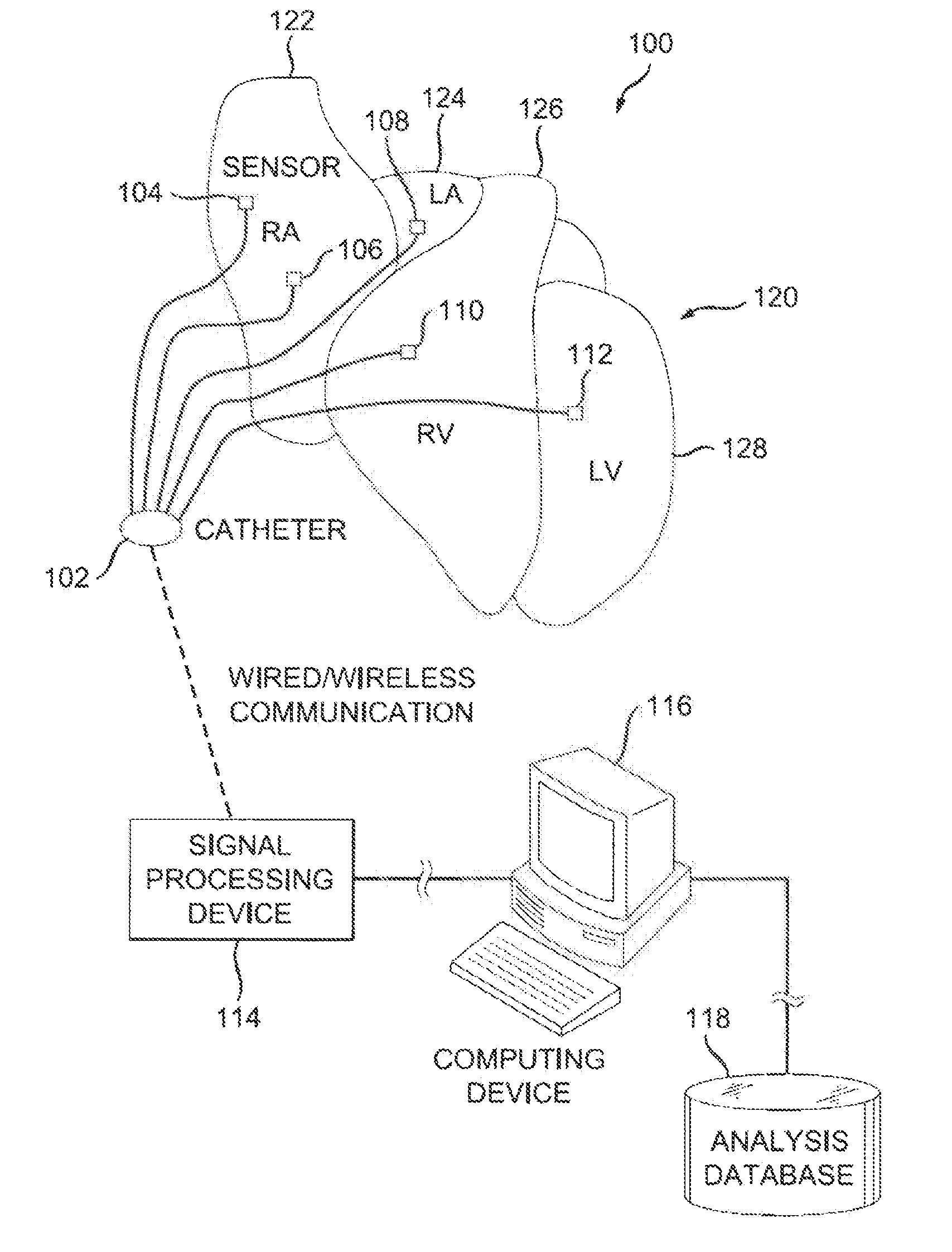
System and method of identifying sources for biological rhythms
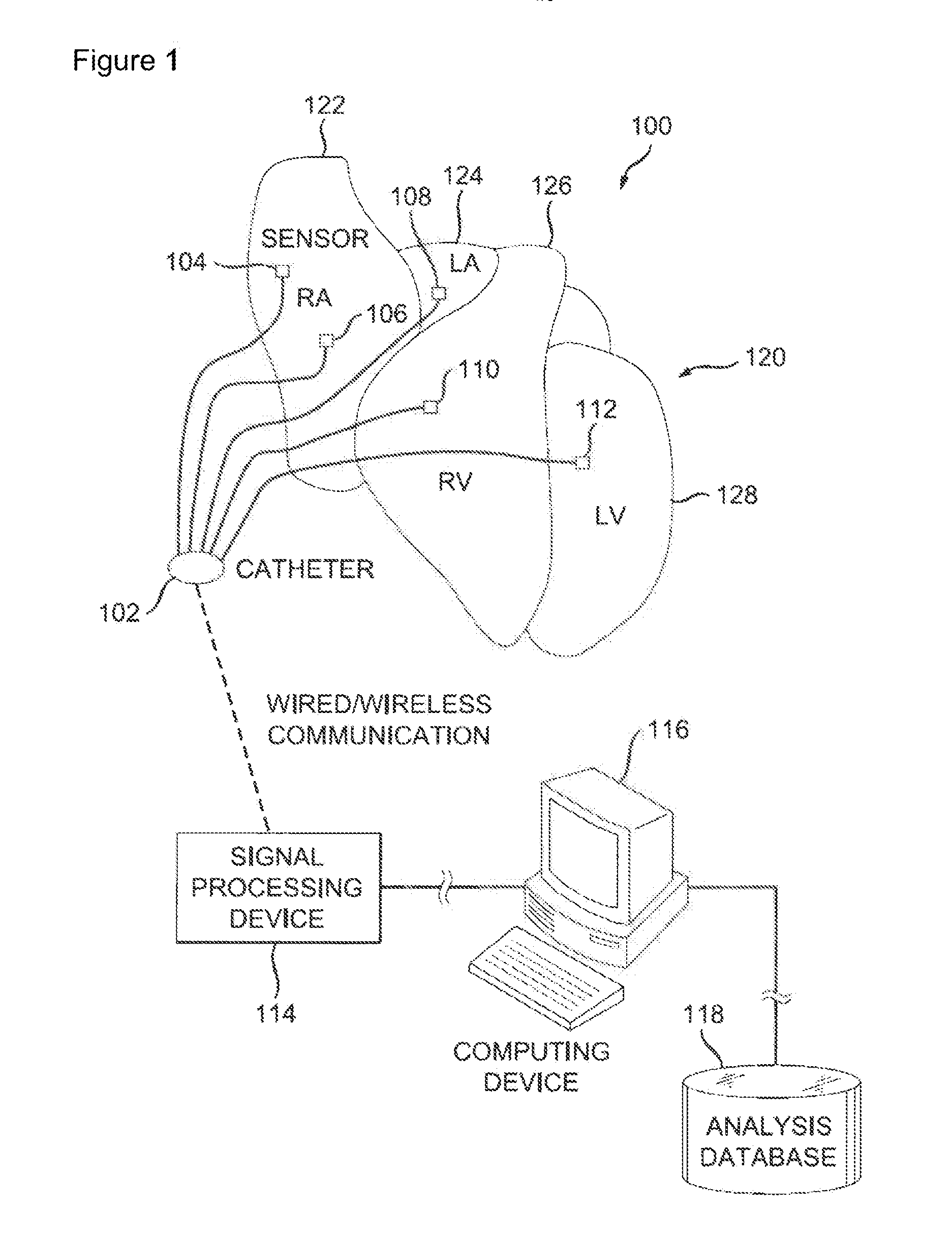
ActiveUS20130150740A1Accurately activatedAmeliorate disorderElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEngineeringCoefficient of variation
An example system and method of locating a source of a heart rhythm disorder are disclosed. In accordance with the method, a first pair of cardiac signals is processed to define a first coefficient associated with variability of the first pair of signals at a first region of the heart. Further, a second pair of cardiac signals is processed to define a second coefficient associated with variability of the second pair of signals at a second region of the heart. Thereafter, the first coefficient of variability is compared to the second coefficient of variability to determine a direction towards the source of the rhythm disorder.
Owner:TOPERA +2
System and method for improving ultrasound image acquisition and replication for repeatable measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS7074187B2ElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionAnatomical landmarkUltrasonic sensor
High resolution B-mode ultrasound images of the common carotid artery are obtained with an ultrasound transducer using a standardized methodology. Subjects are supine with the head counter-rotated 45 degrees using a head pillow. The jugular vein and carotid artery are located and positioned in a vertical stacked orientation. The transducer is rotated 90 degrees around the centerline of the transverse image of the stacked structure to obtain a longitudinal image while maintaining the vessels in a stacked position. A computerized methodology assists operators to accurately replicate images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. By viewing both images, whether simultaneously or alternately, while manually adjusting the ultrasound transducer, an operator is able to bring into view the real-time image that best matches a selected image from the earlier ultrasound examination. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. All images contain anatomical landmarks for reproducing probe angulation, including visualization of the carotid bulb, stacking of the jugular vein above the carotid artery, and initial instrumentation settings, used at a baseline measurement are maintained during all follow-up examinations.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Method and system for color correction of tiled display device
InactiveCN103354087AImprove calibration efficiencyAvoid time wastingCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
Provided is a method for color correction of a tiled display device. The method comprises steps: determining respectively R, G, and B original target tristimulus values according to R, G, and B original target color coordinates and original target brightness prestored in the tiled display device; determining respectively R, G, and B target tristimulus values according to R, G, and B original target color coordinates and original target brightness of each display unit prestored in the tiled display device; determining respectively proportionality coefficients of variation of the R, G, and B tristimulus values according to the R, G, and B original target tristimulus values and target tristimulus values; determining respectively relative values of the R, G, and B tristimulus values of each display unit according to each proportionality coefficient and relative values of the R, G, and B original tristimulus values prestored in each display unit; and performing consistency calibration on colors of the tiled display device according to the relative value of each R, G, and B tristimulus value. The invention provides a corresponding system which improves calibration efficiency of each display unit of the tiled display device.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Split-screen display system and standardized methods for ultrasound image acquisition and processing for improved measurements of vascular structures
InactiveUS6979294B1Accurately and cost-effectively screenOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesSub-pixel resolutionSonification
A standardized acquisition methodology assists operators to accurately replicate high resolution B-mode ultrasound images obtained over several spaced-apart examinations. The methodology utilizes a split-screen display in which the arterial ultrasound image from an earlier examination is displayed on one side of the screen while a real-time “live” ultrasound image from a current examination is displayed next to the earlier image on the opposite side of the screen. A computerized echo edge recognition and tracking methodology automatically identifies ultrasound echo boundaries of the intima-media complex and automatically extracts IMT and arterial dimension measurements, without introducing human measurement error. Measurement accuracy is enhanced by use of sub-pixel resolution for echo edge boundary definition. Utilizing this methodology, measurement of vascular dimensions, such as carotid arterial IMT and diameter, the coefficient of variation is substantially reduced to values approximating from about 1.0% to about 1.25%. Dynamic material properties of arterial structures are measured in a standardized region in accordance with a standardized methodology in order to promote measurement repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
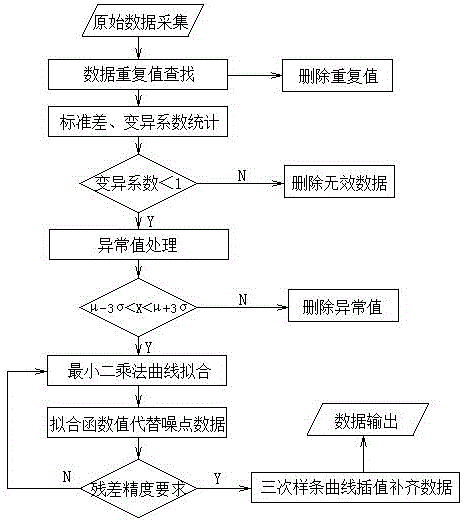
Time-series data cleaning method for pipe net modeling
InactiveCN106649579AAchieve cleaning effectReduce decreaseSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureMissing data
The invention discloses a time-series data cleaning method for pipe net modeling. The time-series data cleaning method for the pipe net modeling comprises the steps of searching and elimination of duplicate values, data dispersion degree analysis, judgment of outliers, denoising noisy points of curve smoothing, interpolation completion of missing data. The time-series data cleaning method for the pipe net modeling introduces variation coefficient to achieve standardization processing of pressure information and flow data of different dimensions, judges the dispersion degree of arrays and screen the dispersion degree of arrays at the same time. The time-series data cleaning method for the pipe net modeling is characterized in that outlier data at first is searched and processed by a utilizing three times standard deviation method and then is fitted by a least square method, which greatly reduces the effects of outliers on fitting results. At the same time, data smoothing of the noisy points is processed by fitting functions, which can further reduce the presence of outlier data. The least square method can satisfy the data processing which does not conform to the normal distribution. Compared with linear interpolation, cubic spline interpolation utilized in the end can make the data inserted more smooth. The time-series data cleaning method for the pipe net modeling has the advantages of preprocessing the data before the data is imported into a model for calculation, achieving the effect of data cleaning, and providing a guarantee for the calculation of the model.
Owner:苏州航天系统工程有限公司
Industrial procedure for identifying preferential seepage channels of oil and gas reservoirs of clastic rock
The invention discloses an industrial procedure for identifying preferential seepage channels of oil and gas reservoirs of clastic rock. The industrial procedure includes steps of 1), dividing n development phases and dividing wells into n groups according to the development phases of well drilling time; 2), dividing data grids of research areas; 3), interpolating permeability parameters of well points of the well groups 1 to obtain permeability planar distribution grids of the development phases 1; 4), sequentially acquiring permeability planar distribution grids R<1>, R<2>, ..., and R<n> of the n development phases by the aid of a method implemented in the step 3); 5), computing a variation coefficient of a permeability value of each grid point by the aid of results obtained in the step 4) so as to obtain variation coefficient grids P; 6), subtracting the R<1> from the R<n>, assigning values of 1 to the grid points with positive difference values and assigning values of -1 to the grid points with negative difference values to obtain grids T; 7), multiplying the grids P by the grids T to obtain grids Q, drawing contour maps of the grids Q, and utilizing regions larger than 0.3 in the contour maps as the preferential seepage channels. The variation coefficients of the permeability values of the grid points change along with change of the development phases. The industrial procedure has the advantage that oilfield water-flooding development and remaining oil prediction can be guided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method and device for sensing touch inputs
ActiveUS20160085333A1Minutely discriminatedDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingSpectral bandsFrequency spectrum
A method for sensing touch inputs to a digital equipment is provided, comprising the steps of sensing a sound / vibration signal generated by a touch, digitally processing the sensed sound / vibration signal, and determining the type of touch means that has generated the touch and the intensity of the touch based on the properties of the processed sound / vibration signal, wherein the properties include at least one of the following properties of the sound / vibration signal in time domain: maximum amplitude, average amplitude, average frequency, mean, standard deviation, standard deviation normalized by overall amplitude, variance, skewness, kurtosis, sum, absolute sum, root mean square (RMS), crest factor, dispersion, entropy, power sum, center of mass, coefficients of variation, cross correlation, zero-crossings, seasonality, DC bias, or the above properties computed for the first, second, third or higher order of derivatives of the sound / vibration signal; and the following properties of the sound / vibration signal in frequency domain: spectral centroid, spectral density, spherical harmonics, total average spectral energy, band energy ratios for every octave, log spectral band ratios, linear prediction-based cepstral coefficients (LPCCs), perceptual linear prediction (PLP) cepstral coefficients, mel-frequency cepstral coefficients, frequency topology, or the above properties computed for the first, second, third or higher order of derivatives of a frequency domain representation of the sound / vibration signal. There is also provided a device for sensing touch inputs.
Owner:QEEXO
Soft magnetic material, dust core, method for manufacturing soft magnetic material, and method for manufacturing dust core
ActiveUS20100044618A1Metal-working apparatusInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureCoefficient of variationMaterials science
A soft magnetic material, a dust core, a method for manufacturing the soft magnetic material, and a method for manufacturing the dust core that can improve DC bias characteristics are provided.A soft magnetic material includes a plurality of metal magnetic particles 10 whose coefficient of variation Cv (σ / μ), which is a ratio of a standard deviation (σ) of a particle size of the metal magnetic particles 10 to an average particle size (μ) thereof, is 0.40 or less and whose circularity Sf is 0.80 or more and 1 or less. The metal magnetic particles 10 preferably have an average particle size of 1 μm or more and 70 μm or less. The soft magnetic material preferably further includes an insulating coated film that surrounds a surface of each of the metal magnetic particles 10.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Rapid image text detection method based on multi-channel and multi-dimensional cascade filter
InactiveCN106384112AEasy to detectImprove detection recallCharacter recognitionText detectionMaximally stable extremal regions
The present invention discloses a rapid image text detection method based on a multi-channel and multi-dimensional cascade filter. The problem is mainly solved that the recall ratio is low and the speed is slow in the prior art. The method comprises: 1) extracting a maximum stable extremum region in the different channels and scales of an input image as a character candidate region; 2) removing the background region in the character candidate region by employing a cascade filter from coarse to fine, namely setting a threshold value for the morphological features of the character candidate region, and performing the first grade coarse filtration; setting thresholds for the stroke width and the stroke width variable coefficient of the character candidate region, performing the second grade coarse filtration, then removing the overlapping regions, and employing a convolution neural network binary classifier perform fine filtration; and 3) aggregating the region into the character string according to the geometry and the position feature of the character candidate region after cascade filter through a graph model. The rapid image text detection method based on the multi-channel and multi-dimensional cascade filter has high recall ratio, high accuracy and fast speed, and can be used for detection of image text at various interference surroundings.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods of Making Libraries of Nucleic Acids Using Porous Particles
InactiveUS20110195459A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementParticle compositionPorous particle
The invention provides particle compositions having applications in nucleic acid analysis. Nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention allow polynucleotides to be attached throughout their volumes for higher loading capacities than those achievable solely with surface attachment. In one aspect, nucleic acid polymer particles of the invention comprise polyacrylamide particles with uniform size distributions having low coefficients of variations, which result in reduced particle-to-particle variation in analytical assays. Such particle compositions are used in various amplification reactions to make amplicon libraries from nucleic acid fragment libraries.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Multi-process scheme planning method based on combination weighting method
The invention discloses a multi-process scheme planning method based on a combination weighting method. The multi-process scheme planning method comprises the following steps: analyzing various factors influencing the quality of a process scheme, and establishing two layers of evaluating systems; carrying out standardizing treatment on evaluating index data by adopting a subjection function; respectively weighting evaluating indexes by adopting a fuzzy integrated evaluating method and a variation coefficient method based on process knowledge data; in combination with the weighting results of the fuzzy integrated evaluating method and the variation coefficient method, taking minimal sum of weight error squares as a target function, and calculating combination weight by adopting a Lagrangian multiplier method; based on the combination weight, in combination with a gray relative analysis method, according to the design of two layers of evaluating structures, establishing two layers of gray relative analysis models, and selecting an optimal process scheme by correlation degree of candidate process schemes obtained by calculating the models. According to the multi-process scheme planning method disclosed by the invention, the distribution deviation of optimized target weights is reduced, and the performability of the process scheme is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
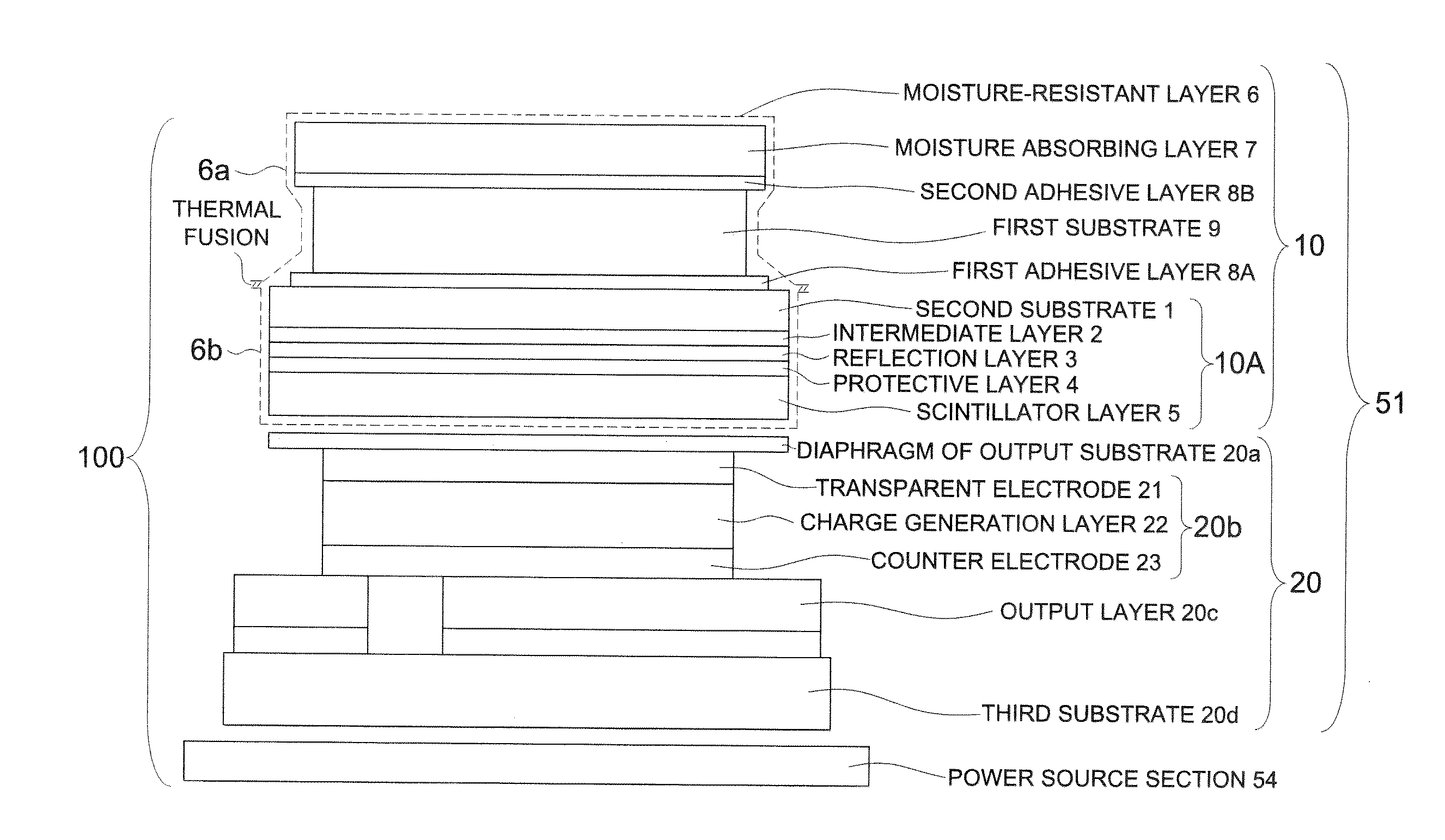
Radiation detector
InactiveUS20120001282A1Few image defectX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLuminescent compositionsPhosphorFill factor
A radiation detector of a compact size and producing almost no image defect is disclosed, comprising a first radiation-transmissive substrate, a first adhesive layer, a second radiation-transmissive substrate, a scintillator layer and an output substrate provided with a photoelectric conversion element layer which are provided sequentially in this order, wherein an arrangement region of the scintillator layer in a planar direction of the layer includes an arrangement region of the photoelectric conversion element layer in a planar direction of the layer and an arrangement region of the first substrate in a planar direction of the substrate, and the arrangement region of the first substrate includes the arrangement region of the photoelectric conversion element layer; and when the arrangement region of the scintillator layer is divided to plural areas, a coefficient of variation of filling factor is 20% or less which is defined as a standard deviation of filling factor of phosphor of the plural areas, divided by an average value of the filling factor.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Electroluminescent phosphor, method for producing the same and device containing the same
InactiveUS20060192486A1Solve low luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorStacking fault
An electroluminescent phosphor comprising: ZnS-based phosphor particles and a coating layer provided on a surface of the particle, wherein the particles have an average particle size of from 0.1 to 20 μm, and a coefficient of variation in a particle size distribution of less than 35%, and a content of particles having 10 or more stacking faults with an interplanar spacing of 5 nm or less is 30% or more based on all of the ZnS-based phosphor particles.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com