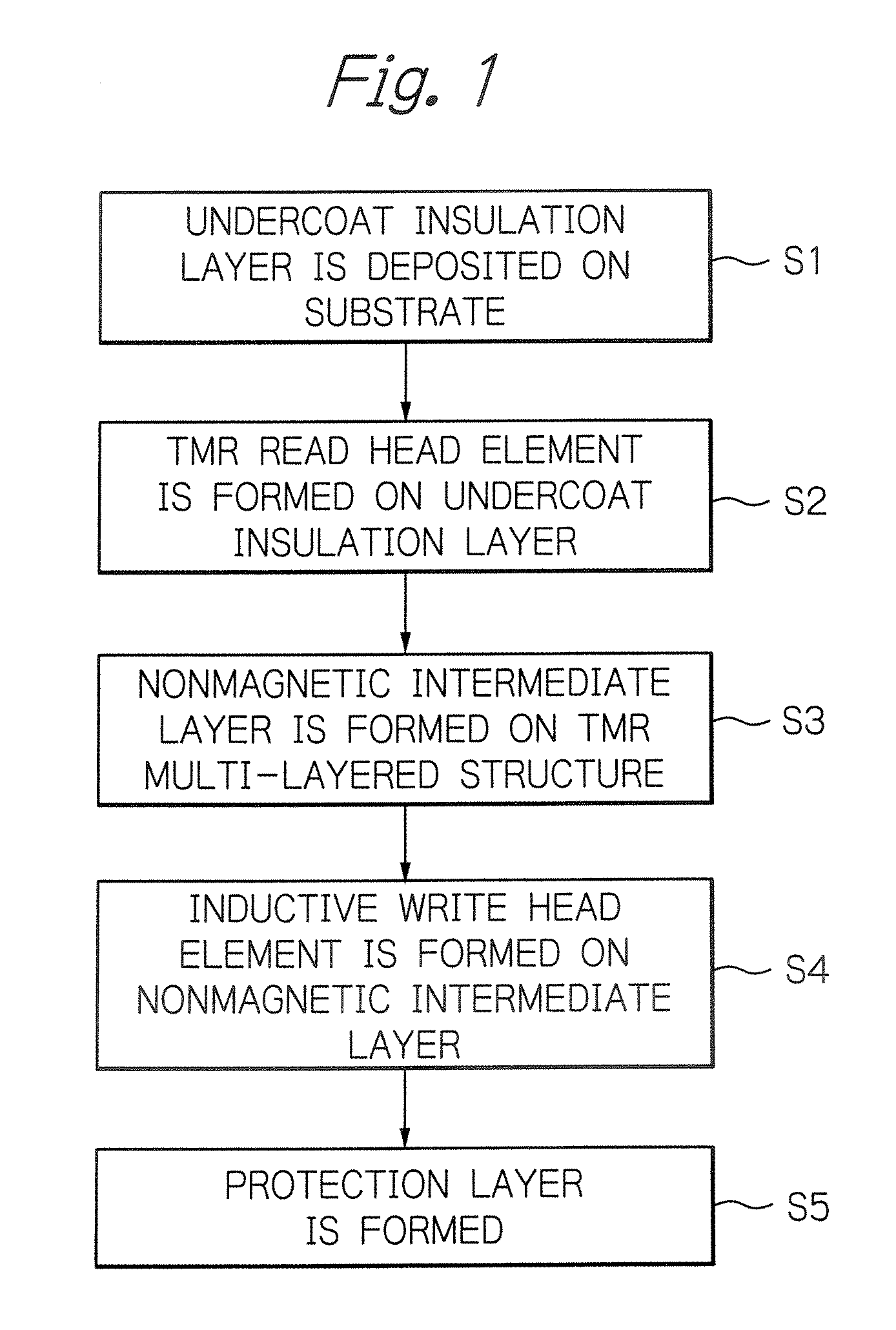
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "High MR ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
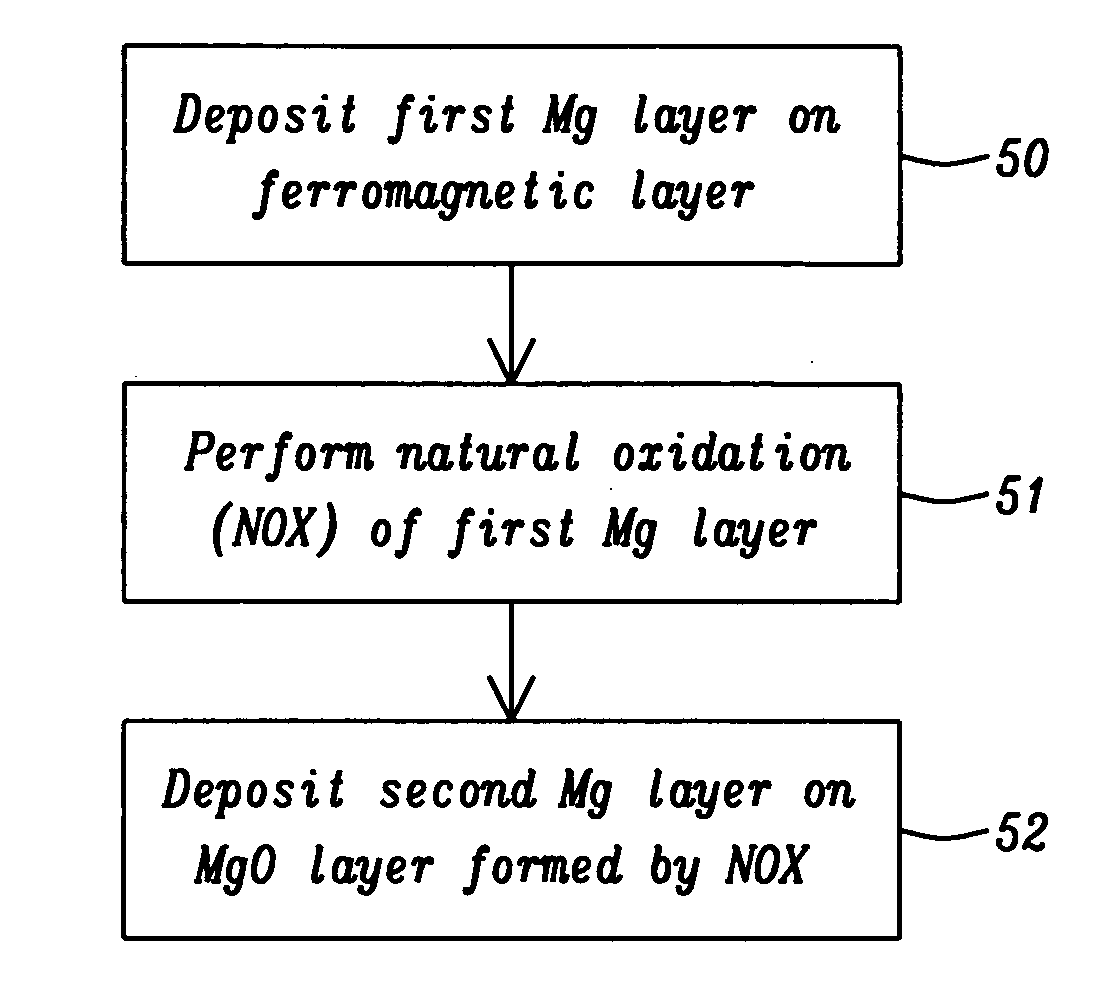
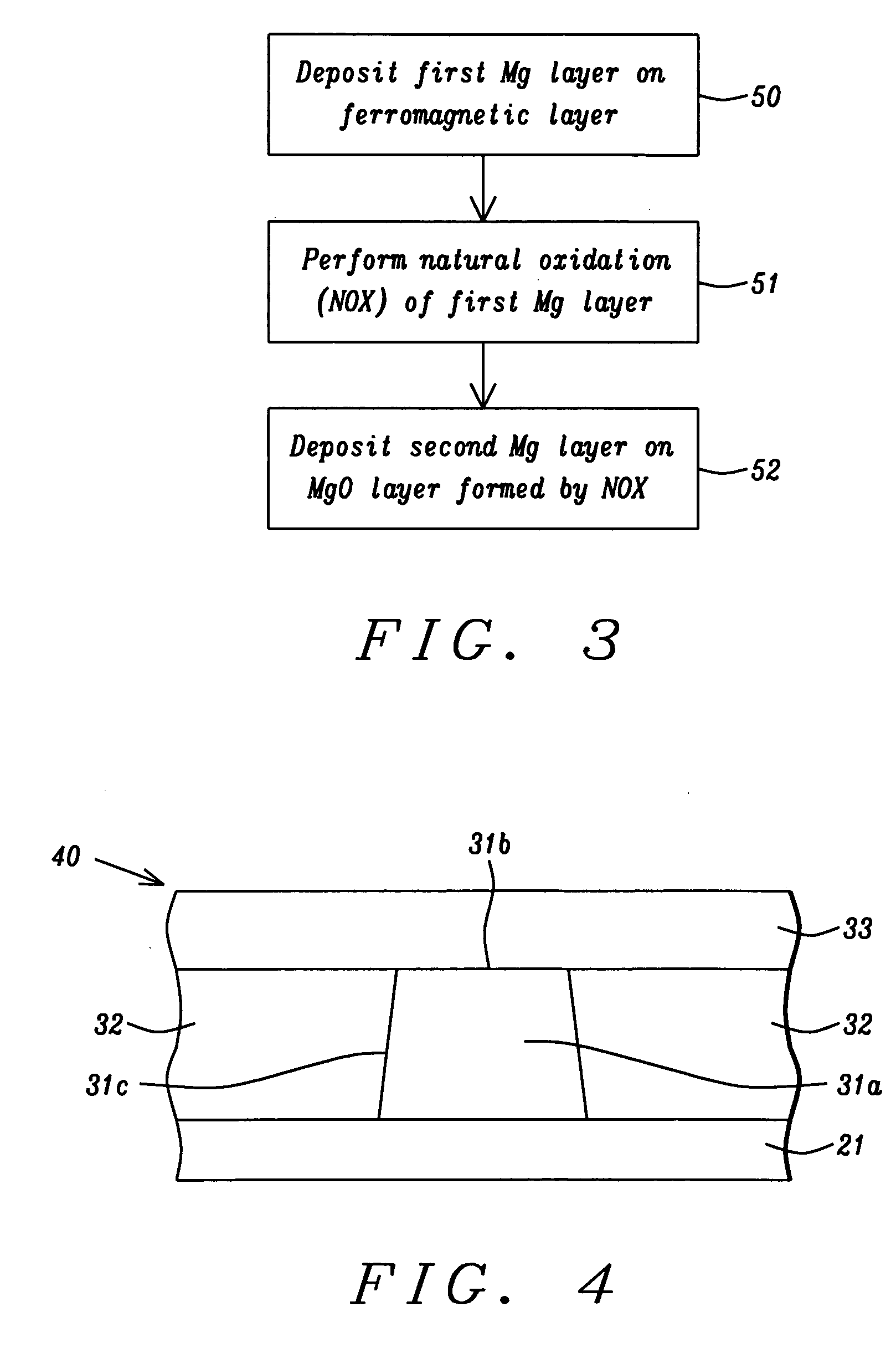
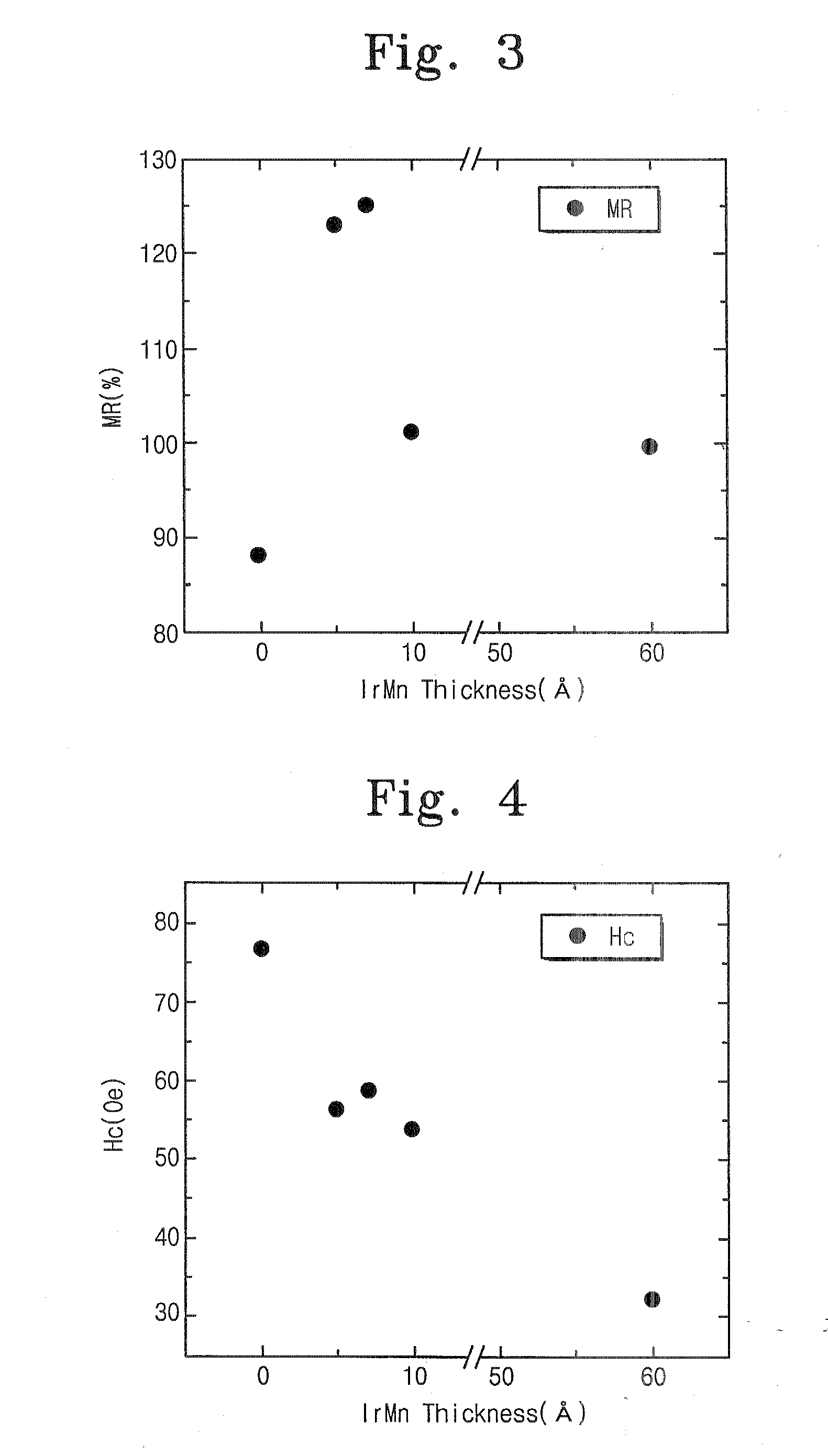
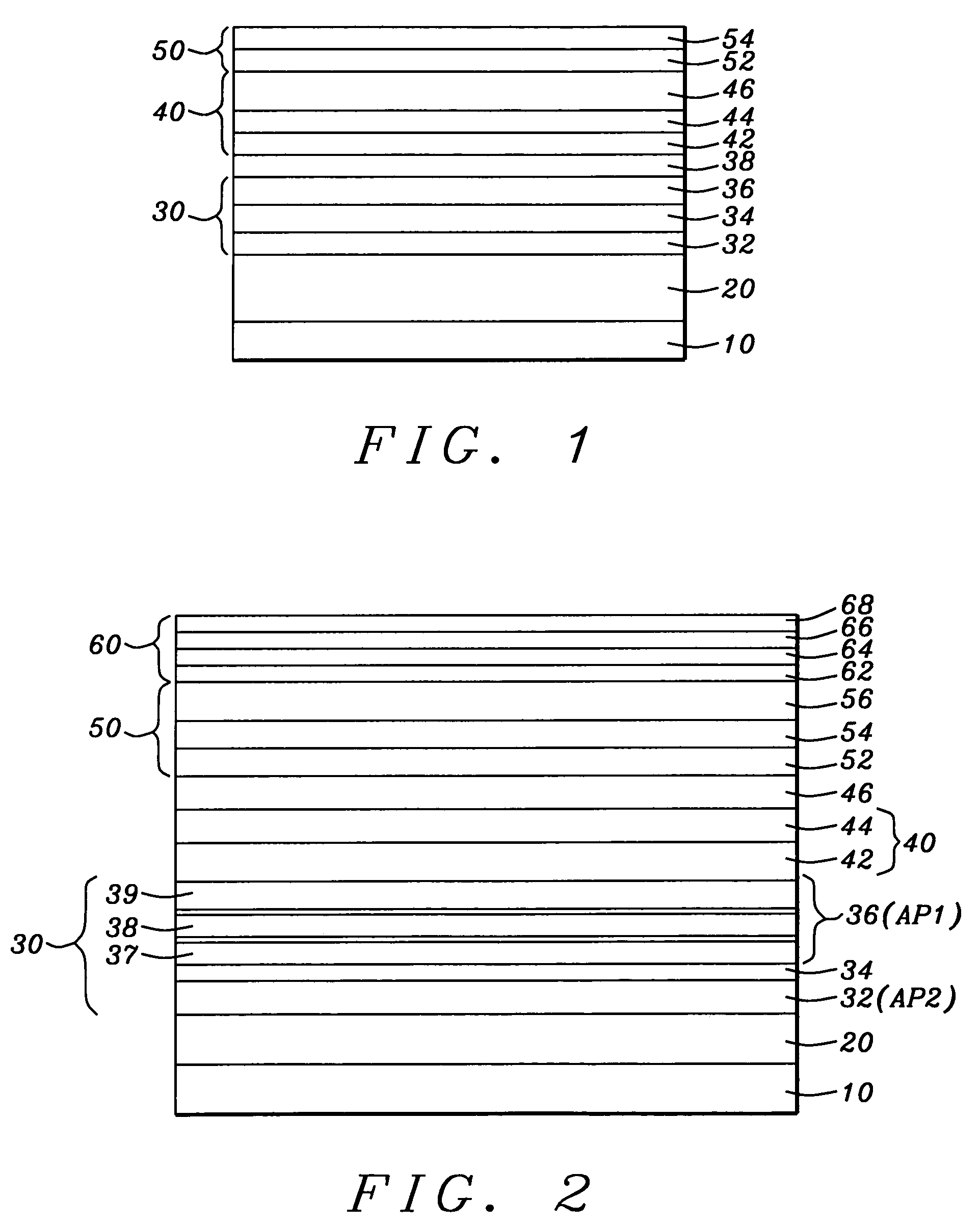
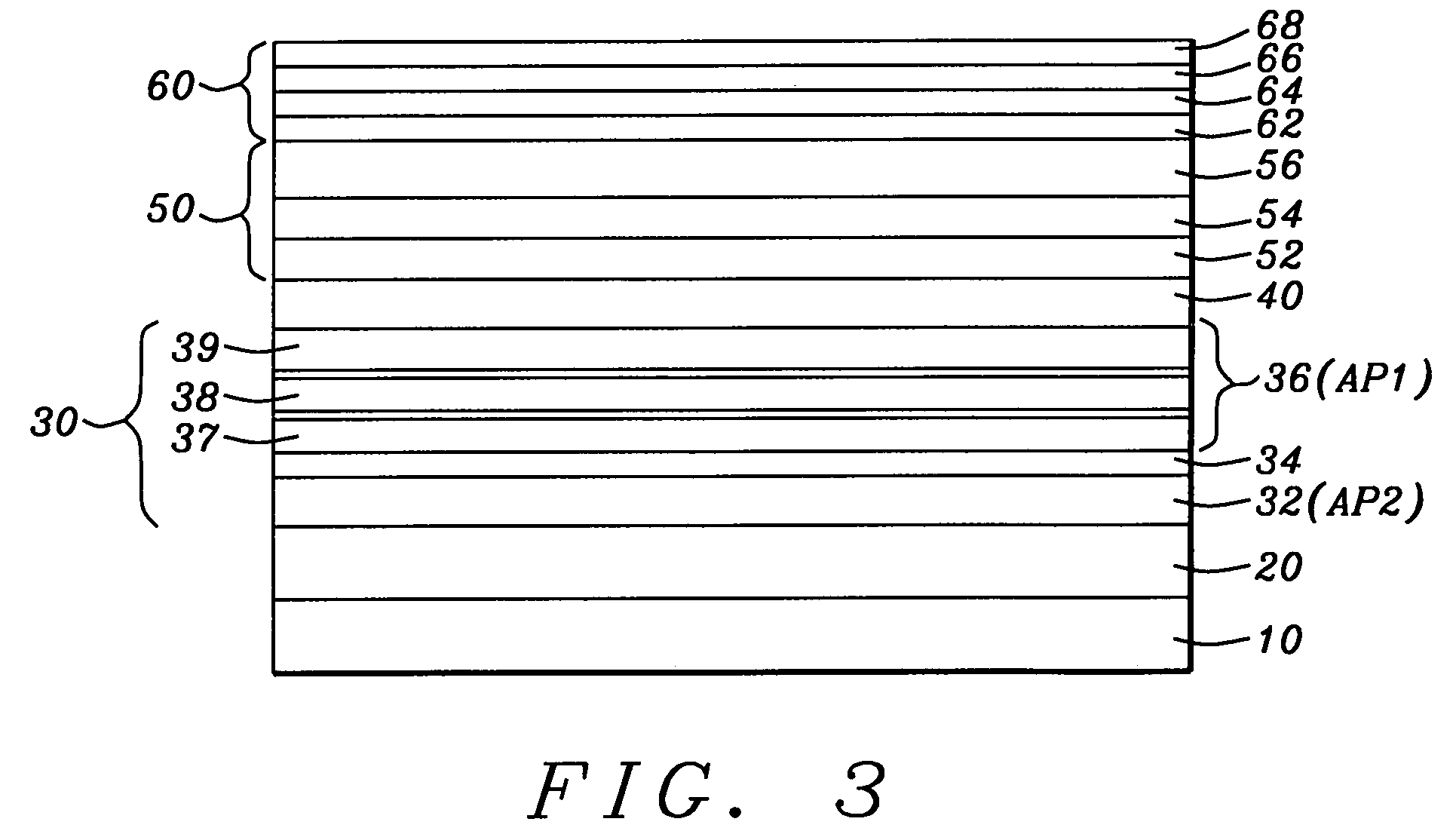
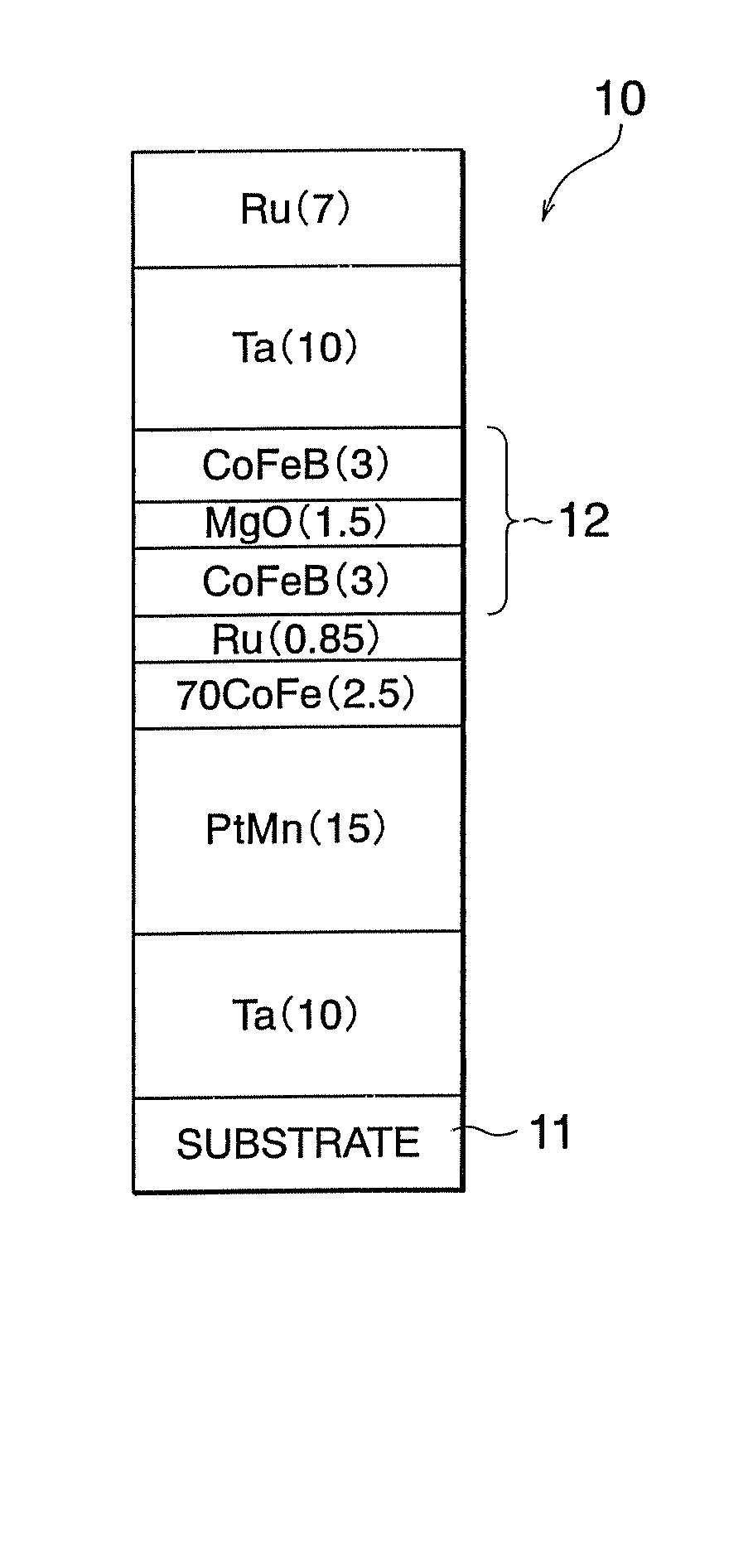
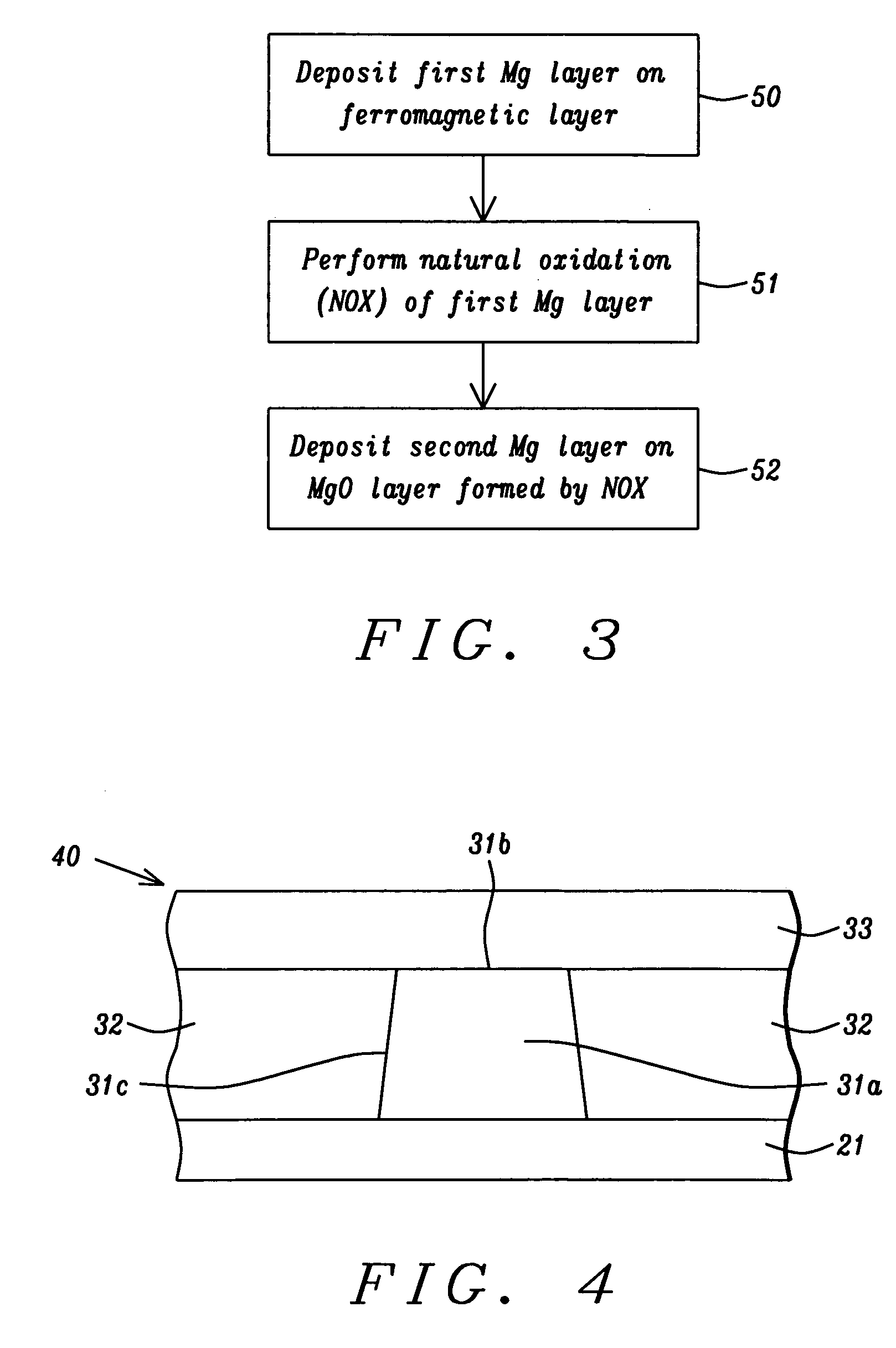
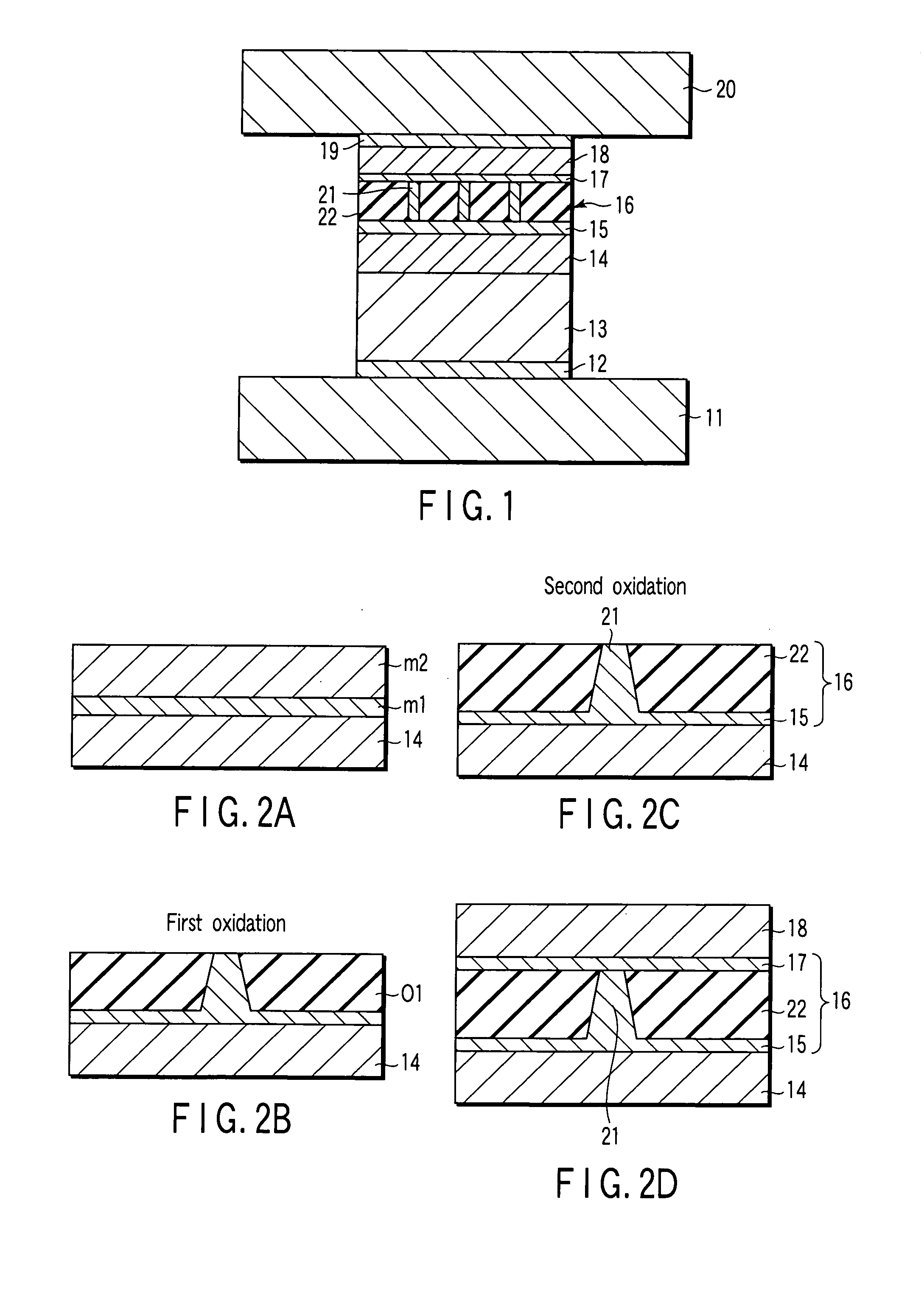
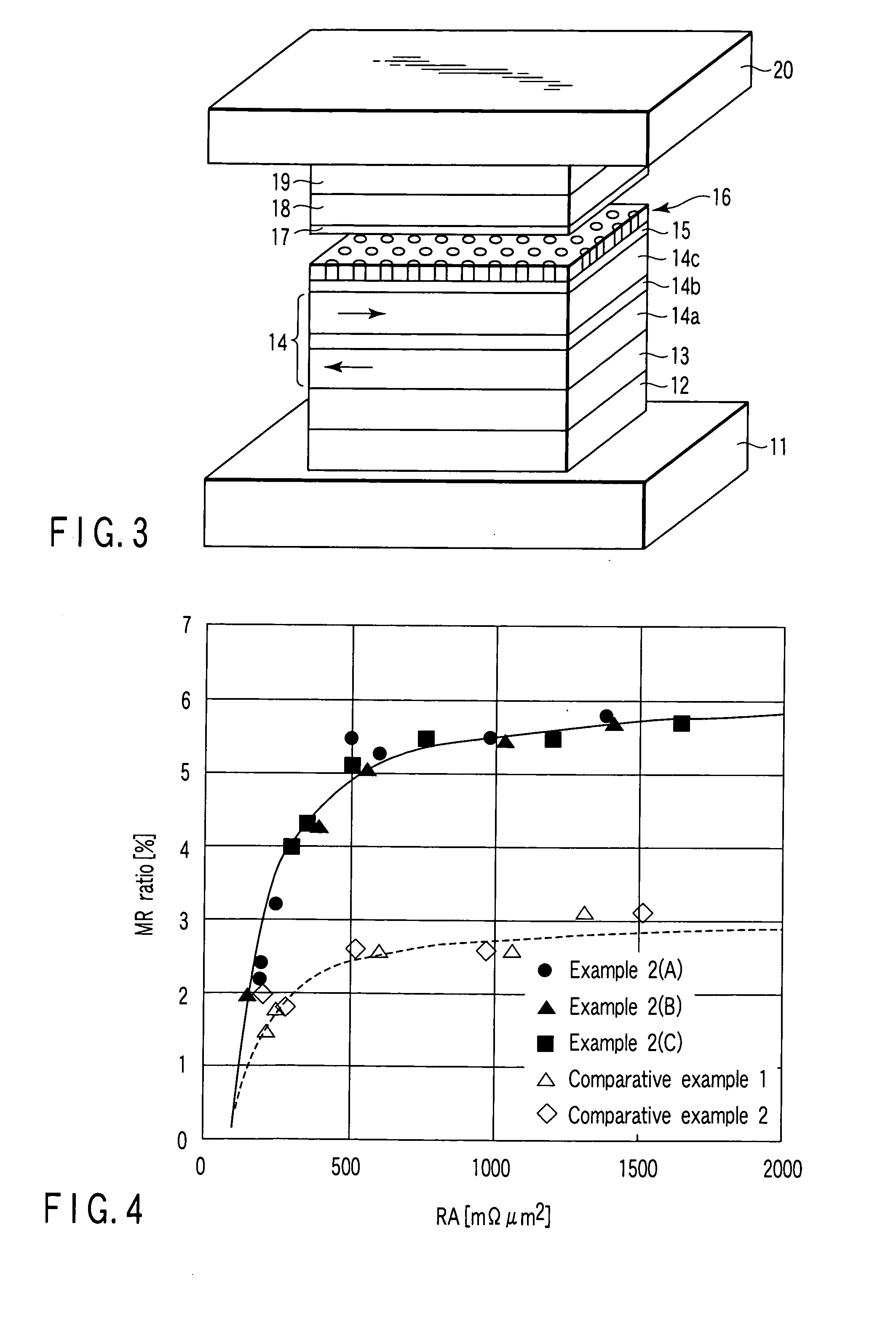
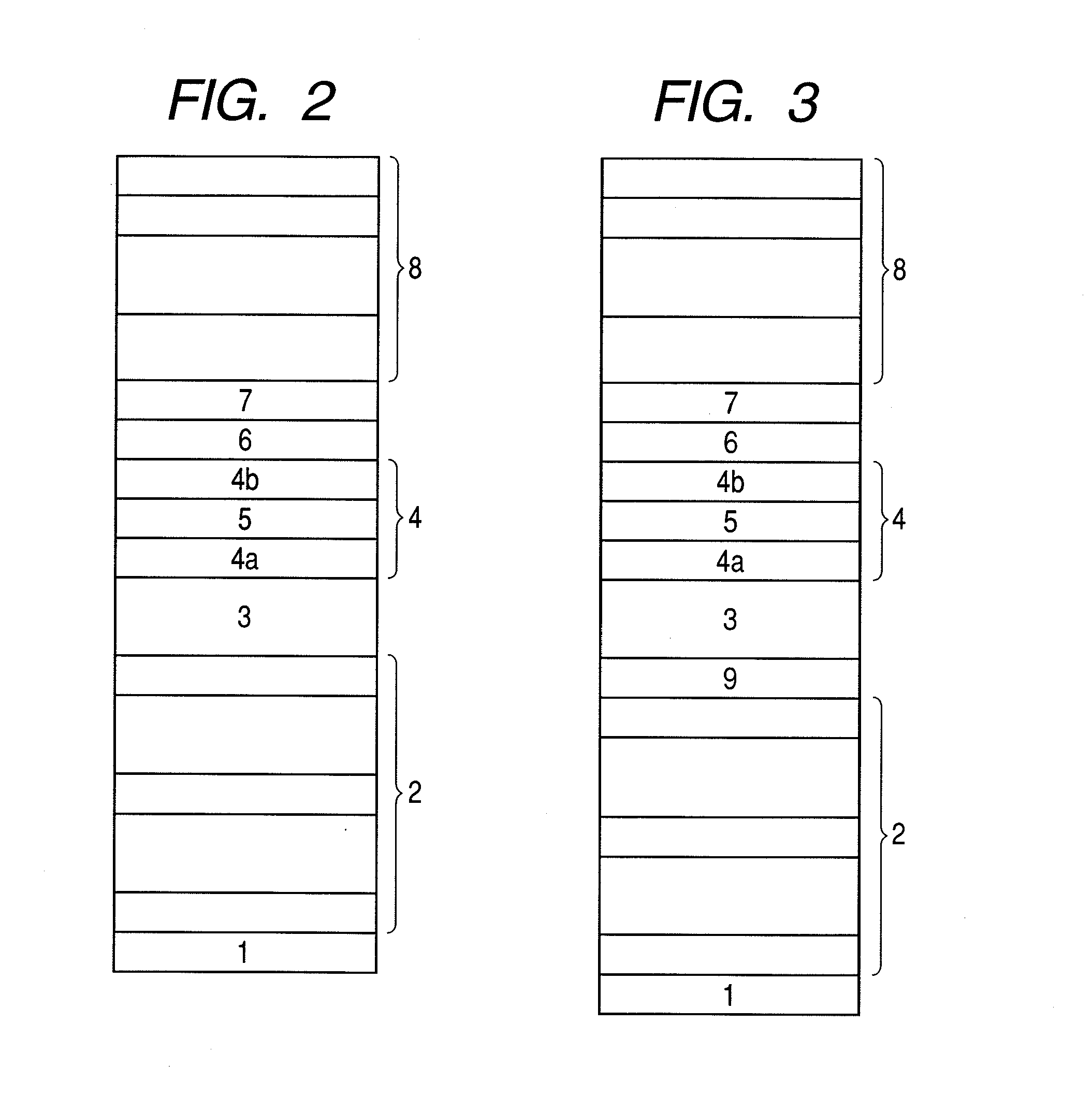
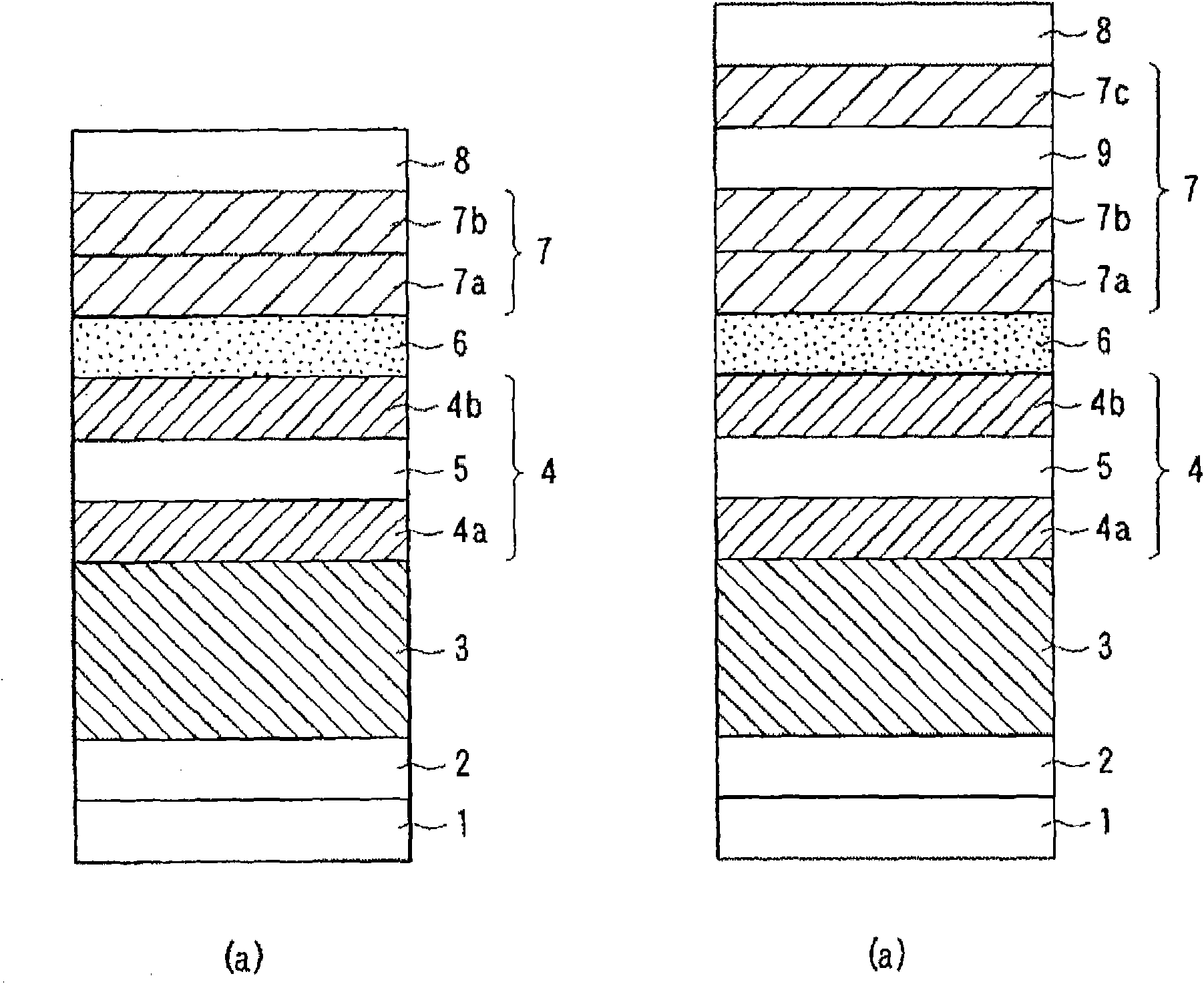
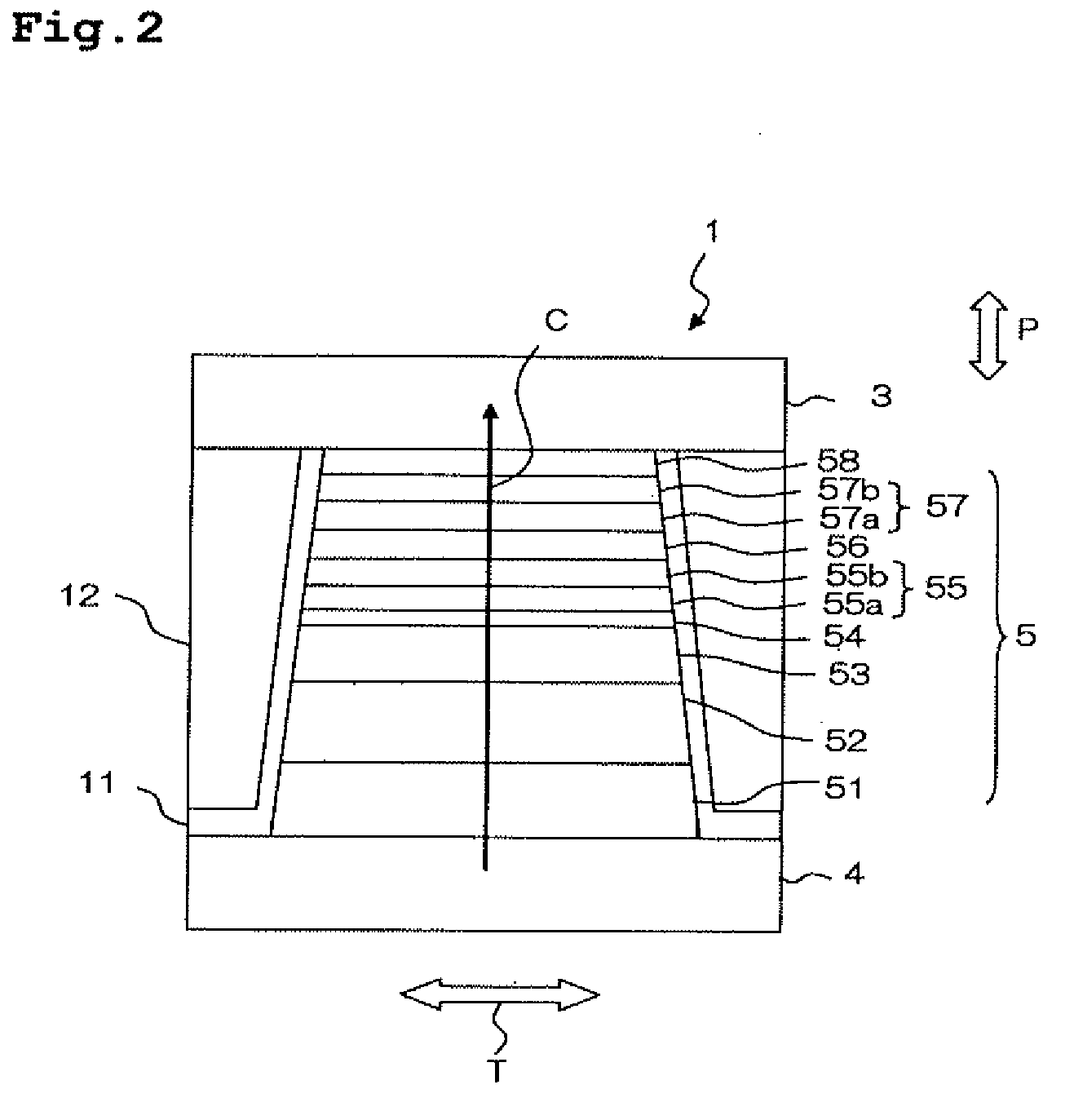
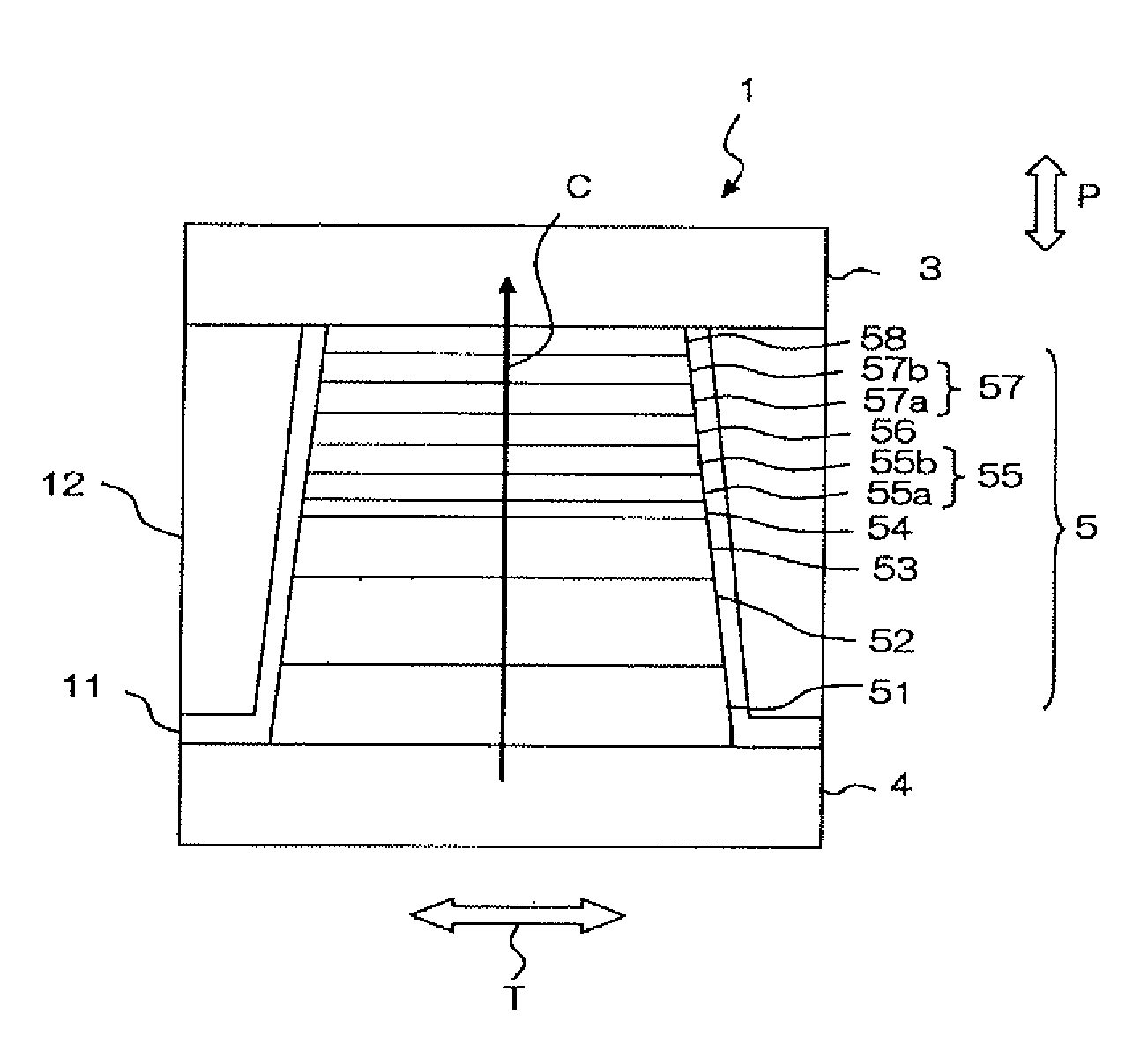
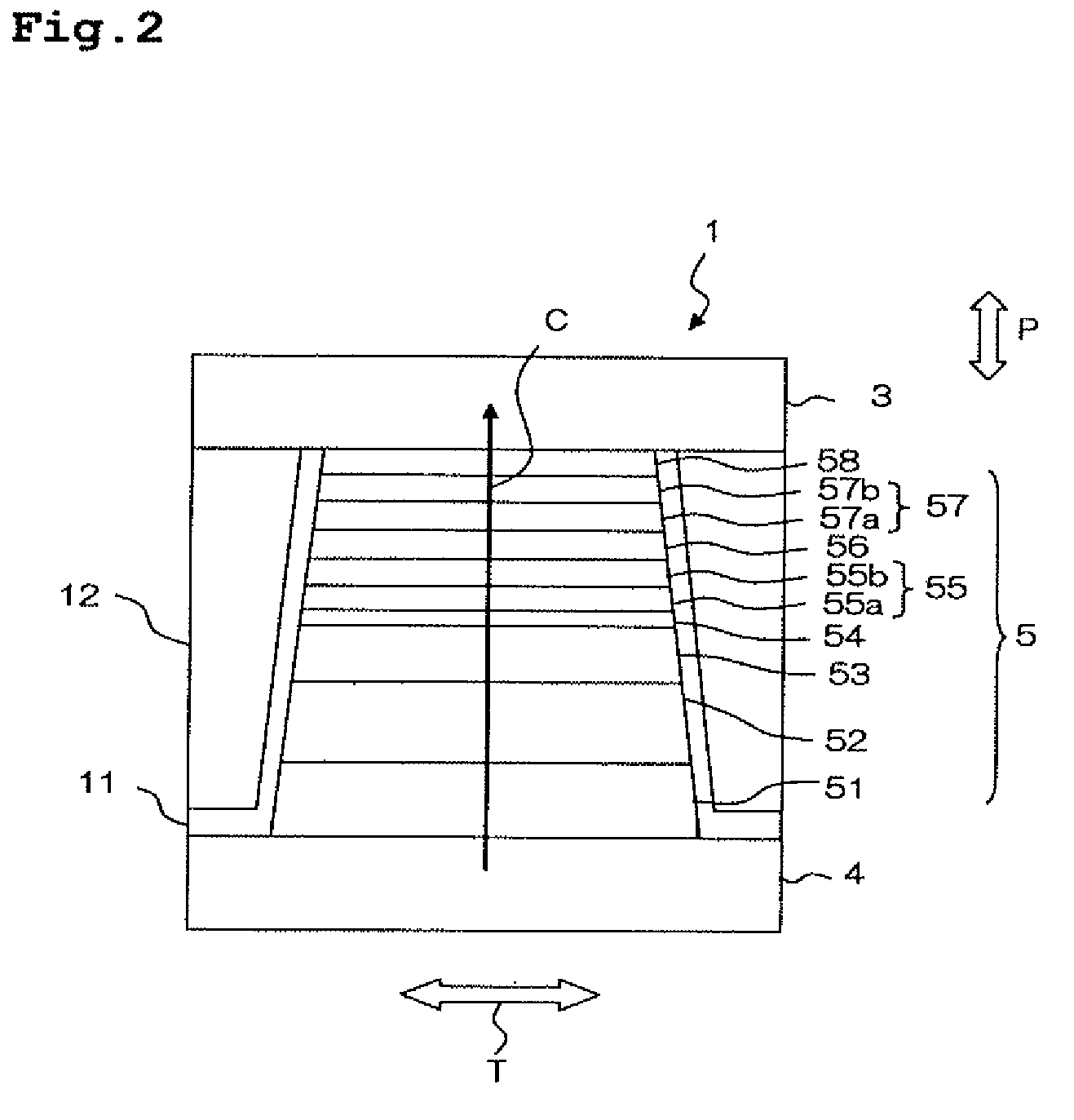
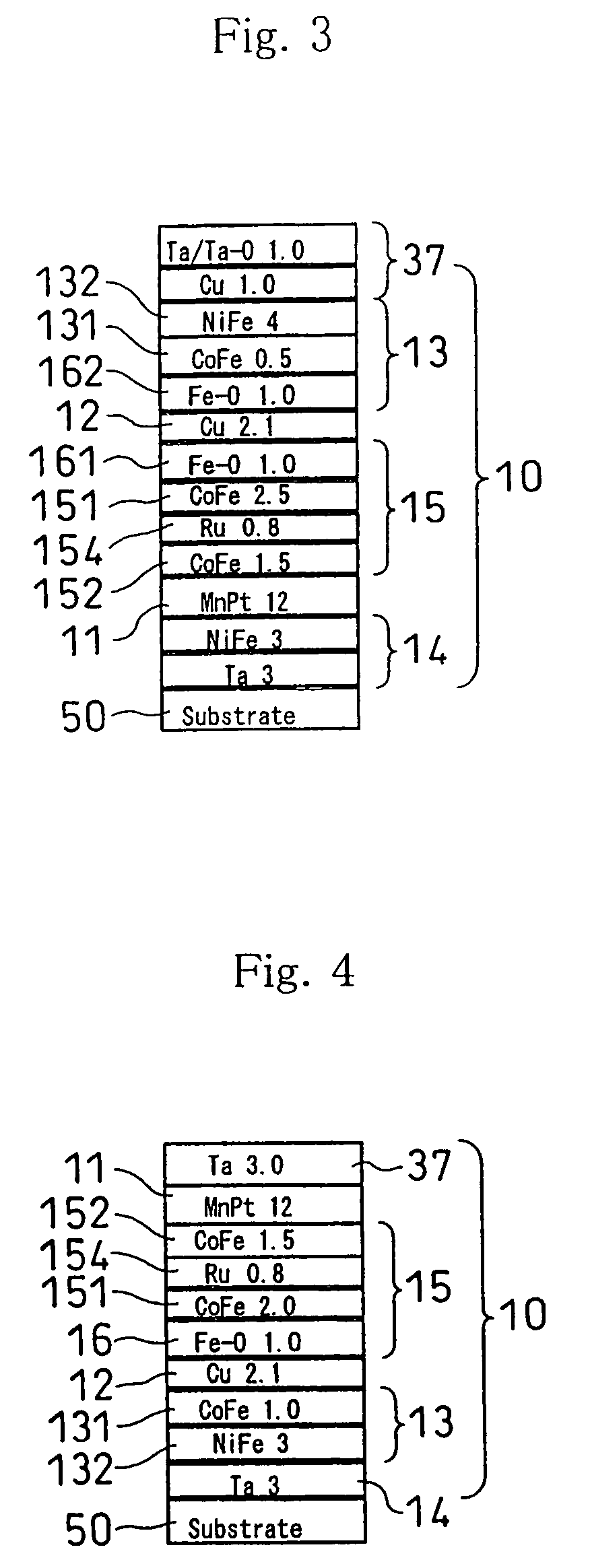
Low resistance tunneling magnetoresistive sensor with natural oxidized double MgO barrier
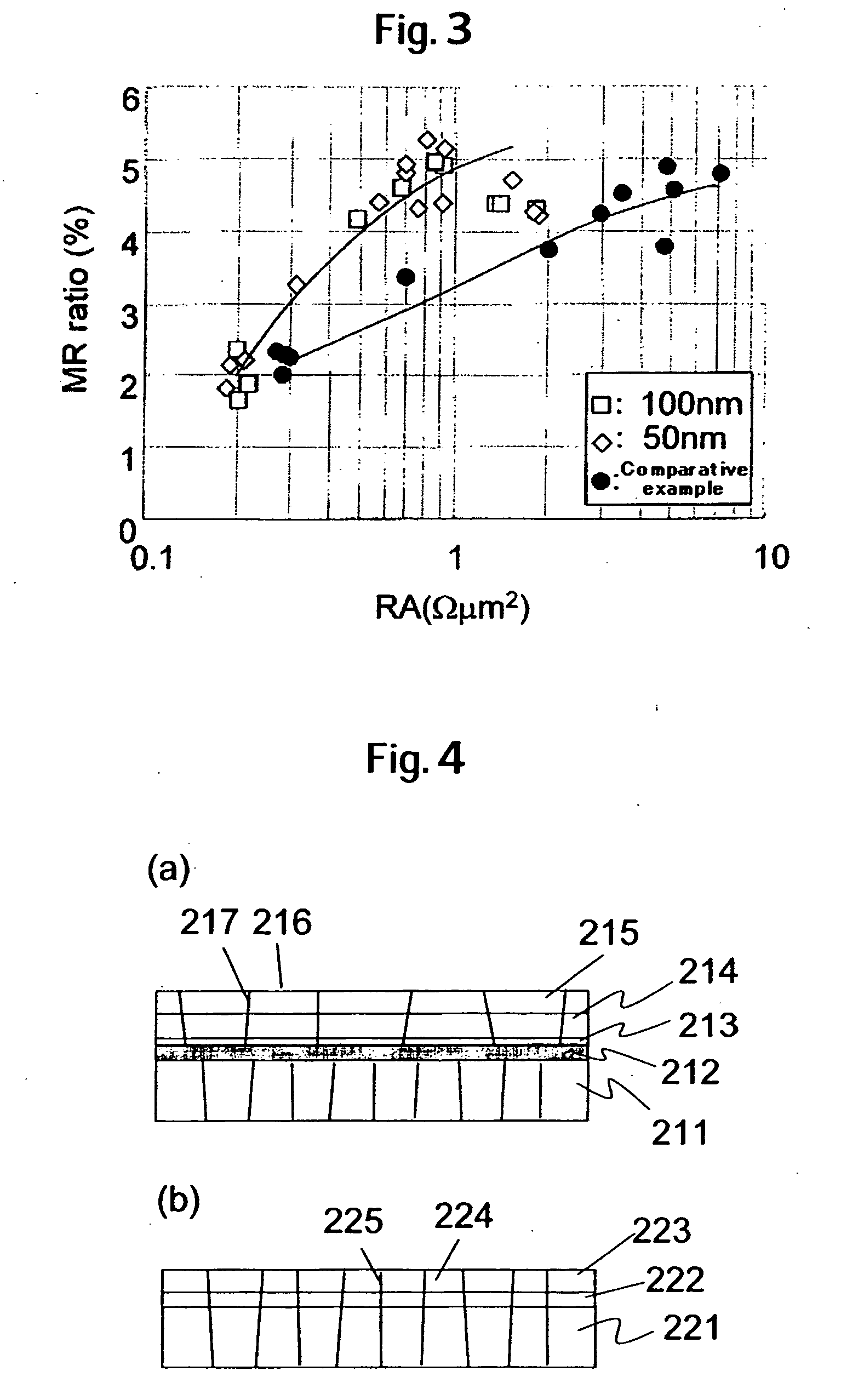
ActiveUS20070111332A1Improve uniformityHigh MR ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsSpin valveMaterials science
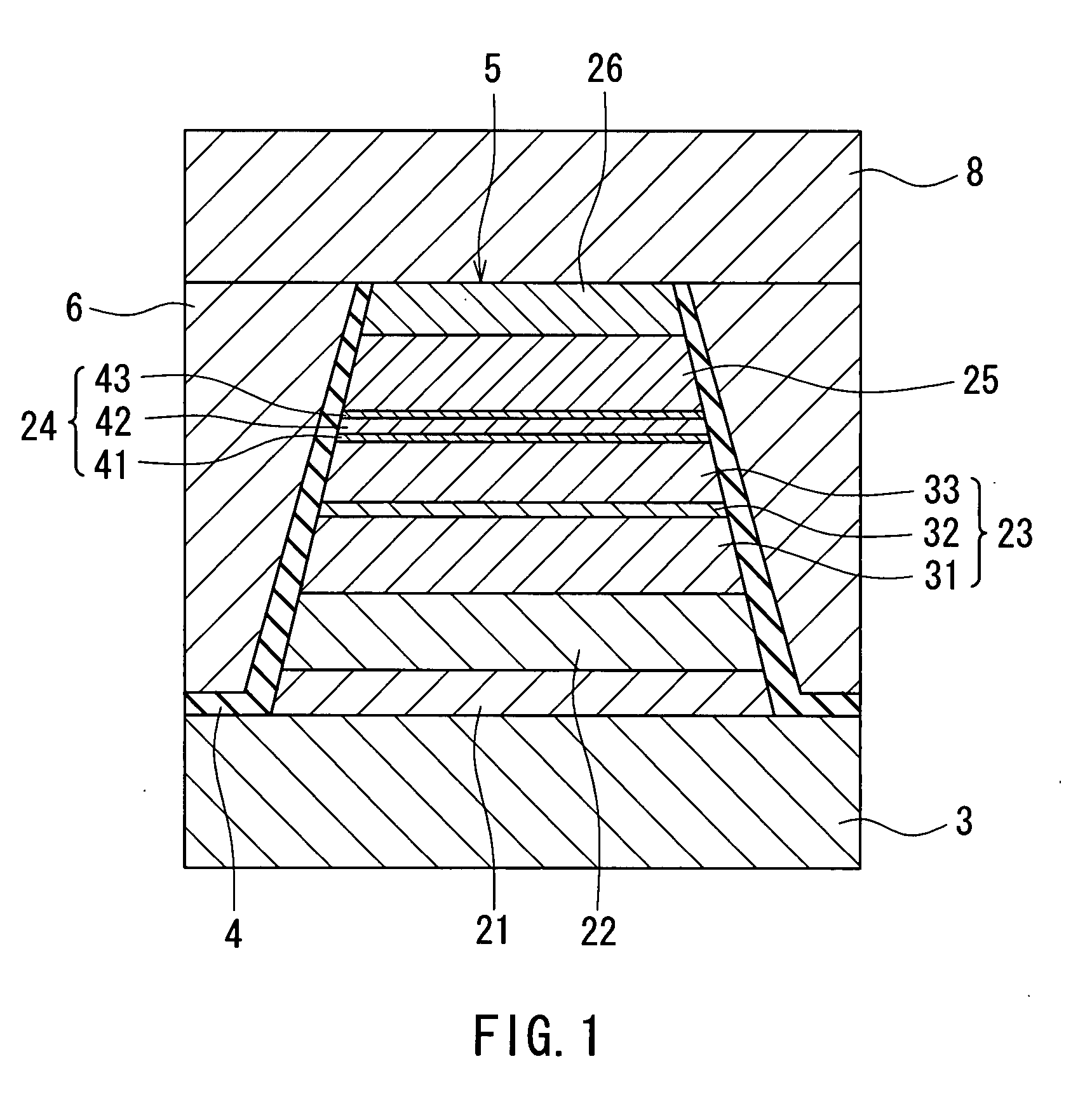
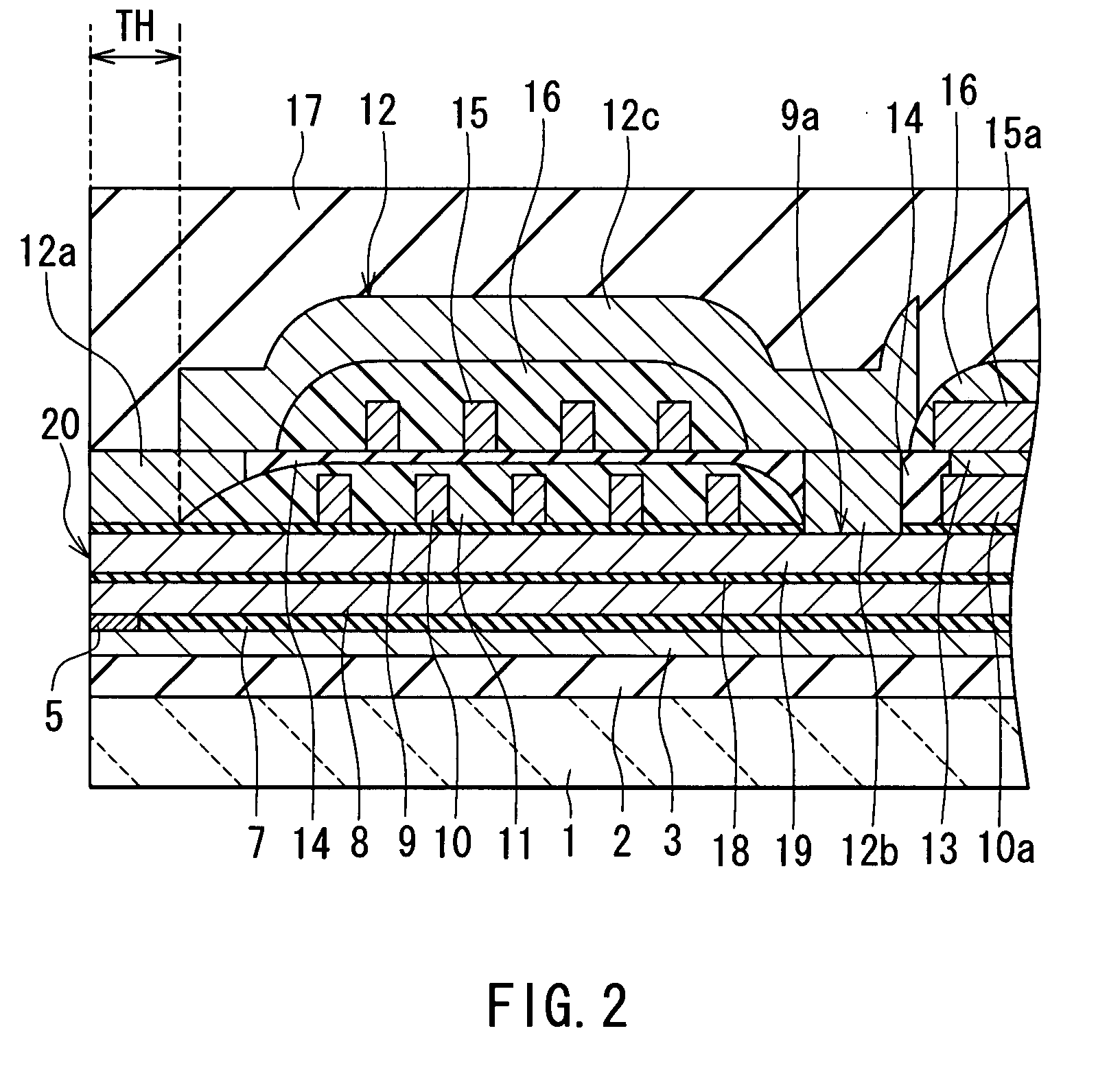
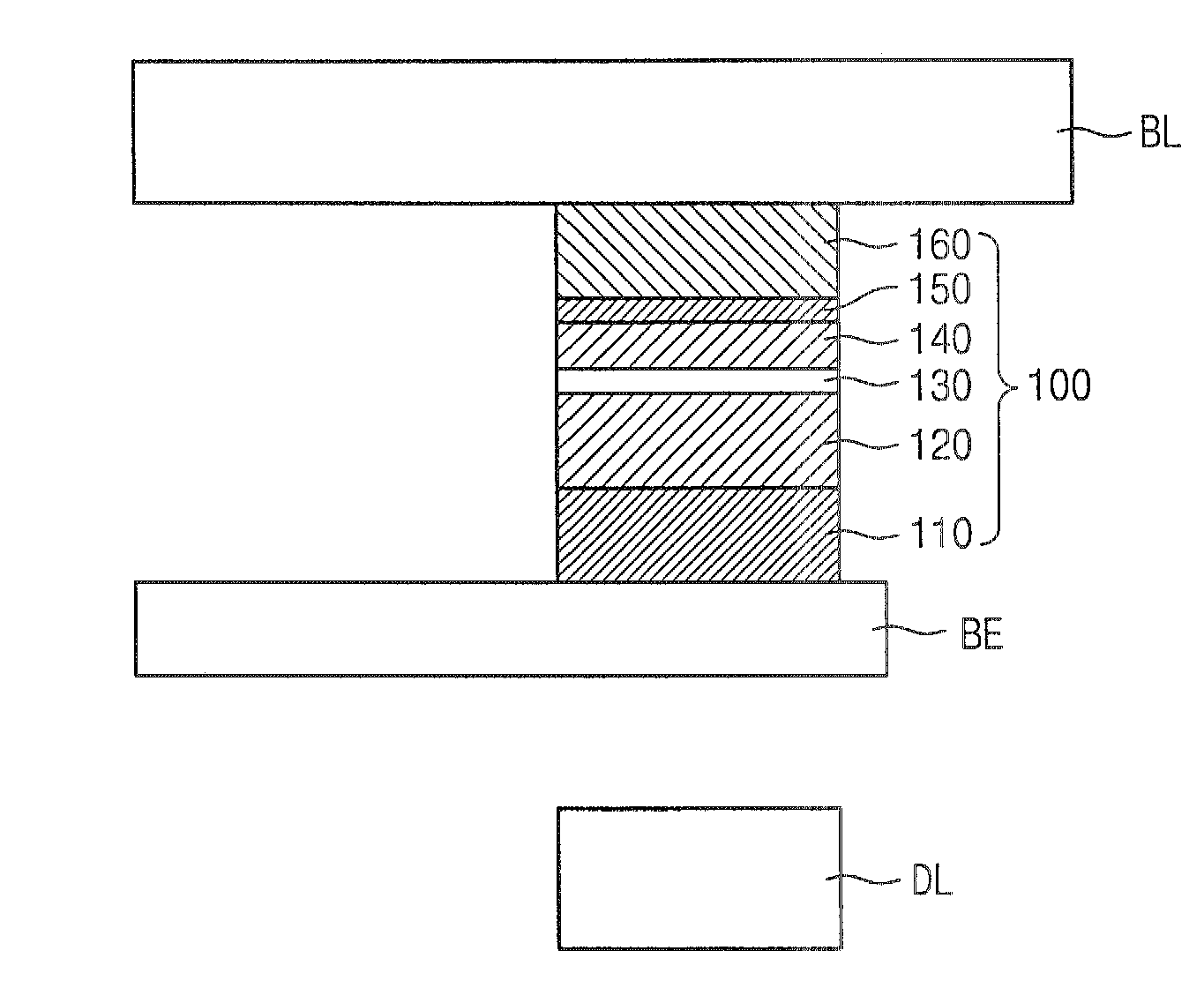
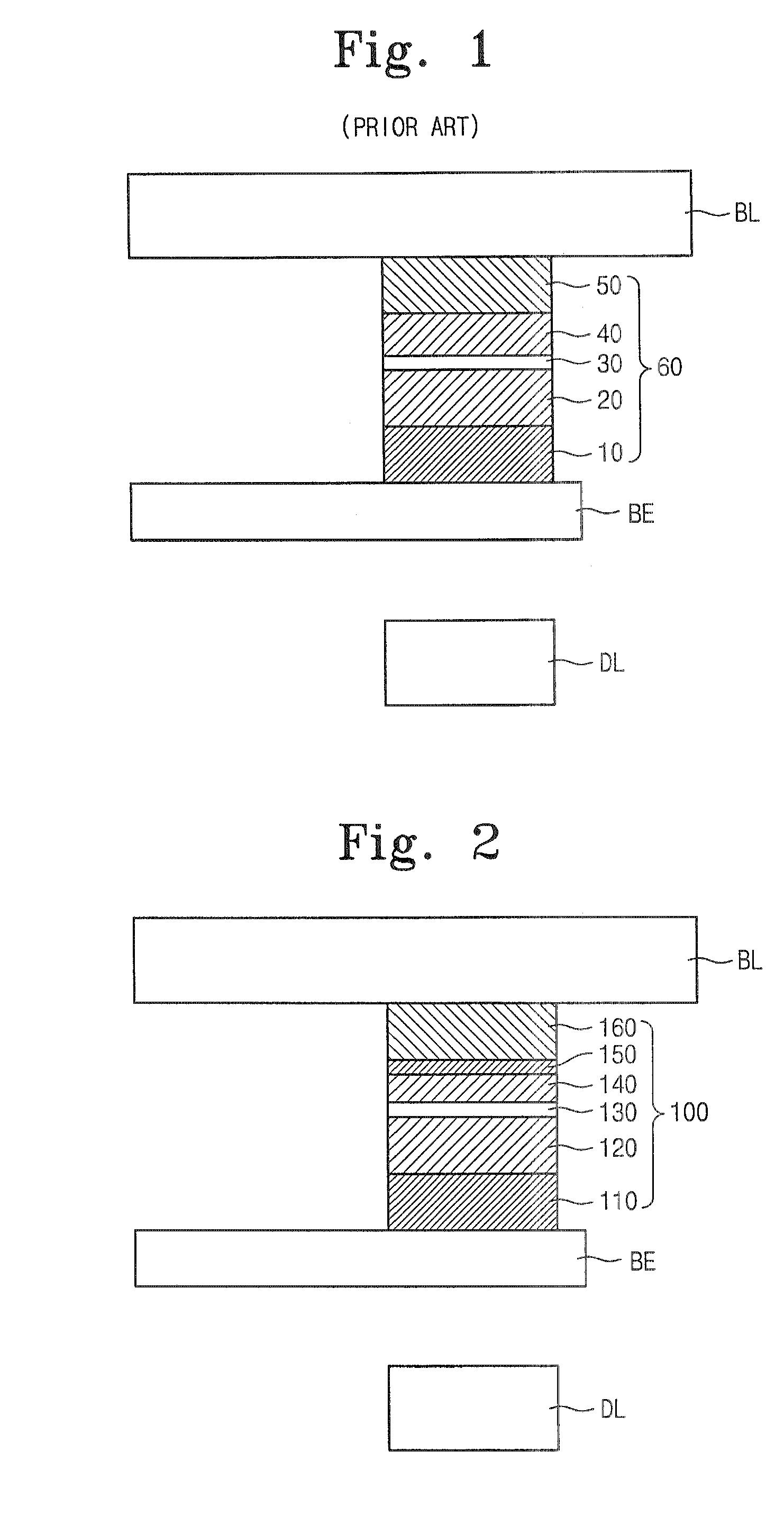
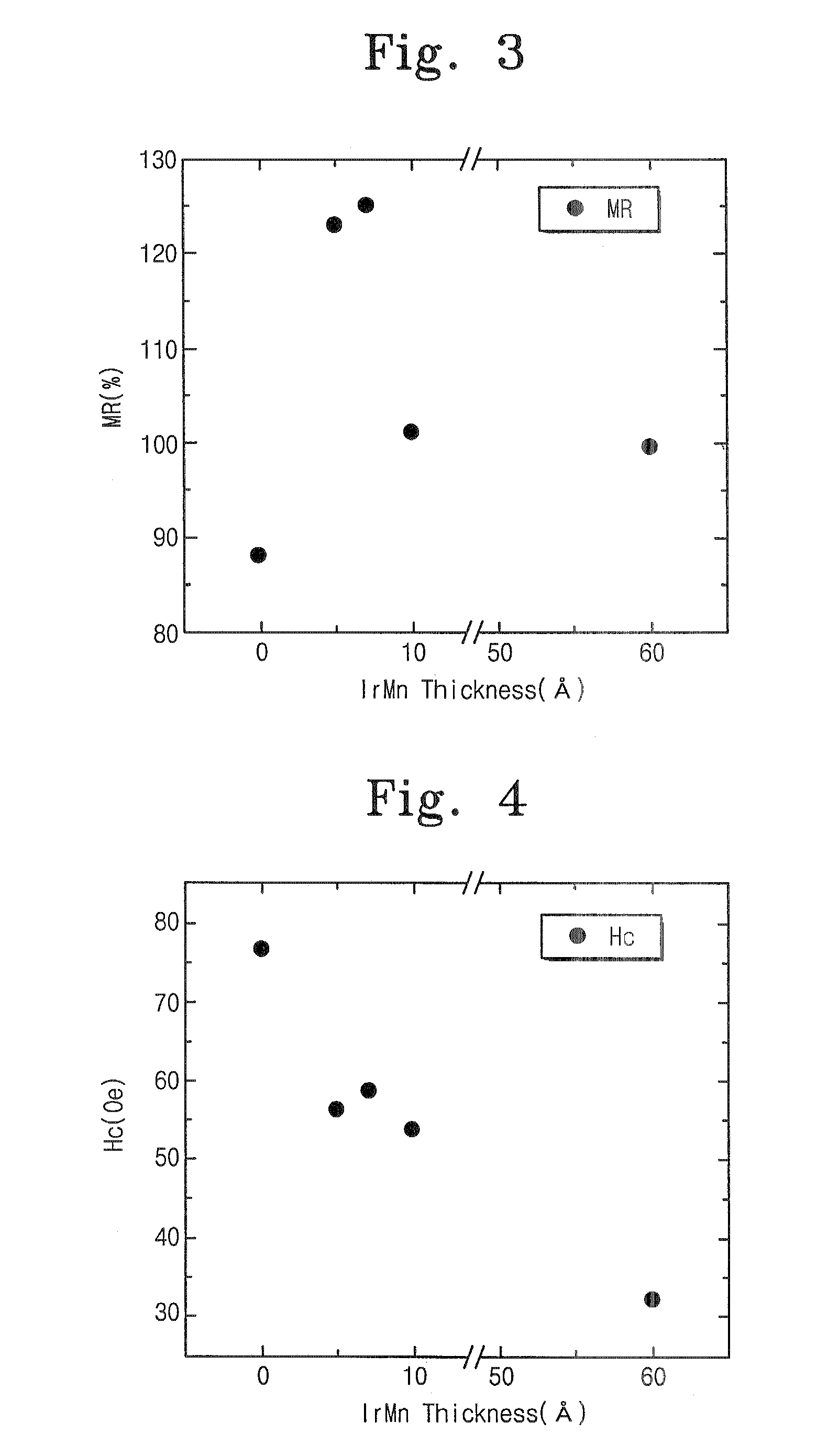
A high performance TMR sensor is fabricated by incorporating a tunnel barrier having a Mg / MgO / Mg configuration. The 4 to 14 Angstroms thick lower Mg layer and 2 to 8 Angstroms thick upper Mg layer are deposited by a DC sputtering method while the MgO layer is formed by a NOX process involving oxygen pressure from 0.1 mTorr to 1 Torr for 15 to 300 seconds. NOX time and pressure may be varied to achieve a MR ratio of at least 34% and a RA value of 2.1 ohm-um2. The NOX process provides a more uniform MgO layer than sputtering methods. The second Mg layer is employed to prevent oxidation of an adjacent ferromagnetic layer. In a bottom spin valve configuration, a Ta / Ru seed layer, IrMn AFM layer, CoFe / Ru / CoFeB pinned layer, Mg / MgO / Mg barrier, CoFe / NiFe free layer, and a cap layer are sequentially formed on a bottom shield in a read head.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
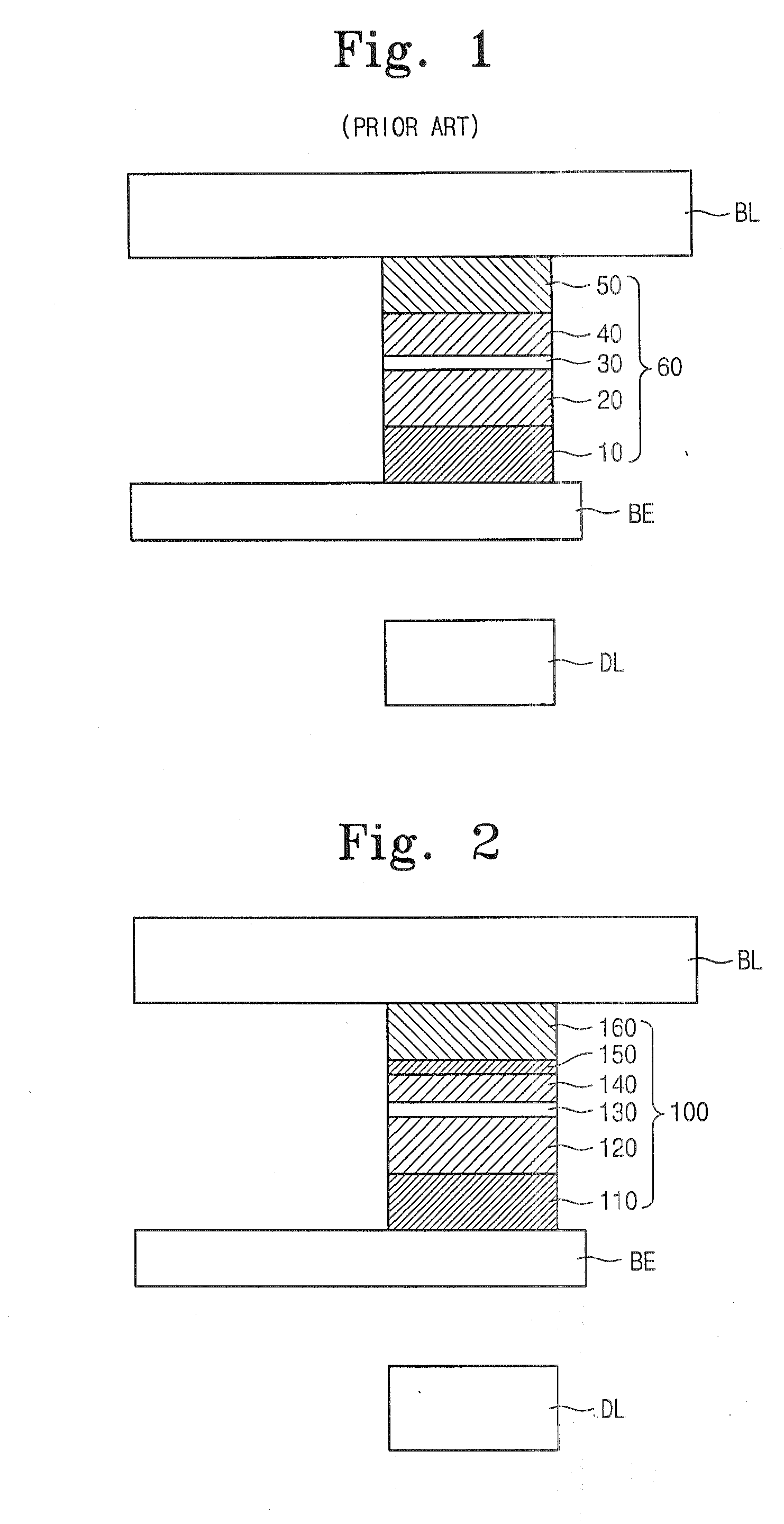
Magnetic memory device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070176251A1High MR ratioNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetoresistanceSemiconductor
A magnetic memory device includes a pinning layer, a pinned layer, an insulation layer, which are sequentially stacked on a semiconductor substrate. The magnetic memory device further includes a free layer disposed on the insulation layer, a capping layer disposed on the free layer and an MR (magnetoresistance) enhancing layer interposed between the free layer and the capping layer. The MR enhancing layer is formed of at least one anti-ferromagnetic material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetoresistance effect device and method of production of the same
InactiveUS20060056115A1Increase valueMaintain good propertiesNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMethods of productionMolecular physics
A magnetoresistance effect device including a multilayer structure having a pair of ferromagnetic layers and a barrier layer positioned between them, wherein at least one ferromagnetic layer has at least the part contacting the barrier layer made amorphous and the barrier layer is an MgO layer having a highly oriented texture structure.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP +1
MRAM with super-paramagnetic sensing layer
ActiveUS20070034919A1Minimize stray fieldLow HcMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMolecular physicsExternal field
An MRAM is disclosed that has a MTJ comprised of a ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization direction along a first axis, a super-paramagnetic (SP) free layer, and an insulating layer formed therebetween. The SP free layer has a remnant magnetization that is substantially zero in the absence of an external field, and in which magnetization is roughly proportional to an external field until reaching a saturation value. In one embodiment, a separate storage layer is formed above, below, or adjacent to the MTJ and has uniaxial anisotropy with a magnetization direction along its easy axis which parallels the first axis. In a second embodiment, the storage layer is formed on a non-magnetic conducting spacer layer within the MTJ and is patterned simultaneously with the MTJ. The SP free layer may be multiple layers or laminated layers of CoFeB. The storage layer may have a SyAP configuration and a laminated structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetoresistive spin valve sensor with tri-layer free layer
ActiveUS7333306B2High MR ratioLow coercivityNanomagnetismElectrical transducersMagnetic reluctanceThin layer
A TMR sensor, a CPP GMR sensor and a CCP CPP GMR sensor all include a tri-layered free layer that is of the form CoFe / CoFeB / NiFe, where the atom percentage of Fe can vary between 5% and 90% and the atom percentage of B can vary between 5% and 30%. The sensors also include SyAP pinned layers which, in the case of the GMR sensors include at least one layer of CoFe laminated onto a thin layer of Cu. In the CCP CPP sensor, a layer of oxidized aluminum containing segregated particles of copper is formed between the spacer layer and the free layer. All three configurations exhibit extremely good values of coercivity, areal resistance, GMR ratio and magnetostriction.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetoresistance effect device
InactiveUS20080055793A1High MR ratioImprove mass productionNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMolecular physicsMagnetic layer
A magnetoresistance effect device including a multilayer structure having a pair of ferromagnetic layers and a barrier layer positioned between them, wherein at least one ferromagnetic layer has at least the part contacting the barrier layer made amorphous and the barrier layer is an MgO layer having a highly oriented texture structure.
Owner:ANELVA CORP +1
Low resistance tunneling magnetoresistive sensor with natural oxidized double MgO barrier
A high performance TMR sensor is fabricated by incorporating a tunnel barrier having a Mg / MgO / Mg configuration. The 4 to 14 Angstroms thick lower Mg layer and 2 to 8 Angstroms thick upper Mg layer are deposited by a DC sputtering method while the MgO layer is formed by a NOX process involving oxygen pressure from 0.1 mTorr to 1 Torr for 15 to 300 seconds. NOX time and pressure may be varied to achieve a MR ratio of at least 34% and a RA value of 2.1 ohm-um2. The NOX process provides a more uniform MgO layer than sputtering methods. The second Mg layer is employed to prevent oxidation of an adjacent ferromagnetic layer. In a bottom spin valve configuration, a Ta / Ru seed layer, IrMn AFM layer, CoFe / Ru / CoFeB pinned layer, Mg / MgO / Mg barrier, CoFe / NiFe free layer, and a cap layer are sequentially formed on a bottom shield in a read head.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
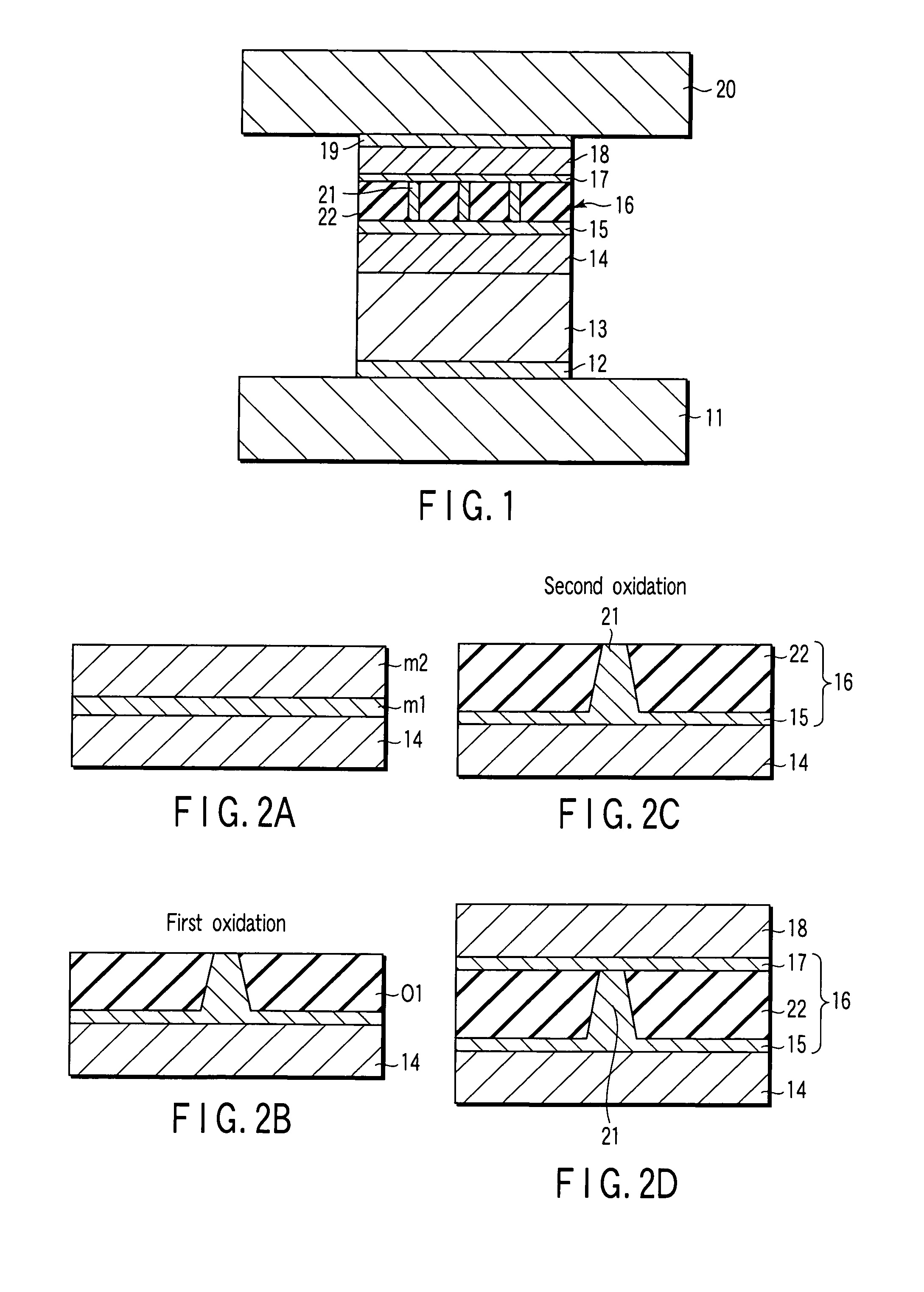
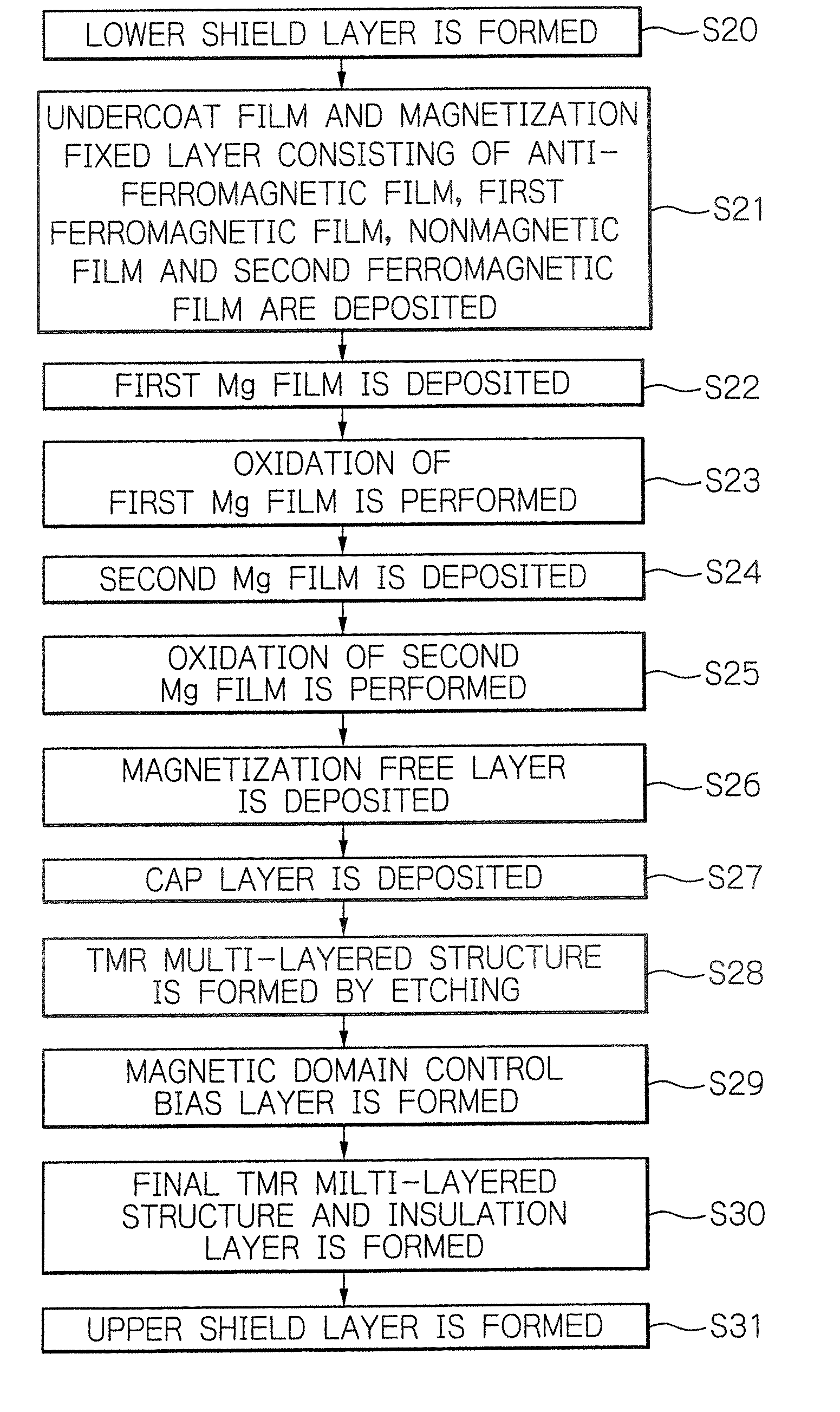
Manufacturing method of tunnel magnetoresistive effect element, manufacturing method of thin-film magnetic head, and manufacturing method of magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070264728A1High MR ratioStably obtain TMR elementsNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetoresistanceMetallic materials
A manufacturing method of a TMR element having a magnetization fixed layer, a magnetization free layer and a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between the magnetization fixed layer and the magnetization free layer. A fabricating process of the tunnel barrier layer includes a step of depositing a first metallic material film on the magnetization fixed layer or the magnetization free layer, and a step of oxidizing the deposited first metallic material film under an environment with an impurity concentration of 1E-02 or less.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
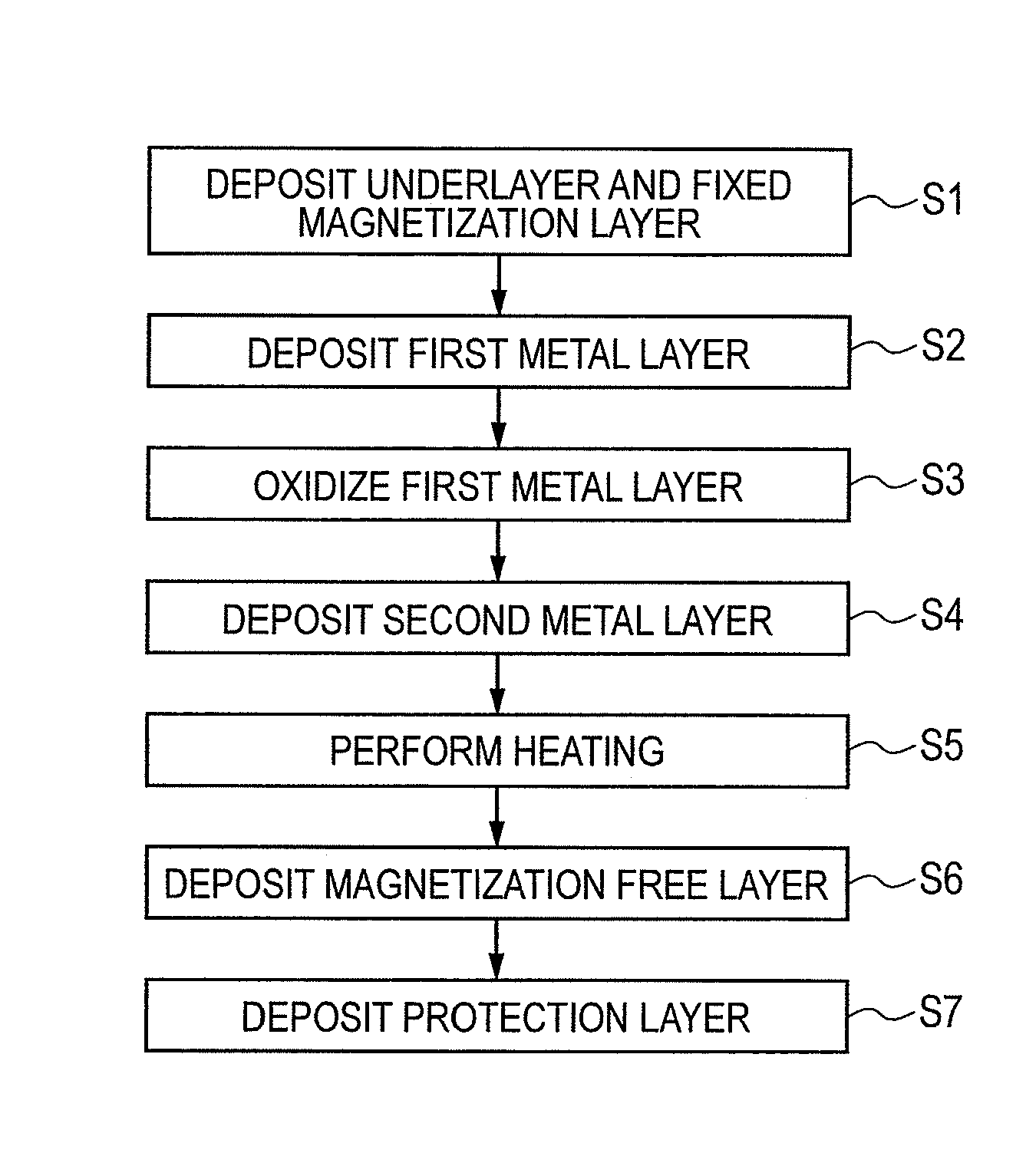
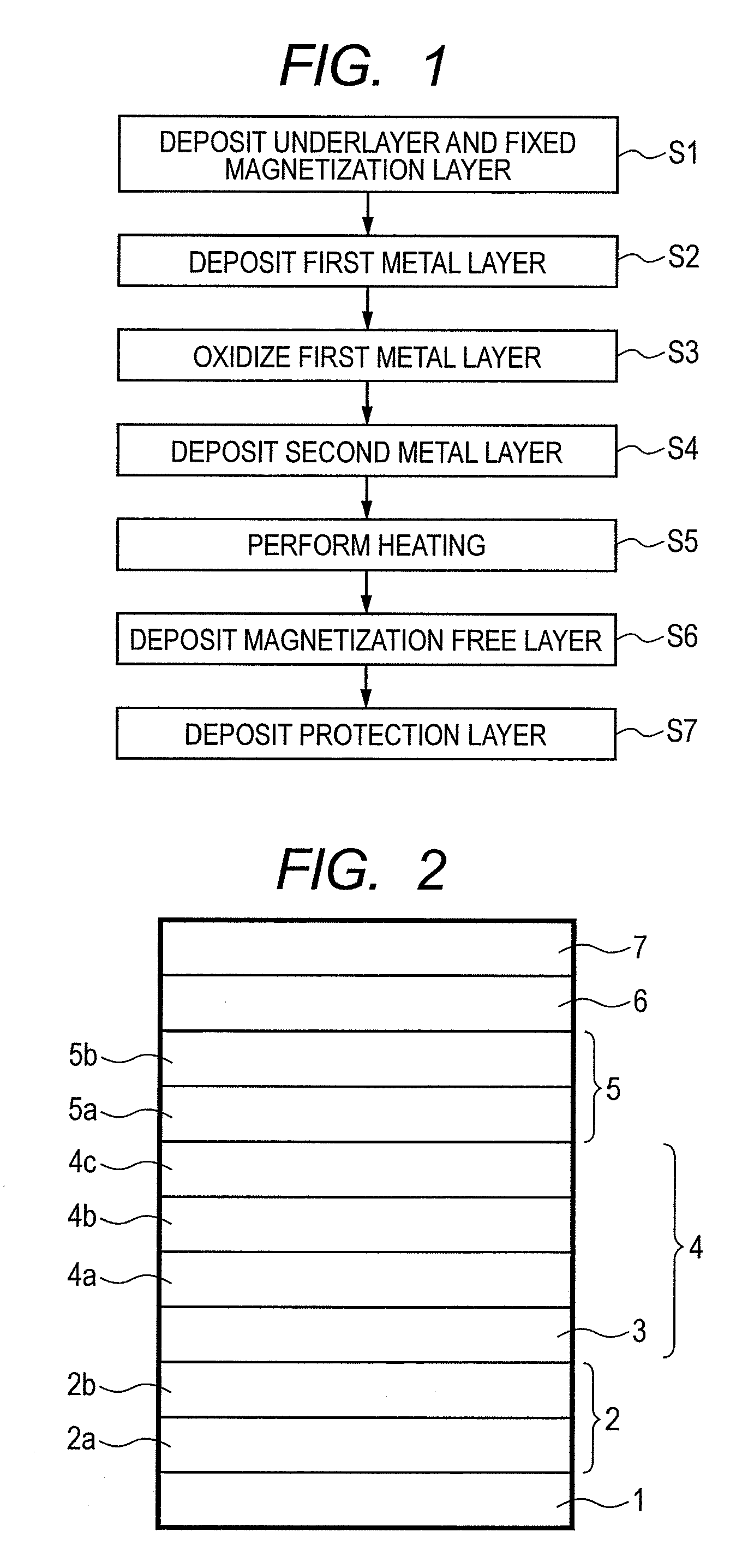
Manufacturing method of magneto-resistive element
ActiveUS20120288963A1High MR ratioReduce the numberNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceMagneto
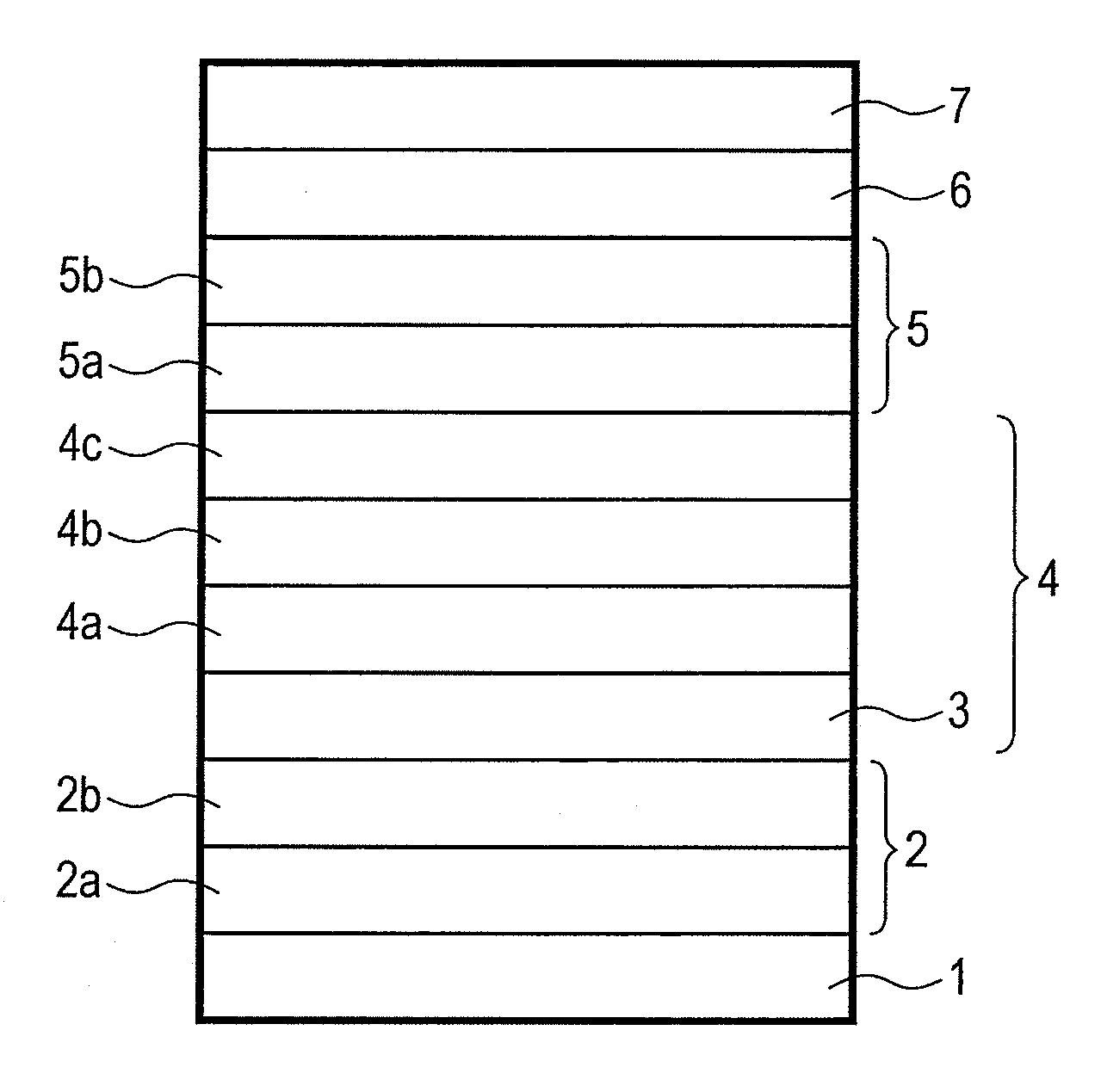
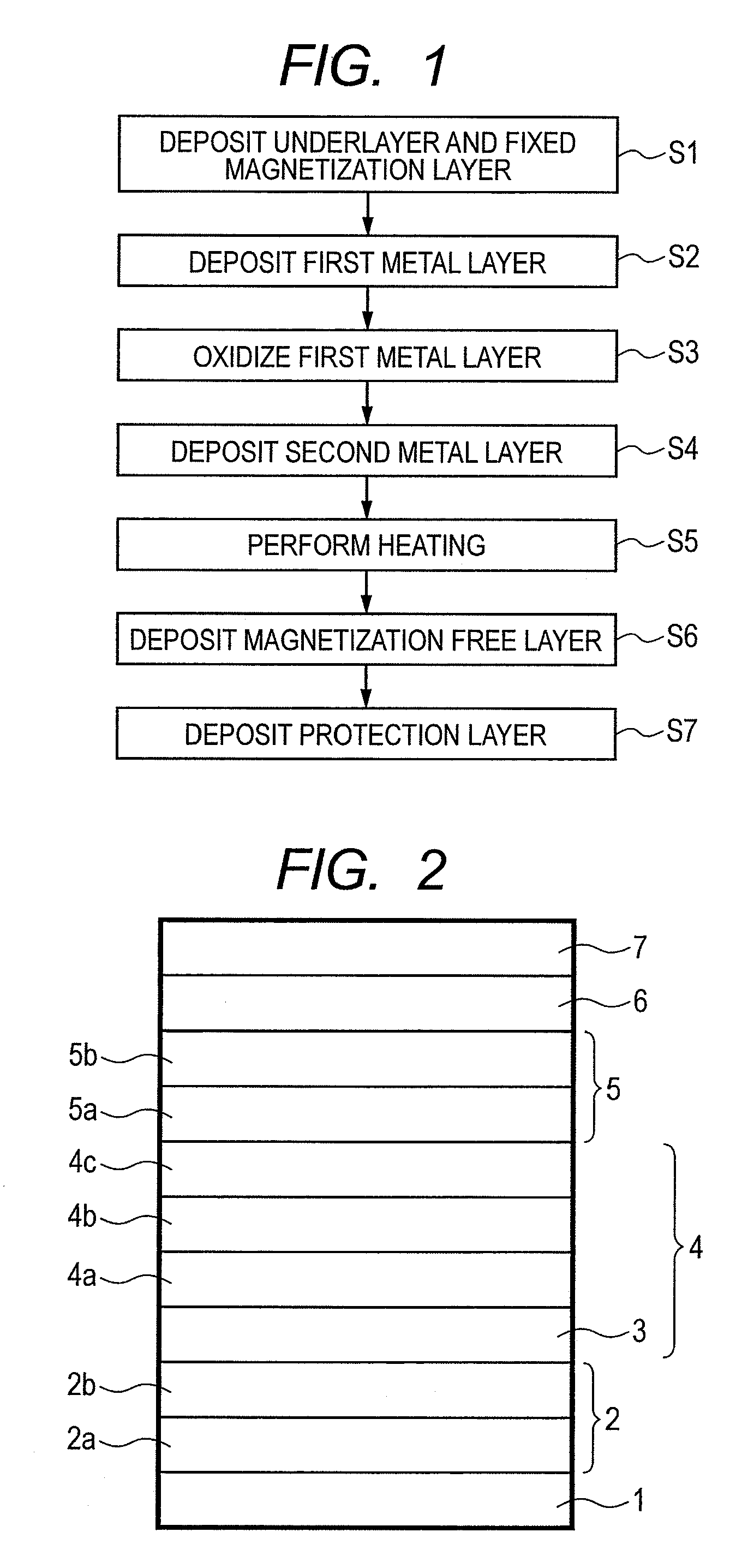
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a magneto-resistive element capable of obtaining a higher MR ratio, in a method of forming a metal oxide layer (e.g., MgO layer) by oxidation treatment of a metal layer (e.g., Mg layer). An embodiment of the present invention includes the steps of; providing a substrate having a first ferromagnetic layer; fabricating a tunnel barrier layer on the first ferromagnetic layer; and forming a second ferromagnetic layer on the tunnel barrier layer. The step of fabricating the tunnel barrier layer includes; the steps of; depositing a first metal layer on the first ferromagnetic layer;oxidizing the first metal layer; depositing a second metal layer on the oxidized first metal layer; and performing heating treatment on the oxidized first metal layer and the second metal layer at a temperature at which the second metal layer boils.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Method for manufacturing magnetoresistive element
InactiveUS20070092639A1High purityFavorable areal resistance RANanomagnetismNanoinformaticsNoble gasMagnetic reluctance
There is provided a method for manufacturing a magnetoresistive element having a magnetization pinned layer, a magnetization free layer, and a spacer layer including an insulating layer arranged between the magnetization pinned layer and the magnetization free layer and current paths passing through the insulating layer. The method includes, in producing the spacer layer, depositing a first non-magnetic metal layer forming the current paths, depositing a second metal layer to be converted into the insulating layer on the first non-magnetic metal layer, and performing two stages of oxidation treatments in which a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a first oxidation treatment is set to 1 / 10 or less of a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a second oxidation treatment, and the second metal layer being irradiated with an ion beam or a RF plasma of a rare gas in the first oxidation treatment.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method of fabricating and apparatus of fabricating tunnel magnetic resistive element
InactiveUS20130134032A1High MR ratioLow RANanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetic layer
One embodiment of the present invention is a method of fabricating a tunnel magnetic resistive element including a first ferromagnetic layer, a tunnel barrier layer and a second ferromagnetic layer, comprising a step of making the tunnel barrier layer, comprising the step of making the tunnel barrier layer includes the steps of: forming a first layer on the first ferromagnetic layer by applying DC power to a metal target and introducing sputtering gas without introducing oxygen gas in a sputtering chamber; and forming a second layer on the first layer by applying DC power to the metal target and introducing the sputtering gas and oxygen gas with the DC power to be applied to the metal target from the step of forming the first layer in the sputtering chamber, wherein the second layer is oxygen-doped.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Composite free layer within magnetic tunnel junction for MRAM applications
ActiveUS20120280337A1Enhances MRAM performanceImprove performanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionBit linePower flow
A MTJ in an MRAM array is disclosed with a composite free layer having a FL1 / FL2 / FL3 configuration where FL1 and FL2 are crystalline magnetic layers and FL3 is an amorphous NiFeX layer for improved bit switching performance. FL1 layer is CoFe which affords a high magnetoresistive (MR) ratio when forming an interface with a MgO tunnel barrier. FL2 is Fe to improve switching performance. NiFeX thickness where X is Hf is preferably between 20 to 40 Angstroms to substantially reduce bit line switching current and number of shorted bits. Annealing at 330° C. to 360° C. provides a high MR ratio of 190%. Furthermore, low Hc and Hk are simultaneously achieved with improved bit switching performance and fewer shorts without compromising other MTJ properties such as MR ratio. As a result of high MR ratio and lower bit-to-bit resistance variation, higher reading margin is realized.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method for manufacturing magnetoresistive element
InactiveUS7785662B2High purityFavorable areal resistance RANanomagnetismChemical vapor deposition applicationNoble gasMagnetization
There is provided a method for manufacturing a magnetoresistive element having a magnetization pinned layer, a magnetization free layer, and a spacer layer including an insulating layer arranged between the magnetization pinned layer and the magnetization free layer and current paths passing through the insulating layer. The method includes, in producing the spacer layer, depositing a first non-magnetic metal layer forming the current paths, depositing a second metal layer to be converted into the insulating layer on the first non-magnetic metal layer, and performing two stages of oxidation treatments in which a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a first oxidation treatment is set to 1 / 10 or less of a partial pressure of an oxidizing gas in a second oxidation treatment, and the second metal layer being irradiated with an ion beam or a RF plasma of a rare gas in the first oxidation treatment.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Tunnel magnetoresistive thin film and magnetic multilayer film formation apparatus
InactiveCN101689599AHigh MR ratioImprove featuresNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetization
This invention provides a tunnel magnetoresistive thin film which can simultaneously realize a high MR ratio and low magnetostriction. The tunnel magnetoresistive thin film comprises a magnetization fixed layer, a tunnel barrier layer, and a magnetization free layer. The tunnel barrier layer is a magnesium oxide film comprising magnesium oxide crystal grains having (001) orientation. The magnetization free layer has a laminated structure comprising a first magnetization free layer formed of an alloy having (001) orientation having a body centered cubic structure containing a Co atom, an Fe atom, and a B atom or a body centered cubic structure containing a Co atom, an Ni atom, an Fe atom, and a B atom, and a second magnetization free layer formed of an alloy having a face centered cubic structure containing an Fe atom and an Ni atom.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Magneto-resistive effect element provided with GaN spacer layer
ActiveUS20100232066A1Raise the ratioSimple structureNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetizationGallium nitride
A magneto-resistive effect (MR) element includes a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer in which a relative angle of magnetization directions of the first and second magnetic layers changes according to an external magnetic field; and a spacer layer that is provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The spacer layer contains gallium nitride (GaN) as a main component. A thin film magnetic head according to one embodiment of the present invention is provided with the following structures: an MR element mentioned above that has a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer, as free layers, in which the magnetization direction in the two layers changes according to the external magnetic field; a bias magnetic field application layer that applies a bias magnetic field to the first and second magnetic layers in an orthogonal direction to an air bearing surface (ABS); the bias magnetic field application layer is formed in a rear side of the MR element seen from the ABS; and a sense current flows in an orthogonal direction to a layer surface of the MR element.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Manufacturing method of magneto-resistive element
ActiveUS8728830B2High MR ratioReduce the numberNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceMagneto
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a magneto-resistive element capable of obtaining a higher MR ratio, in a method of forming a metal oxide layer (e.g., MgO layer) by oxidation treatment of a metal layer (e.g., Mg layer). An embodiment of the present invention includes the steps of; providing a substrate having a first ferromagnetic layer; fabricating a tunnel barrier layer on the first ferromagnetic layer; and forming a second ferromagnetic layer on the tunnel barrier layer. The step of fabricating the tunnel barrier layer includes; the steps of; depositing a first metal layer on the first ferromagnetic layer; oxidizing the first metal layer; depositing a second metal layer on the oxidized first metal layer; and performing heating treatment on the oxidized first metal layer and the second metal layer at a temperature at which the second metal layer boils.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Manufacturing method of tunnel magnetoresistive effect element, manufacturing method of thin-film magnetic head, and manufacturing method of magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070264423A1High mr ratioStably obtainNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetoresistanceTunnel barrier
A manufacturing method of a TMR element having a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between lower and upper ferromagnetic layers. A fabricating process of the tunnel barrier layer includes a step of depositing a first metallic material film on the lower ferromagnetic layer, a step of oxidizing the deposited first metallic material film using an oxygen gas with a first pressure, a step of depositing a second metallic material film of the same material as that of the first metallic film or of metallic material containing primarily the same material as that of the first metallic film, on the oxidized first metallic film, and a step of oxidizing the deposited second metallic material film using an oxygen gas with a second pressure that is lower than the first pressure.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic tunnel junction element and magnetic memory
ActiveUS20190304526A1Large atomic weightImprove heat resistanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetizationMagnetic memory
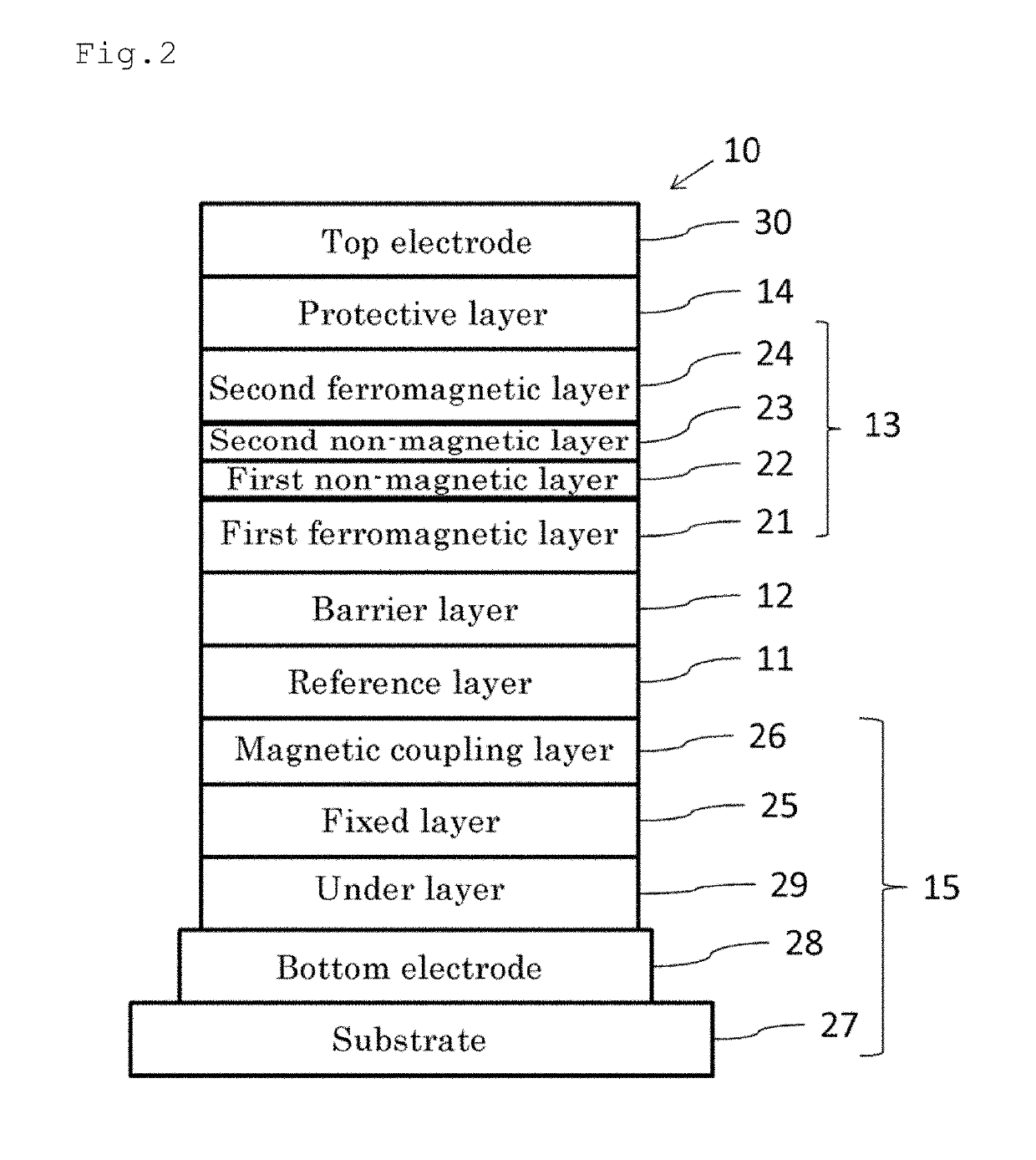
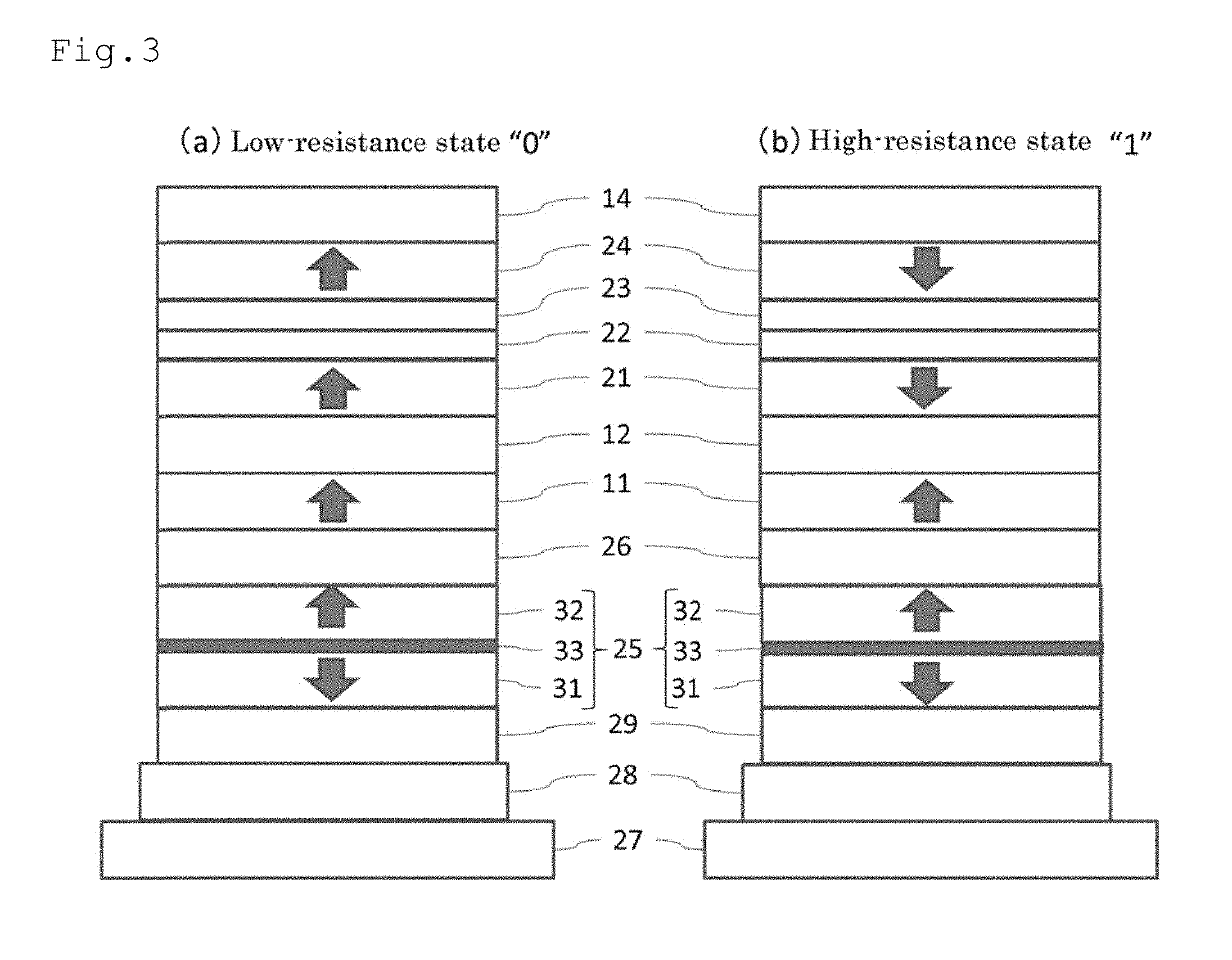
A magnetic tunnel junction element with a high MR ratio, and can prevent a recording layer from being damaged, and magnetic memory. A reference layer includes a ferromagnetic body, and has magnetization direction fixed in the vertical direction. A barrier layer includes non-magnetic body, and disposed on one surface side of the reference layer. A recording layer is disposed to sandwich barrier layer between itself and reference layer. The recording layer includes a first ferromagnetic layer including at least one of Co and Fe, and having a magnetization direction variable in vertical direction; a first non-magnetic layer including at least one of Mg, MgO, C, Li, Al, and Si, second non-magnetic layer including at least one of Ta, Hf, W, Mo, Nb, Zr, Y, Sc, Ti, V, and Cr, and second ferromagnetic layer including at least one of Co and Fe, and having a magnetization direction variable in vertical direction.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
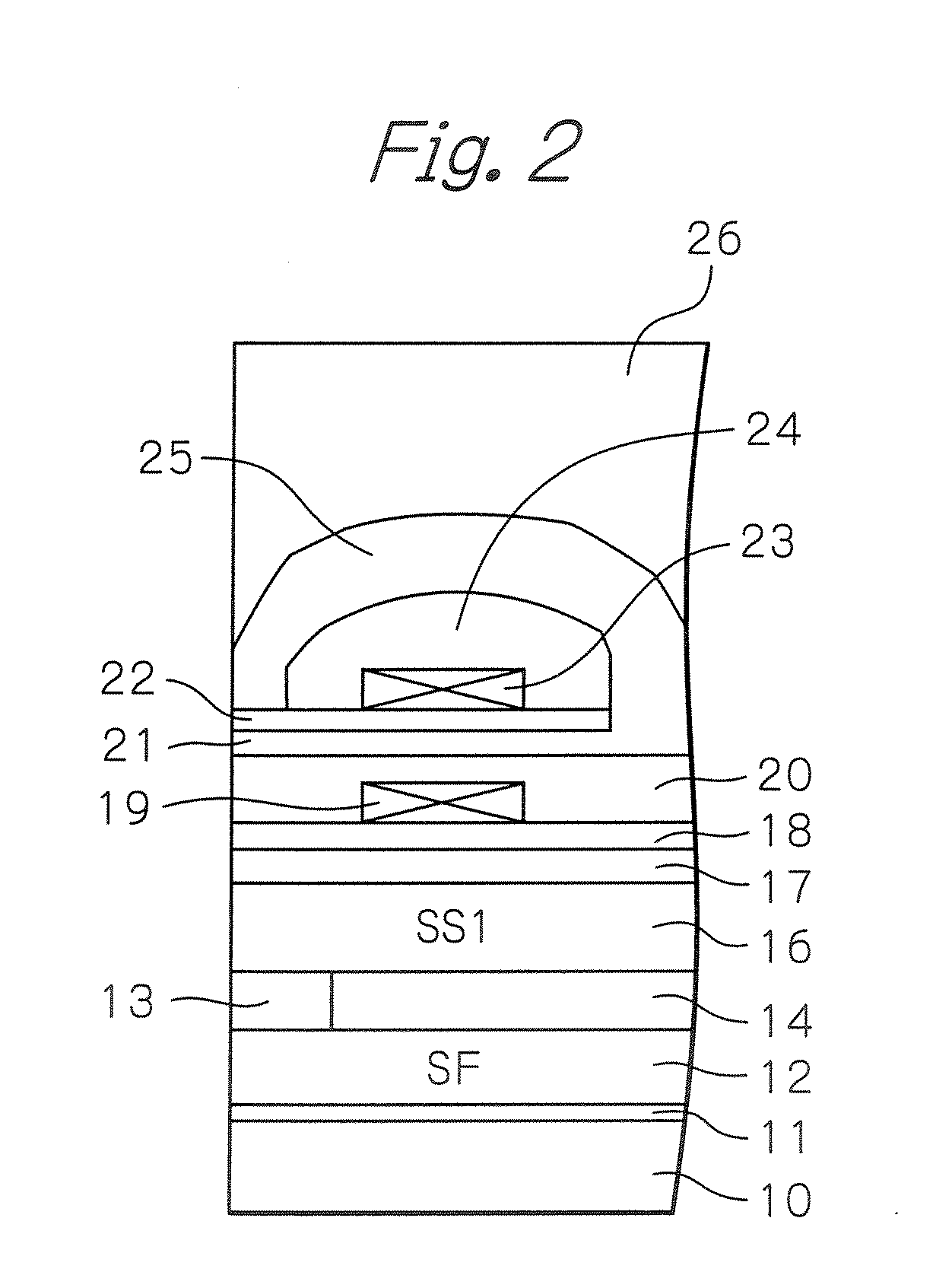
Magnetoresistive head and magnetic storage apparatus
InactiveUS20070188944A1High MR ratioReduce decreaseRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMagnetic storageCrystallinity
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention provide a Current Perpendicular to the Plane-Giant Magnetoresistive (CPP-GMR) head exhibiting a high magnetoresistance (MR) ratio with a low area-resistance product. A lower shield is made up of a first shield layer / a crystalline reset layer / a second shield layer, and an amorphous material is used in at least a part of the crystalline reset layer, thereby controlling crystallinity of the second lower shield / the CPP-GMR head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
CPP-type magnetoresistive element having spacer layer that includes semiconductor layer
InactiveUS20080218912A1High characteristicsRaise the ratioNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsSchottky barrierMagnetization
An MR element includes: a free layer whose direction of magnetization changes in response to a signal magnetic field; a pinned layer whose direction of magnetization is fixed; and a spacer layer disposed between these layers. The spacer layer includes: a semiconductor layer made of an n-type semiconductor; and a Schottky barrier forming layer made of a metal material having a work function higher than that of the n-type semiconductor that the semiconductor layer is made of, the Schottky barrier forming layer being disposed in at least one of a position between the semiconductor layer and the free layer and a position between the semiconductor layer and the pinned layer, touching the semiconductor layer and forming a Schottky barrier at an interface between the semiconductor layer and itself The semiconductor layer is 1.1 to 1.7 nm in thickness, and the Schottky barrier forming layer is 0.1 to 0.3 nm in thickness.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magneto-resistive effect element provided with GaN spacer layer
ActiveUS8274764B2Raise the ratioSimple structureNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetizationGallium nitride
A magneto-resistive effect (MR) element includes a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer in which a relative angle of magnetization directions of the first and second magnetic layers changes according to an external magnetic field; and a spacer layer that is provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer. The spacer layer contains gallium nitride (GaN) as a main component. A thin film magnetic head according to one embodiment of the present invention is provided with the following structures: an MR element mentioned above that has a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer, as free layers, in which the magnetization direction in the two layers changes according to the external magnetic field; a bias magnetic field application layer that applies a bias magnetic field to the first and second magnetic layers in an orthogonal direction to an air bearing surface (ABS); the bias magnetic field application layer is formed in a rear side of the MR element seen from the ABS; and a sense current flows in an orthogonal direction to a layer surface of the MR element.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
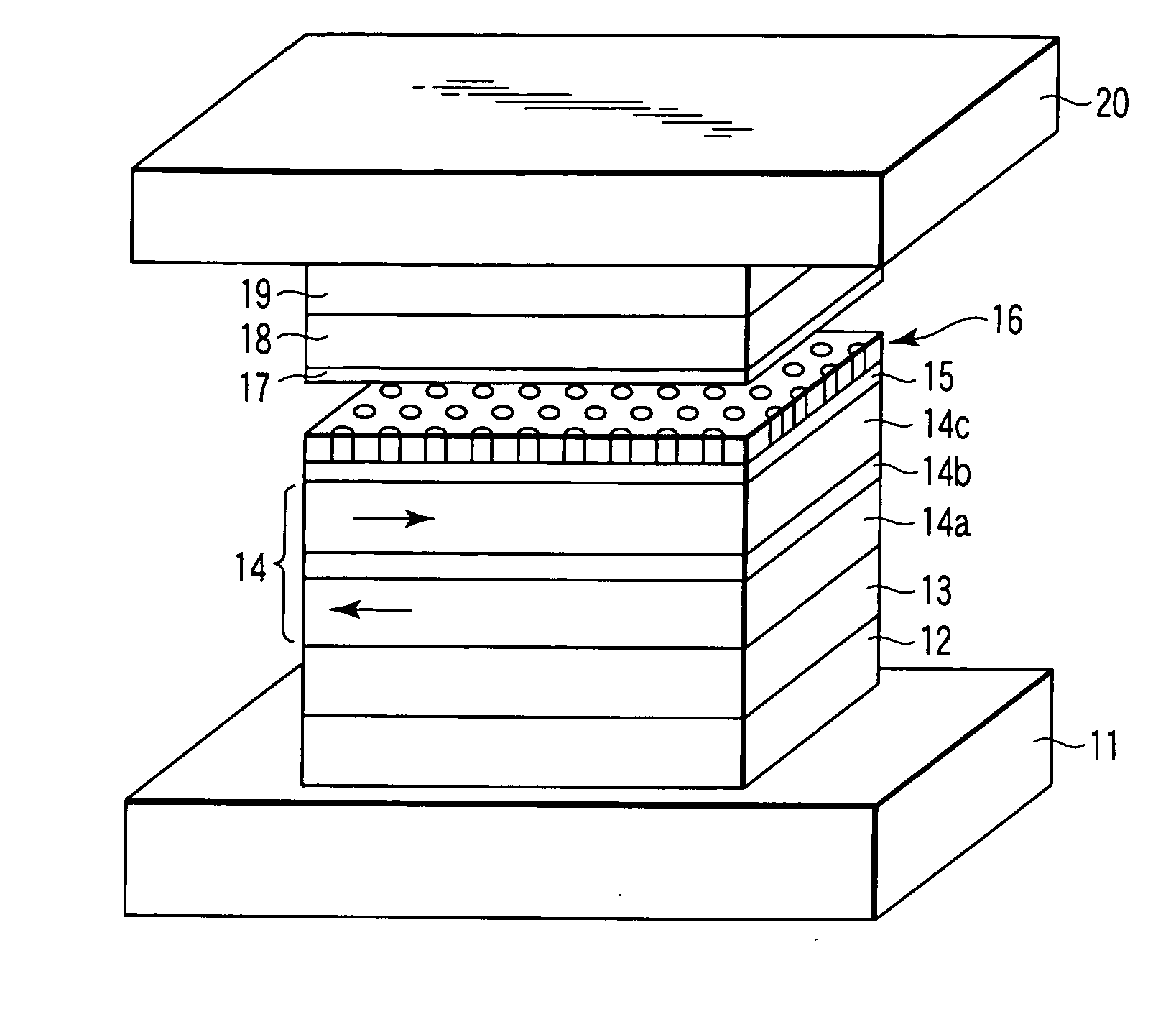
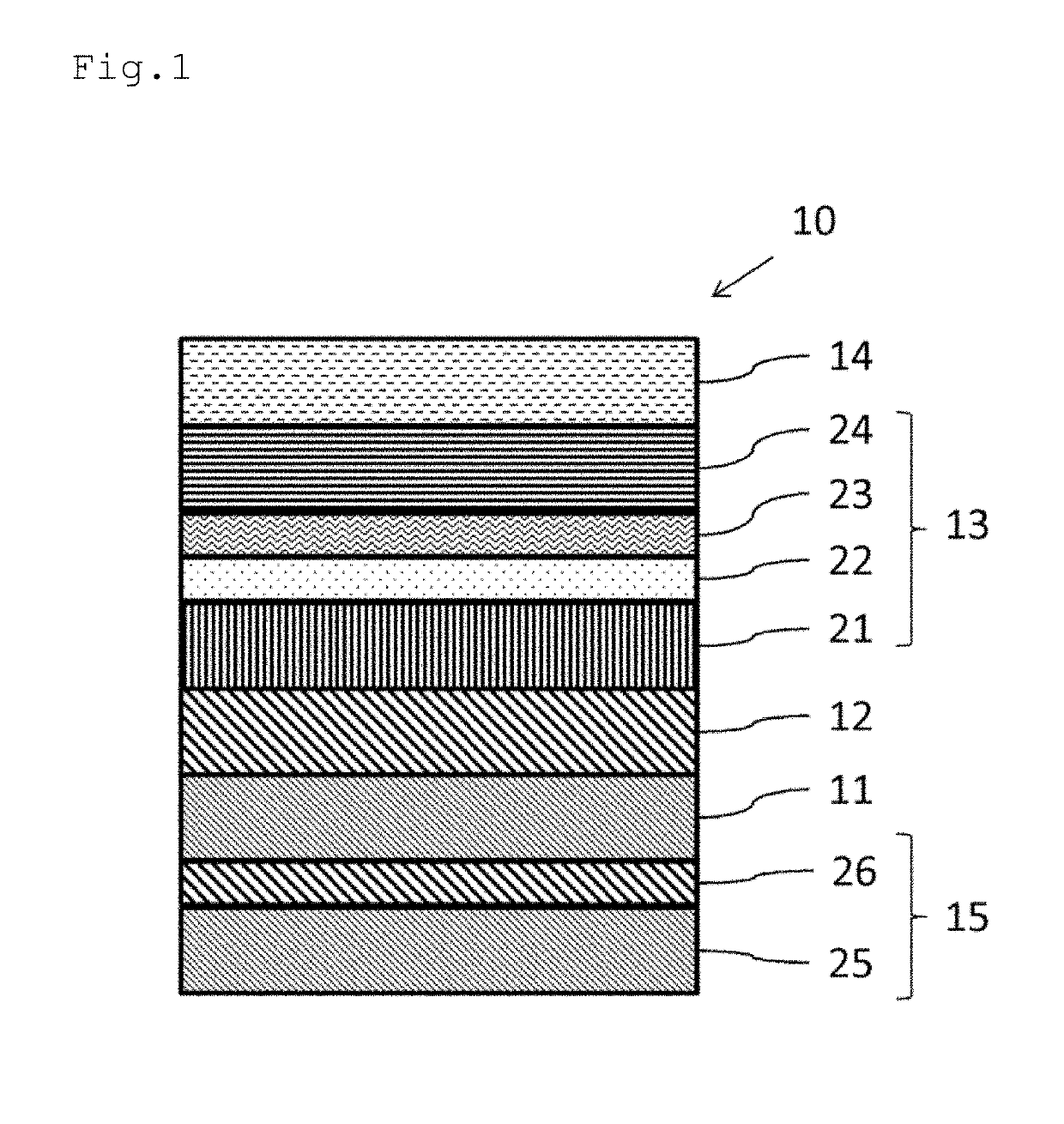
Magnetroresistive element, method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic multilayered film manufacturing apparatus
ActiveCN101304070AImprove thermal stabilityHigh MR ratioChemical vapor deposition applicationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOptoelectronicsAntiferromagnetism
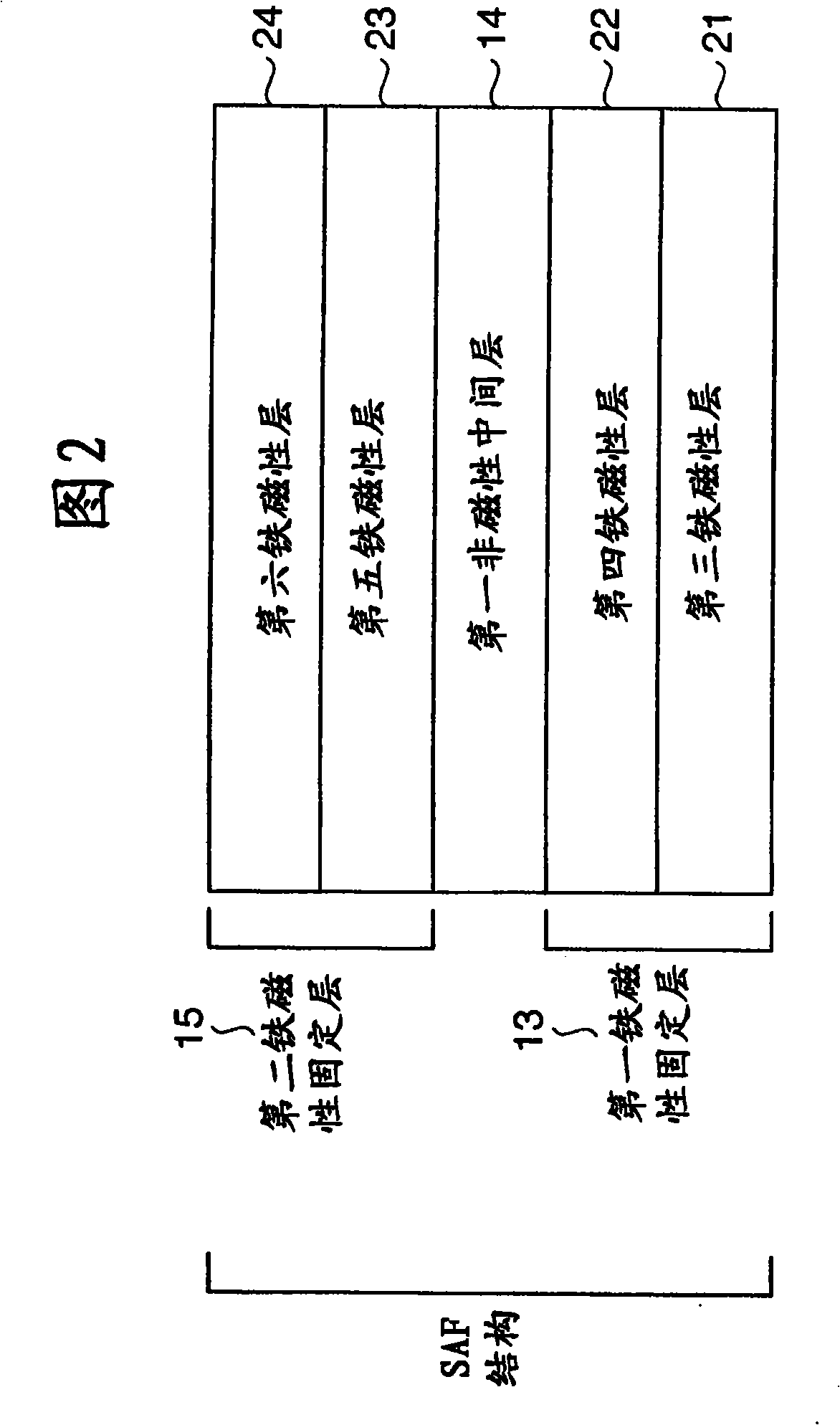
A magnetoresistive element includes an antiferromagnetic layer formed from a layer containing manganese, a layered magnetization fixed layer which includes a first magnetization fixed layer located over a side of the antiferromagnetic layer and formed from a layer containing a ferromagnetic material and a platinum group metal, a second magnetization fixed layer formed from a layer containing a ferromagnetic material, and a first nonmagnetic intermediate layer located between the first magnetization fixed layer and the second magnetization fixed layer, a magnetic free layer formed from a layer containing a ferromagnetic material, and a second nonmagnetic intermediate layer located between the layered magnetization fixed layer and the magnetic free layer.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Magnetic memory device and method of fabricating the same
A magnetic memory device includes a pinning layer, a pinned layer, an insulation layer, which are sequentially stacked on a semiconductor substrate. The magnetic memory device further includes a free layer disposed on the insulation layer, a capping layer disposed on the free layer and an MR (magnetoresistance) enhancing layer interposed between the free layer and the capping layer. The MR enhancing layer is formed of at least one anti-ferromagnetic material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Magnetoresistive element, manufacturing method thereof and magnetic sensor
ActiveUS20190148626A1High repeatability in oxidizationLess variationMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetizationMagnetic reluctance
A magnetoresistive element has a magnetization free layer whose magnetization direction changes in an external magnetic field; a magnetization pinned layer whose magnetization direction is pinned in the external magnetic field; and a barrier layer that is positioned between the magnetization free layer and the magnetization pinned layer and that exhibits a magnetoresistive effect. The barrier layer is an oxide of an alloy that includes Mg and Al, and the barrier layer includes a crystalline region and a non-crystalline region.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetoresistive element with oxide magnetic layers and metal magnetic films deposited thereon
InactiveUS7265948B2High MR ratioImprove long-term reliabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagnetic reluctanceNon magnetic
No related magnetoresistive multi-layered films made from a metal magnetic film provide sufficient reproducing output power. A high-polarized layer with a thickness of 10 nm or less is formed as a Fe-rich Fe—O layer in contact with the interface of a non-magnetic intermediate layer and the resulting layers are heat treated to form a multi-layered film of ferromagnetic Fe—O layers, achieving a magnetoresistive element having high magnetoresistance.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
MRAM with super-paramagnetic sensing layer
ActiveUS7696548B2Low HcHigh MR ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetizationNon magnetic
An MRAM is disclosed that has a MTJ comprised of a ferromagnetic layer with a magnetization direction along a first axis, a super-paramagnetic (SP) free layer, and an insulating layer formed therebetween. The SP free layer has a remnant magnetization that is substantially zero in the absence of an external field, and in which magnetization is roughly proportional to an external field until reaching a saturation value. In one embodiment, a separate storage layer is formed above, below, or adjacent to the MTJ and has uniaxial anisotropy with a magnetization direction along its easy axis which parallels the first axis. In a second embodiment, the storage layer is formed on a non-magnetic conducting spacer layer within the MTJ and is patterned simultaneously with the MTJ. The SP free layer may be multiple layers or laminated layers of CoFeB. The storage layer may have a SyAP configuration and a laminated structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetoresistive device, magnetic head, magnetic storage apparatus, and magnetic memory
InactiveCN101252166ARaise the output levelHigh MR ratioNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
A CPP-type magnetoresistive device includes a magnetization pinned layer, a magnetization free layer, and a non-magnetic layer provided between the magnetization pinned layer and the magnetization free layer. At least one of the magnetization free layer and the magnetization pinned layer is formed of CoFeGe, and the CoFeGe has a composition falling within a range defined by line segments connecting coordinate points A, B, C, and D in a ternary composition diagram where the point A is (42.5, 30, 27.5), the point B is (35, 52.5, 12.5), the point C is (57.5, 30.0, 12.5), and the point D is (45.0, 27.5, 27.5), and where each of the coordinate points is represented by content percentage of (Co, Fe, Ge) expressed by atomic percent (at. %).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Composite free layer within magnetic tunnel junction for MRAM applications
ActiveUS9159908B2Improve performanceHigh MR ratioNanostructure applicationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSwitched currentPower flow
A magnetic tunneling junction (MTJ) in an MRAM array is disclosed with a composite free layer having a FL1 / FL2 / FL3 configuration where FL1 and FL2 are crystalline magnetic layers and FL3 is an amorphous NiFeX layer for improved bit switching performance. FL1 layer is CoFe which affords a high magnetoresistive (MR) ratio when forming an interface with a MgO tunnel barrier. FL2 is Fe to improve switching performance. NiFeX thickness where X is Hf is preferably between 20 to 40 Angstroms to substantially reduce bit line switching current and number of shorted bits. Annealing at 330° C. to 360° C. provides a high MR ratio of 190%. Furthermore, low Hc and Hk are simultaneously achieved with improved bit switching performance and fewer shorts without compromising other MTJ properties such as MR ratio. As a result of high MR ratio and lower bit-to-bit resistance variation, higher reading margin is realized.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetoresistance effect element
ActiveUS20180090670A1Small sizeHigh thermal disturbance resistanceMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesNon magneticCadmium Cation
A magnetoresistance effect element has favorable symmetry of an MR ratio even if the sign of a bias voltage is different, which is capable of reversing magnetization to a current, which has a high MR ratio. A magnetoresistance effect element includes a laminate in which an underlayer, a first ferromagnetic metal layer, a tunnel barrier layer, and a second ferromagnetic metal layer are laminated in that order, wherein the underlayer is made of one or more selected from a group containing of TiN, VN, NbN, and TaN, or mixed crystals thereof, and wherein the tunnel barrier layer is made of a compound having a spinel structure and represented by the following composition formula (1). (1): AxGa2Oy where A is a non-magnetic divalent cation and represents a cation of at least one element selected from the group consisting of magnesium, zinc, and cadmium, x is a number that satisfies 0<x≦2, and y is a number that satisfies 0<y≦4.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Manufacturing method of magnetoresistive effect element
ActiveUS20160240772A1Enhancing MR ratioRaise the ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetizationOptoelectronics
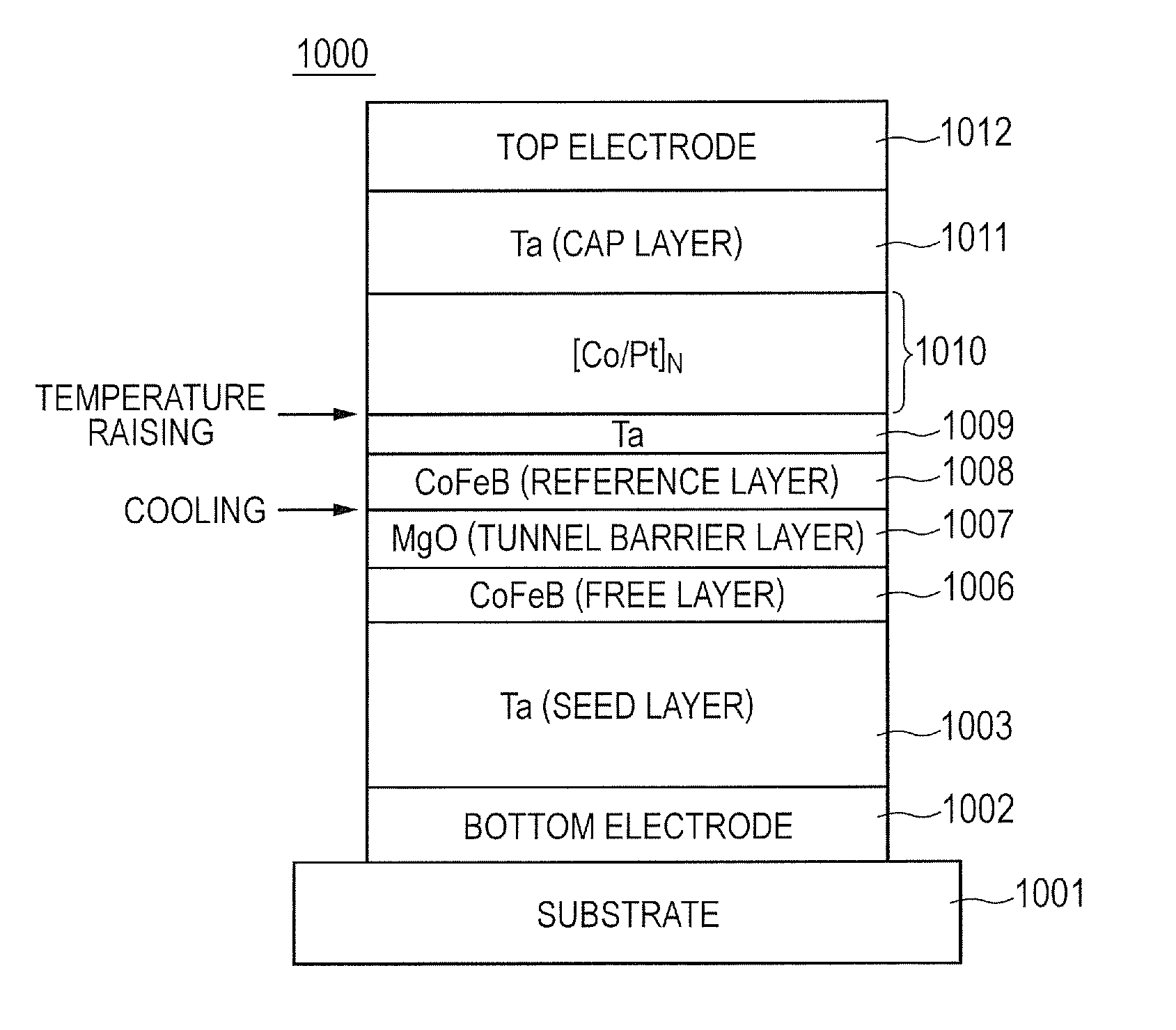
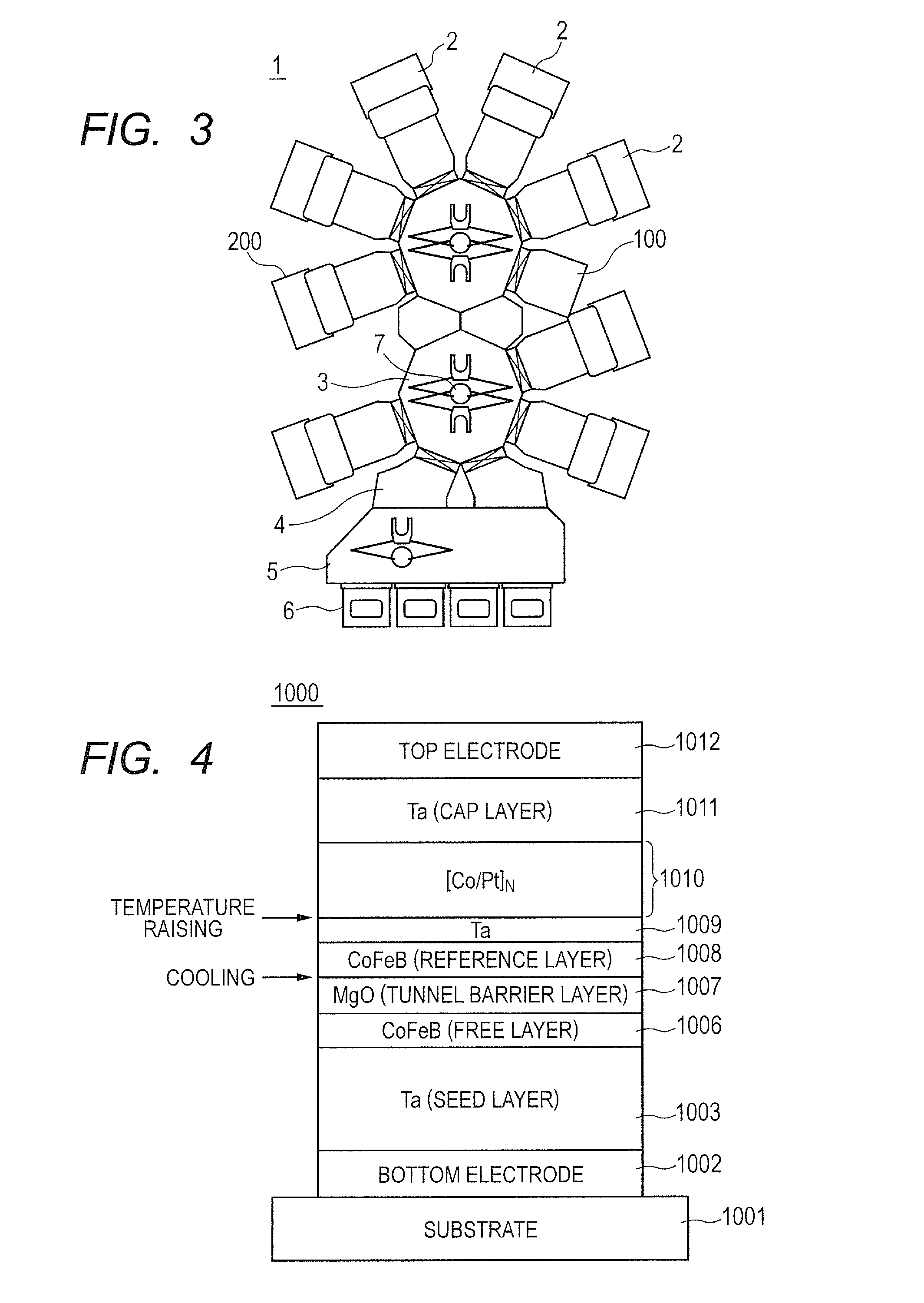
This invention provides a manufacturing method of a magnetoresistive effect element having a higher MR ratio than a conventional element. A manufacturing method of a magnetoresistive effect element of an embodiment of the invention includes: a step of forming a tunnel barrier layer on a substrate, on a surface of which one of a magnetization free layer and a magnetization fixed layer is formed; a step of cooling the substrate after the step of forming a tunnel barrier layer; a step of forming an other one of the magnetization free layer and the magnetization fixed layer on the tunnel barrier layer after the step of cooling; and a step of raising a temperature of the substrate after the step of forming the other one of the magnetization free layer and the magnetization fixed layer.
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com