Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58 results about "Hot mirror" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
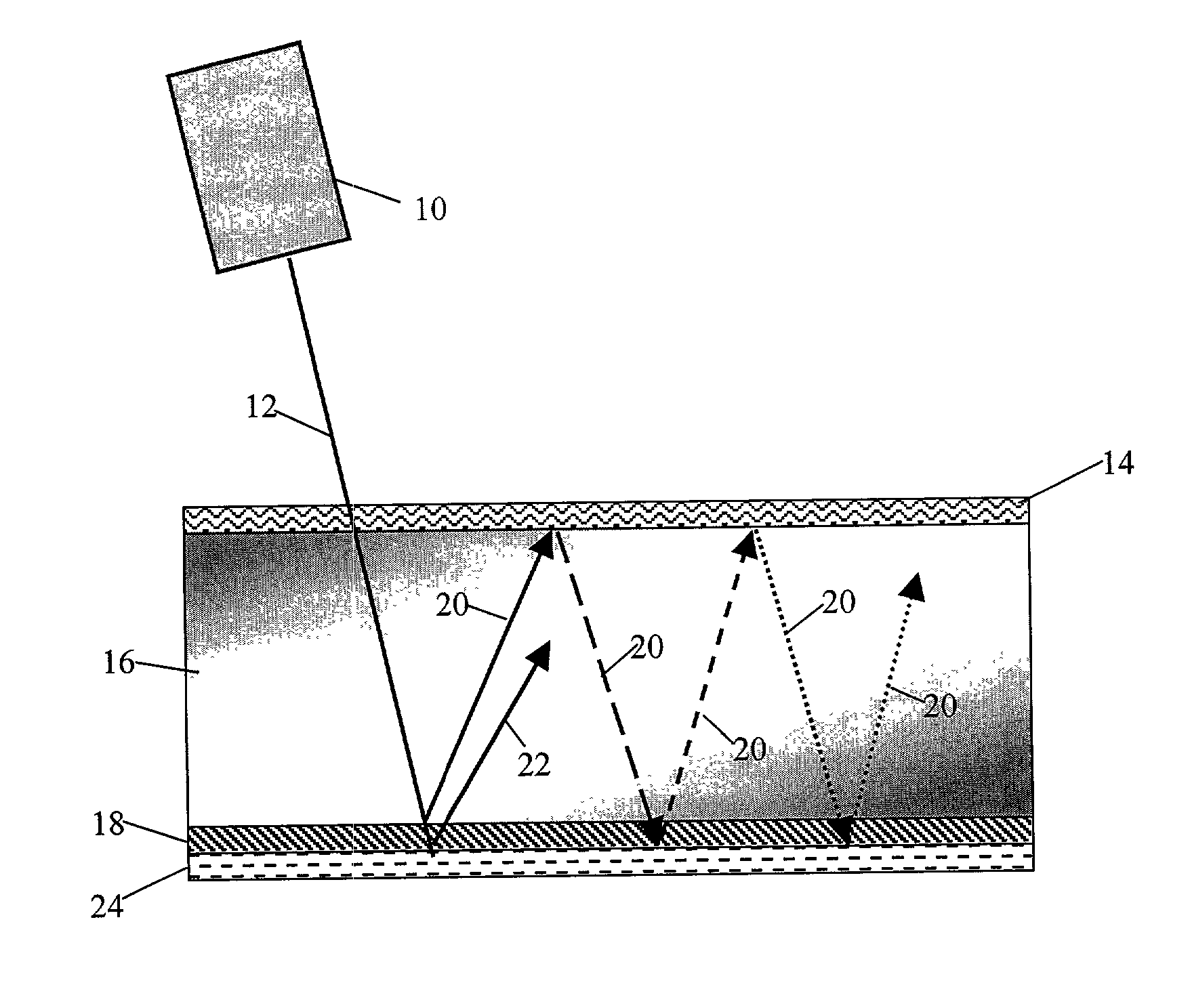
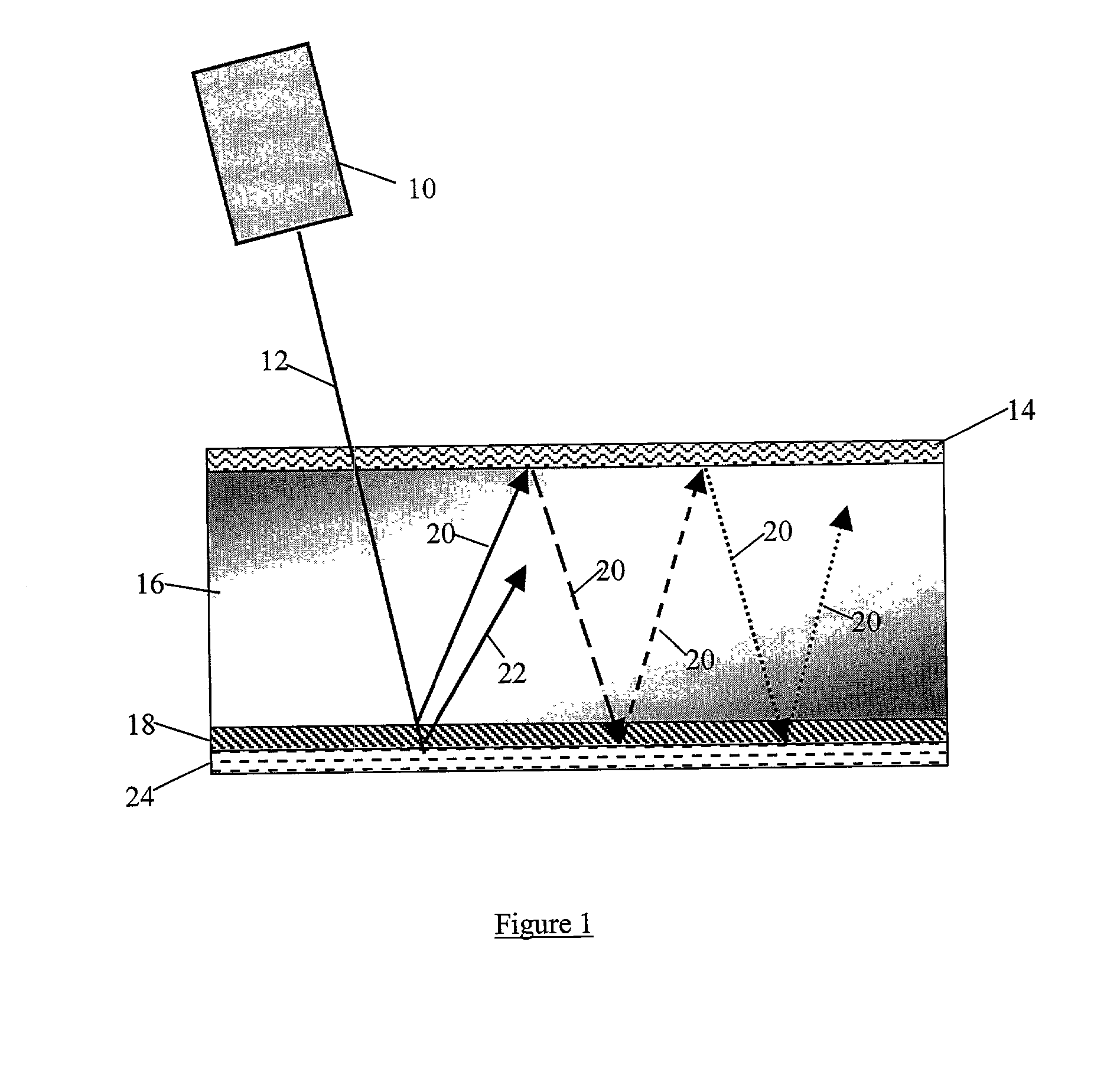
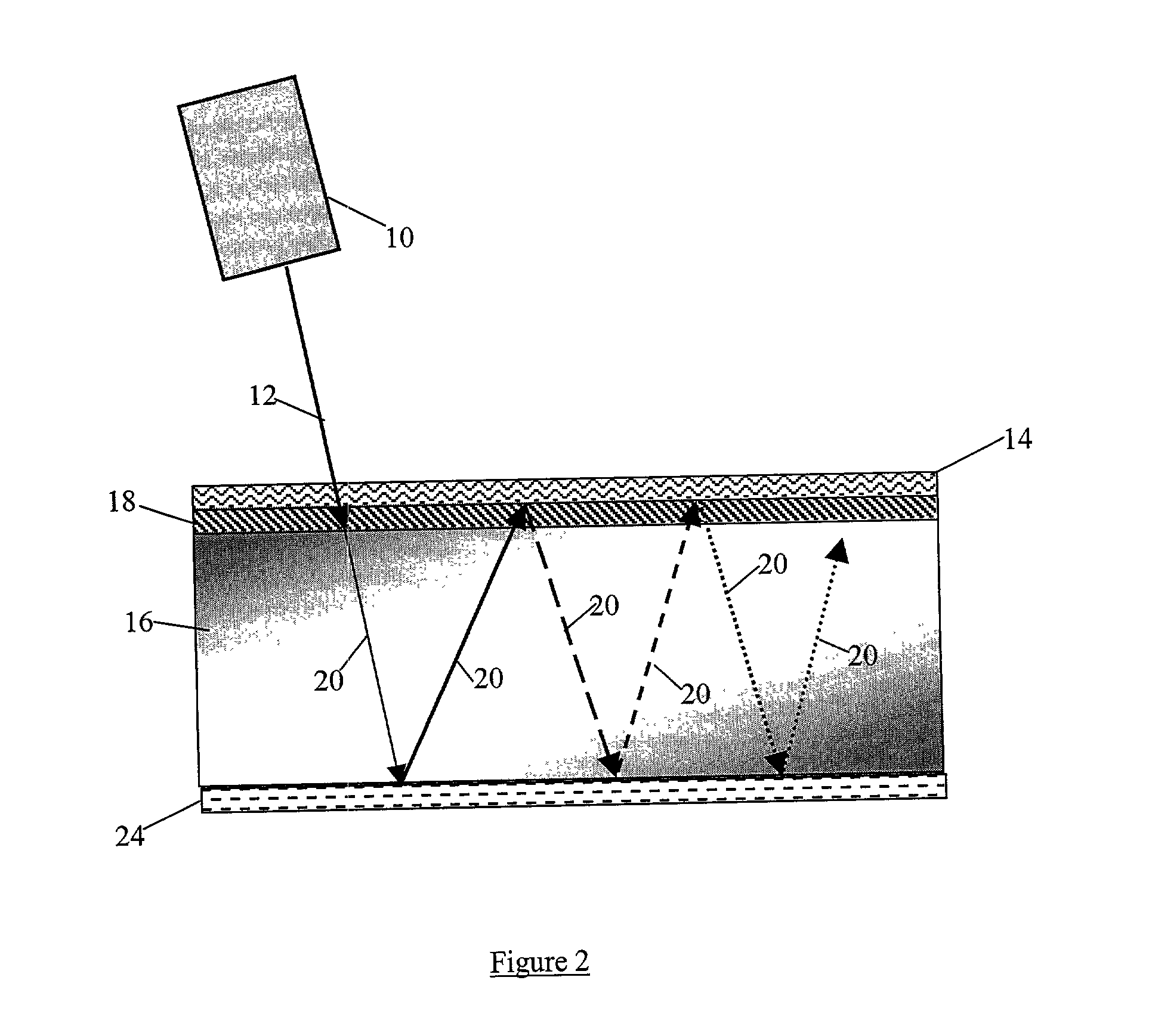
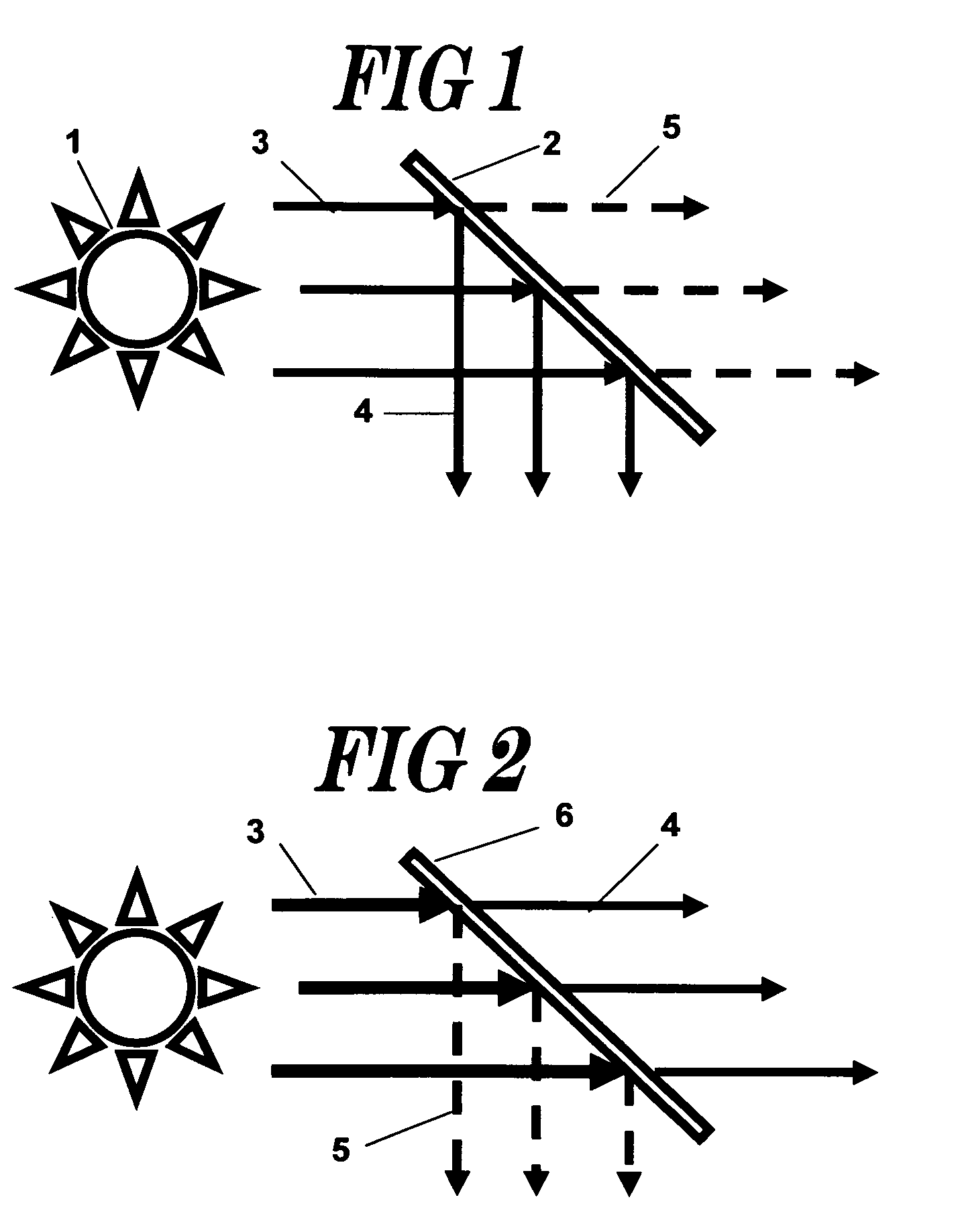
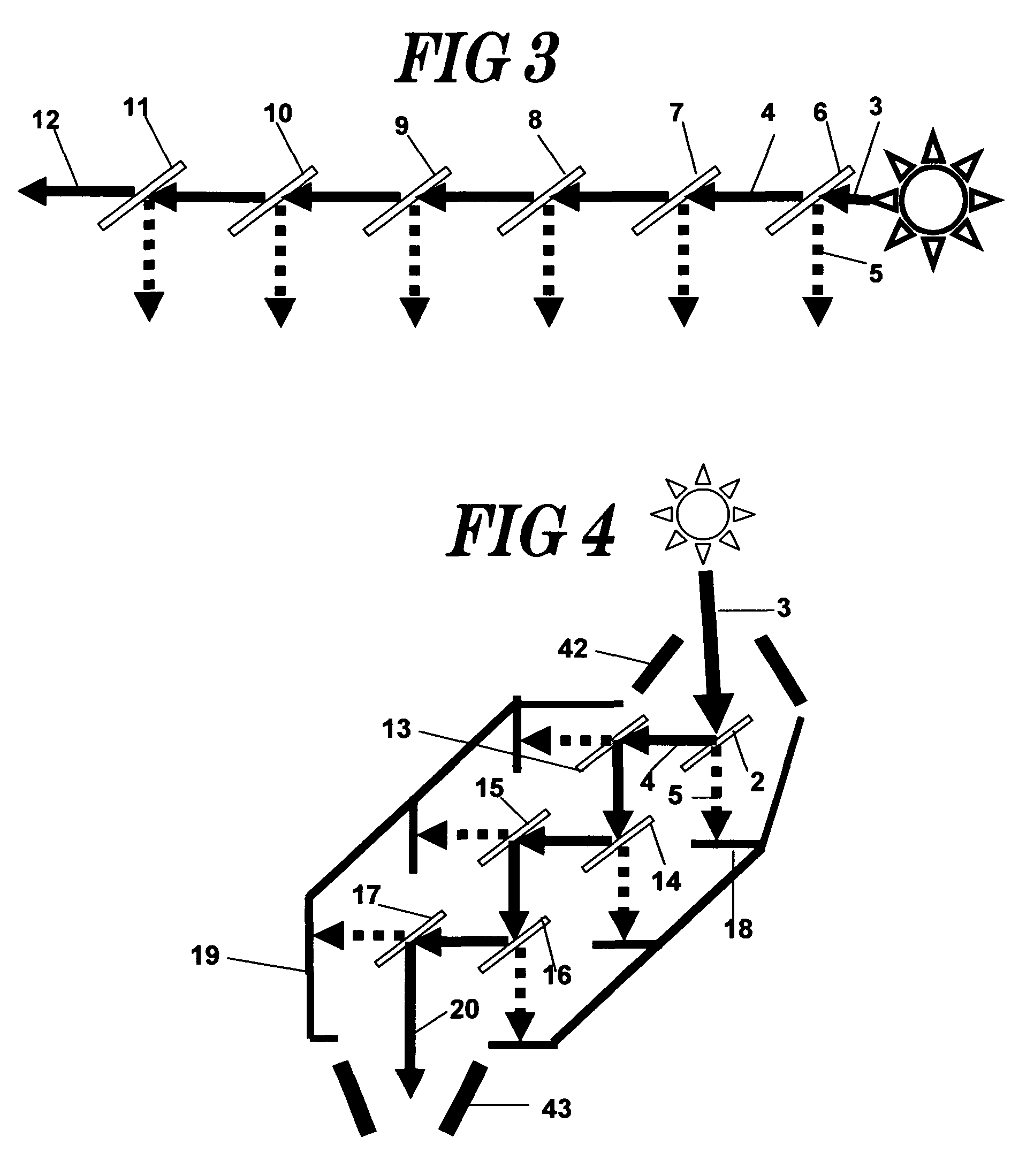
A hot mirror is a specialized dielectric mirror, a dichroic filter, often employed to protect optical systems by reflecting infrared light back into a light source, while allowing visible light to pass. Hot mirrors can be designed to be inserted into the optical system at an incidence angle varying between zero and 45 degrees, and are useful in a variety of applications where the buildup of waste heat can damage components or adversely affect spectral characteristics of the illumination source. Wavelengths reflected by an infrared hot mirror range from about 750 to 1250 nanometers. By transmitting visible light wavelengths while reflecting infrared, hot mirrors can also serve as dichromatic beam splitters for specialized applications in fluorescence microscopy or optical eye tracking.
Enhanced heat mirror films
ActiveUS7215473B2Function increaseImprove interlayer adhesionMirrorsSynthetic resin layered productsMetal alloyHot mirror
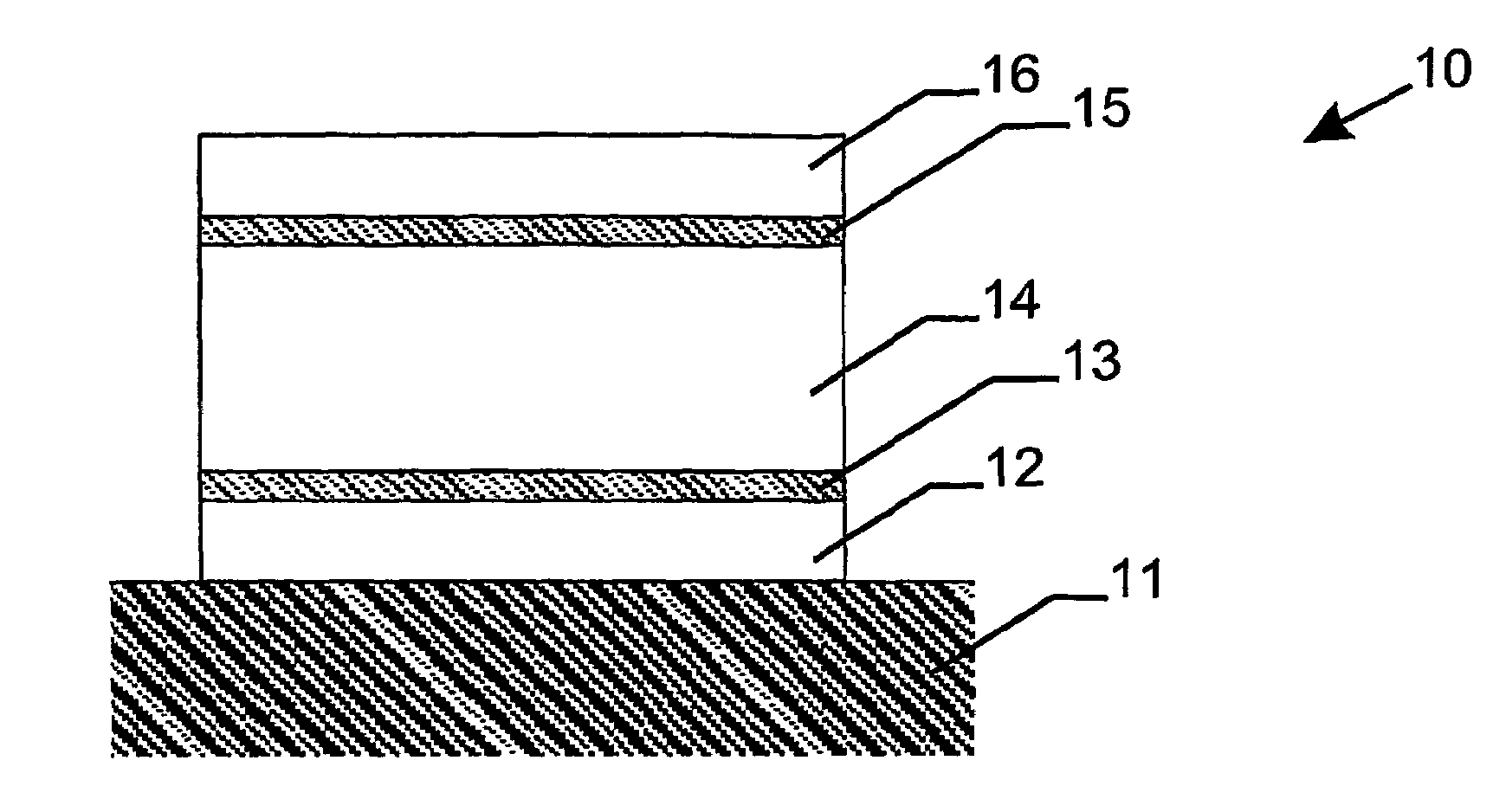
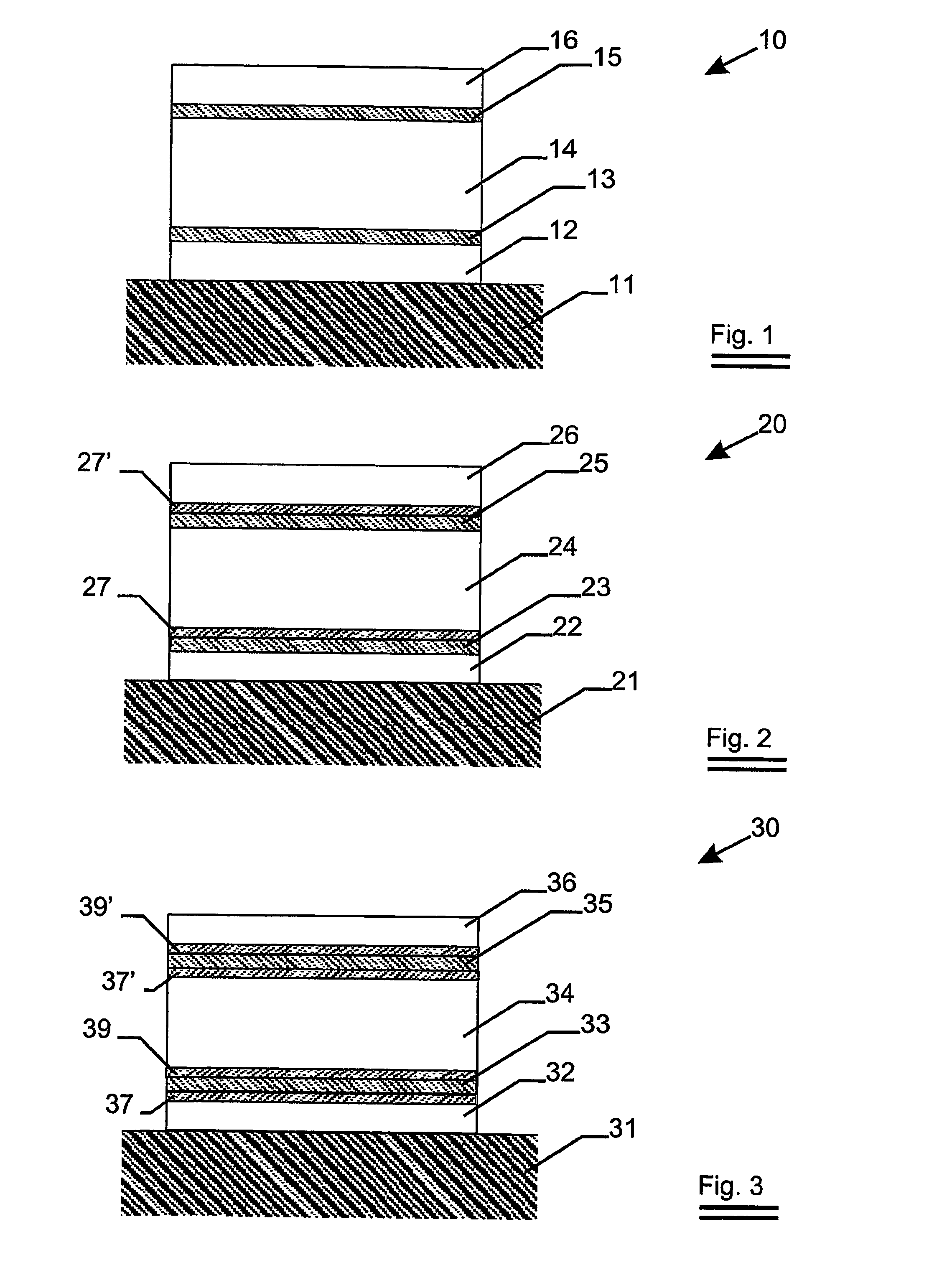
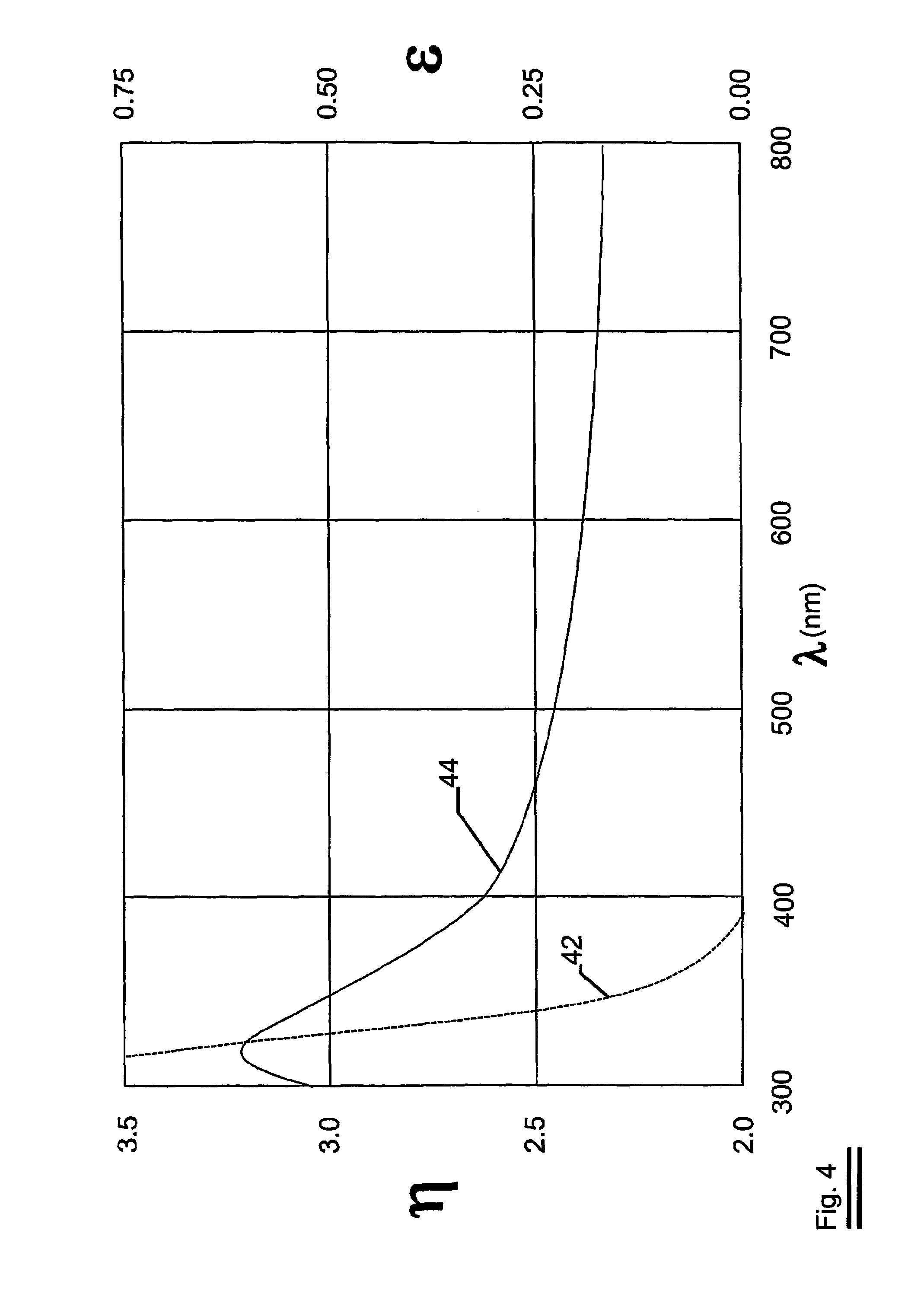
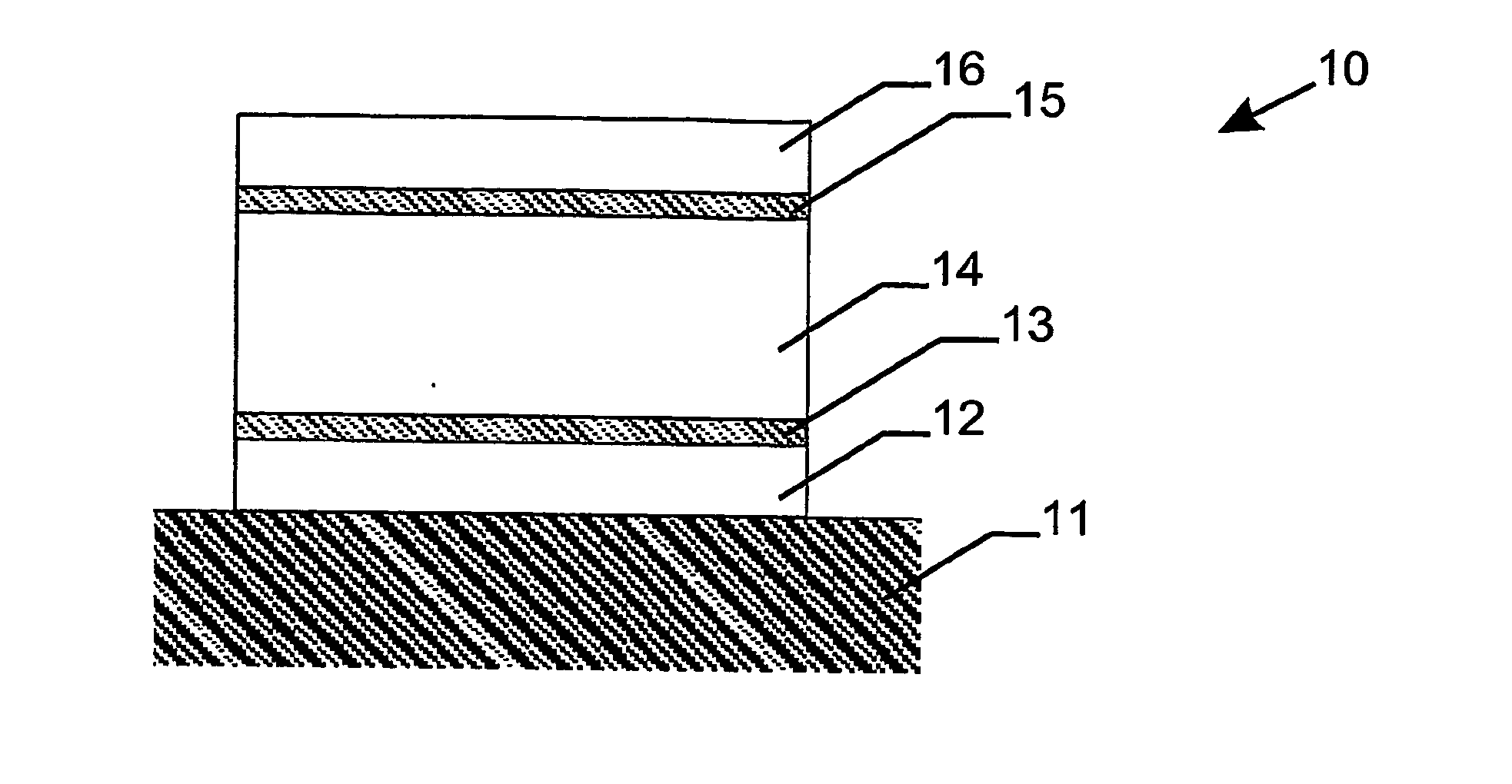
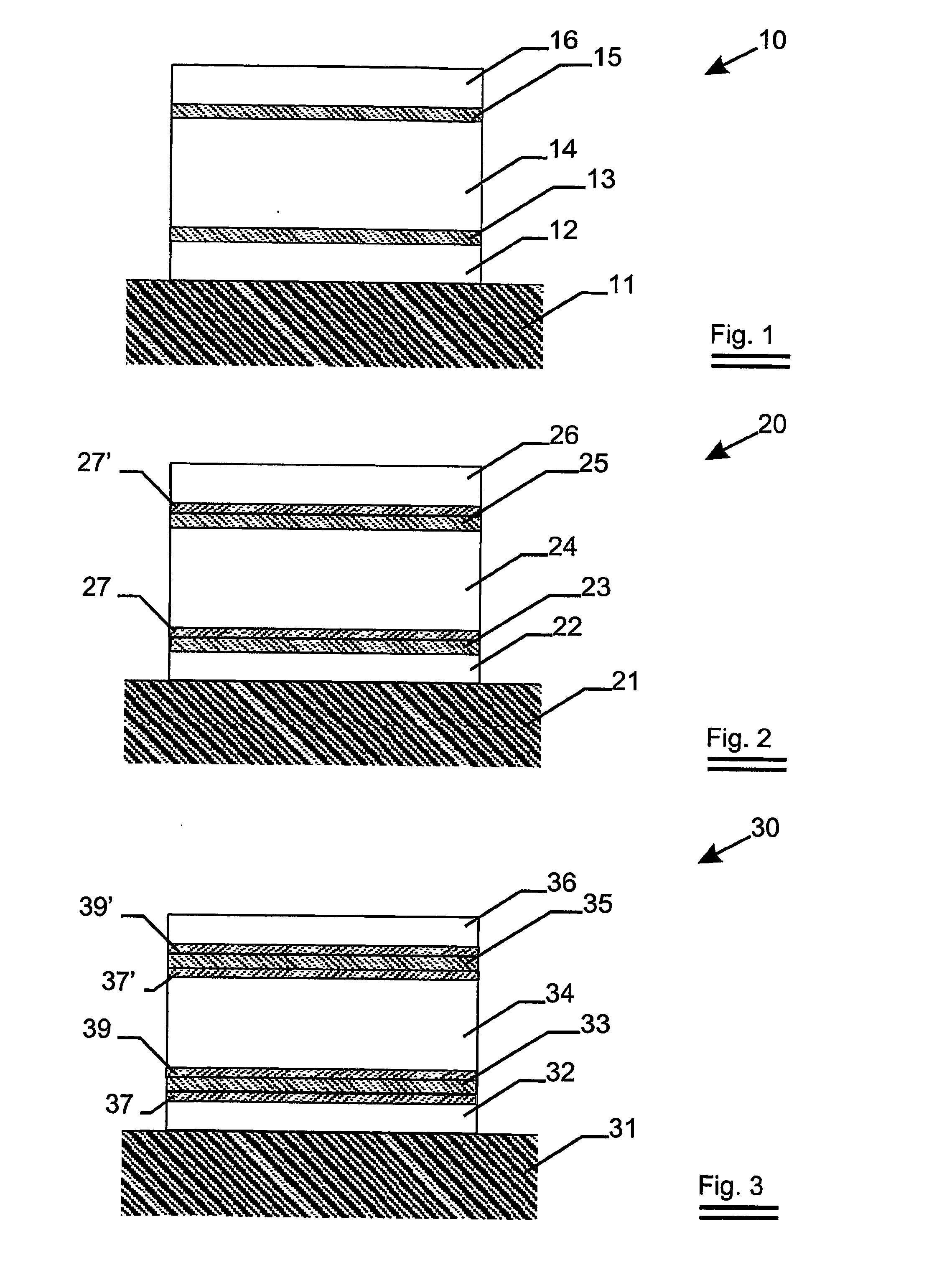
A heat mirror film containing visible light-transmissive and infrared reflective film comprising a birefringent dielectric multilayer support that reflects at least 50% of light in a band at least 100 nm wide in a wavelength region of interest, a metal or metal alloy layer whose thickness is such that the film is visible light-transmissive and its reflection band is broadened, and a crosslinked polymeric layer has improved infrared reflecting properties. The film can be joined or laminated into glazing (especially non-planar vehicular safety glazing) with reduced likelihood that the metal or metal alloy layer will be damaged or distorted.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
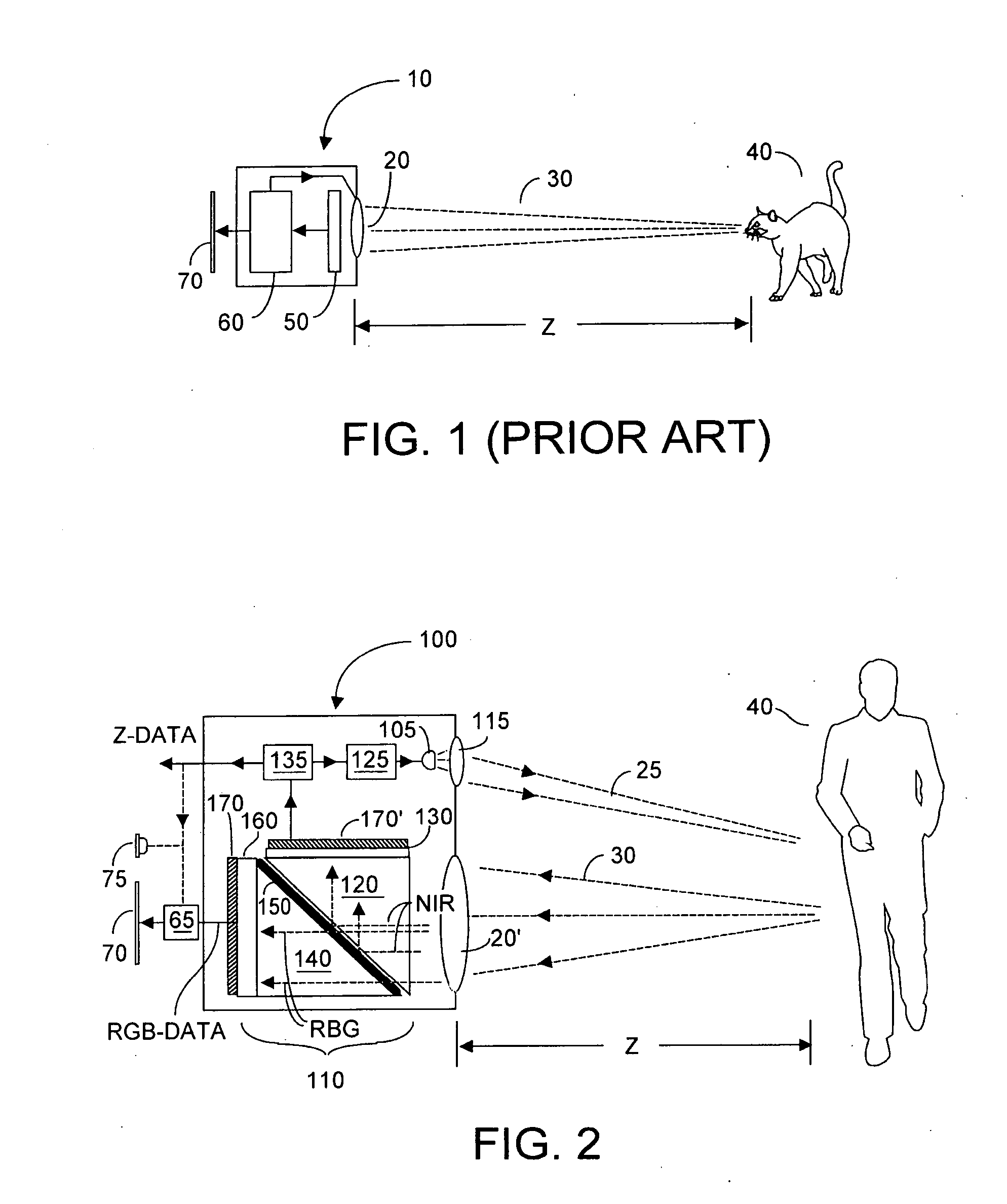
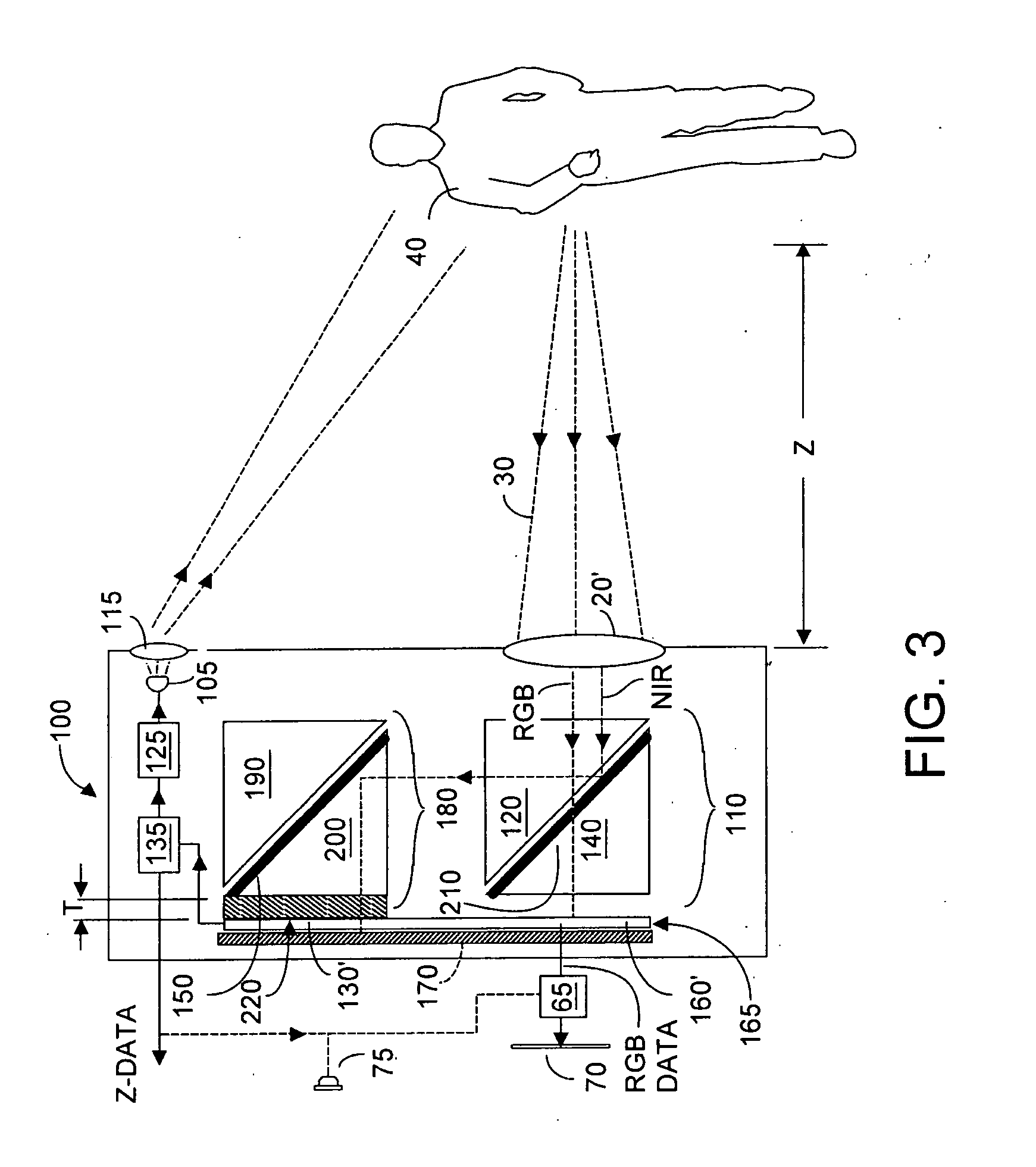
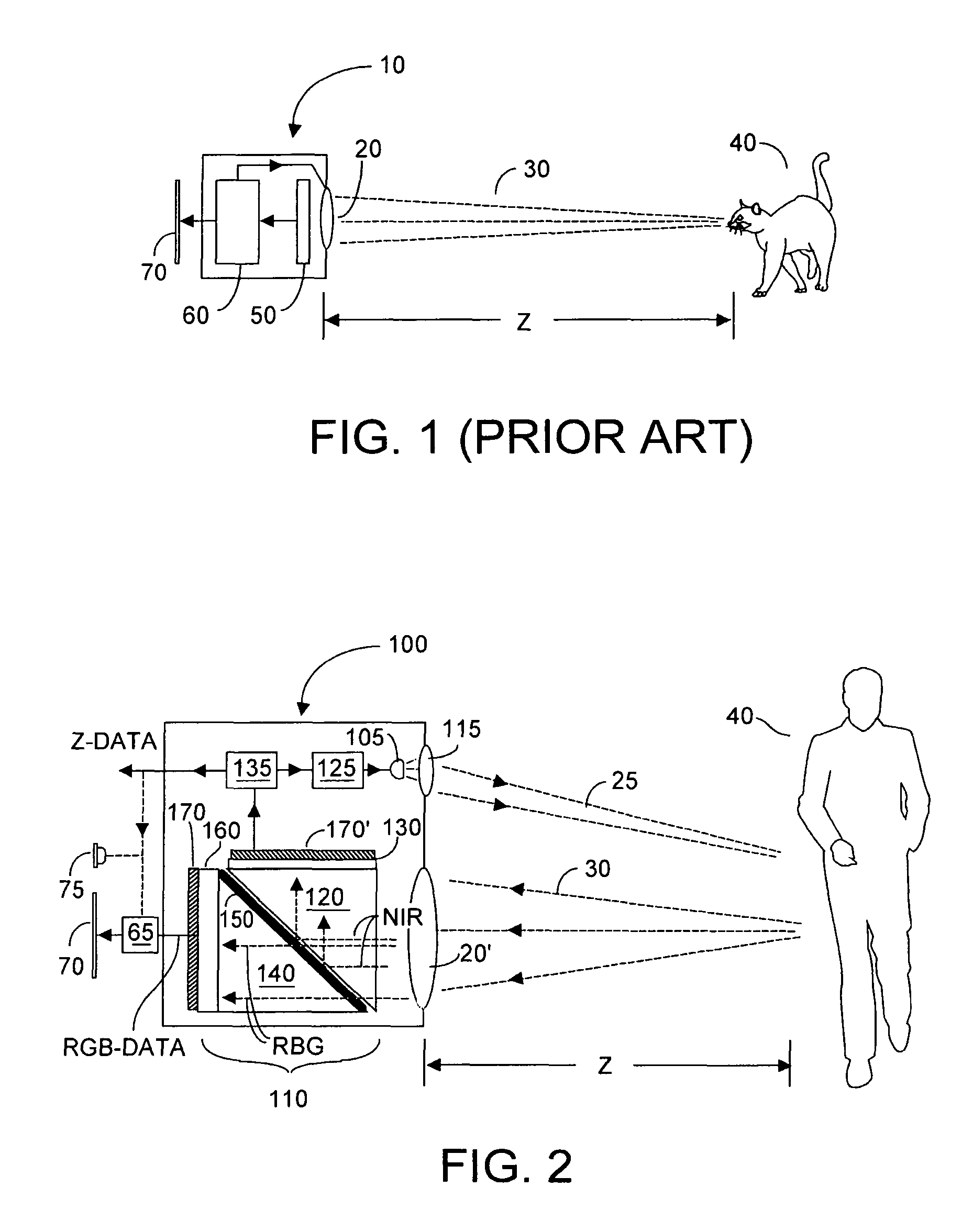
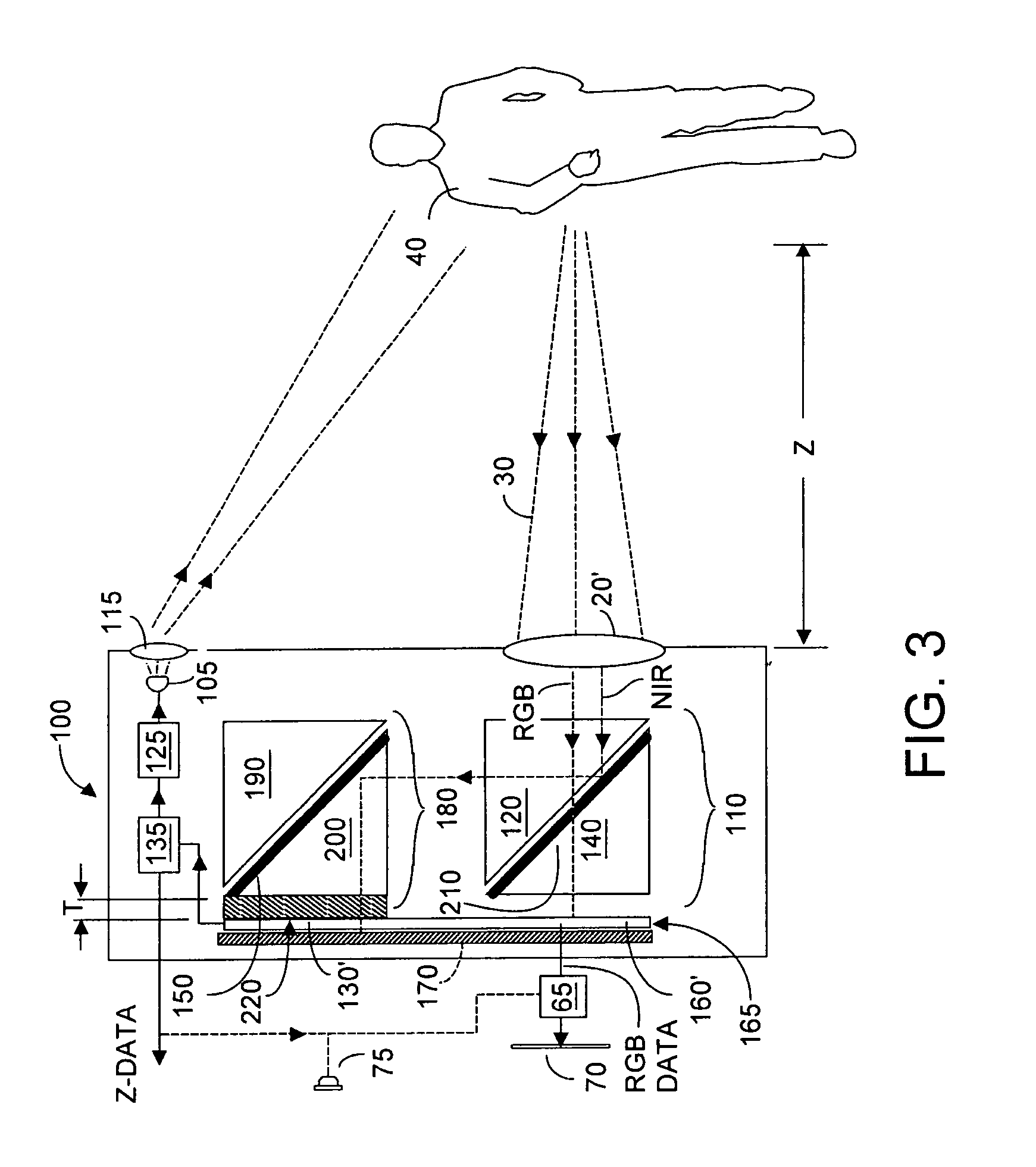
Single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor
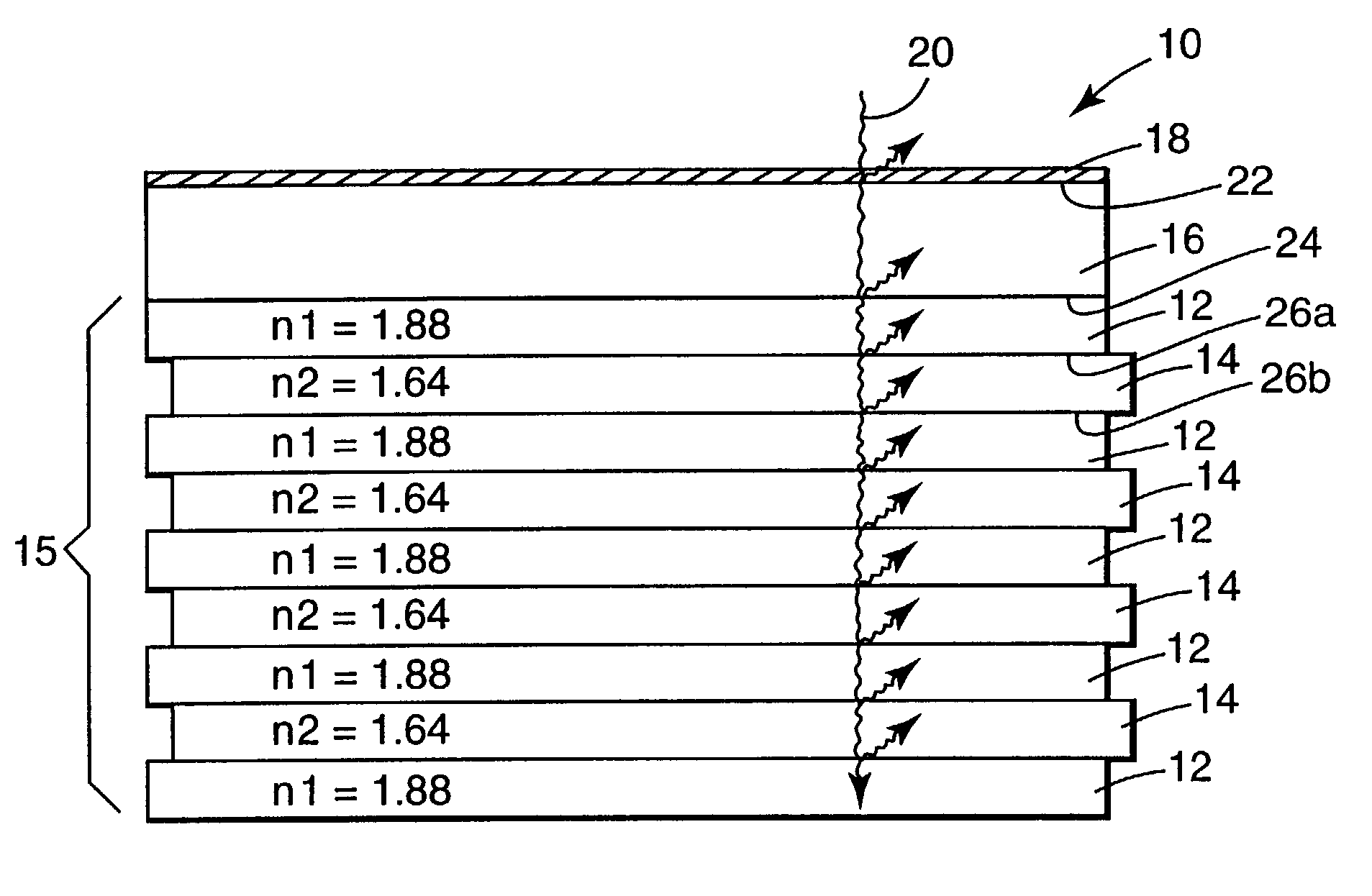
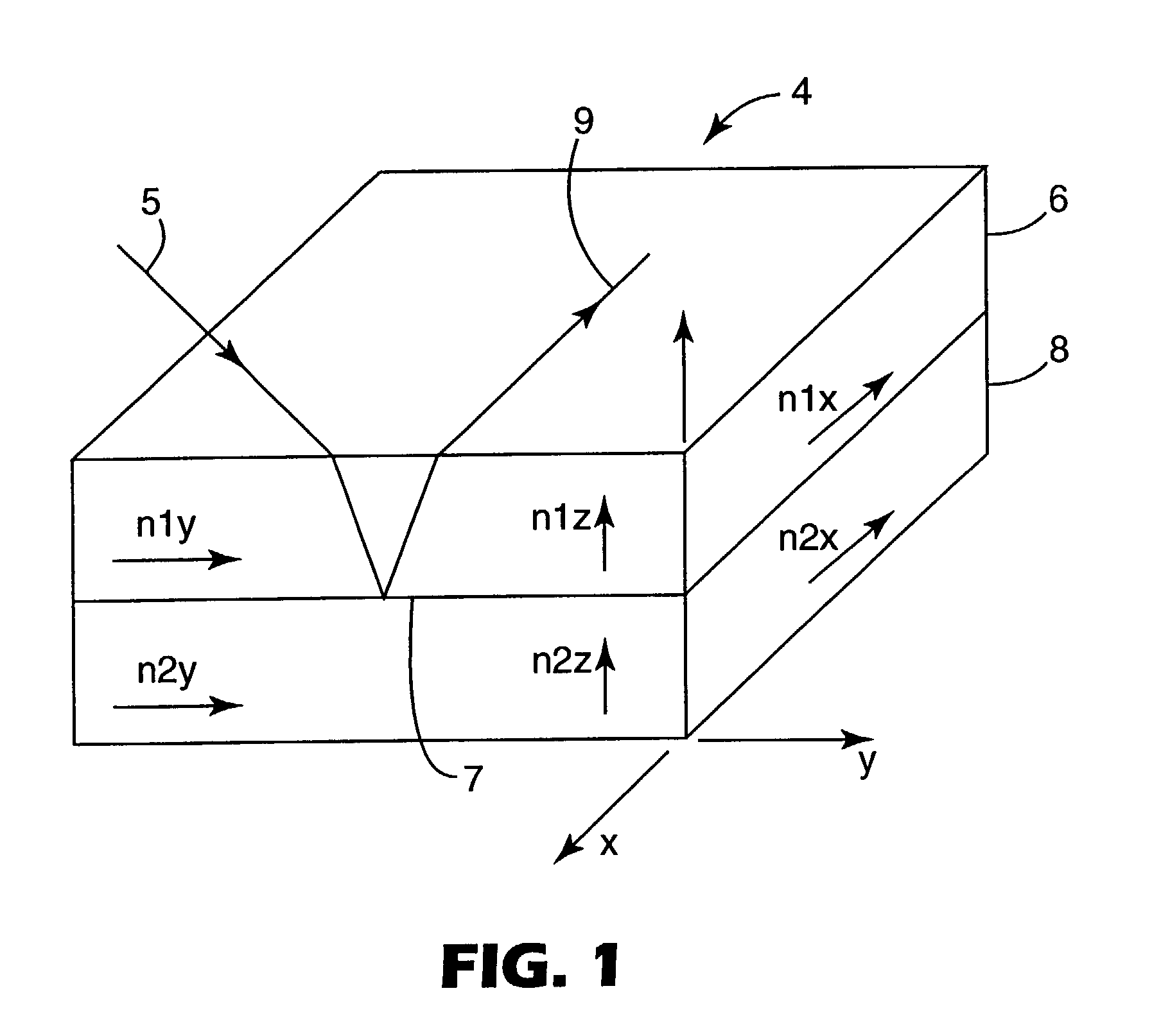
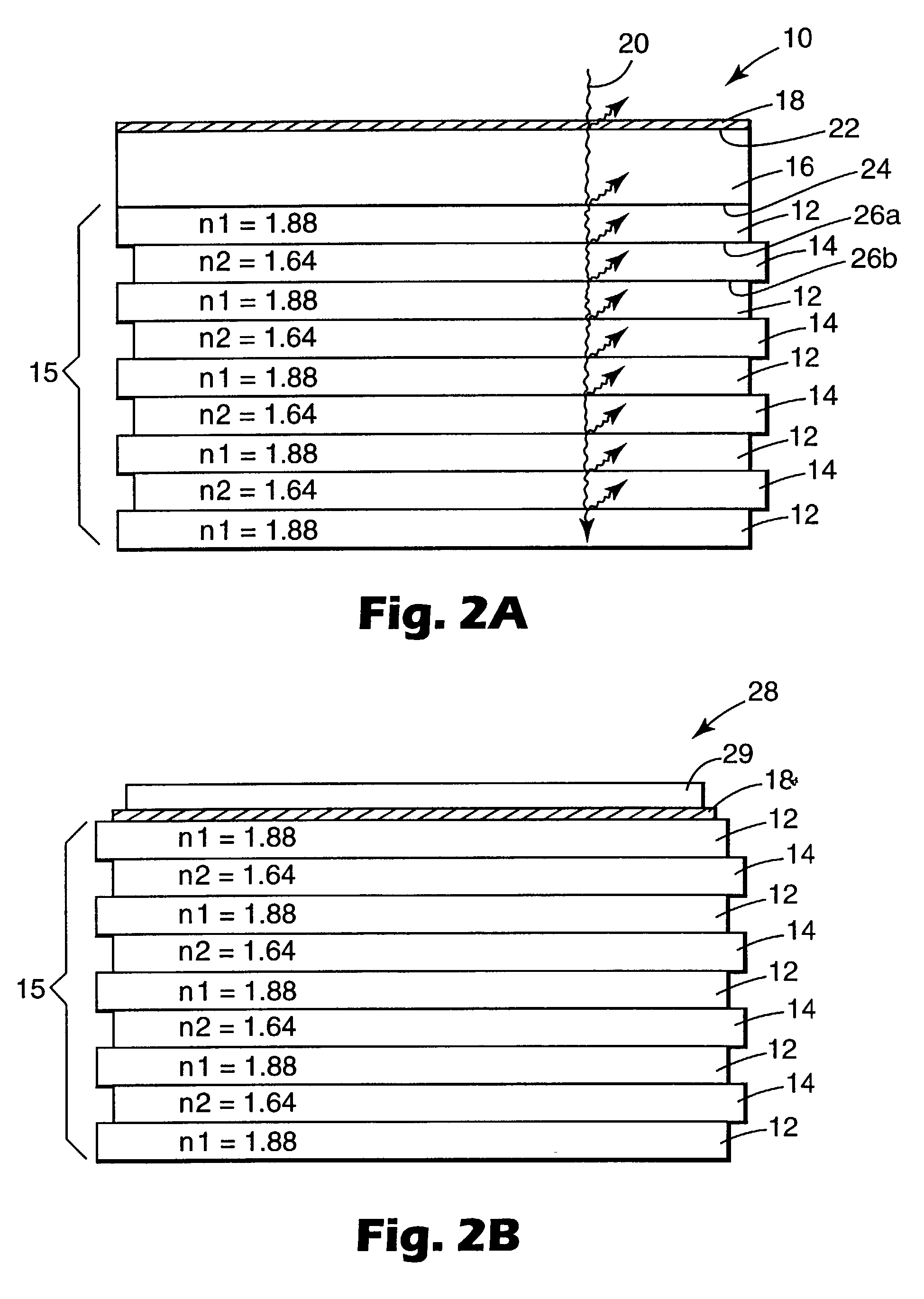
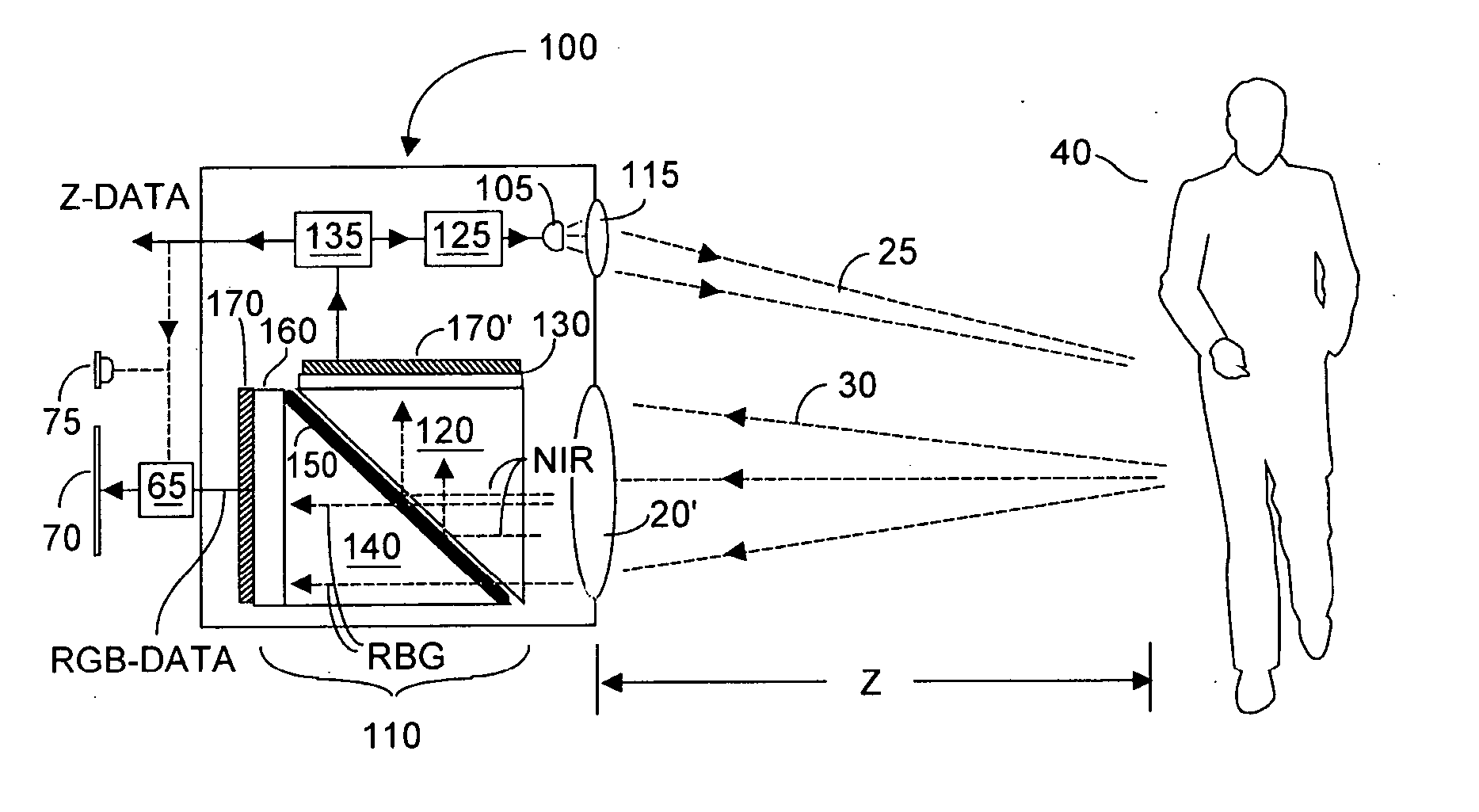
ActiveUS20050285966A1Quick identificationHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersBeam splitterSpectral bands
An RGB-Z sensor is implementable on a single IC chip. A beam splitter such as a hot mirror receives and separates incoming first and second spectral band optical energy from a target object into preferably RGB image components and preferably NIR Z components. The RGB image and Z components are detected by respective RGB and NIR pixel detector array regions, which output respective image data and Z data. The pixel size and array resolutions of these regions need not be equal, and both array regions may be formed on a common IC chip. A display using the image data can be augmented with Z data to help recognize a target object. The resultant structure combines optical efficiency of beam splitting with the simplicity of a single IC chip implementation. A method of using the single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
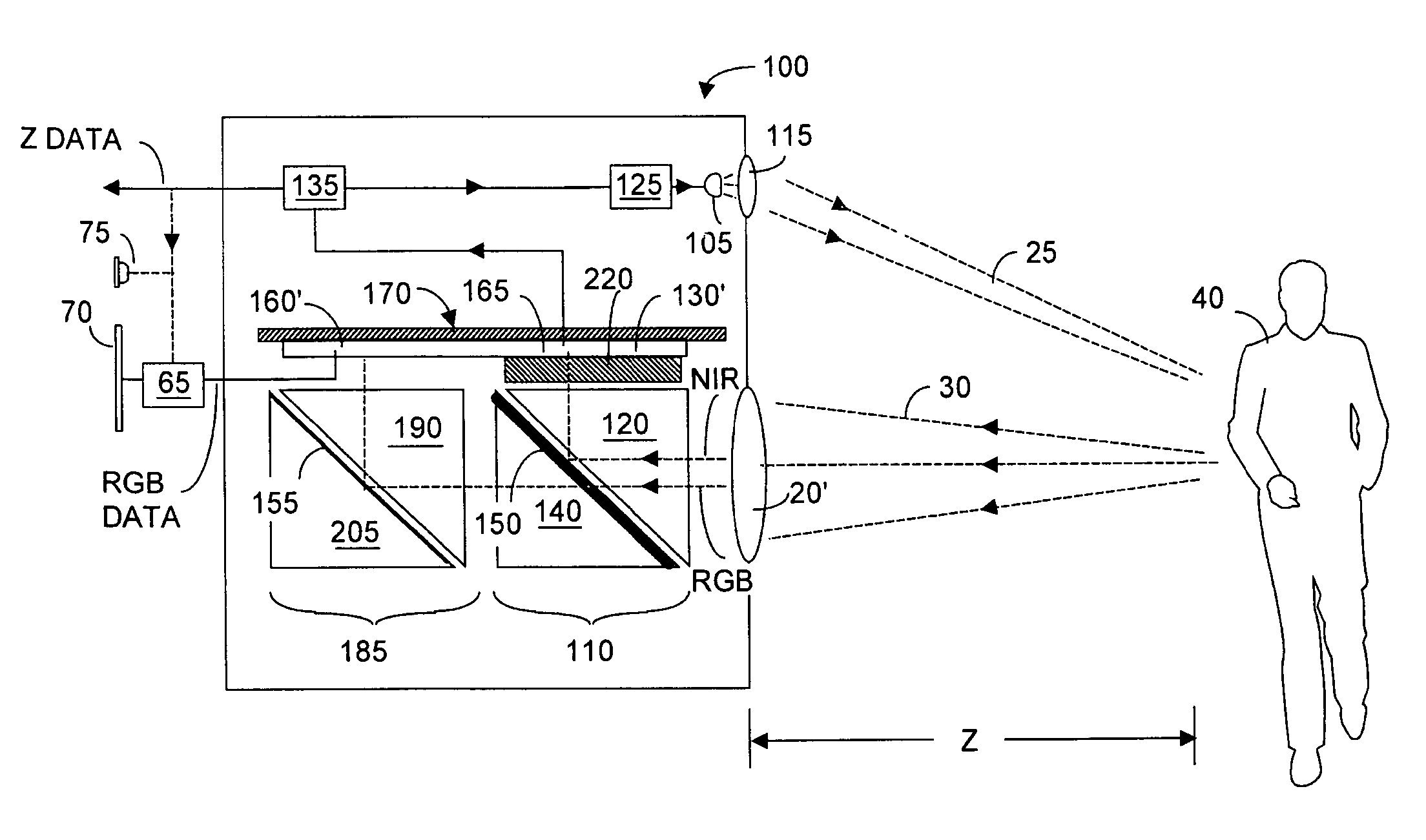
Single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor
ActiveUS8139141B2High resolutionQuick identificationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersBeam splitterSpectral bands
An RGB-Z sensor is implementable on a single IC chip. A beam splitter such as a hot mirror receives and separates incoming first and second spectral band optical energy from a target object into preferably RGB image components and preferably NIR Z components. The RGB image and Z components are detected by respective RGB and NIR pixel detector array regions, which output respective image data and Z data. The pixel size and array resolutions of these regions need not be equal, and both array regions may be formed on a common IC chip. A display using the image data can be augmented with Z data to help recognize a target object. The resultant structure combines optical efficiency of beam splitting with the simplicity of a single IC chip implementation. A method of using the single chip red, green, blue, distance (RGB-Z) sensor is also disclosed.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Personal identification
InactiveUS6309069B1Comfortable to useReduce intensityPerson identificationAcquiring/recognising eyesDisplay deviceHot mirror
An optical apparatus records light reflected from one or more of a user's facial features. While the image is captured, visible light from a display or other scene to be viewed by the user passes to the user's eye. A portable iris pattern capture device is used. Near-infrared light is directed towards the user's eye from where it is reflected back into the apparatus. Visible light from an LCD display mounted at the rear of the apparatus travels out to the user's eye from the apparatus. A hot mirror inside the apparatus directs the near-infrared light reflected from the user's eye to a camera unit, and does not significantly attenuate the visible light emanating from the display.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Infra-red reflecting layered structure
ActiveUS7709095B2Good visible light transmittanceLow solar heat gain coefficientElectric discharge tubesMagnetic/electric field screeningGain coefficientRefractive index
The invention relates to an infra-red reflecting layered structure comprising a transparent substrate layer; a first metal oxide layer; a first silver containing layer, a second metal oxide layer; a second silver containing layer and a third metal oxide layer. The first, second and third metal oxide layer have a refractive index of at least 2.40 at a wavelength of 500 nm. The layered structure according to the present invention laminated on glass has a visual light transmittance (VLT) higher than 70% and a solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) lower than 0.44. The invention further relates to the use of a layered structure as a transparent heat-mirror.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CHAINEUX
Eye imaging with an off-axis imager
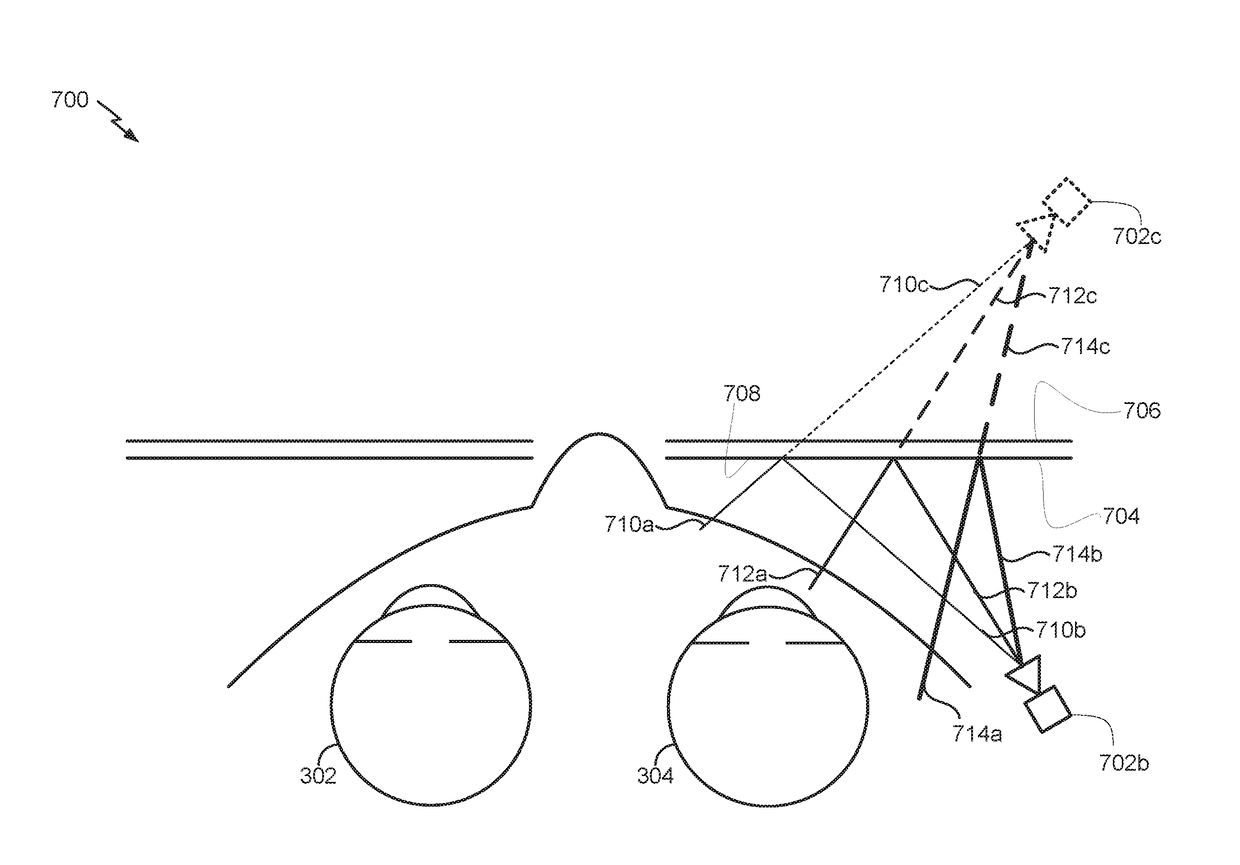
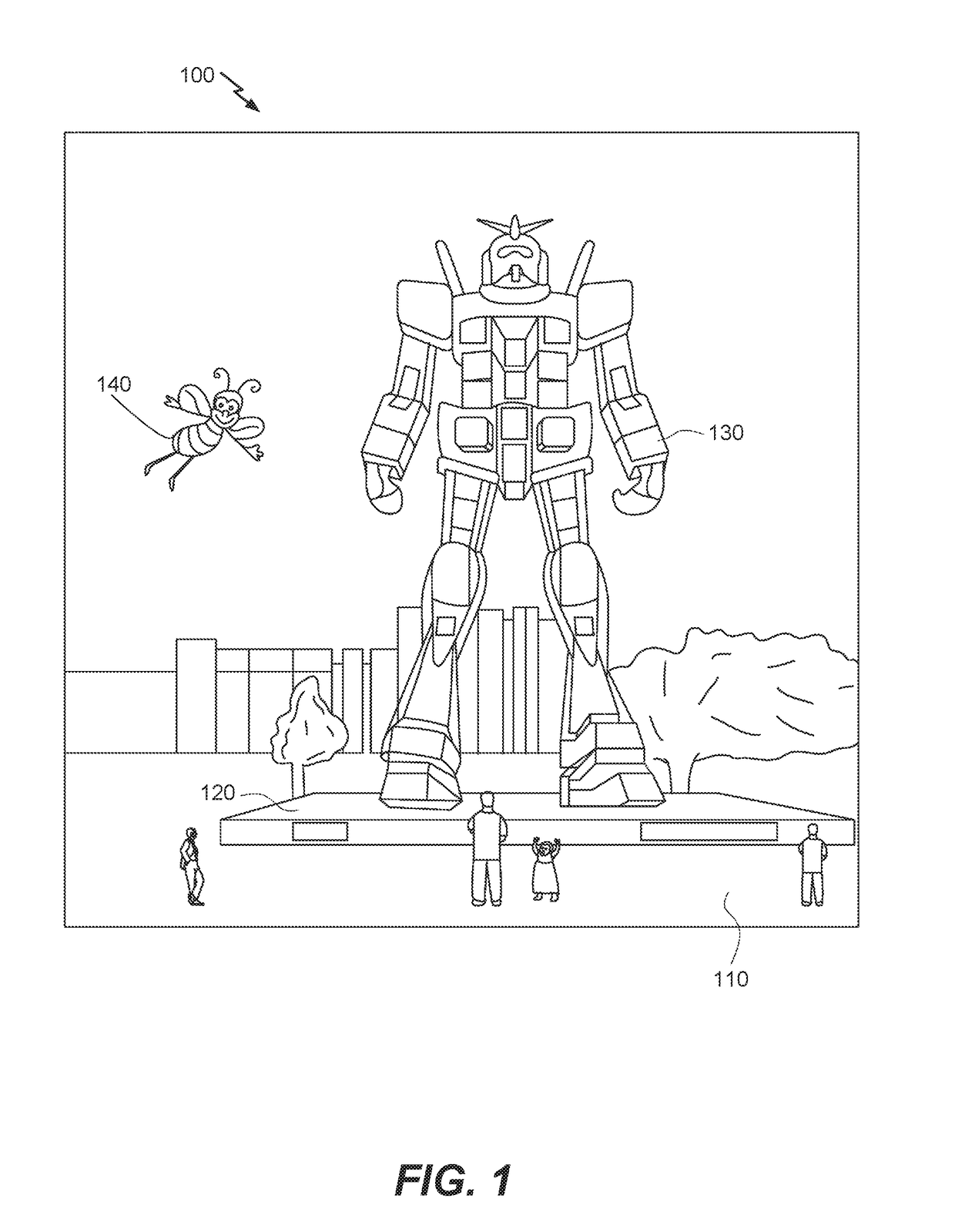
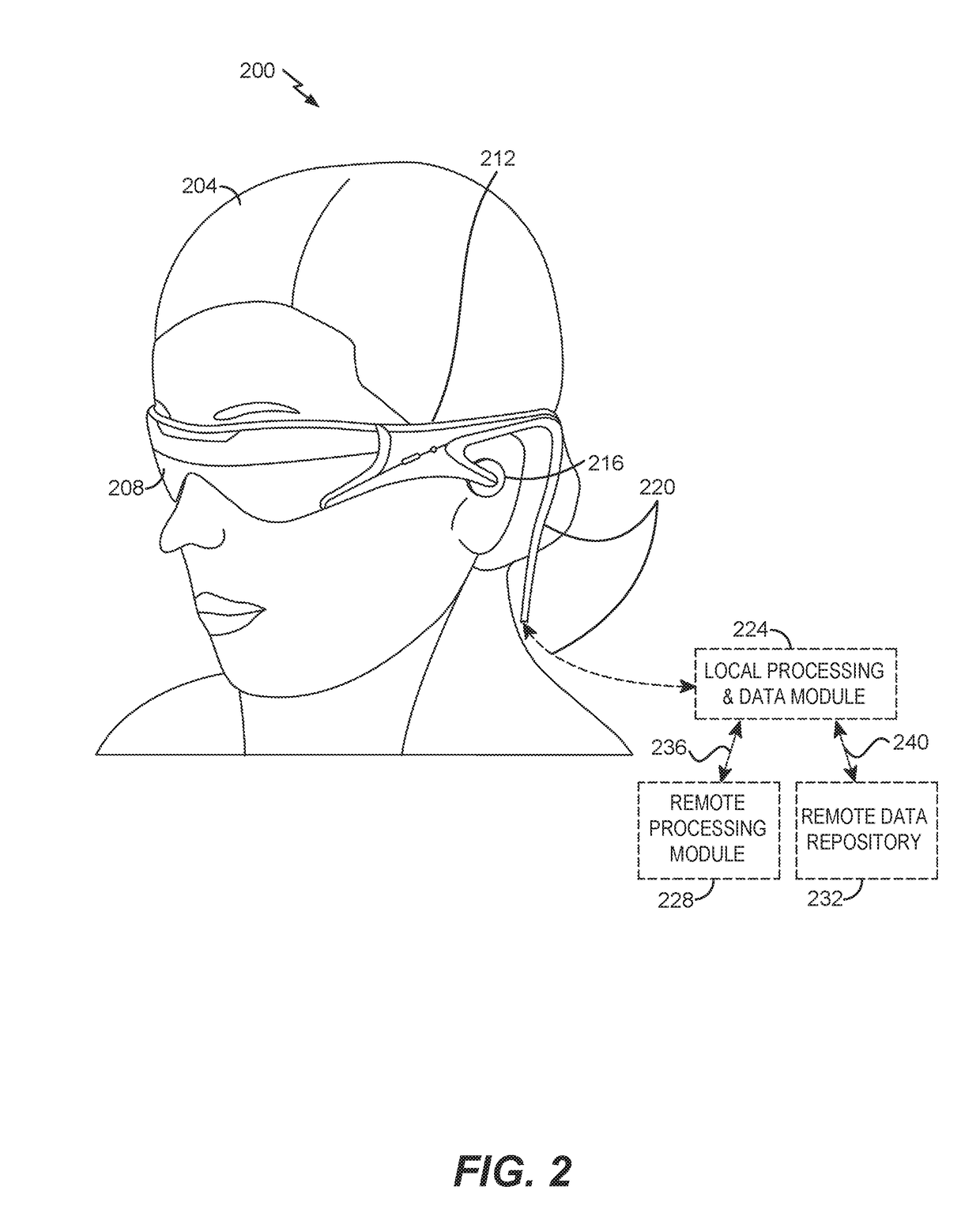
Examples of an imaging system for use with a head mounted display (HMD) are disclosed. The imaging system can include a forward-facing imaging camera and a surface of a display of the HMD can include an off-axis diffractive optical element (DOE) or hot mirror configured to reflect light to the imaging camera. The DOE or hot mirror can be segmented. The imaging system can be used for eye tracking, biometric identification, multiscopic reconstruction of the three-dimensional shape of the eye, etc.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Infra-red reflecting layered structure
ActiveUS20060057399A1Good visible light transmittanceLow solar heat gain coefficientElectric discharge tubesMagnetic/electric field screeningInfraredRefractive index
The invention relates to an infra-red reflecting layered structure comprising a transparent substrate layer; a first metal oxide layer; a first silver containing layer, a second metal oxide layer; a second silver containing layer and a third metal oxide layer. The first, second and third metal oxide layer have a refractive index of at least 2.40 at a wavelength of 500 nm. The layered structure according to the present invention laminated on glass has a visual light transmittance (VLT) higher than 70% and a solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) lower than 0.44. The invention further relates to the use of a layered structure as a transparent heat-mirror.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN PERFORMANCE PLASTICS CHAINEUX
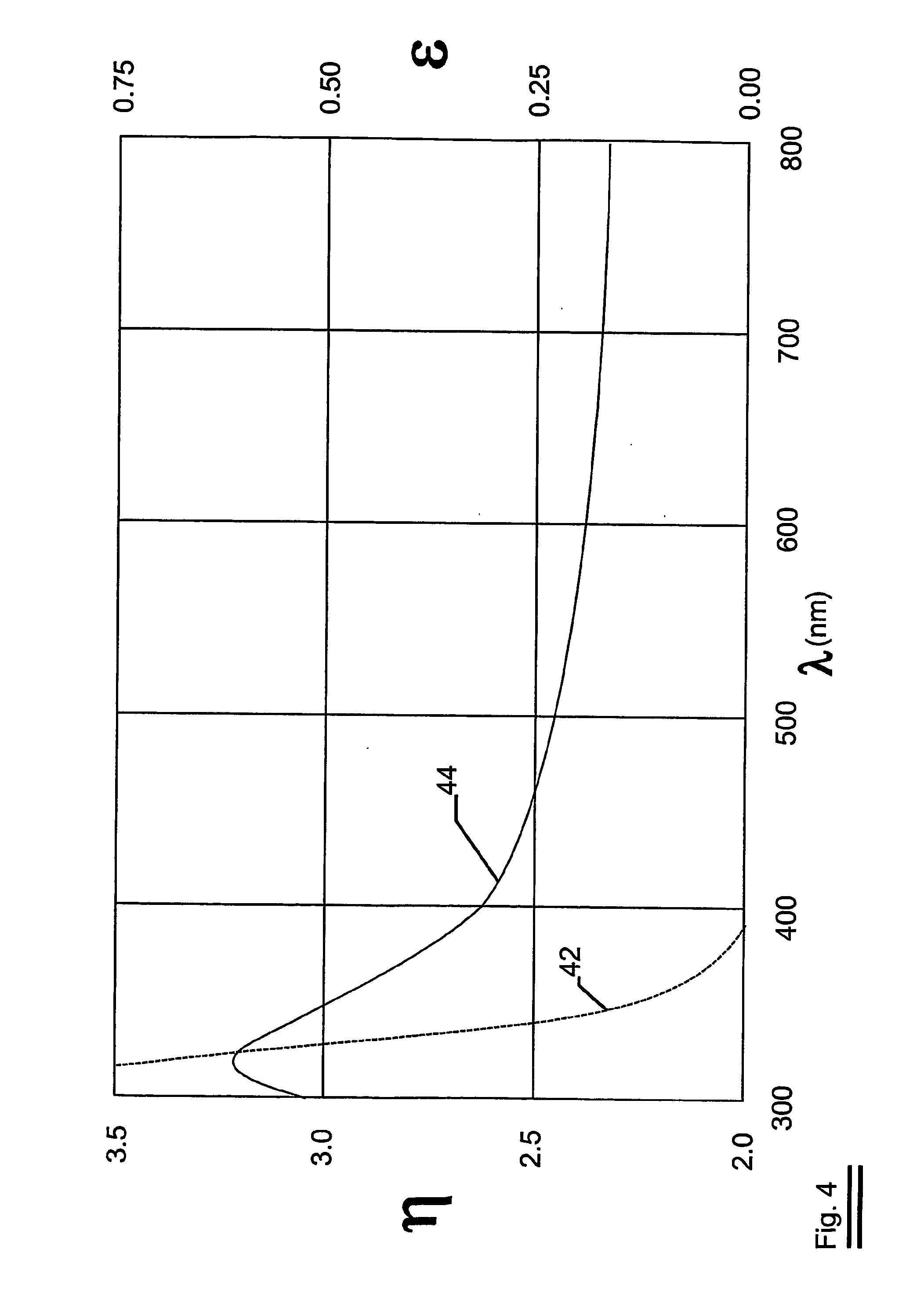
Eye imaging with an off-axis imager
Examples of an imaging system for use with a head mounted display (HMD) are disclosed. The imaging system can include a forward-facing imaging camera and a surface of a display of the HMD can include an off-axis diffractive optical element (DOE) or hot mirror configured to reflect light to the imaging camera. The DOE or hot mirror can be segmented. The imaging system can be used for eye tracking, biometric identification, multiscopic reconstruction of the three-dimensional shape of the eye, etc.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Photocell with fluorescent conversion layer
A photocell device having enhanced conversion efficiency. The device is adapted to convert light energy to electrical energy in a semiconductor layer, to convert a first, monochromatic light, to a second light of different wavelength, in a fluorescent layer, to transmit the first light through a hot mirror layer, to reflect light from the hot mirror layer, and to reflect light from a mirror layer disposed at a second surface of the device.
Owner:BIOMED SOLUTIONS
Double-component silicone structural sealant for heat mirror hollow glass and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103820072AIncreased crosslink depthFast bondingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCross-linkMicrosphere
The invention discloses a double-component silicone structural sealant for heat mirror hollow glass and a preparation method of the sealant. The sealant comprises a component A and a component B, wherein the component A comprises hydroxyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane, alkyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane, hollow microsphere, ceramic microbead, metal hydroxide, metal oxide, activated calcium carbonate, inorganic pigment and a surfactant; the component B comprises alkyl-terminated polydimethylsiloxane, a coupling agent, a cross-linking agent, a catalyst, an inhibitor, a thickening agent, and silicon dioxide. The preparation method of the sealant comprises the following steps: 1) taking each ingredient in the component A to be mixed uniformly under the vacuum condition; 2) taking each ingredient in the component B to be mixed uniformly under the vacuum condition; 3) mixing the component A and the component B at room temperature according to the weight ratio of (8:1) to (20:1), and at last obtaining the sealant. The double-component silicone structural sealant is good in adhesiveness, high in curing speed, good in sealing performance, high in hardness and modulus, and excellent in thermal barrier effect, and suitable for sealing and bonding of heat mirror film, glass and metal materials etc.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU ZHONGYUAN SILANDE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Capture and identification system for blending images of palm veins and palm prints
InactiveCN103116741AThe acquisition equipment is simpleAccurate collectionCharacter and pattern recognitionPalm printParalemmin
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
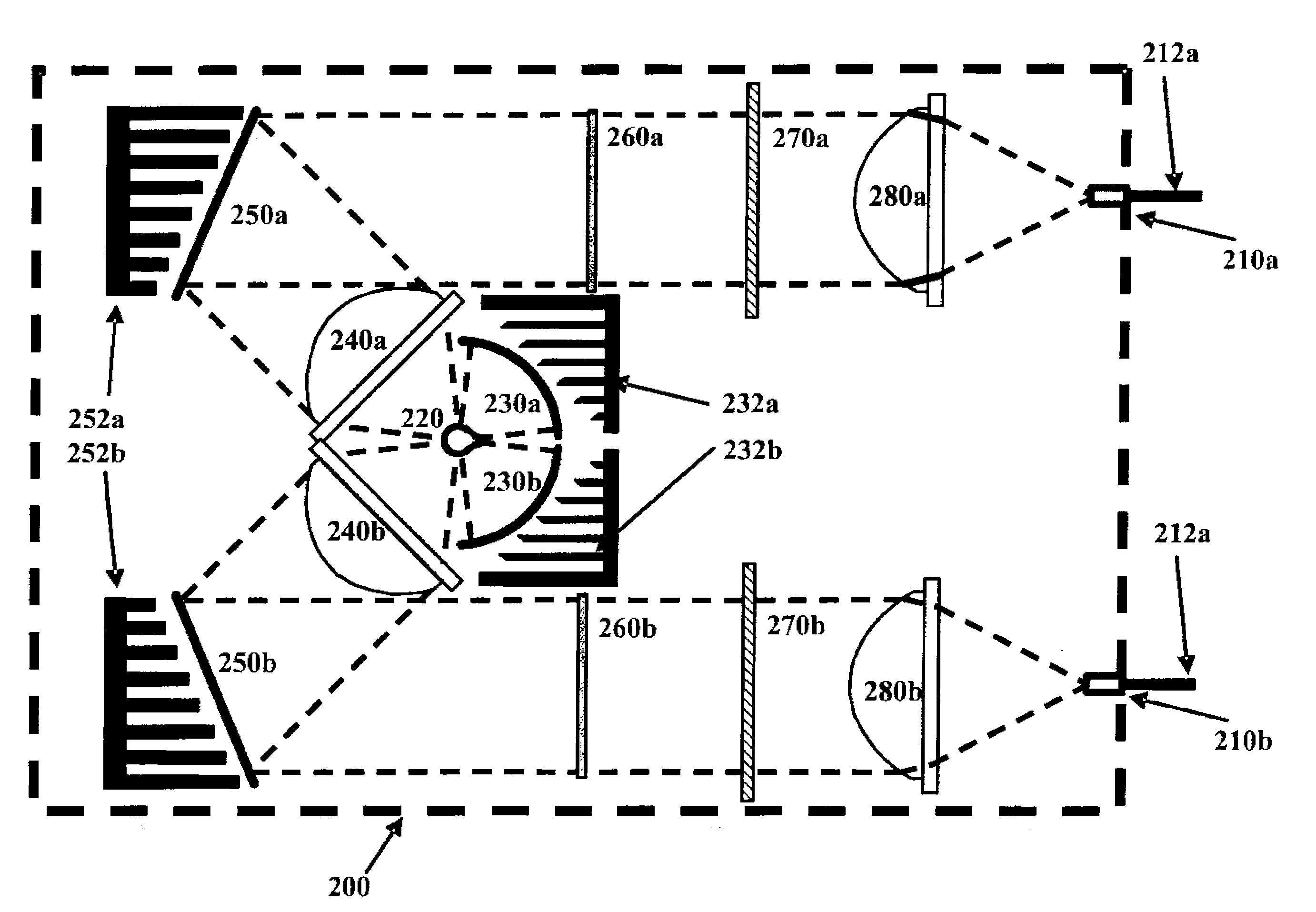
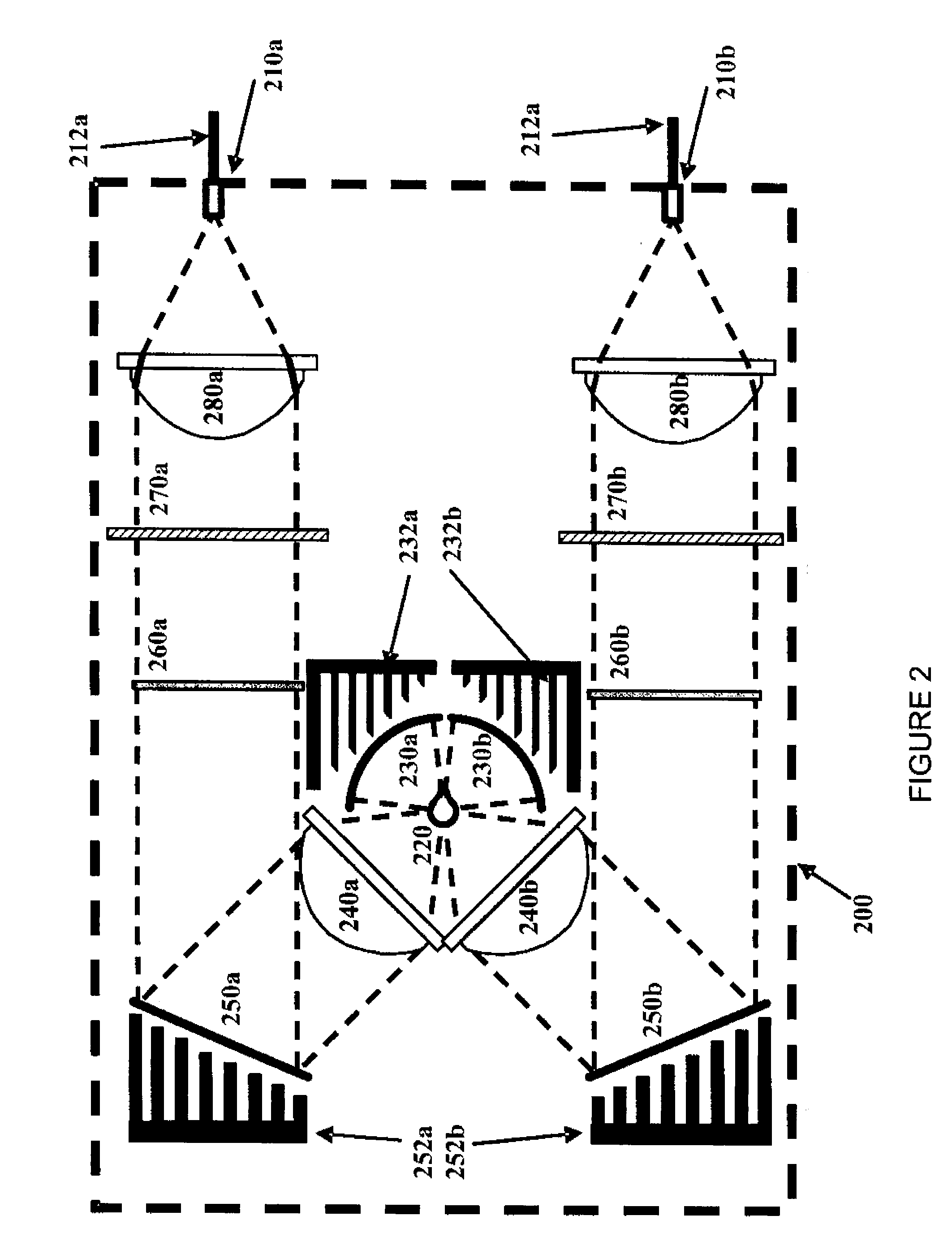
Heat protection and homogenizing system for a luminaire utilizing a lamp with an intense hotspot
An automated luminaire which allows for the selection of a diffuser or a hot mirror which is mounted to engage the light beam at an angle non perpendicular to the central axis of the light beam and nonparallel or not in the same plane as the diffuser. The selector is articulated in a manner to automatically engage a selector based on what other light modulators are selected to engage the light beam and to automatically oscillate or scan when there is a likelihood of damage to the hot mirror or diffuser based on how long it is engaged and / or light intensity and / or other modulators selected and or temperature sensor data in the luminaire.
Owner:ROBE LIGHTING
System and method for the removal of undesired wavelengths from light
InactiveUS20080175002A1Reduce undesired wavelengthSafe and durableMirrorsEye surgeryLength waveHot mirror
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system and method for filtering light. More particularly, embodiments of the present invention may filter light provided as a source of illumination by using one or more mirrors in an optical path. In a specific embodiment, one or more cold mirrors in the optical path are coated such that they are operable to reflect light in the desired wavelengths while transmitting other wavelengths of light. Thus, as light from a light source is reflected off these cold mirrors undesired wavelengths of light may be substantially removed from the light before it is utilized to illuminate an area. In other embodiments, one or more hot mirrors mirror may also be provided in the optical path, where these hot mirrors are coated such that they are operable to transmit the desired wavelengths of light and reflect undesired wavelengths.
Owner:ALCON INC
Optical coherence tomographic imaging system
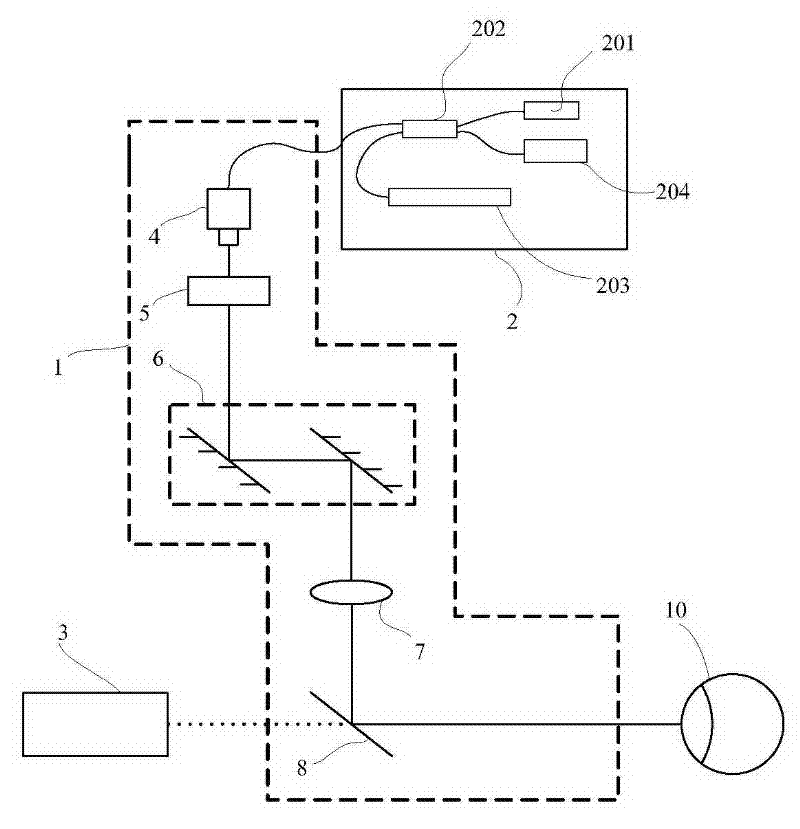
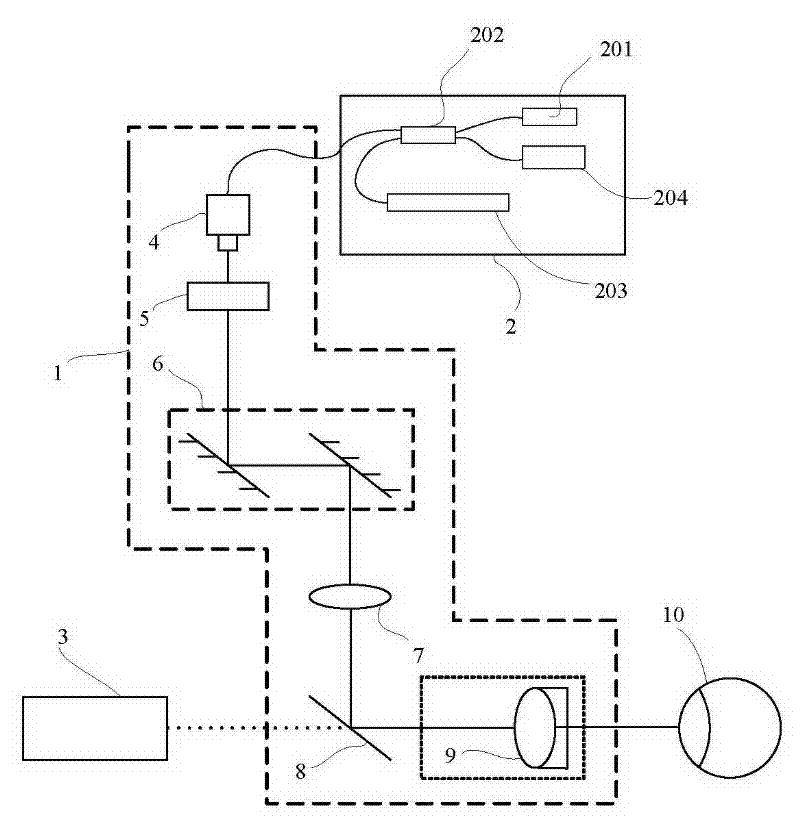
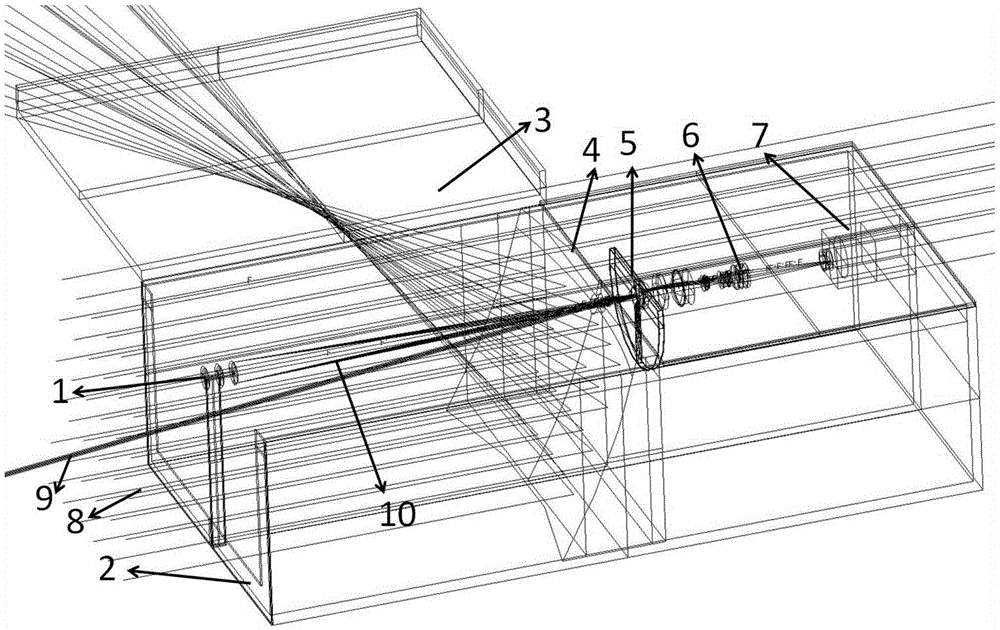
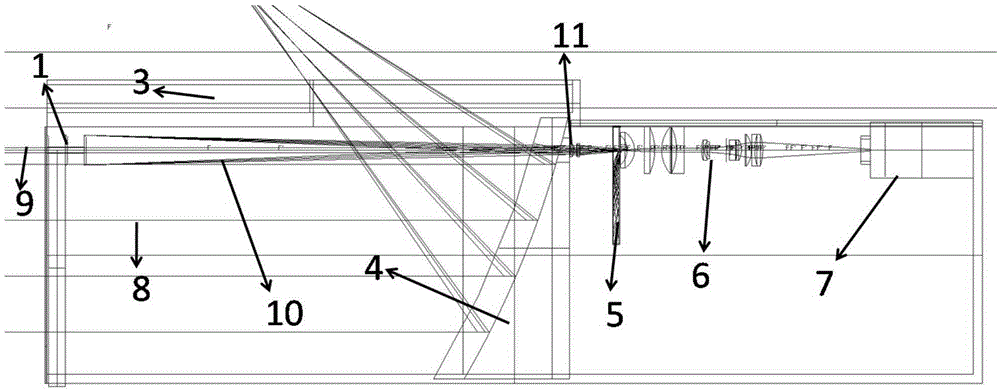
The invention discloses an optical coherence tomographic imaging system, which comprises an OCT (optical coherence tomography) infrared source reference arm, an acquisition portion and a detection arm. The detection arm is provided with optical fibers, a collimator, an optical path galvanometer scanning system, a lens and a heat mirror along an optical path from the OCT infrared source reference arm to human eyes, infrared emitted from the lens is reflected by the heat mirror to human eyes, a slit lamp system is arranged on an optical path opposite to the optical path from the heat mirror to the human eyes, and white light from the slit lamp system passes through the heat mirror to be emitted into the human eyes. The optical coherence tomographic imaging system combines slip lamps with OCT, the OCT system is independent relatively, and mutual imaging is unaffected and mutually supplementary. OCT imaging and slip lamp imaging share a common focus, so that fundus surface or anterior segment surface information and deep structural information can be obtained simultaneously without more adjustment. The optical coherence tomographic imaging system is more reasonable in structure and more stable in imaging.
Owner:GUANGDONG FORTUNE NEWVISION TECH
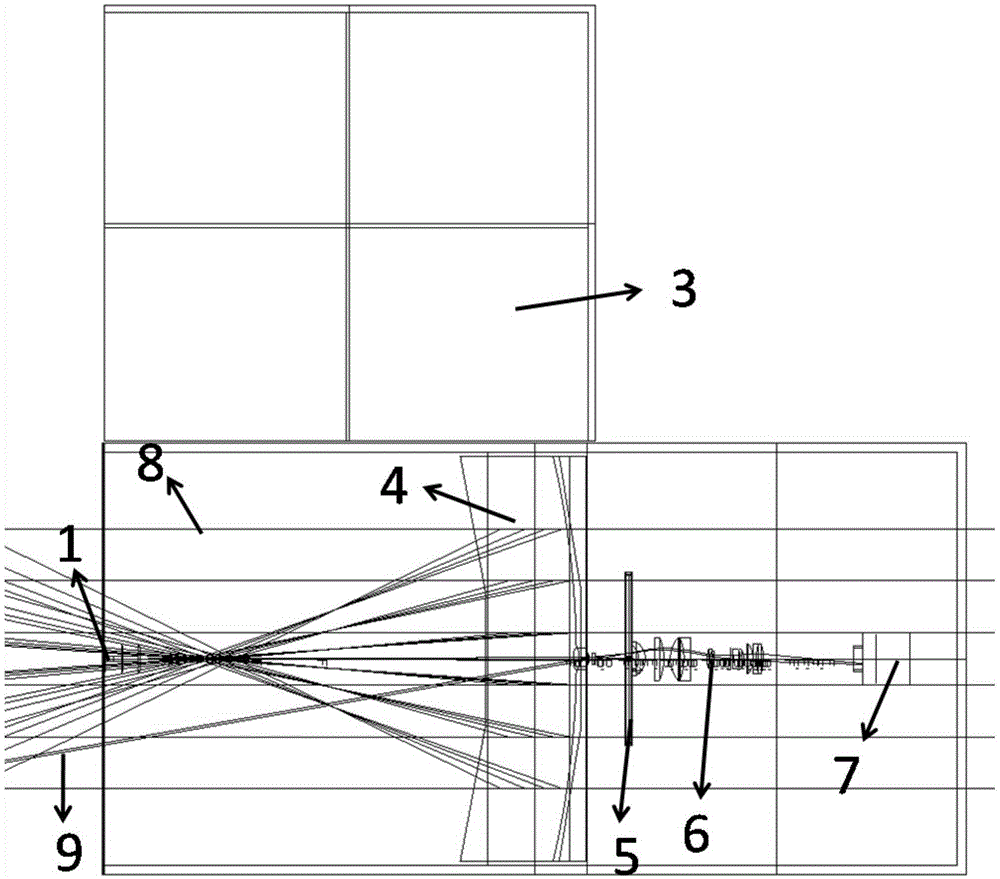
Semi-open type full circumferential coronagraph apparatus with large field of view
InactiveCN105388617ALower performance requirementsSize reduction requirementsOptical elementsSemi openOptical axis
The invention relates to a semi-open type full circumferential coronagraph apparatus with a large field of view. The coronagraph apparatus comprises in sequence from left to right: an outer shielding body, an outer window, a heat collecting lens, an inner shielding body, an inner shielding body light-absorbing groove, an imaging system and a CCD camera. The outer shielding body and the inner shielding body are disposed on the optical axis of an optical path. The inner shielding body is positioned in an imaging position where the outer shielding body passes through an object lens unit. The coronagraph apparatus, as a whole, is of a semi-open square structure, and is reduced in size and weight. The heat collecting lens is a reflector with a square centrally-recessed structure, and the recessed surface of the centrally-recessed structure faces one side of the outer window. The heat collecting lens is arranged in an inclined manner. The lower end of the heat collecting lens goes toward one side of the outer window relative to the upper end of the heat collecting lens. Incident sun direct light is focused by the heat collecting lens outside the semi-open square structure, so the influence of scattered stray light on the surface of the heat collecting lens is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
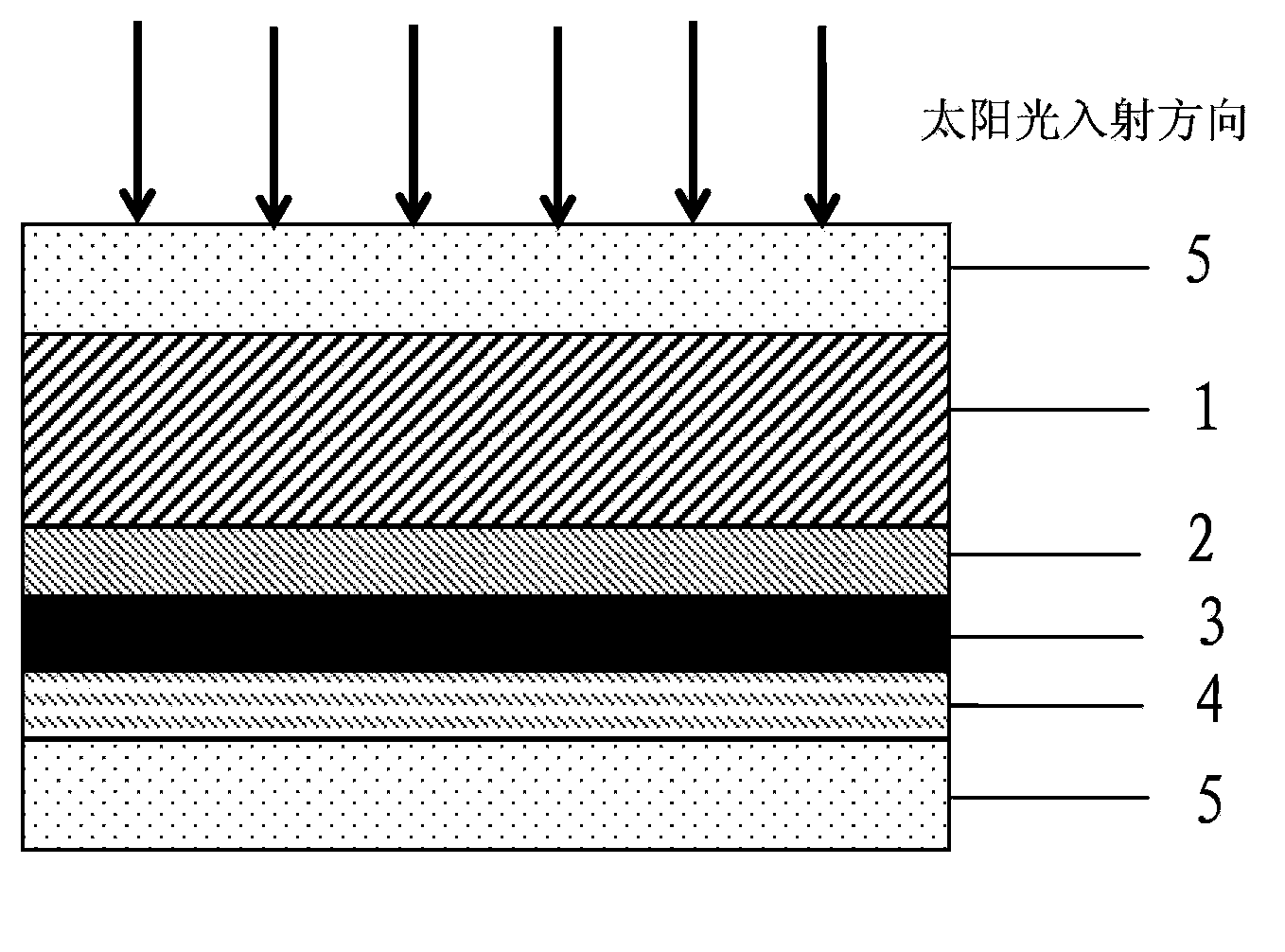
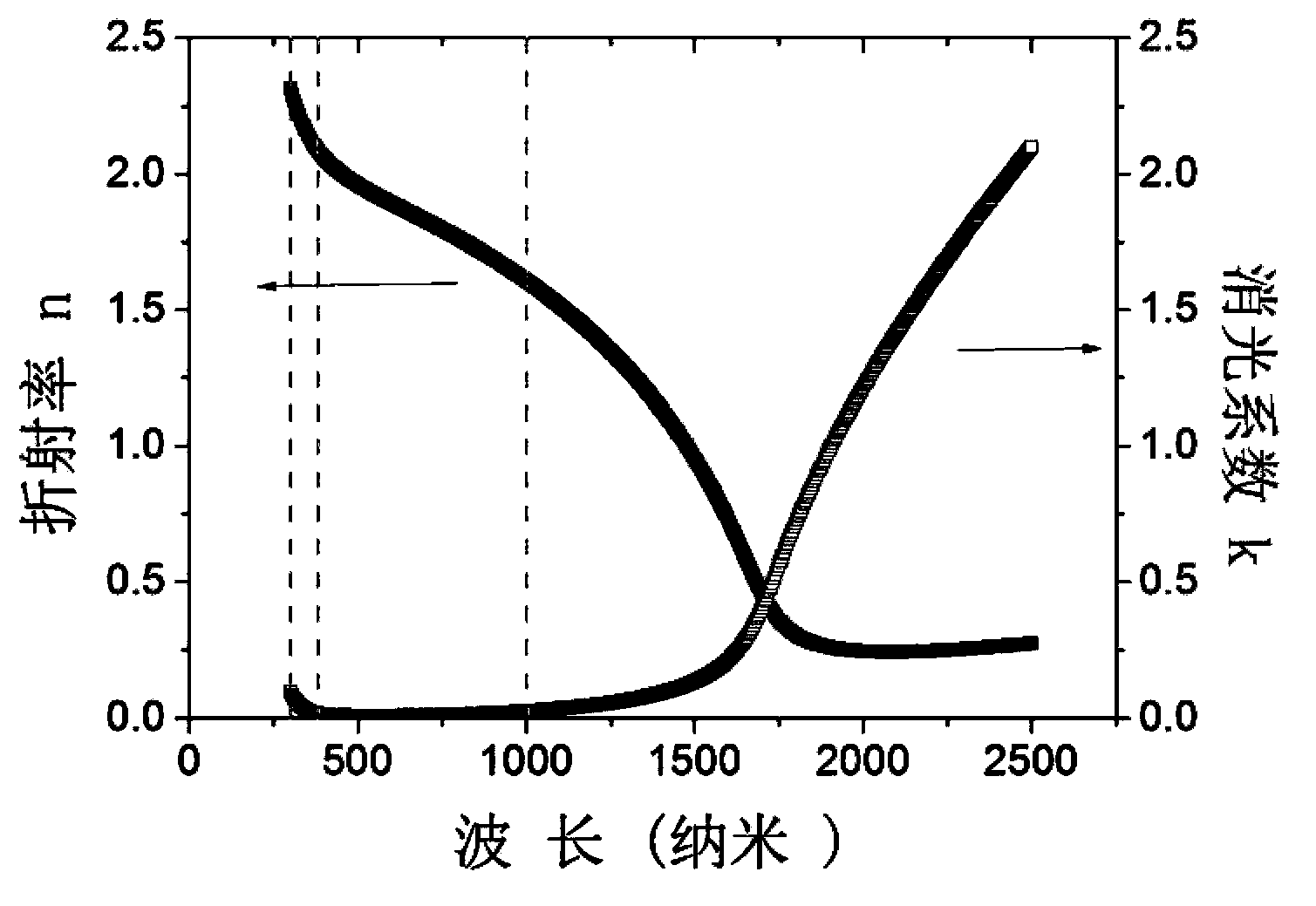
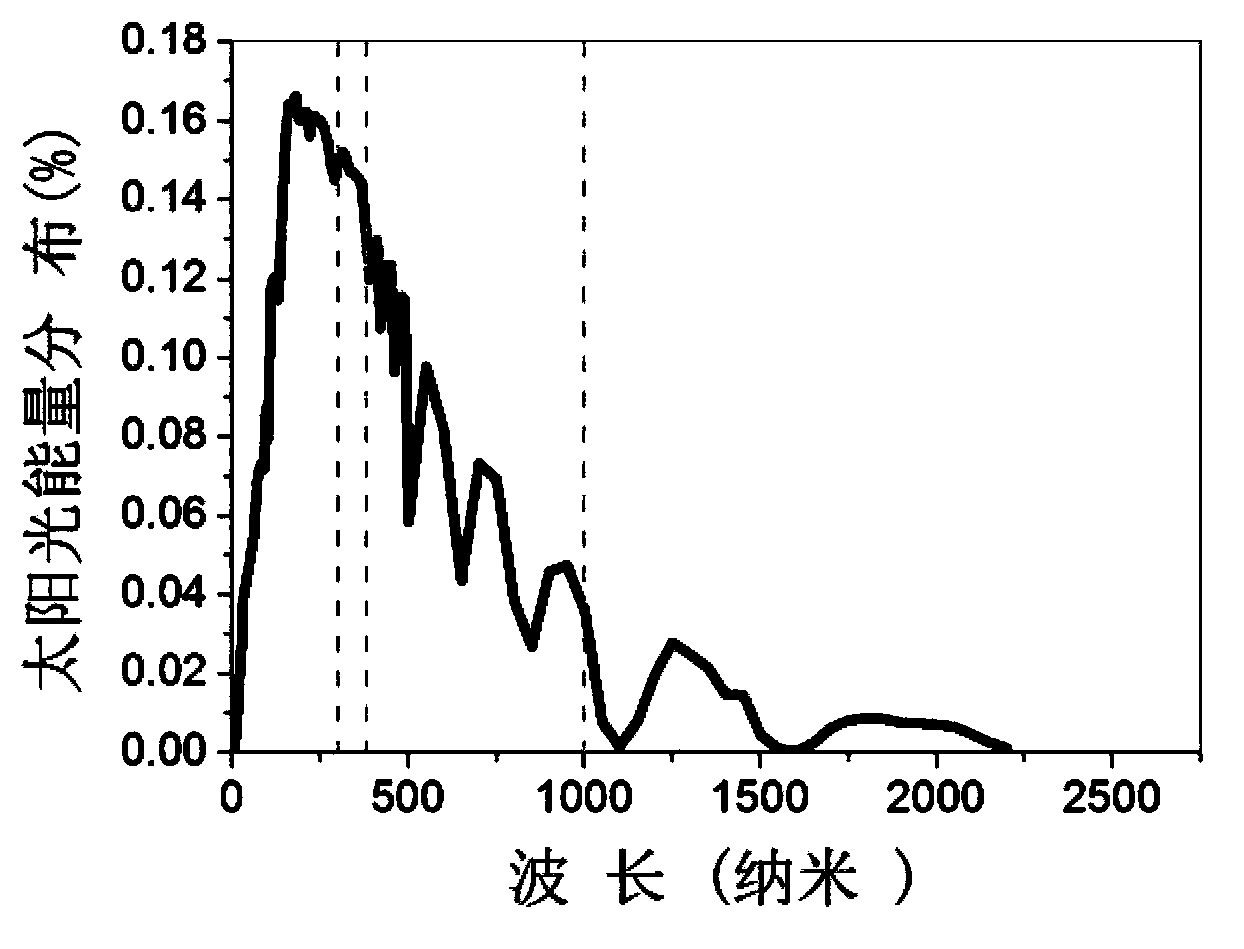
Transparent heat mirror of solar photothermal conversion heat collector and manufacturing method of transparent heat mirror
ActiveCN103884122AHigh visible light transmittanceImprove transmittanceSolar heat devicesSolar ray transmission and prevent heat radiationRadianceRefractive index
The invention discloses a transparent heat mirror of a solar photothermal conversion heat collector and a manufacturing method of the transparent heat mirror. The transparent heat mirror comprises a GLASS / D1 / ITO / D2 or Porous-SiO2 / GLASS / D1 / ITO / D2 / Porous-SiO2 or GLASS / ITO / D2 / D1 film system structure. An ITO film is not only an infrared heat reflection function layer, and is matched with a high-low-refractivity antireflection film system from the perspective of optical design, so that spectral selectivity of the transparent heat mirror is higher than that of a single-layer transparent heat mirror, and solar spectrum (300-2500nm) transmissivity of the transparent heat mirror is improved by 10% when compared with that of a single-layer TCO-film transparent heat mirror with identical radiance and manufactured under the conditions of a same transparent substrate and same processes.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
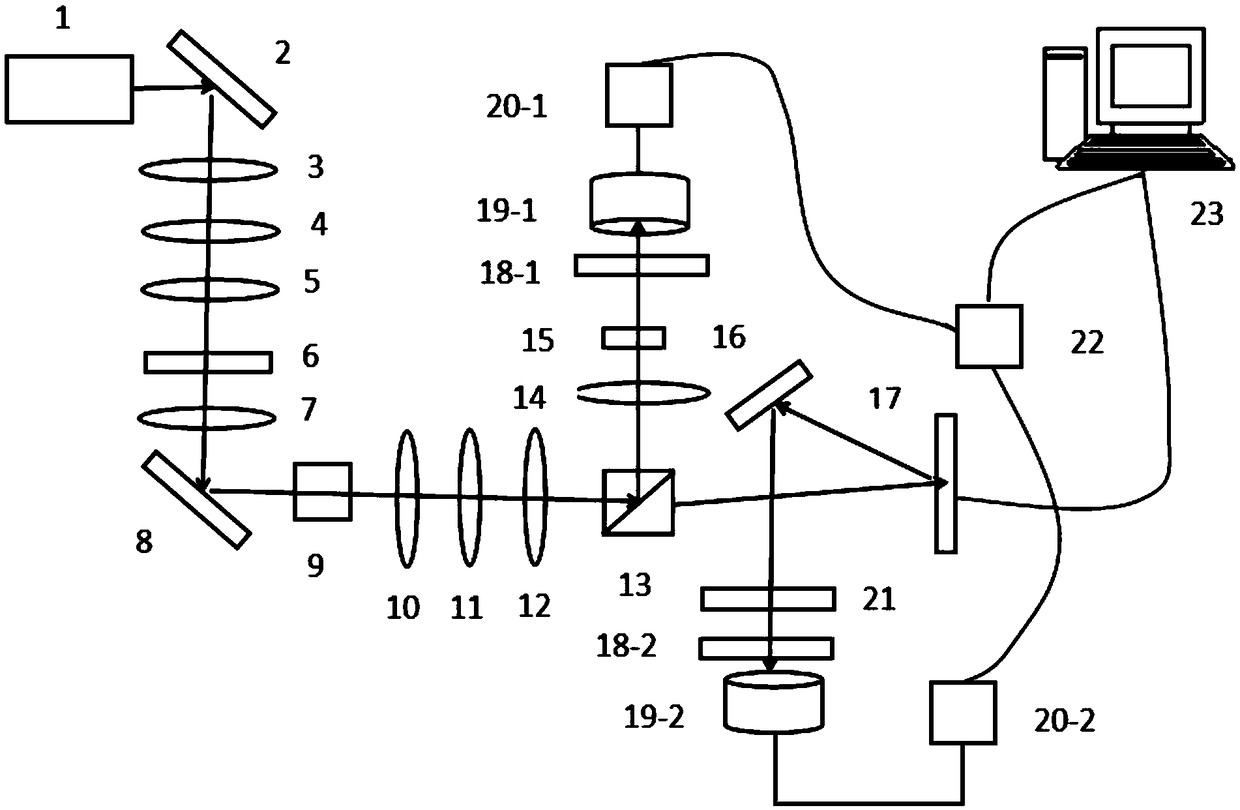
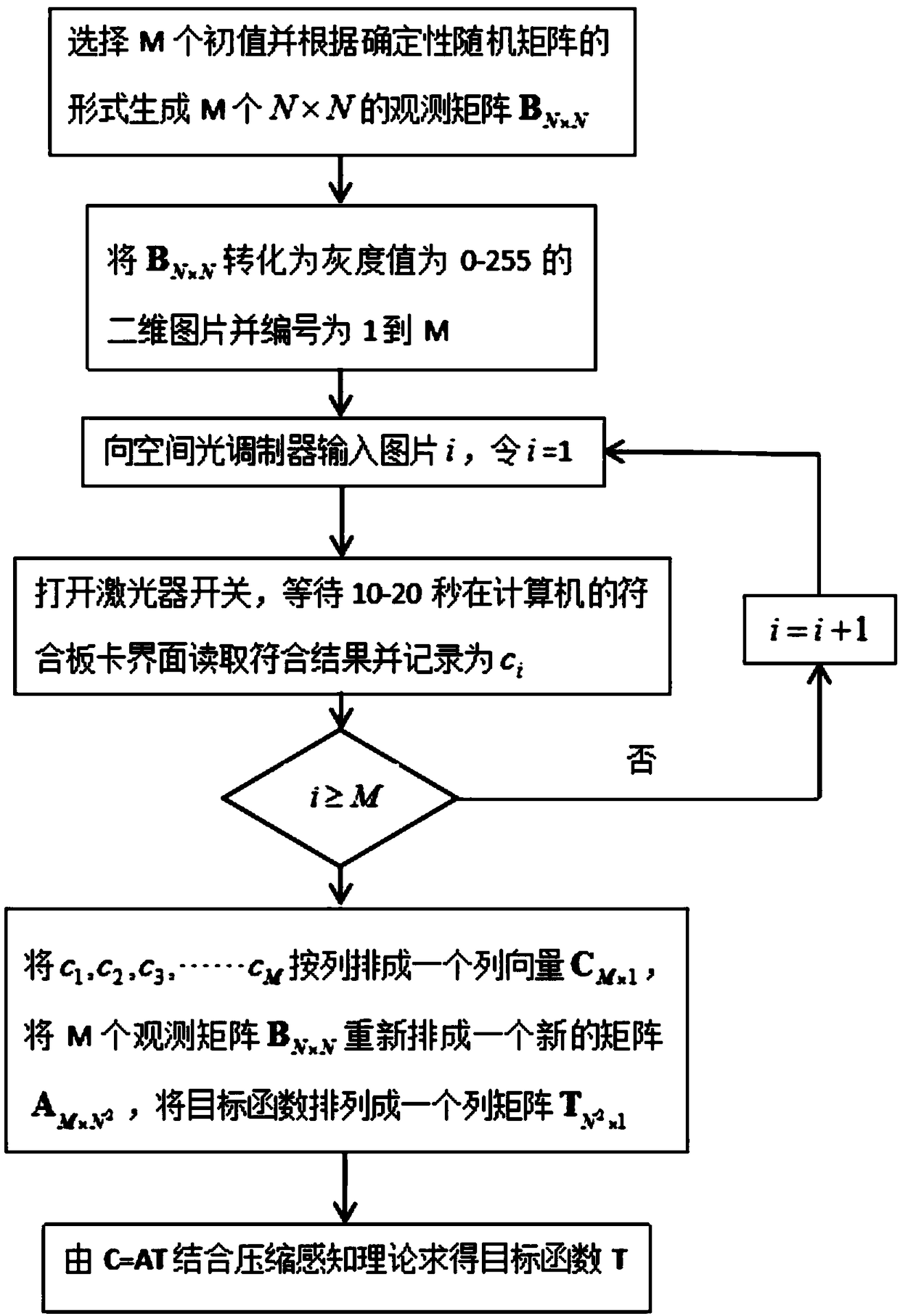
Compressed sensing imaging device and method based on entangled two-photon signal
ActiveCN108844464AReduce storagePromote recoveryImage enhancementUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorImaging quality
The invention discloses a compressed sensing imaging device and method based on an entangled two-photon signal, and solves the problem of not high imaging quality under the condition of low sampling number. According to the method, a deterministic determinacy random matrix is loaded in a spatial light modulator of an original quantum imaging device to complete imaging of a target object; and during preparation of entangled light, a telescoping system and a 0-degree incident heat mirror and a low-pass narrow-band filter which are placed along a laser transmission direction among the telescopingsystem are adopted to process laser. The imaging method includes producing a picture for being input to a spatial light modulator; inputting the picture to the spatial light modulator; preparing entangled light; obtaining a matched result value; loading a plurality of sets of modulated observation matrices and obtaining M matched results; constructing a quantum imaging mathematical model; and adopting a compressed sensing algorithm to solve a quantum imaging relational expression to restore an image of the target object. The entangled light prepared by the compressed sensing imaging device and method provided by the invention is high in purity and can well restore the image of the target object under the condition of a low sampling rate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Heat protection and homogenizing system for a luminaire utilizing a lamp with an intense hotspot
An automated luminaire which allows for the selection of a diffuser or a hot mirror which is mounted to engage the light beam at an angle non perpendicular to the central axis of the light beam and nonparallel or not in the same plane as the diffuser. The selector is articulated in a manner to automatically engage a selector based on what other light modulators are selected to engage the light beam and to automatically oscillate or scan when there is a likelihood of damage to the hot mirror or diffuser based on how long it is engaged and / or light intensity and / or other modulators selected and or temperature sensor data in the luminaire.
Owner:ROBE LIGHTING
Preparation method of energy-saving heat mirror film insulating glass
The invention relates to a preparation method of energy-saving heat mirror film insulating glass, which belongs to the field of glass processing technology, according to the preparation method, a professional laminating process can be developed, heat stretched process parameters are further adjusted, the process can be simply and easily operated, process parameters are easy to control, the phenomenon of film winkles and aluminum strip dislocation due to the fact that the laminated film is easy to be uneven when the heat mirror film is laminated can be solved, the extensibility of the heat mirror film is very good, and the appearance and performance are very good.
Owner:TIANJIN NORTH GLASS IND TECHN
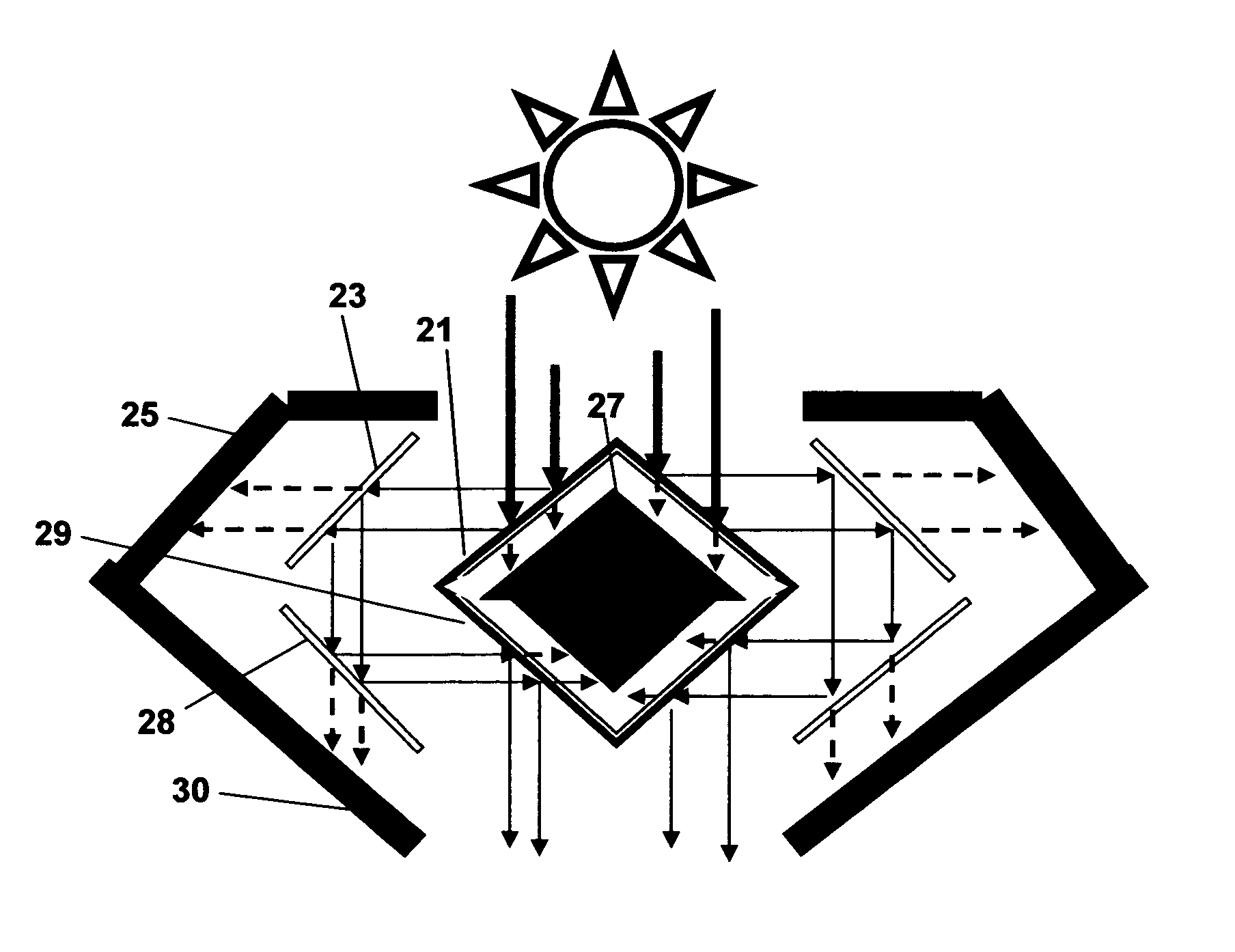
Solar photon filter
This invention relates to a solar photon filter, hereafter known as the SPF, which is a combination band-pass filtering system consisting of a multiple set of cold or hot mirrors and infra-red absorbers set in a 360-degree or linear arrangement. The system removes almost all of the photons carried by waves having lengths longer than 1000 nm (nanometers)+ / −100 nm, while passing almost all of the incoming photons carried by waves having lengths shorter than 1000 nm+ / −100 nm and / or variations thereof. This is accomplished by positioning a set of cold or hot mirrors in constant optical track with the sun. Such an assembly of cold or hot mirrors allows solar photons carried by light to be split into two distinct bands of frequencies for use requiring such filtering separation.
Owner:TILFORD ARTHUR ROBERT +1
Transparent heat-insulation energy-saving nano paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103602263AEnvironmentally friendlyEnergy savingRadiation-absorbing paintsInfraredEngineering
The invention discloses a transparent heat-insulation energy-saving nano paint and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of functional paints. The paint is composed of a metal oxide inorganic nano water-based dispersion with optical thermal properties, a defoaming agent, a leveling agent and a diluter. The coated film formed by the paint has high reflecting power (higher than 80%) for thermal infrared rays with the wave range of 2.5-40 mu m; and therefore, the glass coated with the paint can act as a hot mirror to prevent outdoor heat radiation from entering the room so as to save the air conditioning cost in summer, and reflect most indoor heat radiation back to rooms in winter so as to ensure no indoor heat dissipation to the outside, thereby saving the heating cost.
Owner:BEIJING SHUNYUAN TIANHE NEW MATERIAL TECH
Eyeball tracking structure
ActiveCN110426845AAvoid harmHigh precisionTelevision system detailsInput/output processes for data processingInfraredDisplay device
An eyeball tracking structure comprises a heat mirror, an infrared light source and a camera. The heat mirror is arranged between a displayer in a head-mounted display device and a human eye; the camera is arranged on one side of the displayer in the head-mounted display device, connected with a control circuit and used for capturing an image of an infrared pattern reflected by the heat mirror, capturing an eye image of the human eye and transmitting an obtained composite image to the control circuit, so that the control circuit conducts compensation calculation through a sight image function,the position of a sight point on the displayer is calculated, and then the displayer is controlled to feed back and display information corresponding to the position. Therefore, speckles of infraredbeams are projected onto the heat mirror instead of being directly projected into the eyeball, and the situation that the infrared rays are directly projected onto the eyeball and cause harm can be avoided.
Owner:INTERFACE TECH CHENGDU CO LTD +2
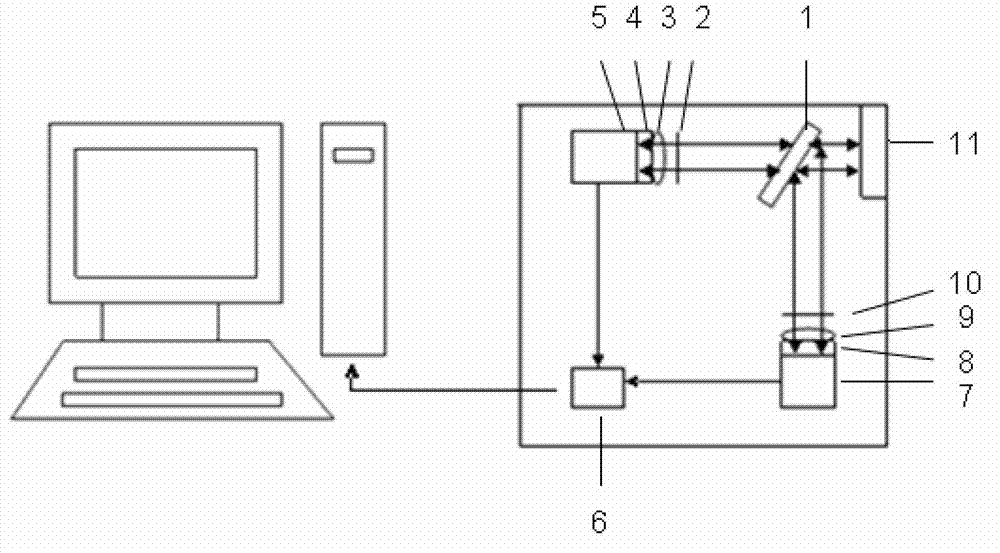
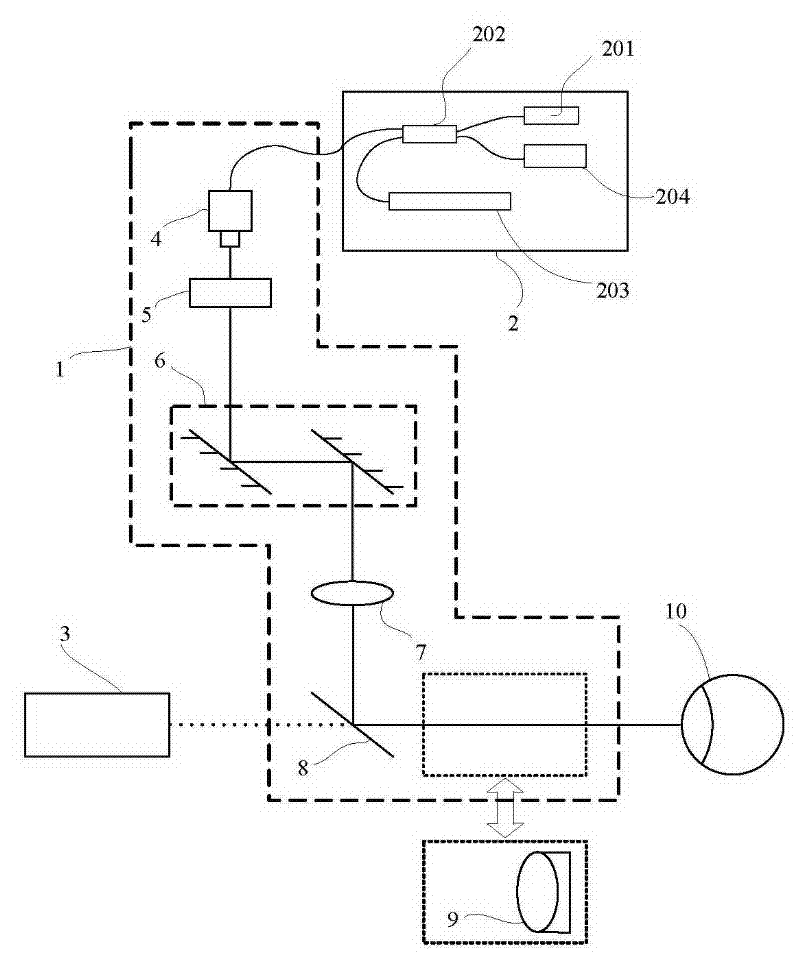
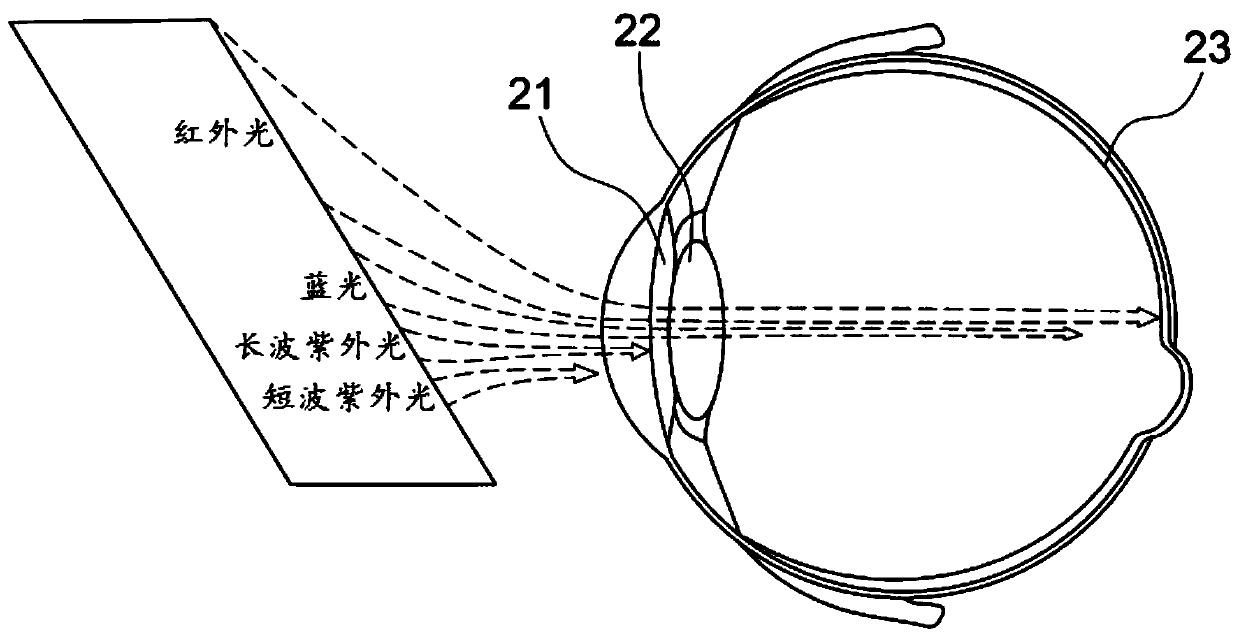
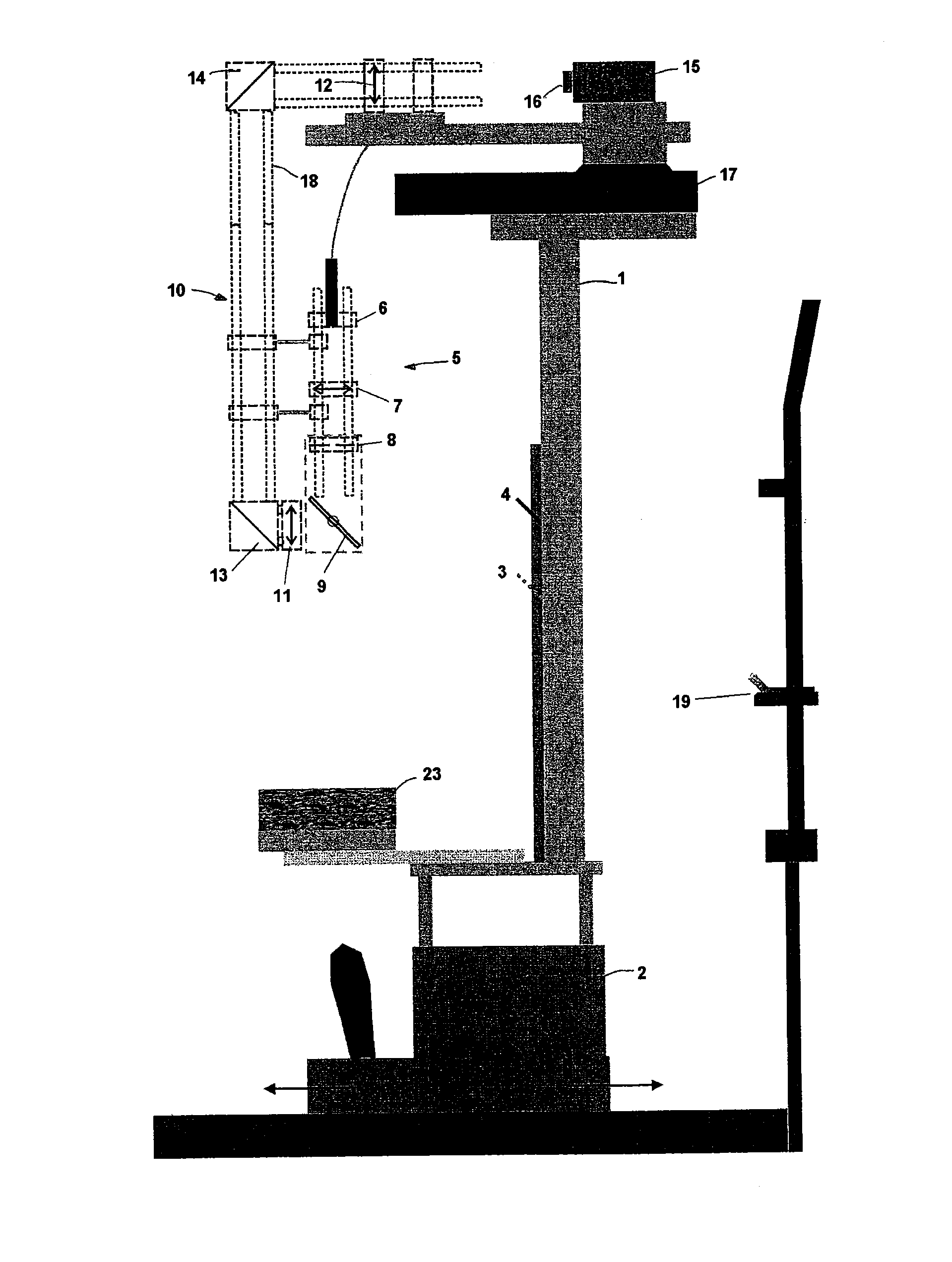
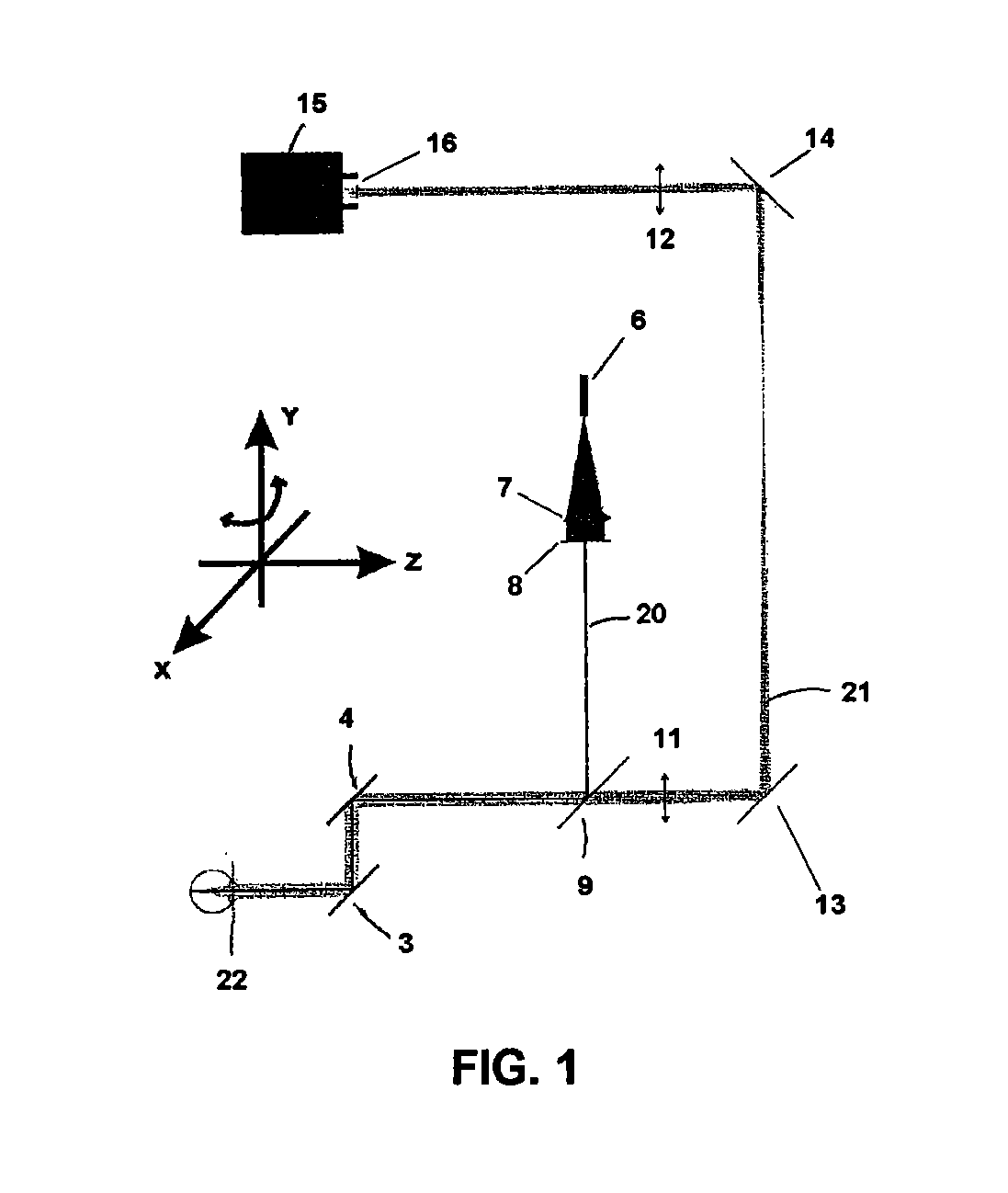
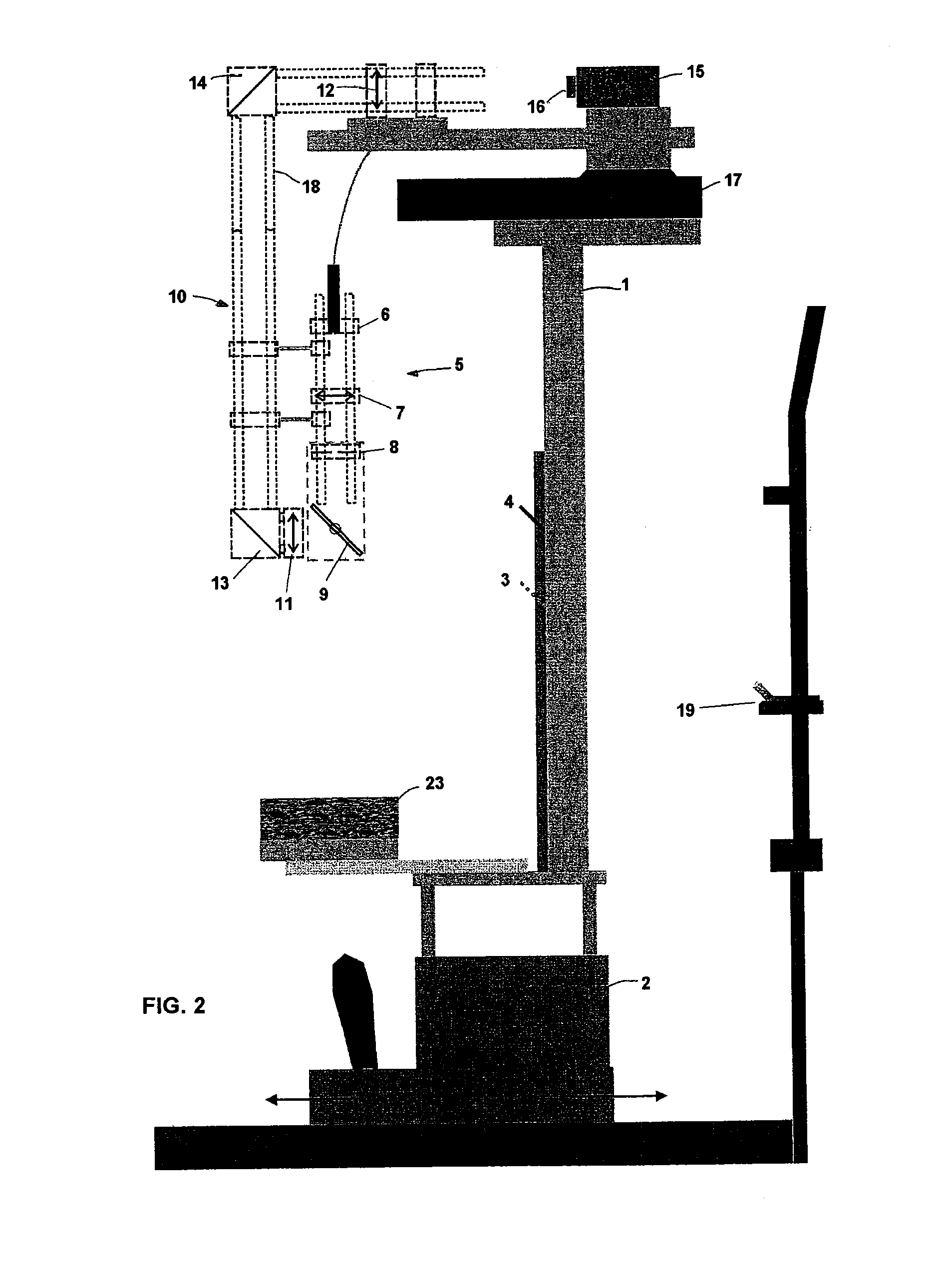
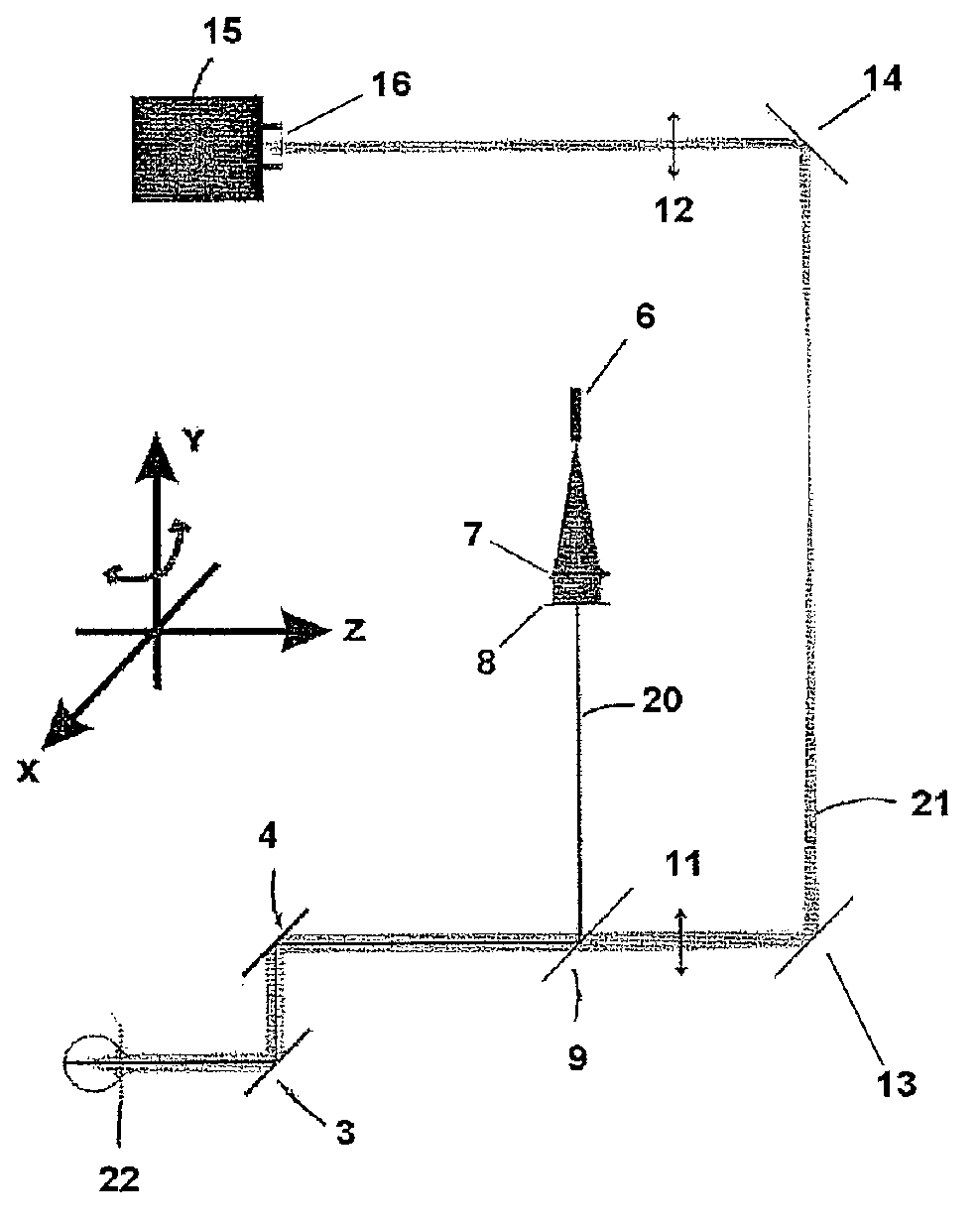
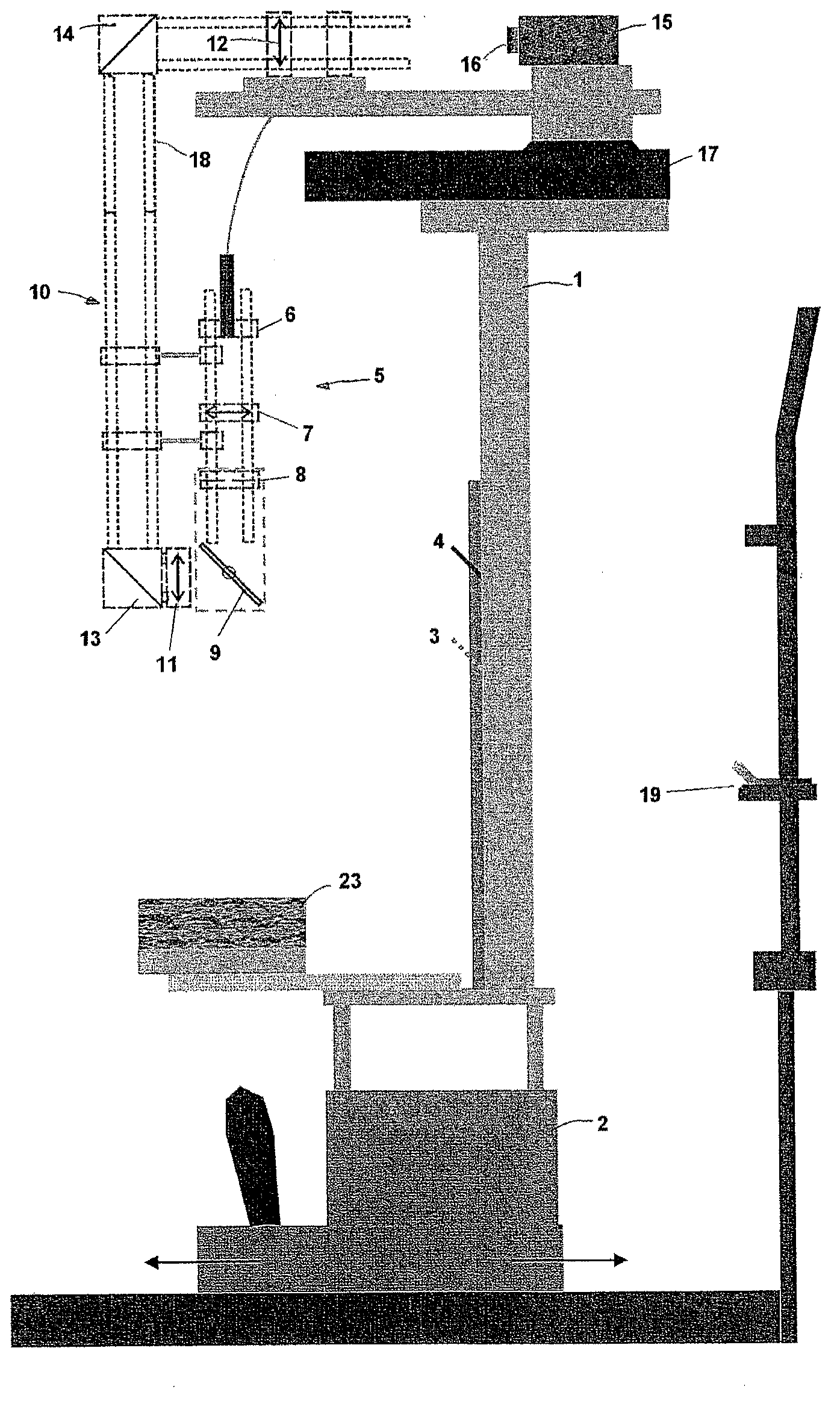
Instrument for rapid measurement of the optical properties of the eye in the entire field of vision
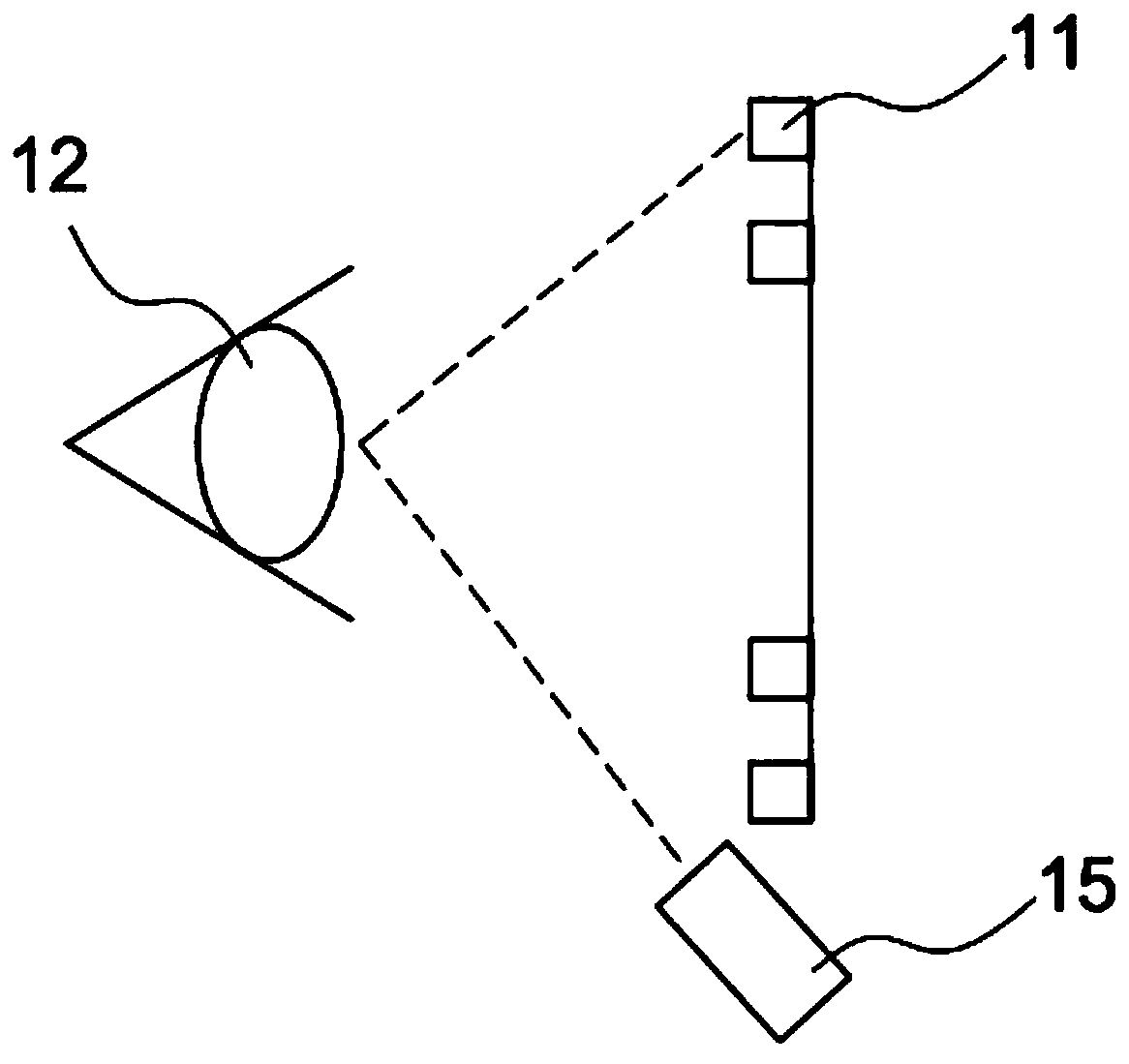
An instrument measuring optical properties of an eye in an entire field of vision, including refraction and aberrations, including: a frame mounted on an ophthalmologic table that can be oriented in three perpendicular directions X, Y, Z; a support surface for a head of the subject; a hot mirror; a long mirror; an illumination sub-assembly including a fiber optic head; a lens; a diaphragm; a beam splitter; and a measurement sub-assembly with two lens and two mirrors; a camera including a matrix of micro-lenses on the inlet of camera, the camera being placed on the focal plane of the micro-lenses; the frame including a motor, a shaft of which rotates in the Y direction, to which an arm is attached that can rotate on the shaft; components of the illumination sub-assembly, components of a measurement sub-assembly, and the camera with the matrix of micro-lenses being mounted on the arm.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MURCIA
Projection type vein indicating instrument
InactiveCN104757940AReduce labor intensityRelieve stressDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsVeinHot mirror
Disclosed is a projection type vein indicating instrument. The projection type vein indicating instrument comprises a light equalization slice, an infrared light emitting diode group, a hot mirror made of optical glass material, an infrared filter, an infrared CCD (charge coupled device), a micro projector and a single chip computer system, wherein the light equalization slice is located at the bottom, the infrared light emitting diode group composed of infrared light emitting diodes circularly arranged is arranged above the light equalization slice, the hot mirror made of the optical glass material is arranged on the upper portion of the infrared light emitting diode group, the infrared filter is arranged on the hot mirror, the infrared filter is connected with the single chip computer system through the infrared CCD, the infrared light emitting diode group emits infrared light 760-940nm in wavelength, the single chip computer system processes an obtained original image so as to convert the original image into a clear vein image, and the single chip computer system transmits the obtained clear vein image to the micro projector. The projection type vein indicating instrument is simple in structure design, high in detection speed, high in detection accuracy, and high in reliability.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Container performance acceleration method based on nonvolatile memory
ActiveCN110096333AMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersAccess frequencyHot mirror
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing SnO2-doped ZnO sputtering target material
ActiveCN106222618AImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDisplay deviceElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a method for preparing a SnO2-doped ZnO sputtering target material. The method includes the steps that SnO2 and ZnO powder with the grain size being 1-5 um and the purity being larger than or equal to 99.95% is selected as raw materials, the raw materials are evenly mixed in proportion through mixing equipment, and the SnO2 powder accounts for 20%-50% mass weight of mixed powder; a graphite mold is assembled, the surface of an inner cavity of the graphite mold is coated with a high temperature resistant ZrO2 protective coating with the thickness being 0.5mm; the mixed powder is placed into the assembled graphite mold, and tamping is performed with a special tool; the tamped graphite mold with the powder is placed into a nitrogen atmosphere shielded furnace to be heated and pressurized, namely hot pressing is performed; and the heating temperature inside the furnace is 1000-1300 DEG C, pressure is 5-30MPa, and heating and pressurizing time is 2-6 hours. By means of doping, the overall performance of a ZnO thin film is improved, and ZnO-based transparent conducting thin films can be widely applied on the aspects of solar cells, flat-panel displays, electromagnetic shielding, hot mirrors, ultraviolet detectors and the like.
Owner:GEMCH MATERIAL TECH SUZHOU
Production process of two-glass three-cavity hot mirror film hollow glass
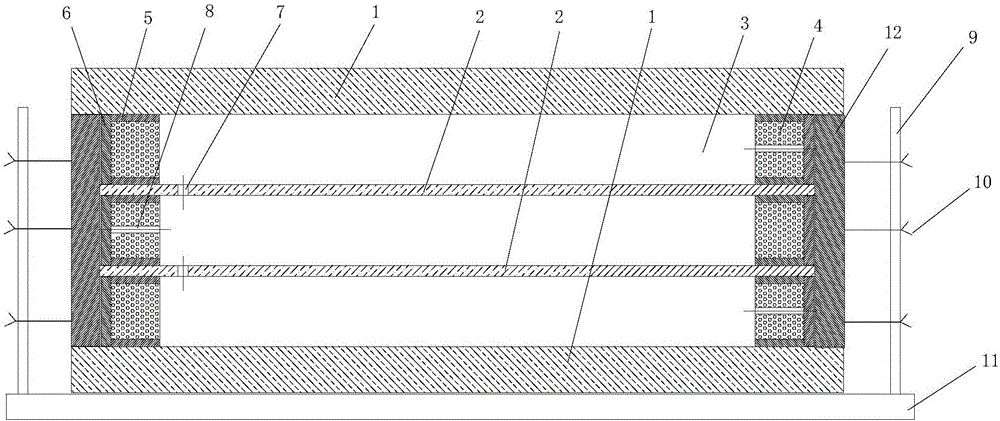
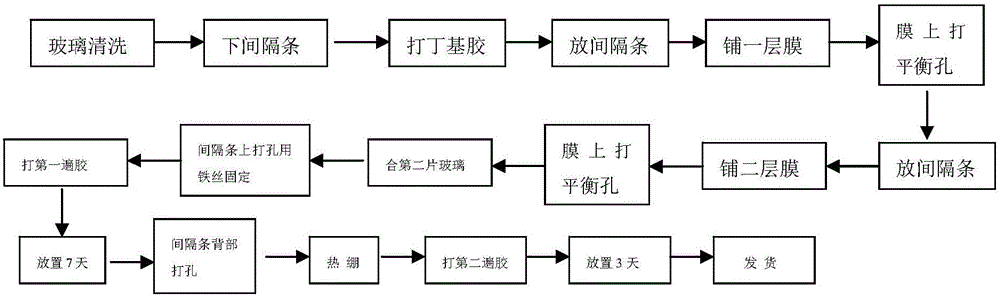
The invention relates to a production process of two-glass three-cavity hot mirror film hollow glass. The production process of the two-glass three-cavity hot mirror film hollow glass has the beneficial effects that two layers of hot mirror films are arranged between two pieces of glass; the weight of the obtained hollow glass with three air layers is far smaller than that of the common four-glass three-cavity glass, so the energy saving problem can be solved to a greater extent and the wastage of the material (sheet glass) is also reduced to a great extent; the three air layers have the effect of improving the properties of the hollow glass to a greater extent; by designing customized auxiliary tools, namely positioning blocks and fixing rods, spacing bars are positioned accurately, are convenient to construct and are also not easy to misplace or incline; by forming balancing holes in the hot mirror films, the air pressures of hollow cavities at the two sides are consistent, thus eliminating the phenomena of unevenness in spreading, edge wrinkle, etc.
Owner:TIANJIN NORTH GLASS IND TECHN
Instrument for rapid measurement of the optical properties of the eye across the whole field of vision
Instrument for measuring the optical properties of the eye across the whole field of vision, including refraction and aberrations, which comprises a frame (1) mounted on an ophthalmological table (2) that may be oriented in three perpendicular directions X, Y, Z and has a support surface (19) for the head, a hot mirror (3) and a long mirror (4), both rigidly secured to the frame (1) in front of the head. It also comprises a lighting subassembly (5) made up of a fibre optic head (6), a lens L1 (7), a diaphragm D (8) and a beam splitter BS (9), and a measuring subassembly (10) with two lenses L2 (11) and L3 (12), two mirrors M1 (13) and M2 (14) and a special camera (15) with a microlens array (16) at the input thereof, such that said camera (15) is positioned in the focal plane of the microlenses. The frame (1) has a motor (17) of which the shaft can rotate in the direction Y, to which is coupled an arm (18) that can rotate with said shaft, the components of the lighting subassembly (5), the components of the measuring subassembly (10) and the camera (15) with the microlens array (16) being mounted on said arm (18).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MURCIA
Method for acquiring RGB and infrared images by using conventional digital camera
The invention discloses a method for acquiring RGB and infrared images by using a conventional digital camera. The method comprises: step one, calculating an independent G channel value and an independent NIR channel value by using data at a G position after hot mirror removing in a Bayer array mode; step two, calculating G channel value and NIR channel values of all pixel positions by using an interpolation method; and step three, calculating an R channel value and a B channel value of each pixel position. Therefore, R, G, B, and NIR channel values of all pixel positions are obtained finallyand thus a complete RGB image and NIR image. The method is simple and the image effect is good.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
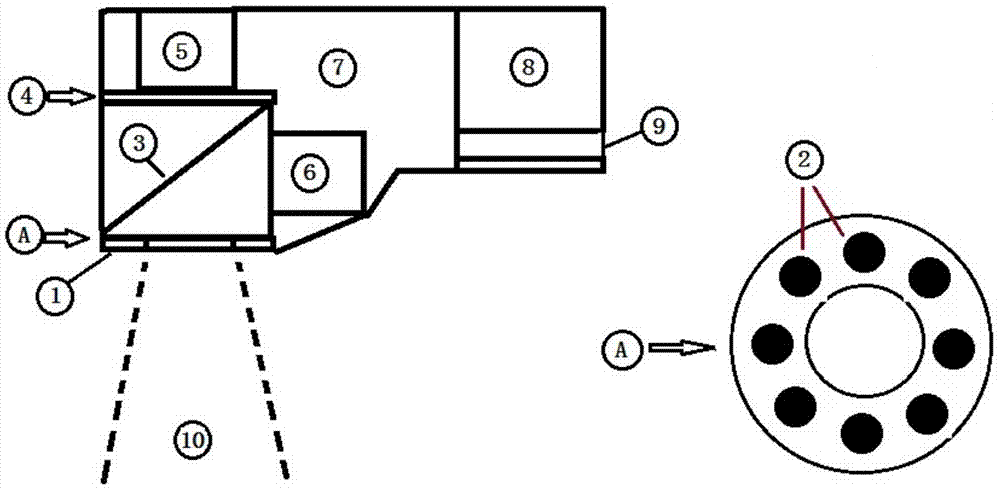
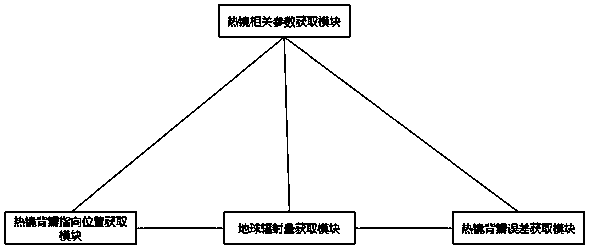
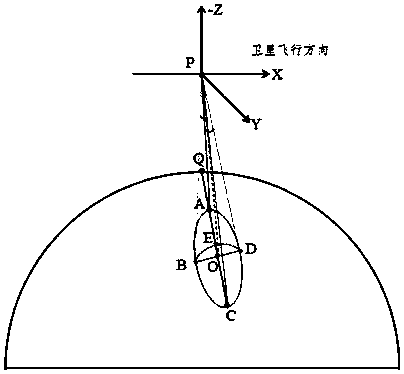
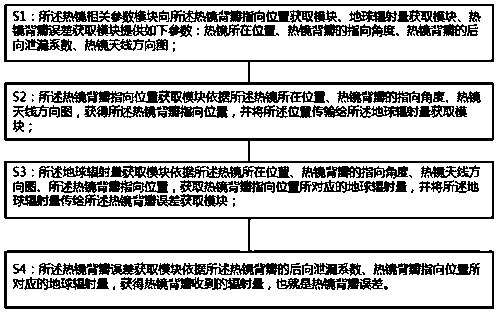
System and method for correcting on-orbit error of heat mirror dorsal valve of satellite-borne microwave imager
ActiveCN110764153ACalculation errorImprove calibration accuracyDetection using electromagnetic wavesEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention provides a system and method for correcting on-orbit error of a heat mirror dorsal valve of a satellite-borne microwave imager. The method comprises the following steps: S1, a heat mirror relevant parameter module provides parameters for a heat mirror dorsal valve orientation position acquisition module, an earth radiation quantity acquisition module and a heat mirror dorsal valve error acquisition module; S2, the heat mirror dorsal valve orientation position acquisition module acquires the orientation position of the heat mirror dorsal valve according to the parameter, and transmits the position to the earth radiation quantity acquisition module ; S3e , the earth radiation quantity acquisition module acquires the earth radiation quantity corresponding to the orientation position of the heat mirror dorsal valve according to the parameter and the position, and sends the earth radiation quantity to the heat mirror dorsal valve error acquisition module; and S4, the heat mirror dorsal valve error acquisition module acquires the heat mirror dorsal valve error according to the parameter and the earth radiation quantity. By adoption of the method provided by the invention, the on-orbit error of the heat mirror dorsal valve of the satellite-borne microwave imager can be acquired effectively and precisely; and moreover, the method is scientific and reasonable, and is easyto realize.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT INST OF TT&C & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com