Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Phrenic nerve stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
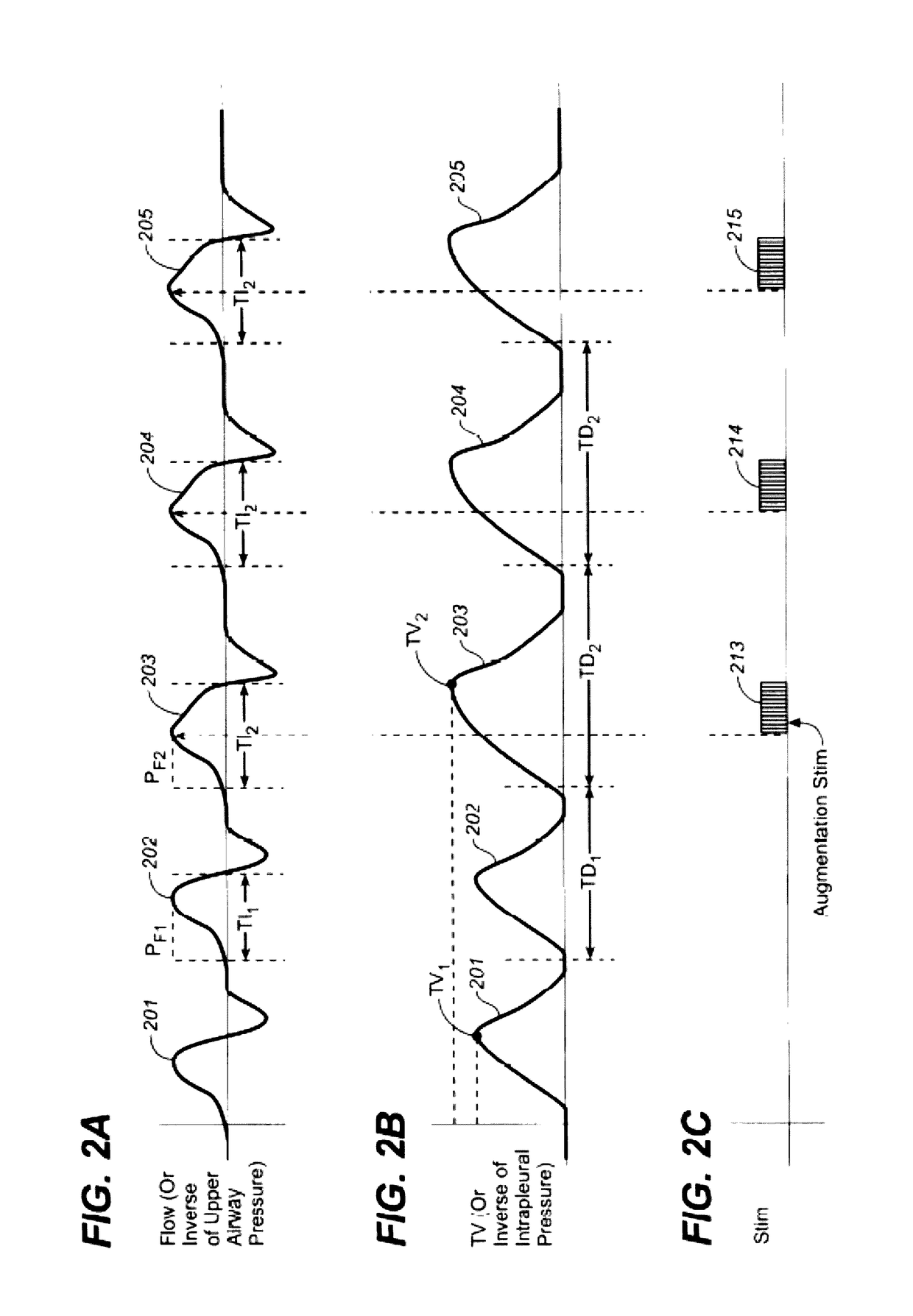
Phrenic nerve stimulation, also known as diaphragm pacing, is the electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerve using a surgically implanted device. This device contracts the diaphragm rhythmically, improving breathing function in patients with respiratory insufficiency.
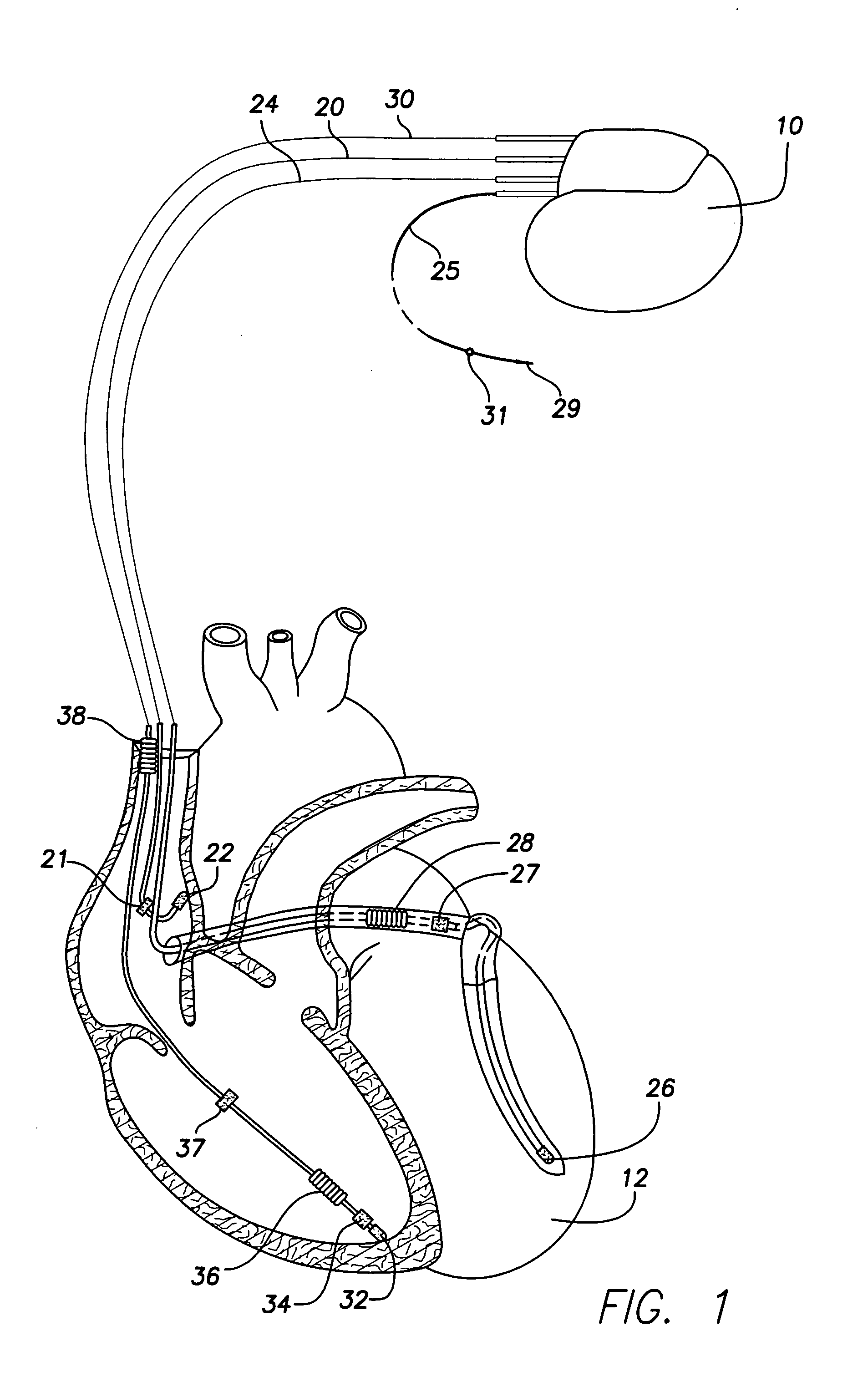
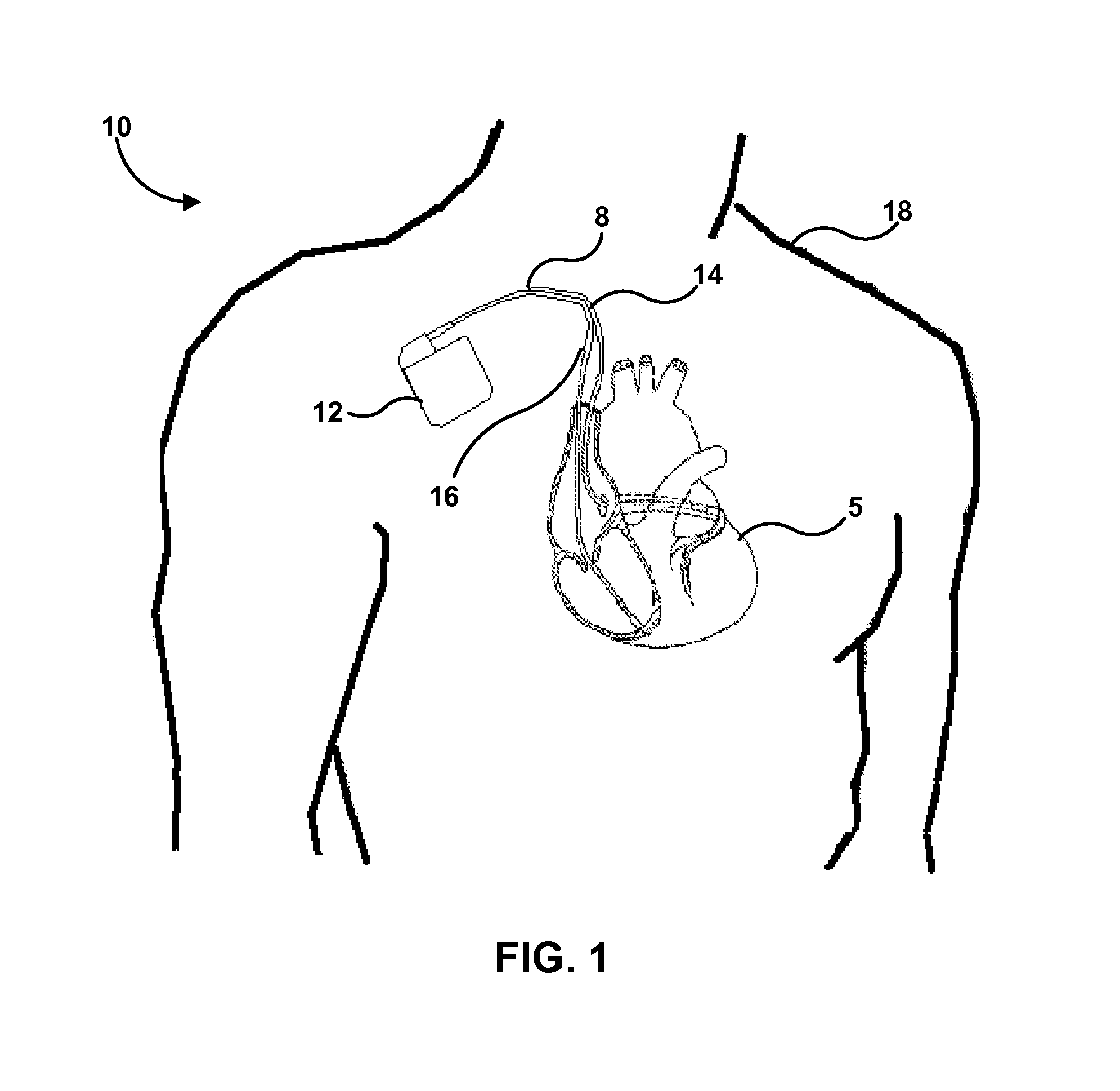
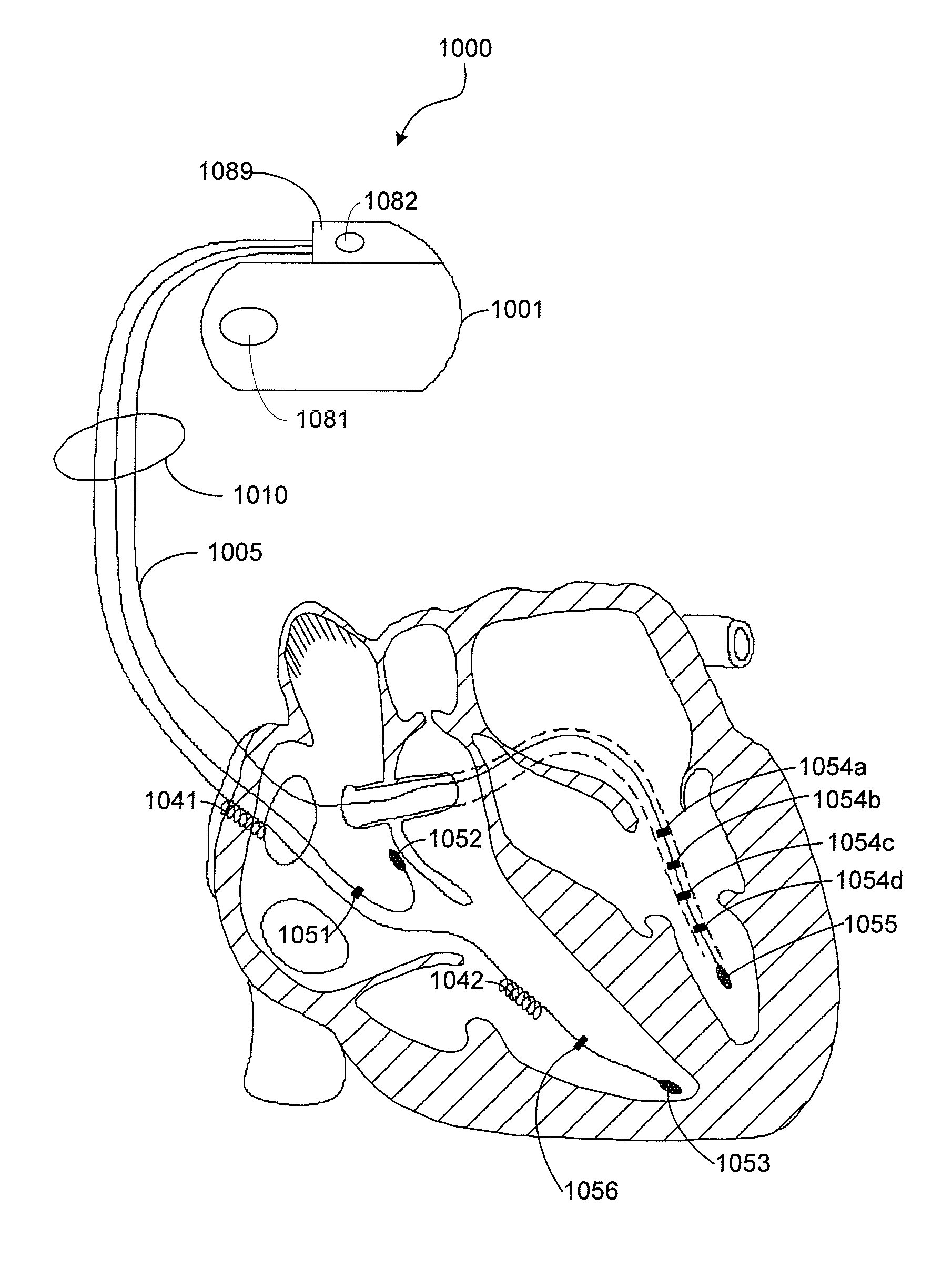
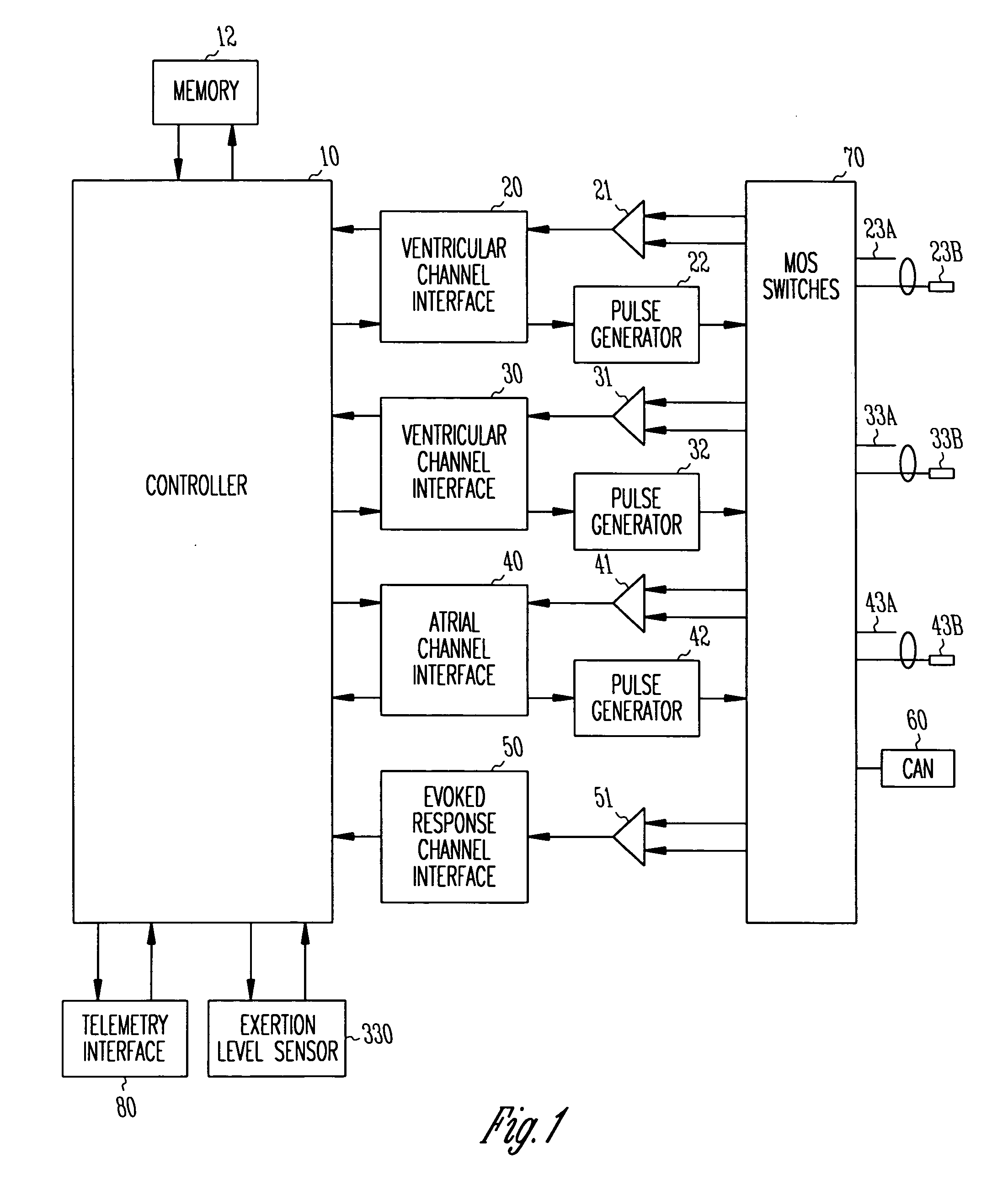
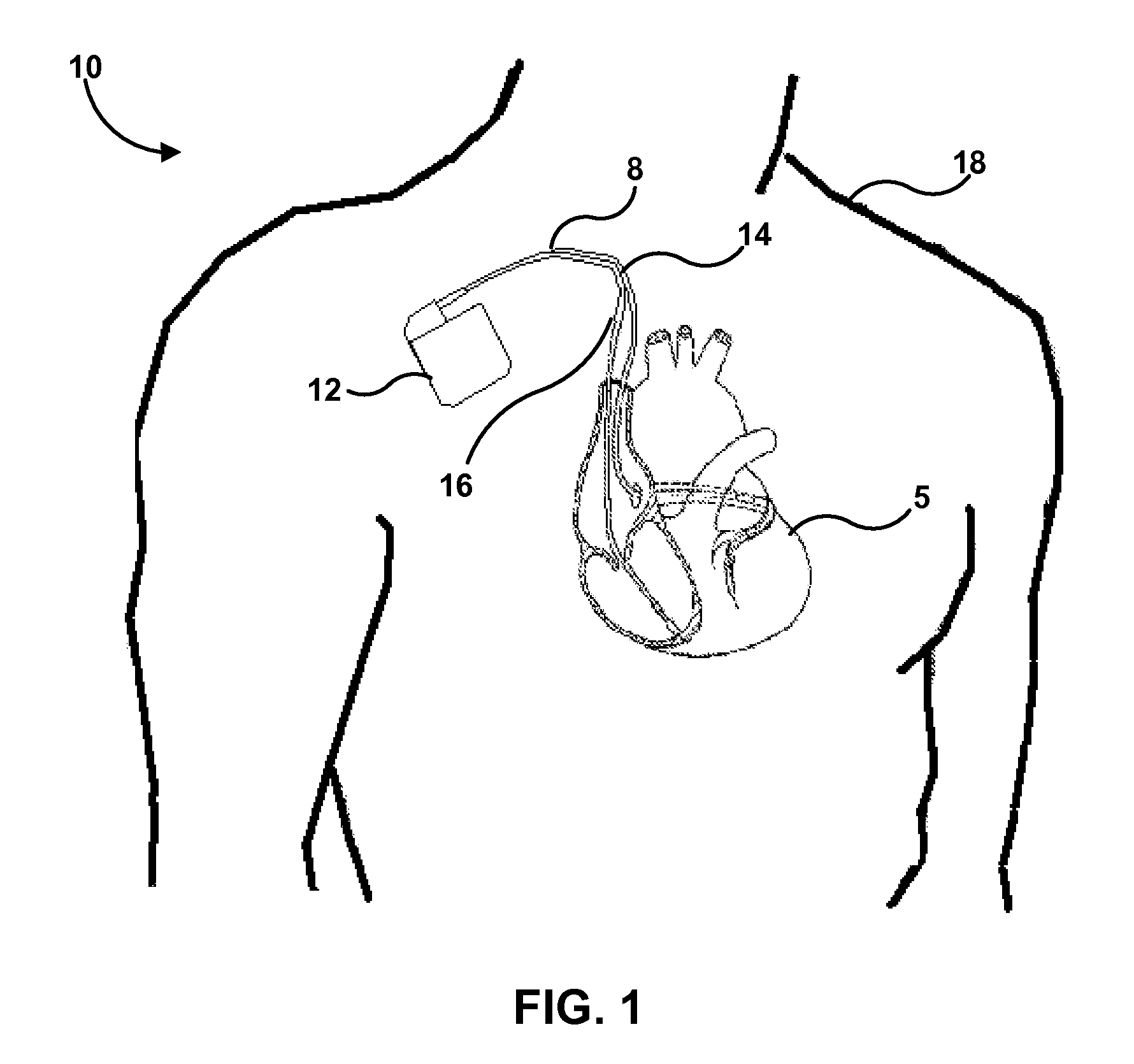
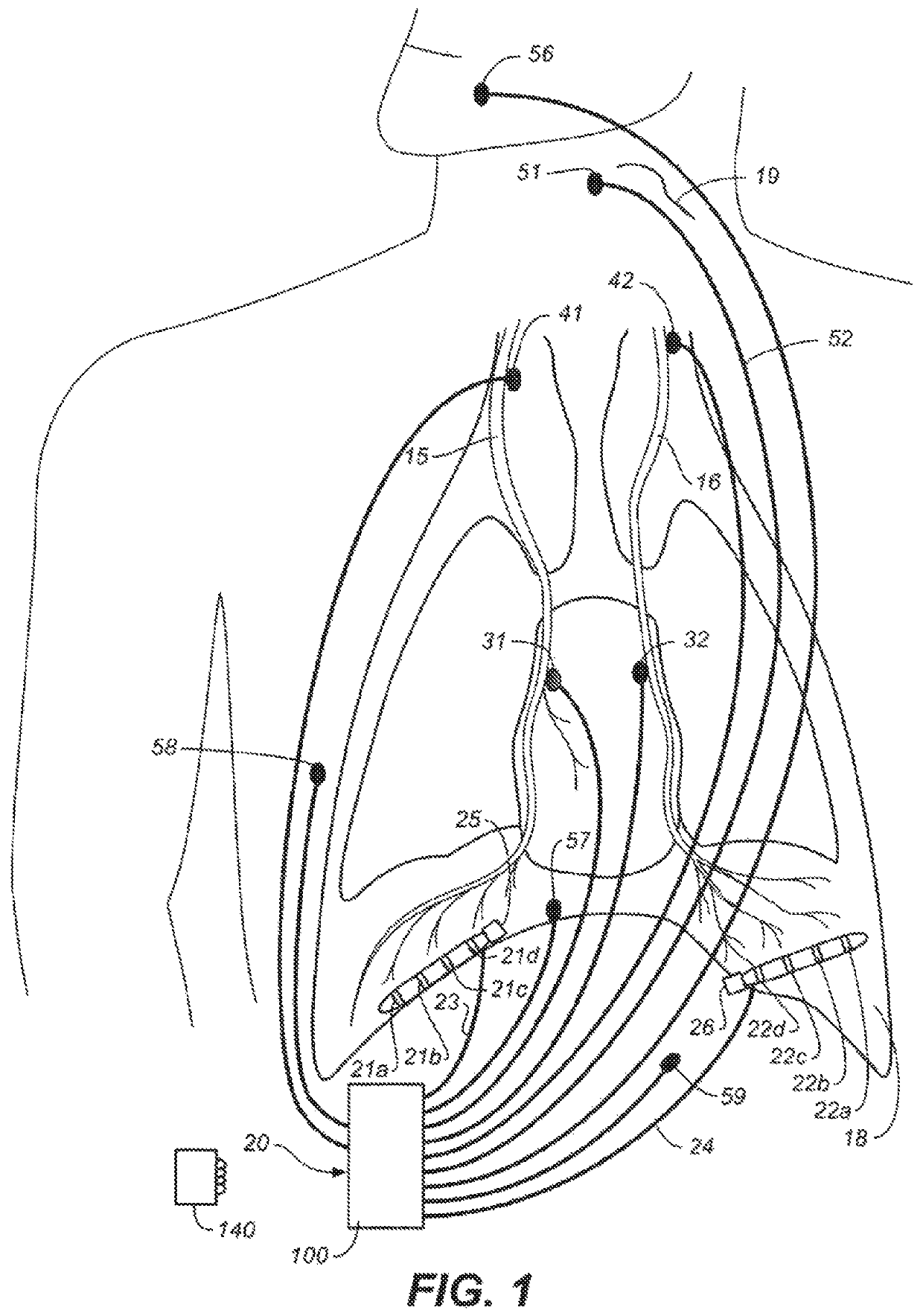
Method and system for optimizing left-heart lead placement
InactiveUS20070055124A1Easy to placePredict successUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac wallBlood flow
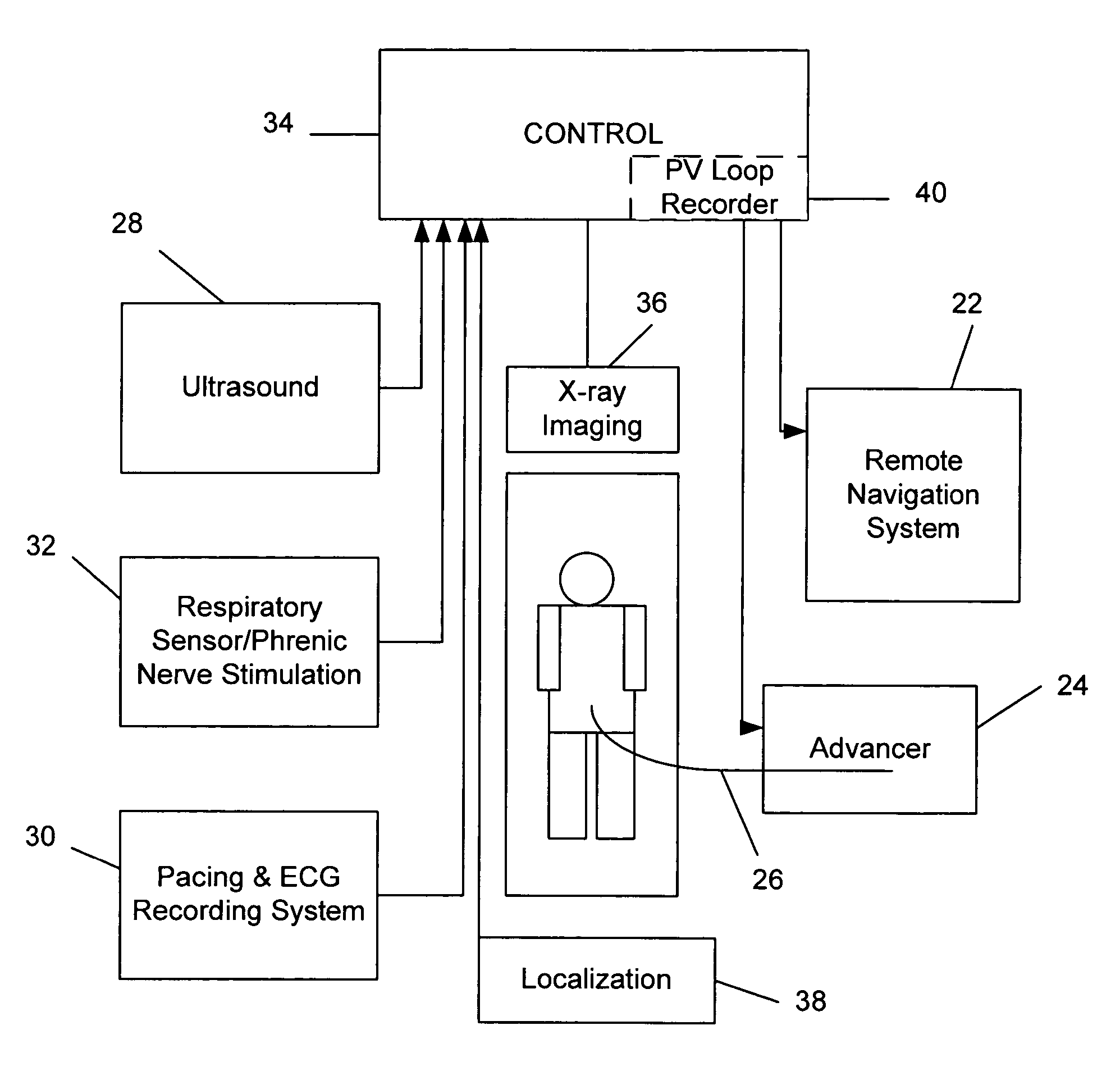
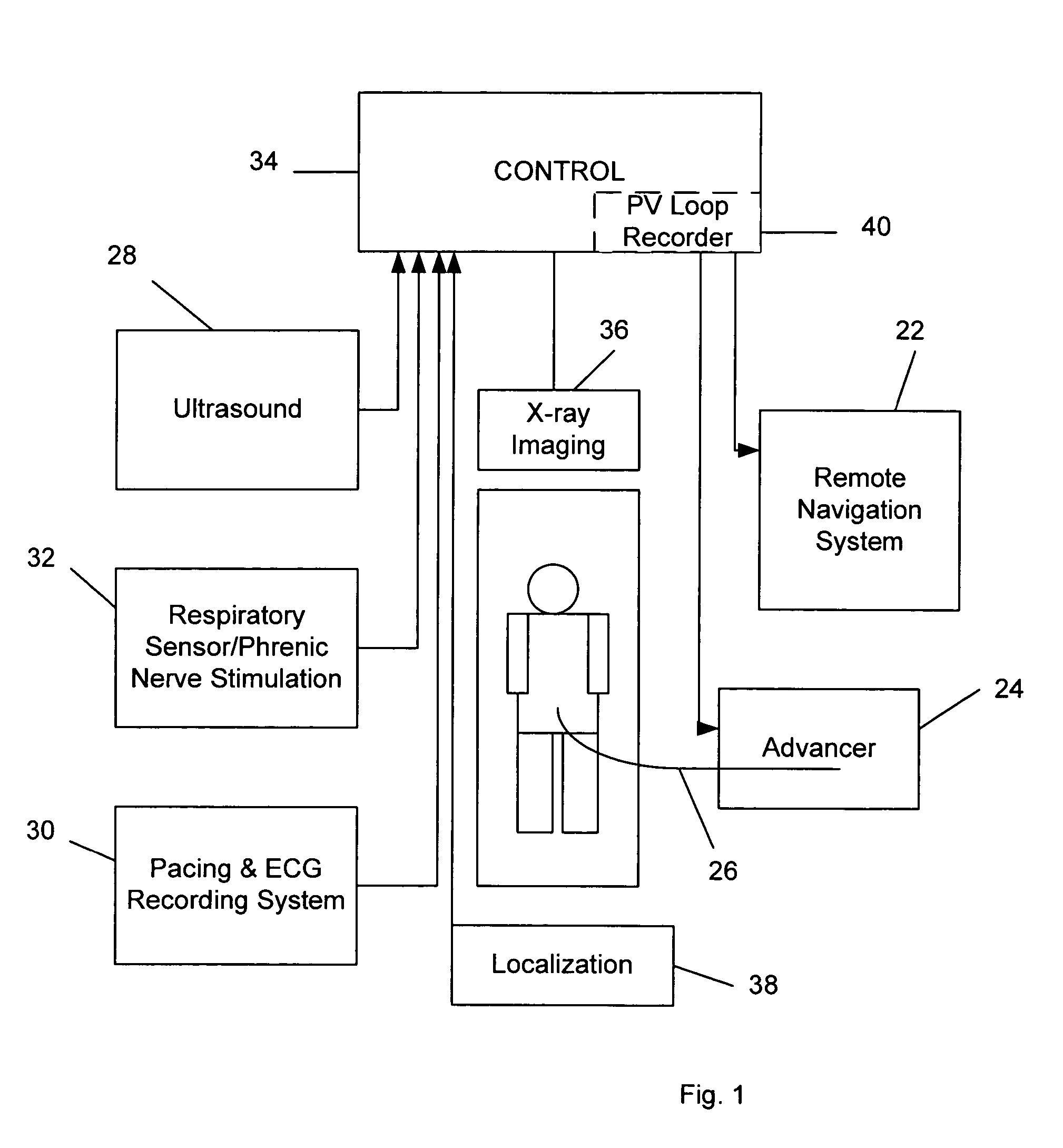
A system for identifying locations for pacing the heart, the system comprising a pacing electrode, a remote navigation system for positioning the pacing electrode at each of a plurality of locations; a system for determining Pressure-Volume loop data resulting from pacing at each location; an ECG system, a phrenic nerve stimulation detection system, and a means of identifying at least one preferred location based upon at least the Pressure-Volume loop, ECG, and phrenic nerve stimulation data at each location. A method of identifying locations for pacing the heart, the method comprising: navigating a pacing electrode to each of a plurality of locations in the heart; pacing the heart at each of the plurality of locations; and assessing the effectiveness of the pacing at each location by measuring cardiac blood flow and cardiac wall strain.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
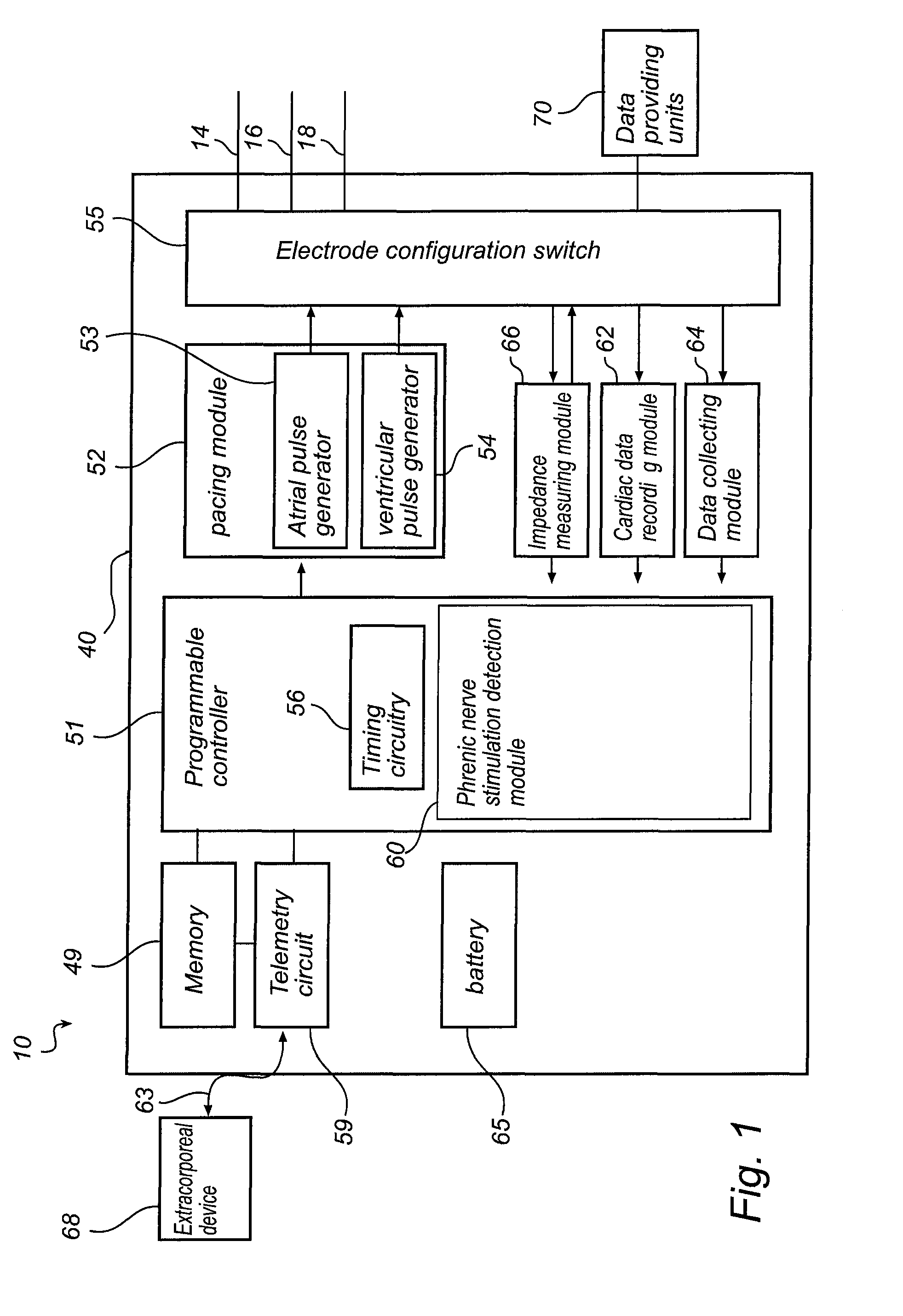
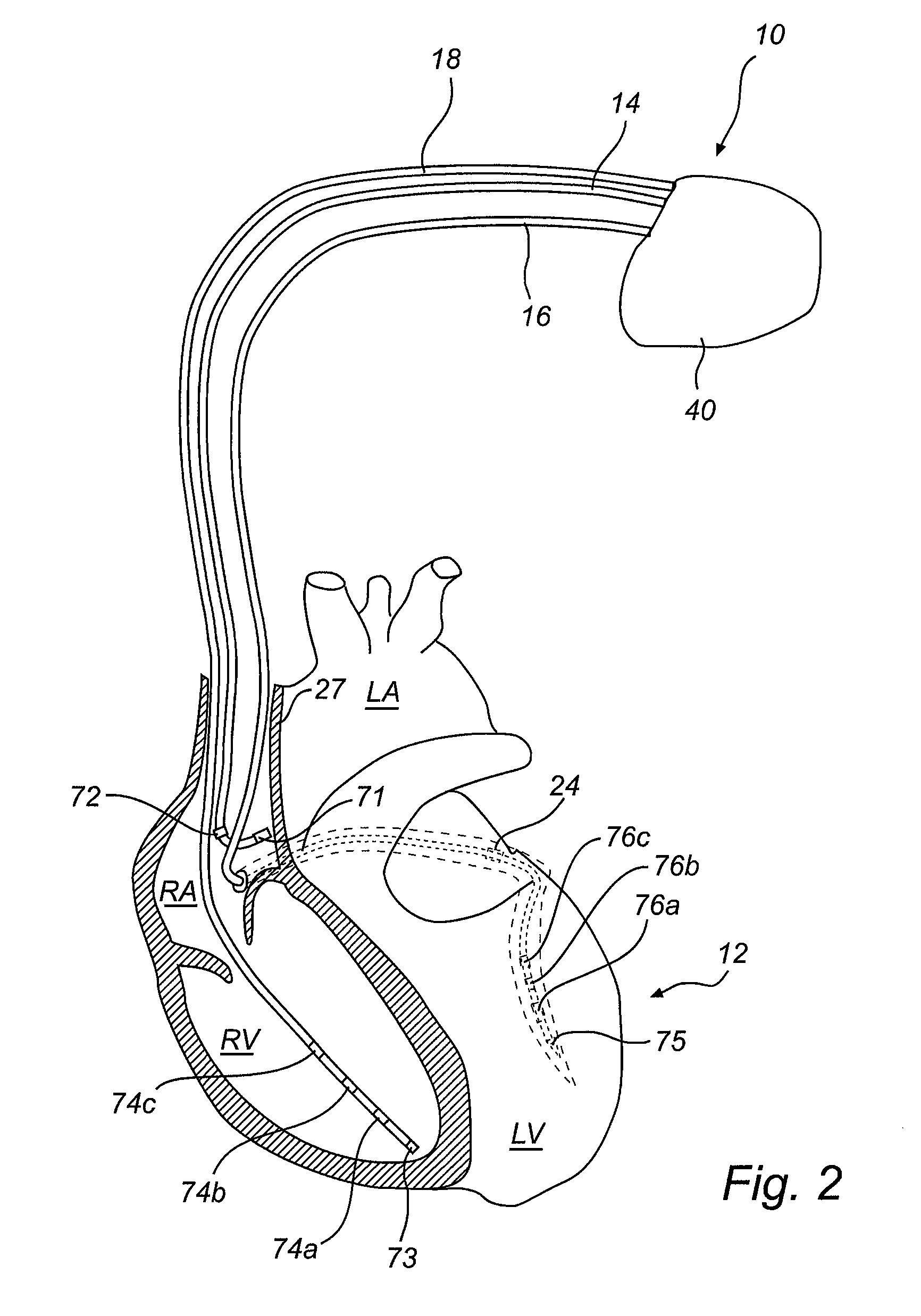
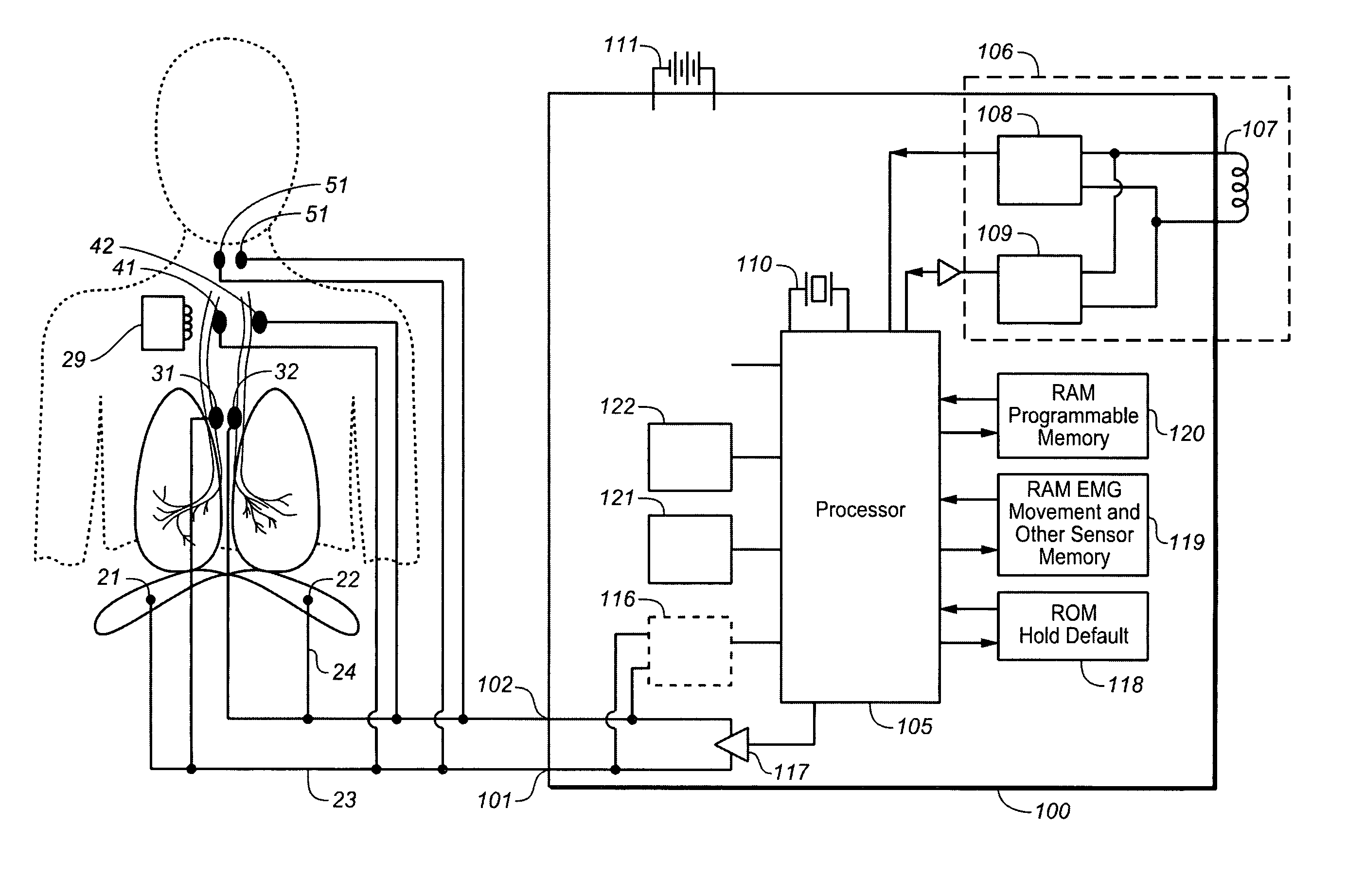
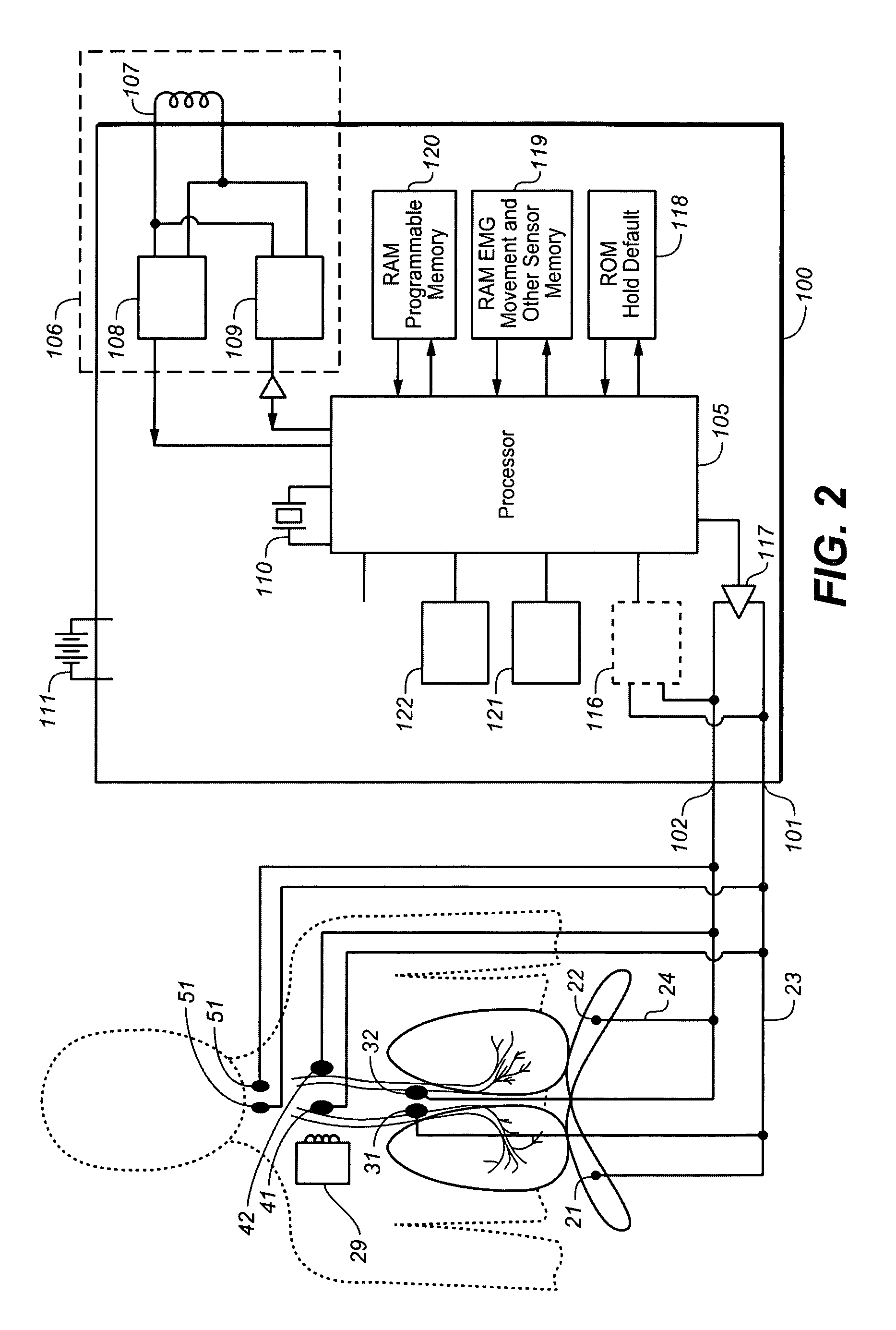
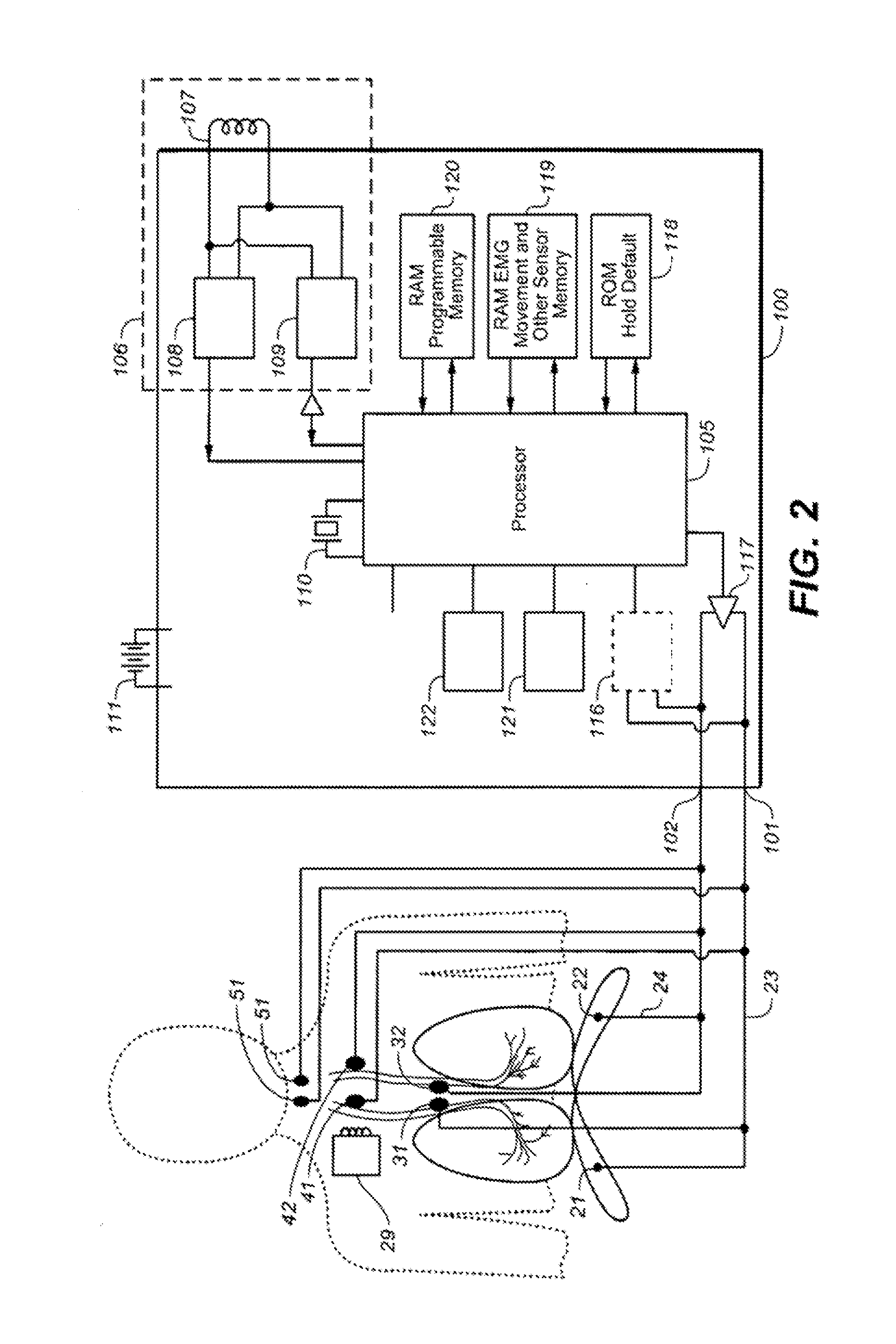
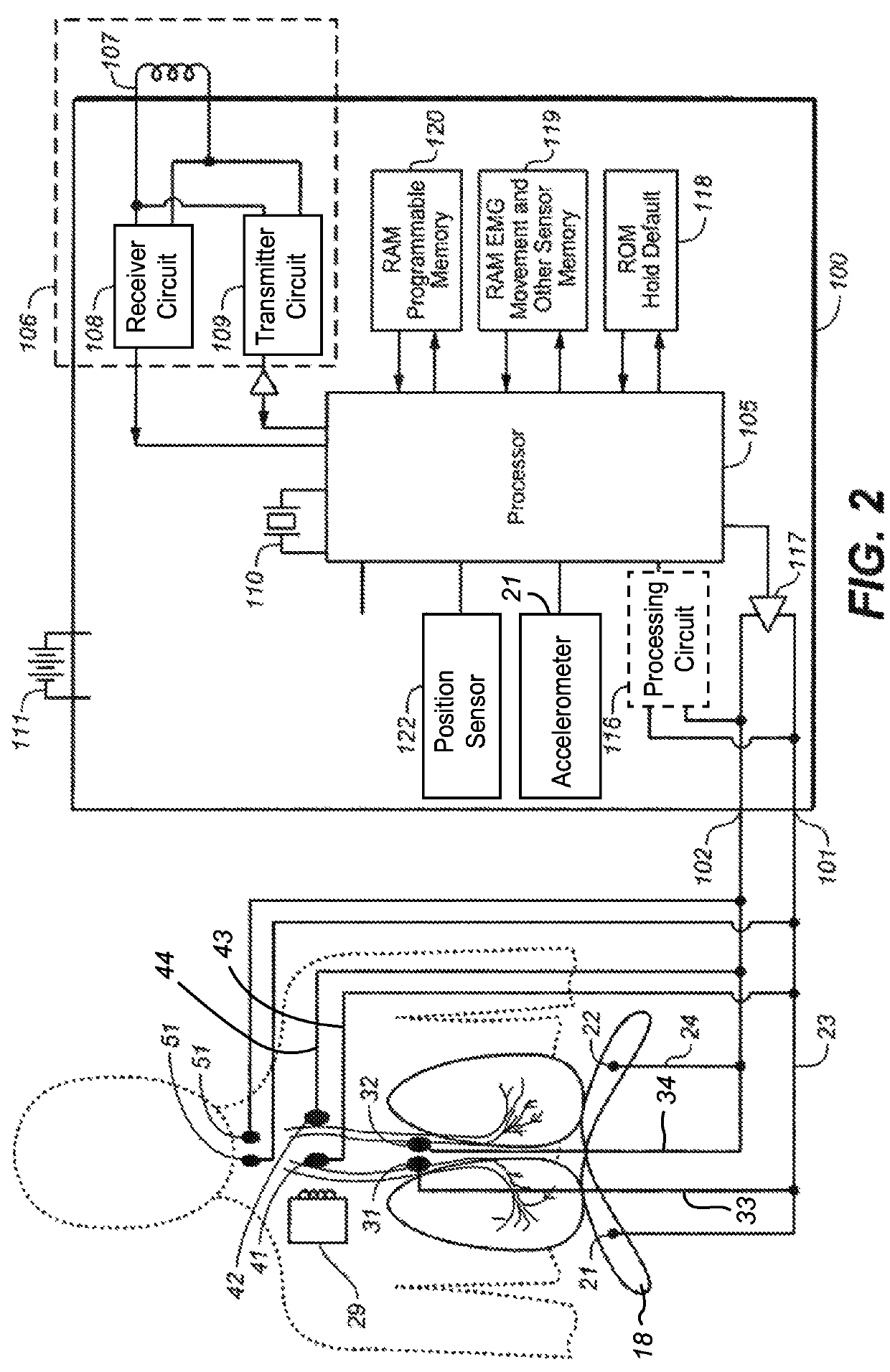
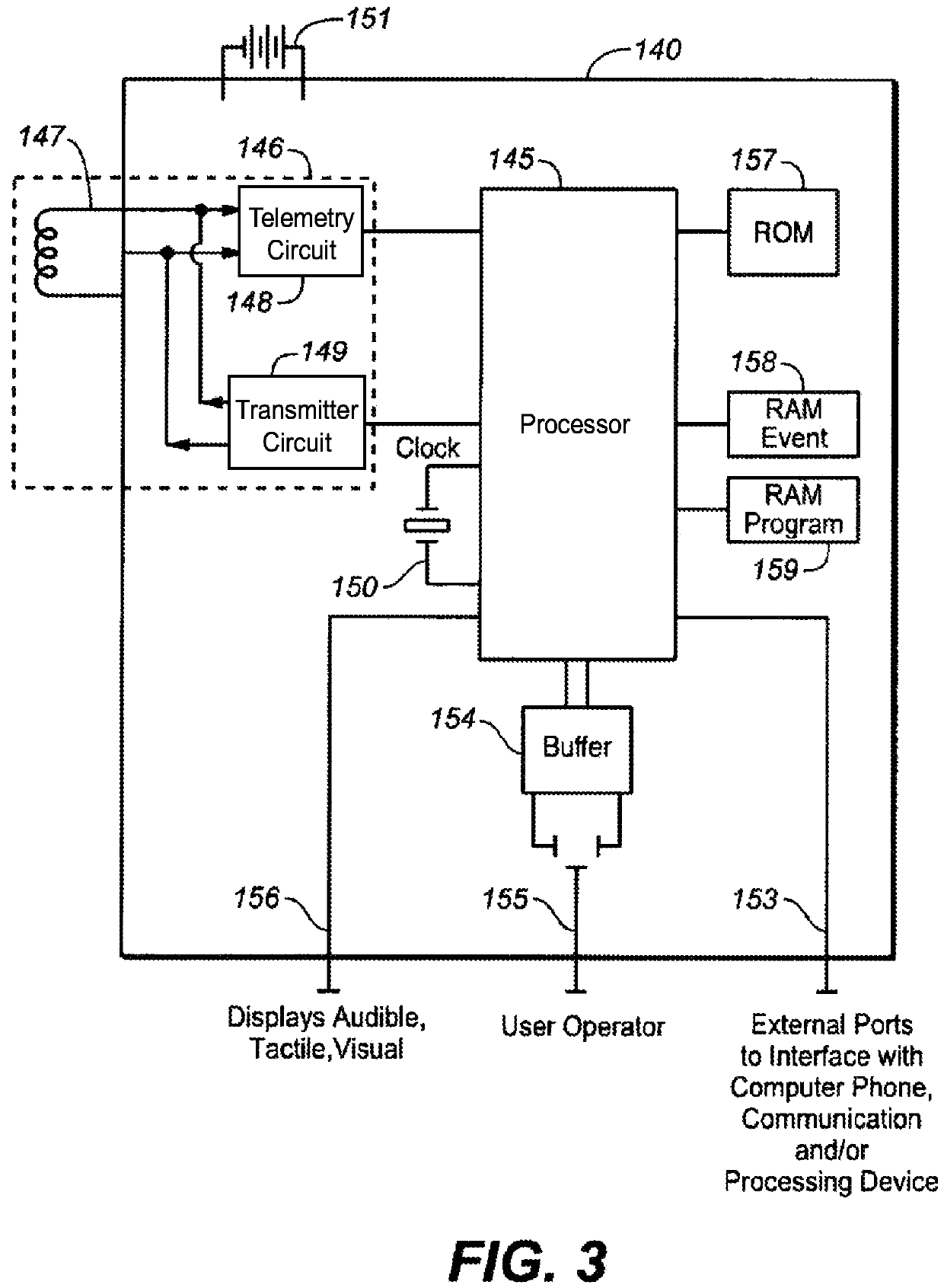
Implantable cardiac device and method for reduced phrenic nerve stimulation
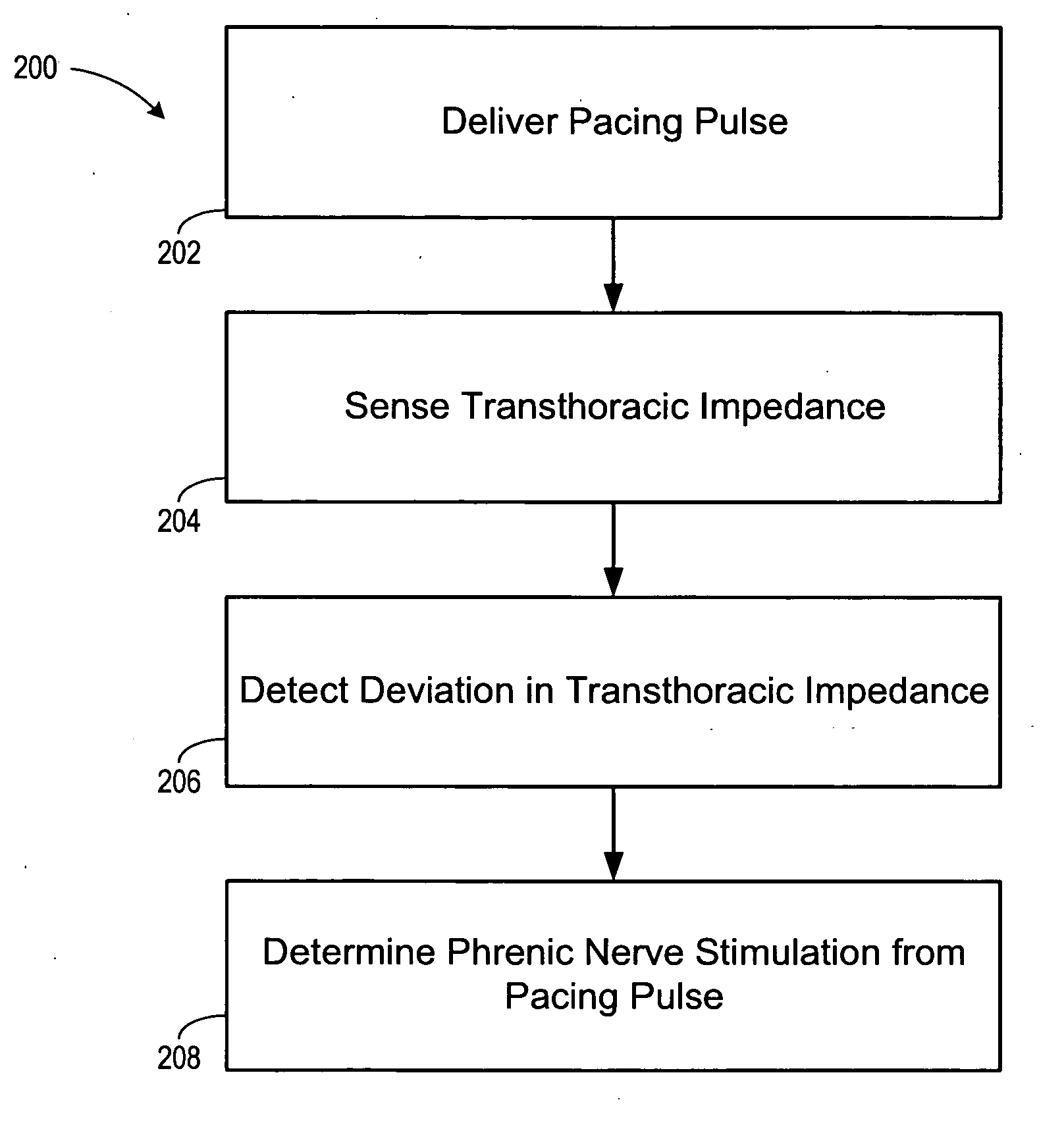
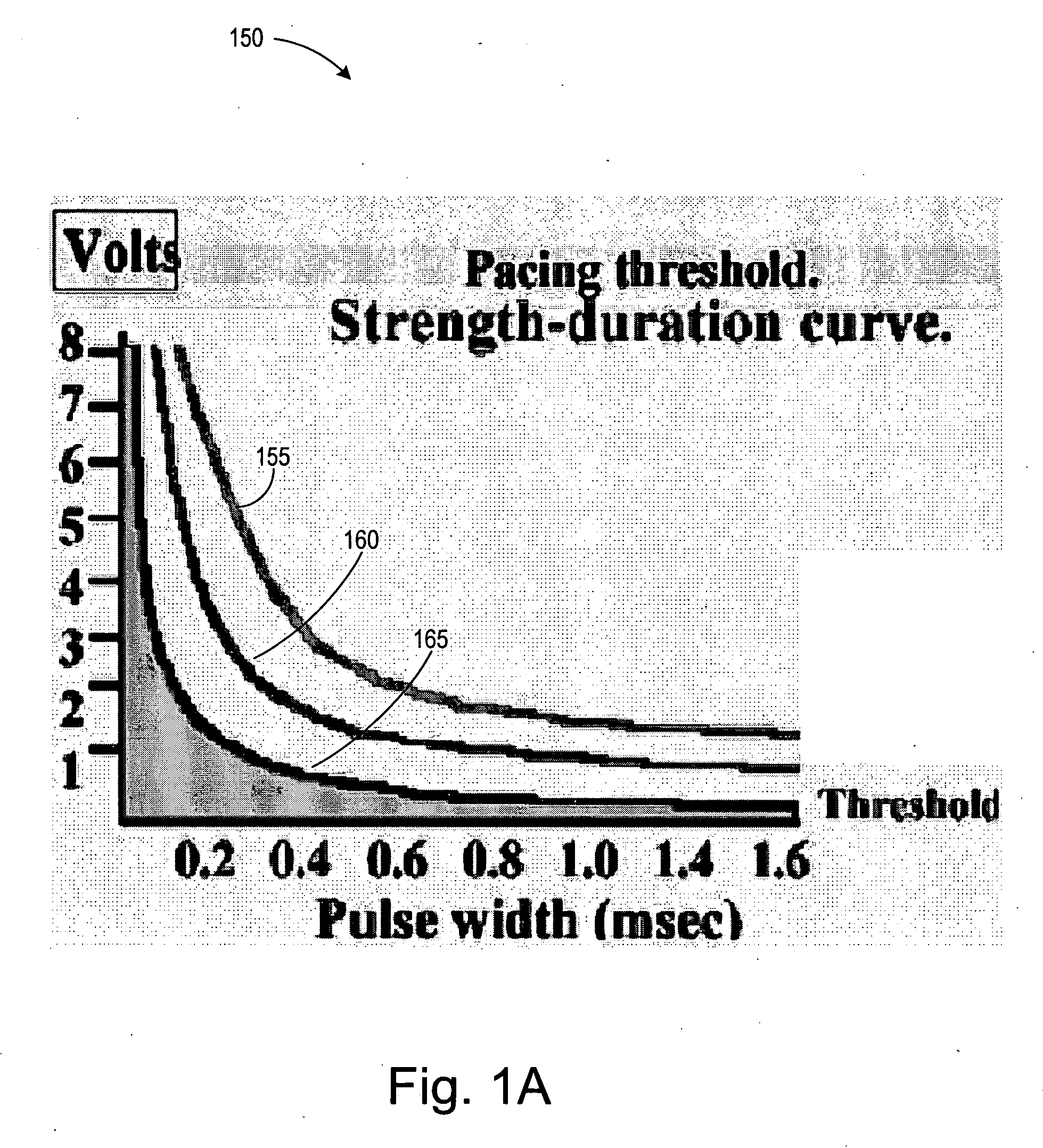
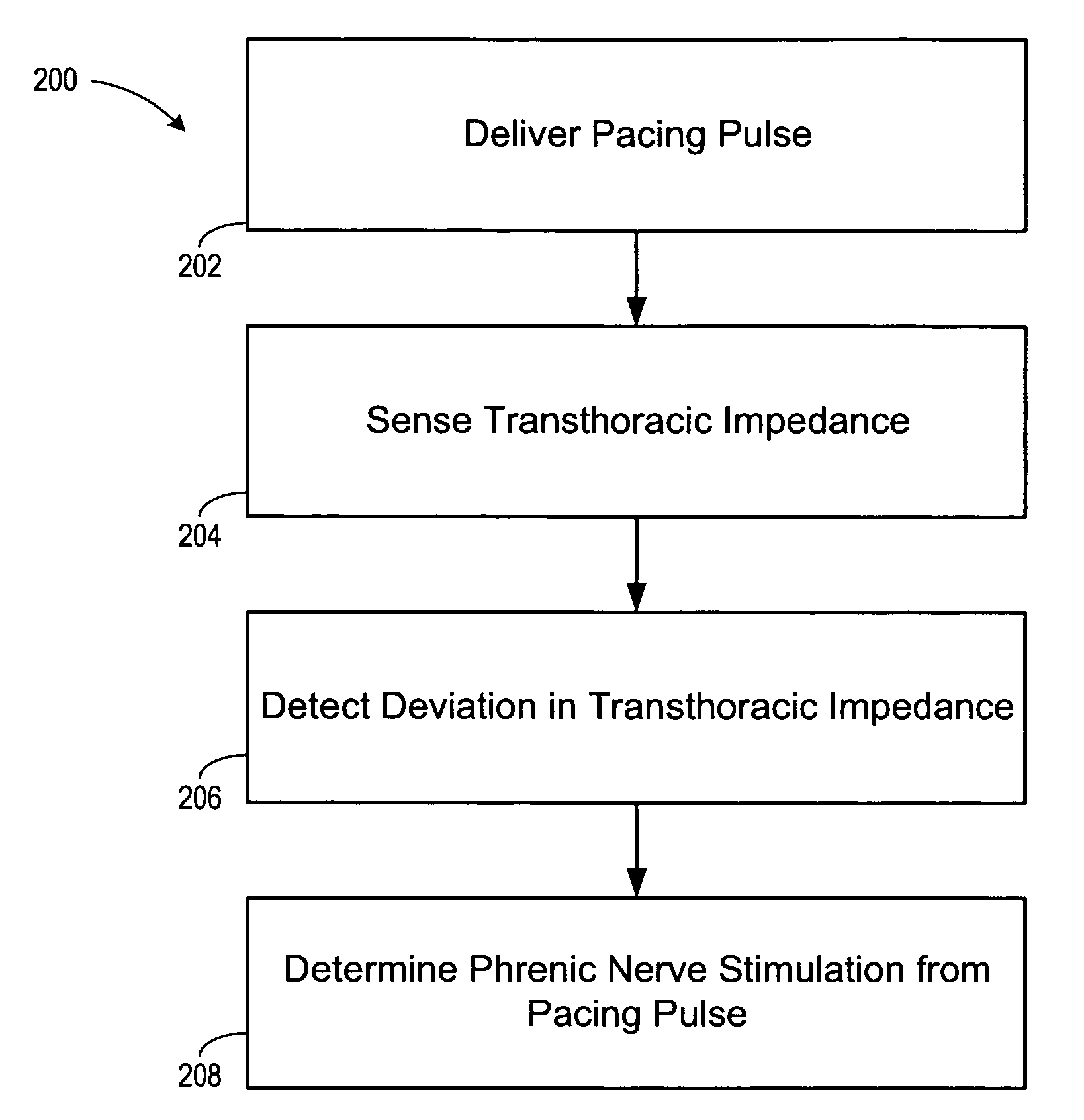
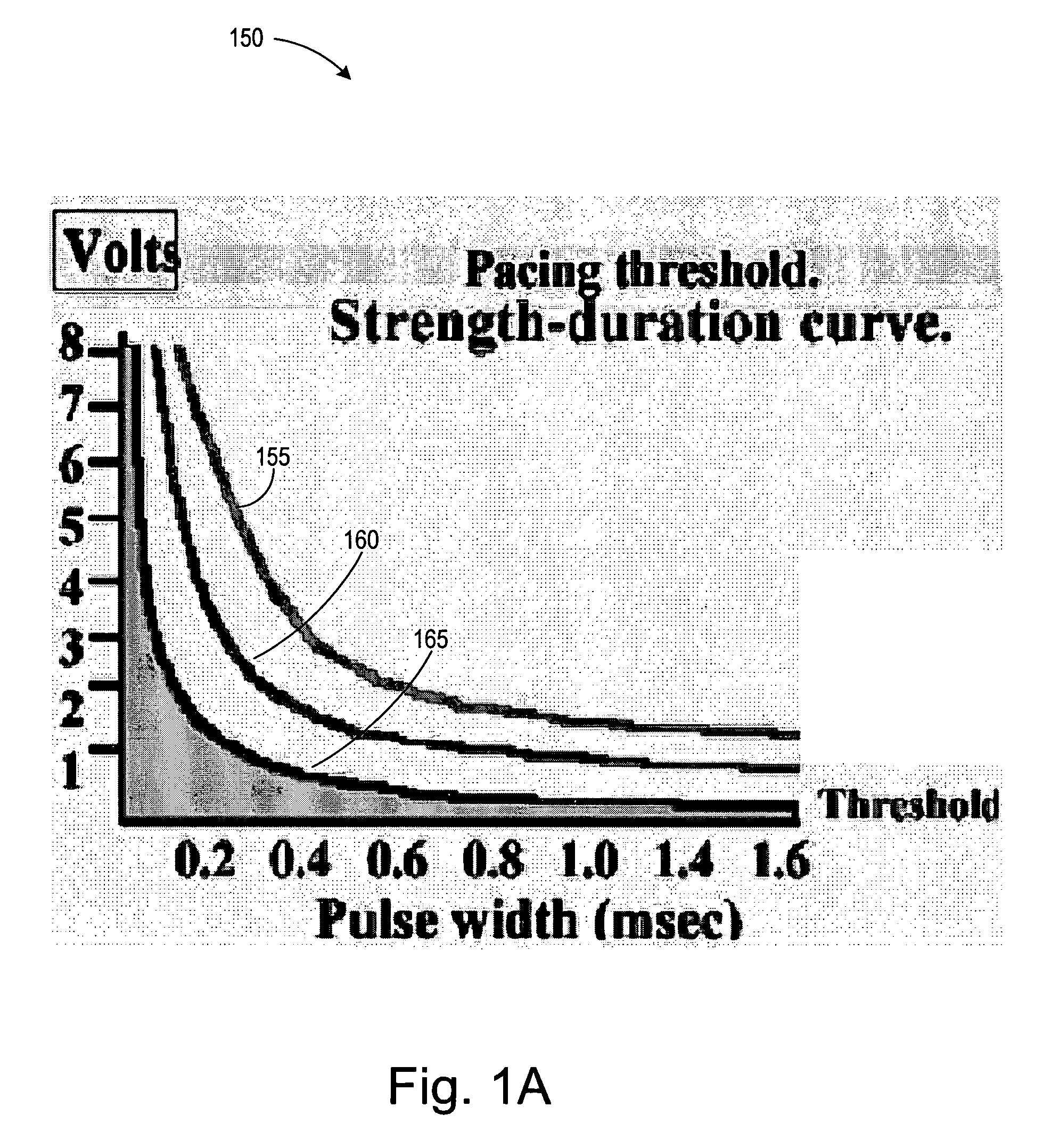
ActiveUS20060241711A1Reducing phrenic nerve stimulationHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringStrength duration curveRadiology
Methods and devices for reducing phrenic nerve stimulation of cardiac pacing systems involve delivering a pacing pulse to a ventricle of a heart. A transthoracic impedance signal is sensed, and a deviation in the signal resulting from the pacing pulse may be used to determine phrenic nerve stimulation. Methods may further involve detecting the phrenic nerve stimulation from the pacing pulse by delivering two or more pacing pulse to the ventricle of the heart, and determining a temporal relationship. A pacing vector may be selected from the two or more vectors that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing voltage and / or pulse width may be selected that provides cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. In other embodiments, a pacing pulse width and a pacing voltage may be selected from a patient's strength-duration curve that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
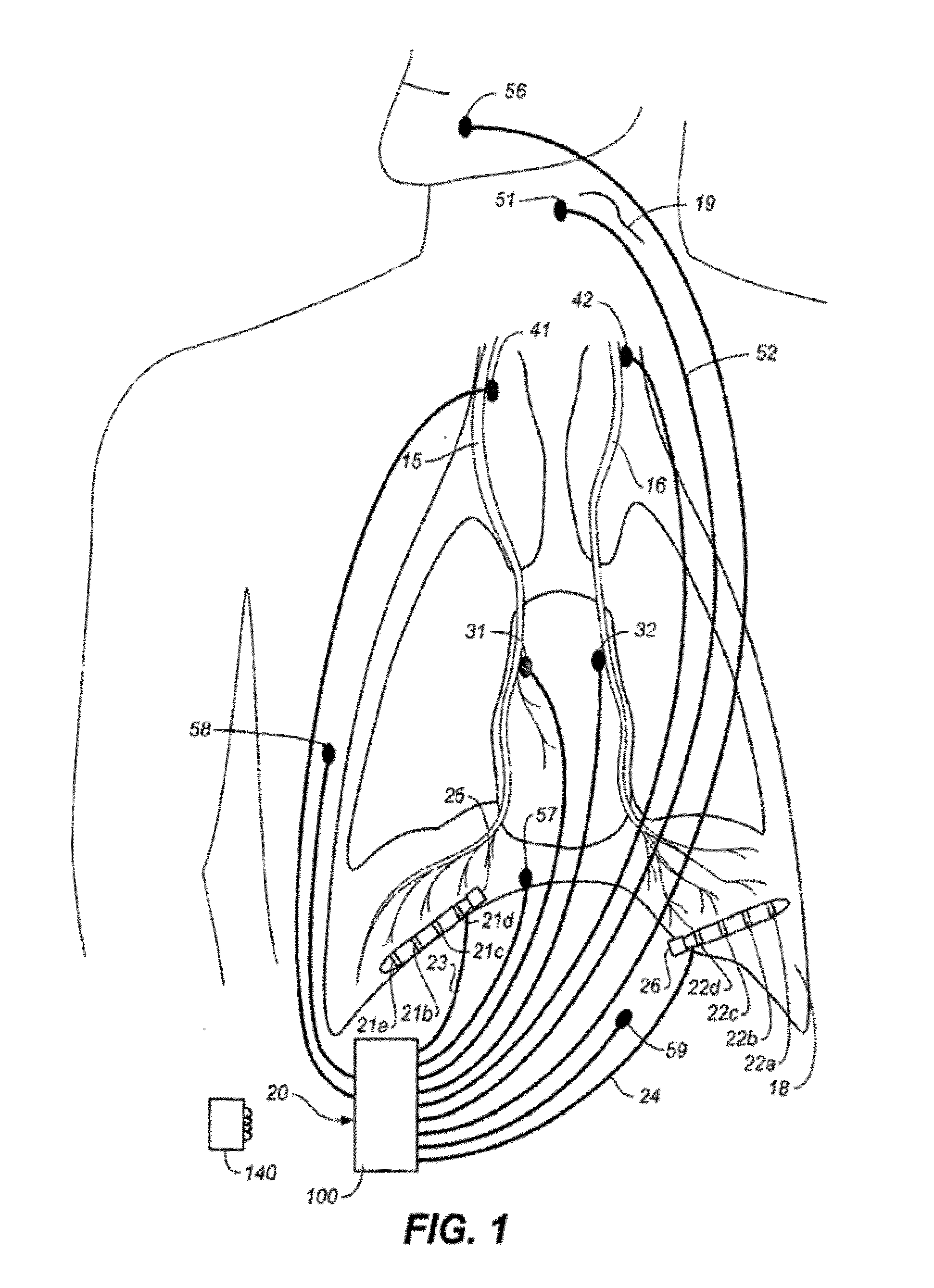
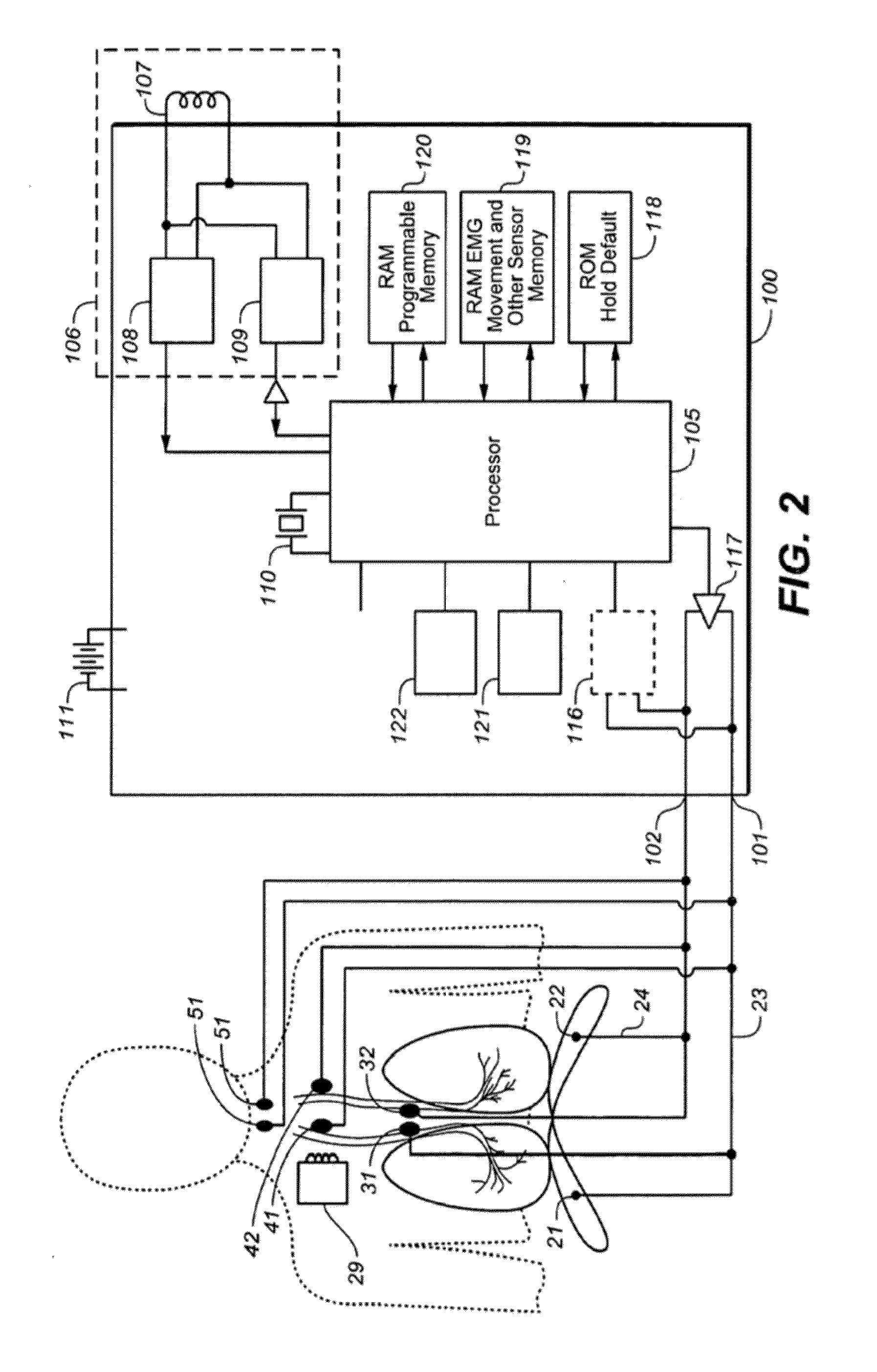
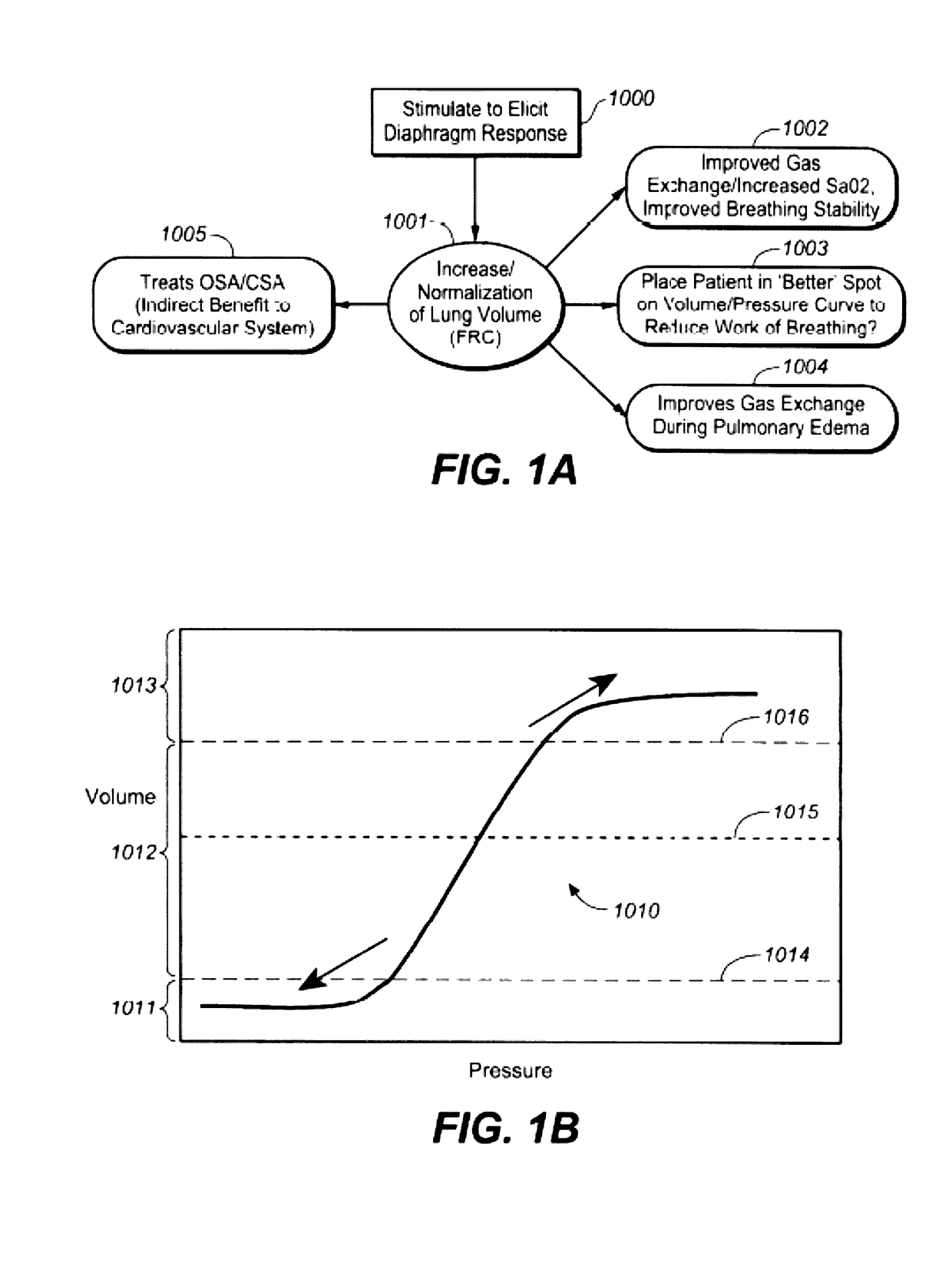
Therapeutic diaphragm stimulation device and method
ActiveUS20080167695A1Steady breathingReduce and avoid arousal eventElectrotherapyElectromyographyDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
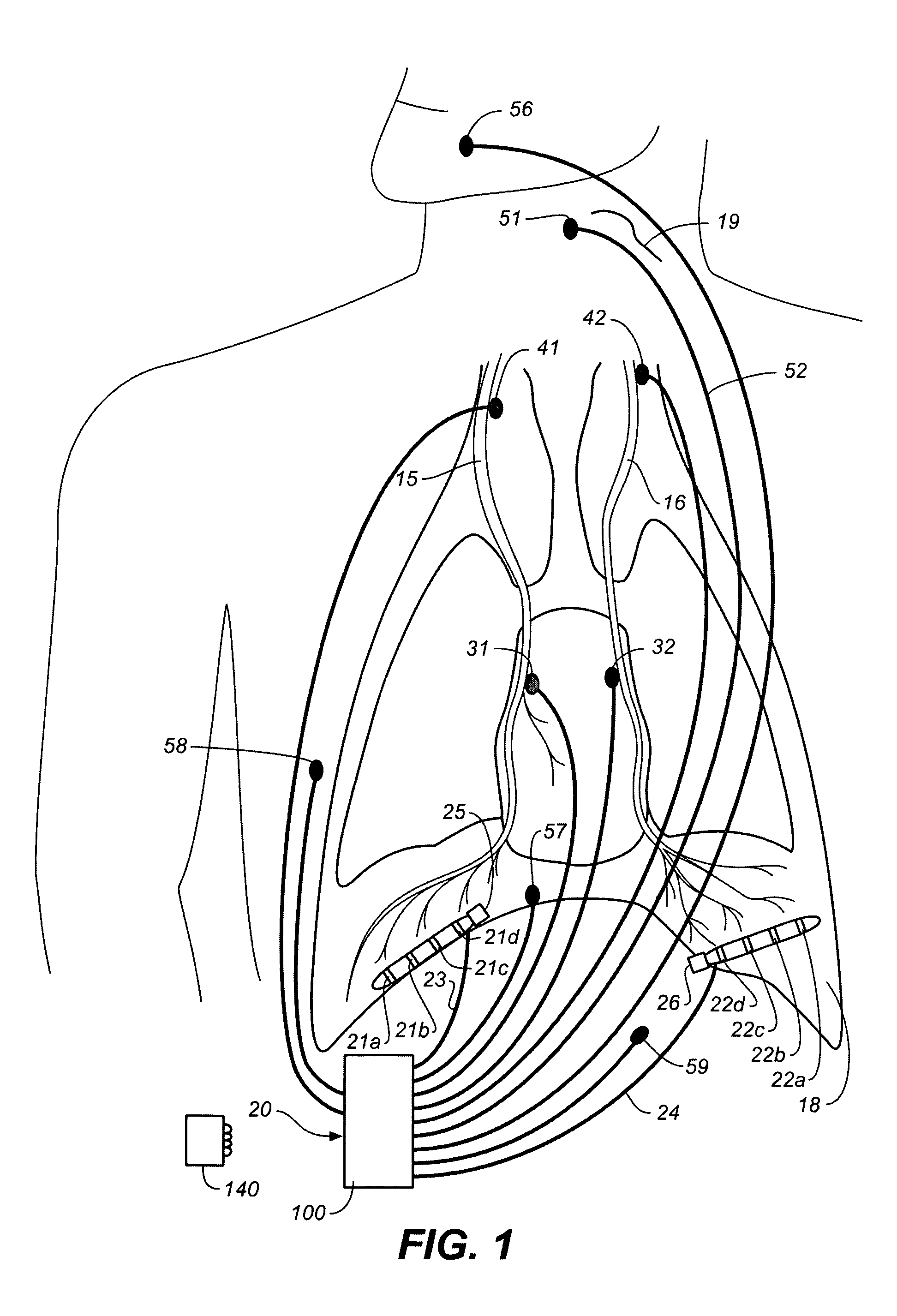
Implantable Devices and Methods for Stimulation of Cardiac or Other Tissues
An implantable stimulation system is provided for stimulation of the heart, phrenic nerve, gastric system, or other tissue structures accessible via a patient's upper gastrointestinal system or airway. The stimulation system includes an implantable controller housing including a pulse generator; at least one electrical lead attachable to the pulse generator; and at least one electrode carried by the electrical lead that is positionable and fixable within the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway. The controller housing may be adaptable for subcutaneous implantation, or within the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway, wherein the controller housing is proportioned to substantially permit fluid and solid flow through the upper gastrointestinal tract or airway about the controller housing. The pulse generator may be operable to deliver one or more electrical pulses effective in cardiac pacing, cardiac defibrillation, cardioversion, cardiac resynchronization therapy, diaphragm pacing, phrenic nerve stimulation, gastric electrical stimulation, or a combination thereof.
Owner:E PACING
Therapeutic diaphragm stimulation device and method
InactiveUS20110288609A1Increase gas exchangeReduces sympathetic biasRespiratorsElectrotherapyDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
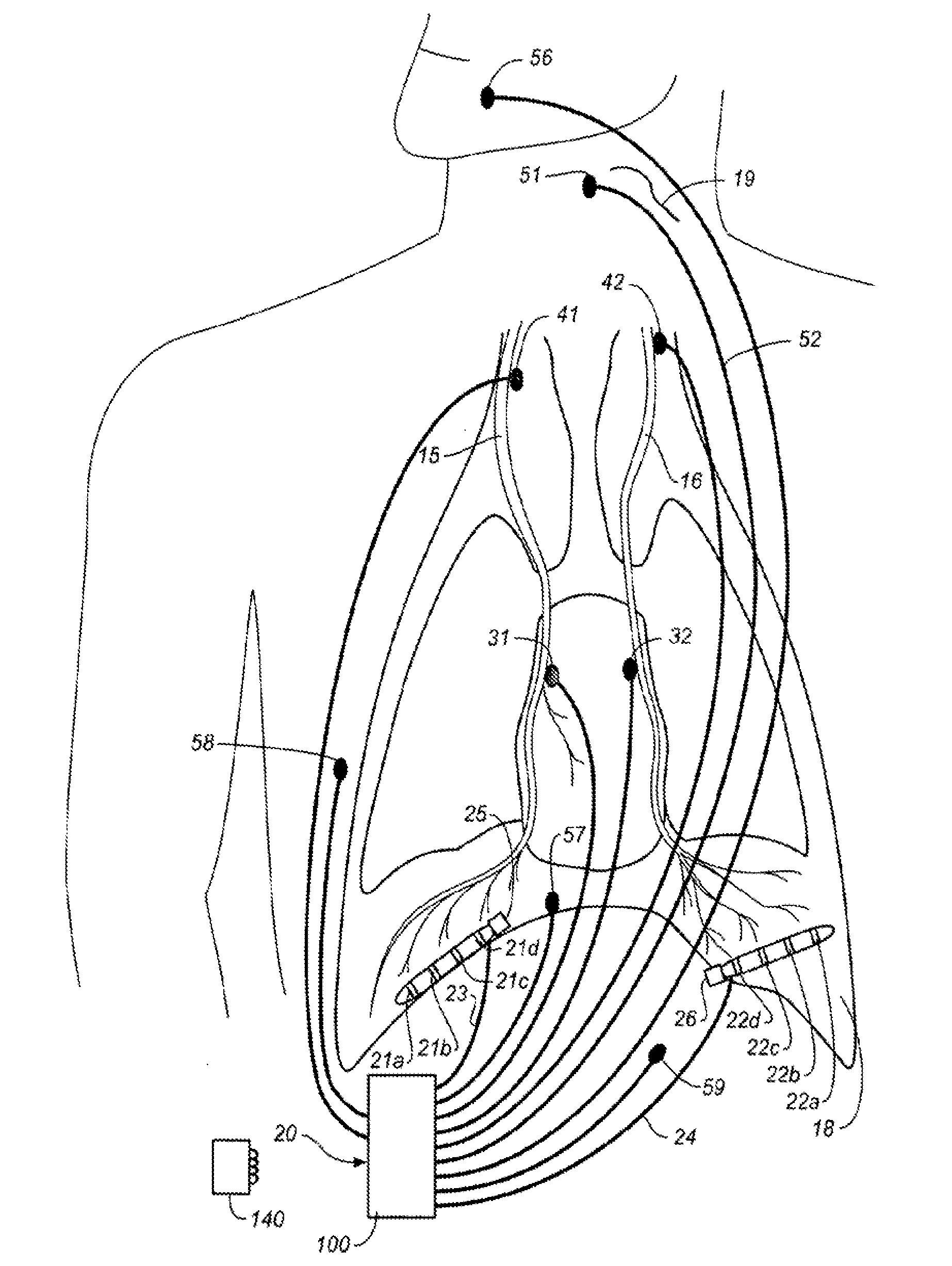
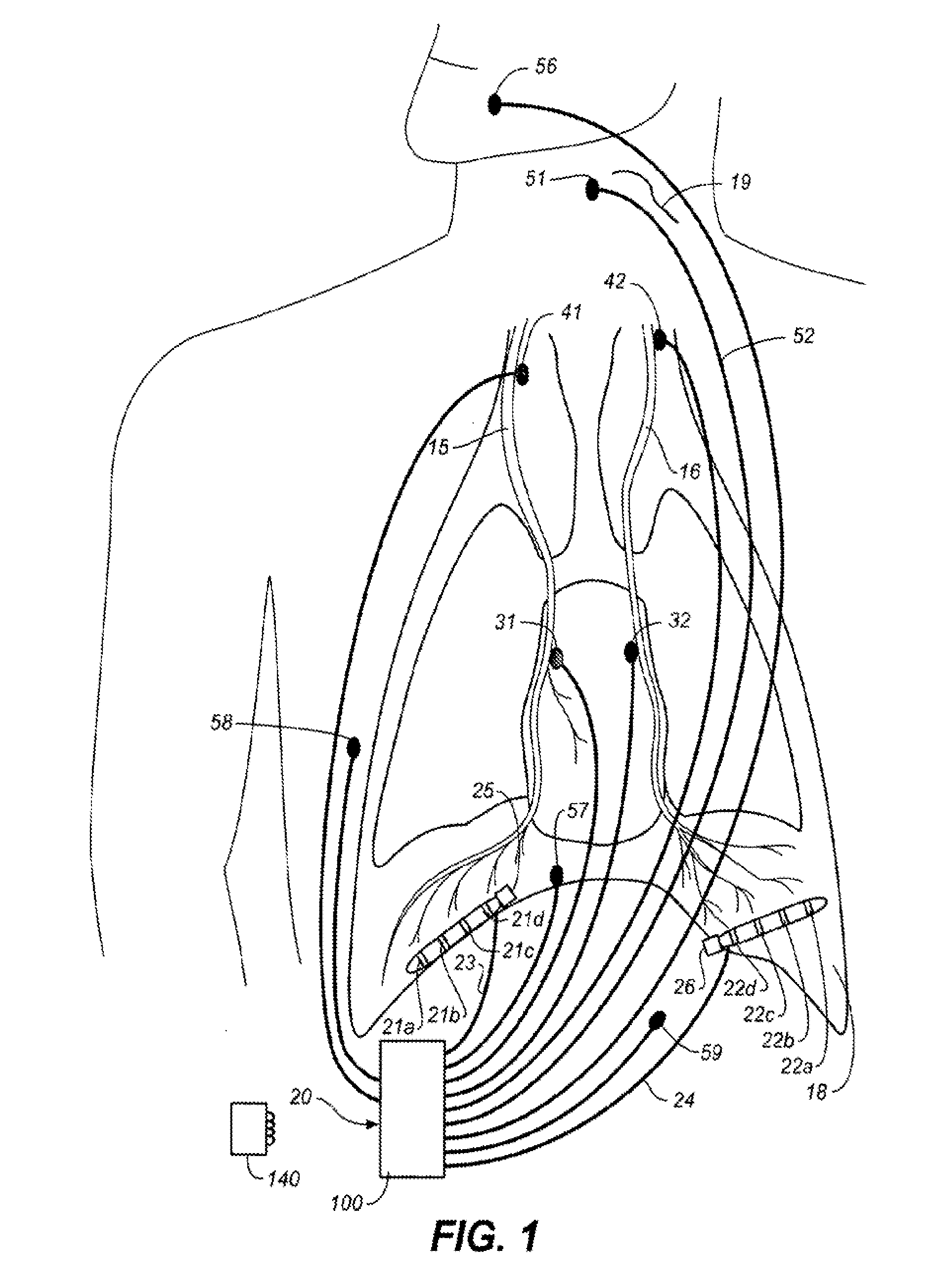
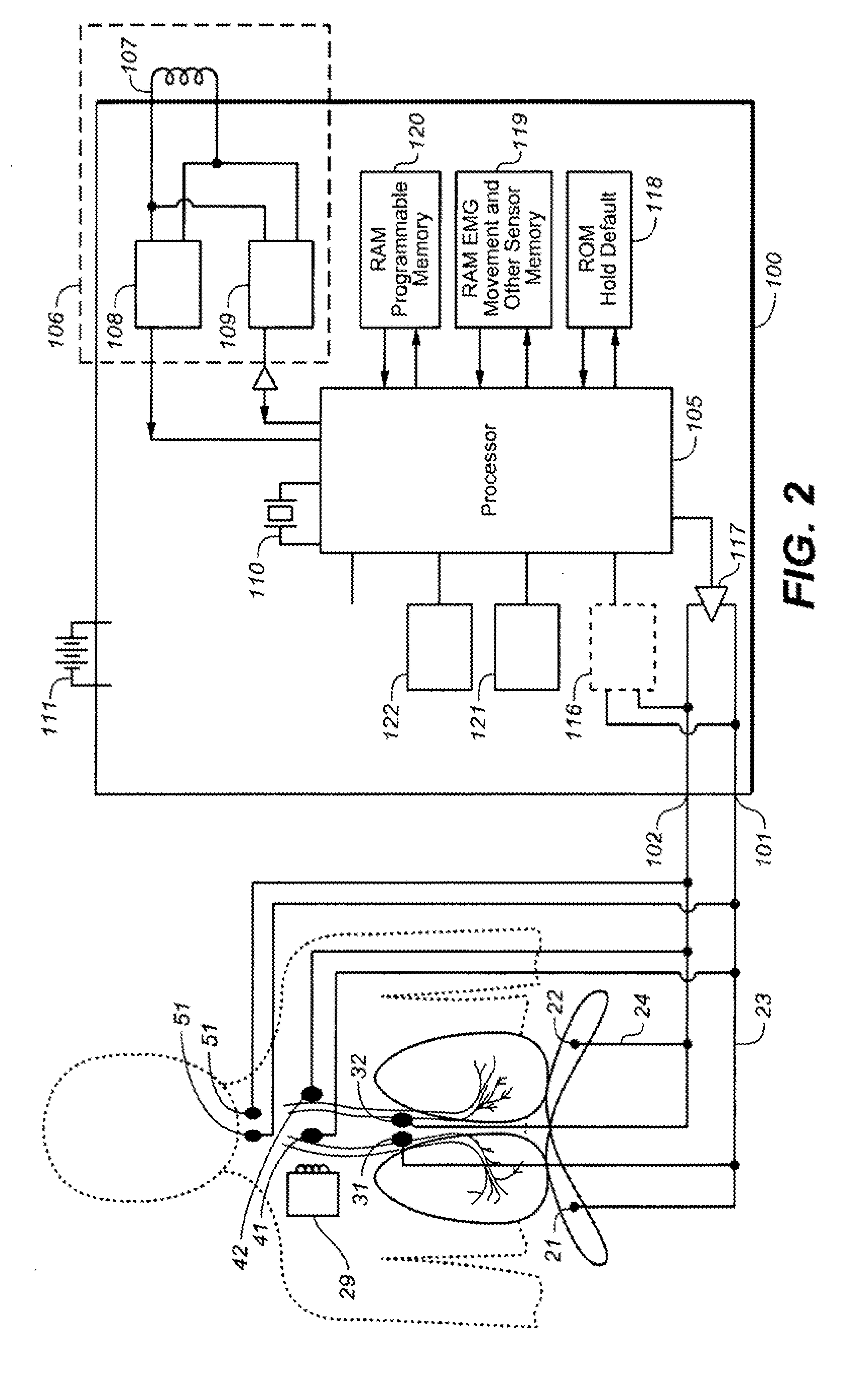
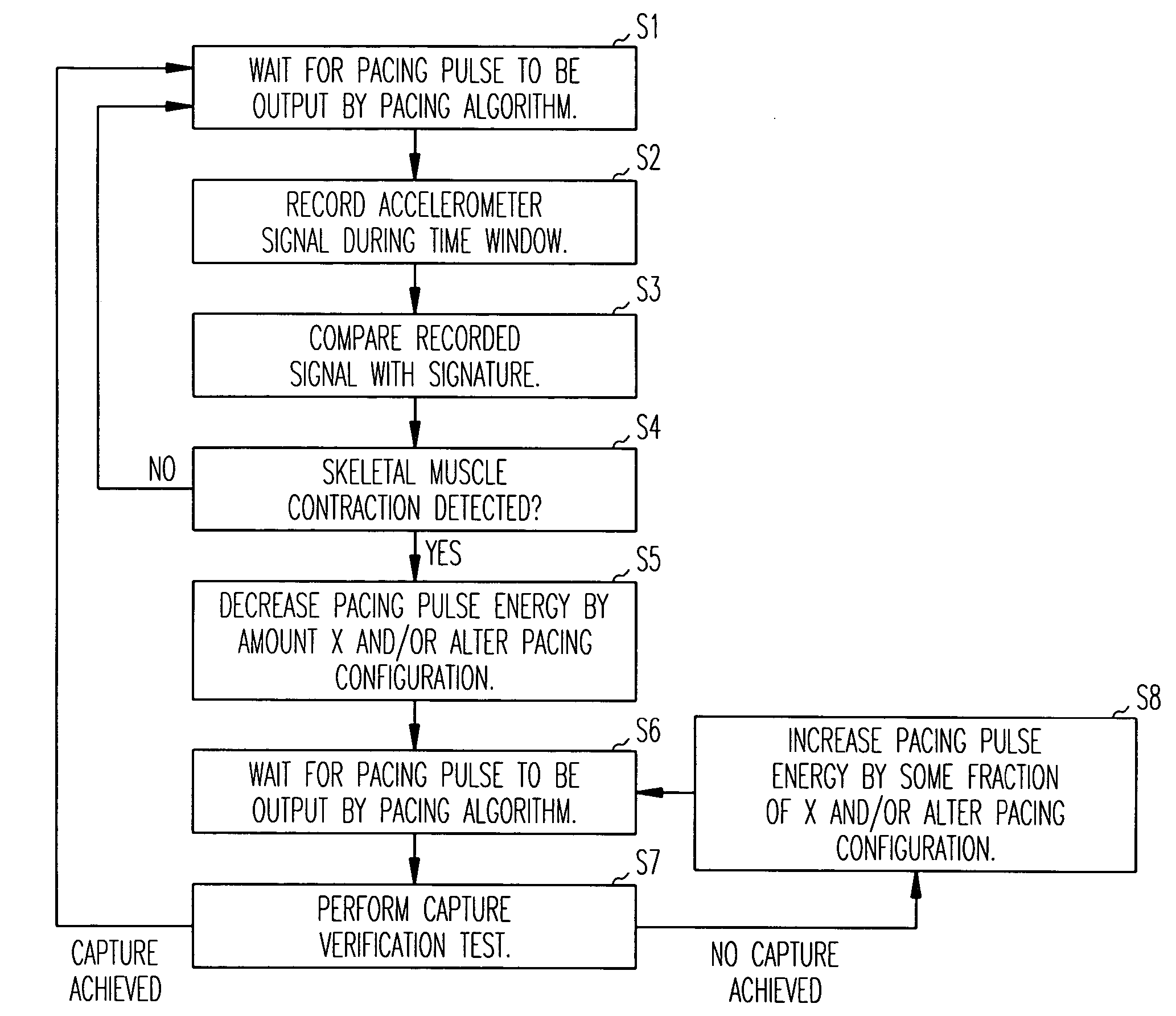
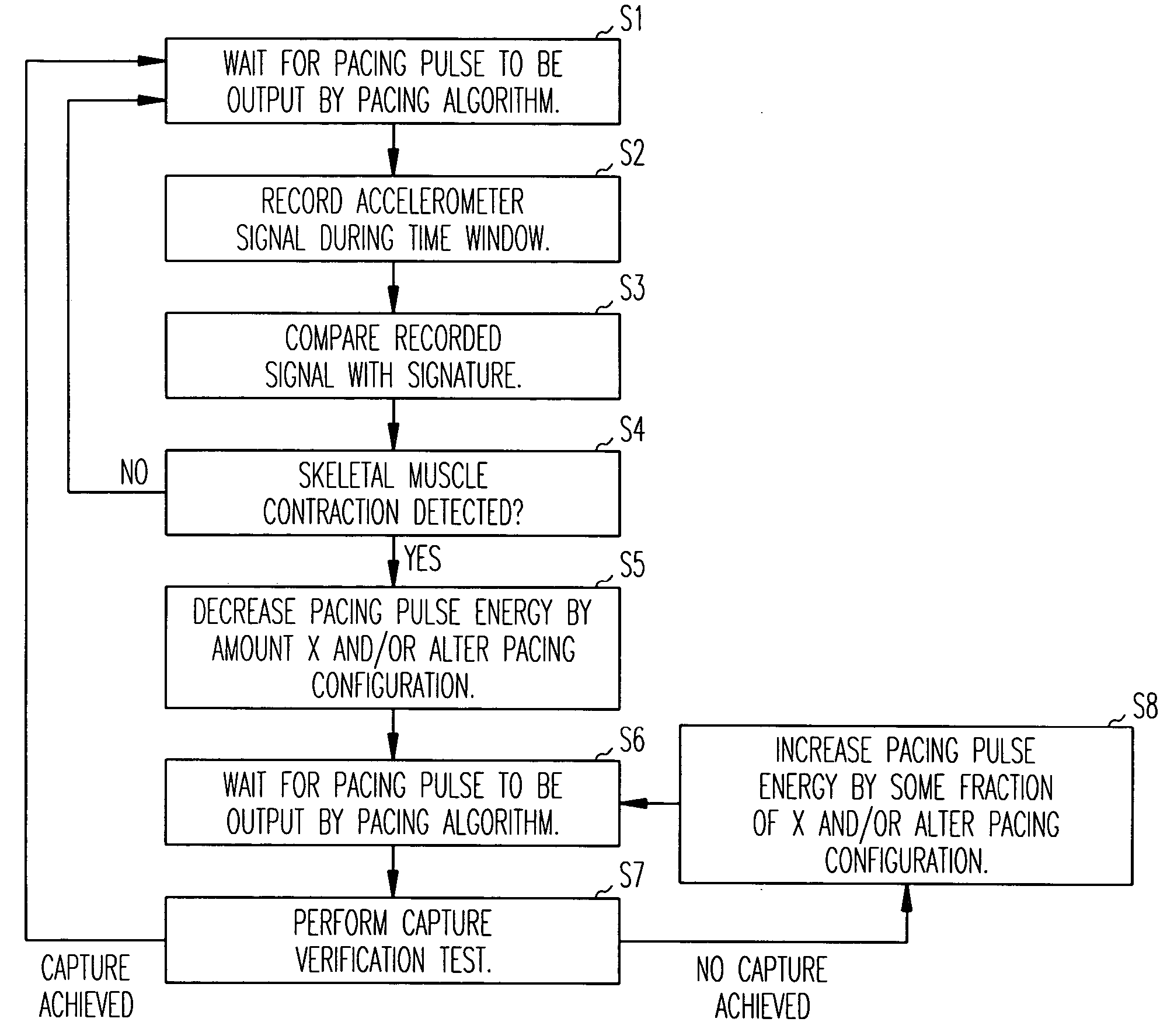
Method and apparatus for avoidance of phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac pacing
A cardiac rhythm management device in which an accelerometer is used to detect diaphragmatic or other skeletal muscle contraction associated with the output of a pacing pulse. Upon detection of diaphragmatic contraction, the device may be configured to automatically adjust the pacing pulse energy and / or pacing configuration.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
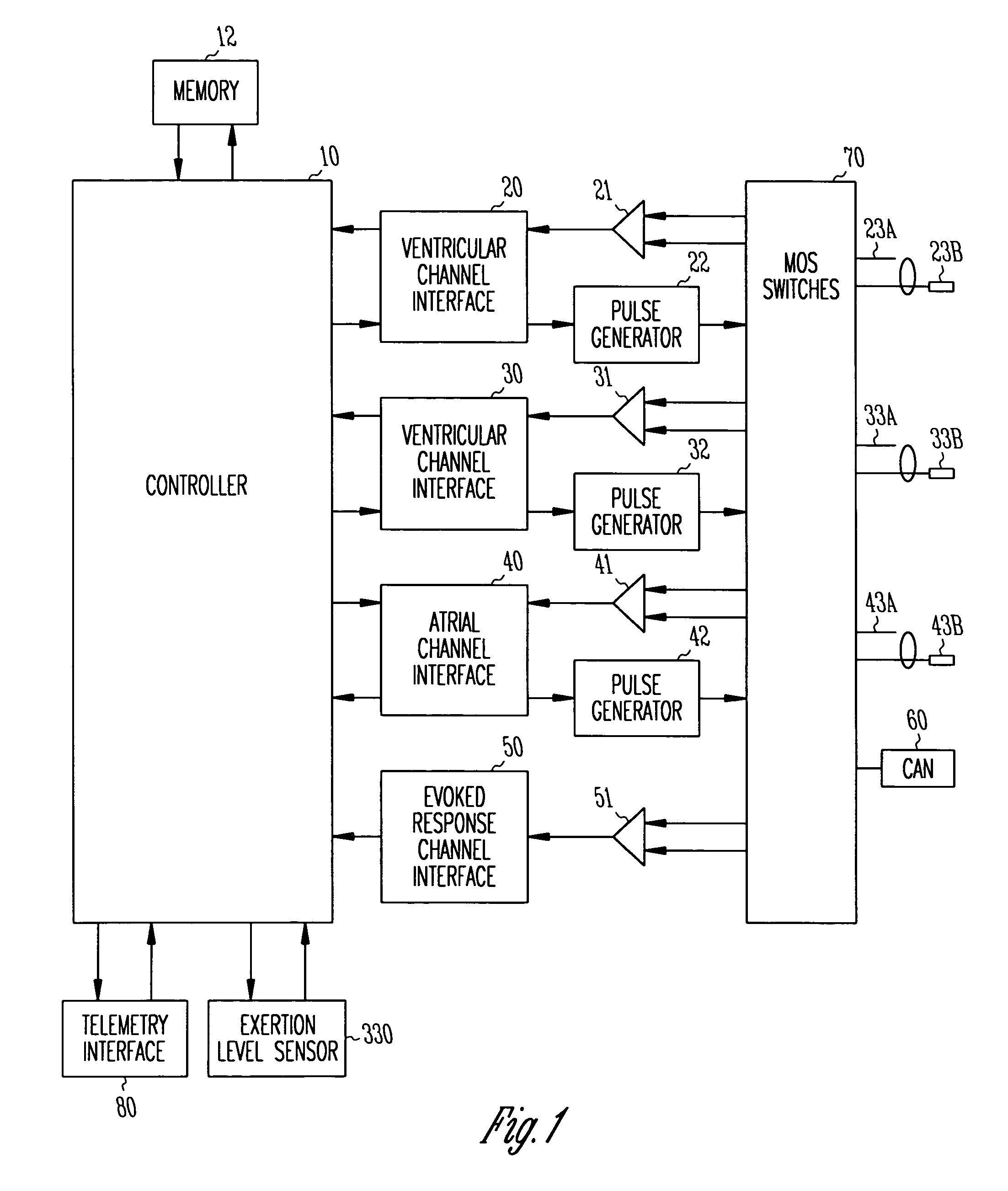
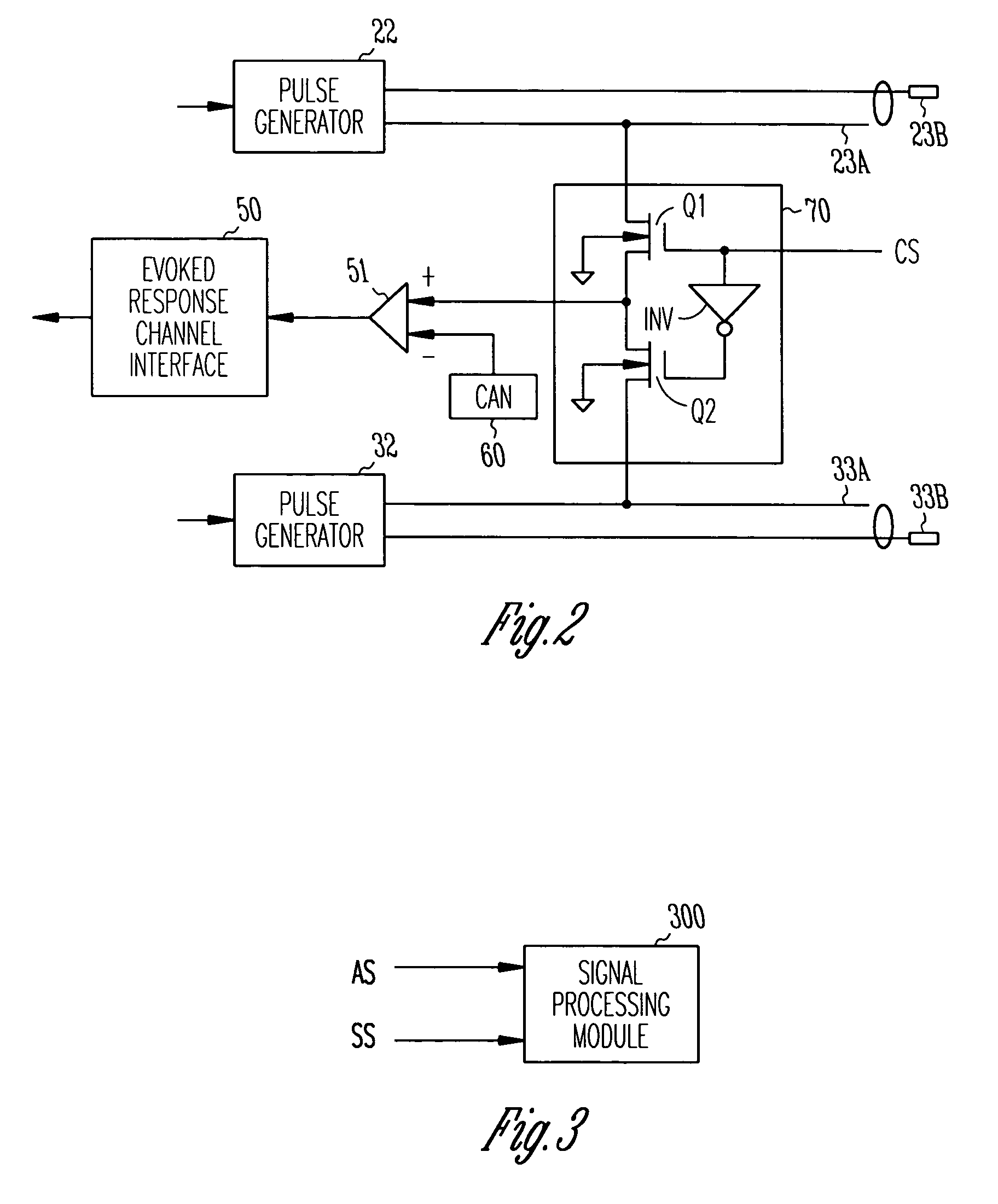
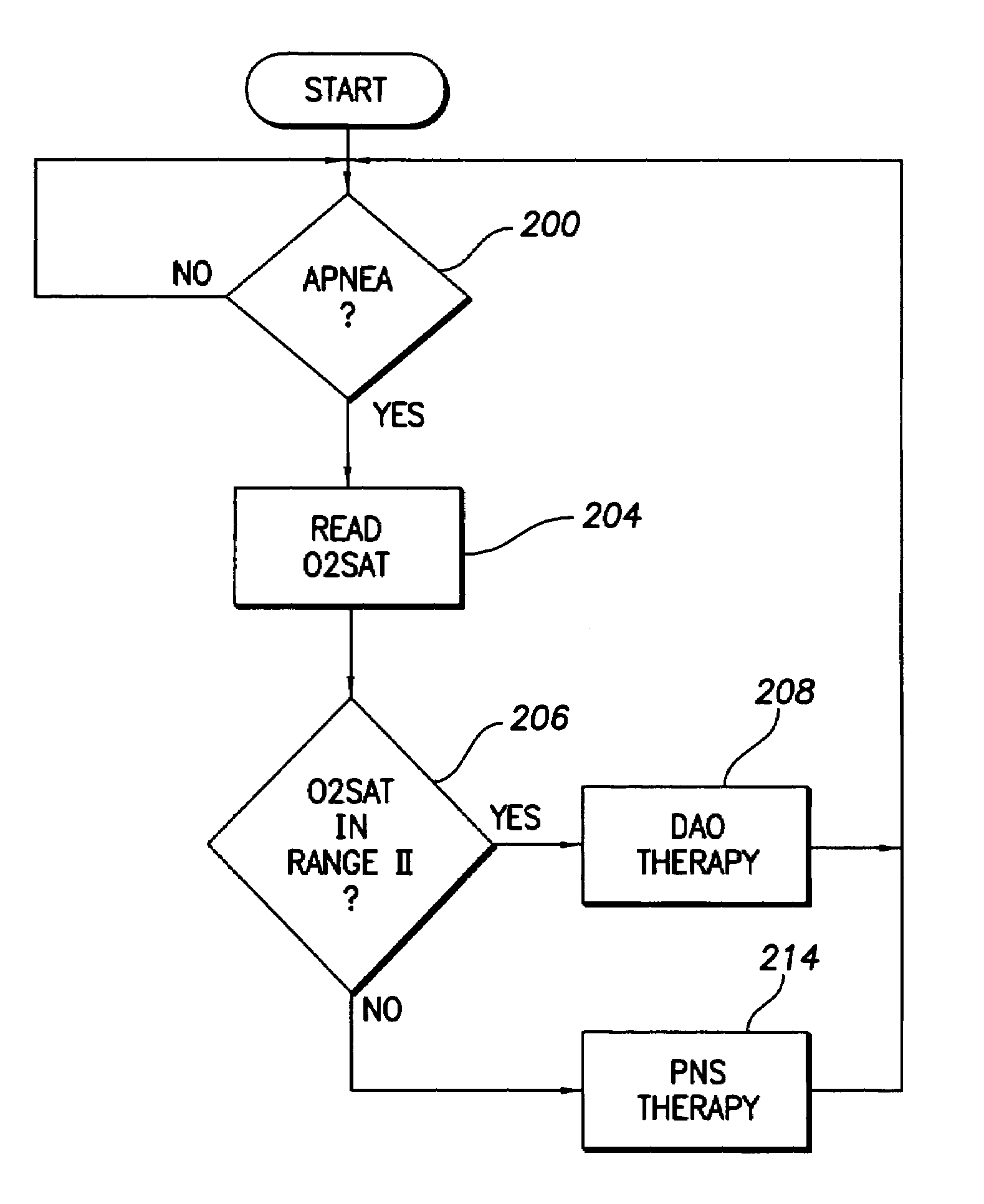
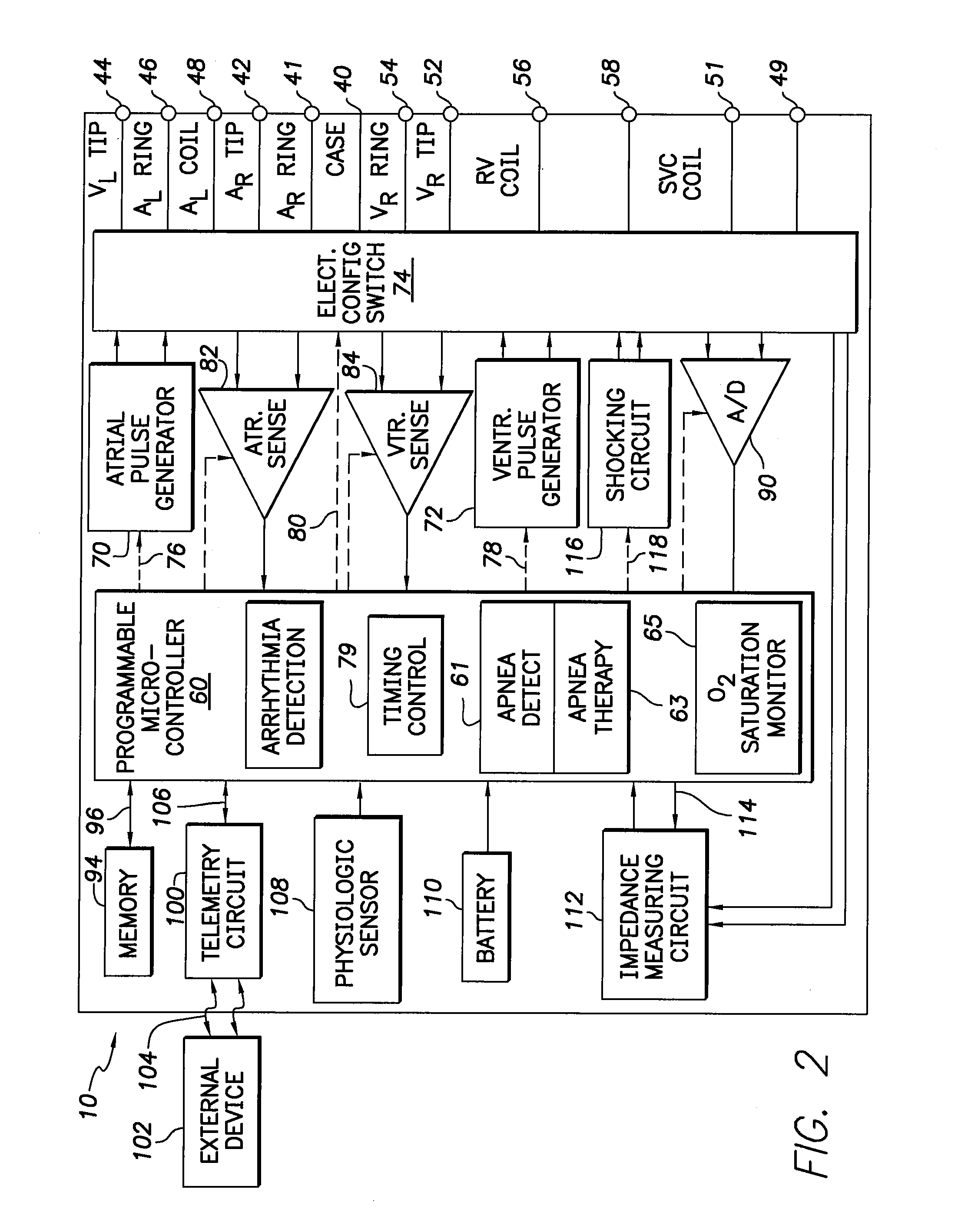
Implantable cardiac device with selectable tiered sleep apnea therapies and method
An implantable cardiac stimulation device treats apnea with either phrenic nerve stimulation pulses or cardiac stimulation pulses. The device includes an apnea detector that detects apnea of a patient, a blood oxygen saturation monitor that measures a blood oxygen saturation level of the patient responsive to detection of apnea, and a tiered therapy circuit that provides phrenic nerve stimulation pulses if the measured blood oxygen saturation level is within a first range and cardiac stimulation pulses if the measured blood oxygen saturation level is within a second range. The cardiac stimulation pulses are preferably provided in a DAO pacing mode.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
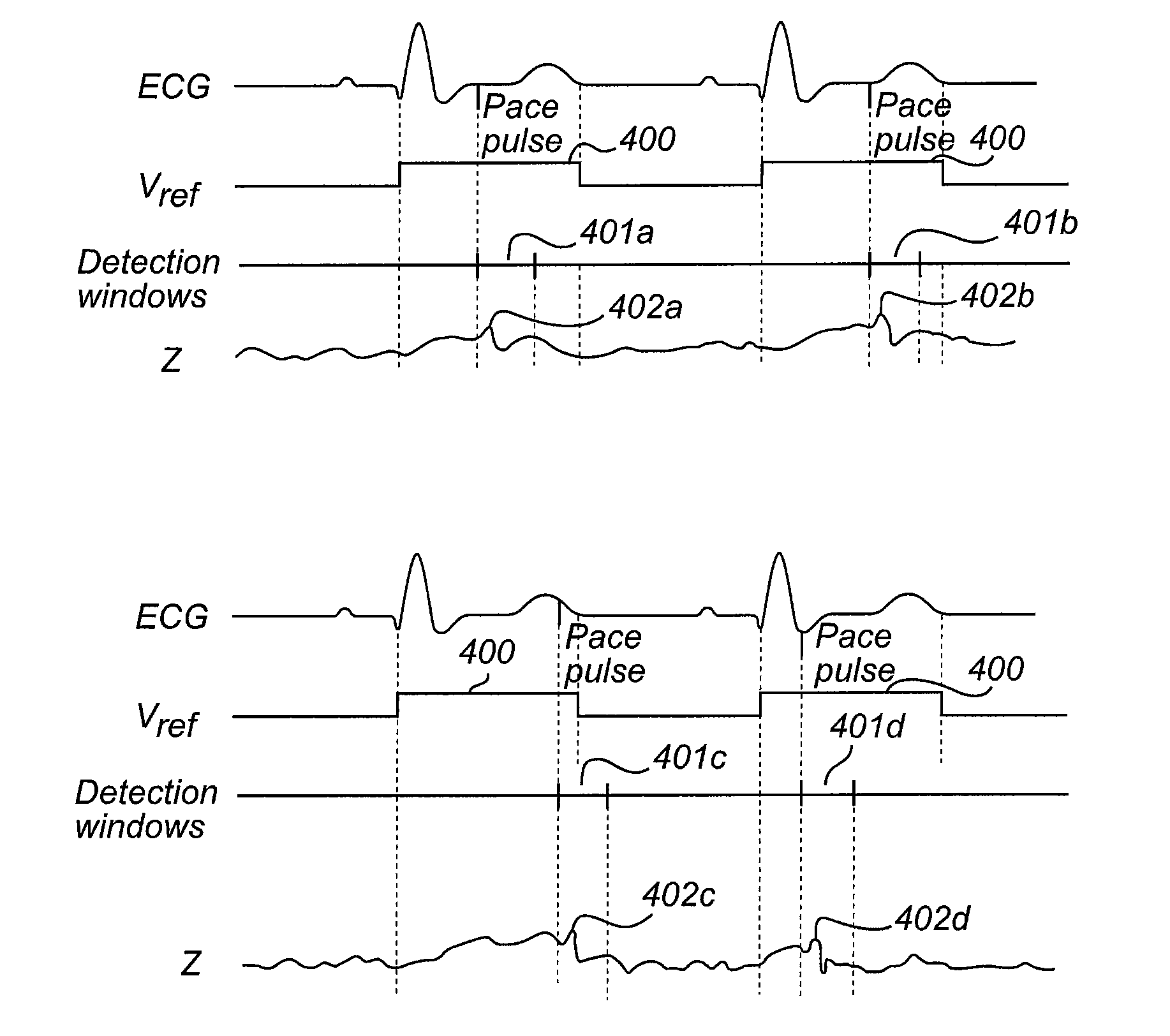
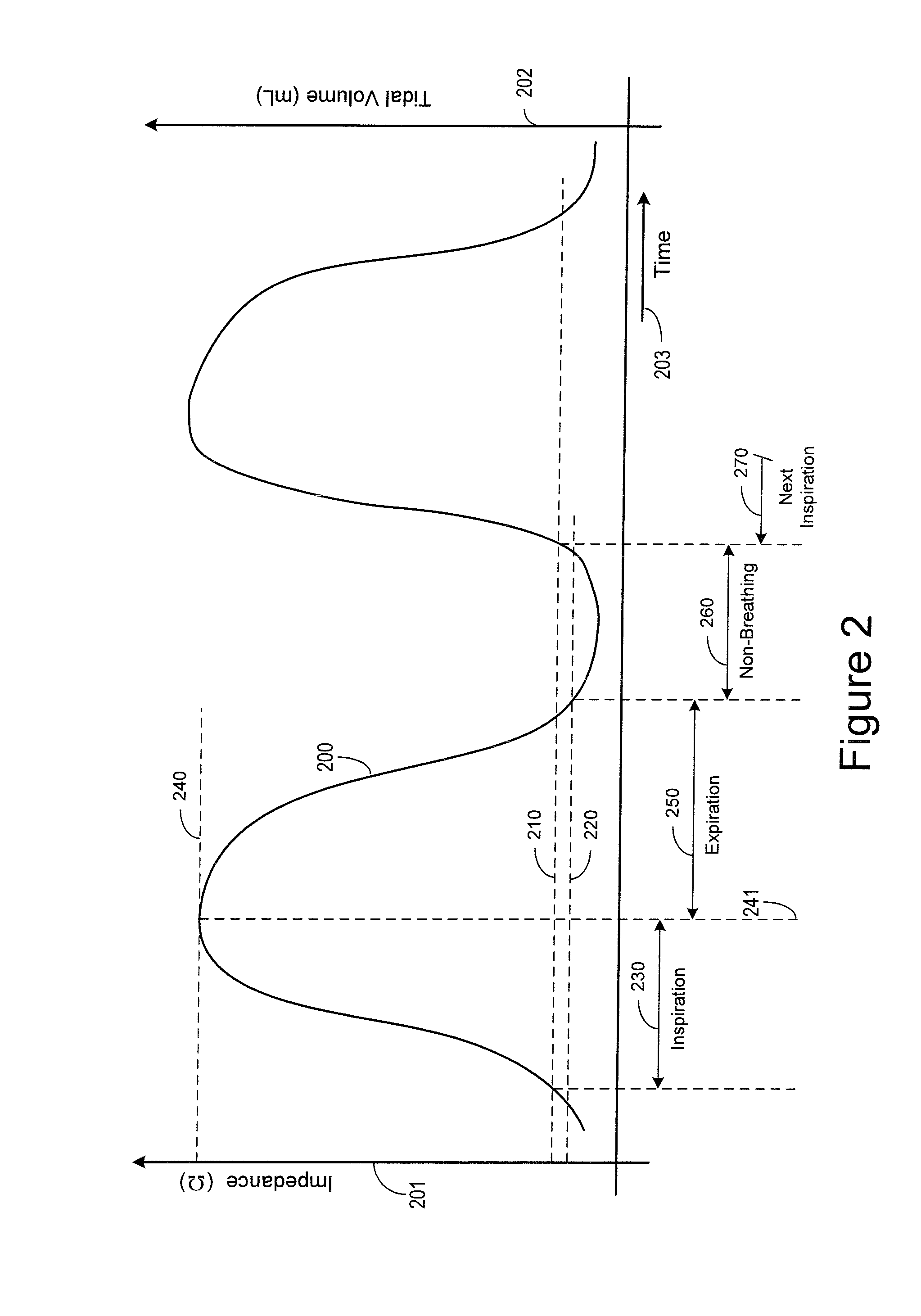
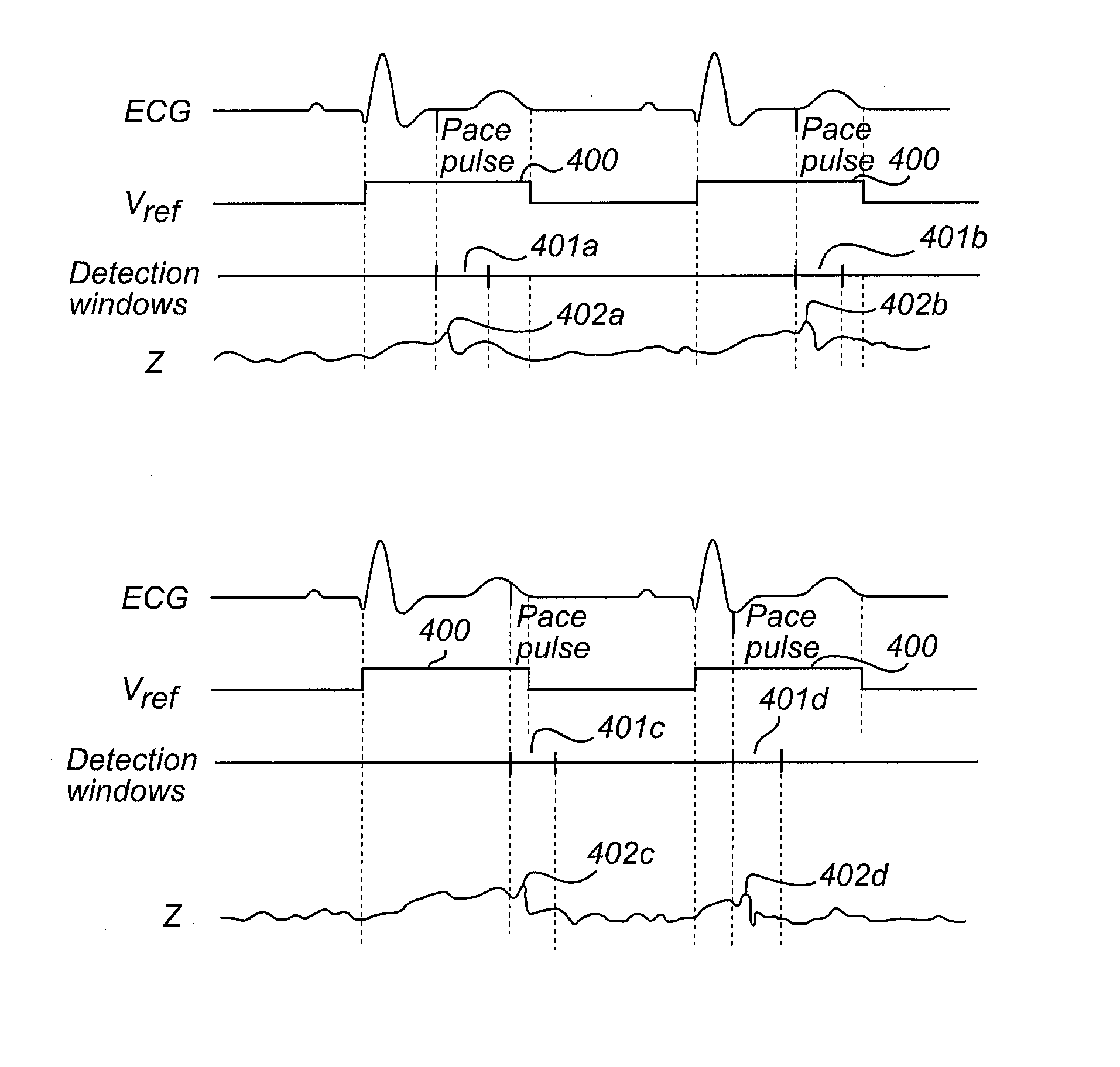
Baseline determination for phrenic nerve stimulation detection
Some method examples may include pacing a heart with cardiac paces, sensing a physiological signal for use in detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation, performing a baseline level determination process to identify a baseline level for the sensed physiological signal, and detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation using the sensed physiological signal and the calculated baseline level. Detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation may include sampling the sensed physiological signal during each of a plurality of cardiac cycles to provide sampled signals and calculating the baseline level for the physiological signal using the sampled signals. Sampling the sensed physiological signal may include sampling the signal during a time window defined using a pace time with each of the cardiac cycles to avoid cardiac components and phrenic nerve stimulation components in the sampled signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Implantable cardiac device and method for reduced phrenic nerve stimulation
Methods and devices for reducing phrenic nerve stimulation of cardiac pacing systems involve delivering a pacing pulse to a ventricle of a heart. A transthoracic impedance signal is sensed, and a deviation in the signal resulting from the pacing pulse may be used to determine phrenic nerve stimulation. Methods may further involve detecting the phrenic nerve stimulation from the pacing pulse by delivering two or more pacing pulse to the ventricle of the heart, and determining a temporal relationship. A pacing vector may be selected from the two or more vectors that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing voltage and / or pulse width may be selected that provides cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. In other embodiments, a pacing pulse width and a pacing voltage may be selected from a patient's strength-duration curve that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
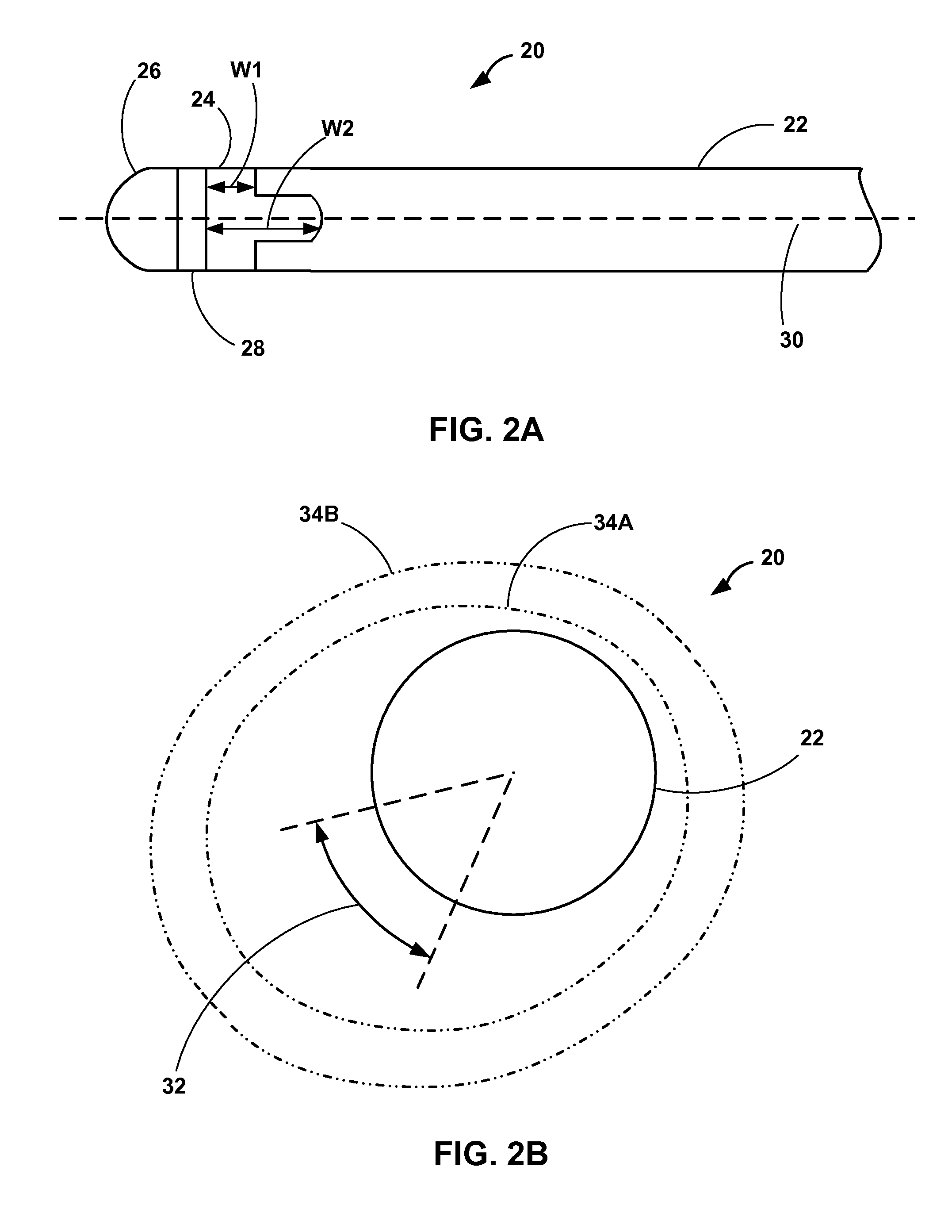
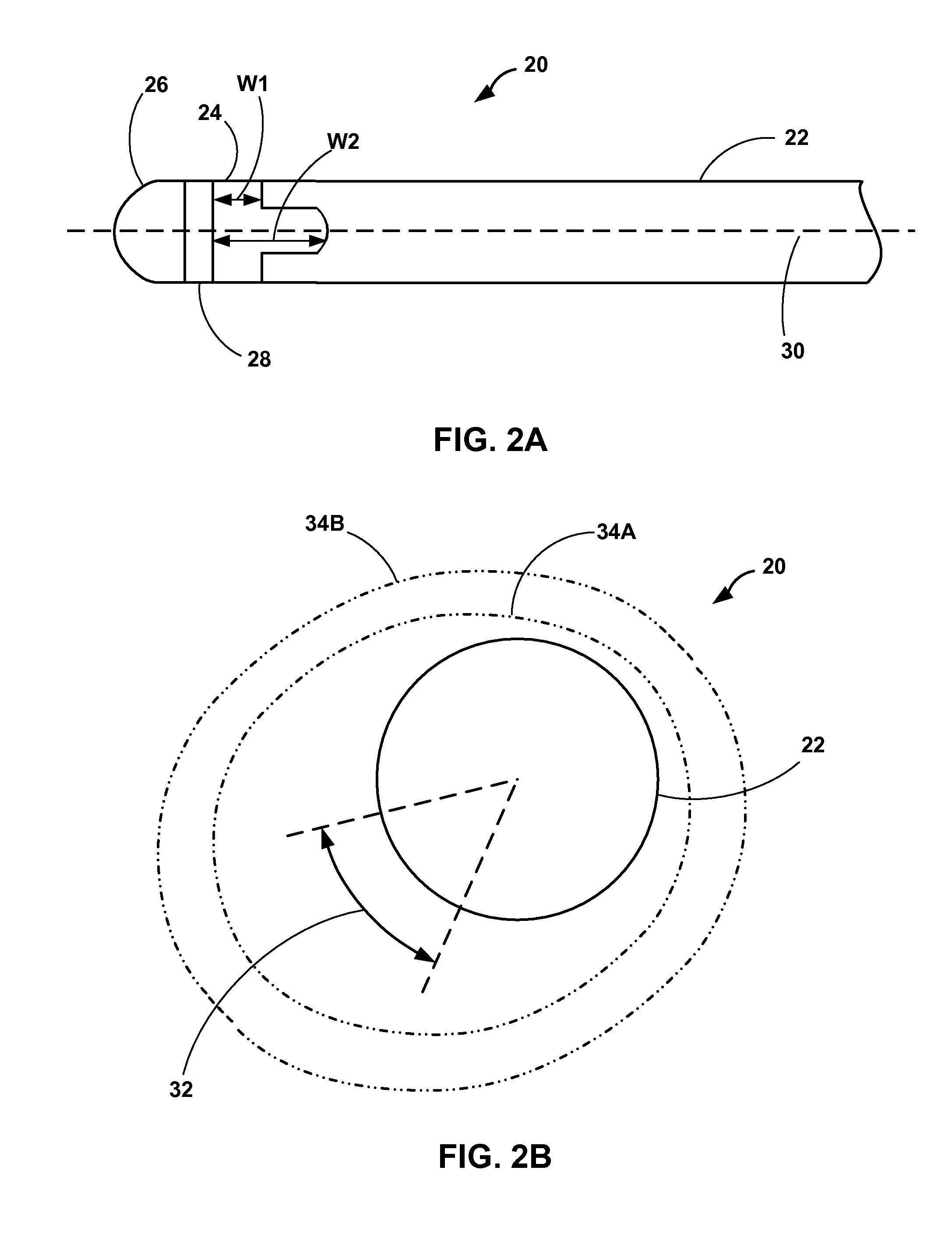
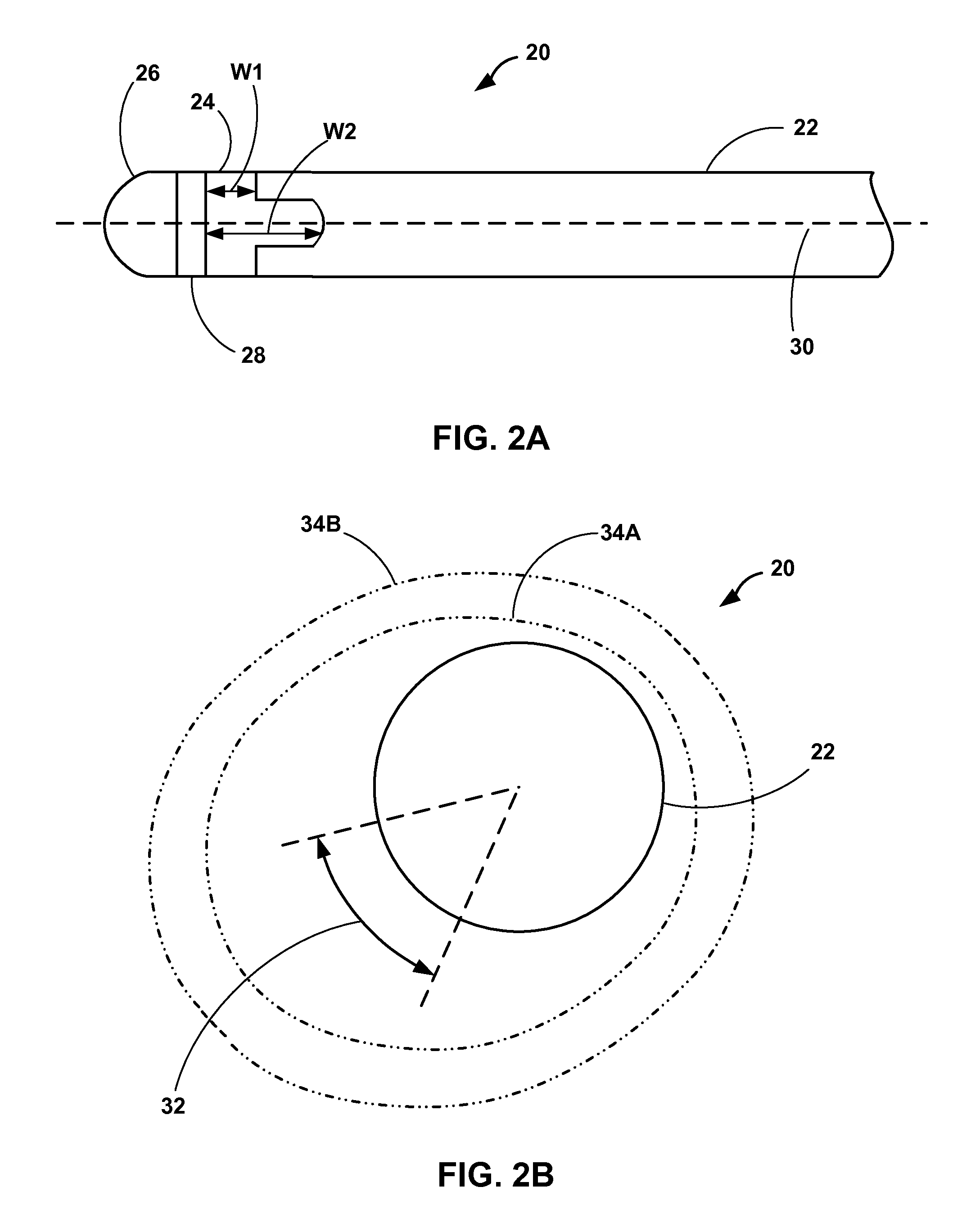
Implantable medical lead with biased electrode
This disclosure describes implantable medical leads that include a lead body and an electrode. A width of the electrode as measured along a longitudinal direction of the lead varies about the perimeter of the lead. The uneven width of the electrode may bias a stimulation field in a particular direction, e.g., a radial or transverse direction relative to the longitudinal axis of the lead. Electrodes with an uneven width may be useful for controlling the direction of propagation of the stimulation field in order to, for example, avoid phrenic nerve stimulation during LV pacing or neck muscle stimulation during vagal neurostimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
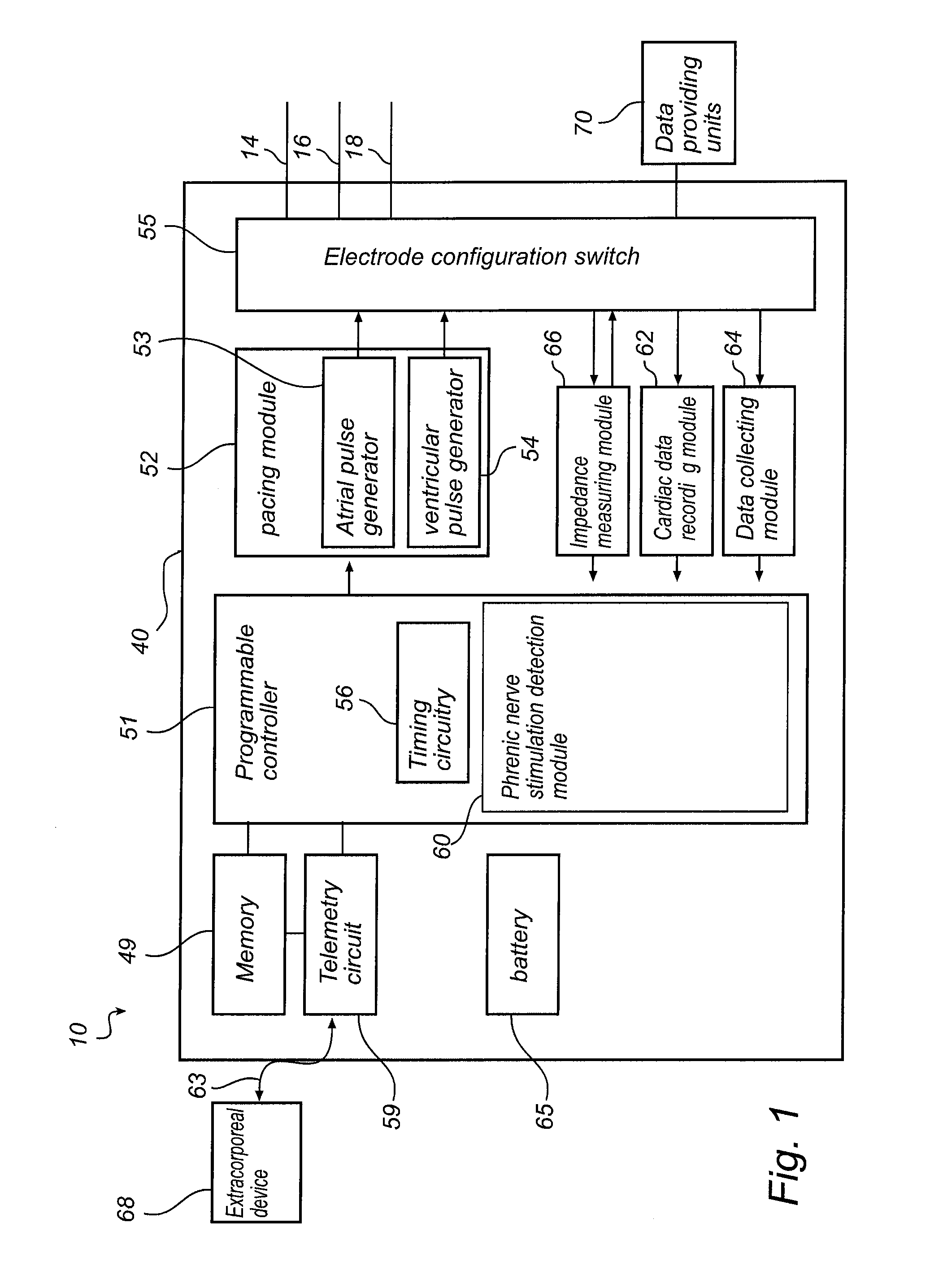
Detection and reduction of phrenic nerve stimulation
The present invention provides implantable medical devices for detecting phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing module is configured to deliver pacing pulses having a predetermined pulse amplitude and / or width within the refractory period of the left ventricle. The pacing pulses are repeatedly delivered during a number of cardiac cycles, and the pacing pulses are delivered at different delays relative to an onset of the refractory period of the left ventricle in different cardiac cycles. An impedance measurement module is configured to measure impedance signals in time windows synchronized with the delivery of pacing pulses in the refractory period of the left ventricle. A phrenic nerve stimulation, PNS, detection module is configured to gather at least one impedance signal from each time window, create aggregated impedance signals using the impedance signals from the different time windows, and analyze the aggregated impedance signals to detect PNS.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Therapeutic diaphragm stimulation device and method
ActiveUS8140164B2Increase volumeCapacity remains stableElectrotherapyElectromyographyDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
Implantable medical lead with biased electrode
This disclosure describes implantable medical leads that include a lead body and an electrode. A width of the electrode as measured along a longitudinal direction of the lead varies about the perimeter of the lead. The uneven width of the electrode may bias a stimulation field in a particular direction, e.g., a radial or transverse direction relative to the longitudinal axis of the lead. Electrodes with an uneven width may be useful for controlling the direction of propagation of the stimulation field in order to, for example, avoid phrenic nerve stimulation during LV pacing or neck muscle stimulation during vagal neurostimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Therapeutic diaphragm stimulation device and method
InactiveUS20120158091A1Steady breathingReduce and avoid arousal eventElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
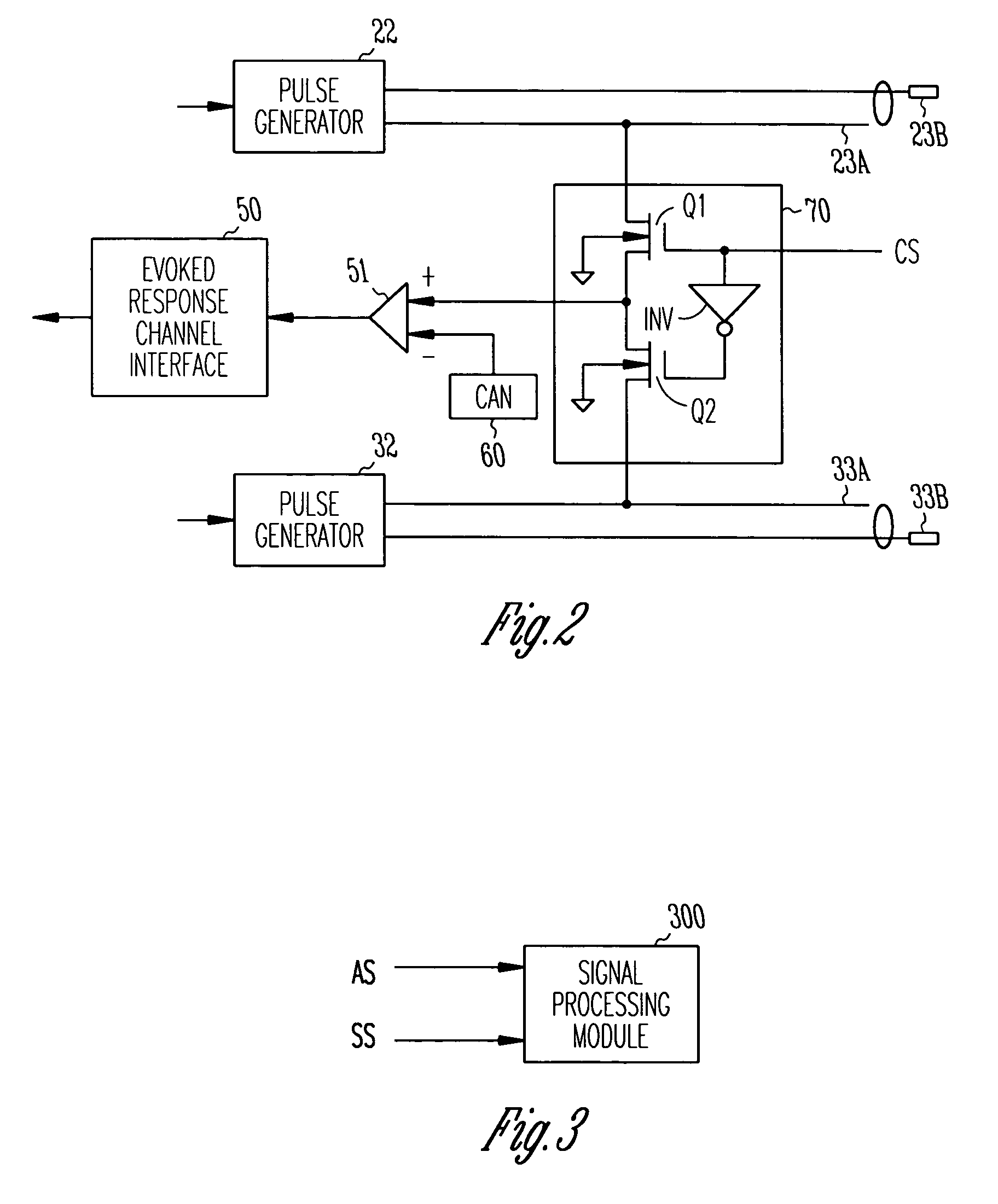
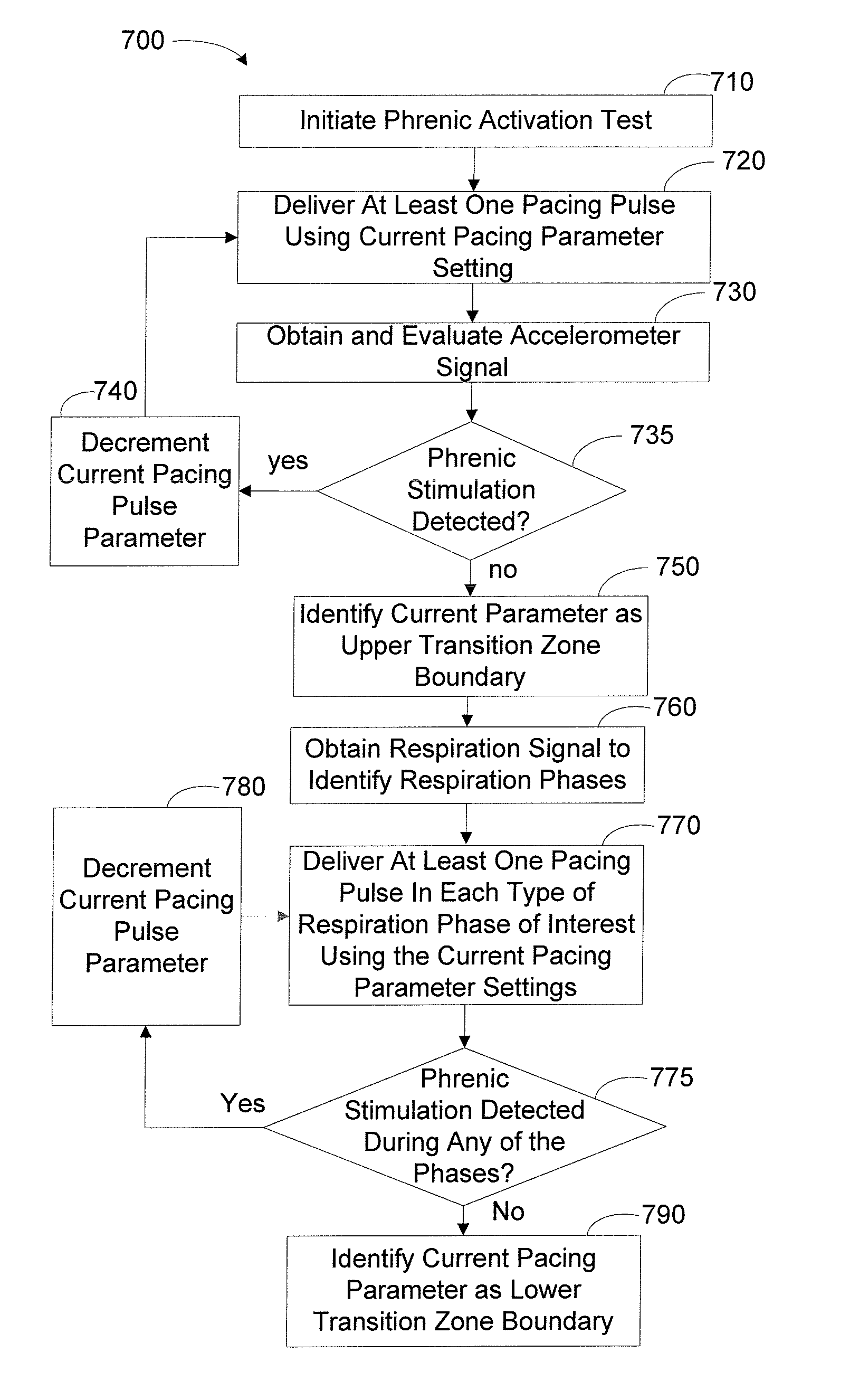
Method and Apparatus for Phrenic Nerve Activation Detection with Respiration Cross-Checking
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Therapeutic diaphragm stimulation device and method
InactiveUS20150034081A1Increase volumeCapacity remains stableRespiratorsElectrotherapyDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
Devices and methods for reducing intrathoracic pressure
ActiveUS20170143973A1Reduce rateReduce high blood pressureElectrotherapyArtificial respirationIntrathoracic usePulmonary artery
Devices and methods are provided to treat acute and chronic heart failure by using one or more implantable or non-implantable sensors along with phrenic nerve stimulation to reduce intrathoracic pressure and thereby reduce pulmonary artery, atrial, and ventricular pressures leading to reduced complications and hospitalization.
Owner:RMX
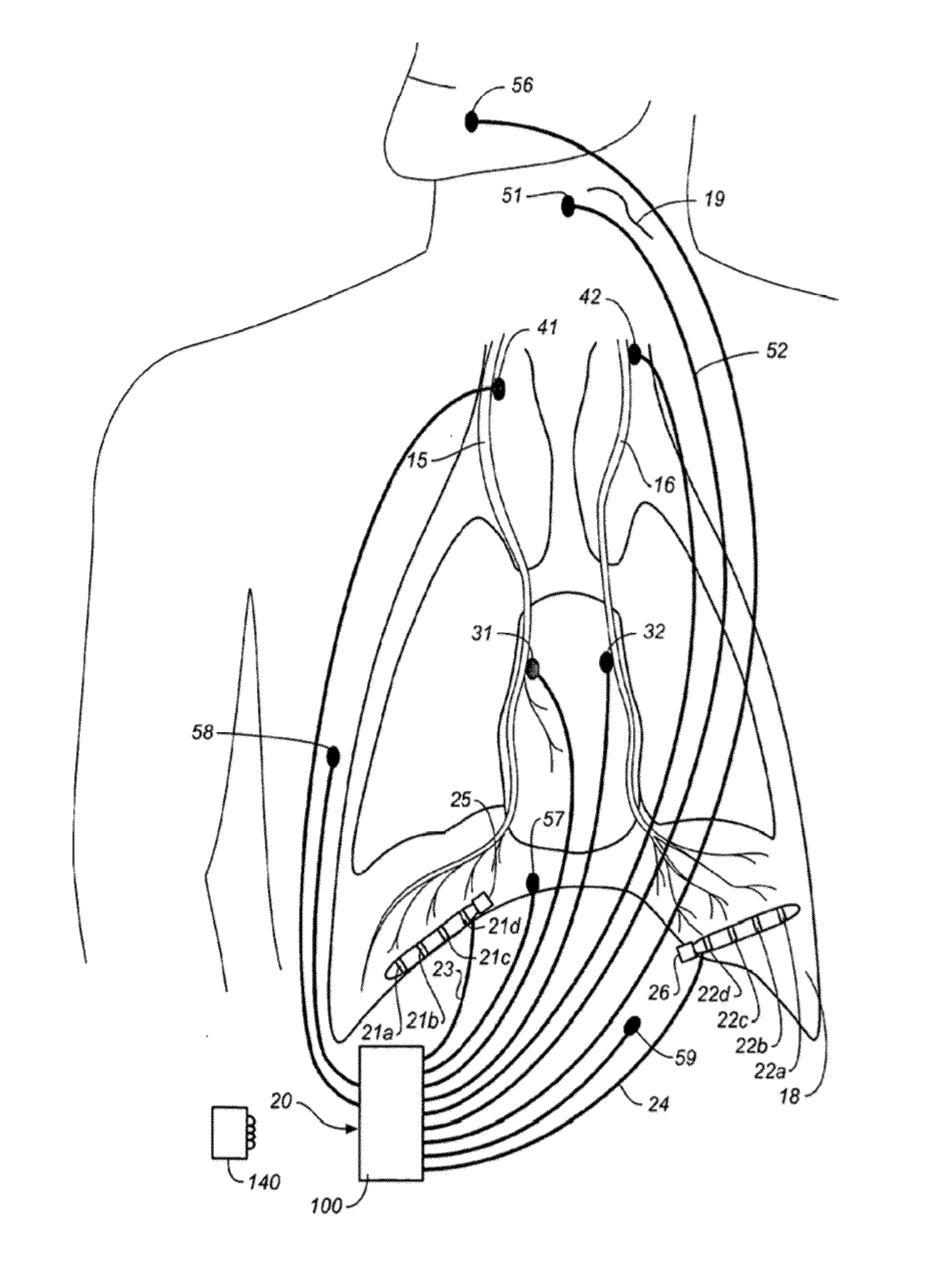
Method and apparatus for using phonomyography to prevent nerve damage during a medical procedure
InactiveUS20140358135A1Preventing phrenic nerve injuryReducing ablation energyElectrotherapyCatheterMedical treatmentMedical procedure
A method and system for preventing phrenic nerve injury during a cardiac ablation procedure. The method generally includes stimulating a phrenic nerve with a pacing electrode at a location proximate a target treatment location, ablating tissue at the target treatment location with a treatment element, obtaining a heart audio signal with an audio sensor positioned proximate the target treatment location, and determining whether phrenic nerve stimulation (PNS) is present based as least in part on the obtained heart audio signal. A processor may be used to compare an amplitude of the obtained heart audio signal to a predetermined threshold amplitude. The processor may determine that PNS is present if the amplitude of the obtained audio signal is greater than the threshold amplitude. If PNS is present, ablation of the tissue may continue at the current or greater energy level and / or at the current treatment location without injuring the phrenic nerve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC CRYOCATH LP
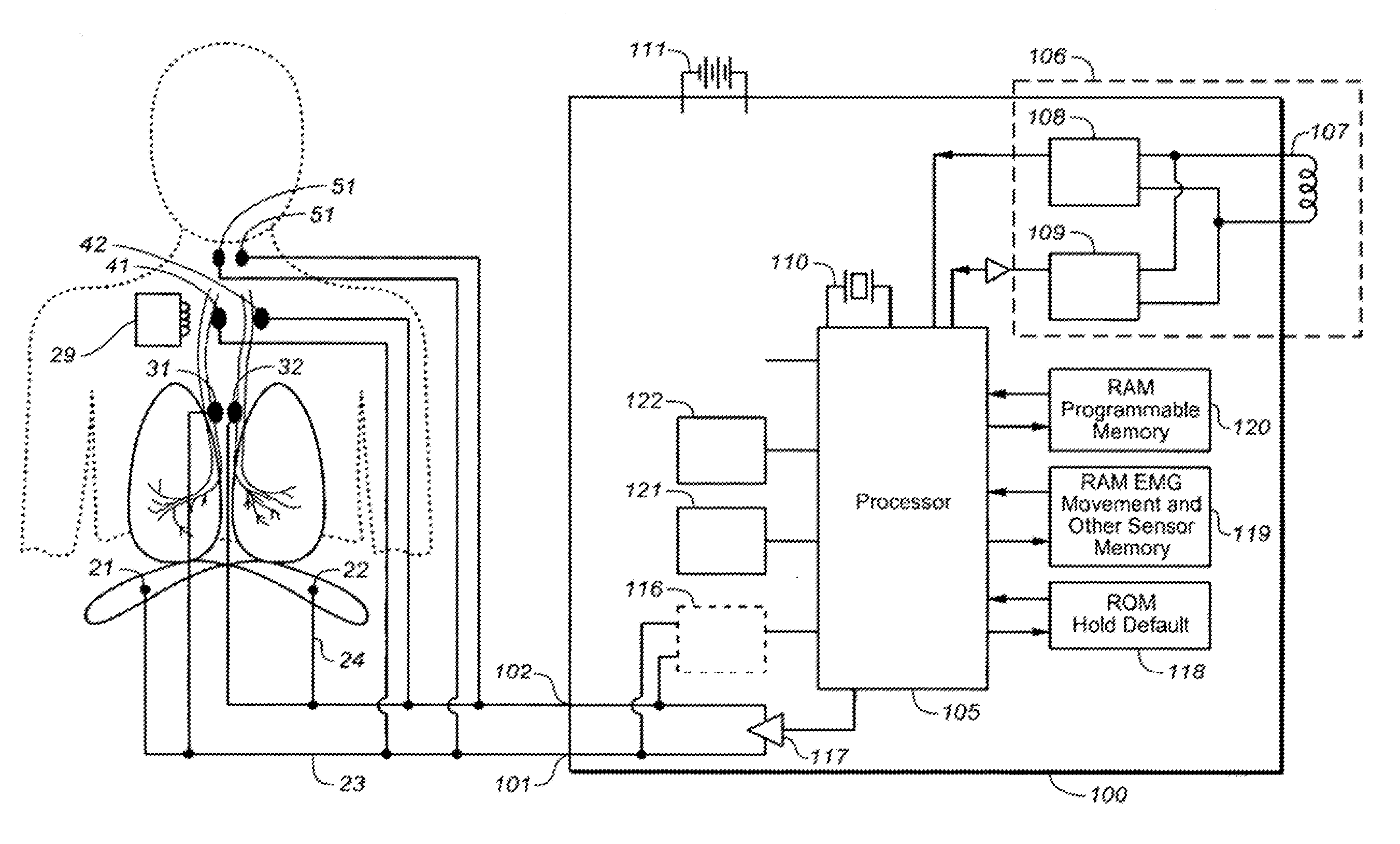
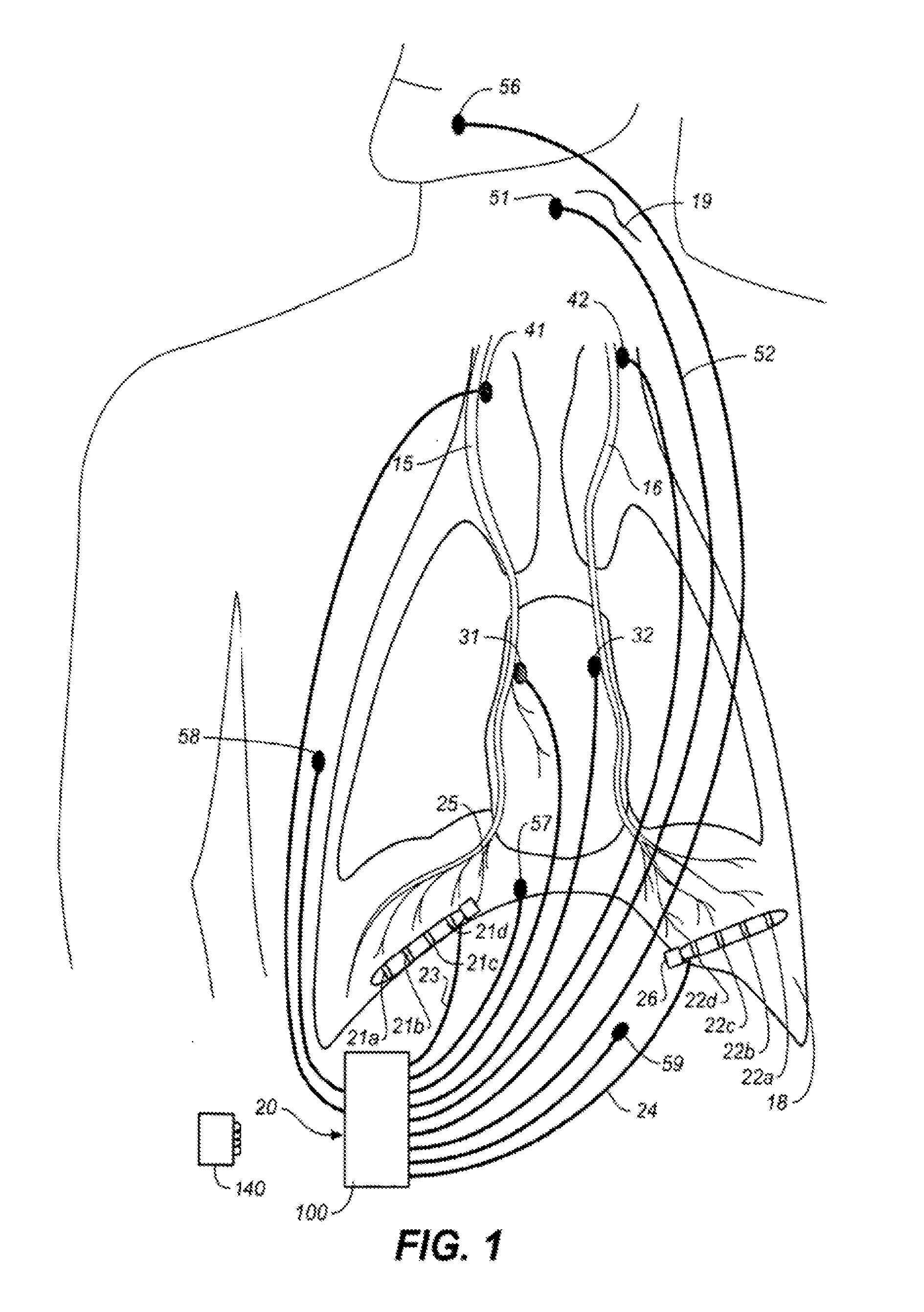
Comprehensive feedback type pulmonary rehabilitation assessment treatment instrument
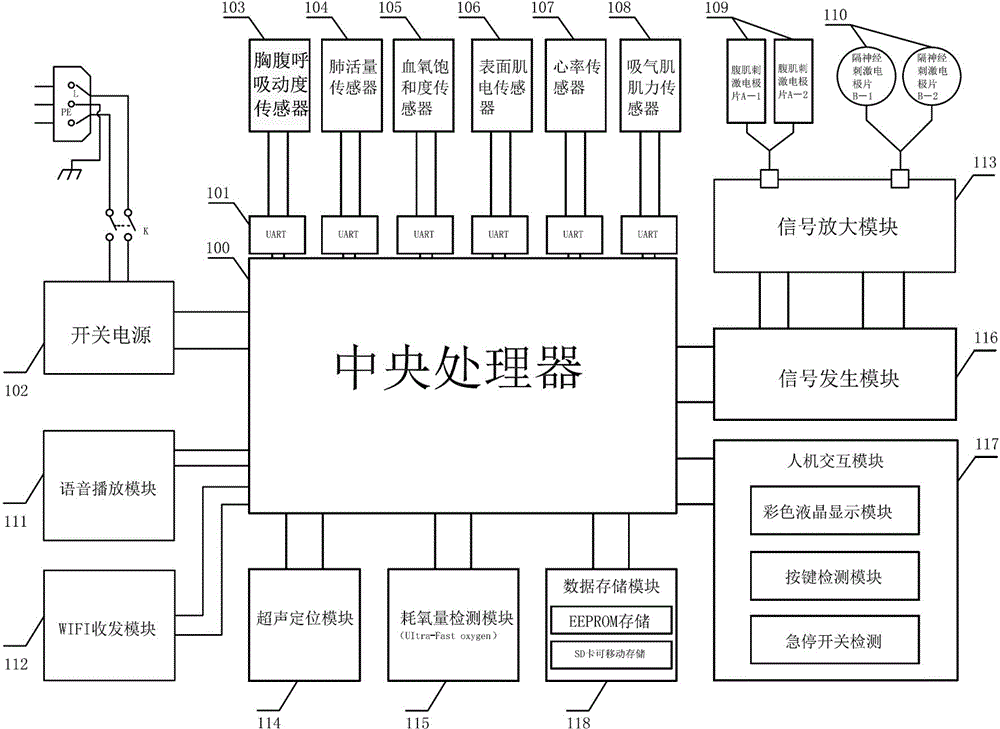
ActiveCN104939815AReal-time human-computer interactionReal-time data display for synchronous real-time human-computer interactionDiagnostic signal processingGymnastic exercisingUniversal asynchronous receiver/transmitterVital capacity
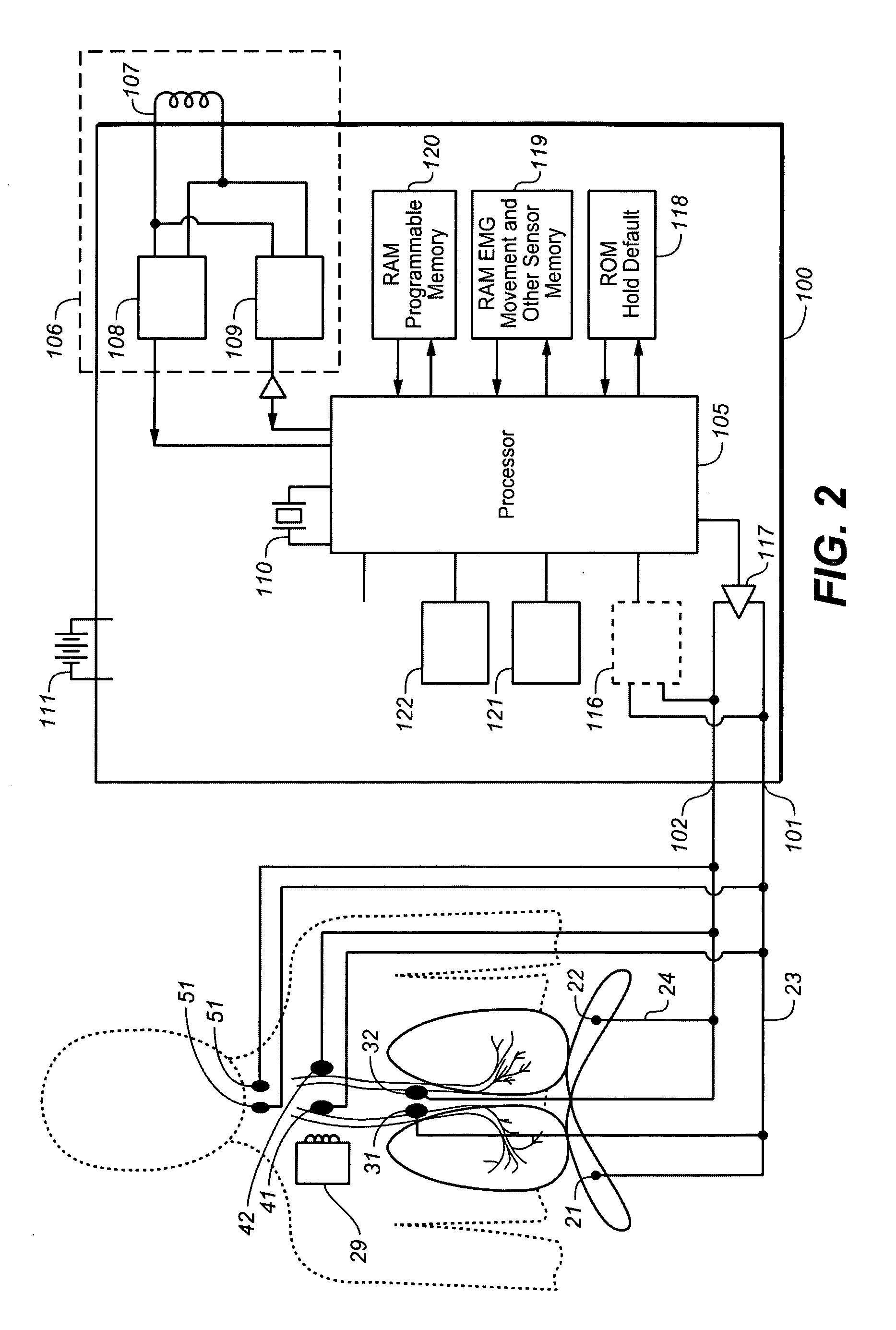
The invention relates to a comprehensive feedback type pulmonary rehabilitation assessment treatment instrument. The instrument comprises a central processor (100), a UART (universal asynchronous receiver / transmitter), a switching power supply (102), a thoracoabdominal breathing movement sensor (103), a vital capacity sensor (104), a blood oxygen saturation degree sensor (105), a surface myoelectricity sensor (106), a heart rate sensor (107), an inspiratory muscle force sensor (108), a signal generation module (116), a signal amplification module (113), an abdominal muscle stimulation electrode (109), a phrenic nerve stimulation electrode (110), a voice playing module (111), a WIFI (wireless fidelity) transceiving module (112), an ultrasonic positioning module (114), an oxygen consumption detection module (115), a man-machine interaction module (117) and a data storage module (118). The sensors of the instrument are used for monitoring various indexes including breathing, circulation, myoelectricity and the like respectively; the sensors are independently or unitedly used for various feedback treatment and also sequential low-frequency current stimulation on phrenic nerves on the neck and abdominal muscles, and a patient is trained to master correct and effective breathing movement. Various data are displayed and processed synchronously in real time, so that man-machine interaction is more convenient and more efficient.
Owner:张鸣生
Method and apparatus for avoidance of phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac pacing
A cardiac rhythm management device in which an accelerometer is used to detect diaphragmatic or other skeletal muscle contraction associated with the output of a pacing pulse. Upon detection of diaphragmatic contraction, the device may be configured to automatically adjust the pacing pulse energy and / or pacing configuration.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for phrenic nerve activation detection with respiration cross-checking
The present invention concerns phrenic nerve activation detection algorithms for characterization of phrenic nerve activation and phrenic nerve activation avoidance in cardiac pacing therapy.Various embodiments concern receiving a respiration signal indicative of respiratory activity of the patient, identifying respiratory phases based on the respiration signal, delivering cardiac pacing pulses within each of the identified respiratory phases, receiving a phrenic nerve activation signal indicative of activation of the patient's phrenic nerve, analyzing the phrenic nerve stimulation signal to determine if one or more of the pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient, and determining if at least one of the delivered pacing pulses activated the phrenic nerve of the patient based on the phrenic nerve activation signal indicating activation of the patient's phrenic nerve associated with delivery of the at least one cardiac pacing pulse.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Detection and reduction of phrenic nerve stimulation
ActiveUS8532774B1Undesired attenuationImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleTime windows
The present invention provides methods for detecting phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing module is instructed to deliver pacing pulses having a predetermined pulse amplitude and / or width within the refractory period of the left ventricle. The pacing pulses are repeatedly delivered during a number of cardiac cycles and wherein the pacing pulses are delivered at different delays relative to an onset of the refractory period of the left ventricle in different cardiac cycles. Impedance signals are measured in time windows synchronized with the delivery of pacing pulses in the refractory period of the left ventricle using at least one electrode configuration. At least one impedance signal is gathered from each time window, aggregated impedance signals are created using the impedance signals from the different time windows, and the aggregated impedance signals are analyzed to detect PNS.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Implantable medical lead with biased electrode
This disclosure describes implantable medical leads that include a lead body and an electrode. A width of the electrode as measured along a longitudinal direction of the lead varies about the perimeter of the lead. The uneven width of the electrode may bias a stimulation field in a particular direction, e.g., a radial or transverse direction relative to the longitudinal axis of the lead. Electrodes with an uneven width may be useful for controlling the direction of propagation of the stimulation field in order to, for example, avoid phrenic nerve stimulation during LV pacing or neck muscle stimulation during vagal neurostimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
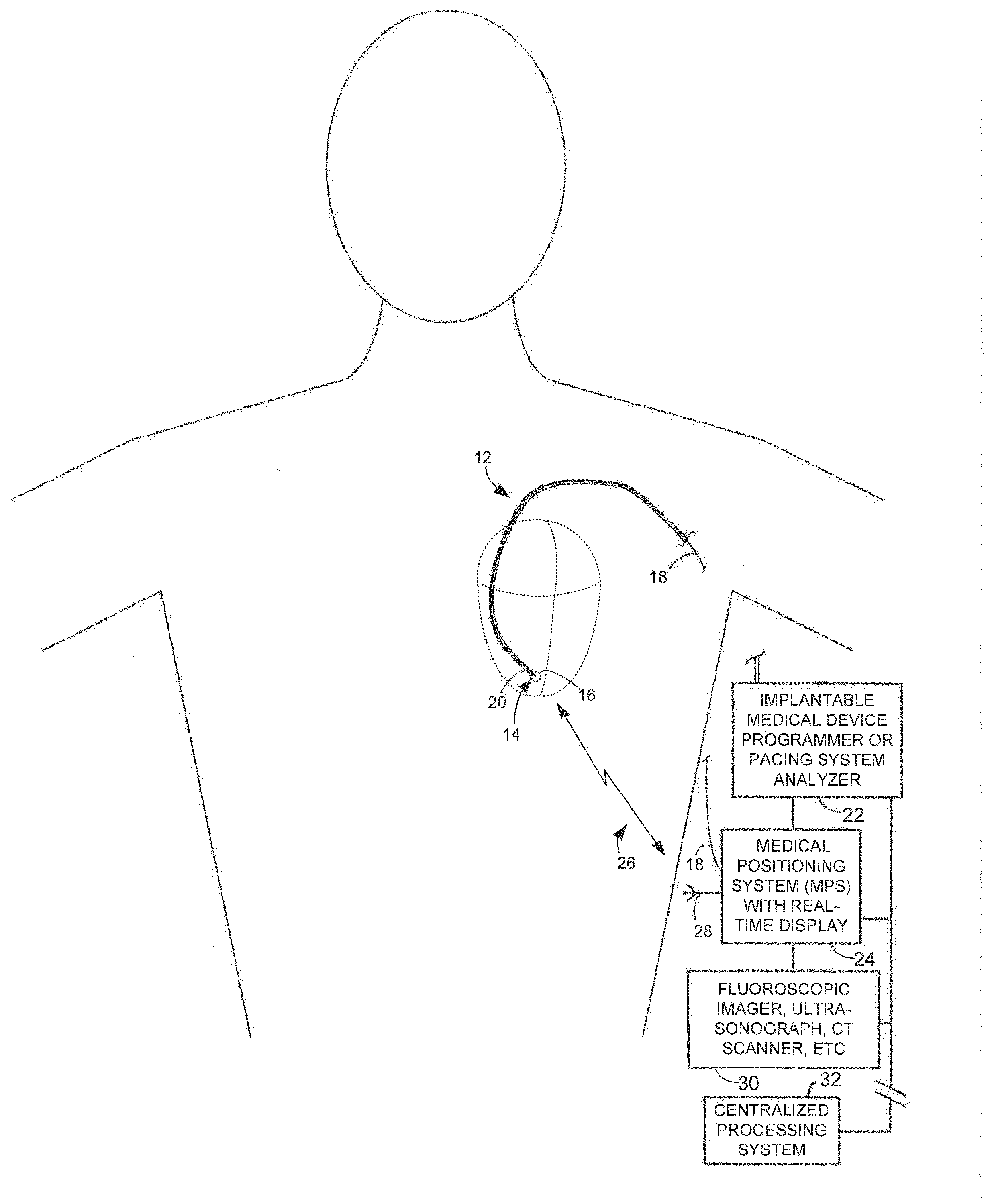
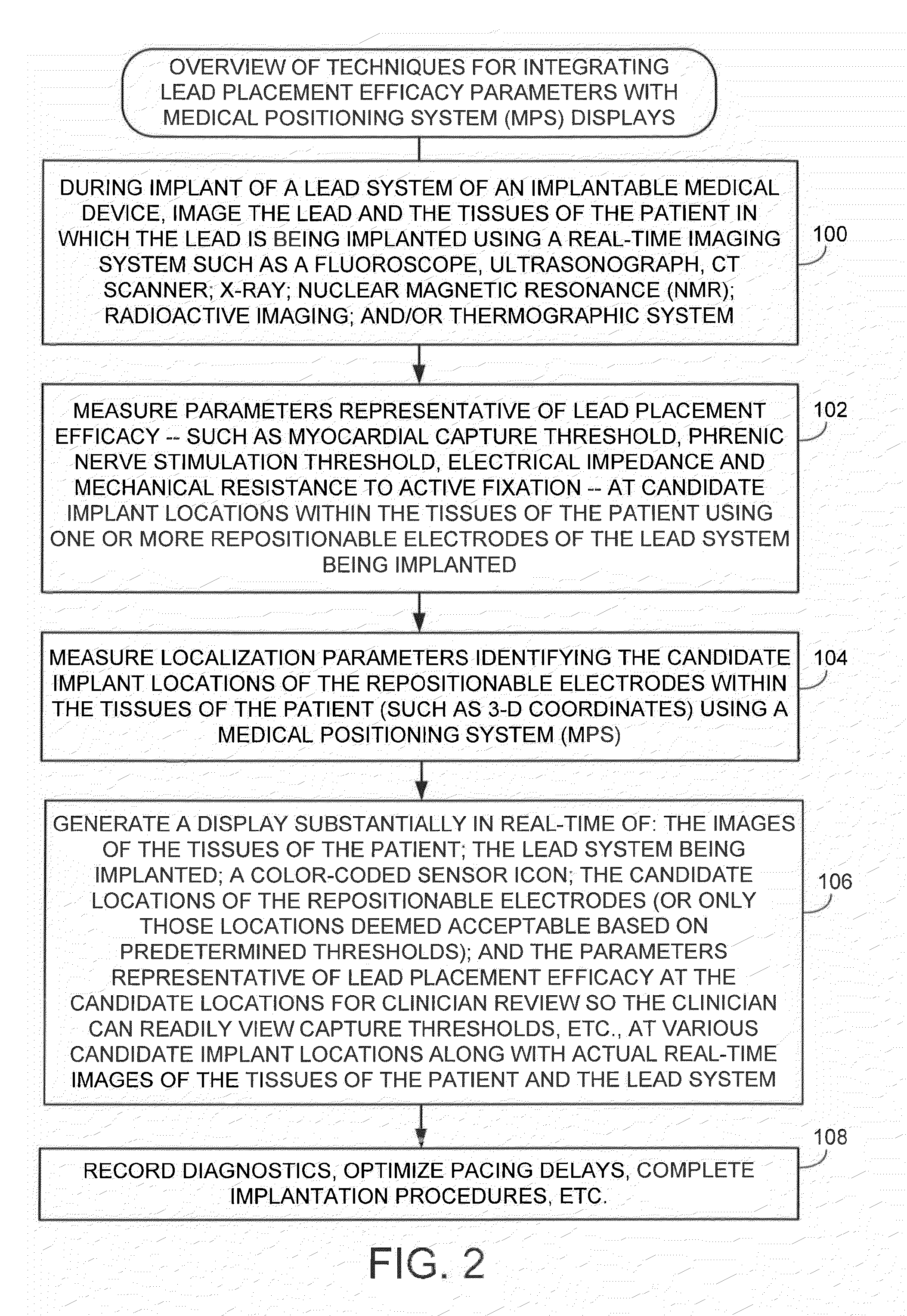
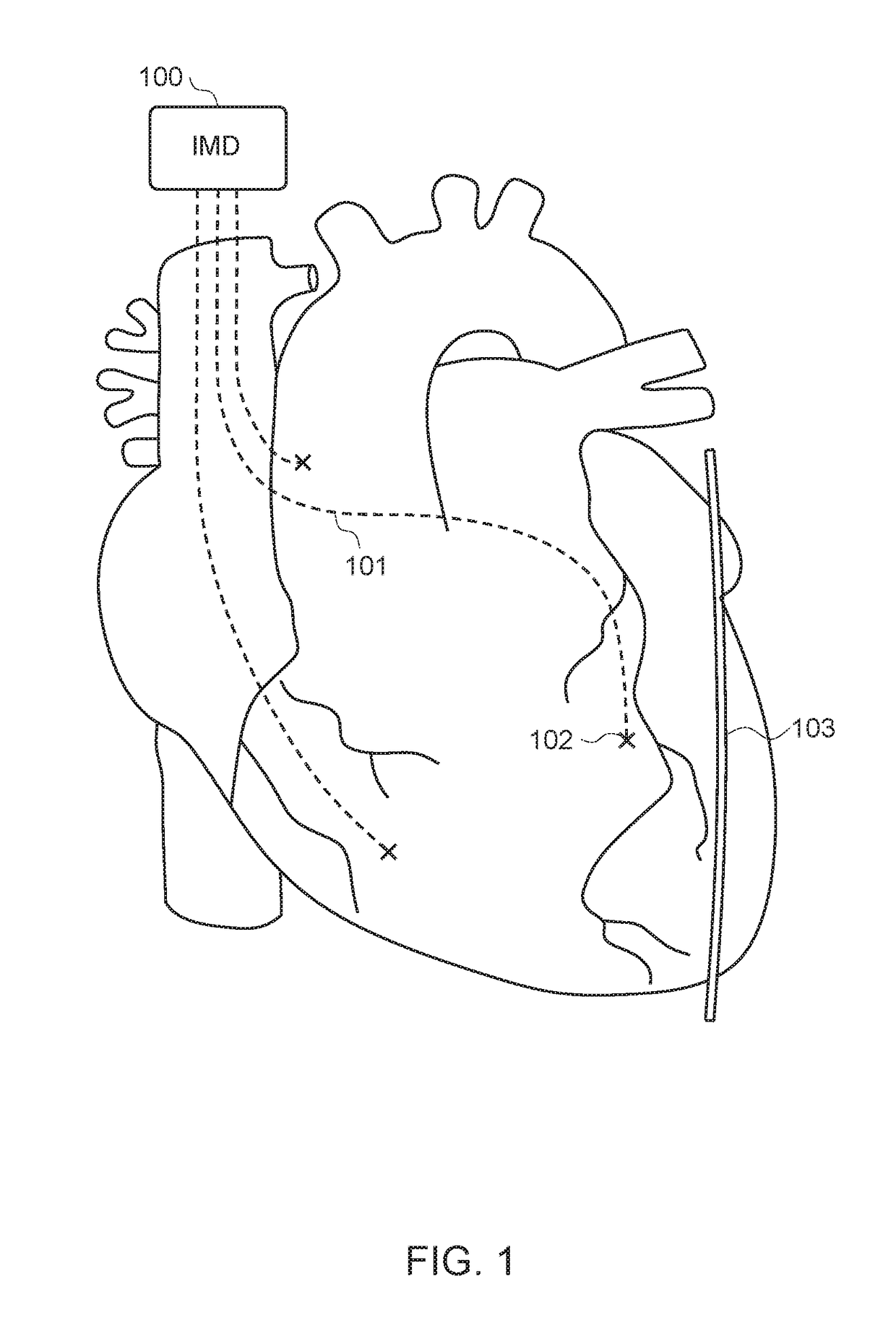
System and method for integrating candidate implant location test results with real-time tissue images for use with implantable device leads
ActiveUS20150018907A1Improve visualizationAvoid confusionTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical navigation systemsFluoroscopic imagingMechanical resistance
Patient tissues are imaged using, e.g., a real-time fluoroscopic imaging system, along with a lead system being implanted. Parameters representative of lead placement efficacy—such as capture thresholds, phrenic nerve stimulation thresholds, impedance values or screw-in tip mechanical resistance values—are measured at candidate implant locations. Localization parameters identifying the candidate implant locations are also measured. In one example, a display is generated substantially in real-time showing: images of the tissues of the patient and the lead system being implanted: candidate locations of the electrodes; and parameters representative of lead placement efficacy at the candidate locations. In this manner, the implanting clinician can readily view capture thresholds and other helpful parameters at various candidate locations along with actual real-time images of the tissues of the patient and the lead system being implanted. Recorded images can also be displayed and, in some examples, multiple images can be superimposed over one another.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
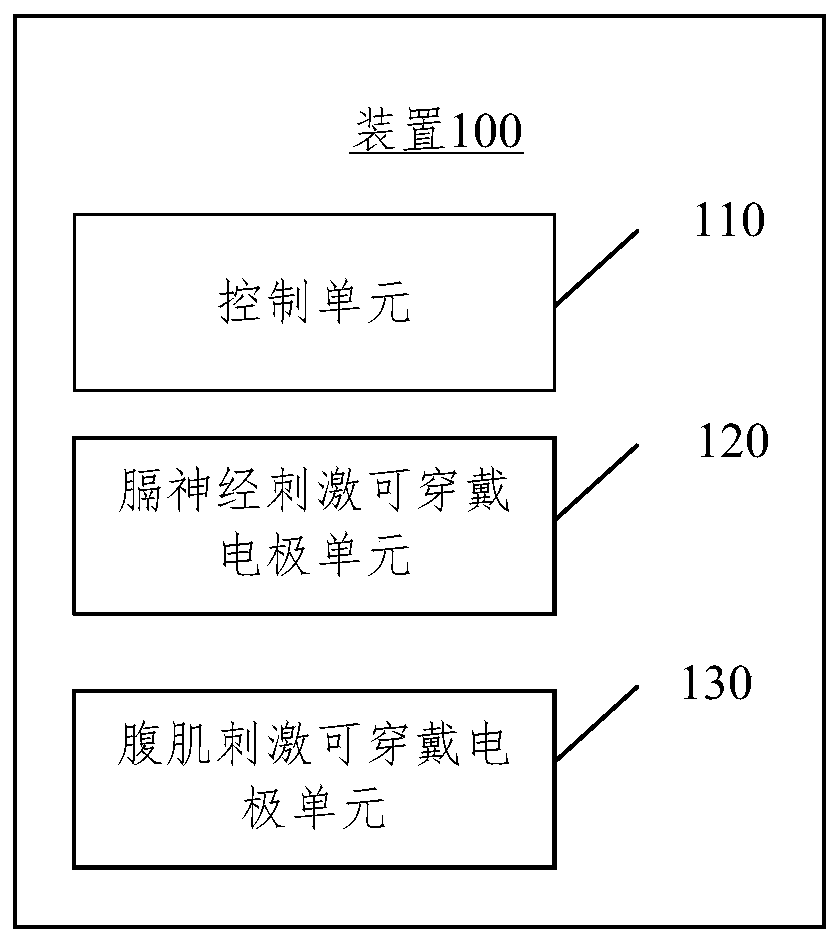
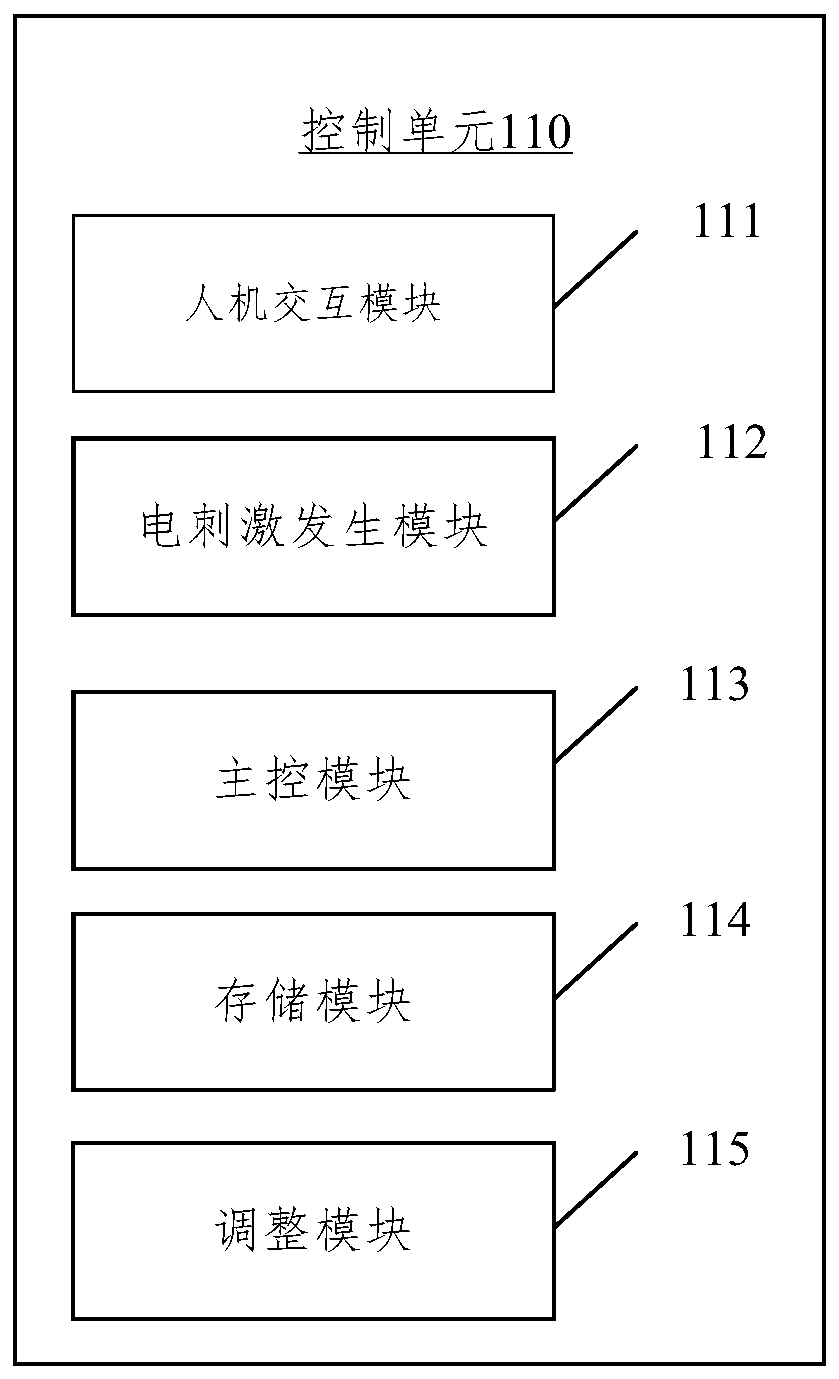
Wearable respiratory myoelectricity stimulation device
ActiveCN110327546AEasy to wearReturn to spontaneous breathingExternal electrodesArtificial respirationMuscle strengthPower flow
The embodiment of the present disclosure relates to a wearable respiratory myoelectricity stimulation device. The device comprises: a control unit which is used for generating corresponding electric stimulation current according to input information; and a phrenic nerve stimulation wearable electrode unit and an abdominal muscle stimulation wearable electrode unit which are both connected to the control unit and used for receiving the current, wherein the current acts on nerves or muscles, wherein the electrode position of the phrenic nerve stimulation wearable electrode unit corresponds to the phrenic nerve after being worn, and the electrode position of the abdominal muscle stimulation wearable electrode unit corresponds to rectus abdominis and obliquus abdominis. The embodiment of the present disclosure provides the wearable device suitable for household, the device is convenient for a user to wear, the electrode is aligned with a part needing electric stimulation after wearing, theoperation is simple, and the user can be helped to recover the spontaneous respiration by training the muscle strength and endurance of the diaphragm muscle and the abdominal muscle.
Owner:YAGUO
Non-invasive detection of phrenic nerve stimulation
InactiveCN106456979AHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphical user interfaceAnesthesia
Systems, methods, and graphical user interfaces are described herein for non-invasively detecting phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac pacing therapy. Phrenic nerve stimulation information may be generated for one or more electrical pacing vectors at one or more power configurations. The phrenic nerve stimulation information may be displayed to a user for use in configuring and / or evaluating cardiac pacing therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
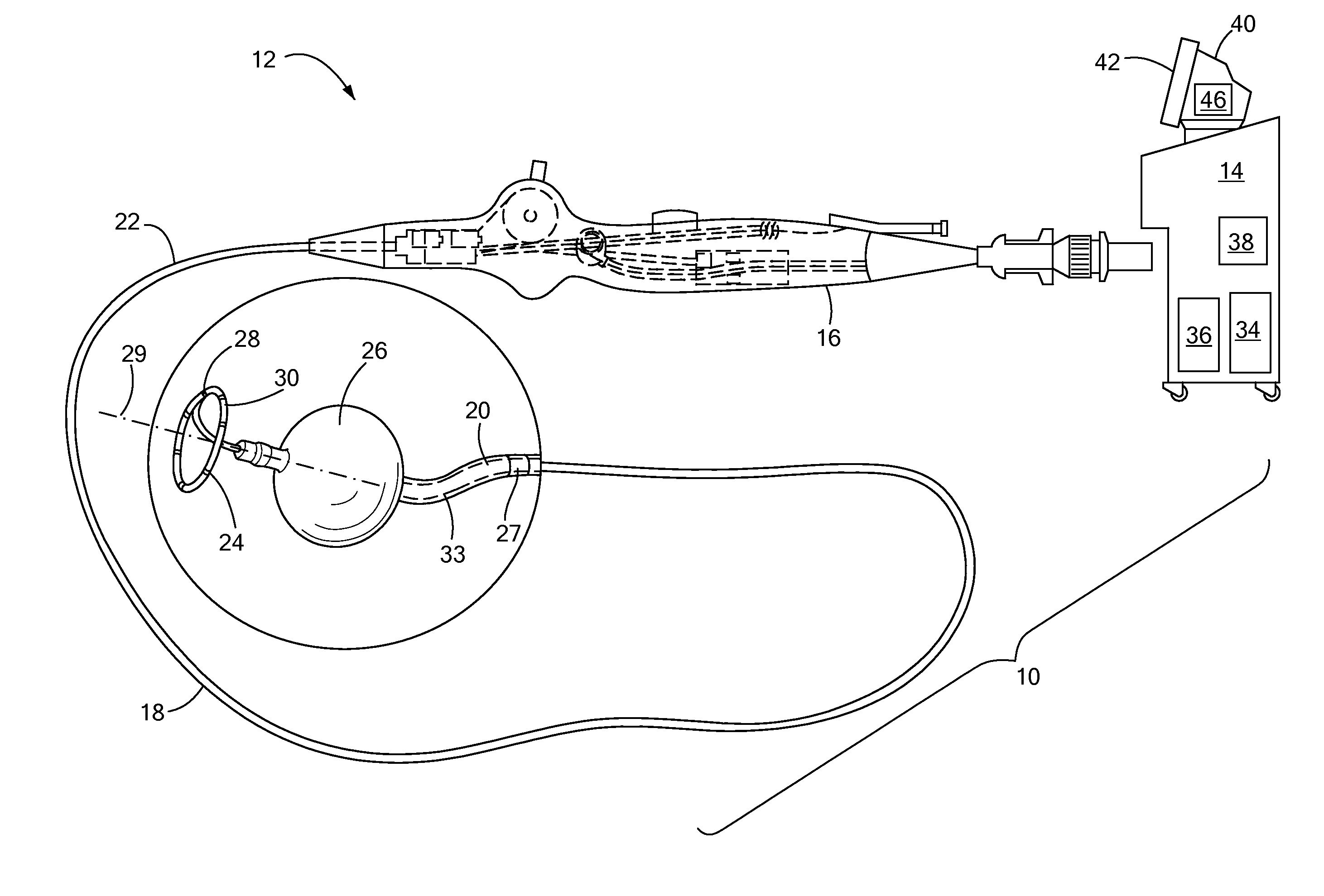
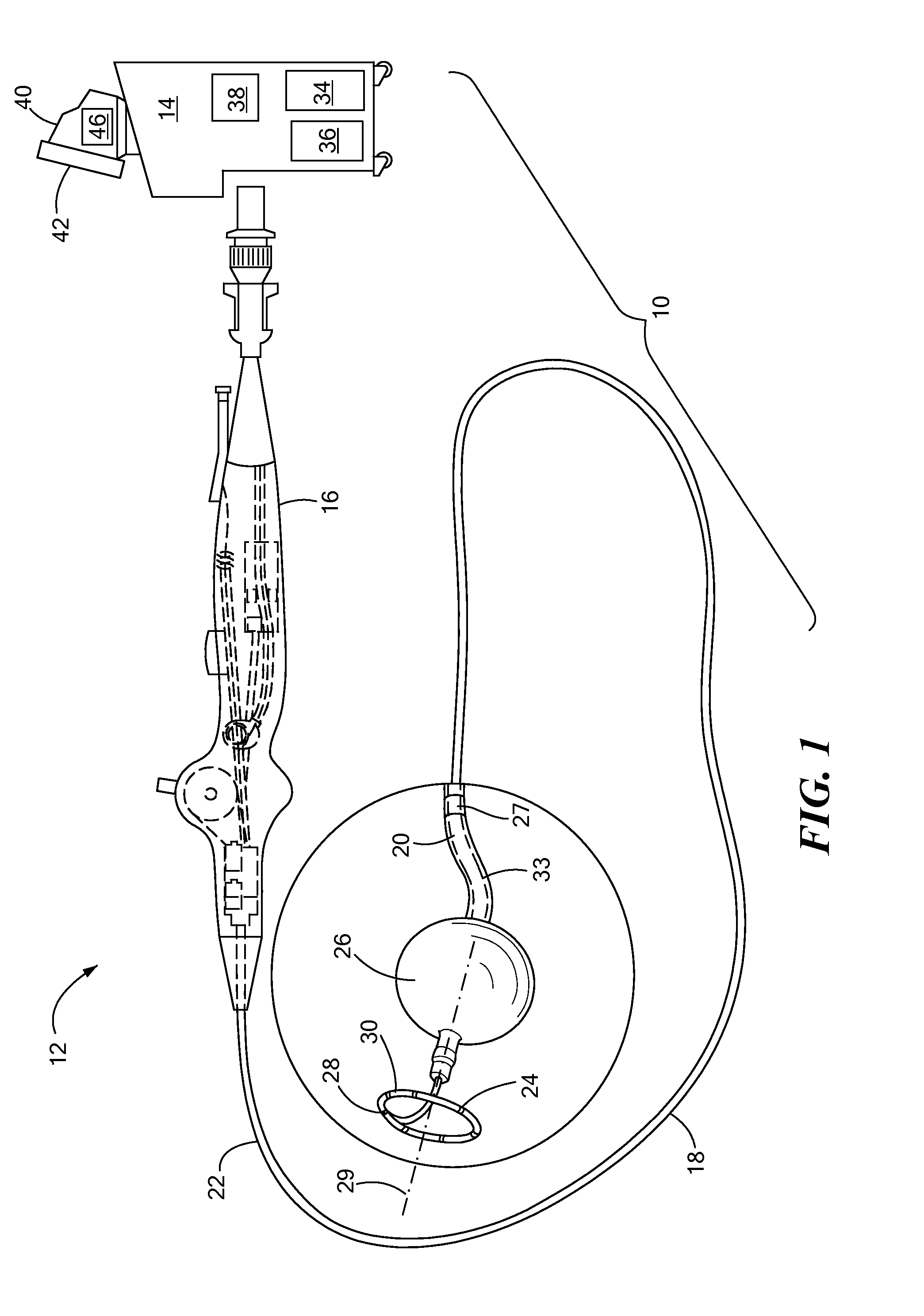
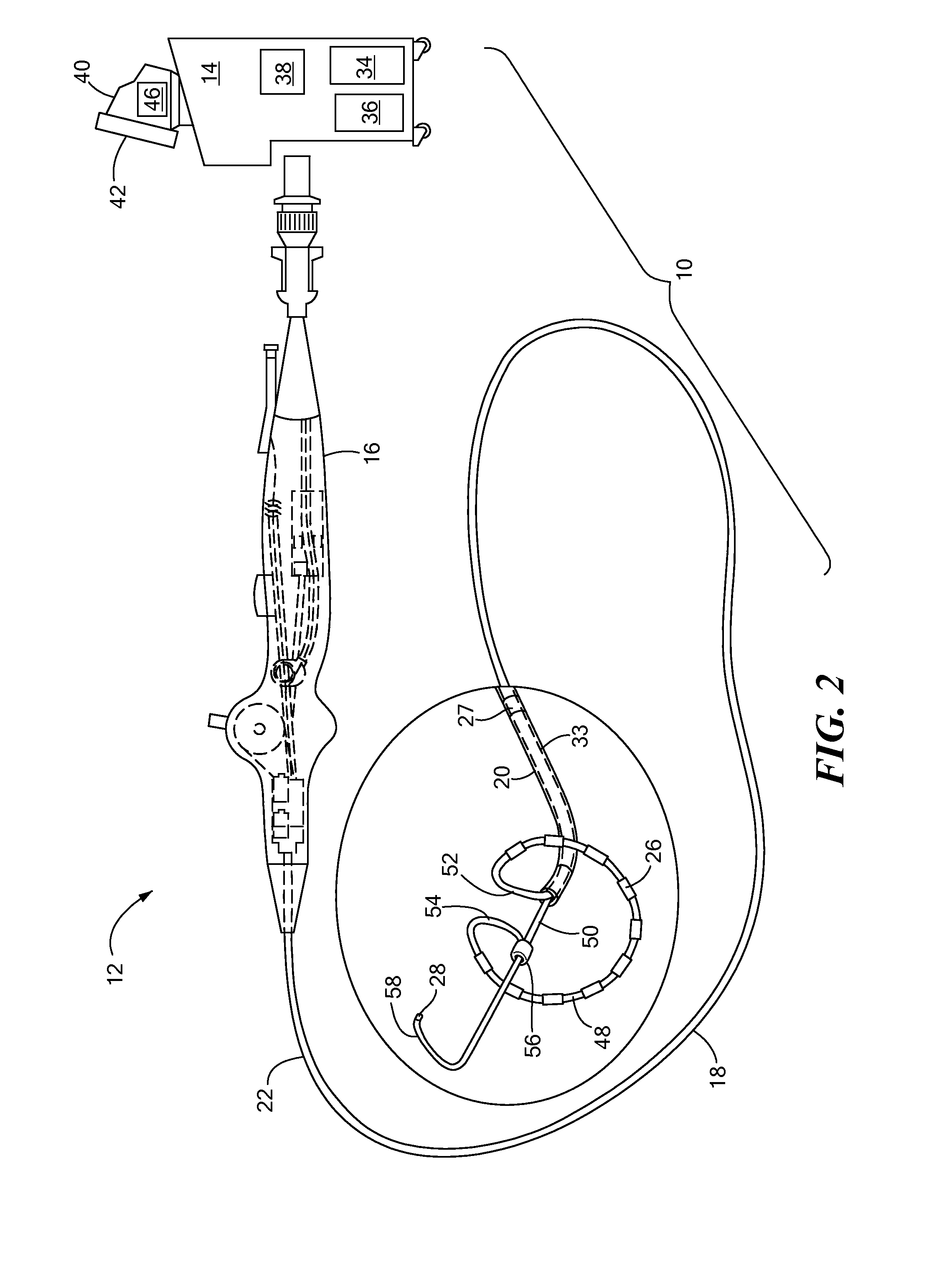
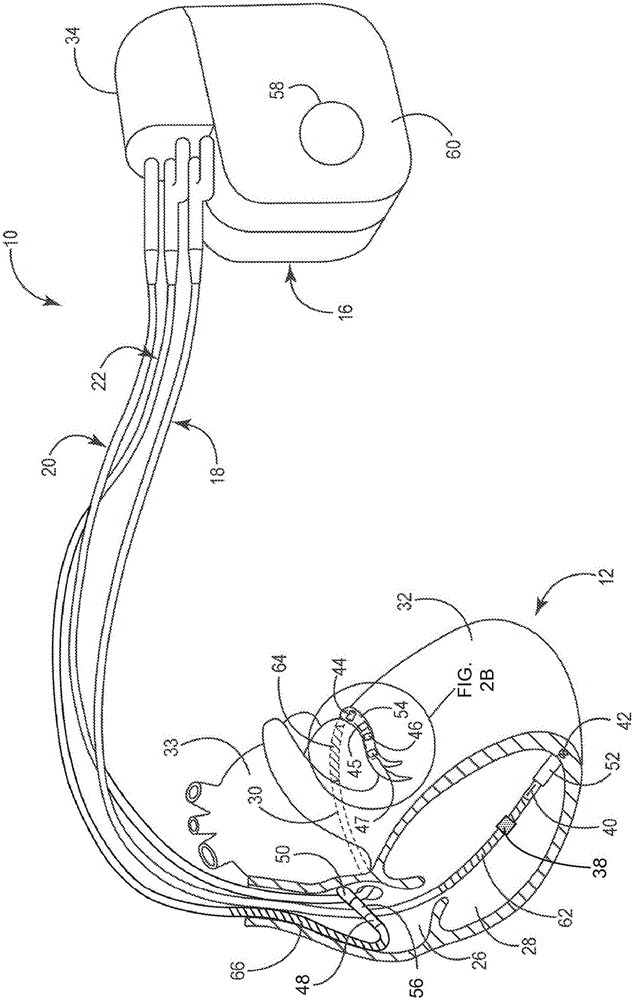
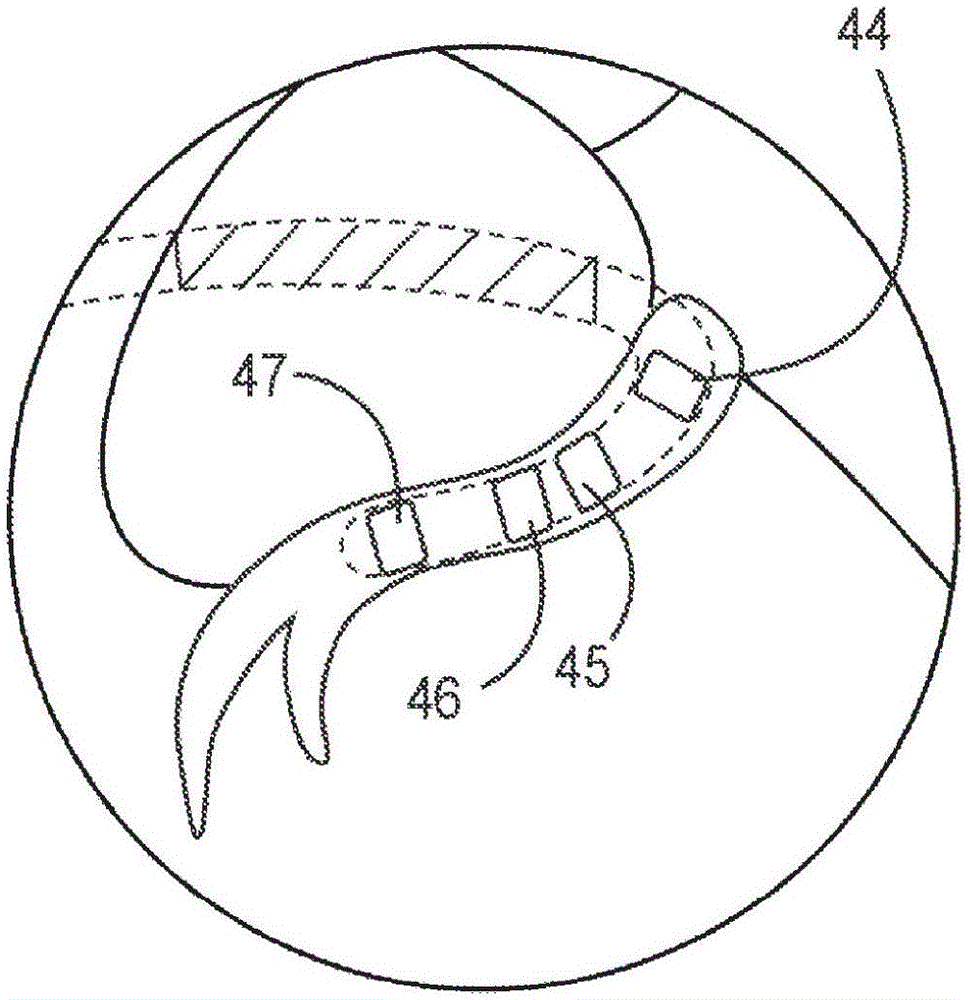
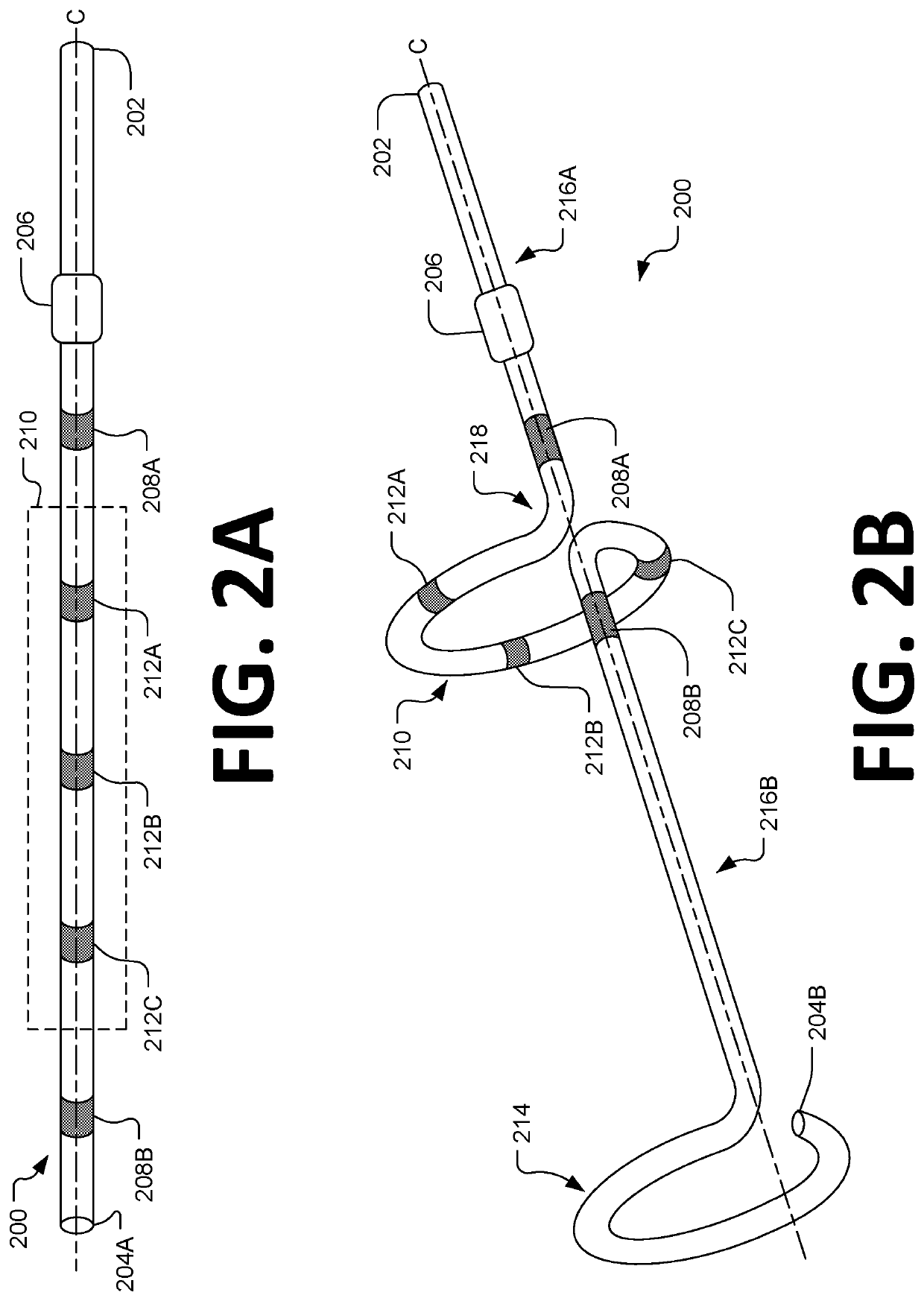
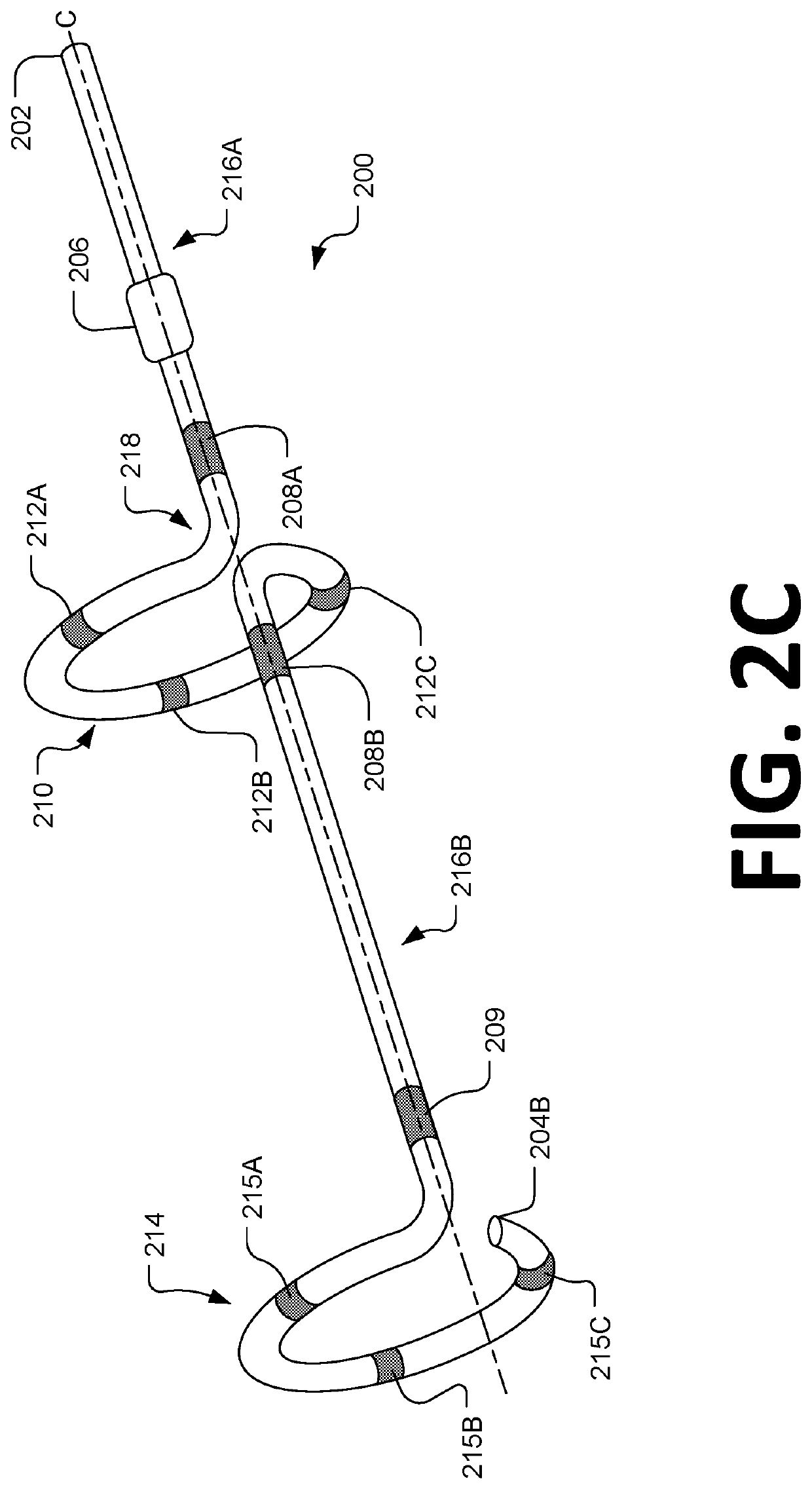
Intravenous phrenic nerve stimulation lead
Aspects of this disclosure describe methods and systems for phrenic nerve stimulation using a stimulation lead placed in a blood vessel. The stimulation lead includes at least one deformable segment that has at least two configurations. For example, the deformable segment may have an elongate configuration and a non-elongate configuration. In the elongate configuration, the deformable segment may be substantially straight, thereby allowing placement of the stimulation lead using a catheter. In the non-elongate configuration, the deformable segment may be a circle or spiral. The deformable segment may transition from the elongate configuration to the non-elongate configuration after the stimulation lead is positioned in the vein. The stimulation lead may be fixated to the vein at a fixation element. Additionally, the stimulation lead may include electrodes distributed along the deformable segment and at least one elongate segment.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Non-invasive detection of phrenic nerve stimulation
PendingCN113398475AHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphical user interfacePhysical therapy
Systems, methods, and graphical user interfaces are described herein for non-invasively detecting phrenic nerve stimulation during cardiac pacing therapy. Phrenic nerve stimulation information may be generated for one or more electrical pacing vectors at one or more power configurations. The phrenic nerve stimulation information may be displayed to a user for use in configuring and / or evaluating cardiac pacing therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Airway diagnostics utilizing phrenic nerve stimulation device and method
ActiveUS11266838B1Steady breathingLower levelSpinal electrodesInertial sensorsDiseasePhysical therapy
A device and method for treating a variety of conditions, disorders or diseases with diaphragm / phrenic nerve stimulation is provided.
Owner:RMX
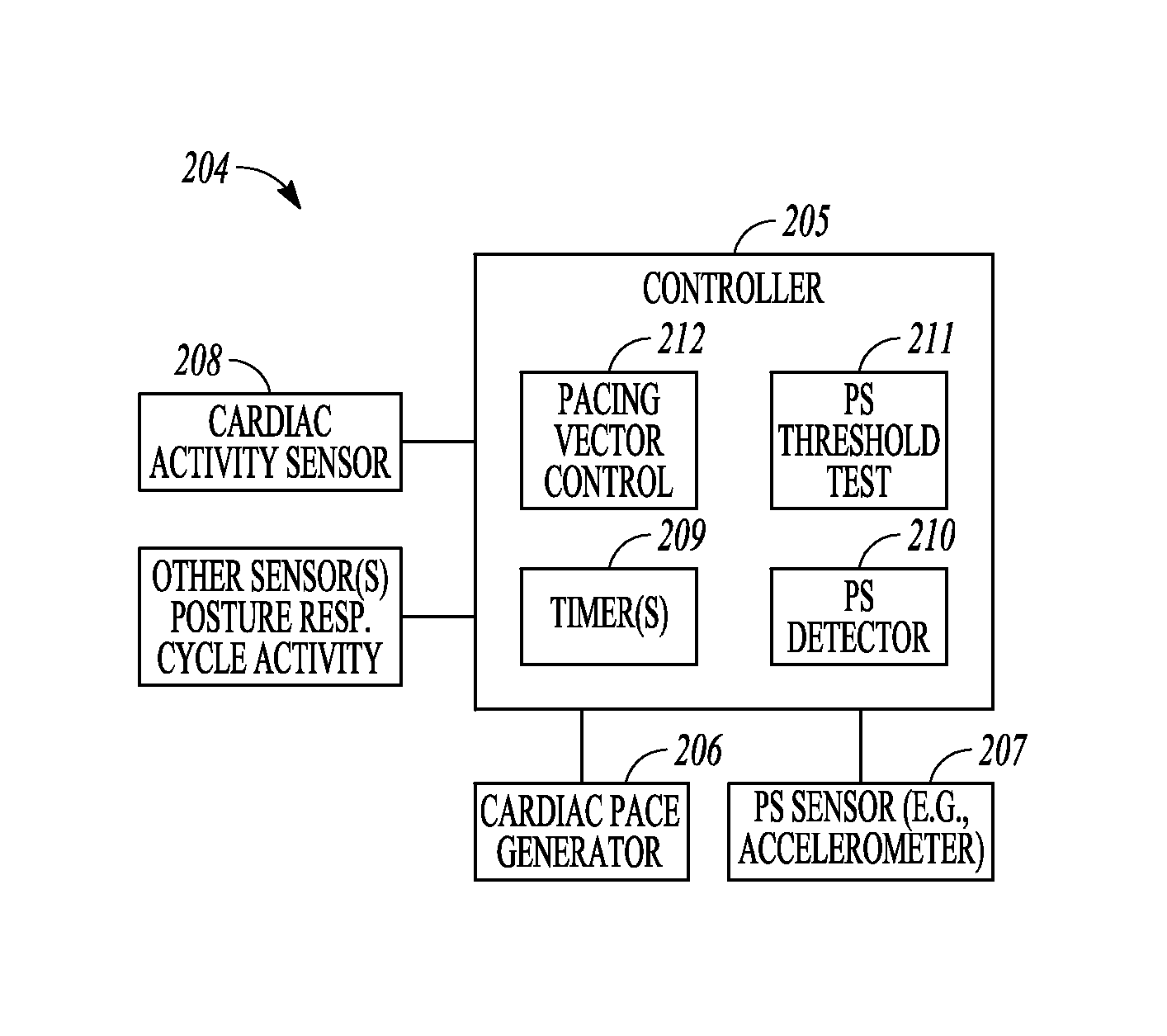
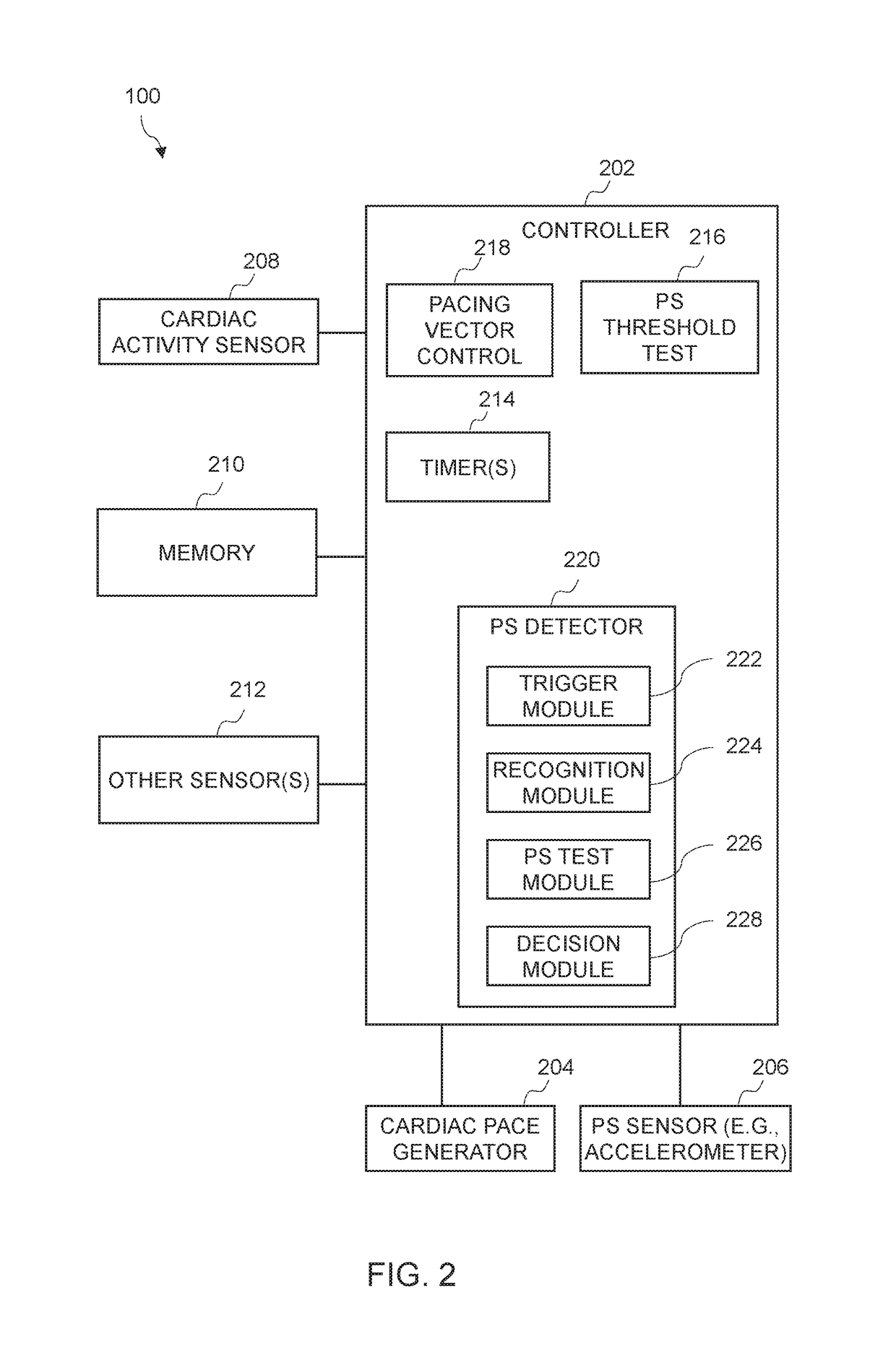
Ambulatory phrenic nerve stimulation detection
An example of a system includes an implantable medical device (IMD) for implantation in a patient, where the IMD includes a cardiac pace generator, phrenic nerve stimulation (PS) sensor, a memory, and a controller, and where the controller is operably connected to the cardiac pace generator to generate cardiac paces. The controller is configured to provide a trigger for conducting a PS detection procedure and perform the PS detection procedure in response to the trigger. In performing the PS detection procedure the controller is configured to receive a signal from the sensor, detect PS using the signal from the sensor, and record the PS detection in storage within the IMD.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com