Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
98 results about "Cardiac pace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
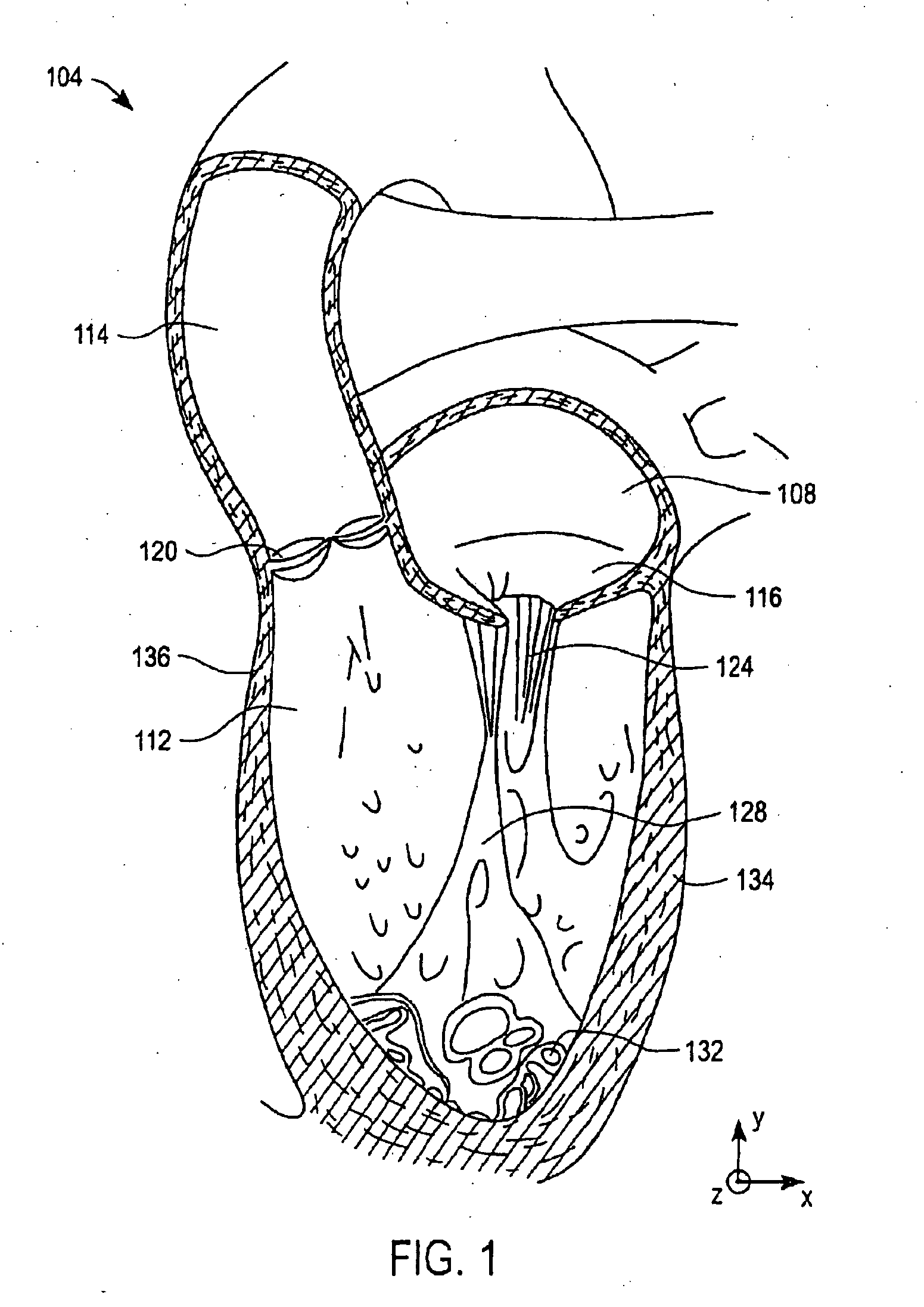
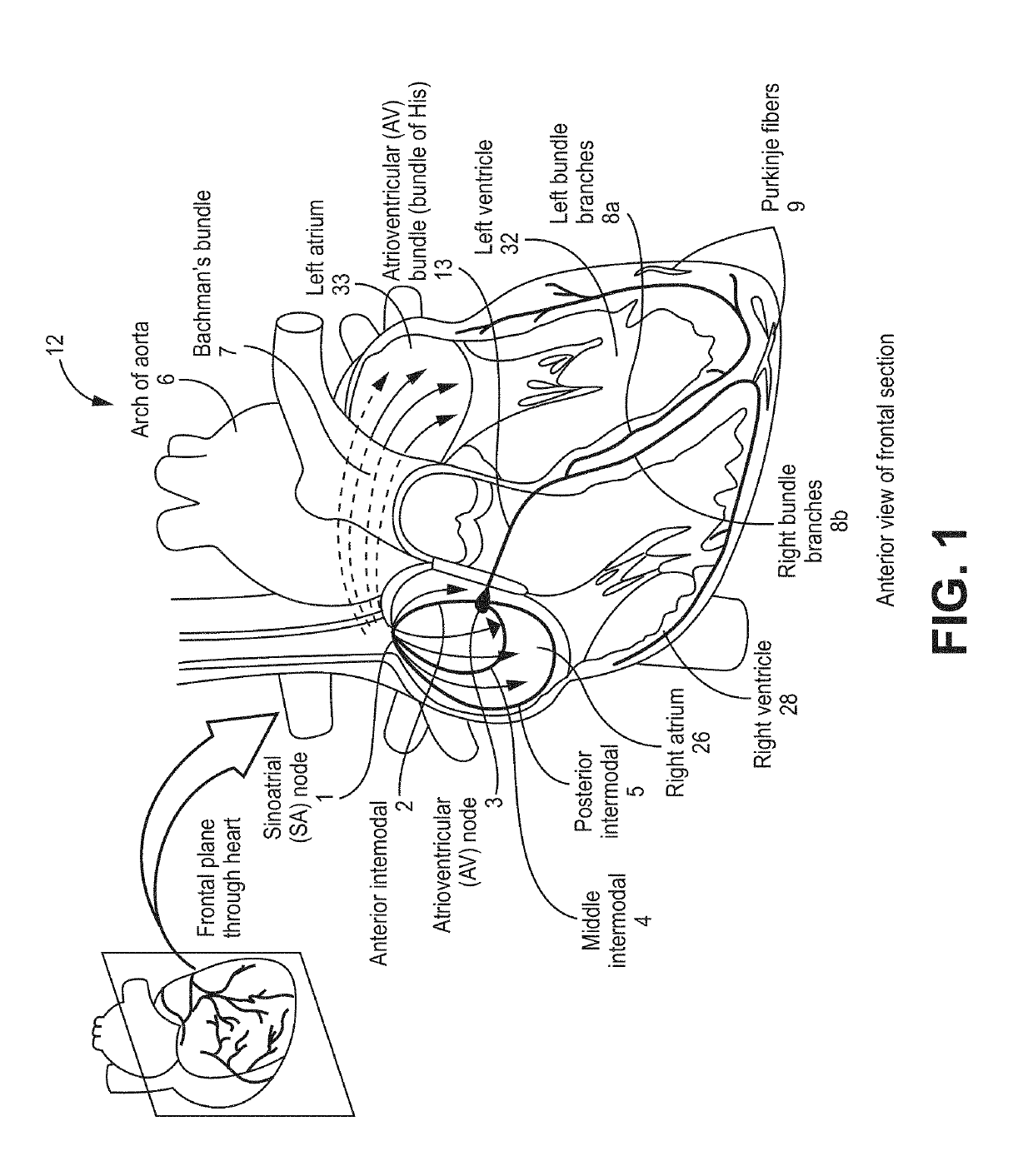
Cardiac pacemaker a small mass of specialized muscle tissue in the heart that sets a rhythm of contraction and relaxation for the other parts of the heart, resulting in the heartbeat. Usually the pacemaker site is the sinoatrial node, near the junction with the superior vena cava.
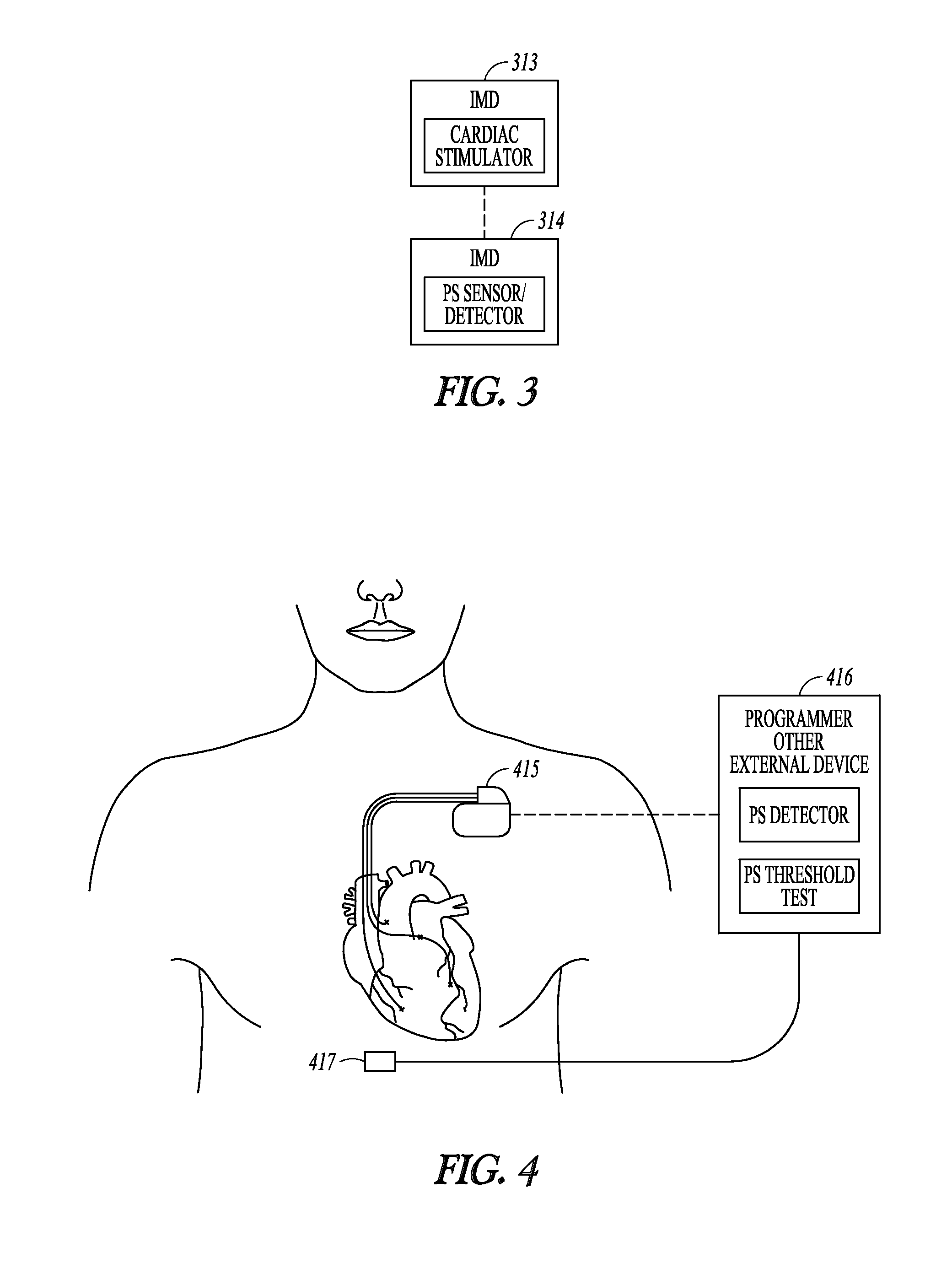
Method and system for optimizing left-heart lead placement
InactiveUS20070055124A1Easy to placePredict successUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyCardiac wallBlood flow
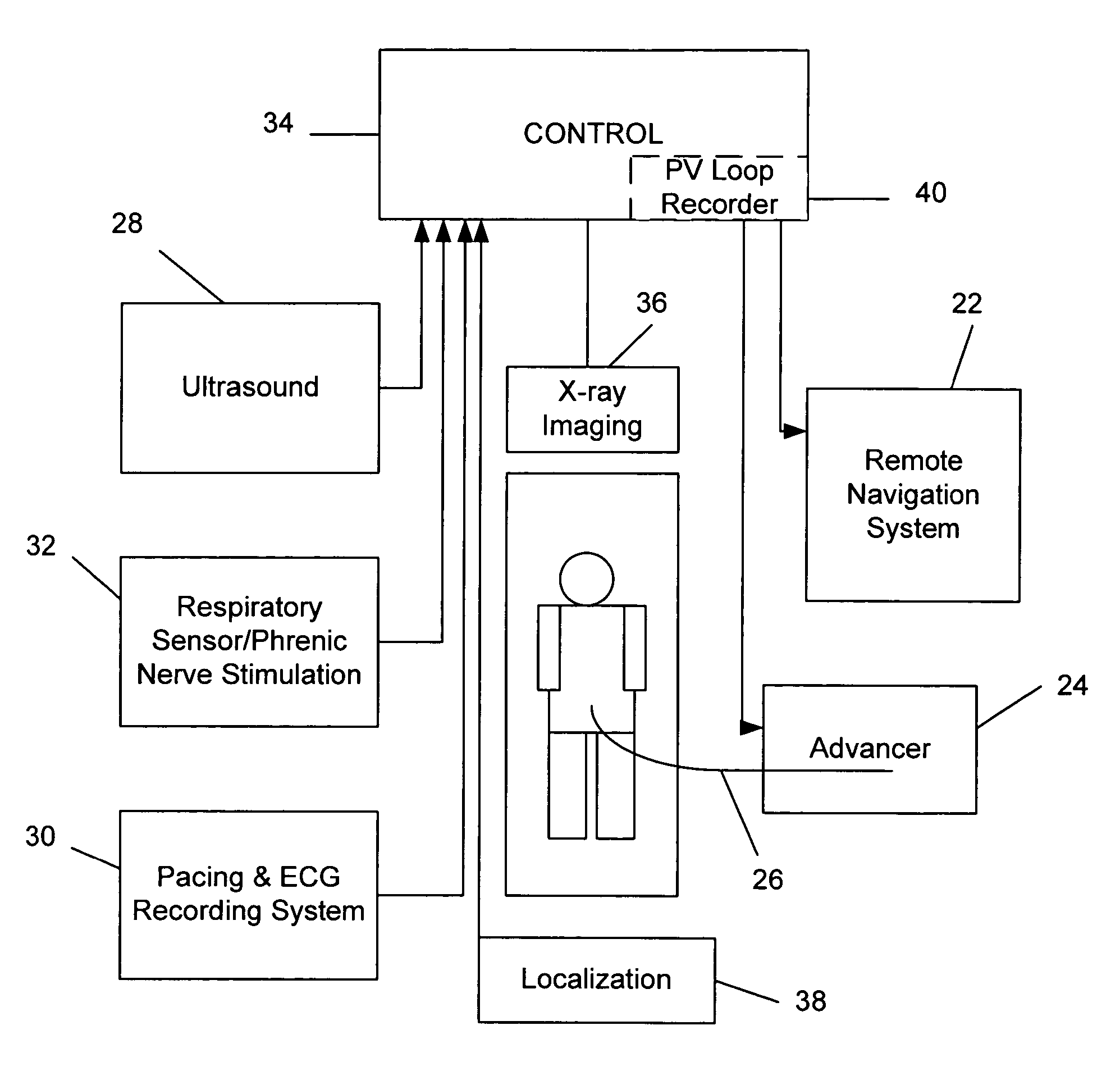
A system for identifying locations for pacing the heart, the system comprising a pacing electrode, a remote navigation system for positioning the pacing electrode at each of a plurality of locations; a system for determining Pressure-Volume loop data resulting from pacing at each location; an ECG system, a phrenic nerve stimulation detection system, and a means of identifying at least one preferred location based upon at least the Pressure-Volume loop, ECG, and phrenic nerve stimulation data at each location. A method of identifying locations for pacing the heart, the method comprising: navigating a pacing electrode to each of a plurality of locations in the heart; pacing the heart at each of the plurality of locations; and assessing the effectiveness of the pacing at each location by measuring cardiac blood flow and cardiac wall strain.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Leadless Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
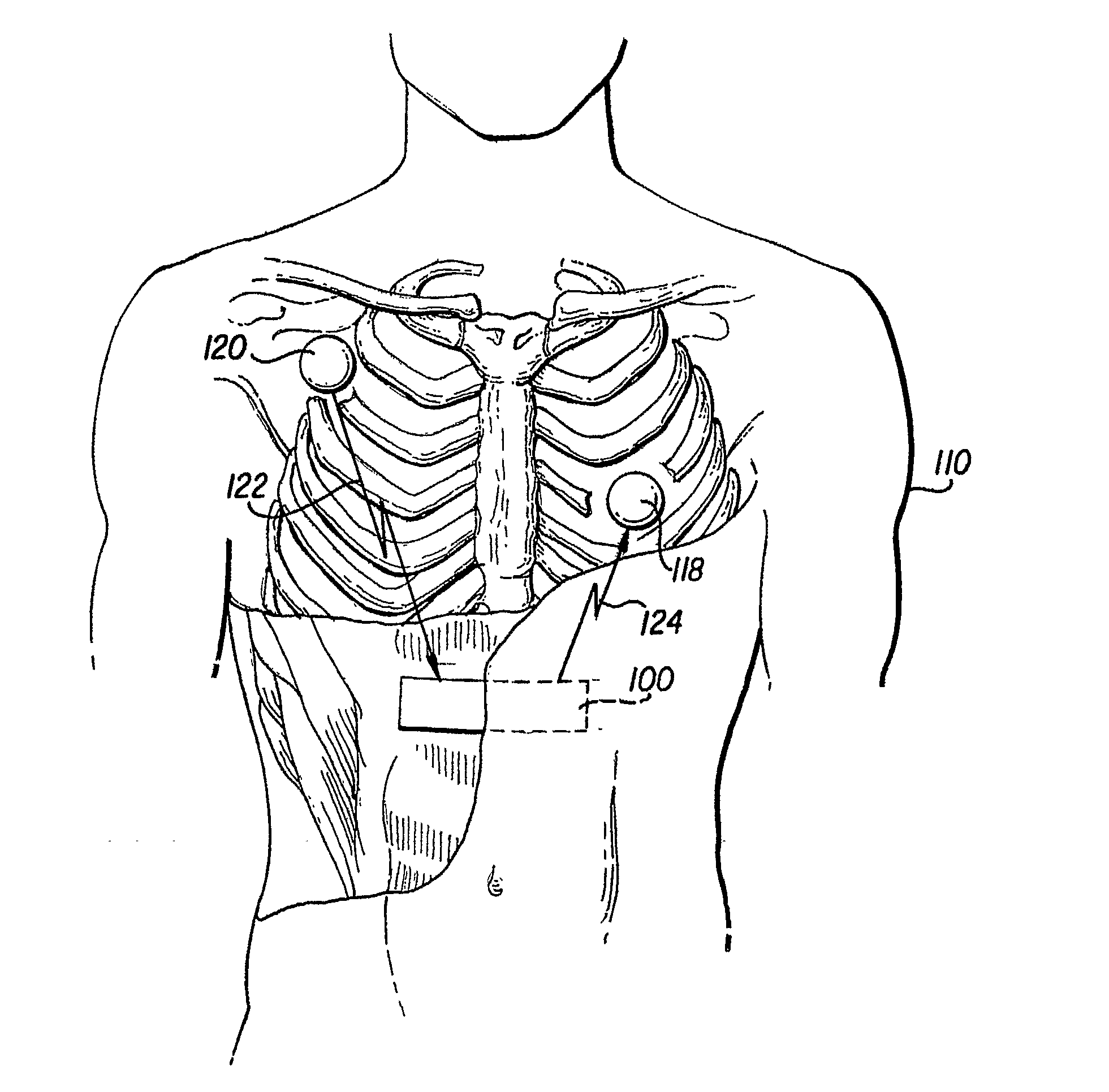
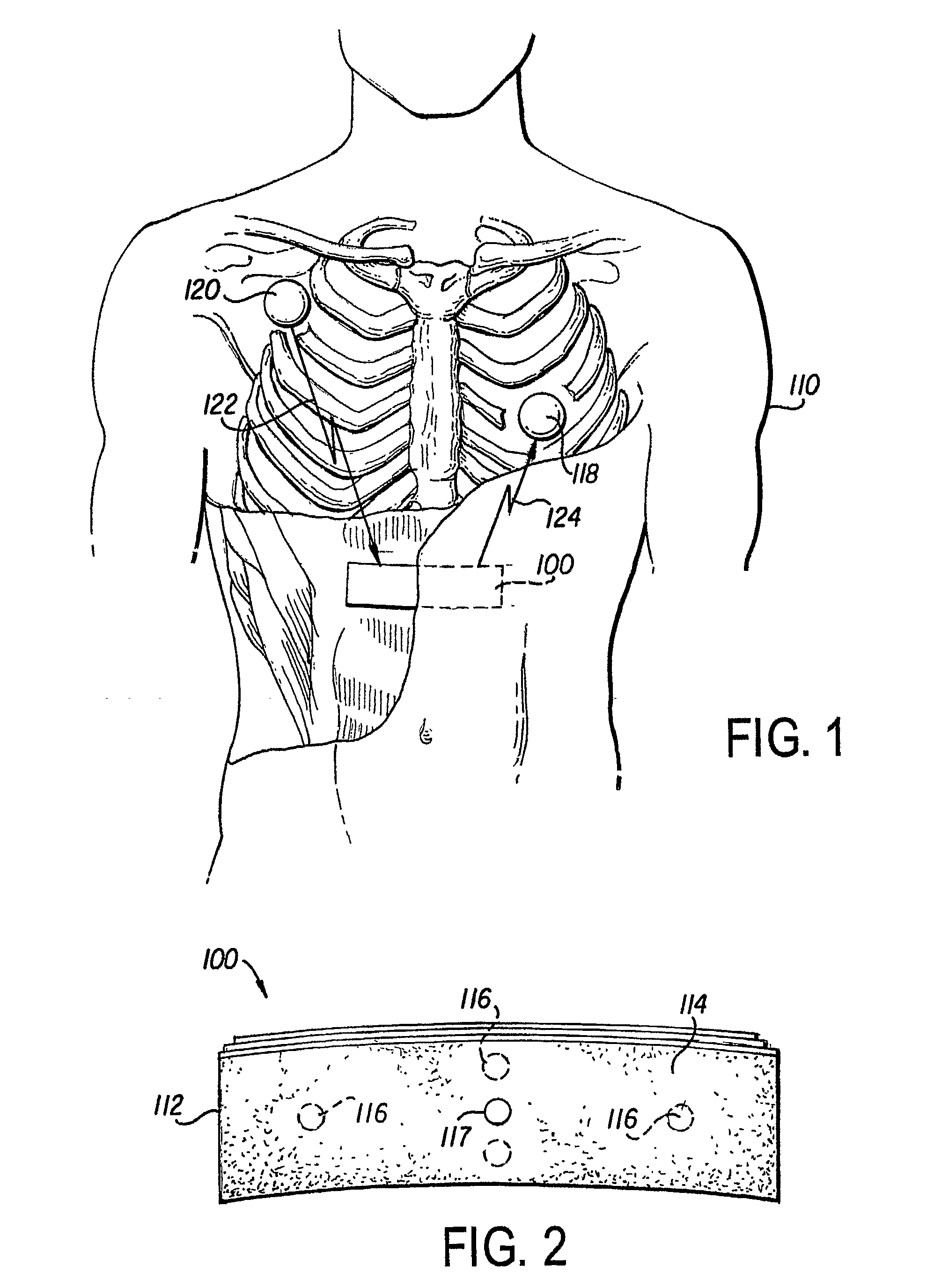
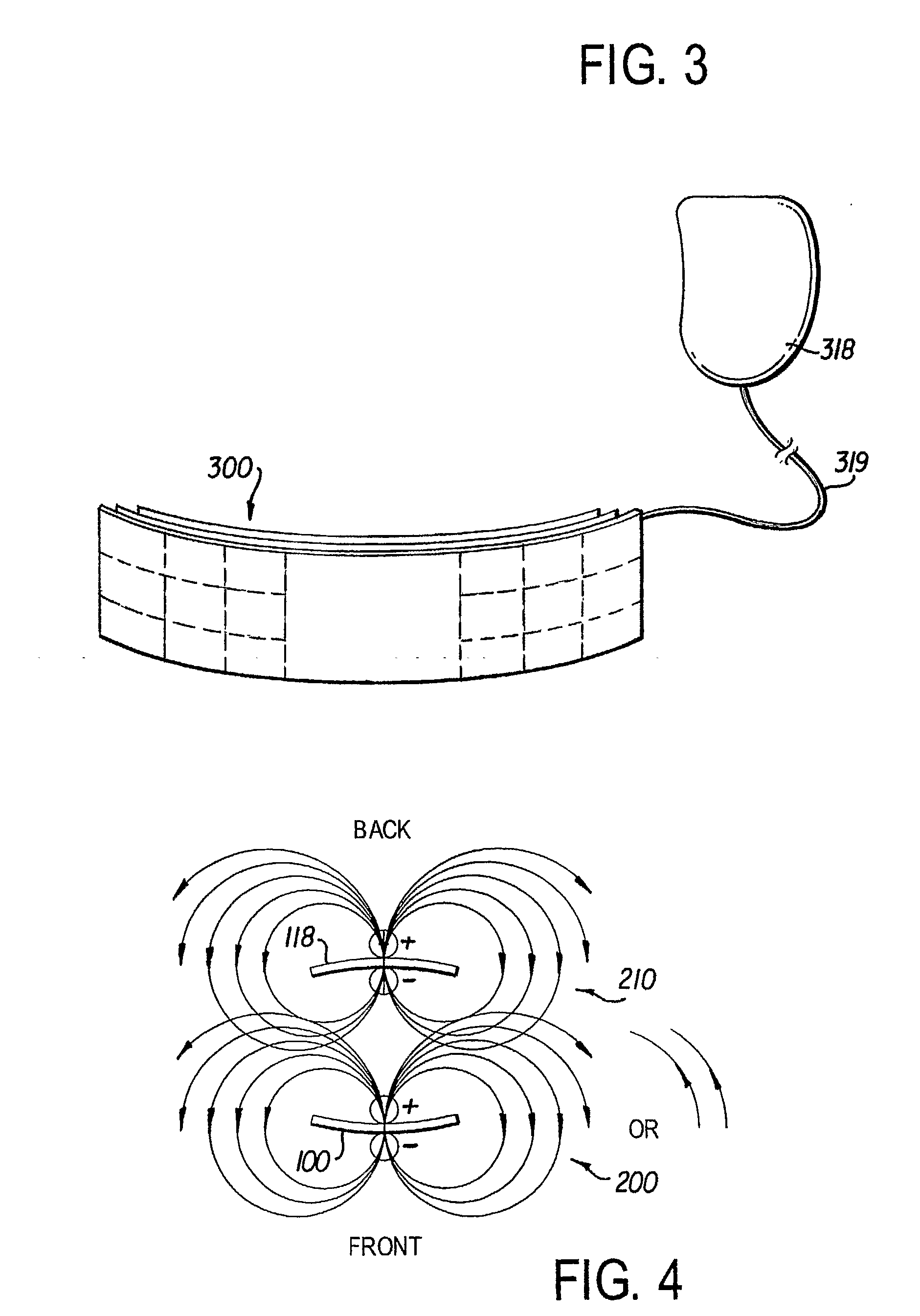
A leadless implantable cardioverter defibrillator (5) for treatment of sudden cardiac death includes a controller and at least one remote module. The defibrillator does not require transvenous / vascular access for intracardiac lead placement. The controller is leadless and uses subcutaneous tissue in proximity of the chest and abdomen for both sensing and defibrillation. The controller and one or more remote sensors sense a need for defibrillation and wireless communicate with the controller. The controller and one of the sensors discharge a synchronized defibrillation pulse to the surrounding subcutaneous tissue in proximity to the heart.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
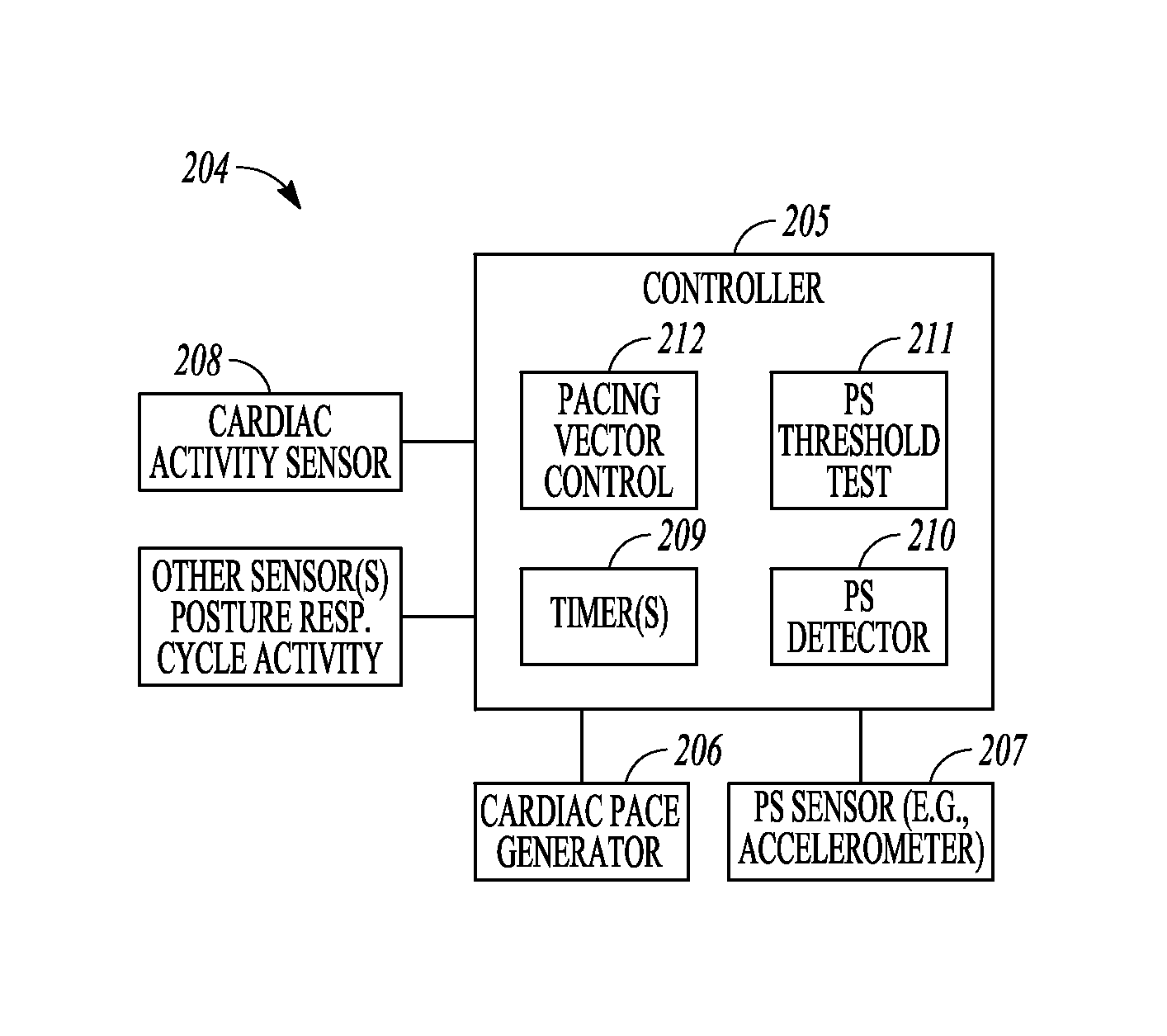
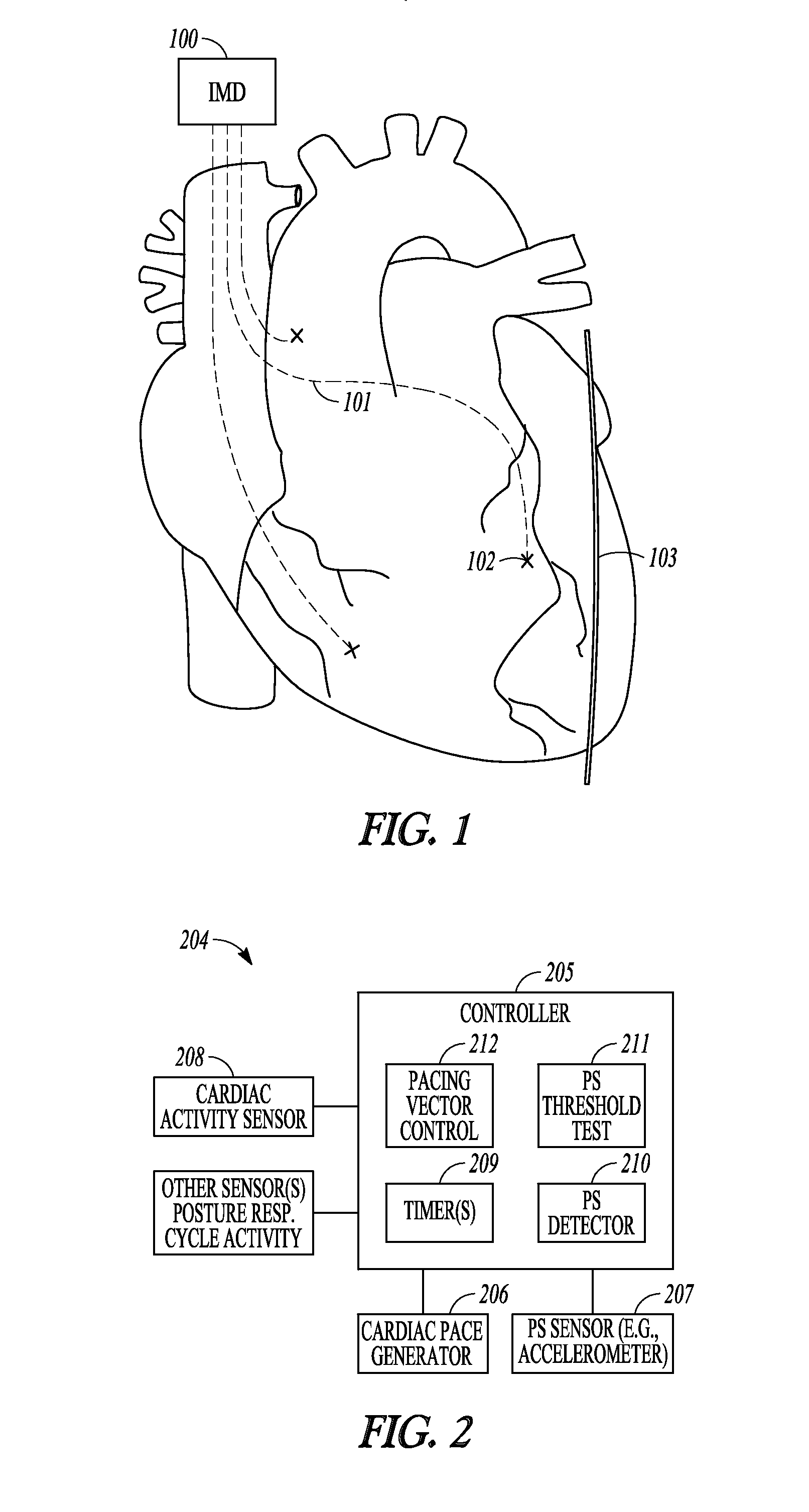
Baseline determination for phrenic nerve stimulation detection
Some method examples may include pacing a heart with cardiac paces, sensing a physiological signal for use in detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation, performing a baseline level determination process to identify a baseline level for the sensed physiological signal, and detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation using the sensed physiological signal and the calculated baseline level. Detecting pace-induced phrenic nerve stimulation may include sampling the sensed physiological signal during each of a plurality of cardiac cycles to provide sampled signals and calculating the baseline level for the physiological signal using the sampled signals. Sampling the sensed physiological signal may include sampling the signal during a time window defined using a pace time with each of the cardiac cycles to avoid cardiac components and phrenic nerve stimulation components in the sampled signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
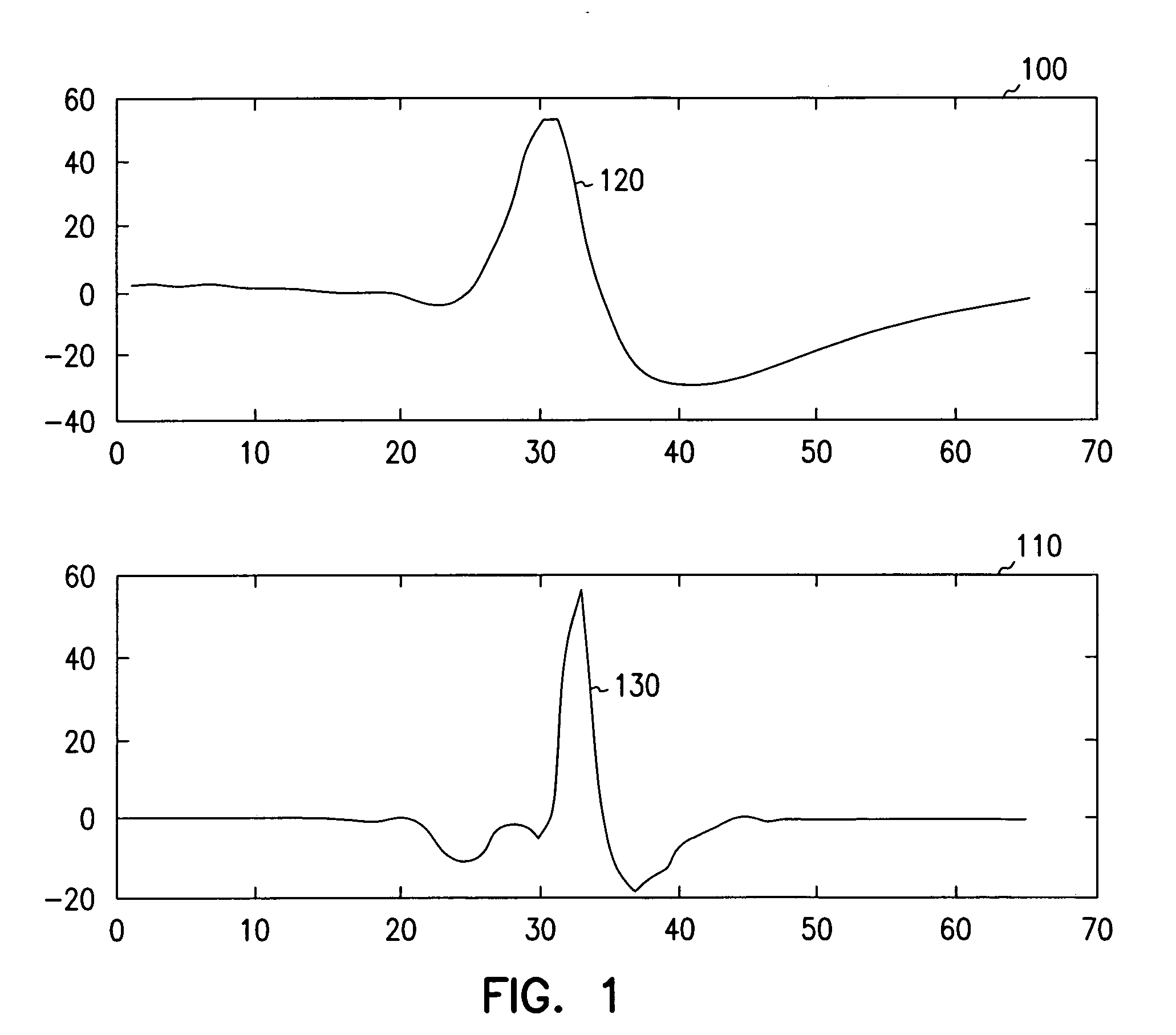
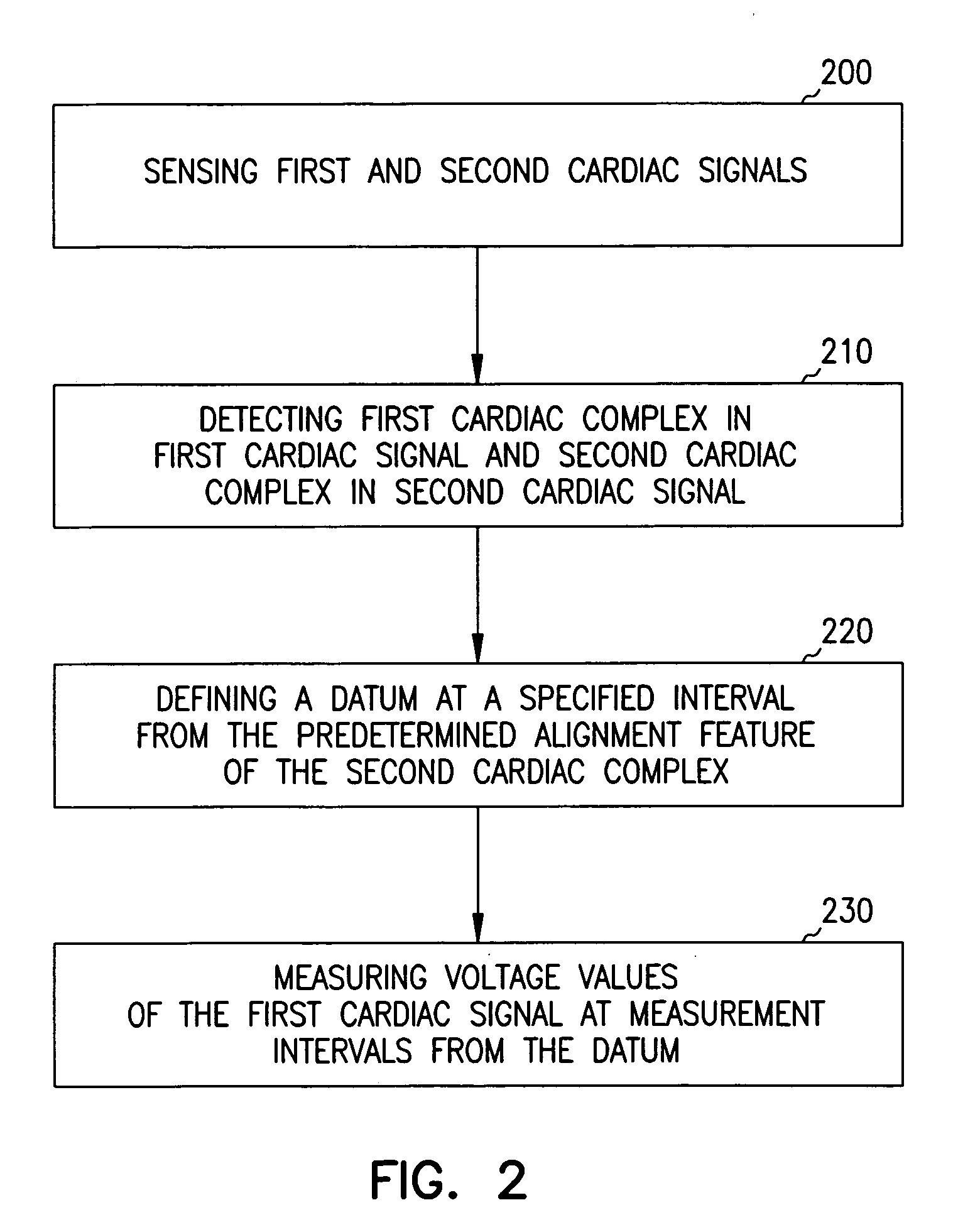
Classification of supraventricular and ventricular cardiac rhythms using cross channel timing algorithm
InactiveUS20050159781A1ElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac cycleVentricular tachycardia
A system and method for classifying cardiac complexes sensed during a tachycardia episode. A first cardiac signal and a second cardiac signal are sensed, where the first cardiac signal has a voltage. A first cardiac complex and a second cardiac complex of a cardiac cycle are detected in the first and second cardiac signal, respectively. A predetermined alignment feature is identified in the second cardiac complex. A datum is defined, or positioned, at a specified interval from the predetermined alignment feature of the second cardiac complex. Voltage values are then measured from the first cardiac complex at each of two or more measurement intervals from the datum. The voltage values are then compared voltage values measured from NSR cardiac complexes to classify the first cardiac complex is either a ventricular tachycardia complex or a supraventricular tachycardiac complex.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and devices for modulation of heart valve function
Methods and devices for modulating heart valve function are provided. In the subject methods, a heart valve is first in structurally modified. Blood flow through the structurally modified heart valve is then monitored, and the heart is paced in response to the monitored blood flow. Also provided are devices, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
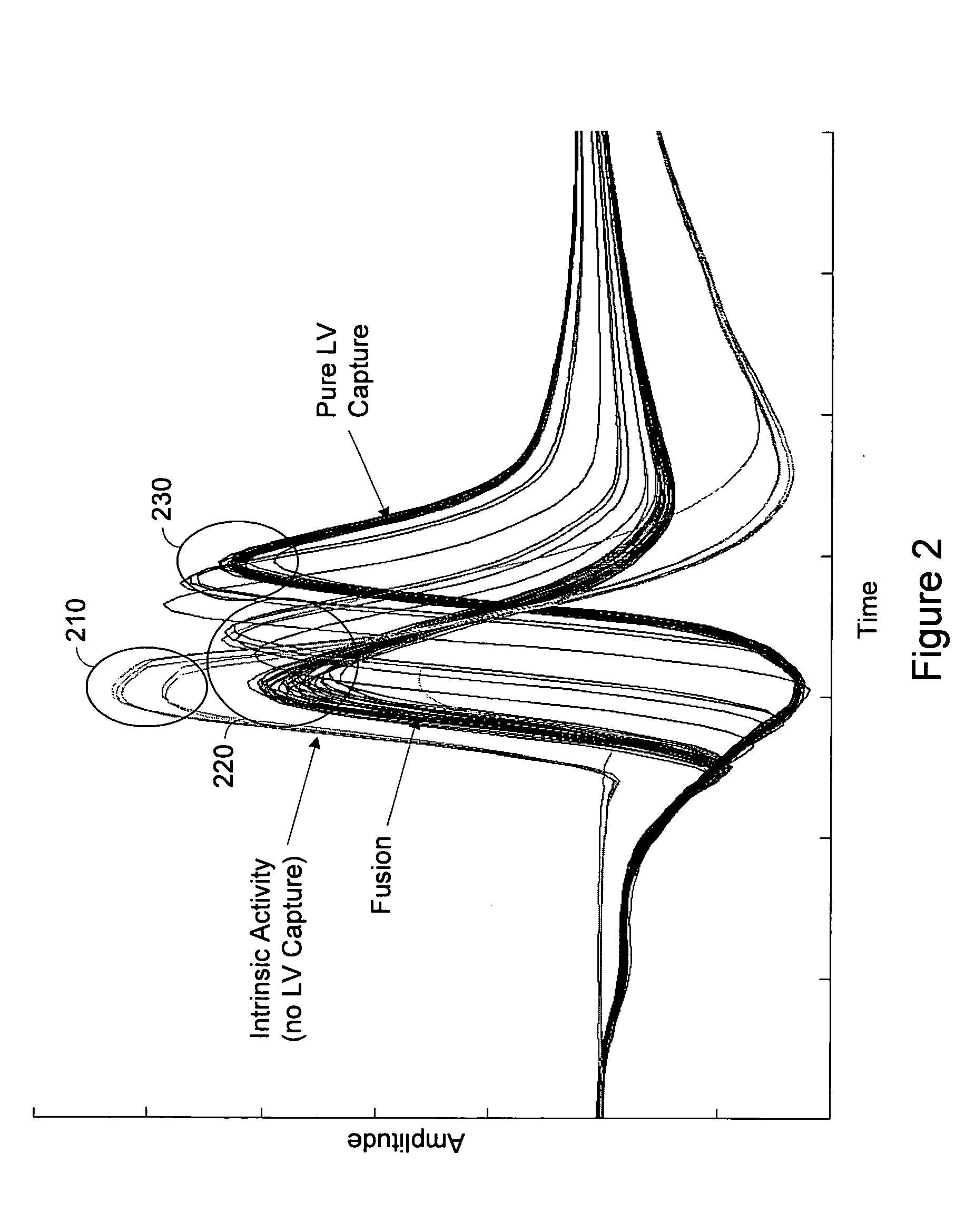
Baseline adaptation for cardiac pacing response classification
ActiveUS7330761B2Heart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEvaluation IntervalClassification methods
Methods and devices for establishing and using baseline for cardiac pacing response detection are described. A baseline amplitude of the cardiac signal may be established using data acquired in an evaluation interval prior to the delivery of the pacing pulse. An amplitude of the cardiac signal following delivery of the pacing pulse may be referenced using the baseline amplitude. An evoked response from the pacing pulse is detected using the referenced cardiac signal amplitude.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
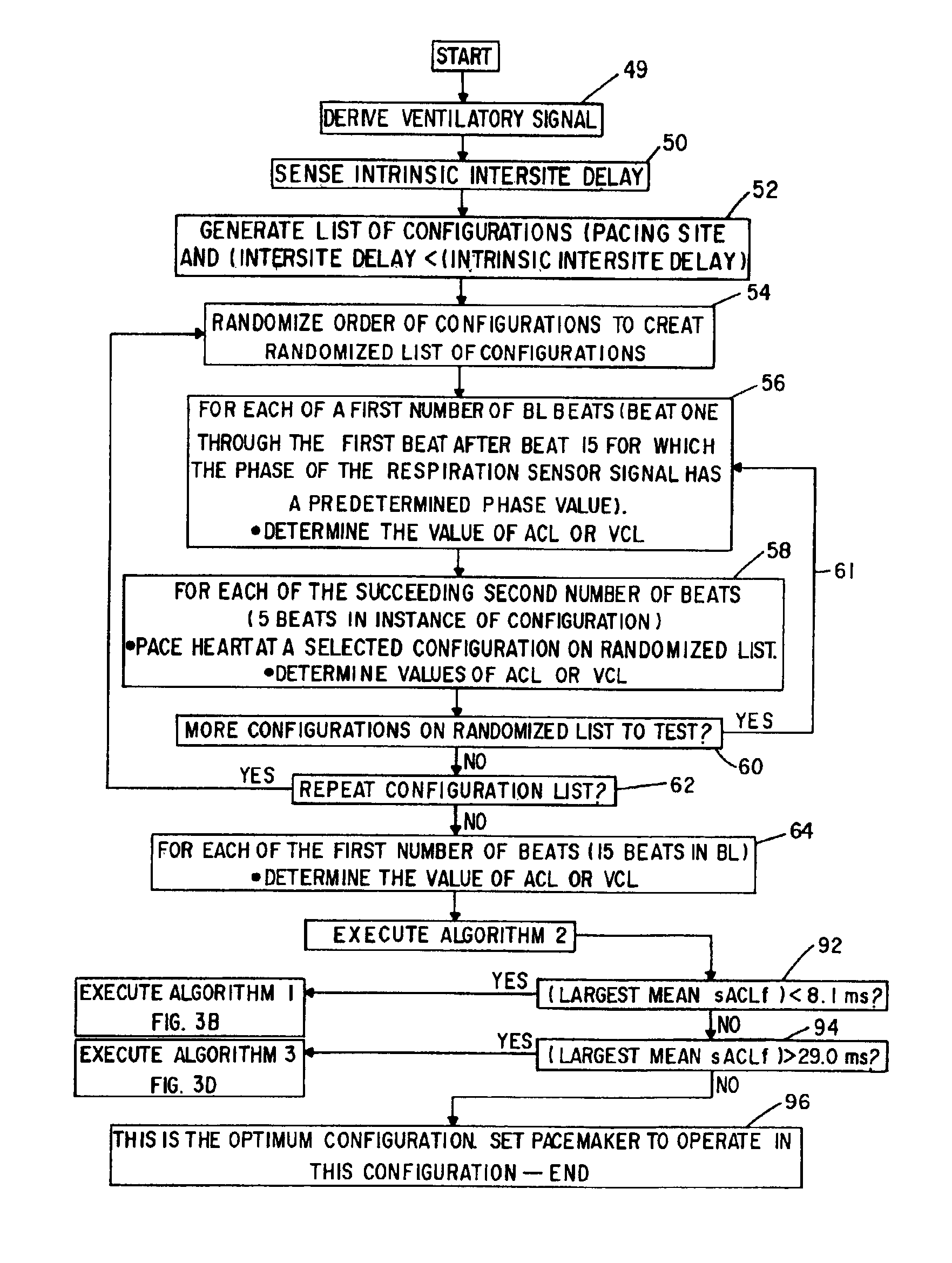
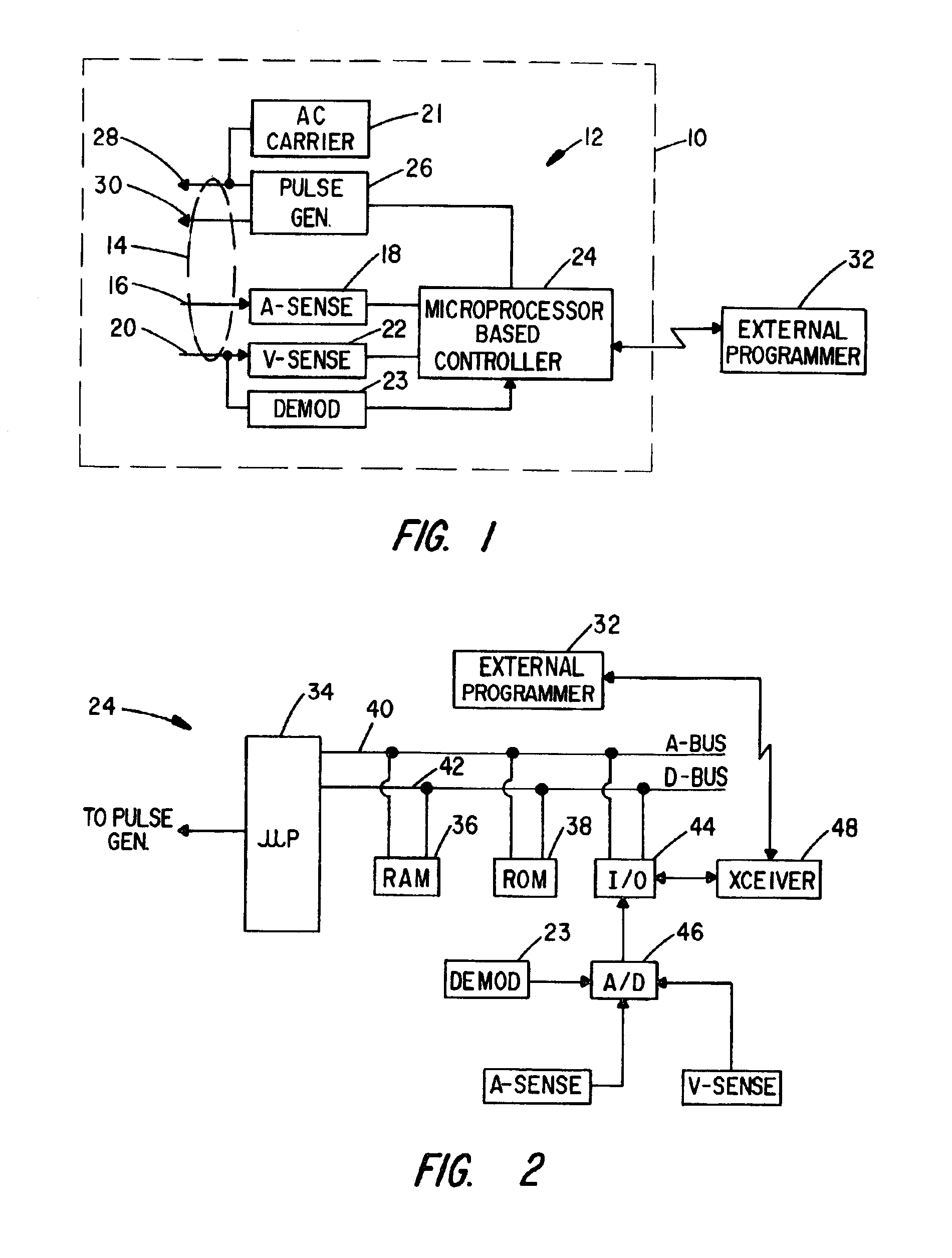
Cardiac rhythm management system with respiration synchronous optimization of cardiac performance using atrial cycle length
ActiveUS6876881B2Improve performanceSimple methodHeart stimulatorsMicrocontrollerCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device includes a dual chamber pacemaker, especially designed for treating congestive heart failure. The device incorporates a program microcontroller which is operative to adjust the pacing site, AV delay and interventricular delay of the pacemaker so as to achieve optimum hemodynamic performance. Atrial cycle lengths measured during transient (immediate) time intervals following a change in the site, AV delay and interventricular delay are signal processed and a determination can then be made as to which particular configuration yields the optimum performance. Paced transient beats following periods of baseline beats are synchronized to the patient's respiratory cycle to minimize effects of respiratory noise on atrial cycle length measurements.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Baseline adaptation for cardiac pacing response classification
ActiveUS20060129198A1ElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringEvaluation IntervalClassification methods
Methods and devices for establishing and using baseline for cardiac pacing response detection are described. A baseline amplitude of the cardiac signal may be established using data acquired in an evaluation interval prior to the delivery of the pacing pulse. An amplitude of the cardiac signal following delivery of the pacing pulse may be referenced using the baseline amplitude. An evoked response from the pacing pulse is detected using the referenced cardiac signal amplitude.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Far-field P-wave sensing in near real-time for timing delivery of pacng therapy in a cardiac medical device and medical device system
A medical device system for controlling ventricular pacing therapy during cardiac resynchronization therapy that includes a sensing device to sense a cardiac signal and emit a trigger signal in response to the sensed cardiac signal, a therapy delivery device to deliver the ventricular pacing in response to the emitted trigger signal, and a processor configured to identify a fiducial point of the cardiac signal sensed in real-time, set a window comprising a start point positioned a first distance prior to the fiducial point and an endpoint positioned a second distance less than the first distance subsequent to the fiducial point, determine a signal characteristic of the cardiac signal within the window, determine whether a P-wave is detected in response to the signal characteristic, determine whether an atrio-ventricular interval timer has expired, and emit a trigger signal to deliver the ventricular pacing timed off of the local maximum in response to the P-wave being detected and not timed off of the local maximum in response to the timer being expired.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cardiac pacing response classification based on waveform feature variability
Methods and systems involve determining the cardiac response to pacing pulses. The variability cardiac signal features detected during initialization is used to establish a variability threshold. A cardiac signal associated with a pacing pulse is sensed and one or more features of the cardiac signal are detected. The variability of the one or more features is compared to the variability threshold. The cardiac response to the pacing pulse is determined based on the feature variability.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Cardiac harness having electrodes and epicardial leads
InactiveUS20050137673A1Limit cardiac functionFunction increaseEpicardial electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesVeinSystole
A system for treating the heart includes a cardiac harness associated with a cardiac rhythm management device which includes at least one electrode associated with the cardiac harness, epicardial leads attached directly to the heart, and a power source connected to the leads. The system may also include transvenous leads that are located within a chamber of the heart and attached to the power source. The cardiac harness applies a compressive force on the heart during diastole and systole, and the electrodes will deliver an electrical shock to the heart for defibrillation and / or can be used for pacing / sensing. The cardiac harness and electrodes are delivered and implanted on the heart by minimally invasive access.
Owner:PARACOR MEDICAL INC
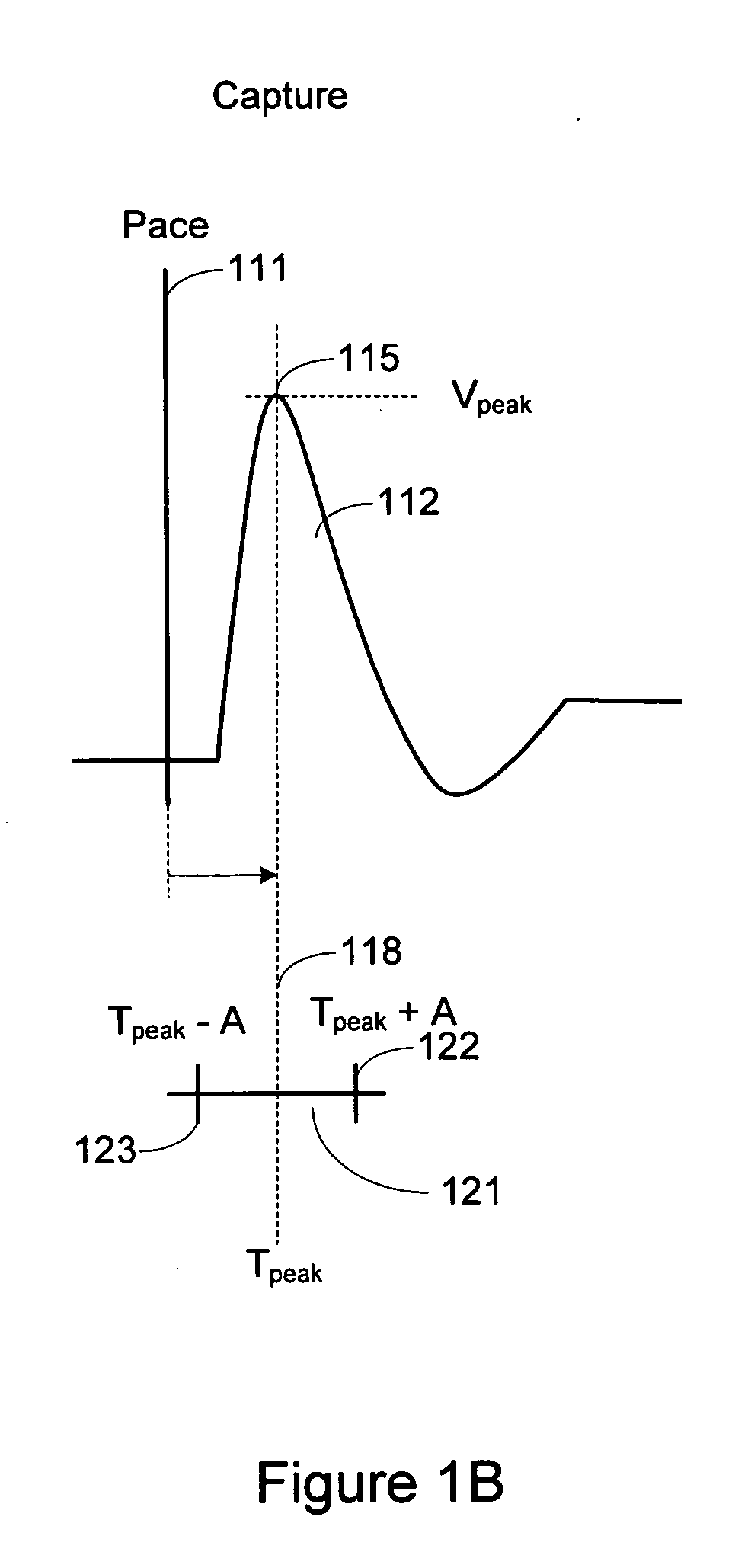
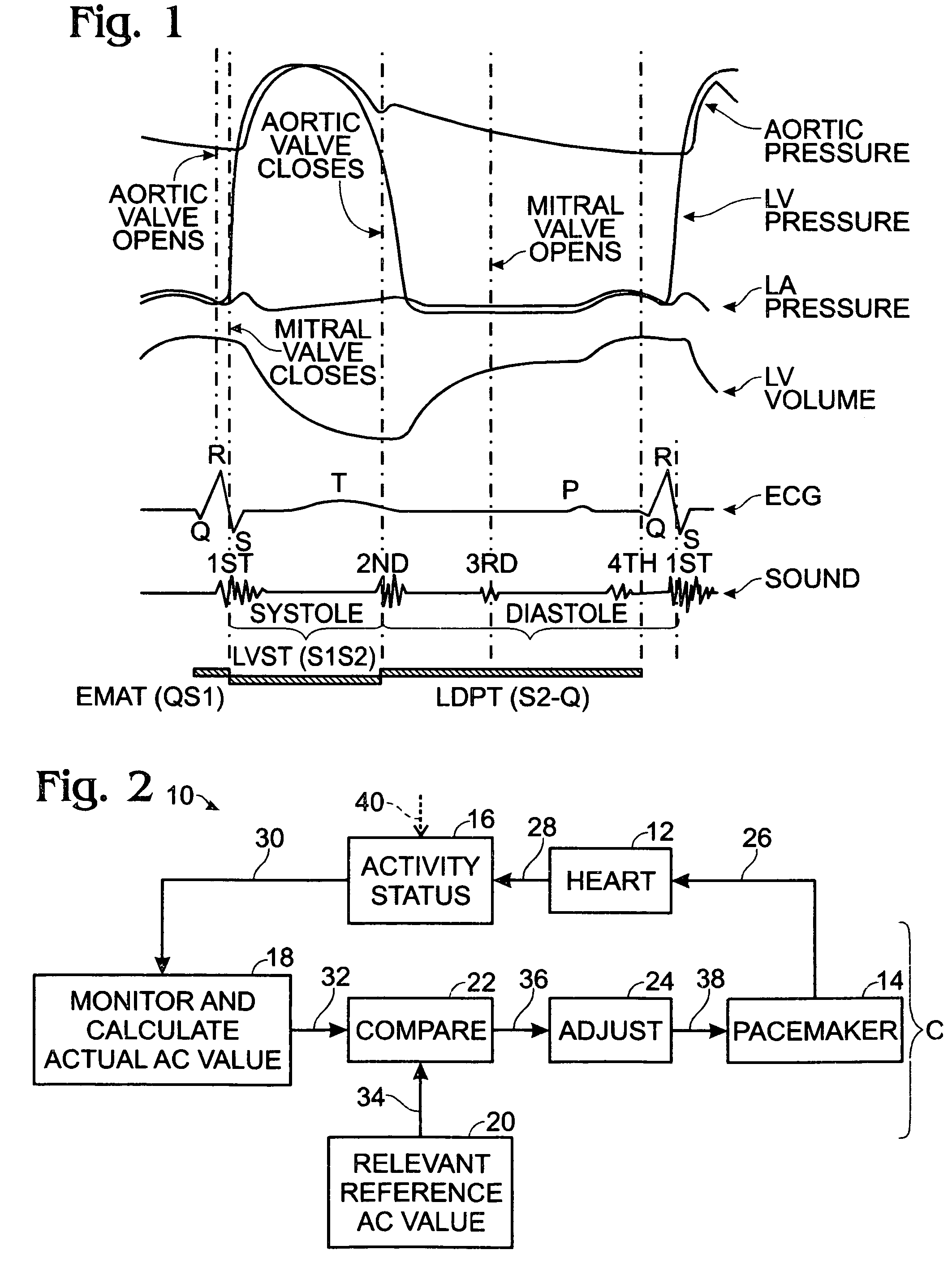
Rest phase heart pacing
A computer method, employable during an at-rest period of a pacemaker patient, for controlling the operation of the pacemaker so as maximally to support the patient's hemodynamic behavior in a context involving inhibiting fluid overload. The method involves (a) collecting simultaneously occurring ECG and heart-sound information, (b) processing the collected information to obtain at least S3 data, and in certain instances also EMAT and / or % LVST data, (c) utilizing such obtained data, and during the at-rest period, applying (a) pacing rate, (b) pacing intensity, (c) atrio-ventricular delay, and (d) inter-ventricular delay control to the pacemaker. Processing involves (a) calculating from the obtained data an actual, real-time, acoustic cardiographic therapy (AC) value which is to be employed in relation to controlling pacemaker activity, and (b) comparing the actual AC value to a pre-established, related, rest-period-associated, reference AC value to detect differences therebetween, with the utilizing and applying steps being implemented so as to minimize such differences.
Owner:INOVISE MEDICAL
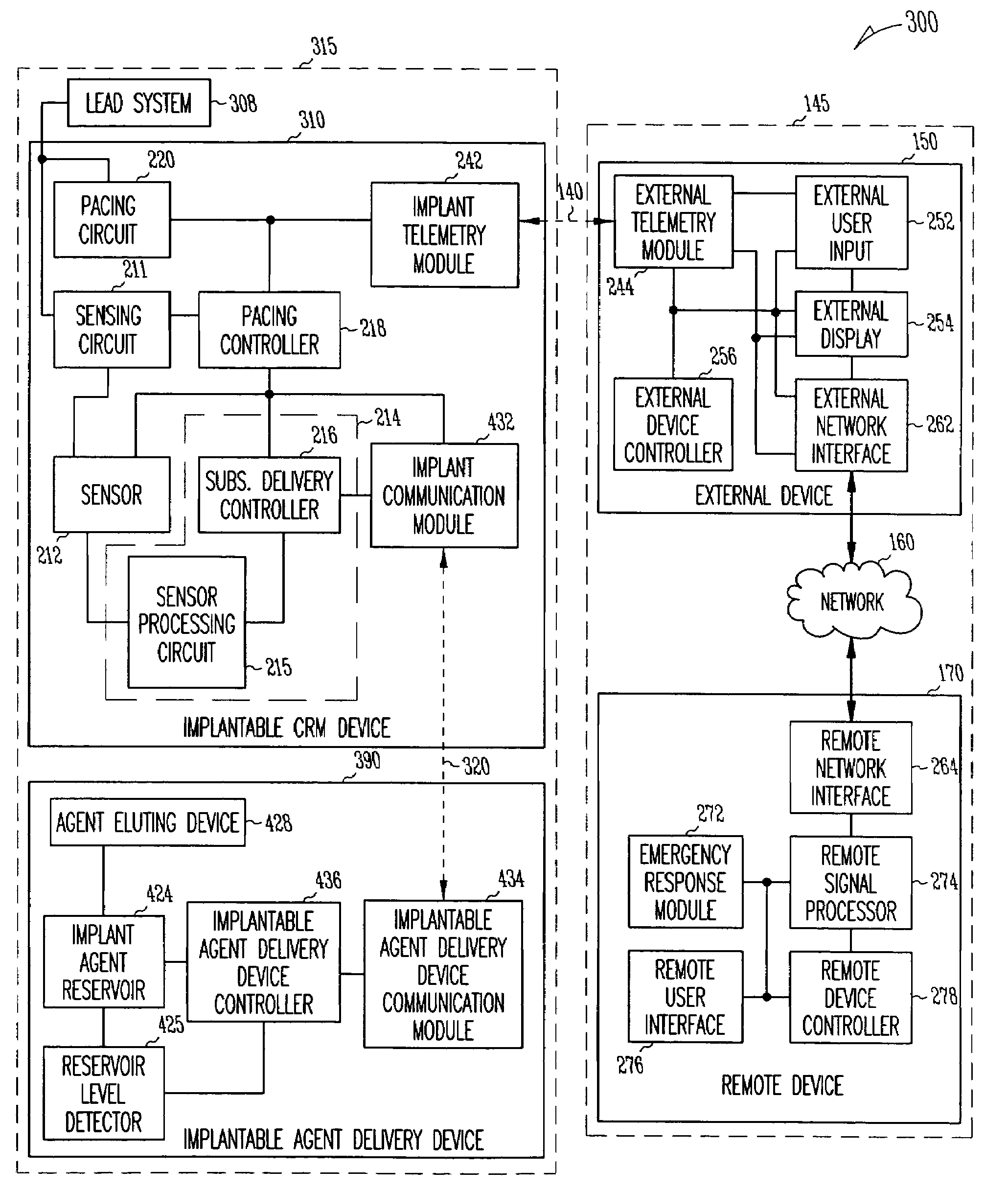
Method and apparatus to modulate cellular regeneration post myocardial infarct
InactiveUS7764995B2Easy to adjustModulate tissue growthMedical devicesPressure infusionCardiac muscleImplanted device
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
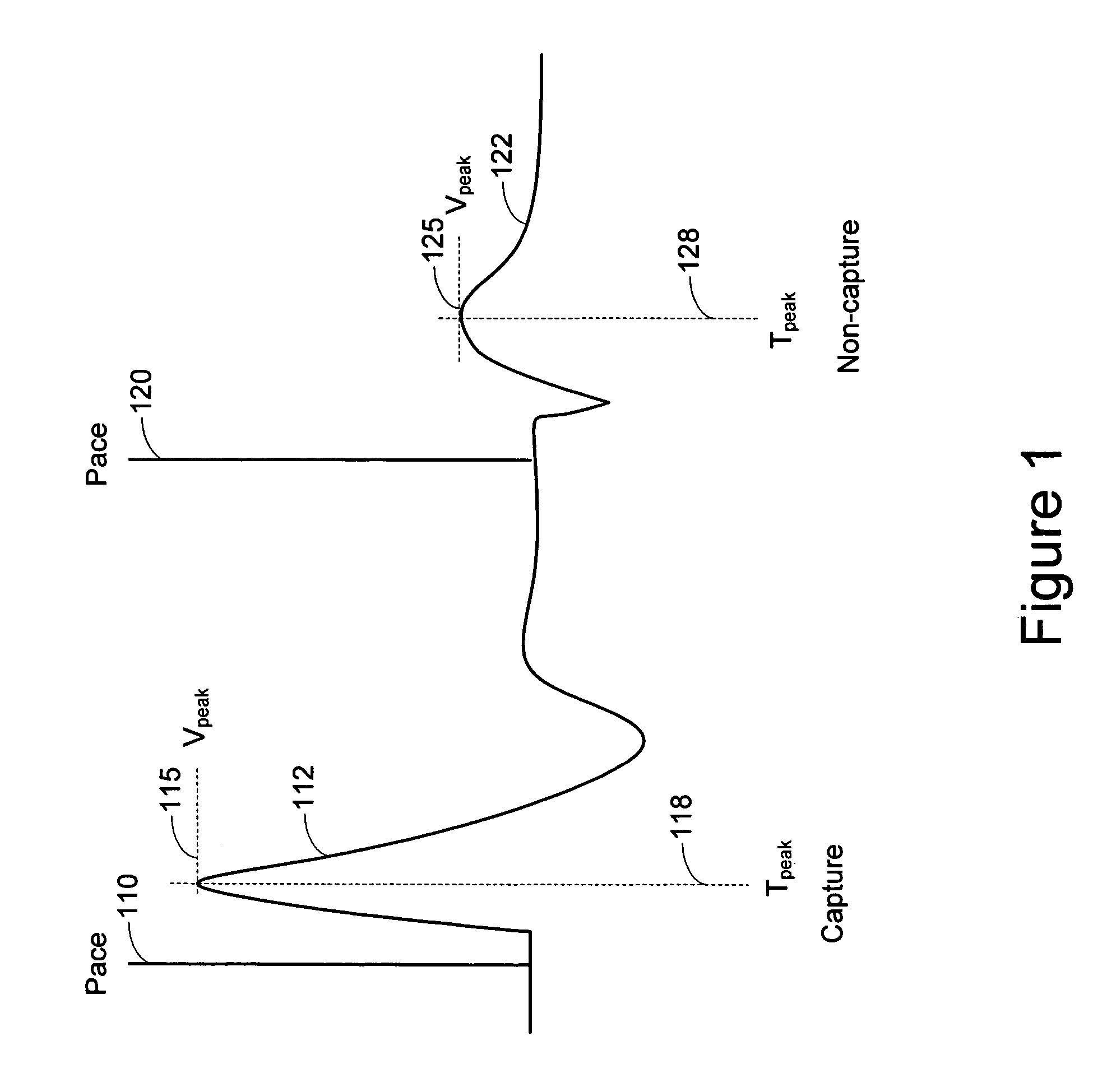
Autocapture pacing/sensing configuration
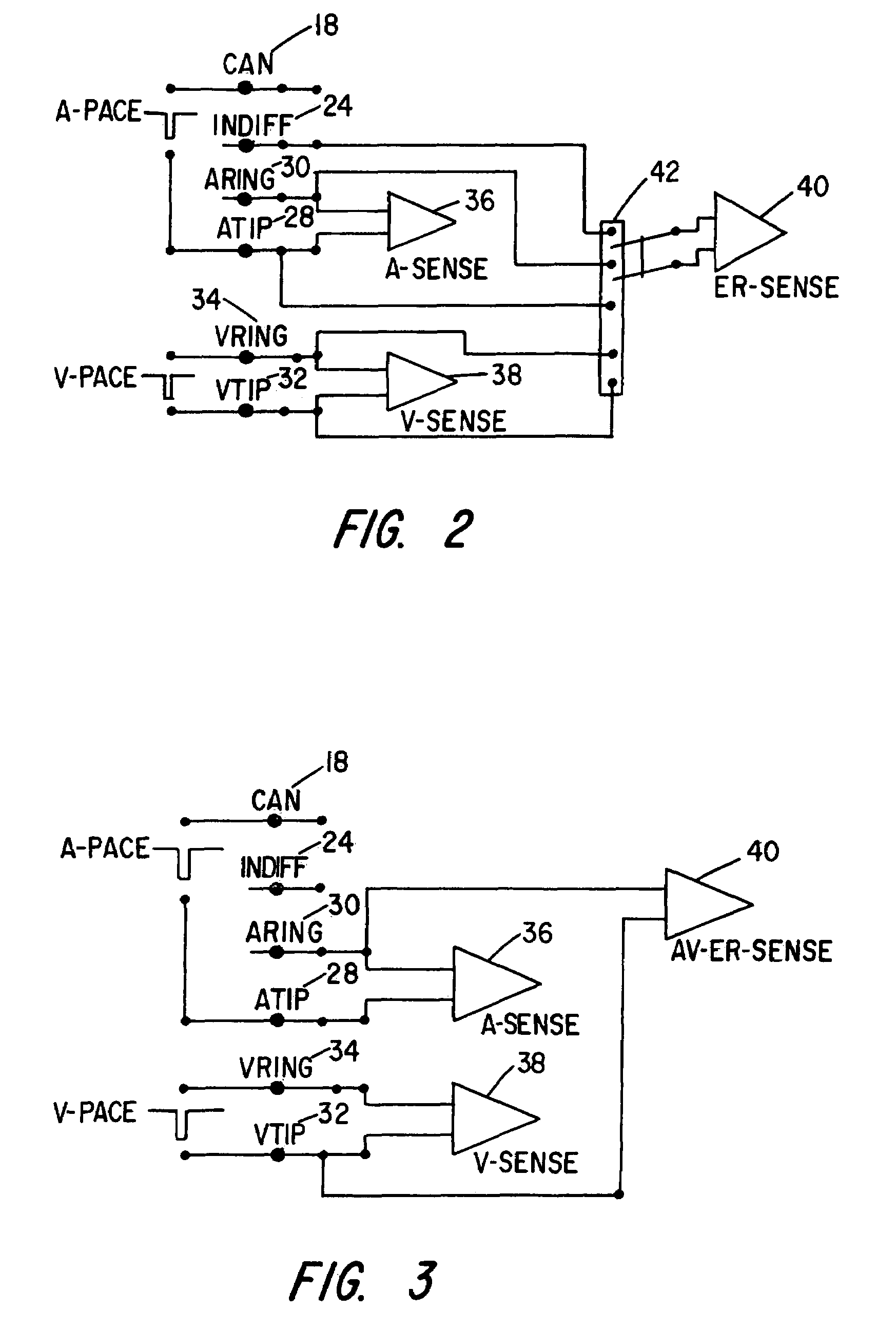
InactiveUS7092756B2Period be reduceEasy to detectHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacing
A cardiac pacing system that enhances the ability of a cardiac pacer to automatically detect whether a pacing stimulus results in heart capture or contraction. The cardiac pacing system includes a pacing circuit that attenuates polarization voltages or “afterpotential” which develop at the heart tissue / electrode interface following the delivery of a stimulus to the heart tissue, which thereby allows the pacing electrodes to be utilized to sense an evoked response to the pacing stimulus. The cardiac pacing system utilizes the pacing electrodes to sense an evoked response, thereby eliminating the necessity for an indifferent electrode to sense an evoked response. The present invention allows accurate detection of an evoked response of the heart, to thereby determine whether each pacing stimulus results in capture.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Tandem cardiac pacemaker system
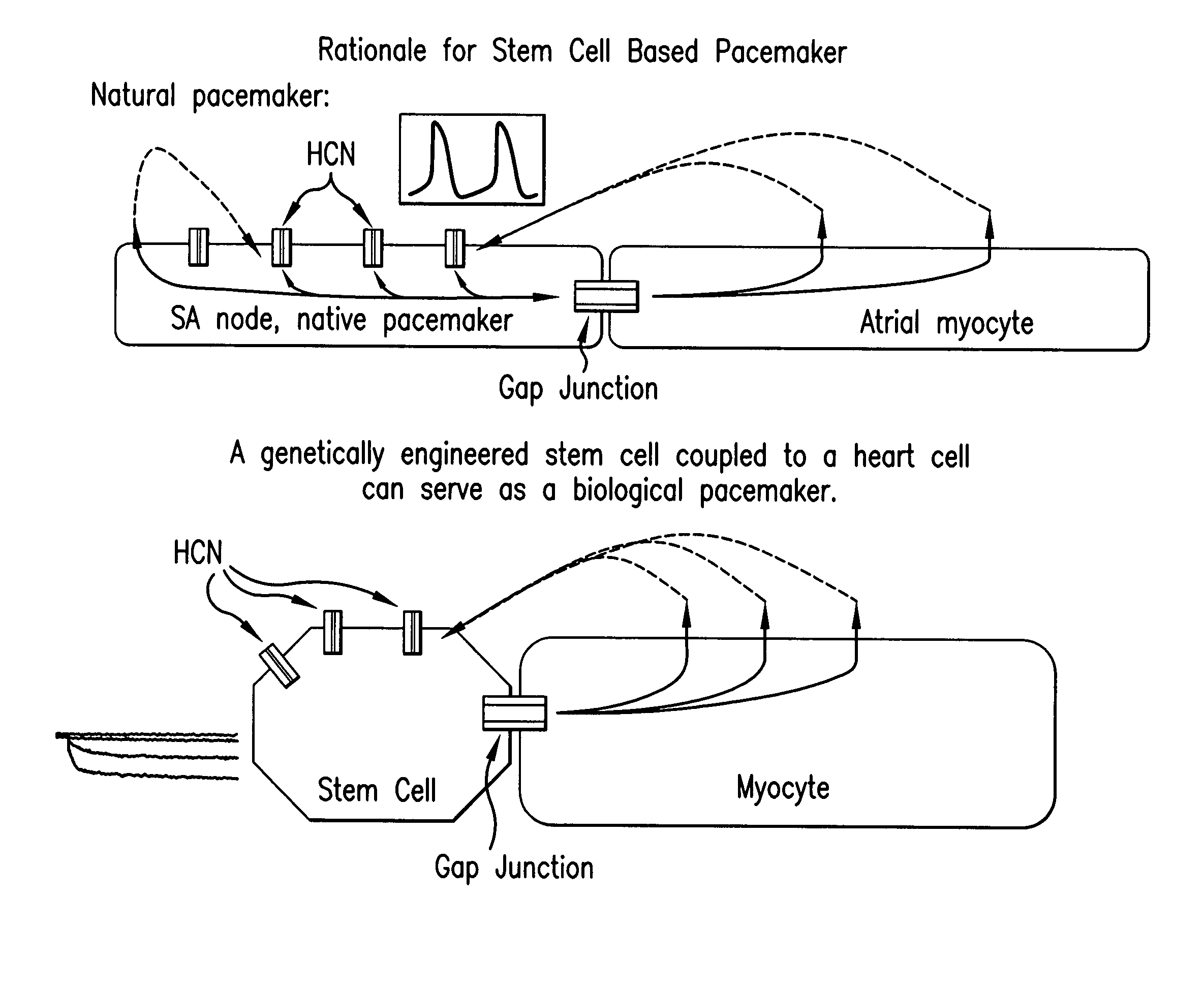
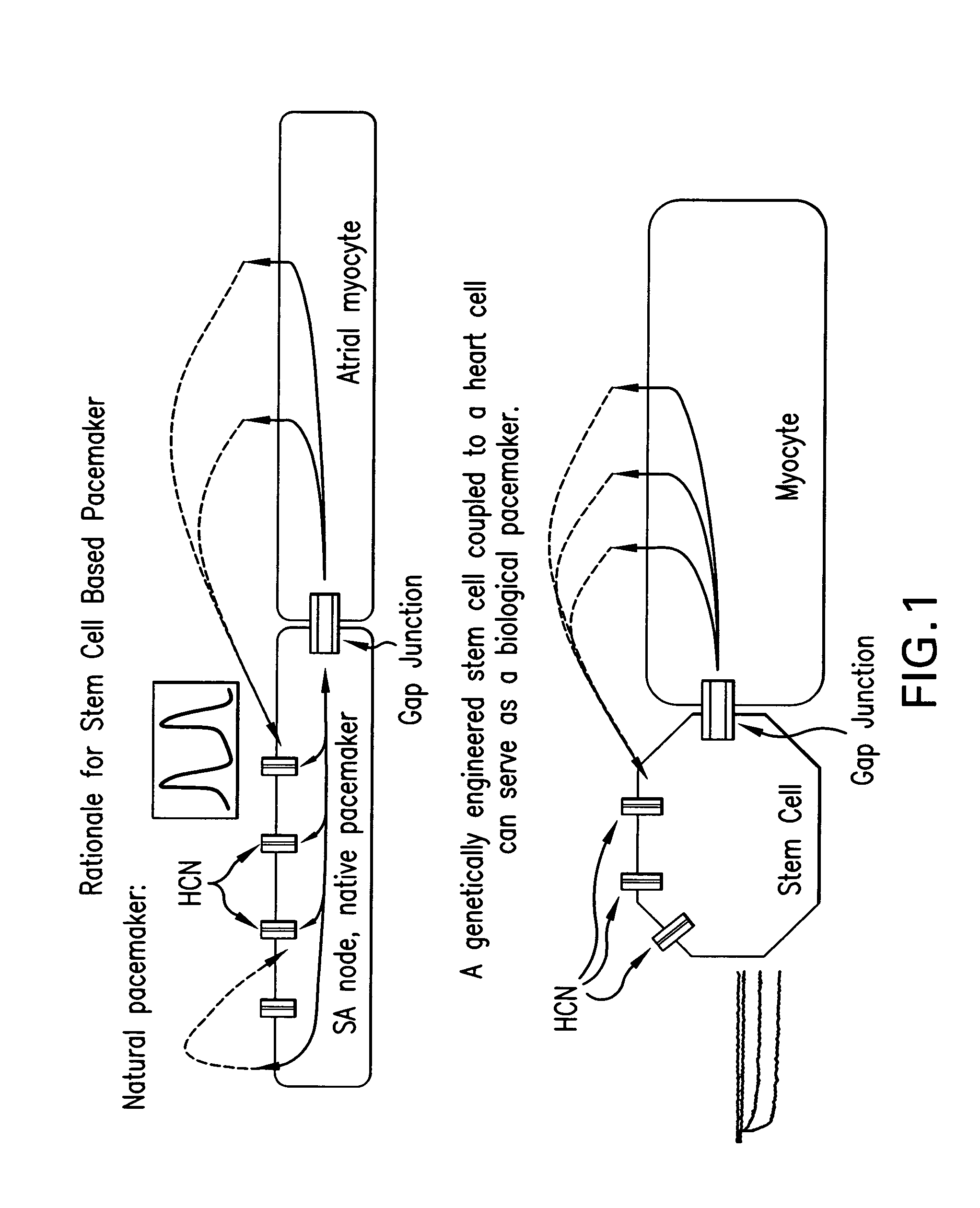
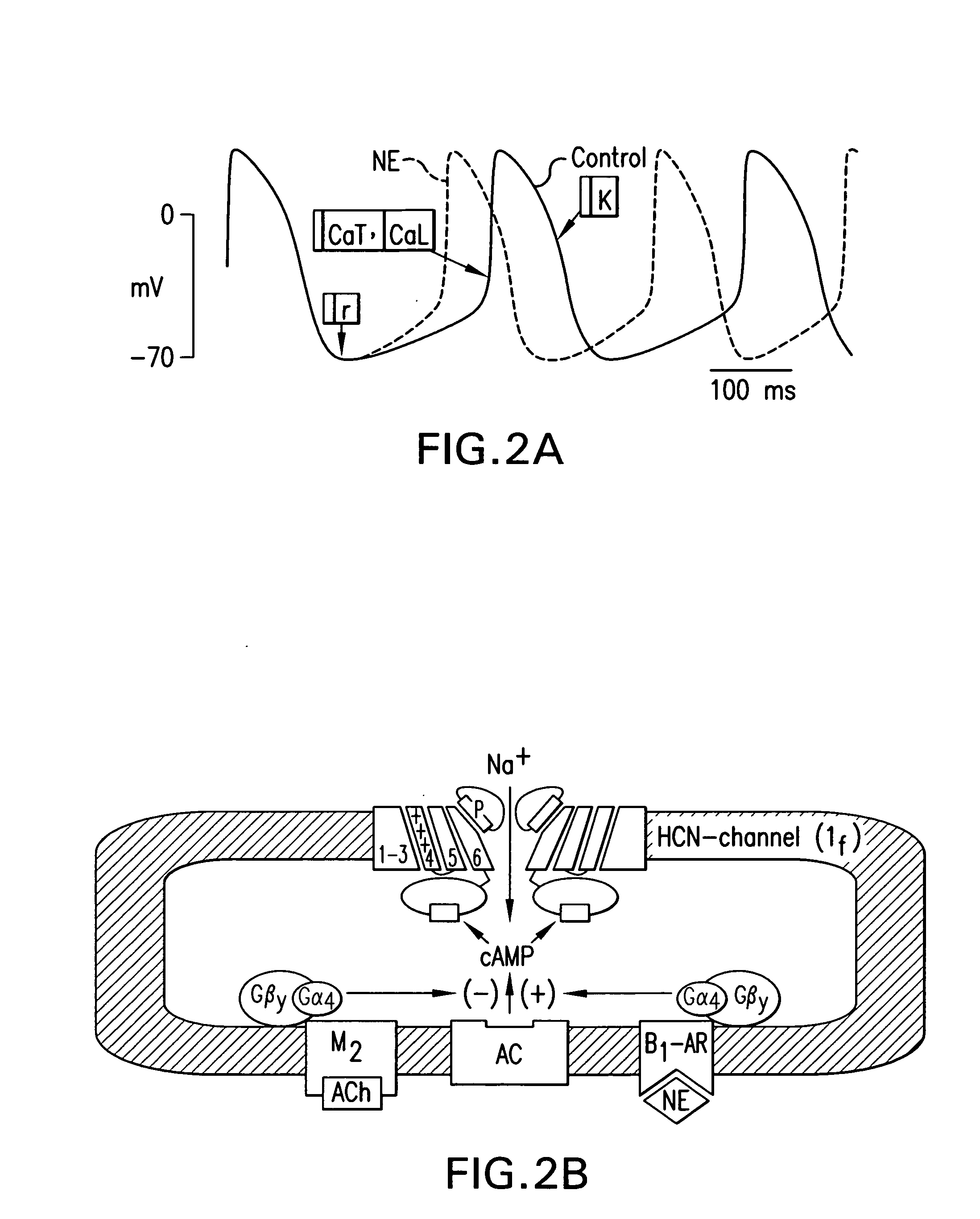
InactiveUS20090053180A1High basal signal frequencyLess negative maximum diastolic potentialBiocideGenetically modified cellsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
This invention provides pacemaker systems comprising (1) an electronic pacemaker, and (2) a biological pacemaker, wherein the biological pacemaker comprises a cell that functionally expresses a chimeric hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) ion channel at a level effective to induce pacemaker current in the cell. The invention also provides related biological pacemakers, atrioventricular bridges, methods of making same, and methods of treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac rhythm disorder.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +2
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS20080081942A1Facilitate positive or reverse remodelingImprove efficiencyHeart valvesInternal electrodesMyofibrilFunctional disturbance
Owner:BAY INNOVATION GROUP
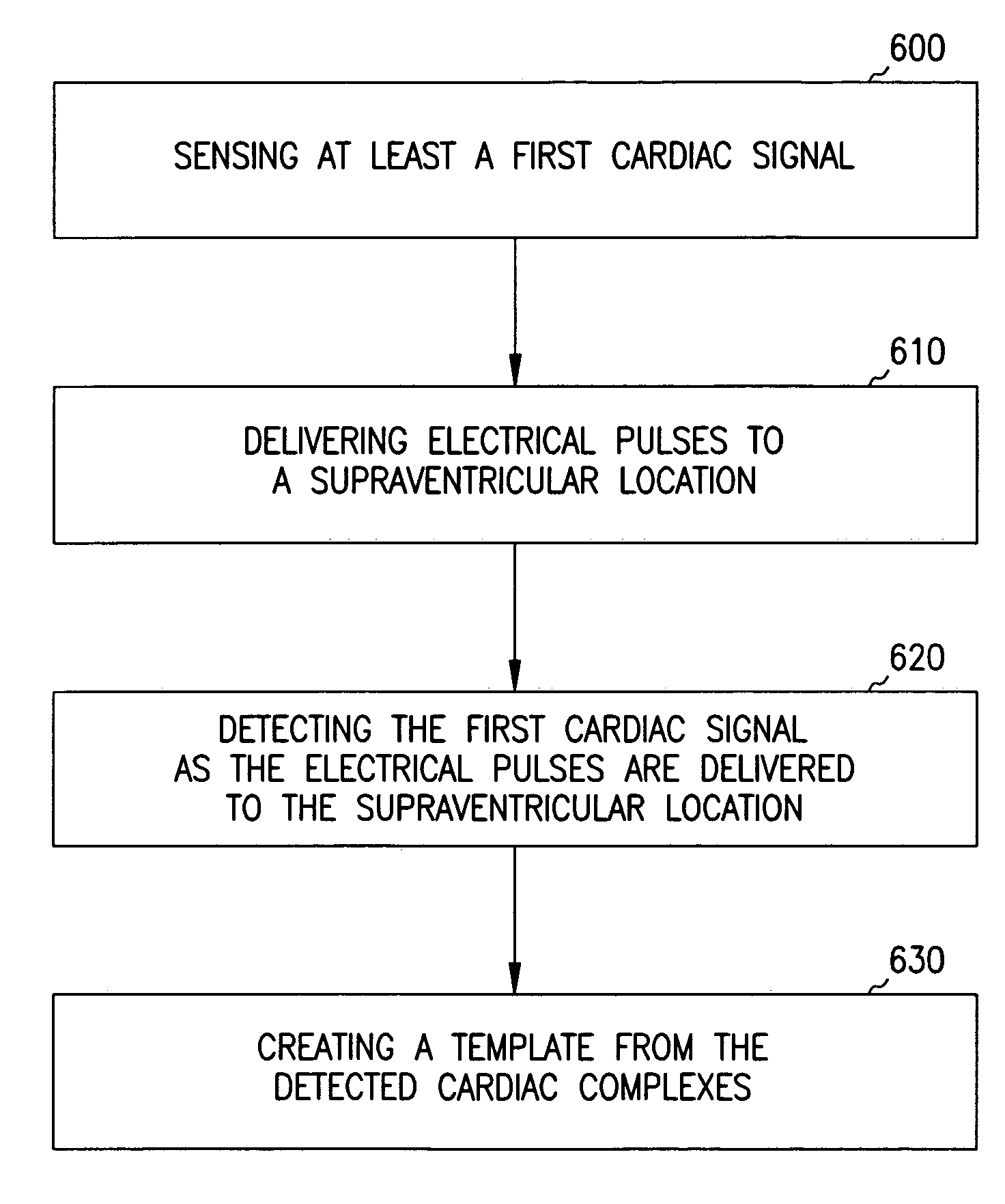
Pacing interval adjustment for cardiac pacing response determination
InactiveUS20070078489A1Enhances cardiac pacing response determinationImprove responseElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalSingle chamber
The waveform morphology of a propagated pacing response signal may be adjusted to achieve a waveform morphology that enhances cardiac pacing response determination. One or more pacing intervals may be adjusted to achieve at least one cardiac pacing response waveform morphology that enhances determination of the cardiac pacing response. The heart is paced using the one or more adjusted pacing intervals and the cardiac response to the pacing is determined. The one or more adjusted pacing intervals may include an atrioventricular pacing delay, an interatrial pacing delay, an interventricular pacing delay, or other inter-chamber or inter-site pacing delays. Adjusting the one or more pacing intervals may be used to increase a difference between a first waveform morphology associated with multi-chamber capture and a second waveform morphology associated with single chamber capture.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and devices for modulation of heart valve function
Methods and devices for modulating heart valve function are provided. In the subject methods, a heart valve is first in structurally modified. Blood flow through the structurally modified heart valve is then monitored, and the heart is paced in response to the monitored blood flow. Also provided are devices, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Method for orienting inducing and differentiating heart pacemaker cell by embryo source pluripotent stem cell
Cell transplantation for constructing biological heart pacemaker is used embryo source dry / ancestral cell and adult mesogalia dry cell as cell sources. The process is carried out by oriented differentiation inducing for heart pacemaker cell by embryo source multifunctional dry cell, bone marrow adhering to obtain primary culture cell, clone culturing to obtain purifying system by diluting, applying paracrine factor endothelin-1 or nervous adjusting protein-1, extracellular matrix laminated adherent protein and fiber connecting protein etc. substrate glue, trans-dyeing pacemaker gene HCN4, and in-vitro inducing embryo source multifunctional dry cell. It is various and non-immunogenicity. It can be used to treat sick sinus syndrome.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
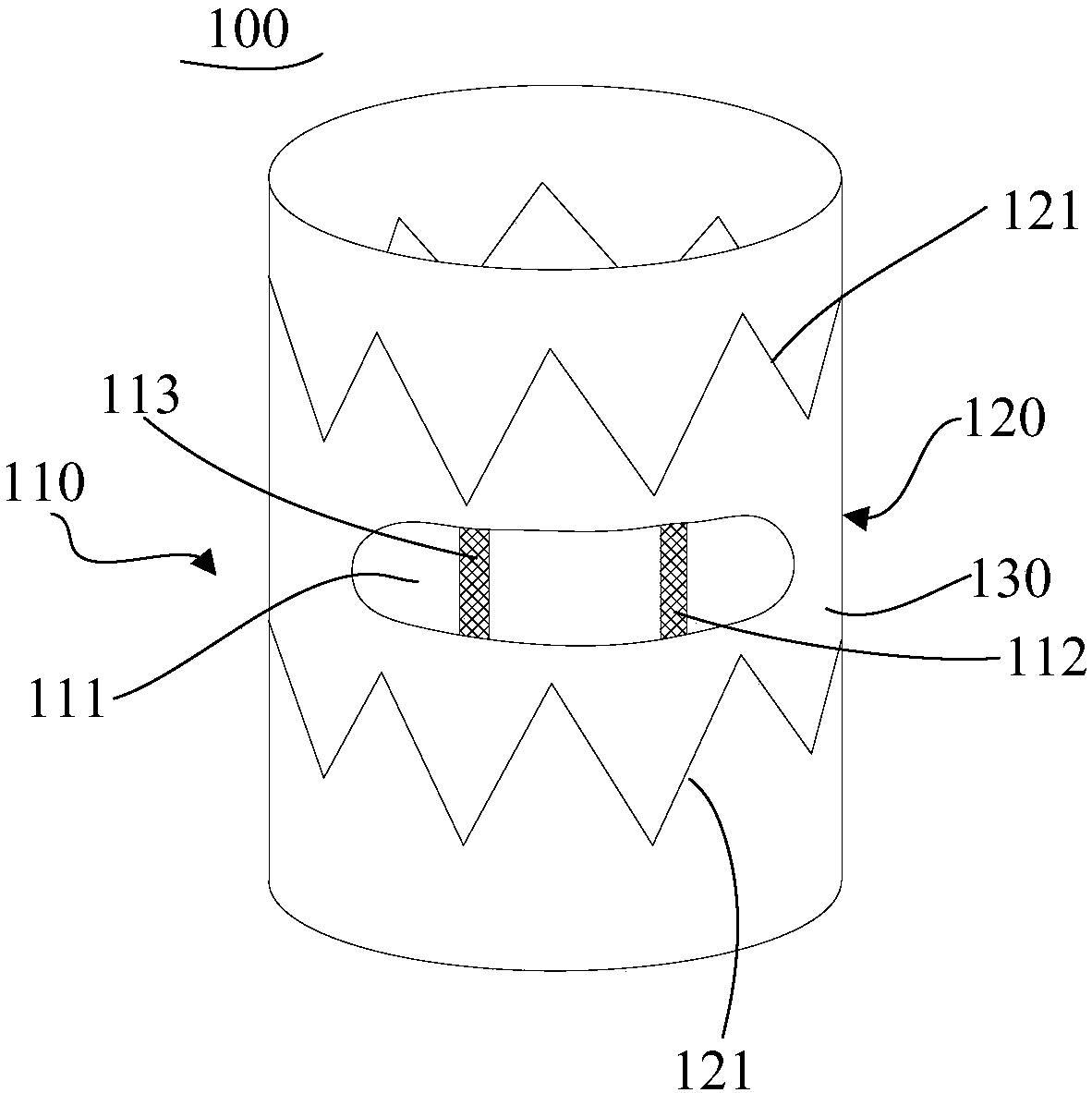
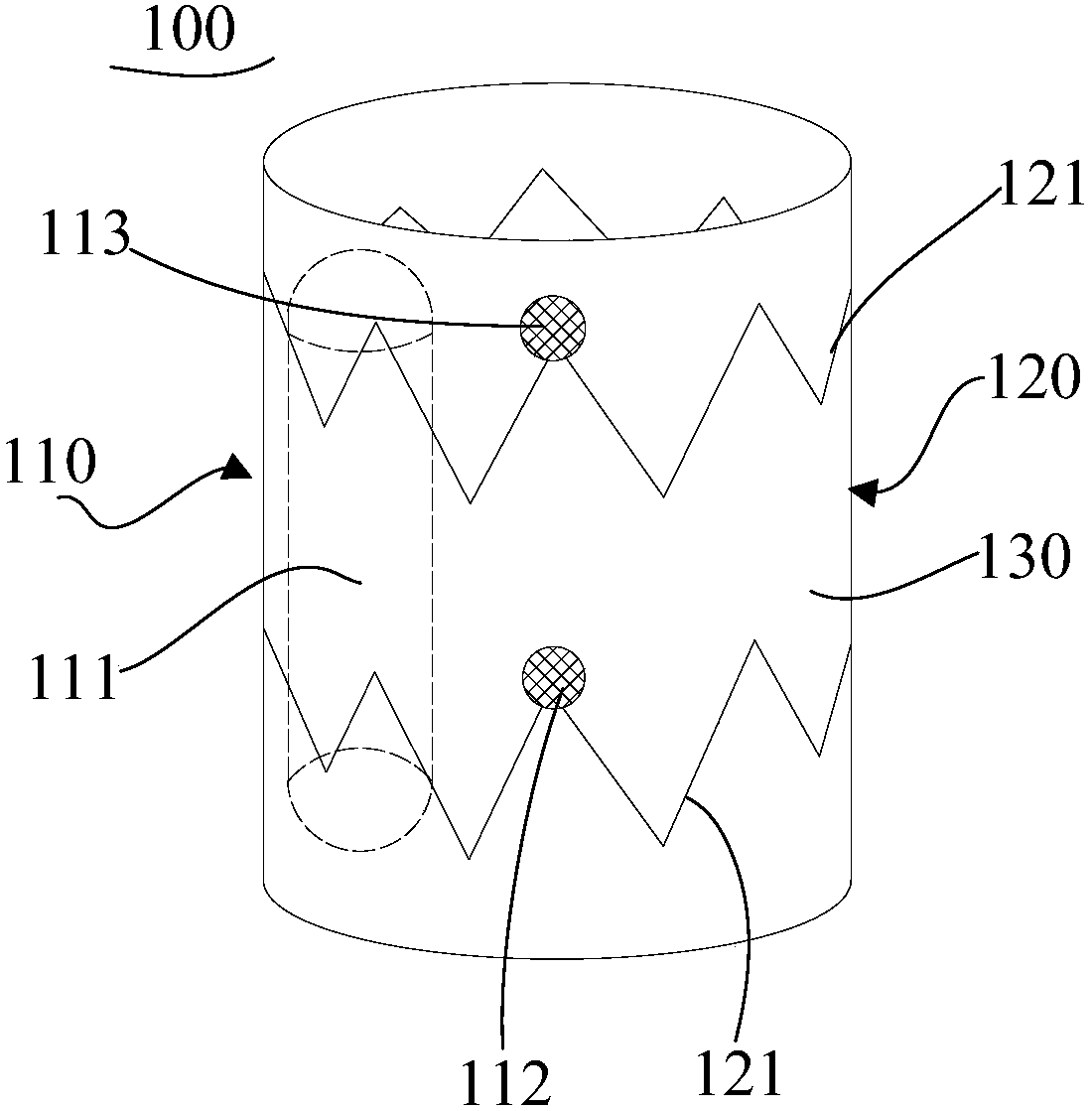
Heart pacing device, and fixing method and conveying system thereof
ActiveCN108079437AAchieve dual chamber pacing functionSynchronized Physiological PacingHeart stimulatorsVeinHeart chamber
The invention provides a heart pacing device, and a fixing method and a conveying system thereof; the heart pacing device comprises an annular support and a wireless pacing unit at least partially arranged on the annular support; the annular support has a first size with the rebound limited by the first environment, and expands to a second size under the second environment. The heart pacing devicecan be fixed in human body tissues of different wall thicknesses and sizes, and can be easily fixed in a boundary place between the postcava and the right atrium, realizing dual-cavity pacing of thewireless pacing unit, and ensuring the atrium-chamber synchronization physiological pacing. The heart pacing device uses the self-expansion features of the annular support to tightly attach the annular support with protogenesis blood vessel walls, thus fixing the heart pacing device in the heart chamber with a good fixing effect, and preventing heart chamber perforating risks.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRMSHANGHAICO LTD
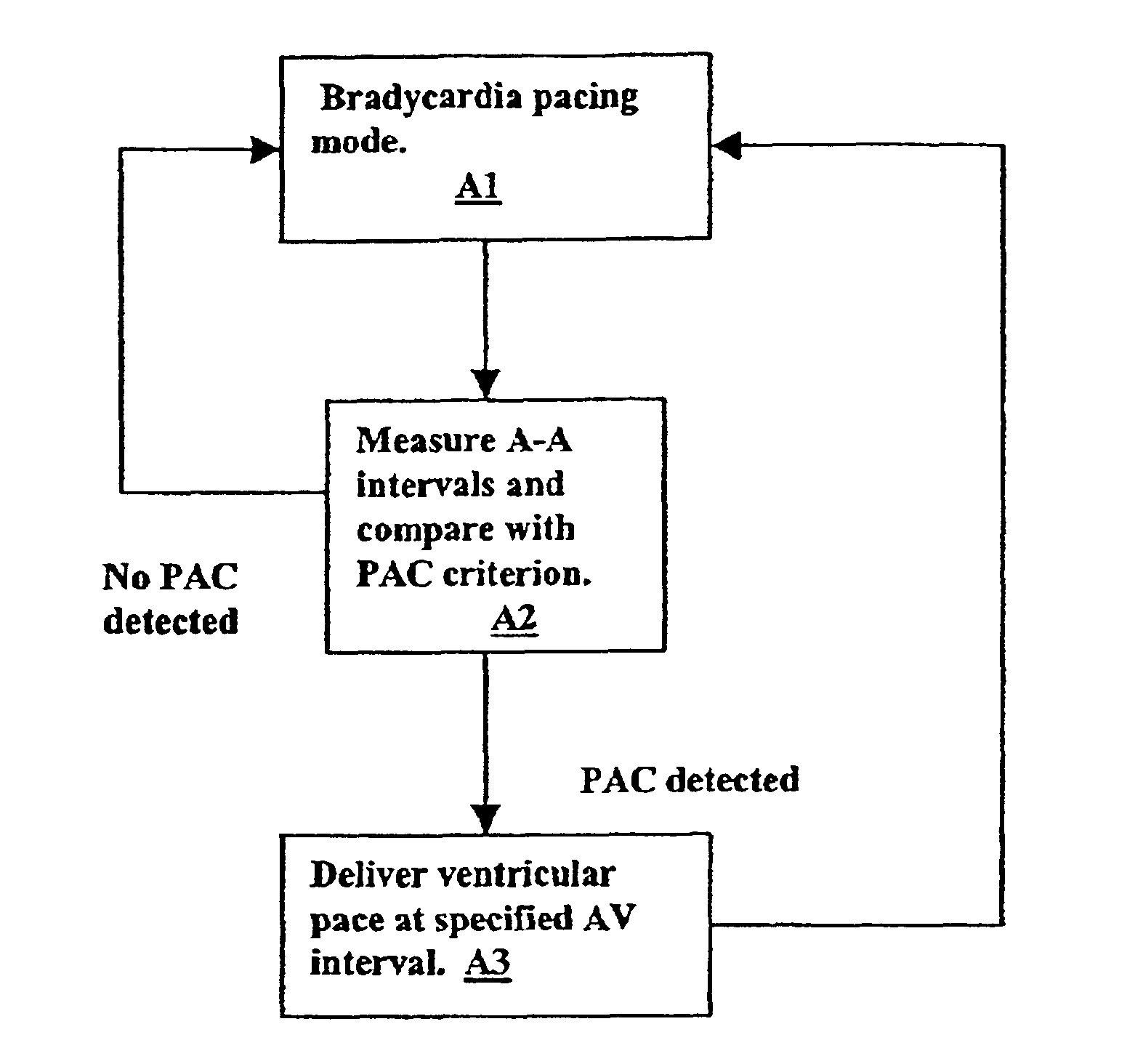
Ventricular pacing for prevention of atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS6957104B2Preventing atrial fibrillationAvoid typingHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular depolarizationPremature atrial contraction
A method and apparatus for preventing atrial fibrillation arising from a premature atrial contraction. Upon detection of a premature atrial contraction, a pace is delivered to a ventricle at a specified AV interval selected as either a late-pace or early-pace value. The resulting ventricular depolarization then occurs during a time when the atria are not vulnerable to the triggering of fibrillation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Bundle branch pacing devices and methods
PendingUS20190111264A1High outputGood synchronizationElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesBundle branchesCathode electrode
The present disclosure relates generally to pacing of cardiac tissue, and more particularly to adjusting delivery of His bundle or bundle branch pacing in a cardiac pacing system to achieve synchronized ventricular activation. A left bundle branch (LBB) cathode electrode may be implanted a left side of the septum of the patient's heart proximate to the LBB, and a right bundle branch (RBB) cathode electrode may be implanted on a right side of the septum of the patient's heart proximate to the RBB. One or both cathode electrodes may be used to deliver synchronized left and right bundle-branch pacing based on one or both of an atrial event and a ventricular event. A device for bundle branch pacing may be implanted based on determining whether an LBB block pattern or an RBB block pattern is present in monitored electrical activity.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Flexible ventricular assist device
ActiveCN111921027AReduce postoperative discomfortReduce weightSuction devicesEngineeringLeft ventricle wall
The invention discloses a flexible ventricle assist device which comprises an elastic shell attached to the outer wall of the heart and at least two sets of pneumatic muscles embedded in the elastic shell and corresponding to the left ventricle and the right ventricle of the heart respectively. An air passage for communicating the air bags in all the pneumatic muscles is arranged in the elastic shell, and is led out through an air inlet and an air outlet in the elastic shell to be connected with an external air source; and a strain limiting layer is arranged on the outer side air bag wall, away from the heart, of the pneumatic muscle. The heart pump blood function of a heart failure patient can be assisted; the whole device is simple in structure, and the elastic shell can be designed to be lighter and thinner; the load of the implantation device on the body of the patient is reduced; the whole elastic structure can better adapt to different biological characteristics adapting to hearts of different patients, is wider in adaptability, can act on the heart to conduct adaptive deformation on torsion of the heart in the heart process, reduces damage to cardiac myocardium of the heart,and enables the heart of the heart failure patient to reach the normal blood pumping level through heart pacing signal feedback control.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Tissue-engineered atrioventricular node and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical engineering. At present, the research about the construction of a tissue-engineered atrioventricular node is not reported in China and foreign countries. The invention provides a method for constructing the tissue-engineered atrioventricular node by using cardiac pacing cells and conduction cells which are obtained by inducing collagen sponge and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are induced into the pacing cells through co-culture with sinoatrial node cells, and are induced into the cardiac pacing cells by a method for co-culture with auricular appendage muscle cells; and the two kinds of cells are used as seed cells, the collagen sponge is taken as a bracket, and the tissue-engineered atrioventricular node with a pacing characteristic and an electrocardio-conduction characteristic is constructed in vitro. Through animal experiments, the successfully constructed tissue-engineered atrioventricular node is transplanted to treat atrioventricular conduction block, and a good treatment effect is achieved. The tissue-engineered atrioventricular node which has the electrocardio-conduction characteristic and can be transplanted for treatment is obtained, and hope is brought to treatment of arrhythmia caused by heart atrioventricular conduction block.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
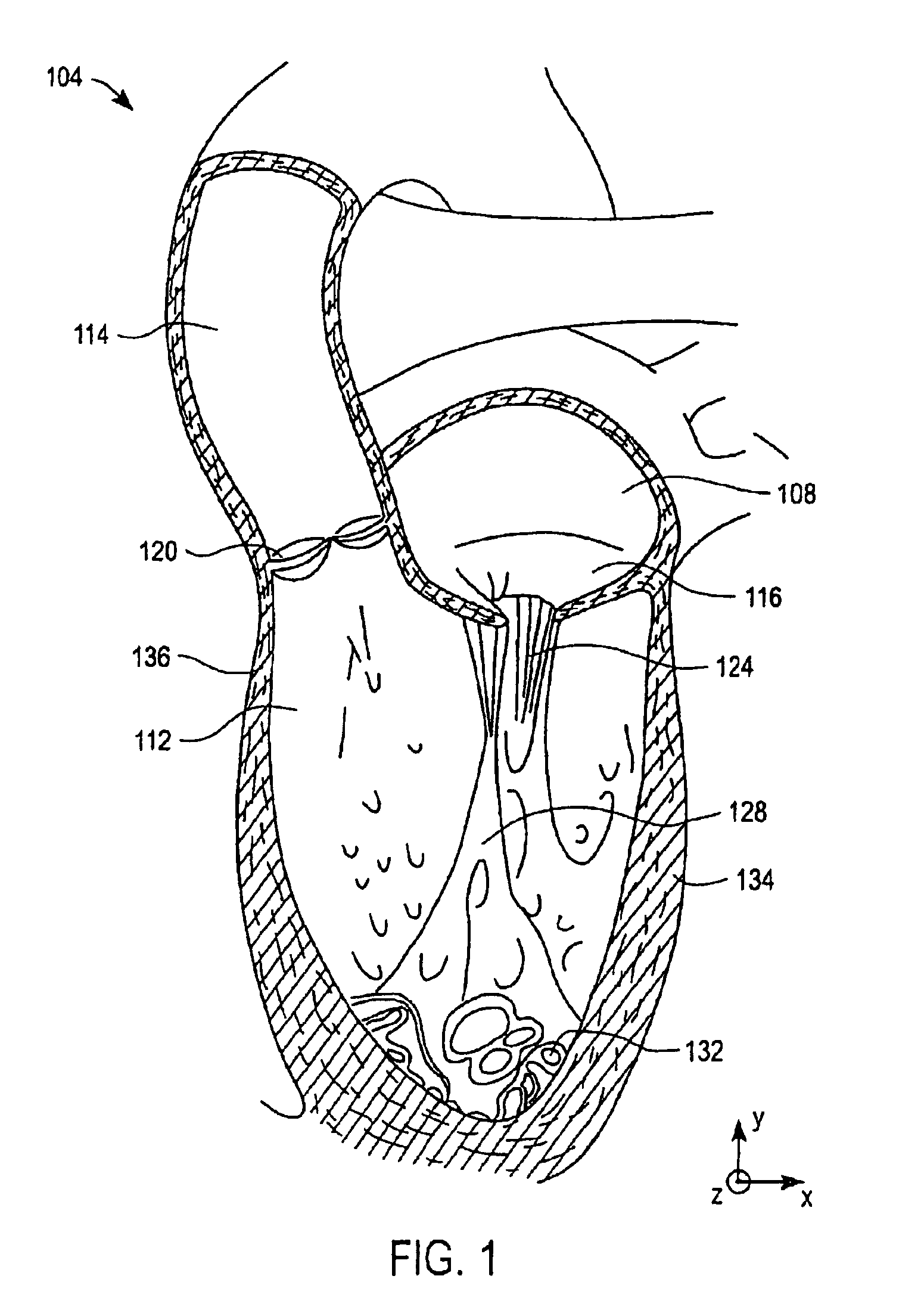
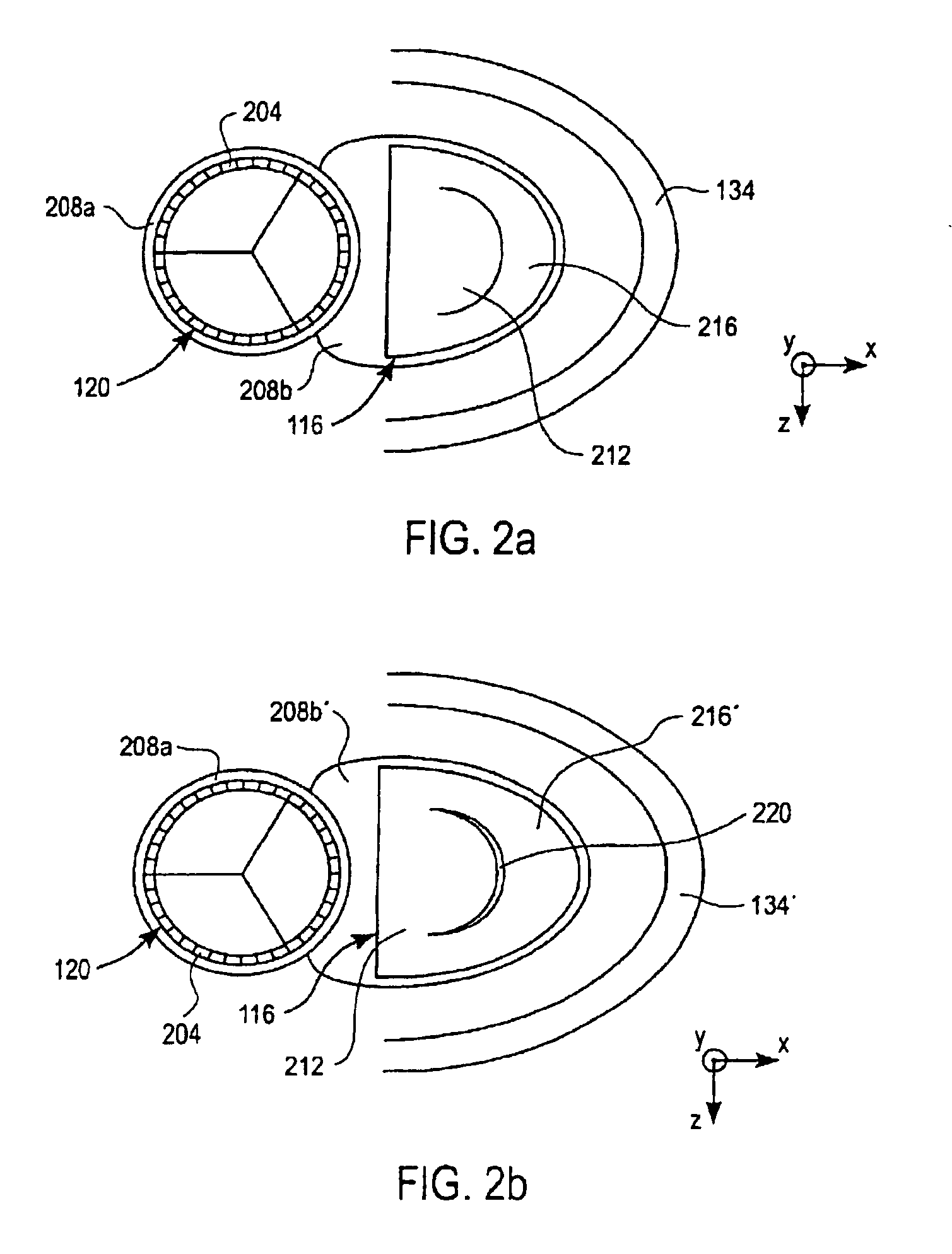
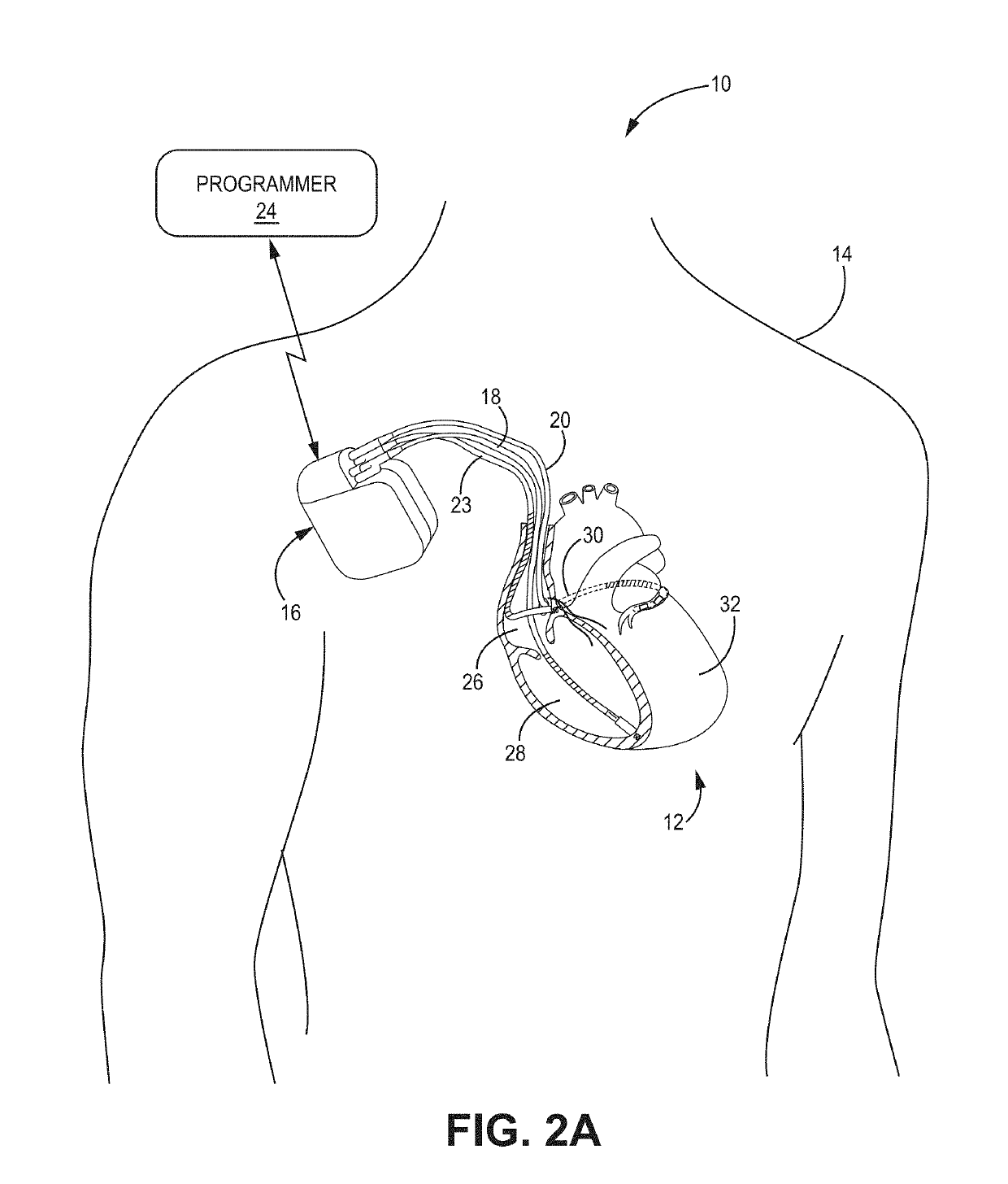
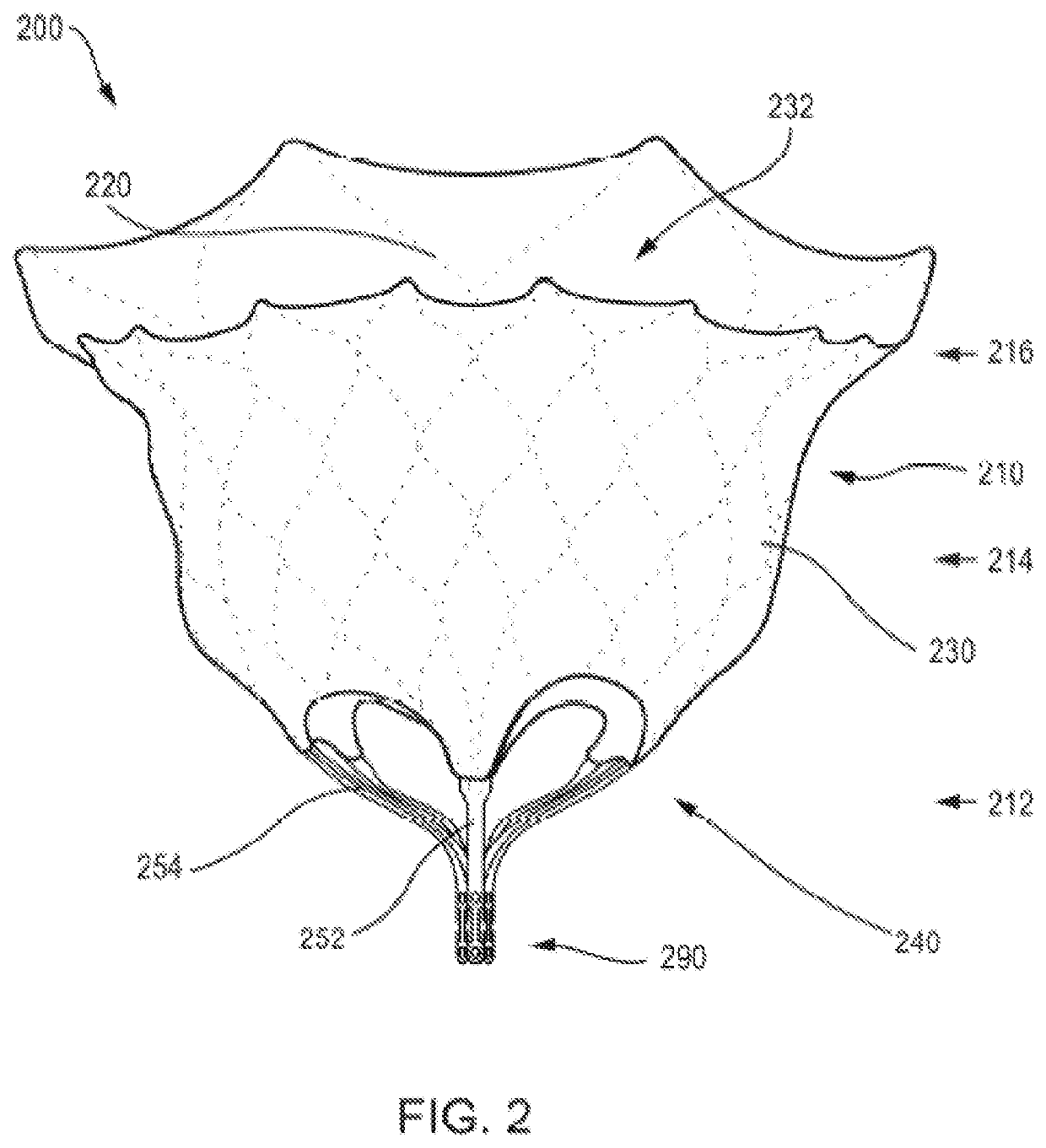
Prosthetic Heart Valve And Methods For Cardiac Hemodynamic Optimization And Monitoring
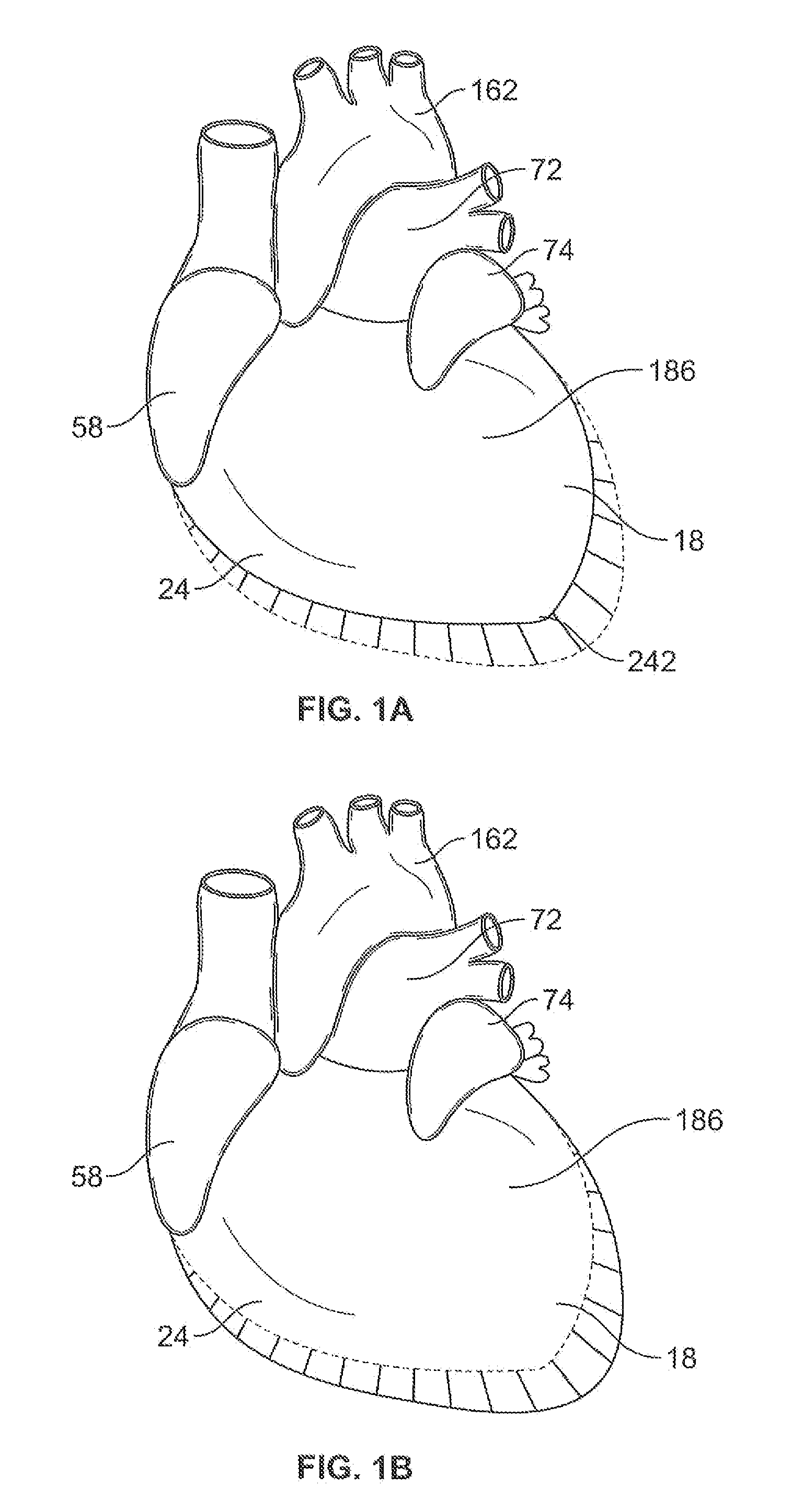
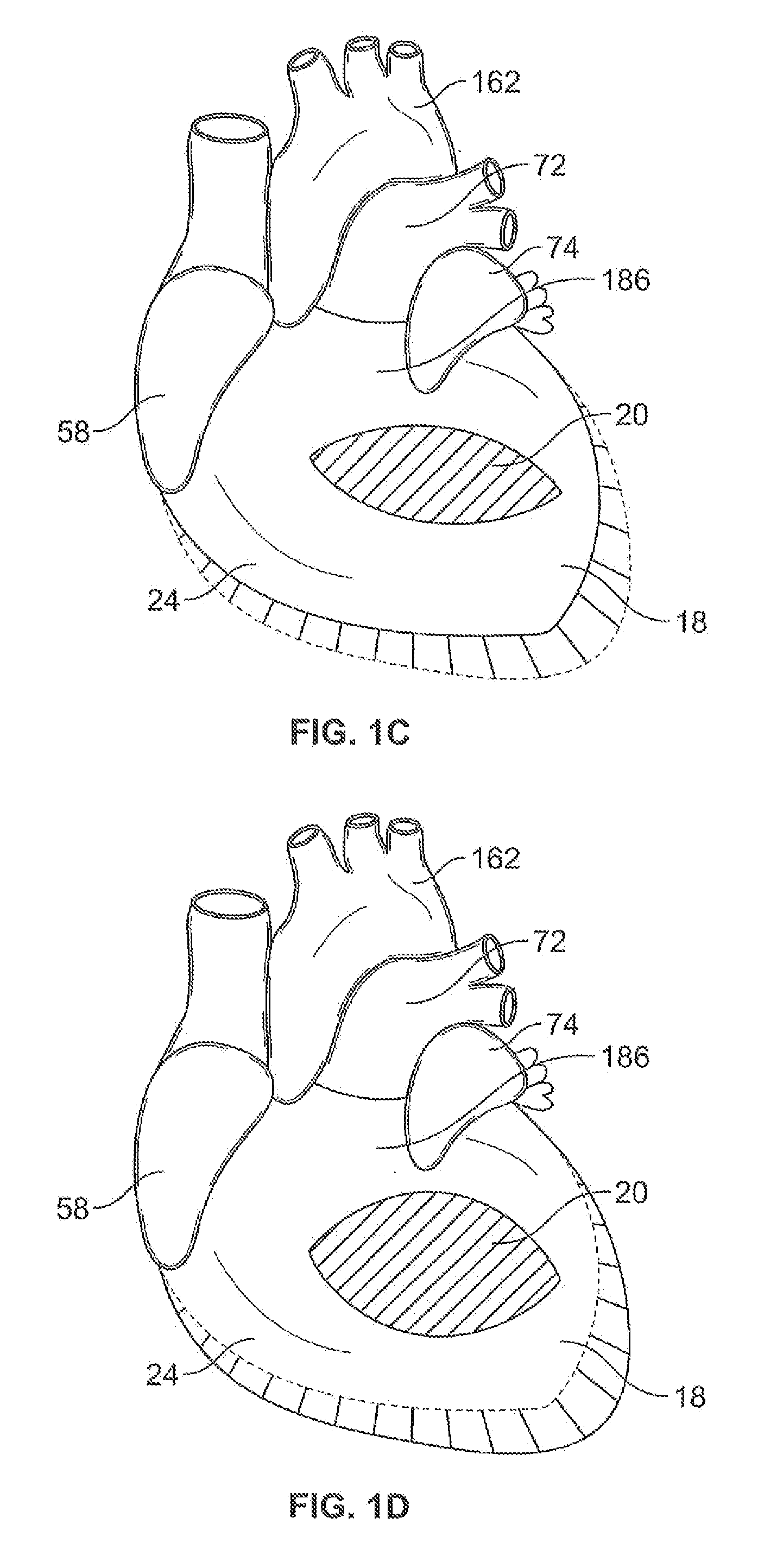
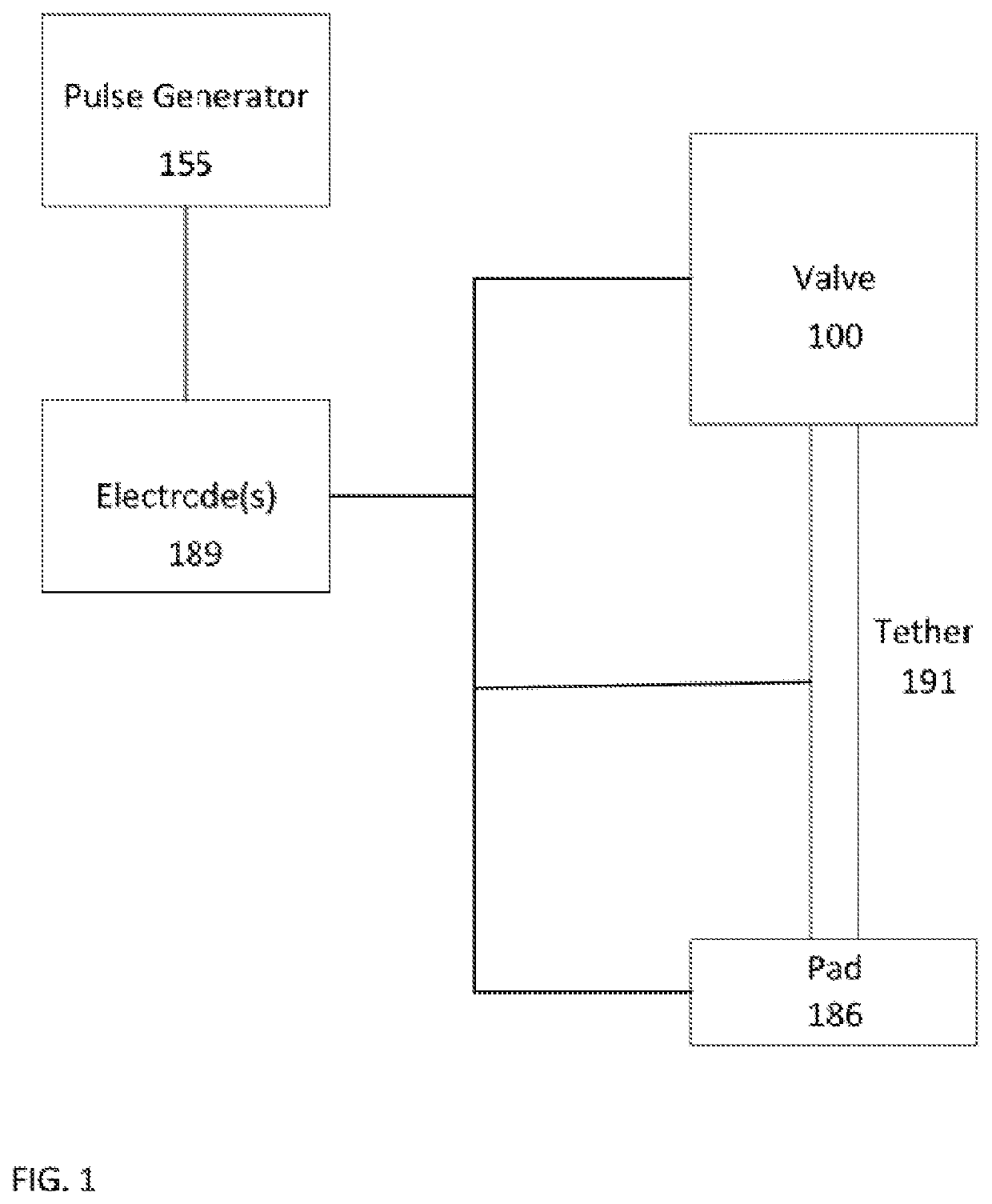
In some embodiments, a method includes delivering to a native valve annulus (e.g., a native mitral valve annulus) of a heart a prosthetic heart valve (200) having a body (242) expandable from a collapsed, delivery configuration to an expanded, deployed configuration. The method can further include, after the delivering, causing the prosthetic heart valve to move from the delivery configuration to the deployed configuration. With the prosthetic heart valve in its deployed configuration, an anchoring tether (191) extending from the prosthetic heart valve can be secured to a wall (Vw) of the heart (H). An electrode (189) coupled to at least one of the prosthetic heart valve or the anchoring tether can then be used to at least one of pace the heart or sense a signal associated with the heart.
Owner:TENDYNE HLDG
System and method for achieving regular slow ventricular rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System of epicardial sensing and pacing for synchronizing a heart assist device
A network of electrodes configured to sense and / or pace the heart, wherein the network of electrodes are in contact with an epicardial surface of the heart, within a wrapping sleeve that assist the heart as a whole, wherein the network of electrodes sense the heart by quantifying intrinsic electrical activities of the heart, and wherein the network of electrodes pace the heart by inducing an electrical impulse to the heart to control its contractile activities. The network may be interfaced with a controller system, wherein the controller uses spatial and temporal electrical activities of the heart muscles to generate electrical impulse to synchronize the wrapping sleeve around the heart with the heart. Also disclosed is a system configured to construct space-time mapping of cardiac electrical activities and / or propagation, and sensing effects of a first assist event of a prior beat and controlling a second assist event.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
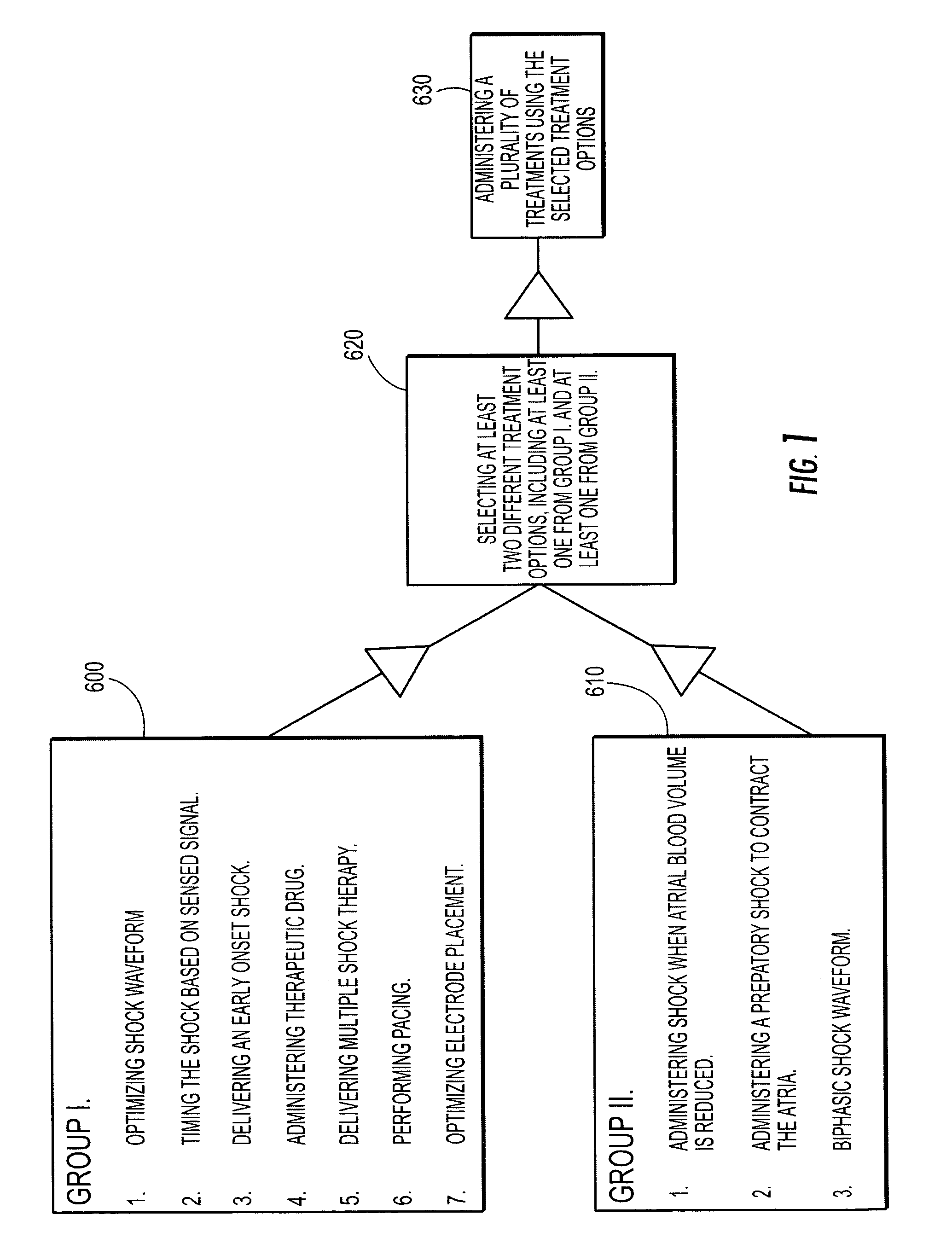
Methods and systems for reducing discomfort from cardiac defibrillation shocks
InactiveUS20060155334A1Reduce discomfortGood clinical efficacyHeart defibrillatorsSolid-state devicesDrugDefibrillation threshold
Methods, systems and computer program products for combining atrial defibrillation treatment techniques include techniques for reducing the discomfort associated with defibrillation and / or reducing the defibrillation threshold. Techniques include timing the defibrillation shock to reduce discomfort based on a sensed signal, giving the shock relatively early during atrial fibrillation, therapeutic drugs, administering more than one shock in succession, pacing the heart before, after, or during the defibrillation shock or shocks, and placing the shock electrodes in locations that may reduce discomfort.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Systems, devices, and methods for his bundle cardiac pacing
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for cardiac pacing therapy. Disclosed herein are methods for His bundle cardiac pacing; cardiac leads and leadless cardiac pacemakers that enables pacing and sensing of the His bundle as well as the right atrium and right ventricle; and delivery sheaths for placing the cardiac lead or leadless cardiac pacemaker in the heart. The devices and methods disclosed increase the success at which His bundle pacing can be implemented.
Owner:EPQUANT LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com