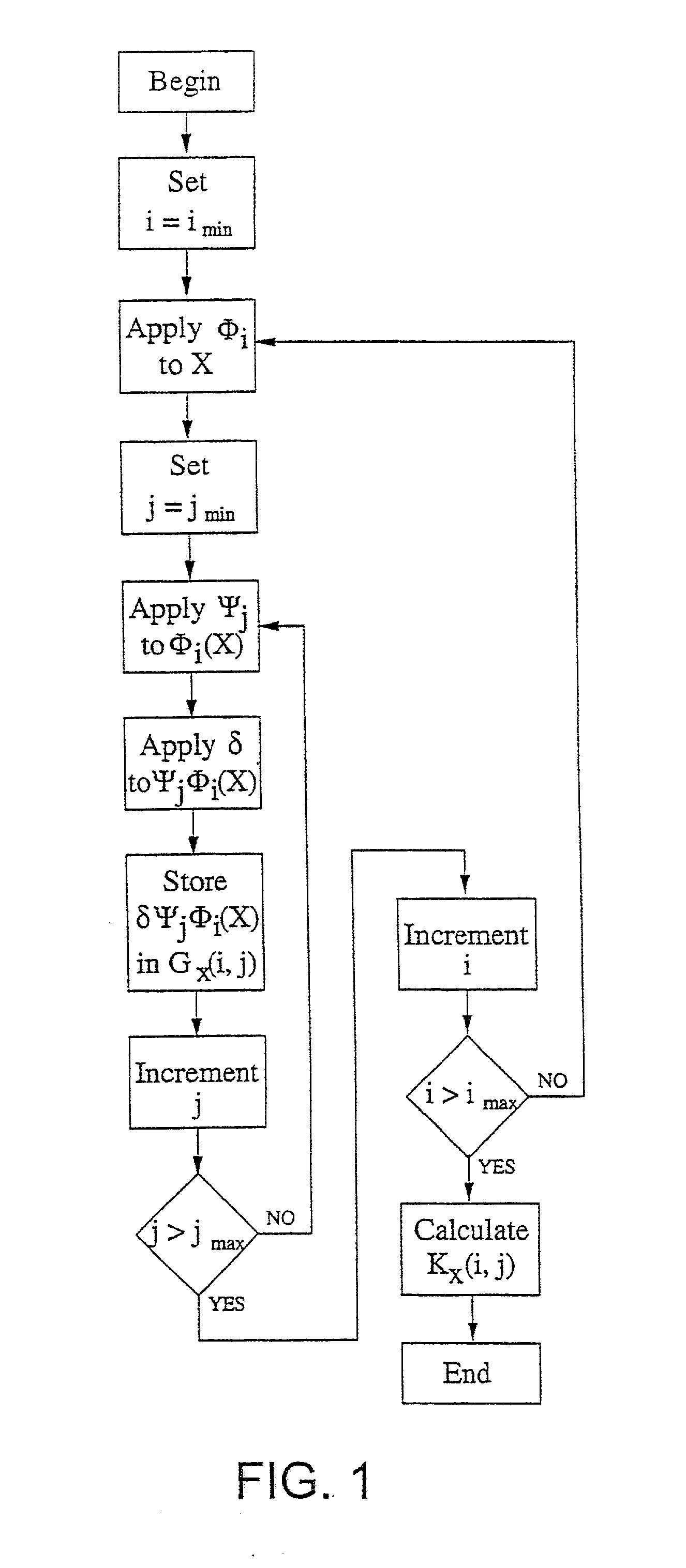
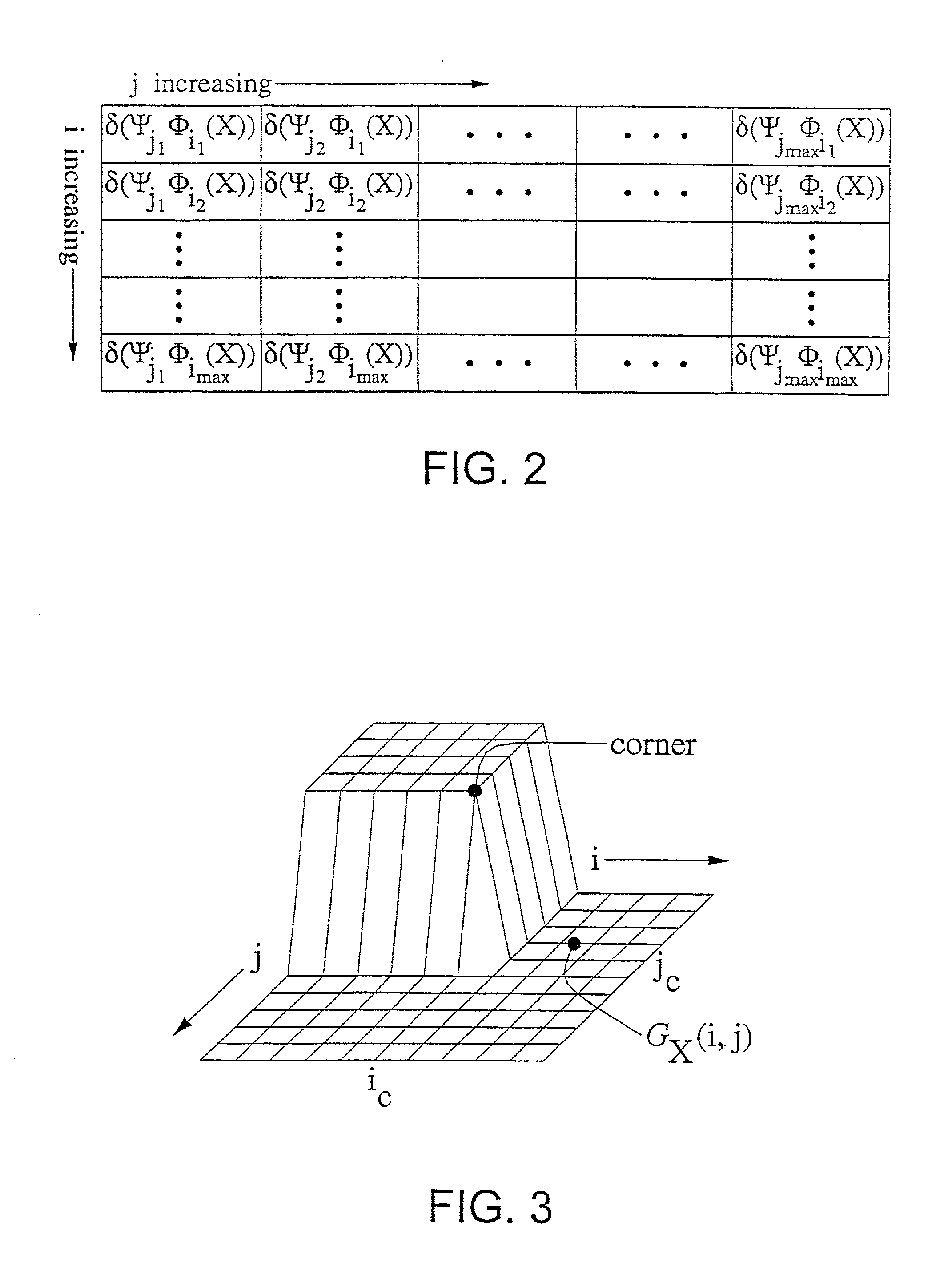
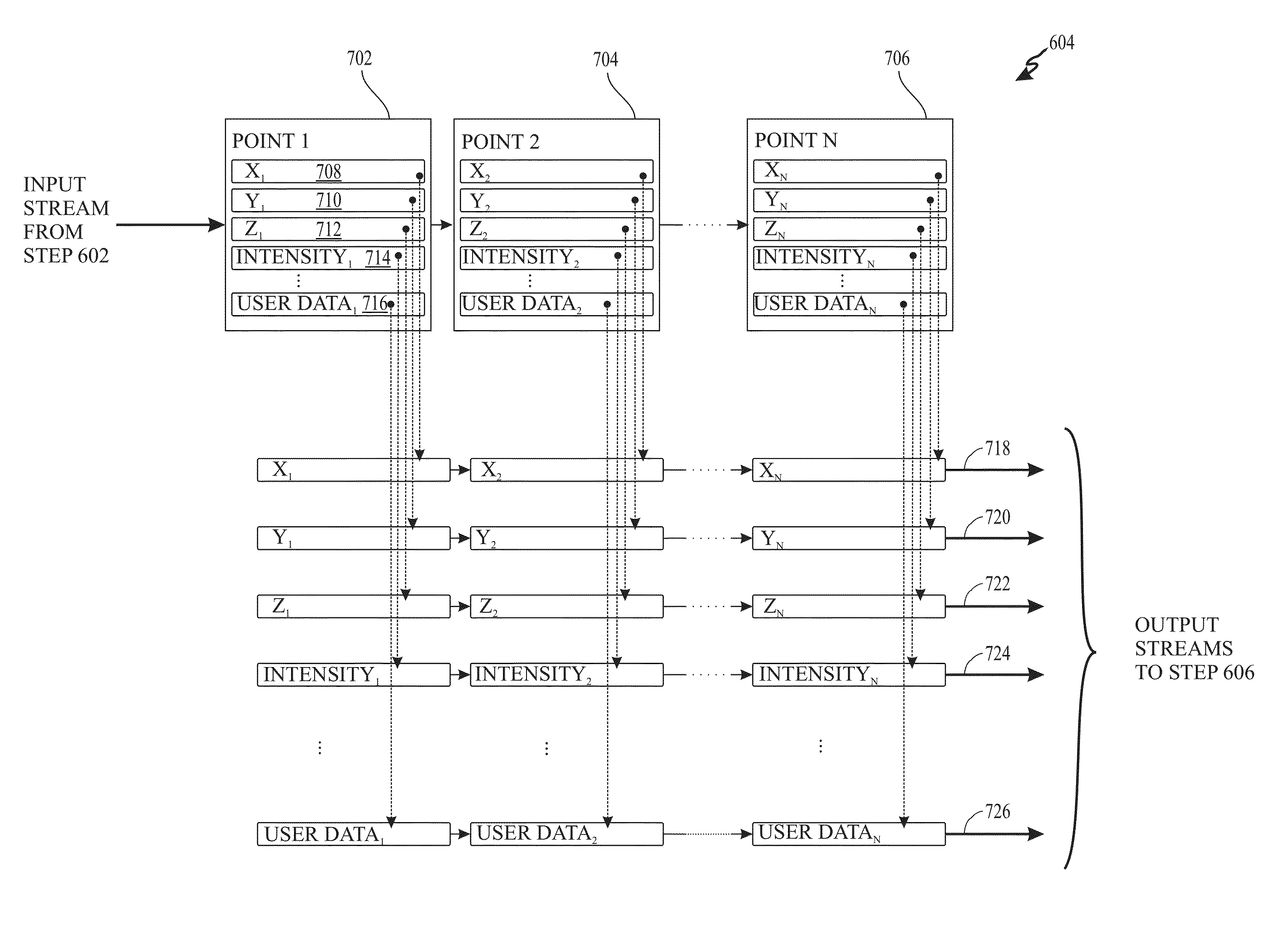
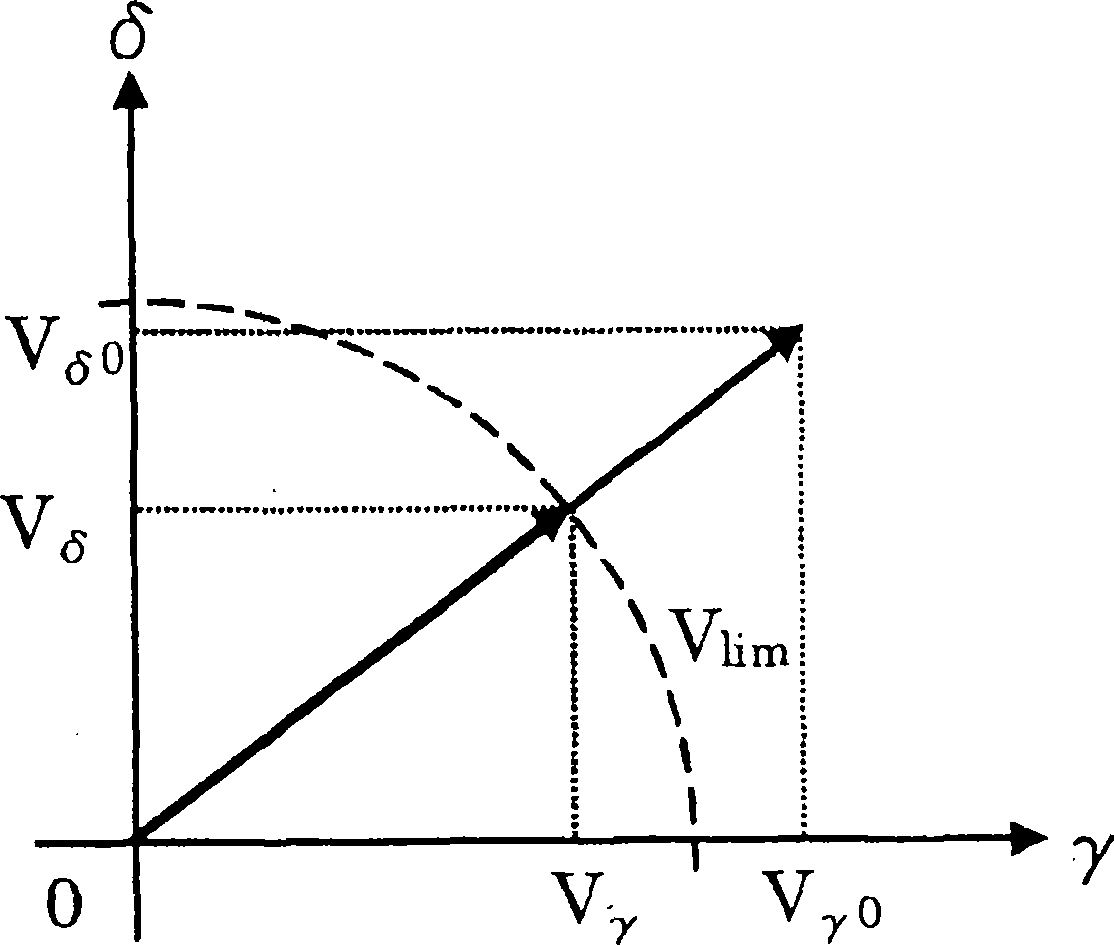Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
131 results about "Scalar Value" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A scalar variable, or scalar field, is a variable that holds one value at a time. It is a single component that assumes a range of number or string values. A scalar value is associated with every point in a space. In computing, the term scalar is derived from the scalar processor, which processes one data item at a time.
Gesture cataloging and recognition
ActiveUS20090183193A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionScalar ValueCataloging
Methods and apparatus for cataloging and recognizing gestures are disclosed. A gesture may be detected using sample motion data. An energy value and a baseline value may be computed. The baseline value may be updated if the energy value is below a calm energy threshold. The sample motion data may be adjusted based on the updated baseline value. A local variance may be calculated over a predetermined number of samples. Sample motion data values may be recorded if the local variance exceeds a threshold. Sample motion data recording may stop if a local variance scalar value falls below a drop threshold. Input Gestures may be recognized by computing a total variance for sample values in an Input Gesture; calculating a figure of merit using sample values from the Input Gesture and one or more Catalog Gestures; and determining whether the Input Gesture matches a Catalog Gesture from the figure of merit.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
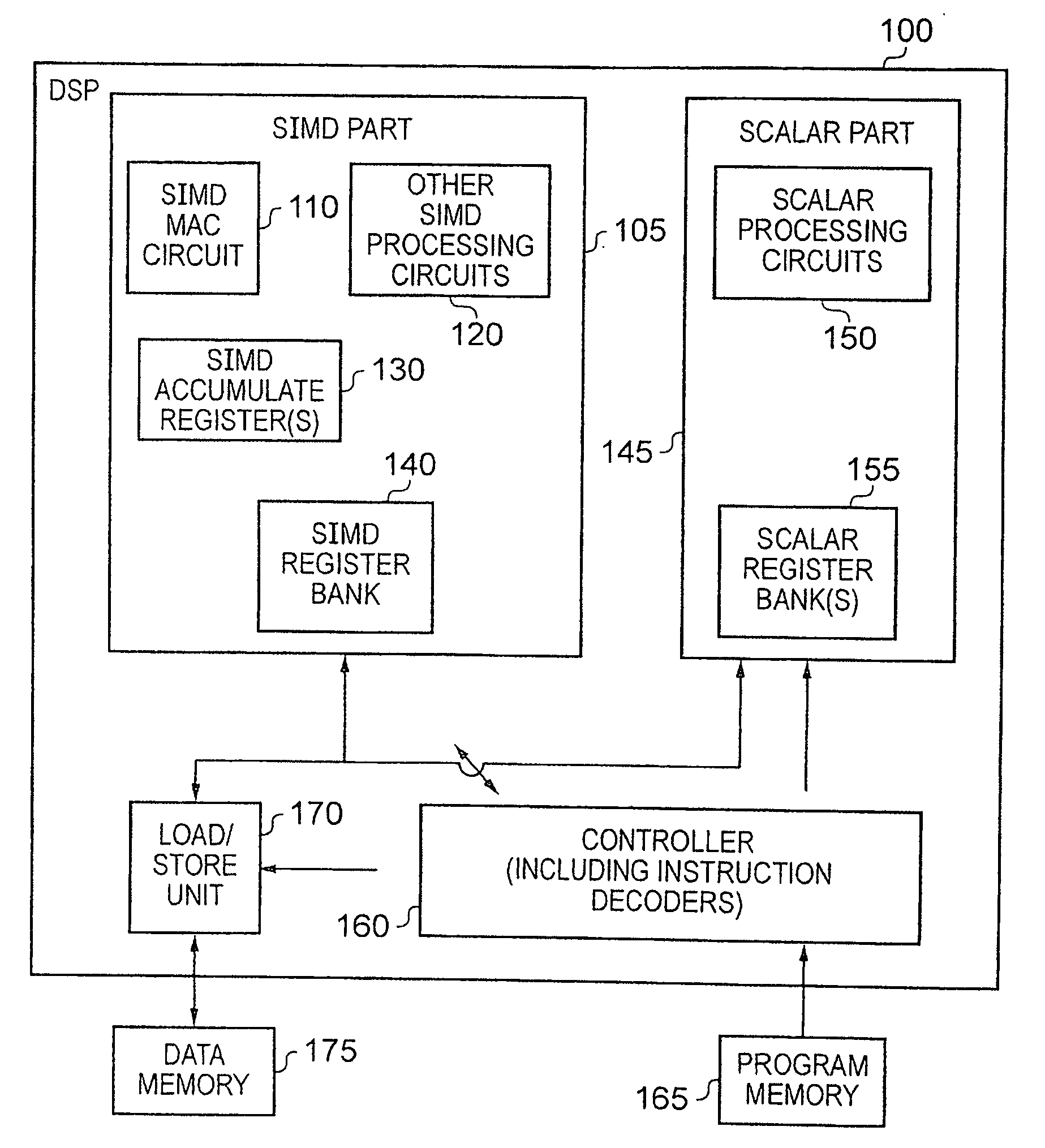
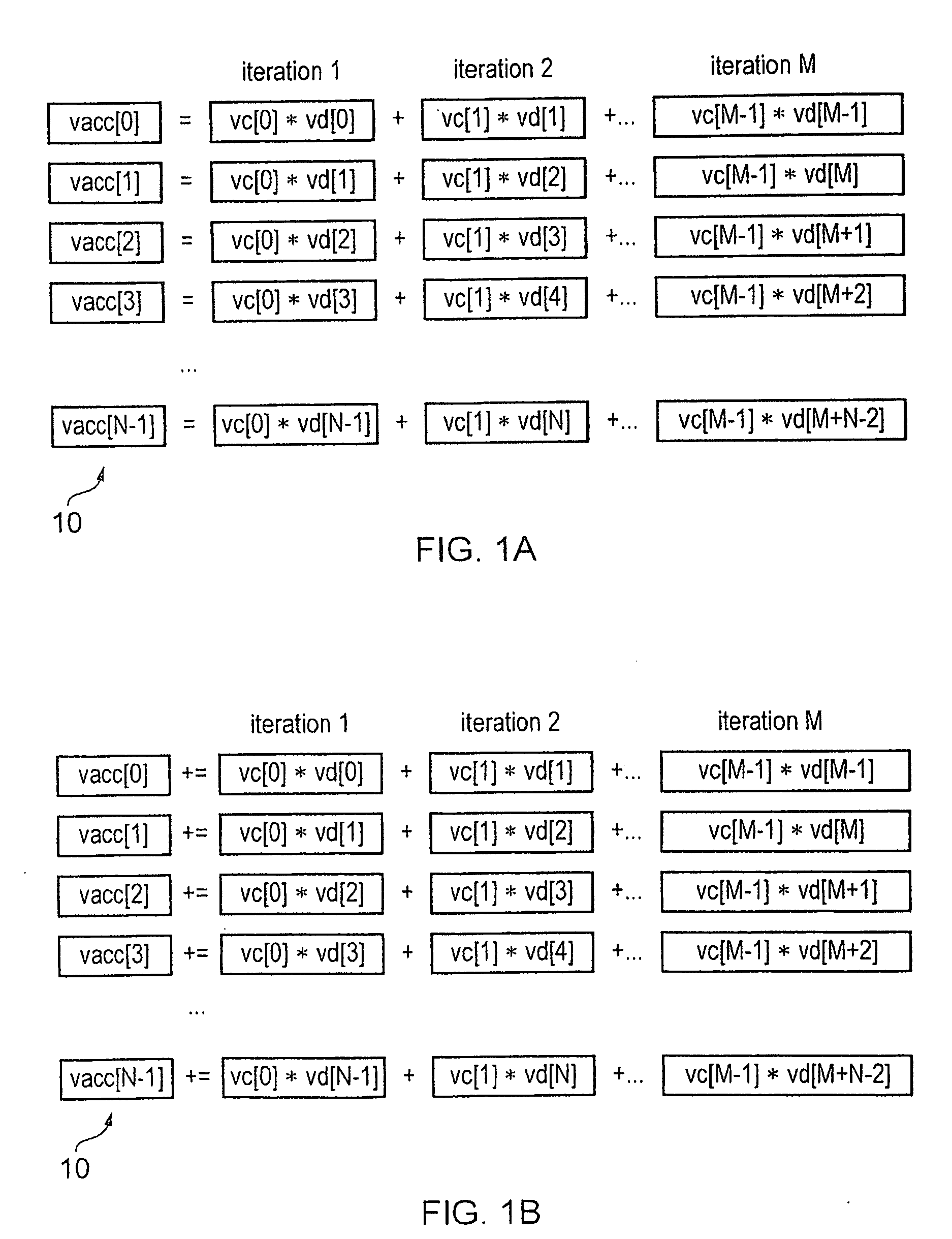
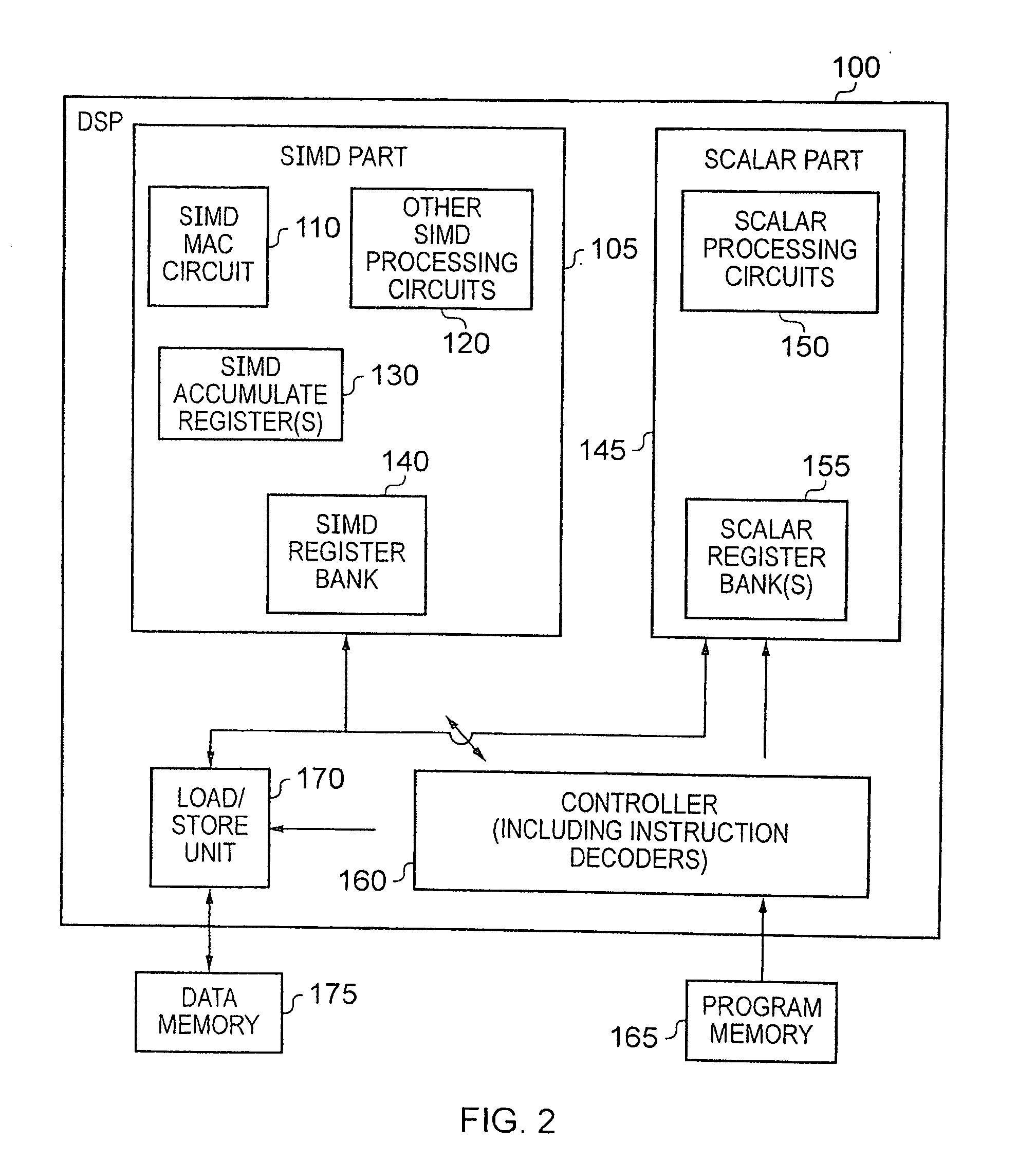
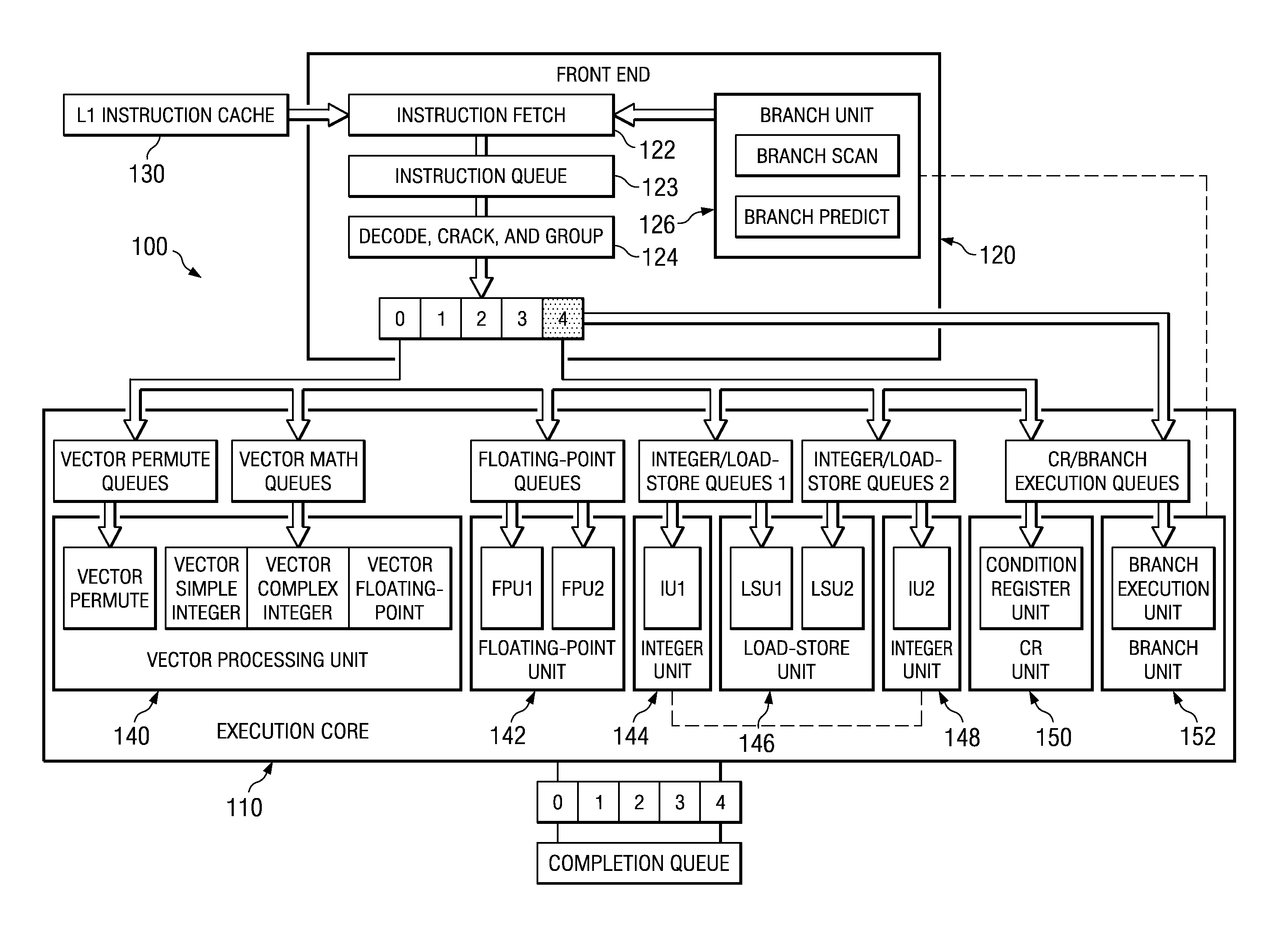
Apparatus and Method for Performing SIMD Multiply-Accumulate Operations
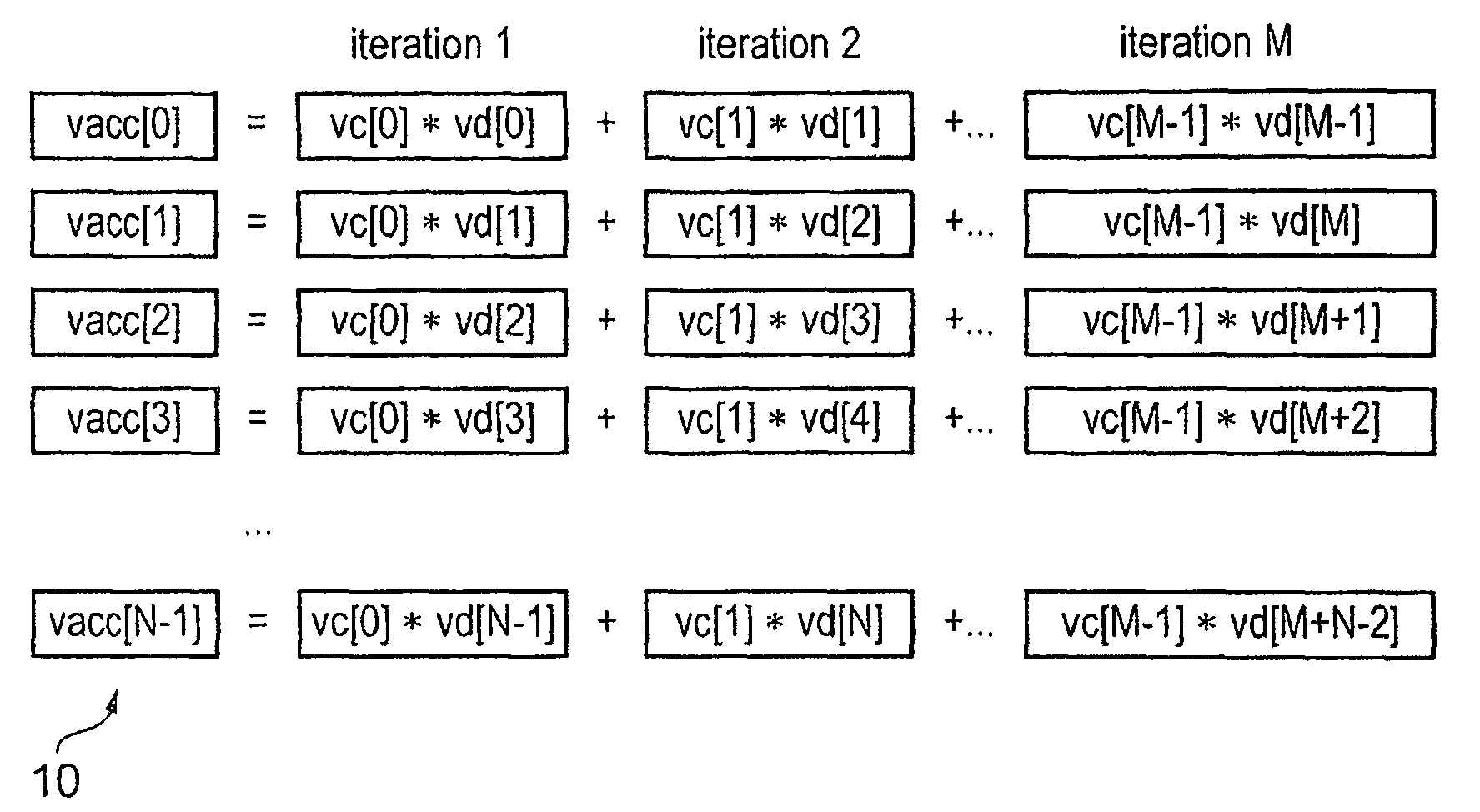
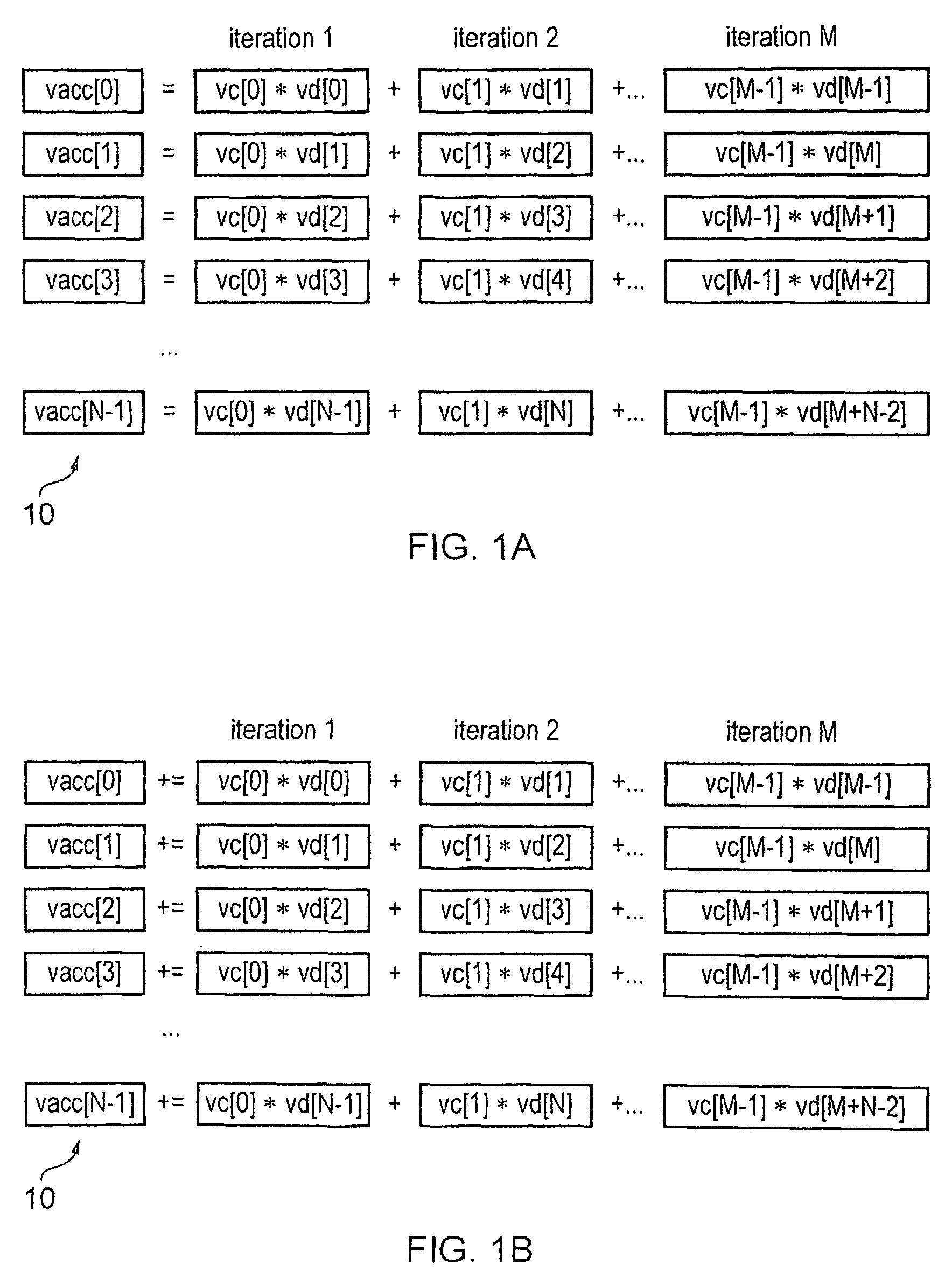
ActiveUS20100274990A1Reduce unnecessary power consumptionSignificant power savingAssociative processorsProgram control using wired connectionsProgram instructionScalar Value
An apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations includes SIMD data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations in parallel on multiple data elements. Instruction decoder circuitry is coupled to the SIMD data processing circuitry and is responsive to program instructions to generate the required control signals. The instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a single instruction (referred to herein as a repeating multiply-accumulate instruction) having as input operands a first vector of input data elements, a second vector of coefficient data elements, and a scalar value indicative of a plurality of iterations required, to generate control signals to control the SIMD processing circuitry. In response to those control signals, the SIMD data processing circuitry performs the plurality of iterations of a multiply-accumulate process, each iteration involving performance of N multiply-accumulate operations in parallel in order to produce N multiply-accumulate data elements. For each iteration, the SIMD data processing circuitry determines N input data elements from said first vector and a single coefficient data element from the second vector to be multiplied with each of the N input data elements. The N multiply-accumulate data elements produced in a final iteration of the multiply-accumulate process are then used to produce N multiply-accumulate results. This mechanism provides a particularly energy efficient mechanism for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations, as for example are required for FIR filter processes.
Owner:U-BLOX
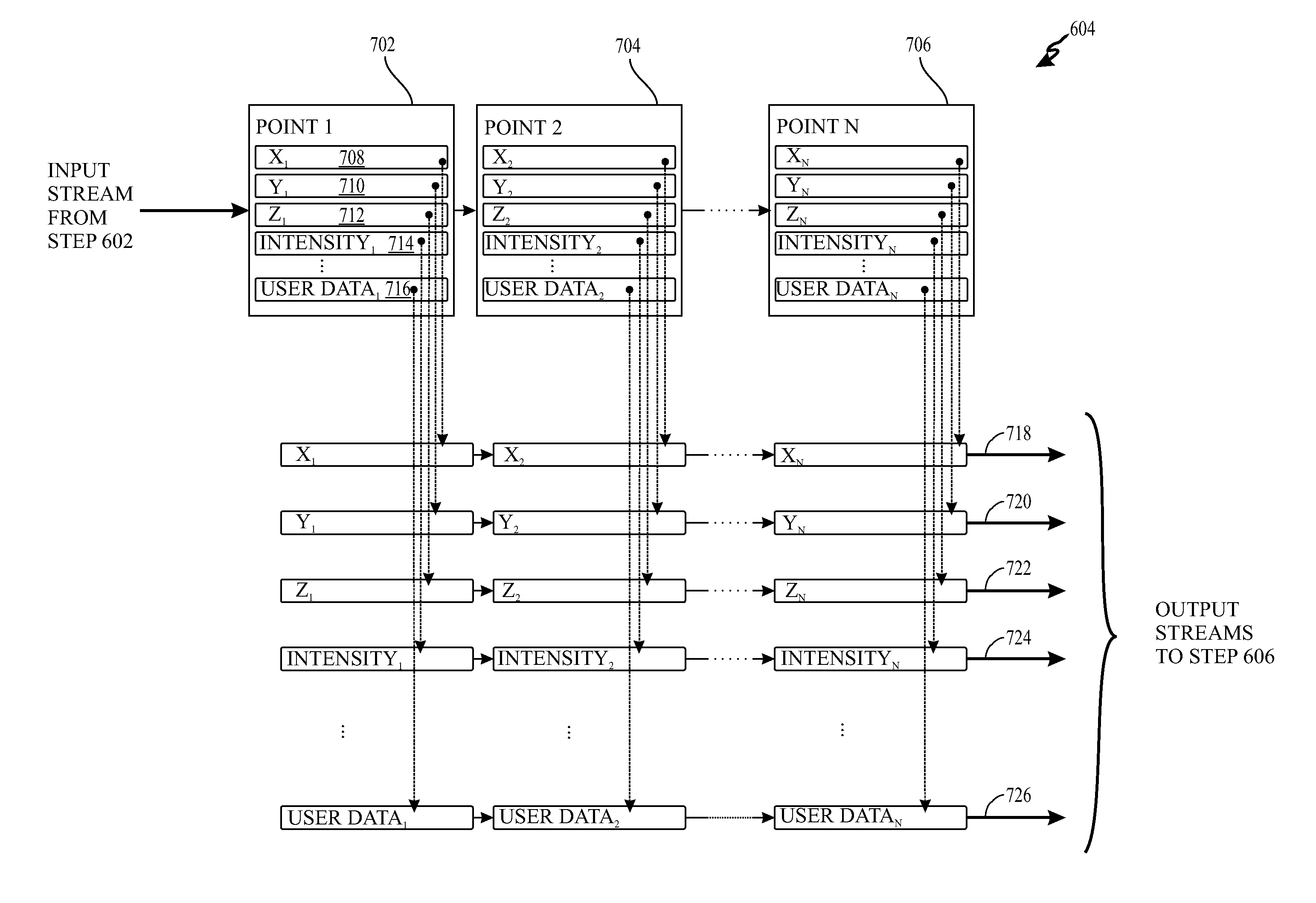
LIGHT DETECTION AND RANGING (LiDAR)DATA COMPRESSION AND DECOMPRESSION METHODS AND APPARATUS
ActiveUS20120124113A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsData compressionScalar Value
Methods and apparatus for lossless LiDAR LAS file compression and decompression are provided that include predictive coding, variable-length coding, and arithmetic coding. The predictive coding uses four different predictors including three predictors for x, y, and z coordinates and a constant predictor for scalar values, associated with each LiDAR data point.
Owner:UNIV OF MARIBOR LAB FOR GEOMETRIC MODELLING & MULTIMEDIA ALGORITHMS
Compilation for a SIMD RISC processor
InactiveUS20070124722A1Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemScalar Value
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer usable code are provided for generating code to perform scalar computations on a Single-Instruction Multiple-Data (SIMD) Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architecture. The illustrative embodiments generate code directed at loading at least one scalar value and generate code using at least one vector operation to generate a scalar result, wherein all scalar computation for integer and floating point data is performed in a SIMD vector execution unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for image texture analysis
A method and apparatus for image texture analysis in which the image is mapped into a first set of binary representation by a monotonically varying operator, such as a threshold operator. Each binary representation in the first set of binary representations is mapped to a further set of binary representations using a second monotonically varying operator, such as a spatial operator. The result of the two mappings is a matrix of binary image representations. Each binary image representation is allocated a scalar value to form an array of scalar values which may be analysed to identify defined texture characteristics.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ADELAIDE +9
Light detection and ranging (LiDAR)data compression and decompression methods and apparatus
Owner:UNIV OF MARIBOR LAB FOR GEOMETRIC MODELLING & MULTIMEDIA ALGORITHMS
Force-feedback input device
InactiveUS20050099387A1DistanceLess attractiveInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsScalar ValueForce generation
In a force-feedback input device, when the cursor moves on a line parallel to a line between a center of a first button and a center of a second button, an area is determined between a first position, which corresponds to the center of the first button, and a second position, which corresponds to the center of the second button, such that the area extends a distance W on both sides of a mid-point between the first and second positions. In this area, the first and second external-force generation portions are controlled so that a scalar value |F| of an attractive force exerted on an operating portion is decreased according to the equation |F|=d / W·|F| as the cursor moves closer to the mid-point, where d is a distance between the cursor and the mid-point.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Handling permanent and transient errors using a SIMD unit
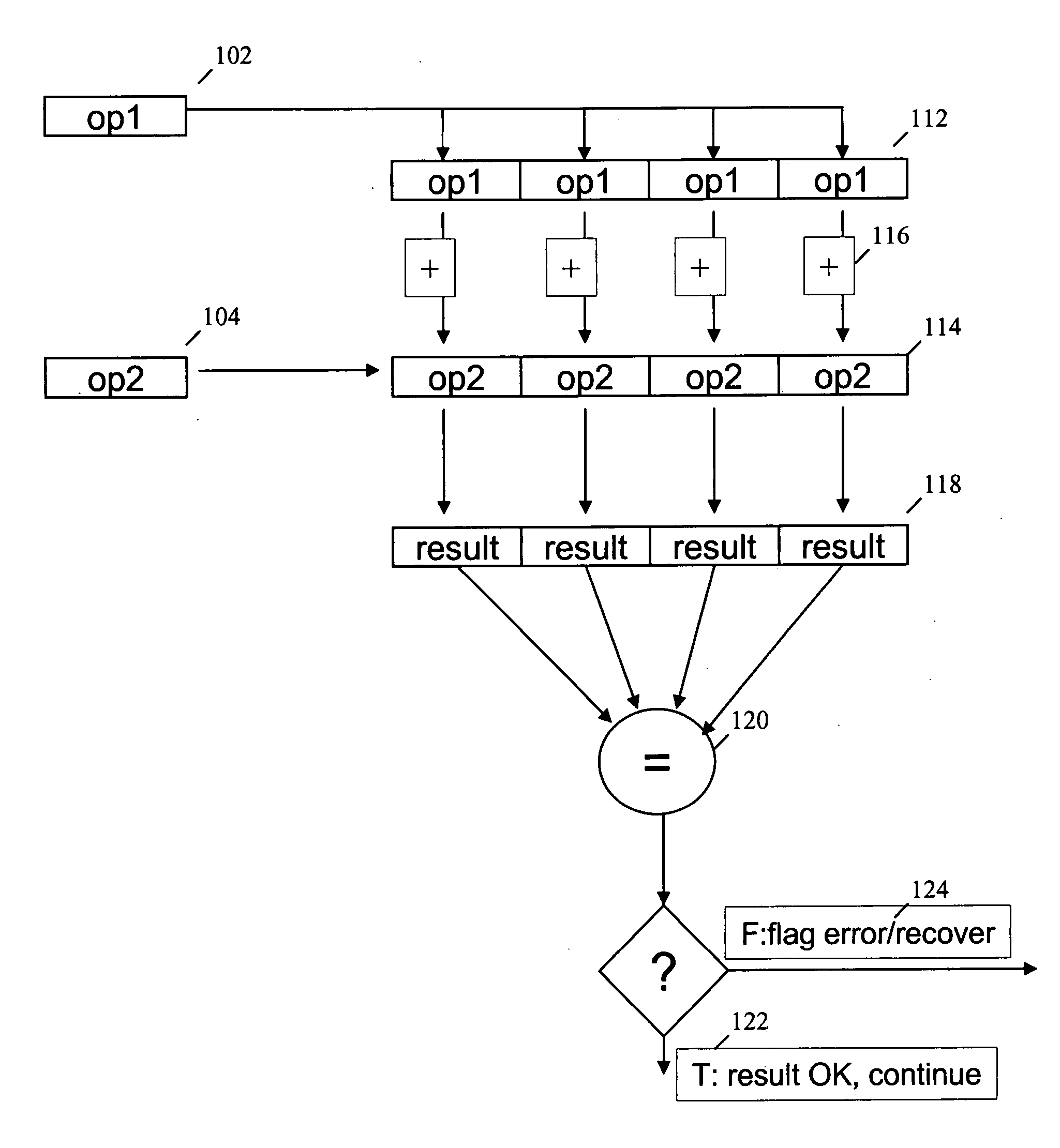
InactiveUS20060190700A1Error detection/correctionGeneral purpose stored program computerScalar ValueExecution unit
A method for handling permanent and transient errors in a microprocessor is disclosed. The method includes reading a scalar value and a scalar operation from an execution unit of the microprocessor. The method further includes writing a copy of the scalar value into each of a plurality of elements of a vector register of a Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) unit of the microprocessor and executing the scalar operation on each scalar value in each of the plurality of elements of the vector register of the SIMED unit using a vector operation. The method further includes comparing each result of the scalar operation on each scalar value in each of the plurality of elements of the vector register and detecting a permanent or transient error if all of the results are not identical.
Owner:IBM CORP
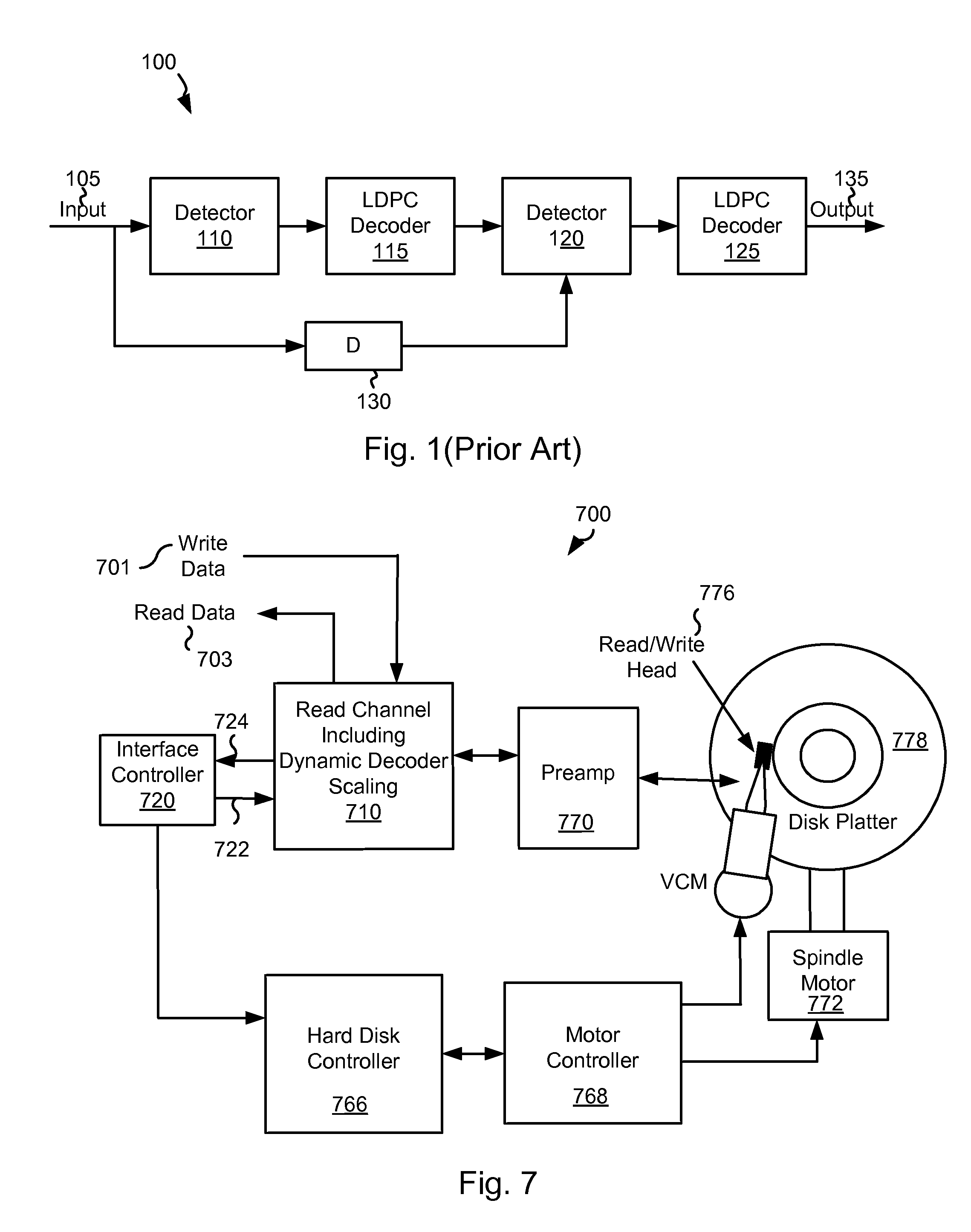
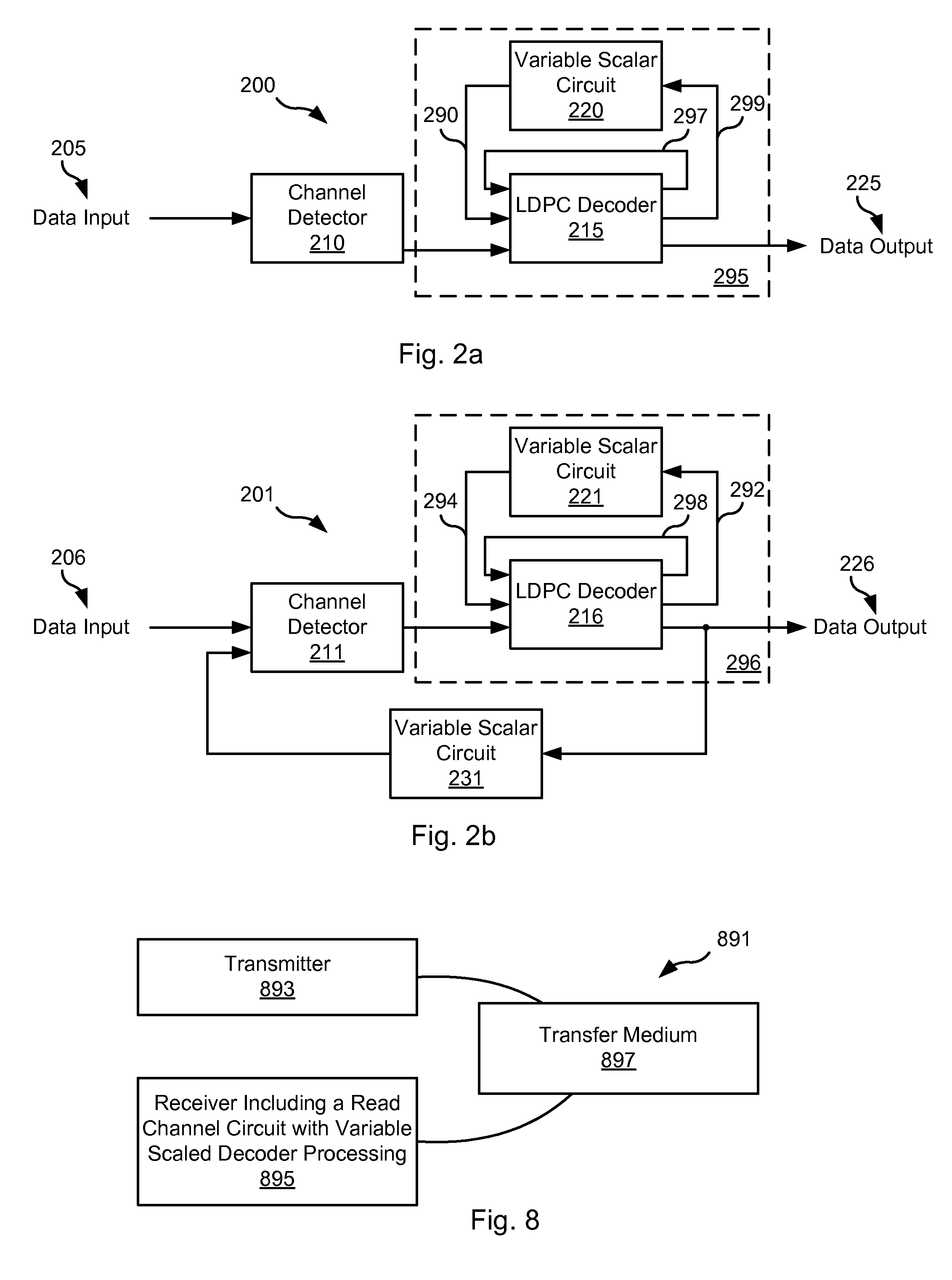
Systems and Methods for Dynamic Scaling in a Data Decoding System
ActiveUS20110258508A1Encourage rapid convergenceEnhanced informationError preventionTransmission systemsScalar ValueComputer engineering
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data processing. As an example, a data processing circuit is disclosed that includes a decoder circuit and a scalar circuit. The decoder circuit is operable to perform a data decoding algorithm by processing at least one decoder message, and the scalar circuit is operable to multiply the decoder message by a variable scalar value.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
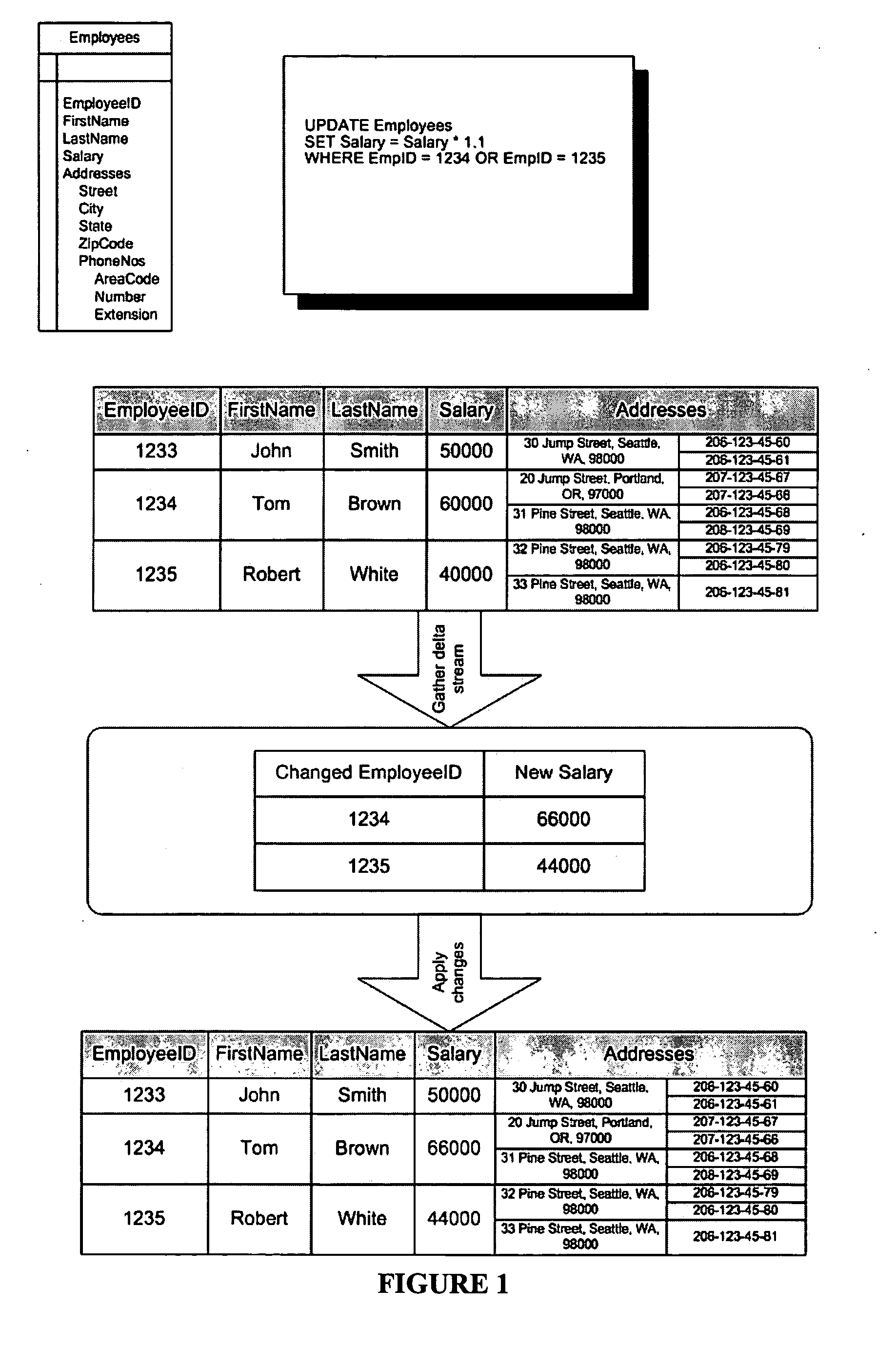
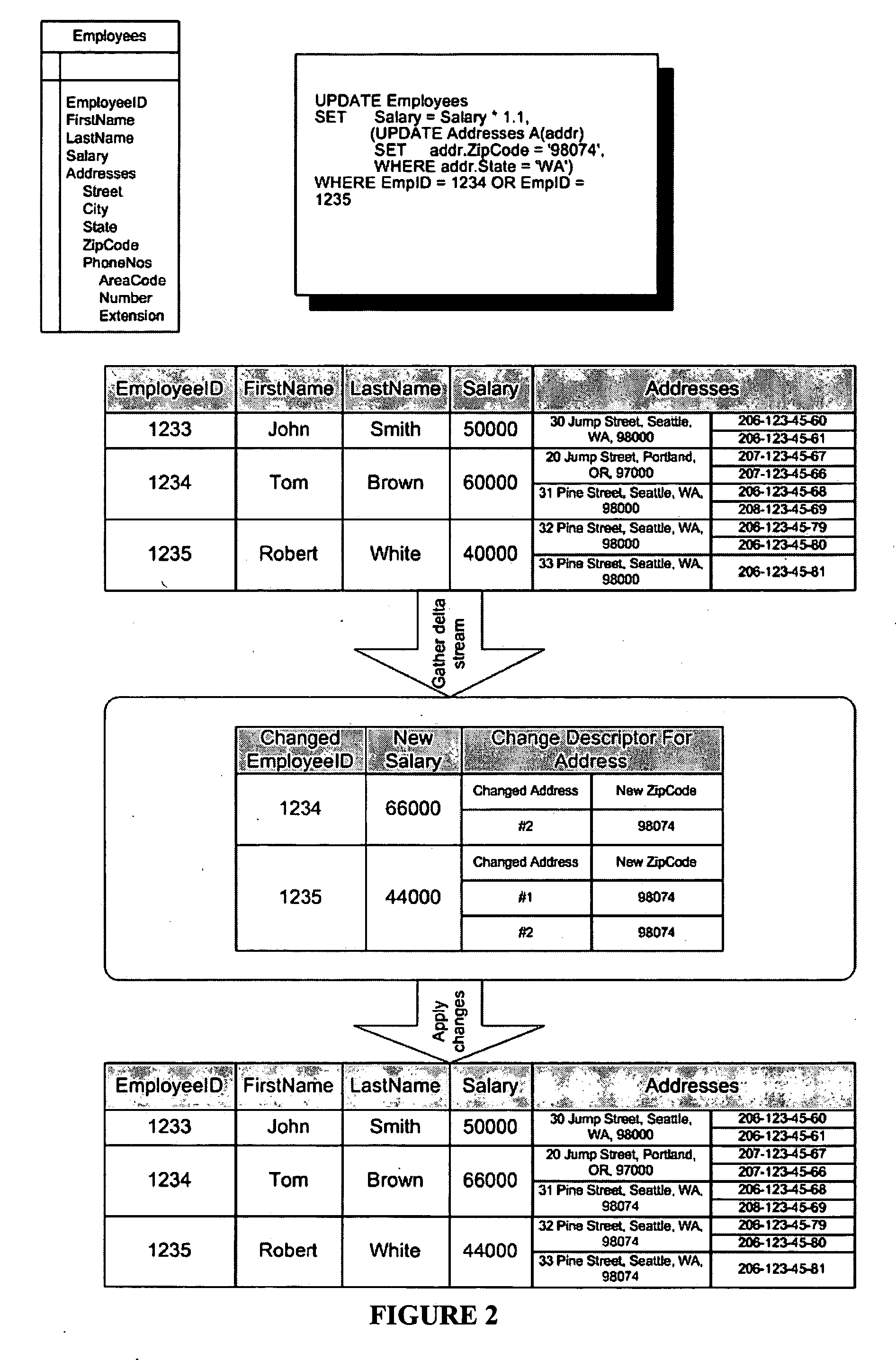
SQL language extensions for modifying collection-valued and scalar valued columns in a single statement
InactiveUS20050091256A1Easy to understandEfficient processingData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDepth levelRelational table
A technique for updating collection-valued and other complex structured columns in a nested table using a nested extension of an UPDATE statement that uses syntax and semantics to modify collection-valued columns in a way that is analogous to the syntax and semantics of the UPDATE statement that is used to modify scalar-valued columns of the table (called the outer UPDATE). Using the same syntactic and semantic constructs as the table at the outer level allows an existing implementation that processes modifications to relational tables to reuse its implementation techniques for processing outer updates to modify collection-valued columns as well. The UPDATE extensions enable the specification of updates to nested collections embedded at arbitrary levels of depth in the object model. The new syntax is embedded inside the outer UPDATE statement in a way that parallels the structure of the data itself and thus maps more directly to the user's conceptual model of the data. The method for implementing the UPDATE extensions uses a change descriptor, which is a data structure that aggregates substantially all changes, both scalar and collection-valued into a single value that can be applied to the changed collection-valued column. This technique can also be used for modifications to other kinds of complex-structured columns such as objects or xml. The change descriptor includes hierarchical information for the cell, thereby enabling efficient application of multiple updates at various granularity levels in a single operation and enabling the implementation of efficient index maintenance algorithms by updating only the indexes affected by the UPDATE operation and updating only those index rows that were affected by the UPDATE operation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
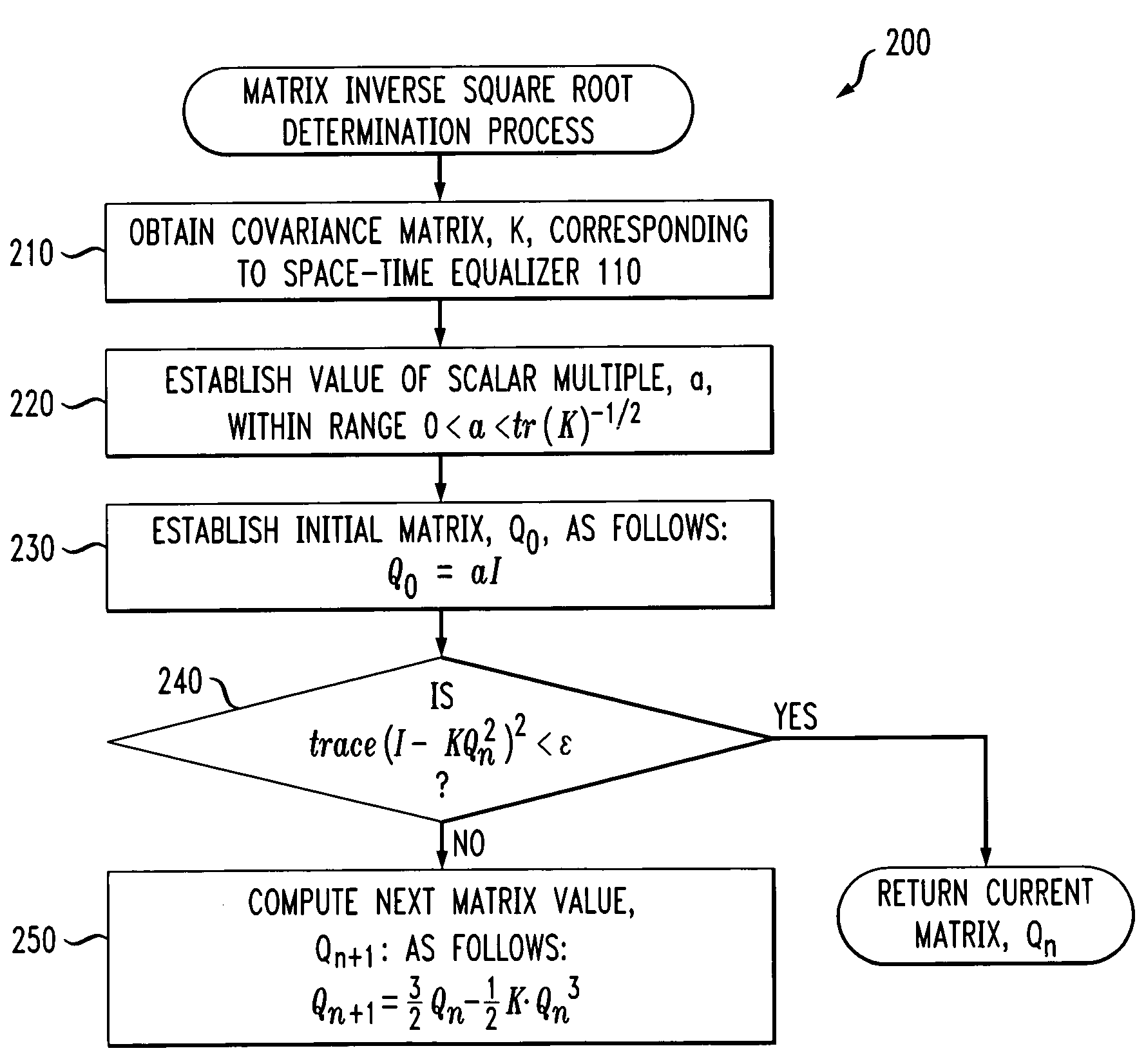
Method and apparatus for determining an inverse square root of a given positive-definite hermitian matrix
Generally, a method and apparatus are provided for computing a matrix inverse square root of a given positive-definite Hermitian matrix, K. The disclosed technique for computing an inverse square root of a matrix may be implemented, for example, by the noise whitener of a MIMO receiver. Conventional noise whitening algorithms whiten a non-white vector, X, by applying a matrix, Q, to X, such that the resulting vector, Y, equal to Q·X, is a white vector. Thus, the noise whitening algorithms attempt to identify a matrix, Q, that when multiplied by the non-white vector, will convert the vector to a white vector. The disclosed iterative algorithm determines the matrix, Q, given the covariance matrix, K. The disclosed matrix inverse square root determination process initially establishes an initial matrix, Q0, by multiplying an identity matrix by a scalar value and then continues to iterate and compute another value of the matrix, Qn+1, until a convergence threshold is satisfied. The disclosed iterative algorithm only requires multiplication and addition operations and allows incremental updates when the covariance matrix, K, changes.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS +1
System and Method for Compiling Scalar Code for a Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) Execution Engine
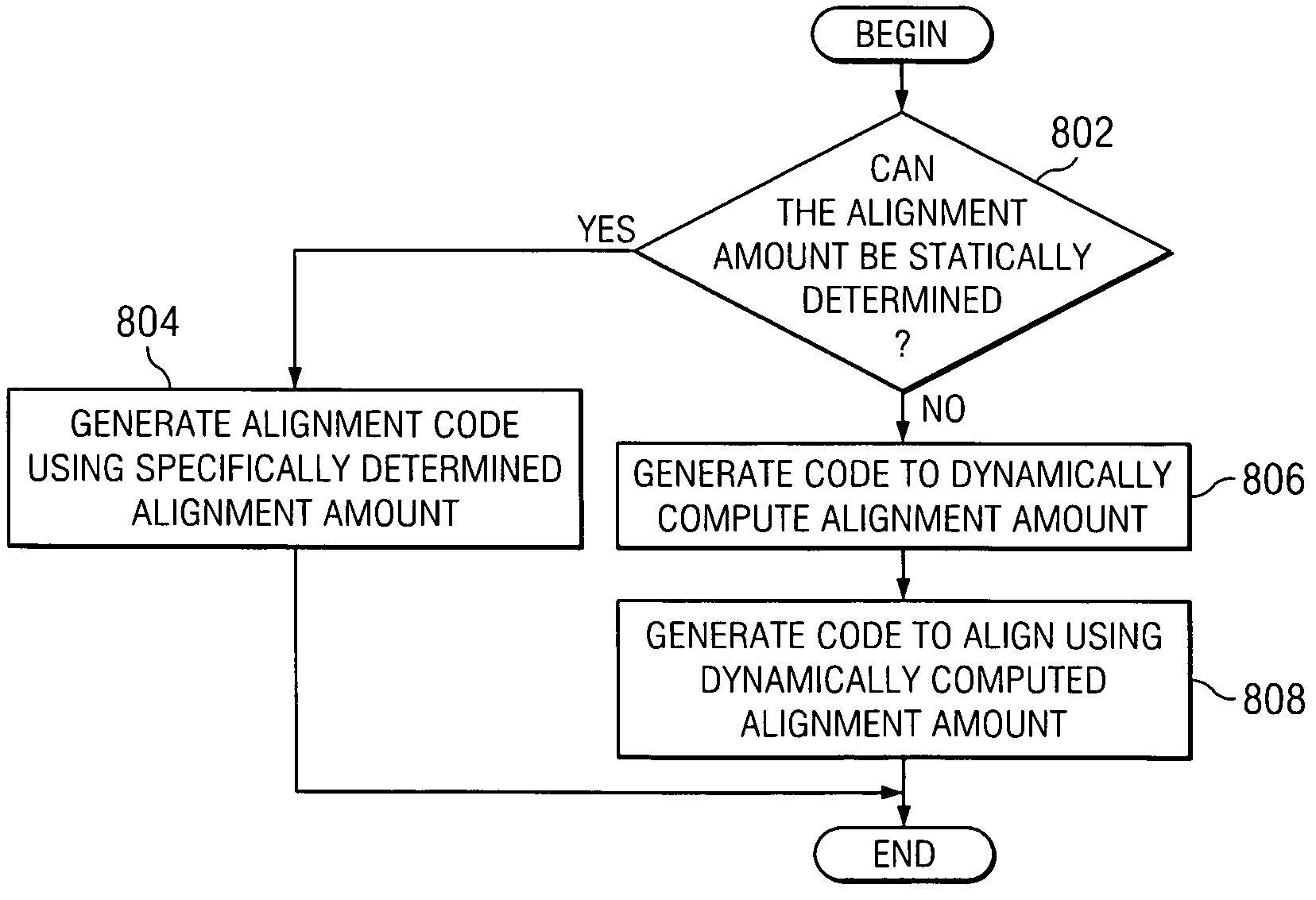
InactiveUS20080229066A1Low costIncrease choiceRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerDynamic compilationLoad instruction
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for performing scalar operations using a SIMD data parallel execution unit. With the mechanisms of the illustrative embodiments, scalar operations in application code are identified that may be executed using vector operations in a SIMD data parallel execution unit. The scalar operations are converted, such as by a static or dynamic compiler, into one or more vector load instructions and one or more vector computation instructions. In addition, control words may be generated to adjust the alignment of the scalar values for the scalar operation within the vector registers to which these scalar values are loaded using the vector load instructions. The alignment amounts for adjusting the scalar values within the vector registers may be statically or dynamically determined.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
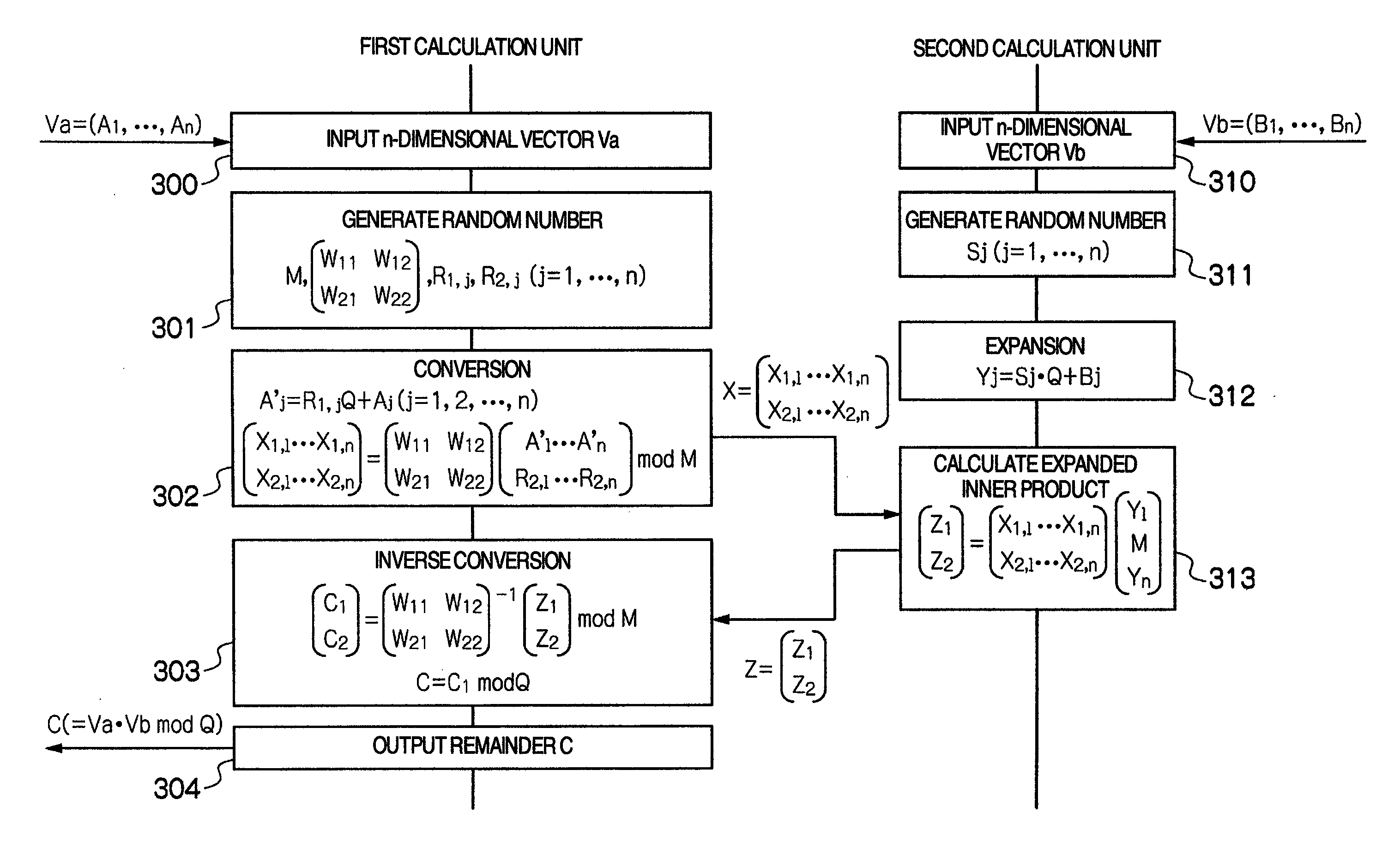
Privacy-preserving scalar product calculation system, privacy-preserving scalar product calculation method and cryptographic key sharing system
InactiveUS20090279694A1Calculation cost is highReduce computing costKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsScalar ValuePrivacy preserving
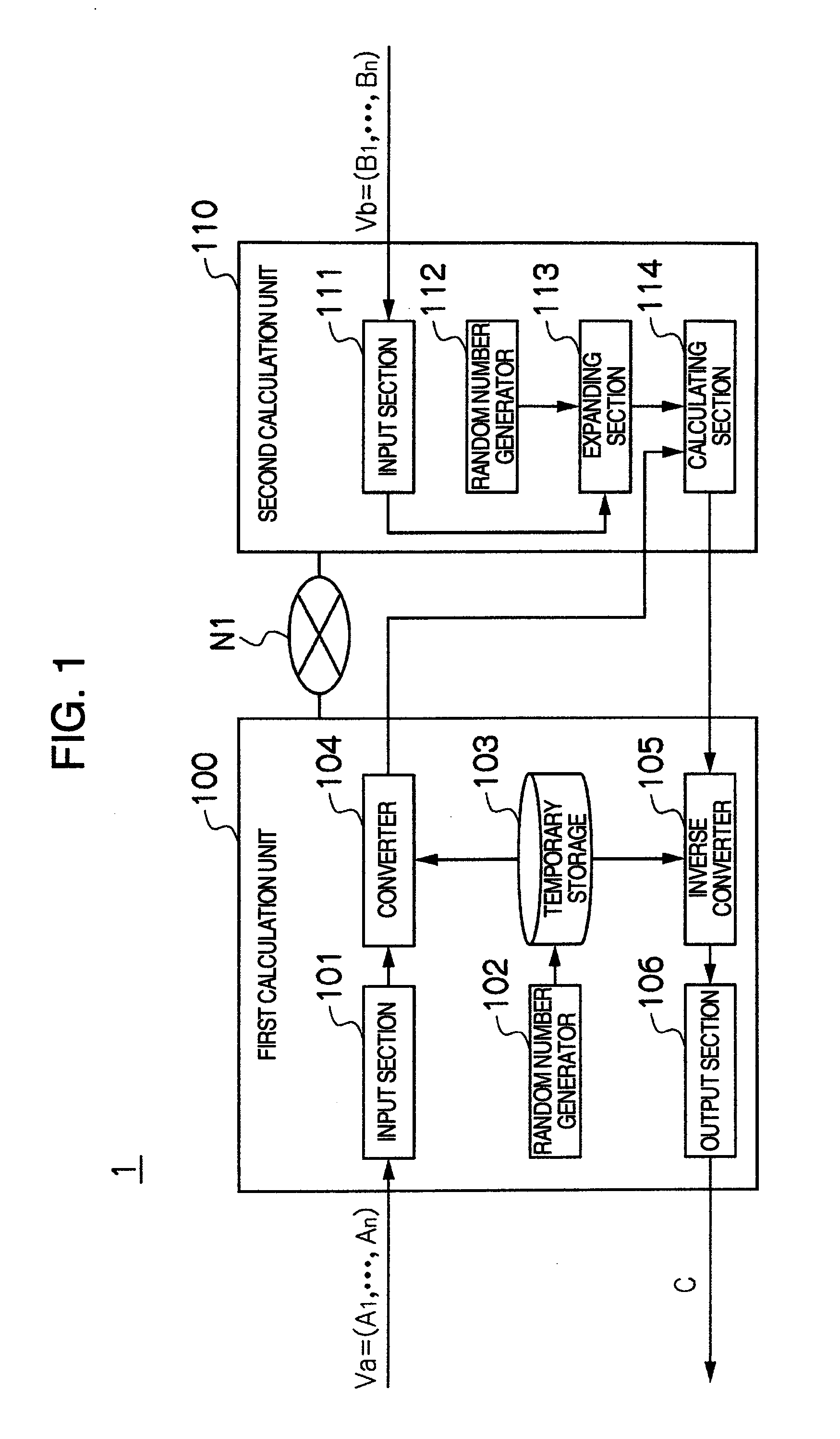
A privacy-preserving scalar product calculation system is provided. A first unit linearly transforms an n-dimensional vector Va into an n-dimensional vector based on a scalar value based on a random number Wi and a random number Rj to calculate a remainder by dividing each element of the linearly transformed n-dimensional vector by a random number Mi, and transmits an n-dimensional converted vector X including each of the remainders as its element to the second unit, the second unit calculates an inner product value Z based on the received n-dimensional converted vector X and an n-dimensional vector Vb, and transmits the inner product value Z to the first unit, and the first unit further calculates, based on a reciprocal of the scalar value and the receive inner product value, a scalar value and which calculates a remainder by dividing the scalar value by the random number Mi.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
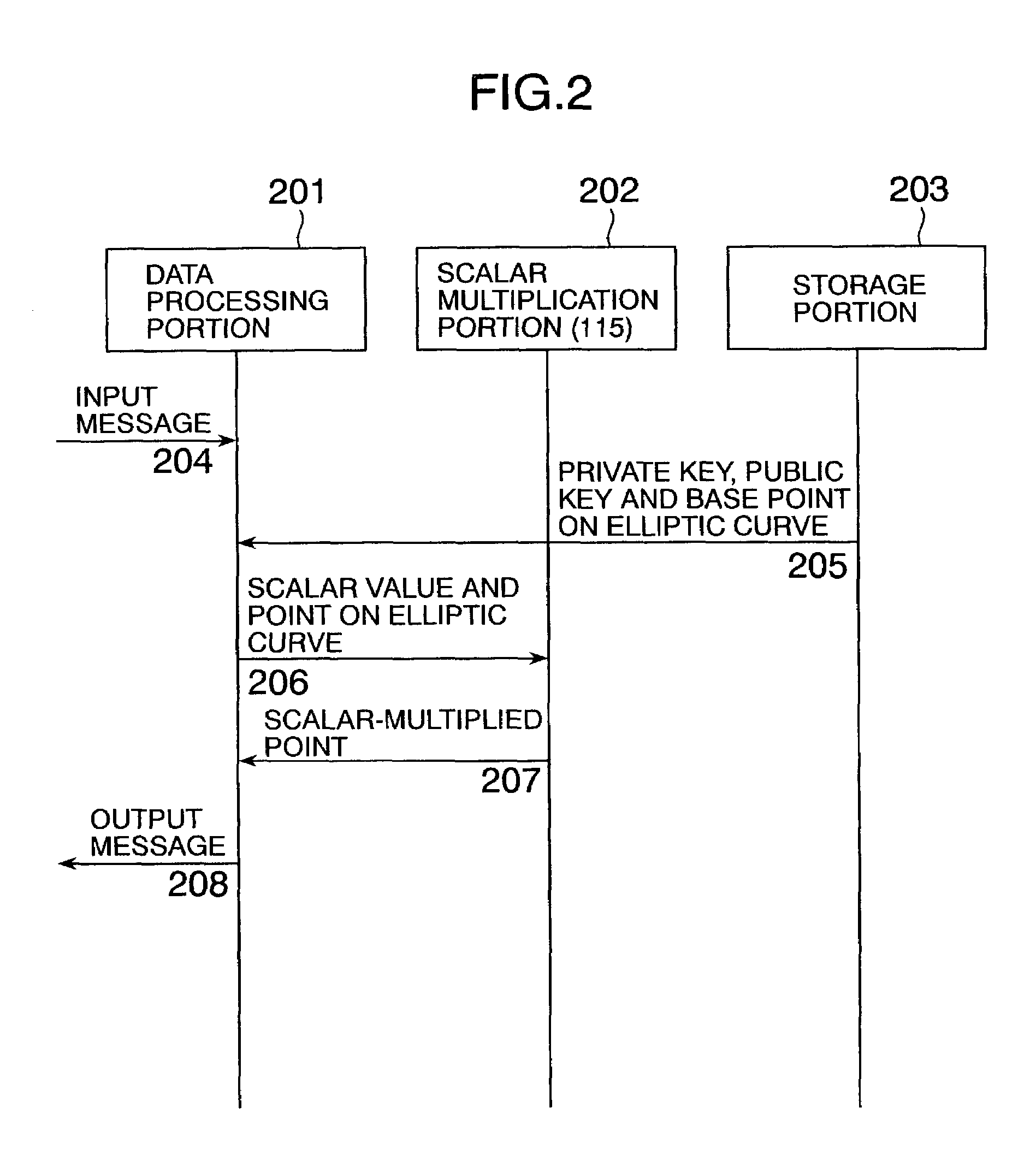
Elliptic scalar multiplication system
InactiveUS7308096B2Increase speedPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationAlgorithmScalar Value
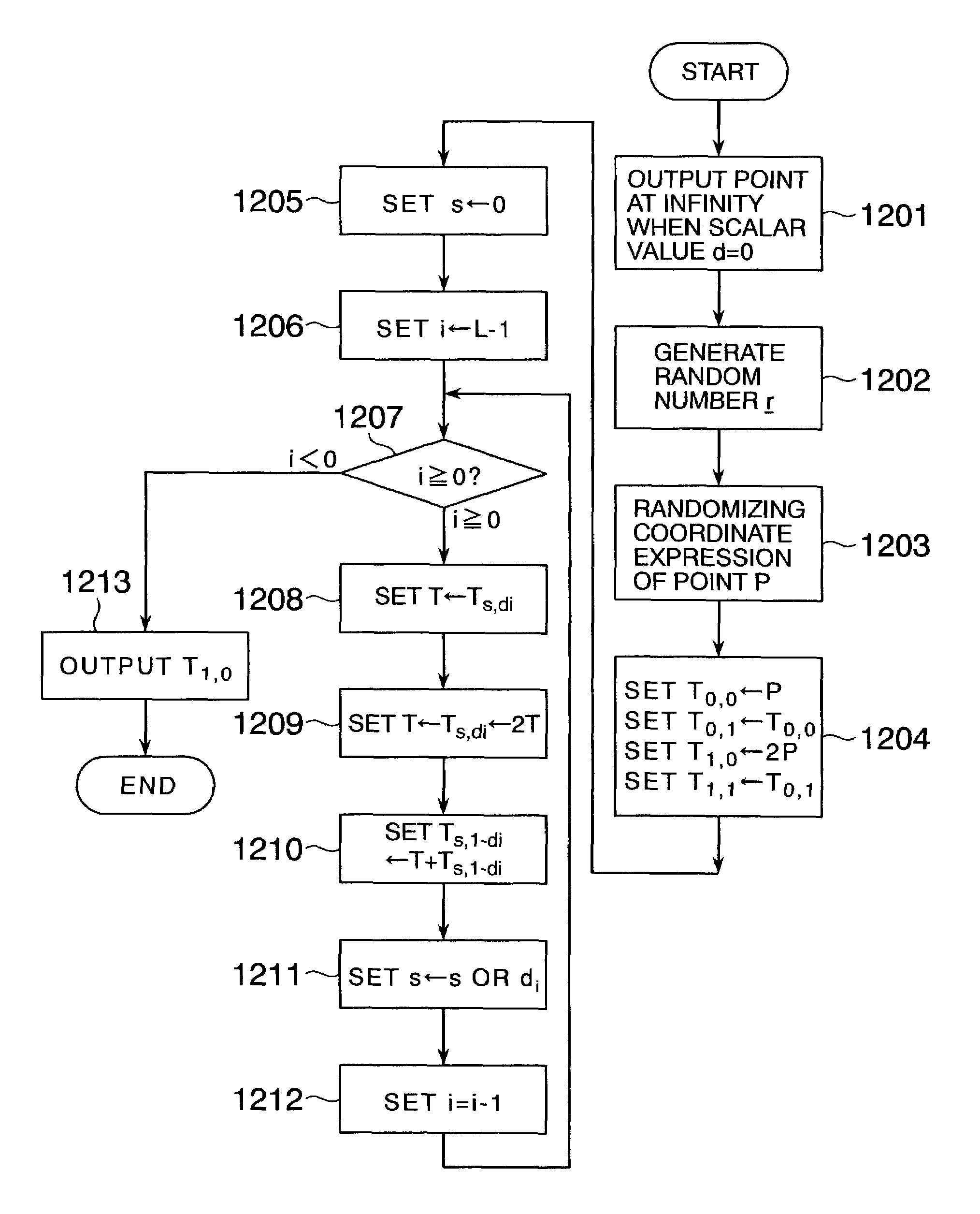
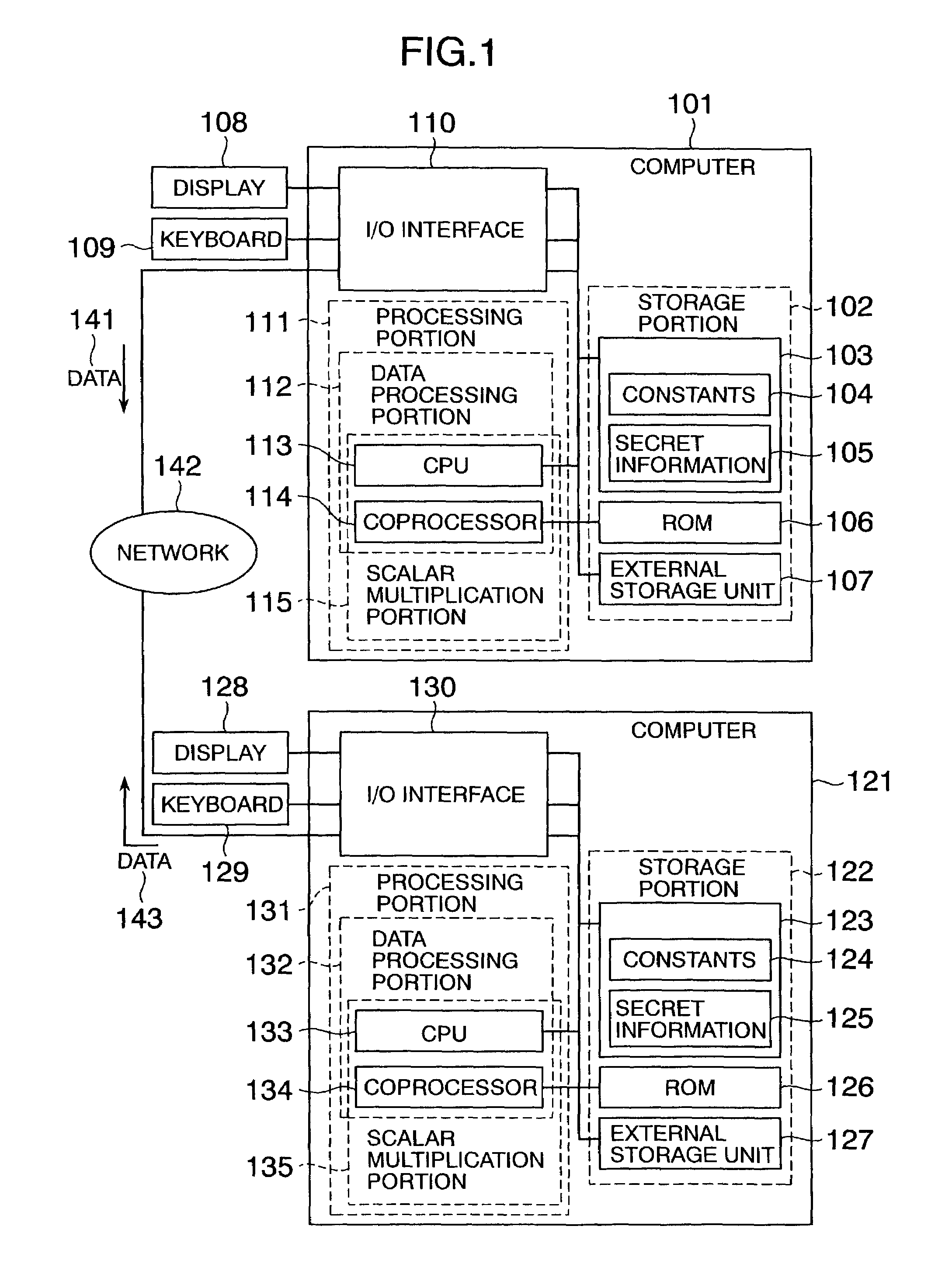
In scalar multiplication method in which a point on an elliptic curve is randomized, but yet scalar multiplication can be calculated by the computational cost as much as that without randomization, an operation is carried out upon a point randomized and a point not randomized in a scalar multiplication method to calculate a scalar-multiplied point from a scalar value and a point on an elliptic curve. The result of the operation is randomized while the computational cost becomes as much as that without randomization.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
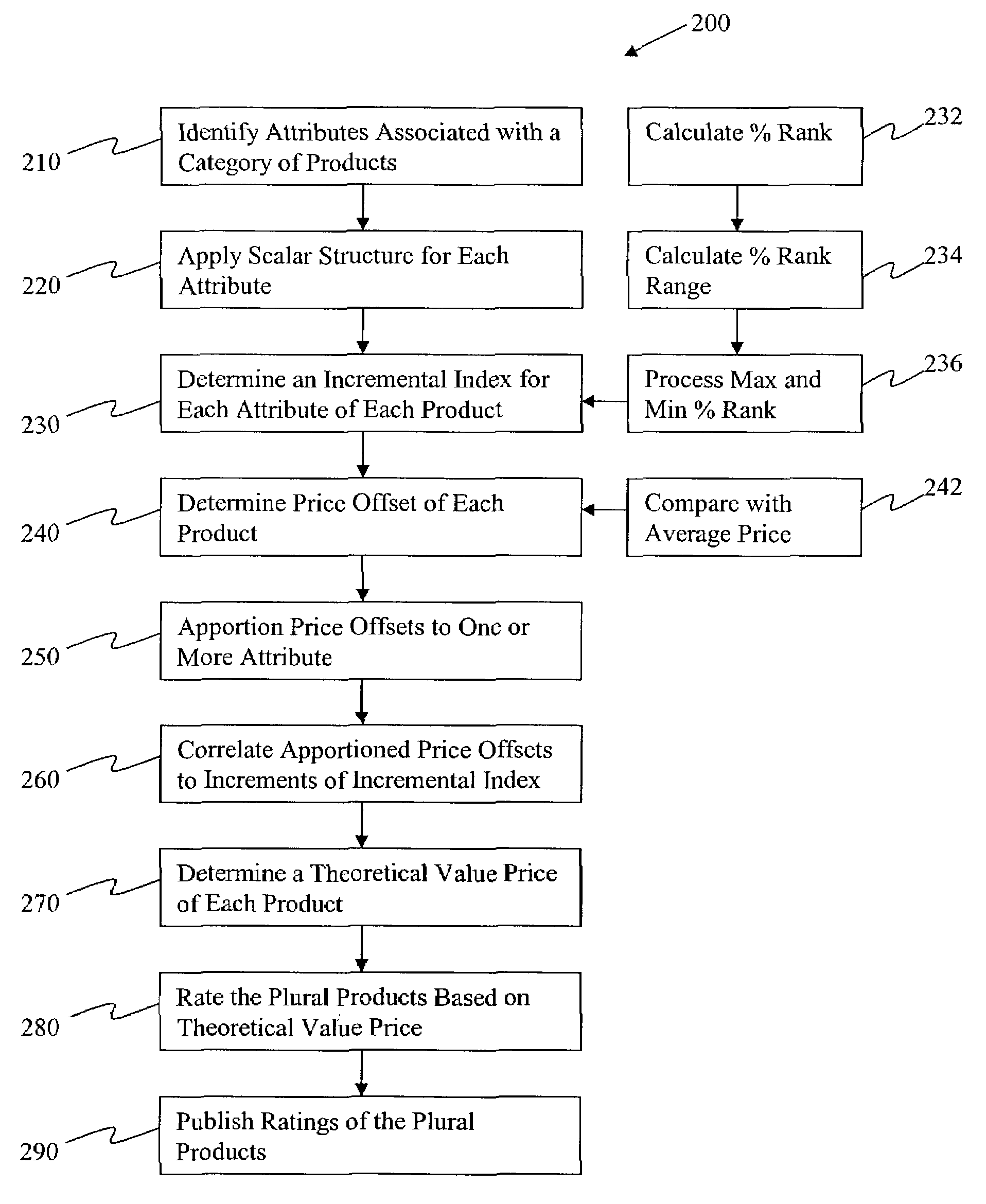
System and method for rating plural products
ActiveUS7627486B2Buying/selling/leasing transactionsElectric/magnetic computingScalar ValueProduct base
A system and method for rating of each of plural products comprising identifying a plurality of attributes associated with a category of product, applying a scalar structure for each attribute to provide a scalar value for each attribute of each of the plural products, determining an incremental competitive index for each attribute of each product based on the scalar value of each attribute and a number of products having the scalar value, and rating each product based on the determined competitive index.
Owner:CBS INTERACTIVE INC
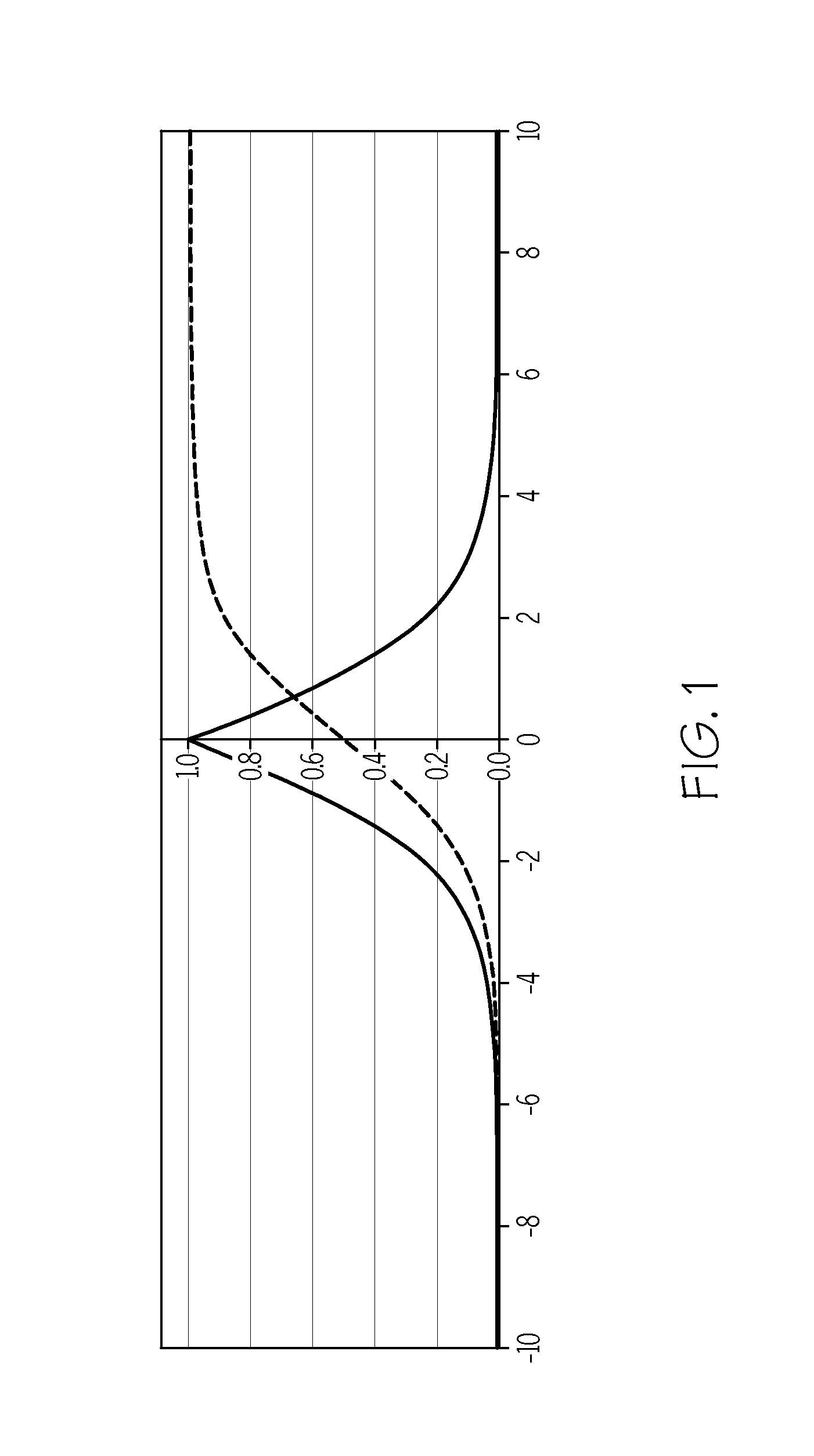
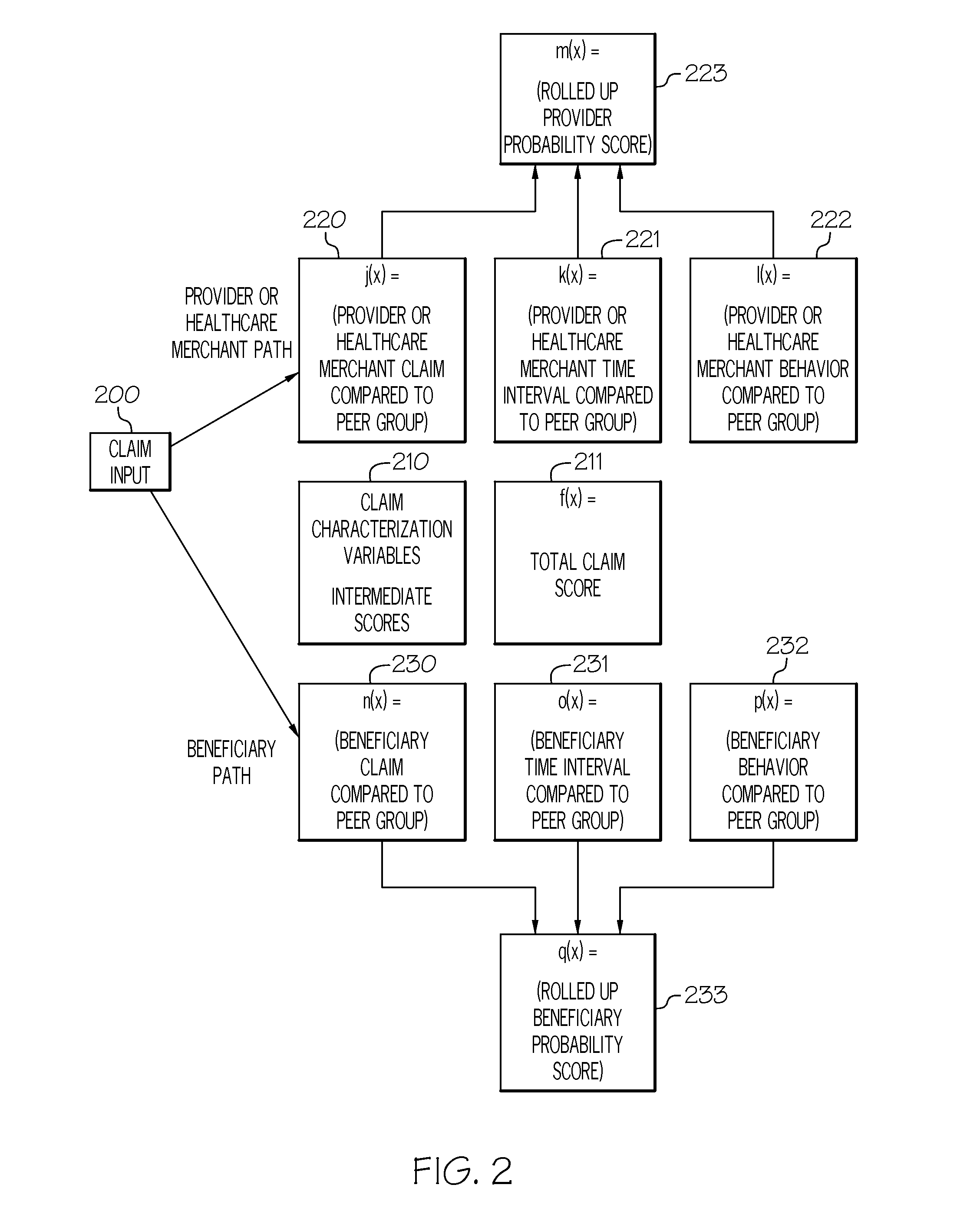
Characterizing healthcare provider, claim, beneficiary and healthcare merchant normal behavior using non-parametric statistical outlier detection scoring techniques
InactiveUS20130085769A1Predictive performanceHigh false positive rateOffice automationPatient-specific dataScalar ValueCrowds
This invention uses non-parametric statistical measures and probability mathematical techniques to calculate deviations of variable values, on both the high and low side of a data distribution, from the midpoint of the data distribution. It transforms the data values and then combines all of the individual variable values into a single scalar value that is a “good-ness” score. This “good-ness” behavior score model characterizes “normal” or typical behavior, rather than predicting fraudulent, abusive, or “bad”, behavior. The “good” score is a measure of how likely it is that the subject's behavior characteristics are from a population representing a “good” or “normal” provider, claim, beneficiary or healthcare merchant behavior. The “good” score can replace or compliment a score model that predicts “bad” behavior in order to reduce false positive rates. The optimal risk management prevention program should include both a “good” behavior score model and a “bad” behavior score model.
Owner:RISK MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
Hash functions using elliptic curve cryptography
InactiveUS20100166174A1Finite divisionUser identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsComputer hardwareHash function
The hash functions using elliptic curve cryptography are hash functions that are produced using both an elliptic curve and a twist of the elliptic curve. Hash points are assigned values that either correspond to points on the elliptic curve or to points on the twist, depending upon whether the scalar value of the corresponding message block produces a quadratic residue or a quadratic non-residue when substituted as the x-value into the elliptic curve equation. The corresponding hash point x-coordinates are concatenated to form the hash bit string. The hash points may be doubled, and the hash functions may be applied to multimedia data by applying a media compression method to the message data before computing the hash points.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method of multi-dimensional analysis of viscoelastic materials for stress, strain, and deformation
A method for solving any arbitrary multi-dimensional scientific or engineering design problem requiring solutions for stress, strain and deformation, and which therefore demands the incorporation of a material constitutive equation into the mathematical solution and wherein that constitutive equation, which quantitatively defines the relationship between stress and strain, incorporates independent tensor valued coefficients and a scalar valued constitutive function / s, and where the values of the tensor valued coefficients and the form of the constitutive function / s is specific to any particular material under consideration.
Owner:TRUNK FR J
System and method for a vector difference mean filter for noise suppression
InactiveUS20060103892A1Suppress noiseReduce noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionAverage filter
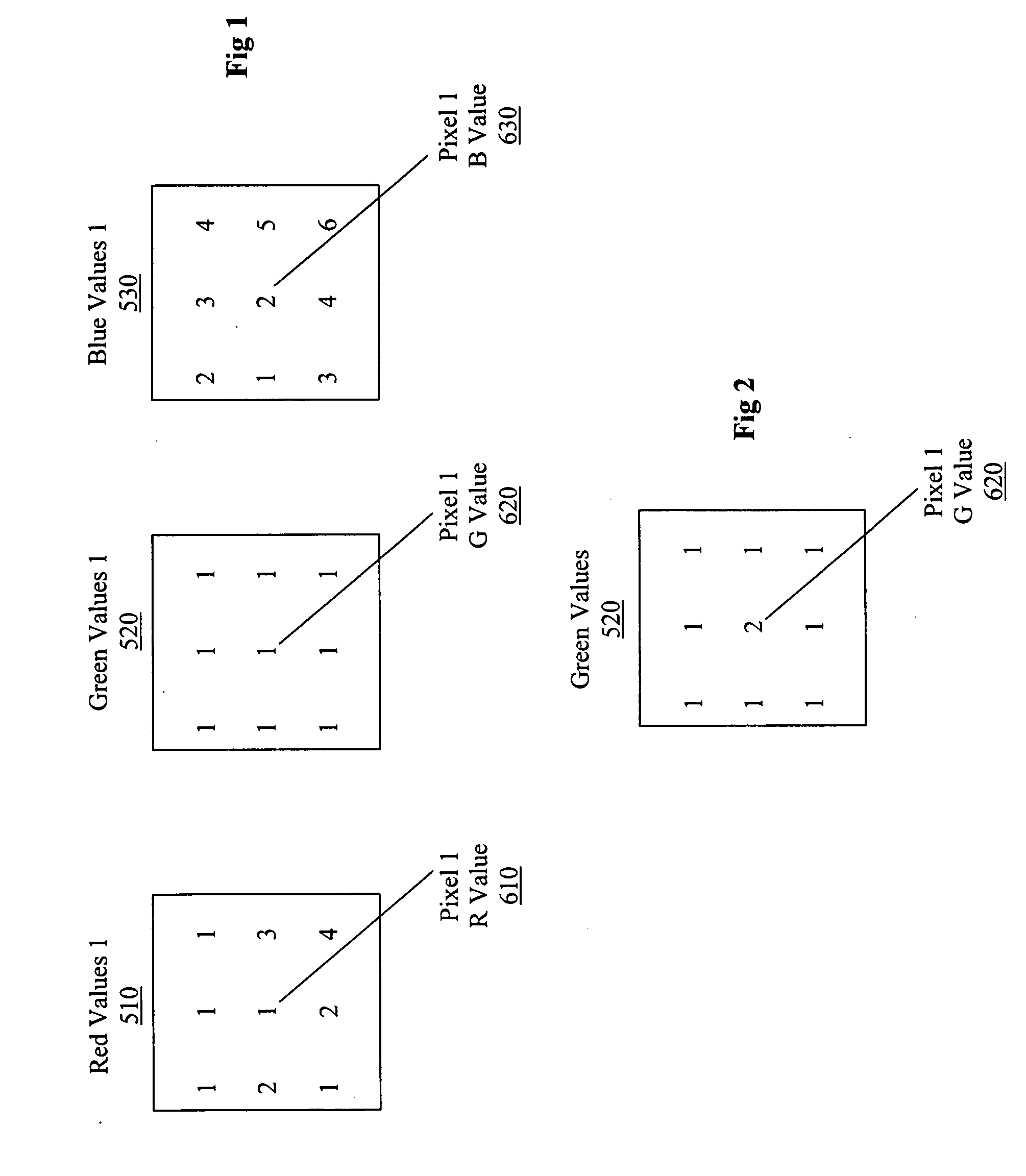
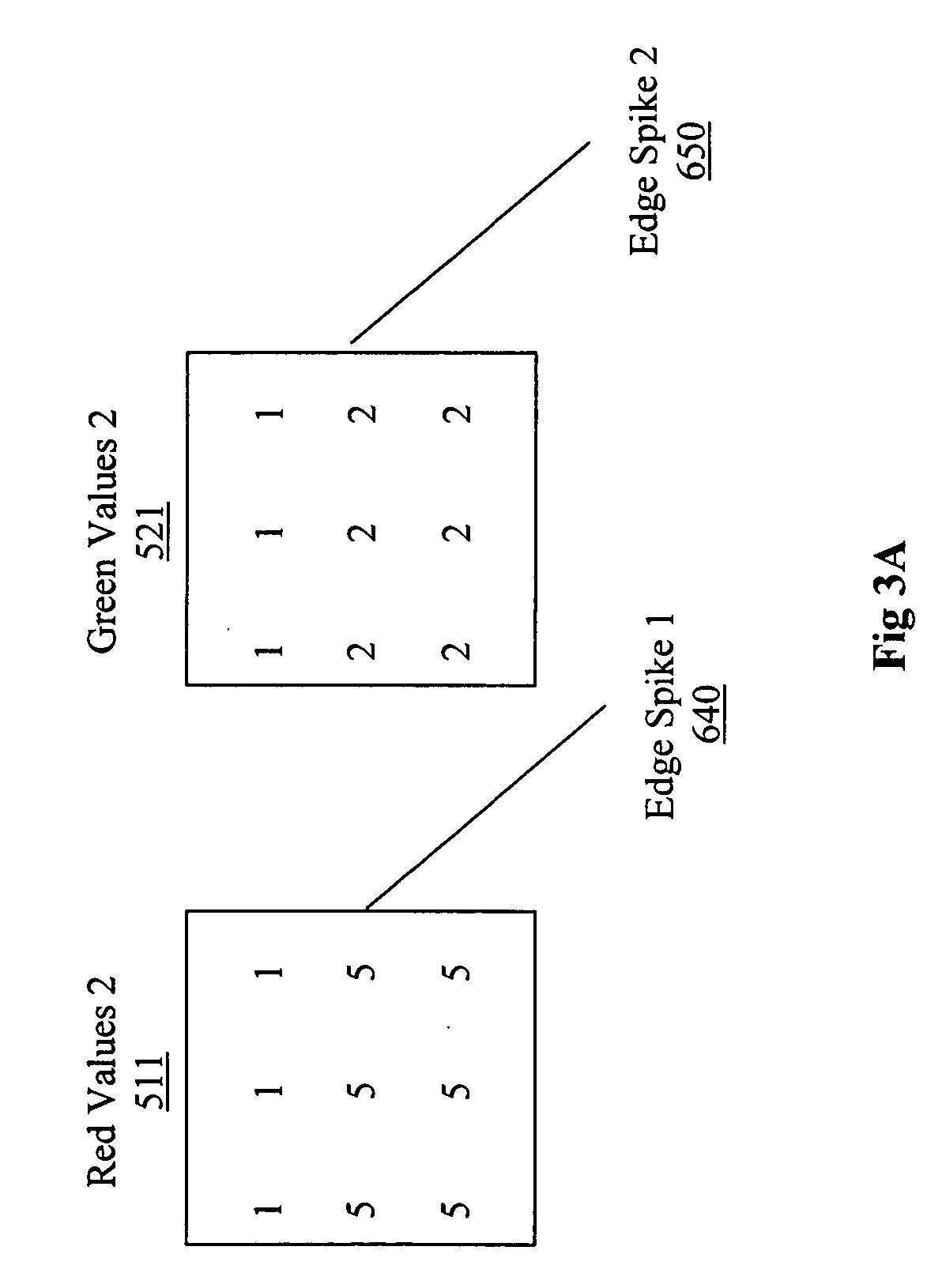
Reduction of noise in digitized multi-spectral images is provided by filtering based on vector values rather than independent scalar values. Vector values refer to a pixel with two or more values. For this method, a metric is defined for pixel vector magnitude. A sliding processing kernel is also defined, with a specified shape, a specified number of pixels to be included in the kernel, and a specified value contrast threshold to avoid distorting edges and fine details. The metric and kernel are used to select pixels for computing filtering of the center pixel in a kernel. A statistical measurement is computed, for example by mean averaging the specified pixels, and the resulting value is made the value of the center pixel of the kernel. The filtering process is applied throughout the image by making each pixel the center of a processing kernel.
Owner:SOZOTEK
System and method for compiling scalar code for a single instruction multiple data (SIMD) execution engine
InactiveUS20070233766A1Low costIncrease choiceRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerDynamic compilationLoad instruction
A system, method, and computer program product are provided for performing scalar operations using a SIMD data parallel execution unit. With the mechanisms of the illustrative embodiments, scalar operations in application code are identified that may be executed using vector operations in a SIMD data parallel execution unit. The scalar operations are converted, such as by a static or dynamic compiler, into one or more vector load instructions and one or more vector computation instructions. In addition, control words may be generated to adjust the alignment of the scalar values for the scalar operation within the vector registers to which these scalar values are loaded using the vector load instructions. The alignment amounts for adjusting the scalar values within the vector registers may be statically or dynamically determined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for differential precoding and base station supporting same
InactiveUS20130070723A1Reduce interference between usersIncrease sum rateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesScalar ValueSide information
Provided is a differential precoding method for reducing inter-user interference and increasing the sum rate. The differential precoding method comprises initializing a precoding matrix with a first (Precoding Matrix Indicator (PMI) for a channel between a mobile station and a base station; and updating the precoding matrix with a second PMI for the channel and side information for adaptively updating the precoding matrix according to a change speed of a state of the channel, wherein the side information has a quantized scalar value.
Owner:HUMAX CO LTD
Electromotor diver and compressor diver
ActiveCN101449456ALow costReduce higher harmonic contentVector control systemsAc-dc conversionPower inverterScalar Value
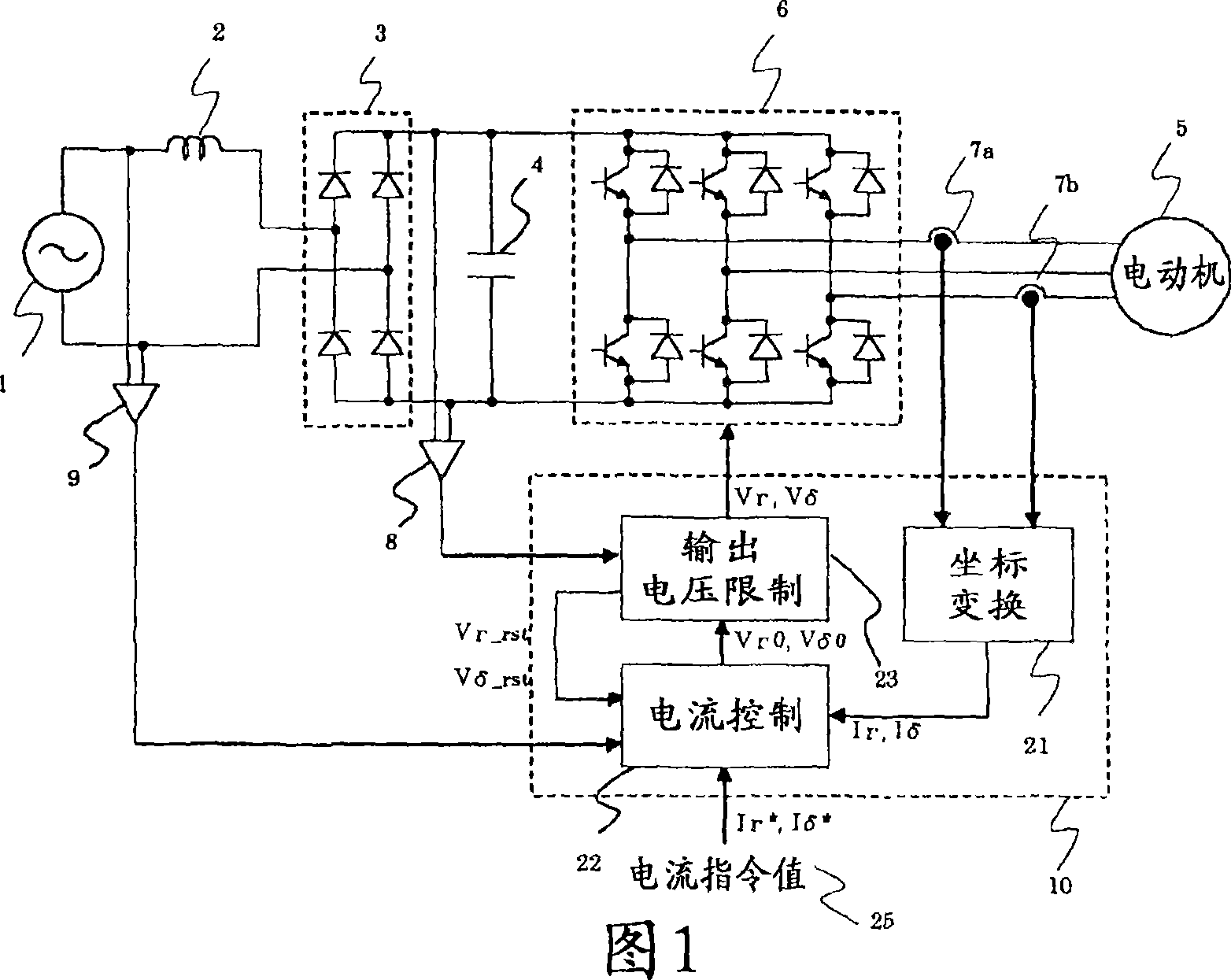
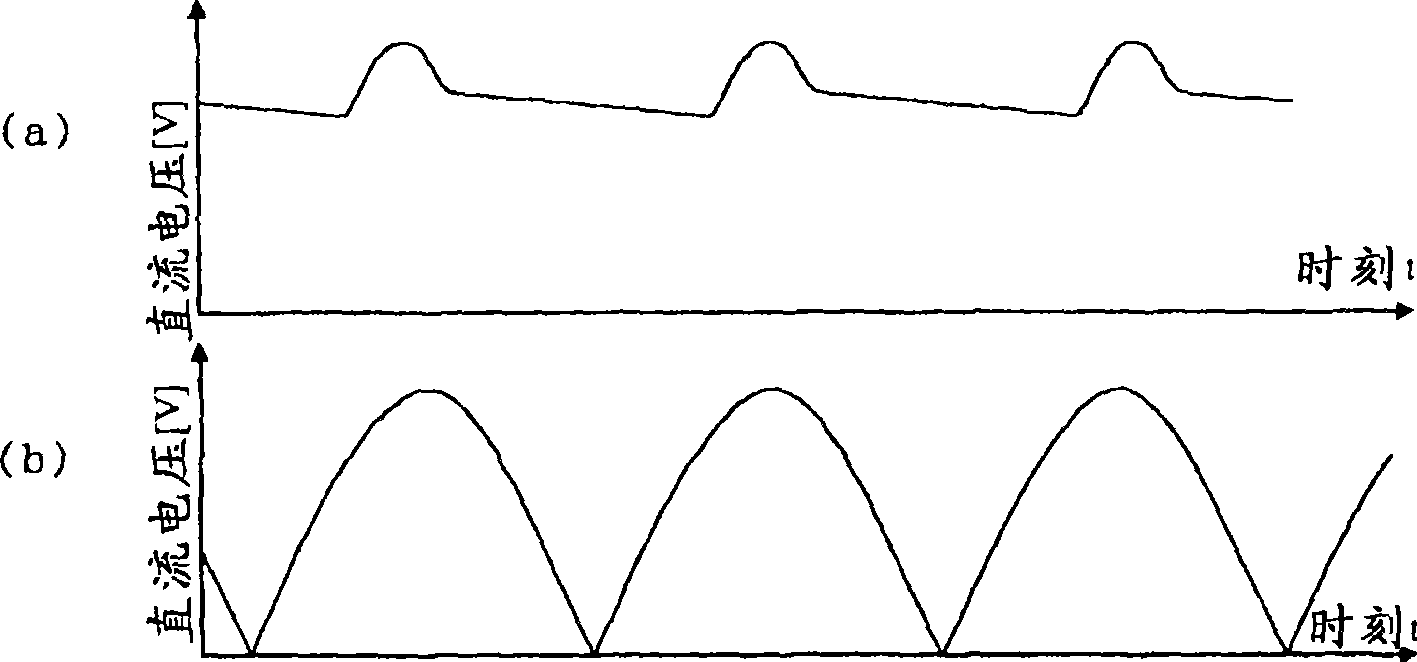
This invention claims an electromotor driver and compressor driver loading the motor driver. The motor driver makes the capacitor smoothing the commutated direct voltage of alternating current power be small capacity or do not be set. It realizes small size, light weight and low cost, furthermore, it can reduce higher harmonic current of input current effectively. The electromotor driver comprises a rectifying unit (3) for rectifying the AC voltage from AC supply to DC voltage, an inverter main circuit part (6) for transforming the DC voltage output by the rectifying unit (3) to AC voltage and applying the AC voltage to the electromotor (5); and a control unit (10) for controlling the voltage from the inverter main circuit part (6)applied to the electromotor (5), wherein the control unit (10) is provided with an output voltage limiting unit (23) for limiting the voltage applied to the electromotor (5) to let the scalar value of the voltage applied to the electromotor below the fixed maximum voltage output by the rectifying unit (3) and feed the voltage limitation of the output voltage limiting unit (23) to the control unit (10).
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Monitoring Device Having Multiple Data Communication Paths
InactiveUS20090265583A1Maximize processing efficiencyAvoid maintenanceProgramme controlFault responseDigital dataScalar Value
A machine monitoring apparatus collects, processes and communicates machine data to be used for process control purposes and to be used in analyzing the machine performance. The apparatus includes one or more sensors that may be attached to or adjacent the machine for generating signals indicative of a performance parameter of the machine. An analog-to-digital converter converts the signals generated by the one or more sensors to bulk digital data corresponding to the sensed performance parameter. A processor receives and analyzes the bulk digital data and generates control digital data based on the bulk digital data. The control digital data may include one or more scalar values or status messages related to the operational performance of the machine as indicated by the bulk digital data. The apparatus includes a control data interface for providing access to the control digital data via a control data network, and a bulk data interface for providing access to the bulk digital data.
Owner:CSI TECH
Music searching methods based on human perception
ActiveUS8326584B1Easy to compareMetadata audio data retrievalMultimedia data retrievalScalar ValuePattern perception
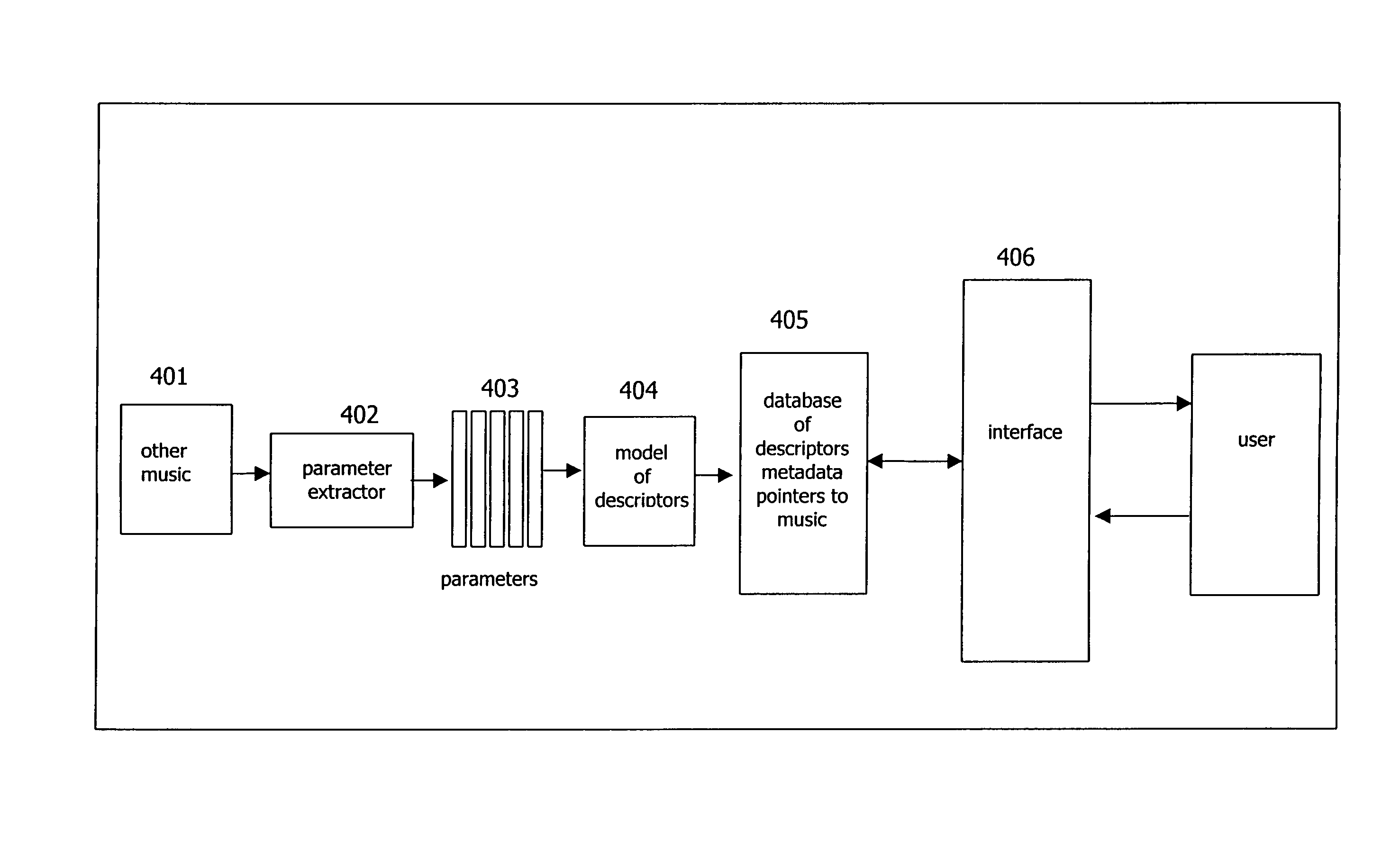
A method for characterizing a musical recording as a set of scalar descriptors, each of which is based on human perception. A group of people listens to a large number of musical recordings and assigns to each one many scalar values, each value describing a characteristic of the music as judged by the human listeners. Typical scalar values include energy level, happiness, danceability, melodicness, tempo, and anger. Each of the pieces of music judged by the listeners is then computationally processed to extract a large number of parameters which characterize the electronic signal within the recording. Algorithms are empirically generated which correlate the extracted parameters with the judgments based on human perception to build a model for each of the scalars of human perception. These models can then be applied to other music which has not been judged by the group of listeners to give to each piece of music a set of scalar values based on human perception. The set of scalar values can be used to find other pieces that sound similar to humans or vary in a dimension of one of the scalars.
Owner:CDDB INC D B A GRACENOTE
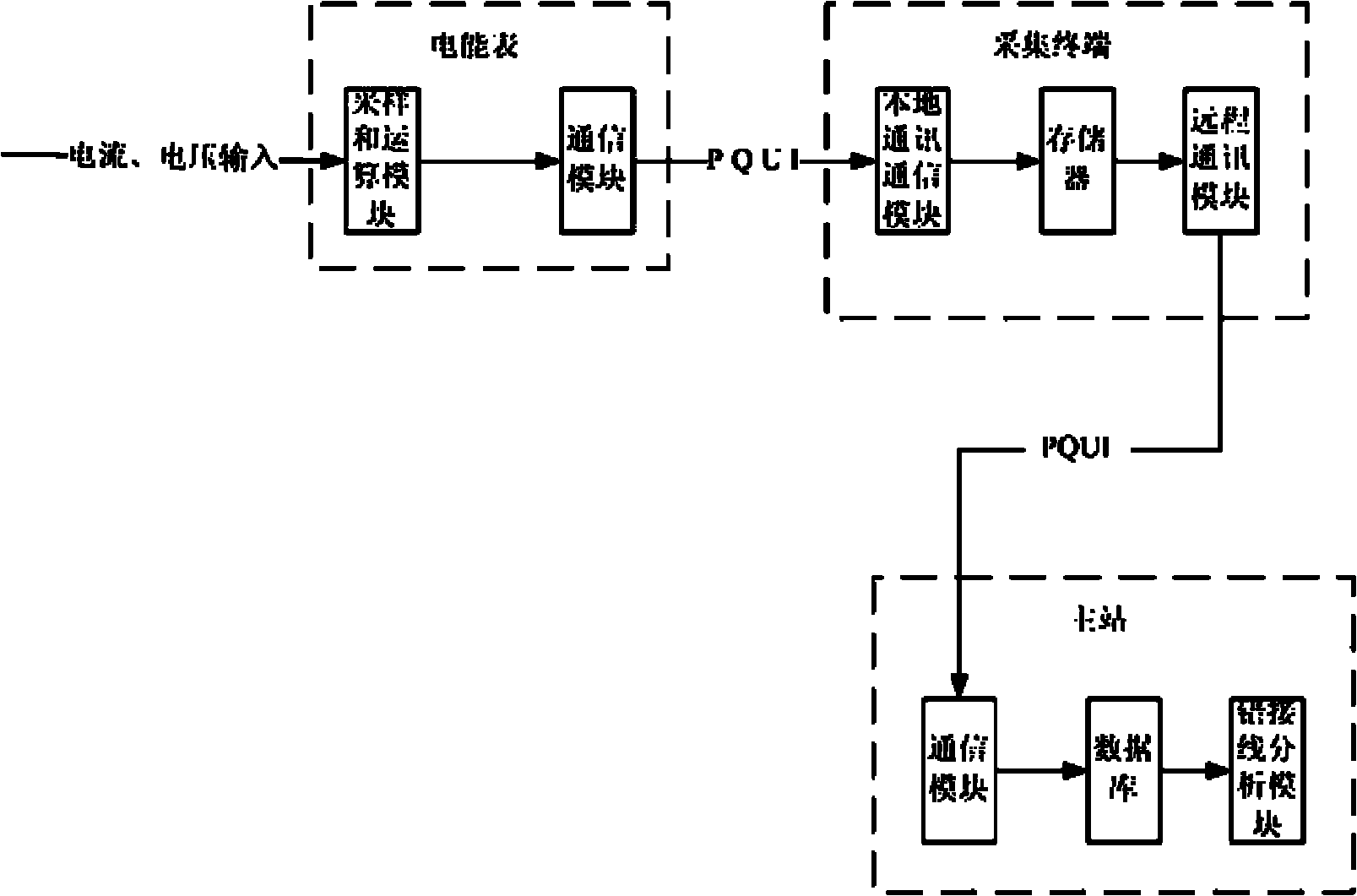
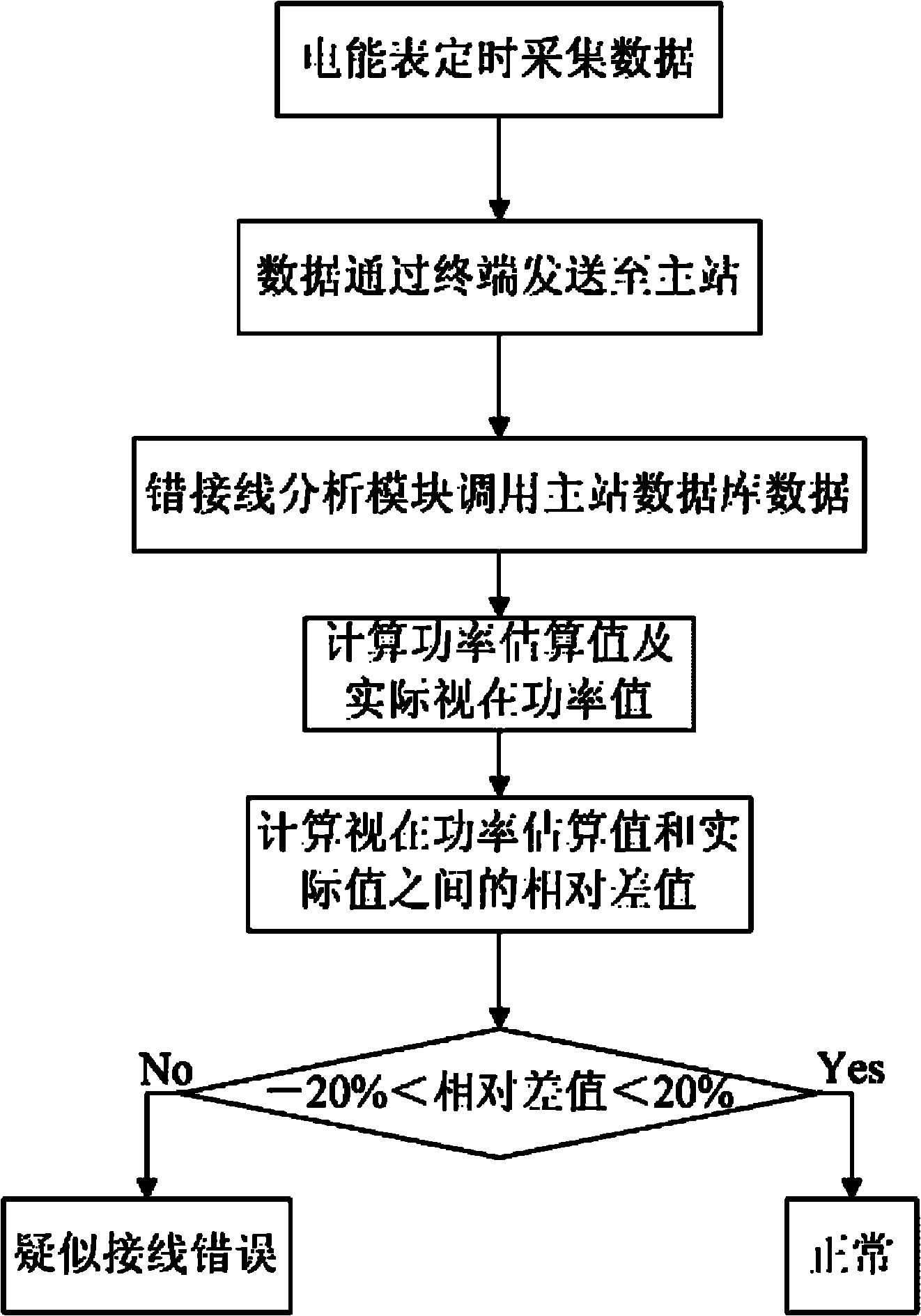
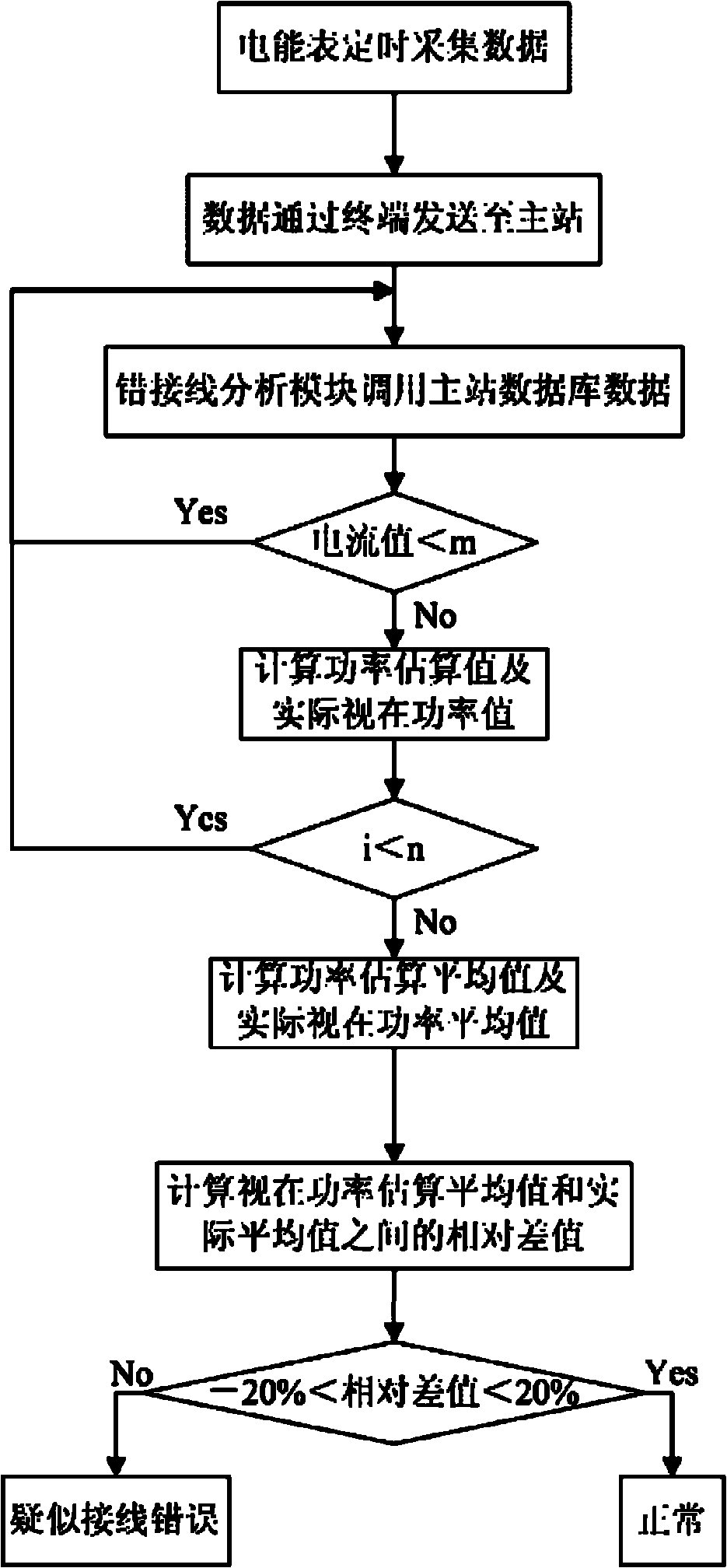
Method for judging wrong wiring of electric energy meter based on apparent power estimation
InactiveCN102033185AAutomate managementImprove judgment efficiencyElectrical testingScalar ValueElectric energy
The invention relates to a method for judging the wrong wiring of an electric energy meter based on apparent power estimation, belonging to the field of the electric energy measurement of a power system. At present, usually the phase angle of current and voltage is detected to judge the wrong wiring of the electric energy meter, and devices such as an on-site calibrator and the like are needed to carry to a site for detection during operation, which causes low efficiency. By using the method, the scalar values of the three-phase current and the three-phase voltage which are collected by the electric energy meter in a timing way are used for estimating the apparent power, and the possibility of the wrong wiring is judged according to the comparison of differences between the estimated apparent power and the actual apparent power. The method realizes large-scale, long-distance and continuous judgment, replaces a method of using the phase angle of the current and the voltage for judging and detecting the wrong wiring of the electric energy meter, improves judgment efficiency, reduces manpower and material resources, and achieves automatic management.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Compilation for a SIMD RISC processor
InactiveUS7840954B2Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemScalar Value
A computer implemented method, data processing system, and computer usable code are provided for generating code to perform scalar computations on a Single-Instruction Multiple-Data (SIMD) Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) architecture. The illustrative embodiments generate code directed at loading at least one scalar value and generate code using at least one vector operation to generate a scalar result, wherein all scalar computation for integer and floating point data is performed in a SIMD vector execution unit.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
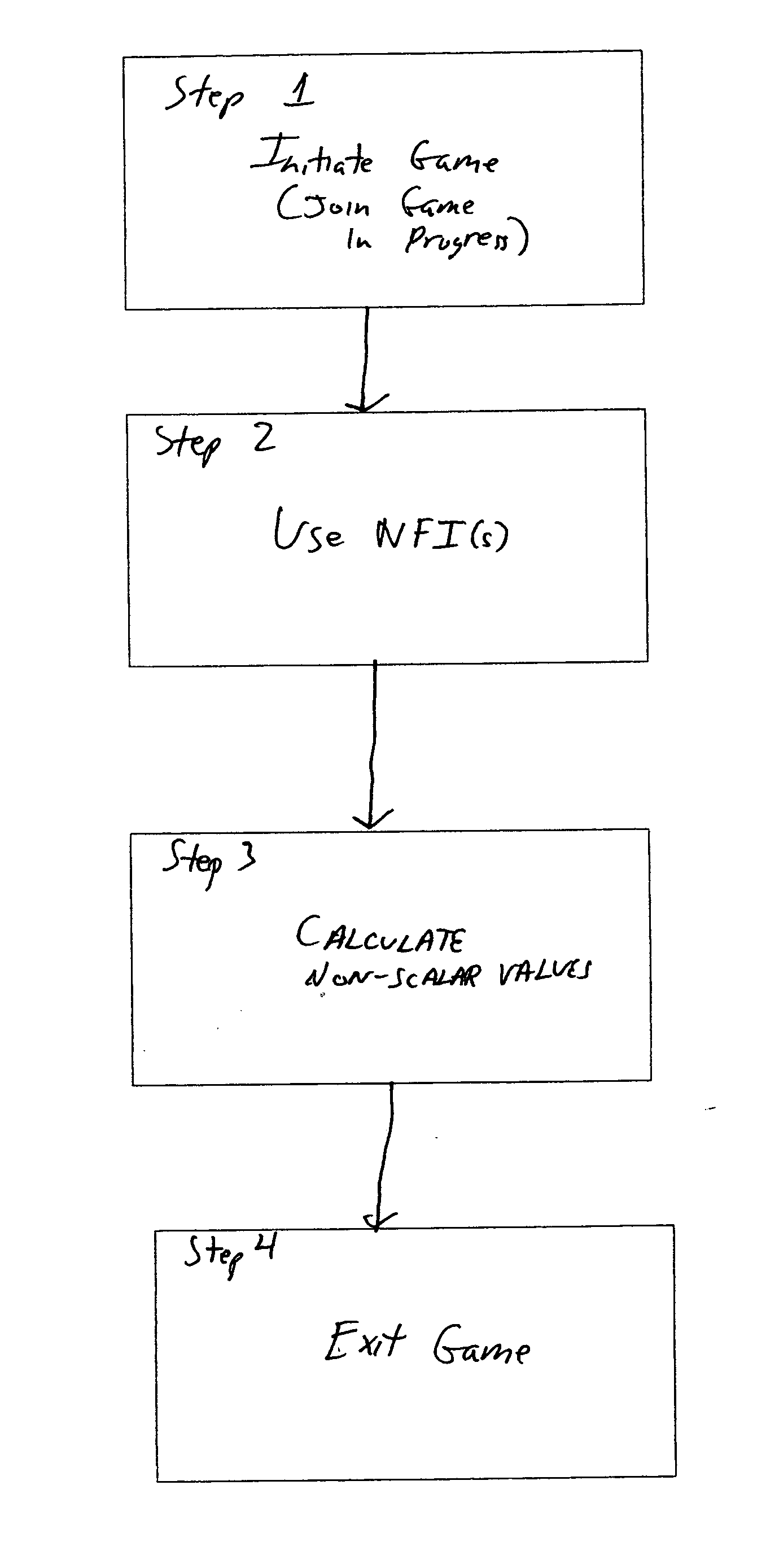
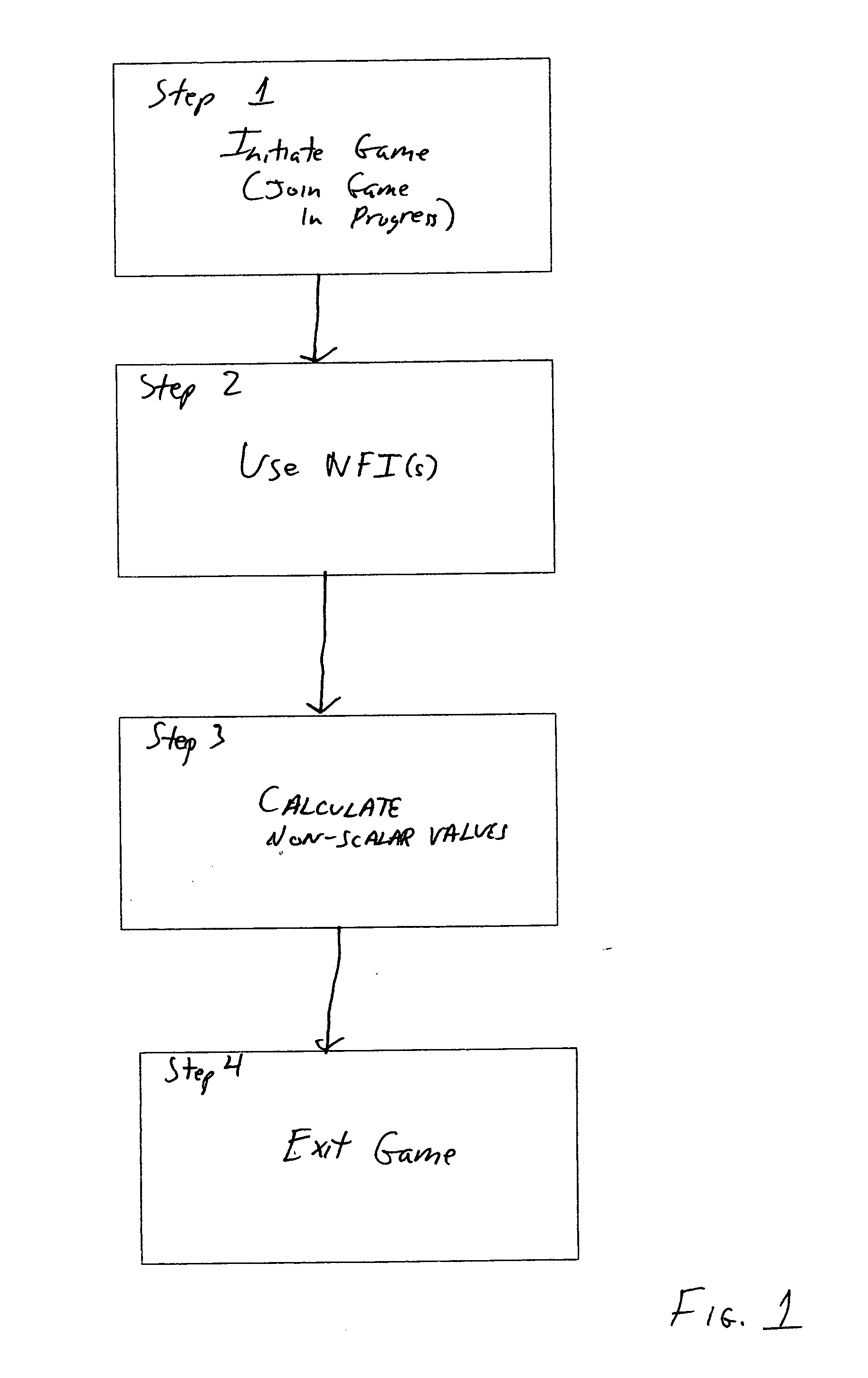
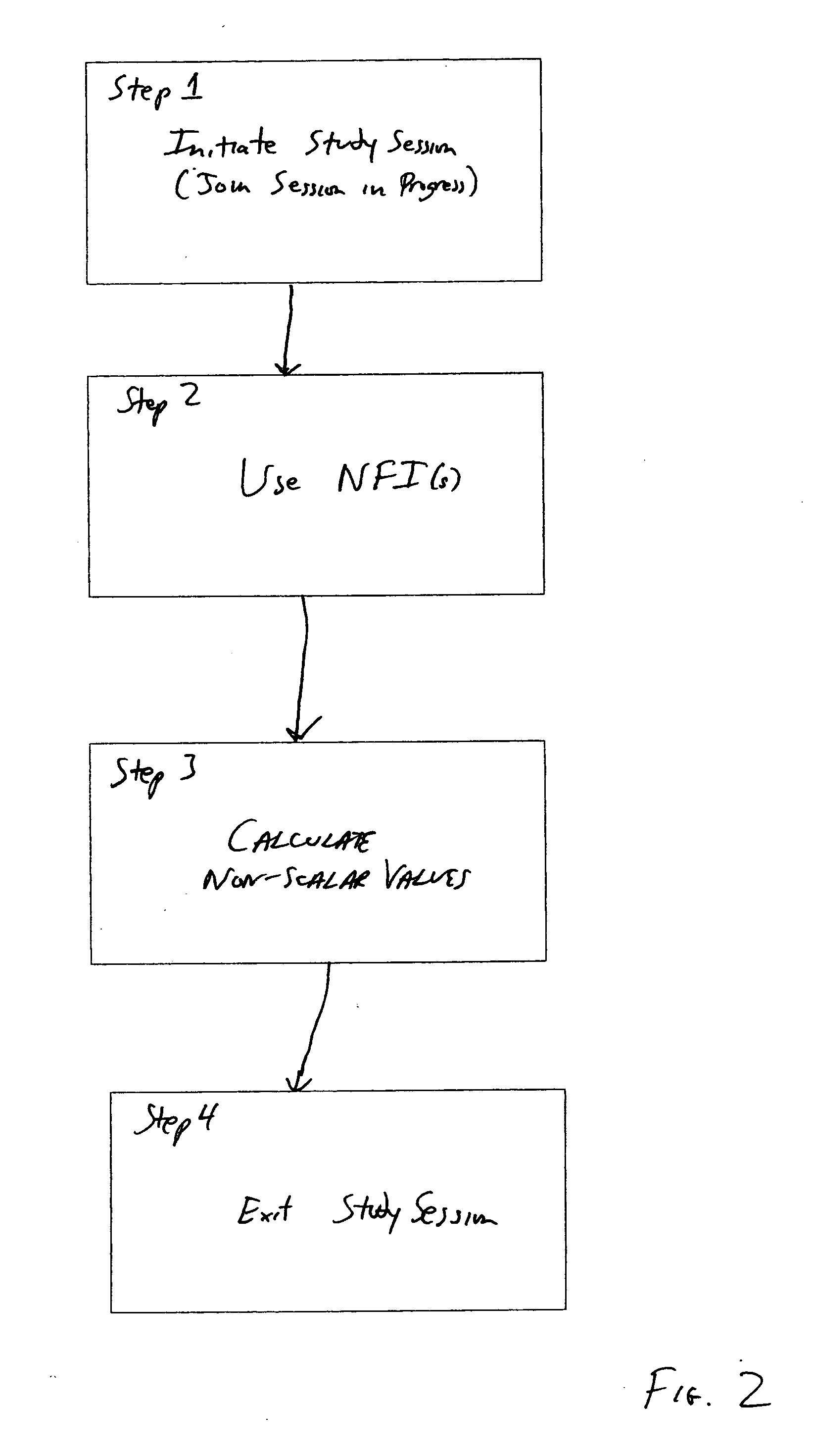
Non-scalar-valued financial instruments
A method and system is disclosed for creating and using non-scalar valued financial instruments. The method and system addresses the problems caused by limiting the value of financial instruments to scalar quantities. Applications of the method and system include recreation, education, therapeutic intervention, and finance.
Owner:GROZ MARC MICHAEL
Generation method of planar spiral and annular milling tracks
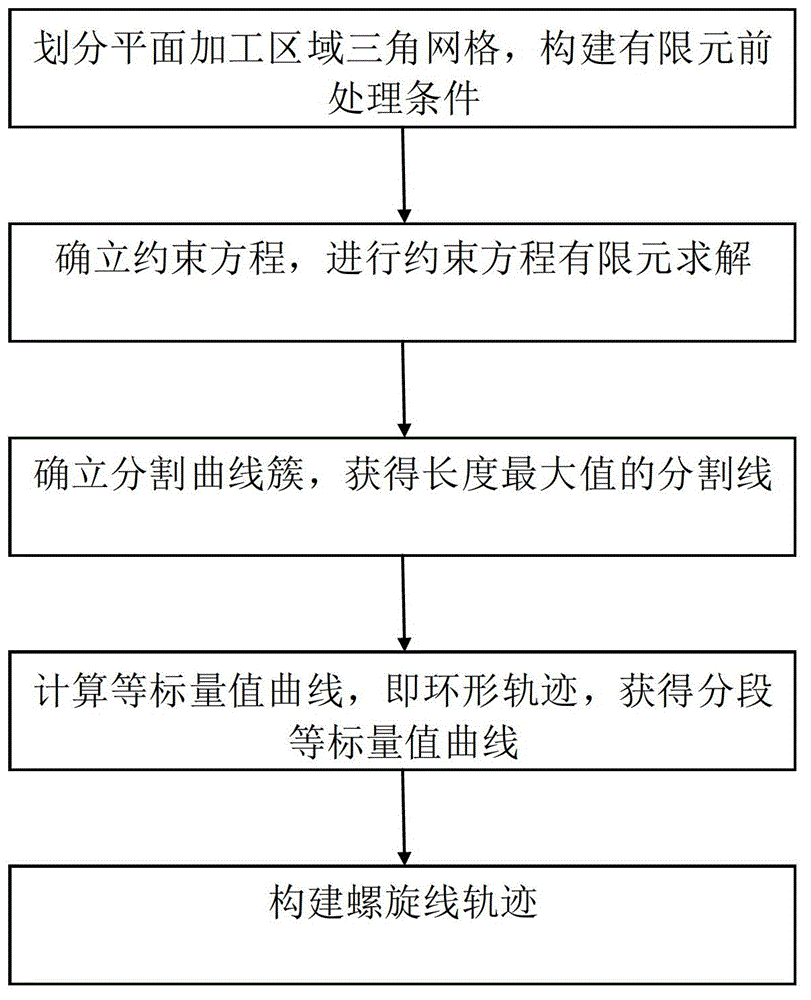
ActiveCN102945019AReduce lossReduce vibrationProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlField function
The invention discloses a generation method of planar spiral and annular milling tracks. The generation method comprises the following steps: acquiring a plane machining region of a multi-shaft cutter, performing triangle grid division on the plane machining region to construct an energy field; establishing a constraint equation of the energy field, performing finite element solution on the constraint equation to obtain a field function; establishing a divide curve family according to the finite element solution to acquire a cutting line of a length maximum value; calculating equal scalar value curves according to the cutting line of the length maximum value, and cutting the plane machining region into m sub-regions, wherein m is an positive integer; and respectively performing interpolation on each pair of equal scalar value curves in the m sub-regions to obtain spiral lines. According to the generation method of the planar spiral and annular milling tracks, the vibration generated in the machining process of a numerical control machine tool can be reduced, at the same time, the processing efficiency is improved, and the loss of the cutter is reduced.
Owner:FOSHAN HUASHU ROBOTICS CO LTD
Apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations
ActiveUS8443170B2Reduce energy consumptionImprove energy consumptionAssociative processorsNext instruction address formationProgram instructionControl signal
An apparatus and method for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations includes SIMD data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations in parallel on multiple data elements. Instruction decoder circuitry is coupled to the SIMD data processing circuitry and is responsive to program instructions to generate the required control signals. The instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a single instruction (referred to herein as a repeating multiply-accumulate instruction) having as input operands a first vector of input data elements, a second vector of coefficient data elements, and a scalar value indicative of a plurality of iterations required, to generate control signals to control the SIMD processing circuitry. In response to those control signals, the SIMD data processing circuitry performs the plurality of iterations of a multiply-accumulate process, each iteration involving performance of N multiply-accumulate operations in parallel in order to produce N multiply-accumulate data elements. For each iteration, the SIMD data processing circuitry determines N input data elements from said first vector and a single coefficient data element from the second vector to be multiplied with each of the N input data elements. The N multiply-accumulate data elements produced in a final iteration of the multiply-accumulate process are then used to produce N multiply-accumulate results. This mechanism provides a particularly energy efficient mechanism for performing SIMD multiply-accumulate operations, as for example are required for FIR filter processes.
Owner:U-BLOX
System and method for sharpening vector-valued digital images
InactiveUS20060182364A1Improve noiseReduce noiseImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionScalar ValueLow-pass filter
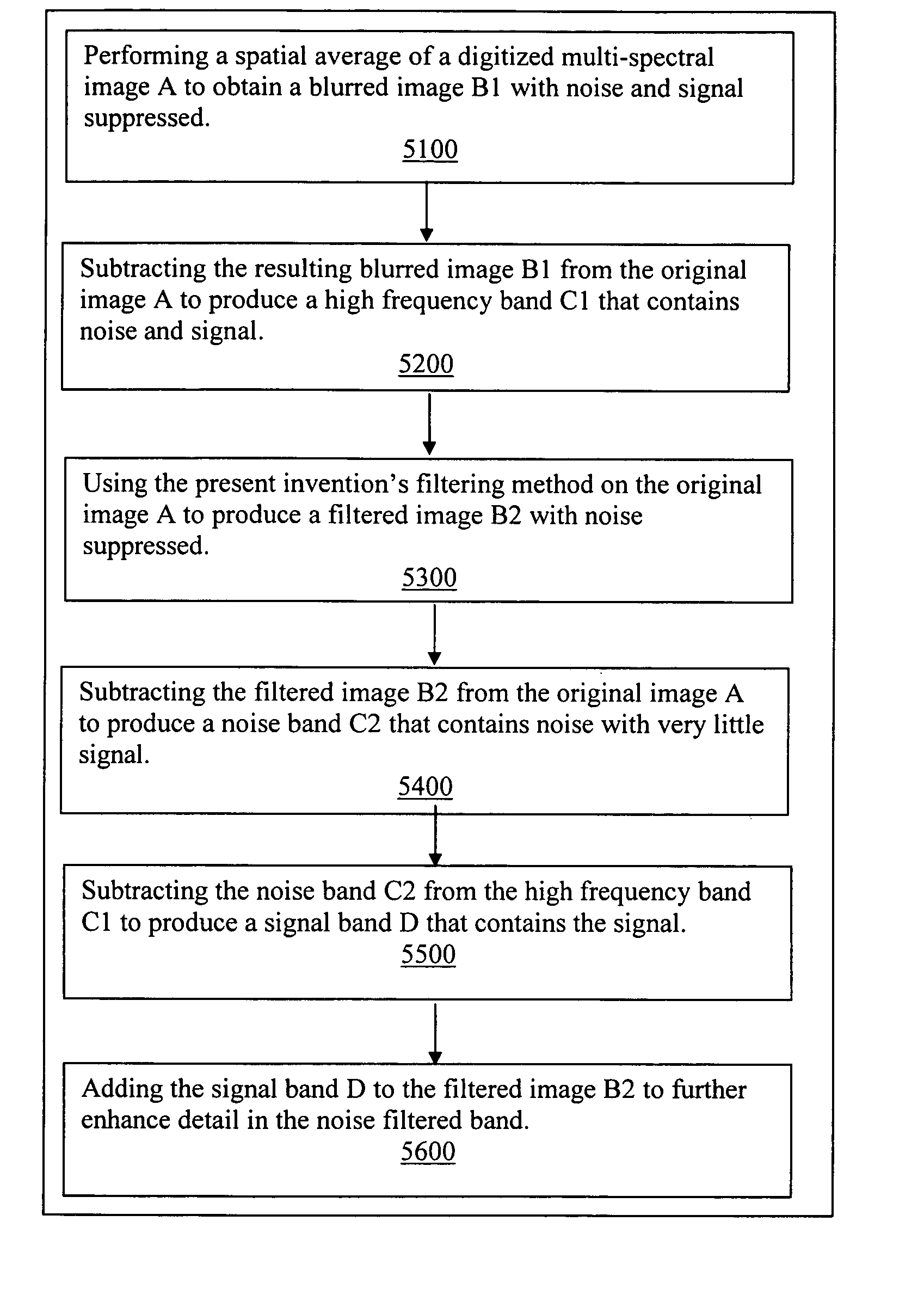
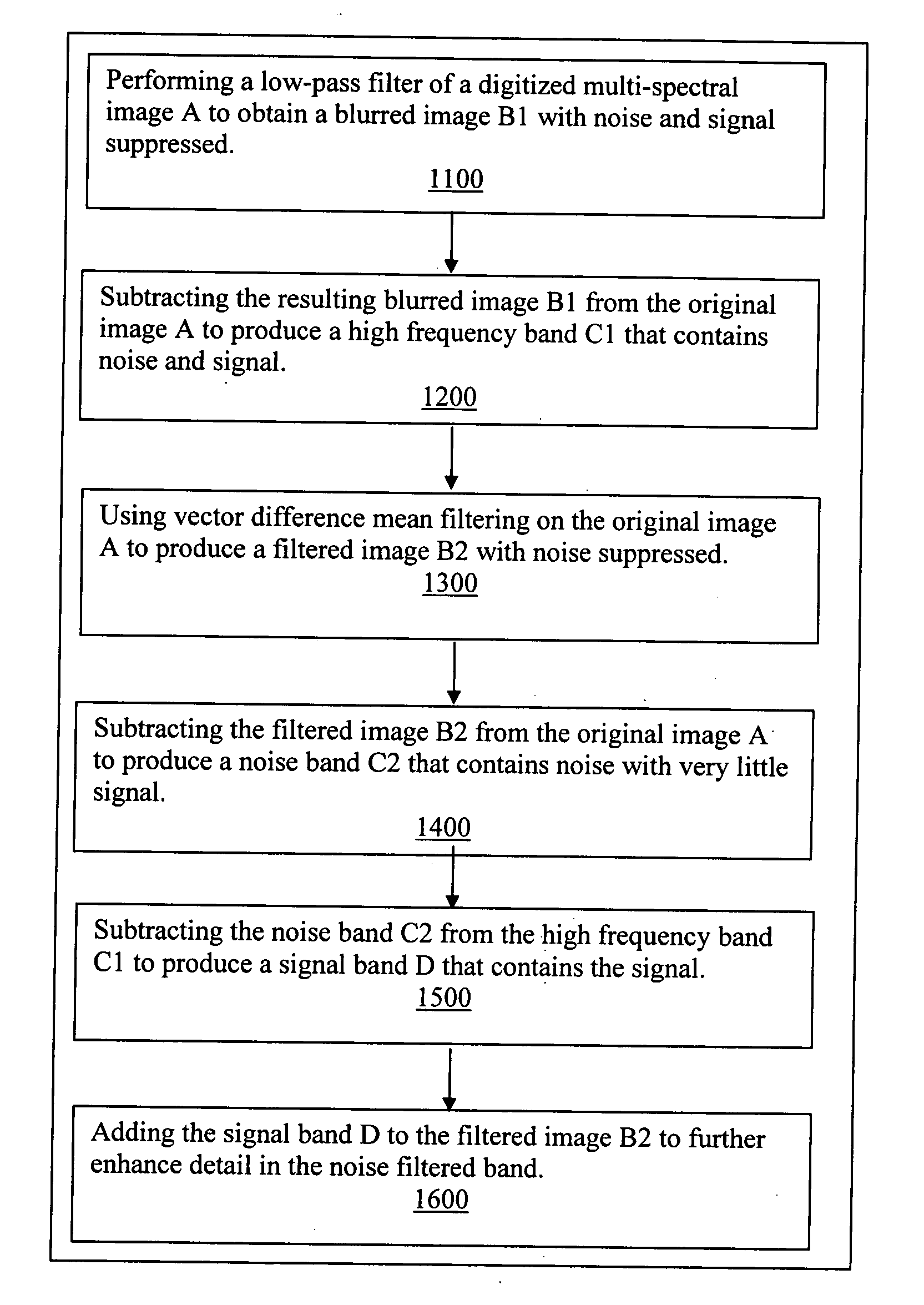
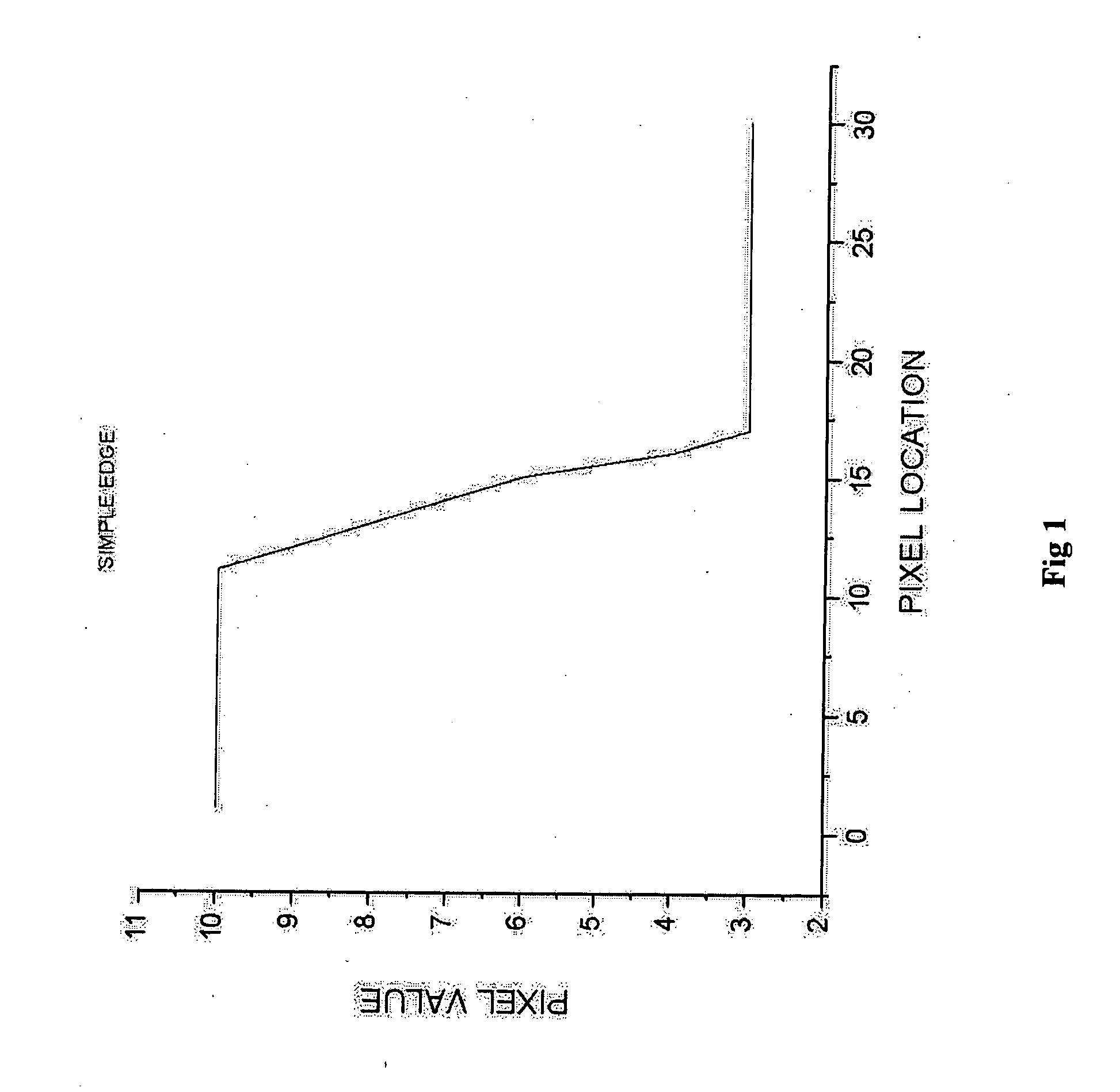
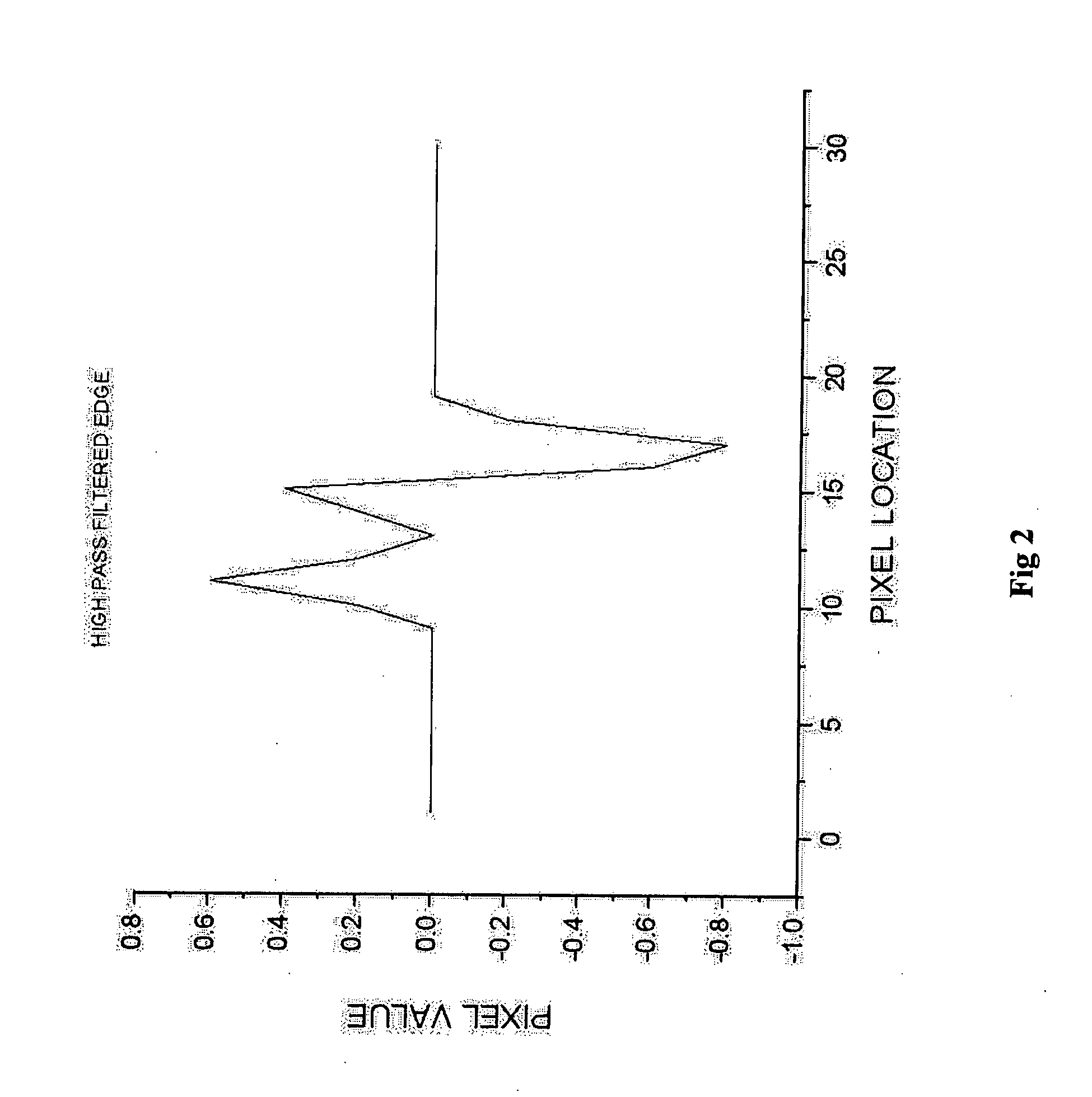
Sharpening multi-spectral digital images without increasing noise is accomplished by filtering vector values rather than independent scalar values. A low-pass filter is performed on image A to obtain a blurred image B1 with noise and signal suppressed. The resulting blurred image B1 is subtracted from the original image A to produce a high frequency band C1 that contains noise and signal. Vector difference mean filtering is performed on the original image A to produce a filtered image B2 with noise suppressed. The filtered image B2 is subtracted from the original image A to produce a noise band C2 that contains noise with very little signal. The noise band C2 is subtracted from the high frequency band C1 to produce a signal band D that contains the signal. The signal band D is then added to the filtered image B2 to further enhance detail in the noise filtered band.
Owner:SOZOTEK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com