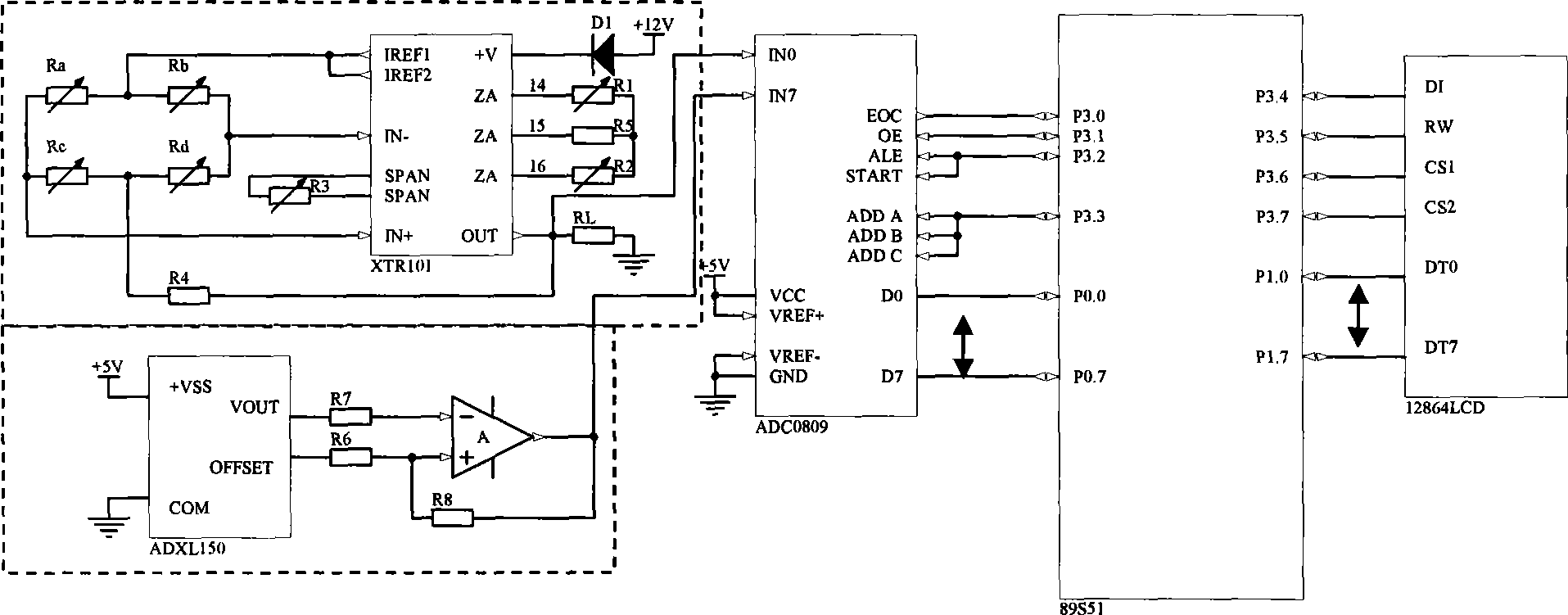
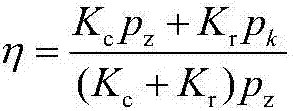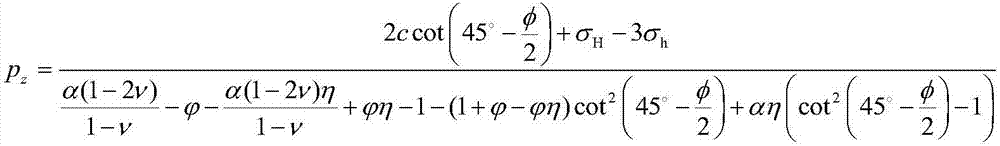Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Wall stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
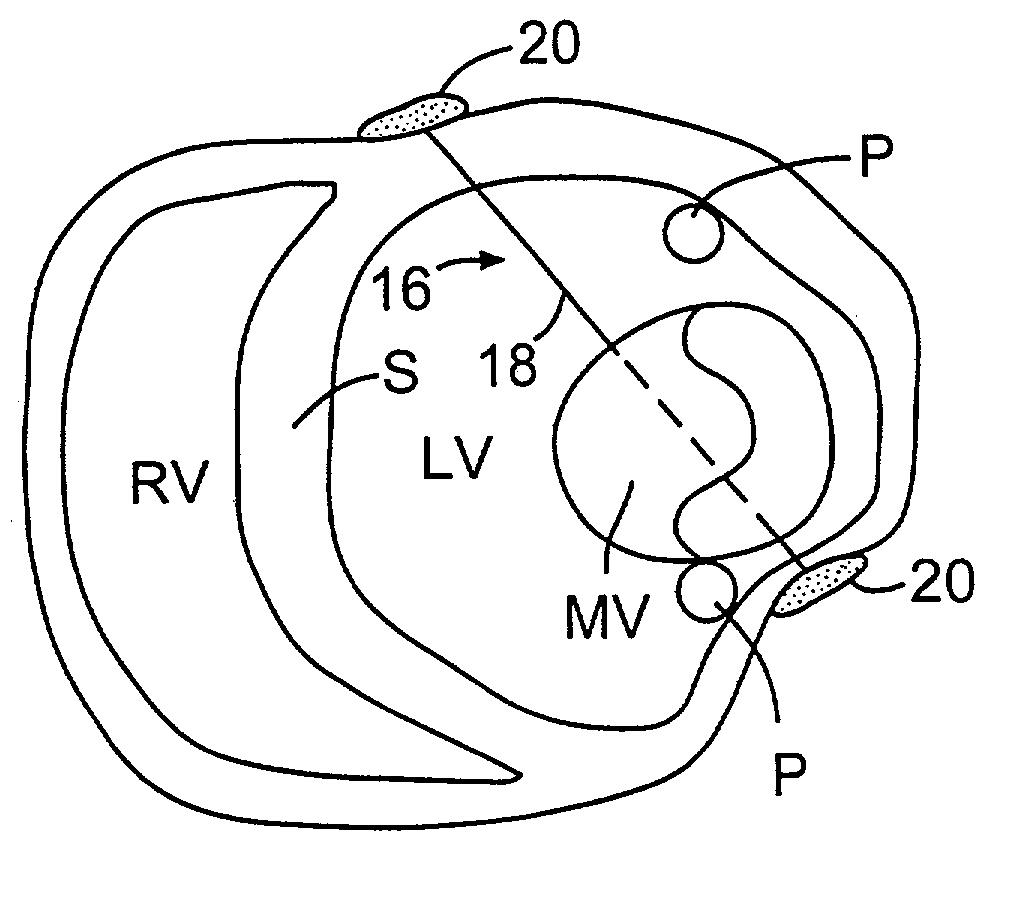
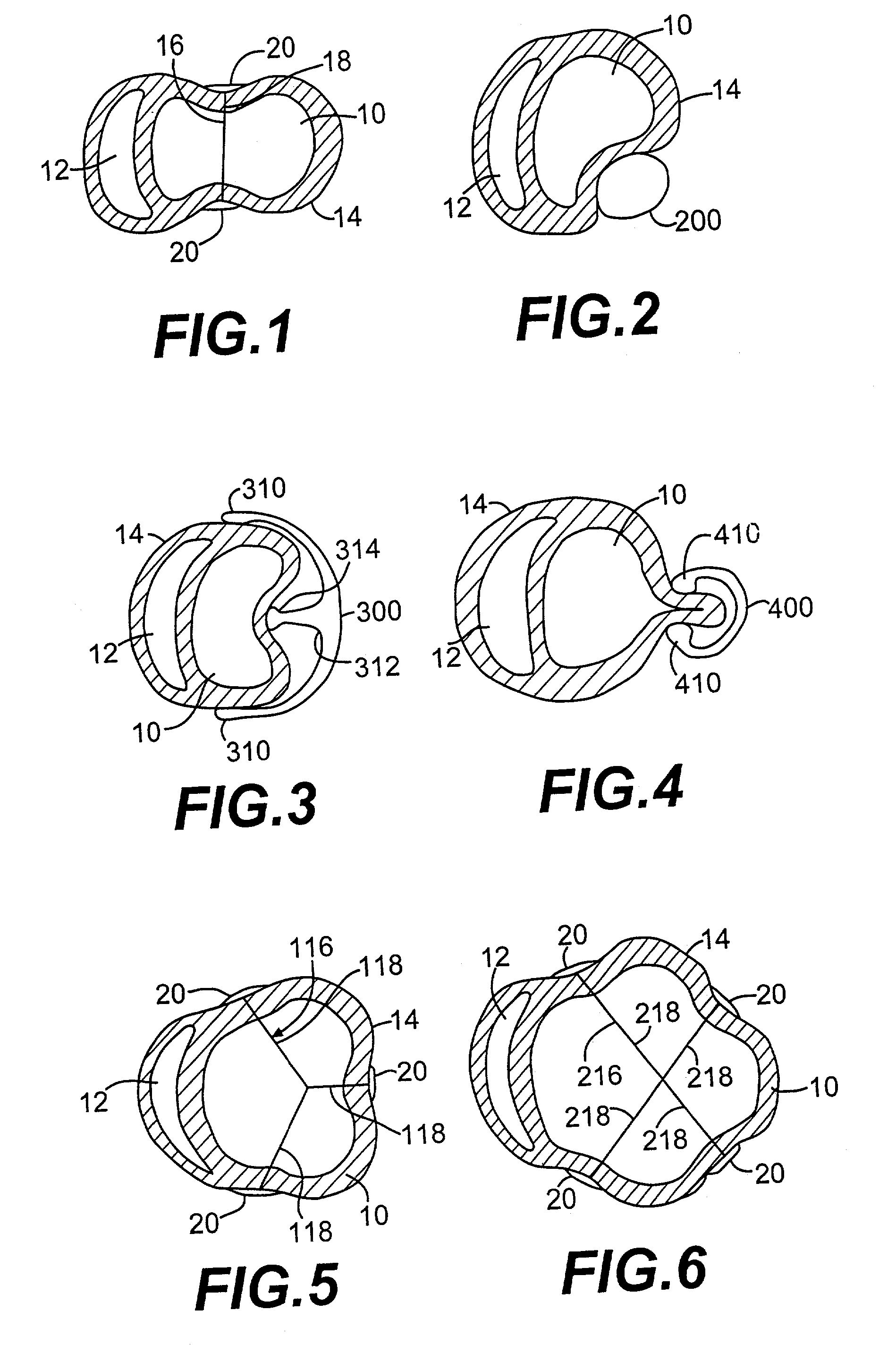
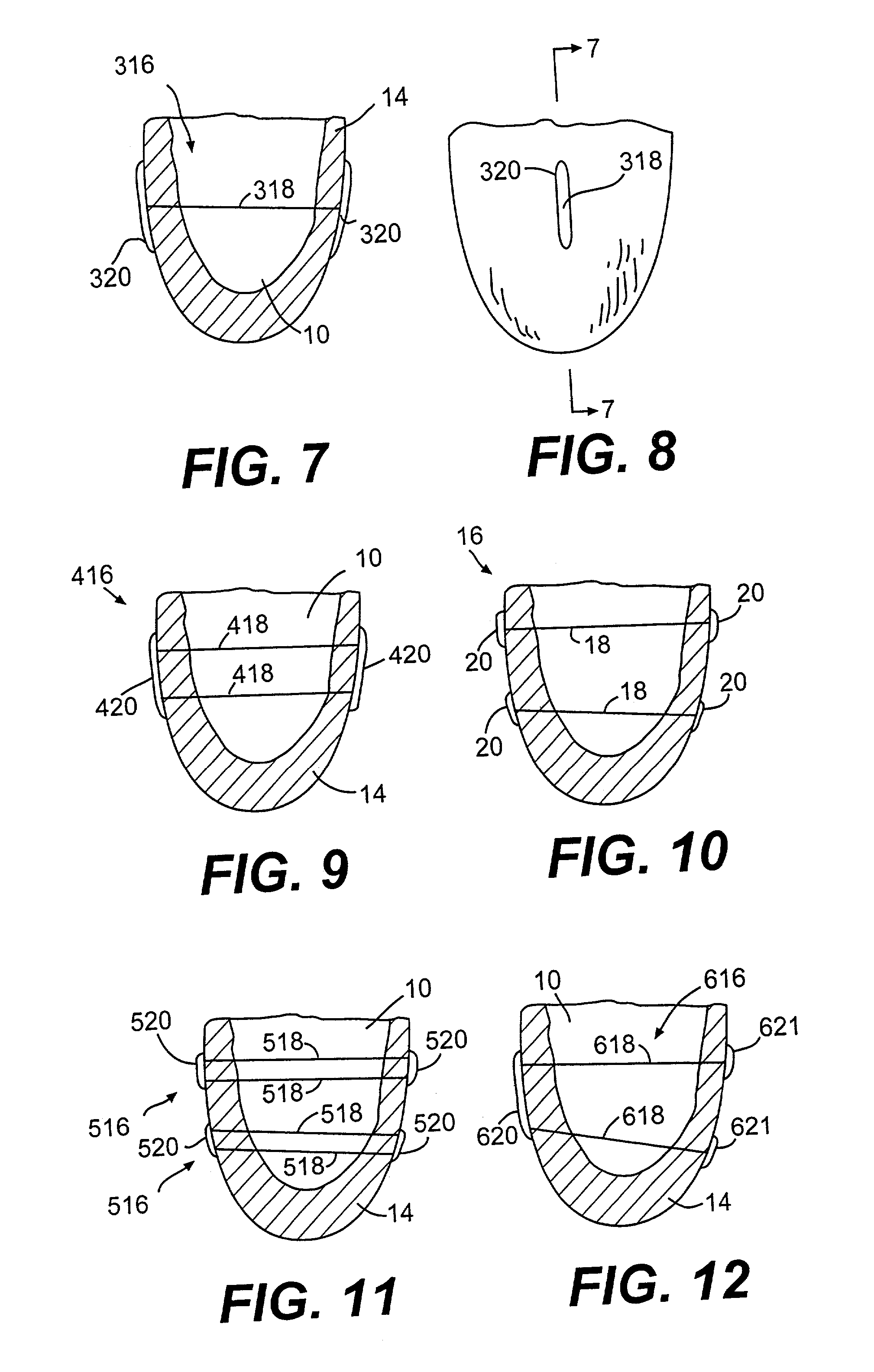
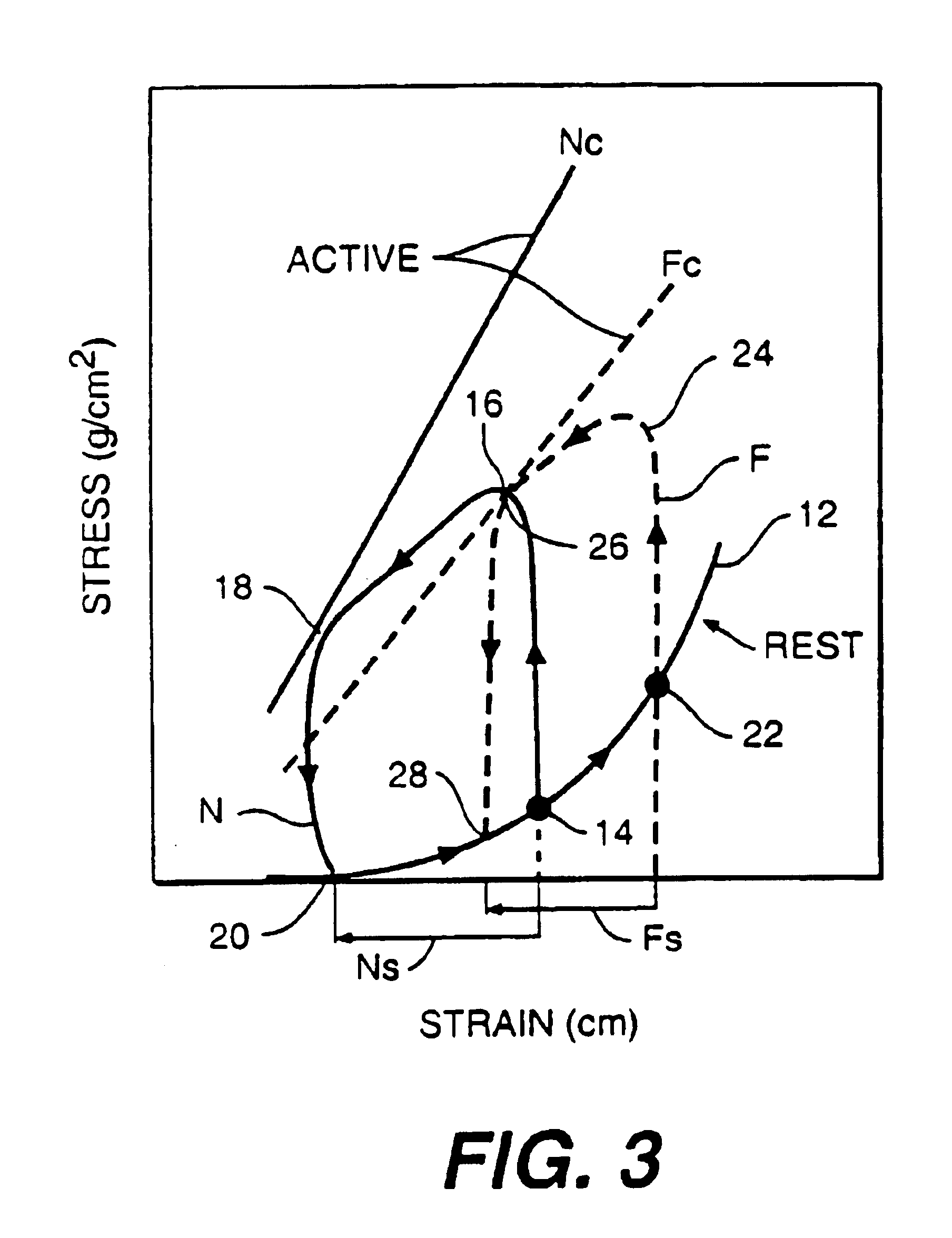
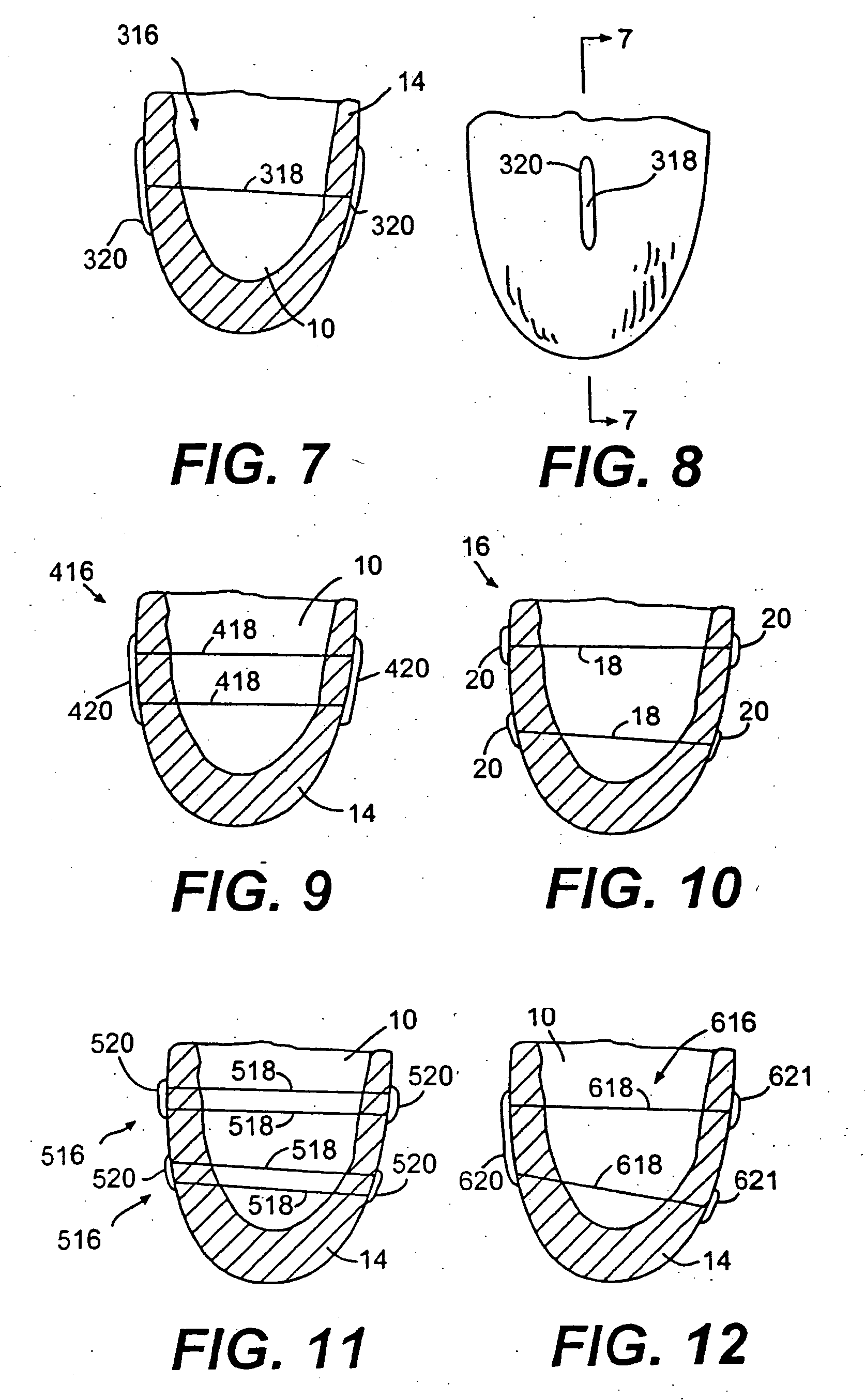
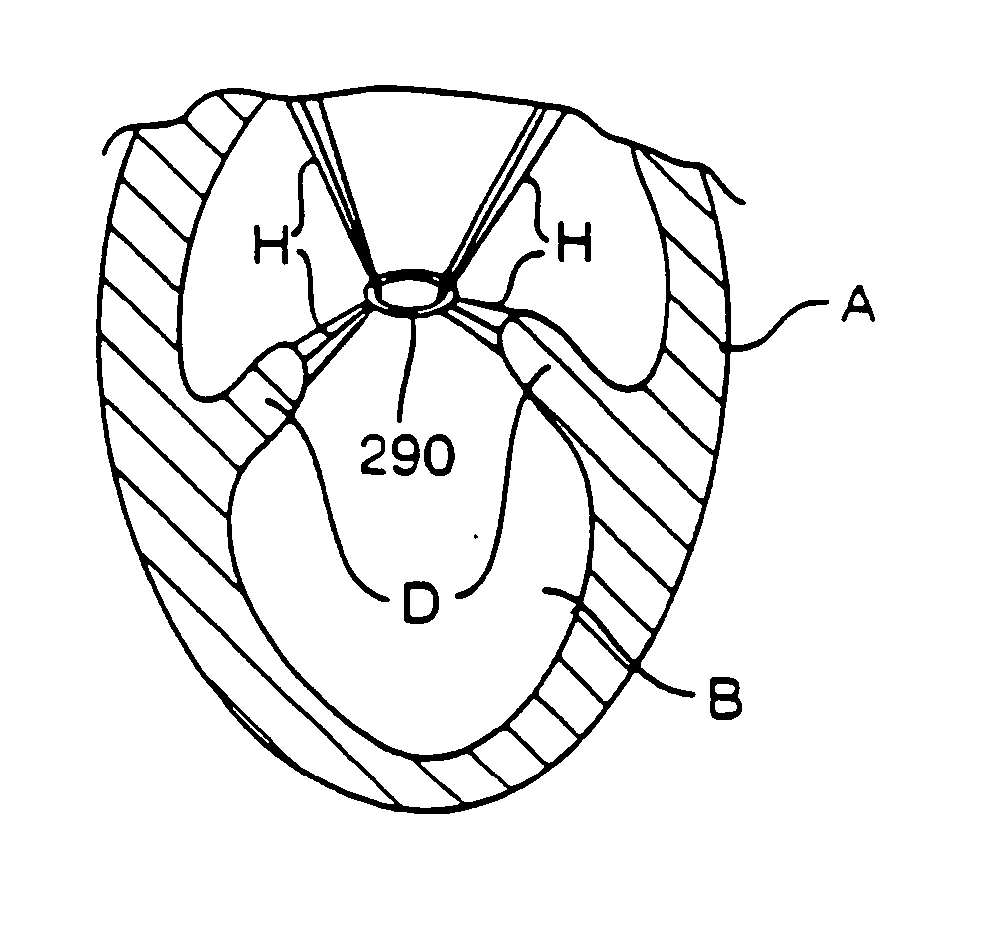
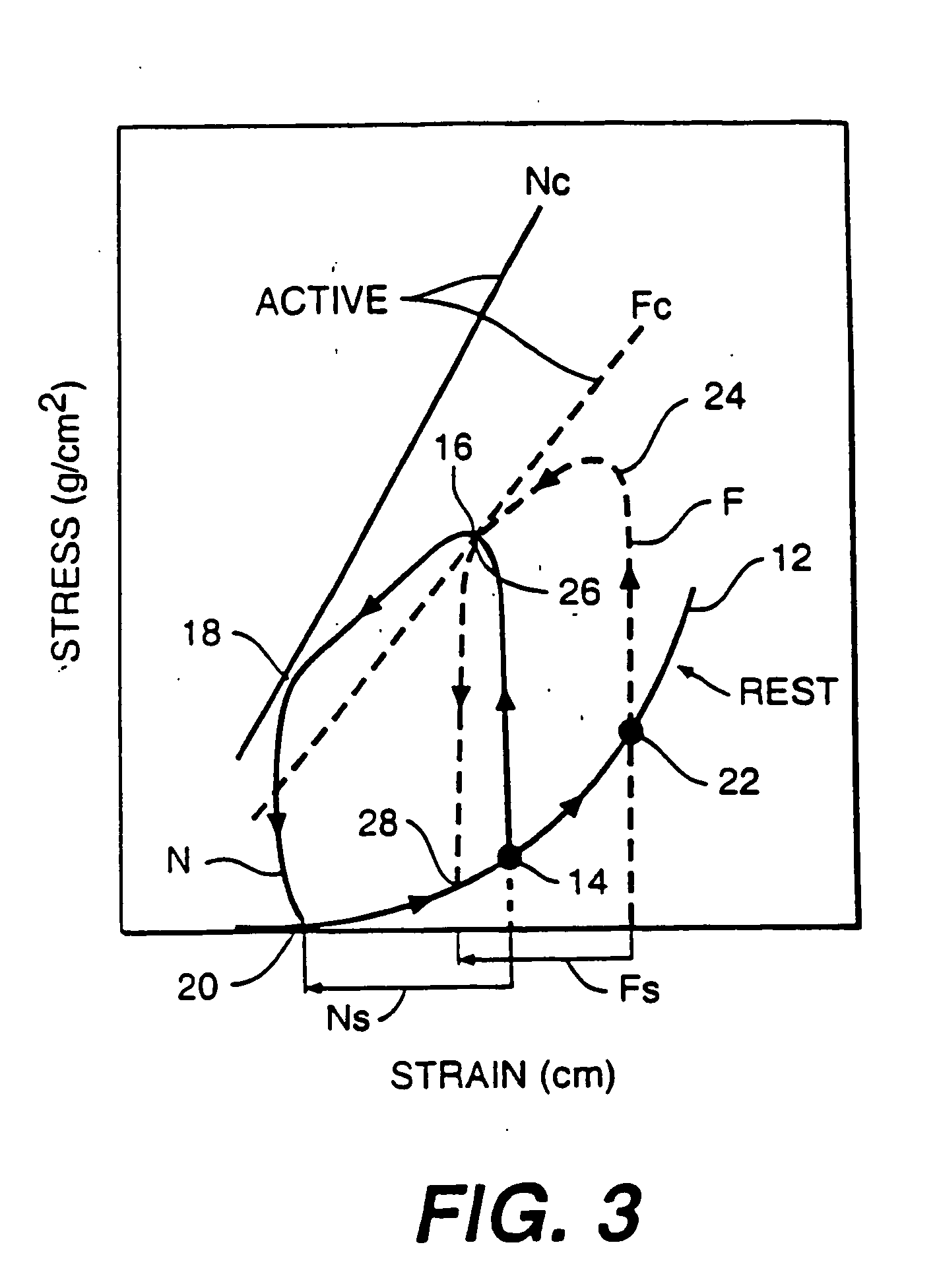
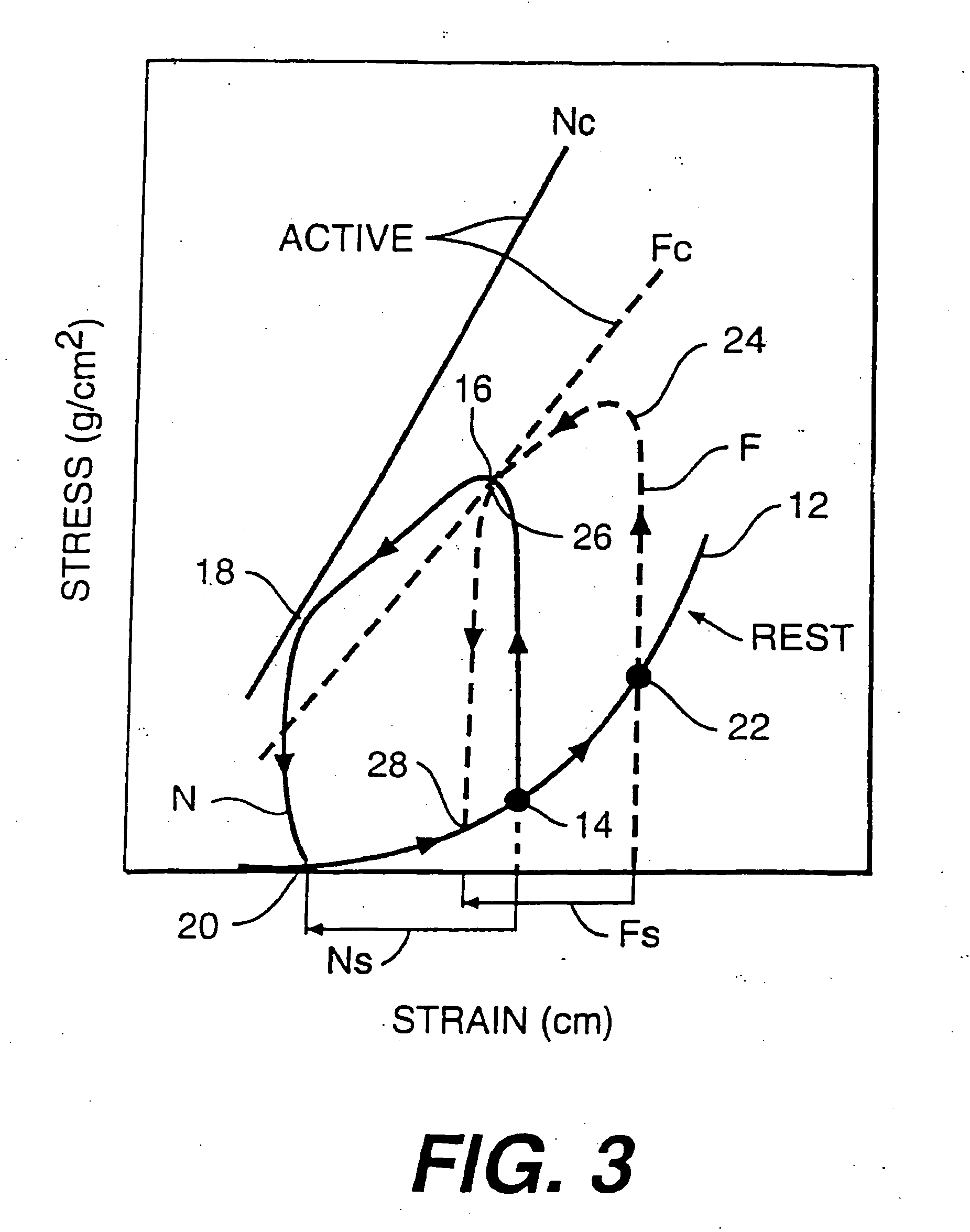
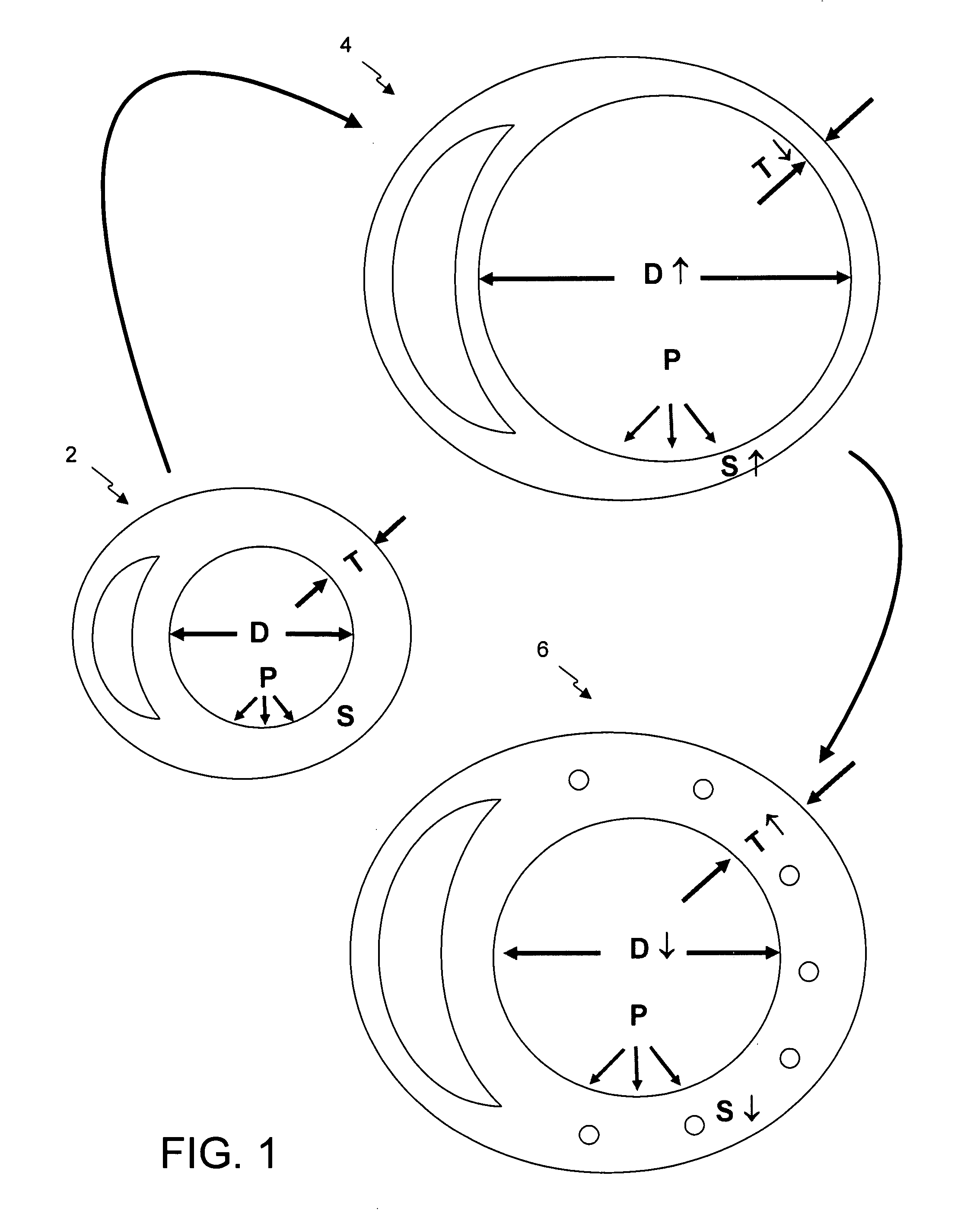
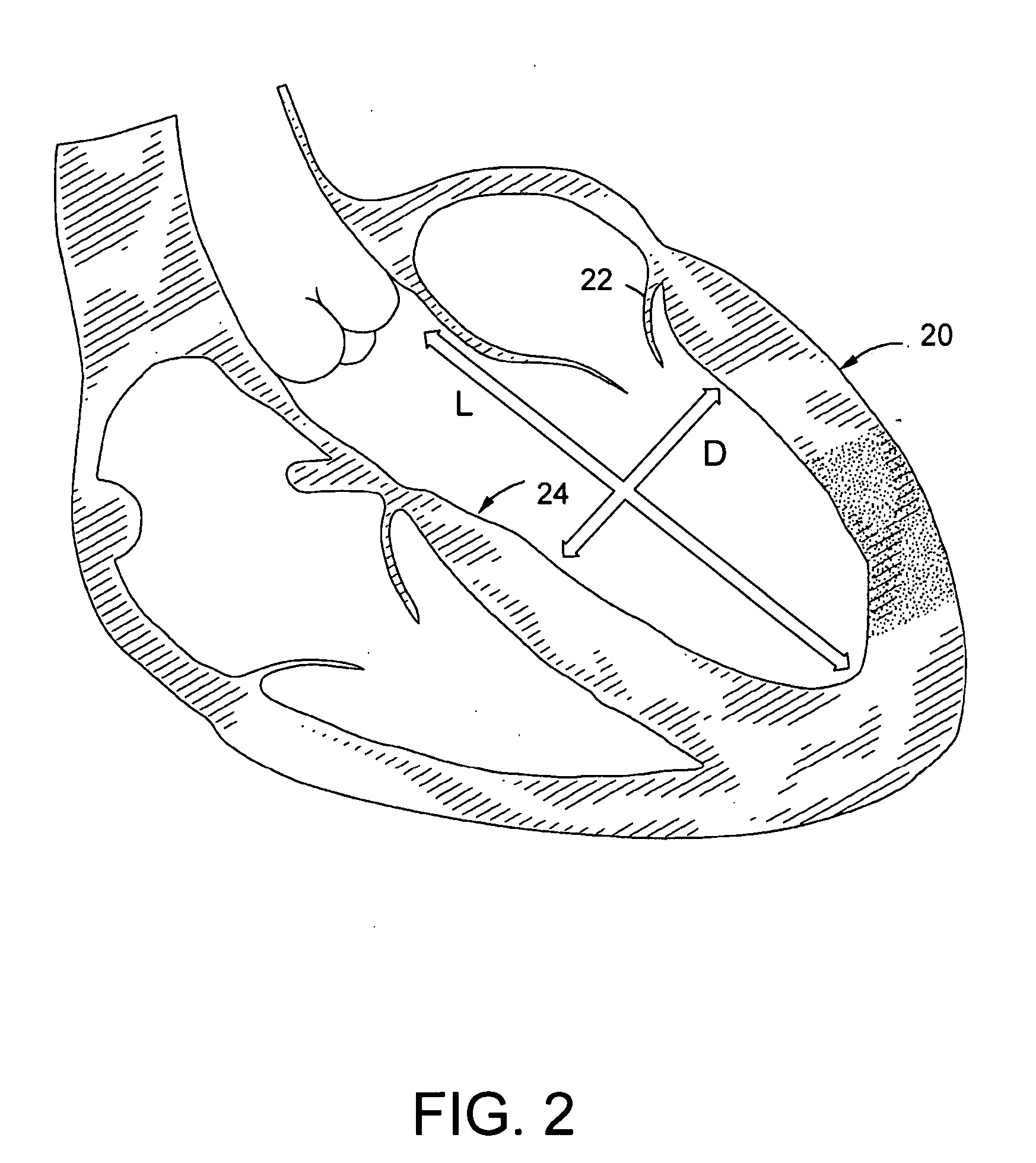
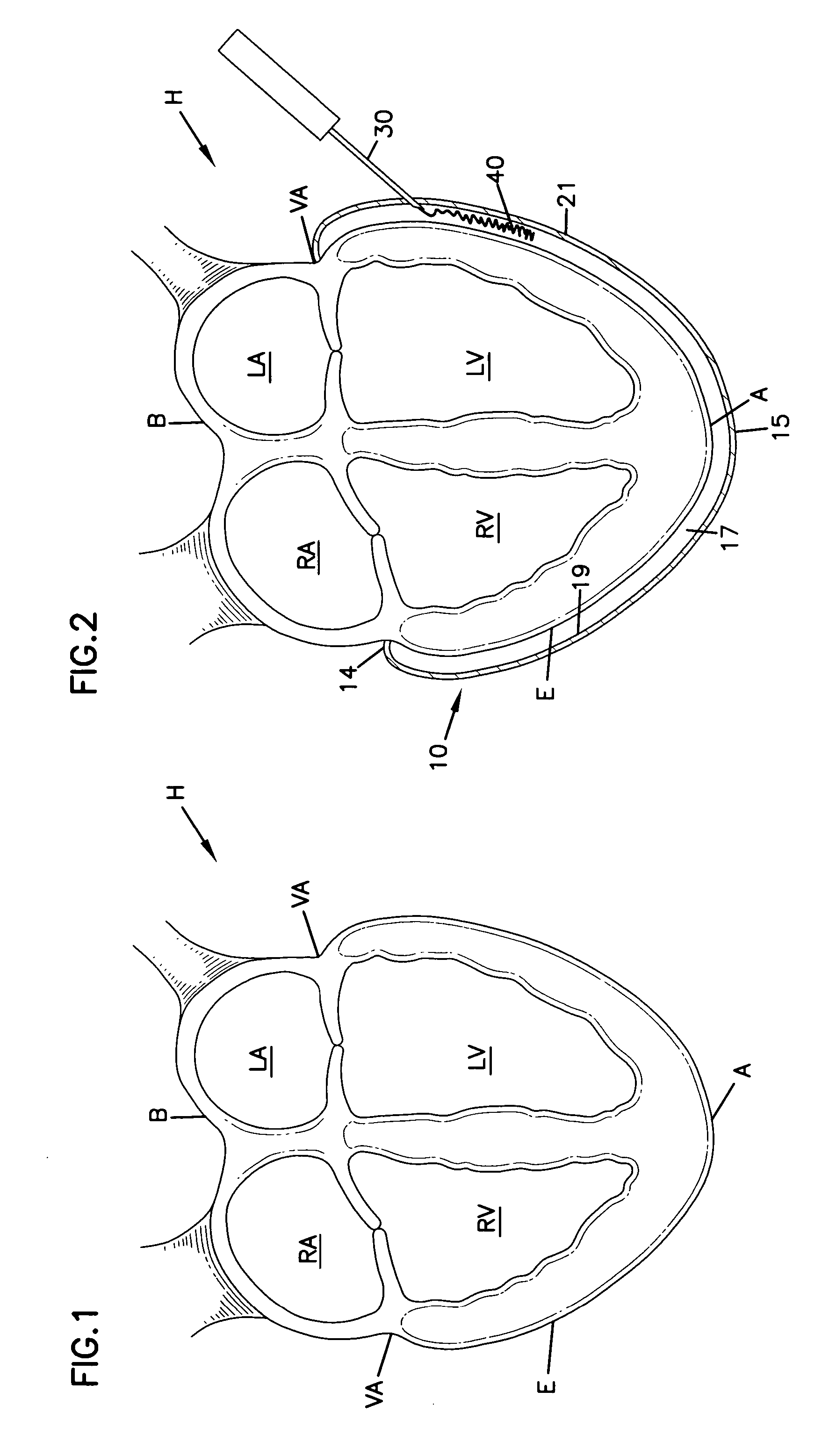
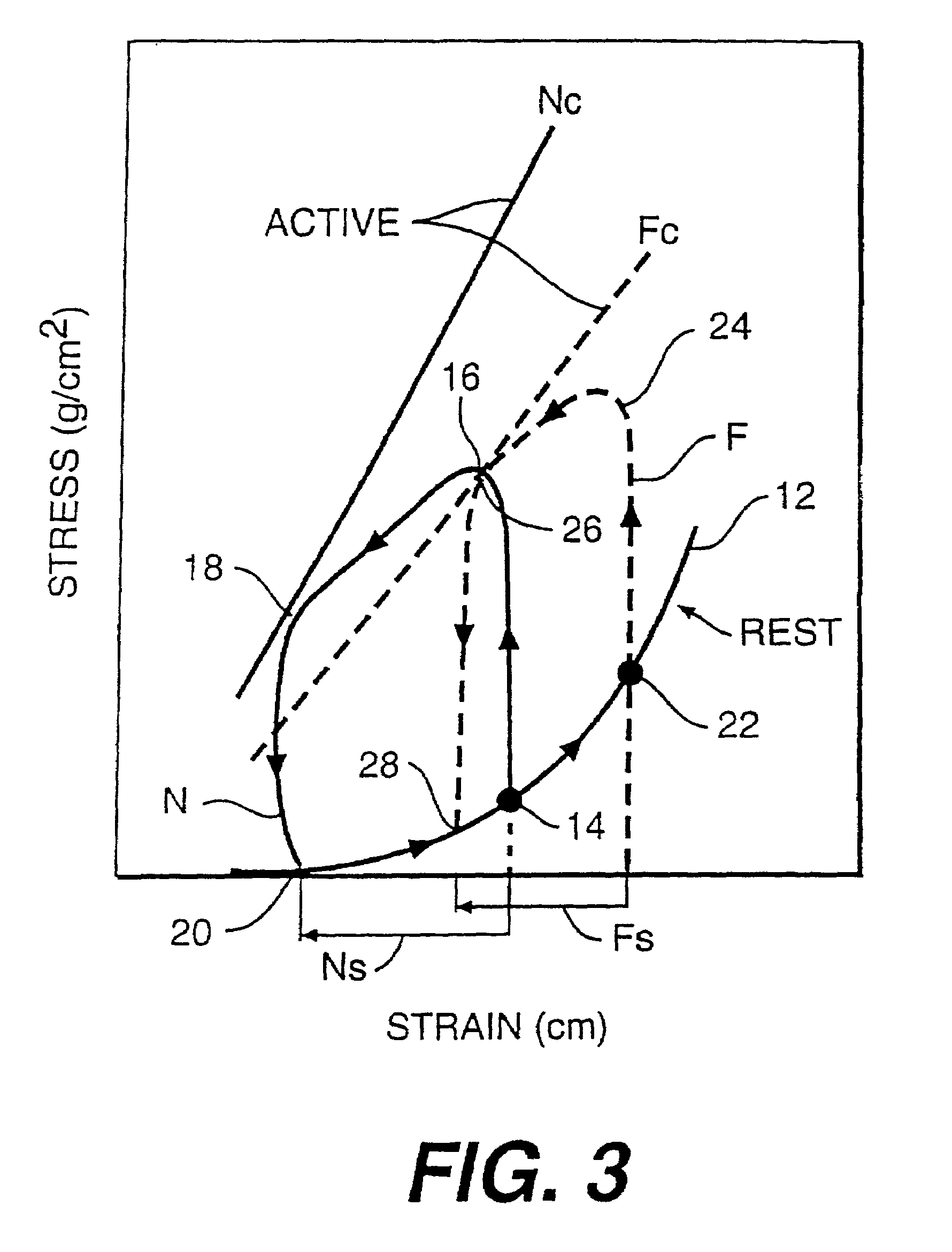
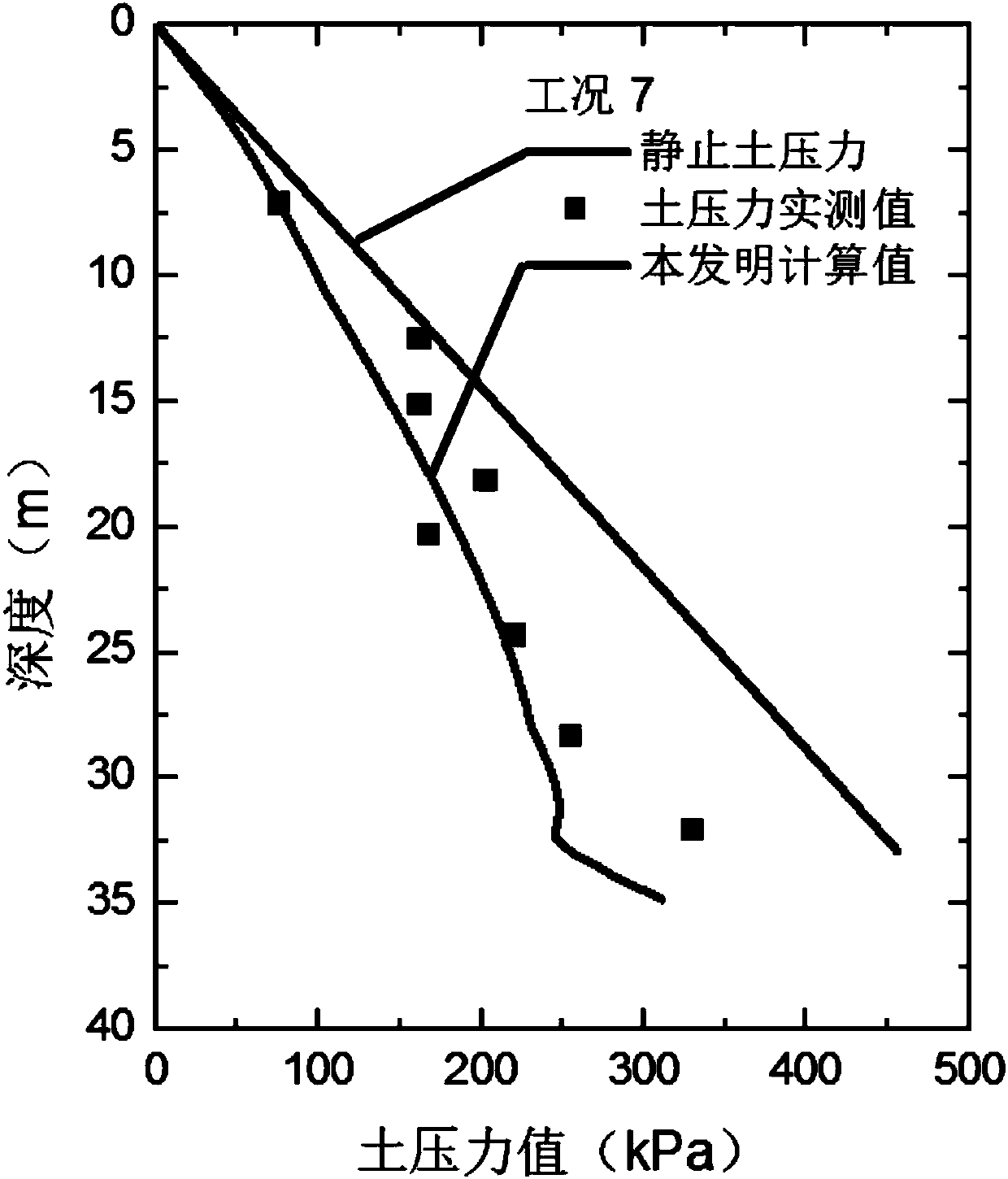
The dilated ventricle requires more wall stress in the wall to generate the same pressure. The wall stress, here the left ventricle's wall stress, is produced by the force acting against the myocardial cells. This wall stress is directly proportional to left ventricle's pressure and radius.
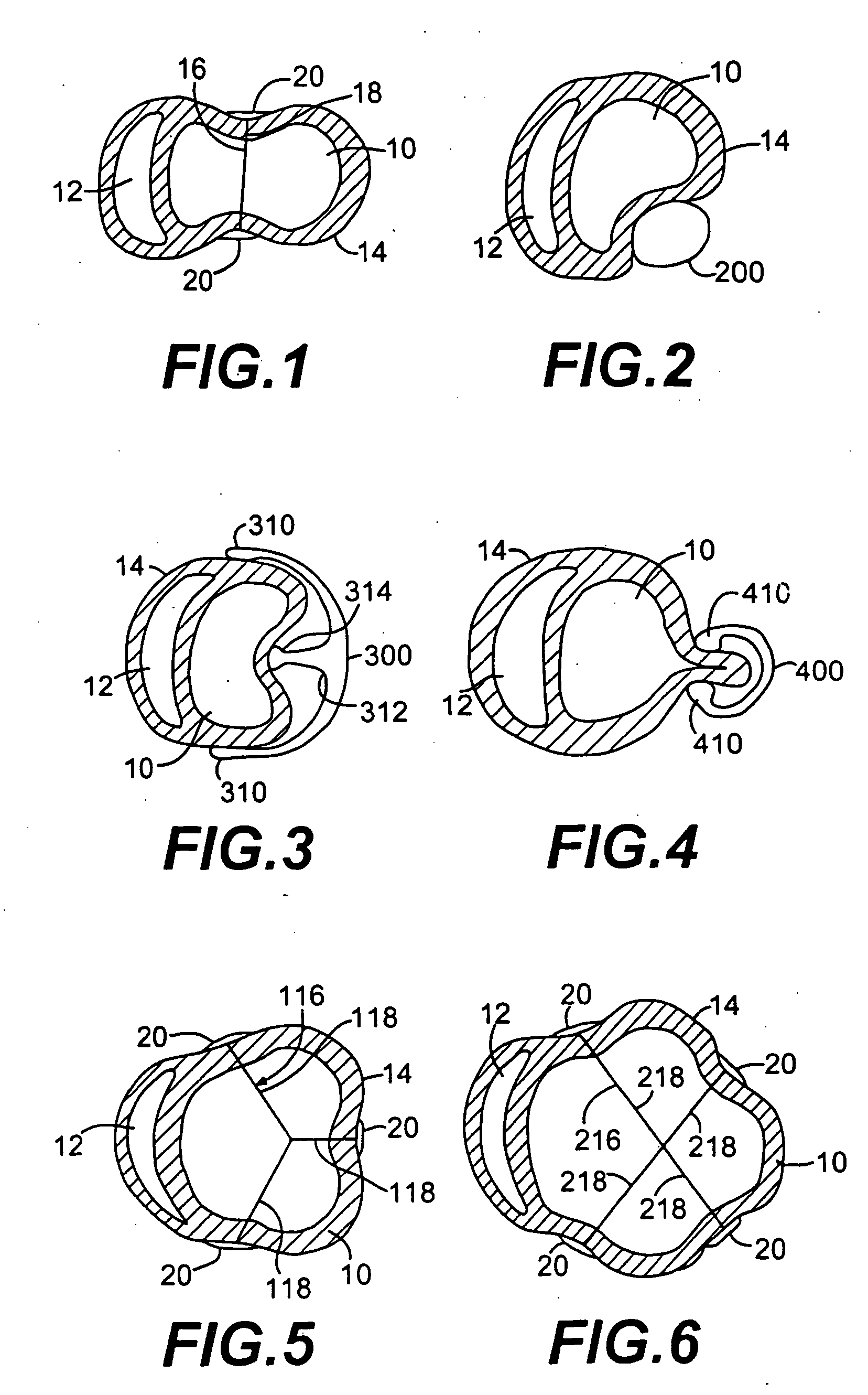
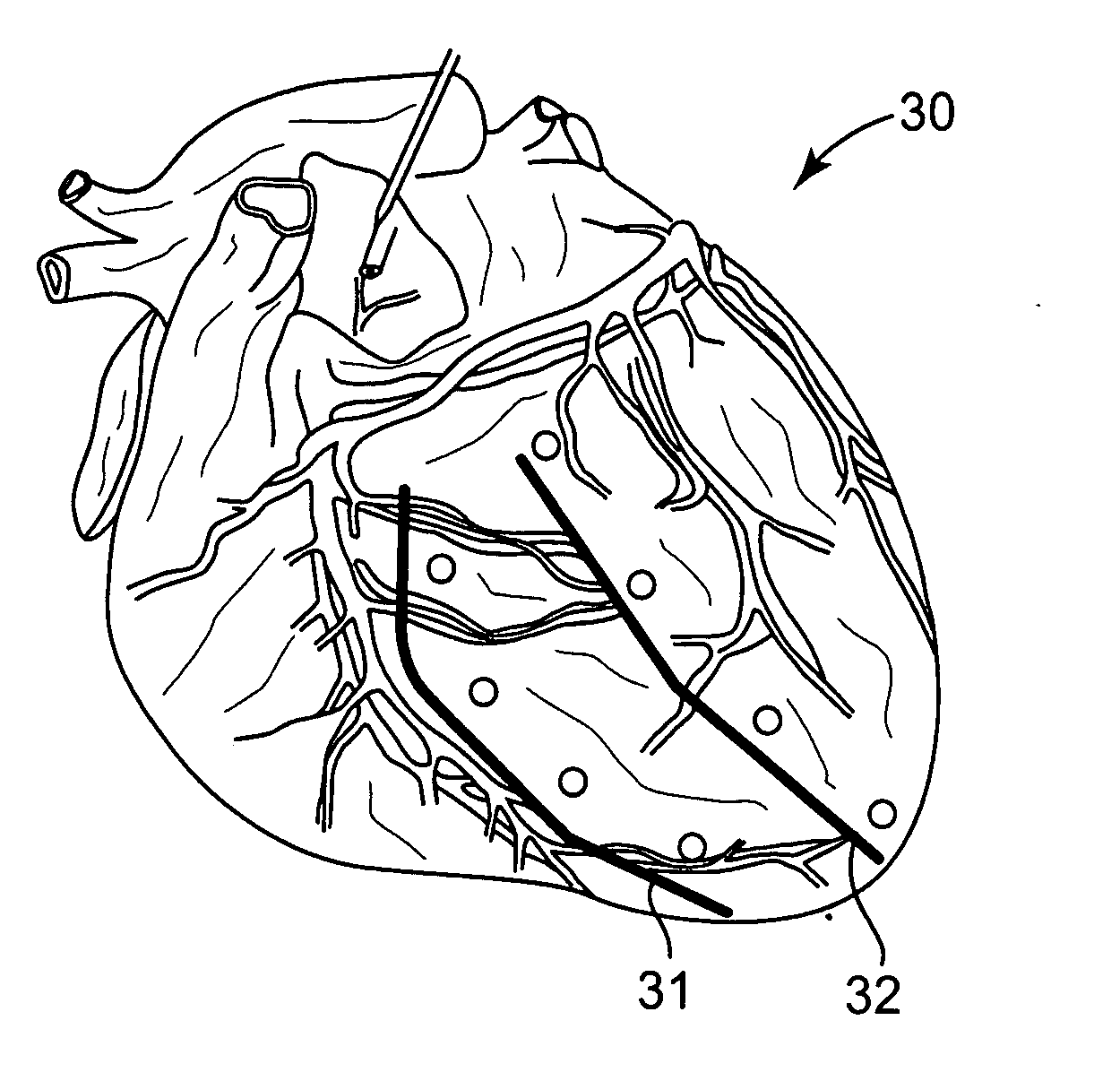
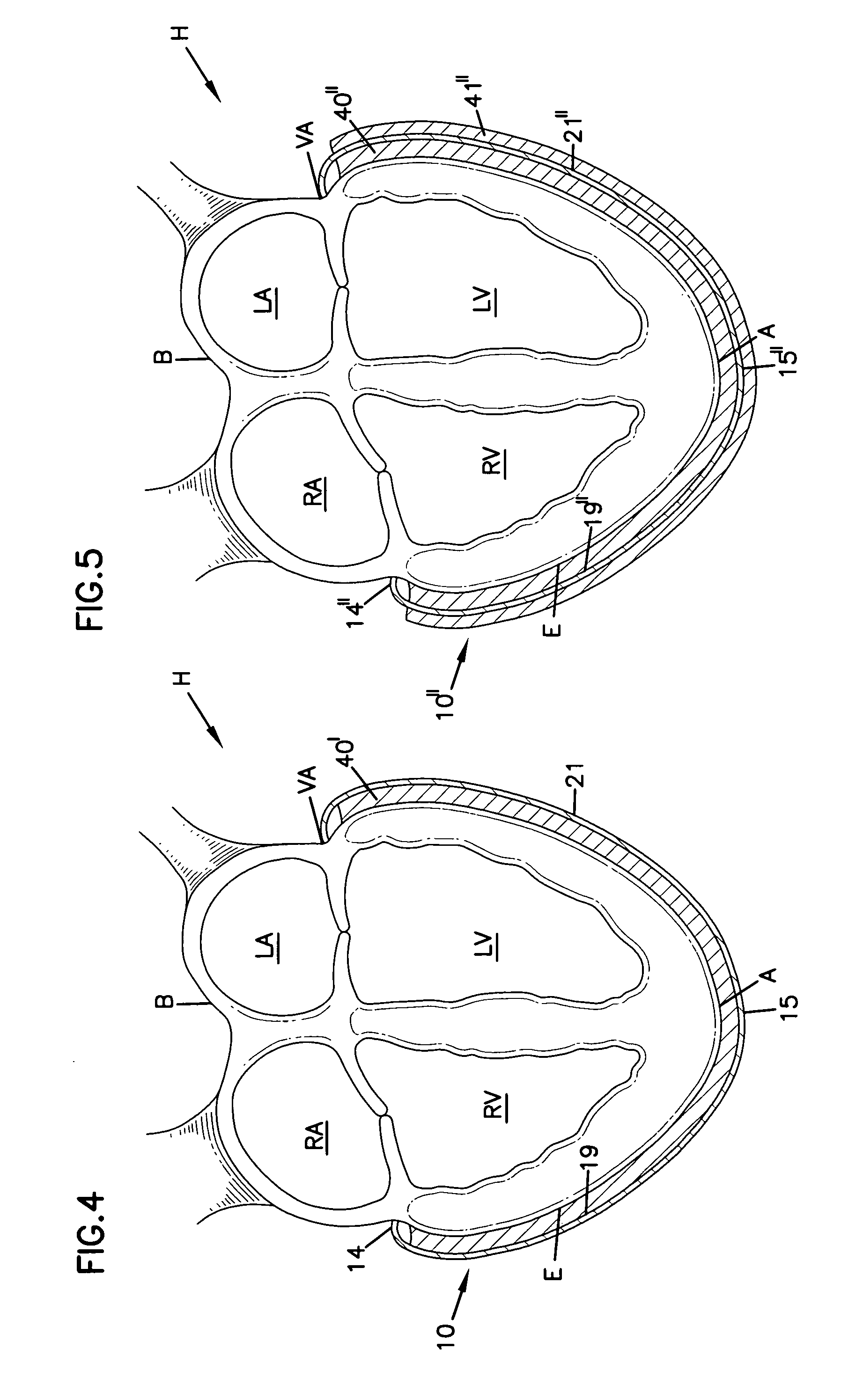
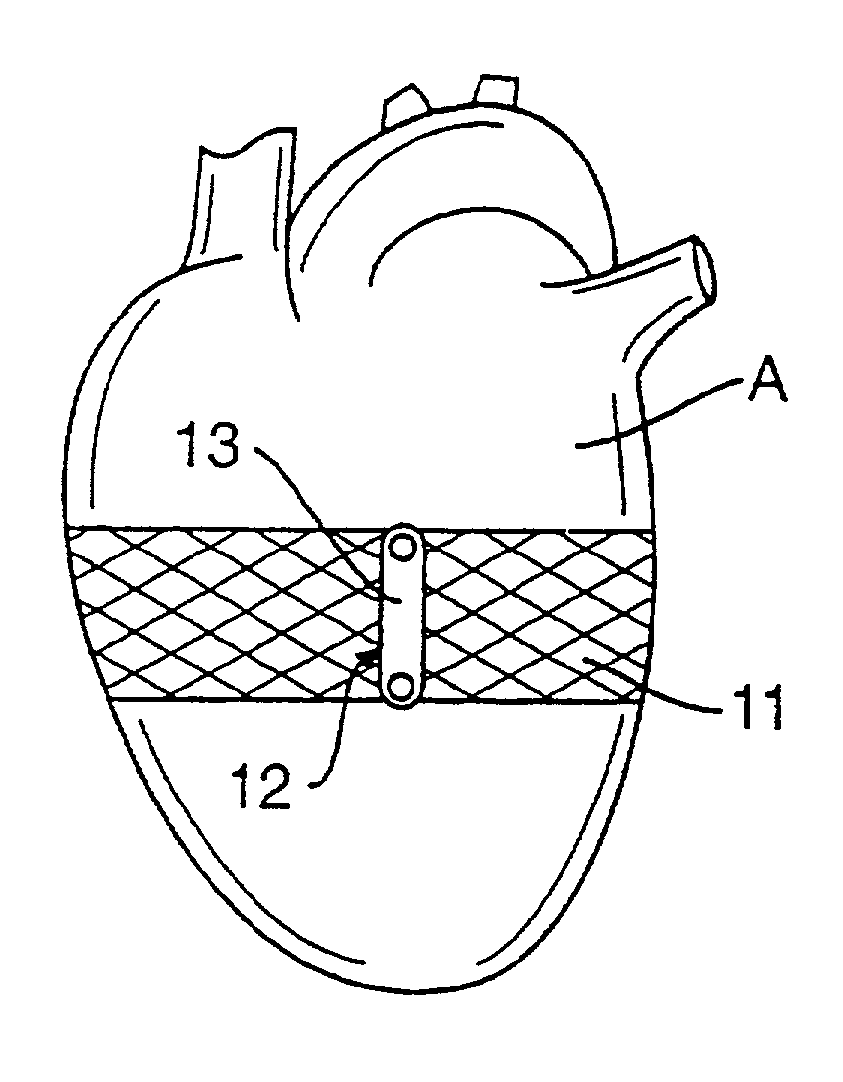
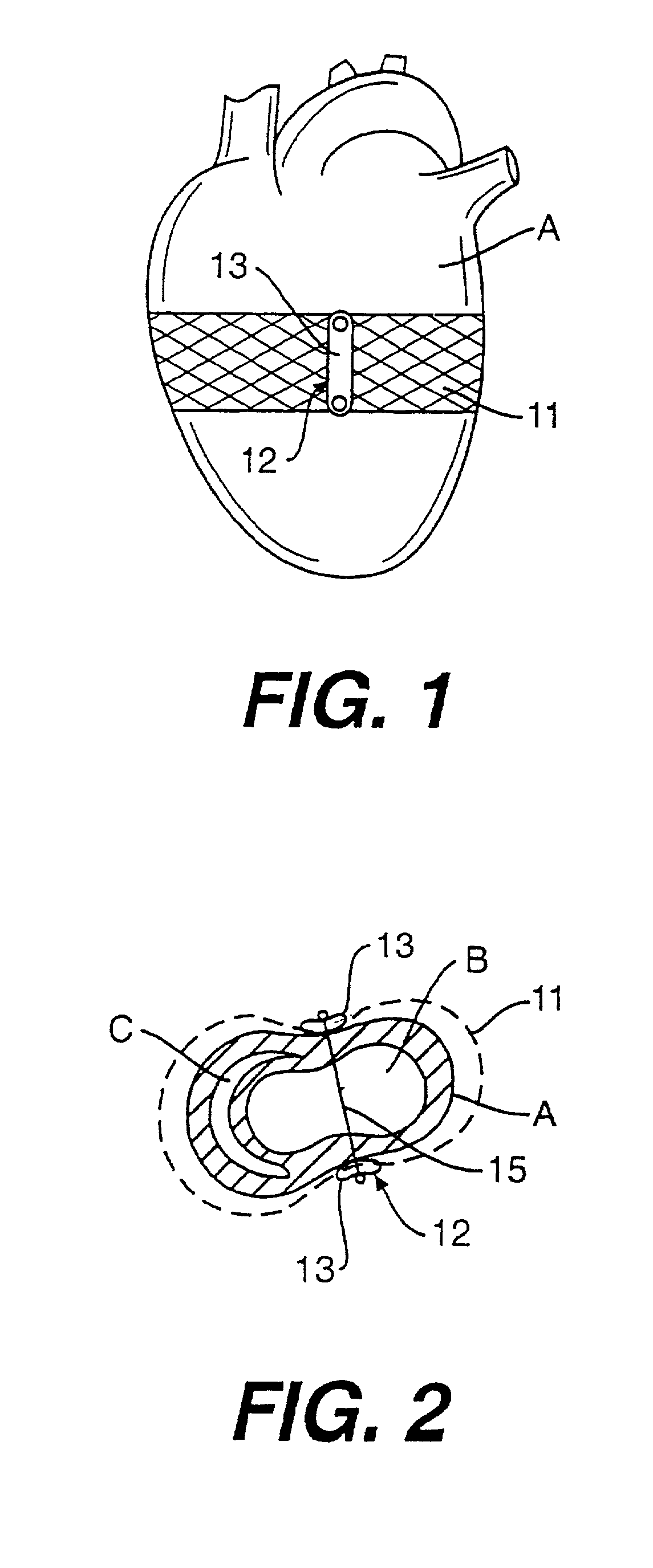
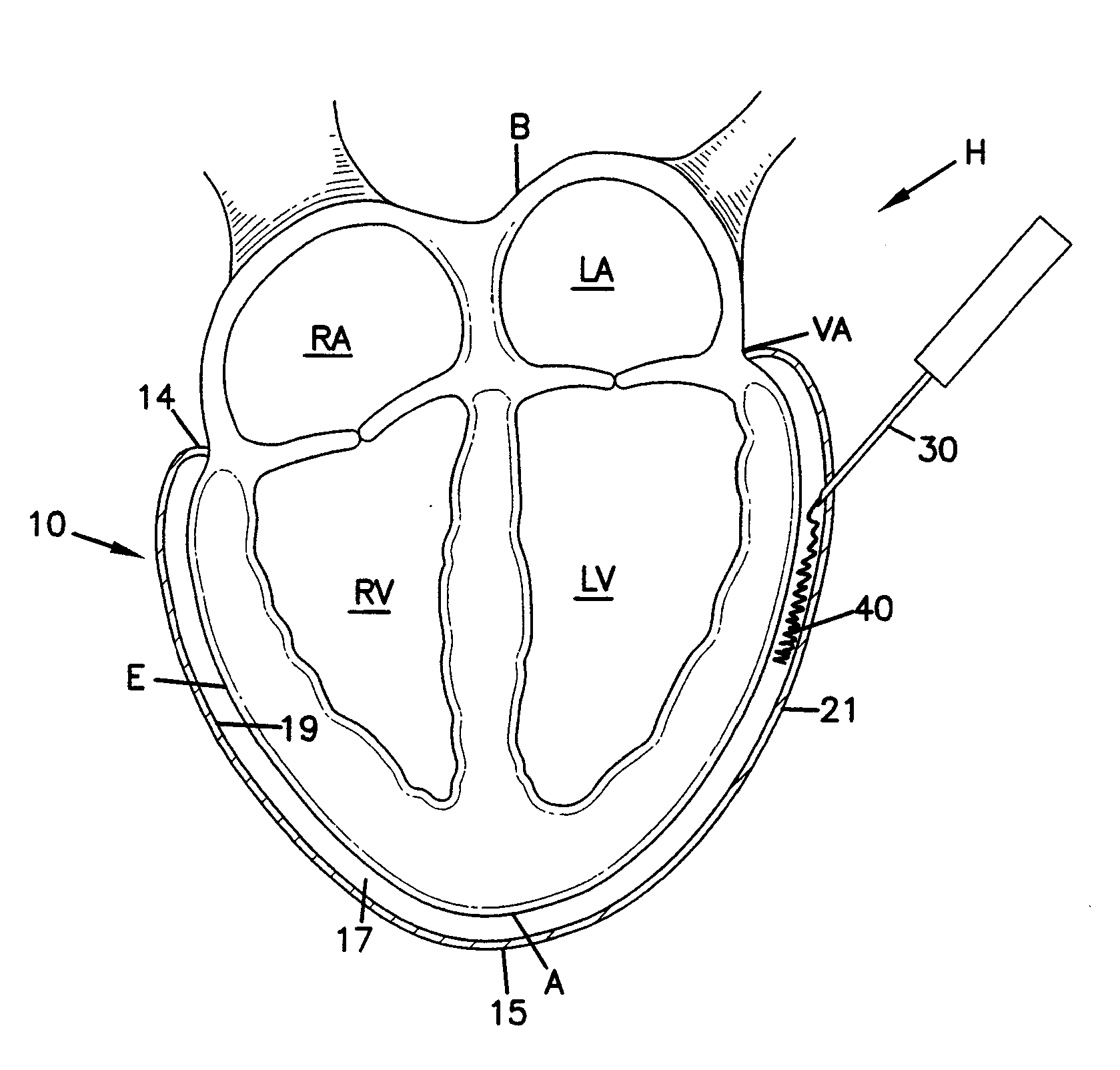
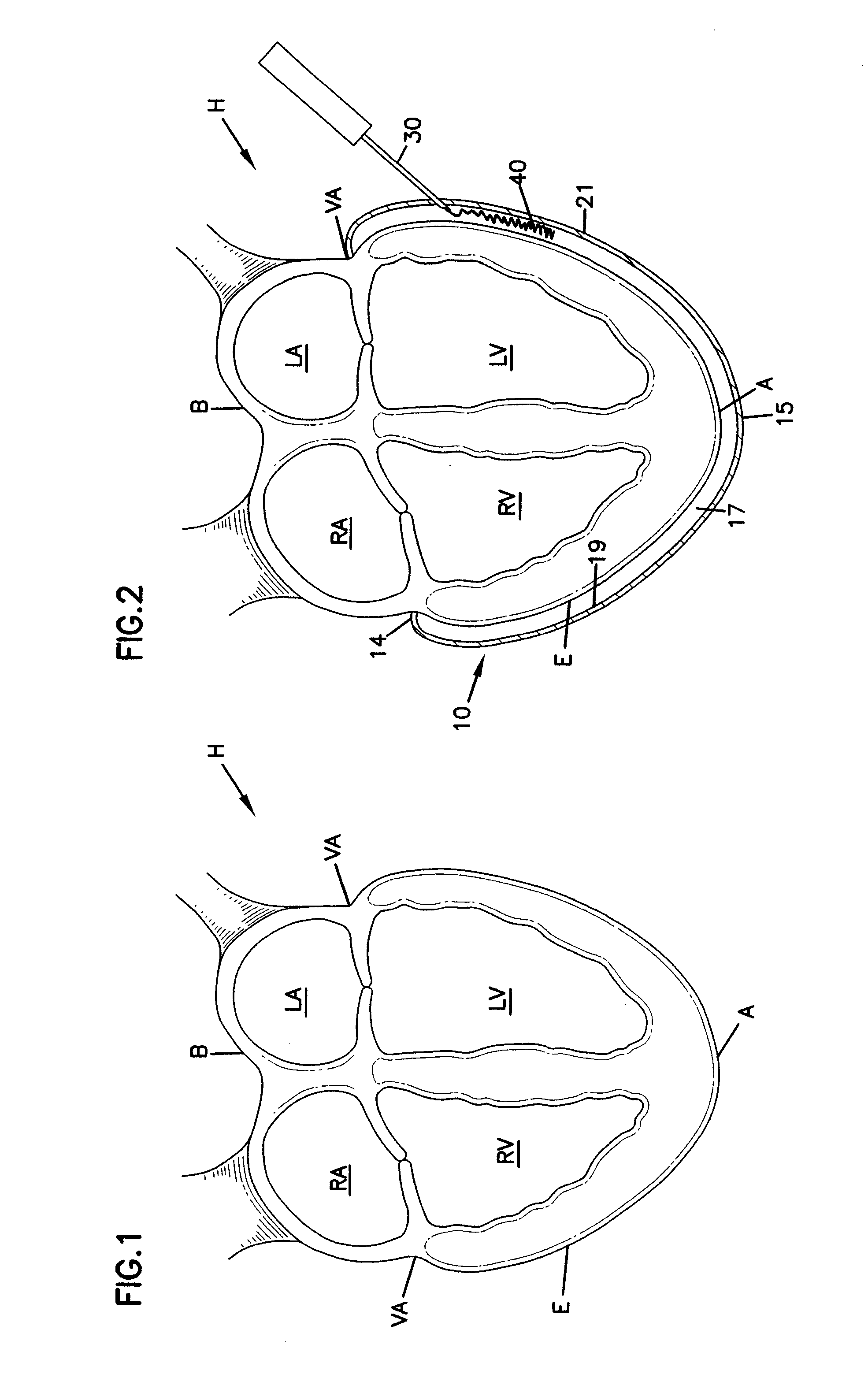
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS7189199B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesIliac AneurysmWall stress
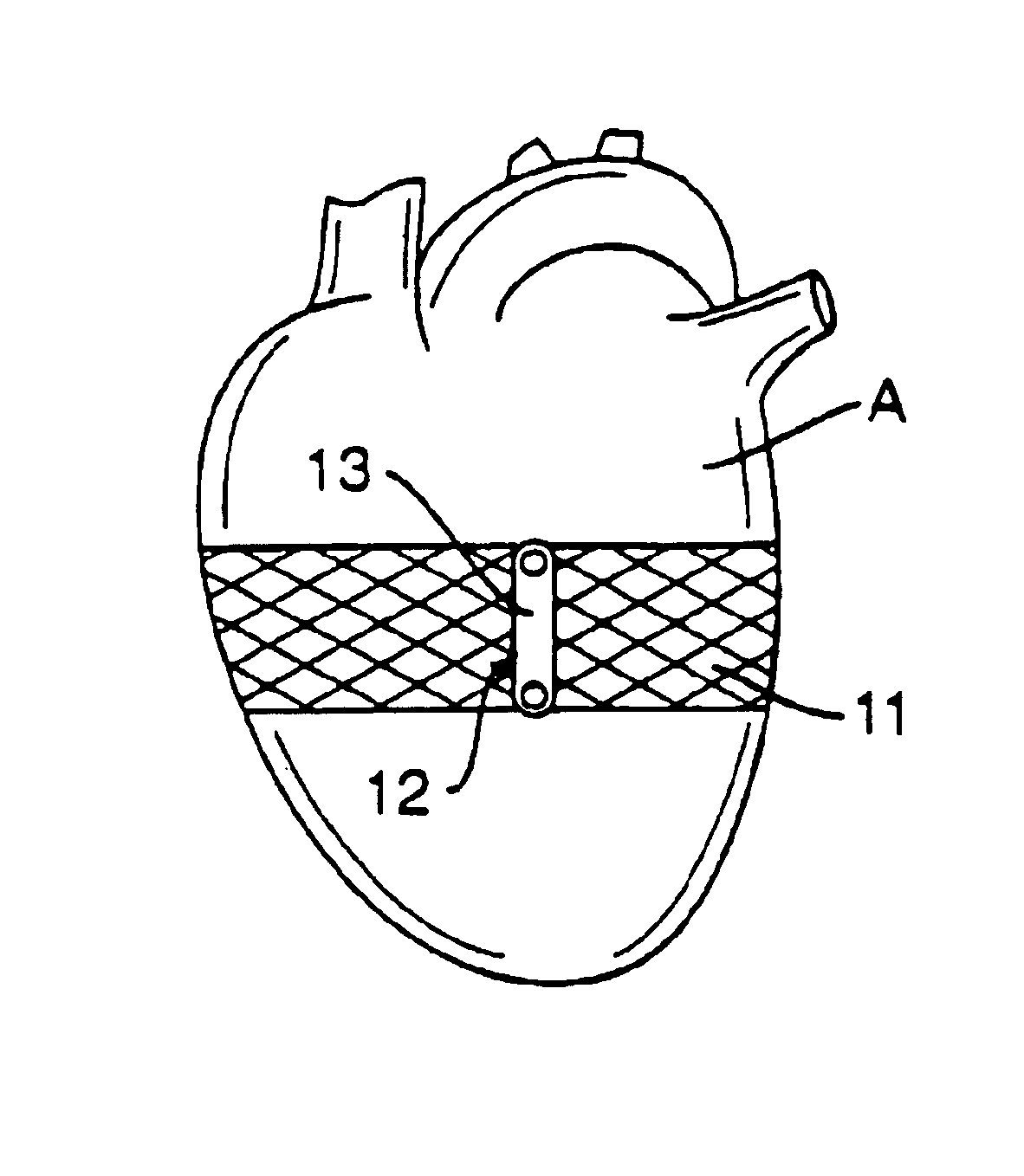
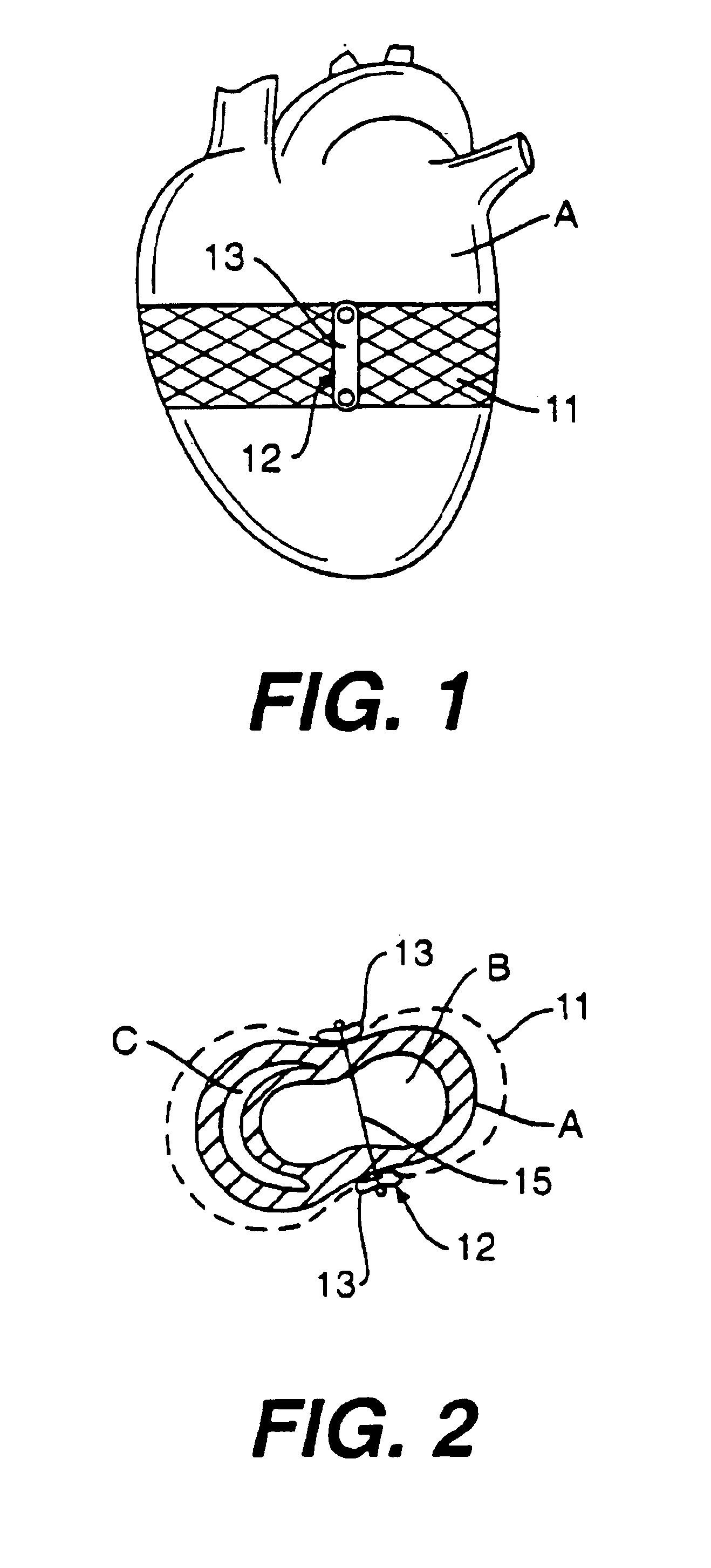
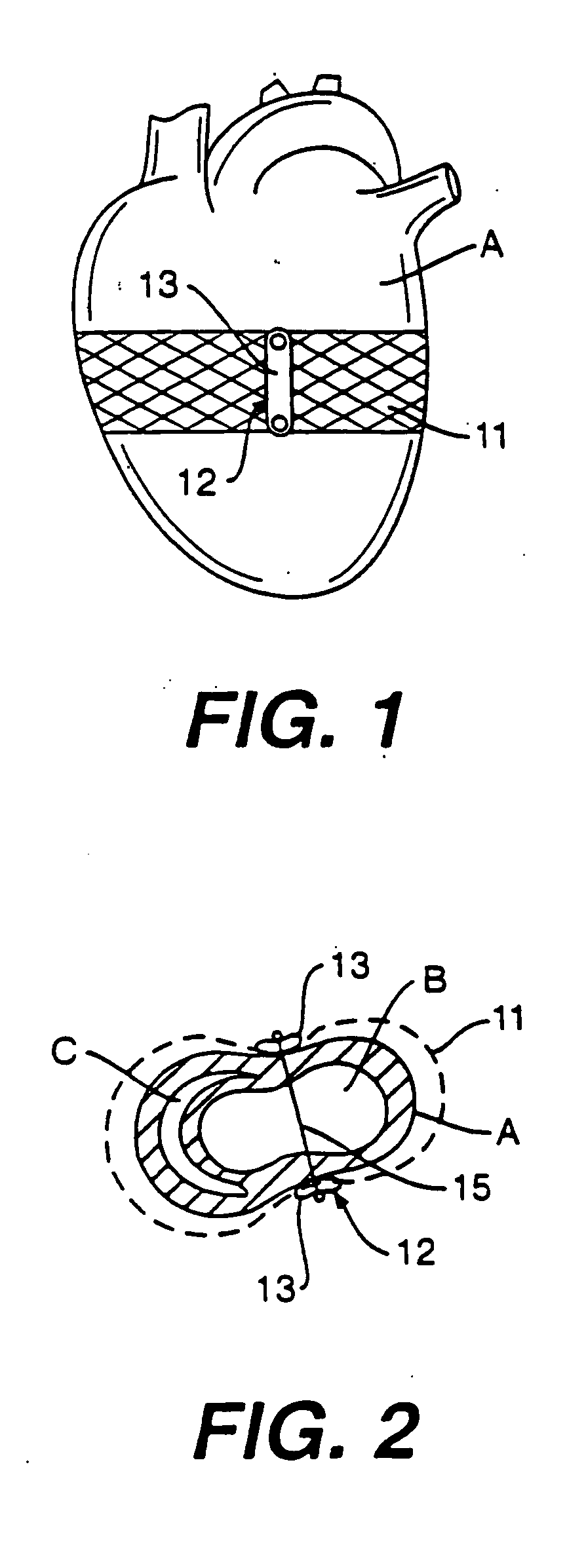
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS20060161040A1Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMedicineCardiac wall
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
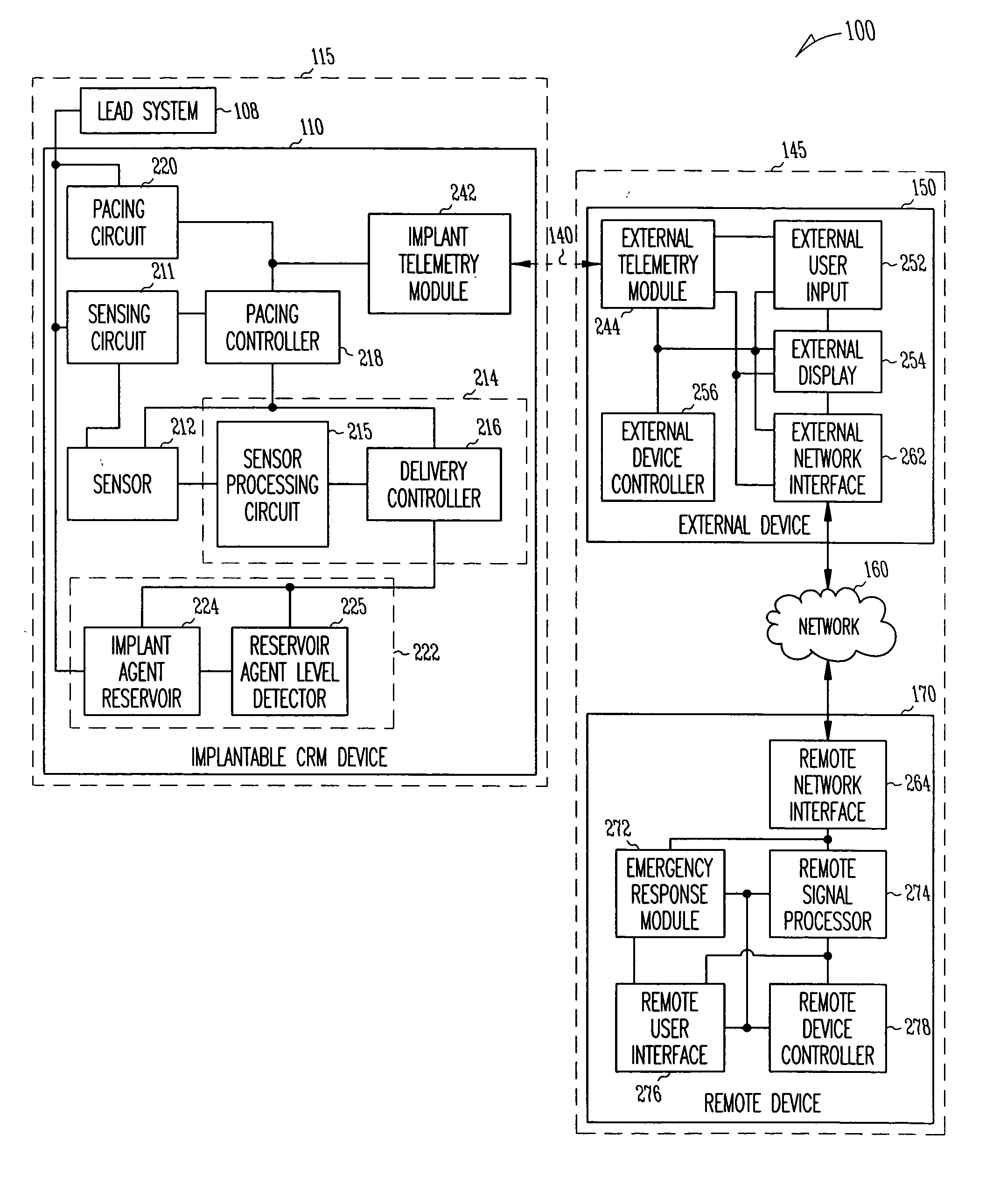
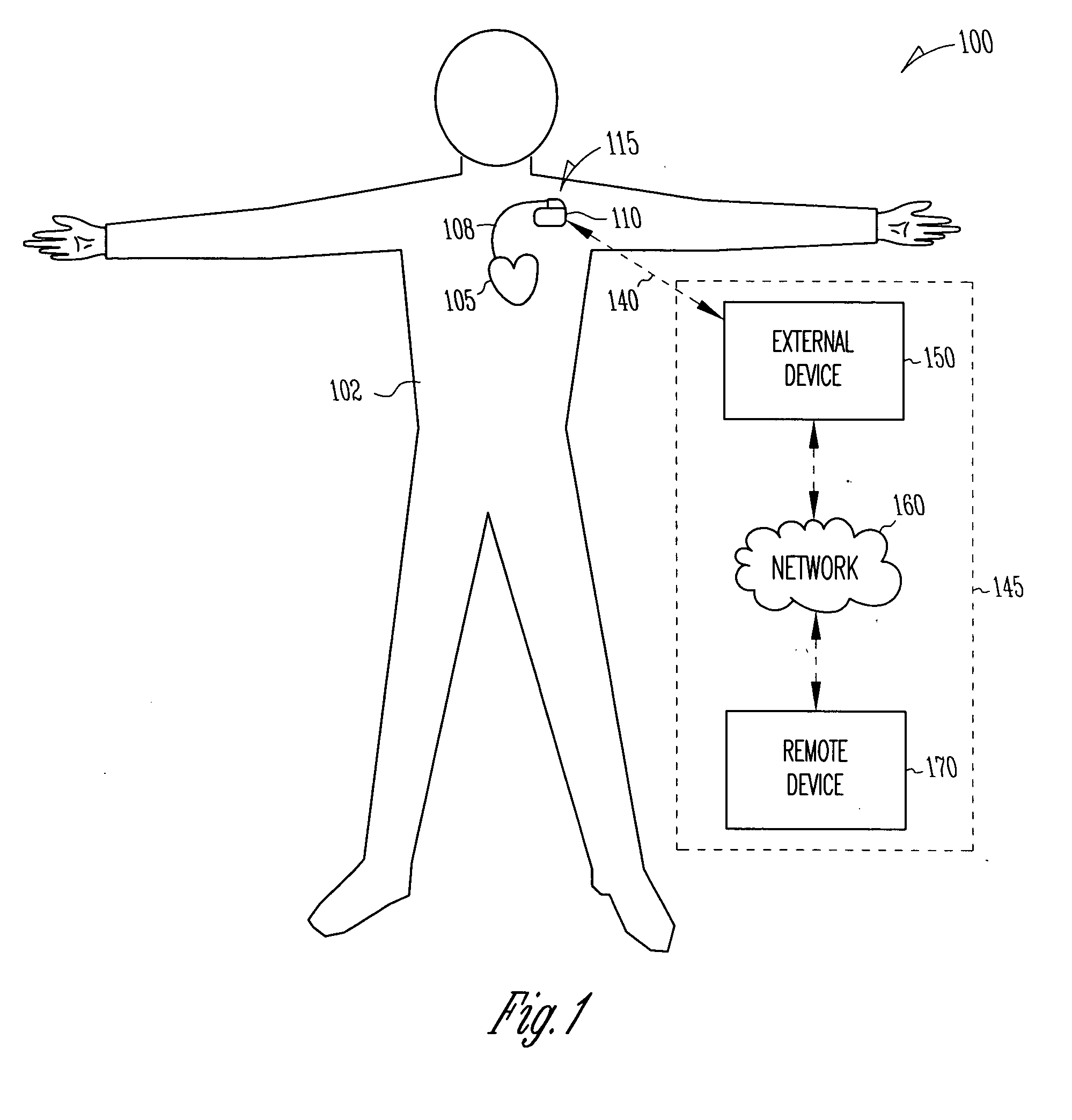
Method and apparatus to modulate cellular regeneration post myocardial infarct
InactiveUS20050288721A1Easy to adjustModulate tissue growthMedical devicesPressure infusionCardiac muscleWorkload
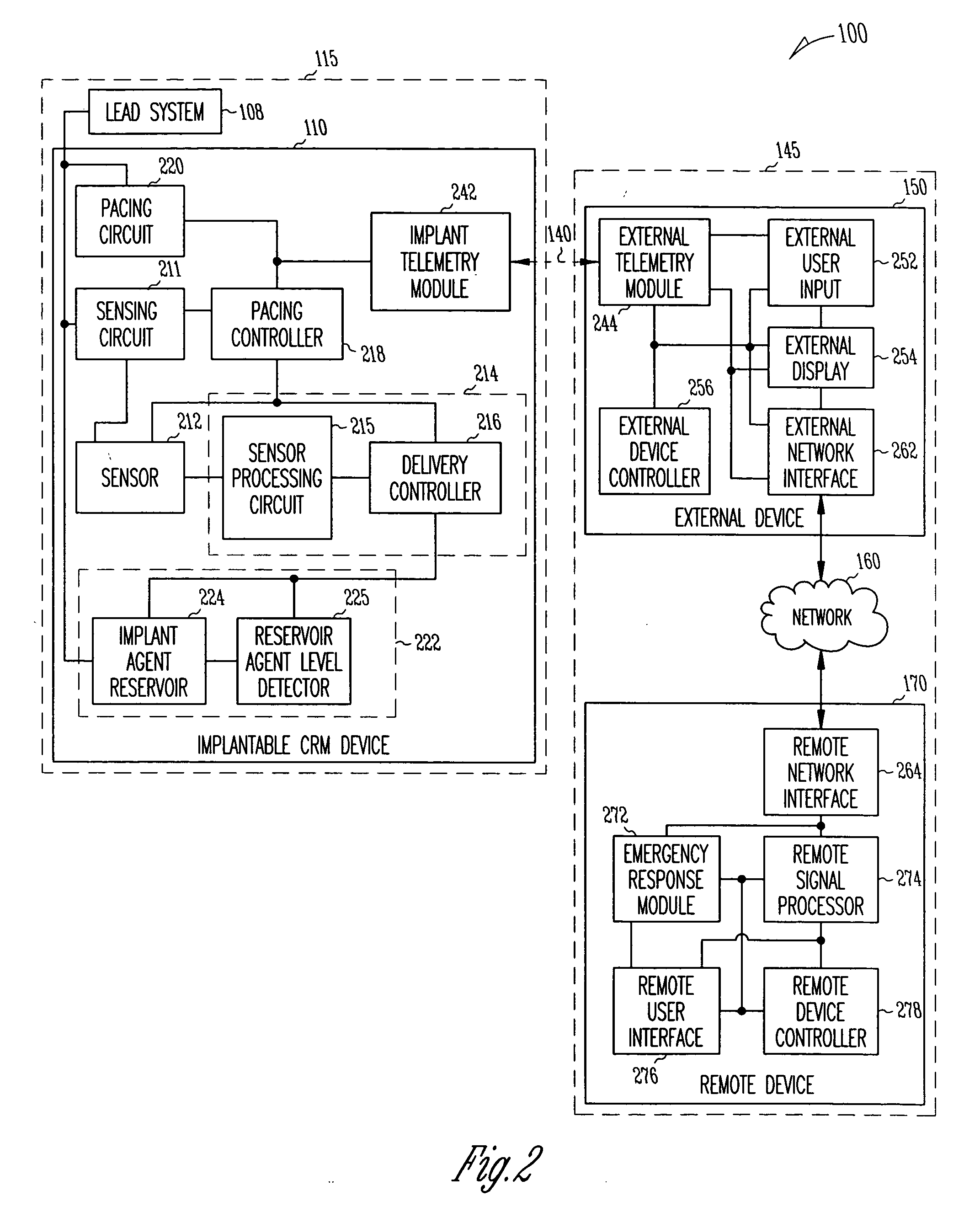
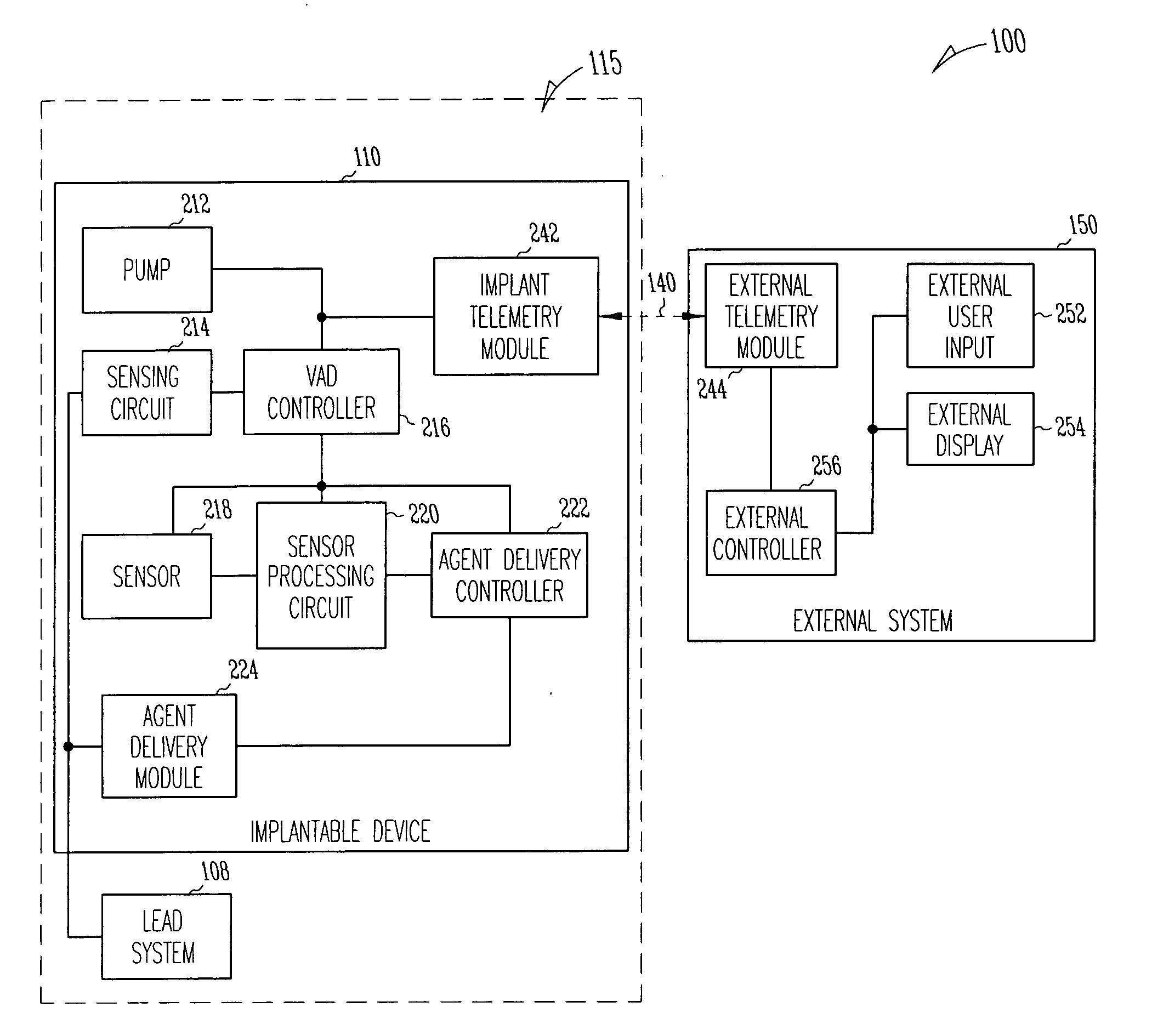
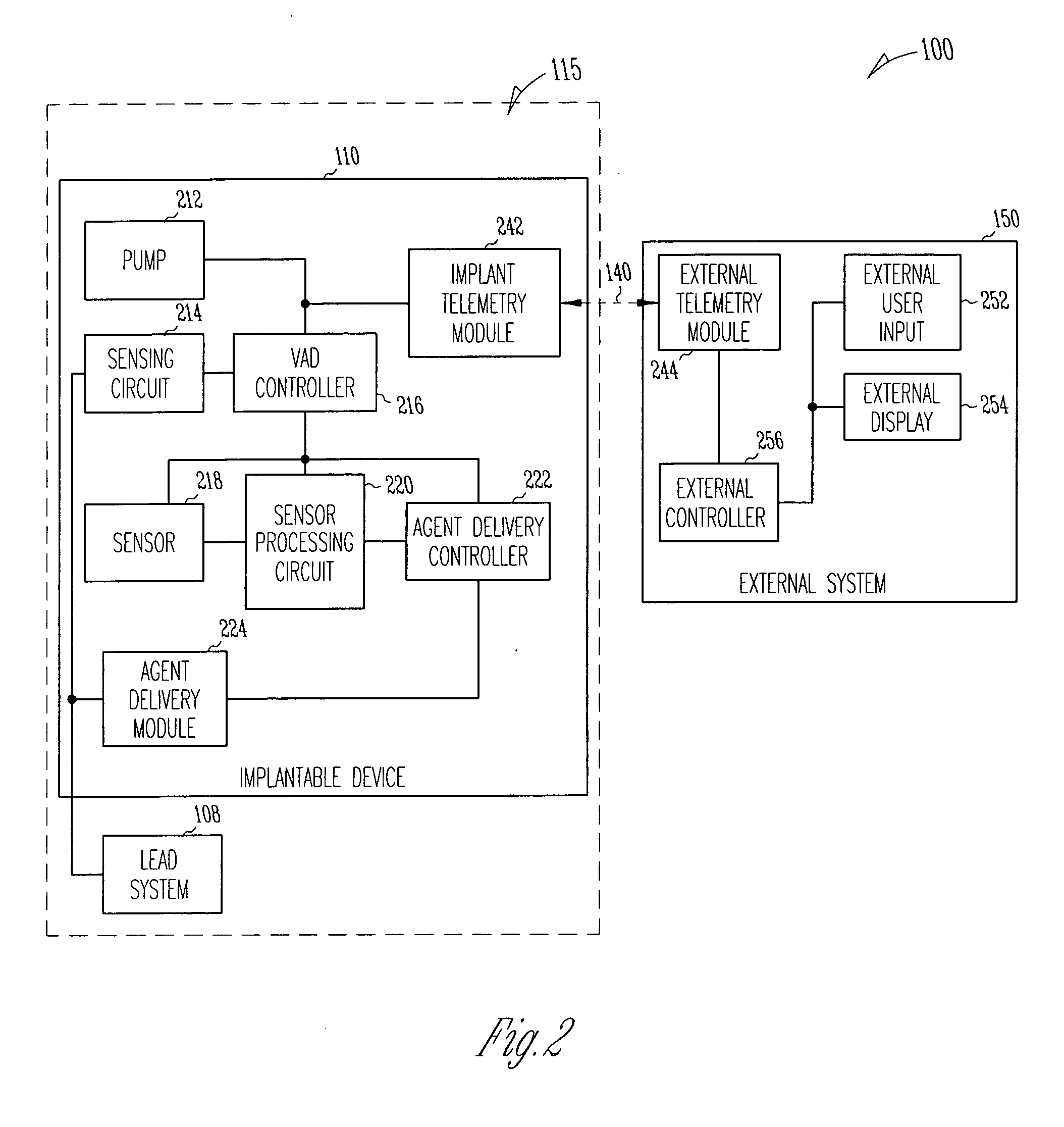
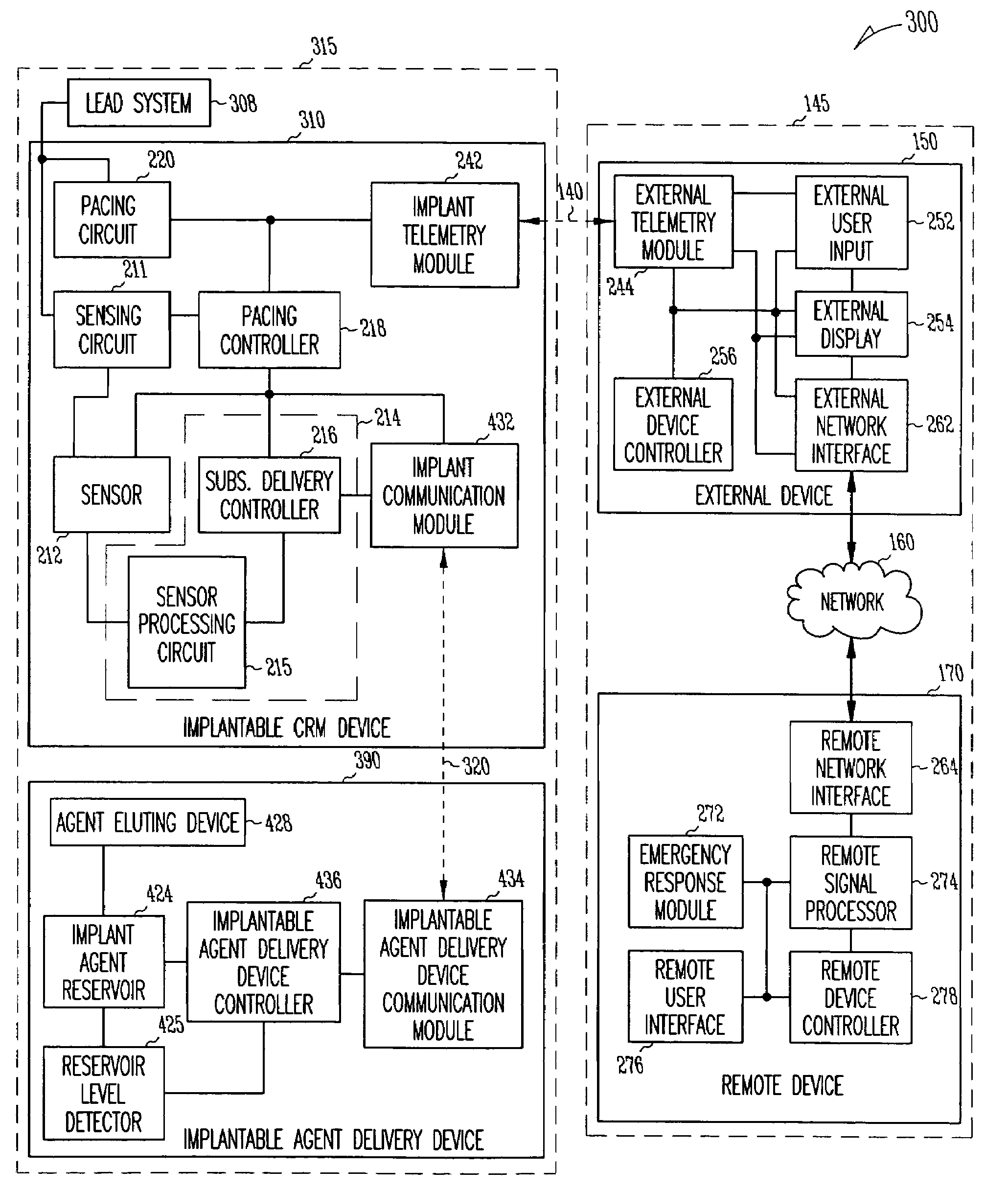
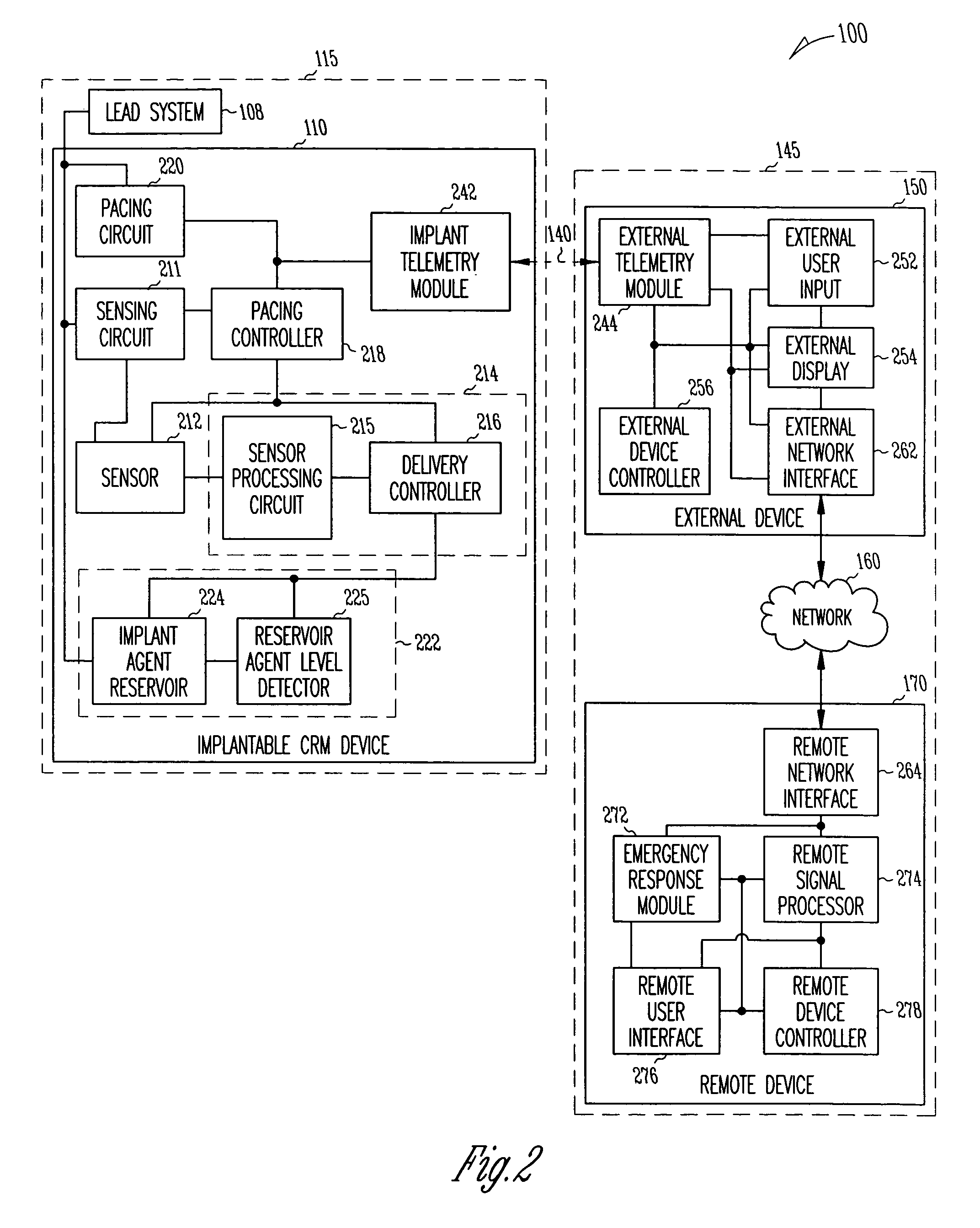
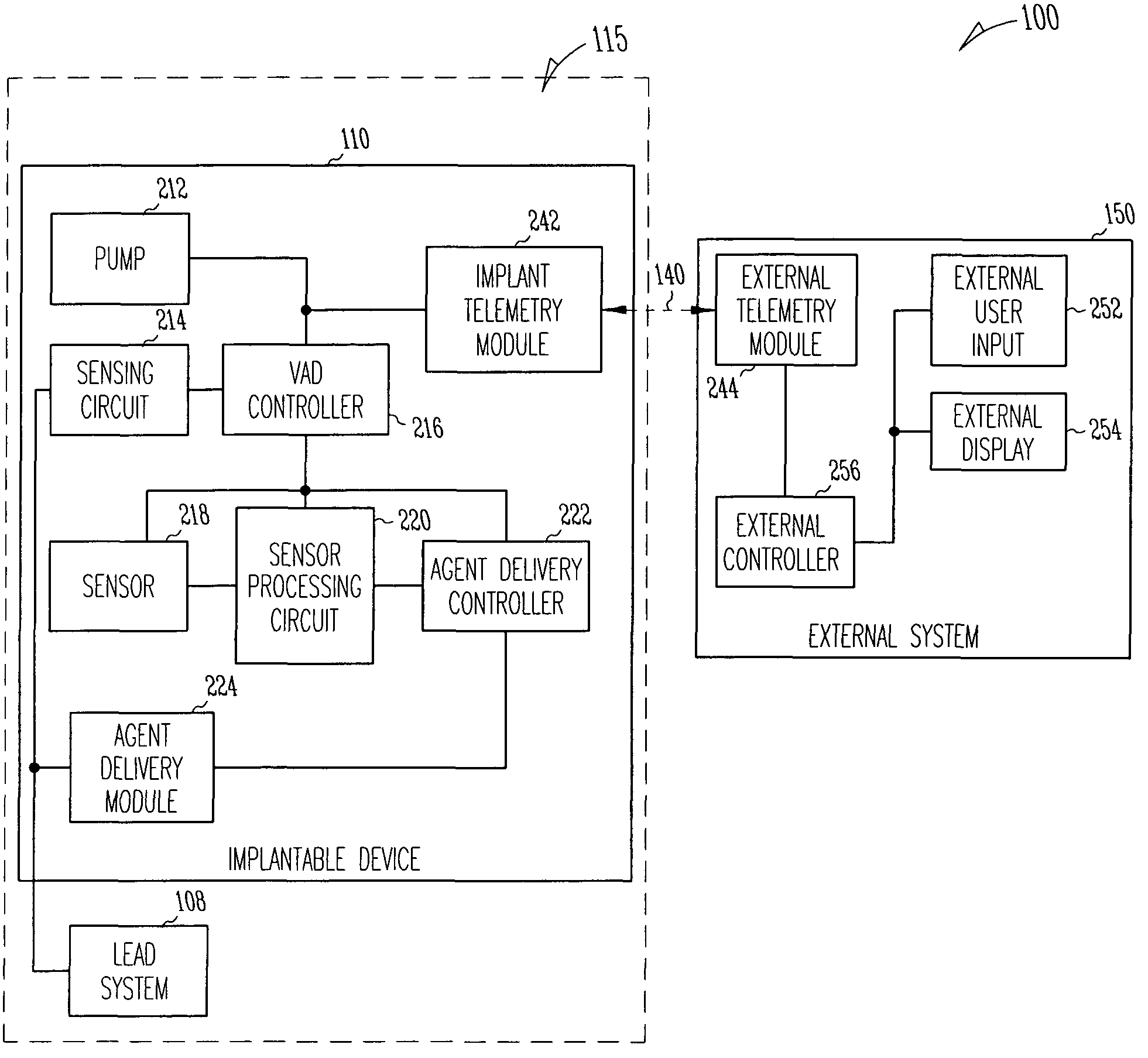
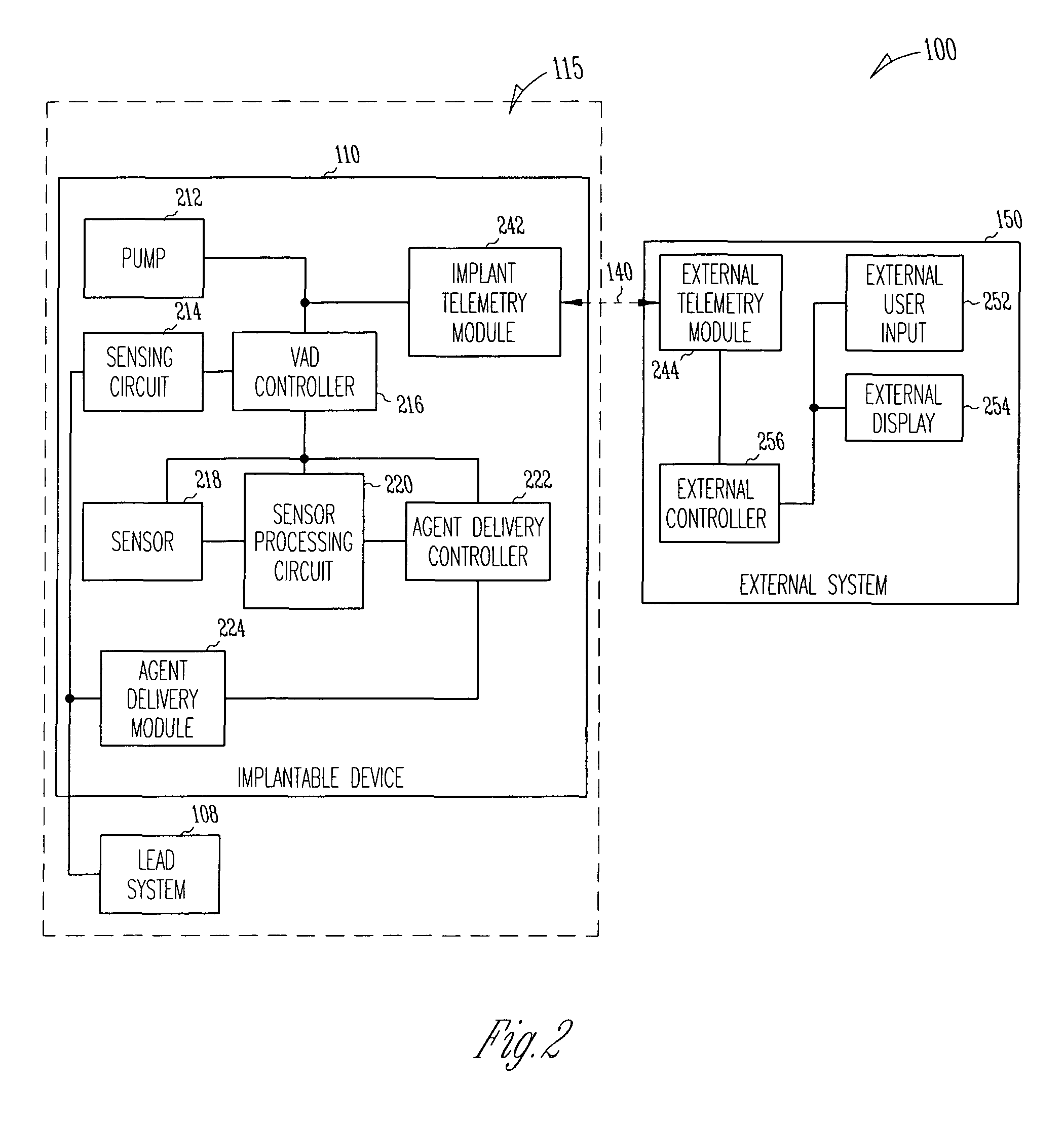
A system delivers cardiac pacing therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a cardiac rhythm management (CRM) device to deliver pacing pulses to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by altering myocardial wall stress and cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable CRM device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
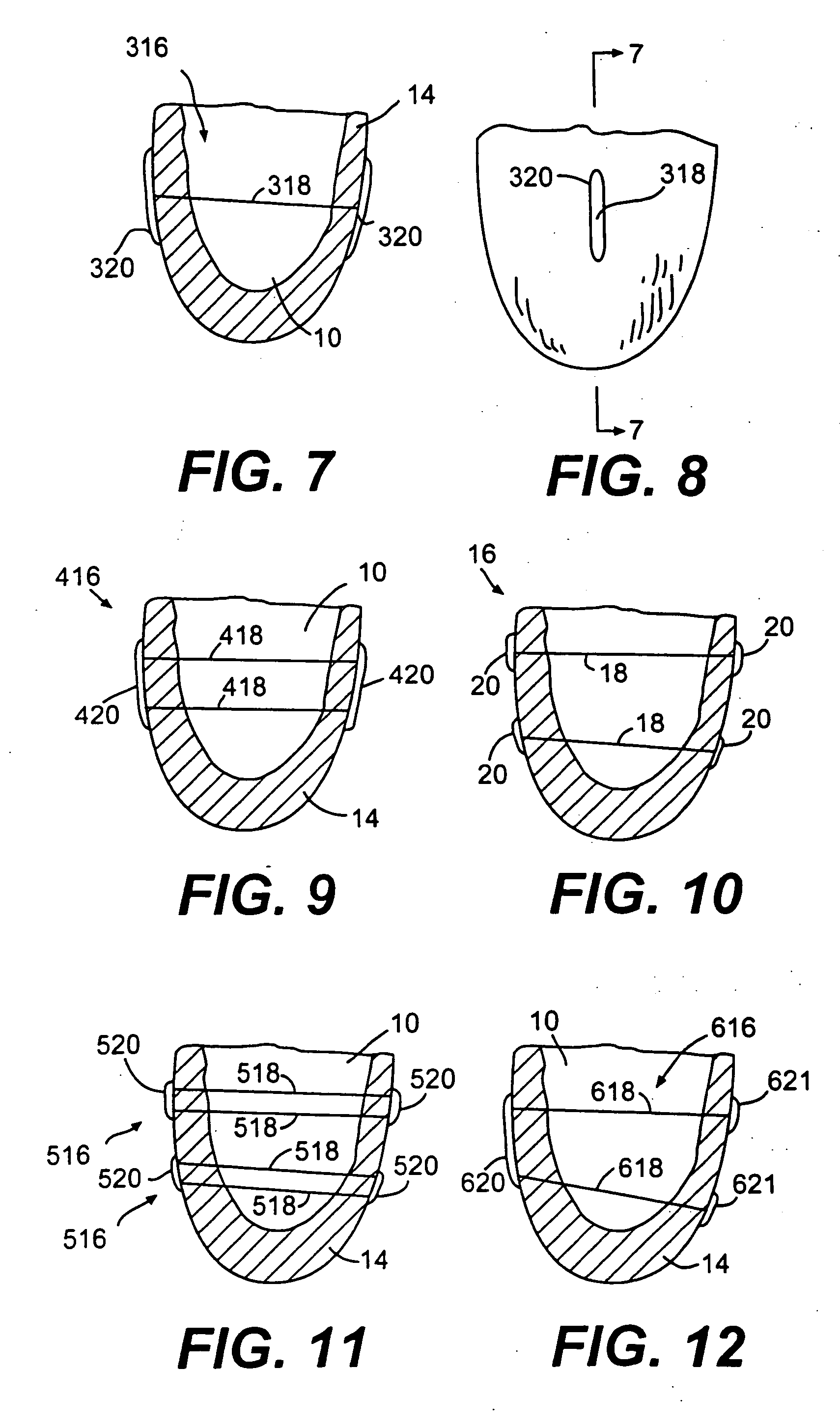
Stress reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS6908424B2Reduce maximum wall stress experienceRelieve pressureSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleStress reduction
The device and method for reducing heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle. The device can be configured to begin to engage, to reduce wall stress during diastolic filling, or begin to engage to reduce wall stress during systolic contraction. Furthermore, the device can be configured to include at least two elements, one of which engages full cycle and the other which engages only during a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Methods and devices for improving cardiac function in hearts
InactiveUS20070112244A1Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesWall stressAneurysm
Various methods and devices are disclosed for improving cardiac function in hearts having zones of infarcted (akinetic) and aneurysmal (dyskinetic) tissue regions. The methods and devices reduce the radius of curvature in walls of the heart proximal infarcted and aneurysmal regions to reduce wall stress and improve pumping efficiency. The inventive methods and related devices include splinting of the chamber wall proximal the infarcted region and various other devices and methods including suture and patch techniques.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Stress reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050143620A1Relieve pressureRelieve muscle stressSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleStress reduction
The device and method for reducing heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle. The device can be configured to begin to engage, to reduce wall stress during diastolic filling, or begin to engage to reduce wall stress during systolic contraction. Furthermore, the device can be configured to include at least two elements, one of which engages full cycle and the other which engages only during a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Method and apparatus for modulating cellular growth and regeneration using ventricular assist device
InactiveUS20060036126A1Good effectPromote tissue growthControl devicesBlood pumpsCardiac muscleVentricular assistance
A system delivers combined ventricular assist device (VAD) therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a VAD to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by reducing myocardial wall stress and the overall cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable VAD for long-term use in a patient.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
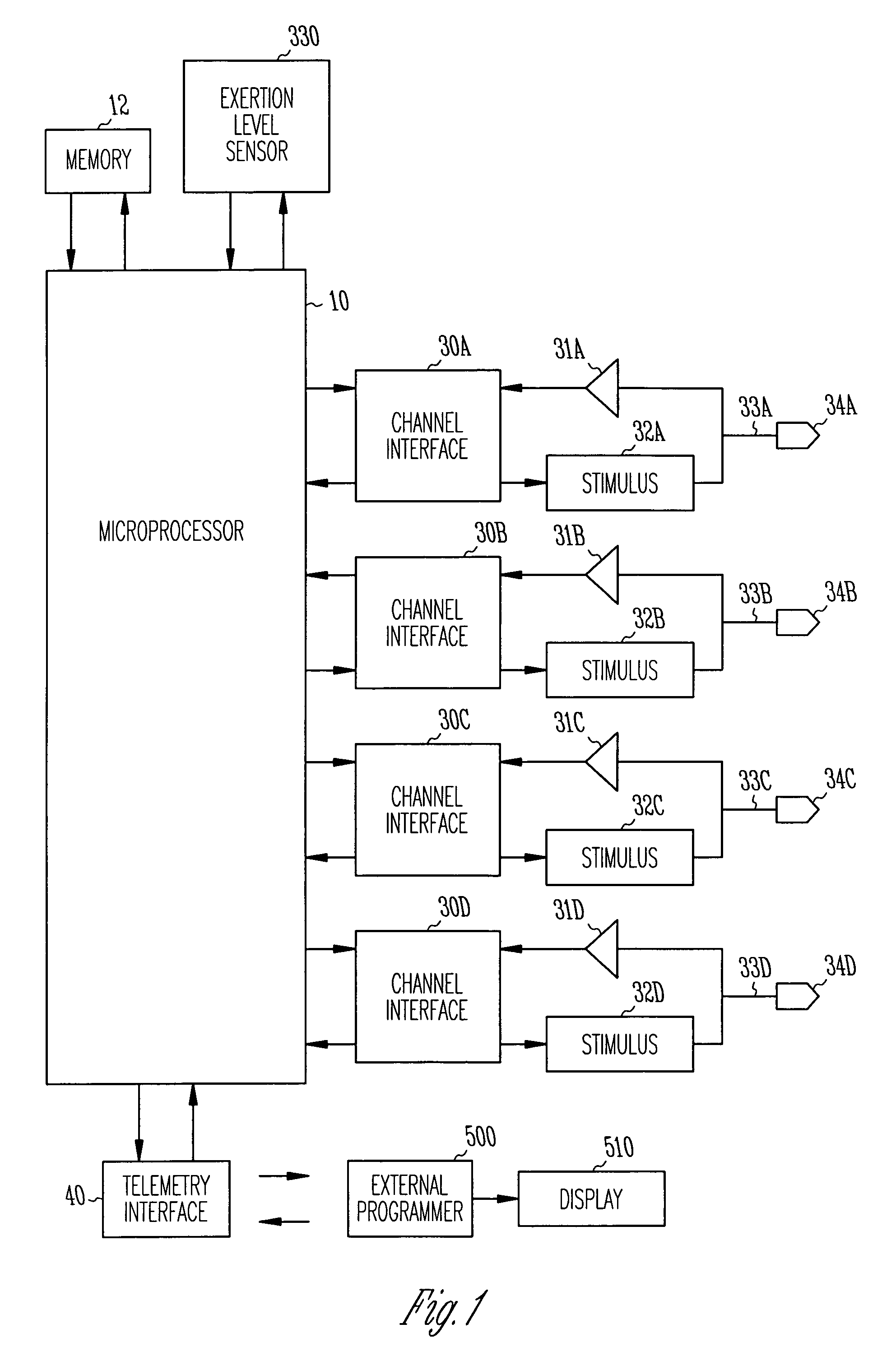
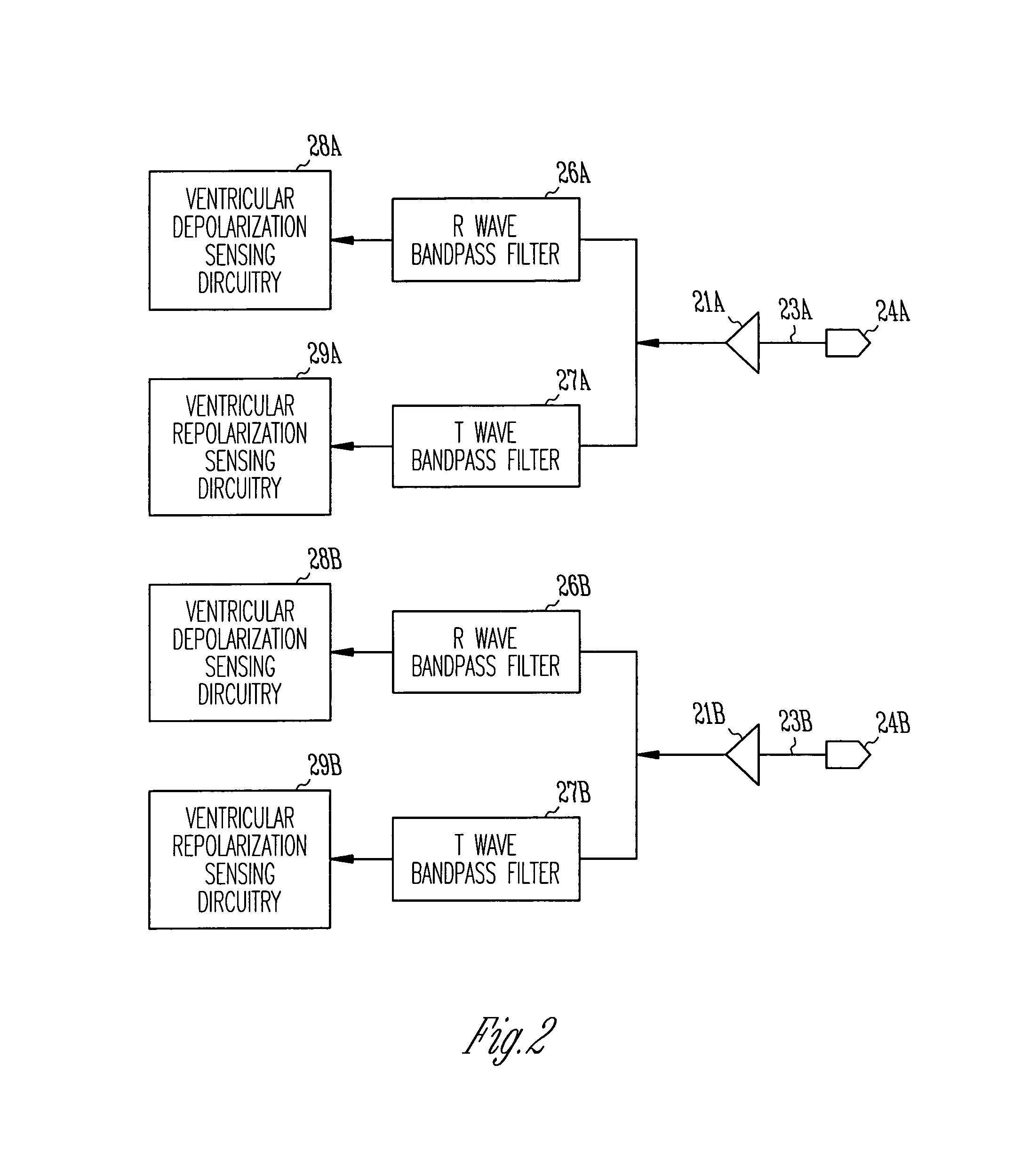
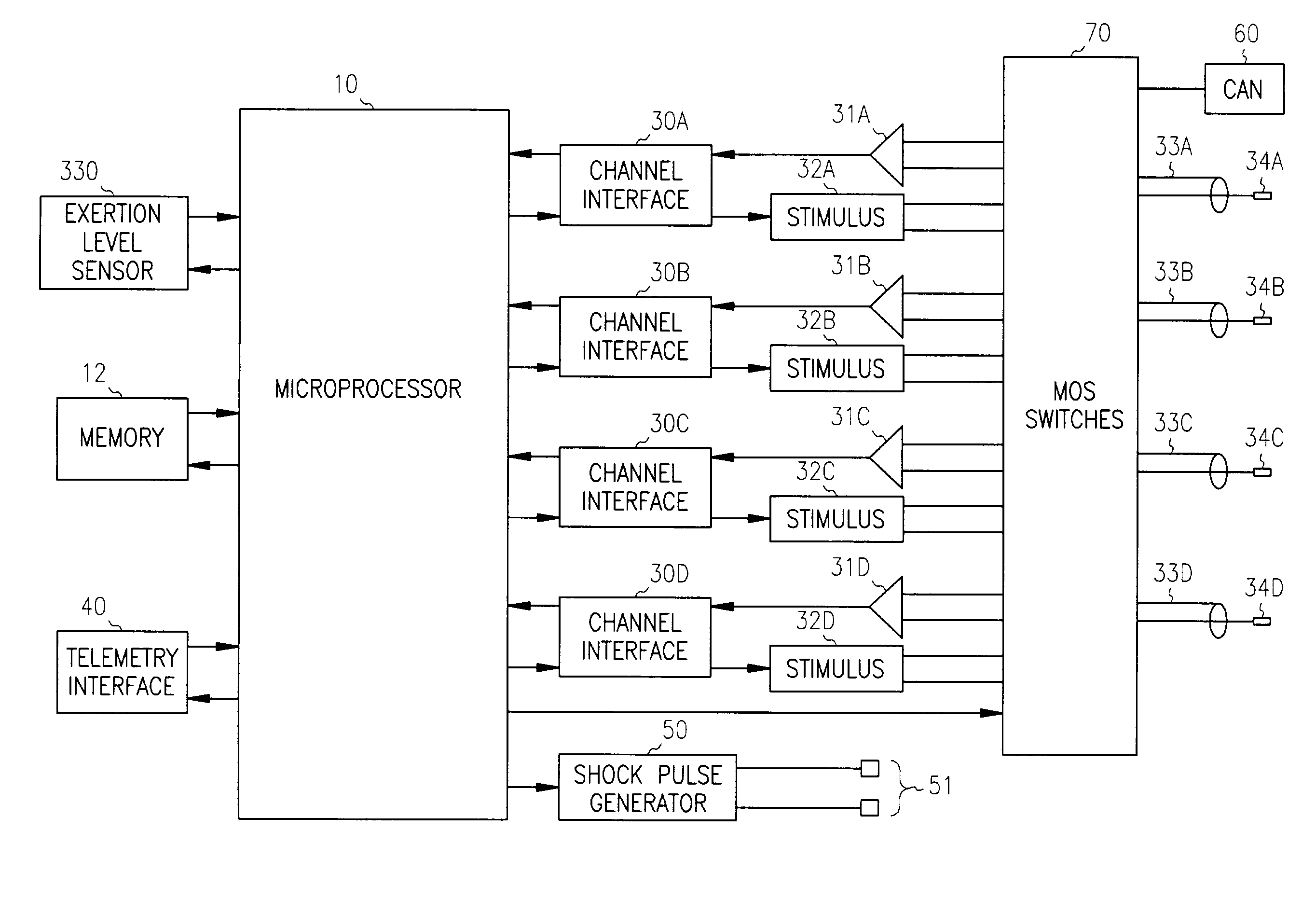
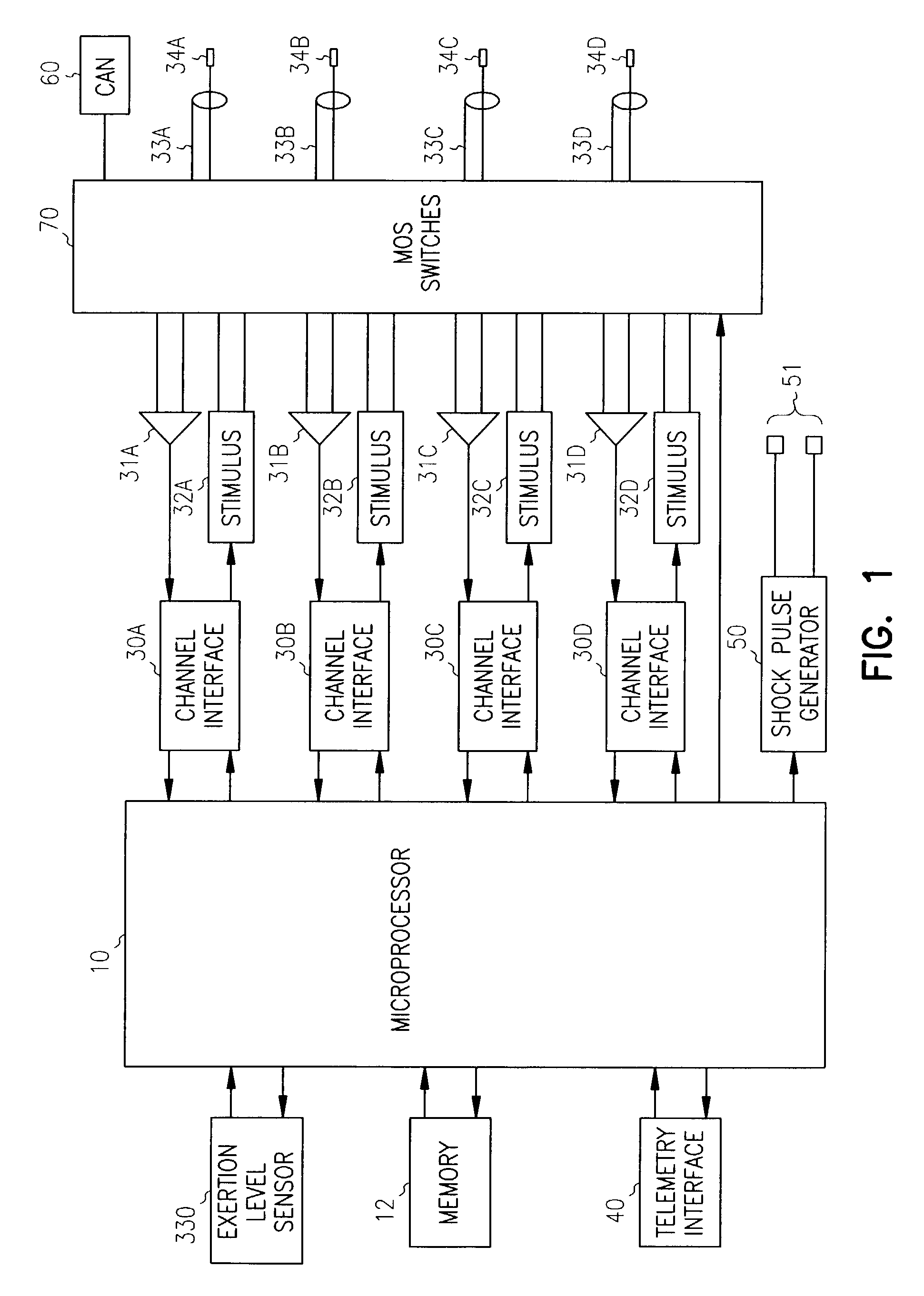
Method and apparatus for assessing and treating myocardial wall stress
InactiveUS6965797B2Prevent and reverse myocardial remodelingHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSystoleElectric stimulation therapy
An apparatus and method for assessing myocardial wall stress is disclosed. The method may be used in conjunction with electro-stimulatory therapy for preventing or reversing ventricular remodeling. In such therapy, one or more stimulatory pulses are delivered to the heart such that a stressed region of the myocardium is pre-excited relative to other regions, thereby subjecting the stressed region to a lessened preload and afterload during systole. The unloading of the stressed myocardium over time effects reversal of undesirable ventricular remodeling.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Stress reduction pacing mode for arrhythmia prevention
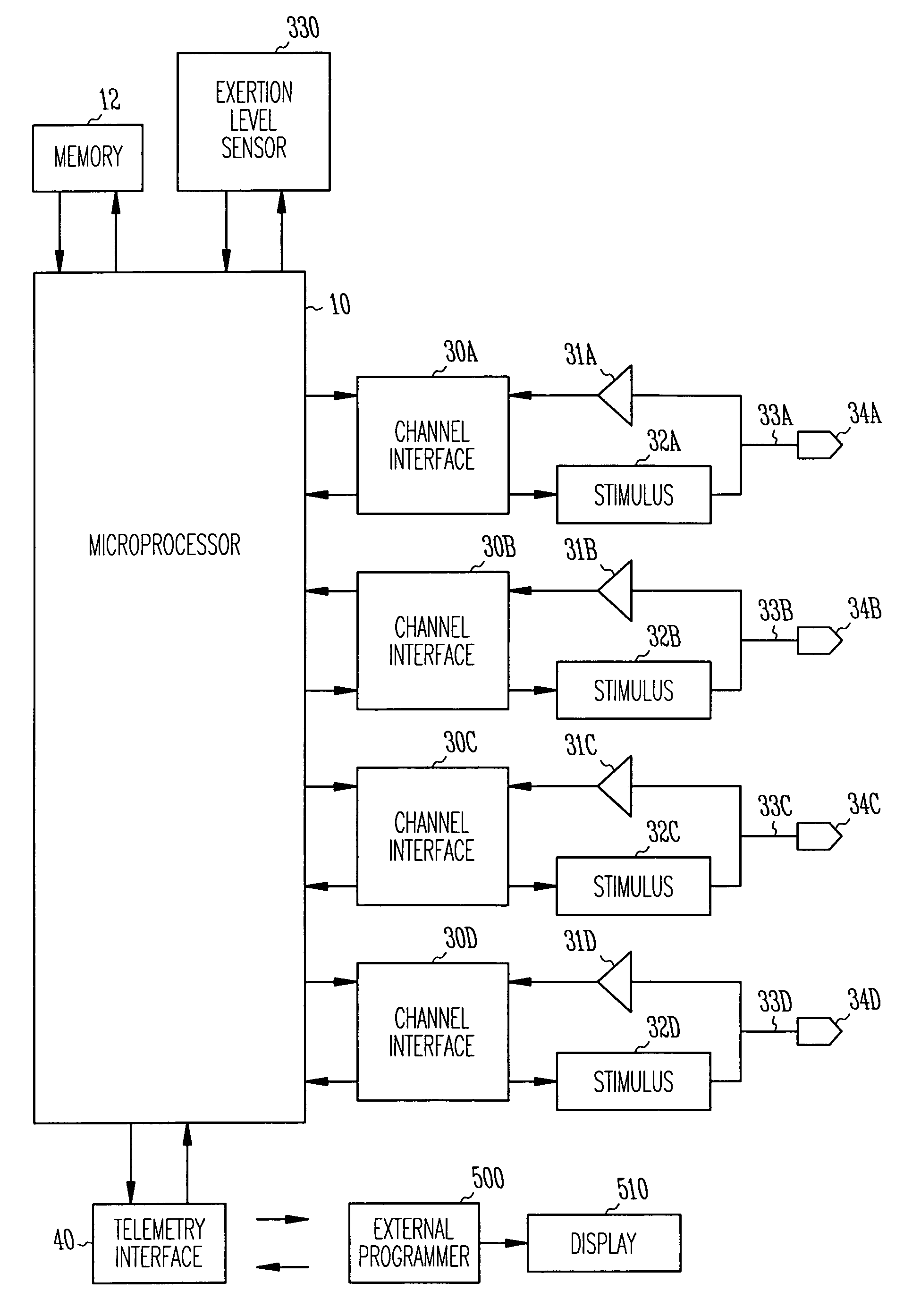
An apparatus and method preventing cardiac arrhythmias with pacing therapy is disclosed. Upon detection of a pre-arrhythmic condition, an implantable cardiac rhythm management device is configured to deliver pacing therapy in a manner that pre-excites particular myocardial sites that have been identified as stressed sites and likely locations for the origination of arrhythmias. Such pacing results in a reduction in myocardial wall stress at those sites during systole and reduces the probability of an arrhythmia occurring.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050131277A1Reduce maximum wall stressReduce tensionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleFailing heart
Devices and methods for treatment of a failing heart by reducing the heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Intramyocardial patterning for global cardiac resizing and reshaping
ActiveUS20080065048A1Thickening myocardiumReducing systolic volumeInfusion syringesHeart valvesVentricular dysrhythmiaCardiac wall
Cardiomyopathy may be treated by distributing space-occupying agent within the myocardium in a pattern about one or more chambers of the heart, such that the space-modifying agent integrates into and thickens at least part of the cardiac wall about the chamber so as globally to reduce wall stress and stabilize or even reduce chamber size. Some patterns also cause a beneficial global reshaping of the chamber. These changes occur quickly and are sustainable, and have a rapid and sustainable therapeutic effect on cardiac function. Over time the relief of wall stress reduces oxygen consumption and promotes healing. Moreover, various long-term therapeutic effects may be realized depending on the properties of the space-occupying agent, including combinations with other therapeutic materials. Specific cardiac conditions treatable by these systems and methods include, for example, dilated cardiomyopathy (with or without overt aneurismal formations), congestive heart failure, and ventricular arrhythmias. Patterns of distribution of space-occupying agent within the myocardium for global resizing may also be used or augmented to treat localized conditions such as myocardial infarctions, overt aneurysm of the ventricular wall as typically forms in response to large transmural myocardial infarctions, and mitral regurgitation due to a noncompliant mitral valve. These techniques may also be used to treat localized conditions that may not yet have progressed to cardiomyopathy.
Horizontal hole ground stress measurement device based on BWSRM (Borehole Wall Stress Relief Method) principle
InactiveCN102979520ASmall sizeReduce broken coreConstructionsBorehole/well accessoriesStress measurementMeasuring instrument
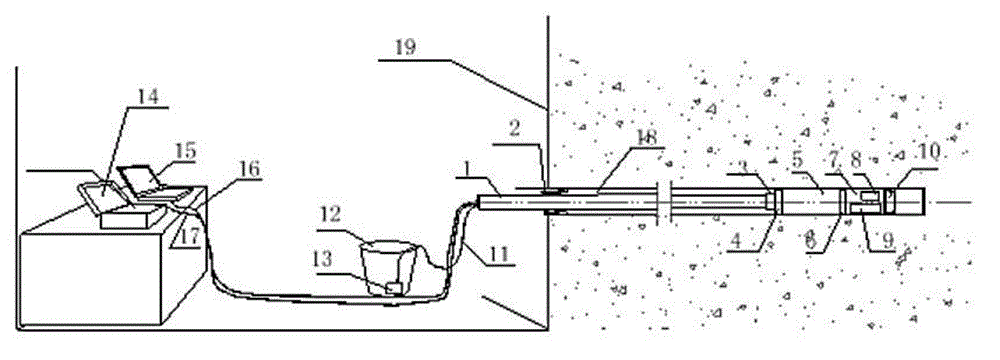
The invention relates to a horizontal hole ground stress measurement device based on a BWSRM (Borehole Wall Stress Relief Method) principle, which is used for the technical field of measurement of stress of rocks in an underground cavity or a mine opening. The horizontal hole ground stress measurement device comprises a sealed cable joint, a stress measurement main working part, a multiway stress measuring instrument, a measurement control unit and a detection part, wherein the sealed cable joint is connected with the front end of the stress measurement main working part to be used as an output port for a power cable and a communication cable of the integral device; the stress measurement main working part is sequentially connected with the multiway stress measuring instrument, the measurement control unit and the detection part; the multiway stress measuring instrument is used for recording variation of stress on a working surface in the process that a thin-walled diamond core drill implements ring-shaped cutting on surrounding rocks of the hole wall of a borehole; and the detection part is used for observing and recording the quality condition of the hole wall of the borehole in the process of propelling integral equipment into the horizontal borehole to a working hole depth and providing reference basis for a local hole section which is selected to be subjected to stress relief. According to the invention, the integral measuring process is controlled sufficiently by an electromechanical integration technology through adopting a main control module; and test reliability and measurement accuracy can be greatly improved. The horizontal hole ground stress measurement device is convenient to carry and apply in the field and easy to operate in the field and can carry out three-dimensional ground stress actual measurement easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cardiac wall tension relief with cell loss management
InactiveUS20050095268A1Reduce loss rateDecreasing wall stressElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac wallCardiac muscle
Method and apparatus are disclosed for treating congestive heart failure. The method includes relieving wall stress on a diseased heart by an amount to decrease a rate of myocardial cell loss. Further, the method includes pharmacologically encouraging a myocardial cell gain. Cell gain may be encouraged by cell replication, cell recruitment or inhibition of cell death. Further embodiments of the method include a passive cardiac constraint selected to reduce wall stress on the heart. An apparatus of the present invention includes a passive cardiac constraint and a pharmacological agent to encourage cell gain.
Owner:ACORN CARDIOVASCULAR
Method and apparatus to modulate cellular regeneration post myocardial infarct
InactiveUS7764995B2Easy to adjustModulate tissue growthMedical devicesPressure infusionCardiac muscleImplanted device
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Intramyocardial patterning for treating localized anomalies of the heart
Cardiomyopathy may be treated by distributing space-occupying agent within the myocardium in a pattern about one or more chambers of the heart, such that the space-modifying agent integrates into and thickens at least part of the cardiac wall about the chamber so as globally to reduce wall stress and stabilize or even reduce chamber size. Some patterns also cause a beneficial global reshaping of the chamber. These changes occur quickly and are sustainable, and have a rapid and sustainable therapeutic effect on cardiac function. Over time the relief of wall stress reduces oxygen consumption and promotes healing. Moreover, various long-term therapeutic effects may be realized depending on the properties of the space-occupying agent, including combinations with other therapeutic materials. Specific cardiac conditions treatable by these systems and methods include, for example, dilated cardiomyopathy (with or without overt aneurismal formations), congestive heart failure, and ventricular arrhythmias. Patterns of distribution of space-occupying agent within the myocardium for global resizing may also be used or augmented to treat localized conditions such as myocardial infarctions, overt aneurysm of the ventricular wall as typically forms in response to large transmural myocardial infarctions, and mitral regurgitation due to a noncompliant mitral valve. These techniques may also be used to treat localized conditions that may not yet have progressed to cardiomyopathy.
Owner:CARDIOPOLYMERS +2
Method and apparatus for testing stress of cavern wall
InactiveCN1963423AReduce measurement errorSuitable for on-site operationMining devicesForce measurementRock coreTangential stress
This invention discloses one spot measurement carve stress test method and device for channel stress test, which uses one same rock core and stress for stress elimination measurement and stress restore device, wherein, the rock wall stress test device comprises upper and down saddle pressure blocks to form round hole size and its load rock chip diameter matched; the saddle arc size is smaller than semi-round; the upper and down saddle pressure blocks arc tank and rock chip are set with at least one layer of film underlay pad.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
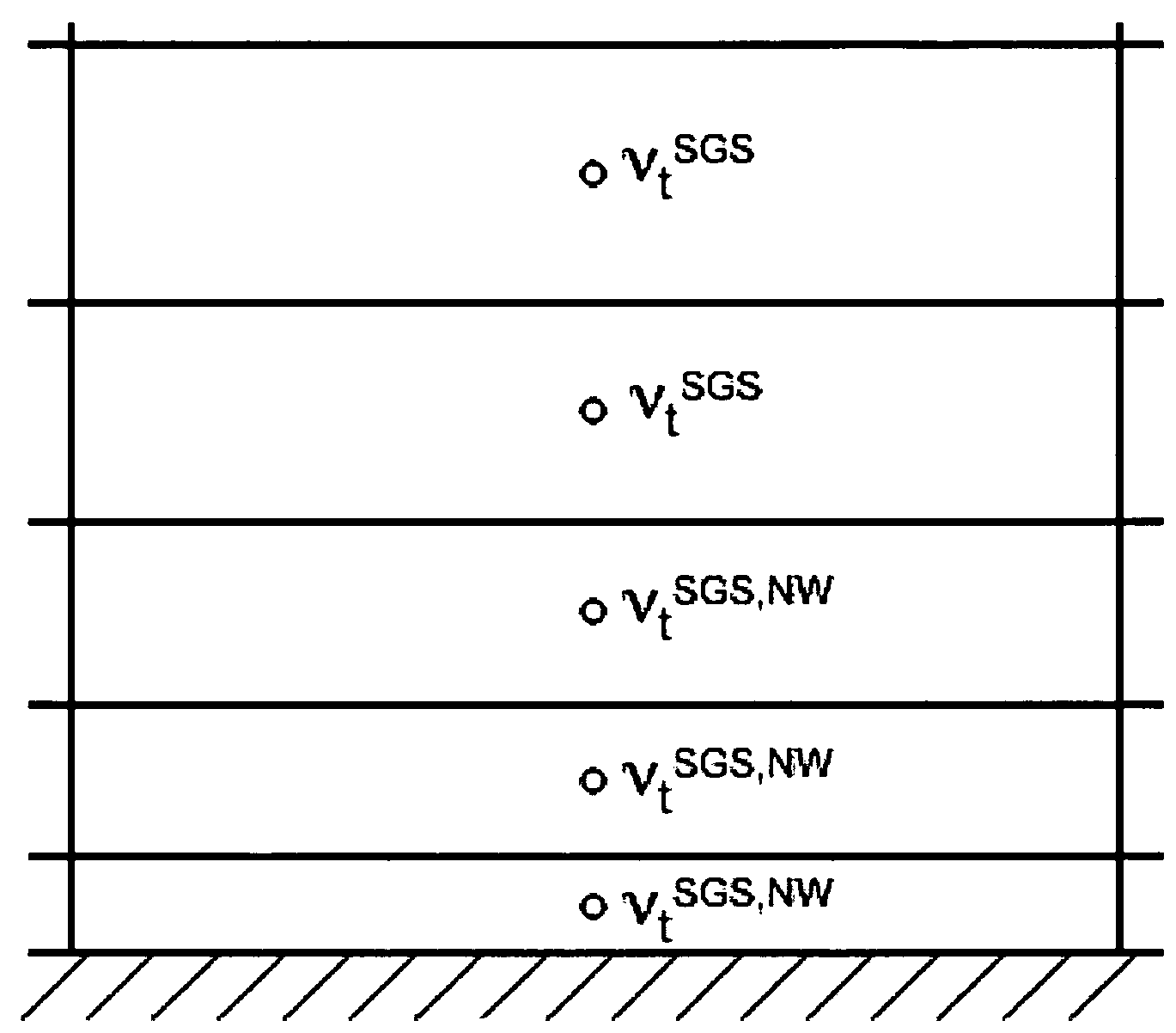
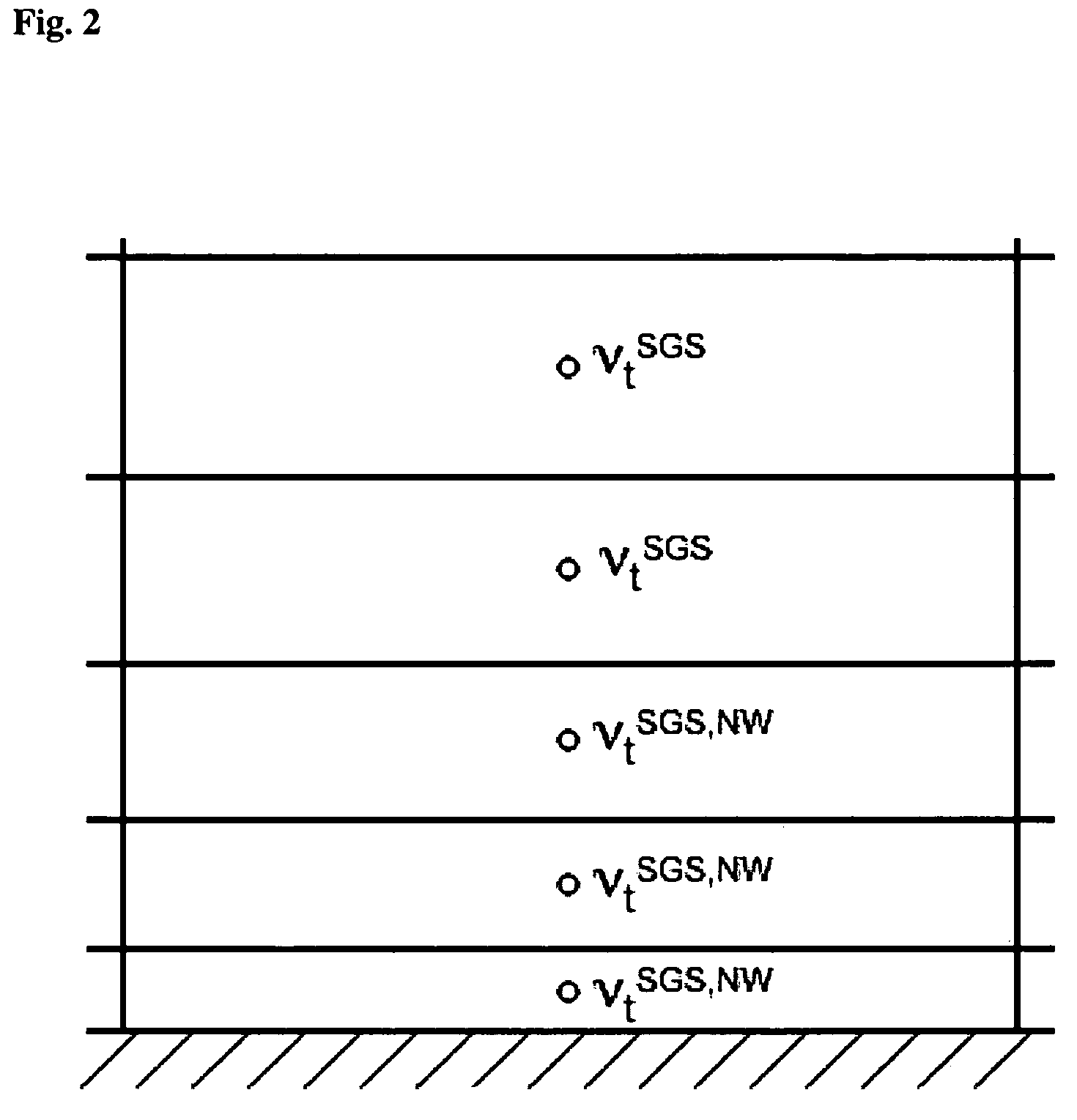
Method for computing turbulent flow using a near-wall eddy-viscosity formulation
InactiveUS20080015825A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationNavier stokesEngineering
A technique that improves large-eddy simulation consists in replacing the instantaneous sub-grid scale eddy-viscosity (such as the dynamic Smagorinsky model eddy-viscosity) in the near-wall region with an eddy-viscosity computed from Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes eddy-viscosity and corrected dynamically using the resolved turbulent stress. The near-wall eddy-viscosity formulation is applied either with a wall stress model on coarse grids that do not resolve the wall or with wall-resolved grids coarsened in the wall-parallel directions. Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes eddy-viscosity is computed either from a look-up table or from a simultaneous solution of a Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes turbulence model.
Owner:KALITZIN GEORGI +2
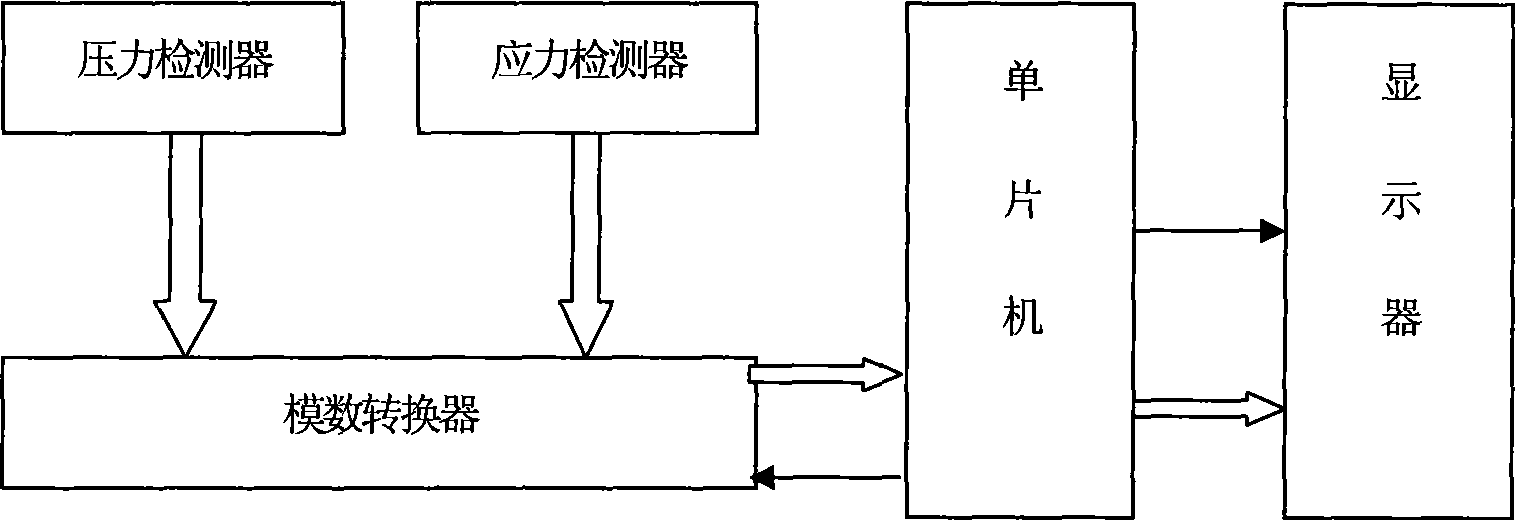
Device and method for detecting coal seam gas pressure and coal wall stress
InactiveCN101446193AReduce stress recovery timePrevent air leakageSurveyMining devicesMicrocontrollerDisplay device
The invention relates to a device and a method for detecting coal seam gas pressure and coal wall stress. The detection device comprises a pressure detector and a stress detector which penetrate the rock layer to be positioned in a drilled hole on a coal wall and an analog-to-digital converter, a monolithic processor and a display which are arranged outside the drilled hole on the coal wall, and the detection method comprises the following steps: a hole is drilled on a coal seam, the pressure detector and the stress detector are transported inside the drilled hole and respectively used for detecting the gas pressure inside the coal seam and the coal wall stress, wherein, the pressure detector transforms the detected information into a standard current signal, the stress detector transforms the detected information into a voltage signal for amplification, and the current signal and the voltage signal are transmitted to the outside of the drilled hole through wires, and are transformed into digital signals through the analog-to-digital converter; and after program operation and processing of the monolithic processor, the numerical values of the coal seam gas pressure and the coal wall stress can be displayed on the display screen. Therefore, not only the measurement time of the coal seam gas pressure can be greatly shortened, but also the technical requirements for hole sealing are lowered, and the cost is saved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Self-propelled diameter-variable stress rosette pasting device used for geostress measuring
The invention discloses a self-propelled diameter-variable stress rosette pasting device used for geostress measuring and relates to the technical field of surveying of geological and mineral energy resources and geotechnical engineering. The self-propelled diameter-variable stress rosette pasting device comprises an orientor, an automatic climbing system, a colloid storing and extruding mechanism, a stress rosette fixing and pasting mechanism and a drive-by-wire operator controlling the automatic climbing system, and the orientor, the automatic climbing system, the colloid storing and extruding mechanism and the stress rosette fixing and pasting mechanism are connected sequentially. By the self-propelled diameter-variable stress rosette pasting device, functions of mounting-in-place and pasting of strain gauges in the process of geostress testing through a hole wall stress relieving method can be realized, the problems that a strain meter is complex in mounting process and low in success rate, testing depth is limited by length of a mounting guide rod and the like when a conventional hollow inclusion method is adopted for geostress measuring are solved effectively, application range of the hole wall stress relieving method for geostress measuring is expanded, and testing efficiency is improved. The self-propelled diameter-variable stress rosette pasting device has the advantages of low testing cost, convenience in carrying, simplicity and convenience in on-site operation and the like.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS7883539B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleFailing heart
Devices and methods for treatment of a failing heart by reducing the heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
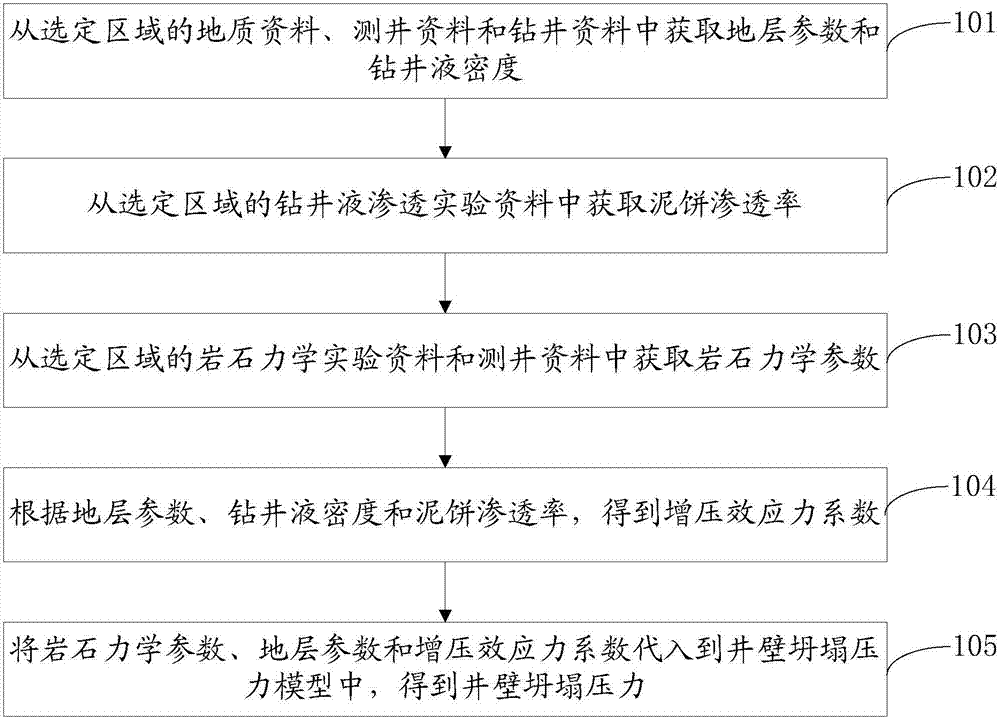
Supercharging effect force-considering hole-wall collapsing pressure calculation method
InactiveCN107038290ATruly reflect the stress characteristicsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsWell drillingOil drilling
The invention discloses a supercharging effect force-considering hole-wall collapsing pressure calculation method, and belongs to the field of oil drilling. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a stratum parameter and a drilling fluid density from geological information, logging information and drilling information of a selected area; obtaining a mud cake penetration rate from drilling fluid penetration experiment information of the selected area; obtaining a rock mechanical parameter from rock mechanical experiment information and the logging information of the selected area; obtaining a supercharging effect force coefficient according to the stratum parameter, the drilling fluid density and the mud cake penetration rate; and substituting the rock mechanical parameter, the stratum parameter and the supercharging effect force coefficient into a hole-wall collapsing pressure model to obtain hole-wall collapsing pressure. According to the method, the hole-wall stress features under drilling fluid environment can be reflected more really, and basis is provided or the selection of reasonable drilling fluid density in the drilling process.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Cardiac wall tension relief with cell loss management
InactiveUS20080125622A1Reduce loss rateEncouraging a myocardial cell gainElectrotherapyHeart valvesCardiac wallCardiac muscle
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for treating congestive heart failure. The method includes relieving wall stress on a diseased heart by an amount to decrease a rate of myocardial cell loss. Further, the method includes pharmacologically encouraging a myocardial cell gain. Cell gain may be encouraged by cell replication, cell recruitment or inhibition of cell death. Further embodiments of the method include a passive cardiac constraint selected to reduce wall stress on the heart. An apparatus of the present invention includes a passive cardiac constraint and a pharmacological agent to encourage cell gain.
Owner:ACORN CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for computing turbulent flow using a near-wall eddy-viscosity formulation
InactiveUS7668705B2Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMedicineNavier stokes
A technique that improves large-eddy simulation consists in replacing the instantaneous sub-grid scale eddy-viscosity (such as the dynamic Smagorinsky model eddy-viscosity) in the near-wall region with an eddy-viscosity computed from Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes eddy-viscosity and corrected dynamically using the resolved turbulent stress. The near-wall eddy-viscosity formulation is applied either with a wall stress model on coarse grids that do not resolve the wall or with wall-resolved grids coarsened in the wall-parallel directions. Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes eddy-viscosity is computed either from a look-up table or from a simultaneous solution of a Reynolds Averaged Navier-Stokes turbulence model.
Owner:KALITZIN GEORGI +2
Method and apparatus for modulating cellular growth and regeneration using ventricular assist device
InactiveUS7828711B2Assists the heart in blood pumpingGood effectControl devicesBlood pumpsCardiac muscleVentricular assistance
A system delivers combined ventricular assist device (VAD) therapy and chemical and / or biological therapy to modulate myocardial tissue growth in a heart after myocardial infarction (MI). The system includes an agent delivery device to release one or more agents to an MI region to modulate myocardial tissue growth in that region, and a VAD to enhance the effects of the one or more agents by reducing myocardial wall stress and the overall cardiac workload. In one embodiment, the system is an implantable system including an implantable agent delivery device and an implantable VAD for long-term use in a patient.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Sublevel-open-stoping-method pressure-relief stoping method for high-dipping medium-thick ore body
InactiveCN107178367AExtend recovery timeAccelerate recovery cycleDisloding machinesUnderground miningDetonationRock blasting
The invention belongs to the technical field of mining, and particularly relates to a sublevel-open-stoping-method pressure-relief stoping method for a high-dipping medium-thick ore body. The method achieves pressure-relief type stoping by means of the steps that a cut parvis is formed through blasting in groups, and then the ore body is divided into three subsections in the vertical direction of the ore body; the ore body is divided into a plurality of stopes in each subsection, and each stope is divided into I-VI rows of grouped concentrated blasting subareas to conduct blasting in groups; broken ores are formed after blasting is conducted, a route for transmitting hanging wall stress to heading wall through the ore body is cut off, and pressure-relief grooves in stair shapes are formed in the vertical direction of the ore body. In addition, through multi-group concentrated blasting, a hole-by-hole millisecond blasting detonation technology is adopted, disturbance and damage to rock mass caused by multi-group blasting of traditional operation are reduced, the blasting efficiency is enhanced, the stope room stoping period is shortened, and the ore production efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
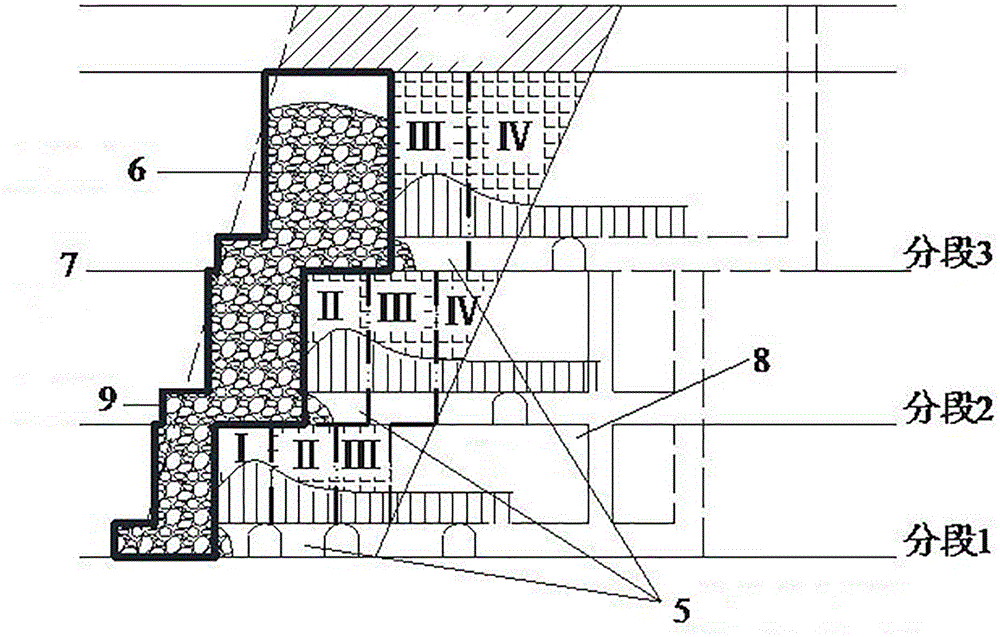
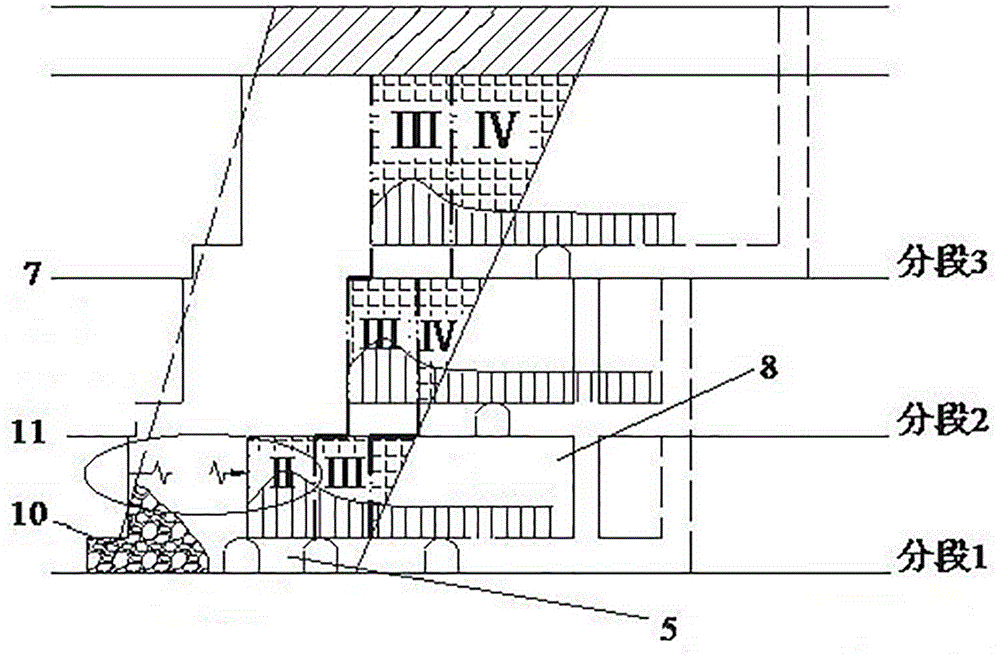
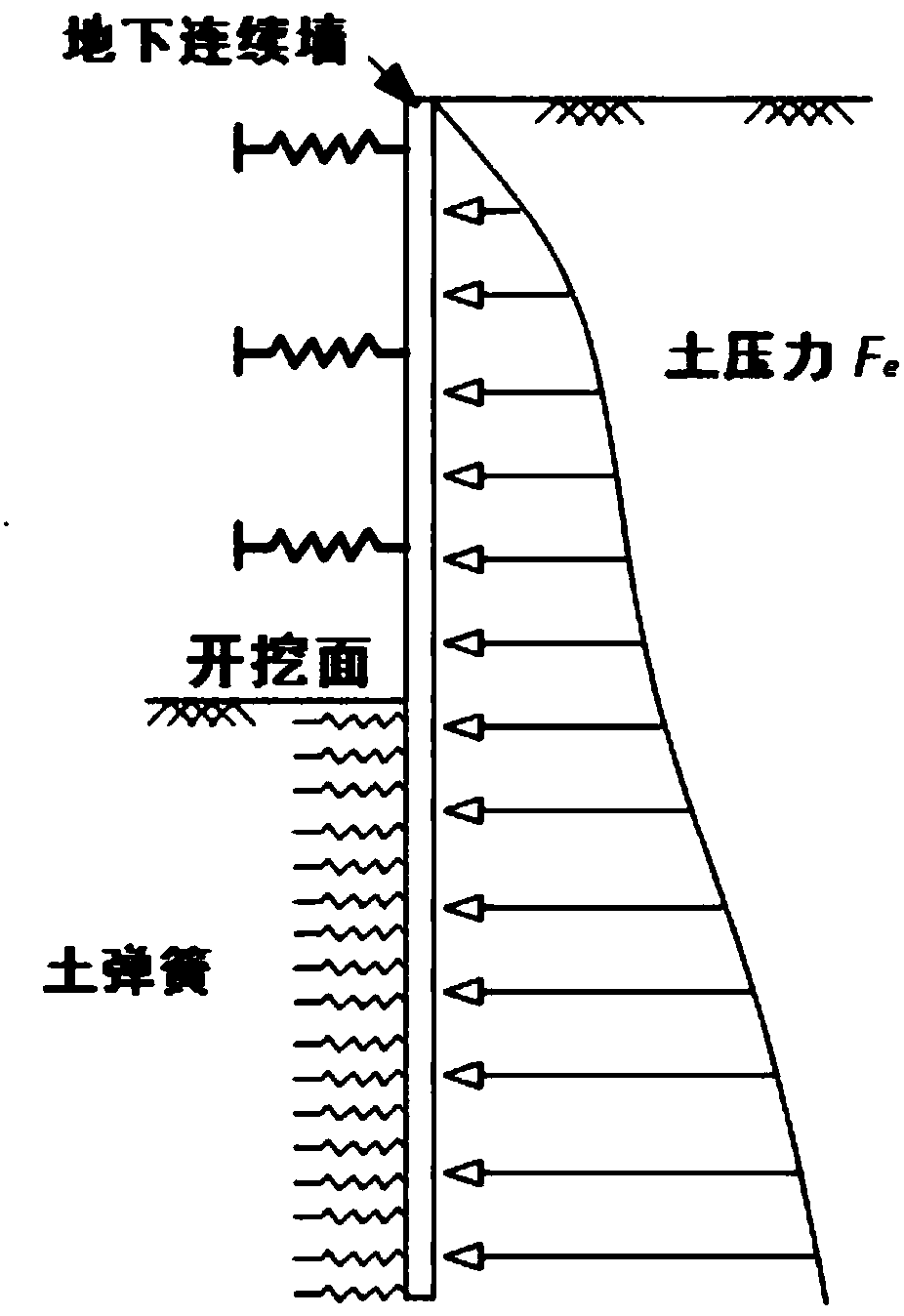
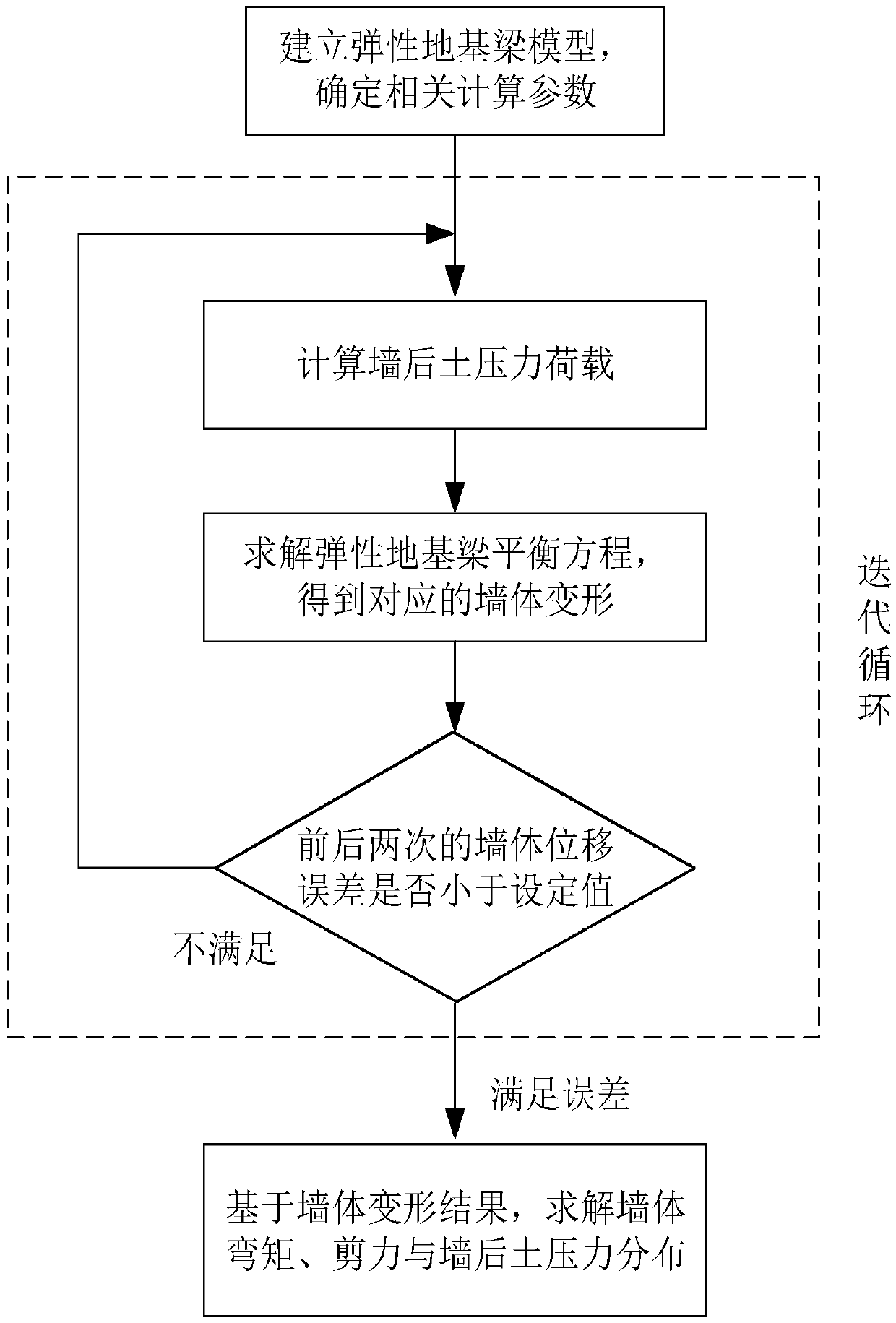
Deep foundation pit enclosure wall stress deformation quick calculating method in consideration of wall soil coupling
The invention provides a deep foundation pit enclosure wall stress deformation quick calculating method in consideration of wall soil coupling; and the method fully considers a coupling relation of wall soil deformation in the foundation pit excavation unloading process, and has the advantages of high calculating efficiency, more accordance with actual conditions and the like. The method comprisesthe following steps: (1) an elastic foundation beam model is built (an elastic beam is adopted to simulate a ground continuous wall, a spring unit is adopted to simulate a support, a soil spring unitis adopted to simulate in-pit soil, and the soil pressure adopts a non-limit soil pressure model), and related calculating parameters are determined; (2) the after-wall soil pressure distribution iscalculated (the supposed wall deformation is firstly calculated as zero); (3) a stress balance equation of the ground continuous wall is calculated to obtain corresponding wall deformation; (4) wall deformation errors calculated by two times are judged to restrain to a set value; and if requirements are not met, the steps (2) to (4) are repeated until the errors are restrained to the set value toobtain a final wall deformation value; and (5) the wall bending moment and shearing force and the after-wall soil pressure distribution are calculated based on the wall deformation value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cardiac Patterning for Improving Diastolic Function
InactiveUS20130211182A1Function increaseThickening myocardiumSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac wallCardiac functioning
Cardiomyopathy may be treated by distributing a space-occupying diastole-assist agent within the myocardium or within the cardiac venous system in a pattern about one or more chambers of the heart, such that the space-modifying agent integrates into and thickens at least part of the cardiac wall about the chamber so as globally to reduce wall stress, stabilize or even reduce chamber size, and / or improve diastolic function. Some patterns also cause a beneficial global reshaping of the chamber. These changes occur quickly and are sustainable, and have a rapid and sustainable therapeutic effect on cardiac function. Patterns of distribution of space-occupying agent within the myocardium for global resizing may also be used or augmented to treat localized conditions such as myocardial infarctions, overt aneurysm of the ventricular wall as typically forms in response to large transmural myocardial infarctions, and mitral regurgitation due to a noncompliant mitral valve. These techniques may also be used to treat localized conditions that may not yet have progressed to cardiomyopathy.
Owner:SABBAH HANI N +2
Stress peak detection method through laser shock peening hole wall
ActiveCN107389241ASimple and fast operationImprove detection efficiencyApparatus for force/torque/work measurementElement modelStatistical analysis
The invention provides a stress peak detection method through a laser shock peening hole wall. The stress peak detection method comprises the following steps that a finite element model of the laser shock peening hole is established; simulation calculation is performed; a laser loading curve is determined according to the laser shock process parameters; a shock trajectory path is set; a simulation calculation module is started; hole opening finite element simulation is started; laser shock peening simulation is performed on the acting area of laser shock, and then hole opening simulation is performed on the shock center area; the laser shock process parameters are changed and the steps are repeated; a relation curve between the residual stress and the hole wall stress peak of the hole wall surface theory is drawn; the sample is prepared, and laser shock peening processing and hole opening are performed on the sample; the surface residual stress of the hole of the sample is measured for statistical analysis; and the actual residual stress peak of the hole wall is estimated. The surface residual stress near the hole angle can be measured according to the relation curve between the laser shock peening surface residual stress near the hole angle and the hole wall stress peak.
Owner:东台城东科技创业园管理有限公司
Pressure regulation type children pigeon breast appliance
InactiveCN104970910AEasy to adjust the degree of compressionAvoid damageOrthopedic corsetsPigeon breastEngineering
The present invention relates to a pressure regulation type children pigeon breast appliance. The pressure regulation type children pigeon breast appliance is provided with a chest orthopedic stand, a fixing strap, a pressure fixing plate, a pressure monitoring gauge, fixing tying belts, tying belt fixing buttons and fixing shoulder straps, wherein two ends of the fixing strap are connected with the fixing tying belts, two ends of the chest orthopedic stand are connected with the tying belt fixing buttons, the tying belt fixing buttons coordinate with the fixing tying belts, the fixing shoulder straps are connected between the chest orthopedic stand and the fixing strap, inner sides of both the chest orthopedic stand and the fixing strap are provided with liners, the pressure monitoring gauge is disposed at an outer side face of the chest orthopedic stand, the pressure fixing plate is disposed at the inner side face of the chest orthopedic stand, and a thin film pressure sensor is disposed on the inner surface of the pressure fixing plate. The pressure regulation type children pigeon breast appliance has the advantages that the orthopedic pressure can be displayed and is adjustable, chest wall stressed situations can be monitored, the chest wall pressure degree can be conveniently adjusted, and tissue injuries caused by excessive pressure are prevented.
Owner:XIN HUA HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
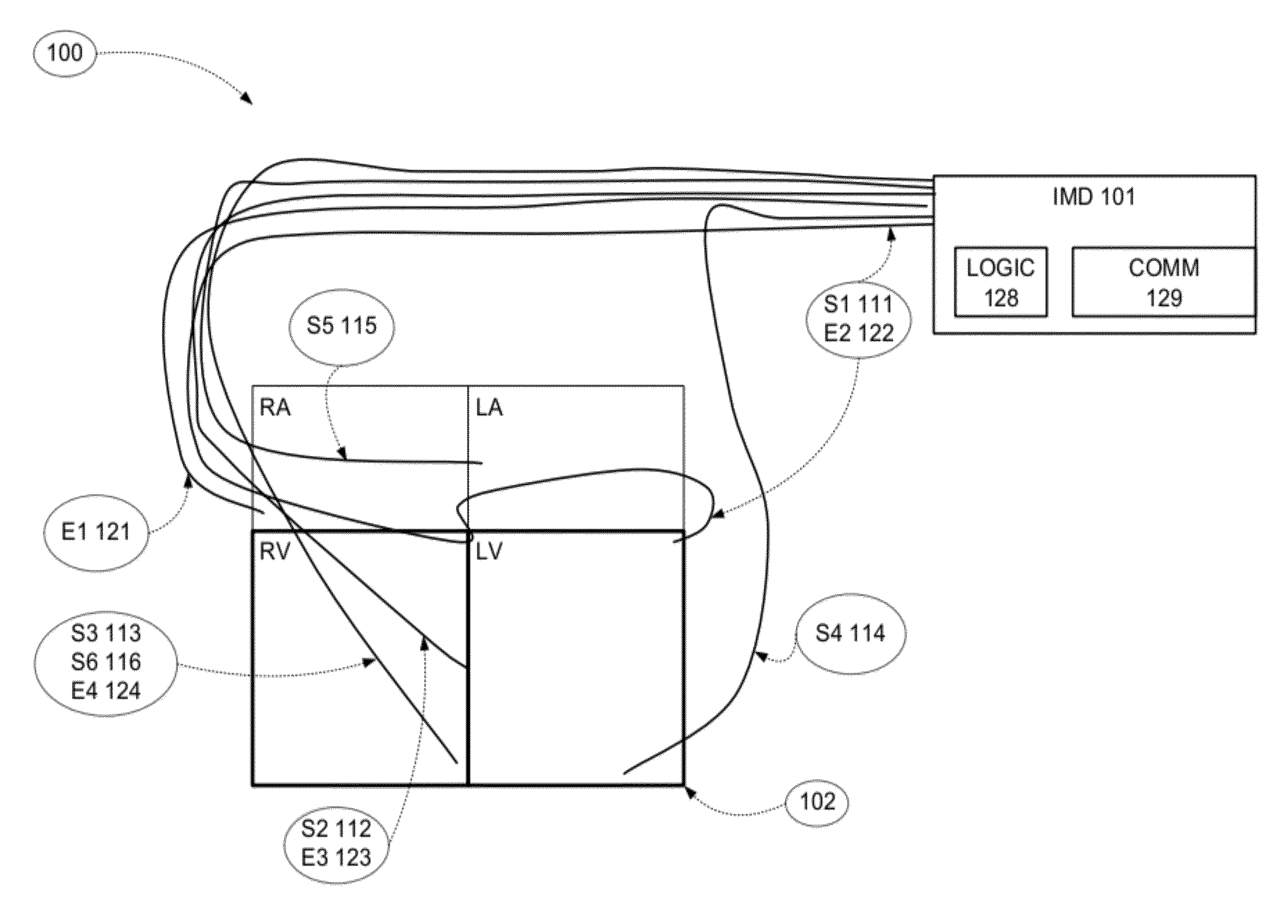
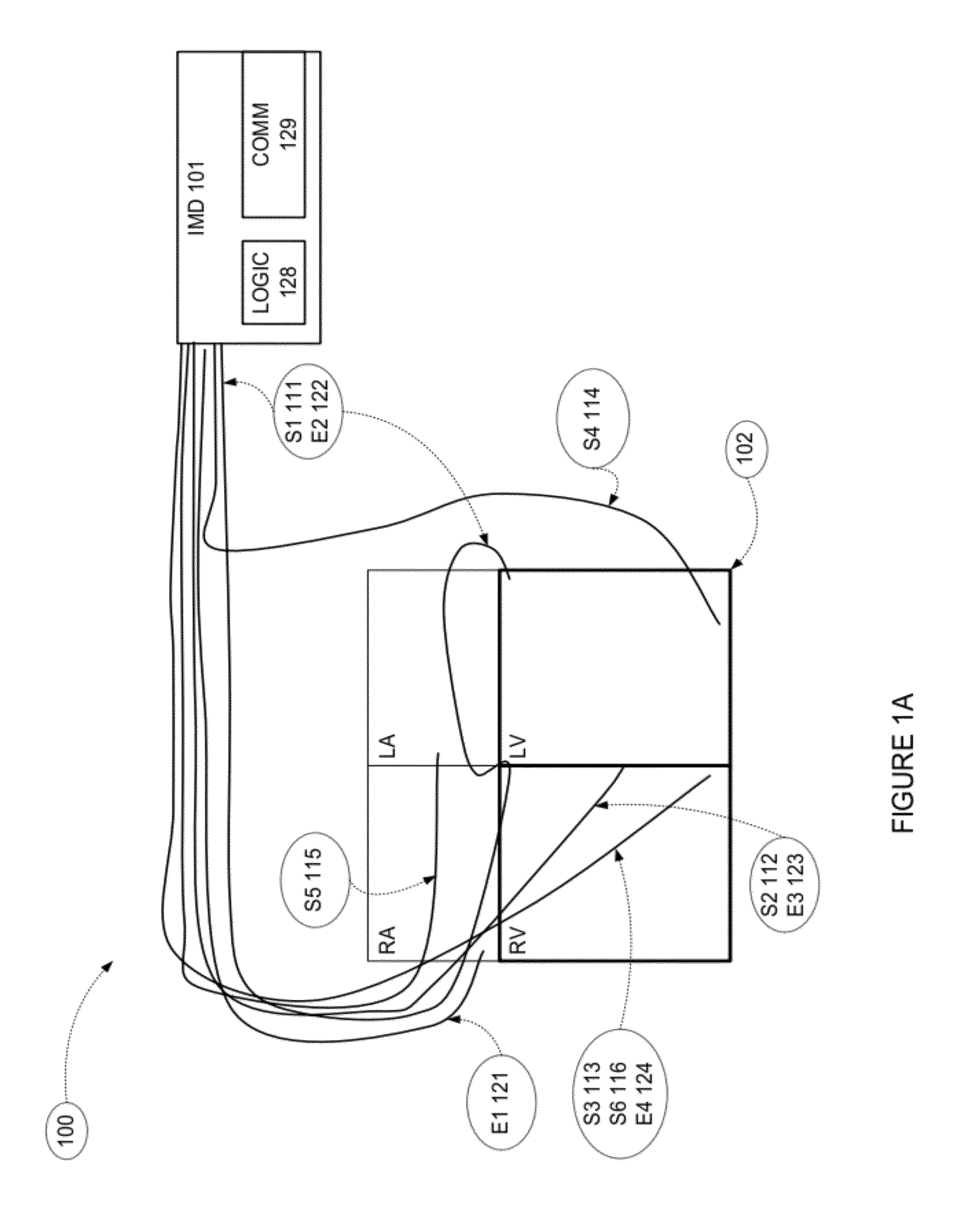
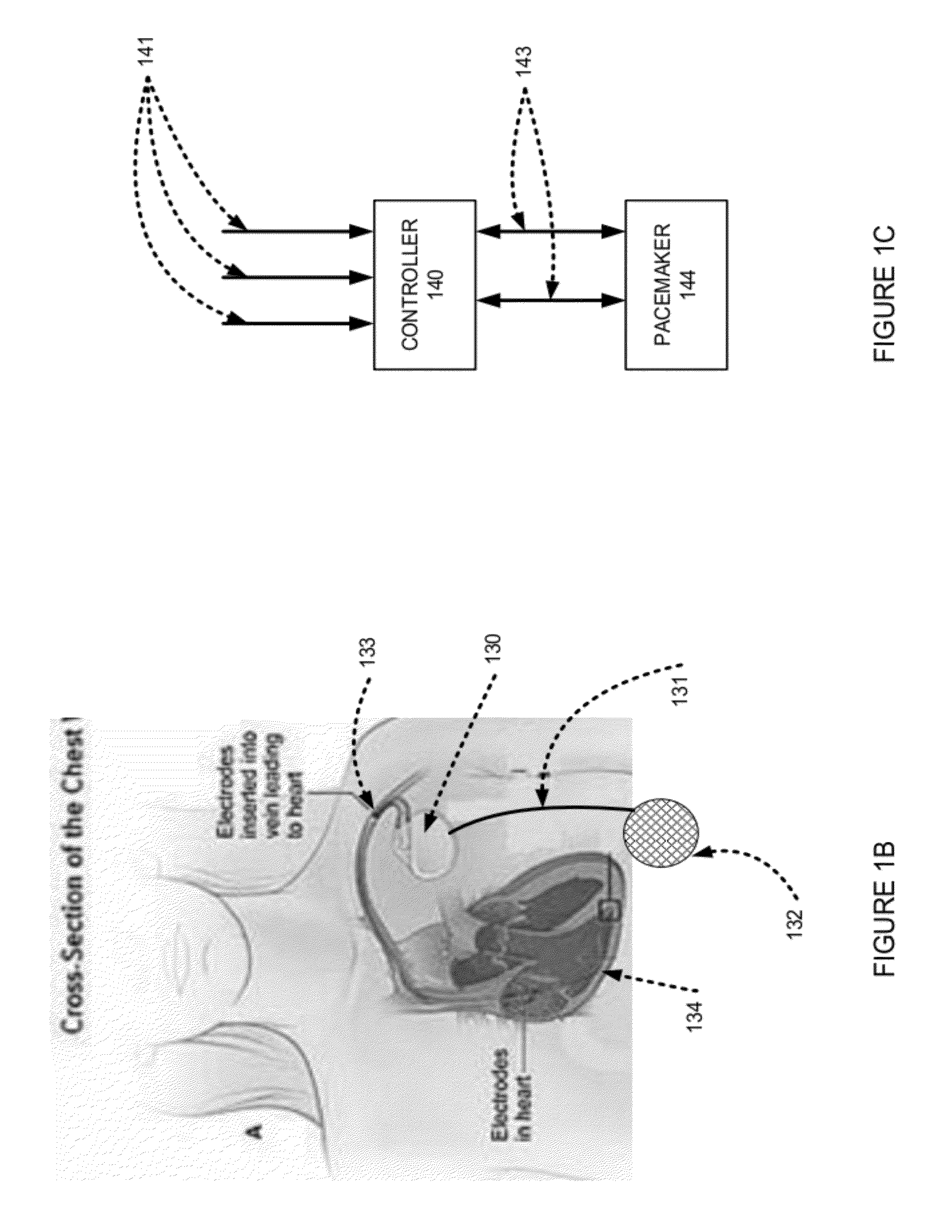
Methods and apparatus for optimizing cardiac output, preventing backward heart failure, and minimizing diastolic myocardial wall stress by controlling left ventricular filling
InactiveUS20120172944A1Less timeIncrease heart rateElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsIncreased heart rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
Apparatus for diastole trimming including a controller for producing a diastole ending signal, and one or more leads connected to the controller, for carrying the signal to lead connections to a heart, characterized by the controller detecting when a left ventricle (LV) of the heart is mostly full, and producing the diastole ending signal such that the diastole duration is trimmed. Apparatus for diastole trimming including a controller for producing a diastole ending signal, and a connection to a pacemaker, characterized by the controller having decision rules for indicating to the pacemaker when to fire and end the diastole. A method of programming a pacemaker characterized by increasing cardiac output by trimming duration of diastole. A method for increasing cardiac output including producing a signal to trim diastole duration, thereby increasing heart rate (HR) and increasing a product of stroke volume (SV) times HR. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:D H S MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com