Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Failing heart" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
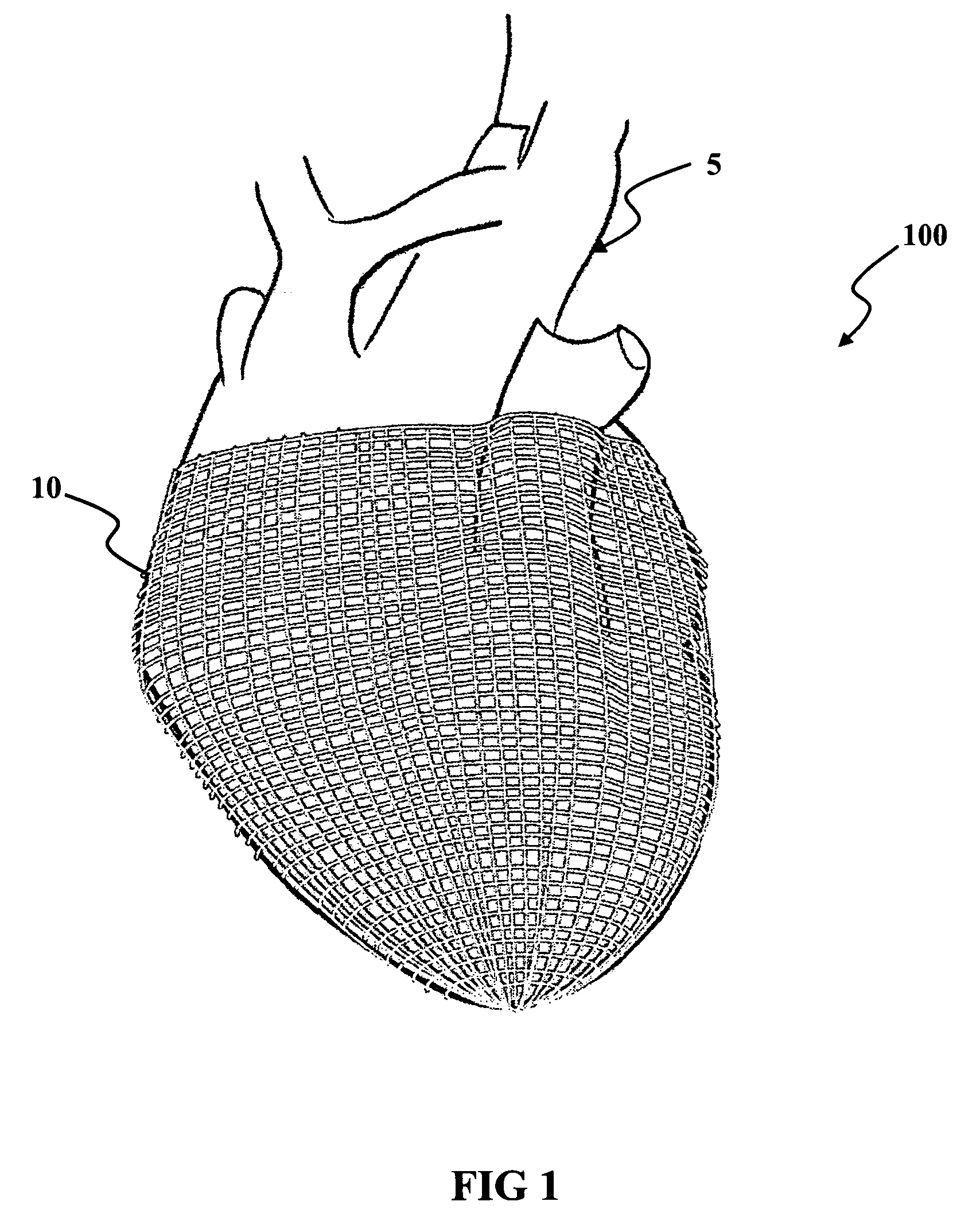
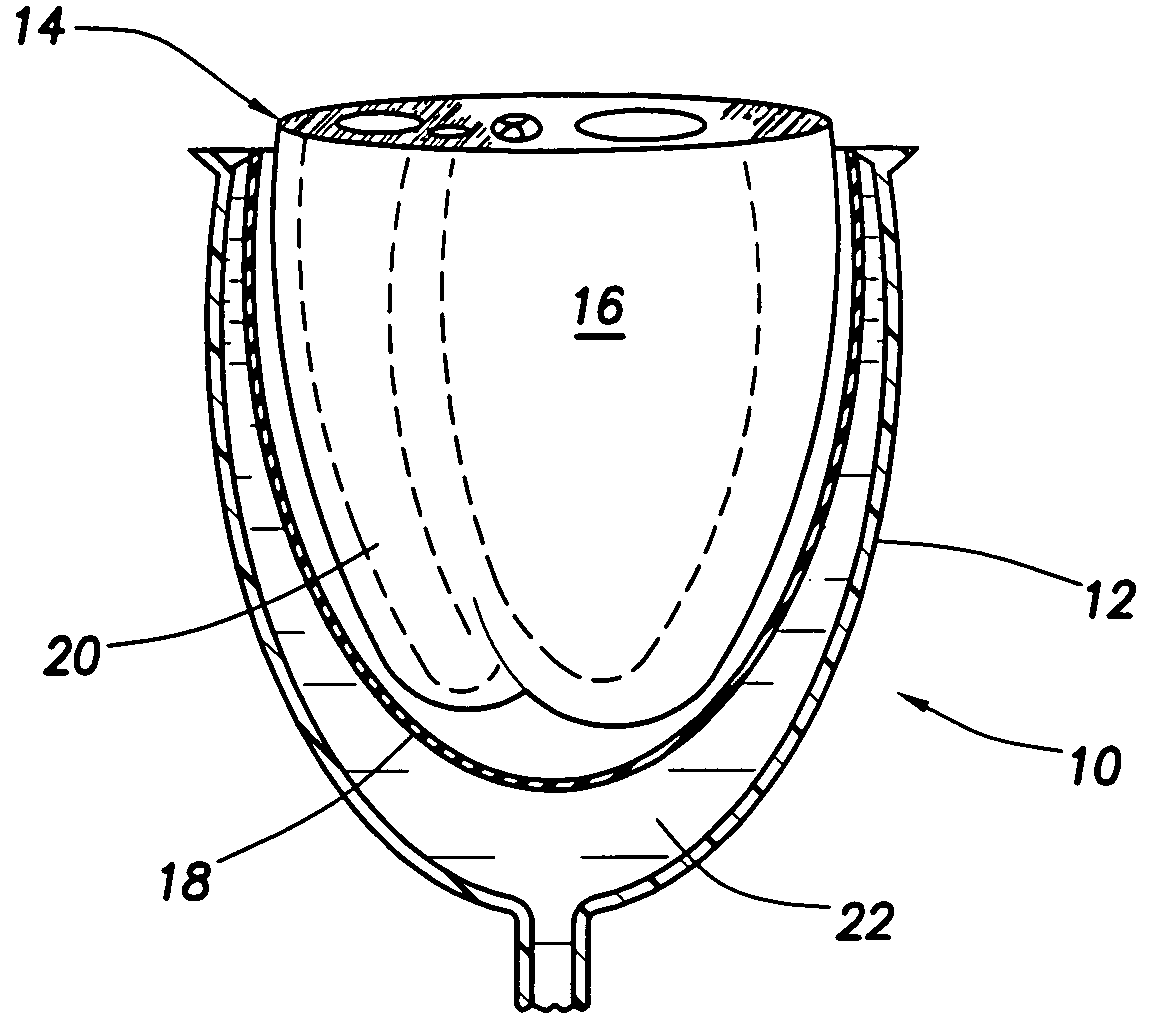
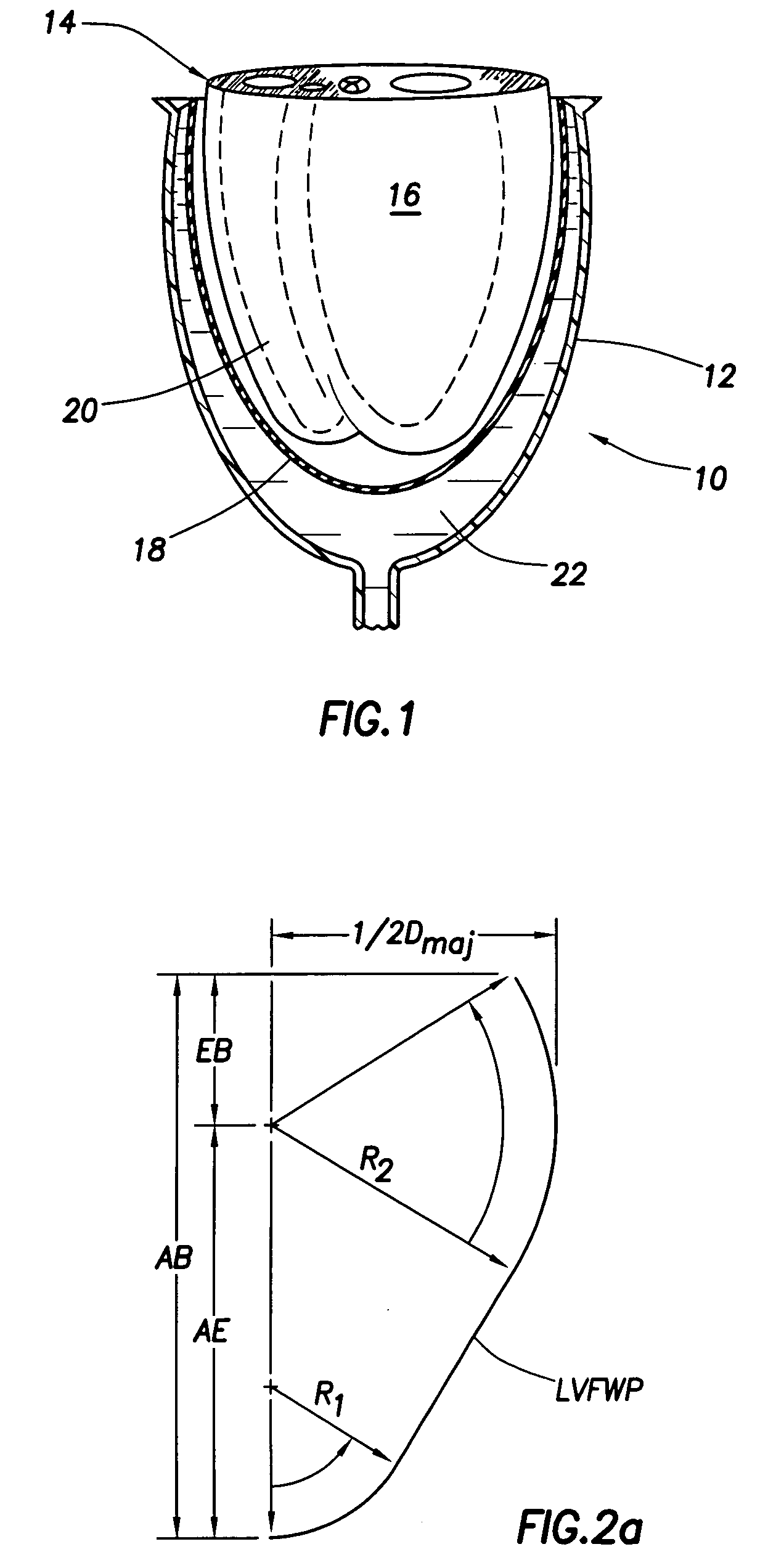
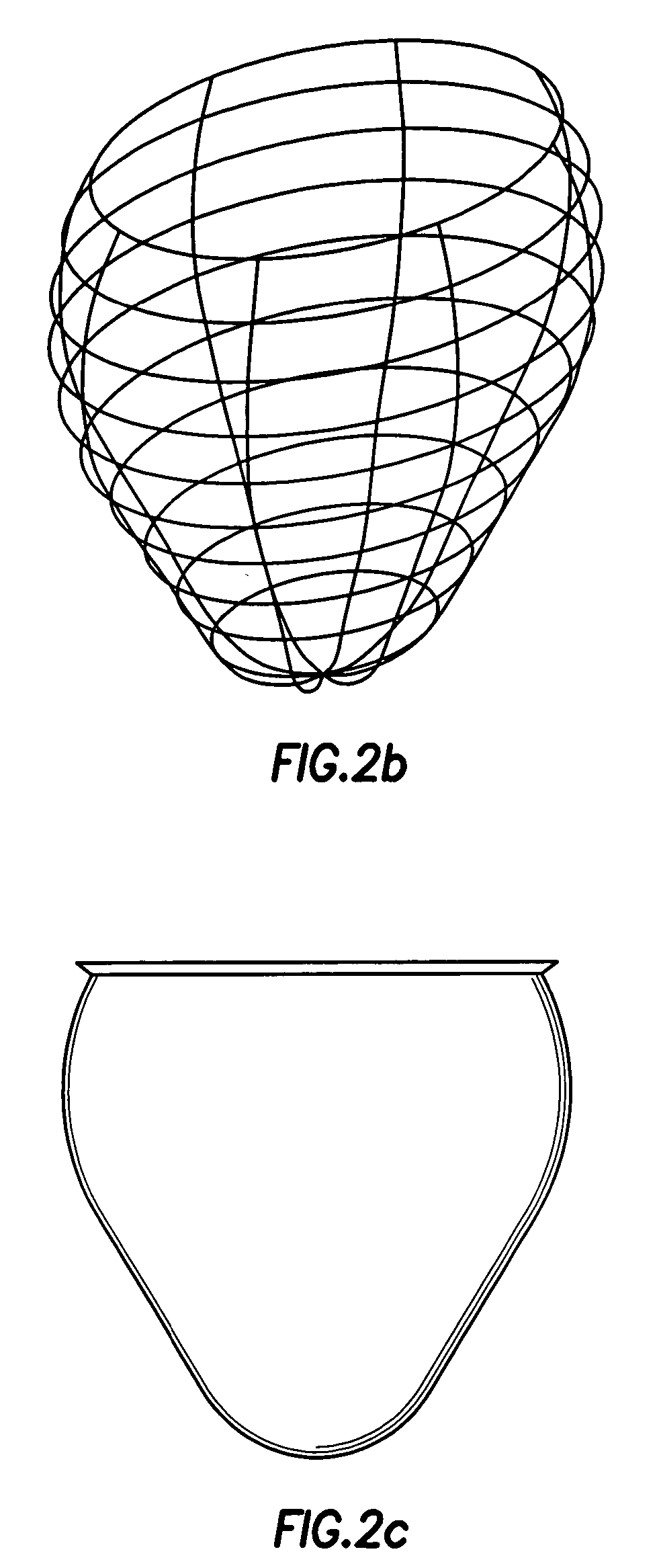
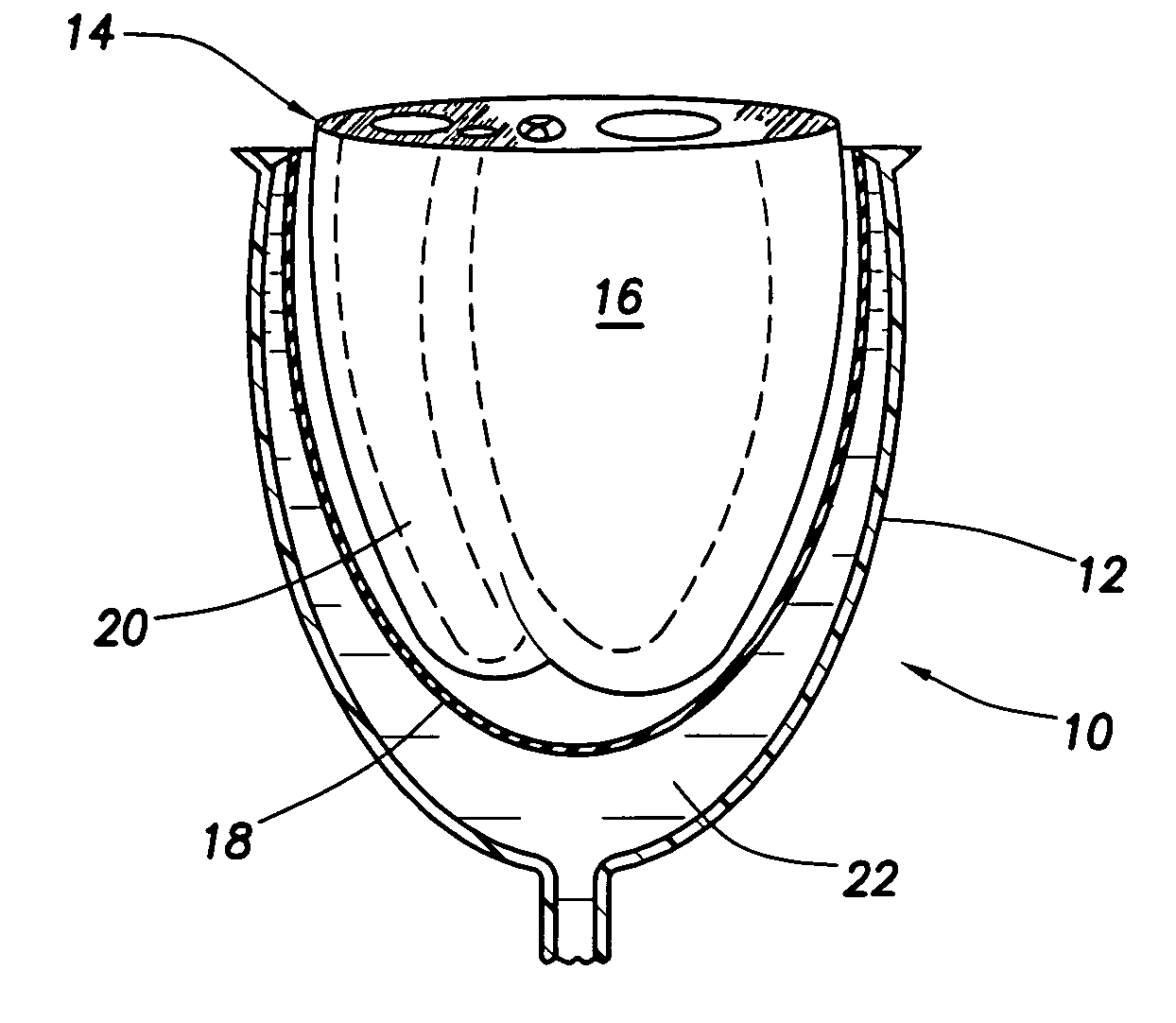
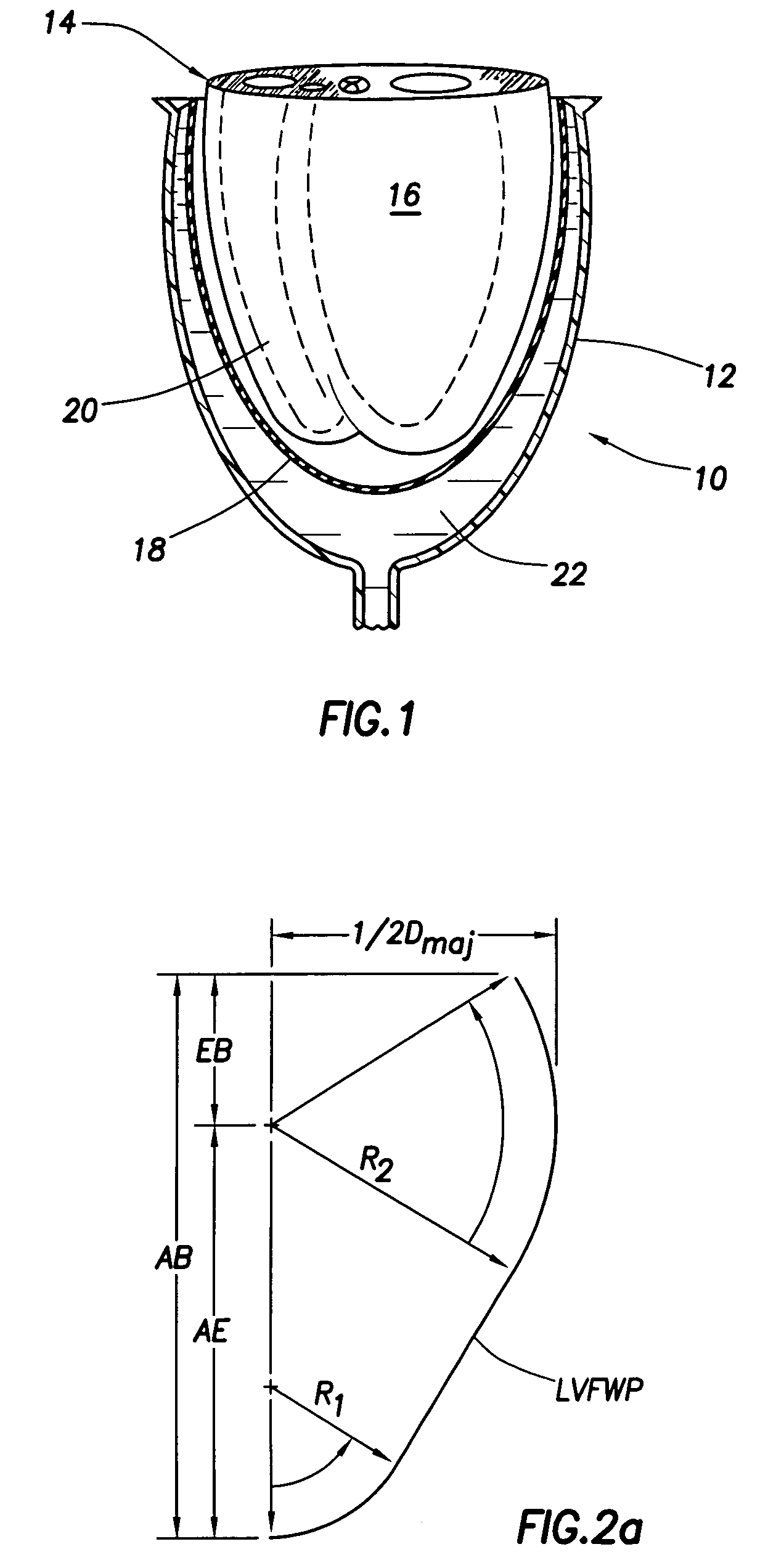
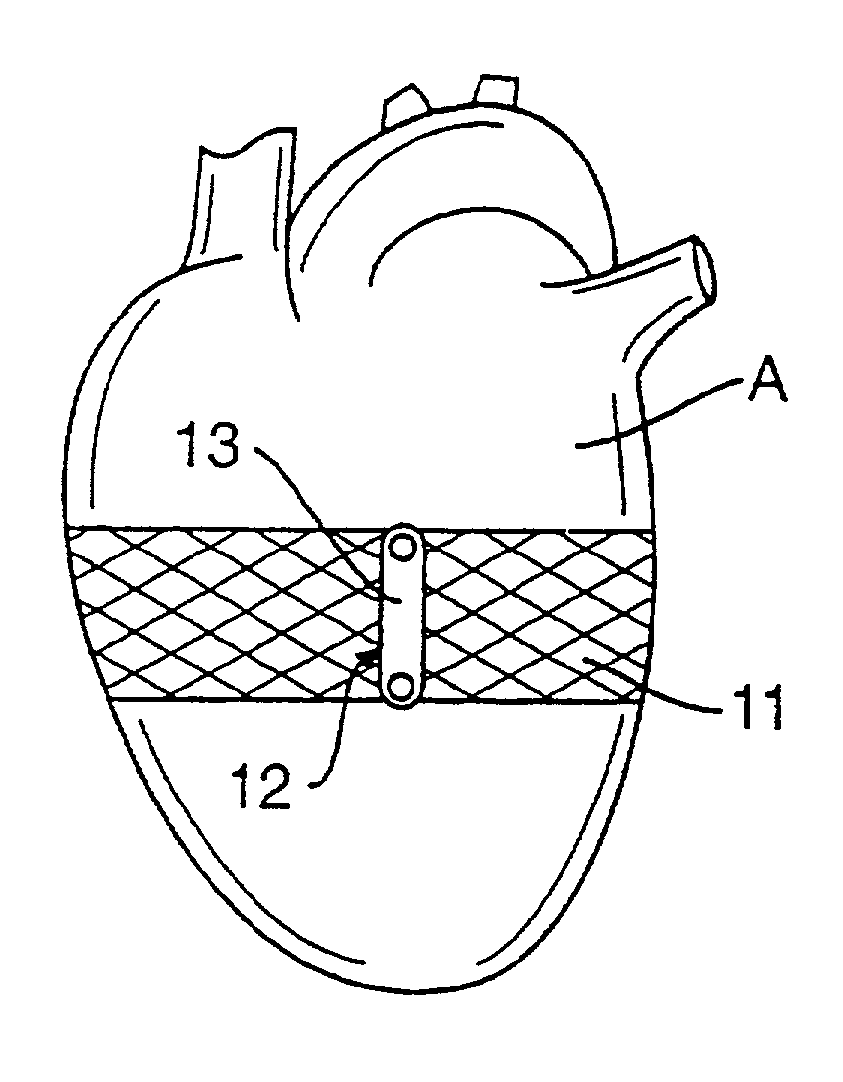
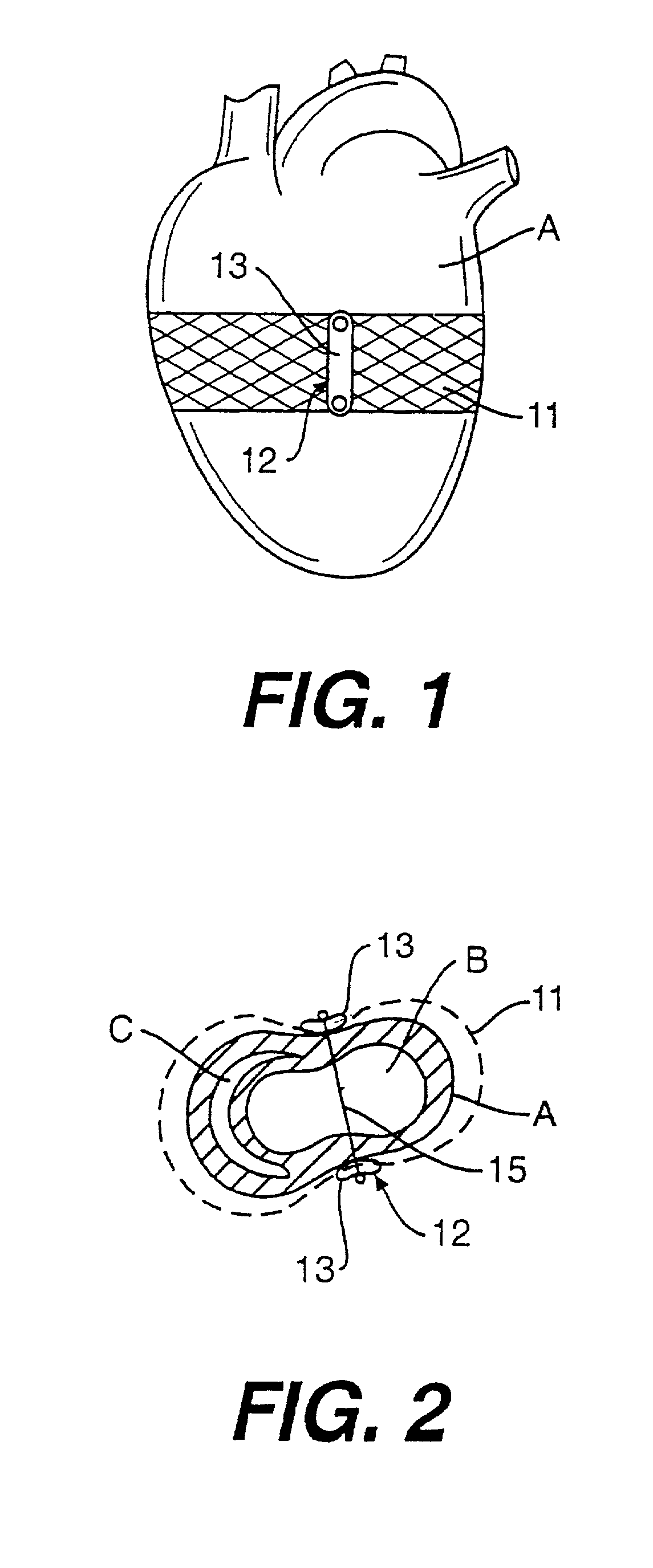
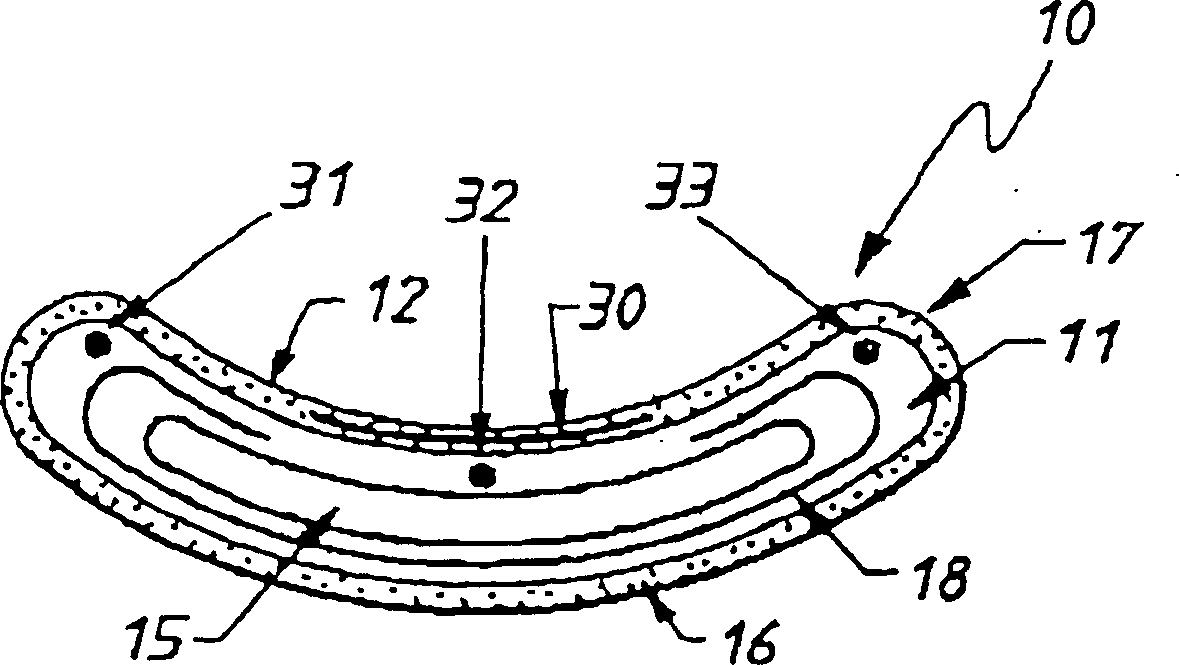
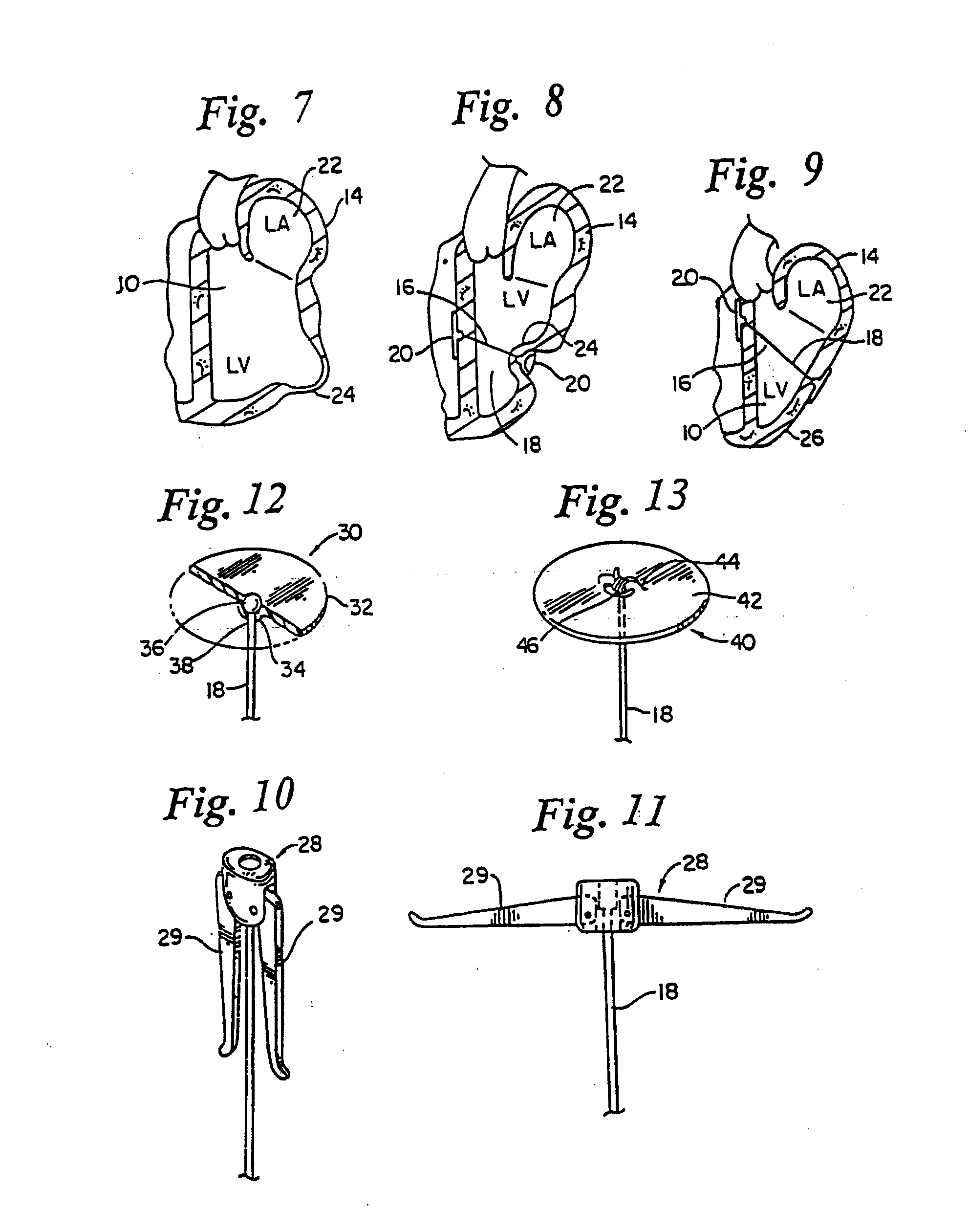
Heart valve prosthesis and method
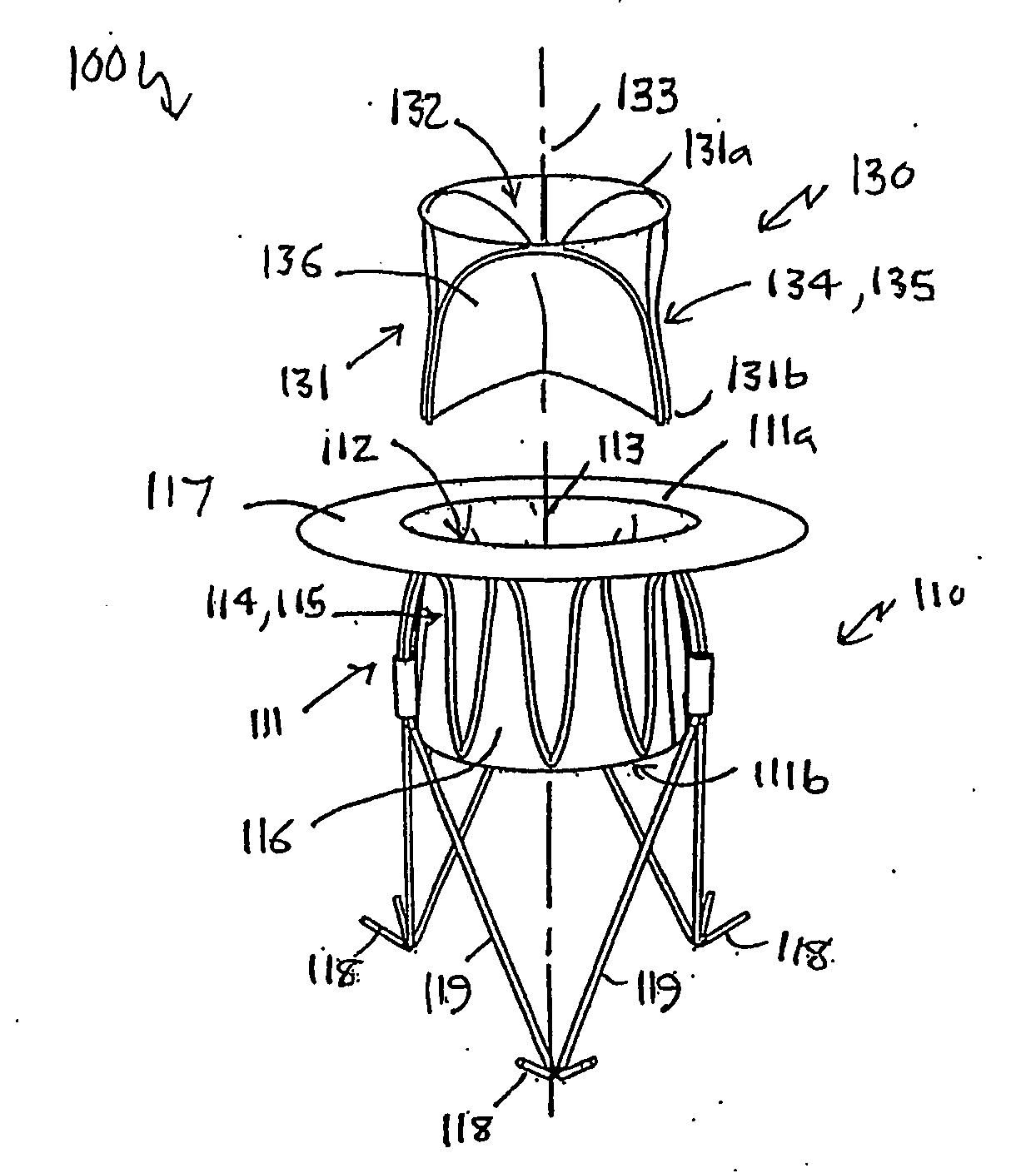
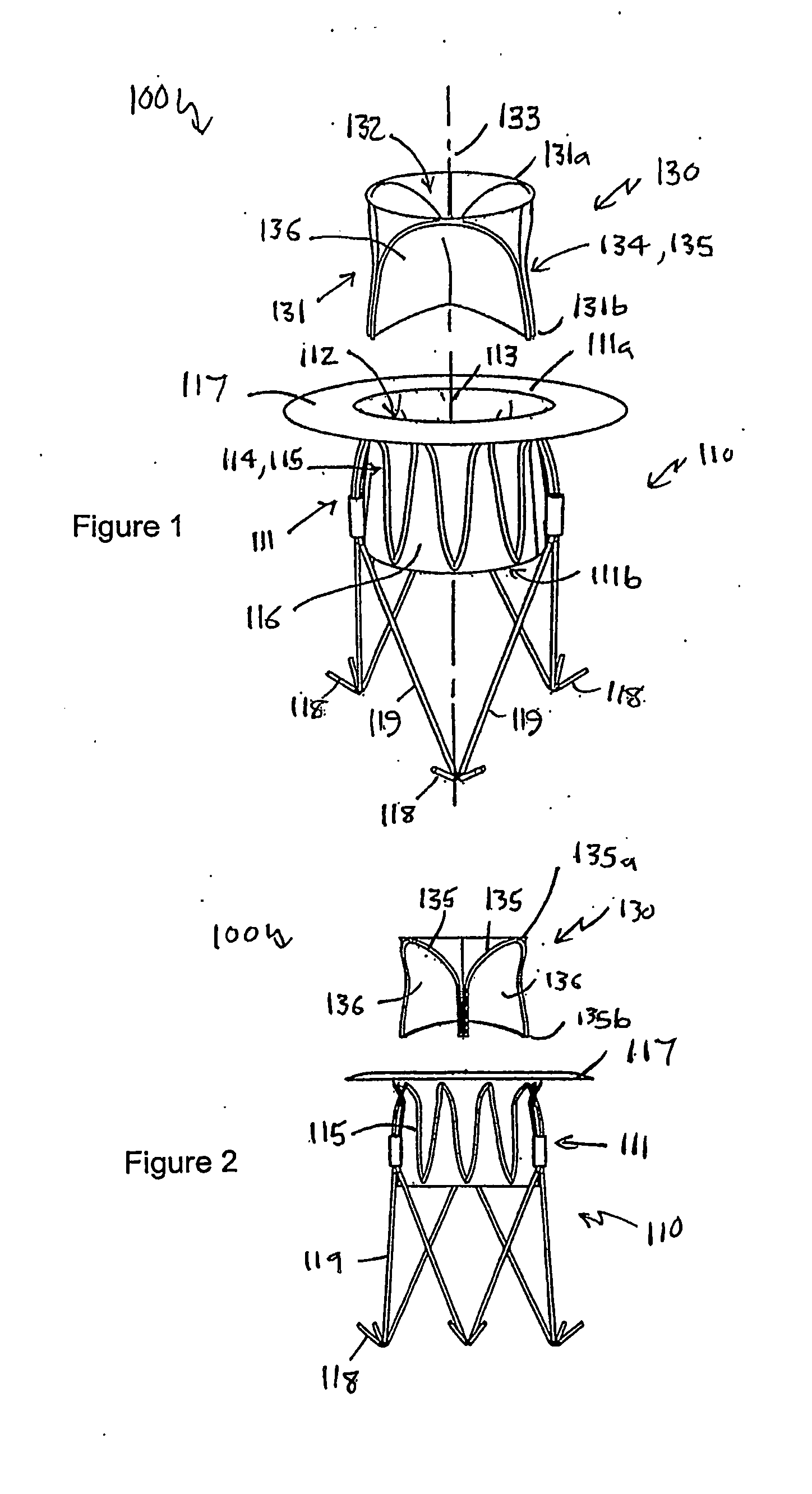
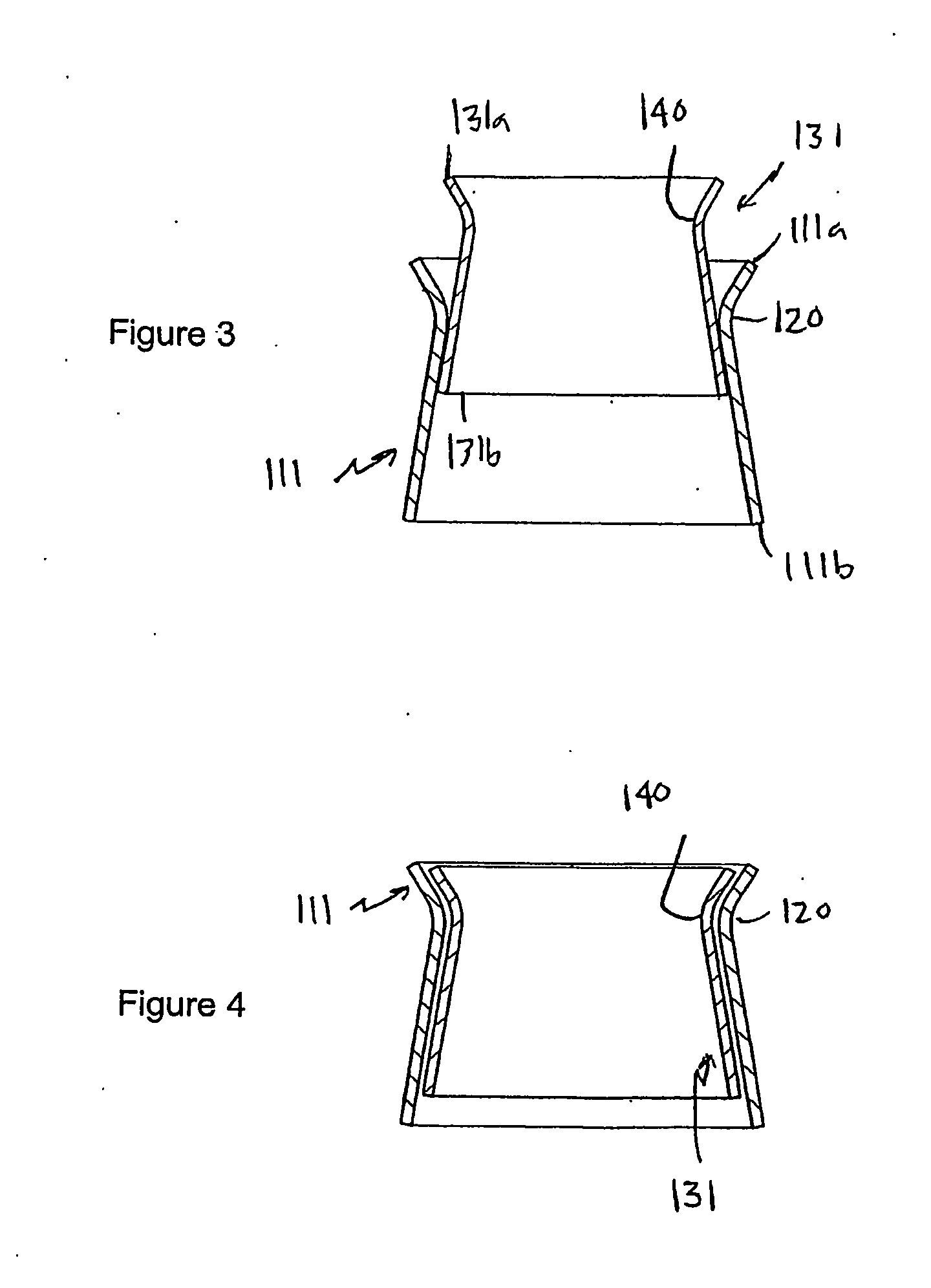
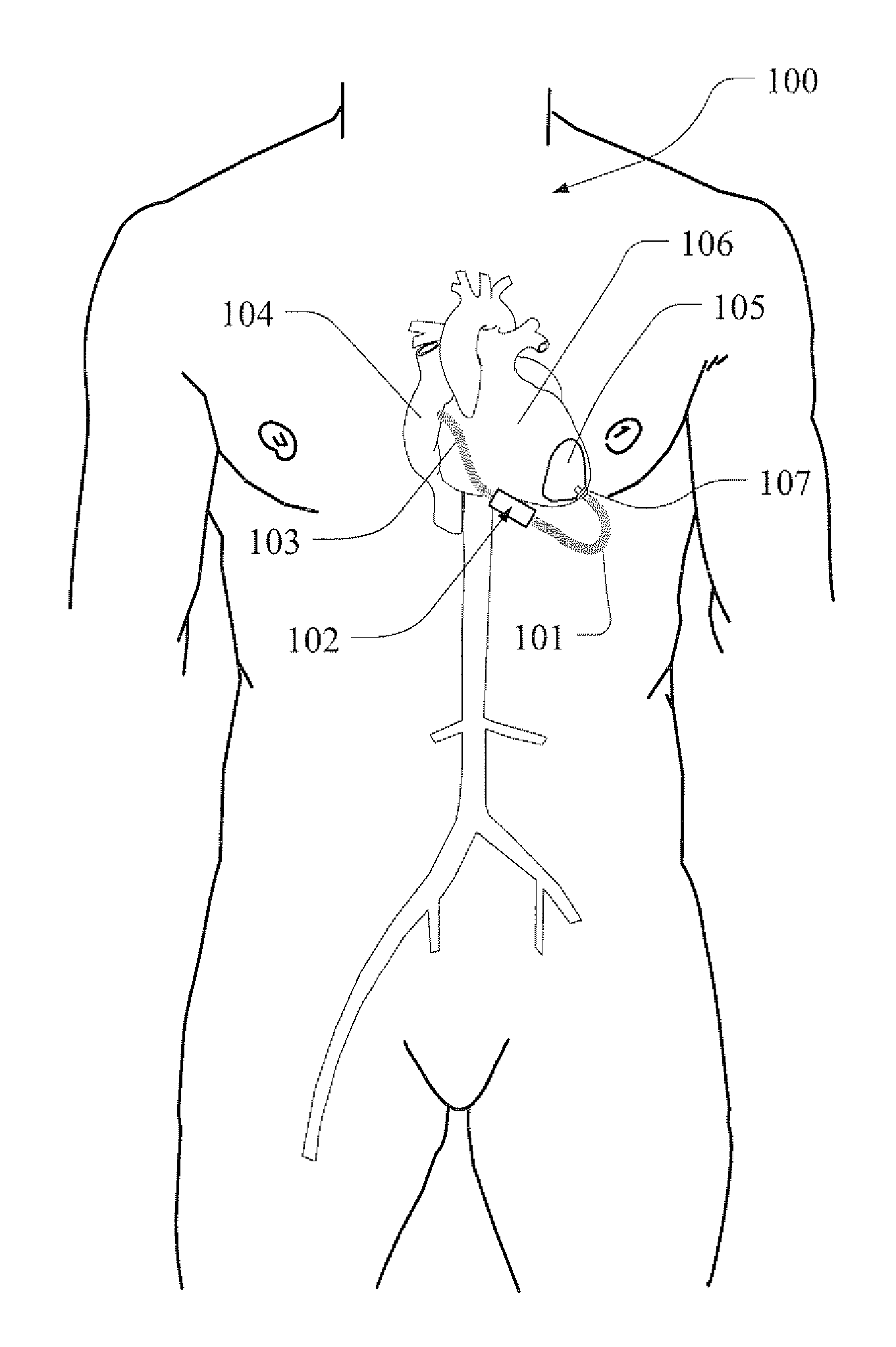
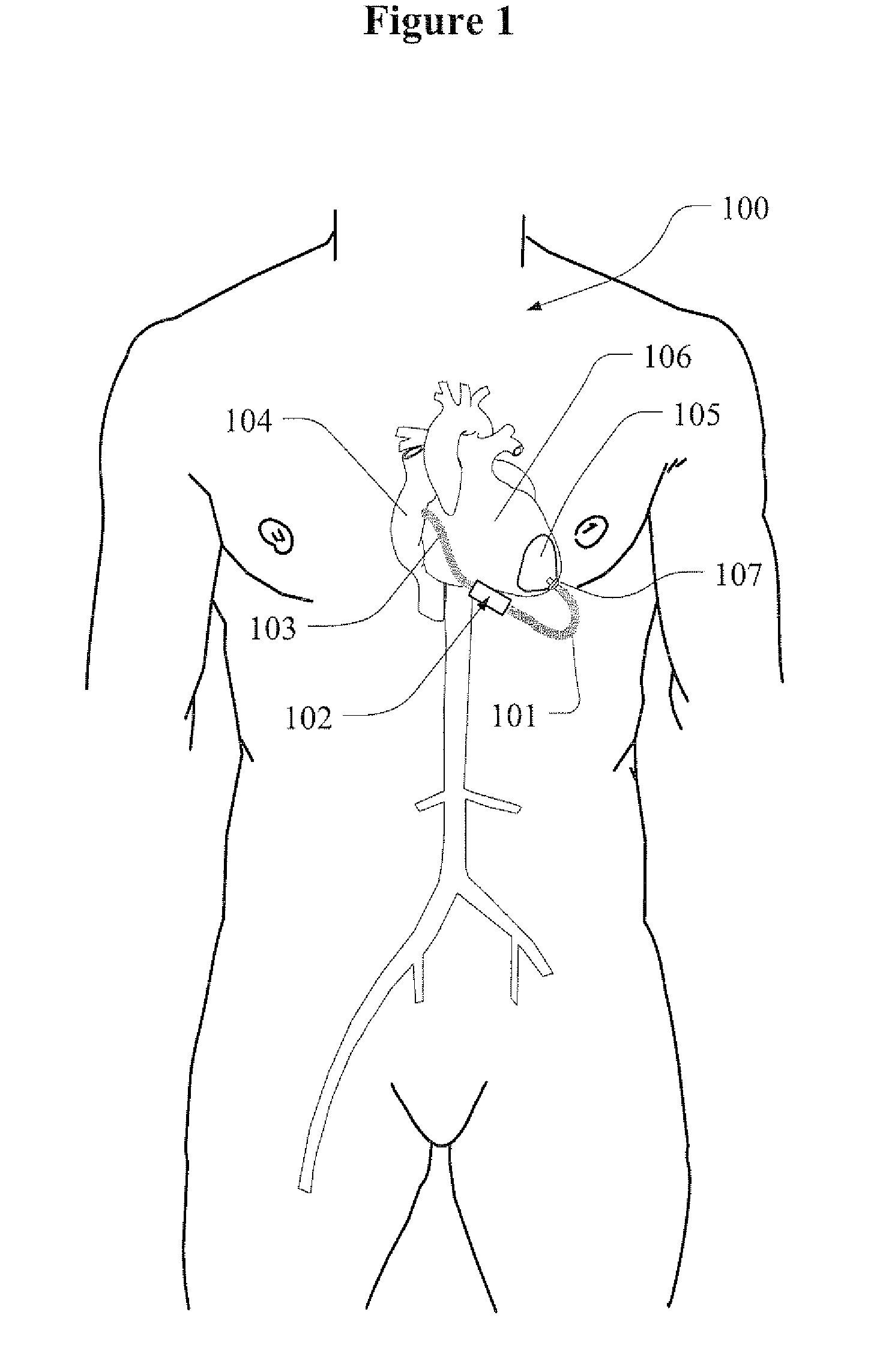
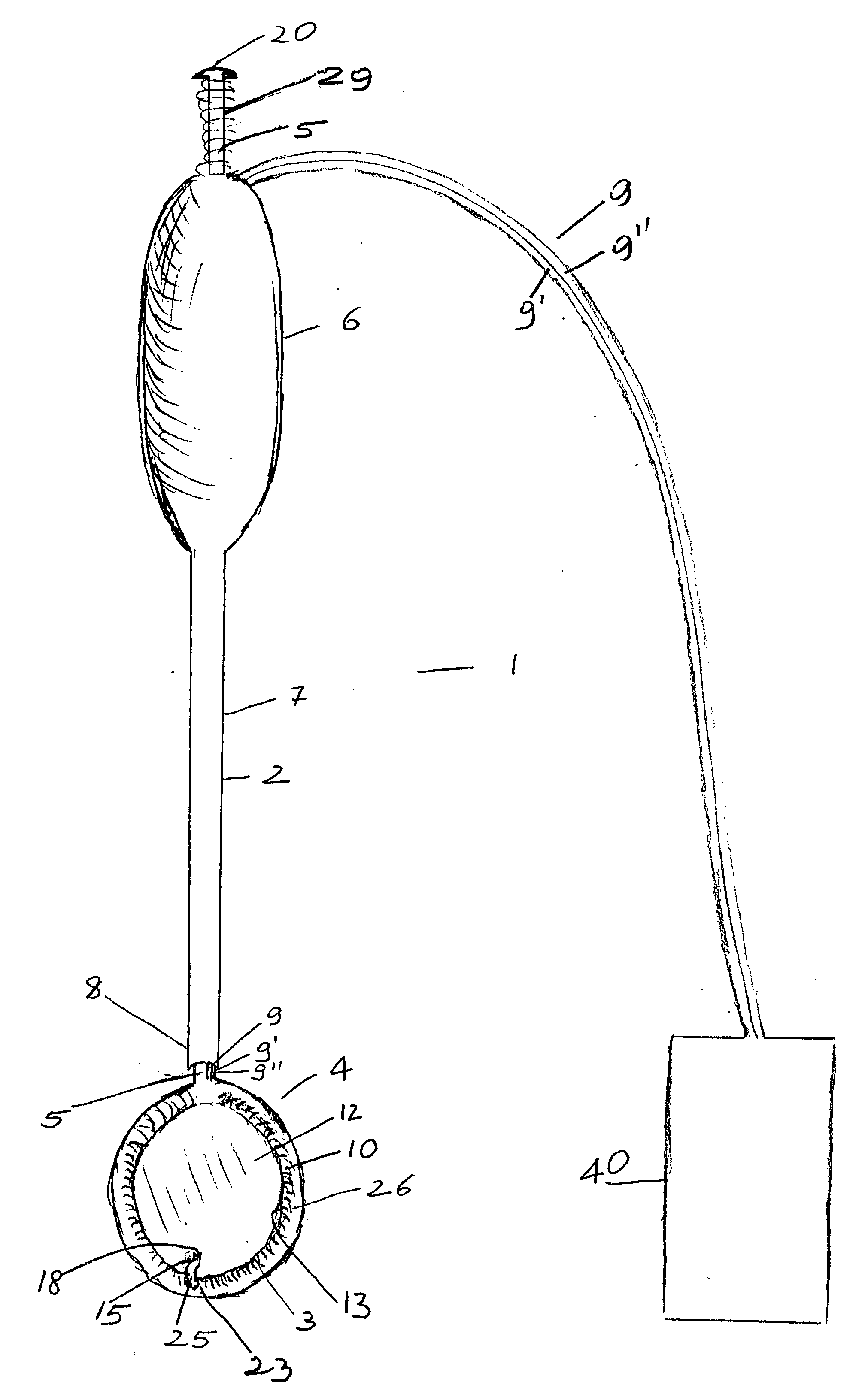
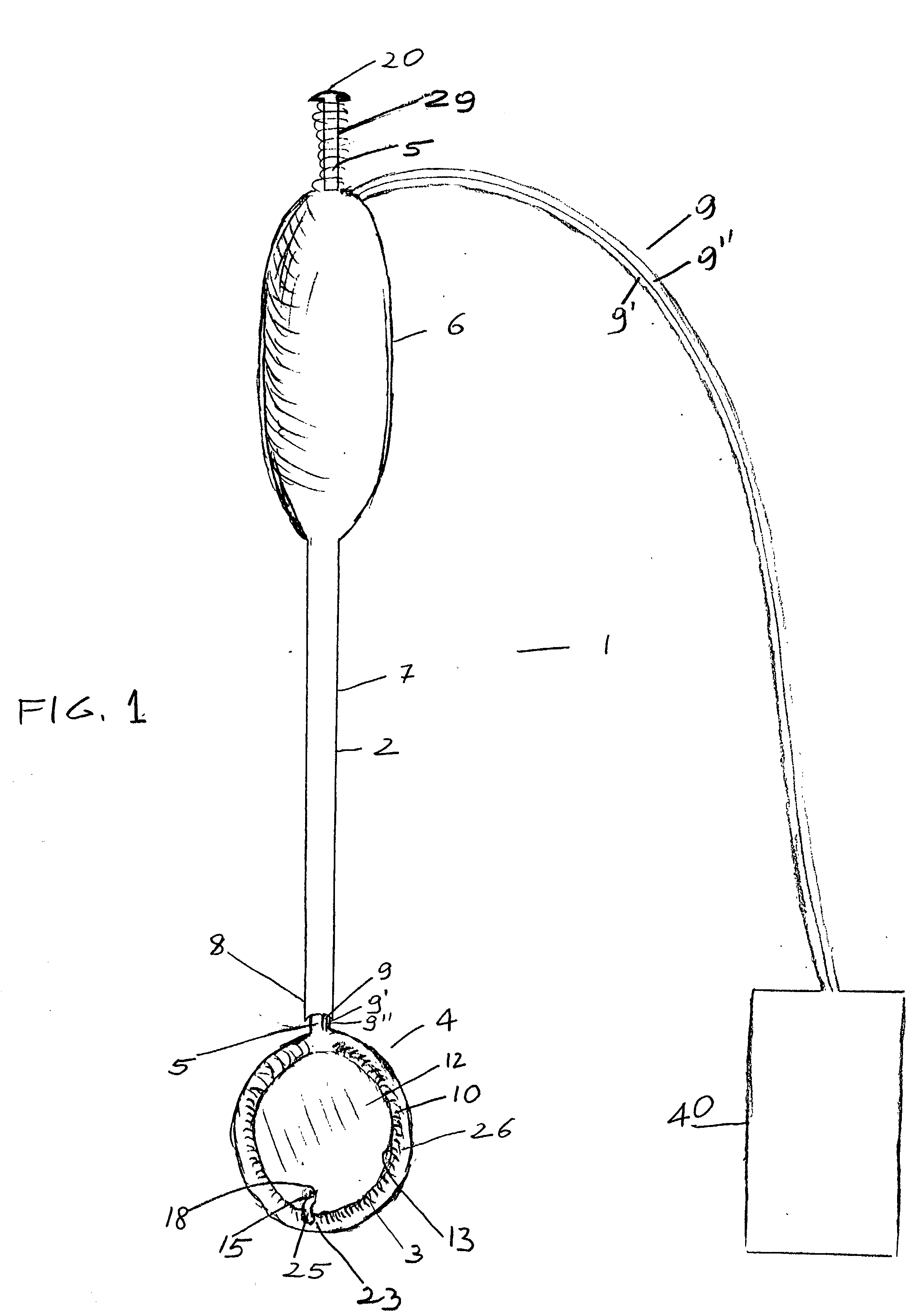
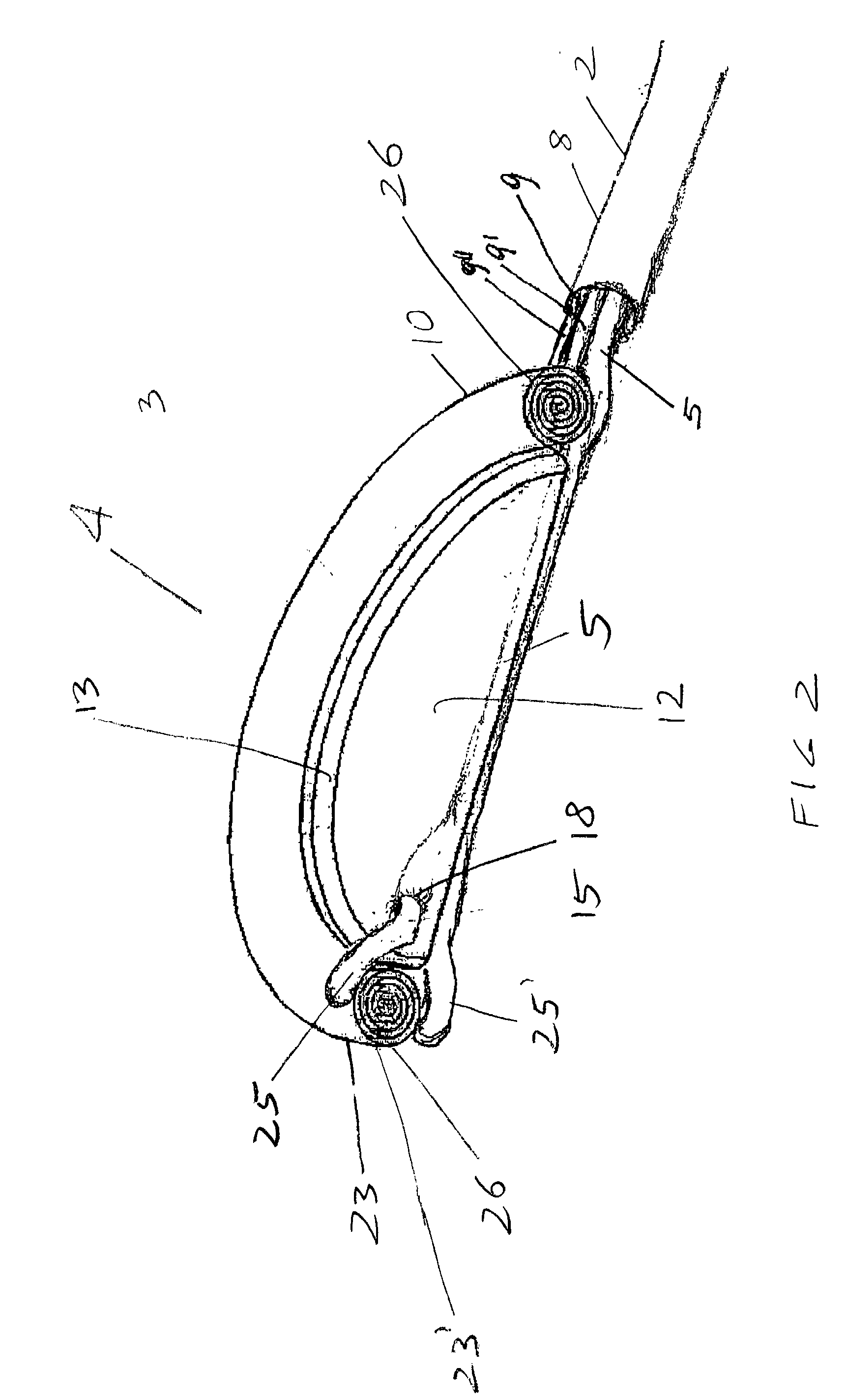
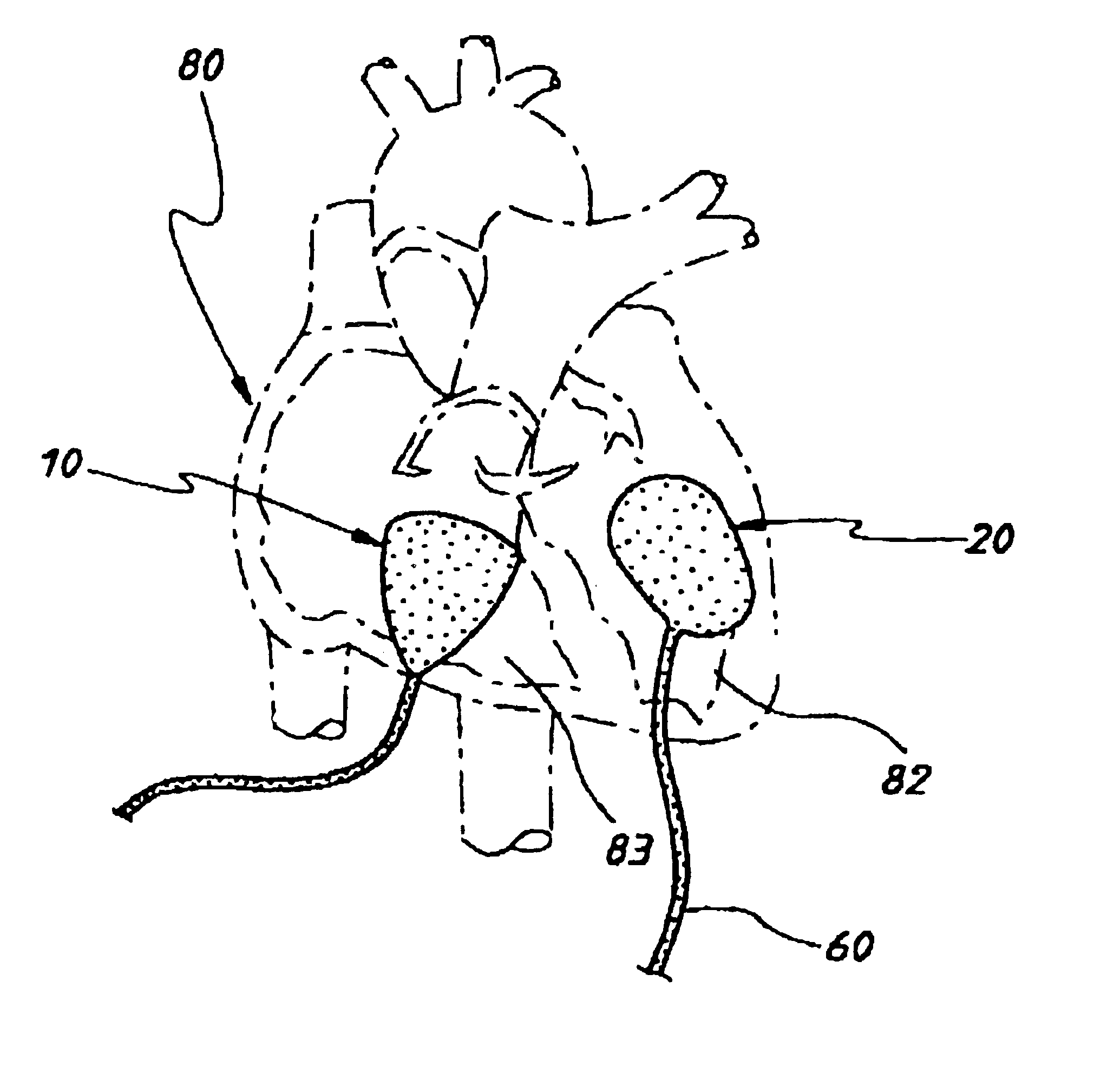
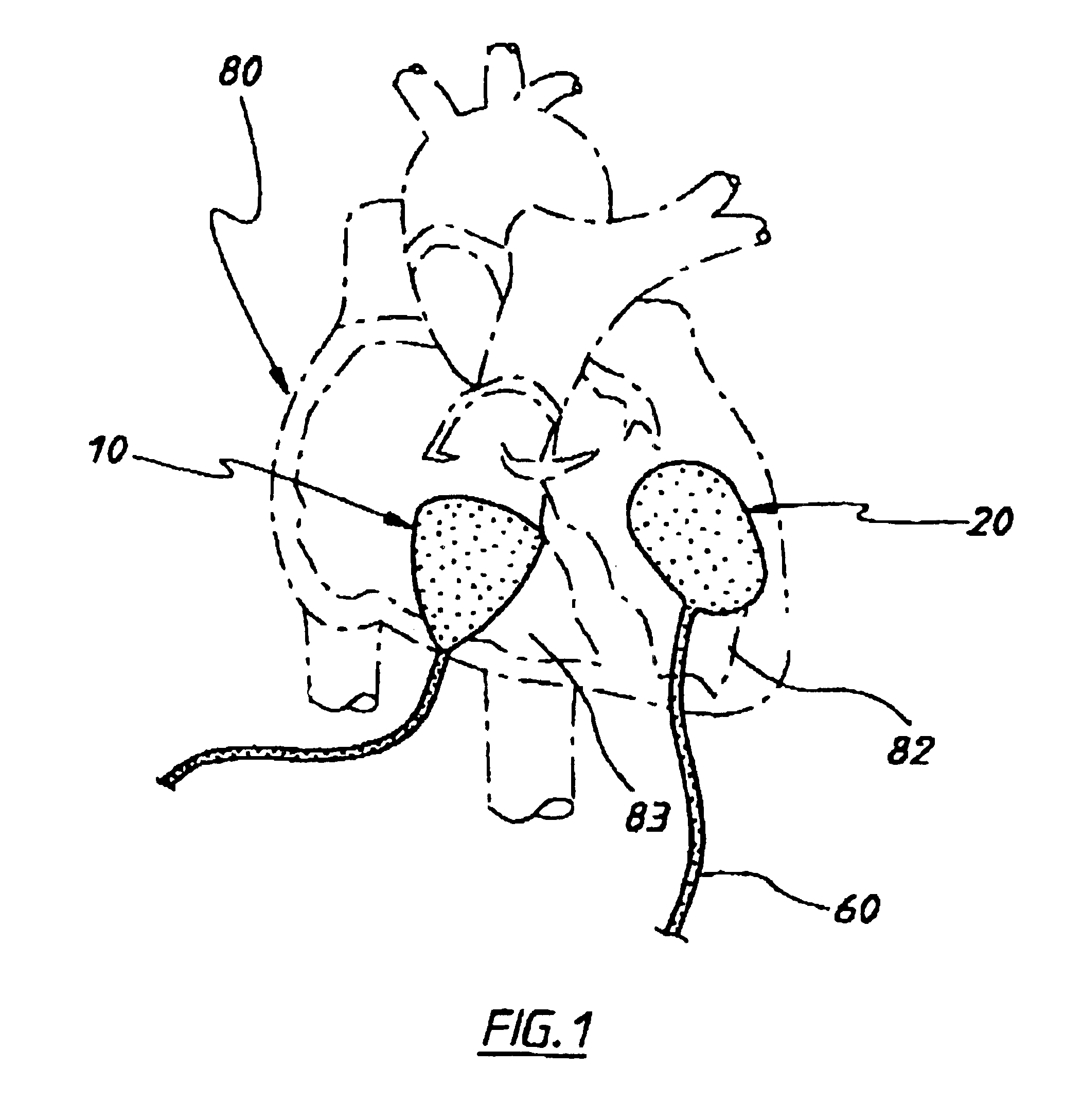
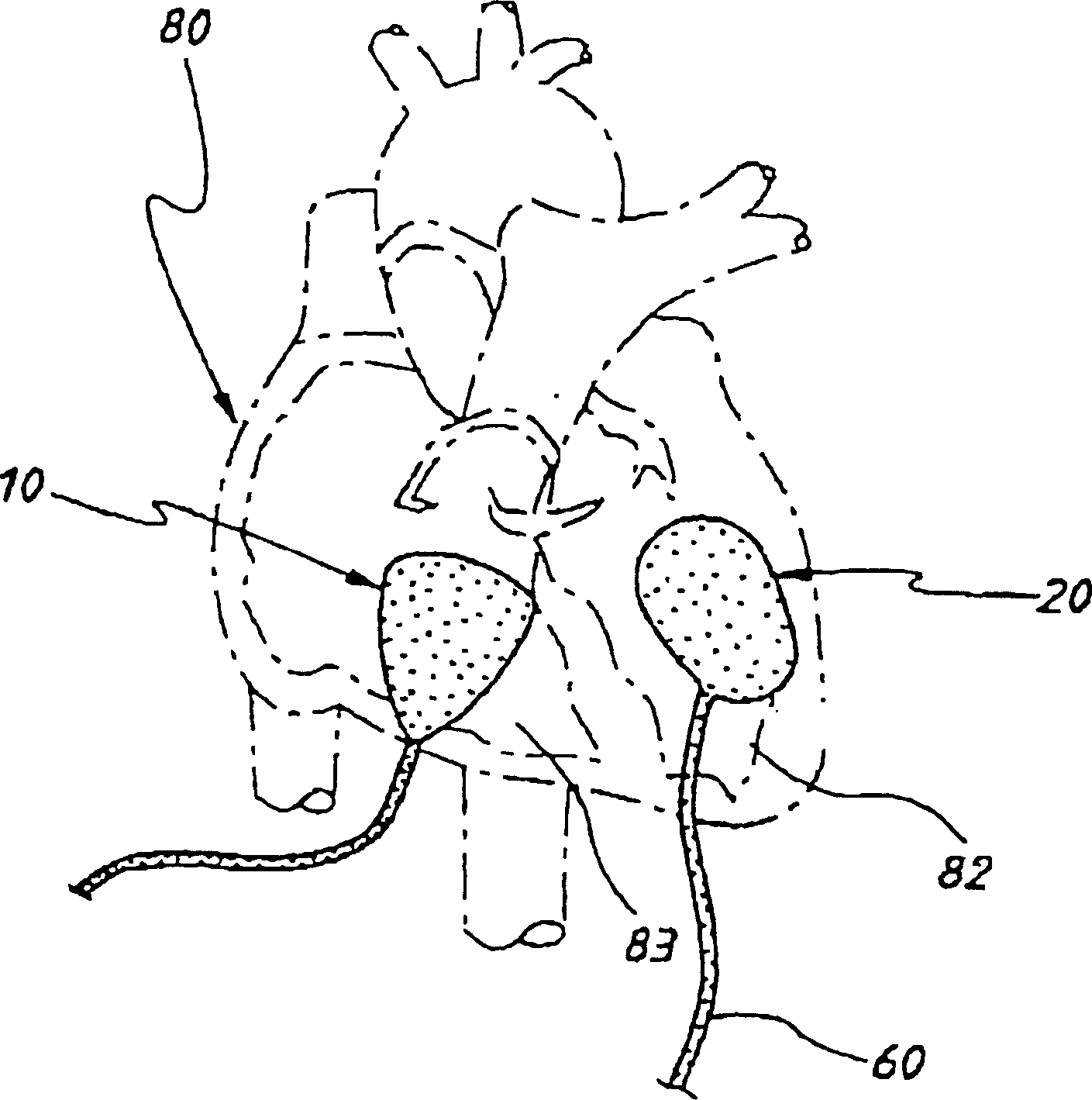
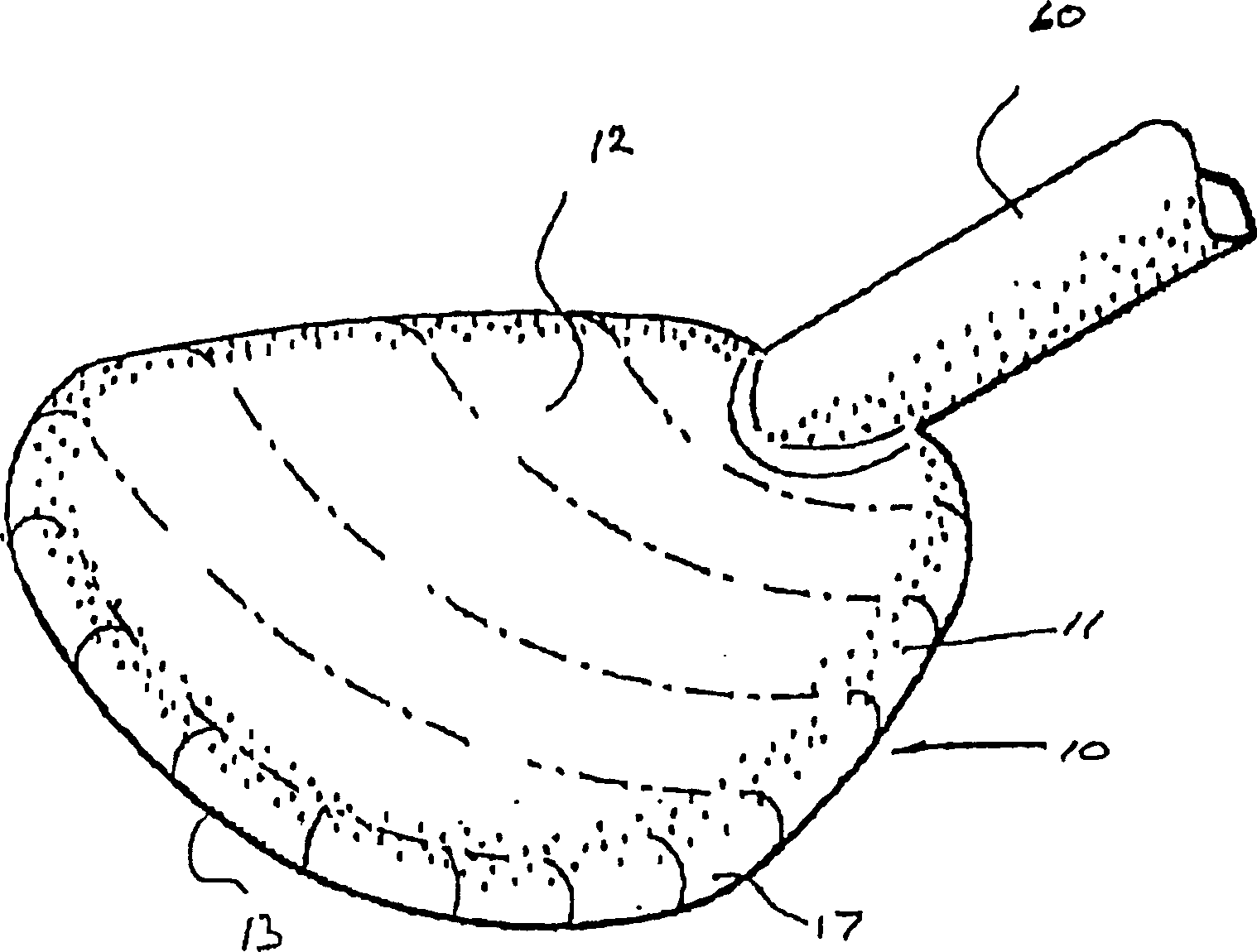
A heart valve prosthesis (100) comprises a housing component (110) and a valve component (130). The housing component (110) comprises a housing body (111) having a housing passage (112) extending therethrough. The housing body (111) is configured to be located in, or adjacent to and communicating with, a native valve orifice (16) of a heart (10) and to engage structure of the heart (10) to fix the housing body (111) in relation to the valve orifice (161). The housing component (111) is collapsible for delivery via catheter (2). The valve component (130) comprises a valve body (131) having a valve passage (132) extending therethrough. The valve body (131) is configured to be fixed within the housing passage (112) with the valve passage (132) extending along the housing passage (112). One or more flexible valve elements (131) is / are secured to the valve body and extend across the valve passage (132) for blocking blood flow in a first direction through the valve passage (132) whilst allowing blood flow in the opposing direction. The valve component (130) is collapsible for delivery via catheter (2) separate to the housing component (110). An associated method of replacing a failed or failing heart valve utilising the heart valve prosthesis (100) is also disclosed.
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS
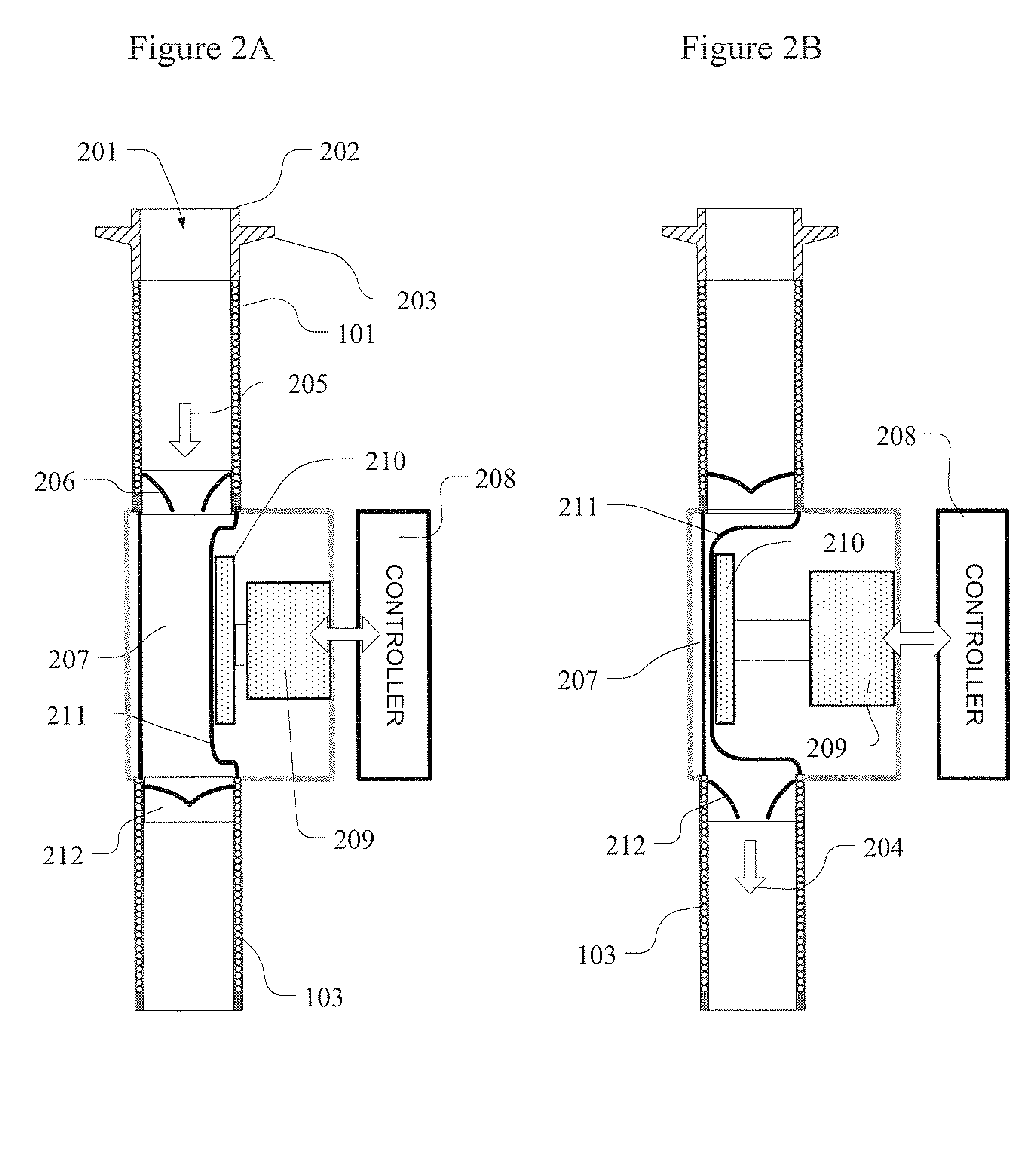
Method and apparatus to unload a failing heart
InactiveUS20070208210A1Lowering LVEDPPrevent of lung congestionElectrocardiographyHeart valvesValved conduitMedicine
A method and apparatus for treatment of heart failure by reducing LV diastolic volume and pressure by pumping blood out of the LV during diastole. A pump is synchronized to the heart cycle, connected to the apex of the LV and discharging into the right atrium of the heart. A left ventricle to aorta one-way valved conduit with added compliance decreases blood pressure in the aorta and the resistance to the ejection of blood by the heart decreases the energy requirements of the heart.
Owner:G&L CONSULTING
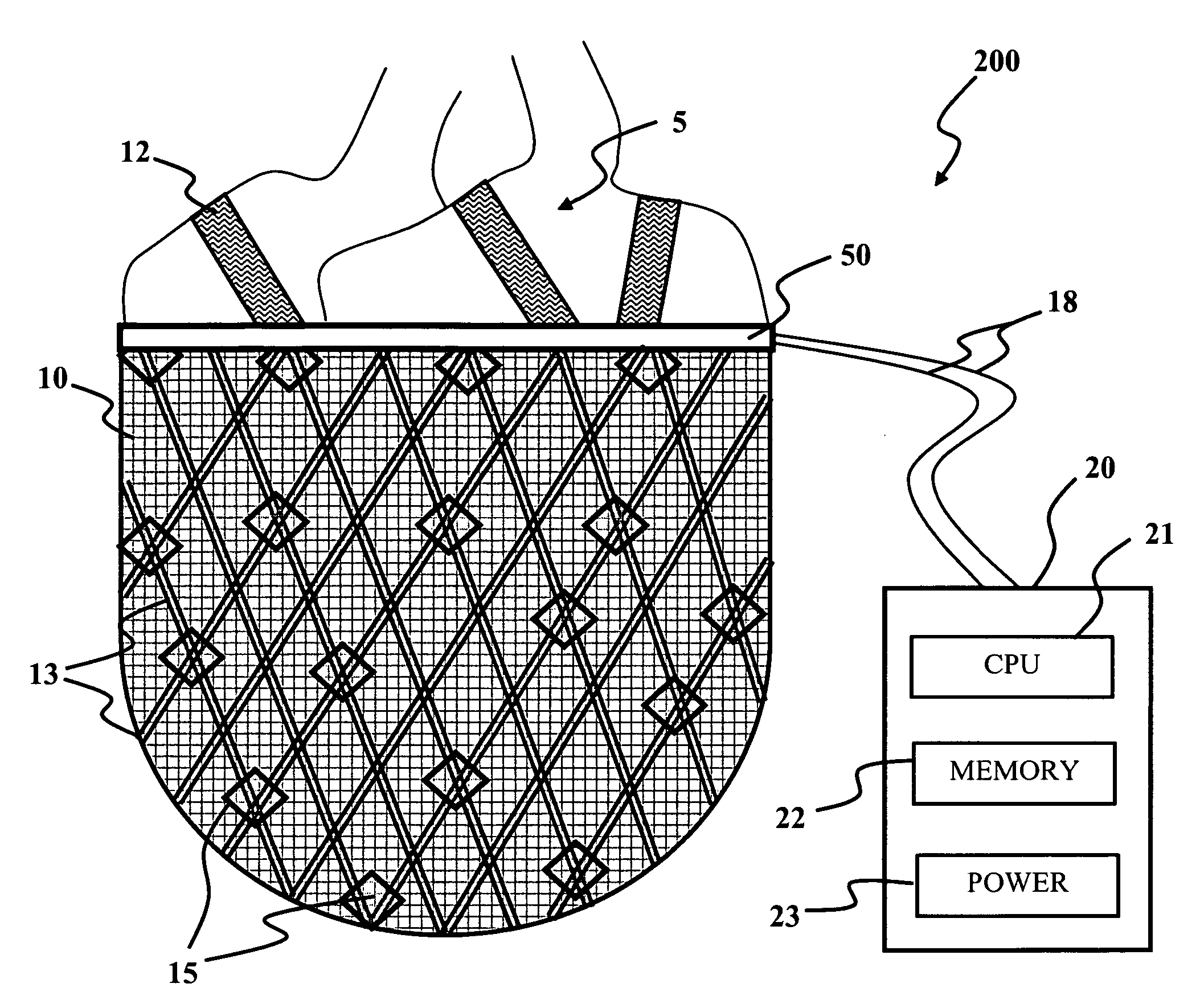
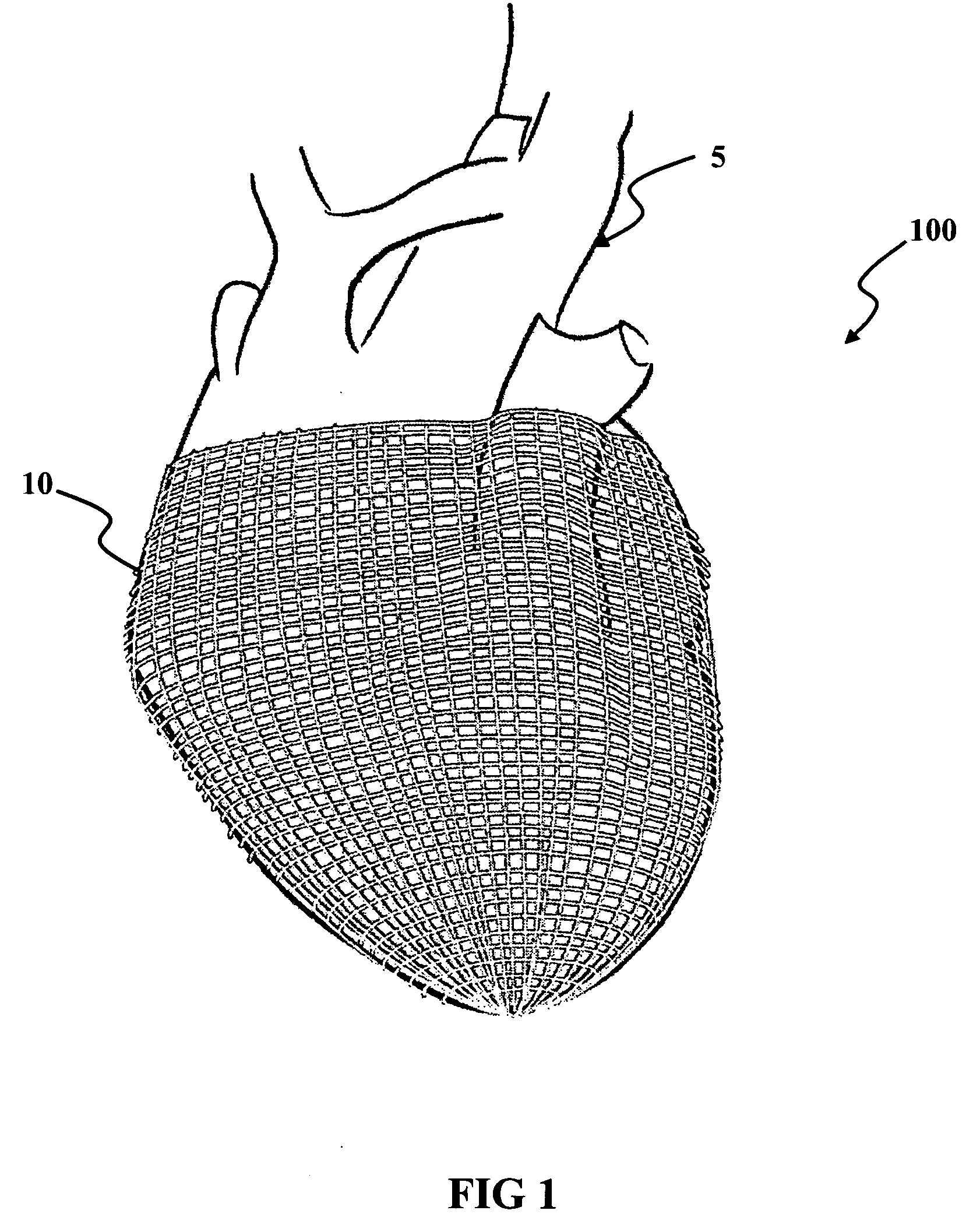
Electromechanical machine-based artificial muscles, bio-valves and related devices
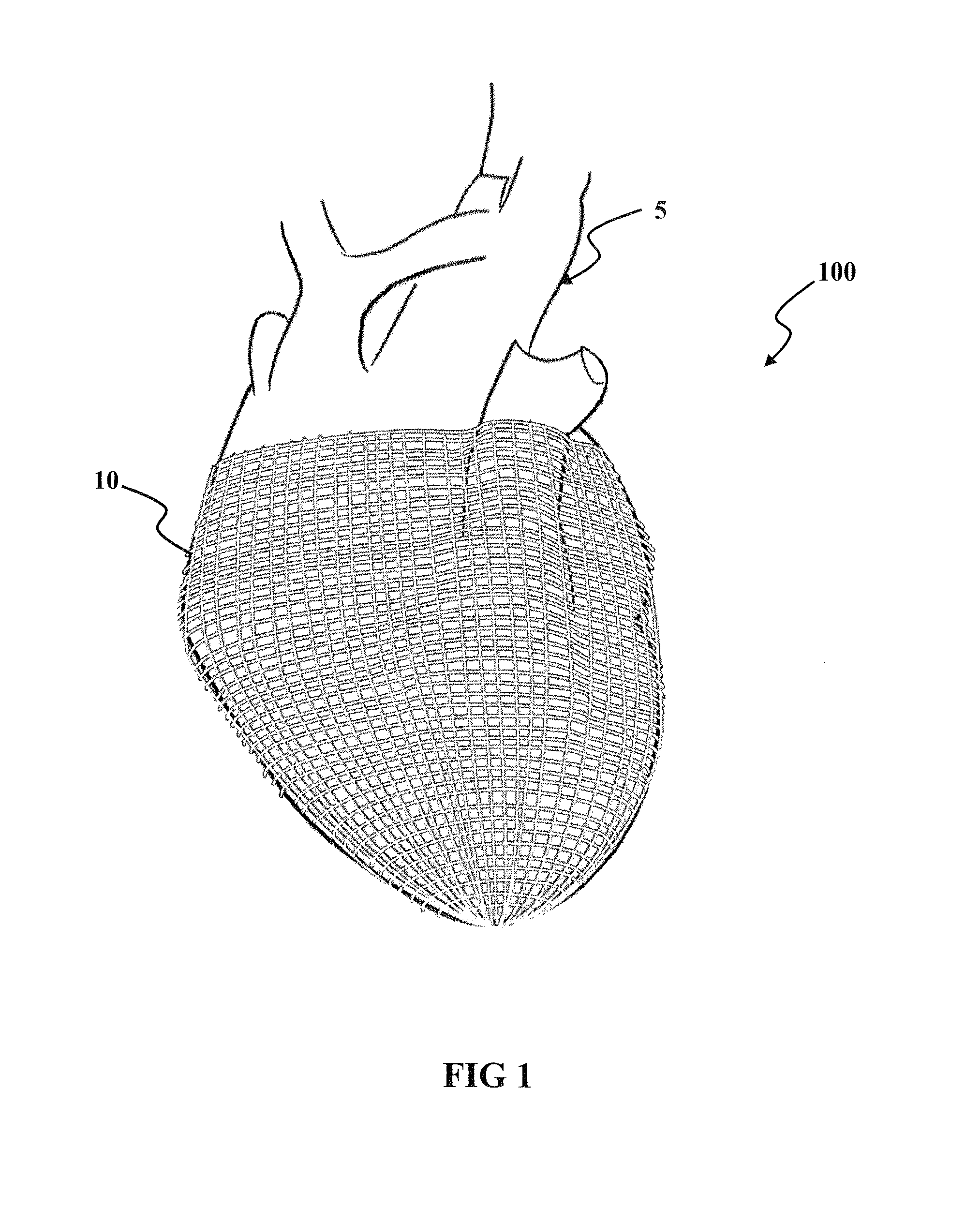
InactiveUS20060041183A1Easy to understandAnti-incontinence devicesHeart valvesSphincterFailing heart
A biological function assist apparatus composed an electromechanically-based system wrapped in protective coating and controlled by a controller, which also provides power to the electromechanically-based system. The electromechanically-based system can be formed as a mesh using MEMS or a larger electromechanically grid and wrapped around a failing heart, or the electromechanical system can be formed in a circle forming an artificial valve (e.g., sphincter). The electromechanically-based system can operate as a bone-muscle interface, thereby functioning in place of tendons.
Owner:ORSEN
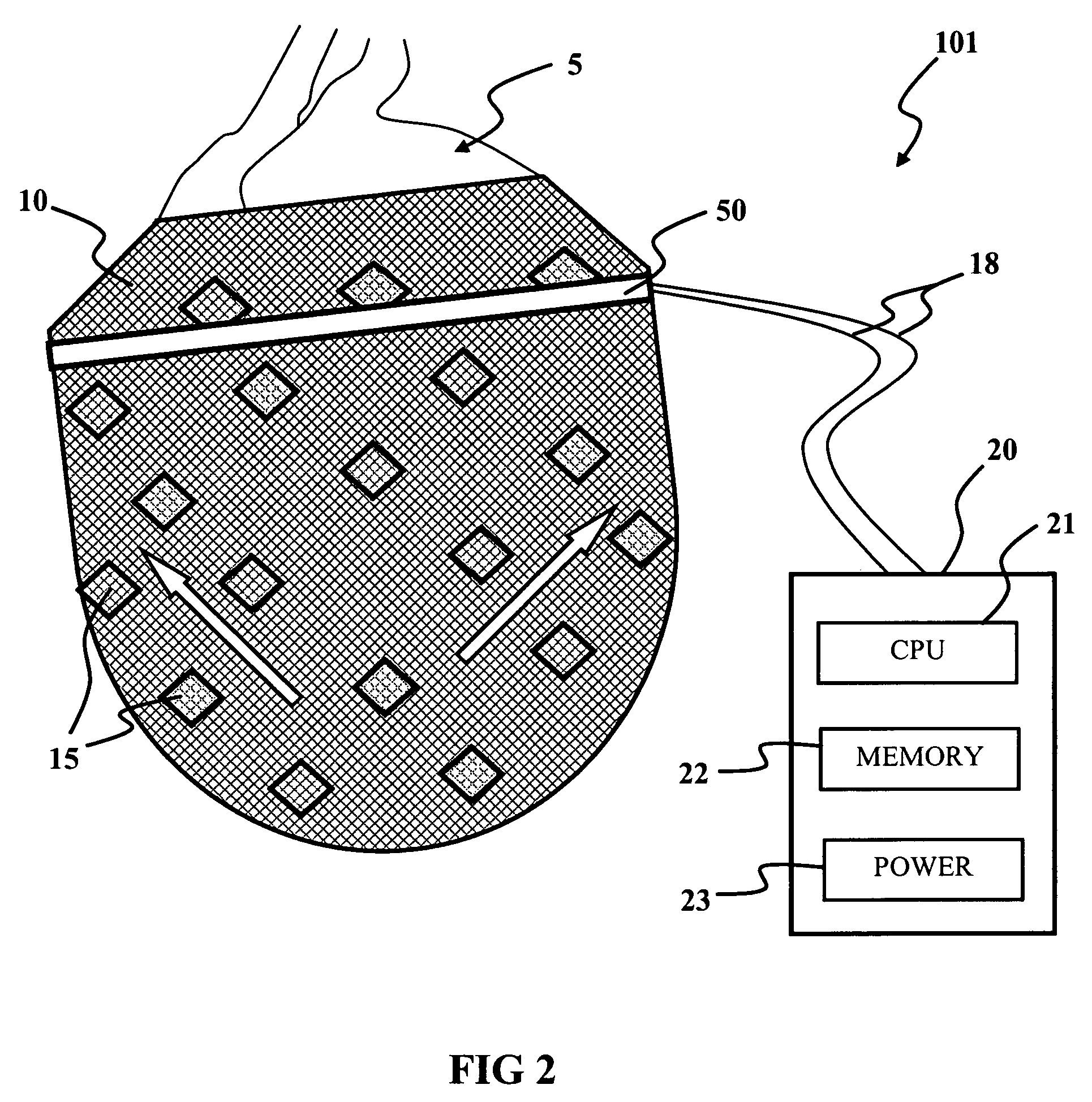
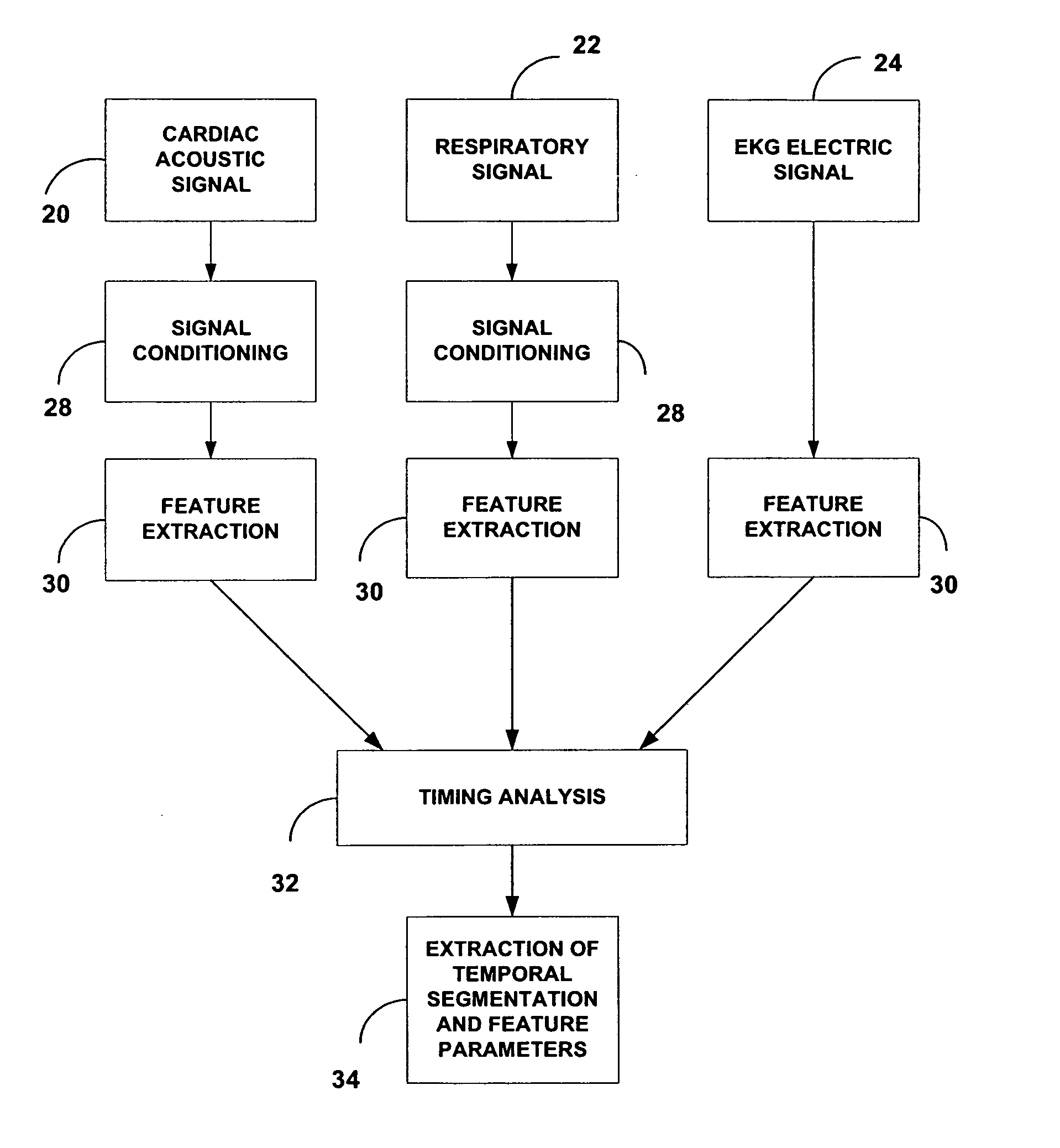
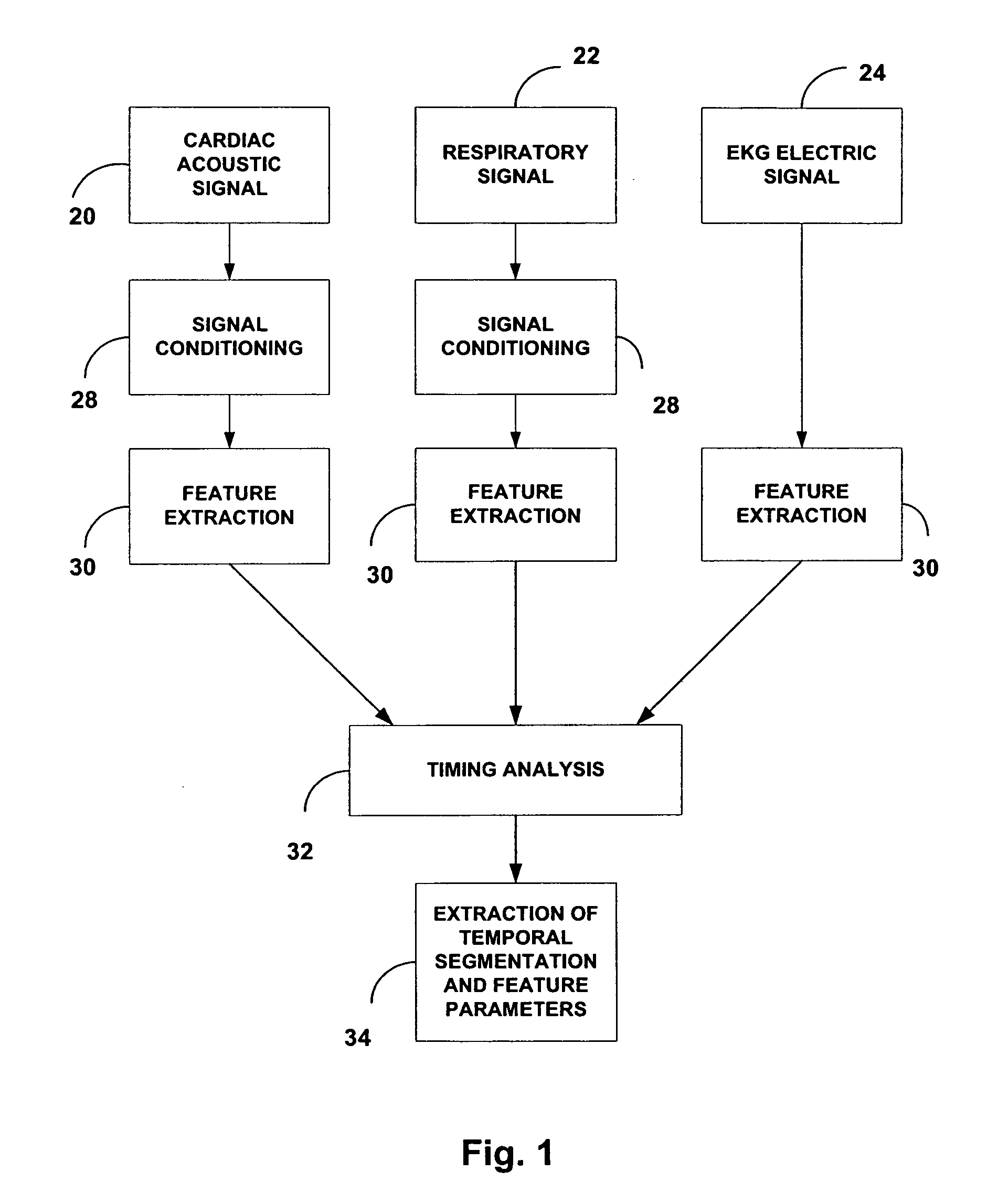
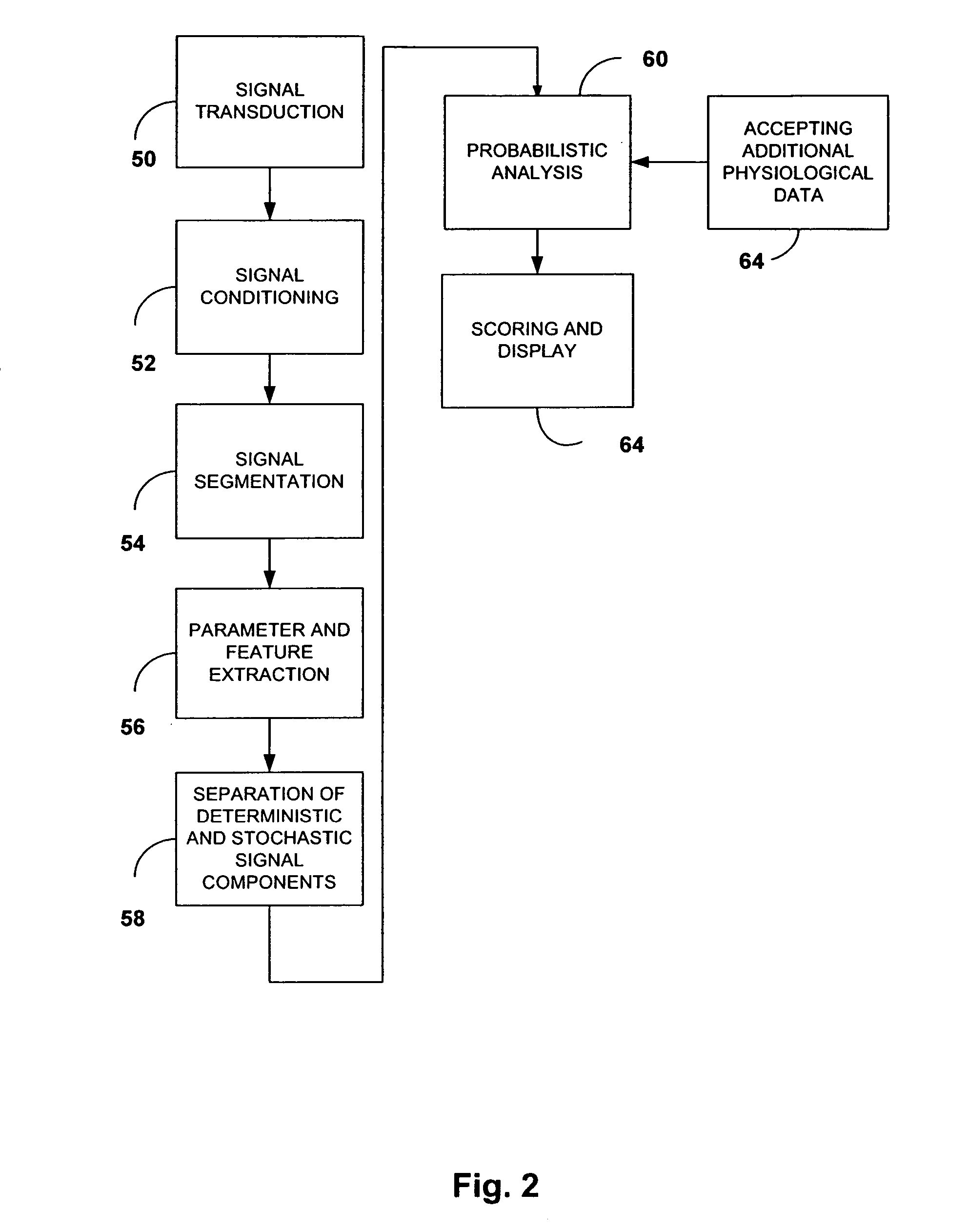
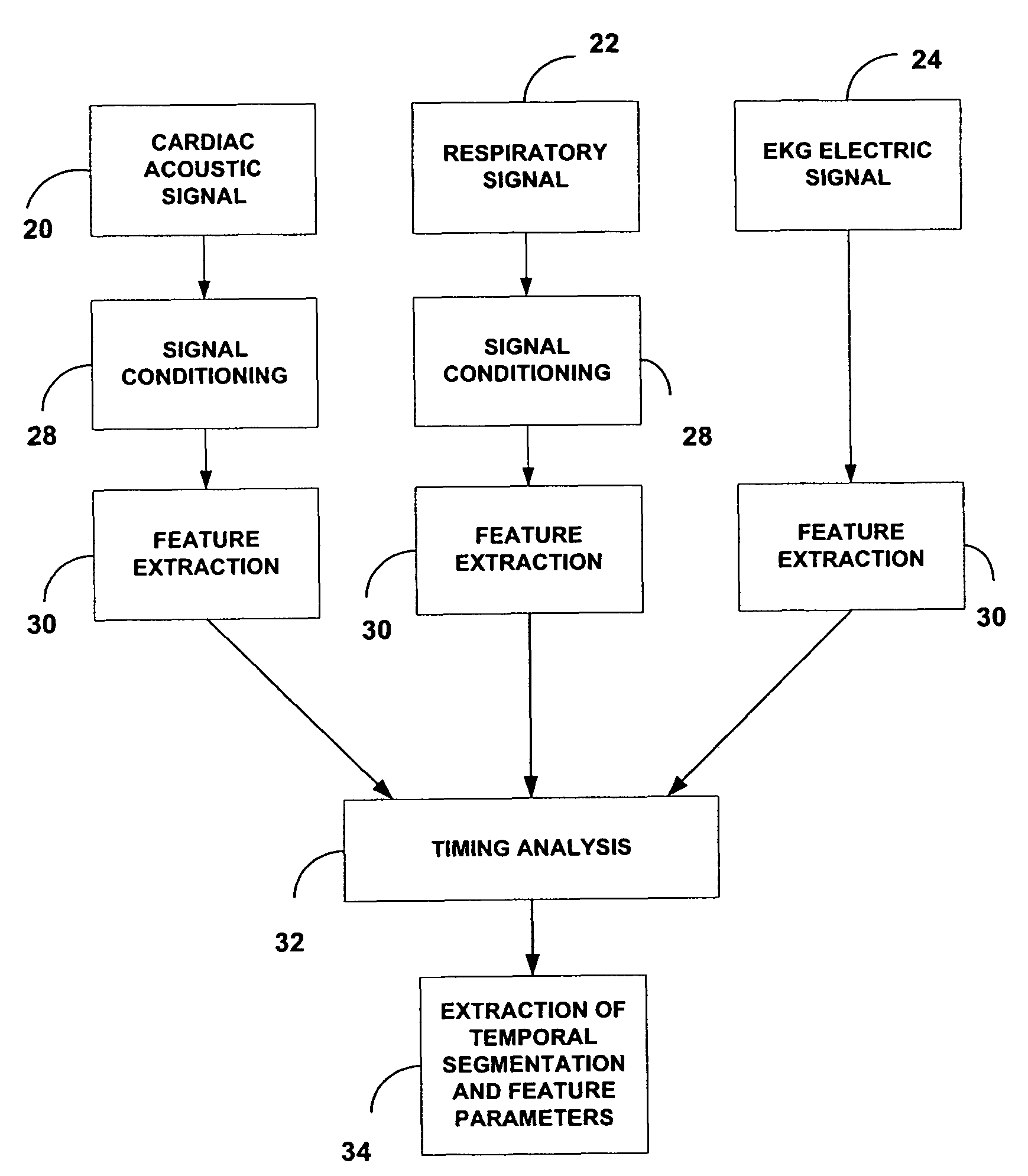
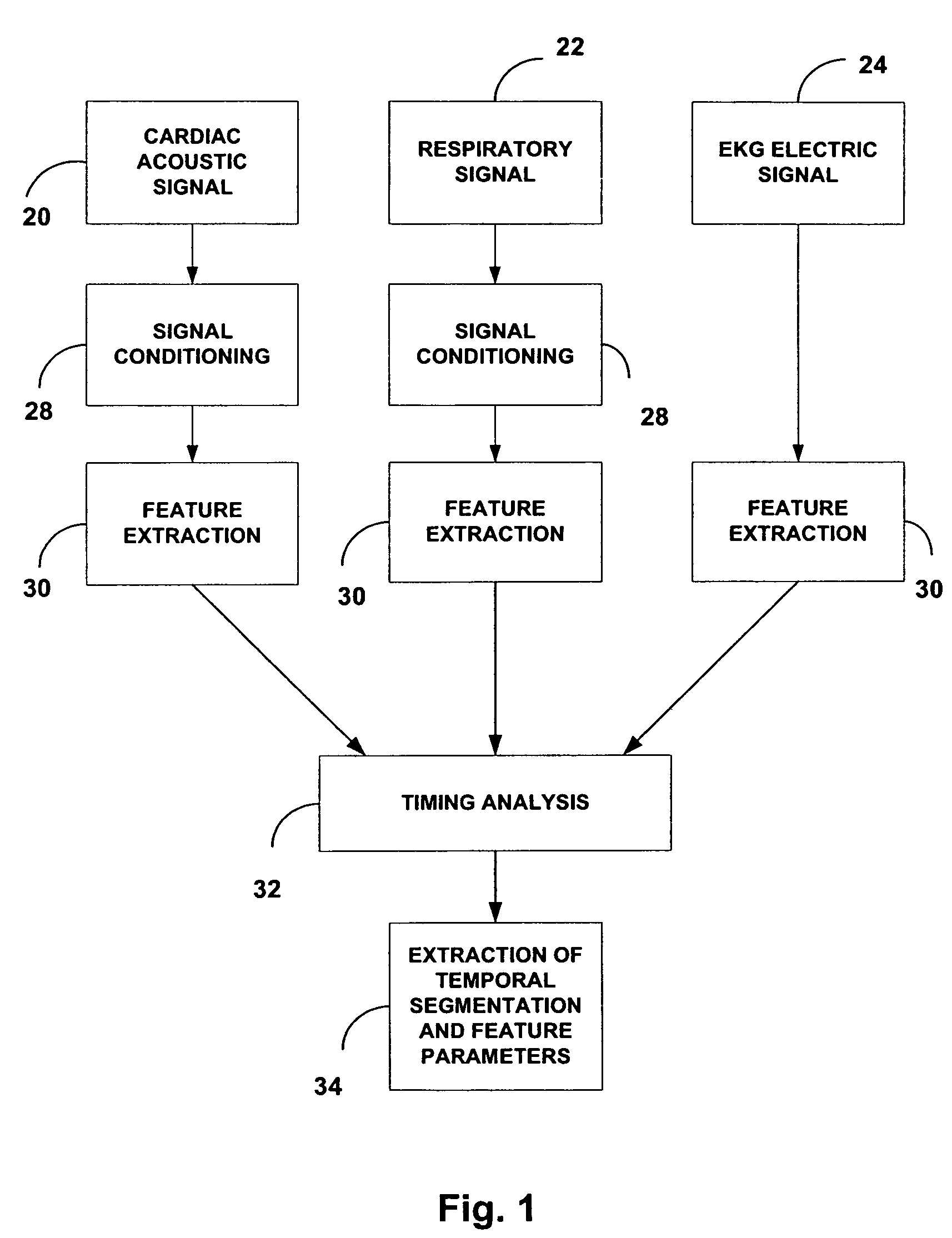
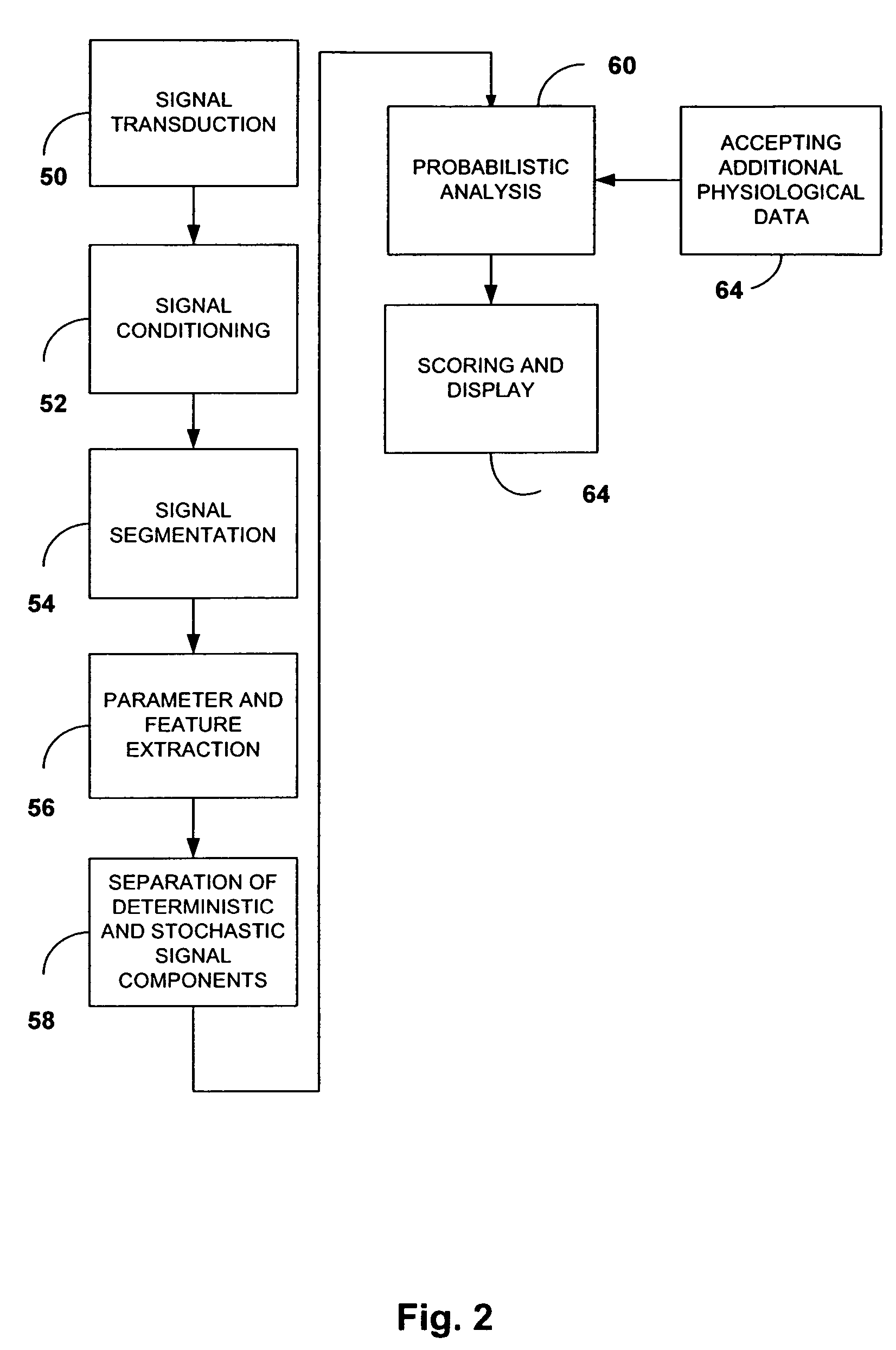
Acoustic cardiac assessment
A non-invasive method and apparatus for monitoring of the function of the heart and lungs in vulnerable patients. An analysis of the activity of the heart is made in correspondence to the respiratory system. Using the method of the invention, precise tracking of the changes of the mutual heart-lung interactions cycle are made, enabling better definitions of heart conditions. Within breath variability factor is introduced for tracking heart condition. Failing heart assisting methods and improved diagnostic methods are facilitated using the monitoring system of the invention.
Owner:GAVRIELY NOAM +1
Acoustic assessment of the heart
A non-invasive method and apparatus for monitoring of the function of the heart and lungs in vulnerable patients. An analysis of the activity of the heart is made in correspondence to the respiratory system. Using the method of the invention, precise tracking of the changes of the mutual heart-lung interactions cycle are made, enabling better definitions of heart conditions. Within breath variability factor is introduced for tracking heart condition. Failing heart assisting methods and improved diagnostic methods are facilitated using the monitoring system of the invention.
Owner:GAVRIELY NOAM +1
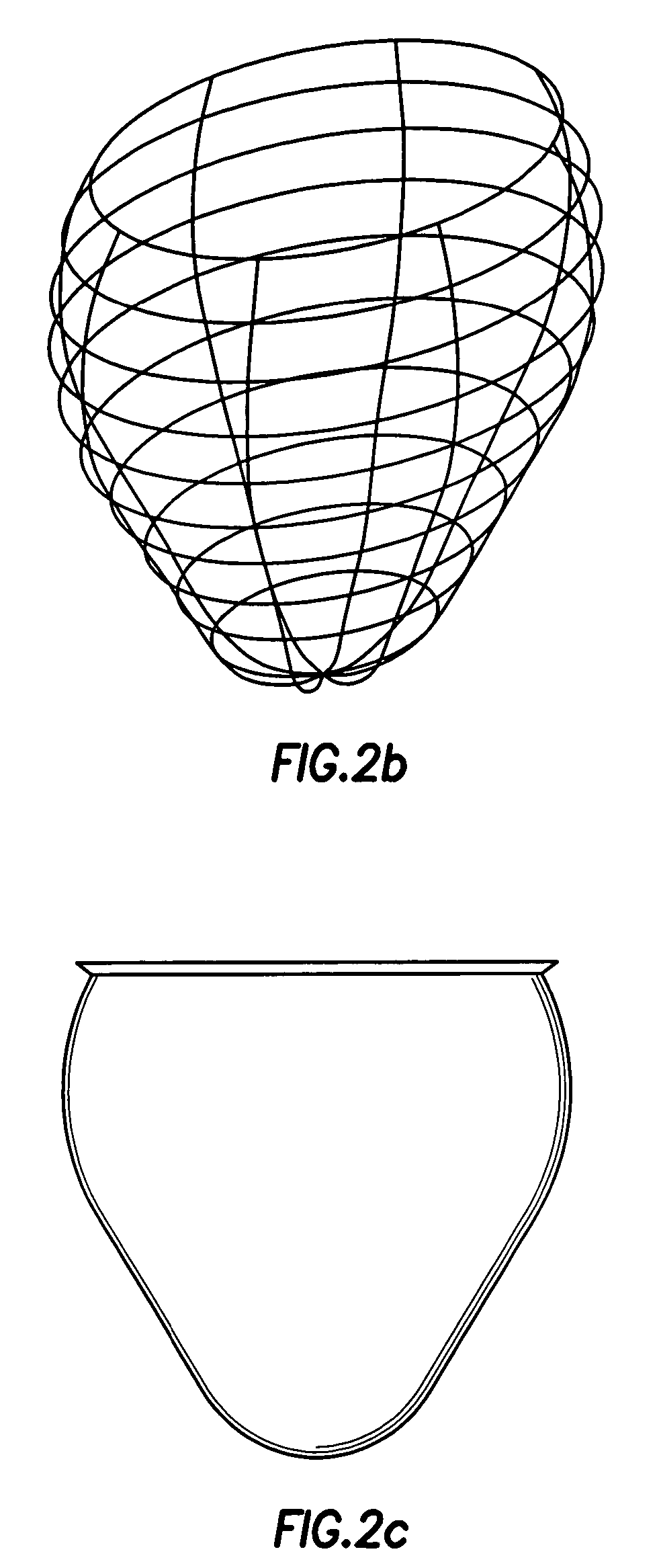
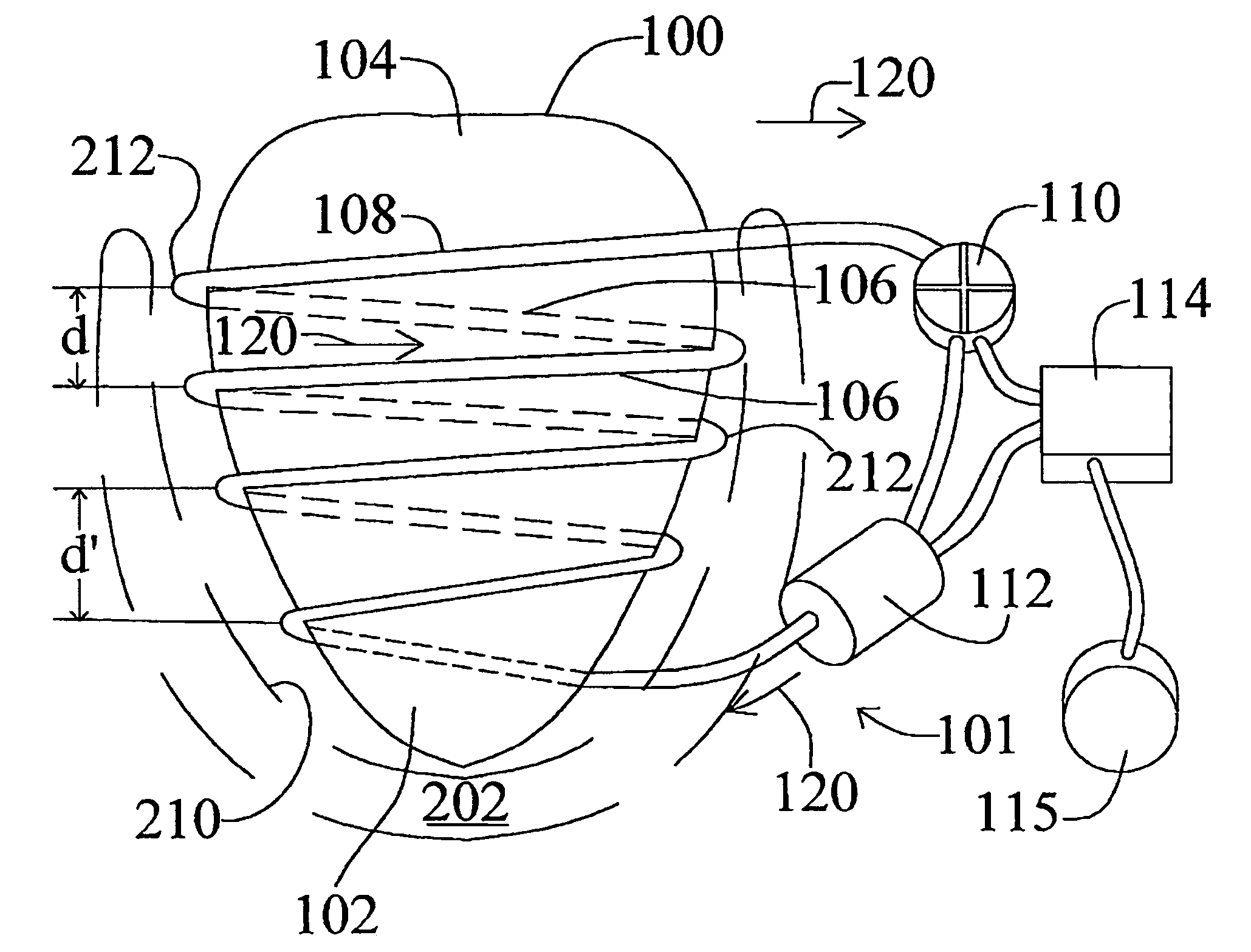
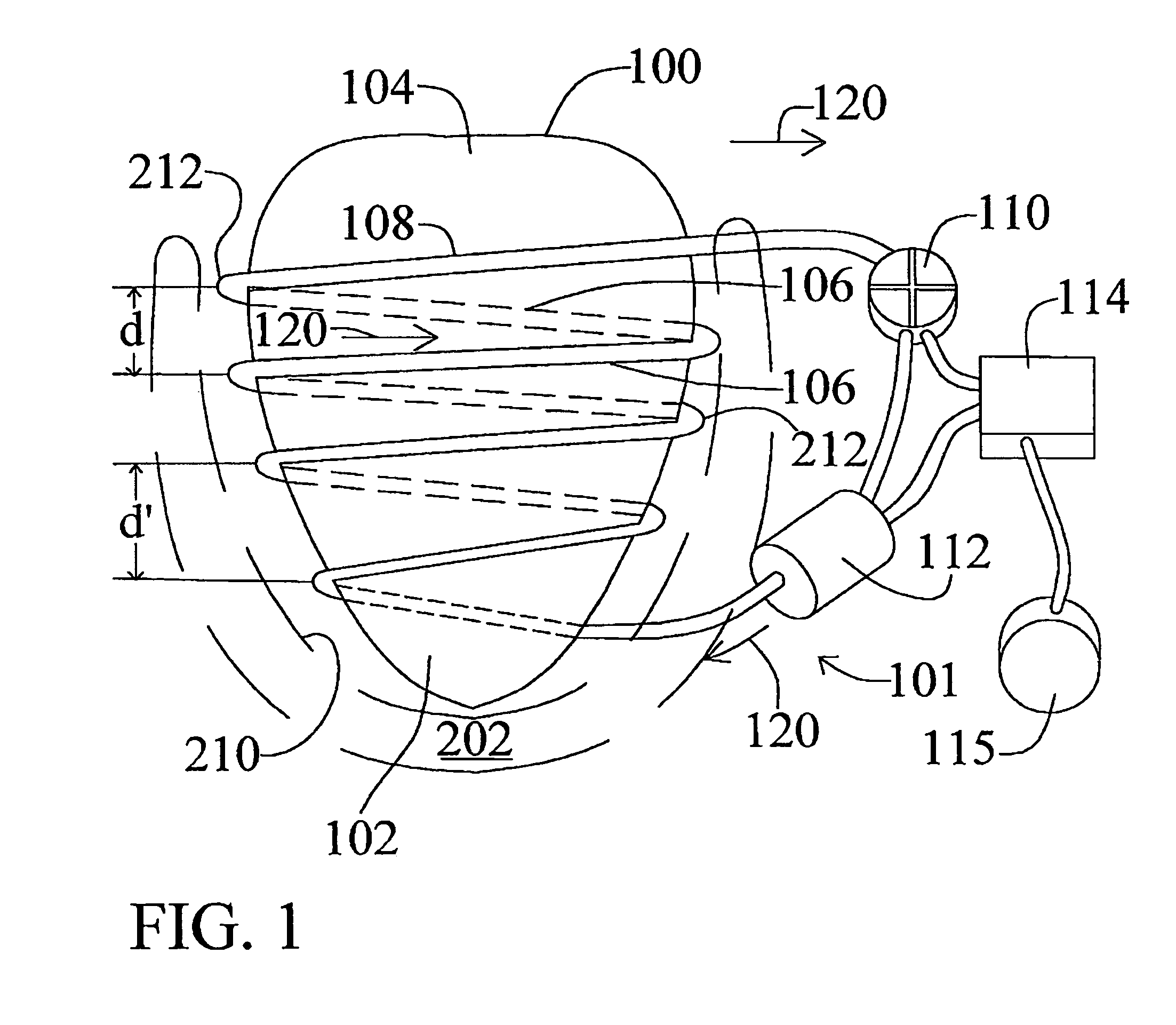
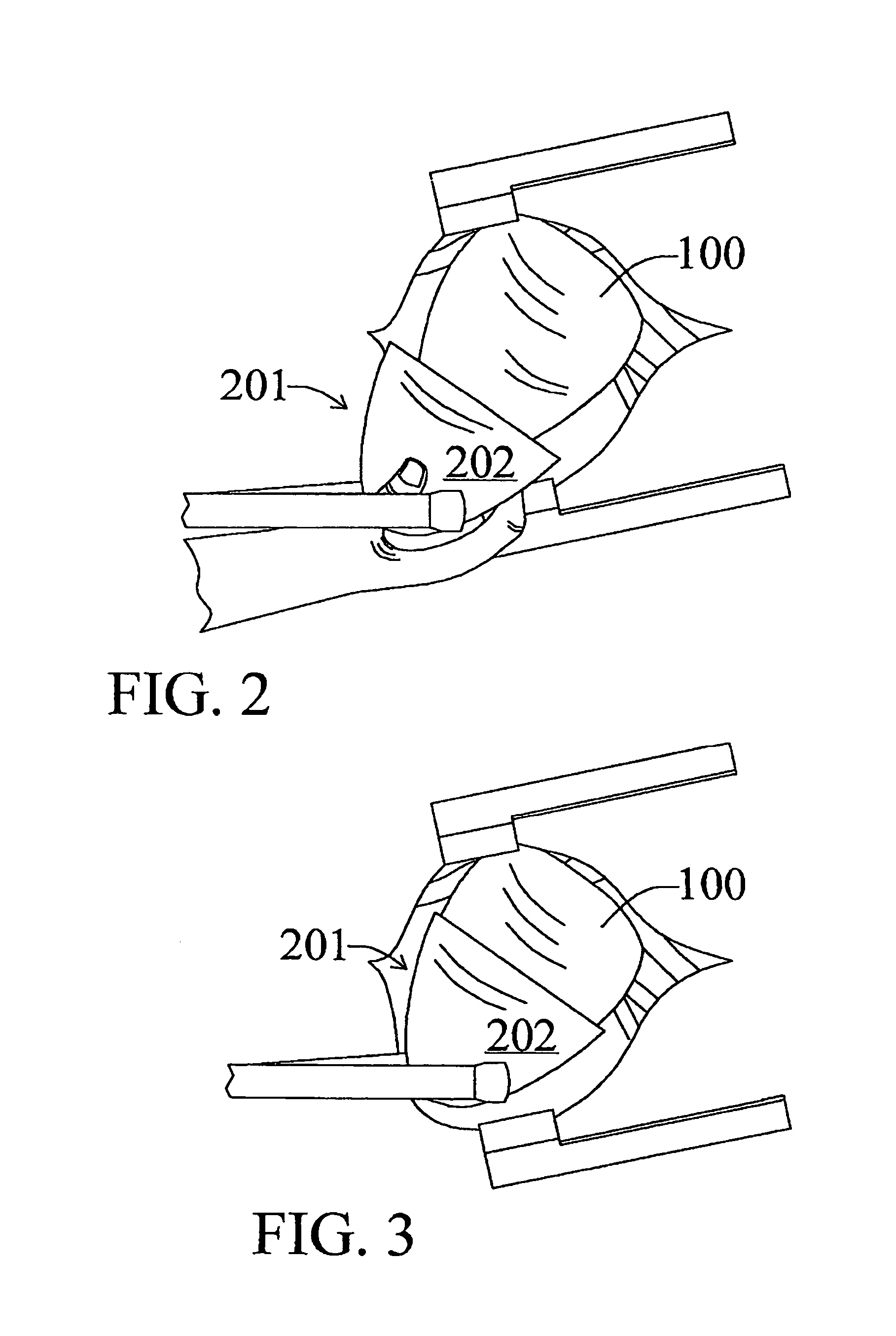
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS7695425B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberFailing heart
An apparatus for treatment of a failing heart by reducing the wall tension therein. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a tension member for drawing at least two walls of a heart chamber toward each other. Methods for placing the apparatus on the heart are also provided.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050131277A1Reduce maximum wall stressReduce tensionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleFailing heart
Devices and methods for treatment of a failing heart by reducing the heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Linear electromechanical device-based artificial muscles, bio-valves and related applications
A biological function assist apparatus composed a linear electronmechanical device or system wrapped in protective coating and controlled by a controller, which also provides power to the electromechanically-based system. The electromechanically-based system can be formed as a mesh using linear motors or linear actuators, or a larger electromechanically grid and wrapped around a failing heart. The electromechanical system can be formed in a circle forming an artificial valve (e.g., sphincter). The electromechanically-based system can operate as a bone-muscle interface, thereby functioning in place of tendons.
Owner:ORSEN
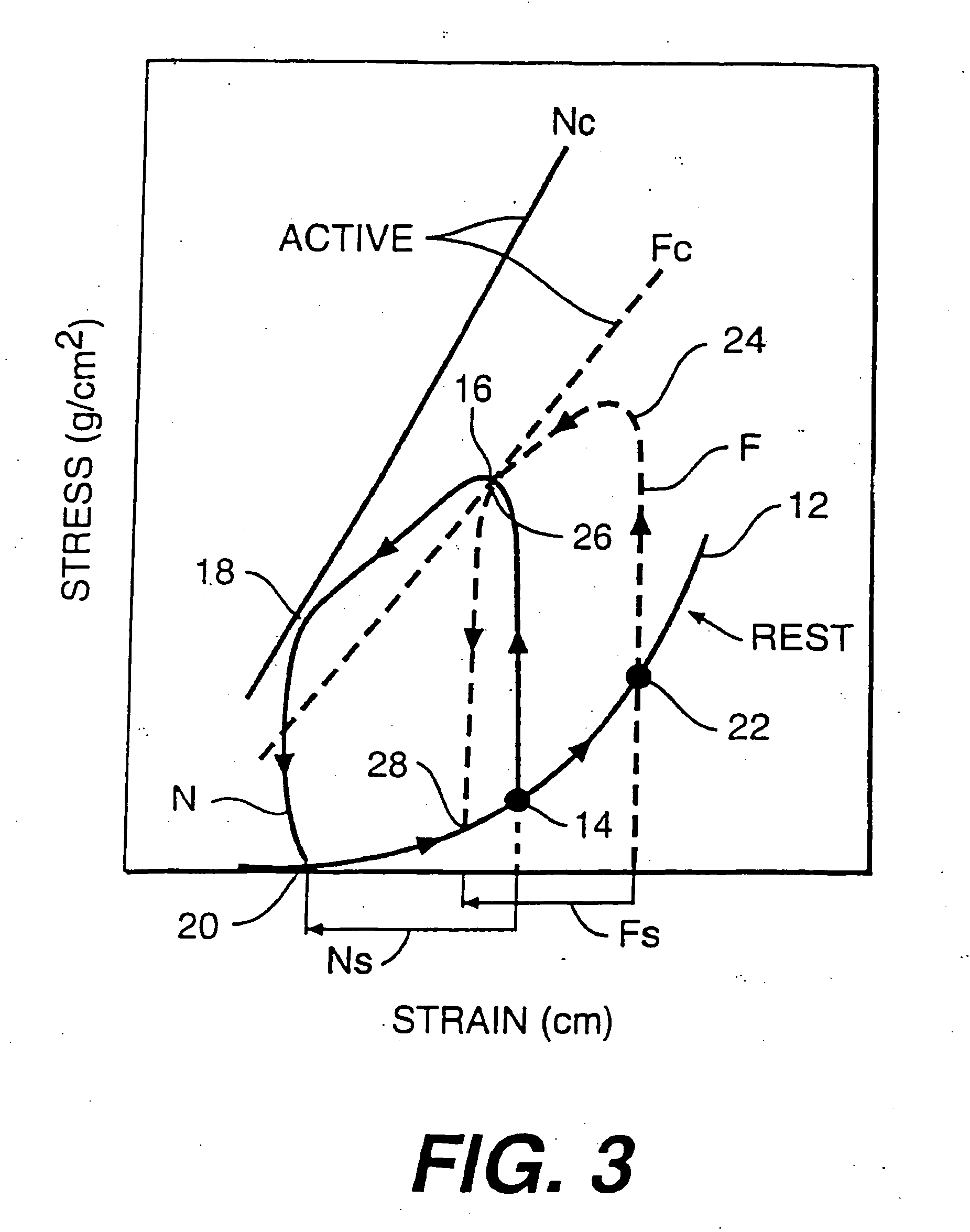
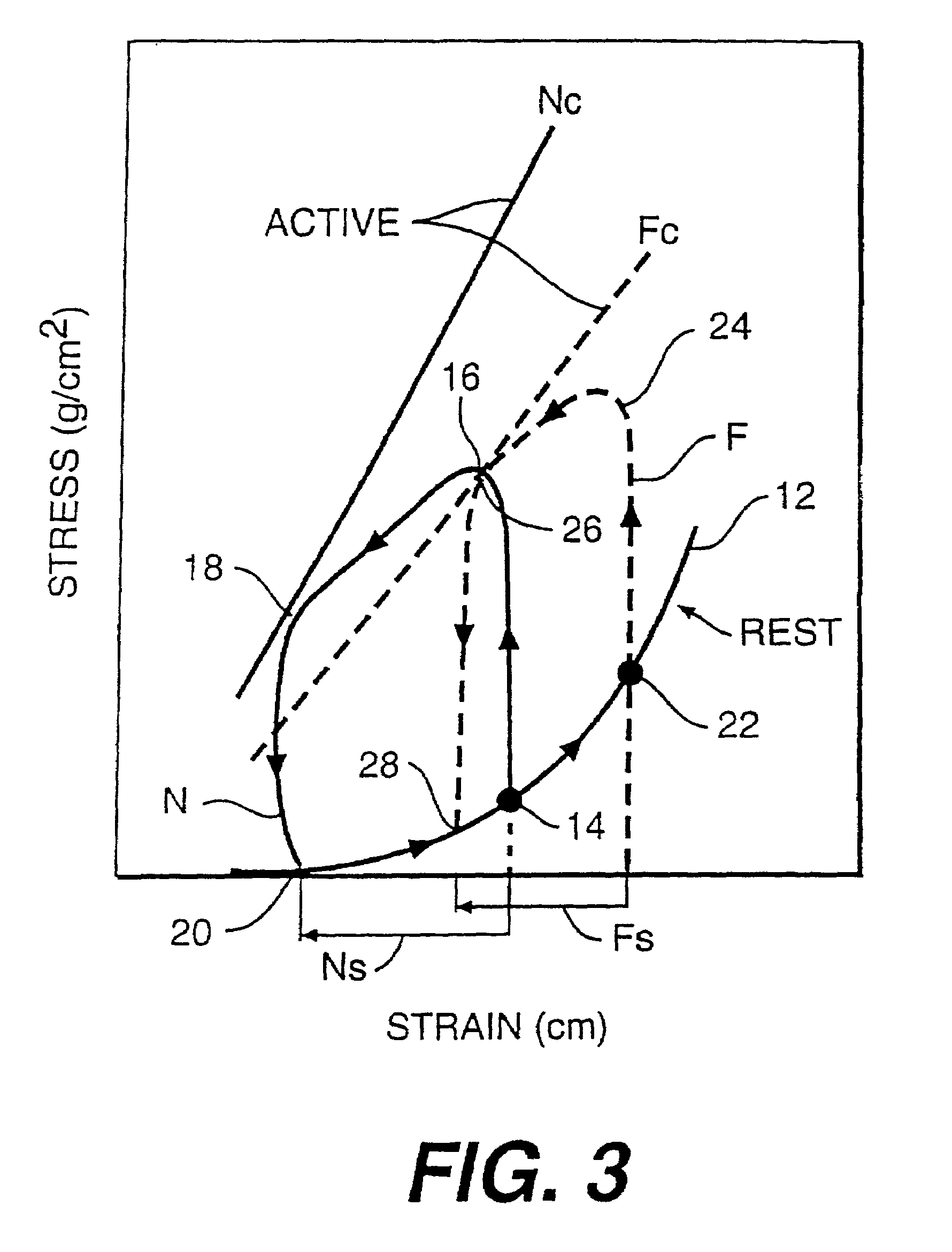
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
ActiveUS20050004420A1Maintain strainReduces apoptosis in the myocardiumHeart valvesIntravenous devicesCardiac muscleApoptosis
A direct cardiac assist device which may aid in ventricular recovery. The device proactively modulates cardiac strain pattern to produce a contraction strain pattern that induces beneficial growth and remodeling of the myocardium or prevents or reduces apoptosis of the myocytes. The device may include an outer shell. membrane, or mesh and an inner membrane. The space between the outer member and the membrane may be filled with fluid that is pressurized during contraction. The device prescribes a beneficial strain pattern during heart contraction. This strain pattern does not invert the curvatures or grossly alter the curvatures of the heart and may assist in myocyte regrowth and healing of the failing heart.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
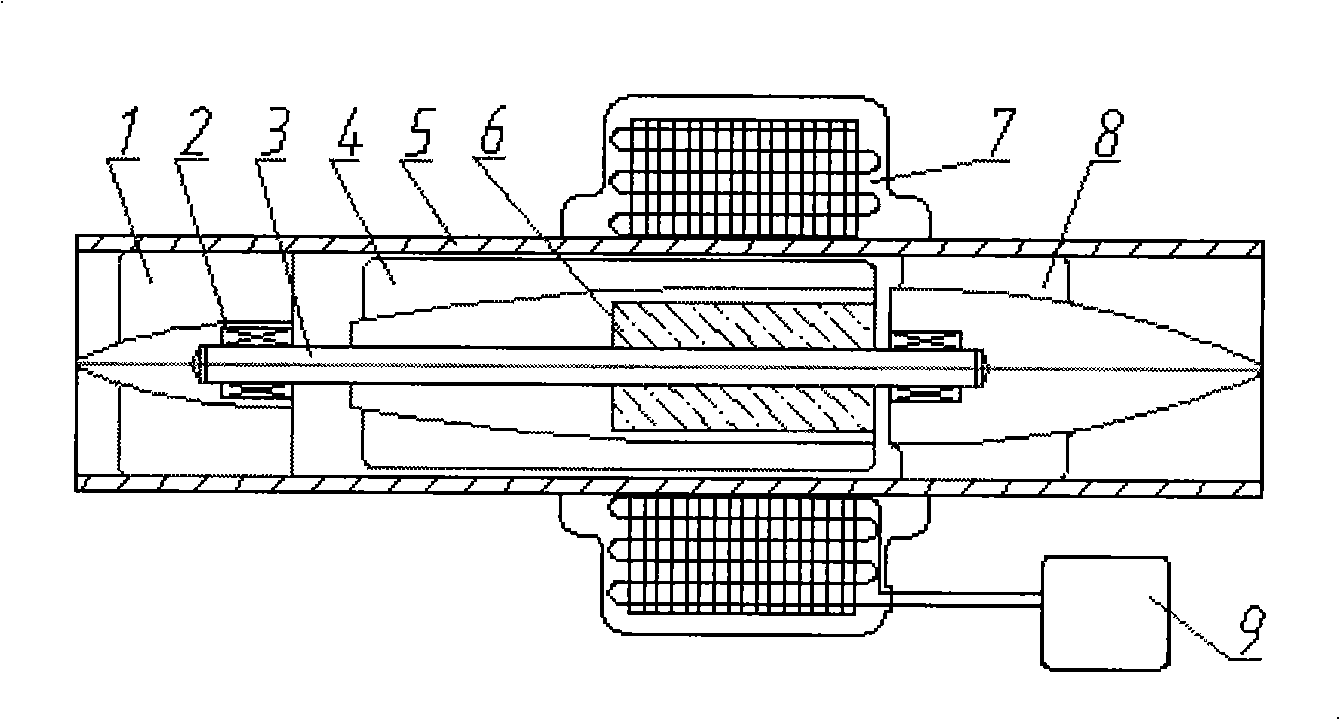
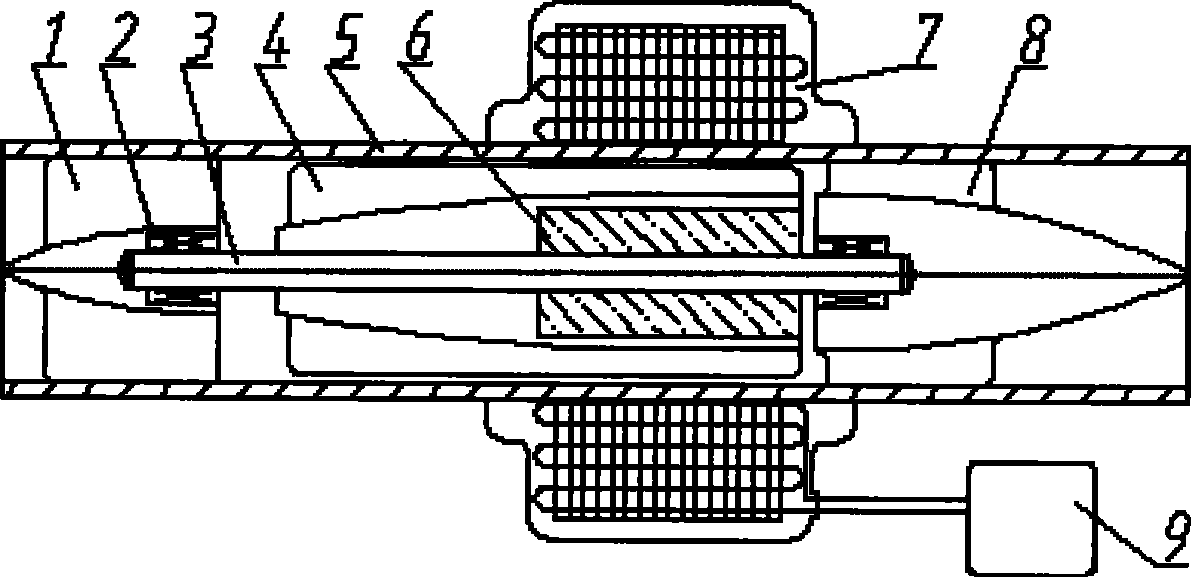
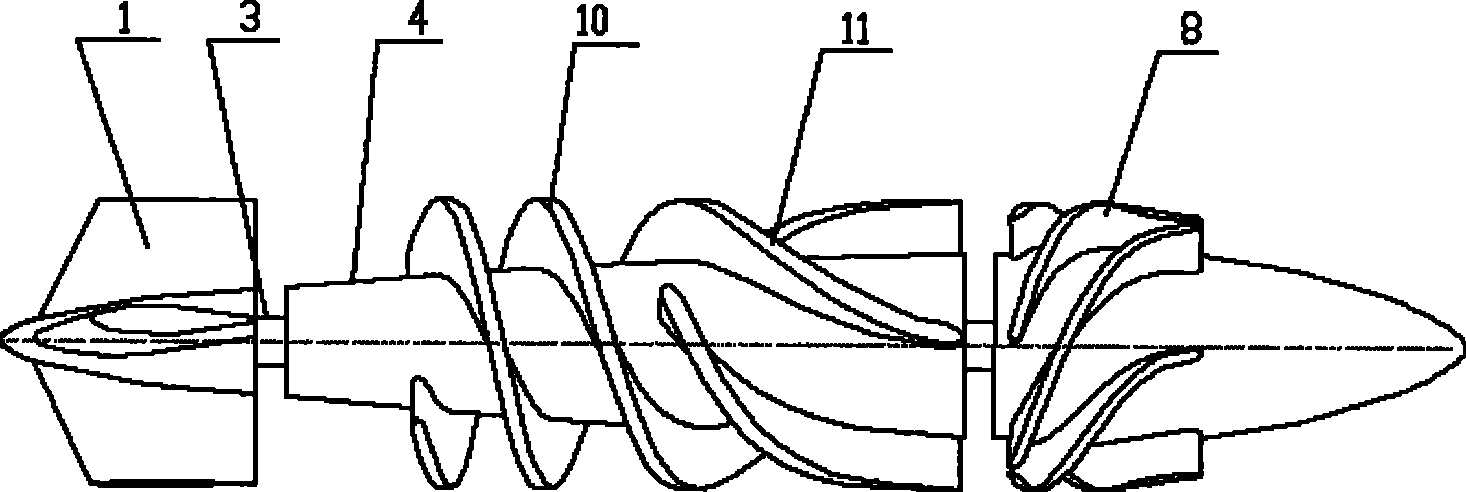
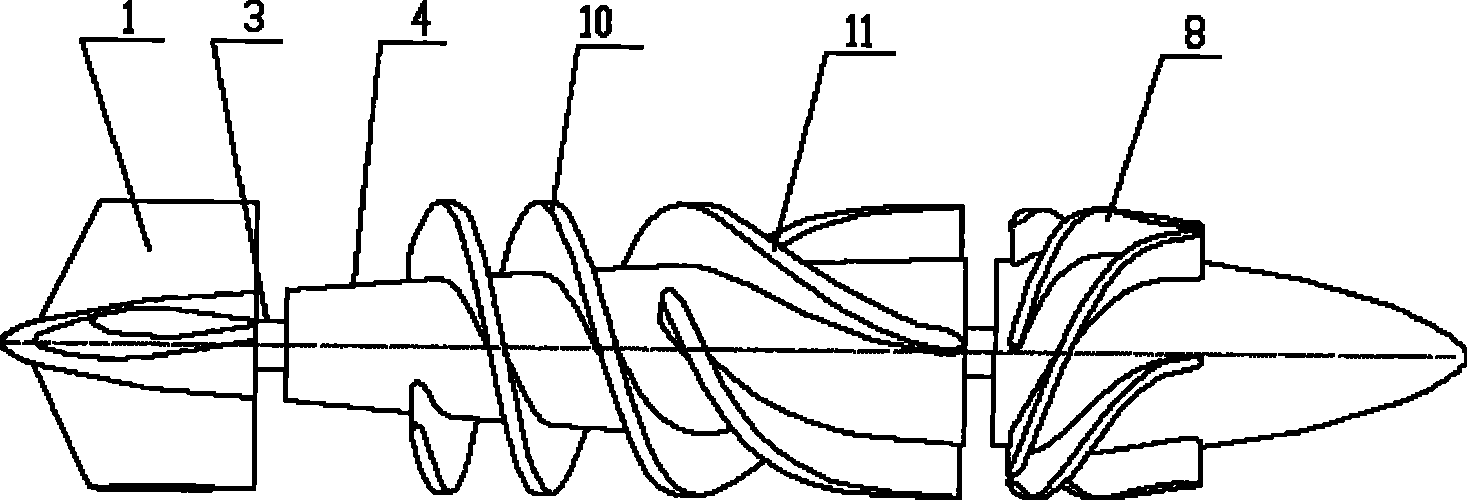
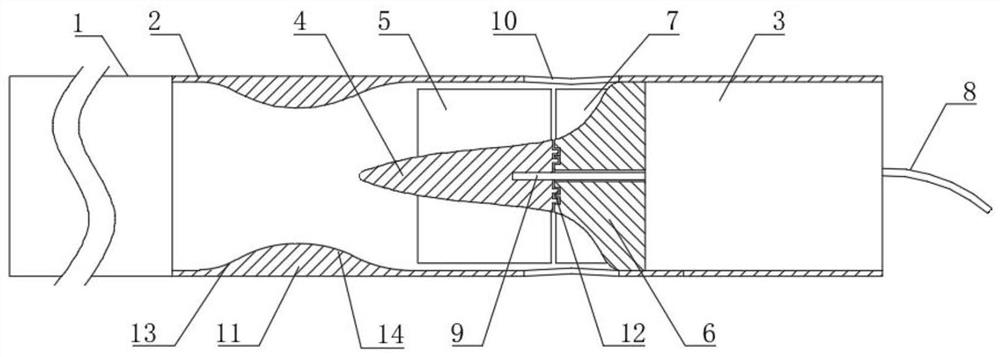
Implanted miniature streamlined shaft bloodshed pump
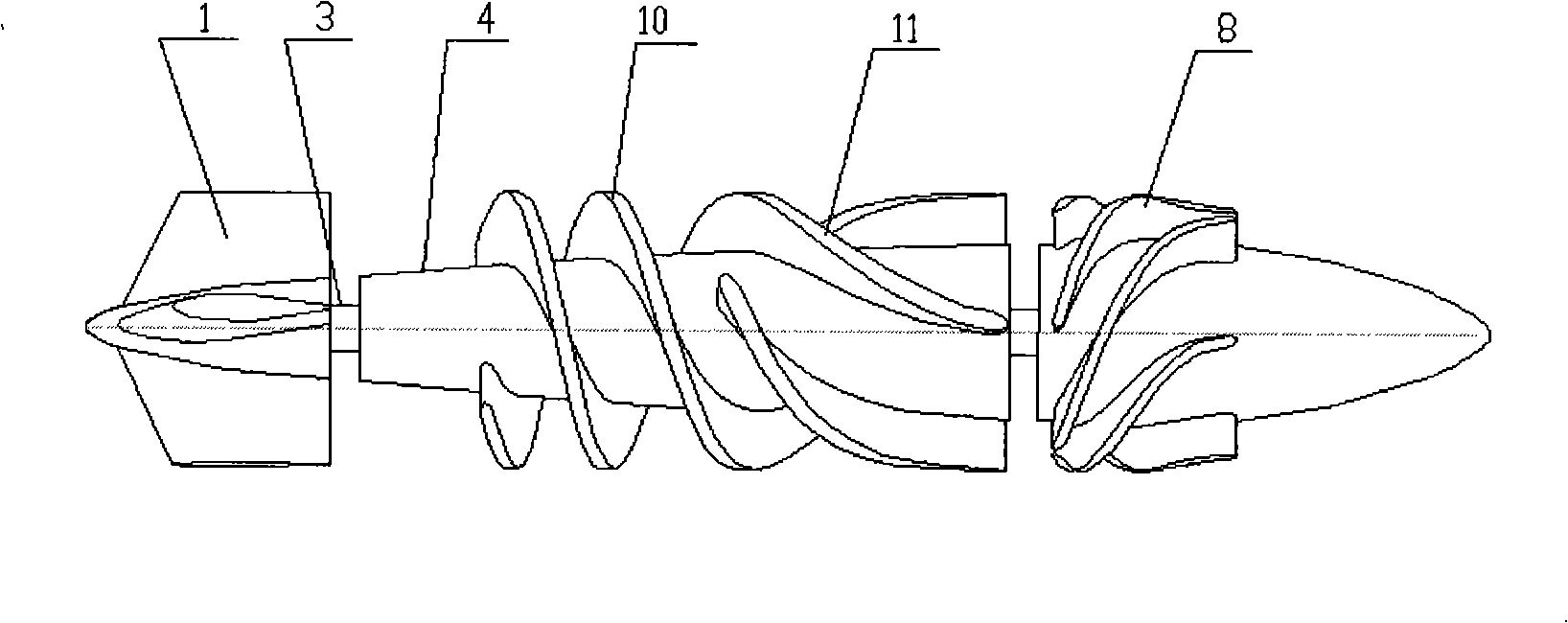
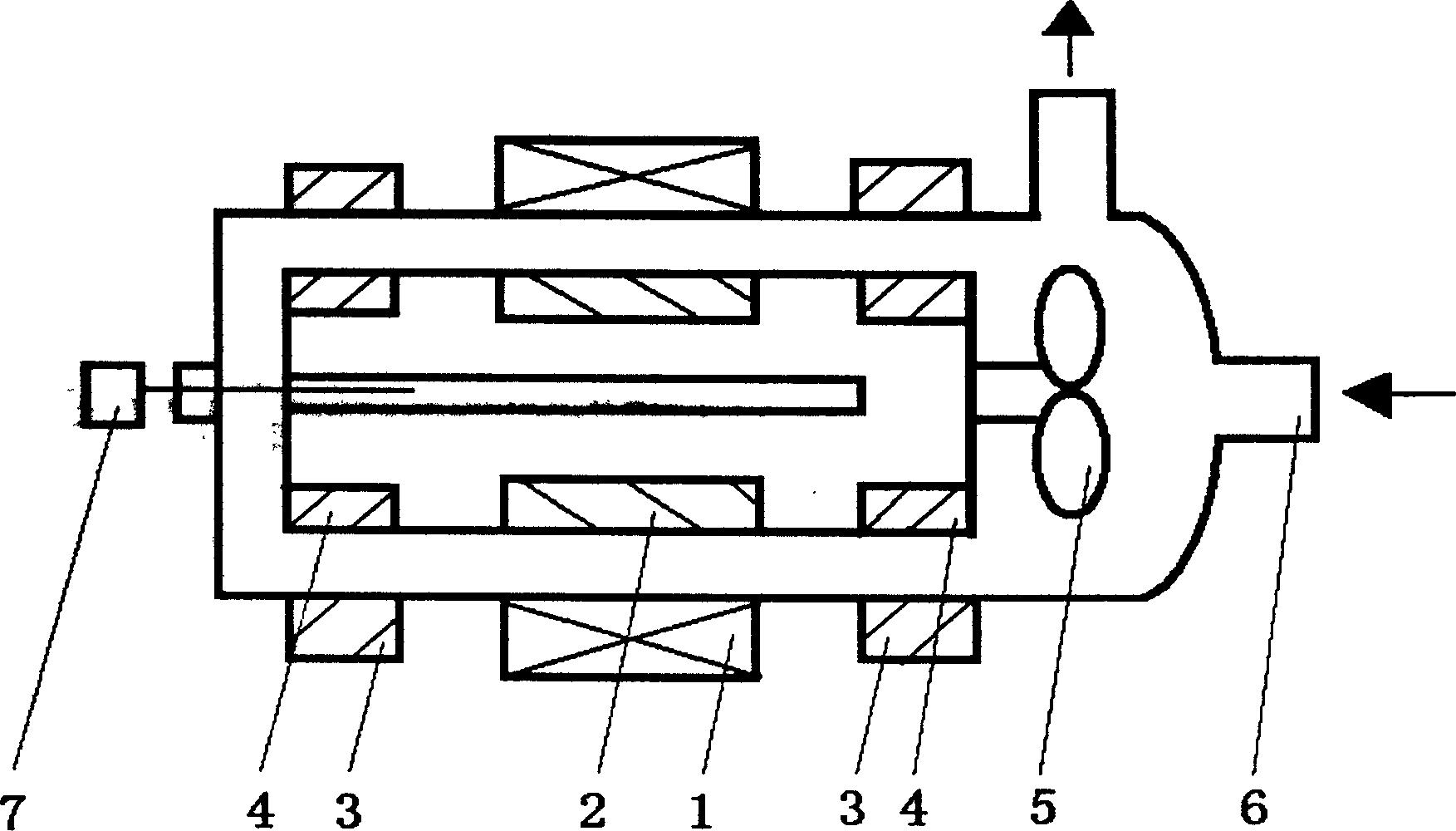
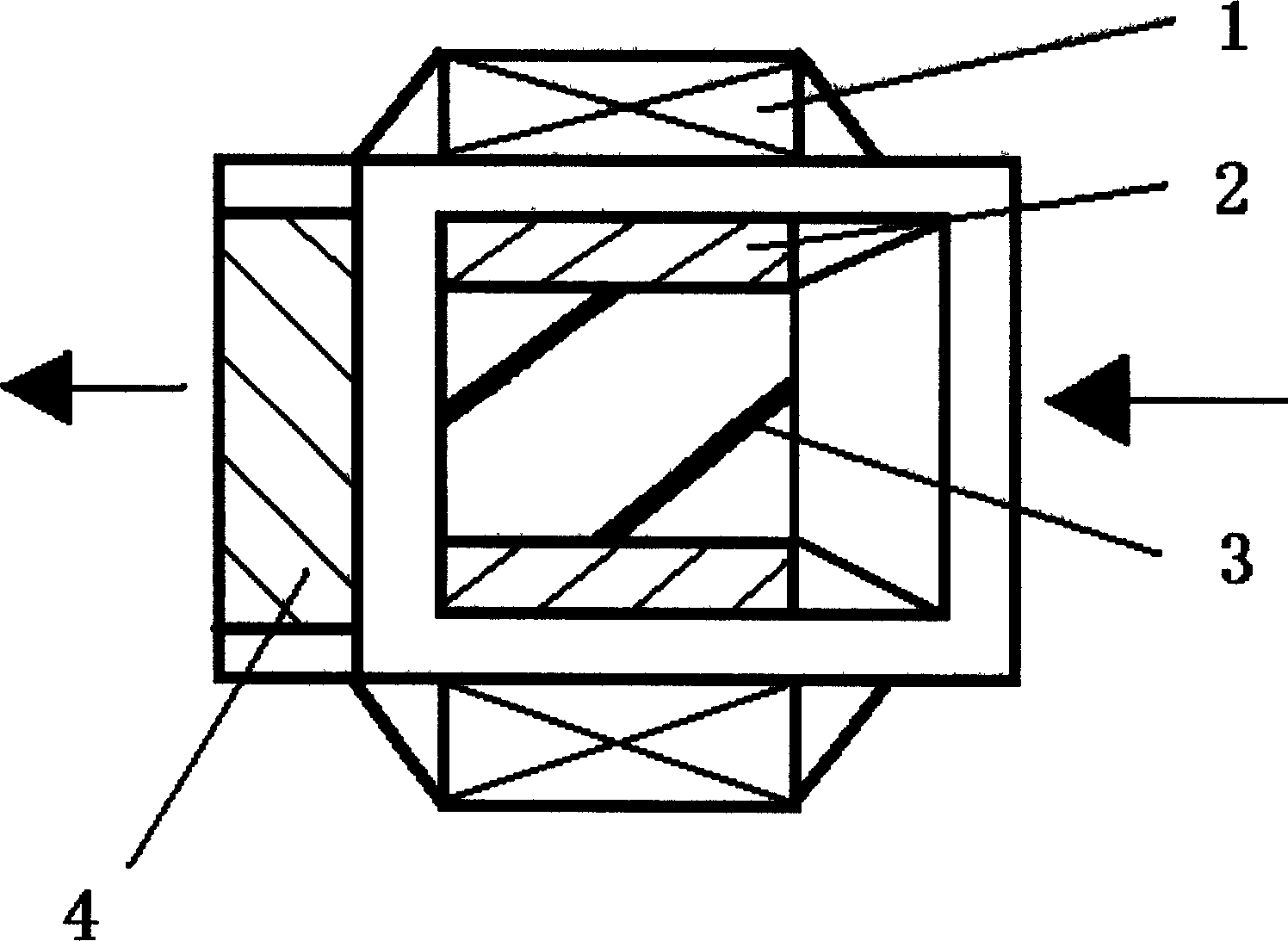
The invention relates to an embedded micro streamline axial flow blood pump, which can be used for assisting blood circulation of failed heart. The blood pump comprises a pump body arranged in a sleeve body and a driving device arranged outside the pump body, wherein the pump body comprises the sleeve body, a front guide vane, a rotor and a back guide vane; the hubs of the front guide vane, a rotor and the back guide vane are designed integrally in an integral streamline form; and the front half part of the rotor is provided with an inductive blade. The blood pump can reduce the on-way pressure loss of the blood in the flow channel of the blood pump, improve efficiency and reduce hemolysis; and can promote the circumferential speed of the blood after entering into a rotor area due to the inductive blade arranged on the front half part of the rotor, and avoids the occurrence of vacuole phenomenon.
Owner:中山好特人工心脏实验室有限公司
Minimally invasive percutaneous ventricular assist device
InactiveUS20040102674A1The process is simple and fastHigh outputControl devicesSurgeryCardiorespiratory arrestVentricular assistance
A Minimally Invasive Ventricular Assist Device for circulatory support of a failing heart apt to be inserted percutaneously bluntly via a thoracostomy a into a chest cavity of a patient in cardiac failure or cardiac arrest without the need for wide surgical opening of the chest. The device once deployed inside the chest is capable of compressing and decompressing the heart via pneumatic or mechanical means providing circulatory support to patients in cardiac failure or cardiac arrest. Due to its design and structure the Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Ventricular Assist Device can be deployed rapidly and safely at bedside by health care professionals properly trained in the procedure.
Owner:ZADINI FILIBERTO P +1
Assist device for the failing heart
InactiveUS6918870B1Assisted movementDifferent degree of stiffnessControl devicesMedical devicesCardiac wallFailing heart
A heart actuator device for use in heart assist apparatus, which device includes a paddle-like main body. The main body has a heart compressing wall, which in use is adapted to be affixed to at least a region of heart, and a distal wall, which in use is adapted to be distal that region of the heart. The heart compressing wall is movable in a direction relatively away from the distal wall, so as, in use to compress at least that region of the heart thereby assisting movement of the heart wall.
Owner:HEART ASSIST TECH PTY LTD
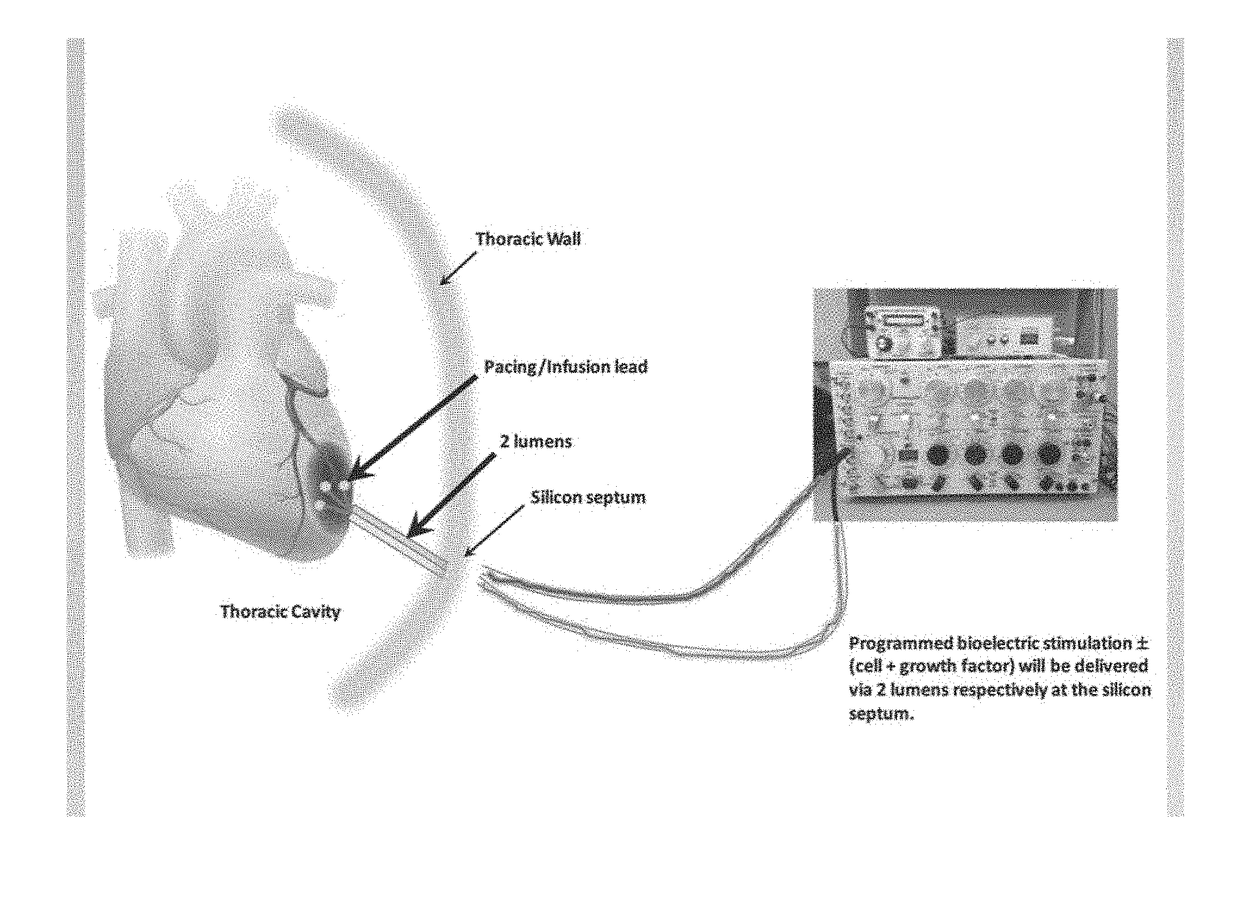
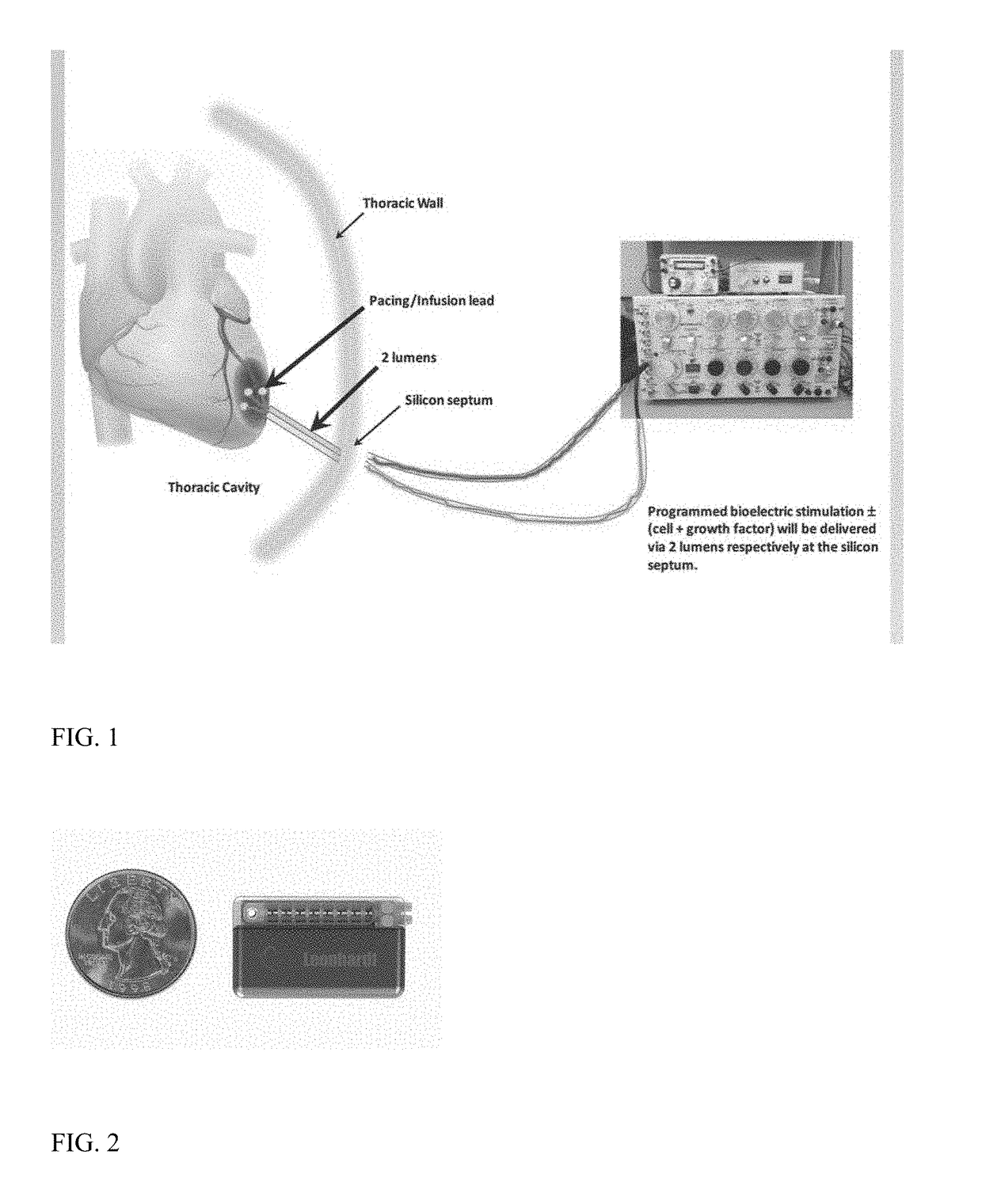
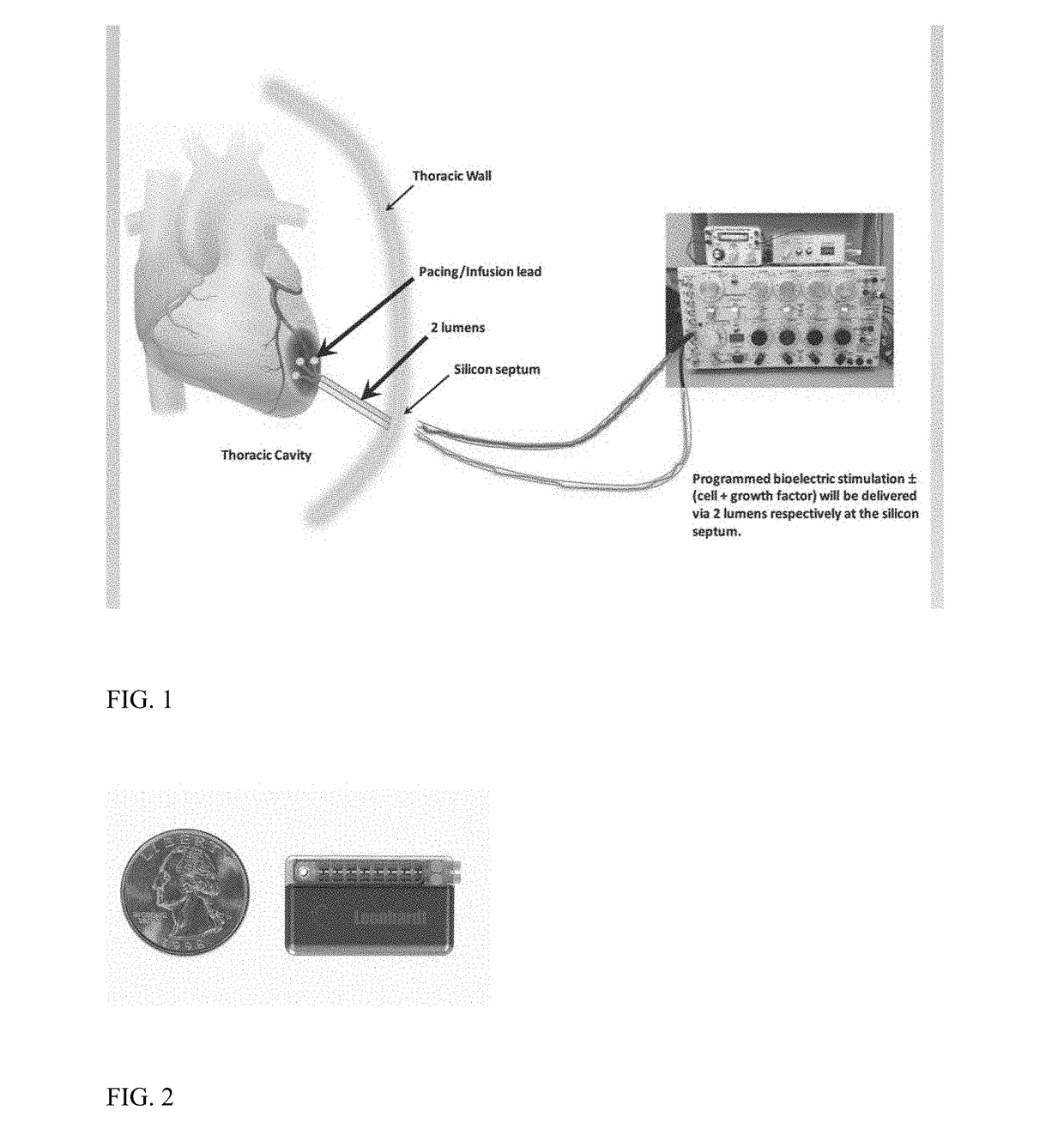
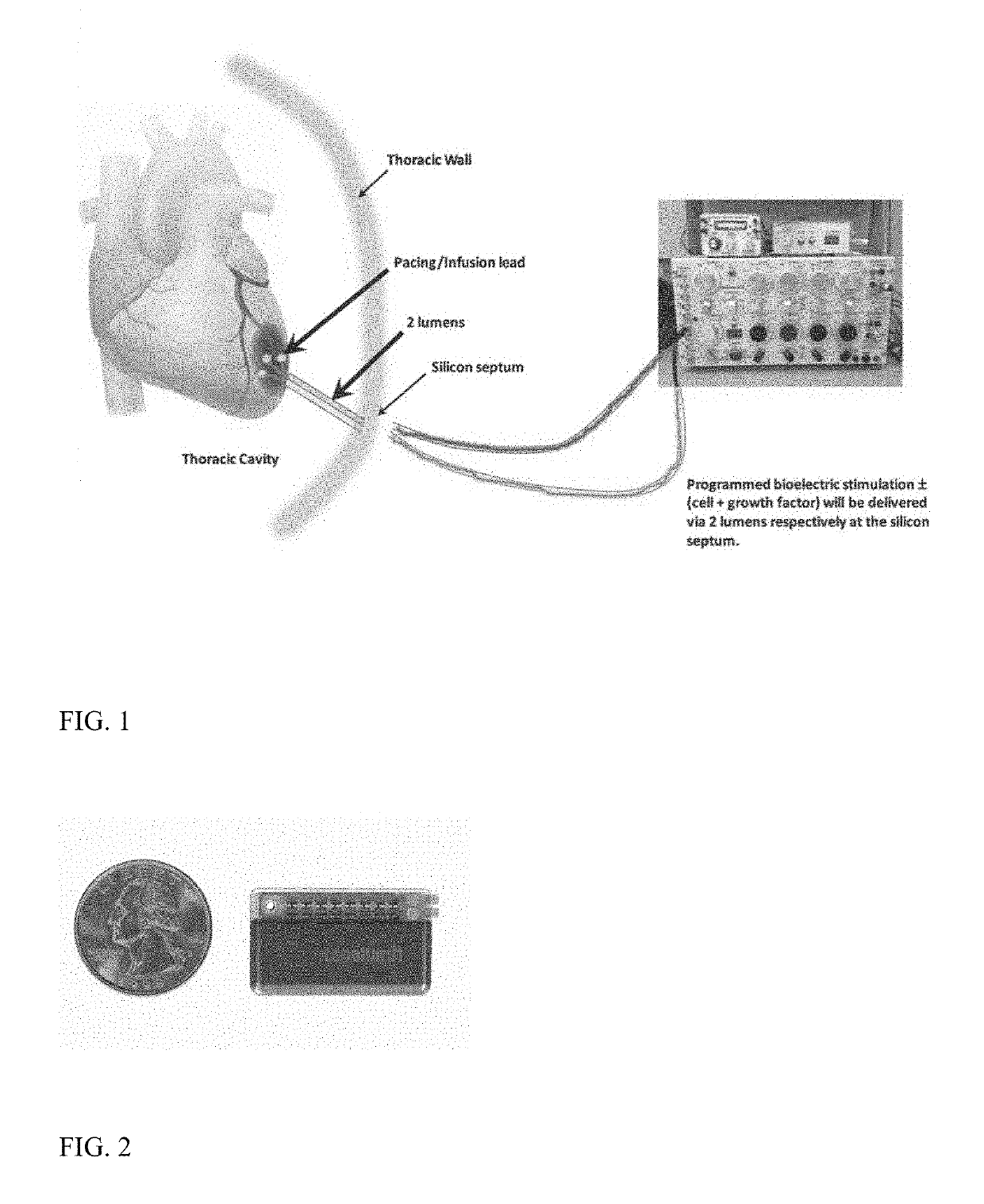
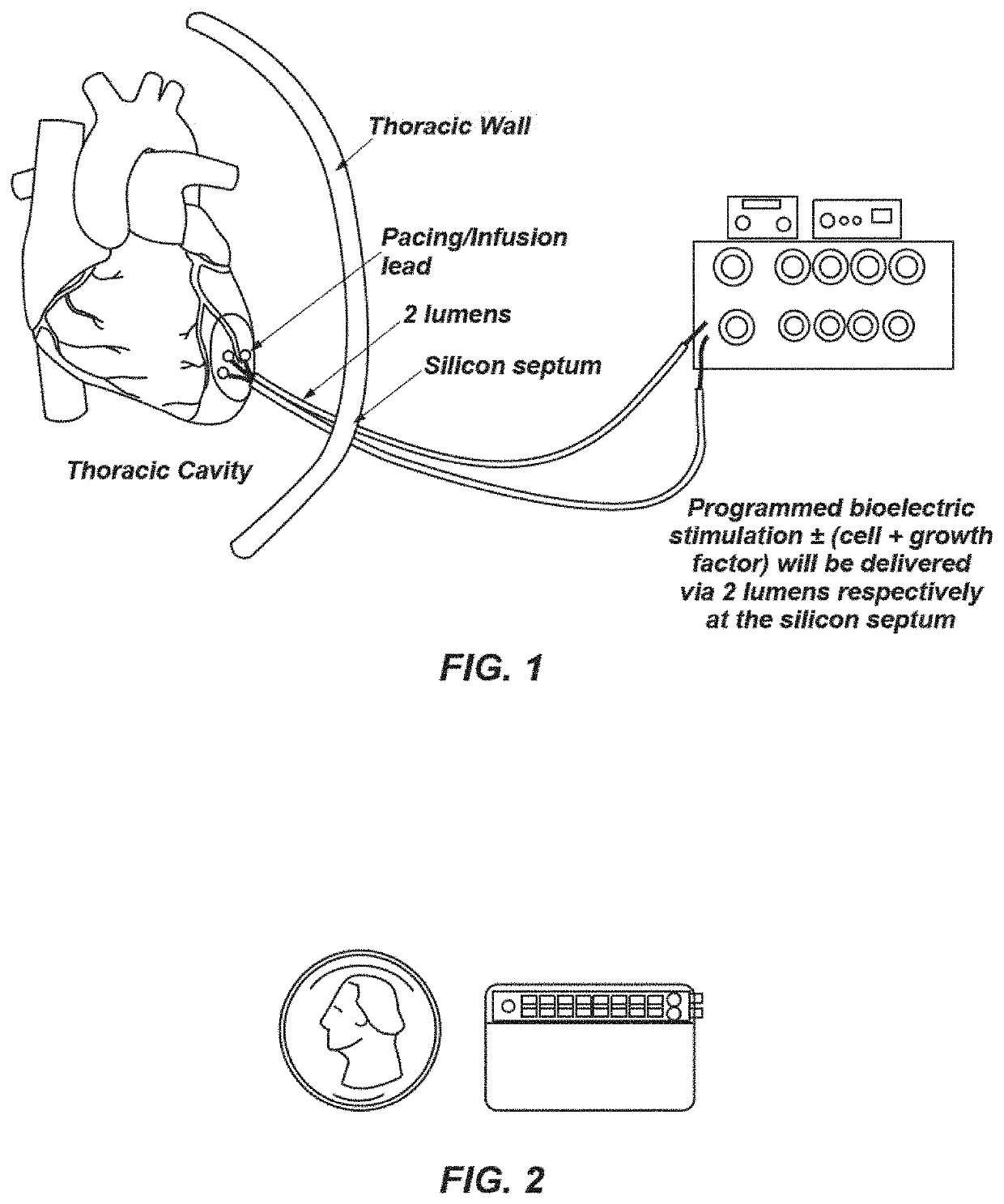
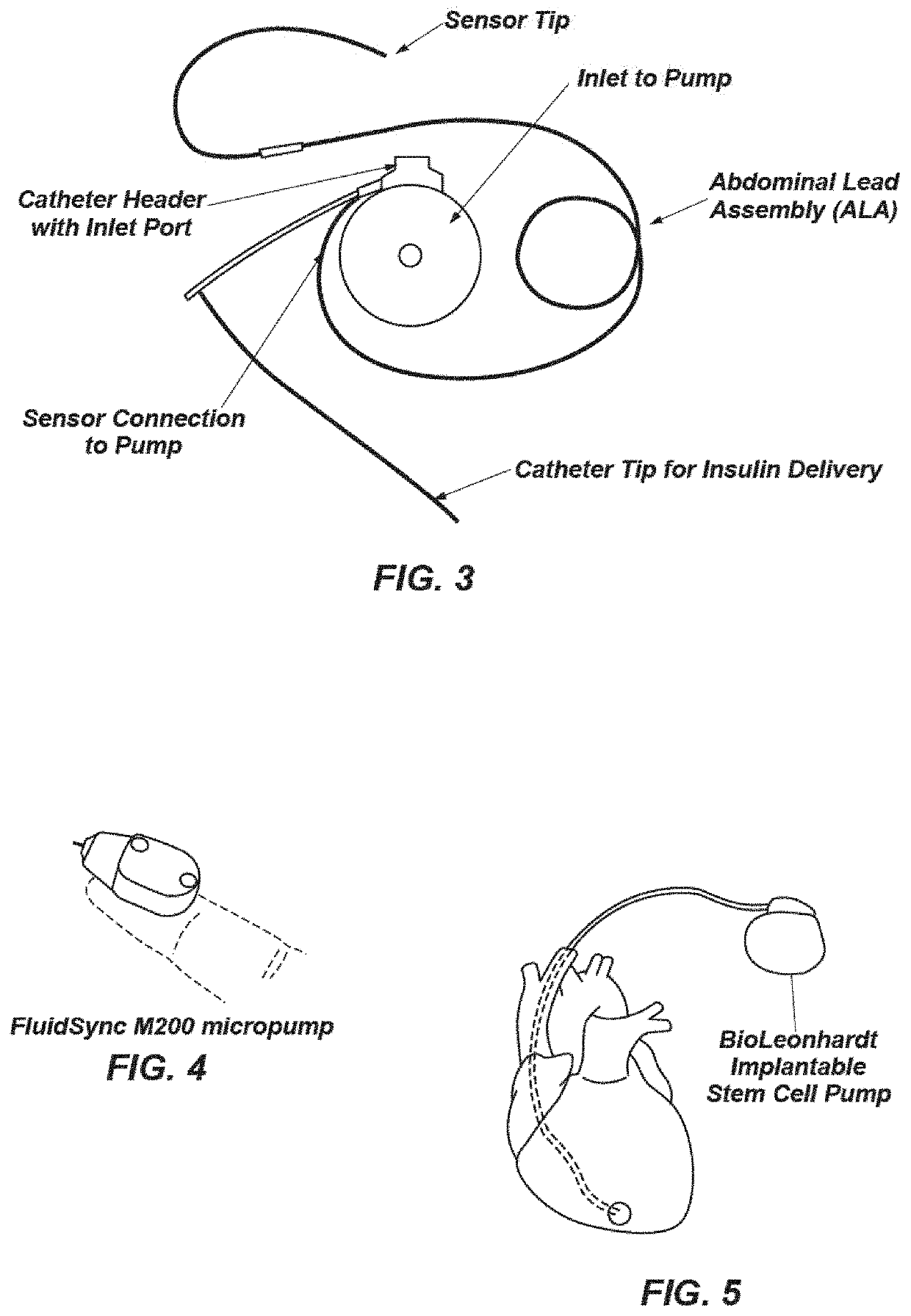
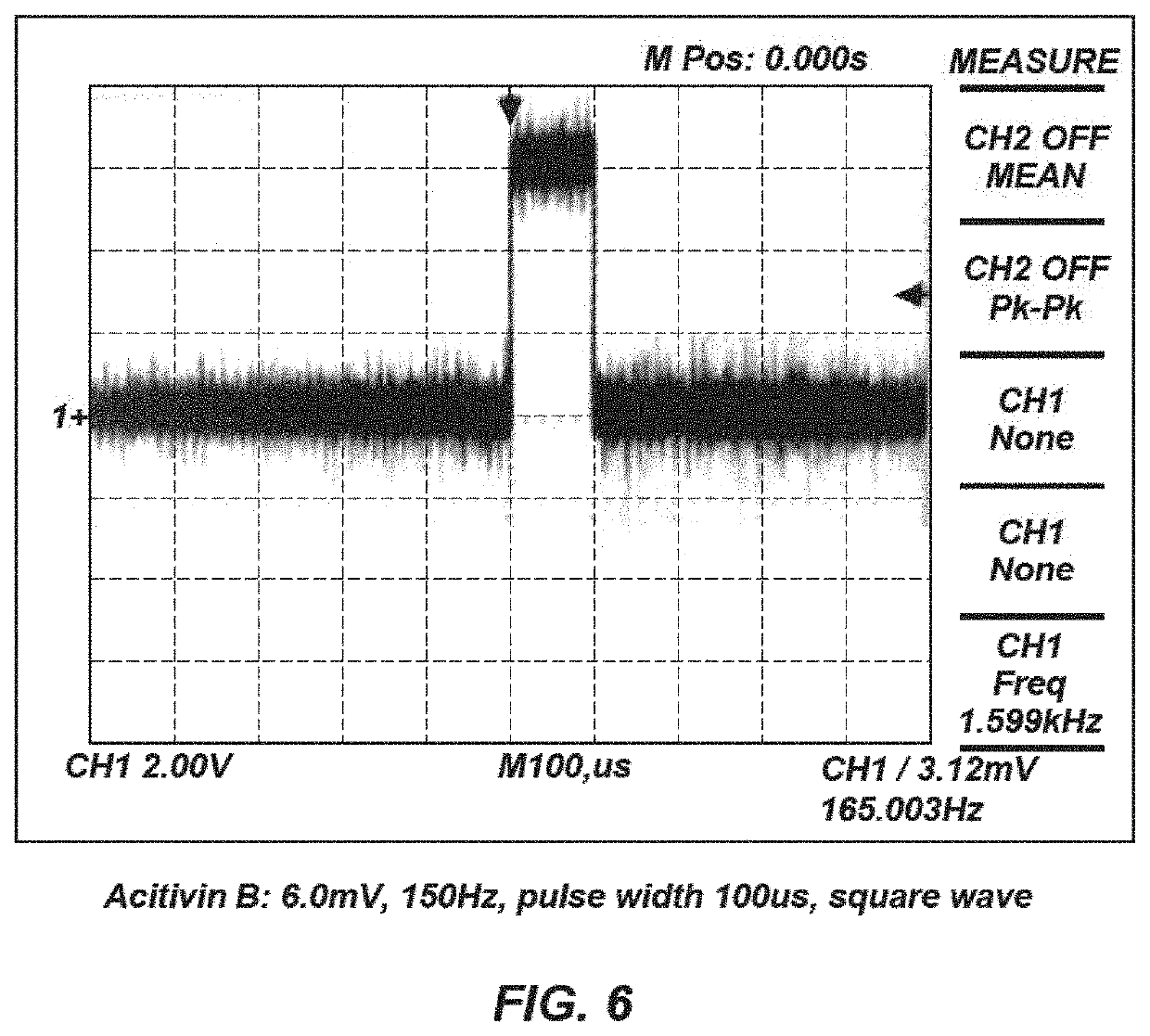
Bioelectric stimulator
ActiveUS20180064935A1Quality improvementExpansion quantityElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseControl release
Described is a low voltage, pulsed electrical stimulation device for controlling expression of, for example, follistatin, a muscle formation promotion protein, by tissues. Epicardial stimulation is especially useful for heart treatment. Follistatin controlled release is also useful for treating other ailments, such as erectile dysfunction, aortic aneurysm, and failing heart valves.
Owner:LEONHARDT VENTURES LLC
Device for proactive modulation of cardiac strain patterns
ActiveUS7445593B2Reduces apoptosis in the myocardiumPromote growthHeart valvesIntravenous devicesApoptosisCardiac muscle
A direct cardiac assist device which may aid in ventricular recovery. The device proactively modulates cardiac strain pattern to produce a contraction strain pattern that induces beneficial growth and remodeling of the myocardium or prevents or reduces apoptosis of the myocytes. The device may include an outer shell. membrane, or mesh and an inner membrane. The space between the outer member and the membrane may be filled with fluid that is pressurized during contraction. The device prescribes a beneficial strain pattern during heart contraction. This strain pattern does not invert the curvatures or grossly alter the curvatures of the heart and may assist in myocyte regrowth and healing of the failing heart.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Implantable cardiac assist device
InactiveUS7118525B2Inhibit migrationMinimal movementControl devicesBlood pumpsHuman bodyTherapeutic Devices
The present invention relates to therapeutic devices to work in conjunction with a diseased or failing heart to satisfy the hemodynamic needs of a patient. More particularly, the invention relates to a fully implantable device for assisting a heart to pump blood by intermittently applying pressure to at least a portion of the ventricular surface of the heart (if not the entire surface), preferably both the atrial and ventricular surfaces, at predetermined or possibly pre-programmed intervals to assist the heart to provide adequate hemodynamic output by sensing demand of the human body. In short, the present invention assists the maintenance of, or reestablishes, the normal contraction sequence of a healthy heart.
Owner:COLEMAN EDWARD J DR
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus and method
InactiveUS7883539B2Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCardiac cycleFailing heart
Devices and methods for treatment of a failing heart by reducing the heart wall stress. The device can be one which reduces wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle or only a portion of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
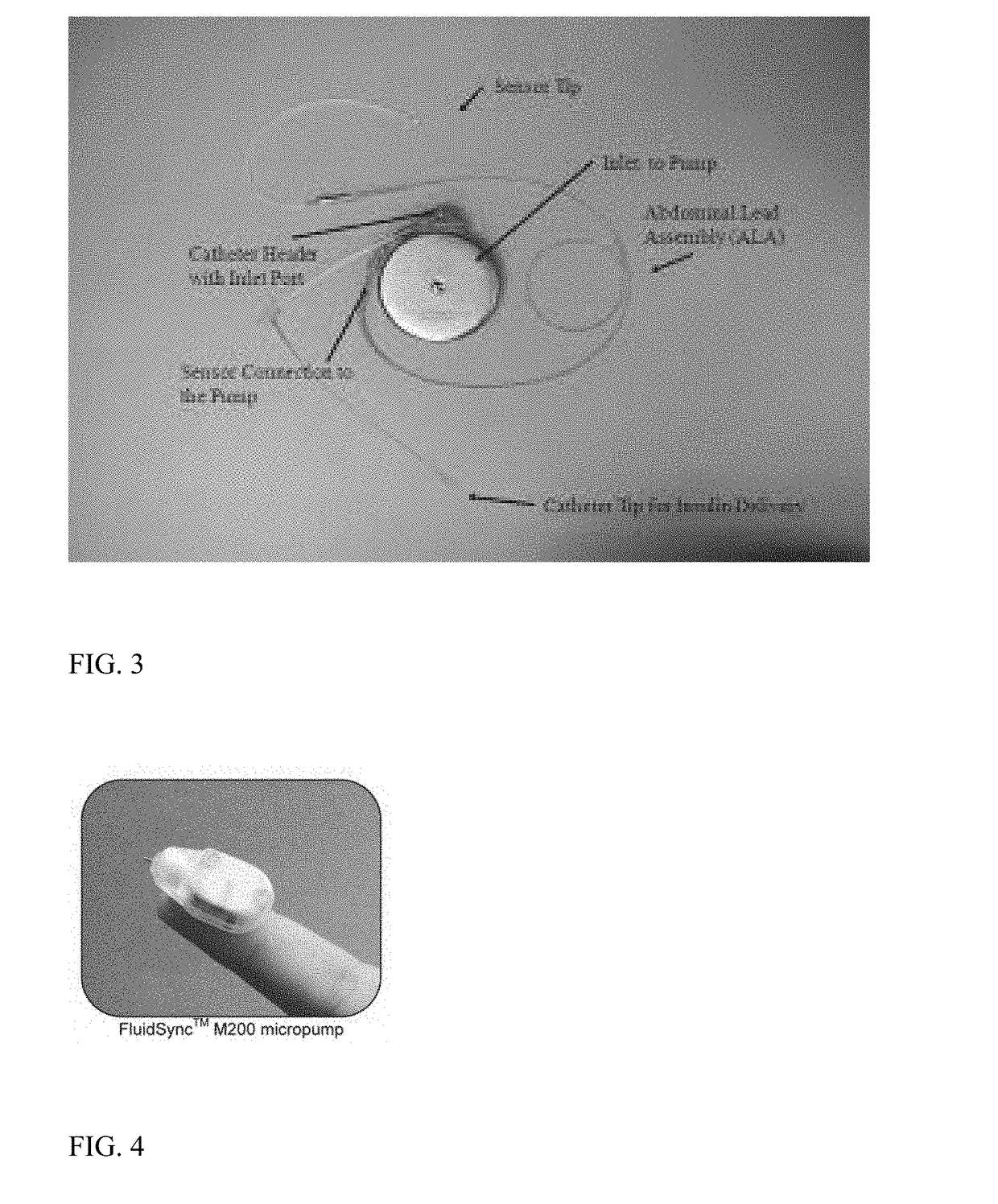
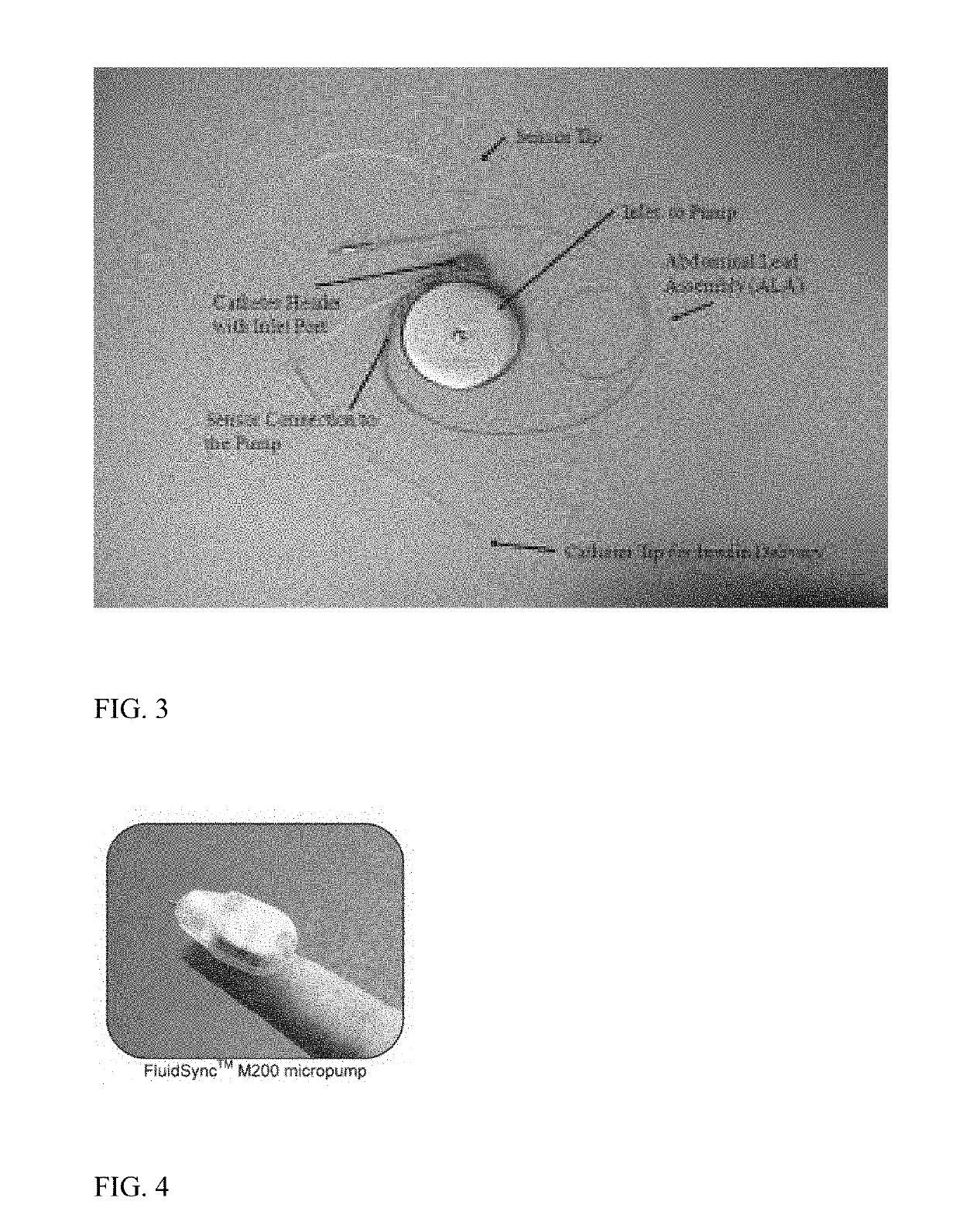
Stimulator, pump & composition
Described is a low voltage, pulsed electrical stimulation device for controlling expression of, for example, follistatin, a muscle formation promotion protein, by tissues. Epicardial stimulation is especially useful for heart treatment. Follistatin controlled release is also useful for treating other ailments, such as erectile dysfunction, aortic aneurysm, and failing heart valves.
Owner:LEONHARDT VENTURES LLC
Linear electromechanical device-based artificial muscles, bio-valves and related applications
A biological function assist apparatus composed of a linear electronmechanical device or system wrapped in protective coating and controlled by a controller, which also provides power to the electromechanically-based system. The electromechanically-based system can be formed as a mesh using linear motors or linear actuators or a larger electromechanically grid and wrapped around a failing heart. The electromechanical system can be formed in a circle forming an artificial valve (e.g., sphincter). The electromechanically-based system can also operate as a bone-muscle interface, thereby functioning in place of tendons.
Owner:ORSEN
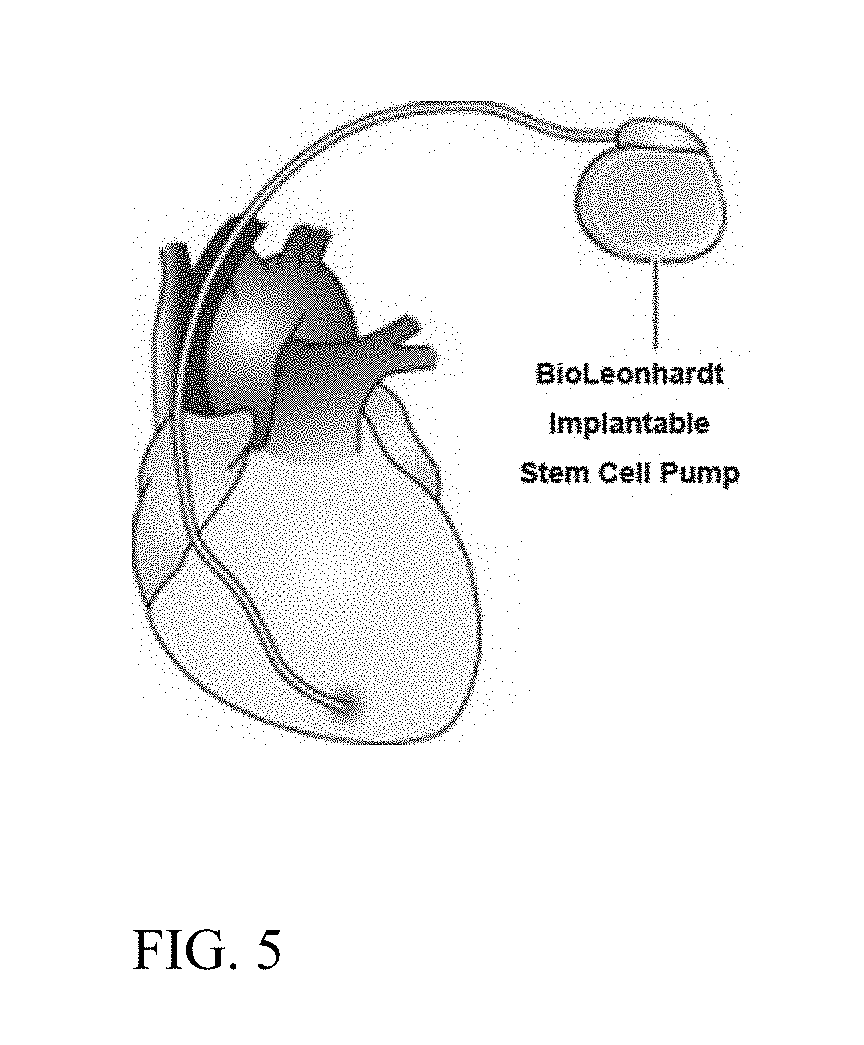
Methods and apparatus for in vivo cell therapy
InactiveUS20060122696A1Promote cell growthRecovery functionHeart valvesBlood vesselsMyogenesisHeart disease
The present invention includes a method and apparatus to transplant functional cells into failing heart muscle to cure heart disease. In particular, the present invention relates to a method and apparatus to deliver cell-composed medical device and / or three-dimensional cell composite per minimally invasive intracornonary approach to the infarct-related artery, allowing functional cells to home in and engraft to the zone of the infarct and peri-infarct tissue, in order to regenerate infarcted, scarred or non-functioning myocardial tissue into functioning muscle (“myogenesis”), also to create growth and proliferation of new blood vessel (“angiogenesis”) in the area.
Owner:ZHANG PING YE +1
Passive magnetik floating permanent heart ventricle auxiliary propeller-type blood pump
A permanent propeller-type blood pump for helping the failed heart is composed of rotor and stator. It features that a permanent-magnet bearing is used to realize passive magnetic floating for separating rotor from stator to avoid mechanical abrasion, and the physiological saline and heparin and directly introduced to it for avoiding blood coagulation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Artificial cardiac valve pump
An artificial cardiac valve pump for helping the failing heart by installing it in the heart is coposed of the rotor consisting of magnetic steel and blade wheel made of ferromagnetic material and the stator consisting of coil, iron core and guide blade at output position. Its shape and volume are same as those of natural valve.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Assist device for failing heart
A heart actuator device for use in heart assist apparatus, which device includes a paddle-like main body. The main body has a heart compressing wall, which in use is adapted to be affixed to at least a region of heart, and a distal wall, which in use is adapted to be distal that region of the heart. The heart compressing wall is movable in a direction relatively away from the distal wall, so as, in use to compress at least that region of the heart thereby assisting movement of the heart wall.
Owner:HEART ASSIST TECH PTY LTD
Implanted miniature streamlined shaft bloodshed pump
The invention relates to an embedded micro streamline axial flow blood pump, which can be used for assisting blood circulation of failed heart. The blood pump comprises a pump body arranged in a sleeve body and a driving device arranged outside the pump body, wherein the pump body comprises the sleeve body, a front guide vane, a rotor and a back guide vane; the hubs of the front guide vane, a rotor and the back guide vane are designed integrally in an integral streamline form; and the front half part of the rotor is provided with an inductive blade. The blood pump can reduce the on-way pressure loss of the blood in the flow channel of the blood pump, improve efficiency and reduce hemolysis; and can promote the circumferential speed of the blood after entering into a rotor area due to the inductive blade arranged on the front half part of the rotor, and avoids the occurrence of vacuole phenomenon.
Owner:中山好特人工心脏实验室有限公司
Stimulator, pump and composition
Described is a low voltage, pulsed electrical stimulation device for controlling expression of, for example, follistatin, a muscle formation promotion protein, by tissues. Epicardial stimulation is especially useful for heart treatment. Follistatin controlled release is also useful for treating other ailments, such as erectile dysfunction, aortic aneurysm, and failing heart valves.
Owner:LEONHARDT VENTURES LLC
Minimally invasive intervention-type artificial heart axial flow blood pump
ActiveCN112807564AReduce resistanceReduce disturbanceBlood pumpsMedical devicesBlood pumpFailing heart
Disclosed is a minimally invasive intervention-type artificial heart axial flow blood pump. The minimally invasive intervention-type artificial heart axial flow blood pump is used for assisting in blood circulation of a failing heart. The blood pump comprises a front catheter, a sleeve, a pump body and a micro motor, wherein the pump body and the micro motor are arranged in the sleeve, the micro motor is fixed on the sleeve, and the pump body comprises a rotor hub, rotor blades, a rear guide vane hub and rear guide vane blades. The blood pump is mainly characterized in that the gradually-varying inner diameter is adopted, the minimum sectional area of the gradually-varying inner diameter is the same as the sectional area of a flow field area in the middle of a rotor, and the rotor hub is connected with the rear guide vane hub through a tooth-shaped sealing structure. Under the condition that the sectional area of the flow field of the rotor area is basically unchanged, the energy loss caused by the change of the sectional area of the flow field is effectively reduced, so that the working efficiency of the blood pump is improved. Meanwhile, invasion of blood cells in gap areas is avoided, the problem that damage to the blood cells in the gap areas of the rotor hub and the rear guide vane hub of an existing minimally invasive intervention-type axial flow blood pump is large is solved, which remarkably enhances the reliability of the blood pump accordingly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Heart wall tension reduction apparatus
InactiveUS20150105611A1Reduce tensionReduce energy consumptionSuture equipmentsHeart valvesHeart chamberFailing heart
An apparatus and method for treatment of a failing heart. In one embodiment, the apparatus and method includes a deploying a tension member for drawing at least two portions of the heart toward each other across a heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Inhibition of mypb-c binding to myosin as a treatment for heart failure
InactiveUS20130345135A1Improve athletic abilityReduce pressurePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesMyosin-binding protein CFailing heart
The present invention provides for methods of treating and slowing the onset of heart failure. The inventors have determined that myosin binding to unphosphorylated Myosin Binding Protein C (MyBP-C) plays a key role in the diminution of cardiac contractile force and frequency in heart failure. The present invention provides peptide inhibitors of the MyBP-C / myosin interaction, thereby increasing both cardiac contractile force and frequency in the failing heart, as well as in patients not yet exhibiting frank heart failure.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Bioelectric stimulator
ActiveUS10960206B2Quality improvementExpansion quantityMedical devicesPressure infusionEngineeringBiology
Described is a low voltage, pulsed electrical stimulation device for controlling expression of, for example, follistatin, a muscle formation promotion protein, by tissues. Epicardial stimulation is especially useful for heart treatment. Follistatin controlled release is also useful for treating other ailments, such as erectile dysfunction, aortic aneurysm, and failing heart valves.
Owner:LEONHARDT VENTURES LLC
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of cardiomyopathies
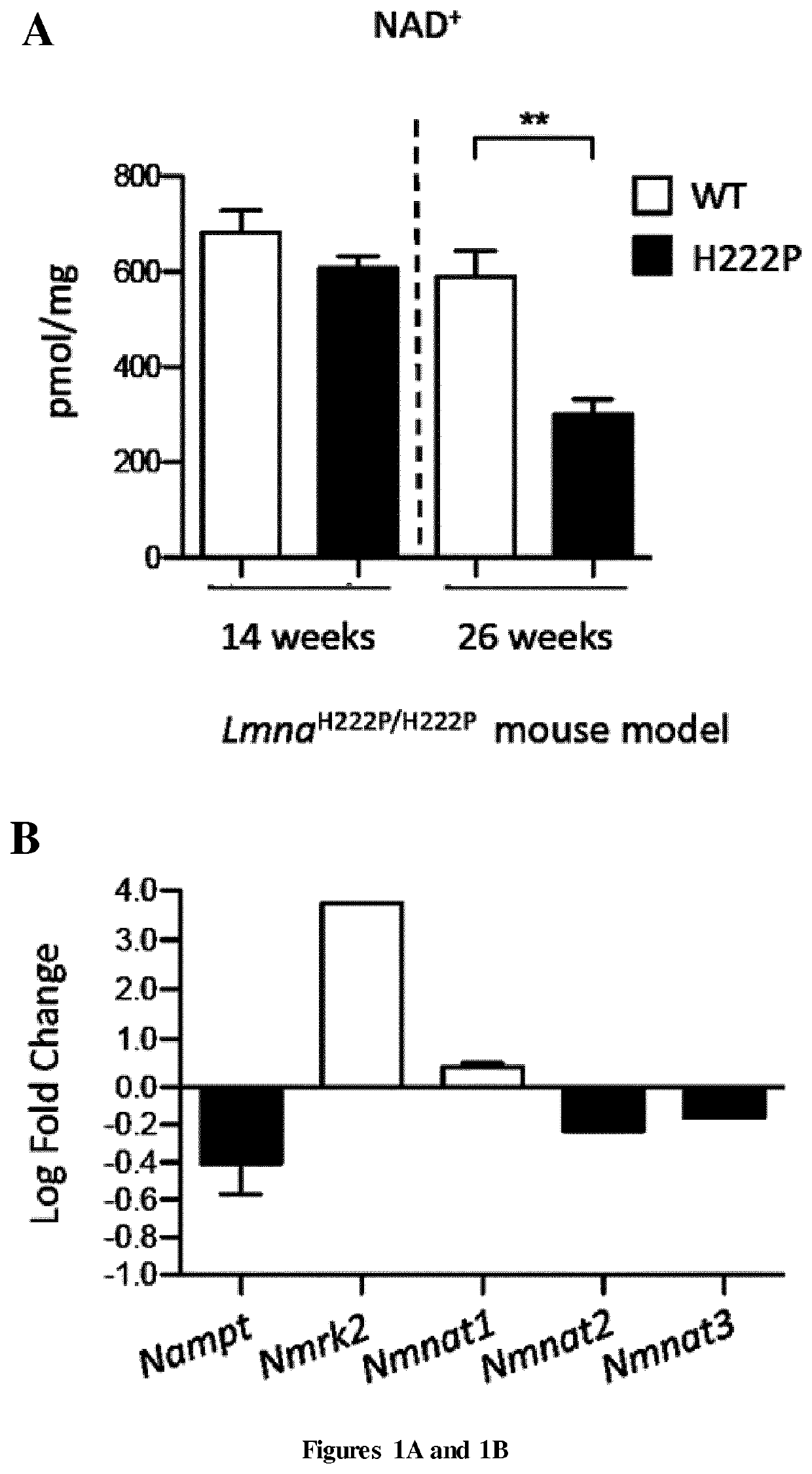
InactiveUS20190350955A1Improve heart functionReduces eccentric remodelingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNicotinamide riboside kinaseNicotinamide riboside
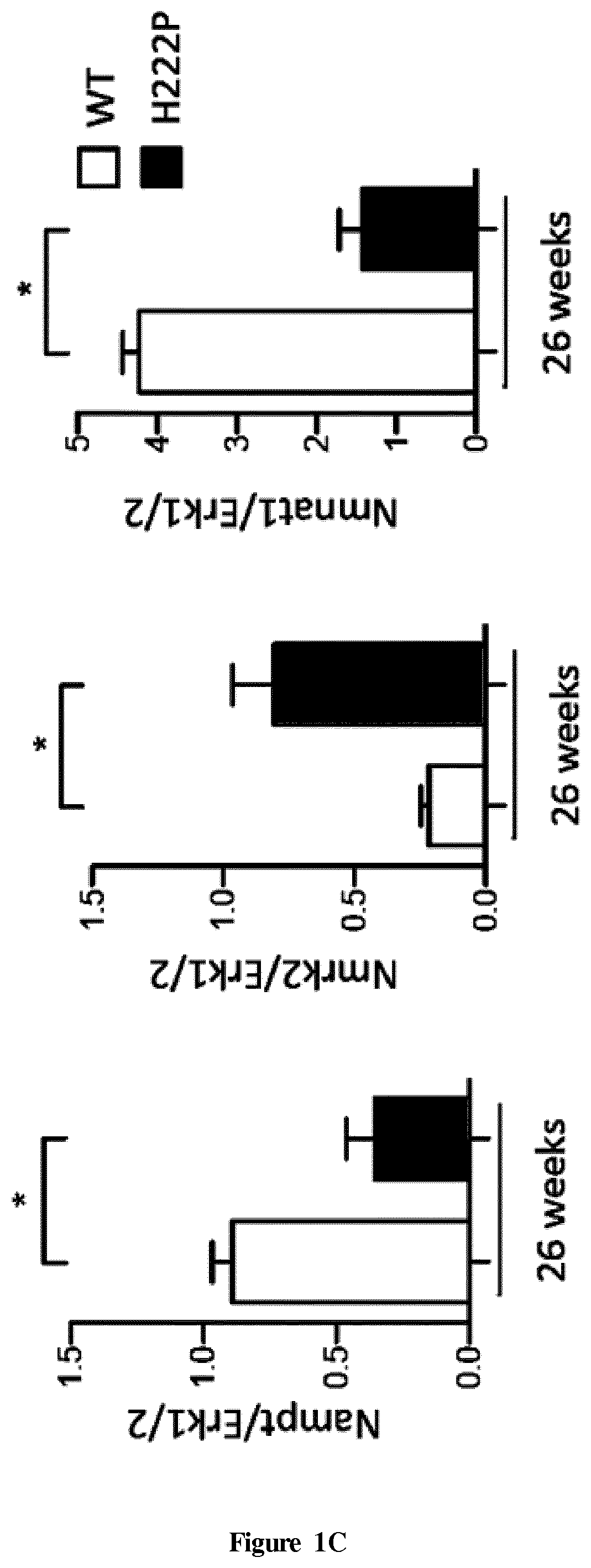
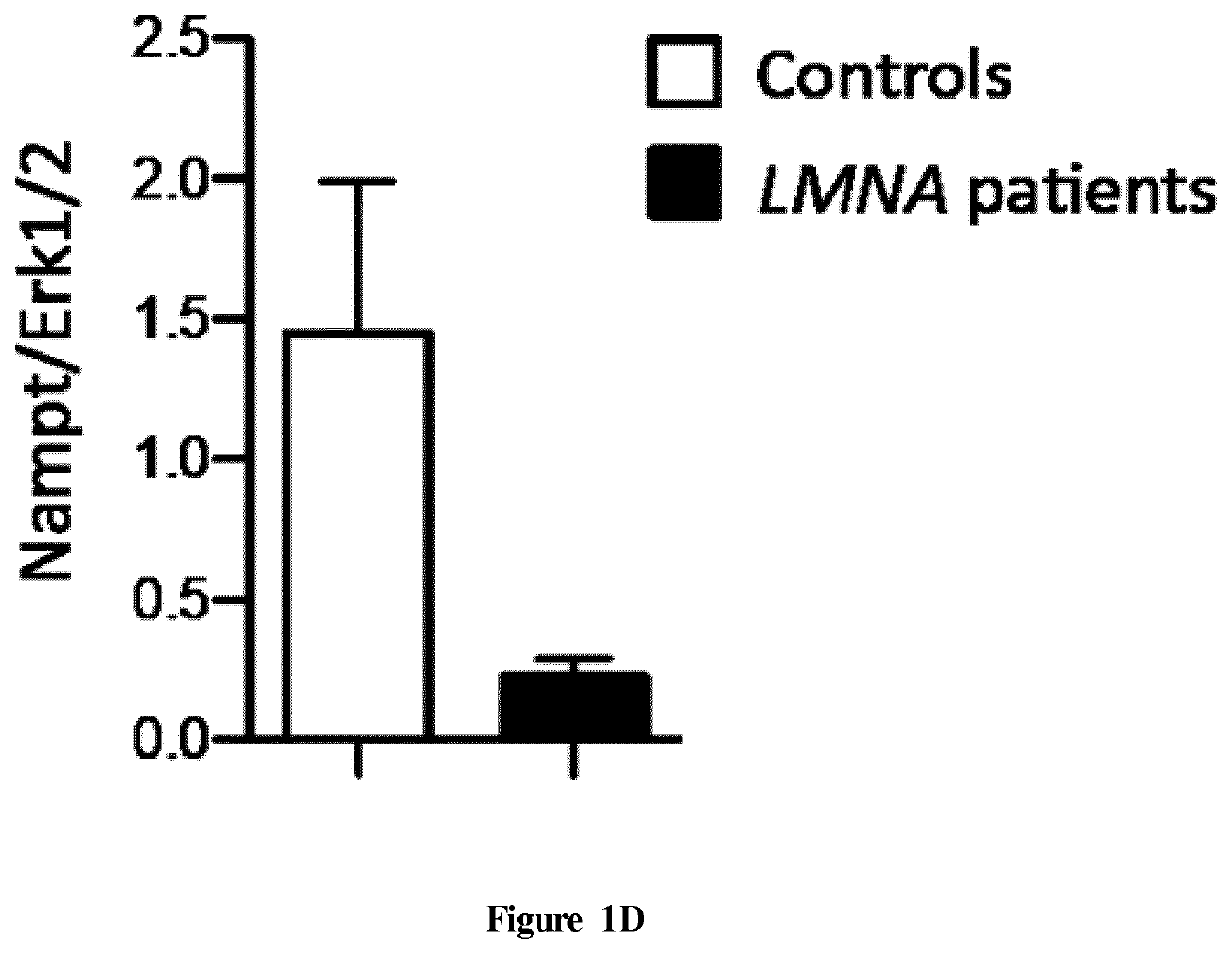
The present invention relates to methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of cardiomyopathies. The inventors showed that the nicotinamide riboside kinase Nmrk2 gene involved in NAD+ biosynthetic pathway is strongly induced in the heart of the mouse models of dilated cardiomyopathy and that Nmrk2 is an AMPK and PPARα responsive gene. They also showed that the NMRK enzymes substrate nicotinamide riboside supplementation in food markedly improves cardiac functions and reduces eccentric remodeling. The inventors demonstrated that both the NMRK1 and NMRK2 protein are expressed in the human healthy heart, that NMRK2 protein level is increased in human failing hearts as it is the case in mouse failing hearts in several models of heart failure and cardiomyopathies. In particular, the present invention relates to nicotinamide riboside for use in the treatment of cardiomyopathy in a human subject in need thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +3
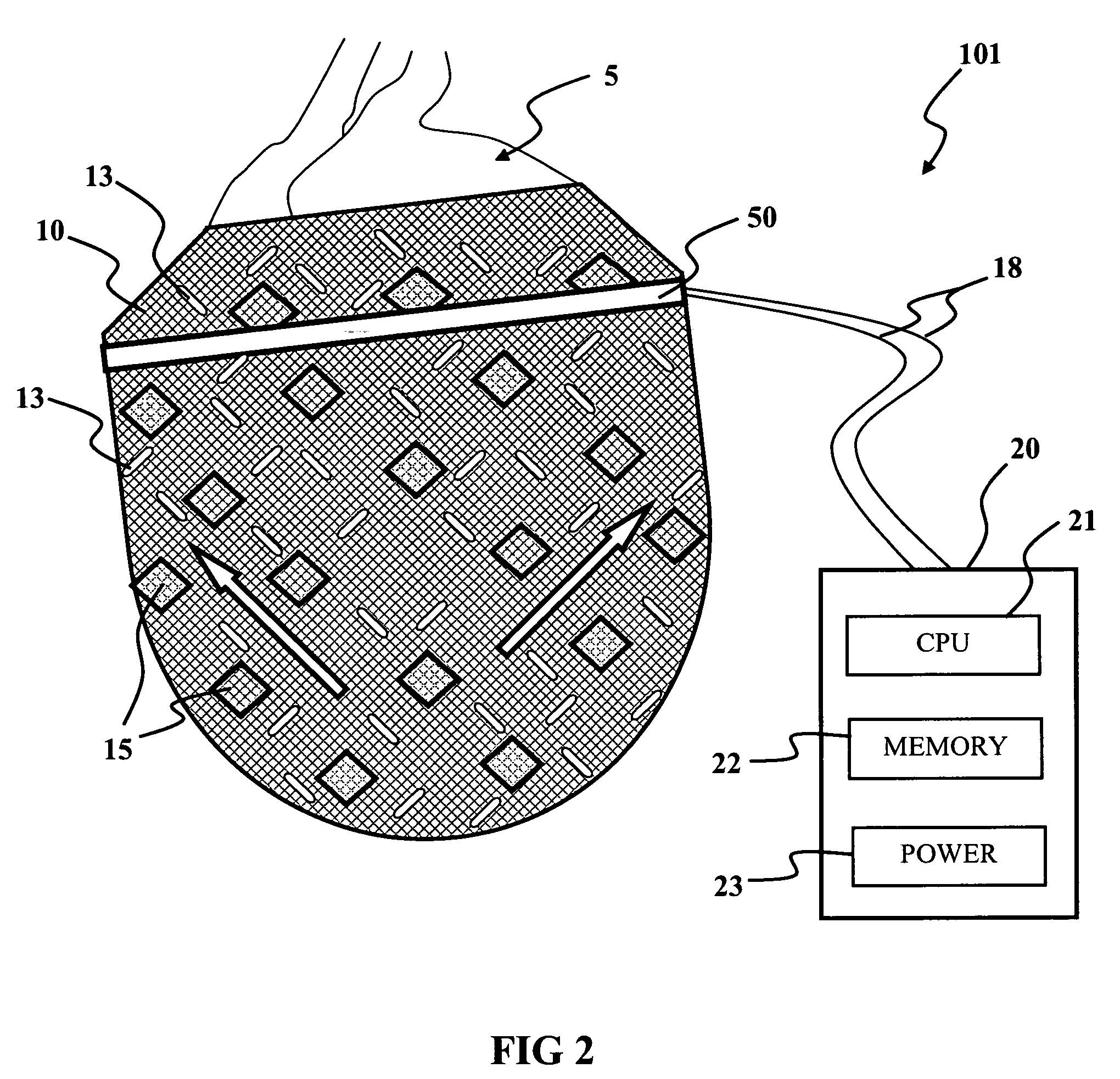
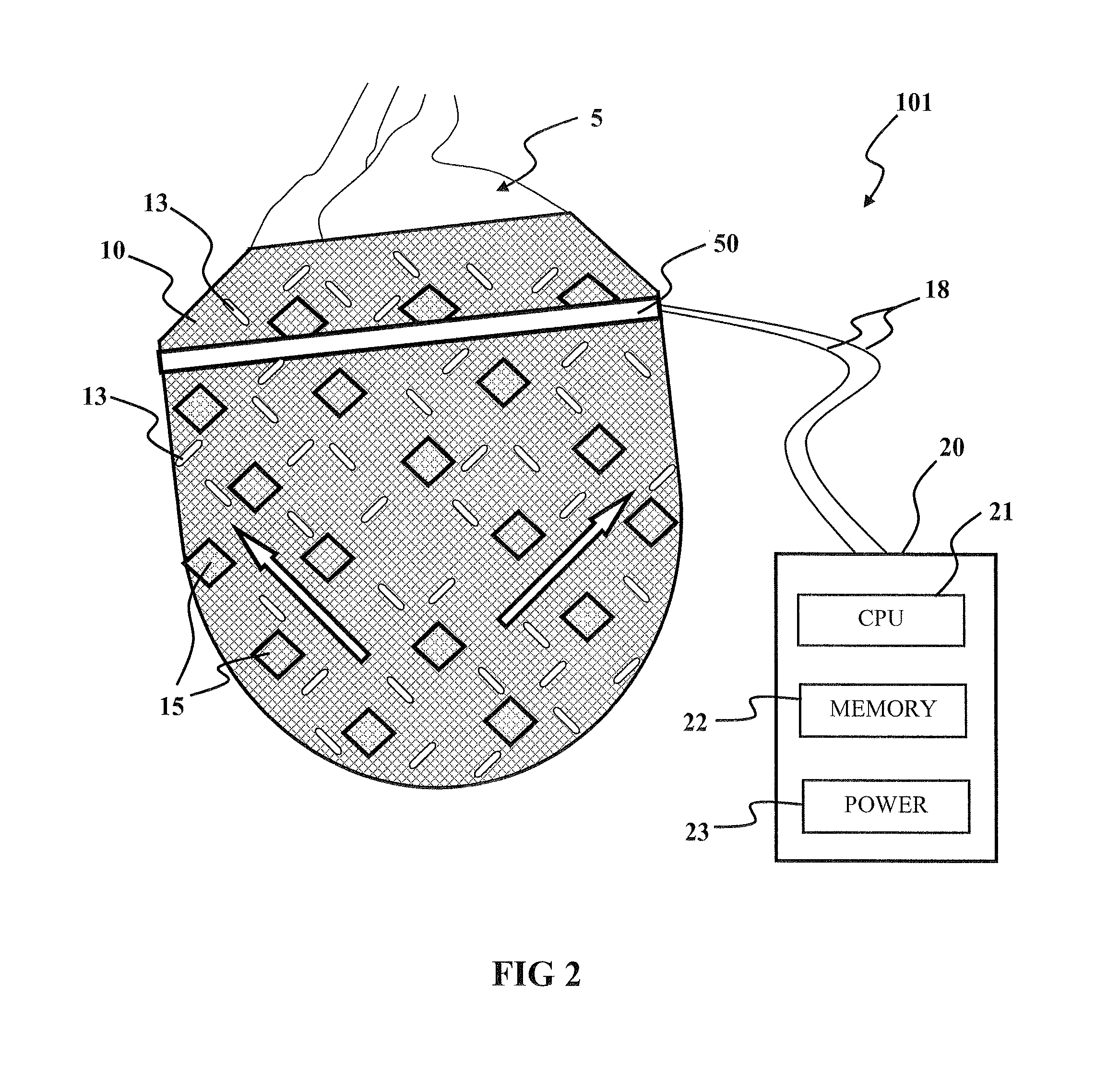
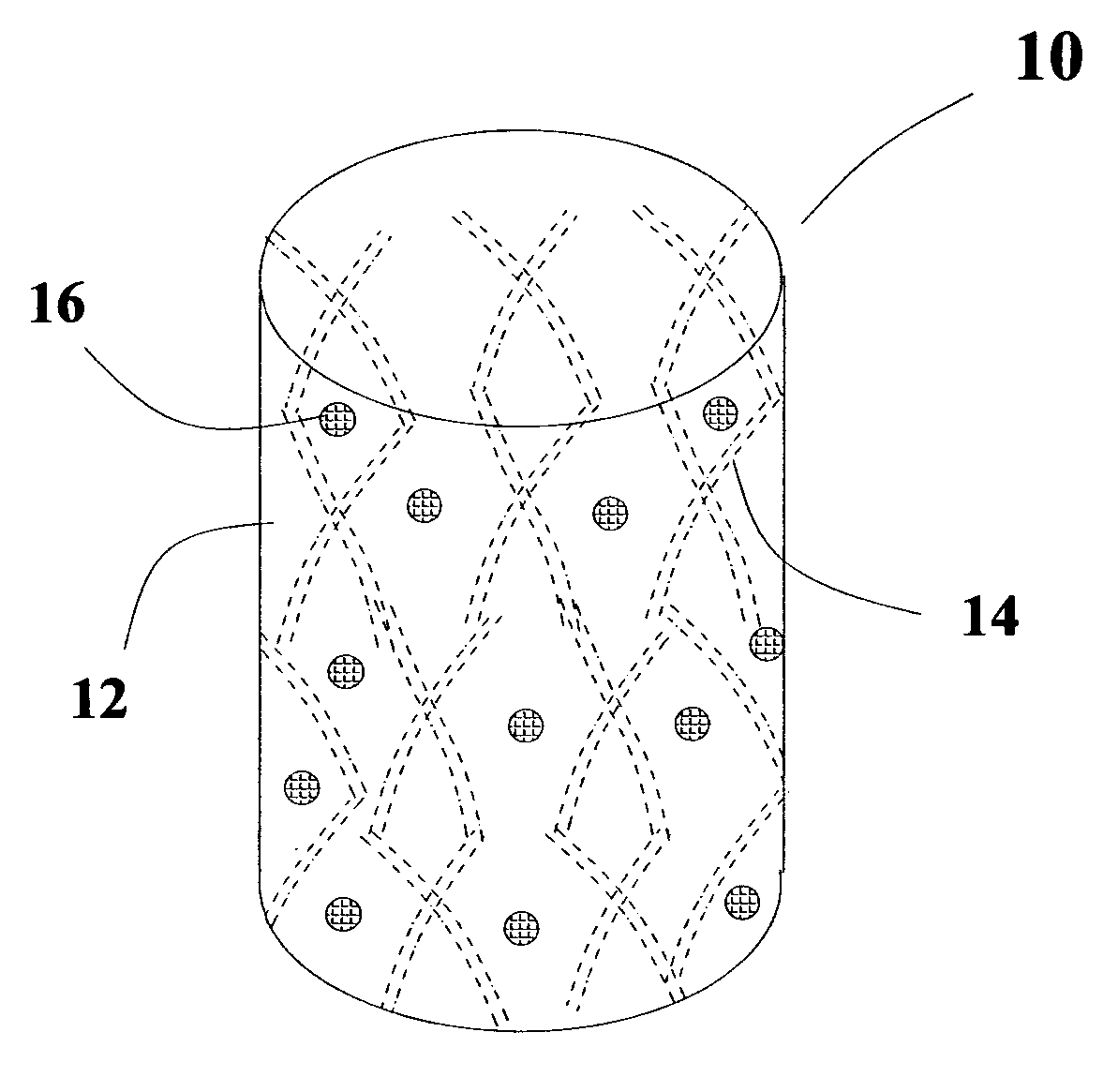
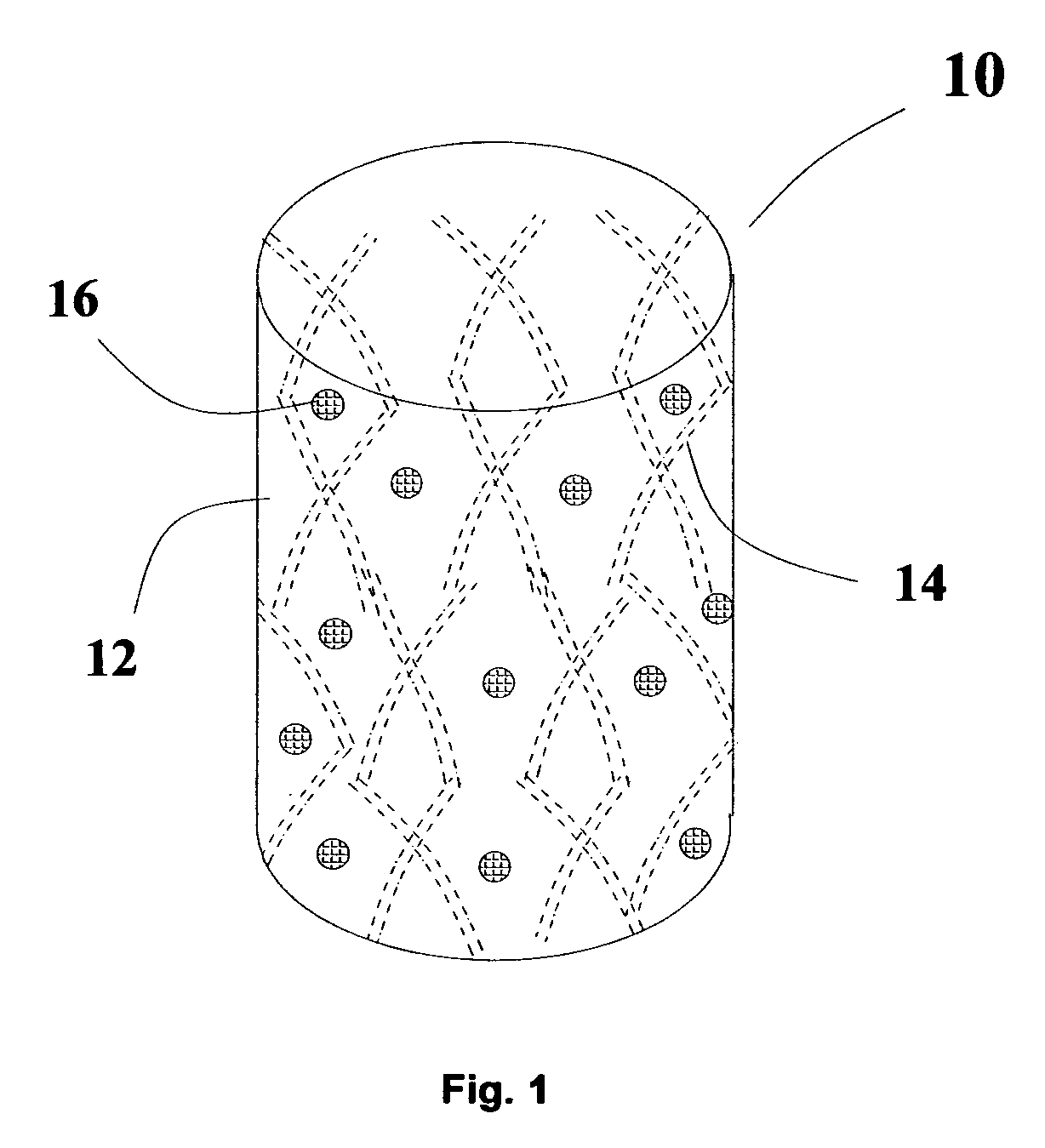
Intelligent Nanomagnetic Cardiac Assist Device for a Failing Heart
The present invention is directed to a contractible and expandable jacket configured to encase at least a portion of a patient's heart. The jacket has a plurality of individual contractile cells with each of the cells having a first electrically conductive coil and a second electrically conductive coil spaced from the first coil. The first coil preferably defines at least in part a first periphery of an inner nucleus of the cell and the second coil preferably defining at least in part an outer portion of the cell spaced outwardly from the inner nucleus. When electrical current passes through the first and second coils in opposite directions, the cell contracts and when electrical current passes through the first and second coils in the same direction the cell expands. Each of the individual cells has conductive appendages for conducting information to and from the individual cells.
Owner:MIRHOSEINI MAHMOOD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com