Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Heart mitral valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
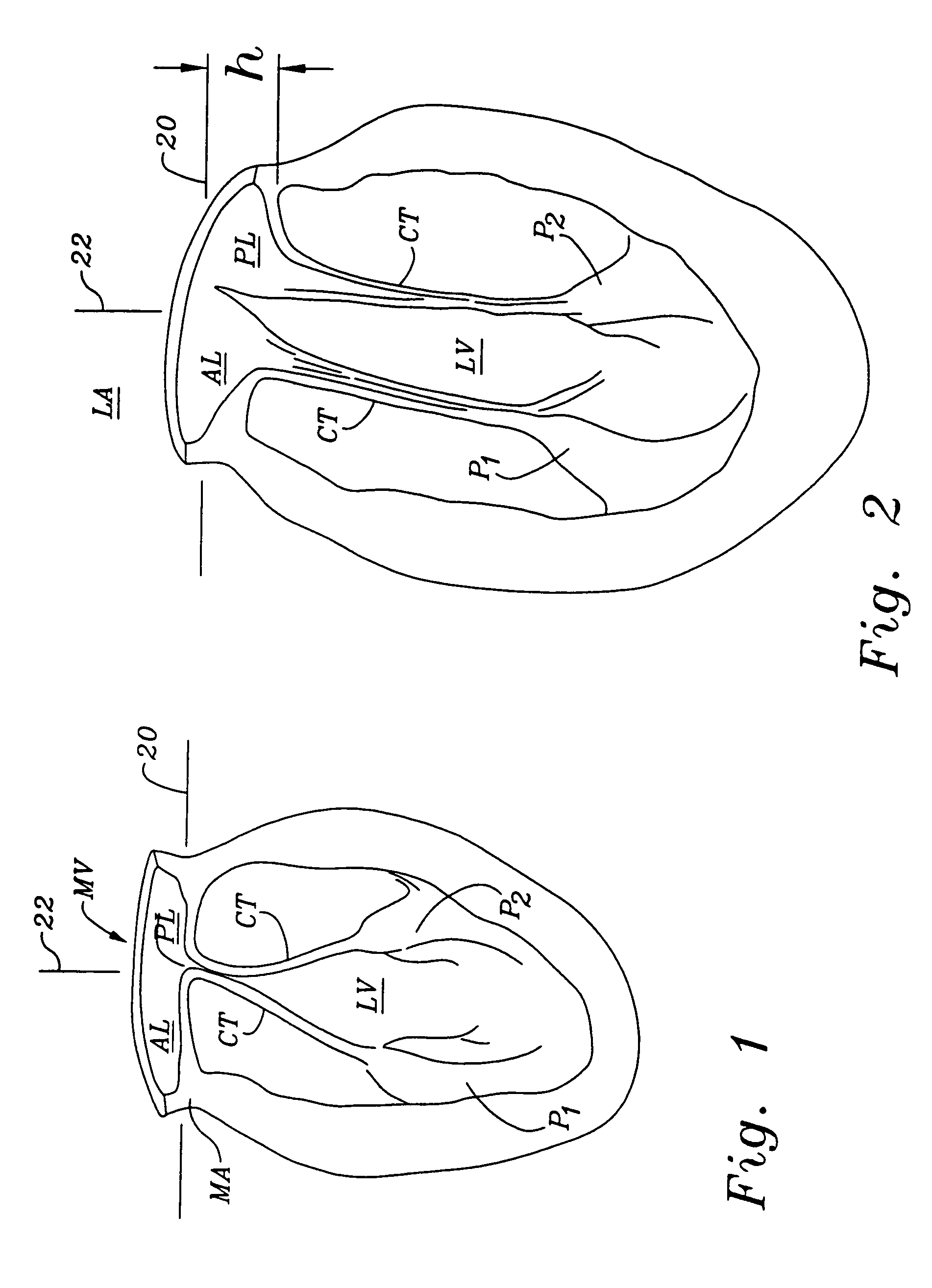
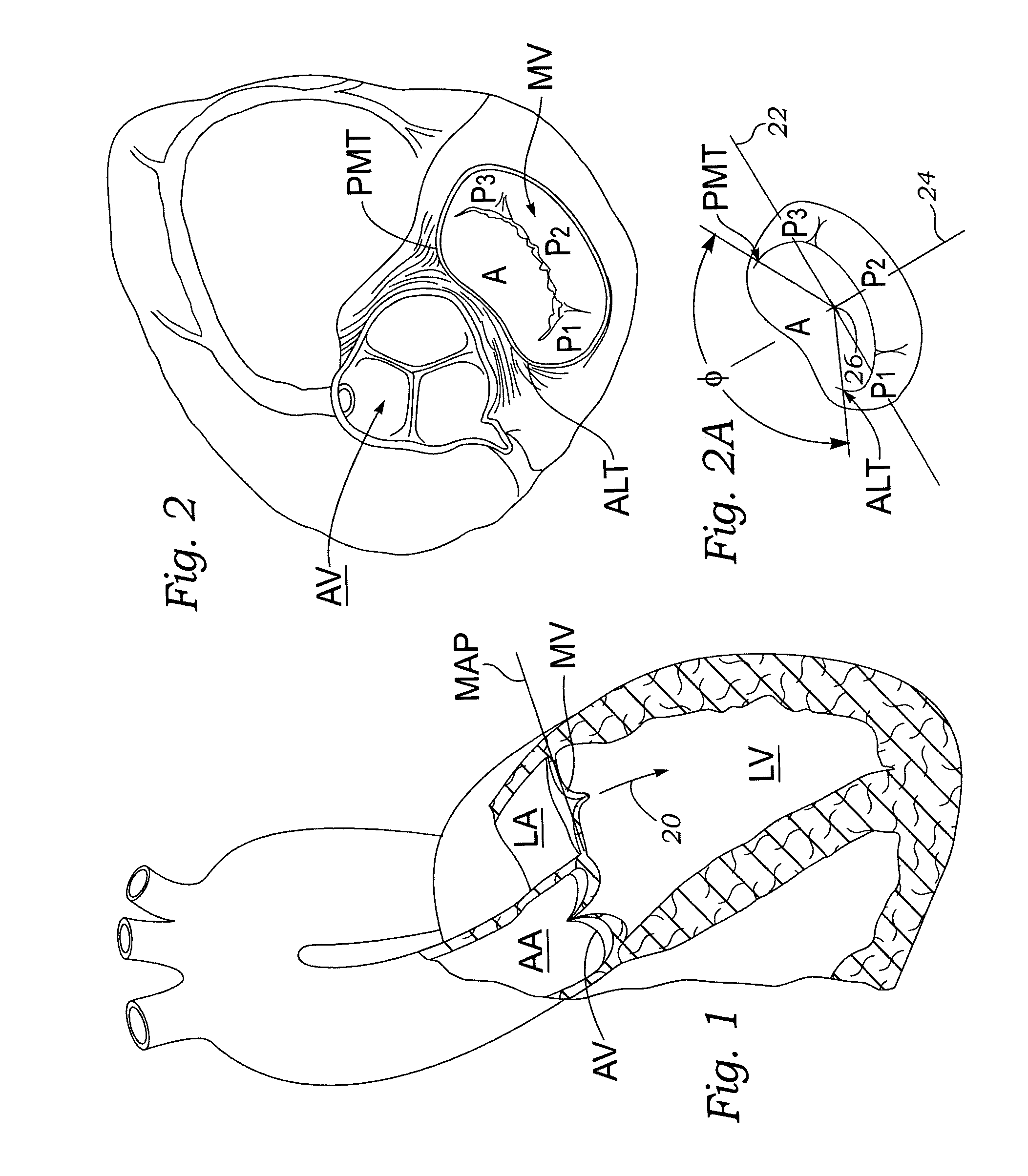
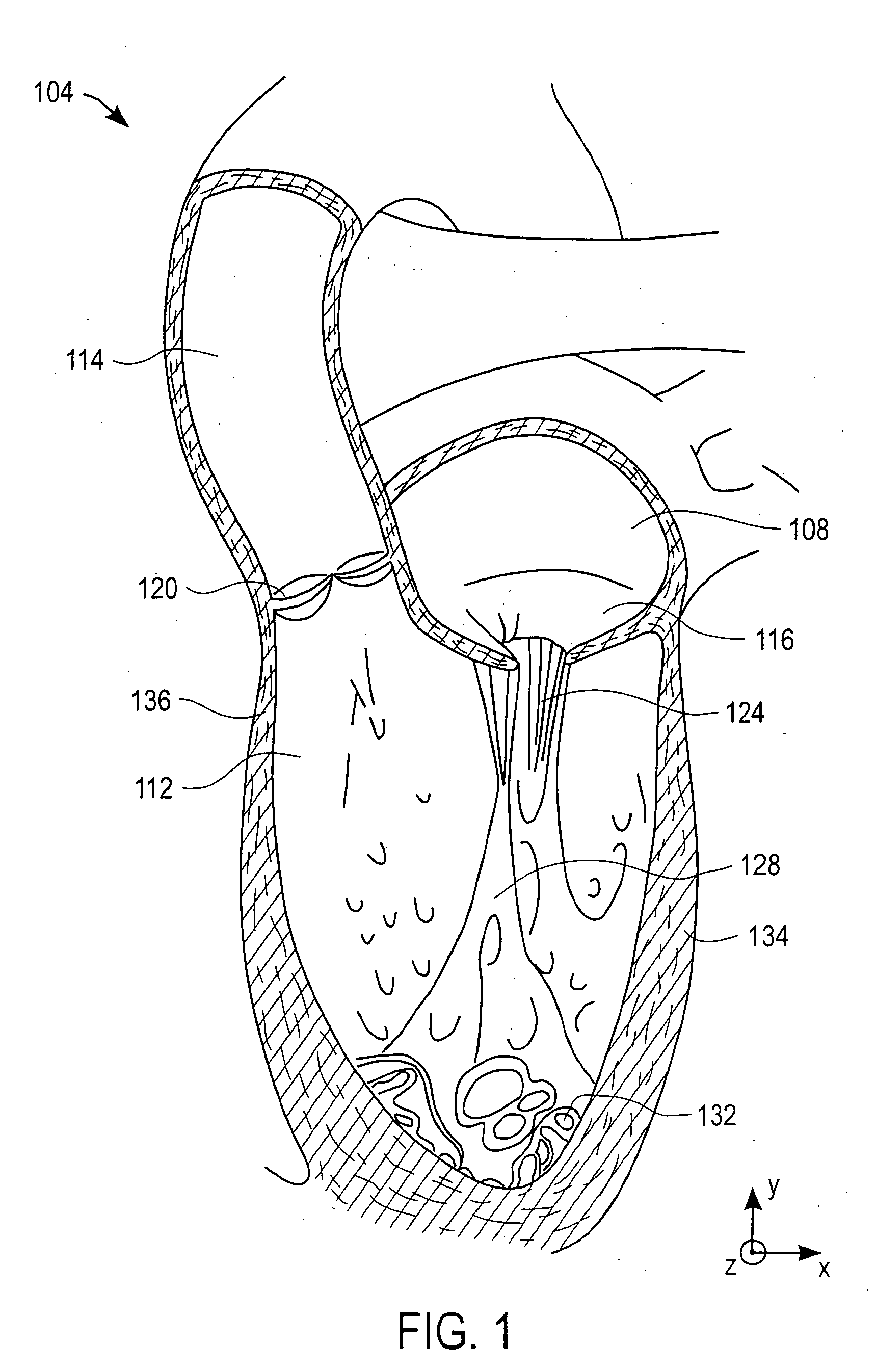
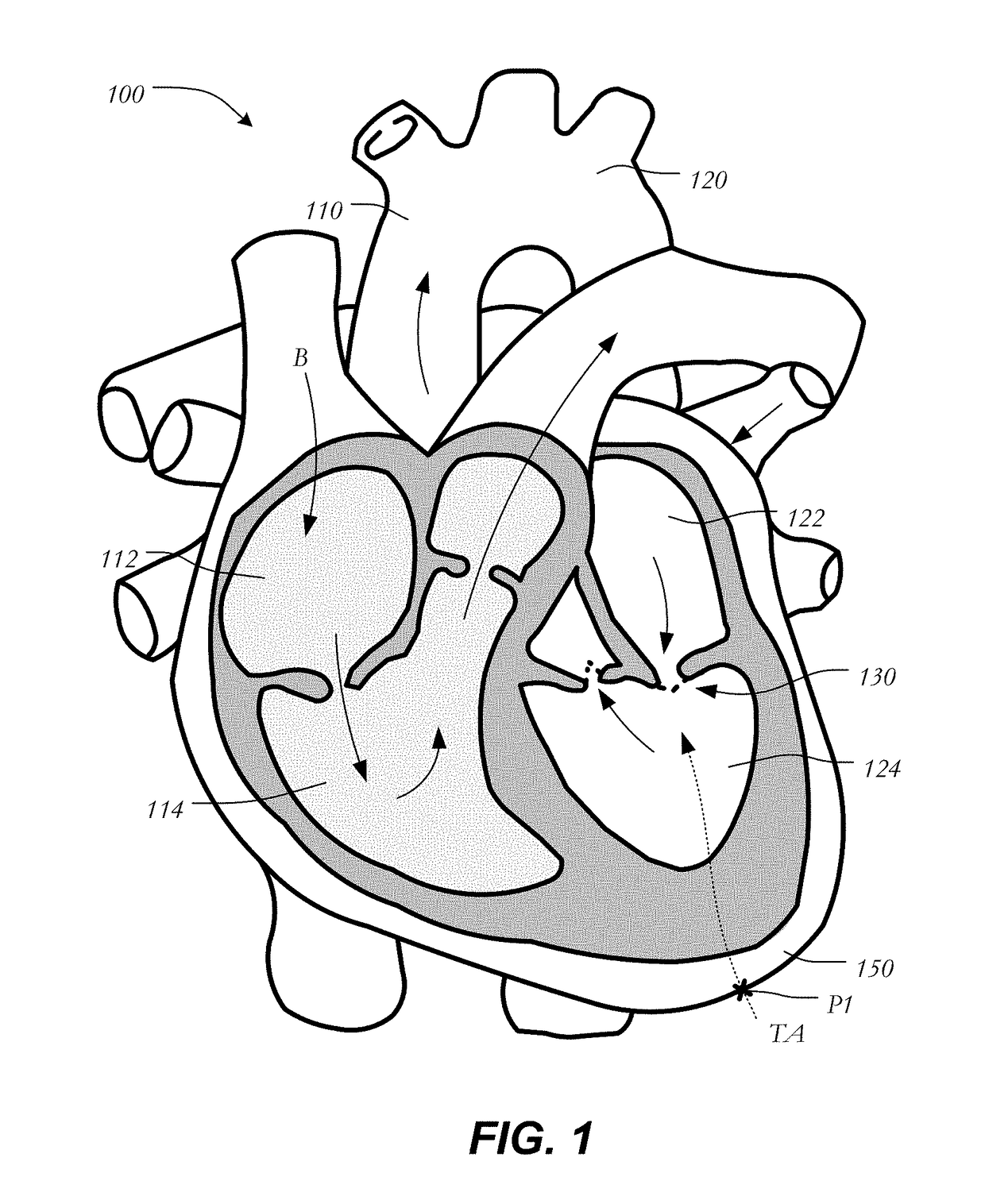
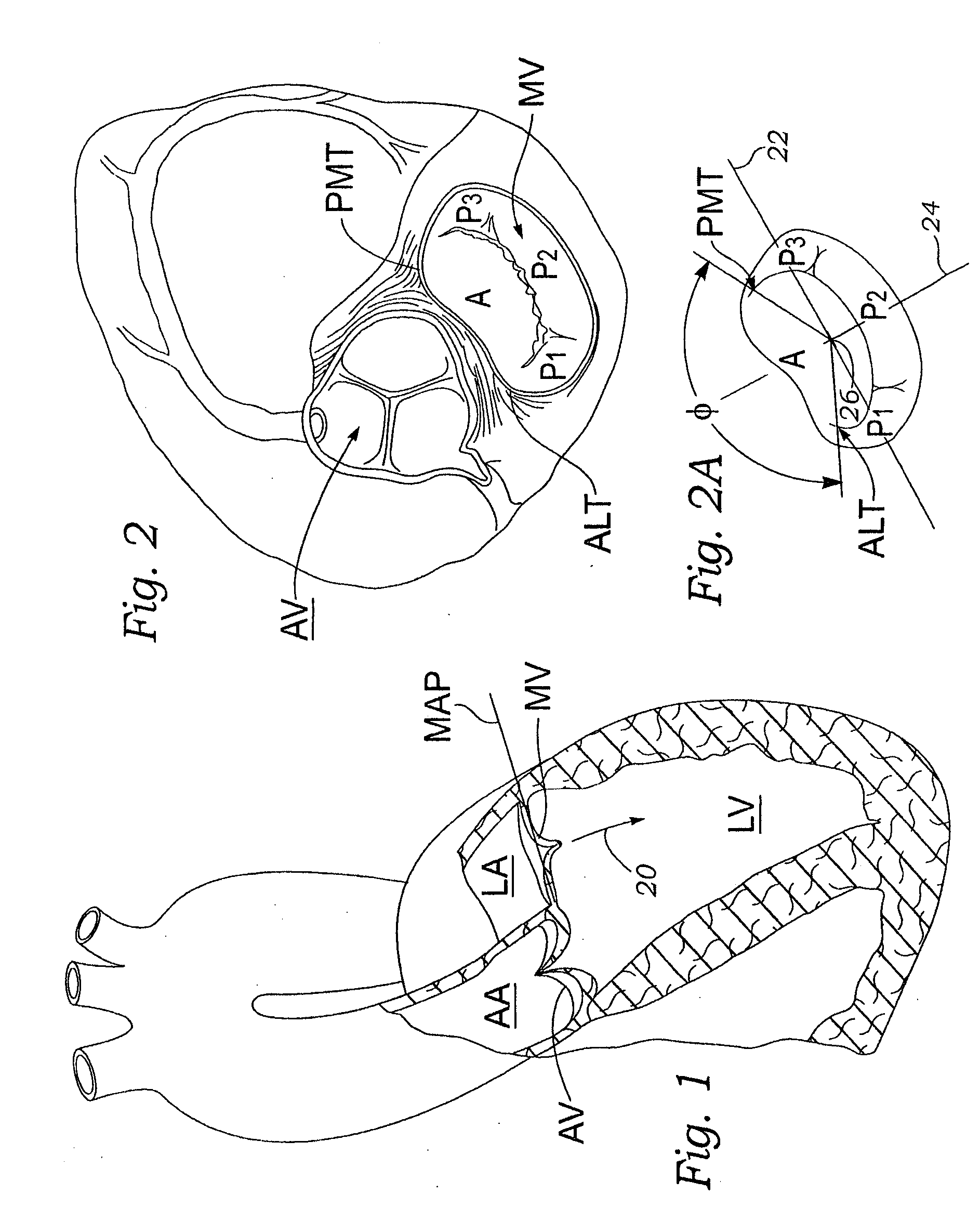
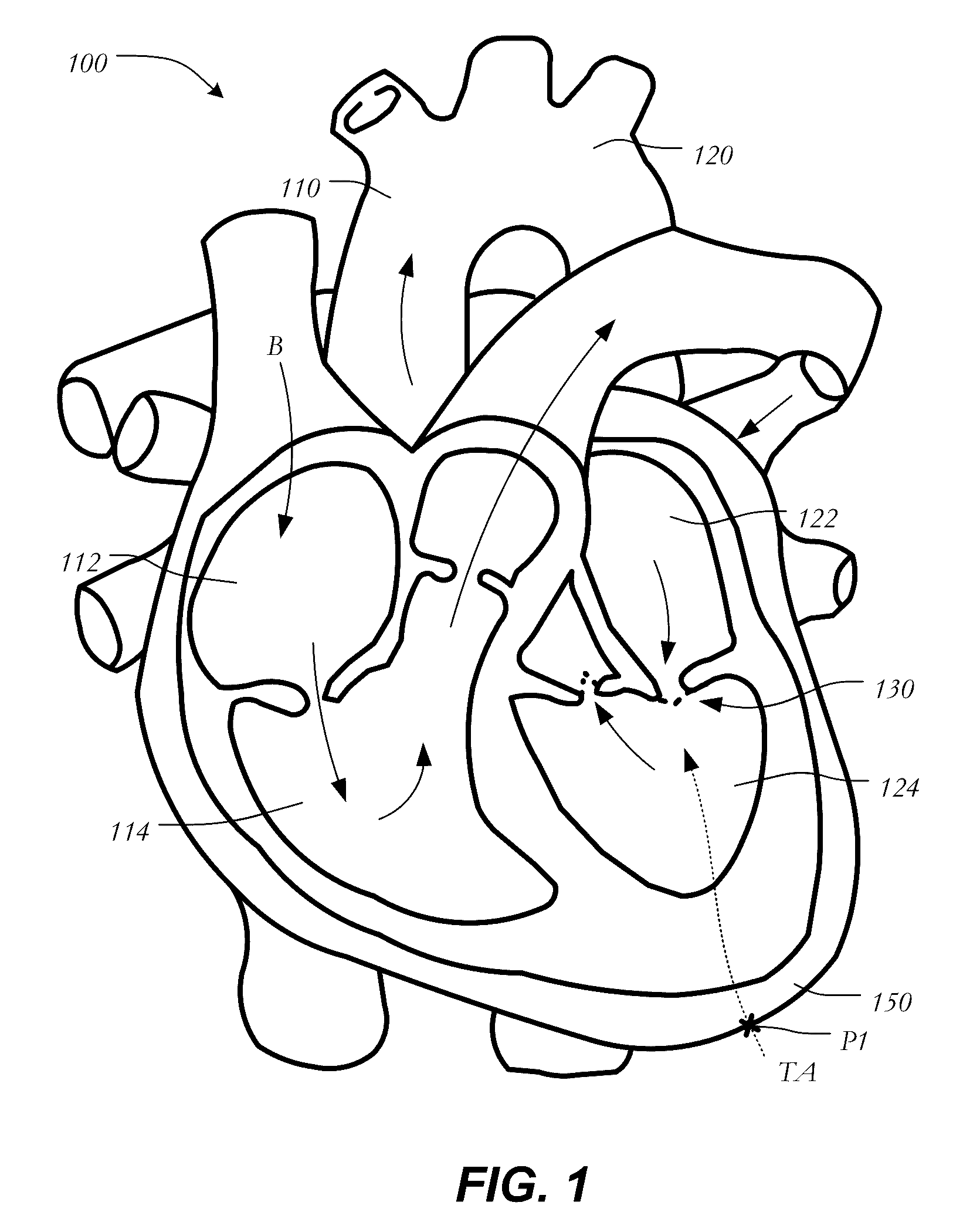
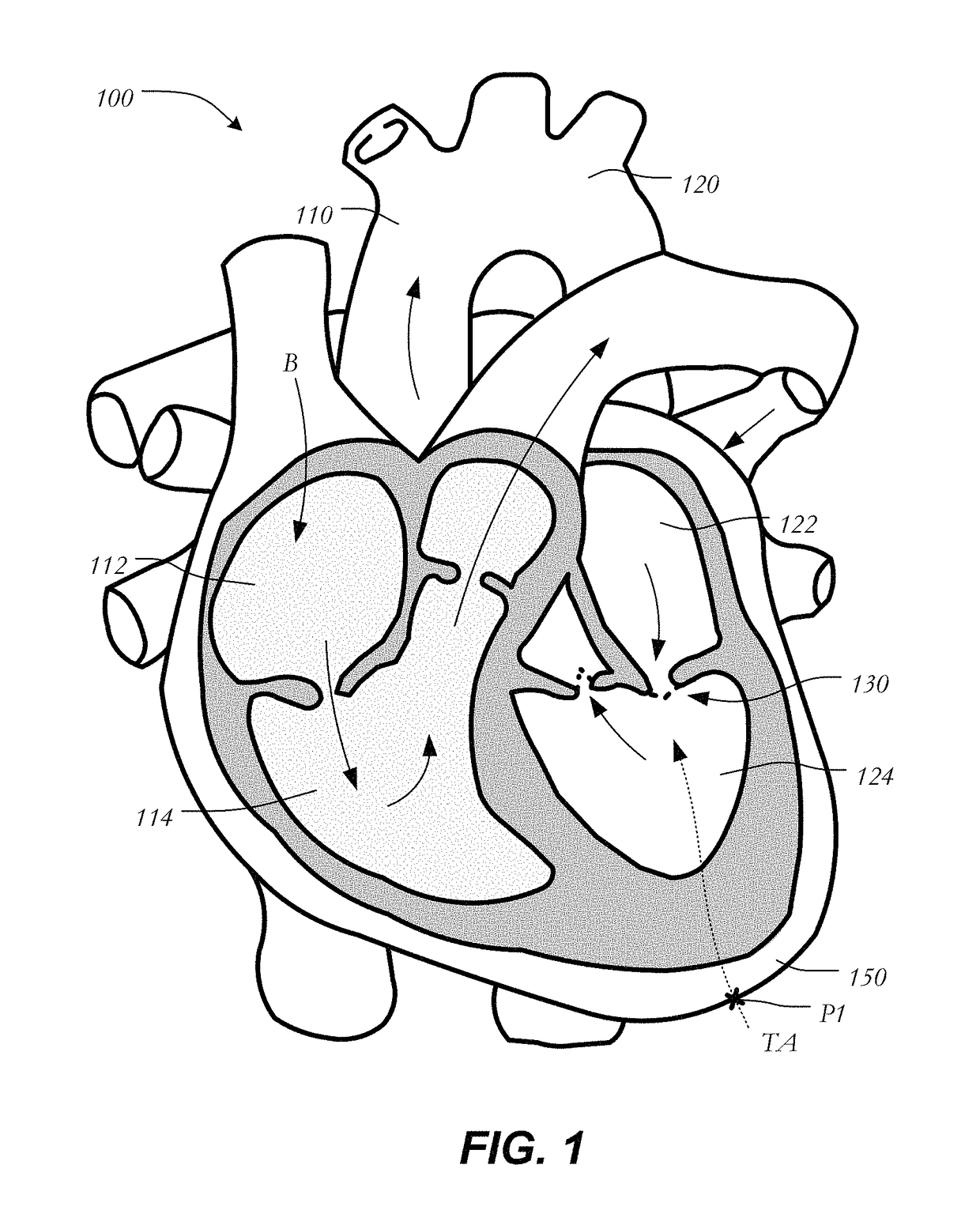
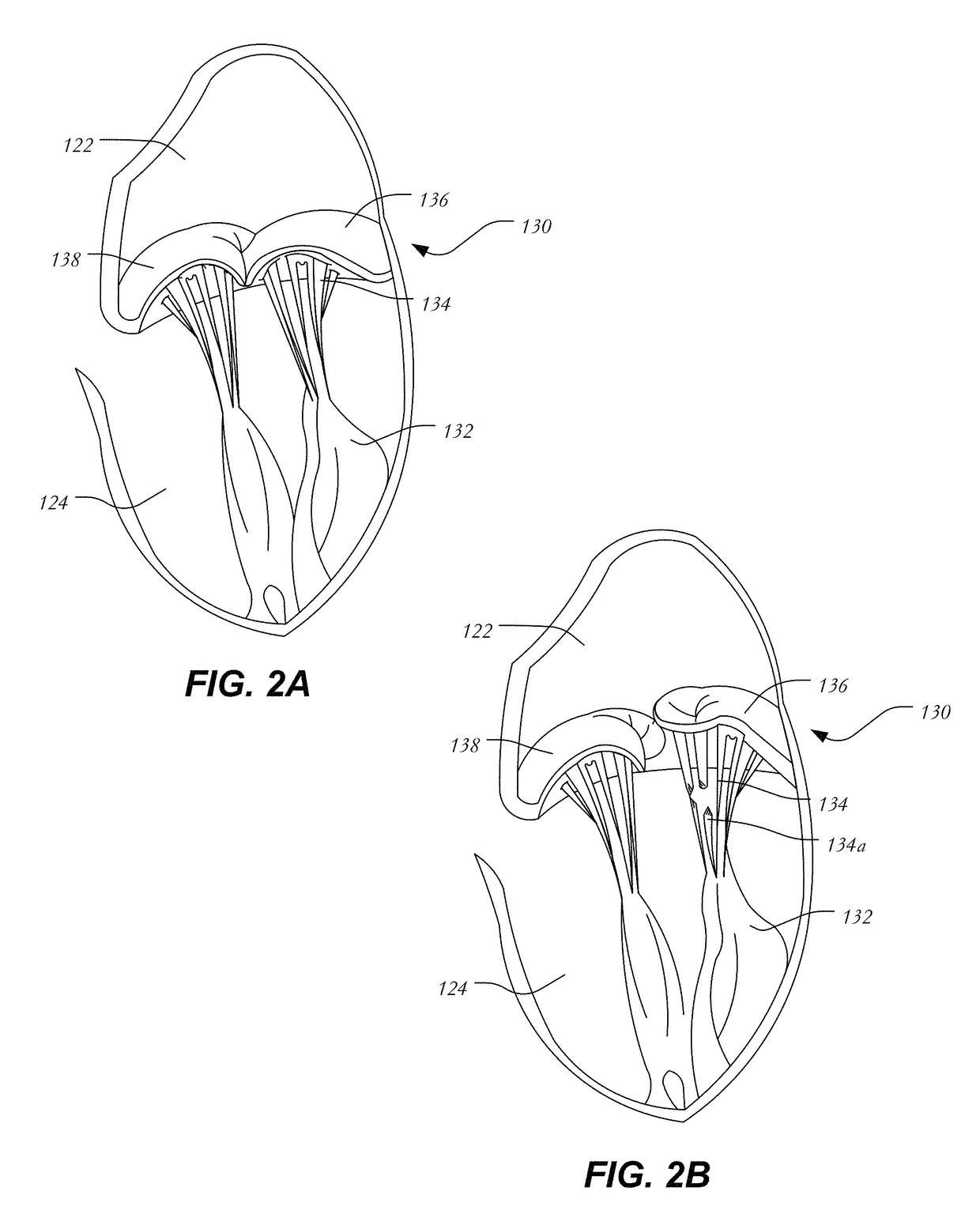
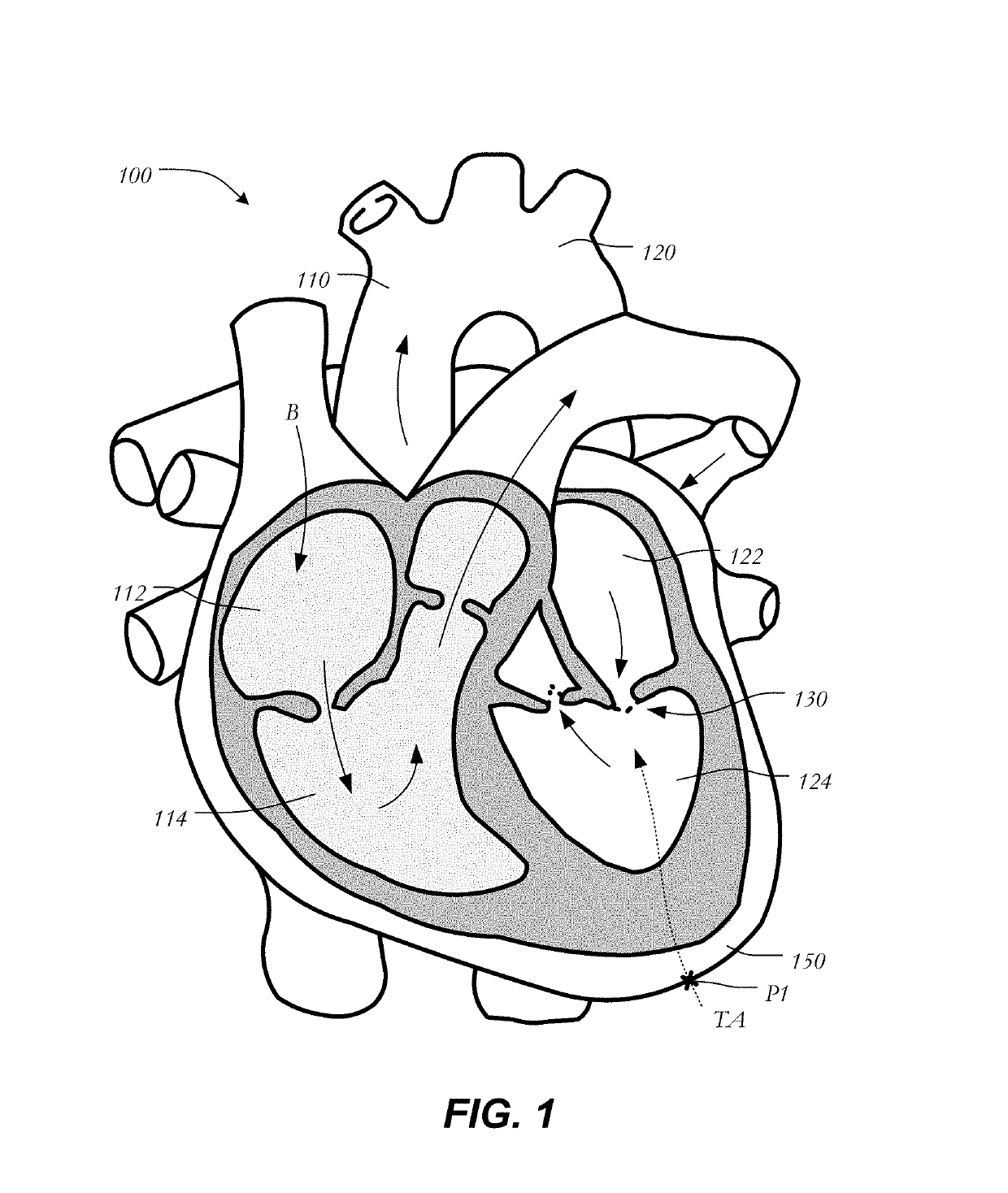
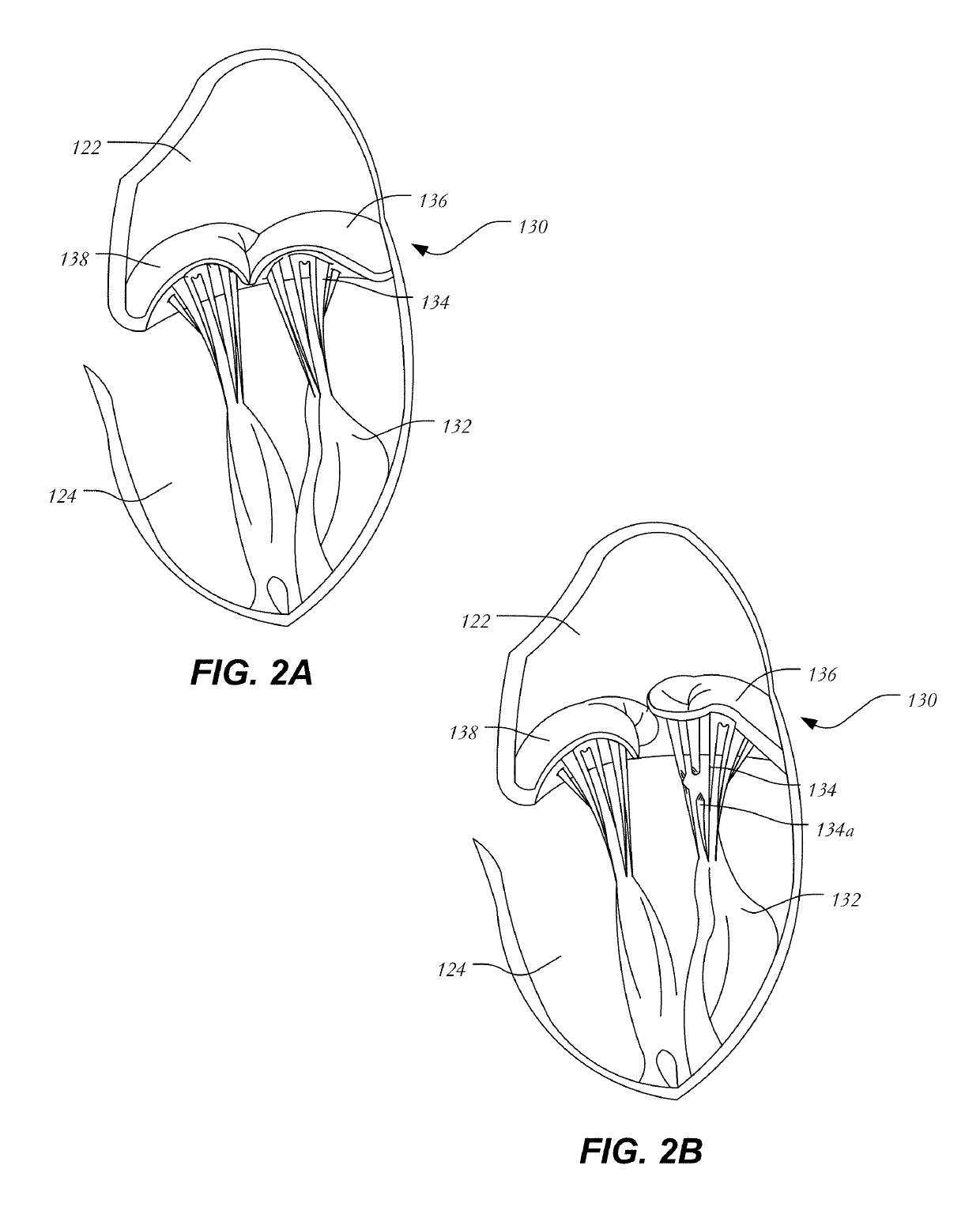
Anatomical terminology. [edit on Wikidata] The mitral valve (/ˈmaɪtrəl/), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is a valve with two flaps in the heart, that lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
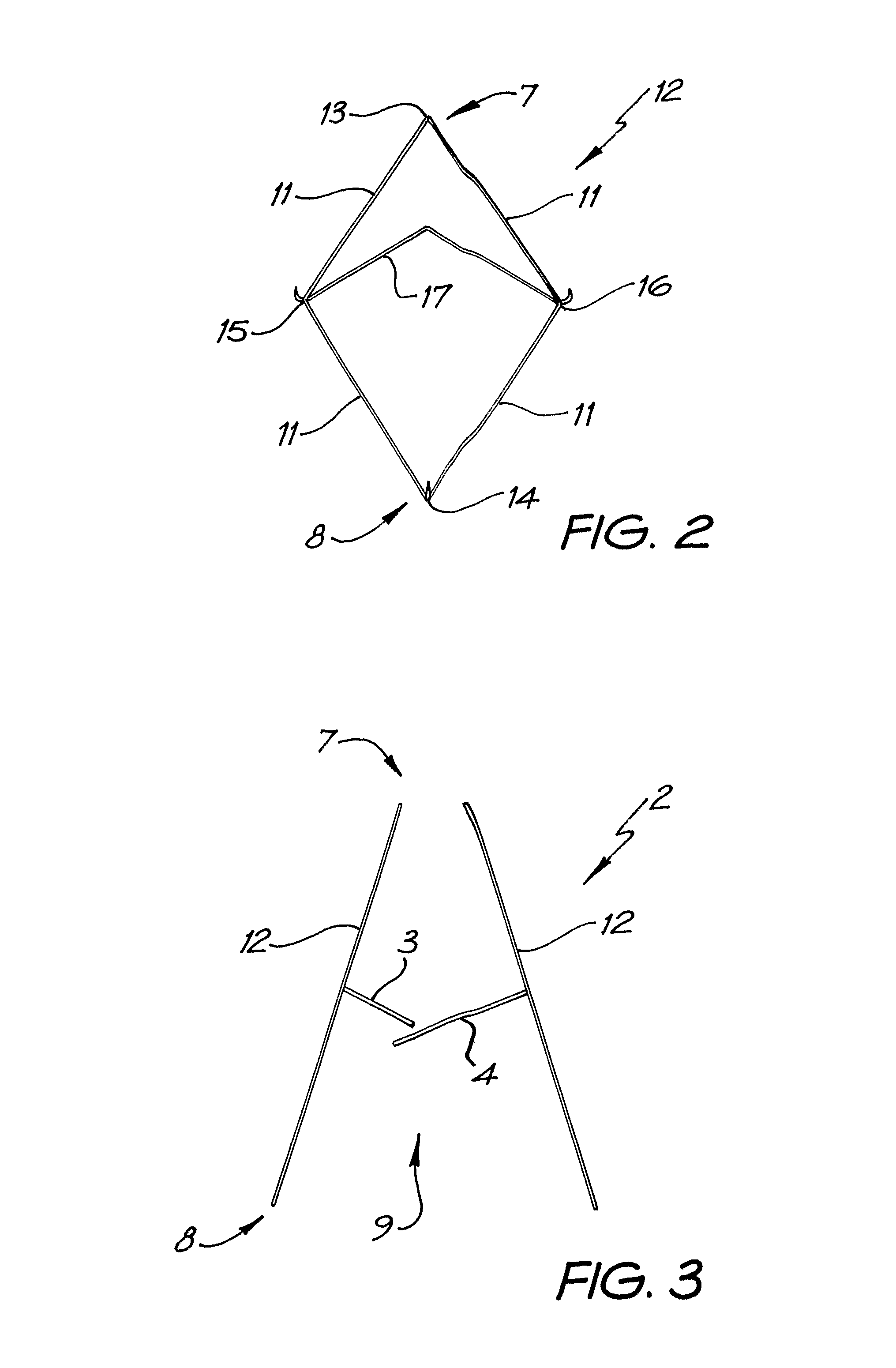
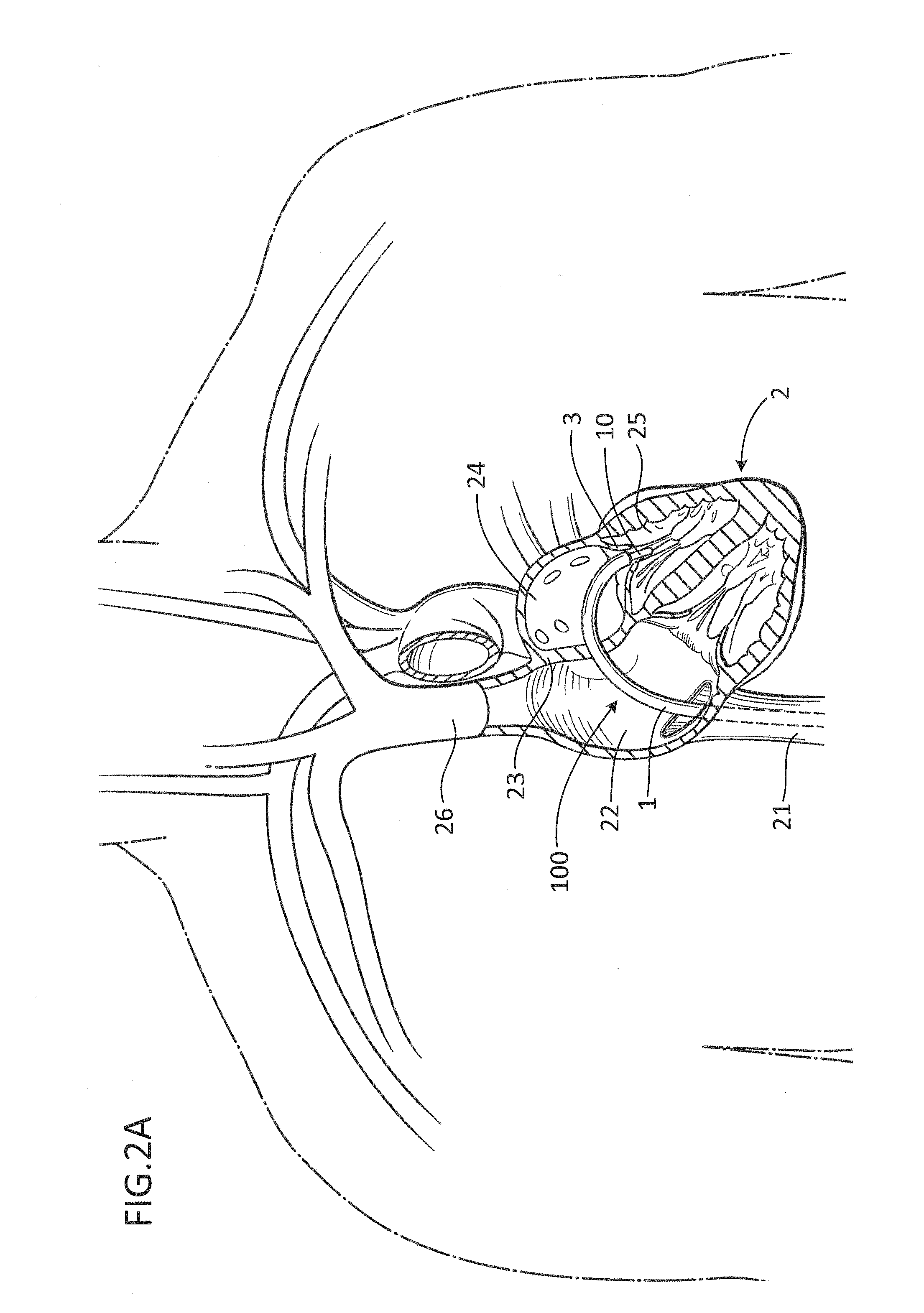
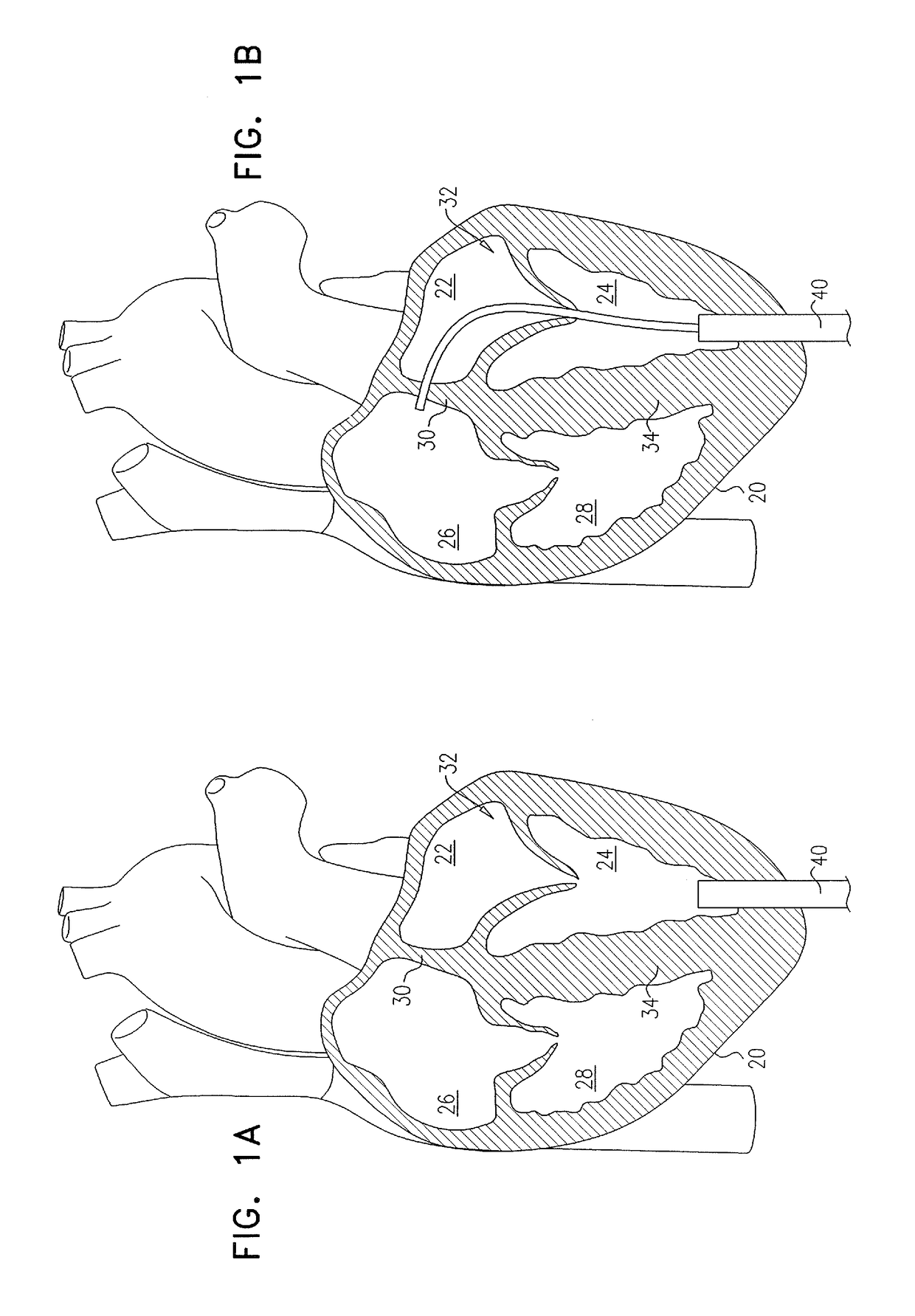
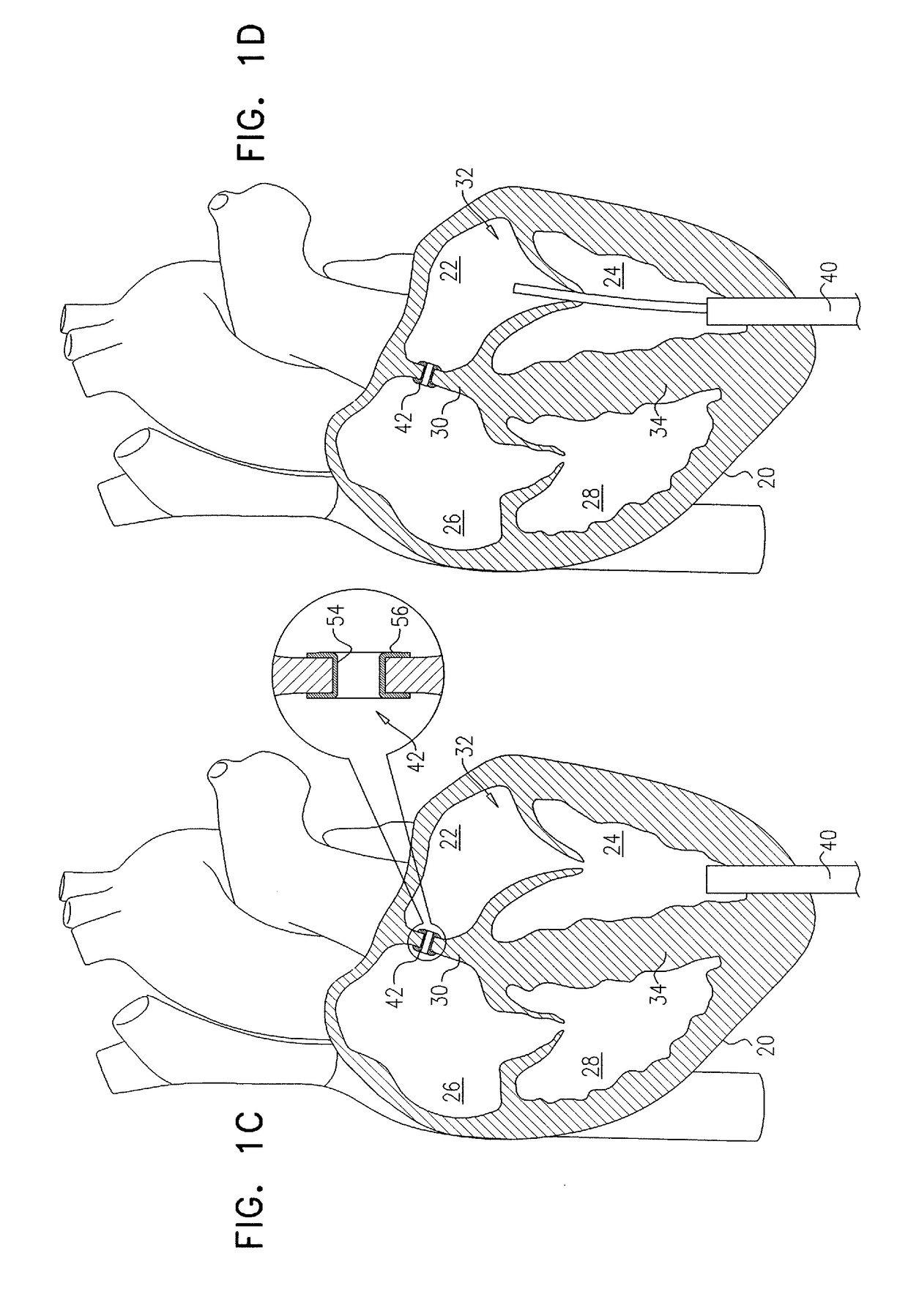
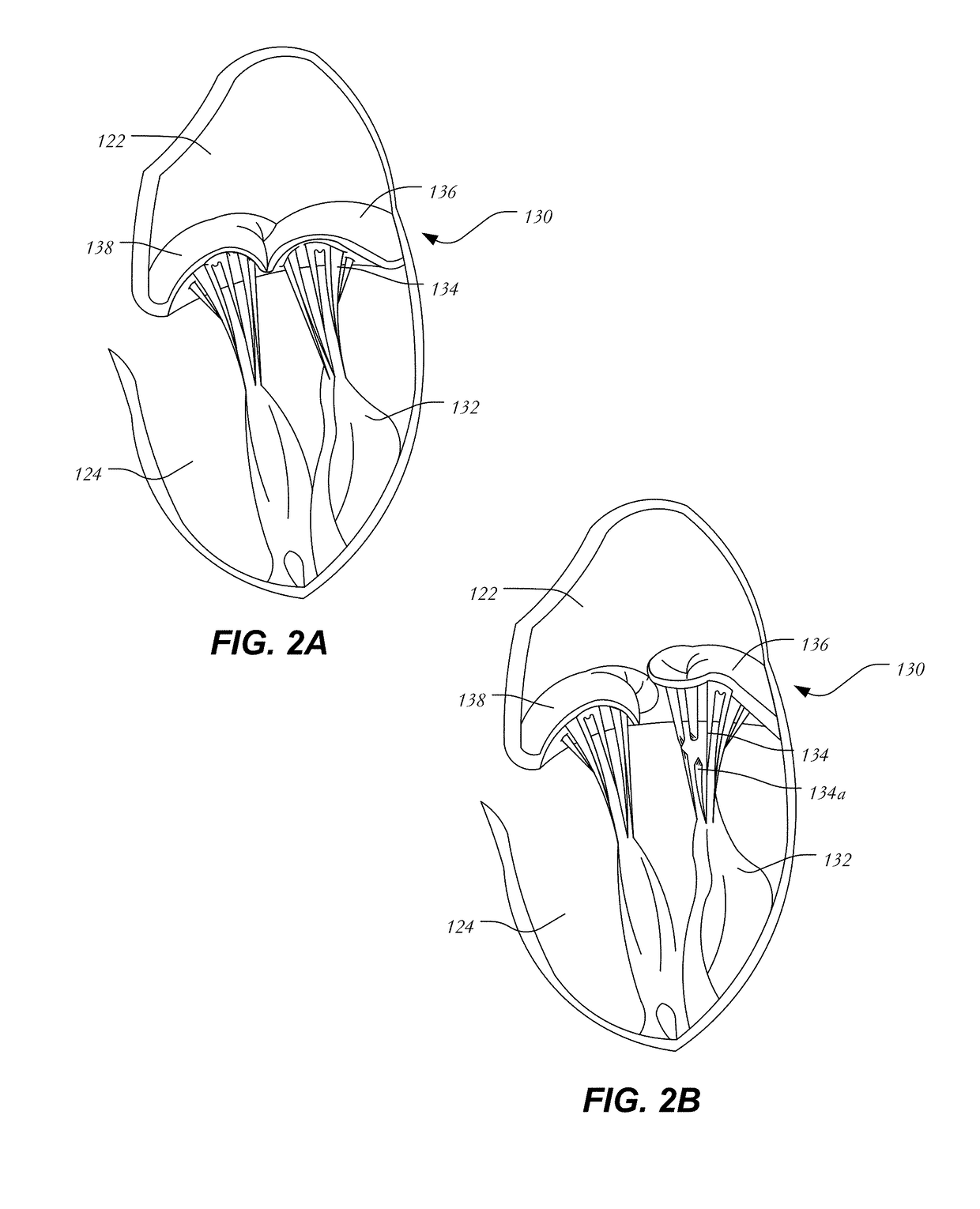
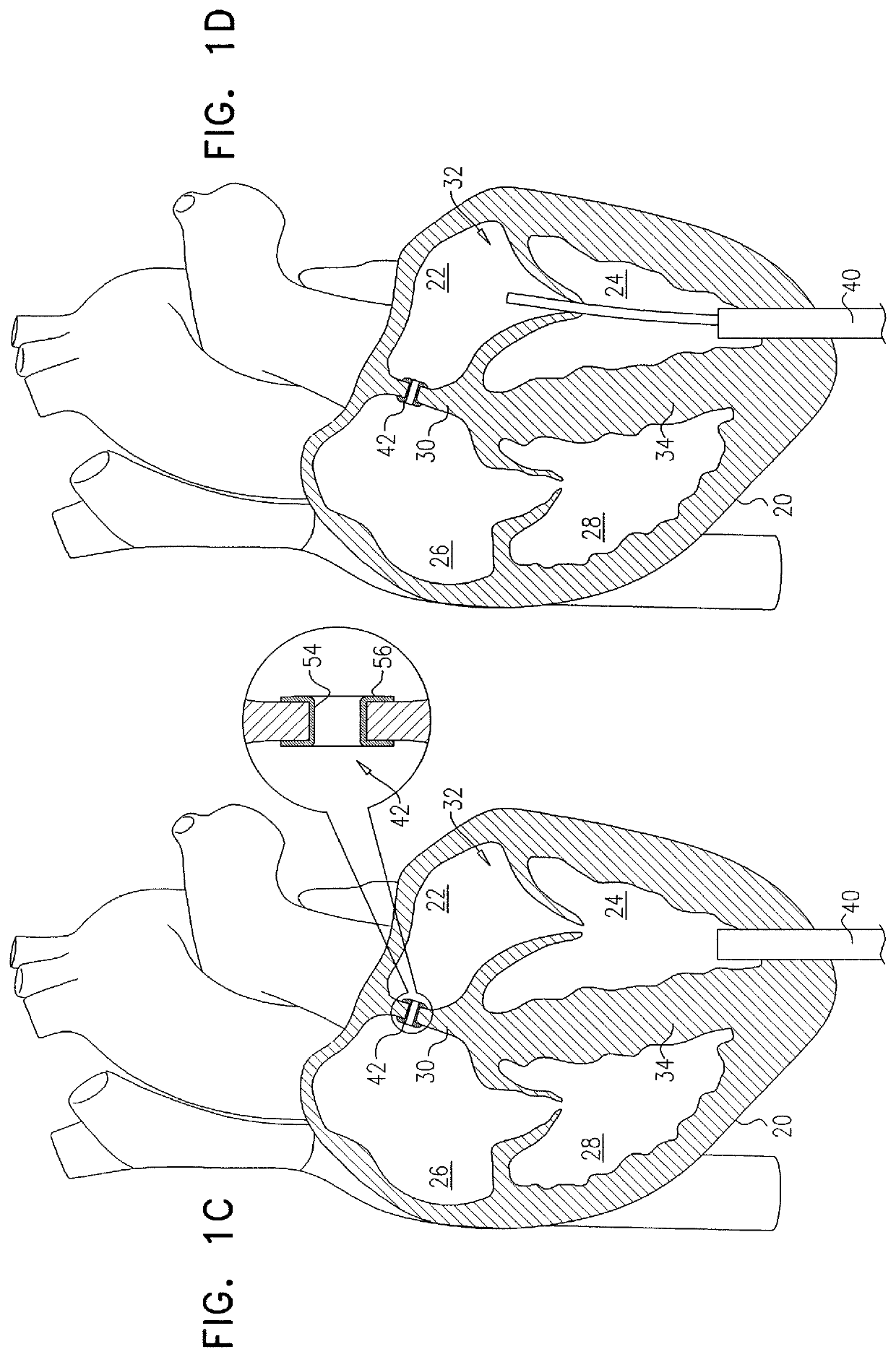
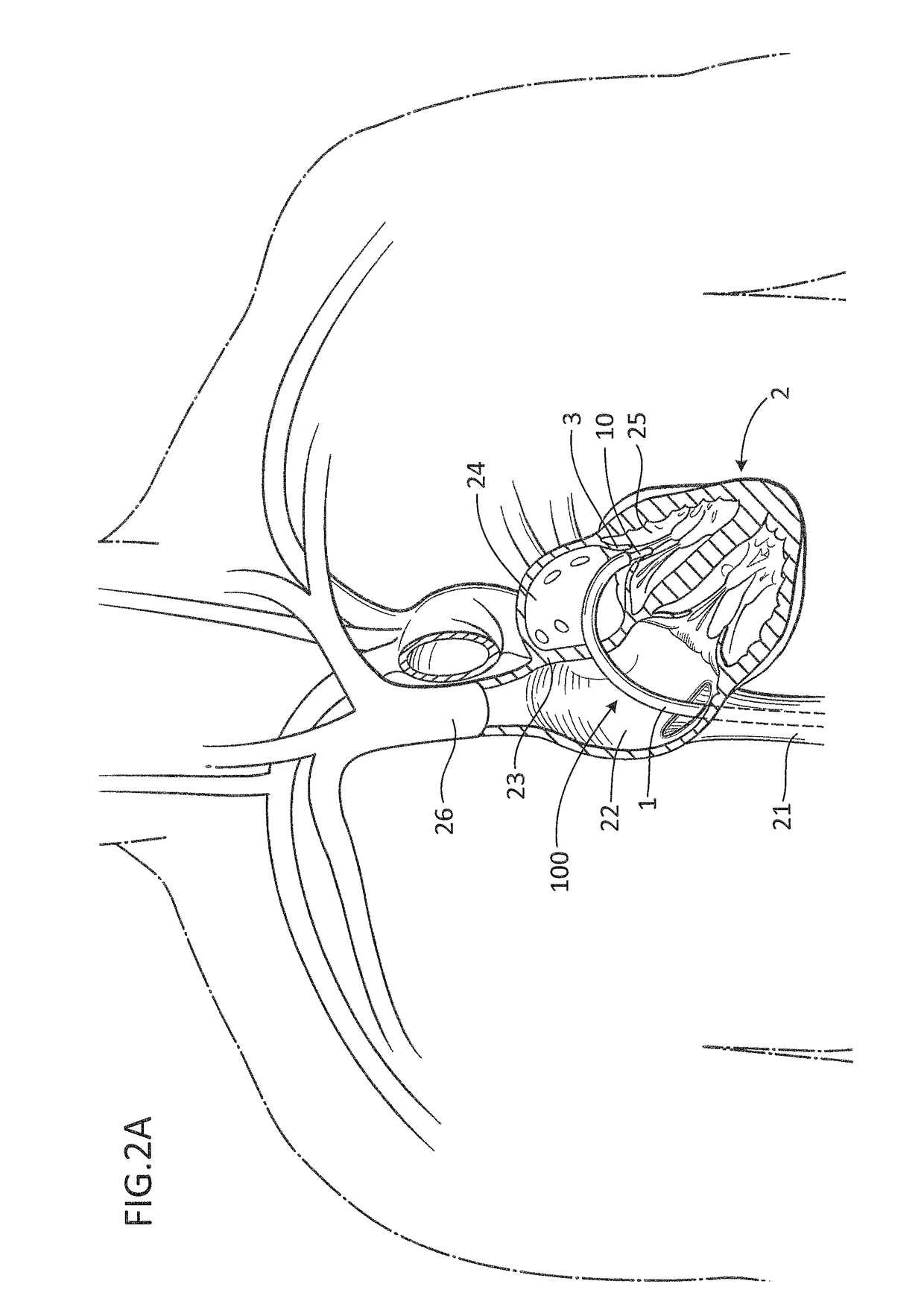
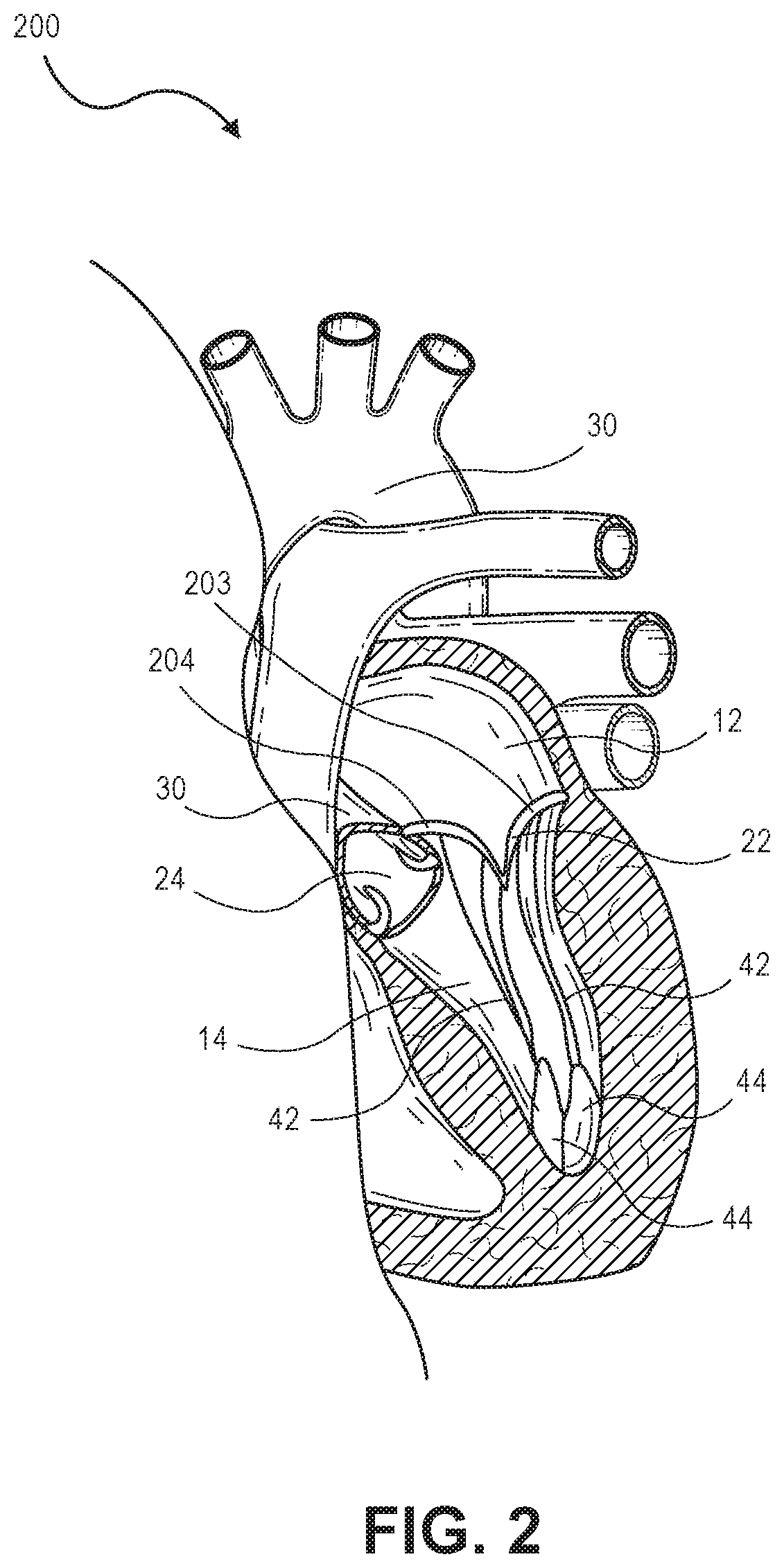
Percutaneous Heart Valve Prosthesis
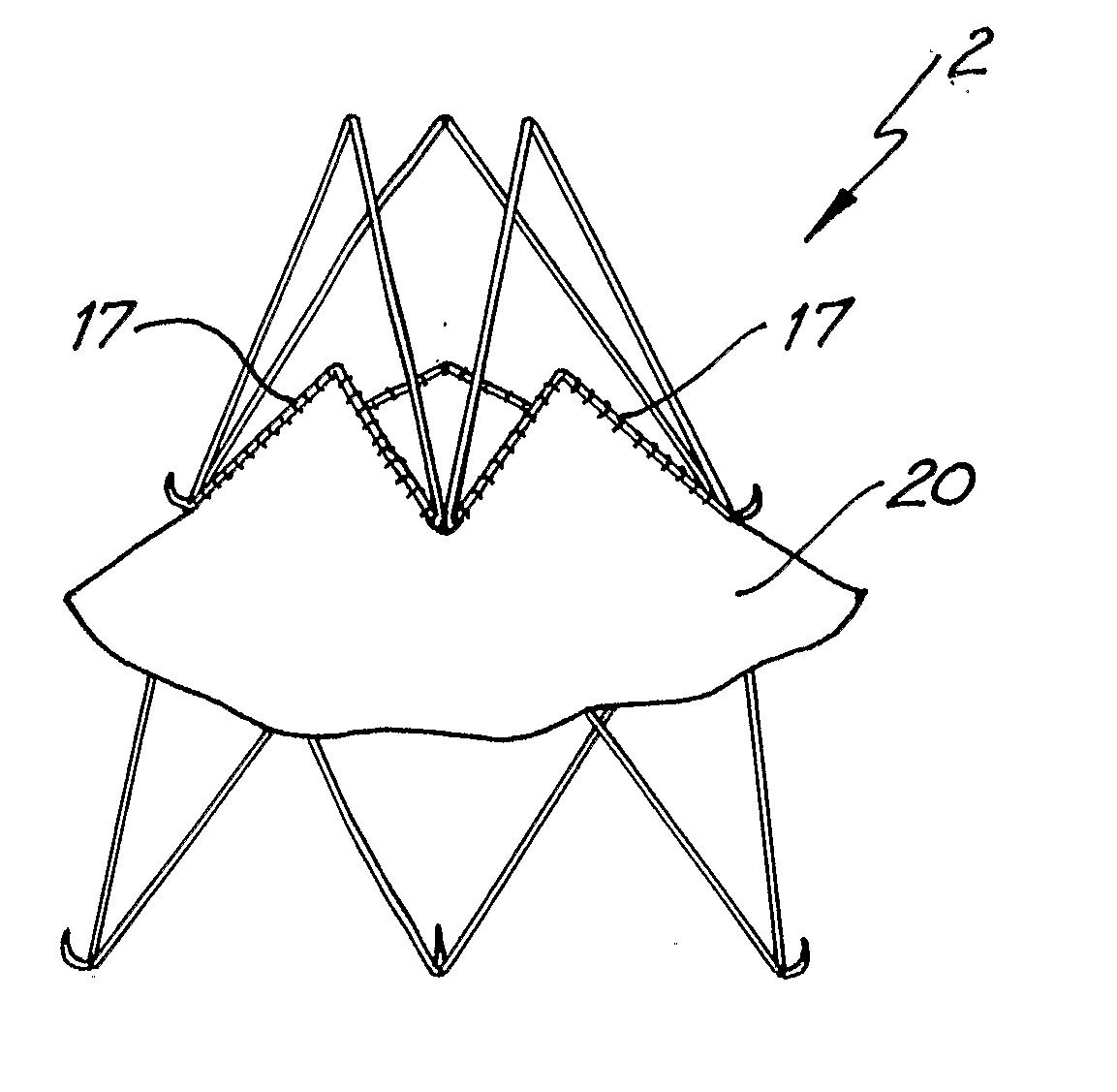
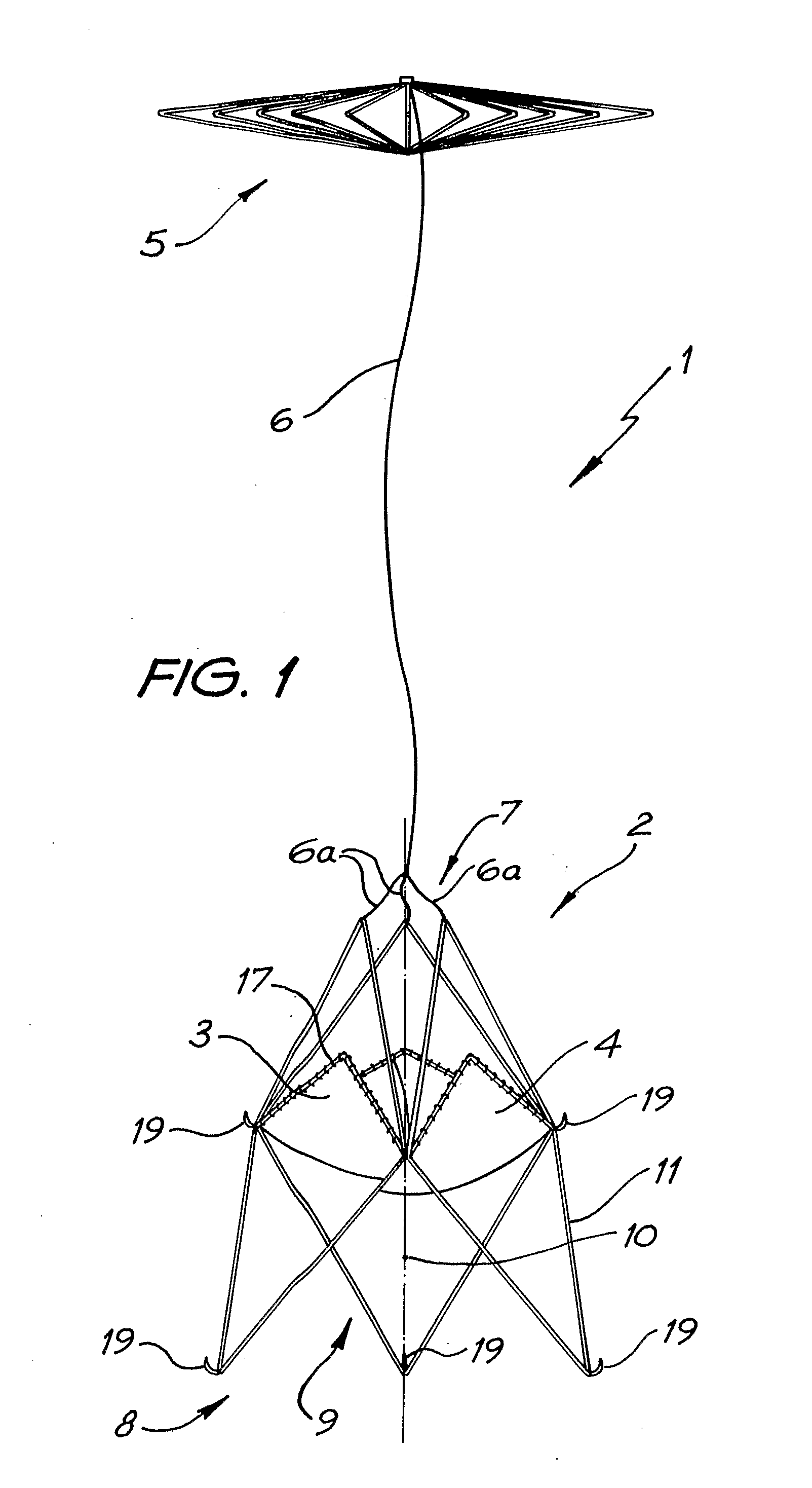
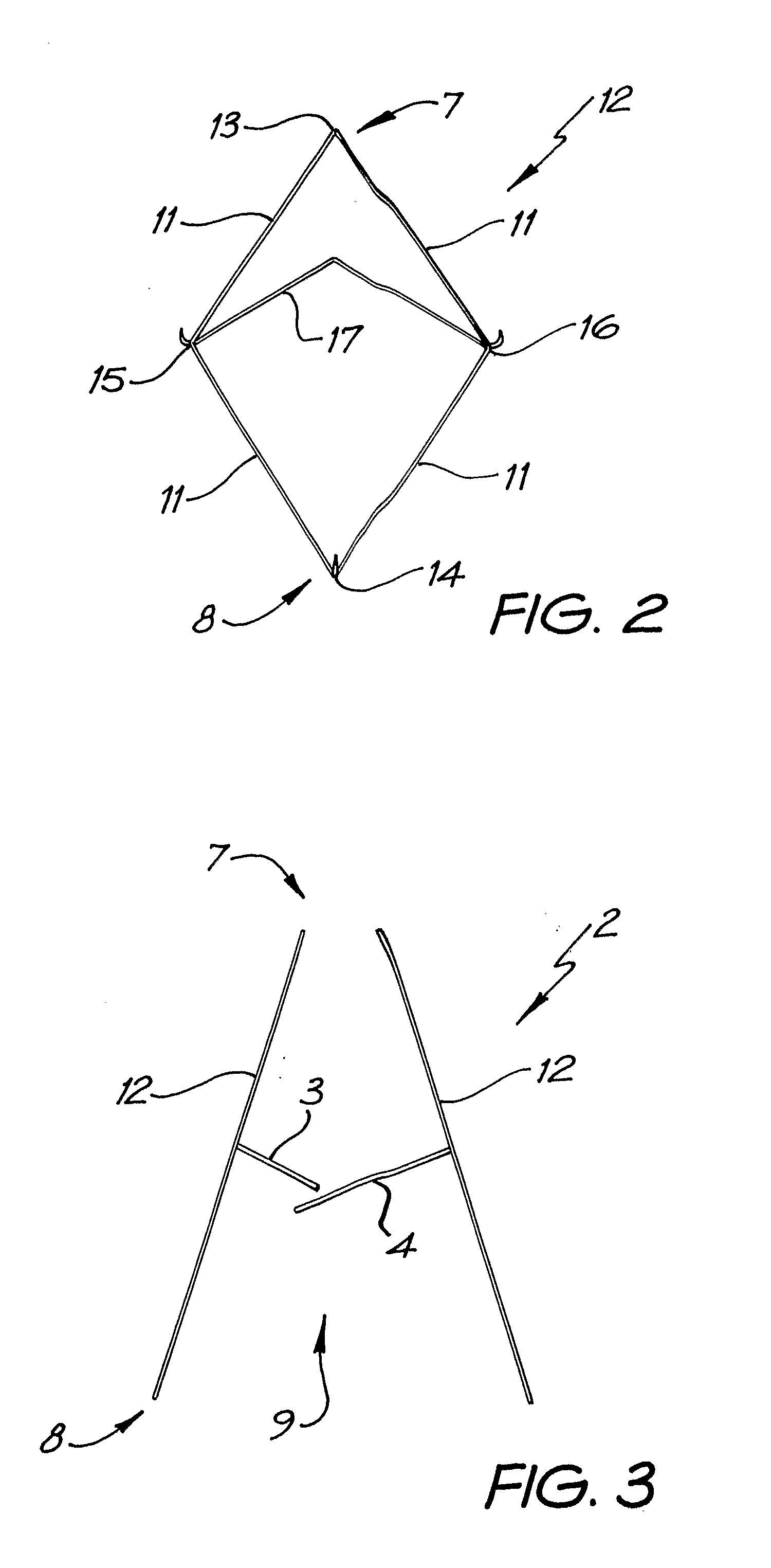
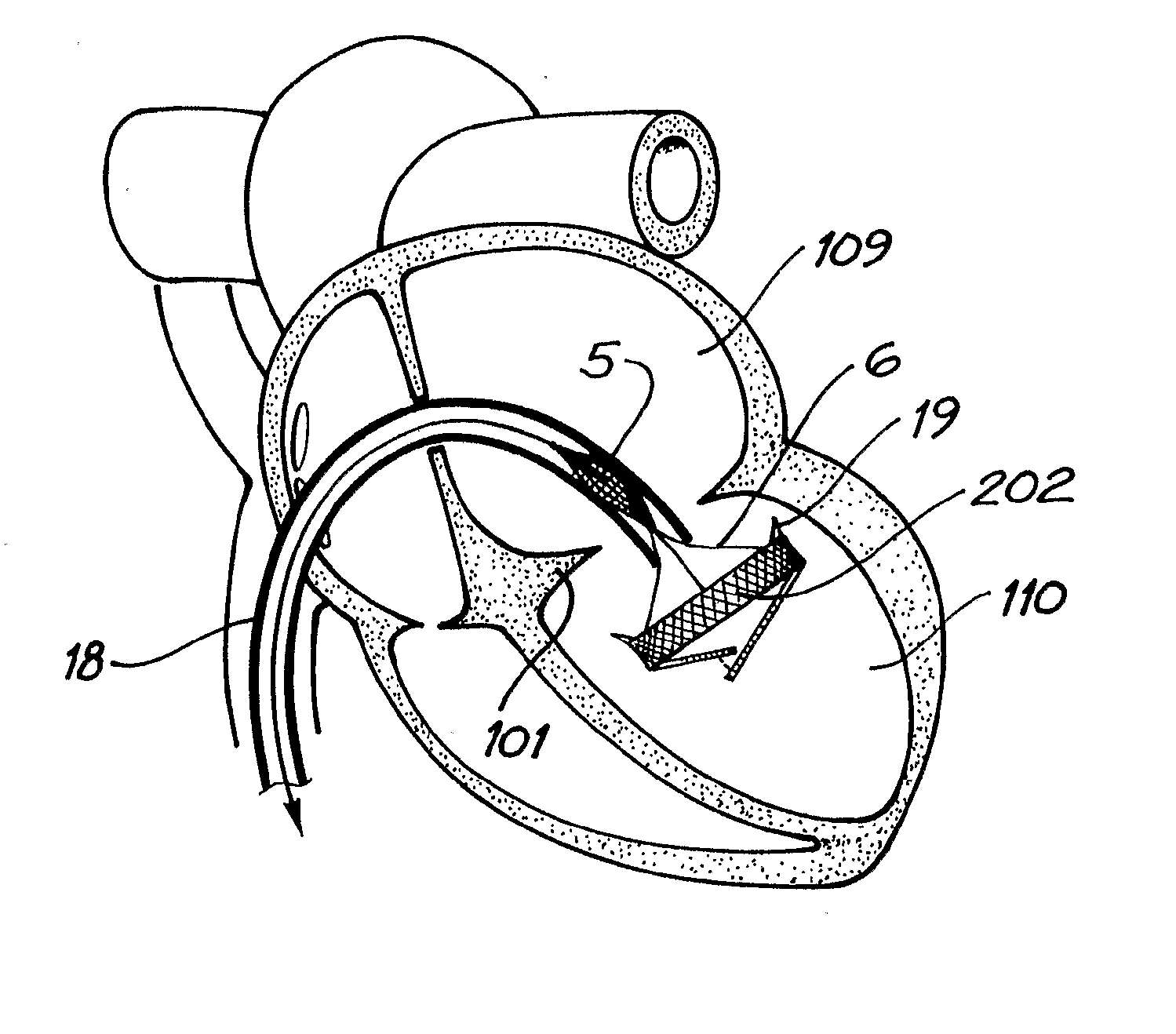
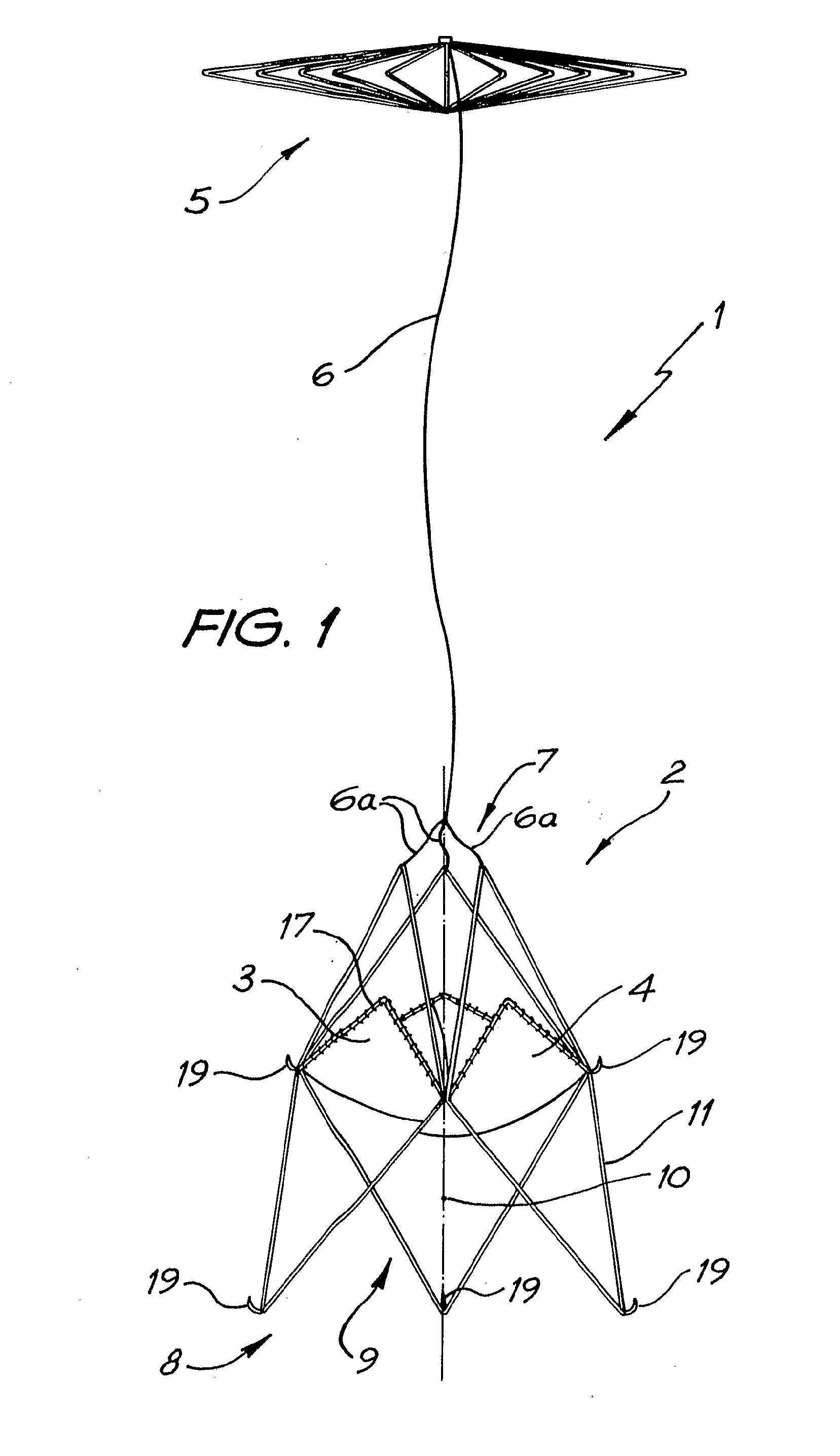
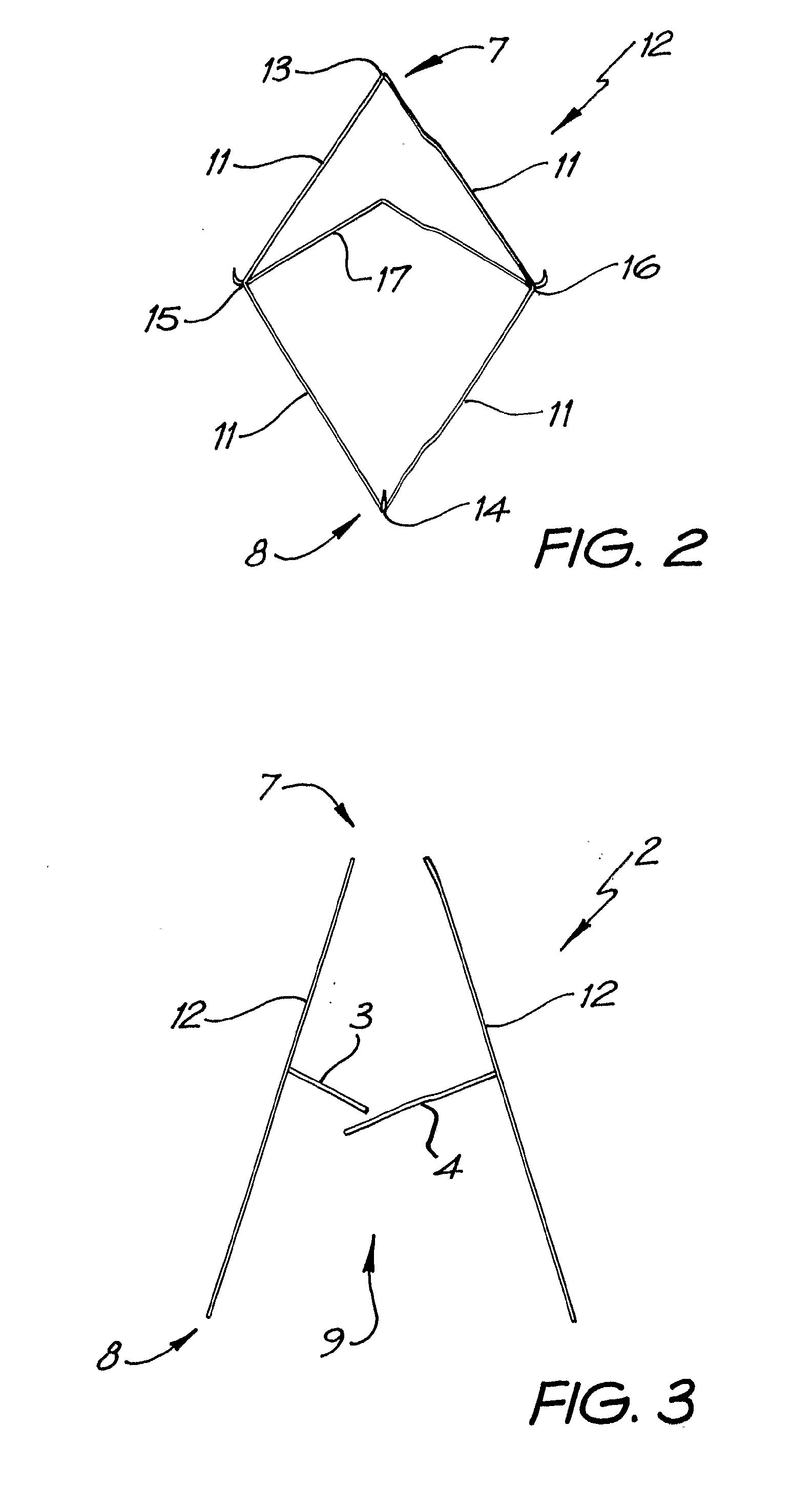
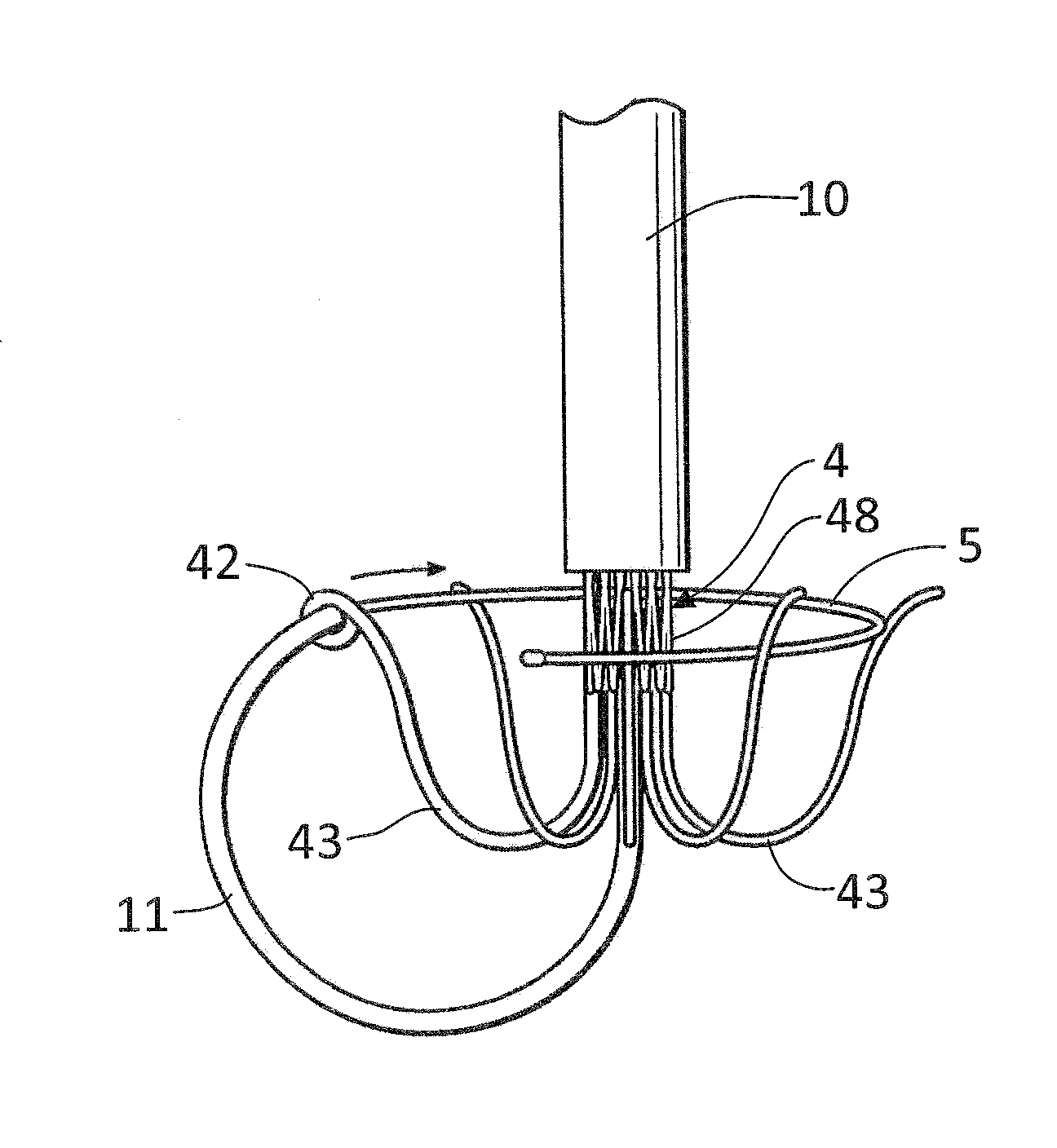
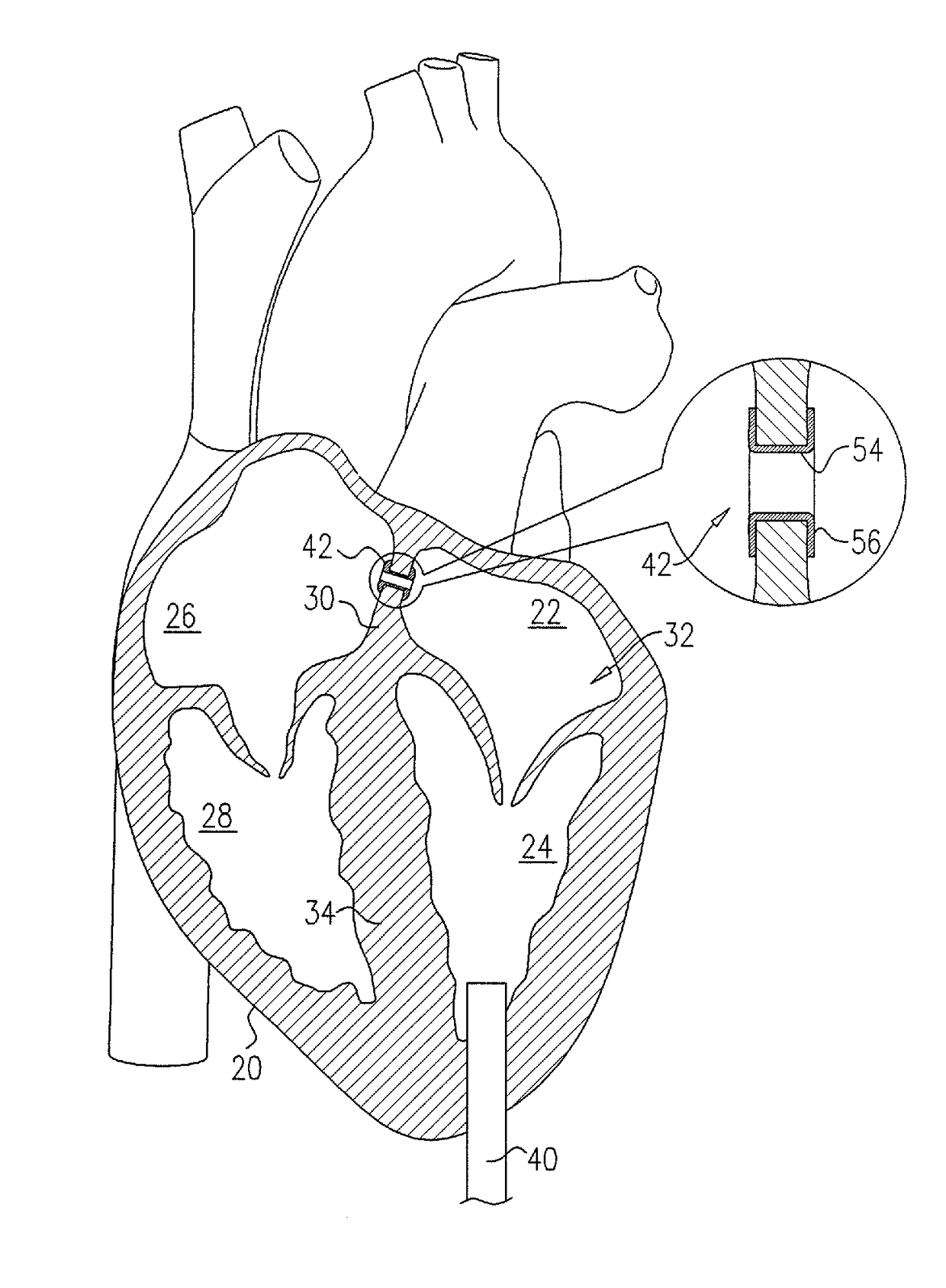
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS
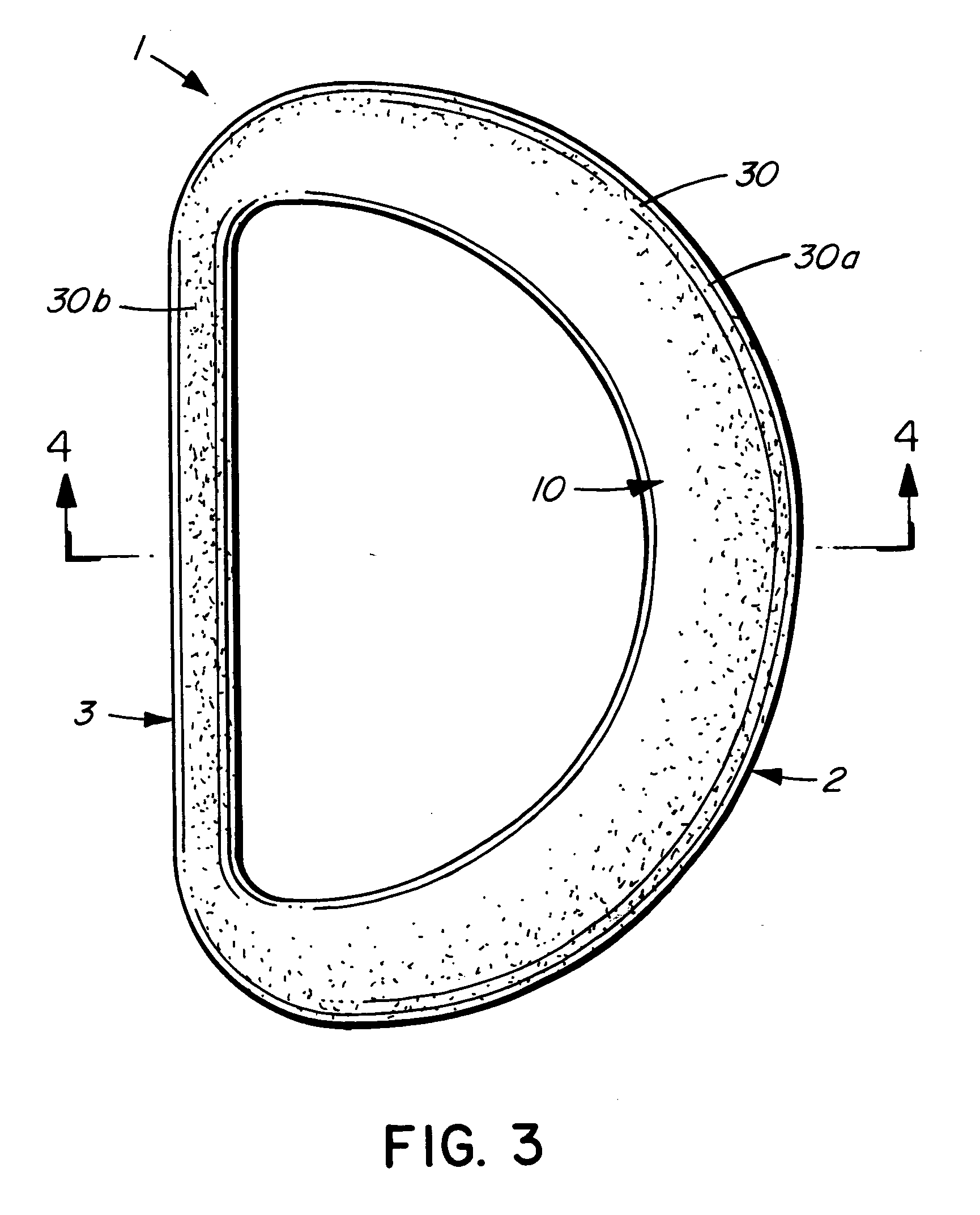
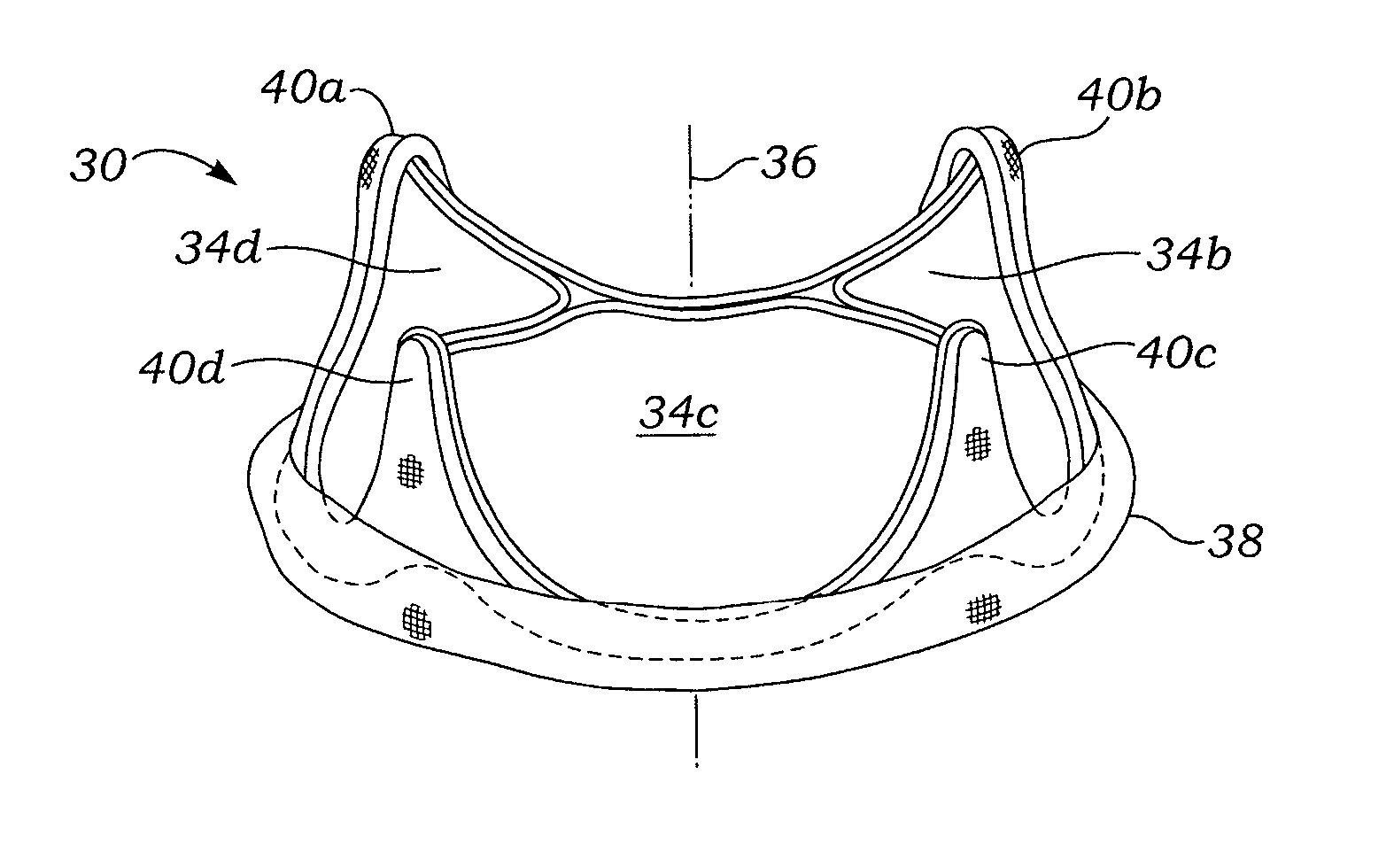
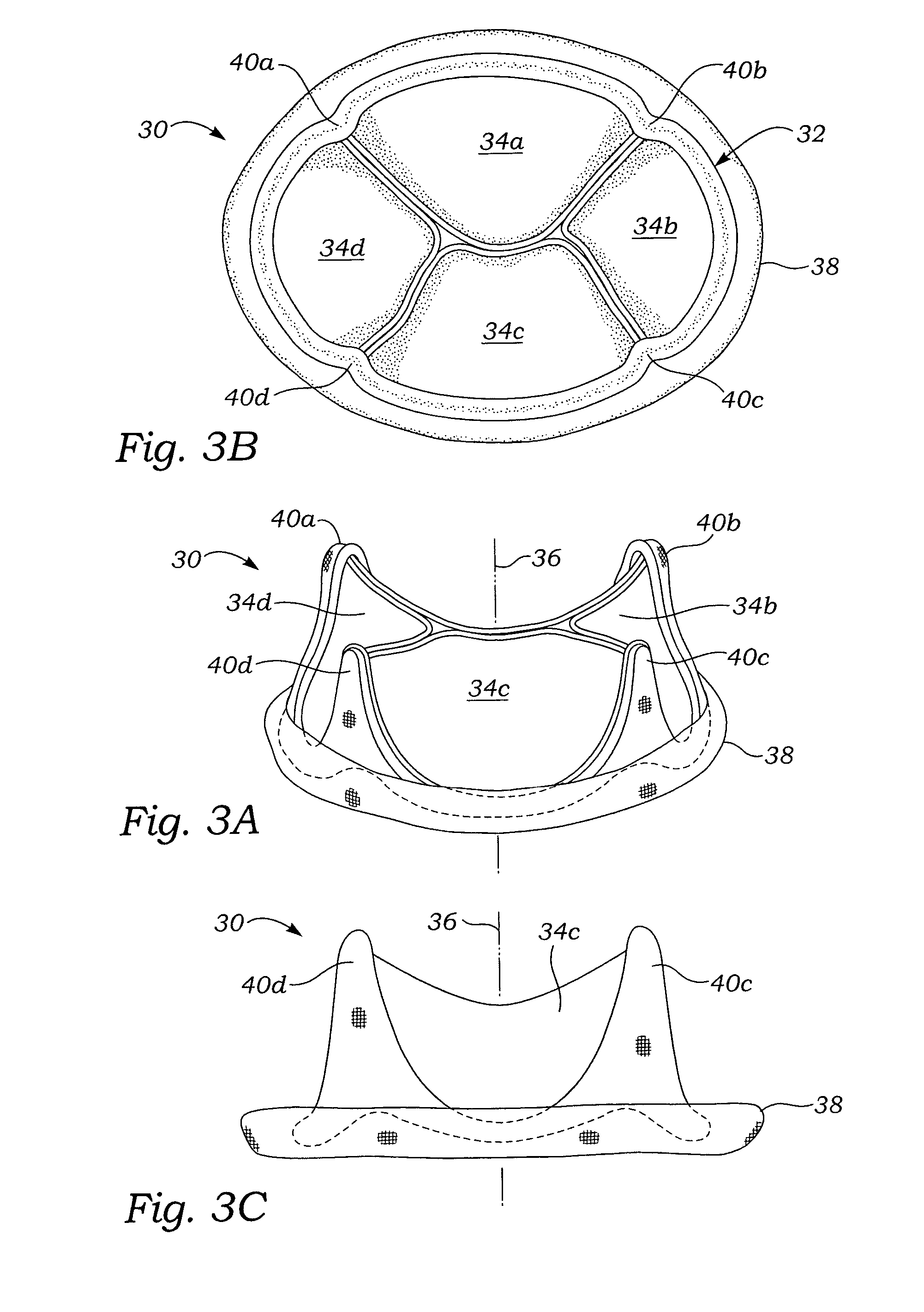
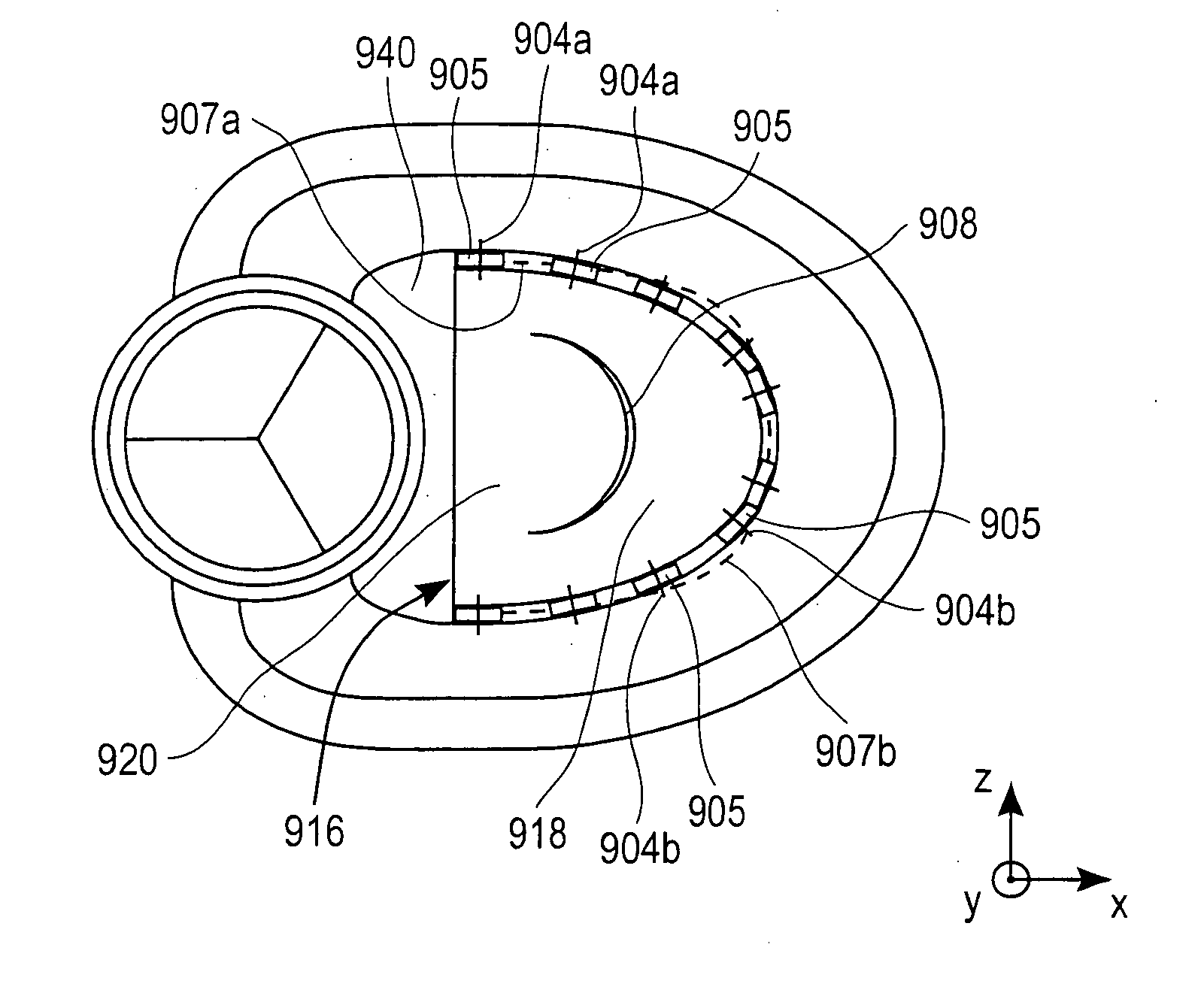
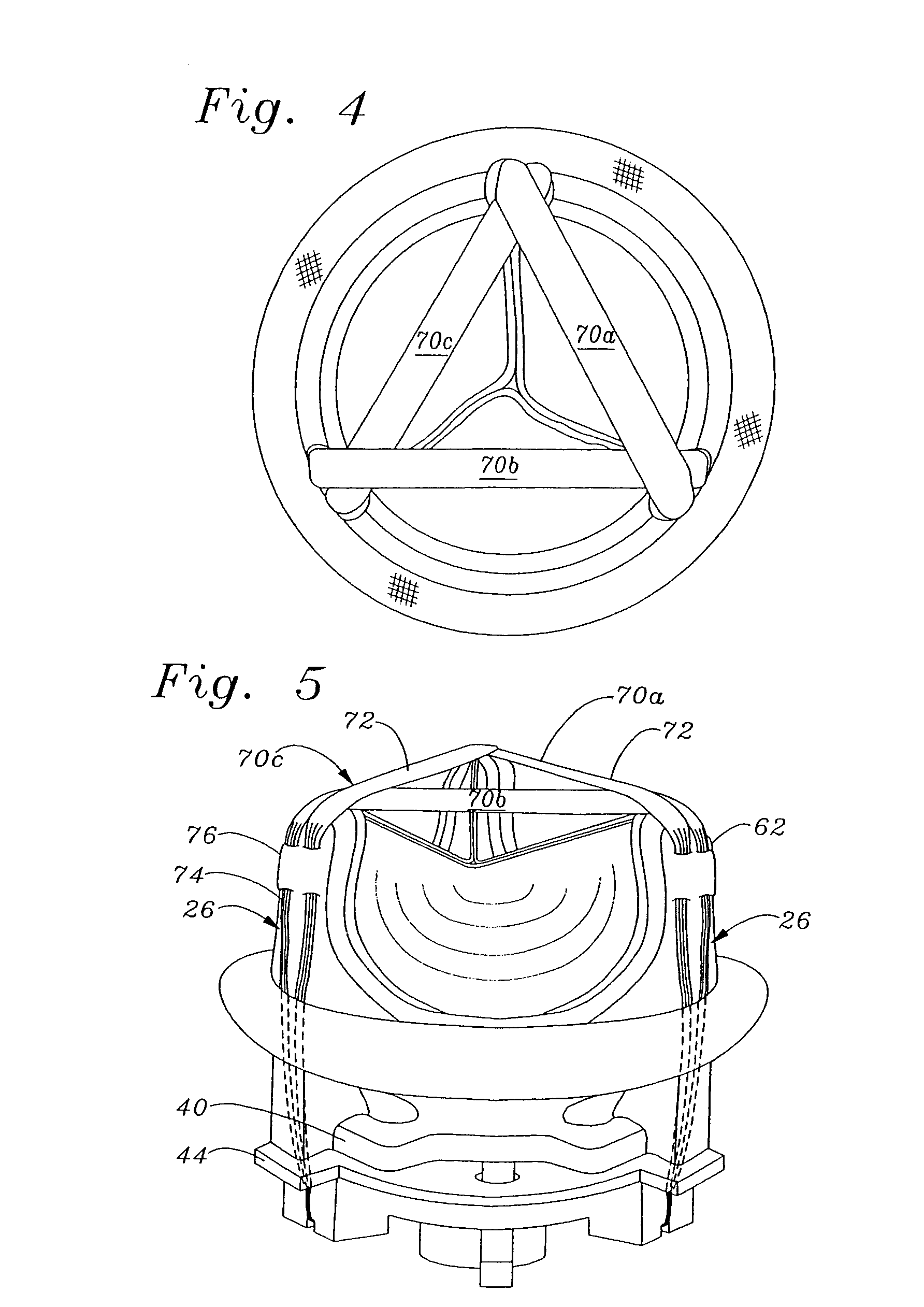
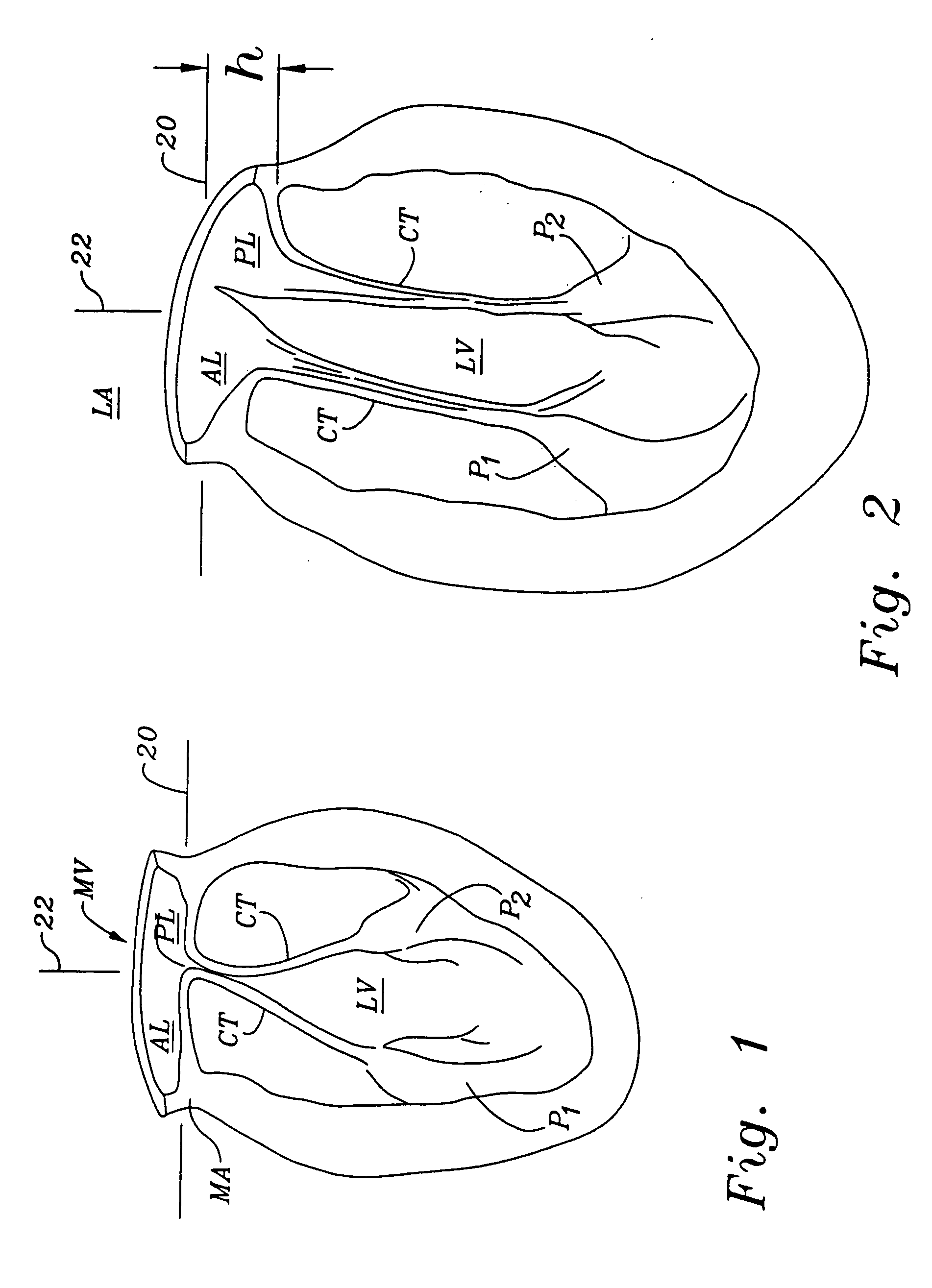
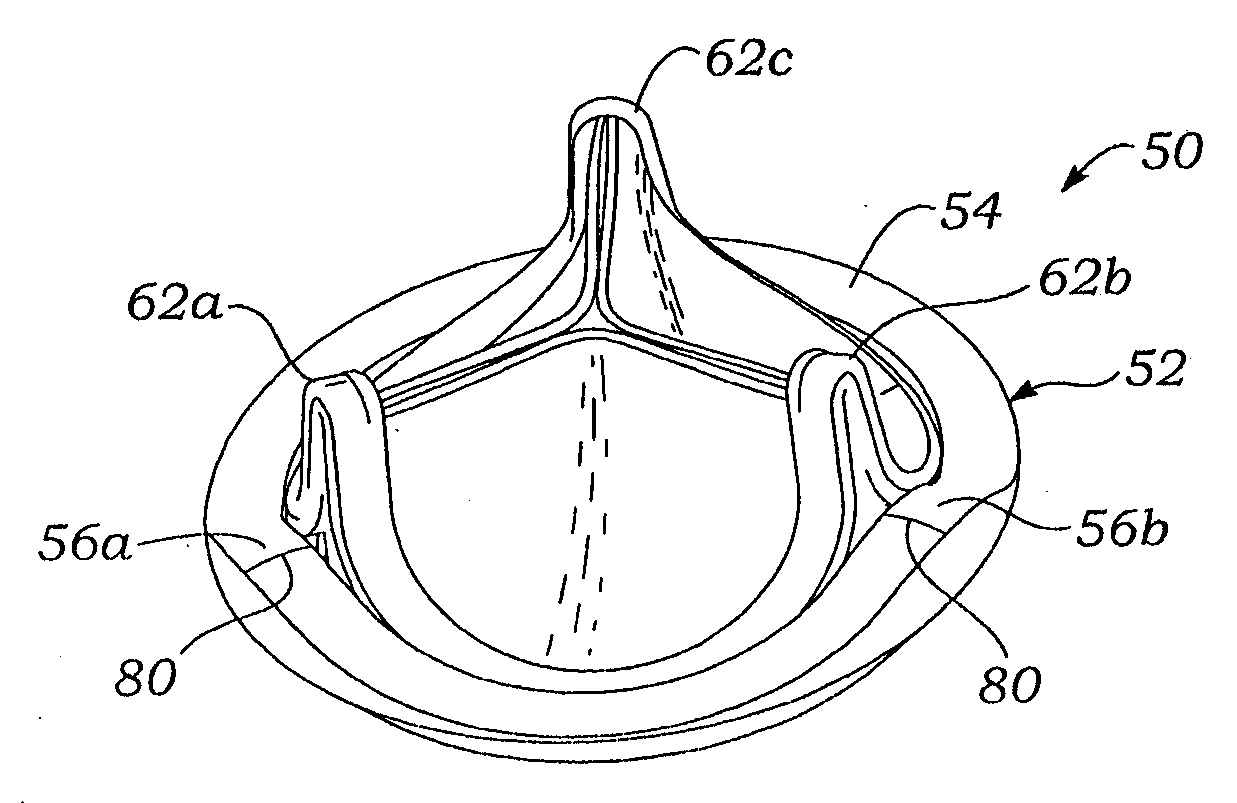
Mitral valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow
A mitral heart valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow that conforms to an abnormal posterior aspect of the mitral annulus. The ring may be generally oval having a major axis and a minor axis, wherein the posterior bow may be centered along the minor axis or offset in a posterior section. The ring may be substantially planar, or may include upward bows on either side of the posterior bow. The ring may include a ring body surrounded by a suture-permeable fabric sheath, and the ring body may be formed of a plurality of concentric ring elements. The ring is semi-rigid and the posterior bow is stiff enough to withstand deformation once implanted and subjected to normal physiologic stresses. The ring elements may be bands of semi-rigid material. A method of repairing an abnormal mitral heart valve annulus having a depressed posterior aspect includes providing a ring with a posterior bow and implanting the ring to support the annulus without unduly stressing the attachment sutures.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Percutaneous heart valve prosthesis
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS PTY LTD
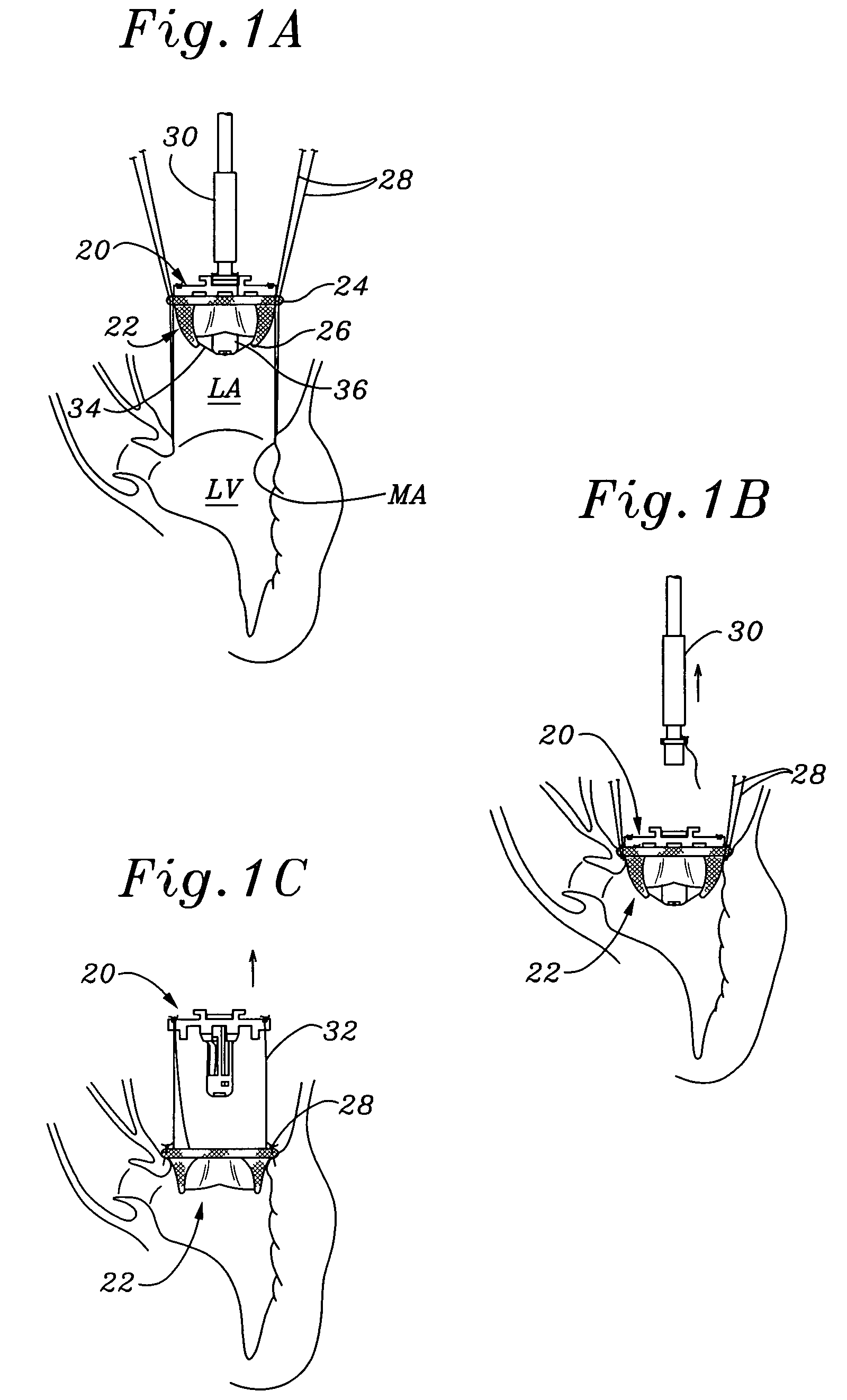
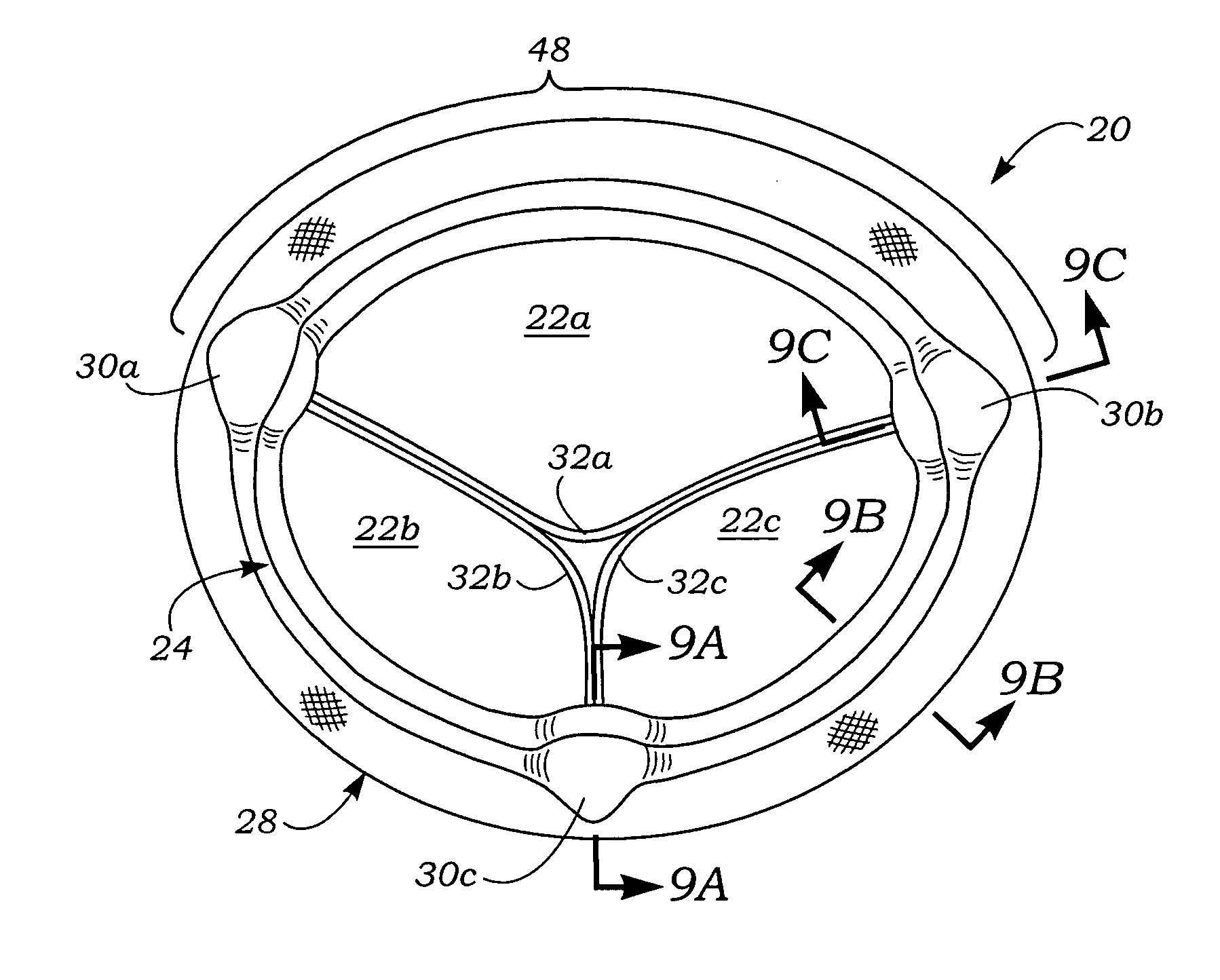
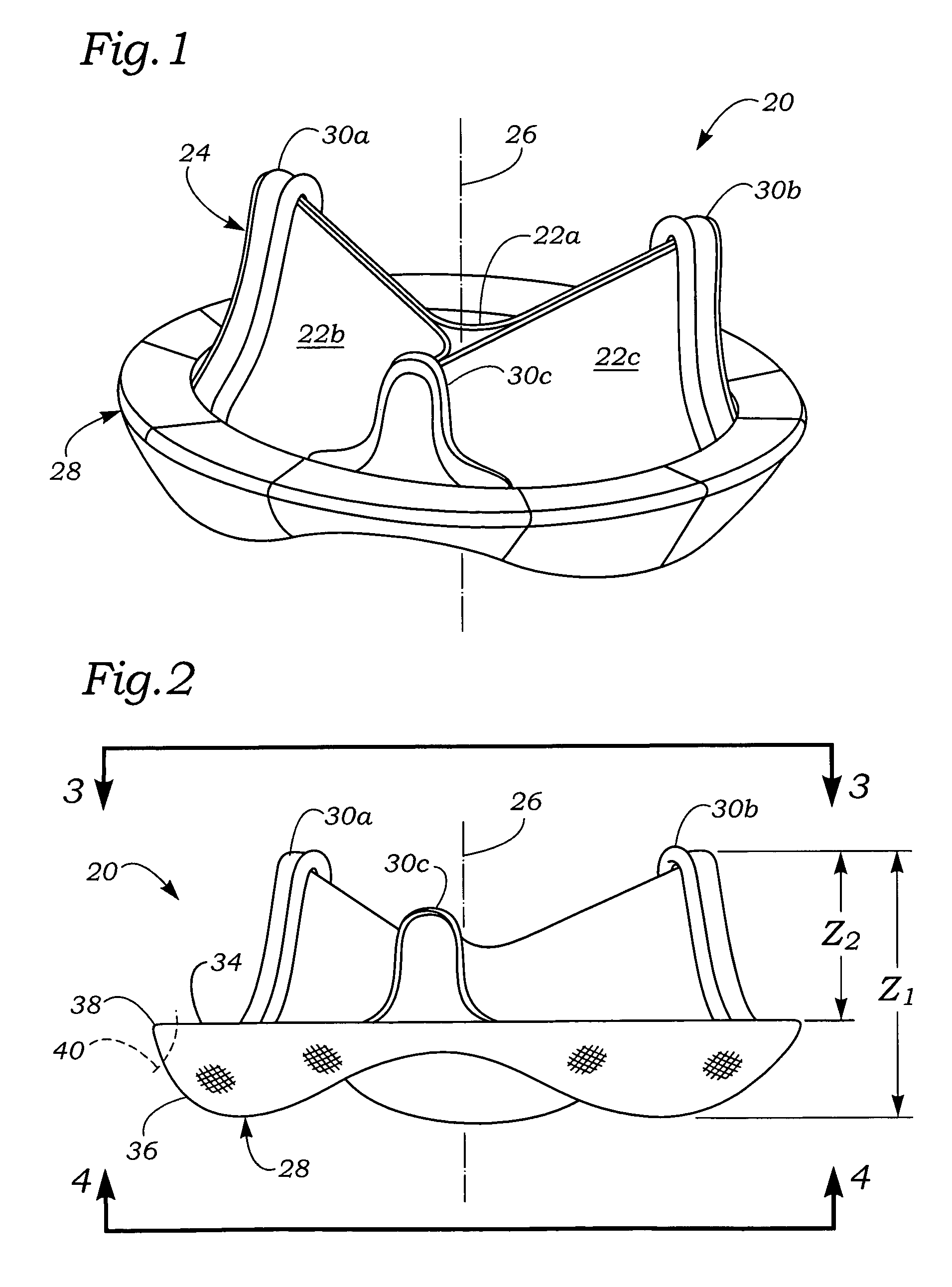
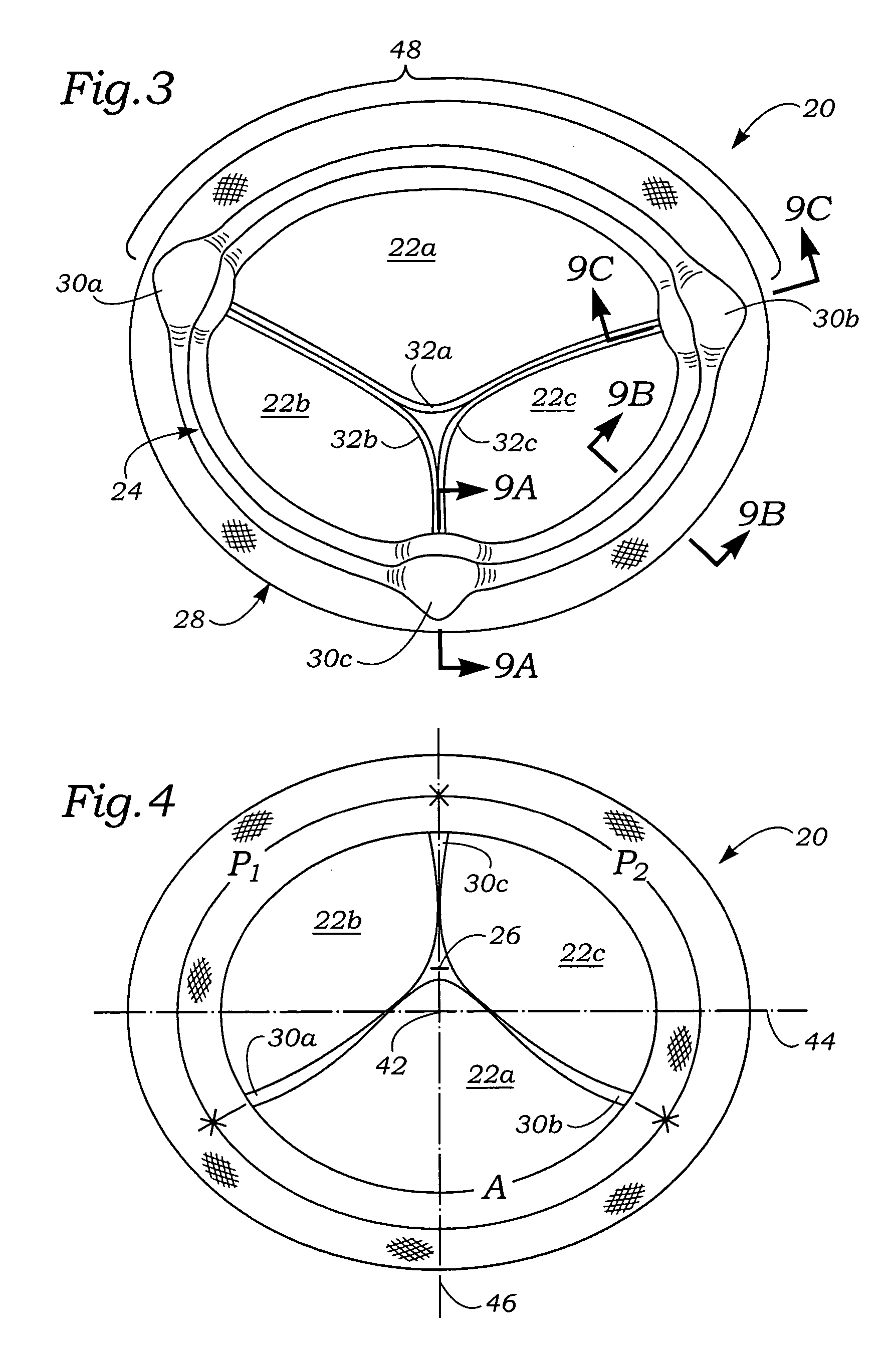
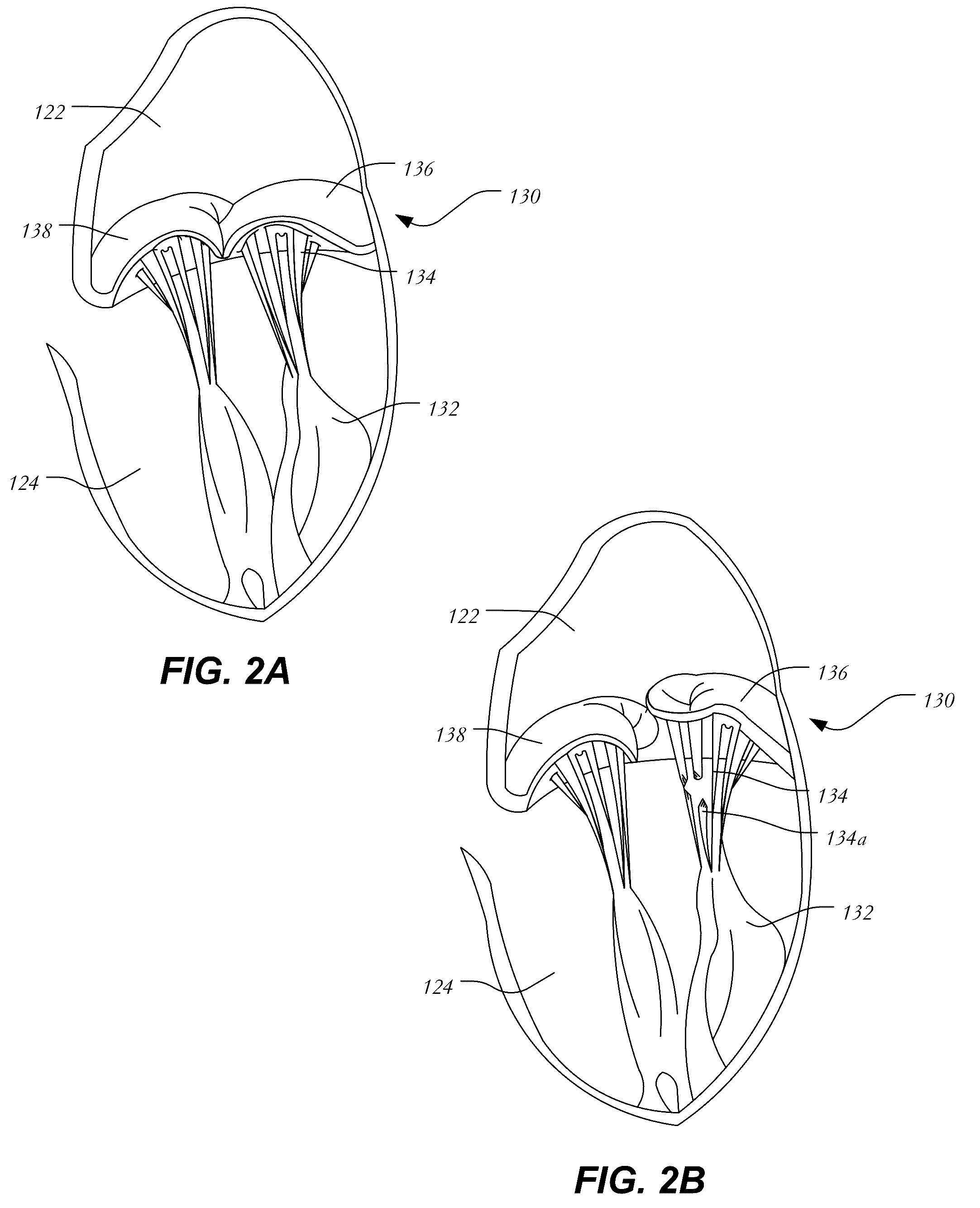
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS20060293745A1Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsAnterior leafletMitral annulus
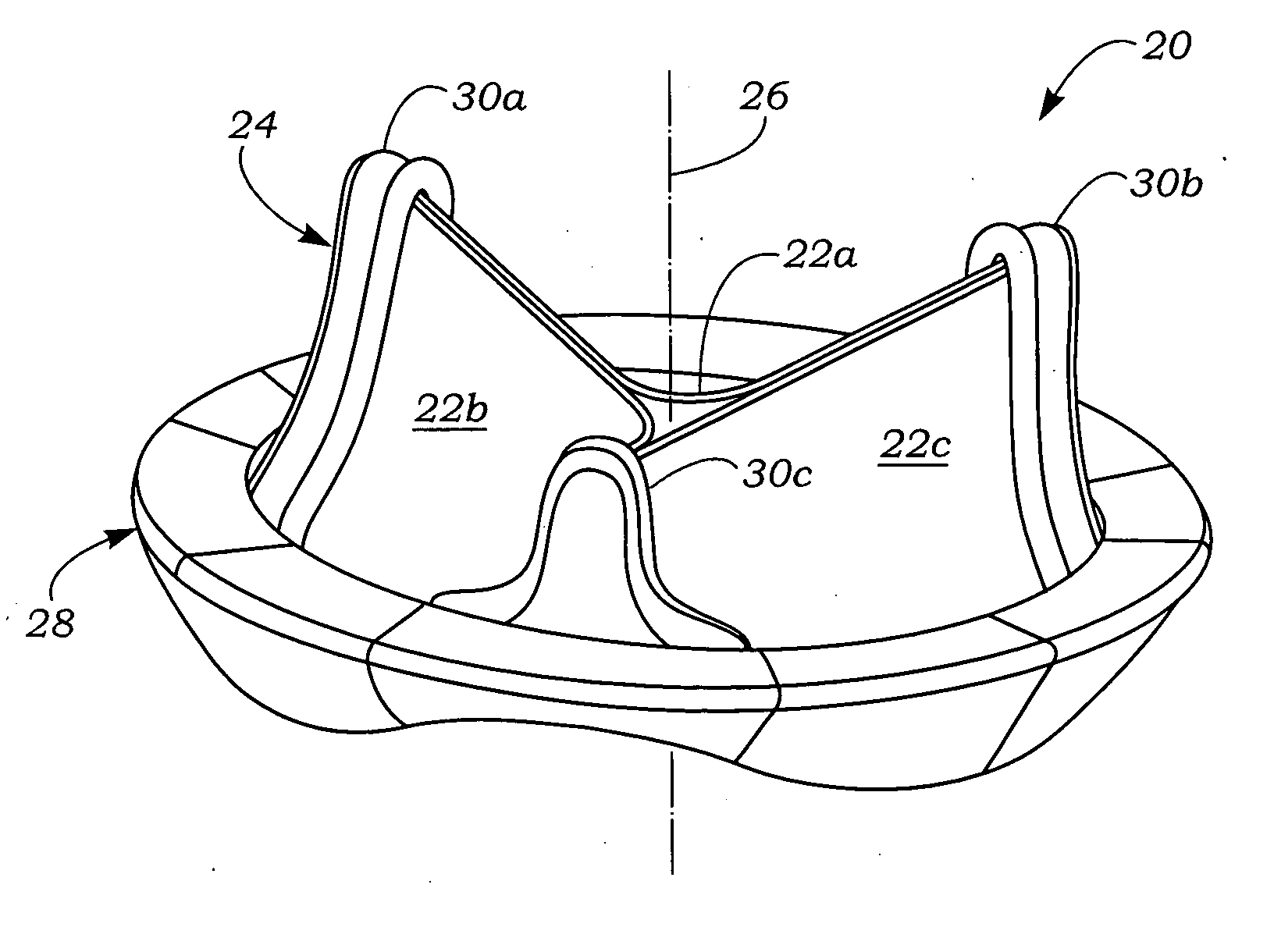
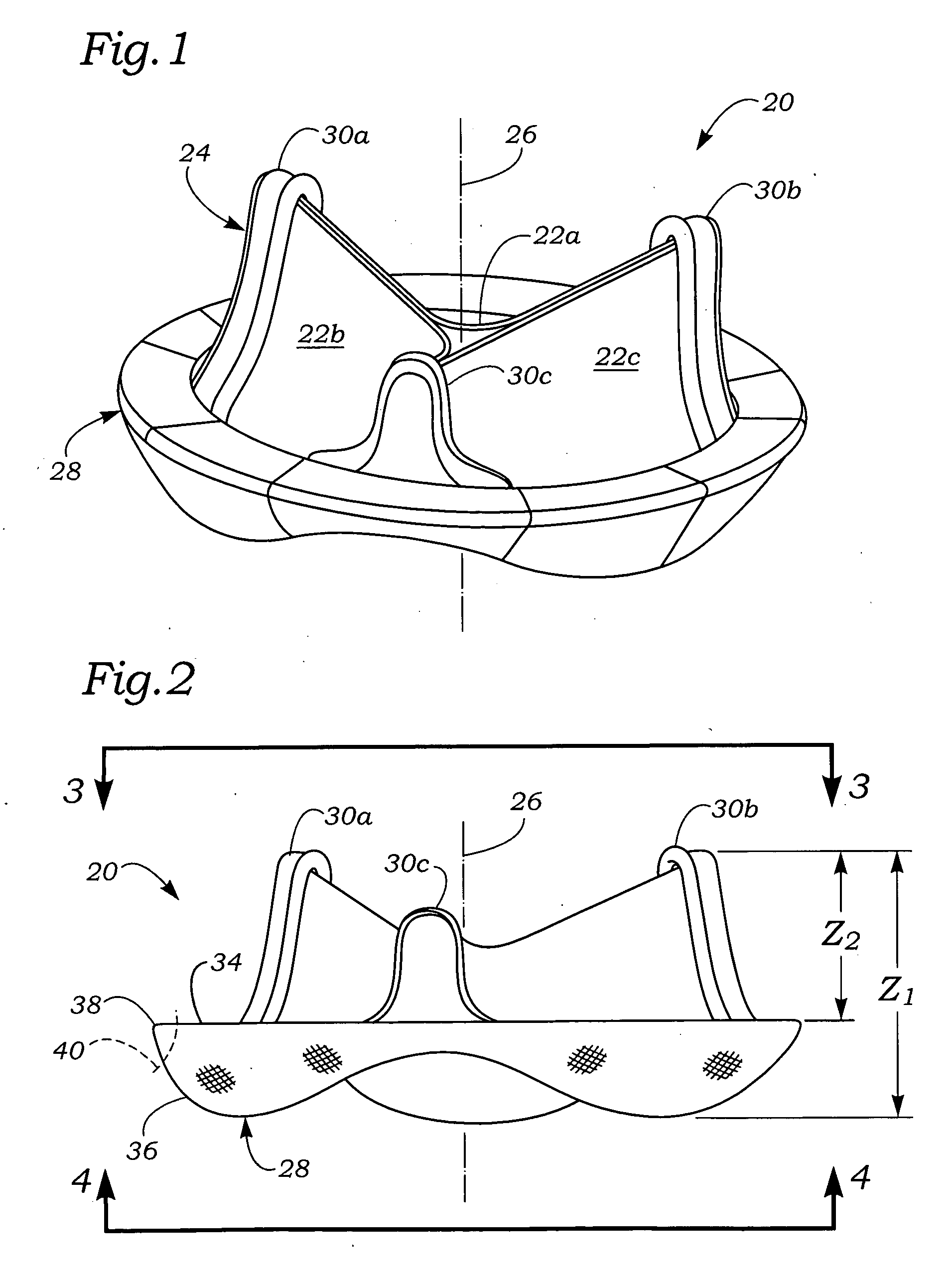
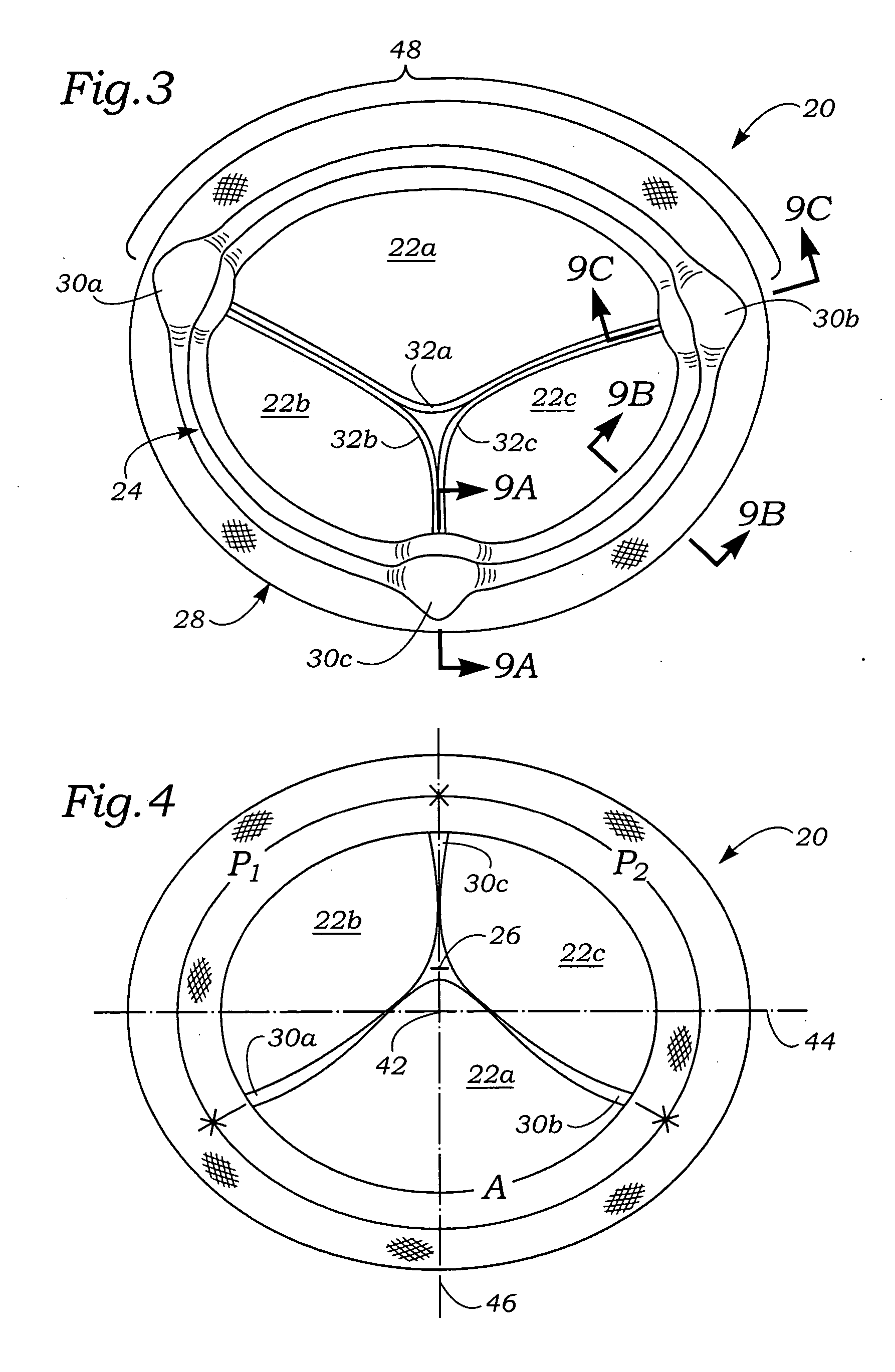
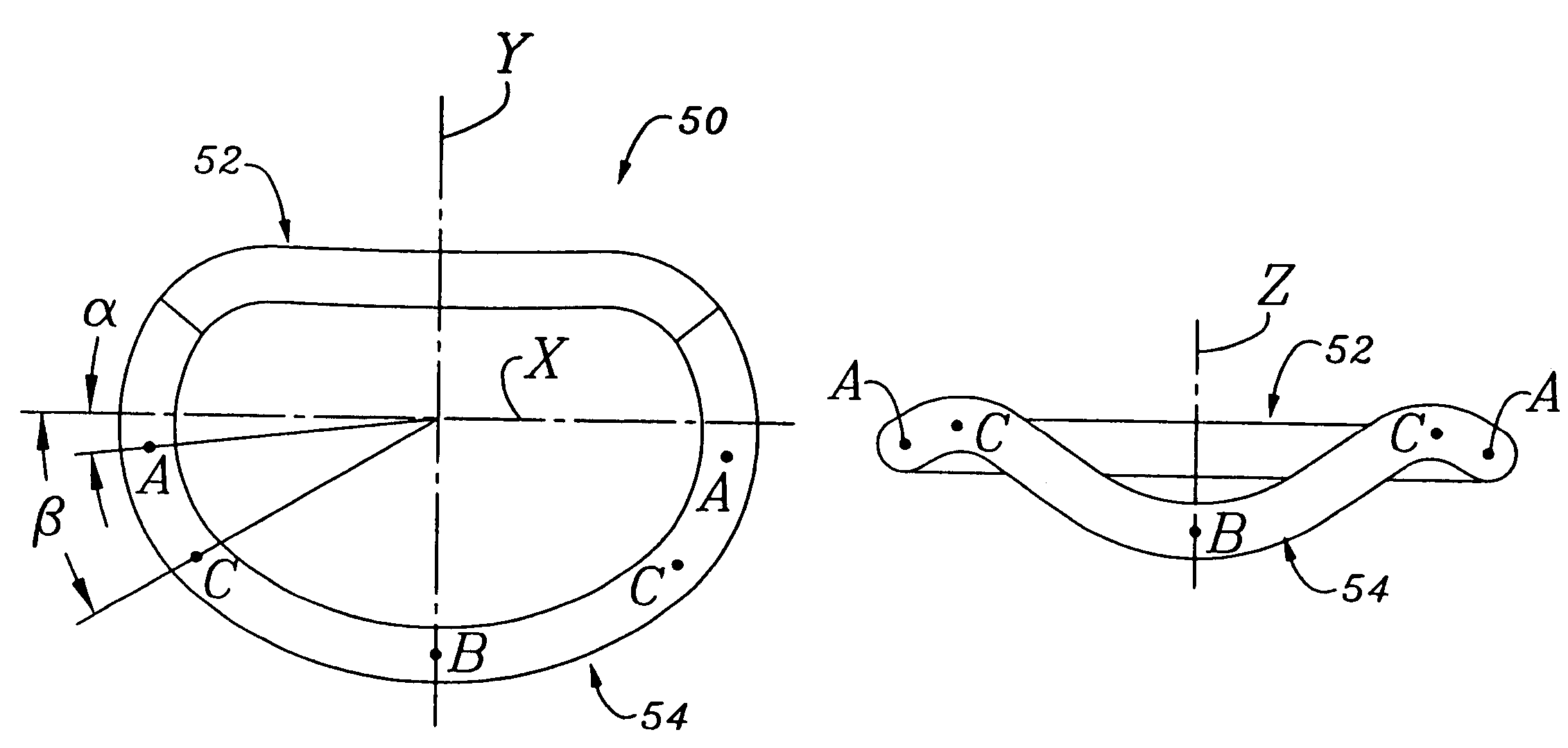
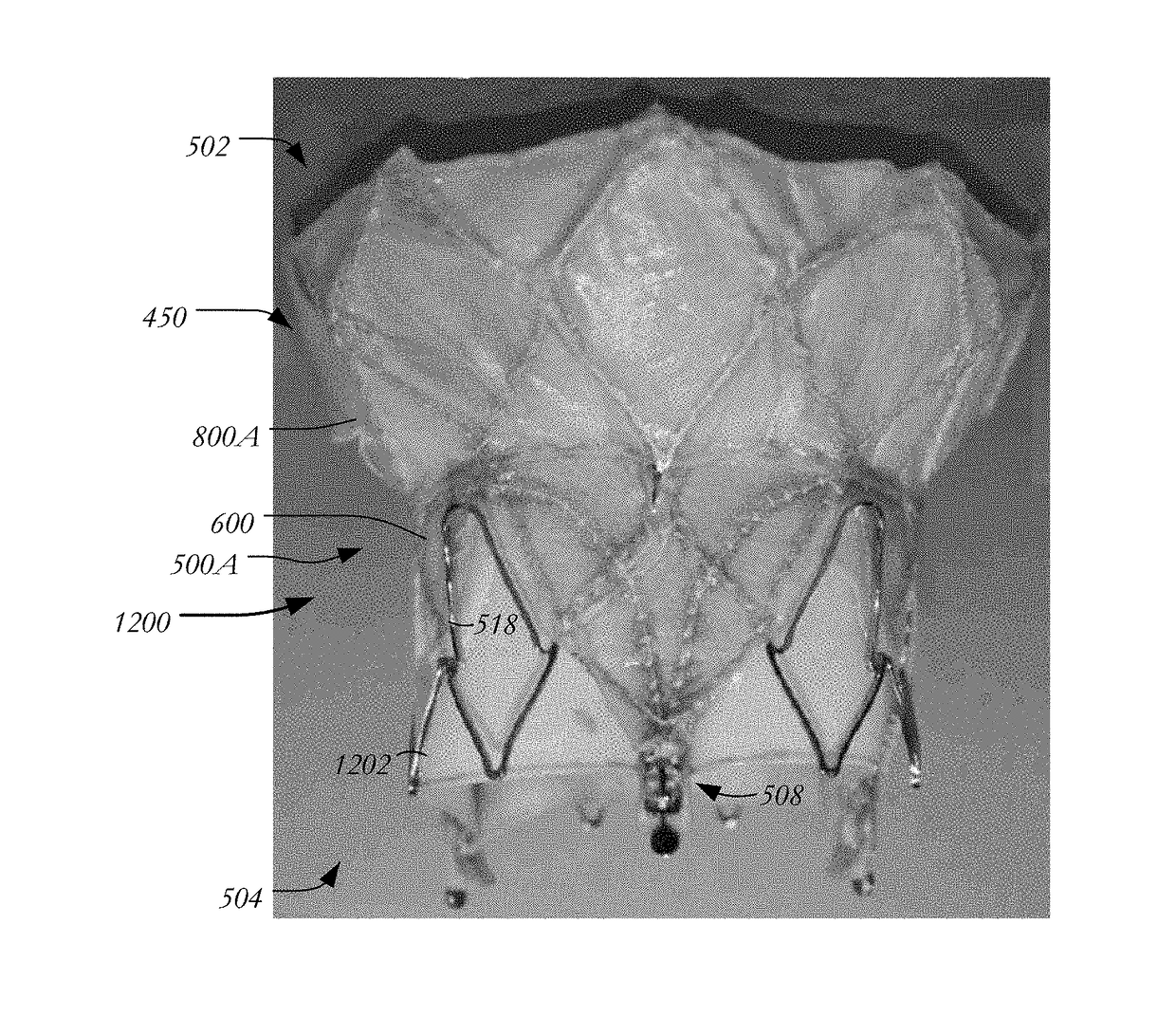
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Percutaneous heart valve prosthesis
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS PTY LTD
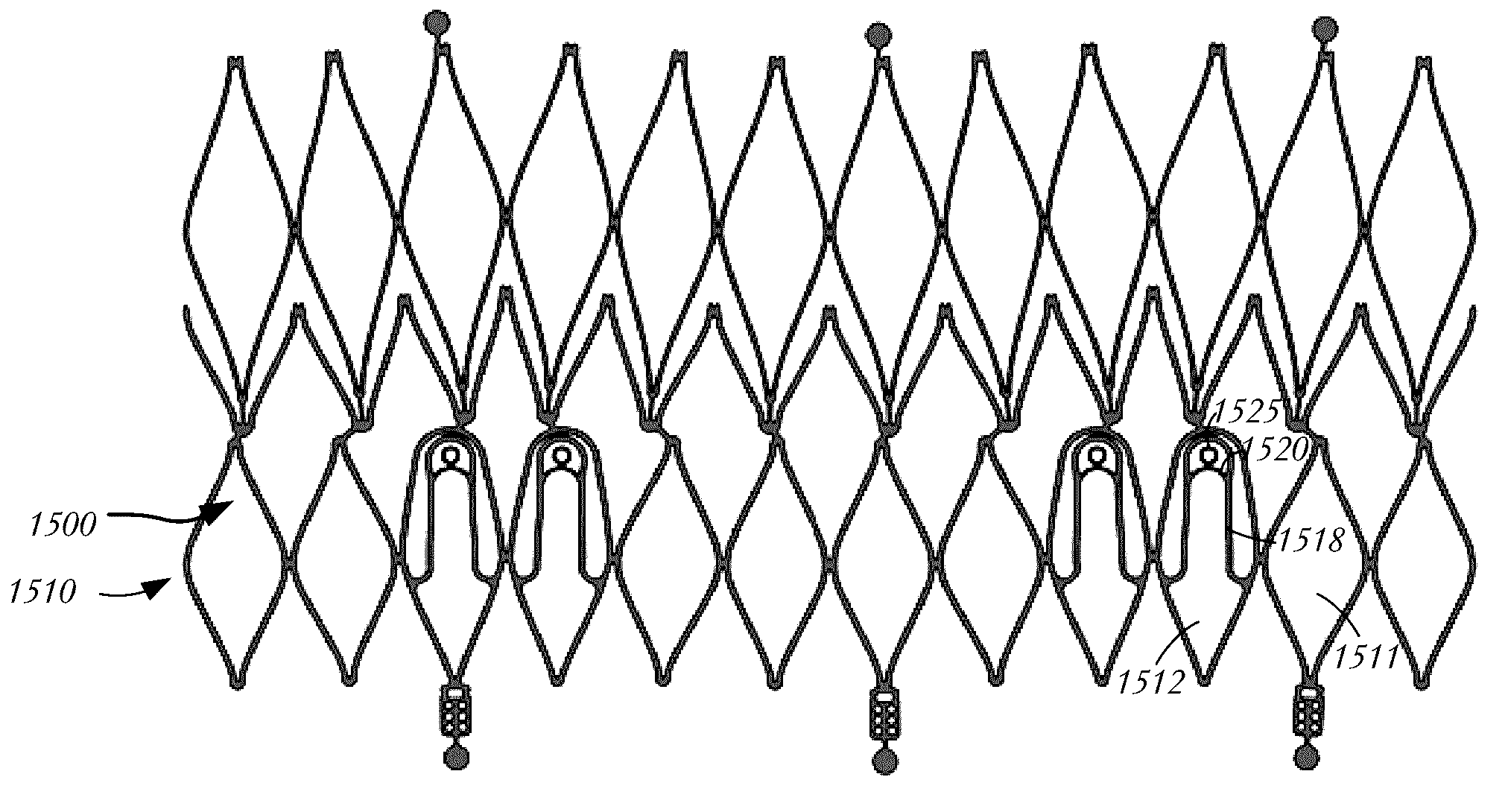
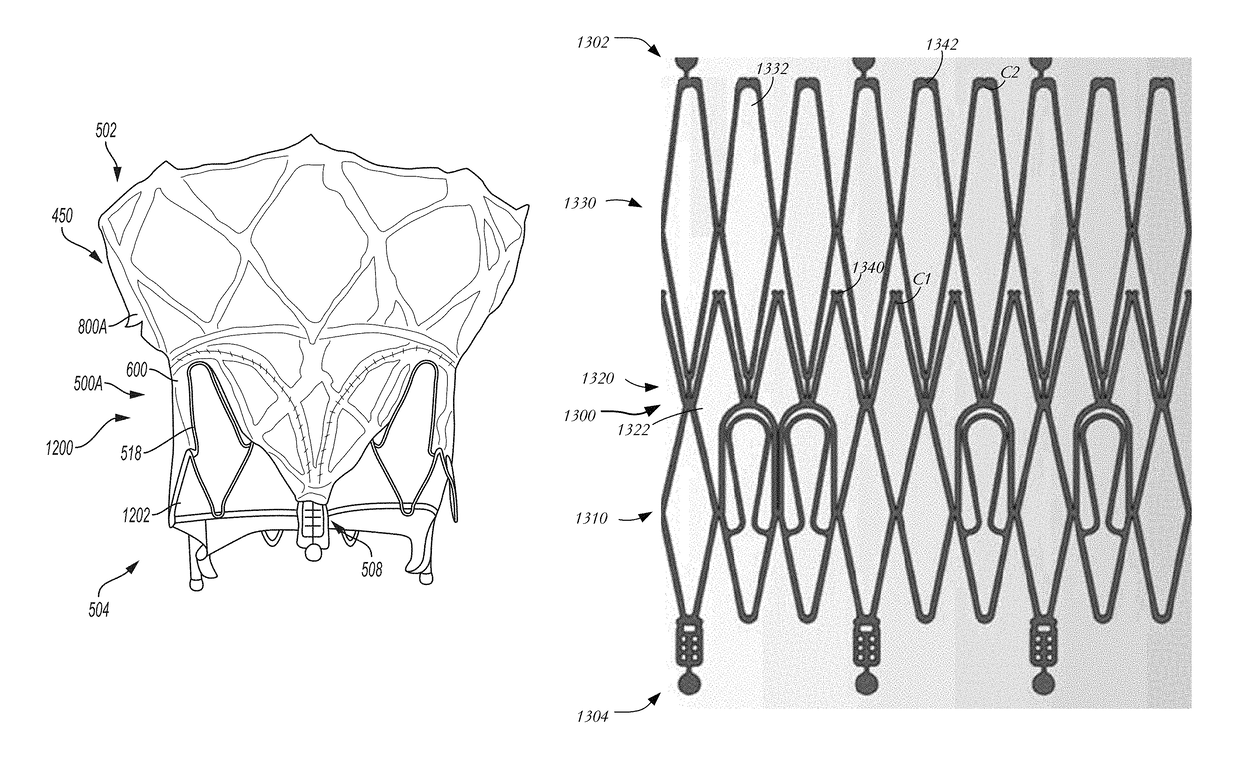
Devices, systems and methods for delivering a prosthetic mitral valve and anchoring device
Prosthetic mitral heart valves and anchors for use with such valves are provided that allow for an improved implantation procedure. In various embodiments, a helical anchoring device is formed as a coiled or twisted anchor that includes one or more turns that twist or curve around a central axis. Curved arms attached to the frame of the valve guide the helical anchoring device into position beneath the valve leaflets and around the mitral valve annulus as it exits the delivery catheter, and the expandable prosthetic mitral valve is held within the coil of the anchoring device. The anchoring device and the valve can be delivered together, simplifying the valve replacement procedure.
Owner:MITRAL VALVE TECHNOLOGIES SARL
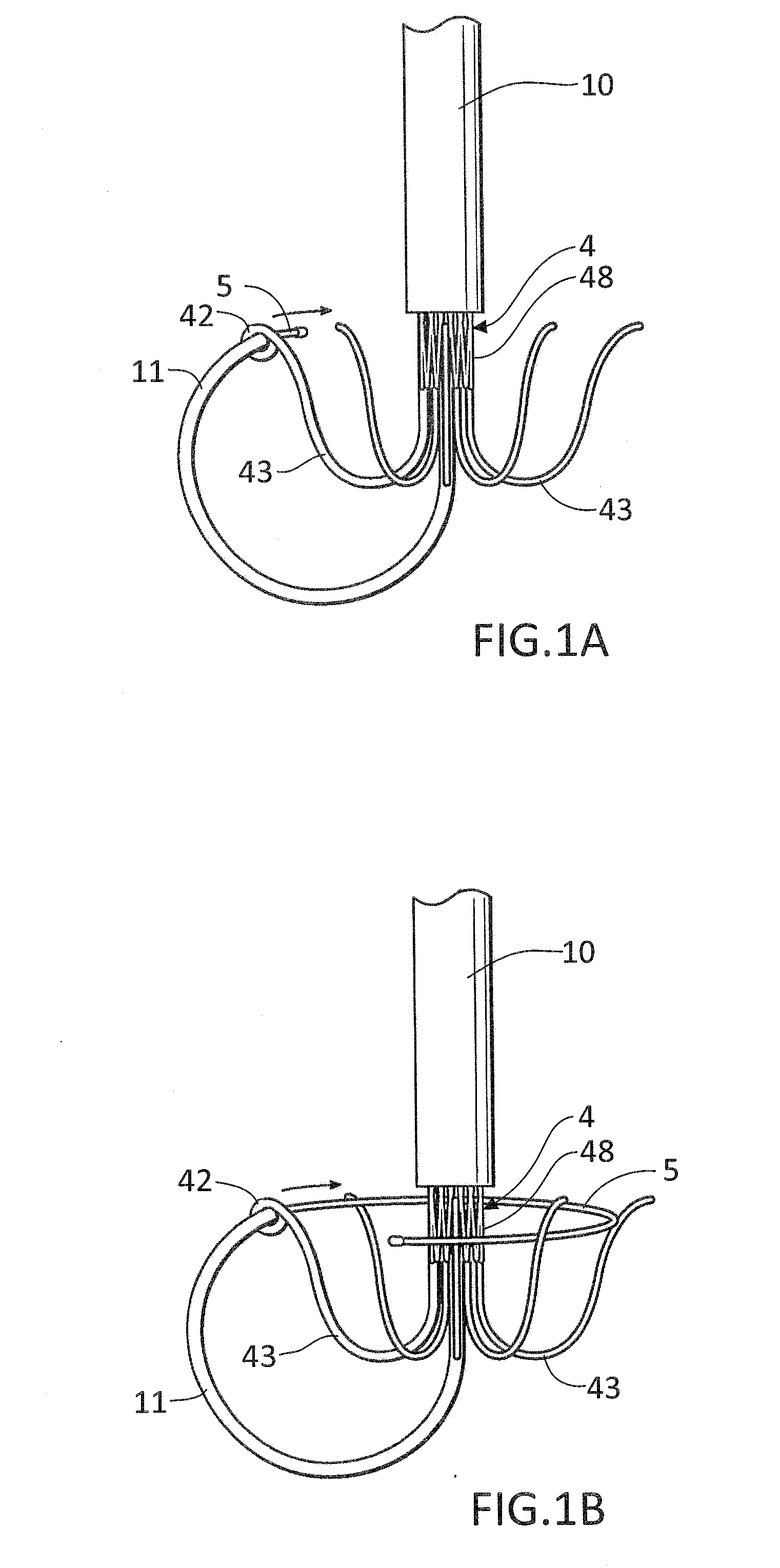
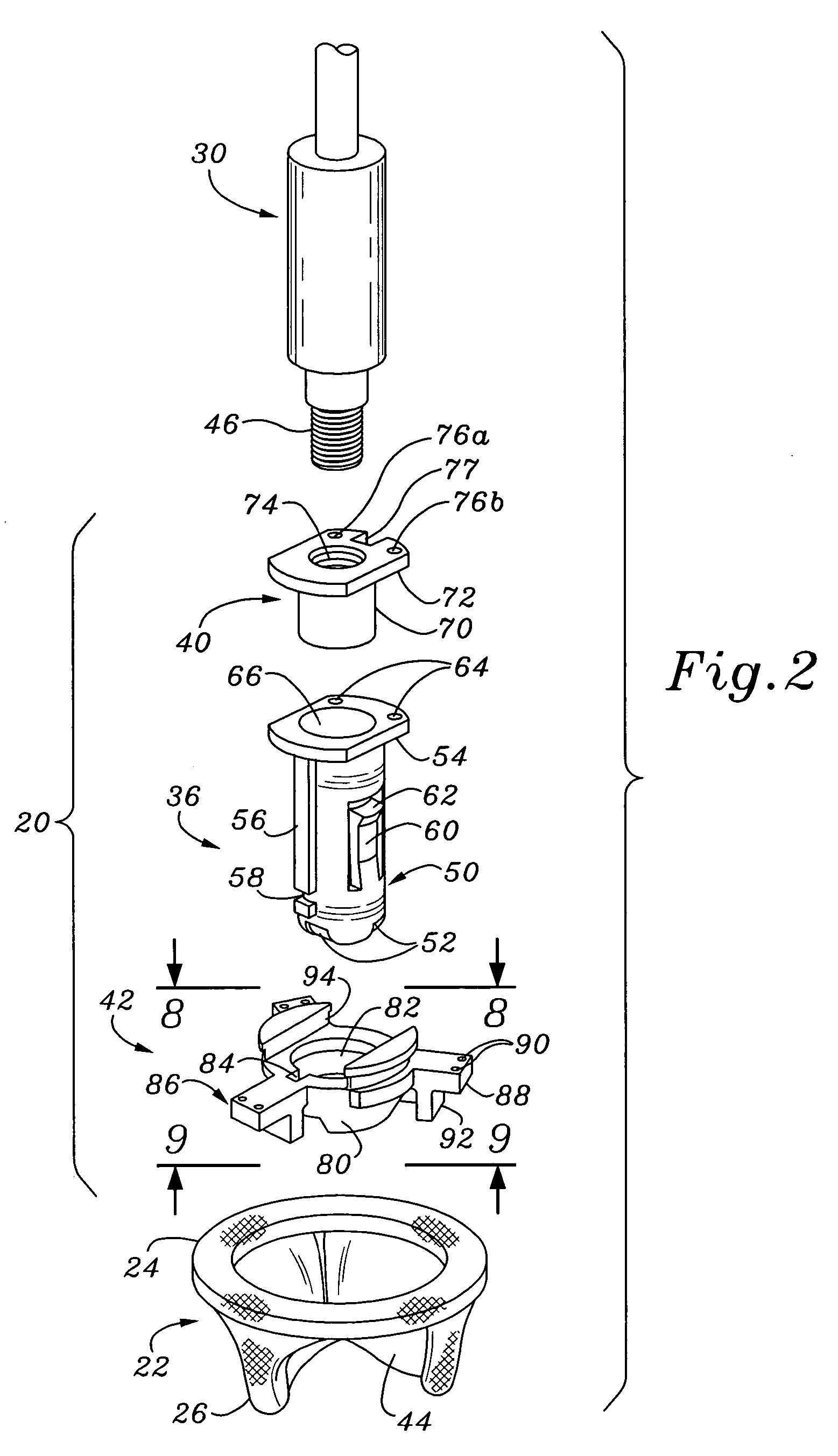
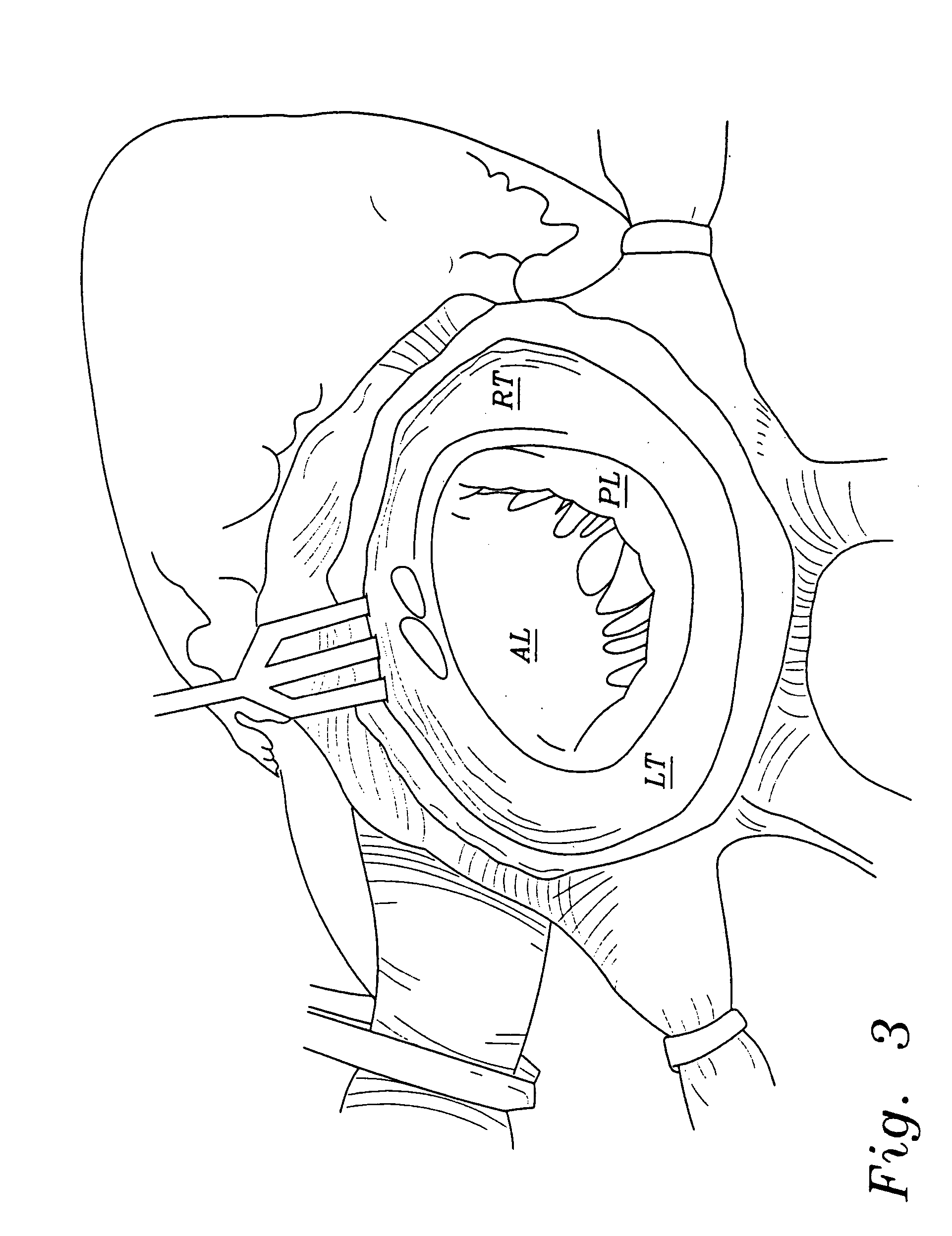
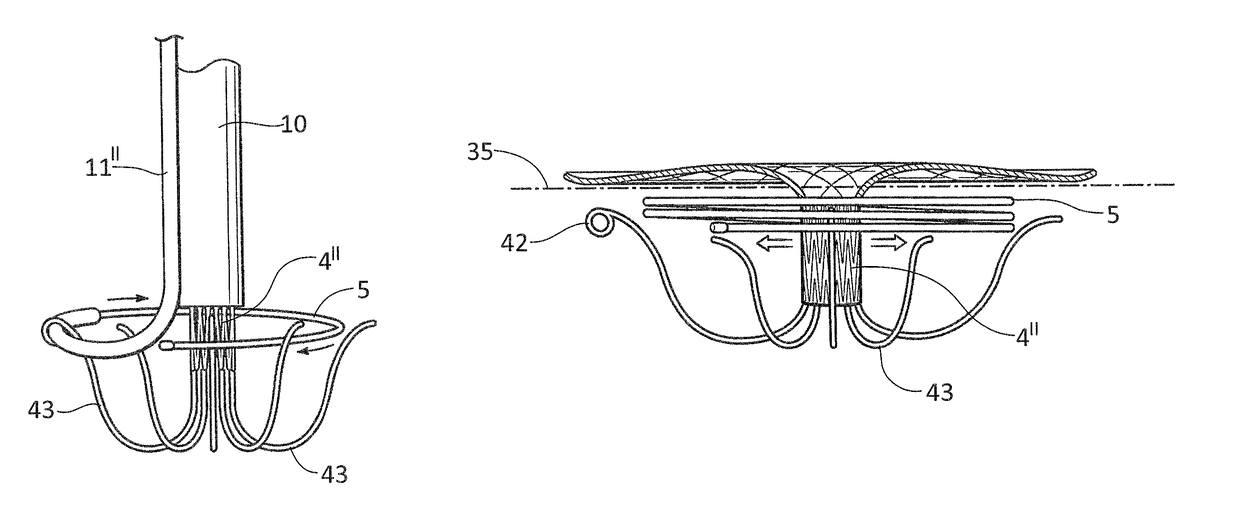
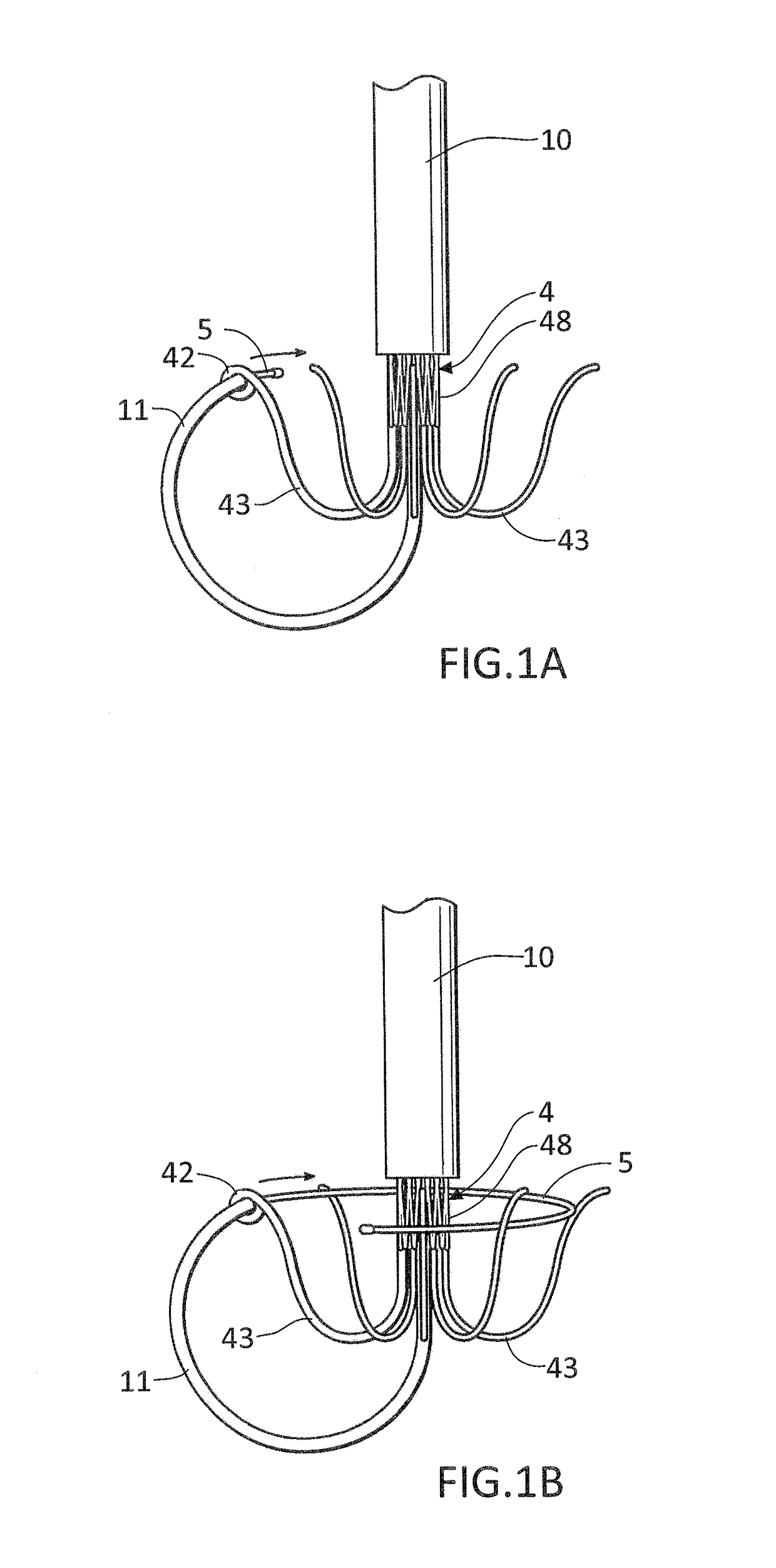
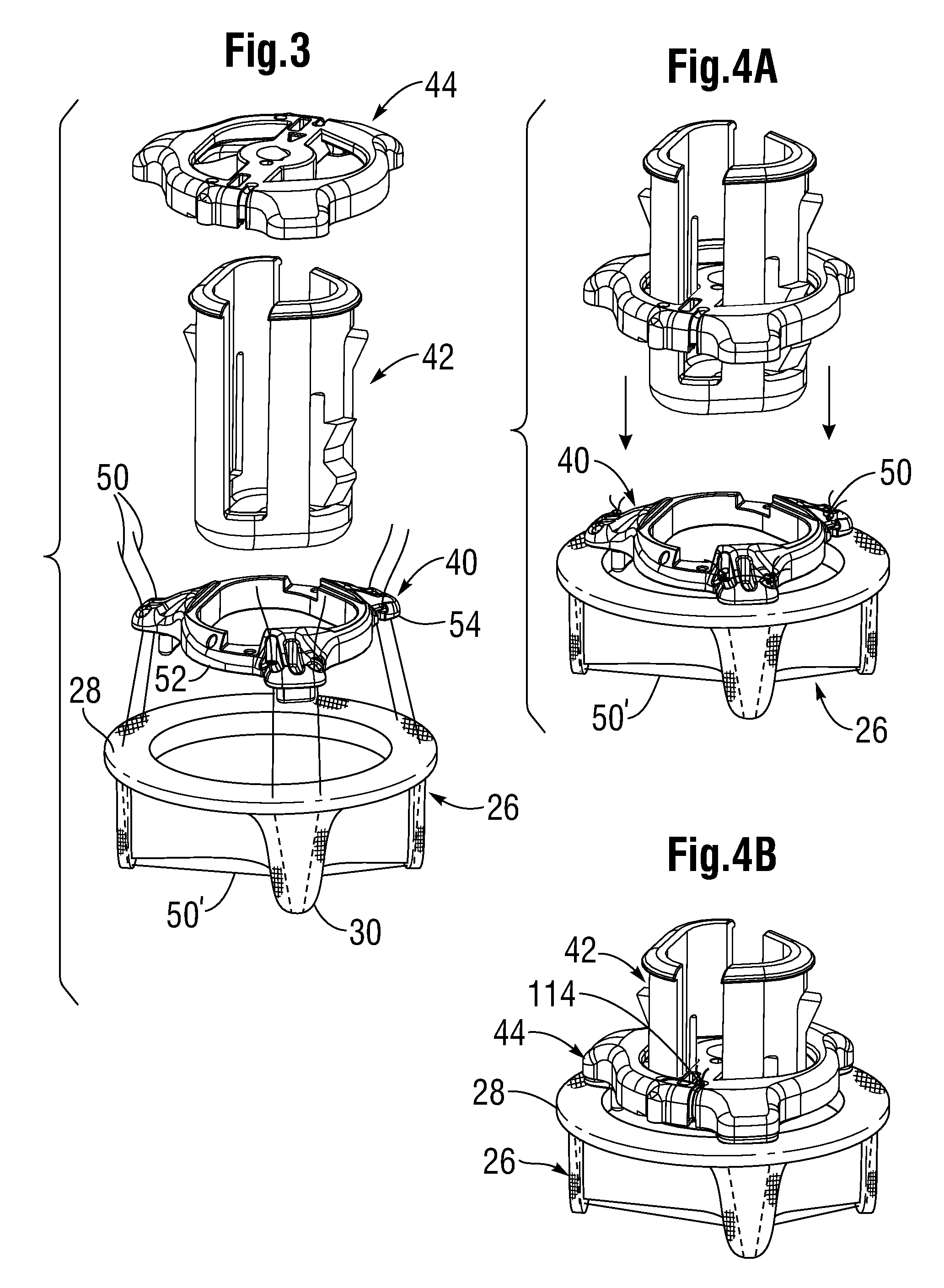
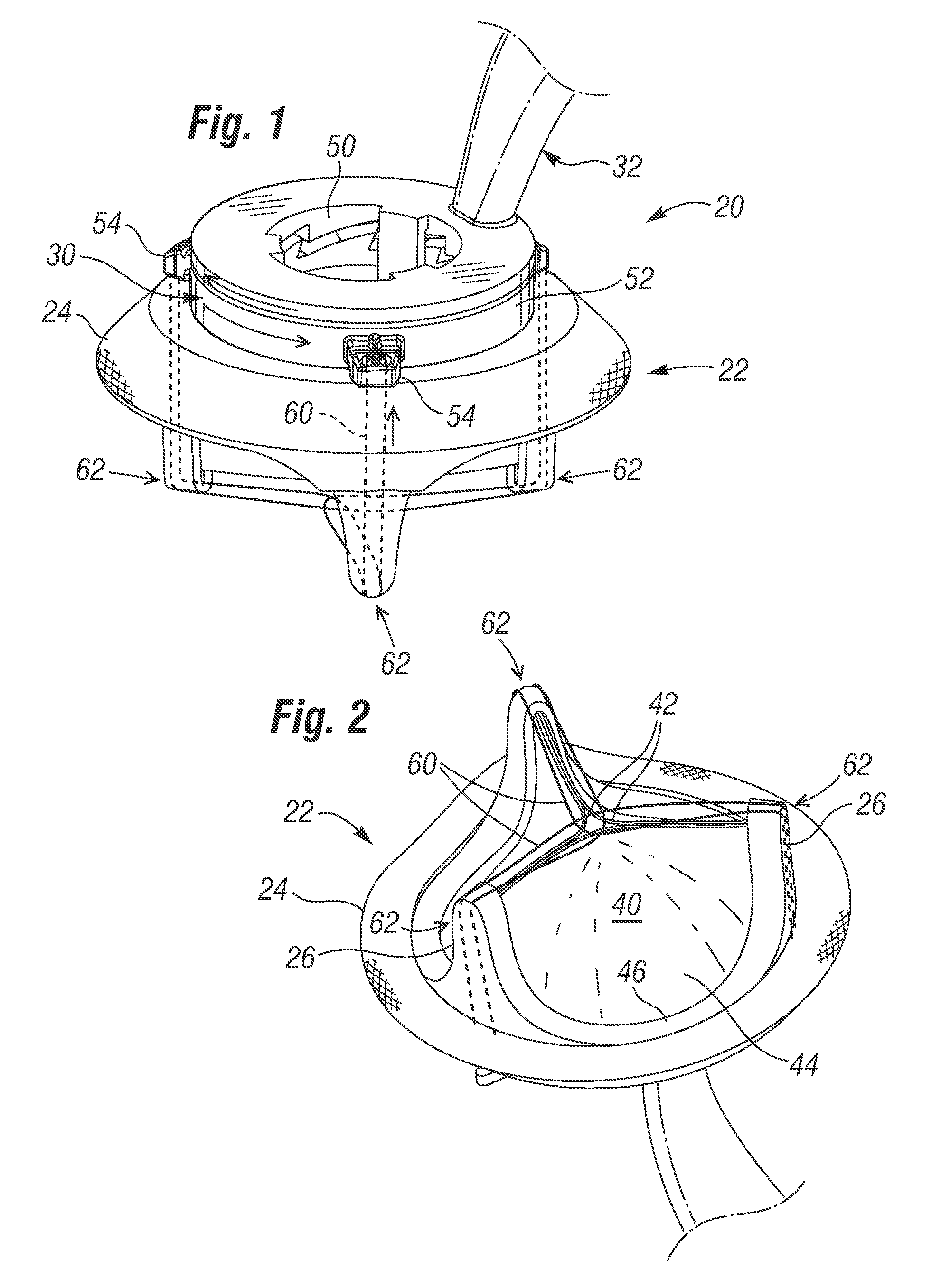
Heart valve holder and method for resisting suture looping
An improved holder and method for implanting a tissue-type prosthetic mitral heart valve that prevents suture looping and may also constrict the commissure posts of the valve. An upstanding or shaft member axially positioned on the holder causes the lengths of attachment sutures to extend axially beyond the commissure post tips to create a tent and prevent looping of any of an array of pre-implanted sutures around the tips during deployment of the valve. The shaft member may be axially movable such that it can be initially retracted and then actuated just prior to valve deployment. The shaft member may have notches on its distal tip for capturing the attachment sutures, which are crossed over along the valve axis to ensure engagement by the notches. The attachment sutures may be strands or filaments, or may be wider bands of flexible biocompatible material. If bands are used, they desirably cover the commissure post tips to further help prevent suture looping thereover. The flexible lengths of material extend directly between commissures of the valve, or may extending radially inward from each commissure to a central upstanding member.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow
A mitral heart valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow that conforms to an abnormal posterior aspect of the mitral annulus. The ring may be generally oval having a major axis and a minor axis, wherein the posterior bow may be centered along the minor axis or offset in a posterior section. The ring may be substantially planar, or may include upward bows on either side of the posterior bow. The ring may include a ring body surrounded by a suture-permeable fabric sheath formed of a plurality of concentric ring elements or bands. The posterior bow is stiff enough to withstand deformation once implanted and subjected to normal physiologic stresses. A method of repairing an abnormal mitral heart valve annulus having a depressed posterior aspect includes providing a ring with a posterior bow and implanting the ring to support the annulus without unduly stressing the attachment sutures.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
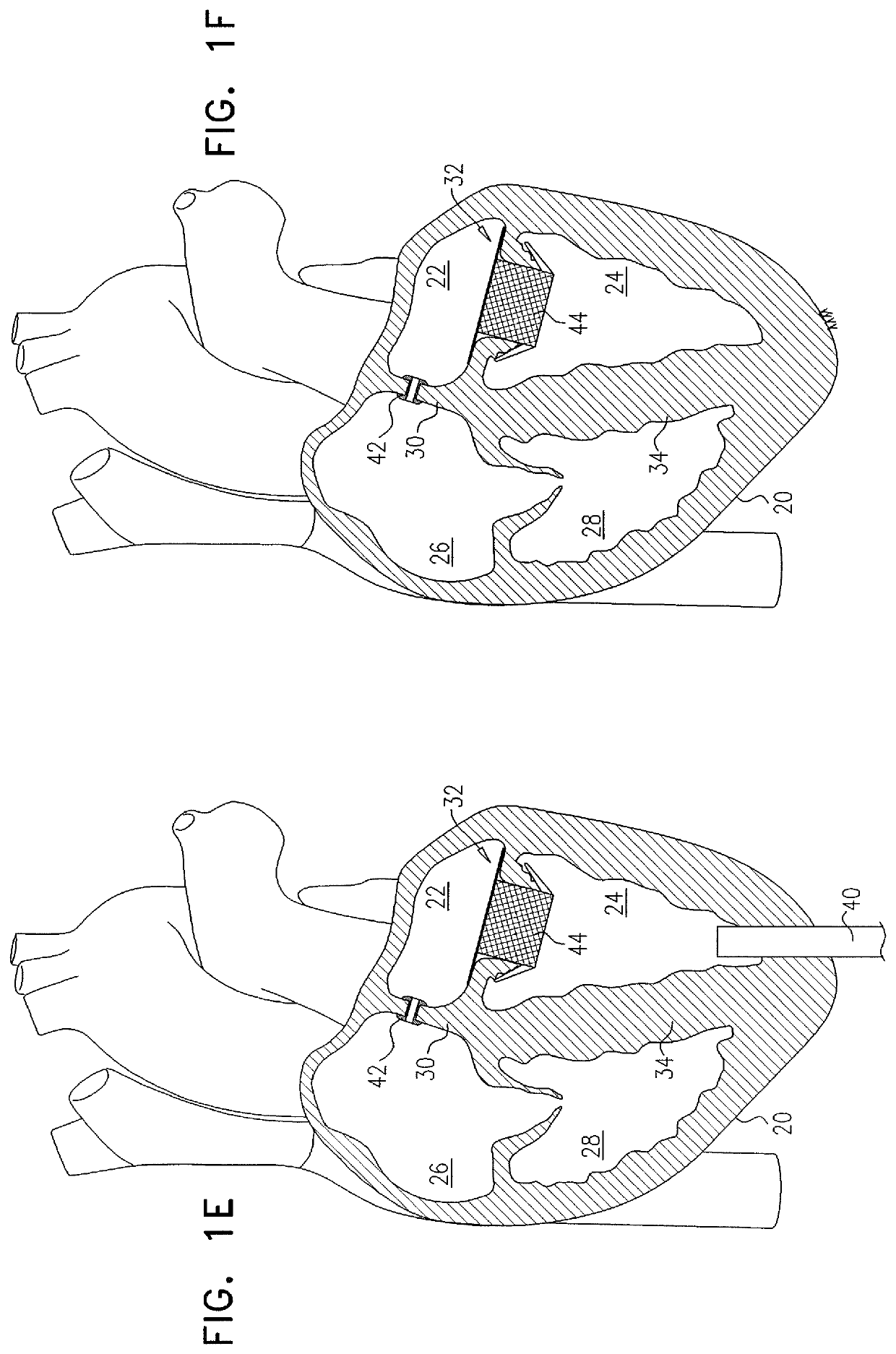
Valve prosthesis including a prosthetic leaflet
InactiveUS20050038509A1Improve effectivenessIncreased durabilityBone implantAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic valveProsthesis
A prosthesis for repairing a damaged valve such as a heart mitral valve is disclosed. The prothesis comprises a prosthetic valve leaflet mounted on a frame. When implanted in a mitral valve, the leaflet replaces the function of an endogenous valve leaflet and coapts with an opposed endogenous valve leaflet. The prosthesis may further comprise a strut or other member to which the edge of an opposed valve leaflet can be sutured, and which can be used to correct deformities of a ventricle wall. Further disclosed is a method of repairing a damaged heart valve by providing a prosthetic valve leaflet or by providing a prosthetic valve leaflet and prosthetic attachment points for an opposed valve leaflet.
Owner:ASHE KASSEM ALI
Four-leaflet stented mitral heart valve
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method and apparatus for performing catheter-based annuloplasty using local plications
InactiveUS20050184122A1Complicated surgical procedure can be avoidedImprove the quality of lifeSuture equipmentsStapling toolsMitral valve leafletCatheter device
A minimally invasive method of performing annuloplasty. According to one aspect, a method for performing annuloplasty includes creating a first plication in the tissue near a mitral valve of a heart, using at least a first plication element, and creating a second plication in the tissue near the mitral valve such that the second plication is substantially coupled to the first plication.
Owner:MITRALIGN INC
Heart valve holder that resist suture looping
An improved holder, system and method for implanting a tissue-type prosthetic mitral heart valve that prevents suture looping and may also constrict the commissure posts of the valve. The holder may include two relatively movable plates, one of which attaches to the valve sewing on the inflow end of the valve ring and the other which attaches via sutures or similar expedient to the valve commissures on the outflow end. Separation of the plates places the sutures in tension and constricts the commissures. The sutures may be strands or filaments, or may be wider bands of flexible biocompatible material. If bands are used, they desirably cover the commissure post tips to further help prevent suture looping thereover. The flexible lengths of material extend directly between commissures of the valve, or may extending radially inward from each commissure to a central upstanding member. Desirably, a slide is created by the flexible lengths of material adjacent each commissure post, for example by crossing over suture filaments at or radially inward from the commissure posts. If an upstanding member is used, the lengths of suture extend axially beyond the commissure post tips to create a tent that wards off sutures that otherwise might loop around the tips during advancement of the valve along an array of pre-implanted sutures.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS7871435B2Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic heartLeft ventricle wall
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
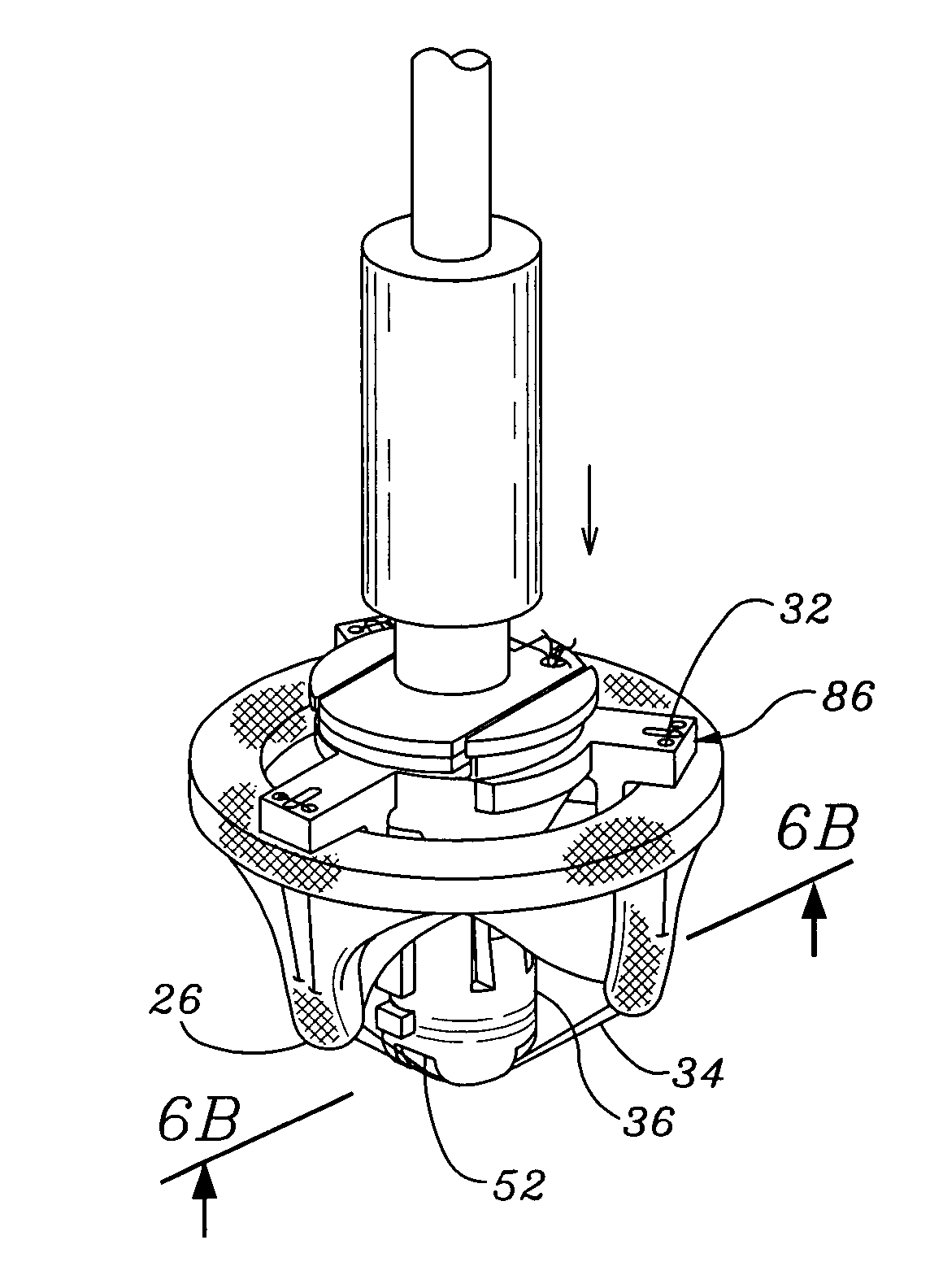
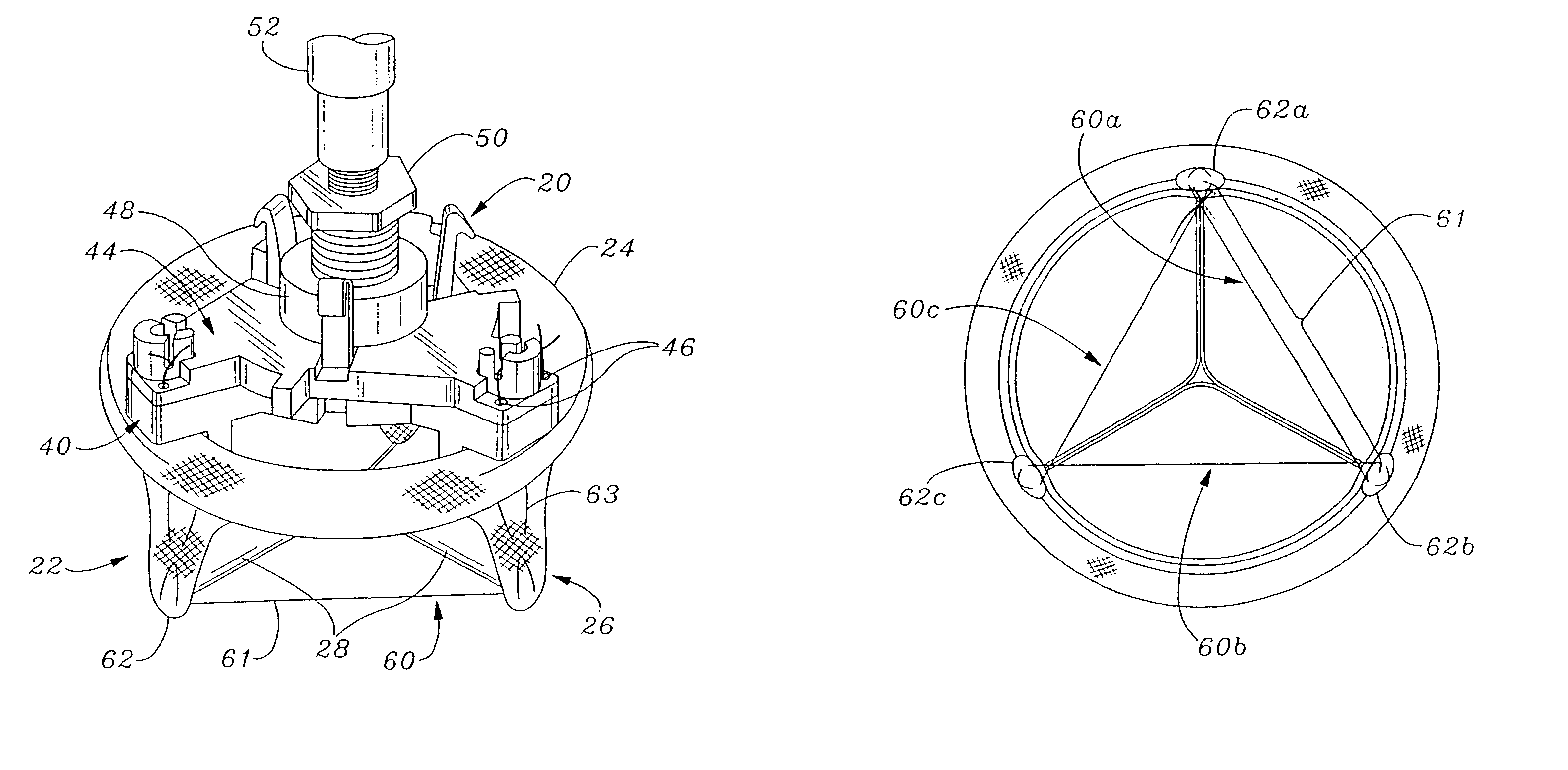
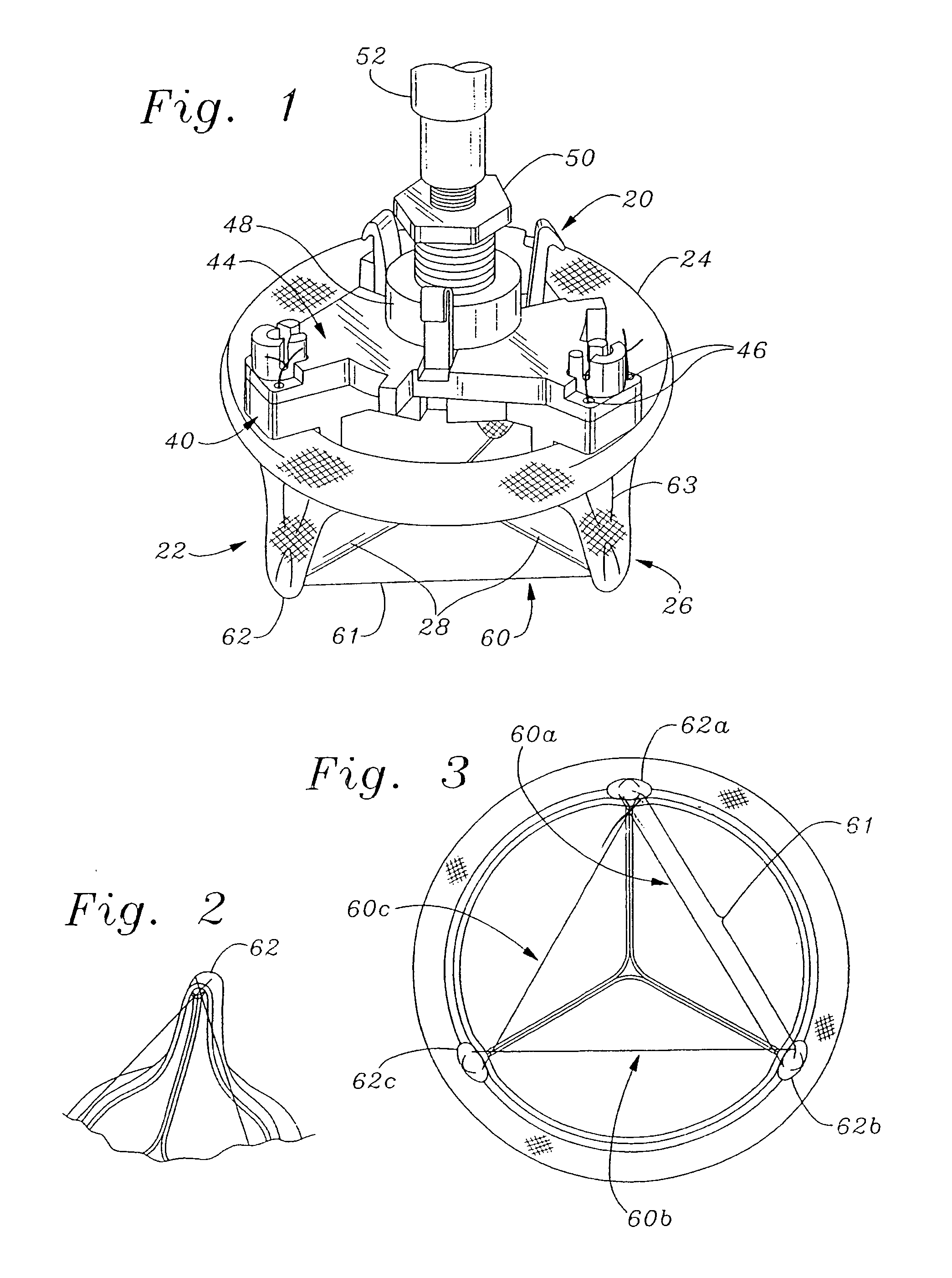
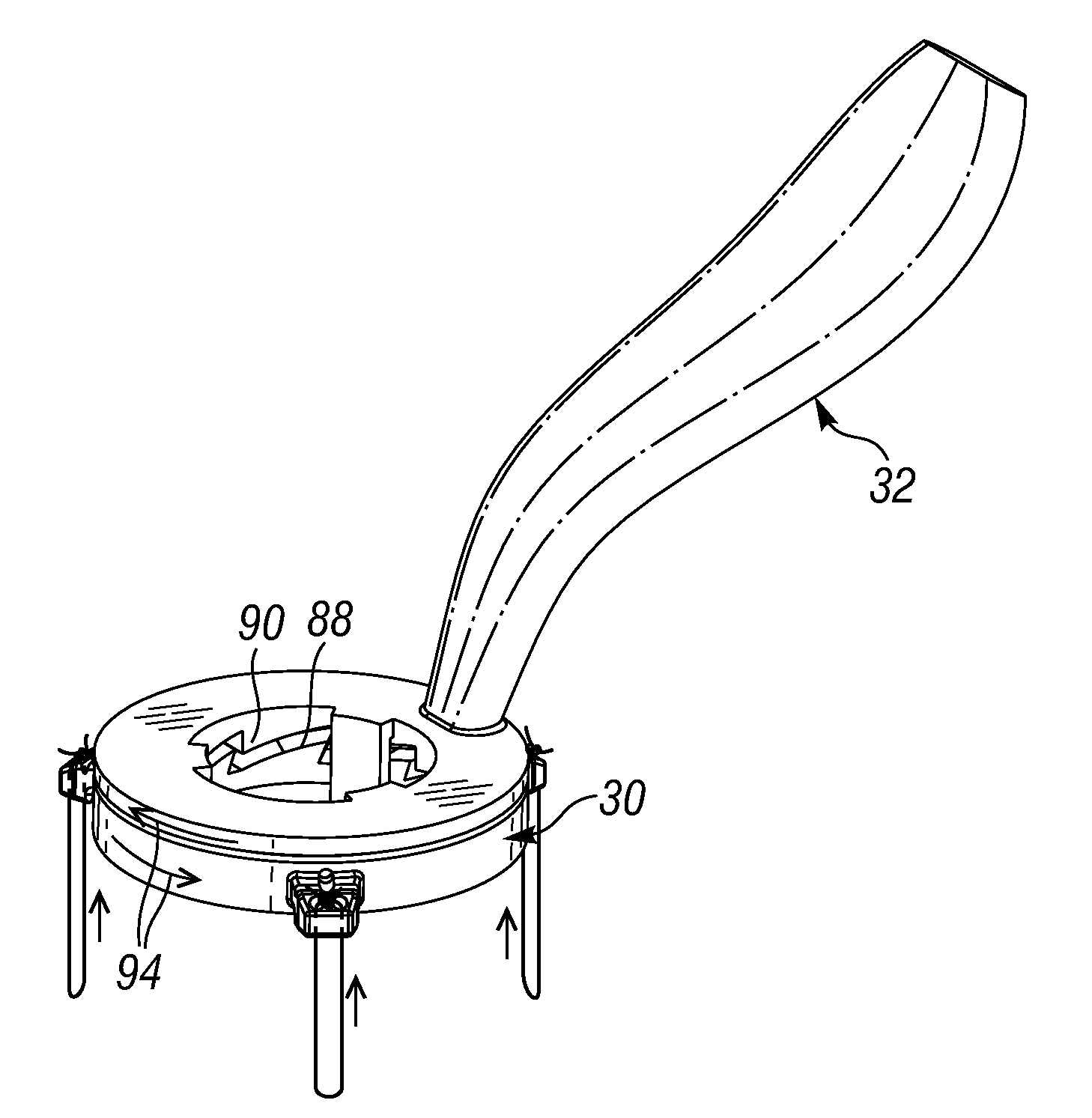
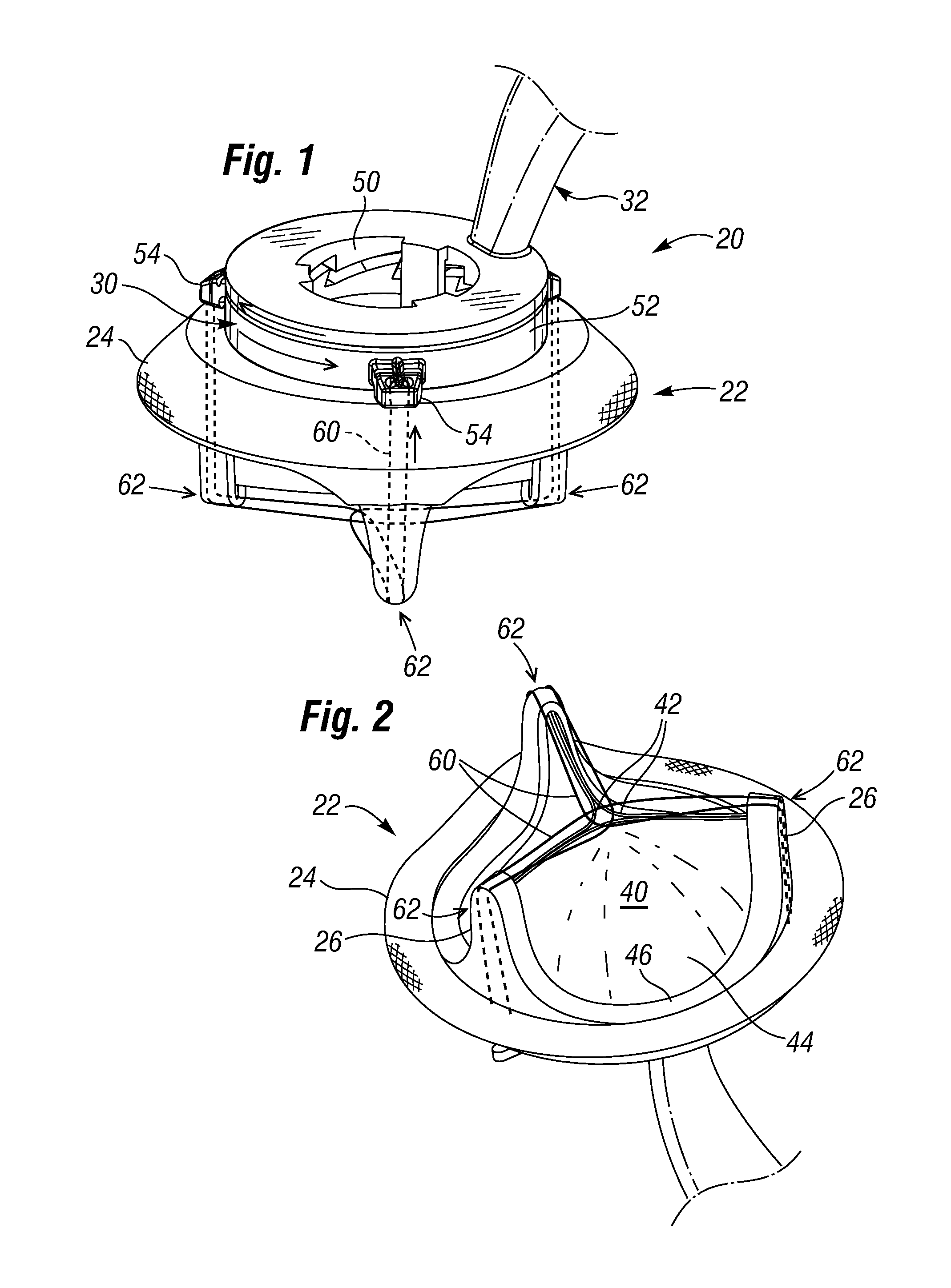
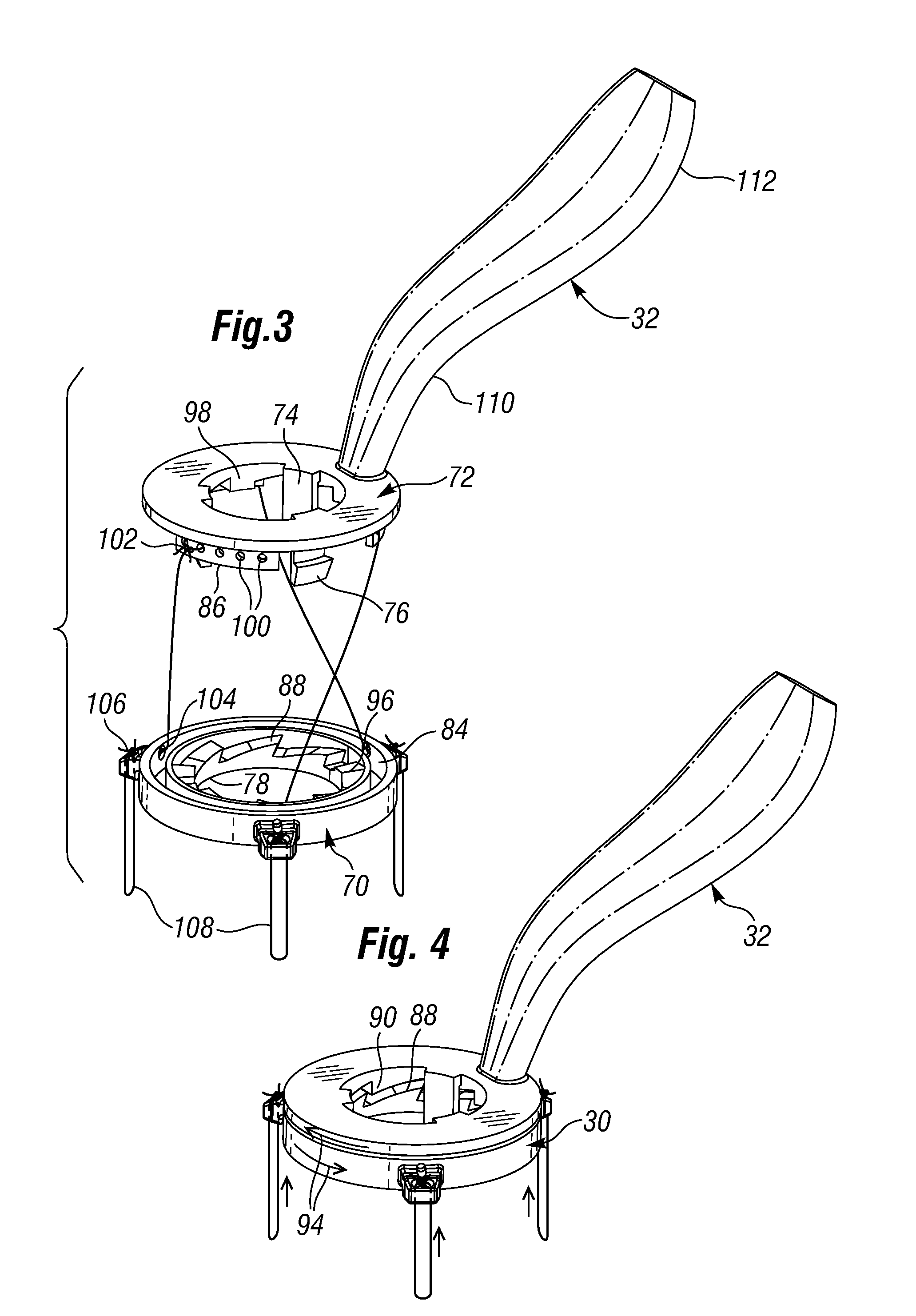
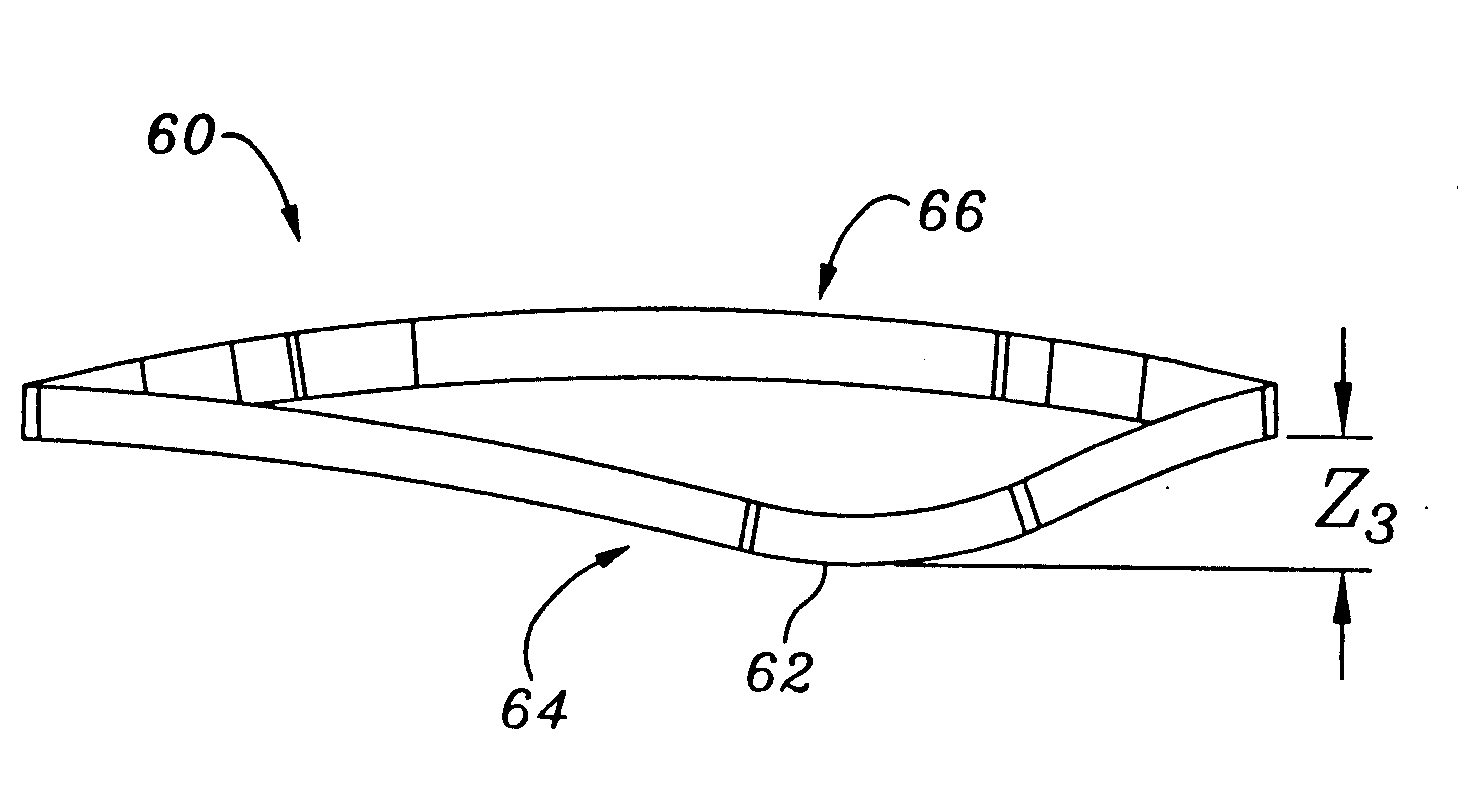
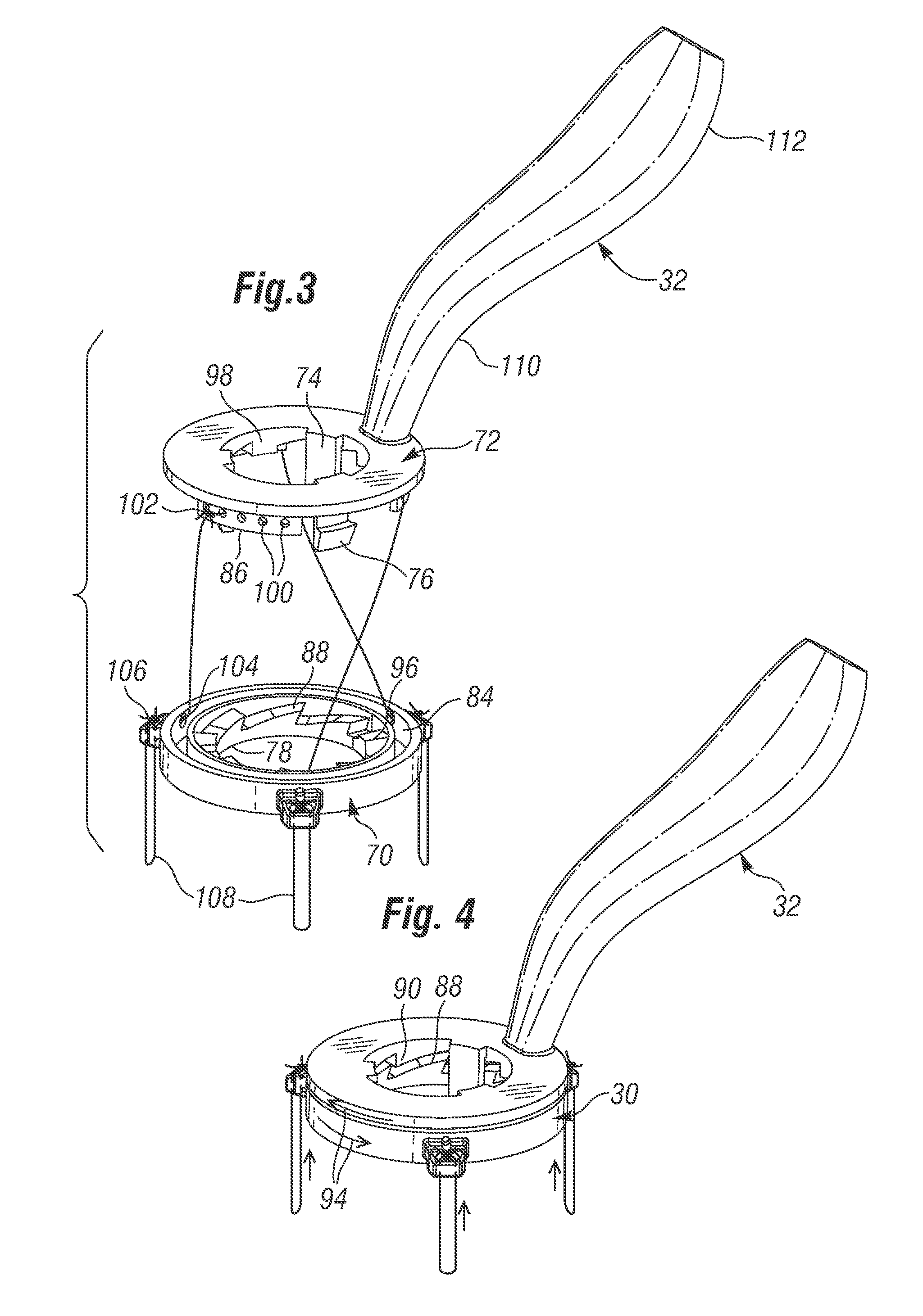
Ergonomic mitral heart valve holders
ActiveUS20120136434A1Prevent suture loopingEasy accessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMetallic materialsProsthesis
A holder for a prosthetic mitral heart valve that attaches to an inflow end of the valve and includes a simple tensioning mechanism that flexes the heart valve commissure posts inward to help prevent suture looping. The tensioning mechanism may include relatively movable rings of the holder or a generally unitary holder with a tensor, or rotatable knob. Connecting sutures thread through internal passages in the holder and travel in the outflow direction along valve commissure posts, emerging at the post tips and mutually crossing over the outflow side of the valve. A handle attaches off-center on the holder to increase visualization of and access to the heart valve through a central window. The holder is constructed of non-metallic materials so as to avoid interfering with imaging devices, and the handle is ergonomically curved and shaped to facilitate manipulation. The holder may be shaped as a ring with an open inner diameter for enhanced access to the commissure posts and leaflets.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow
A mitral heart valve annuloplasty ring having a posterior bow that conforms to an abnormal posterior aspect of the mitral annulus. The ring may be generally oval having a major axis and a minor axis, wherein the posterior bow may be centered along the minor axis or offset in a posterior section. The ring may be substantially planar, or may include upward bows on either side of the posterior bow. The ring may include a ring body surrounded by a suture-permeable fabric sheath, and the ring body may be formed of a plurality of concentric ring elements. The ring is semi-rigid and the posterior bow is stiff enough to withstand deformation once implanted and subjected to normal physiologic stresses. The ring elements may be bands of semi-rigid material. A method of repairing an abnormal mitral heart valve annulus having a depressed posterior aspect includes providing a ring with a posterior bow and implanting the ring to support the annulus without unduly stressing the attachment sutures.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral heart valve prosthesis and associated delivery catheter
InactiveUS20140309727A1Prevent paravalvular leakagePrevent leakageHeart valvesDocking stationPosterior leaflet
The invention relates to a mitral heart valve prosthesis and a delivery catheter to carry and deploy such a prosthesis. The invention allows to effectively treat a pathology related to moderate to severe mitral regurgitation. Such a prosthesis implantable by catheterism includes mainly a docking station and a leaflet cooperating with the docking station. The leaflet is advantageously arranged in a configuration close to a posterior leaflet of a native mitral valve of a patient.
Owner:ST GEORGE MEDICAL INC BVI
Techniques for providing a replacement valve and transseptal communication
ActiveUS20170231766A1Good blood pressureEasy to moveHeart valvesWound drainsHeart apexProsthetic valve
A method is provided, comprising: (1) making a transapical puncture into a left ventricle of the heart; (2) making a transseptal fenestration in the heart; (3) delivering a prosthetic valve via the transapical puncture and implanting the prosthetic valve at a mitral valve of the heart; and (4) subsequently to delivering the prosthetic valve and making the transseptal fenestration, closing the transapical puncture. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Mitral heart valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve having an inflow end, an outflow end and a longitudinal axis extending from the inflow end to the outflow end includes a collapsible and expandable stent including a plurality of cells arranged in at least one row extending around a circumference of the stent. The stent further includes at least one engaging arm joined to one of the cells adjacent the outflow end and having a free end extending toward the inflow end, the engaging arm being movable between a loaded condition in which the engaging arm is oriented substantially parallel with the longitudinal axis of the stent, a partially-released condition in which the engaging arm forms a first angle with the longitudinal axis of the stent, and a fully-released condition in which the engaging arm forms a second angle with the longitudinal axis of the stent, the first angle being larger than the second angle.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
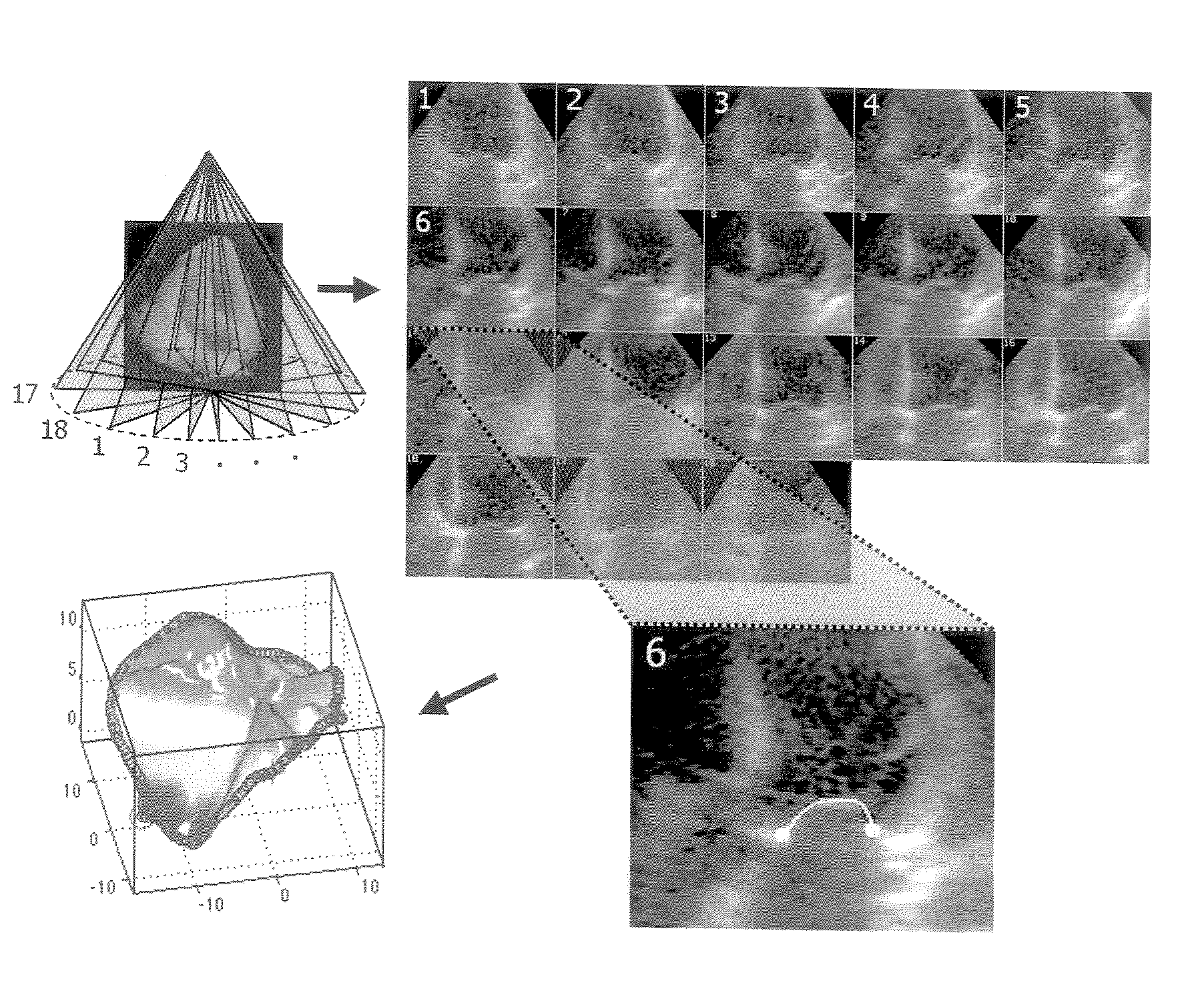
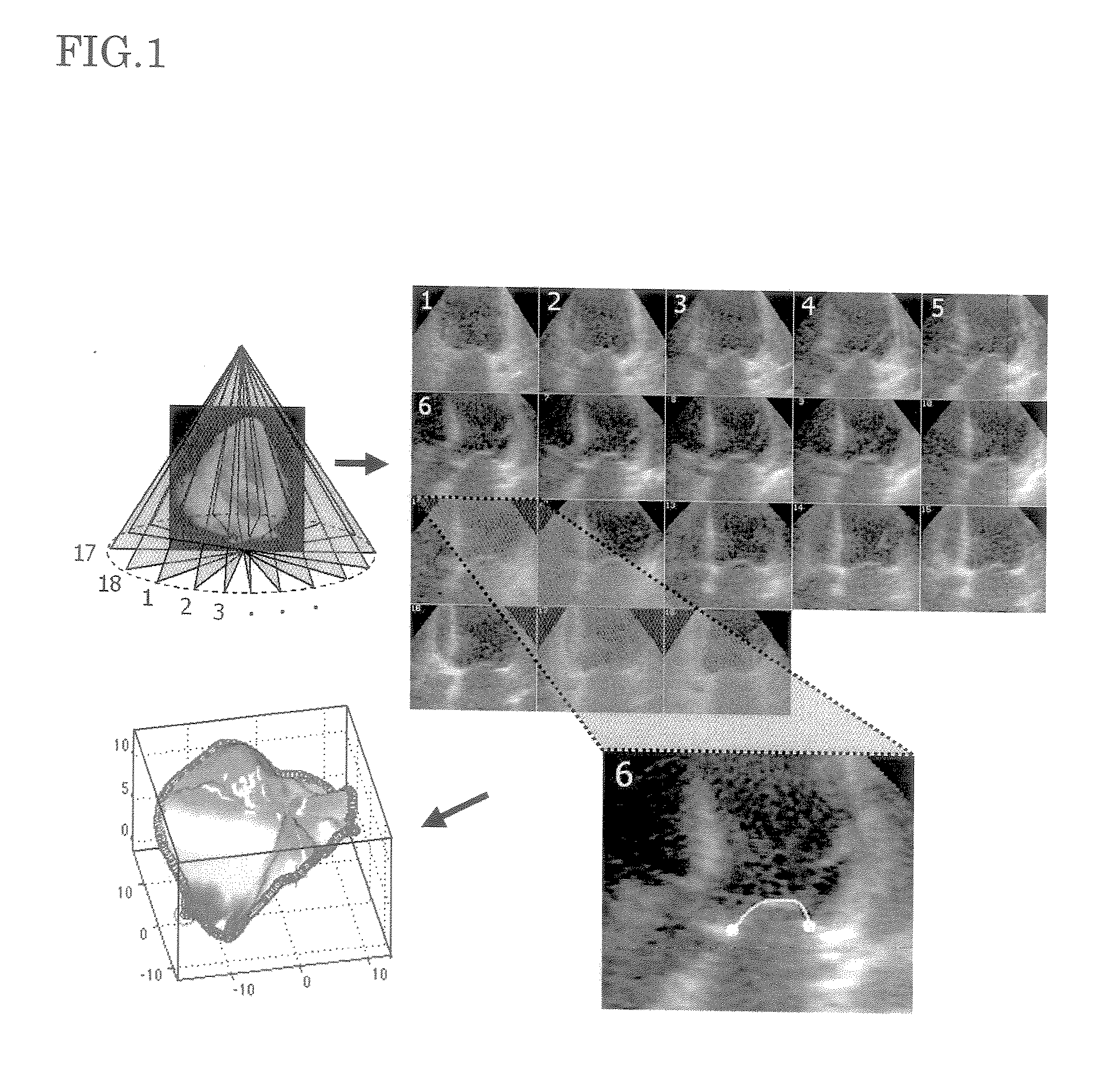
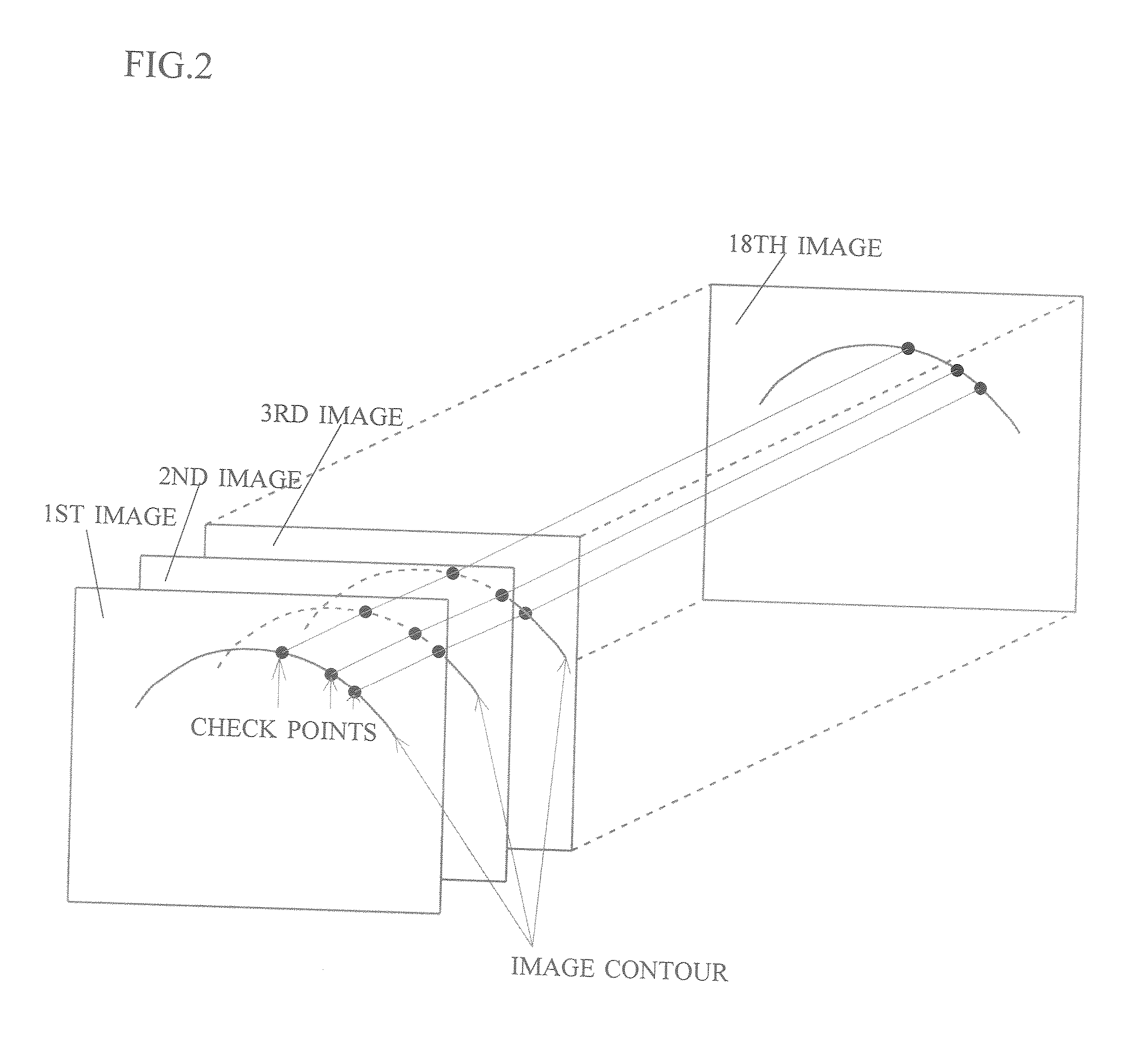
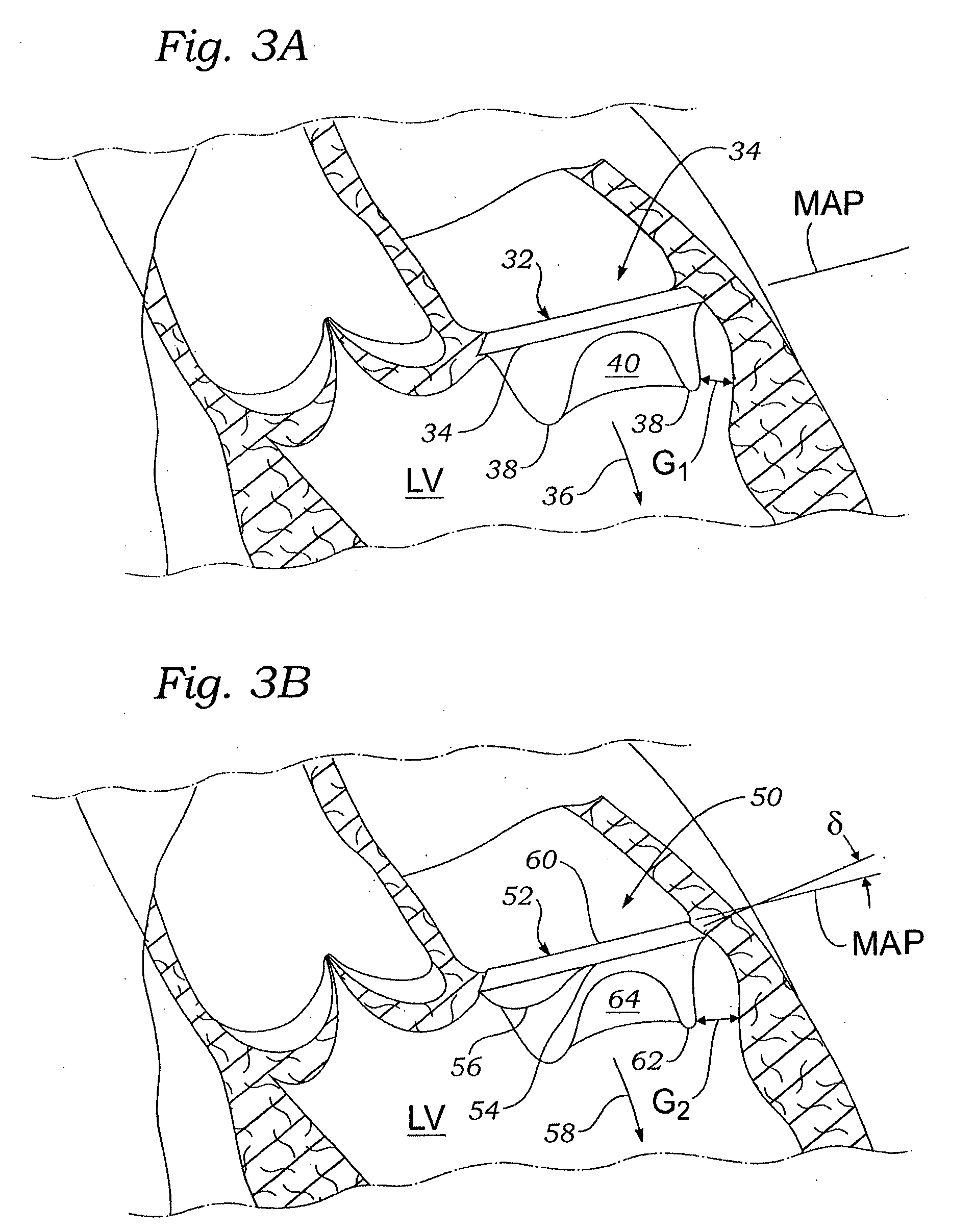
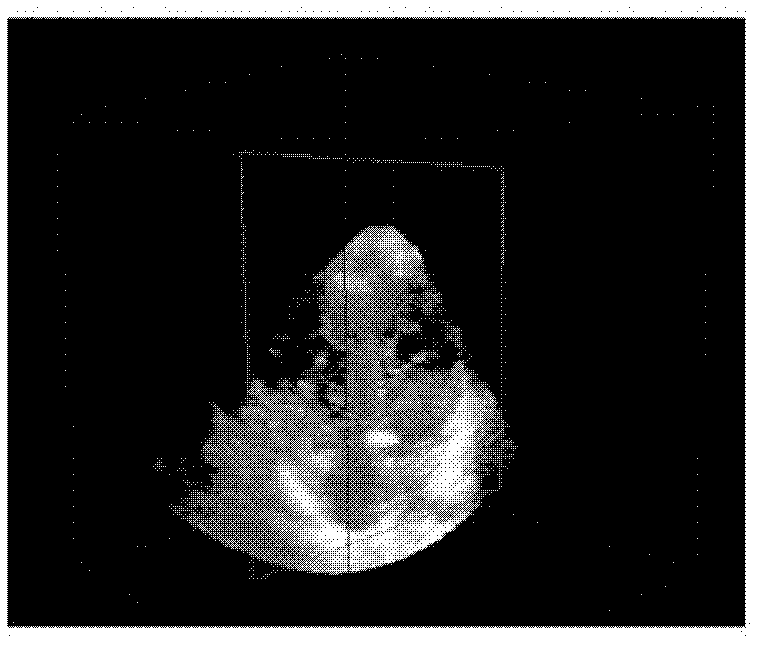
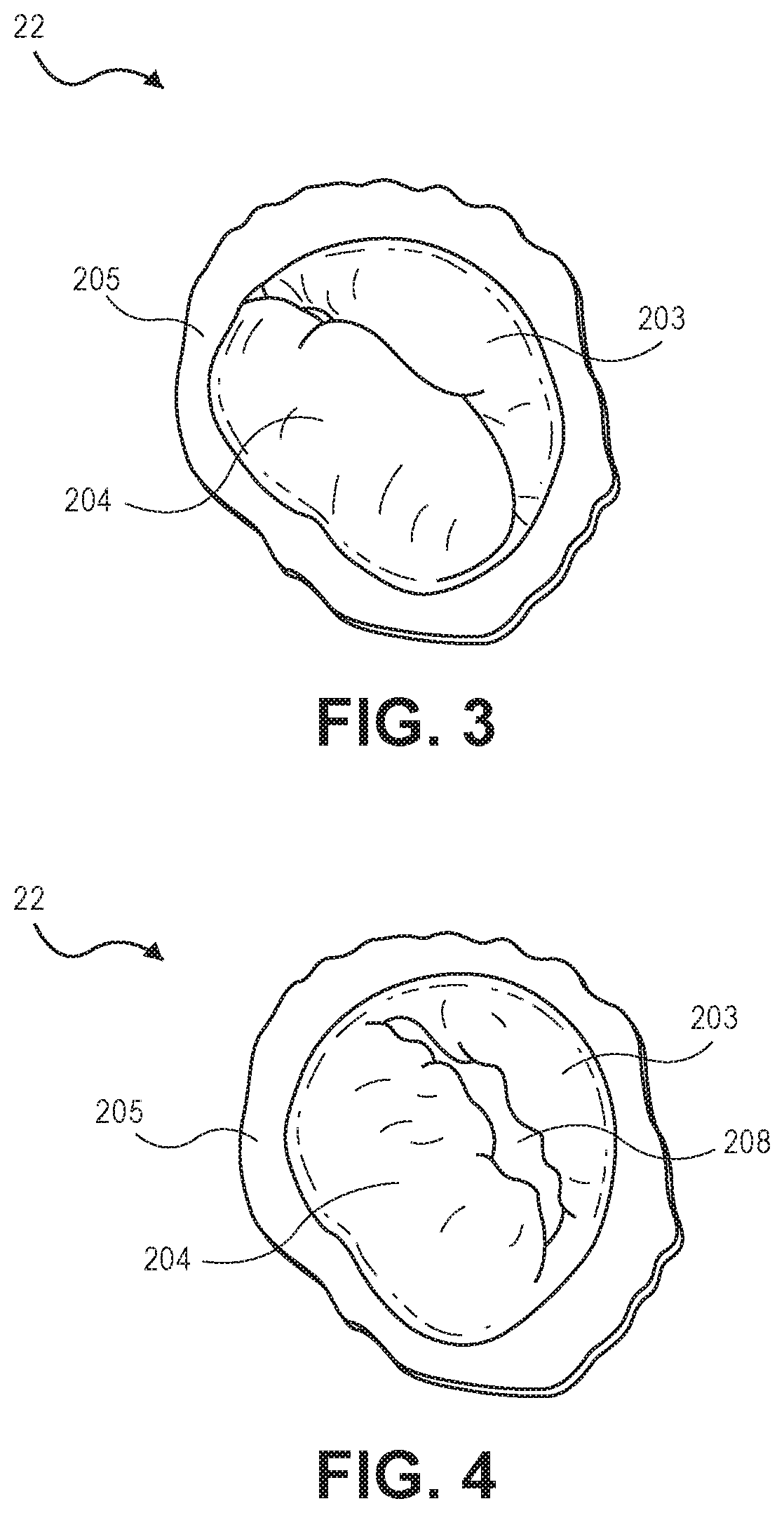
Cardiac Valve Data Measuring Method And Device
InactiveUS20080085043A1Time and labor consumingImage enhancementImage analysisPhysical shape2 dimensional echocardiography
An object of the present invention is to acquire information regarding the cardiac valve required in the clinical field, such as the tenting volume, tenting area, tenting height of the mitral valve of the heart, the area, the circumferential length, and height (the difference between the highest portion and the lowest portion) of the mitral annulus, etc. A method of obtaining a three-dimensional cardiac-valve image for measuring clinically required data regarding the cardiac valve, in which method a three-dimensional echocardiogram is created from two-dimensional echocardiograms obtained through scanning by means of an echocardiograph, and the three-dimensional cardiac-valve image is automatically extracted from the three-dimensional echocardiogram by computer processing The method is characterized in that a fitting evaluation function (potential energy) of a model of the mitral annulus in a fitting model prepared in consideration of the physical shapes of the heart and the mitral annulus is optimized by the replica exchange method and extended simulated annealing method.
Owner:YD +4
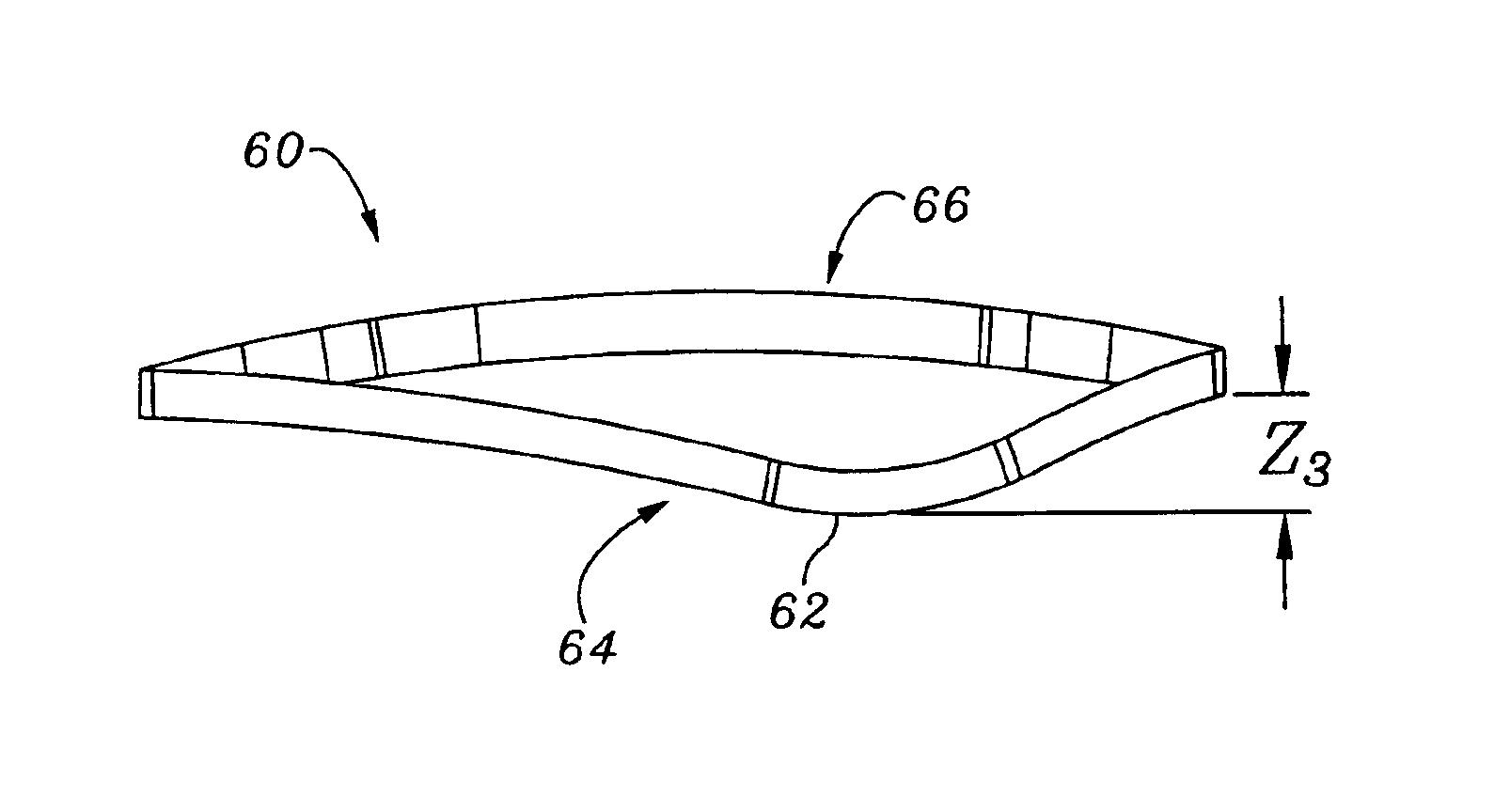
Methods of implanting a prosthetic mitral heart valve having a contoured sewing ring
A prosthetic mitral heart valve including a contoured sewing ring that better matches the mitral valve annulus. The sewing ring includes an inflow end and an outflow end, the outflow and having at least one raised portion. There may be two raised portions located approximately 120° apart from each other and designed to register with two anterior trigones of the mitral valve annulus. The sewing ring may be formed by a suture-permeable annular member surrounded by a fabric covering, the annular member desirably being molded of silicone. The raised portion(s) may gently curve upward to a height of about 2 mm above the adjacent portions of the outflow end of the sewing ring. The sewing ring may also be constructed so as to be more flexible around a posterior aspect than around an anterior aspect to accommodate calcified tissue more commonly found around the posterior annulus. The contoured sewing ring can be combined with various types of heart valve including bioprosthetic and mechanical valves. A bioprosthetic heart valve of the present invention may include a support stent having three outflow commissures alternating with three inflow cusps, with two of the commissures being located at the same place as two raised portions of the sewing ring. A method of implant includes tilting the prosthetic heart valve in the mitral annulus so that a posterior commissure angles away from the ventricular wall and reduces the chance of contact therebetween.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Techniques for providing a replacement valve and transseptal communication
A method is provided, comprising: (1) making a transapical puncture into a left ventricle of the heart; (2) making a transseptal fenestration in the heart; (3) delivering a prosthetic valve via the transapical puncture and implanting the prosthetic valve at a mitral valve of the heart; and (4) subsequently to delivering the prosthetic valve and making the transseptal fenestration, closing the transapical puncture. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:CARDIOVALVE LTD
Prosthetic mitral heart valve having a contoured sewing ring
A prosthetic mitral heart valve including a contoured sewing ring that better matches the mitral valve annulus. The sewing ring includes an inflow end and an outflow end, the outflow and having at least one raised portion. There may be two raised portions located approximately 120° apart from each other and designed to register with two anterior trigones of the mitral valve annulus. The sewing ring may be formed by a suture-permeable annular member surrounded by a fabric covering, the annular member desirably being molded of silicone. The raised portion(s) may gently curve upward to a height of about 2 mm above the adjacent portions of the outflow end of the sewing ring. The sewing ring may also be constructed so as to be more flexible around a posterior aspect than around an anterior aspect to accommodate calcified tissue more commonly found around the posterior annulus. The contoured sewing ring can be combined with various types of heart valve including bioprosthetic and mechanical valves. A bioprosthetic heart valve of the present invention may include a support stent having three outflow commissures alternating with three inflow cusps, with two of the commissures being located at the same place as two raised portions of the sewing ring. A method of implant includes tilting the prosthetic heart valve in the mitral annulus so that a posterior commissure angles away from the ventricular wall and reduces the chance of contact therebetween.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral heart valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve having an inflow end and an outflow end includes a collapsible and expandable stent including a plurality of cells arranged in rows extending around a circumference of the stent, at least one of the rows forming a flared portion having a diameter that is larger than diameters of others of the rows. The stent further includes engaging arms disposed adjacent the outflow end and extending toward the inflow end, the engaging arms being configured to couple to heart tissue to anchor the stent. A collapsible and expandable valve assembly has a plurality of leaflets disposed within the stent.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Devices, systems and methods for delivering a prosthetic mitral valve and anchoring device
Prosthetic mitral heart valves and anchors for use with such valves are provided that allow for an improved implantation procedure. In various embodiments, a helical anchoring device is formed as a coiled or twisted anchor that includes one or more turns that twist or curve around a central axis. Curved arms attached to the frame of the valve guide the helical anchoring device into position beneath the valve leaflets and around the mitral valve annulus as it exits the delivery catheter, and the expandable prosthetic mitral valve is held within the coil of the anchoring device. The anchoring device and the valve can be delivered together, simplifying the valve replacement procedure.
Owner:MITRAL VALVE TECHNOLOGIES SARL
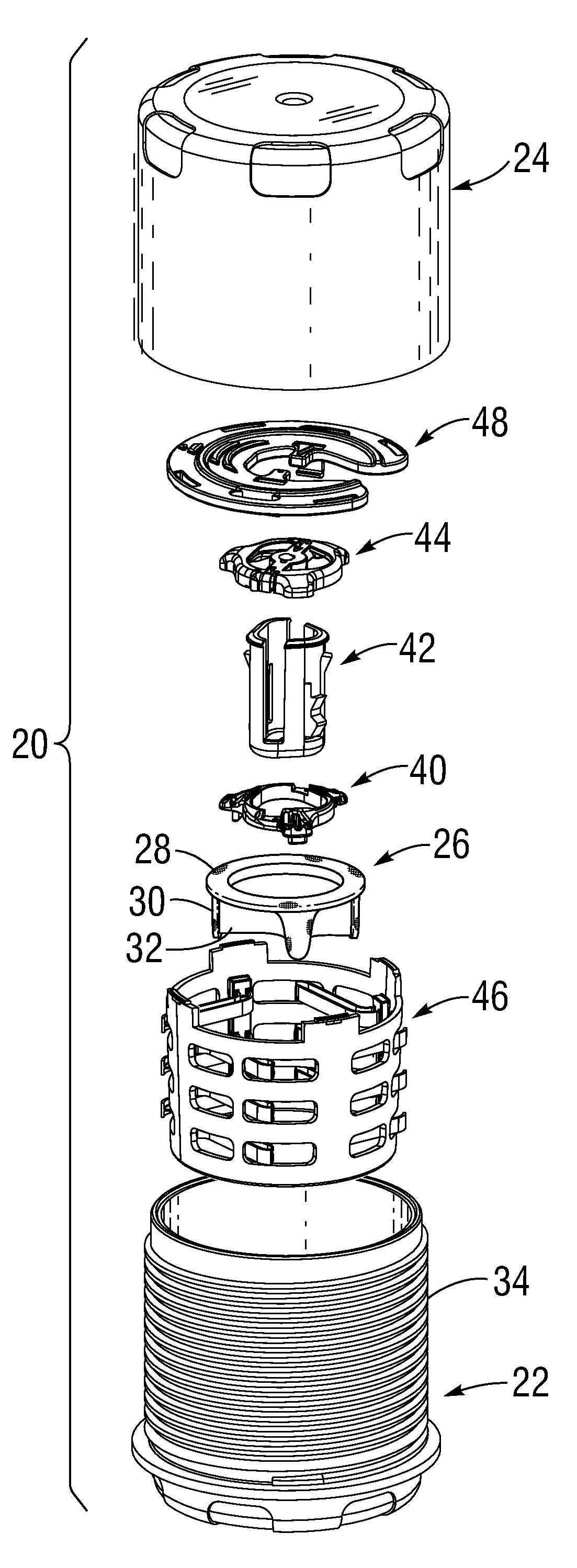
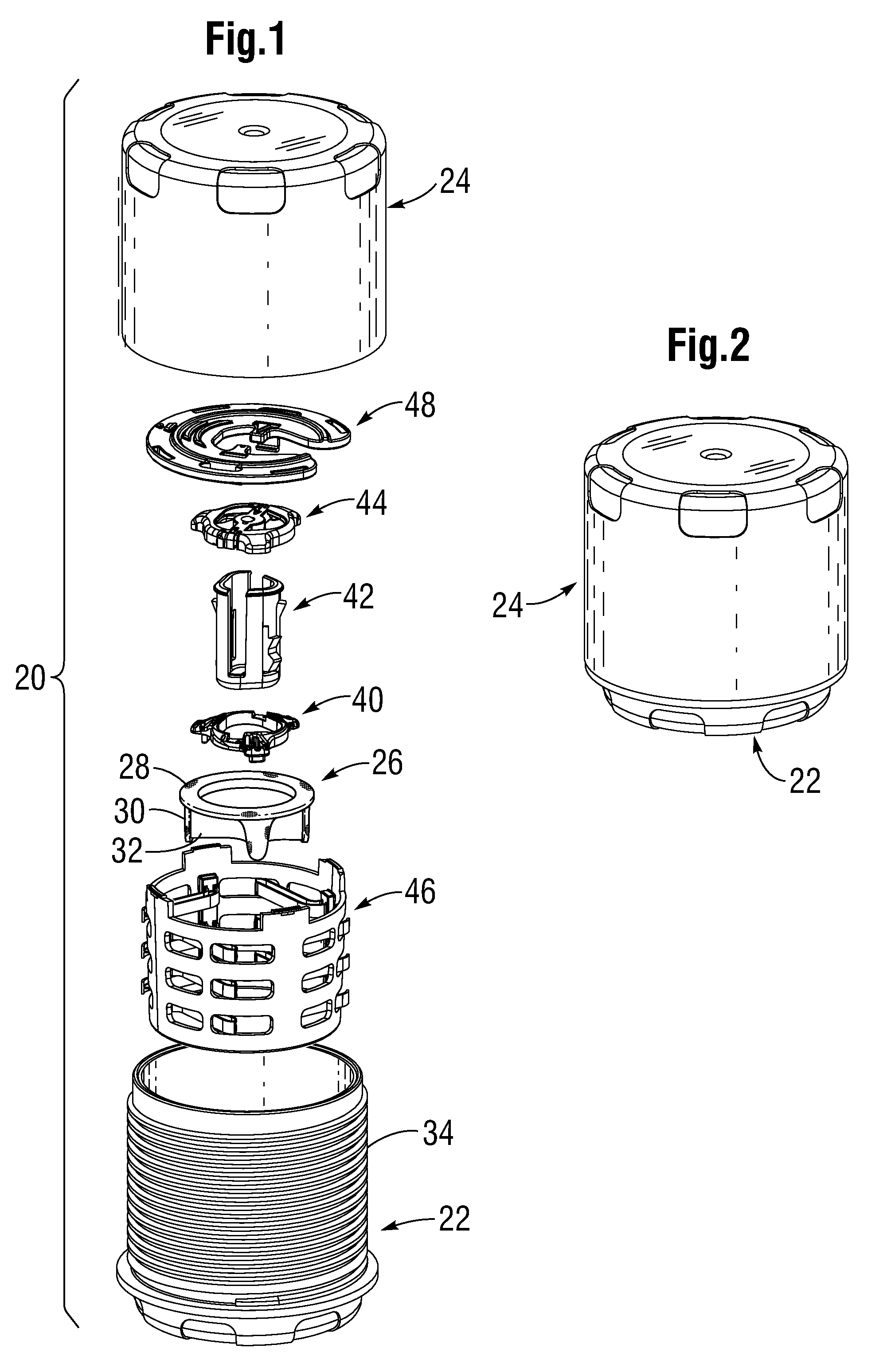
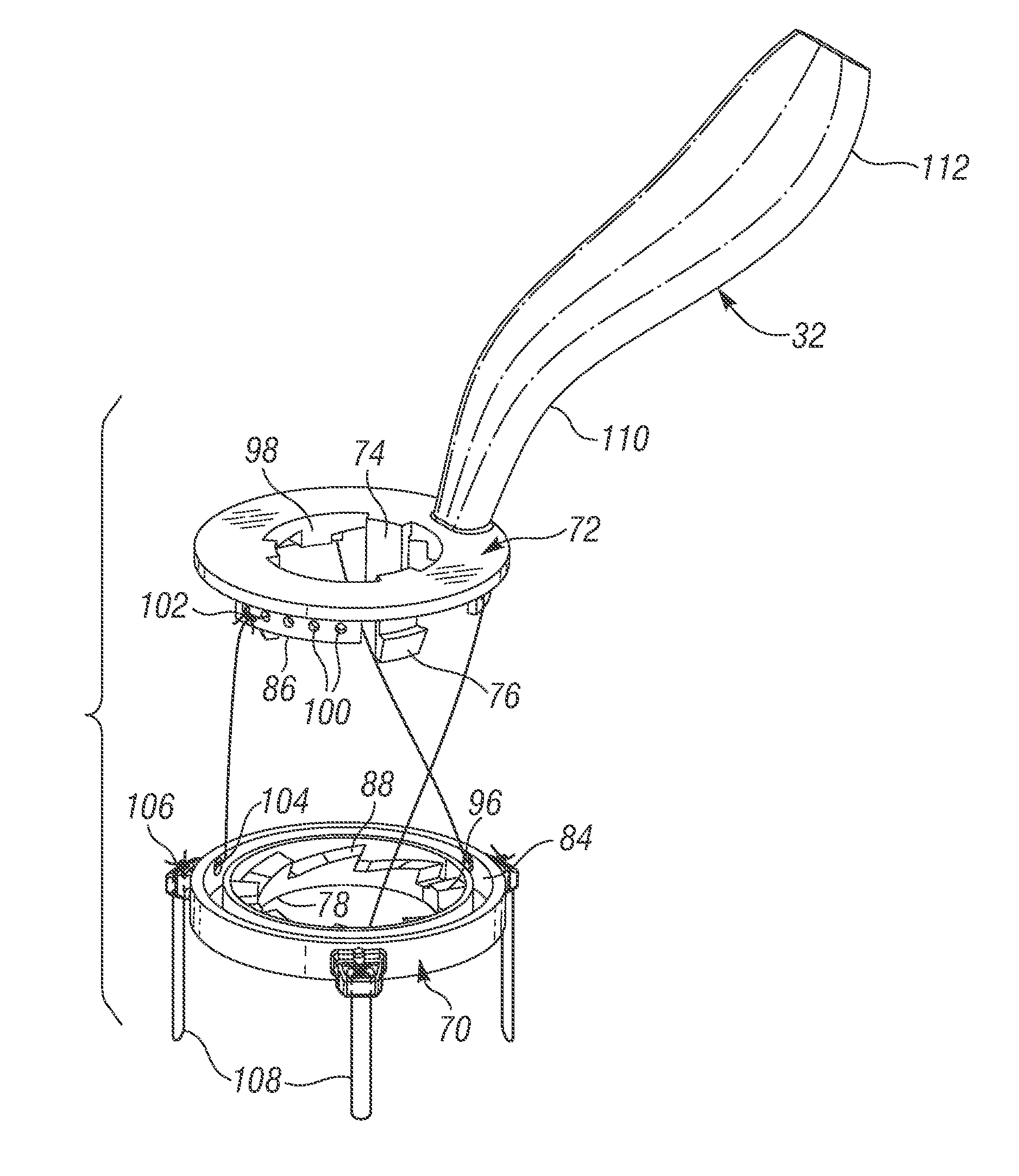
Mitral heart valve holder and storage system
An improved holder and storage system for a tissue-type prosthetic mitral heart valve that constricts the commissure posts of the valve and prevents suture looping. A rod axially movable relative to the holder tensions lengths of attachment sutures that extend between the commissure post tips to create a tent and flex the tips inward, thus helping to prevent looping of any of an array of pre-implanted sutures around the leading tips during delivery of the valve. The holder has a safety mechanism that prevents valve delivery before the rod is deployed. One embodiment automatically deploys the rod upon opening a storage jar. One embodiment permits a delivery handle to directly deploy the rod, while another uses a separate worm screw and coupling. A holder clip that attaches to a packaging sleeve may be formed of flexible members meshed together from which the heart valve and holder are easily pulled free to eliminate a step of decoupling the clip from the sleeve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Mitral heart valve replacement
A prosthetic heart valve having an inflow end and an outflow end includes a collapsible and expandable stent including a plurality of cells arranged in rows extending around a circumference of the stent, at least one of the rows forming a flared portion having a diameter that is larger than diameters of others of the rows. The stent further includes engaging arms disposed adjacent the outflow end and extending toward the inflow end, the engaging arms being configured to couple to heart tissue to anchor the stent. A collapsible and expandable valve assembly has a plurality of leaflets disposed within the stent.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Mitral heart valve replacement
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
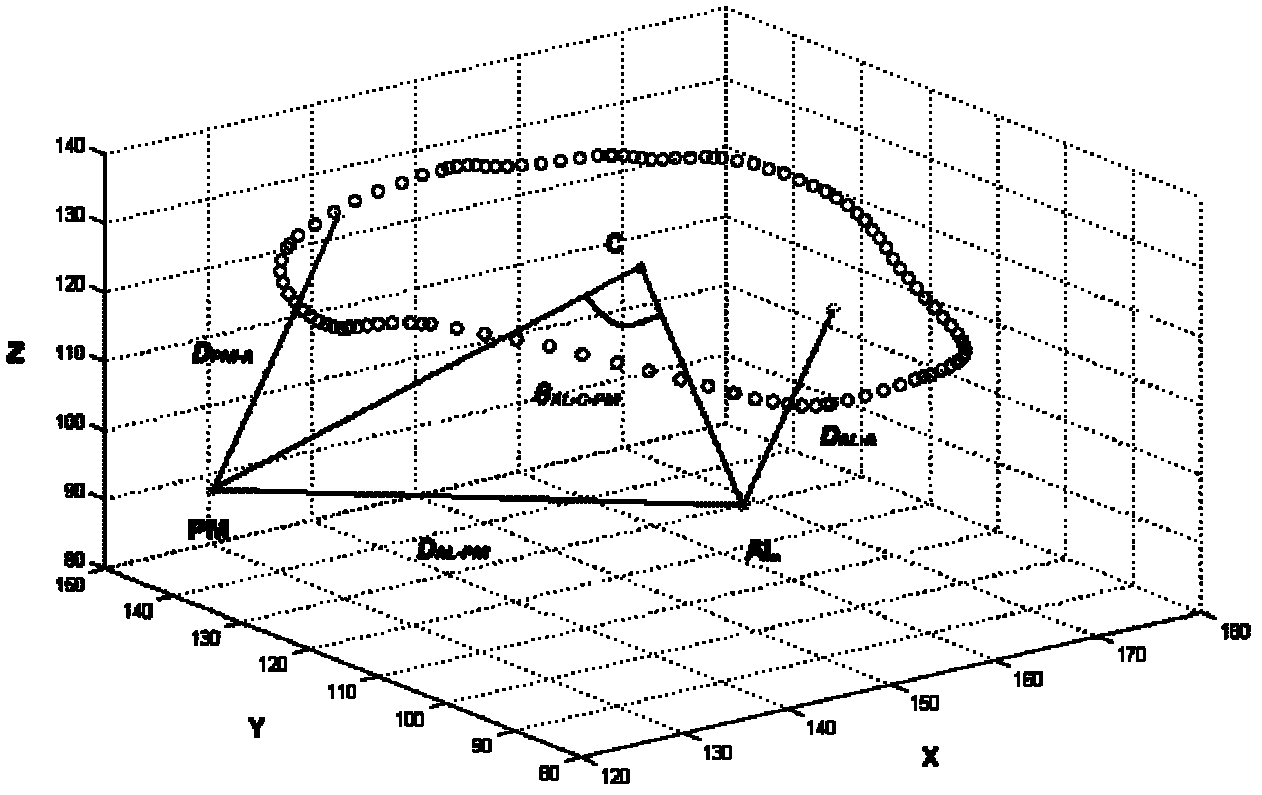
Quantitative analysis method for three-dimensional geometric structure of heart mitral valve device
InactiveCN102207995AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesSupport vector machineImaging modalities
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method for a three-dimensional geometric structure of a heart mitral valve device in the technical field of computer application. Quantitative analysis is realized by establishing a three-dimensional simplified model of the mitral valve device and using three-dimensional geometric structure parameters of a local coordinate system of the mitral valve device as the input of a support vector machine-based classification system. According to the method, reconstruction of the mitral valve device is not affected by an imaging mode, and the simplified three-dimensional model of the mitral valve device is obtained. The local coordinate system of the mitral valve device is established on the basis of simplified expression, so that the mitral valve device is independent of the influence factors such as the position of a sampling probe, heart motion displacement and displacement of a detected main body and the like, the three-dimensional geometric structure parameters of the mitral valve device are calculated, and the structure and the function of the mitral valve device and the spatial structure relation between the components of the mitral valve device are described.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Ergonomic mitral heart valve holders
ActiveUS20150313712A1Increase visualization of and accessExpand accessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMetallic materialsProsthesis
A holder for a prosthetic mitral heart valve that attaches to an inflow end of the valve and includes a simple tensioning mechanism that flexes the heart valve commissure posts inward to help prevent suture looping. The tensioning mechanism may include relatively movable rings of the holder or a generally unitary holder with a tensor, or rotatable knob. Connecting sutures thread through internal passages in the holder and travel in the outflow direction along valve commissure posts, emerging at the post tips and mutually crossing over the outflow side of the valve. A handle attaches off-center on the holder to increase visualization of and access to the heart valve through a central window for enhanced access to the commissure posts and leaflets. The holder is constructed of non-metallic materials so as to avoid interfering with imaging devices, and the handle is ergonomically curved and shaped to facilitate manipulation.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Beating-heart mitral valve chordae replacement
Methods and devices for the treatment of cardiac valve dysfunction through the placement of lines and anchors. The lines and anchors can form artificial chordae between valve leaflets and the ventricular wall or papillary muscles or connect the two valve leaflets together. The methods and devices offer a mechanism for performing this technique with the heart still beating, and allows for the placement of multiple lines with a single device.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com