Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Plant genomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
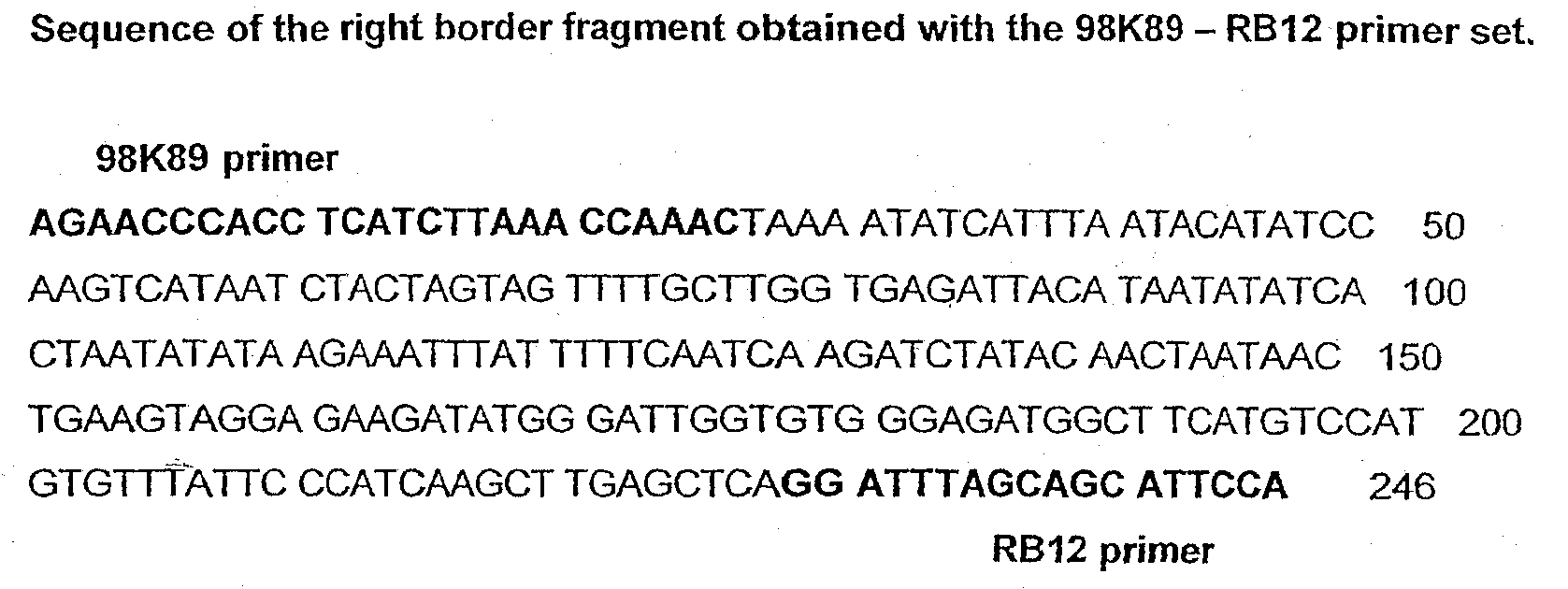
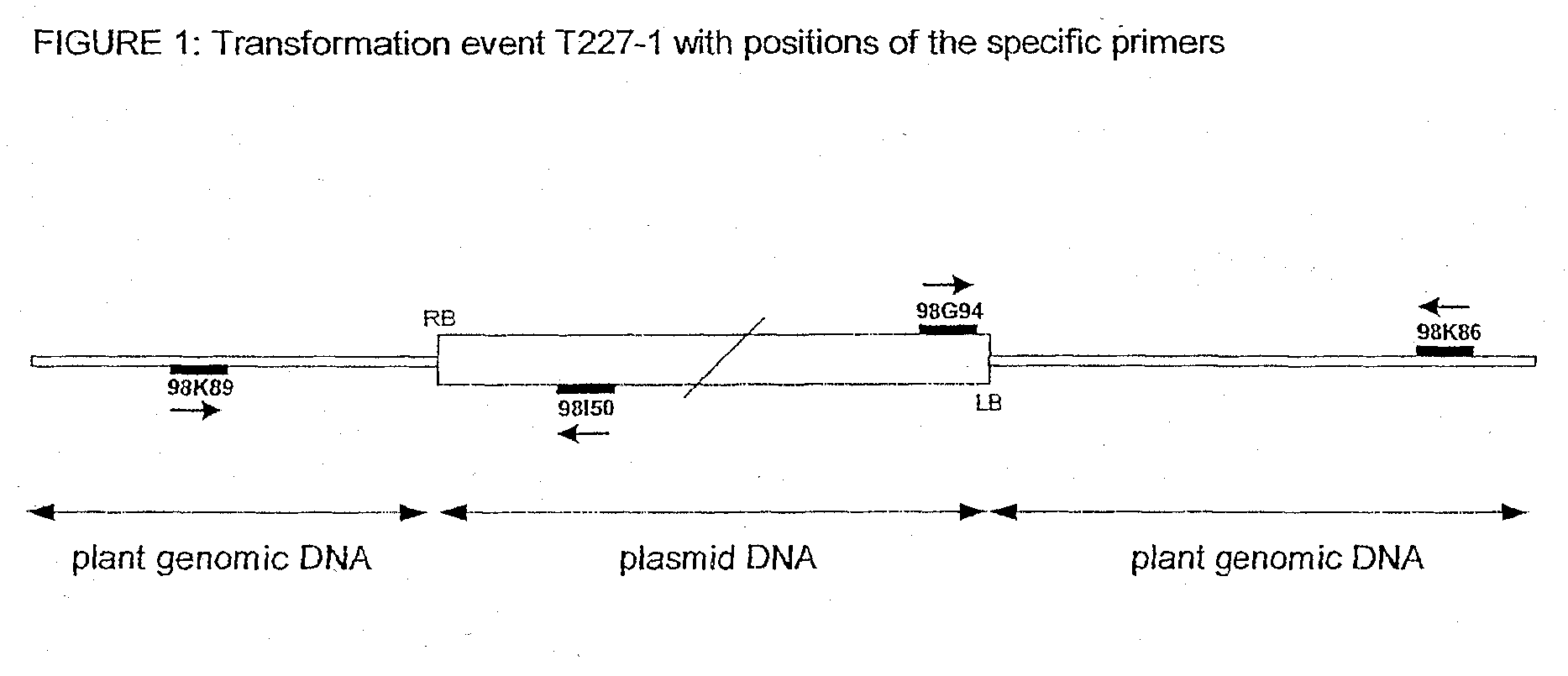
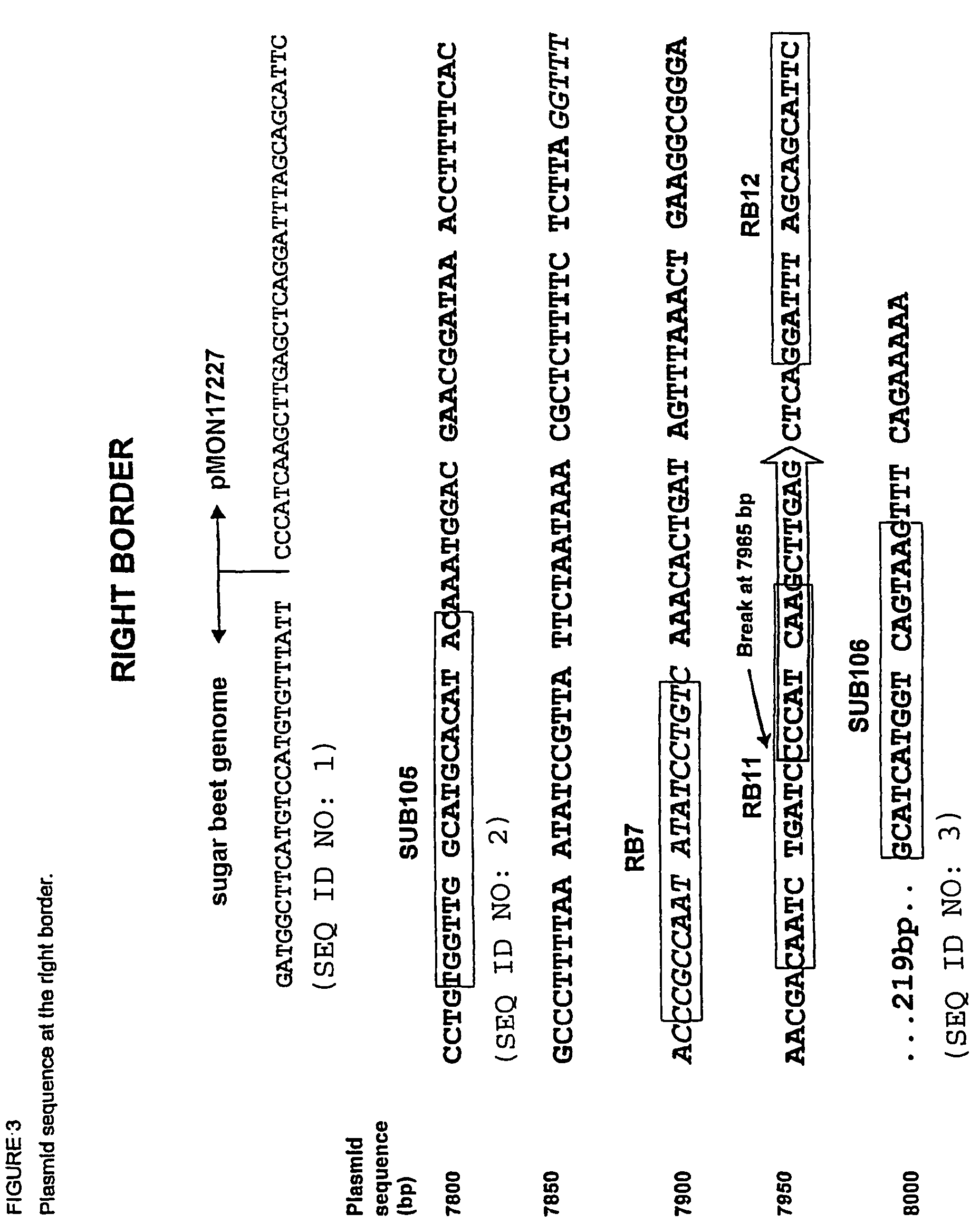
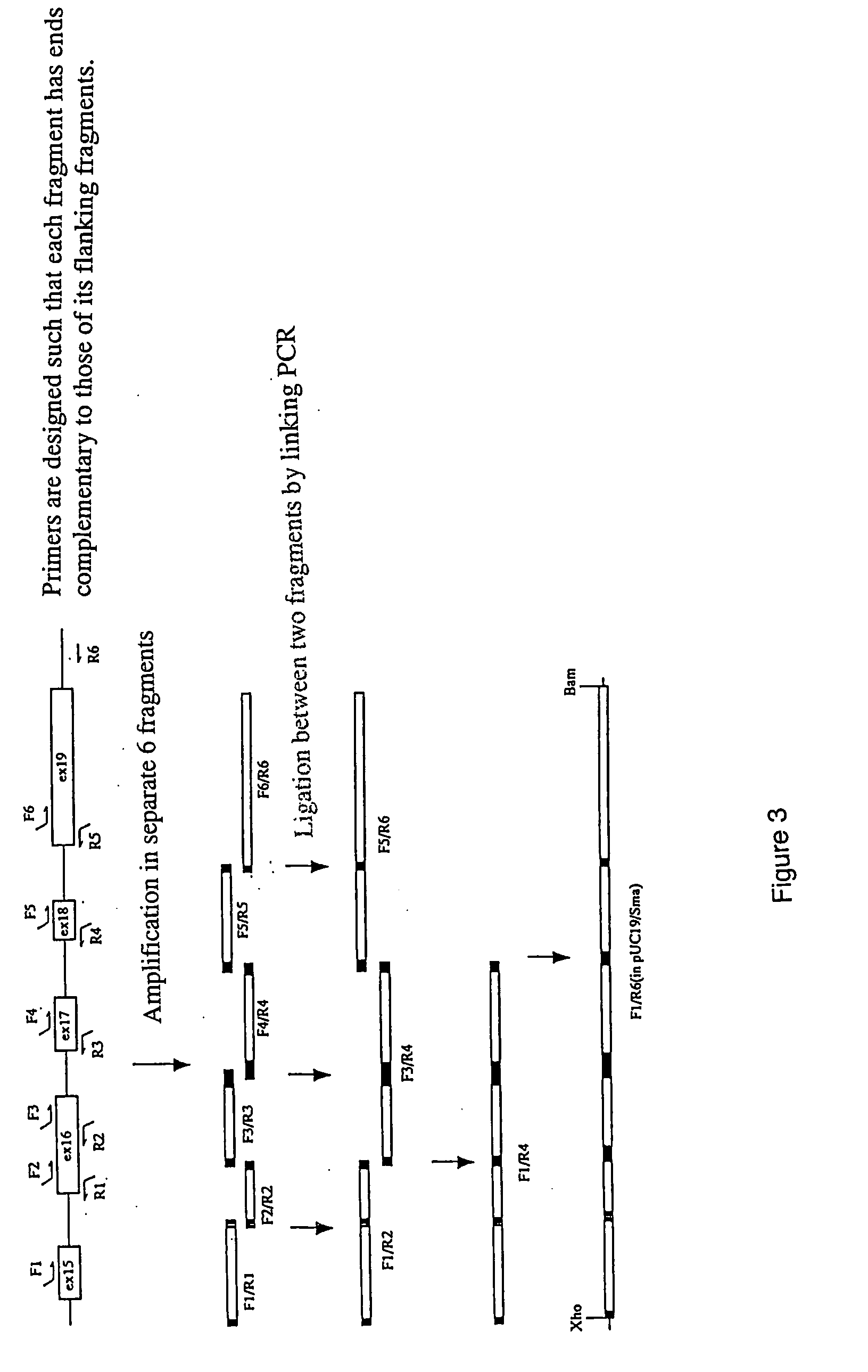
T227-1 flanking sequence
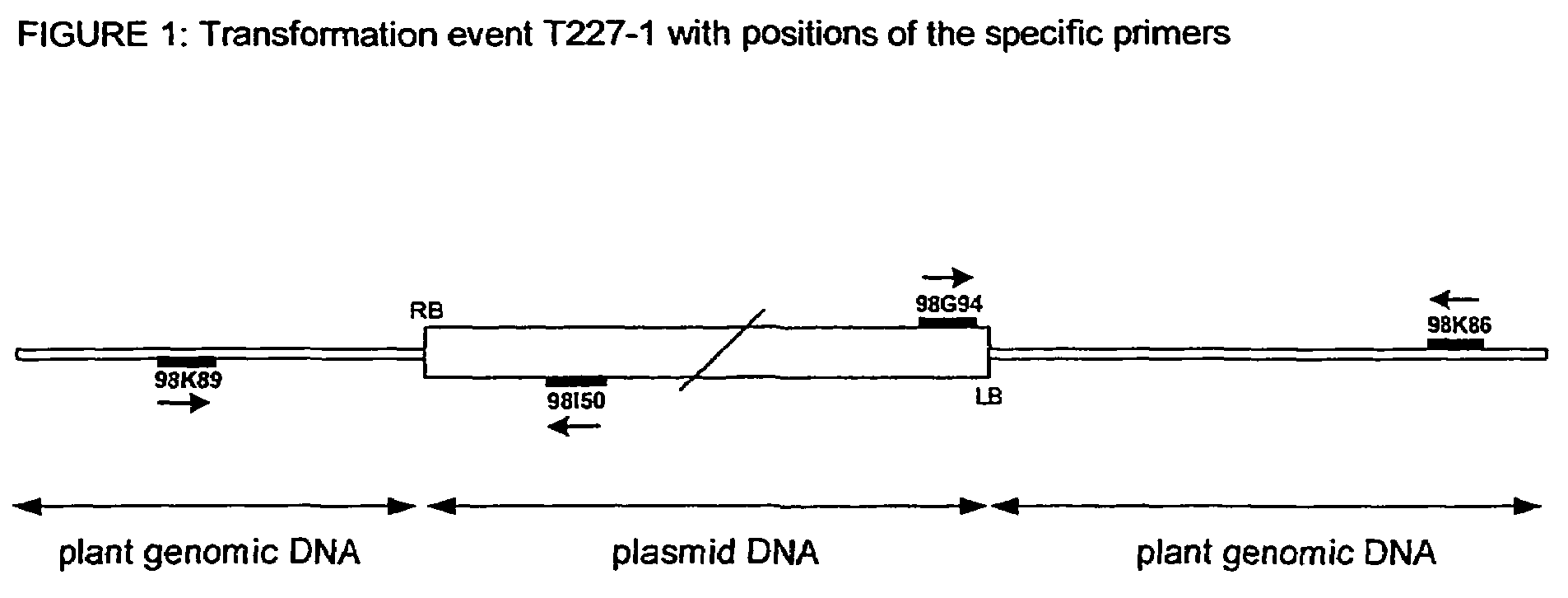
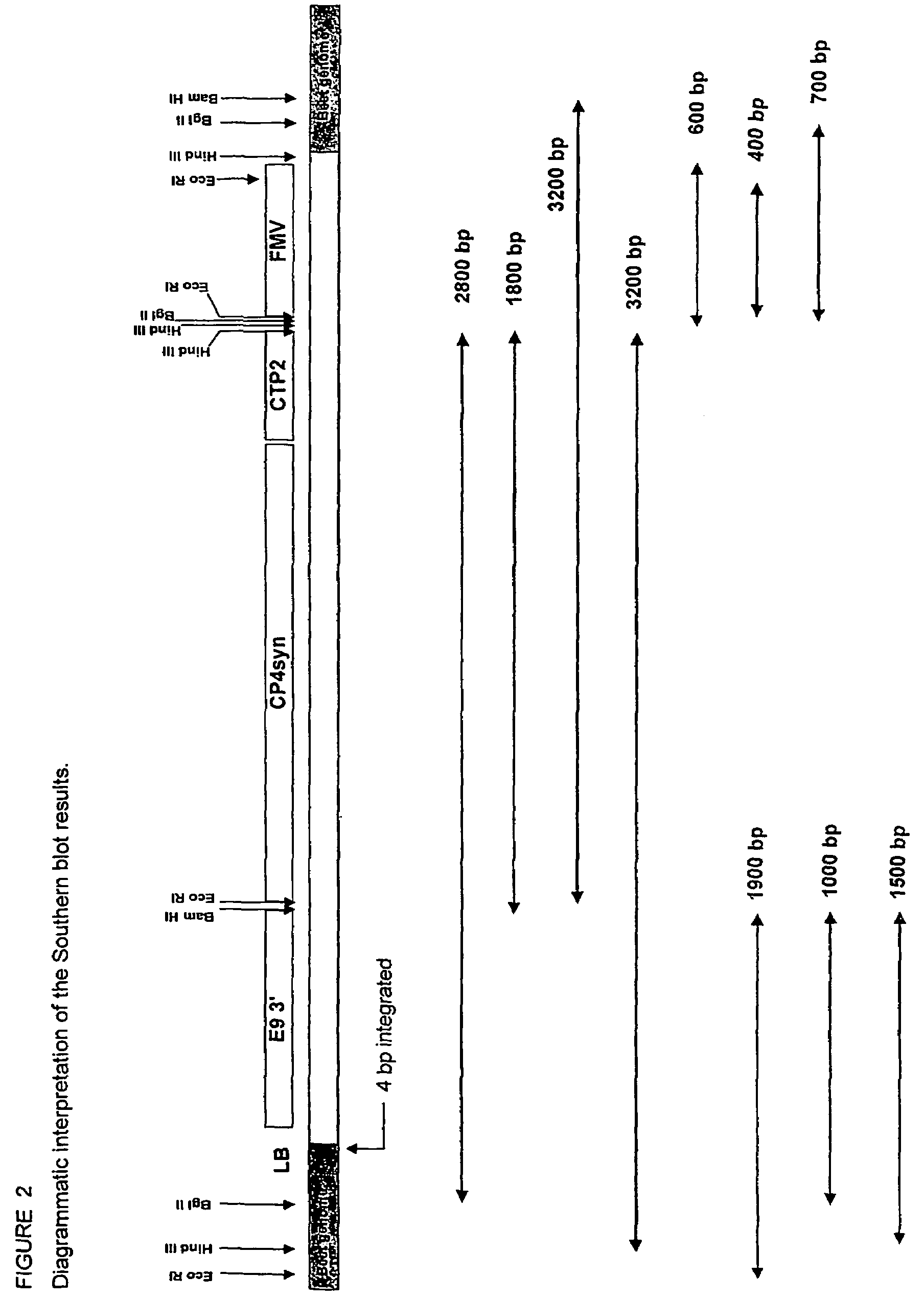
A herbicide resistant transformed sugar beet that is detectable by the specific primers developed to match the DNA sequences that flank the left and / or right border region of the inserted transgenic DNA and the method of identifying primer pairs containing plant genomic DNA / plasmid DNA. More specifically, the present invention covers a specific glyphosate resistant sugar beet plant having an insertion of the transgenic material identified as the T227-1 event. The present invention additionally covers primer pairs: plant genomic DNA / Plasmid DNA that are herein identified. Additionally, these primer pairs for either the left or the right flanking regions make an event specific test for the T227-1 insert of transgenic material.
Owner:SES EURO N V
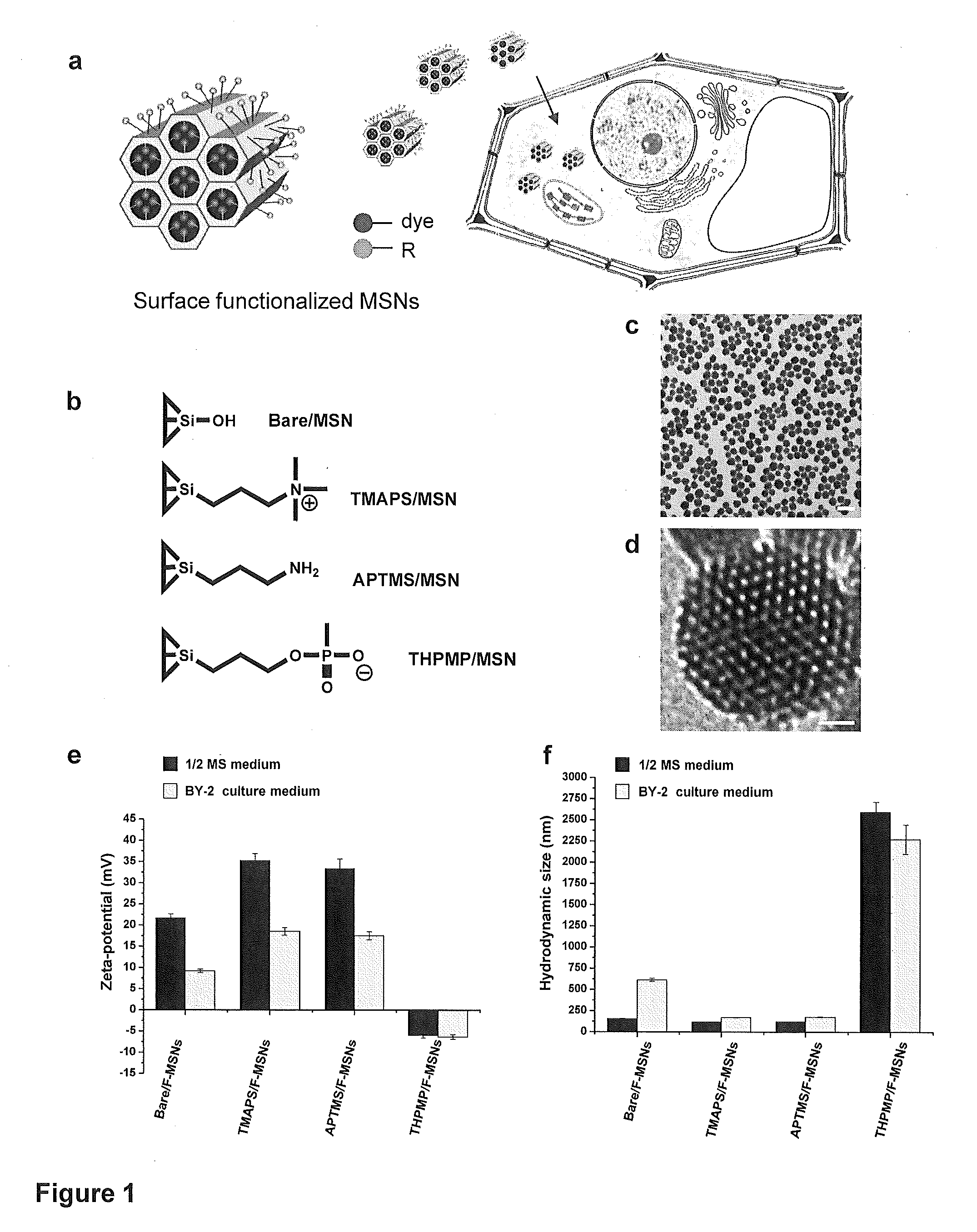
Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-mediated delivery of DNA into arabidopsis root
InactiveUS20130185823A1MicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesGerm layerGene delivery
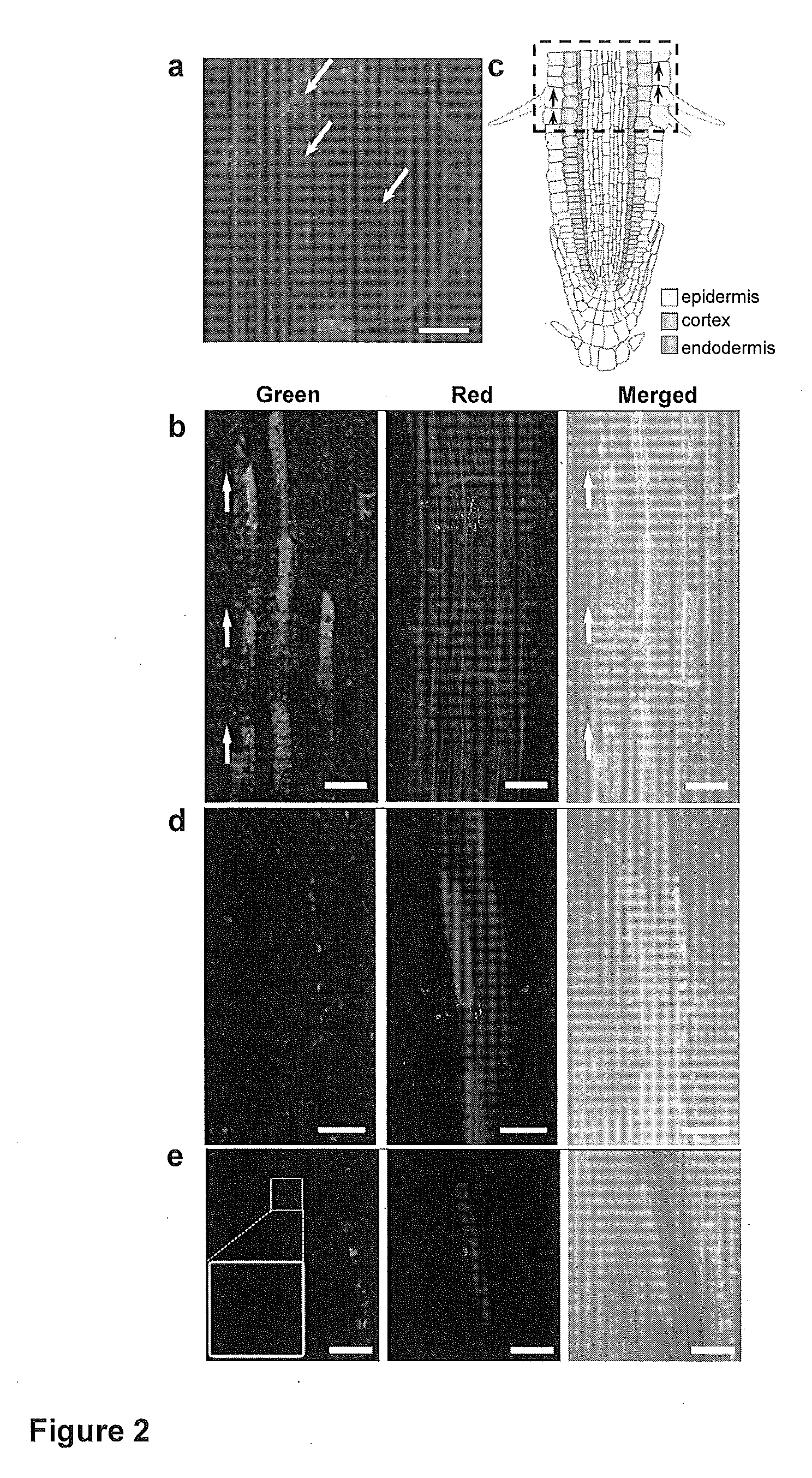
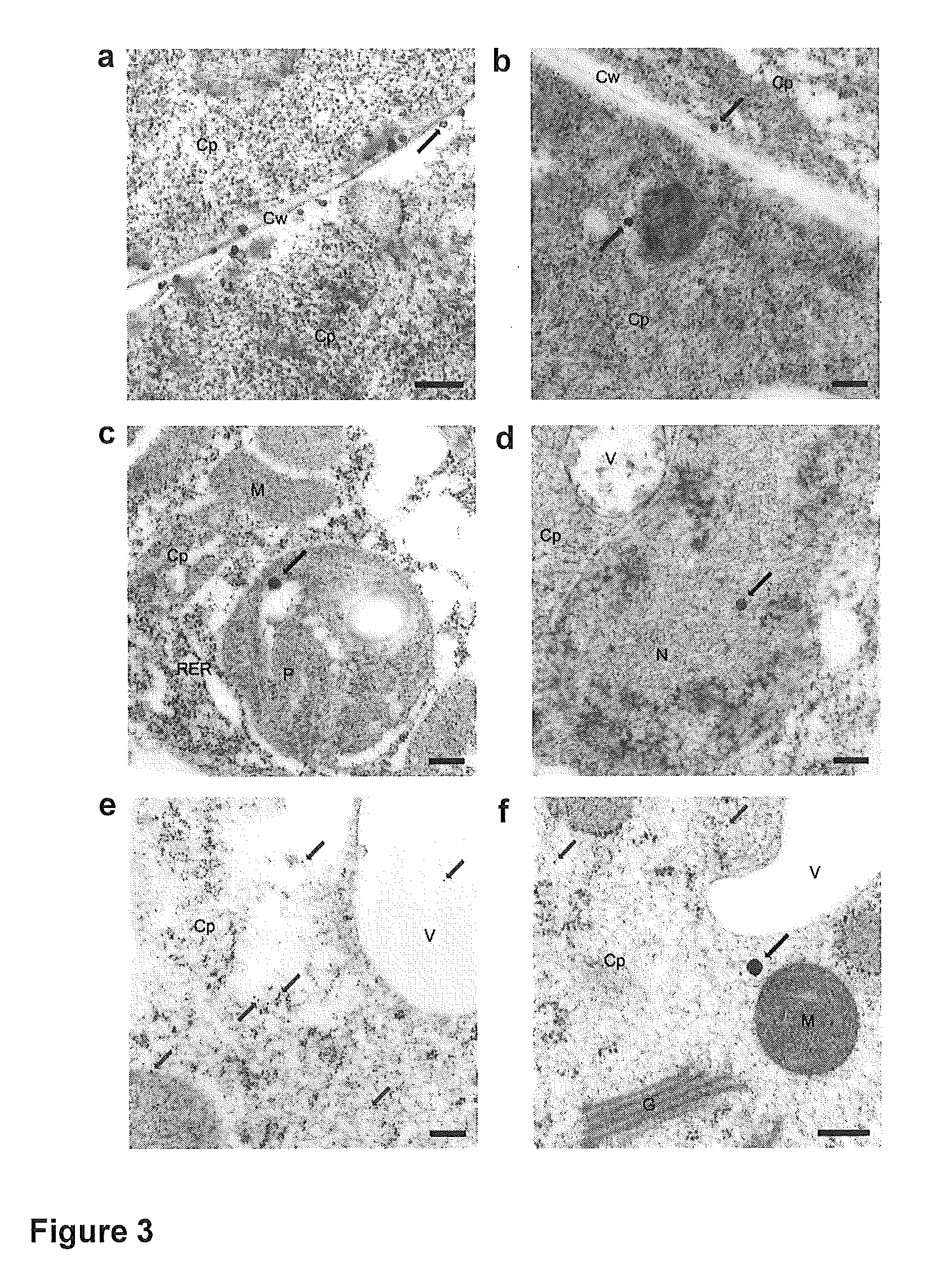
Transient gene expression is a powerful tool for plant genomics studies. Recently, the use of nanomaterials has drawn great interest. Delivery with mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) has many advantages. We used surface-functionalized MSNs to deliver and express foreign DNA in Arabidopsis thaliana root cells without the aid of particle bombardment. Gene expression was detected in the epidermis layer and in the more inner cortex and endodermis root tissues. This method is superior to the conventional gene-gun method to deliver DNA, which delivers the gene to the epidermis layer only. Less DNA is needed for the MSN method. Our system is the first use of nanoparticles to deliver DNA to plants with good efficiency and without external aids. MSNs, with multifunctionality and the capability of cargo delivery to plant cells as we demonstrated, provide a versatile system for biomolecule delivery, organelle targeting, and even agriculture, such as improved nutrient uptake.
Owner:ACAD SINIC +1
Glyphosate-resistant plants
This invention relates to glyphosate-resistant transgenic plants and methods of making the same. In a preferred embodiment, a DNA fragment which comprises an EPSPS 5′ regulatory sequence and a glyphosate-resistant EPSPS coding sequence is introduced into regenerable plant cells. The encoded EPSPS has a chloroplast transit peptide. The DNA fragment does not contain a non-EPSPS enhancer. Cells are selected for stable transformation, and the selected cells can be used to regenerate glyphosate-resistant transgenic plants. The DNA fragment used for transformation preferably comprises a modified plant genomic sequence, such as SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO:4 or SEQ ID NO: 6. In one embodiment, two DNA fragments of this invention are stably transformed into a plant to confer glyphosate-resistance.
Owner:MERTEC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080263730A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionImmunoglobulinsFermentationNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070016974A1Desirable effectIncrease profitSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from rice are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BUEHLER ROBERT E +3
Nucleic acid molecule SEQ ID NO. 68811 and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from cotton are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080168583A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from cotton are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:FINCHER KAREN L +3
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from cotton are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:FINCHER KAREN L +3
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BUEHLER ROBERT E +3
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070283459A1Desirable effectIncrease profitImmunoglobulinsFermentationNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
T227-1 flanking sequence
InactiveUS7241567B2Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGlyphosatePlasmid dna
A herbicide resistant transformed sugar beet that is detectable by the specific primers developed to match the DNA sequences that flank the left and / or right border region of the inserted transgenic DNA and the method of identifying primer pairs containing plant genomic DNA / plasmid DNA. More specifically the present invention covers a specific glyphosate resistant sugar beet plant having an insertion of the transgenic material identified as the T227-1 event. The present invention additionally covers primer pairs: plant genomic DNA / Plasmid DNA that are herein identified. Additionally, these primer pairs for either the left or the right flanking regions make an event specific test for the T227-1 insert of transgenic material.
Owner:SES EURO N V
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from cotton are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080104729A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:CONNER TIMOTHY +1
Nucleic Acid Molecules and Other Molecules Associated with Plants
InactiveUS20100024079A1Increase profitSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGenetics genomicsNovel gene
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Quick extraction method of plant genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
ActiveCN107475248AHigh purityImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationEnzyme digestionCell membrane
The invention discloses a quick extraction method of plant genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid). The quick extraction method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1), taking a plant tissue sample, adding liquid nitrogen, grinding the plant tissue sample into powder and collecting into a centrifugal tube, and the like. SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate) in a Buffer A in the quick extraction method can be used for cracking a cell membrane to denature protein; a Buffer B can act with the SDS; impurities of the protein, a polysaccharide and the like can be effectively removed; moreover, PVP40 (Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone 40) in the Buffer A can be used for effectively removing substances of the polysaccharide and polyphenol in plant tissue; the purity of the DNA is improved; the completeness of the DNA is enabled to be better; the quick extraction method can be directly used for a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and various enzyme digestion reaction; meanwhile, the quick extraction method does not need to use organic solvents of phenol chloroform and the like in the entire extraction process; therefore, steps of ethanol precipitation and the like do not need to be carried out; the extraction method provided by the invention, compared with a conventional extraction method, can be used for more quickly, simply and conveniently extracting the DNA; the operation, on a single sample, of the quick extraction method can be completed within 1 hour and the extraction time is greatly shortened.
Owner:成都晟博源生物工程有限公司
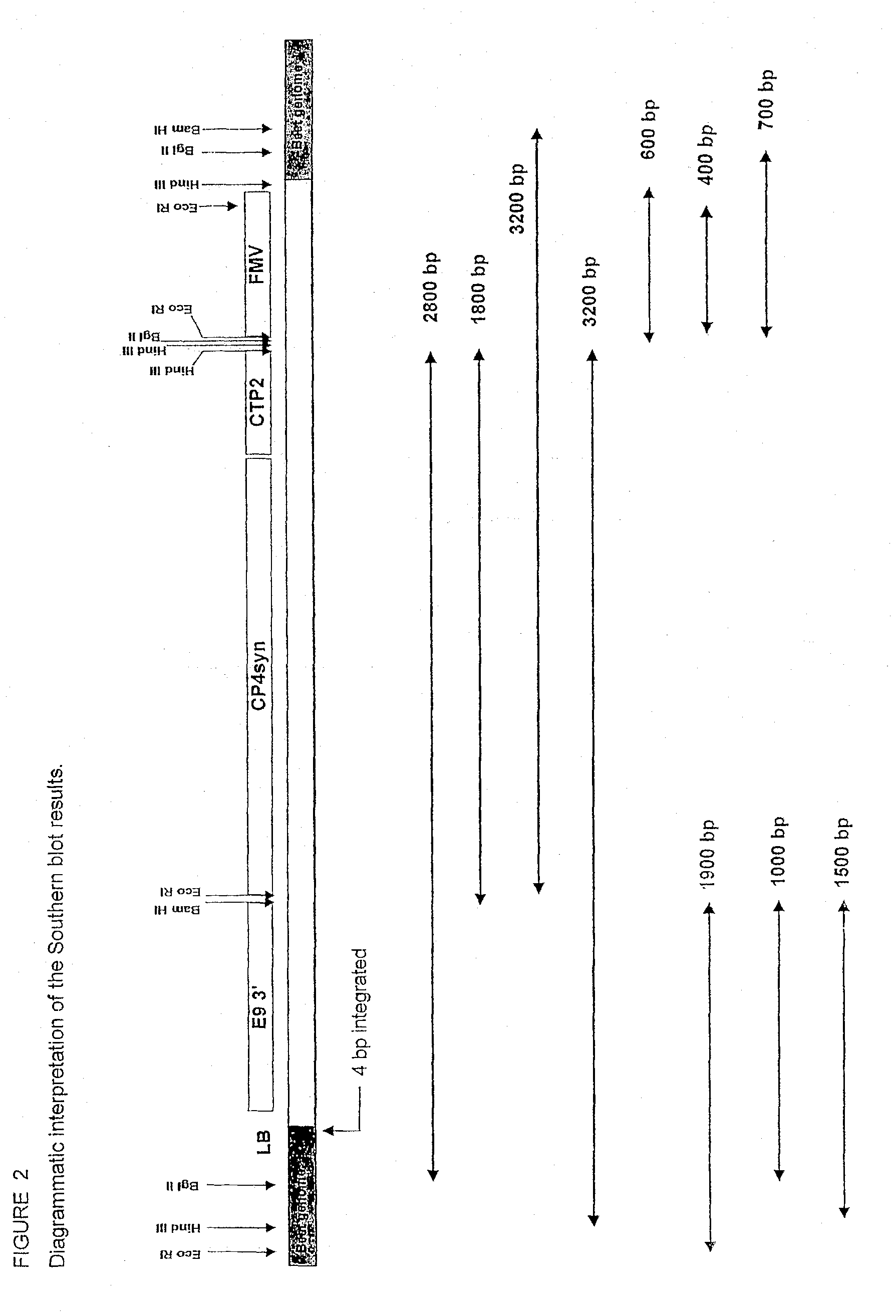
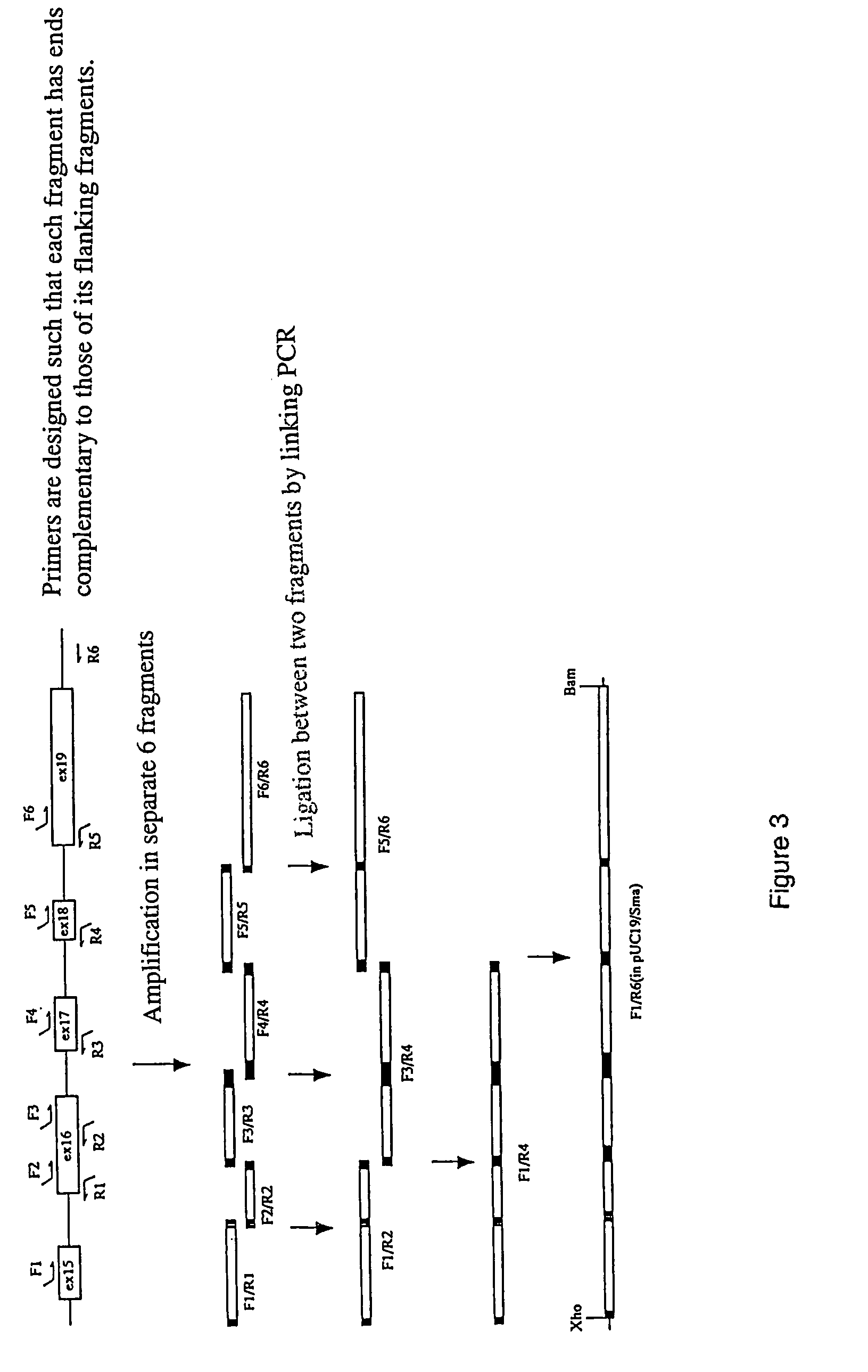
High through-put analysis of transgene borders
InactiveUS20120258867A1Easy to applyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationTransgeneInsertion site
The present invention is a method to identify unknown DNA sequences which flank known DNA sequences. The invention improves the accuracy, sensitivity, and reproducibility for determining unknown DNA sequences which flank a known DNA sequence. This claimed method can be deployed as a high throughput method to quickly and efficiently identify plant genomic chromosomal sequences which flank a transgene. Further analysis of these unknown sequences can be used to characterize the transgene insertion site for the identification of rearrangements, insertions and deletions which result from the integration of the transgene. In addition, analysis of the chromosomal flanking sequences can be used to identify the location of the transgene on the chromosome.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
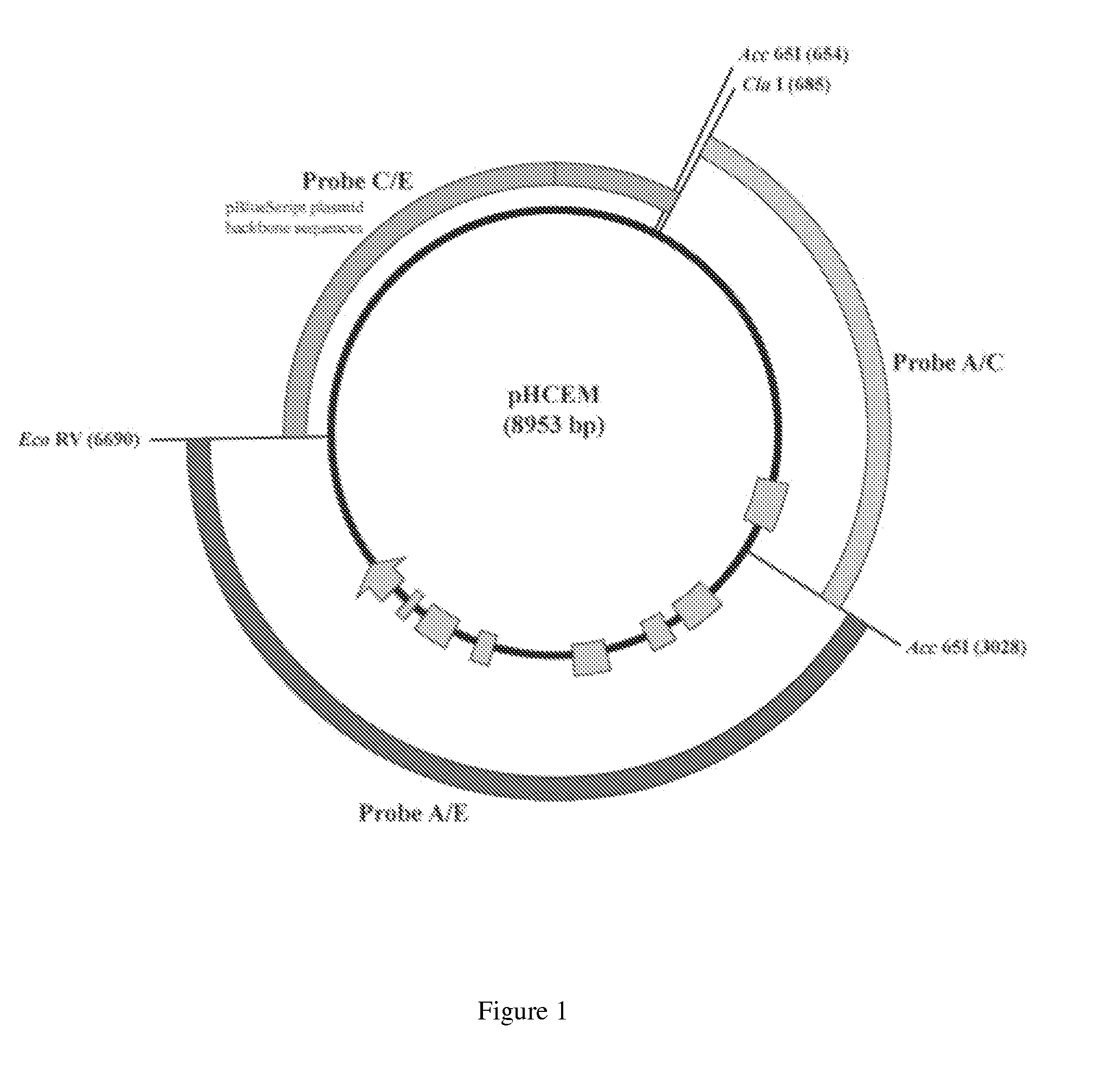
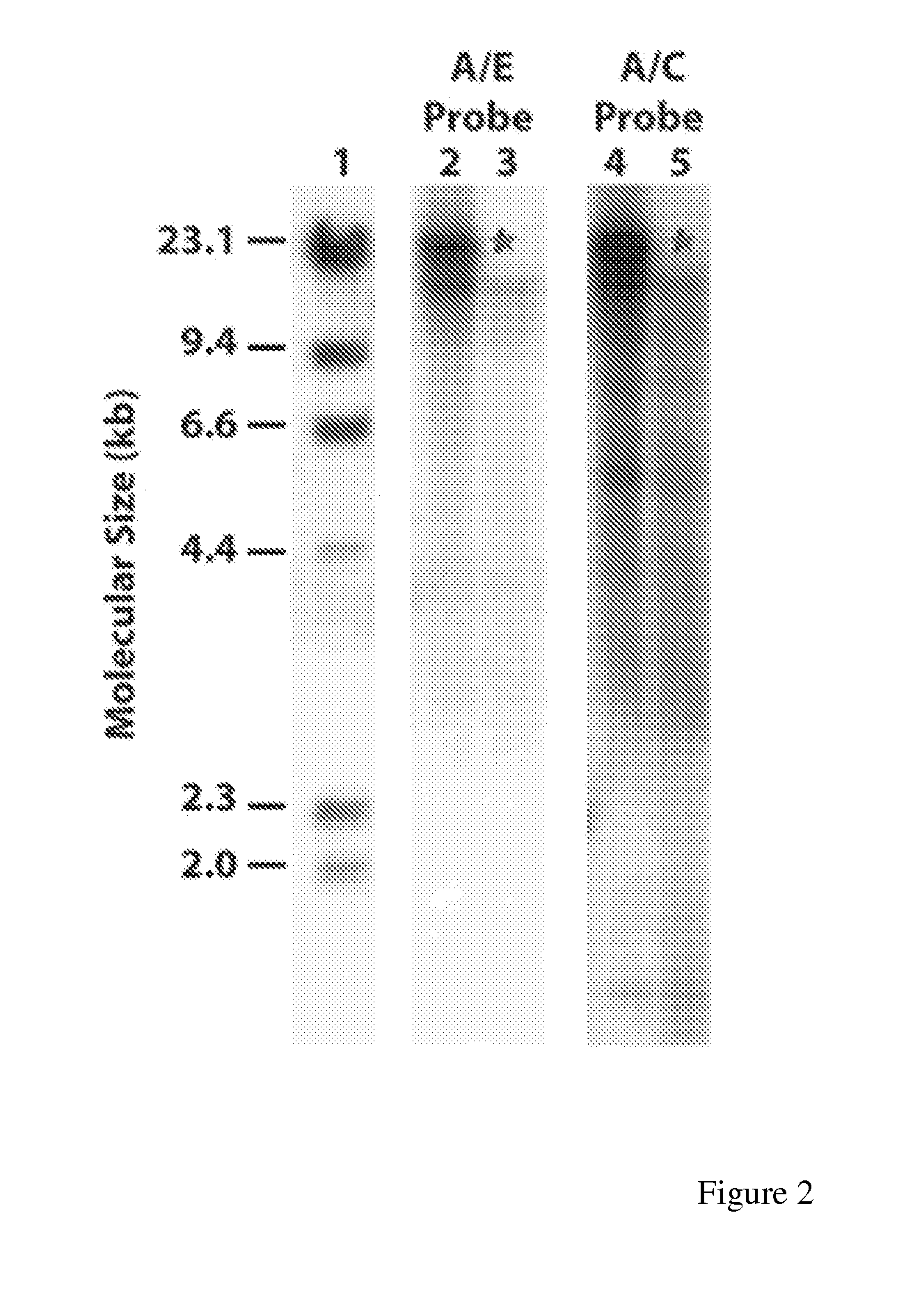
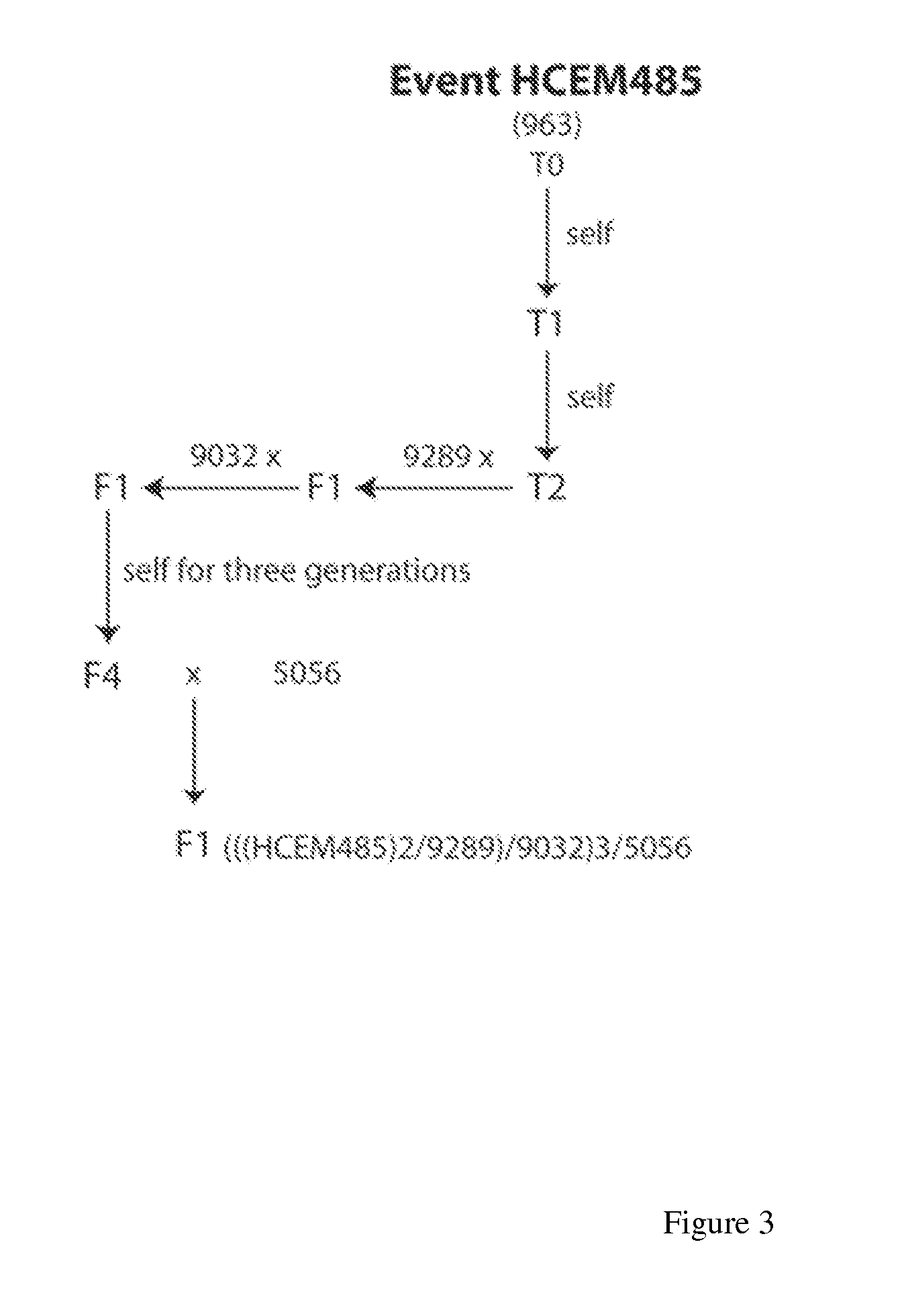
Maize event HCEM485, compositions and methods for detecting and use thereof
Maize event HCEM485 is provided, in which plants comprising the event are tolerant to exposure to a glyphosate herbicide. Maize genomic polynucleotides flanking the insert DNA providing glyphosate tolerance are provided. The plant or part thereof having the event comprises a junction region of the insert DNA and maize plant genomic sequences. Methods and primers and probes to detect the presence of the event are provided, as well as kits which employ such primers and probes.
Owner:STINE SEED FARM
Method for identifying cymbidium rapidly
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
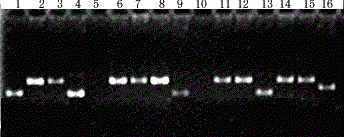
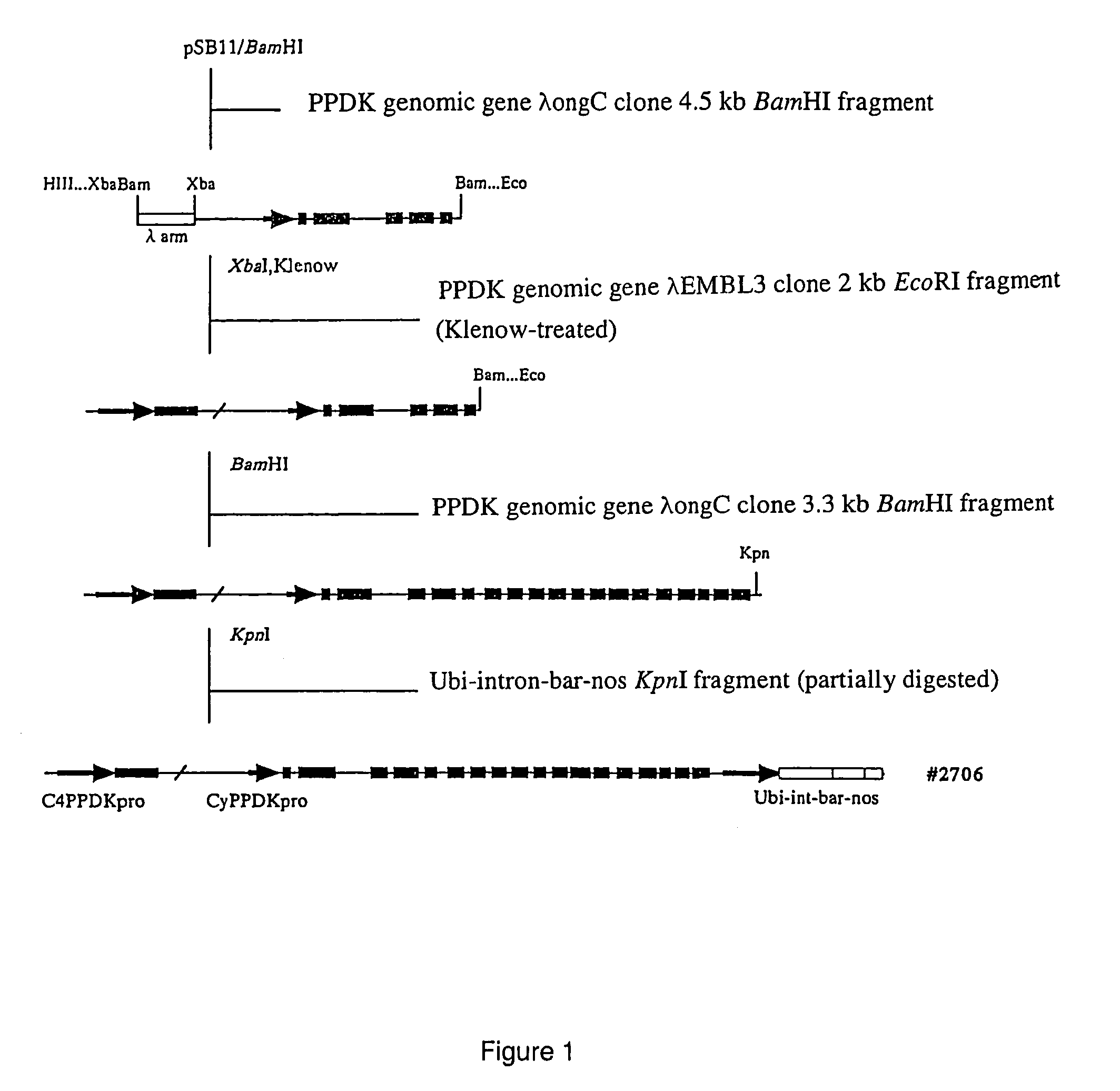
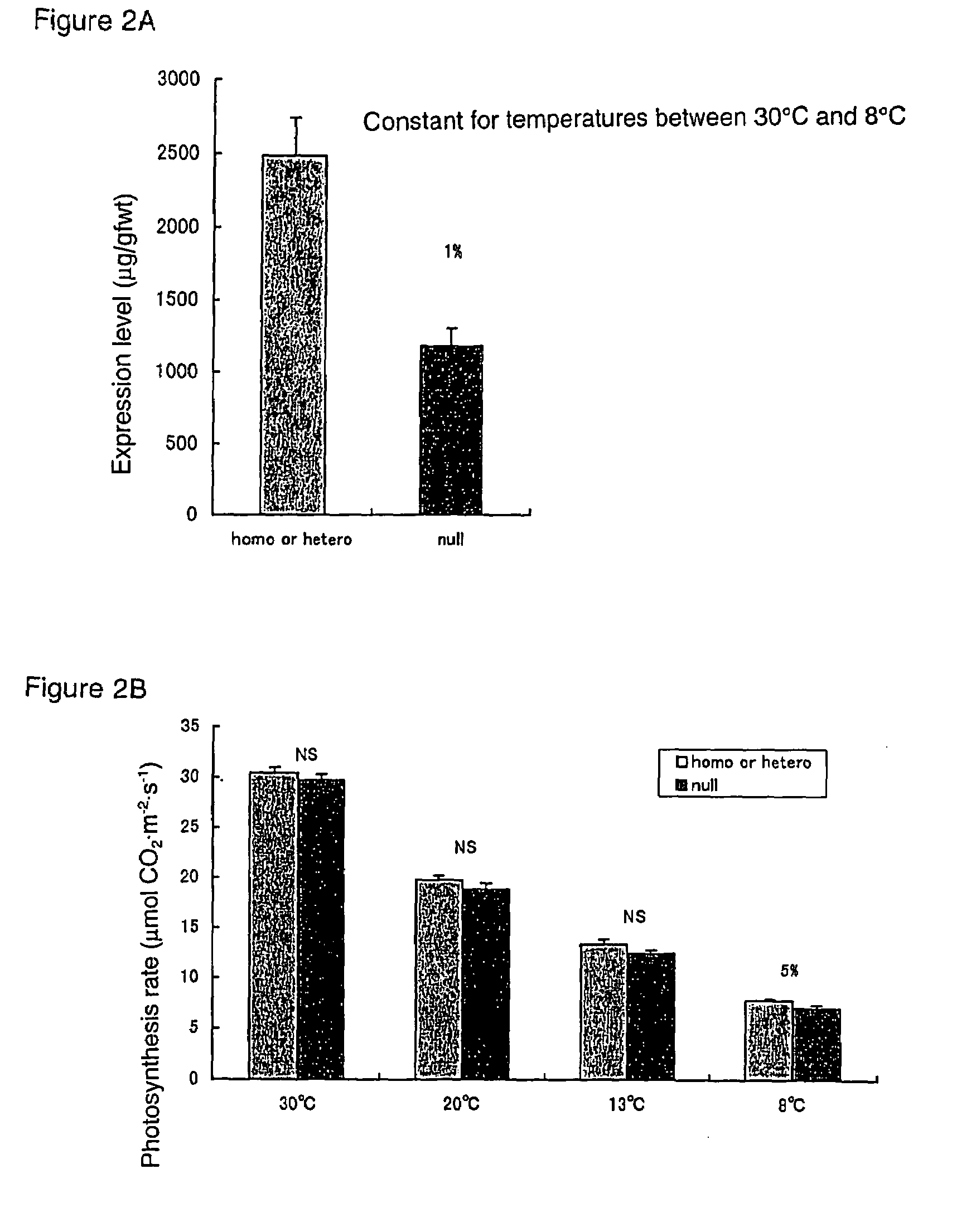
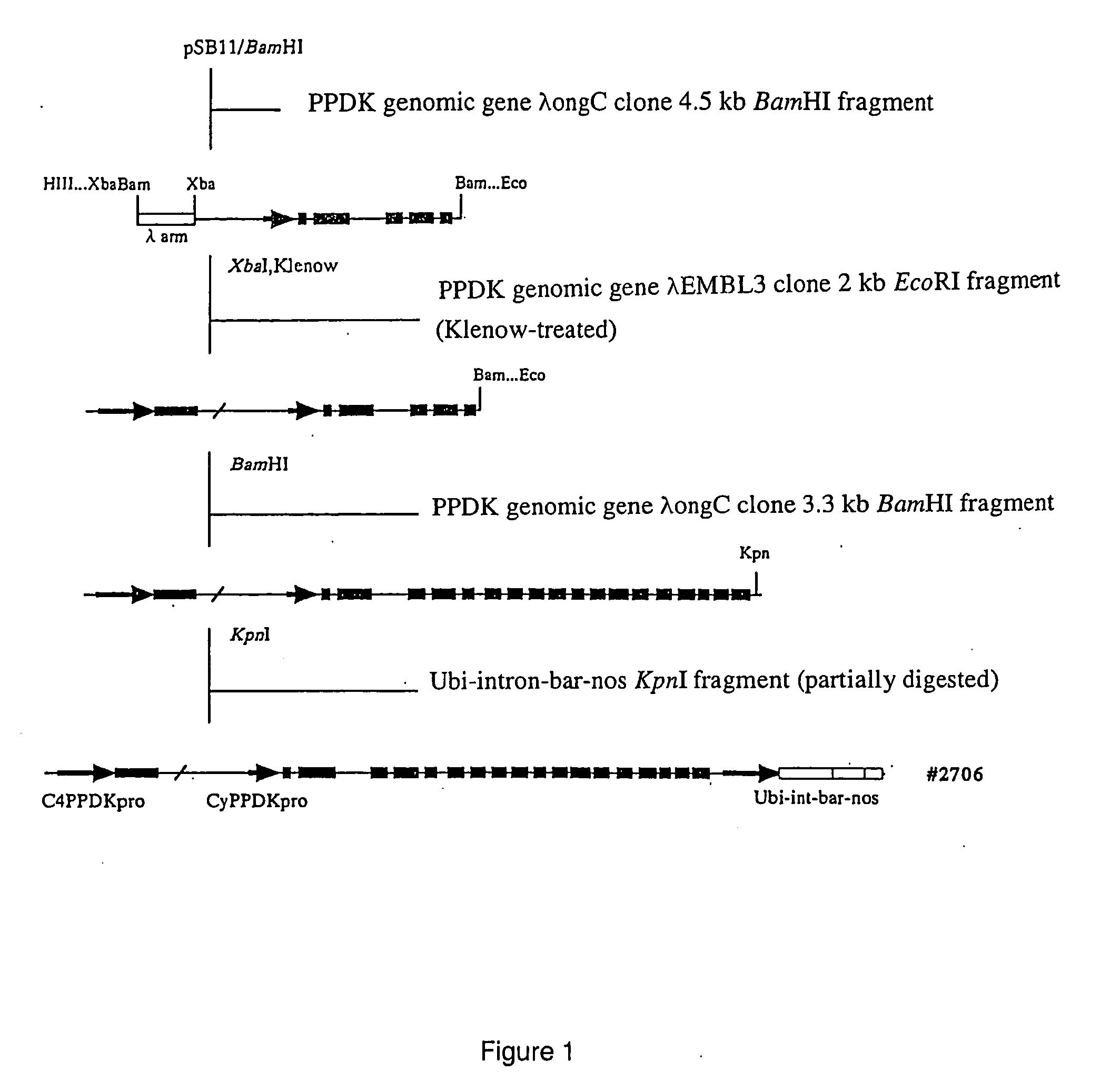
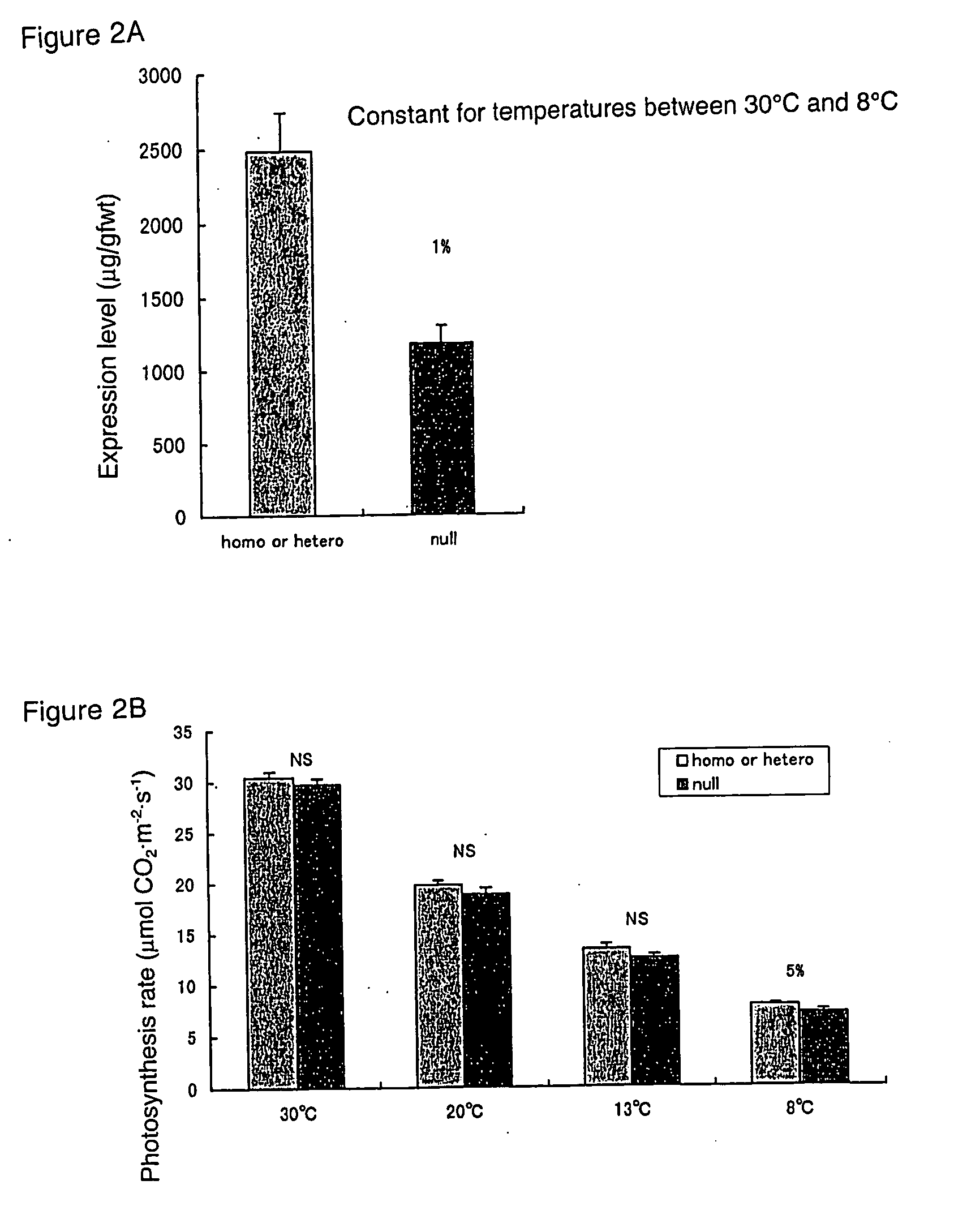
Method of elevating photosynthesis speed of plant by improving pyruvate phosphate dikinase
The present invention relates to the transformation of C4 plants. It also relates to the high-level expression of foreign genes in C4 plants. More specifically, the present invention relates to the creation of C4 plants retaining an excellent photosynthetic capacity at low temperature by achieving high-level expression of an enzyme constituting the C4 photosynthetic pathway. In the present invention, C4 plants are transformed using an expression cassette that comprises a promoter, a C4 plant genomic gene, under control of said promoter, encoding an enzyme constituting a photosynthetic pathway, and a terminator. The C4 plant genomic gene encoding an enzyme constituting a photosynthetic pathway is preferably a C4 plant genome-derived PPDK gene or a modified form thereof. The present invention is particularly useful in improving the production of C4 plants having PPDK (especially, in improving the production of maize under low temperature conditions).
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080256662A1Increase profitSugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH R +2
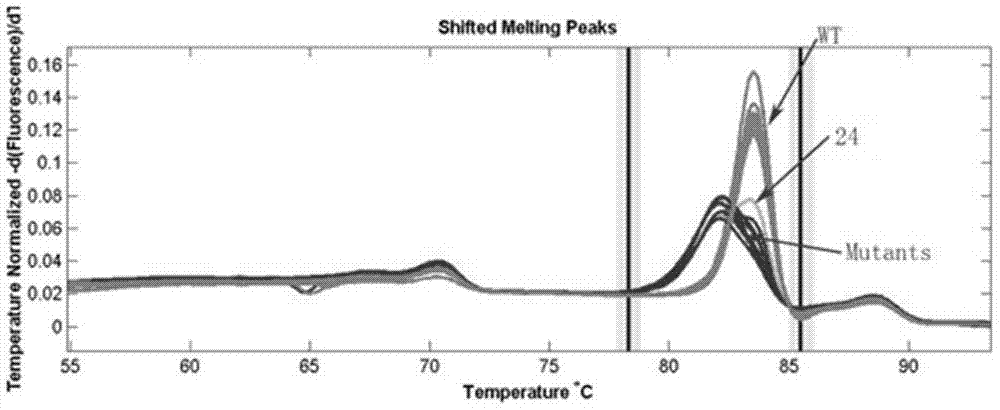
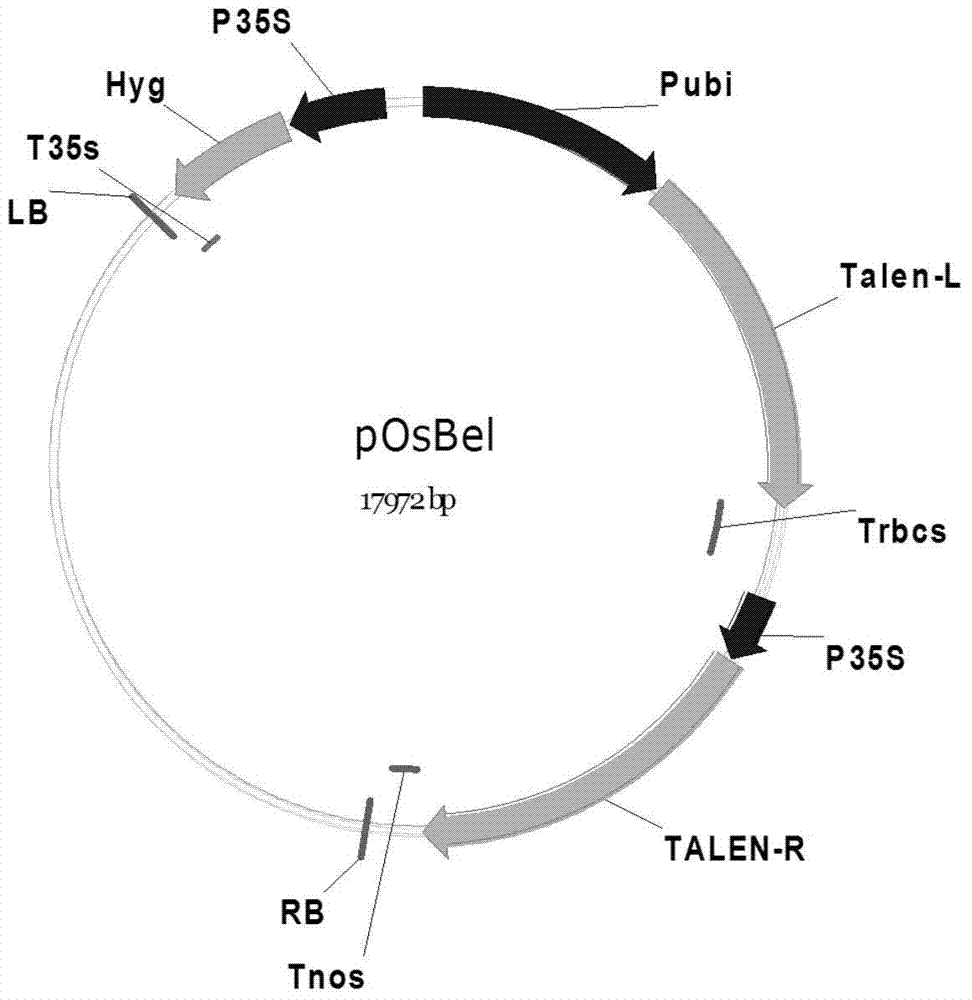
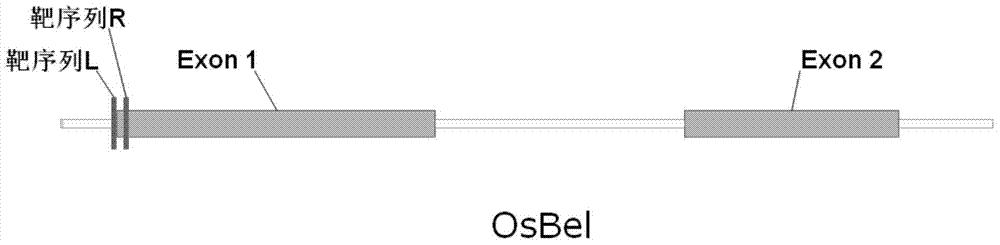
Fixed-point knockout system for Bel gene of paddy rice and application thereof
The invention discloses a fixed-point knockout system for the Bel gene of paddy rice and application thereof, specifically a fixed-point knockout method for the bentazone gene of paddy rice and application thereof, belonging to the field of plant genetic engineering. The invention provides a TALEN site-specific mutagenesis system preferably directed at plant genomic DNA. The TALEN site-specific mutagenesis system includes four recognition modules. Compared with conventional bentazone-sensitive plant creating technology, the TALEN site-specific mutagenesis system provided by the invention has the advantages of convenience and rapidness; with the TALEN site-specific mutagenesis system, one scientific research personnel can acquire a plurality of homozygous mutant plants with different mutation sites in one and a half years, so labor and material resources are substantially saved; obtained mutants do not contain transgenic components, so misgivings of people about transgene are eliminated; and the TALEN site-specific mutagenesis system is of great significance to creation of novel germplasm resources through plant genetic engineering.
Owner:FRONTIER LAB OF SYST CROP DESIGN CO LTD +2
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080066199A1Desirable effectSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNovel genePlant genomics
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
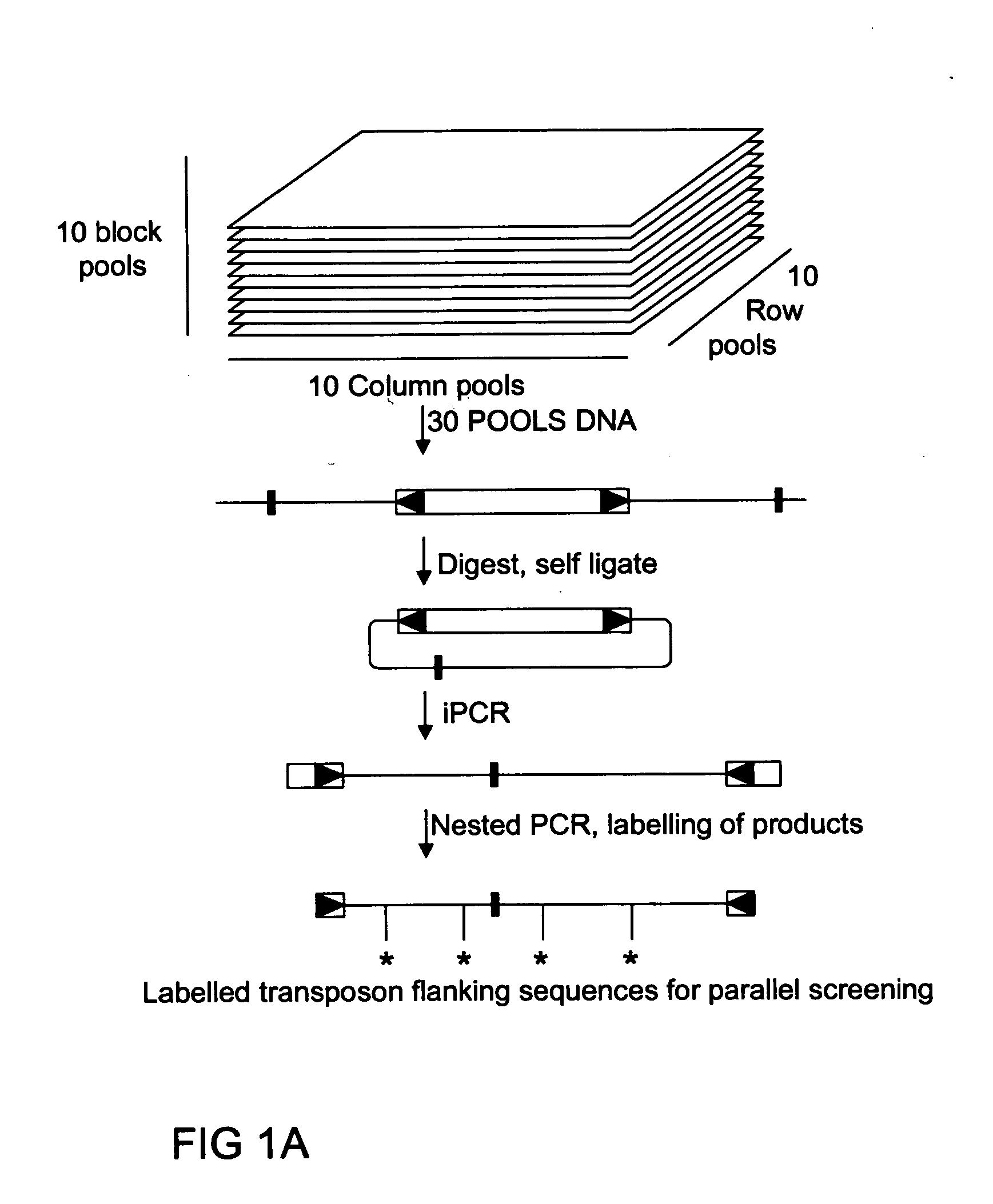
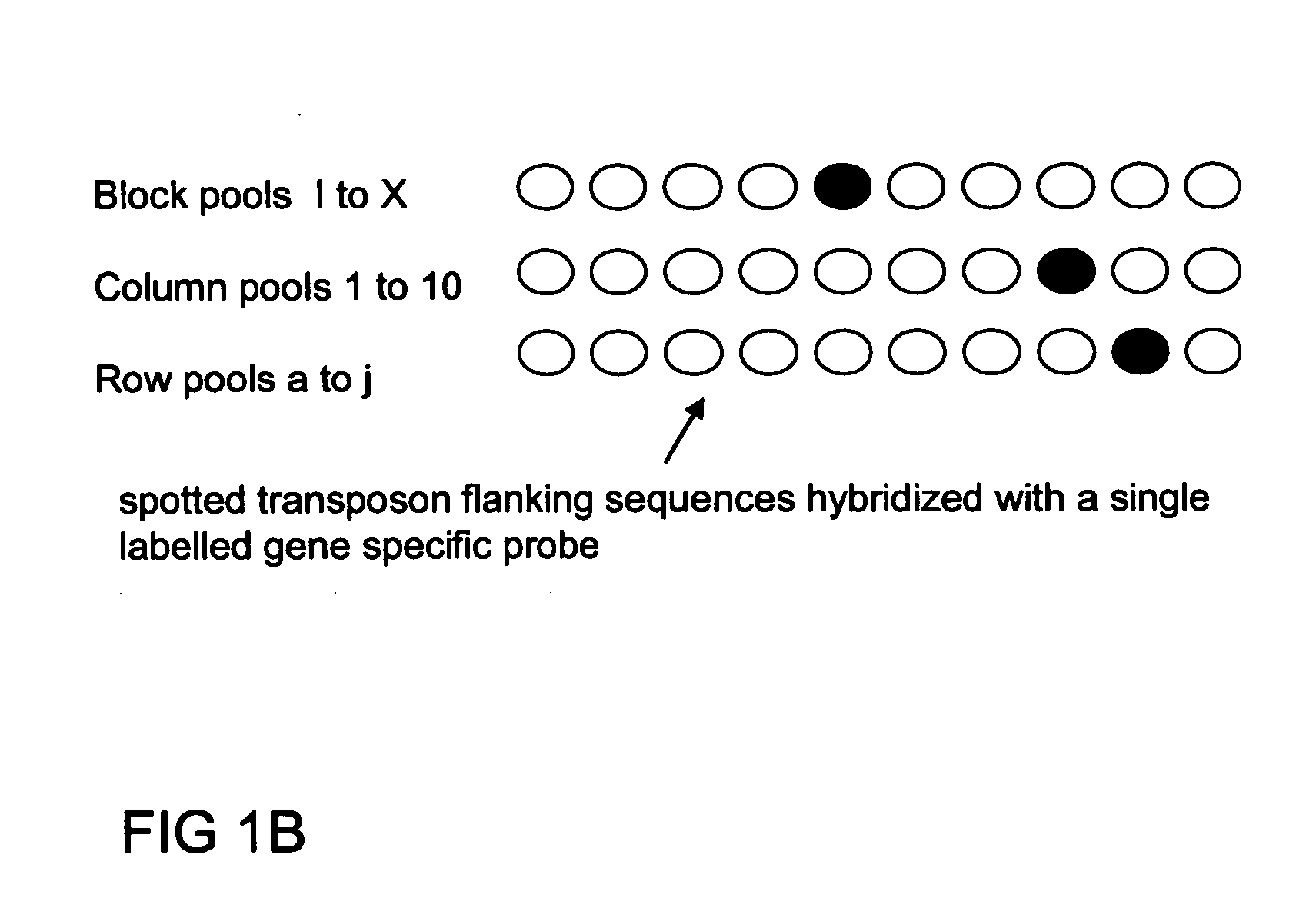
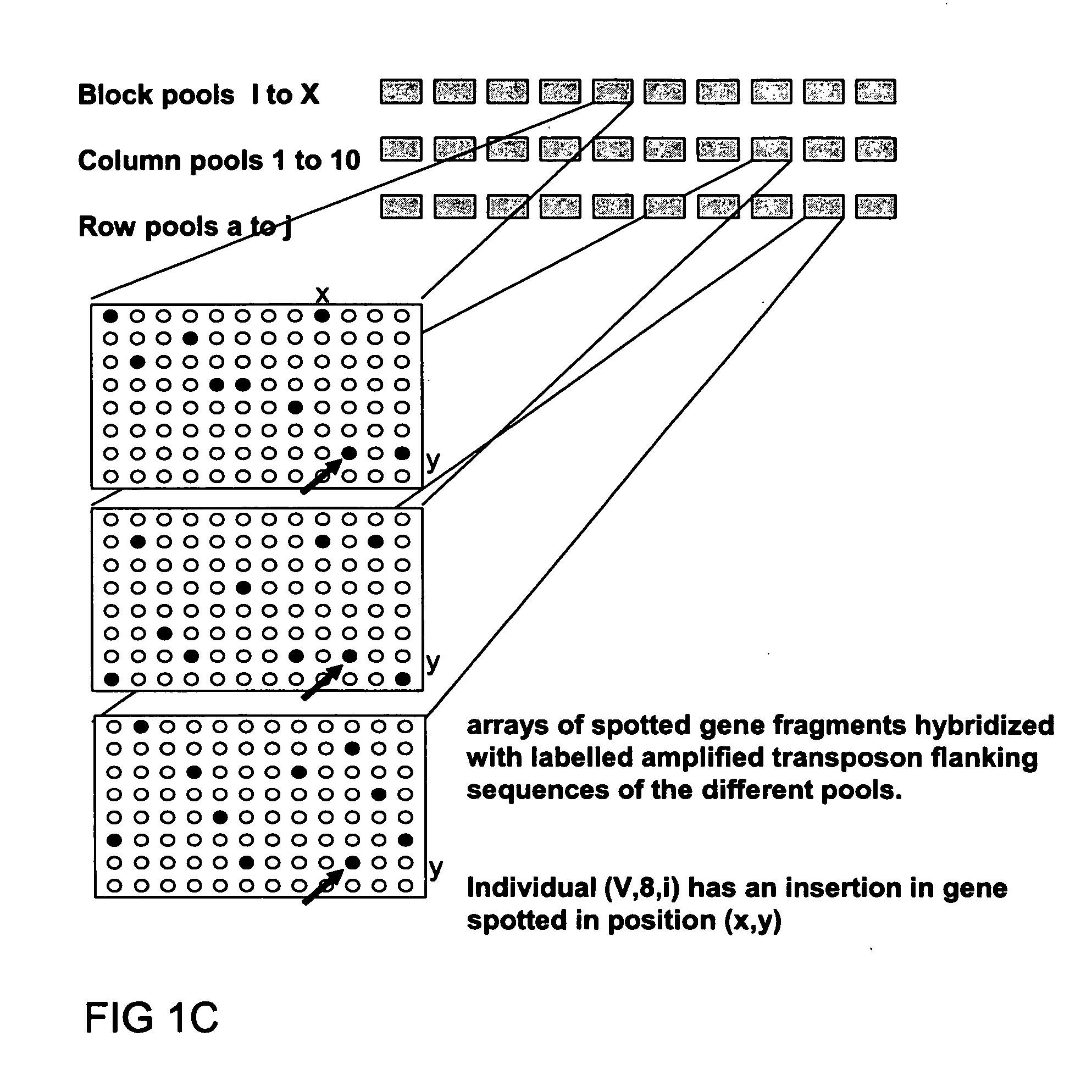
Method of parallel screening for insertion mutants and a kit to perform this method
InactiveUS20050059057A1Improve screening efficiencyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationModel systemScreening method
The current invention is a novel approach termed “parallel screening” which allows simultaneously screening of a population for insertions in all genes cloned from that or a closely related organism. In order to test this approach, the flowering plant Petunia hybrida was used as a model system. Petunia hybrida line W137 contains a high copy number of the endogenous transposable element dTph1 and has been previously presented as a genetic tool. A 3D library of the plant genomic DNA of 1000 Petunia hybrida W137 plants was generated. The 3D library consists of 30 pools of DNA from 100 plants each. These were used to generate 30 pools of insertion flanking sequences by nested iPCR using a set of transposon-specific primers or by Transposon Display PCR. Insertions into a gene were detected by hybridizing the amplified insertion flanking sequences fixed to a filter with a gene-specific probe, an approach termed simple screening for insertion elements. Alternatively, the amplified insertion element flanking sequences were labeled and used as a probe to hybridize a filter displaying multiple gene targets, an approach termed parallel screening for insertion elements, which allows the simultaneous screening for insertions in all genes of an organism, appearing in a population of insertion mutants.
Owner:MAES TAMARA +1
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070234438A1Desirable effectIncrease profitSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided m the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:ABAD MARK S +1
Method of elevating photosynthesis speed of plant by improving pyruvate phosphate dikinase
InactiveUS20060064783A1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesHigh level expressionPlant genomics
The present invention relates to the transformation of C4 plants. It also relates to the high-level expression of foreign genes in C4 plants. More specifically, the present invention relates to the creation of C4 plants retaining an excellent photosynthetic capacity at low temperature by achieving high-level expression of an enzyme constituting the C4 photosynthetic pathway. In the present invention, C4 plants are transformed using an expression cassette that comprises a promoter, a C4 plant genomic gene, under control of said promoter, encoding an enzyme constituting a photosynthetic pathway, and a terminator. The C4 plant genomic gene encoding an enzyme constituting a photosynthetic pathway is preferably a C4 plant genome-derived PPDK gene or a modified form thereof. The present invention is particularly useful in improving the production of C4 plants having PPDK (especially, in improving the production of maize under low temperature conditions).
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH R +2
Glyphosate-resistant plants
InactiveUS20060225147A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationGlyphosatePlant cell
This invention relates to glyphosate-resistant transgenic plants and methods of making the same. In a preferred embodiment, a DNA fragment which comprises an EPSPS 5′ regulatory sequence and a glyphosate-resistant EPSPS coding sequence is introduced into regenerable plant cells. The encoded EPSPS has a chloroplast transit peptide. The DNA fragment does not contain a non-EPSPS enhancer. Cells are selected for stable transformation, and the selected cells can be used to regenerate glyphosate-resistant transgenic plants. The DNA fragment used for transformation preferably comprises a modified plant genomic sequence, such as SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO:4 or SEQ ID NO: 6. In one embodiment, two DNA fragments of this invention are stably transformed into a plant to confer glyphosate-resistance.
Owner:MERTEC
Method for extracting total DNA from agriophyllum squarrosum tissue
InactiveCN106047866AStable extractionHigh quantity and qualityDNA preparationGenomic DNADNA extraction
A method for extracting total DNA from an agriophyllum squarrosum tissue includes the steps of kit equipment extraction pretreatment, extraction, and quality detection. According to the method, aiming at the defects of a conventional agriophyllum squarrosum DNA extraction technique, with combination of beta-mercaptoethanol and a commercial DNA extraction kit Plant Genomic DNA Kit of Tiangen biotech (Beijing) Co., Ltd., and through optimization tests, the method for extracting the total DNA with high quality, high yield and no protein and RNA pollution is developed for the agriophyllum squarrosum tissue; the method not only lays the foundation for development of agriophyllum squarrosum genome and mining of stress resistance resources, but also provides a model for extraction of high-quality whole genomic DNA of desert plants.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com