Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "Genetics genomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
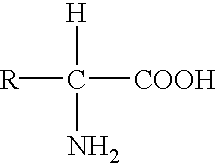
WHO definitions of genetics and genomics. Genetics is the study of heredity.1 Genomics is defined as the study of genes and their functions, and related techniques. 1,2 The main difference between genomics and genetics is that genetics scrutinizes the functioning and composition of the single gene where as genomics addresses all genes...
Ecdysone receptor-based inducible gene expression system
This invention relates to the field of biotechnology or genetic engineering. Specifically, this invention relates to the field of gene expression. More specifically, this invention relates to a novel inducible gene expression system and methods of modulating gene expression in a host cell for applications such as gene therapy, large-scale production of proteins and antibodies, cell-based high throughput screetng assays, functional genomics and regulation of traits in transgenic plants and animals.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1 and application
ActiveCN105441460AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1. The lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and codes a protein with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY1, functional genomics related technical research verifies that the LrWRKY1 gene has the function of increasing the fungus resistance of plants; when the antifungal LrWRKY1 gene is constructed to a plant expression vector and is transferred to tobaccos for overexpression, transgenic tobacco plants have strong in-vitro antifungal activities, and experimental results show that the LrWRKY1 overexpressed transgenic tobaccos have obvious inhibiting effects on the growth of four fungi including botryosphaeria, sclerotinite, botrytis cinerea and fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
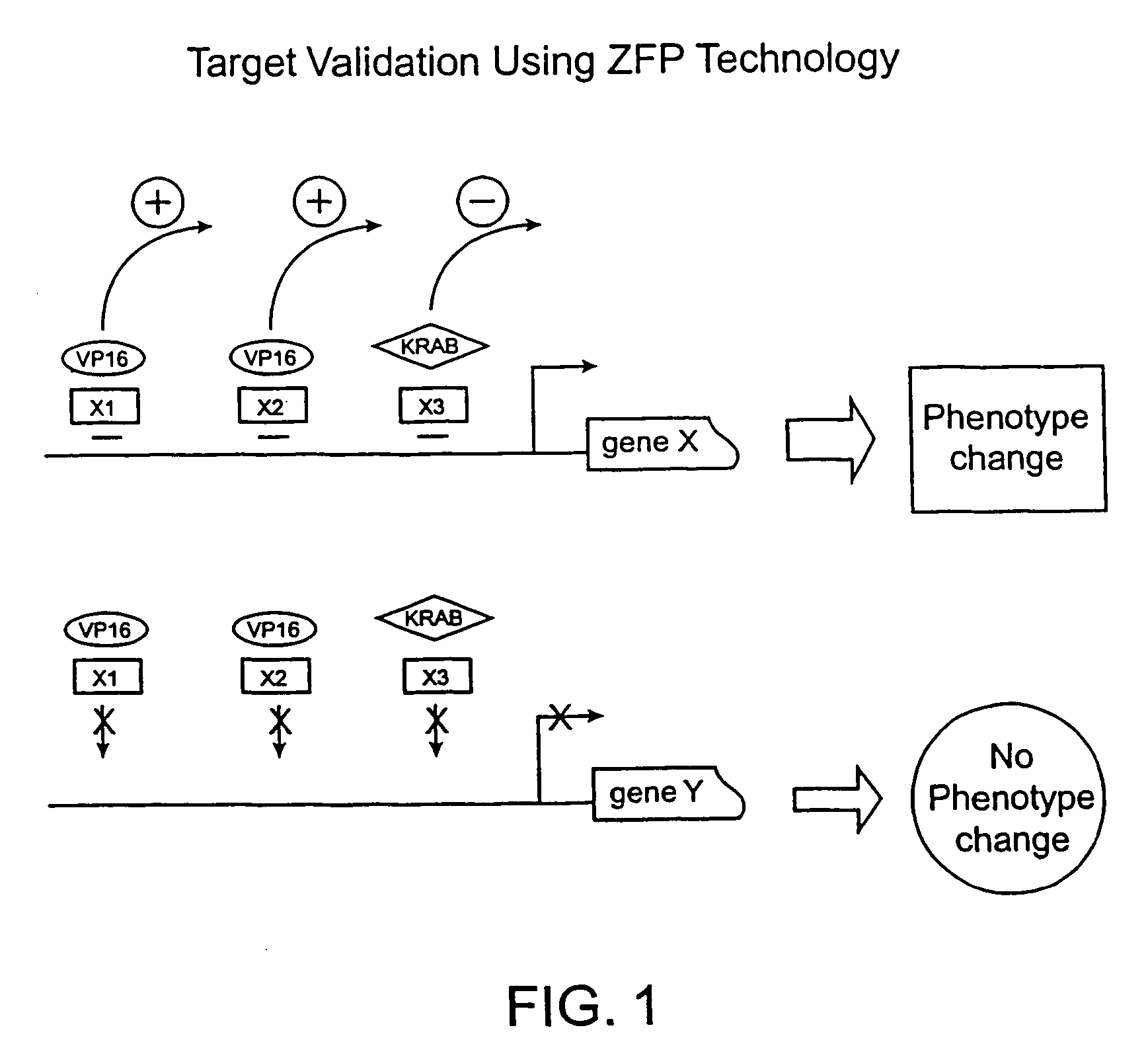
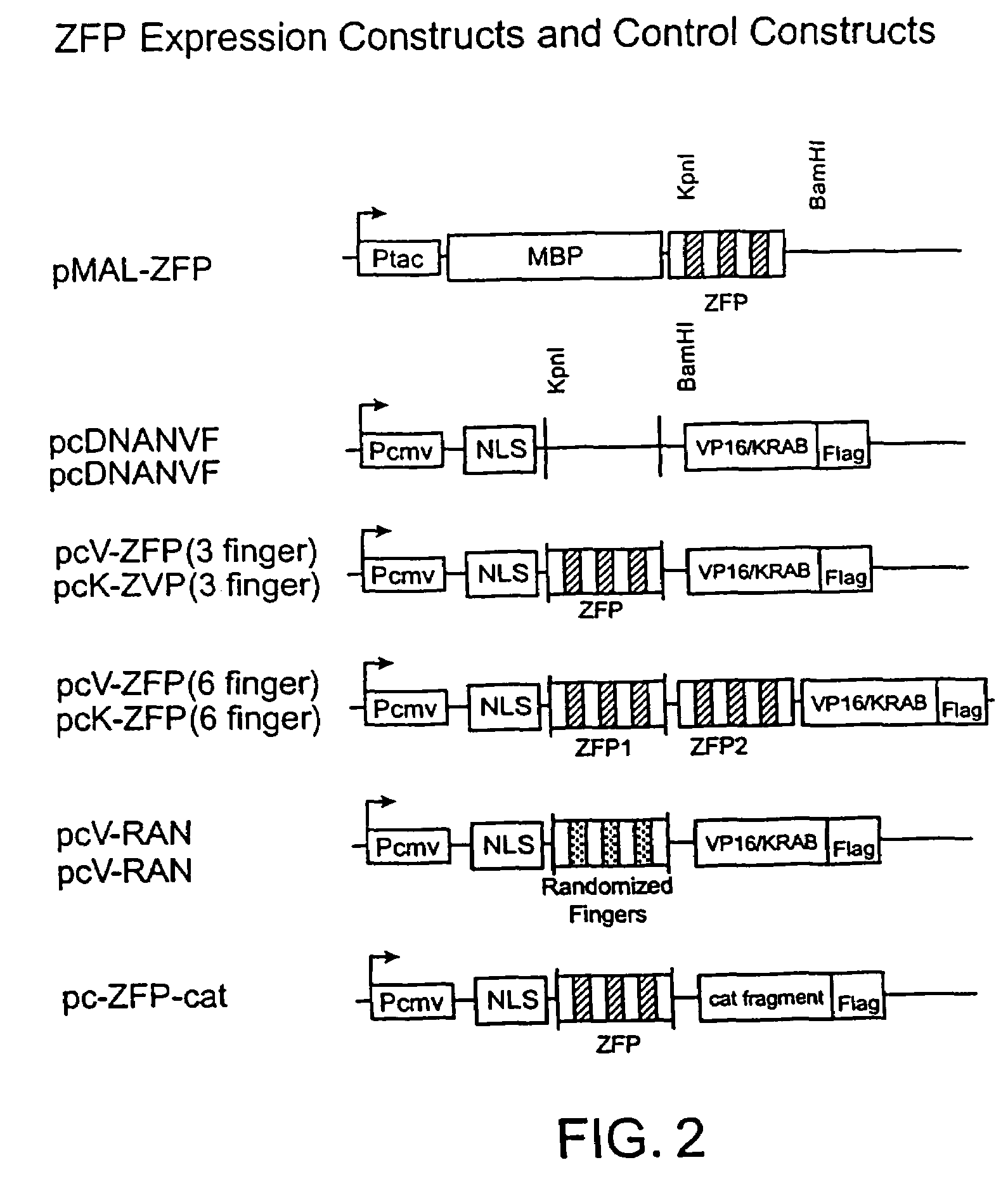
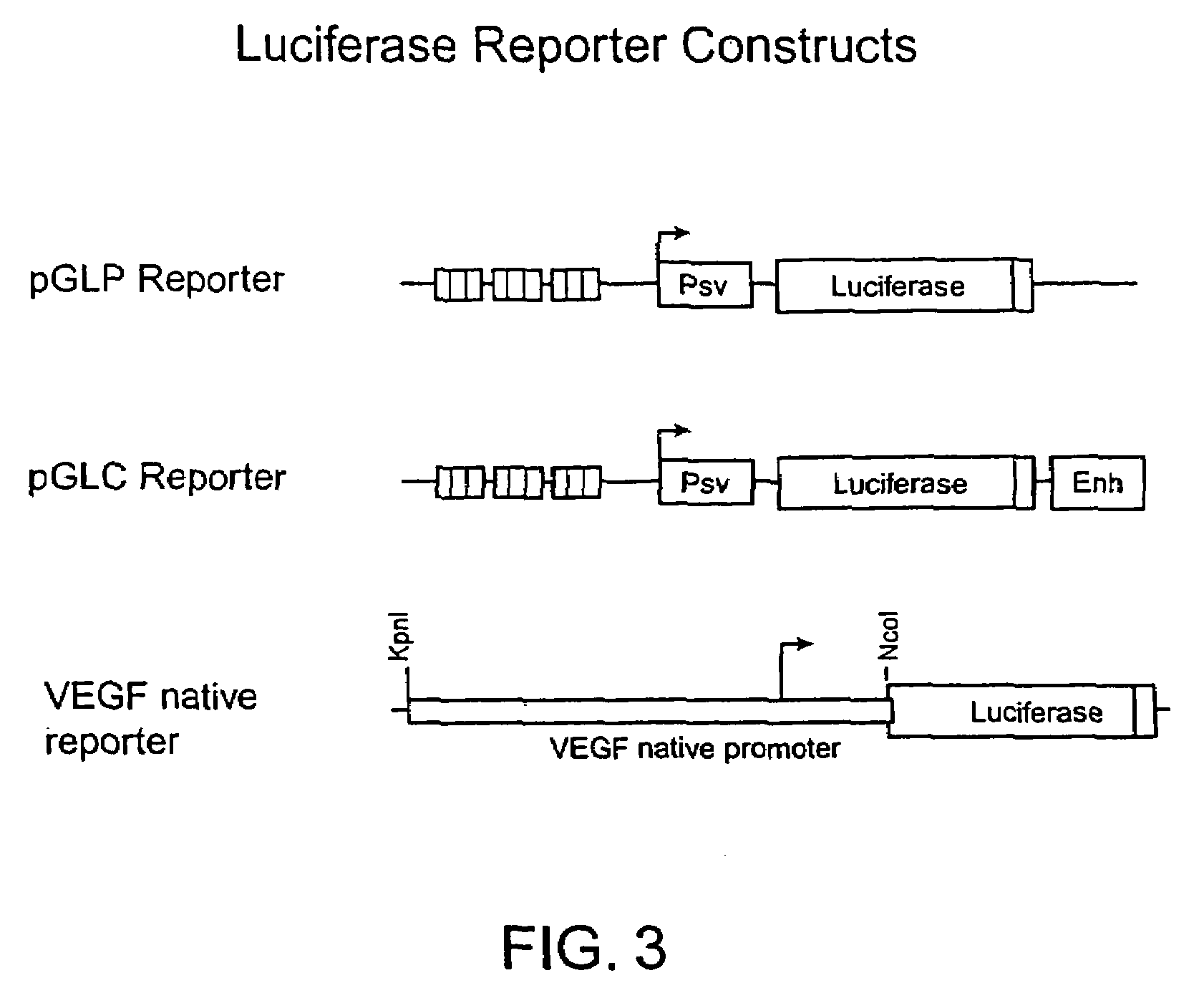
Functional genomics using zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS7235354B2Prevents repressionInhibition of activationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsZinc
The present invention provides methods of regulating gene expression using recombinant zinc finger proteins, for functional genomics and target validation applications.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080263730A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionImmunoglobulinsFermentationNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BUEHLER ROBERT E +3
Lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 and application thereof
ActiveCN110734482AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyAntifungal
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4. The nucleotide sequence of the lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 is described as in the SEQ ID NO:1,and the coded protein of the lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY4 corresponds to the amino acid sequence described in the SEQ ID NO:2. According to the lilium regale WRKY transcriptionfactor gene LrWRKY4, it is proved that the LrWRKY4 gene has the function of improving the antifungal ability of plants through the technical research related to the functional genomics, the antifungal LrWRKY4 gene is constructed to a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco for overexpression, the transgenic tobacco has very high antifungal activity, and the experimental result showsthat the tobacco with the LrWRKY4 gene overexpressed is highly resistant to infestation of nigrospora oryzae, fusarium graminearum, fusarium graminearum, botryosphaeria and fusarium solanum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
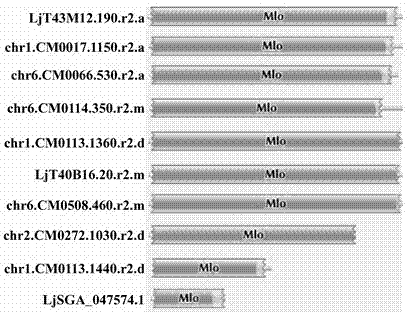
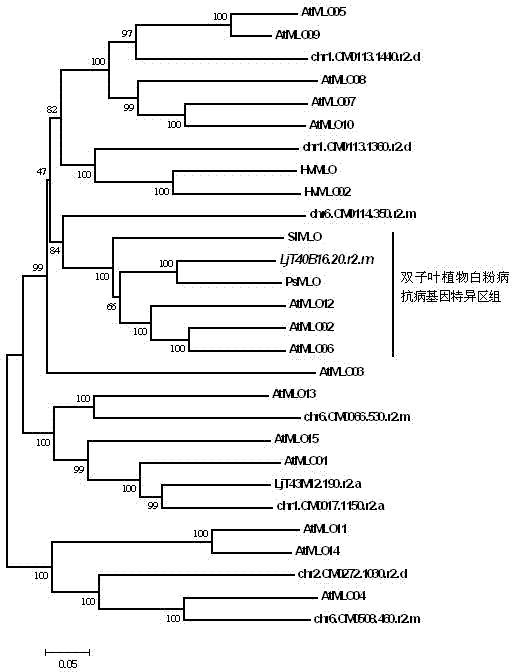
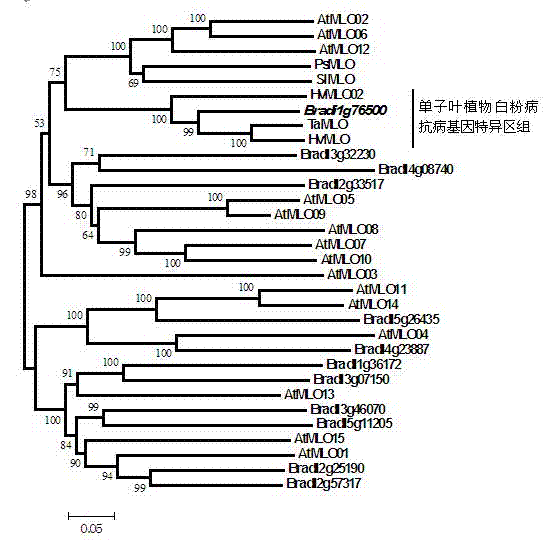
Rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing comparative genomics
InactiveCN102703463AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGenetics genomics
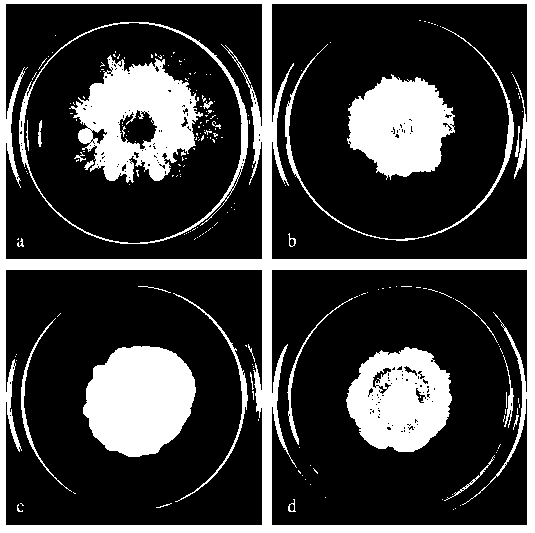
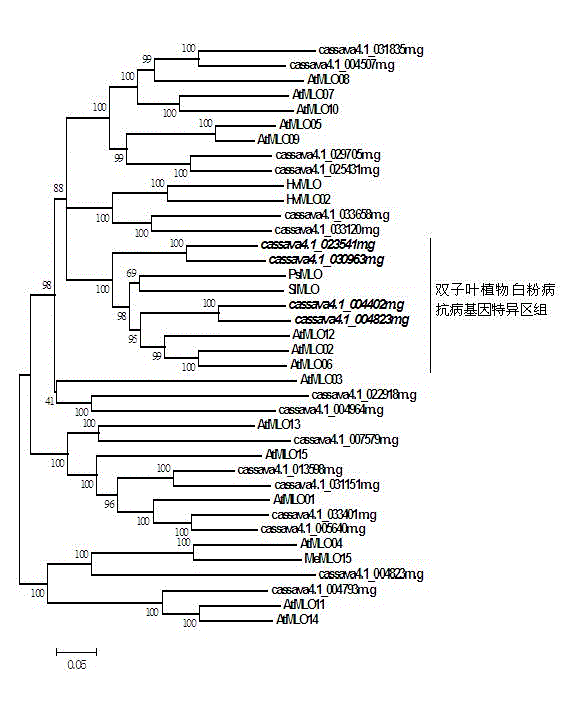
The invention relates to rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing comparative genomics, relates to knowledge of subjects such as plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, and belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing the comparative genomics mainly includes the steps of firstly, downloading full genomic sequences of Lotus corniculatus and collecting MLO (mildew resistance locus o) genes; secondly, identifying the MLO genes; thirdly, identifying phylogenetic relationship of the MLO genes; and fourthly comparing the MLO powdery mildew resistance genes. By the rapid identification, mining cycle of the powdery mildew resistance genes is shortened, and the powdery mildew resistance genes can be identified quickly. Corresponding co-separation functional marks (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), Scar and the like) can be developed through candidate powdery mildew resistance genes identified, the rapid identification is also available for molecular marker-assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance genes, and accuracy is high. The rapid identification can also be used with other molecular markers for resistance genes to create multiresistance breeding materials, and accordingly breeding period is shortened, breeding efficiency is improved, and basis for elaborating powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus molecular mechanisms is laid.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Nucleic acid molecule SEQ ID NO. 68811 and other molecules associated with plants
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080168583A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from cotton are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:FINCHER KAREN L +3
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1
ActiveCN105087599AIncrease contentHigh expressionFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjERF1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjERF1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and AP2 / ERF transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjERF1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11 and application thereof
ActiveCN110747202AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetics genomics
The invention discloses a Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11. The Lilium regale Wilson WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY11 has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and encodes a protein having an amino acid sequences shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. According to the invention, genomic studies have confirmed that the LrWRKY11 gene can improve anti-fungal functions of plants. Being constructed onto a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco so as to be subjected to overexpression, the anti-fungal LrWRKY11 gene disclosed by the invention is capable of endowing the transgenic tobacco with very strong resistance to fungal pathogens. Experimental results have shown that transgenic tobacco with overexpression of the LrWRKY11 gene has very high level of resistance to infection of Nigrospora oryzae, Fusarium verticillioides, Botryosphaeria dothidea, Fusarium solani and Alternaria panax.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and application thereof
ActiveCN110818782AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a lilium regale WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY3 and a preparation method thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and a protein with an aminoacid sequence shown as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; according to the invention, functional genomics related technical researches prove that the LrWRKY3 gene has the function of improving the antifungal performance of plants; the antifungal LrWRKY3 gene disclosed by the invention is constructed on a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco for overexpression; the transgenic tobacco plantshave very strong fungus infection resistance, and experimental results show that transgenic tobacco leaves with over-expression of LrWRKY3 have very strong resistance to infection of five pathogenicfungi such as alternaria oryzae, Botryosphaeria dothidea, fusarium graminearum, Fusarium rotunda and fusarium solani.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lilium regale antifungal gene Lr14-3-3 and application thereof
InactiveCN103194456AIncreased fungal resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAntifungal
The invention discloses a lilium regale gene Lr14-3-3 with antifungal activity. The gene Lr14-3-3 has the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and encodes protein 14-3-3. A relevant technology of functional genomics proves that the gene Lr14-3-3 has a function of improving the plant antifungal activity. The antifungal gene Lr14-3-3 is constructed to a plant expression vector and is transferred into tobacco to perform overexpression; the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in vitro antifungal activity; and the transgenic tobacco expressing the Lr14-3-3 has obvious inhibition effects on the growth of botryosphaeria dothidea, phomopsis fungi, fusarium oxysporum and alternaria.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
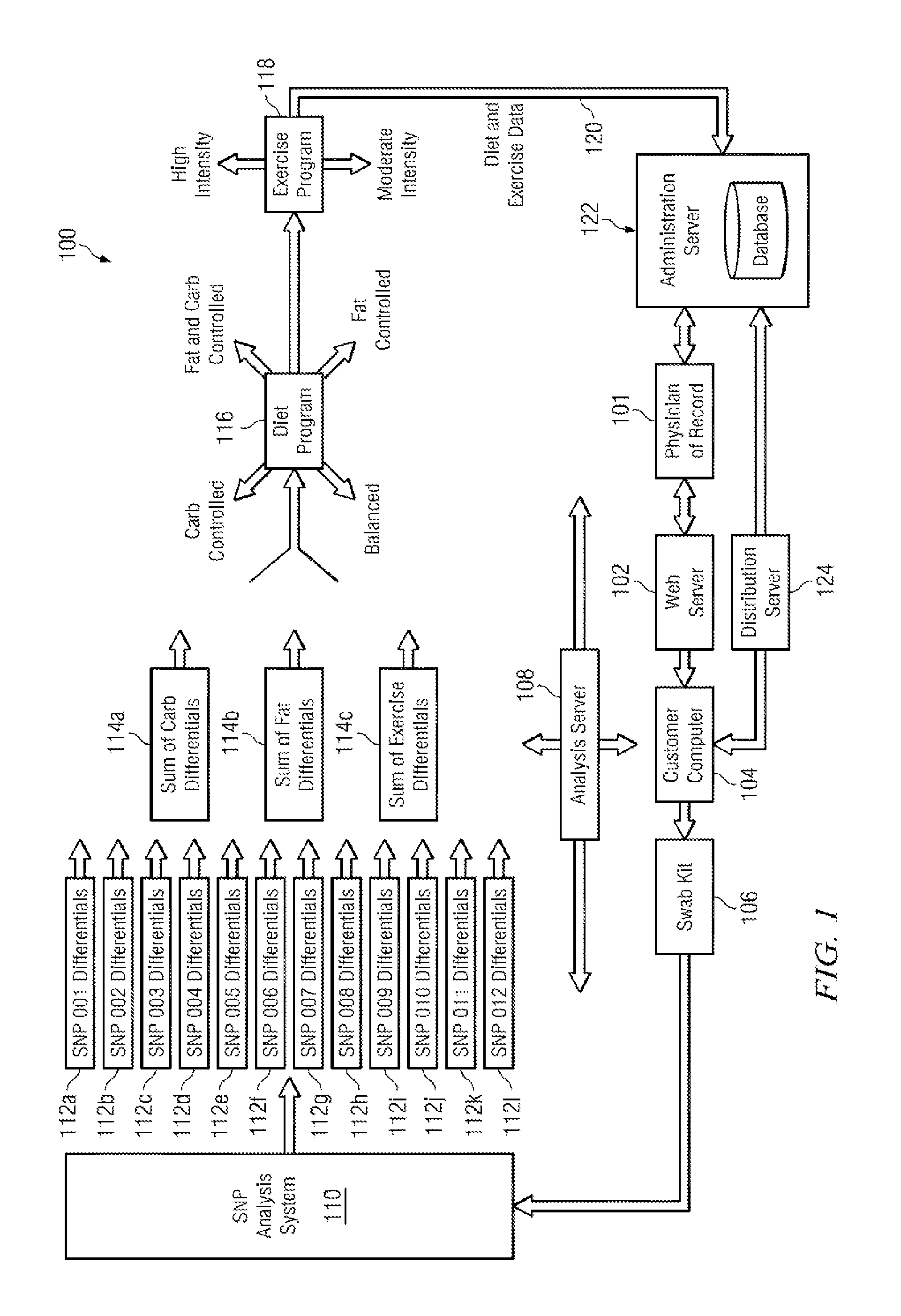
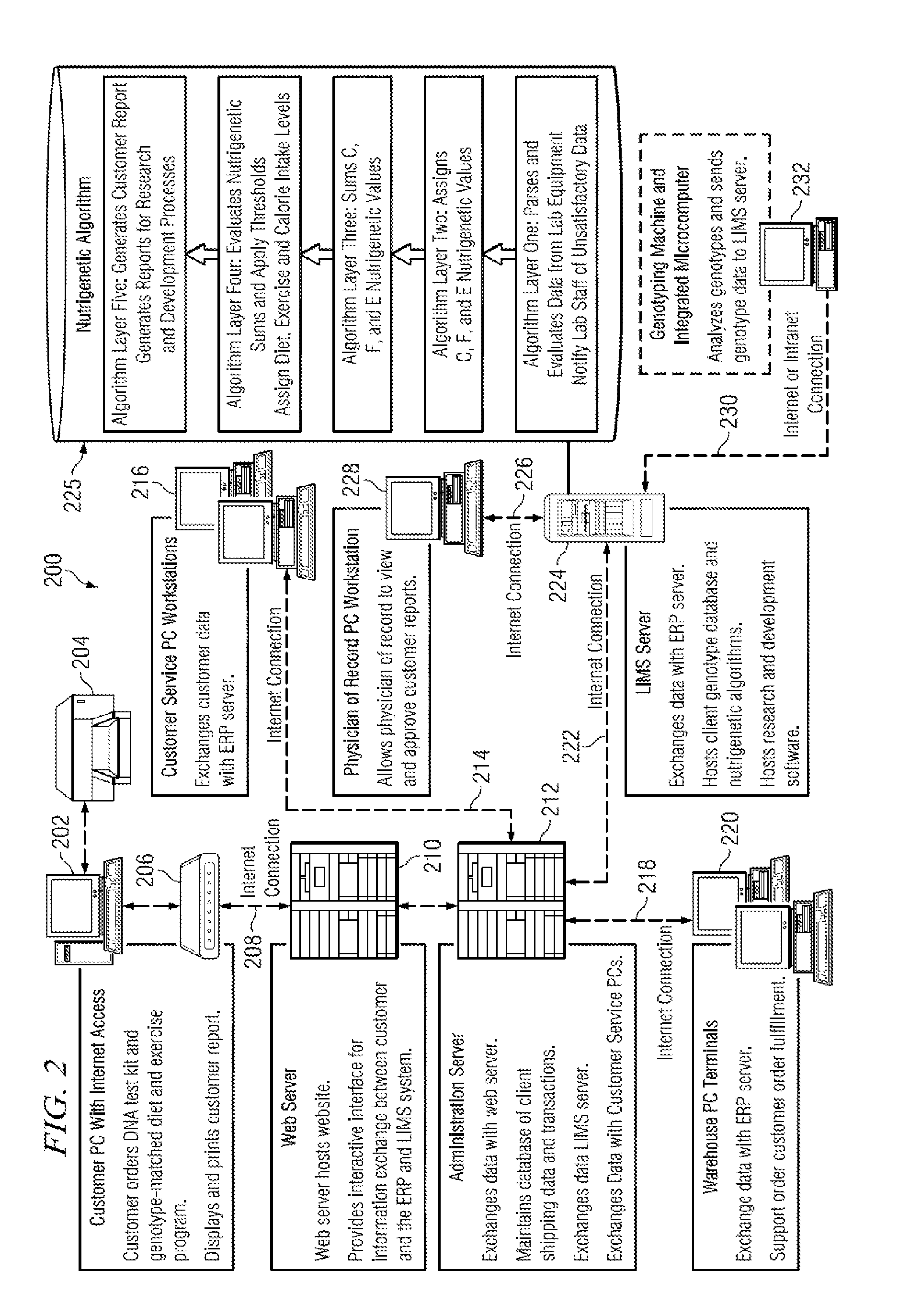
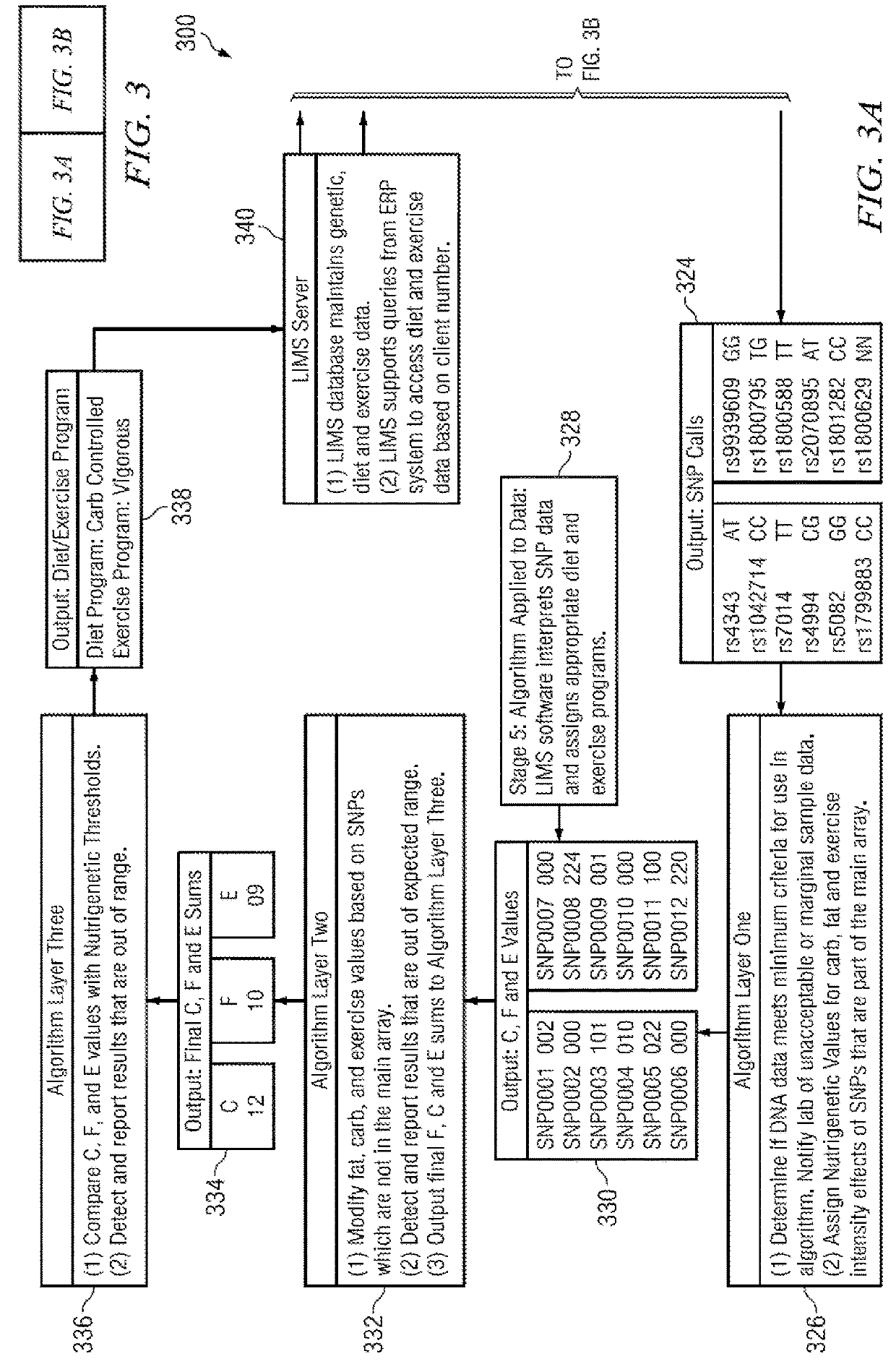
Weight management genetic test systems and methods
InactiveUS20120295256A1Healthy weightIncreased susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPersonalizationProgram planning
Disclosed herein is a nutritional genomic weight management algorithm running on a computer system, and more specifically, a nutritional genomic weight management algorithm where an analysis of a customer's unique DNA results in individualized diet and exercise plans, in accordance with the present invention. Methods of weight management, weight management business methods, and panels of alleles for nutritional genomics are also disclosed.
Owner:GENOVIVE
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20070283459A1Desirable effectIncrease profitImmunoglobulinsFermentationNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from soybean are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:BYRUM JOSEPH +2
Method for quickly identifying manihot esculenta mildew-resistance locus (MLO) gene by applying comparative genomics
InactiveCN102796745AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesDiseaseGenetics genomics
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying a manihot esculenta mildew-resistance locus (MLO) gene, relates to knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics, bioinformatics and the like and belongs to the field of plant biotechnology science. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1) downloading a manihot esculenta whole genome sequence, and collecting the MLO gene; 2) identifying the MLO gene; 3) identifying the MLO gene according to the MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparing the MLO genes. By the method, the discovery cycle of the manihot esculenta MLO gene is shortened effectively, and the MLO gene can be quickly identified; corresponding coseparation functional markers (single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and specific combining ability (SCA)) can be developed by the identified candidate MLO gene, and the method can be quickly used for molecular marker auxiliary selection of the MLO gene, and is high in accuracy; by combining other disease-resistant gene molecular markers, multiresistance breeding materials can be prepared, the breeding cycle is shortened, and the breeding efficiency is improved; and the foundation is laid for elaborating a manihot esculenta MLO gene molecular mechanism.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Weight management genetic test systems and methods
InactiveUS20180182479A1Healthy weightIncreased susceptibilityPhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationProgram planningAllele
Disclosed herein is a nutritional genomic weight management algorithm running on a computer system, and more specifically, a nutritional genomic weight management algorithm where an analysis of a customer's unique DNA results in individualized diet and exercise plans, in accordance with the present invention. Methods of weight management, weight management business methods, and panels of alleles for nutritional genomics are also disclosed.
Owner:GENOVIVE
Pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY9 and application thereof
ActiveCN112831504AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyNigrospora oryzae
The invention discloses a pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY9 and the application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the PnWRKY9 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and the PnWRKY9 gene encodes a WRKY transcription factor; according to the application, molecular biology and functional genomics related technical researches prove that the PnWRKY9 gene has the function of improving the fungal disease resistance of plants, the antifungal gene PnWRKY9 is constructed on a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco for overexpression, and the transgenic tobacco plant has very strong in-vitro antifungal activity; according to the present invention, the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of Alternaria Compacta, Fusarium solani, and Nigrospora oryzae, and the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of the Alternaria Compacta, the Fusarium solani, and the Nigrospora oryzae, such that the PnWRKY9 overexpressed transgenic tobacco has the significant inhibition effect on the growth of the Nigrospora oryzae,.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of lilium regale wilson pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene LrPR10-5
InactiveCN104131015AIncrease resistanceReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomicsNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses an application of a lilium regale wilson pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene LrPR10-5. A nucleotide sequence of the LrPR10-5 is as shown in SEQIDNO:1, and the pathogenesis-related protein 10 gene is encoded. The research proves that the LrPR10-5 gene has the function of improving the plant antifungal capability by functional genomics-related technologies, the antifungal LrPR10-5 gene is built on a plant expression vector and is switched into tobacco to perform overexpression, the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in-vitro antifungal activity in the result, and the experiment result shows that the transgenic tobacco for overexpression of the LrPR10-5 has an obvious inhibiting effect on growth of a plurality of fungi, such as botrytis cinerea, rhizoctonia solani and sclerotinia sclerotiorum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon
InactiveCN102703462AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention relates to rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon, relates to the knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics, biological information and other subjects, and belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon comprises the main steps of: (1) downloading full genome sequences of Brachypodium distachyon and collecting MLO (mildew resistance locus o) type gene; (2) identifying the MLO type gene; (3) analyzing the MLO type gene historical development relation; and (4) comparing the MLO type powdery mildew gene. According to the rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon provided by the invention, the excavation period of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon is effectively shortened, and the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene is facilitated; the identified powdery mildew gene can be used for developing corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), SCAR (sequence-characterized amplified region), and the like), and can also be rapidly used for assisted selection of molecule markers of anti-powdery-mildew gene, and the accuracy is high; development of multi-resistance breeding materials can be carried out by combining with other anti-disease gene molecule markers, the breeding time is shortened and the breeding efficiency is improved; and foundation is established for expounding the molecular mechanism of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Novel feruloyl esterase, mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111748538ARich sources of bacteriaRich sourcesHydrolasesFood processingEscherichia coliGenetics genomics
The invention discloses novel feruloyl esterase, a mutant and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, successfully screening out a feruloyl esterase gene from anaerobic fungi Neocallimatix sp. by utilizing a genomics technology; according to the preference of a prokaryotic system codon, the GC content of a feruloyl esterase gene and the secondary structure of mRNA, and codon optimization is carried out on the feruloyl esterase gene to obtain a novel feruloyl esterase gene sequence. The enzyme has an esterase regionand a glucoside hydrolase 11 region, site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on the two regions; the obtained mutant gene is also expressed in escherichia coli; separation and purification results show that the novel feruloyl esterase and the mutant thereof are successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and the esterase activity of the mutant is far lower than that of a non-mutant, so that the strain source of the feruloyl esterase is enriched, and the feruloyl esterase has theoretical guiding significance in the aspects of improving the digestibility of feed fibers and improving the production performance of animals.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid molecules and other molecules associated with plants
InactiveUS20080104729A1Reduces and depresses expression of proteinReduce protein expressionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNovel genePlant genomics
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:CONNER TIMOTHY +1
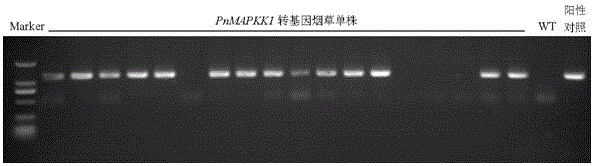
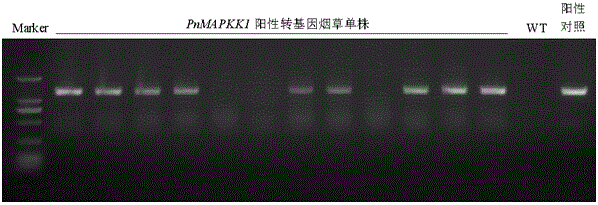
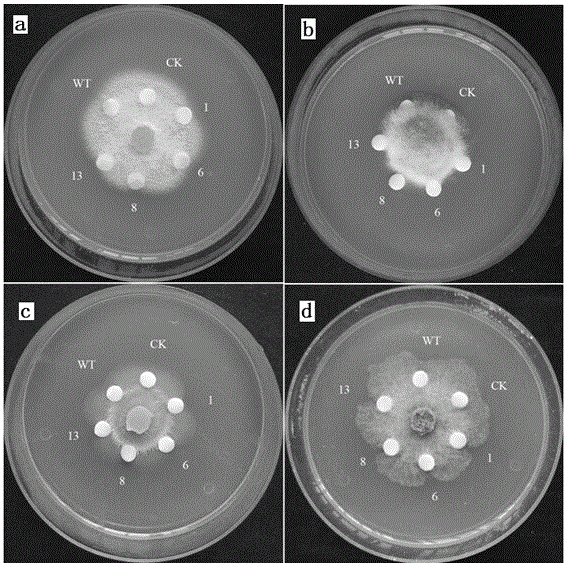
Radix notoginseng mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase gene PnMAPKK1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a radix notoginseng mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase gene PnMAPKK1.A nucleotide sequence of the gene PnMAPKK1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the gene PnMAPKK1 codes mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.According to functional genomics related technical researches, the gene PnMAPKK1 has a function of improving pathogenic fungus resistance of plants.After the antifungal gene PnMAPKK1 is constructed to a plant expression vector and transferred into tobaccos to realize overexpression, transgenic tobacco plants have extremely high in-vitro antifungal activity.The transgenic tobacco plants with PnMAPKK1 overexpressed have an evident inhibition effect on growth of fusarium solani, colletotrichum gloeosporioides, verticillium fusarium and botryosphaeria.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hansenula polymorpha with double selection marker and application thereof
InactiveCN102226154AMaintain physiological and biochemical characteristicsHigh copy numberFungiMicroorganism based processesGenomicsHigh level expression
The invention discloses hansenula polymorpha with a double selection marker and an application thereof. The hansenula polymorpha with a double selection marker provided by the invention is uracil-synthesized and tryptophan-synthesized double-deficient hansenula polymorpha HUT-31 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.4778. The strain has a uracil and tryptophan double-auxotrophic selection marker, maintains the physiological biochemical characteristics of wild-type strains, facilitates the culture of recombinant strains and the high-level expression of heterologous protein; not only recombinant strains can be selected easily and rapidly, but also the double selection marker can increase the copy number of target genes integrated on a chromosome, can increase the expression level of targetprotein, and has important industrial application value. Meanwhile, the double selection marker is also applicable to the polygene genetic modification of hansenula polymorpha in functional genomics,synthetic biology, and metabolic engineering.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
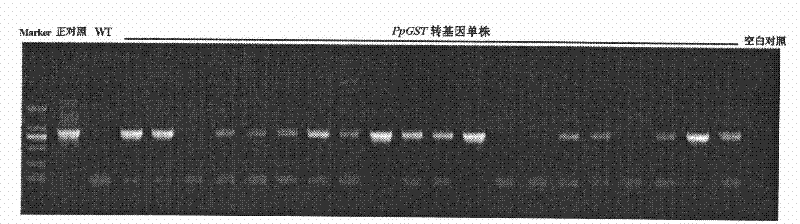
Torch pear haloduric gene PpGST and application thereof
InactiveCN101748144AIncrease resistanceImprove stress resistanceFermentationGenetic engineeringPEARNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to a torch pear haloduric gene PpGST and an application thereof. The PpGST gene is provided with base sequence as SEQ ID indicates and encoded glutathione S-transferring enzyme. In the invention, the PpGST gene is proven to have the function of improving plant resisting salt stress by the technology related to functional genomics; and when the haloduric gene PpGST is structured on a plant expression vector and shifted to over expression in tobacco, the obtained transgenic tobacco enjoys very strong haloduric activity.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nucleic Acid Molecules and Other Molecules Associated with Plants
InactiveUS20100024079A1Increase profitSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationGenetics genomicsNovel gene
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) isolated from maize are disclosed. The ESTs provide a unique molecular tool for the targeting and isolation of novel genes for plant protection and improvement. The disclosed ESTs have utility in the development of new strategies for understanding critical plant developmental and metabolic pathways. The disclosed ESTs have particular utility in isolating genes and promoters, identifying and mapping the genes involved in developmental and metabolic pathways, and determining gene function. Sequence homology analyses using the ESTs provided in the present invention, will result in more efficient gene screening for desirable agronomic traits. An expanding database of these select pieces of the plant genomics puzzle will quickly expand the knowledge necessary for subsequent functional validation, a key limitation in current plant biotechnology efforts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for constructing pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate
PendingCN108617502AImprove anti-aphid performanceHigh yieldPlant genotype modificationGenomicsEthylmethane Sulfonate
The invention discloses a method for constructing a pepper mutant library from ethylmethane sulfonate. The method is characterized in that a Zunla 1 is used as a mutagenesis object; on the premise ofpointing out the influence of treating fluid dose and excluding space of each seed on germination percentage, semi-lethal dose is determined by comparing the germination percentage of pepper seeds with EMS treating fluid with different concentrations at different mutagenesis time; the pepper seeds are treated by mutagenesis of the semi-lethal dose; mutation frequency and mutation types of M2 generation are investigated, a mutant capable of stably inheriting of M4 generation is identified and a mutant library is constructed; the mutation types of leaves, stems, fruits, growth period, flower organs, fertility and the like are obtained and create abundant materials for functional genomics reach of pepper; and meanwhile, partial beneficial mutation can be directly applied to breeding practice.
Owner:GUIZHOU SERICULTURE RES INST GUIZHOU PEPPER RES INST
Lilium regale wilson LrPAL-1 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110938617AHigh degree of lignificationImprove lodging resistanceCarbon-nitrogen lyasesClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a lilium regale wilson LrPAL-1 gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the LrPAL-1 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and the coded amino acid sequence of the LrPAL-1 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The overexpression vector containing the LrPAL-1 gene is transferred into tobacco, the lignification degree of an obtained transgenic tobacco plant is increased,the lodging resistance of the plant is improved, and particularly, the upright state of fresh cut lily flowers can be maintained. The transgenic plant has an obvious inhibition effect on pathogenic bacteria botrytis cinerea and alternaria alternata. Meanwhile, the functional genomics researches prove that the lilium regale wilson LrPAL-1 gene has an important biological function of changing the morphology of plant leaves. The invention provides an important target for molecular genetic improvement of lilium plants; the lilium regale wilson LrPAL-1 gene has an important value and significance for cultivation and production of new varieties of plants with ornamental value and landscape ecological value; and a technical support is provided for cultivation of new lilium germplasm with dual values of lodging resistance and pathogenic bacteria resistance.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
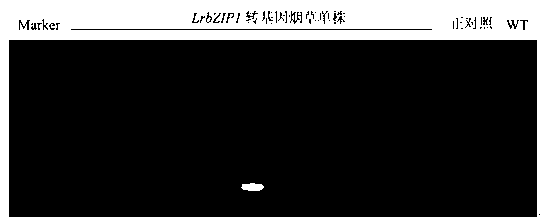
Lilium regle bZIP transcription factor LrbZIP1 and application
InactiveCN103320448AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationLiliumNicotiana tabacum
The inventing discloses a Lilium regle bZIP transcription factor LrbZIP1. According to the invention, the nucleotide sequence of the gene LrbZIP1 is as shown in SEQ ID No:1, and the gene LrbZIP1 encodes a protein of a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No:2. Functional genomics related technical research proves that LrbZIP1 has a function for improving the antifungal property of plants, after the antifungal LrbZIP1 gene is constructed in a plant expression vector and transferred to tobacco for overexpression, the result shows that the transgenic tobacco plant has strong in-vitro antifungal activity, so the experiment shows that the LrbZIP1-overexpressed transgenic tobacco has an obvious inhibiting effect on growth of various fungus such as ascomycetes and fusarium oxysporum.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY15 and application
ActiveCN112831505AIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a pseudo-ginseng WRKY transcription factor gene PnWRKY15. The nucleotide sequence of which is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, the PnWRKY15 gene is proved to have a function of improving the antifungal function of plants through functional genomics related technical research, and the antifungal PnWRKY15 gene is constructed to a plant expression vector and transferred into tobacco for overexpression, transgenic tobacco plants have very strong fungal infection resistance, and experimental results show that the PnWRKY15 overexpression transgenic tobacco leaf total protein obviously inhibits mycelial growth of fusarium chlamydosporum and alternaria compacta.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com