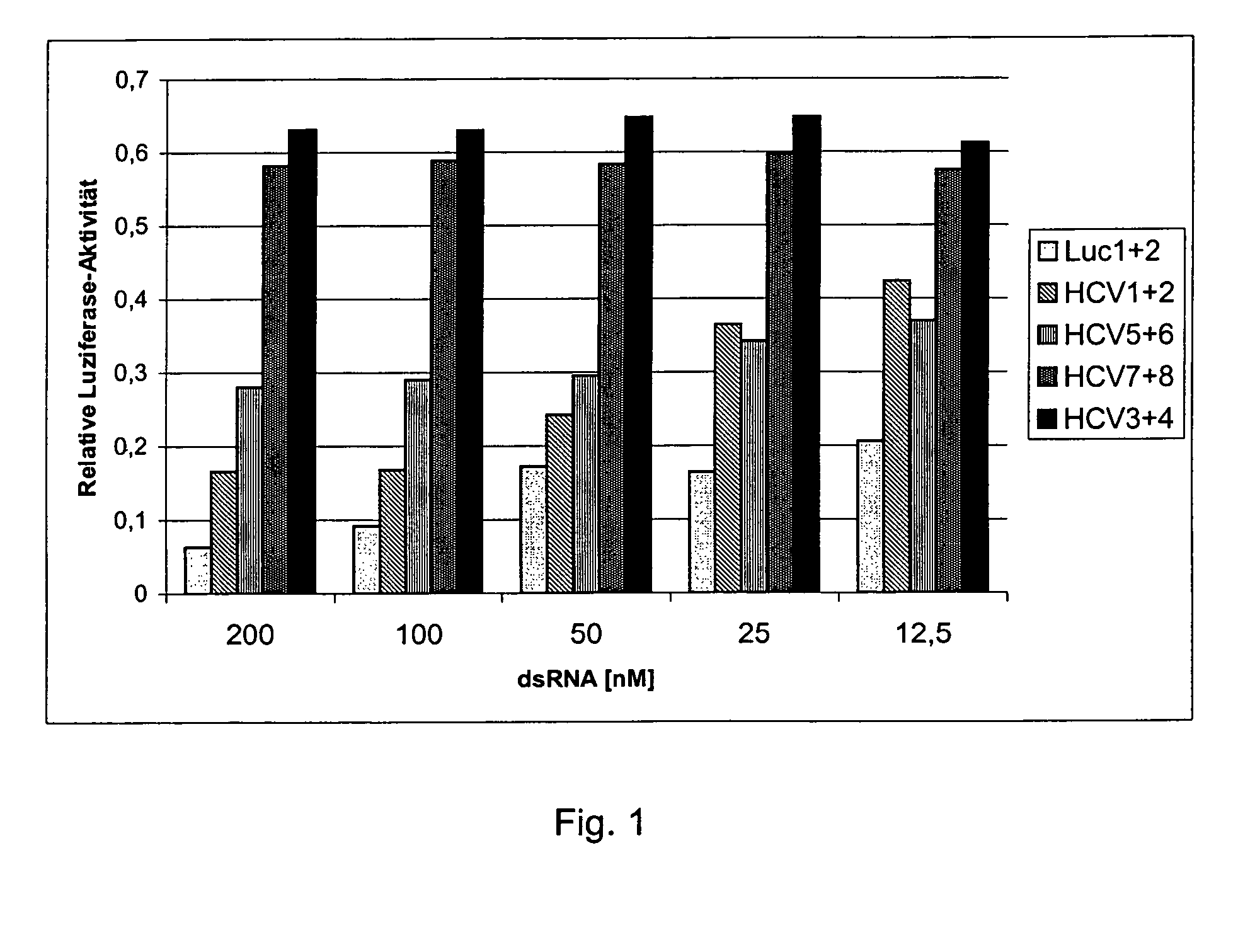
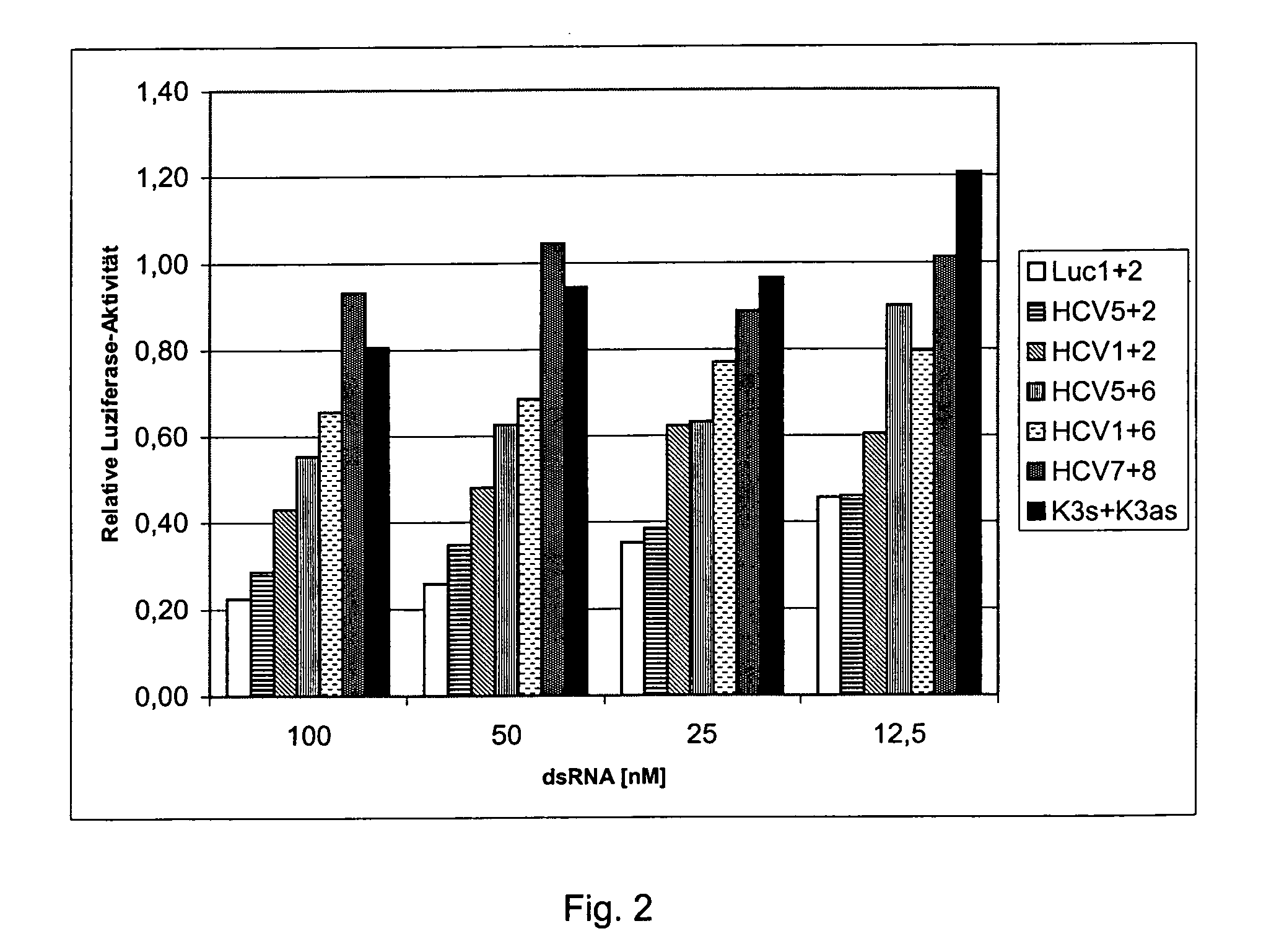
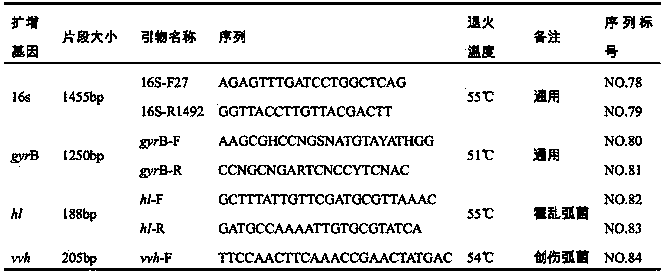
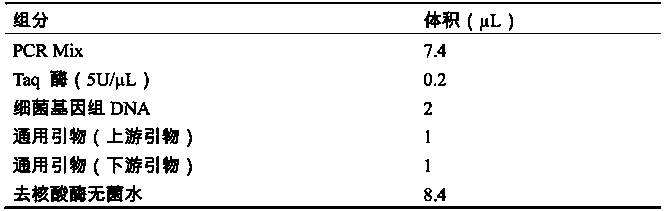
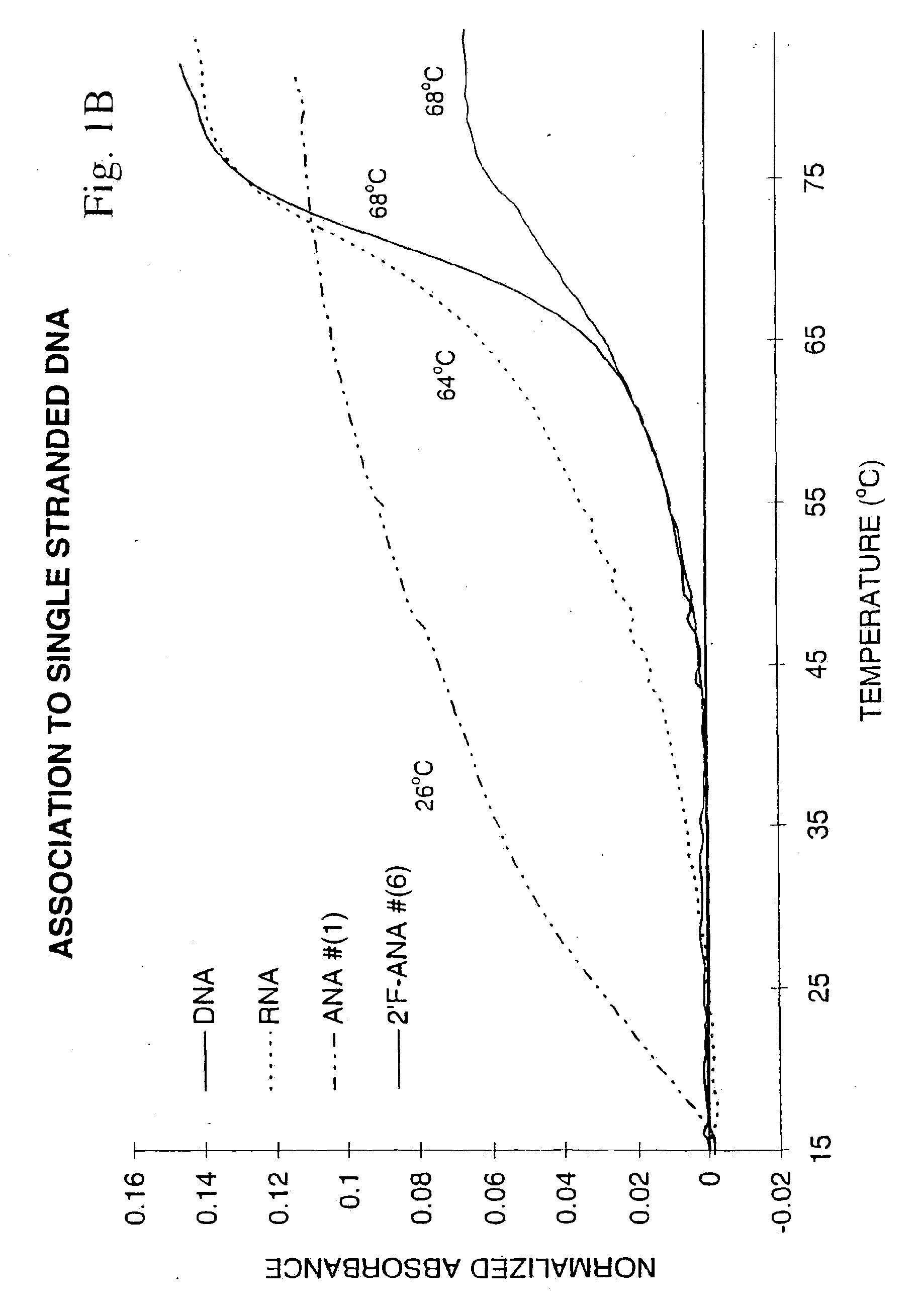
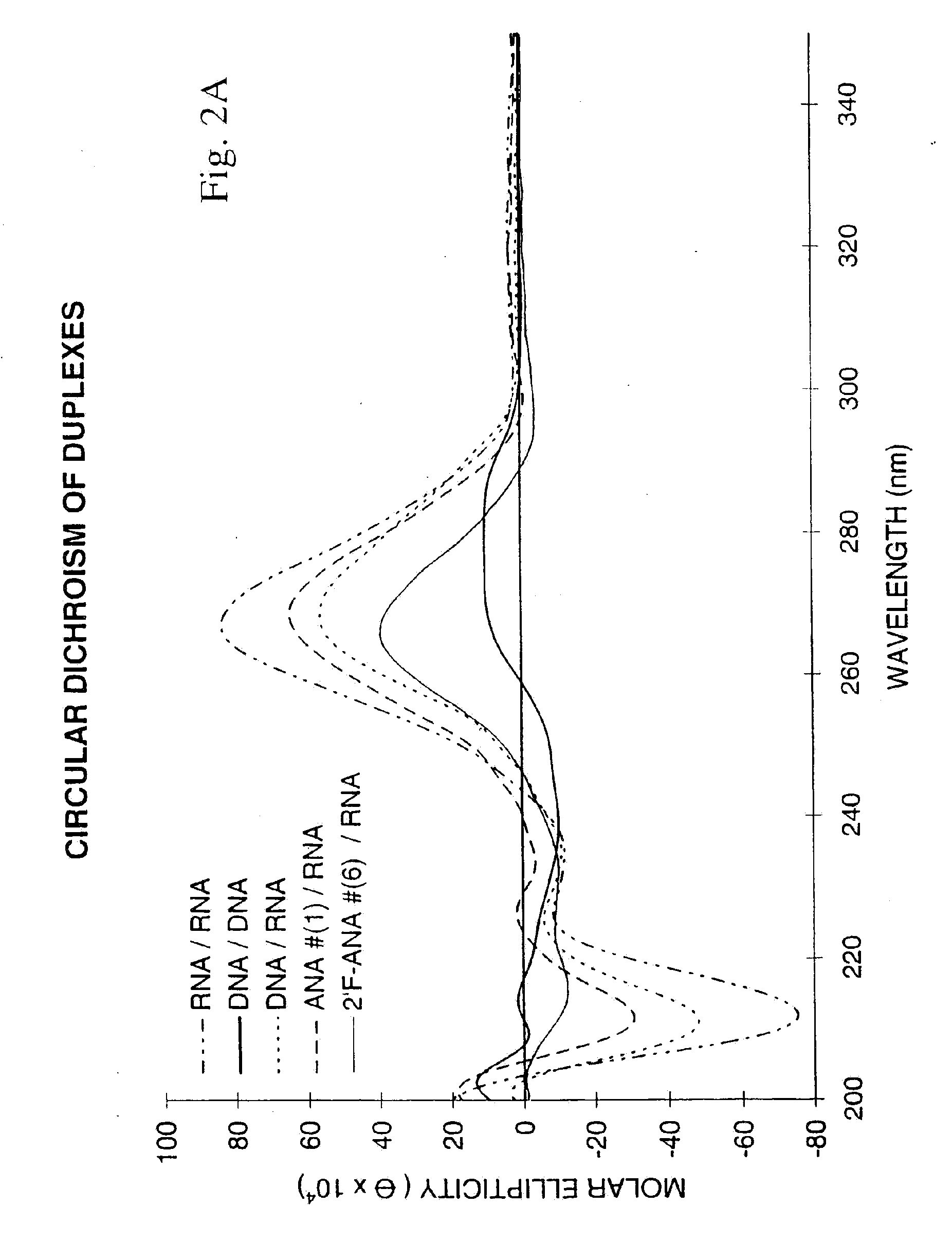
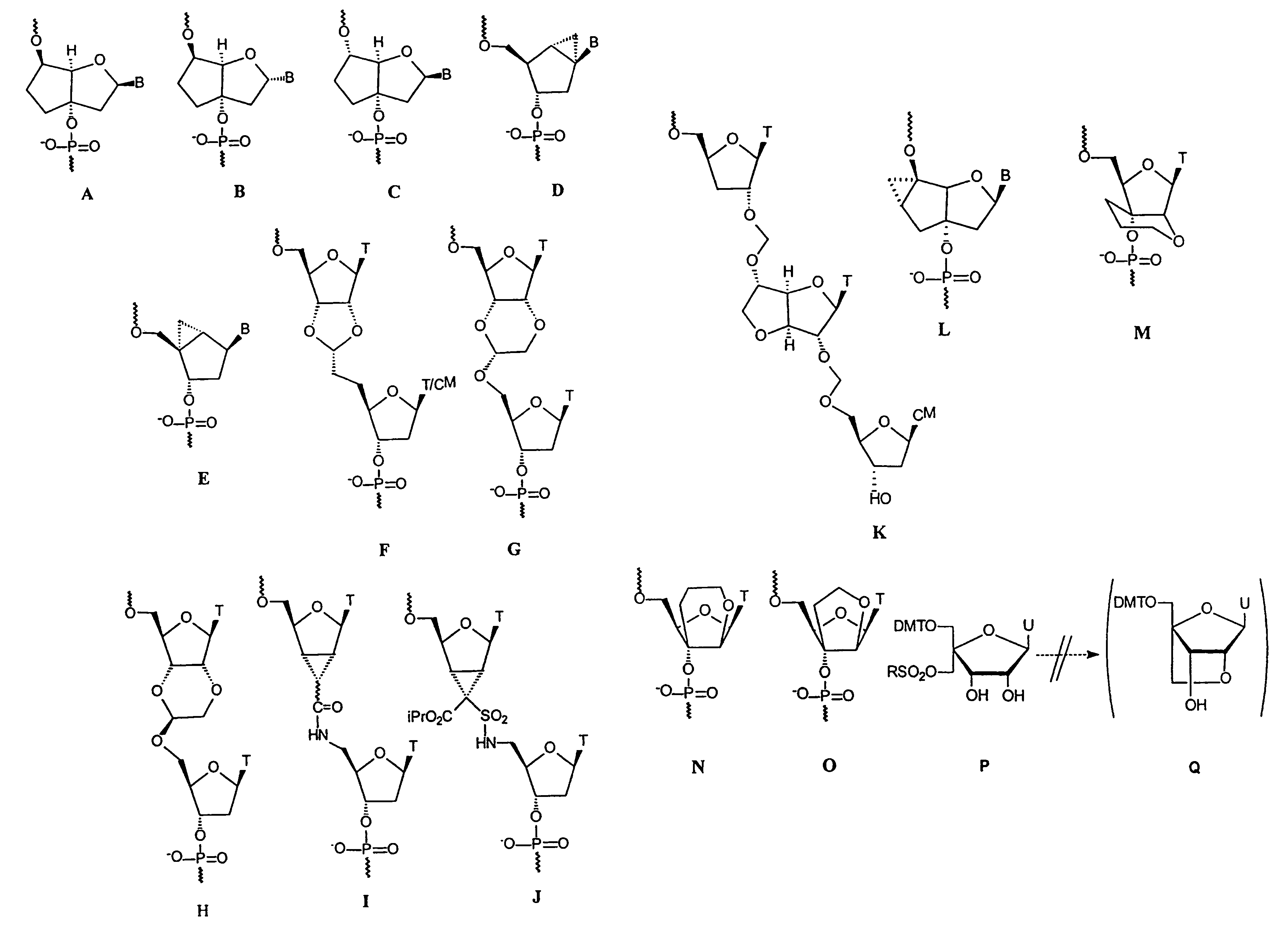Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Complementary rna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
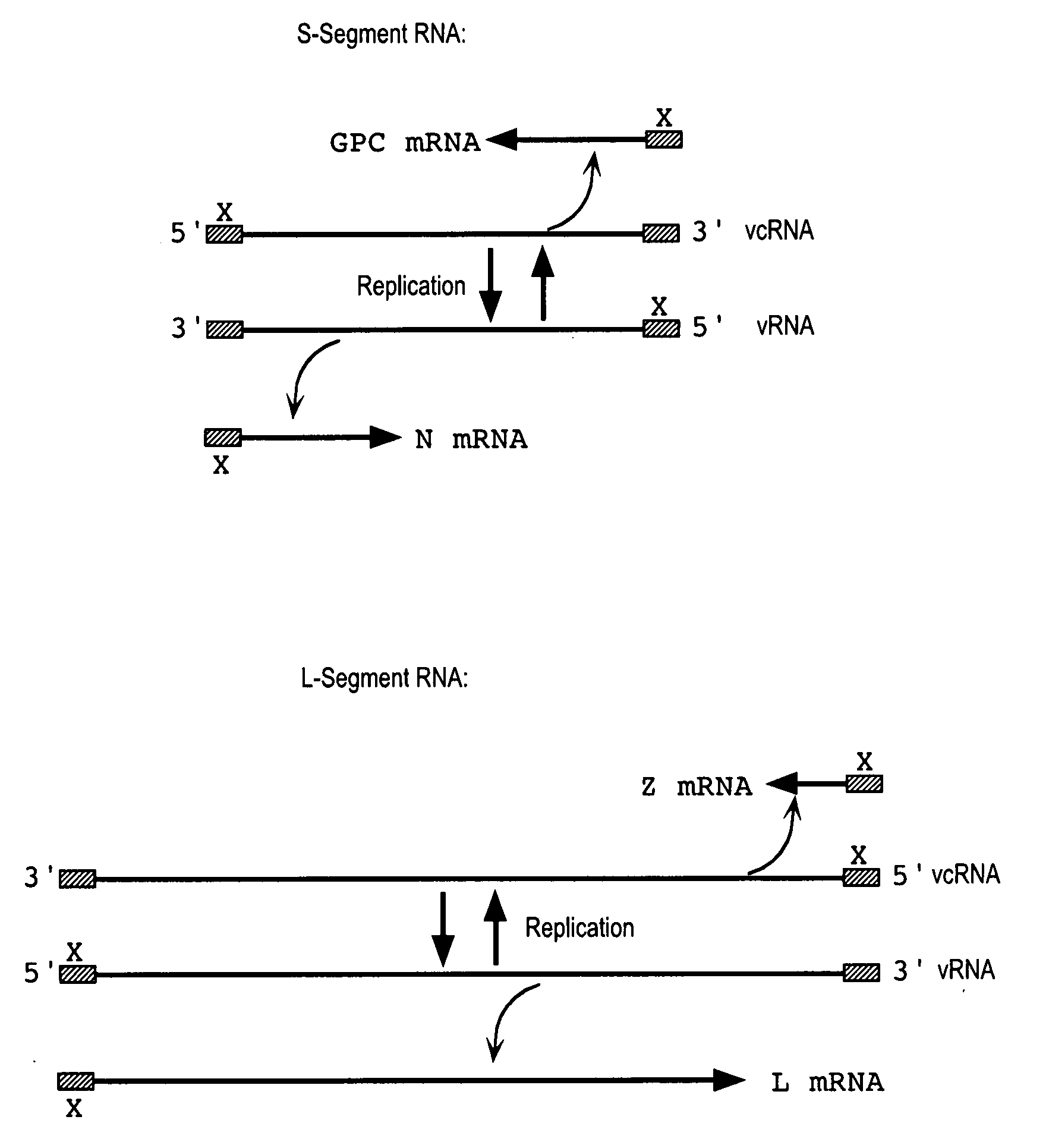
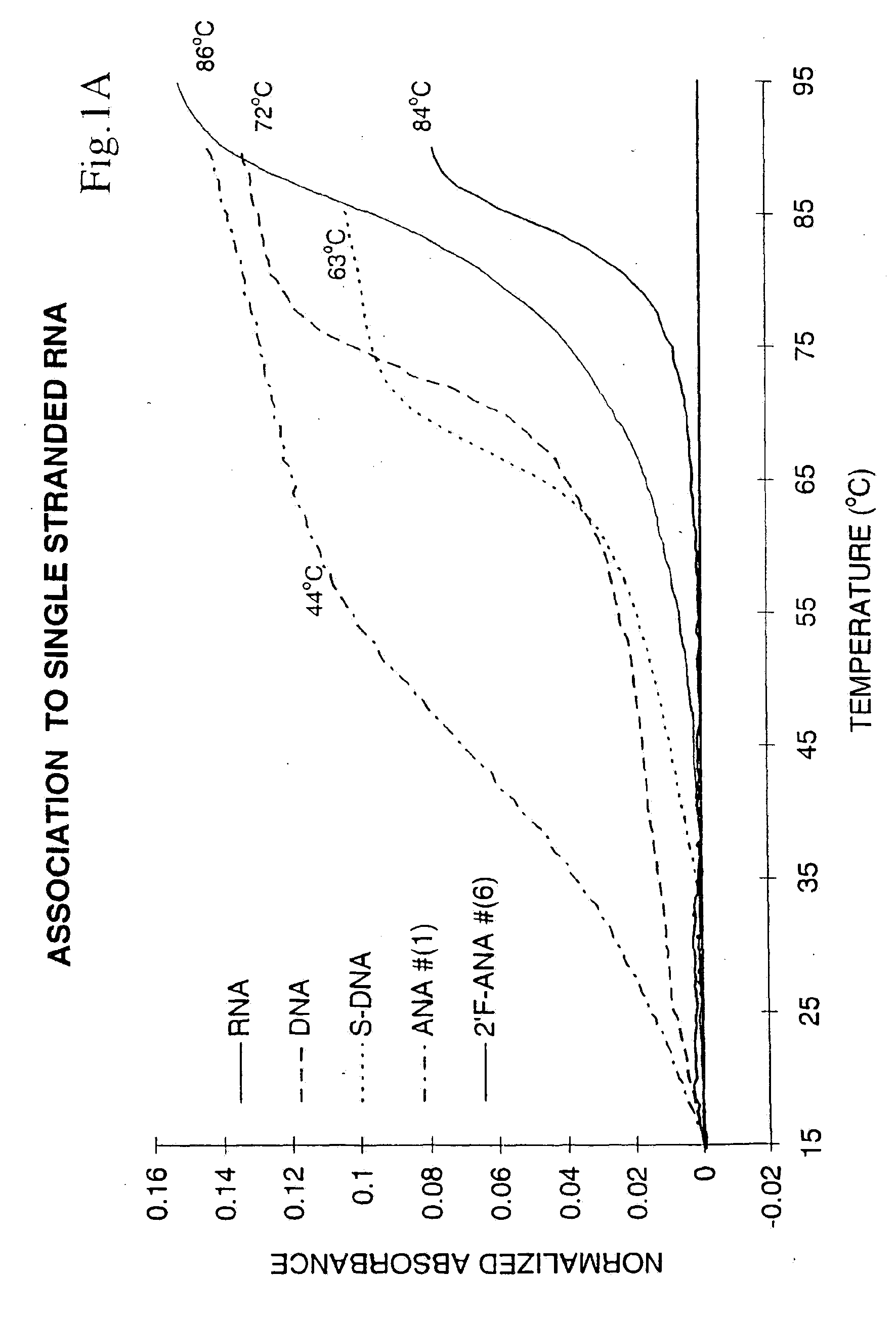
Complementary RNA A complementary RNA sequence that binds to a naturally occurring (sense) mRNA molecule, thus blocking its translation. The complementary RNA molecule is synthesized according to base-pairing rules, except that uracil is the complementary base to adenine.
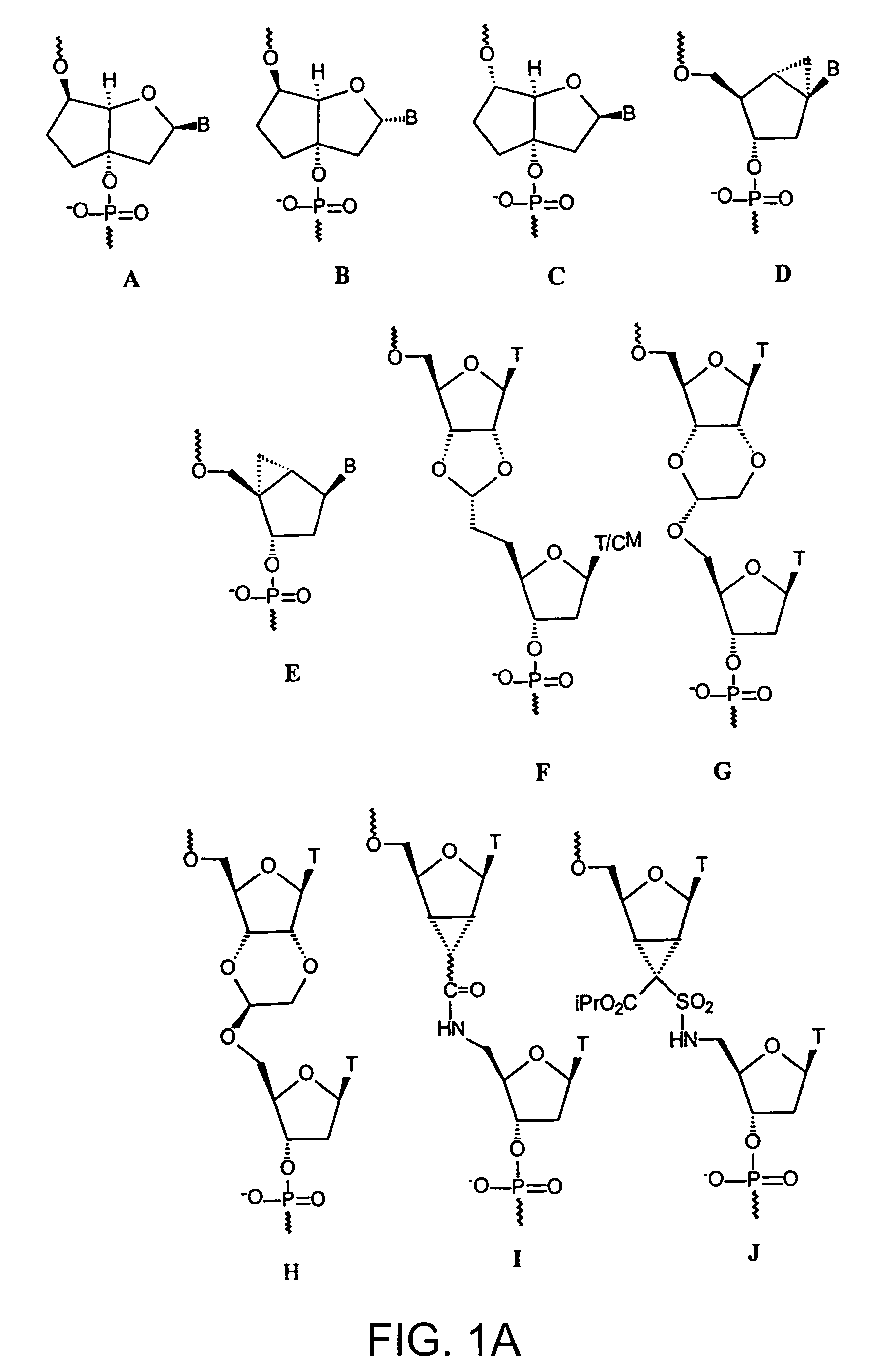
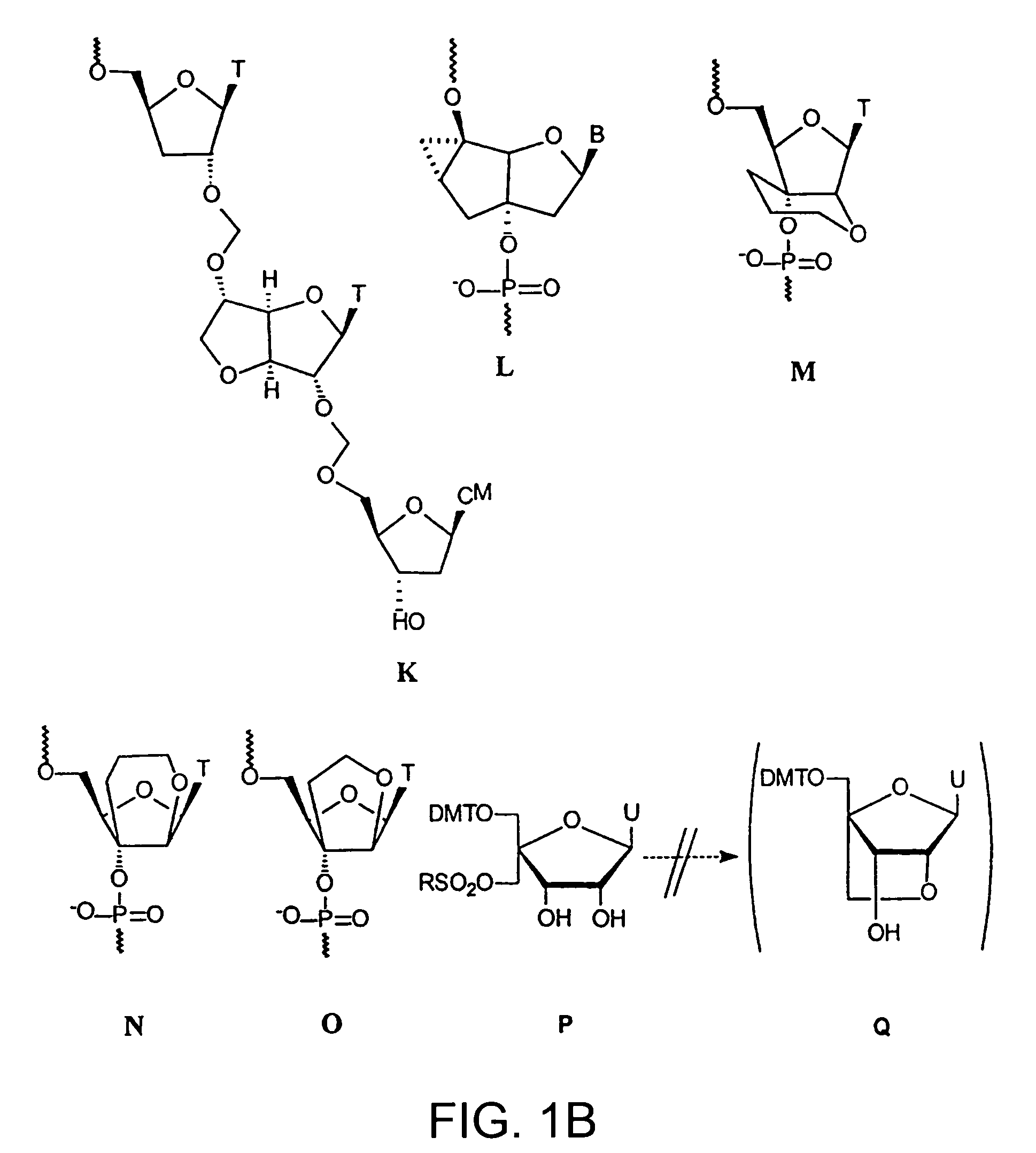
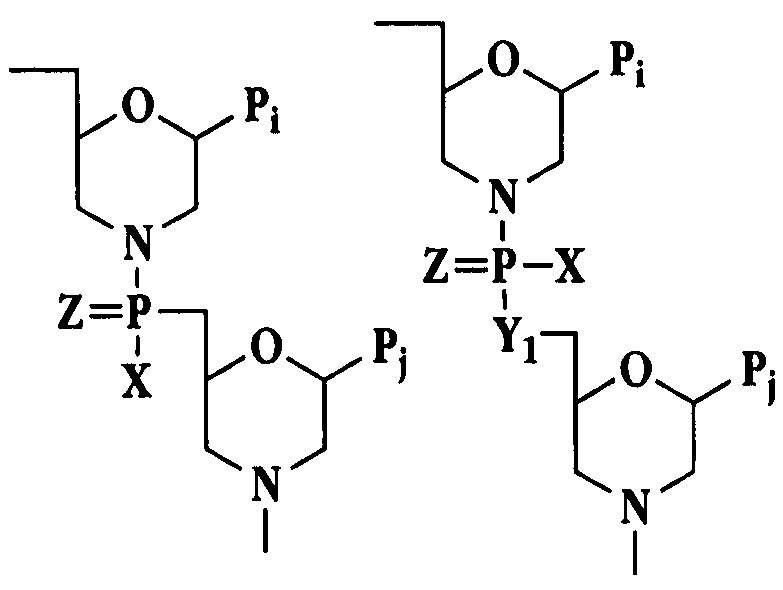
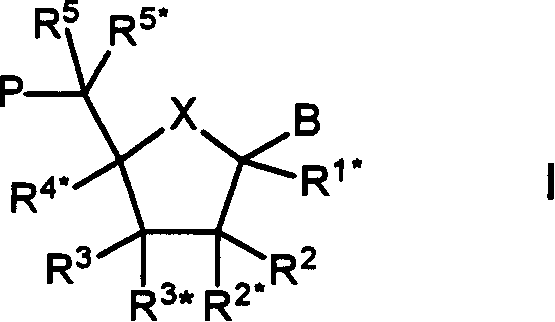
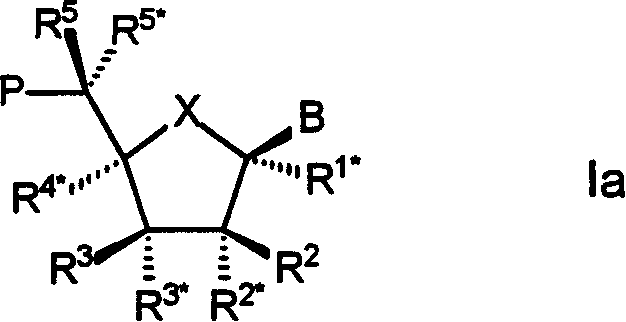
Oligonucleotide analogues
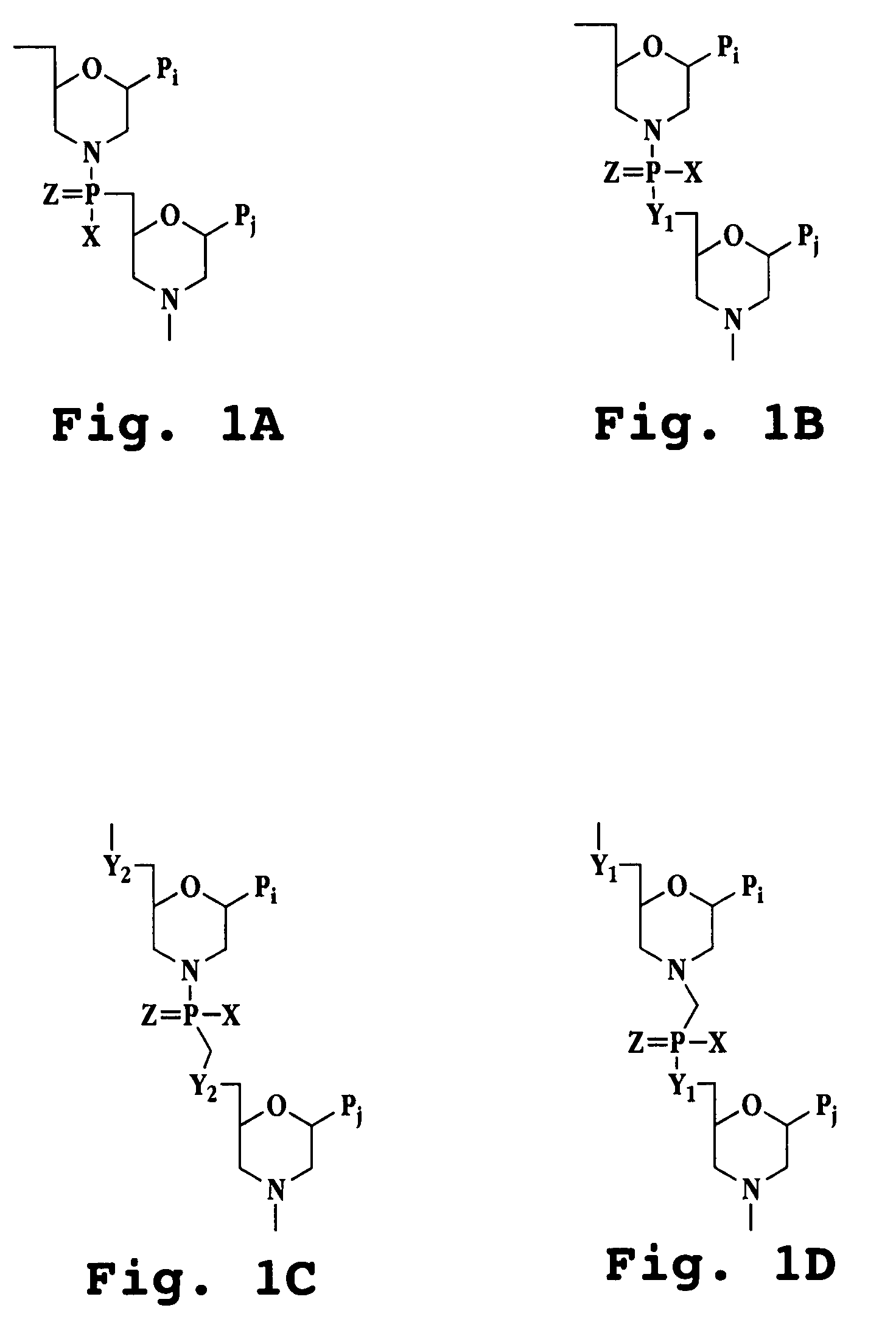
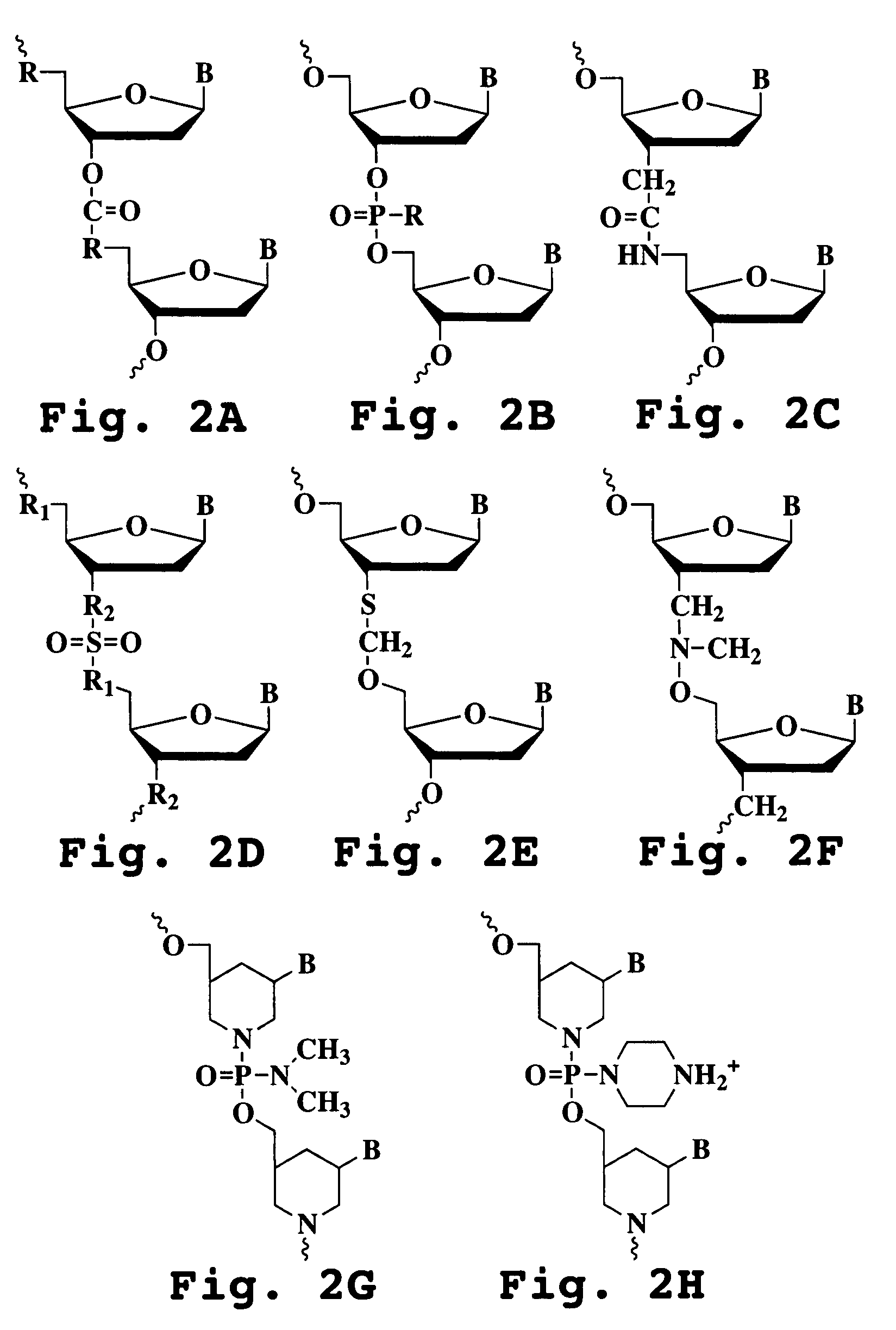
The present invention relates to novel bicyclic and tricyclic nucleoside and nucleotide analogues as well as to oligonucleotides comprising such elements. The nucleotide analogues, LNAs (Locked Nucleoside Analogues), are able to provide valuable improvements to oligonucleotides with respect to affinity and specificity towards complementary RNA and DNA oligomers. The novel type of LNA modified oligonucleotides, as well as the LNAs as such, are useful in a wide range of diagnostic applications as well as therapeutic applications. Among these can be mentioned antisense applications, PCR applications, strand displacement oligomers, as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, as nucleotide based drugs, etc. The present invention also relates to such applications.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Modified nucleotide compounds
ActiveUS7495088B1Increased nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyModified nucleosides
Disclosed is a nuclease resistant nucleotide compound capable of hybridizing with a complementary RNA in a manner which inhibits the function thereof, which modified nucleotide compound includes at least one component selected from the group consisting of MN3M, B(N)xM and M(N)xB wherein N is a phosphodiester-linked modified 2′-deoxynucleoside moiety; M is a moiety that confers endonuclease resistance on said component and that contains at least one modified or unmodified nucleic acid base; B is a moiety that confers exonuclease resistance to the terminus to which it is attached; and x is an integer of at least 2.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating arenavirus infection
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Arenaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Arenavirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 19 nucleotide region of the 5′-terminal regions of the viral RNA, viral complementary RNA and / or mRNA identified by SEQ ID NO:1.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Amplification method
InactiveUS20070105090A1Maintaining representationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTemplate switchingPolymerase
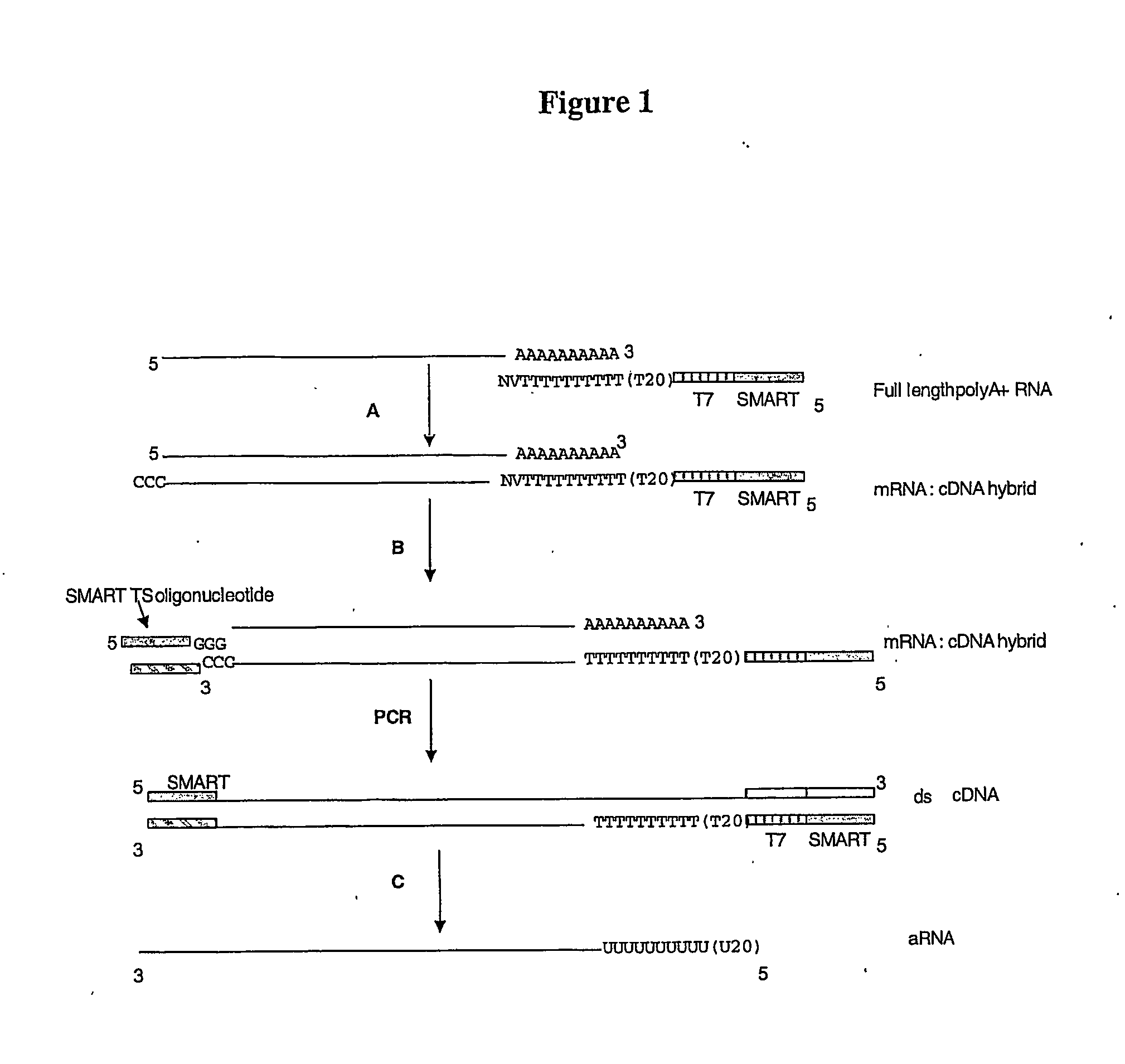
The present invention combines the use of template switching with nucleic acid amplification—such as PCR—to generate amplification products representative of an entire RNA population. An RNA polymerase promoter sequence allows transcription-based amplification to be performed on the derived amplification products such that antisense amplified RNA (aRNA) or complementary RNA (cRNA) is produced for subsequent downstream applications.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Oligonucleotide analogues
The present invention relates to novel bicyclic and tricyclic nucleoside and nucleotide analogues as well as to oligonucleotides comprising such elements. The nucleotide analogues, LNAs (Locked Nucleoside Analogues), are able to provide valuable improvements to oligonucleotides with respect to affinity and specificity towards complementary RNA and DNA oligomers. The novel type of LNA modified oligonucleotides, as well as the LNAs as such, are useful in a wide range of diagnostic applications as well as therapeutic applications. Among these can be mentioned antisense applications, PCR applications, strand displacement oligomers, as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, as nucleotide based drugs, etc. The present invention also relates to such applications.
Owner:EXIQON AS
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of a mutant gene
InactiveUS20050074757A1Inhibit expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsWild typeDouble stranded
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of a mutant gene, comprising a complementary RNA strand having a complementary region that is substantially complementary to a portion of the mutant gene, and which is partially complementary to the corresponding wild-type gene. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene. The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the target gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Arrays with modified oligonucleotide and polynucleotide compositions
InactiveUS20040121352A1Extend cycle timeMaintain structural integrityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleasePolynucleotide
The present invention provides arrays having associated modified oligonucleotides that selectively bind to DNA or RNA, methods of making such arrays, assays for using such arrays, and the like. In one embodiment, the arrays of the invention exhibit an increased binding affinity with complementary nucleic acids, and in particular with complementary RNA. In another embodiment, the associated nucleic acids of the array of the invention exhibit substantial acid resistance, allowing the arrays to be treated with low pH solutions. In another embodiment, the modified associated nucleic acids of the array of the invention exhibit substantial resistance to nuclease degradation.
Owner:LAKEWOOD AMEDEX
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of a mutant gene
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of a mutant gene, comprising a complementary RNA strand having a complementary region that is substantially complementary to a portion of the mutant gene, and which is partially complementary to the corresponding wild-type gene. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene. The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the target gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products
InactiveCN103820558AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMicrobiologyComplementary DNA
The invention relates to a gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products and a kit thereof. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe, wherein the oligonucleotide probe includes one or more selected from the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences selected from genes of a vibrio hollisae, a vibrio vulnificus, a vibrio cholera, a vibrio parahemolyticus, a vibrio harveyi, a vibrio alginolyticus, a vibrio furnissi, a vibrio mimicus and a vibrio damsel, 2) complementary DNA sequences of the DNA sequences selected in the DNA sequences in 1), 3) complementary RNA sequences of the selected DNA sequences in 1) or 2). The kit comprises the gene chips. The gene chip for detecting nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products and the kit thereof provided by the invention are used for detecting the nine pathogenicity vibrios in marine products, and have the advantages of simplicity in operation, good sensitivity and strong repeatability.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN INST OF CALIBRATION & TESTING FOR QUALITY & TECHNICAL SUPERVISION
Gene chip for detecting important pathogenic bacteria in aquatic product and kit thereof
InactiveCN102311993AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacillus cereusStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a gene chip for detecting important pathogenic bacteria in an aquatic product and a kit thereof. The gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe; the oligonucleotide probe comprises one or more of the following nucleotide sequences: (1) DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequences selected from proteus mirabilis 1, proteus vulgaris, salmonella, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio cholerae, Listeria monocytogenes, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus pyogenes, vibrio vulnificus, bacillus cereus cluster, Shigella and pathogenic Y. enterocolitica ail gene; (2) complementary DNA sequences of the DNA sequences selected in the (1); (3) complementary RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) sequences of the DNA sequences in the (1) or (2). The kit comprises the gene chip. The gene chip and the kit can be used for detecting the important pathogenic bacteria in an aquatic product, are convenient to operate, high in precision and strong in repeatability.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Compositions and methods for inhibiting expression of a mutant gene
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of a mutant gene, comprising a complementary RNA strand having a complementary region that is substantially complementary to a portion of the mutant gene, and which is partially complementary to the corresponding wild-type gene. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene. The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the target gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Method and apparatus for detection or identification of DNA
InactiveUS20050048501A1High sensitivityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNAEnzyme
DNA is detected using complementary RNA probes and an enzyme that attacks and hydrolyzes the RNA probes only when it has hybridized with target DNA. A low concentration of target DNA can therefore successively hydrolyze a larger amount of RNA whose loss may then be detected to indirectly determine the presence of the target DNA.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Antisense antiviral compound and method for treating arenavirus infection
ActiveUS20070274957A1Avoid virus infectionAvoid infectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsArenaviridaeCompound (substance)
The invention provides antisense antiviral compounds and methods of their use and production in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Arenaviridae family and in the treatment of a viral infection. The compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of Arenavirus infection in a mammal. The antisense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides have a sequence of 12-40 subunits, including at least 12 subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with viral RNA sequences within a 19 nucleotide region of the 5′-terminal regions of the viral RNA, viral complementary RNA and / or mRNA identified by SEQ ID NO:1.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Gene chip for evaluating transport stress model and application of gene chip for evaluating transport stress model
InactiveCN103031374AShorten the timeSave moneyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganismDeoxyribose
The invention relates to a gene chip for evaluating a transport stress model and an application of the gene chip for evaluating the transport stress model. The gene chip comprises one or a plurality of probes used for detecting ribos nucleic acid (RNA), complementary RNA (cRNA) or complementary deoxyribose nucleic acid (cDNA) which is generated by the following genes: Gdnf, Lifr, Ppp3rl, Sphkl, B4galtl, Phldal, Il24, Adm, Gsdmal, Acvrl, Naip2, Aqp2, Ptprc, Bcl2l1, Rela, Ctnnb1, Pdcd6ip, Tgfbr1, Hmox1, Sort1, Tpt1, Aldh1a1, Actc1, Rhot2 and Bax. According to the chip, the typical variations of indexes after livestock and poultry are subjected to transport stress are comprehensively evaluated in a multilayer multi-target point manner through once real-time synchronous high throughput detection of the variation of nerve-immunity-internal secretion indexes, and guiding significance in livestock and poultry organism conditions and production performances during a transport evaluating process is obtained. The chip not only has the characteristics of sample saving and time saving in new drug research, but also saves money and has an important practical meaning.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compositions and Methods for Inhibiting Expression of a Mutant Gene
The present invention relates to a double-stranded ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) for inhibiting the expression of a mutant gene, comprising a complementary RNA strand having a complementary region that is substantially complementary to a portion of the mutant gene, and which is partially complementary to the corresponding wild-type gene. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the dsRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The pharmaceutical compositions are useful for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as for treating diseases caused by expression of the target gene. The invention also relates to methods for inhibiting the expression of a target mutant gene, as well as methods for treating diseases caused by the expression of the target gene.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
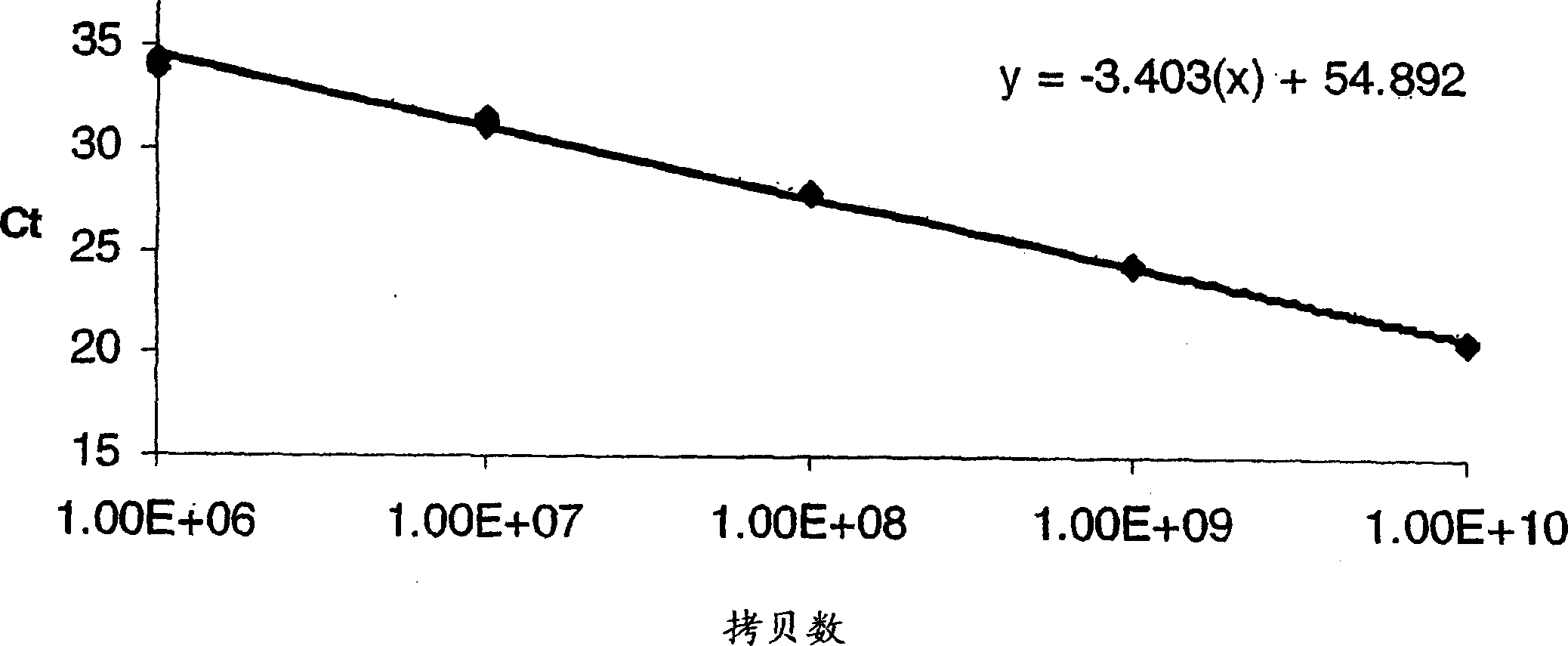
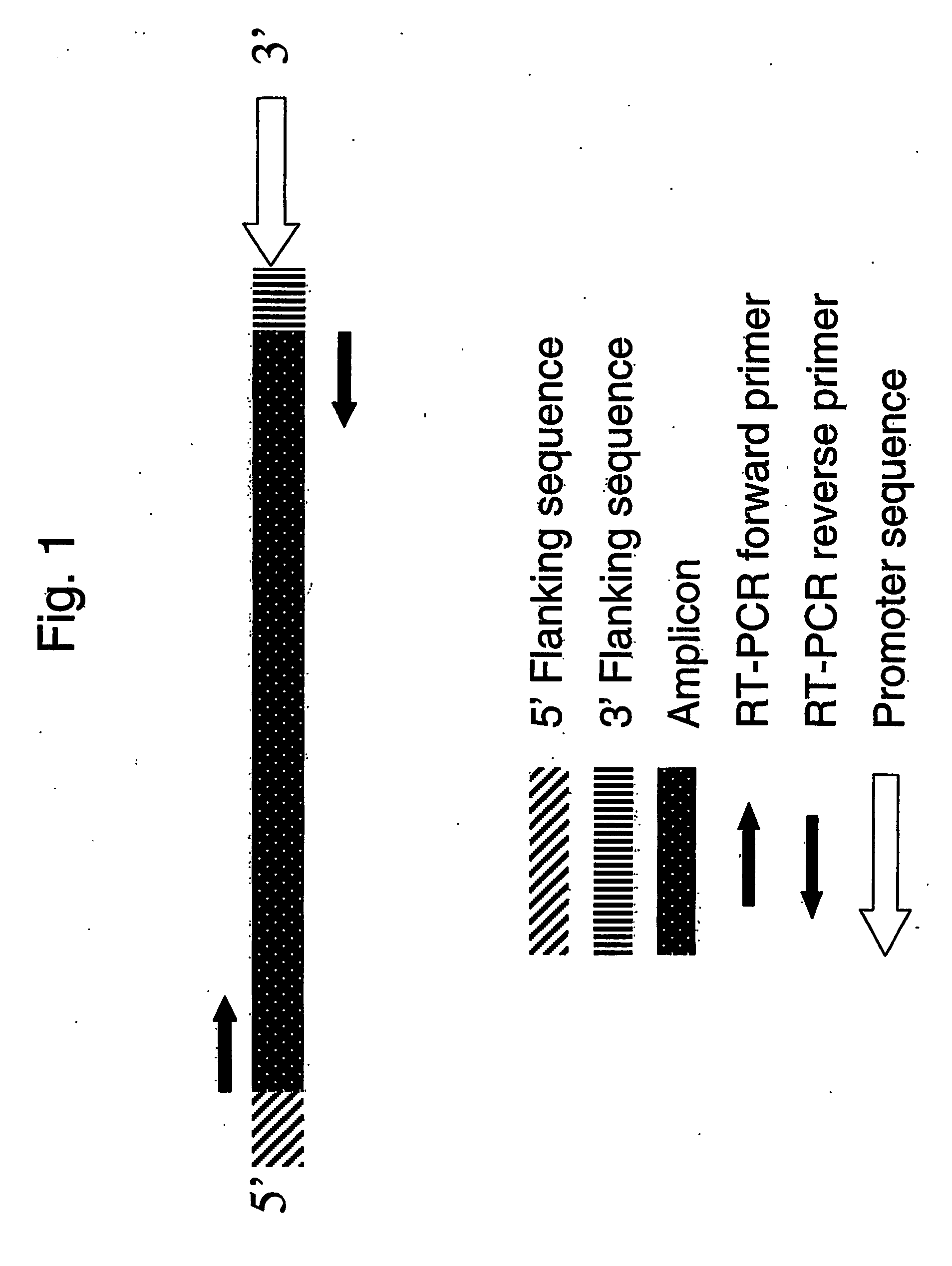
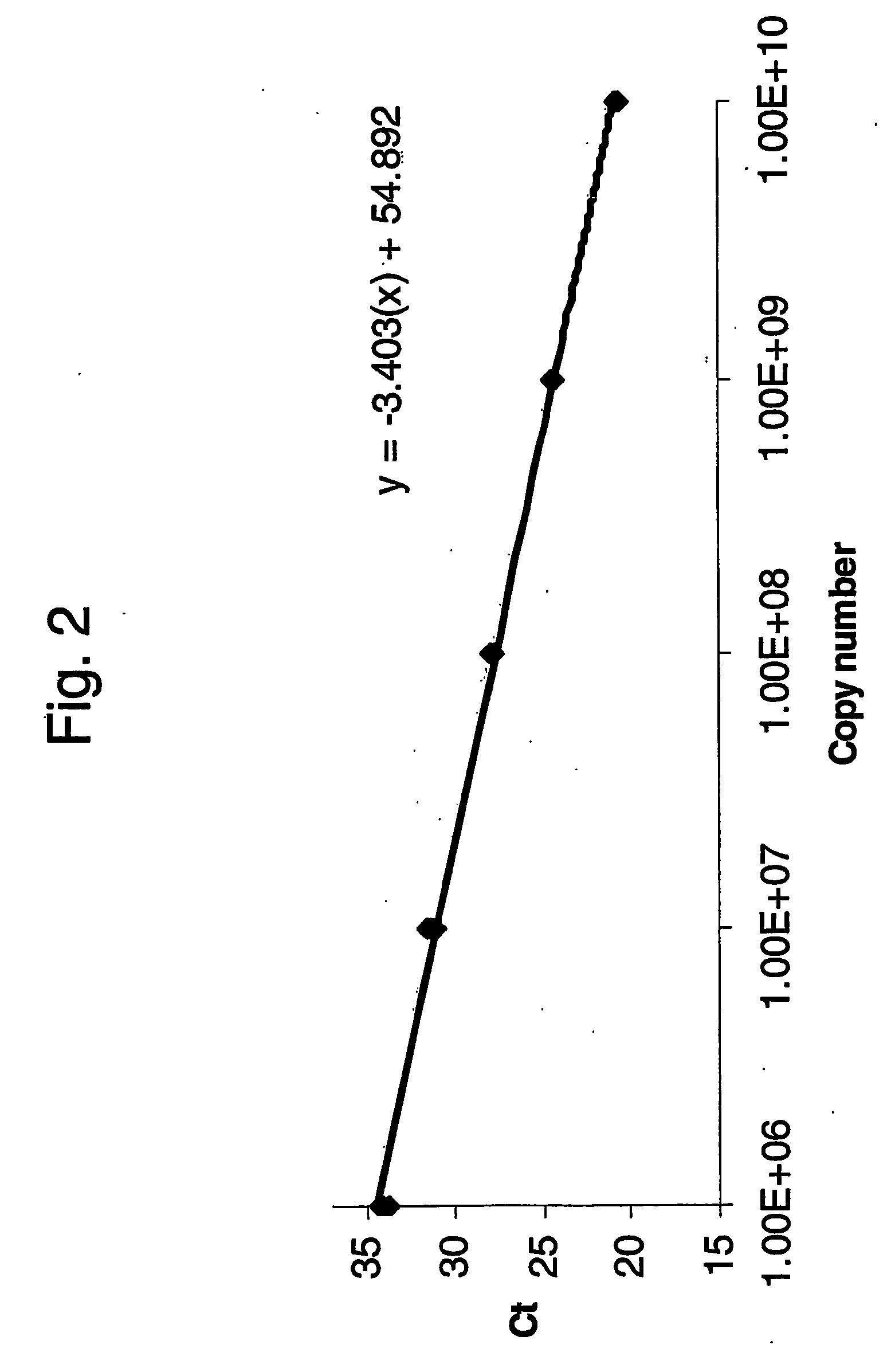
Absolute quantitation of nucleic acids by RT-PCR
InactiveCN1759190AMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical preparationsBioinformaticsComplementary rna
A method for obtaining a cRNA for use in generating calibration data, e.g., a standard curve, for absolute quantitation of RNA by RT-PCR is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: providing a synthetic oligonucleotide comprising an amplicon, a promoter sequence located 3' relative to the amplicon; synthesizing complementary RNA (cRNA) by in vitro transcription of the synthetic oligonucleotide; quantitatively assaying the cRNA by an independent method; and generating calibration data using a known quantity of the cRNA.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Absolute quantitation of nucleic acids by rt-pcr
InactiveUS20060149484A1Microbiological testing/measurementMedical preparationsBioinformaticsComplementary rna
A method for obtaining a cRNA for use in generating calibration data, e.g., a standard curve, for absolute quantitation of RNA by RT-PCR is disclosed. The method includes the steps of: providing a synthetic oligonucleotide comprising an amplicon, a promoter sequence located 3′ relative to the amplicon; synthesizing complementary RNA (cRNA) by in vitro transcription of the synthetic oligonucleotide; quantitatively assaying the cRNA by an independent method; and generating calibration data using a known quantity of the cRNA.
Owner:BIOGEN IDEC MA INC
Chimeric antisense oligonucleotides of arabinofuranose analogue and deoxyribose nucleotides
ActiveUS8178348B2Inhibit productionEnhances cellular uptake of such oligonucleotide.Organic active ingredientsSugar derivatives3-deoxyriboseMessenger RNA
The present invention relates to novel oligonucleotide chimera used as therapeutic agents to selectively prevent gene transcription and expression in a sequence-specific manner. In particular, this invention is directed to the selective inhibition of protein biosynthesis via antisense strategy using oligonucleotides constructed from arabinonucleotide or modified arabinonucleotide residues, flanking a series of deoxyribose nucleotide residues of variable length. Particularly this invention relates to the use of antisense oligonucleotides constructed from arabinonucleotide or modified arabinonucleotide residues, flanking a series of deoxyribose nucleotide residues of variable length, to hybridize to complementary RNA such as cellular messenger RNA, viral RNA, etc. More particularly this invention relates to the use of antisense oligonucleotides constructed from arabinonucleotide or modified arabinonucleotide residues, flanking a series of deoxyribose nucleotide residues of variable length, to hybridize to and induce cleavage of (via RNaseH activation) the complementary RNA.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Method for detecting (CAG)n repeated sequence by utilizing RNase H
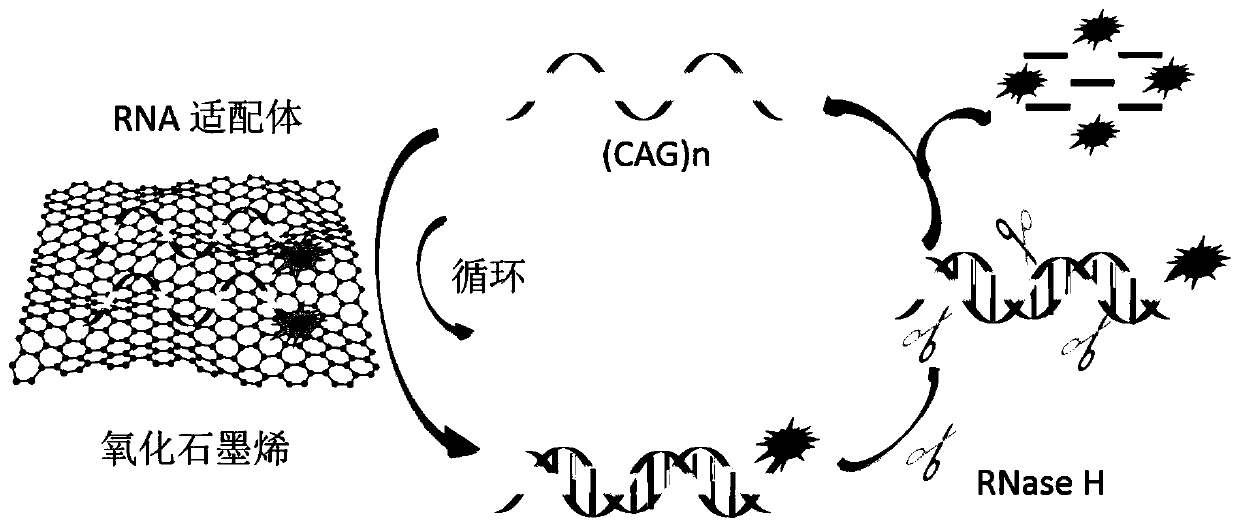
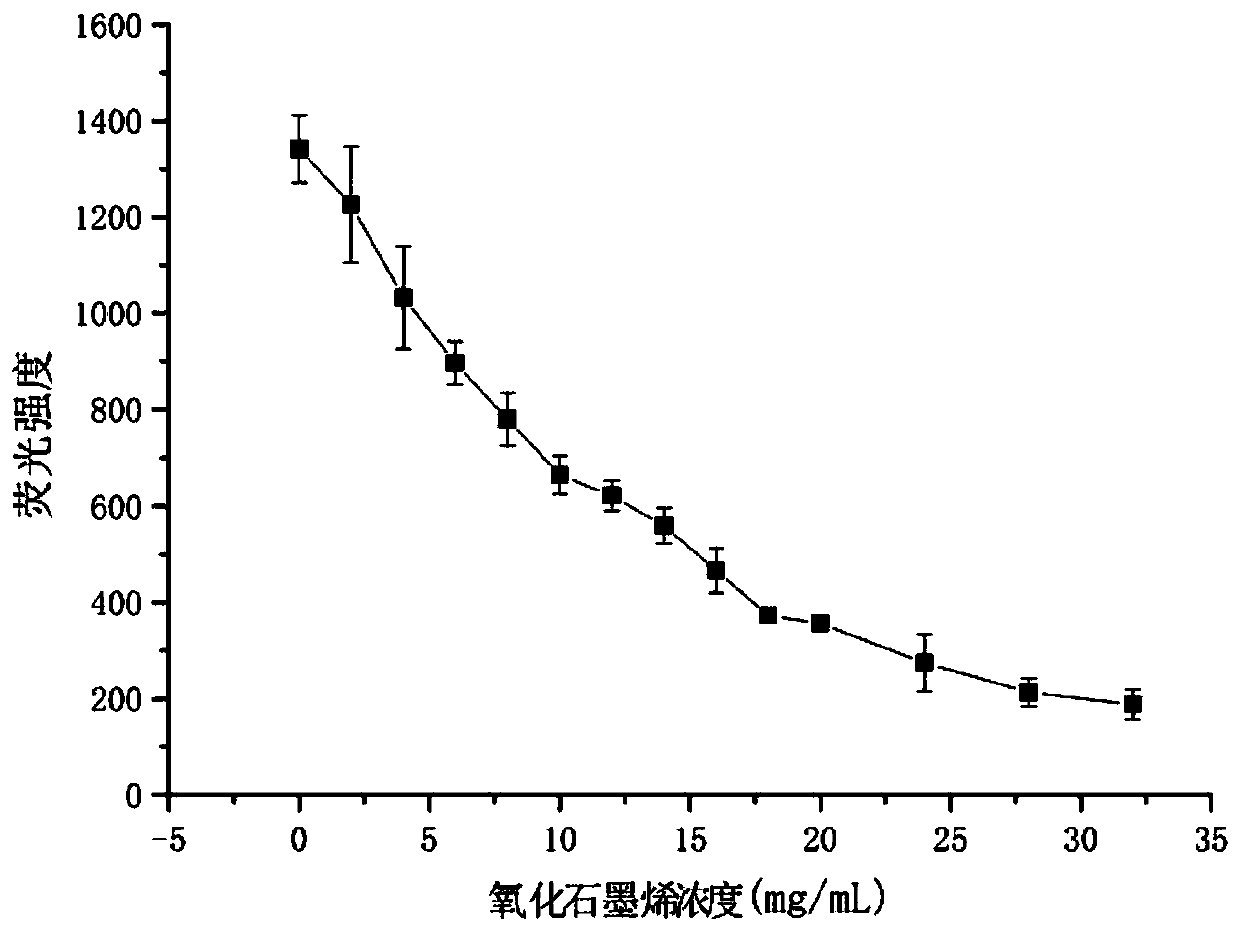
ActiveCN110055305AIncrease profitHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEnzyme digestionSpectrofluorometer
The invention discloses a method for detecting a (CAG)n repeated sequence by utilizing RNase H and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the method, a (CAG)n is mixed witha fluorescein-labeled complementary RNA aptamer; enzyme digestion reaction of restrictive endonuclease RNase H is executed: the mixed solution of (CAG)n and the aptamer with a solution of restrictiveendonuclease RNase H uniformly mixed for incubation; fluorescence detection is executed: graphene oxide is added into the solution subjected to the enzyme digestion reaction, uniformly mixing is executed for incubation to obtain a solution to be detected, and the fluorescence intensity is detected by using a fluorescence spectrophotometer. The method is simple to operate, rapid in detection and high in sensitivity, and the detection limit of (CAG)n can reach 1.12*10-10 mol / L, and it is detected that the DNA sequence containing (CAG)n has very high specificity.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Microwave-driven rna polymerization by rna polymerases of caliciviruses
InactiveCN103119177APromote polymerizationOvercoming Degradation DefectsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSingle strandPolynucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for polymerising a complementary RNA strand on a single-stranded polynucleotide template comprising the step of irradiating a composition containing said template and an RNA polymerase of a virus of the Caliciviridae family under RNA polymerisation conditions in the presence or absence of a primer hybridised to the template, with an effective amount of microwave energy. Further subject matter of the invention relates to a method for transferring one or more ribonucleotides to the 3' end of a single-stranded polynucleotide template comprising the step of irradiating a composition containing an RNA polymerase of a virus of the Caliciviridae family in the presence of rATP or rGTP or rUTP or rCTP or a modified or labelled analogue thereof with an effective amount of microwave energy.
Owner:RIBOXX
RNA molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140316126A1High expressionSugar derivativesVector-based foreign material introductionNon-coding RNANucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a method of designing a short RNA molecule to increase the expression of a target gene in a cell through the down-regulation of a non-coding RNA transcript, said method comprising the steps of: a) obtaining the nucleotide sequence of the coding strand of the target gene, at least between 200 nucleotides upstream of the gene's transcription start site and 200 nucleotides downstream of the gene's transcription start site; b) determining the reverse complementary RNA sequence to the nucleotide sequence determined in step a); and c) designing a short RNA molecule which is the reverse complement or has at least 80% sequence identity with the reverse complement of a region of the sequence determined in step b); wherein said method does not include a step in which the existence of said non-coding RNA transcript is determined; and to such short RNA molecules and uses thereof.
Owner:MINA THERAPEUTICS
Gene chip and test kit for detecting important pathogenic bacteria in aquatic products
InactiveCN101724686BImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisVirulent characteristicsStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a gene chip and a test kit for detecting important pathogenic bacteria in aquatic products, wherein the gene chip comprises a solid matrix and an oligonucleotide probe composed of one or more serials selected from the following serials: (1) DNA serials selected from the spacers of 16S-23rS DNA of salmonella, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholerae, Listeria monocytogenes, staphylococcus aureus, Suppurative streptococcus, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus Vulgaris and Paneth Proteus, and ipaH Virulence gene of Shigella; (2) complement DNA serials of the DNA serials selected from (1); (3) complement RNA serials of the DNA serials selected from (1) or (2). The chip and the test kit comprise simple and convenient operation, high veracity and strong repeatability in detecting the important pathogenic bacteria in aquatic products.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Method for treating Usher syndrome and composition thereof
PendingCN113122577ATreatment advantageGuaranteed functionSenses disorderNervous system cellsBase JDisease
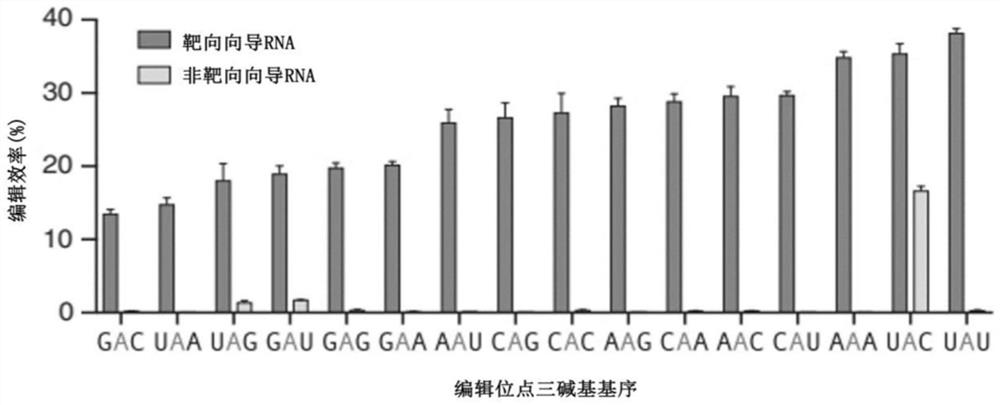
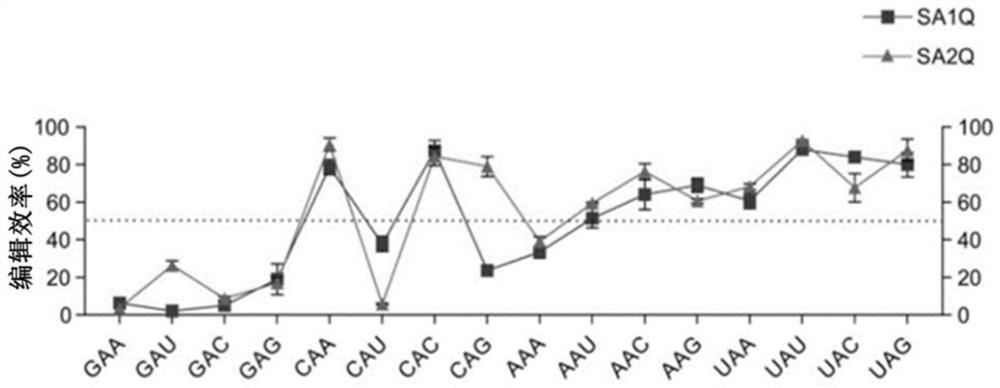
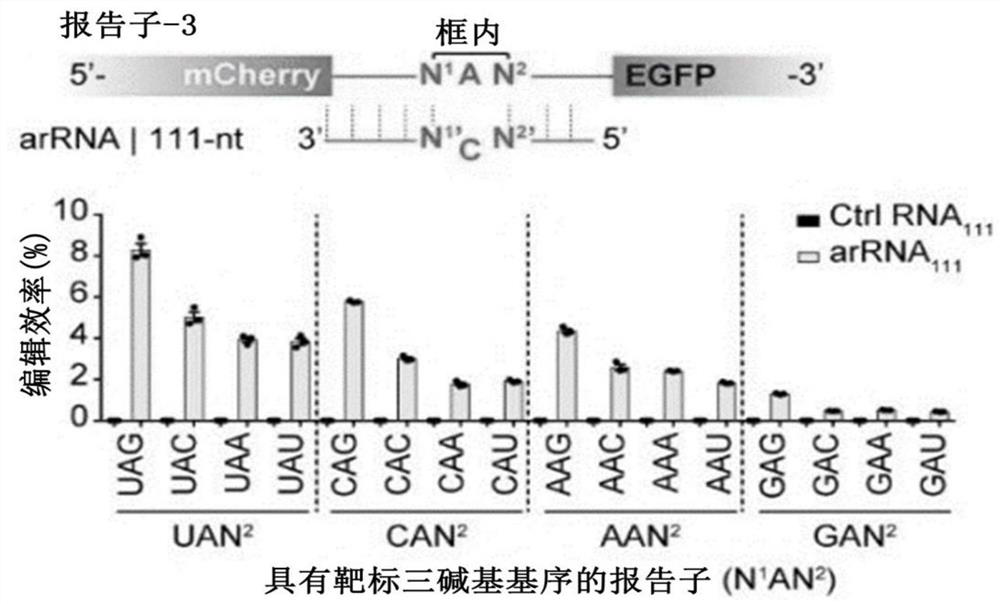
The invention relates to a method for targeted editing of target RNA containing G-to-A mutation in a USH2A gene transcript based on a LEAPER technology, comprising the following steps that adenosine deaminase recruitment RNA (arRNA) for editing the target RNA or a construct encoding the arRNA is introduced into cells, the arRNA comprises a complementary RNA sequence hybridized with the target RNA, the arRNA can recruit adenosine deaminaseacting on RNA (ADAR) so as to deaminize target adenosine in the target RNA, in-vivo editing from A to I bases on RNA is safely and effectively carried out, pathogenic mutation sites are repaired, and the purpose of treating diseases such as Usher syndrome is achieved.
Owner:EDIGENE INC
gi Genotype Norovirus Reverse Transcription Rolling Circle Amplification Method
InactiveCN104313187BStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideArcobacter
The invention relates to a GI genome type norovirus reverse transcription roll loop amplification detection method. A gene chip comprises a solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises one or more selected from the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences selected from genes of vibrio hollisae, vibrio vulnificus, vibrio cholera, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio harveyi, vibrio alginolyticus, vibrio furnissii, vibrio mimicus and vibrio damsel; 2) complementary DNA sequences of the DNA sequences selected from the 1); 3) complementary DNA sequences of the DNA sequences selected from 1) or 2). A kit comprises the gene chip. The gene chip and the kit provided by the invention are used for detecting nine pathogenic vibrios in ocean products, and are simple and convenient to operate, good in sensitivity and high in repeatability.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN INST OF CALIBRATION & TESTING FOR QUALITY & TECHNICAL SUPERVISION
Improved RNA editing method
PendingCN113897359AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenomic cloneComplementary rna
The invention relates to a method of editing a target RNA at a position of a target residue in a host cell. The method comprises the steps: introducing a deaminase recruitment RNA (arRNA) or a construct coding the arRNA into the host cell, wherein the arRNA comprises a complementary RNA sequence that hybridizes to the target RNA, wherein the target residue is located in a tribase motif, the tribase motif comprises a 5'-nearest neighbor residue of the target residue in the target RNA (upstream residue), the target residue, and a 3'-nearest neighbor residue of the target residue in the target RNA (downstream residue), wherein the tribase motif is not UAG, and wherein the complementary RNA sequence comprises a mismatch directly opposed to the upstream or downstream residue of the target RNA. The invention also relates to the arRNA used in the method, RNA obtained through the RNA editing method, the host cell containing the RNA and application of the RNA editing method in treatment of diseases.
Owner:EDIGENE THERAPEUTICS (BEIJING) INC
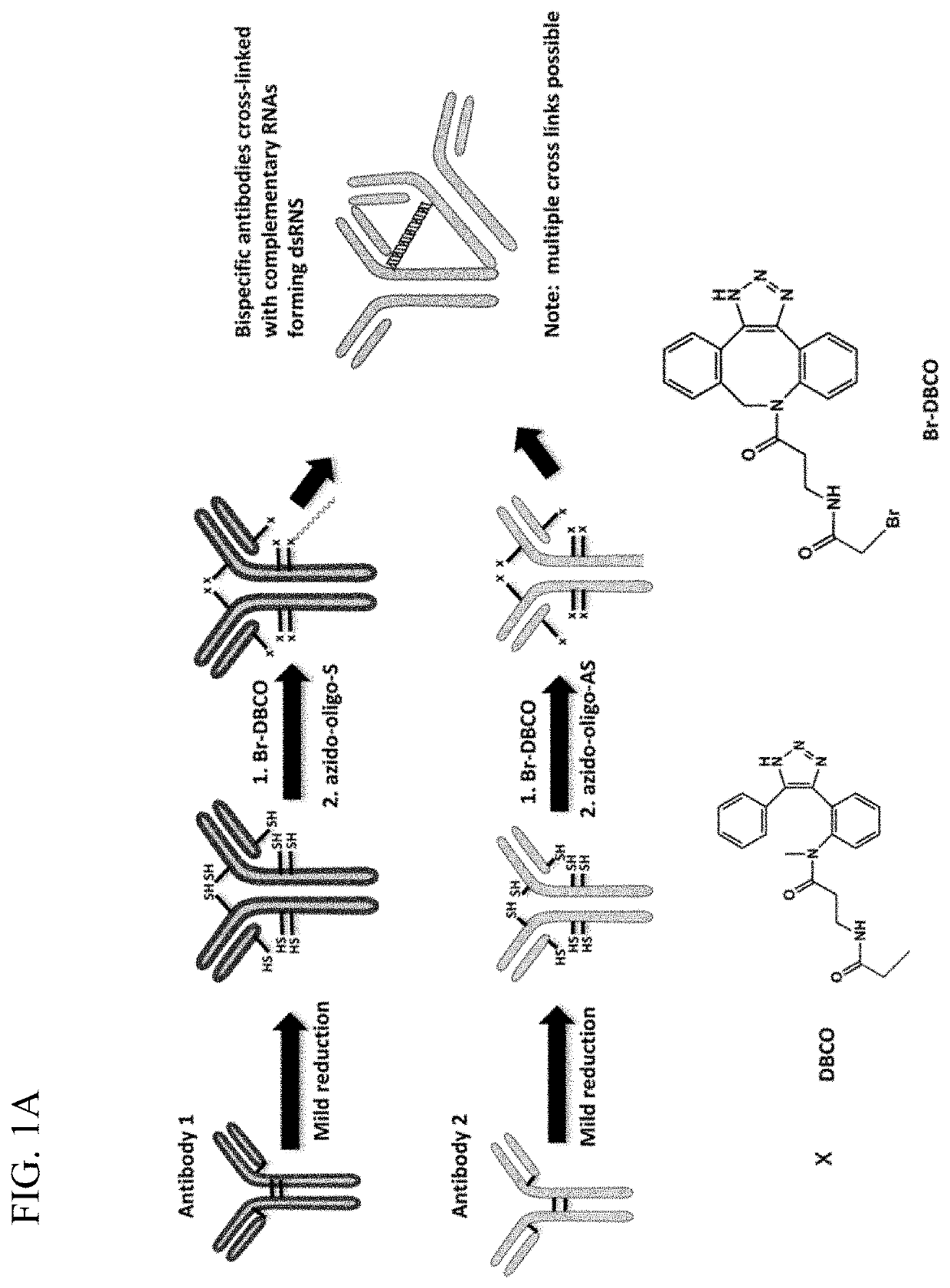
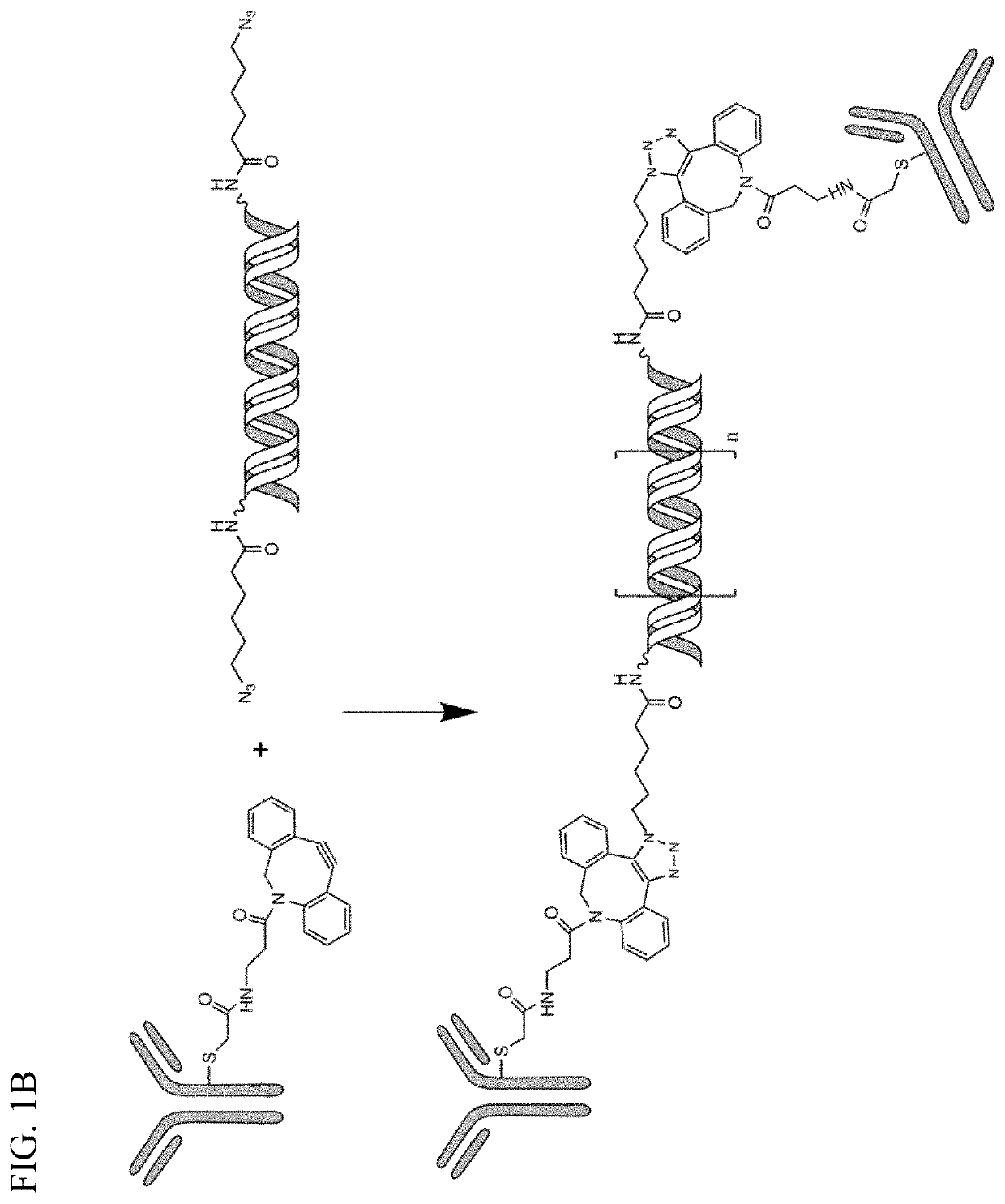
Complementary RNA linked bispecific t-cell engaging antibodies
PendingUS20220119552A1Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRibonucleotide bindingAutoimmune condition
The compositions and methods provide herein include, inter alia, antibodies attached to single-stranded oligoribonucleotides. Two antibodies are capable of forming complexes in vivo through hybridization of the respective complementary oligoribonucleotides they are bound to. For example, a first antibody bound to a first oligoribonucleotide through a first chemical linker may be administered to a subject, bind to a cell surface antigen in vivo and subsequently form an antibody complex in vivo with a second antibody bound to a second oligoribonucleotide through a second chemical linker, through complementary base-pairing between the first and the second oligoribonucleotide. The compositions and methods provided herein are, inter alia, useful for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, for example, the treatment of cancer or autoimmune disease.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Bi-and tri-cyclic nucleoside, nucleotide and oligonucleotide analoguse
The present invention relates to novel bicyclic and tricyclic nucleoside and nucleotide analogues as well as to oligonucleotides comprising such elements. The nucleotide analogues, LNAs (Locked Nucleoside Analogues), are able to provide valuable improvements to oligonucleotides with respect to affinity and specificity towards complementary RNA and DNA oligomers. The novel type of LNA modified oligonucleotides, as well as the LNAs as such, are useful in a wide range of diagnostic applications as well as therapeutic applications. Among these can be mentionned antisense applications, PCR applications, strand displacement oligomers, as substrates for nucleic acid polymerases, as nucleotide based drugs, etc. The present invention also relates to such applications.
Owner:EXIQON AS
RNA molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20170107514A1High expressionSystems biologyVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideNon-coding RNA
The invention relates to a method of designing a short RNA molecule to increase the expression of a target gene in a cell through the down-regulation of a non-coding RNA transcript, said method comprising the steps of: a) obtaining the nucleotide sequence of the coding strand of the target gene, at least between 200 nucleotides upstream of the gene's transcription start site and 200 nucleotides downstream of the gene's transcription start site; b) determining the reverse complementary RNA sequence to the nucleotide sequence determined in step a); and c) designing a short RNA molecule which is the reverse complement or has at least 80% sequence identity with the reverse complement of a region of the sequence determined in step b); wherein said method does not include a step in which the existence of said non-coding RNA transcript is determined; and to such short RNA molecules and uses thereof.
Owner:MINA THERAPEUTICS
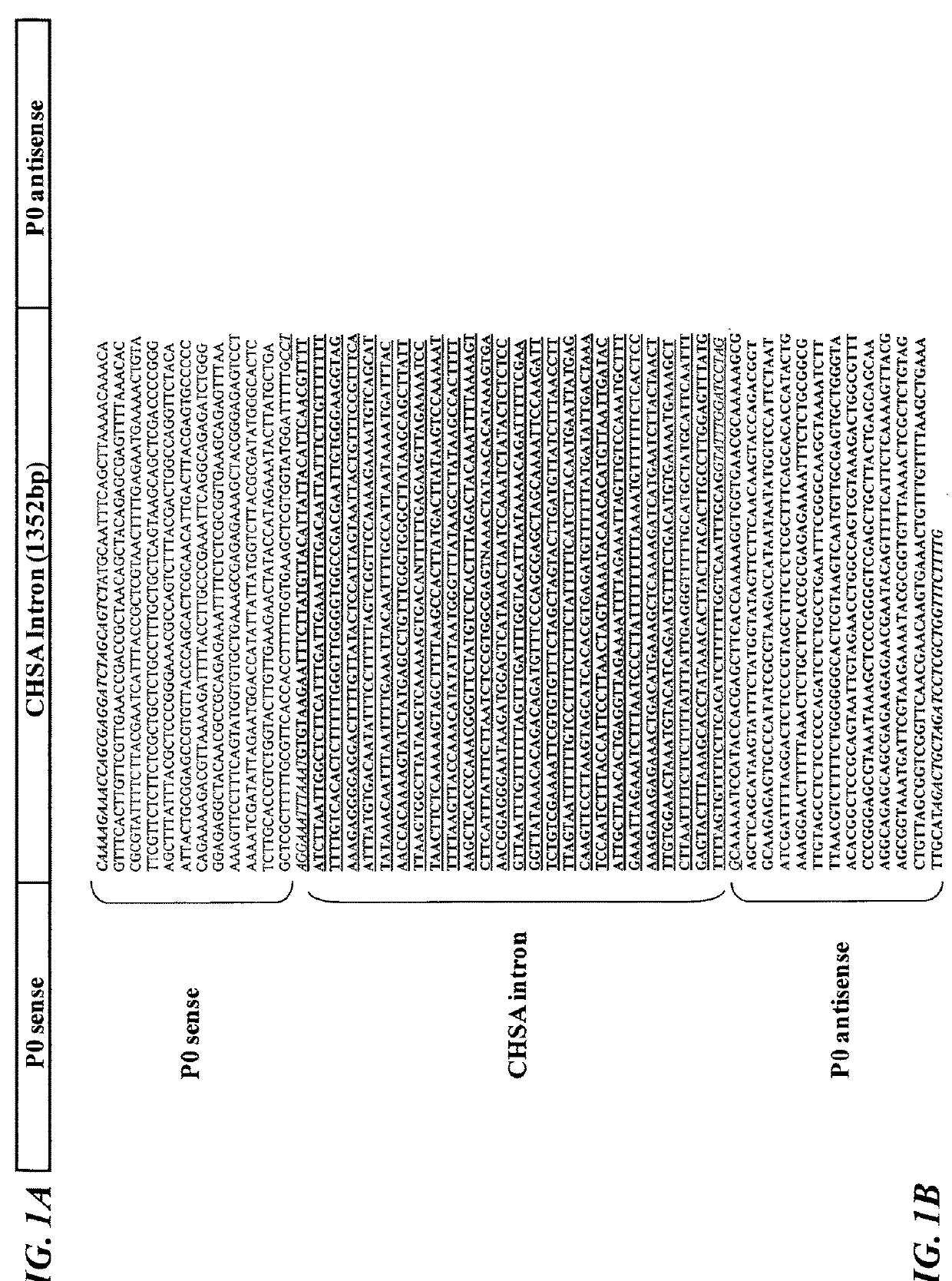
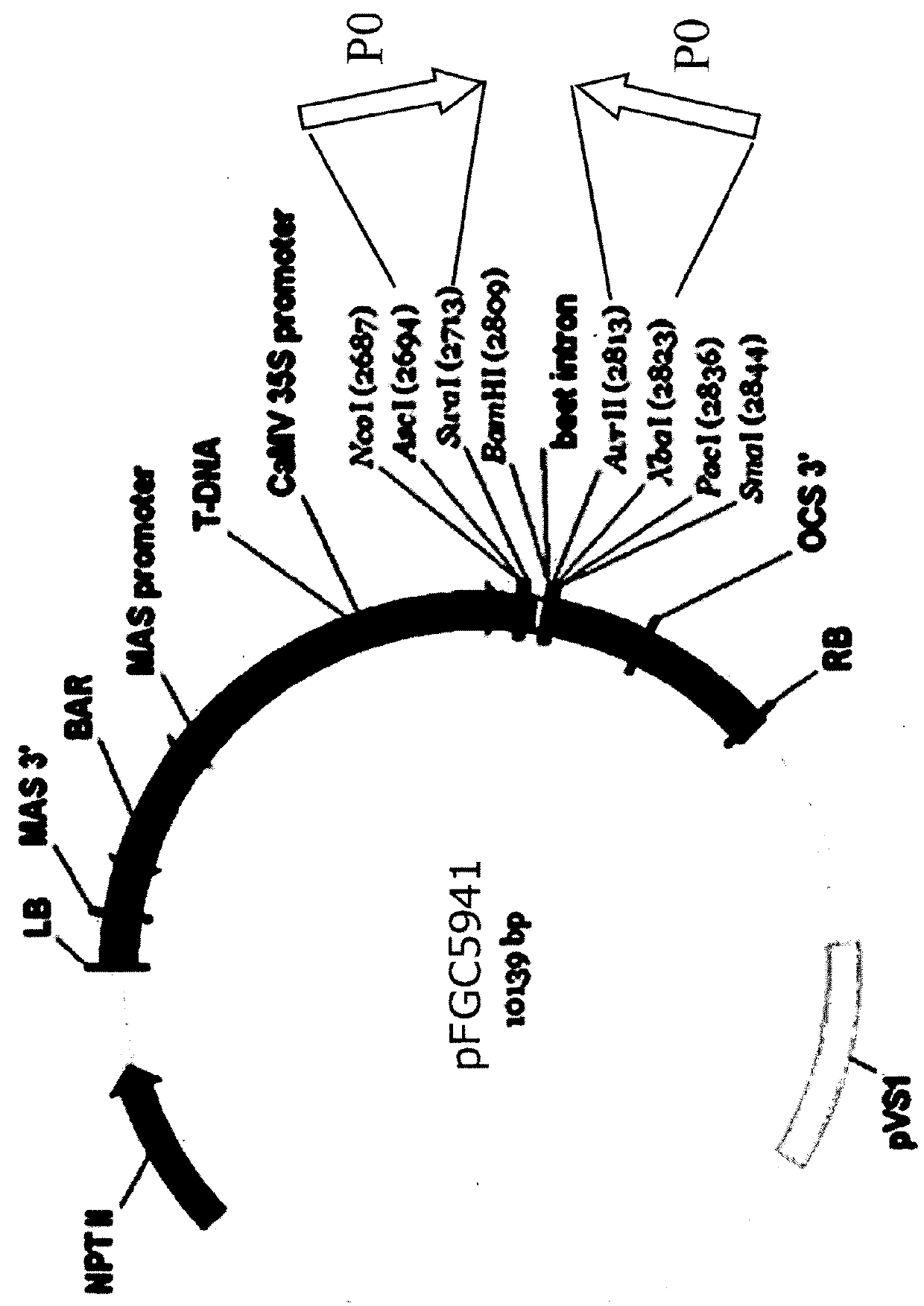
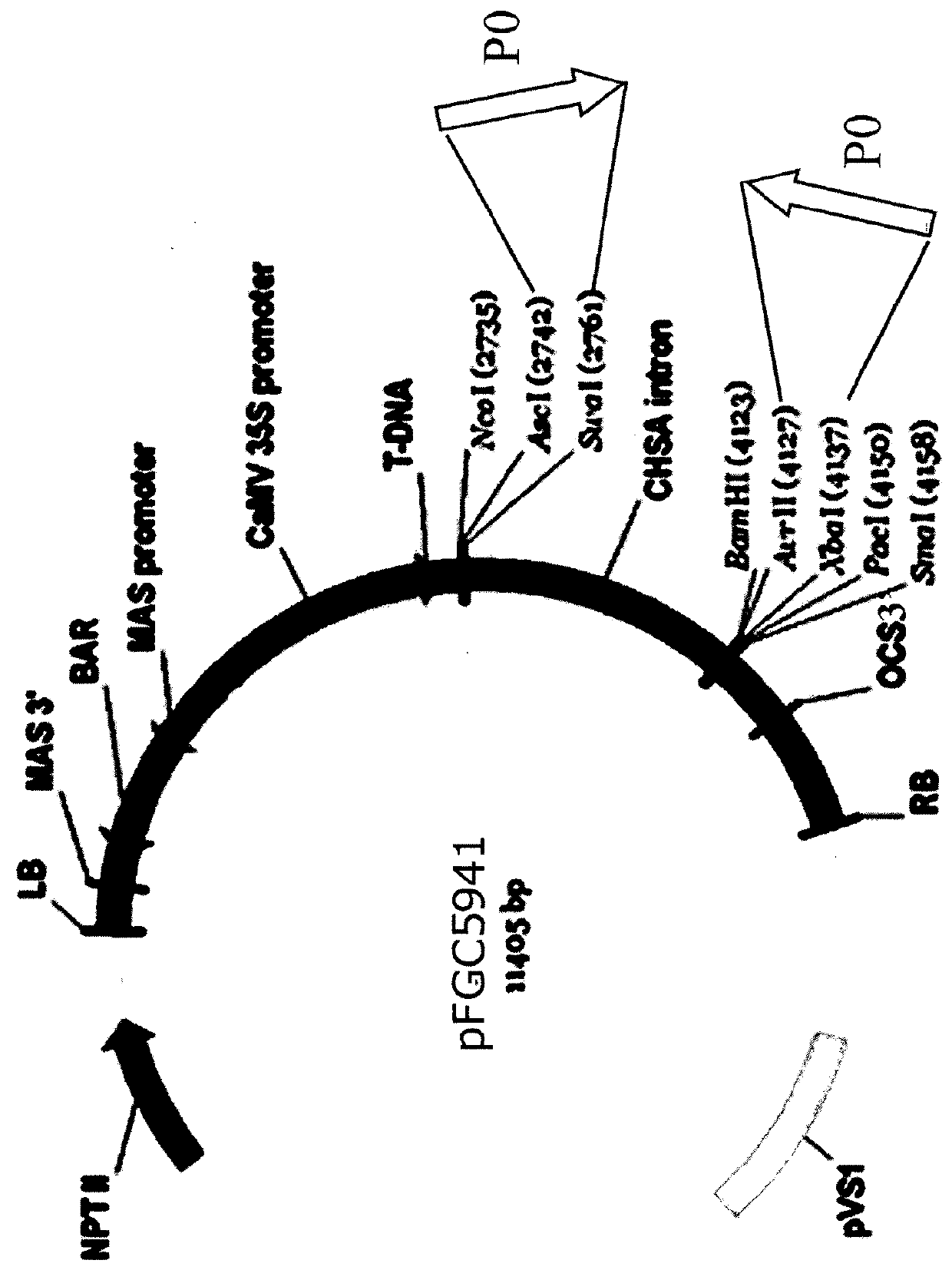
P0 gene silencing constructs and use
ActiveUS20180265888A1Vector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRNA SequenceNucleotide sequencing
A recombinant BMYV P0 viral nucleotide sequence when transcribed in a cell is capable of forming a double stranded self-complementary RNA sequence.
Owner:SESVANDERHAVE
Antisense oligonucleotide constructs based on beta-arabinofuranose and its analogues
InactiveUS20090105467A1High affinityInhibit expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMessenger RNAADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to modified oligonucleotide therapeutic agents to selectively prevent gene transcription and expression in a sequence-specific manner. In particular, this invention relates to the selective inhibition of protein biosynthesis via antisense strategy using oligonucleotides constructed from arabinonucleotide or modified arabinonucleotide residues. More particularly this invention relates to the use of antisense oligonucleotides having arabinose sugars to hybridize to complementary RNA such as cellular messenger RNA, viral RNA, etc.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com