Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Southern blot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
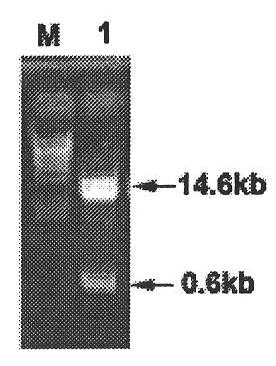
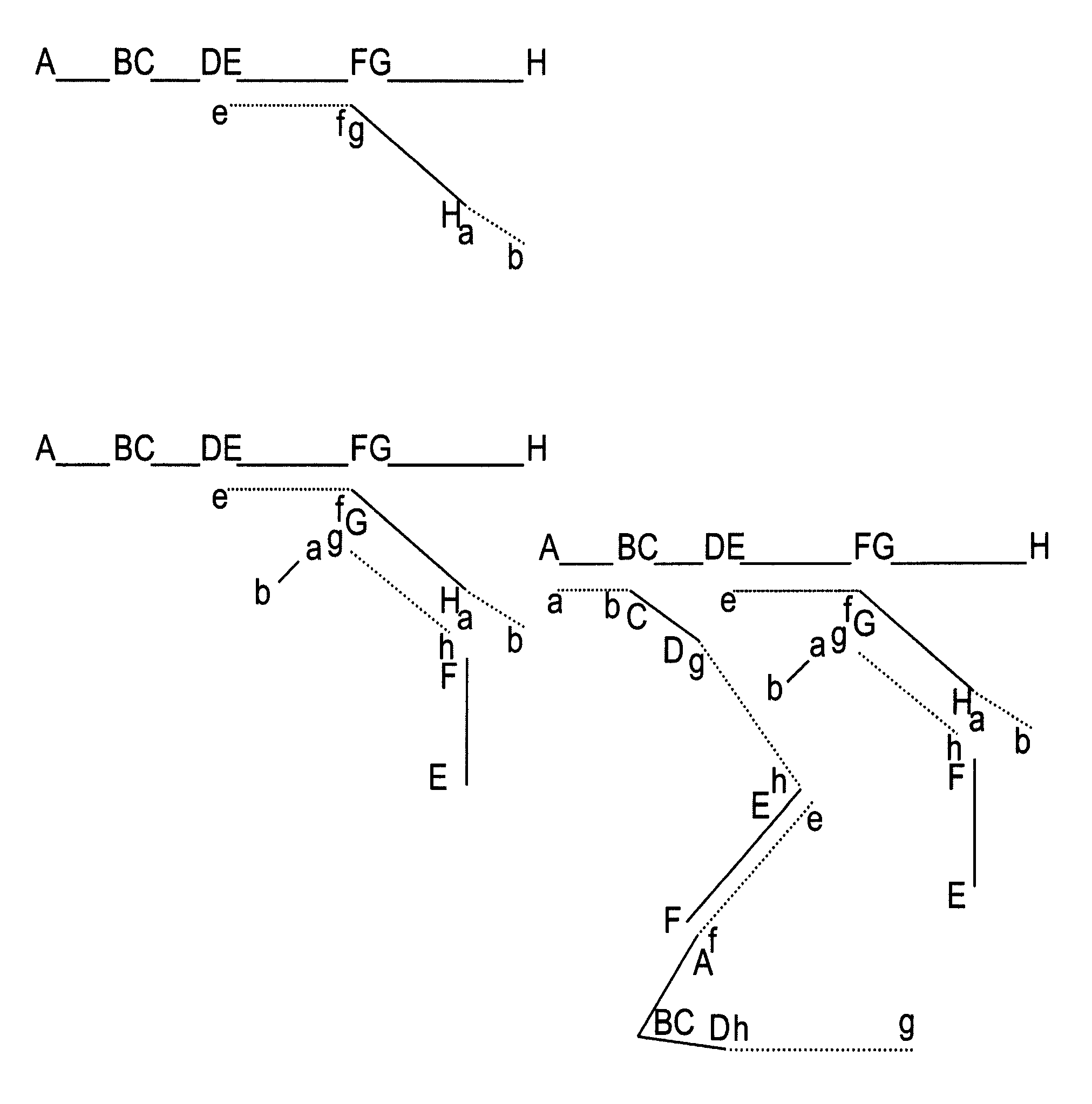
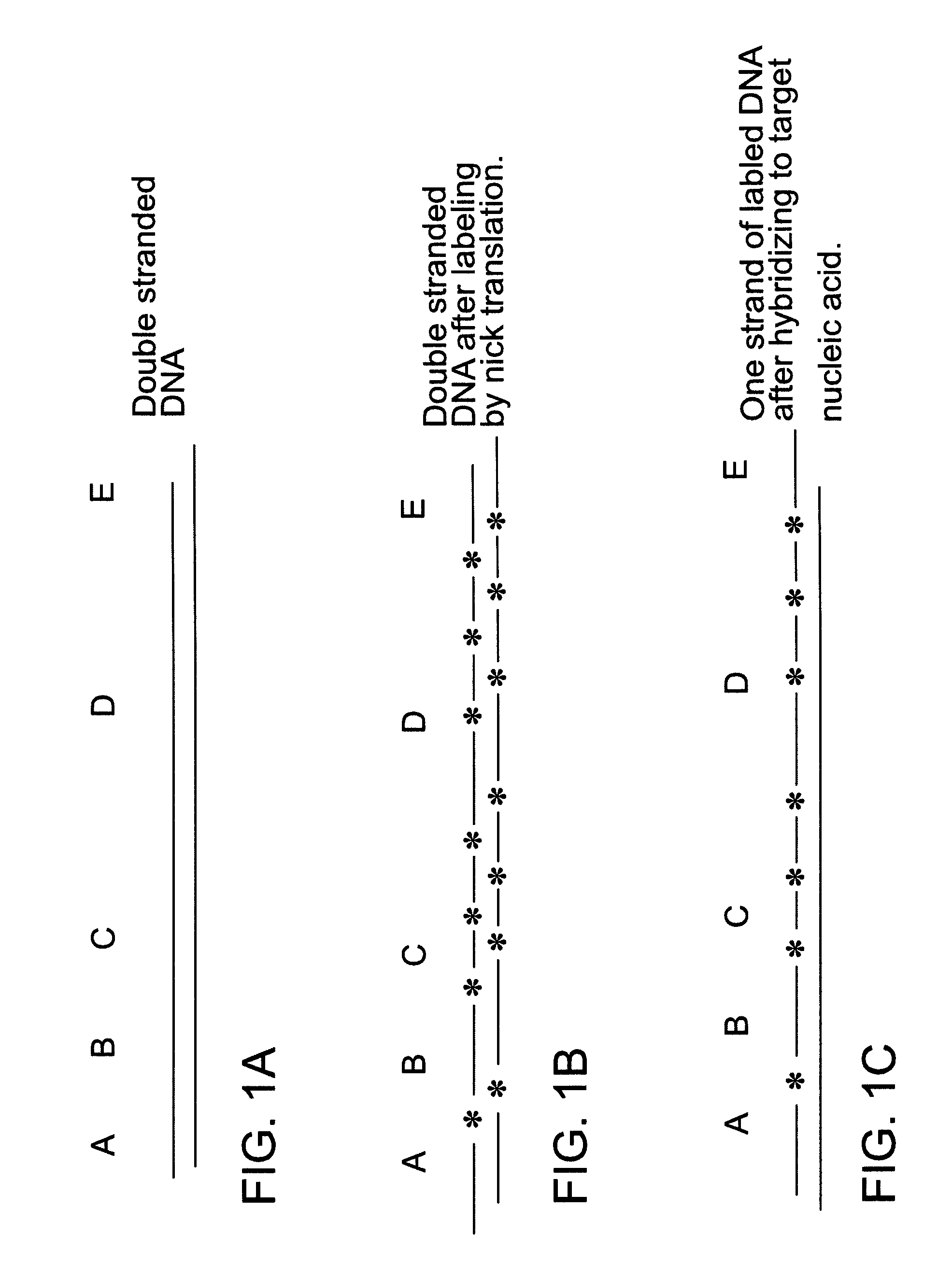
A Southern blot is a method used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples. Southern blotting combines transfer of electrophoresis-separated DNA fragments to a filter membrane and subsequent fragment detection by probe hybridization.
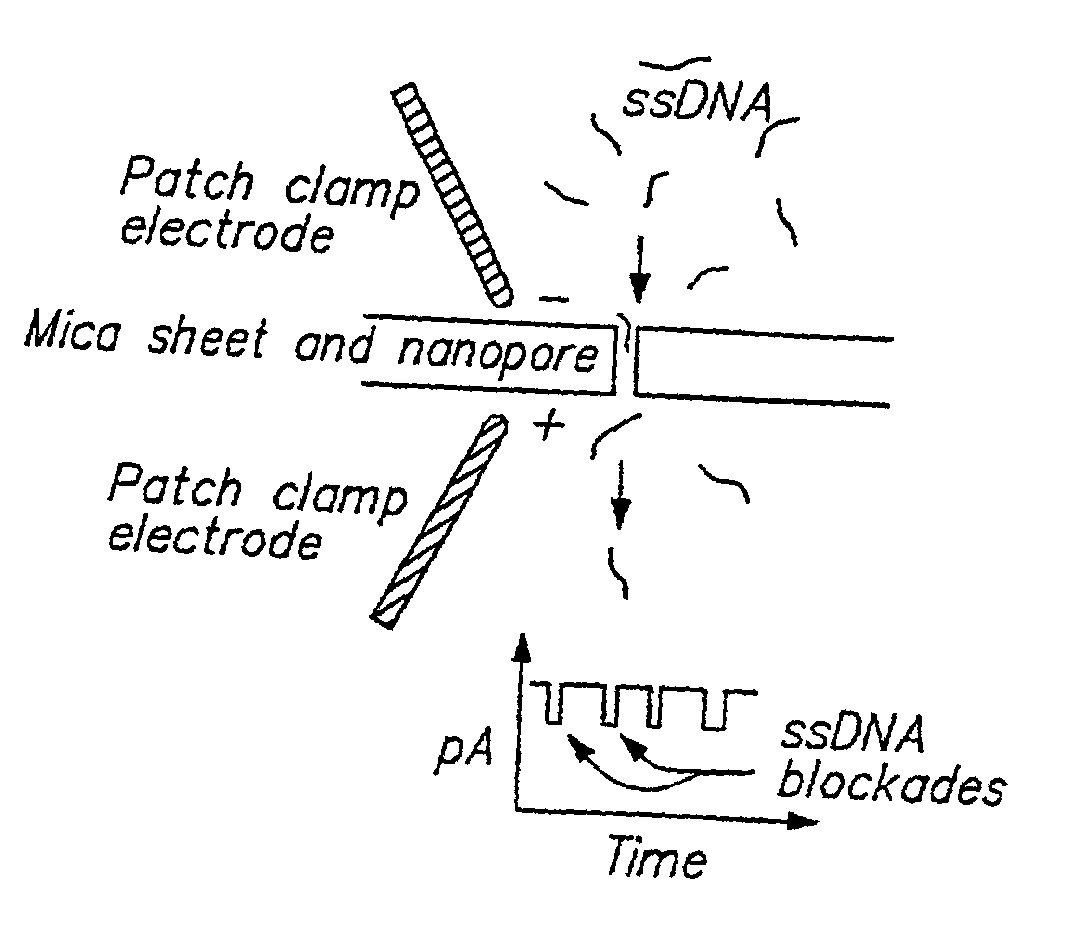
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS6428959B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
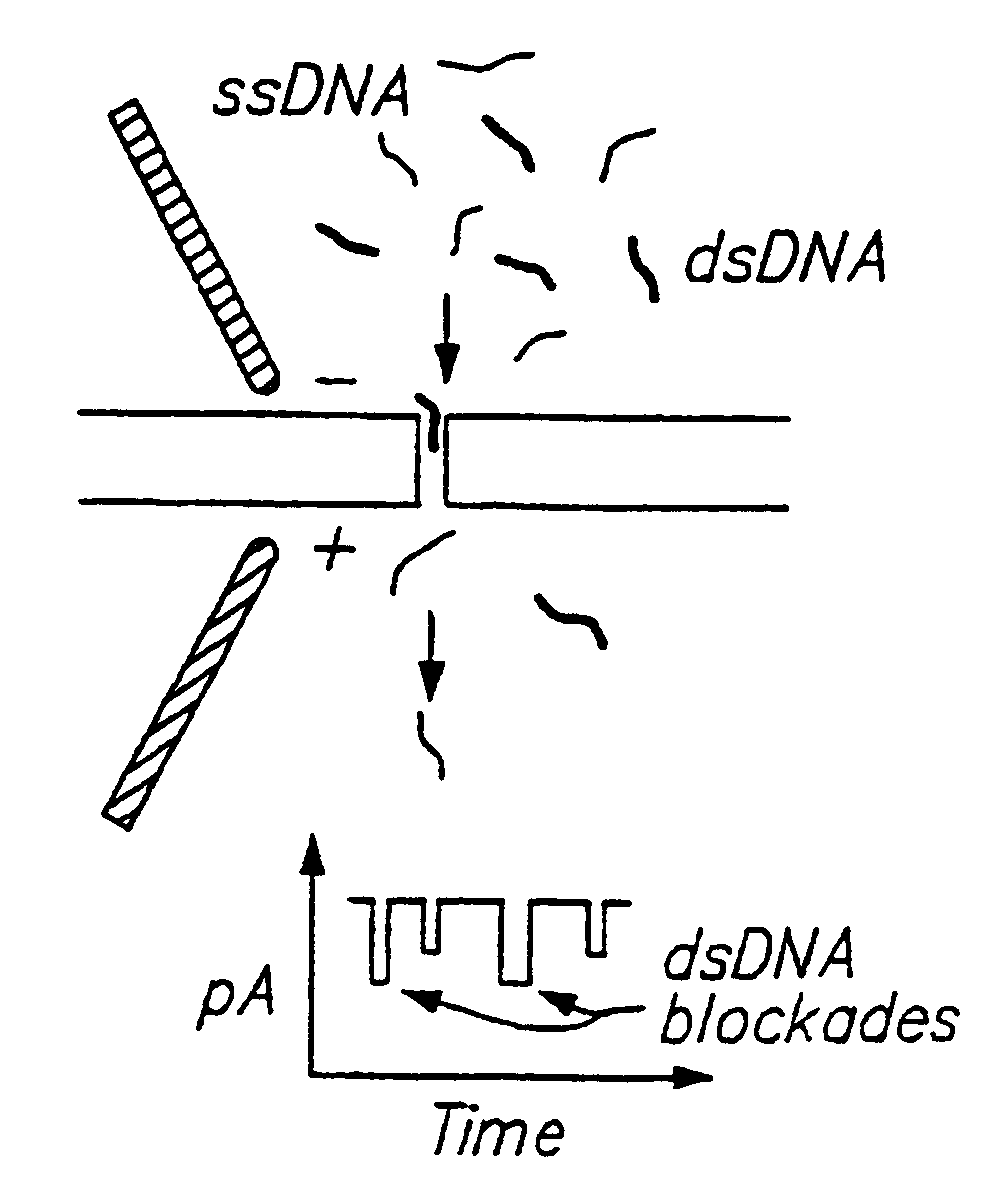
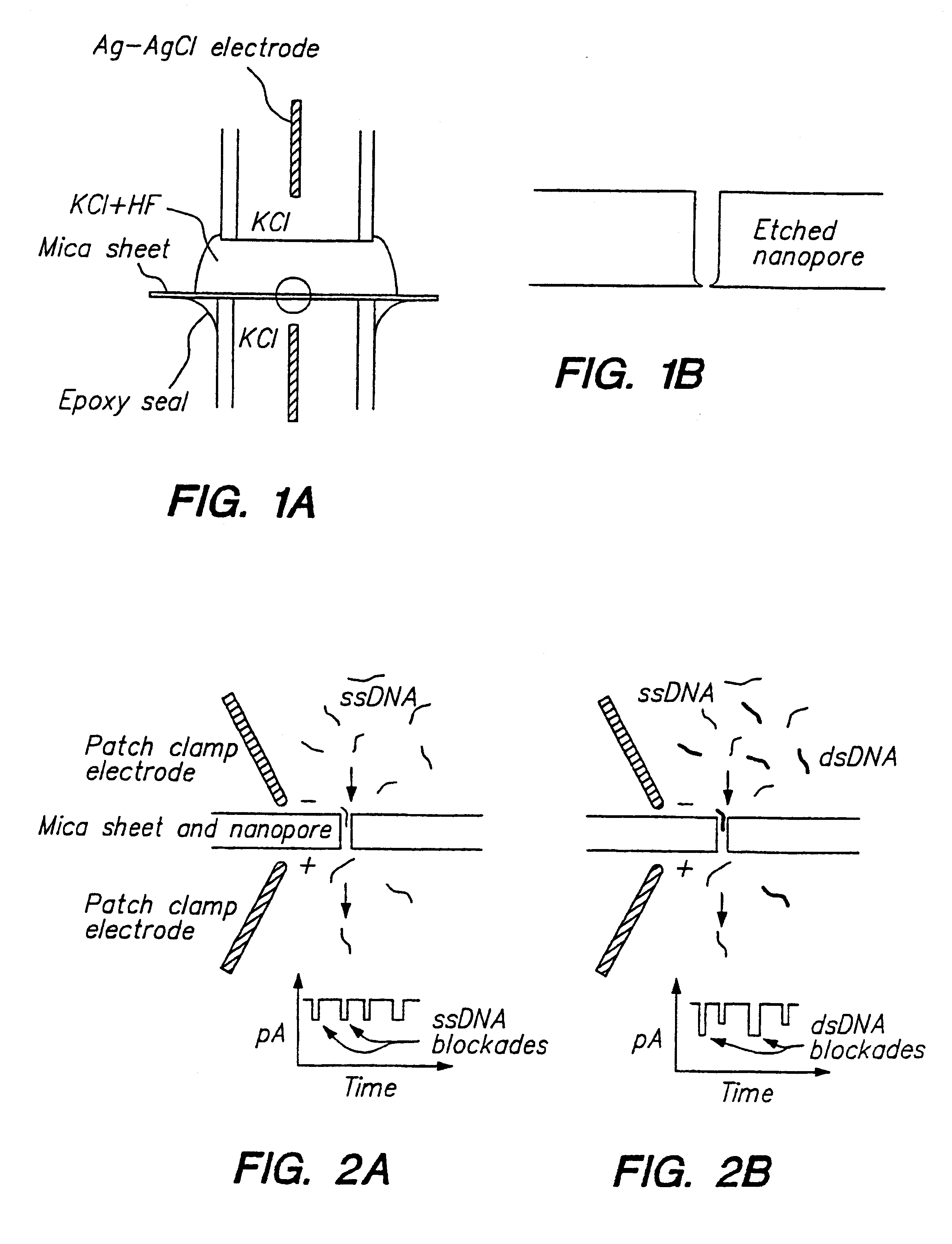
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
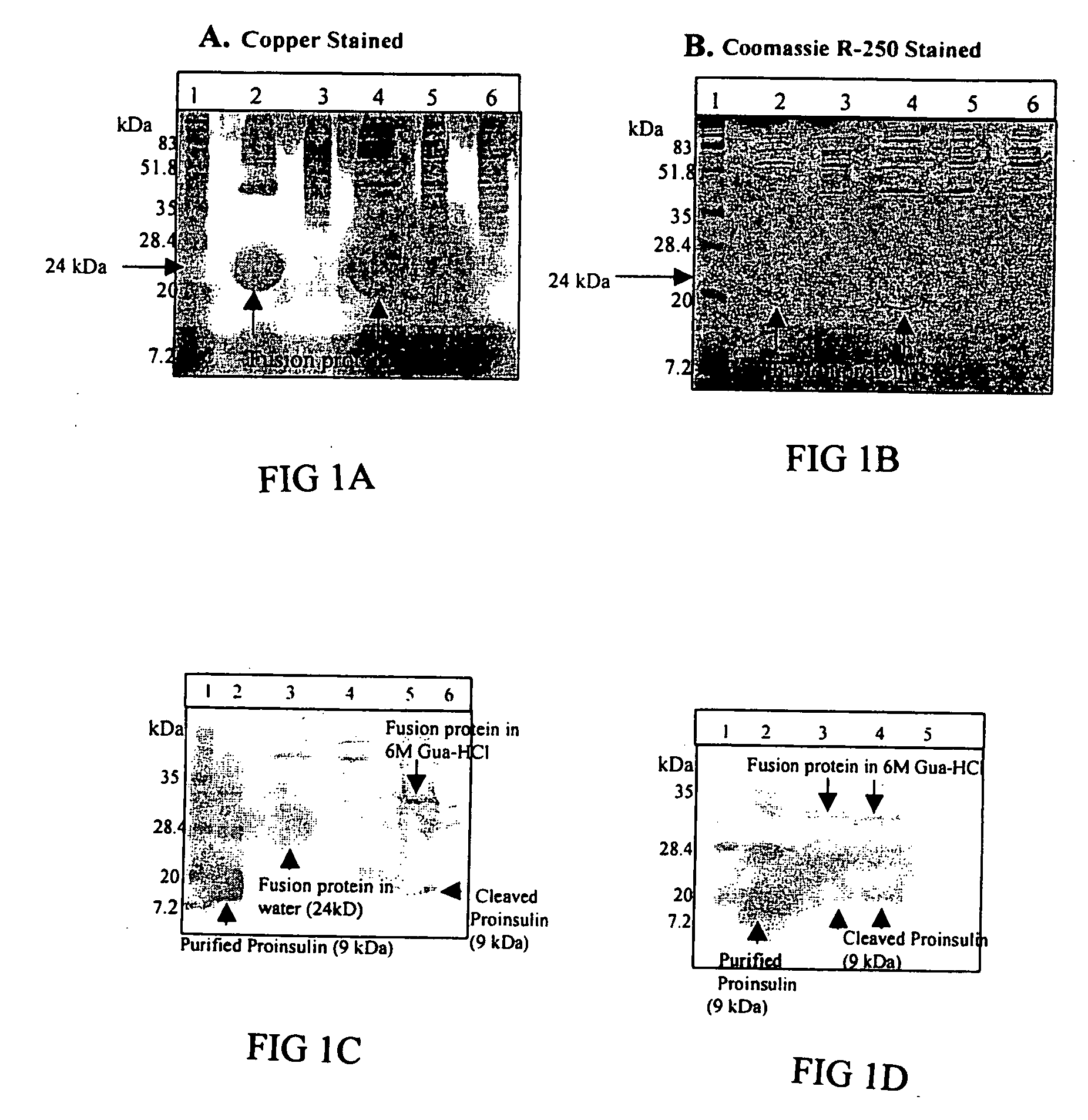
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin, insulin, native cholera toxic b submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20030204864A1Eliminate needLarge biomassBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliInsulin-like growth factor
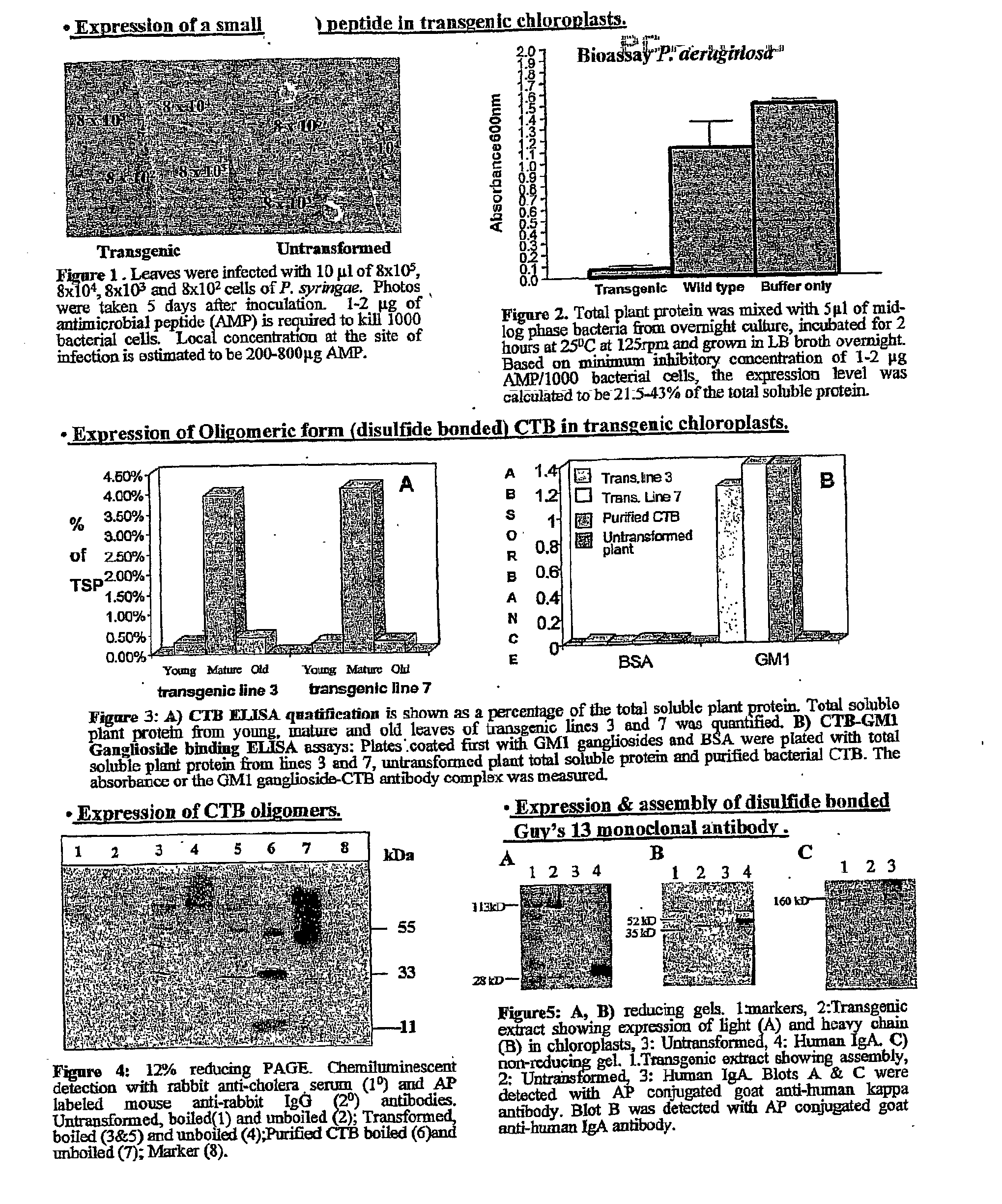
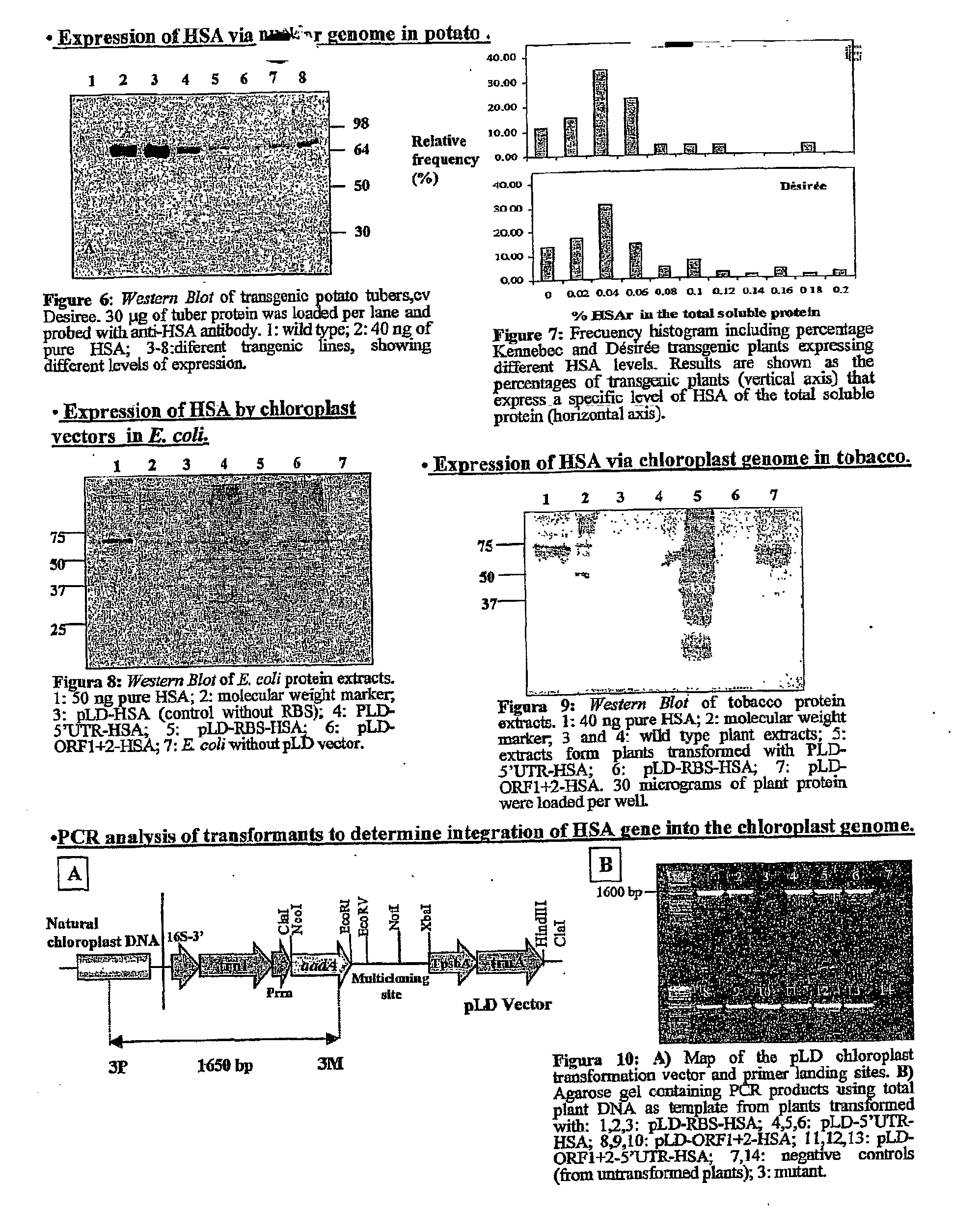
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1,-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV +1
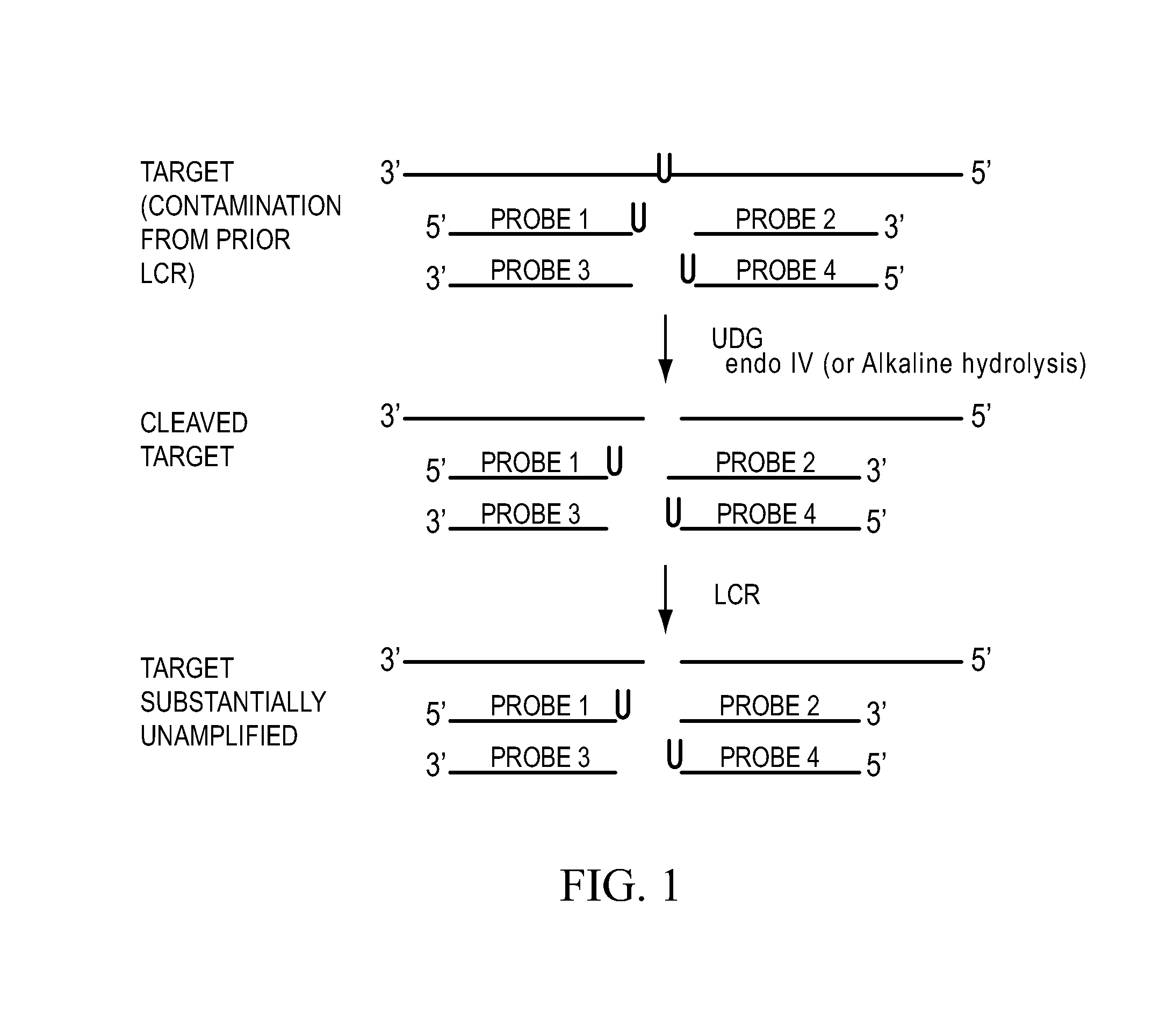
Process for controlling contamination of nucleic acid amplification reactions
ActiveUS7687247B1Eliminate productionImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePhosphate
This invention relates to a method of incorporating an exo-sample nucleotide into the amplified product strands resulting from a nucleic acid amplification process. Once the product strands have been obtained and analyzed (e.g., by hybridization, Southern blot, etc.), the exo-sample strands can be selectively destroyed by acting on the incorporated exo-sample nucleotide.Two embodiments are presented. In a first embodiment, the exo-sample nucleotide is incorporated by carrying out the amplification to reaction in the presence of an excess of exo-sample nucleotide tri-phosphate.In a second embodiment, the exo-sample nucleotide is incorporated by carrying out the amplification reaction in the presence of an oligonucleotide which has, as part of its sequence, one or more exo-sample nucleotides.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP +1
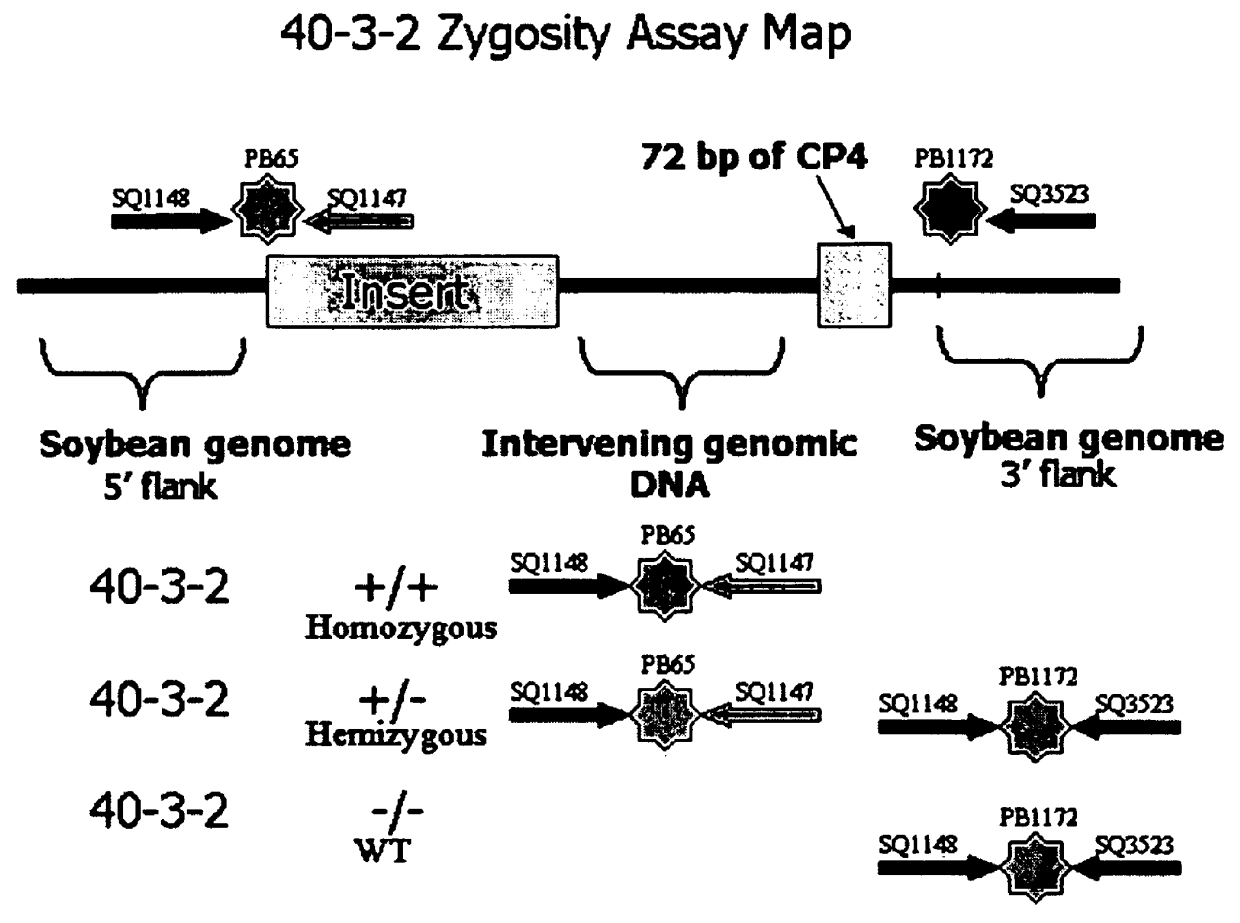
Flanking sequence of foreign insert segment in maize genetic modification event IE034 and application of flanking sequence
The invention belongs to the field of plant biotechnology, and particularly relates to a flanking sequence of a foreign insert segment in the maize genetic modification event IE034 and application of the flanking sequence. Testing by the Southern blot method show that an insertion side is present in the maize genetic modification event IE034, and a 5'-end flanking sequence of the foreign insert segment on the insertion site is showed as SEQ ID No.1. The invention provides a primer for detecting the flanking sequence, such as nucleotide sequences showed in SEQ ID No.4 and SEQ ID No.5. Testing of the flanking sequence of the foreign insert segment in the maize genetic modification event IE034 is applicable to detection of genetic modification IE034 of insect-resistant maize (including parents, hybrids F1 and offspring) and products of the insect-resistant maize ( including plants, tissues and seeds and products of these).
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
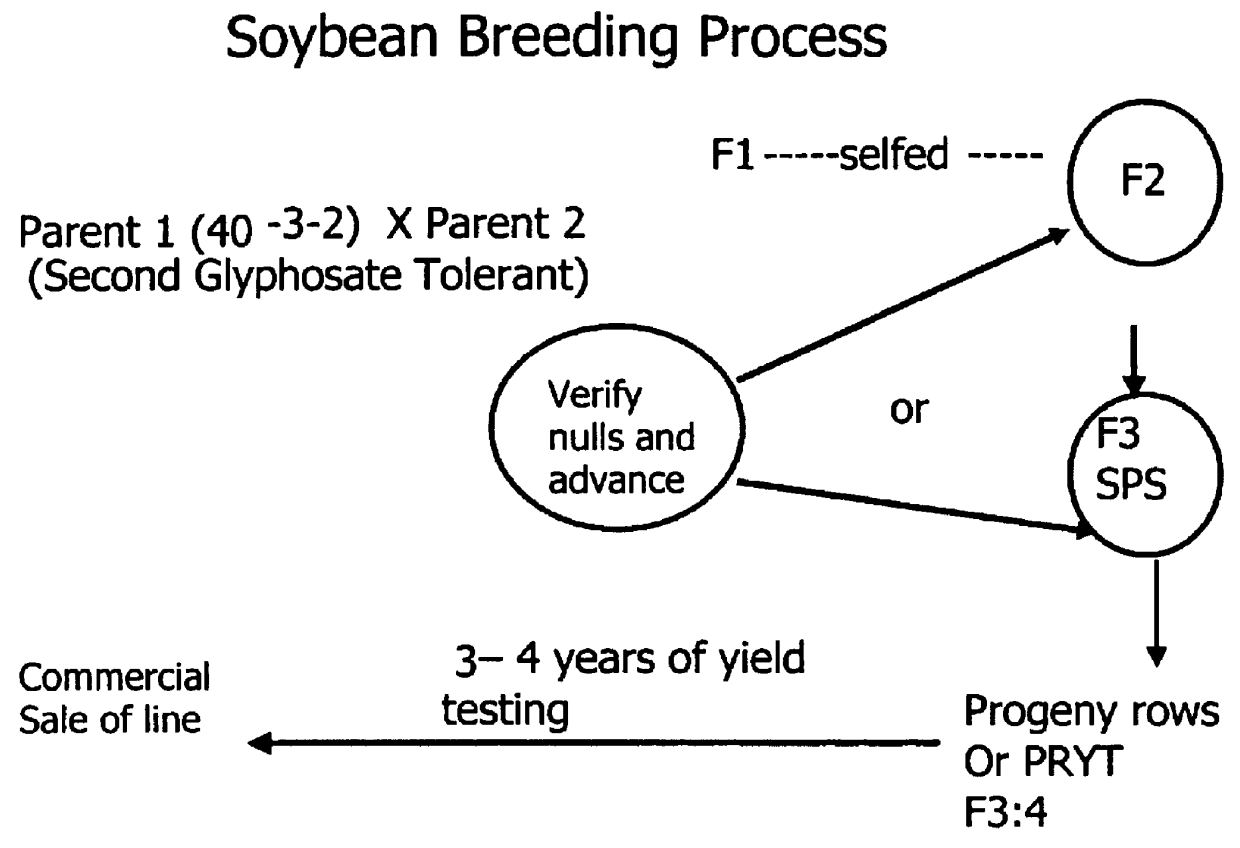
Development of novel germplasm using segregates from transgenic crosses
ActiveUS20070136836A1Improve efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGermplasmEvolutionary biology
This invention provides a method for the development of novel plant germplasm using segregates from a transgenic line combined with PCR-based zygosity testing and, optionally, Southern blot analysis.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS20020137089A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
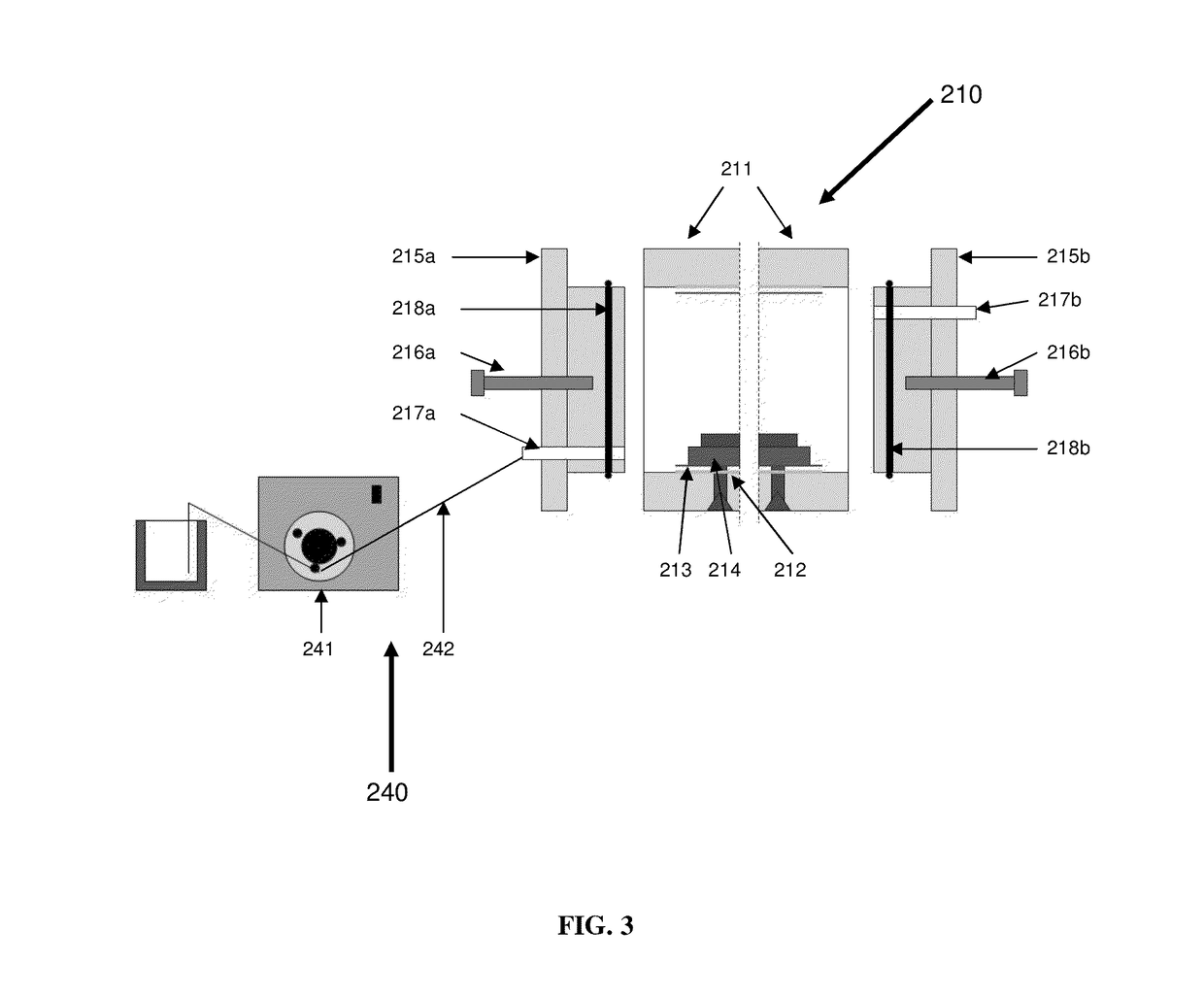
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS8470541B1Evaluating efficacyOptimize patient therapyElectrophoretic profilingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
Method for authenticating copy number of target genes in transgenic animal
InactiveCN101892295ASimple methodConsistent resultMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceGenome
The invention discloses a method for authenticating the copy number of target genes in a transgenic animal. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: taking genome DNA of the transgenic animal as a template; performing fluorescence quantitative PCR by respectively using a target gene primer and a reference gene primer to respectively obtain a fluorescence quantitative PCR result of the target genes and reference genes of the transgenic animal; taking a standard substance with the target genes in a different copy number as the template; performing the fluorescence quantitative PCR by using the target gene primer and the reference gene primer respectively to obtain the fluorescence quantitative PCR result of the target genes and the reference genes in the standard substance; establishing a standard curve relative to the difference values of the cycle indexes of the target genes and the reference genes and the natural logarithm of the copy number of the target genes; and determining the copy number of the target genes in the transgenic animal. The method has the characteristics of simplicity, easy implementation, and accuracy and reliability because the results are consistent by using a conventional Southern blot method.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
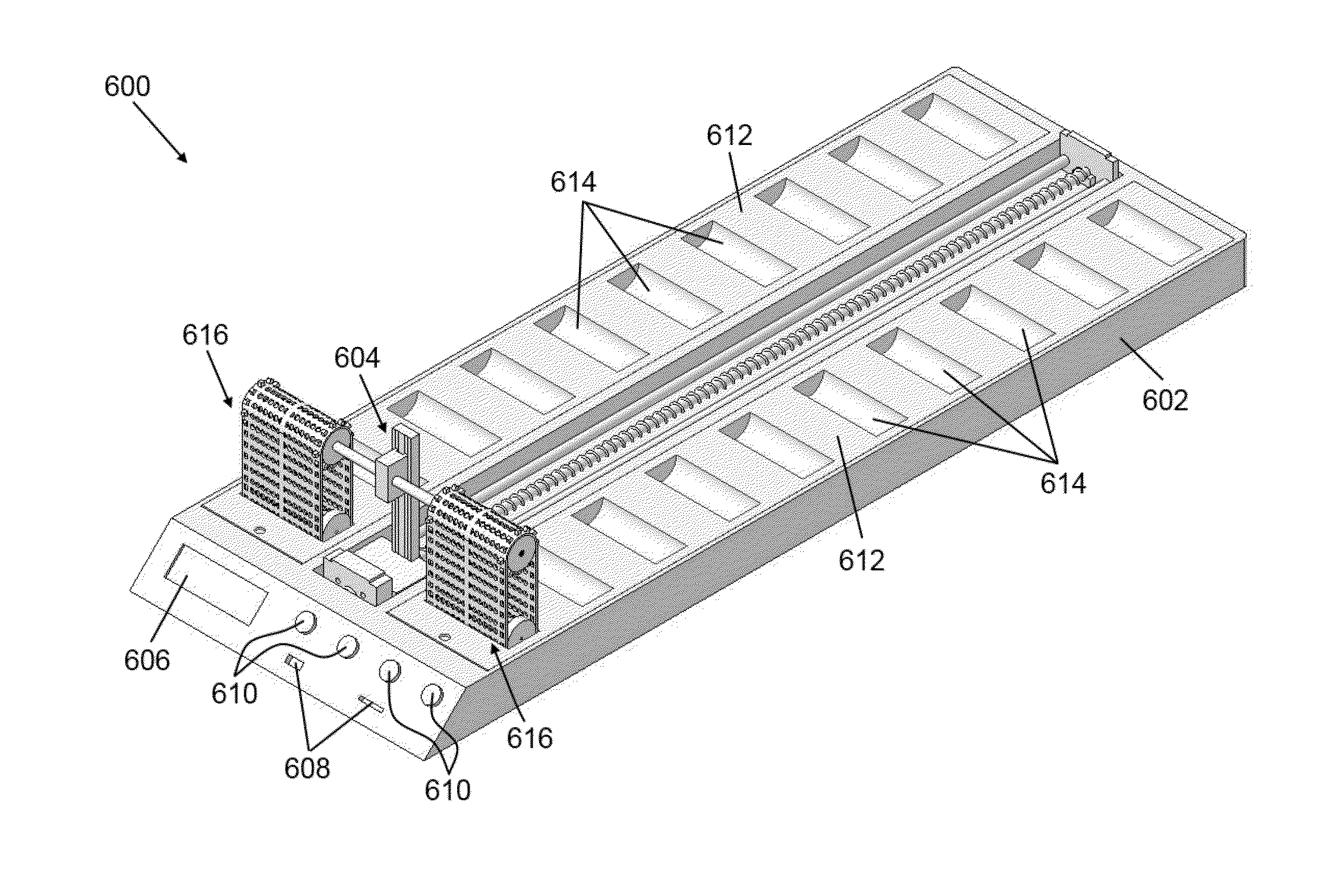
Apparatus for processing biological samples and method thereof
ActiveUS20130203072A1Avoid cloggingShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComputer scienceAutomatic processing
The present invention provides devices, apparatuses and methods for automated processing of biological samples. This invention provides automated devices and automated methods of sequentially treating a biological sample with processing fluids in more than one washing basin. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of western blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of Southern blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of northern blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of staining biomolecules on solid supports. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of nucleic acid separation and isolation.
Owner:TIAN FENG +2
Pharmaceutical proteins, human therapeutics, human serum albumin insulin, native cholera toxic B submitted on transgenic plastids
InactiveUS20060117412A1Eliminate needLarge biomassSerum albuminDepsipeptidesInsulin-like growth factorEscherichia coli
Transgenic chloroplast technology could provide a viable solution to the production of Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I), Human Serum Albumin (HSA), or interferons (IFN) because of hyper-expression capabilities, ability to fold and process eukaryotic proteins with disulfide bridges (thereby eliminating the need for expensive post-purification processing). Tobacco is an ideal choice because of its large biomass, ease of scale-up (million seeds per plant), genetic manipulation and impending need to explore alternate uses for this hazardous crop. Therefore, all three human proteins will be expressed as follows: a) Develop recombinant DNA vectors for enhanced expression via tobacco chloroplast genomes b) generate transgenic plants c) characterize transgenic expression of proteins or fusion proteins using molecular and biochemical methods d) large scale purification of therapeutic proteins from transgenic tobacco and comparison of current purification / processing methods in E. coli or yeast e) Characterization and comparison of therapeutic proteins (yield, purity, functionality) produced in yeast or E. coli with transgenic tobacco f) animal testing and pre-clinical trials for effectiveness of the therapeutic proteins. Mass production of affordable vaccines can be achieved by genetically engineering plants to produce recombinant proteins that are candidate vaccine antigens. The B subunits of Enteroxigenic E. coli (LTB) and cholera toxin of Vibrio cholerae (CTB) are examples of such antigens. When the native LTB gene was expressed via the tobacco nuclear genome, LTB accumulated at levels less than 0.01% of the total soluble leaf protein. Production of effective levels of LTB in plants, required extensive codon modification. Amplification of an unmodified CTB coding sequence in chloroplasts, up to 10,000 copies per cell, resulted in the accumulation of up to 4.1% of total soluble tobacco leaf protein as oligomers (about 410 fold higher expression levels than that of the unmodified LTB gene). PCR and Southern blot analyses confirmed stable integration of the CTB gene into the chloroplast genome. Western blot analysis showed that chloroplast synthesized CTB assembled into oligomers and was antigenically identical to purified native CTB. Also, GM1-ganglioside binding assays confirmed that chloroplast synthesized CTB binds to the intestinal membrane receptor of cholera toxin, indicating correct folding and disulfide bond formation within the chloroplast. In contrast to stunted nuclear transgenic plants, chloroplast transgenic plants were morphologically indistinguishable from untransformed plants, when CTB was constitutively expressed. The introduced gene was stably inherited in the subsequent generation as confirmed by PCR and Southern blot analyses. Incrased production of an efficient transmucosal carrier molecule and delivery system, like CTB, in transgenic chloroplasts makes plant based oral vaccines and fusion proteins with CTB needing oral administration a much more practical approach.
Owner:DANIELL HENRY
Flanking sequences of transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-resistant maize CM8101 exogenous insertion fragment and application thereof
InactiveCN109536490AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide sequencing
The invention belongs to the plant biotechnical field, and in particular, relates to flanking sequences of a transgenic insect-resistant herbicide-resistant maize CM8101 exogenous insertion fragment and an application thereof. The transgenic maize CM8101 provided by the invention is identified to have an insertion site by Southern blot. The flanking sequences of 5' end and 3' end of the exogenousinsertion fragment of the insertion site are shown in SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. The invention provides primer pairs for detecting the flanking sequences, wherein the primer pairs have nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID No.3-4 and SEQ ID No.5-6 respectively. The identification of the flanking sequences of the transgenic insect-resistant and herbicide-resistant maize CM8101 exogenous insertionfragment is suitable for the detection of the transgenic maize CM8101 including parents, hybrid F1 and offspring, and plants, tissues, seeds and products.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as method and application for gene fixe-point knock-in in Xenopus laevis genome
InactiveCN104611368ARealize fixed-point insertionGenetic stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryA-DNAEmbryo
The invention provides a carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as a method and an application for gene fixe-point knock-in in a Xenopus laevis genome. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), guide RNA (ribonucleic acid), Cas9 nuclease and a donor carrier with a pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label and a Cas9 target fragment are contained in a fertilized egg of Xenopus laevis; (2) under the joint action of guide RNA and Cas9 nuclease, a target gene in the Xenopus laevis genome and the double-chain Cas9 target fragment on the donor carrier are shorn; (3), gene fixed-point knock-in of the Xenopus laevis genome is realized through a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recovery function of Xenopus laevis cells; (4), G0-generation embryos are screened through the pancreas ela-fluorescent screening label, and F1 is subjected to southern blot identification. The carrier incapable of generating frameshift mutation after recombination as well as the method and the application for gene fixe-point knock-in in the Xenopus laevis genome lay a foundation for research of genetics and human diseases with Xenopus laevis as a model animal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Codon optimized fatty acid desaturase gene sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN102533807AEfficient productionReduce production processFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionControl cellChinese hamster
The invention relates to a codon optimized fatty acid desaturase (FatI for short) gene sequence and application thereof. A eukaryotic expression vector is constructed, and is transfected in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO), and a cell strain which stably expresses FatI is obtained through G418 screening; through genome polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Southern Blot determination, an exogenous gene is integrated into a genome, and the exogenous gene can be transcribed into mRNA in the cell; a n-3 / n-6 value of a cell of the successfully transfected CHO cell line is improved by 8.47 percent than that of a control cell; and therefore, the FatI gene sequence can promote n-6 fatty acid in the cell to be converted into n-3 fatty acid.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
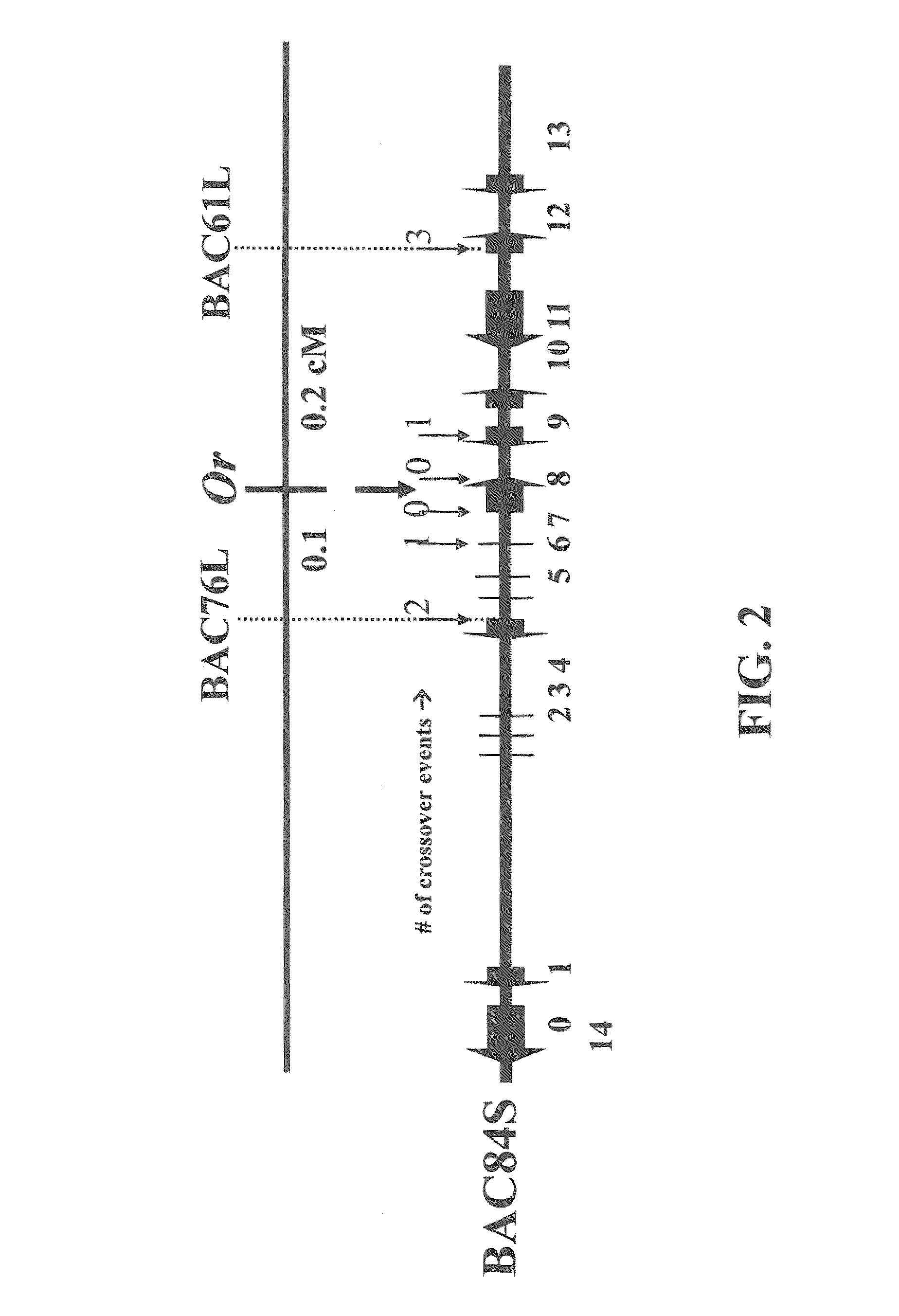
Or gene and its use in manipulating carotenoid content and composition in plants and other organisms
InactiveUS20070199104A1Increase carotenoid contentSugar derivativesTransferasesBeta-CaroteneHigh level expression
The cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis) Or gene is a semi-dominant, single-locus mutation. It induces the accumulation of high levels of beta-carotene in various tissues that are normally devoid of carotenoids, turning them orange. Using a map-based cloning strategy, we identified a single gene representing Or and successfully verified its identity by functional complementation in the wild type cauliflower. The Or gene encodes a plastid membrane protein containing the DnaJ zinc figure domain. A likely gain-of-function mutation from a 4.3-kb retrotransposon insertion in the Or allele confers the orange phenotype in the mutant. Southern blot analysis revealed that Or is a single-copy sequence in the cauliflower genome. High level of expression of the Or gene and the protein was found in very young leaves, curds, and flowers at comparable abundance between wild type and the Or mutant. Or likely functions in regulating the differentiation of some non-photosynthetic plastids into chromoplasts, which provide the deposition “sink” for carotenoid accumulation. Successful demonstration of Or in conferring carotenoid accumulation in potato tubers indicates its potential use to improve the nutritional value in staple crops.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS20130248370A1Safe and efficient and cost-effectiveEfficient and cost-effectiveCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
Plant expression vector and construction method thereof, and method for producing chicken alpha interferon by utilizing crowtoe as bioreactor
InactiveCN102121029AExtensive managementLong grass seasonFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyWestern blot
The invention relates to a plant expression vector and a construction method thereof, and a method for producing chicken alpha interferon by utilizing crowtoe as a bioreactor, belonging to the technical field of biology. The plane expression vector pSFRLH is shown as the figure 1 in the specification. In the invention, main stem sections, rachis stem sections and tender leaves of crowtoe are used as explants, and a constructed plane expression vector chicken alpha interferon gene ChIFN-alpha is subjected to genetic transformation and regeneration and then subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction), Southern blot, Western blot and ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay). Proved by a detection result, the ChIFN-alpha gene is integrated into a crowtoe chromosome genome and correctly transcribed, translated and expressed, and recombinant protein can be neutralized by a ChIFN-alpha antibody. The invention lays the foundation for producing animal medical protein by utilizing crowtoe pasture grass as a bioreactor and provides a new thinking for the control of animal epidemic diseases.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Regeneration and genetic transformation of Acacia mangium
InactiveUS6846971B1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationCauliflower mosaic virusOrganogenesis
The present invention is directed to a method of Acacia mangium regeneration through organogenesis and a method of genetic transformation of Acacia mangium. The method of regeneration comprises inducing callus from different parts of seedlings and vegetatively micropropagated plantlets as explants; adventitious bud induction followed by pinnate leaf and bud elongation and eventually, elongated shoots were induced to root. Based on the regeneration system, a marker gene GUS under cauliflower mosaic virus promoter was introduced to Acacia mangium via Agrobacterium infection. GUS staining in the regenerated plants and Southern blot hybridization prove the incorporation of the foreign gene into the host genome and expression of the foreign gene.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
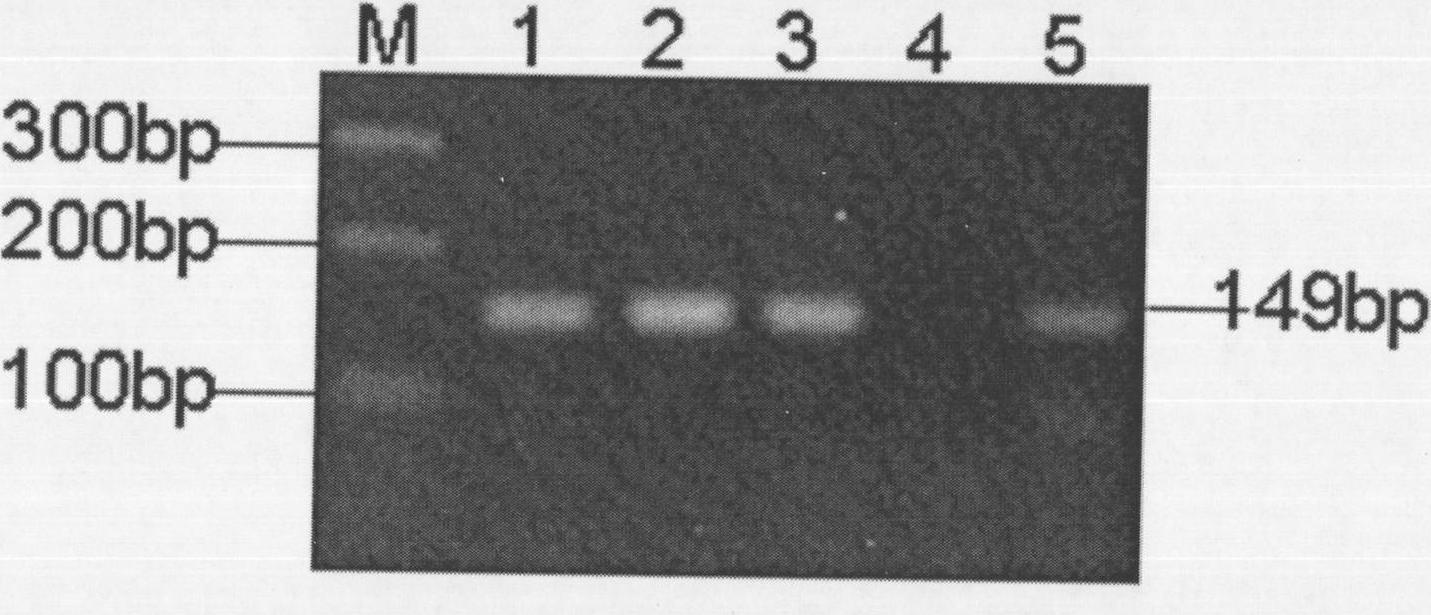
PCR kit used for detecting CGC replication number and AGG insert information of fragile X syndrome
InactiveCN103981253AAccurate analysisIncrease the difficultyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMathematical model
The invention provides a PCR kit used for detecting the CGC replication number and AGG insert information of fragile X syndrome. The PCR kit comprises a DNA polymerase emboitement, a PCR reinforcing agent, a primer group and a correction Marker; and the primer group comprises primers F and R used for detecting the CGG replication number, and detection primers M1 and R1 and verification primers M2 and F1 used for detecting the AGG insert information. The kit can accurately and rapidly analyze the CGC replication number and the AGG insert information of a sample, can breakthrough the problems of high sequencing difficulty, long time and high cost of present fragile X syndrome detection methods adopting a fluorescence probe, MLPA and Southern Blot, and can directly analyze the range of the CGC replication number and the AGG insert information according to a gel electrophoresis result in order to rapidly diagnose the characteristics of the sample; and the product resolution can be obtained by separating products through a high-resolution device, and the CGC replication number and the AGG insert information are obtained through a mathematic model.
Owner:江苏佰龄全基因生物医学技术有限公司
Development of novel germplasm using segregates from transgenic crosses
ActiveUSH2258H1Improve efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGermplasmEvolutionary biology
This invention provides a method for the development of novel plant germplasm using segregates from a transgenic line combined with PCR-based zygosity testing and, optionally, Southern blot analysis.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
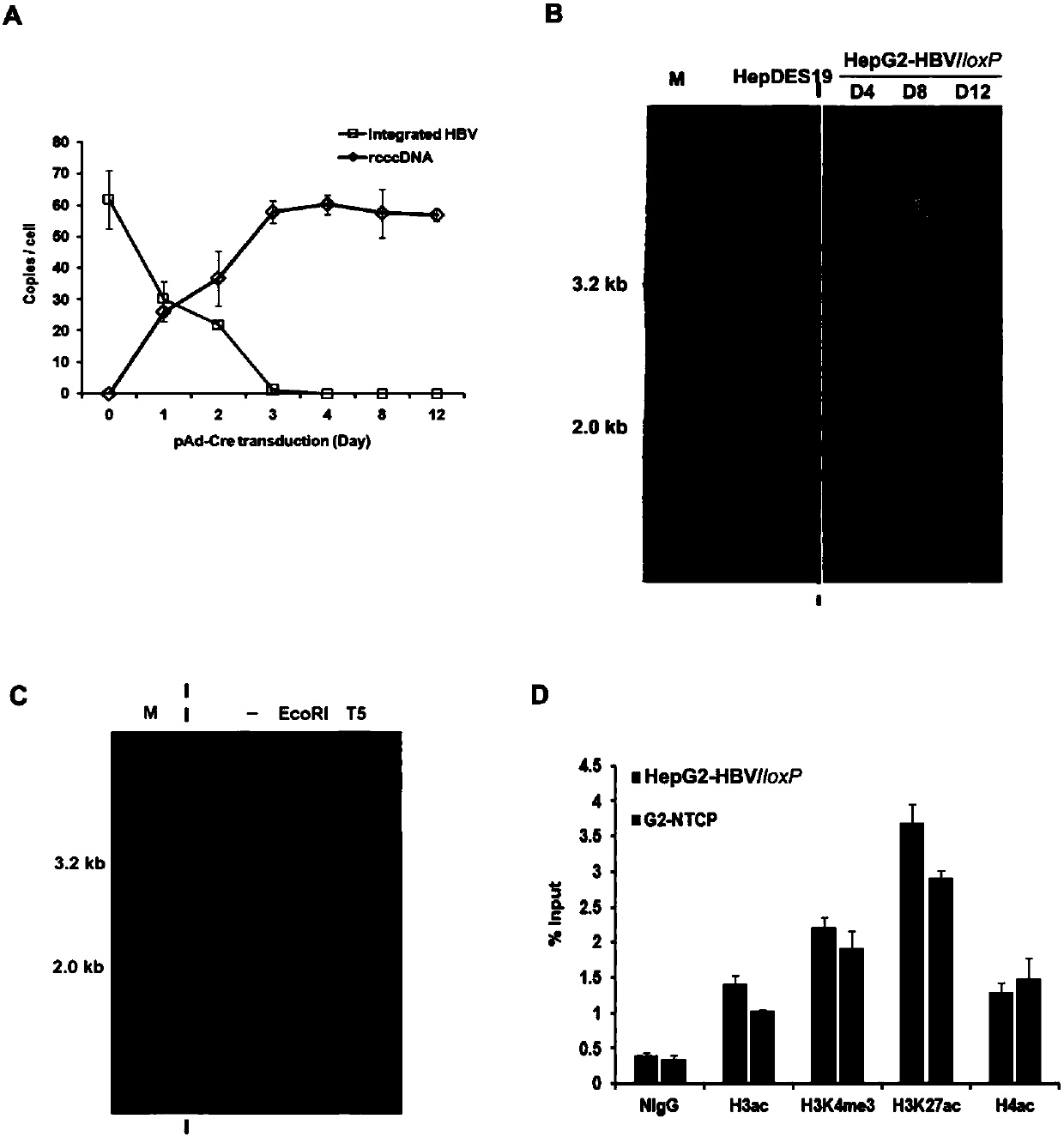
Cell system for simply and efficiently generating hepatitis B virus (HBV) recombinant cccDNA
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism animal cell lines, and relates to a cell system for generating hepatitis B virus (HBV) recombinant cccDNA. Through a transposon system, HBV single-copy genomes with two ends provided with loxP sites are integrated into HepG2 cells, a clone HepG2-HBV / loxP cell line integrated with the different-copy-number HBV genomes is obtained, the cell line does not express HBsAg, after cyclization recombination enzyme (Cre) is introduced through adenovirus transduction, the rcccDNA is generated and the HBsAg is expressed, and expression of the HBsAg is closely relevant to the generation and level of the rcccDNA; the rcccDNA is rapidly and stably generated, the structure feature of the rcccDNA is similar to that of real HBV cccDNA, and transcription, copy and protein expression of viruses can be supported; the rcccDNA can be quantitatively detected through quantitative PCR by designing a specific primer, and Southern Blot detection can be carried out by utilizing a digoxin marking system. The cell system can be used for establishing a platform for HBV cccDNA relevant biological research and screening and evaluation of anti-HBV medicines.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Methods for producing nucleic acid hybridization probes that amplify hybridization signal by promoting network formation
This invention describes methods for the generation of nucleic acid probes that improve the sensitivity of hybridization assays. The sensitivity increase results from structural modifications of nucleic acids that promote network formation during hybridization with the result that a single target molecule becomes attached to a complex of many probe molecules. The structural modification involves fragmentation of the probe nucleic acid followed by joining the fragments together such that their order and orientation and number is altered from the original probe molecule. The result is the generation of permuted probe libraries. Probes made according to this invention can be used in many kinds of hybridization assays including Southern blots. Northern blots. Dot blots. Nucleic acid Array hybridization, ‘in situ’ hybridization with fluorescent or other labels (FISH) and various kinds of sandwich hybridization assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method for extracting rice genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
The invention discloses a method for extracting rice genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The method comprises the steps of splitting, extracting, carrying out centrifugal separation and enzymolysis, precipitating, etc. After the method is adopted, the large-fragment rice genome DNA can be simply and effectively extracted; compared with the prior art, the method is simplified in the operation steps, reduced in the centrifugation times and rotating speed and reduced in the number of the needed reagents; the quality of the DNA completely meets the common subsequent experiment requirements such as genomic library building, genomic sequence amplification, Southern blot, tail-polymerase chain reaction (PCR), etc.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Regeneration and genetic transformation of acacia mangium
InactiveUS20050155116A1BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesCauliflower mosaic virusOrganogenesis
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Cultivation method of glyphosate-resistant transgenic Glycine max(L.).Merr
ActiveCN112322631AGenetic stabilityToleratedMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGlyphosatePlant cultivation
The invention provides a cultivation method of glyphosate-resistant transgenic Glycine max(L.).Merr, and relates to the field of plant cultivation by utilizing genetic engineering. The cultivation method comprises the following steps of constructing a vector pTWGM1 containing a target gene I.variabilis-EPSPS*, infecting and co-culturing an agrobacterium strain containing the expression vector pTWGM1 and a Glycine max(L.).Merr cotyledonary node explant, inducing cluster buds through glyphosate screening, and performing rooting culture when the induced buds grow to be about 3 cm to obtain transgenic T0-generation seedlings; in the growth period of T0-generation plants, screening positive plants, identifying the copy number of the positive plants through Southern blot, and collecting and planting the single-copy plants; and in the T1 generation, planting transgenic plants according to families, spraying glyphosate through field observation, and selecting the transgenic families with goodglyphosate tolerance and no obvious change of agronomic traits. The transgenic Glycine max(L.).Merr exogenous gene obtained by the method can be stably inherited in the later generations and has glyphosate herbicide tolerance, the labor cost in production management can be reduced, and the planting benefit is improved.
Owner:武汉天问生物科技有限公司
A method for producing banana plants with tolerance to fusarium oxysporum cubensis tr4
PendingUS20200275624A1Plant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsFusarium oxysporumBanana Plant
Provided is a method for producing a banana plant with tolerance or resistance to Fusarium oxysporum Cubensis TR4 and such plants. The method includes (a) exposing one or more banana meristems, in one or more propagating cycles, to a medium including a demethylating agent (in vitro mutagenesis) to thereby provide one or more banana meristems exhibiting expression and thereby amplification of retrotransposable elements in their plant genome as determined by Southern blot hybridization analysis, and (b) rooting the meristems that exhibited the amplification and regenerating therefrom one or more regenerated banana plants, at least one of the regenerated banana plants having tolerance or resistance to Fusarium oxysporum Cubensis TR4.
Owner:RAHAN MERISTEM 1998
Method for identifying age of ginseng by utilizing length of ginseng telomere
ActiveCN104357560AHigh degree of fitImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMathematical modelGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for identifying the age of ginseng by utilizing the length of a ginseng telomere. The method comprises the following steps: (A) establishing a mathematical model: (a1) selecting a plurality of samples from the positions 1-2 cm below the rhizomes of the ginseng of known age and extracting genomic DNA from each sample; (a2) taking each genomic DNA as a template, conducting qPCR on a primer pair distinguished from the ginseng telomere to obtain a Ct value and marking the Ct value as T, and conducting qPCR on a primer pair distinguished from a single copy gene of the ginseng to obtain another Ct value and marking the Ct value as S; (a3) calculating the T / S ratio for each ginseng; (a4) taking the ages of the ginseng as the abscissa values and taking all the calculated T / S ratios as the ordinate values to draw a standard linear curve and obtain a curve equation; (B) adopting the mathematical model to identify the age of ginseng to be measured: obtaining the T / S ratio for the ginseng to be measured according to the operations from step (a1) to step (a3), and substituting the T / S ratio into the mathematical model to obtain the age of the ginseng to be measured. The method has the advantages that the identified age of ginseng is highly identical with the actual age of the ginseng, the cost is low, and the flux is high. Compared with the traditional Southern blot technology adopted for measuring the length of a ginseng telomere, the method provided by the invention has less demand for DNA and a shorter test period.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Method for enhancing aphis resistance of chrysanthemum by using transgenosis
InactiveCN101831460AImprove insect resistanceImprove breeding efficiencyGenetic engineeringFermentationGenomic DNAAphis
The invention relates to a method for enhancing the aphis resistance of chrysanthemum by using transgenosis, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: adopting binary plant expression vectors comprising hpalXoo genes coding harpinXoo proteins and glufosinate-resistant bar genes; integrating the hpalXoo genes and the bar genes on chrysanthemum genomic DNA; performing glufosinate resistance-based sieving to obtain resistant transformed plants; testing positive by using PCR and genomic southern blot to obtain transgenic chrysanthemum plants; and performing a biological aphis-resistance test on leaves and the whole plants to obtain aphis-resistant transgenic plants. Through the method, the aphis resistance of the chrysanthemum is improved by transforming foreign hpalXoo genes, performing normal transcriptome expression and inserting the foreign hpalXoo genes into chrysanthemum to induce a broad spectrum aphis-resistant signal to conduct relative gene NPR1 expression. The novel and practical method is provided for gene engineering technology to select and breed aphis-resistant chrysanthemum varieties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUB TROPICS CROP INST
Or gene and its use in manipulating carotenoid content and composition in plants and other organisms
InactiveUS8071841B2Increase carotenoid contentSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBeta-CaroteneHigh level expression
The cauliflower (Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis) Or gene is a semi-dominant, single-locus mutation. It induces the accumulation of high levels of beta-carotene in various tissues that are normally devoid of carotenoids, turning them orange. Using a map-based cloning strategy, we identified a single gene representing Or and successfully verified its identity by functional complementation in the wild type cauliflower. The Or gene encodes a plastid membrane protein containing the DnaJ zinc figure domain. A likely gain-of-function mutation from a 4.3-kb retrotransposon insertion in the Or allele confers the orange phenotype in the mutant. Southern blot analysis revealed that Or is a single-copy sequence in the cauliflower genome. High level of expression of the Or gene and the protein was found in very young leaves, curds, and flowers at comparable abundance between wild type and the Or mutant. Or likely functions in regulating the differentiation of some non-photosynthetic plastids into chromoplasts, which provide the deposition “sink” for carotenoid accumulation. Successful demonstration of Or in conferring carotenoid accumulation in potato tubers indicates its potential use to improve the nutritional value in staple crops.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
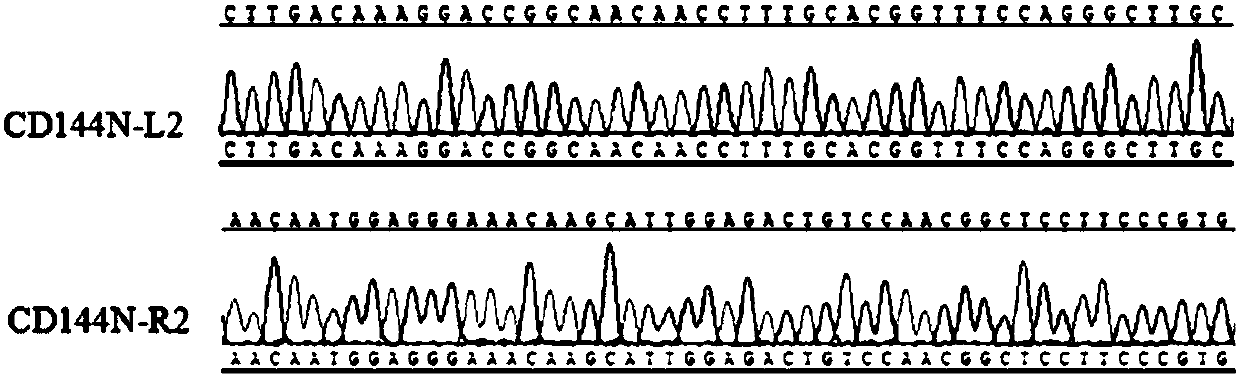
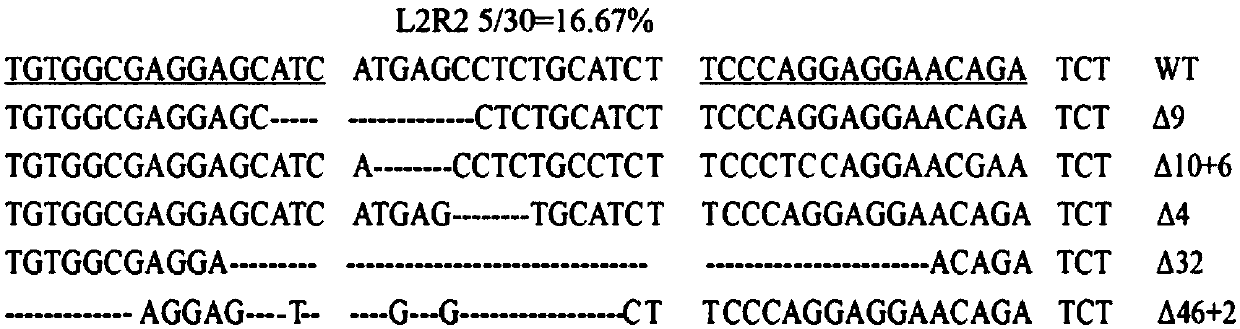
Method for constructing hESC indicating cell line for specifically tracing endothelial cell differentiation
ActiveCN107805627AGenetically modified cellsPeptidesEnzyme digestionEndothelial cell differentiation
The invention discloses a method for constructing an hESC indicating cell line for specifically tracing endothelial cell differentiation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a plasmid CD144N-GFP; (2) constructing plasmid TALENs, wherein the plasmid TALENs include a plasmid CD144N-L2 and a plasmid CD144N-R2; and (3) nuclearly transferring the plasmid CD144N-GFP and the plasmid TALENs to ESCs, carrying out G418 screening, picking a monoclone, carrying out PCR preliminary identification by using a cross-5' homologous arm primer F1 / R1 and a cross-3' homologous arm primer F2 / R2, carrying out Southern blot identification on bilaterally positive cells, and carrying out hybridization identification on probes on the long homologous arm by using Kpn I enzyme digestion to obtain positive cells that are the hESC indicating cell line for specifically tracing endothelial cell differentiation.
Owner:SHANGHAI PINPOINT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for identifying copy number of T-DAN tandem repeat sequences in transgenic plant through real-time fluorescence quantification PCR method
InactiveCN104745696AShielding effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFluorescenceWild type
The invention discloses a method for identifying the copy number of T-DAN tandem repeat sequences in a transgenic plant through a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR method. The method comprises the following steps: connecting an HMGA gene to a plant expression vector Pski015 containing a screening gene BAR through a Southern Buddhism mediated plant transformation method; then transfecting wild Col-4 arabidopsis; connecting the vector with two reference plasmids; extracting RNA of glyphosate-screened transgenic arabidopsis and carrying out inverse transcription to obtain cDNA as a detection template; and detecting the copy number of a mutant plant in a way of real-time quantification PCR respectively by virtue of quantitative primers of a glyphosate-resistance gene and the HMGA gene. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the influence of a T-DAN tandem structure on identification of the copy number of a transgenic plant can be effectively shielded; and compared with Southern blot, quantification PCR is more convenient and more efficient.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com