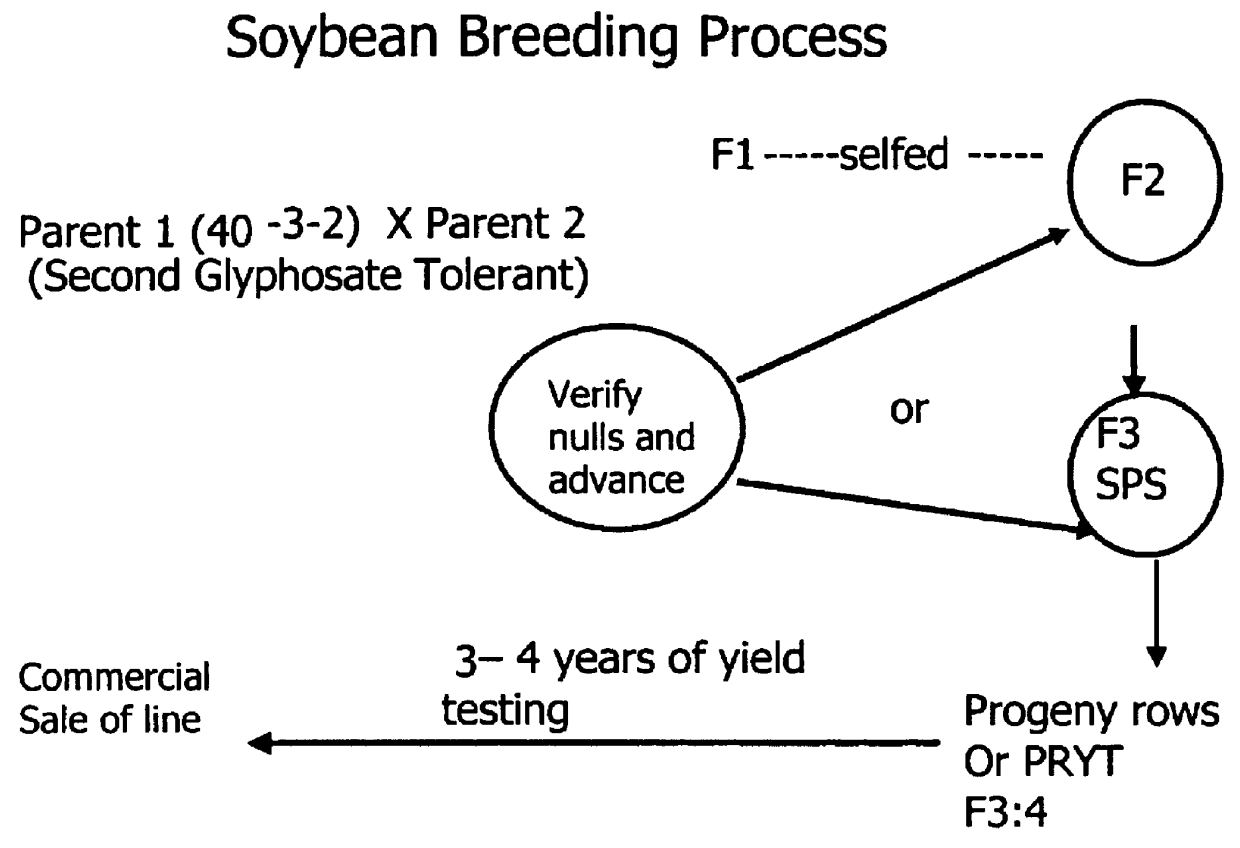
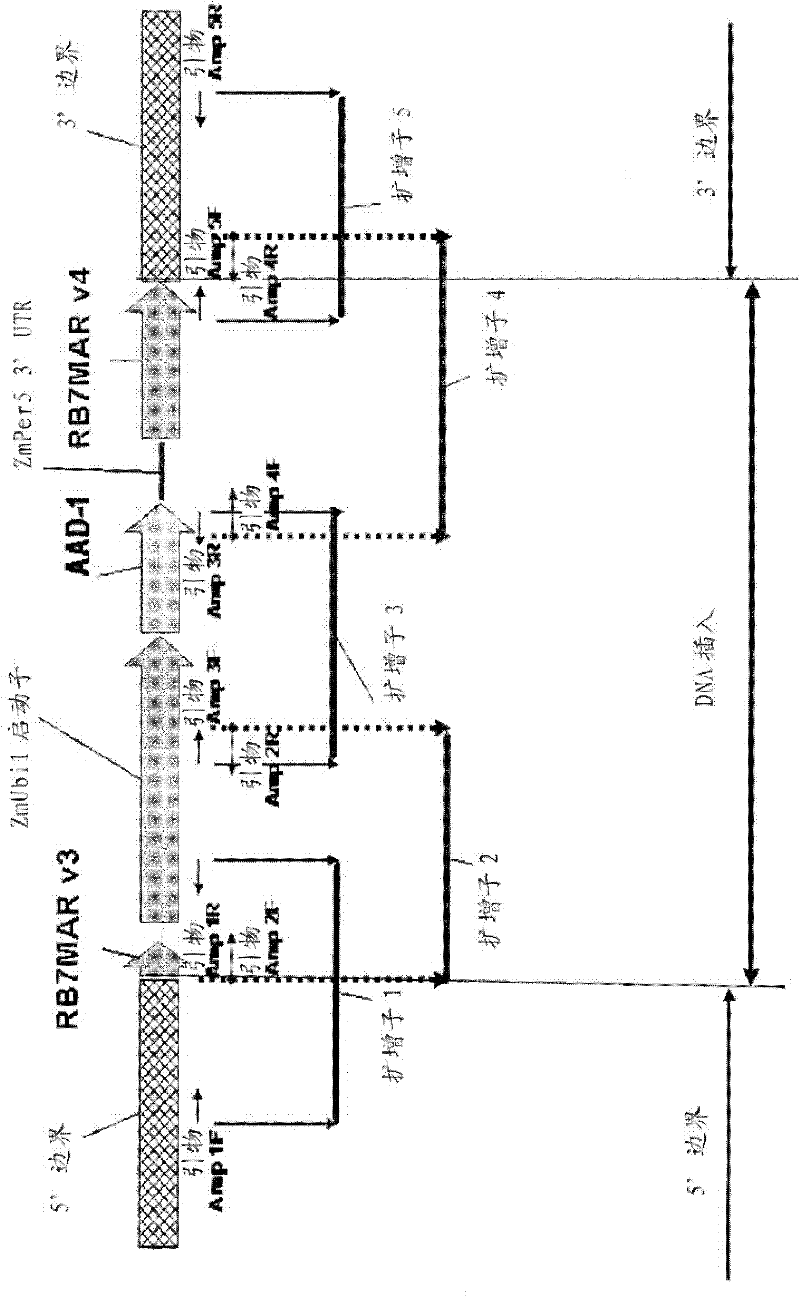
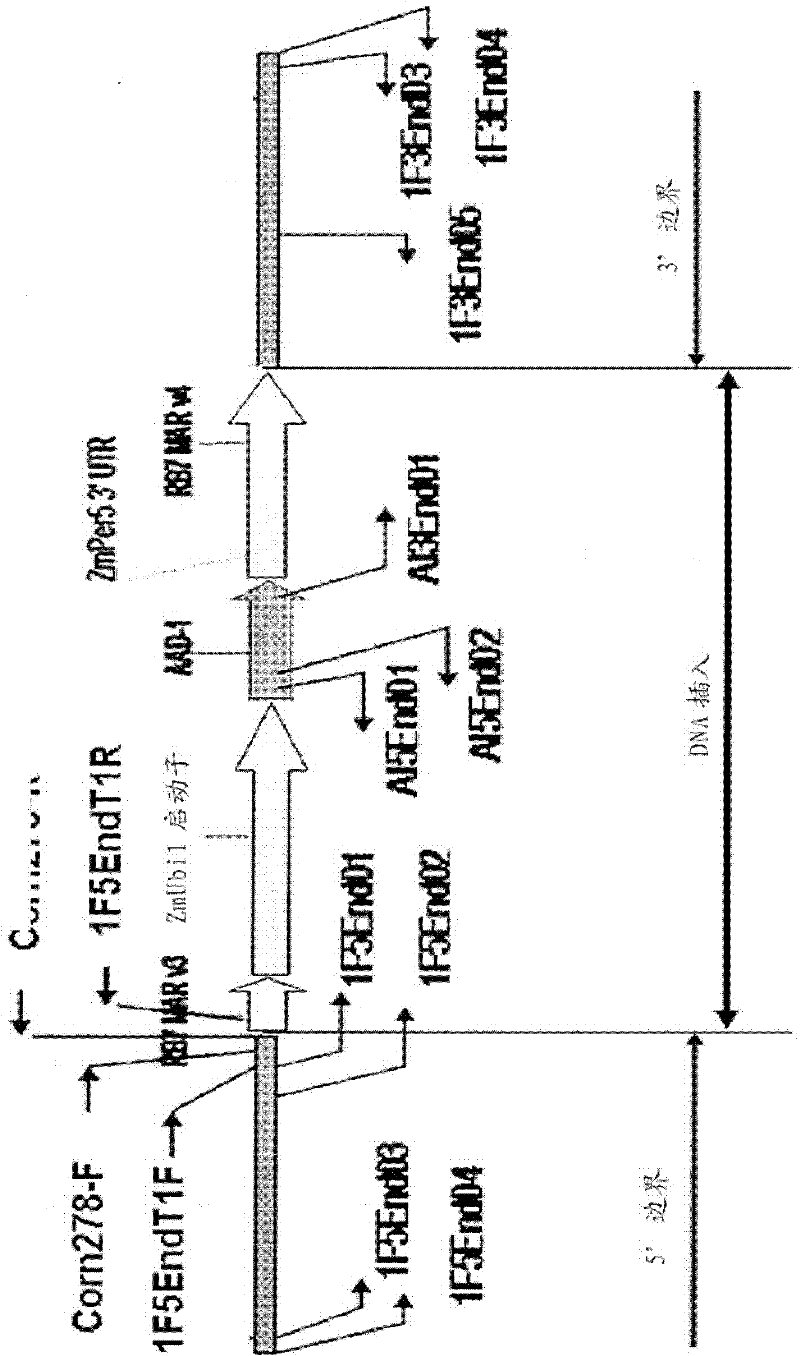
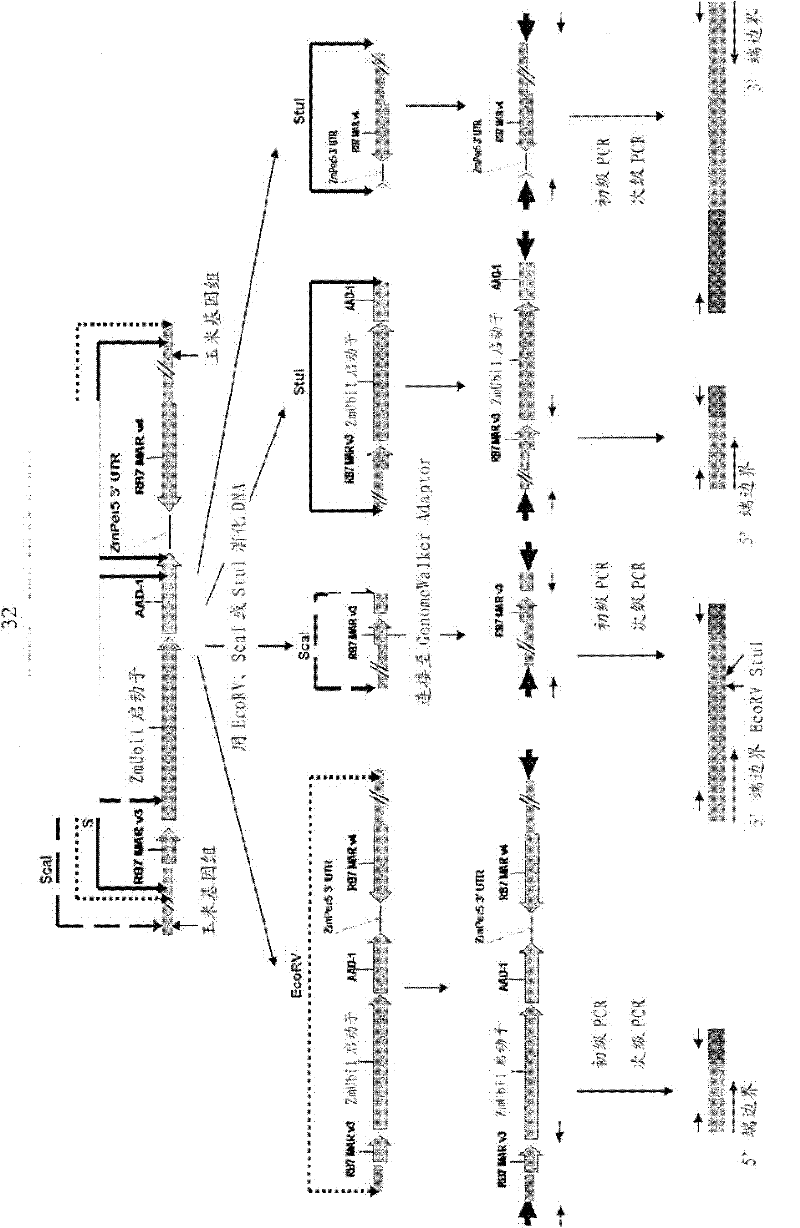
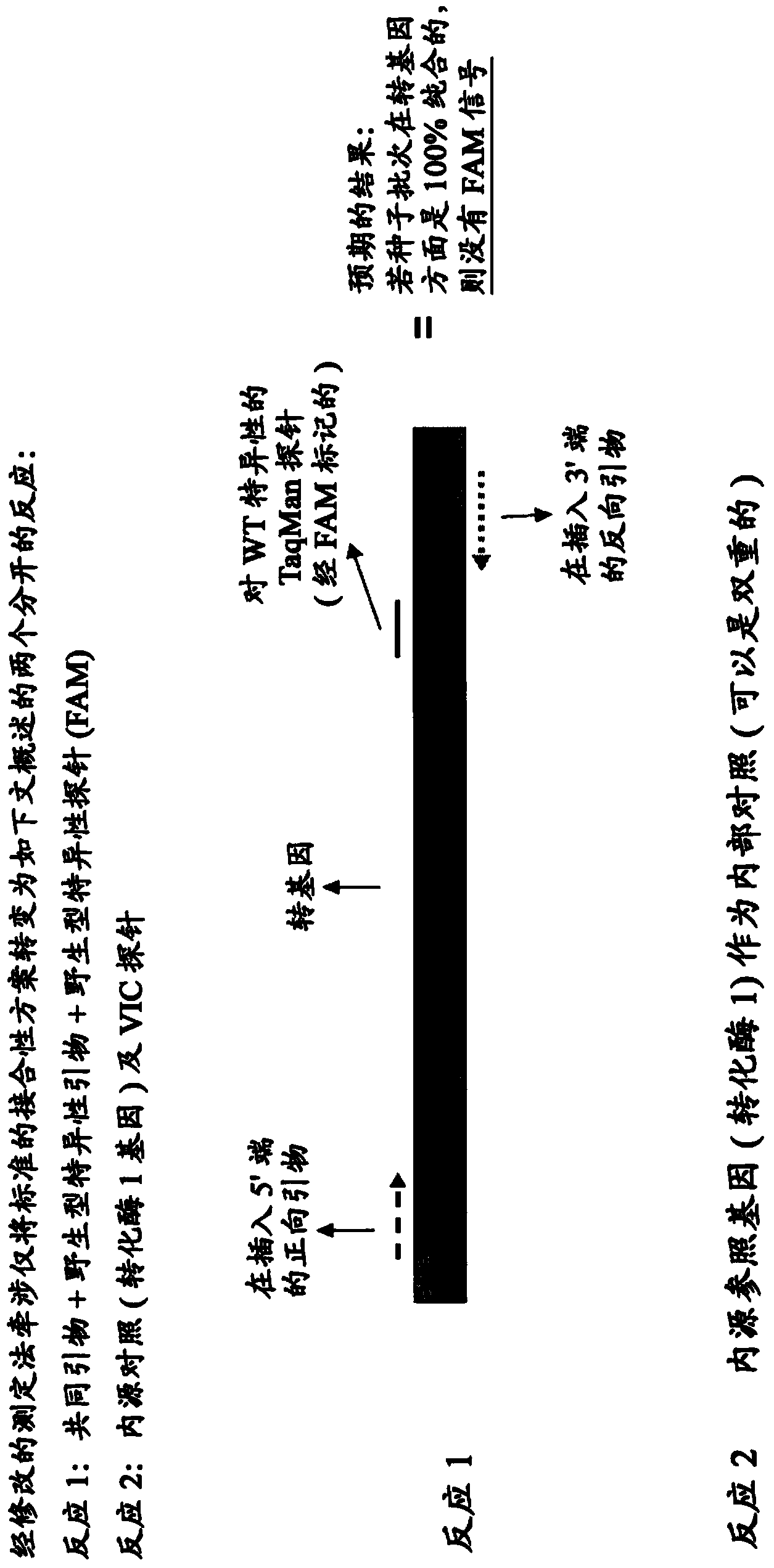
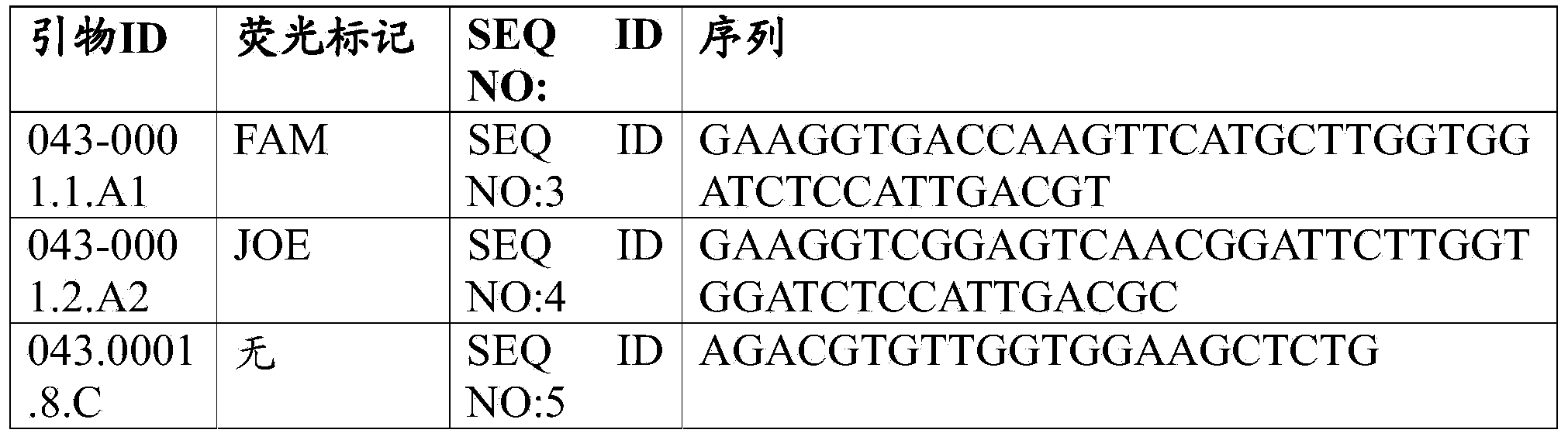
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
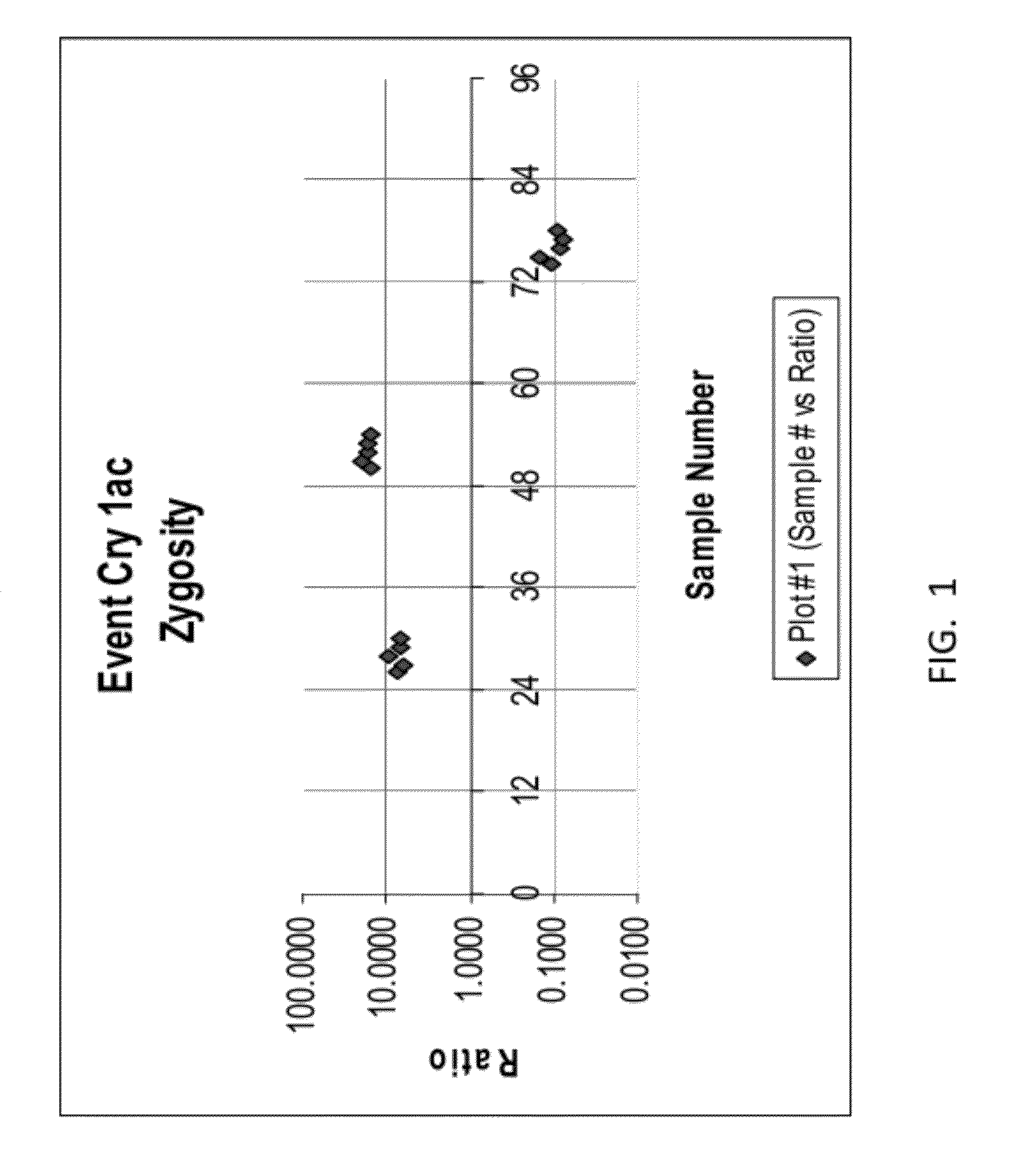
39 results about "Zygosity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek zygotos "yoked," from zygon "yoke") (/zaɪˈɡɒsɪti/) is the degree of similarity of the alleles for a trait in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous.
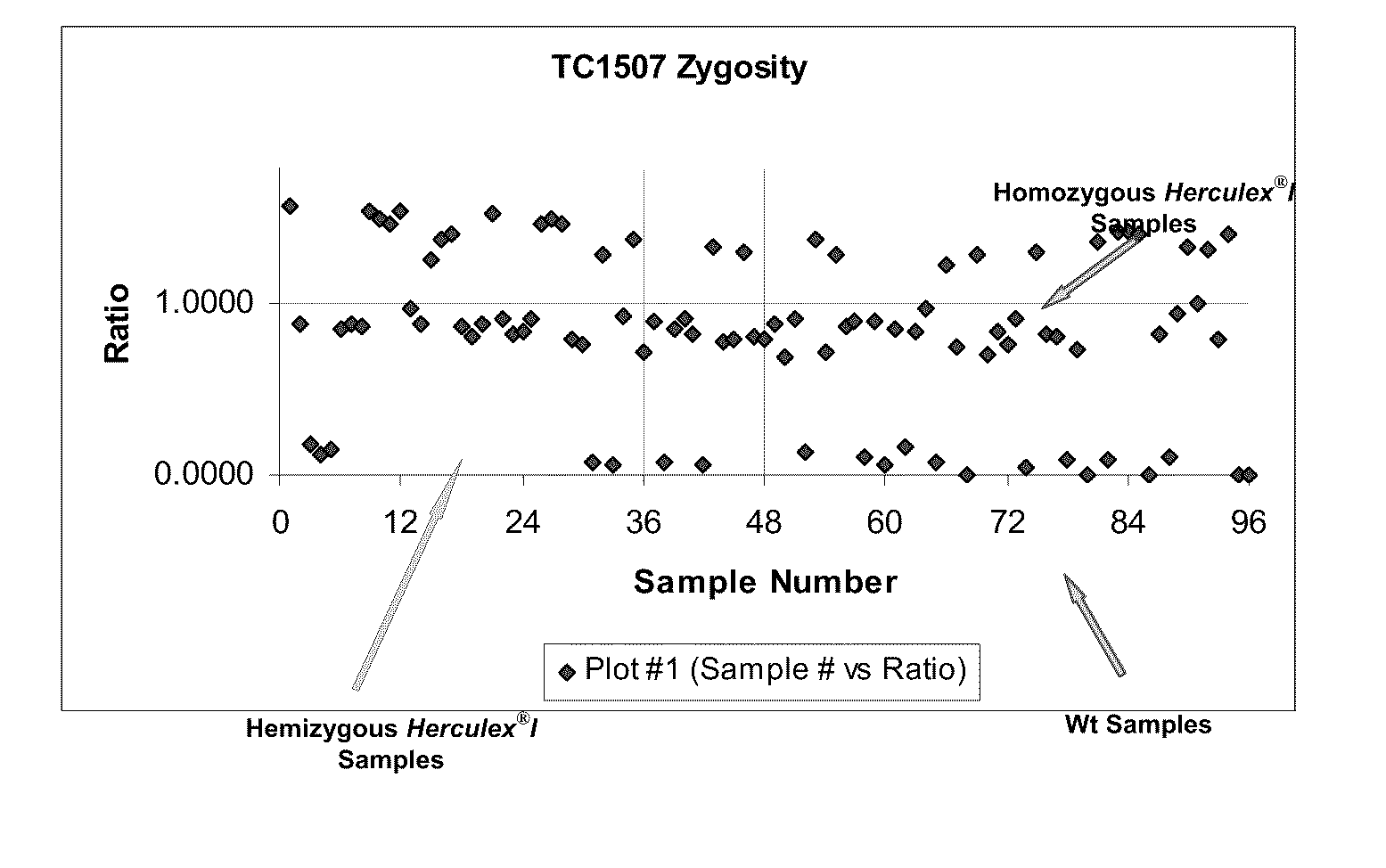
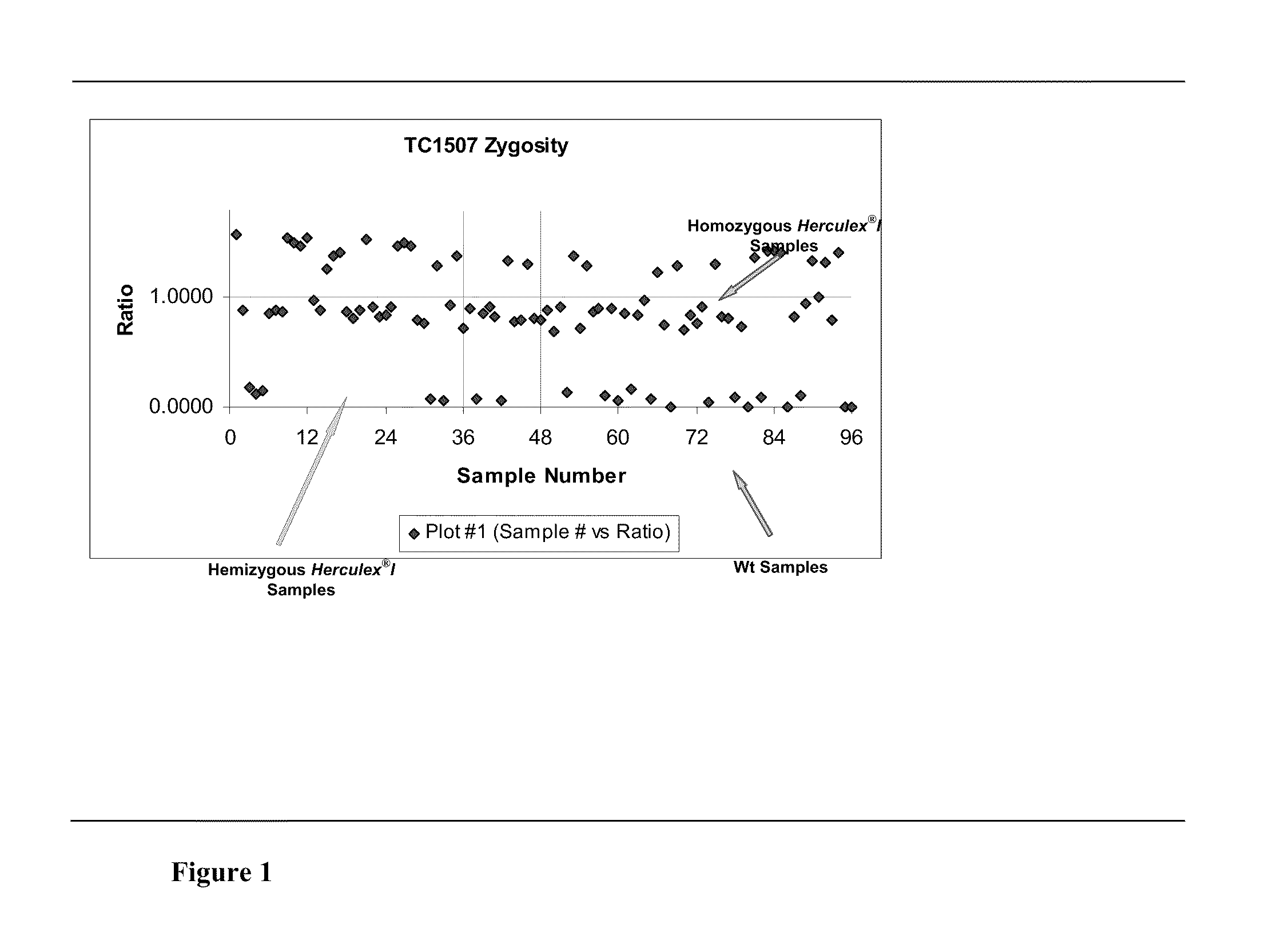
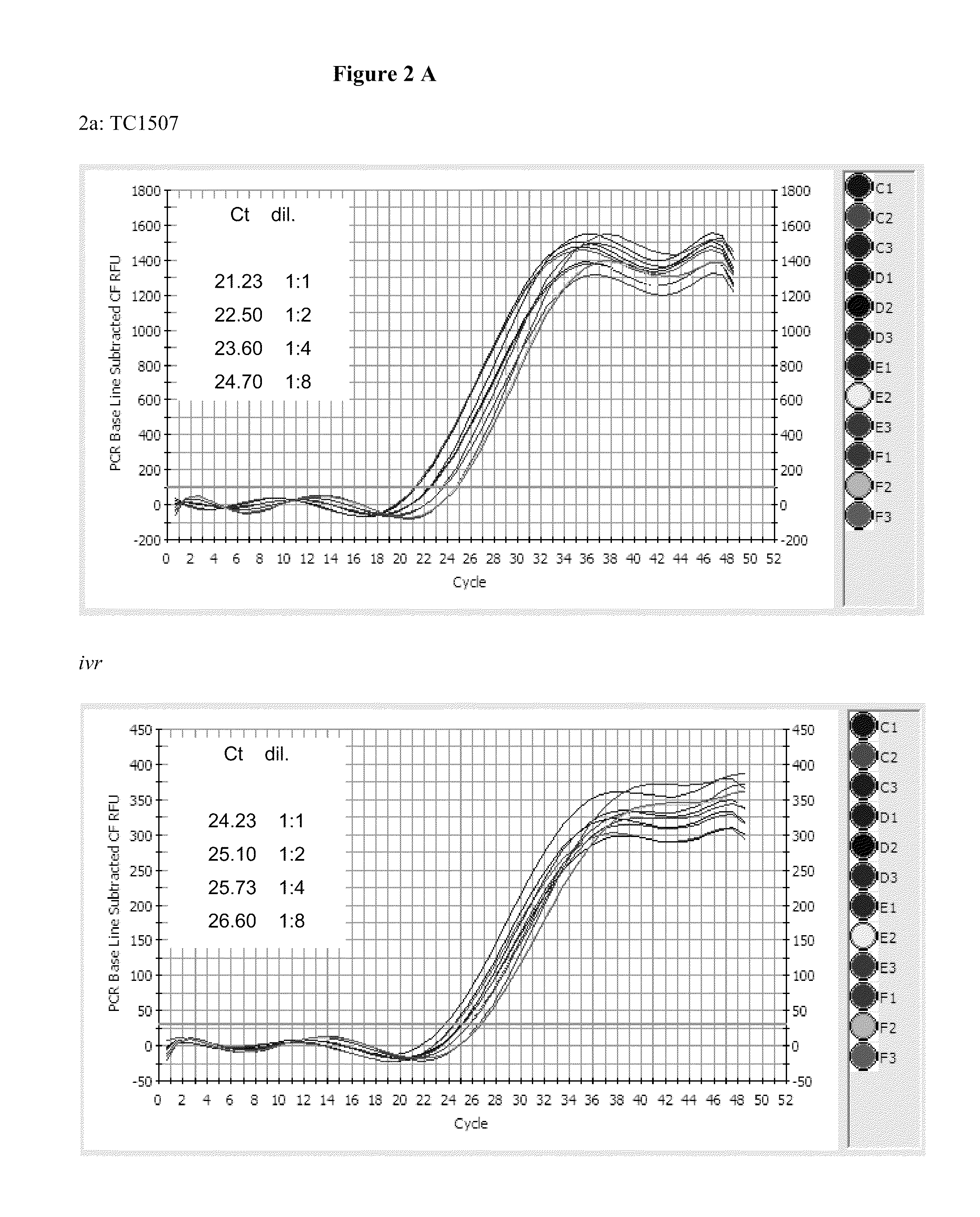
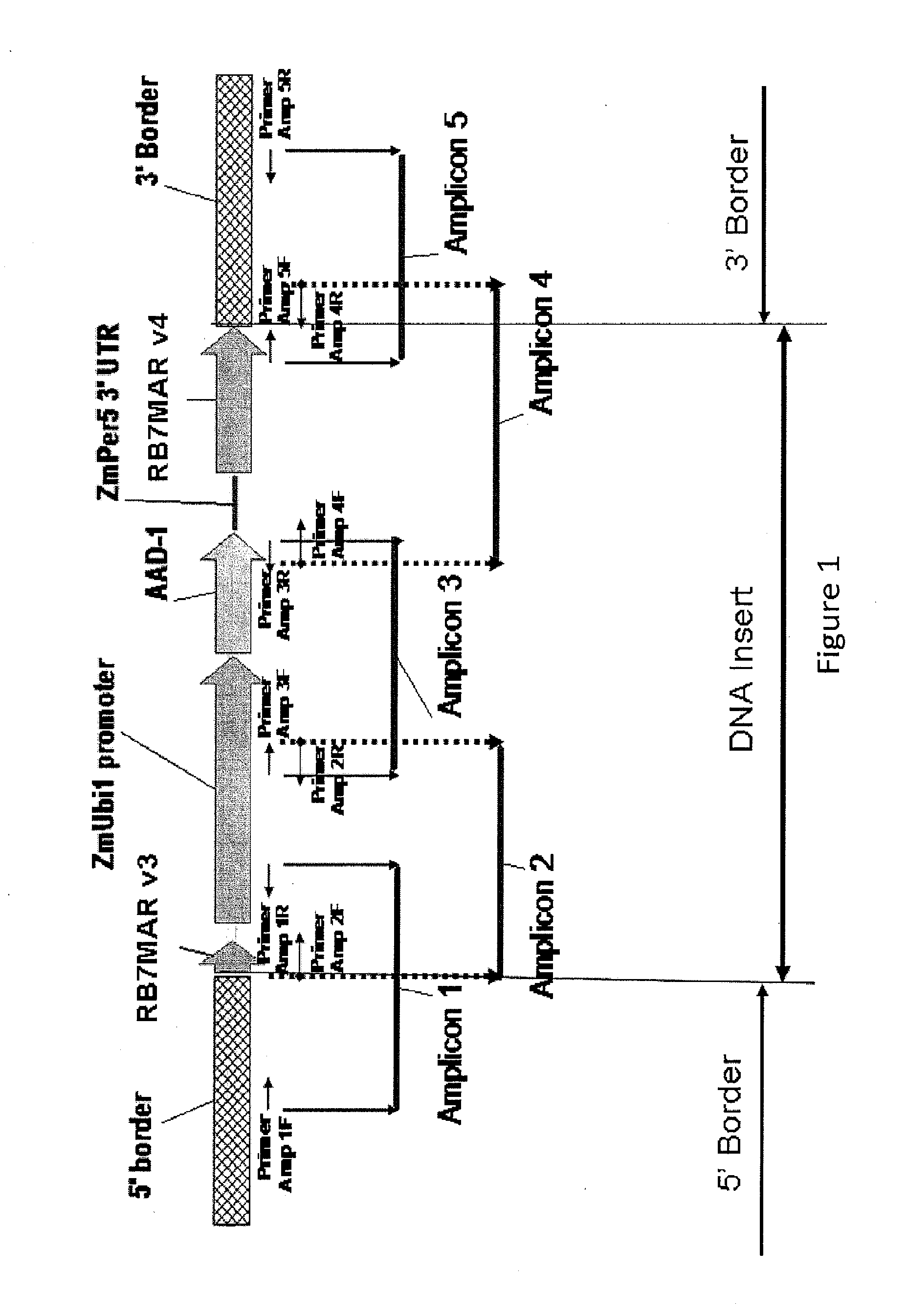
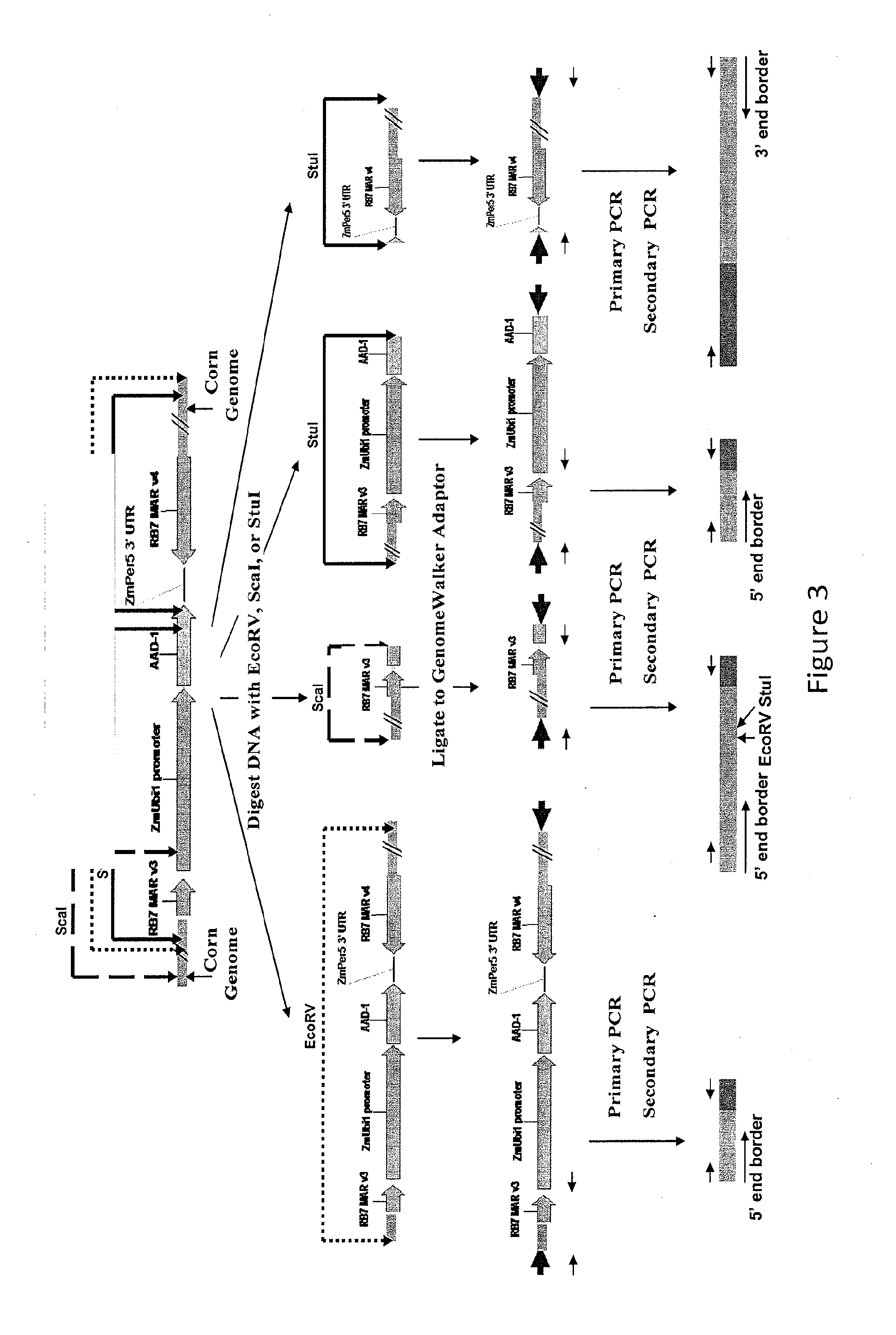
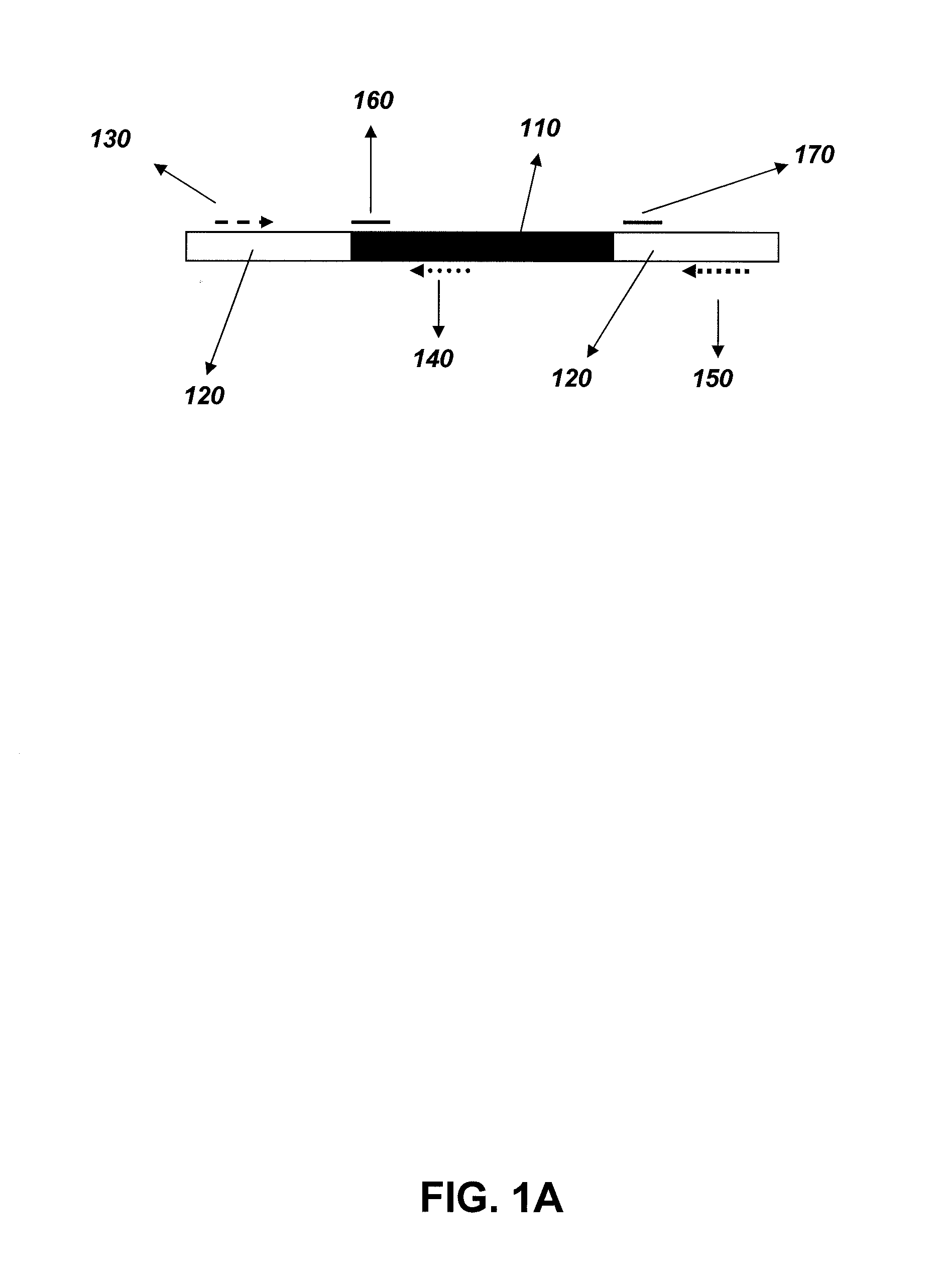
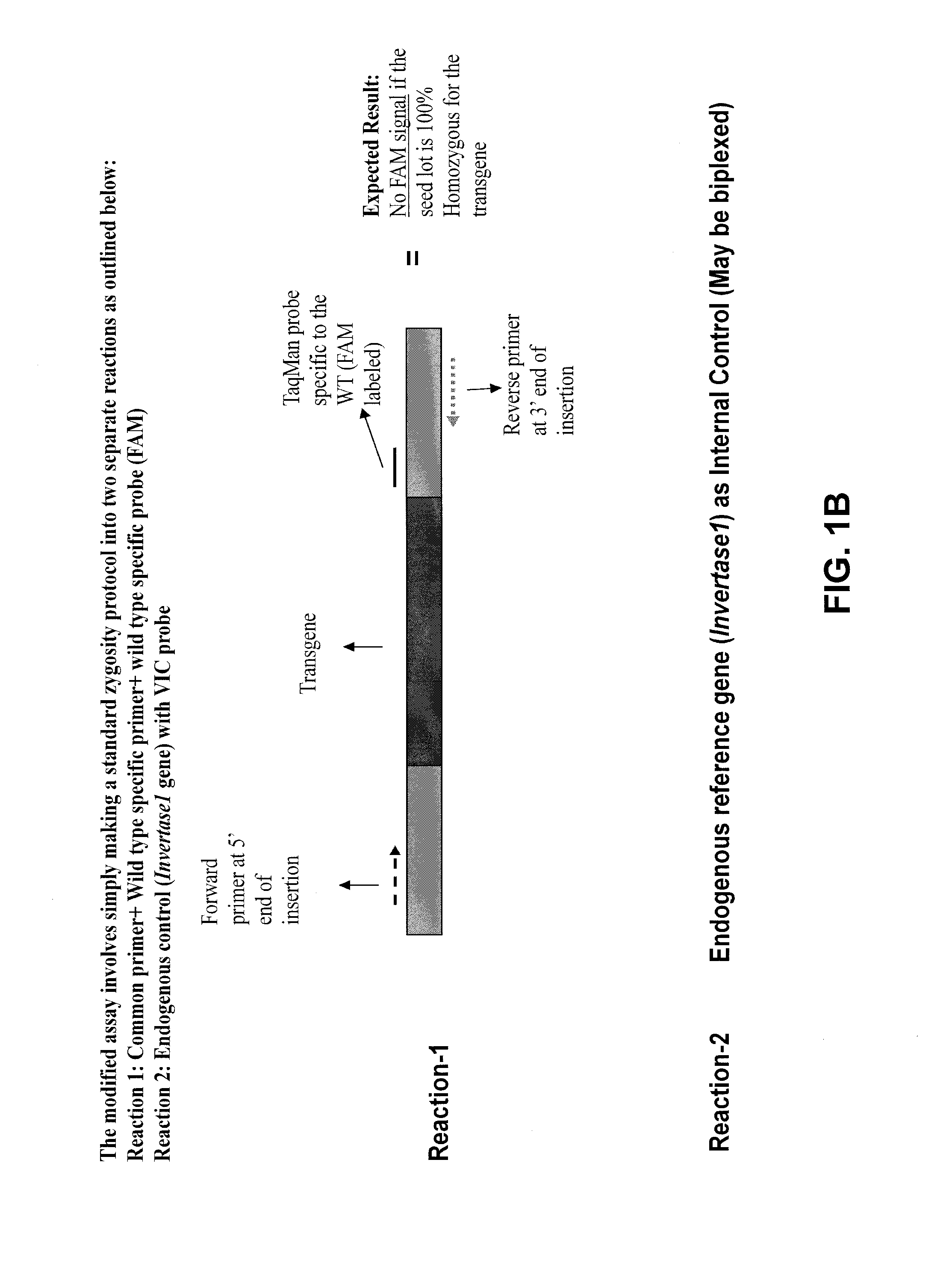
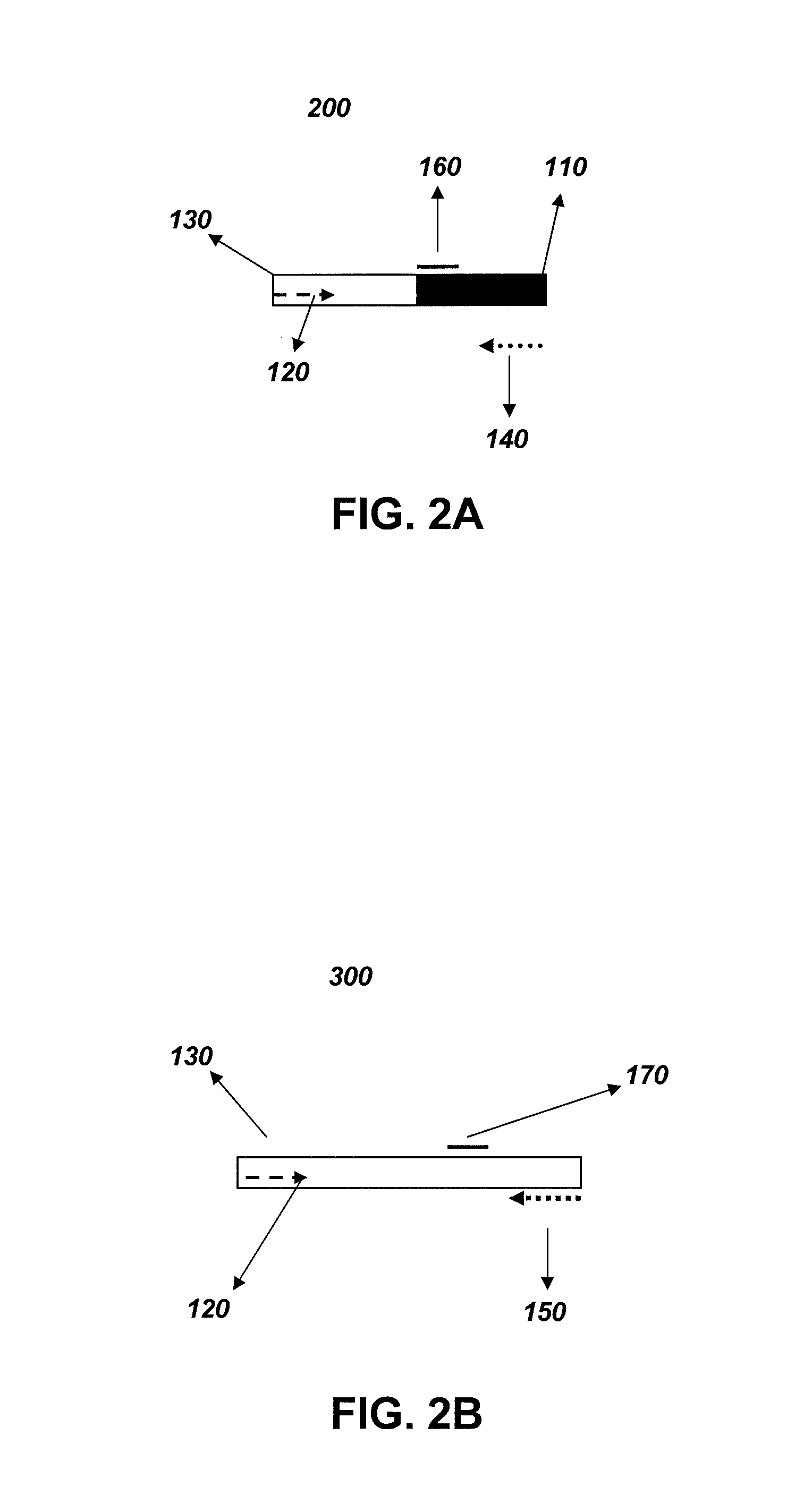
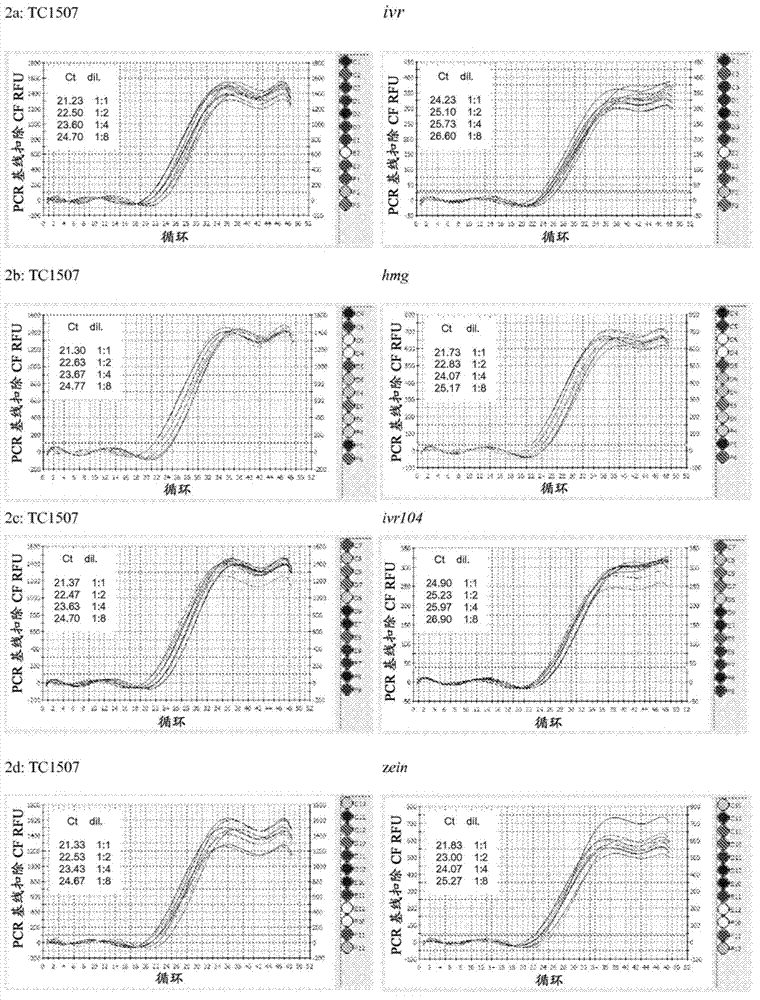
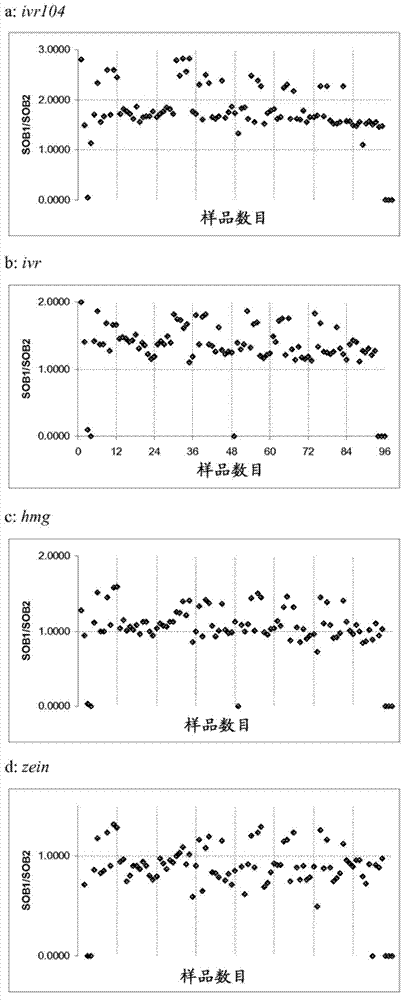
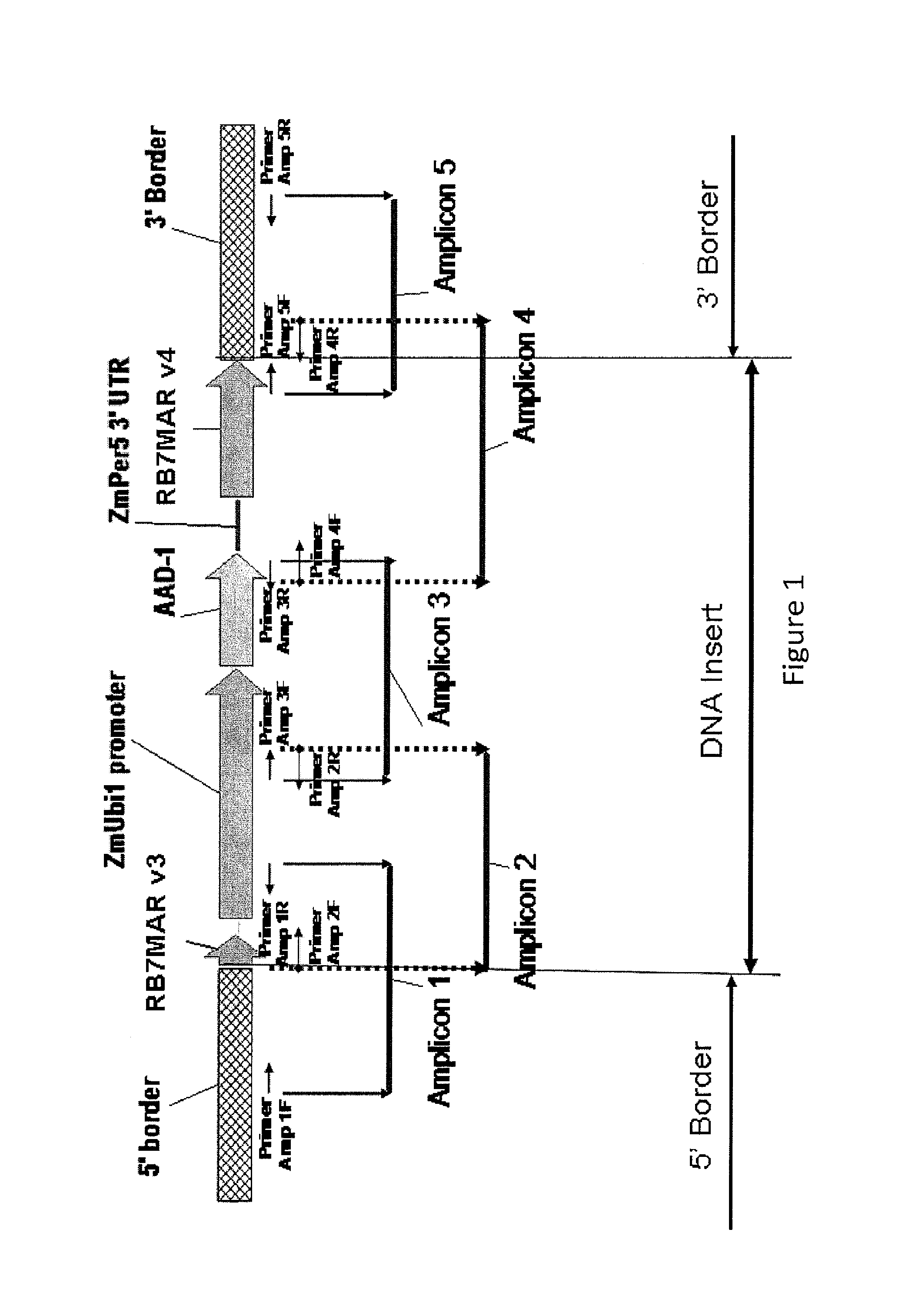
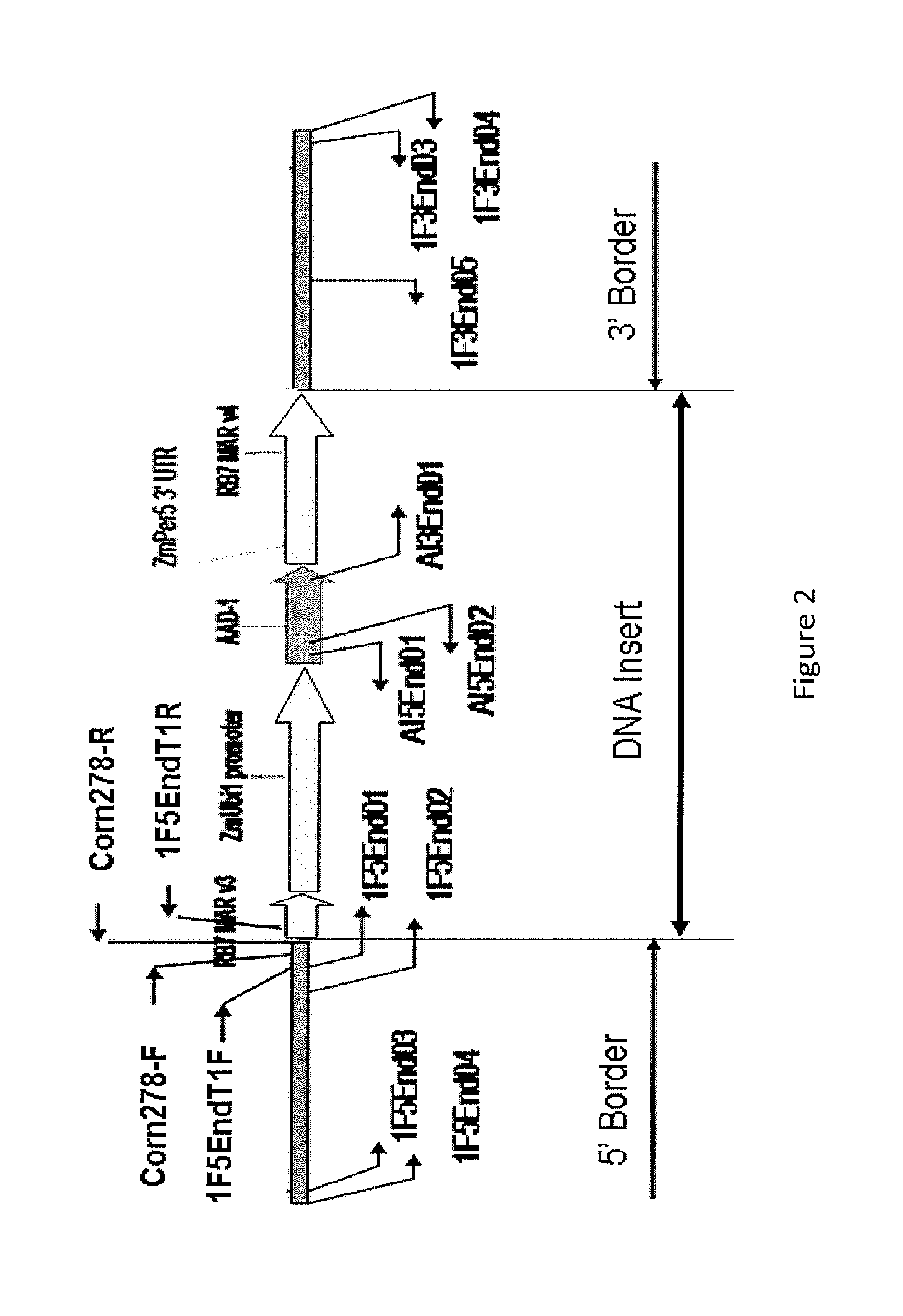
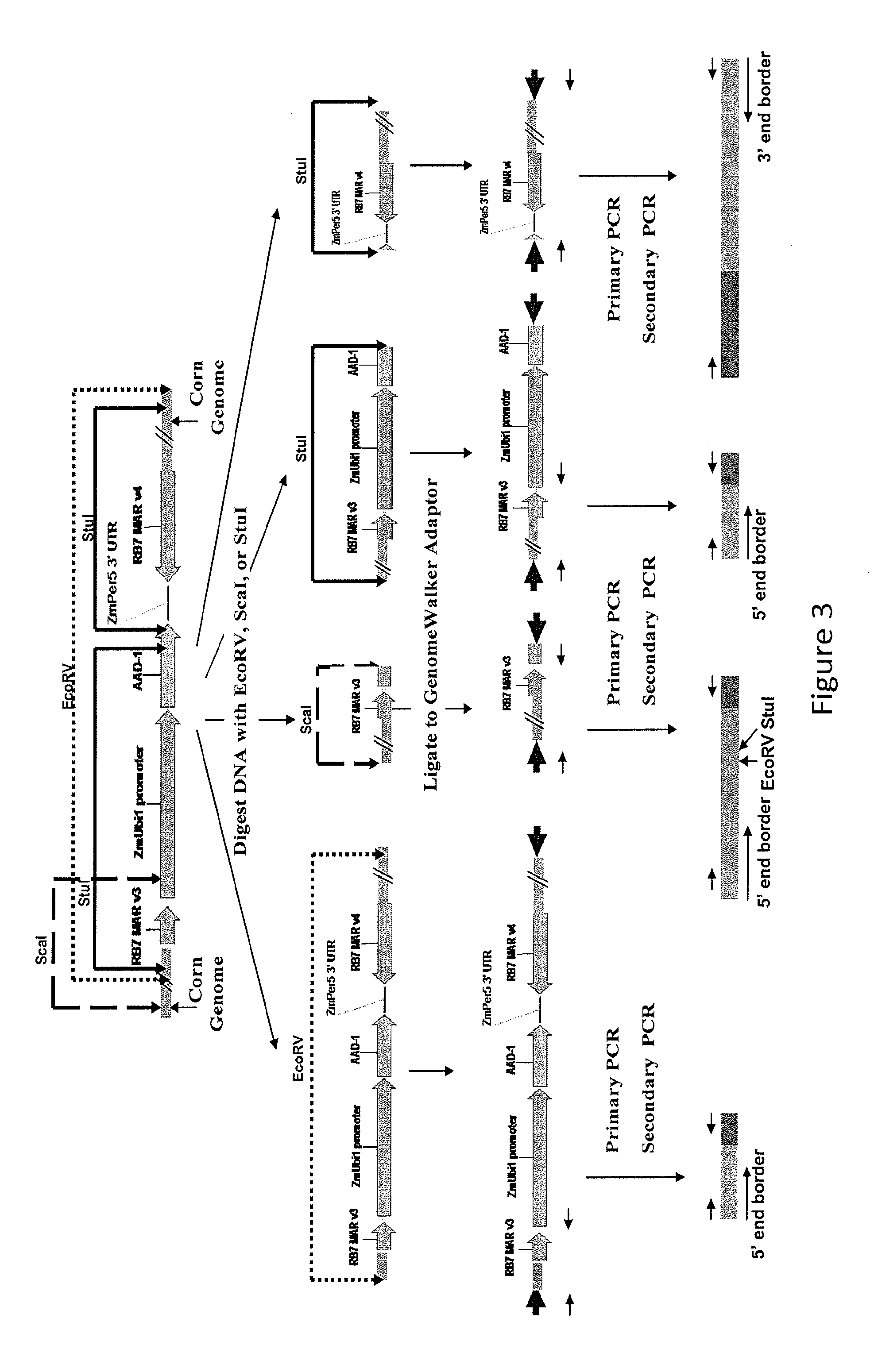
Endpoint taqman methods for determining zygosity of corn comprising tc1507 events
InactiveUS20110151441A1High throughput zygosity analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesPcr assay
A method for zygosity analysis of the maize Cry1F event TC1507 is provided. The method provides TC1507 event-specific and maize endogenous reference gene-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of producing robust genotype calls for assisting in molecular breeding of TC1507.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
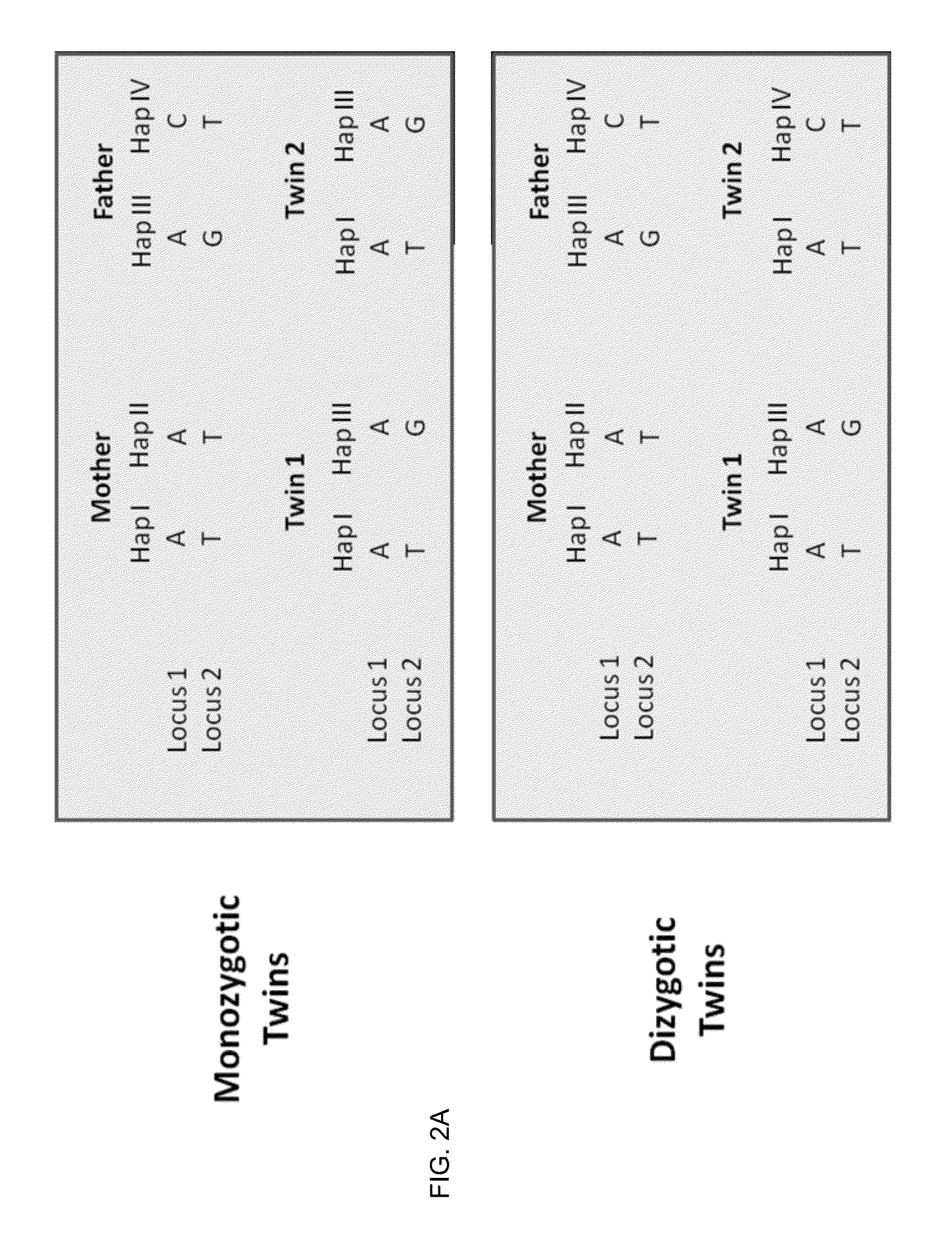
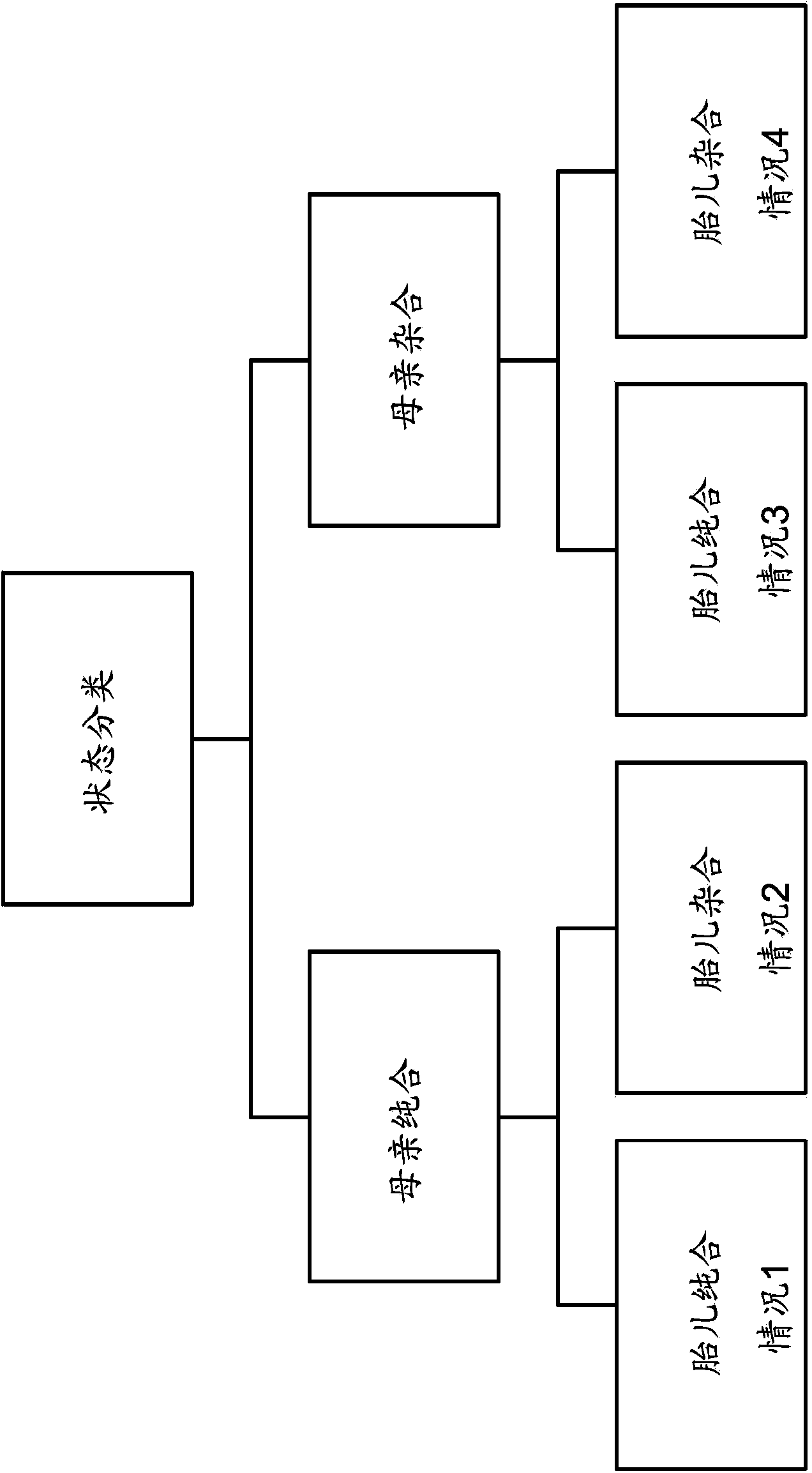
Molecular testing of multiple pregnancies
ActiveUS20130059733A1Non invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningSpecific chromosomeGenetic divergence
Methods, systems, and apparatus are provided for determining zygosity of a multiple-fetus pregnancy using a biological sample taken from the mother. The fetal and maternal DNA in the sample (e.g. plasma) can be analyzed for a particular chromosomal region to identify genetic differences in the fetuses. For example, a normalized parameter for the measure of a primary or secondary allele can show variances for different chromosomal regions when fetuses are dizygotic. Such a variance can be determined relative to an expected value if the fetuses were genetically identical. Statistical methods are provided for analyzing the variation of the normalized parameters to determine fetal DNA concentration and the maternal-fetal mixed genotype at various loci. Parental genotype and haplotype information can also be used to identify inheritance of different parental haplotypes to indicate genetic differences among the fetuses.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
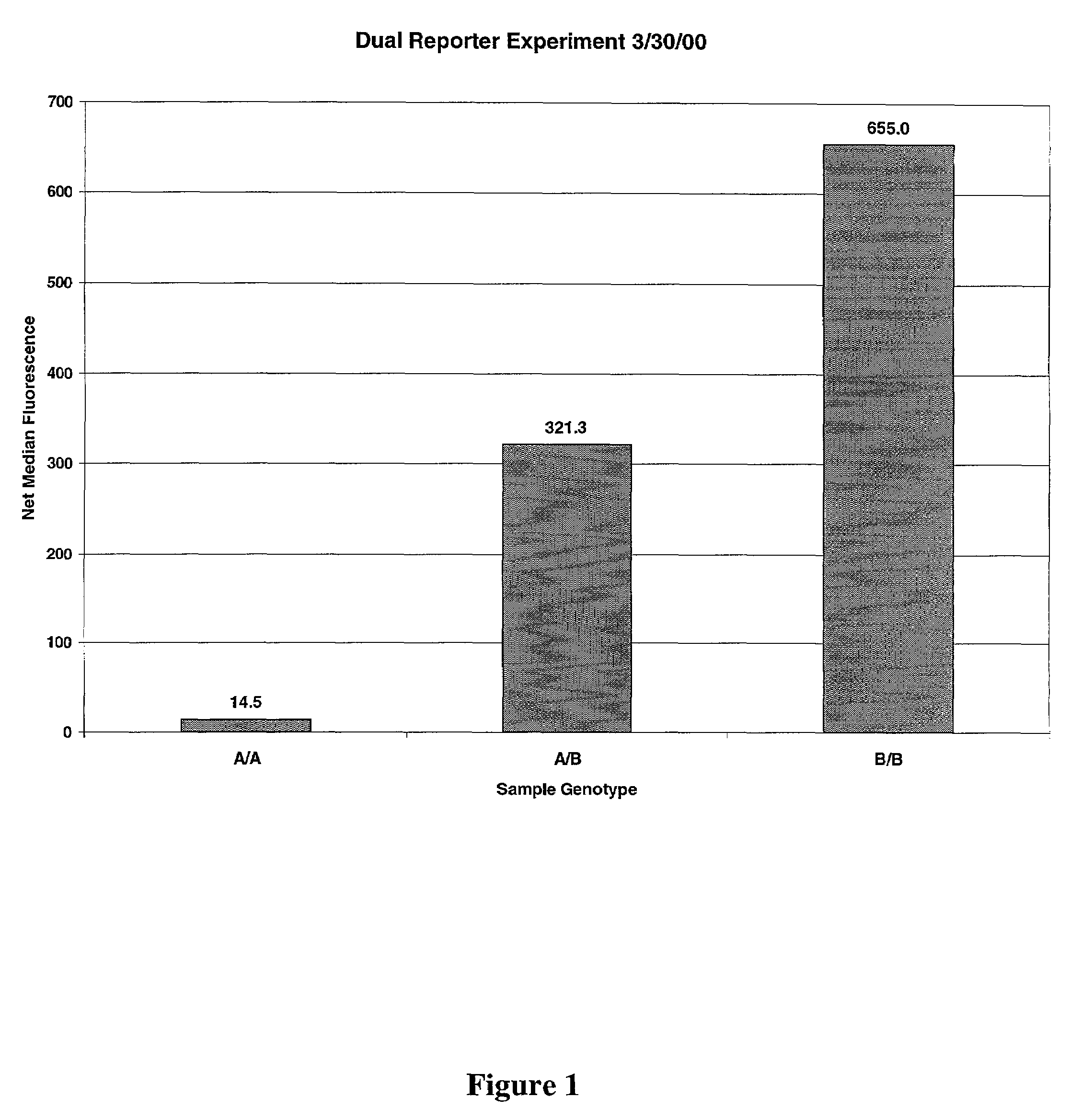
Multiple reporter read-out for bioassays
ActiveUS7465540B2Convenient and accurateImprove detection limitPeptide librariesNucleotide librariesAnalyteMicrosphere
A method for detecting a plurality of reactive sites on an analyte, comprising allowing reactants on an addressable microsphere and the reactive sites to react, forming reactant-reactive site pairs distinguishable by fluorescence intensity. The invention also provides a method for detecting a plurality of analytes in a sample using addressable microspheres in combination with one or more reporter reagents. Also provided are a method for determining allele zygosity of a genetic locus having two alleles or more alleles using microparticles, and a method for detecting a plurality of SNPs in nucleic acid molecules. The instant invention also provides a composition comprising an addressable microsphere carrying at least two fluorescent reactants capable of forming reactant-analyte pairs distinguishable by their fluorescence intensity, and kits comprising the inventive composition and a plurality of reporter reagents.
Owner:LUMINEX
Development of novel germplasm using segregates from transgenic crosses
ActiveUS20070136836A1Improve efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGermplasmEvolutionary biology
This invention provides a method for the development of novel plant germplasm using segregates from a transgenic line combined with PCR-based zygosity testing and, optionally, Southern blot analysis.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Detection of aad1 event das-40278-9
ActiveUS20120244533A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotechnologyReference genes
This invention relates in part to detecting herbicide tolerant plants—more specifically, an aad-1 transformation event in corn plants. The subject invention also provides assays for detecting the presence of the subject event in a sample (of corn grain, for example). Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. The subject invention also relates in part to plant breeding using the subject methods. In some embodiments, said event / polynucleotide sequence can be “stacked” with other traits. More specifically, the invention relates in part to an endpoint TaqMan PCR assay for AAD-1 corn event 40278-9. Some embodiments are directed to assays that are capable of high throughput zygosity analysis. The subject invention further relates, in part, to the use of a preferred reference gene for use in determining zygosity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
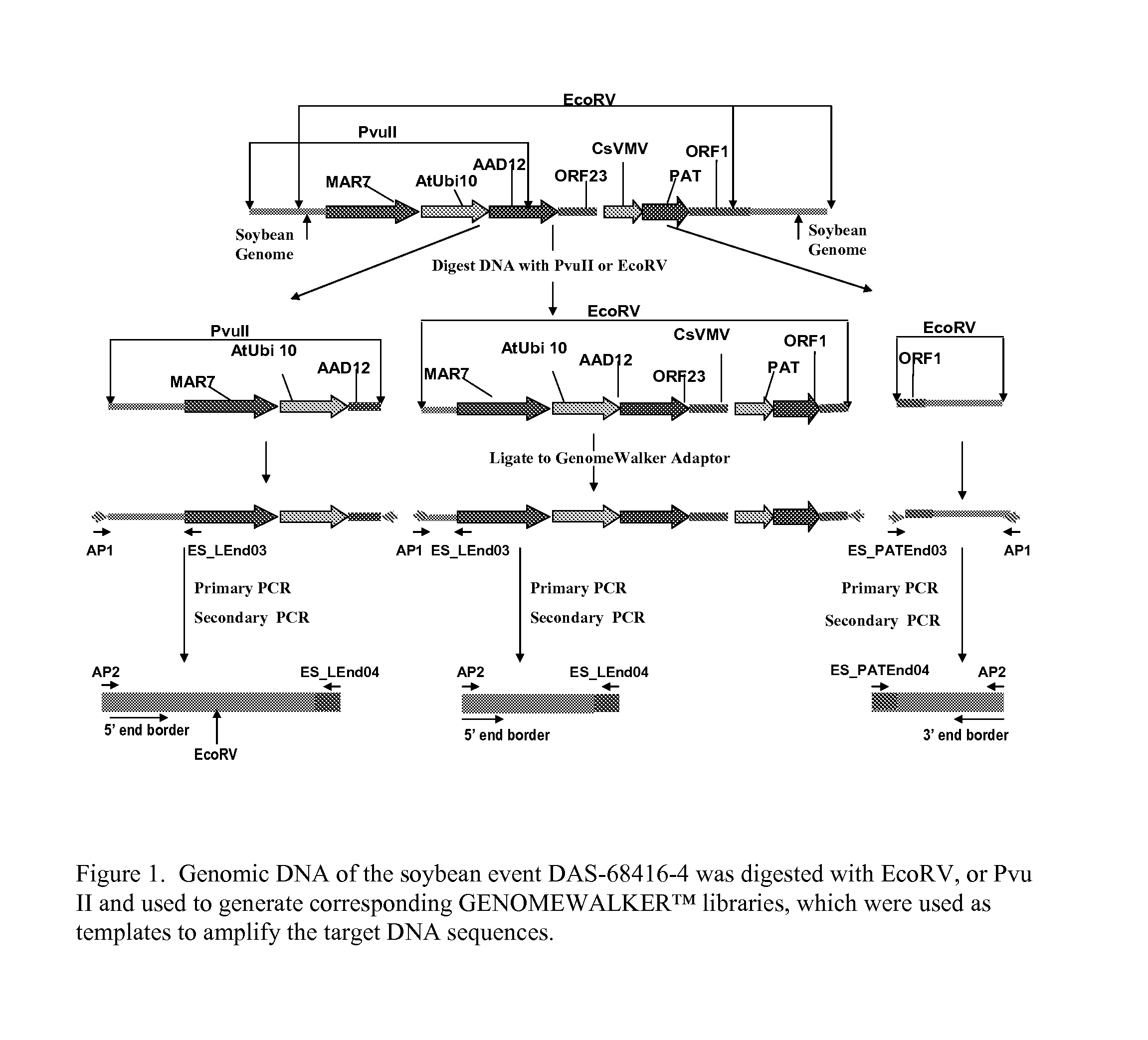
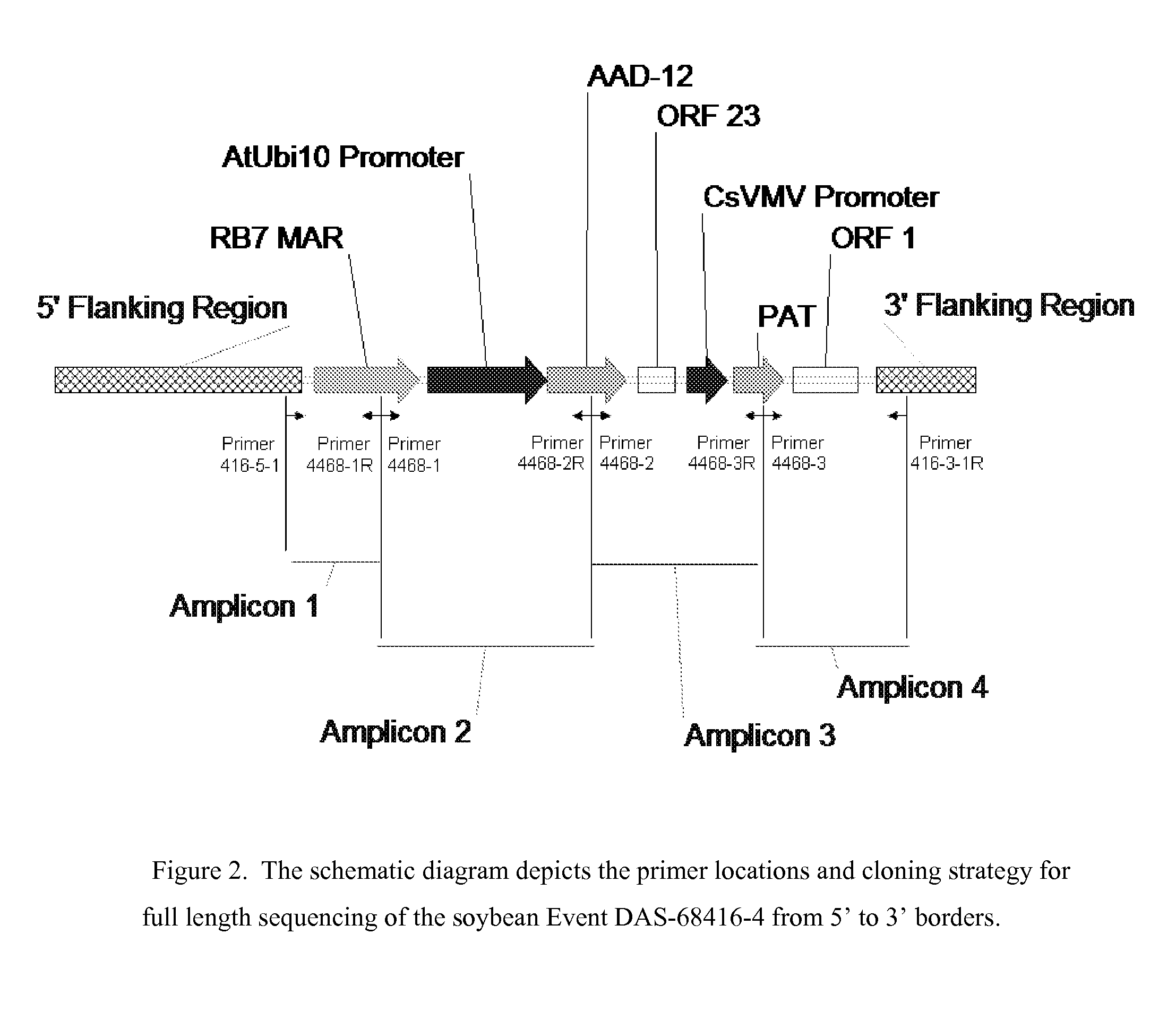
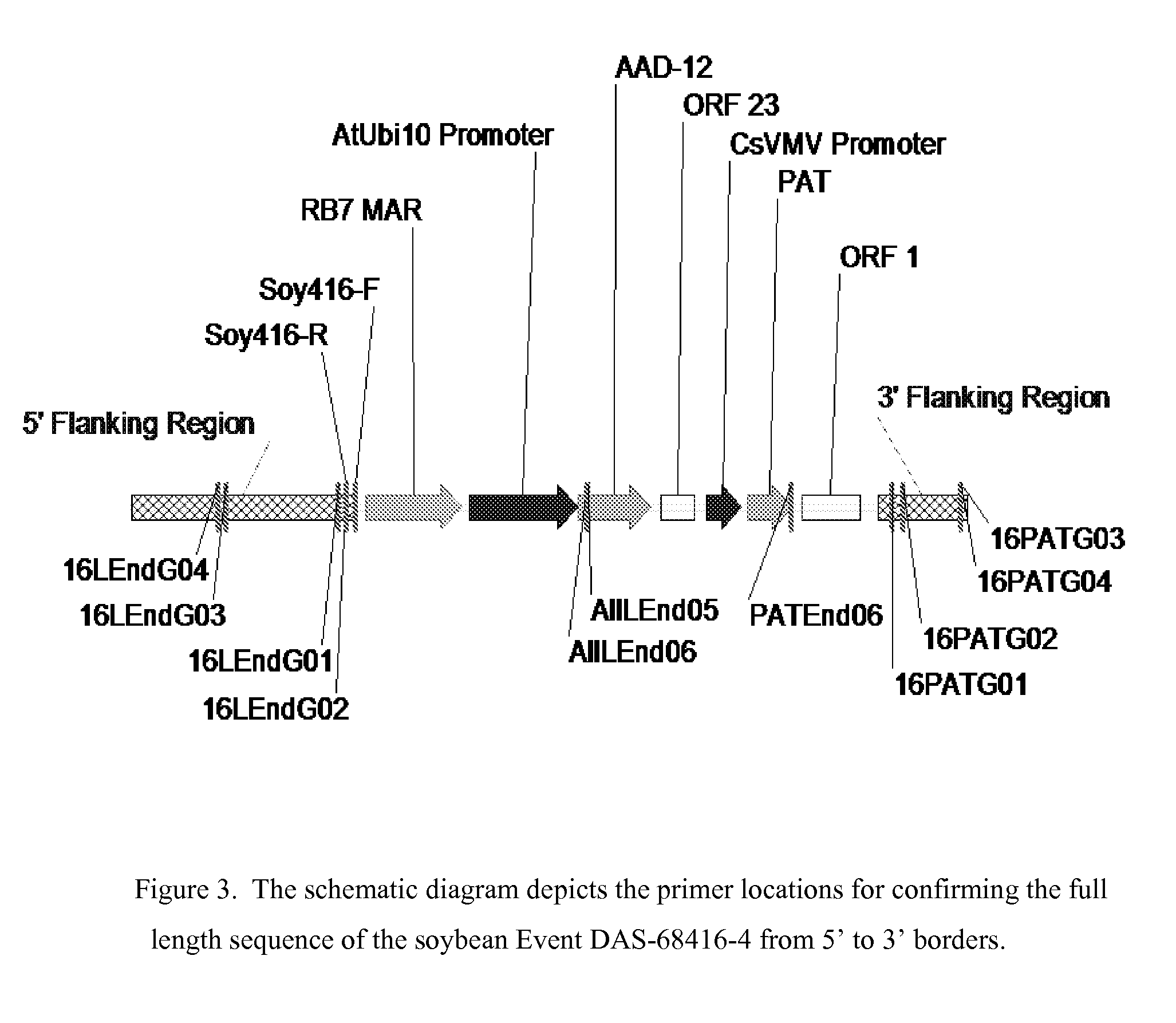
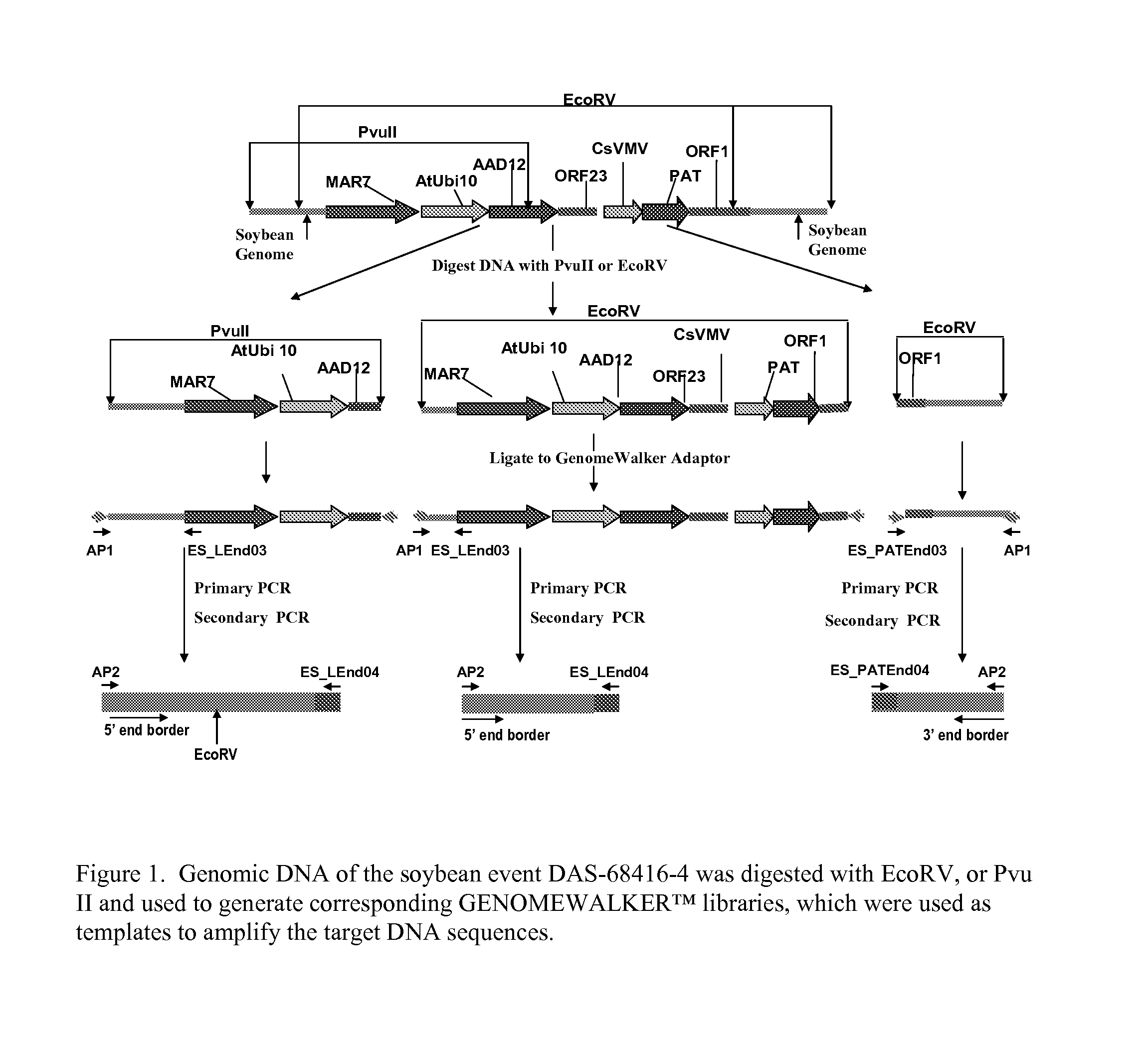
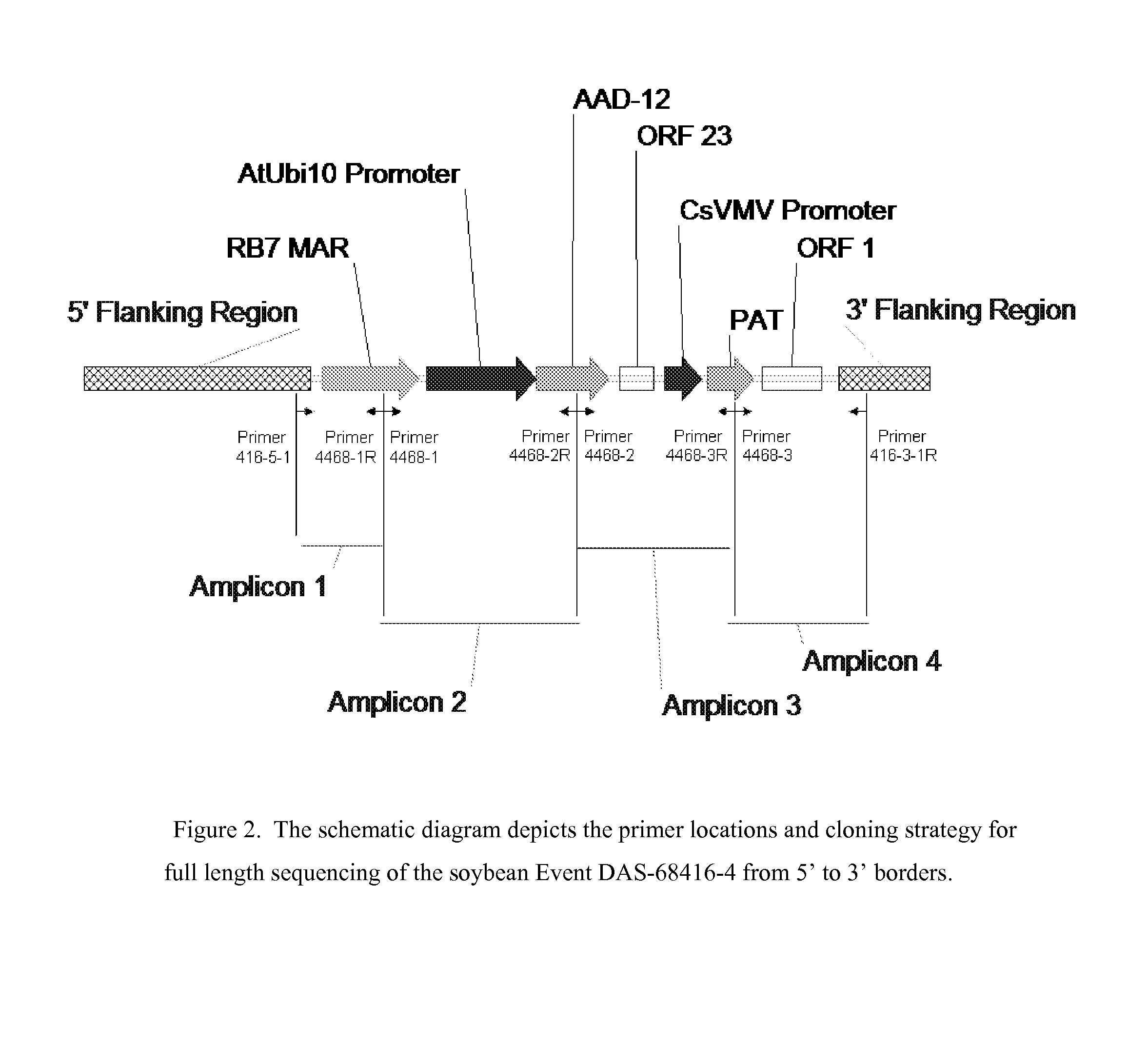
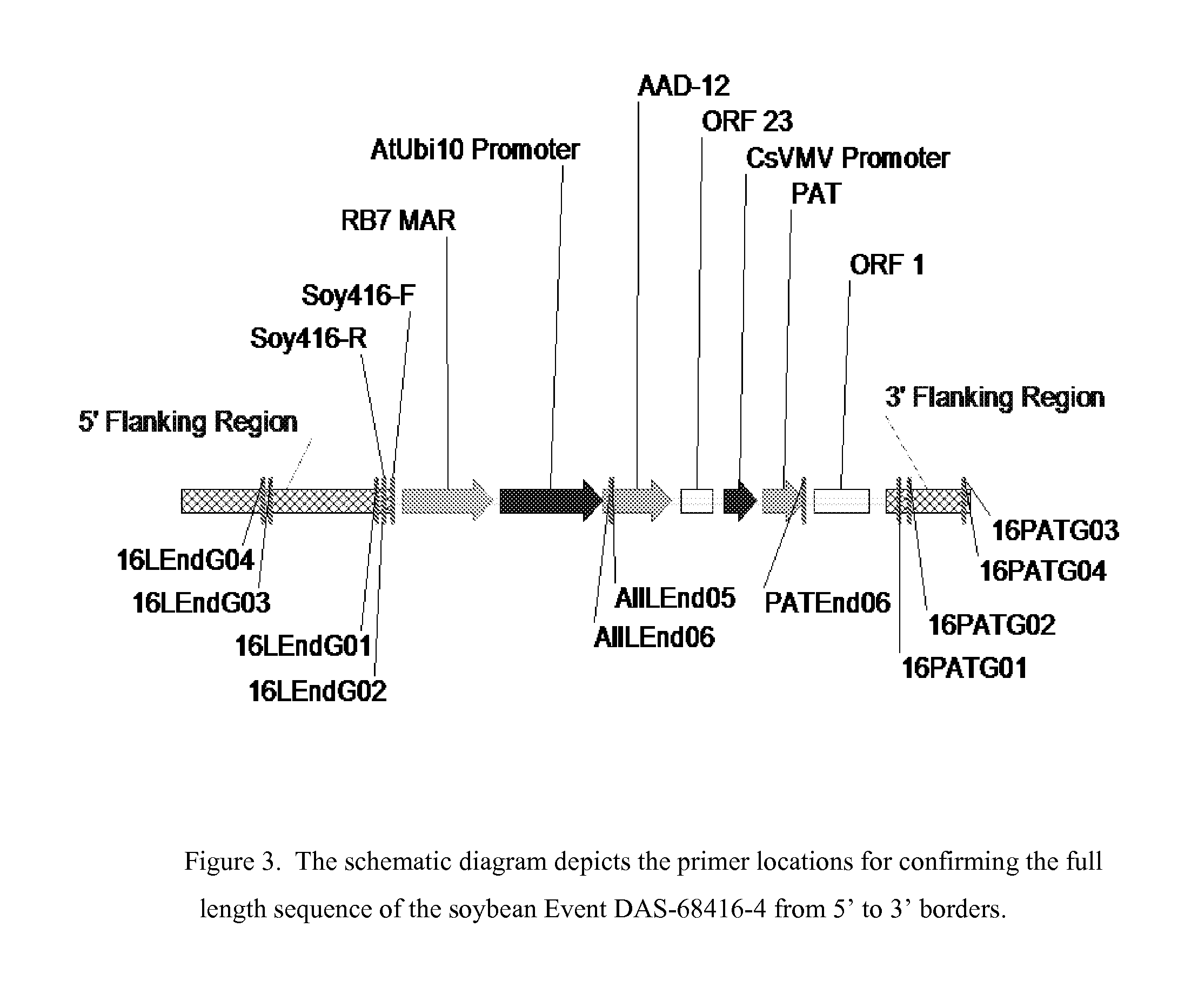
Detection of AAD-12 soybean event 416
The invention relates in part to methods of detecting an AAD-12 soybean event. The subject invention provides assays for detecting the presence of the subject event in a sample (of soybeans, for example). Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. More specifically, the present invention relates in part to an endpoint TaqMan PCR assay for the AAD-12 soybean event. Some embodiments are directed to assays that are capable of high throughput zygosity analysis. The subject invention further relates, in part, to the discovery of a preferred reference gene for use in determining zygosity. This invention also relates in part to plant breeding using any of the subject methods. In some embodiments, said event / polynucleotide sequence can be “stacked” with other traits. The subject procedures can be used to uniquely identify soybean lines comprising the event of the subject invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
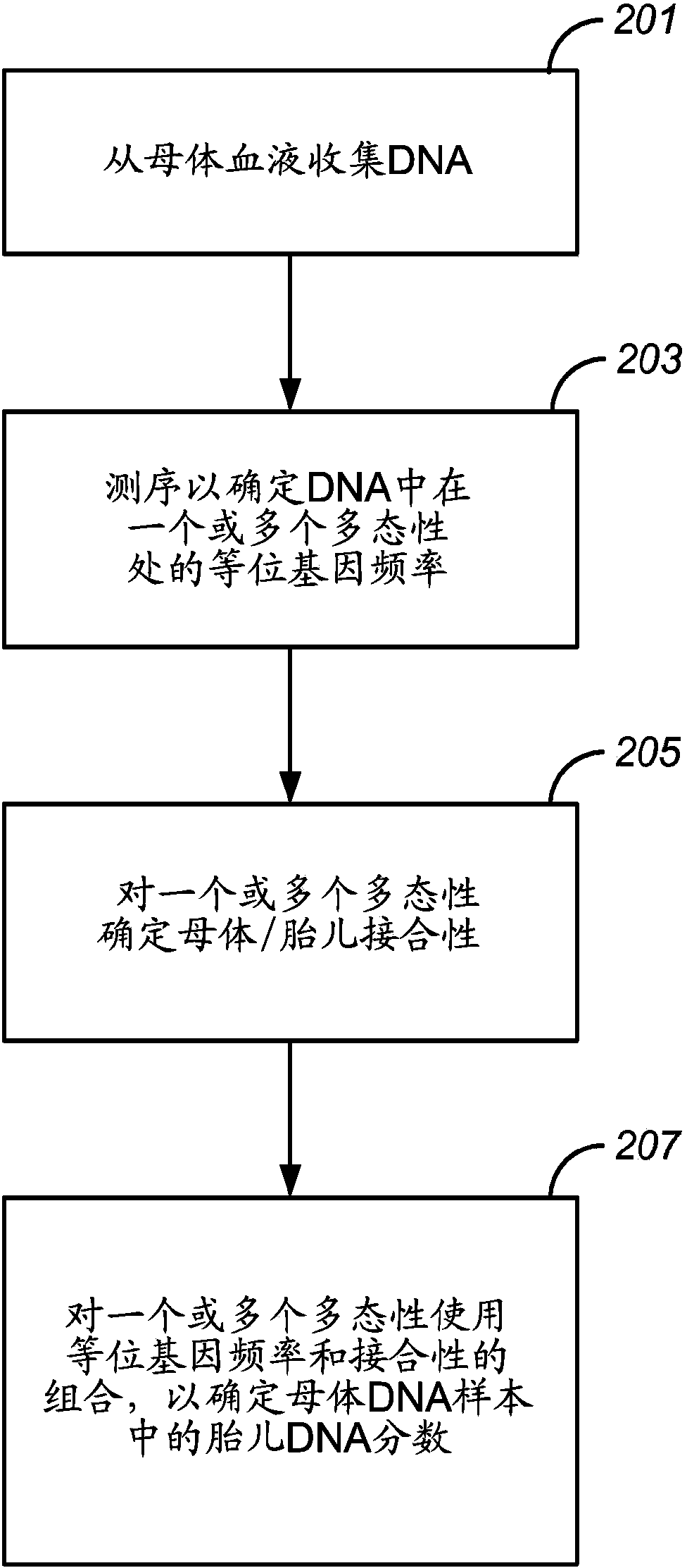
Resolving genome fractions using polymorphism counts
ActiveCN103797129AMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationRe sequencingInsertion deletion
Methods of reliably estimating genomic fraction (e.g., fetal fraction) from polymorphisms such as small base variations or insertions-deletions are disclosed. Sequenced data from a multigenomic source is used to determine allele counts for one or more of the polymorphisms. For one or more of the polymorphisms, zygosity is assigned, and genomic fraction is determined from the zygosity and allele counts. Certain embodiments employ SNPs as the relevant polymorphism. The disclosed methods can be applied as part of an intentional, pre-designed re-sequencing study targeted against known polymorphisms or can be used in a retrospective analysis of variations found by coincidence in overlapping sequences generated from maternal plasma (or any other setting where a mixture of DNA from several people are present).
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
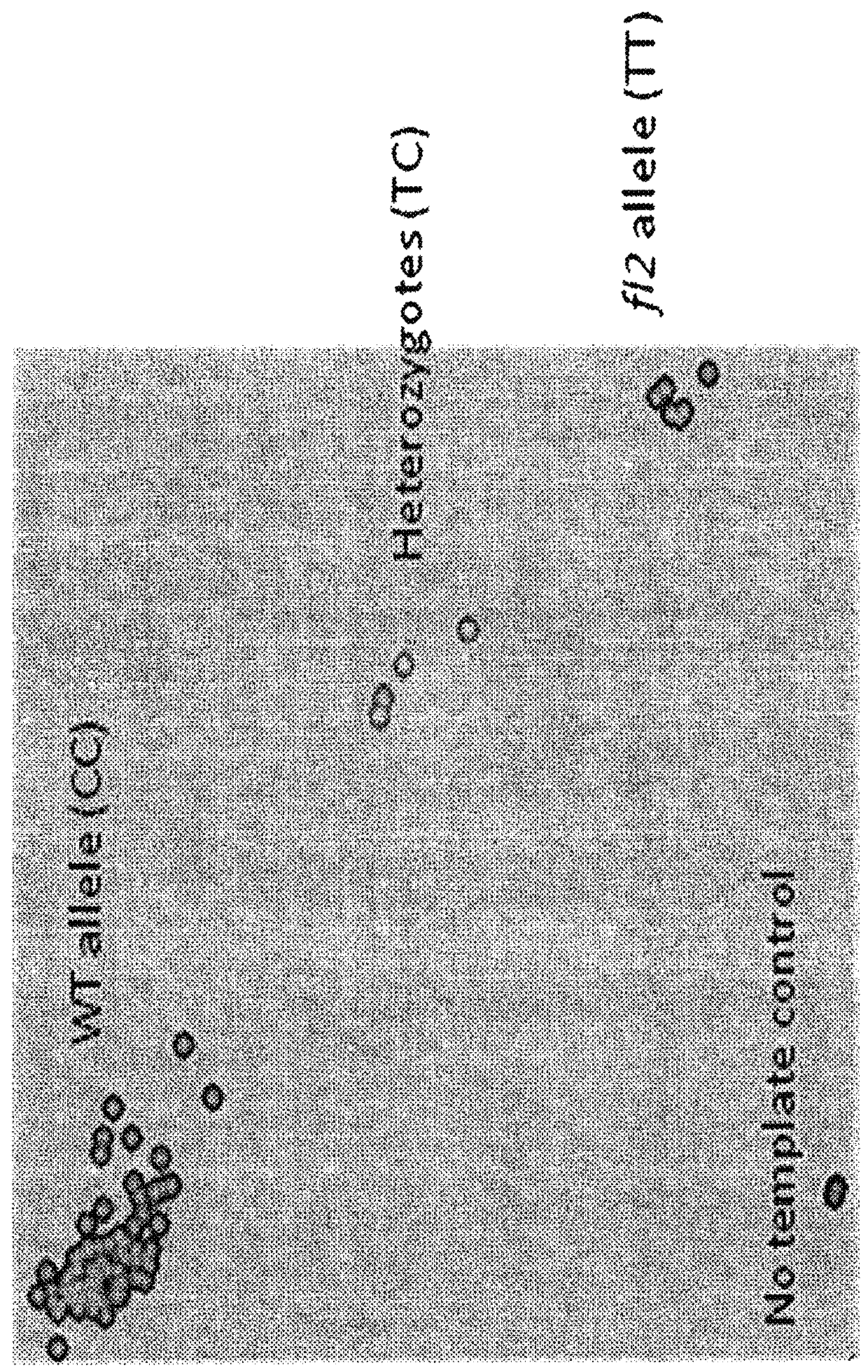
Floury 2 gene-specific assay in maize for floury (FL2) trait introgression
ActiveUS20160153055A1Reliably and predictably introgressingHigh in lysineBryophytesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular breedingGermplasm
The disclosure concerns compositions and methods for determining the zygosity of corn plants containing one or more floury2 (fl2) mutations. In embodiments, the disclosure concerns a gene specific PCR-based molecular (KASPar®) assay for identifying the floury2 trait in plants. In certain embodiments, compositions and methods are disclosed for determining the zygosity of corn plants with respect to the fl2 allele. In particular embodiments, the assay may be used for fl2 germplasm identification, accelerating introgression and molecular breeding programs in corn and other plants.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Development of novel germplasm using segregates from transgenic crosses
ActiveUSH2258H1Improve efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationGermplasmEvolutionary biology
This invention provides a method for the development of novel plant germplasm using segregates from a transgenic line combined with PCR-based zygosity testing and, optionally, Southern blot analysis.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Detection of AAD-1 event DAS-40278-9
This invention relates in part to detecting herbicide tolerant plants - more specifically, an aad-1 transformation event in corn plants. The subject invention also provides assays for detecting the presence of the subject event in a sample (of corn grain, for example). Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. The subject invention also relates in part to plant breeding using the subject methods. In some embodiments, said event / polynucleotide sequence can be "stacked" with other traits. More specifically, the invention relates in part to an endpoint TaqMan PCR assay for AAD-1 corn event 40278-9. Some embodiments are directed to assays that are capable of high throughput zygosity analysis. The subject invention further relates, in part, to the use of a preferred reference gene for use in determining zygosity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
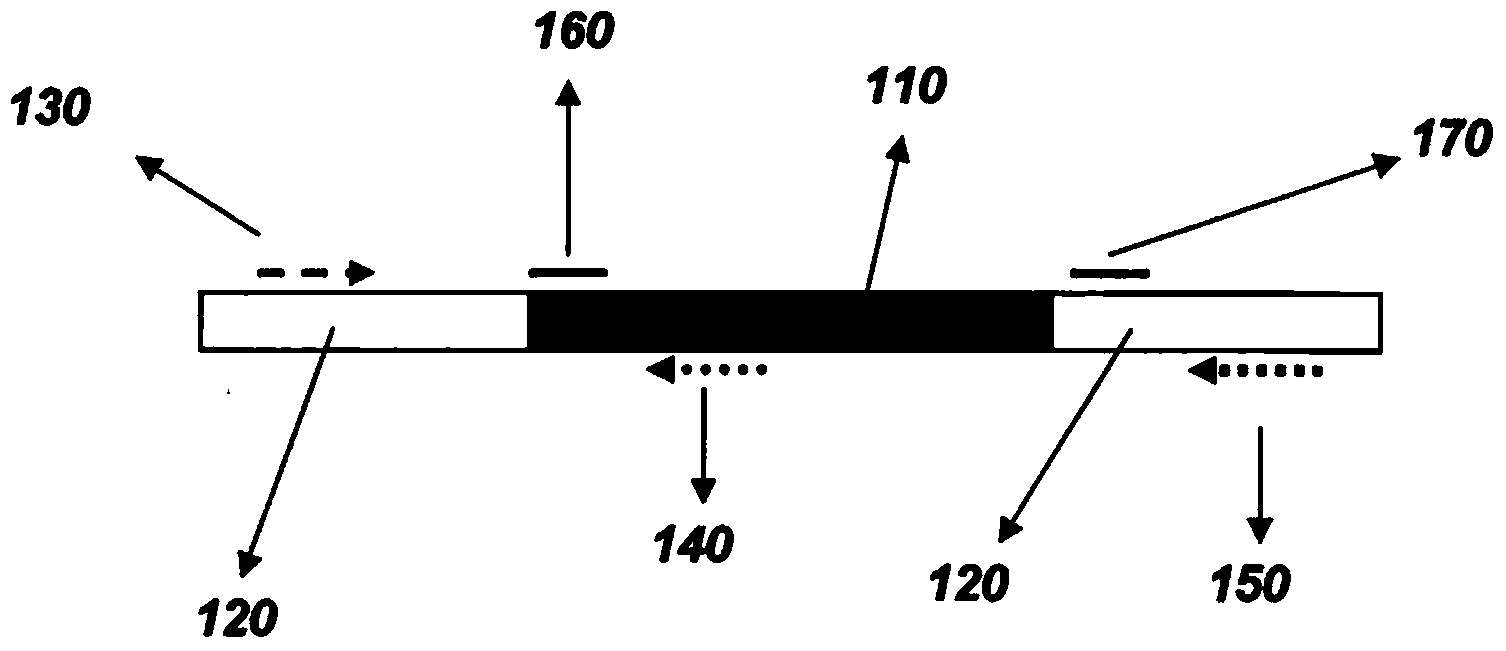
Methods to determine zygosity in a bulked sample
Methods of determining the presence or absence of an inserted nucleotide sequence at a particular insertion site in a nucleic acid include: isolating a nucleic acid from the bulked tissue sample; contacting the nucleic acid with a forward primer able to bind to the nucleic acid upstream of the insertion site, a first reverse primer specific for the inserted nucleotide sequence, and a second reverse primer able to bind to the nucleic acid downstream of the insertion site. The primers may be used to reproduce nucleic acids between the primers. The reproduced nucleic acids may be analyzed to determine if an inserted nucleotide sequence is present or absent in the sample.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
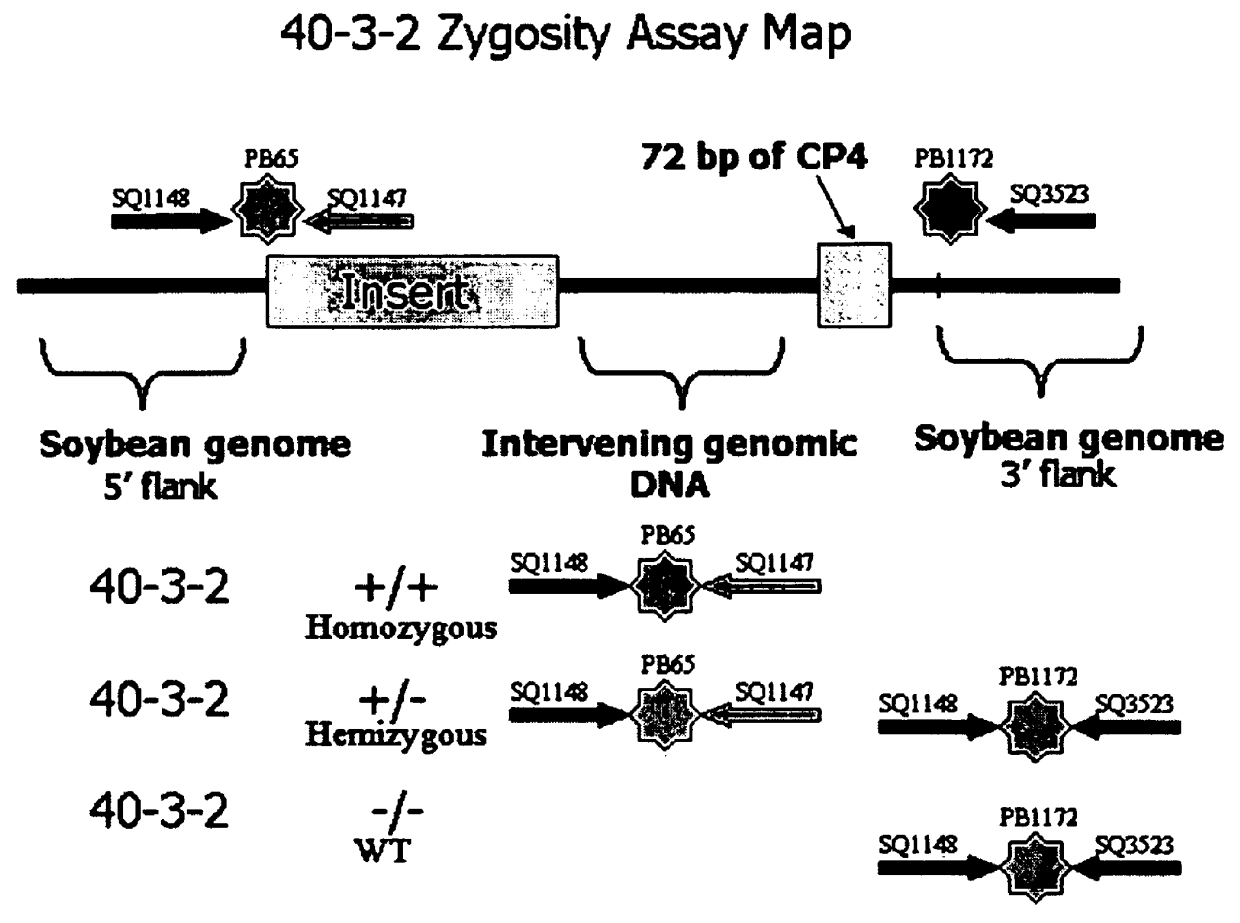
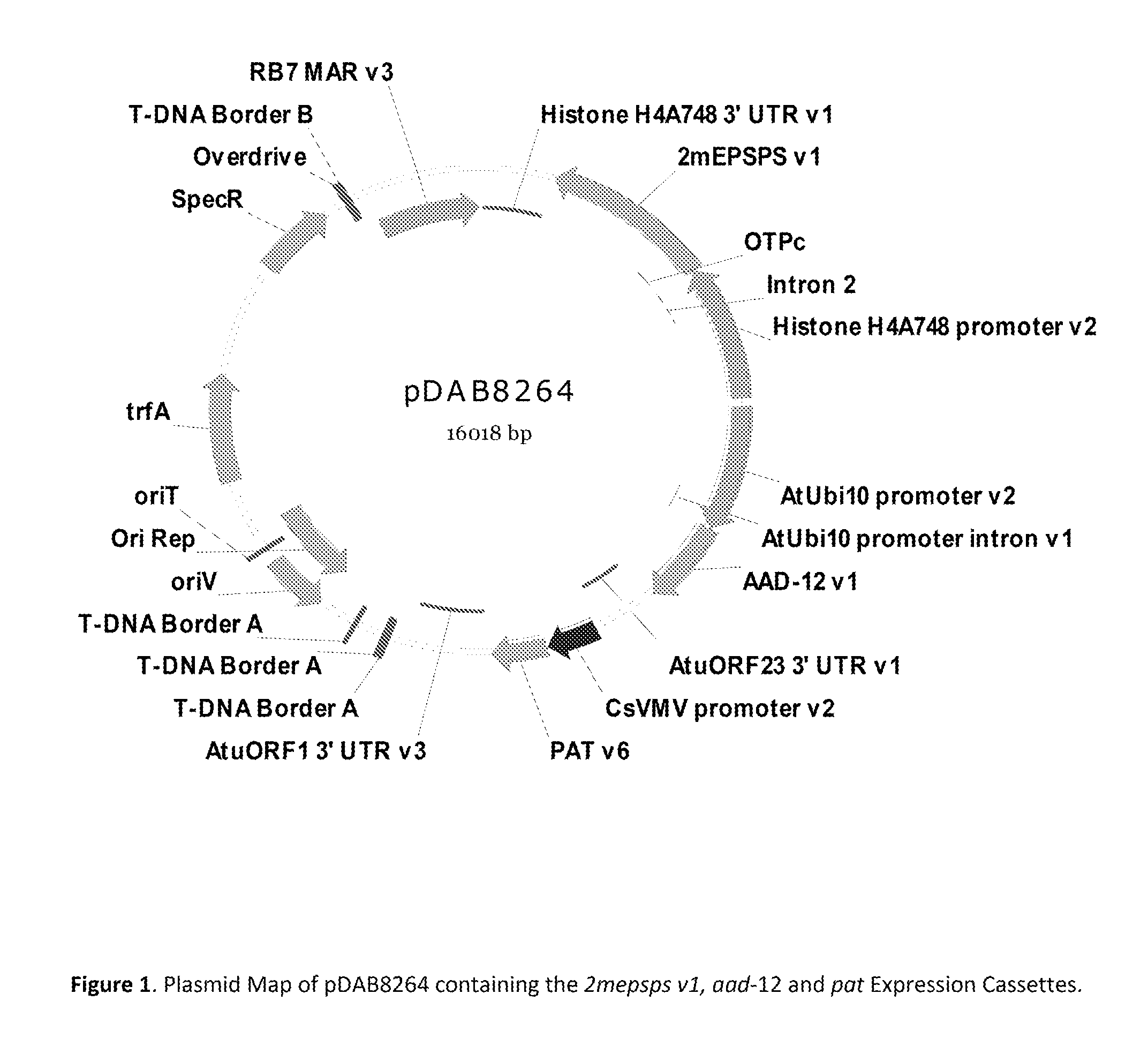
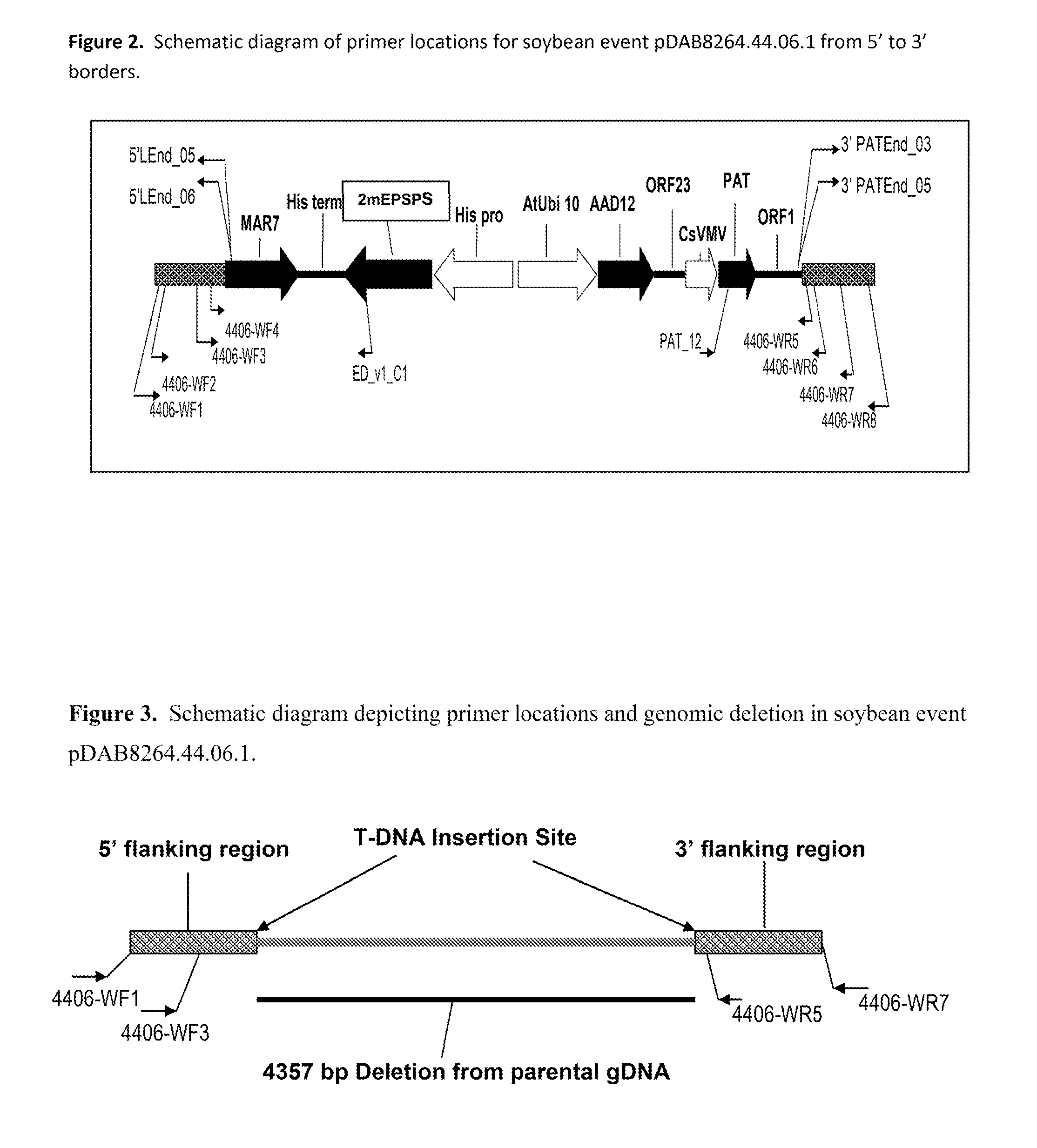
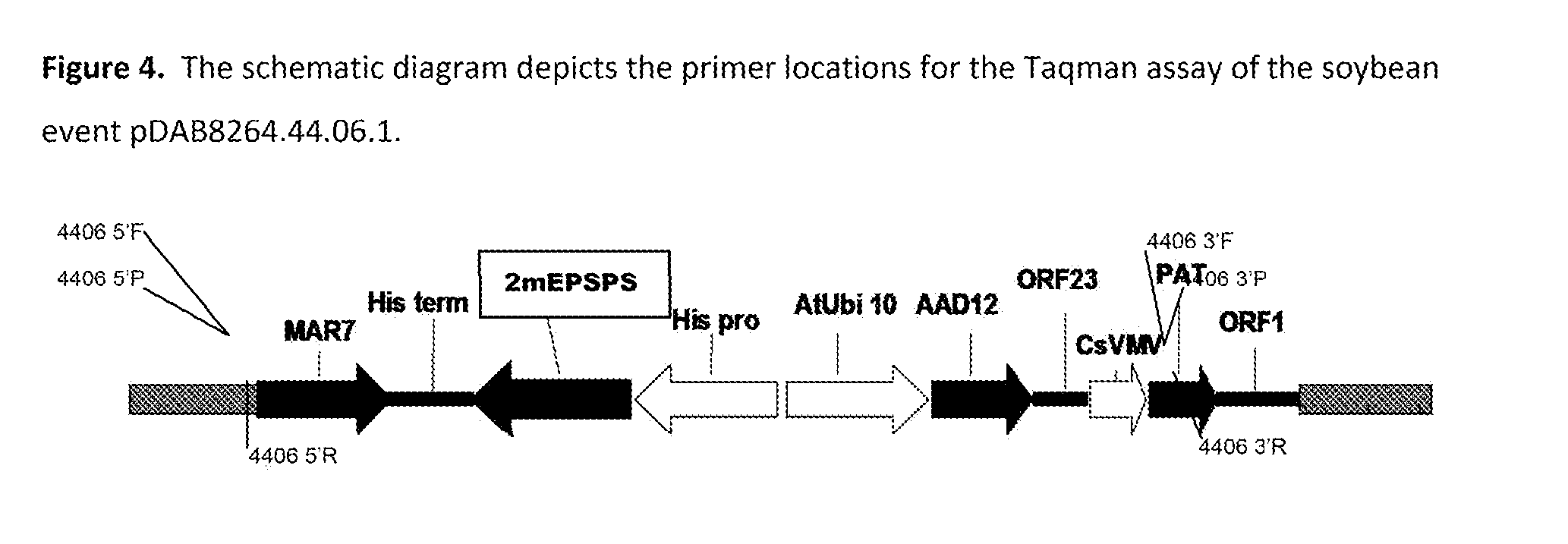
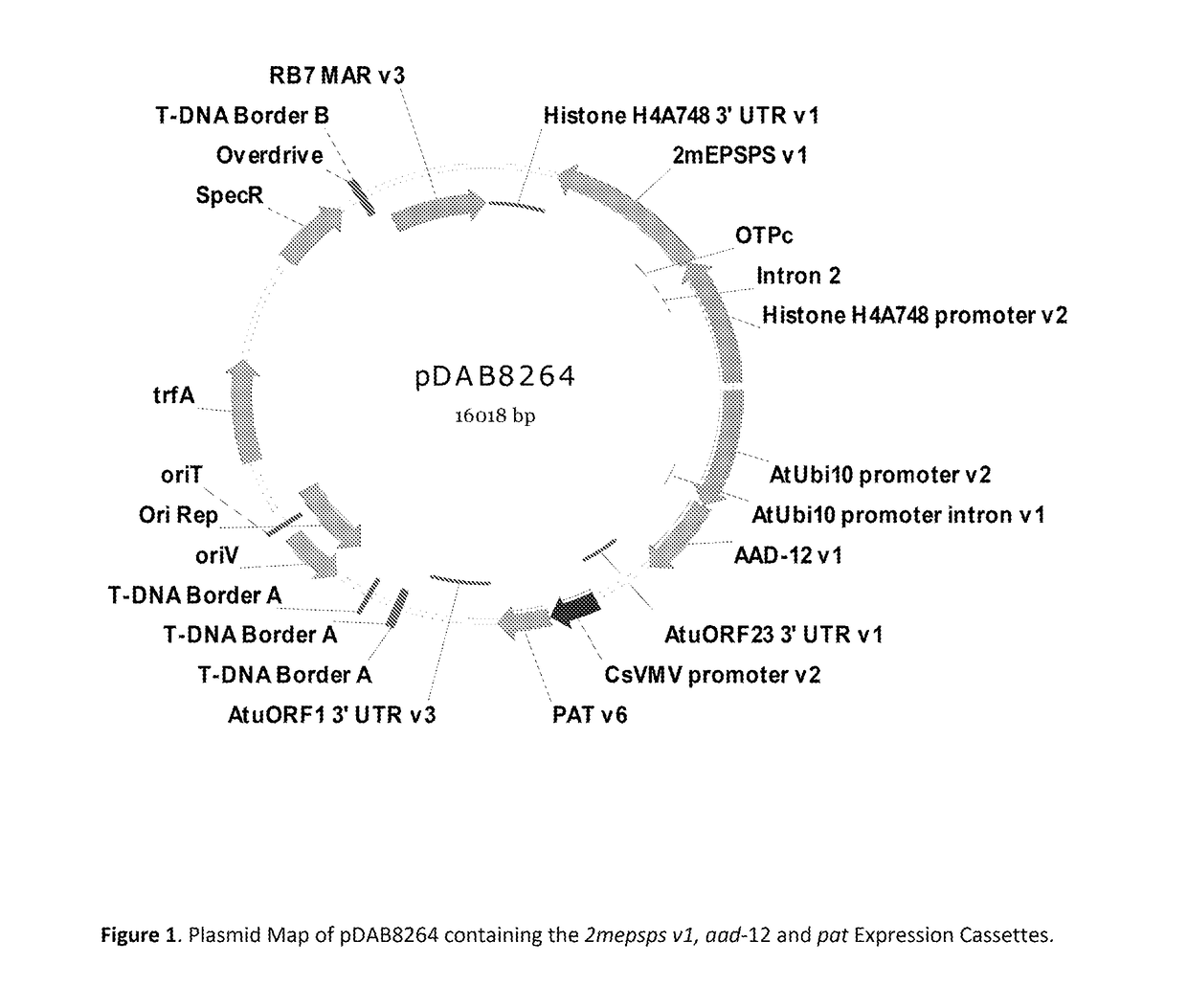
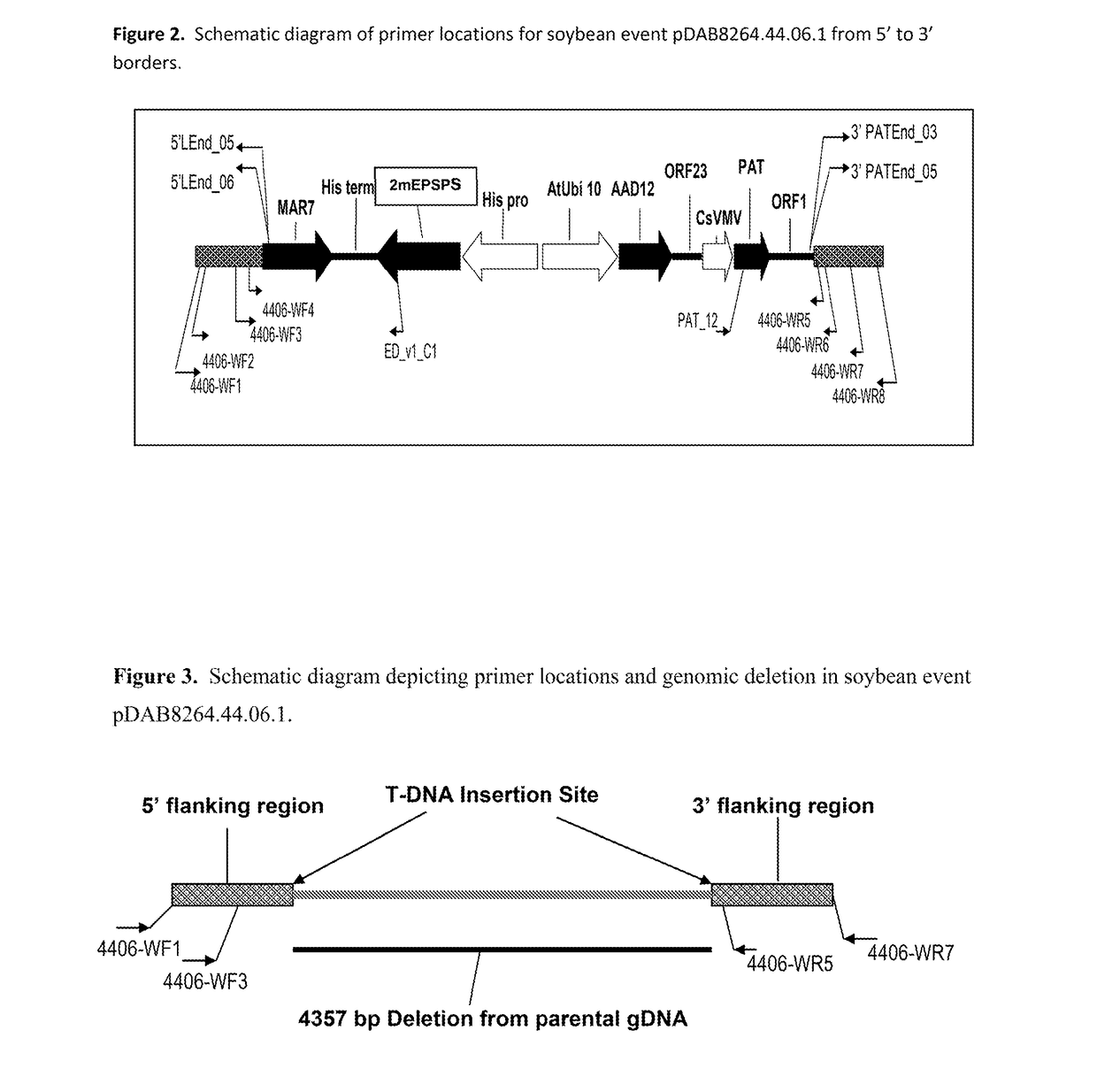
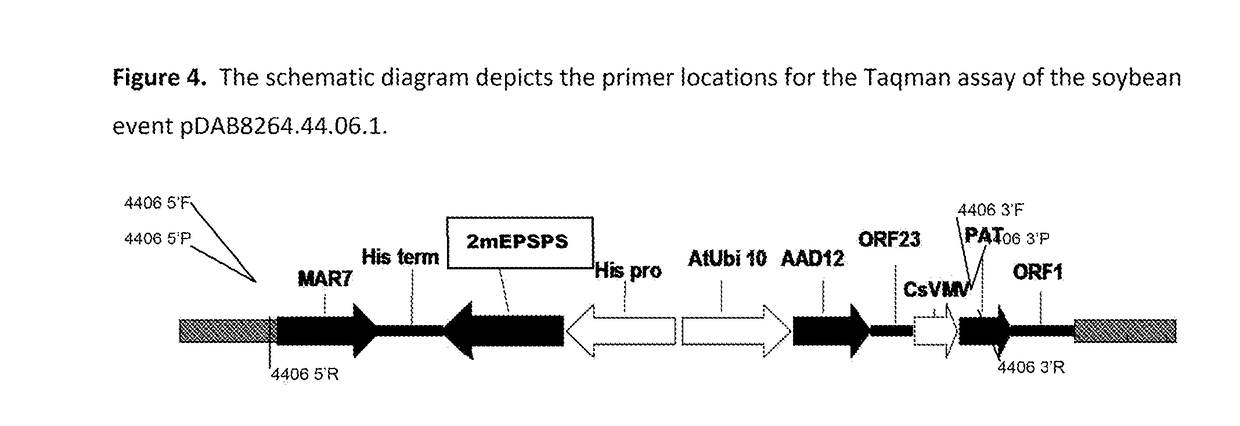
Stacked herbicide tolerance event 8264.44.06.1, related transgenic soybean lines, and detection thereof
ActiveUS20140041083A1Preserve usefulnessIncrease flexibilityBiocideSeed and root treatmentMultiple traitsPlant breeding
This invention relates in part to soybean event pDAB8264.44.06.1 and includes a novel expression cassettes and transgenic inserts comprising multiple traits conferring resistance to glyphosate, aryloxyalkanoate, and glufosinate herbicides. This invention also relates in part to methods of controlling resistant weeds, plant breeding and herbicide tolerant plants. In some embodiments, the event sequence can be “stacked” with other traits, including, for example, other herbicide tolerance gene(s) and / or insect-inhibitory proteins. This invention further relates in part to endpoint TaqMan PCR assays for the detection of Event pDAB8264.44.06.1 in soybeans and related plant material. Some embodiments can perform high throughput zygosity analysis of plant material and other embodiments can be used to uniquely identify the zygosity of and breed soybean lines comprising the event of the subject invention. Kits and conditions useful in conducting these assays are also provided.
Owner:M S TECH +1
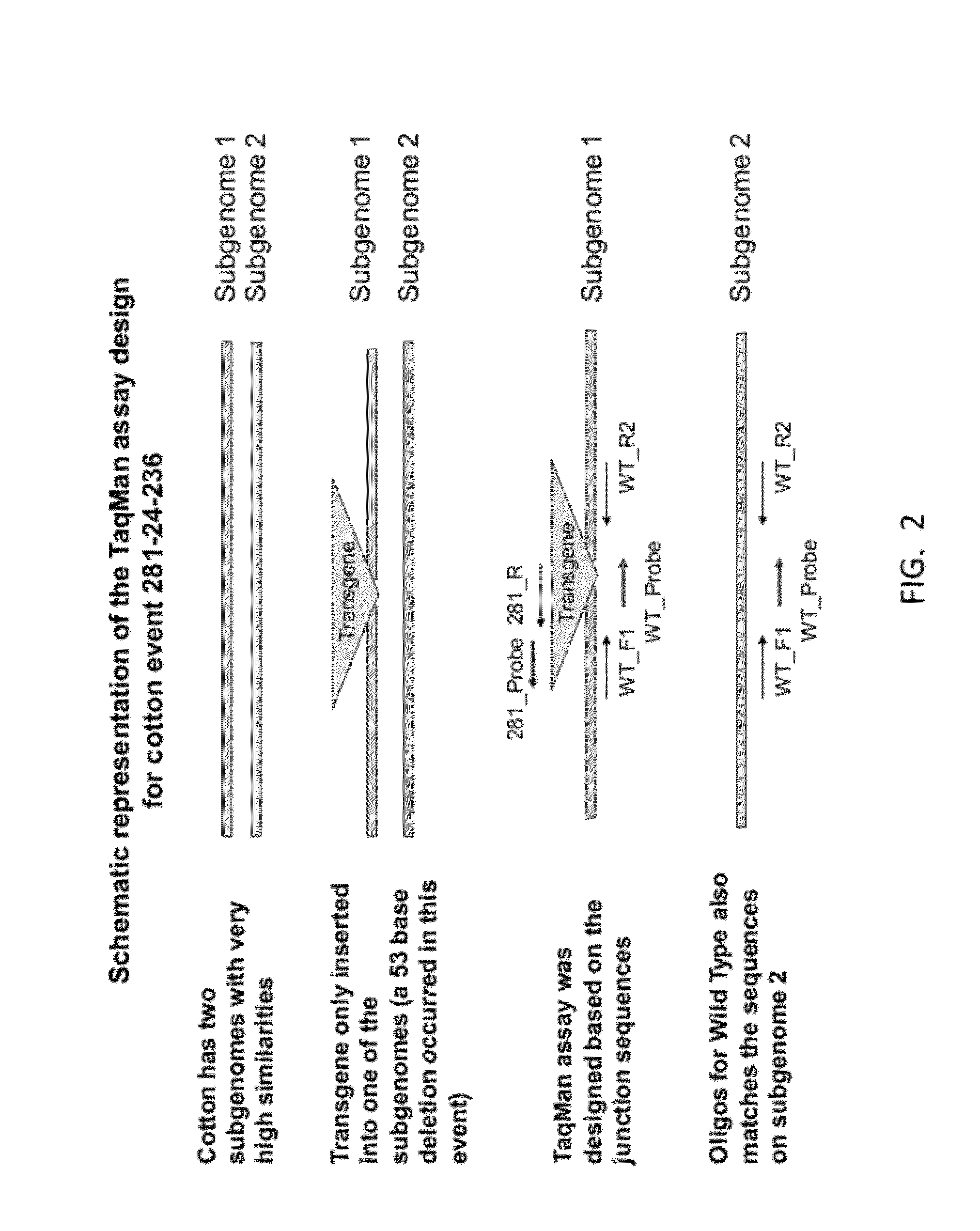
ENDPOINT TAQMAN METHODS FOR DETERMINING ZYGOSITY OF COTTON COMPRISING Cry1F EVENT 281-24-236
InactiveUS20120115141A1High throughput zygosity analysisEliminates denaturation stepMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationAgricultural sciencePcr assay
A method for zygosity analysis of the cotton Cry1F event 281-24-236 is provided. The method provides 281-24-236 event-specific and cotton endogenous reference gene-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of determining event zygosity and for assisting in event introgression and breeding.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
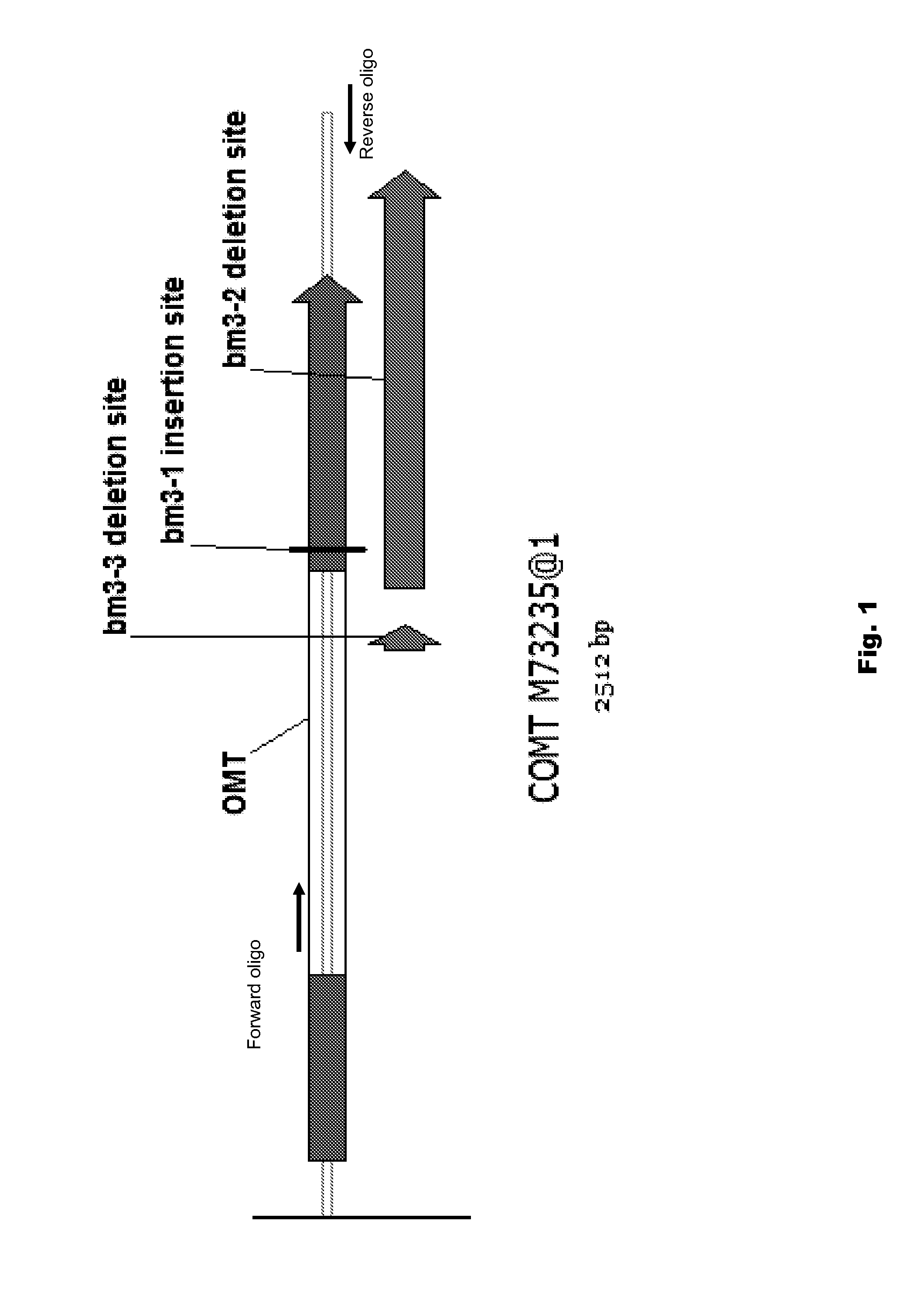
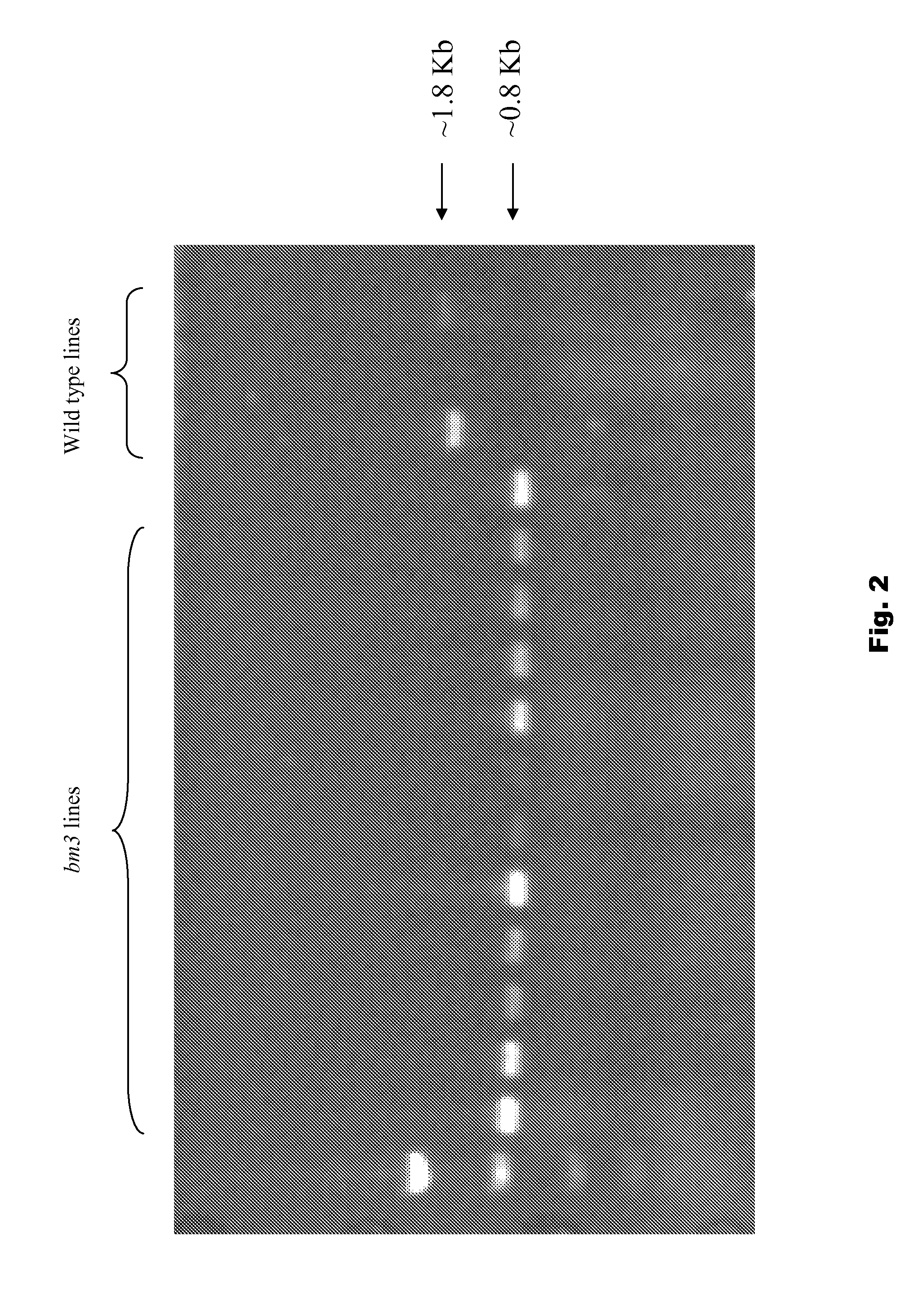
Use of brown midrib-3 gene specific markers in maize for trait introgression
ActiveUS20110283427A1Easy to breedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiotechnologyAllele
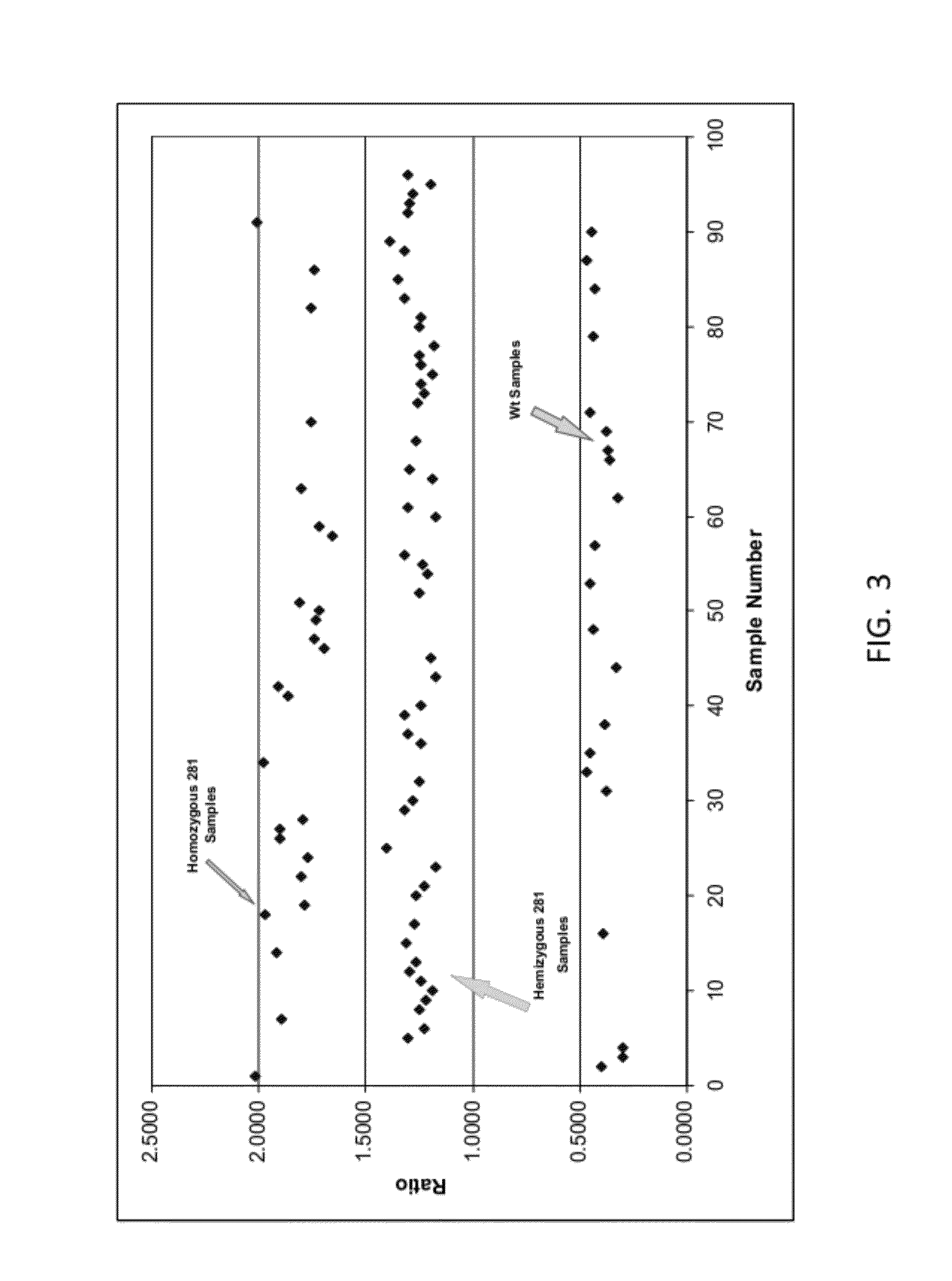
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for determining the zygosity of corn plants containing one or more brown midrib (BMR) mutations. The disclosure also concerns methods that are useful for enhancing the breeding process for BMR corn. In certain embodiments, compositions and methods for determining the zygosity of corn plants with respect to the bm3 allele.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
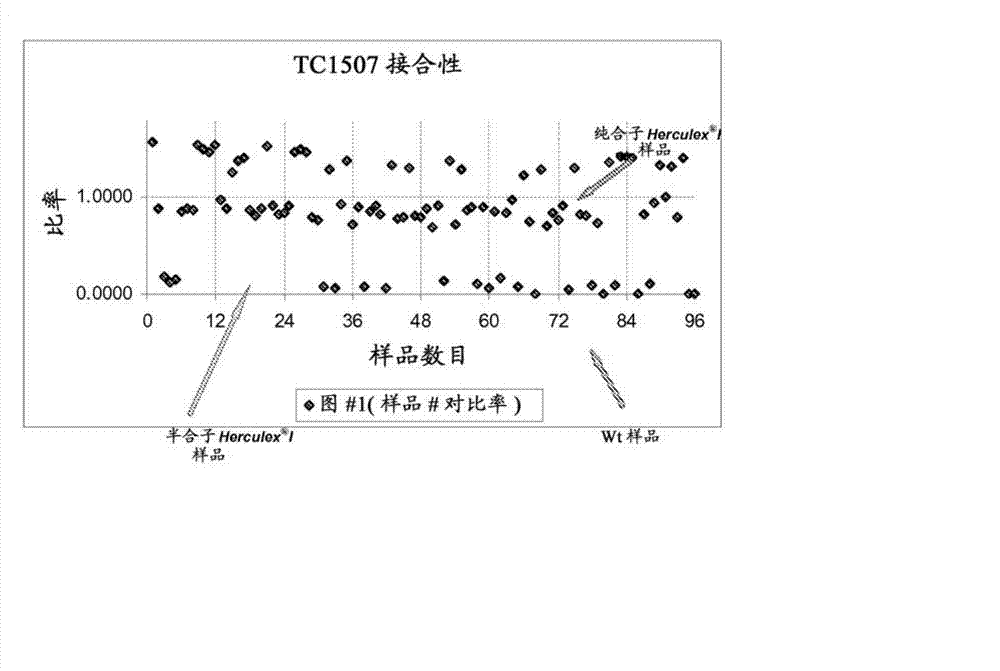
Endpoint TAQMAN methods for determining zygosity of corn comprising TC1507 events
A method for zygosity analysis of the maize Cry 1F event TC 1507 is provided. The method provides TC1507 event-specific and maize endogenous reference gene-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of producing robust genotype calls for assisting in molecular breeding of TC1507.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Stacked herbicide tolerance event 8264.44.06.1, related transgenic soybean lines, and detection thereof
ActiveUS20170112128A1Preserve usefulnessIncrease flexibilityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAssayGenetically modified soybean
This invention relates in part to soybean event pDAB8264.44.06.1 and includes a novel expression cassettes and transgenic inserts comprising multiple traits conferring resistance to glyphosate, aryloxyalkanoate, and glufosinate herbicides. This invention also relates in part to methods of controlling resistant weeds, plant breeding and herbicide tolerant plants. In some embodiments, the event sequence can be “stacked” with other traits, including, for example, other herbicide tolerance gene(s) and / or insect-inhibitory proteins. This invention further relates in part to endpoint TaqMan PCR assays for the detection of Event pDAB8264.44.06.1 in soybeans and related plant material. Some embodiments can perform high throughput zygosity analysis of plant material and other embodiments can be used to uniquely identify the zygosity of and breed soybean lines comprising the event of the subject invention. Kits and conditions useful in conducting these assays are also provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
Floury 2 gene-specific assay in maize for floury (fl2) trait introgression
ActiveUS9994919B2Easy to breedReliably and predictably introgressingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular breedingGermplasm
The disclosure concerns compositions and methods for determining the zygosity of corn plants containing one or more floury2 (fl2) mutations. In embodiments, the disclosure concerns a gene specific PCR-based molecular (KASPar®) assay for identifying the floury2 trait in plants. In certain embodiments, compositions and methods are disclosed for determining the zygosity of corn plants with respect to the fl2 allele. In particular embodiments, the assay may be used for fl2 germplasm identification, accelerating introgression and molecular breeding programs in corn and other plants.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Detection of aad-12 soybean event 416
ActiveUS20130029329A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyReference genes
The invention relates in part to methods of detecting an AAD-12 soybean event. The subject invention provides assays for detecting the presence of the subject event in a sample (of soybeans, for example). Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. More specifically, the present invention relates in part to an endpoint TaqMan PCR assay for the AAD-12 soybean event. Some embodiments are directed to assays that are capable of high throughput zygosity analysis. The subject invention further relates, in part, to the discovery of a preferred reference gene for use in determining zygosity. This invention also relates in part to plant breeding using any of the subject methods. In some embodiments, said event / polynucleotide sequence can be “stacked” with other traits. The subject procedures can be used to uniquely identify soybean lines comprising the event of the subject invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
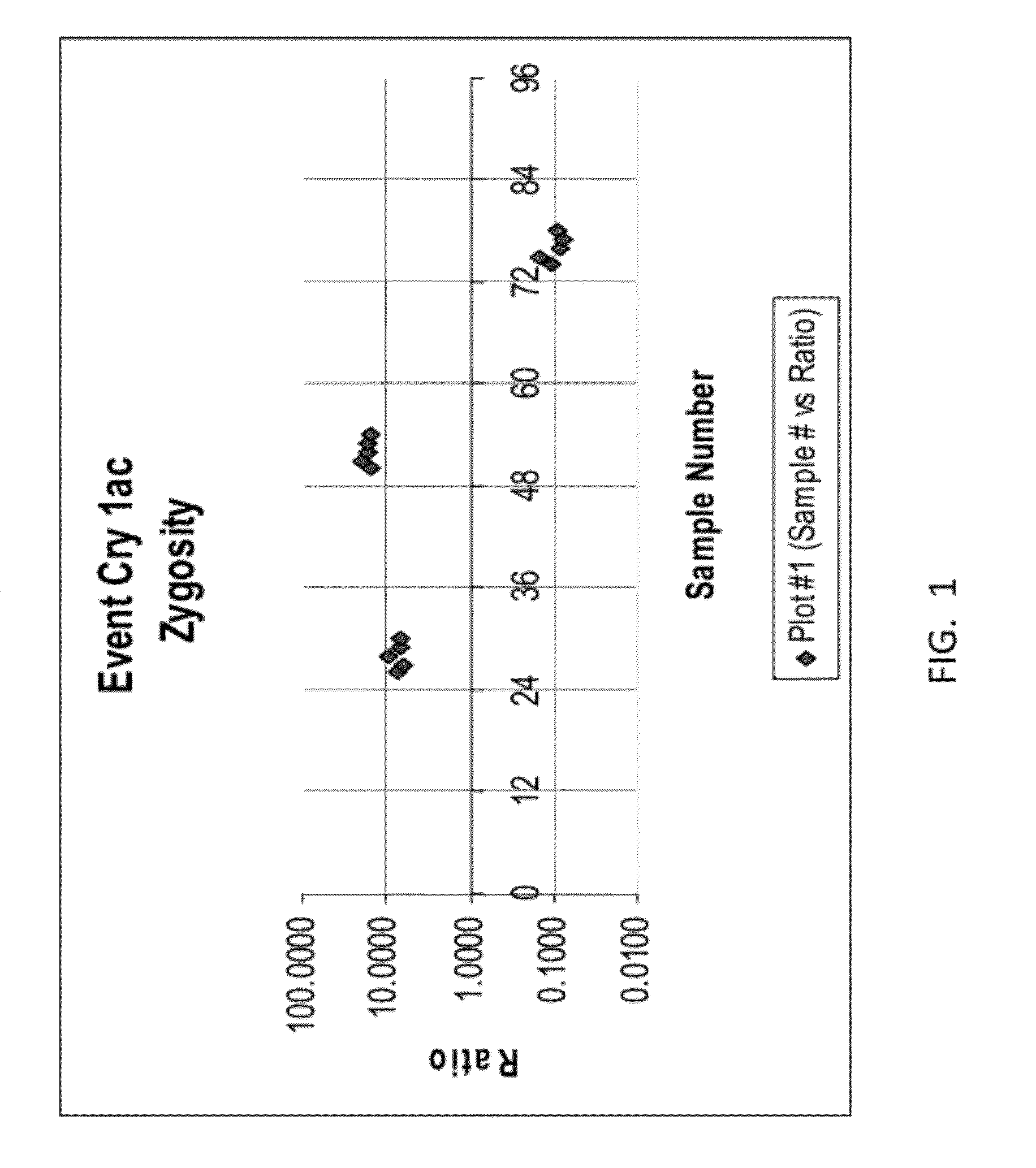
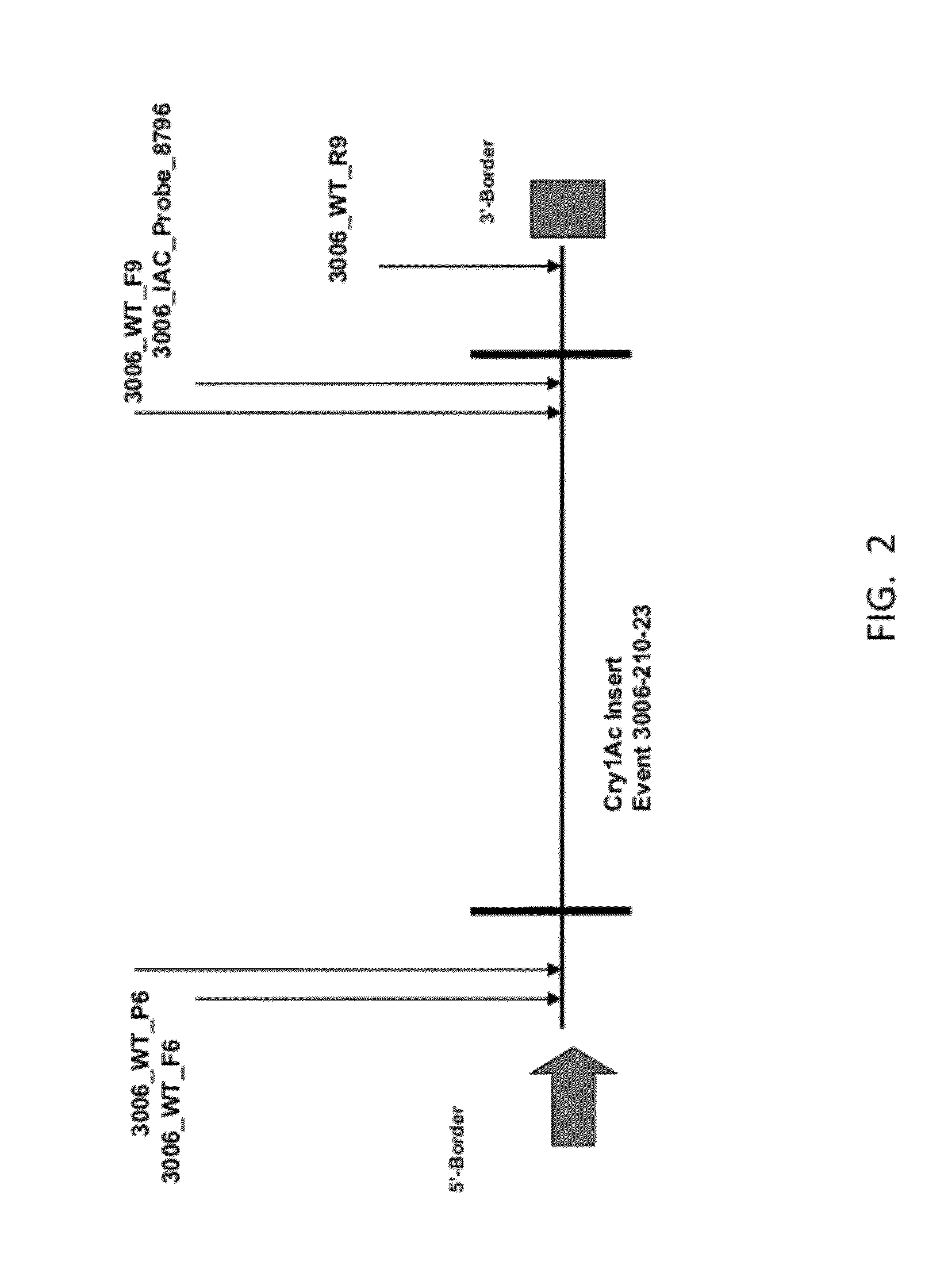
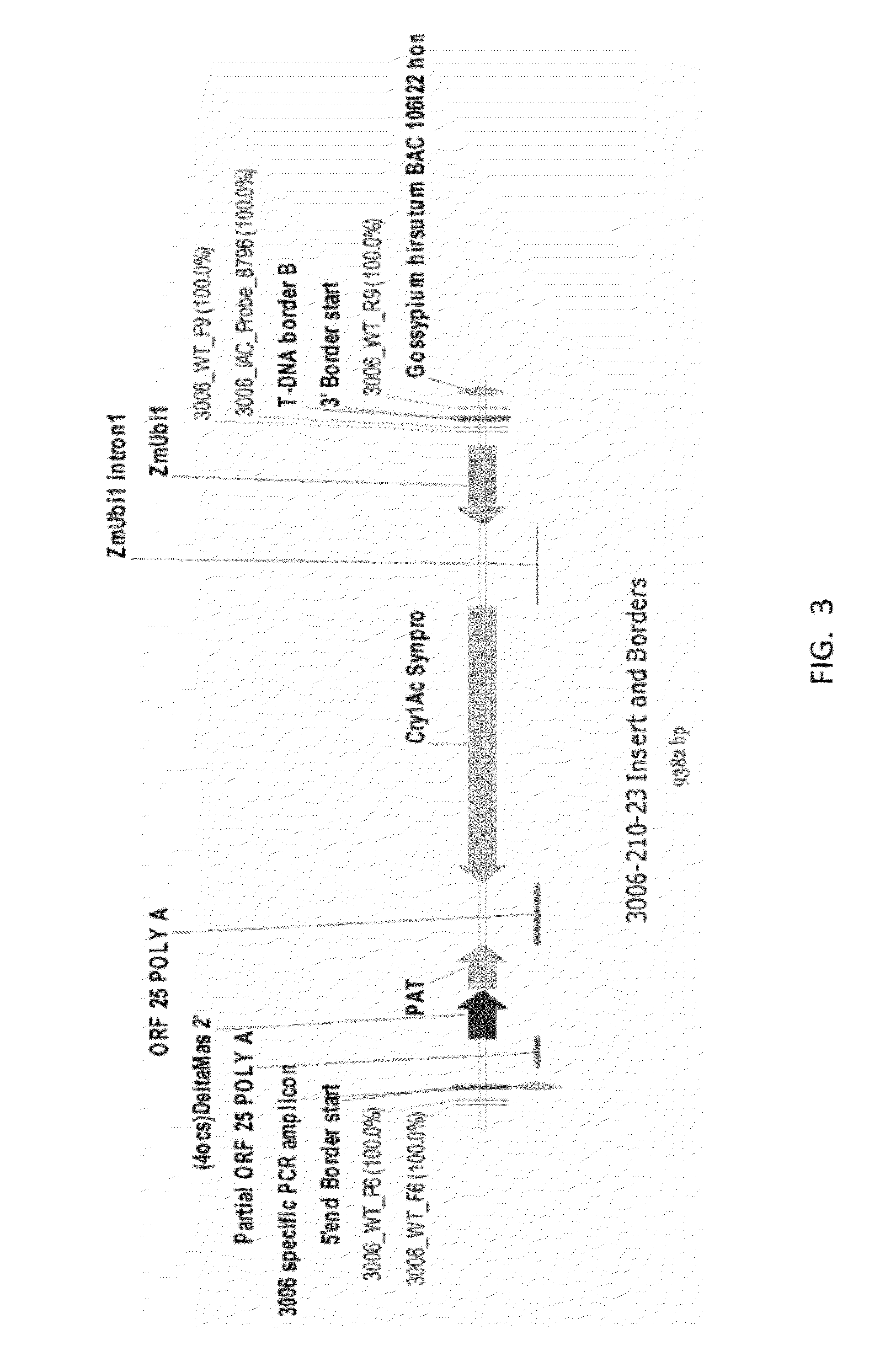
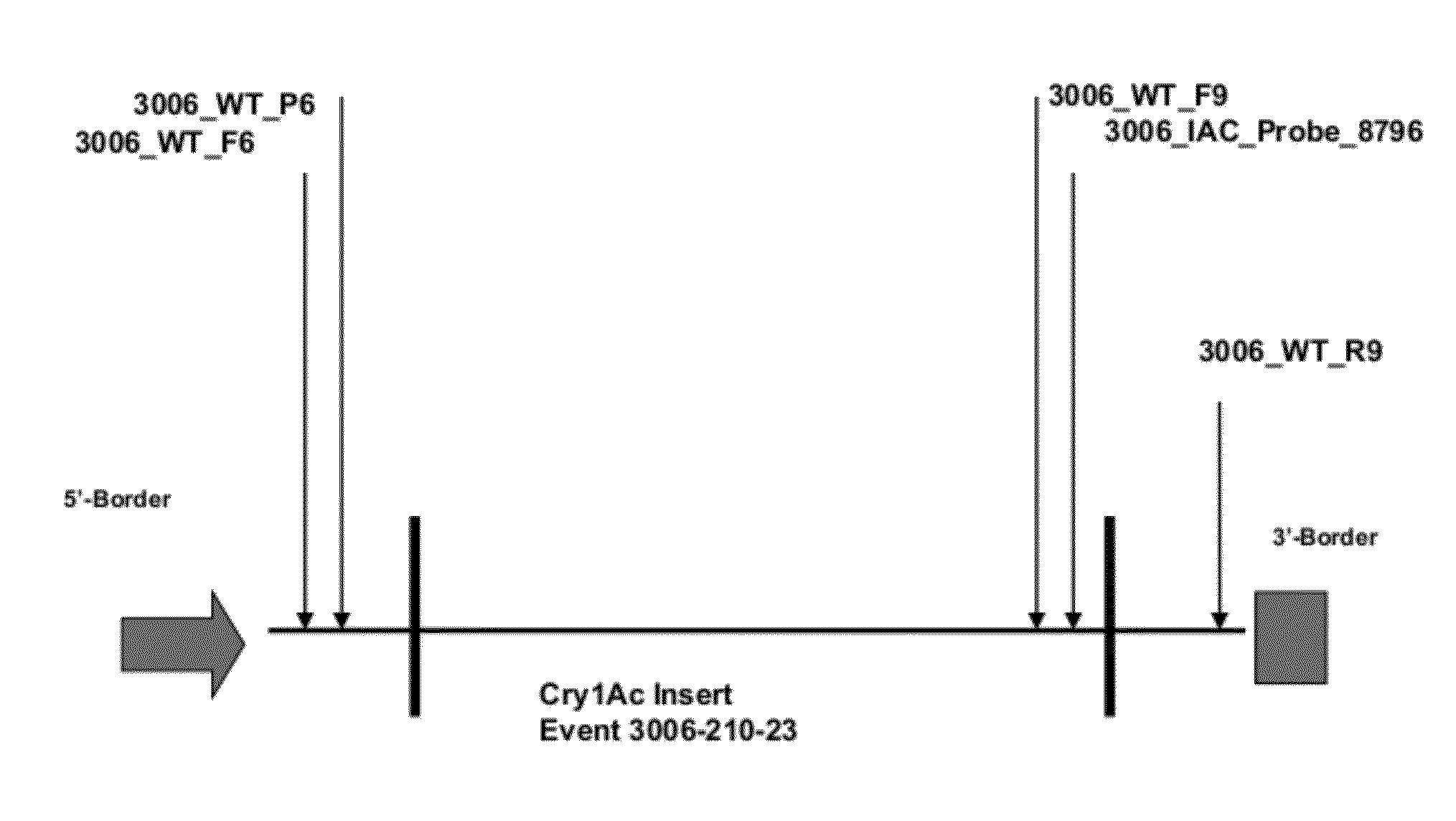
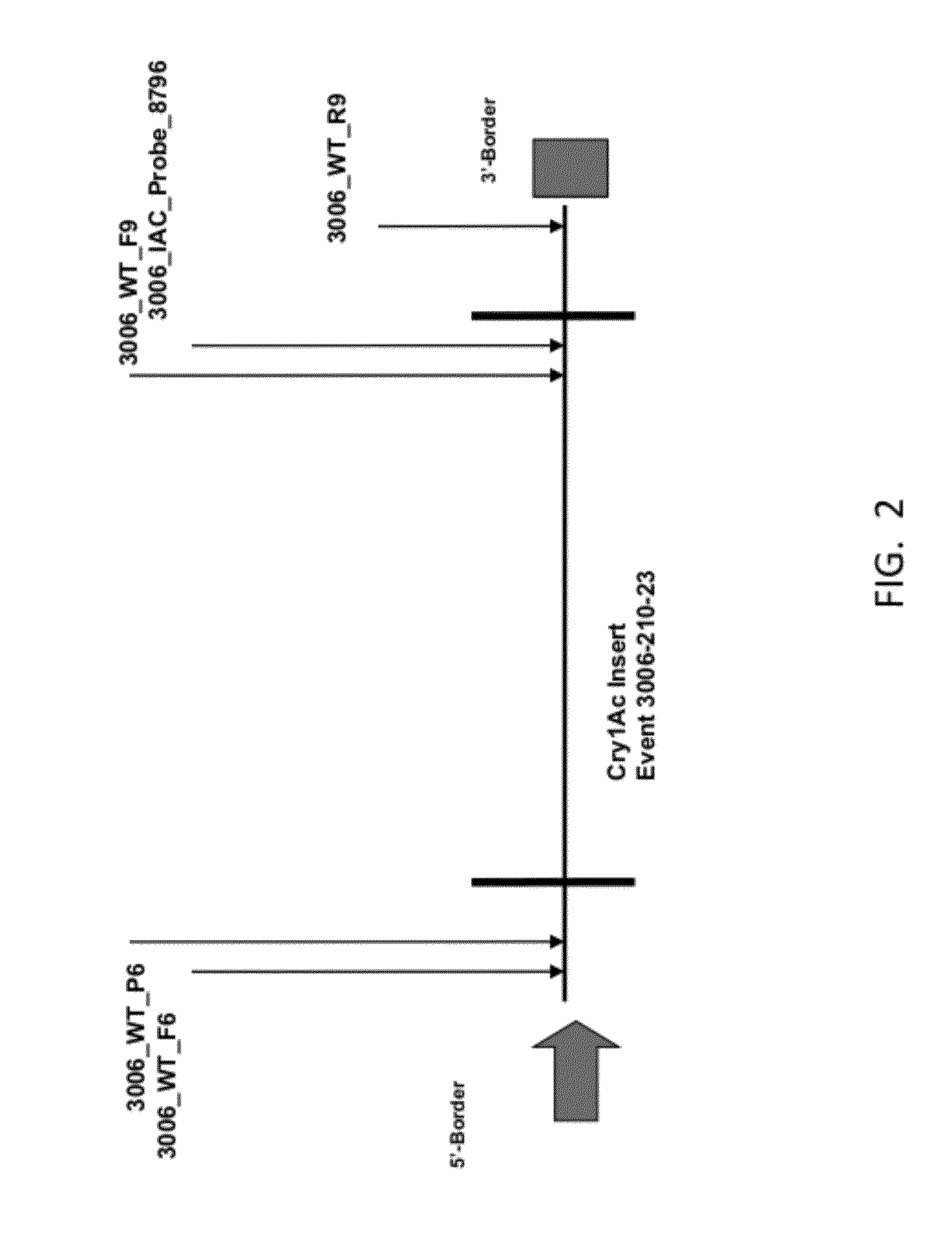
ENDPOINT TAQMAN METHODS FOR DETERMINING ZYGOSITY OF COTTON COMPRISING Cry1Ac EVENT 3006-210-23
ActiveUS20120115142A1High throughput zygosity analysisEliminates denaturation stepMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayBiology
A method for zygosity analysis of the cotton Cry1Ac event 3006-210-23 is provided. The method provides 3006-210-23 event-specific and cotton-genome-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of determining event zygosity and for assisting in event introgression and breeding.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
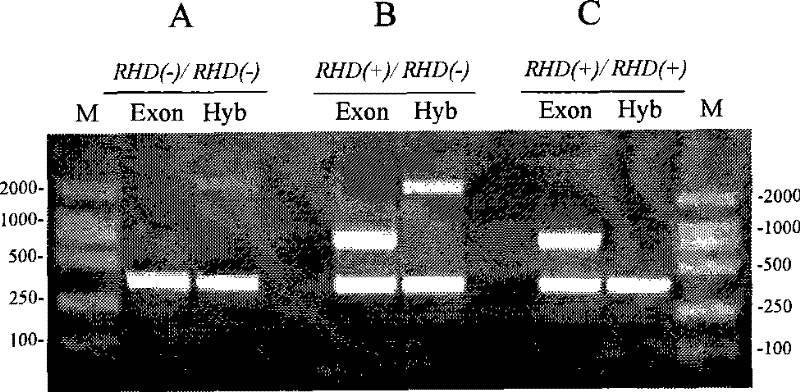
PCR primer and kit for measuring individual RHD gene zygosity and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101748202BImprove accuracyImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRhD antigenOligonucleotide Primer
The invention relates to a PCR primer and a kit for measuring individual RHD gene zygosity and a measuring method thereof. The primer of the invention is used for detecting a first exon of an RHD gene, a 3' end position of an upstream primer is at a -554 basic group opposite to a first basic group position of an RHD gene code area, and a 3' end position of an downstream primer is at a 18th basic group of a first intron of the RHD gene. The kit and the measuring method of the invention based on the specific oligonucleotide primer has sophistication, specificity and high accuracy rate, and has simple and easy operation in the process of measuring.
Owner:SHENZHEN BLOOD CENT
Methods to determine zygosity in a bulked sample
InactiveCN103403185AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerNucleotide
Methods of determining the presence or absence of an inserted nucleotide sequence at a particular insertion site in a nucleic acid include: isolating a nucleic acid from the bulked tissue sample; contacting the nucleic acid with a forward primer able to bind to the nucleic acid upstream of the insertion site, a first reverse primer specific for the inserted nucleotide sequence, and a second reverse primer able to bind to the nucleic acid downstream of the insertion site. The primers may be used to reproduce nucleic acids between the primers. The reproduced nucleic acids may be analyzed to determine if an inserted nucleotide sequence is present or absent in the sample.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
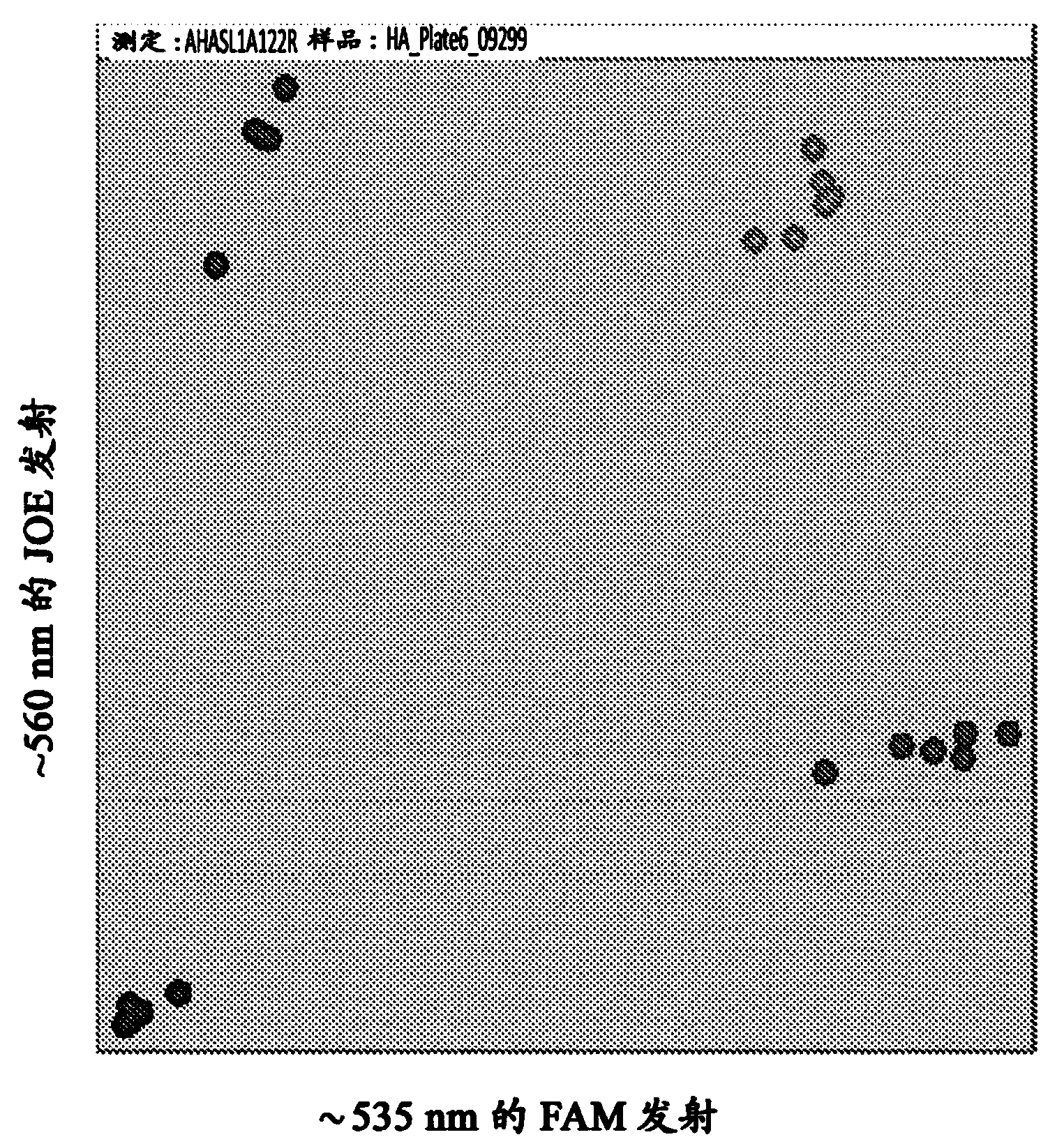
High throughput single nucleotide polymorphism assay
A method consisting of a homogeneous assay detection system for a PCR process using FRET for detection and zygosity analysis of the HaAHASL1-A122(At)T single nucleotide polymorphism in sunflower is provided. The method provides specific sunflower-genome primers that can be used to detect the presence or absence of the HaAHASL1-A122(At)T single nucleotide polymorphism. The primer combinations for use in an endpoint PCR assay capable of determining zygosity and for assisting in breeding introgression are described.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Molecular diagnostics for galactosemia
InactiveUS20010024791A1Specific detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideLactose
A process for detecting mutations in the gene responsible for galactosemia, galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT), is described. In one embodiment, the process can be used to detect over 85% of the mutations known to cause galactosemia in the United States population by using six different oligonucleotide probes, which span single-nucleotide Missense or nonsense mutations in the GALT gene. Hybridization conditions which can distinguish a single nucleotide mismatch are used to detect both the presence and zygosity of mutations in the GALT gene to aid in genetic counseling. A kit for use in detecting mutations in the GALT gene is also disclosed.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
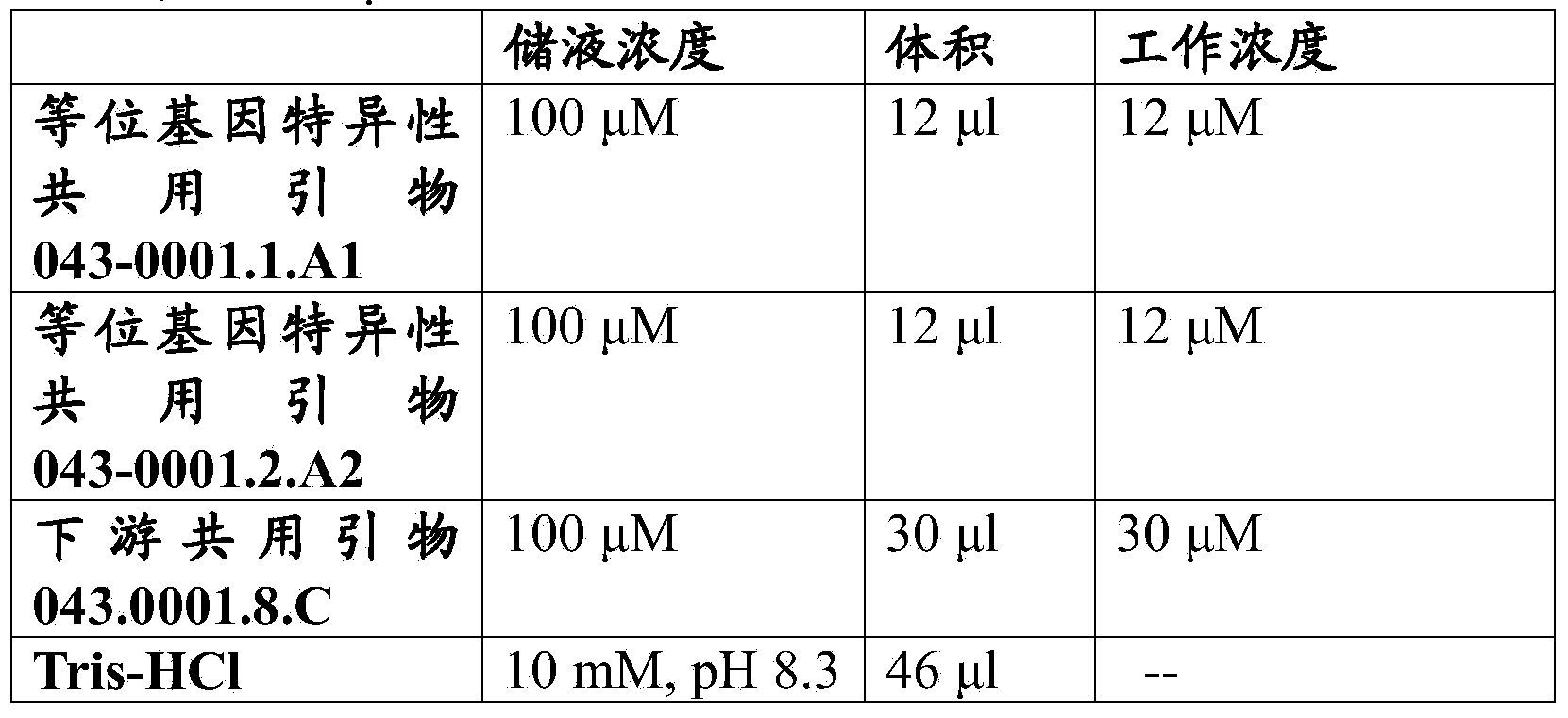
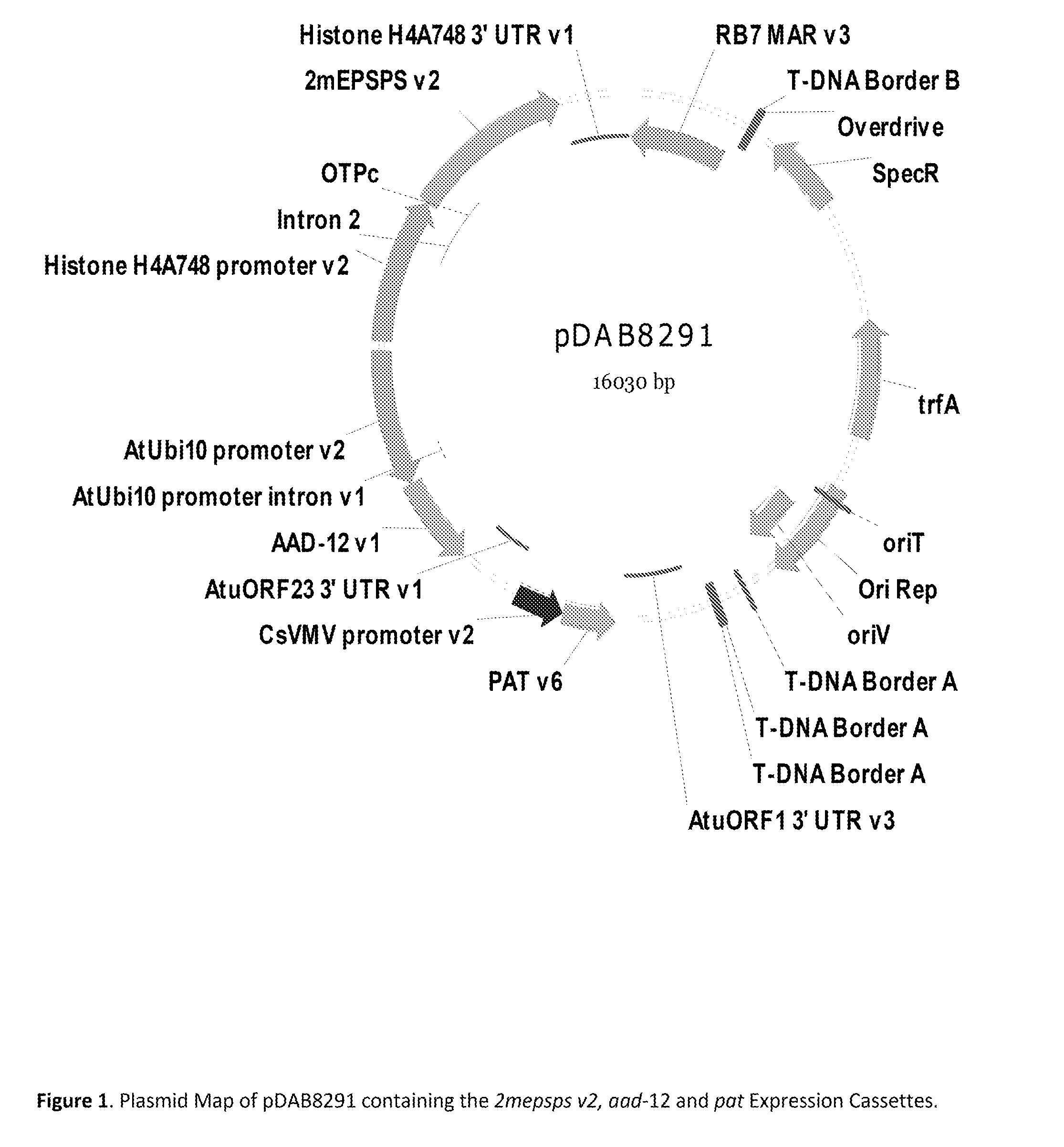
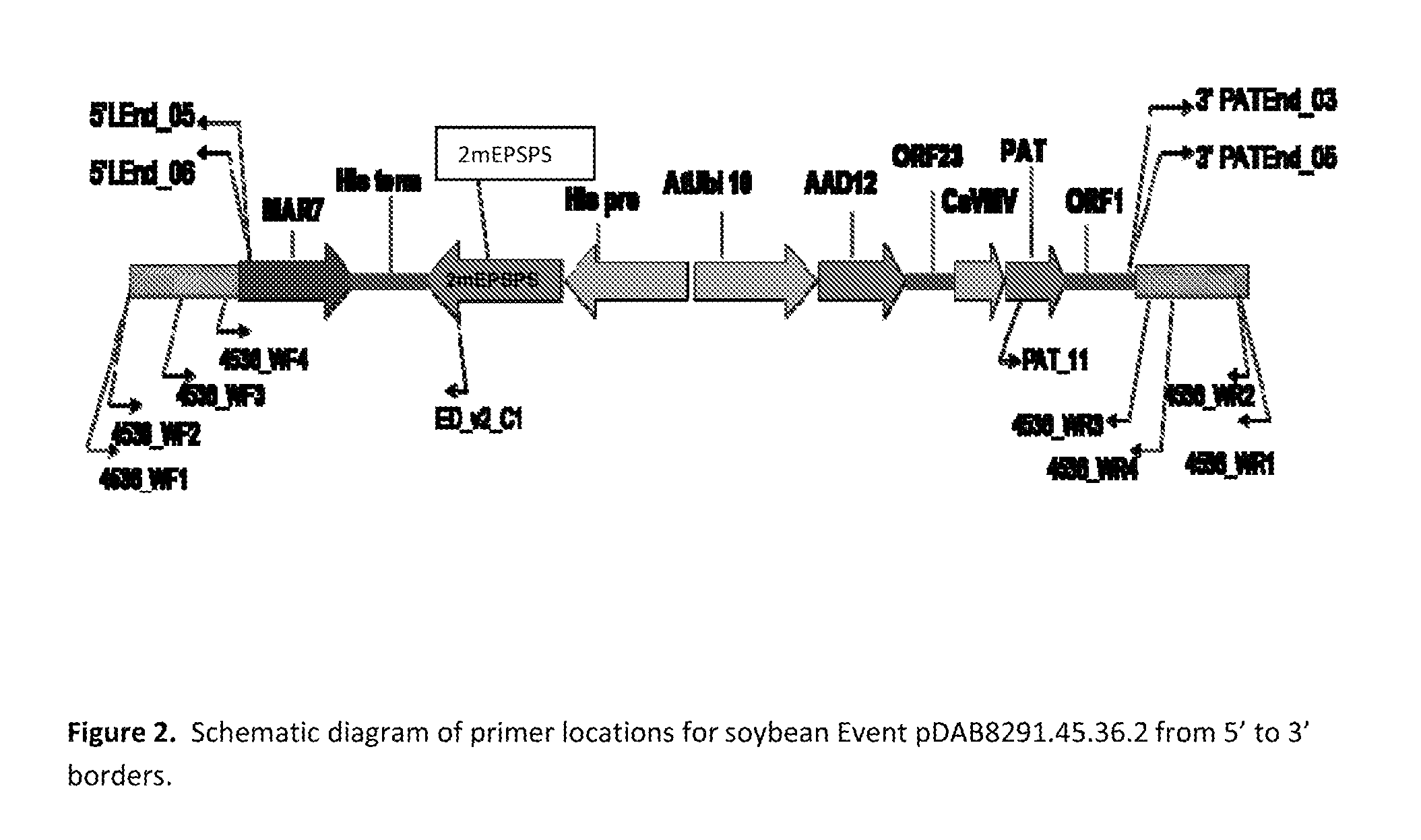
Stacked herbicide tolerance event 8291.45.36.2, related transgenic soybean lines, and detection thereof
ActiveUS20130338006A1Preserve usefulnessIncrease flexibilityBiocideSugar derivativesMultiple traitsBiology
This invention relates to soybean event pDAB8291.45.36.2, which includes a novel expression cassette comprising multiple traits conferring resistance to glyphosate, aryloxyalkanoate, and glufosinate herbicides. This invention also relates in part to methods of controlling resistant weeds, plant breeding, and herbicide tolerant plants. In some embodiments, the event sequence can be “stacked” with other traits, including, for example, other herbicide tolerance gene(s) and / or insect-inhibitory proteins. This invention further relates in part to detection methods, including endpoint TaqMan PCR assays, for the detection of Event pDAB8291.45.36.2 in soybeans and related plant material. Some embodiments can perform high throughput zygosity analysis of plant material and other embodiments can be used to uniquely identify the zygosity of and breed soybean lines comprising the event of the subject invention. Kits and conditions useful in conducting these assays are also provided.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
Detection of AAD1 event DAS-40278-9
ActiveUS9204599B2Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionReference genesPcr assay
This invention relates in part to detecting herbicide tolerant plants-more specifically, an aad-1 transformation event in corn plants. The subject invention also provides assays for detecting the presence of the subject event in a sample (of corn grain, for example). Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. The subject invention also relates in part to plant breeding using the subject methods. In some embodiments, this event / polynucleotide sequence can be “stacked” with other traits. More specifically, the invention relates in part to an endpoint Taqman PCR assay for AAD-1 corn event 40278-9. Some embodiments are directed to assays that are capable of high throughput zygosity analysis. The subject invention further relates, in part, to the use of a preferred reference gene for use in determining zygosity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
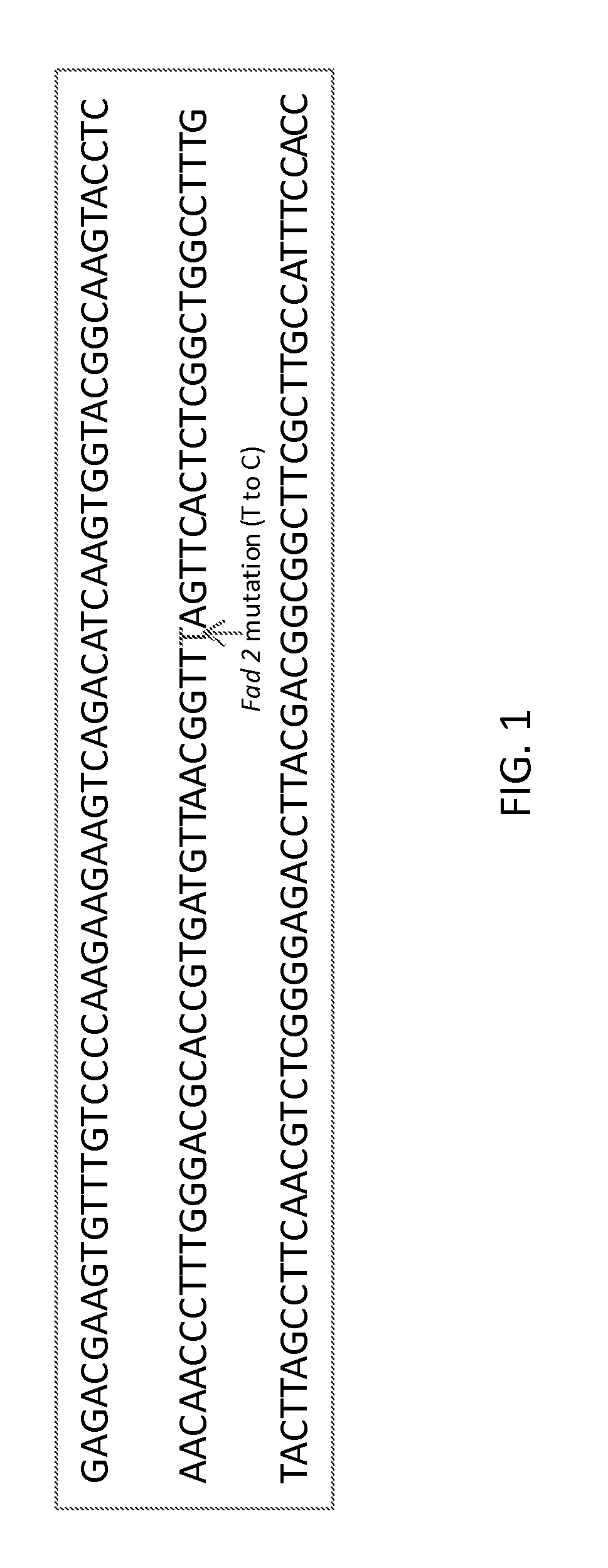
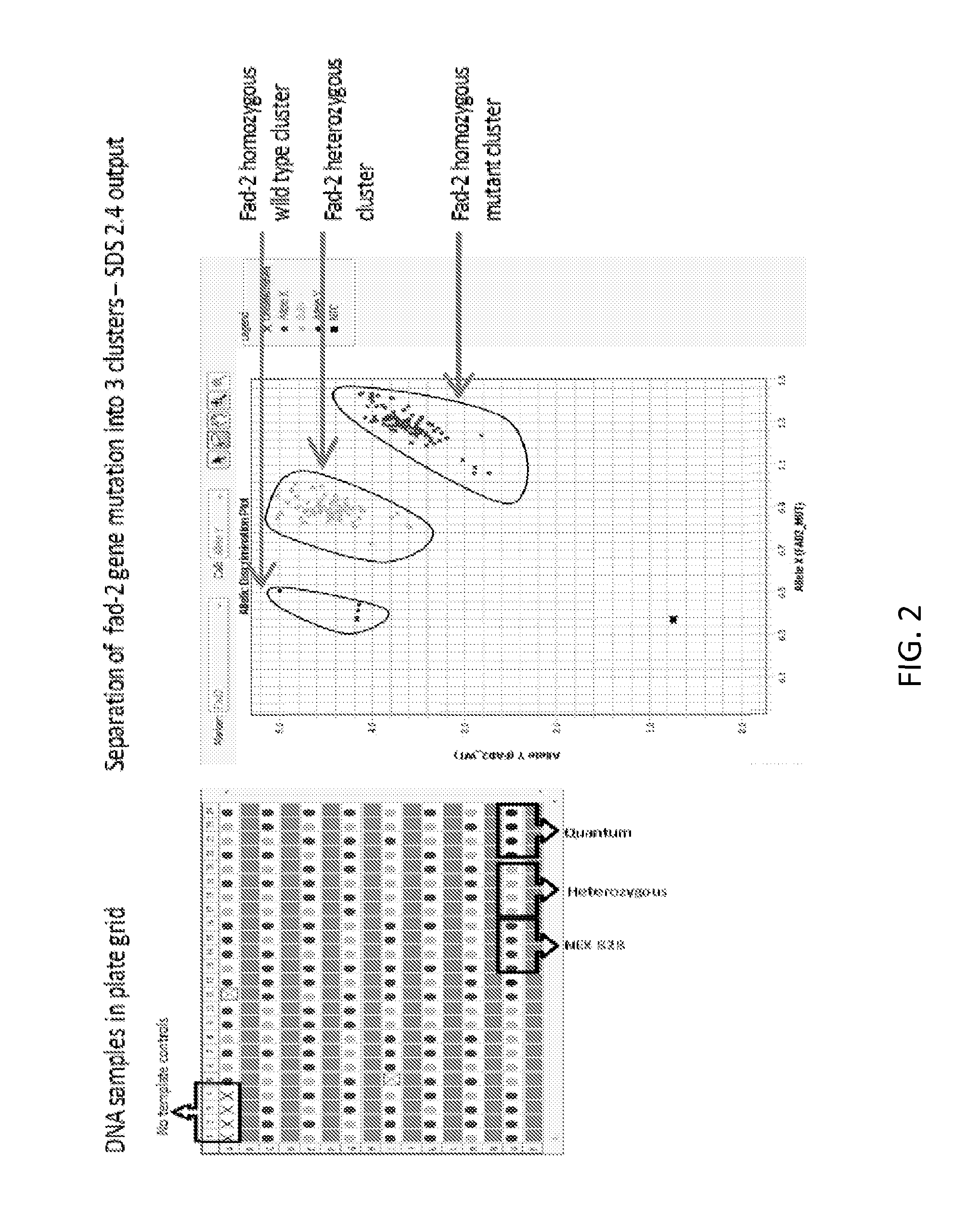
Method to determine zygosity of the fad2 gene in canola using end-point taqman PCR
InactiveUS20130102001A1Improve throughputReliable and accurate and high throughputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayWild type
The subject disclosure relates in part to endpoint TaqMan® PCR assays for the detection and high throughput zygosity analysis of the fad-2 gene in canola. The subject disclosure further relates, in part, to the use of wild type DNA as a reference for use in determining zygosity. These and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify the zygosity and variety of canola lines comprising the subject gene. The subject disclosure also provides related kits for determining zygosity from a sample of a canola plant or seed, for example.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
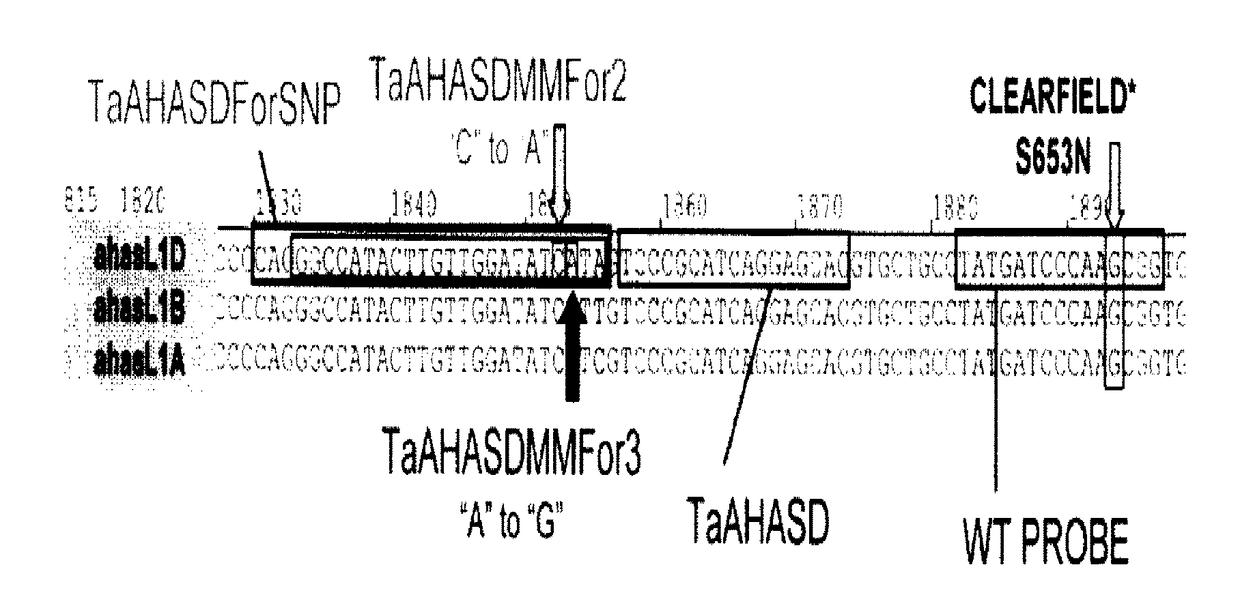
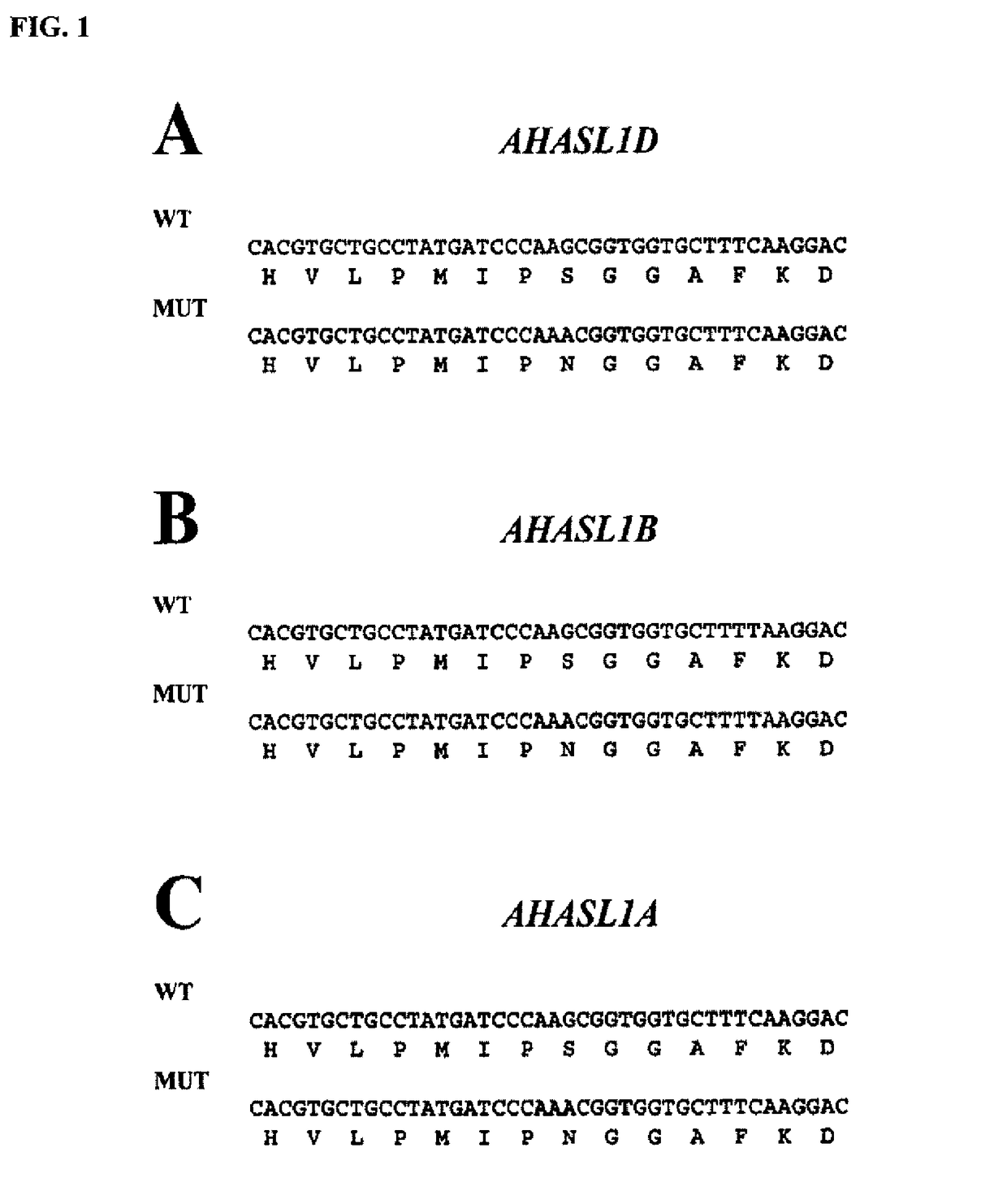
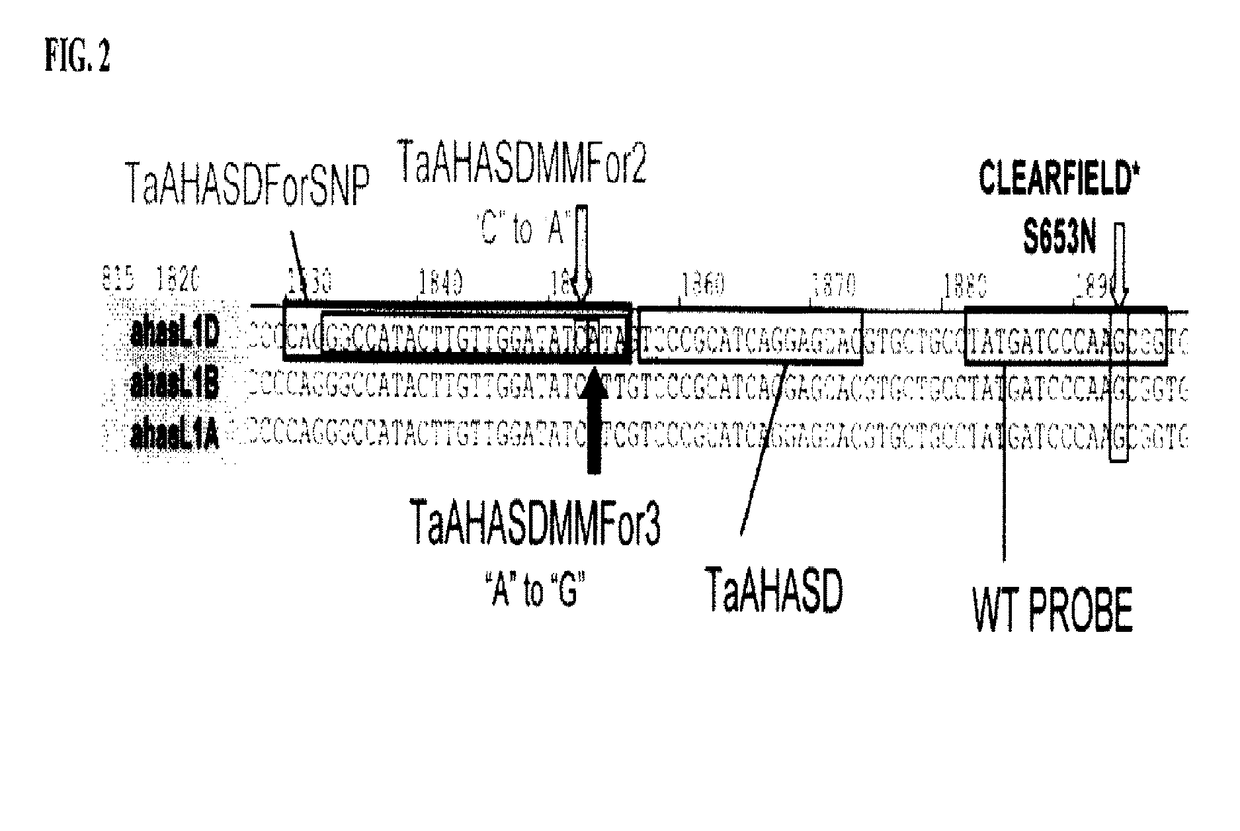
Methods and compositions for analyzing AHASL genes in wheat
ActiveUS9856538B2Low detection sensitivityHigh detection specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyForward primer
Owner:BASF AGROCHEMICAL PROD BV
Endpoint TaqMan methods for determining zygosity of cotton comprising Cry1Ac event 3006-210-23
ActiveUS9243287B2High throughput zygosity analysisExemption stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPcr assayGenome
A method for zygosity analysis of the cotton Cry1Ac event 3006-210-23 is provided. The method provides 3006-210-23 event-specific and cotton-genome-specific primers and TaqMan probe combinations for use in an endpoint biplex TaqMan PCR assay capable of determining event zygosity and for assisting in event introgression and breeding.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
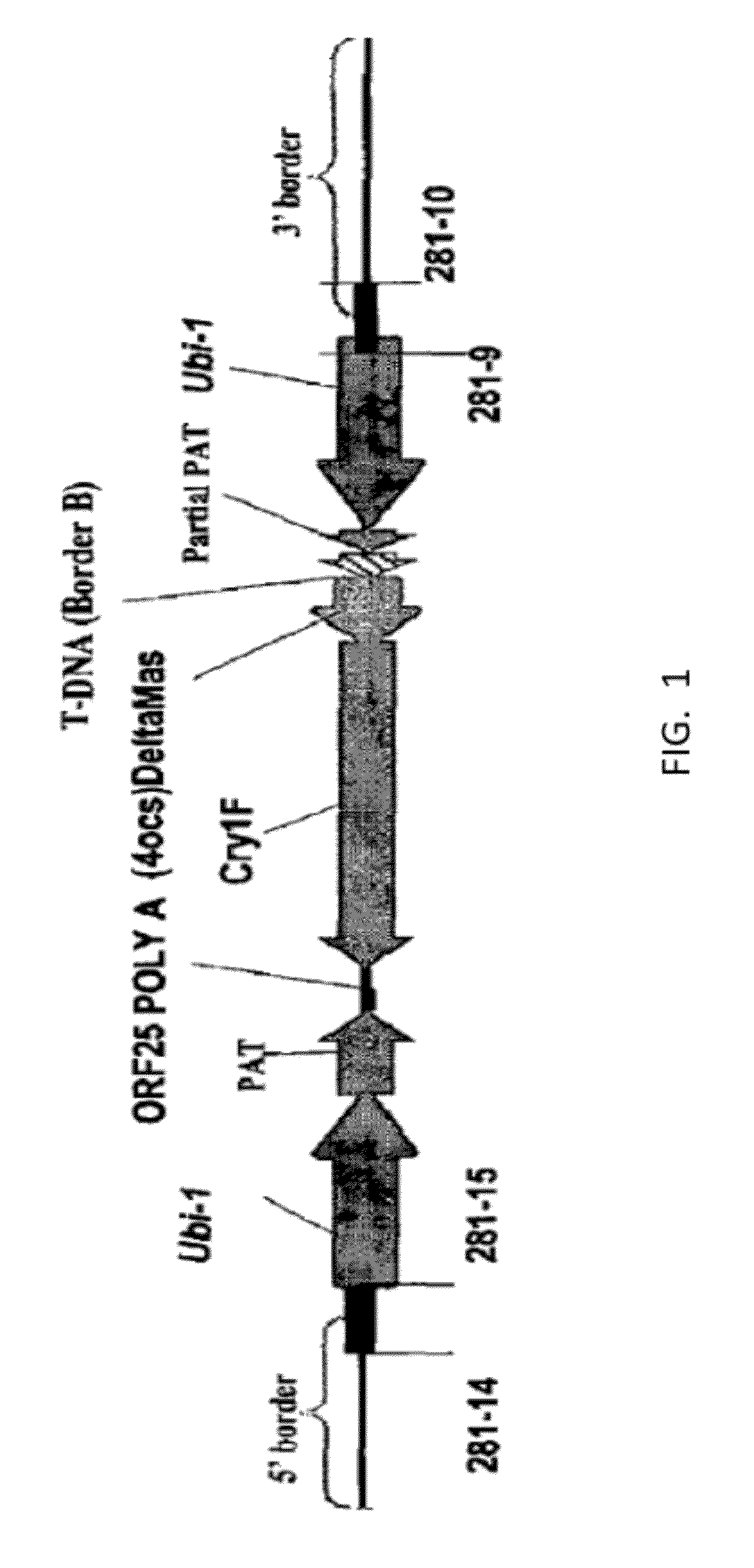
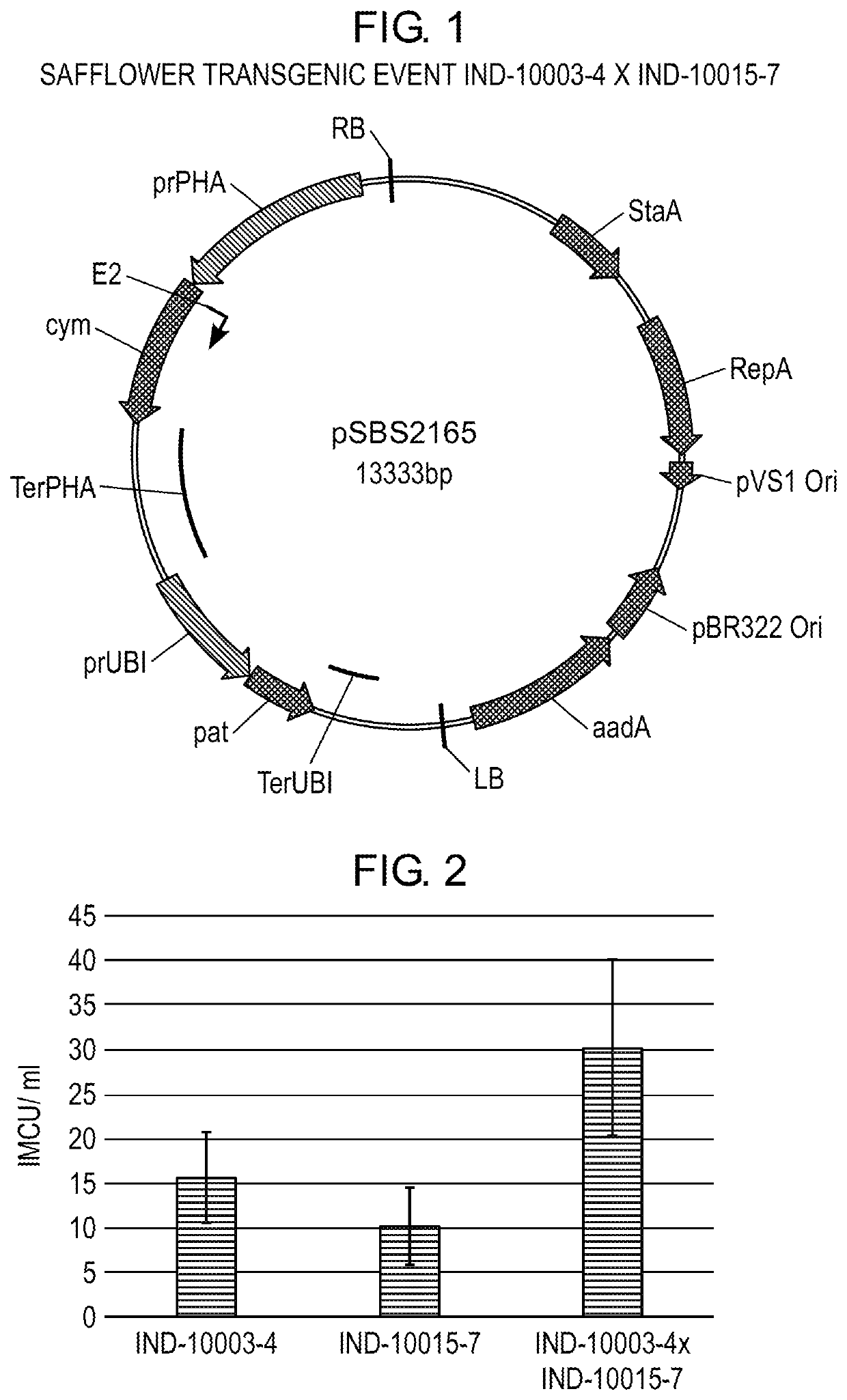
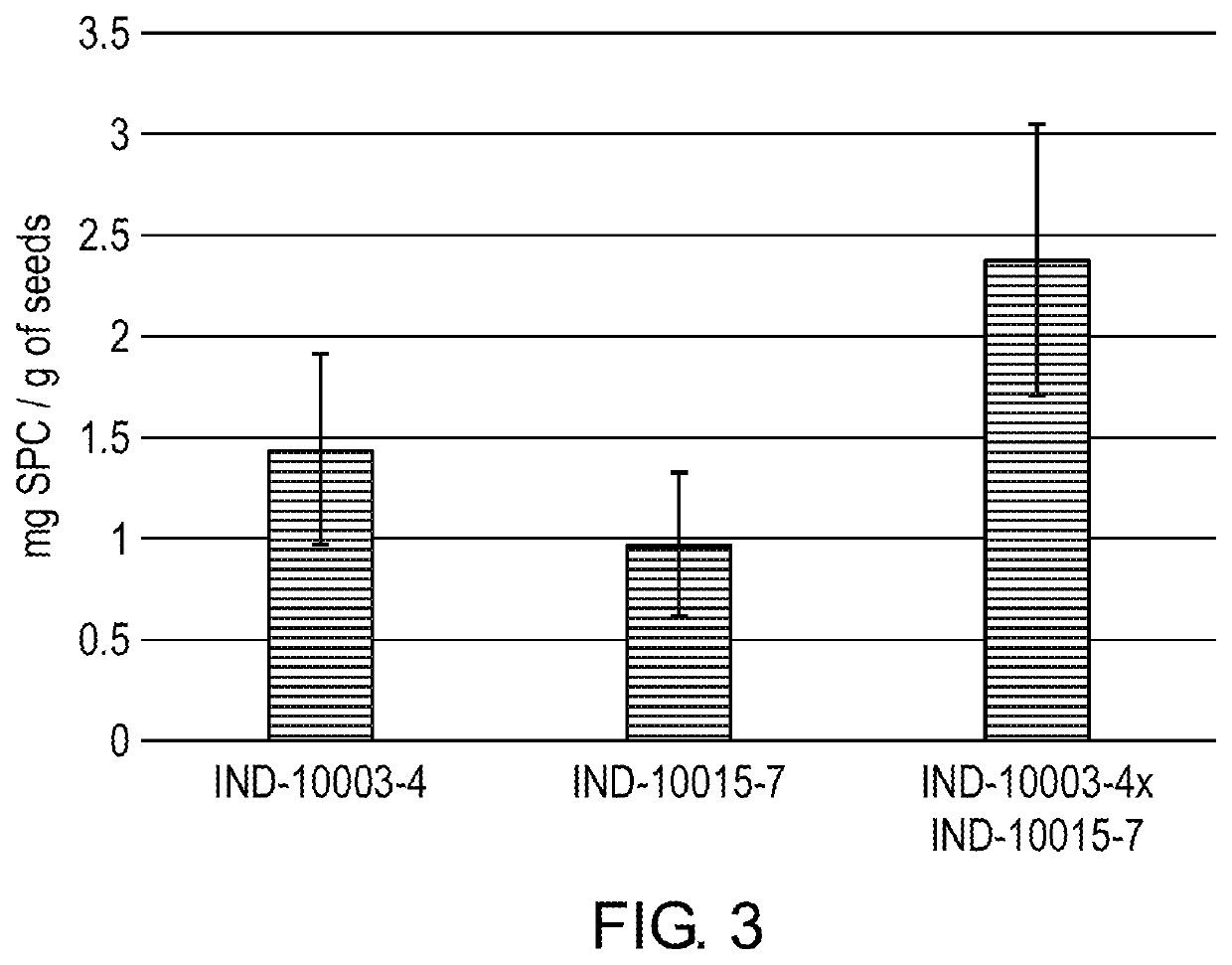
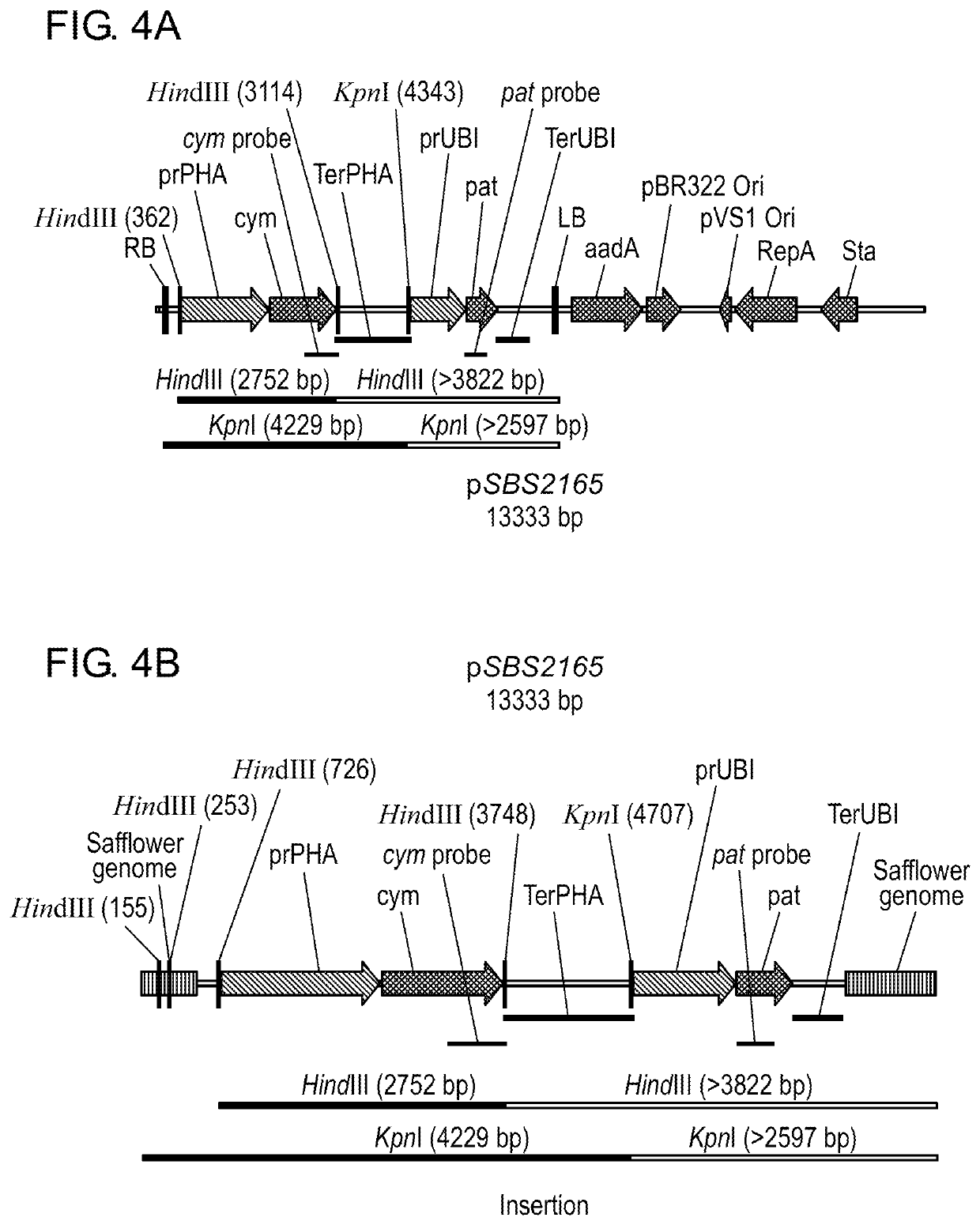
Transgenic Safflower Event Stack IND-1ØØØ3-4 X IND-1ØØ15-7 and Methods to Use It
PendingUS20220056463A1Microbiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiodieselNucleotide
The present invention relates to a safflower plant or part thereof involving the molecular stacking of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7, wherein the plant produces and accumulates chymosin in seed under agricultural conditions. A plant seed involving the molecular stacking of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7. A consumer product produced from the seed, defined as chymosin, and additionally as ground grain, flour, flakes, oil, biodiesel, biogas, or another biomaterial. Also, the present invention include a recombinant DNA molecule involved in the molecular stacking of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7. A DNA polynucleotide primer molecule comprising at least 15 contiguous nucleotides of the DNA molecule involved in the molecular stacking of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7, or its complement which is useful in a DNA amplification method to produce a diagnostic amplicon for the event IND-1ØØØ3-4 and IND-1ØØ15-7, or each of them separately IND-1ØØØ3-4 and IND-1ØØ15-7. A vector of functional expression in plants and the microorganism that comprises it. A DNA detection kit comprising at least one DNA molecule comprising a nucleotide sequence with a sufficient length of contiguous nucleotides of the recombinant DNA molecule involved in the molecular stacking of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7. Furthermore, the present invention involves methods of producing a safflower plant that accumulates chymosin in seeds under agricultural conditions; methods of producing a chymosin-producing safflower plant; methods to detect the presence of DNA corresponding to the molecular stack of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7, or each of them separately IND-1ØØØ3-4 and IND-1ØØ15-7; methods for determining the zygosity of the safflower genome containing DNA from the molecular stack of safflower events IND-1ØØØ3-4×IND-1ØØ15-7, or each of them separately IND-1ØØØ3-4 or IND-1ØØ15-7; and methods of producing a consumer product made from safflower.
Owner:AG BIOMOLECULES LLC
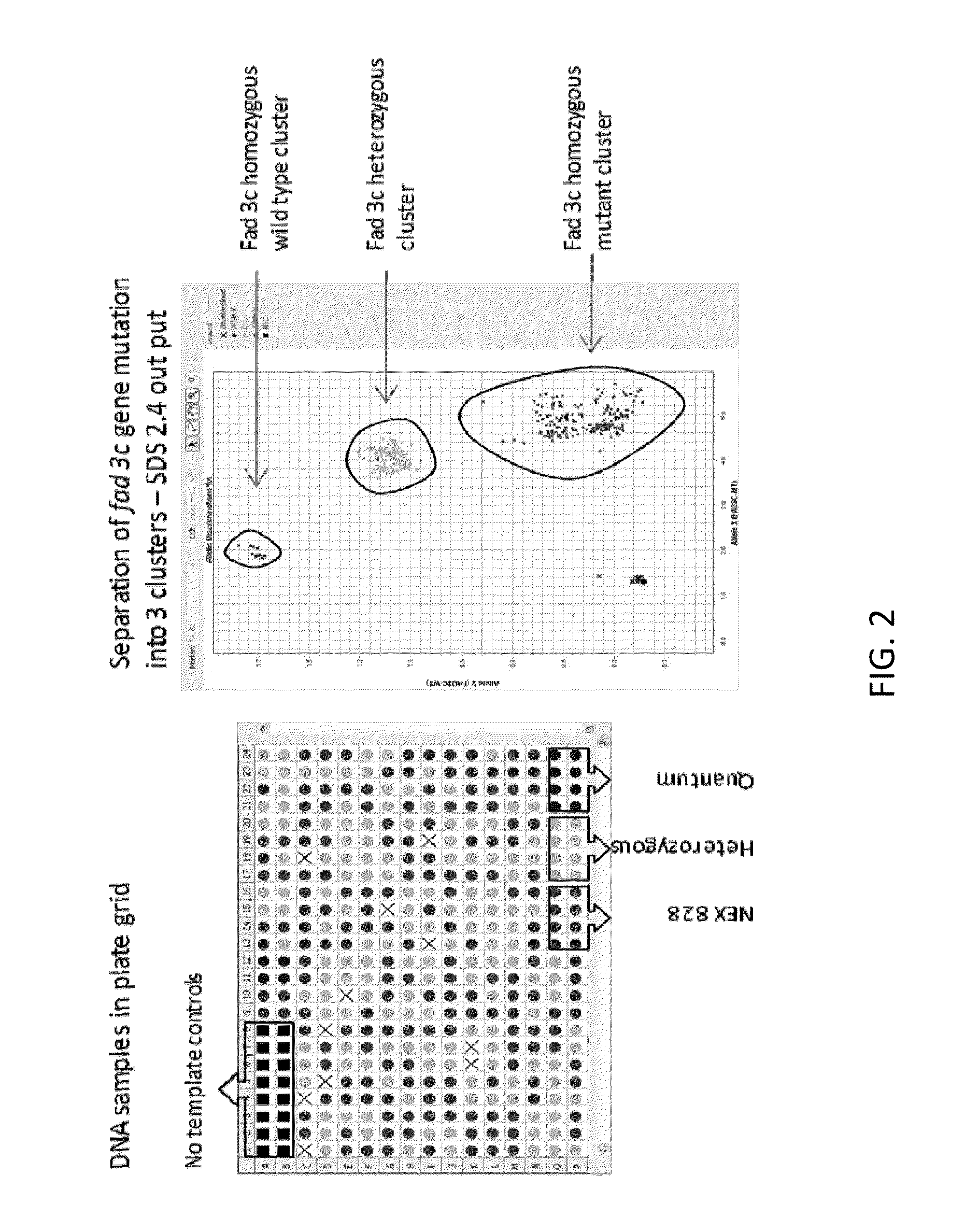
Method to determine zygosity of the fad3 gene in canola using end-point taqman® PCR
ActiveUS20130102002A1Reliable and accurate and high throughputImprove throughputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayWild type
The subject disclosure relates in part to endpoint TaqMan® PCR assays for the detection and high throughput zygosity analysis of the fad-3c gene in canola. The subject disclosure further relates, in part, to the use of wild type DNA as a reference for use in determining zygosity. These and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify the zygosity and variety of canola lines comprising the subject gene. The subject disclosure also provides related kits for determining zygosity from a sample of a canola plant or seed, for example.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com