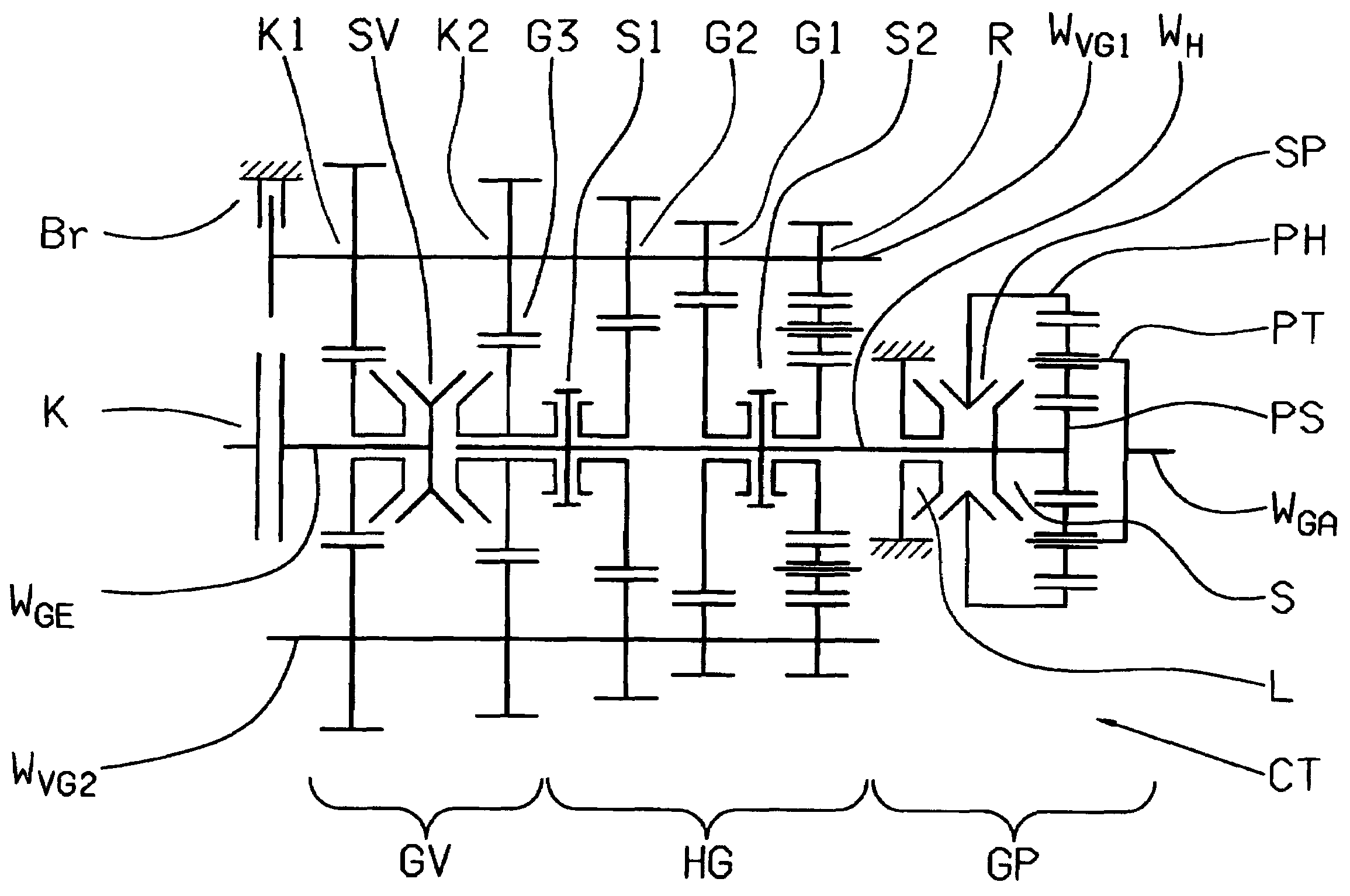
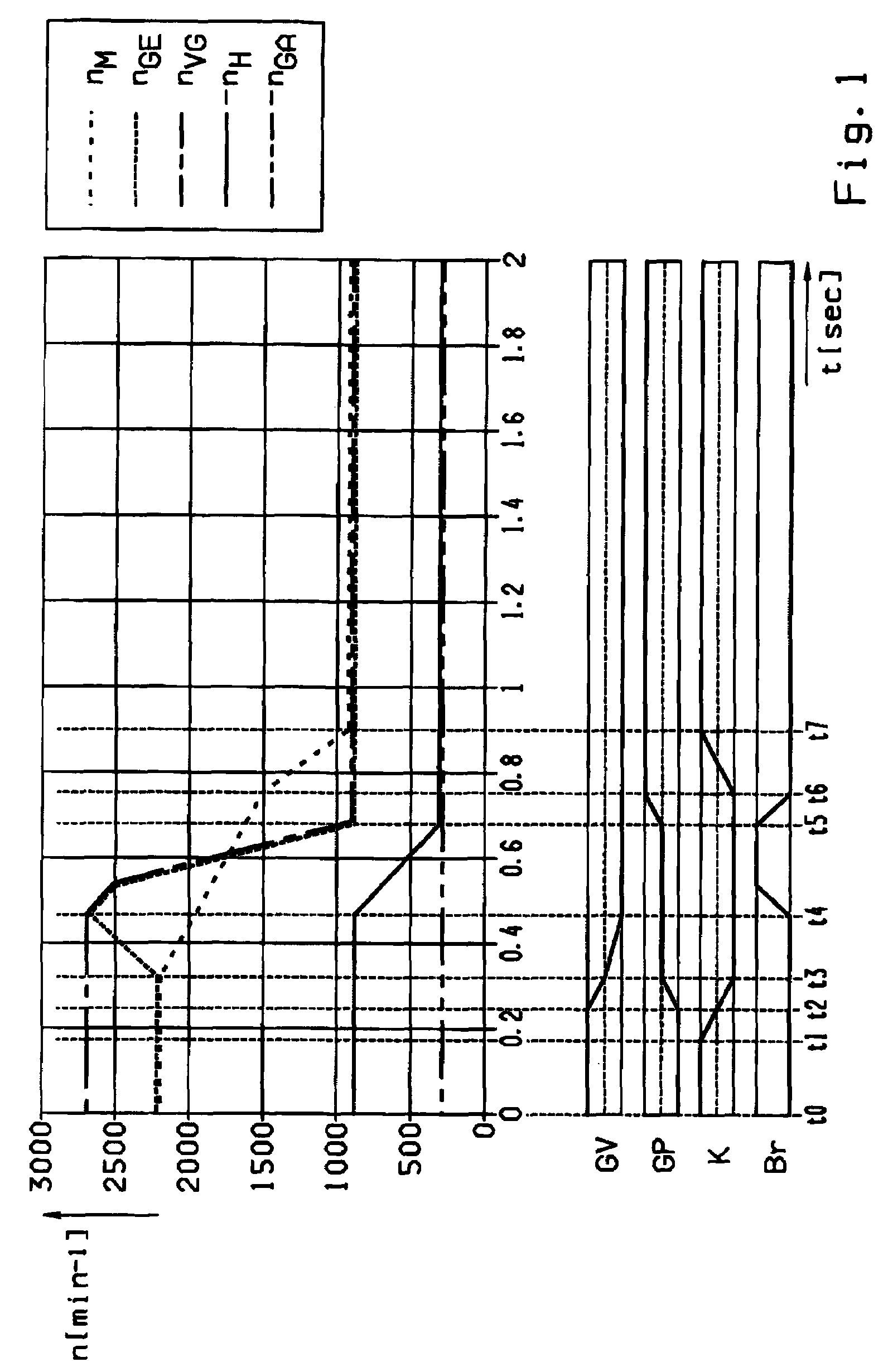
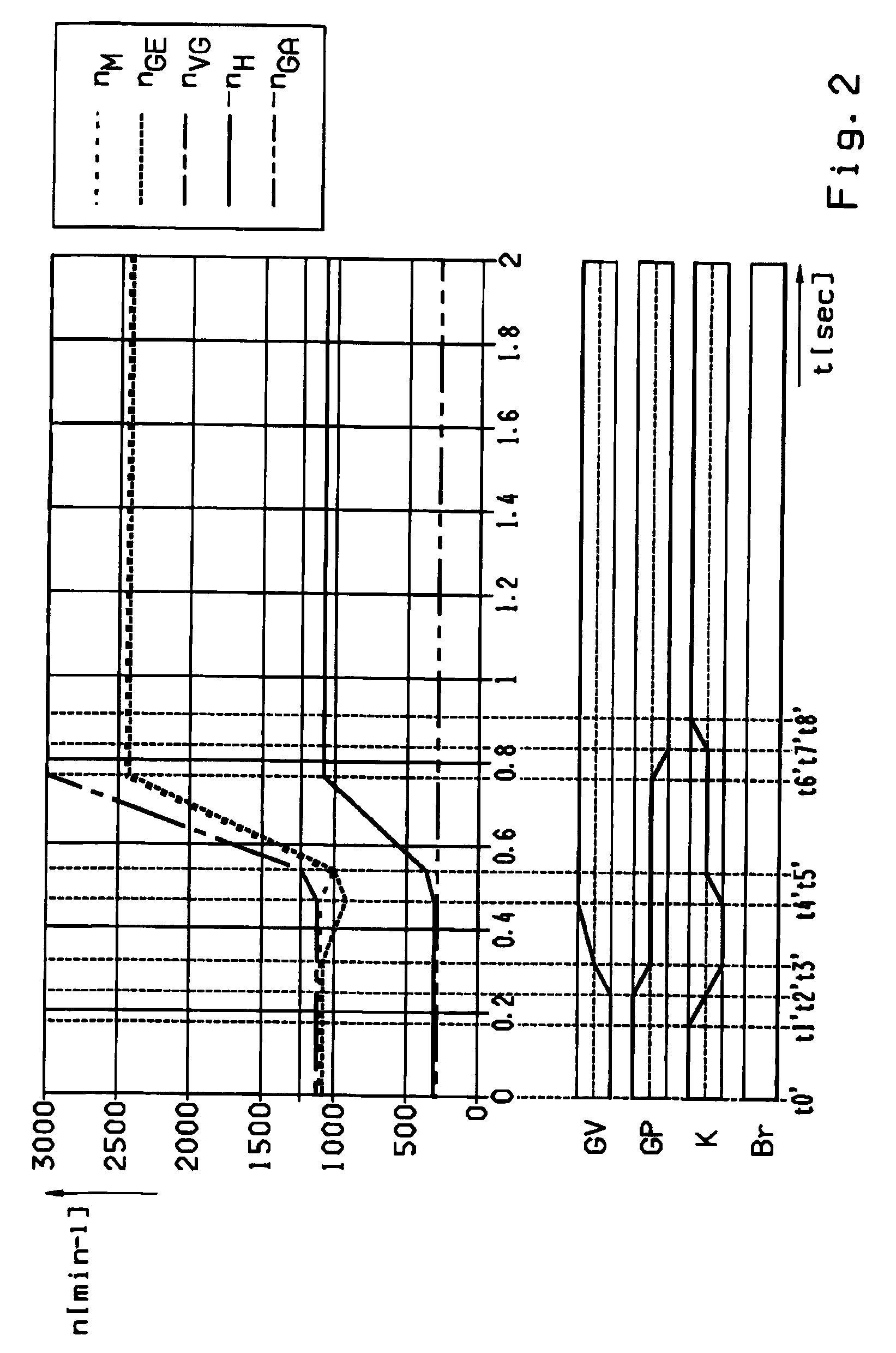
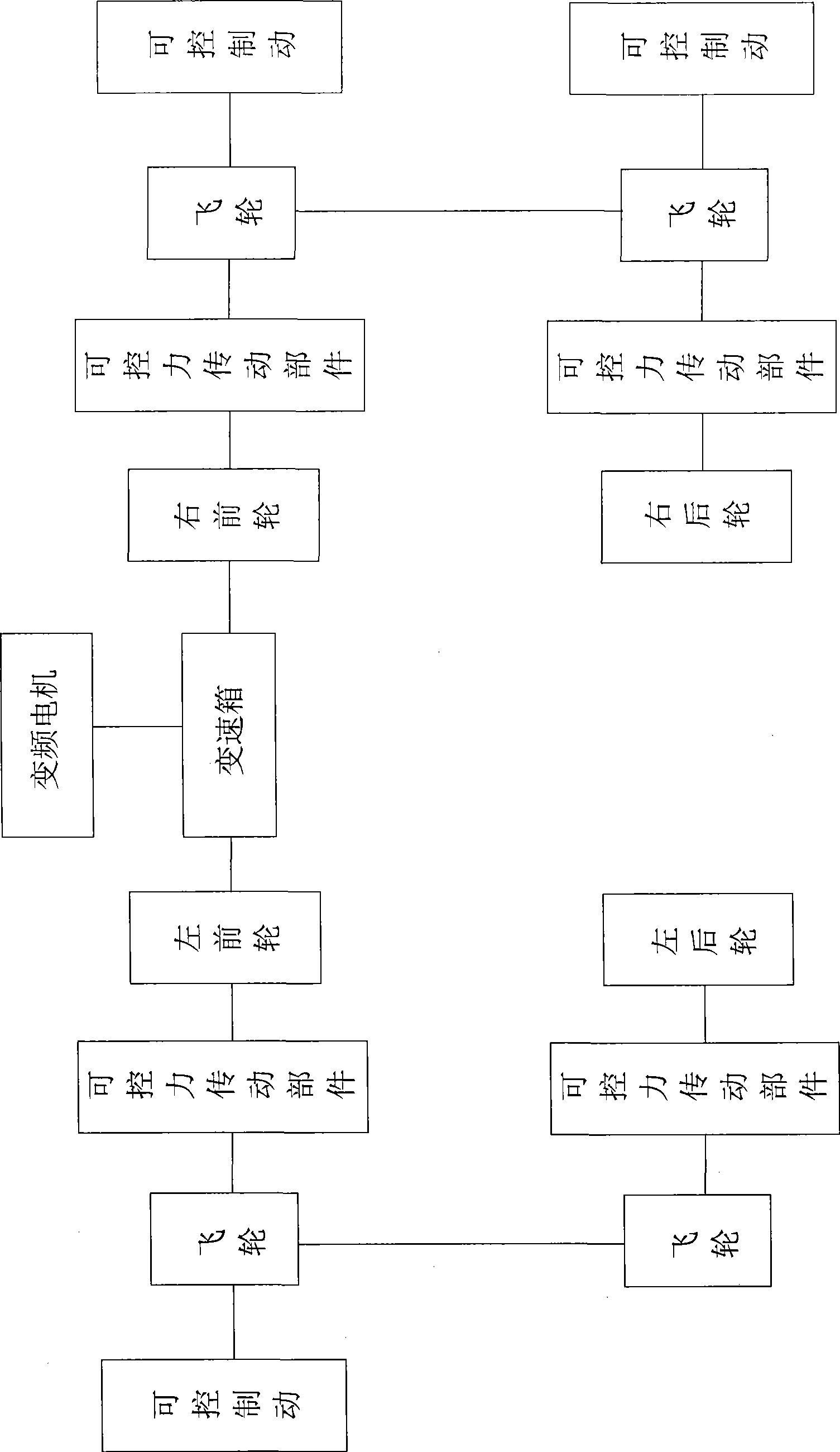
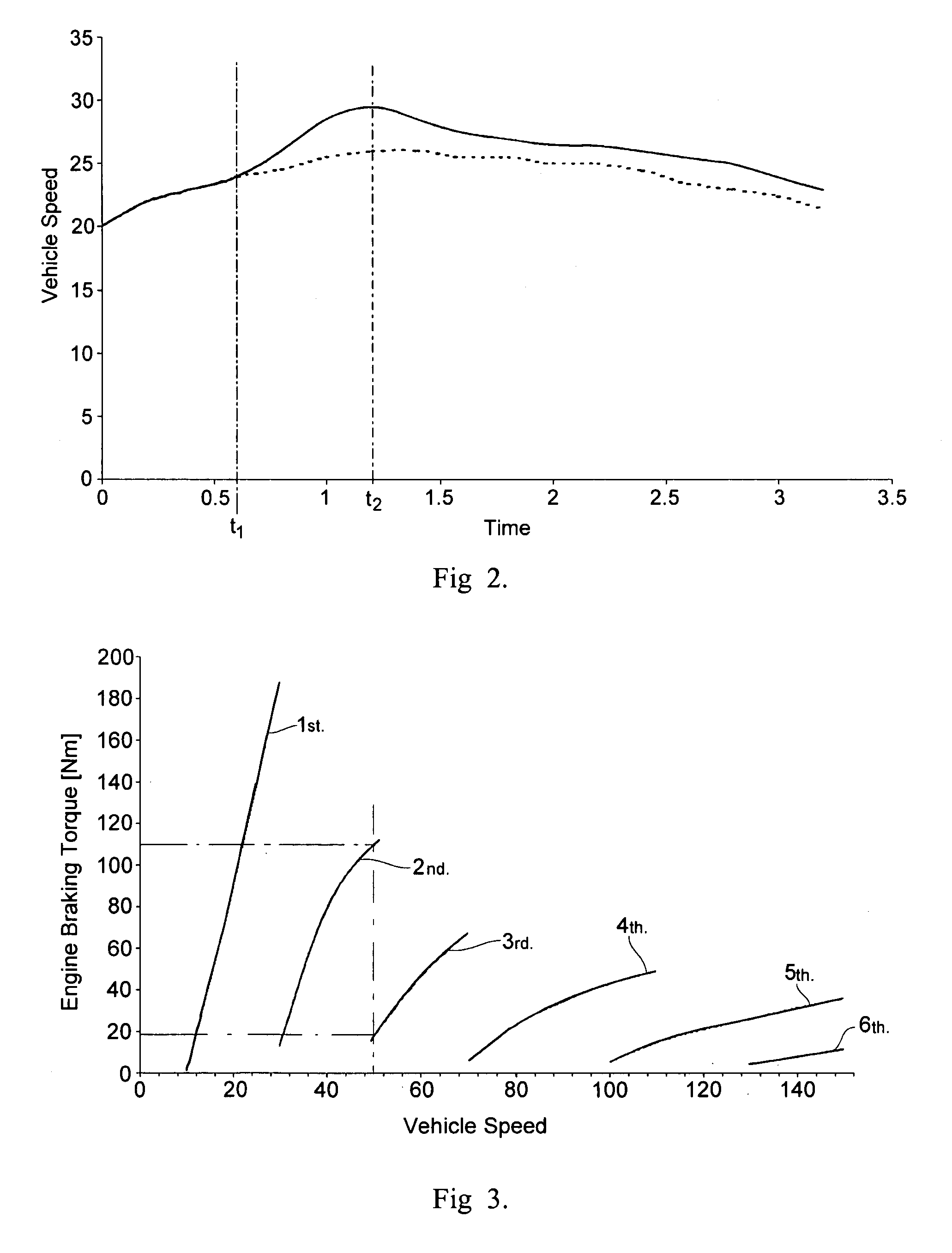
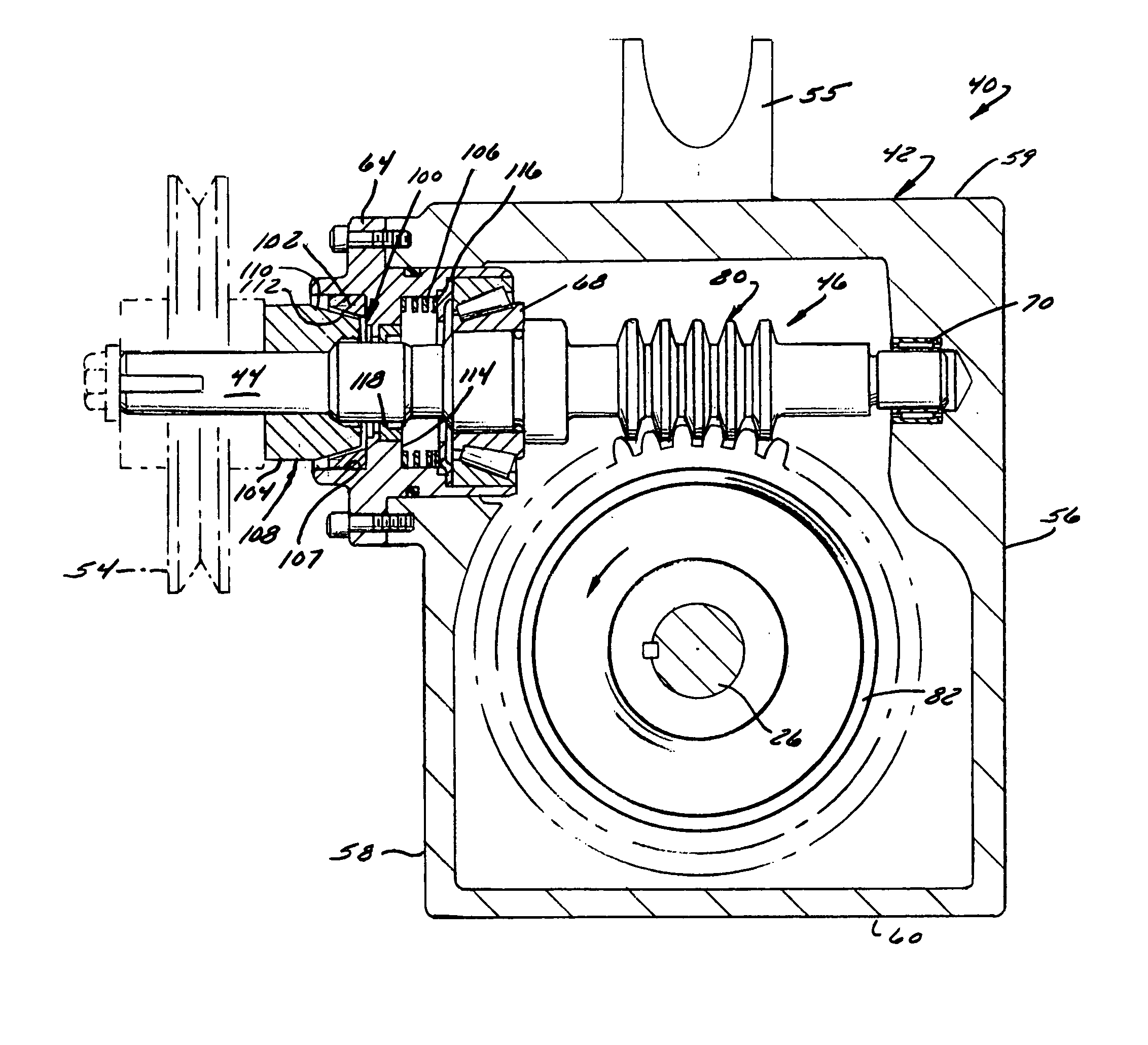
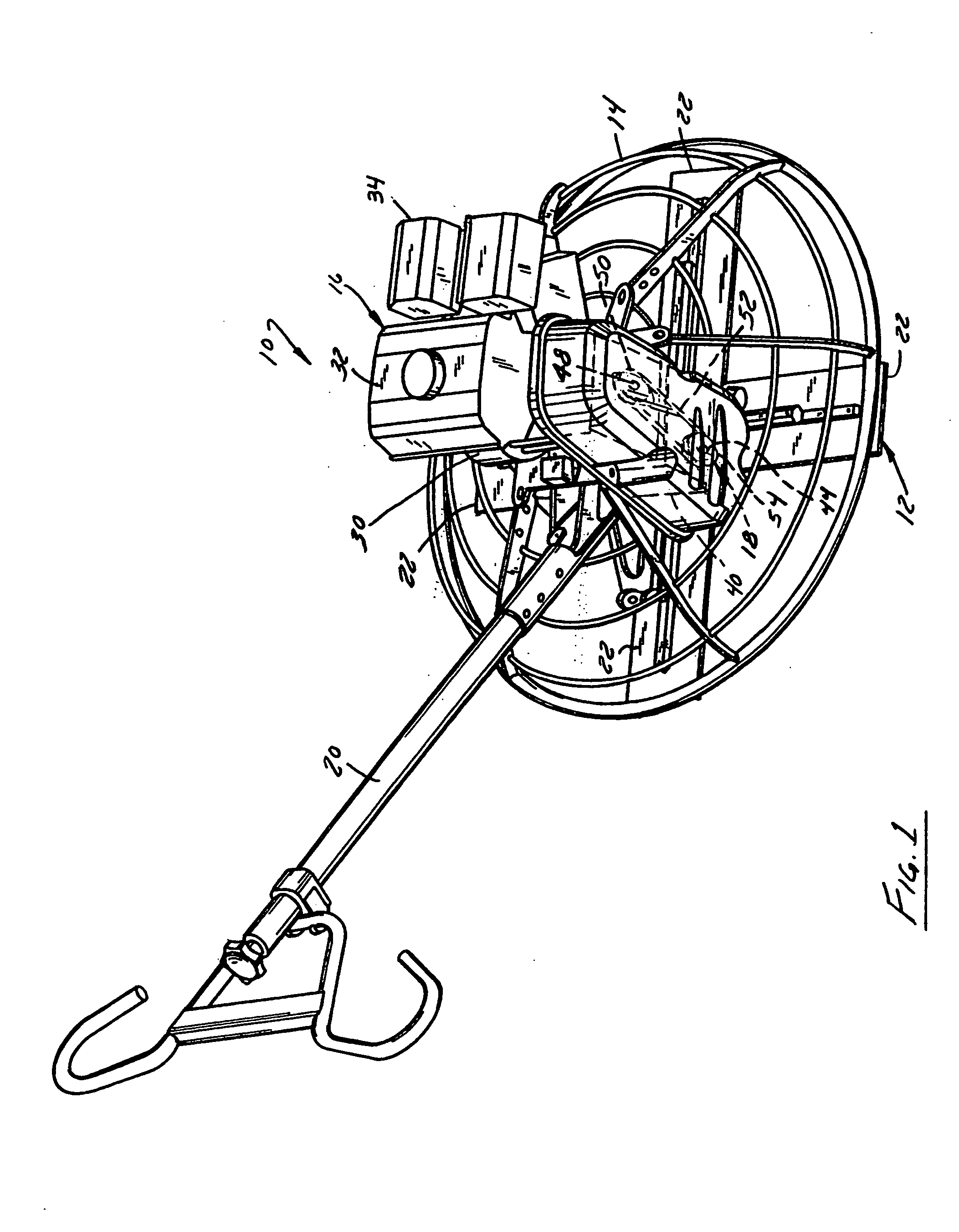
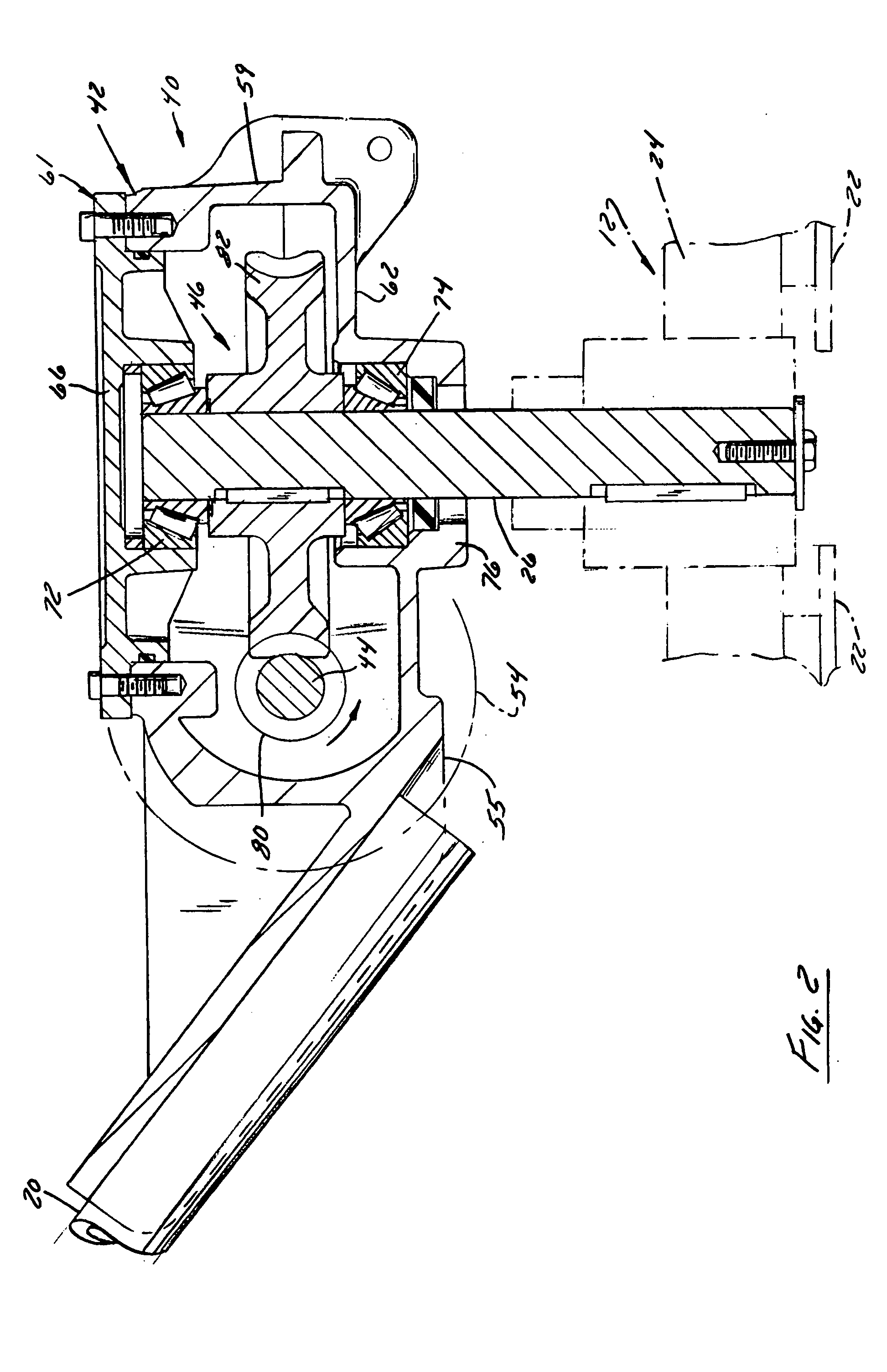
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
128 results about "Transmission brake" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
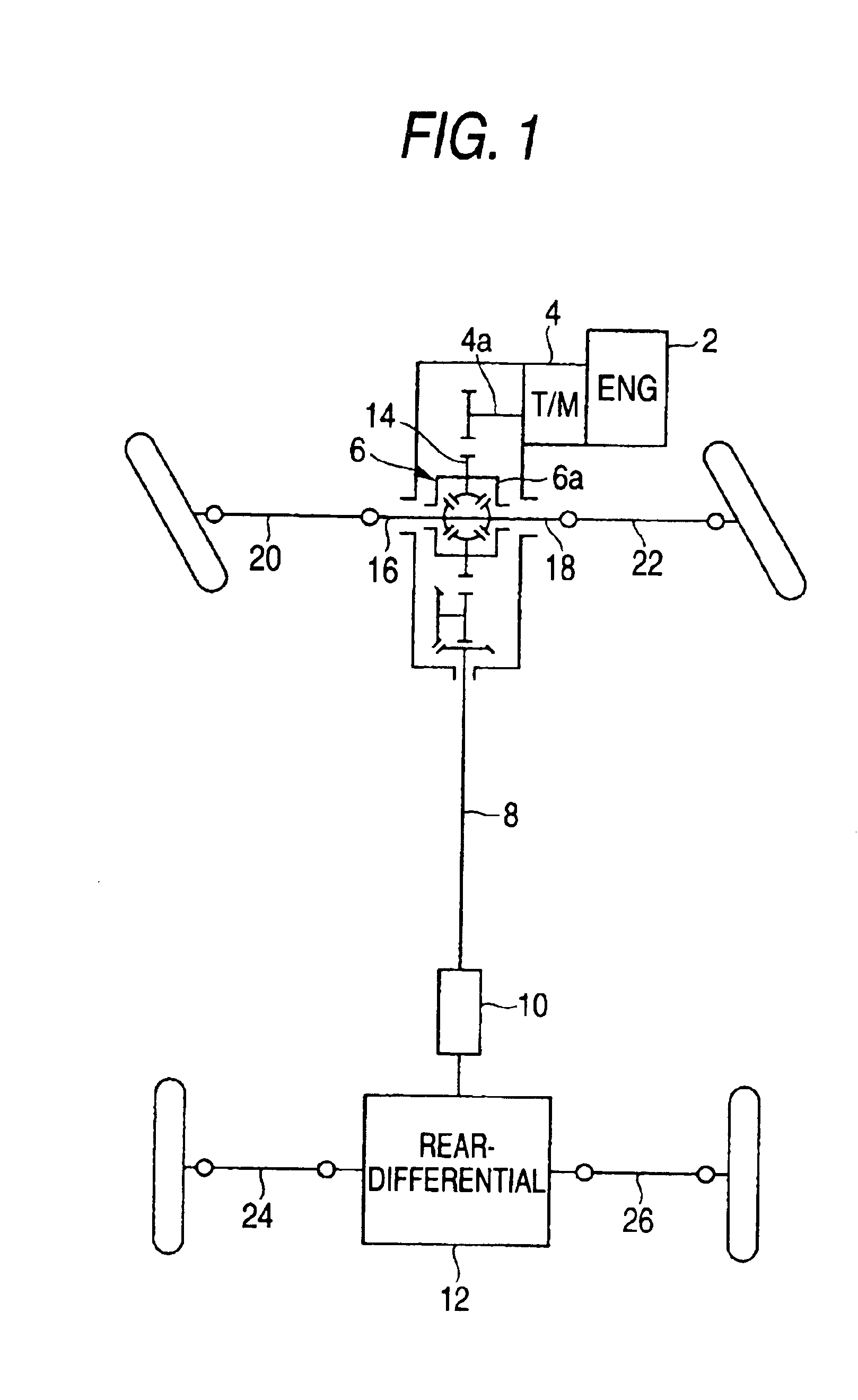
A transmission brake or driveline parking brake is an inboard vehicle brake that is applied to the drivetrain rather than to the wheels. Historically, some early cars used transmission brakes as the normal driving brake and often had wheel brakes on only one axle, if that. In current vehicles, these brakes are now rare. They are found in some makes, notably Land Rover, usually for light off-road vehicles. Simple transmission brakes could be found in large vehicles too, such as the 16 inch single disc parking brake used in the M19 Tank Transporter of World War II. . Such a system was also used on the HMMWV.
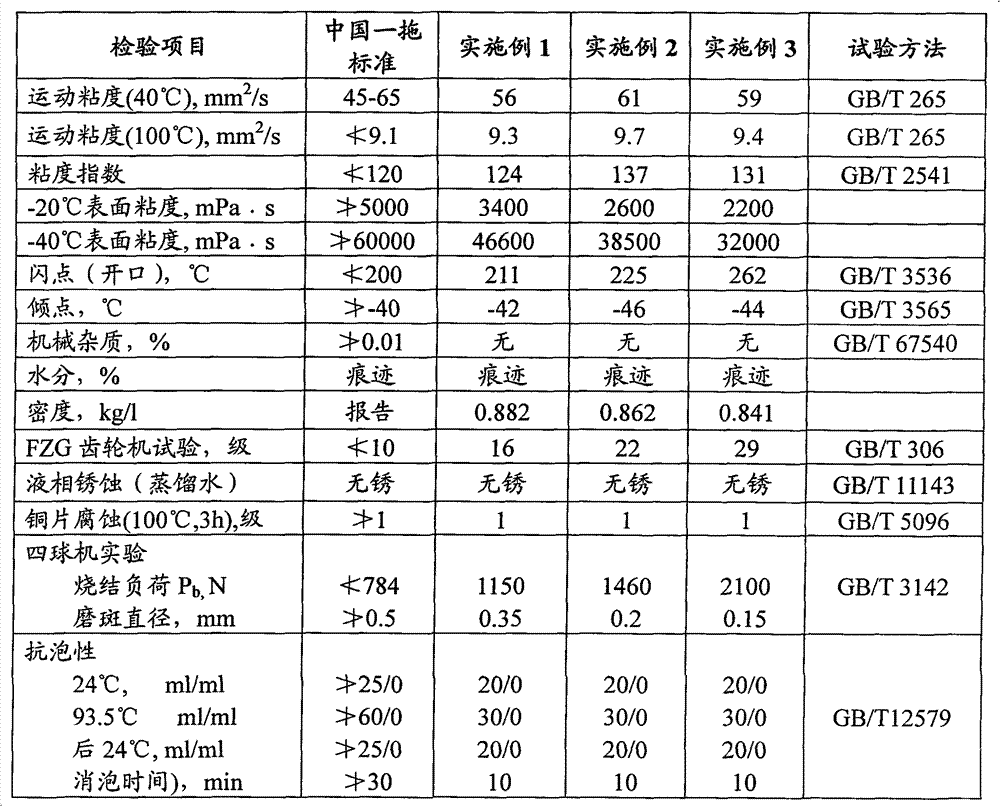
Hydraulic-transmission-braking three-use lubricating oil composition
InactiveCN102952617AAvoid wear and tearPrevent rustLubricant compositionFriction reductionTransmission brake
The present invention relates to a hydraulic-transmission- braking three-use lubricating oil composition, which is prepared by mixing the following raw materials, by weight, 85-98% of high viscosity index base oil, 0.1-5% of an extreme pressure wear resistance agent, 0.1-4% of an antioxidant, 0.1-3% of a metal deactivator / antirust agent, 0.1-5% of a friction modifier, and 0.1-2% of a dispersing agent. The hydraulic-transmission- braking three-use lubricating oil composition has beneficial effects of good low temperature fluidity, friction reduction, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, rust resistance, emulsification resistance and foaming resistance, and can meet requirements of universal hydraulic transmission oil used by large-medium-sized tractors and construction machinery so as to achieve complete lubricating protection on hydraulic parts, transmission parts, gear parts, power output parts and braking parts, such that a long service life is provided, equipment operation stability is easily improved, and energy saving and consumption reduction are provided.
Owner:BEIJING ALLUBE PETROCHEM
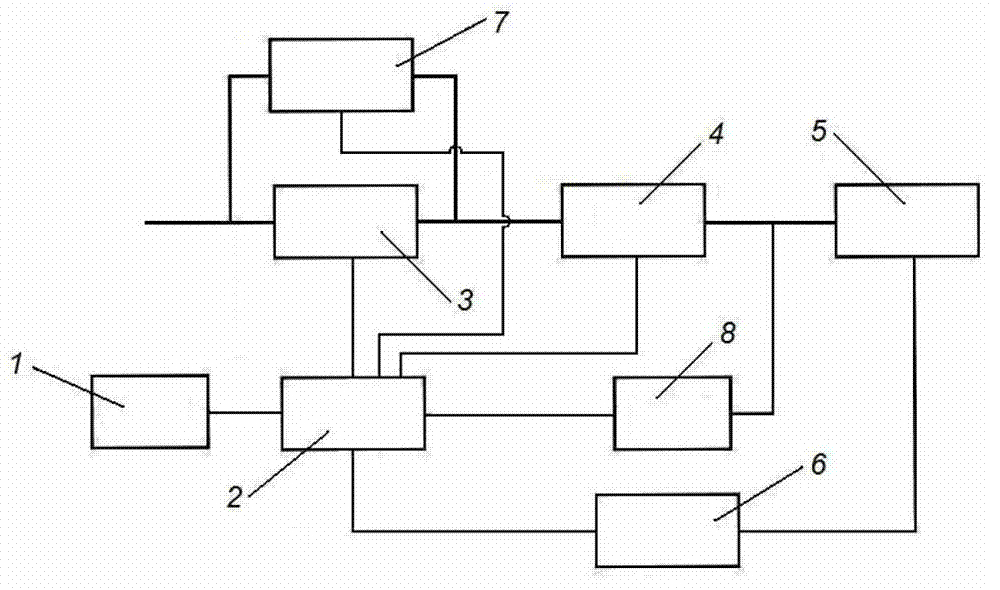
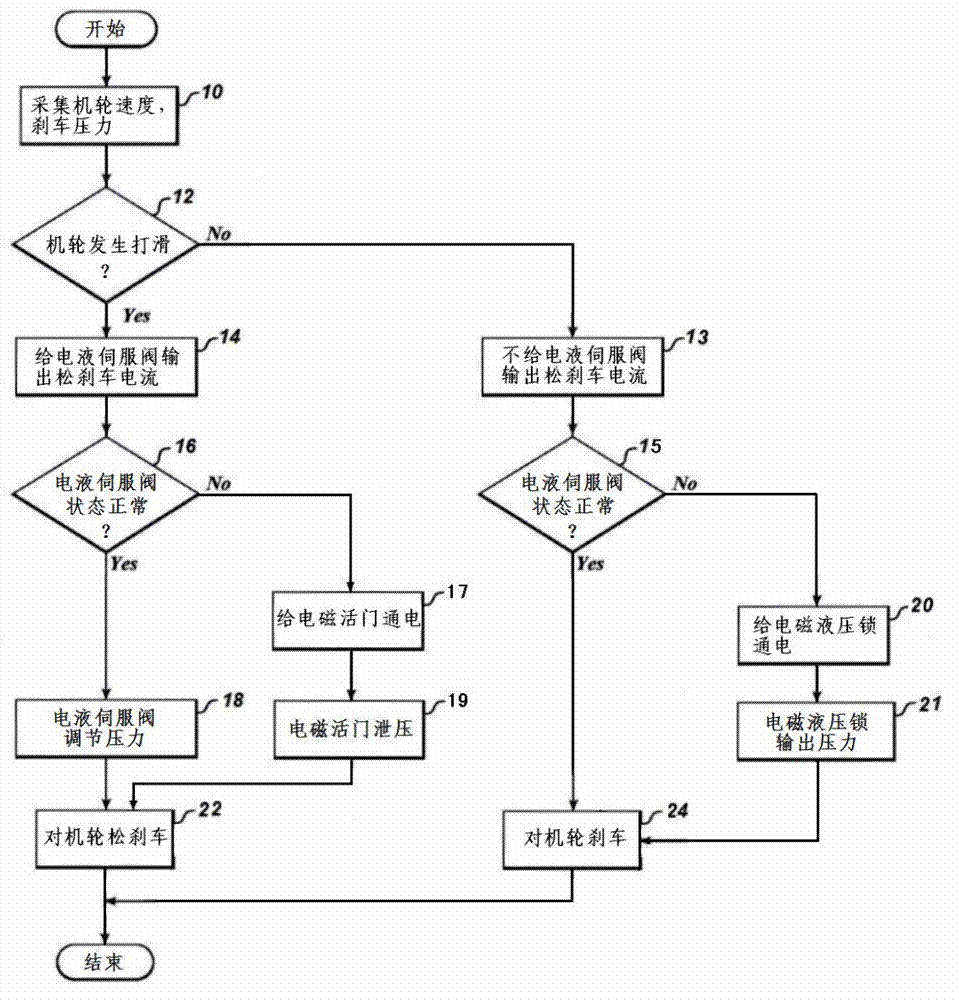
Airplane electrical signal transmission brake antiskid control system
InactiveCN103158867AAutomatic recording of failure status modesGuaranteed uptimeBrake regulatorsTransmission brakeControl system
The invention relates to an airplane electrical signal transmission brake antiskid control system. When brake is carried out, an electro hydraulic servo valve can not output brake pressure, a control box emits a control signal to an electromagnetic hydraulic lock, the electromagnetic hydraulic lock unlocks by energization, the hydraulic power source is switched on, and the brake is carried out on a brake machine wheel with maximum brake pressure. During a brake process, if the machine wheel slips, the control box controls the electromagnetic valve for energization to release pressure. The system is simple and easy to be carried out, the reliability and security of the brake system operation can be greatly increased during taking off, landing rollout processes, the work load of a driver is reduced, even the electro hydraulic servo valve generates fault, the tire burst can be effectively avoided, and the airplane usage safety is ensured.
Owner:XIAN AVIATION BRAKE TECH
Gearbox brake for mining machinery
InactiveUS7493992B2Increasing envelopeEasy maintenanceSelf acting brakesMechanically actuated brakesTransmission brakeEngineering
A gearbox having an integral wet brake assembly is provided to replace the prior gearbox assembly of an underground mining machine. The brake housing is configured and contoured to be nestingly received upon the gearbox housing and without intrusion upon the output drive flanges. The brake housing includes concentric parking and service brake pistons adapted to engage and disengage a brake disc stack provided within a cavity machined into an end plate of the gear box assembly. An intermediate shaft of the gearbox is provided with a hub to engage the rotary discs of the brake disc stack. The parking brake is normally engaged by a spring and released by hydraulic pressure, while the service brake is normally released by a spring and engaged by hydraulic pressure.
Owner:PT TECH INC
Method for shifting actuation of an automated group transmission
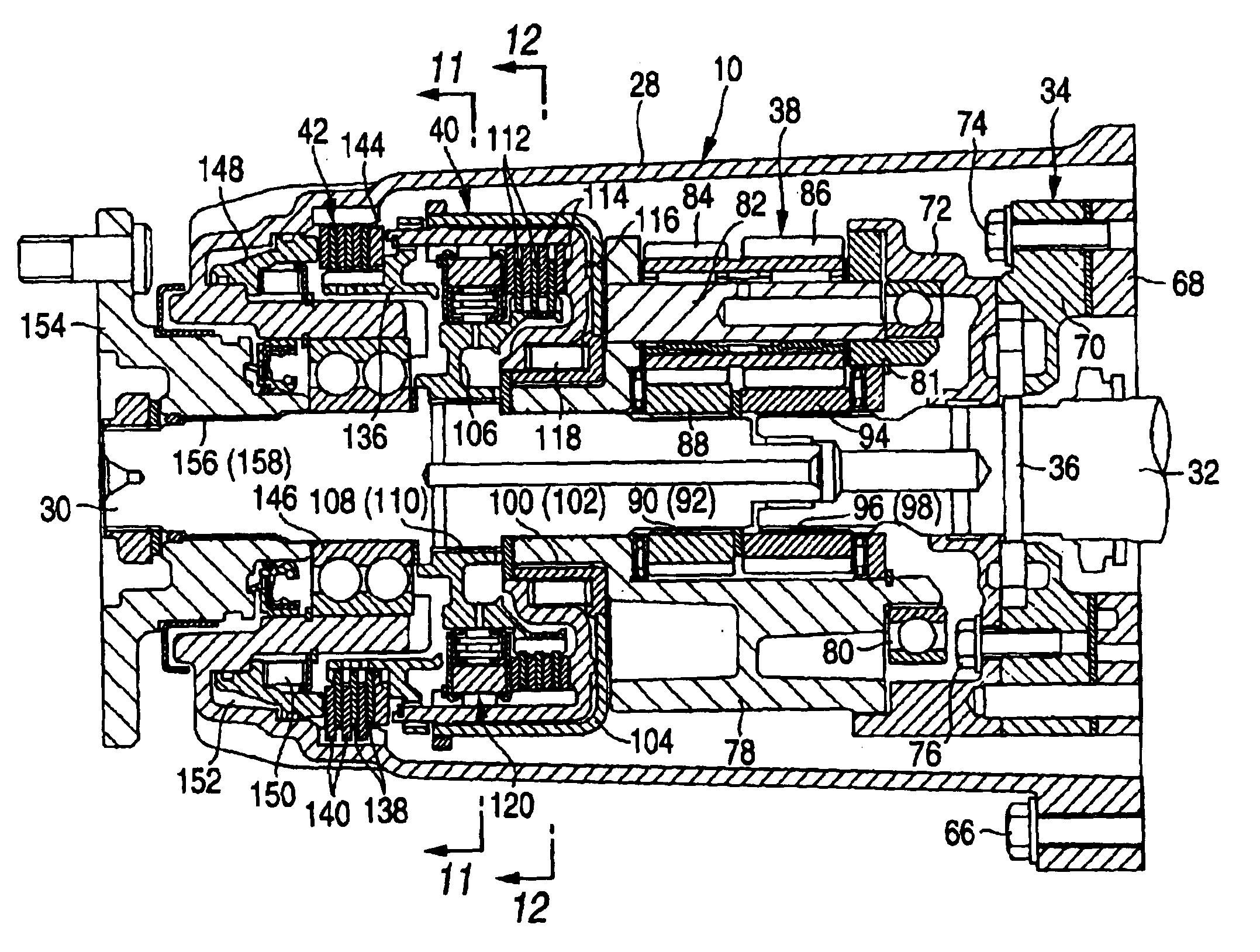
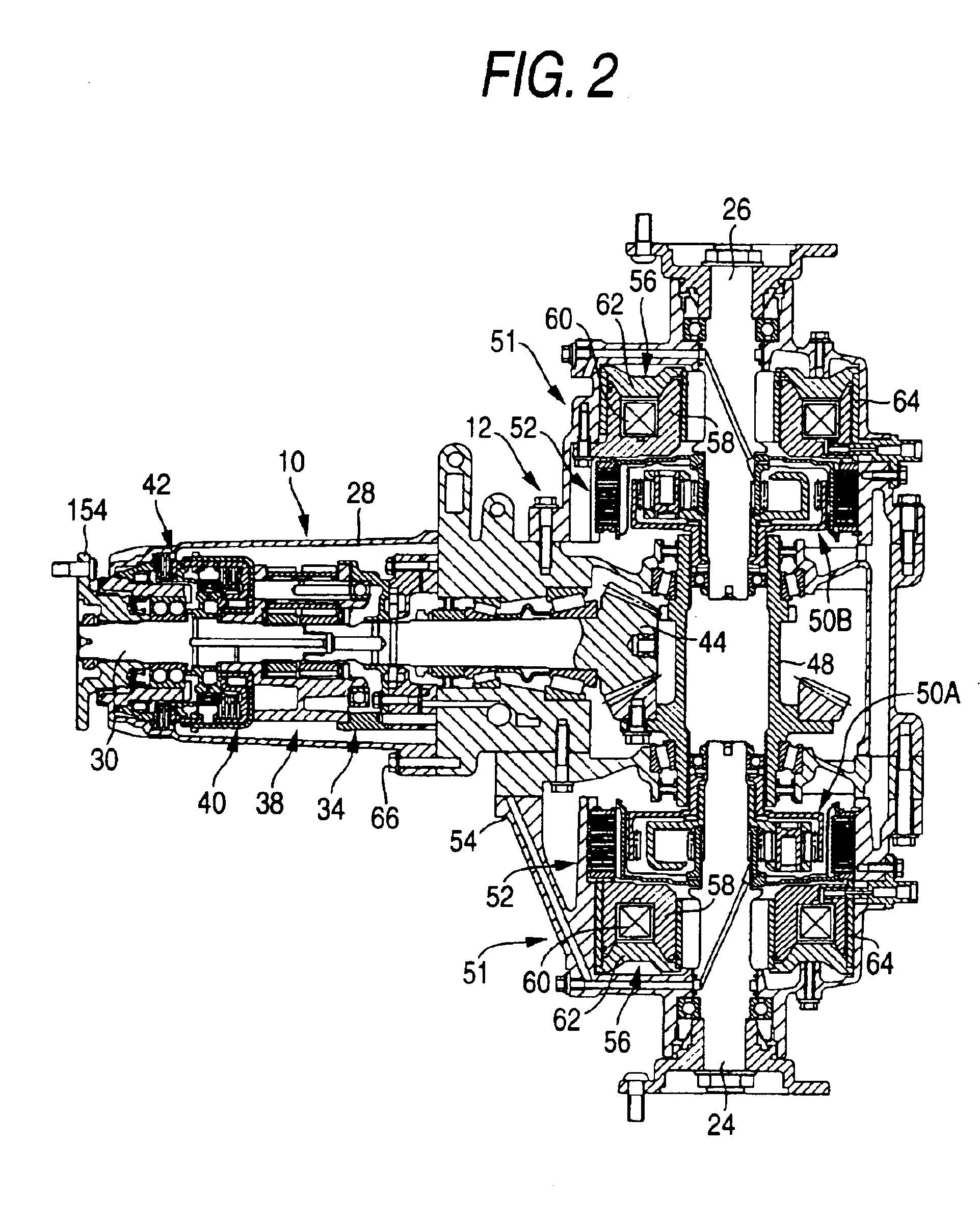
InactiveUS20090071277A1Open fastAcceptable shifting comfortGearingGearing controlMobile vehicleTransmission brake
A method for shifting an automated transmission situated in a drive train of a motor vehicle between an engine and a drive axle and having at least one multi-speed main transmission and a two-speed range change group rear-mounted thereon. The main transmission has at least one counter shaft with a transmission brake. A clutch engages the prime mover and the main transmission and the range change group is shifted via unsynchronized dog clutches which are combined in pairs in a common shift set and have two shift positions and one neutral position such that, during a range change gear shift both in the main transmission and the range change group a change between two ratio stages occurs. A range change up-shift includes synchronizing the input shaft and the target gear utilizing the transmission brake and passively synchronizing the dog shifted transmission parts by the edge beveling of the concerned dog clutches.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Disengaging systems
A lever system for actuating a clutch or a brake for a vehicle, such as a motor vehicle. The actuating force for the clutch or transmission brake is changeable by displacing a fulcrum with respect to a lever. An energy storage mechanism may act at one end portion of the lever and a pressure plate of a clutch or a transmission brake may act, directly or indirectly, on the other end portion.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Method for controlling shifts in an automated step-down transmission
ActiveUS20090239704A1Great shifting reliabilityShort shift timesHybrid vehiclesGearing controlTransmission brakeDrivetrain
A method of controlling an automated step-down transmission, arranged in a drivetrain between an engine and a drive axle, which includes a multi-stage main transmission and a range group. The main transmission has an intermediate transmission style with a countershaft having a transmission brake and an input shaft connected, via a clutch, to the engine. The main transmission shifts, without being synchronized, and the range group shifts, after synchronization, such that the engaged gear ratio of the main transmission remains engaged during a range shift operation. The range shift is accomplished by firstly reducing drive engine torque; secondly, disengaging the existing gear ratio of the range group; thirdly, remotely synchronizing the target gear ratio in the range group; fourthly, engaging the target gear ratio in the range group; and fifthly, increasing the drive engine torque.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
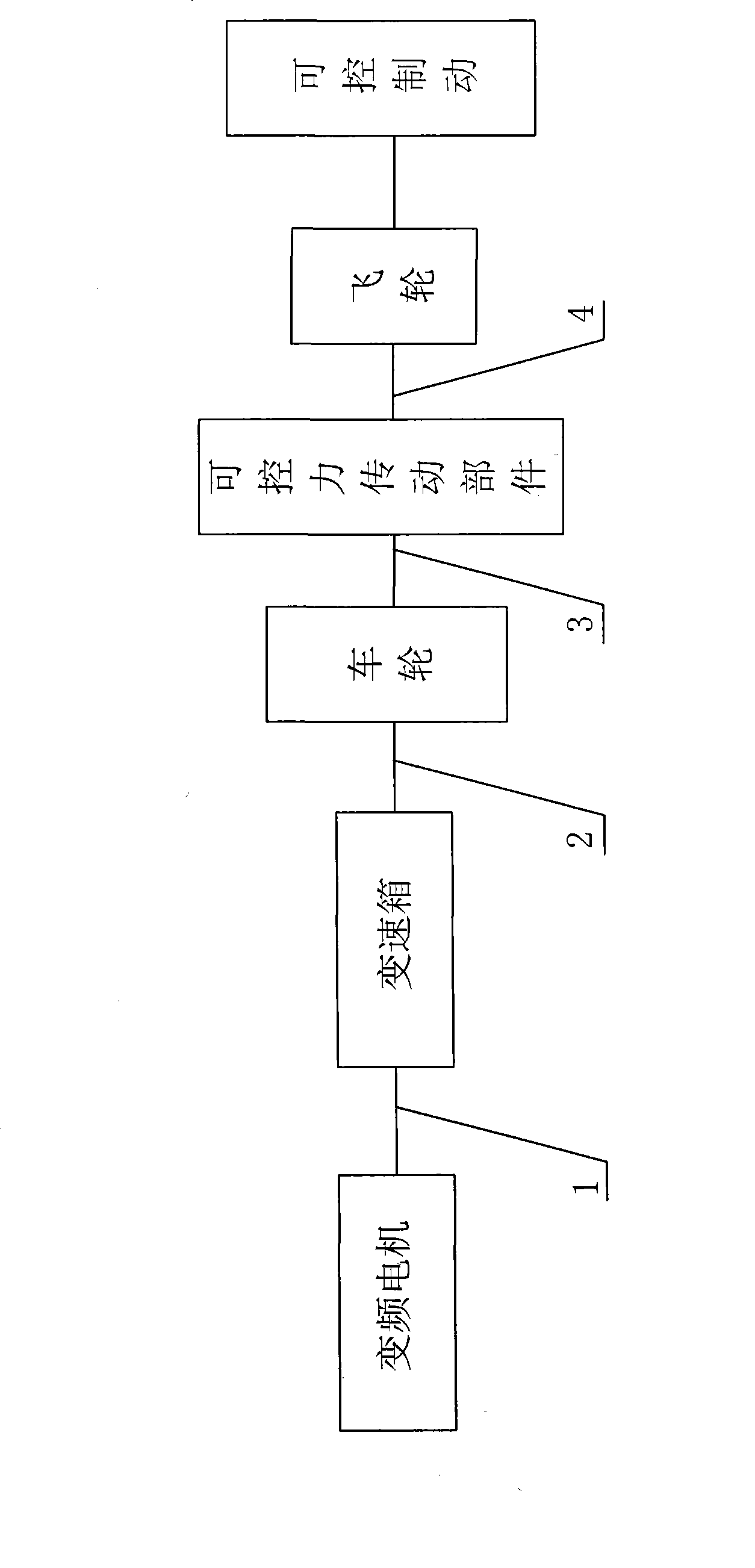
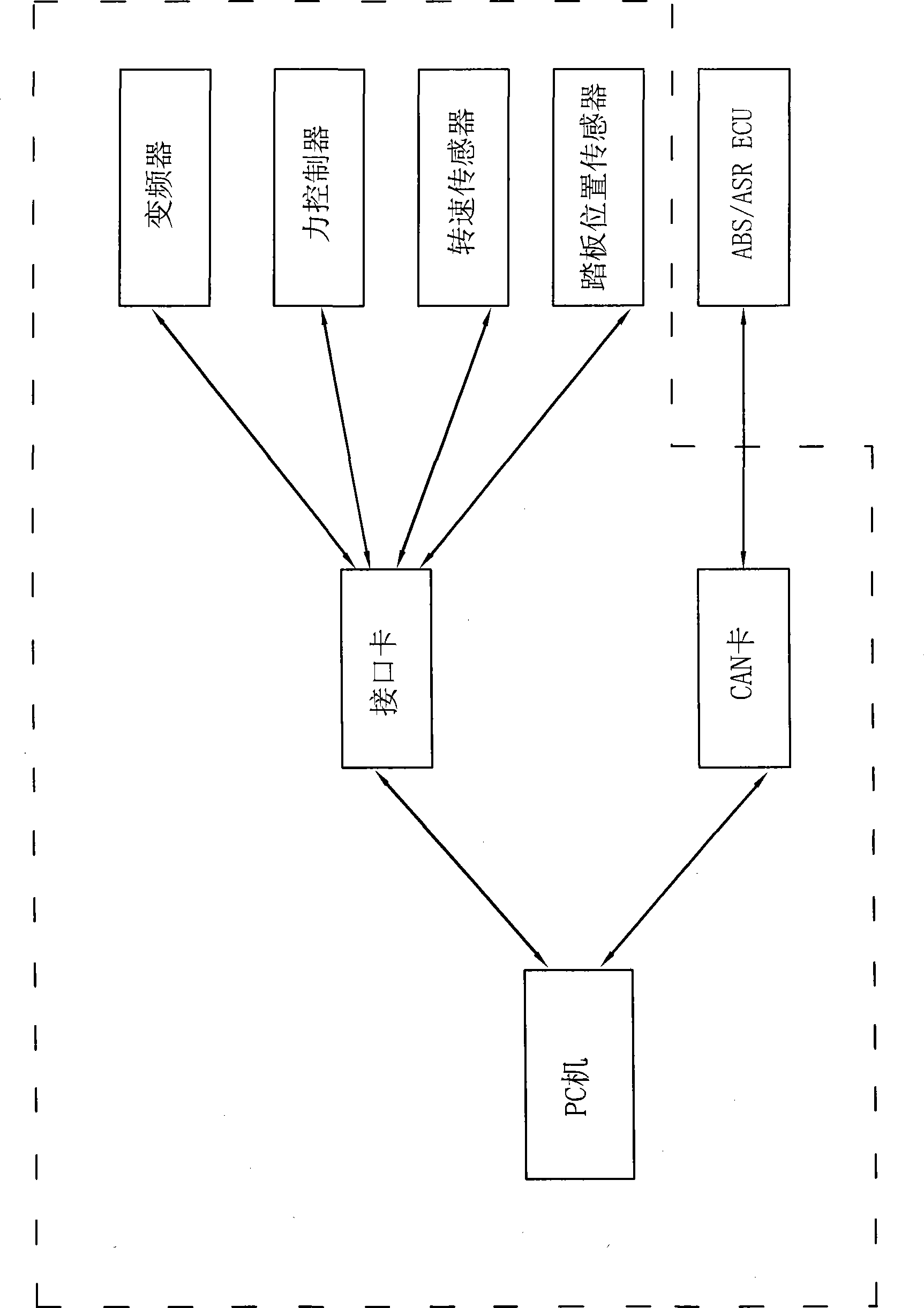
Hardware-in-loop semi-physical vehicle transmission-integrated simulation experiment bench
InactiveCN101476985AConvenient teachingReduce experimental expensesCosmonautic condition simulationsMachine gearing/transmission testingTransmission brakeFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a hardware-in-loop semi-physical automobile transmission-braking integrated simulation test table. The test table comprises a mechanical system part of the test table and an electric system part of the test table; the mechanical system part of the test table comprises a wheel, a flywheel and a rotating shaft; the wheel is provided with an ABS braking system; a wheel axle of the wheel and a flywheel axle of the flywheel are connected together by a controllable force transmission part; the flywheel axle of the flywheel is also connected with a controllable braking part; the mechanical system part also comprises an accelerating pedal, a braking pedal, a clutch pedal, a frequency conversion motor and a gearbox; an output shaft of the gearbox and the wheel axle of the wheel are connected together; an input shaft of the gearbox is connected with the frequency conversion motor; and the electric system part of the test table comprises a PC machine, an interface card, a CAN card, a pedal position sensor, a rotational speed sensor, a force controller and a transducer.
Owner:WEIHAISHIWEILI TOP GRADE TOOL CO
Energy storage system based on track transport
InactiveCN102157951ASmooth power fluctuationsGuaranteed safe operationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingTransmission brakeHeavy load
The invention relates to an energy storage system based on rail transport. The energy storage system comprises high and low load fields for load parking, a transport track for load transportation, a power transmission line for providing traction power and transmission brake power generation, a traction / brake unit, a load unit, a storage track, a safety track, a control center and a power grid access module. In the invention, by means of combination of energy storage based on electrified track transport and brake power generation, in the case of excess electricity of the system, an electric traction locomotive carries heavy load from a low place to a high place so as to convert electric energy into potential energy for storage; and in the case of high demand of the electricity of the system, brake power generation is performed during the process that the electric locomotive carries the heavy load from the high place to the low place so as to convert the potential energy into the electric energy and transfer the electric energy to a power grid. The energy storage system has the advantages that energy with super-large and controllable volume and high density can be stored, the operation management method is simple, and the energy cycle efficiency is ultrahigh.
Owner:无锡爱索思电力科技有限公司
Automatic gearbox with a hydraulically actuated shifting element
InactiveUS20060163020A1Appreciable time gainSufficient roomFluid actuated brakesFluid actuated clutchesTransmission brakeDisk pack
An automatic gearbox for a vehicle with at least one hydraulically actuated shifting element made as a transmission brake or transmission clutch. The shifting element has an inner disk carrier and an outer disk carrier where inner disks and outer disks are arranged rotationally fixed but axially displaceably. The disks are arranged in alternating sequence one after the other to form a disk pack which can be acted upon by an actuator with an axial actuation force to close the shifting element, and in which one disk carrier is connected to non-rotating or rotating gearbox components and the other disk carrier can be connected via a synchronization device to rotating gearbox components. To reduce the shifting time that can be achieved with such a gearbox in carrying out a transmission ratio change process, a synchronization device can be actuated by way of a second actuator of its own.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Method for shifting actuation of an automated group transmission
InactiveUS7976431B2Acceptable shifting comfortGearingGearing controlTransmission brakeAutomatic transmission
A method for shifting an automated transmission situated in a drive train of a motor vehicle between an engine and a drive axle and having at least one multi-speed main transmission and a two-speed range change group rear-mounted thereon. The main transmission has at least one counter shaft with a transmission brake. A clutch engages the prime mover and the main transmission and the range change group is shifted via unsynchronized dog clutches which are combined in pairs in a common shift set and have two shift positions and one neutral position such that, during a range change gear shift both in the main transmission and the range change group a change between two ratio stages occurs. A range change up-shift includes synchronizing the input shaft and the target gear utilizing the transmission brake and passively synchronizing the dog shifted transmission parts by the edge beveling of the concerned dog clutches.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Gearbox brake for mining machinery
InactiveUS20070034458A1Increasing envelopeEasy maintenanceSelf acting brakesMechanically actuated brakesTransmission brakeParking brake
A gearbox having an integral wet brake assembly is provided to replace the prior gearbox assembly of an underground mining machine. The brake housing is configured and contoured to be nestingly received upon the gearbox housing and without intrusion upon the output drive flanges. The brake housing includes concentric parking and service brake pistons adapted to engage and disengage a brake disc stack provided within a cavity machined into an end plate of the gear box assembly. An intermediate shaft of the gearbox is provided with a hub to engage the rotary discs of the brake disc stack. The parking brake is normally engaged by a spring and released by hydraulic pressure, while the service brake is normally released by a spring and engaged by hydraulic pressure.
Owner:PT TECH INC
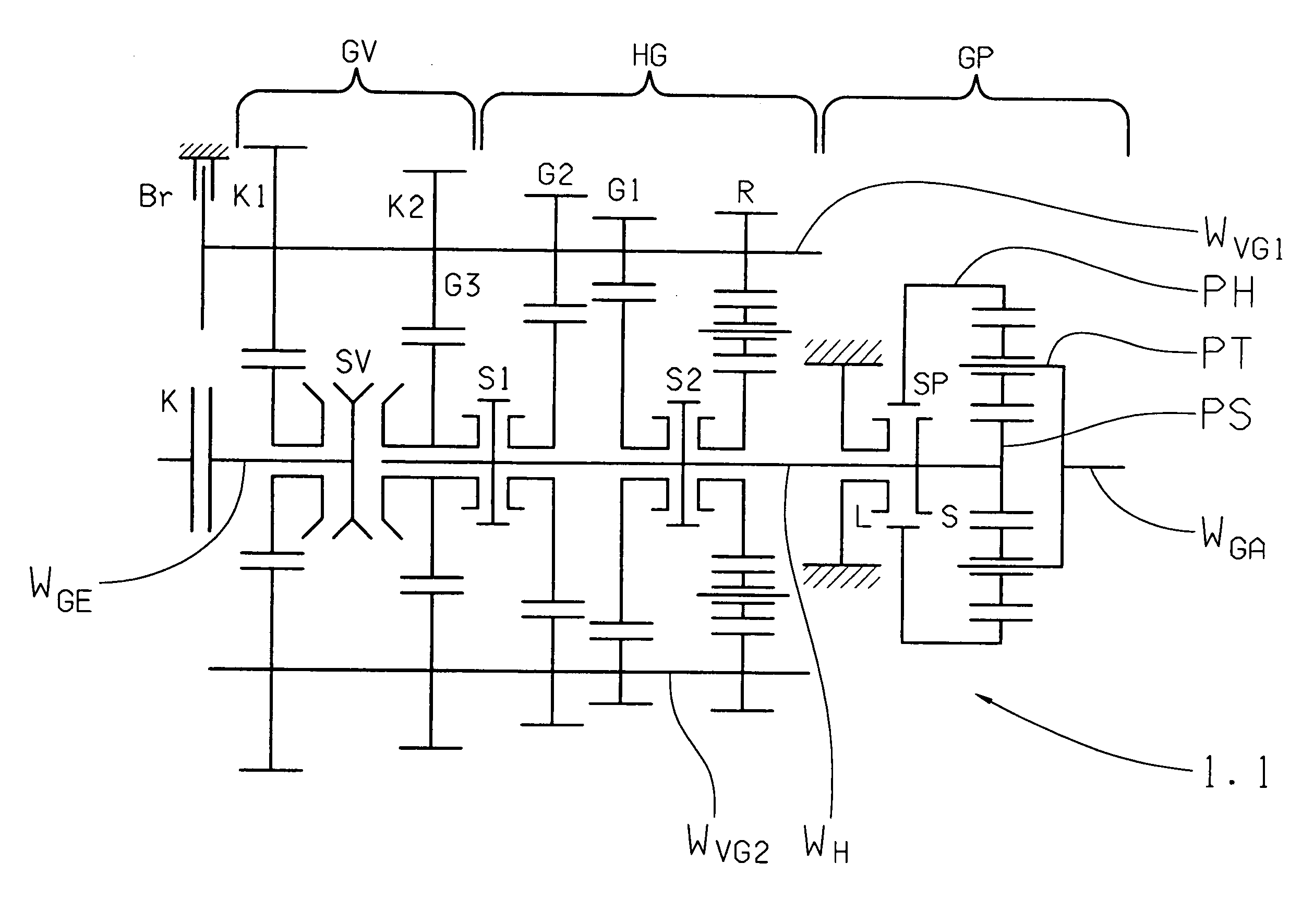
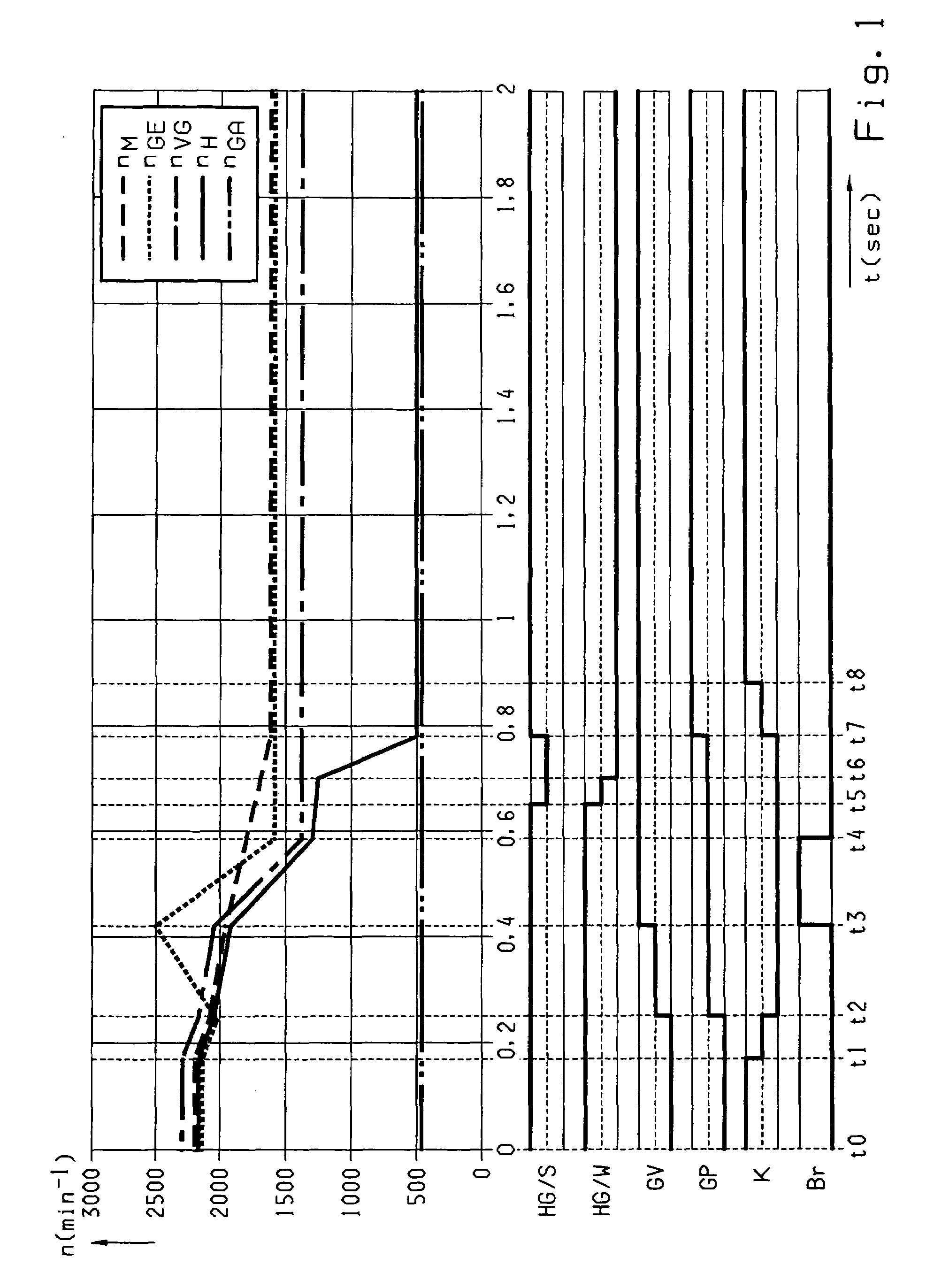
Shift Control Method For An Automatic Gearbox
ActiveUS20080113847A1Small sizeShifting sequenceGearing controlEngine controllersTransmission brakeElectric machine
A shift control method of a range group transmission with a multi-speed main transmission, which connects with a drive motor, via a clutch (K) and an input shaft. A transmission brake optionally engages the input shaft. At least a two range group is located downstream of the main transmission. A range change shift is accomplished by changing a gear of the main transmission and the range group. The shifting sequence is accelerated by: reducing motor torque and disengaging the clutch (K); disengaging a previous range group gear; synchronizing a new range group gear; disengaging a previous main transmission gear; engaging the new range group gear; synchronizing a new main transmission gear; engaging the new main transmission gear; and engaging the clutch (K) and increasing the motor torque, such that synchronization of the new gear occurs by influencing the input shaft of the main transmission.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
One-way braking device for wind power pitch system
InactiveCN102287332ASafe parkingPrevent lockWind motor controlMachines/enginesTransmission brakeEngineering
A unidirectional braking device for a wind power pitch system, the end cover is fixed on the shell, the mandrel passes through the shell and the end cover, and the mandrel is fitted between the mandrel and the shell and between the mandrel and the end cover Bearing; the mandrel gear is fixed on the mandrel, and the outer teeth of the mandrel gear mesh with the inner teeth of the transmission disc; one end of the brake spring is on the housing and the other end is on the brake pad, and the braking surface of the brake pad is in contact with the transmission disc. The disc surfaces of the discs match each other, the electromagnetic coil is fixed on the casing and the direction of its electromagnetic force is aligned with the brake pad, and the electromagnetic coil is electrically connected to the main power supply circuit. The invention utilizes brake springs, brake pads and electromagnetic coils to cooperate with one-way clutches to control the pitch system. When the main power supply circuit is powered off and the backup power supply fails, the fan blades can be safely returned. The paddle can prevent the motor braking device from locking up, and can return the blade to a safe position, so that the wind turbine can run and stop safely.
Owner:BEIJING WENCHUANG YOULIKE NEW ENERGY TECH
Method for controlling shifts in an automated step-down transmission
A method of controlling an automated step-down transmission, arranged in a drivetrain between an engine and a drive axle, which includes a multi-stage main transmission and a range group. The main transmission has an intermediate transmission style with a countershaft having a transmission brake and an input shaft connected, via a clutch, to the engine. The main transmission shifts, without being synchronized, and the range group shifts, after synchronization, such that the engaged gear ratio of the main transmission remains engaged during a range shift operation. The range shift is accomplished by firstly reducing drive engine torque; secondly, disengaging the existing gear ratio of the range group; thirdly, remotely synchronizing the target gear ratio in the range group; fourthly, engaging the target gear ratio in the range group; and fifthly, increasing the drive engine torque.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Automatic gearbox with a hydraulically actuated shifting element
InactiveUS7357235B2Appreciable time gainSufficient roomFluid actuated brakesFluid actuated clutchesCircular discTransmission brake
An automatic gearbox for a vehicle with at least one hydraulically actuated shifting element made as a transmission brake or transmission clutch. The shifting element has an inner disk carrier and an outer disk carrier where inner disks and outer disks are arranged rotationally fixed but axially displaceably. The disks are arranged in alternating sequence one after the otherto form a disk pack which can be acted upon by an actuator with an axial actuation force to engage the shifting element, and in which one disk carrier is connected to one of a non-rotating or a rotating gearbox component and the other disk carrier can be connected, via a synchronization device, to a rotating gearbox component. To reduce the shifting time that can be achieved with such a gearbox when carrying out a transmission ratio change process, a synchronization device is actuated by way of a second actuator.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Rotating speed synchronous control method for non-synchronizer type AMT transmission in gear shifting process
InactiveCN104791480AAccurate speed difference controlEasy to controlGearing controlTransmission brakeSynchronous control
The invention discloses a rotating speed synchronous control method for a non-synchronizer type AMT transmission in the gear shifting process. The method includes the following steps that first, the AMT transmission begins to shift a gear; second, the AMT controls a gear-shifting sliding sleeve to act, and the sliding sleeve is made to prepare for engaging a gear; third, the AMT judges whether up-shifting or down-shifting is conducted; fourth, if up-shifting happens, the AMT calculates the rotating speed n needing to be reached by an engine in the up-shifting process and controls the engine to further control a transmission brake to act; fifth, if down-shifting happens, the AMT calculates the rotating speed n' needing to be reached by the engine in the down-shifting process and controls a clutch to be engaged; sixth, the synchronizing process of the rotating speed is ended, and a TCU controls the gear-shifting sliding sleeve to act, so that a needed gear is engaged. The AMT is used for calculating the rotating speed, corresponding to a target shift gear, needing to be reached by the engine in the up-shifting or down-shifting process, the transmission brake is controlled to brake or the clutch is controlled to be engaged, the rotating speed of the target shift gear is made to be decreased or increased, the difference of the rotating speed of the sliding sleeve of a gear-shifting mechanism and the rotating speed of the target shift gear is controlled more accurately, and the synchronizing process is quicker.
Owner:SINO TRUK JINAN POWER
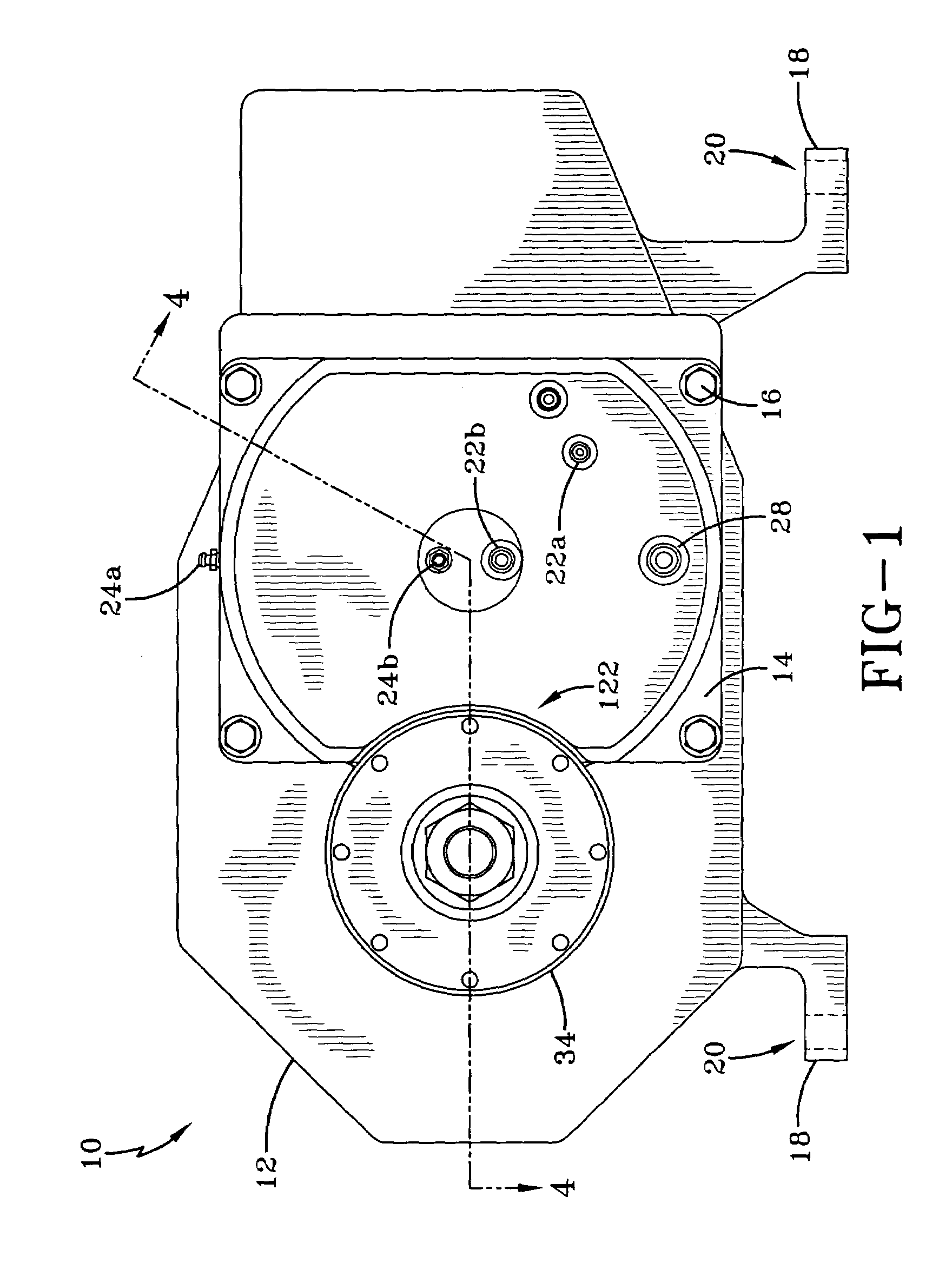
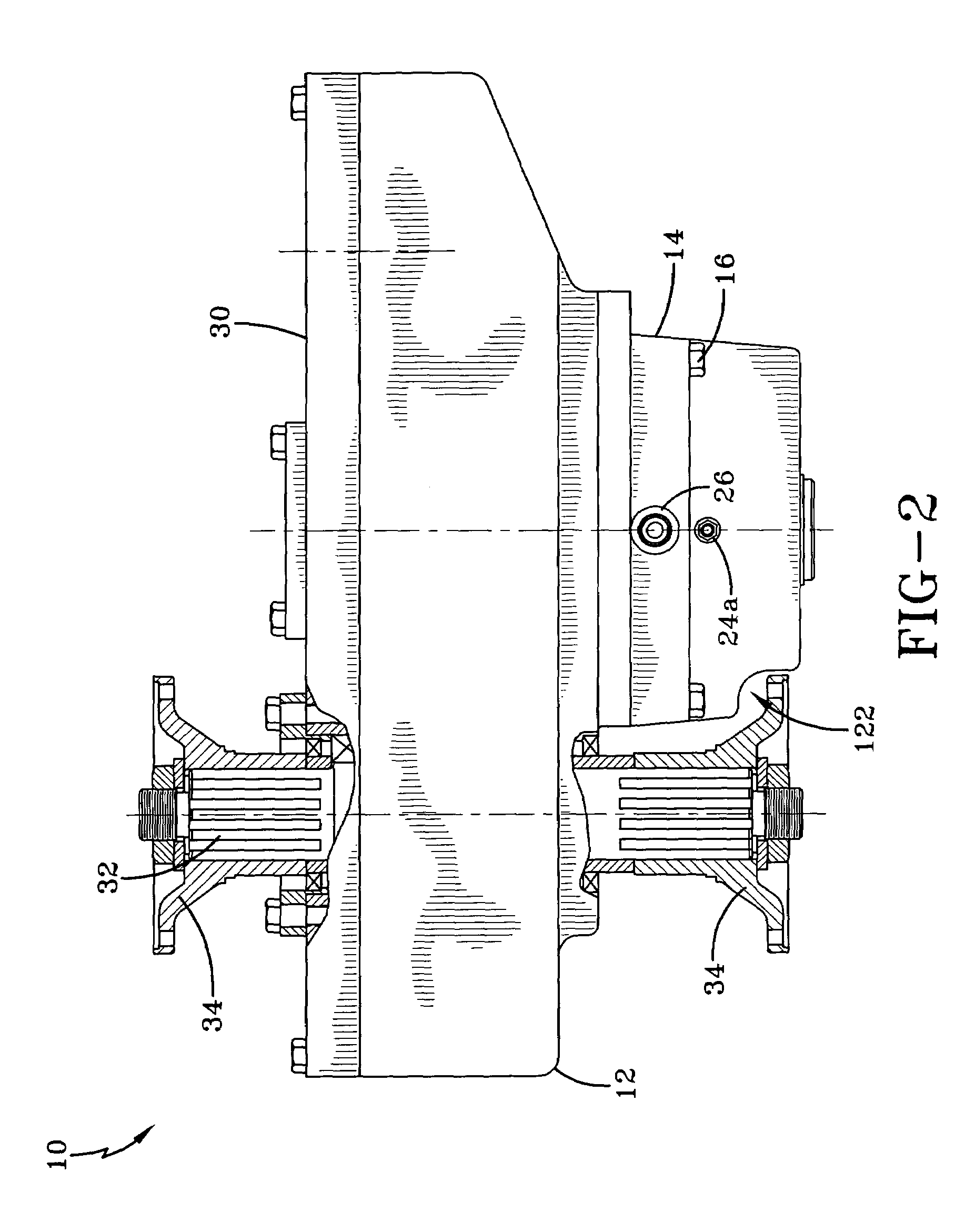
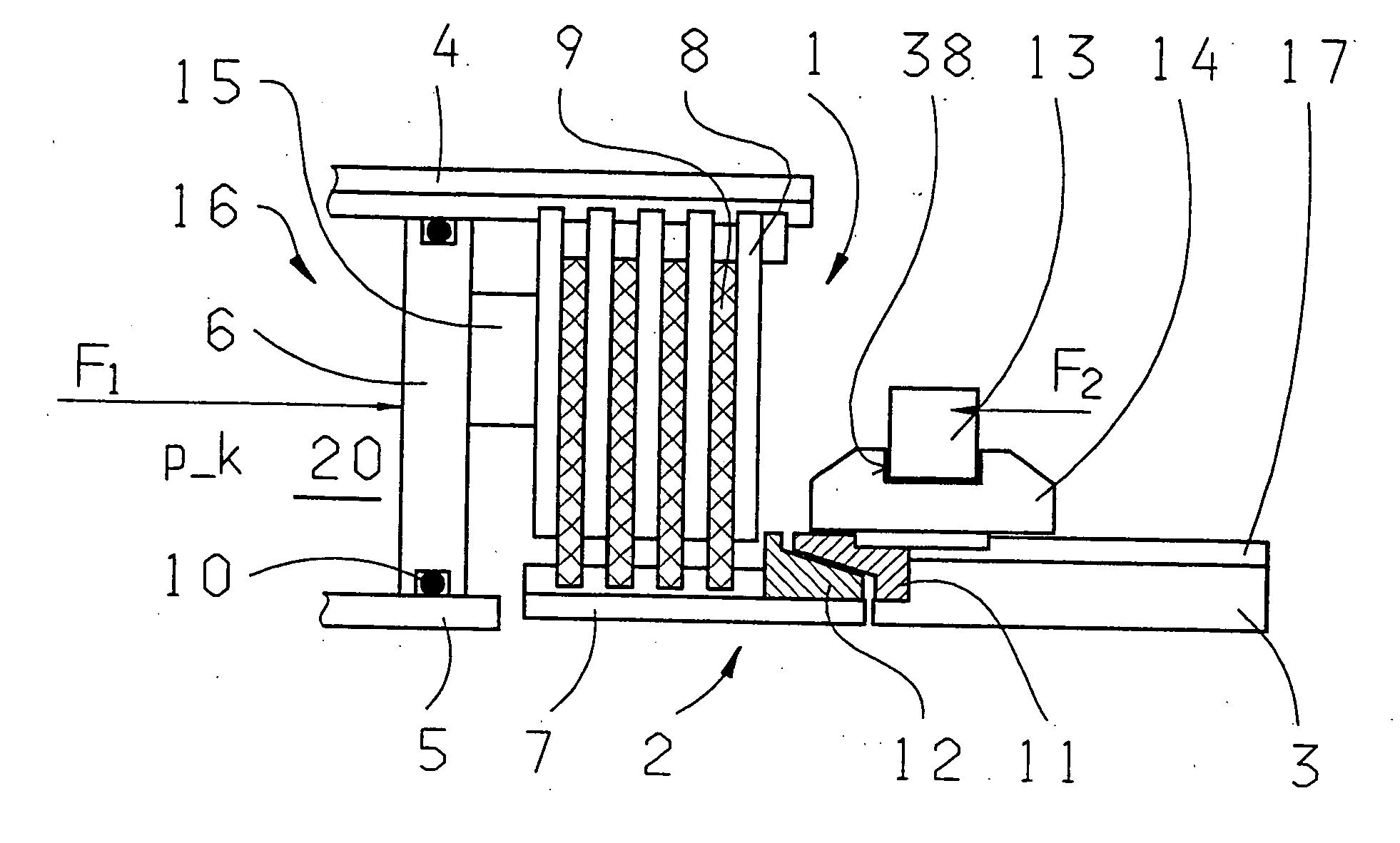
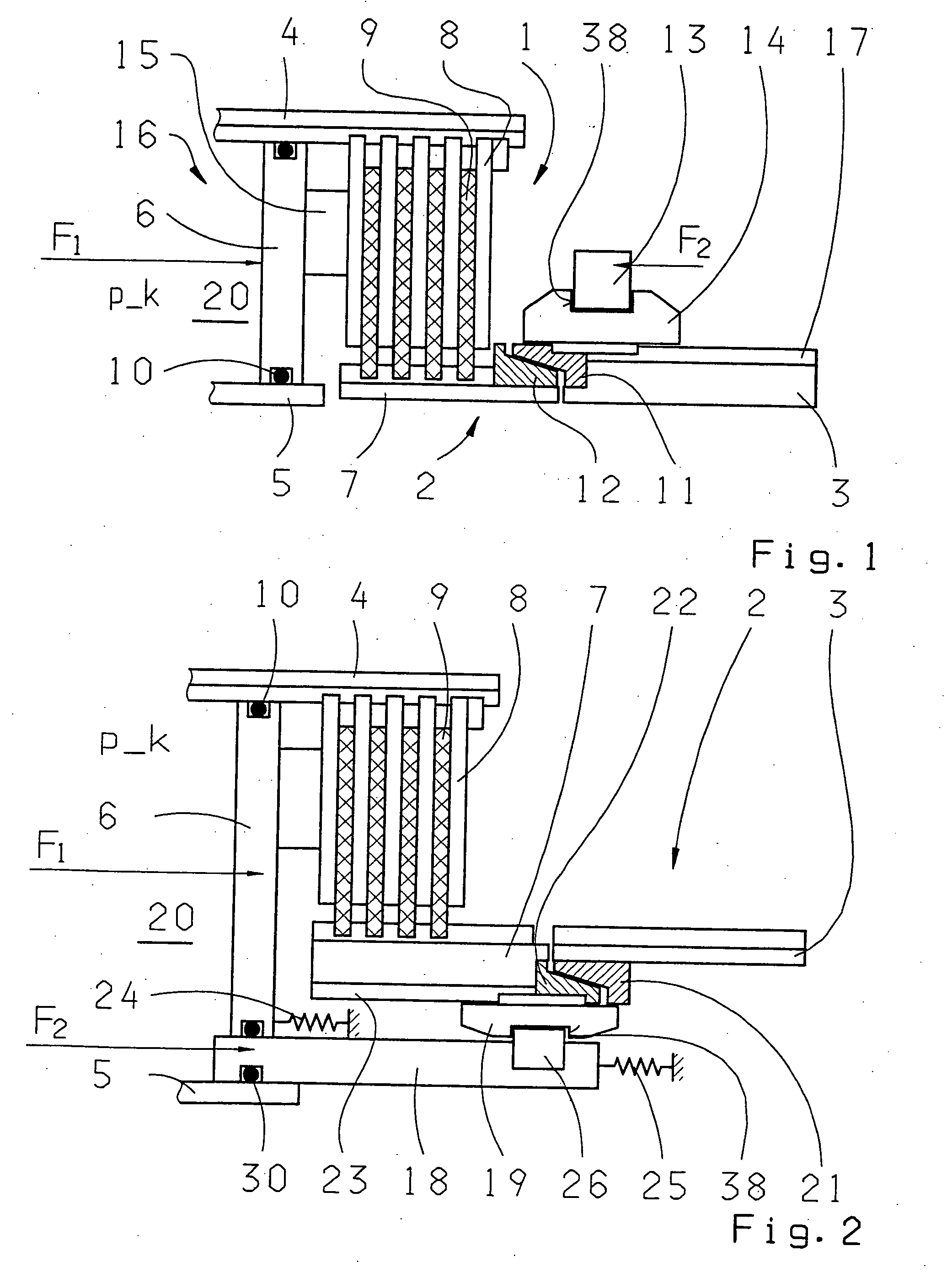
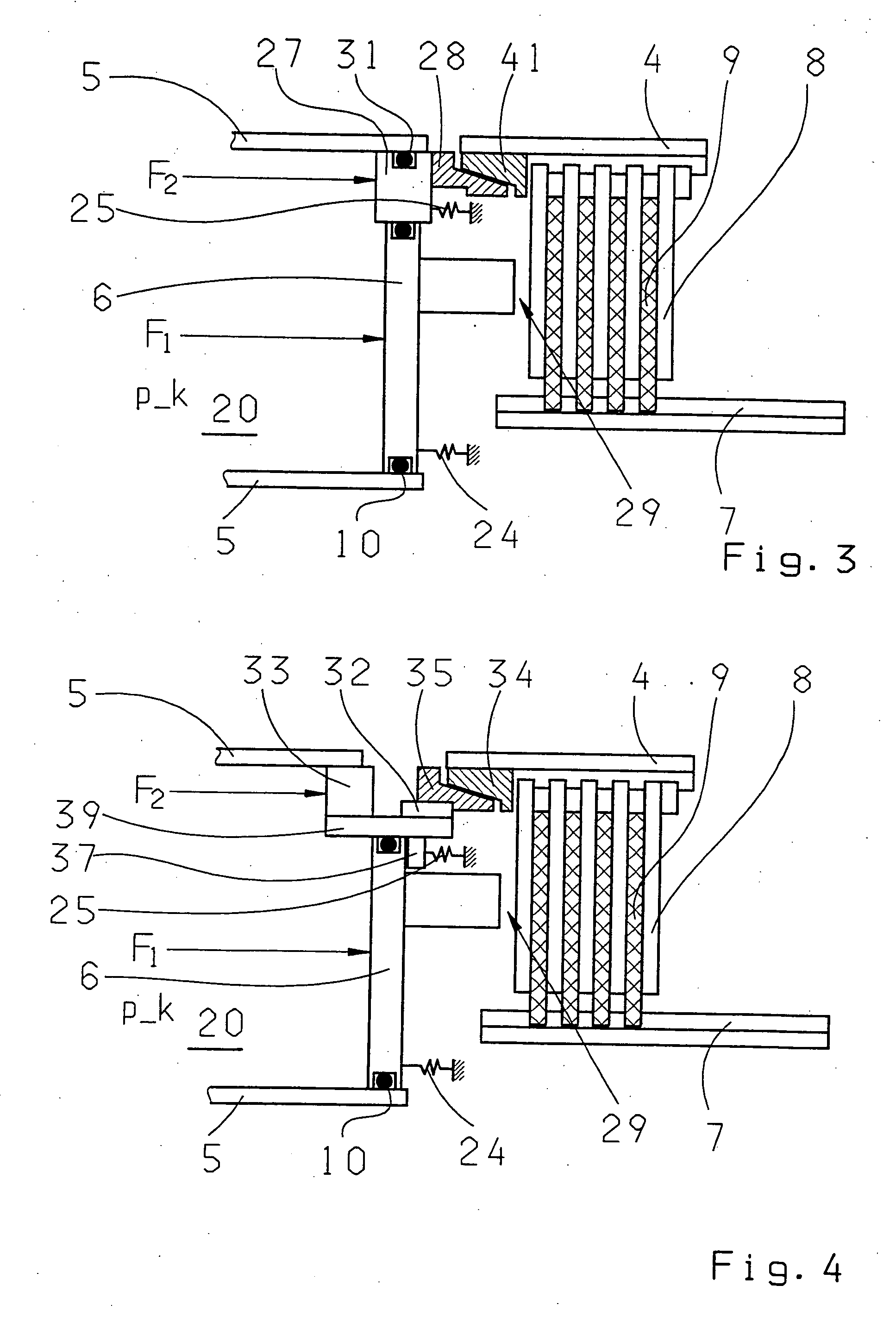
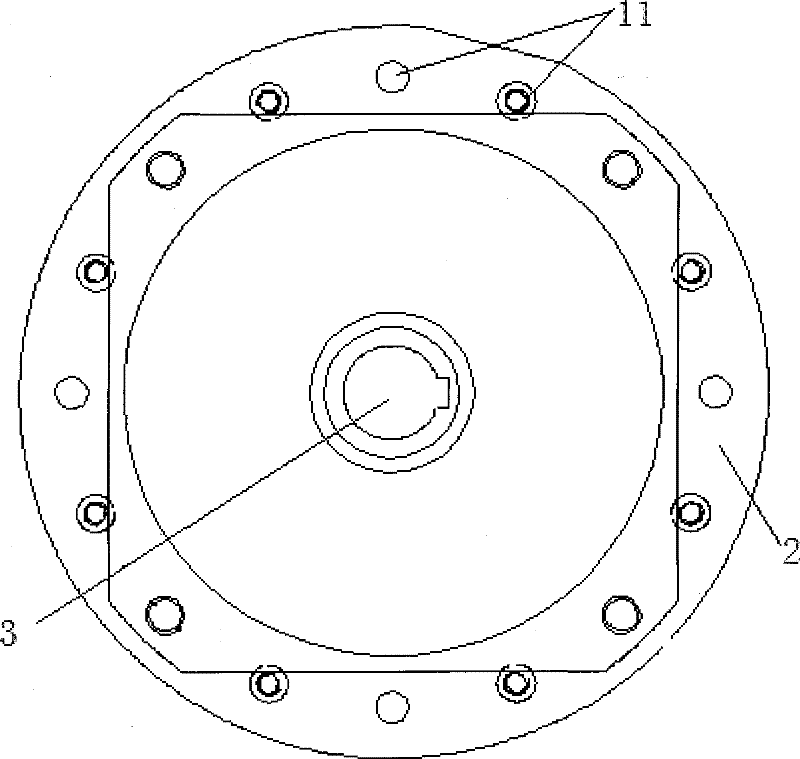
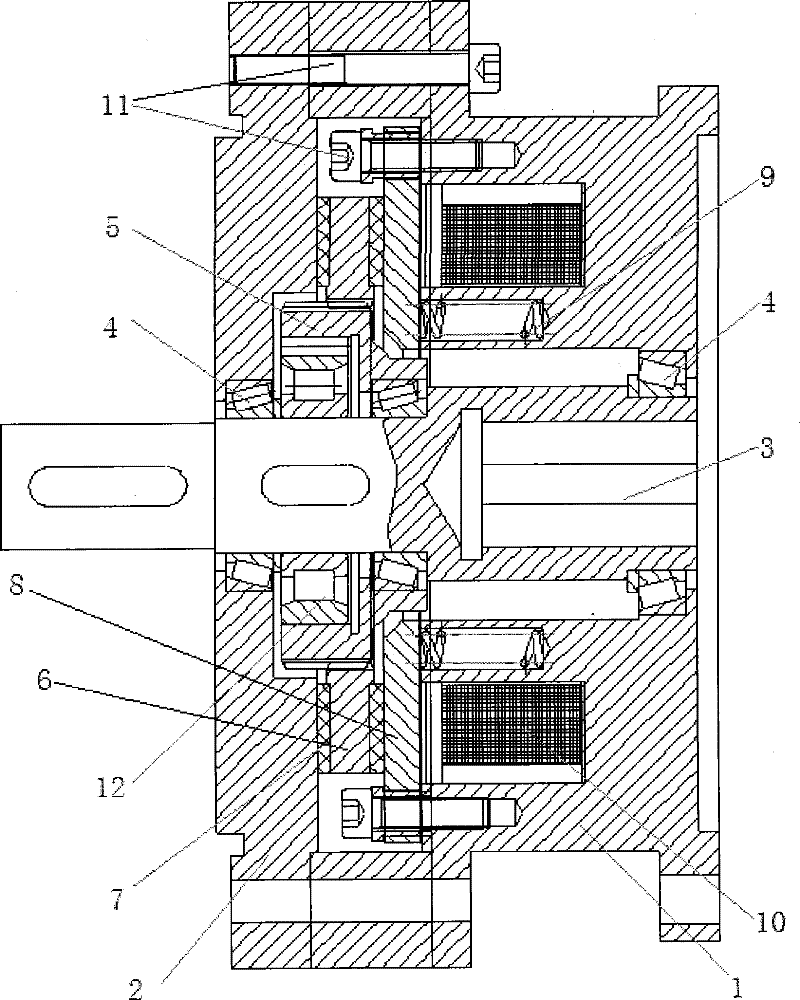
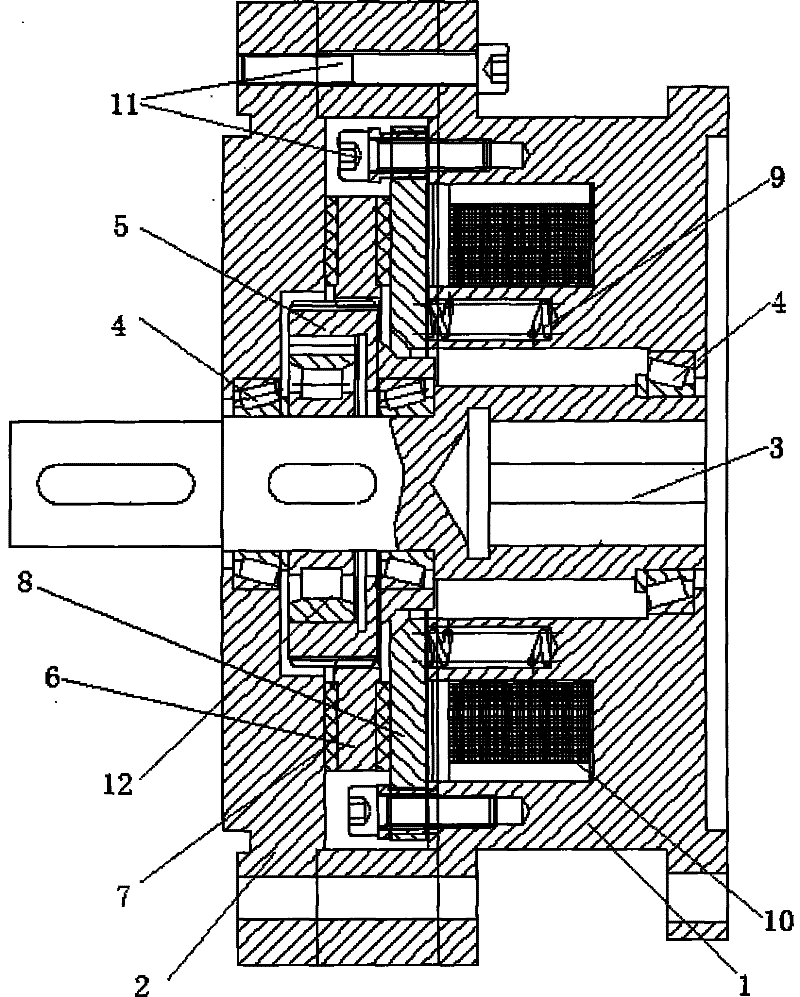
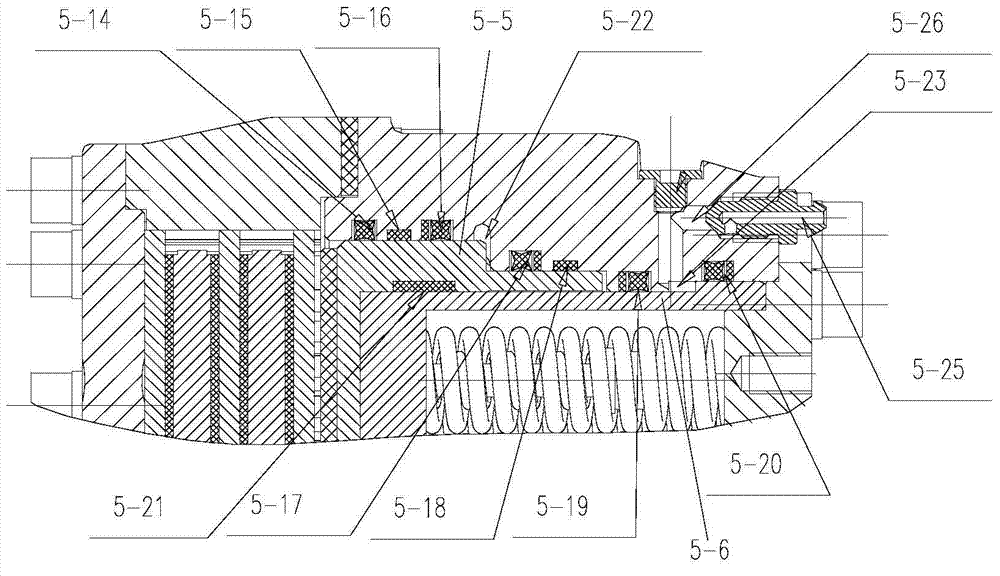
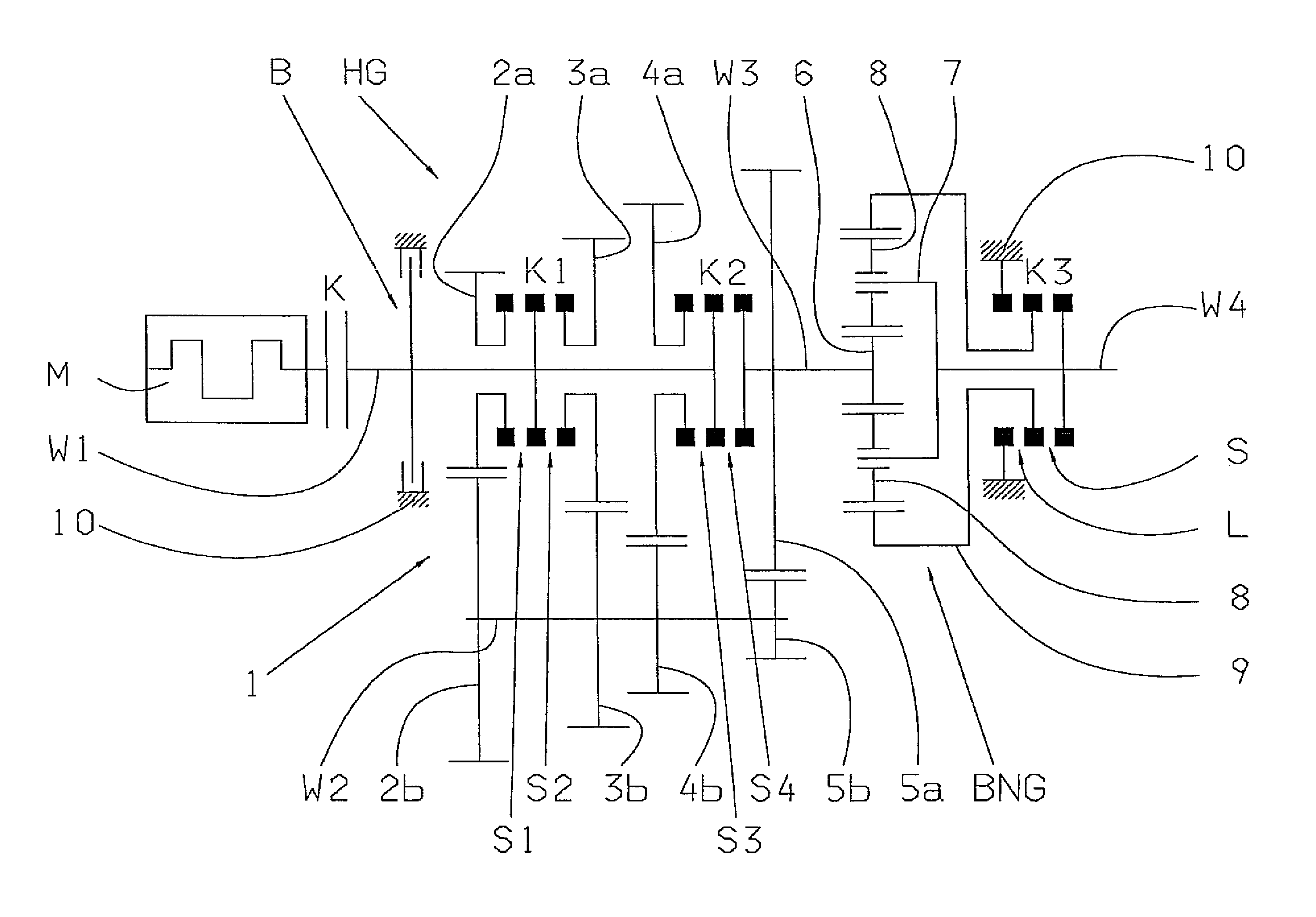
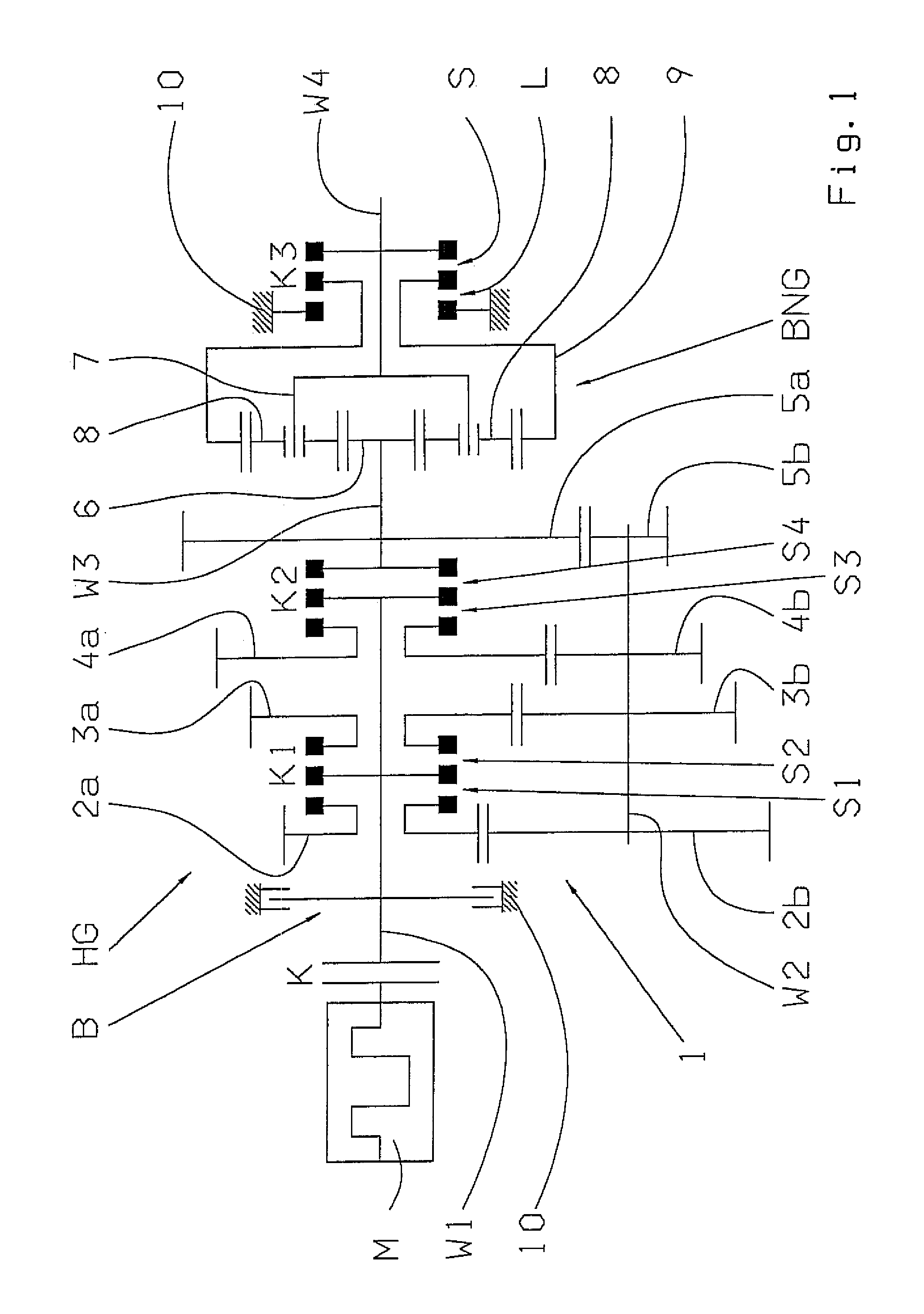
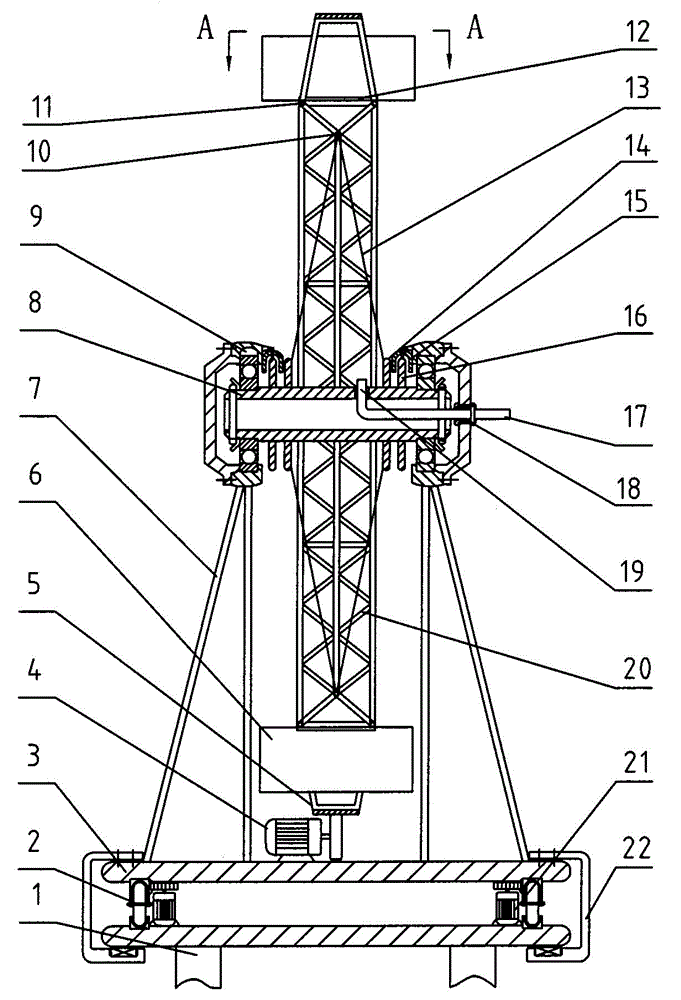
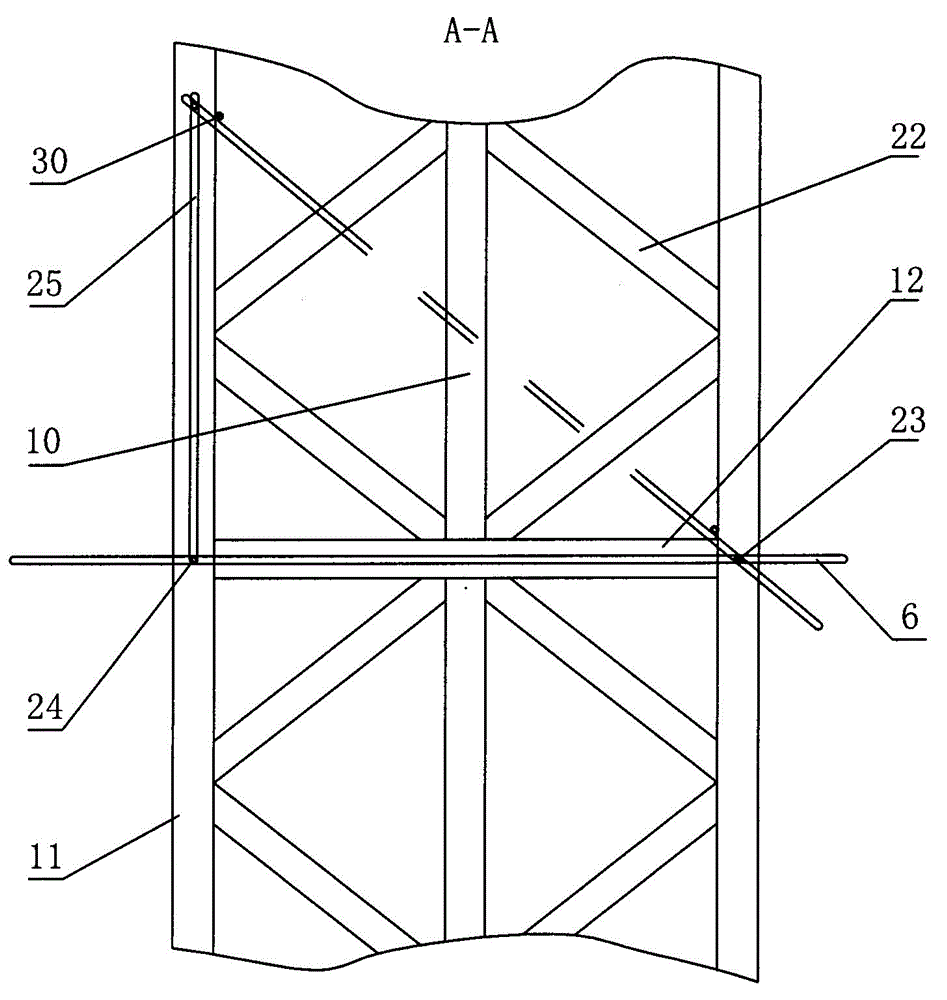
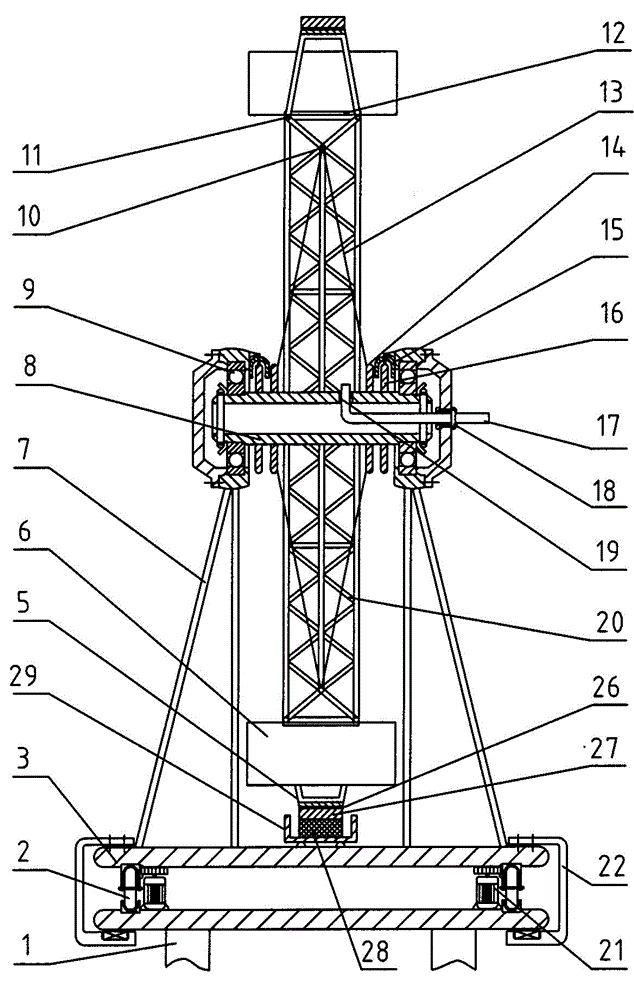
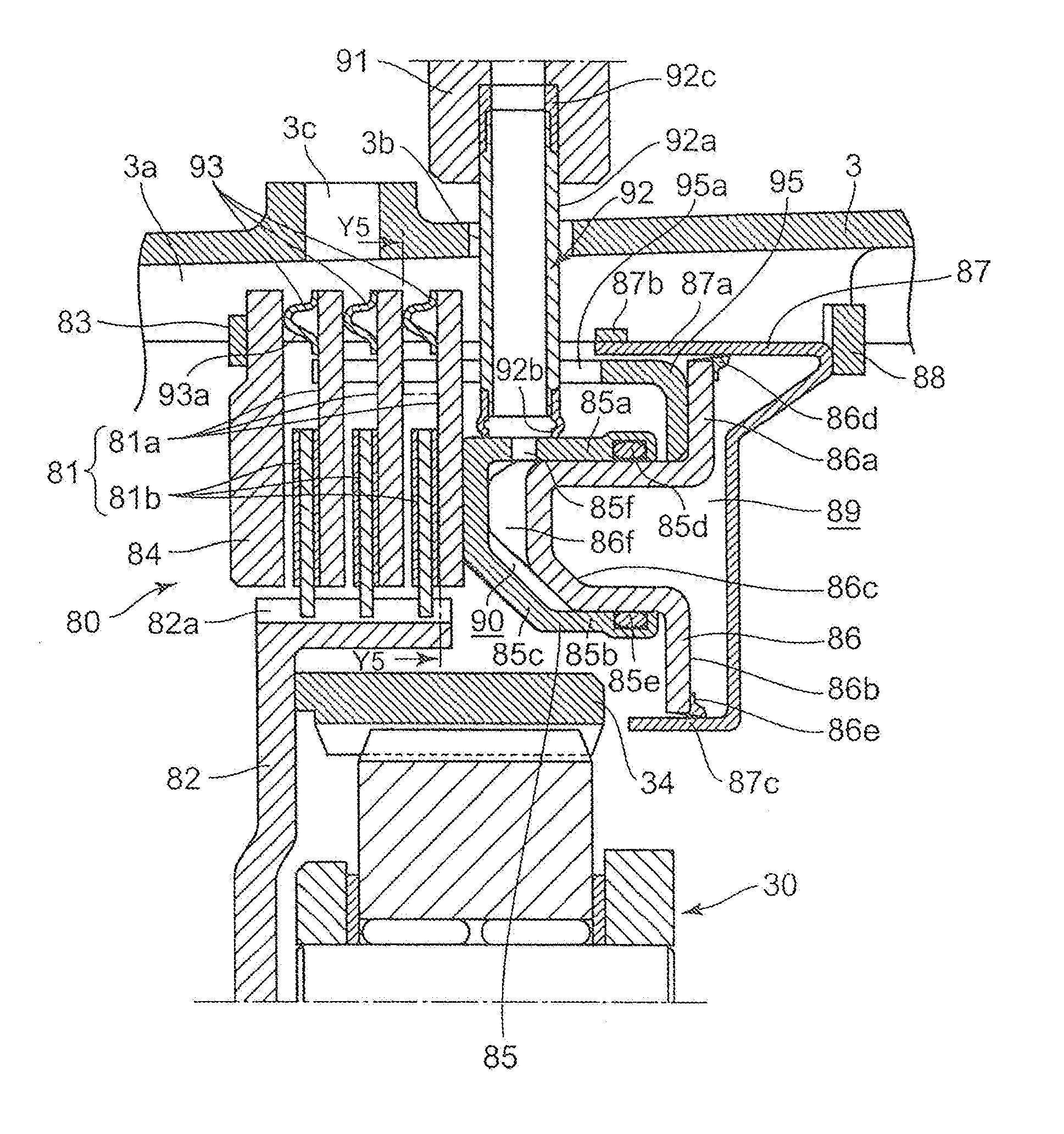
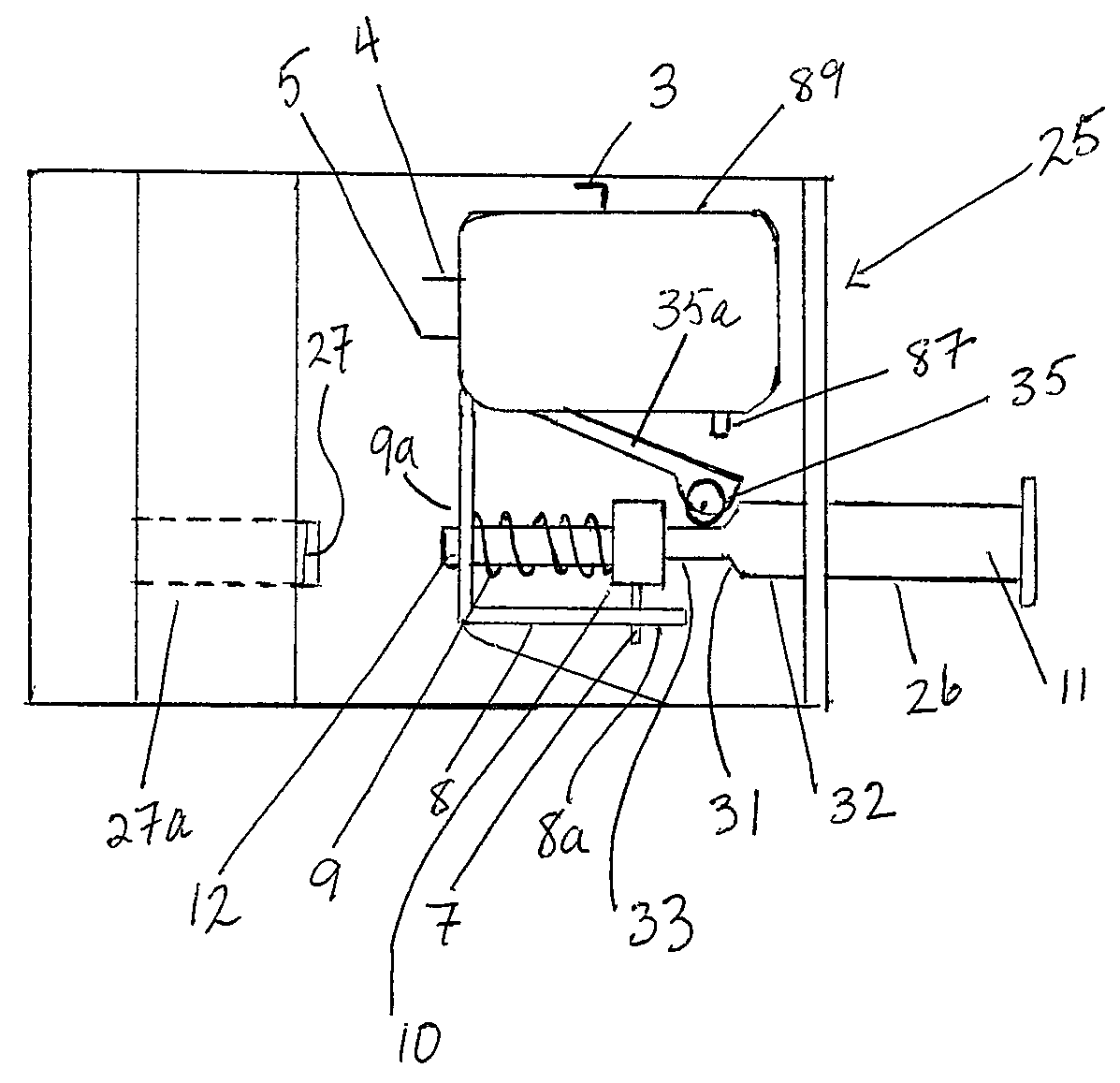
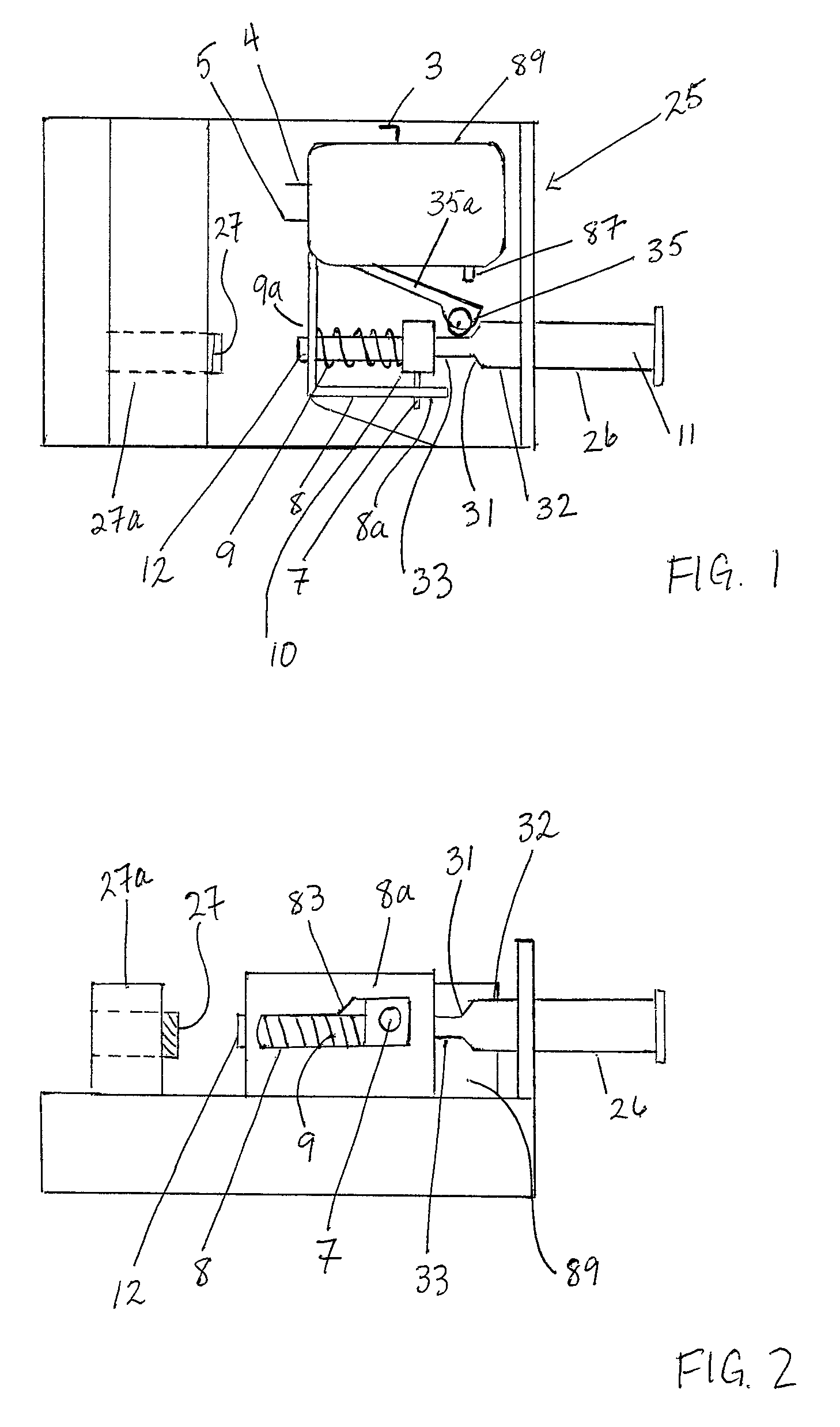
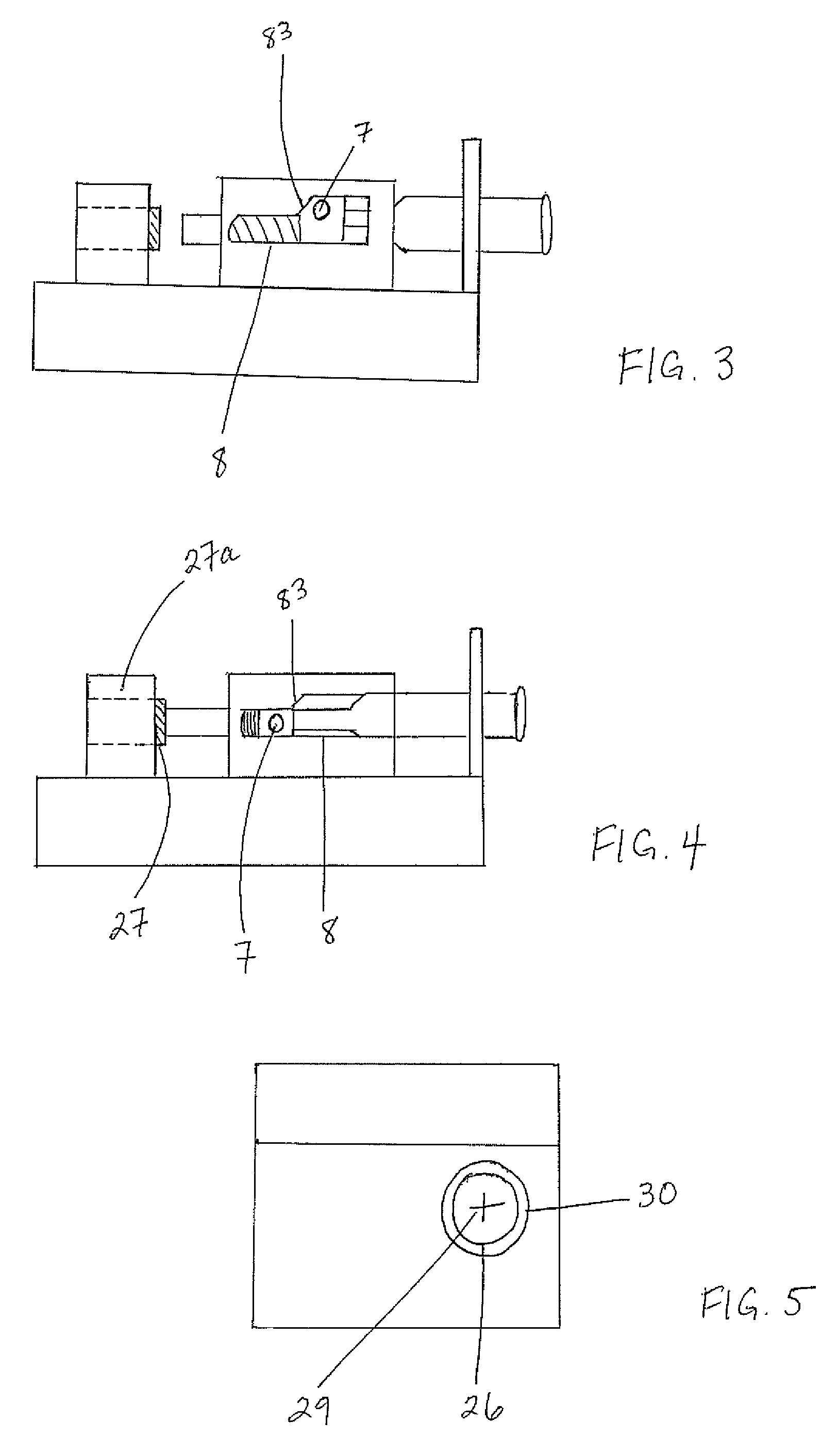
Transmission brake integrated device for vehicle
ActiveCN104773140AReduce volumeCompact structureBraking element arrangementsControl devicesTransmission brakeVehicle frame
The invention relates to a transmission brake integrated device for a vehicle, and belongs to the technical field of vehicles. The device comprises a brake positioned in a rim, and a speed reducer, wherein one side of the rim is provided with an open end disk which is fixedly connected with an output flange; friction plates which are distributed at intervals are arranged at one end of the brake close to the end disk; brake discs are arranged between adjacent friction plates; an oil cylinder block is arranged on one side of a friction pair constructed by the friction plates and the brake discs; a travel braking oil cylinder and a parking braking oil cylinder are arranged in the oil cylinder block; a travel piston and a parking piston are arranged in the travel braking oil cylinder and the parking braking oil cylinder respectively; parking springs containing a return mechanism are distributed at intervals along the outer circumference of the parking piston; the speed reducer extends into a cavity in the middle part of the oil cylinder from the open end of the rim; an output shaft on the middle part of the speed reducer is fixedly connected with an output flange; a shell and a brake shell are fixedly connected with a frame. On the premise of ensuring the original functions, the structure can be as compact as possible, and the research and development demands of novel vehicles with narrow structural spaces can be met practically.
Owner:CRRC QISHUYAN INSTITUTE CO LTD
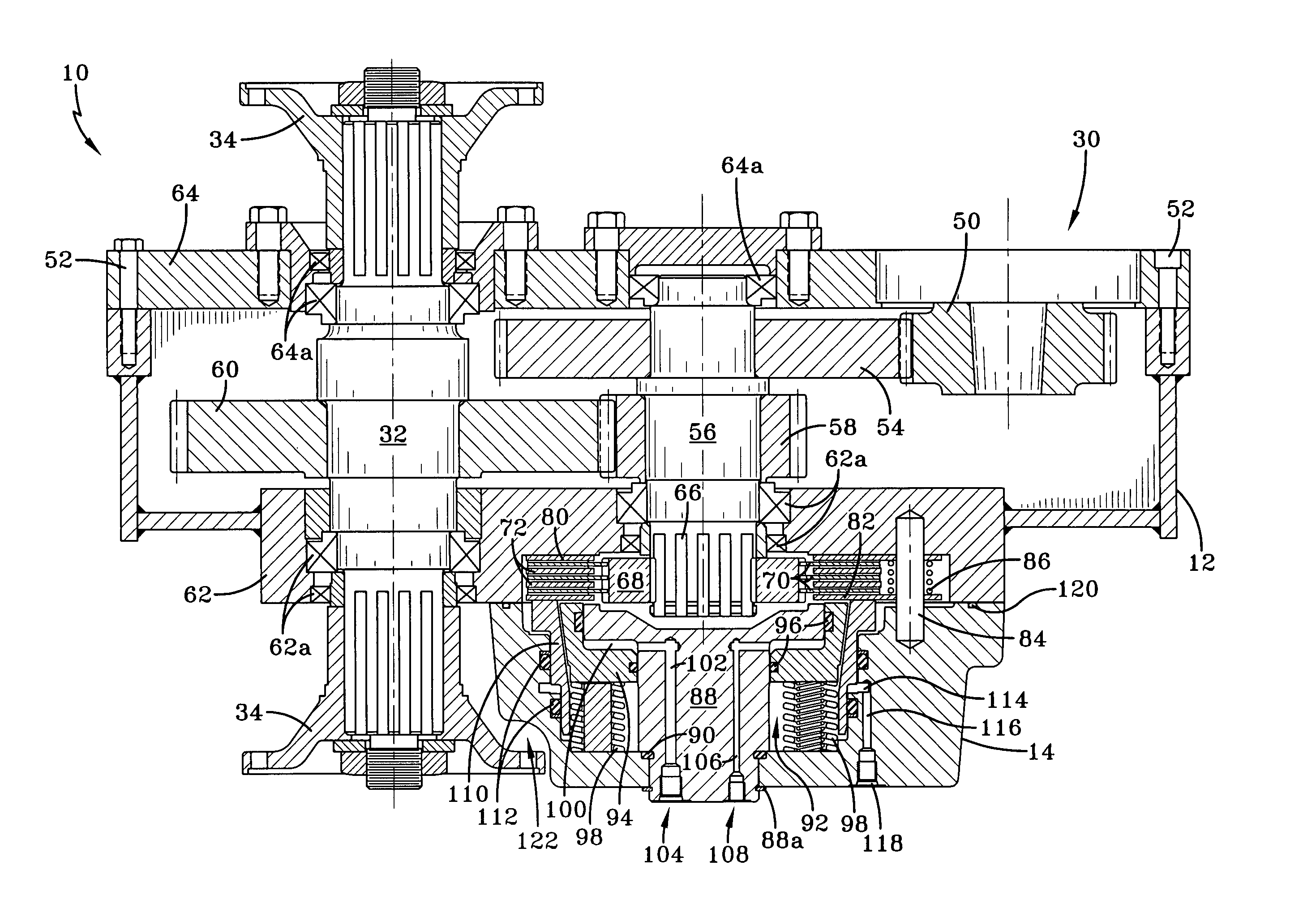
Power transfer apparatus
A power transfer apparatus including a clutch having a biasing device for biasing the clutch piston in a direction in which the clutch discs engage with the clutch plates, a transmission brake disposed in line in an axial direction of the clutch, an actuator disposed in line in an axial direction of the transmission brake for disengaging the clutch at the same time of applying the transmission brake, and a planetary carrier sub-assembly disposed in line in the axial direction of the clutch, wherein the power transfer apparatus provided between an input shaft and an output shaft which are accommodated within a casing for selectively changing the speed of the output shaft.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
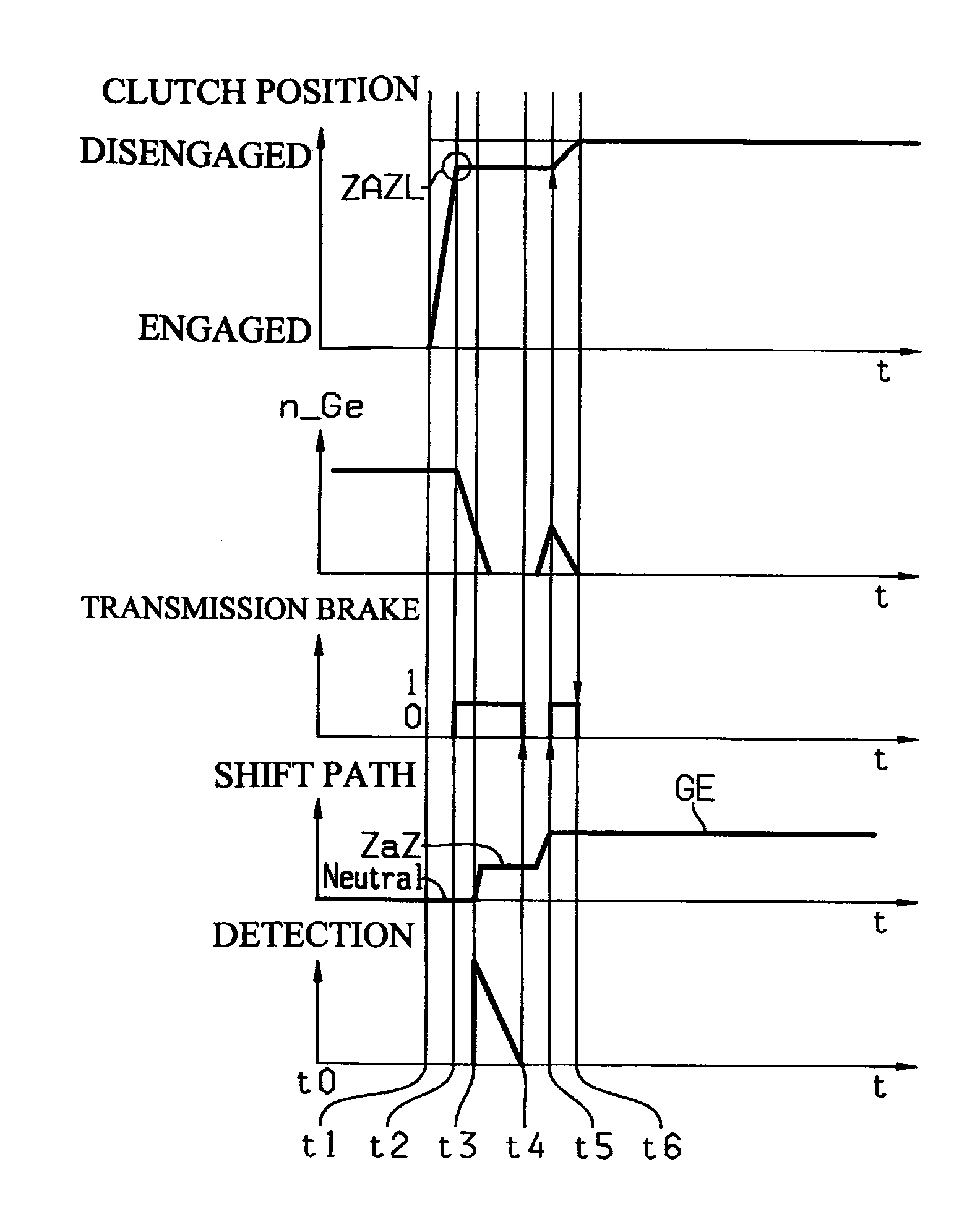
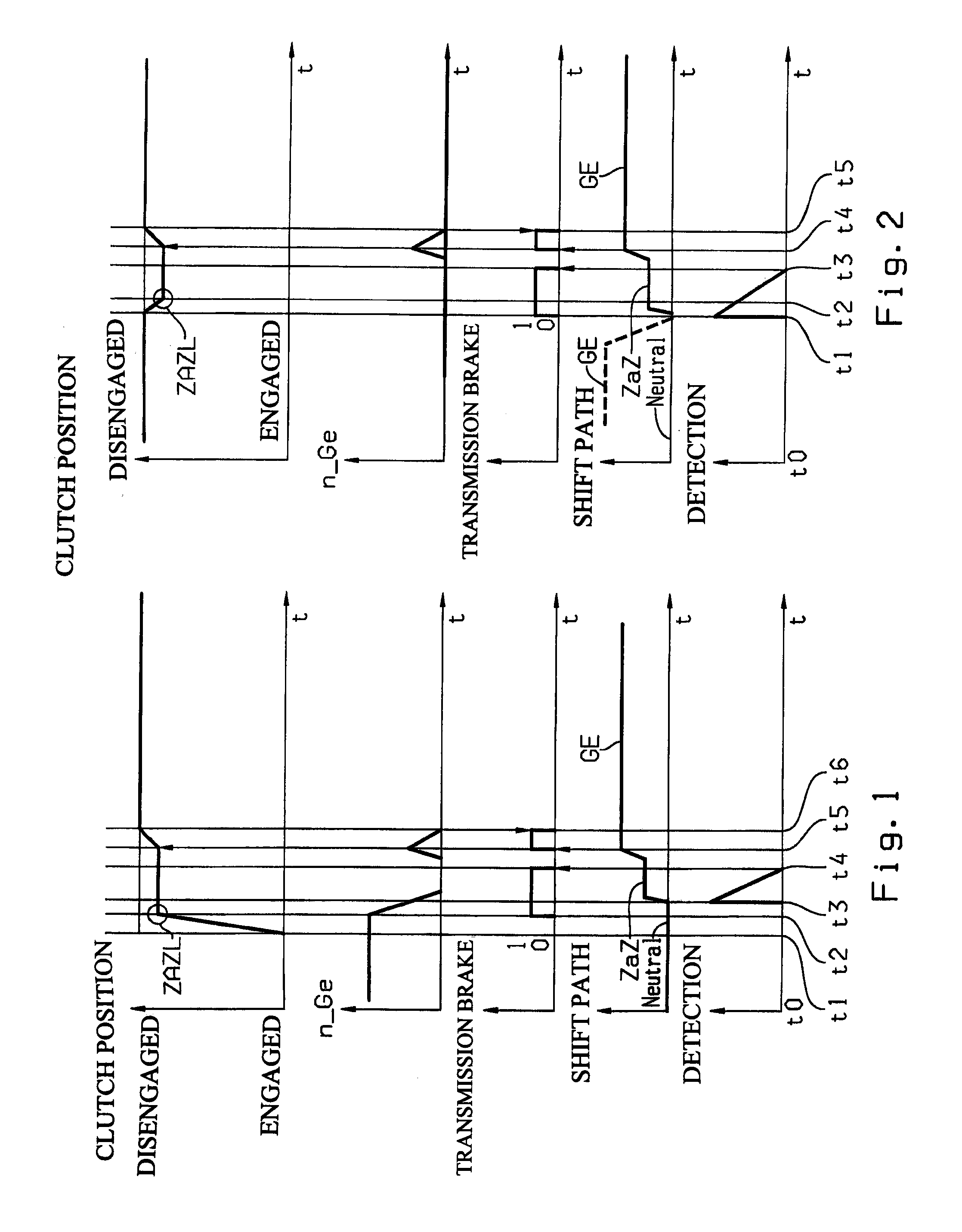
Method for overcoming tooth butt conditions when engaging gears in transmissions
ActiveUS20100041513A1Good effectAccurate transmissionGearing controlEngine controllersTransmission brakeDrive shaft
The present invention relates to a method for overcoming tooth butt conditions (ZaZ) when engaging gears in transmissions. A sensitive adjustment of the clutch to apply torque for rotating the drive shaft of the transmission in order to overcome tooth butt conditions has certain limits because of the proportion of the power required and desired for making said sensitive adjustment. This may cause unpleasant jerking of the vehicle or a clearly audible locking noise of the involved positively connected elements and undesired mechanical stress to said elements.The method according to the present invention provides a remedy due to the fact that during each shifting process, regardless of the occurrence of a tooth butt condition, the clutch is brought into a position allowing minimum predetermined torque transmission to the drive shaft of the transmission, and this torque is supported on a transmission brake, which is often already available. Due to its substantially smaller size, the transmission brake can much more quickly and accurately adjust a desired net torque curve and torque progress on the drive shaft of the transmission when a tooth butt condition occurs and thus make it significantly easier to overcome the tooth butt condition.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
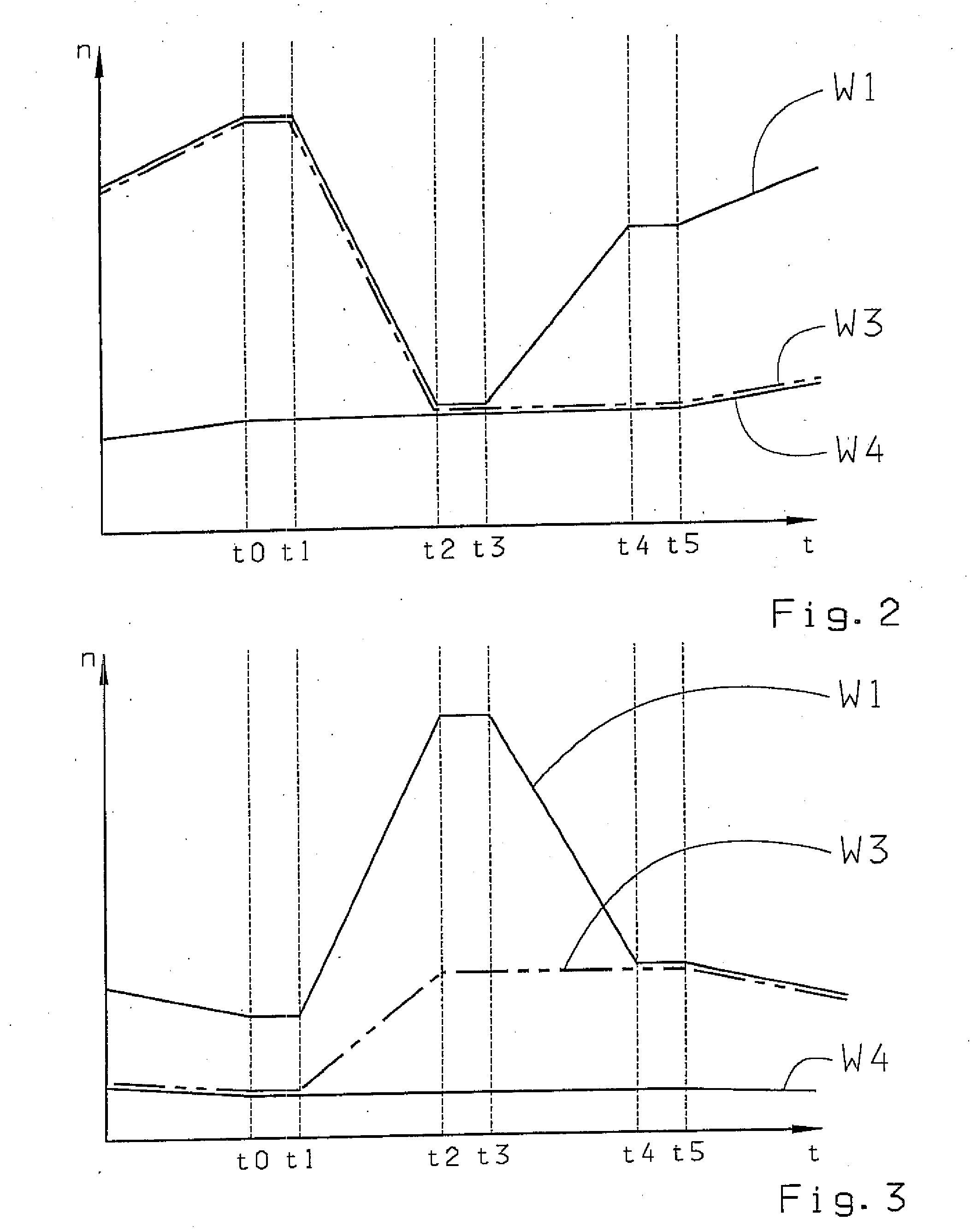
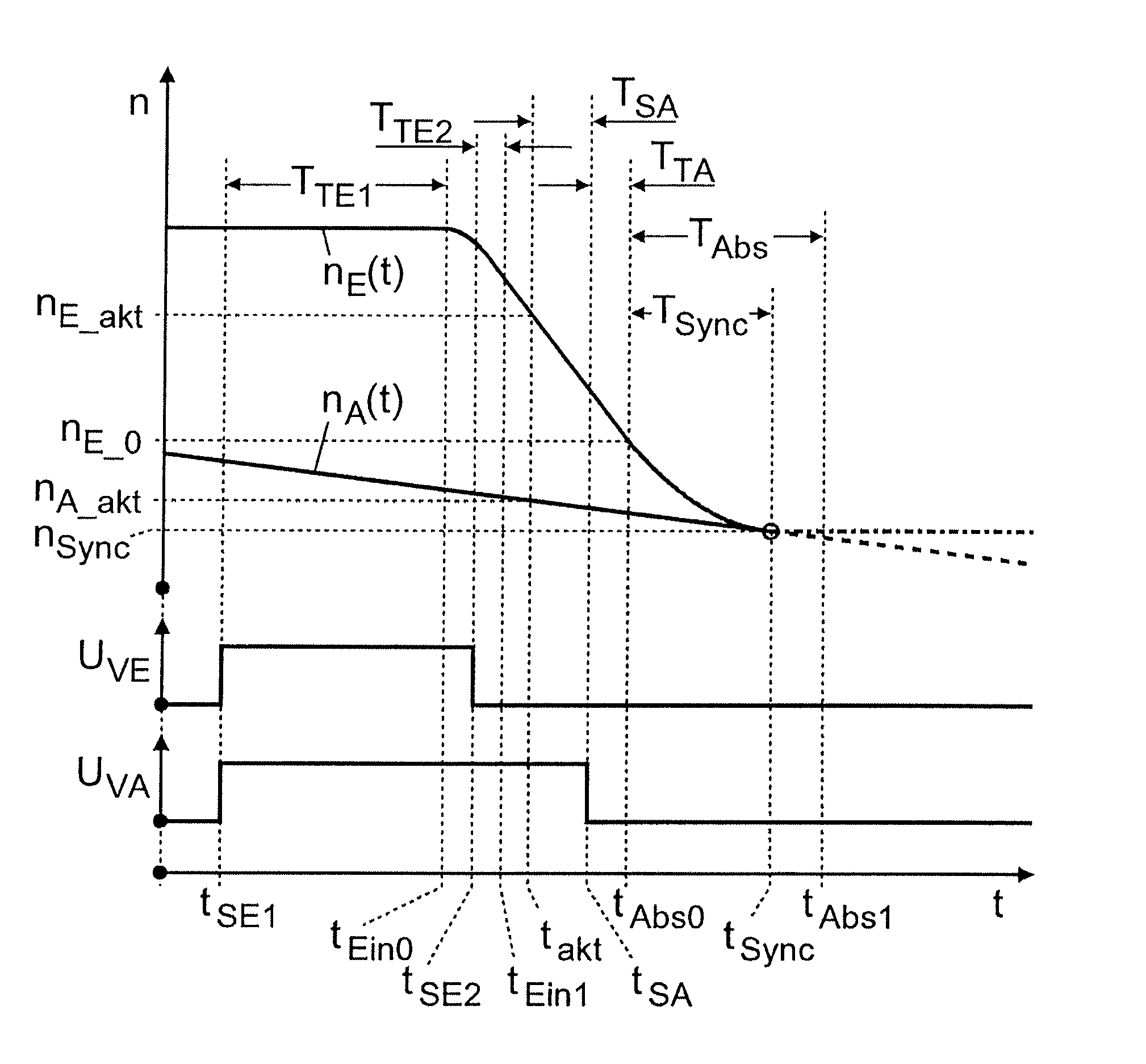
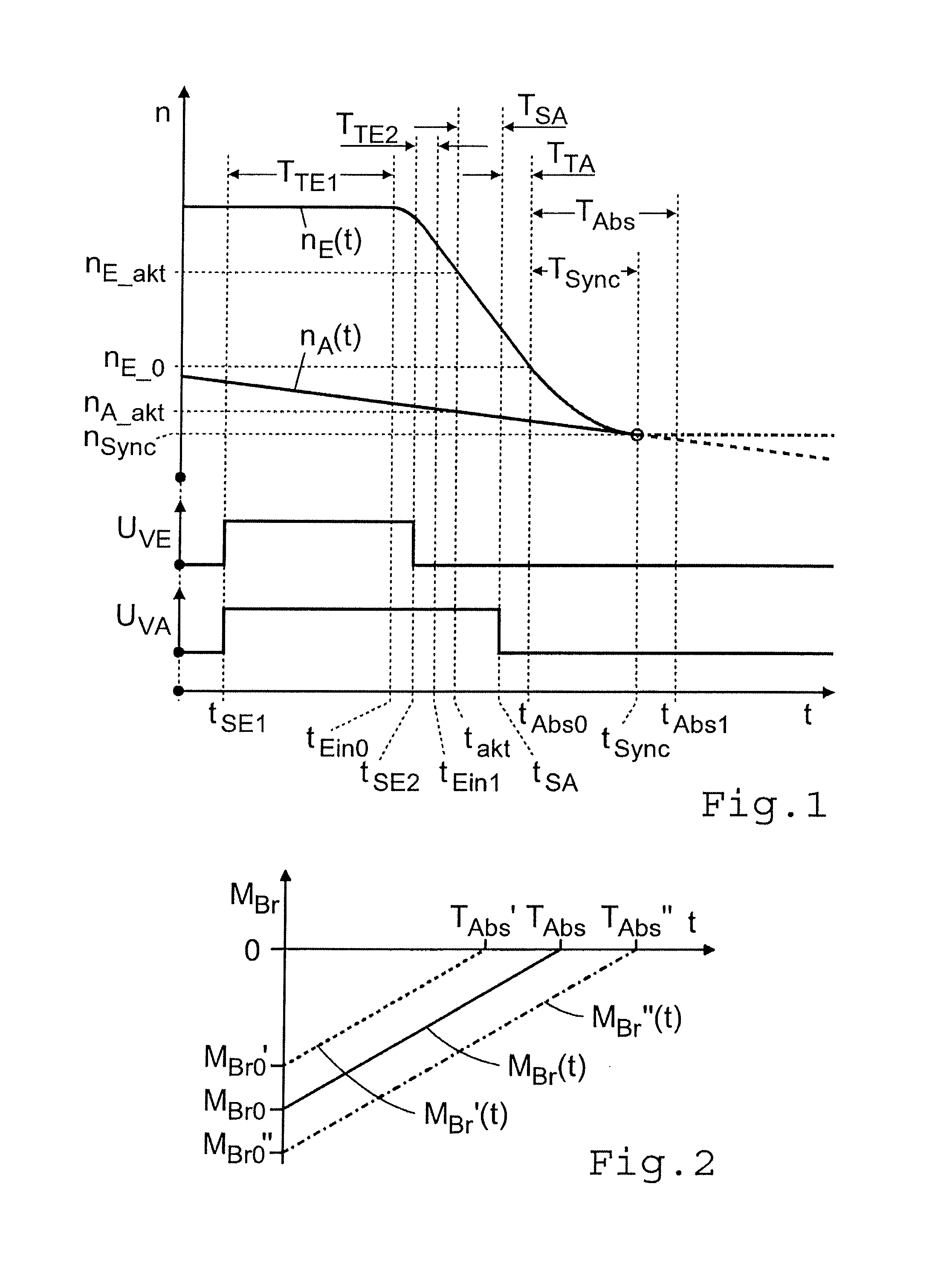
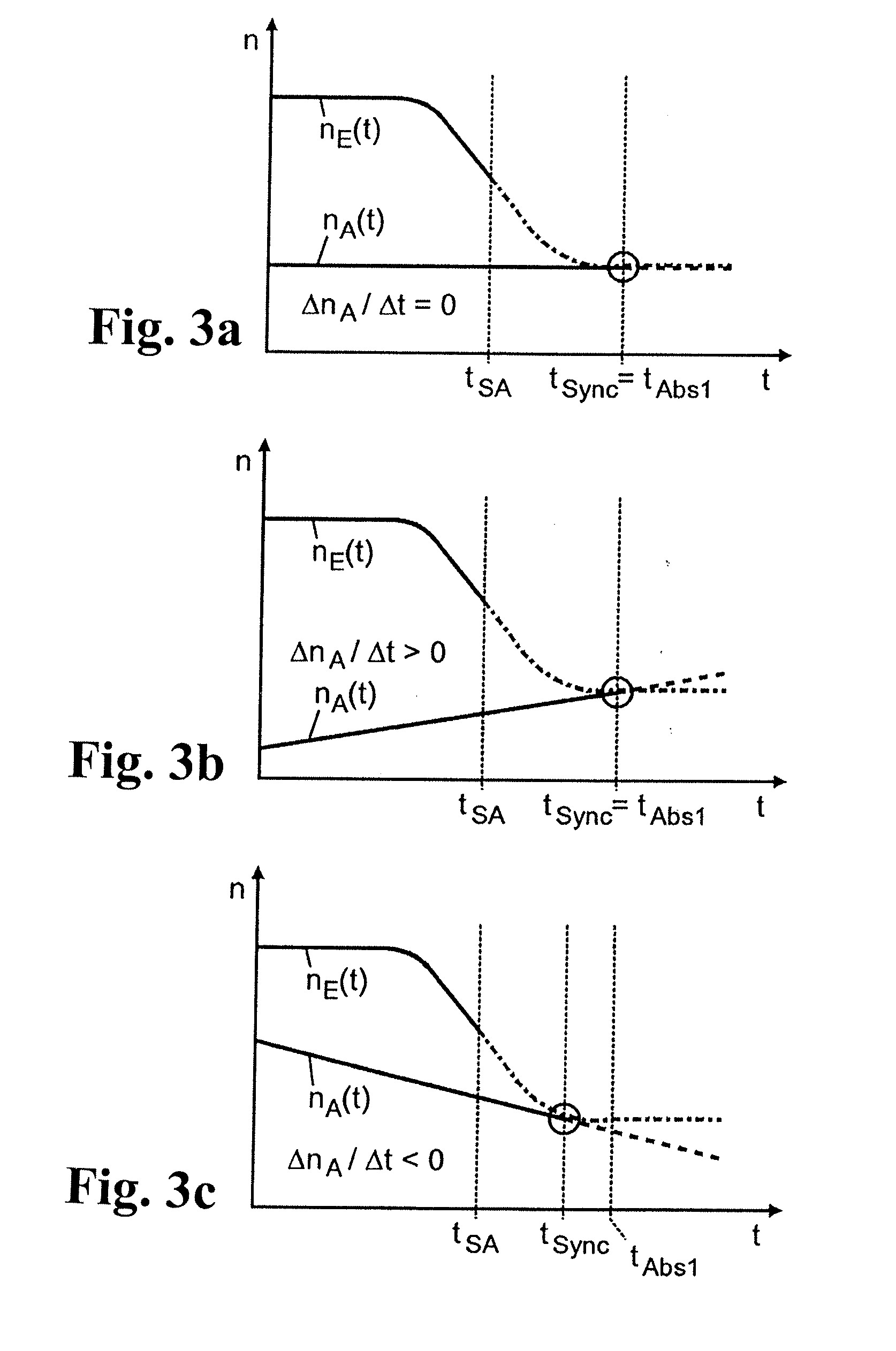
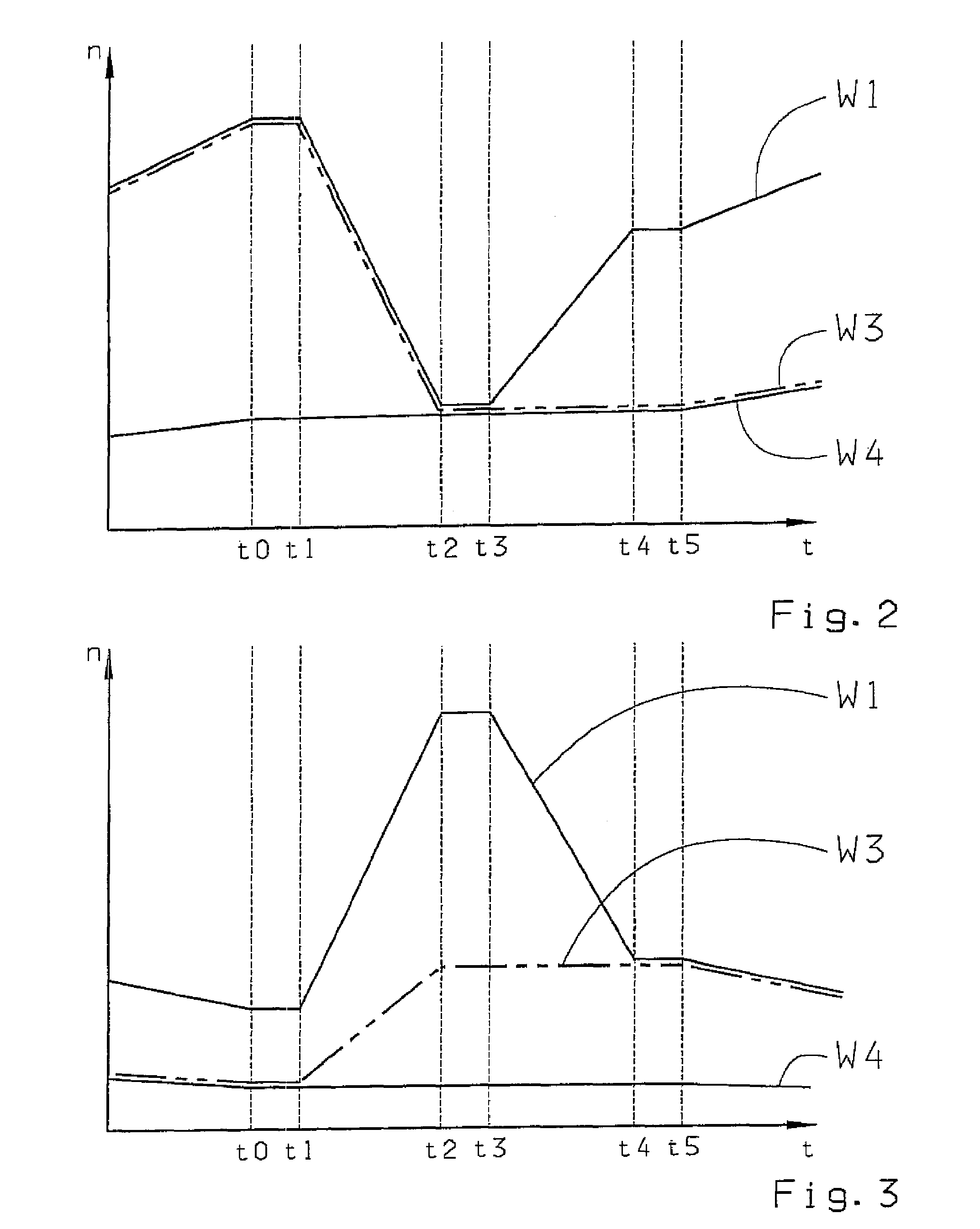
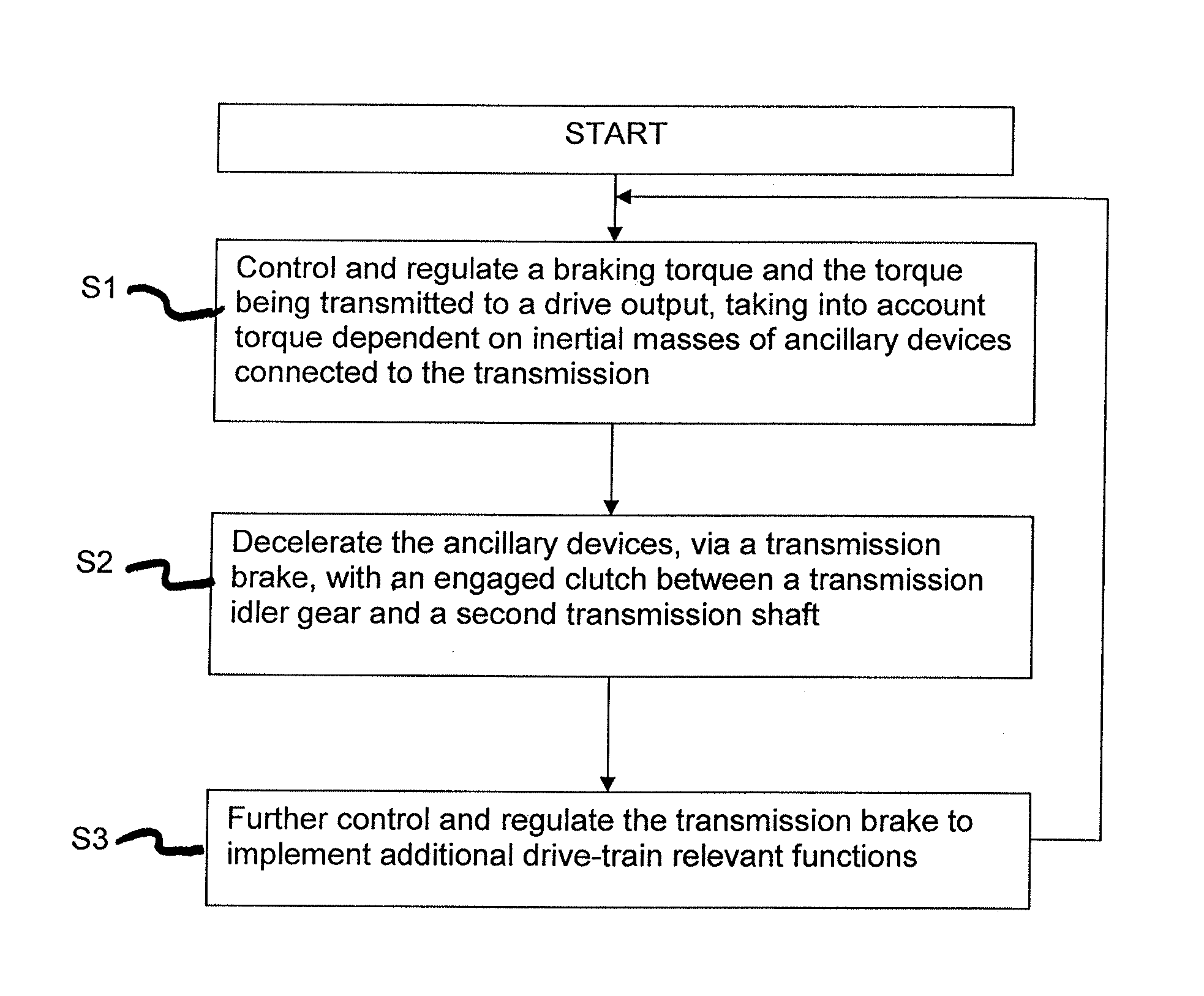
Method for controlling a transmission brake
ActiveUS20120330519A1Improved shift qualityProperty is limitedDigital data processing detailsToothed gearingsDead timeTransmission brake
A method of controlling a transmission brake that is actuated by inlet and outlet valves. For determining when to transmit a disengagement signal for opening the outlet valve, the current input and output speeds are determined and the respective gradients of these speeds are calculated. Variation of the input speed, during the disengagement of the brake, is determined as a function of the input gradient, the optimum time for reaching the synchronous speed, during brake disengagement, is determined from the input speed variation as a function of the output gradient, and the time interval until transmission of the disengagement signal is determined as a function of the current input and output speeds and their gradients, by a back-calculation from the time when the synchronous speed is reached, taking a disengagement dead time of the brake, between transmitting the disengagement signal and start of disengagement, into account.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Shift control method for an automatic gearbox
ActiveUS7632211B2Small sizeShifting sequenceGearing controlEngine controllersTransmission brakeElectric machine
A shift control method of a range group transmission with a multi-speed main transmission, which connects with a drive motor, via a clutch (K) and an input shaft. A transmission brake optionally engages the input shaft. At least a two range group is located downstream of the main transmission. A range change shift is accomplished by changing a gear of the main transmission and the range group. The shifting sequence is accelerated by: reducing motor torque and disengaging the clutch (K); disengaging a previous range group gear; synchronizing a new range group gear; disengaging a previous main transmission gear; engaging the new range group gear; synchronizing a new main transmission gear; engaging the new main transmission gear; and engaging the clutch (K) and increasing the motor torque, such that synchronization of the new gear occurs by influencing the input shaft of the main transmission.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Full-blade-tip wind driven generator
ActiveCN103147926ASimple structureEven by forceWind motor controlMachines/enginesWind drivenTransmission brake
The invention discloses a full-blade-tip wind driven generator, which is used for solving the problems of low blade efficiency, poor mechanical strength, high implementing difficulty and the like existing in the conventional wind driven generator. The full-blade-tip wind driven generator comprises a yawing platform, a horizontal shaft impeller unit, a generator and a hydraulic pipeline, wherein the yawing platform is fixed on towers; and the horizontal shaft impeller unit is assembled on the yawing platform. Technical key points are that the horizontal shaft impeller unit comprises a wheel body, a blade assembled on the outer rim of the wheel body through a blade variable-pitch device, and a transmission braking integral ring fixed on the periphery of the wheel body; the wheel body and a hollow revolving shaft are connected together by using a stay cable support; the hinged end of the blade variable-pitch device is fixed at the bottom end of the blade; a hydraulic cylinder is arranged at the movable support end of the blade; pitch variation of the blade is finished through the extension and contraction of a piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder; and main brake clamps are distributed on both sides of a main brake disc of the hollow revolving shaft. The full-blade-tip wind driven generator has the advantages of reasonable design, simple blade structure, complete hydraulic yawing and pitch varying functions, uniform stress on a full blade tip, convenience in installing and adjusting, using safety and reliability, and prolonging of the service life of an entire machine.
Owner:戚永维
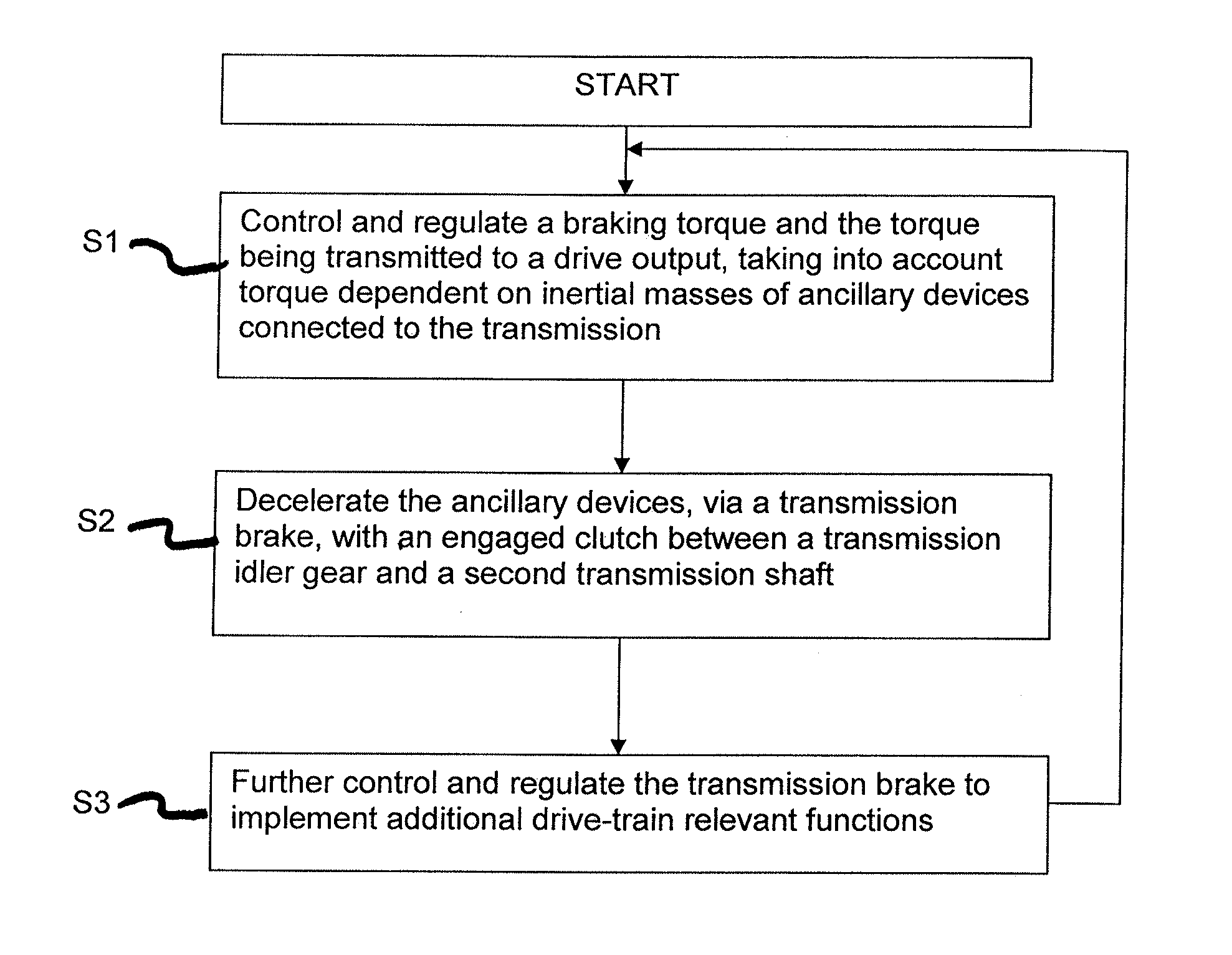
Method for broadening the function of a transmission brake
ActiveUS20130296134A1Extended functional scopeImprovement of comfort and speedClutchesGearing controlTransmission brakeHardware complexity
A method of controlling and regulating a transmission brake which, for the purpose of synchronization, determines a target rotational speed of a shaft to be synchronized on the basis of an actual rotational speed of a transmission shaft, and controls a transmission brake such that the determined target rotational speed is set for the shaft that is to be synchronized. The transmission brake also carries out additional functions. These functions require no, or only minimal, additional hardware complexity in a cost-neutral way, but considerably increase the functional and practical value of the transmission brake. The comfort and speed of shifting operations, the protection or, as the case may be, the detection of error states in sensors, a clutch, a main clutch or a motor control are improved, and undesirable transmission states avoided. It is also possible to account for and influence other conditions, such as the operation of ancillary devices.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Transmission brake device
ActiveUS20170009831A1Reduce resistanceBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesTransmission brakeEngineering
A transmission brake device includes: a friction plate set configured such that a plurality of rotation-side friction plates; an engaging piston disposed on an axial side of the friction plate set; a clearance adjustment piston disposed on a side of the engaging piston opposite to the friction plate set,; a clearance adjustment hydraulic chamber configured to move the clearance adjustment piston; and an engaging hydraulic chamber configured to move the engaging piston; a biasing member disposed between each adjacent pair of the fixed-side friction plates, the biasing member being configured to bias each adjacent pair of the fixed-side friction plates in directions away from each other. The biasing member distributes the clutch clearance in a gap between each adjacent pair of the fixed-side friction plates when a hydraulic pressure is supplied only to the clearance adjustment hydraulic chamber.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Transmission brake disengagement switch and method of operation
ActiveUS8950564B1Braking element arrangementsContact driving mechanismsTransmission brakeEngineering
Controls for a transmission brake include a switch that employs resistance to motion of an axially movable plunger in order to provide tactile feedback to the operator as to the current position of the plunger, thus reflecting a particular state of the switch. In a fully depressed position of the plunger, the transmission brake is on. Shortly before this position is reached, resistance is encountered at an intermediate position at which the transmission brake is already engaged, thereby giving the user of the option of depressing the plunger further in order to provide a longer travel time of plunger back to its normal spring-biased position in which the brake is disengaged. Some embodiments activate other brake control components at partially depressed plunger positions preceding the intermediate position, whereby controlled creeping of the vehicle can be accomplished before the transmission brake is returned to a continuously engaged state.
Owner:PENNER ERNEST PETER
Full Blade Tip Wind Turbine
ActiveCN103147926BSimple structureEven by forceWind motor controlMachines/enginesHydraulic cylinderImpeller
A wind turbine with full blade tips comprises a yaw platform (3) fixed on a tower (1), a horizontal blade impeller set mounted on the yaw platform (3), a power generator (4), and a hydraulic pipeline. The horizontal blade impeller set comprises an impeller body, blades (6) mounted on the outer edge (11) of the impeller body by a blade pitch varying device (12), and a transmission-braking integrated ring (5) fixed on the periphery of the impeller body; the impeller body and a hollow rotation shaft (8) are supported and connected together by a stay cable (13), a hinged end of the blade pitch varying device (12) is fixed on the bottom end of the blade (6), a blade motion supporting end (24) is provided on a hydraulic cylinder, and the pitch of the blade (6) is varied by stretching out and drawing back a piston rod of the hydraulic cylinder; and master brake calipers (15) are disposed at two sides of a master brake disc (16) on the hollow rotation shaft (8). The impeller body is designed rationally, the blade structure is simple, the wind turbine has complete hydraulic yaw and pitch varying functions, and all blade tips are evenly stressed, so the mounting and adjustment are simple and it is safe and reliable to use the wind turbine, thereby prolonging the service life of the whole machine.
Owner:戚永维
Automated transmission systems
An automated transmission system includes a transmission brake which is used to apply a braking torque to the transmission, while the engine torque is negative and a transmission clutch is disengaged to effect a gear downshift, in order to avoid acceleration of the vehicle when the clutch is released and abrupt deceleration of the vehicle upon completion of the gear downshift.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
GPS-based road and vehicle use information acquisition method
ActiveCN104751534AEasy to useMeet the reliability of useRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTransmission brakeAtmospheric pressure
The invention relates to a GPS-based road and vehicle use information acquisition method. GPS equipment is used for measuring the slope information I, the current engine torque value T and the current engine rotating speed, and is used for acquiring the current gear transmission speed ratio ig, the vehicle speed value U<alpha> and the acceleration magnitude du / dt; the current vehicle weight G is calculated and the calculated vehicle weight G is sent to a remote enterprise monitoring platform; designers can carry out strength improvement design according to the vehicle required by a client in the environment for meeting the normal reliable use of the vehicle in the environment; the GPS equipment is used for acquiring the countershaft rotating speed omega1, the countershaft rotating speed omega2 during braking ending and the air pressure value P0 of the whole vehicle; the friction coefficient f of a transmission brake is calculated, the GPS equipment sends the calculated friction coefficient f to the remote enterprise monitoring platform, and therefore, the strength of the transmission brake is optimized by technicians, and the using reliability of the transmission brake under warranty is met.
Owner:SINO TRUK JINAN POWER
Trowel gearbox brake
Owner:HUSQVARNA AB
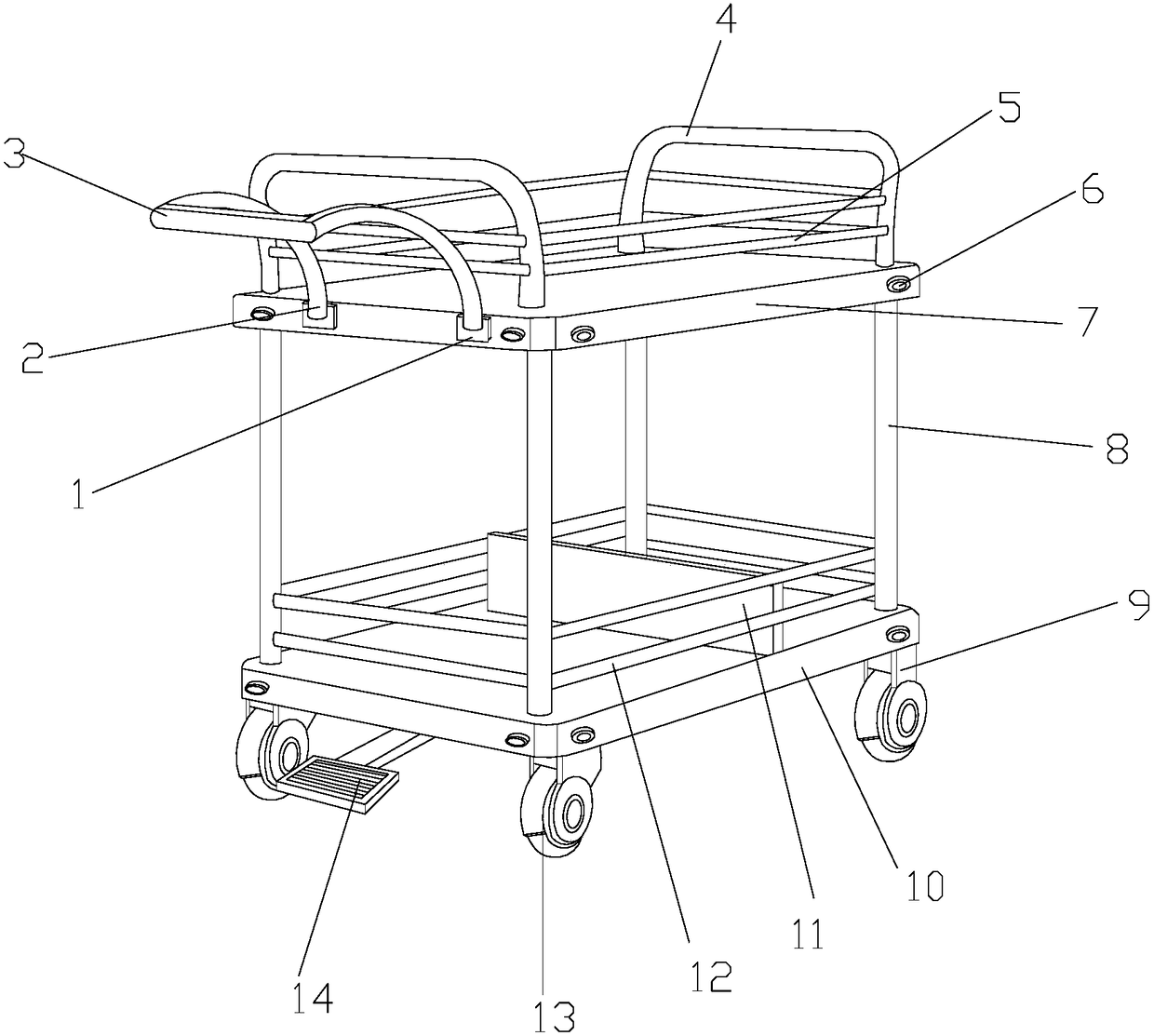
Conveying trolley for logistics assembly
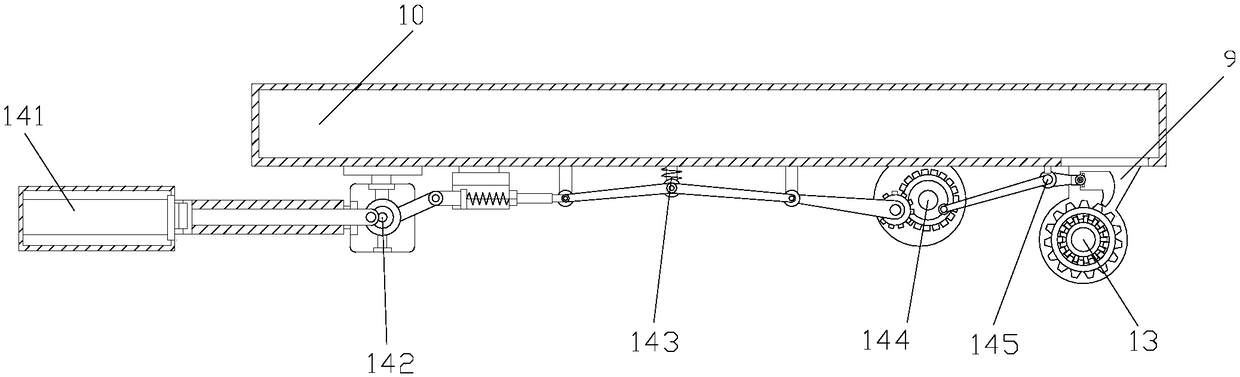
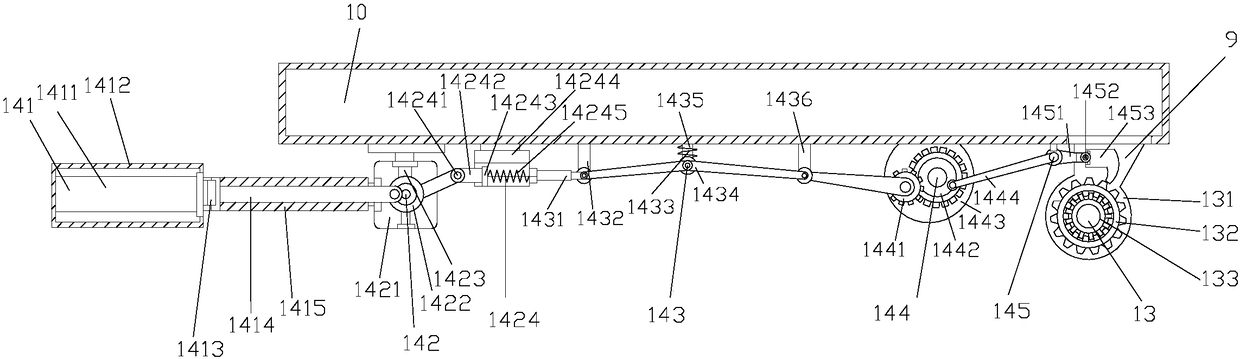
ActiveCN108407851AIncrease frictionPrevent slippingHand carts with multiple axesHand cart accessoriesTransmission brakeEngineering
The invention discloses a conveying trolley for logistics assembly. The conveying trolley structurally comprises a connecting plate, a pushing rod, a holding rod, vertical rods, an upper fence, bolts,an upper supporting plate, supporting rods, fixing plates, a lower supporting plate, a partition plate, a lower fence, castors, a pedal braking device, a pedal device, a pedal traction mechanism, anoperating mechanism, a gear transmission device, and a transmission braking structure. The conveying trolley for logistics assembly is structurally provided with the pedal braking device which is mounted at the bottom of the lower supporting plate in an embedded mode; and according to the pedal braking device, the conveying trolley can be braked in time through the transmission mechanism as long as a foot slightly steps a pedal, and thus the situations that the conveying trolley collides with an object due to delayed braking, consequently the structure is damaged, and the unnecessary loss is caused are avoided.
Owner:安徽驿星智能物流装备制造有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com