Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
505results about "Brake-by-wire" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
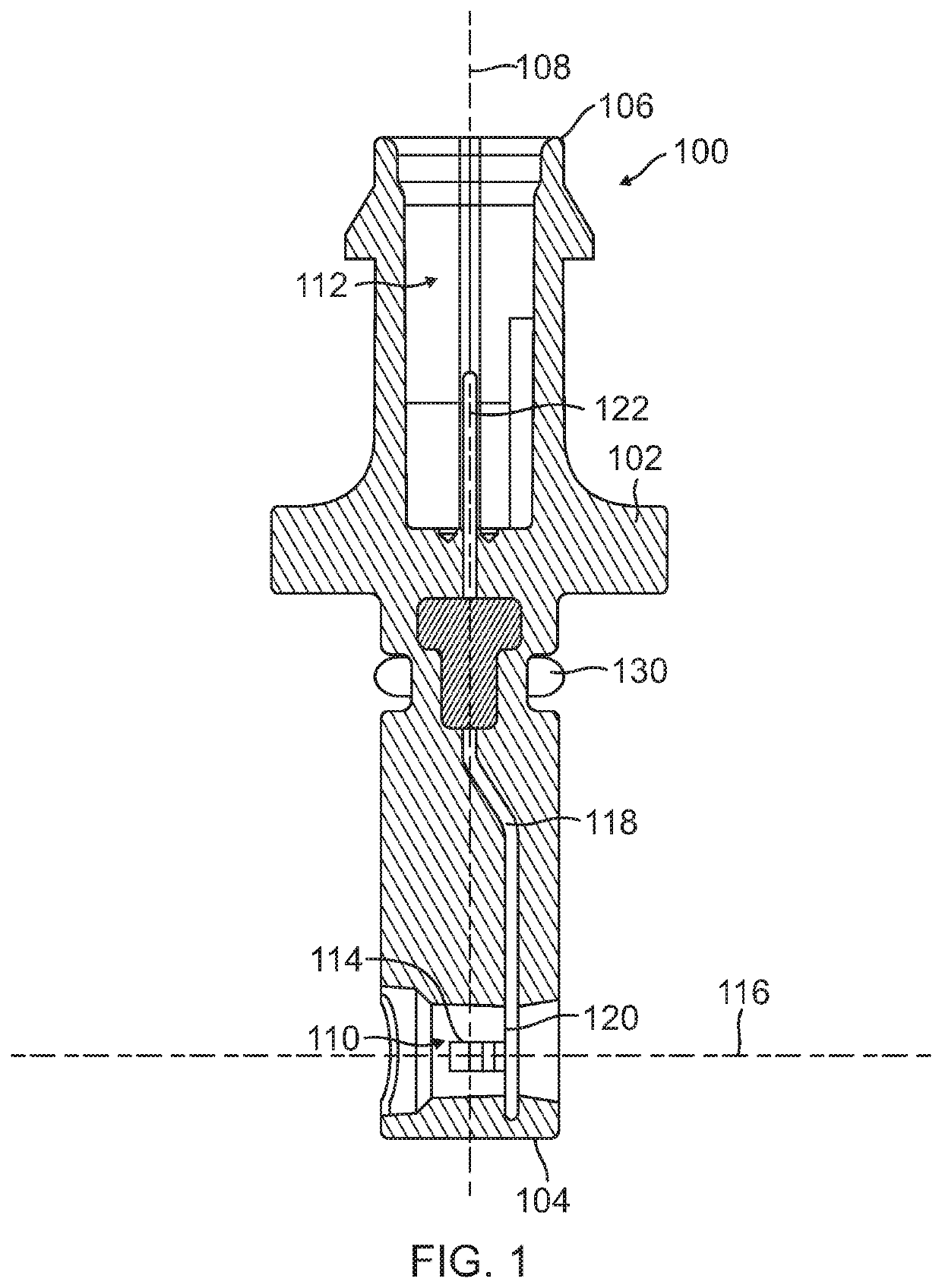
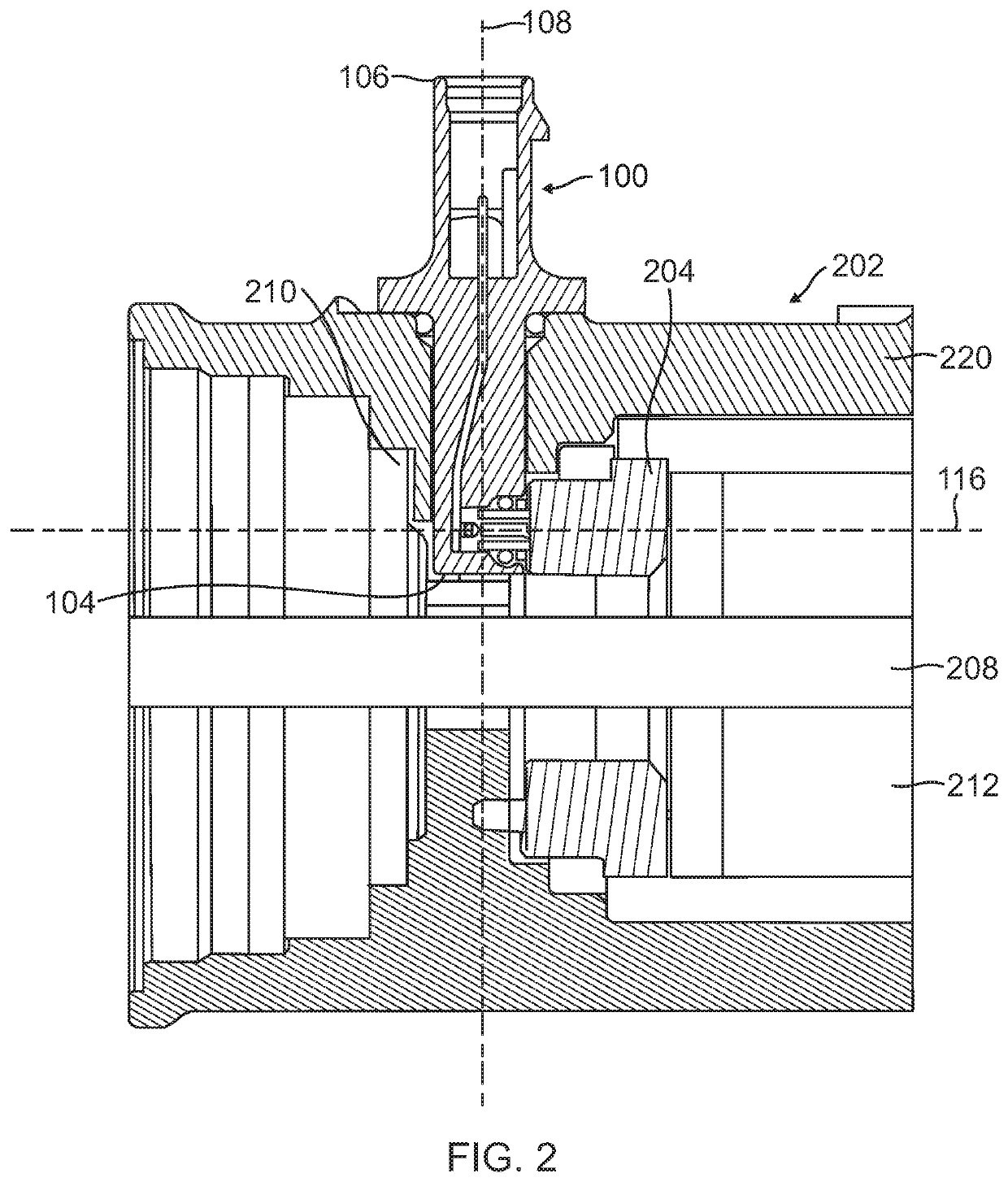
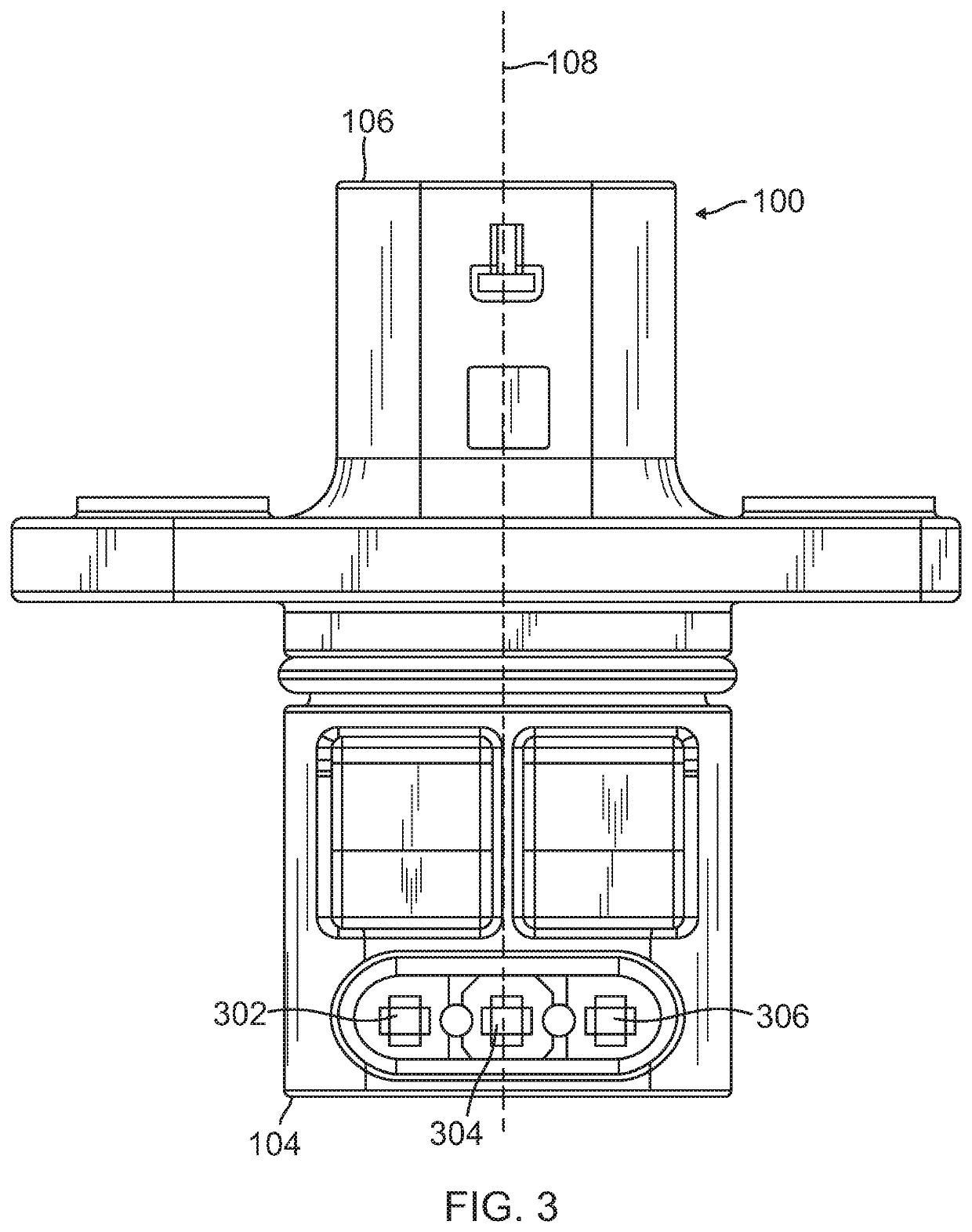
Electromechanical braking connector
ActiveUS20190375383A1Reduce excess spaceImprove the environmentBraking action transmissionCoupling device detailsBody axisElectrical connection
An electromechanical braking (EMB) connector for electrical communication between an interior of a brake caliper assembly and an exterior of the brake caliper assembly is disclosed. The EMB connector includes a body having a distal end for insertion into the interior of the brake caliper assembly and a proximal end for exposure on the exterior of the brake caliper assembly, with the distal end and the proximal end defining a body axis. The EMB connector also includes a load sensor connector for coupling with a load sensor disposed on the interior of the brake caliper assembly. The load sensor connector is compressible along a load sensor axis that is substantially perpendicular to the body axis. The EMB connector further includes a conductive component coupled to the load sensor connector. The conductive component enables electrical connection of the load sensor to the exterior of the brake caliper assembly.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
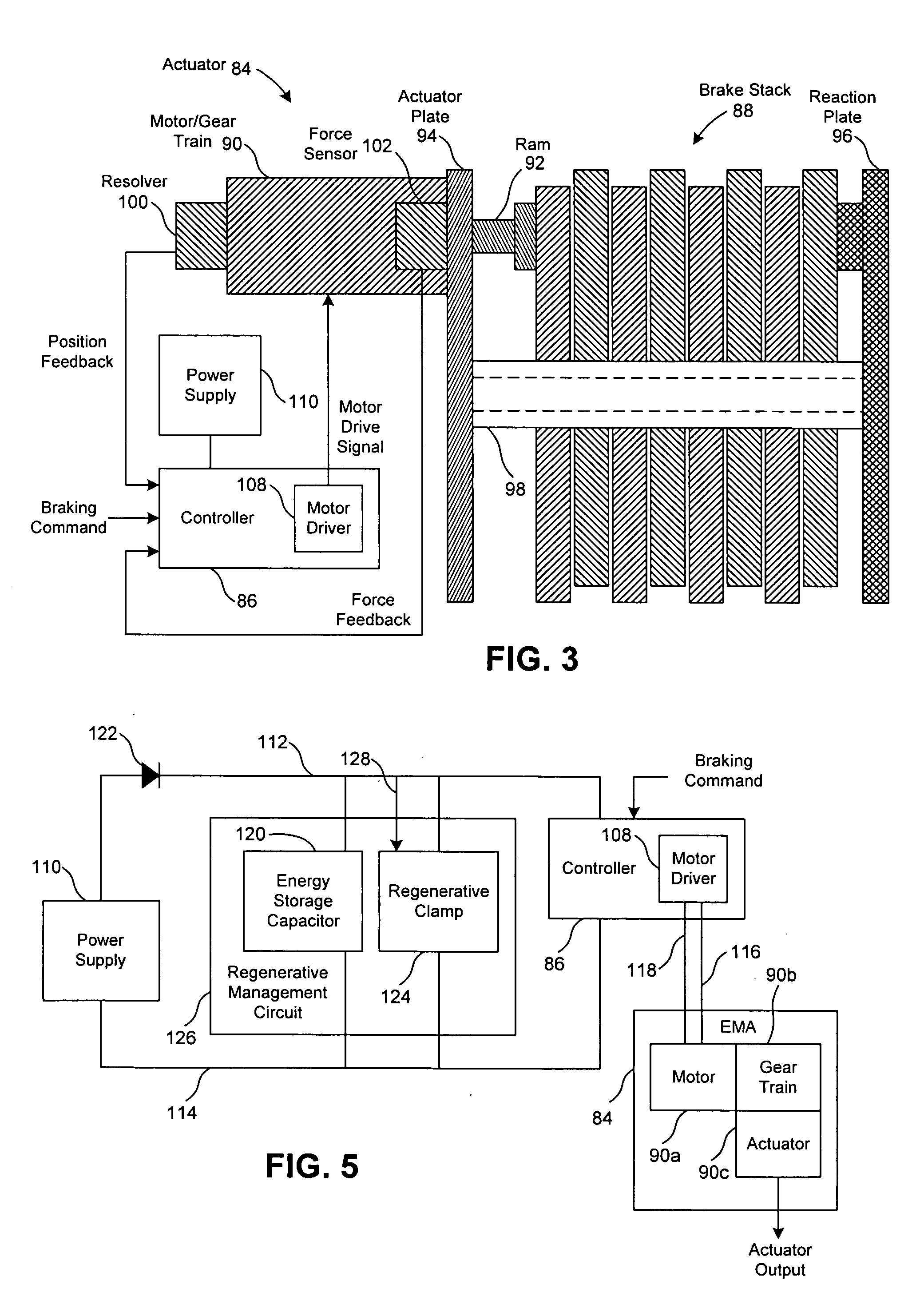
Electromechanical braking system with electrical energy back-up and regenerative energy management
InactiveUS20060108867A1Braking element arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityStored energy
An electromechanical system and system are provided where a controller generates an electrical drive signal for an actuator using power from a power source. A capacitor stores electrical energy and avails the stored energy to the controller when a voltage potential of the store electrical energy is higher than the supply voltage of the power source. The stored electrical energy may originate from the power source and / or regenerative energy produced by the actuator.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
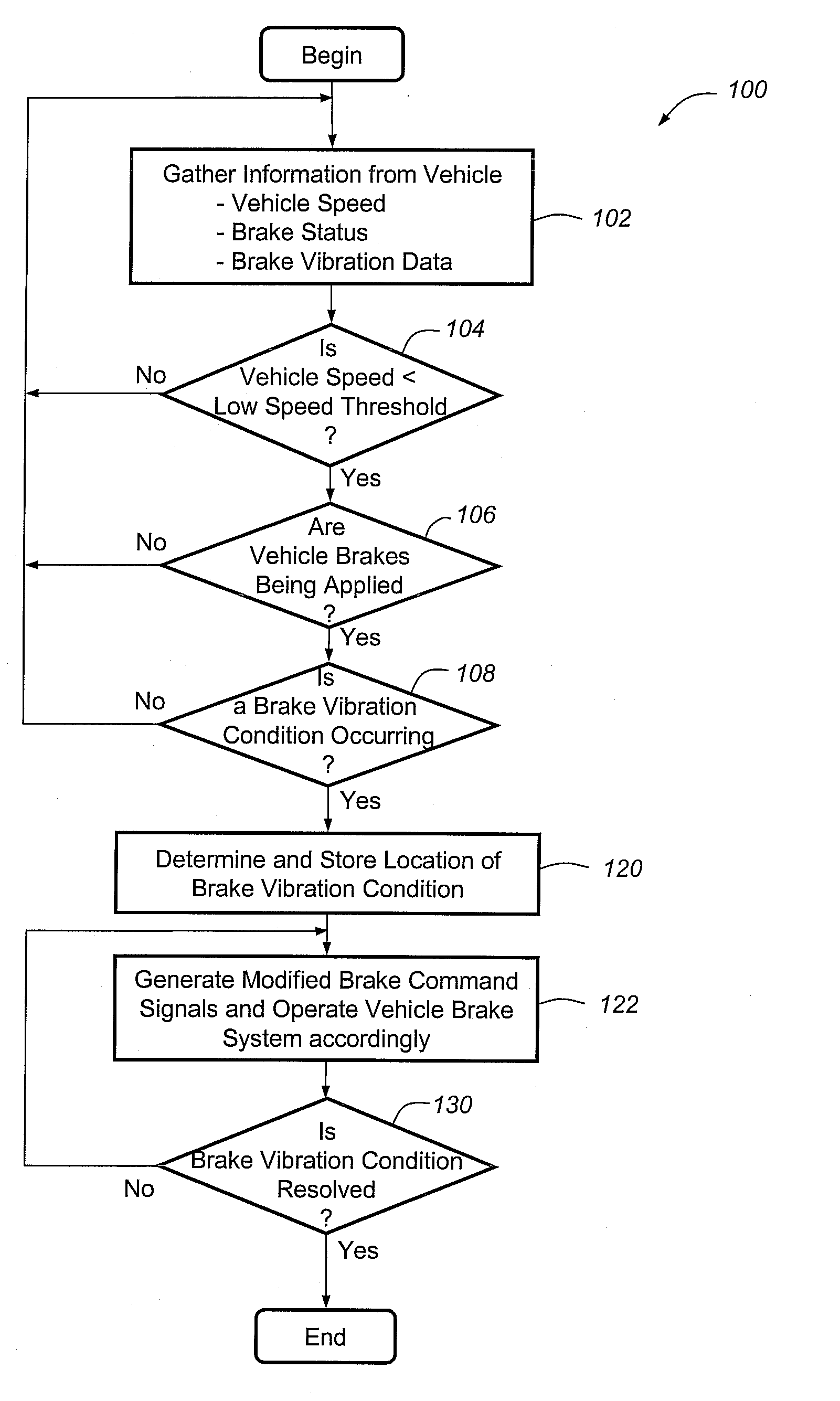
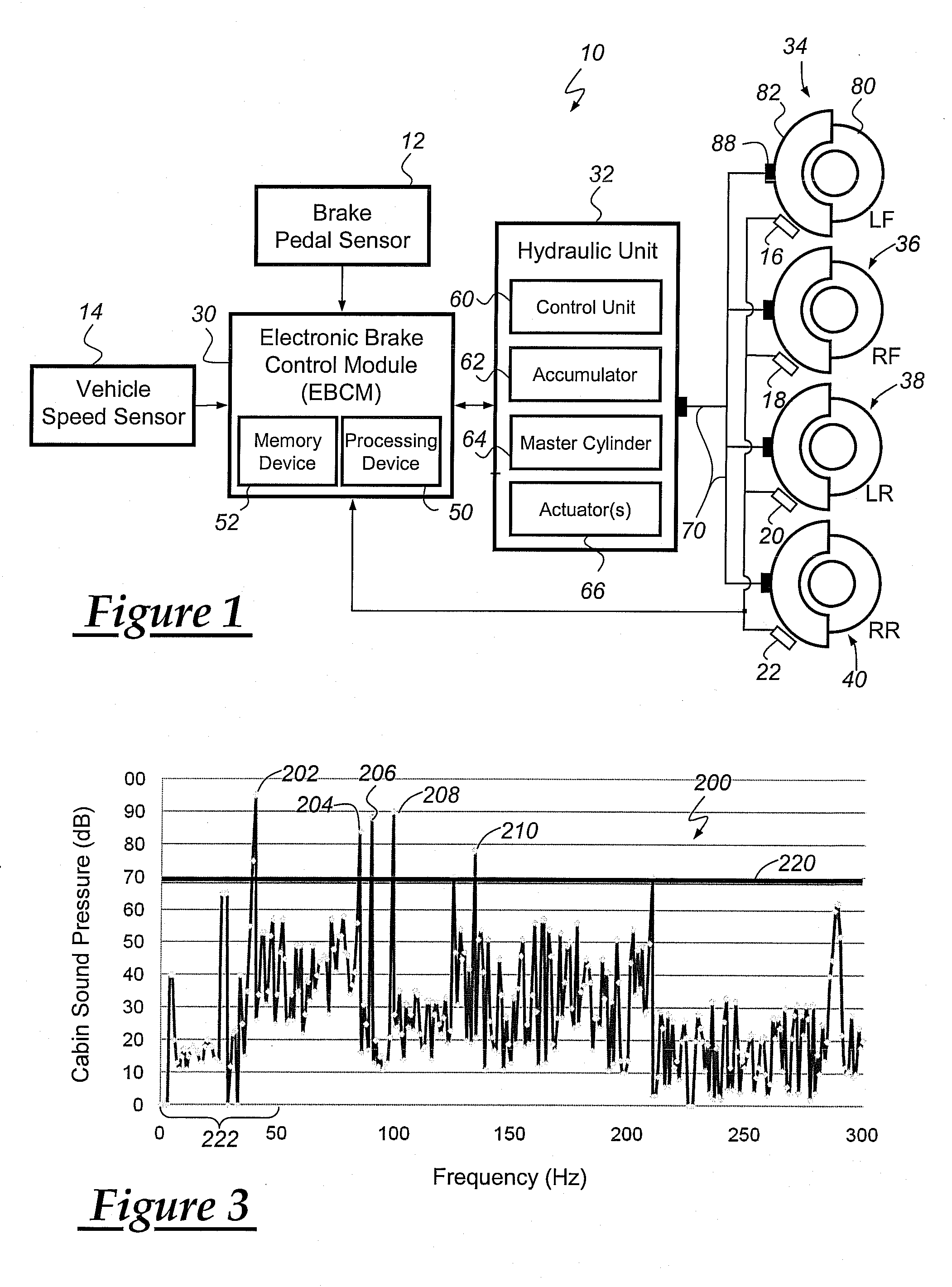
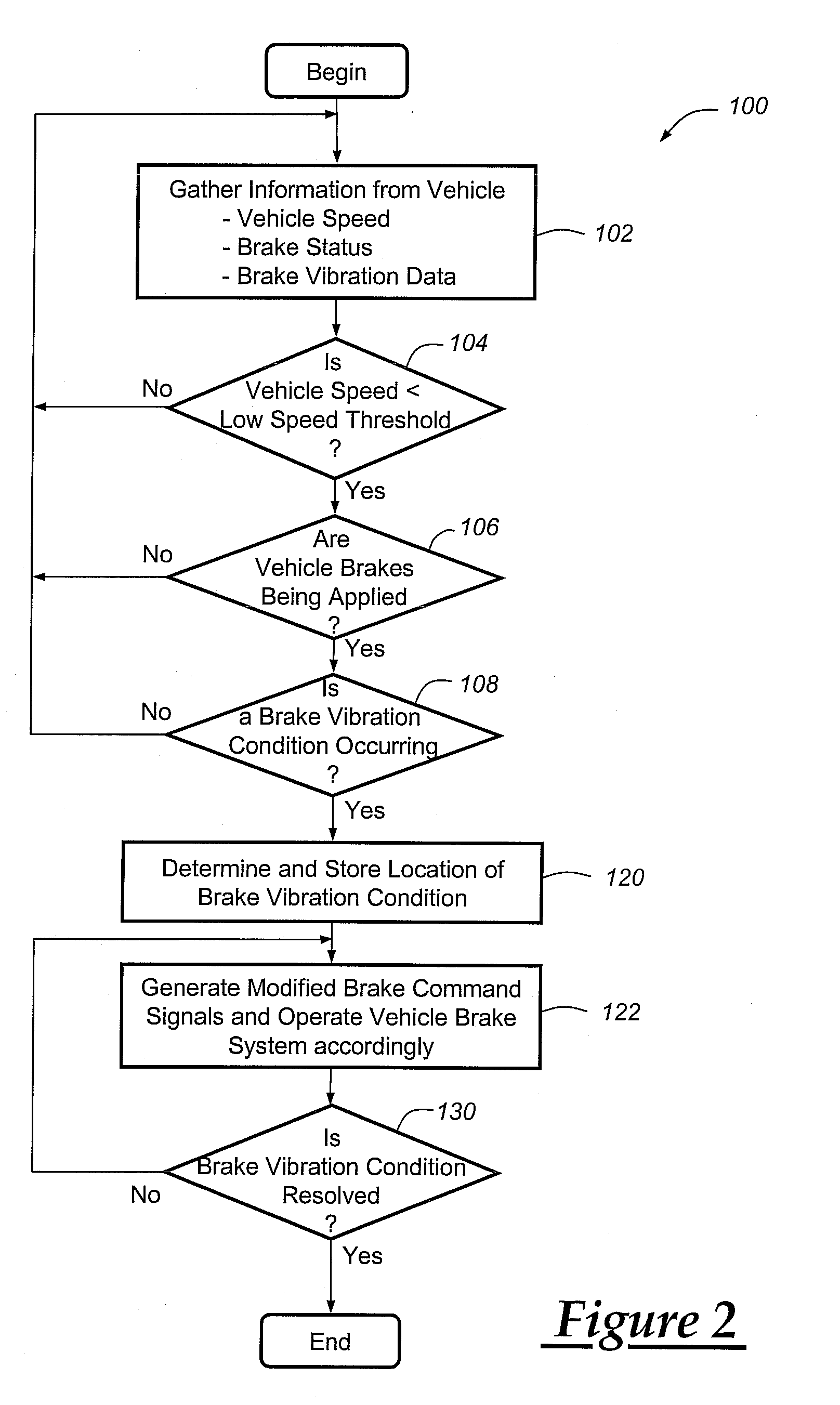
Method for operating a vehicle brake system
InactiveUS20100250081A1Reducing brake groan noiseReduce noiseVehicle testingNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueVehicle brake
A method for reducing or mitigating the effects of vibration in a vehicle brake system, particularly those that can lead to brake groan or other unwanted noise. According to an exemplary embodiment, when the vehicle brake system detects certain vibratory conditions, it makes slight braking adjustments (e.g., adjustments to fluid pressure, brake force, brake torque, etc.) that are aimed to address the brake groan. The vehicle brake system can then determine the effectiveness of the braking adjustments and, if need be, make additional braking adjustments. The method is particularly well suited for use with brake-by-wire systems, but can be used with a number of different vehicle braking systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Re-positionable vehicle control-by-wire assembly, method, and system
ActiveUS20050283288A1Digital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsControl theoryVehicle control
A vehicle control assembly and a method and system for controlling a vehicle. The assembly includes a controller. A steer-by-wire component, a brake-by-wire component, and an accelerator-by-wire component are each operably attached to the controller. A track is operably attached to the vehicle. The controller is laterally re-positionable with respect to the track. The method includes the steps of providing a controller, and steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller. The method further includes the step of re-positioning the controller between a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side. The system includes controller means, and means for steering, braking, and accelerating the vehicle by-wire with the controller means. The system further includes means for reversibly positioning the controller means from a first vehicle side to a second vehicle side.
Owner:FCA US
Fail-safe concept for an electromechanical brake
InactiveUS20050127749A1Security failsFatal consequenceBraking action transmissionMechanically actuated brakesControl systemExercise state
A control system for an electromechanical brake with self-reinforcement has: means for recognizing a brake failure means for detecting the actual state of motion of the device to be braked and means for opening and closing the brake upon recognition of a failure dependent upon the detected state of motion of the device to be braked. The means for recognizing the state of motion detection in particular the rotational velocity of a brake disk assigned to the brake.
Owner:STOP
Brake System for Motor Vehicles and Method for Operating the Brake System
InactiveUS20140225425A1Braking action transmissionBrake action initiationsElectricityMaster cylinder
A brake system includes a brake pedal for actuating a master cylinder having two pistons and corresponding pressure chambers, where the system can be operated in a brake-by-wire mode and also a fallback mode. The system also includes a first electrically controllable pressure source and a second electrically controllable pressure source. The first and second electrically controllable pressure sources each have corresponding output flows that are connected together. The second electrically controllable pressure source can therefore provide output volume flow in the event the first electrically controllable pressure source fails.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Brake System for Motor Vehicles
ActiveUS20130147259A1Sufficient forceEasy to manufactureFoot actuated initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleMaster cylinder
A brake system for motor vehicles comprising a brake master cylinder which can be activated by means of a brake pedal and to which wheel brakes are connected. The brake system also comprises an electrically controllable pressure-generating device, a pressure-regulating valve arrangement to regulate a wheel brake pressure set at a wheel brake, a first electronic control and regulating unit which controls at least one of the pressure-generating device, the pressure-regulating valve arrangement, and an electrically controllable auxiliary pressure-generating device by means of which the brake master cylinder can be activated by means of which a pressure in an intermediate chamber of the brake master cylinder can be controlled or regulated.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
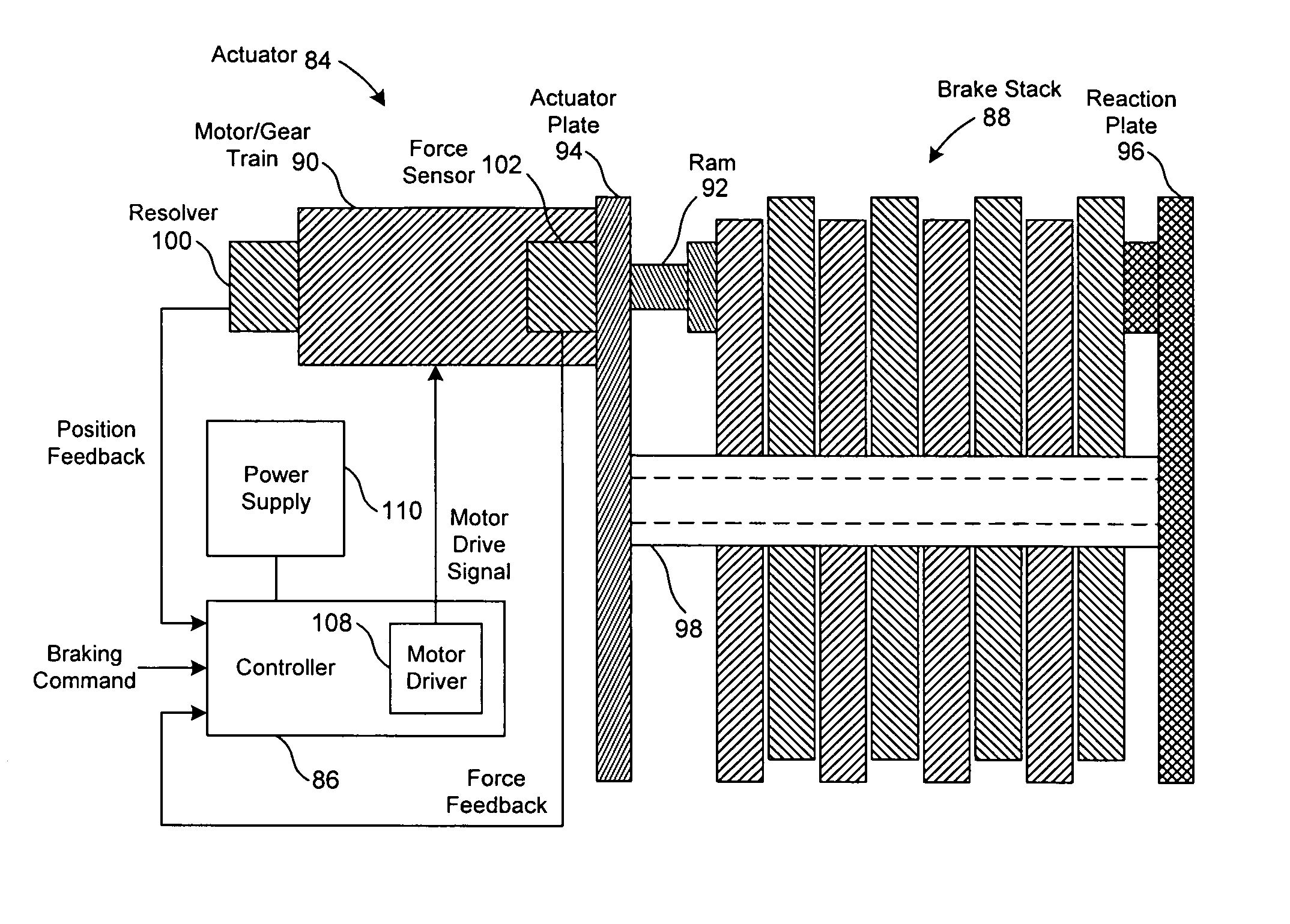
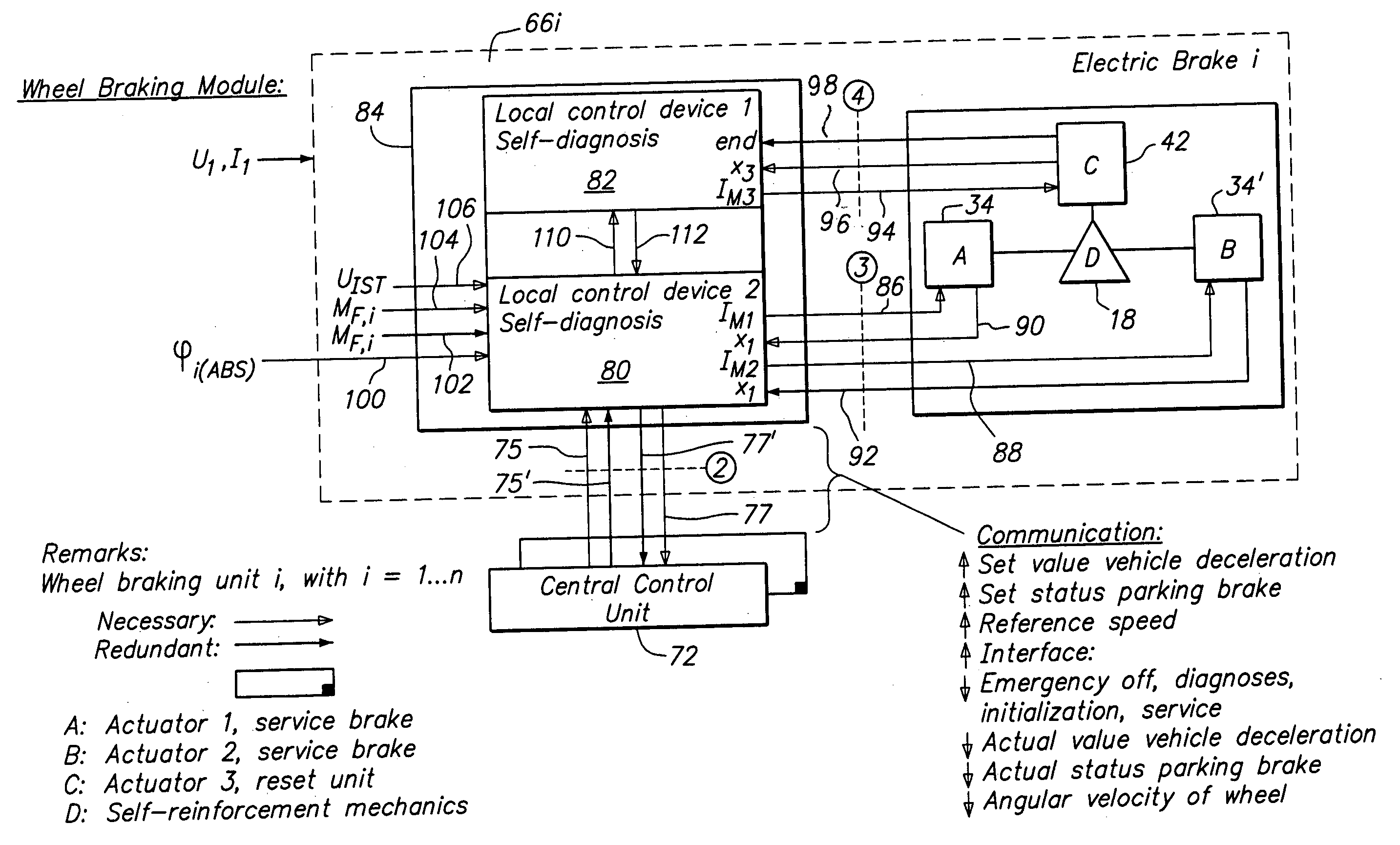
Redundant Brake Actuators For Fail Safe Brake System
InactiveUS20080296106A1Improve usabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesBraking action transmissionControl signalActuator
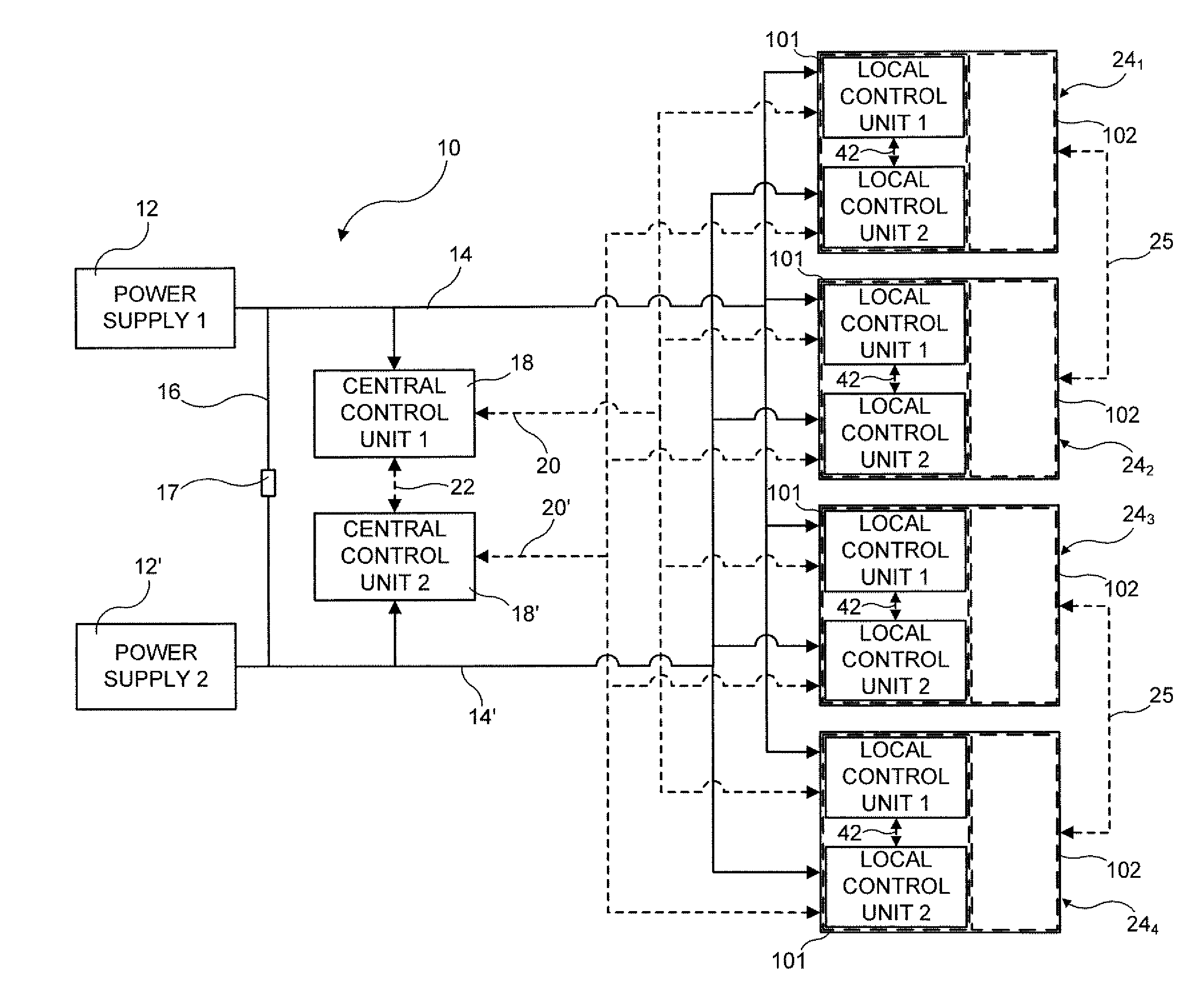
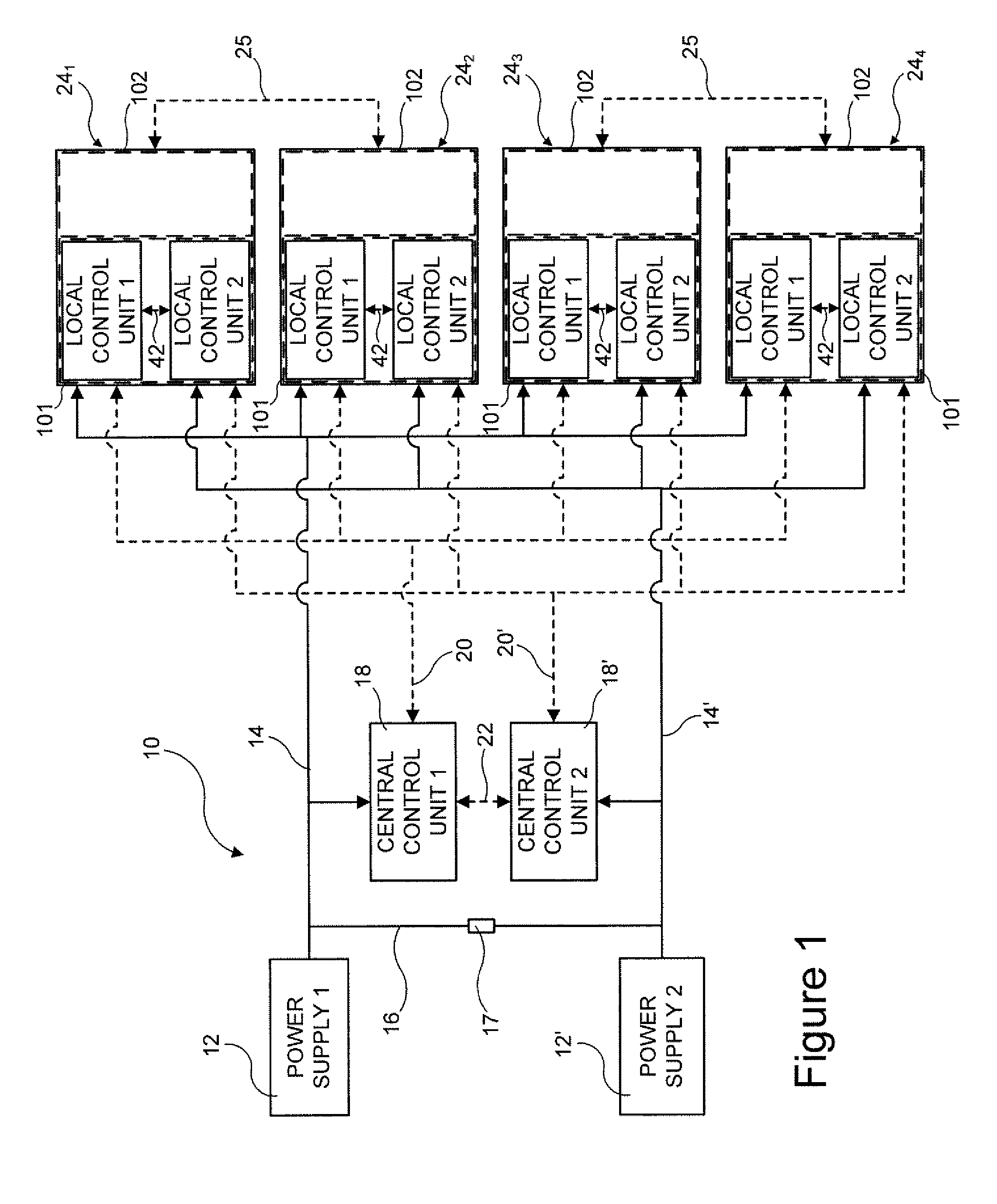
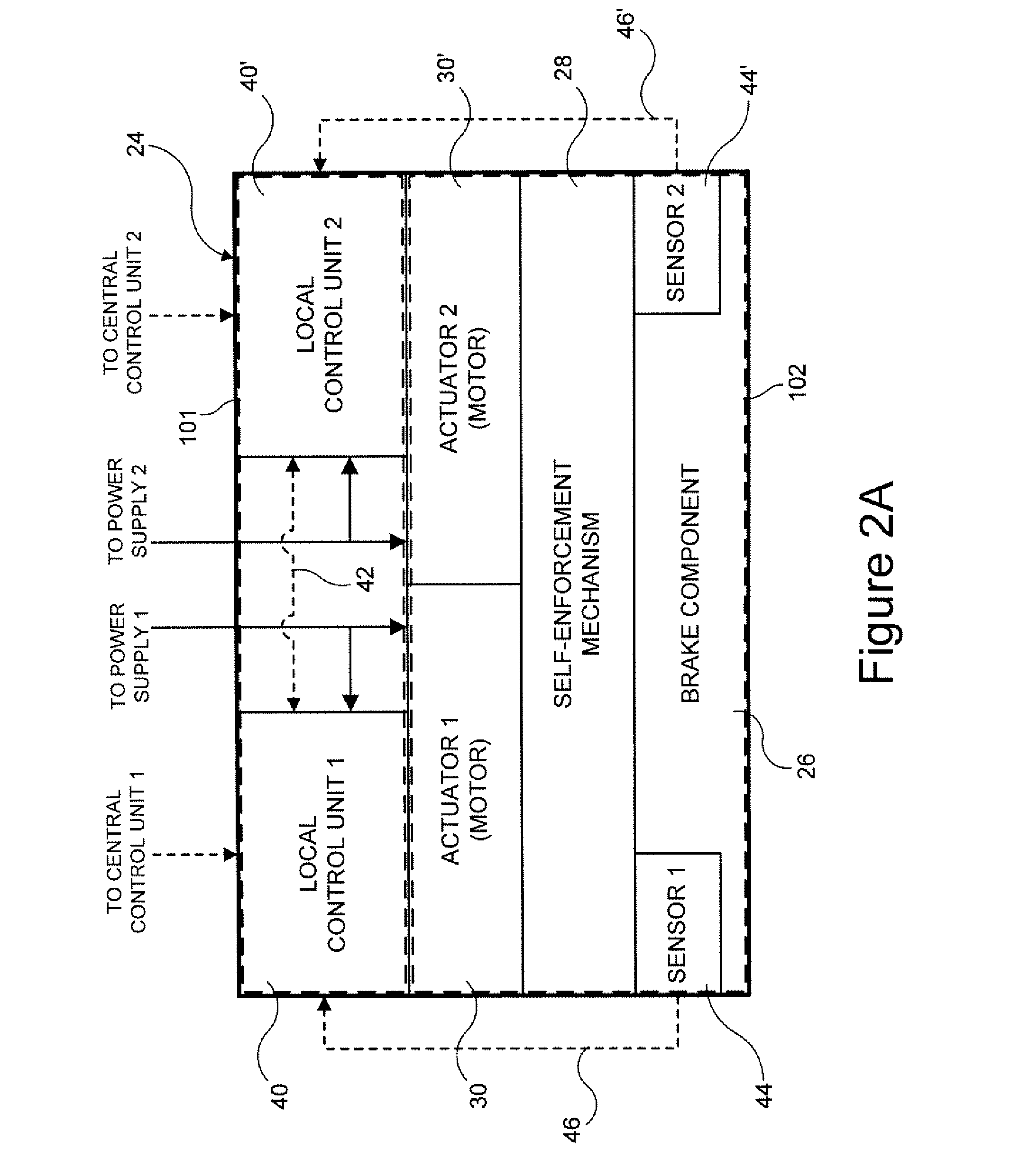
A vehicle brake system includes first and second central control units communicating with, respectively, first and second control networks, and a plurality of brake units. Each brake unit includes a brake component, a self-enforcing mechanism associated with and acting upon the brake component, and first and second actuation mechanisms acting upon the self enforcing mechanism, in response to, respectively, first and second actuation control signals, to cause actuation of the brake component. Each brake unit also includes first and second local control units in direct communication with, respectively, the first and second central control units via, respectively, the first and second control networks. The first and second local control units are in communication with, respectively, the first and second actuation mechanisms and transmit, respectively, the first and second actuation control signals to, respectively, the first and second actuation mechanisms, under certain circumstances, to cause actuation of the brake component.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD AB
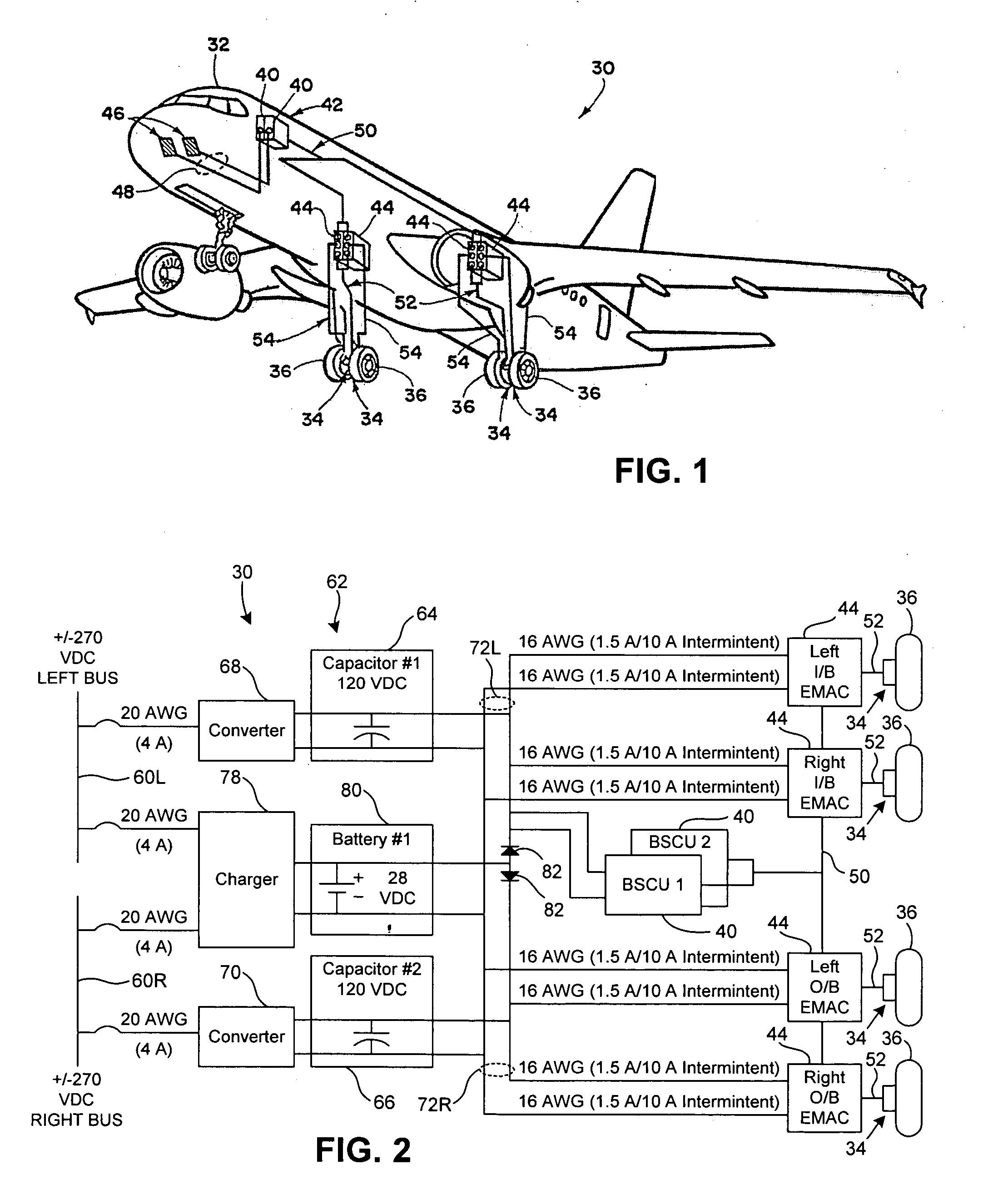
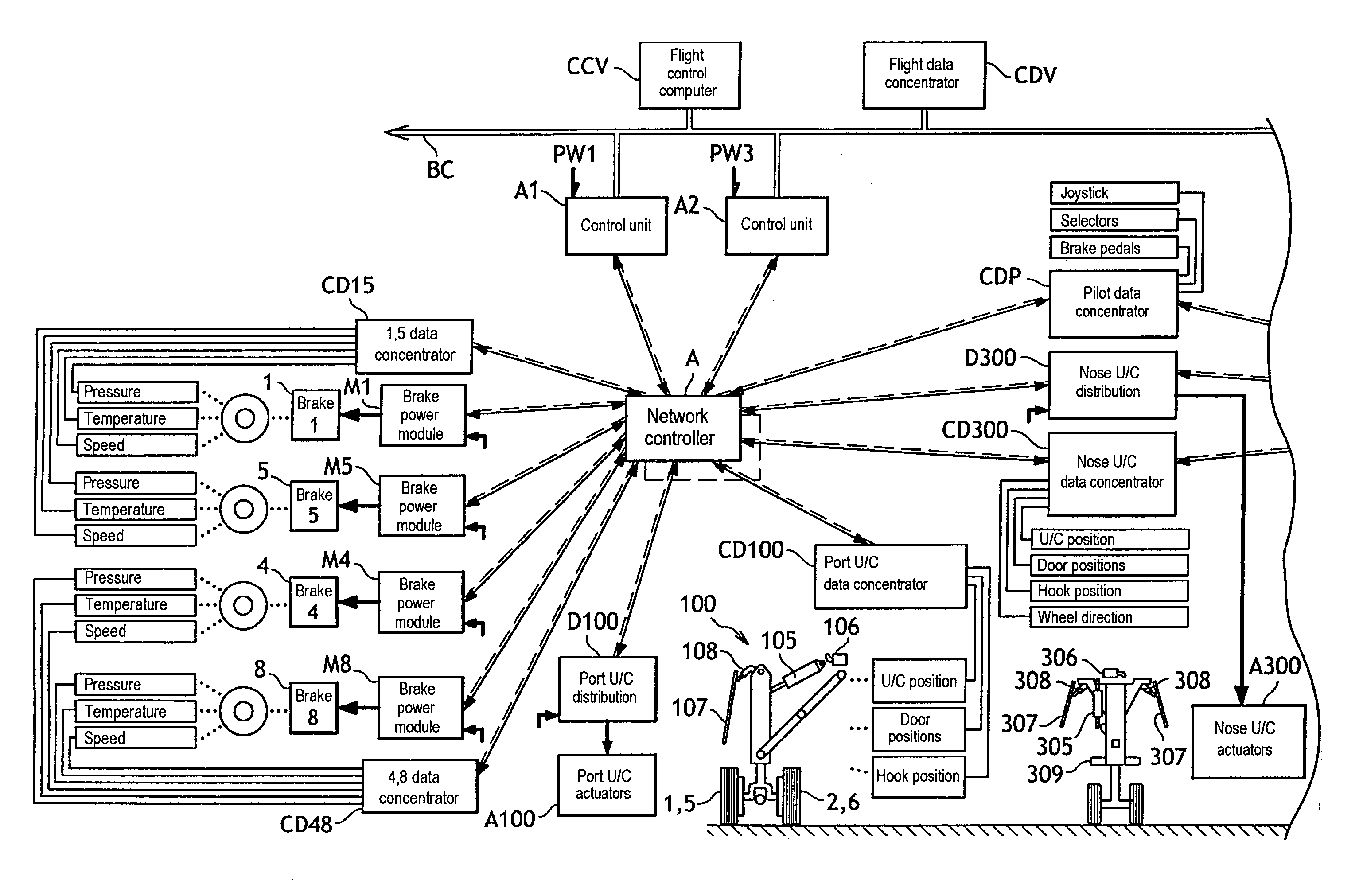
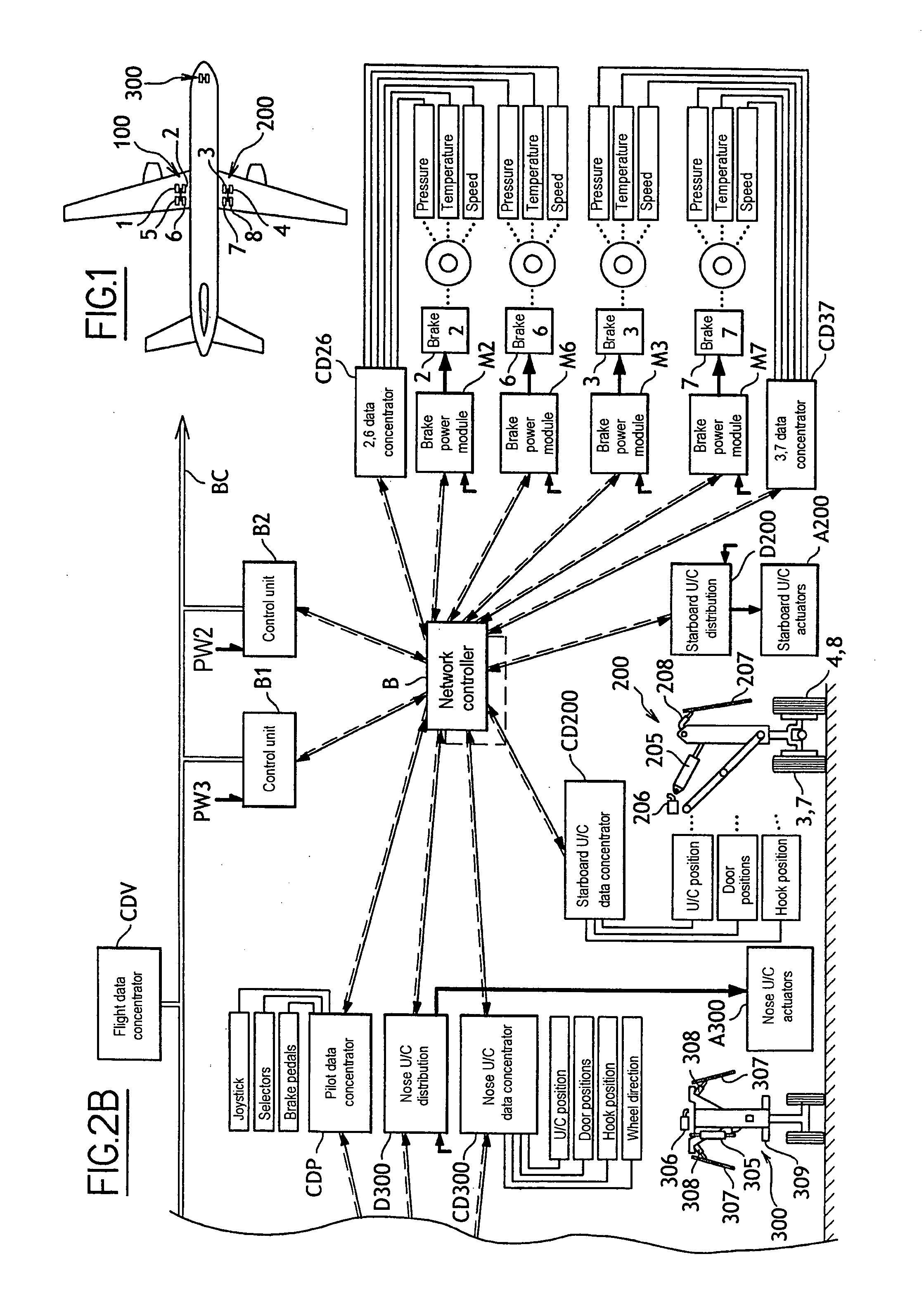
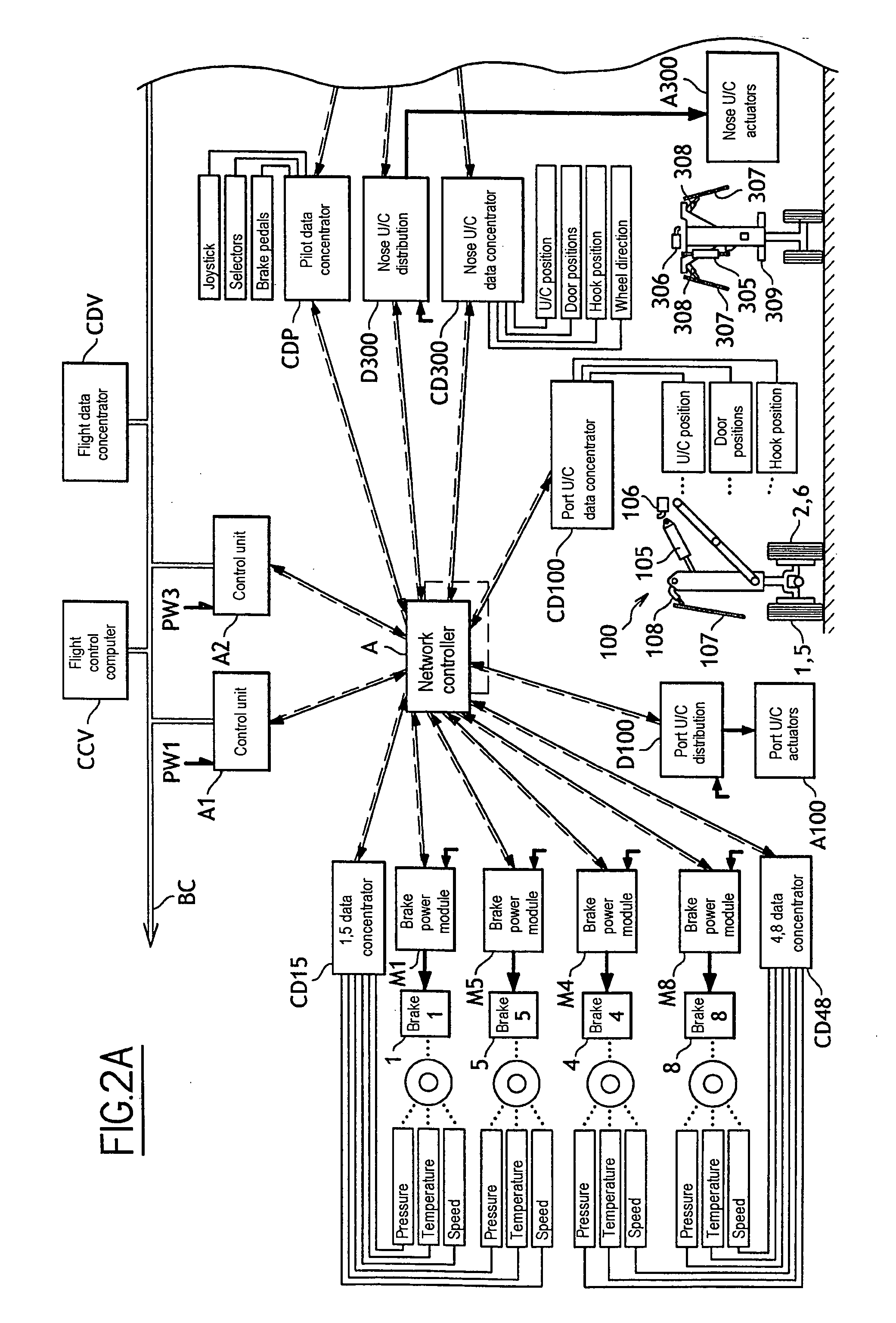
Distributed architecture for a system for managing aircraft landing gear
ActiveUS20060293805A1Simple structureSimplify the management processAnalogue computers for vehiclesDigital data processing detailsAircraft landingEngineering
The invention relates to a system architecture for managing aircraft landing gear and suitable for extending / retracting retractable undercarriages, steering steerable wheels, and braking braked wheels. According to the invention, the architecture comprises a communications network having connected thereto extension / retraction actuators, steering actuators, and braking actuators, together with one or more control units adapted to control all of the actuators connected thereto, the communications network having transmission characteristics that are adapted to enabling the control unit(s) to implement antilock servo-control for controlling the braking actuators.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS
Method for providing haptic information to the driver of a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20150061854A1Simple electronic meansFoot actuated initiationsElectric propulsion mountingDriver/operatorFunctional Relationship
The invention relates to a method for providing haptic information to the driver of a motor vehicle, equipped with a brake-by-wire brake system, about the operating state of the brake system, in which method the brake pedal characteristic is generated by a pedal travel simulator, in the form of a functional relationship between the brake pedal opposing force and the brake pedal travel, and is modified as a function of an operating state. In order to provide the driver with the haptic information channel via which electronically controlled information can be communicated to the driver during braking, without the impression of a defect arising, the invention proposes that a basic brake pedal characteristic is generated by a passive simulator spring which assigns pedal travel, on which pedal return travel transporting the haptic information is superimposed, to a given pedal force in an unchanging, constant relationship.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
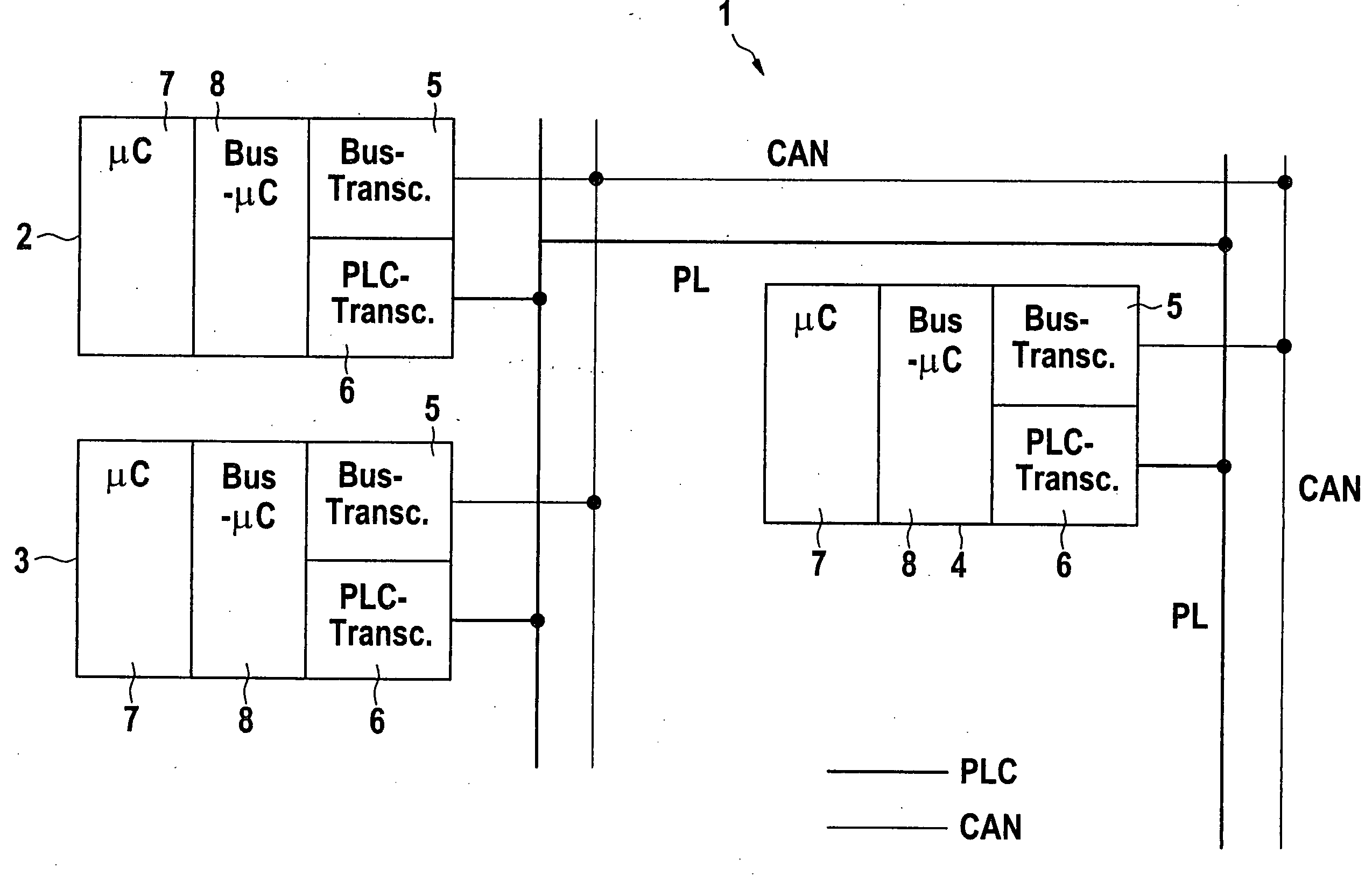
Method and Communications System for Transmitting Information in a Motor Vehicle
InactiveUS20070286225A1Simple and cost-effectiveMultiplex system selection arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionMobile vehicleCommunications system
A communications system for a motor vehicle, including a plurality of electrical components, a data bus structure to which the components are connected in order to transmit information among the components, and a power line structure to which the components are connected in order to be supplied with power. The information is transmitted in successive cycles over the data bus structure, each cycle including at least one time window for transmitting information at specific points in time and at least one event window for transmitting information in response to specific events. The communications system includes an arrangement for redundantly transmitting information which merely transmits the information transmitted in the at least one time window over the data bus structure at least partially over the power line structure as well.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
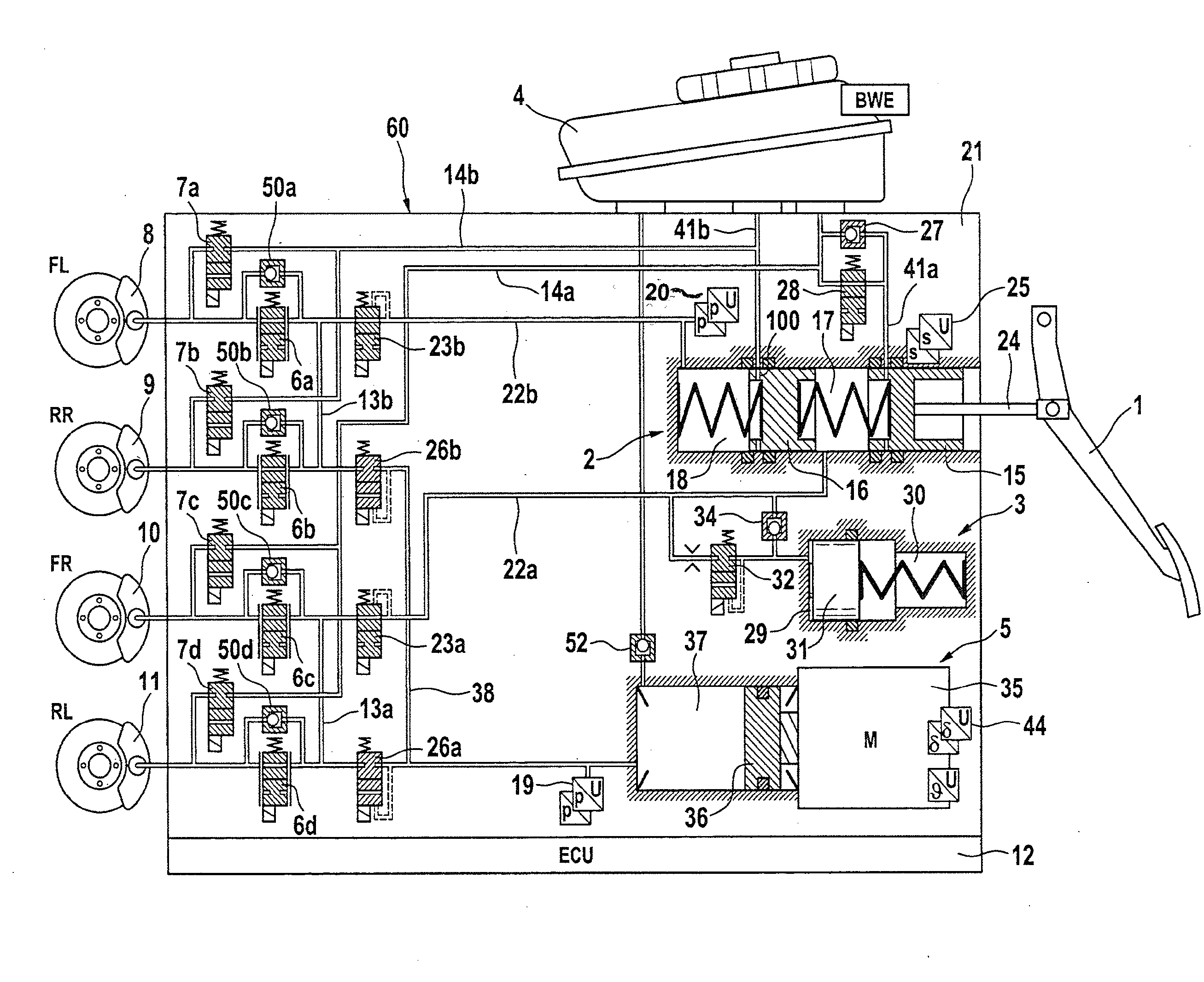
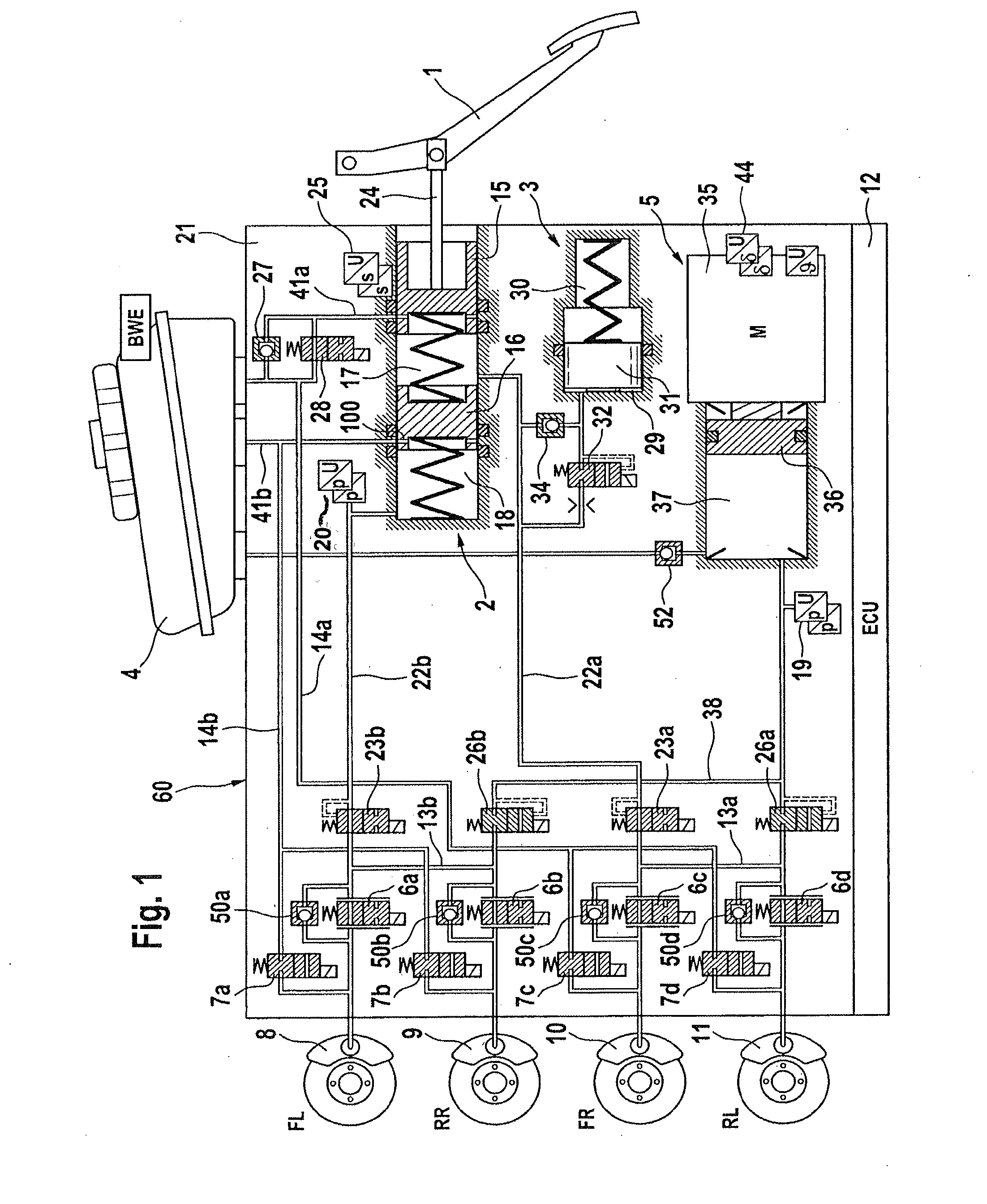
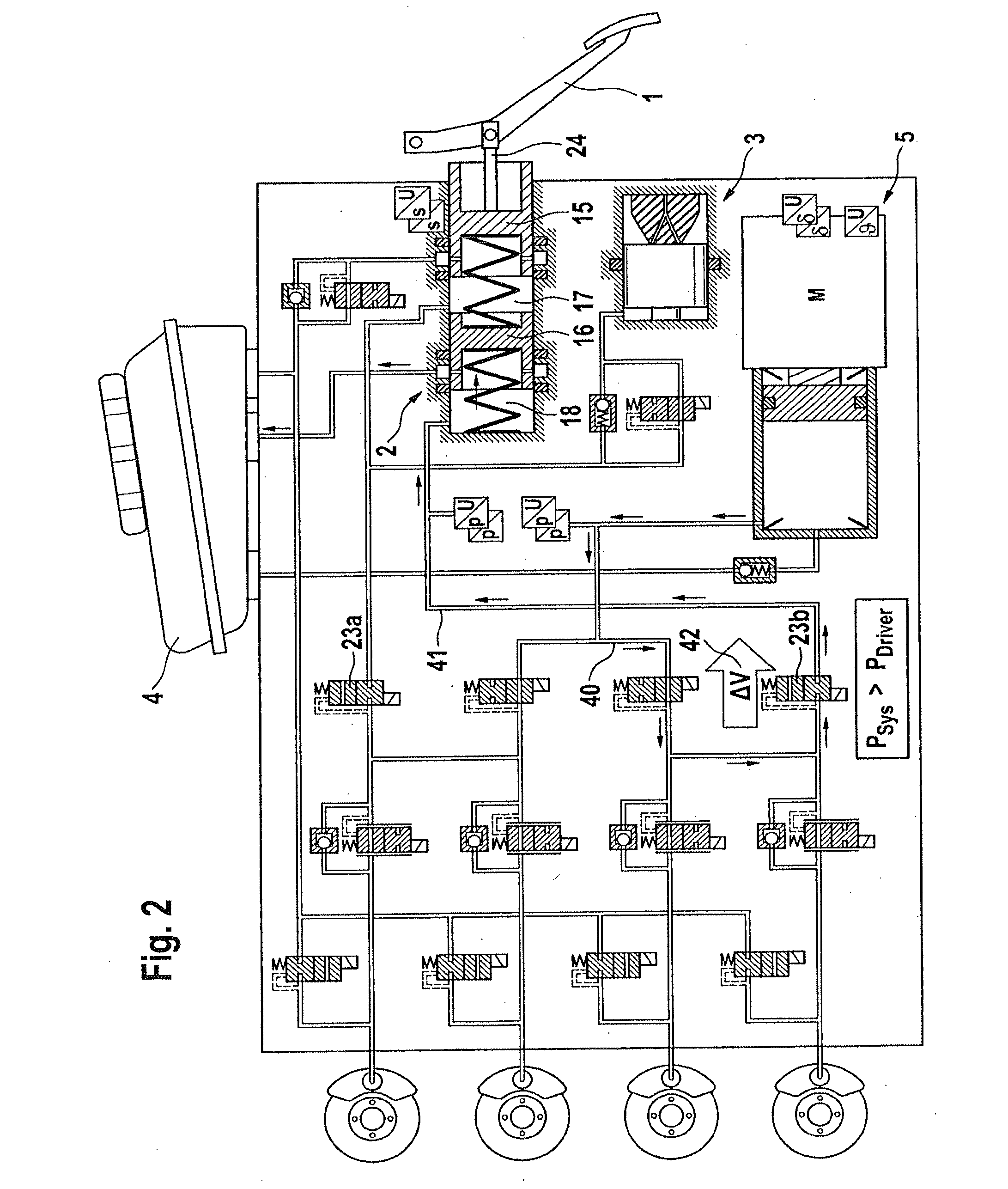
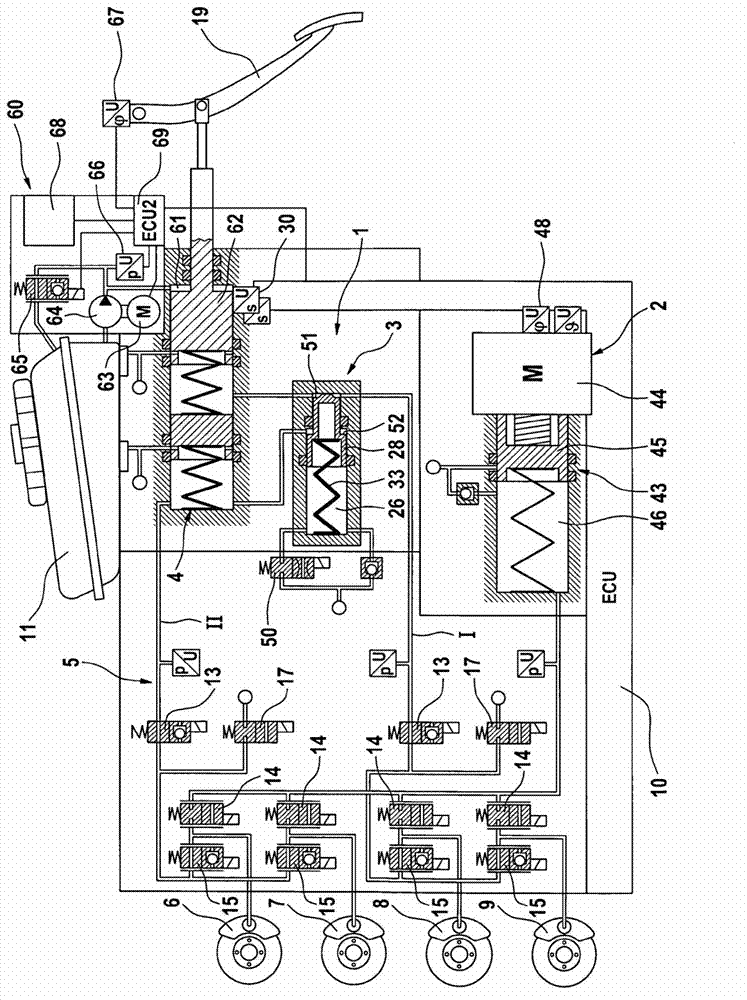
Redundant architecture for brake-by-wire system
ActiveUS7128376B2Relieve stressAutomatic braking sequenceBraking action transmissionEngineeringControl theory
A redundant architecture for a brake-by-wire system is provided. The system includes a pressure source; at least one brake actuator for exerting a braking force on a wheel as a result of pressure provided by the pressure source; at least one servo valve for controlling an amount of pressure provided from the pressure source to the at least one brake actuator in response to a servo valve command signal; a shutoff valve in line with the at least one servo valve for preventing pressure from the pressure source from being provided to the at least one brake actuator in response to a shutoff valve command signal; a processor which executes code in order to carry out brake control operations, the processor outputting the servo command signal and the shutoff valve command signal in response to system inputs provided to the processor; a shutoff valve enable device for performing brake control operations redundant at least in part with the processor and based on the system inputs, and selectively enabling shutoff valve command signals from the processor to be provided to the shutoff valve based on the redundant brake control operations.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Brake system for motor vehicles
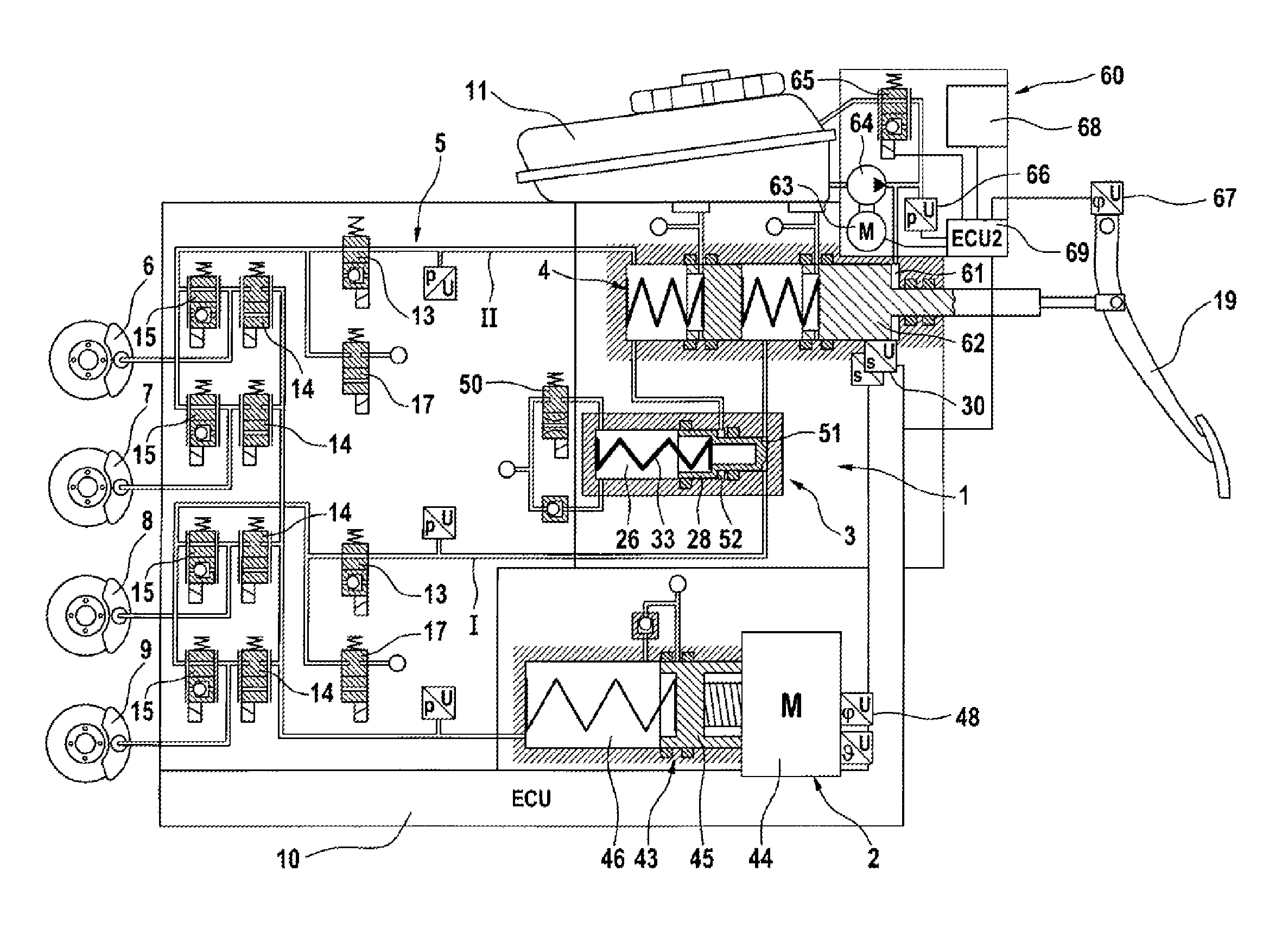
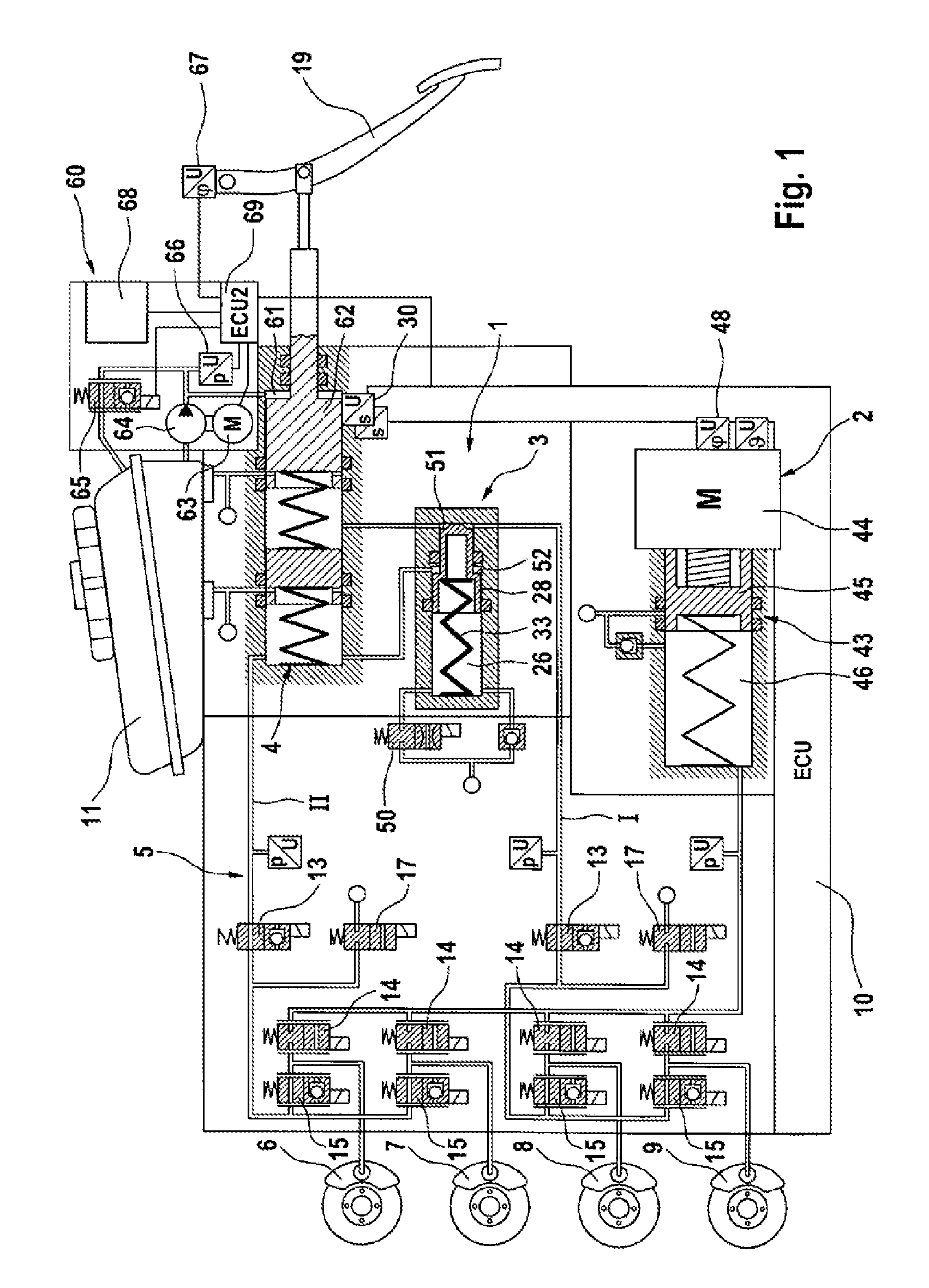
InactiveCN103079914AFoot actuated initiationsFluid braking transmissionMobile vehicleMotor vehicle part
In a brake system for motor vehicles, having a master brake cylinder (4) which can be actuated by means of a brake pedal (19) and to which wheel brakes (6, 7, 8, 9) are connected, having an electrically controllable pressure generating device (2), having a pressure regulating valve arrangement (5) for regulating and / or controlling a wheel brake pressure induced at a wheel brake (6, 7, 8, 9), and having a first electronic control and regulating unit (10) which controls or regulates the pressure generating device (2) and / or the pressure regulating valve arrangement (5), it is sought to a provide brake force assistance means which is independent of the functioning of the pressure generating device. For this purpose, said brake system comprises an electrically controllable auxiliary pressure generating device (60) by means of which the master brake cylinder (4) can be actuated, in particular by means of which a pressure in an intermediate chamber (61) of the master brake cylinder (4) can be controlled or regulated.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
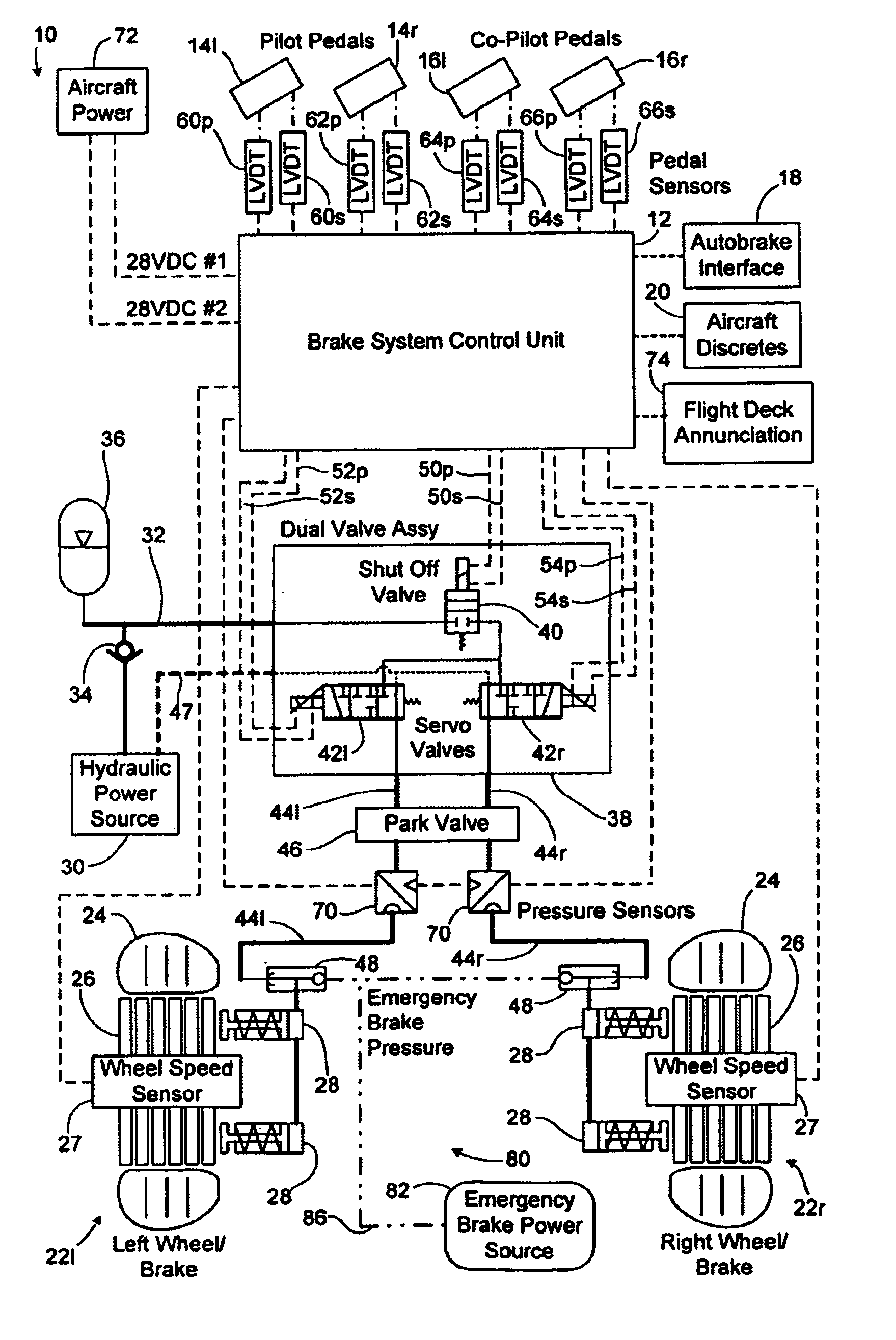
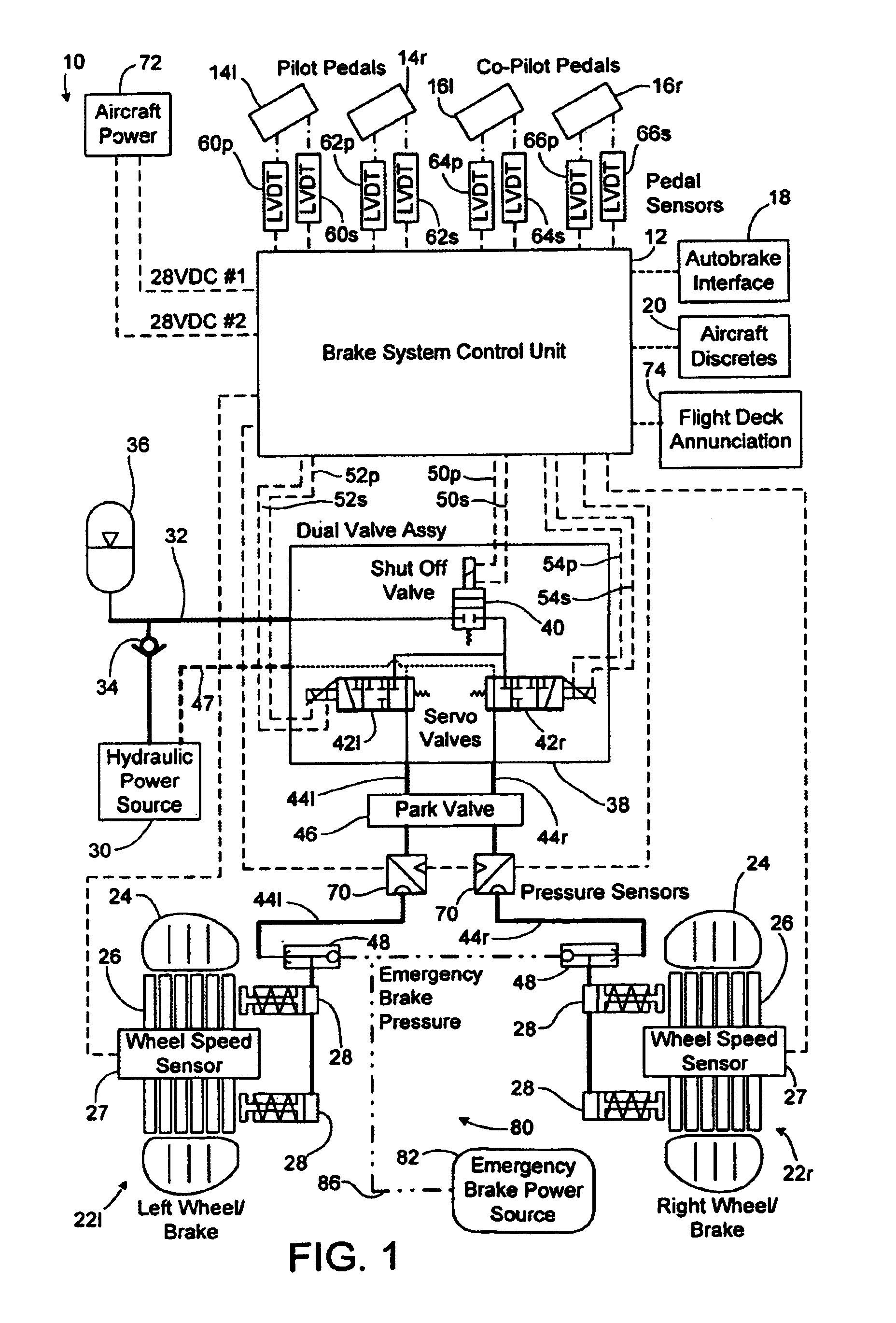
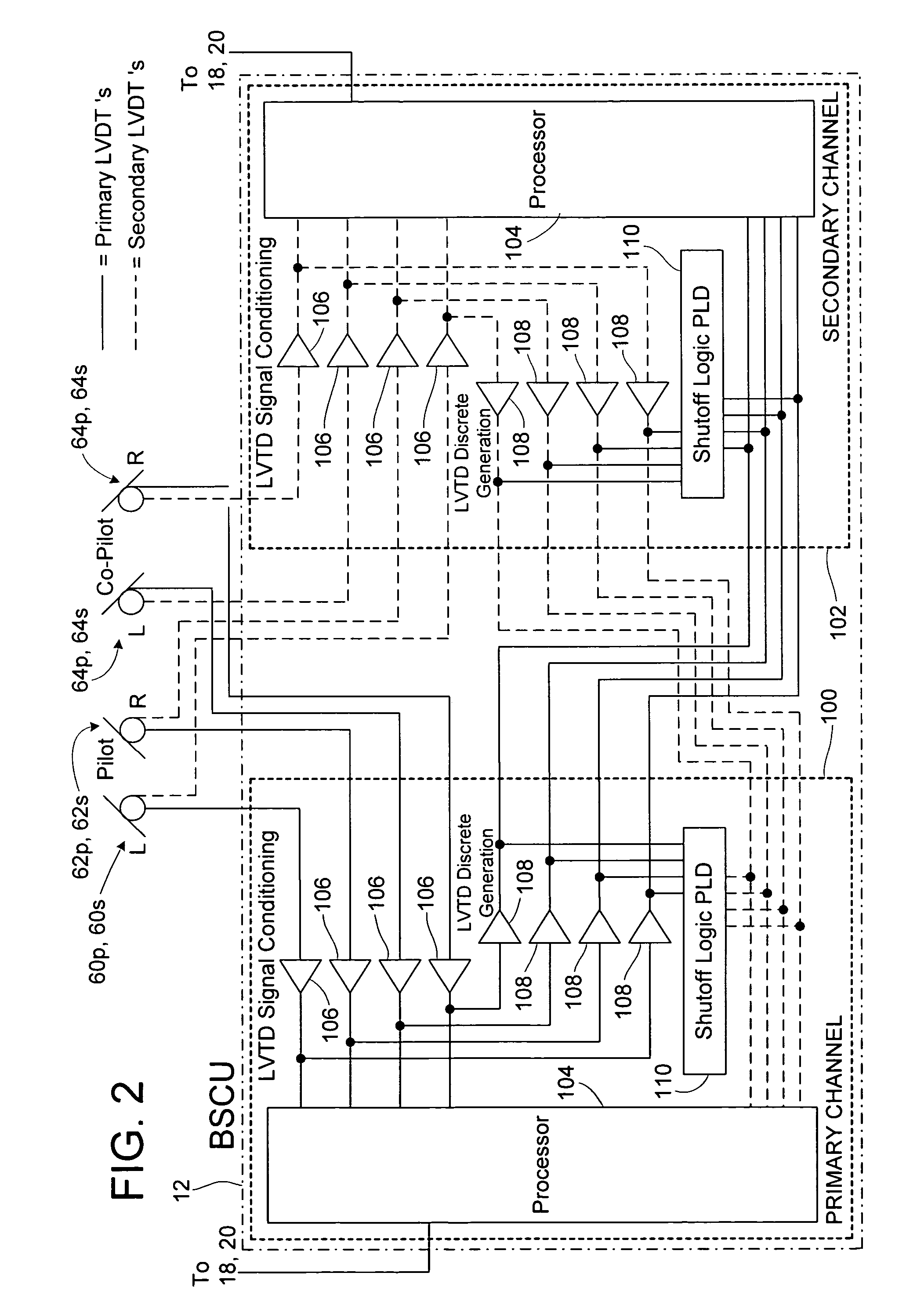
Architecture for an airplane braking system including two computers and capable of withstanding two breakdowns, and a method of managing such an architecture
ActiveUS20050189814A1Braking action transmissionAircraft braking arrangementsJet aeroplaneNormal mode
The invention relates to an architecture for a braking system for an airplane fitted with a plurality of undercarriages each carrying a plurality of wheels, at least some of which are fitted with brakes, the architecture comprising at least two braking computers each having two modules such that in each computer, one of the modules controls a first fraction of the brakes and the other module controls a second fraction of the brakes complementary to the first. According to the invention, the architecture is configured to operate in any one of the following modes of operation: a first normal mode in which both modules of one of the braking computers are active for controlling all of the brakes; a second normal mode in which both modules of the other braking computer are active for controlling all of the brakes; and an alternative mode in which one module of one of the braking computers and one module of the other braking computer are active for controlling all of the brakes.
Owner:SAFRAN LANDING SYSTEMS
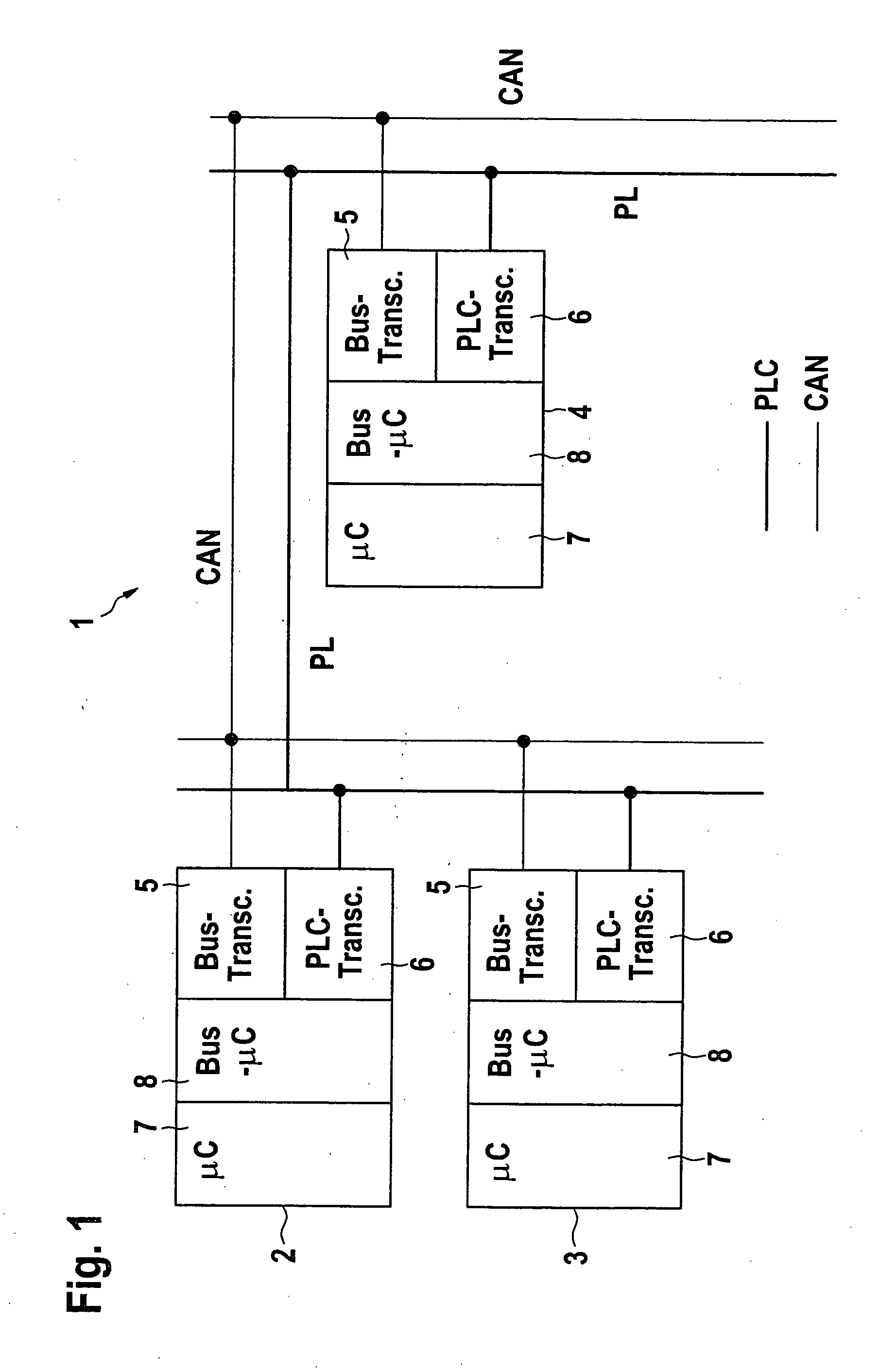
Method and supply line structure for transmitting data between electrical automotive components
InactiveUS20050040709A1Add featureLow costElectric signal transmission systemsError preventionMobile vehicleEngineering
A method and a supply line structure for transmitting information between electrical components in a motor vehicle is described. The information is transmitted over a data bus. At least some of the components are powered via a supply line structure. To make the transmission of information between the components fail-safe, the information is also transmitted over the supply line structure in addition to over the data bus at least after a failure of the data bus.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
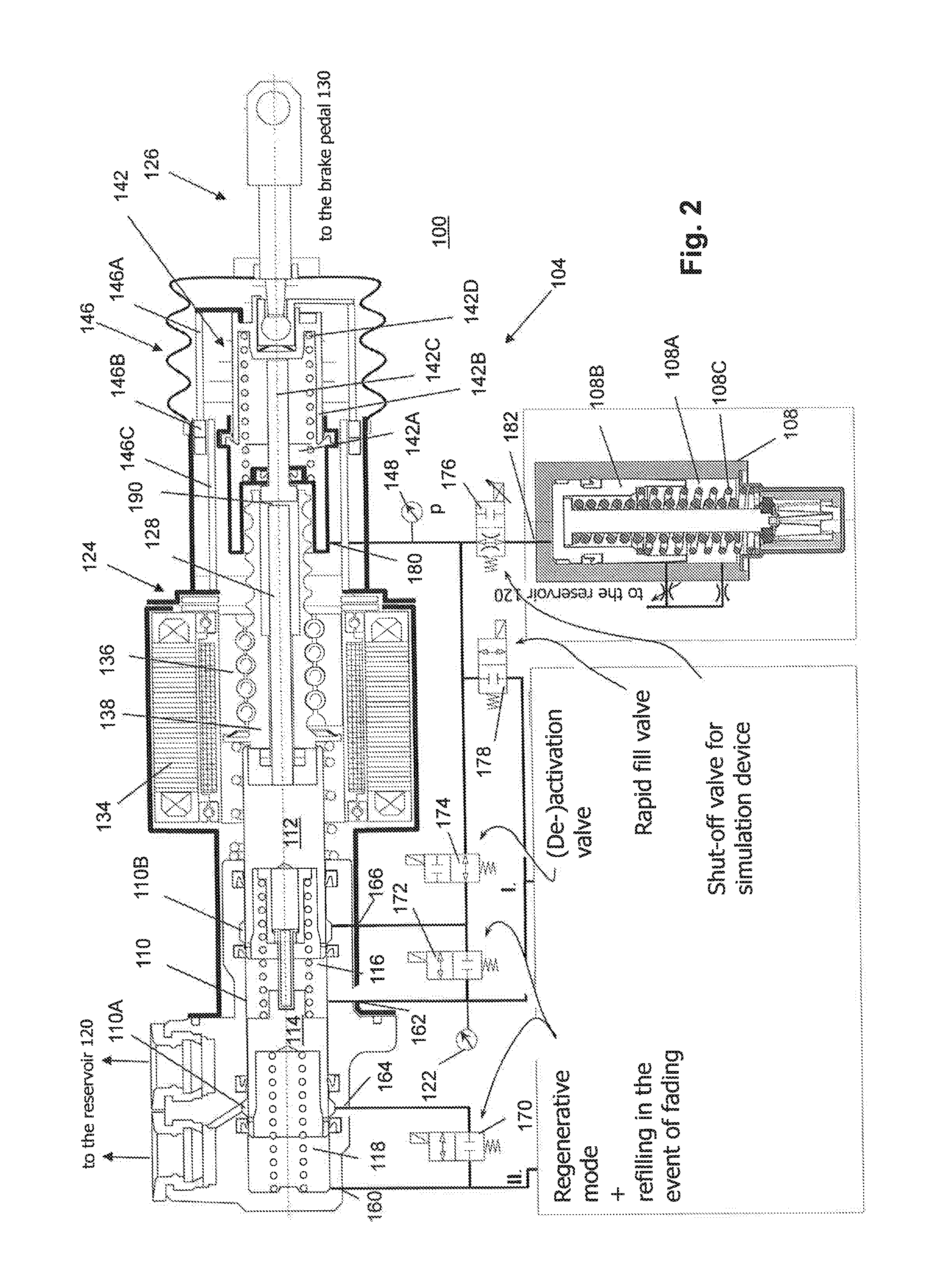
Vehicle Brake System With Dual Acting Plunger Assembly
A plunger assembly for use as a pressure source for a brake system includes a housing having first and second ports. A motor is mounted on the housing for driving an actuator. A piston is connected to the actuator. The piston is slidably mounted within the housing. The piston pressurizes a first chamber when the piston is moving in a first direction to provide fluid out of the first port. The piston pressurizes a second chamber when the piston is moving in a second direction to provide fluid out of the second port.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Control method for hydraulic dual motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system
InactiveCN104309597AEasy to controlGood braking feelBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesDriver/operatorSolenoid valve
The invention discloses a control method for a hydraulic dual motor-driven electronic hydraulic braking system based on torque control. The control method comprises the following steps: judging whether the braking system is in failure, determining the adjustment torque T2 of a second motor in a second electronic control straight line motion module if the braking system is not in failure so as to match the second motor with the force of treading a brake pedal by a driver and regenerative brake force to generate a braking torque, and obtaining target braking force; meanwhile determining the adjustment torque T1 of a first motor in a first electronic control straight line motion module so as to provide the brake pedal feeling of the driver by the first motor; if the braking system is in failure, controlling electromagnetic valves through a switch to realize the switching of system braking modes under different failure conditions. The control method disclosed by the invention is accurate in control and high in response speed, and has good robustness; under the precondition of realizing the braking intention of the driver, a good braking feeling is provided for the driver, and hydraulic force is actively controlled, so that maximum recycling for braking energy is realized, and the braking requirement of automatic driving vehicles is met.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
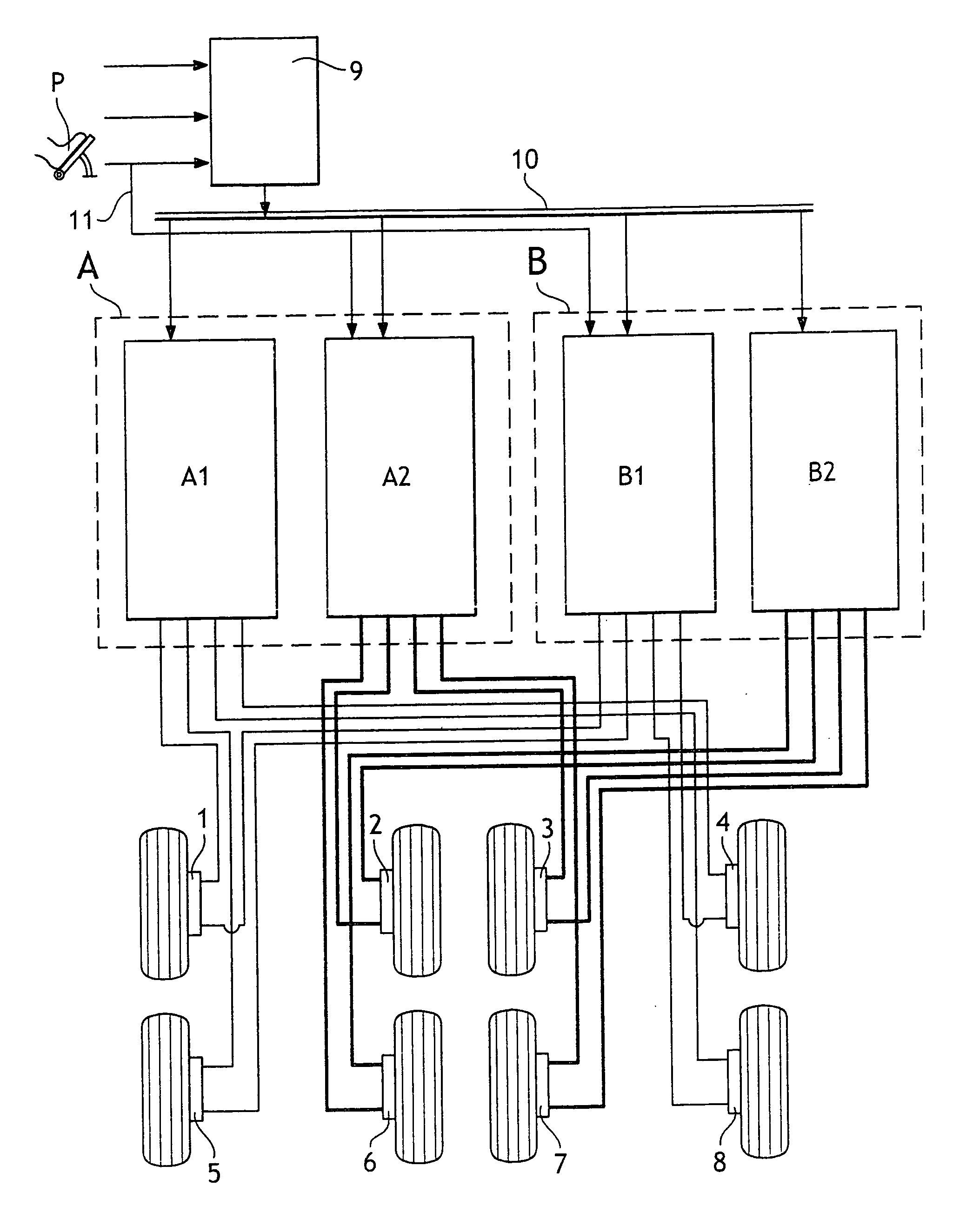
Control network for vehicle dynamics and ride control systems having distributed electronic control units
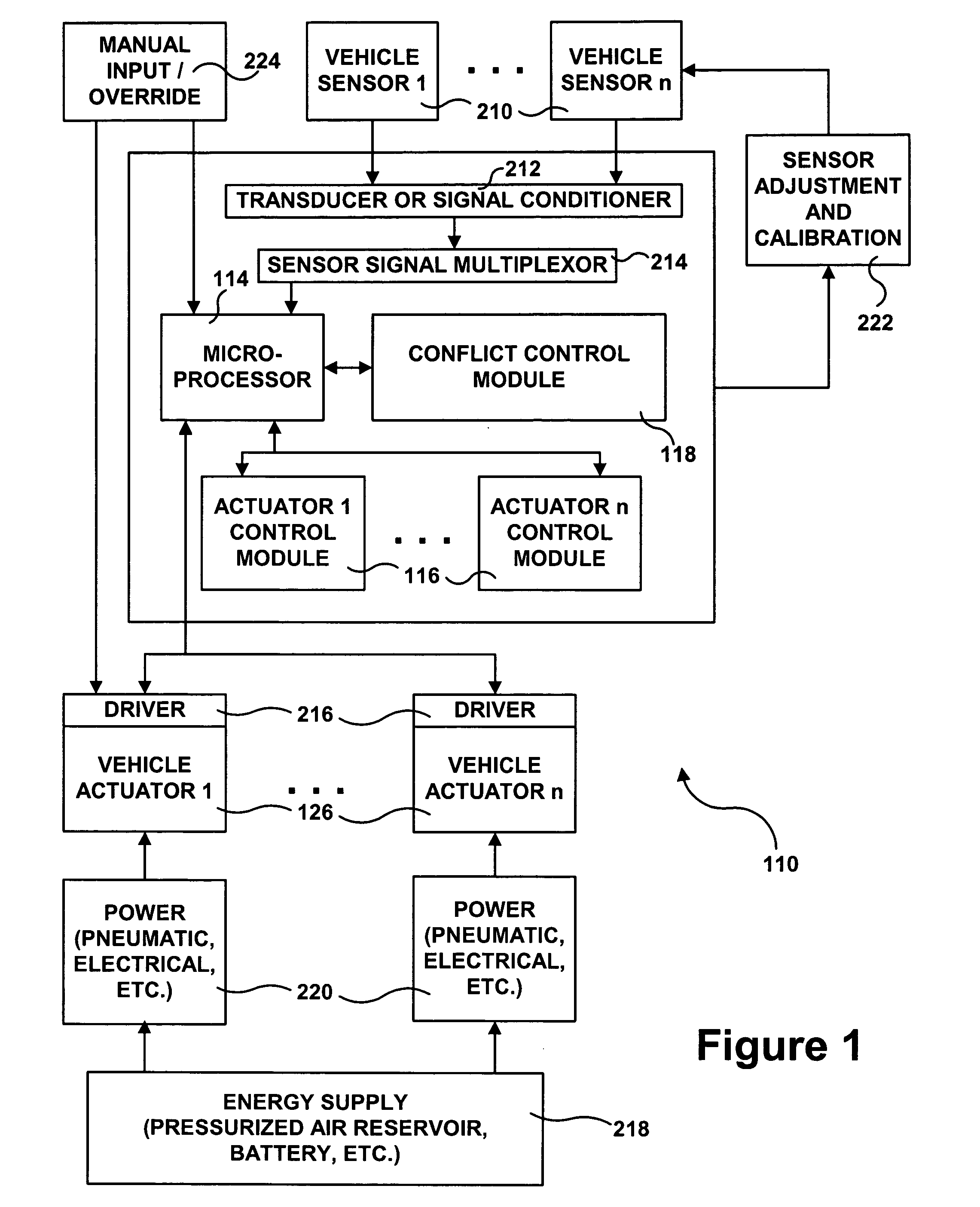
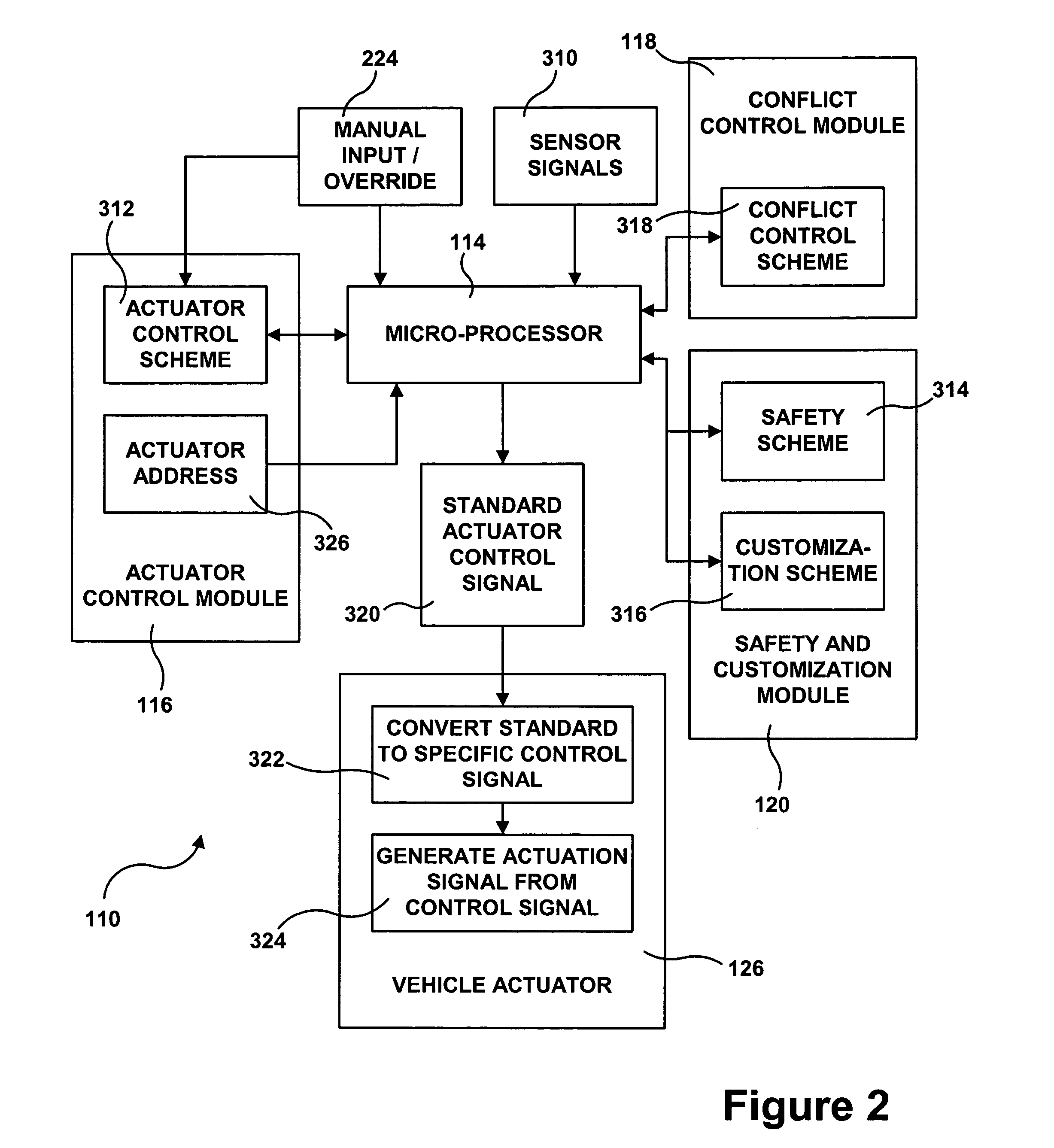
InactiveUS20050001472A1Reduce componentsSimple designBrake system interactionsBraking action transmissionVehicle dynamicsExtensibility
An electrical control network is laid over one or more vehicle dynamics control and / or ride control systems of a heavy vehicle, which control network controls actuation of components thereof. The invention offers many advantages including reduction of components, simplified design, unified communication for numerous different types of system components, simplified resolution of conflicts between competing control strategies, expandability to additional vehicle systems, and flexibility to upgrade for new, improved vehicle control schemes.
Owner:HALDEX BRAKE PROD LTD
Electrohydraulic Motor Vehicle Brake System and Method for Operating the Same
ActiveUS20150344014A1Function increaseTotal current dropAnalogue computers for trafficBraking action transmissionMultiplexingMaster cylinder
The invention relates to a technique for operating an electrohydraulic motor vehicle brake system comprising a master cylinder, an electromechanical actuator for generating a hydraulic pressure at a plurality of wheel brakes and a set of electrically actuable valve arrangements. The set of valve arrangements comprises a first valve arrangement between the master cylinder and every wheel brake. The first valve arrangements can be controlled in the multiplex operation to generate, by means of the electromechanical actuator, the respective brake pressure intended for each of the wheel brakes. According to an aspect of this technique, the method comprises the steps of: generating a feedback current during the multiplex operation by operating an electric motor of the electromechanical actuator as a generator and supplying the feedback current to at least one electrical load.
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Electric brake system and method for leak check of the same
ActiveUS20170158184A1Avoid it happening againBrake safety systemsBrake-by-wireMaster cylinderBraking system
A leakage inspecting method of an electric brake system, which includes a master cylinder connected to a reservoir, a simulation device having one side connected to the master cylinder to provide a reaction force according to the pedal effort of the brake pedal, a simulation valve provided at a flow path connected to the master cylinder or a flow path connected to the reservoir, a hydraulic pressure supply device operated by an electrical signal of a pedal displacement sensor sensing a displacement of the brake pedal and configured to generate hydraulic pressure, and a hydraulic pressure control unit, comprising: executing an inspection mode for inspecting for a leak of the simulation valve and a sealing member provided inside a chamber of the master cylinder by providing an inspection valve at a flow path connecting the master cylinder to the reservoir, wherein the inspection mode includes: (a1) closing a cut valve provided at a flow path connecting the master cylinder to the hydraulic pressure control unit when the inspection valve is open; (b1) pressurizing a piston disposed inside the master cylinder according to the pedal effort of the brake pedal and detecting whether pressure is formed through a pressure sensor; and (c1) determining that a leak does not exist when pressure detected through the pressure sensor satisfies a preset criterion.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Electro-hydraulic brake system and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20160347298A1Increase manufacturing costPrevent deterioration of brake stabilityBraking action transmissionBrake action initiationsDriver/operatorControl signal
An electro-hydraulic brake system may include a brake input device manipulated by a driver to brake a vehicle, a brake input detecting sensor configured to detect a brake input value of the driver through the brake input device, a pressure generating device configured to generate a brake hydraulic pressure, a wheel cylinder configured to receive the brake hydraulic pressure generated from the pressure generating device and to generate braking power for braking rotations of each vehicle wheel, a hydraulic pressure supply line connected between the pressure generating device and the wheel cylinder to transfer the brake hydraulic pressure generated from the pressure generating device to each wheel cylinder, and a controller configured to output a control signal for controlling an operation of the pressure generating device to allow the pressure generating device to generate a target brake hydraulic pressure based on a signal of the brake input detecting sensor.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
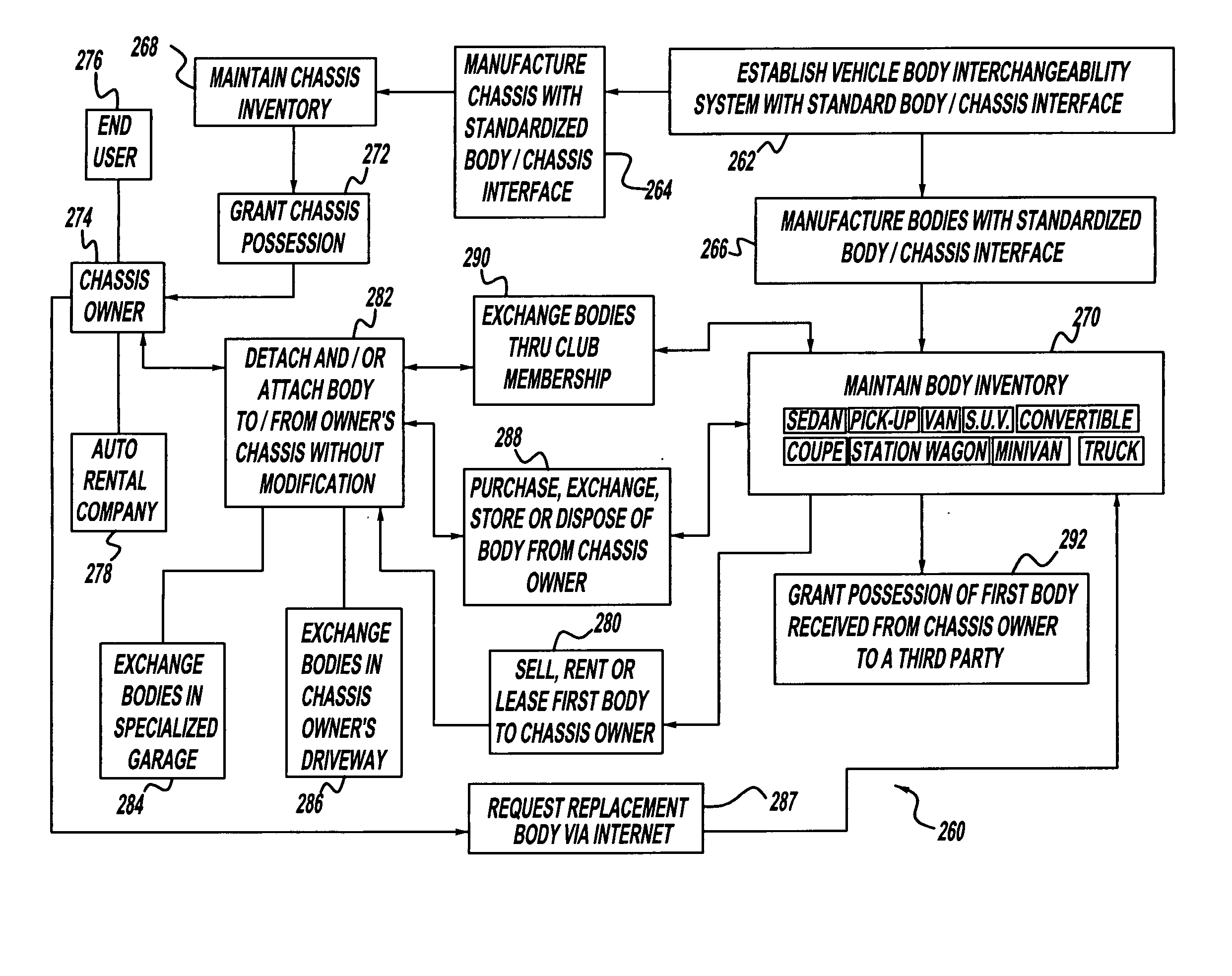
Vehicle body interchangeability
InactiveUS20050049944A1Simple interfaceEliminateAuxillary drivesVehicle seatsReconfigurabilityAutomotive engineering
A method is provided for providing vehicle reconfigurability. The method includes maintaining an inventory containing vehicle body pods each having a substantially identical interface at which each of the body pods is connectable to a chassis such that the body pods are interchangeable on the chassis. The body pods include at least one body pod characterized by a first body pod style and at least one body pod characterized by a second body pod style. The method also includes granting possession to a customer of a vehicle body pod from the inventory independent of a chassis.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Vehicle brake system with dual acting plunger assembly
A plunger assembly for use as a pressure source for a brake system includes a housing having first and second ports. A motor is mounted on the housing for driving an actuator. A piston is connected to the actuator. The piston is slidably mounted within the housing. The piston pressurizes a first chamber when the piston is moving in a first direction to provide fluid out of the first port. The piston pressurizes a second chamber when the piston is moving in a second direction to provide fluid out of the second port.
Owner:KELSEY HAYES CO
Brake control device and brake system for vehicles
ActiveUS20160339885A1Safely brakeImprove performanceBraking action transmissionPump/compressor arrangementsBraking systemVehicle brake
A brake control device for at least four fluidically actuatable, especially hydraulically actuatable, wheel brakes of a vehicle brake system, which device includes at least one input pressure connection, a wheel-specific output pressure connection for every wheel brake, a pressure regulating valve array for setting wheel-specific brake pressures at the output pressure connections and a pressure source the brake control device having a wheel specific input pressure connection for every wheel brake.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
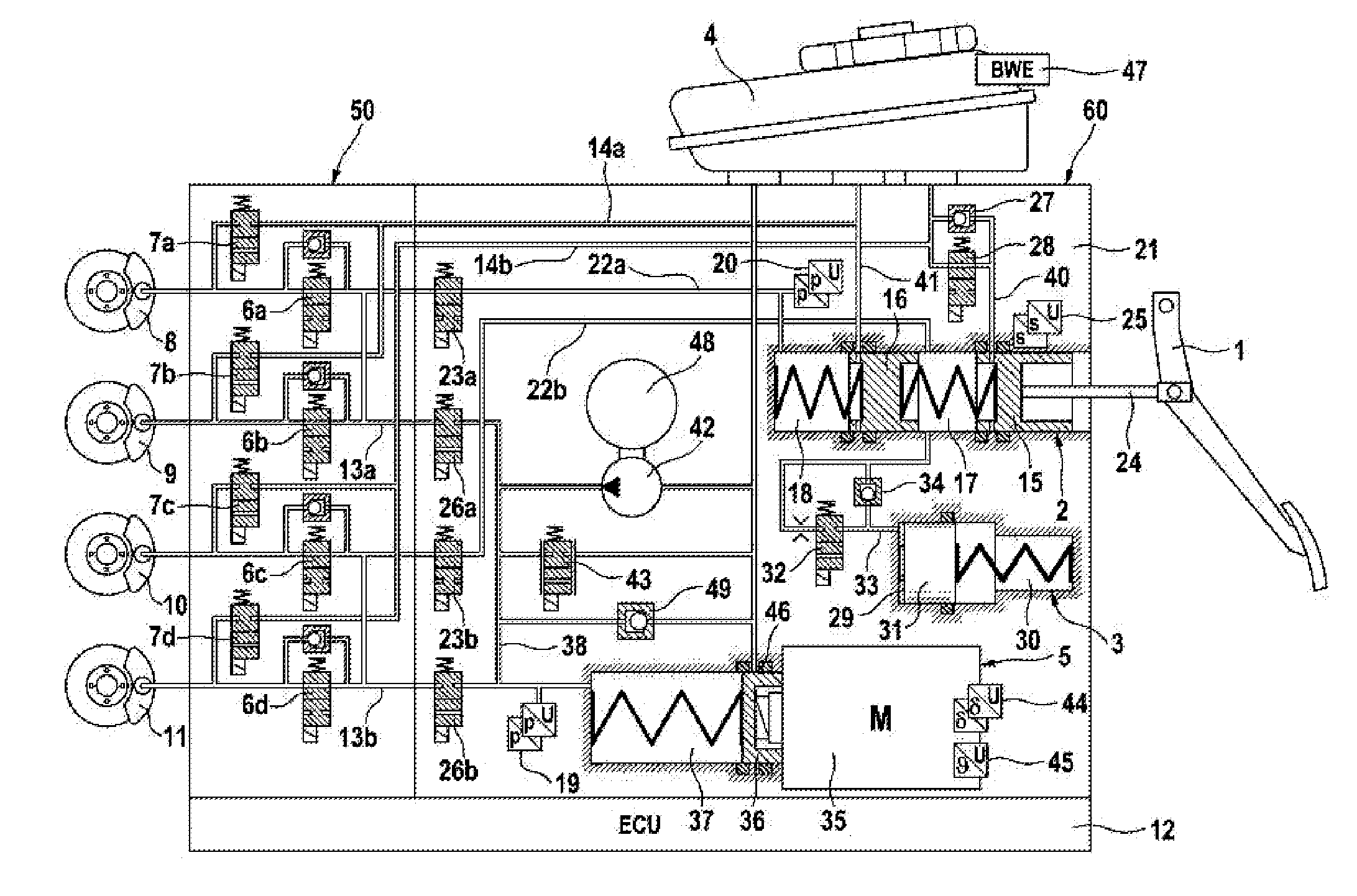
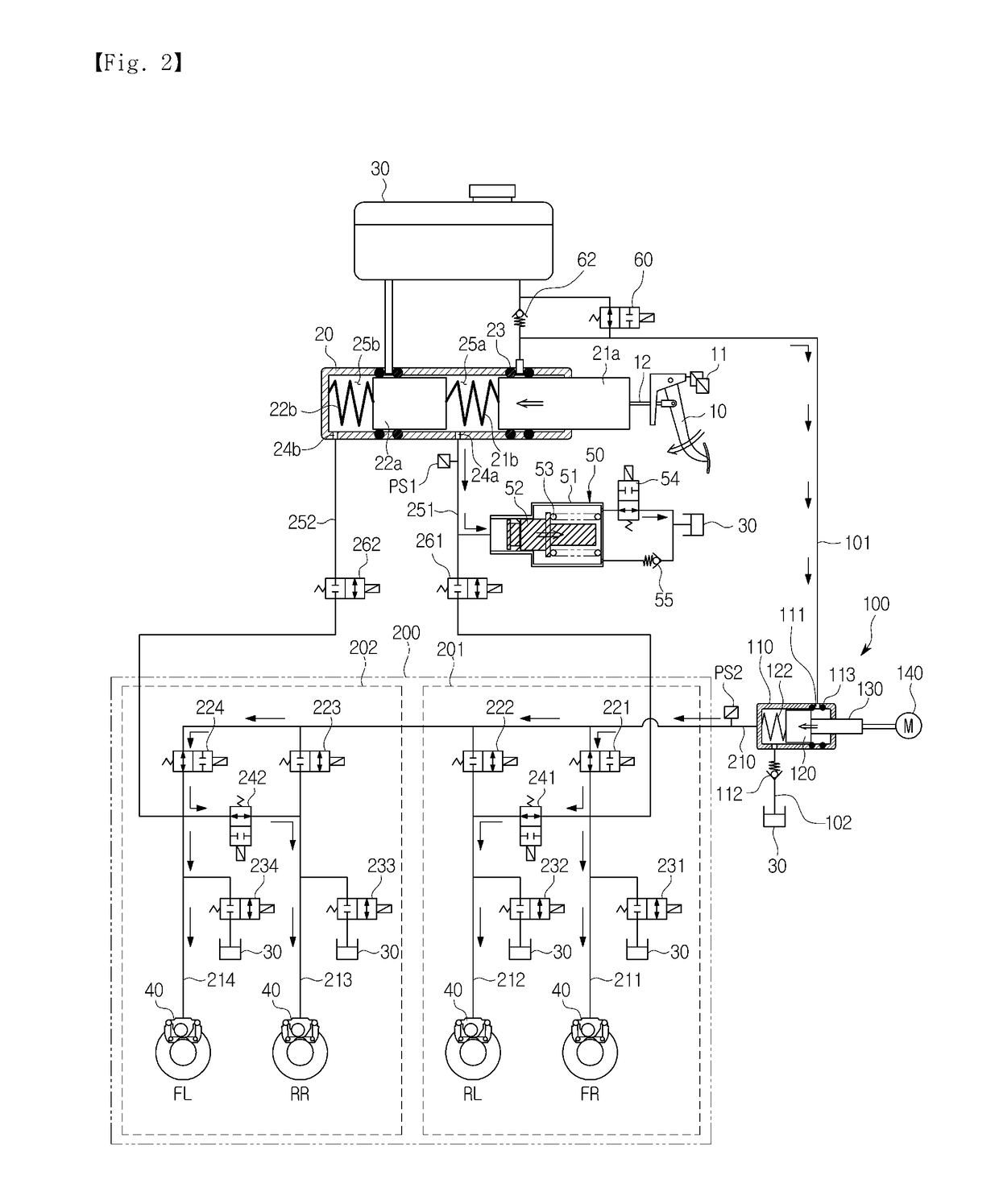
Brake system for motor vehicles
ActiveCN106458192ASmall sizeParked securelyBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsData connectionElectricity
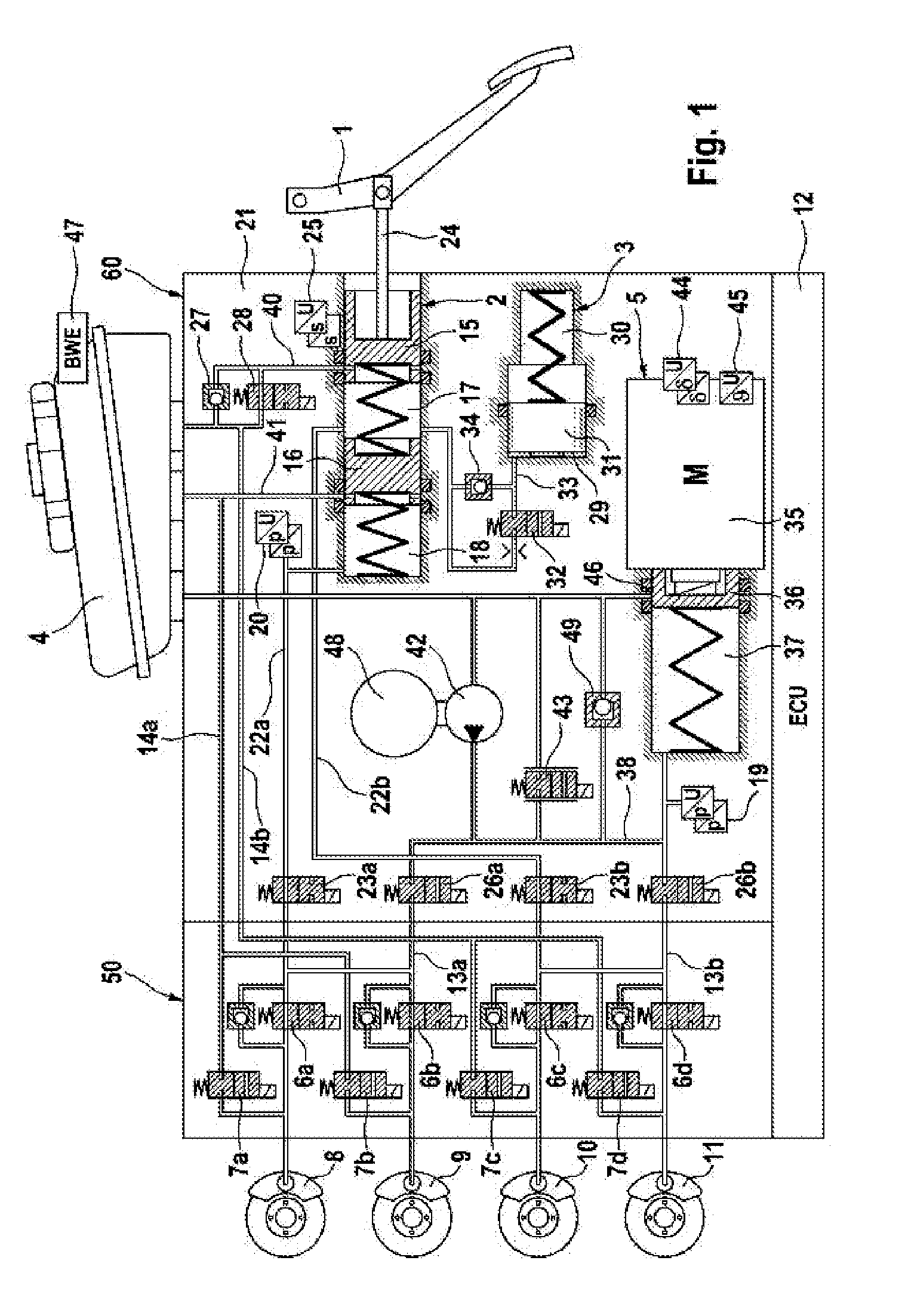
The invention relates to a brake system for motor vehicles, which can be controlled both by a driver and independently of the driver in a "brake-by-wire" operating mode, comprising a brake pedal (1), at least two wheel brakes (8, 9, 10, 11) that can be actuated hydraulically, a first and a second brake actuation sensor (505a, 505b), a first electrically controllable pressure source (301, 5), by means of which the wheel brakes can be actuated, a first electronic control unit (112, 12), which is connected to the first brake actuation sensor (505a) and controls the first pressure source (301, 5), a second electrically controllable pressure source (302, 249), by means of which the wheel brakes can be actuated, a second electronic control unit (139, 39), which is connected to the second brake actuation sensor (505b) and controls the second pressure source (302, 249), a hydraulic control device (300), which comprises, in particular, at least a first solenoid valve (26, 26a, 26b) between the wheel brakes and the first pressure source and a second solenoid valve (23, 23a, 23b) between the wheel brakes and the second pressure source, and a data connection (53) between the first electronic control unit (112, 12) and the second electronic control unit (139, 39), wherein the first electronic control unit (112, 12) has a first interface (601) and the second electronic control unit (139, 39) has a second interface (602), wherein the first interface and the second interface are not connected to each other.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
Brake system and method for controlling a vehicle brake
ActiveUS20110125381A1Improve reliabilityAnalogue computers for trafficComputations using stochastic pulse trainsActuatorMotorized vehicle
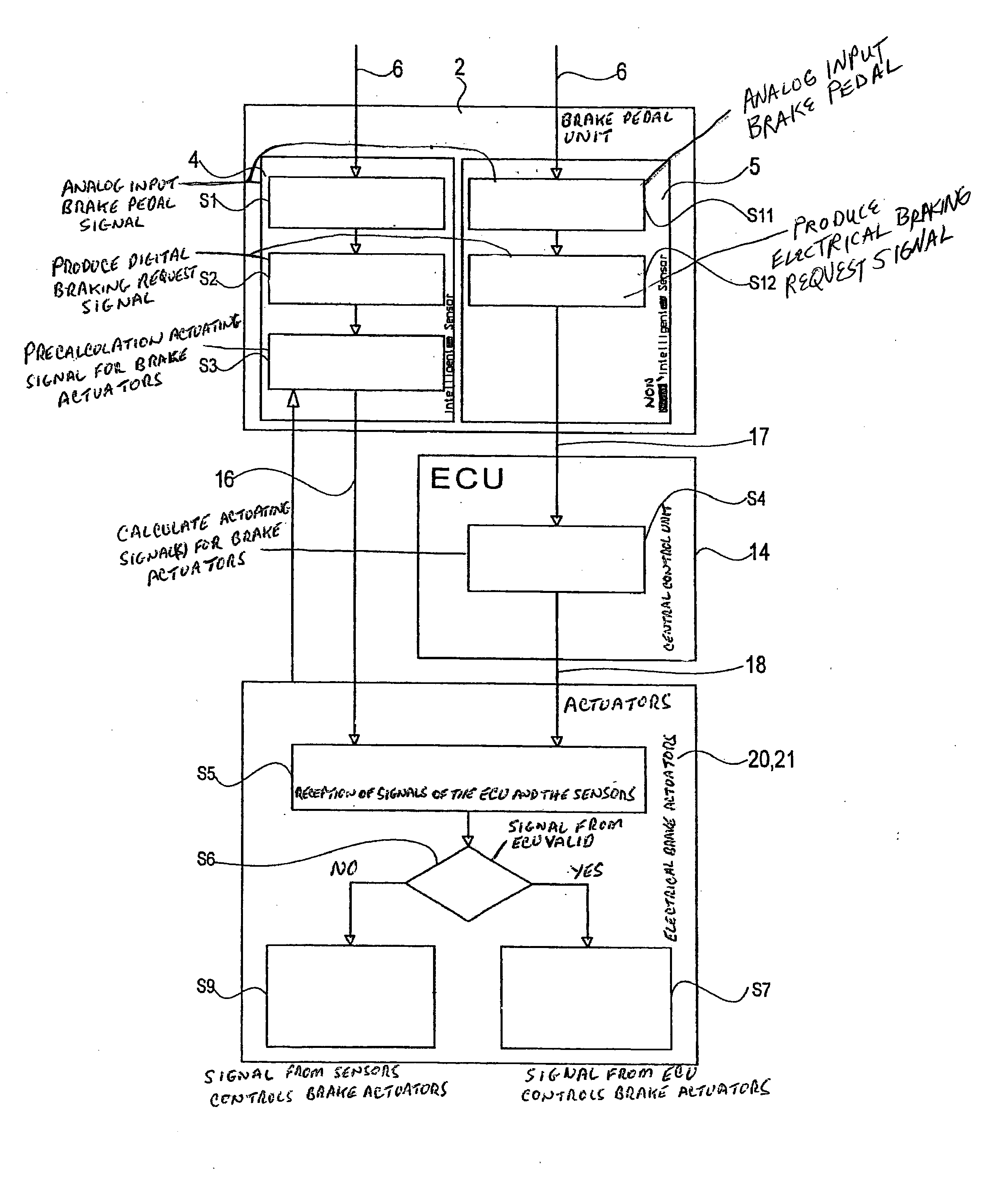
The brake system for motor vehicles has a brake pedal unit having a sensor, which has an intelligence of its own in the form of an electronic processing unit, which directly calculates actuating signals for brake actuators. Furthermore, the brake system has a central electronic control unit, which ascertains actuating signals for the actuators on the basis of an analog or digital signal of the mentioned sensor or of an additional sensor. The actuators have an intelligence of their own in the form of an electronic processing unit, which verifies whether the actuating signal coming from the central electronic control unit is valid. If this is the case, then the actuators are controlled by this signal, otherwise on the basis of the actuating signal calculated by the sensor.
Owner:KNORR-BREMSE SYST FUER NUTZFAHRZEUGE GMBH
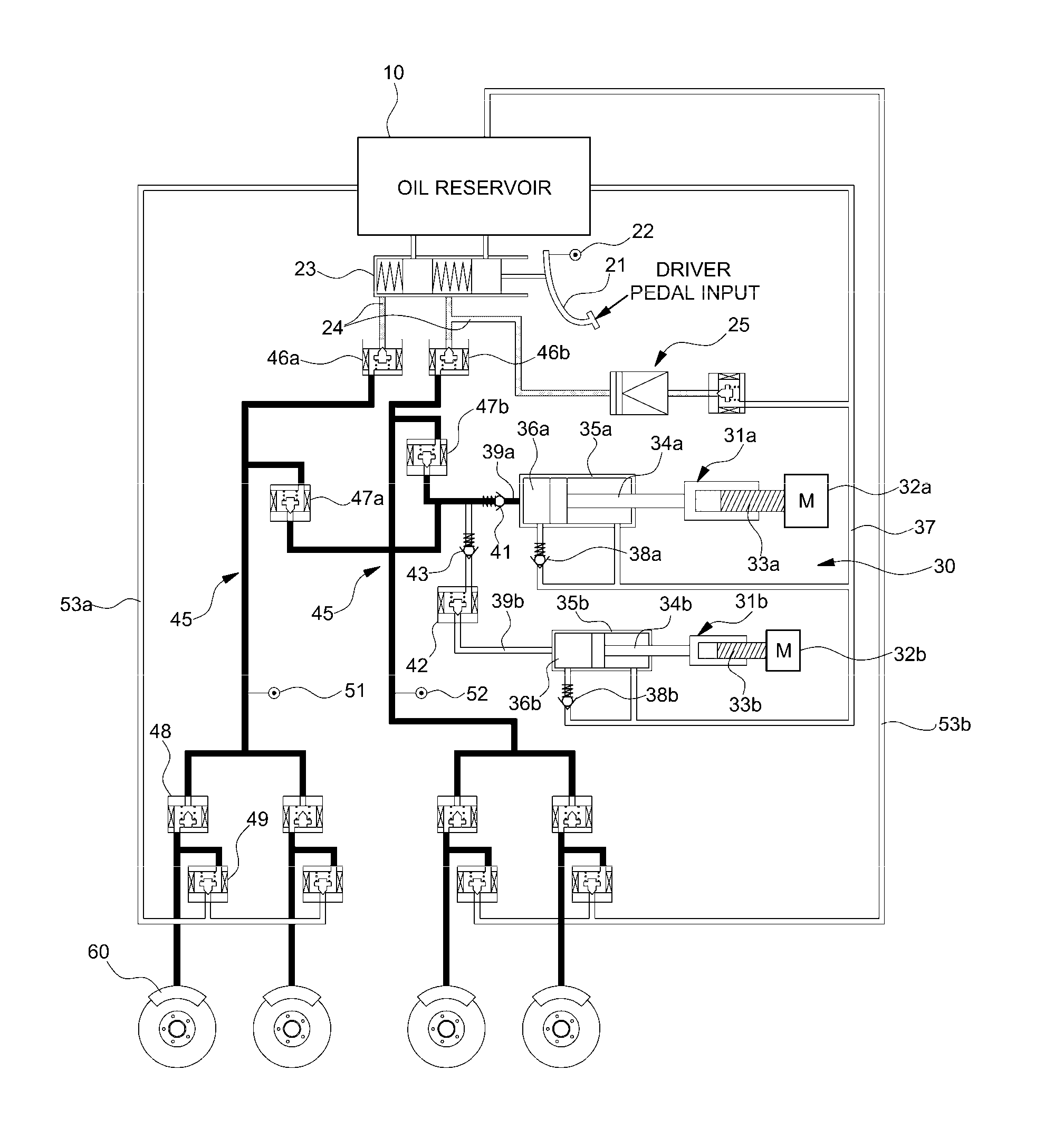
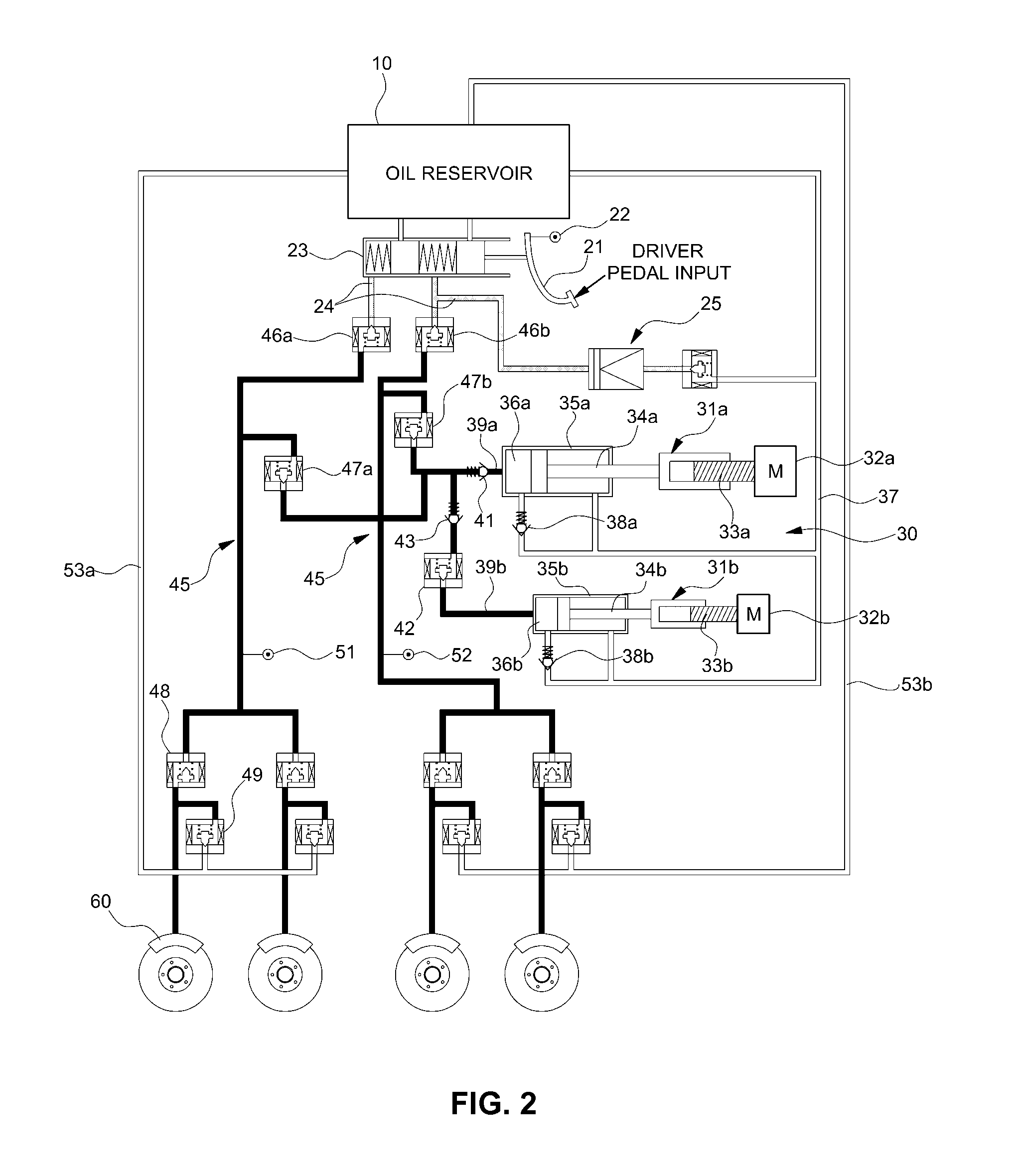
Brake actuation unit
ActiveCN105026232AImprove availabilityImprove reliabilityBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsMicrocontrollerHydraulic cylinder
The invention relates to a brake actuation unit (1) for a "brake-by-wire" motor vehicle brake system, comprising: a brake pedal-actuatable master brake cylinder (2) and an associated pressure-medium reservoir (4); an electrically controllable pressure provision device (5), which is formed by a hydraulic cylinder / piston assembly, the piston (51) of which can be actuated by an electric motor (35), wherein the piston delimits a pressure chamber (50), which is sealed off from the atmosphere by a main sealing element (60); a first group of electrically actuatable valves (6a-6d, 7a-7d) for adjusting respective braking pressures for each wheel; a second group of electrically actuatable valves (23a, 23b, 26a, 26b) for disconnecting the wheel brakes from or connecting the wheel brakes to the master brake cylinder or the pressure provision device; and an electronic open-loop and closed-loop control unit (12, 12'). The pressure chamber (50) is sealed by an additional sealing element (61) after a specified actuation of the piston (51). The electric motor has at least two drive units operable independently of one another, each having at least one winding, for driving the rotor of the electric motor. The electronic open-loop and closed-loop control unit comprises a first microcontroller (201) and a second microcontroller (301). The first microcontroller is designed to control (205) one of the drive units of the electric motor and the second microcontroller is designed to control (305) the other of drive units of the electric motor, and the first and second microcontrollers are designed to control (207, 307) the second group of valves.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
System And Method For Regulated And/Or Limited Speed Control
InactiveUS20160375347A1Improve fitnessHigh strengthBraking element arrangementsDigital data processing detailsSpeed control systemControl system
Provided is a speed control system, a method for using a speed control system, a use of a speed control system, a roller ski using the speed control system, and a ski pole insert for the speed control system. A speed control system (1) for limiting and / or regulating the speed of a wheeled article (2) is provided, wherein the wheeled article (2) comprises a body (4) and one or more wheels (6), the speed control system (1) adapted to, by actuation of a user actuator (12), actuate one or more brake units (10), and a restriction means (14) to limit the magnitude of a braking force applied to the one or more wheels (6) so as to enable a safe and controlled reduction in speed.
Owner:ROLLERSAFE
Braking system of electronic hand brake and control method thereof
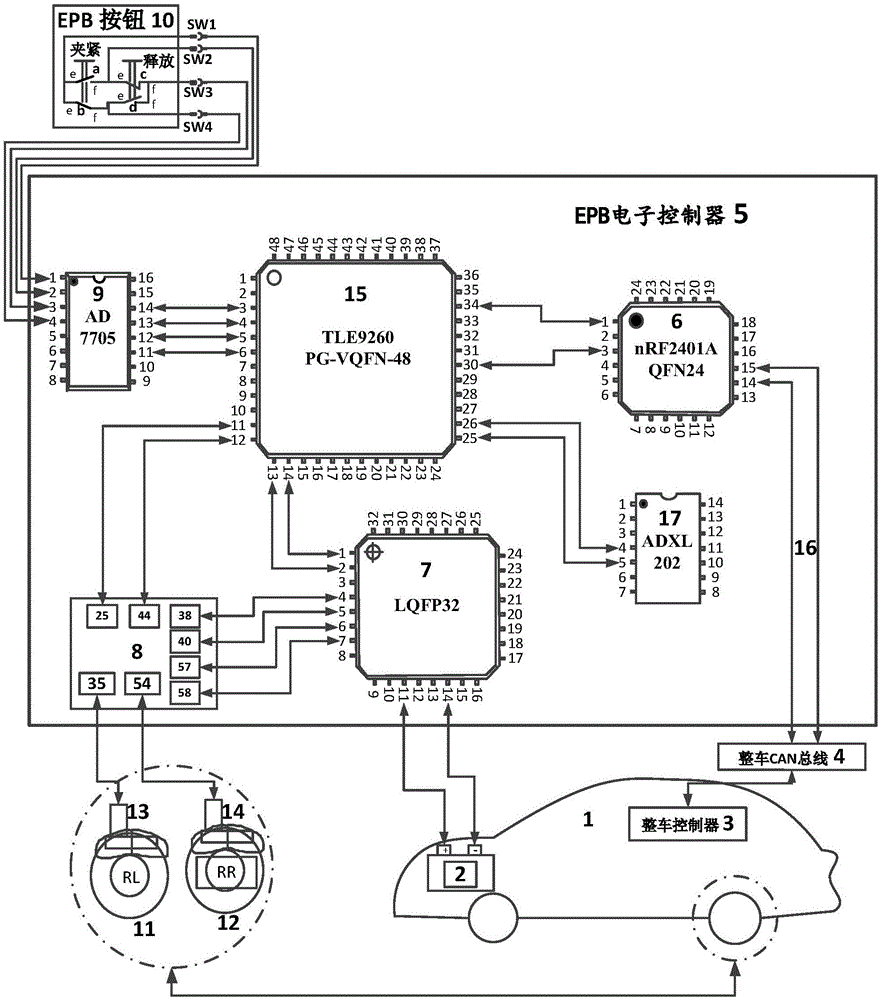
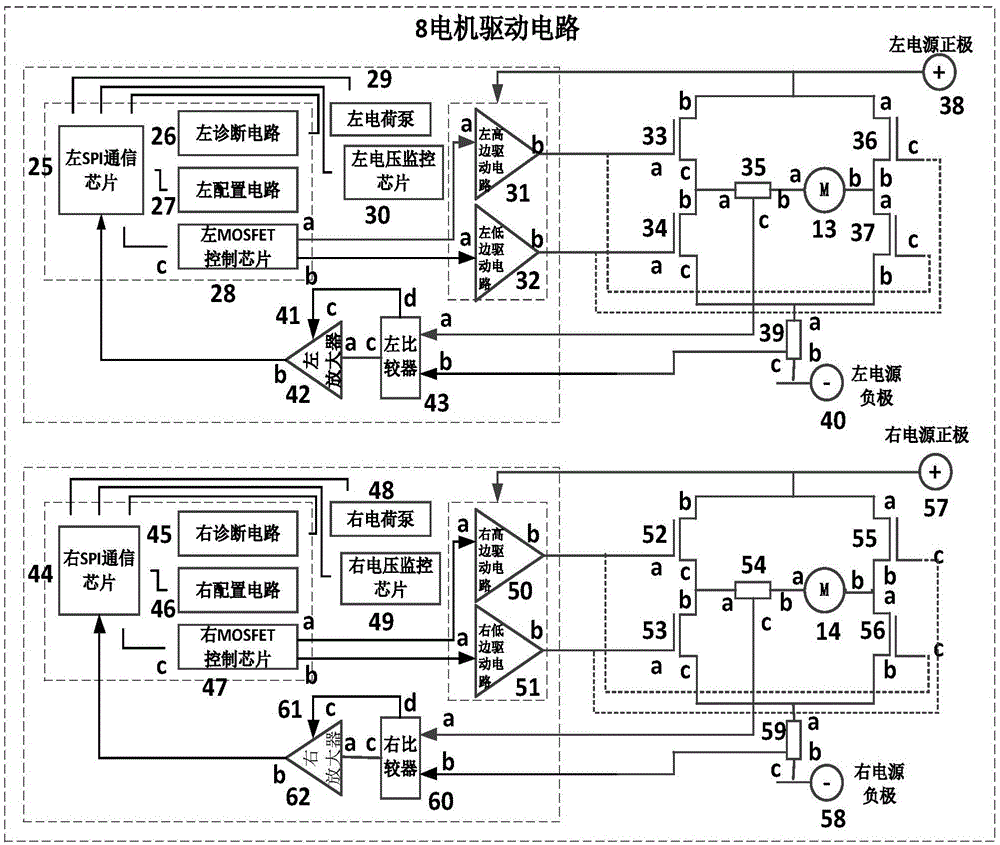
ActiveCN105059282ASolve stuckAvoid stickingBraking action transmissionBrake-by-wireMotor driveElectronic controller
The invention discloses a braking system of an electronic hand brake and a control method thereof and aims at overcoming the problems that a speed changing rod is locked when a gear-P parking system of a speed changing box perform parking on a slope, the speed changing box is damaged in the running process due to misoperation after the a gear P is engaged and a pure electric vehicle is not parked and accordingly slides on the slope when being charged. The braking system of the electronic hand brake comprises an EPB button (10), an EPB electronic controller (5), a rear left brake (11) and a rear right brake (12). The EPB button (10) is in wired connection with a lead 1, a lead 2, a lead 3 and a lead 4 of a button identification chip (9) in the EPB electronic controller (5) through a signal wire SW1, a signal wire SW2, a signal wire SW3 and a signal wire SW4 sequentially, and a motor driving circuit (8) in the EPB electronic controller (5) is connected with a rear left motor (13) and a rear right motor (14) through cables sequentially. The invention further provides the control method of the braking system of the electronic hand brake.
Owner:苏州萨克汽车科技有限公司
Brake system with multiple pressure sources
A brake for operating first, second, third, and fourth wheel brakes includes first and second hydraulic brake circuits each defining a fluid conduit to two of the wheel brakes. Each circuit includes a power transmission unit having a first motor driven piston for pressurizing pressure chambers therein for providing pressurized fluid to the respective fluid conduits. Each circuit includes at least a pair of valves adapted to selectively provide pressurized fluid from the fluid conduits to each one of the wheel brakes. The system includes two separate electronic control units for controlling each of the circuits, namely the power transmission units and the pair of valves.
Owner:ZF ACTIVE SAFETY US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com