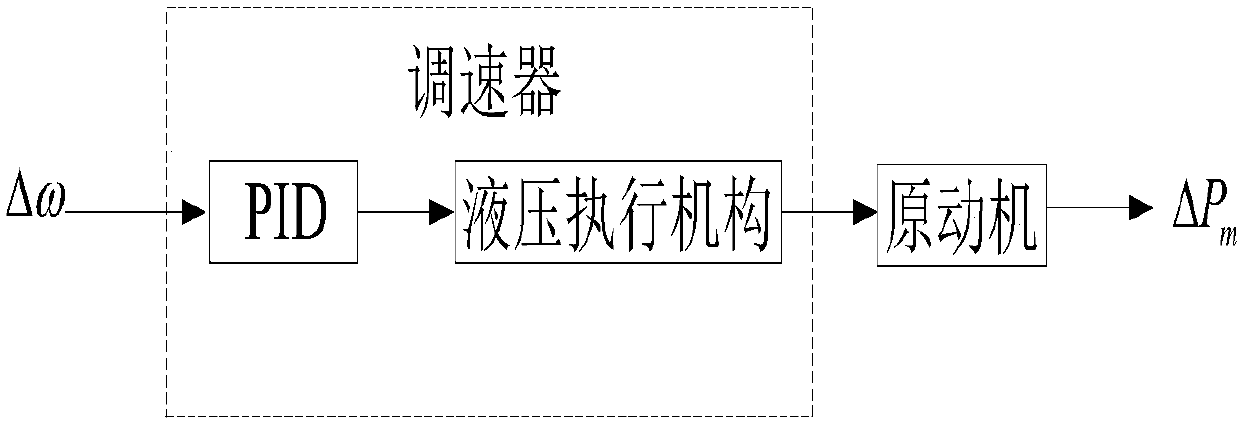
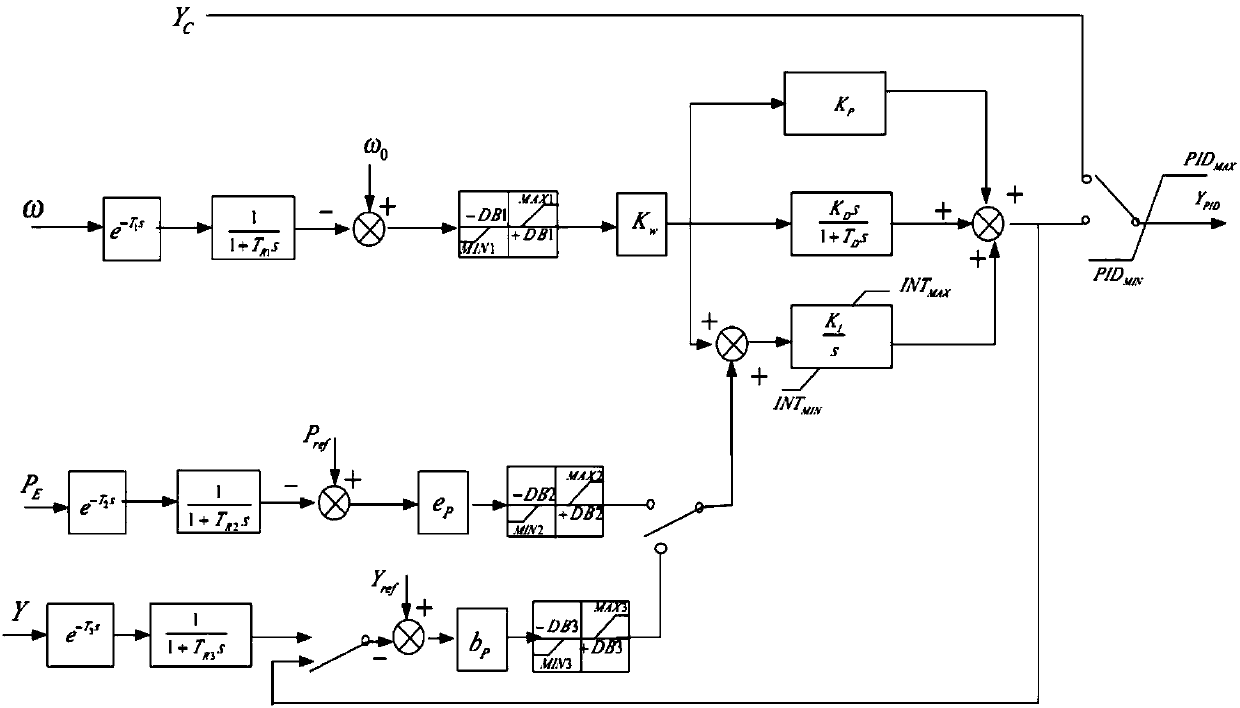
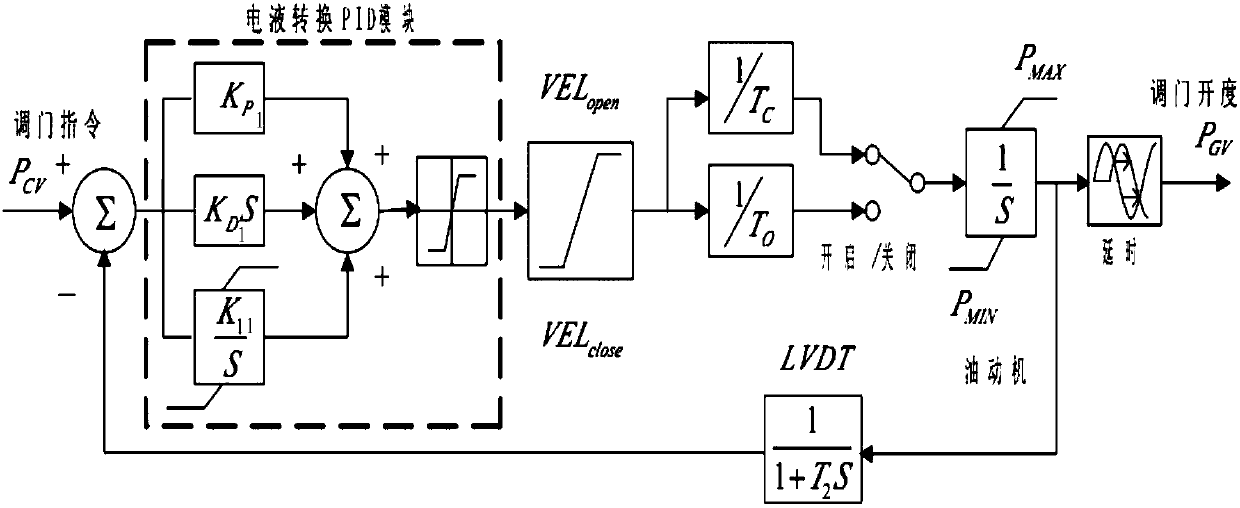
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
304 results about "Damping torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Damper is a generic term used to identify any mechanism used for vibration energy absorption, the shaft vibration suppression, soft start and overload protection device. In order to design an efficient damper, it is imperative that the damping torque is calculated first. Damping torque or damping forces is the speed deviation of an electromechanical torque deviations of a machine while the angle deviation is called synchronizing torque [1].
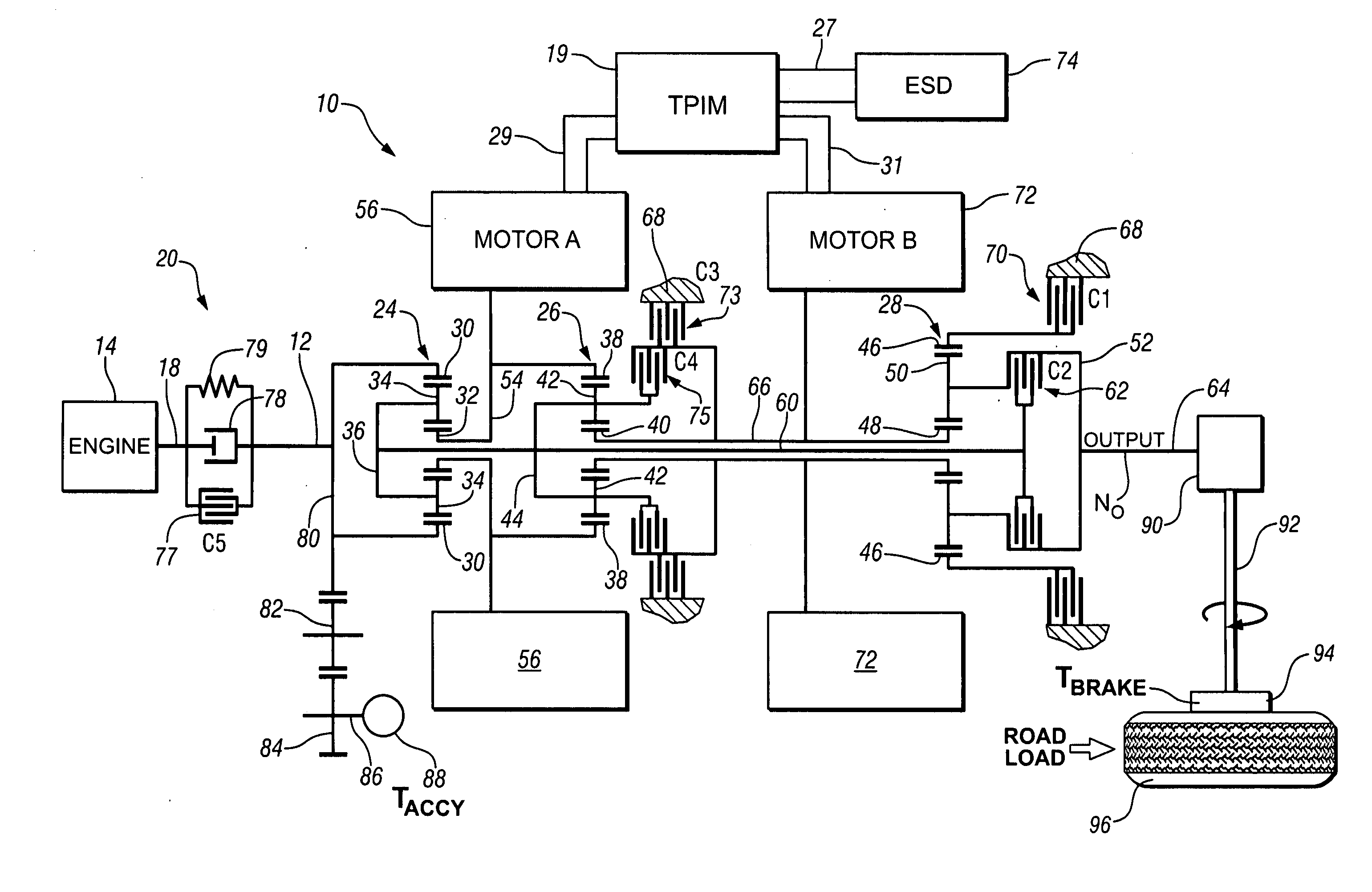
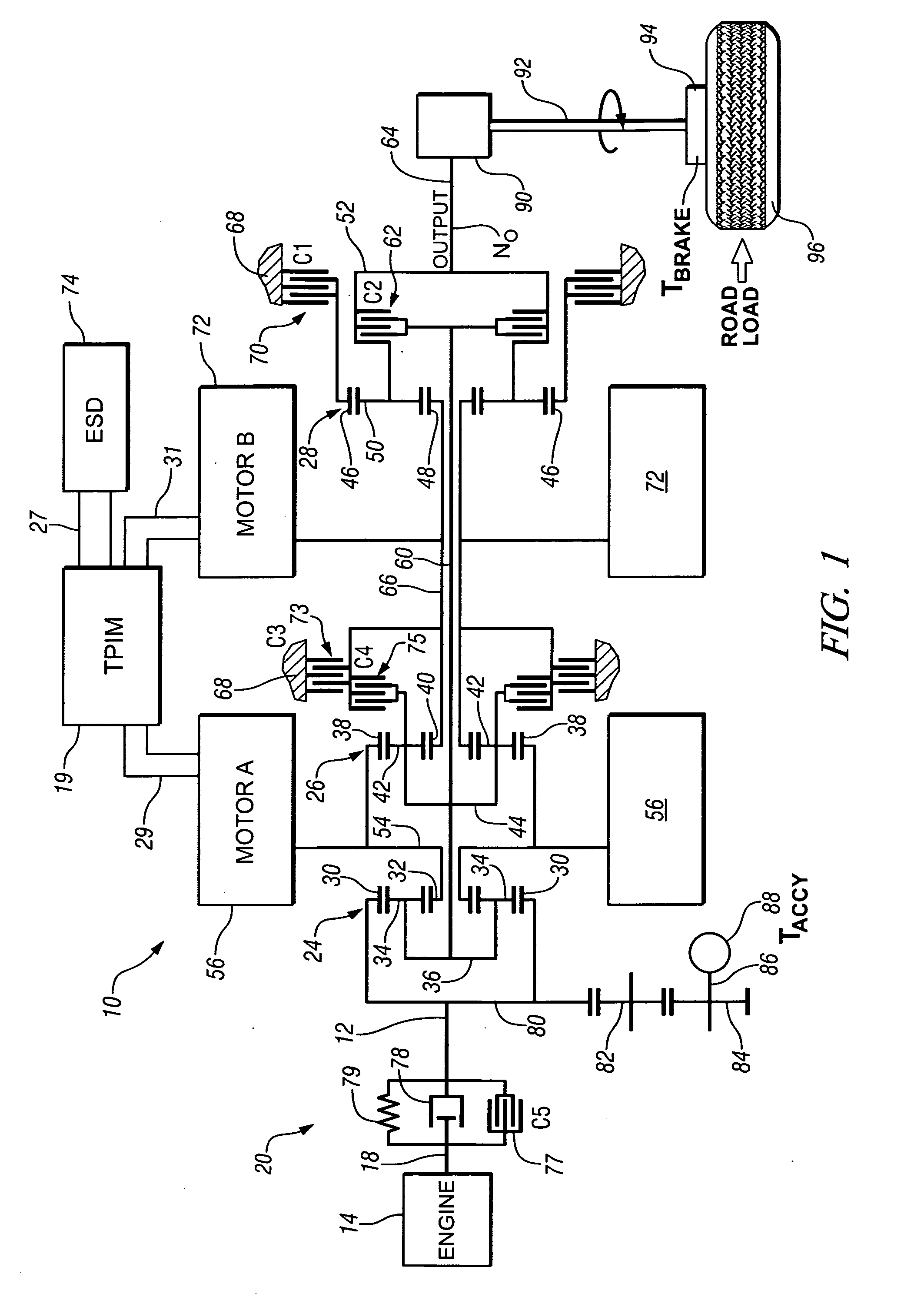
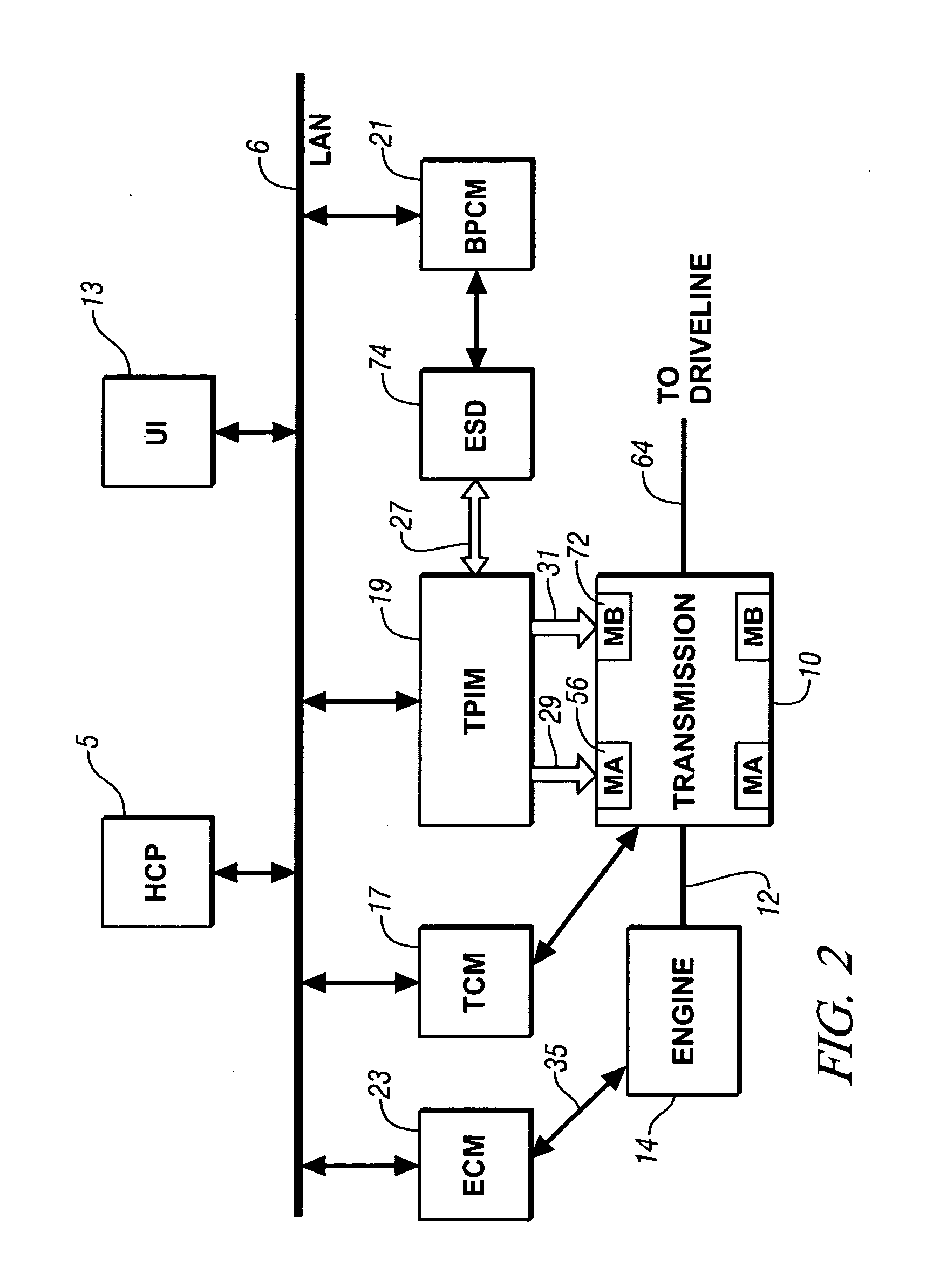
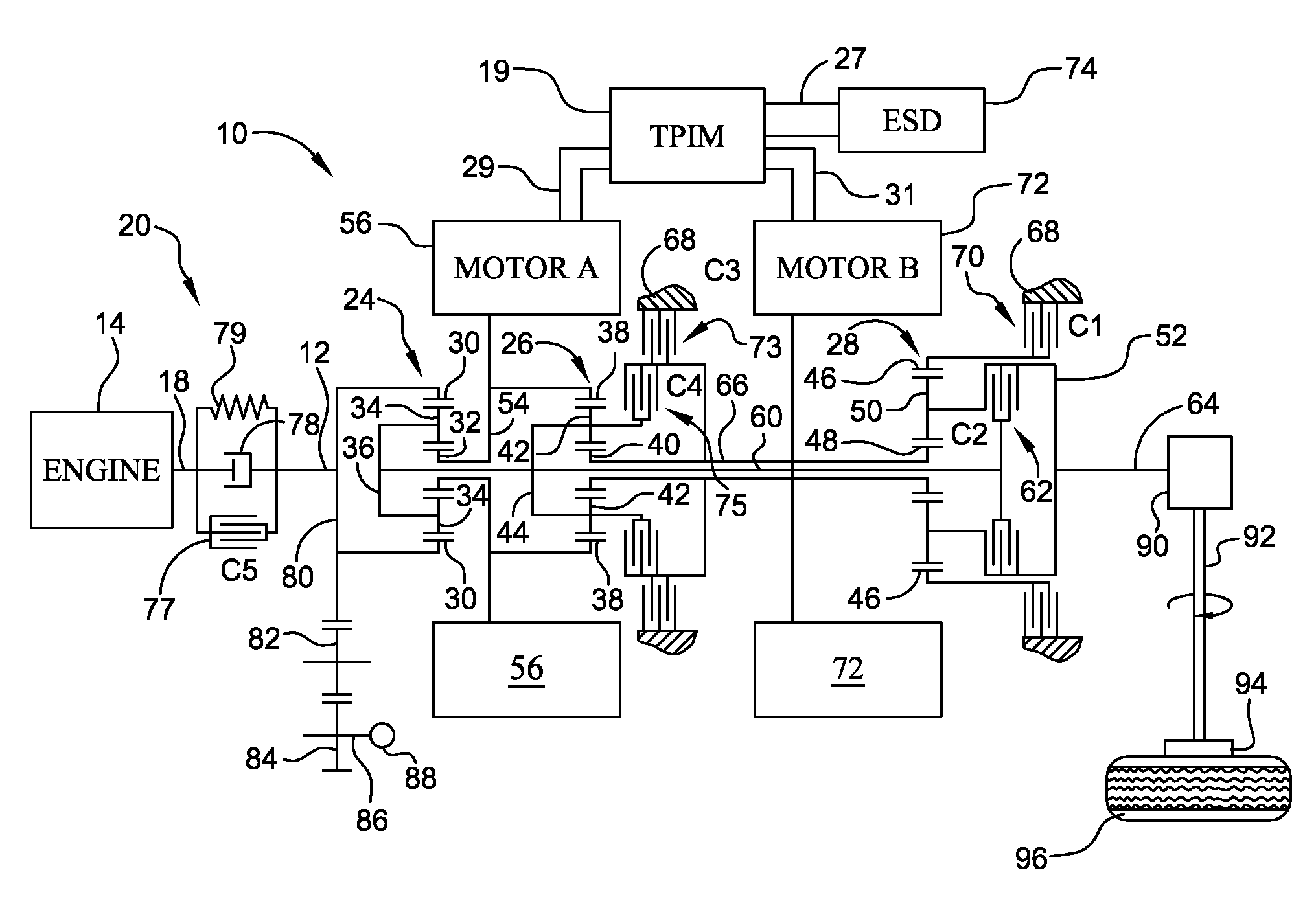
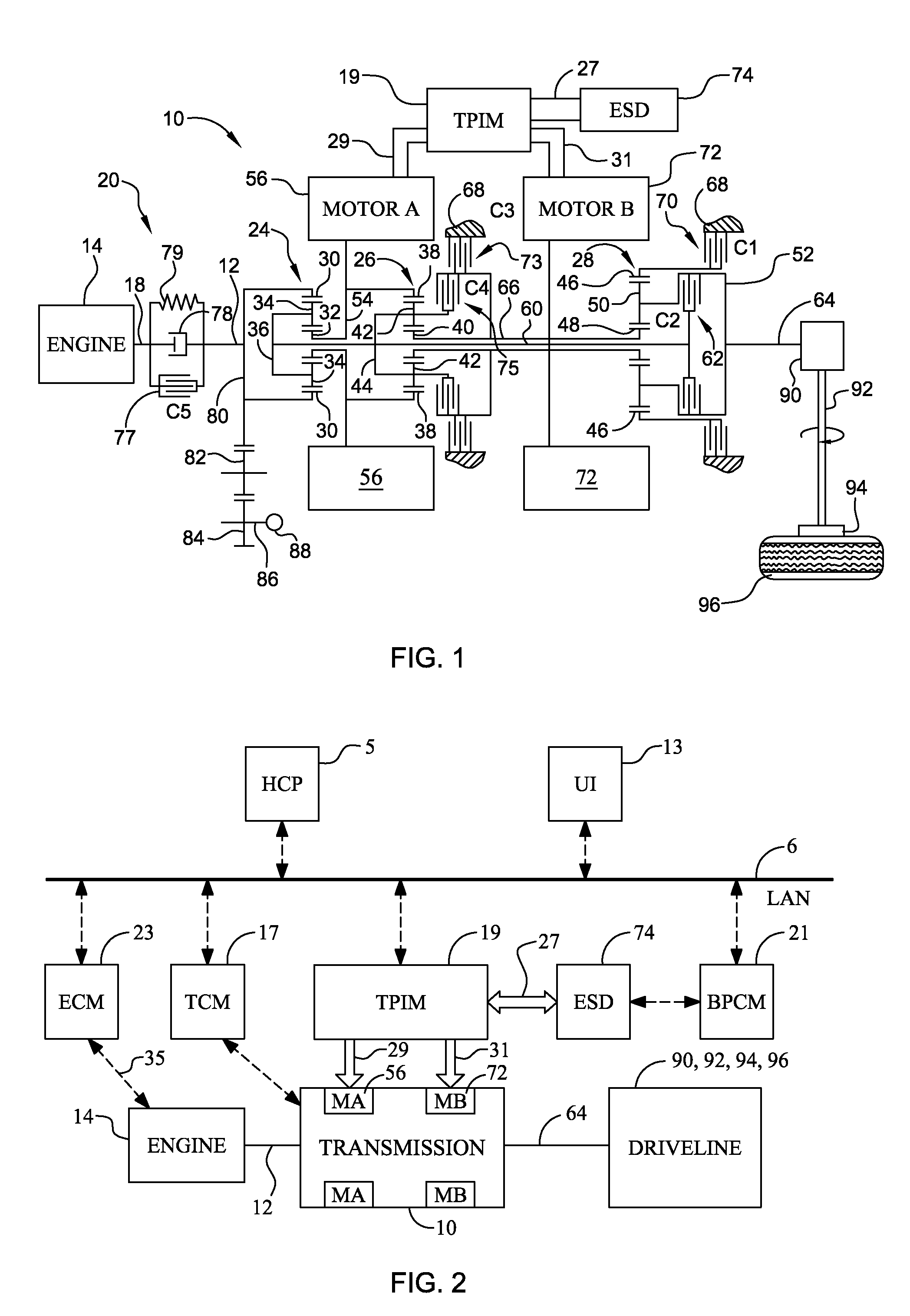
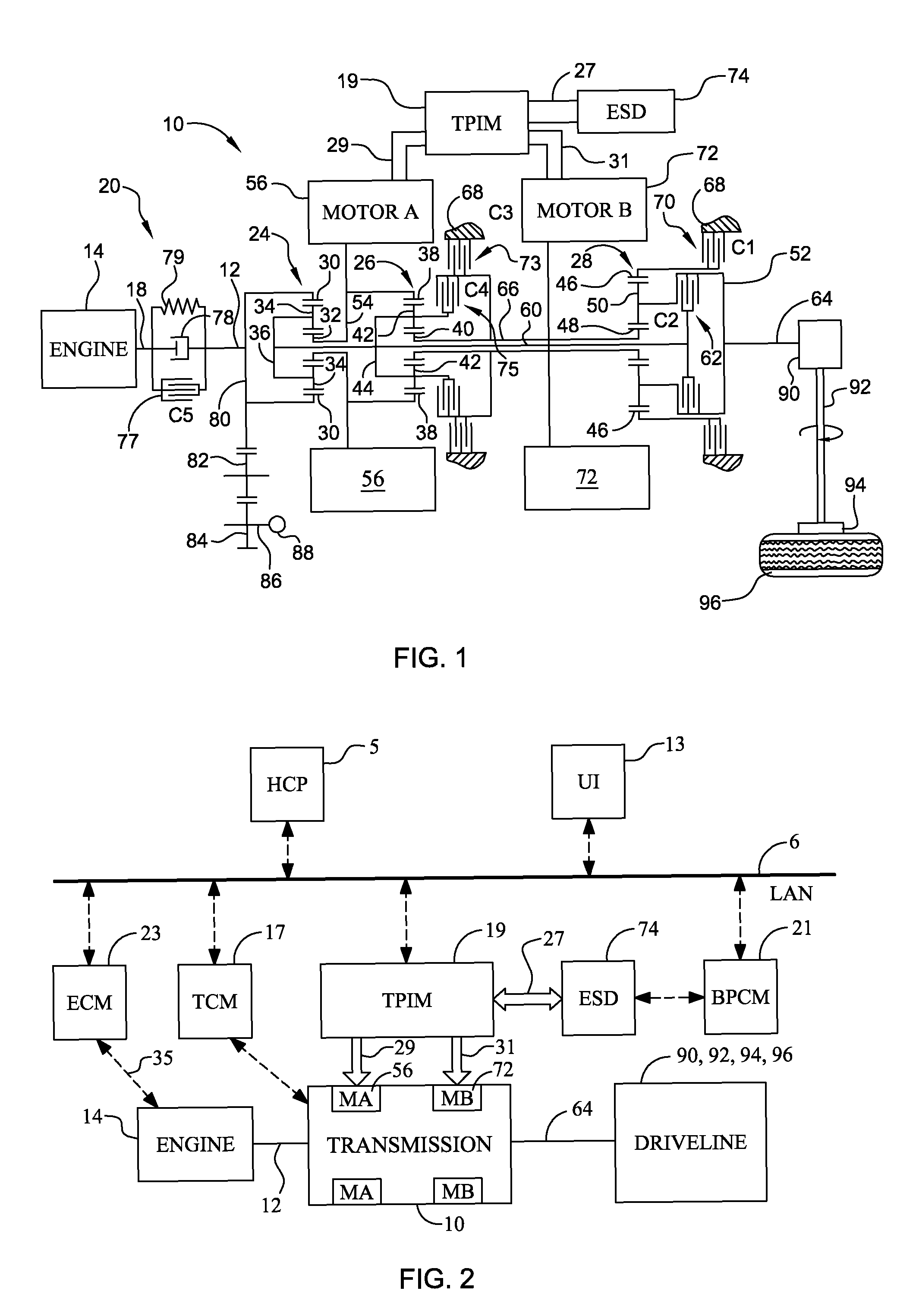
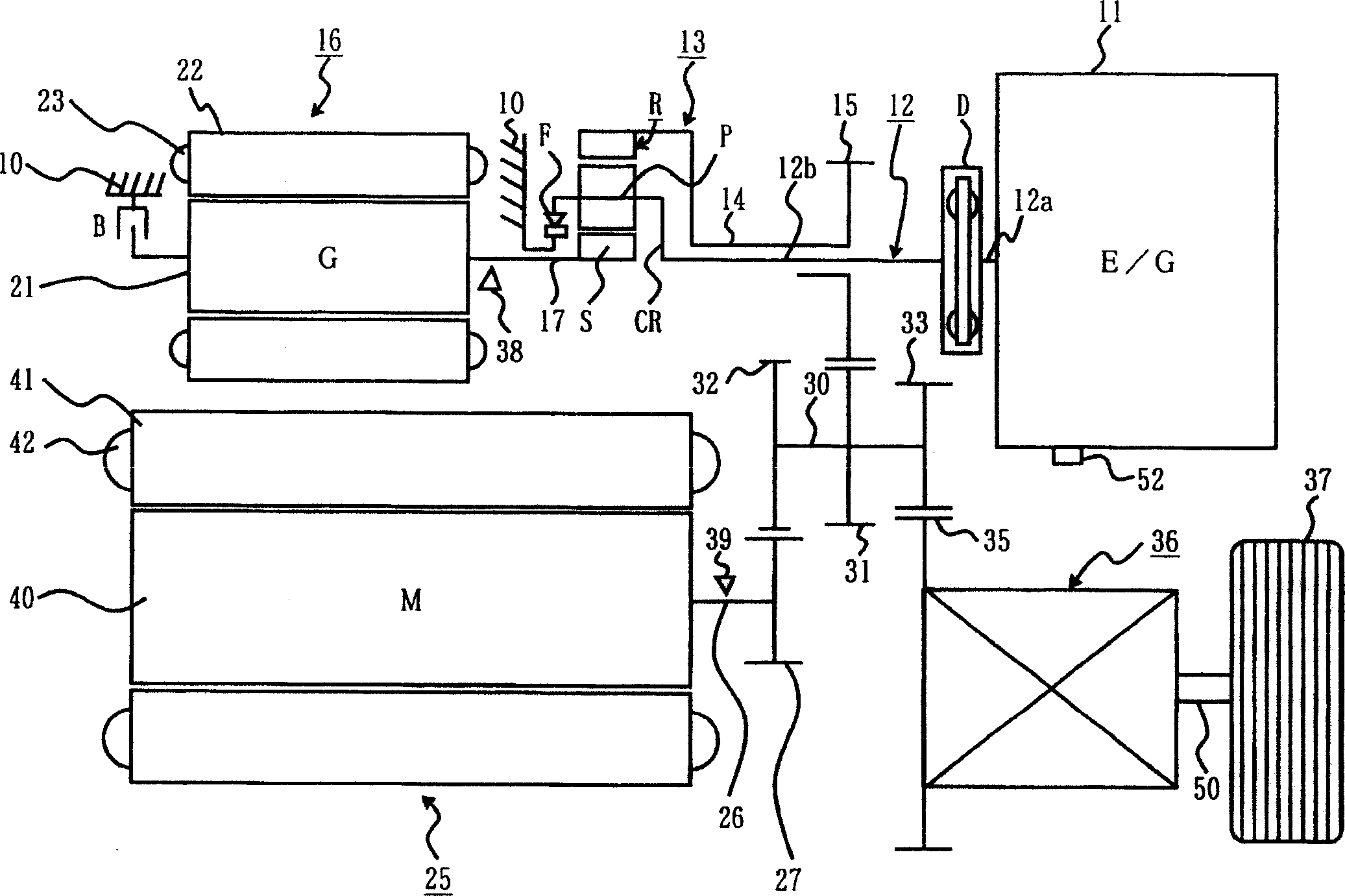
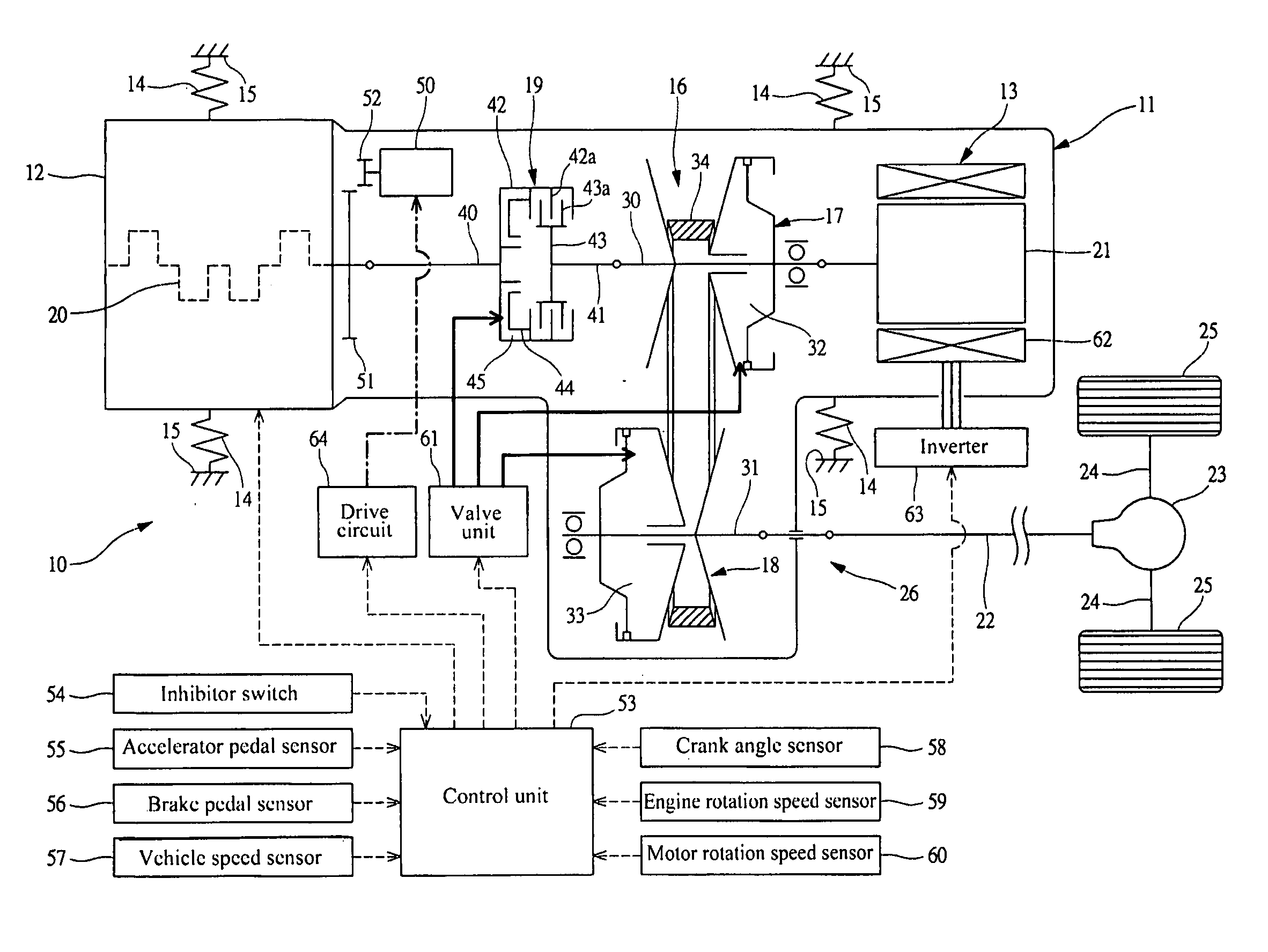
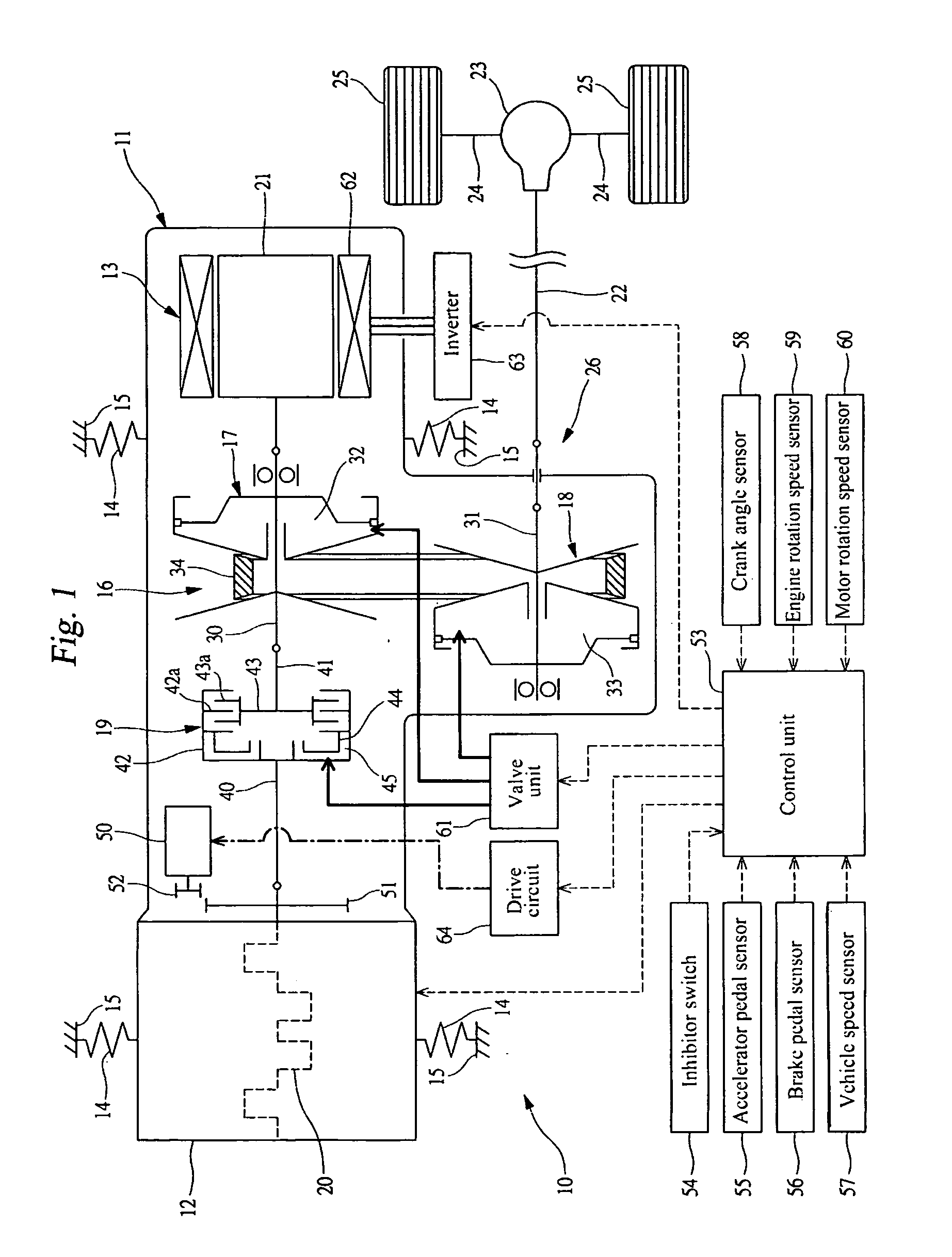
Method and apparatus for multivariate active driveline damping
A multivariate control method and system to control torque output from a powertrain system to a driveline is provided, to reduce driveline oscillations. The powertrain preferably comprises hybrid powertrain having a plurality of torque-generative devices connected to a transmission. Desired powertrain and driveline operating states are determined, as are a plurality of operating state errors. Each torque-generative device is controlled, based upon the operating state errors, and operating mode of the transmission. A damping torque command, additive to a commanded torque, is determined for one or more of the torque-generative devices based upon the determined transmission operating mode. Determined operating states include operator input, and powertrain / driveline including driveline torque; transmission input torque, rotational speed of the torque-generative devices; road load; and, accessory load.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
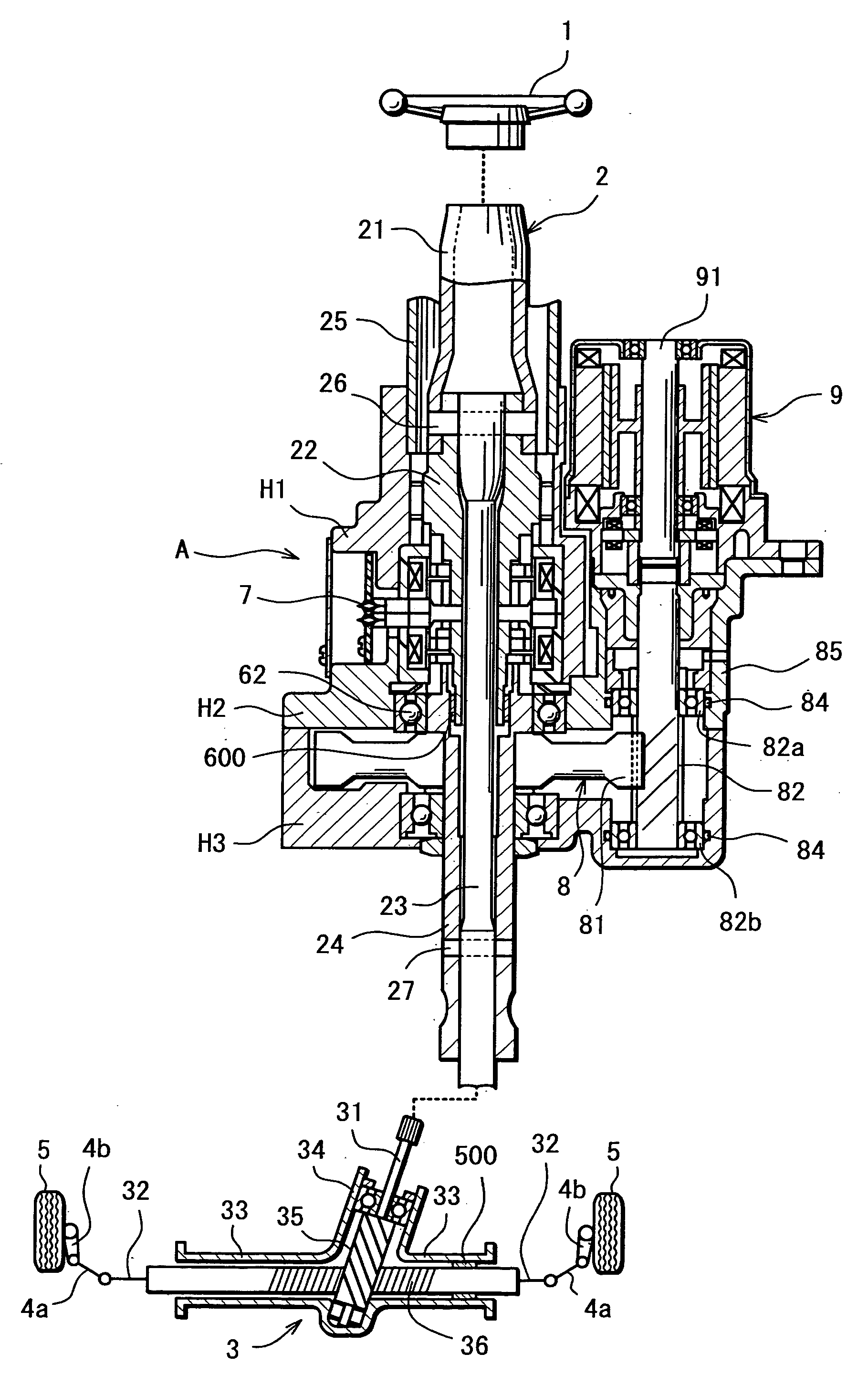
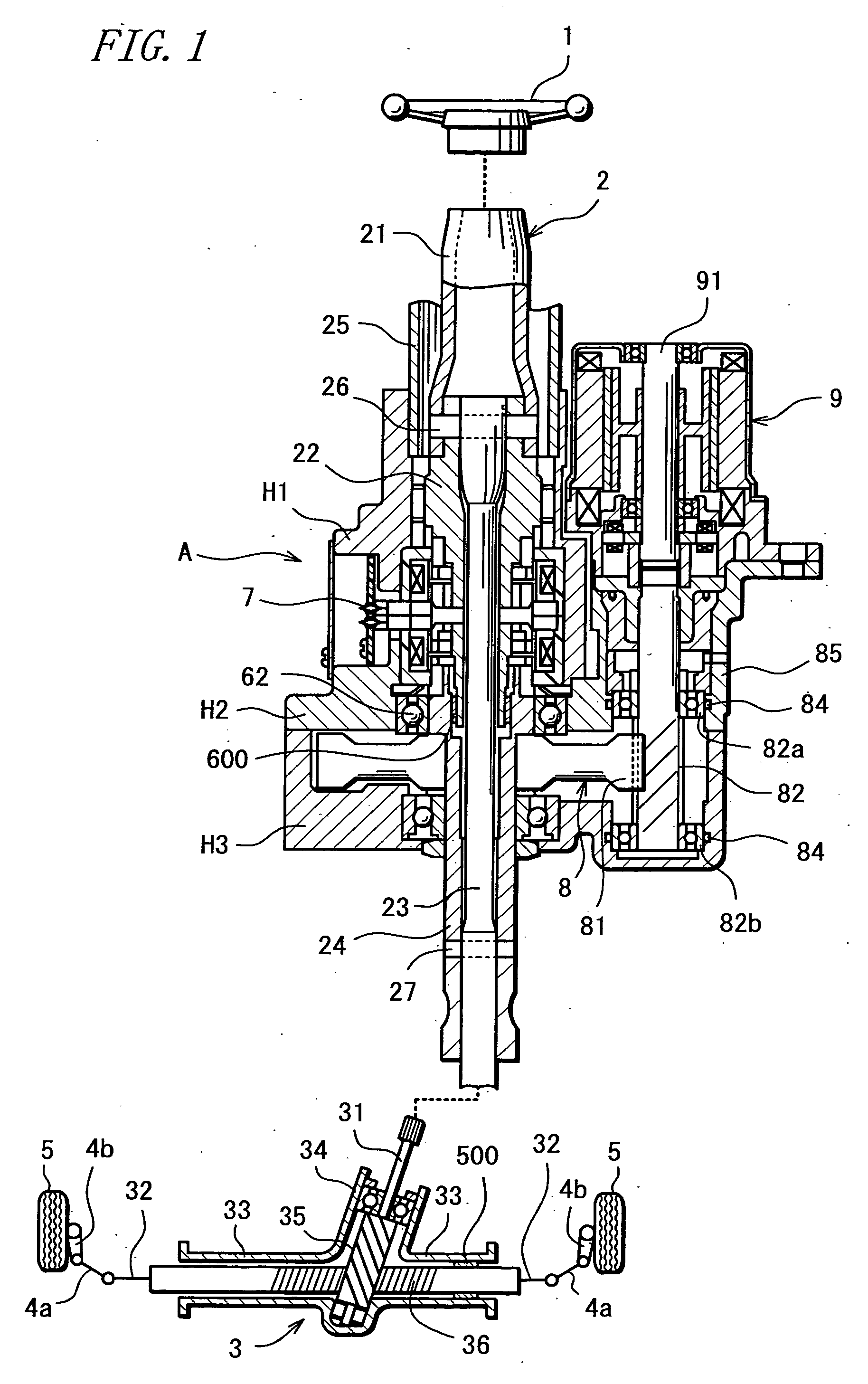
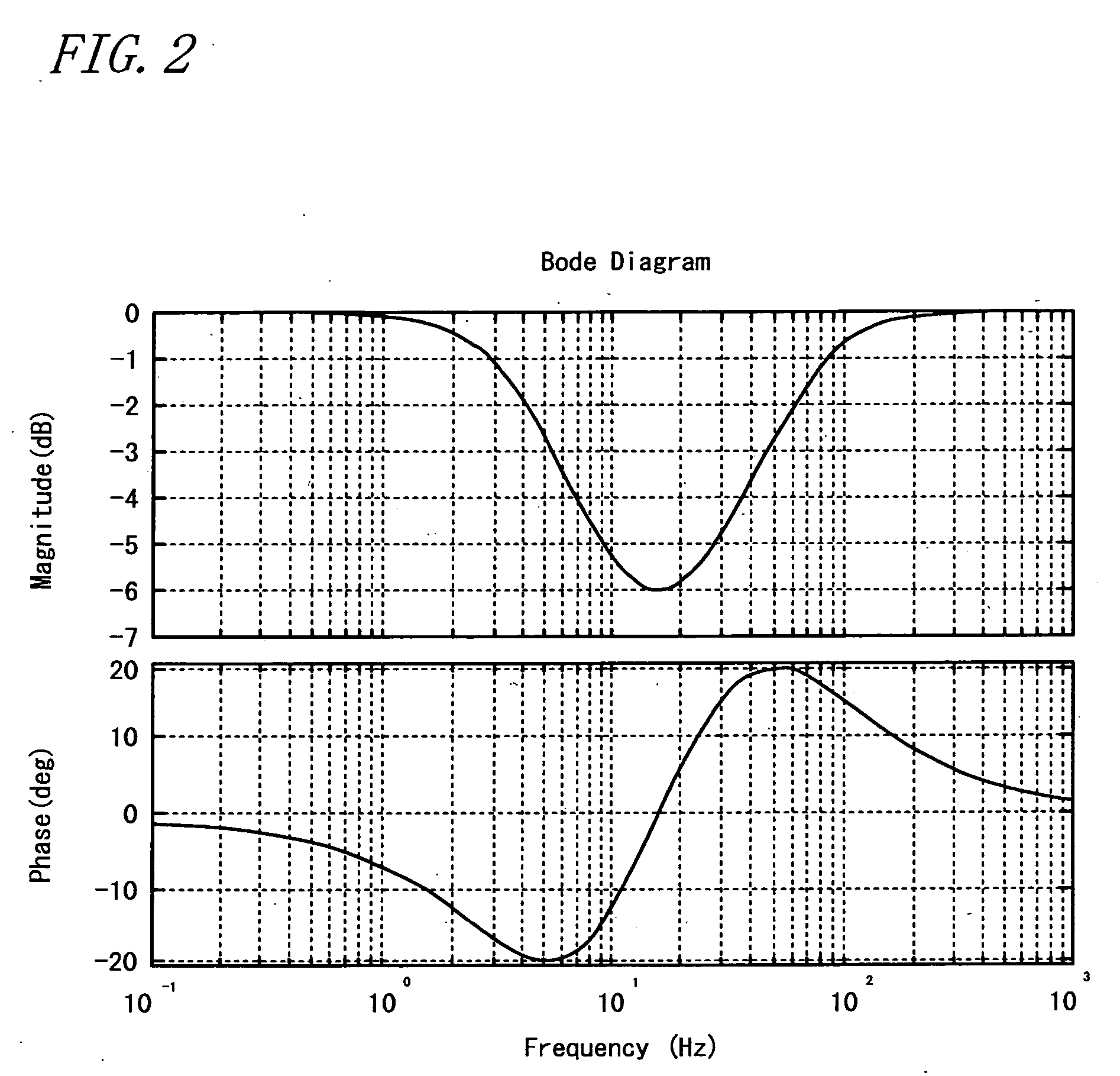
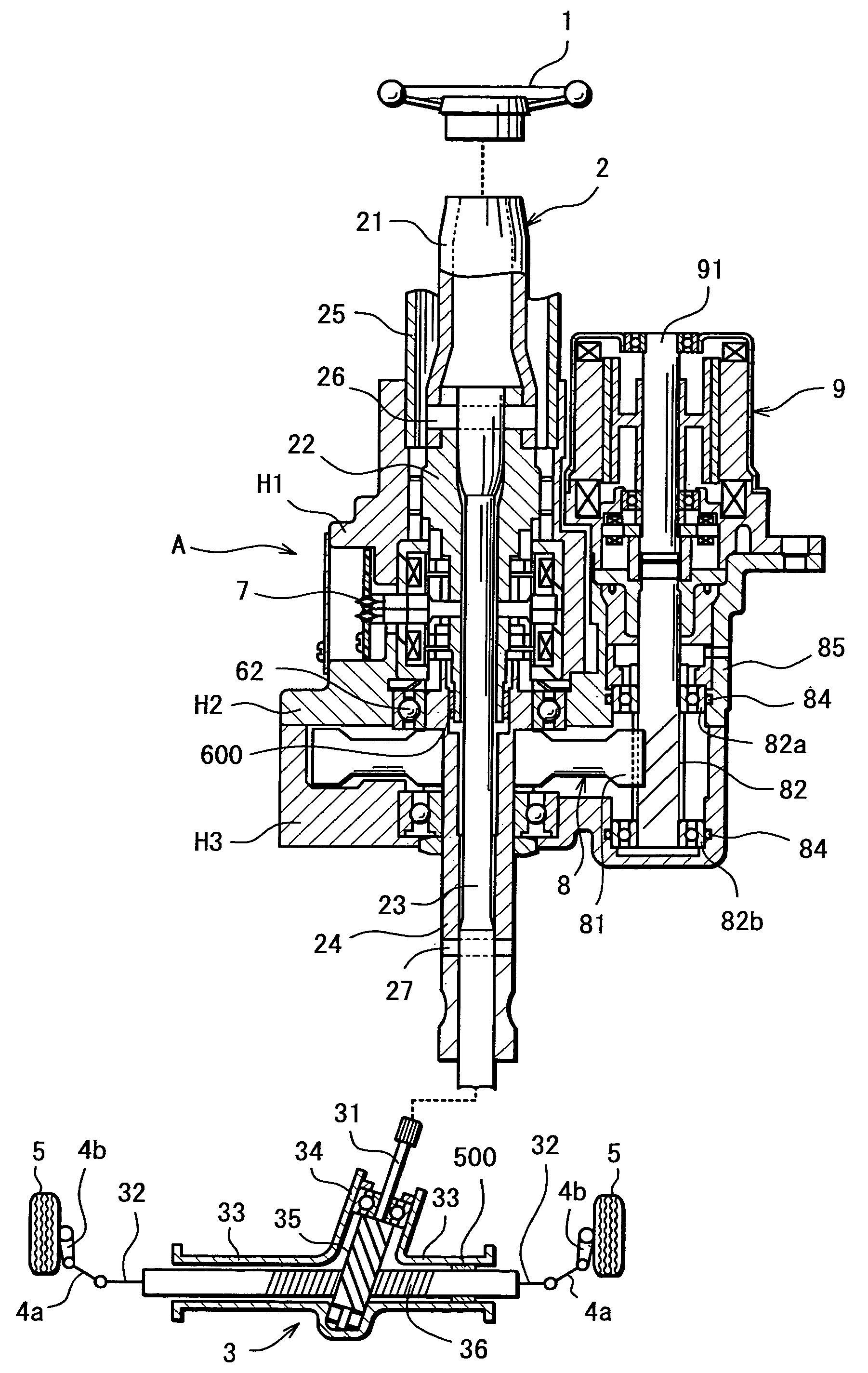
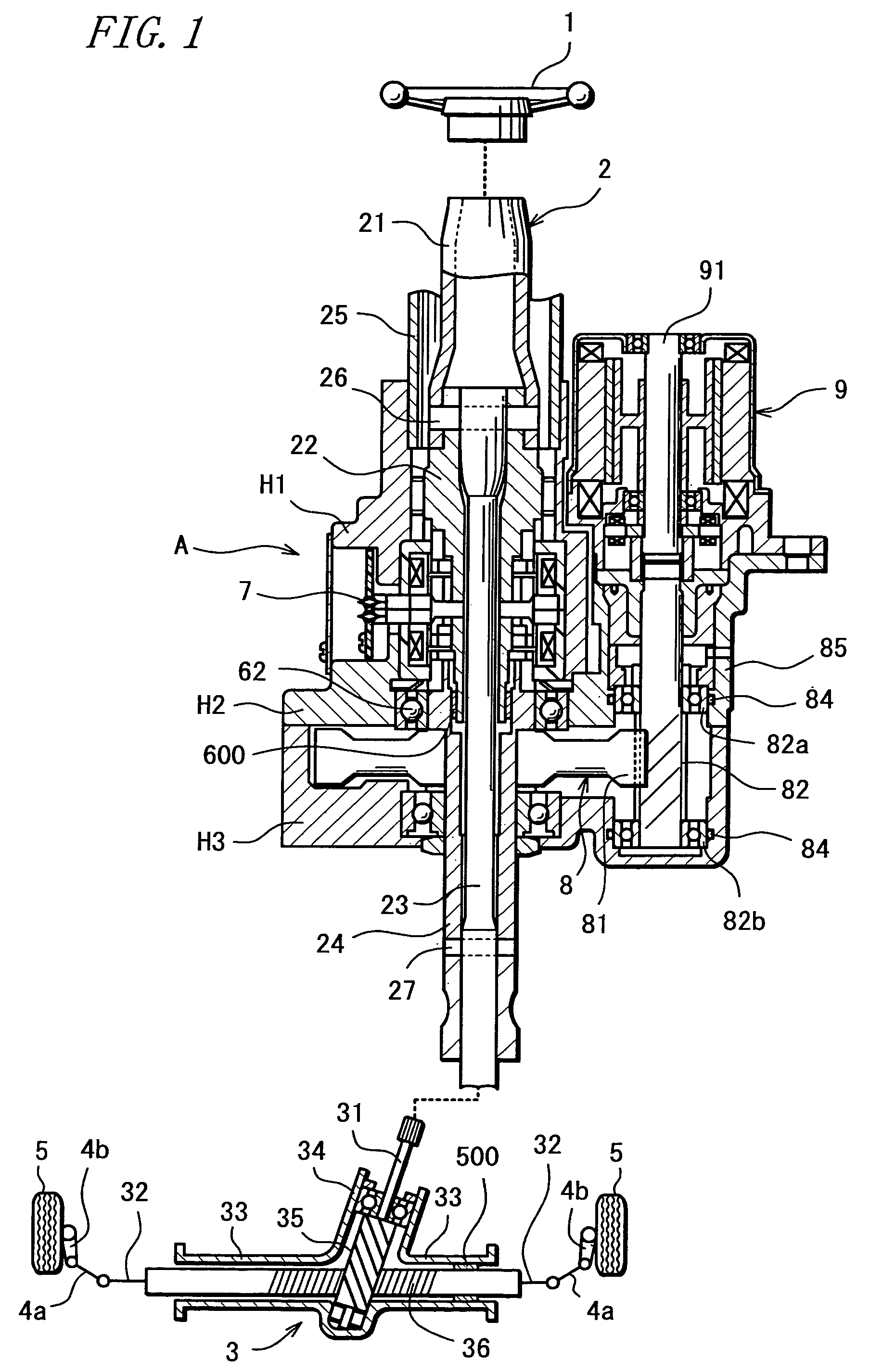
Electric Power Steering System
InactiveUS20070205041A1Favorable steering feelingLess inertia feelingSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringDamping torque
An electric power steering system is provided which is capable of providing a favorable steering feeling without using compensation logics such as of inertia compensation and friction compensation. The electric power steering system includes road-noise suppression control means (213) for controlling a steering assist motor (9) in a manner to damp torque transmission in a higher frequency region representing road noises than a frequency region representing road information. A friction value of a steering mechanism (A) is decreased enough to allow the intrinsic vibrations of the steering mechanism (A) to appear. Rotor inertia of the steering assist motor (9) is set to a value small enough to allow the frequencies of the intrinsic vibrations to be present in the frequency region where the torque transmission is damped by the road-noise suppression control means (213).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
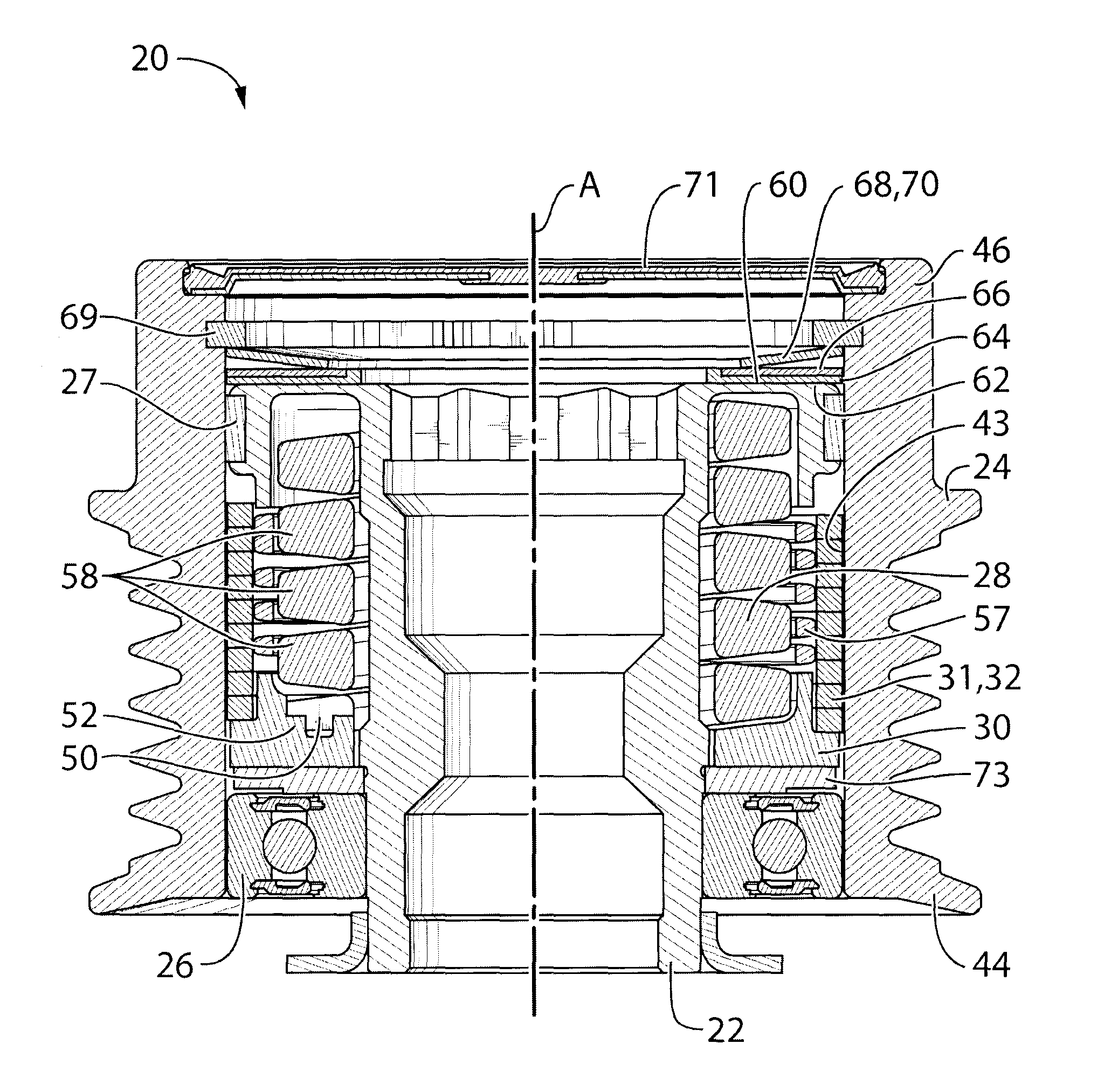
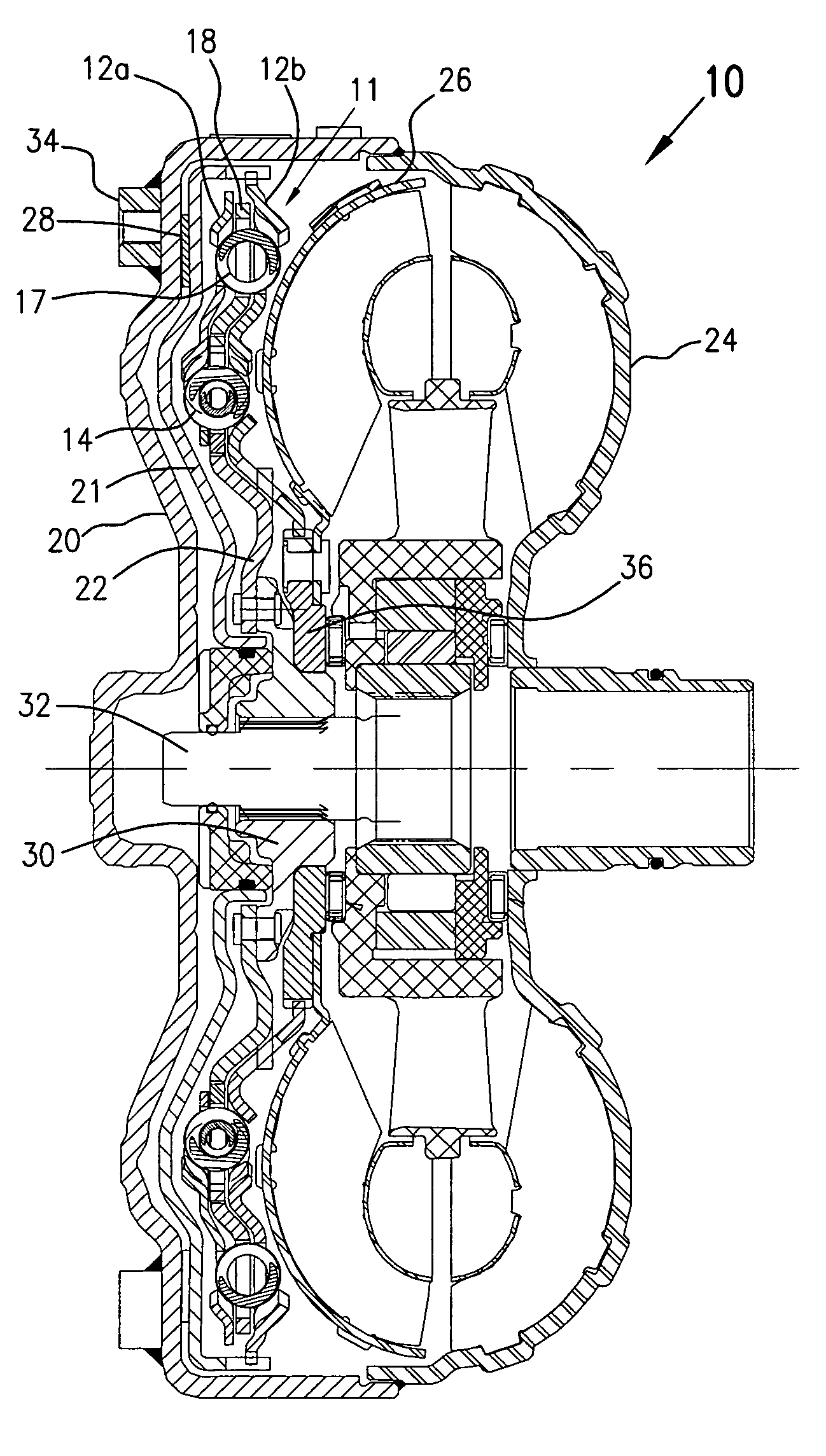
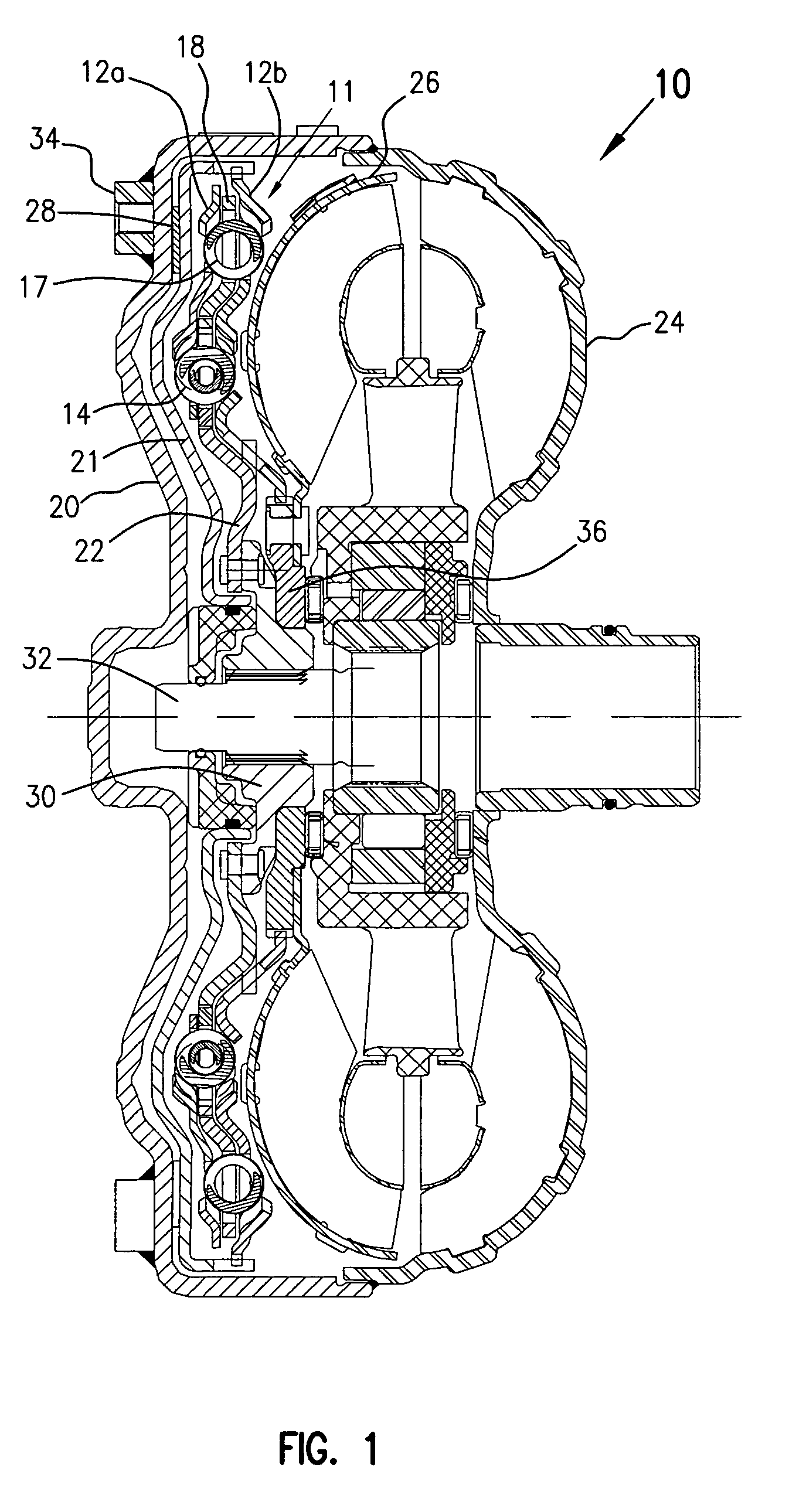
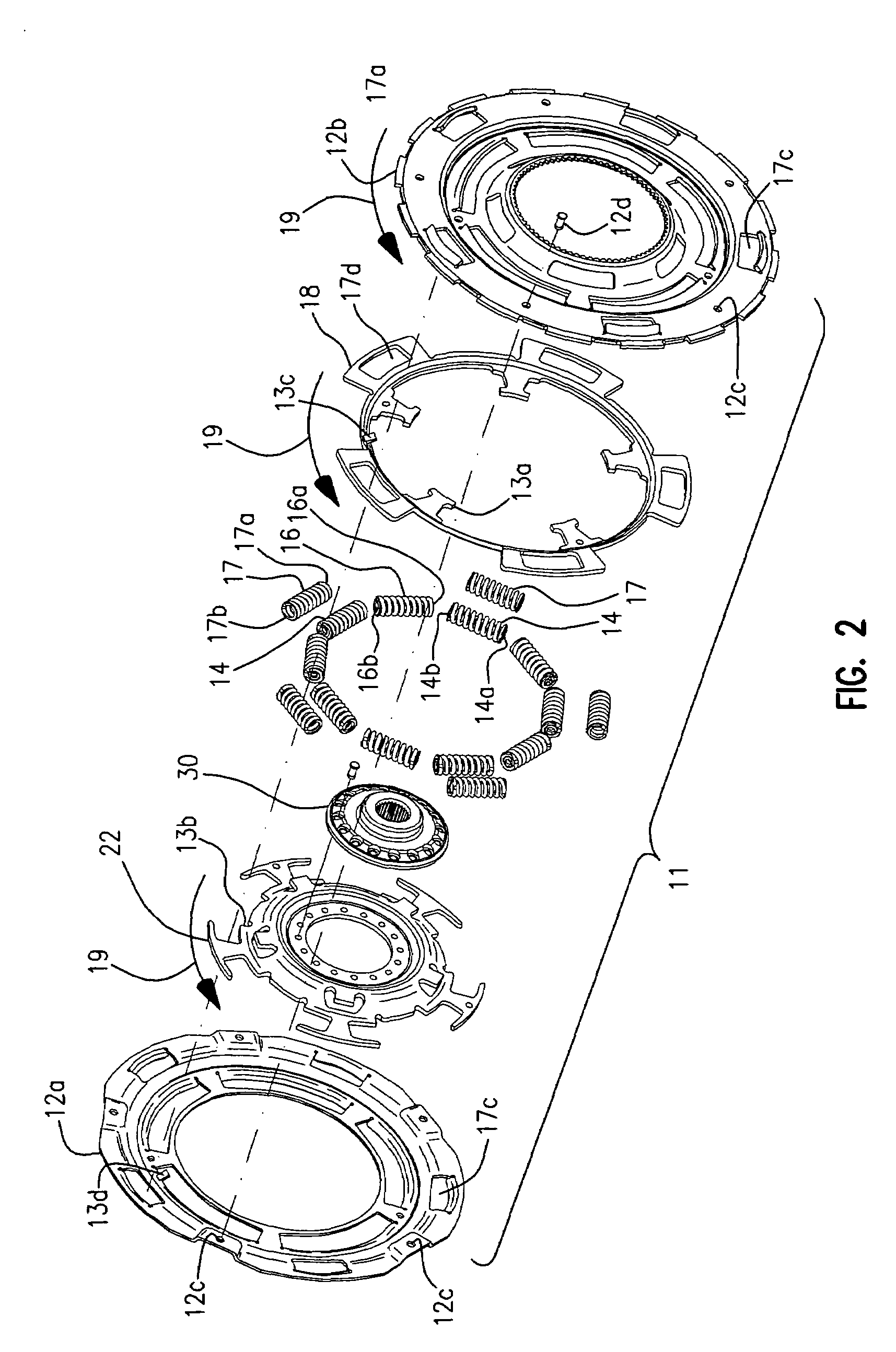
Decoupler with tuned damping and methods associated therewith
ActiveUS20130217524A1Reduce torsional vibrationImprove fatigue lifeAuxillary drivesRotating vibration suppressionEngineeringDamping torque
In an aspect, the invention relates to a decoupler that is positionable between a shaft (eg. for an alternator) and an endless power transmitting element (eg. a belt) on an engine. The decoupler includes a hub that mounts to the shaft, and a pulley that engages the endless power transmitting element, an isolation spring between the hub and the shaft. The decoupler provides at least a selected damping torque between the hub and the pulley.
Owner:LITENS AUTOMOTIVE INC
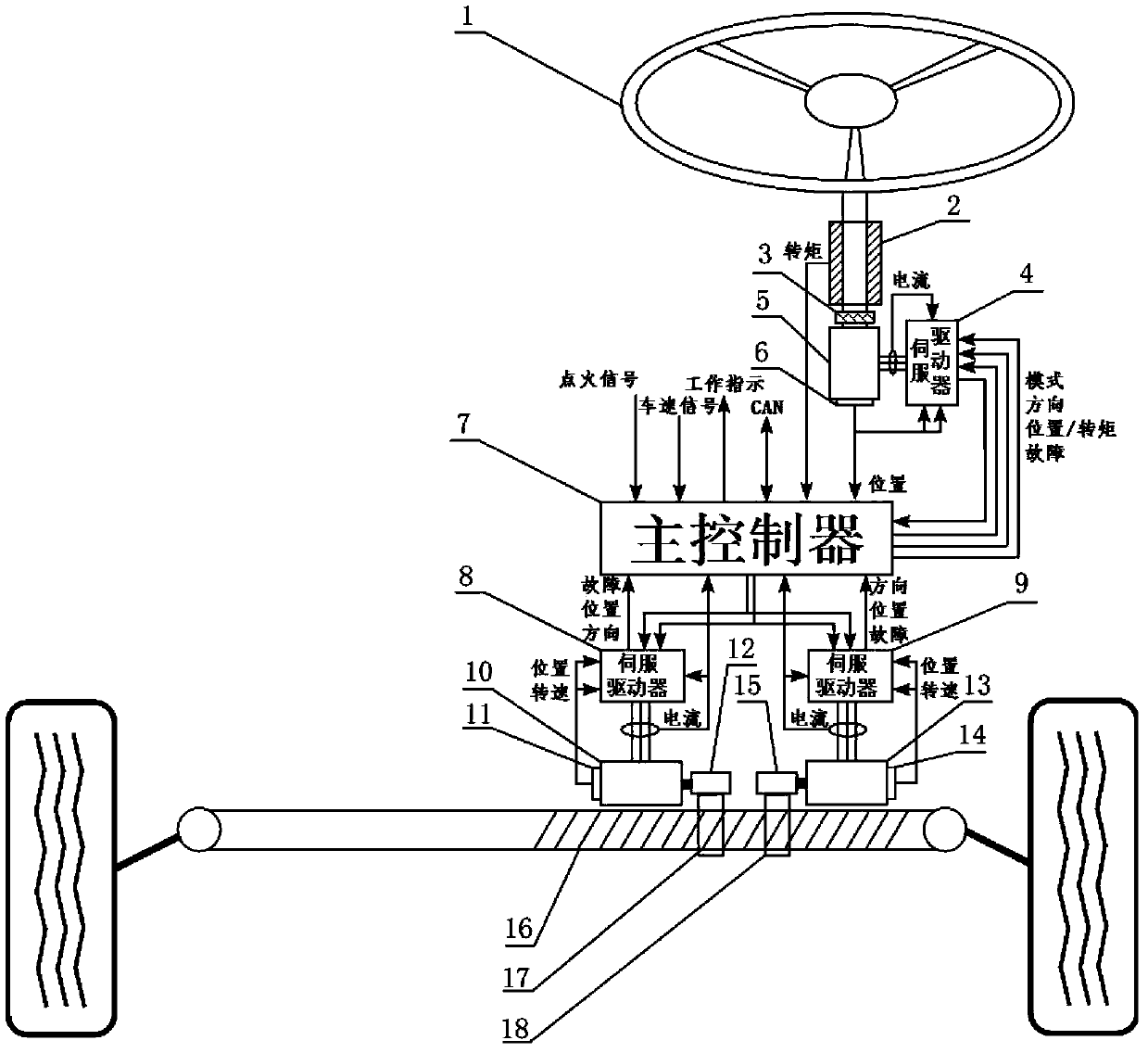
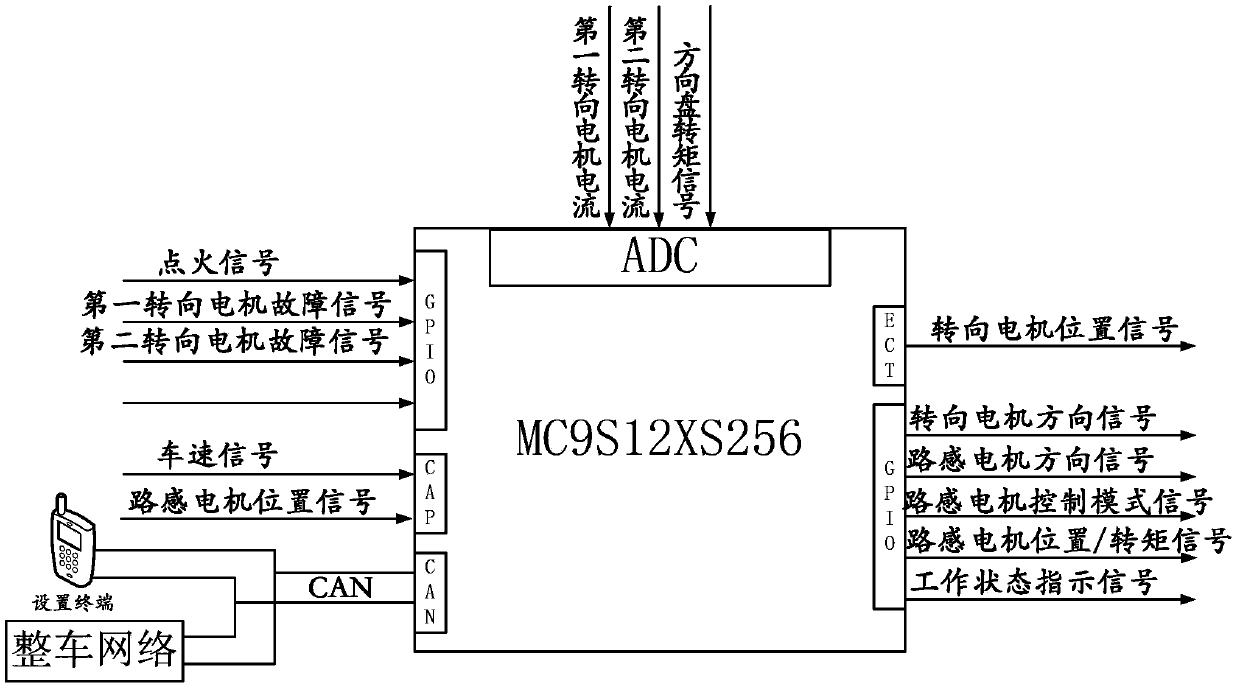
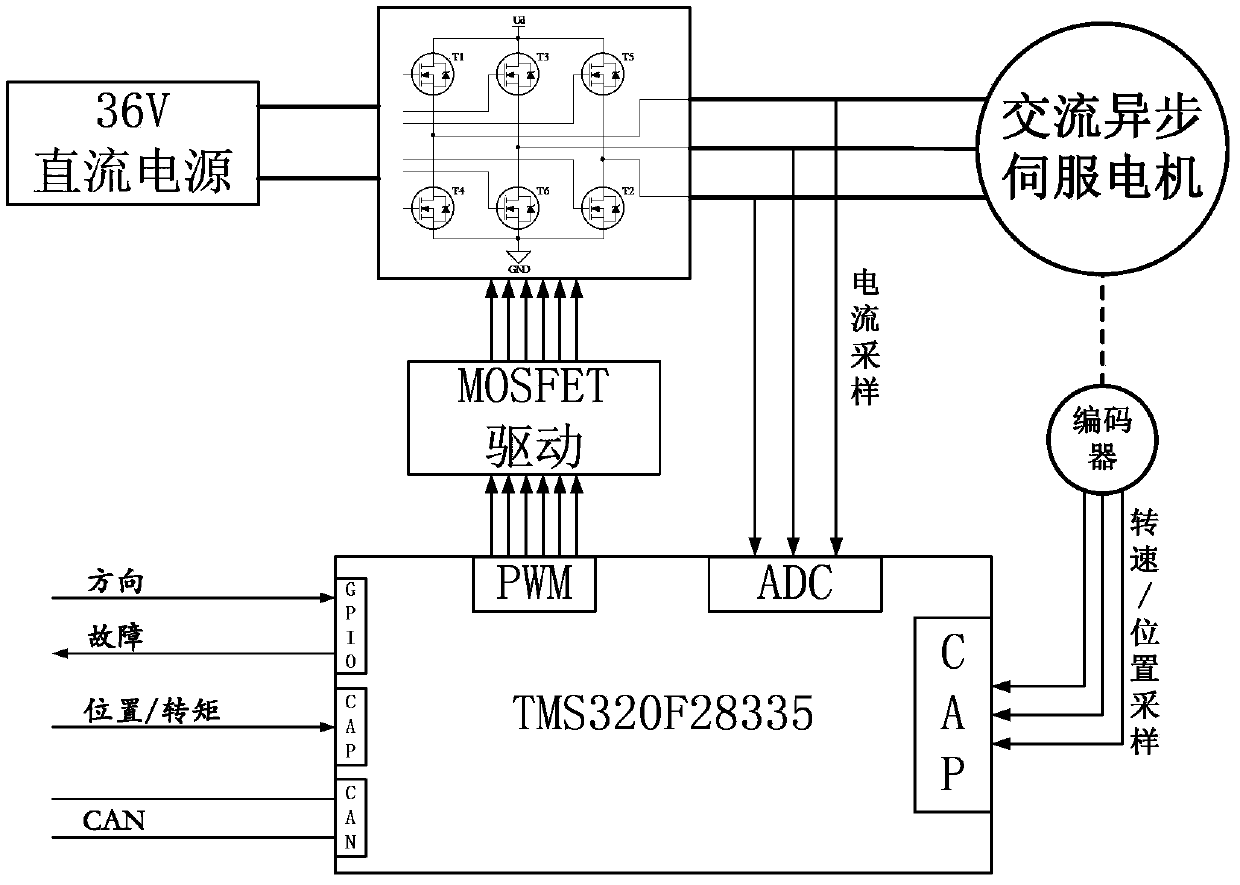
Automobile steering-by-wire system and control method thereof
ActiveCN103419835APrecise angle controlRealize personalized configurationSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlSteering wheelSteering angle
The invention discloses an automobile steering-by-wire system and a control method of the automobile steering-by-wire system. The automobile steering-by-wire system can control the angle of a steering wheel accurately, and a location servo mode of a road sense motor is adopted for limiting the steering angel of the steering wheel instead of a common mechanical limiting mechanism. Double steering motors adopt a redundancy design, simultaneously receive same control instructions sent by a master controller and work in a location servo control mode to drive a steering gear, and therefore not only is reliability of the system ensured, but also the angle of the steering wheel can be controlled accurately. Three-phase alternating current asynchronous motors are adopted for the road sense motor, the first steering motor and the second steering motor, therefore, even if a winding short circuit fault happens, damping torque can not be generated, and safety and reliability of the system are improved. Road sense coefficients of road sense feedback torque can be adjusted according to needs, personalized configuration of road sense intensity is achieved, and driving comfort is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
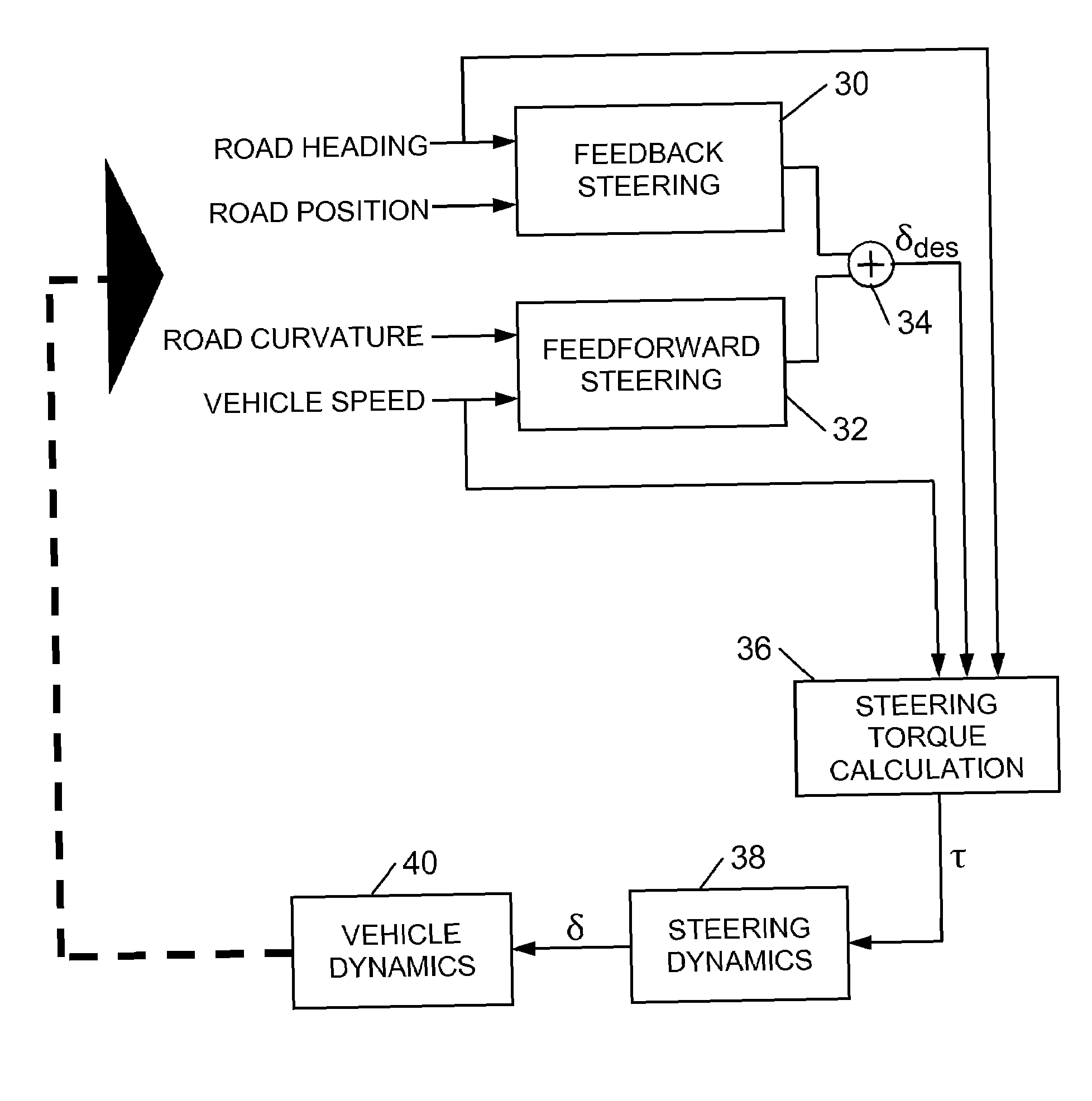
Method for Providing a Lanekeeping Assistance Based on Modifying Mechanical Sources of Steering Torques
ActiveUS20100145575A1Increase driver acceptanceReduce interruptionsDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsSteering angleDamping torque
A method for providing a lanekeeping assistance for a vehicle includes determining road lane characteristics such as a road lane curvature. A vehicle velocity and a vehicle position with respect to a road lane are also determined. A desired steering angle is determined as a function of at least the road lane characteristics. A lanekeeping torque acting on the steering system of the vehicle in order to keep the vehicle on a desired path is determined as a function of at least the desired steering angle. The lanekeeping torque is generated by modifying at least one mechanical steering torque such as a jacking torque, an aligning torque, an inertia torque and a damping torque.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS7604088B2Reduce frictionFeel goodSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringDamping torque
An electric power steering system is provided which is capable of providing a favorable steering feeling without using compensation logics such as of inertia compensation and friction compensation. The electric power steering system includes road-noise suppression control means (213) for controlling a steering assist motor (9) in a manner to damp torque transmission in a higher frequency region representing road noises than a frequency region representing road information. A friction value of a steering mechanism (A) is decreased enough to allow the intrinsic vibrations of the steering mechanism (A) to appear. Rotor inertia of the steering assist motor (9) is set to a value small enough to allow the frequencies of the intrinsic vibrations to be present in the frequency region where the torque transmission is damped by the road-noise suppression control means (213).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
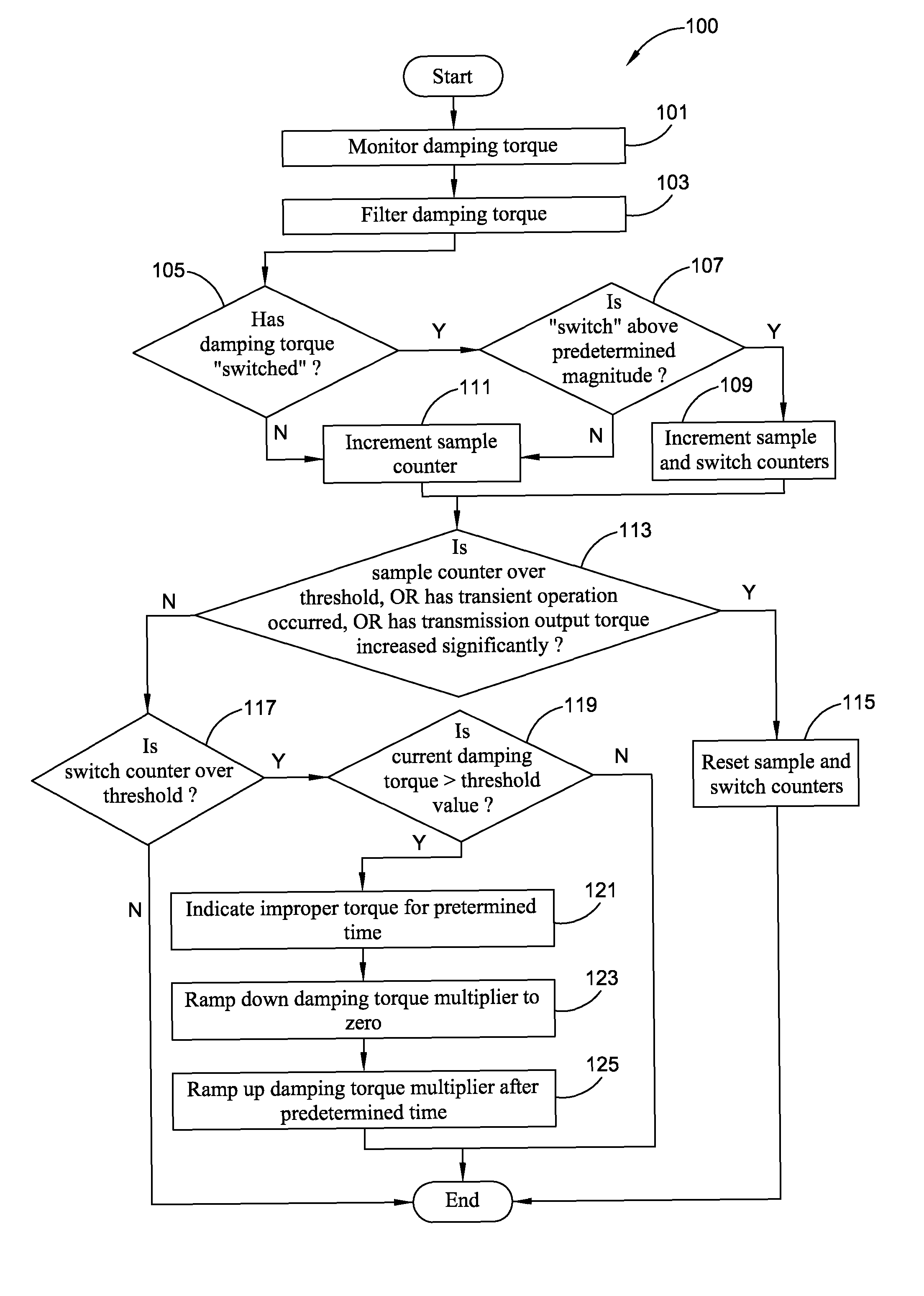
Apparatus and Method for Regulating Active Driveline Damping in Hybrid Vehicle Powertrain
ActiveUS20100087996A1Avoid problemsHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for vehiclesDamping torqueEngineering
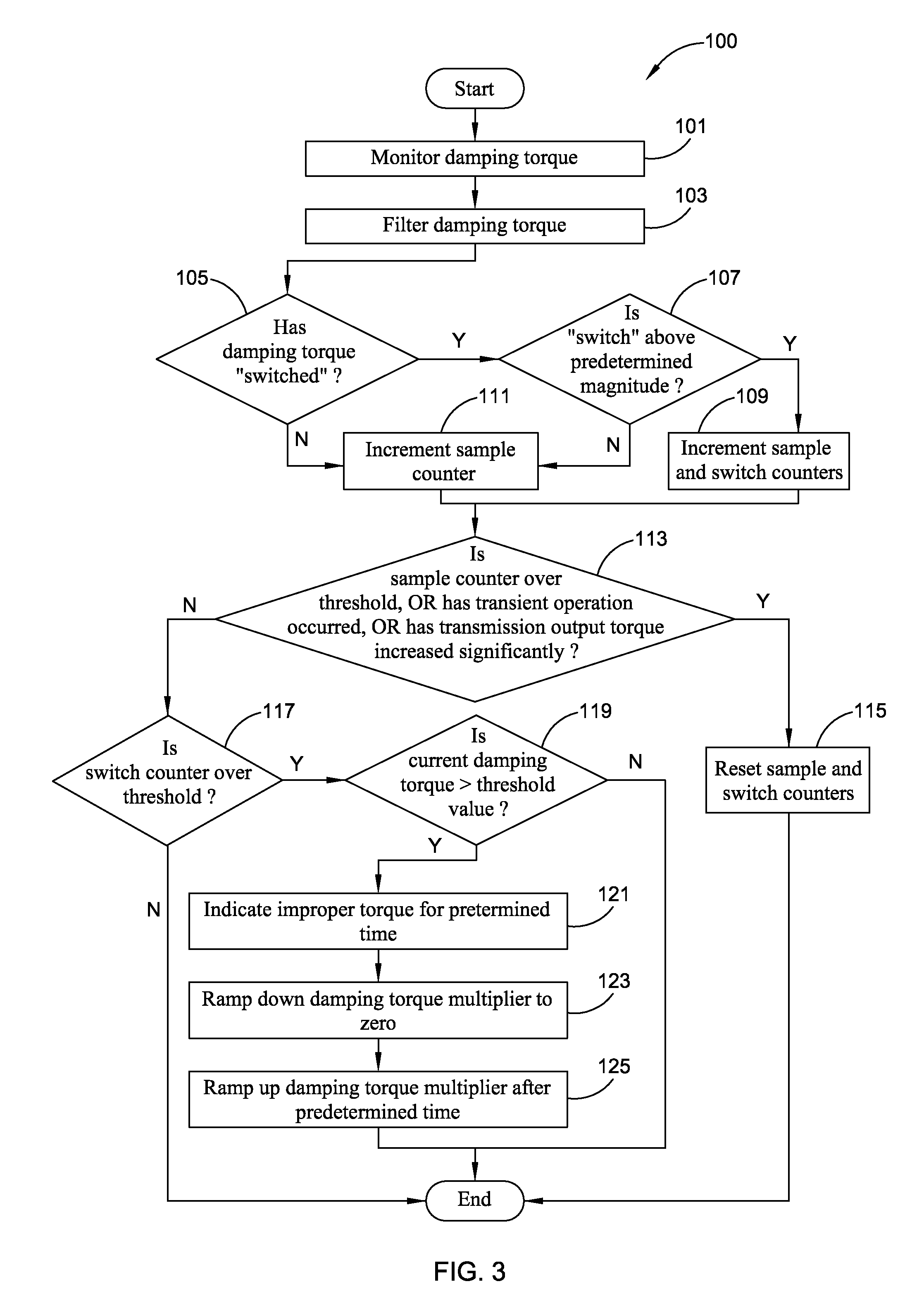
The present invention provides an improved method and apparatus for regulating active damping in a hybrid vehicle powertrain. The method includes: monitoring the damping command sent to the active damping system; determining a mean reference point, which may be a filtered value of the damping torque command; determining if the unfiltered damping torque command value switches from one side to the other of the mean reference point; if a switch is detected, determining if the size of the switch exceeds a predetermined minimum; if it does, then increasing a total number of switches; determining if the total number of switches exceeds a switch threshold; if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold, determining if the current damping torque exceeds a damping torque threshold; and decreasing the damping torque if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold and the current damping torque exceeds the damping torque threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Series-parallel multistage torque converter damper
InactiveUS20070051577A1Raise transfer toLarge capacityYielding couplingRotary clutchesDamping torqueOutput device
A method and apparatus for damping torque output from a torque converter turbine to input to a transmission. The damper includes: (a) an input device for connection to an engine; (b) a first spring set having drive springs; (c) a second spring set having secondary springs; (d) a third spring set having parallel springs; (e) a floating apparatus; and (f) an output device. Springs of the first spring set are compressible in a forward direction toward the output device as a result of torque applied to the input device and compressible in a reverse direction toward the input device as a result of torque applied by the output device. The first and second spring sets are in series between the input device and output device during a first forward compression of the first spring set, and the series is in parallel with the third spring set between the input apparatus and output device during a second compression of the first spring set. The first spring set is in parallel with the third spring set between the input apparatus and output device without the second spring set during a third compression of the first spring set. The floating apparatus is between the input apparatus and the output device and between springs of said first and second spring sets during the first forward compression of the first spring set. The method includes the steps of: (a) operating a spring set one and a spring set two in series between torque input and torque output; (b) placing a spring set three in parallel with spring sets one and two allowing more torque per degree of wind-up than in step (a); and (c) removing spring set two from series with spring set one resulting more torque per degree of wind-up than in step (b).
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
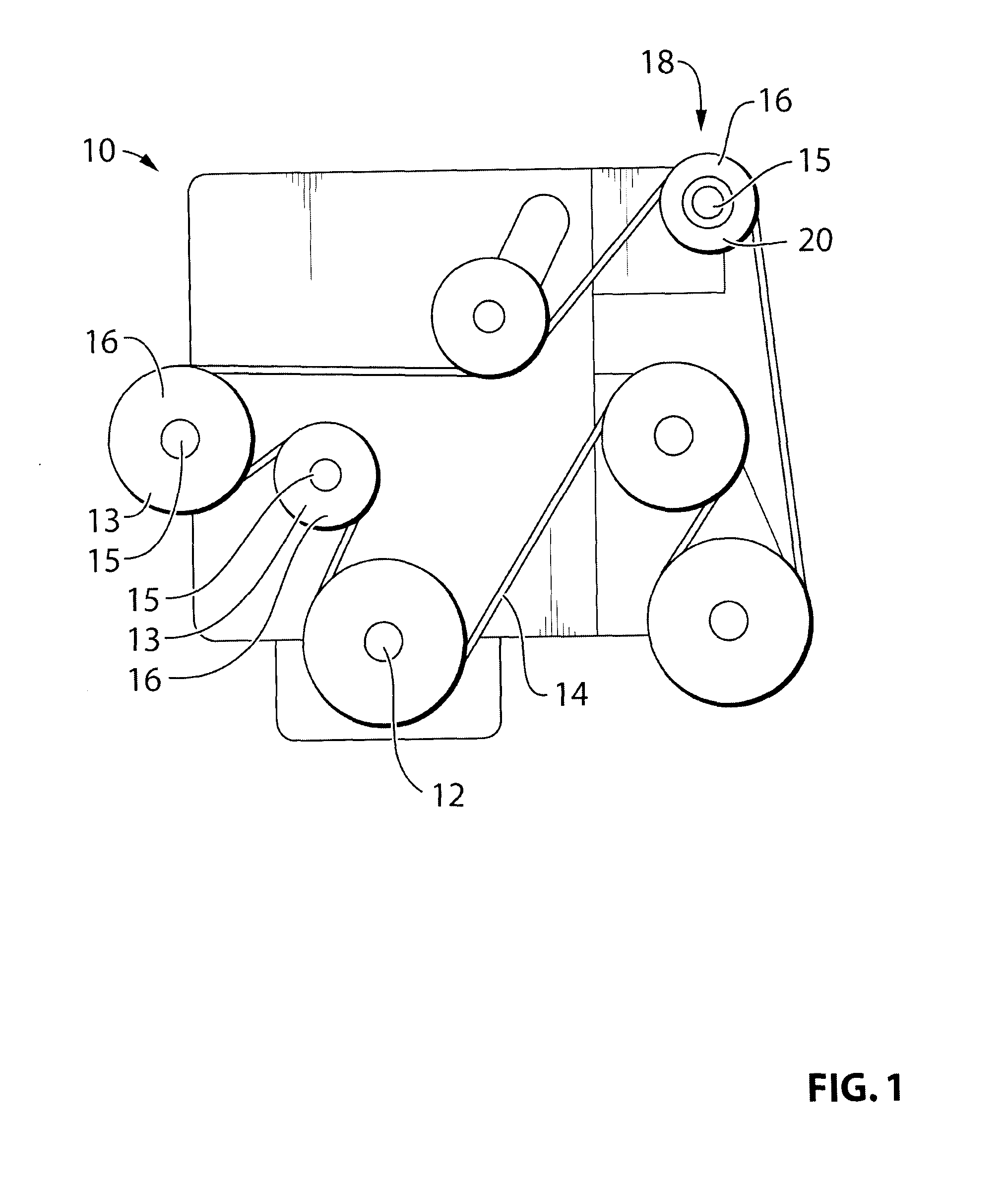
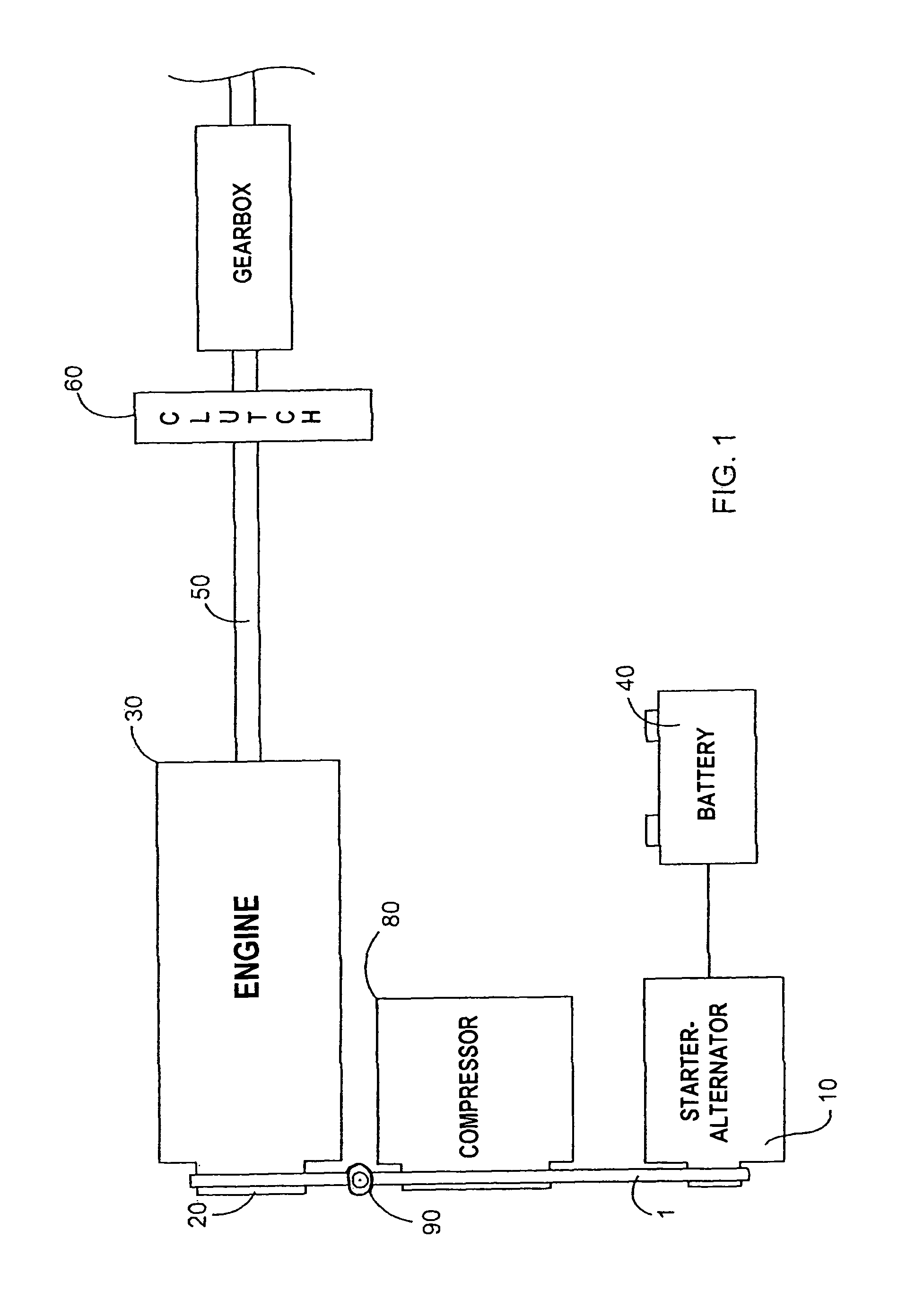
Pulley for a power transmission member, a separate starter-alternator fitted with such a pulley, and an engine drive system
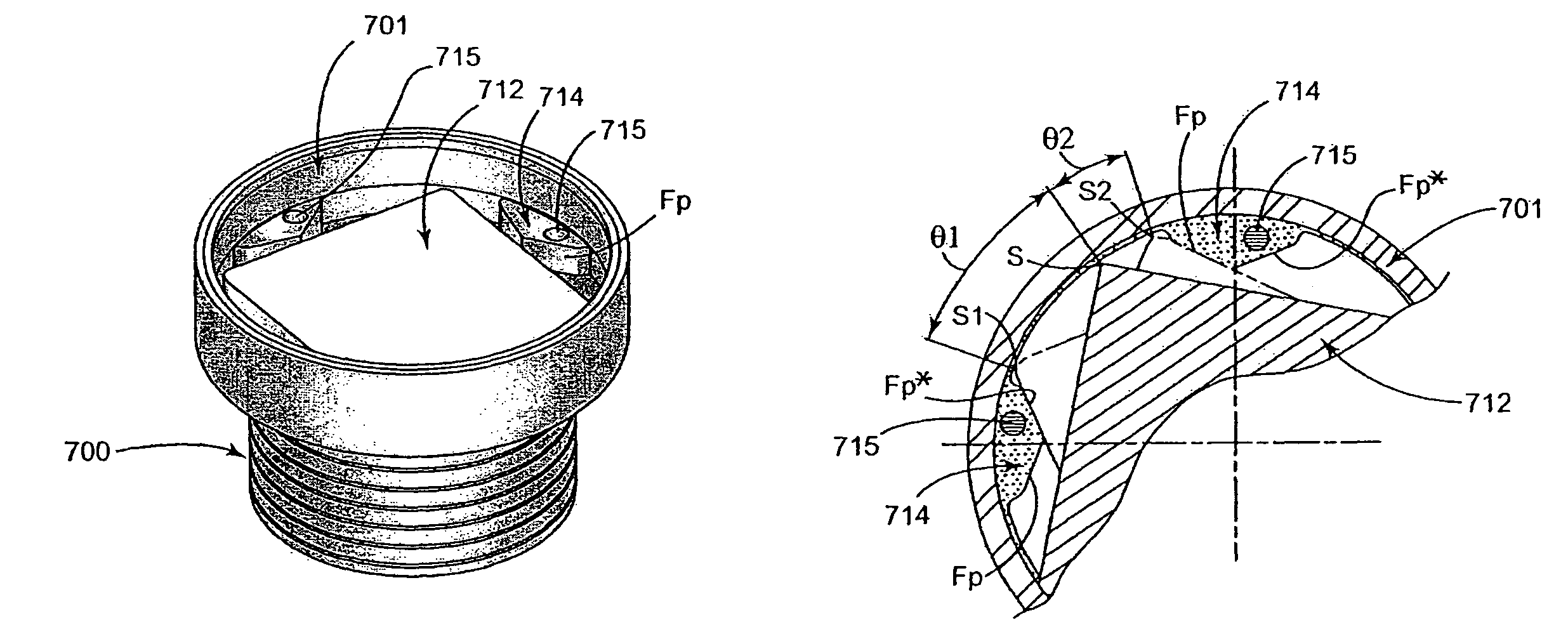
InactiveUS7985150B2Control tensionControlling the riskRotating vibration suppressionYielding couplingAlternatorDamping torque
The invention seeks to provide a transmission system, in particular for a starter-alternator, capable both of damping large variations in torque under starting conditions (drive from the alternator) and of providing effective decoupling under running conditions (alternator driven). In an embodiment, the decoupling located between a central hub and a rim over which a drive belt (not shown) is tensioned, is provided by at least one decoupler element designed to provide optimized stiffness. In addition, the decoupler assembly is associated with at least one deflection limiter having two components: a central plate secured to an outside face of the central hub and coupled to abutments that are regularly distributed around the periphery of an inside face of the rim, the abutments and the plate being shaped so as to come into deforming contact. The resilient assembly provides two stiffness values, whether in the drive direction or in the driven direction. The invention is applicable to starter-alternators, crankshafts, and other power transmission members (compressors, etc.).
Owner:HUTCHINSON SA
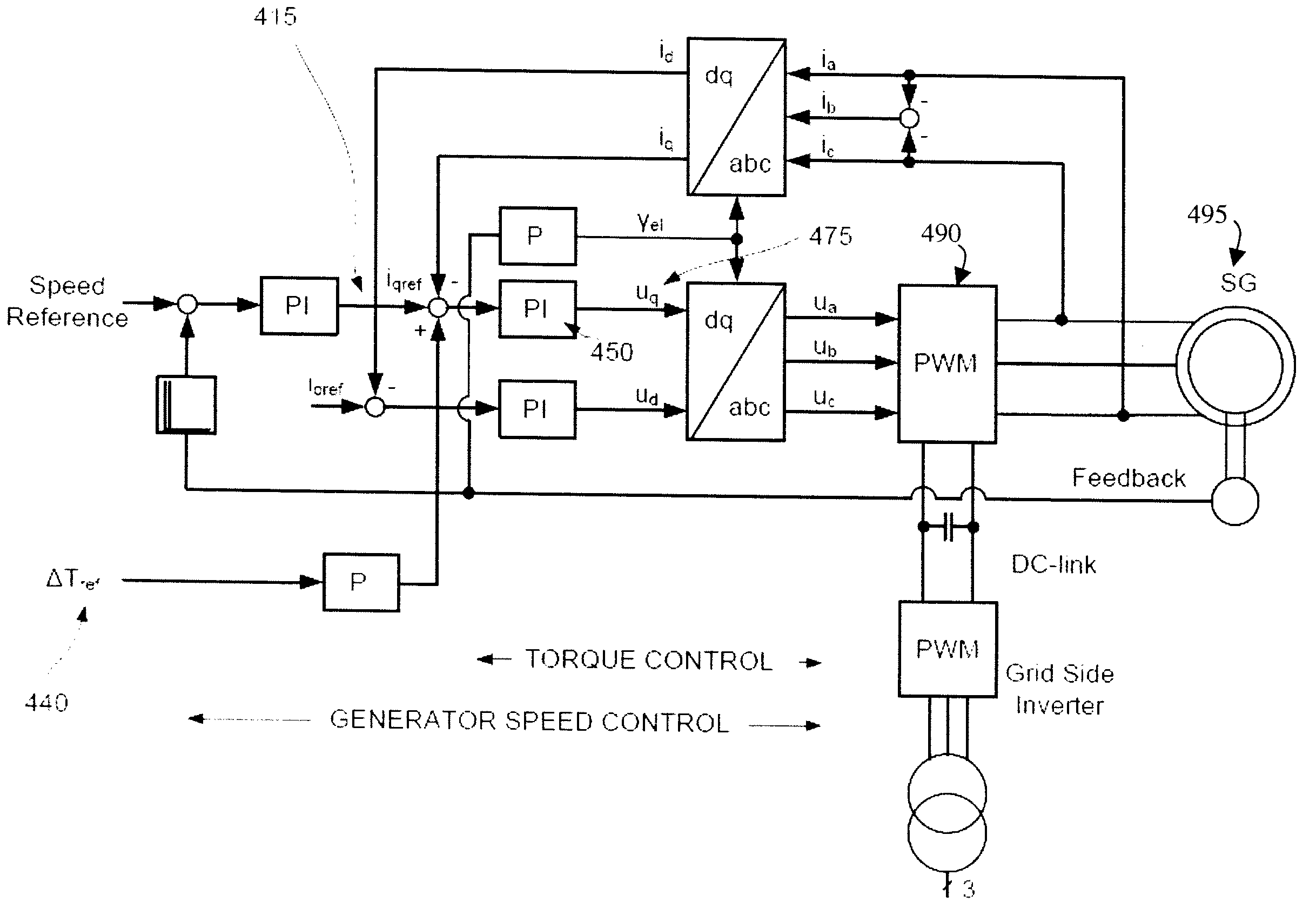
Gearbox Noise Reduction By Electrical Drive Control
ActiveUS20090149999A1Reduce audible noiseReducing audibleNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTemperatue controlPhase shiftedDamping torque
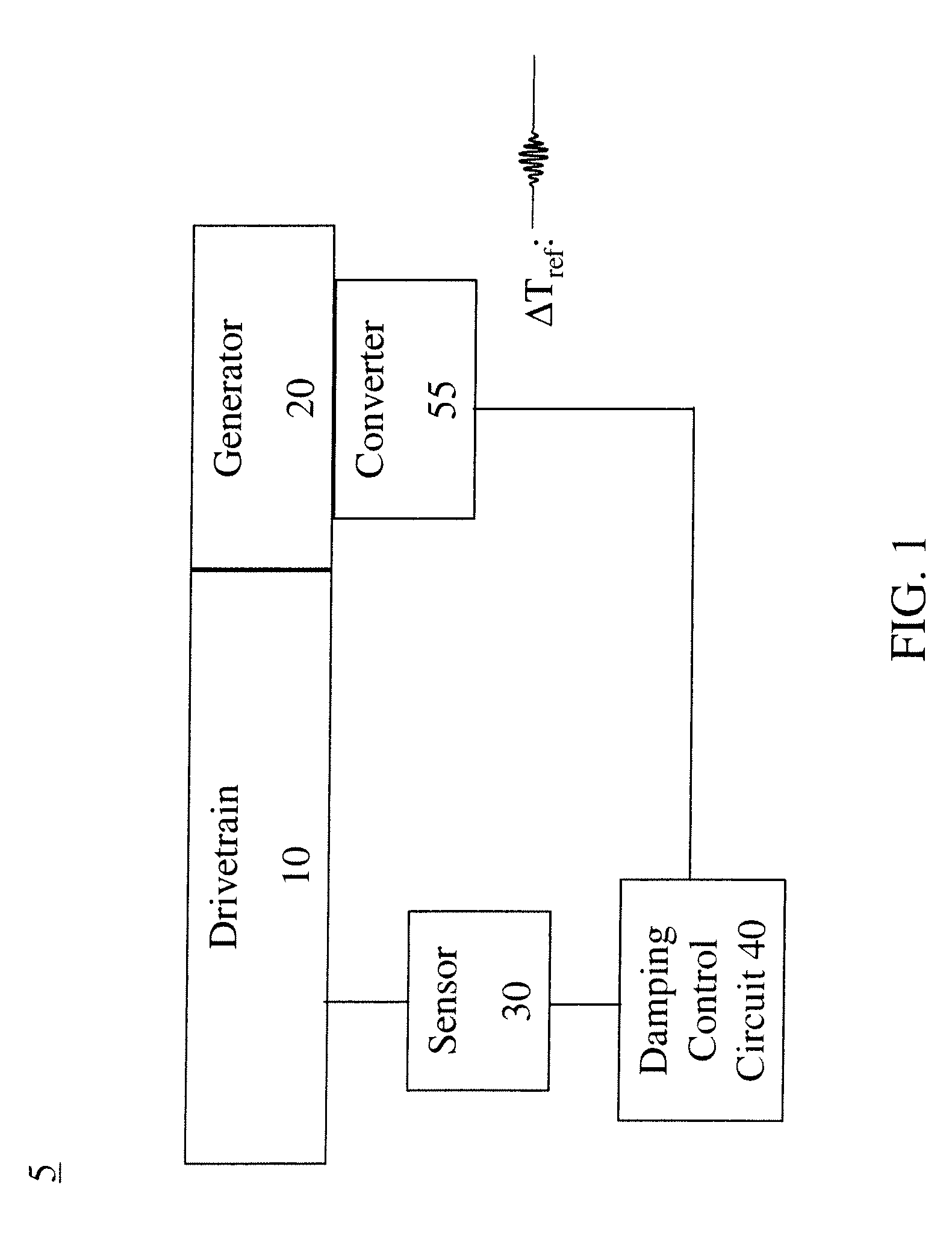
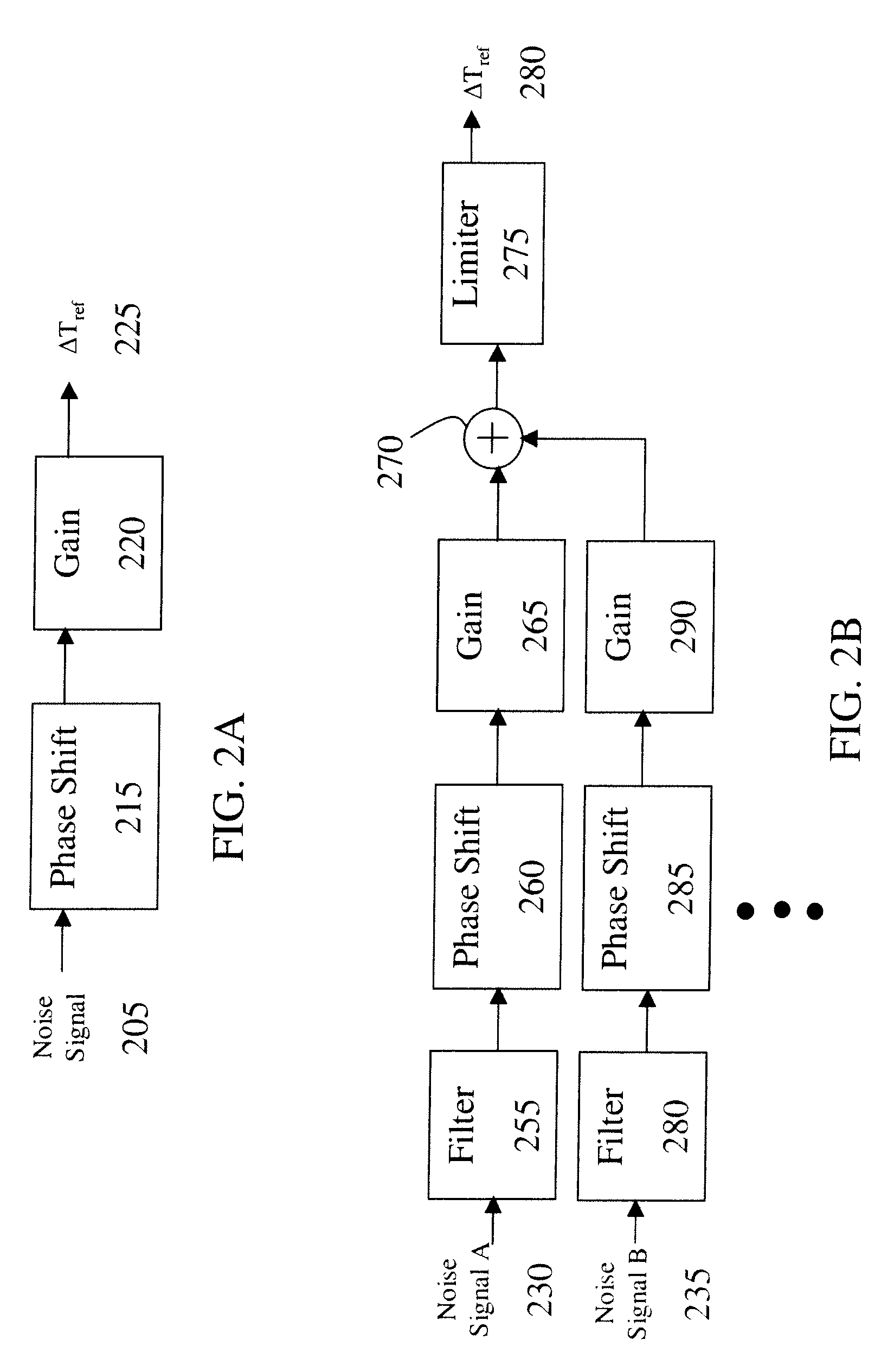
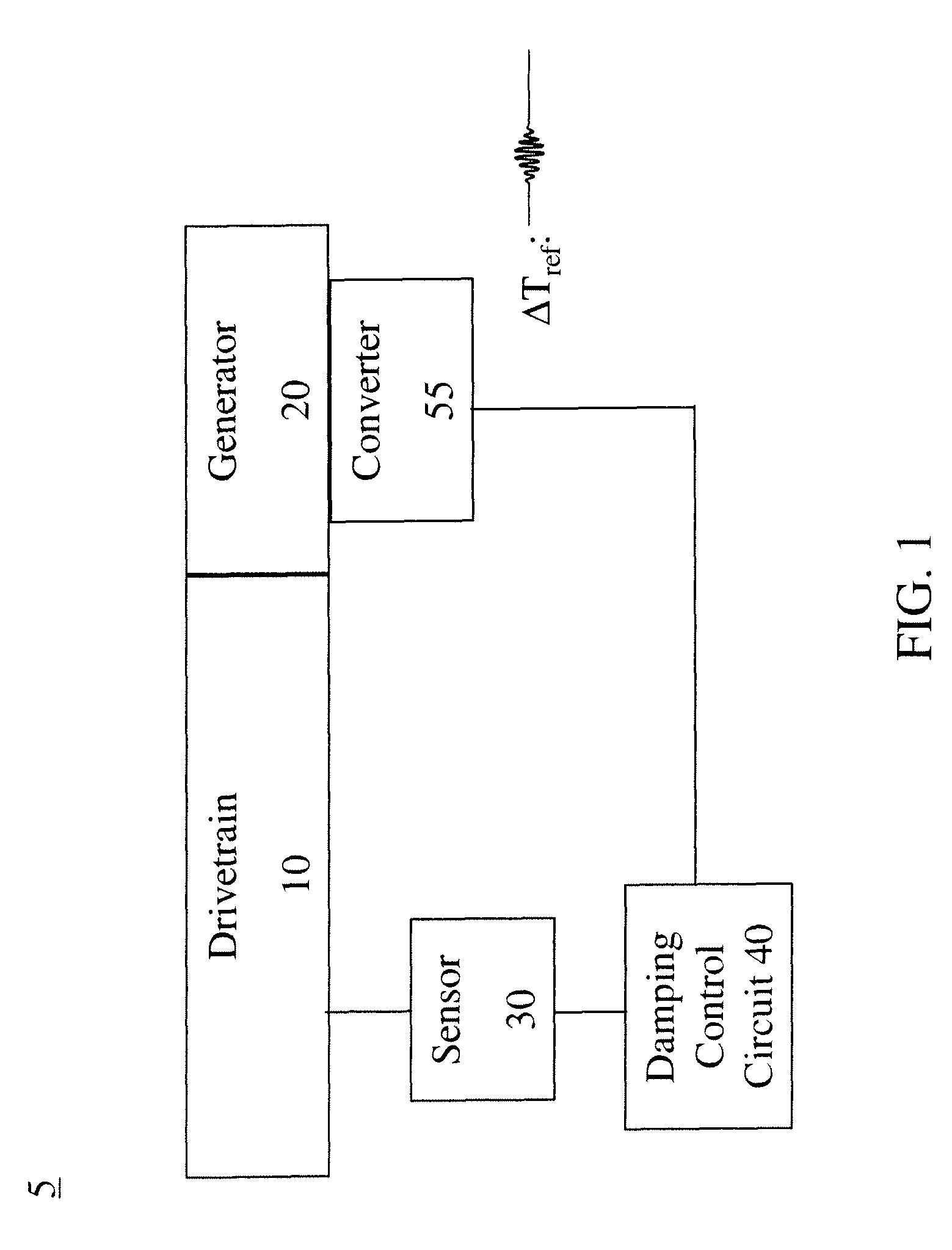
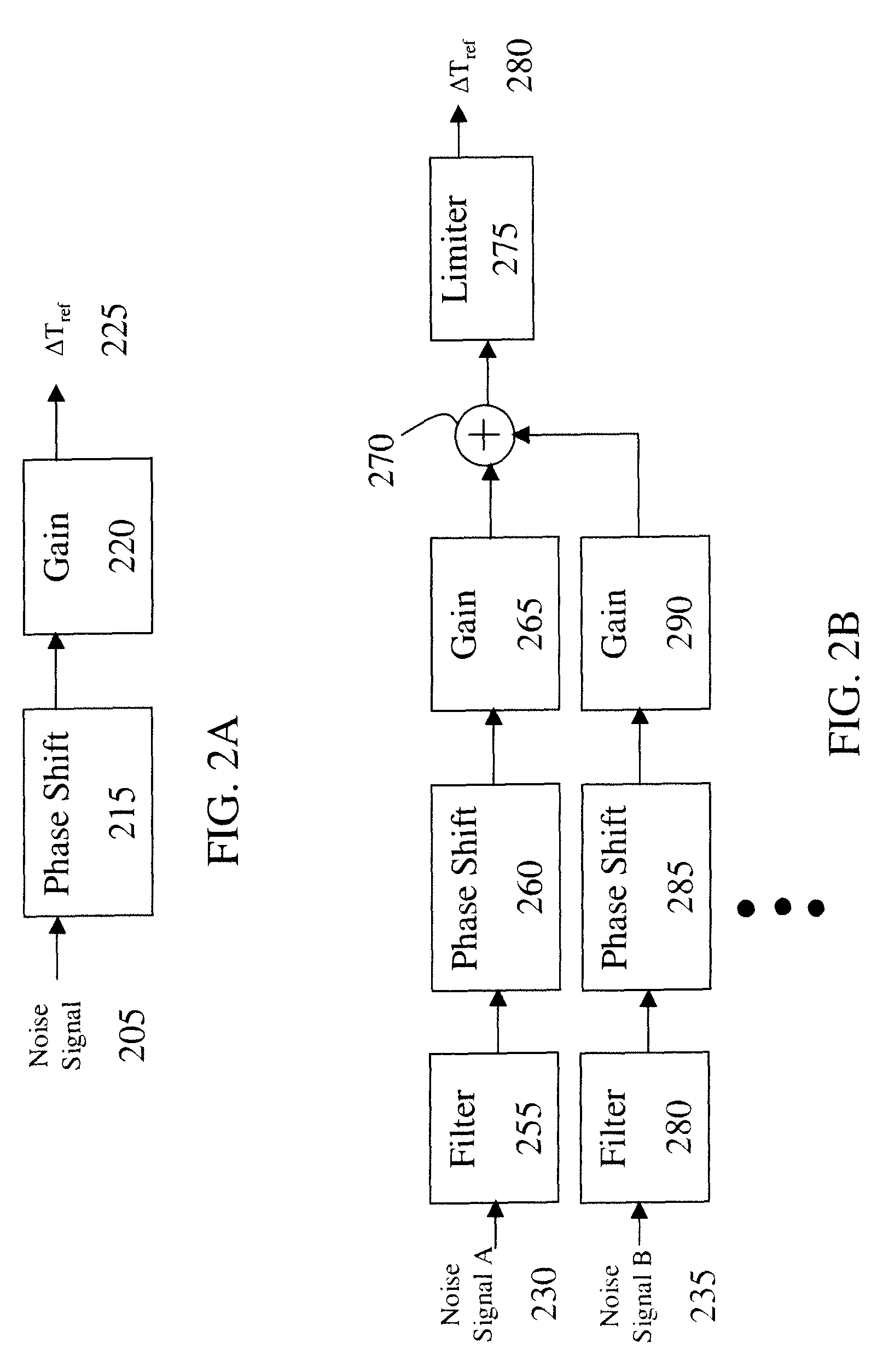
A system for damping audible noise from a drive train. One embodiment is a system with an audible noise signal from a drive train wherein a damping circuit produces a damping torque that is a phase shifted and amplified version of the noise signal that is applied to the air-gap torque of a generator or motor coupled to the drive train and effectively reduces the audible noise.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
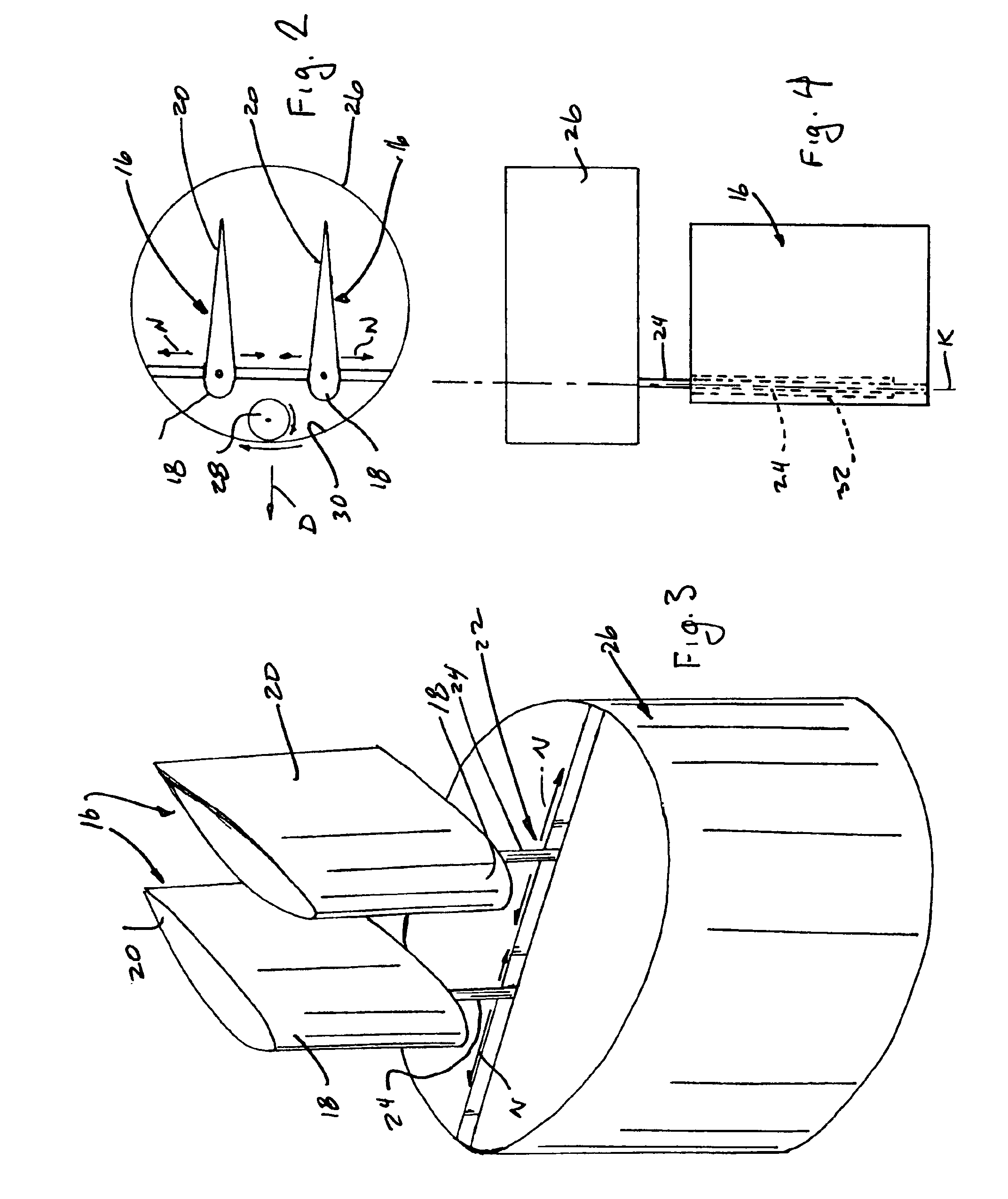
Oscillating foil propulsion system
InactiveUS6877692B2Easy to liftReduce rateMachines/enginesPropulsive elements of non-rotary typeDamping torqueCompressed fluid
The invention provides a propulsion system based on “thuniform” movement of a foil member to achieve desired directional movement of a vehicle such as an unmanned submarine type of vessel. A pair of foil members are mounted to the vehicle body for reciprocating oscillating movement towards and away from each other, creating forward movement due to the compression of a fluid medium between the foil members and the expulsion of the compressed fluid rearwardly of the foil members. Each foil member is mounted to a pivot shaft for limited rotational movement with respect to the vehicle body. Damping means are connected between each pivot shaft and its associated foil member so that during operation of the propulsion system damping torque will offset hydrodynamic loads imposed on the foil members by the fluid medium. The damping means will in turn control the pitch angle of the foil members during operation, meaning that a thrust is generated for rigid foil members when moving at zero forward speed. The propulsion system of the invention exhibits increased efficiency and thrust in comparison to other such propulsion systems. The foil members are mounted to the vehicle body in such a manner that the thrust vector thereof can be directed through a full 360 degrees relative to the vehicle, thereby achieving superb maneuverability when the vehicle is provided with sets of the thrusters suitable located thereon.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
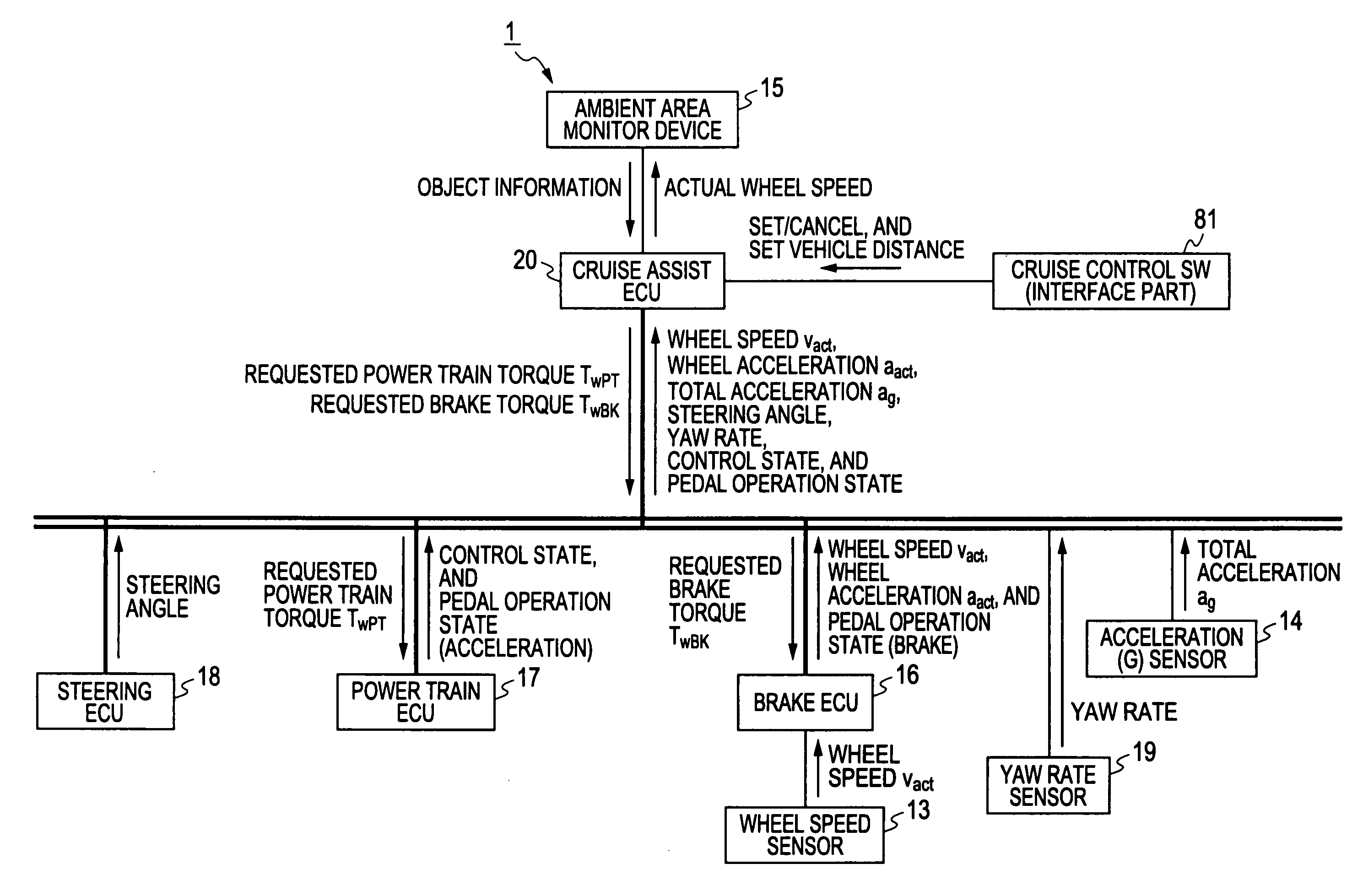
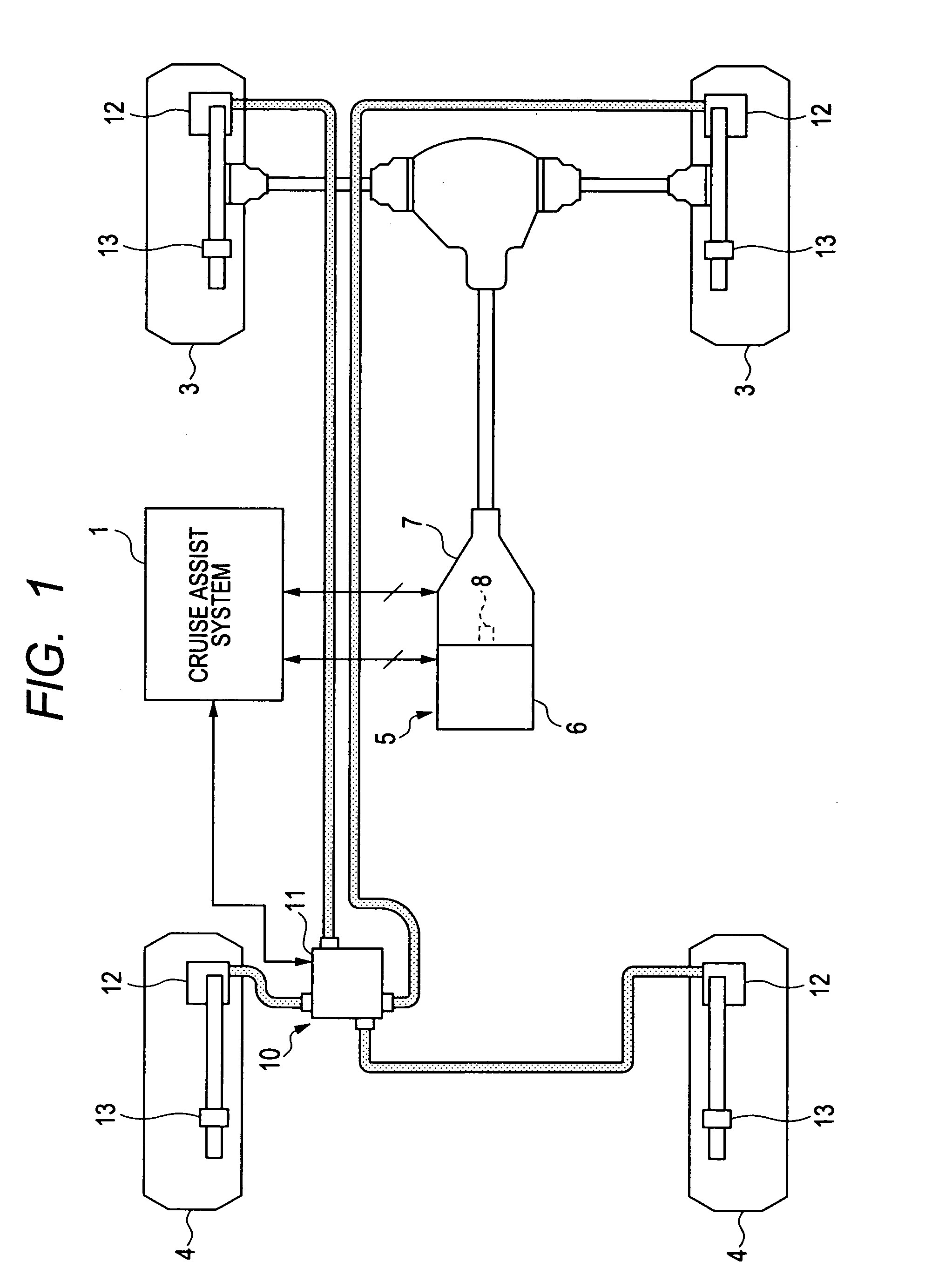
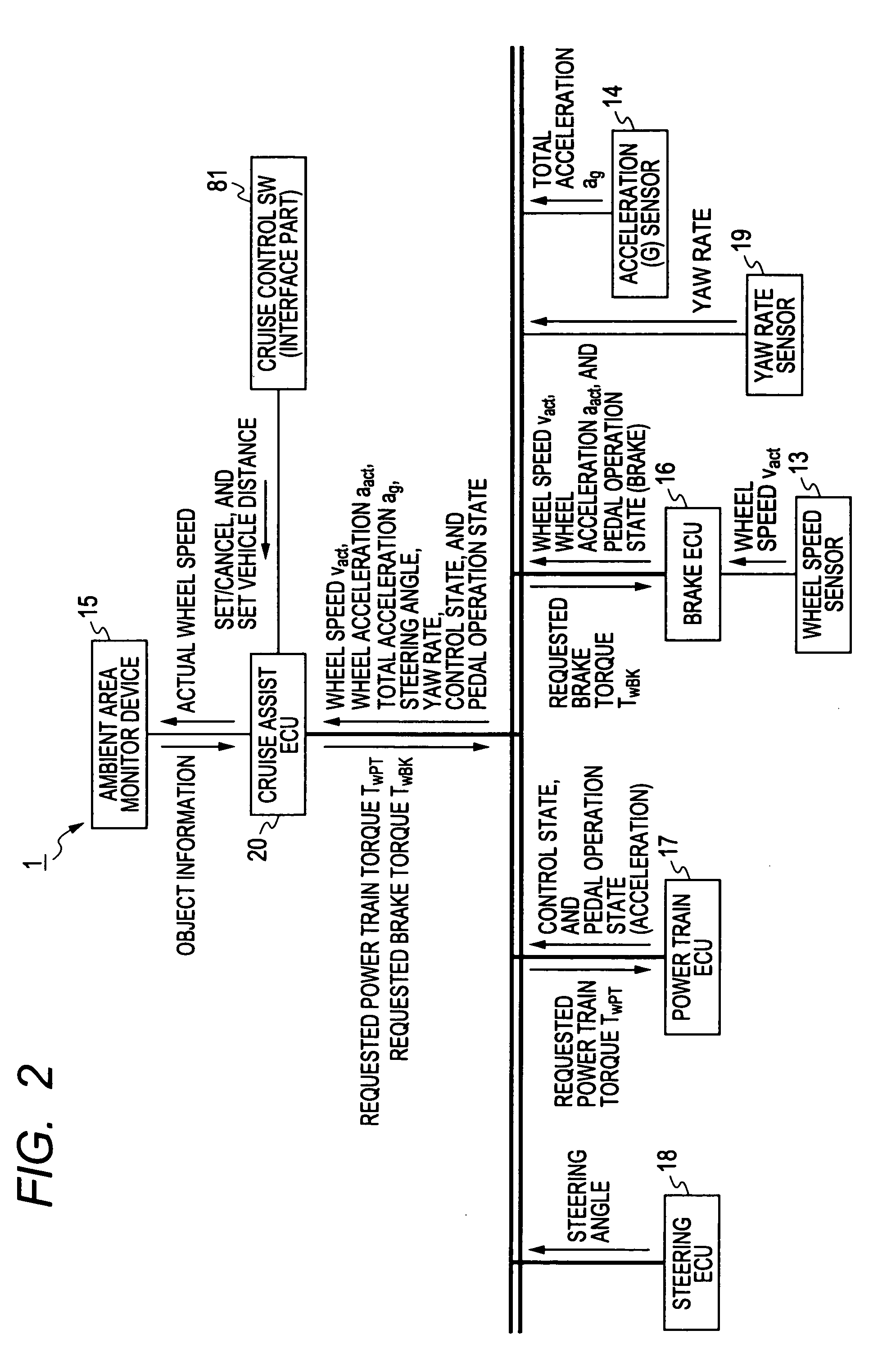
Acceleration control device
InactiveUS20110022284A1Possible to calculateDriving comfortVehicle fittingsAnalogue computers for trafficDamping torqueResponse delay
In a cruise assist ECU, when a vehicle drive state is changed from a running state to a state immediately before vehicle stop or from a stop state to a state immediately after vehicle start, a feedback torque gain compensation part changes a feedback torque gain to a second set value, and maintain it during the state immediately before vehicle stop or the state immediately after vehicle start. Because the second set value is smaller than a first set value, a response delay is increased in feedback control of the feedback torque control part when the first set value of the feedback torque gain is switched to the second set value. This makes it possible to slowly change the FB control value during the transition state in elapse of time, and prevent a brake or damping torque generated in the vehicle from being excessively changed in FB control.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Speed controller parameter optimization method in consideration of primary frequency modulation and ultralow-frequency oscillation suppression
ActiveCN107800146AElectric power transfer ac networkSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsSystem of imprimitivityWater turbine
The invention discloses a speed controller parameter optimization method in consideration of primary frequency modulation and ultralow-frequency oscillation suppression. According to the method, a single machine infinite system containing an optimized unit and an equivalent infinite power supply is established, a comprehensive optimized index function is established under the stimulation of frequency step signals of the primary frequency modulation test requirement by regarding the unit openness / power response curve rise time, stabilization time and reverse regulation power as performance indexes of primary frequency modulation and regarding damping torque coefficients of a speed controller and a water turbine system in an ultralow frequency band as ultralow-frequency oscillation damping performance indexes, the primary frequency modulation performance and the damping level can be considered by obtained speed controller parameters, and technical means is provided for optimization of the speed controller parameters and suppression of ultralow-frequency oscillation.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
Device and method for suppressing subsynchronous oscillation of power system
InactiveCN102340146AReduce dependenceSuppression of subsynchronous oscillationsPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping torqueElectric power system
The invention discloses a device and method for suppressing subsynchronous oscillation of a power system. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, filtering the rotation speed signal of a generator to obtain the subsynchronous rotation speed signal of each mode; processing the subsynchronous rotation speed signal of each mode respectively to obtain a change rate; then, generating an additional control signal through a Sugeno type fuzzy reasoning system; and finally, performing amplification, overlapping and amplitude limiting on the obtained additional control signal, and generating an exciting voltage additional control signal so as to change the exciting current, generate a subsynchronous frequency damping torque and suppress the subsynchronous oscillation. In the method provided by the invention, a training sample of a fuzzy controller is established according to the phase compensation principle, and the parameters of the fuzzy system are optimized and trained by use of a learning algorithm of an error backpropagation neural network. The method solves the problem that the expert experience is difficult to obtain by the fuzzy controller, and the additional exciting damping controller can effectively suppress the subsynchronous oscillation of the power system.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus and method for regulating active driveline damping in hybrid vehicle powertrain
The present invention provides an improved method and apparatus for regulating active damping in a hybrid vehicle powertrain. The method includes: monitoring the damping command sent to the active damping system; determining a mean reference point, which may be a filtered value of the damping torque command; determining if the unfiltered damping torque command value switches from one side to the other of the mean reference point; if a switch is detected, determining if the size of the switch exceeds a predetermined minimum; if it does, then increasing a total number of switches; determining if the total number of switches exceeds a switch threshold; if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold, determining if the current damping torque exceeds a damping torque threshold; and decreasing the damping torque if the total number of switches exceeds the switch threshold and the current damping torque exceeds the damping torque threshold.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
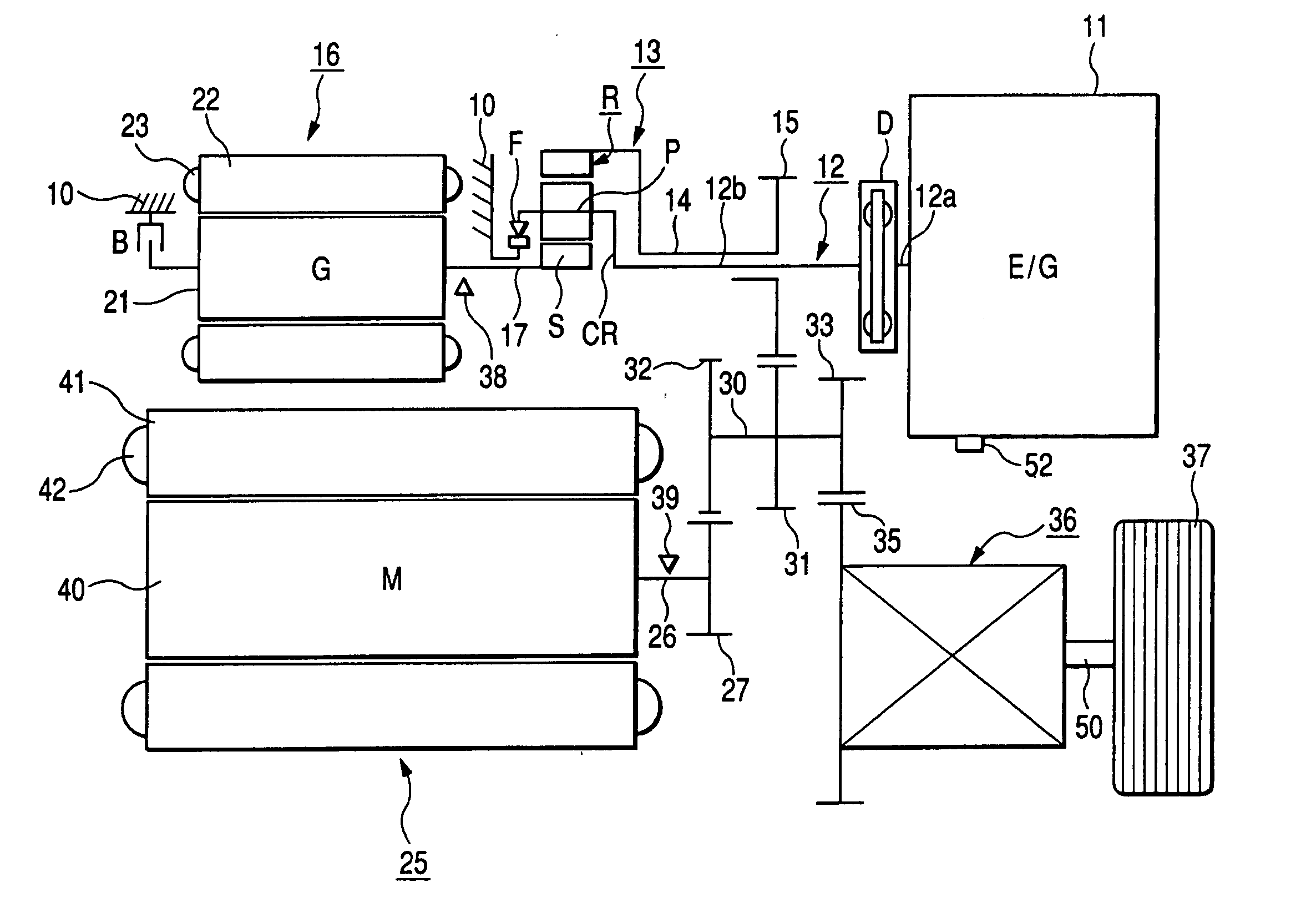
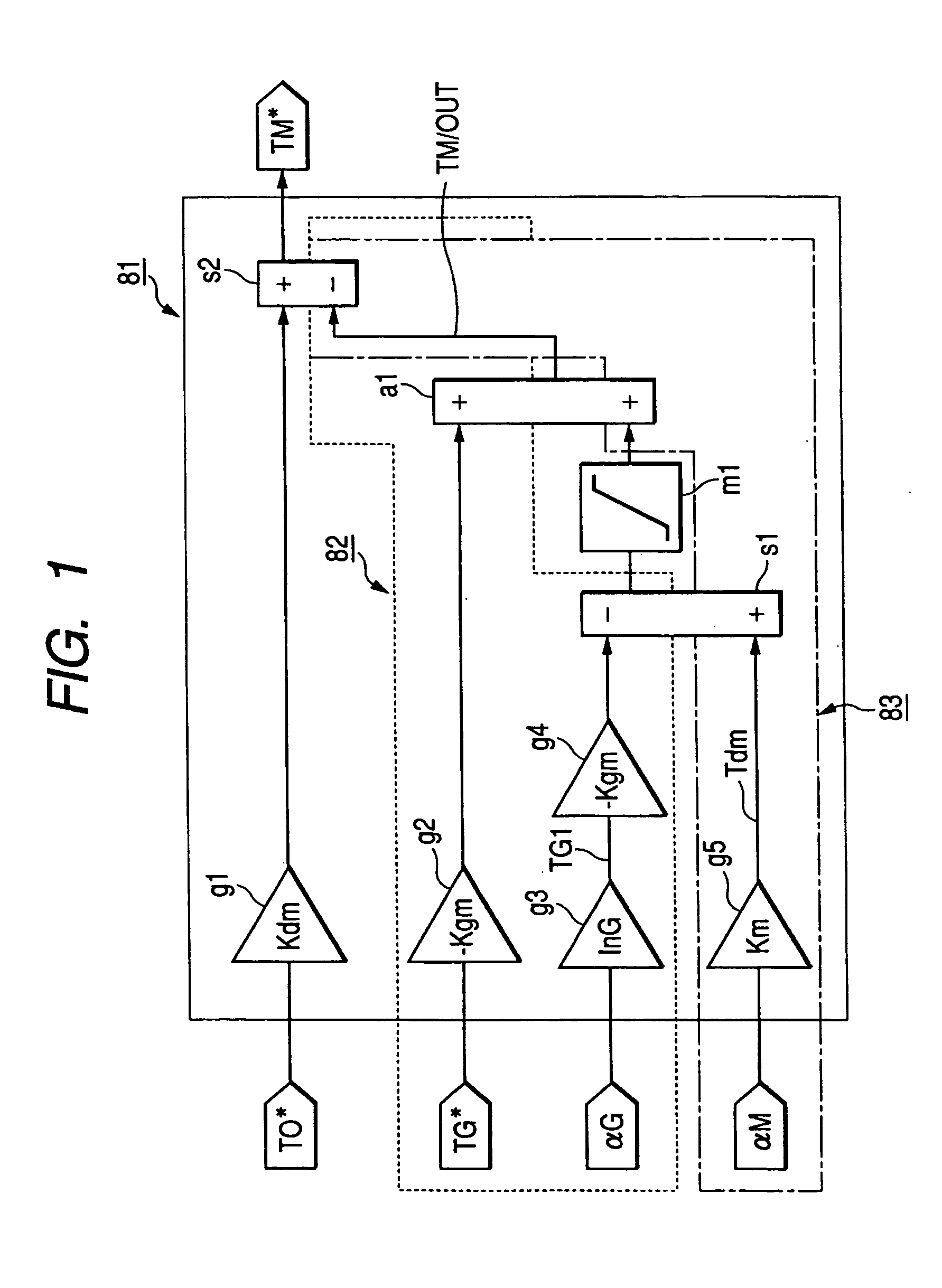
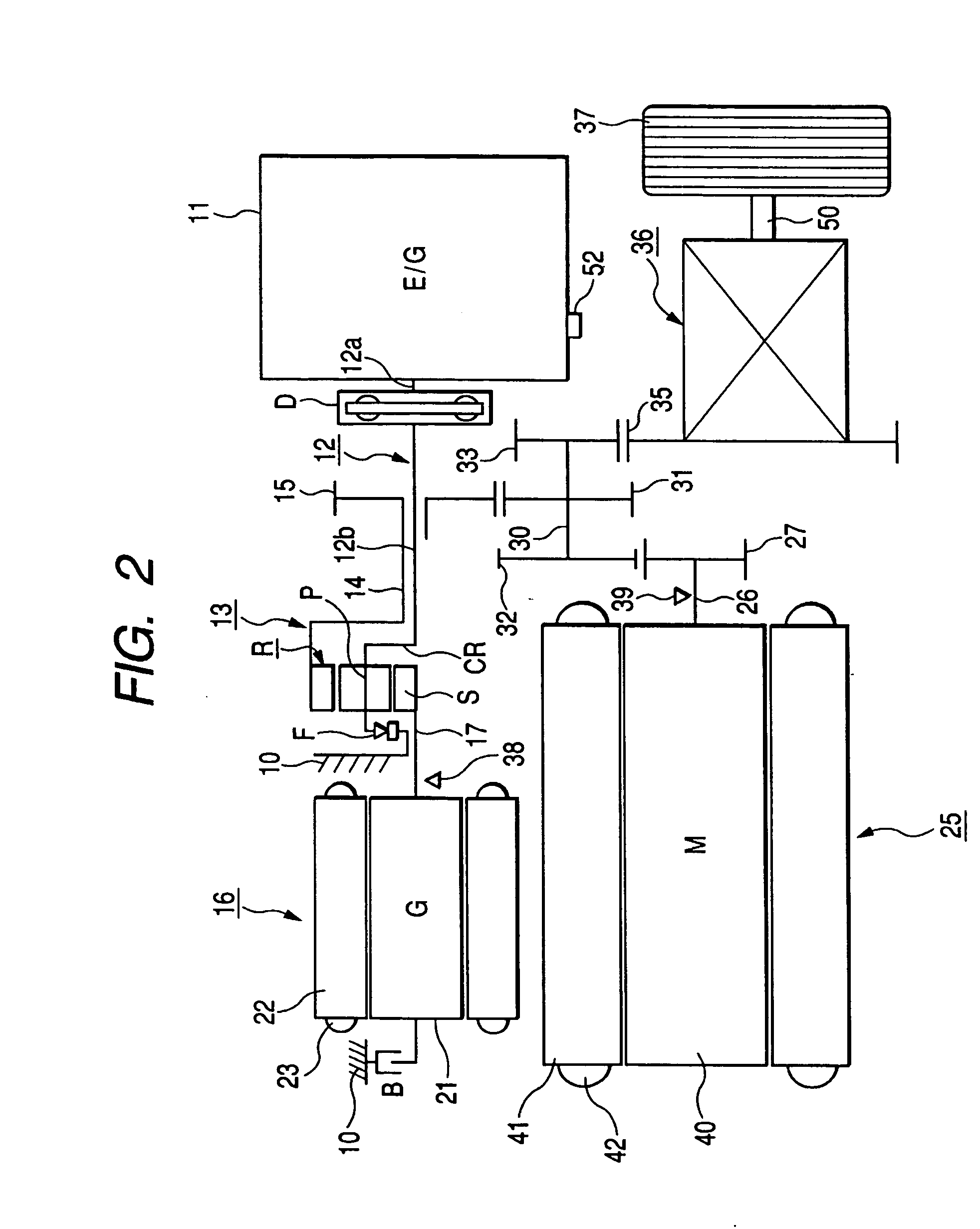
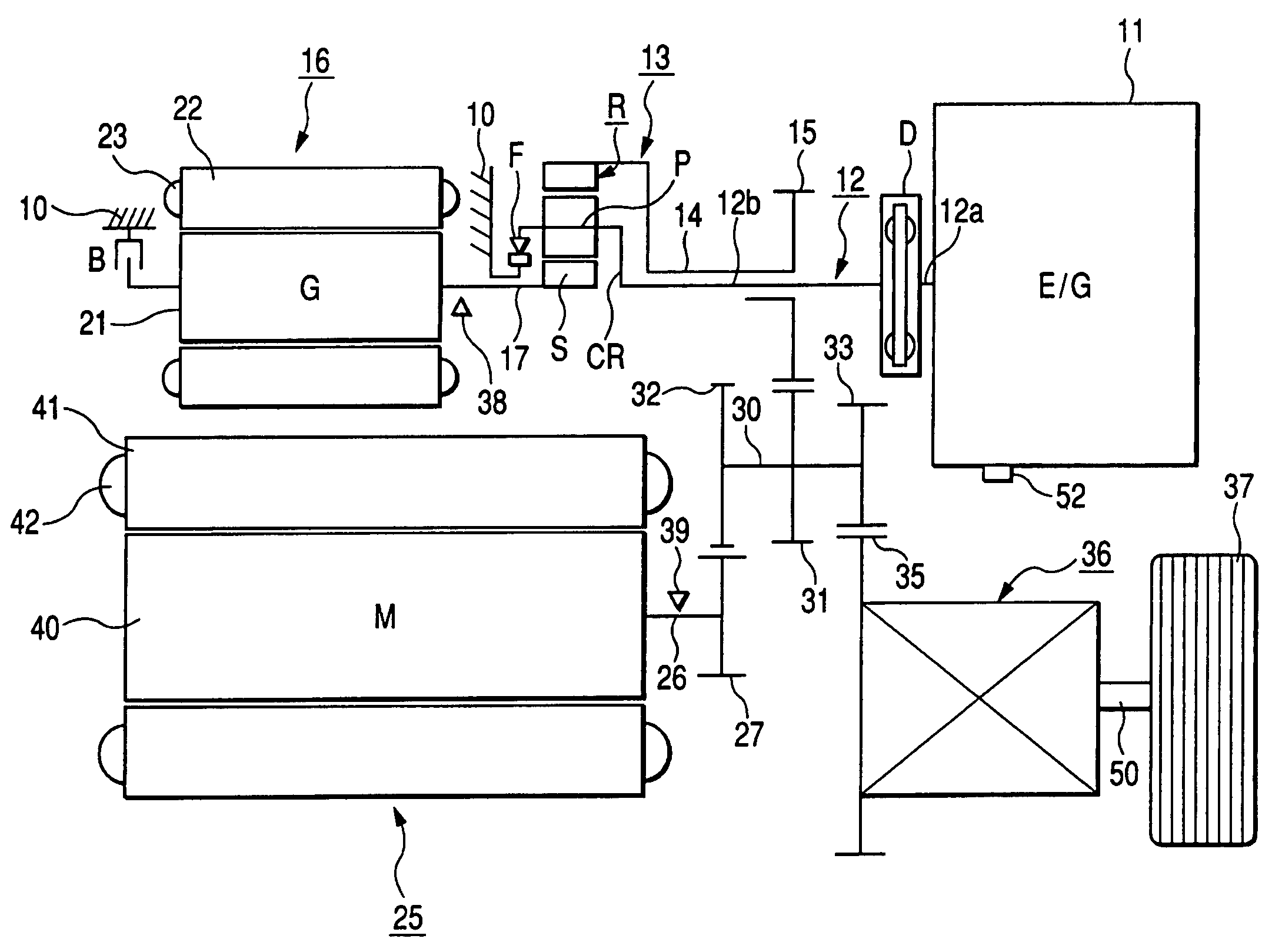
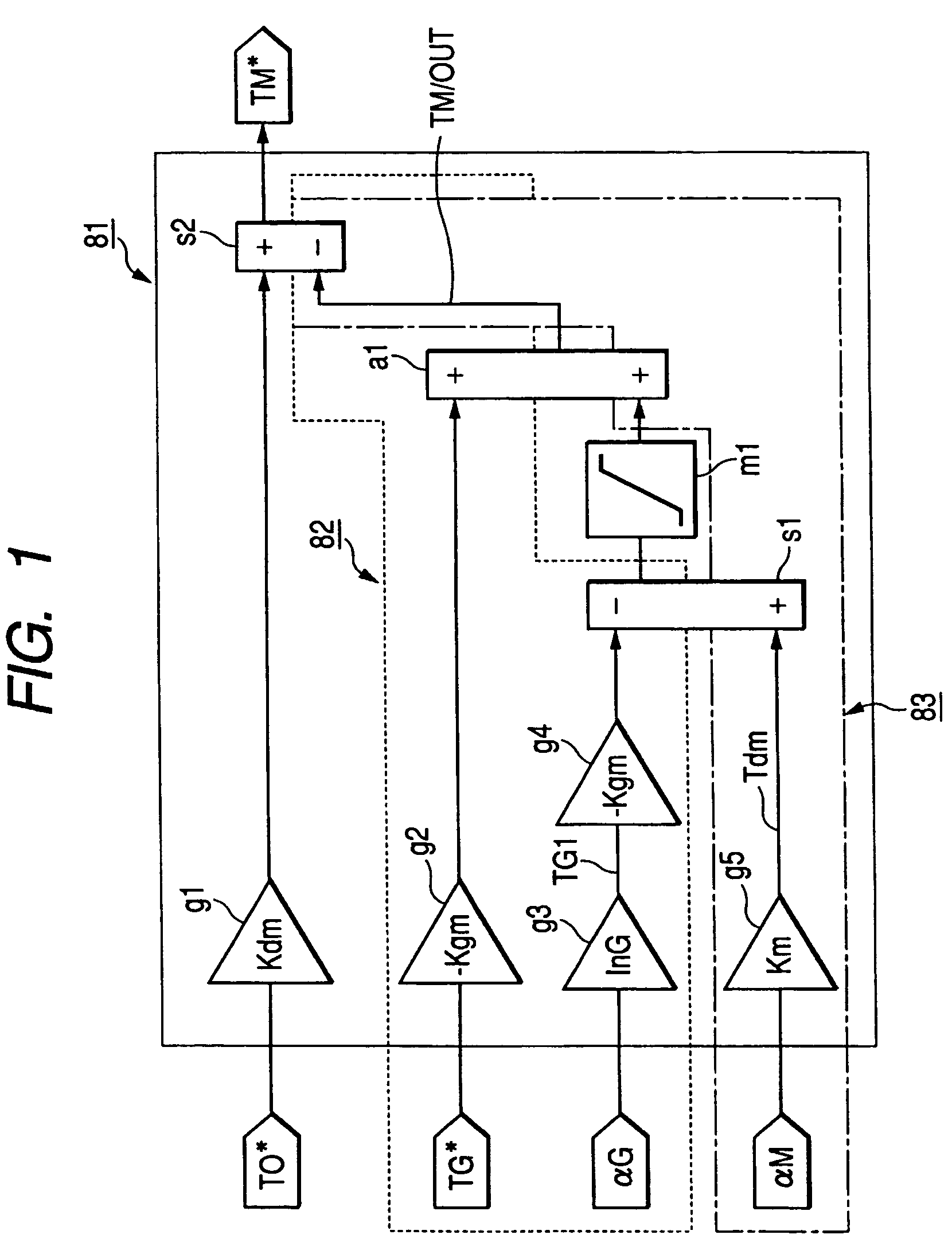
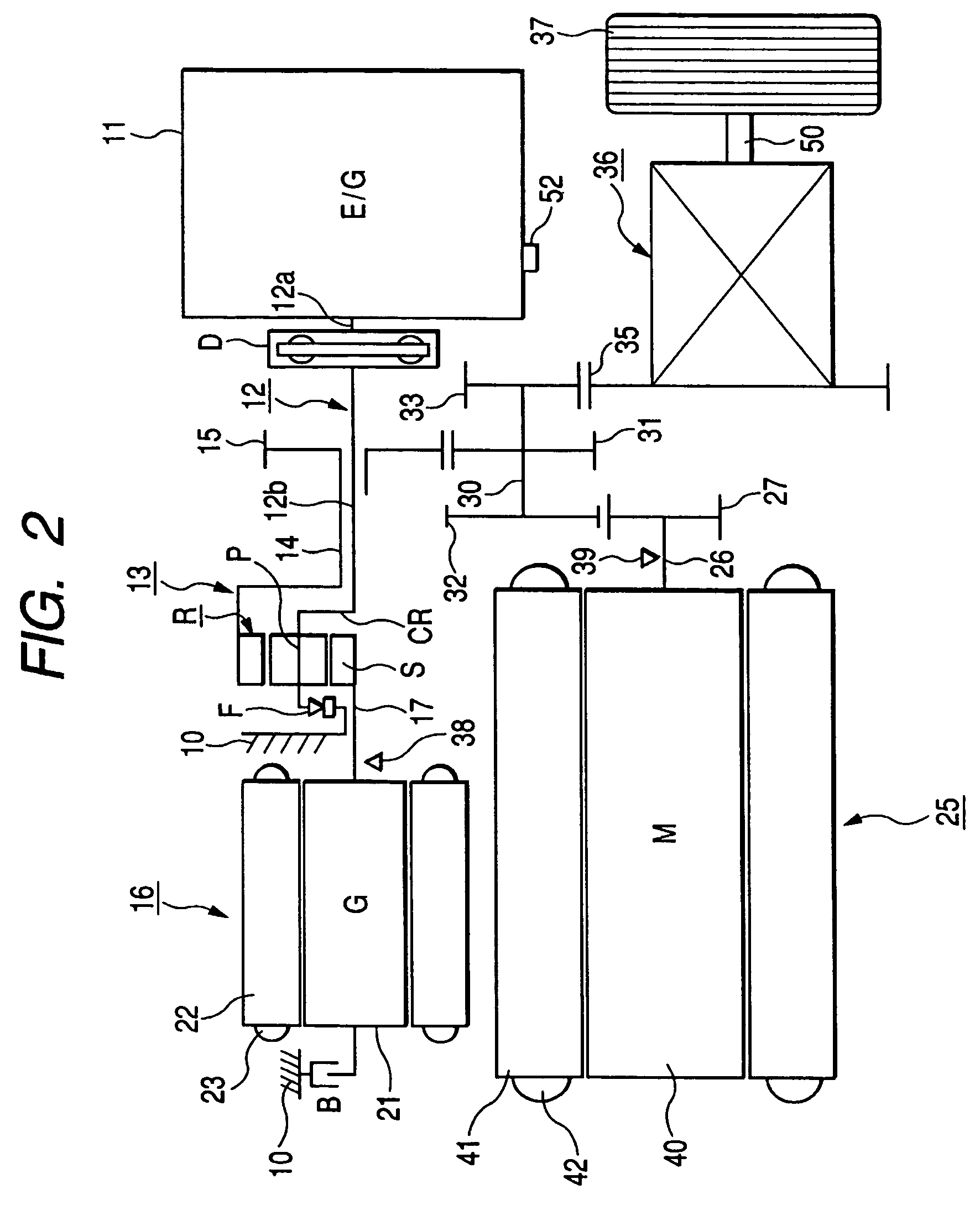
Electrically operated vehicle drive controller and electrically operated vehicle drive control method
ActiveUS20050283283A1Avoid it happening againReliably compensate for the excessive and deficient amountsHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDamping torqueDrive motor
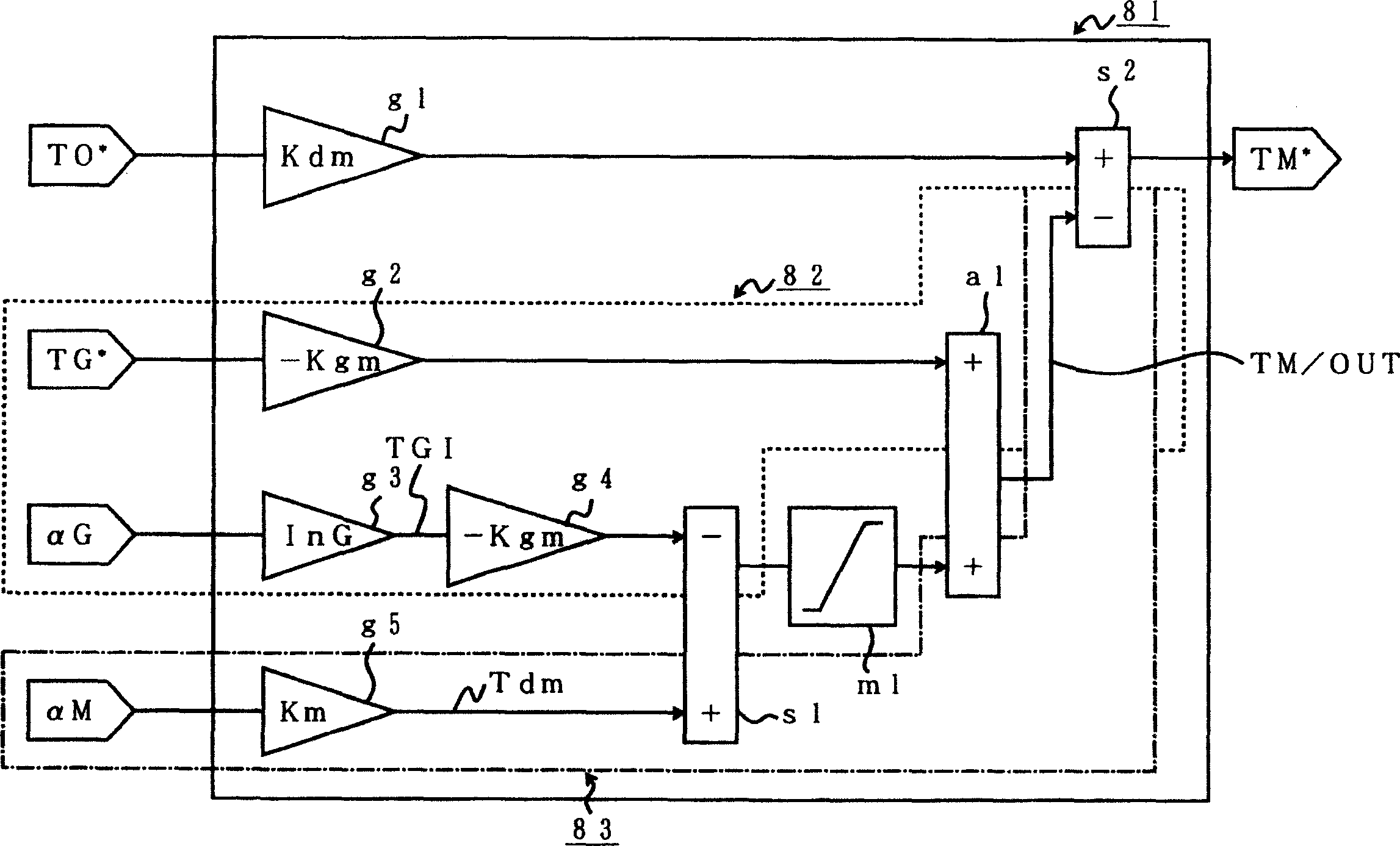
An electrically operated vehicle drive controller has an electric generator target torque calculation processing means for calculating electric generator target torque TG*; an inertia correction torque calculation processing means for calculating inertia correction torque on the basis of inertia torque TGI of an electric generator; a drive motor target torque generation processing means for generating drive motor target torque on the basis of the calculated inertia correction torque; and a damping torque correction processing means for correcting output torque on the basis of an output torque changing index which expresses a change of output torque due to the inertia correction torque.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
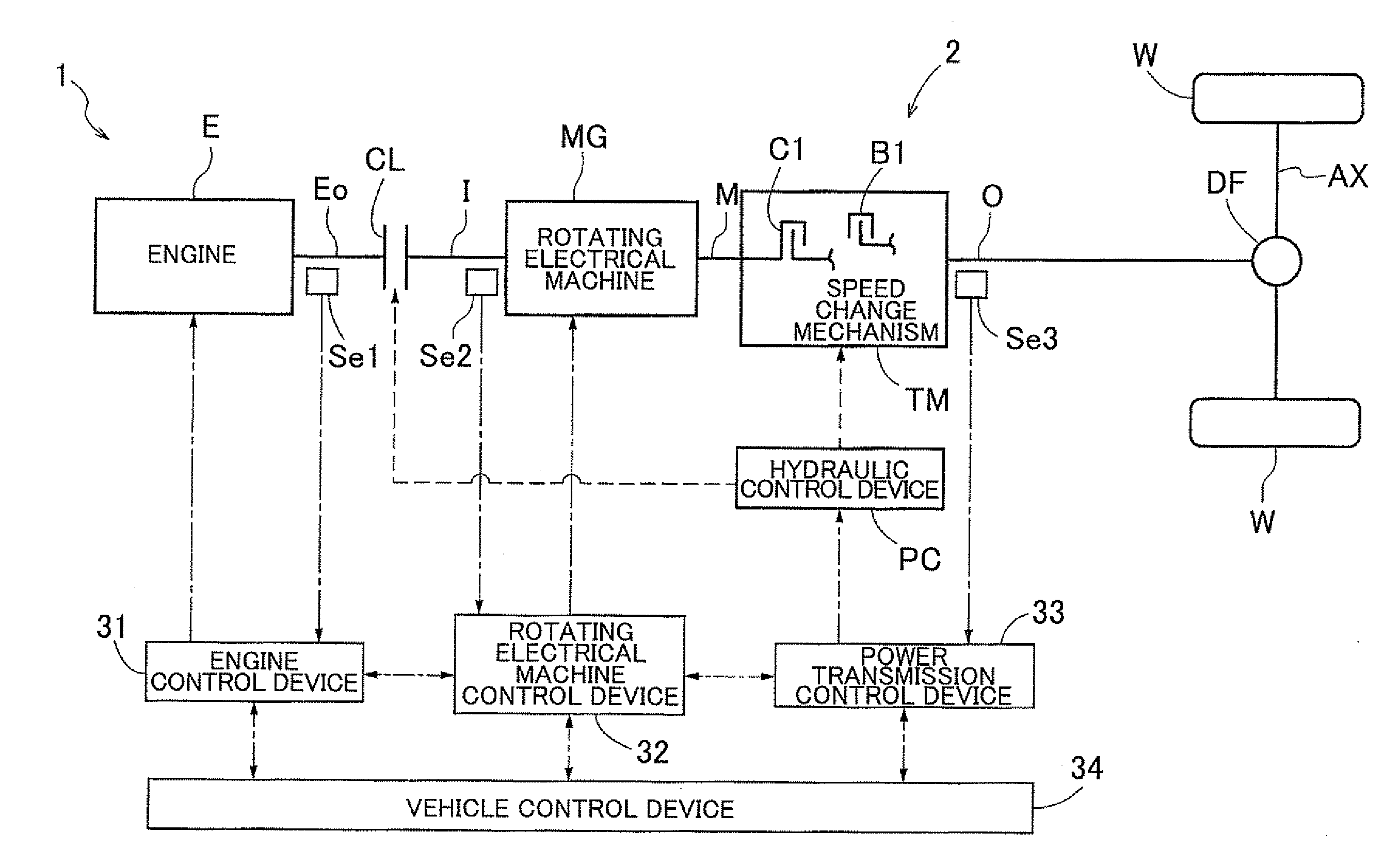
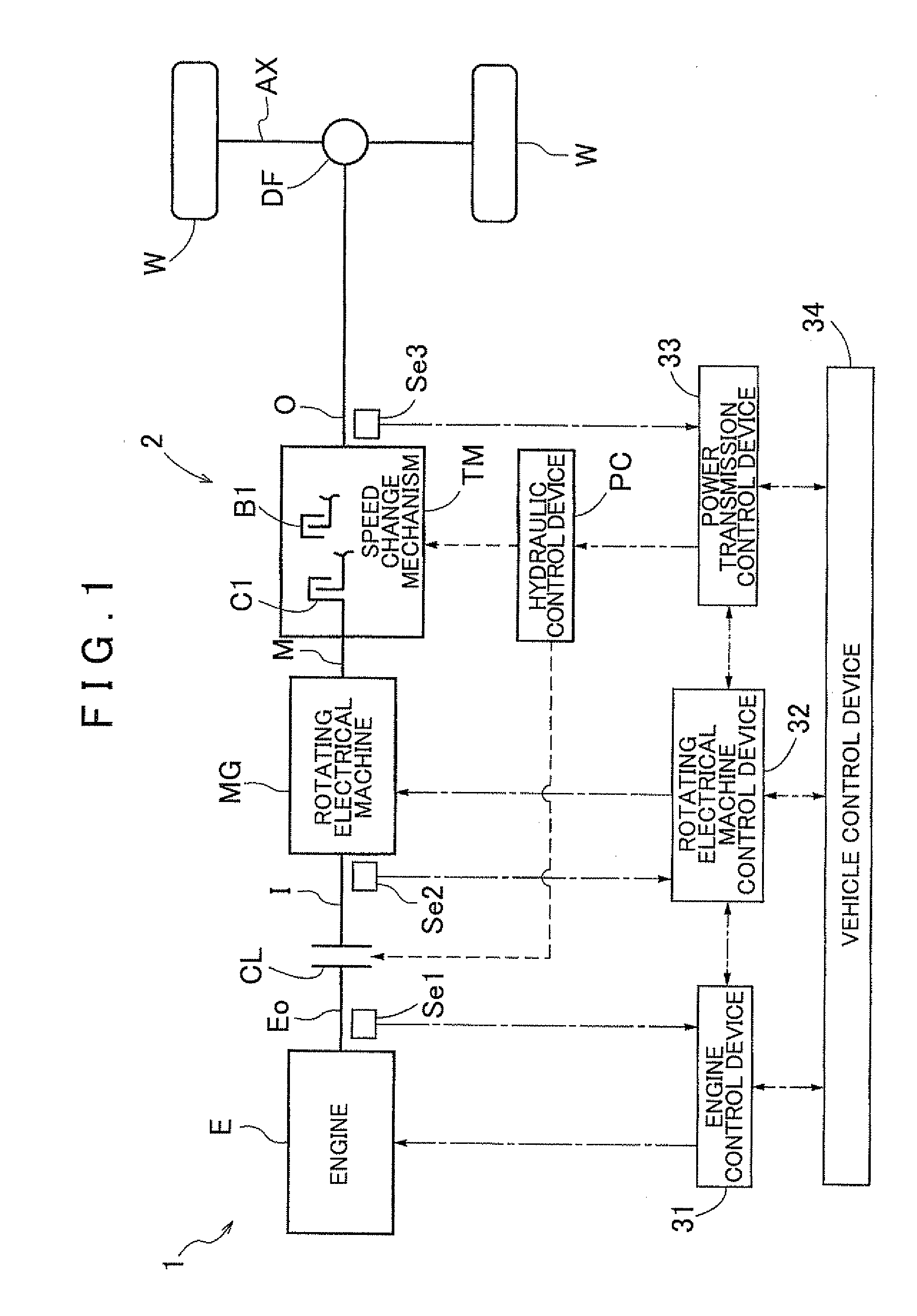
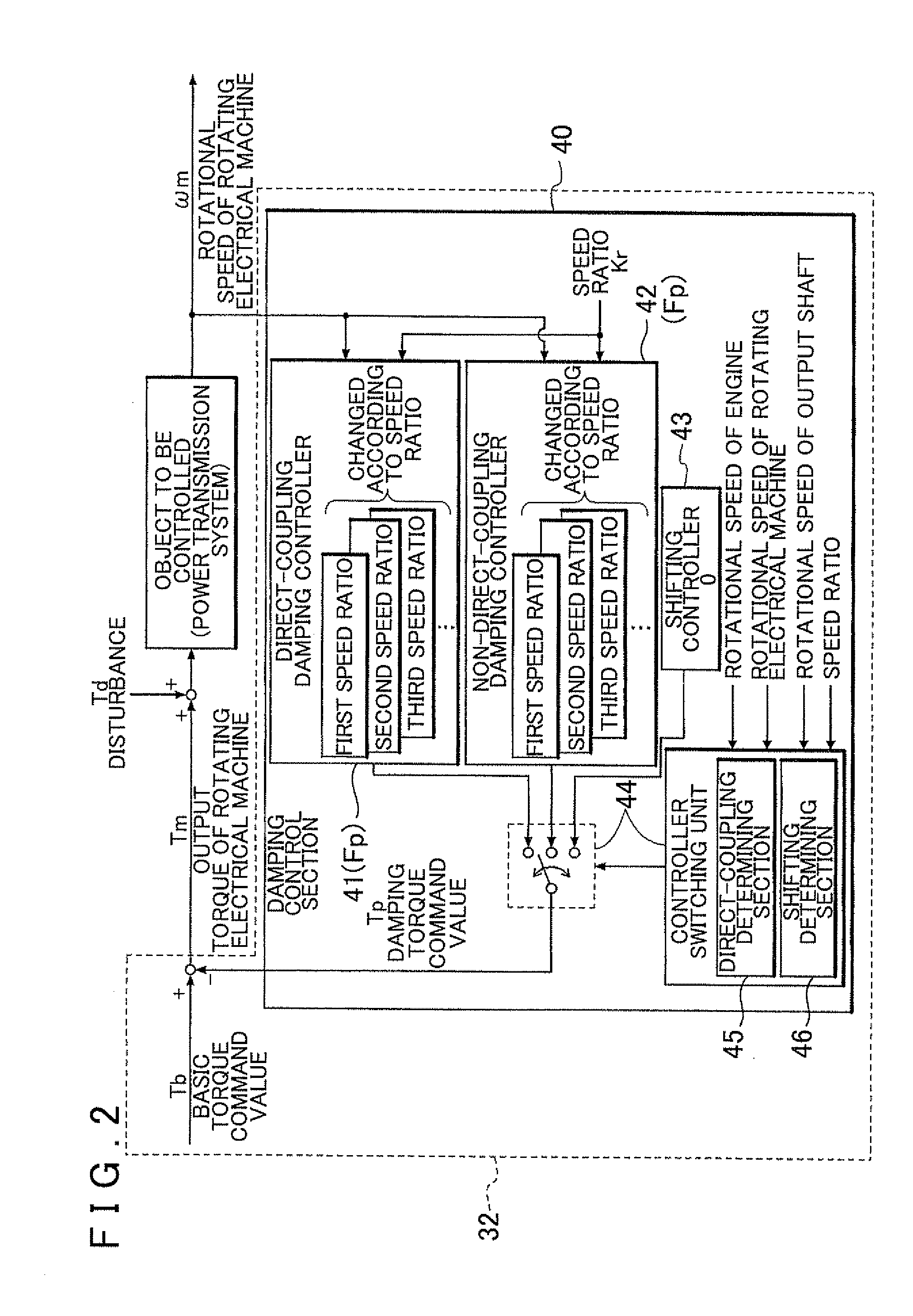
Control device
InactiveUS20120083953A1Limit unnecessary executionReduce output torqueHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineDamping torque
A control device capable of executing damping control of outputting a damping torque command that suppresses vibration of a rotational speed of a rotating electrical machine caused at least by elastic vibration of a power transmission mechanism. This is accomplished by using feedback control based on the rotational speed of the rotating electrical machine. The control device executes the damping control by a direct-coupling damping controller when the engagement state of the engagement device is a direct-coupling engagement state in which there is no rotational speed difference between engagement members, and executes the damping control by a non-direct-coupling damping controller different from the direct-coupling damping controller in a case where the engagement state of the engagement device is a non-direct-coupling engagement state other than the direct-coupling engagement state.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
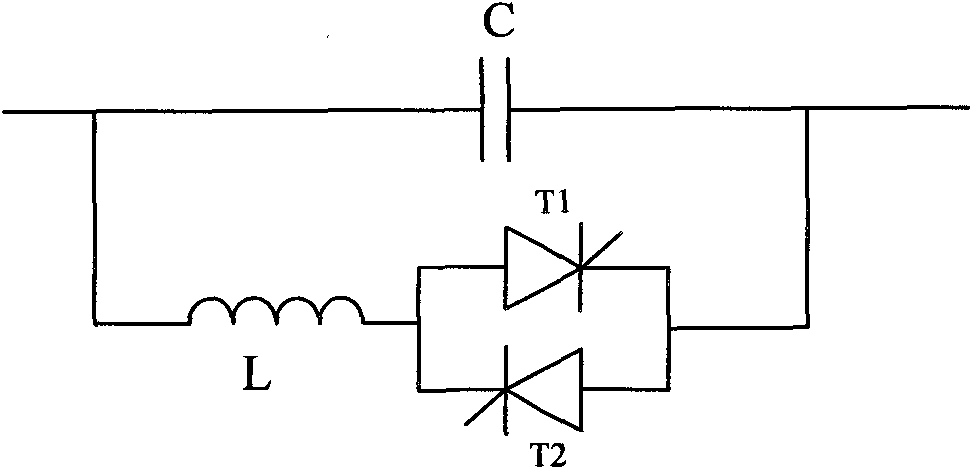
Sub-synchronous oscillation suppression method based on controlled series compensation
InactiveCN101834446APower oscillations reduction/preventionHarmonic reduction arrangementCapacitanceSub synchronous resonance
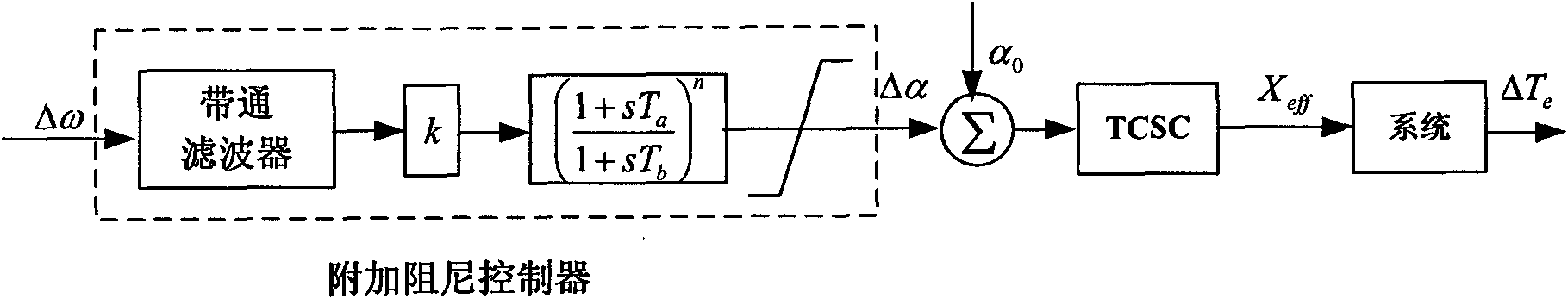
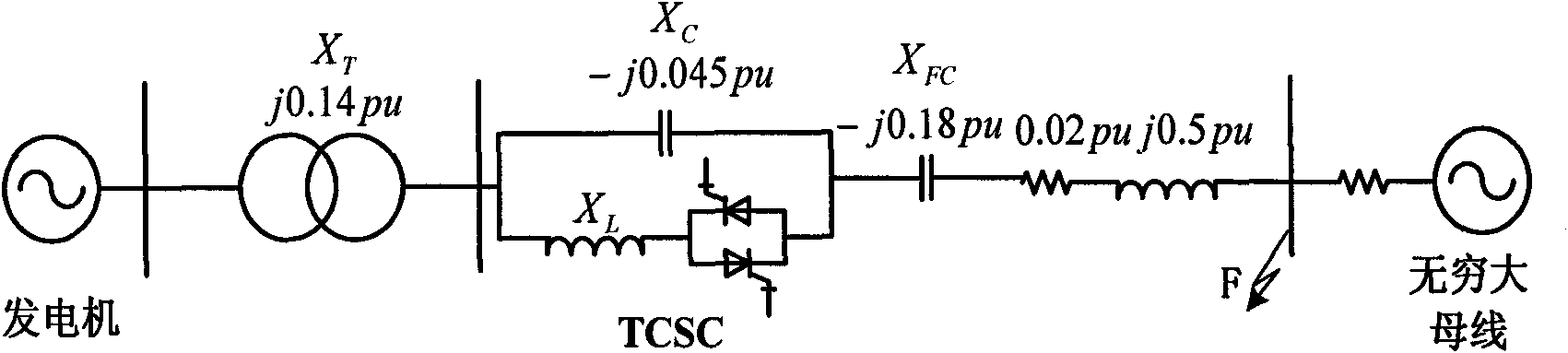
The invention relates to a sub-synchronous oscillation suppression method based on controlled series compensation, which is based on the concept of damping torque, adopts a design method of phase compensation, and carries out proper amplification and phase shift processing on speed signal delta omega to generate an additional control signal to modulate a TCSC (Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor) trigger angle. Therefore, equivalent reactance of the TCSC is changed, the TCSC can provide positive electrical damping in the entire sub-synchronous frequency range, and the problem of SSR (Sub-Synchronous Resonance) caused by series compensation capacitors can be thoroughly eliminated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gearbox noise reduction by electrical drive control
ActiveUS8532828B2Reduce audible noiseReducing audibleNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital data processing detailsDamping torqueEngineering
A system for damping audible noise from a drive train. One embodiment is a system with an audible noise signal from a drive train wherein a damping circuit produces a damping torque that is a phase shifted and amplified version of the noise signal that is applied to the air-gap torque of a generator or motor coupled to the drive train and effectively reduces the audible noise.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
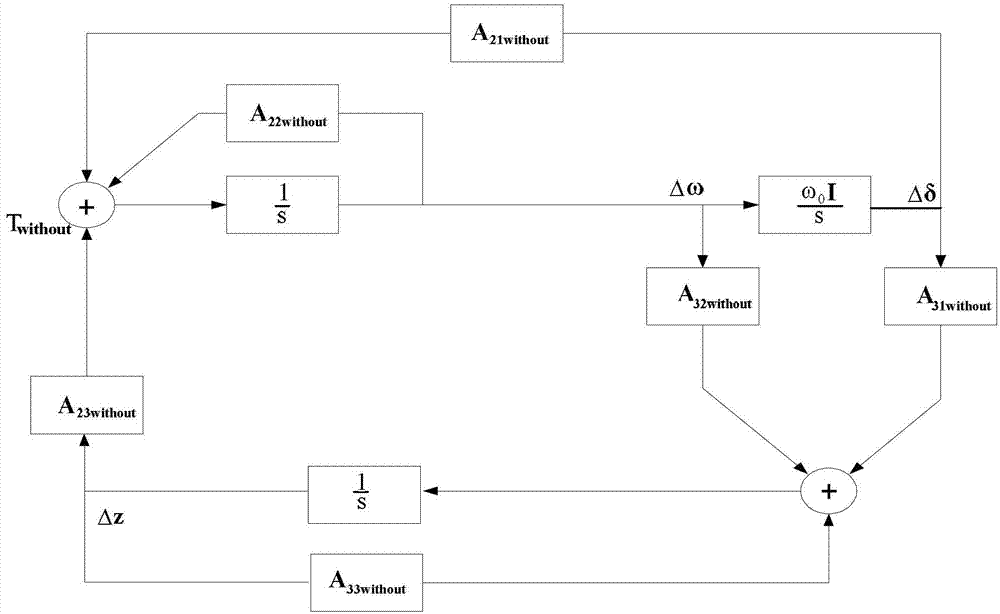
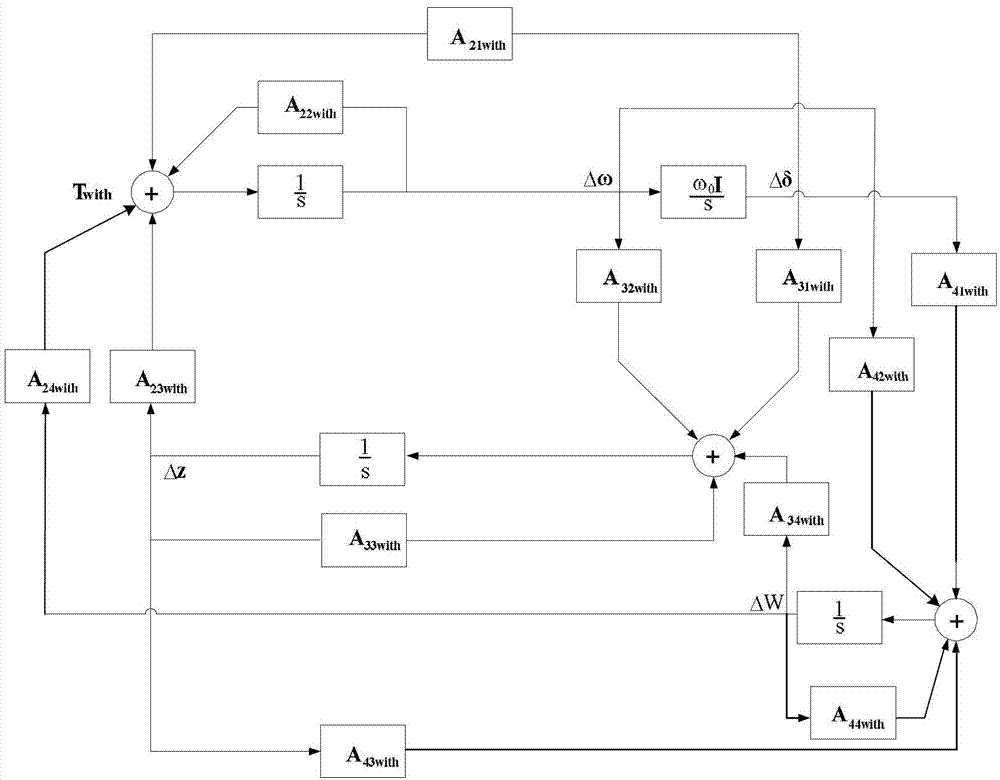
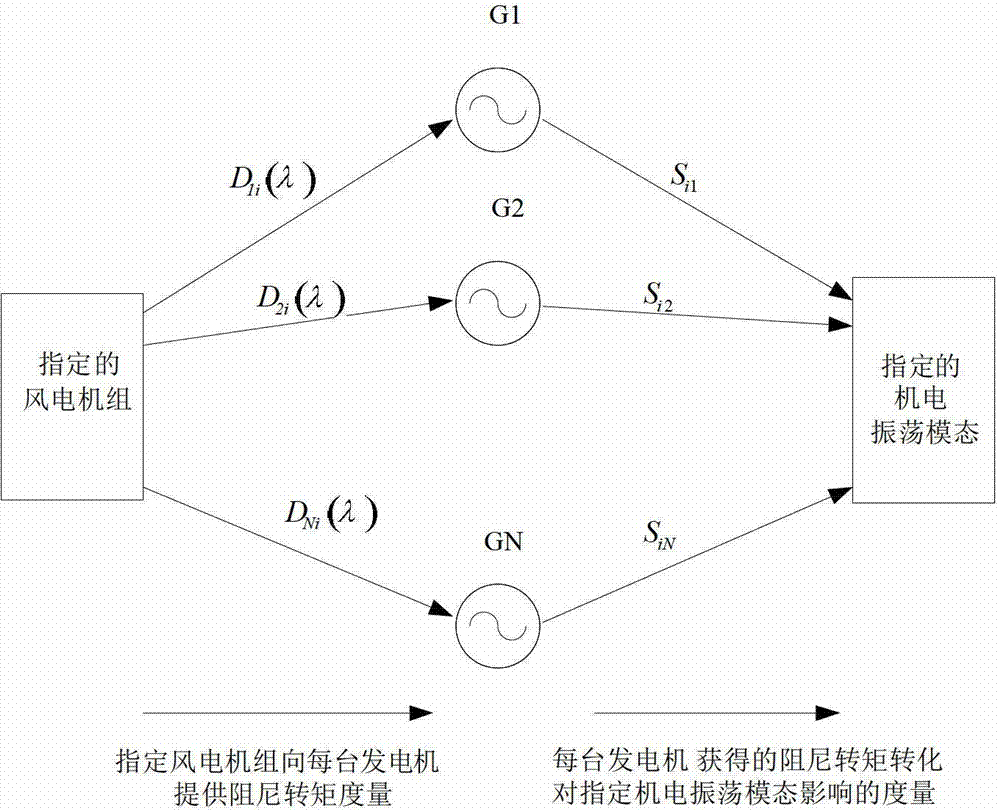
Analyzing method for damping torque having small interfering stable influence on power system caused by wind power integration
InactiveCN103050992ASingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationElectricityLinear matrix
The invention discloses an analyzing method for a damping torque having a small interfering stable influence on a power system caused by wind power integration. The method comprises the following steps: performing depreciating treatment on a system linear matrix containing no fan set and a system linear matrix containing an appointed fan set, thereby obtaining a damping torque matrix provided by a generator before and after the fan is added, and then calculating a participating factor of each generator corresponding to an appointed vibration mode, thereby obtaining the influence of the accessing of a wind fan on the appointed vibration mode. The analyzing method can be utilized to clearly and detailedly give out how the appointed fan influences the electromechanical vibration mode of an appointed power system through each synchronous generator, so that a physical significance guidance is supplied to the small interfering vibrating stability analysis for the power system connected with the fan, the selection and the control design for a fan mounting place.
Owner:杜文娟
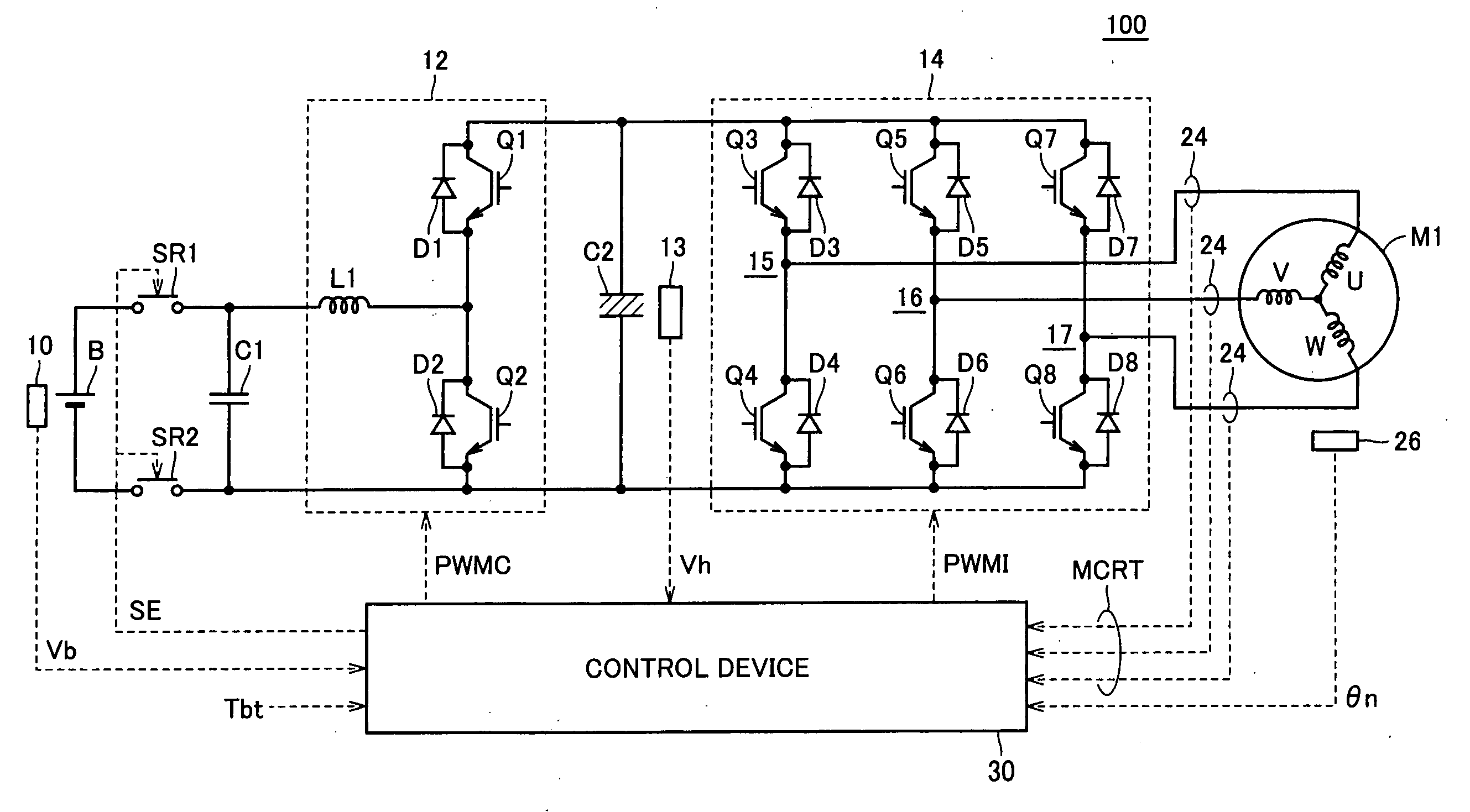
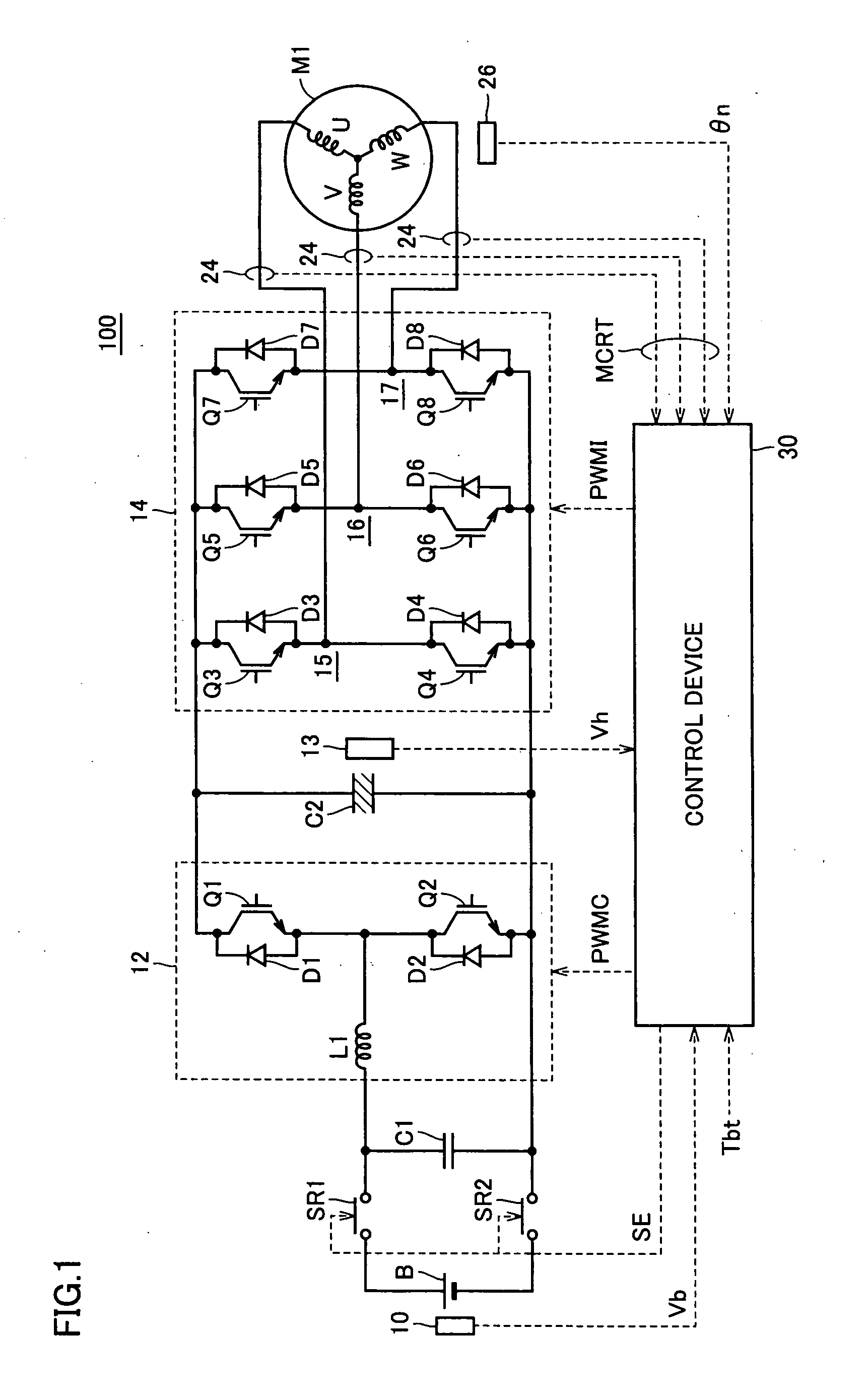
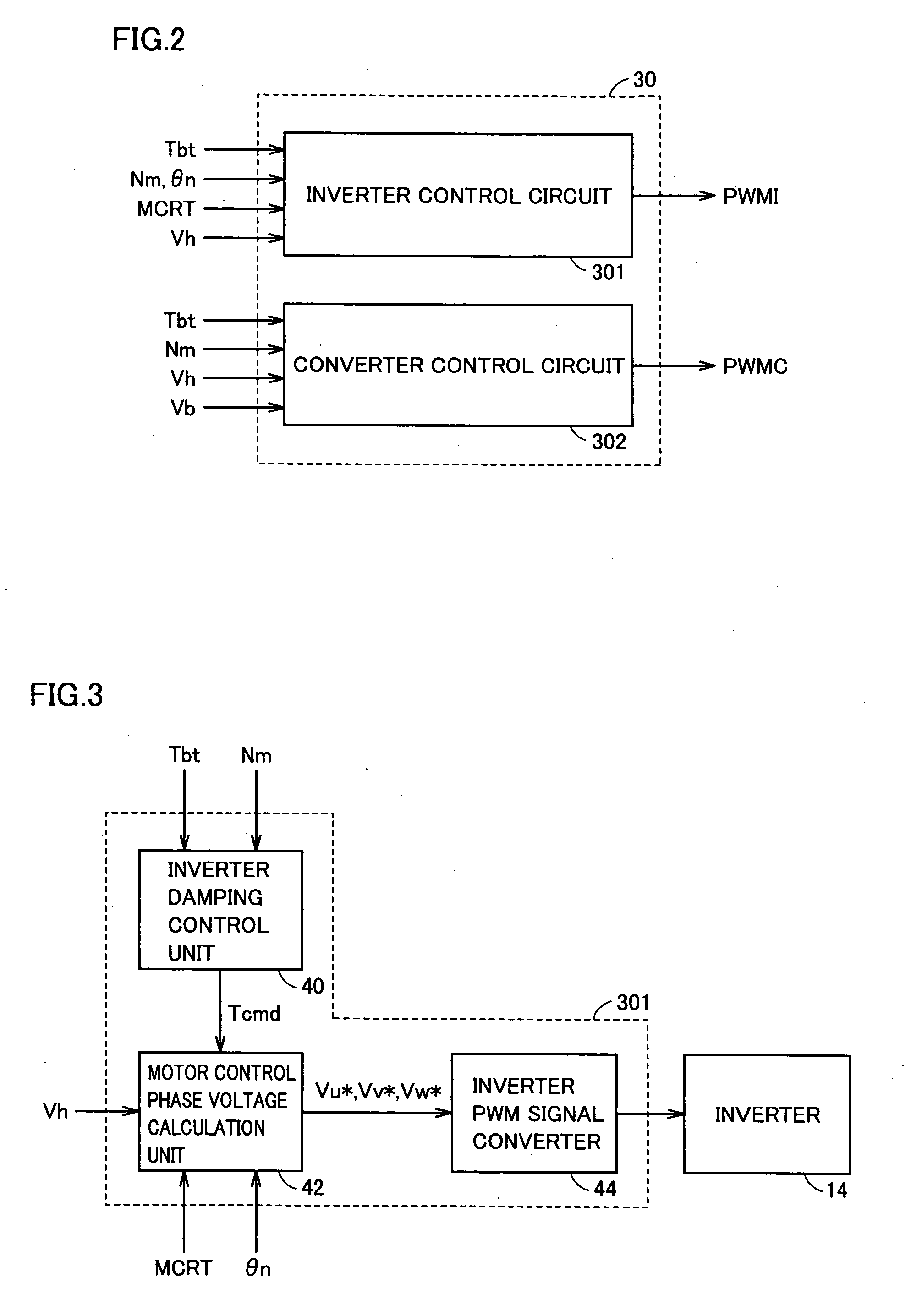
Motor Drive Device and Control Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090160380A1Reduce decreaseTorque ripple controlCommutation monitoringMotor driveDamping torque
A torque command (Tht) used in the calculation of a voltage command (Vht) of a voltage-up converter is generated by adding an upper limit value value (Tc_max) of damping control that can be set by a motor drive device with a target drive torque (Tbt). Accordingly, the torque command (Tht) exhibits a waveform absent of variation, differing from a torque command (Tcmd) that is generated by adding damping torque generated based on revolution count variation component with the target drive torque (Tbt). Therefore, the voltage command (Vht) calculated based on the torque command (Tht) exhibits a waveform absent of variation. Accordingly, increase in current passing through the voltage-up converter caused by variation in the voltage command (Vht) can be suppressed. As a result, power loss at the voltage-up converter is reduced and operation of the motor at high efficiency can be realized. Further, the voltage-up converter can be protected from element fracture.
Owner:DENSO CORP
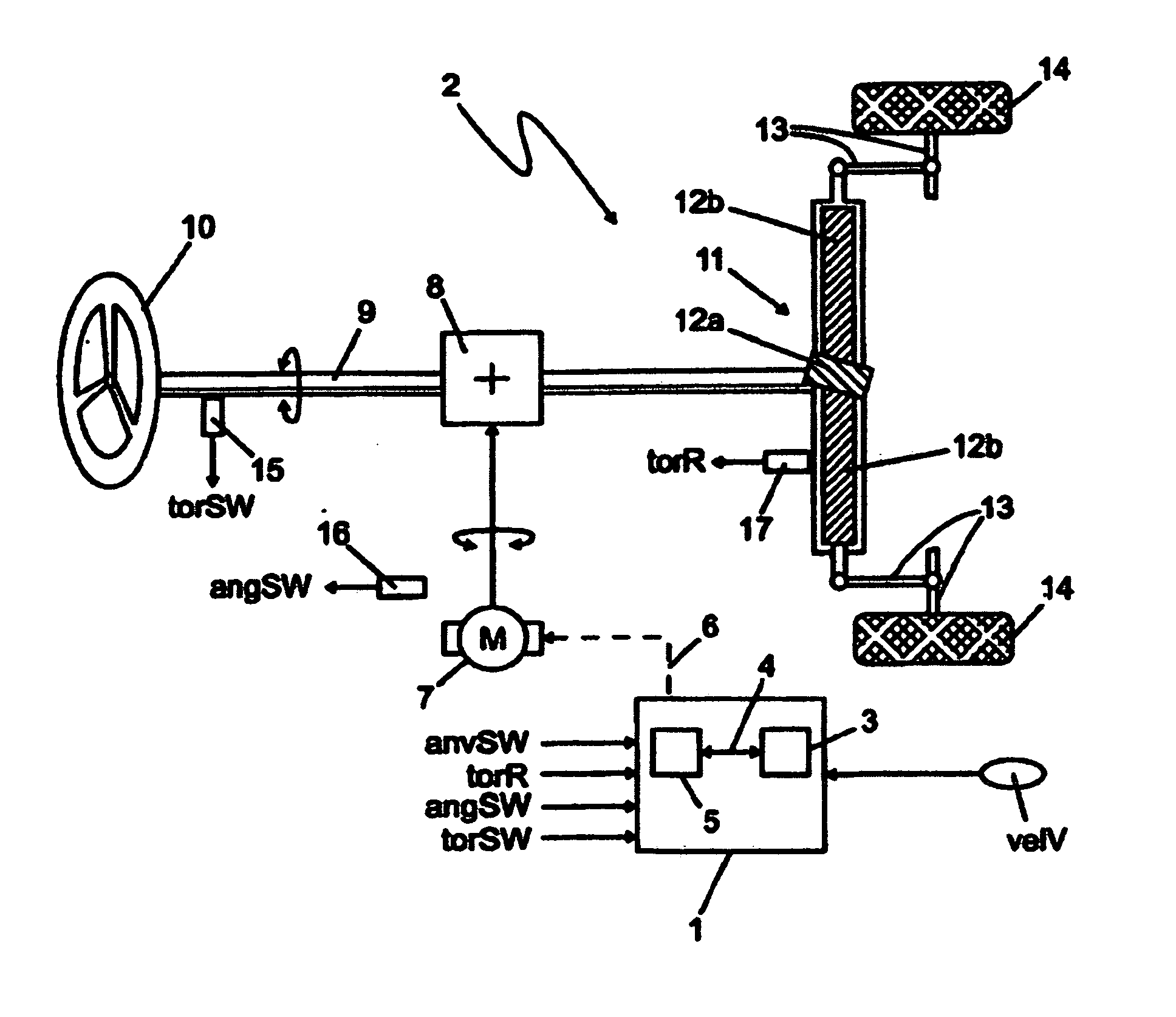
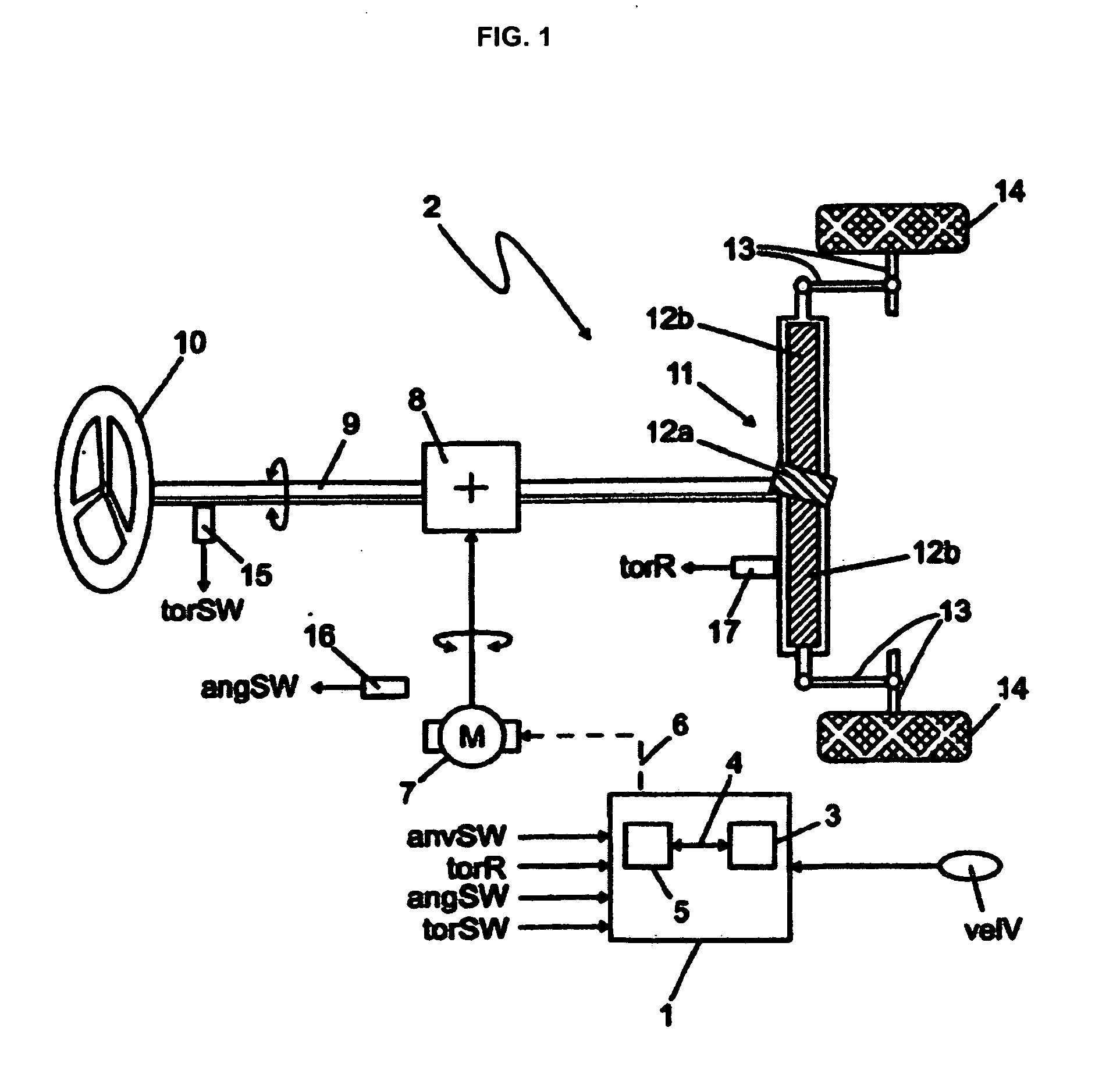
Determining a target steering torque in a steering device
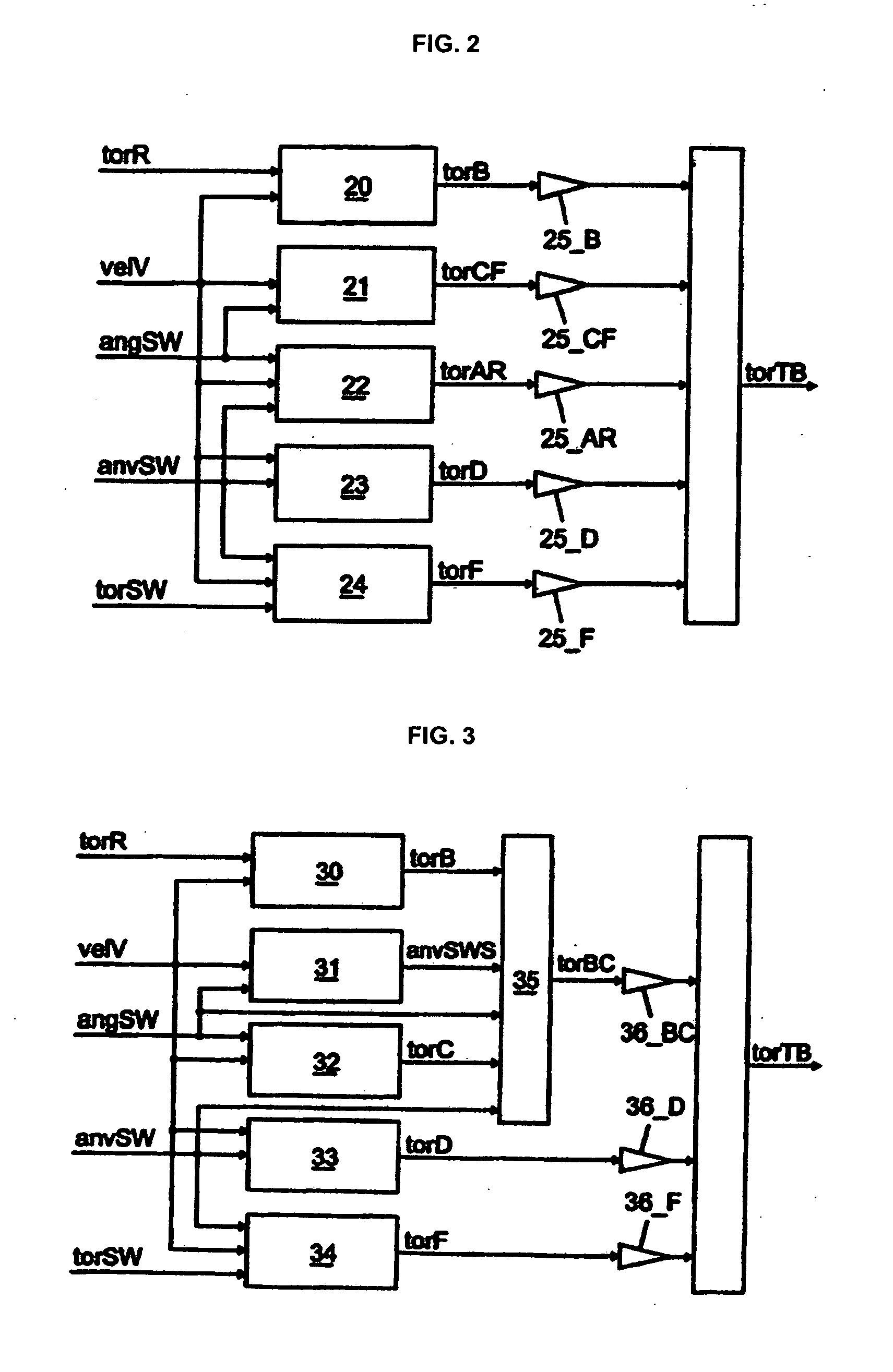
In order to achieve a steering feel for SbW systems and EPS systems having a control design for controlling the steering torque by generating a target steering torque (torTB) that can be adapted to various steering systems, vehicle types, or requirements, in which the resulting steering feel is a steering feel, in all driving conditions and driving situations, which is equivalent to, or better than, hydraulic and electromechanical steering systems available on the market today, according to the invention: a base steering torque (torB) is determined as a function of an externally acting force (torR) and a vehicle speed (velV); a damping torque (torD) is determined as a function of a steering speed (anvSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); a hysteresis torque (torF) is determined as a function of the steering speed (anvSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); a centering torque (torCF; torC) in the direction of the straight-ahead position is determined as a function of a steering wheel angle (angSW) and the vehicle speed (velV); and the base steering torque (torB), the damping torque (torD), the hysteresis torque (torF) and the centering torque (torCF; torC) form individual components, as a function of which the target steering torque (torTB) is determined.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH AUTOMOTIVE STEERING
Prime mover speed control system additional damper control method
ActiveCN106911274ASuppress low frequency oscillation phenomenonEnhanced damping of ultra-low frequency oscillationsPower oscillations reduction/preventionElectric generator controlDamping factorSpeed control system
The invention relates to a prime mover speed control system additional damper control method. The mechanical power which affects the prime mover speed control system is calculated according to a pre-defined prime mover speed control system model. The mechanical power is decomposed into damping torque and synchronization torque components, so as to acquire compensated additional damping coefficients under power closed-loop adjustment and rotation speed closed-loop adjustment. According to the additional damping coefficients, the damping torque interval is determined. A speed control system additional damper model is built to carry out phase compensation on a compensation link corresponding to the phase frequency characteristic of the speed control system, so that the additional damping coefficients are positive. According to the invention, ultra-low frequency oscillation damping caused by the speed control system is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Novel electronic power steering system testing platform and testing method thereof
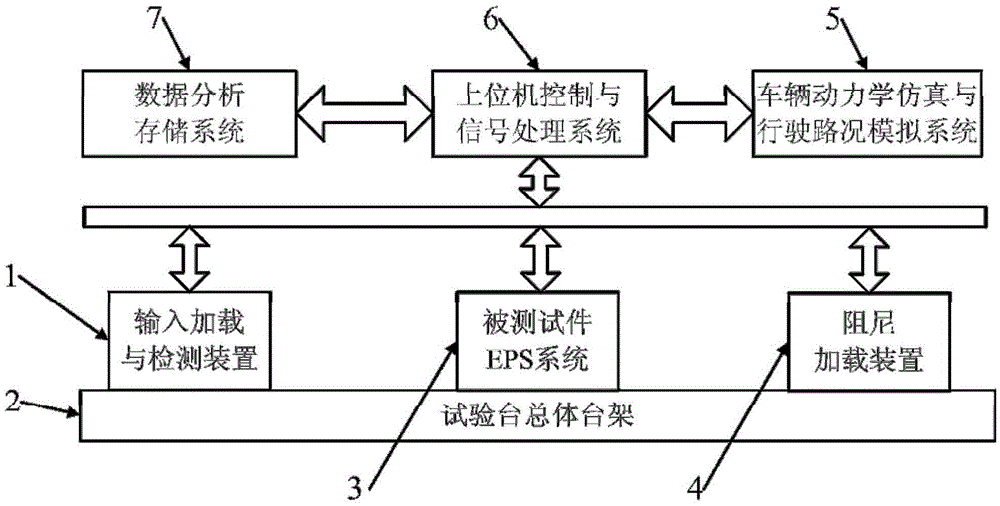
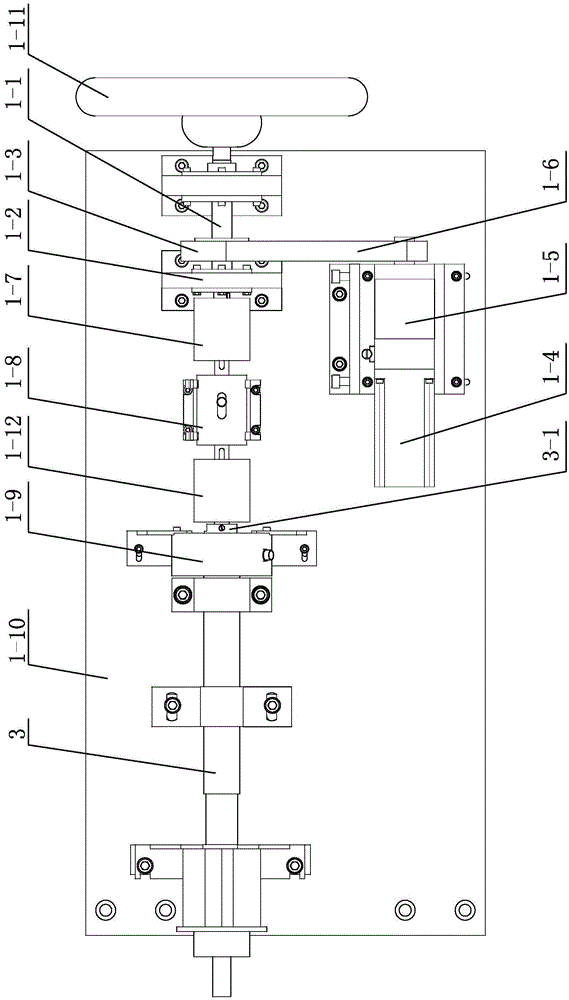
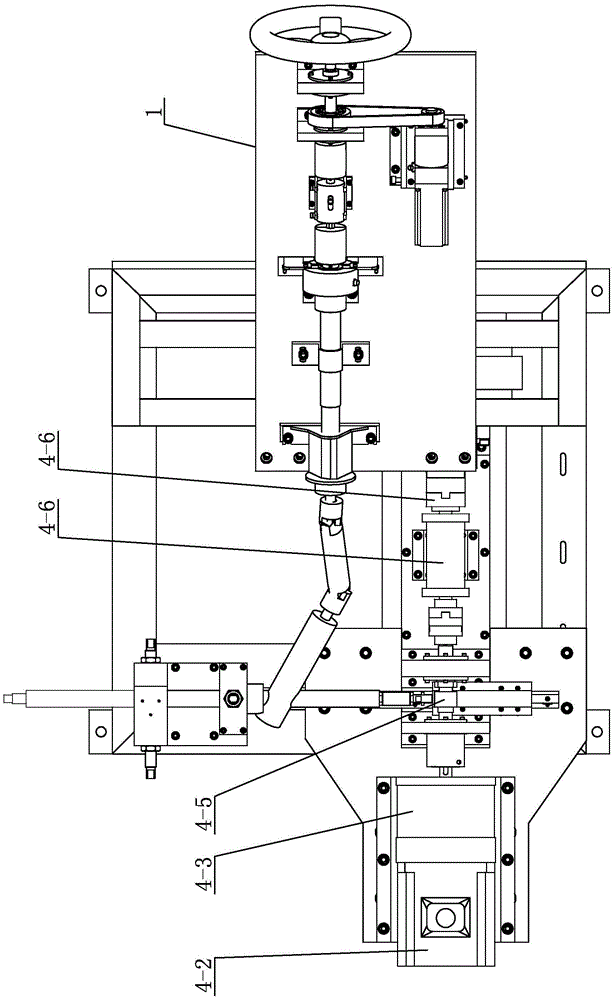
ActiveCN105606382ALow costHigh outputVehicle steering/rolling behaviourElectric power steeringDamping torque
The invention provides a novel electronic power steering system testing platform and a testing method thereof. A steering wheel is installed on an input shaft; a servo motor I uses a reduction box and a synchronous belt to drive the input shaft to make rotation, thereby realizing two kinds of ways of servo loading and hand-operated loading. A torque sensor and an angle sensor are connected to the input shaft. An output terminal of a tested piece electronic power steering (EPS) system a is connected with a damping loading unit by a gear wheel and rack driving mechanism; and bidirectional data transmission among an input loading and detection device, the tested piece EPS system, and an upper computer control and signal processing system is carried out. The upper computer simulates a road condition; and the damping unit is controlled to simulate performance testing and steering hand-feeling testing with a damping moment. The damping loading unit is formed by combination of a magnetic powder brake and a servo motor; the magnetic powder brake outputs a large damping moment; and quick control of the small moment is realized based on characteristics of quick response and precise control of the servo motor. Therefore, precise and quick control of the damping torque of the testing platform is realized on the condition of cost consideration.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Series-parallel multistage torque converter damper
InactiveUS7658679B2Large wind up angleLarge capacityYielding couplingRotary clutchesDamping torqueSnubber
A method and apparatus for damping torque output from a torque converter turbine to input to a transmission. The damper includes: (a) an input device for connection to an engine; (b) a first spring set having drive springs; (c) a second spring set having secondary springs; (d) a third spring set having parallel springs; (e) a floating apparatus; and (f) an output device. Springs of the first spring set are compressible in a forward direction toward the output device as a result of torque applied to the input device and compressible in a reverse direction toward the input device as a result of torque applied by the output device. The first and second spring sets are in series between the input device and output device during a first forward compression of the first spring set, and the series is in parallel with the third spring set between the input apparatus and output device during a second compression of the first spring set. The first spring set is in parallel with the third spring set between the input apparatus and output device without the second spring set during a third compression of the first spring set. The floating apparatus is between the input apparatus and the output device and between springs of said first and second spring sets during the first forward compression of the first spring set. The method includes the steps of: (a) operating a spring set one and a spring set two in series between torque input and torque output; (b) placing a spring set three in parallel with spring sets one and two allowing more torque per degree of wind-up than in step (a); and (c) removing spring set two from series with spring set one resulting more torque per degree of wind-up than in step (b).
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG
Electrically operated vehicle drive controller and electrically operated vehicle drive control method
The present invention provides an electric vehicle drive control device, comprising a generator target torque calculation and processing mechanism for calculating a generator target torque (TG*), and an inertia correction rotor for calculating an inertia correction torque based on the generator inertia torque (TGI). Torque calculation processing means, drive motor target torque generation processing means for generating drive motor target torque based on the calculated inertia correction torque, output torque fluctuation index based on an output torque fluctuation index representing the fluctuation of the output torque caused by the inertia correction torque A damping torque correction processing mechanism for torque correction. By calculating the inertia correction torque and correcting the output torque, it is possible to reliably compensate the excess or deficiency of the output torque with respect to the vehicle required torque (TO*), thereby suppressing the occurrence of vibrations in the vehicle drive device.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Rotary-type magneto-rheological damper
ActiveCN108843720AWide adjustable damping torqueImprove adaptabilitySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionDamping torqueMagneto rheological
The invention discloses a rotary-type magneto-rheological damper. The rotary-type magneto-rheological damper comprises a cylinder tube, a rotatably-arranged rotor assembly, a rotating shaft outer ringarranged on the rotor assembly in a sleeving mode, a first excitation coil arranged on the rotating shaft outer ring, a second excitation coil arranged on the cylinder tube, and a damping channel forming device arranged between the rotating shaft outer ring and the cylinder tube. The damping channel forming device is provided with a first damping channel and a second damping channel which allow magneto-rheological liquid to pass, and the first damping channel and the second damping channel are arranged to be able to be switched between the connecting state and the disconnecting state. According to the rotary-type magneto-rheological damper, by changing the lengths of the damping channels, adjusting control over the magnitude of damping force is achieved, thus the damper has wider-range adjustable damping torque, and the adaptability of the damper is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Single motor driven two-freedom degree joint structure
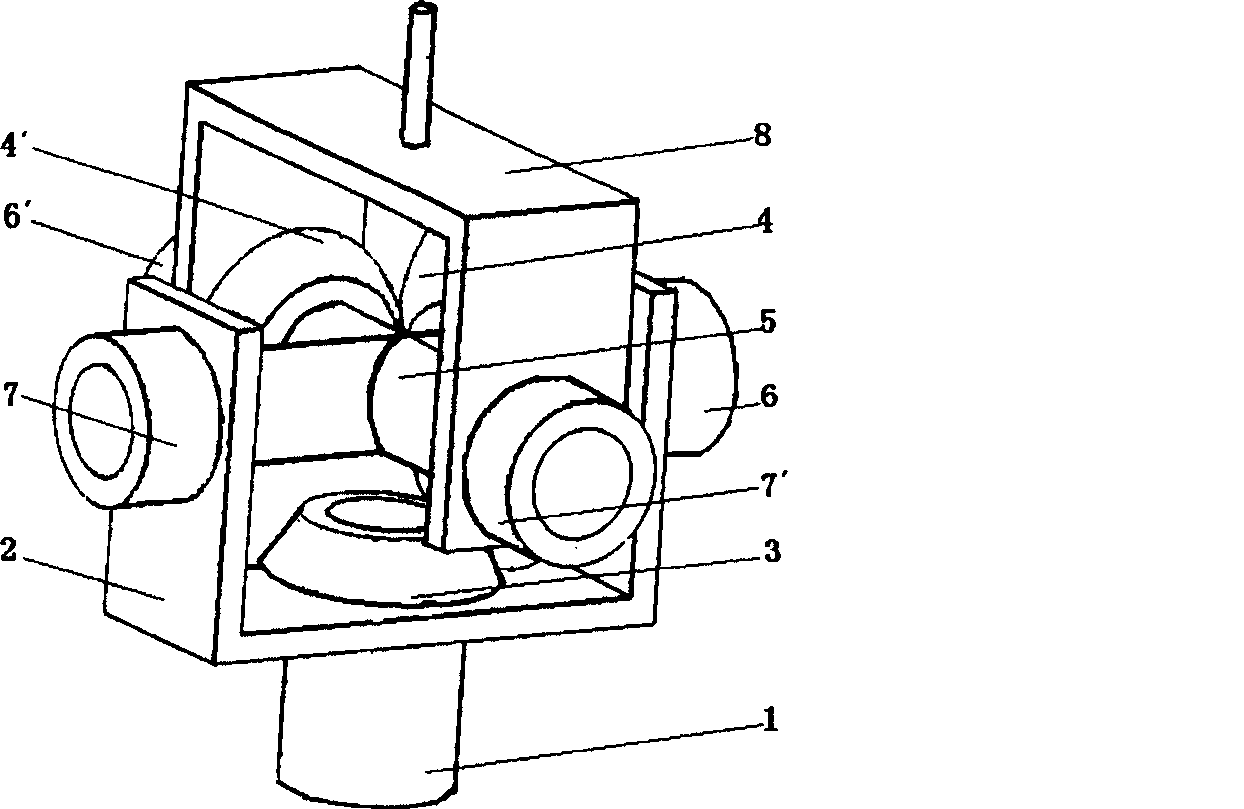
The invention discloses a single motor-driven two-degree-of-freedom joint structure, which consists of a motor (1), a machine frame (2), a motor gear (3), a first gear (4), a second gear (4'), a cross-shaped intersecting axle (5), a first angular displacement sensor (6), a second angular displacement sensor (6'), a first magnetorheological damper (7), a second magnetorheological damper(7') and an actuating part (8). The structure realizes the control of the single motor over the two-degree-of-freedom motion by controlling the output damping torque of the magnetorheological dampers with two controllable end shafts.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS20130085634A1Increase in sizeReduce vibrationDigital data processing detailsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsDrive wheelDamping torque
There is provided a control apparatus for hybrid vehicle. A motor / generator and a drive wheel are connected via a power transmission path. Further, an engine is connected to the power transmission path via a friction clutch. An EV mode using the motor / generator is implemented by disengaging the friction clutch, whereas an HEV mode using the motor / generator and the engine is implemented by engaging the friction clutch. When the engine is started in order to shift to the HEV mode during travel in the EV mode, the engine is rotated by a starter motor, and damping torque Tm2 is output from the motor / generator. Damping torque Tm2′ is then transmitted to the engine via the friction clutch, which is set in a slip condition.
Owner:SUBARU CORP
Electrically operated vehicle drive controller and electrically operated vehicle drive control method
ActiveUS7565938B2Avoid it happening againReliably compensate for the excessive and deficient amountsHybrid vehiclesSpeed controllerDamping torqueEngineering
An electrically operated vehicle drive controller has an electric generator target torque calculation processing means for calculating electric generator target torque TG*; an inertia correction torque calculation processing means for calculating inertia correction torque on the basis of inertia torque TGI of an electric generator; a drive motor target torque generation processing means for generating drive motor target torque on the basis of the calculated inertia correction torque; and a damping torque correction processing means for correcting output torque on the basis of an output torque changing index which expresses a change of output torque due to the inertia correction torque.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com