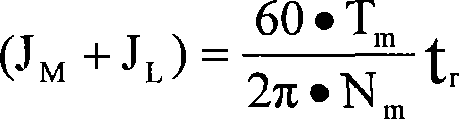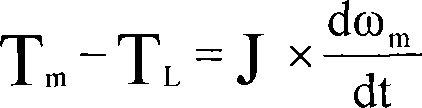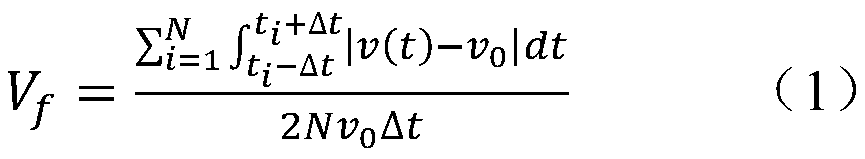Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85 results about "Rotor inertia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rotor inertia is determined by the mass of the blade, and manifests itself in how easily it gains or loses momentum. A low mass blade has low inertia, and will therefore be more easily subject to changes in momentum. A high mass blade has more inertia, and will be less easily subject to changes in momentum.
Electric Power Steering System
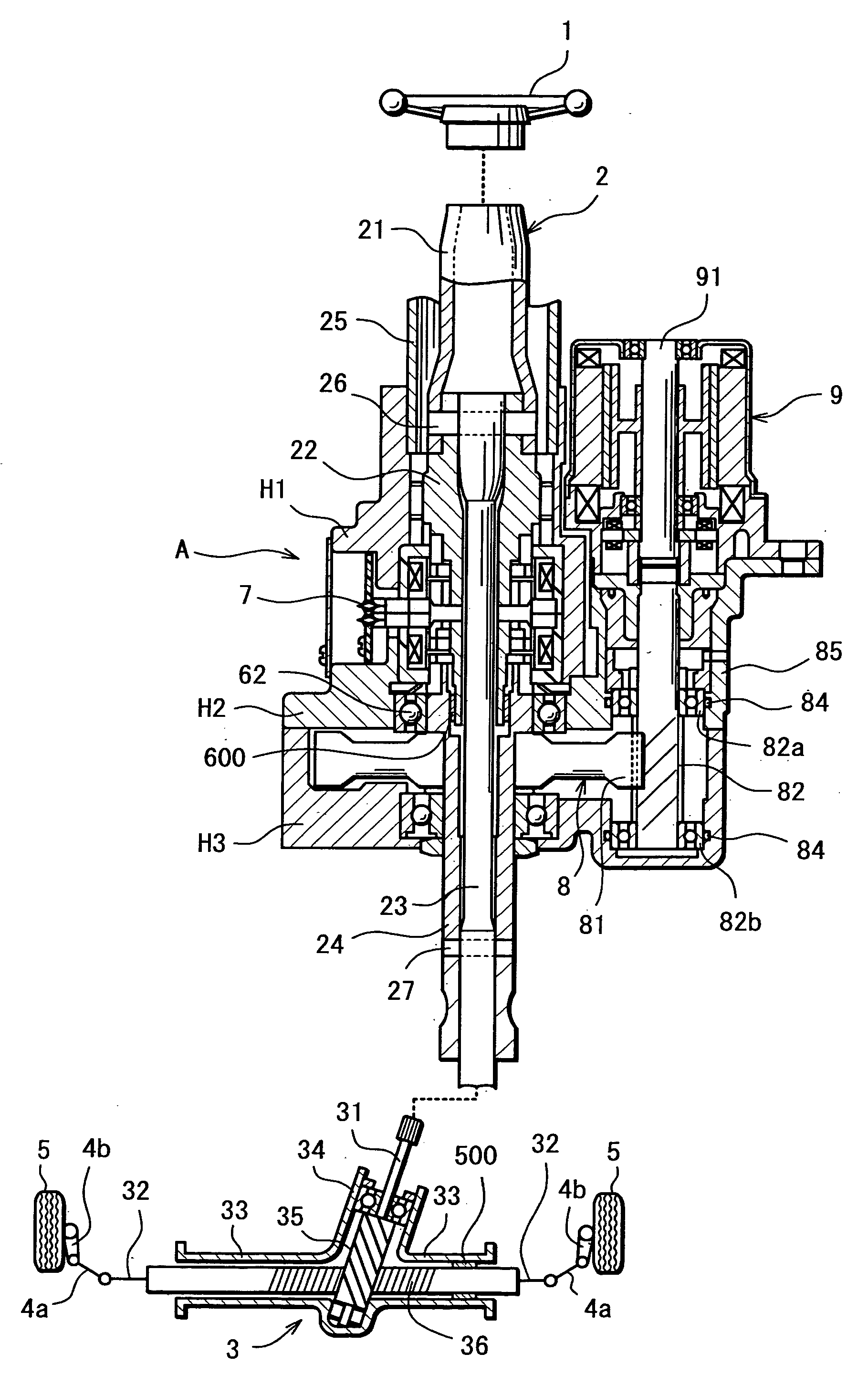
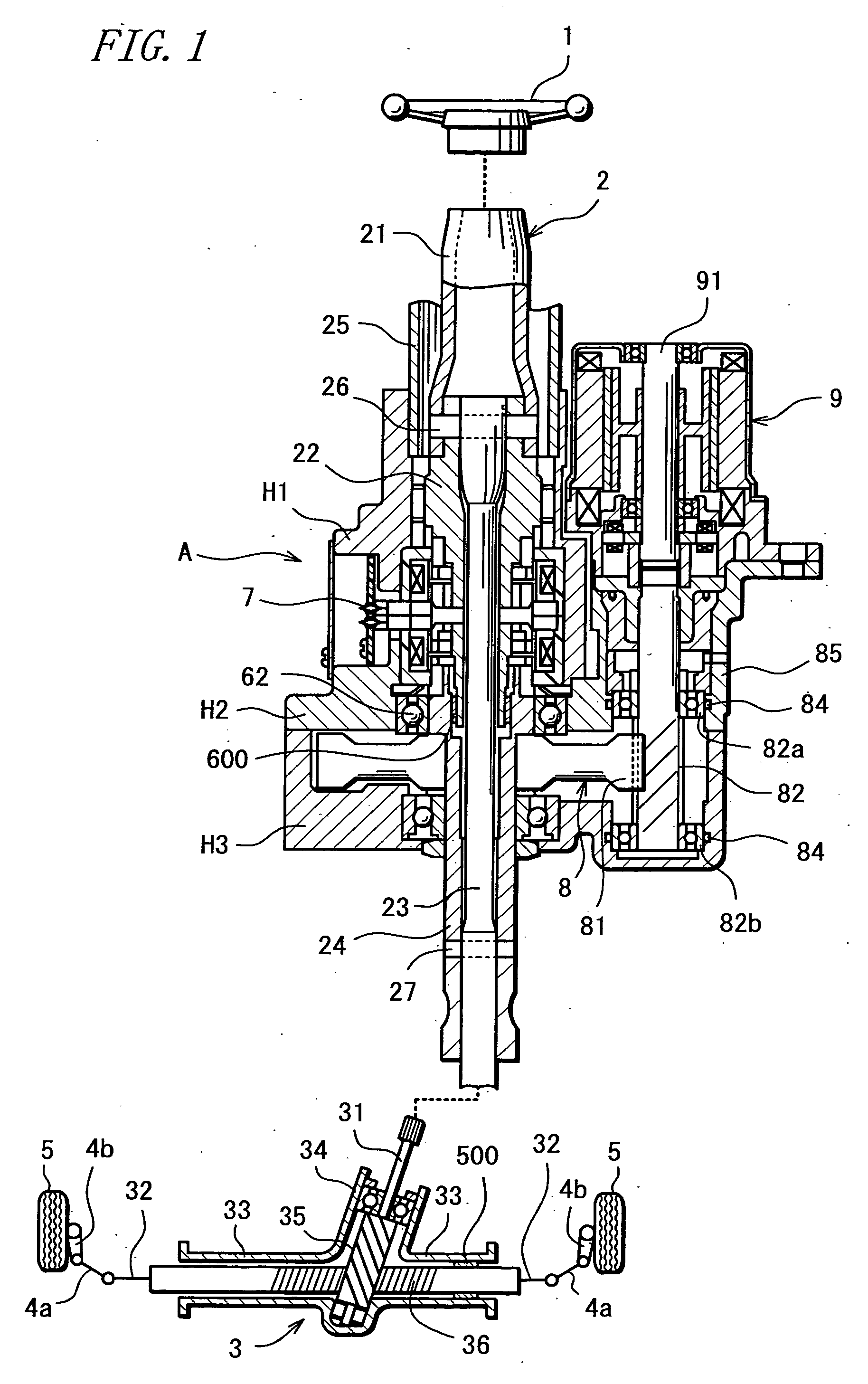
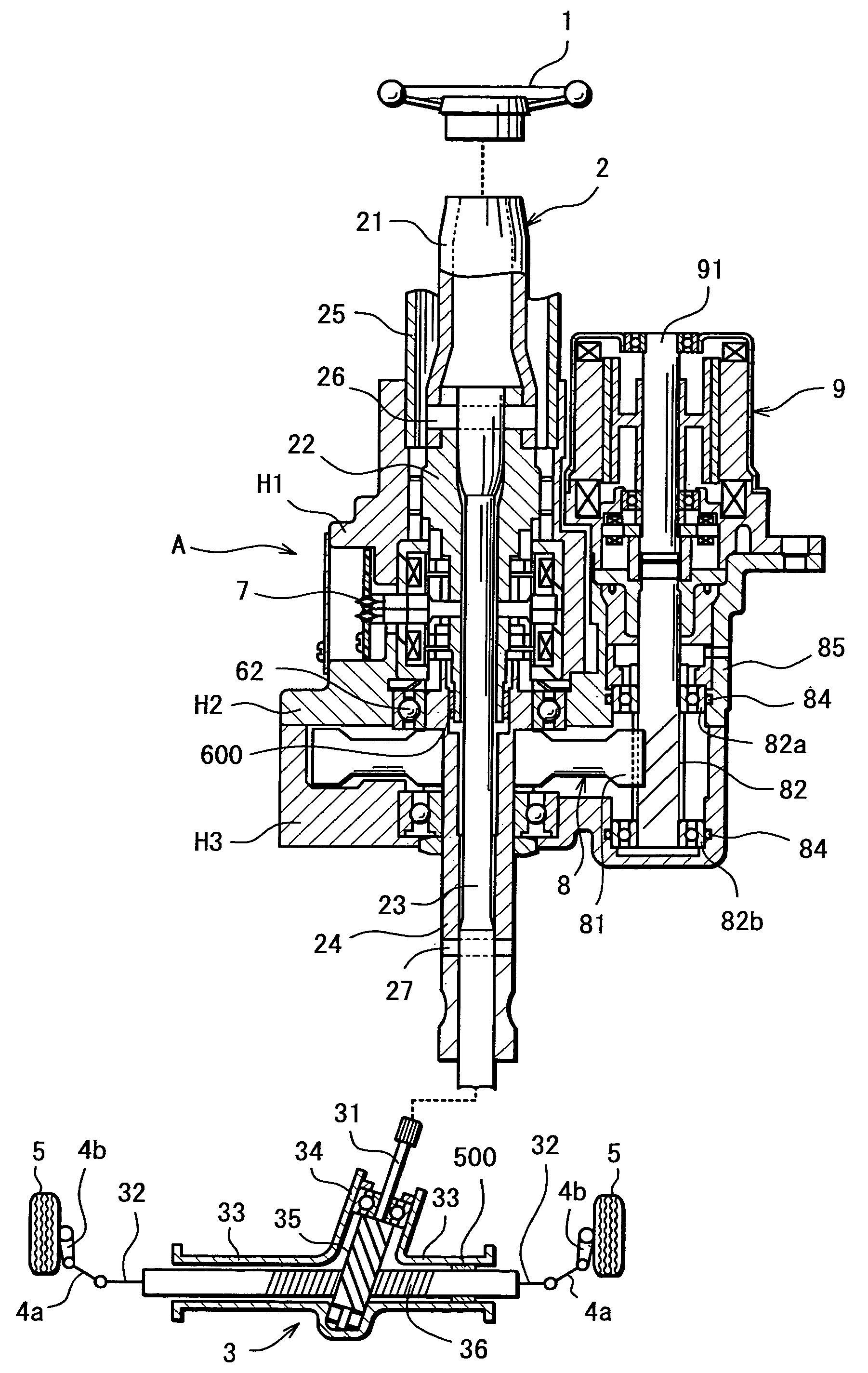
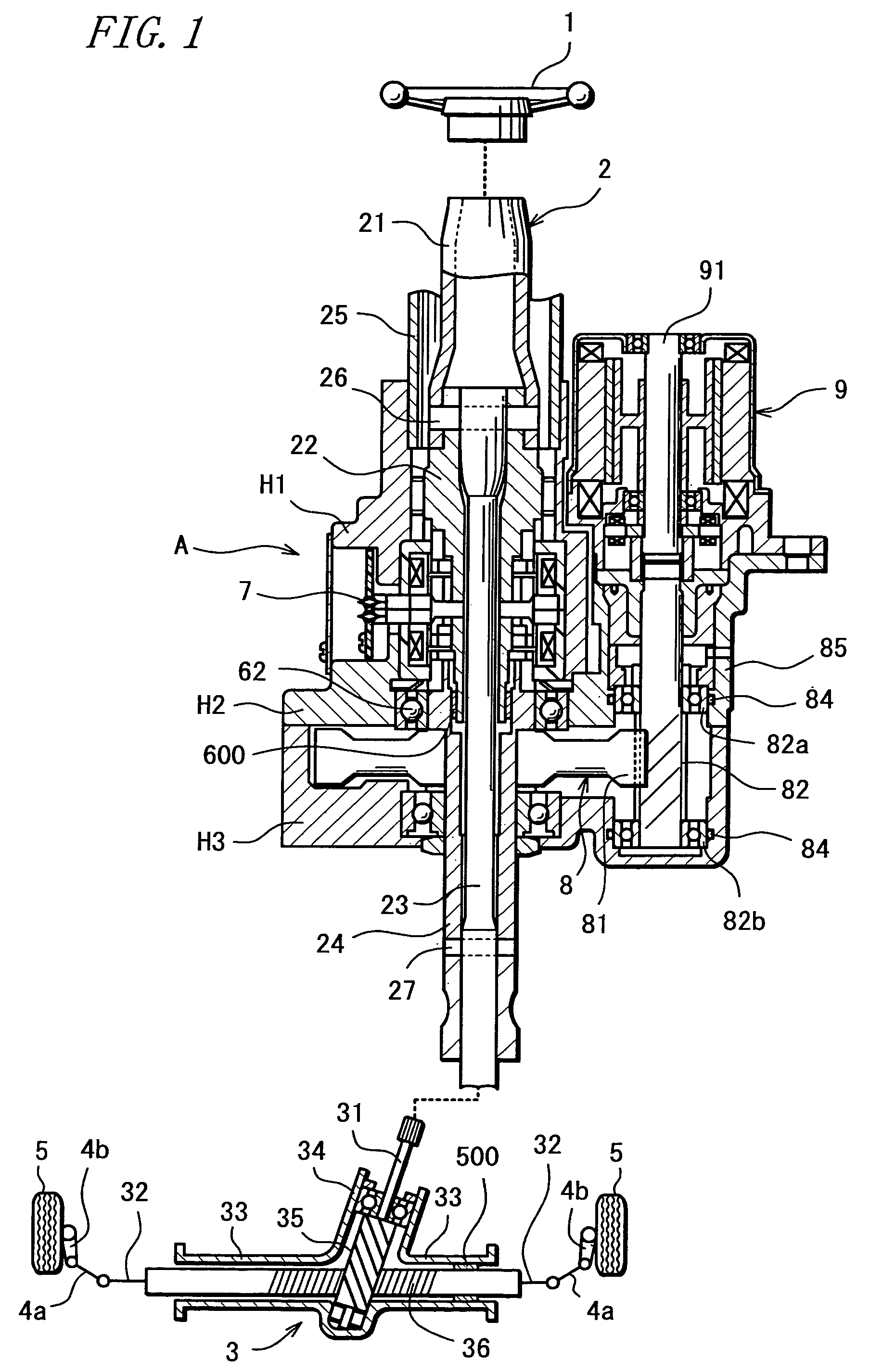
InactiveUS20070205041A1Favorable steering feelingLess inertia feelingSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringDamping torque
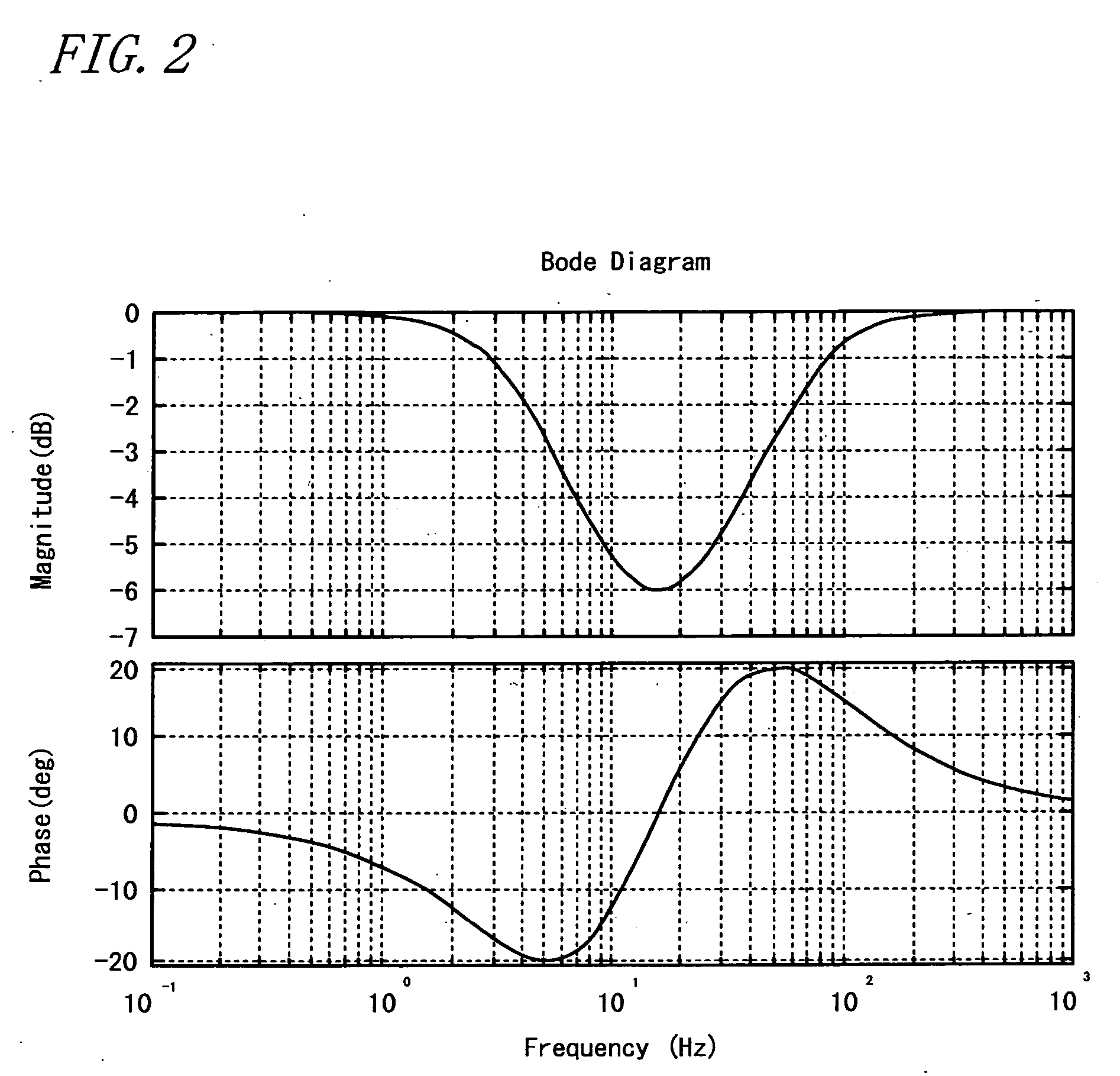
An electric power steering system is provided which is capable of providing a favorable steering feeling without using compensation logics such as of inertia compensation and friction compensation. The electric power steering system includes road-noise suppression control means (213) for controlling a steering assist motor (9) in a manner to damp torque transmission in a higher frequency region representing road noises than a frequency region representing road information. A friction value of a steering mechanism (A) is decreased enough to allow the intrinsic vibrations of the steering mechanism (A) to appear. Rotor inertia of the steering assist motor (9) is set to a value small enough to allow the frequencies of the intrinsic vibrations to be present in the frequency region where the torque transmission is damped by the road-noise suppression control means (213).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS7604088B2Reduce frictionFeel goodSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringDamping torque
An electric power steering system is provided which is capable of providing a favorable steering feeling without using compensation logics such as of inertia compensation and friction compensation. The electric power steering system includes road-noise suppression control means (213) for controlling a steering assist motor (9) in a manner to damp torque transmission in a higher frequency region representing road noises than a frequency region representing road information. A friction value of a steering mechanism (A) is decreased enough to allow the intrinsic vibrations of the steering mechanism (A) to appear. Rotor inertia of the steering assist motor (9) is set to a value small enough to allow the frequencies of the intrinsic vibrations to be present in the frequency region where the torque transmission is damped by the road-noise suppression control means (213).
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Method for identification of rotational inertia of AC servo
InactiveCN101231207AImprove torque performanceGood dynamic responseStatic/dynamic balance measurementElectric controllersServo actuatorLoad torque
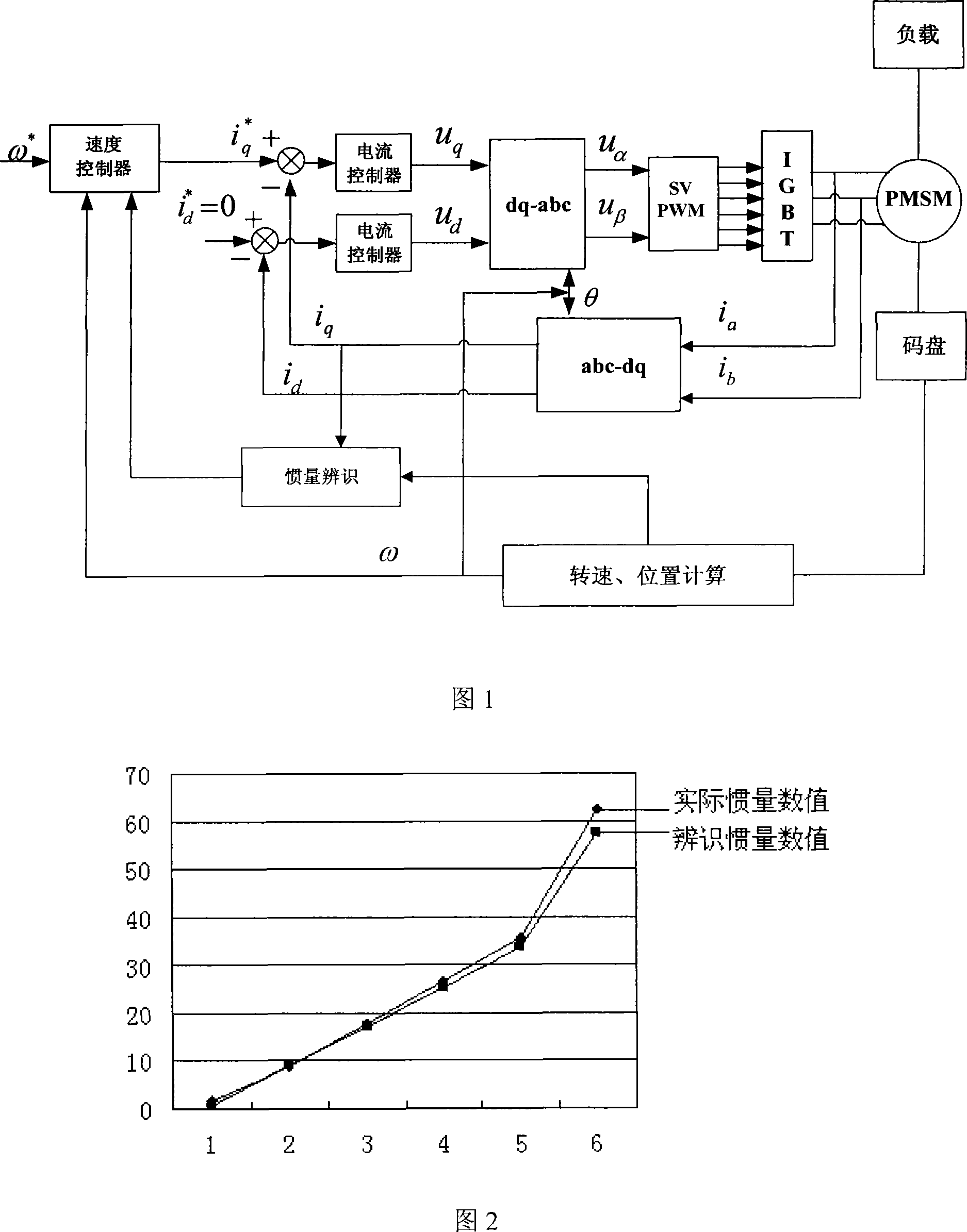
The invention relates to a rotary inertia identification method of an alternating-current servomechanism, the load inertia and the rotor inertia of a motor are regarded as a whole inertia, a servo system does an accelerated motion and a decelerated motion, so as to obtain the system output torque and the motor average rotate speed for a period of time. The average torque of the servo system can be obtained by the system output torque, the value of the whole inertia can be obtained according to the motor average rotate speed, the average torque of the servo system, and the total operation time of the accelerated motion and the decelerated motion of the system, that is, the rotary inertia of the alternating-current servomechanism can be identified. The invention does not need to singly identify the load inertia or the load torque for identifying the system rotary inertia, but causes the load inertia and the motor rotary inertia to be regarded as an inertia, and the identification of the system rotary inertia can be realized by combining the system output torque. The implementation of the method is simple, the use is convenient, the identified inertia precision is higher, and the method can be applied to the servo system inertia detection of a permanent magnetism synchronous servo-actuator.
Owner:ESTUN AUTOMATION TECH
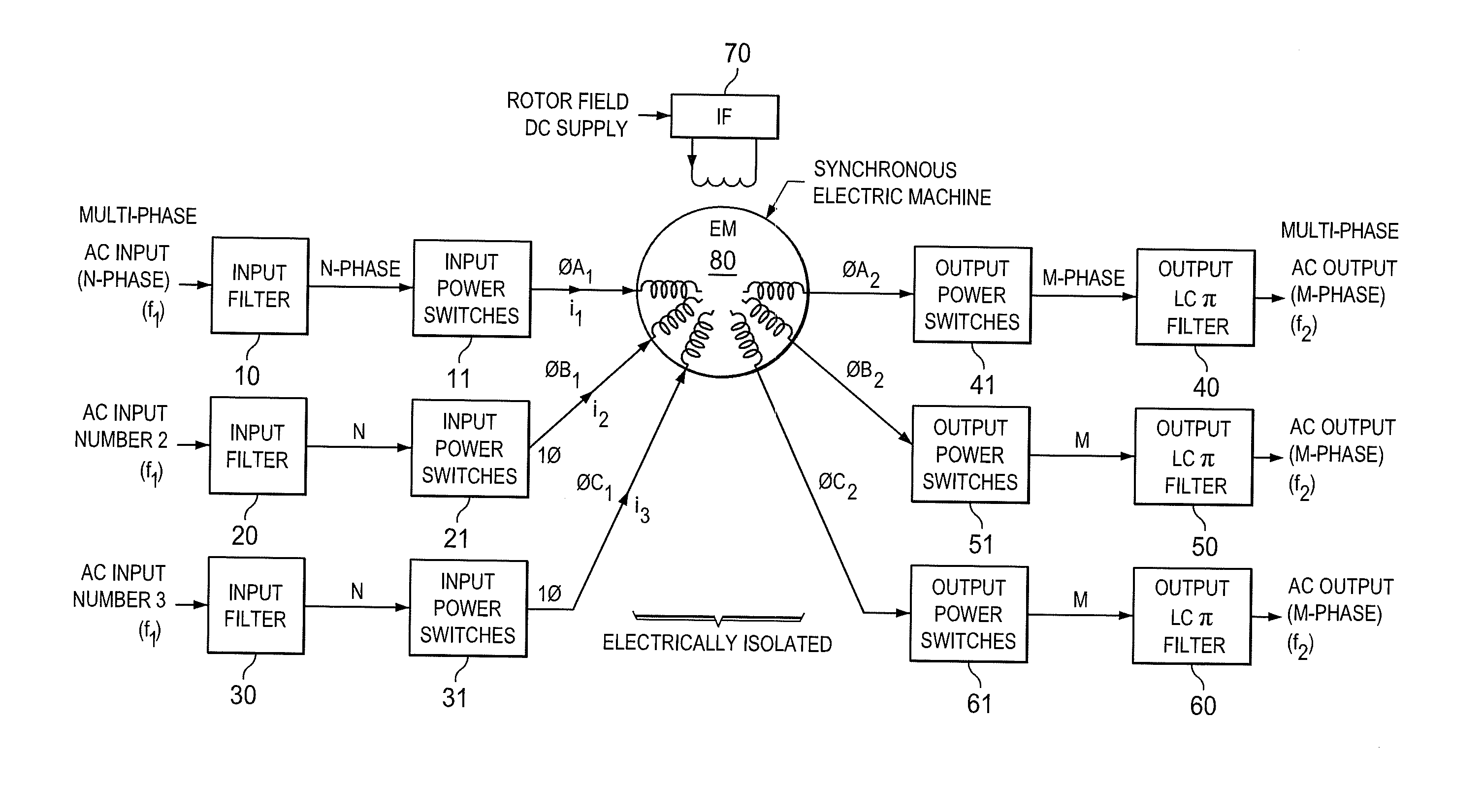
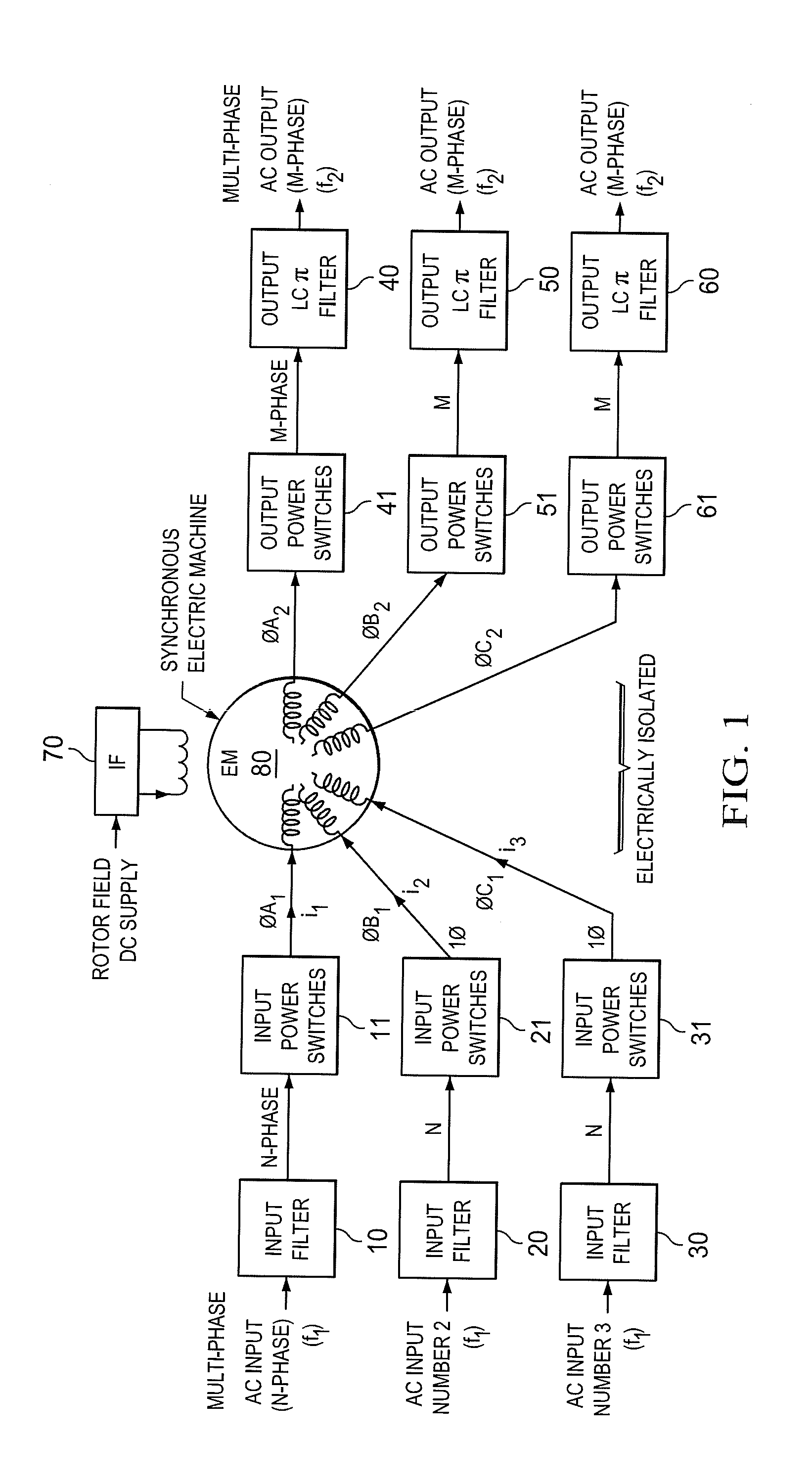
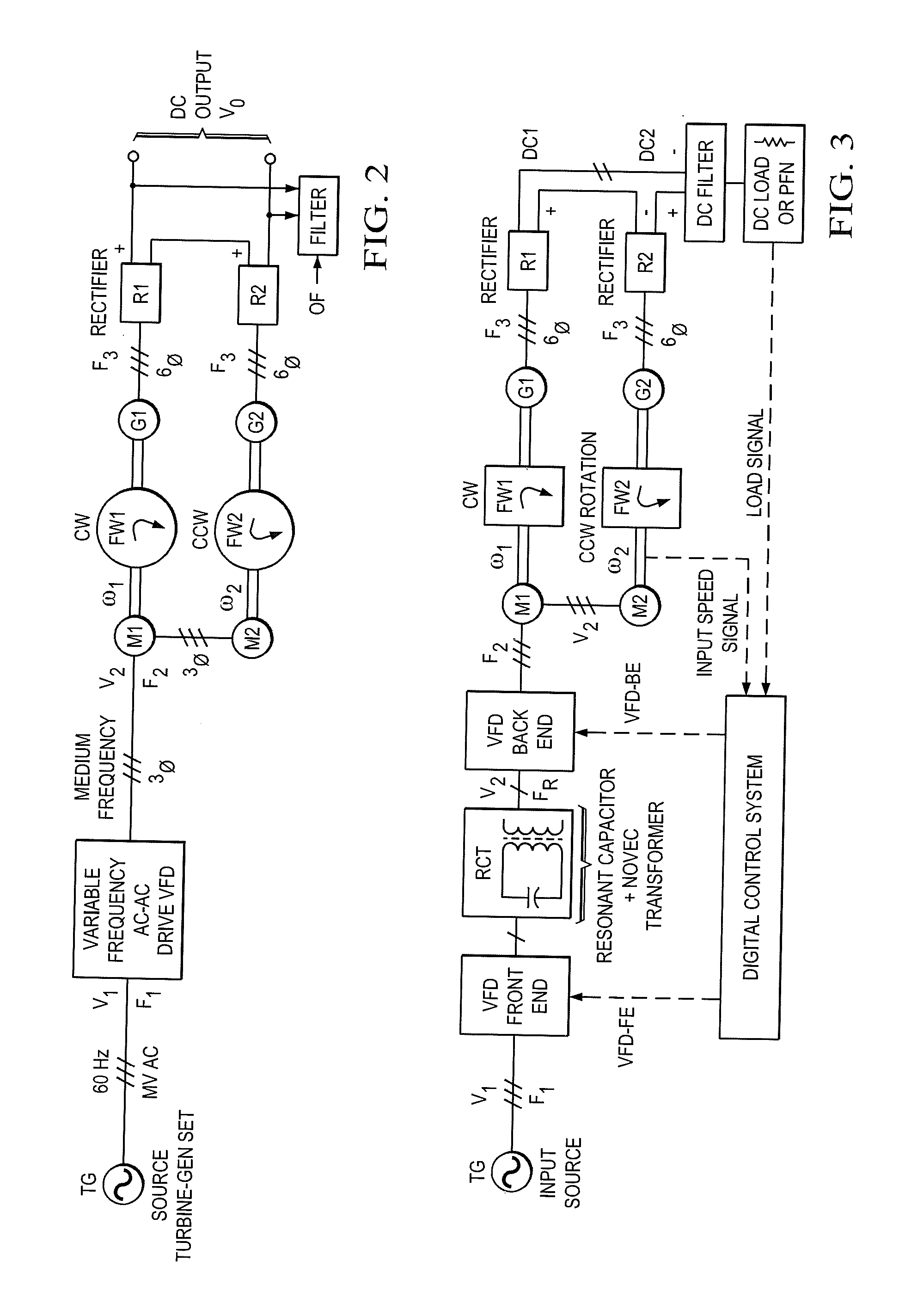
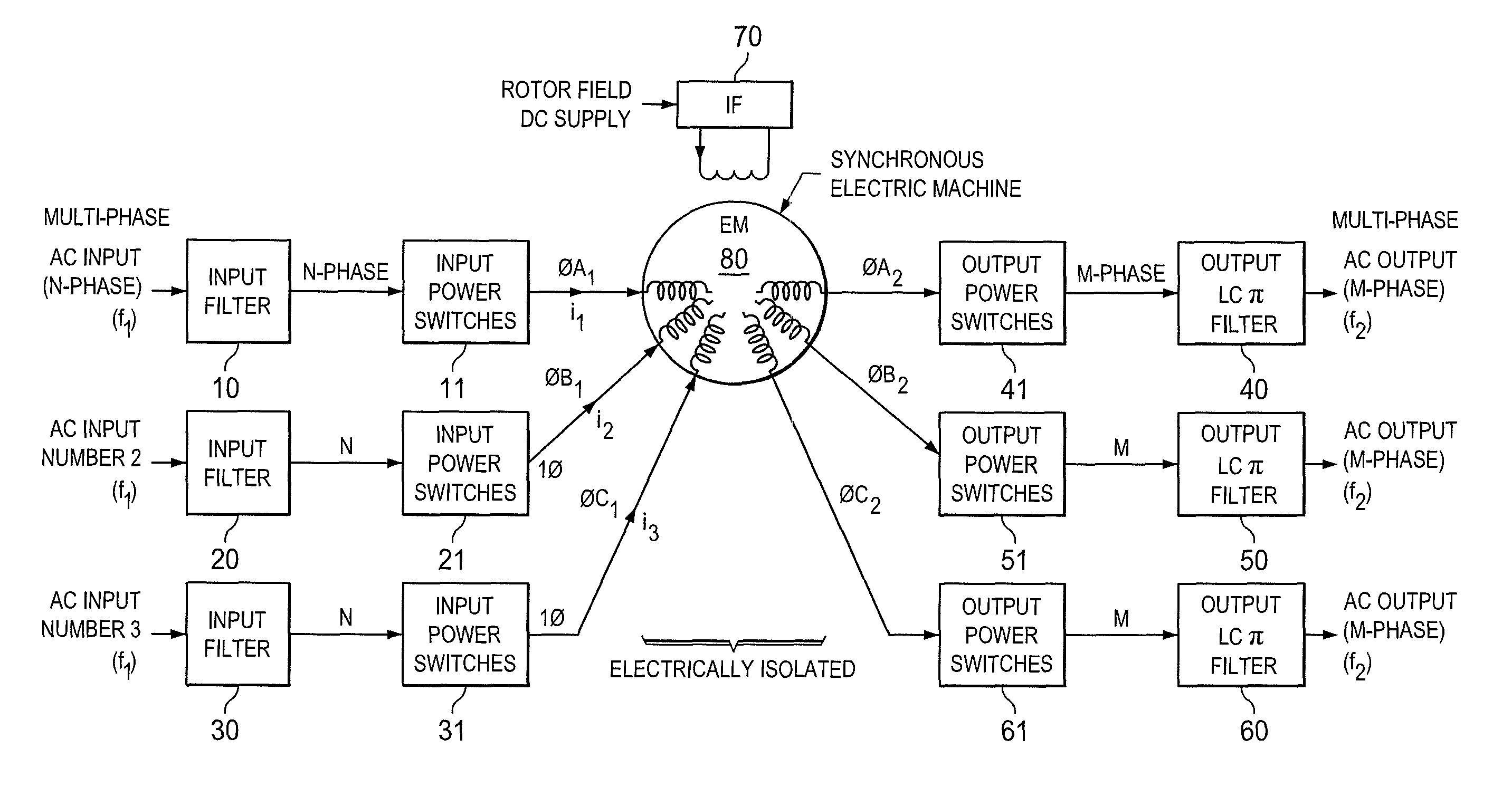
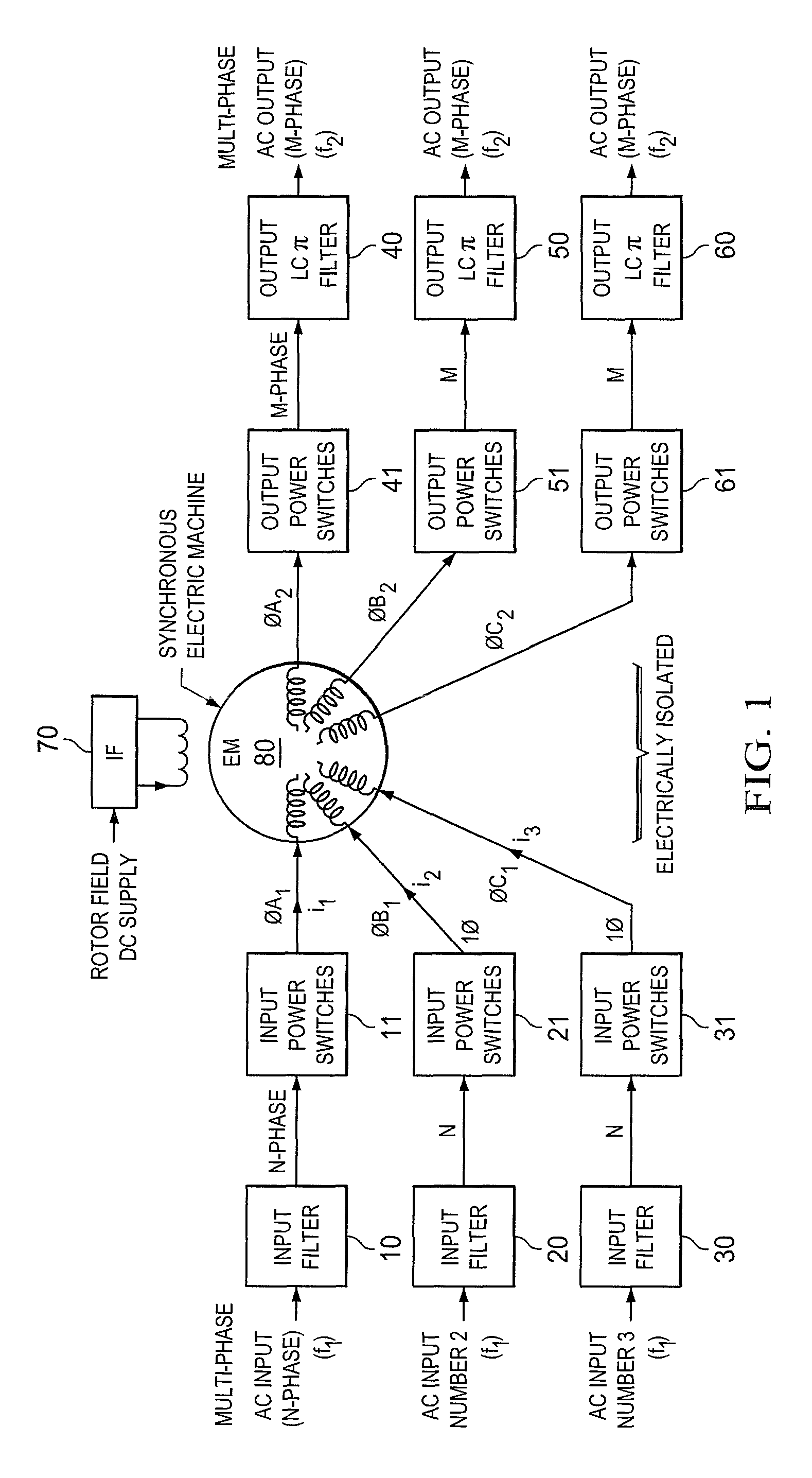
Inertial energy storage system and hydro-fluoro-ether power transformer scheme for radar power systems and large pfn charging
A multi-port storage system includes a dynamo-electric machine with integral rotor inertia forming a primary energy storage system. The dynamo-electric machine has a primary stator winding configured to accept multiple AC input power sources, and has at least two secondary stator windings configured to deliver electric power to multiple loads at different power, frequency and voltage levels. A secondary energy storage system is coupled to the primary energy storage system, and is configured to convert its stored energy to electric power. The dynamo-electric machine is configured to enhance and buffer the secondary energy storage system, and is configured to improve the conversion of the stored energy to electric power. The system may include a step-up transformer responsively coupled to one of the secondary stator windings. The step-up transformer may comprise a single phase or polyphase step-up transformer having internal cooling and electrical insulation between the secondary windings comprising a hydro-fluoro-ether (HFE) vapor and liquid fluid.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Inertial energy storage system and hydro-fluoro-ether power transformer scheme for radar power systems and large PFN charging
A multi-port storage system includes a dynamo-electric machine with integral rotor inertia forming a primary energy storage system. The dynamo-electric machine has a primary stator winding configured to accept multiple AC input power sources, and has at least two secondary stator windings configured to deliver electric power to multiple loads at different power, frequency and voltage levels. A secondary energy storage system is coupled to the primary energy storage system, and is configured to convert its stored energy to electric power. The dynamo-electric machine is configured to enhance and buffer the secondary energy storage system, and is configured to improve the conversion of the stored energy to electric power. The system may include a step-up transformer responsively coupled to one of the secondary stator windings. The step-up transformer may comprise a single phase or polyphase step-up transformer having internal cooling and electrical insulation between the secondary windings comprising a hydro-fluoro-ether (HFE) vapor and liquid fluid.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
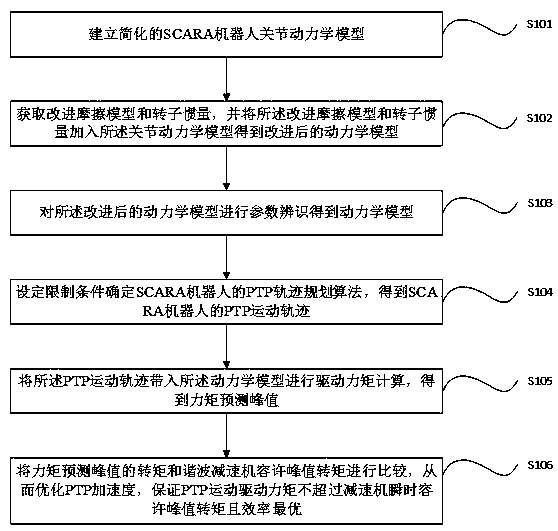
Dynamic parameter identification based PTP (peer to peer) acceleration optimization method and device
InactiveCN108890650AImprove accuracyGuaranteed uptimeProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsEngineering
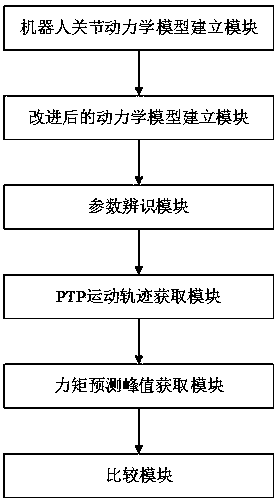
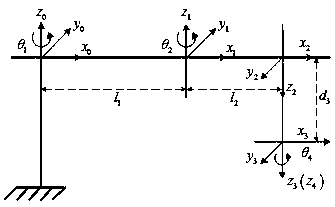
The invention discloses a dynamic parameter identification based PTP (peer to peer) acceleration optimization method and device. The method includes: establishing a simplified joint dynamic model of aSCARA (selective compliance assembly robot arm) robot; acquiring an improved friction model and rotor inertia and adding the improved friction model and the rotor inertia into the joint dynamic modelto obtain an improved dynamic model; performing parameter identification on the improved dynamic model to obtain a dynamic model; setting limiting conditions to determine a PTP trajectory planning algorithm of the SCARA robot to obtain PTP motion trajectories of the SCARA robot; substituting the PTP trajectories into the dynamic model for driving torque calculation to obtain predicted peak moments; comparing torques of the predicted peak moments with permissible peak torques of a harmonic reducer to optimize PTP acceleration and ensure that PTP motion driving moments not to excess instantaneous permissible peak torques of the reducer and to be the optimal. The improved friction model and rotor inertia are added in the dynamic model of the robot to obtain the completely improved dynamic model, and precision in parameter identification and accuracy in torque predication are improved.
Owner:WUXI XINJIE ELECTRICAL
Permanent calibration method in soft bearing dynamic unbalance test of rigid rotor
InactiveCN102175394AAchieve permanent calibrationLow technical requirementsStatic/dynamic balance measurementSupporting systemRigid rotor
The invention discloses a permanent calibration method in soft bearing dynamic unbalance test of a rigid rotor, belonging to the technical field of mechanical measurement. The method can realize permanent system calibration on a soft bearing dynamic unbalance machine and is characterized in that inherent frequency of a vibrating system consisting of a support system and a detected rotor is calculated by acquiring rotary frequencies and amplitudes of the support system at the corresponding moments in the process of rotor acceleration, thereby characterizing the influence of the quality of the rotor on the vibrating amplitude of the rotor by mapping. The influence of the quality and the rotating speed (inertia force of the rotor) of the rotor on calibration is eliminated. The permanent system calibration on the soft bearing dynamic balance machine is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Synchronous motors of different kinds
InactiveUS6441528B1Reduce in quantityLow costMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous motorEngineering
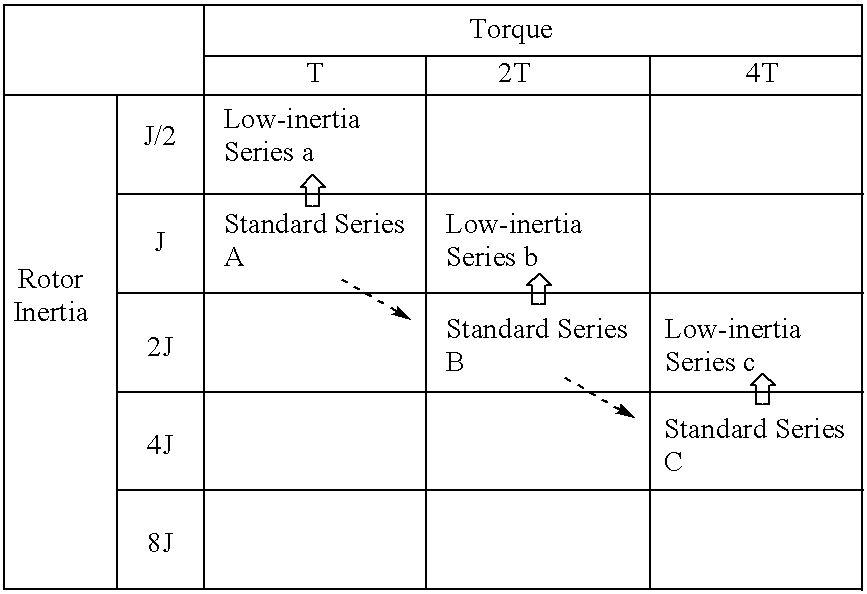
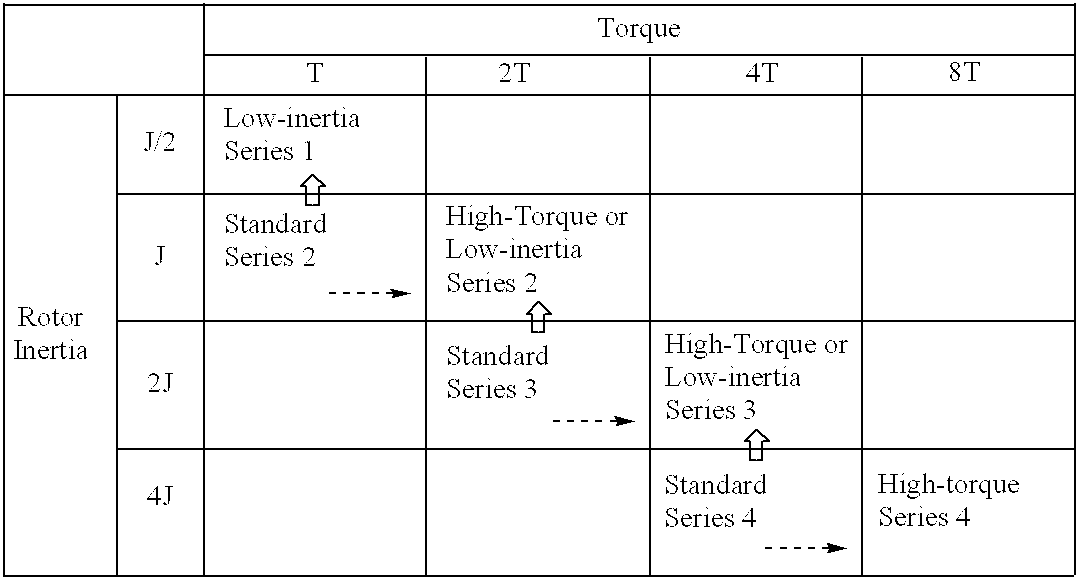
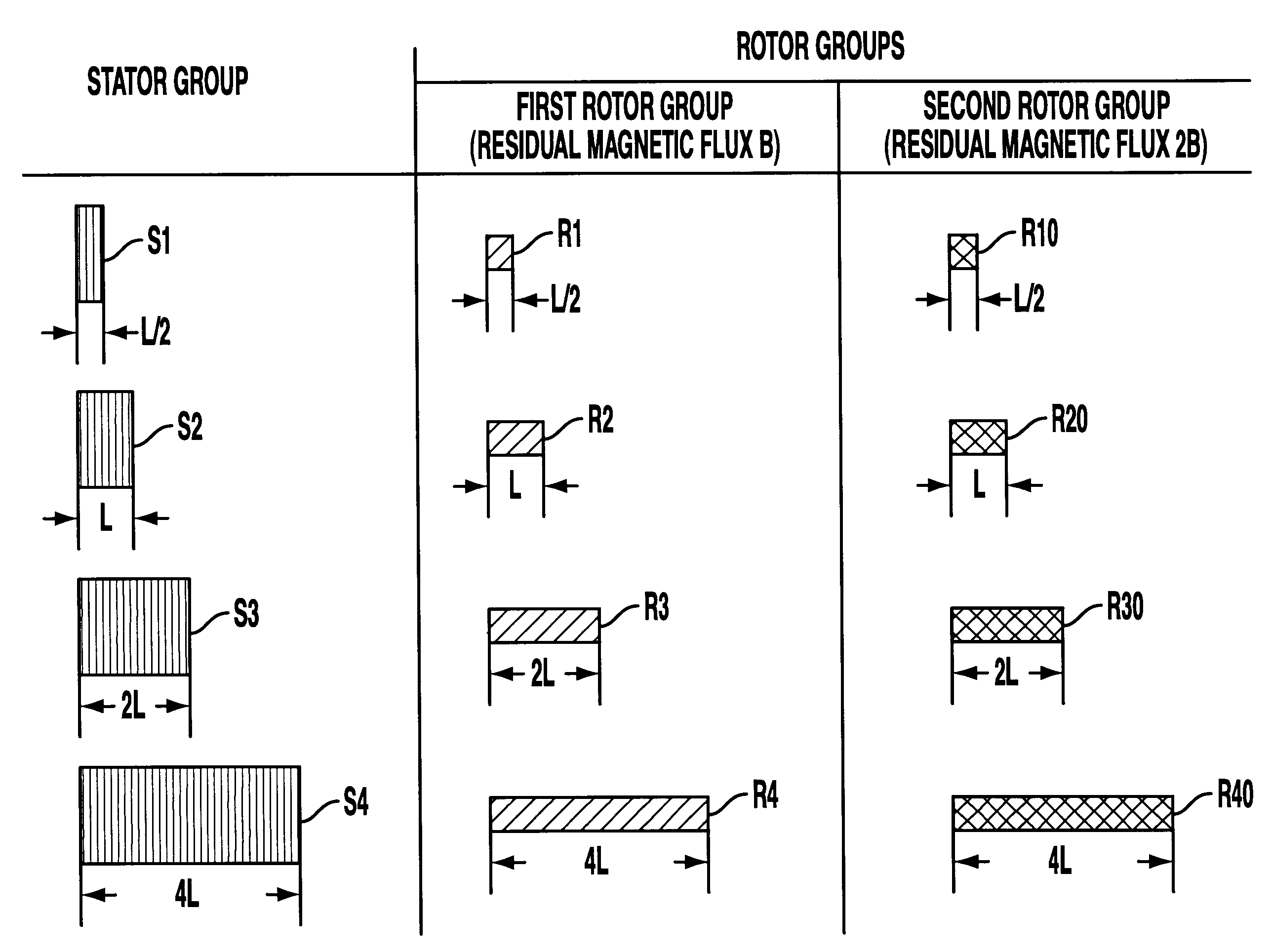
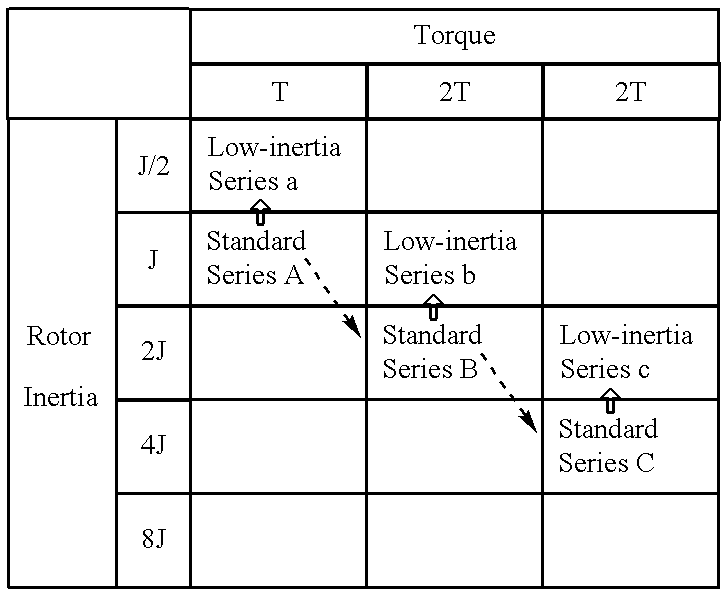
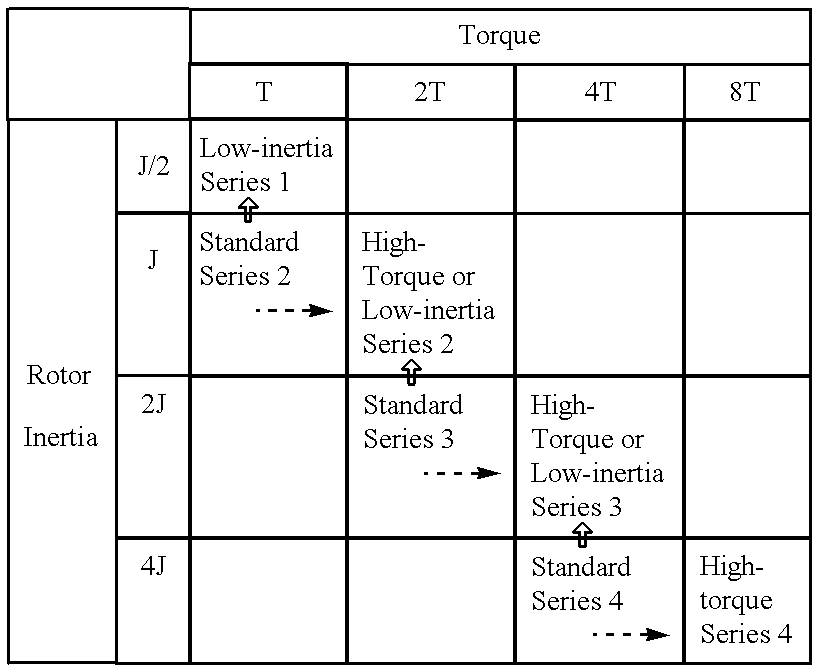
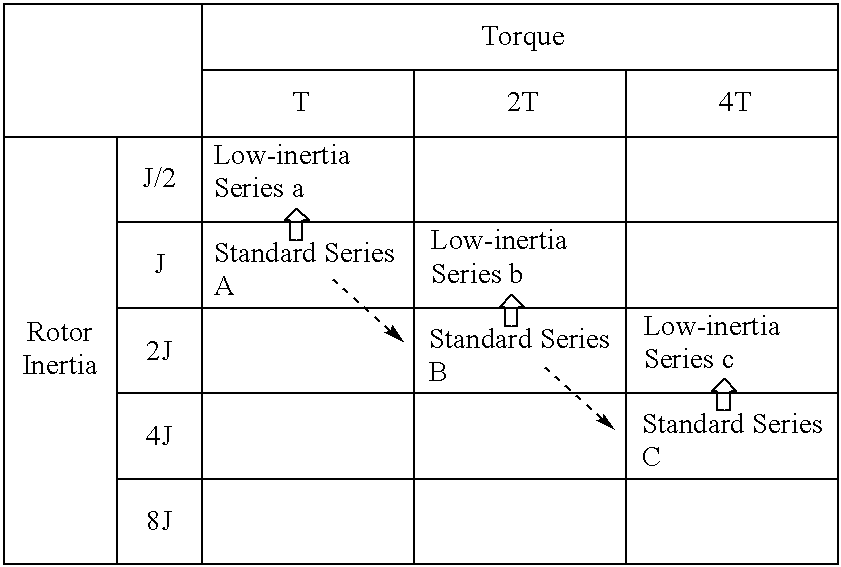
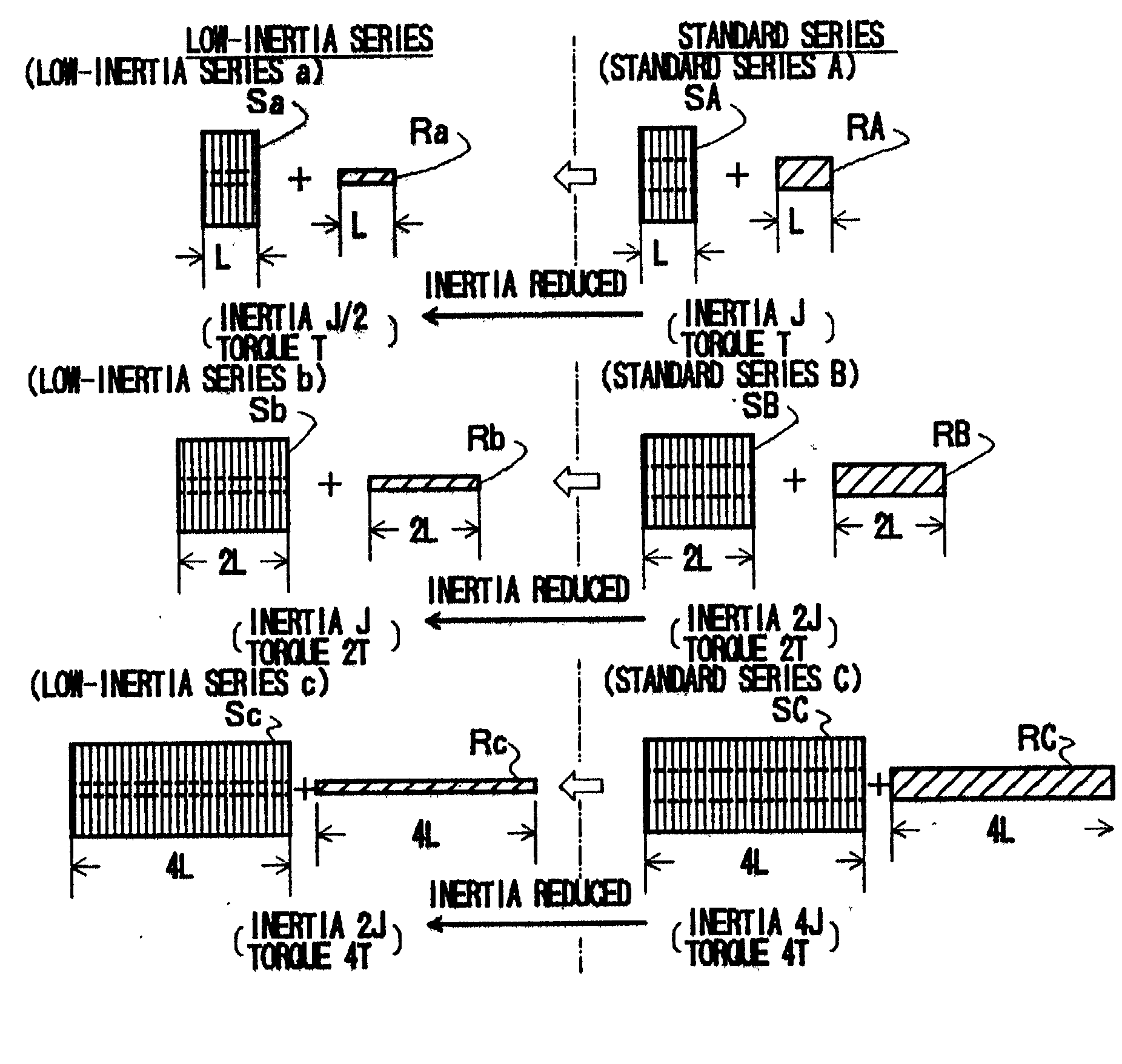
A method of expanding types of synchronous motors capable of reducing the number of required stator types to use stators in common, and a synchronous motor produced by the method. A group of stators are prepared by stacking stator cores of identical shape so that heights of the stators are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental height. A plurality of groups of rotors are prepared so that lengths of the rotors in each group are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental length. The rotors in each group are provided with permanent magnets having a residual magnetic flux density different from that of the permanent magnets of the rotors in the other groups. A stator and a rotor corresponding to a preset output torque specification value and a preset rotor inertia specification value are respectively selected from the group of stators and the rotor groups and are combined with each other, whereby an expanded type of motor is obtained.
Owner:FANUC LTD
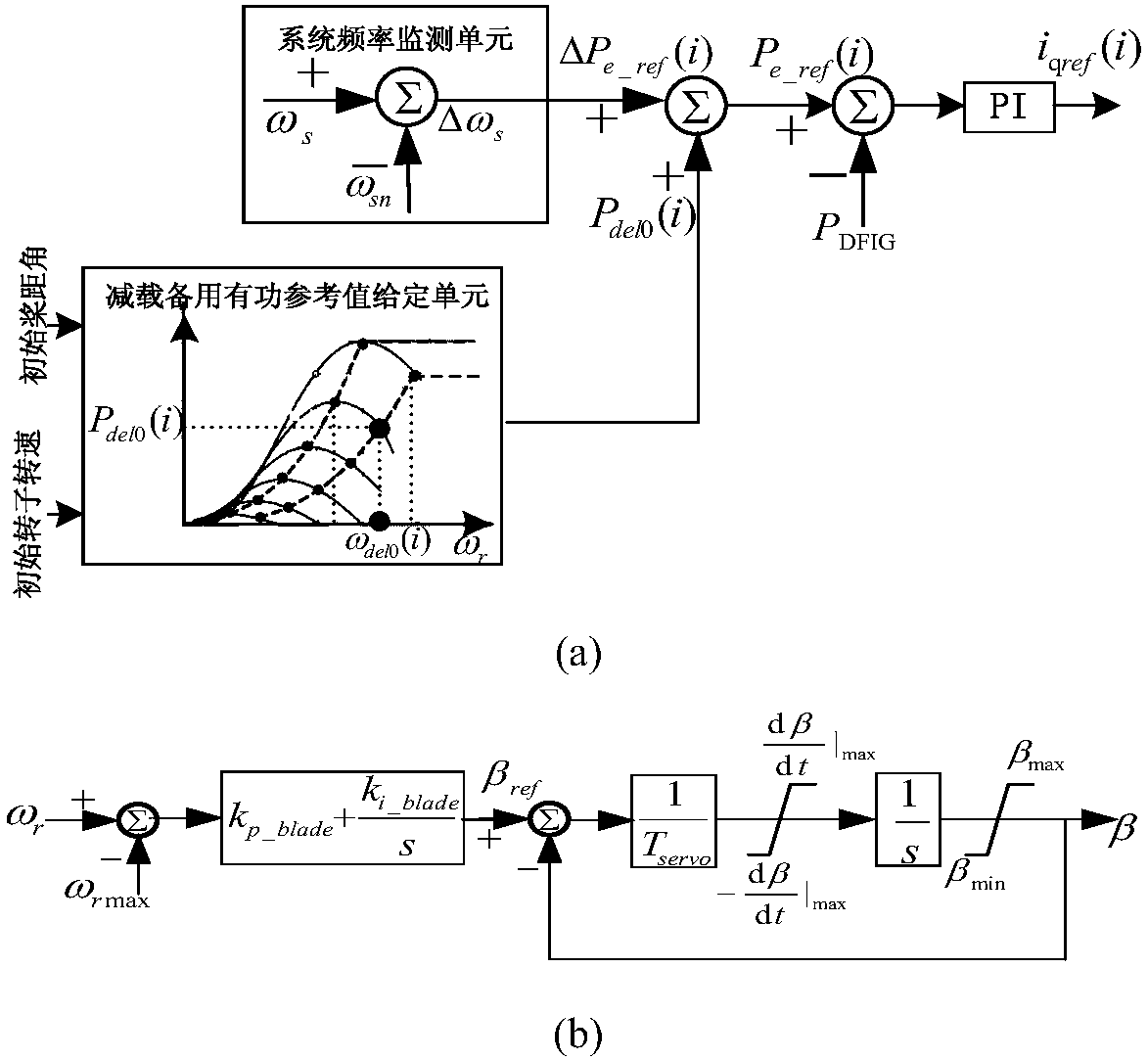
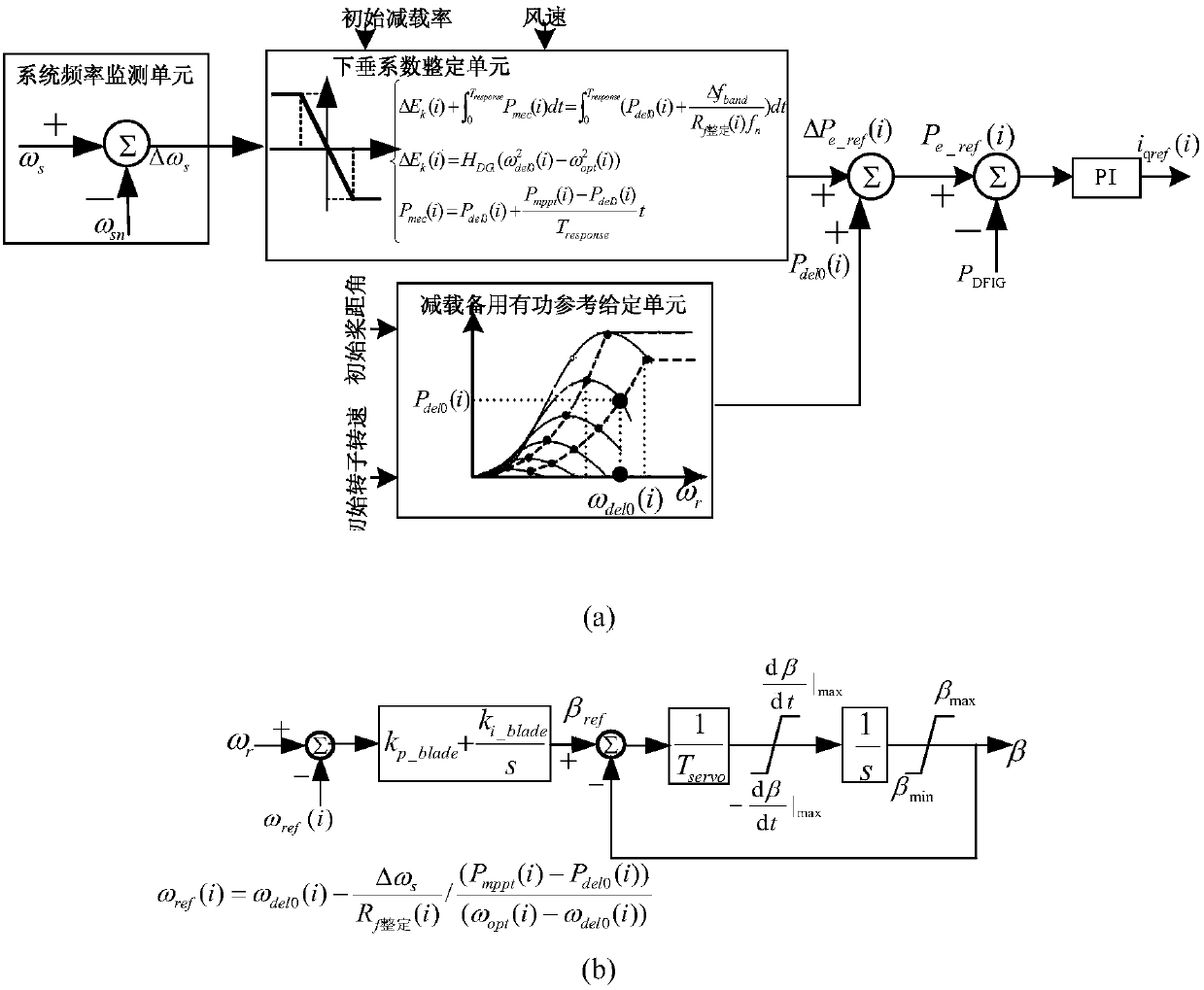
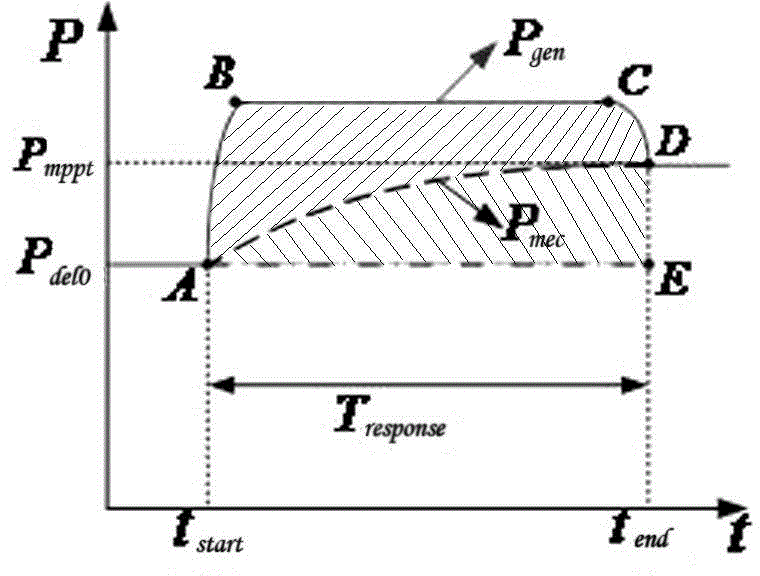
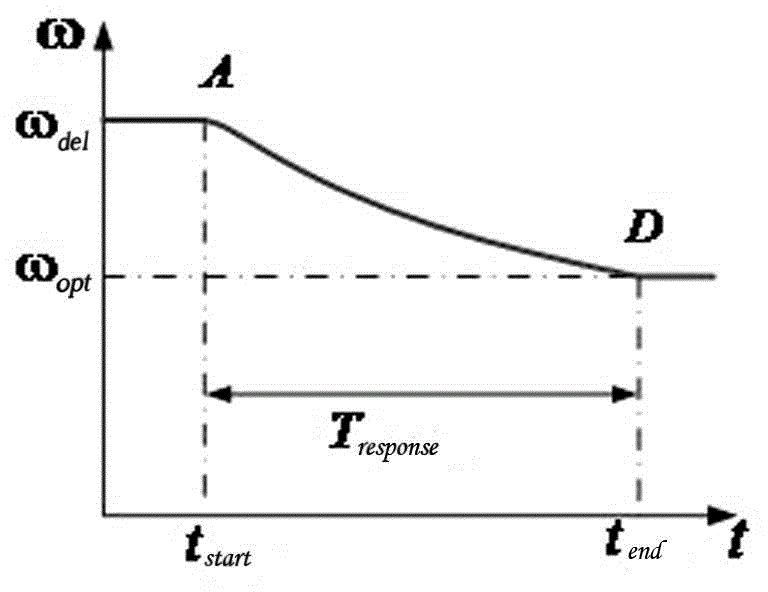
Method for frequency control of doubly-fed wind farm considering optimal rotor inertial kinetic energy
InactiveCN107846030AImprove FM effectSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionLinear controlEngineering
The invention discloses a method for frequency control of a doubly-fed wind farm considering the optimal rotor inertial kinetic energy. The method is based on the proposed method for optimizing the rotating reserve capacity of a wind farm considering the rotor inertial kinetic energy, further adopts a linear control path with the overspeed and the pitch angle coordinated, and adjusts a droop coefficient by taking the sum of the rotor inertia kinetic energy and the pure mechanical load shedding capacity stored in each unit of the double-fed wind farm as the rotating reserve capacity, so that the rotor inertial kinetic energy can be fully utilized in the frequency droop control. The method of the invention can allow the double-fed wind farm to achieve substantially the same frequency modulation effect at a smaller wind curtailment cost as that at a conventional standby operation mode when a standby optimization operation mode is executed; and can allow the double-fed wind farm to obtaina better frequency modulation effect at the same wind curtailment conditions than in a conventional standby mode when a scheduling optimization operation mode is performed.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Vehicle permanent magnetic synchronous motor and stator iron core capable of weakening magnetic resistance moment
InactiveCN101789663AHigh precisionImprove power densityMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsPunchingSynchronous motor
The invention relates to a vehicle permanent magnetic synchronous motor, wherein radial magnetized magnet steels are uniformly inlaid in the circumferential direction of the inside of a rotor iron core, the magnet steels and a pole shoe form a permanent magnetic pole, a fan-shaped cavity is arranged at the inside of the pole shoe, a cambered conductive starting strip and a resin filling are respectively arranged at the outer margin and the inside of the cavity, and the structure can prevent the permanent demagnetization of the magnet steels due to static and dynamic armature reactions, improve starting torque and peak torque, reduce rotor inertia and centrifugal force and improve fast response capability; a stator iron core applied to the synchronous motor is formed by sequentially overlying three layers of iron cores with different stator punching sheet tooth surfaces, wherein the first layer of iron core comprises a stator punching sheet of which the tooth surface is rightwards moved at a theta angle, the second layer of iron core comprises the stator punching sheet of which the tooth surface is leftwards and rightwards moved at a theta / 2 angle, the third layer of iron core comprises the stator punching sheet of which the tooth surface is leftwards moved at the theta angle, the tooth surfaces of the three layers of iron cores are overlaid to form a skewed tooth, and the structure can weaken the magnetic resistance moment, inhabit tooth slot moment fluctuation and avoid the defect of an iron core skewed slot.
Owner:李嘉琛 +1
Correction method for rheological test data of coaxial cylinder rheometer
ActiveCN105928833AUnderstanding RheologyRheological Data Bias CorrectionFlow propertiesApparent viscosityShear stress
The invention discloses a correction method for rheological test data of a coaxial cylinder rheometer. The correction method specifically comprises the following steps: putting a sample to be tested into a coaxial cylinder rheometer test system; carrying out a test under a set mode, and acquiring data; introducing an angle acceleration correction item for shear stress to calculate real shear stress at the boundary of a corrected coaxial cylinder measurement clamp and apparent viscosity of a corrected material. The correction method has the beneficial effects that by introducing a torque correction item and considering torque consumption of a system inertia (a motor rotor inertia and a measurement clamp inertia), deviations of the rheological data acquired by the conventional rheometer can be corrected, and the rheological property of a medium to be tested can be recognized more accurately.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
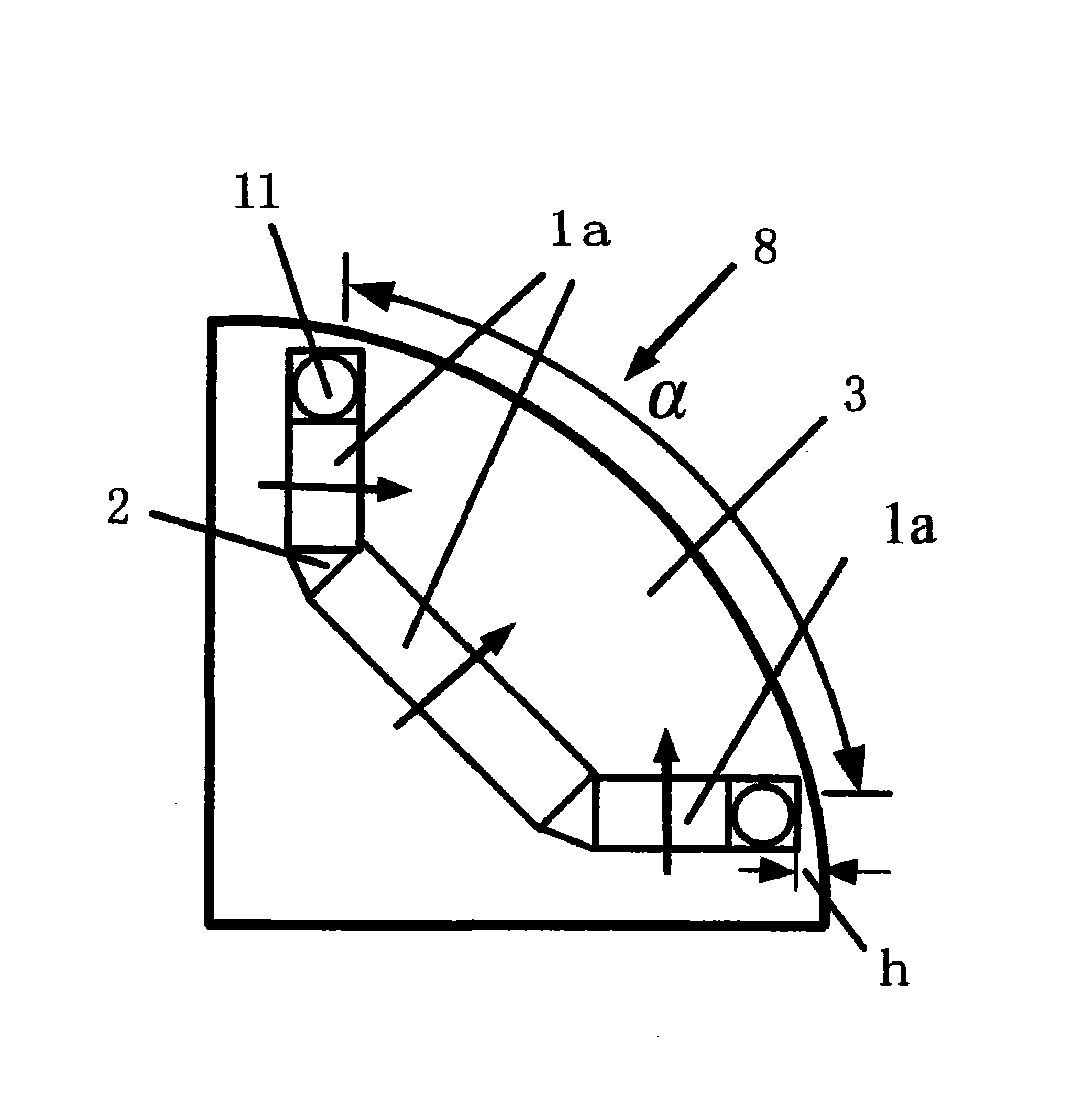
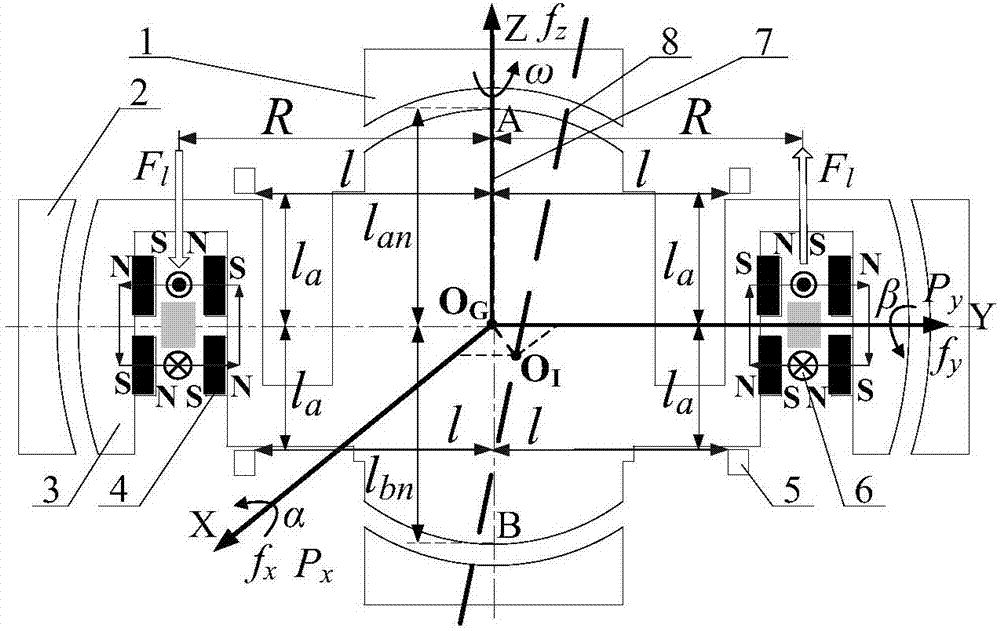
Magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method
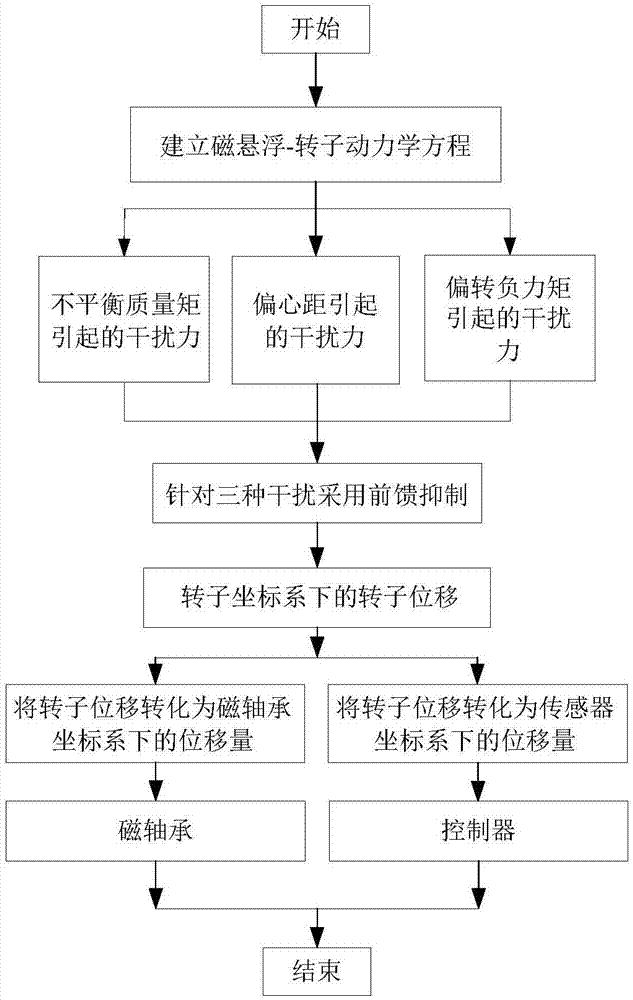
The present invention relates to a magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method. The Newton's second law and the gyro technique equation are employed to establish a magnetic bearing-rotor dynamics equation, based on the D'Alembert's principle, the disturbing force of imbalance mass moment on a rotor caused by deviation of rotor inertial axis from a geometrical axis, the disturbing force of the eccentricity on the rotor caused by the deviation of the rotor mass center from the geometrical axis and the disturbing force of the deflection negative moment on the rotor caused by suspension force passing through the rotor centroid and not passing through the rotor mass center are obtained. Rotor displacement amounts under the three disturbing forces are converted to the displacement amount under a sensor coordinate system and the displacement amount under a magnetic bearing coordinate system through a conversion matrix, the two displacement amounts are respectively acted in the controller and the magnetic bearing, and the feedforward inhibition method is employed to perform inhibition of the three disturbing forces. The magnetic suspension spherical flywheel imbalance vibration inhibition method can effectively improve the control precision of the imbalance vibration of the magnetic bearing-rotor system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
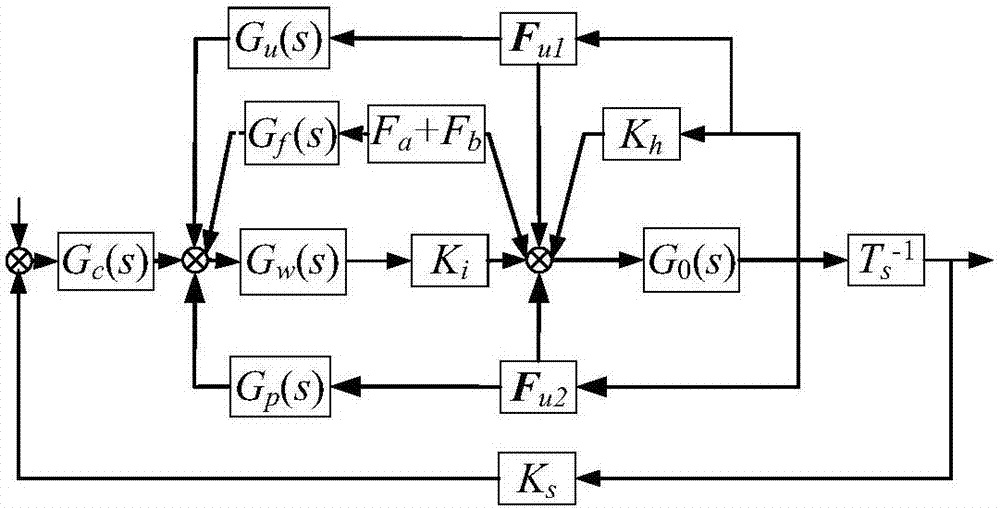
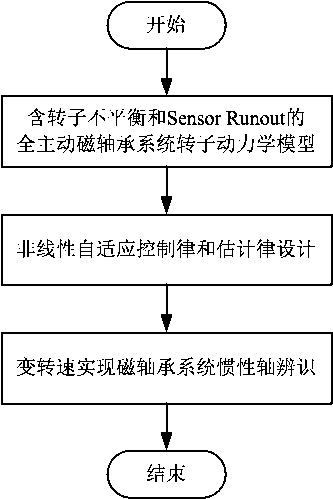
Identifying method for inertia shaft of full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control
InactiveCN107727088AOvercome the disadvantage of large identification errorRealize identificationRotary gyroscopesAdaptive controlMagnetic bearingSystem stability
The invention discloses an identifying method for an inertia shaft of a full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a full-automatic magnetic bearing rotor dynamics model with rotor imbalance and displacement sensor harmonic noise is established; secondarily, a nonlinear self-adaption control rule and estimation rule are provided, the system stability and astringency of estimation parameters are proved, it is guaranteed that a magnetic suspension rotor inertia shaft displacement estimation value is convergent to zero, and meanwhile the high-level harmonic component fourier coefficient of displacement sensor harmonic noise is estimated; then, a variable rotation speed strategy is adopted, the same frequency component of displacement sensor harmonic noise and recognizable degree of rotor imbalance are improved, the fourier coefficient values of two same frequency components are solved, and finallyidentifying for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system is achieved. According to the identifying method for the inertia shaft of the full-automatic magnetic bearing system based on nonlinear self-adaption control, speed raising or speed reduction for one time is only needed, and identifying of the magnetic bearing inertia shaft can be achieved online, so that a magnetic suspension rotor rotates around the inertia shaft.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
A low carbon steel hollow tube rotor structure for permanent magnet motor
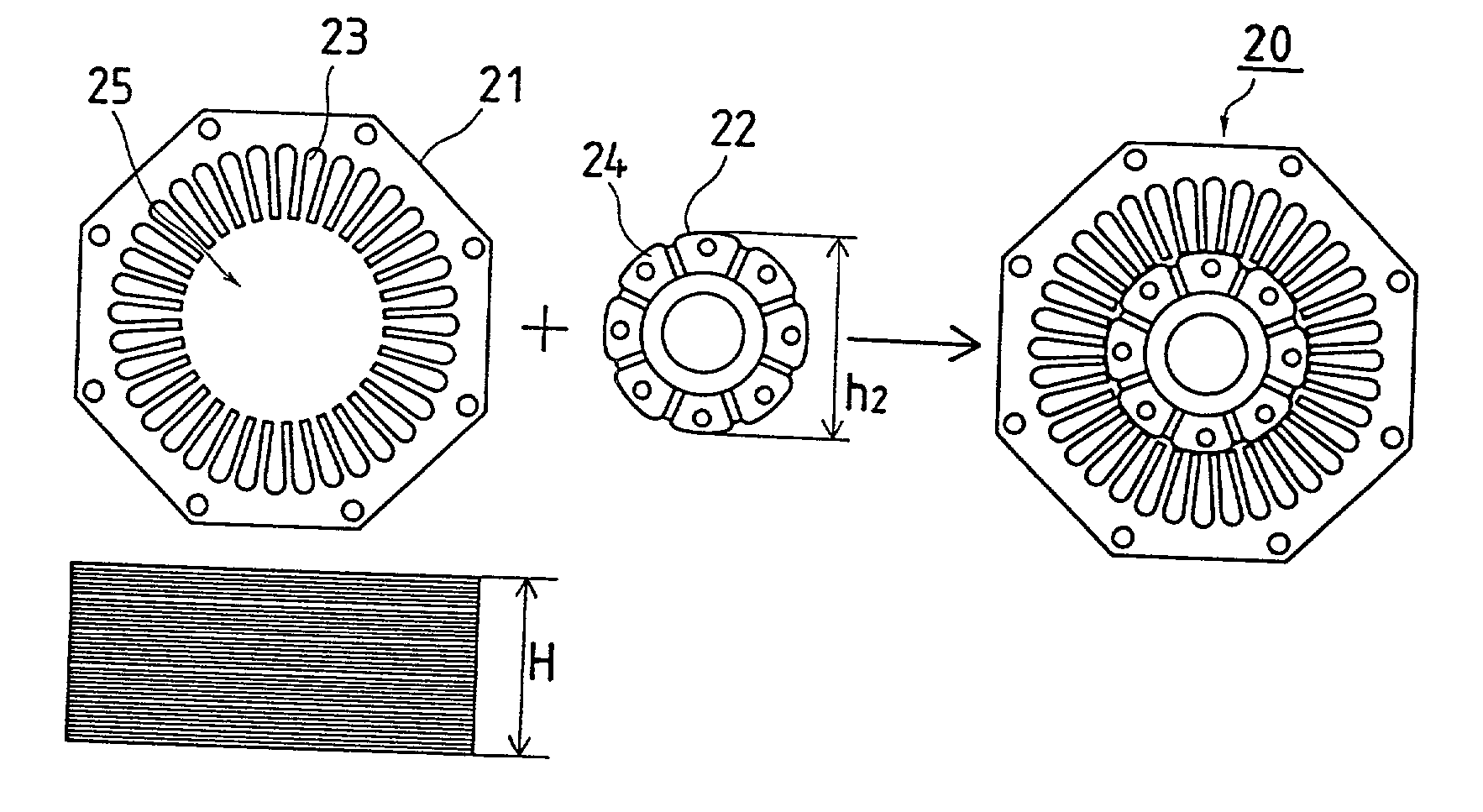
InactiveCN102263448ASolve the problem that it is difficult to use built-in magnetic steelSolve the problem that requires a small moment of inertiaMagnetic circuit rotating partsFiberAdhesive
The invention relates to a low-carbon steel hollow circular tube rotor structure of a permanent magnet motor, which is provided with a rotor sleeve, a shaft extension end shaft, a non-shaft extension end shaft, screws, arc-shaped magnetic steel, anaerobic glue, and carbon fiber cloth. The two ends of the rotor sleeve are respectively fastened to the shaft extension end shaft and the non-shaft extension end shaft through spigots and screws. The outer circle of the rotor sleeve is pasted with arc-shaped magnetic steel with anaerobic adhesive, and the outer circle of the magnetic steel is wrapped with carbon fiber cloth. Heat to cure. When the invention is used, the arc-shaped magnetic steel is evenly distributed on the outer circle of the rotor sleeve, which solves the problem that the rotor of a multi-pole permanent magnet motor is not easy to use built-in magnetic steel, especially solves the requirement for the rotor to rotate in the servo motor Small inertia problem. The structure is reasonable, simple, convenient and practical, and is especially suitable for the rotor structure of a high-power permanent magnet synchronous torque servo motor.
Owner:SHANDONG LIJIU SPECIAL PURPOSE ELECTROMOTOR CO LTD
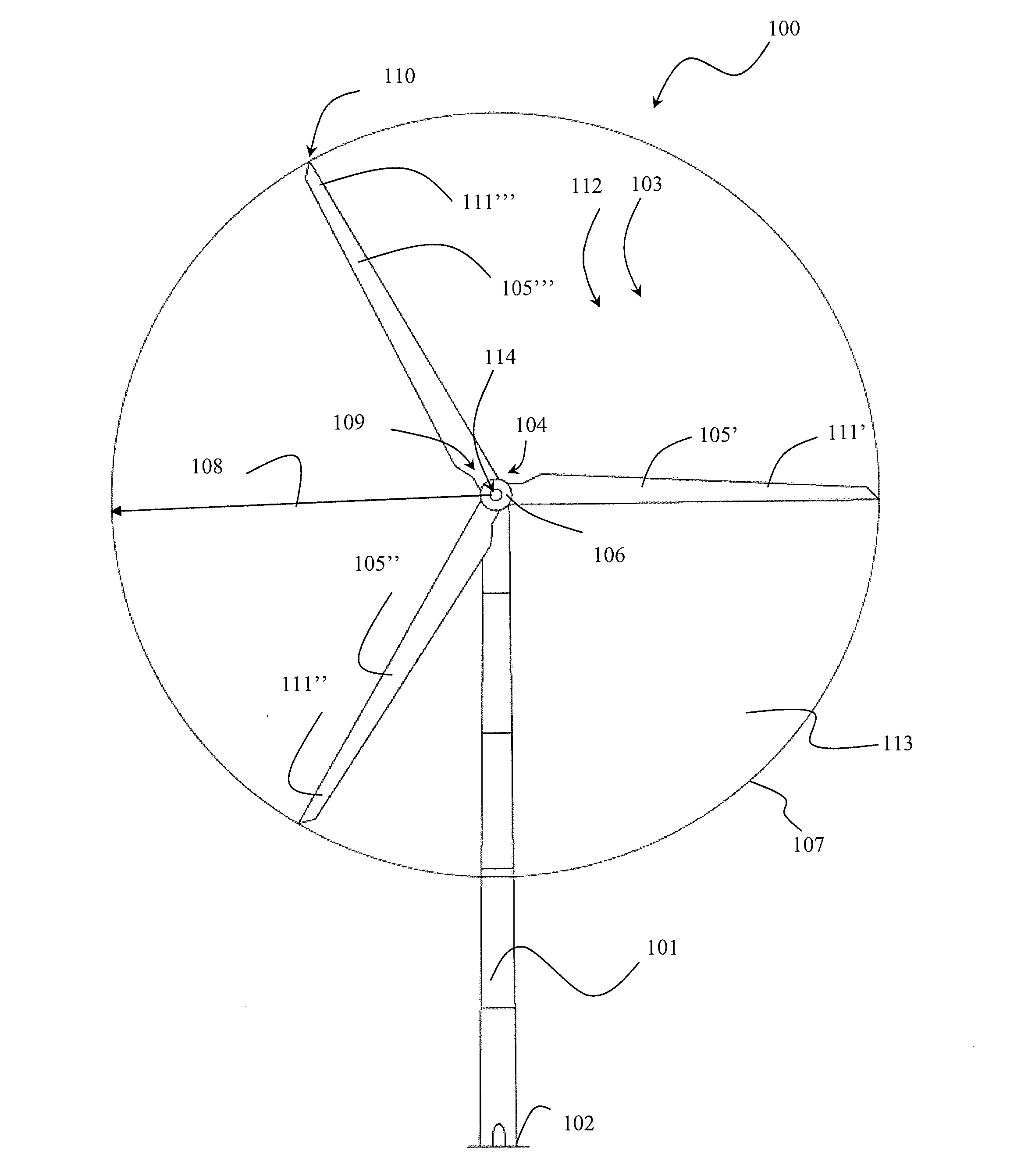
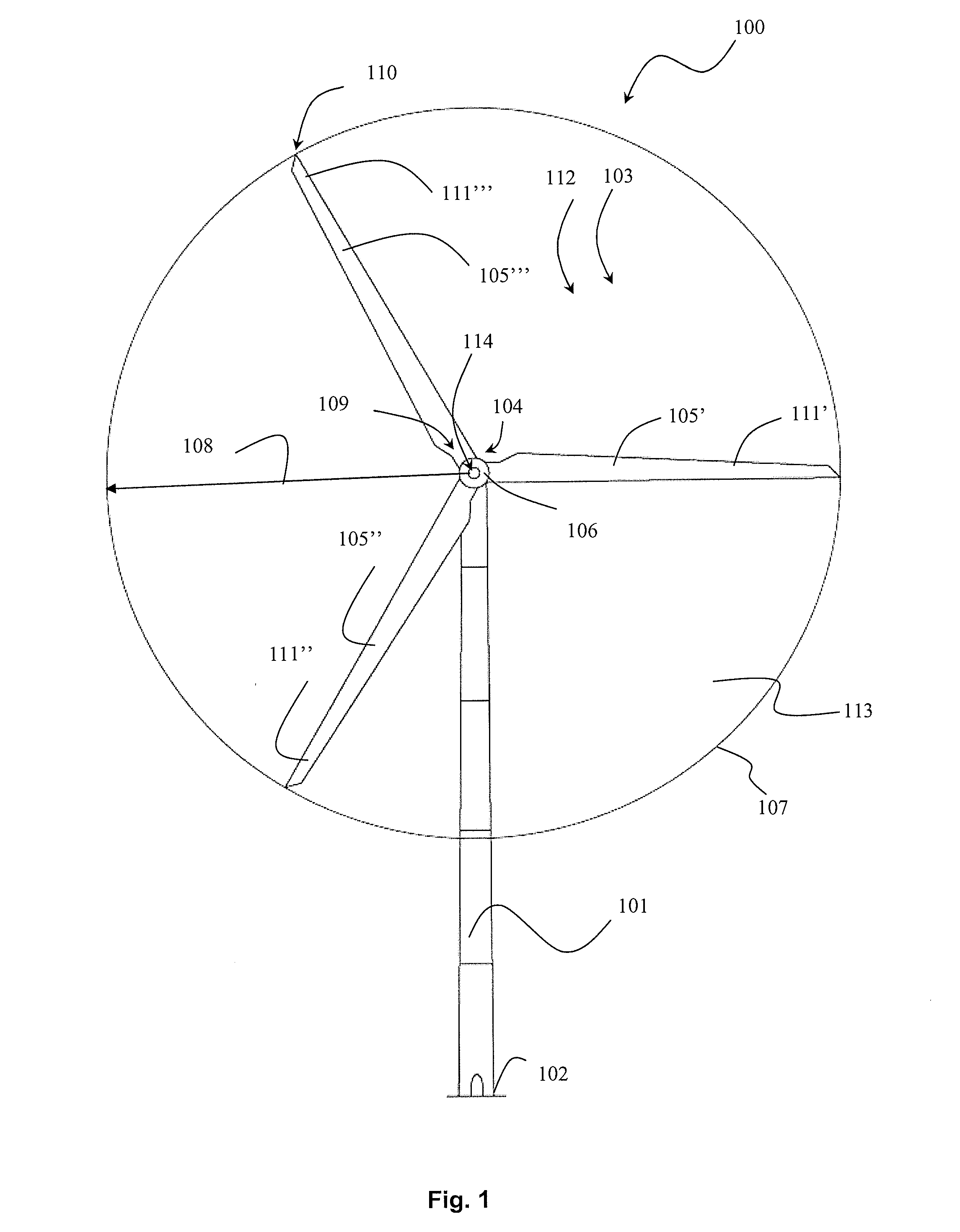
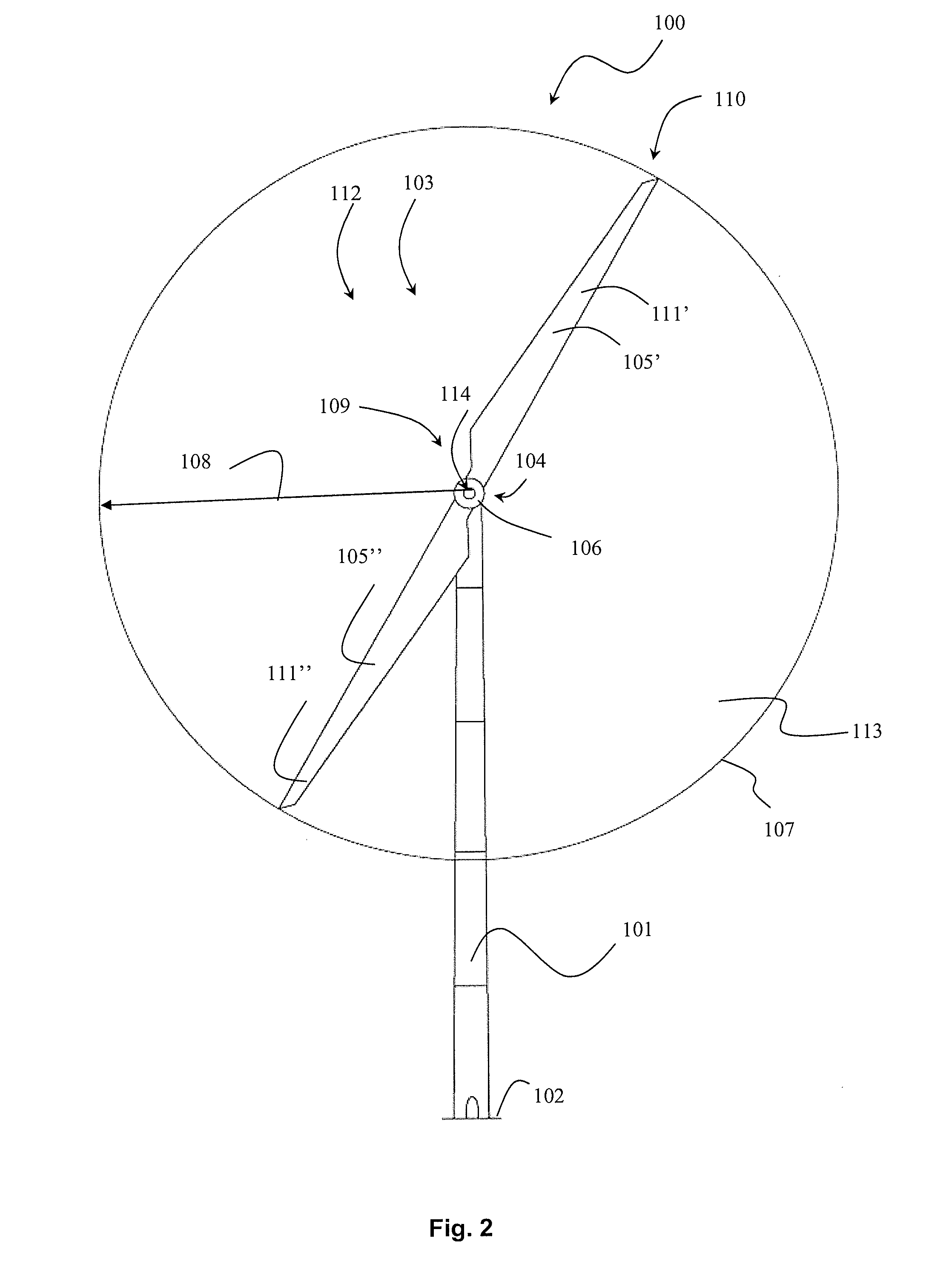
Wind turbine with additional rotor moment of inertia and a method for controlling a wind turbine with additional rotor moment of inertia
InactiveUS20130119663A1Eliminate needReduce rotation speedWind motor controlMachines/enginesGrid codeElectricity
This invention relates to a wind turbine having an additional mass each placed between a mounting end and a free end of at least two rotor blades. This invention further relates to a method for controlling a wind turbine with a pitch system for pitching a blade in a pitch angle and with blades with a mass for increased inertia, which wind turbine is operated in a normal operation mode in which a generator has a generator speed at a generator torque, and which wind turbine is to remain electrically coupled to a grid during a low voltage condition and with supplied current specifications, torque reference, power references, or according to a grid code.
Owner:ENVISION ENERGY DENMARK
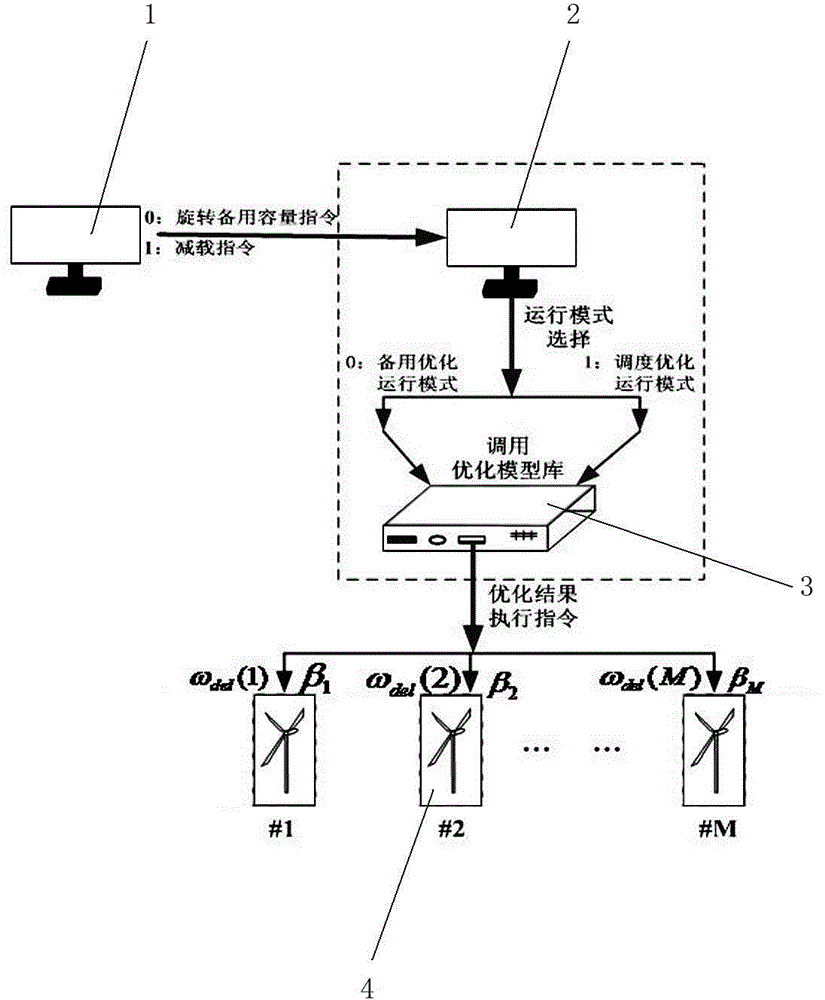
Wind power farm spinning reserve capacity optimization method considering rotor inertia kinetic energy
InactiveCN104701887AMinimized air curtailmentGuaranteed uptimeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationOperation modeFrequency regulation
The invention discloses a wind power farm spinning reserve capacity optimization method considering rotor inertia kinetic energy. Rotor inertia kinetic energy is brought into spinning reserve capacity, a reserve optimization operation mode and a dispatching optimization operation mode are built, a wind power farm control center selects the operation modes according to dispatching instructions issued by a dispatching master station, calculates and acquires optimization results and finally issues the optimization results to wind turbine groups, and wind turbine generators in the wind turbine groups execute the operation modes. The potential of frequency adjustment or emergency reserve of the rotor inertia kinetic energy can be maximally mined, wind curtailment capacity can be minimized when the reserve optimization operation mode is executed in a common operation scene of a wind power farm, considerable economic benefits are brought for wind power farm businessmen, spinning reserve capacity is maximized when the dispatching optimization operation mode is executed, and particularly, the method plays a very positive role in stable operation of a power grid when the power grid runs short of the spinning reserve capacity.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
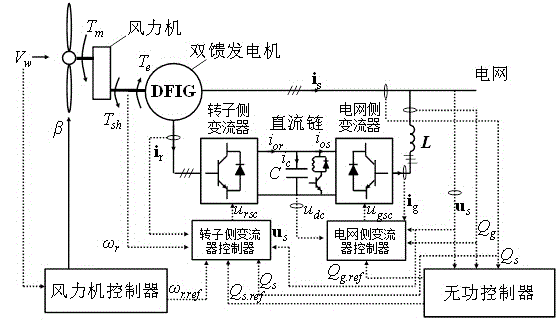
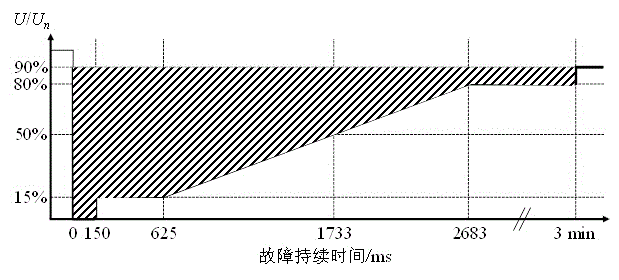
Wind energy caching low voltage ride through and reactive supporting control method for double-feed draught fan
InactiveCN104158225ASmall currentShorten the acceleration processSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingWind drivenGrid fault
The invention discloses a wind energy caching low voltage ride through and reactive supporting control method for a double-feed draught fan and belongs to the technical field of automatic control over wind driven generators. The purpose of reducing the currents of a rotor is achieved by switching electromagnetic torque reference values in a rotor side (RSC) control circuit under grid faults and temporarily storing surplus wind energy captured under the faults into rotor inertia energy. After the voltage recovers, a traditional circuit is switched back by an RSC, after the switch, overcurrent of the voltage recovery segment is avoided by temporarily limiting the electromagnetic torque of the RSC, and energy balance recovers safely. After a cascading feedback type reactive controller is applied, a fan can also provide reactive supporting safely for a grid in the whole low voltage ride through process. Compared with the prior art, the method is high in control strategy speed, new hardware is not introduced in, fault current in the fan can be effectively reduced, grid leaving time is prolonged, and nearby voltage can be obviously stabilized.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD
Taking-off and landing method of aircraft and device thereof
ActiveCN106882386ASolve the problem of not being able to take off verticallySolve the problem of vertical landingGround installationsRotocraftAviationButt joint
The invention provides a taking-off and landing method of an aircraft and a device thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aviation. The taking-off and landing device comprises a fixed wing aircraft, a multi-rotor type aircraft and a multi-rotor type aircraft parking platform; the fixed wing aircraft is provided with a GPS navigation device, an inertia sensor, an infrared illuminator, a communication module and an adsorption plane; the multi-rotor type aircraft comprises a flight control computer, a multi-rotor inertia sensor, an infrared thermal imager, a multi-rotor GPS navigation device, a multi-rotor communication module, avacuum generator, a sucking disc, a connecting rod and a connecting rod vertical device. The multi-rotor type aircraft separates from the fixed wing aircraft after hoisting the fixed wing aircraft to lift off, and taking-off of the fixed wing aircraft is achieved; the multi-rotor type aircraft flies to midair and is combined with the fixed wing aircraft, and hoists landing of the fixed wing aircraft. According to the taking-off and landing method of the aircraft and the device thereof, the advantages of the multi-rotor type aircraft that the multi-rotor type aircraft can vertically take off and land and is flexible and mobile can be utilized, the fixed wing aircraft is in butt joint with the multi-rotor type aircraft, and the problem that a traditional fixed wing aircraft cannot vertically take off and land is solved.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANYI AIRPORT SPECIAL EQUIP CO LTD
Starting method for Hall-less single-phase BLDCM
InactiveUS7242160B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersEngineeringSpecific time
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method of expanding types of synchronous motors and synchronous motors produced by the method
InactiveUS20020035775A1Reduce in quantityLow costMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesSynchronous motorEngineering
A method of expanding types of synchronous motors capable of reducing the number of required stator types to use stators in common, and a synchronous motor produced by the method. A group of stators are prepared by stacking stator cores of identical shape so that heights of the stators are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental height. A plurality of groups of rotors are prepared so that lengths of the rotors in each group are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental length. The rotors in each group are provided with permanent magnets having a residual magnetic flux density different from that of the permanent magnets of the rotors in the other groups. A stator and a rotor corresponding to a preset output torque specification value and a preset rotor inertia specification value are respectively selected from the group of stators and the rotor groups and are combined with each other, whereby an expanded type of motor is obtained.
Owner:FANUC LTD
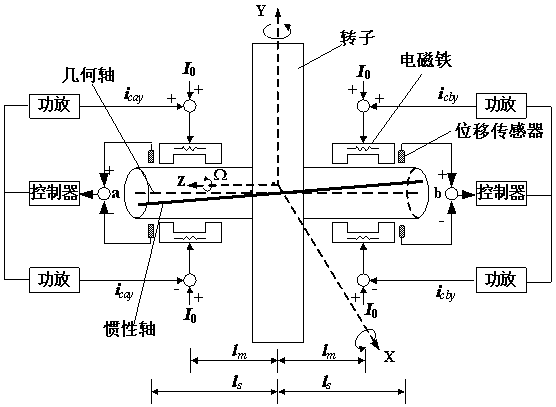
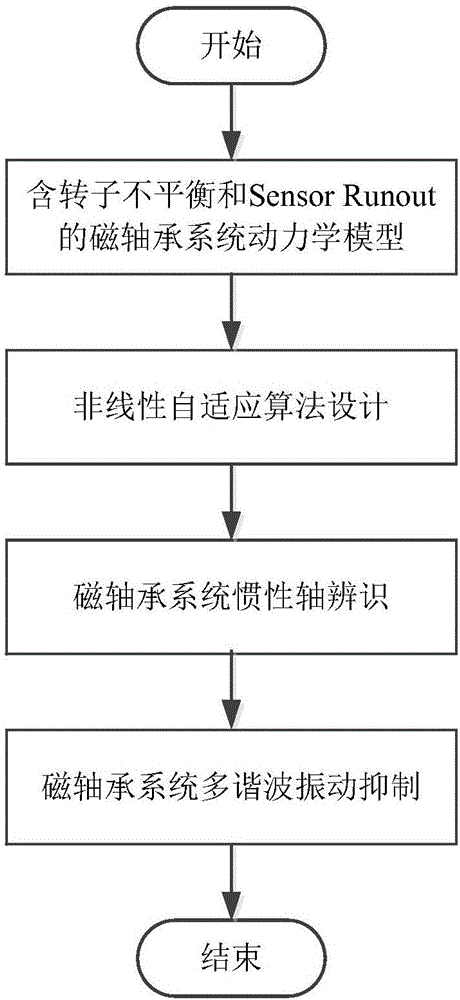
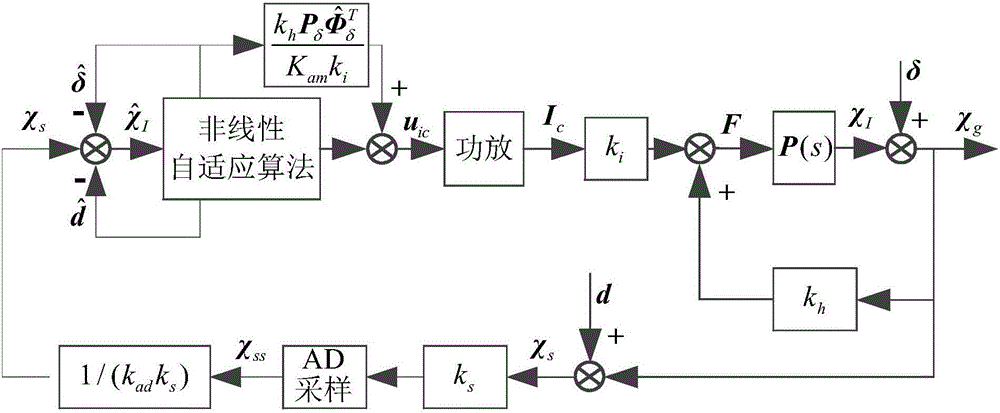
Magnetic bearing system inertia axis identification method based on nonlinear self-adaptive algorithm
ActiveCN106289208AImprove performanceOvercome the disadvantage of large identification errorRotary gyroscopesMagnetic bearingDynamic models
The invention relates to a magnetic bearing system inertia axis identification method based on a nonlinear self-adaptive algorithm. Firstly, a magnetic bearing system rotor dynamics model including unbalance and Sensor Runout is established; secondly, a nonlinear self-adaptive control law and an estimation law are provided, and Fourier coefficients of Sensor Runout higher harmonic components can be also estimated while the estimated value of the inertia center displacement of a magnetic suspension rotor tends to zero; then, identification of Sensor Runout synchronous components and the unbalance amount of the rotor is achieved by changing the rotation speed strategy of the rotor and increasing the observability degree of a system, namely the identification of inertia axis is achieved; finally, the Fourier coefficients of the synchronous components in a self-adaptive algorithm are corrected, multi-harmonic current is accurately inhibited, displacement stiffness is compensated, and multi-harmonic vibration control of a magnetic-suspension inertia executing mechanism is achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Inertia compensator based on virtual synchronous generator rotor inertia power decoupling
ActiveCN108683213AHigh inertiaImprove stabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower oscillations reduction/preventionVirtual synchronous generatorElectric power system
The invention relates to an inertia compensator based on virtual synchronous generator rotor inertia power decoupling. The inertia compensator comprises a power storage element, a DC / DC converter, a filter circuit, an inverter and a controller. The power storage element is connected to a power grid through the DC / DC converter, the inverter and the filter circuit in order. When a system load changes stepwise, the controller controls the DC / DC converter and the inverter to output inertial power and exhibit attenuated oscillation characteristics to compensate the moment of inertia of a system. Compared with the prior art, the inertia compensator has the advantages that the inertia of a power system is increased in a targeted way while a traditional grid-connected mode of a distributed power supply is not changed, thus the stability of the power system is improved, the adaptability of distributed power grid connection is enhanced, a virtual synchronous generator can be replaced, and thus the shortcomings of a complex control algorithm and high equipment investment of the virtual synchronous generator are avoided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
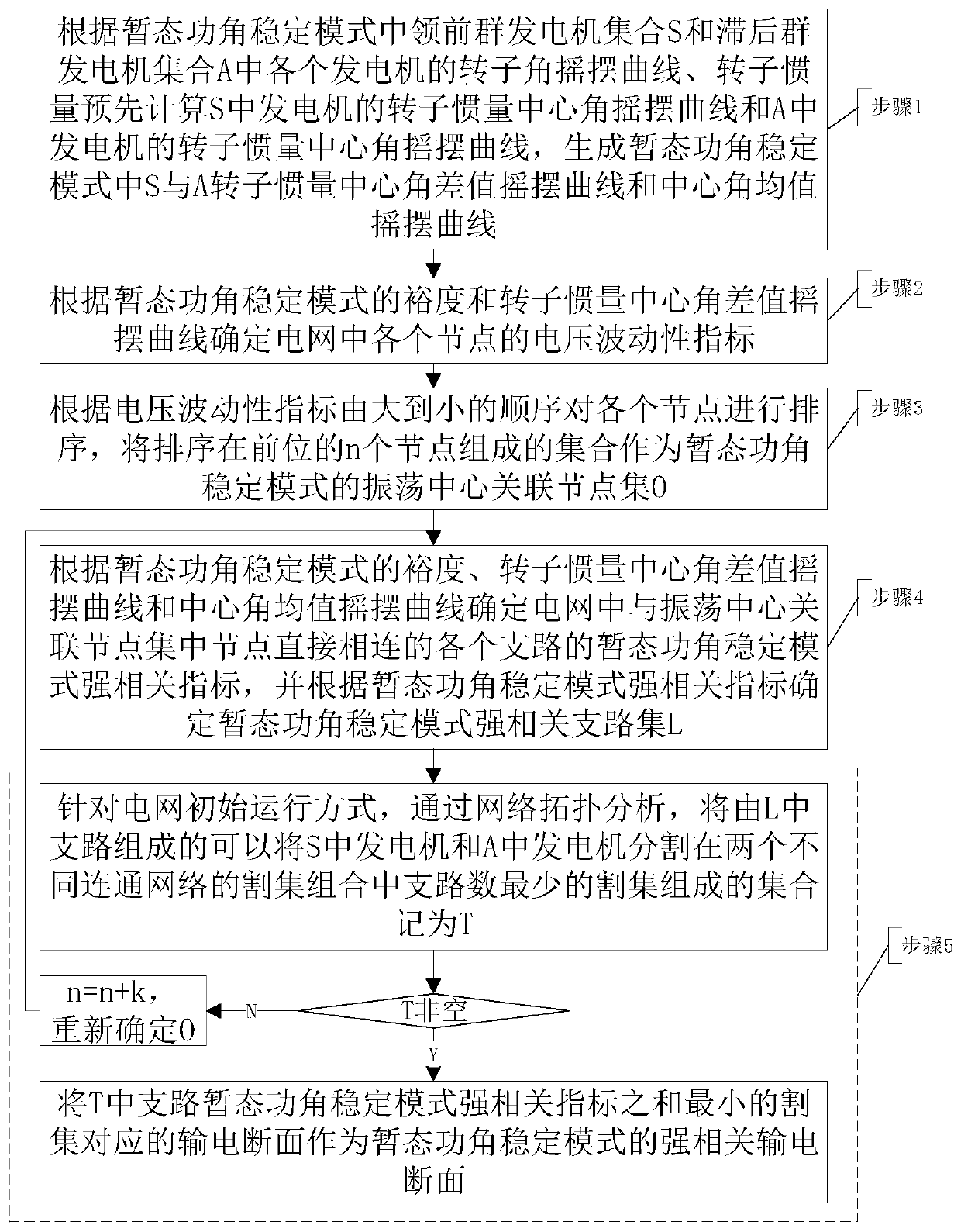
Method and system for identifying strong correlation power transmission section in transient power angle stabilization mode
ActiveCN109873418AIndicator results are accurateConforms to the analysis theory of electrical transient oscillation characteristicsAc network circuit arrangementsTransient statePower grid
The invention discloses a method and a system for identifying a strong correlation power transmission section in a transient power angle stabilization mode. A node, in which the node voltage is greater than a ratio of an initial value average fluctuation amplitude and an initial value, is taken as an oscillation center correlation node in a transient power angle stabilization mode, when the rotorinertia central angle difference value of a leading front group generator and a lagging group generator in the transient power angle stabilization mode reaches the maximum value or close to 180 degrees; the maximum value in the average deviation between each point voltage phase angle in the direct connection branch of the oscillation center correlation node at the corresponding moment and the rotor inertia central angle mean value of a complementary group generator is used as a transient power angle stability mode strong correlation index of the branch; the leading front group generator and the lagging group generator are cut into a cutting combination of two different communication networks, and the power transmission section corresponding to the cutting combination with the least branches and the minimum sum of the branch transient power angle stability mode strong correlation index as the strong related power transmission section of the transient power angle stabilization mode; andthe power transmission section is matched with the actual requirements of the power grid regulation and control operation personnel and is convenient to master.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +3
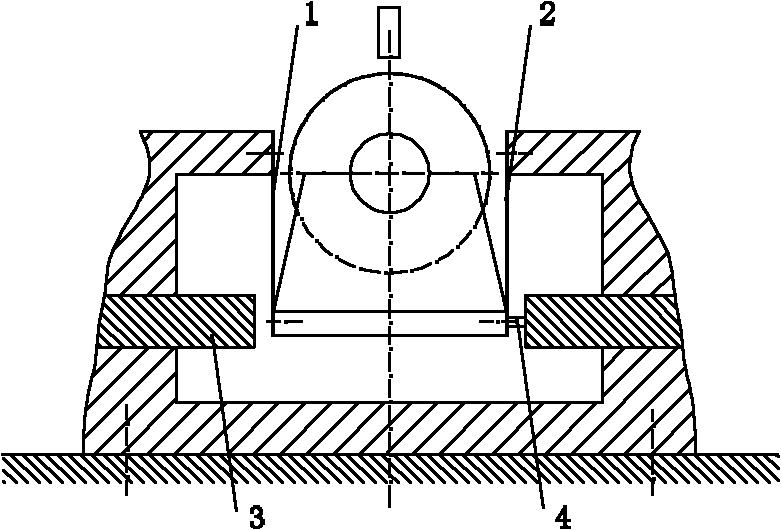
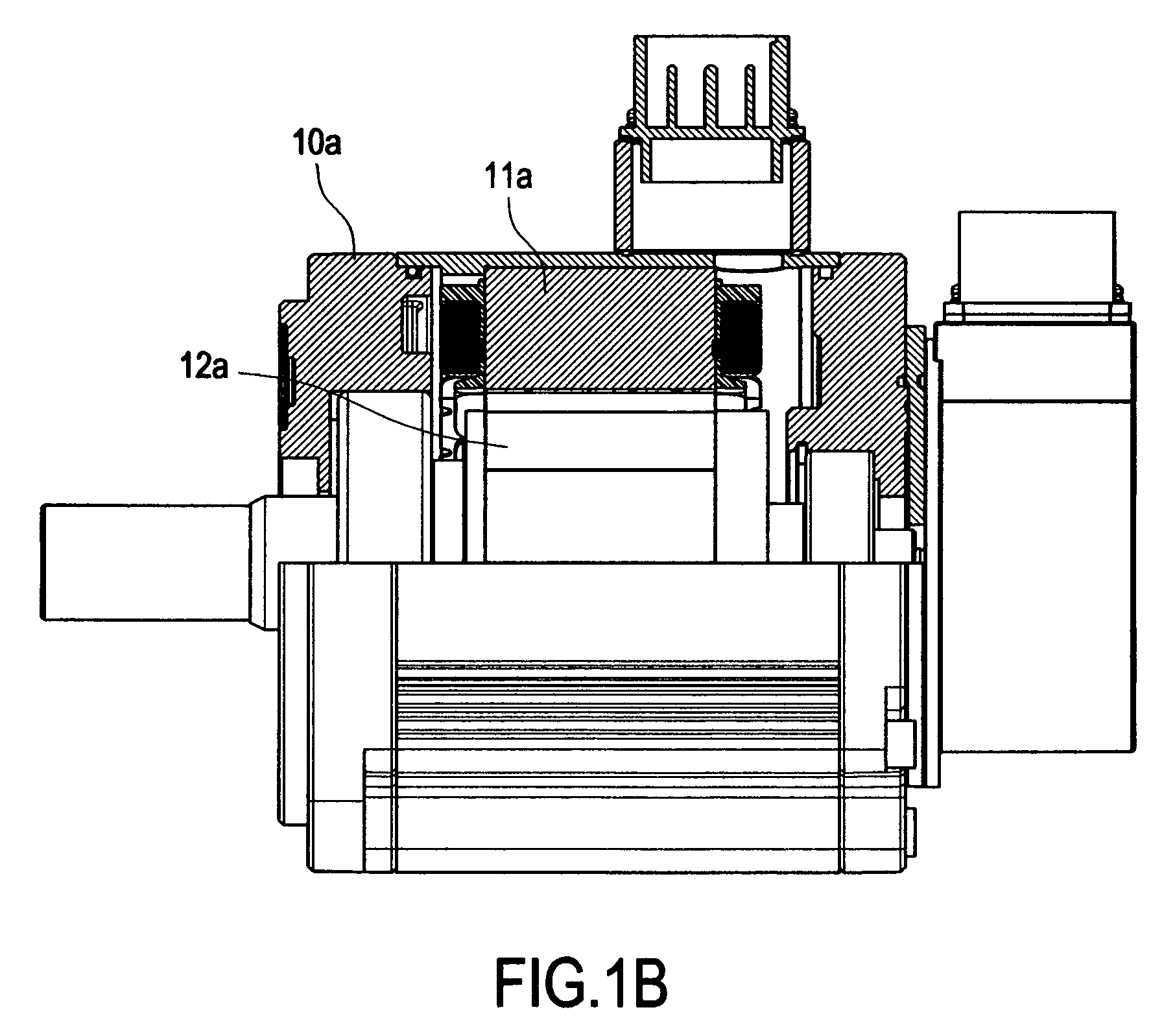
Servo motor with large rotor inertia
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Method of instant estimation of a load motor inertia
InactiveUS20040148110A1Electric motor controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementMean squareAdaptive filter
A method of instant estimation of the rotor inertia of a load motor is disclosed. The adaptive filter accompanied with the Least Mean Square Rule is introduced to instantly estimate the rotor inertia of a load motor. One input of the adaptive filter is the current signal of a model motor whose rotor inertia is known, and the other is the deviation current signal between the model motor and the drive motor. Once the two inputs are determined, the rotor inertia of the load motor will then be calculated using the Least Mean Square Rule and the adaptive filter.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Motor control apparatus generating command limited by motor torque
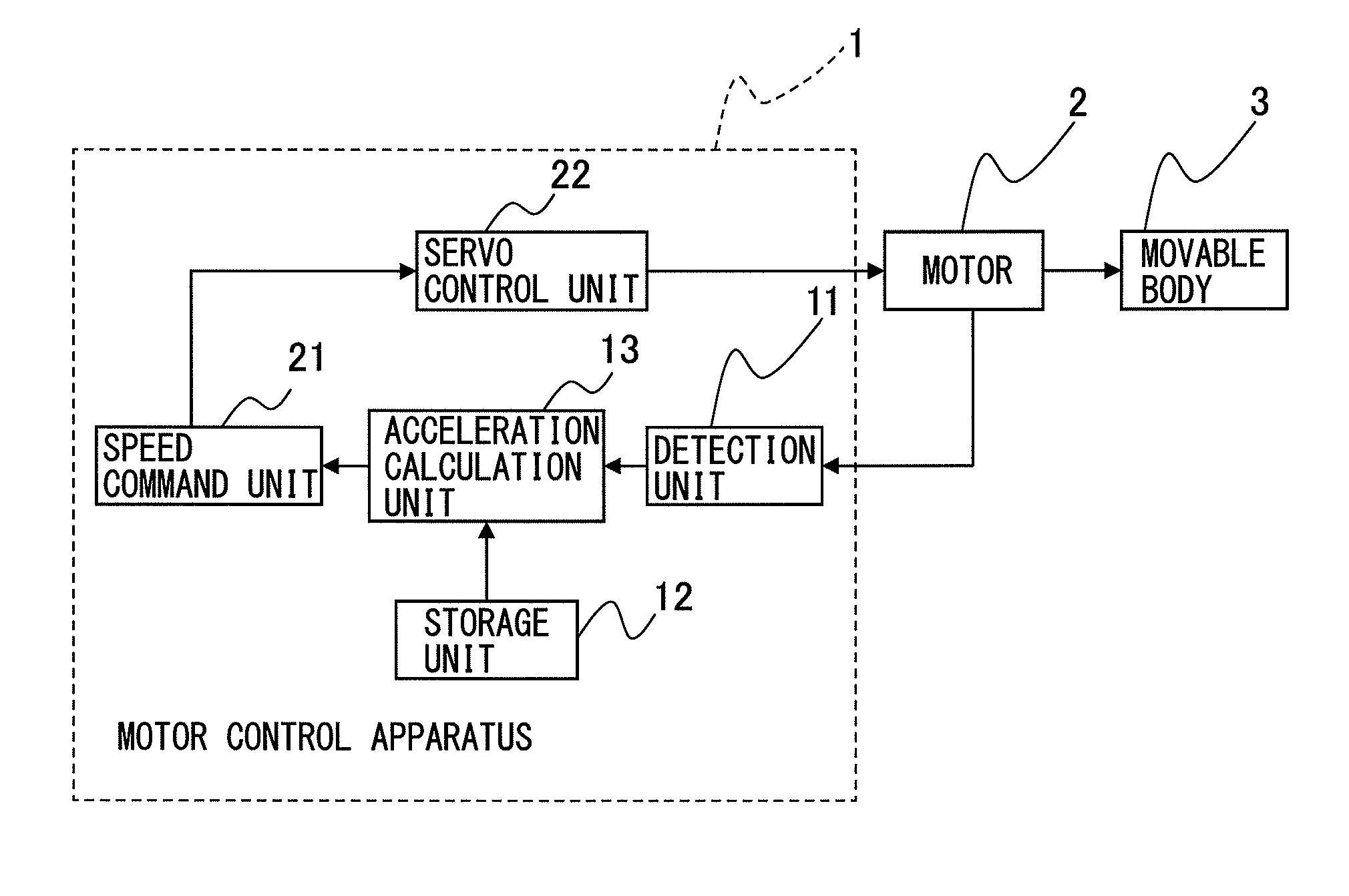
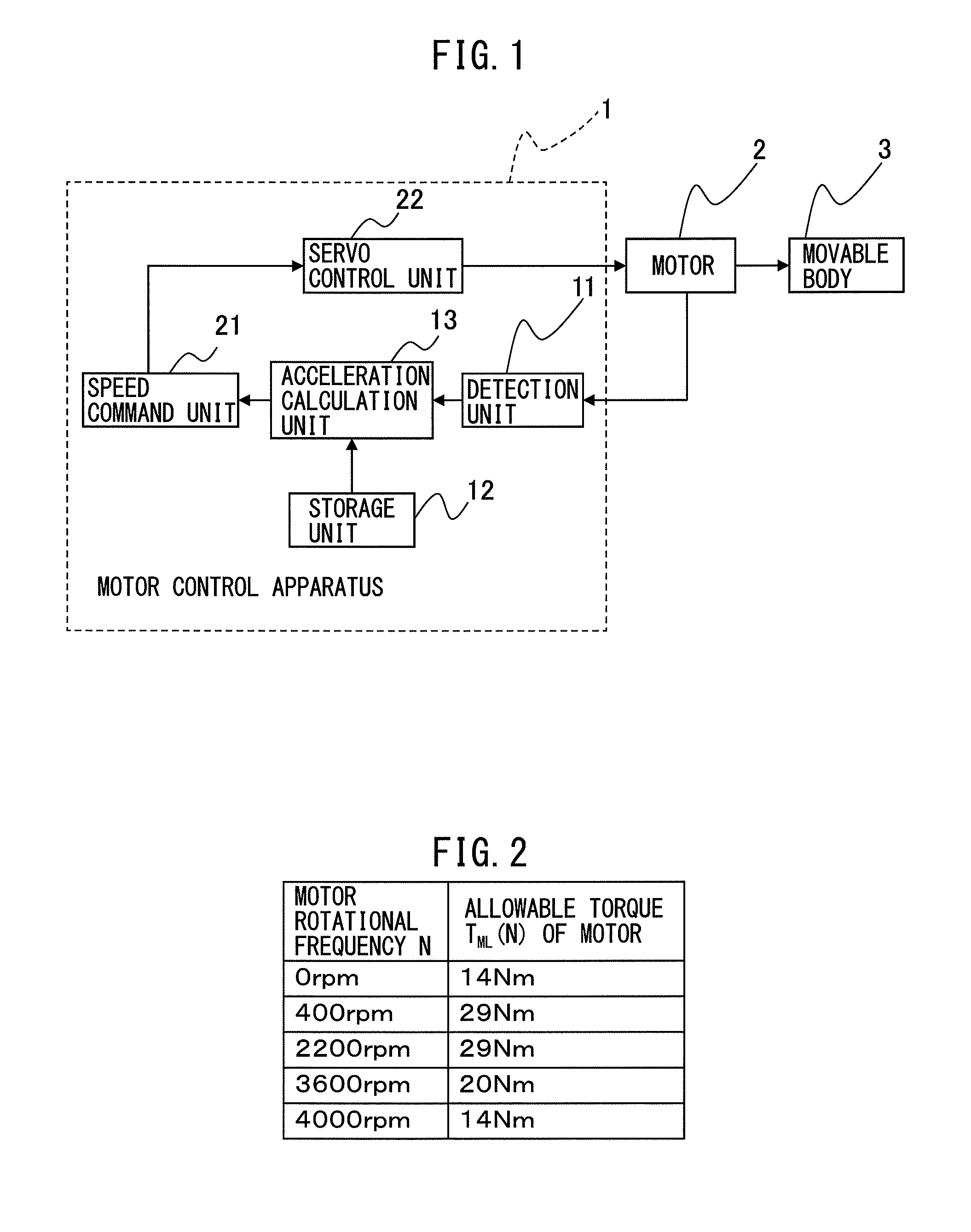
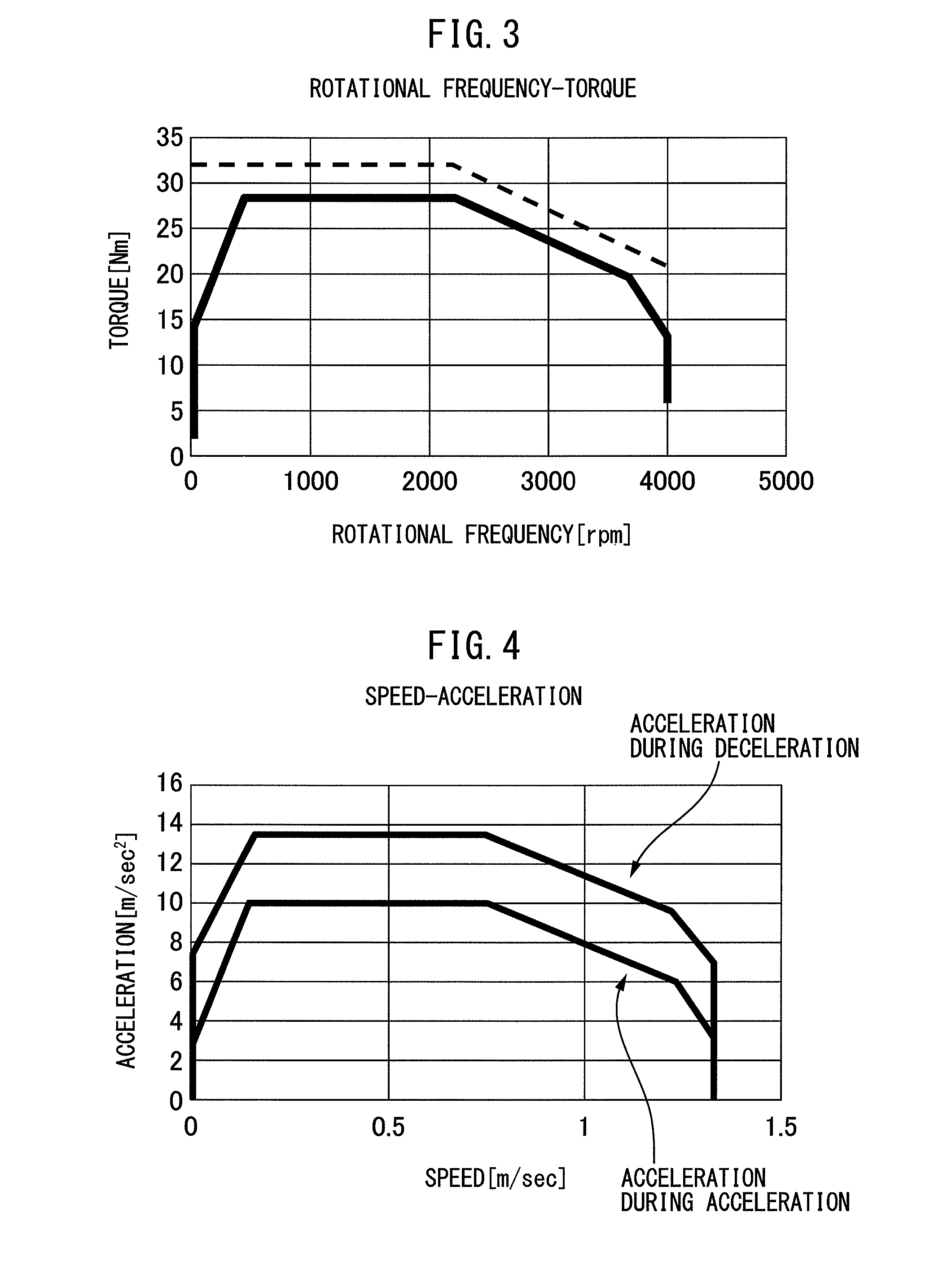
ActiveUS20160132041A1Easy to useImprove motor performanceComputer controlSimulator controlLinear motionConversion factor
A motor control apparatus includes a detection unit detecting a motor rotational frequency, a storage unit storing an allowable torque at the motor rotational frequency detected by detection unit, a first torque offset generated in a direction opposite to a moving direction of a movable body, a second torque offset generated in one direction regardless of the moving direction of the movable body, a rotor inertia moment, a load inertia moment, and a conversion factor for converting a motor rotation angle in rotary motion of the motor to a moving distance in linear motion of the movable body, and an acceleration calculation unit calculating an acceleration command of the motor for each moving direction of the movable body and each acceleration operation and deceleration operation using the allowable torque, the first torque offset, the second torque offset, the rotor inertia moment, the load inertia moment, and the conversion factor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Servo motor with large rotor inertia
ActiveUS20070188031A1Increase rotation inertiaMechanical energy handlingMagnetic circuit shape/form/constructionMoment of inertiaEngineering
A servo motor with large rotor inertia includes a casing, a stator, a rotor and an inertial disk. The casing includes a hollow chamber and axial stages at front side and rear side thereof. The stator is arranged in the chamber and includes a ring and a plurality of coils around the ring. A through hole is defined at the center of the ring. A rotation shaft of the rotor is fixed to the stage and a magnet body is capped to the rotation shaft, where the magnet body is arranged in the through hole. The inertial disk is fixed to the rotation shaft of the rotor. The rotational inertia of the rotor is increased by rotating the inertial disk when the rotor is rotated by magnetize the stator. Therefore, the inertial disks of various sizes can be fixed to the rotor for matching different load inertia.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Low rotor inertia dry type dual clutch
InactiveCN101196217ASmall moment of inertiaImprove ride comfort performanceFriction clutchesEngineeringMoment of inertia
The invention discloses a dry type double clutch with low rotation inertia, which aims at resolving the problem of great rotation inertia in double clutch. The invention adds and improves a transition disc (2), an I clutch compressing disc (3), a flywheel (5) and an I clutch shell body (10). The transition disc (2) is connected solidly with a flange disc at an crankshaft output end of an engine (21); the flywheel (5) is connected solidly with the transition disc (2); a II clutch shell body (11) at the right side of the flywheel (5) is connected solidly with the flywheel (5); the I clutch compressing disc (3) is positioned at the left side of the flywheel (5); the I clutch shell body (10) is positioned at the right side of the II clutch shell body (11); a bent extruding ear on the I clutch compressing disc (3) passes through a cutting slot on the flywheel (5) and connects solidly with the bent extruding ear on I clutch shell body (10). In addition, the invention has two input axles being configured as parallel axle type gear box with concentric sleeve shaft.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of expanding types of synchronous motors and synchronous motors produced by the method
InactiveUS20020167240A1Reduce in quantityLow costWave amplification devicesDC commutatorSynchronous motorEngineering
A method of expanding types of synchronous motors capable of reducing the number of required stator types to use stators in common, and a synchronous motor produced by the method. A group of stators are prepared by stacking stator cores of identical shape so that heights of the stators are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental height. A plurality of groups of rotors are prepared so that lengths of the rotors in each group are different from one another to be multiples of a fundamental length. The rotors in each group are provided with permanent magnets having a residual magnetic flux density different from that of the permanent magnets for the rotors in the other groups. A stator and a rotor corresponding to a preset output torque specification value and a preset rotor inertia specification value are respectively selected from the group of stators and the rotor groups and are combined with each other, whereby an expanded type of motor is obtained.
Owner:FANUC LTD
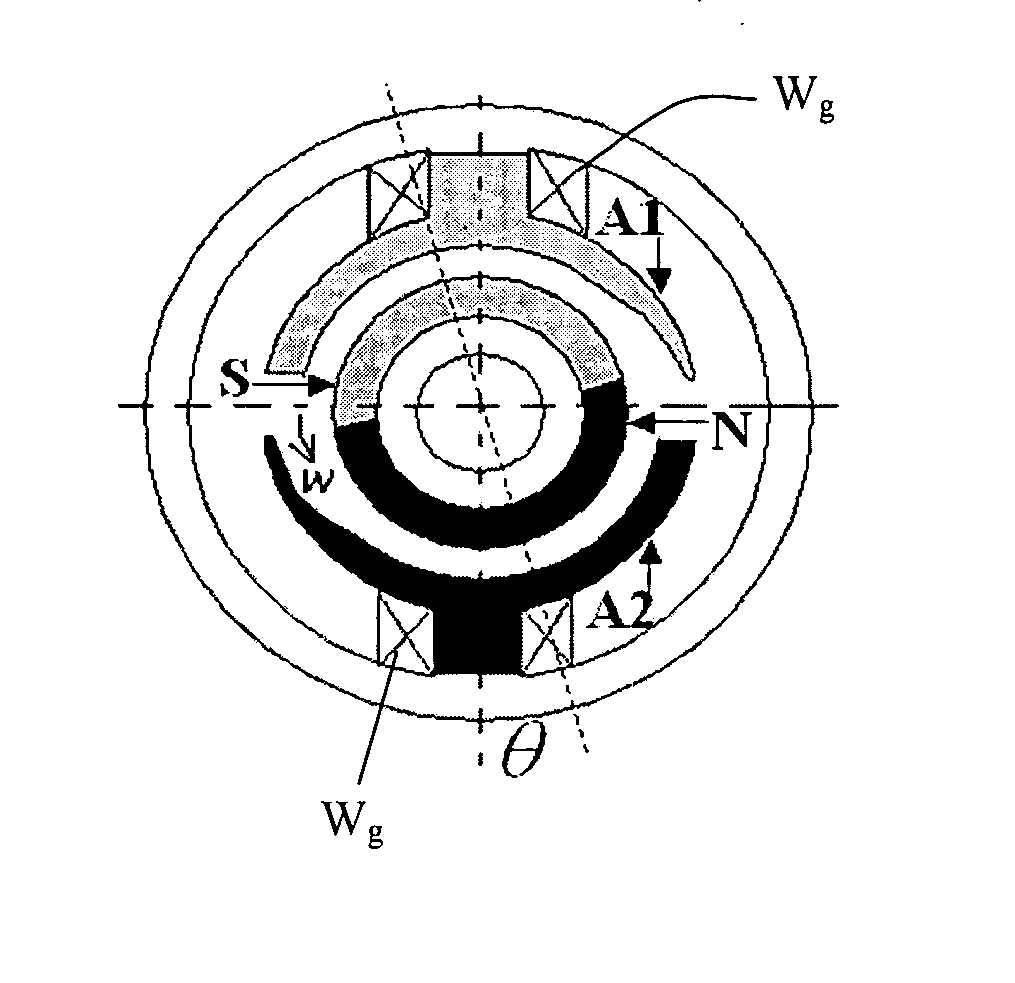
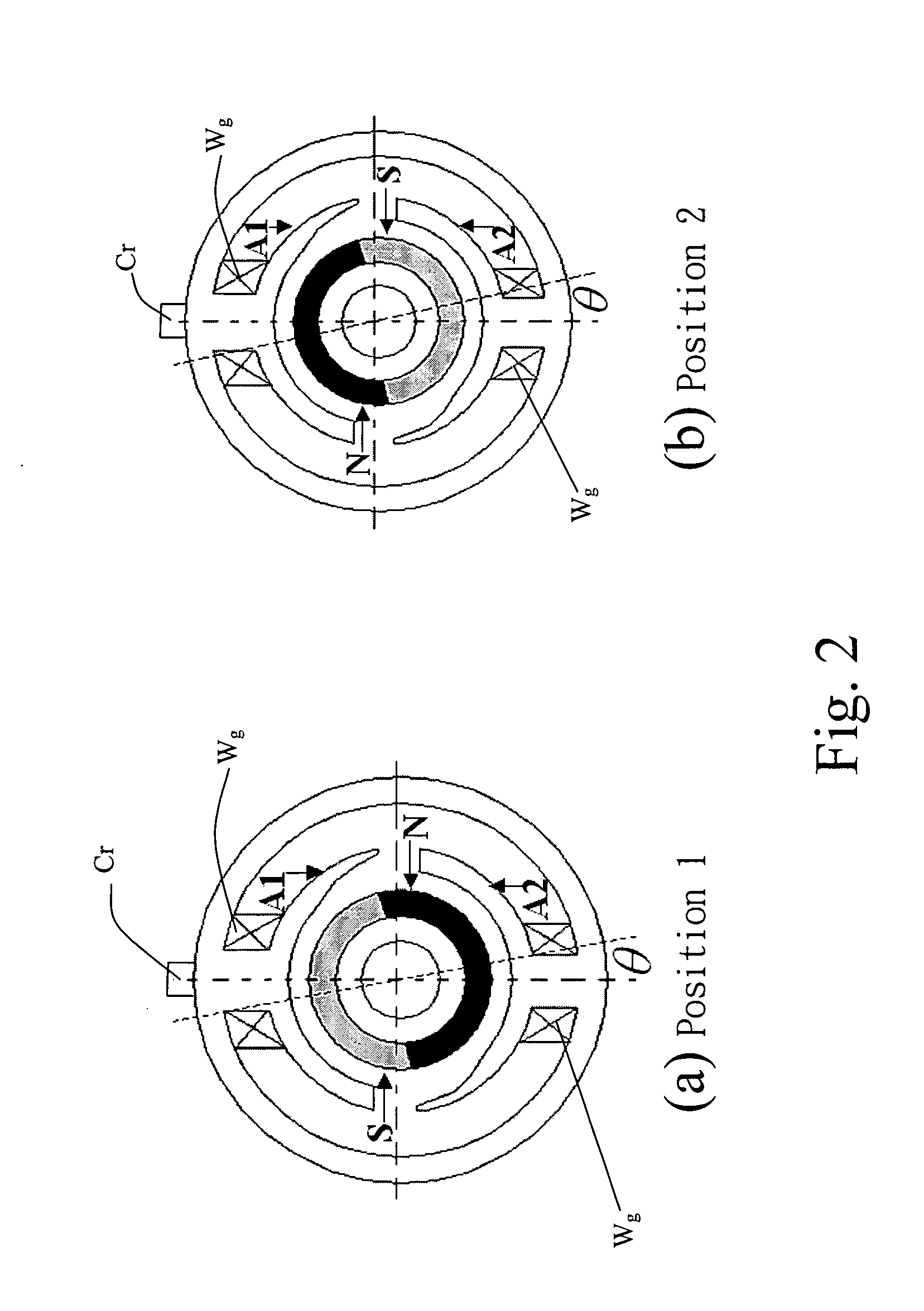
Starting method for hall-less single-phase BLDCM
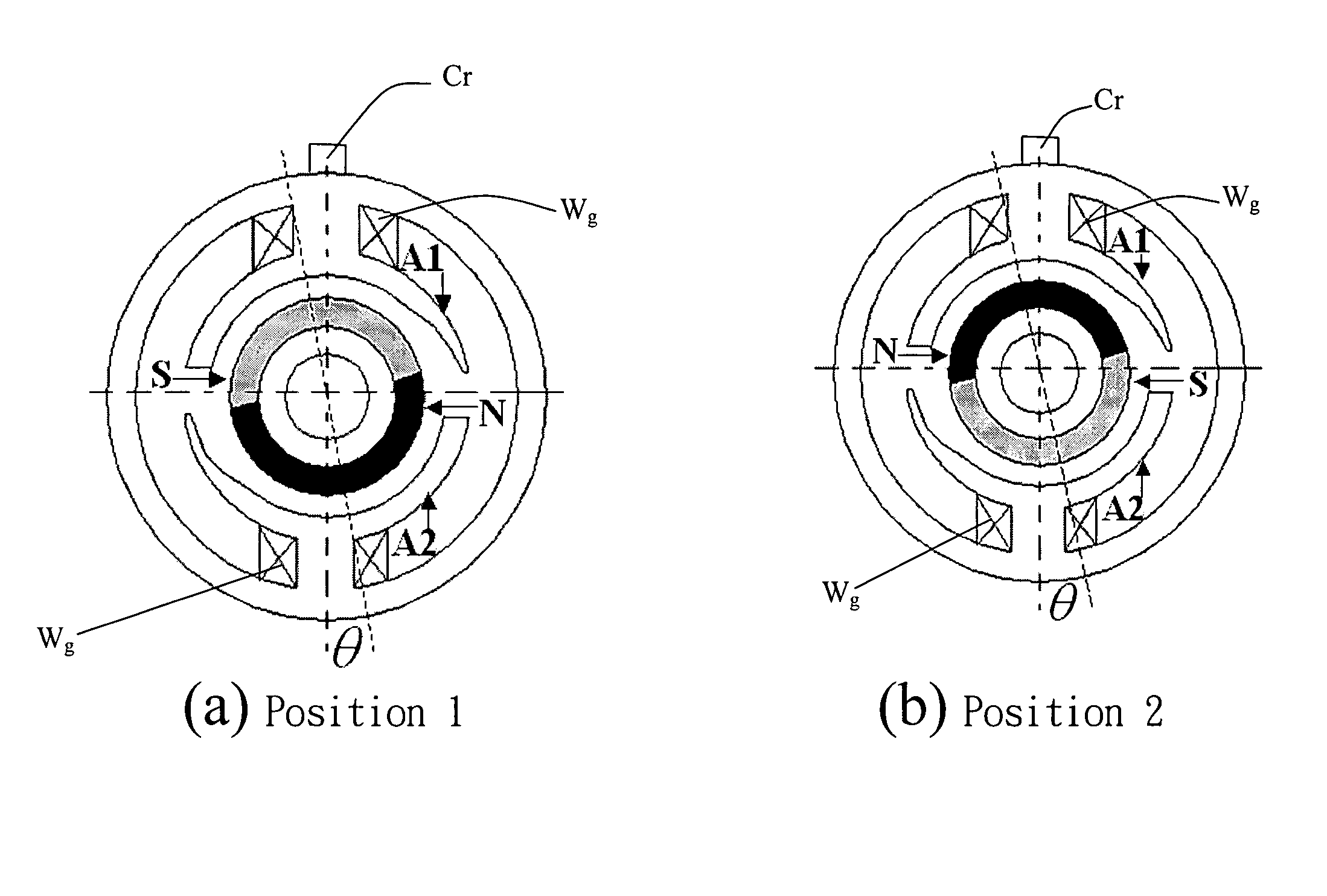
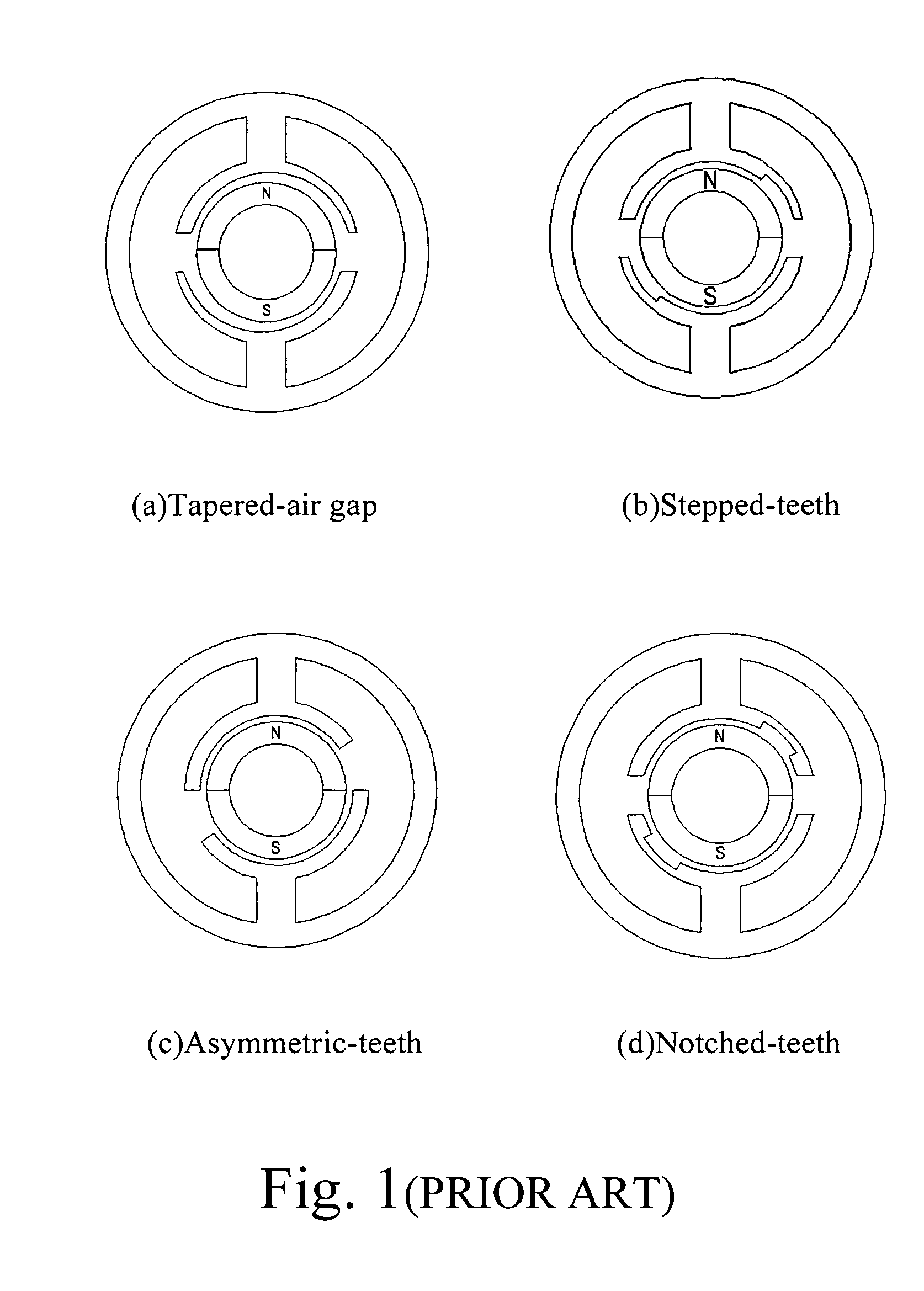
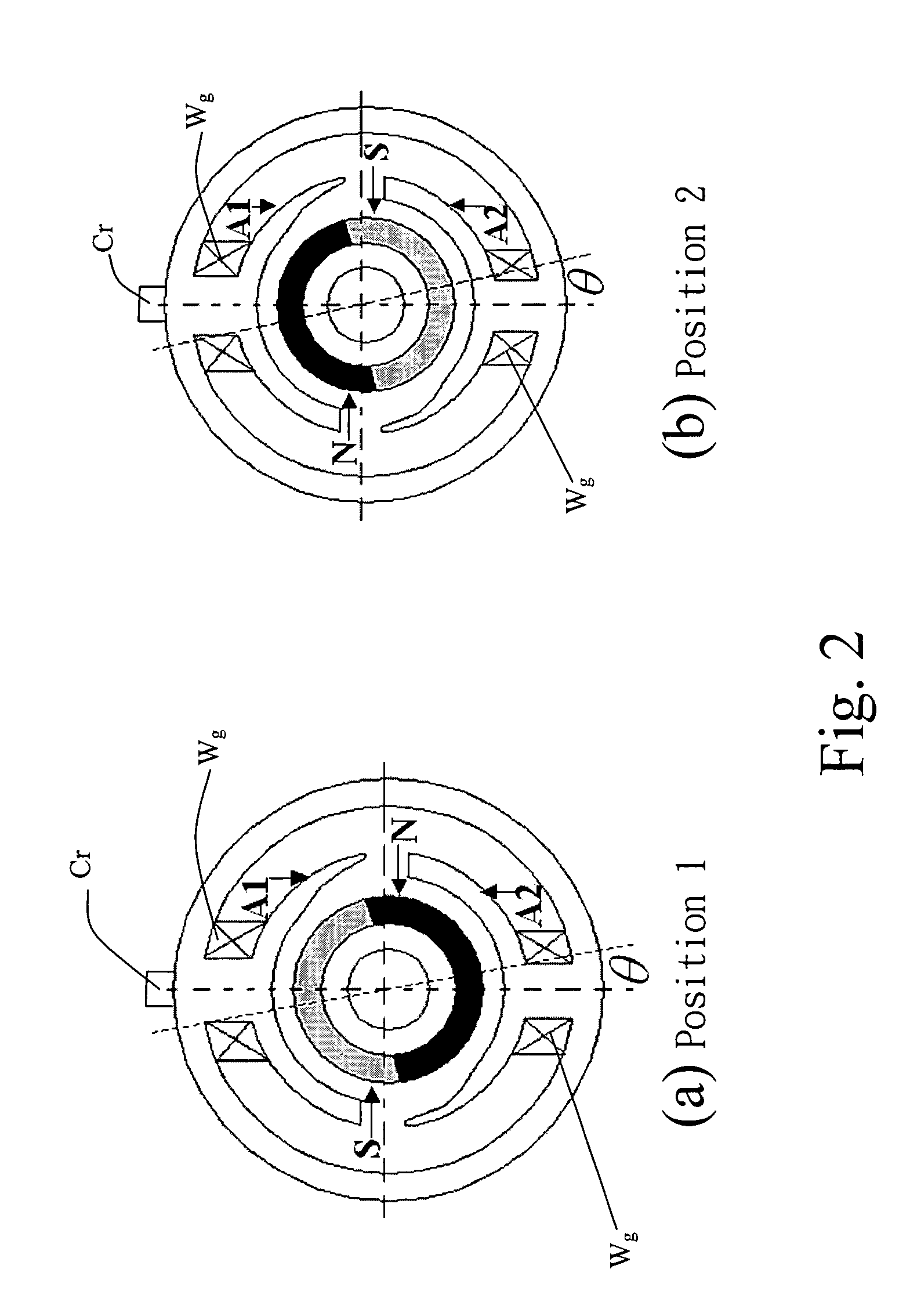
The methods for starting a Hall-less single-phase BLDCM having an asymmetrical air gap are proposed. The provided methods are employed to input a specific amount of current impulse and stop the current impulse at a specific time such that the rotor of the single-phase BLDCM having an asymmetrical air gap can be realized to rotate in the pre-determined direction through one of the cogging torque and the rotor inertia after that specific time so as to accomplish the normal starting of a motor without the Hall-effect sensor.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com