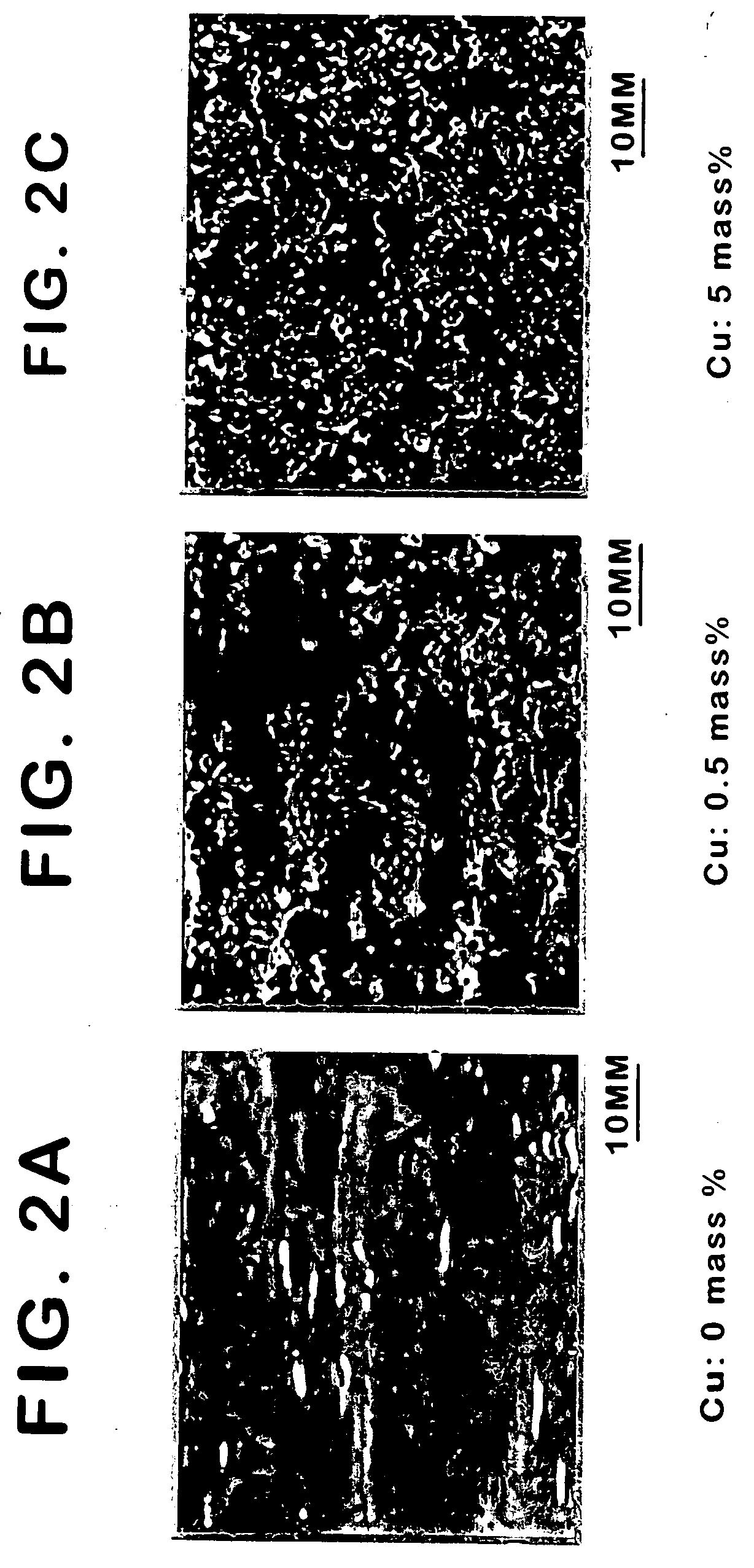
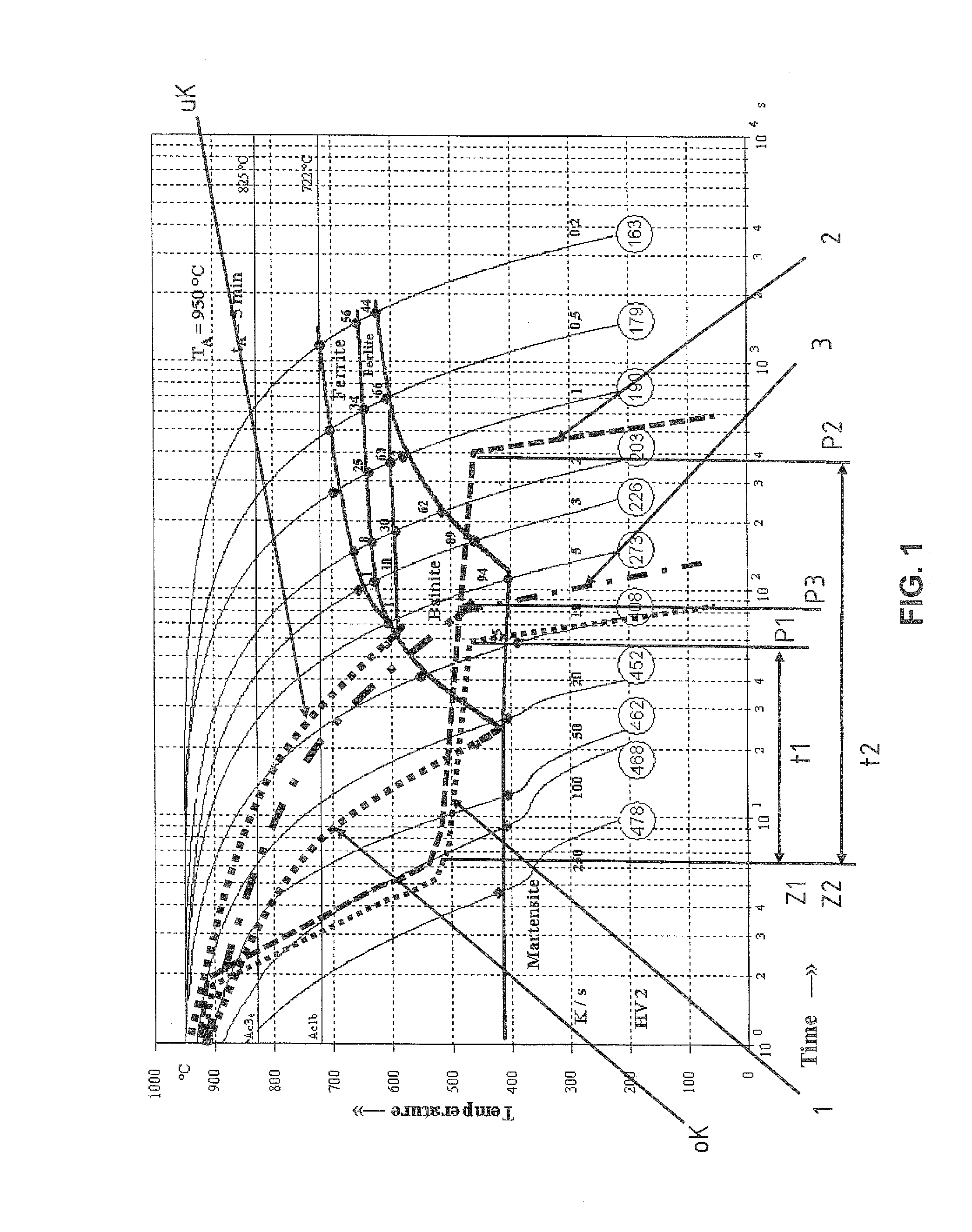
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
330results about How to "Low ductility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
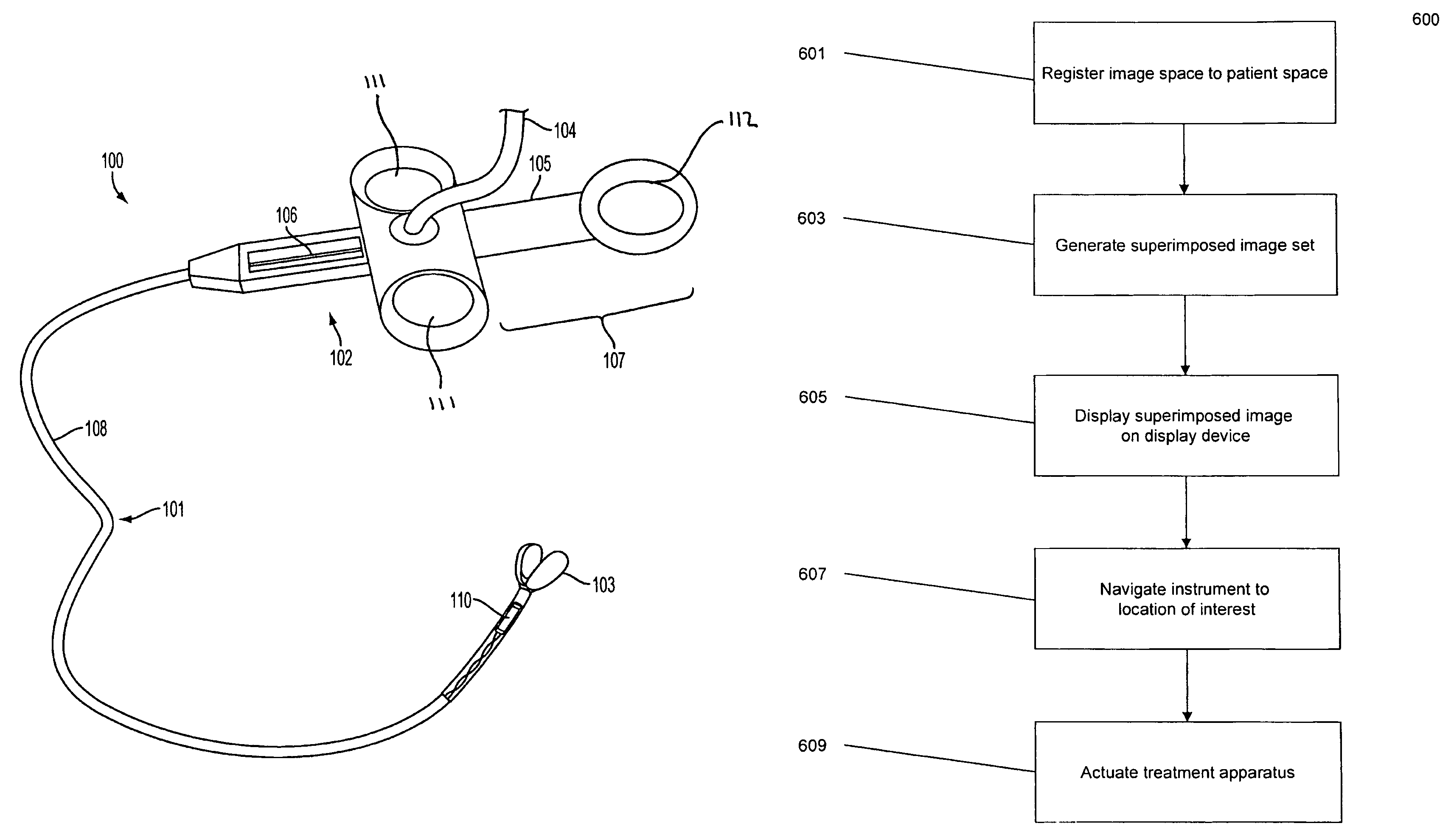
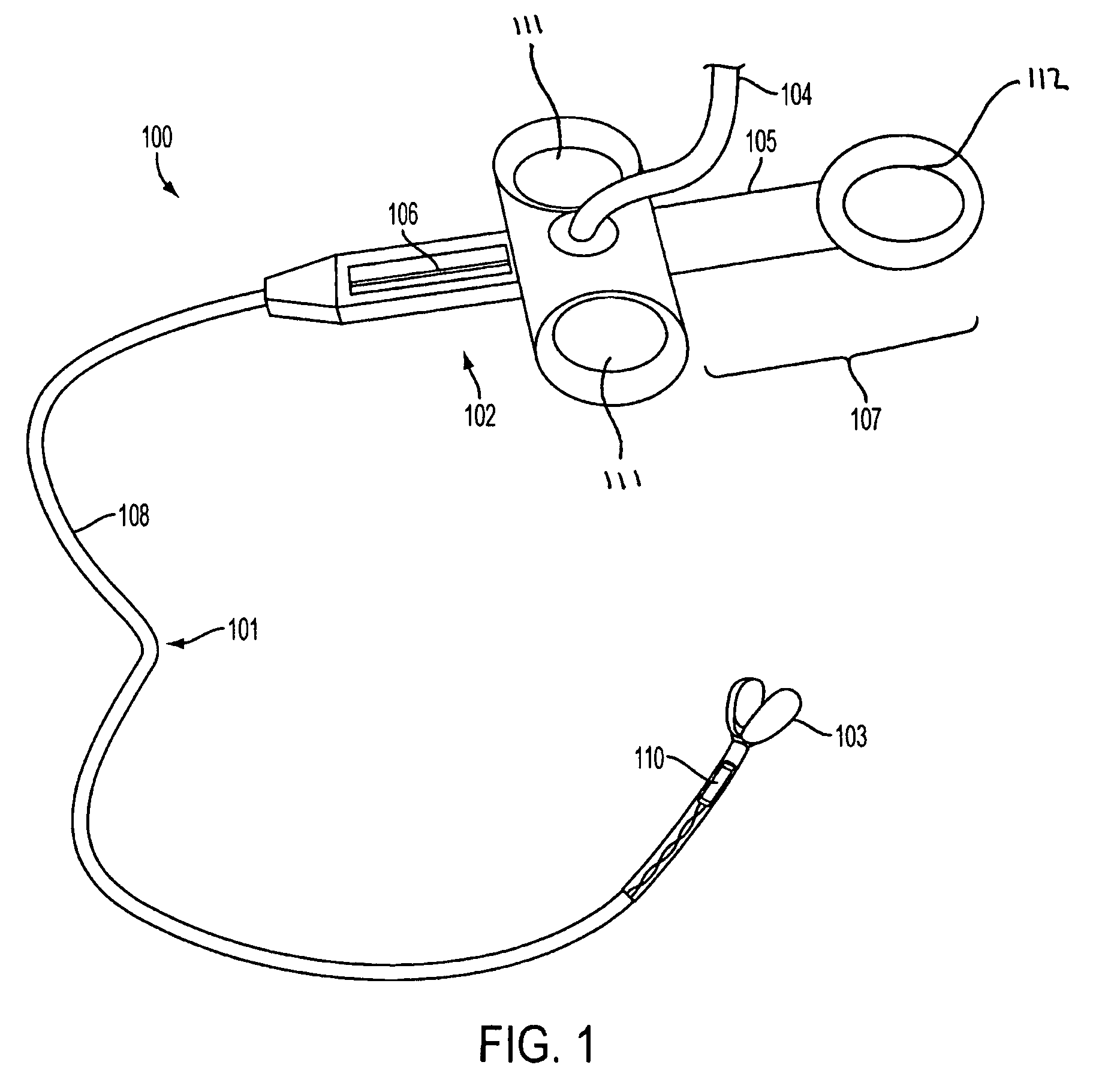
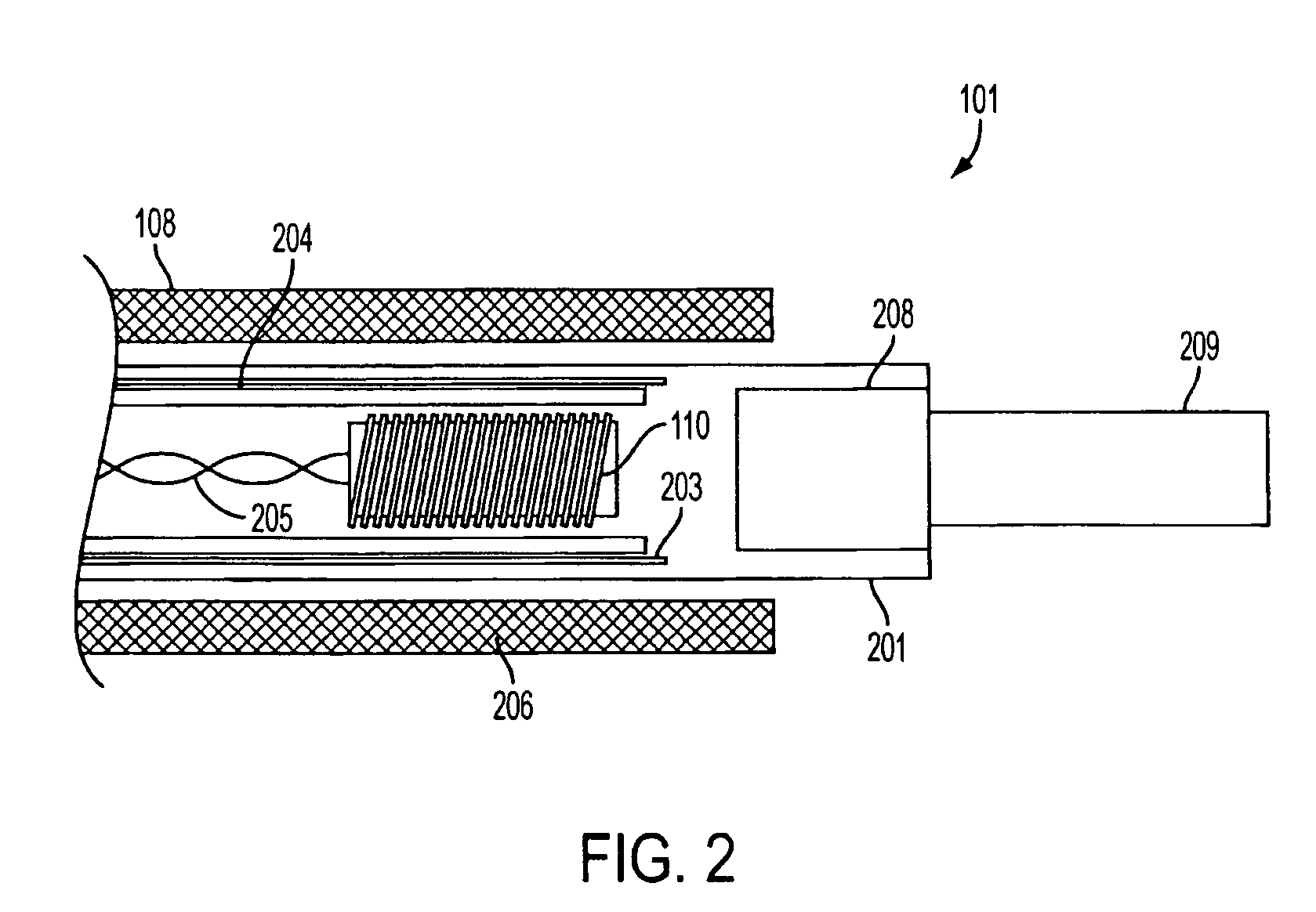
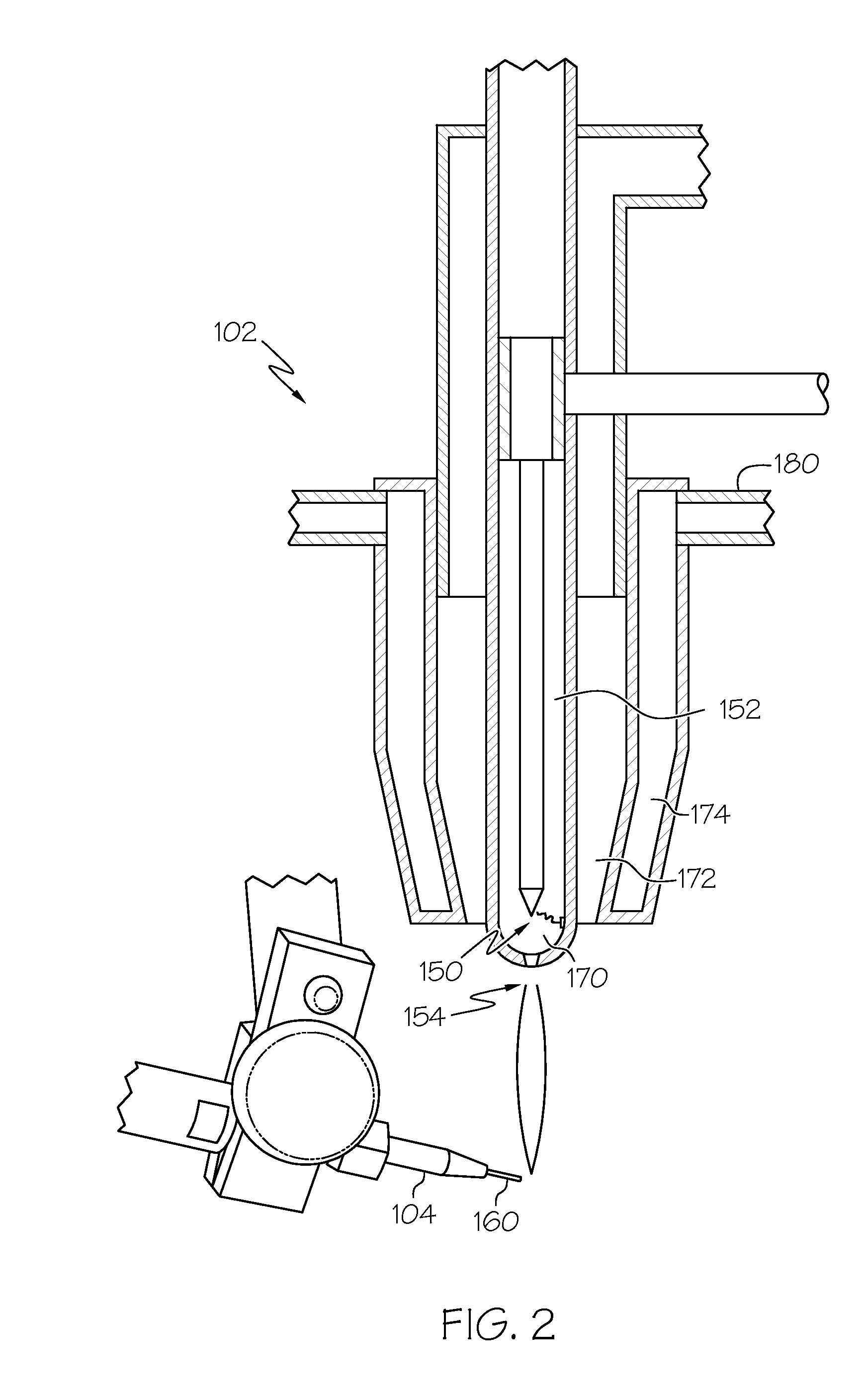
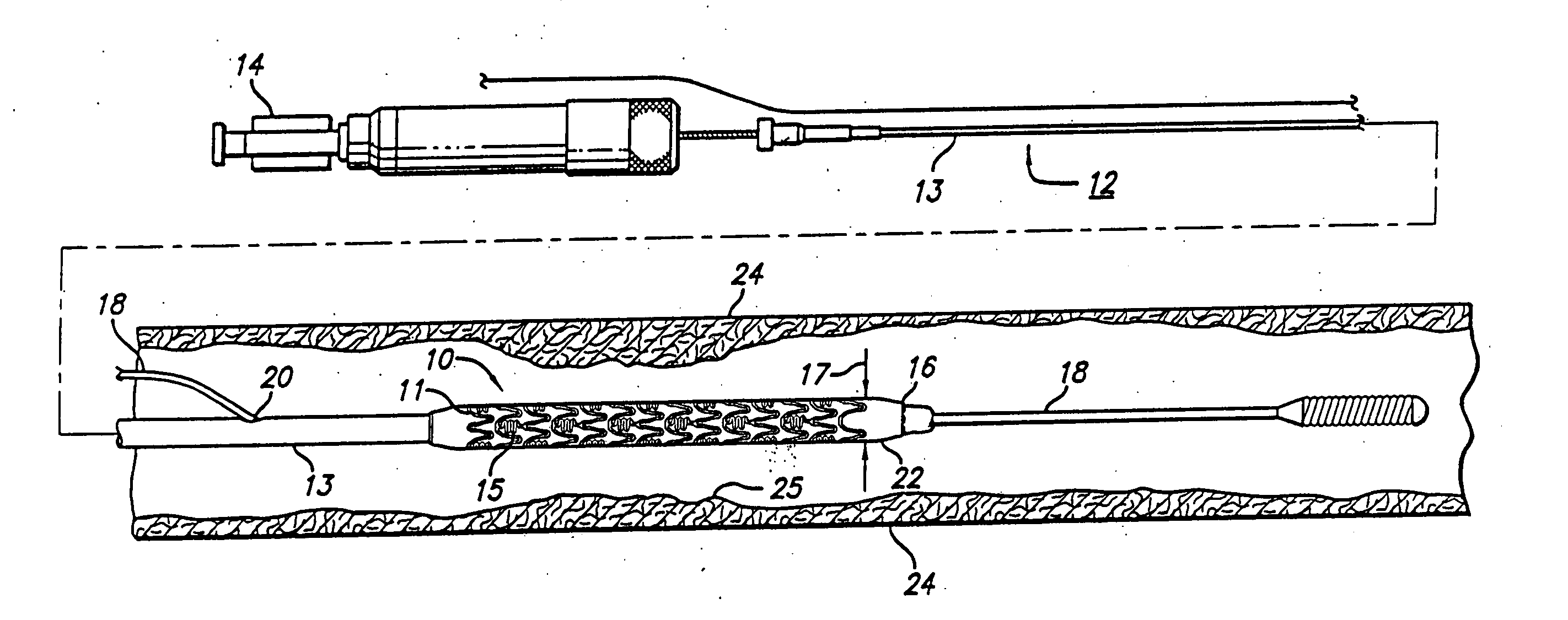
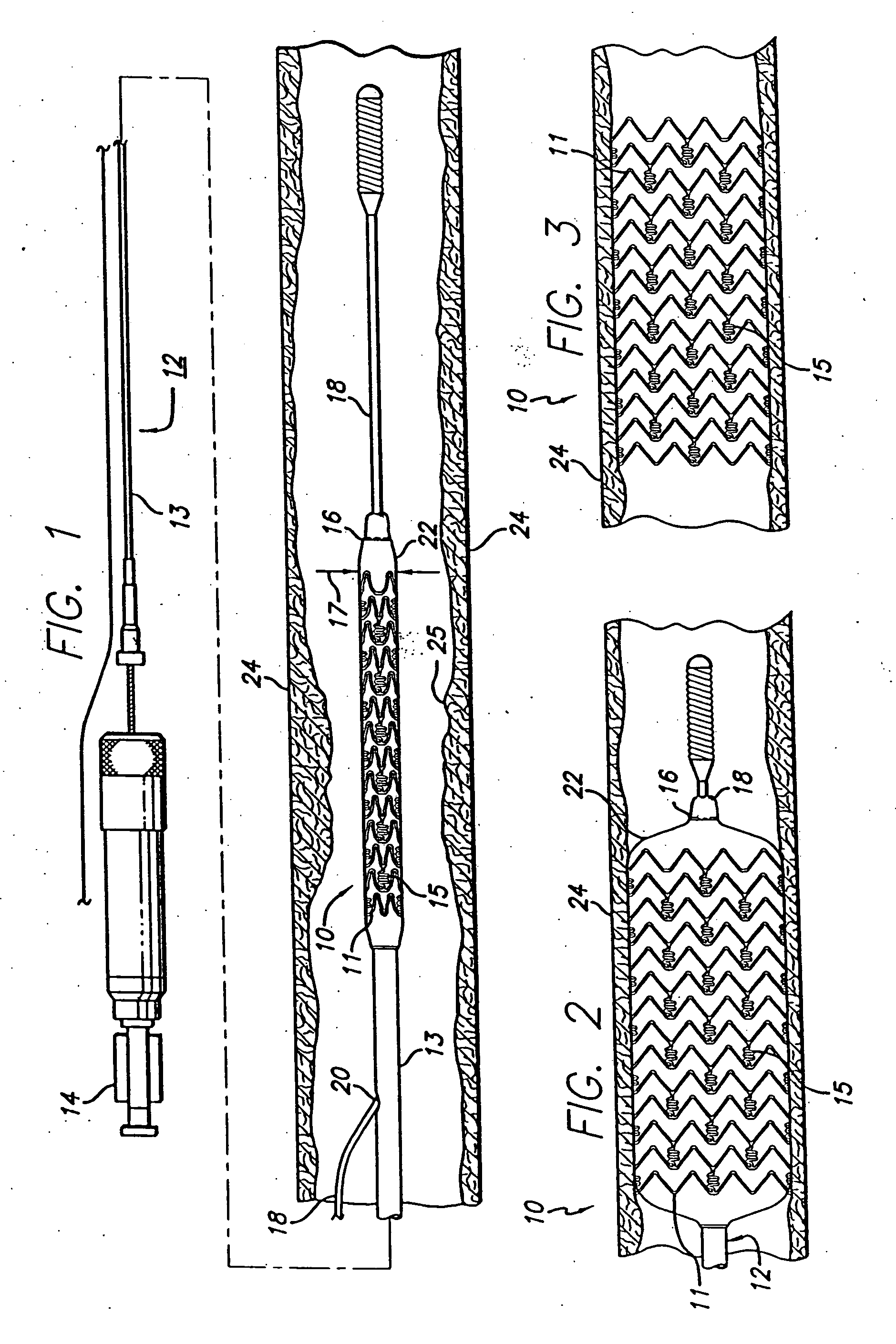
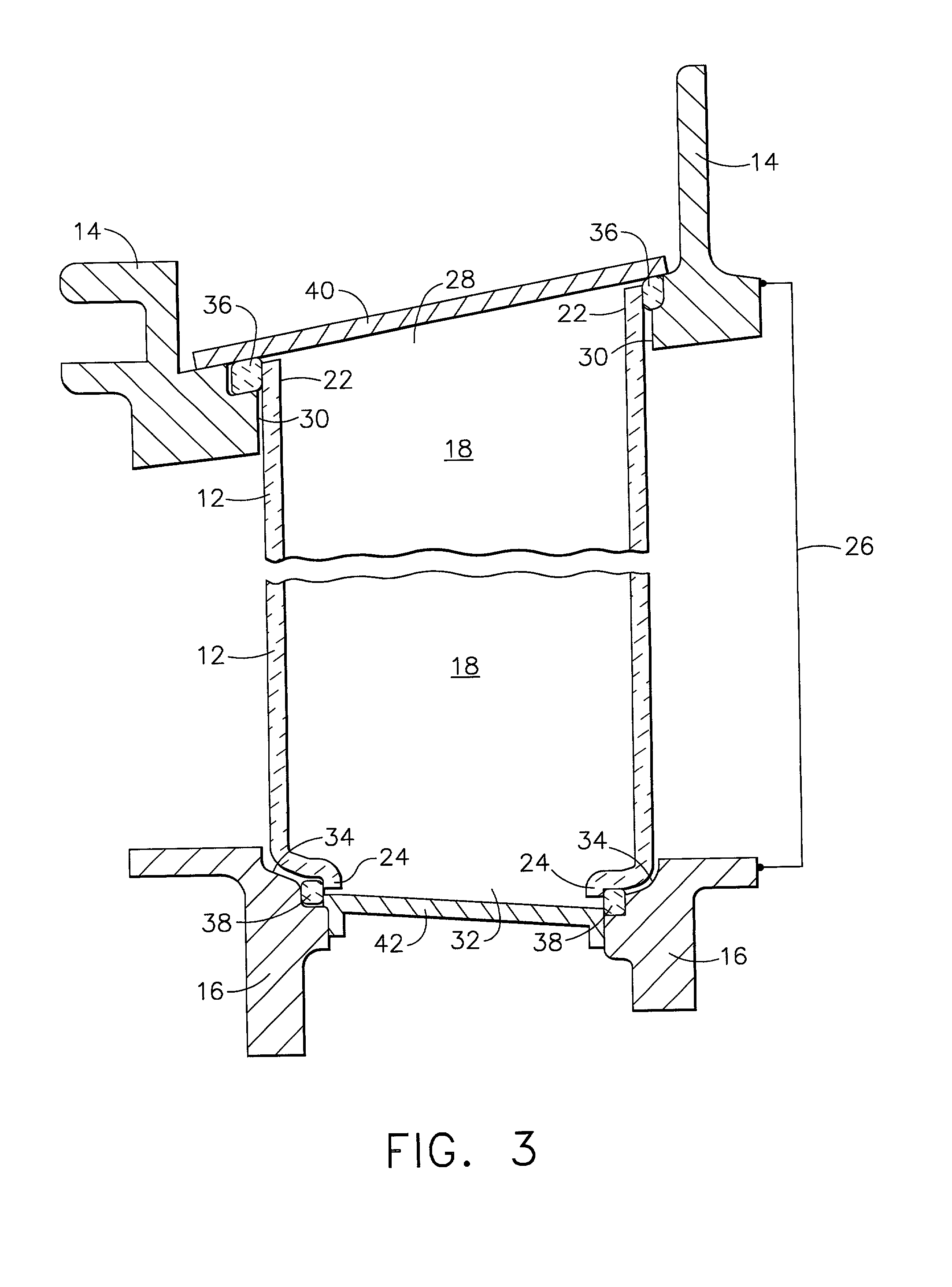
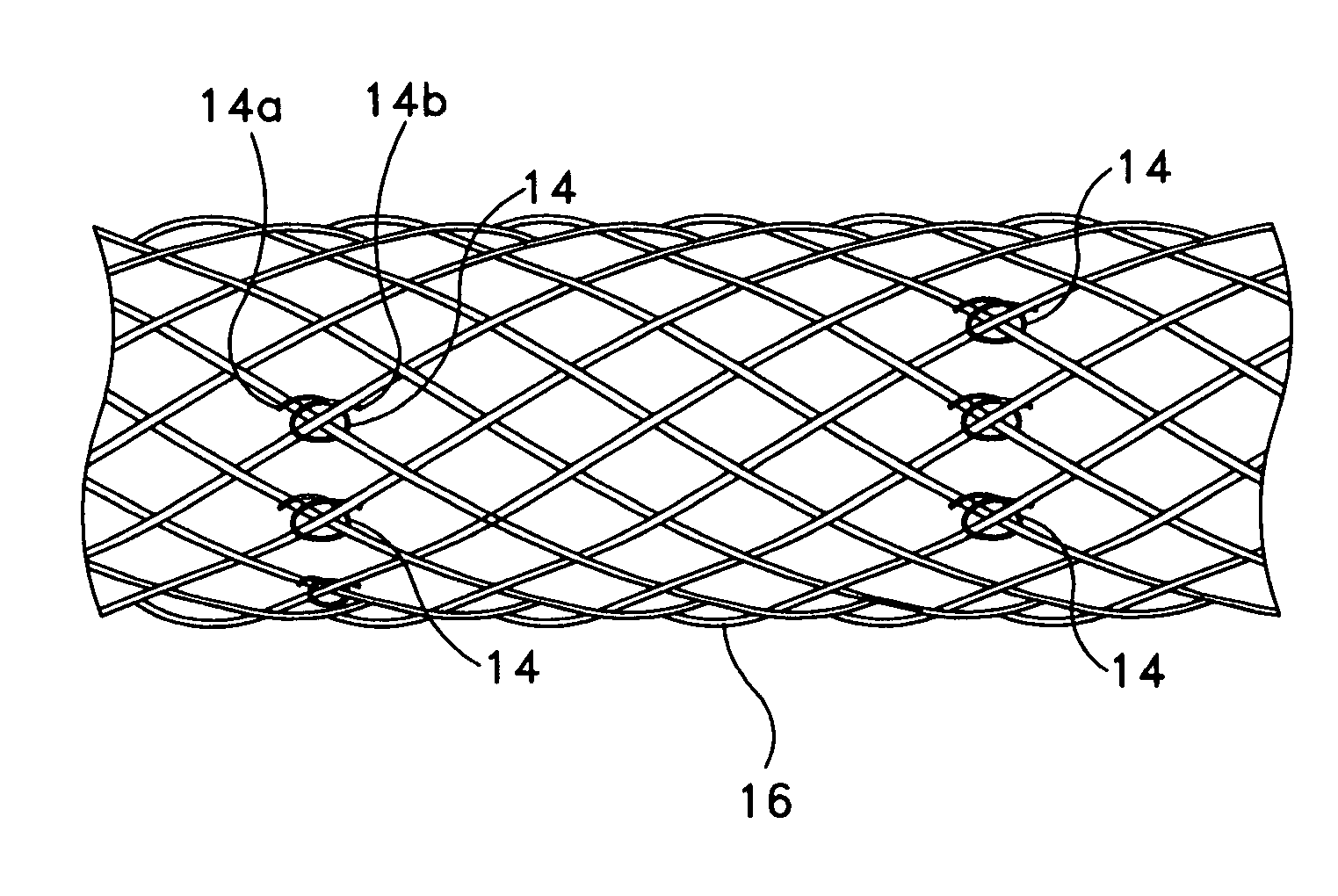
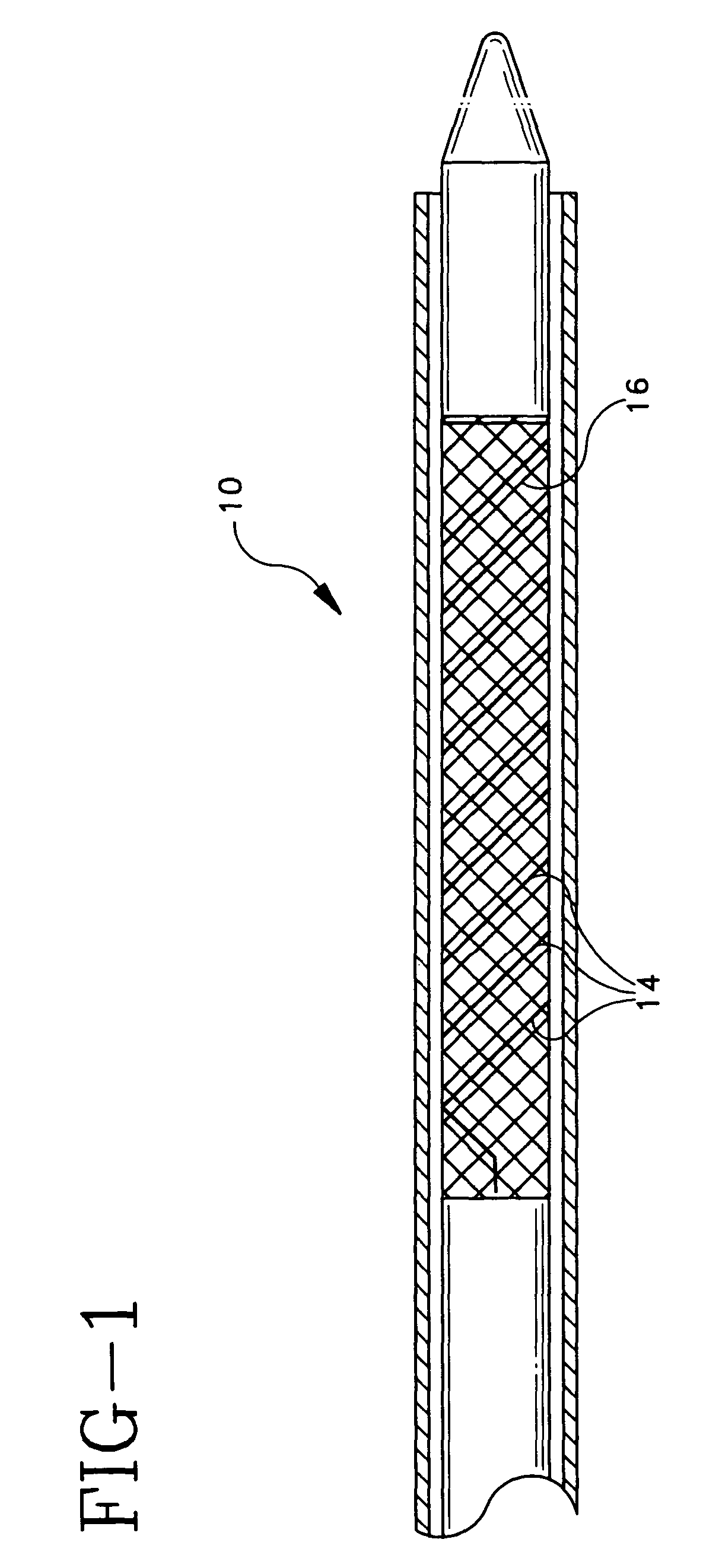
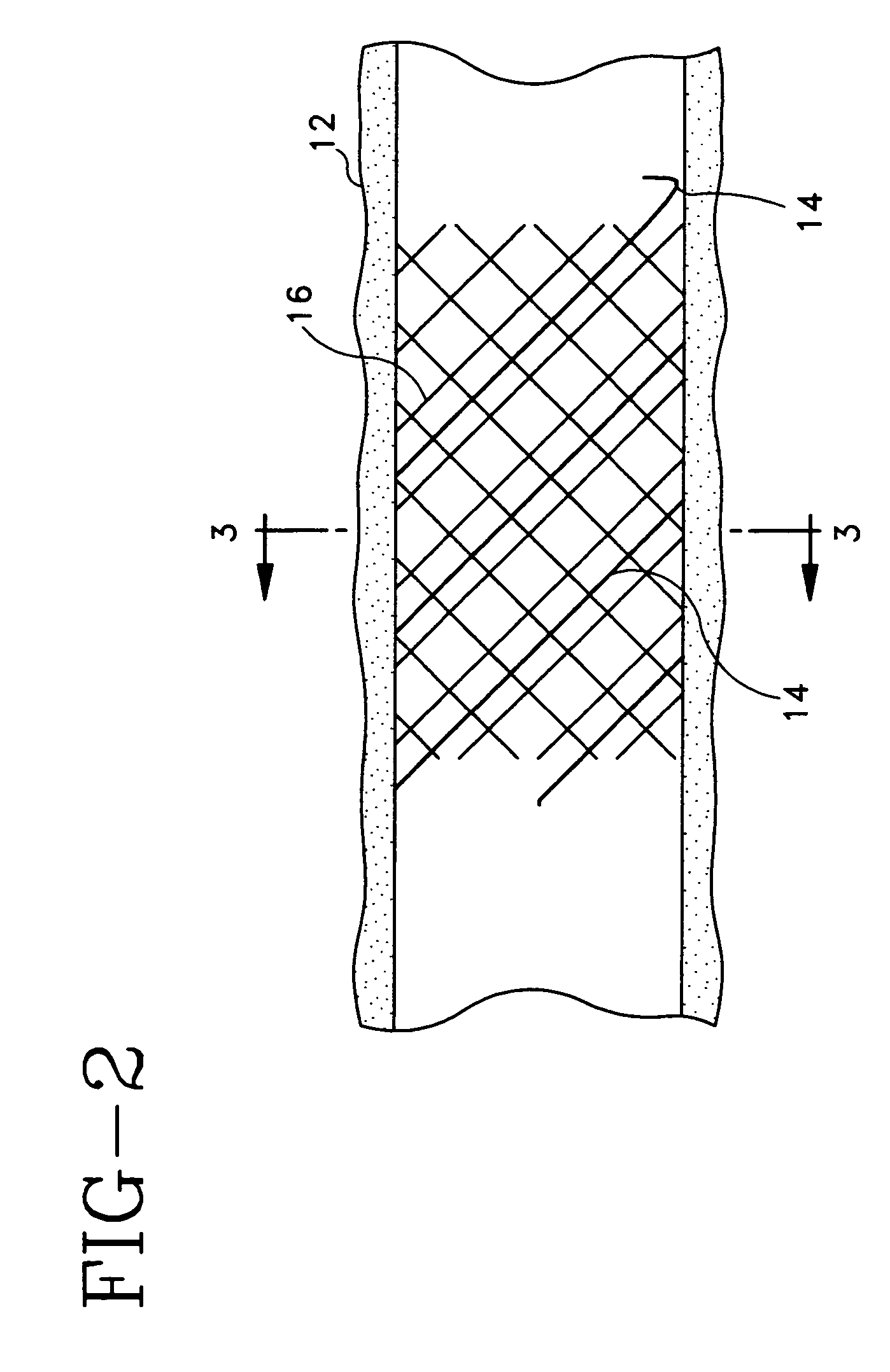
System, method and apparatus for navigated therapy and diagnosis
ActiveUS8632461B2Increase thrustHigh torque transmissionSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesEngineeringMedical instruments
The invention provides an image-guided medical instrument that utilizes a tracking device to track the location of at least a portion of the instrument on at least one image of a patient's anatomy. The instrument may include a handle having an operating element, an elongated flexible body member connected to the handle, wherein the body member includes a lumen, a transmission element housed within the lumen of the body member, and a treatment apparatus connected to end of the transmission element, wherein actuation of the operating element actuates the treatment apparatus via the transmission element. The body member also includes at least one sensor element that is utilized by the tracking device to determine position information regarding the treatment apparatus that is used to display the location of the treatment apparatus on the at least one image of the patient's anatomy.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
High performance non-combustible gypsum-cement compositions with enhanced water durability and thermal stability for reinforced cementitious lightweight structural cement panels
ActiveUS8038790B1Reduce weightPerformance requirementConstruction materialSolid waste managementOperating energyAir entrainment
Structural cement panel for resisting transverse and shear loads equal to transverse and shear loads provided by plywood and oriented strain board, when fastened to framing for use in shear walls, flooring and roofing systems. The panels provide reduced thermal transmission compared to other structural cement panels. The panels employ one or more layers of a continuous phase resulting from curing an aqueous mixture of calcium sulfate alpha hemihydrate, hydraulic cement, coated expanded perlite particles filler, optional additional fillers, active pozzolan and lime. The coated perlite has a particle size of 1-500 microns, a median diameter of 20-150 microns, and an effective particle density (specific gravity) of less than 0.50 g / cc. The panels are reinforced with fibers, for example alkali-resistant glass fibers. The preferred panel contains no intentionally added entrained air. A method of improving fire resistance in a building is also disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
System, method and apparatus for navigated therapy and diagnosis
ActiveUS20070032723A1Increase thrustHigh torque transmissionSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesTherapeutic DevicesEngineering
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
Moment-resistant structure, sustainer and method of resisting episodic loads
The present invention relates to a moment-resistant structure, sustainer, and method of construction for deformably resisting episodic loads, particularly those of high intensity. The episodic loads may be due to earthquake, impact, or other intense episodic sources. The structure and sustainer may be in buildings, bridges, or other civil works, land vehicles, watercraft, aircraft, spacecraft, machinery, or other structural systems or apparati. Deformation capacity is enhanced by the use of multiple dissipative zones. Dissipative zones that function in a manner similar to plastic hinges are determined by one or more voids that are located in the web of a sustainer. The one or more voids are of a size, shape, and configuration to assure that the dissipative zones deform inelastically when a critical stress, i.e., a maximum allowable demand, is reached, thereby developing the action of a structural fuse, preventing the occurrence of stress and strain demands sufficient to cause fracture of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones, i.e., preventing the stress and strain demands from exceeding the strength capacity of the connection welds or adjacent heat-affected zones. The sustainers may be removably connected to the remainder of the structure, facilitating their replacement after inelastic deformation. The structure, sustainer, and method of construction may be utilized in new construction and in the rehabilitation of existing construction. Mechanical equipment and utilities may pass through the voids.
Owner:ASCHHEIM MARK AMOS
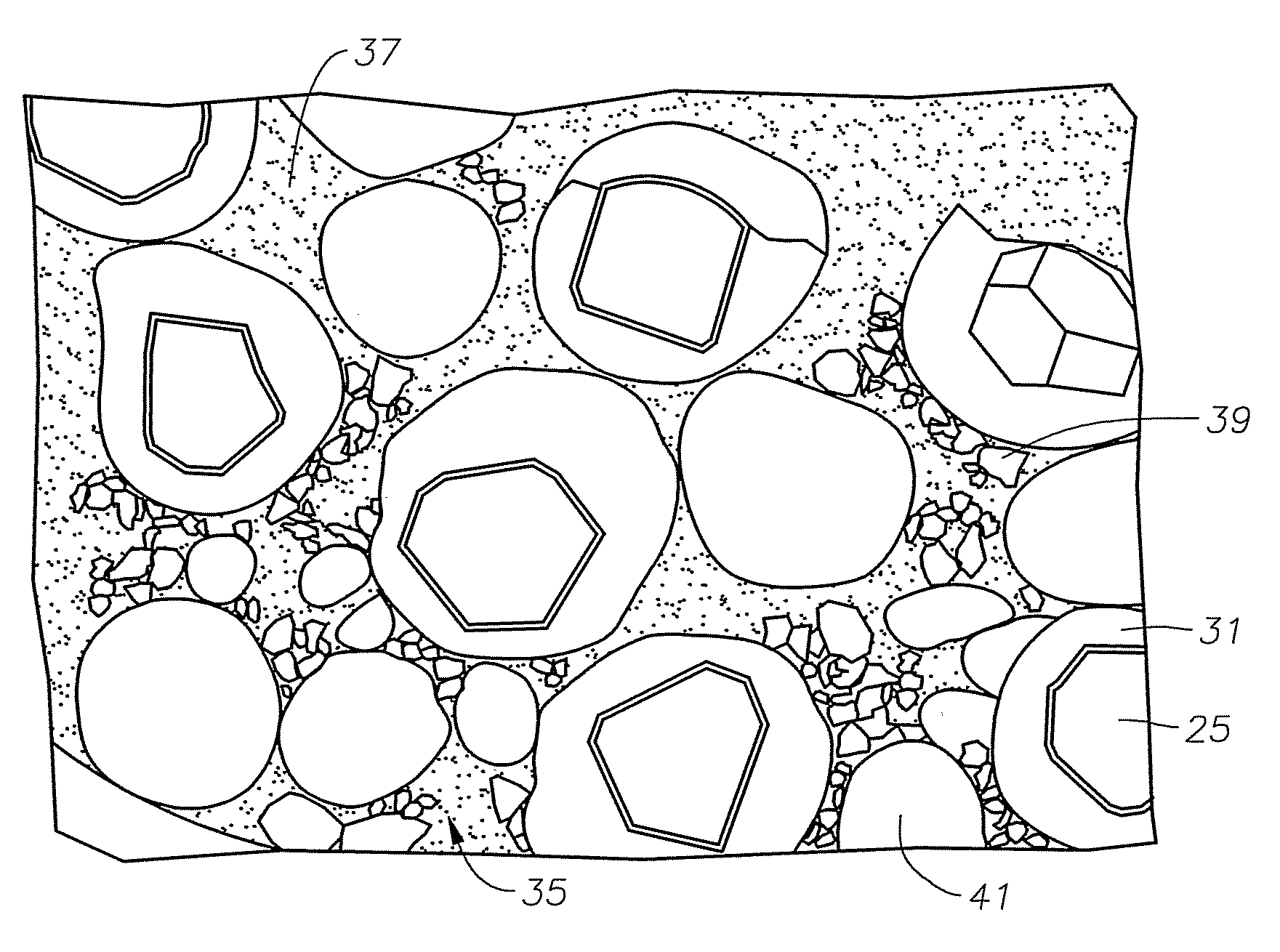
Multi-Layer Encapsulation of Diamond Grit for Use in Earth-Boring Bits
ActiveUS20080202821A1High retention rateOptimize allocationDrill bitsTransportation and packagingCarbideAtmospheric pressure
A method of constructing an earth-boring, diamond-impregnated drill bit has a first step of coating diamond grit with tungsten to create tungsten-coated diamond particles. These coated particles are then encapsulated in a layer of carbide powder held by an organic green binder material. The encapsulated granules are then mixed along with a matrix material and placed in a mold. The matrix material includes a matrix binder and abrasive particles. The mixture is heated in the mold at atmospheric pressure to cause the matrix binder to melt and infiltrate the encapsulated granules and abrasive particles.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
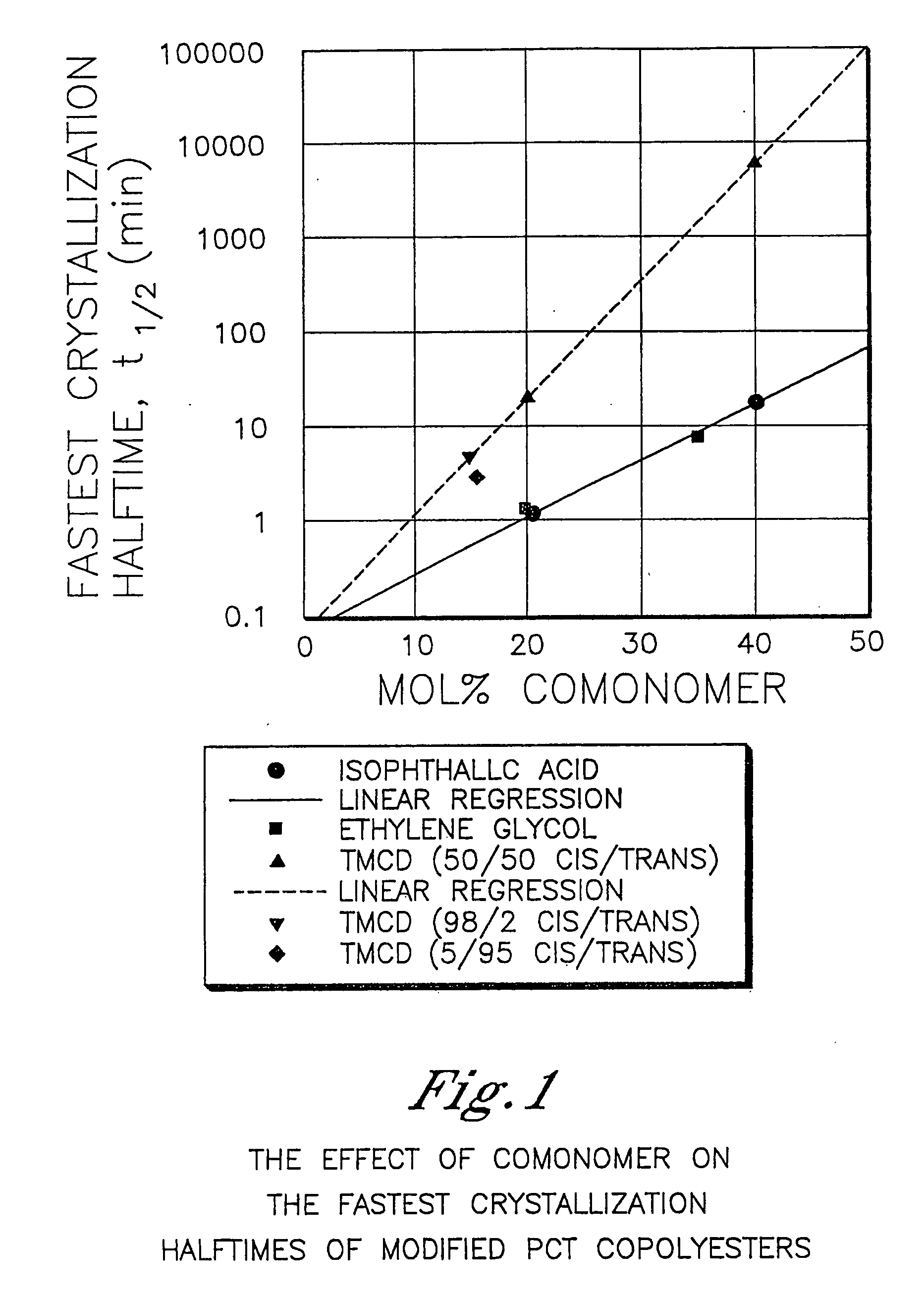
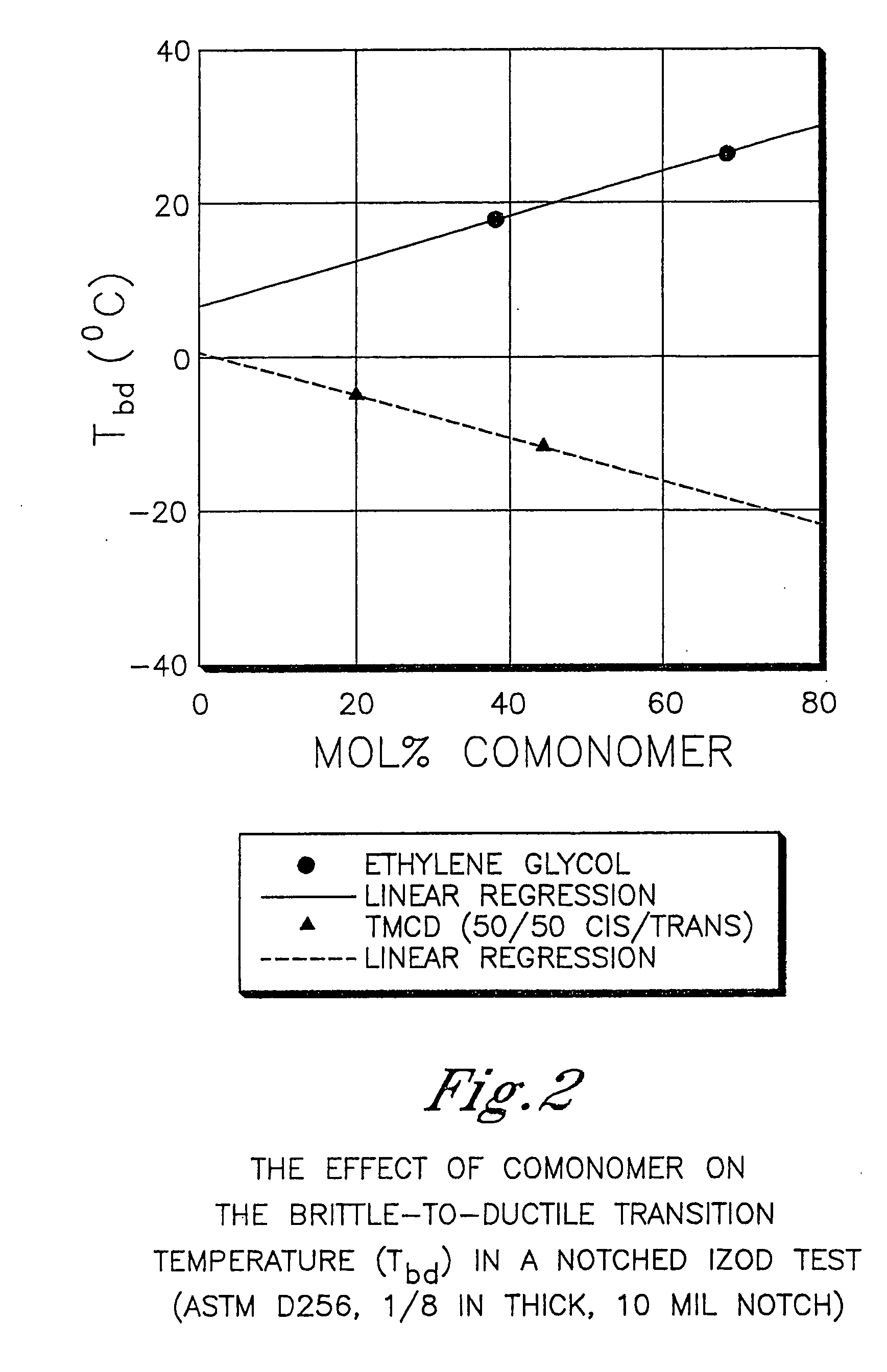
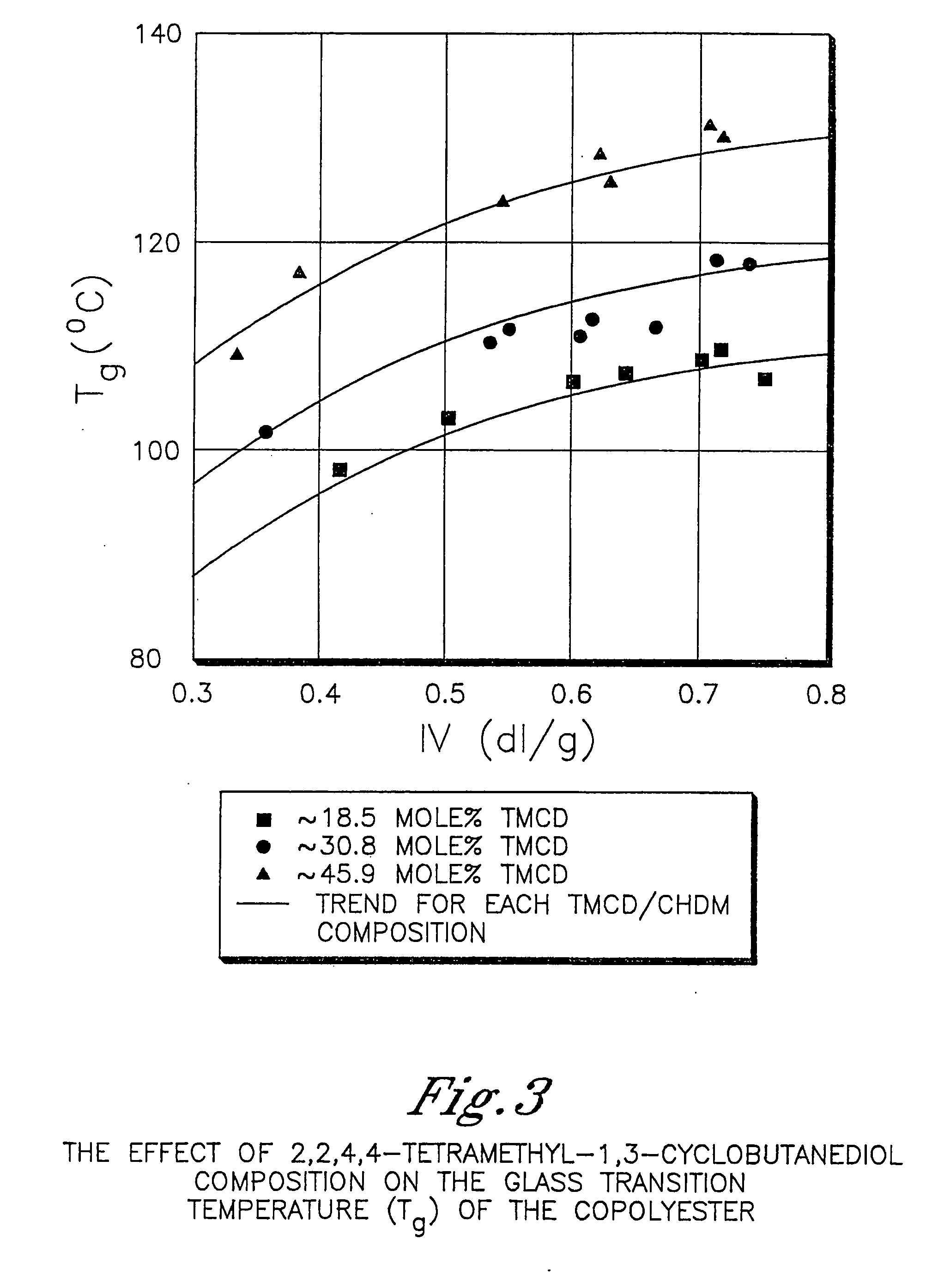
Polyester compositions containing cyclobutanediol having a certain combination of inherent viscosity and moderate glass transition temperature and articles made therefrom
ActiveUS20060293495A1Easy to optimizeHigh impact strengthDialysis systemsDialysisFiberCyclohexanedimethanol
Described are polyesters comprising (a) a dicarboxylic acid component comprising terephthalic acid residues; optionally, aromatic dicarboxylic acid residues or aliphatic dicarboxylic acid residues; 2,2,4,4-tetramethyl-1,3-cyclobutanediol residues; and 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol residues. The polyesters may be manufactured into articles such as fibers, films, bottles or sheets.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Heat-resistant austenitic stainless steel and a production process thereof
InactiveUS20050194073A1Low costHigh-temperature strengthAustenitic stainless steelWorking temperature
Owner:DAIDO STEEL CO LTD
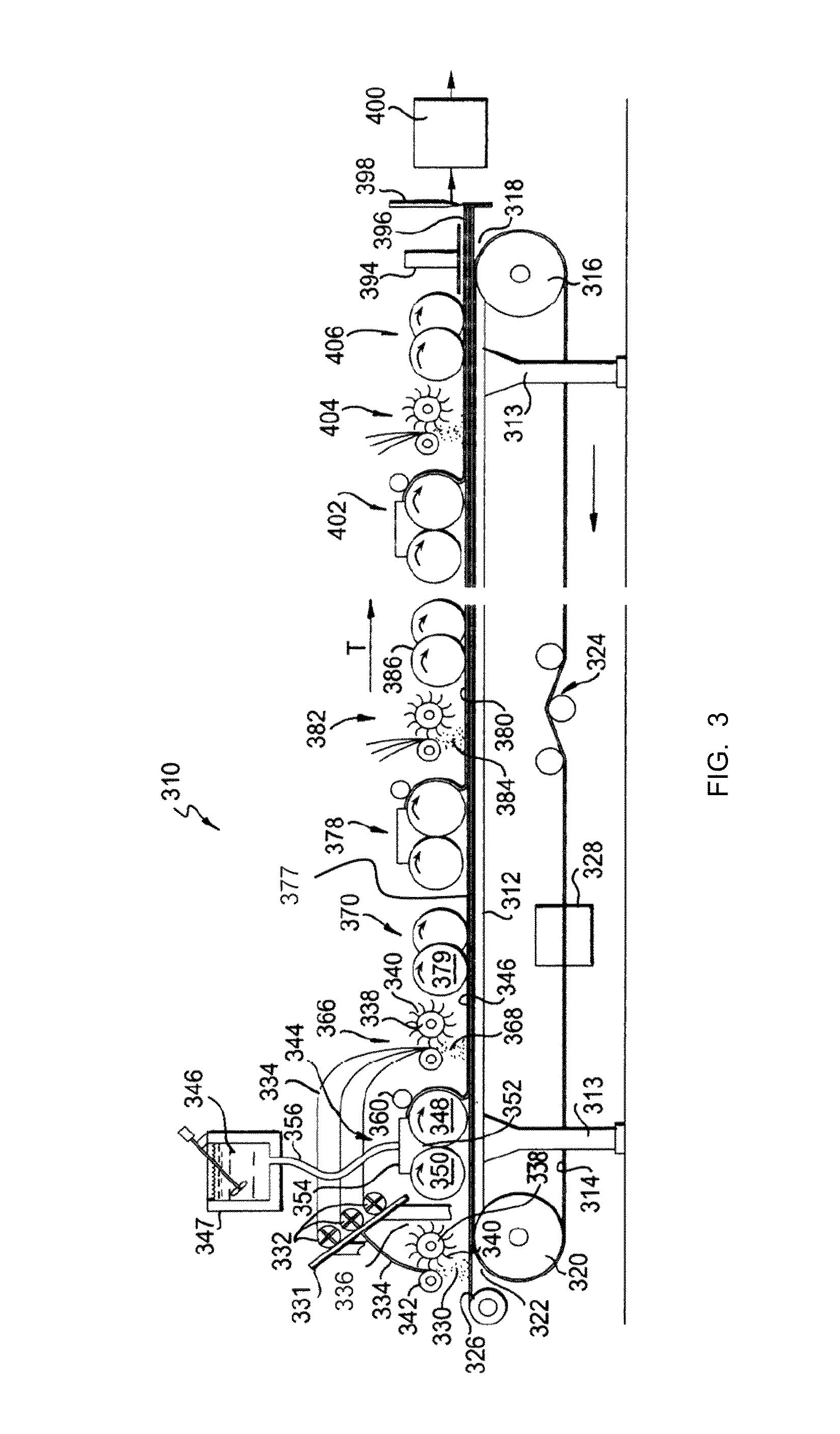
Deposition of materials with low ductility using solid free-form fabrication
InactiveUS20100193480A1Minimize occurrenceLow ductilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusFree formTransition temperature
A solid free-form (SFF) method is used to manufacture a component from successive layers of feedstock material with low ductility. A plasma stream is created by energizing a flowing gas using an arc electrode, the arc electrode having a variable magnitude current supplied thereto. The plasma stream is directed to a predetermined targeted region to preheat the predetermined targeted region prior to deposition. The current is adjusted and the feedstock material is introduced into the plasma stream to deposit molten feedstock in the predetermined targeted region. The current is adjusted and the molten feedstock is slowly cooled at an elevated temperature, typically above the brittle to ductile transition temperature of the feedstock material, in a cooling phase to minimize the occurrence of material stresses.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
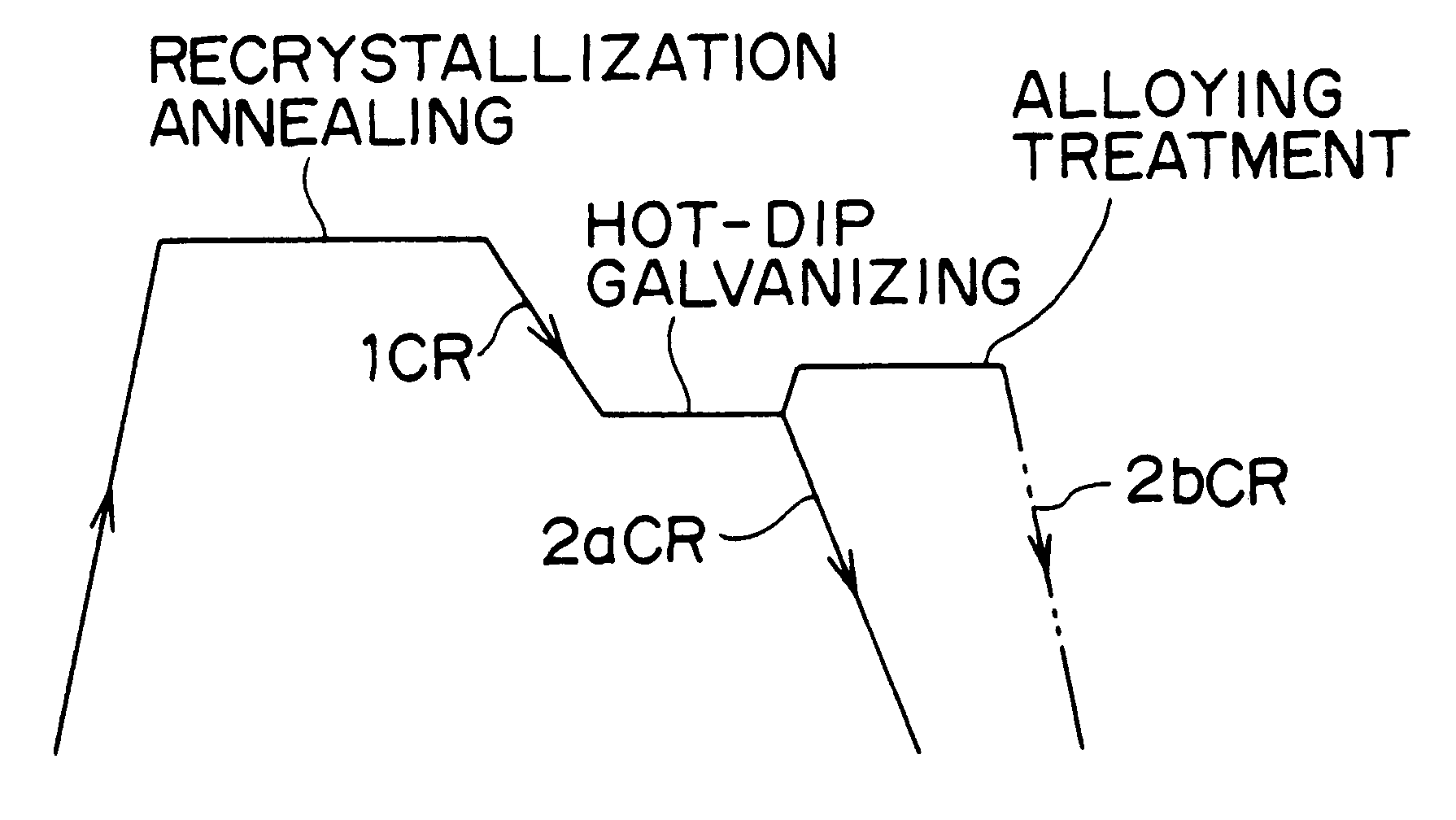
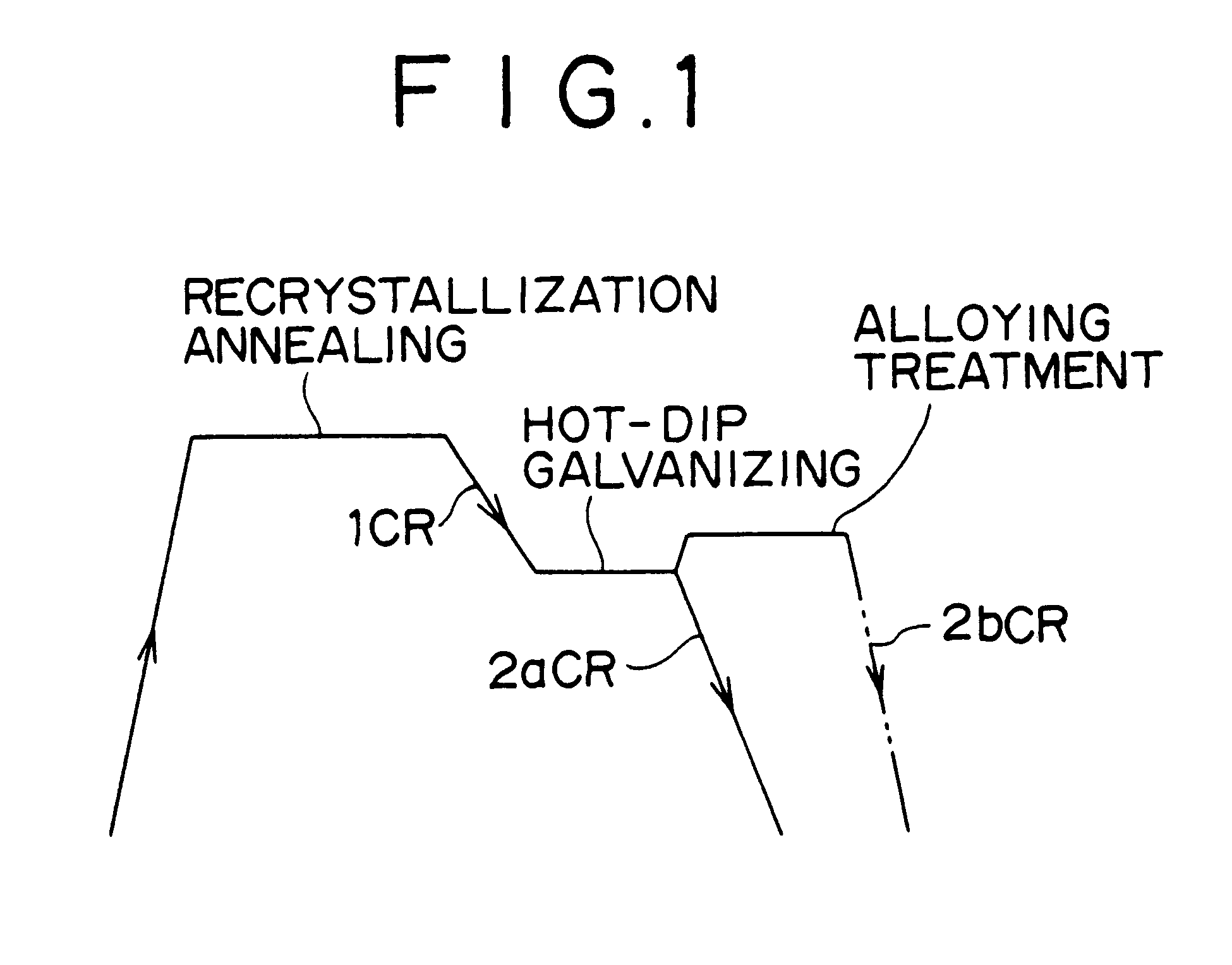
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and process for production thereof
InactiveUS6306527B1Ductility deterioratesImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsHot-dip galvanizationDuctility
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet which is produced from a cold-rolled steel sheet, as a base steel sheet, consisting essentially of C: 0.010-0.06 wt %, Si: no more than 0.5 wt %, Mn: no less than 0.5 wt % and less than 2.0 wt %, P: no more than 0.20 wt %, S: no more than 0.01 wt %, Al: 0.005-0.10 wt %, N: no more than 0.005 wt %, Cr: no more than 1.0 wt %, Mn+1.3Cr: 1.9-2.3 wt %, Fe: remainder, and having a structure composed of ferrite and a second phase containing martensite, said second phase in the structure accounting for no more than 20% in terms of area and martensite in the second phase accounting for no less than 50%, and which has a zinc-plated layer formed on the surface thereof by hot-dip galvanizing or hot-dip galvannealing. A process for production of said hot-dip galvanized steel sheet. This steel sheet has a composite structure containing martensite and yet it has a low strength (no higher than 500 MPa) and also has good strength-ductility balance.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
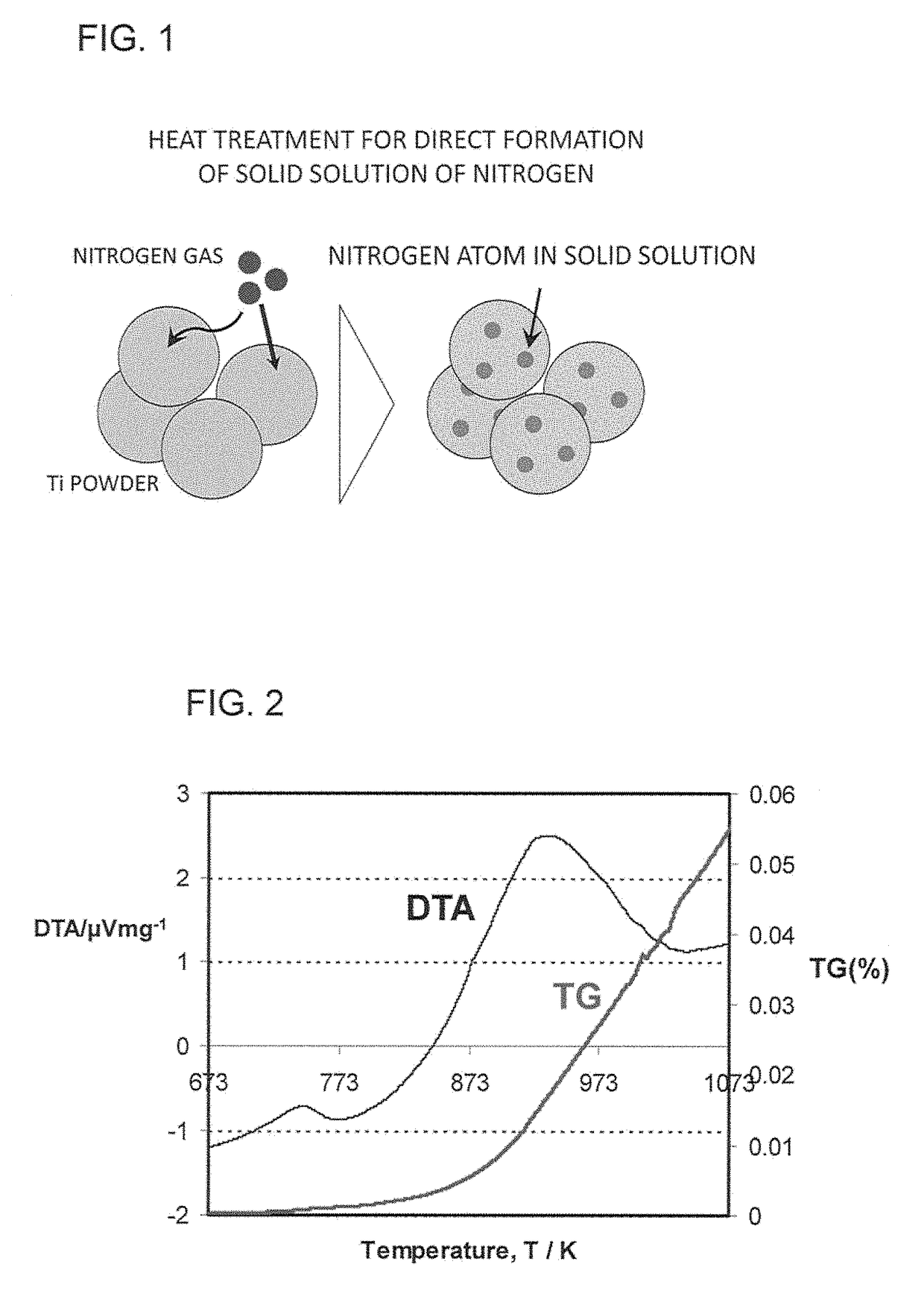
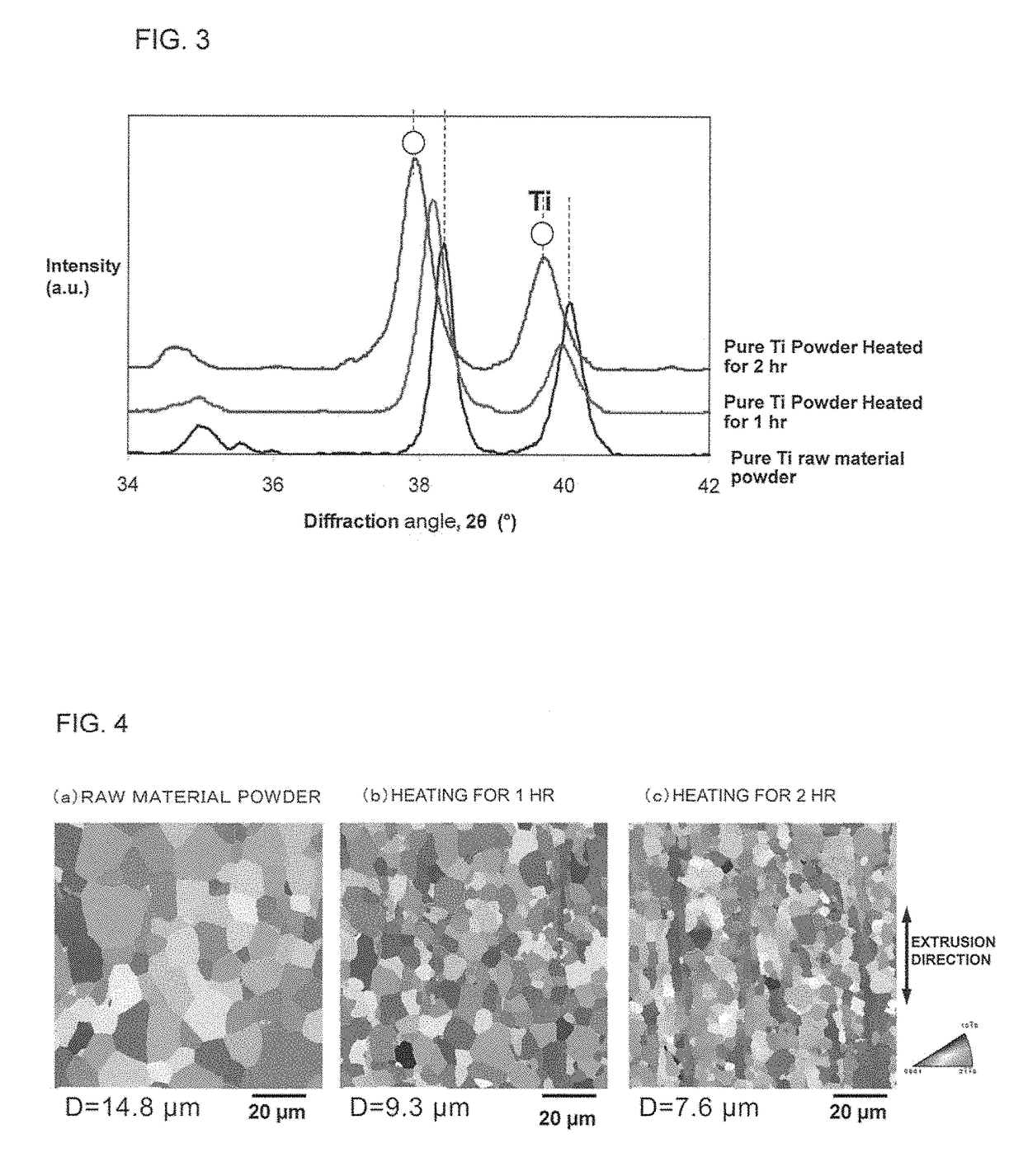
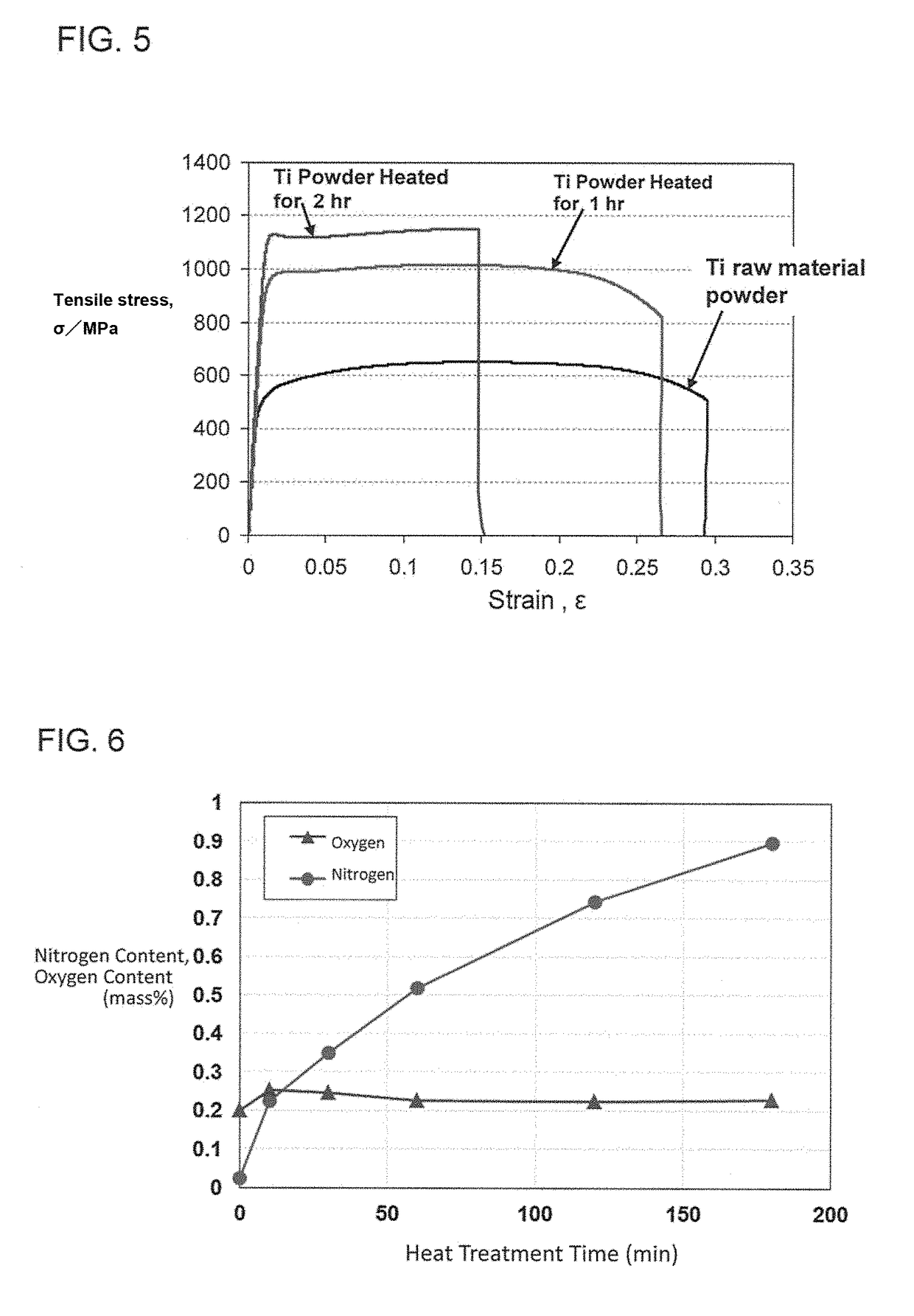
Titanium powder containing solid-soluted nitrogen, titanium material, and method for producing titanium powder containing solid-soluted nitrogen
ActiveUS10213837B2Low ductilitySpread evenlyTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSolid solutionTitanium powder
Owner:HI-LEX CORPORATION +1
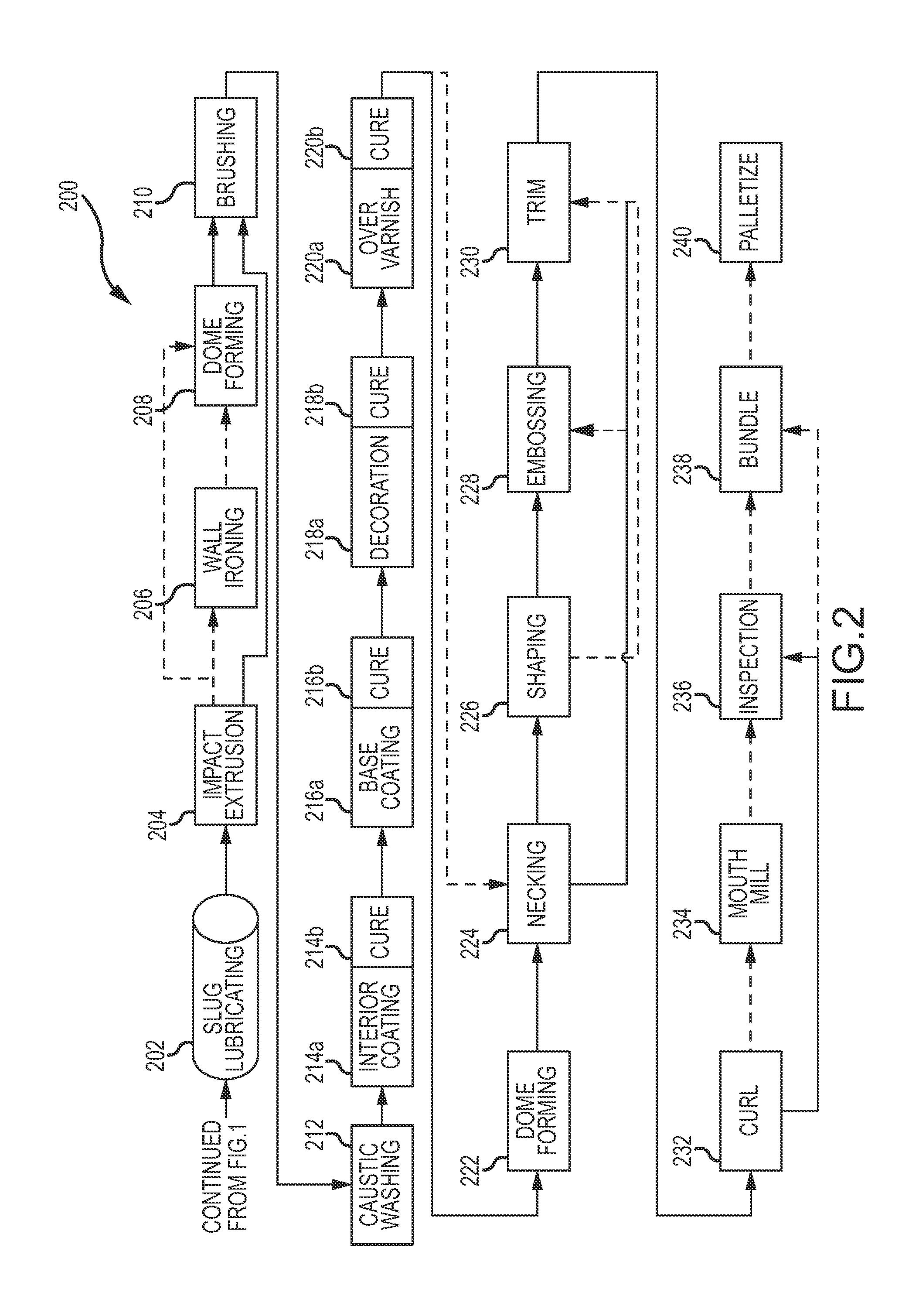
Impact extruded containers from recycled aluminum scrap
ActiveUS20130068352A1Increase resistanceReduction in weight and metal contentLiquid dispensingScrapEnvironmentally friendly
Novel aluminum alloys are provided for use in an impact extrusion manufacturing process to create shaped containers and other articles of manufacture. In one embodiment blends of recycled scrap aluminum are used in conjunction with relatively pure aluminum to create novel compositions which may be formed and shaped in an environmentally friendly process. Other embodiments include methods for manufacturing a slug material comprising recycled aluminum for use in the impact extraction process.
Owner:BALL CORP
Bioabsorbable medical device
An implantable medical device is provided that degrades upon contact with body fluids so as to limit its residence time within the body. The device is formed of an iron carbon alloy that is subjected to DET heat treatment to impart high strength and high ductility in combination with an accelerated corrosion rate.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Method for producing hardened parts from sheet steel
ActiveUS20070000117A1Fast coolingEasy to integrateHot-dipping/immersion processesMetal rolling stand detailsPunchingSheet steel
The invention relates to a method for producing hardened structural parts from sheet steel. The method includes shaping at least one shaped part made of sheet steel provided with a cathodic corrosion protection coating, performing any required final trim of the shaped part and possibly any required punching, or the creation of a perforation pattern, subsequently heating the shaped part, at least over partial areas, under the admission of atmospheric oxygen to a temperature which permits austenizing of the steel material, and thereafter transferring the structural part to a mold-hardening tool and performing mold-hardening in the mold-hardening tool, wherein the structural part is cooled by the contact with and pressing by the mold-hardening tool and is hardened thereby.
Owner:VOESTALPINE STAHL GMBH
Preparation of nanostructured materials having improved ductility
A method for preparing a nanostructured aluminum alloy involves heating an aluminum alloy workpiece at temperature sufficient to produce a single phase coarse grained aluminum alloy, then refining the grain size of the workpiece at a temperature at or below room temperature, and then aging the workpiece to precipitate second phase particles in the nanosized grains of the workpiece that increase the ductility without decreasing the strength of the workpiece.
Moldable polyester compositions, processes of manufacture, and articles thereof
A thermoplastic composition comprises, based on the total weight of the composition: 51-90 wt % of a polyester, 10-49 wt % of an ABS impact modifier; 0 to 20 wt % of a multifunctional epoxy compound; 0-40 wt % of a filler; 0-2 wt % of a fibrillated fluoropolymer; and from more than 0 to 5 wt % of a stabilizer composition. An article blow molded or injection molded from the composition has a multi-axial impact total energy from 40-100 Joules at −30° C.; a ductility of more than 90%, a permeability of more than 0 to less than or equal to 1.5g / m2-day, measured after exposure Fuel C vapor for 20 weeks at 40° C.; an MVR of 1-20 cc / 10 min; a flexural modulus of greater than 1300 MPa; and retains at least 75% of its initial tensile elongation at break after exposure to Fuel E85 for 28 days at 70° C.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Turbine vane assembly including a low ductility vane
At least one airfoil shaped vane made of a low ductility material, for example a ceramic base material such as a ceramic matrix composite or an intermetallic material such as NiAl material, is releasably carried in a turbine vane assembly including inner and outer vane supports by at least one high temperature resistant compliant seal. The seal isolates the vane from at least one of the vane supports and allows independent thermal expansion and contraction of the vane in respect to the support.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
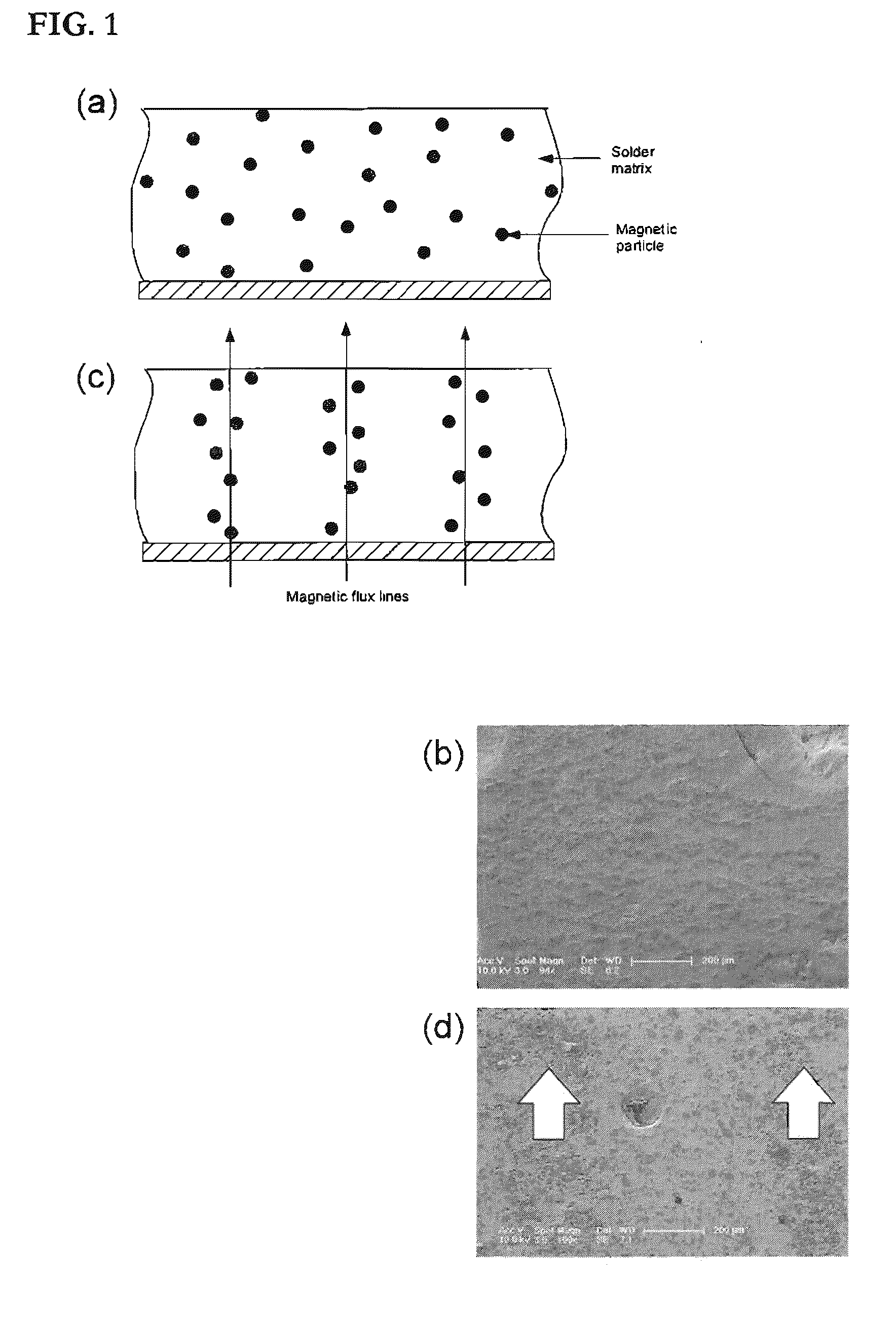
Low melting temperature alloys with magnetic dispersions
InactiveUS20110210283A1Enhanced mechanical propertyPromotes an increase in inductionNanomagnetismMagnetic liquidsMelting temperatureMelting point
A low melting temperature composite material including an alloy having about 0.1% by weight to about 99% by weight of tin and about 0.1% by weight to about 90% by weight of an element selected from the group consisting of silver and gold, and about 0.1% by weight to about 50% by weight of magnetic particles dispersed in the alloy. Method of heating such a composite material, remotely manipulating such a composite material with magnetic fields, enhancing the mechanical properties of such a material, and making such a material are also disclosed.
Owner:YALE UNIV
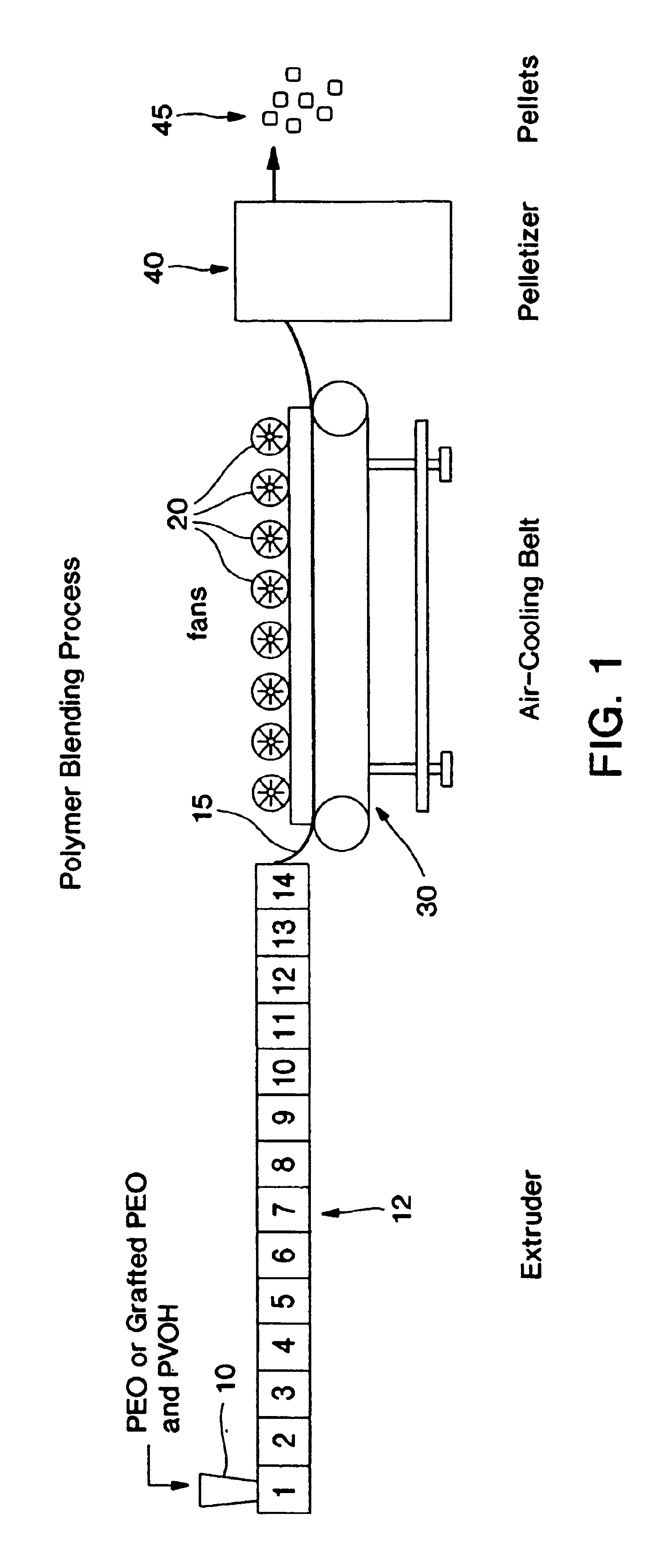
Method of making blends of poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(ethylene oxide)
The present invention discloses water-soluble compositions comprising a blend of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(vinyl alcohol) that have improved ductility over water-soluble compositions comprising poly(vinyl alcohol) alone. In one desirable embodiment of the present invention, the poly(ethylene oxide) component of the blend is grafted. Grafted poly(ethylene oxide) resins have improved processability and improved blend compatibility with poly(vinyl alcohol). Films comprising a melt blend of poly(vinyl alcohol) and grafted poly(ethylene oxide) have improved melt processability as well as other improved properties. Films comprising compositions of the present invention have improved ductility over films comprising poly(vinyl alcohol) alone while retaining much of the high strength and water solubility exhibited by such poly(vinyl alcohol) films.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Bioabsorbable marker having radiopaque constituents
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
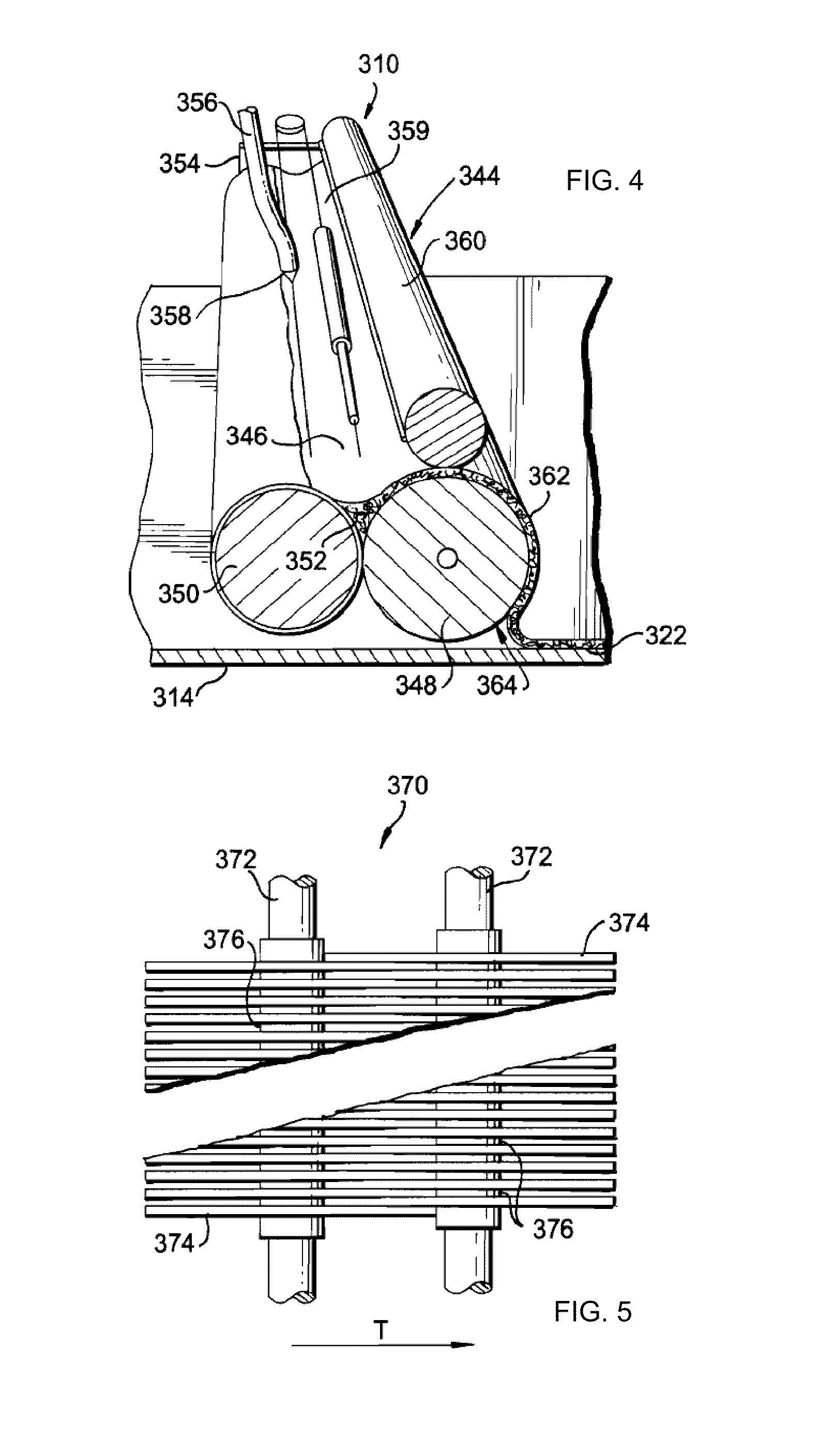
Method and apparatus for forming materials with low ductility
InactiveUS20130062003A1Low ductilityShaping toolsLamination ancillary operationsMechanical engineeringDuctility
The invention provides an apparatus and a method of forming a material of low ductility including providing a first sheet made from a material of low ductility, providing an integrated forming device comprising a heat source and a forming element, and moving the forming element relative to the first sheet along a forming direction while simultaneously heating a localized portion of the first sheet along the forming direction at a substantially constant predetermined distance in front of the forming element. The predetermined distance is selected so as to yield a predetermined temperature to achieve a predetermined ductility at the localized portion of the first sheet when the forming element reaches the localized portion of the first sheet.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
Heat resistant austenitic stainless steel
InactiveUS6485679B1High creep rupture strengthGood steam oxidation resistanceRigid pipesHeat exchange apparatusAustenitic stainless steelTungsten
A heat resistant austenitic stainless steel with high strength at elevated temperatures, good steam oxidation resistance, good fire side corrosion resistance, and a sufficient structural stability, suitable for use in boilers operating at high temperatures has a composition (by weight) of. 0.04 to 0.10% carbon (C), not more than 0.4% silicon (Si), not more than 0.6% manganese (MN), 20 to 27% chromium (Cr), 22.5 to 32% nickel (Ni), not more than 0.5% molybdenum (Mo), 0,20 to 0.60% niobium (Nb), 0.4 to 4.0% tungsten (W), 0.10 to 0.30% nitrogen (N), 0.002 to 0.008% boron (B), less than 0.05% aluminium (Al), at least one of the elements Mg and Ca in amounts less than 0.010% Mg and less than 0.010% Ca, and the balance being iron and inevitable impuities.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
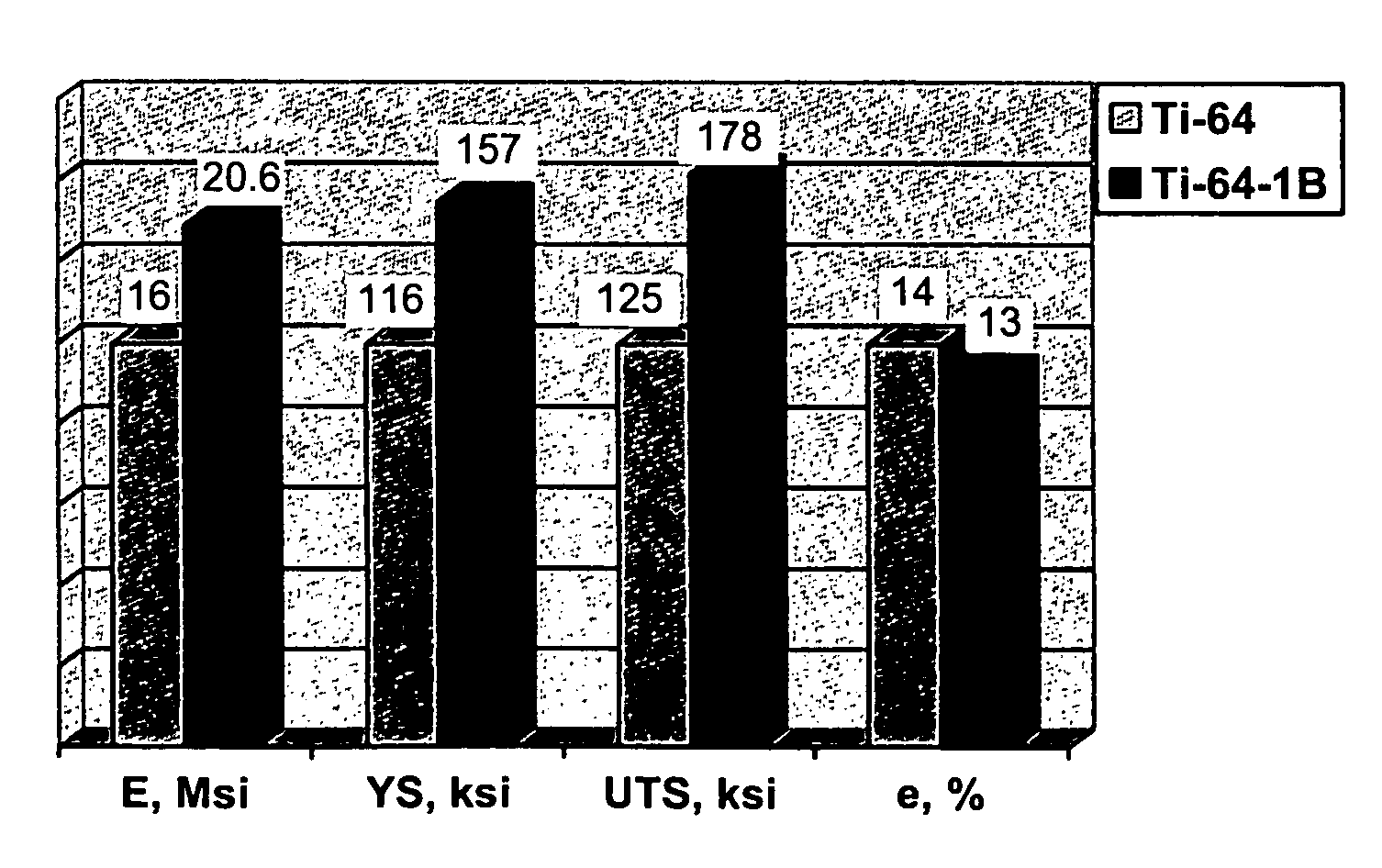
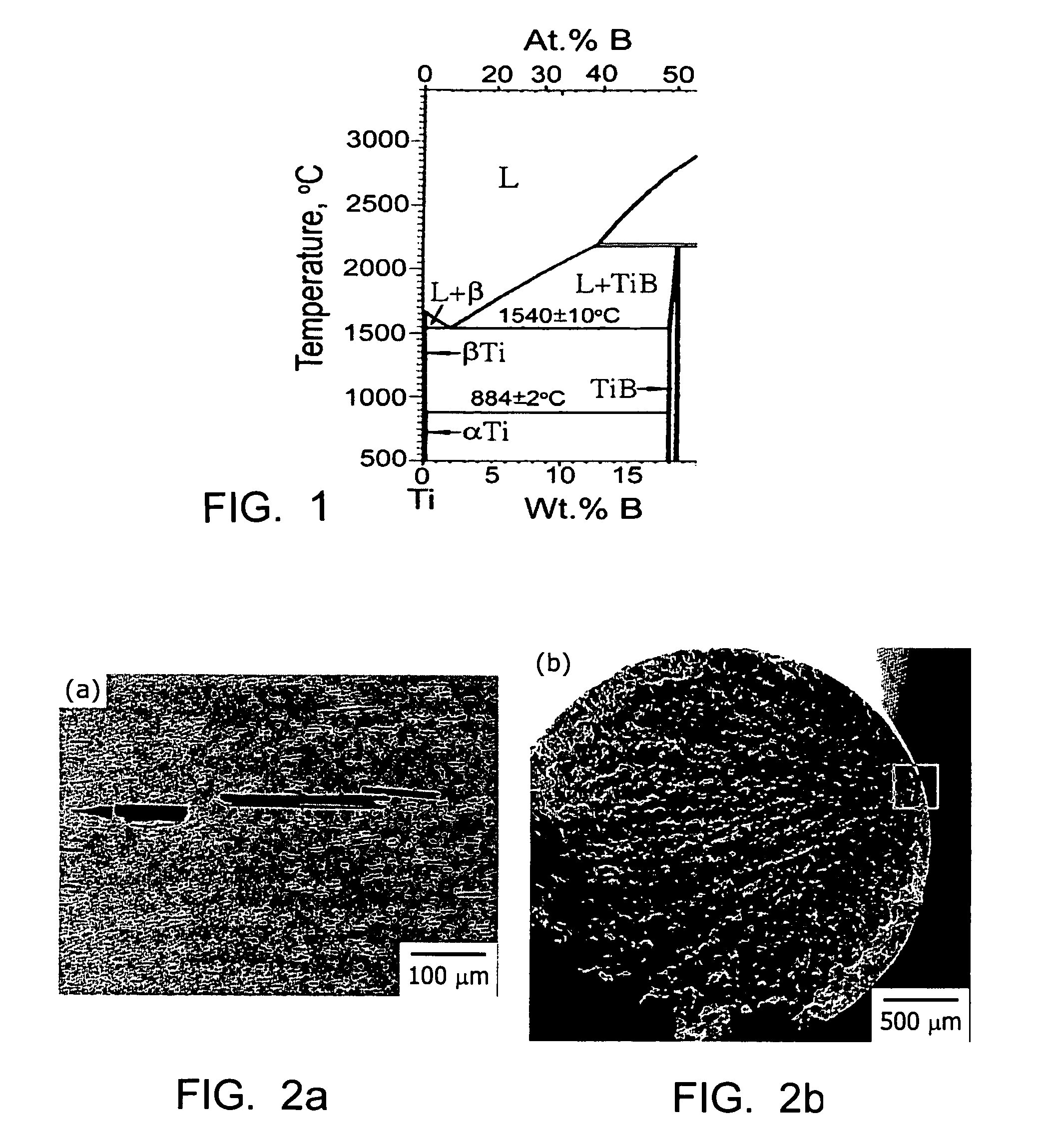
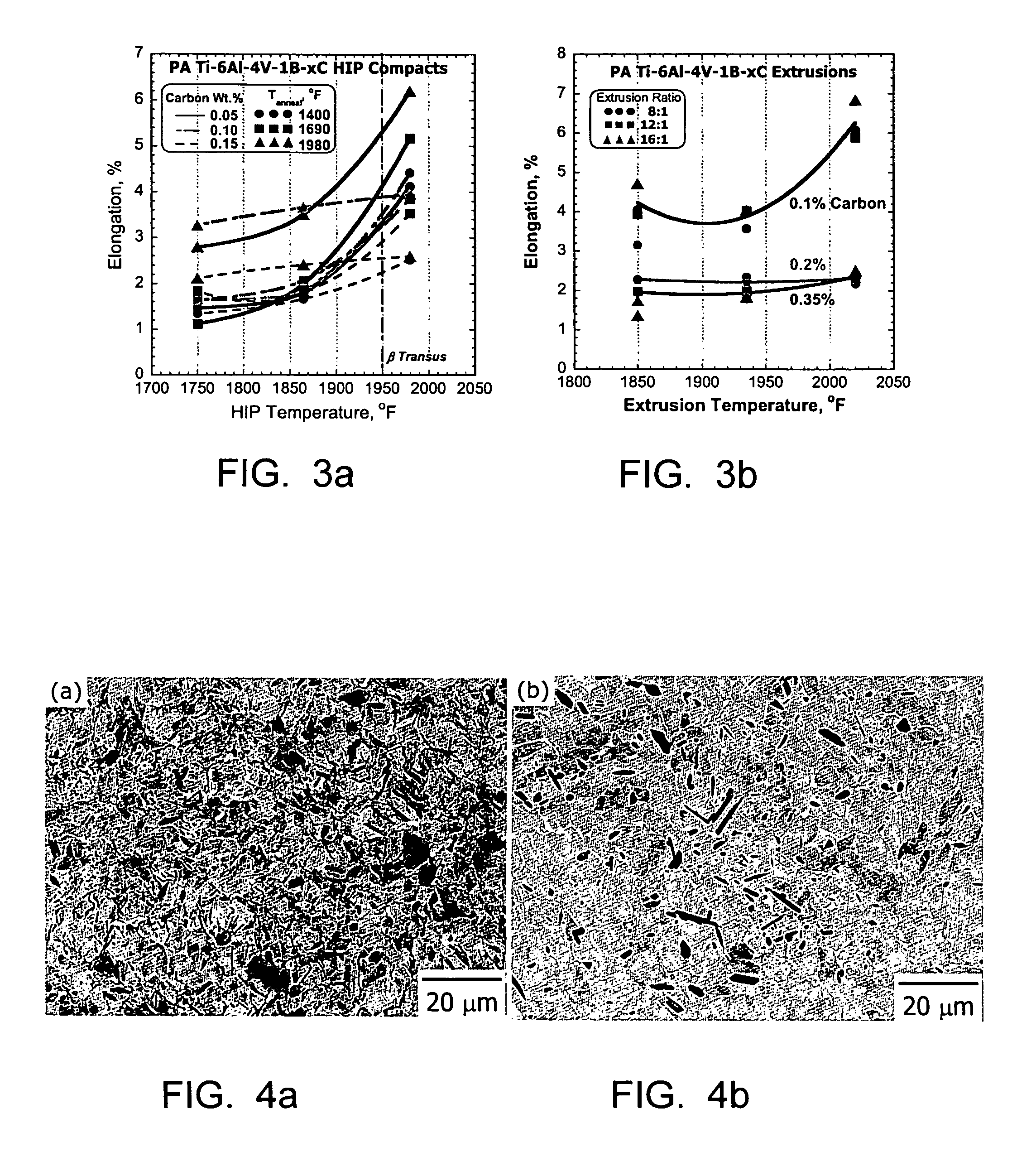
Method of producing high strength, high stiffness and high ductility titanium alloys
A method of producing a high strength, high stiffness and high ductility titanium alloy, comprising combining the titanium alloy with boron so that the boron concentration in the boron-modified titanium alloy does not exceed the eutectic limit. The carbon concentration of the boron-modified titanium alloy is maintained below a predetermined limit to avoid embrittlement. The boron-modified alloy is heated to a temperature above the beta transus temperature to eliminate any supersaturated excess boron. The boron-modified titanium alloy is deformed at a speed slow enough to prevent microstructural damage and reduced ductility.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES +2
Multi-layer encapsulation of diamond grit for use in earth-boring bits
ActiveUS7810588B2High retention rateOptimize allocationDrill bitsMetal-working drilling toolsCarbideAtmospheric pressure
A method of constructing an earth-boring, diamond-impregnated drill bit has a first step of coating diamond grit with tungsten to create tungsten-coated diamond particles. These coated particles are then encapsulated in a layer of carbide powder held by an organic green binder material. The encapsulated granules are then mixed along with a matrix material and placed in a mold. The matrix material includes a matrix binder and abrasive particles. The mixture is heated in the mold at atmospheric pressure to cause the matrix binder to melt and infiltrate the encapsulated granules and abrasive particles.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Lead-free solder with low copper dissolution
InactiveUS20070172381A1Minimize formation of oxideAdvantageously producedWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDissolutionImpurity
Lead-free solder compositions suitable for joining electronic devices to printed wiring boards, which comprises by weight 0.2 to 0.9% copper, 0.006 to 0.07% nickel, 0.03 to 0.08% bismuth, less than 0.5% silver, less than 0.010% phosphorus, and a balance of tin and inevitable impurities. A solder composition embodying this invention finds particular application in automated wave-soldering machines where conventional lead-free solders dissolve excessive copper from printed wiring circuitry and component terminations.
Owner:KESTER
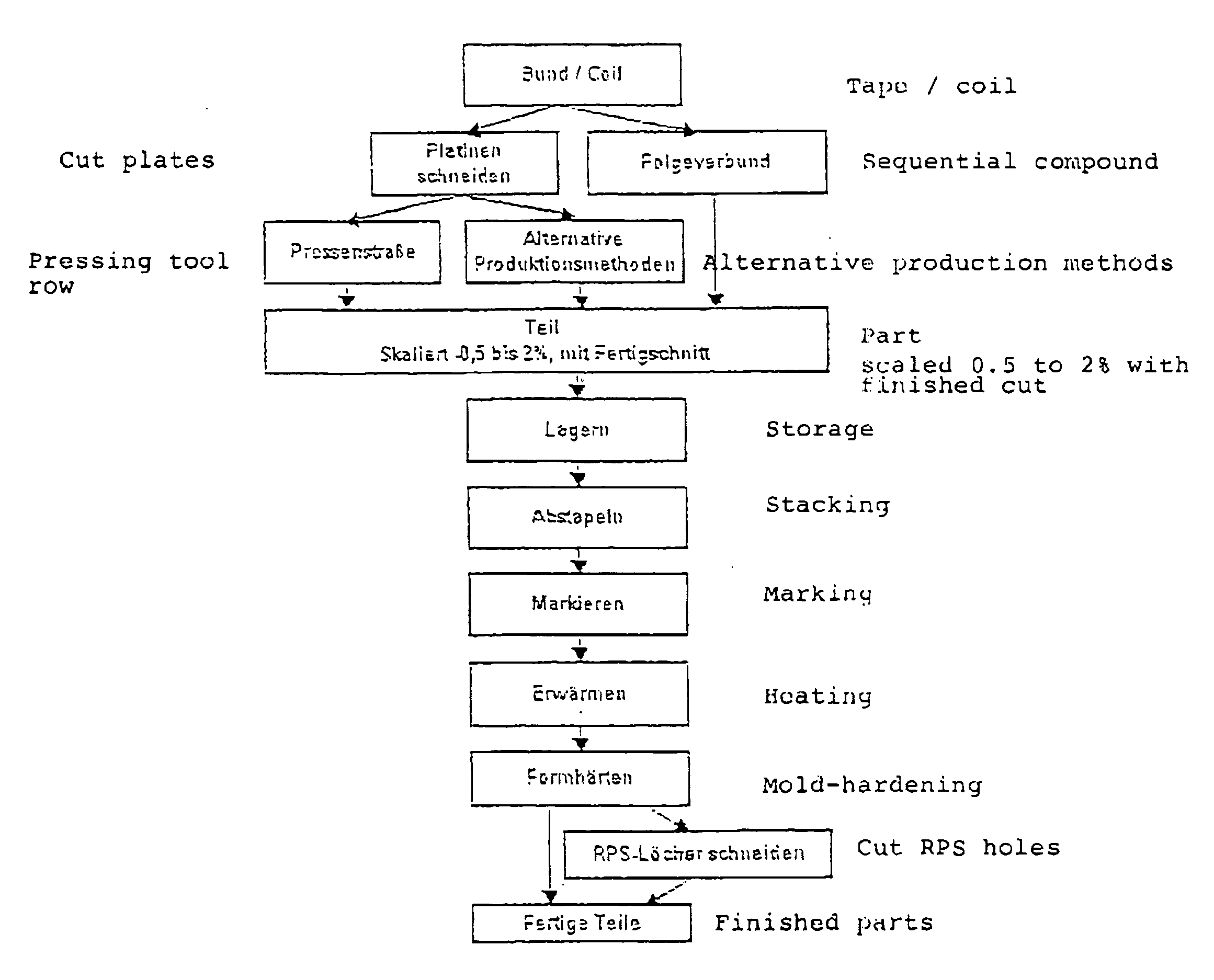
Press-forming method of component with l shape
ActiveUS20120297853A1Inhibit the generation of cracksSuppress generationVehicle componentsEngineeringMetal sheet
The present invention provides a forming method that forms a press component with an L shape from a blank metal sheet, the press component having a top sheet section and a vertical wall section which is connected to the top sheet section via a bent section having a part curved in an arc shape and which has a flange section on an opposite side to the bent section, the top sheet section being arranged on an outside of the arc of the vertical wall section, the method including: disposing the blank metal sheet between a die and both of a pad and a bending die; and forming the vertical wall section and the flange section while at least a part of the blank metal sheet is caused to slide on a part of the die corresponding to the top sheet section, the forming of the vertical wall section and the flange section being performed in a state where the pad is made close to or brought into contact with the blank metal sheet.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Aluminum alloys for casting, aluminum alloy castings and manufacturing method thereof
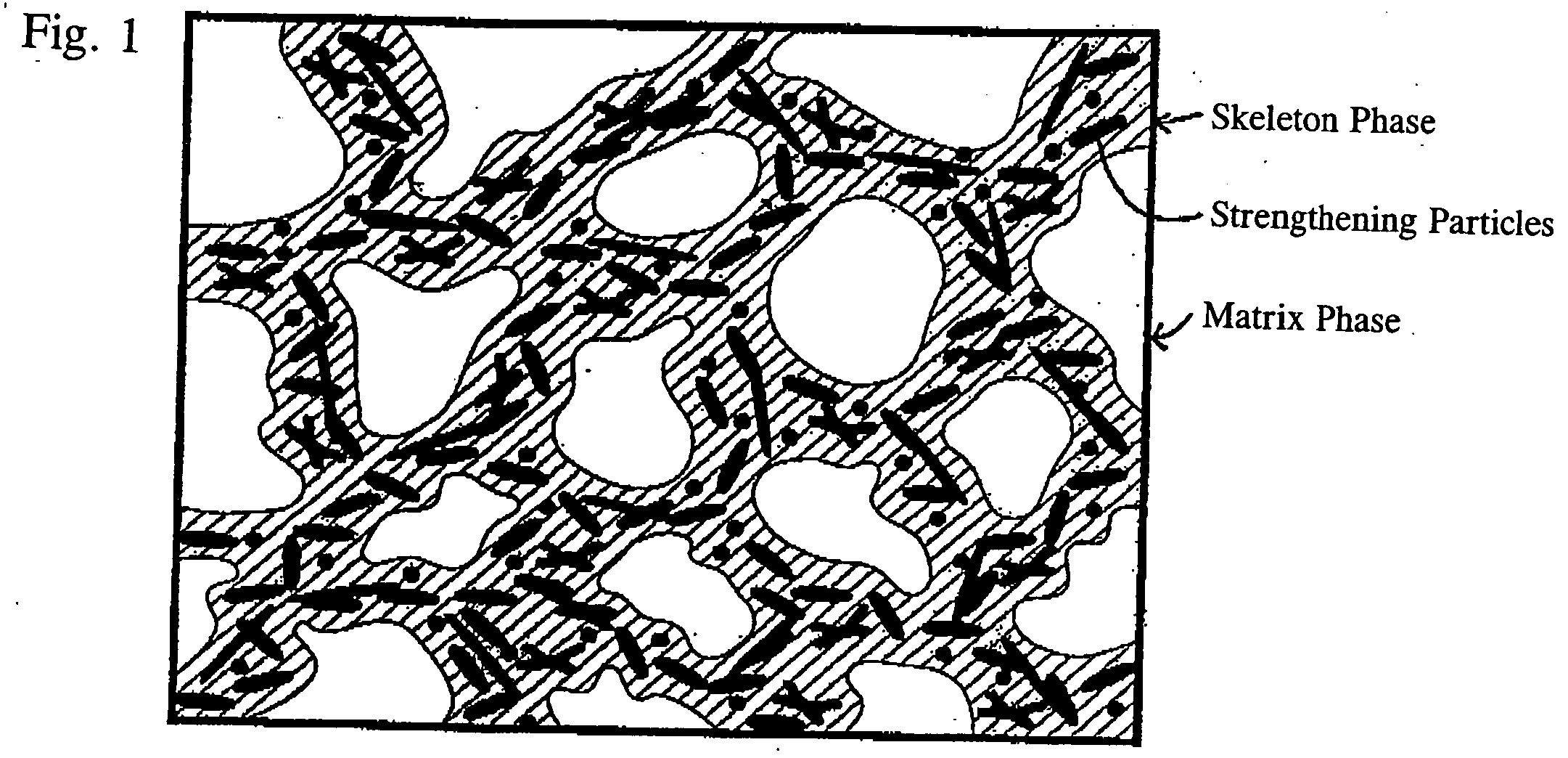
Aluminum alloys and castings are provided that have excellent practical fatigue resistances. The alloy includes, based upon 100 mass %, 4-12 mass % of Si, less than 0.2 mass % of Cu, 0.1-0.5 mass % of Mg, 0.2-3.0 mass % of Ni, 0.1-0.7 mass % of Fe, 0.15-0.3 mass % of Ti, and the balance of aluminum (Al) and impurities. The alloy has a metallographic structure, which includes a matrix phase primarily of α-Al and a skeleton phase crystallizing around the matrix phase in a network shape. The matrix phase is strengthened by precipitates containing Mg. Because of the strengthened matrix phase, and the skeleton phase that surrounds it, the castings have high strength, high fatigue strength, and high thermo-mechanical fatigue resistance.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Method for producing a hot-formed and press-hardened metal component
ActiveUS20120090741A1Reduce weightLow component weightSuperstructure subunitsQuenching devicesHardnessMetal
The present invention relates to a method for producing a hot-formed and press-hardened metal component for an automobile having at least two regions of different hardness. A hardenable sheet-metal blank is heated to at least an austenizing temperature and a first region of the sheet-metal blank is intermediately cooled at a cooling speed greater than the lower critical cooling speed of the material of the sheet-metal blank. The sheet-metal blank is then hot-formed and press-hardened in a press-hardening tool by quenching the first region from a bainitic structure transformation stage, thereby adjusting a mixed structure of martensite and bainite in the first region.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
Graphene dye sensitized solar cell and production method thereof
InactiveCN102148099AMaterials are readily availableLow costLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureSputteringSolar cell
The invention discloses a graphene dye sensitized solar cell and a production method thereof. The solar cell comprises a light anode comprising transparent upper base material and graphene conducting layer, a porous nano semiconductor film and a dye sensitizer, oxidation reduction electrolyte solution, a counter electrode comprising a lower base and graphene conducting layer and a composite catalytic layer as well as a film shell. The production method comprises the steps of preparing the light anode, preparing the counter electrode, encapsulating and injecting the electrolyte solution. In the invention, graphene with an available raw material, low cost, good conductive performance, extremely high flexibility and good ductibility is adopted as the conducting layer, the flexible transparent material is adopted as a substrate, and platinum metal particles are embedded on the graphene conducting layer of the counter electrode by adopting adsorption instead of magnetron sputtering to form the composite catalytic layer. Thus, the invention has the characteristics that the raw material is available, the production cost is low, the production process is simple and reliable, the flexible solar cell can be produced and applied to the flexible field, and the application range is effectively expanded.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High tensile strength cold rolled steel sheet having excellent strain age hardening characteristics and the production thereof
InactiveUS20030145920A1Easy to shapeImproving size precisionFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesSheet steelSolid solution
The present invention presents a high tensile strength cold rolled steel sheet having excellent formability, impact resistance and strain age hardening characteristics, and the production thereof. As a specific means, a slab having a composition which contains, by mass %, 0.15% or less of C, 0.02% or less of Al, and 0.0050 to 0.0250% of N at N / Al of 0.3 or higher, and has N in a solid solution state at 0.0010% or more, is first hot rolled at the finish rolling delivery-side temperature of 800° C. or above, and is subsequently coiled at the coiling temperature of 750° C. or below to prepare a hot rolled plate. Then, after cold rolling, the hot rolled plate is continuously cooled at a temperature from the recrystallization temperature to 900° C. at a holding time of 10 to 120 seconds, and is cooled by primary cooling in which the hot rolled plate is cooled to 500° C. or below at a cooling rate of 10 to 300° C. / s, and furthermore if necessary, by secondary cooling in which a residence time is 300 seconds or less in a temperature range of the primary cooling stopping temperature or higher and 350° C. or higher. Provided is a steel sheet containing a ferritic phase having an average crystal grain size of 10 mum or less at an area ratio of 50% or more, and if necessary, a martensitic phase at an area ratio of 3% or more as a second phase.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS6939415B2Reliably obtainedImprove high temperature strengthLavatory sanitoryFurnace typesMetallurgyUltimate tensile strength
An austenitic stainless steel excellect in high temperature strength and creep rupture ducitility which comprises, on the percent by mass basis, C: 0.03-0.12%, Si: 0.2-2%, Mn: 0.1-3%, P: 0.03% or less, S: 0.01% or less, Ni: more than 18% and less than 25%, Cr: more than 22% and less than 30%, Co: 0.04-0.8%, Ti: 0.002% or more and less than 0.01%, Nb: 0.1-1%, V: 0.01-1%, B: more than 0.0005% and 0.2% or less, sol. Al: 0.0005% or more and less than 0.03%, N: 0.1-0.35% and O (Oxygen): 0.001-0.008%, with the balance being Fe and impurities. The austenitic stainless steel may contain a specified amount of one or more element(s) of Mo and W, and / or a specified amount of one or more element(s) of Mg, Zr, Ca, REM, Pd and Hf.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com