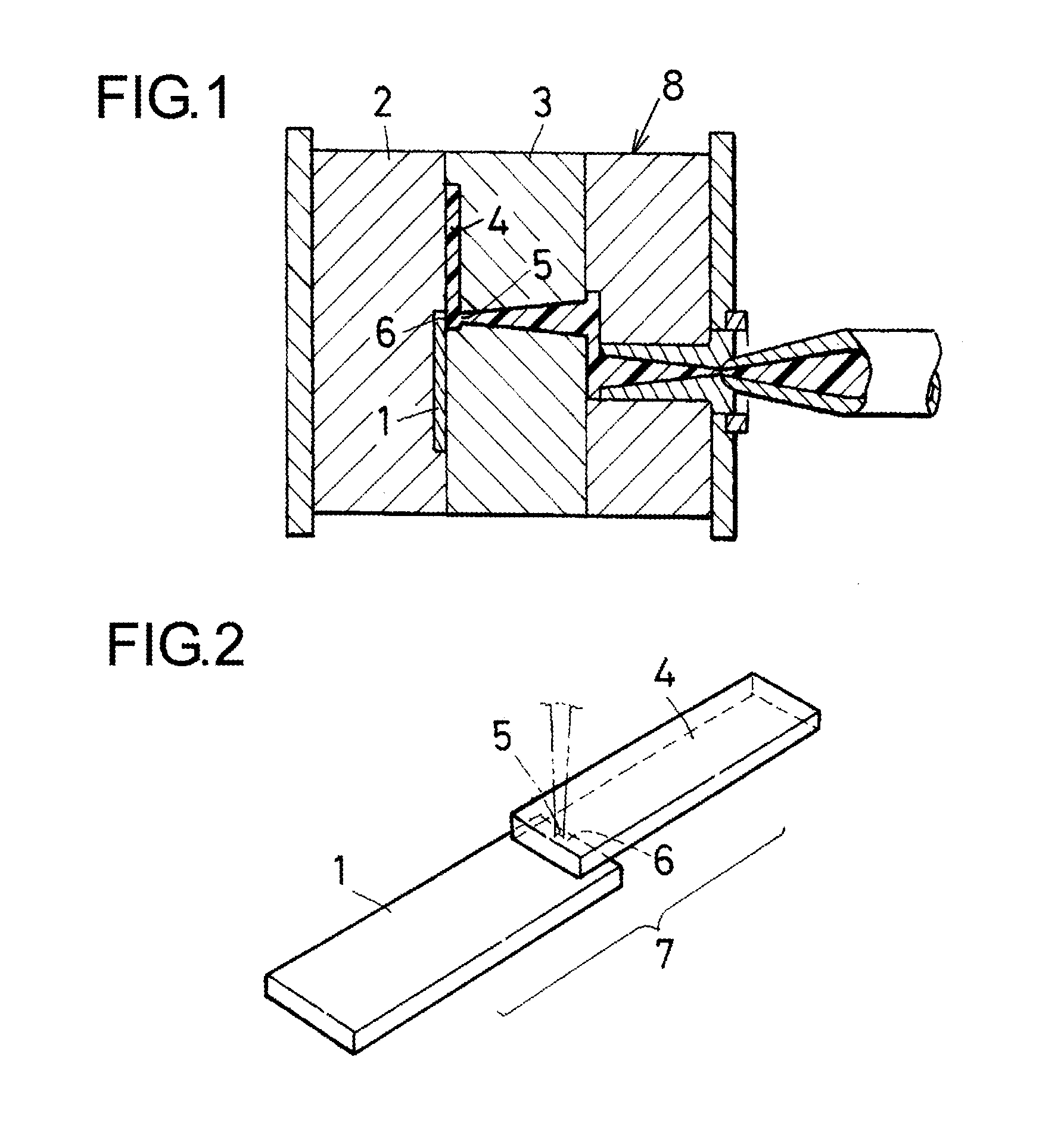
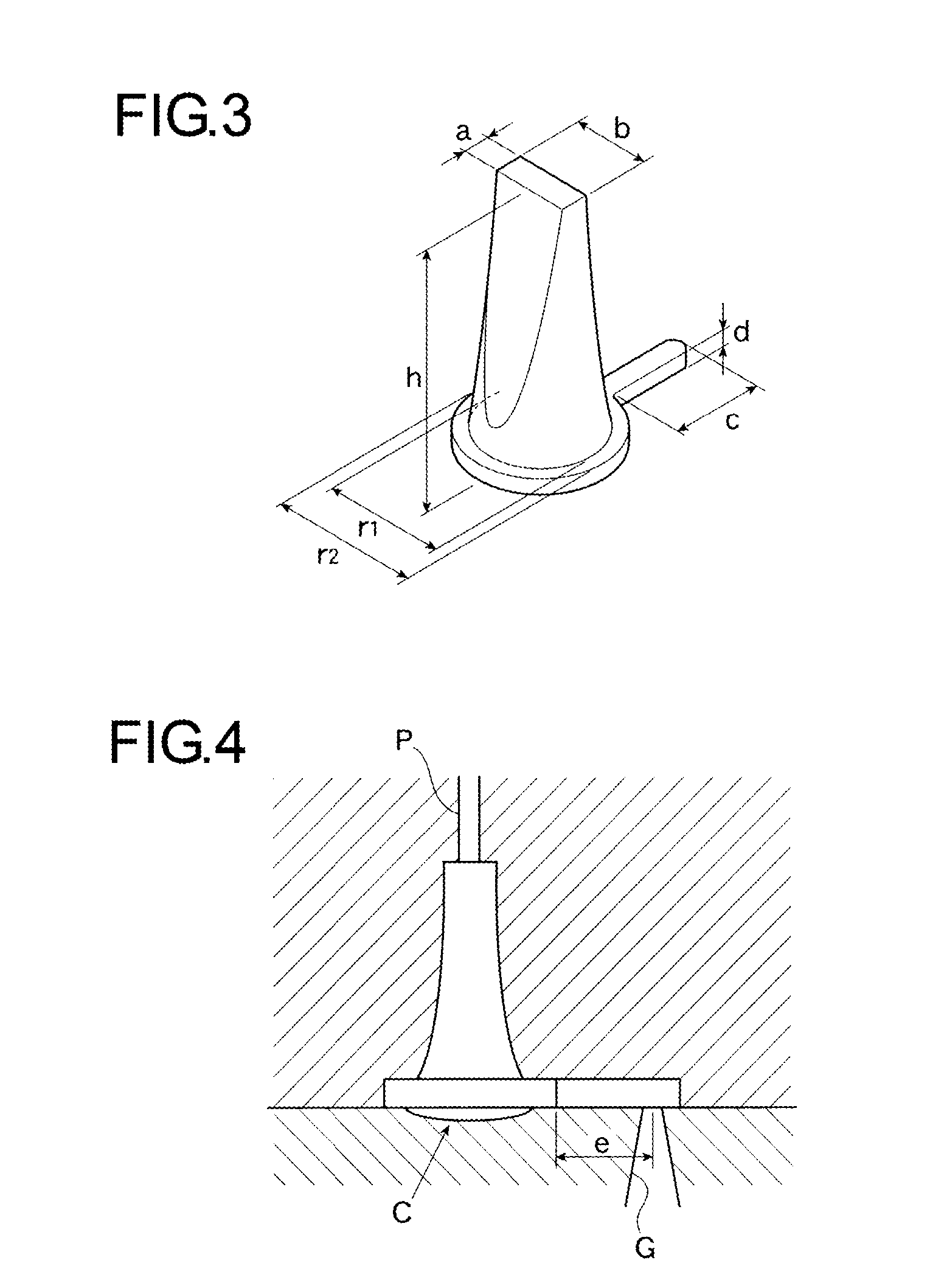
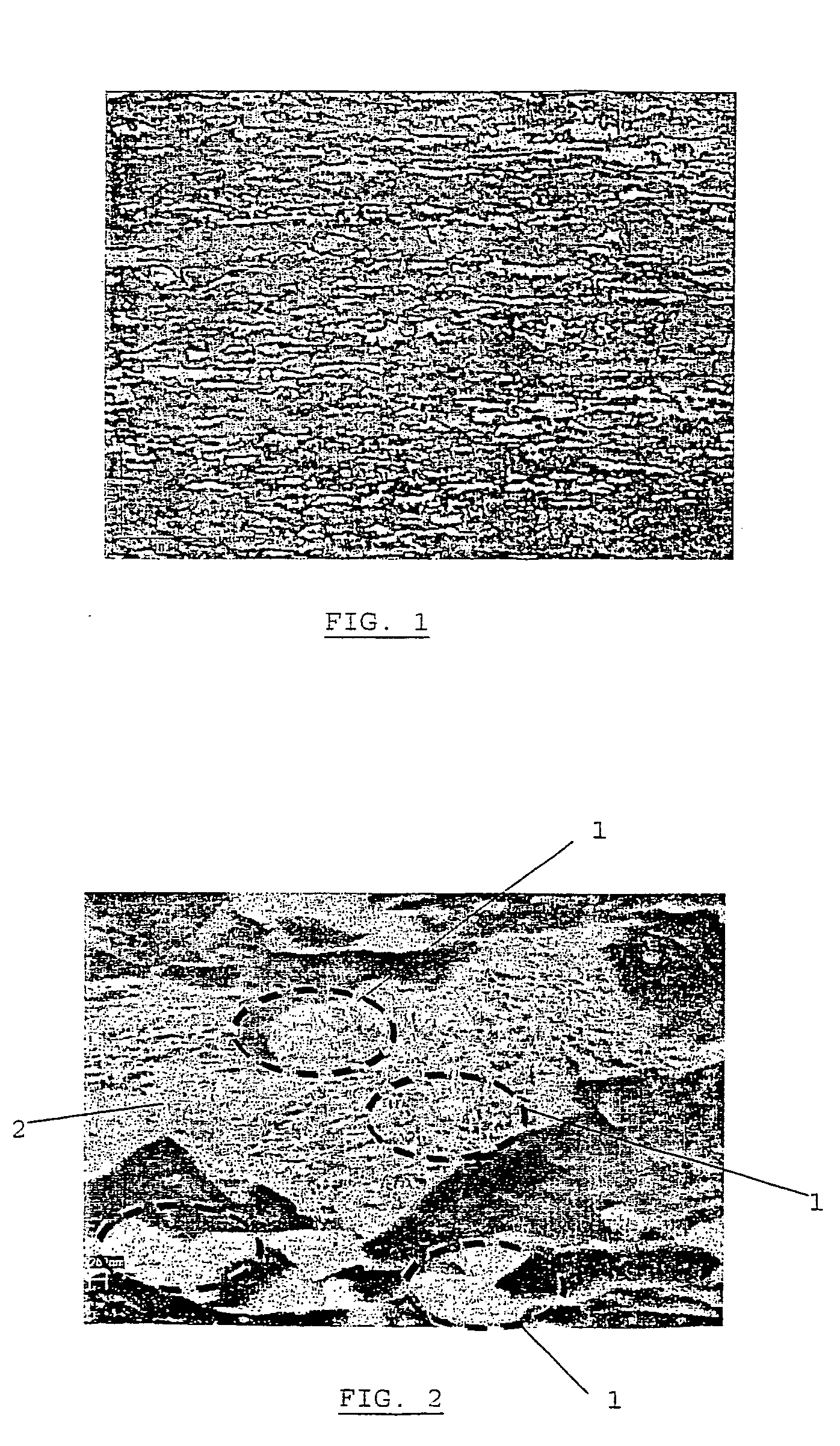
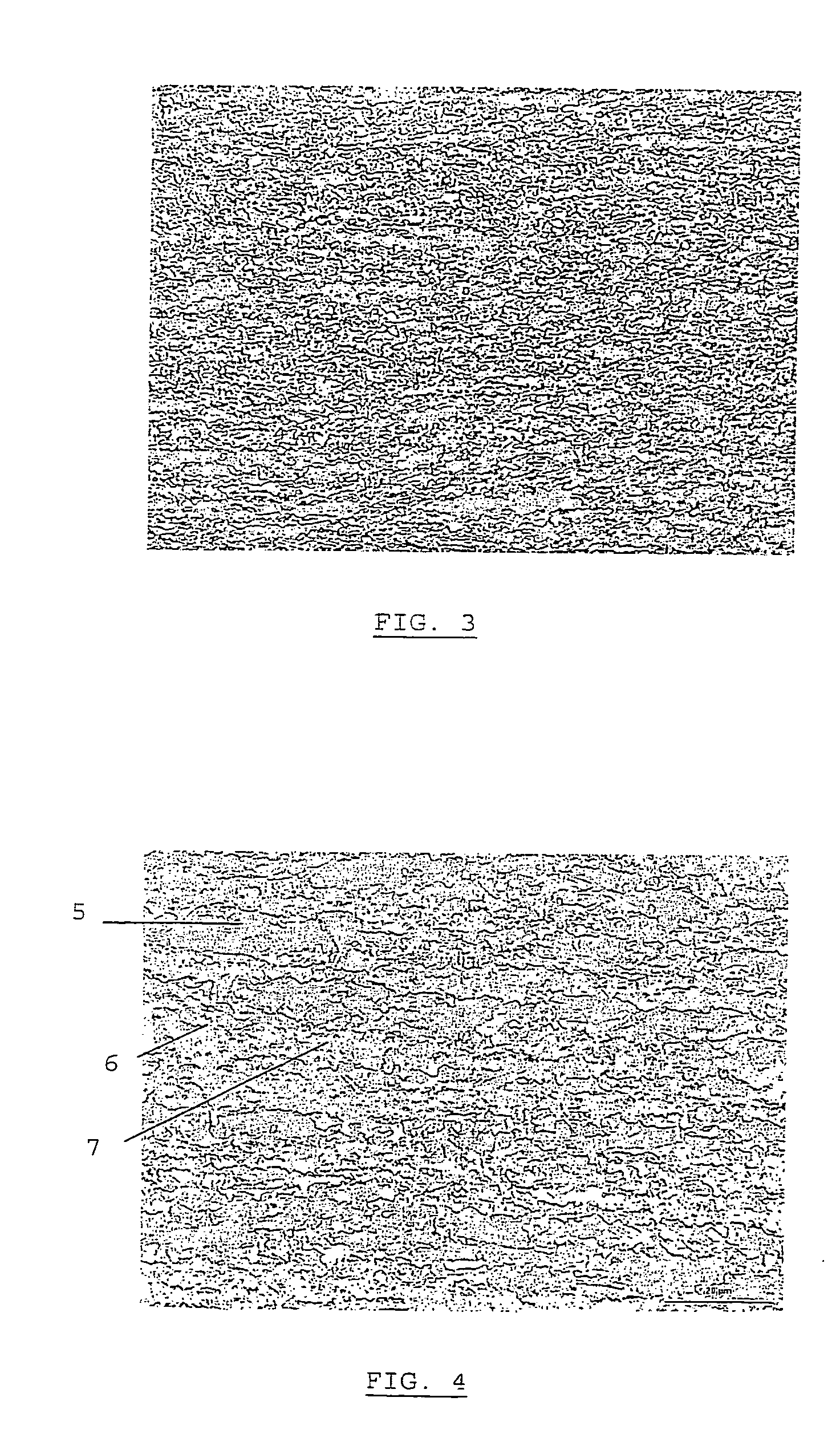
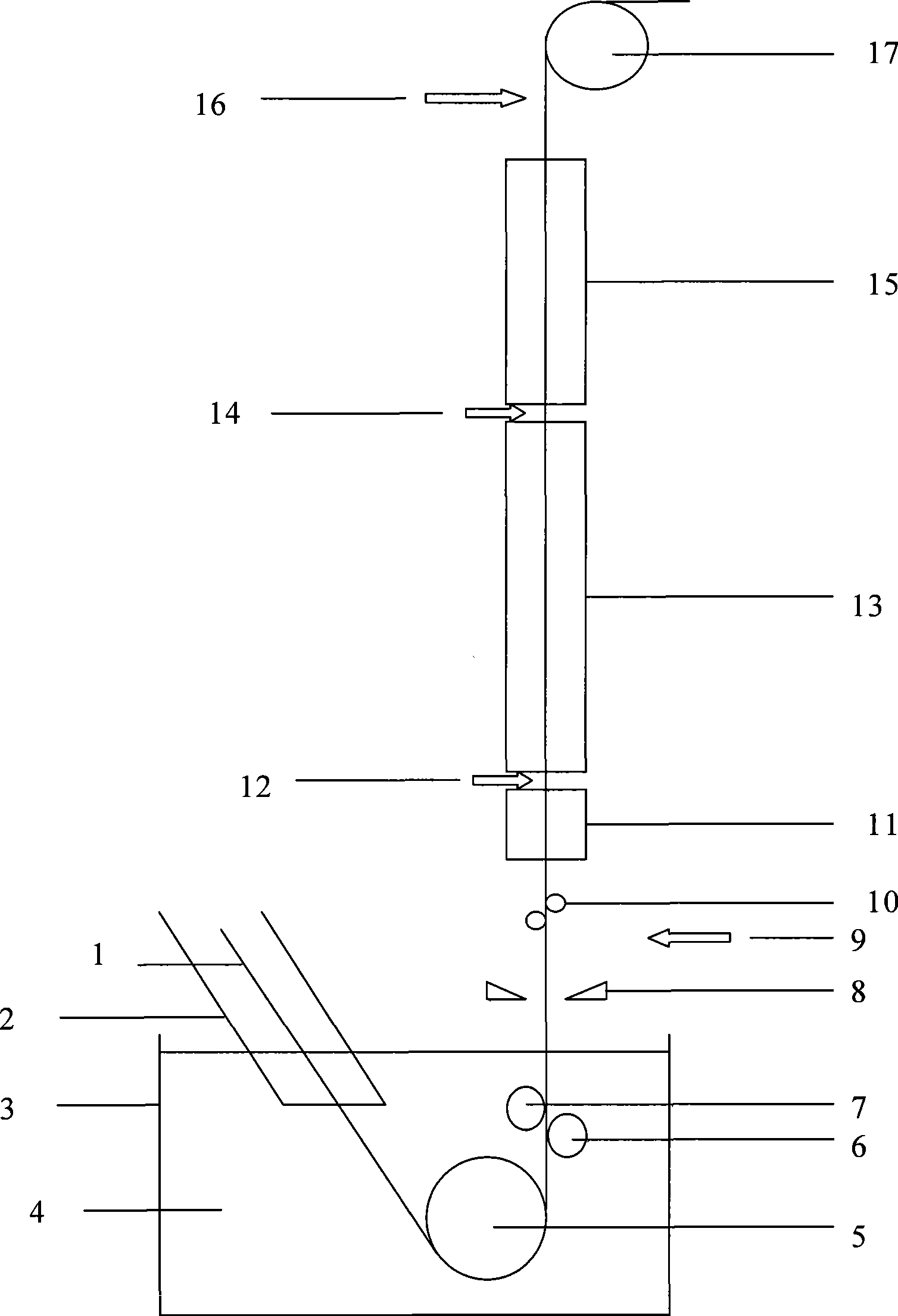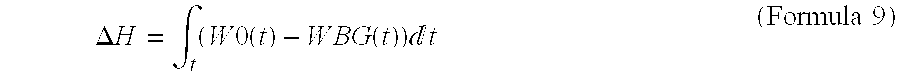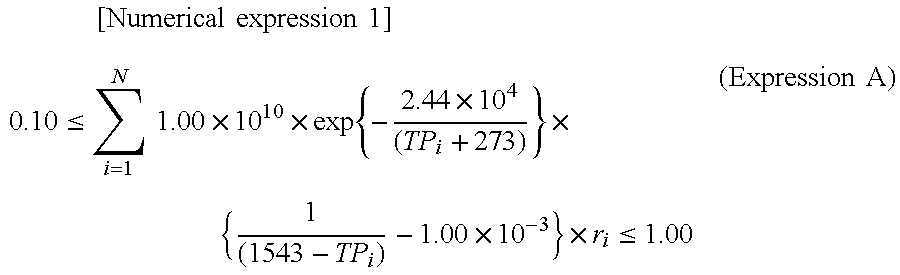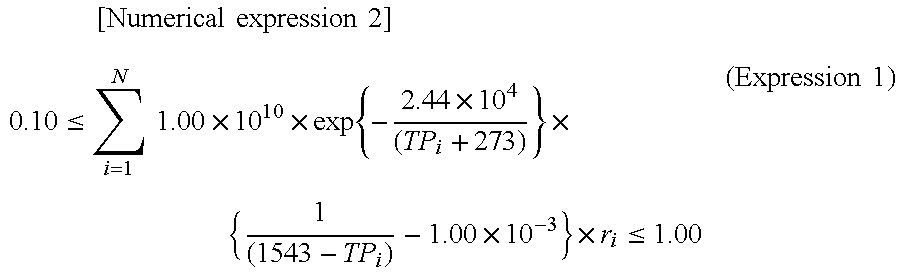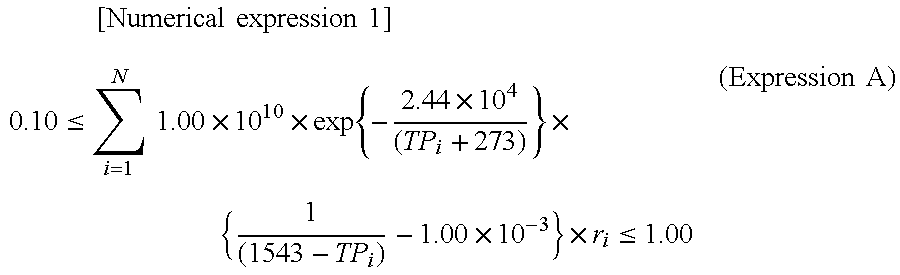Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1014 results about "Hot-dip galvanization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
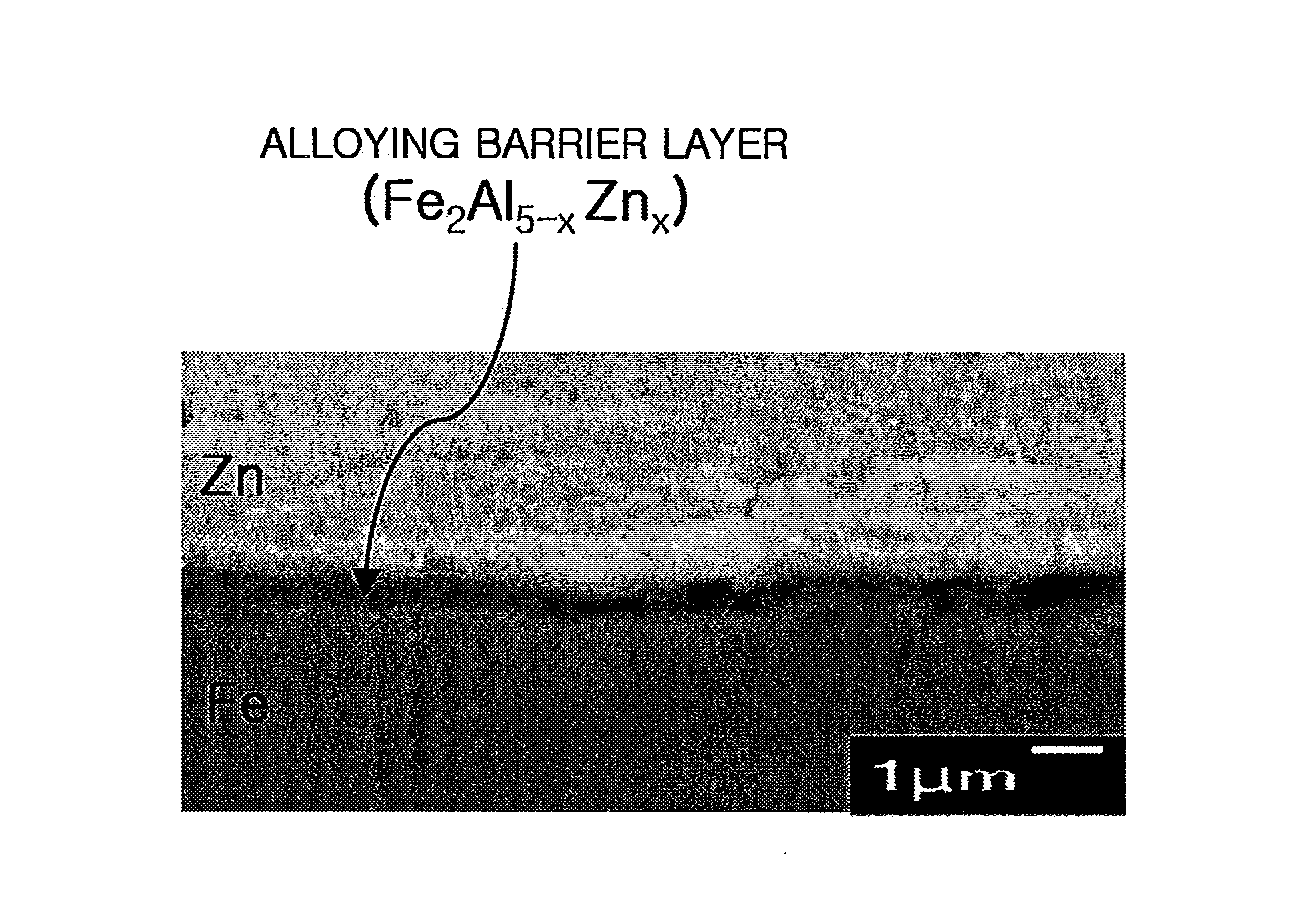
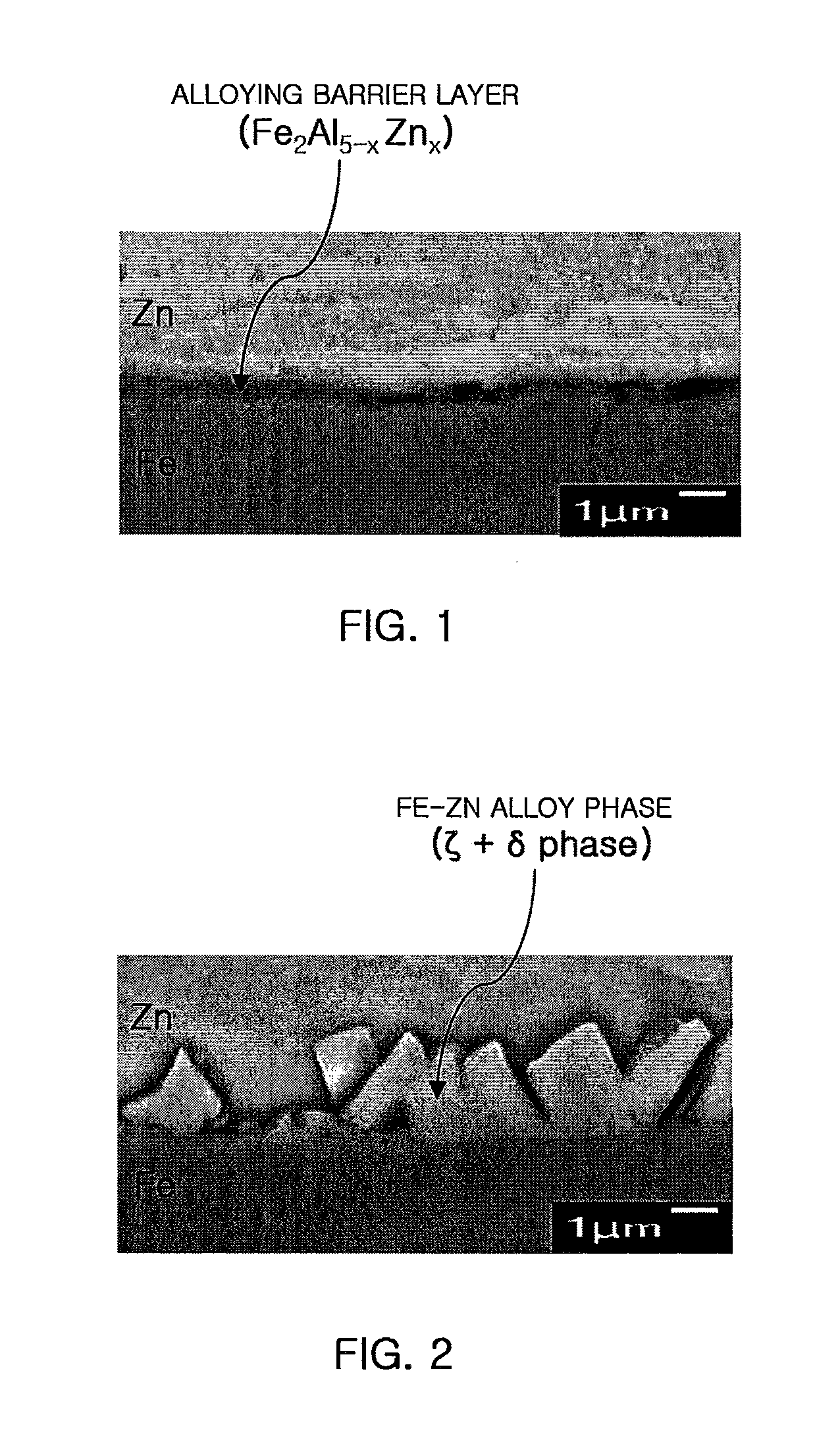
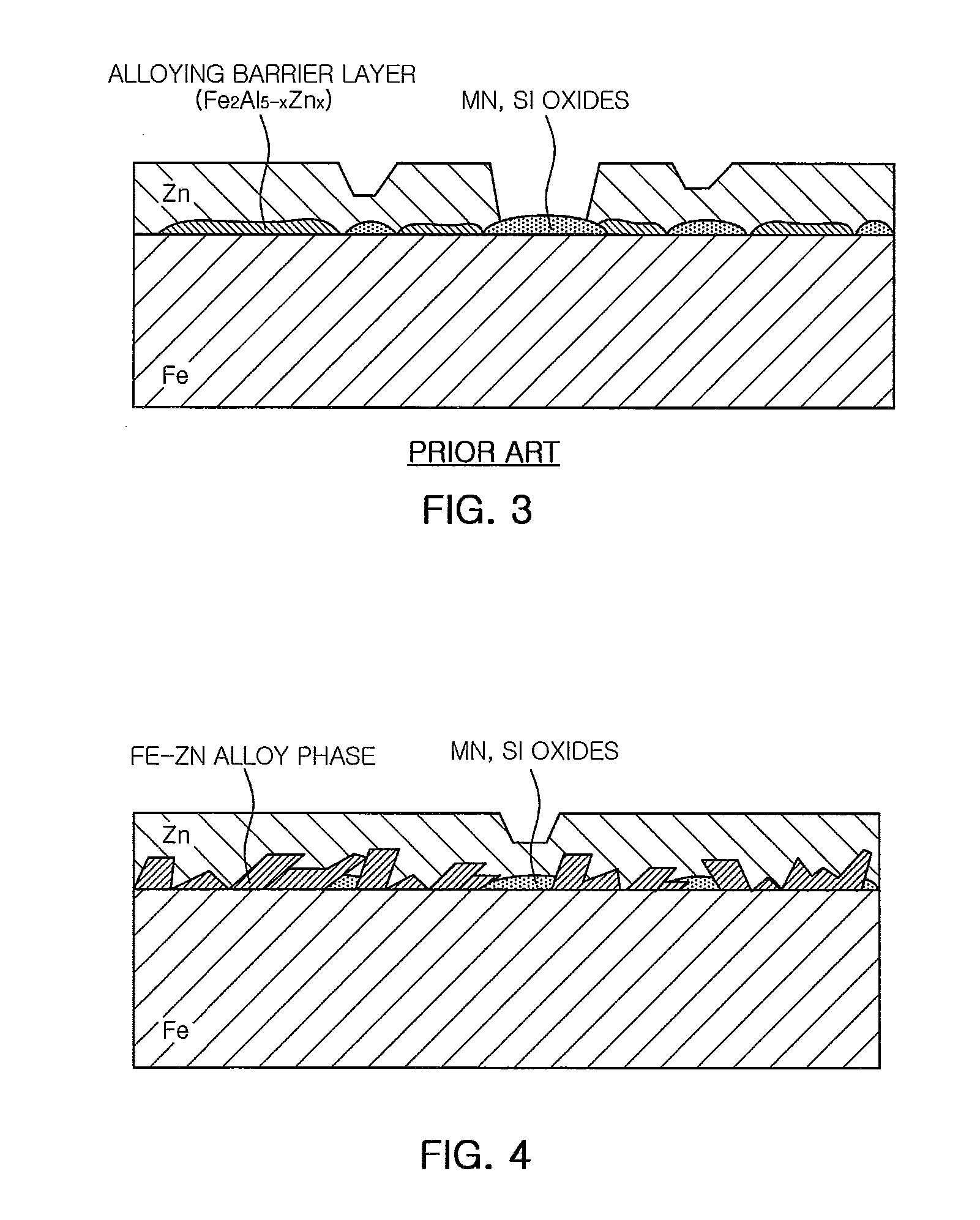
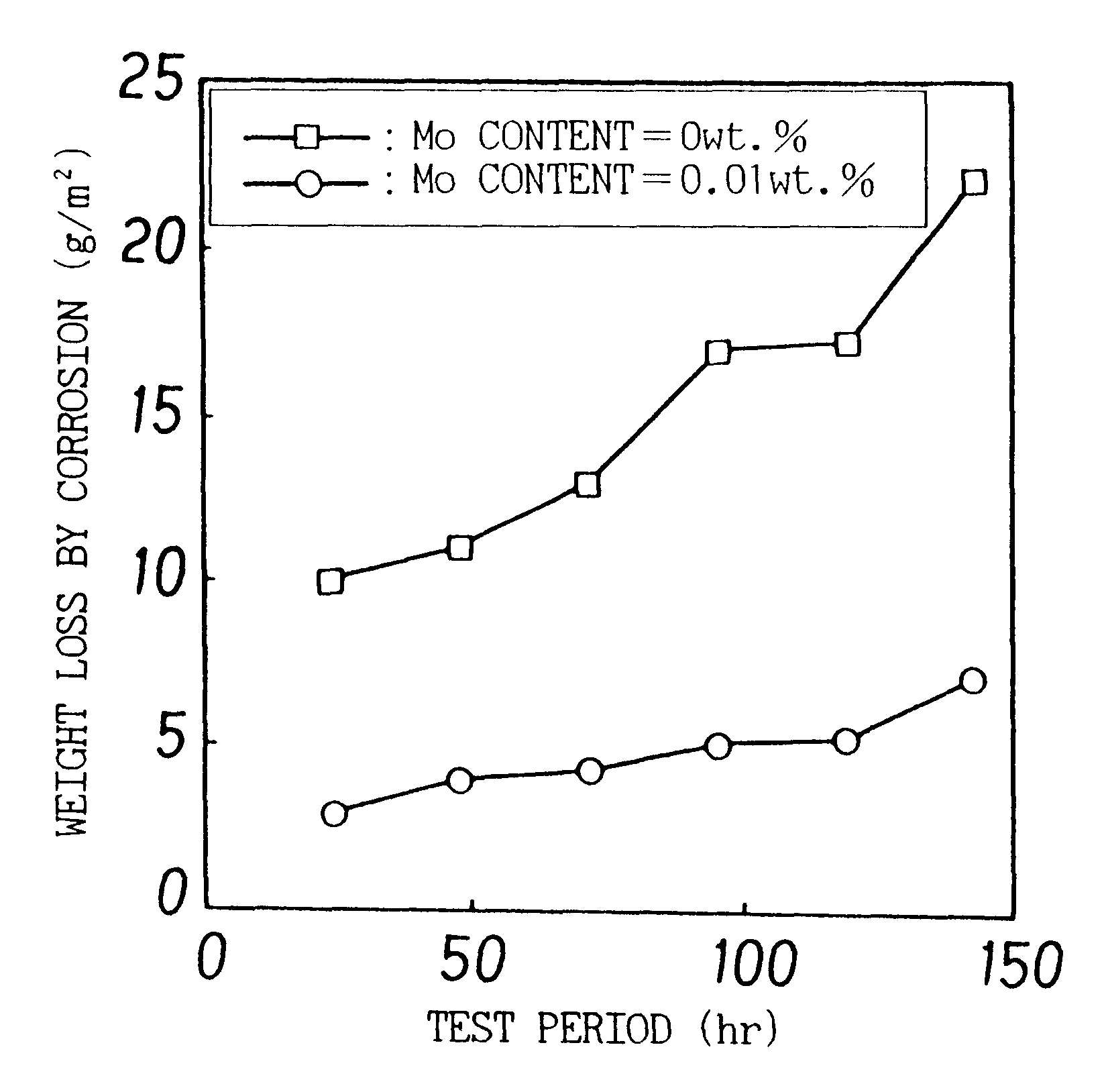
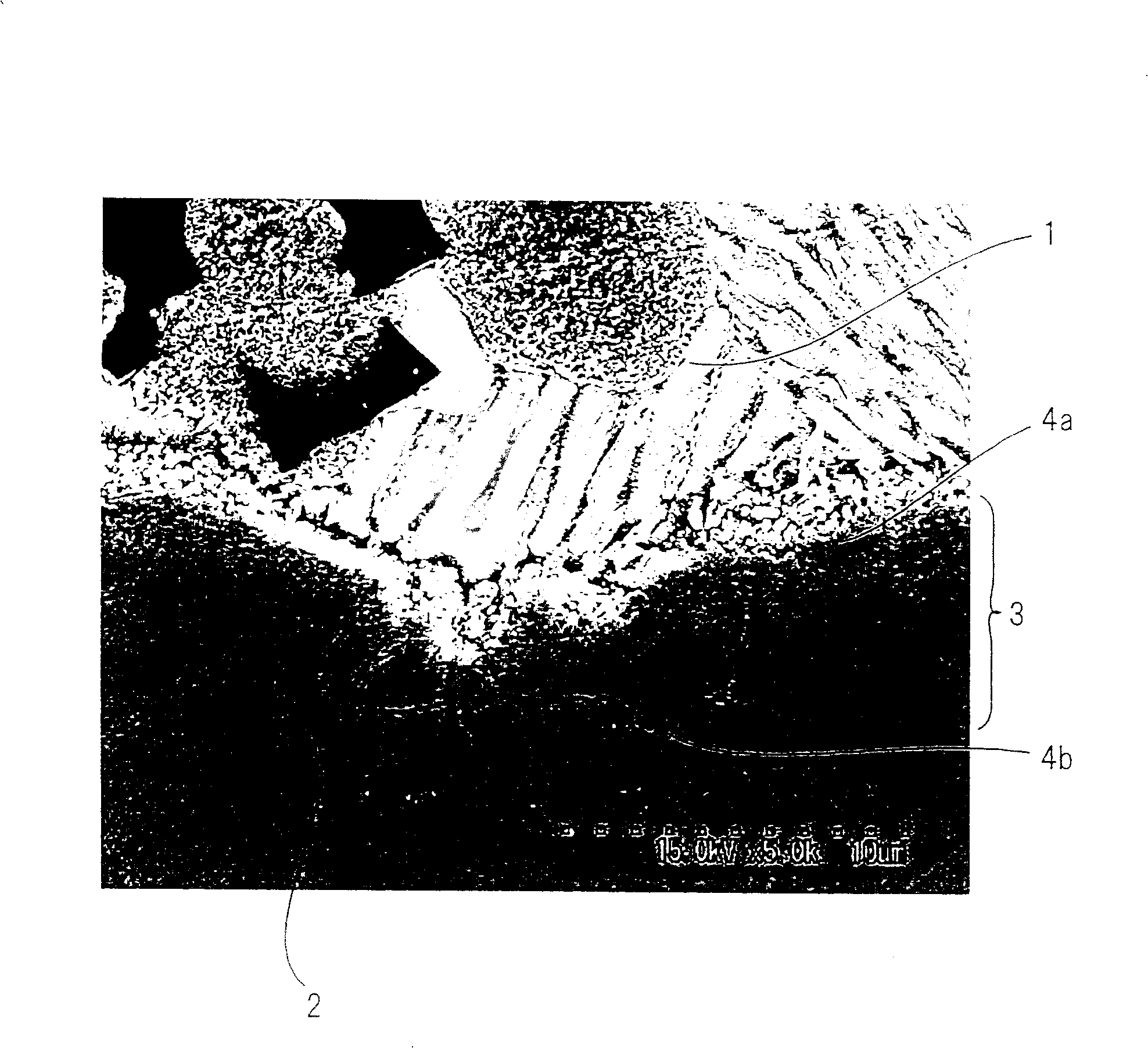
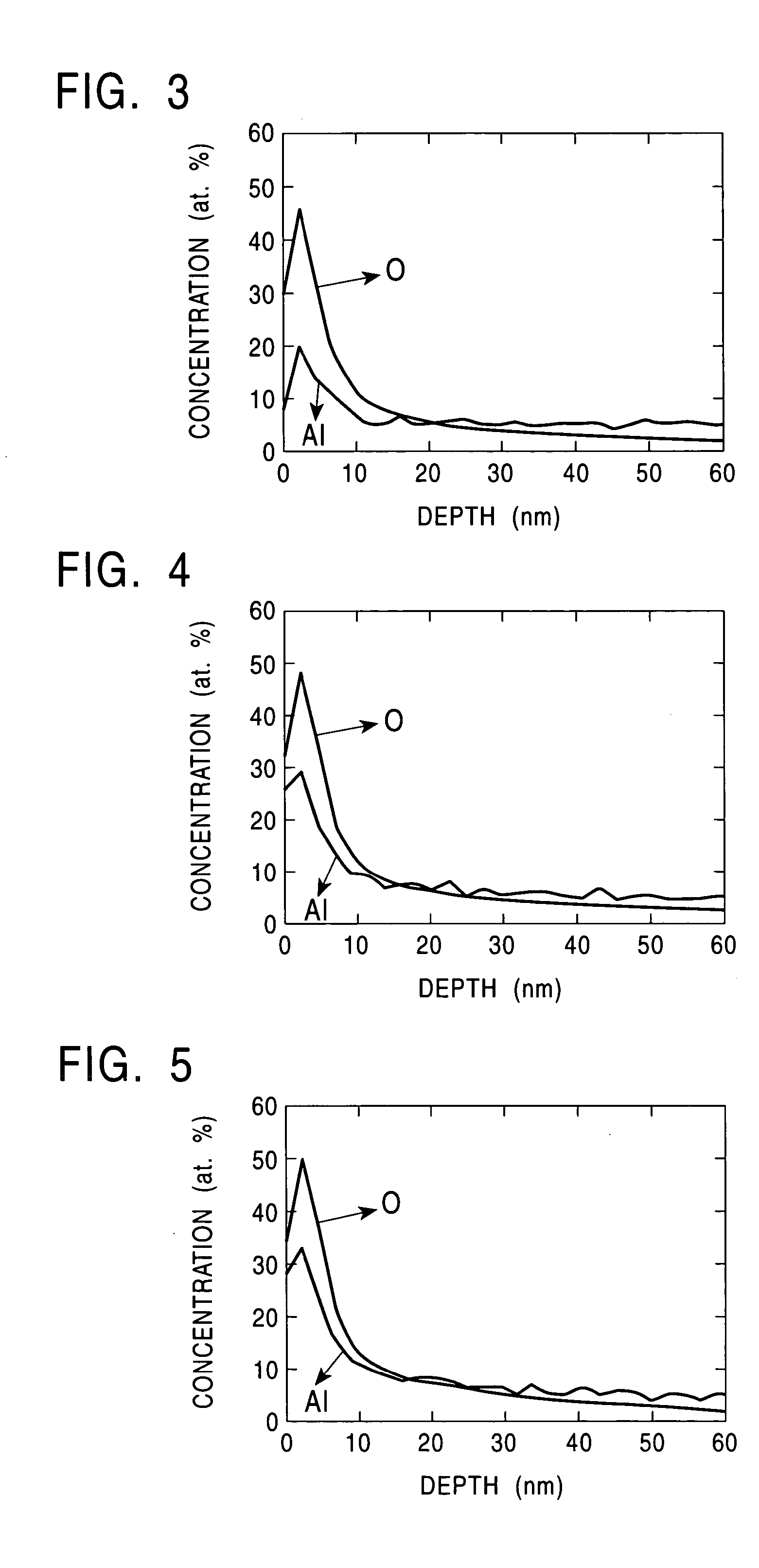
Hot-dip galvanization is a form of galvanization. It is the process of coating iron and steel with zinc, which alloys with the surface of the base metal when immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 449 °C (840 °F). When exposed to the atmosphere, the pure zinc (Zn) reacts with oxygen (O₂) to form zinc oxide (ZnO), which further reacts with carbon dioxide (CO₂) to form zinc carbonate (ZnCO₃), a usually dull grey, fairly strong material that protects the steel underneath from further corrosion in many circumstances. Galvanized steel is widely used in applications where corrosion resistance is needed without the cost of stainless steel, and is considered superior in terms of cost and life-cycle. It can be identified by the crystallization patterning on the surface (often called a "spangle").
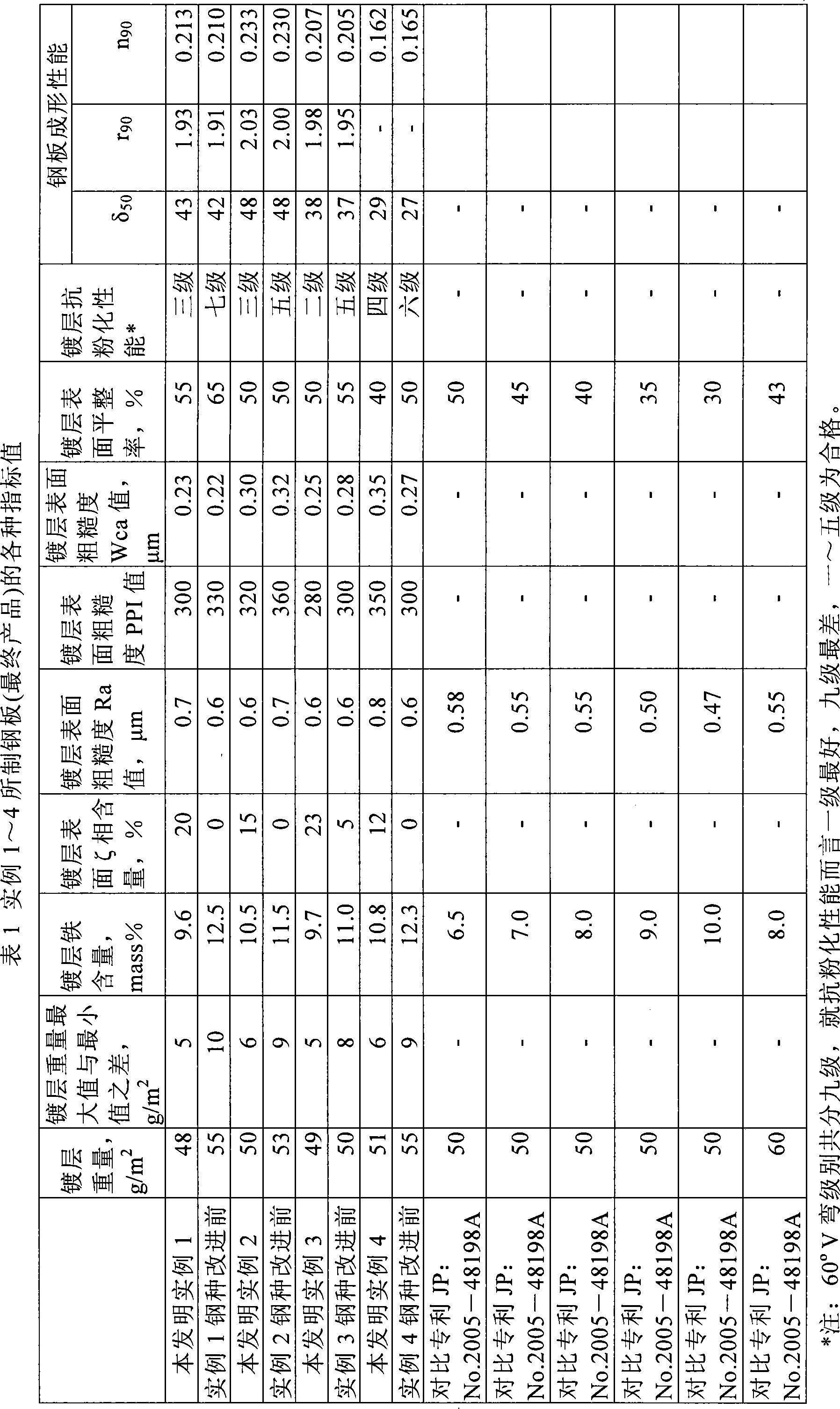
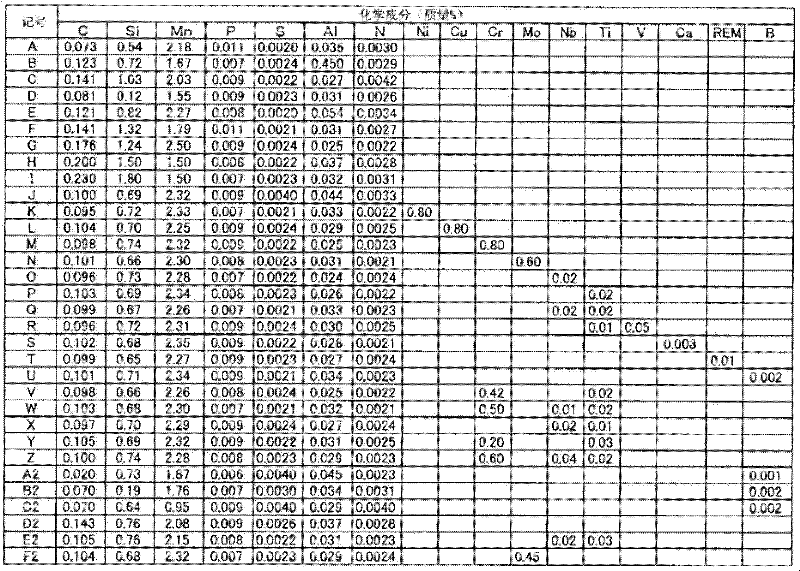
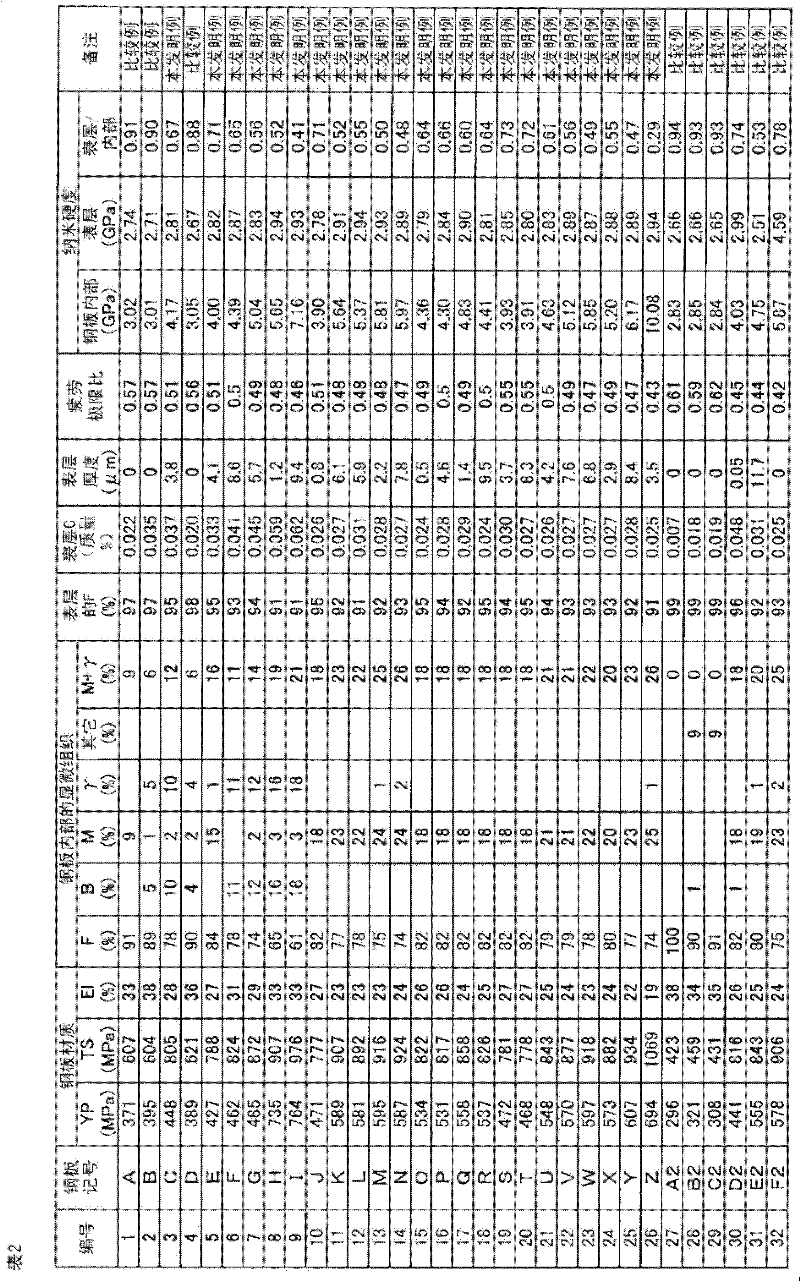
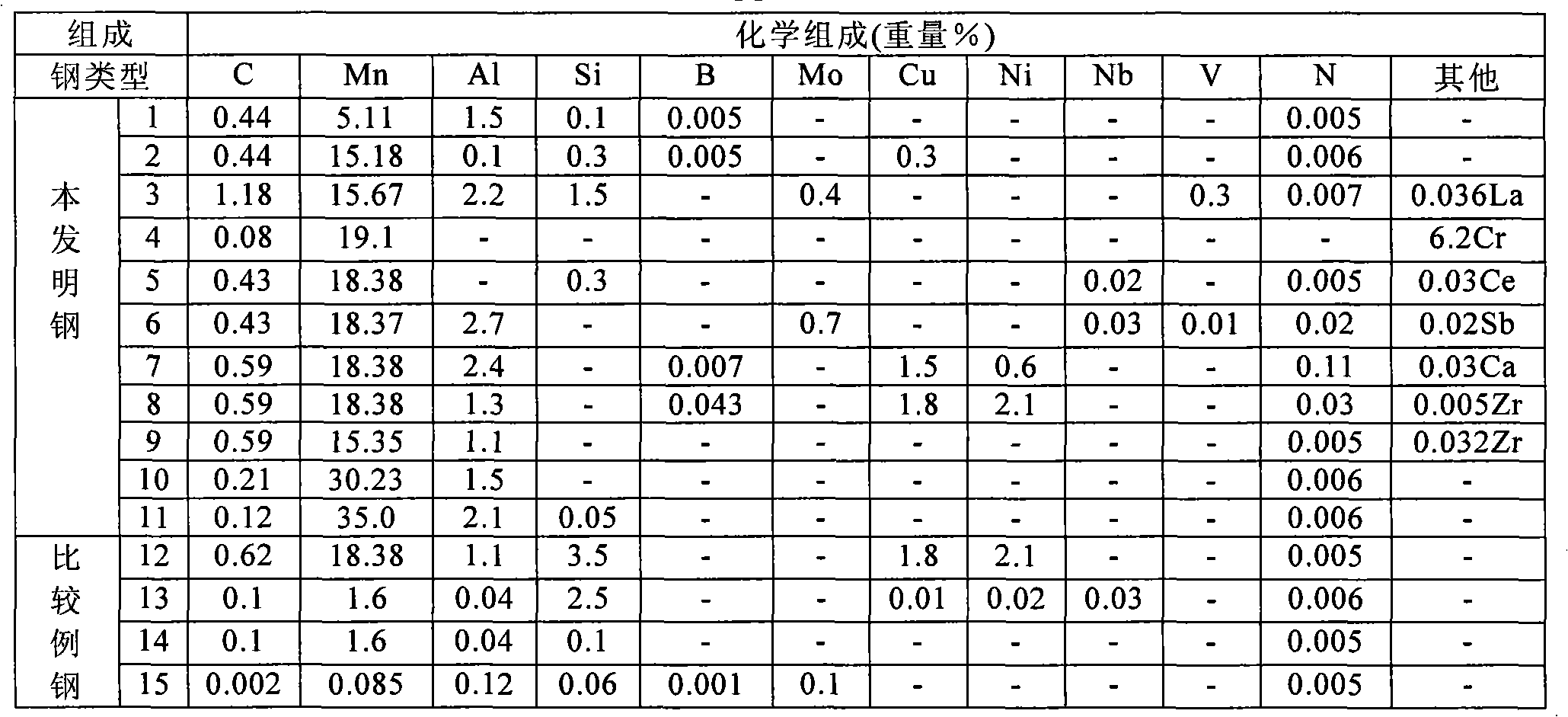
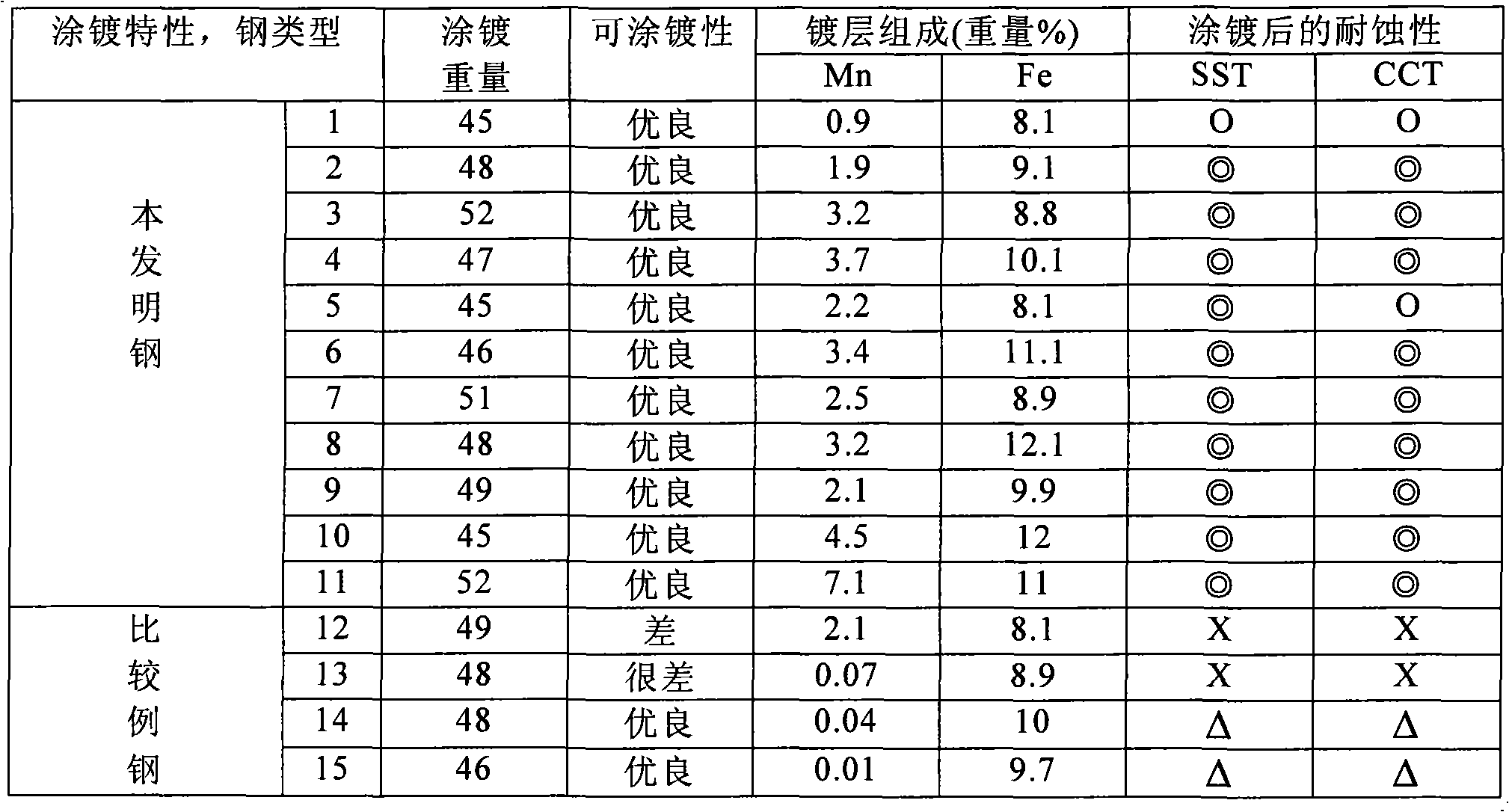
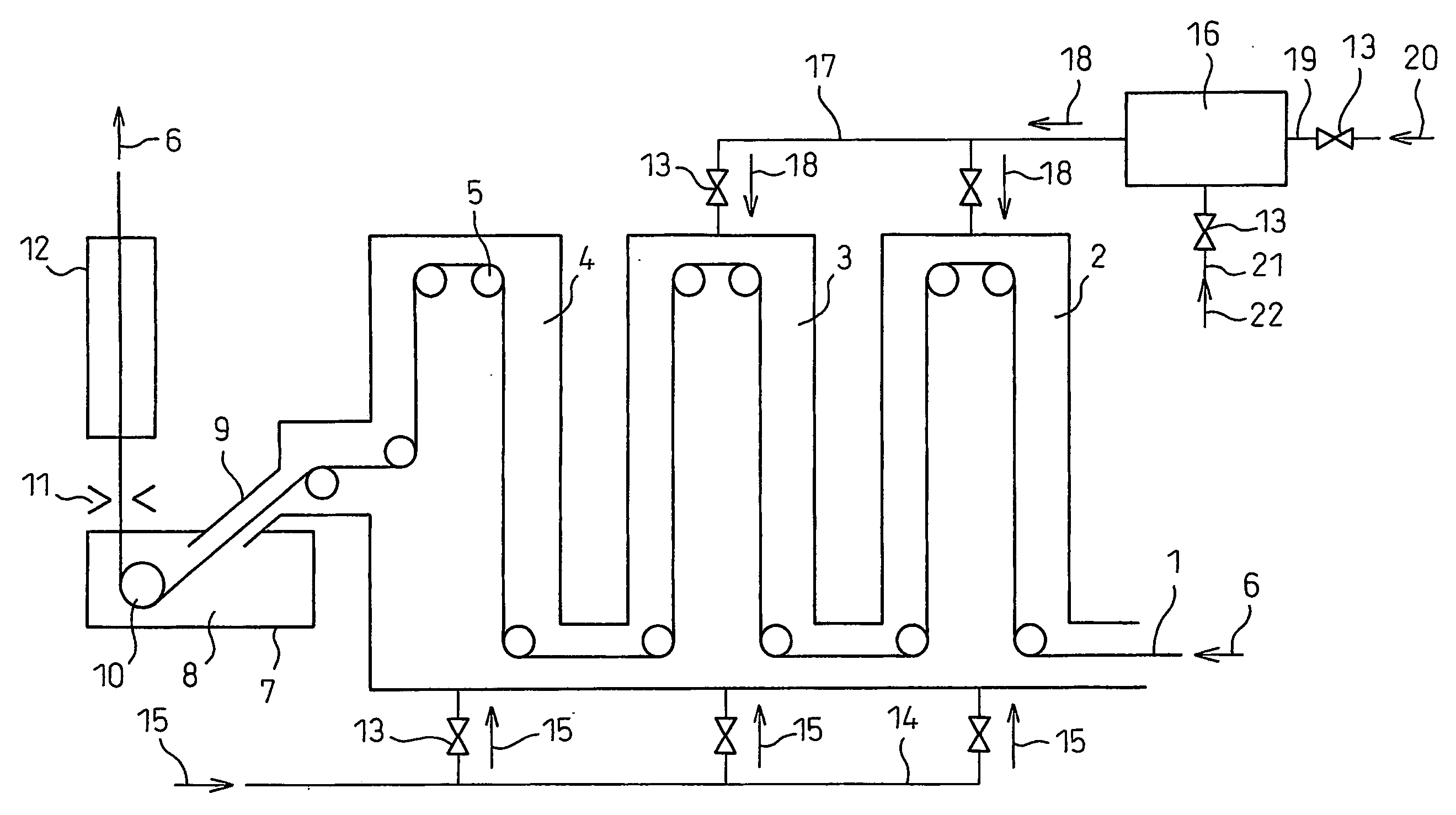
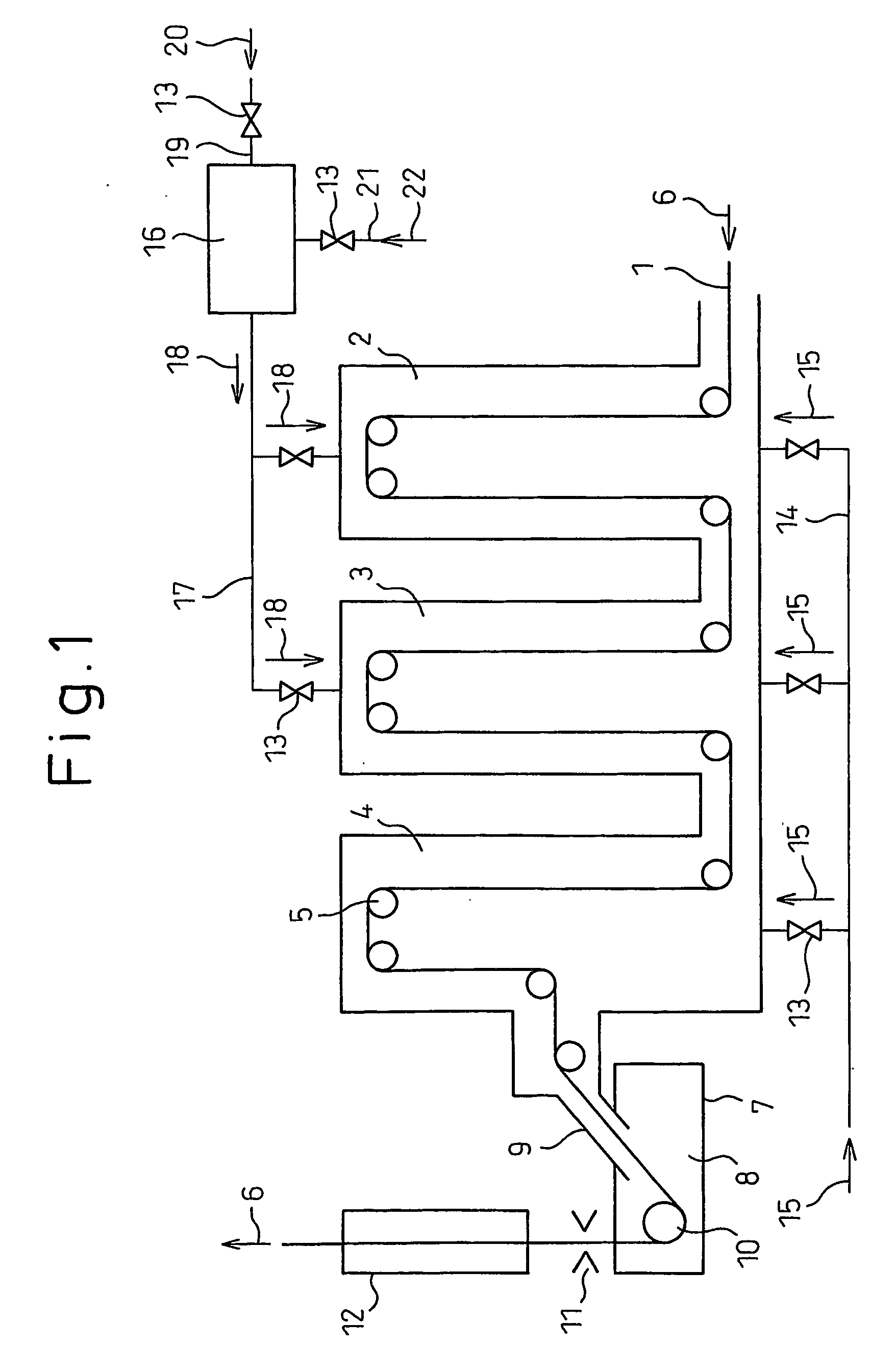
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and production thereof
InactiveUS6312536B1High strengthGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelHigh intensity
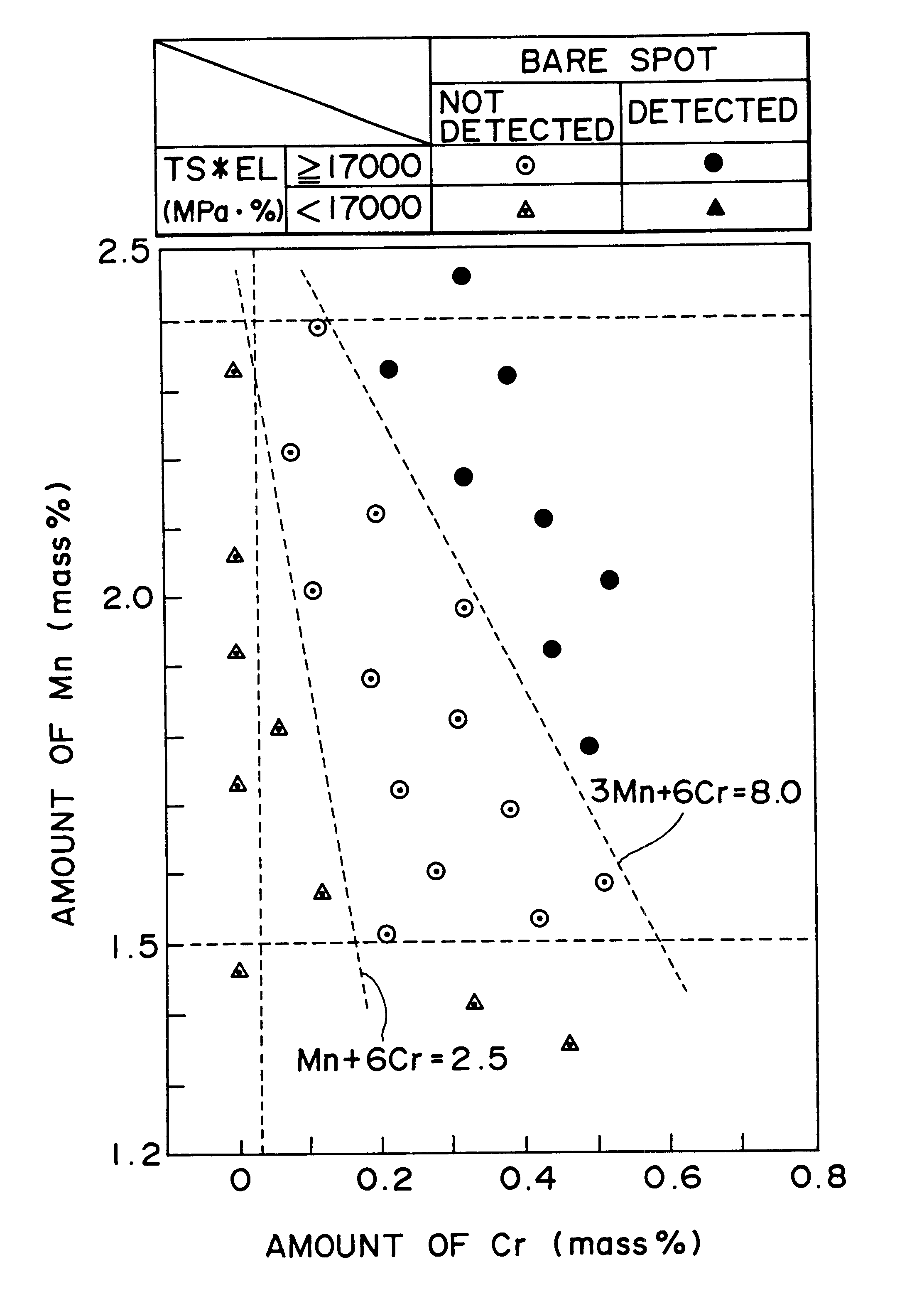
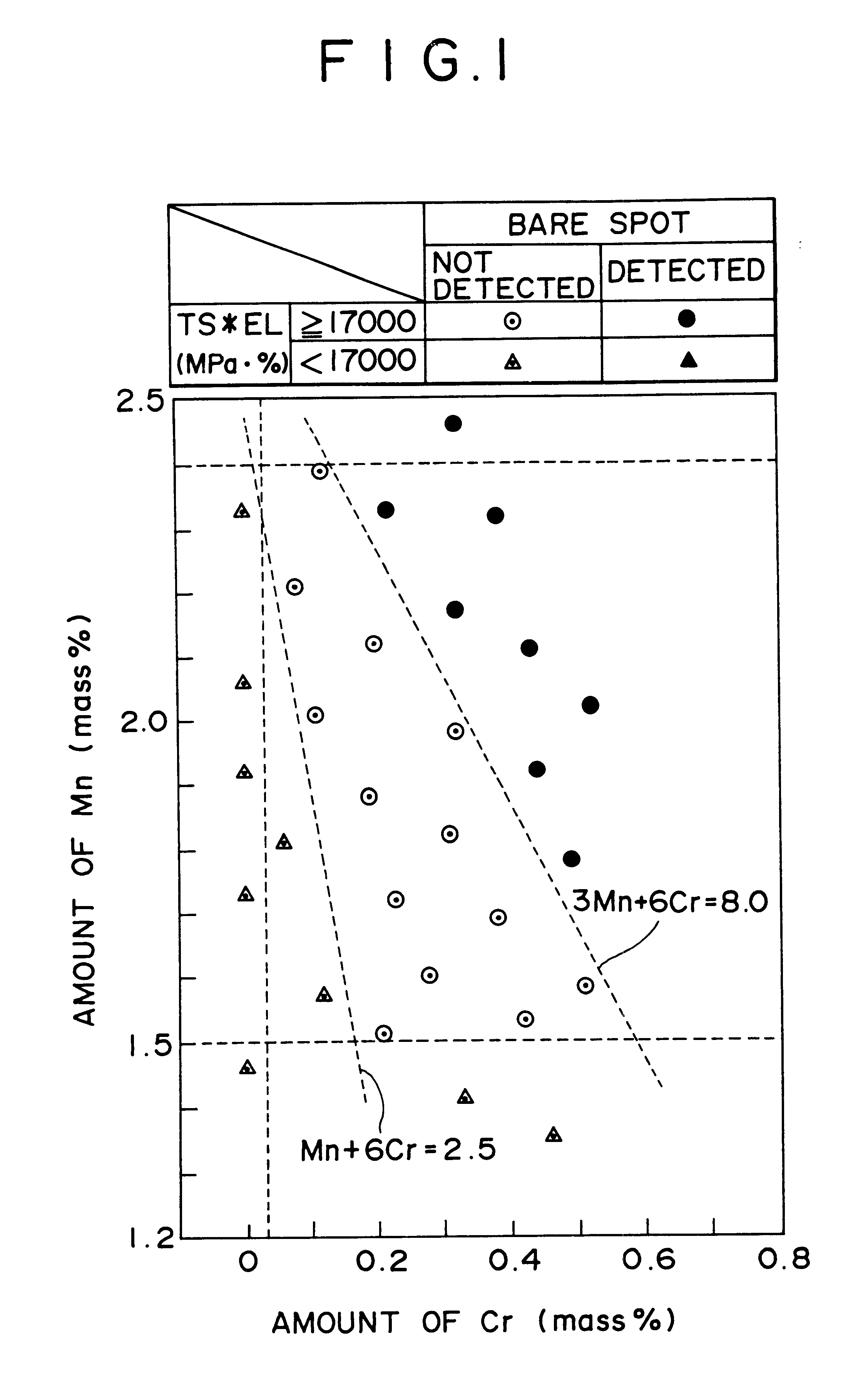
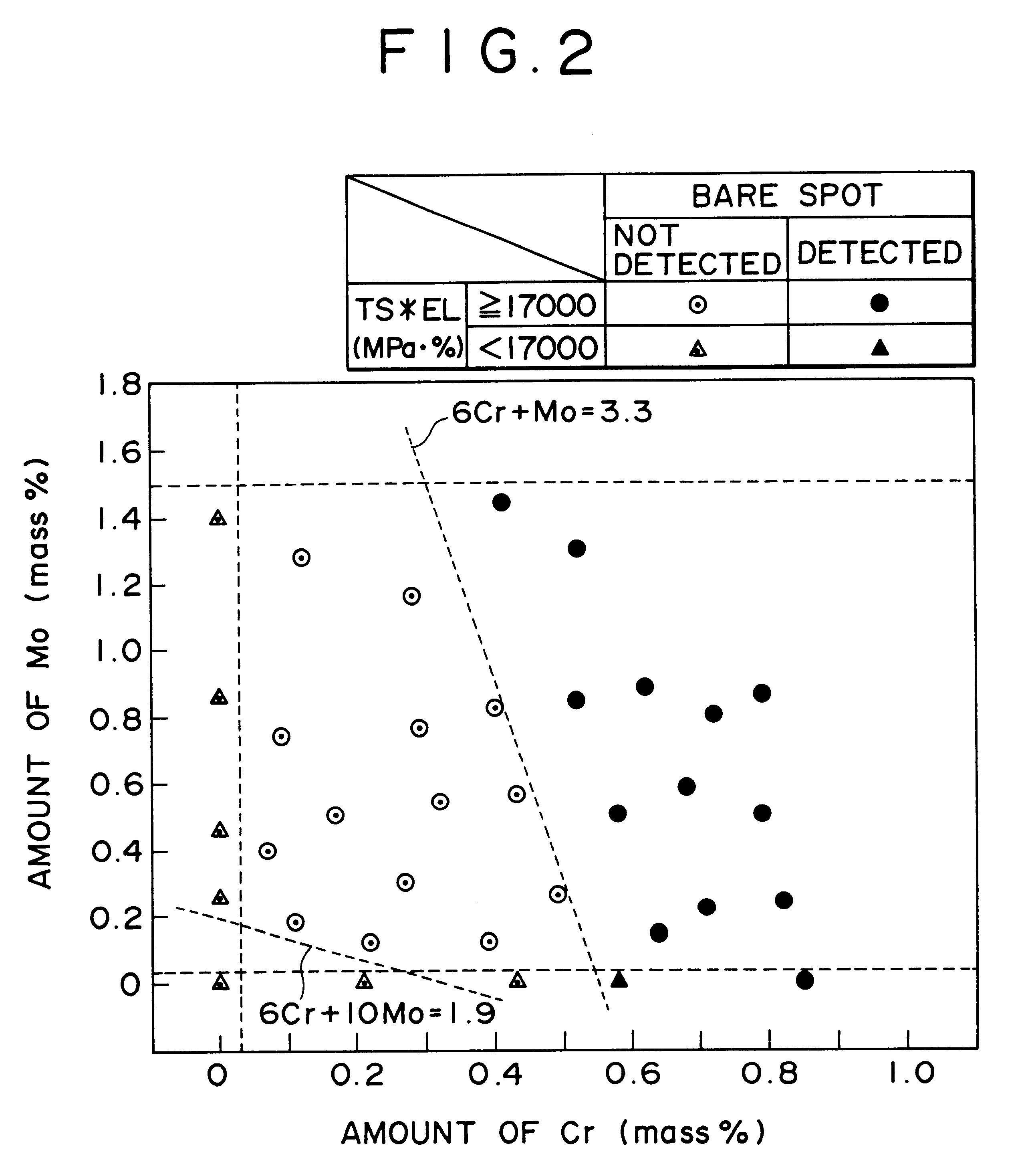
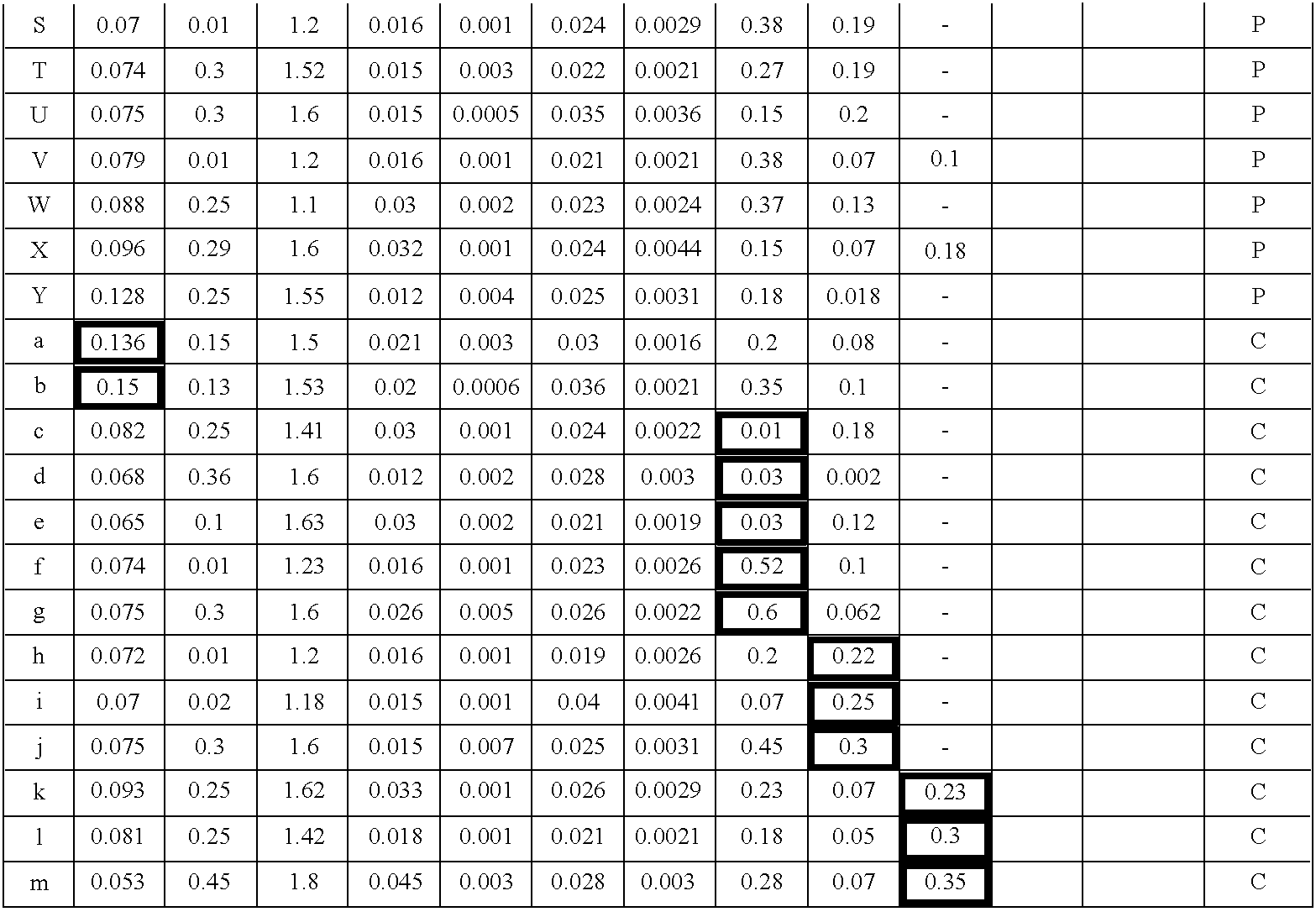
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having both high strength and good formability. A process for producing said hot-dip galvanized steel sheet without requiring additional steps of surface grinding and pre-plating.The hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is produced by forming a hot-dip galvanizing layer on a base cold-rolled steel sheet composed of C (0.02-0.20 mass %), Mn (1.50-2.40 mass %), Cr (0.03-1.50 mass %), Mo (0.03-1.50 mass %), 3Mn+6Cr+Mo (no more than 8.1 mass %), Mn+6Cr+10 Mo (no less than 3.5 mass %), Al (0.010-0.150 mass %), and Fe as the principal component, with Ti limited to 0.01 mass % or less, Si limited to 0.04 mass % or less, P limited to 0.060 mass % or less, and S limited to 0.030 mass % or less, and said base steel sheet having the composite microstructure composed mainly of ferrite and martensite.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Flux and process for hot dip galvanization
InactiveUS20030219543A1Improve the immunityConvenient coatingHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsAlkaline earth metalChloride
A flux for hot dip galvanization comprises from:&Circlesolid;60 to 80 wt. % of zinc chloride (ZnCl2); 7 to 20 wt. % of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl); 2 to 20 wt. % of a fluidity modifying agent comprising at least one alkali or alkaline earth metal; 0.1 to 5 wt. % of a least one of the following compounds: NiCl2, CoCl2, MnCl2; and 0.1 to 1.5 wt. % of at least one of the following compounds: PbCl2, SnCl2, BiCl3, SbCl3.
Owner:FONTAINE HLDG NV
Bonded body of galvanized steel sheet and adherend, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110008644A1Firmly connectedGood adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsPolyolefinSheet steel
The invention is a technique for strongly integrating a galvanized steel sheet and a resin molded article. A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet “Z18” is immersed in an aqueous solution for aluminum degreasing at 75° C. for 7 minutes, to form roughness having an RSm of 0.8 to 2.3 μm and an Rz of 0.3 to 1.0 μm on the surface. The surface is covered with convex protrusions having a diameter of about 100 nm, and a chromate treatment layer appears in the surface. In other words, three conditions suitable for bonding are satisfied thereby. A resin composition comprising 70 to 97 wt % of polyphenylene sulfide and 3 to 30 wt % of a polyolefin resin is injected onto the surface. The resin composition penetrates into ultra-fine irregularities and is cured in that state, whereby a composite in which the galvanized steel sheet and the resin molded article are strongly integrated is obtained. The shear rupture strength of the composite is extremely high, in excess of 20 MPa.
Owner:TAISEI PLAS CO LTD
Ultra high strength steel composition, the process of production of an ultra high strength steel product and the product obtained
ActiveUS20040238080A1Hot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityUltimate tensile strength
The present invention is related to a steel composition, a process for producing a steel product having said composition, and said steel product itself. According to the invention, a cold-rolled, possibly hot dip galvanized steel sheet is produced with thicknesses lower than 1 mm, and tensile strengths between 800 MPa and 1600 MPa, while the A80 elongation is between 5 and 17%, depending on the process parameters. The composition is such that these high strength levels may be obtained, while maintaining good formability and optimal coating quality after galvanising. The invention is equally related to a hot rolled product of the same composition, with higher thickness (typically about 2 mm) and excellent coating quality after galvanising.
Owner:ARCELOR FRANCE SA
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6440584B1Hot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsResidence timeMartensite
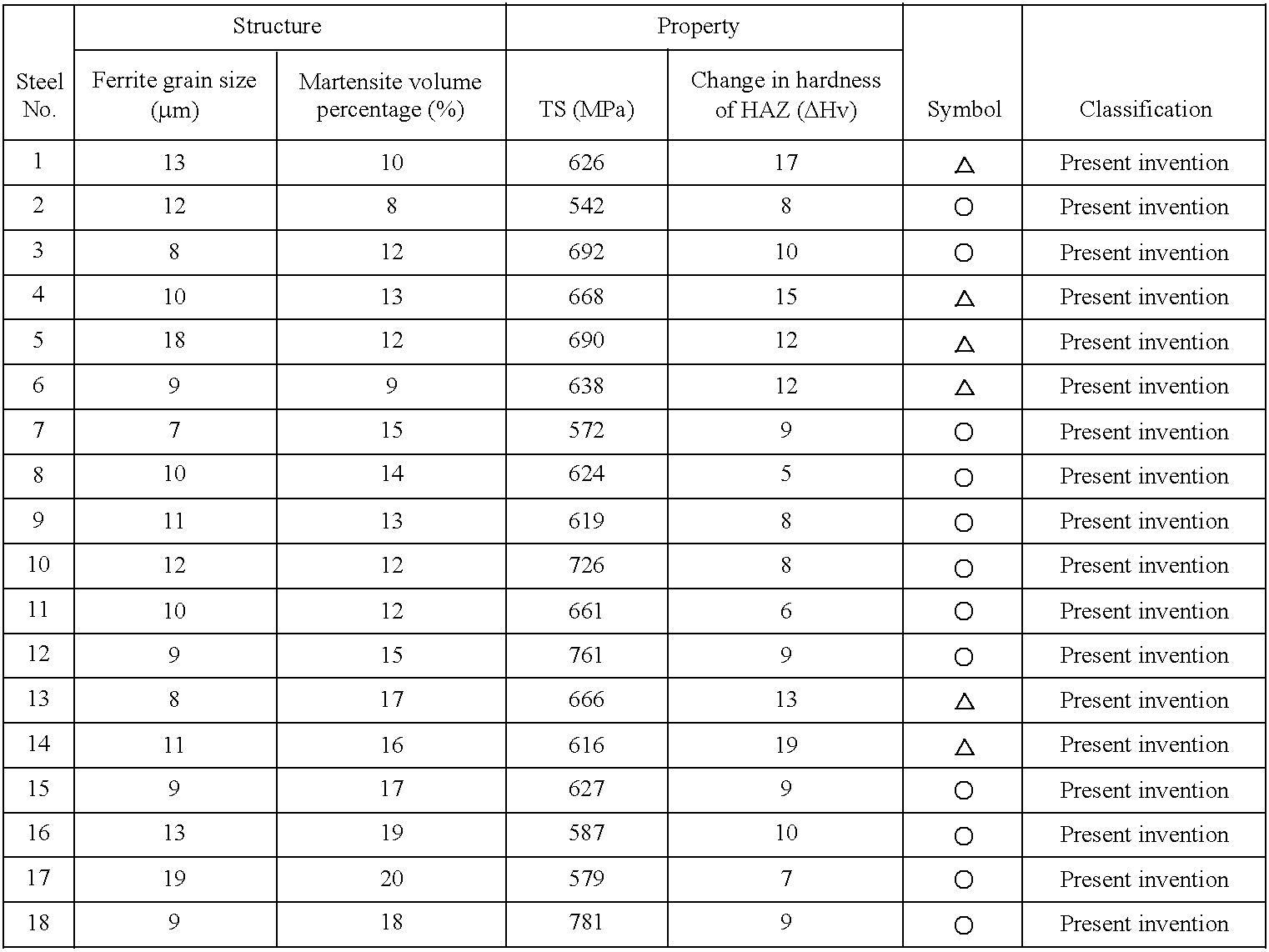
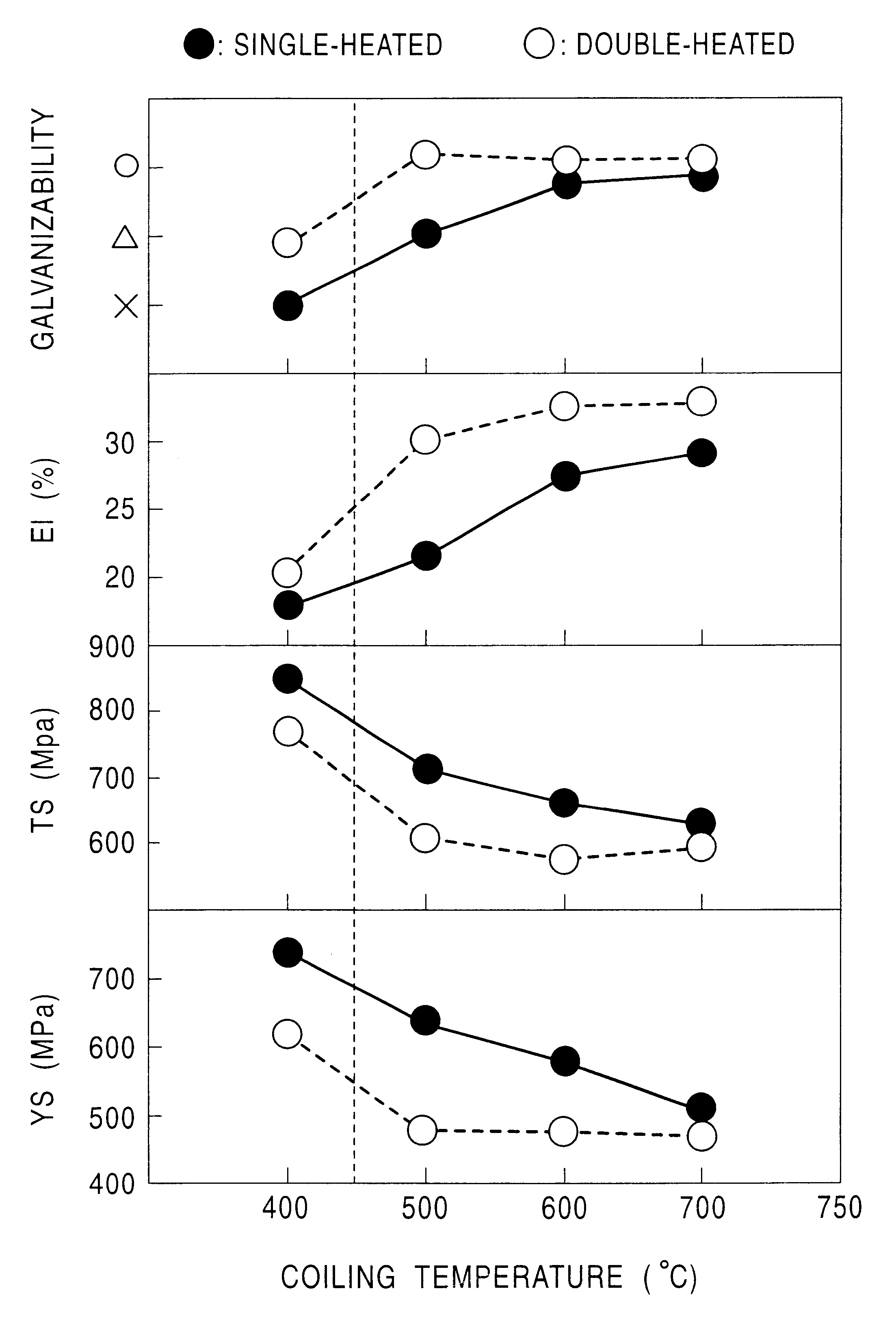
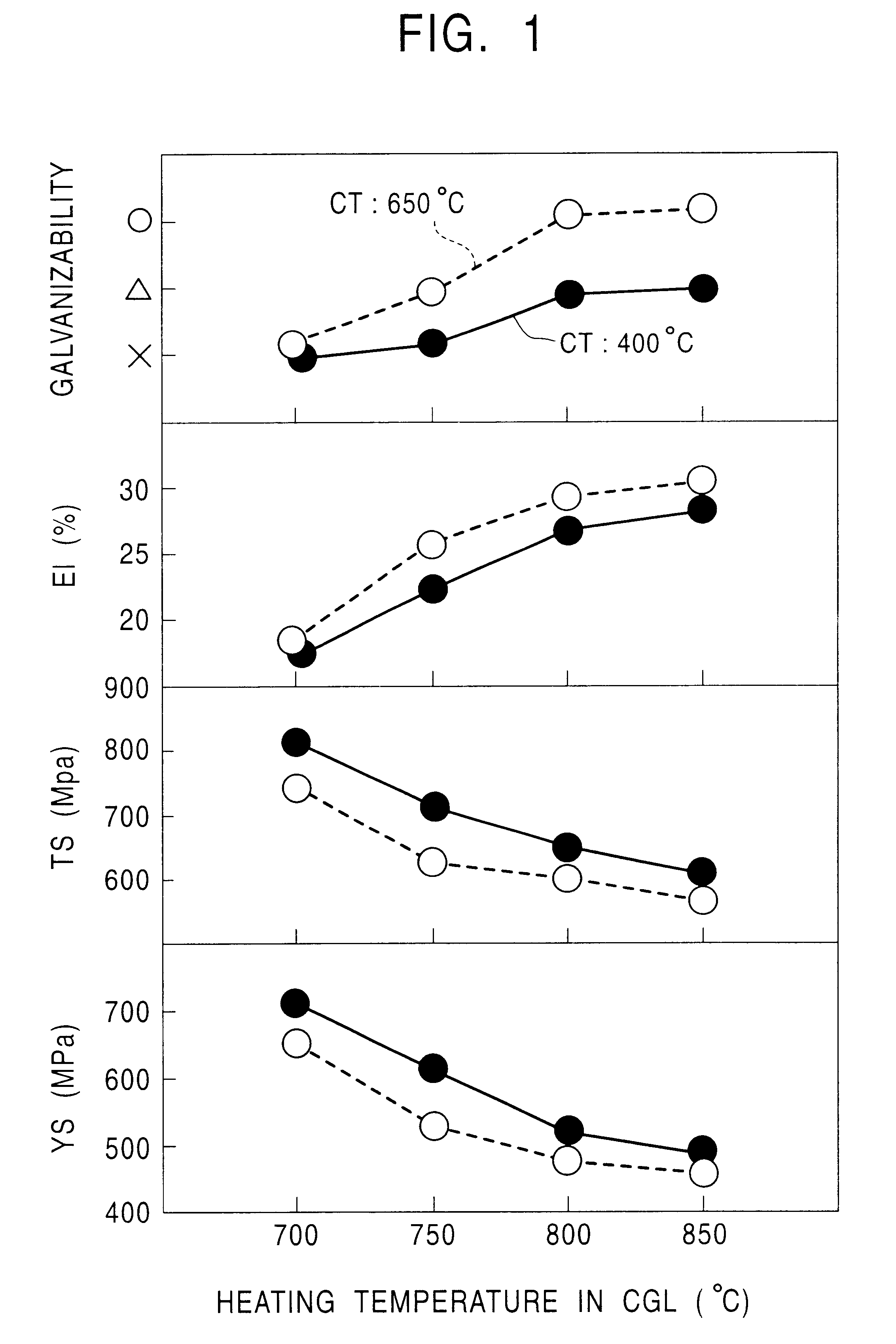
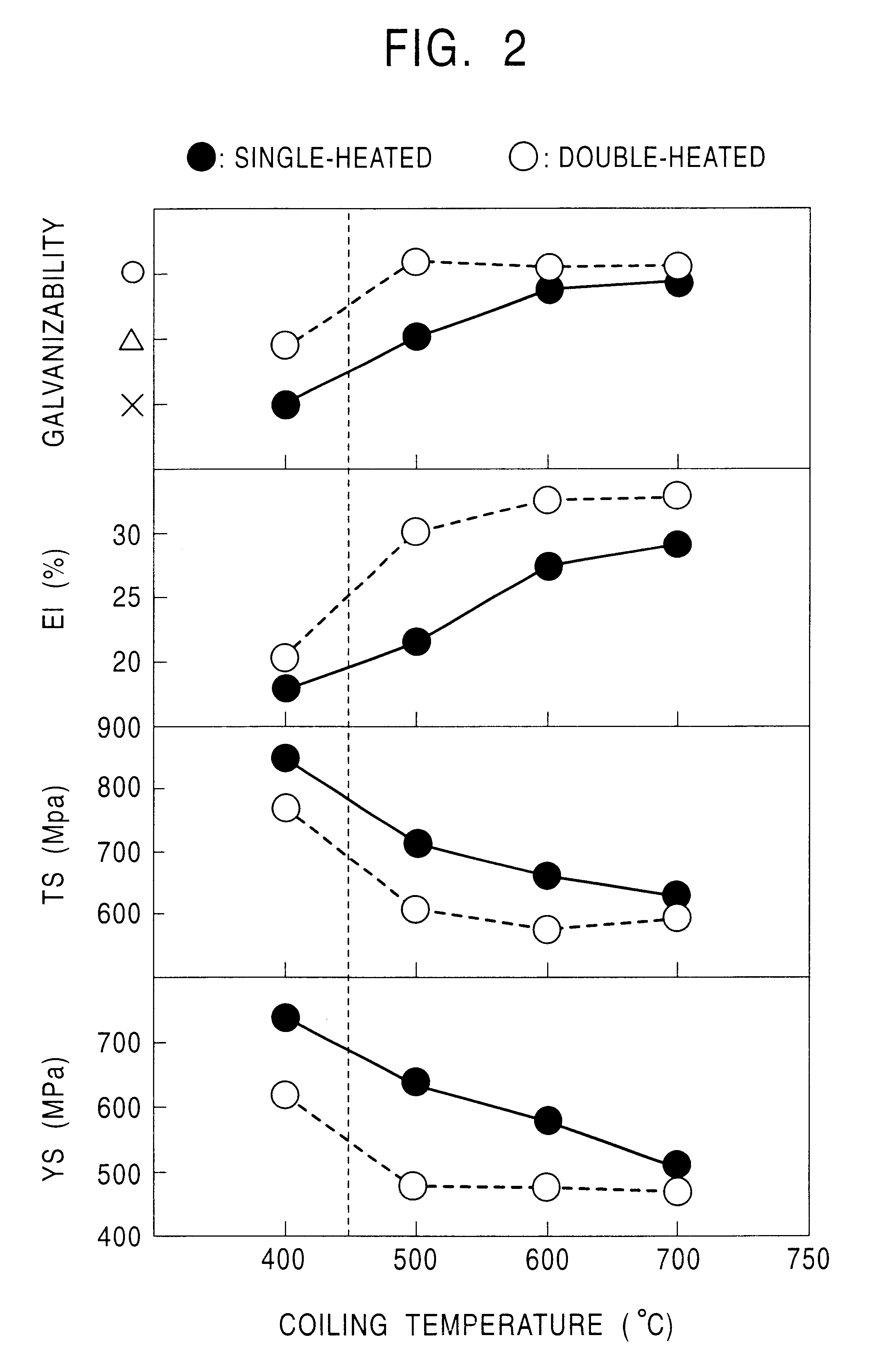
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet is produced by rough rolling a steel, finish rolling the rough rolled steel at a temperature of Ar3 point or more, coiling the finish rolled steel at a temperature of 700° C. or less, and hot-dip galvanizing the coiled steel at a pre-plating heating temperature of Ac1 to Ac3. A continuous hot-dip galvanizing operation is performed by soaking a pickled strip at a temperature of 750 to 850° C., cooling the soaked strip to a temperature range of 600° C. or less at a cooling rate of 1 to 50° C. per second, hot-dip galvanizing the cooled strip, and cooling the galvanized strip so that the residence time at 400 to 600° C. is within 200 seconds. The steel sheet has a structure consisting essentially of ferrite and martensite.
Owner:NIPPON KOKAN KK +1
Method for producing hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having high strength and also being excellent in formability and galvanizing property
InactiveUS6537394B1Satisfactory workabilityHigh strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelBand shape
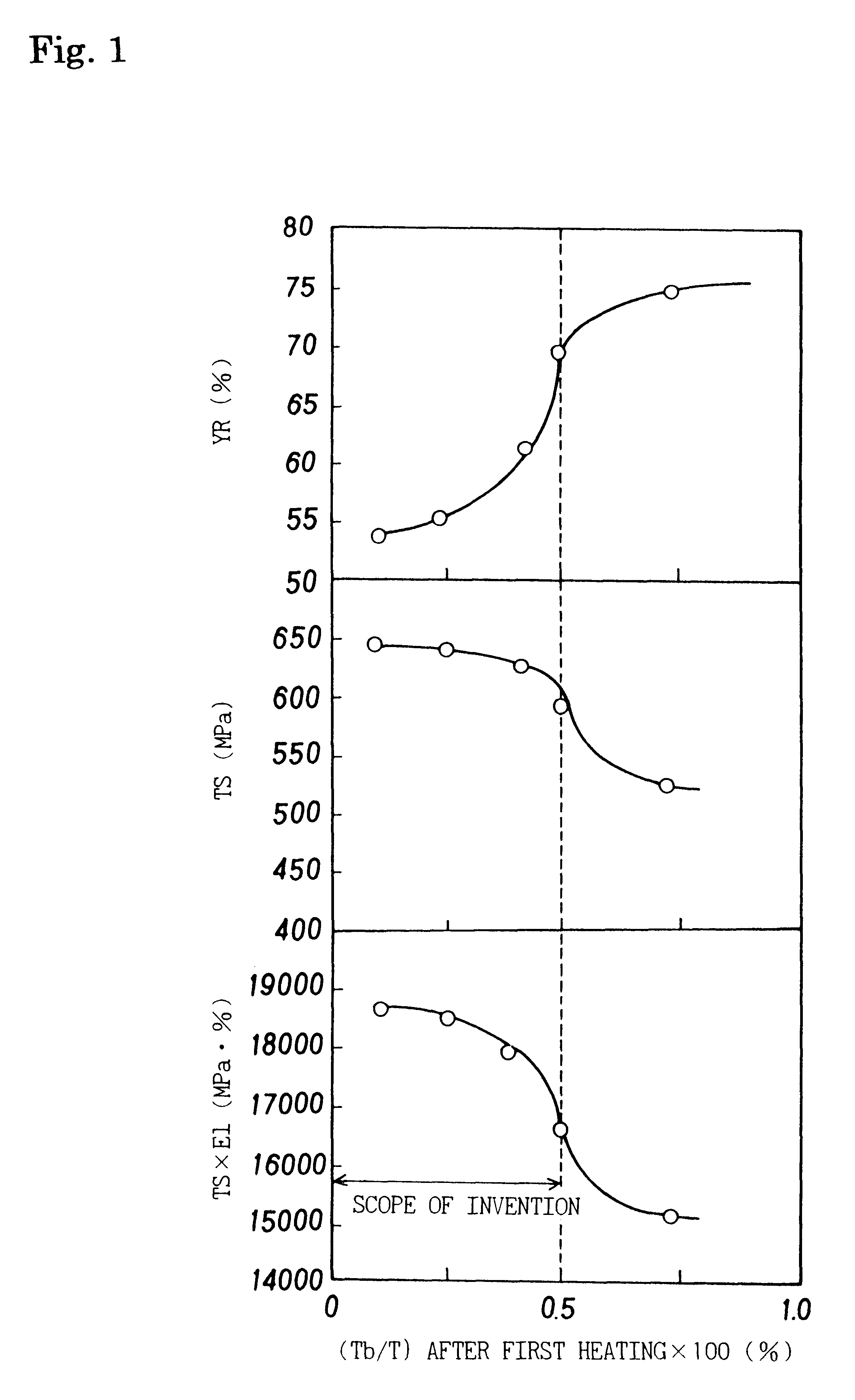
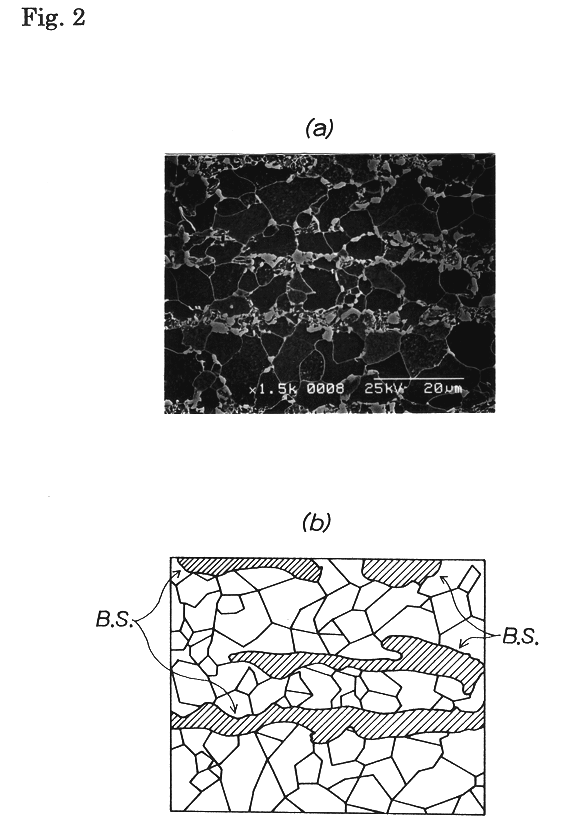
A hot-dip galvanized high-strength steel sheet having superior workability and galvanizability containing:0.01% to 0.20% by weight of C;1.0% by weight or less of Si;more than 1.5% to 3.0% by weight of Mn;0.10% by weight or less of P;0.05% by weight or less of S;0.10% by weight or less of Al;0.010% by weight or less of N;0.010% to 1.0% by weight in total of at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, Nb, and V; andthe balance being Fe and incidental impurities;in which the steel sheet has the metal structure in which the areal rate of the ferrite phase is 50% or more, the ferrite phase has an average grain diameter of 10 mum or less, and the thickness of a band-like structure composed of the second phase satisfies the relationship Tb / T<=0.005, where Tb is the average thickness in the sheet thickness direction of the band-like structure and T is the thickness of the steel sheet, and a method for producing the same. To provide a method for producing a hot-dip galvanized high-strength steel sheet in which superior workability and high strength are obtained and moreover satisfactory galvanizability is obtained when galvanizing is performed using facilities such as a continuous galvanizing line.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
Hot rolled steel plate, cold rolled steel plate and hot dip galvanized steel plate being excellent in strain aging hardening characteristics, and method for their production
InactiveUS20030111144A1Improve stamping formabilityGood strainHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelChemical composition
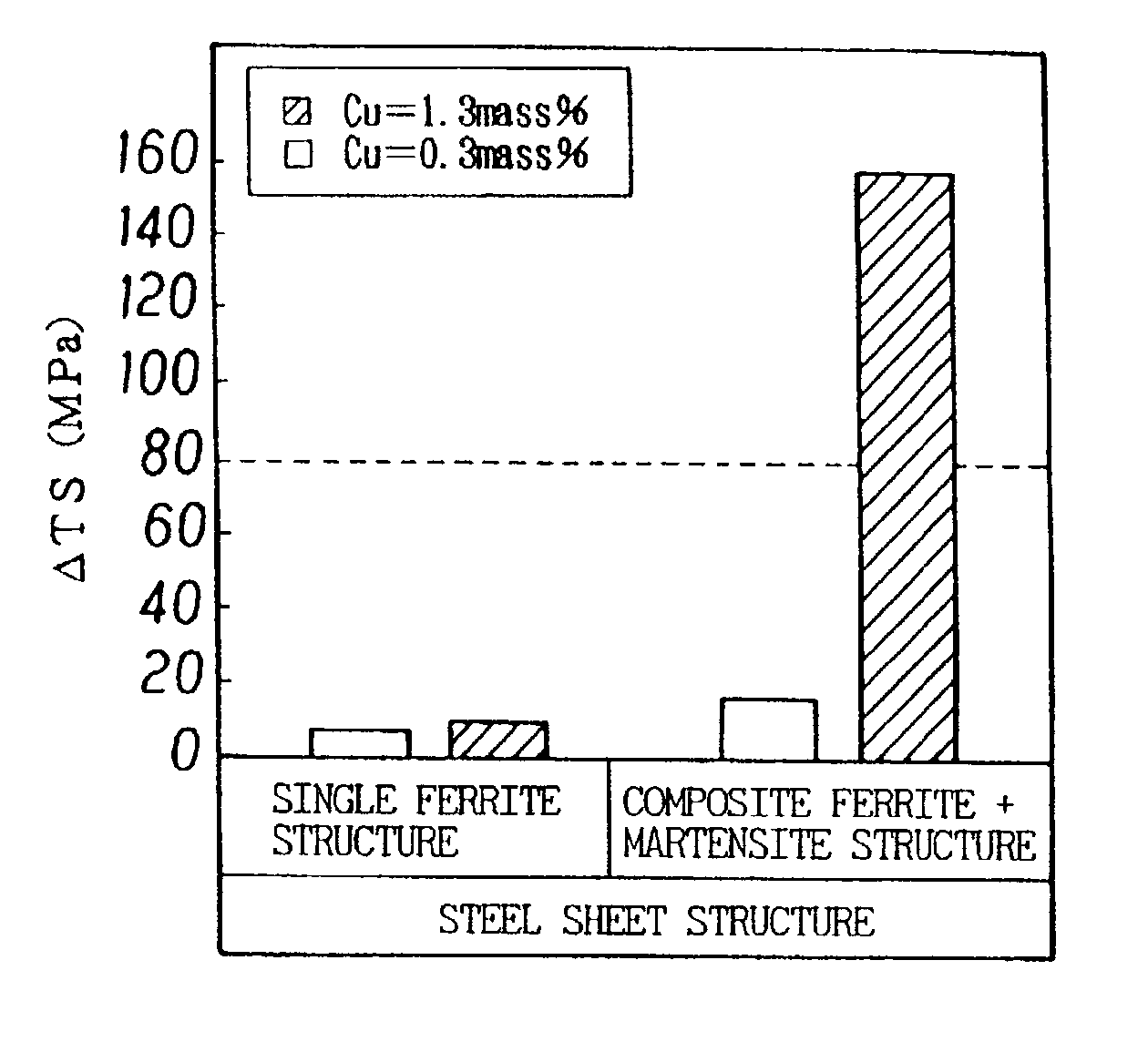
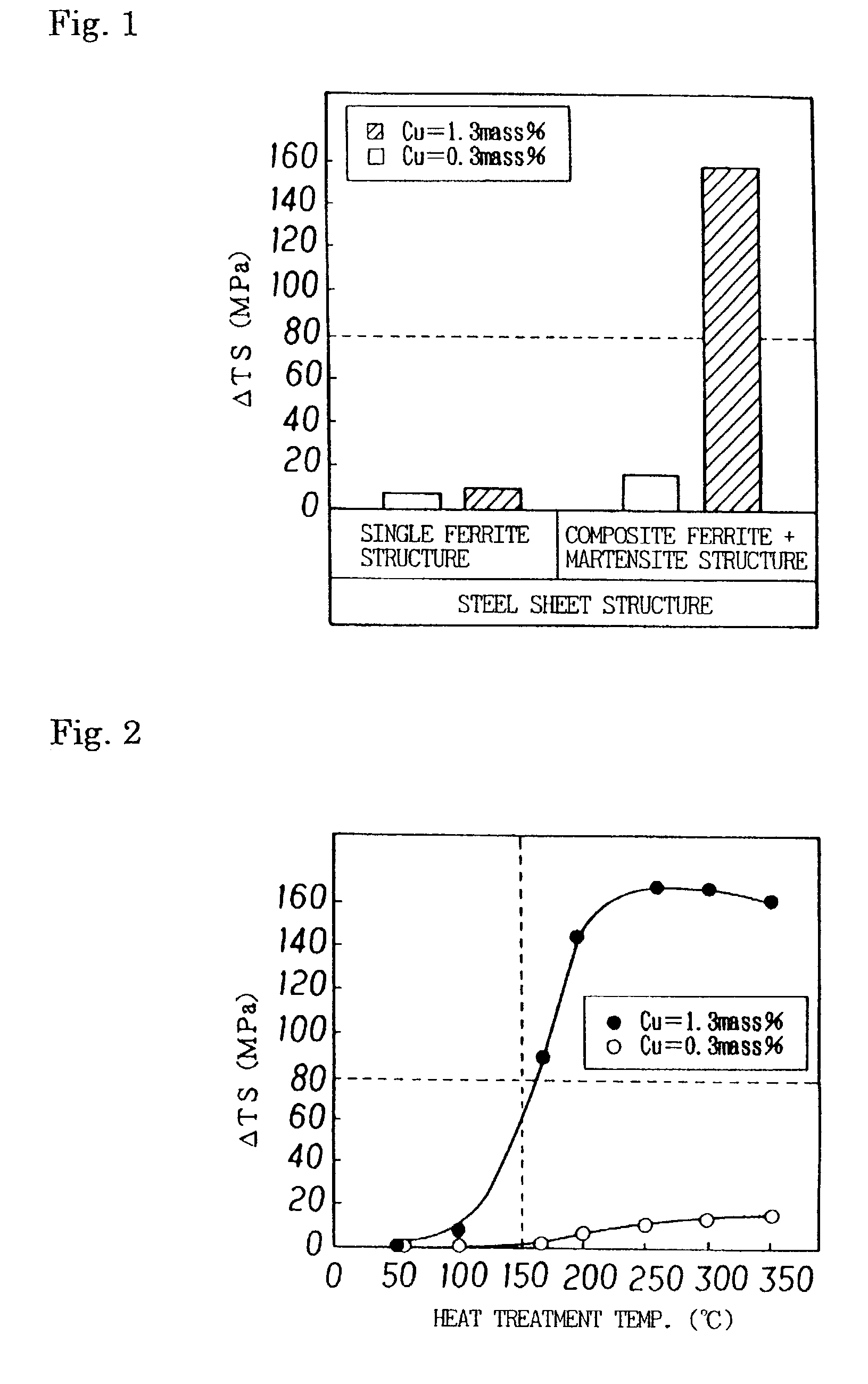
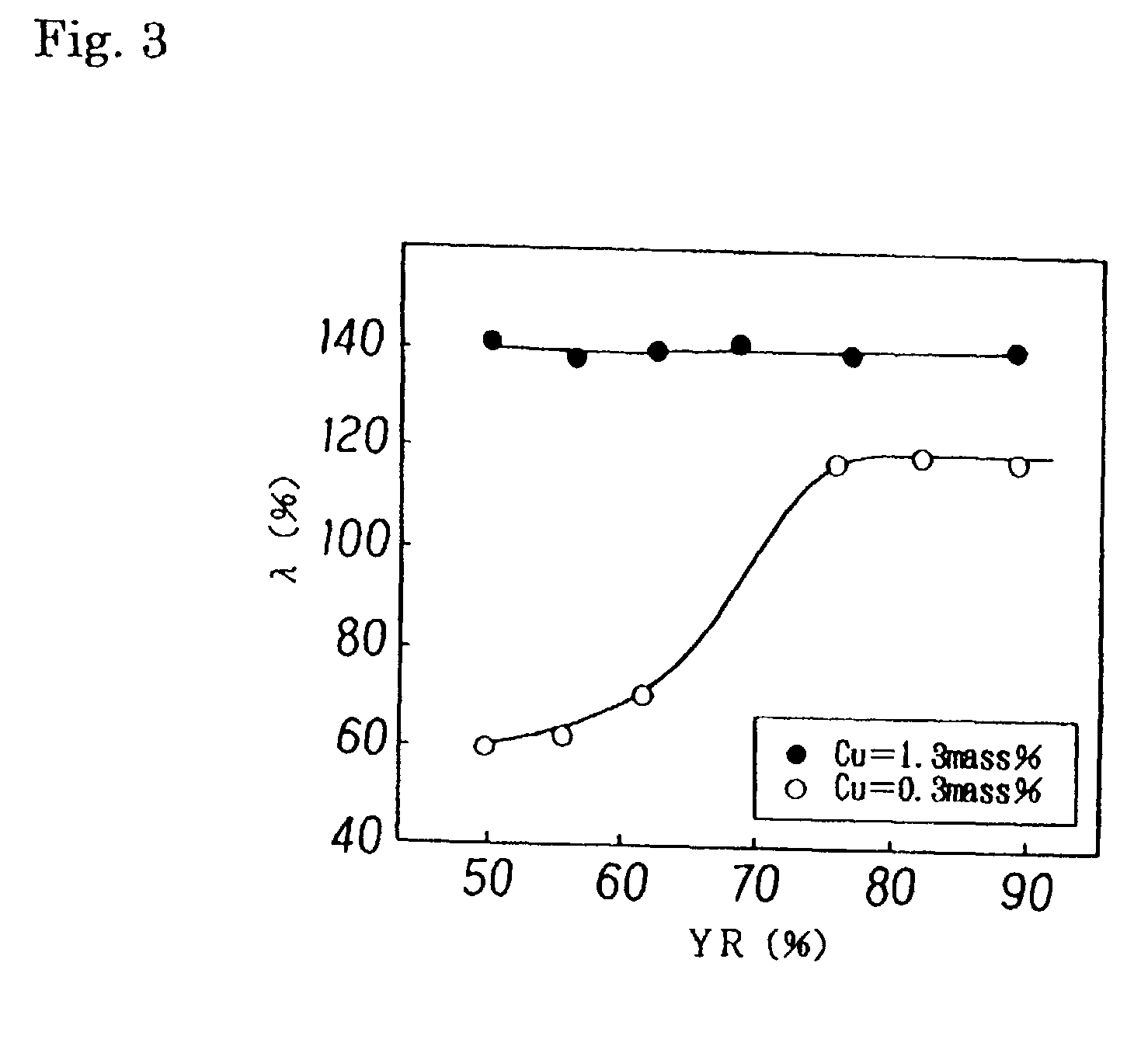
The present invention provides a steel sheet having a chemical composition comprising 0.15% or less C, 2.0% or less Si, 3.0% or less Mn, P, S, Al and N in adjusted amounts, from 0.5 to 3.0% Cu, or one or more of Cr, Mo and W in a total amount of 2.0% or less, and having a composite structure comprising ferrite and martensite having an area ratio of 2% or more. The steel sheet is in the form of a high-strength hot-rolled steel sheet, a high-strength cold-rolled steel sheet, or a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet. There is thus available a steel sheet excellent in press-formability and in strain age hardening property as represented by a DELTATS of 80 MPa or more.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Method for controlling alloyed hot dip galvanizing steel plate coating phase structure and alloyed hot dip galvanizing steel plate
InactiveCN101376956AGood chalking resistanceGood stamping performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelSurface roughness
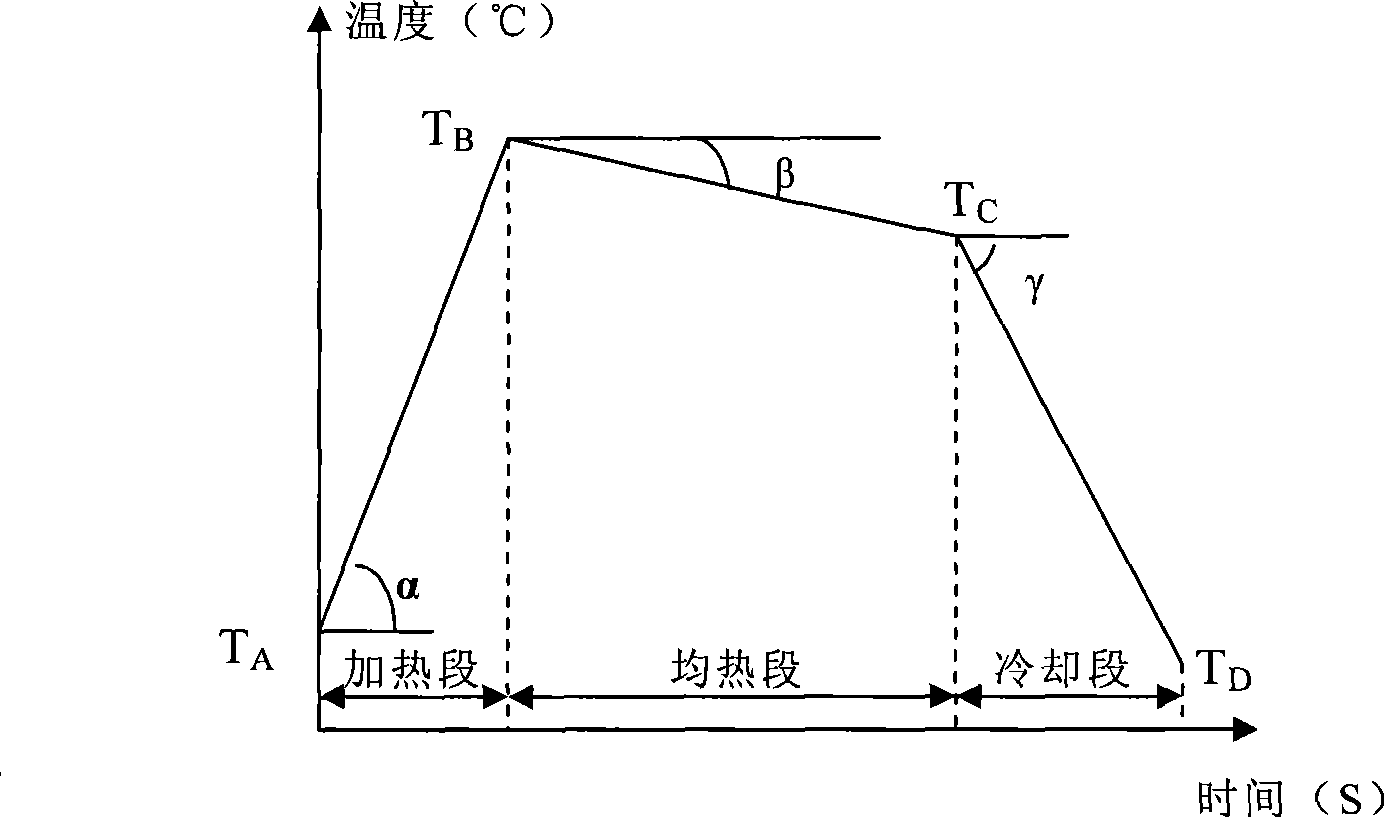
The invention provides a method for controlling alloyed hot-dip galvanized cladding, in particular hot-dip galvanized steel sheet cladding phase structure. The method comprises the following steps: at least a set of strip steel which is provided with a steel stabilizing device and can stably control hot-dip galvanization process parameters and air knife parameters to obtain even thickness of the cladding is arranged between an air knife and a top roller; an inclined alloyed cladding heat treatment annealing curve with even temperature sections from high temperature to low temperature is selected and the strip steel is evenly alloyed, to improve the evenness of the alloying process and the alloying degree of the strip steel cladding; in addition, flat roll surface roughness and flat extensibility are selected, to control the cladding surface roughness and cladding surface flat rate and improve the shaping performance of the steel sheet. The invention also provides an alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet manufactured by the method for controlling the alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet cladding phase structure; the hot-dip galvanized steel sheet has excellent cladding powder resistance and shaping performance, and is very applicable to automobile internal and external plates as well as household electric appliance external plates.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and process for producing same
ActiveCN102482753AImprove fatigue durabilityExcellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlementHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSoft layerHigh intensity
Disclosed is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet which comprises a steel sheet part and a deposit formed on the surface of the steel sheet part and has a tensile strength of 770 MPa or higher, wherein the deposit is a zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating or an alloyed zinc layer formed by hot-dip plating, the steel sheet part comprises a soft layer, which is in direct contact with the deposit, and an inner layer, which is the part other than the soft layer, and the thickness (D) of the soft layer is 0.001 to 5% of the thickness (t) of the steel sheet part. In a cross-section along the thickness direction of the steel sheet part, when the hardness of the soft layer measured by a nanoindentation method is expressed by H1 and the representative hardness of the steel sheet part measured by the nanoindentation method is expressed by Ha, then H1 is 5-75% of Ha.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot dip galvanized composite high strength steel sheet excellent in shapeability and hole enlargement ability and method of production of same
InactiveUS20070190353A1High strengthImprove adhesionHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesMartensite transformationAdditive ingredient
The present invention provides a hot dip galvanized composite high strength steel sheet excellent in shapeability and hole enlargement ability and a method of production of the same, that is, a hot dip galvanized composite high strength steel sheet excellent in shapeability and hole enlargement ability containing C: 0.01 to 0.3%, Si: 0.005 to 0.6%, Mn: 0.1 to 3.3%, P: 0.001 to 0.06%, S: 0.001 to 0.01%, Al: 0.01 to 1.8%, and N: 0.0005 to 0.01% and having a metal structure of ferrite and, by area rate, 5% to 60% of tempered martensite and a method of production of the same comprising hot rolling, then cold rolling a slab including the above ingredients, heating the sheet in the hot dip galvanization heating process to Ac1 l to Ac3+100° C., holding it there for 30 seconds to 30 minutes, then cooling it by a 1° C. / s or higher cooling rate to 450 to 600° C., hot dip galvanizing it at that temperature, then cooling it at a 1° C. / s or higher cooling rate to the martensite transformation point or lower in temperature, holding it there at 200° C. to 500° C. for 1 second to 5 minutes, then cooling it at a 5° C. / s or higher cooling rate to 100° C. or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High Corrosion Resistance Hot dip Galvanized Steel Material
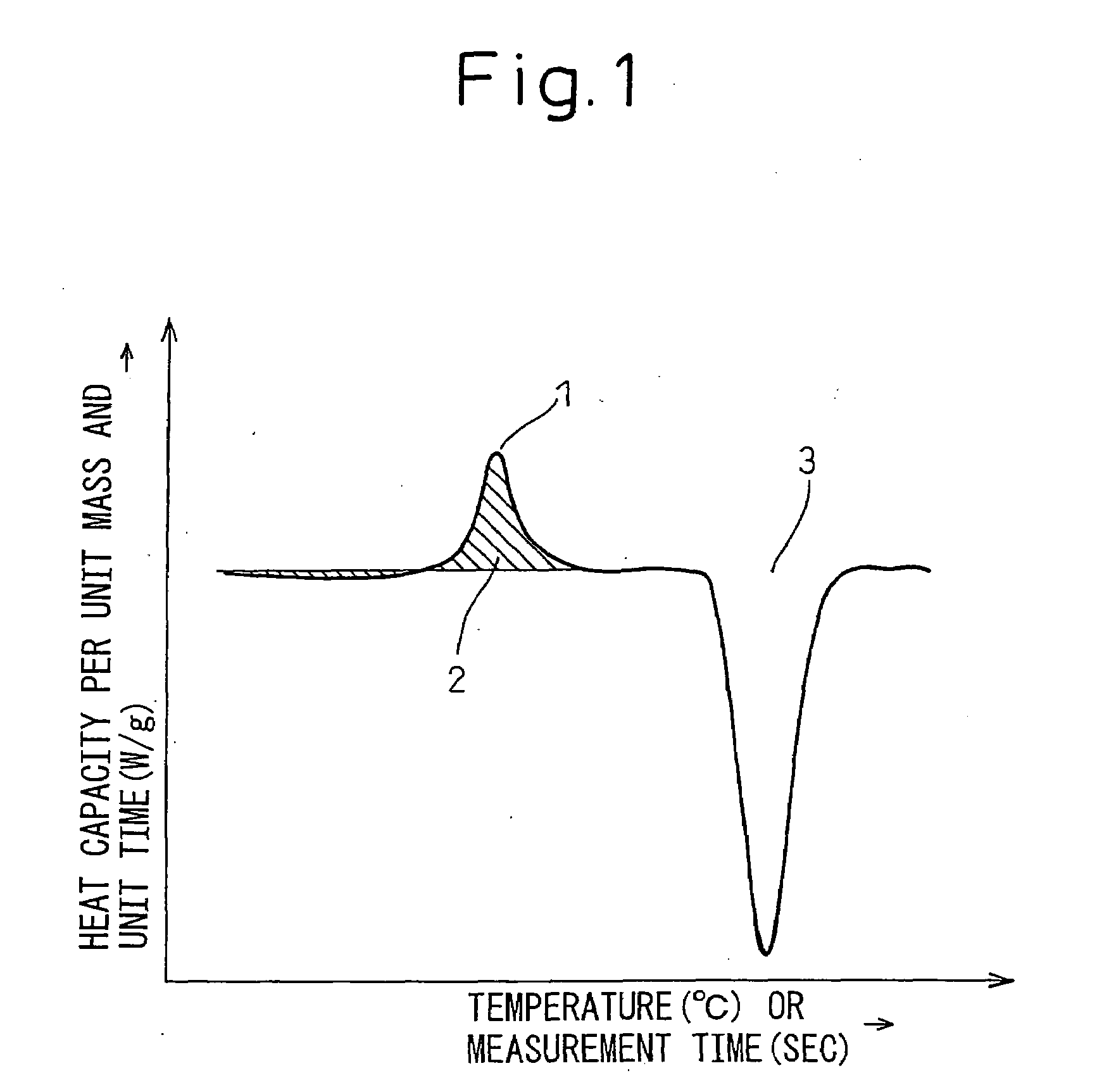
InactiveUS20090053555A1Improve corrosion resistanceSuppressing degradationHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingAmorphous phaseAlloy
The present invention provides a high corrosion resistance hot dip galvannealed steel material comprised of a Zn-based hot dip plated steel material achieving both a higher corrosion resistance of the plated layer itself by the added elements and sacrificial protection of iron metal by the plated layer or workability free of degradation caused of formation of intermetallic compounds by added elements, that is, a high corrosion resistance hot dip Zn plated steel material characterized in that an alloy plated layer containing Zn: 35 mass % or more, preferably 40 mass % or more, contains a non-equilibrium phase having a heat capacity by differential scanning calorimetry of 1 J / g or more. Furthermore, 5% or more, preferably 50% or more in terms of vol % is an amorphous phase. The alloy layer may contain, by mass %, Mg: 1 to 60% and Al: 0.07 to 59%, may further contain one or more elements selected from Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu in a total of 0.1 to 10%, and may in addition contain one or more elements of 0.1 to 10% of La, 0.1 to 10% of Ce, 0.1 to 10% of Ca, 0.1 to 10% of Sn, 0.005 to 2% of P, and 0.02 to 7% of Si.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent plating qualities, plating adhesion and spot weldability and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20120100391A1Extended service lifeImproving the plating qualities and plating adhesion of the galvanized steel sheetHot-dipping/immersion processesPretreated surfacesSheet steelElectroplating
Provided is a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent plating qualities, plating adhesion and spot weldability, in which an alloy phase is formed at the interface between a base steel sheet and a galvanized layer, and a manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and high-strength alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet excellent in mechanical cutting property, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140287263A1High densityImprove work hardening abilityHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesSheet steelSurface layer
There is provided a high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and the like excellent in mechanical cutting property, which are capable of obtaining high ductility while ensuring high strength with maximum tensile strength of 900 MPa or more. The high-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet has a sheet thickness of 0.6 to 5.0 mm and has a plating layer on a surface of a steel sheet with component compositions being set in appropriate ranges, in which the steel sheet structure contains a 40 to 90% ferrite phase and a 3% or more retained austenite phase by volume fraction. In the retained austenite phase, a solid solution carbon amount is 0.70 to 1.00%, an average grain diameter is 2.0 μm or less, an average distance between grains is 0.1 to 5.0 μm, a thickness of a decarburized layer in a steel sheet surface layer portion is 0.01 to 10.0 μm, an average grain diameter of oxides contained in the steel, sheet surface layer portion is 30 to 120 nm and an average density thereof is 1.0×1012 oxides / m2 or more, and moreover, a work hardening coefficient (n value) during a 3 to 7% plastic deformation is 0.080 or more on average.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High strength thin steel sheet, high strength alloyed hot-dip zinc-coated steel sheet, and method for producing them
InactiveUS6410163B1Improve the plating effectImproving threadabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelHigh intensity
The present invention provides a high strength thin excellent workability and galvanizability, having a composition comprising from 0.01 to 0.20 wt. % C, up to 1.0 wt. % Si, from 1.0 to 3.0 wt. % Mn, up to 0.10 wt. % P, up to 0.05 wt. % S, up to 0.10 wt. % Al, up to 0.010 wt. % N, up to 1.0 wt. % Cr, from 0.001 to 1.00 wt. % Mo, and the balance Fe and incidental impurities, wherein a band structure comprising a secondary phase has a thickness satisfying the relation Tb / T<=0.005 (where, Tb: average thickness of the band structure in the thickness direction of steel sheet; T: steel sheet thickness), and a manufacturing method thereof, and a manufacturing method of a high strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet or a high strength galvannealed steel sheet applying hot-dip galvanizing or further galvannealing, and giving an excellent workability, a high tensile strength, and excellent galvanizability, coating adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Owner:KAWASAKI STEEL CORP
High-strength hot-dip zinced steel sheet excellent in moldability and suitability for plating, high-strength alloyed hot-dip zinced steel sheet, and processes and apparatus for producing these
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
High mn steel sheet for high corrosion resistance and method of manufacturing galvanizing the steel sheet
InactiveUS20090053556A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove ductilityHot-dipping/immersion processesLiquid surface applicatorsSheet steelHigh intensity
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High young's modulus steel plate, zinc hot dip galvanized steel sheet using the same, alloyed zinc hot dip galvanized steel sheet, high young's modulus steel pipe, and method for production thereof
InactiveCN1989267AExcellent Young's modulusDeveloped shear textureFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesChemical compositionYoung's modulus
An embodiment of a high Young's modulus steel sheet, wherein it has a chemical composition, in mass %, that C: 0.0005 to 0.30 %, Si: 2.5 % or less, Mn: 2.7 to 5.0 %, P: 0.15 % or less, S: 0.015 % or less, Mo: 0.15 to 1.5 %, B: 0.0006 to 0.01%, Al: 0.15 % or less, and the balance: Fe and inevitable impurities.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Flux and process for hot dip galvanization
ActiveUS20070137731A1Convenient coatingHigh concentrationHot-dipping/immersion processesWelding/cutting media/materialsAlcoholHydrophile
A flux for use in a hot dip galvanization process has an acidic component so that the flux has a pH of about 1.5 or less. The flux also includes an alkali metal chloride and a nonionic surfactant containing polyoxyethylenated straight-chain alcohols with a hydrophile-lipophile balance (HLB) of less than 11. Depending on the particular application, the flux also includes other components, such as ferric chloride, an inhibitor containing an amino derivative and bismuth oxide.
Owner:TECK METALS +1
Batch hot-dip galvanizing chromium-free passivator and application method thereof
ActiveCN104018148AAchieve qualityAchieve corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesOrganic filmChromium free
The invention discloses a batch hot-dip galvanizing chromium-free passivator and an application method thereof. According to the invention, toxic and harmful hexavalent chromium and trivalent chromium used in a traditional passivation process are replaced with an organic film-former, so that a chromium-free passivator which does not contain chromates, can be used at room temperature, is low in cost, good in corrosion resistance and easy to use, and can be practically applied to industrial production is provided for passivation treatment in the batch hot-dip galvanizing industry. The chromium-free passivator mainly comprises an organic film-former, an organic corrosion inhibitor, an oxidant, a surfactant and water. The chromium-free passivator disclosed by the invention is easy to use and simple in operation, and has no change in existing processes.
Owner:宁波华印表面工程材料科技有限公司 +1
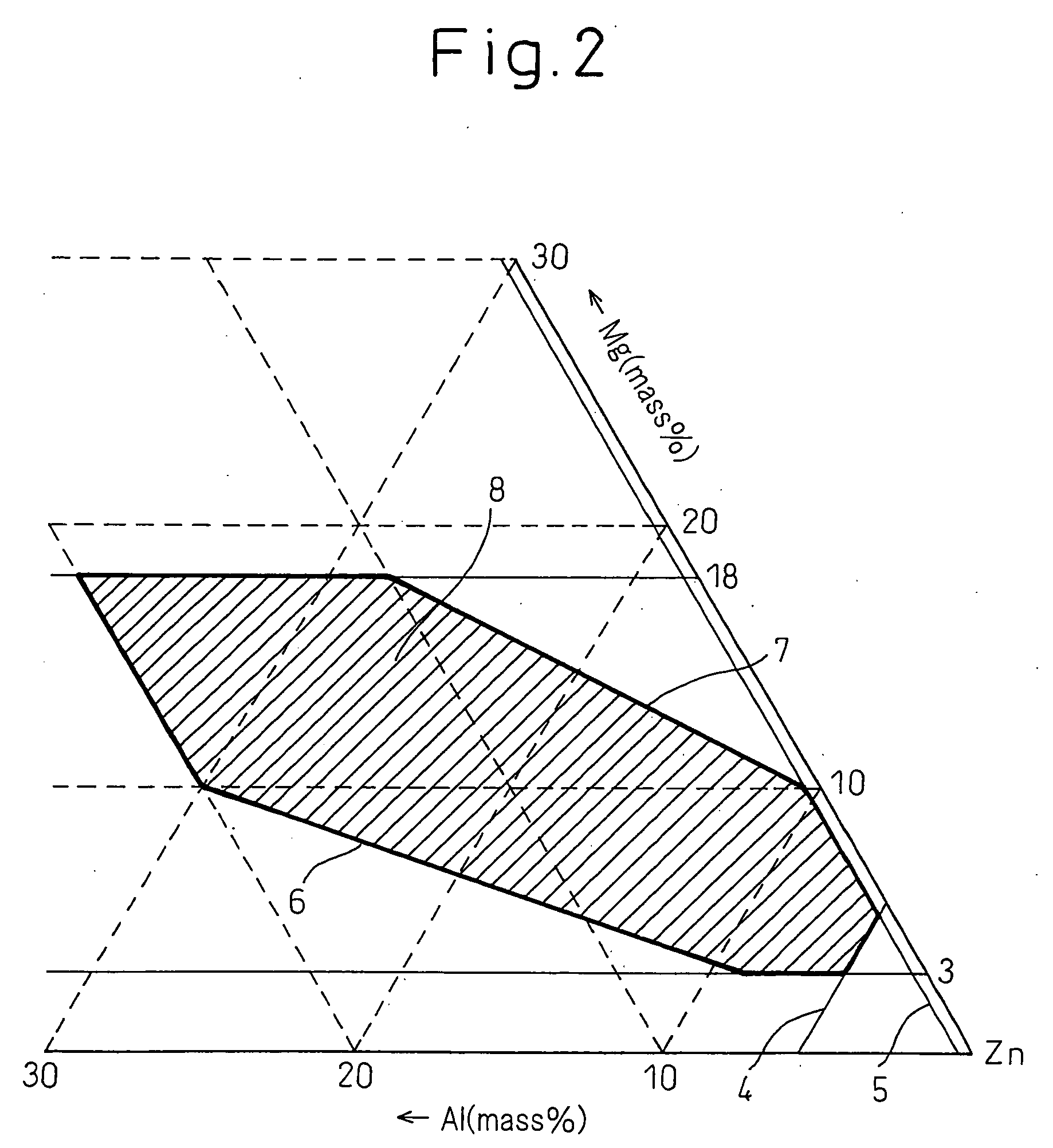
Alloyed zinc aluminum magnesium alloy coated steel plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN103507324AImprove corrosion resistanceGood formabilityHot-dipping/immersion processesMetal layered productsRare earthAir knife
The invention provides an alloyed zinc aluminum magnesium alloy coated steel plate and a production method thereof. The coating has an Fe content of not more than 5%, the coating surface contains an MgZn2 phase, which has a particle size of not greater than 5 micrometers. The coating surface is in the form of equiaxed grains, and in the coating, Mg accounts for 1.5-8wt%, aluminum accounts for 1.5-15wt%, and rare earth accounts for 0-0.2wt%. According to the production method, cold rolled strip steel is subjected to continuous annealing and hot dipping in a continuous hot dip galvanizing unit, and then alloy treatment is carried out on the hot-dip galvanized zinc aluminum magnesium steel plate. Chemically, a plating solution comprises 1.0-11wt% of Al, 0.5-5wt% of Mg, and the balance Zn and inevitable impurities. After the steel plate undergoes annealing by N2 containing 0.5%-30 vol % of H2, the steel plate is immersed in the plating solution at a temperature of 450-650DEG C, the steel plate enters a zinc pot at 420-580DEG C, and the immersion plating time of the steel plate in the plating solution is 1-10s. After air knife cooling, the zinc aluminum magnesium steel plate enters an alloying furnace to undergo alloying treatment, the alloying temperature is 450-650DEG C, the alloying time is 3-20s, and then the steel plate is cooled at a speed of 10-50DEG C / s. The steel plate provided by the invention ensures that the coating does not fall off in a complex forming process, and after forming, the zinc aluminum magnesium coating can put its excellent corrosion resistance to good use, thus prolonging the service life of components.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet excellent in impact resistance property and manufacturing method thereof, and high-strength alloyed hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140227555A1Improve impact resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingDecarburizationSheet structure
A base steel sheet has a hot-dip galvanized layer formed on a surface thereof, in which, in a steel sheet structure in a range of ⅛ thickness to ⅜ thickness centered around ¼ thickness of a sheet thickness from a surface, a volume fraction of a retained austenite phase is 5% or less, and a total volume fraction of phases of bainite, bainitic ferrite, fresh martensite, and tempered martensite is 40% or more, an average effective crystal grain diameter is 5.0 μm or less, a maximum effective crystal grain diameter is 20 μm or less, and a decarburized layer with a thickness of 0.01 μm to 10.0 μm is formed on a surface layer portion, in which a density of oxides dispersed in the decarburized layer is 1.0×1012 to 1.0×1016 oxides / m2, and an average grain diameter of the oxides is 500 nm or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Axle sleeve and bush for zinc plating pot roller and its making method
The present invention relates to an axle sleeve, an axle bush and a manufacture method used on the zinc pot roller in the continuous hot dip galvanizing production line in steel and metallurgy fields. The method of oxygen-fuel gas spray welding or plasma spray welding or laser melting is adopted, the cobalt-based or cobalt-based wire stock or powder is sprayed or melted on the matching surface of the axle sleeve and the axle bush to form a surface strengthened layer with the thickness of 2 to 5 mm. The axle sleeve and the axle bush manufactured through the method of the present invention greatly enhances the zinc resistance or aluminum zinc corrosion and friction resistance performance, the combination performance is good, the present invention is not easy to break off, and the service life is lengthened. The method can be suitable for preparation of a thick coating layer, and is simple and convenient, the cost is lower, and the utilization cost and the production cost of the enterprise can be directly reduced. The method can be used as the processing method of the parts which are mutually contacted and have opposite motion in the similar zinc or aluminum zinc solution corrosion environment to lengthen the service life.
Owner:常州杰耐机械有限公司
High Mn steel sheet for high corrosion resistance and method of manufacturing galvanizing the steel sheet
InactiveCN101346489AImprove ductilityImprove corrosion resistanceHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingSheet steelHigh intensity
Disclosed herein are a high-manganese hot-dip coated steel sheet exhibiting high ductility and high strength, mainly used for inner and outer panels of automobiles, and a method of manufacturing the same. The high-manganese hot-dip coated steel sheet includes a substrate steel sheet having a composition of (in weight %) 0.1 to 1.5 % of C, 5 to 35 % of Mn, and the remainder including Fe and other unavoidable impurities, and a hot-dip zinc coating layer formed on the substrate steel sheet, the hot-dip zinc coating layer containing only Zn, or an alloying hot-dip coating layer formed on the substrate steel sheet, the alloying hot-dip coating layer having a composition of (in weight %) 0.1 to 10 % of Mn, 5 to 15 % of Fe, and the remainder including Zn and other unavoidable impurities. Consequently, the hot-dip coated steel sheet according to the present invention exhibits high corrosion resistance as well as high strength and high ductility.
Owner:POHANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
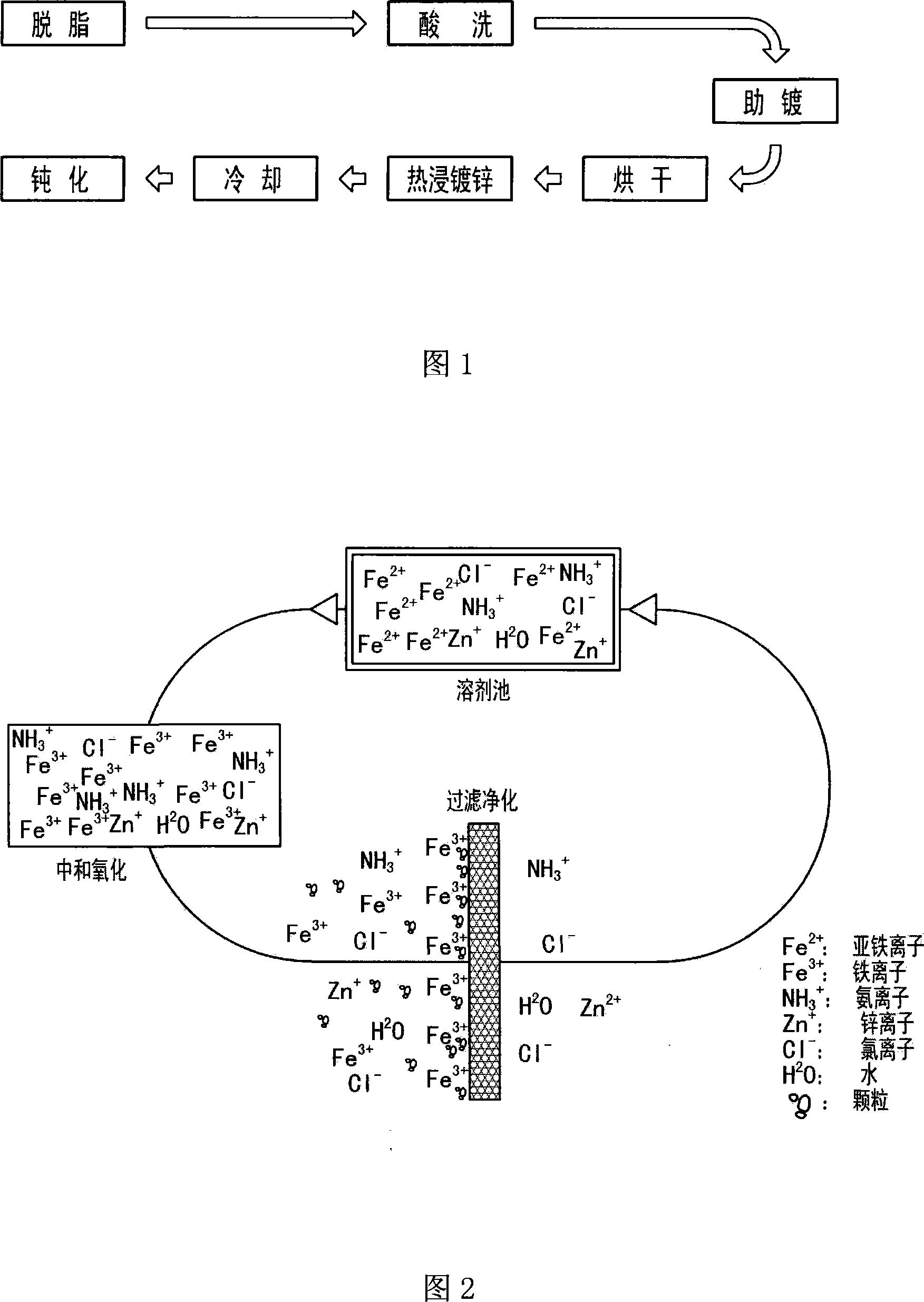
Hot dip galvanizing method of steel structural members
The invention relates to a hot dip galvanizing method of steel structural members, comprising the following steps of: 1) preparing before galvanization; 2) degreasing; 3) cleaning degreased raffinate; 4) pickling; 5) cleaning pickled raffinate; 6) activating a steel structural member matrix; 7) applying a plating-assistant solvent; 8) drying the moisture in the plating-assistant solvent; 9) hot dip galvanizing; 10) cooling in the air and removing residual zinc; 11) cooling in water; 12) drying the moisture; and 13) examining. The invention further provides the relative component formula of various treatment fluids used during the galvanizing process in the above method, and provides the most ideal working condition parameters in each step of the galvanizing process. Processed by the hot dip galvanizing technology, the steel structural members have advantages of excellent integrity of the coating, high bonding strength, flat and smooth appearance and high qualified rate of products.
Owner:BEIJING JJRS TECH DEV +1
High-strength hot-dip galvanized steel sheet having excellent delayed fracture resistance and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20140234659A1Improve fracture resistanceSmall anisotropyHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesDiameter ratioMaterials science
A hot-dip galvanizing layer or an alloyed hot dip galvanizing layer is formed on the surface of a base steel sheet in which in volume fraction, 40 to 90% of a ferrite phase and 5% or less of a retained austenite phase are contained, and a ratio of non-recrystallized ferrite to the entire ferrite phase is 50% or less in volume fraction, and further a grain diameter ratio being a value of, of crystal grains in the ferrite phase, an average grain diameter in the rolling direction divided by an average grain diameter in the sheet width direction is 0.75 to 1.33, a length ratio being a value of, of hard structures dispersed in island shapes, an average length in the rolling direction divided by an average length in the sheet width direction is 0.75 to 1.33, and an average aspect ratio of inclusions is 5.0 or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Hot dip galvanizing method for steel pieces
ActiveCN101092682ALong corrosion lifeImprove uniformityHot-dipping/immersion processesRare-earth elementAlloy
This invention discloses a method for hot-dip galvanizing on steel work piece. The method comprises: checking black work piece, suspending, degreasing, rinsing, washing with acid, rinsing, treating with a galvanizing aid, drying with hot air, hot-dip galvanizing and cooling. During the hot-dip galvanizing process, Al, Ni, Si and rare earth element are added into the galvanizing solution. The galvanizing solution comprises: Al 7-9 wt. %, Ni 3-6 wt. %, Si 0.5-0.8 wt. %, rare earth element 0.5-1.0 wt. %, and Zn as balance. The addition of Si can reduce Fe content in the galvanizing solution, and the formation of Zn-Fe alloy residue. The Zn consumption is lowered by nearly 1%, and the surface quality of galvanized steel is improved.
Owner:南京大吉铁塔制造有限公司
Non-poaching-water common hot-dip galvanizing technique
InactiveCN101215682AZero emissionGuarantee the quality of galvanizingHot-dipping/immersion processesWater sourceRinse water
The invention relates to a hot-dip galvanizing process, in particular to a common hot-dip galvanizing process without rinse water, which aims to solve the technical problems existing in prior art that after being treated, if industrial wastewater which is produced during hot-dip galvanizing is discharged reaching the standard, galvanizing needs to consume a large number of water source, and the treatment cost is greatly increased and the like. The steps of common hot-dip galvanizing process without rinse water of the invention comprises degreasing, cleaning and plating auxiliary, wherein to-be-galvanized workpieces are dipped in assisted plating solution, whose components are aqueous solution of ZnCl2 and NH4Cl, the PH valve of the assisted plating solution is adjusted through adding ammonia water, then Fe2+ on the surface of the workpiece is changed into Fe3+ through hydrogen peroxide solution, and then the Fe3+ is filtered out through a filter purification device, a layer of assisted plating film is formed on the surface of the workpiece, drying, hot-dip galvanizing, cooling and inactivating.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGDA STEEL TOWER +1
Hot-dip zinc aluminum magnesium silicon rare earth coated steel strips taking air as air source of air knife during production
InactiveCN101812653AEvenly distributedUniform tissue structureHot-dipping/immersion processesCeriumAir knife
The invention relates to hot-dip zinc aluminum magnesium silicon rare earth coated steel strips taking air as an air source of an air knife during production. The coating material on the surface of the steel strips comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 9.9 to 12.1 percent of Al, 1.0 to 1.8 percent of Mg, 0.18 to 0.22 percent of Si, 0.01 to 0.3 percent of rare earth (RE), and the balance of Zn. Based on a quaternary component Zn-Al-Mg-Si in Nippon Steel, the rare earth (RE) comprising lanthanum and cerium is added into the coating material so as to become a quintuple component Zn-Al-Mg-Si-RE, and the content of the magnesium is reduced. Because of the addition of the trace RE, the component distribution of the coating can become more uniform, the organizational structure is more uniform, and the corrosion resistance is further improved based on the original corrosion resistance; and because the content of the magnesium is reduced properly, the coating can bear the blowing of the air knife and cannot be oxidized and discolored on the premise of ensuring high corrosion resistance, and meets the requirements of the corrosion resistance and apparent mass.
Owner:梁士臣
Zinc hot dip galvanized steel plate excellent in press formability and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20050139291A1Not degradedHot-dipping/immersion processesSolid state diffusion coatingFormabilityHot-dip galvanization
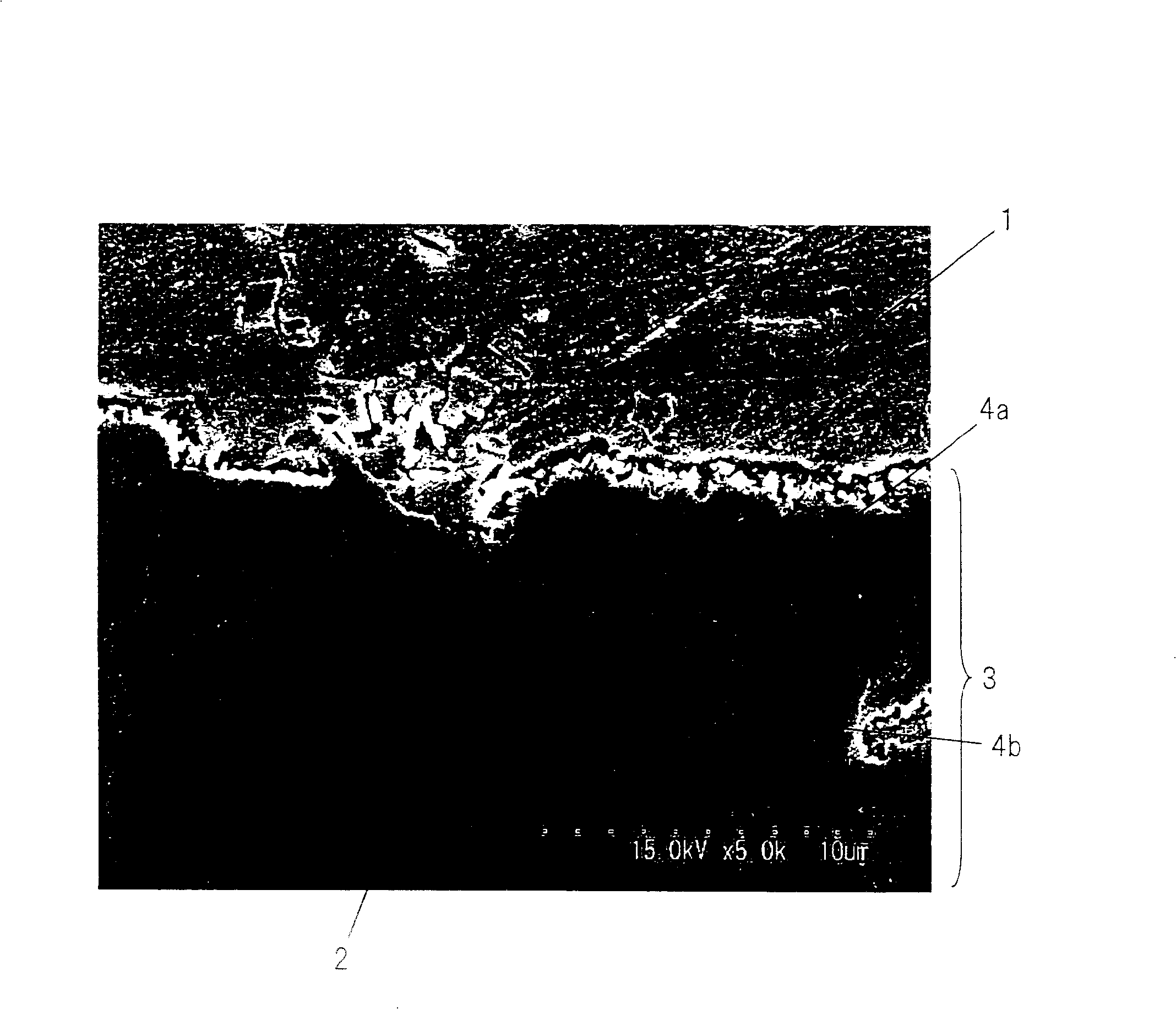
A hot-dip galvanized steel sheet includes a plating layer substantially composed of the η phase and an oxide layer disposed on a surface of the plating layer. The oxide layer has an average thickness of 10 nm or more and includes a Zn-based oxide layer and an Al-based oxide layer. A method for producing the hot-dip galvanized steel sheet includes a hot-dip galvanization step, a temper rolling step, and an oxidation step.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Process of production and production system of high strength galvannealed steel sheet
ActiveUS20070051438A1High strengthHot-dipping/immersion processesFurnace typesHigh intensityEquipment use
A process of production for producing a high strength galvannealed steel sheet by a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet production equipment using an all radiant tube type annealing furnace and a production equipment for the same are provided, comprising continuously hot-dip galvanizing a high strength steel sheet having a content of Si of 0.4 to 2.0 wt % during which making the atmosphere of the reducing zone an atmosphere containing H2 to 1 to 60 wt % and comprised of the balance of N2, H2O, O2, CO2, CO, and unavoidable impurities, controlling the log(PCO2 / PH2) of the carbon dioxide partial pressure and hydrogen partial pressure in the atmosphere to log(PCO2 / PH2)≦−0.5 and the log(PCO2 / PH2) of the water partial pressure and hydrogen partial pressure to log(PH2O / PH2)≦−0.5, and controlling the log(PT / PH2) of the total partial pressure PT of the carbon dioxide partial pressure PCO2 and water partial pressure PH2O and the hydrogen partial pressure to −3≦log(PT / PH2)≦−0.5.
Owner:USINOR SA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com