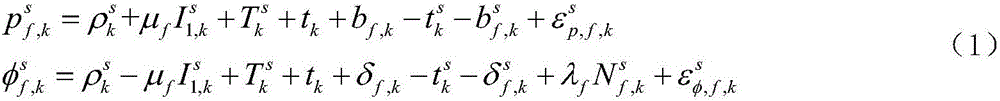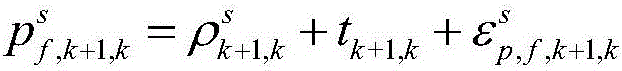Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105 results about "Single difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
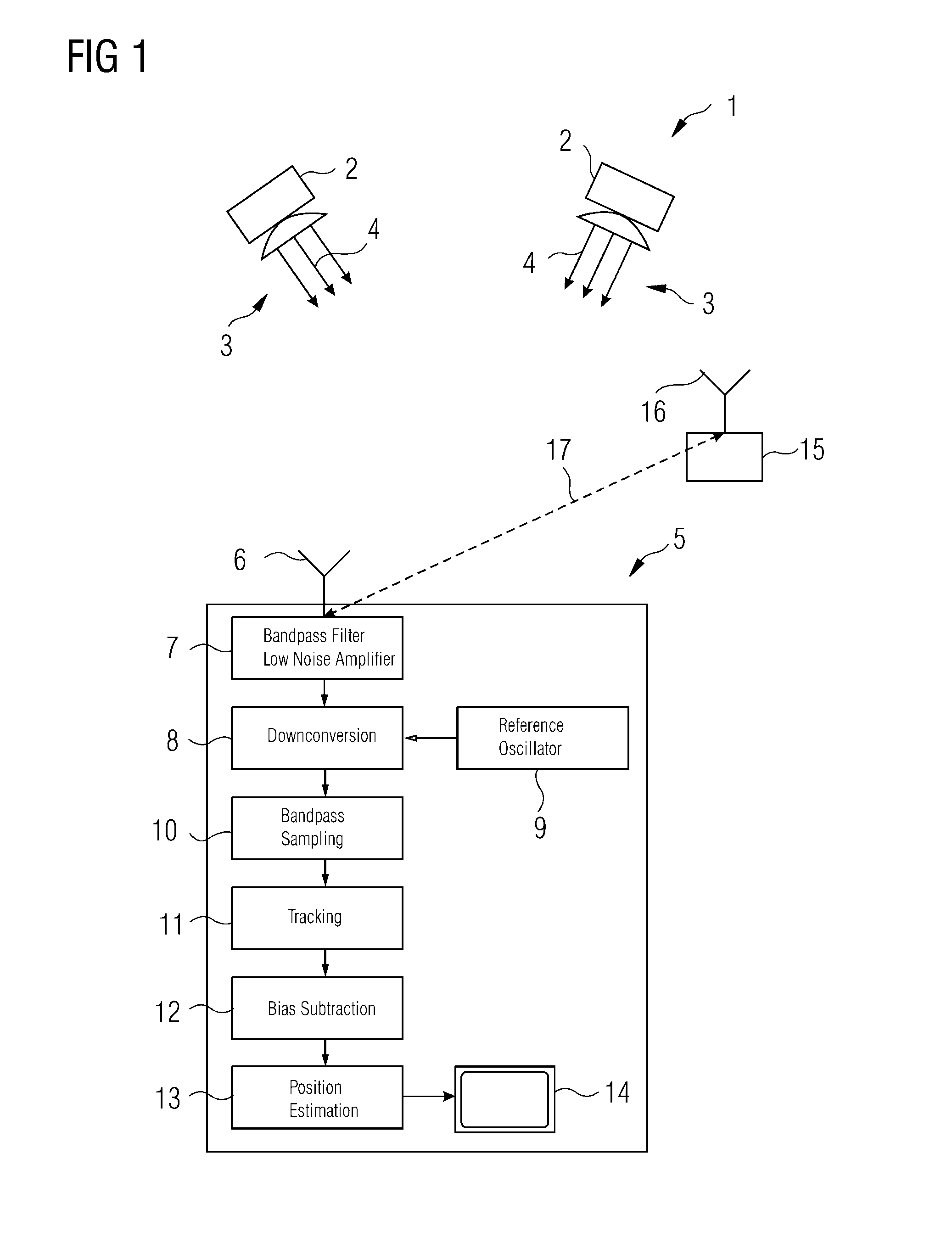
Carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus
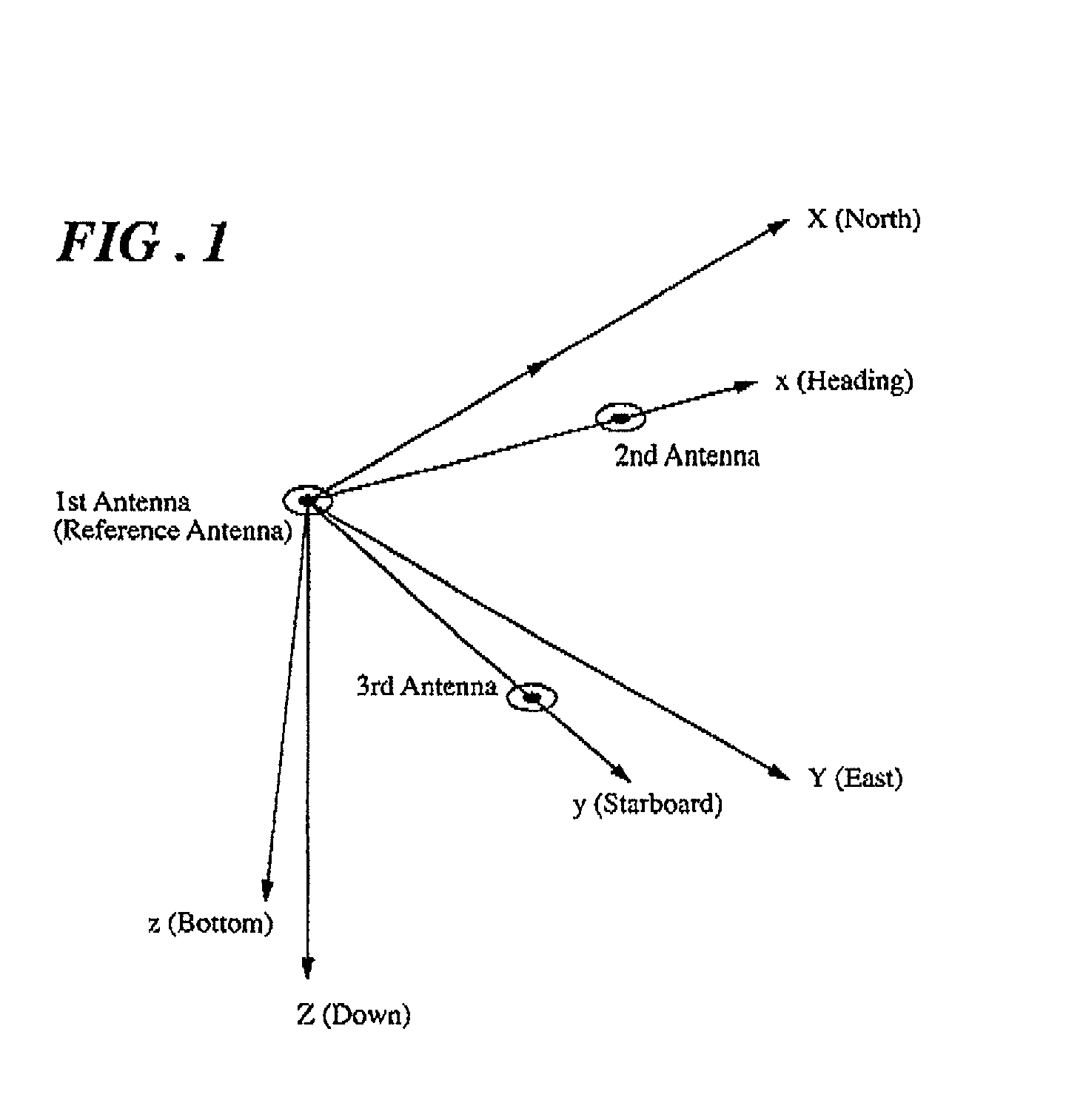
InactiveUS6611228B2Improve reliabilityShorten the timePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceReference antenna
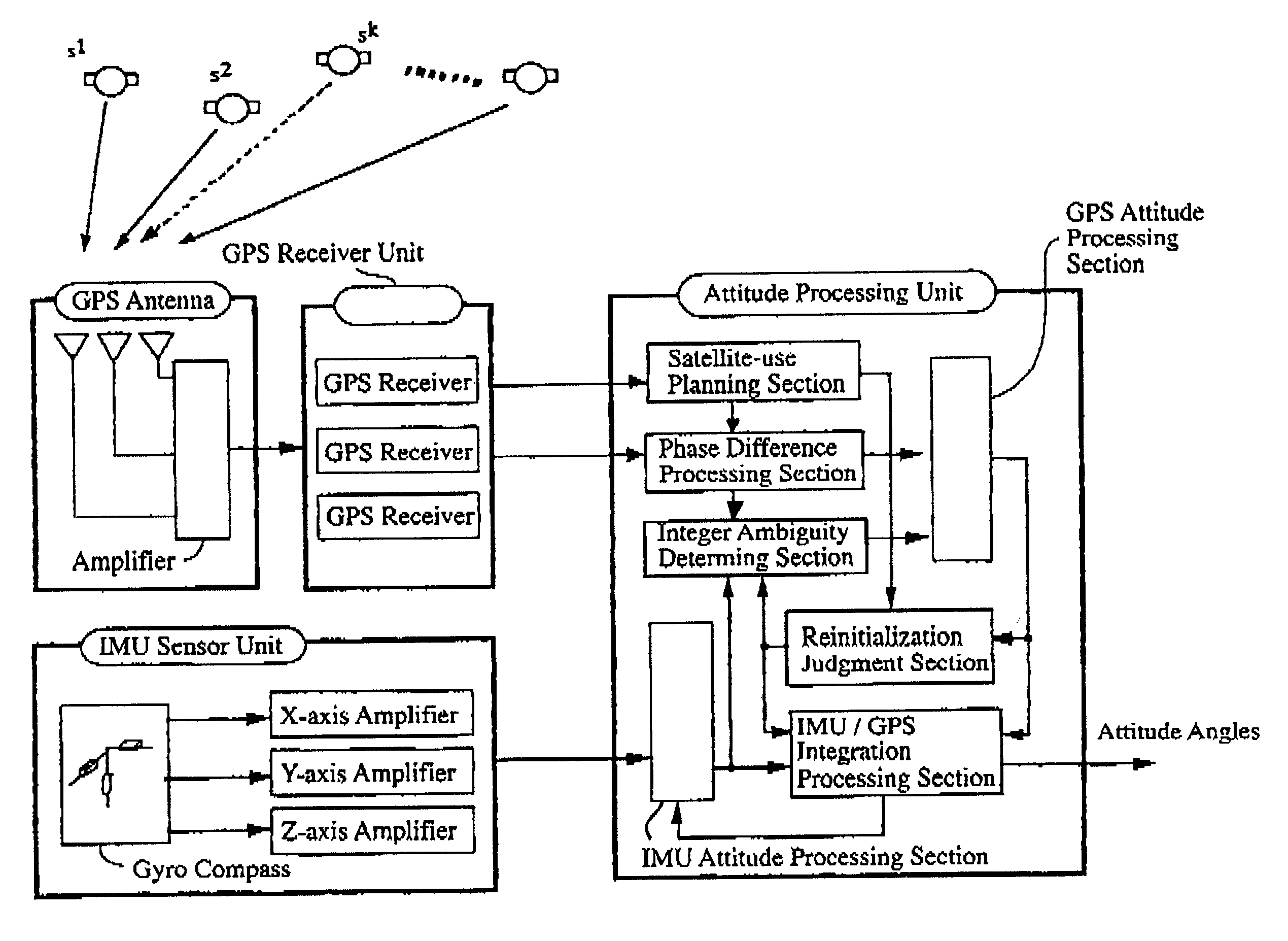
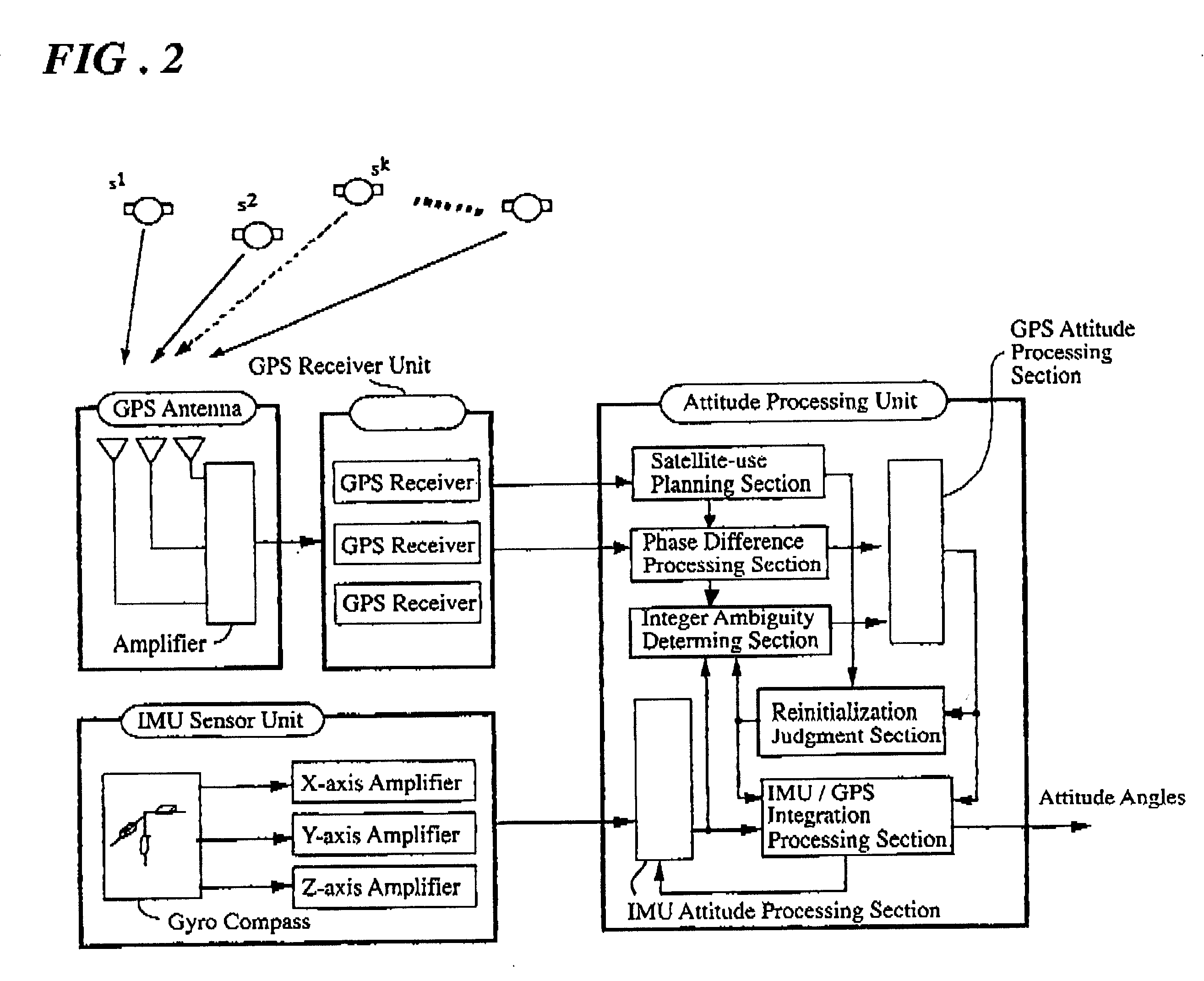
A carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus comprises a plurality of antennas of which at least one is installed on a mobile unit. The apparatus determines the position of each antenna other than one antenna used as a reference antenna relative to the reference antenna by receiving radio signals transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with the multiple antennas, observing a single difference phase or a double difference phase, and calculating an integer ambiguity of the single difference phase or the double difference phase. The apparatus judges that the integer ambiguity has been incorrectly determined if the position of any of the antennas relative to the reference antenna (or the angle of a flat plane formed by those two antennas) falls out of a preset range in which the relative position (the angle of the flat plane) falls under normal conditions.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for estimating phase deviation in precise single-point positioning technology
InactiveCN102353969AImprove robustnessGuaranteed sizeSatellite radio beaconingPoint-to-Point ProtocolIonosphere
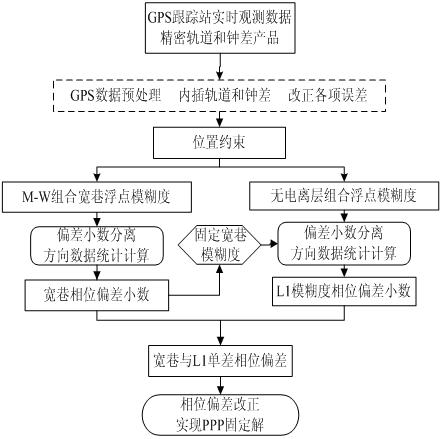
The invention discloses a method for estimating a phase deviation in a precise single-point positioning technology, which comprises the steps of: firstly, carrying out parameter estimation on single-difference non-ionized layer combined ambiguity by using a position as a restraint condition according to data of a reference station in a tracking network; secondly, carrying out parameter estimationon single-difference wide-lane ambiguity by adopting an M-W combination, separating out a decimal part of the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity, and carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using a directional data statistic theory, modifying and fixing the single-difference wide-lane ambiguity as an integer; thirdly, resolving a single-difference L1 ambiguity floating point solution according to a single-difference non-ionized layer ambiguity estimation value and a single-difference wide-lane ambiguity integer solution, separating the decimal part, carrying out decimal deviation calculation by using the direction data statistic theory; and finally, broadcasting the wide-lane and the L1 phase deviation decimal part to a user of a roving station so as to be used for fixing the single-difference integral ambiguity solution of the wide lane and the L1 and further obtaining a PPP (Point to Point Protocol) static solution.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
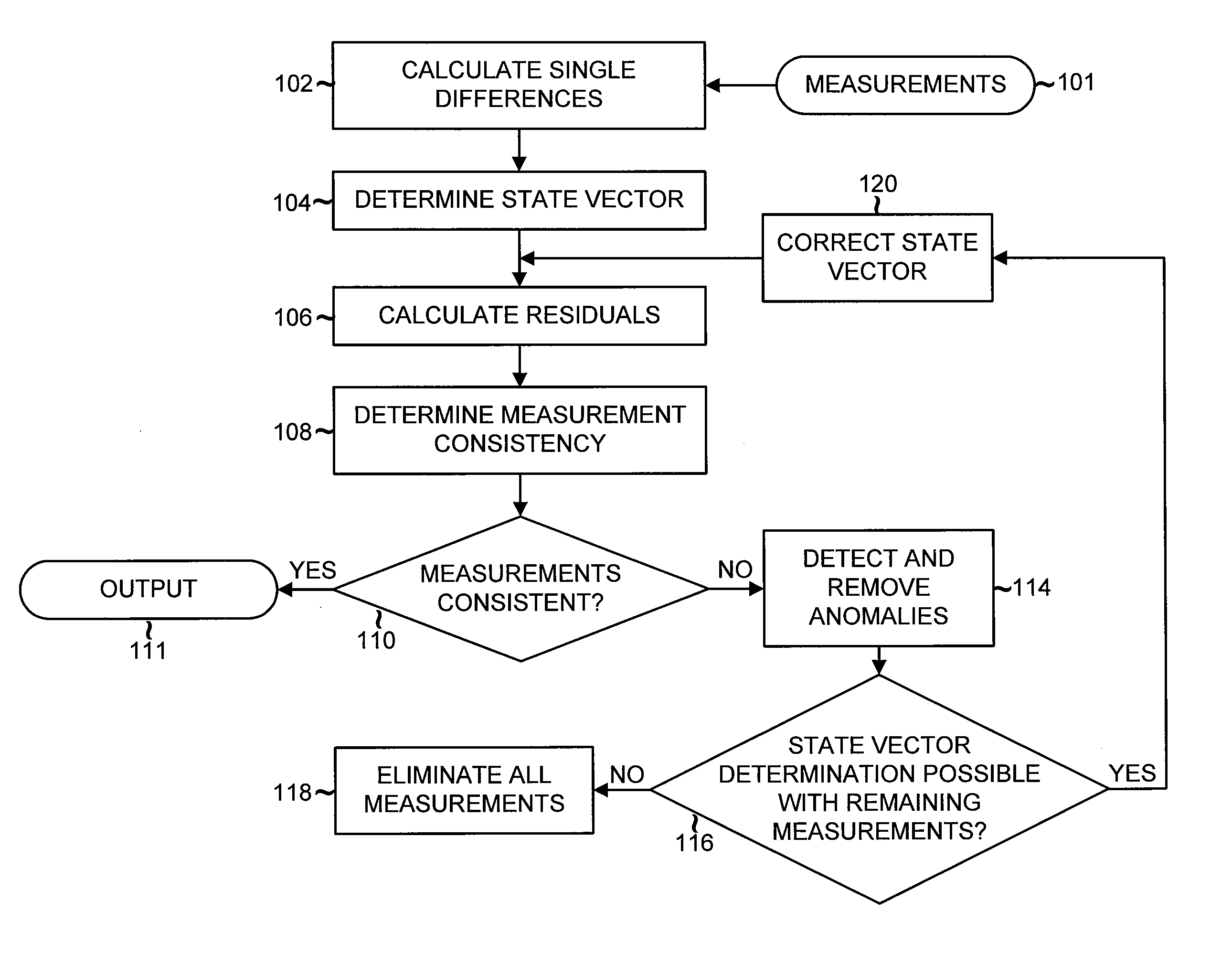
Detection and Correction of Anomalous Measurements and Ambiguity Resolution in a Global ...
A global navigation system includes a first navigation receiver located in a rover and a second navigation receiver located in a base station. Single differences of measurements of satellite signals received at the two receivers are calculated and compared to single differences derived from an observation model. Anomalous measurements are detected and removed prior to performing computations for determining the output position of the rover and resolving integer ambiguities. Detection criteria are based on the residuals between the calculated and the derived single differences. For resolving integer ambiguities, computations based on Cholessky information Kalman filters and Householder transformations are advantageously applied. Changes in the state of the satellite constellation from one epoch to another are included in the computations.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
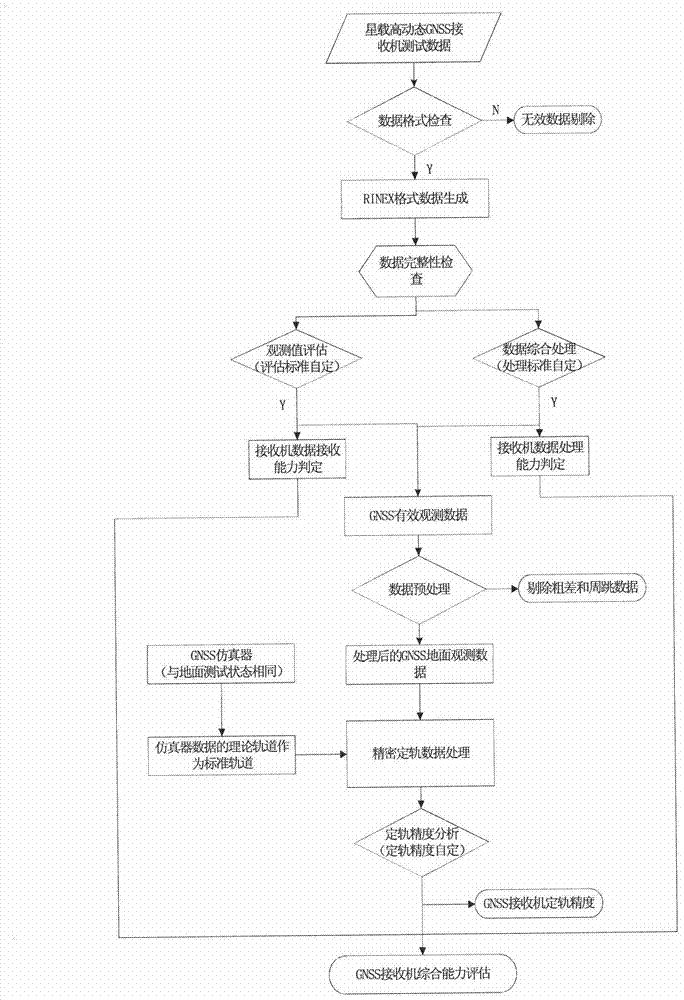
Method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver
ActiveCN103076618AImprove the scope of performance assessmentImprove verification capabilitiesSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteSource Data Verification
The invention provides a method for performing ground check and performance evaluation on a satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly performing observation data verification on observation data generated by the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver; and after verification is finished, further performing orbit determination performance test on the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver by utilizing a geometrical orbit determination method. The process of performing data verification on the observation data mainly comprises four links, namely observation data standard format treatment, observation data type integrity checking, observation data quality evaluation based on calculation on observed value dual difference of different navigational satellites at a same frequency and observed value single difference of a same navigational satellite at different frequencies, and evaluation on pseudo range and carrier noise based on simulation data observation in a zero / short base line under the condition of no satellite; and during orbit determination performance test, by virtue of solving a linearized observation equation and comparing the linearized observation equation with a theoretical value, the orbit determination accuracy of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver is obtained. The method provided by the invention can be used for directly and comprehensively evaluating the performance of the satellite-borne measurement-type GNSS receiver.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method
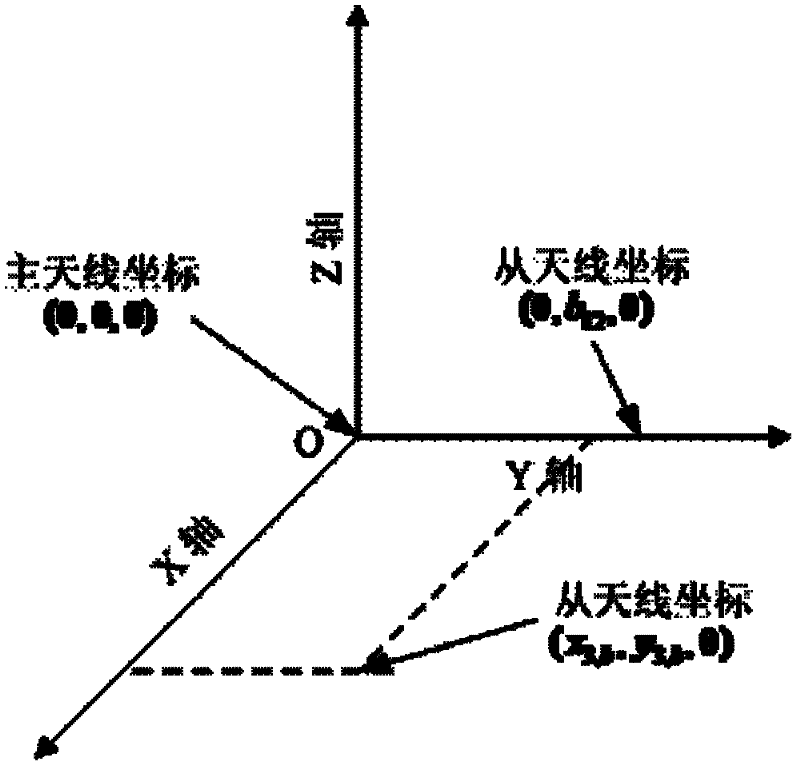
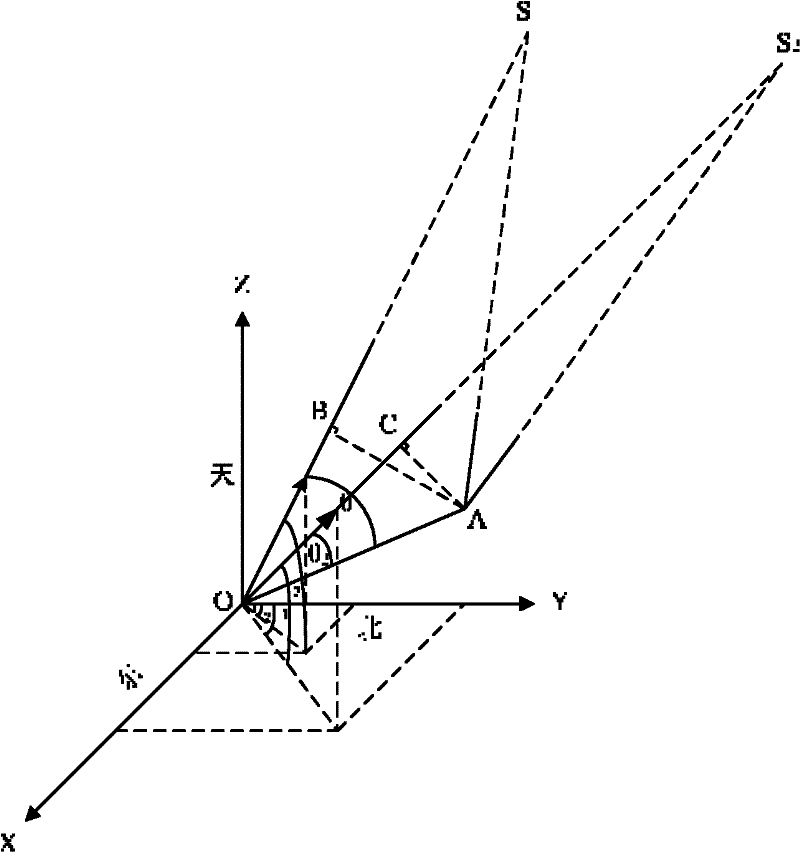
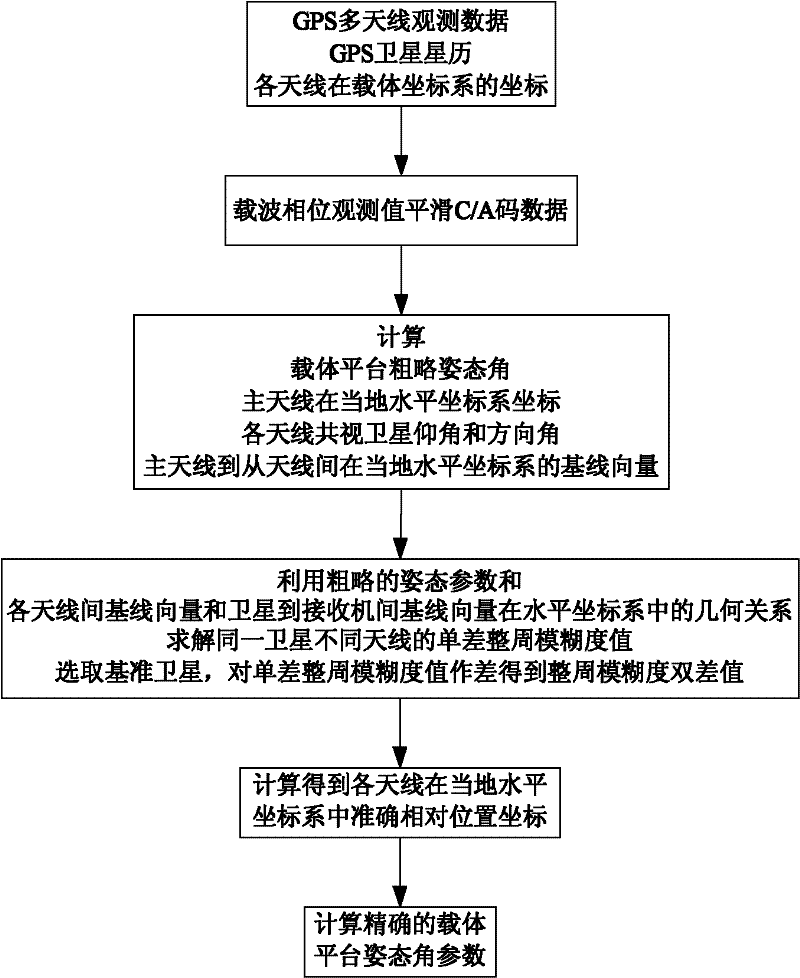
The invention aims at providing a GPS multi-antenna attitude determination method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly GPS multi-antenna observation data, a GPS satellite ephemeris and the coordinates of antennas on a carrier coordinate system are collected; a smoothing procedure is carried out to C / A code observation data with a carrier wave phase observed value; a carrier platform rough attitude angle, the coordinate of the main antenna in a local horizontal coordinate system, the shared vision satellite elevation angles and direction angles of the antennas and the baseline vector from the main antenna to subordinated antennas in the local horizontal coordinate system are calculated; based on the geometry relations of the baseline vectors among the antennas and the baseline vectors from the satellite to a receiver in the horizontal coordinate system, the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value of different antennas of the same satellite is solved; a reference satellite is selected and a difference operation is carried out to the single difference integer cycle fuzziness value to obtain an integer cycle fuzziness double difference value; the integer cycle fuzziness double difference value obtained is substituted into a carrier wave phase double difference model to obtain accurate coordinate components of the antennas and based on the coordinate components of the antennas, accurate attitude parameters are solved so as to realize GPS multi-antenna attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Single-epoch fixing method for enhancing PPP-RTK ambiguity of regional foundation
InactiveCN103176188AReduce ambiguity convergence timeImprove initialization speedSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityIonization
The invention provides a single-epoch fixing method for enhancing PPP-RTK ambiguity of regional foundation. The single-epoch fixing method comprises the following steps of: improving the ambiguity convergence time of a PPP-RTK method by carrying out optimizing ordering on the fixing feasibility of single-difference ambiguity between alternative satellites, respectively modeling for an observed value residual error of a CA / P1 pseudo-range and observed value residual errors of L1 and L2 phase positions by adopting a single-reference station processing mode based on a PPP-RTK technique, and realizing the single-epoch fixing of combined ambiguity of an ionization-free layer through step-by-step solving of the ambiguity in consideration of a linear constraint relationship between the high precision of a pseudo-range observed value, long wavelength of a wide-lane observed value, wide-lane ambiguity and L1 ambiguity after a user refines the models, thus the determination time of the PPP ambiguity is minimized, and the working efficiency of precisely locating the user is improved to the maximum degree.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
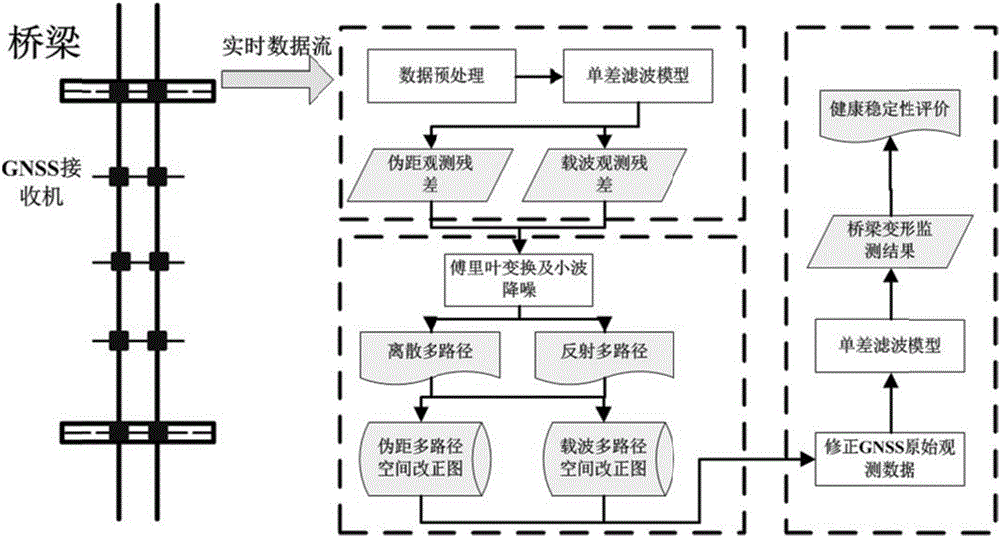
Single-difference filtering-based deformation monitoring GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signal multi-path correction method
ActiveCN106646538ARealize evaluationAchieve transformationSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityDeformation monitoring
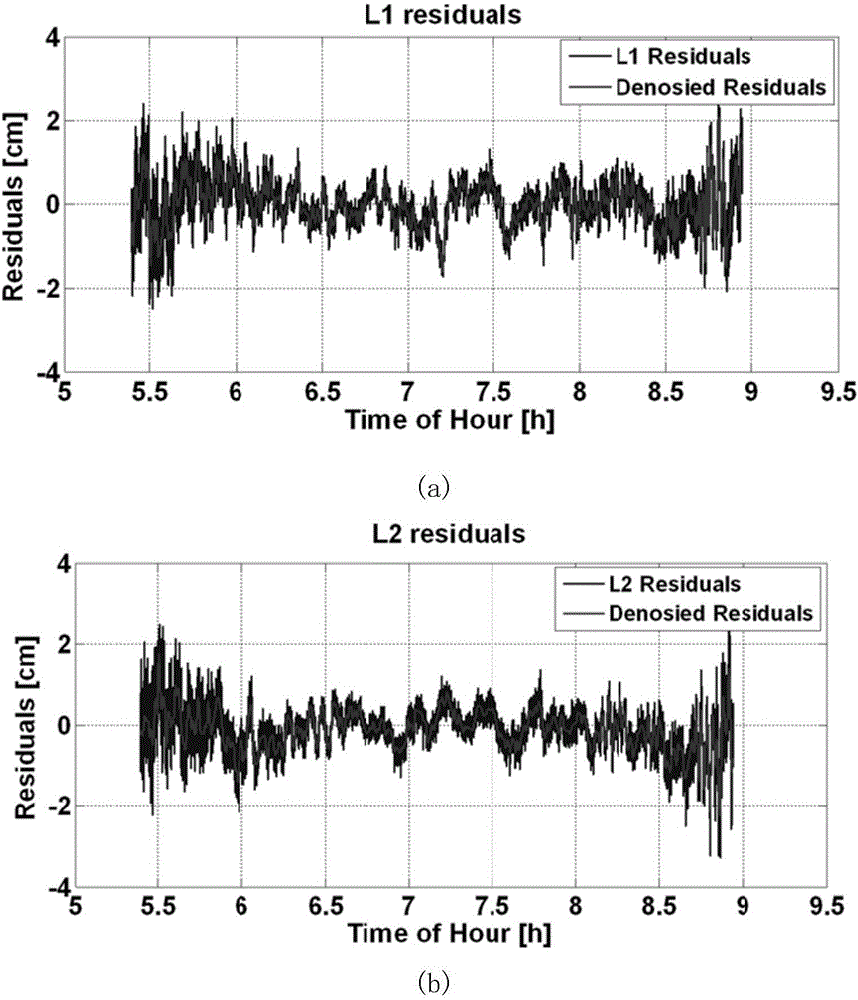
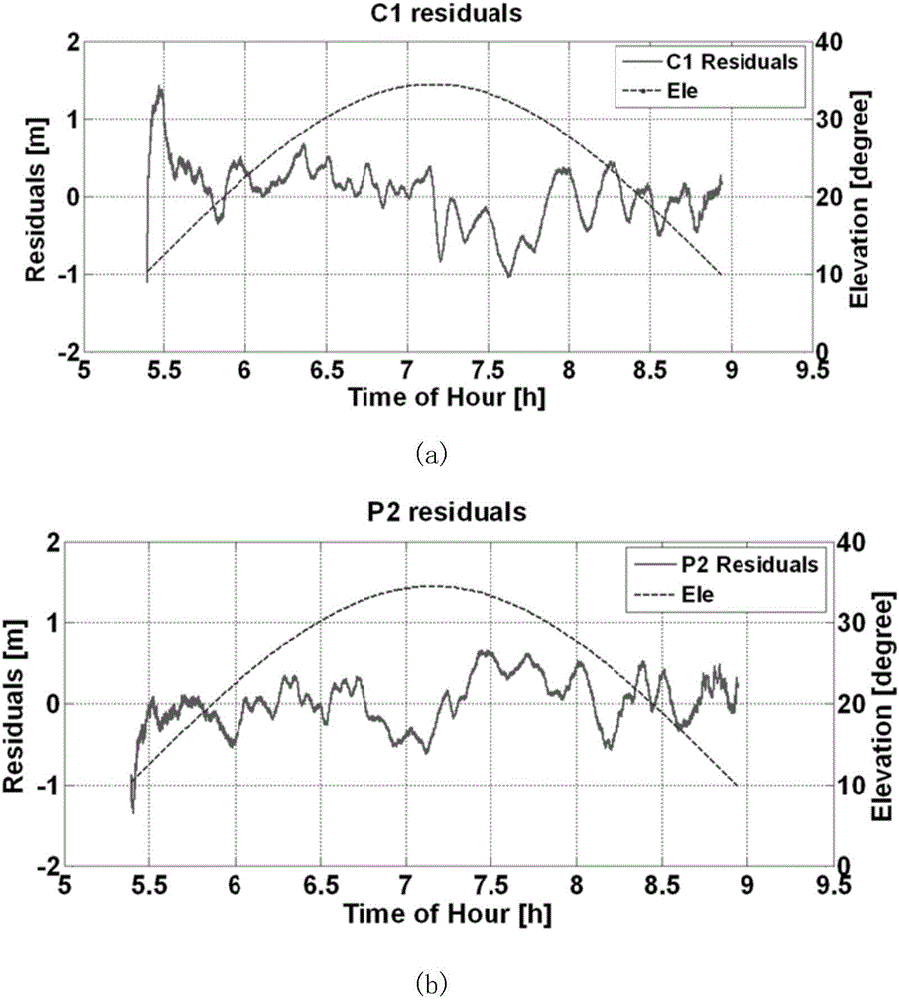
The invention discloses a single-difference filtering-based deformation monitoring GNSS (global navigation satellite system) signal multi-path correction method. On the basis of the spatial correlation characteristics of inter-receiver single-difference observation residuals, a single-difference filtering method is adopted to fix ambiguity and extract a carrier pseudo-range observation residual; fast Fourier transform analysis and wavelet de-noising are performed on the data residual, so that a discrete multi-path correction map and a reflection multi-path spatial correction map are established; and therefore, influence on GNSS carriers and pseudo-range observation values caused by a multipath effect in a bridge deformation monitoring environment can be decreased. According to the method of the invention, the spatiotemporal repetition characteristics of multiple paths are utilized. With the single-difference filtering-based deformation monitoring GNSS signal multi-path correction method adopted, the reliability and success rate of ambiguity fixation can be effectively improved, and single-epoch calculation accuracy of dynamic monitoring can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
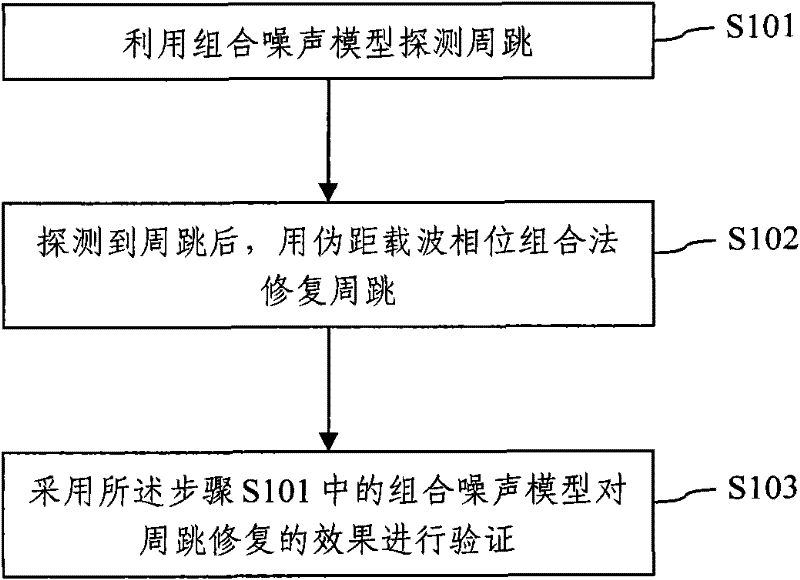
Method for detecting and repairing cycle slip by utilizing BeiDou three-frequency observed quantity
InactiveCN102650692ALong wavelengthReduce noiseVoltage-current phase angleSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNoise detection
The invention discloses a method for detecting and repairing a cycle slip by utilizing a BeiDou three-frequency observed quantity. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, performing linear combination by utilizing the three-frequency observed quantity under the condition of providing a three-frequency signal by a BeiDou satellite navigation system, and constructing a combination noise detection quantity by selecting proper combination coefficients to detect the cycle slip; 2, after the cycle slip is detected, calculating and screening to obtain three sets of combination coefficients with superior performance in a pseudo-range carrier phase combination method, and calculating and repairing the cycle slip by utilizing the pseudo-range carrier phase combination method; and 3, finally, performing verification on a cycle-slip repairing effect by utilizing the combination noise detection quantity. The method for detecting and repairing the cycle slip is not related to the motion state of a carrier, can be used for reliably detecting and repairing the minimum cycle slip of which the time of losing lock reaches up to 30 seconds and can be used for detecting and repairing the cycle slip by the zero-difference, single-difference or double-difference carrier phase observed quantity when static measurement or dynamic measurement is performed.
Owner:中国人民解放军61081部队
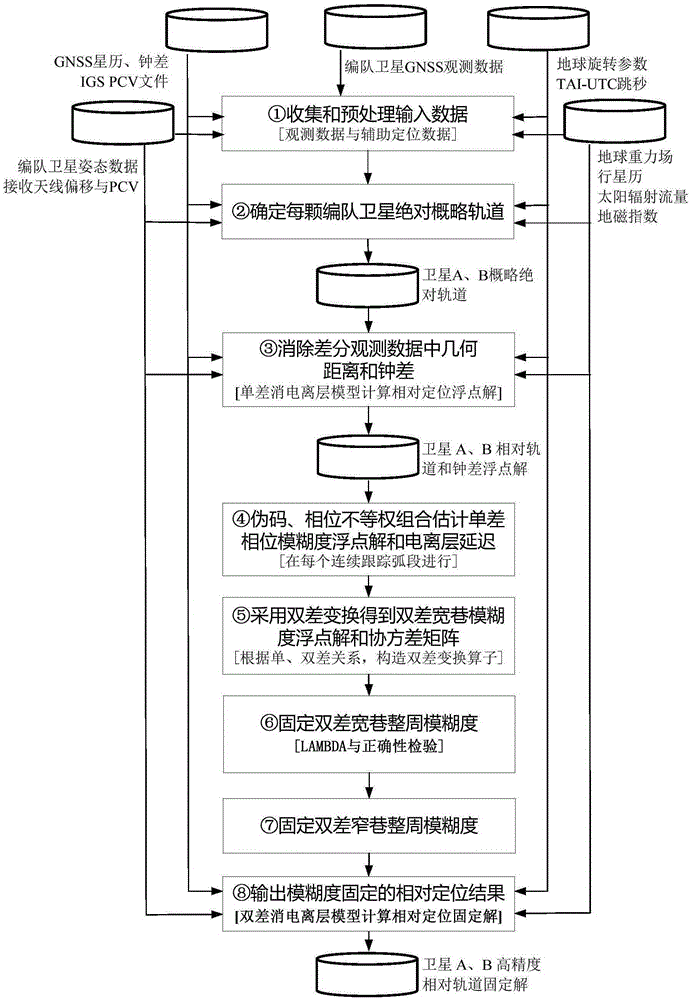
Long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing
ActiveCN105372691AHigh precisionOvercome the shortcoming of easy divergenceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
A long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning method based on ambiguity fixing is provided in order to improve the success rate of ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of relative positioning results. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: first, collecting and pre-processing input data, and determining the absolute general orbit of a formation satellite; then, eliminating the geometric distance and clock error in differential observation data, estimating a single-difference phase ambiguity float solution and a single-difference ionosphere delay parameter, carrying out double-difference transform to get a double-difference wide-lane ambiguity float solution and a covariance matrix, and fixing the double-difference wide-lane integer ambiguity and the double-difference narrow-lane integer ambiguity; and finally, outputting the relative positioning result of ambiguity fixing. By adopting the method of the invention, the problem that ambiguity fixing strongly depends on a pseudo code with low observation precision due to equally-weighted pseudo code and phase processing in M-W combination in the traditional method is avoided, the success rate of long baseline satellite formation GNSS relative positioning ambiguity fixing and the accuracy of final relative positioning results are improved, calculation is stable, and the reliability of relative positioning results is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Orientation attitude determination method oriented to clock synchronization multi-antenna GNSS receiver
ActiveCN104597471AHigh precisionImprove operational efficiencySatellite radio beaconingData streamAmbiguity
The invention provides an orientation attitude determination method oriented to a clock synchronization multi-antenna GNSS receiver. The orientation attitude determination method comprises the steps of establishing a high-accuracy orientation attitude determination model oriented to the clock synchronization multi-antenna GNSS receiver, observing a carrier phase and a pseudo-range in real time and providing a data source for the high-accuracy orientation attitude determination model in a real-time data flow mode, determining parameters to be estimated and constraint information, monitoring and repairing cycle slip, fixing a part of or all ambiguity parameters to an integer value by estimating base line vector parameters and floating point carrier phase ambiguity parameters, using base line length information as additional information, and using the base line length information as pseudo-observation values in the base line vector resolving process to constraint the resolving accuracy of base line vectors; converting the base line vectors into a course angle and a pitch angle to be output through coordinate system conversion. The orientation attitude determination method achieves high-accuracy attitude determination through single difference, is simple in algorithm, can be suitable for high-accuracy real-time orientation attitude determination application under static, quasi-static and dynamic conditions, meanwhile is high in algorithm operating efficiency and is suitable for high-dynamic vehicle-mounted orientation attitude determination.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Detection and correction of anomalous measurements and ambiguity resolution in a global navigation satellite system receiver
A global navigation system includes a first navigation receiver located in a rover and a second navigation receiver located in a base station. Single differences of measurements of satellite signals received at the two receivers are calculated and compared to single differences derived from an observation model. Anomalous measurements are detected and removed prior to performing computations for determining the output position of the rover and resolving integer ambiguities. Detection criteria are based on the residuals between the calculated and the derived single differences. For resolving integer ambiguities, computations based on Cholesky information Kalman filters and Householder transformations are advantageously applied. Changes in the state of the satellite constellation from one epoch to another are included in the computations.
Owner:TOPCON POSITIONING SYST INC
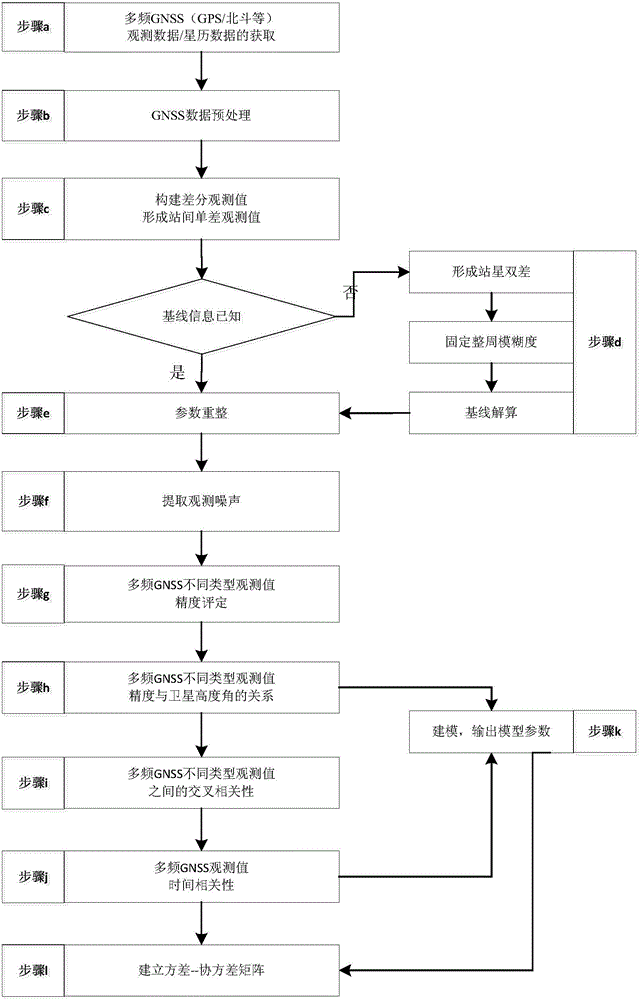
Method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values
InactiveCN104102822ASimple calculationHigh speedSatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention relates to a method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring multi-frequency GNSS observed data, and preprocessing the data; constructing a single difference observation equation to form an intersite single difference observed value; performing parameter reforming on the single difference observation equation according to a base line and fixed double-difference ambiguity; taking the average value of single difference observed values of single-epoch multiple satellites as the least square solution of the reformed parameter, and subtracting the least square solution from the single different observed value of each satellite to obtain single difference observation noise; calculating the accuracy of non-difference observed values of single-epoch multi-frequency GNSS different-type observed values, cross-correlation coefficients of the different-type observed values and temporal correlation coefficients of the same-type observed values by utilizing the extracted observation noise; obtaining a relation between the accuracy of the observed value of each satellite and an elevating angle; modeling, outputting model parameters and establishing a variance-covariance matrix. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simple calculating process, reliability and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
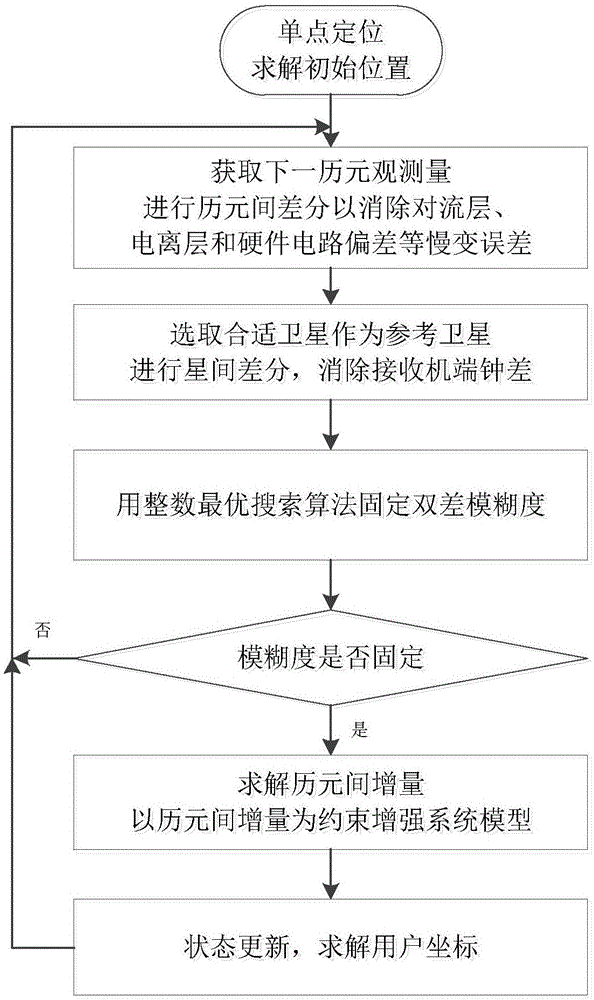
Positioning method based on epoch-satellite difference constraint
ActiveCN106772478AMake up for inaccurate problemsHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation and positioning, and relates to a positioning method based on epoch-satellite difference constraint. The positioning method enhances the intensity of a satellite navigation system model and improves the convergence speed of a system. The positioning method provided by the invention comprises the steps that (1) observation acquired by a receiver is used for precise single point positioning to acquire the initial solution of the position of a user; (2) the observation of two adjacent epochs is used for first difference to acquire single difference observation; and (3) a satellite is selected as a reference satellite, and second difference between satellites is carried out on the single difference observation acquired in the step (2) to acquire double difference observation. According to the method proposed by the invention, epoch-satellite difference is carried out the original observation of the receiver; the whole-week characteristic of double difference ambiguity is recovered; and accurate inter-epoch position increment is acquired.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Carrier phase difference positioning method and device and single-frequency receiver
ActiveCN106646565AImprove fixation efficiencyAvoid cycle slip problemSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
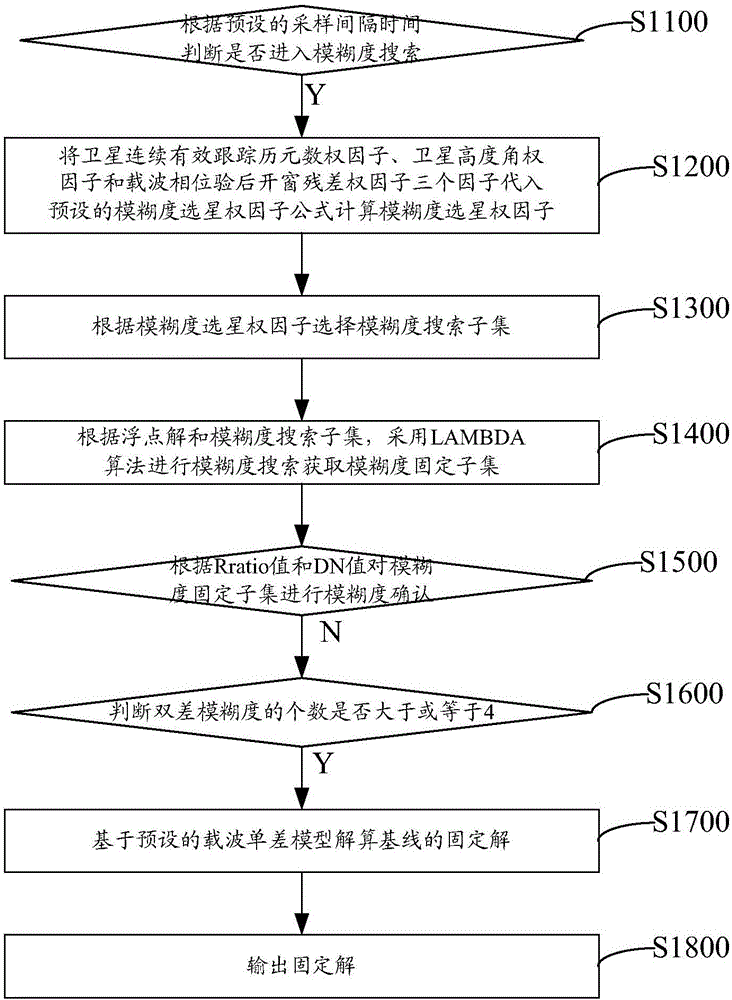
The invention relates to a carrier phase difference positioning method and device and a single-frequency receiver, and the method comprises the steps: judging whether to carry out the ambiguity search or not according to a preset sampling time interval; substituting a satellite continuous and effective tracking epoch number weight factor, a satellite elevation weight factor and a carrier phase posterior windowing residual error weight factor into a preset ambiguity satellite selection weight factor formula if the ambiguity search is carried out, and calculating a ambiguity satellite selection weight factor; selecting a ambiguity search subset according to the ambiguity satellite selection weight factor; carrying out the ambiguity search through employing an LAMBDA algorithm, and obtaining an ambiguity fixed subset; respectively judging whether the obtained ratio value and DN value are greater than a preset first threshold value and a preset second threshold value or not, and carrying out the ambiguity confirmation of the ambiguity fixed subset; judging whether the number of double-difference ambiguities is greater than or equal to 4 or not if the obtained ratio value and DN value are greater than the preset first threshold value and the preset second threshold value; solving a fixed solution of a base line based on a preset carrier single-difference model if the obtained ratio value and DN value are not greater than the preset first threshold value and the preset second threshold value; and outputting the fixed solution. The method can enable the single-frequency receiver to carry out the RTK high-precision positioning.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HI TARGET SURVEYING INSTRUMENT CO LTD
Ground-based high-precision regional positioning navigation system and method
ActiveCN108089204AImplement two-way transmissionTime synchronizationSatellite radio beaconingSignal qualityCarrier signal
The invention relates to the field of satellite navigation and radio positioning, and discloses a ground-based high-precision regional positioning navigation system and a ground-based high-precision regional positioning navigation method. The ground-based high-precision regional positioning navigation system comprises a plurality of distributed navigation base stations, a datum station and a monitoring station, wherein each navigation base station has a navigation signal broadcasting function, is equipped with transmitting and receiving antennas, and adopts a broadband variable-frequency channel design; 2) the navigation base stations and the datum station adopt a bidirectional time synchronization method to achieve time synchronization among the navigation base stations, and the datum station has a GNSS time reference function; the monitoring station has a navigation signal quality monitoring, evaluation and calibration function, and the monitoring station and the datum station can beco-locational. The invention further discloses a high-precision positioning method, which determines initial position coordinates of a receiver based on a single-difference pseudo code phase measurement value, and assists in completion of carrier ambiguity resolution and high-precision positioning. The ground-based high-precision regional positioning navigation system has the advantages of high environment adaptability, high positioning precision, high anti-interference performance, easy deployment, low cost, scalability and GNSS system cooperative work capability.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for positioning GNSS receiver
ActiveCN106291639AHigh positioning accuracyEasy to operateSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceExternal data
Owner:UNICORE COMM INC
Real-time GLONASS phase deviation estimation method based on particle swarm optimization algorithm
ActiveCN106249256AEfficient and accurate searchAvoid unavailabilitySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceLinear correlation
The invention provides a real-time GLONASS phase deviation estimation method based on a particle swarm optimization algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of a satellite positioning system and positioning measuring technique. The method is characterized by carrying out correction on all single difference ambiguity parameters by utilizing IFB change rate particles; carrying out double-difference ambiguity fixation through an LAMBDA method; serving the obtained RATIO value as evaluated fitness of each particle, and searching the swarm optimum position of the IFB change rate particles through a particle swarm optimization algorithm; and finally, obtaining an optimum IFB change rate estimated value. The method solves the problem caused by IFB and ambiguity linear correlation; estimation is carried out on the IFB change rate online in real time, thereby preventing the phenomenon that existing IFB change rate correction parameters are not available due to observation condition change, and the method is suitable for real-time dynamic positioning; and real-time ambiguity fixation is realized through the real-time GLONASS phase deviation estimation method, and the application field of GLONASS is further expanded.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for high-precision dynamic point positioning through big dipper double frequency receiver
ActiveCN105807300AEasy to lockHigh positioning accuracySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterTroposphere
The invention discloses a method for high-precision dynamic point positioning through a big dipper double frequency receiver.Double frequency high-sampling-frequency big dipper data is utilized, only one big dipper double frequency receiver is needed, it is not required to erect a base station or a CORS system or other auxiliary devices at a known point, error sources are eliminated or weakened through algorithms, an iteration least squares elimination method is used, a kalman filter based on single difference ambiguity and troposphere delay parameters is used for parameter calculating, an accurate absolute coordinate position can be obtained, working employment is easy and convenient, the positioning precision is high, the position of a satellite is conveniently locked, and the method is suitable for large working range applications.
Owner:WUHAN GEOSUN NAVIGATION TECH CO LTD
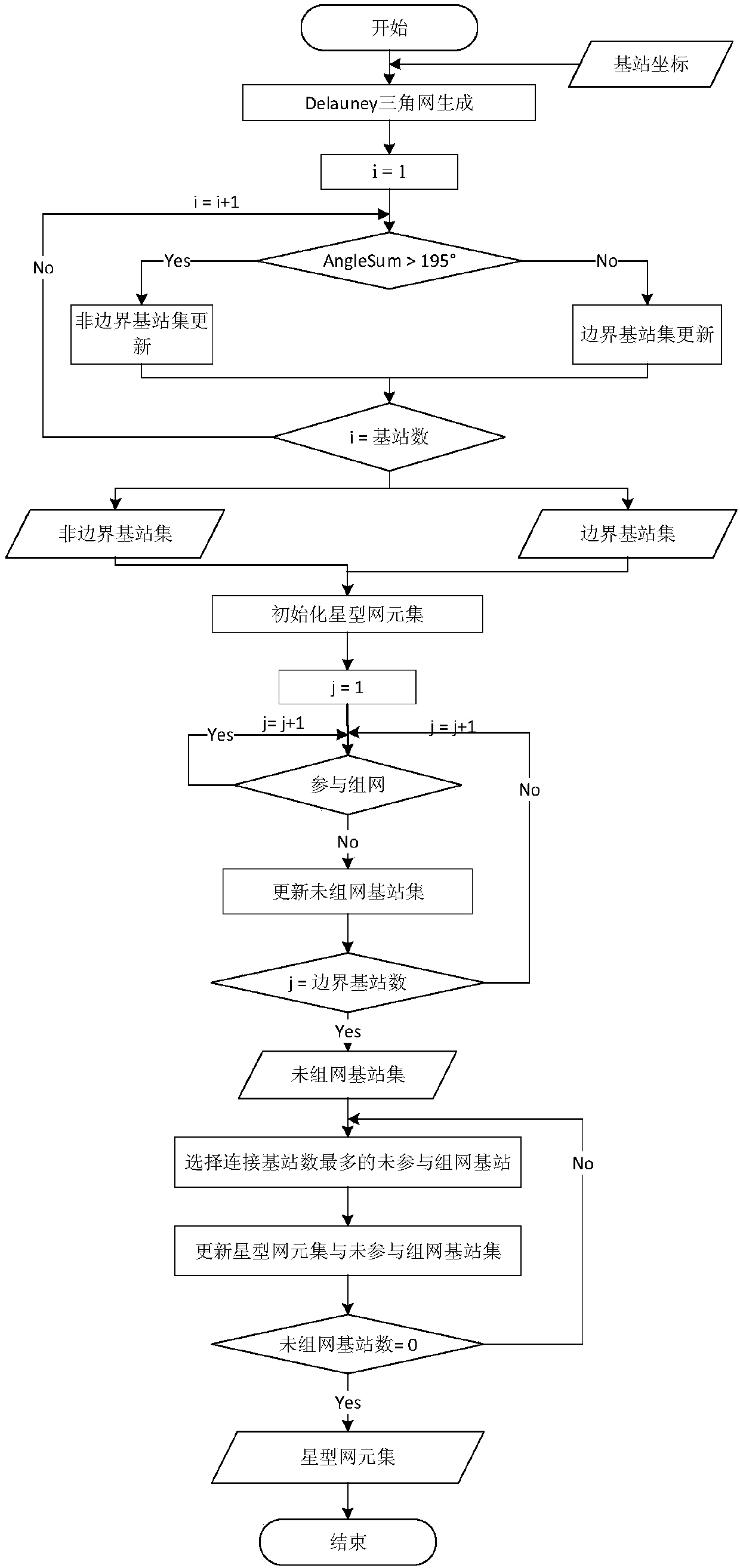
Star-network-based BDS/GPS broadcast type network RTK algorithm
ActiveCN107797126ARedundant observationsUnlimited capacitySatellite radio beaconingAviationPrimary station
The invention discloses a star-network-based BDS / GPS broadcast type network RTK algorithm. All base stations form a triangulation network based on a Delaunay triangulation algorithm; and a controllable full-region star network formed by a plurality of star network elements is generated based on the triangulation network. Data of the base stations are obtained in real time and network element calculation is carried out to generate a baseline atmospheric error. Meanwhile, a server side broadcasts a main station observation value, a base station coordinate and the baseline atmospheric error to auser by using the star network as a unit based on a UDP protocol; the user selects one network element based on an own approximate position and the position of the main station; interpolation is carried out on an inter-station single-difference atmospheric error of the baseline formed by the user and the main station and the obtained atmospheric error is corrected to the observation value of the main station to carry out baseline calculation. Besides, the user also can uploads an approximate coordinate by two-way communication and the server side broadcasts difference data of the network element in which the user is located. And difference data broadcasting by equipment like ground equipment, an aircraft or a satellite is also supported.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
GNSS baseline solution reference satellite selecting method
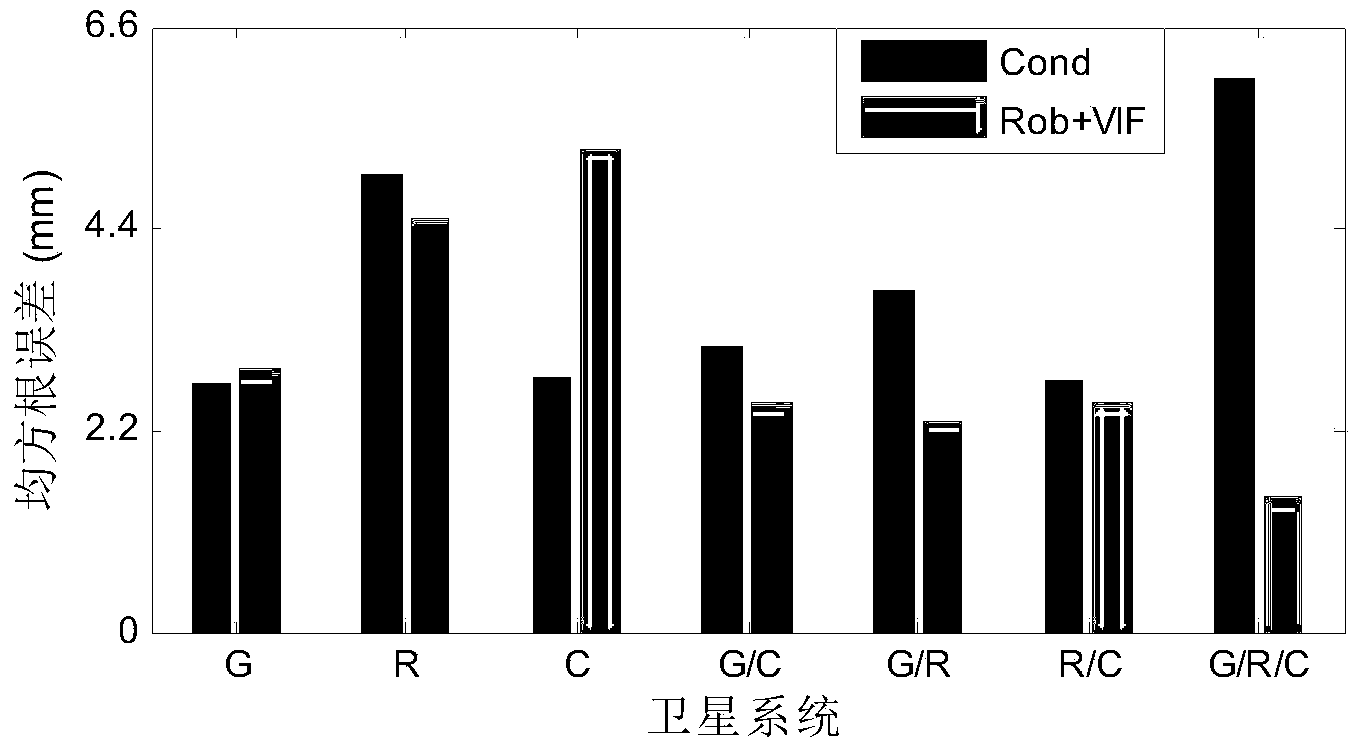
ActiveCN103630914AReduce morbidityExcellent Space Satellite DistributionSatellite radio beaconingSpatial correlationEquivalent weight
The invention discloses a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) baseline solution reference satellite selecting method. The method mainly comprises the steps of establishing an inter-station difference single-difference model according to a GNSS carrier phase observation equation, and weakening influence from spatial correlation error; selecting a satellite according to base station and moving station common-view observation satellite list to construct a dual-difference model, resetting weight of each dual-difference observation value through an equivalent weight model based on an IGGIII model, and inhibiting influence from observation abnormity through a robust estimation model; calculating a variance inflation factor corresponding to each common-view satellite as a reference satellite according to the established dual-difference model; and calculating a VIF value to determine the reference satellite. The method, compared to an existing method, not only takes distribution structure of a spatial satellite into consideration but also focuses on quality of the observation value; therefore, the method can determine the most reasonable reference satellite and greatly improve both positioning accuracy and reliability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Relative inter-vehicle position calculation apparatus, transmission apparatus and program for same
ActiveUS20090140916A1Accurate calculationEasy to calculateBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceOn board
An on-board communication equipment on each of two vehicles receives a radio wave from two or more GPS satellites, and determines a carrier wave phase of the received radio wave. Then, the on-board communication equipment on one vehicle receives, from the other vehicle, information on the carrier wave phase observed in the other vehicle. Further, the on-board communication equipment calculates a relative position of a self vehicle relative to the other vehicle by a Carrier-Phase DGPS positioning based on a difference between two carrier wave phases (e.g., single difference, double difference or the like), that is, one from the self vehicle and one from the other vehicle, both having the same observation time, from among the available carrier wave phases.
Owner:DENSO CORP
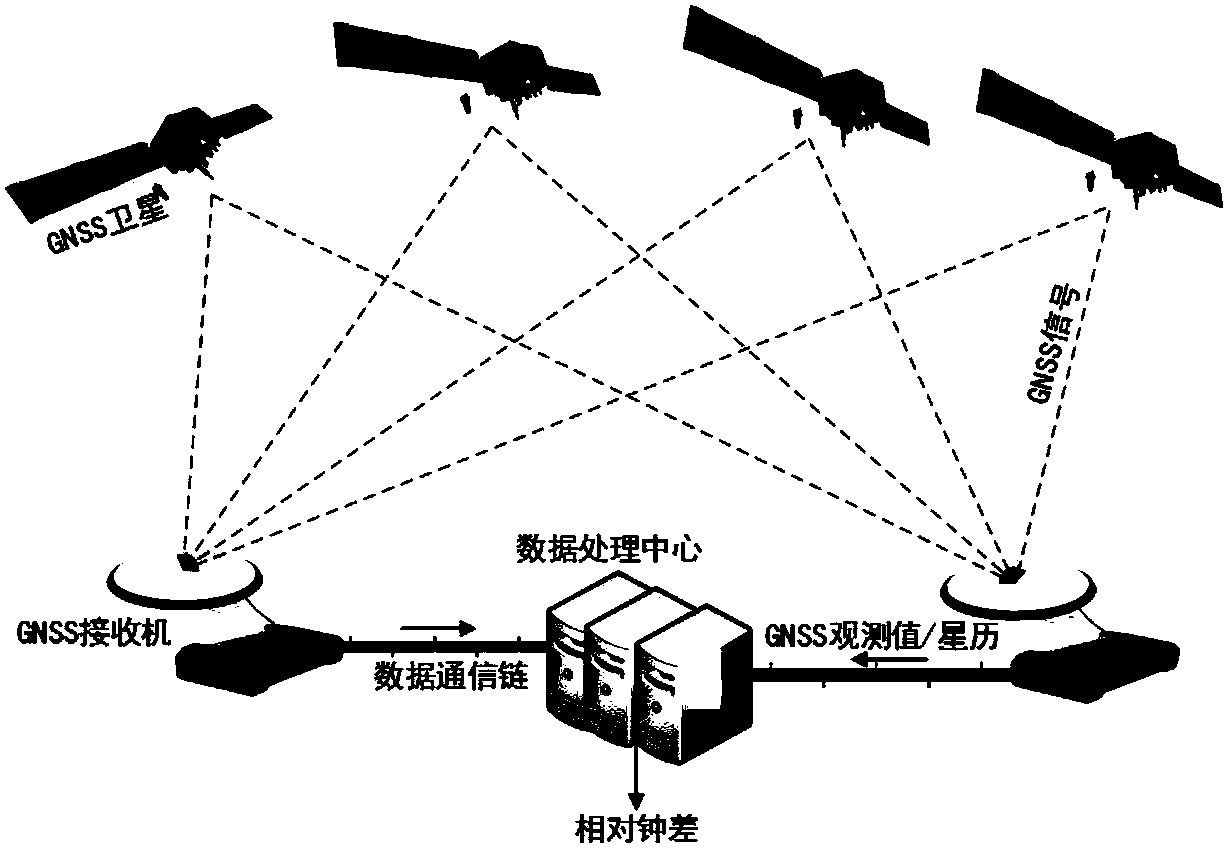
GNSS precise time transmission method based on constraint of fixed solution of double-difference ambiguity
ActiveCN108445518AHigh precisionImprove reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention relates to a GNSS precise time transmission method based on constraint of a fixed solution of a double-difference ambiguity, and belongs to the technical field of precise time service, time synchronization and time frequency transmission. The GNSS precise time transmission method comprises that an inter-station single-difference observation module calculates a relative clock error ofa GNSS receiver; single-difference ambiguity is projected into double-difference ambiguity, and the double-difference ambiguity is fixed; and a relative clock error of the receiver is calculated based on constraint of the fixed solution of the double-difference ambiguity. The GNSS pseudo range and a carrier phase observation value are used, and the inter-station single-difference observation module is utilized to estimate the relative clock error of the receiver. On such basis, the single-difference ambiguity is projected into double-difference ambiguity, and the double-difference ambiguity is fixed. The fixed double-difference ambiguity serves as a constraint condition, the precision of a floating point solution of the single-difference ambiguity is improved, and the time transmission precision and reliability are improved.
Owner:ACAD OF MATHEMATICS & SYSTEMS SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus
InactiveUS20020050943A1Improve reliabilityShorten the timePosition fixationNavigation instrumentsDouble differenceReference antenna
A carrier phase-based relative positioning apparatus comprises a plurality of antennas of which at least one is installed on a mobile unit. The apparatus determines the position of each antenna other than one antenna used as a reference antenna relative to the reference antenna by receiving radio signals transmitted from a plurality of position-fixing satellites with the multiple antennas, observing a single difference phase or a double difference phase, and calculating an integer ambiguity of the single difference phase or the double difference phase. The apparatus judges that the integer ambiguity has been incorrectly determined if the position of any of the antennas relative to the reference antenna (or the angle of a flat plane formed by those two antennas) falls out of a preset range in which the relative position (the angle of the flat plane) falls under normal conditions.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Short arc batch processing-based satellite autonomous orbit determination method and device
InactiveCN105629272AEliminate Clock ParametersMeet real-time requirementsSatellite radio beaconingBatch processingObservation data
The invention discloses a short arc batch processing-based satellite autonomous orbit determination method and device. The method includes the following steps that: S11, GNSS observation data of a current observation arc are acquired, and gross error-free inter-satellite single-difference observation data of the whole observation arc are obtained; S12, the satellite state information of the observation arc at all observation time points is subjected to integral prediction; S13, the satellite state information is iteratively estimated through a batch processing method; S14, a posterior residual sum is calculated based on the iteratively-estimated satellite state information, and the convergence and divergence of the iterative estimation are judged according to the posterior residual sum, if a judgment result indicates that the iterative estimation is convergent, a step S15 is executed; S15, the satellite state information of a next observation arc is subjected to integral prediction; S16, a receiver clock error is calculated according to the GNSS observation data, and a receiver clock error of the next observation arc is predicted in a unified manner; and the receiver clock error of the next observation arc is led into a navigation signal tracking loop, and the method enters the next observation arc. The method provided by the invention can satisfy orbit precision requirements of medium, low and high-orbit satellites.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Method for overcoming deviation of precise orbit determination system of beidou second-generation GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite
ActiveCN103323867AReduce correlationImprove estimation accuracySatellite radio beaconingPrior informationClock offset
The invention provides a method for overcoming deviation of a precise orbit determination system of a beidou second-generation GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite. According to the method, a fuzzy degree fixation process is used and strict judgment criteria are adopted in the beidou fuzzy degree fixation process to guarantee the success rate of the fuzzy degree fixation process; a space relation between a Y-axis direction of a solar panel and a sunlight incidence direction in a zero-offset state is analyzed; corresponding parameters are set for estimating and absorbing a reflection force in a light pressure model, and a reasonable prior information and experience model is built from posterior long-term observation data, so that an effective background constraint to light pressure parameters in a GEO orbit determination process is formed, the influence due to insufficient geometrical observation conditions and other model errors is avoided, and the orbit determination precision is improved; a clock offset model is built within a time allowed by the frequency stability, a relation between epochs is established, a model constraint is built by adopting an inter-satellite single difference method when a satellite clock of a GEO is modeled, the influence of a receiver clock offset of an observation station is eliminated, the purpose of reducing the correlation is reached, and the resolving and forecast accuracy of the beidou GEO is improved finally.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
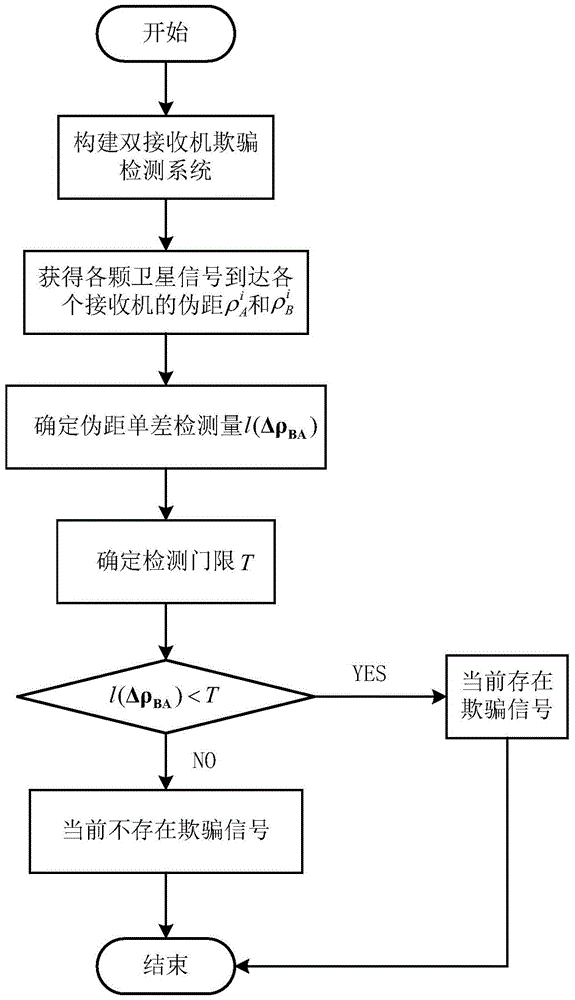
GNSS anti-deception method based on double receivers
ActiveCN105717492AEasy to implementLow costWave based measurement systemsReal signalDetection threshold
The invention discloses a GNSS anti-deception method based on double receivers. The method comprises the following steps that a double-receiver deception detection system is constructed; each receiver processes received navigation satellite signals to obtain pseudo range values from different satellites to the receiver; a single-difference detection quantity of the pseudo range and a detection threshold are determined; when the single-difference detection quantity of the pseudo range is lower than the detection threshold, it is determined that deception interference signals exist at present; and when the single-difference detection quantity of the pseudo range is greater than the detection threshold, a present signal is determined to be a true signal. The GNSS anti-deception method is easy to realize and low in cost, and two common GNSS receivers can form one detection system; the computational complexity is low, detection is rapid, and the single difference of pseudo range can be directly used to complete deception detection; and the application range is wide, and deception detection can be completed if only there is pseudo range output no matter whether signals are strong or weak.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for real-time direction finding of base station antenna ultrashort baseline GNSS double antenna
InactiveCN109613585AEliminate errorsGuaranteed reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceAmbiguity
The invention discloses a method for real-time direction finding of a base station antenna ultrashort baseline GNSS double antenna. The two-dimensional pose of a carrier can be determined by measuringa vector fixed on the carrier. The vector that reflects the two-dimensional pose of the carrier can be formed when the antennas of two receivers are mounted on a rigid carrier. And the heading angleof the carrier can be calculated by accurately determining the direction and distance of the two ends of the vector in space. According to the method for the real-time direction finding of the base station antenna ultrashort baseline GNSS double antenna, the common errors of the satellite and the receiver are eliminated by constructing a double difference model to perform a global solution on thebaseline vector. The problem of the frequent replacement of a reference star is avoided by firstly solving the single-difference ambiguity between fixed stations. The reliability of the baseline vector is ensured by using the EKF solution. The single epoch can be guaranteed to be solved, the real-time performance is effectively ensured, and in particular, various errors in the observation of the low-cost positioning module and the antenna in the absolute positioning are prevented from affecting the receiver antenna and making the high-precision position difficult to obtain.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for a global satellite navigation system
ActiveUS20110122020A1Simple methodEstimation biasPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingAmbiguityCarrier signal
A method for estimating satellite-satellite single difference biases is described. The method uses an ionosphere-free mixed code-carrier combination of maximum ambiguities discrimination defined at the ration between wavelength and noise standard deviation. The accuracy of the biases estimation is further improved by an additional ionosphere-free mixed code-carrier combination of time-difference measurement that is uncorrelated with the first combination. Finally, an alternative method is based on a combination of carrier signals in a common frequency band which allows estimating the biases individually.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) single difference processing method of fixed reference satellite
ActiveCN106569242AStrong service abilitySolve difficult problems that cannot be passed continuouslySatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterNatural satellite
The present invention relates to a GNSS single difference processing method of a fixed reference satellite. The method comprises the following steps of A selecting a synchronous observation satellite which has a larger elevating angle at the beginning moment and is reliable in observation quality as the fixed reference satellite, and hypothesizing the satellite as the No.1 satellite; B constructing a station-between single difference Kalman filtering observation model taking the double-difference ambiguity as a parameter; C constructing a Kalman filtering state model; D starting a Kalman filter, and solving the parameters by taking a double-difference ambiguity parameter as a time invariant parameter. By the design, the problem that due to the change of the reference satellite, the double-difference ambiguity parameters between the epochs and the receiver clock offset parameters can not be transmitted continuously, is solved, and the GNSS single difference processing method of the fixed reference satellite is simple and convenient to operate, and is high in calculation efficiency and strong in GNSS service capability.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
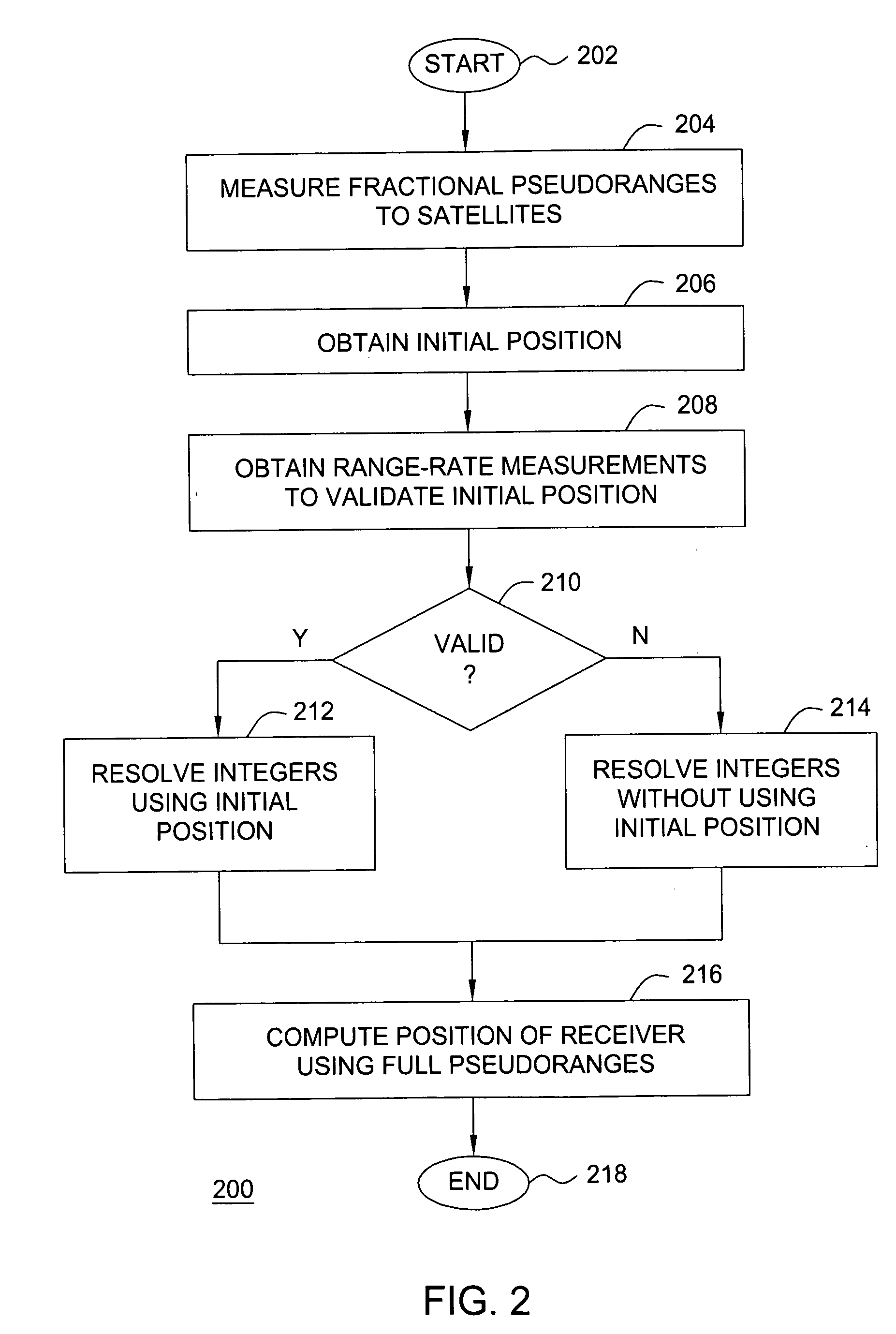
Method and apparatus for validating a position in a satellite positioning system using range-rate measurements
InactiveUS20060273954A1Position fixationSatellite radio beaconingSingle differenceSatellite positioning
Method and apparatus for validating an initial position in a satellite positioning system using range-rate measurements is described. In one example, range-rate measurements are obtained at the remote receiver with respect to a plurality of satellites. Expected range-rates are computed with respect to the plurality of satellites using the initial position. Single differences are computed using the range-rate measurements. Expected single differences are computed using the expected range-rates. Single difference residuals are computed between the single differences and the expected single differences. The single difference residuals are compared to a threshold. The initial position may be deemed valid if the absolute value of each of the single difference residuals is less than or equal to the threshold. A valid initial position may be used to fix the pseudorange integers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com