Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
88results about How to "Improve device density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
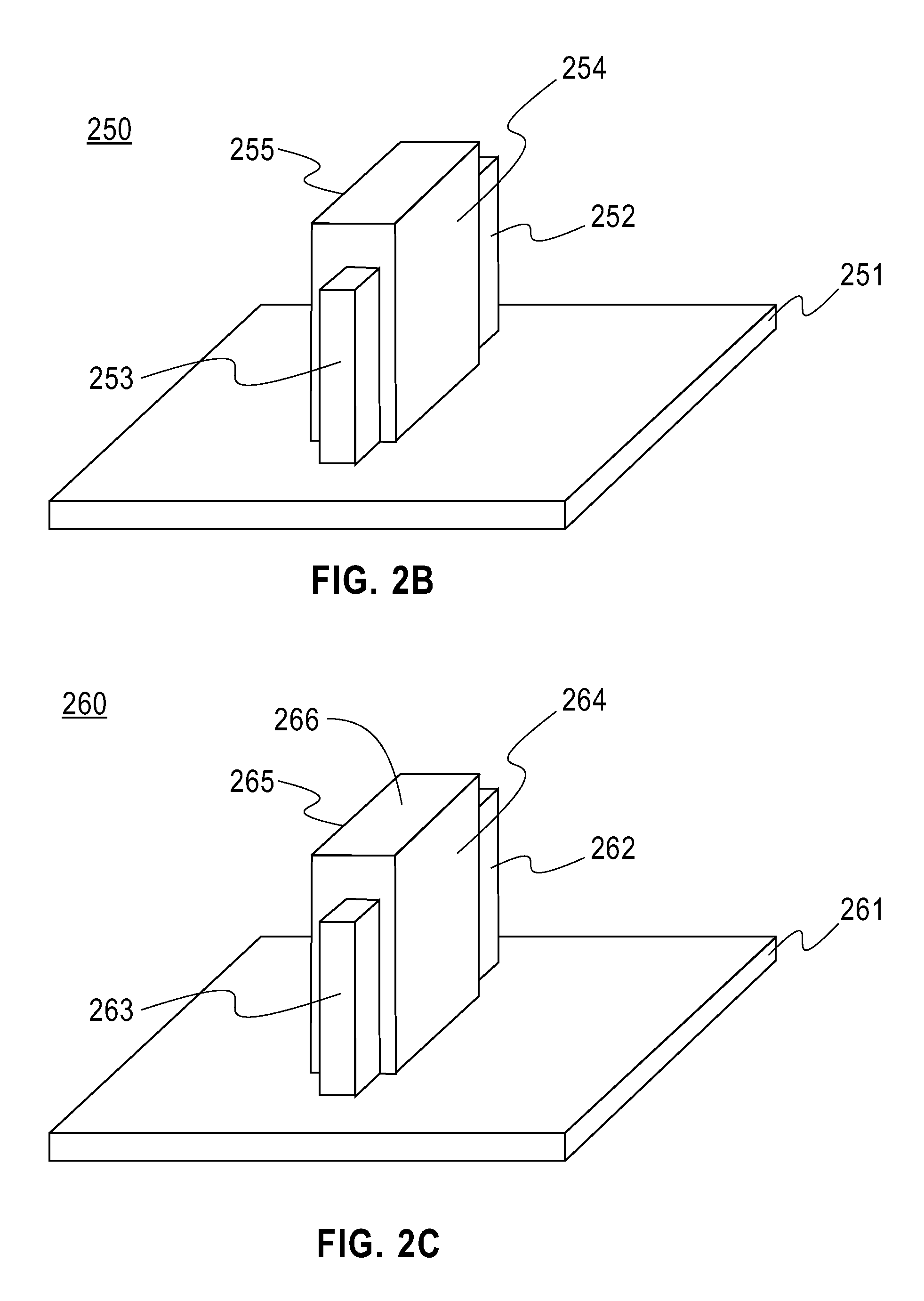
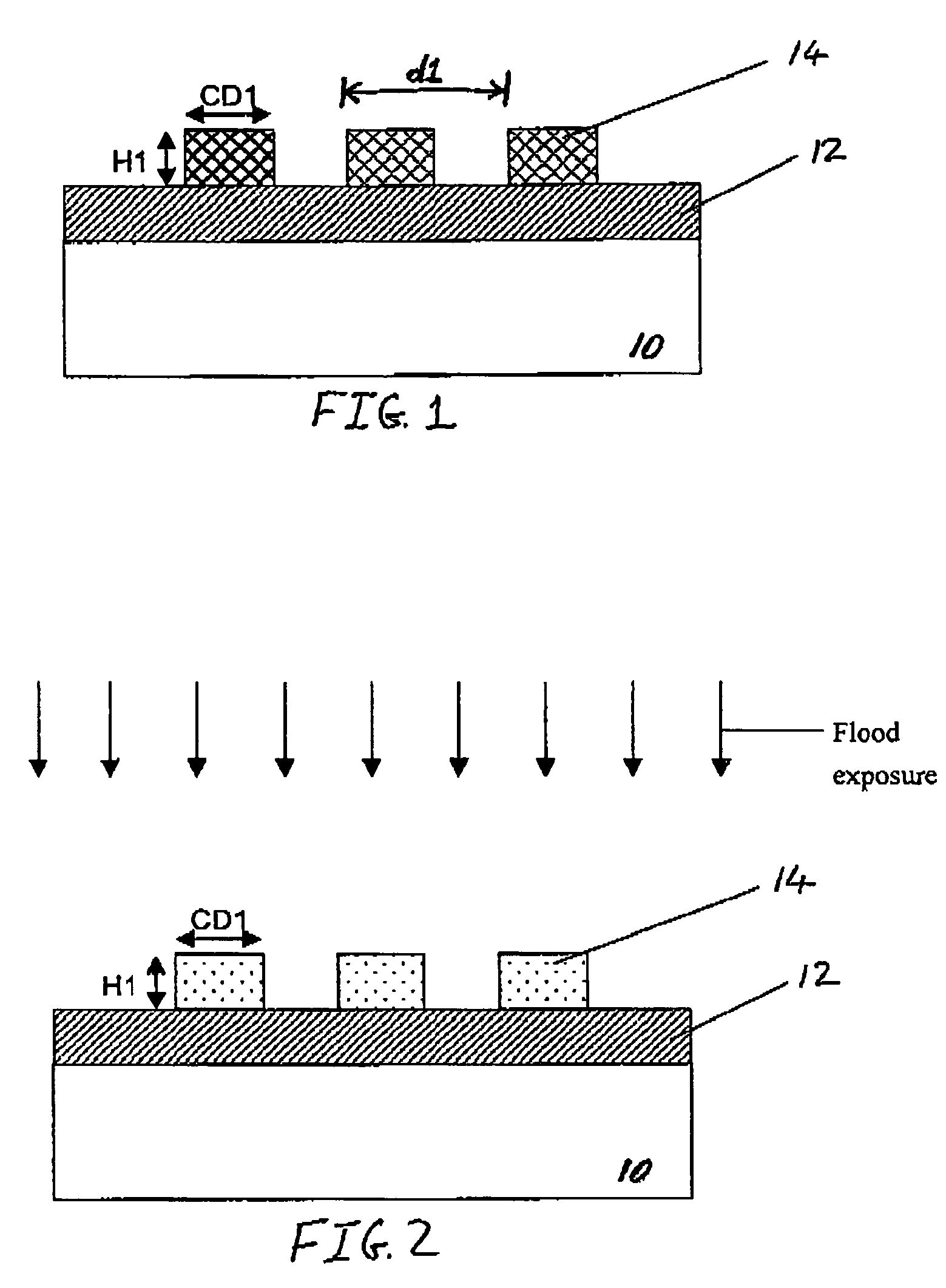
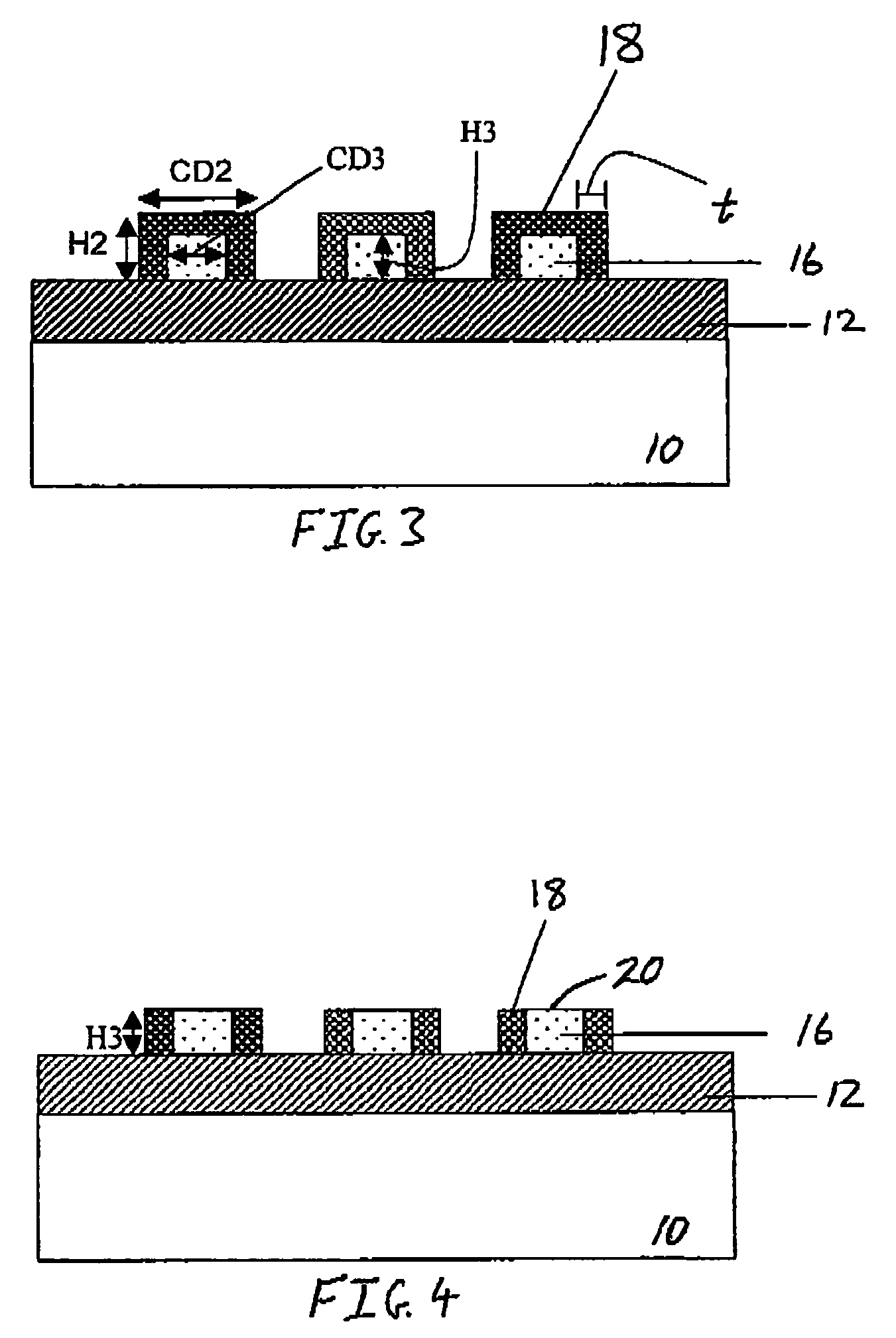
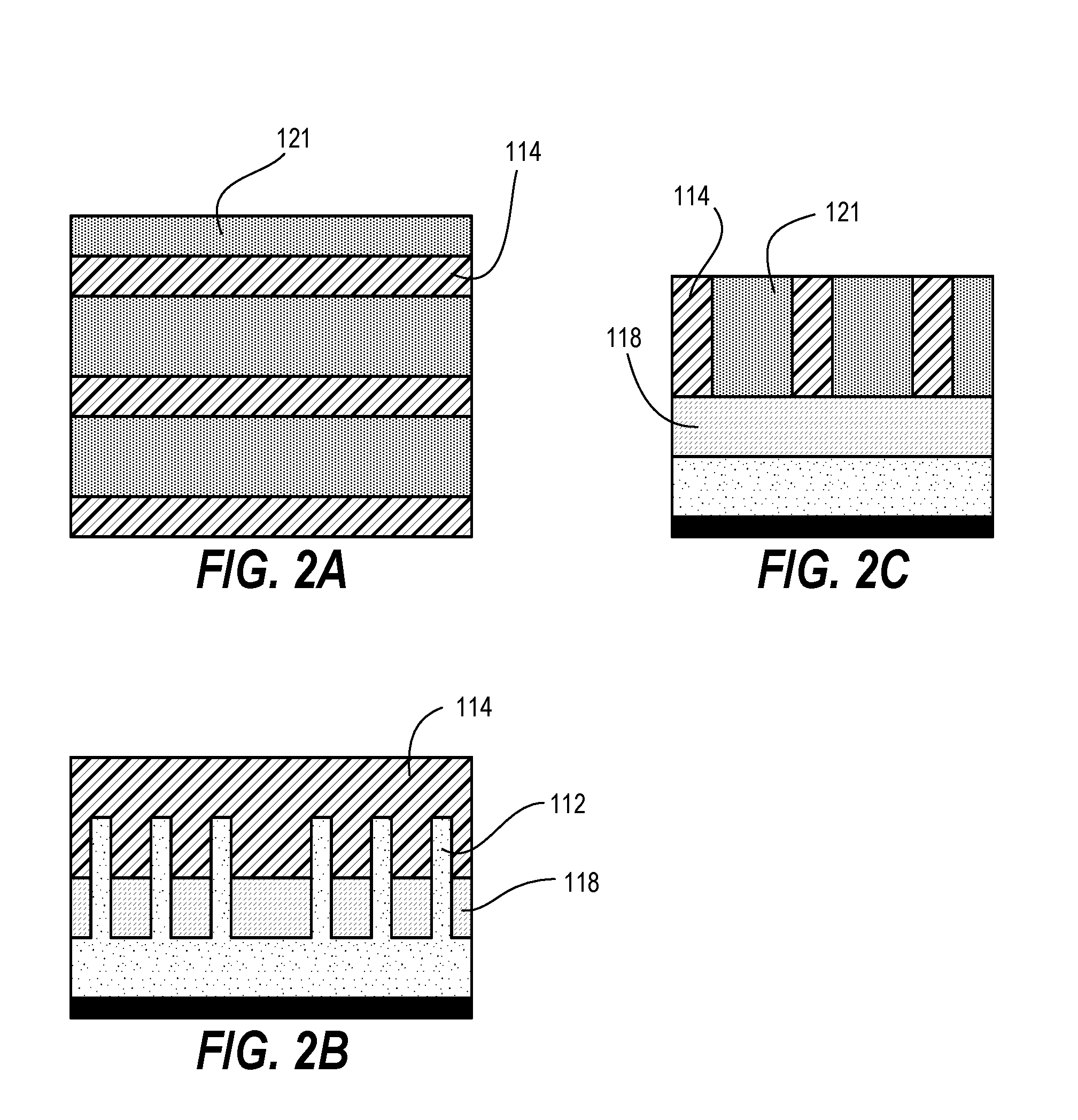
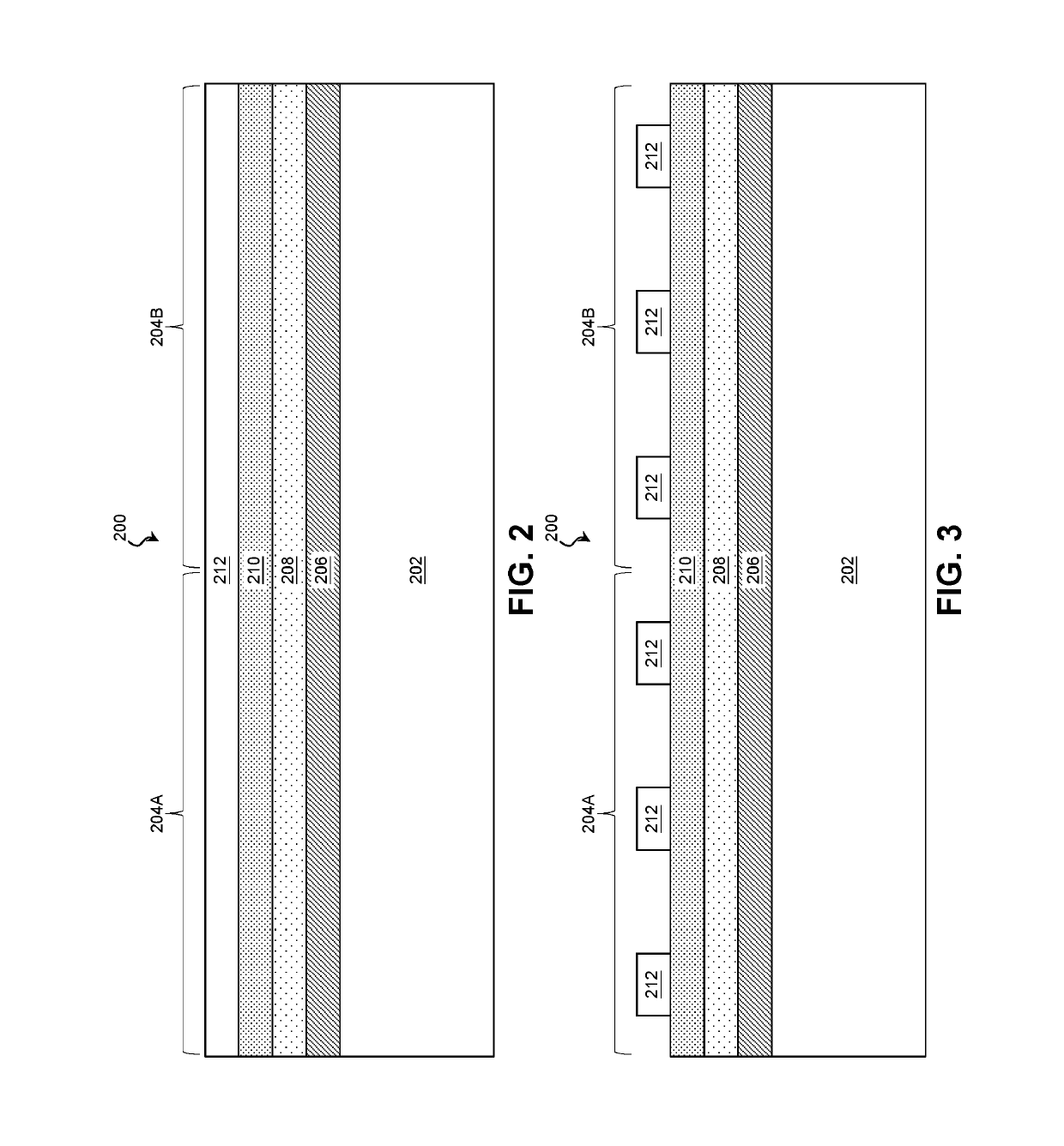
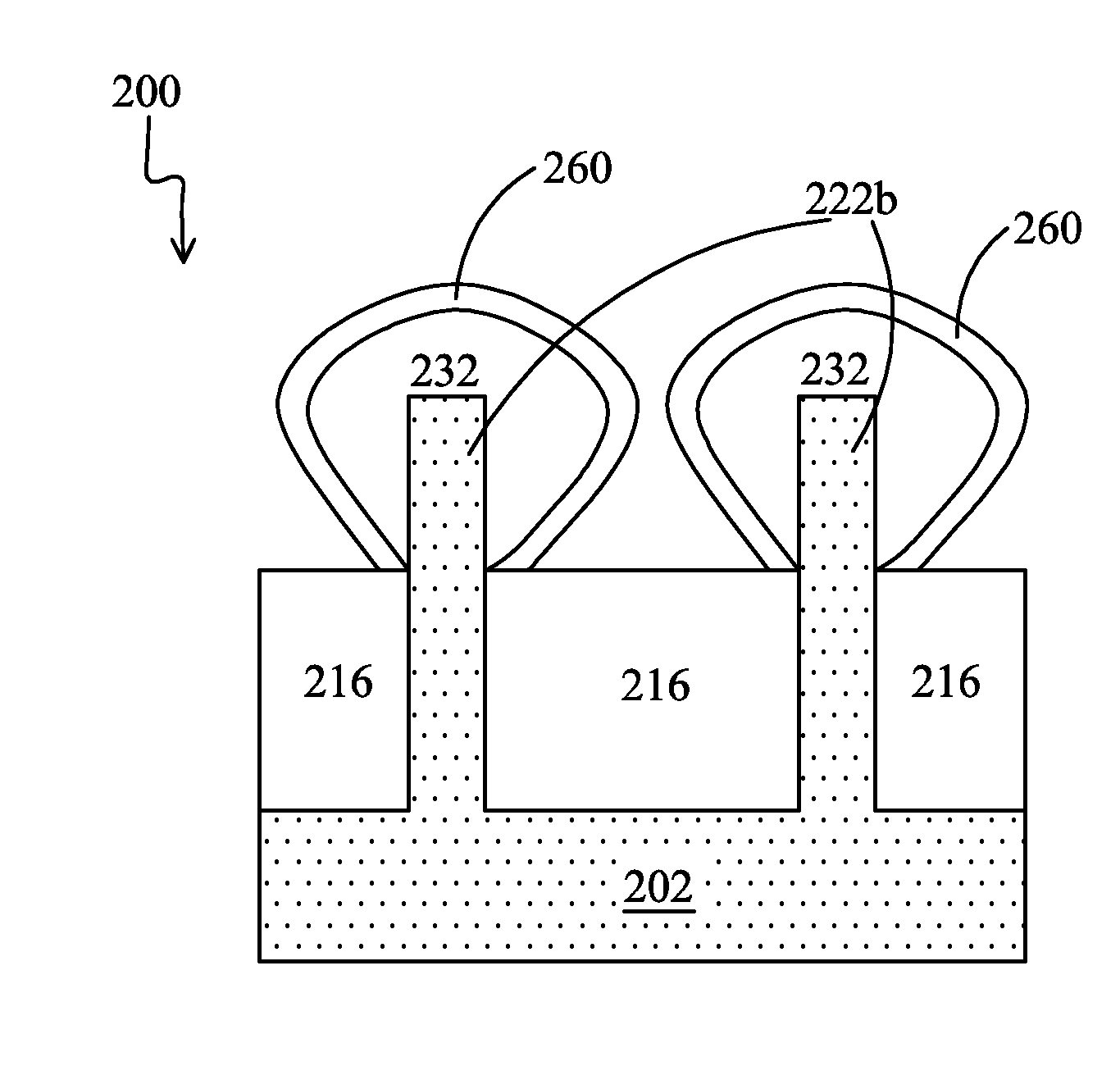
Method for fabricating a FinFET device
ActiveUS8652894B2Improve device densityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Non-uniform channel junction-less transistor
ActiveUS8487378B2Easy to controlImprove device densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
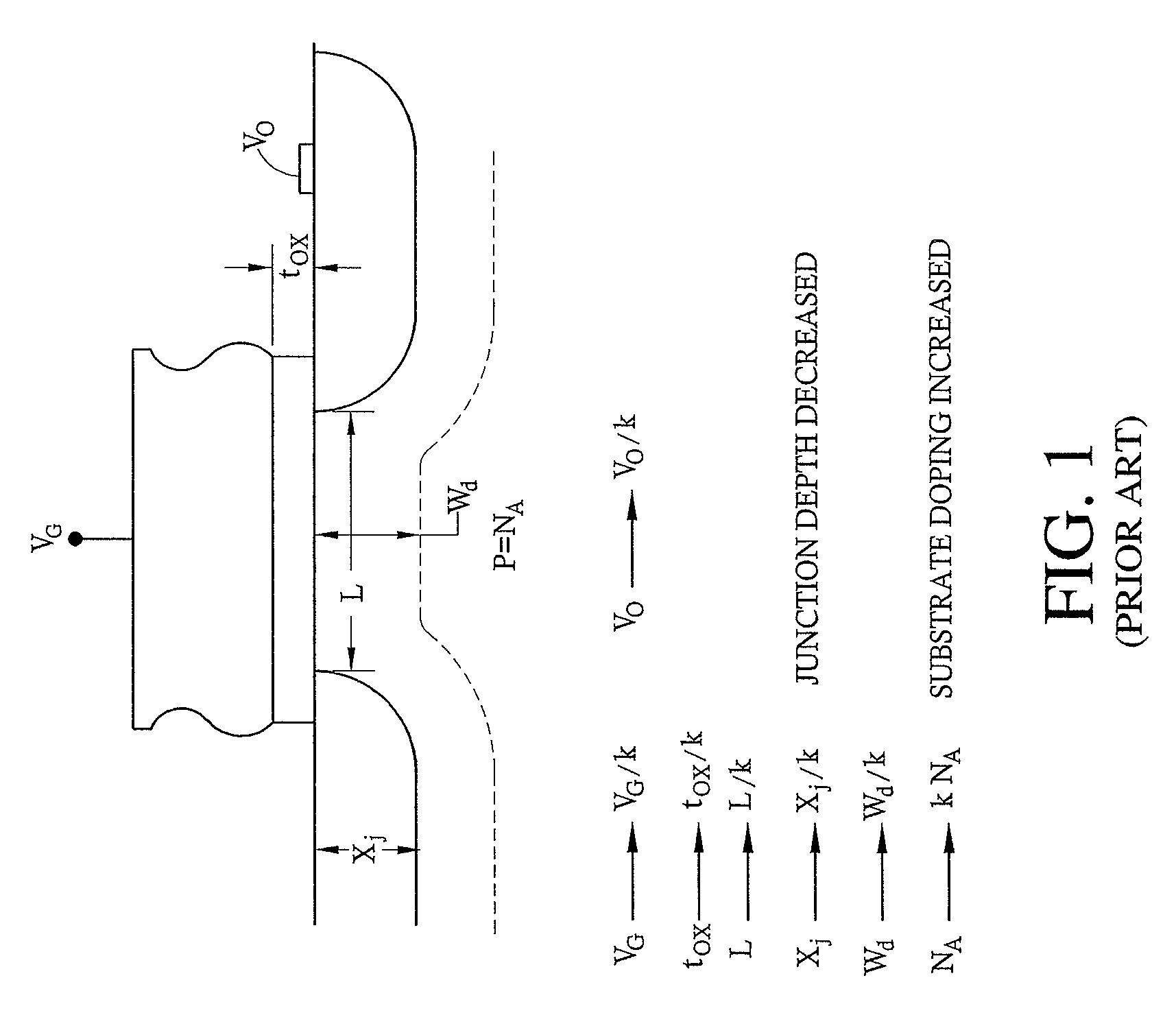
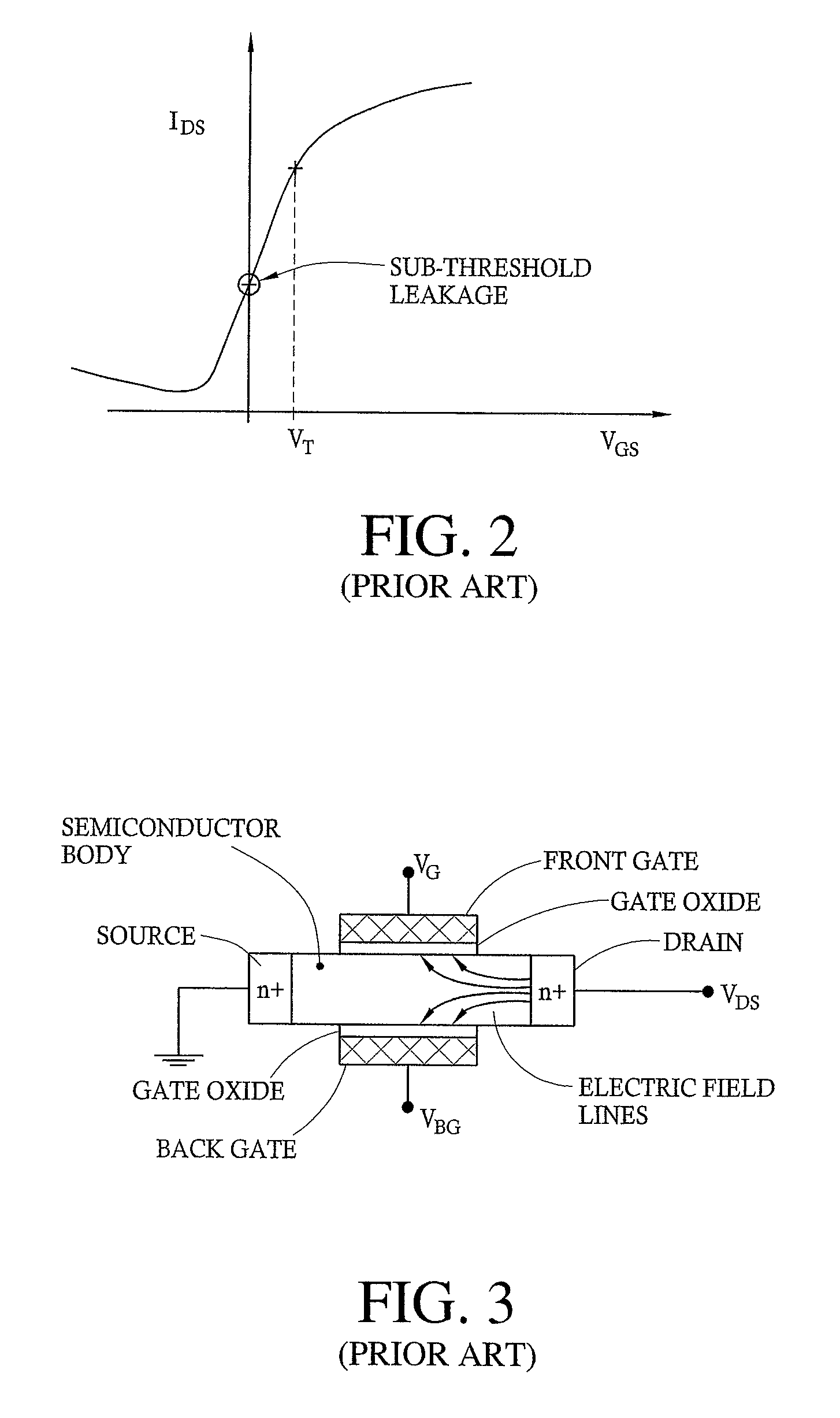
Semiconductor device including back-gated transistors and method of fabricating the device
ActiveUS20060274569A1Improve device densityImprove device stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryDevice material
A memory cell (e.g., static random access memory (SRAM) cell) includes a plurality of back-gated n-type field effect transistors (nFETs), and a plurality of double-gated p-type field effect transistors (pFETs) operatively coupled to the plurality of nFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
High density MRAM using thermal writing
ActiveUS6980468B1Reduce surface areaImprove reliability of deviceDigital storageAspect ratioMagnetic layer
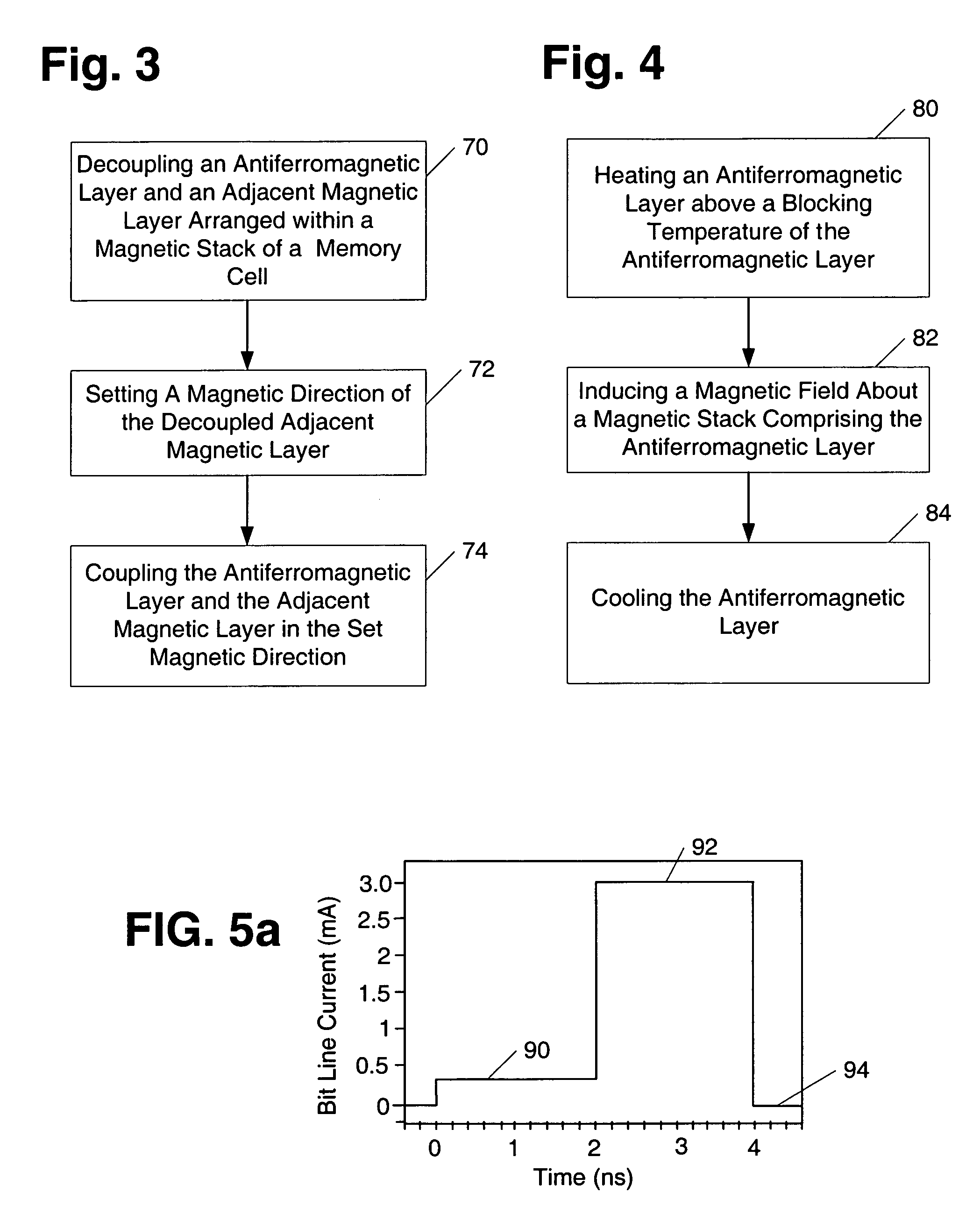
A memory cell includes a magnetic cell junction having an antiferromagnetic layer within a portion of the cell junction that is adapted to characterize a logic state of a bit written to the junction. More specifically, a memory cell includes, an antiferromagnetic layer arranged in contact with an adjacent magnetic layer within a storing portion of a magnetic cell junction. Such a magnetic cell junction configuration and a method for programming a memory cell with such a cell junction configuration may be used to improve the write selectivity of a memory cell array and reduce the amount of current needed to write a bit to a memory cell. Moreover, a memory cell includes a magnetic cell junction having an aspect ratio less than 1.6. In addition, a memory cell includes at least two resistors.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Memory array with ultra-thin etched pillar surround gate access transistors and buried data/bit lines
ActiveUS7371627B1Improved sub-threshold performanceImprove device densityTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineElectrical contacts
A memory array with data / bit lines extending generally in a first direction formed in an upper surface of a substrate and access transistors extending generally upward and aligned generally atop a corresponding data / bit line. The access transistors have a pillar extending generally upward with a source region formed so as to be in electrical communication with the corresponding data / bit line and a drain region formed generally at an upper portion of the pillar and a surround gate structure substantially completely encompassing the pillar in lateral directions and extending substantially the entire vertical extent of the pillar and word lines extending generally in a second direction and in electrical contact with a corresponding surround gate structure at least a first surface thereof such that bias voltage applied to a given word line is communicated substantially uniformly in a laterally symmetric extent about the corresponding pillar via the surround gate structure.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Methods for interconnecting bonding pads between components
InactiveUS8759713B2Cost-effectiveMore cost effective productsElectrically conductive connectionsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityHigh density
The present invention discloses methods and apparatuses for the separations of IC fabrication and assembling of separated IC components to form complete IC structures. In an embodiment, the present fabrication separation of an IC structure into multiple discrete components can take advantages of dedicated IC fabrication facilities and achieve more cost effective products. In another embodiment, the present chip assembling provides high density interconnect wires between bond pads, enabling cost-effective assembling of small chip components. In an aspect, the present process bonds multiple interconnect wires to bond pads with electrical linkages between the bond pads and then subsequently separates the adjacent bond pads.
Owner:TERECIRCUITS CORP
System and method for cryogenic hybrid technology computing and memory
ActiveUS9520180B1Easy to combineTransmission lineCosmetic preparationsQuantum computersLow inductanceDatapath
A system and method for high-speed, low-power cryogenic computing are presented, comprising ultrafast energy-efficient RSFQ superconducting computing circuits, and hybrid magnetic / superconducting memory arrays and interface circuits, operating together in the same cryogenic environment. An arithmetic logic unit and register file with an ultrafast asynchronous wave-pipelined datapath is also provided. The superconducting circuits may comprise inductive elements fabricated using both a high-inductance layer and a low-inductance layer. The memory cells may comprise superconducting tunnel junctions that incorporate magnetic layers. Alternatively, the memory cells may comprise superconducting spin transfer magnetic devices (such as orthogonal spin transfer and spin-Hall effect devices). Together, these technologies may enable the production of an advanced superconducting computer that operates at clock speeds up to 100 GHz.
Owner:SEEQC INC
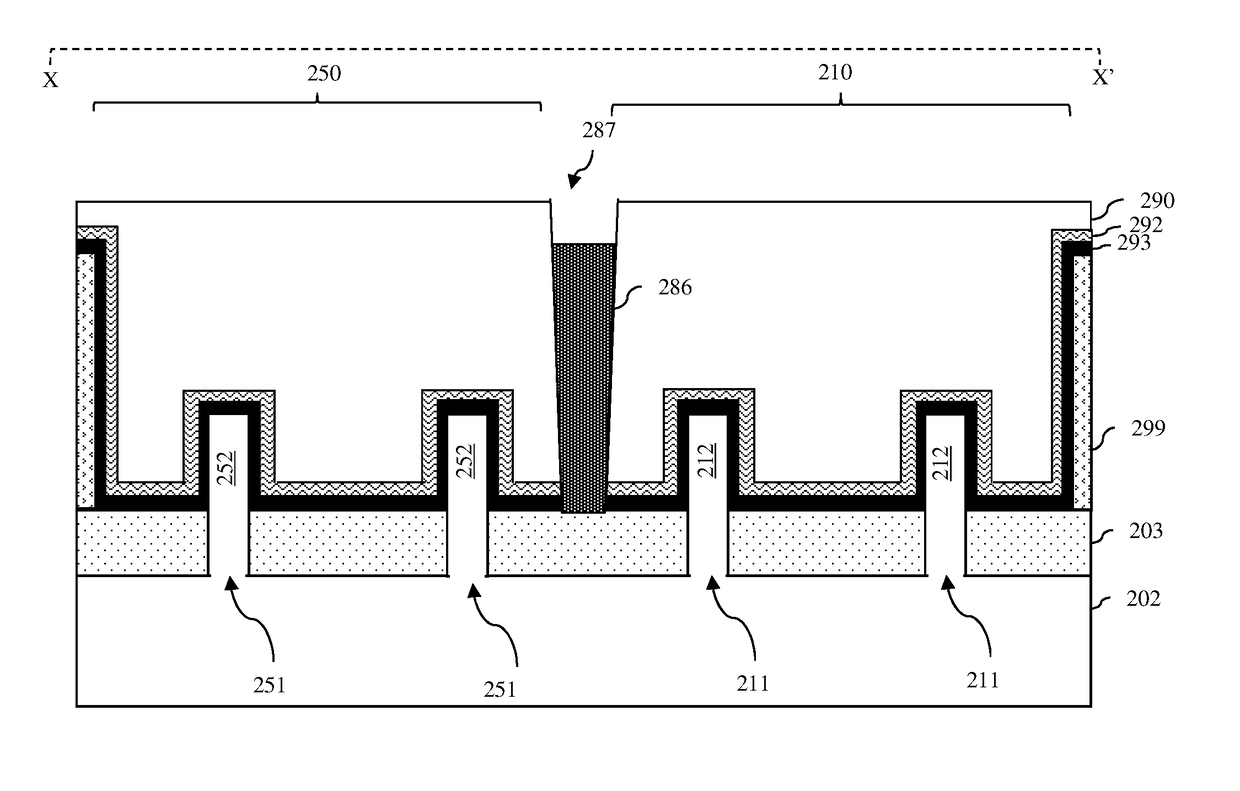
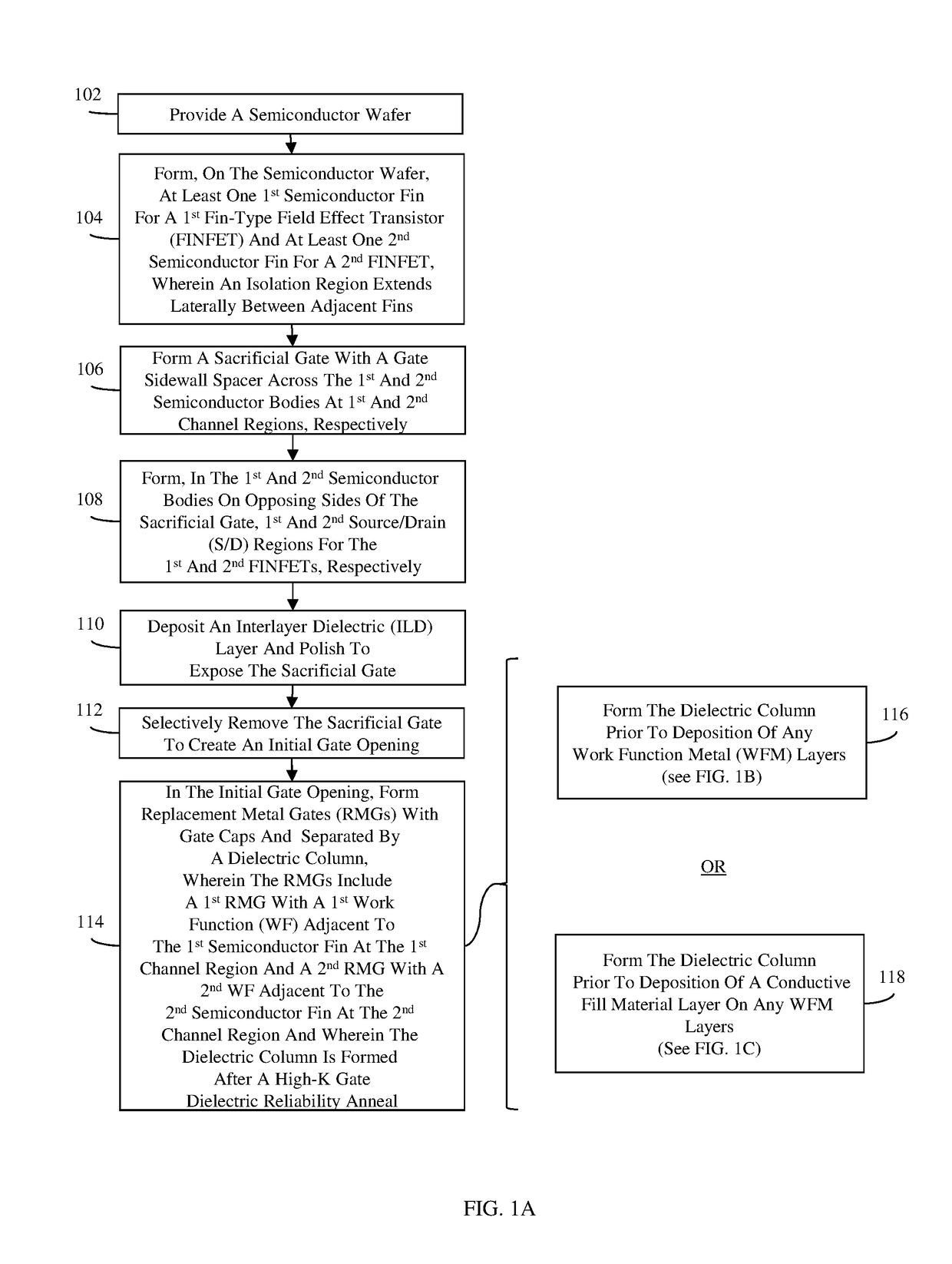
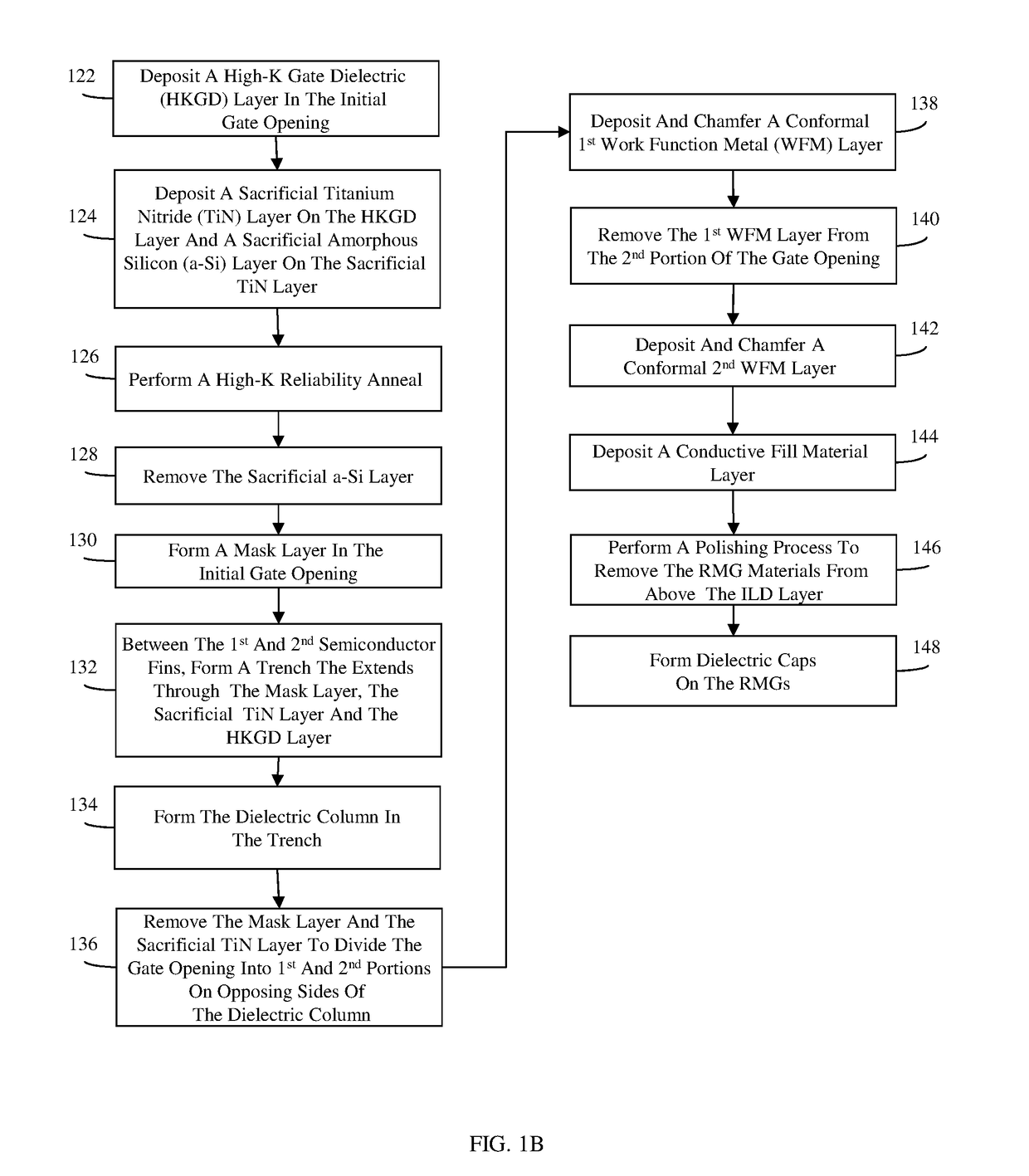
Fin-type field effect transistors (finfets) with replacement metal gates and methods
ActiveUS20180261514A1Minimize riskSecond rmgTransistorSolid-state devicesWork functionIntegrated circuit
Disclosed are method embodiments for forming an integrated circuit (IC) structure with at least one first-type FINFET and at least one second-type FINFET, wherein the first-type FINFET has a first replacement metal gate (RMG) adjacent to a first semiconductor fin, the second-type FINFET has a second RMG adjacent to a second semiconductor fin, and the first RMG is in end-to-end alignment with the second RMG and physically and electrically isolated from the second RMG by a dielectric column. The method embodiments minimize the risk of the occurrence defects within the RMGs by forming the dielectric column during formation of the first and second RMGs and, particularly, after deposition and anneal of a gate dielectric layer for the first and second RMGs, but before deposition of at least one of multiple work function metal layers. Also disclosed herein are IC structure embodiments formed according to the above-described method embodiments.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
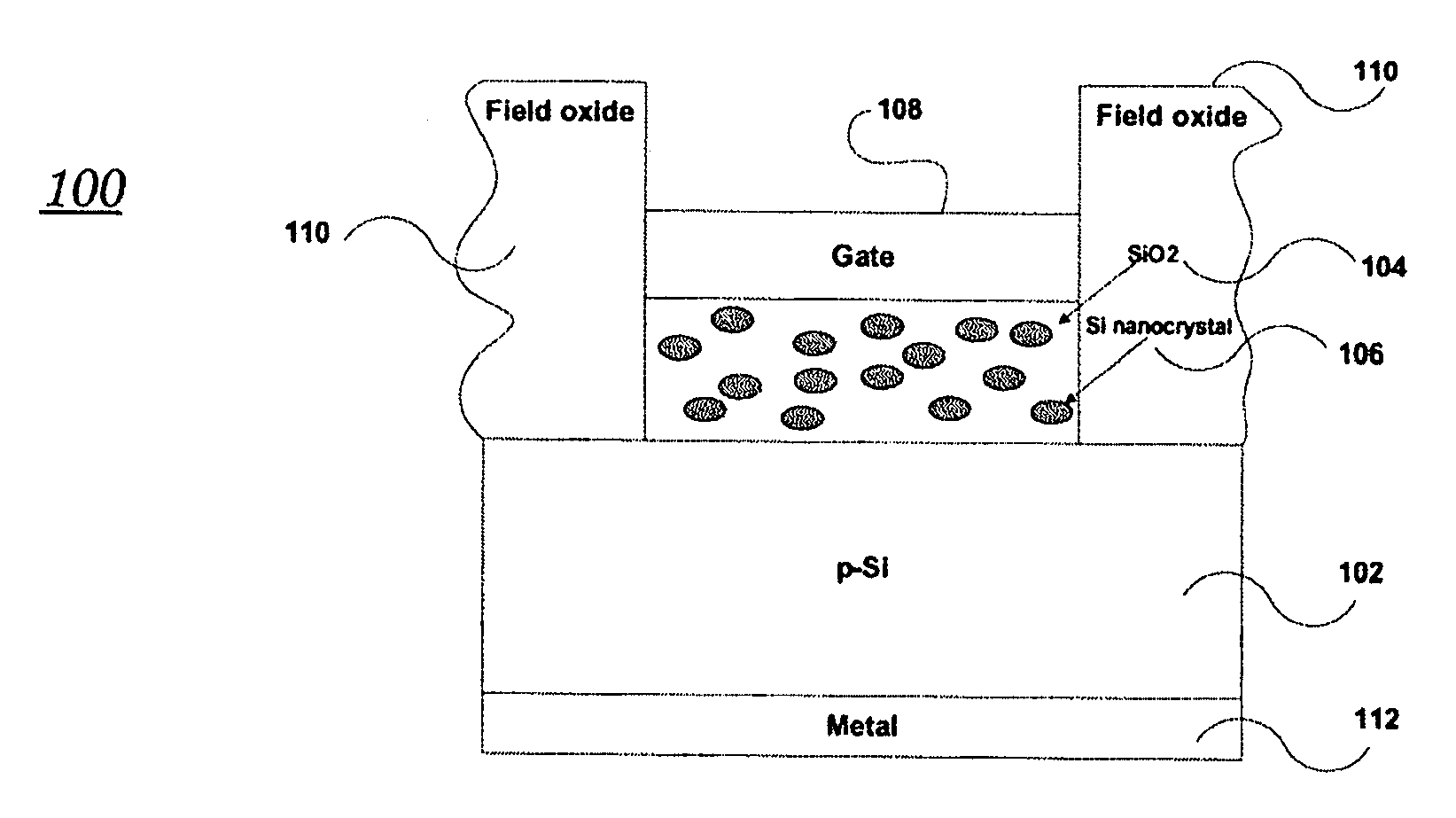
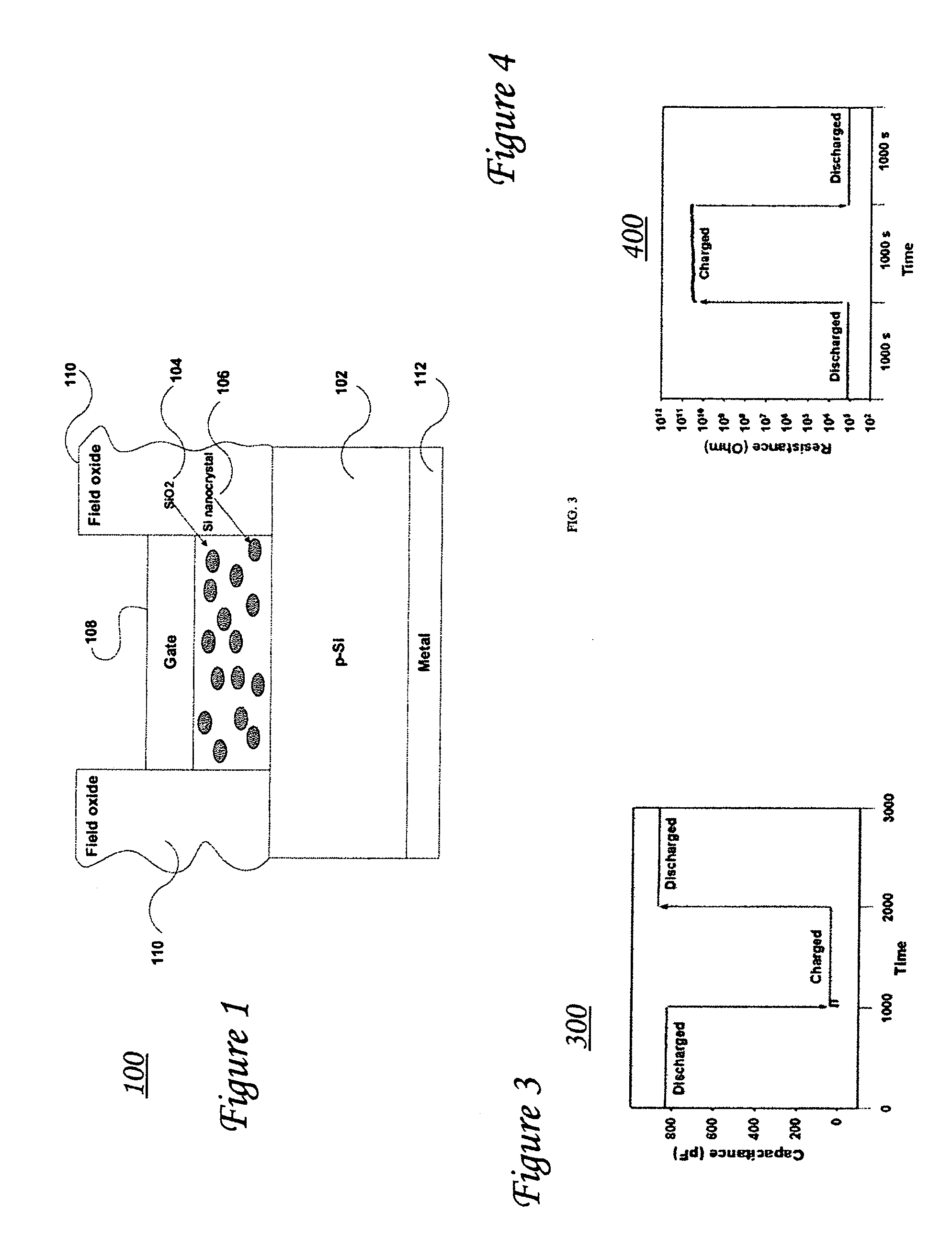
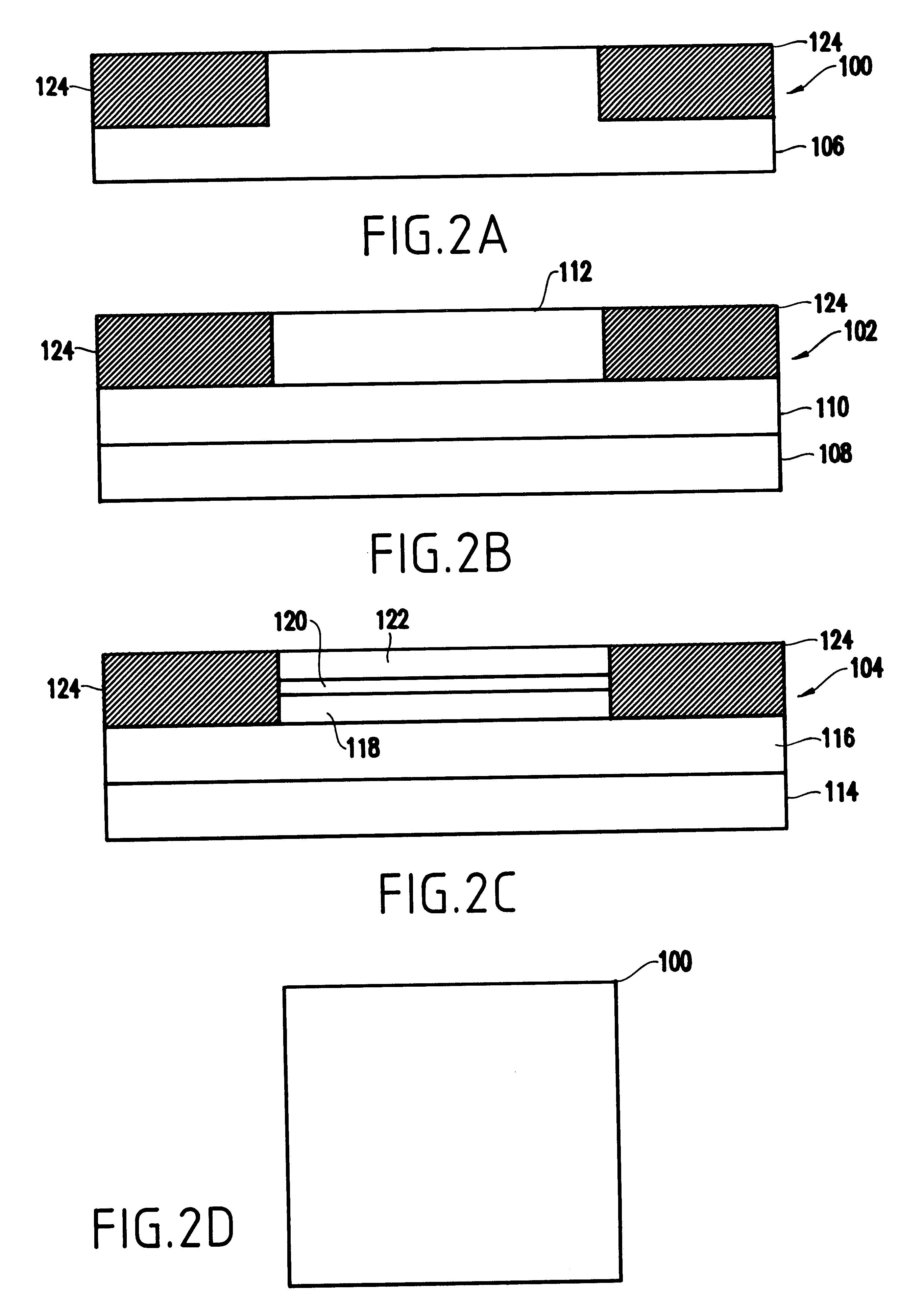
Two-terminal solid-state memory device and two-terminal flexible memory device based on nanocrystals or nanoparticles
InactiveUS20060231889A1Simple designFew stepsNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETManufacturing technology
A two-terminal memory device based on semiconductor (such as Si or Ge) or metal (such as Al or Au) nanocrystals and / or nanoparticles is described wherein each device has a substrate, a dielectric layer (such as SiO2 or organic dielectric materials) nanocrystals and / or nanoparticles distributed throughout the dielectric layer, and a metal (or poly-crystalline Si, or conductive organic materials) gate electrode. The memory states of the device are distinguished by charging and discharging the nanocrystals and / or nanoparticles. This two-terminal memory device is much simpler than the conventional four-terminal MOSFET-based memory device in terms of device structure and fabrication process. In addition, it is flexible if the memory devices are fabricated on flexible substrate with organic materials.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Two-step MOSFET gate formation for high-density devices
InactiveUS6333247B1Reduces device topographyReduces the demands on backend lithographyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETHigh density
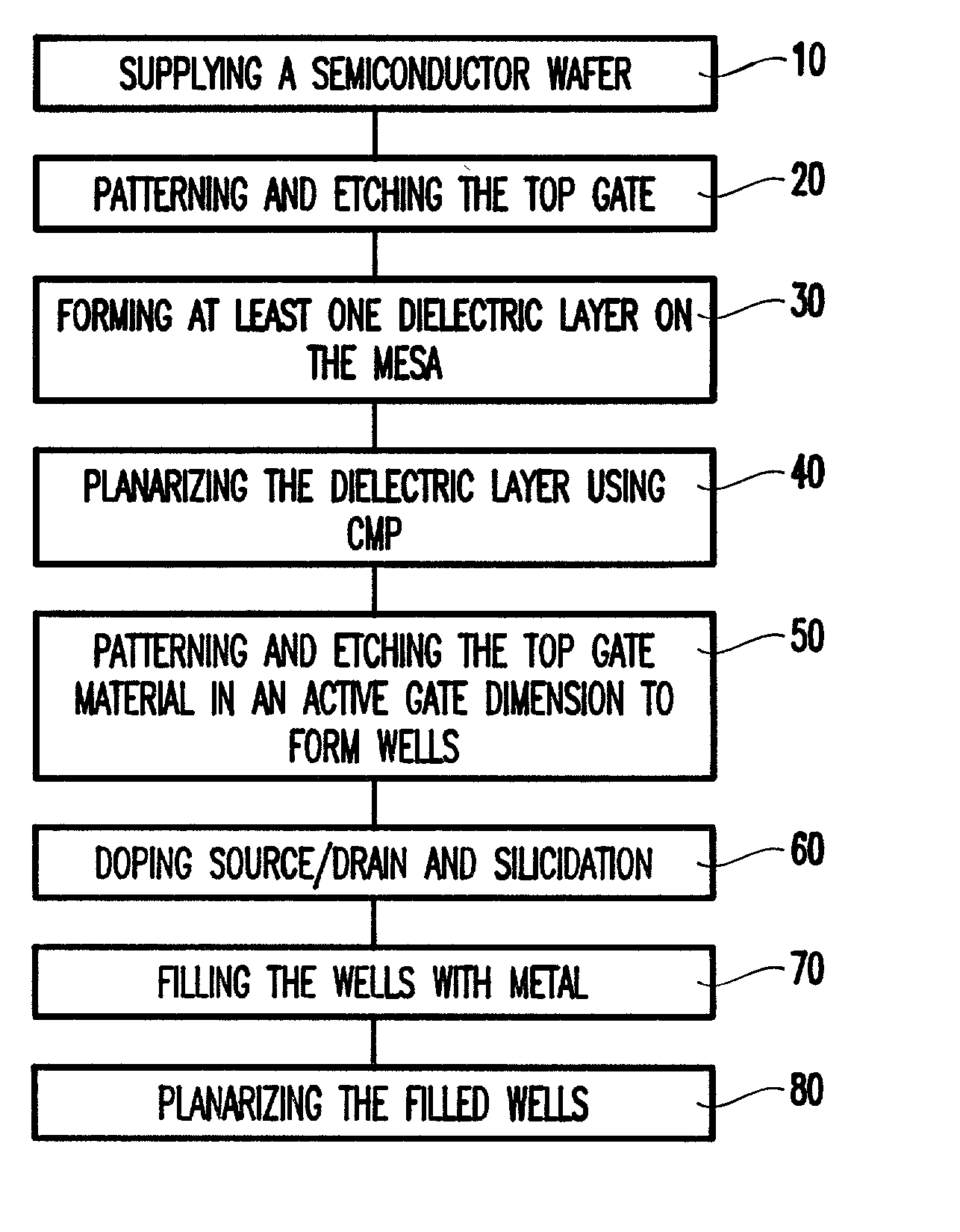
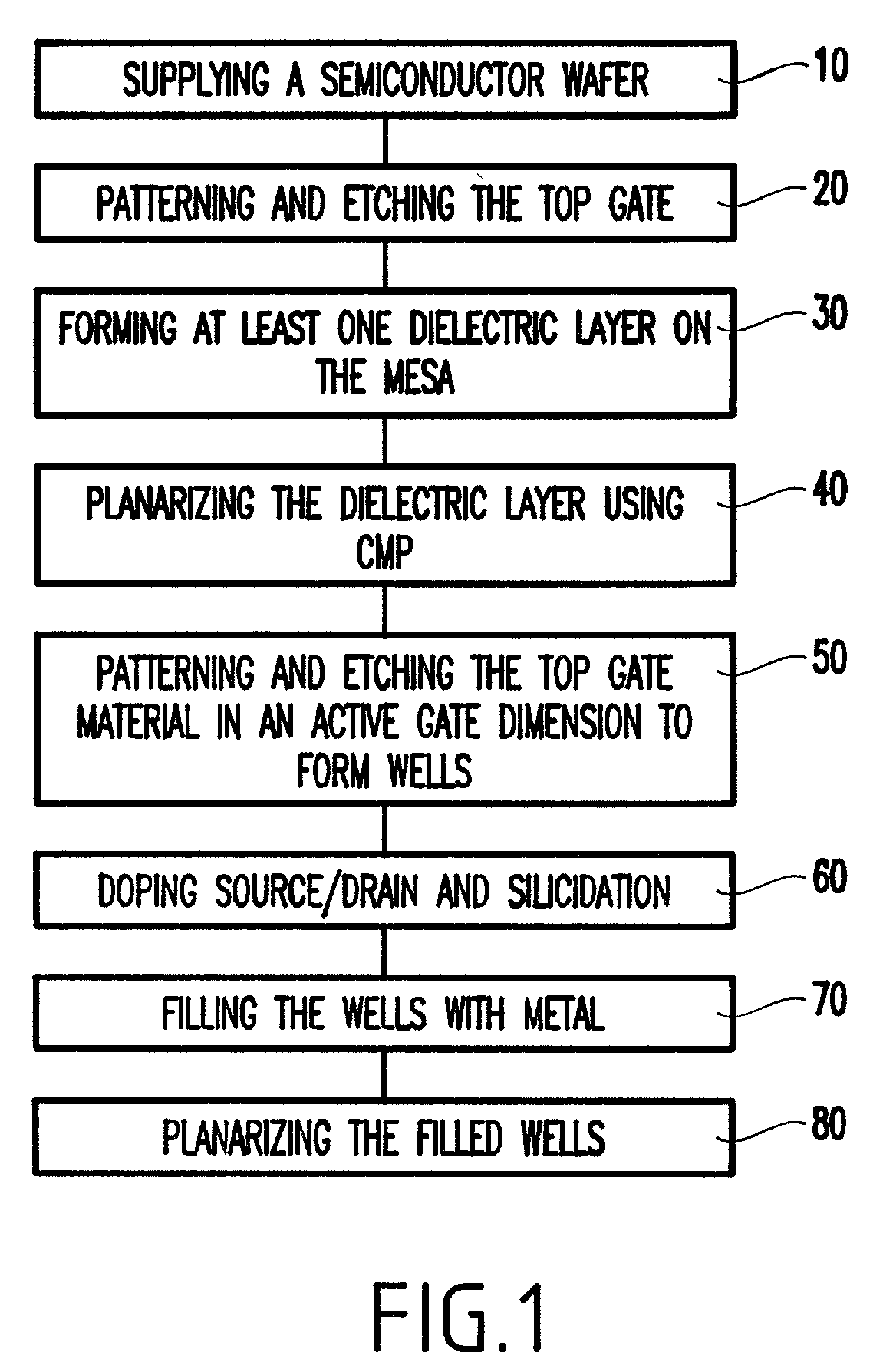
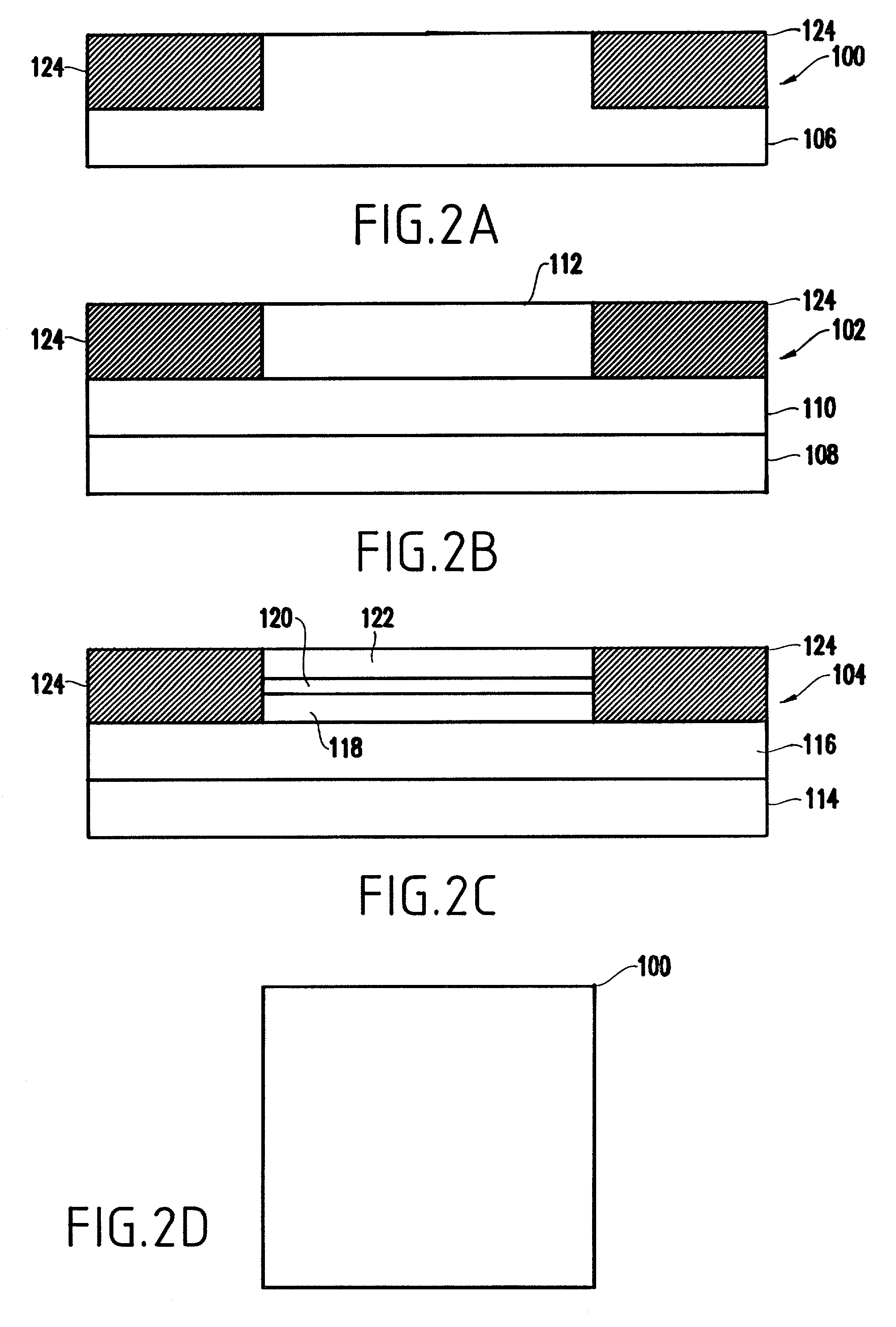
A method of manufacturing a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor MOSFET device gate includes patterning and etching the mesa of a gate material. A dielectric layer is formed on the mesa and is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). The active gate dimension is patterned and etched to form source and drain wells that extend down to an active area on either side of the MOSFET gate. In one further embodiment, the wells are filled with metal and the metal is planarized. The MOSFET device, in one embodiment, includes source and drain wells equally spaced from the active gate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for fabricating a finfet device
ActiveUS20130071980A1Improve device densityImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
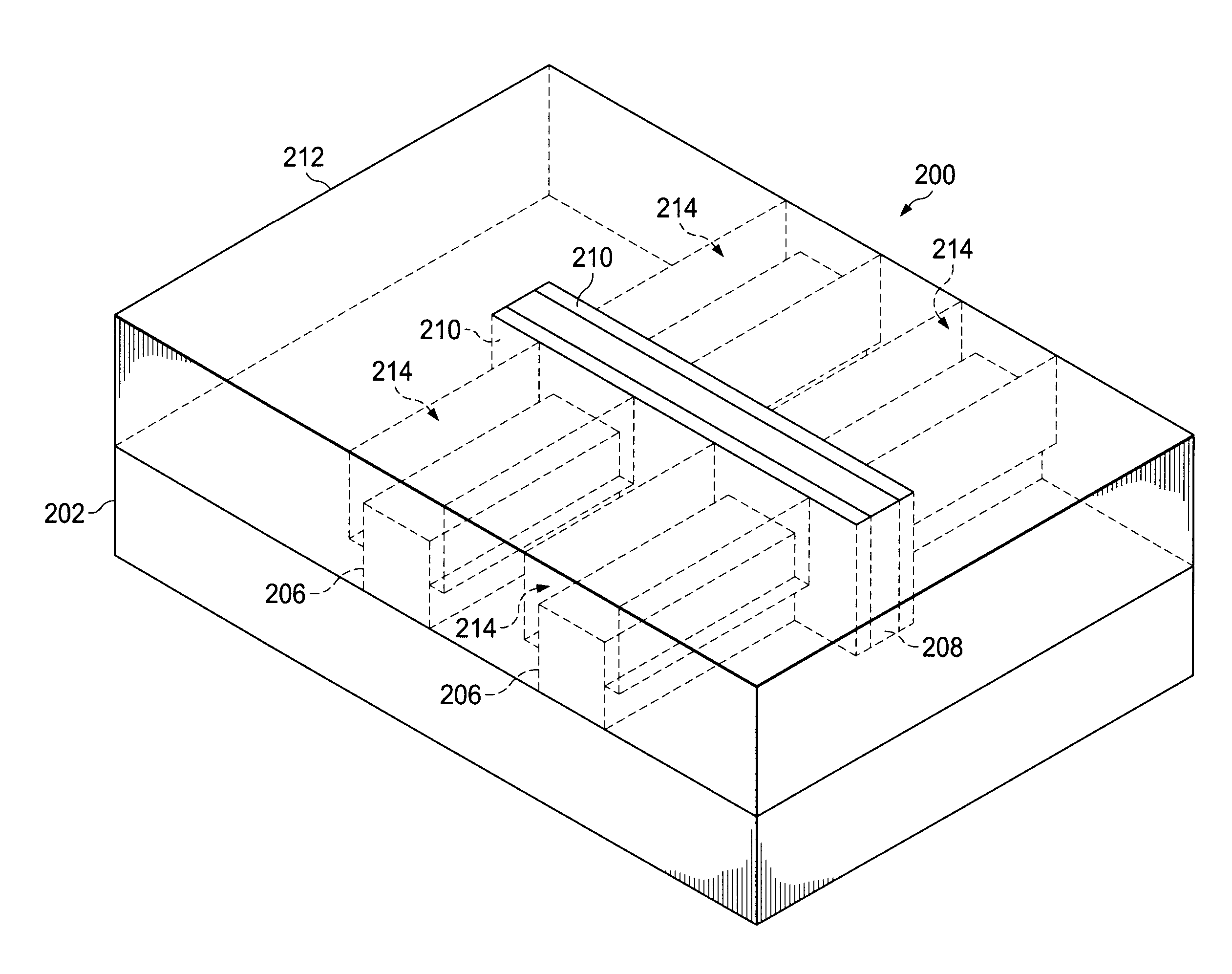
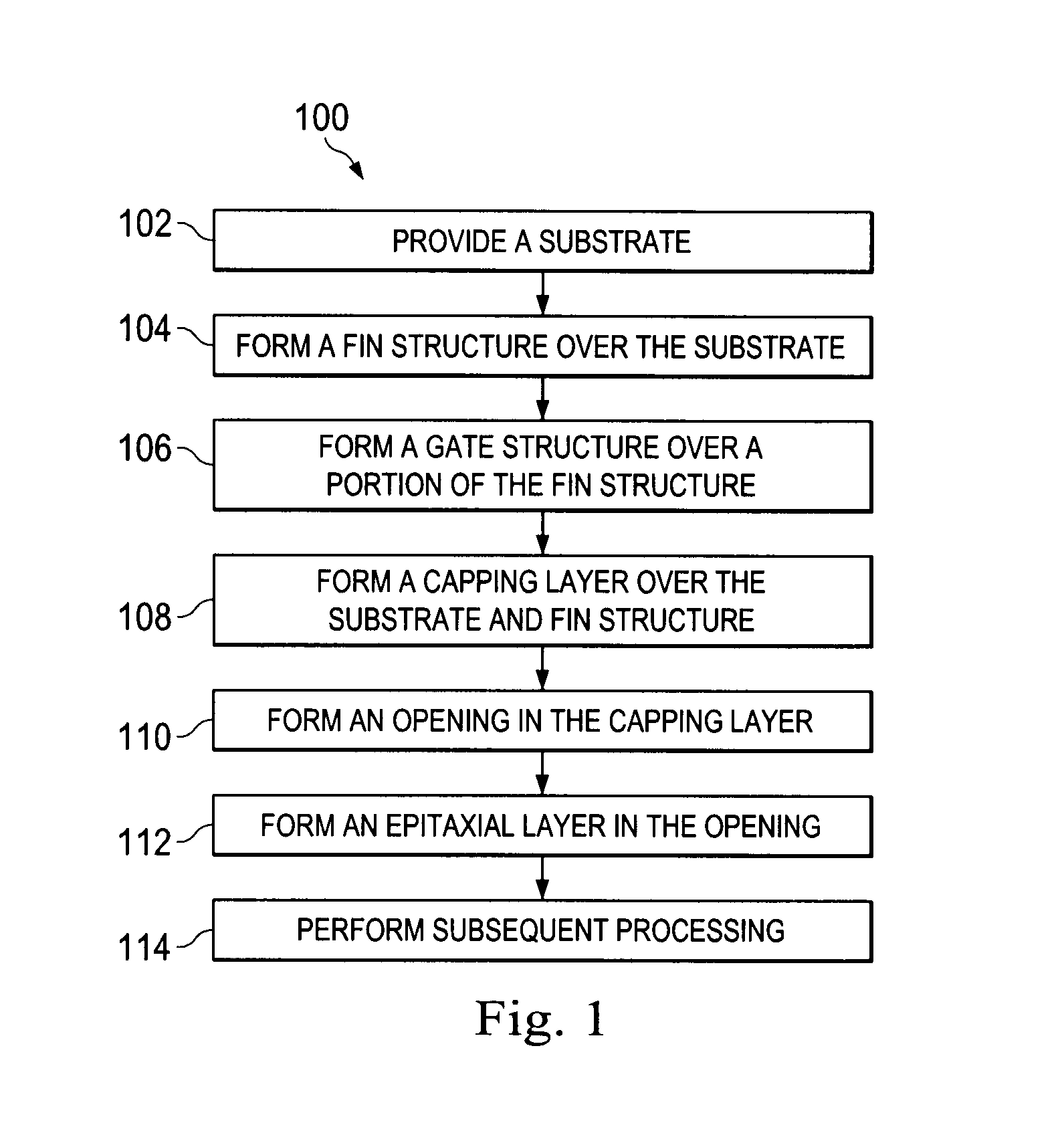
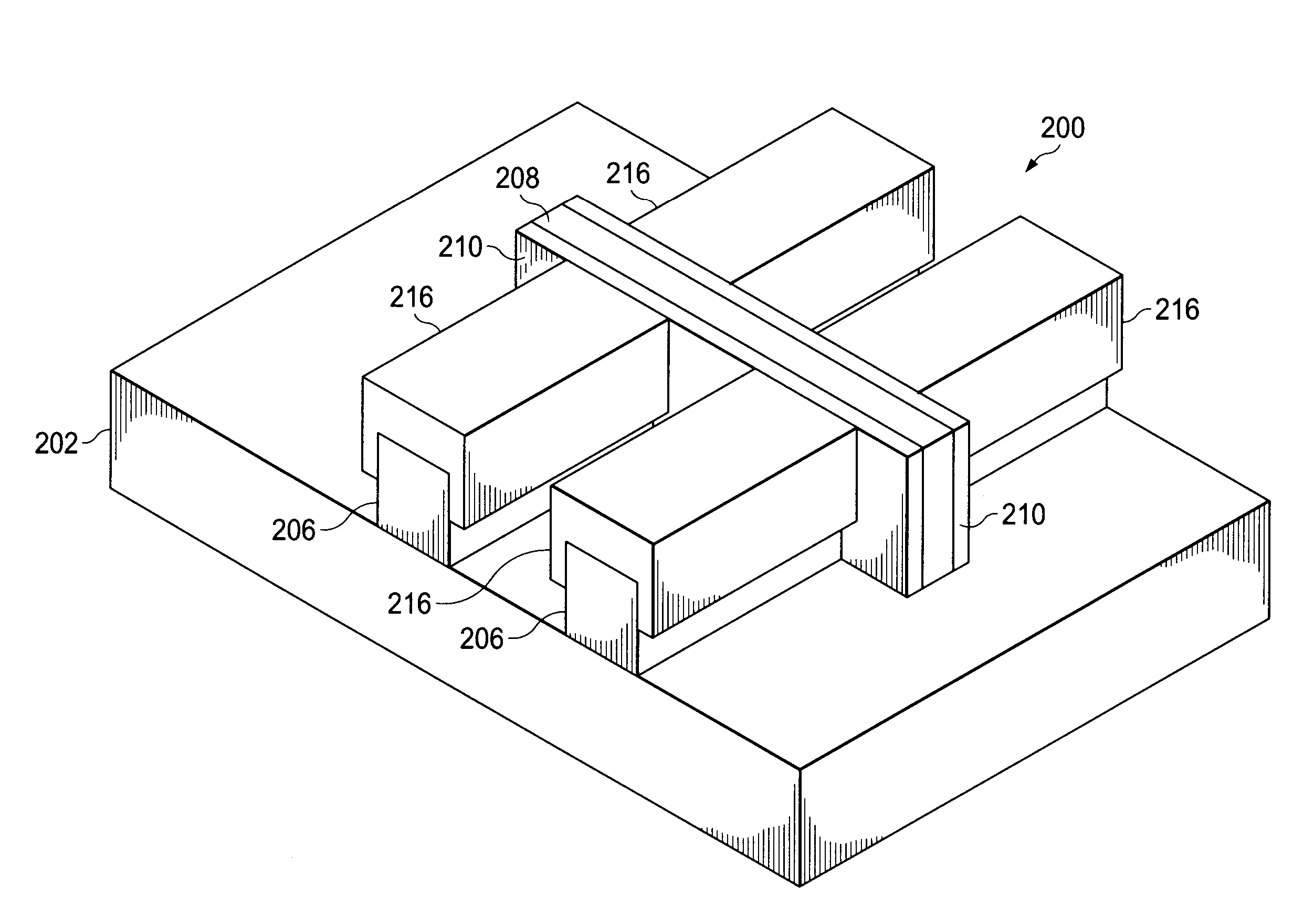
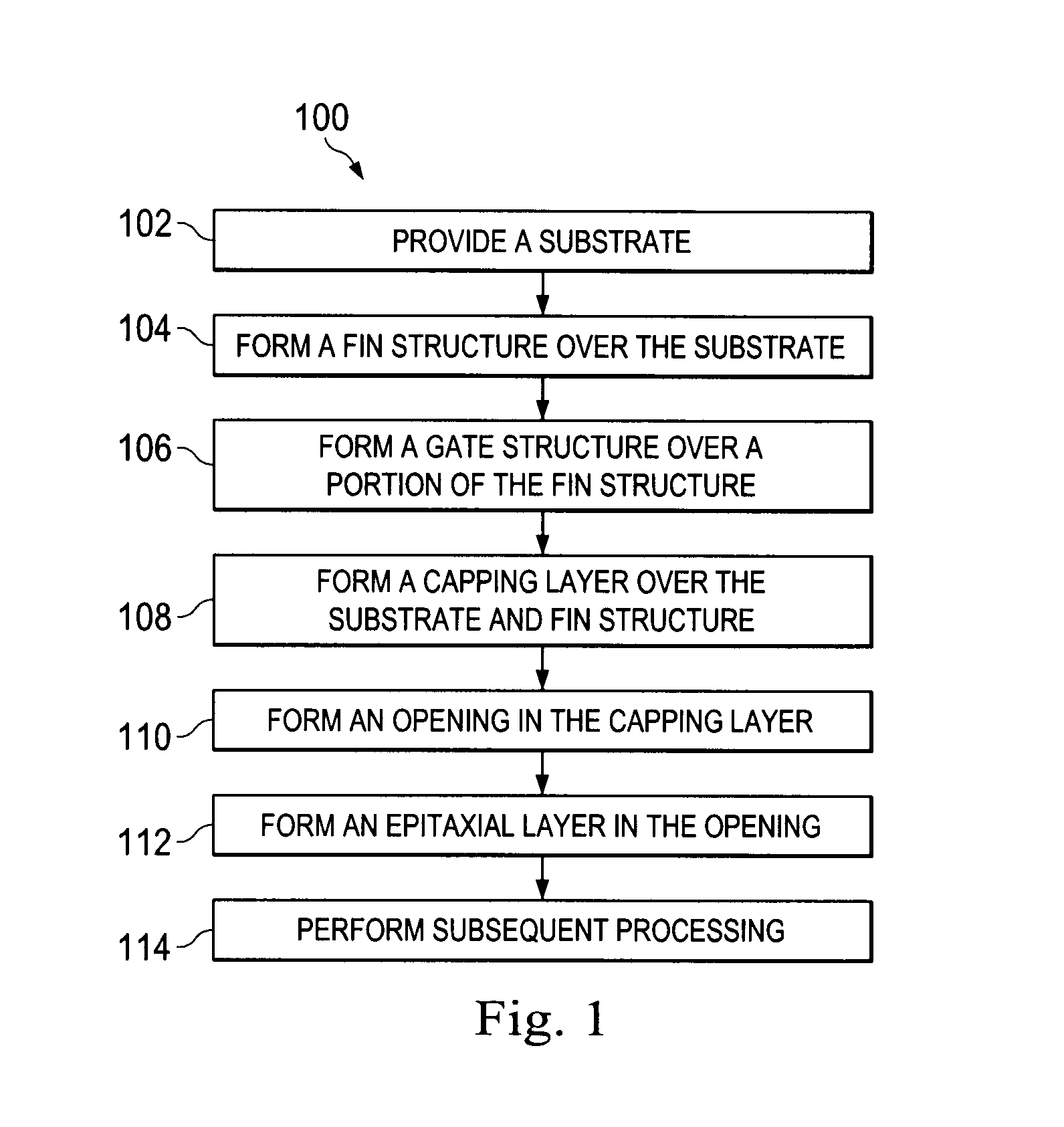
A FinFET device and method for fabricating a FinFET device is disclosed. An exemplary method includes forming a fin structure on a semiconductor substrate and forming a gate structure on the fin structure. A capping layer is then formed over the semiconductor substrate, fin structure, and gate structure. The capping layer is patterned to form an opening exposing a second portion of the fin structure. An epitaxial layer is grown in the opening and on the second portion of the fin structure. At least one of a source region and a drain region is provided in the epitaxial layer. The method may continue to remove the capping layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device including back-gated transistors and method of fabricating the device
ActiveUS7532501B2Improve device densityImprove device stabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryEngineering
A memory cell (e.g., static random access memory (SRAM) cell) includes a plurality of back-gated n-type field effect transistors (nFETs), and a plurality of double-gated p-type field effect transistors (pFETs) operatively coupled to the plurality of nFETs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Memory array with ultra-thin etched pillar surround gate access transistors and buried data/bit lines
ActiveUS7525141B1Easy to controlImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineElectrical contacts
A memory array with data / bit lines extending generally in a first direction formed in an upper surface of a substrate and access transistors extending generally upward and aligned generally atop a corresponding data / bit line. The access transistors have a pillar extending generally upward with a source region formed so as to be in electrical communication with the corresponding data / bit line and a drain region formed generally at an upper portion of the pillar and a surround gate structure substantially completely encompassing the pillar in lateral directions and extending substantially the entire vertical extent of the pillar and word lines extending generally in a second direction and in electrical contact with a corresponding surround gate structure at least a first surface thereof such that bias voltage applied to a given word line is communicated substantially uniformly in a laterally symmetric extent about the corresponding pillar via the surround gate structure.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
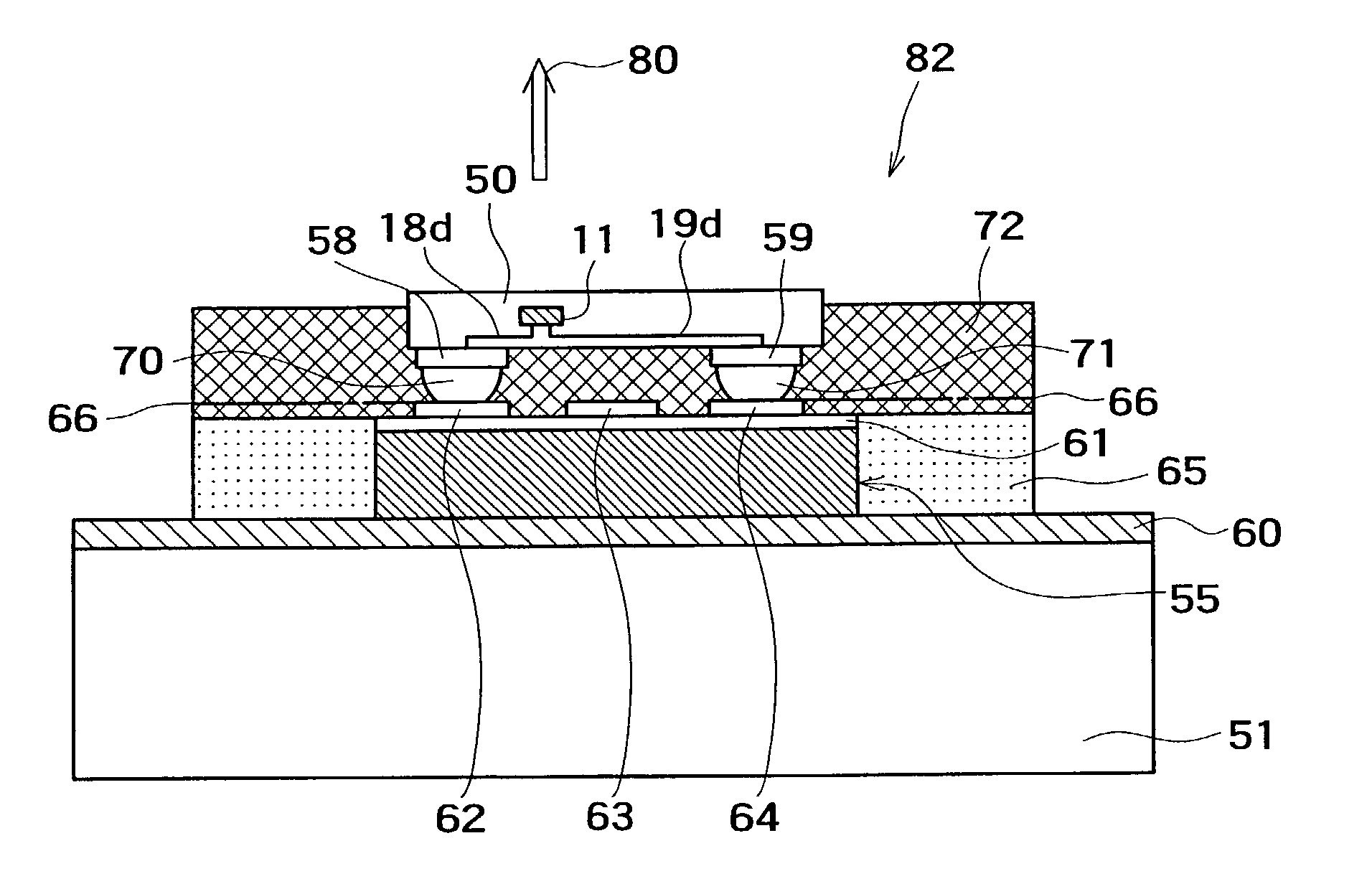
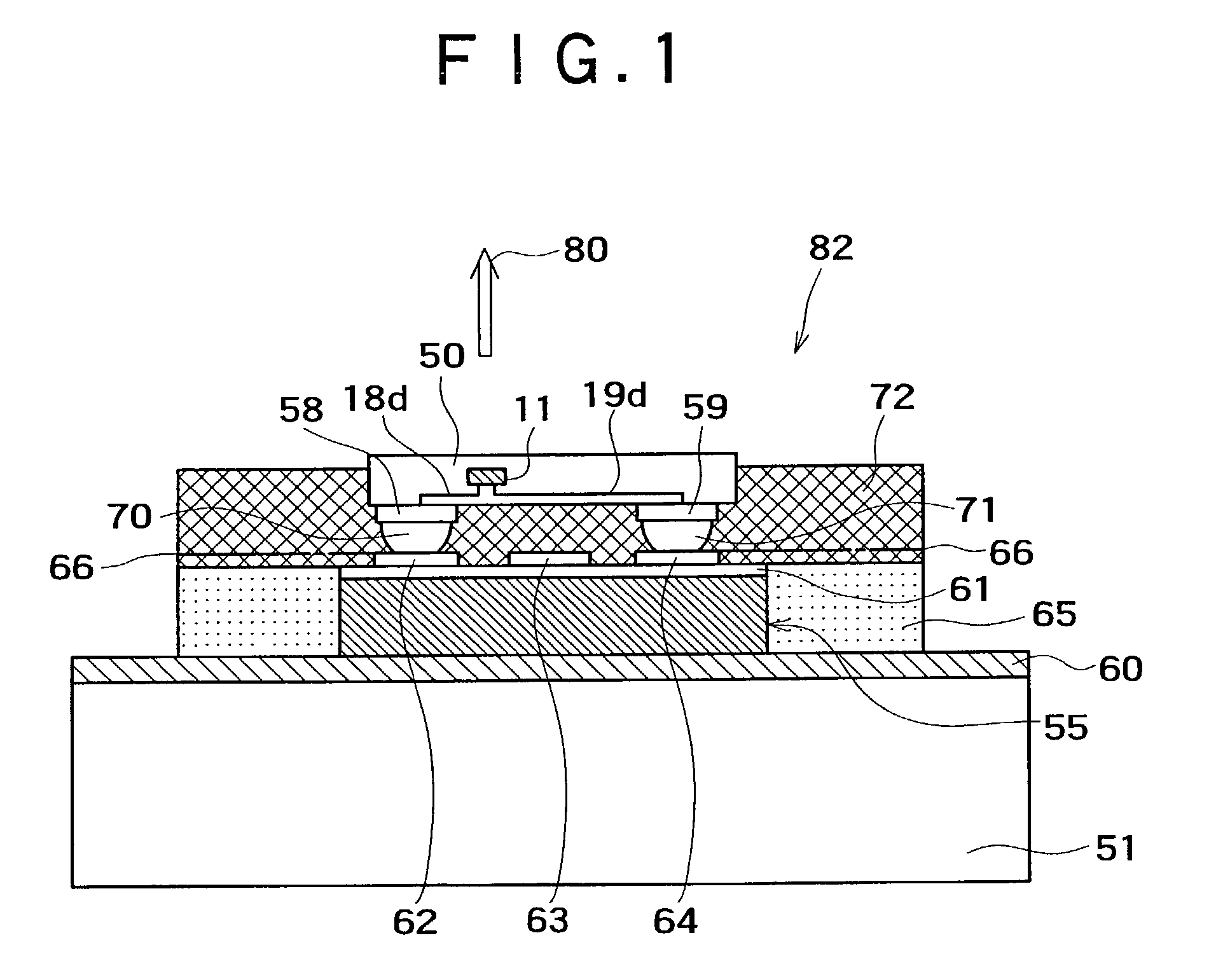
Light emitting unit
InactiveUS7289089B2Improve device densityIncrease diameterSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsPixel densitySemiconductor
A light emitting unit represented by an image display unit includes chips, each of which is formed by burying a light emitting device such as a GaN based semiconductor light emitting device in a resin, wherein external terminals connected to the light emitting device buried in each chip are provided on the chip, and a drive control device such as a pixel transistor for controlling the drive of the light emitting device are connected to the external terminals in a state being at least partially overlapped to the chip. Such an image display unit is advantageous in improving a device density such as a pixel density, enhancing the connection reliability by increasing the diameters of via-holes for wiring without excessively reducing the size of each chip, improving the fabrication yield, facilitating the handling of the chip (or device) at the time of bonding by increasing the apparent area of the chip (or device), and lowering the required specification in terms of alignment accuracy of the chip (or device).
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor device having integrated mosfet and schottky diode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100289075A1High densityImprove efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesTrench mosfetEngineering
A semiconductor device having integrated MOSFET and Schottky diode includes a substrate having a MOSFET region and a Schottky diode region defined thereon; a plurality of first trenches formed in the MOSFET region; and a plurality of second trenches formed in the Schottky diode region. The first trenches respectively including a first insulating layer formed over the sidewalls and bottom of the first trench and a first conductive layer filling the first trench serve as a trenched gate of the trench MOSFET. The second trenches respectively include a second insulating layer formed over the sidewalls and bottom of the second trench and a second conductive layer filling the second trench. A depth and a width of the second trenches are larger than that of the first trenches; and a thickness of the second insulating layer is larger than that of the first insulating layer.
Owner:ANPEC ELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Novel semiconductor device design
InactiveUS20050275043A1Improve device densityReduce crosstalkTransistorSolid-state devicesSram cellIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit having small layout area and a method of forming the same are provided. A slant contact is formed by shifting a portion of a contact a distance less than a whole dimension of the contact along the direction shifted. By using slant contacts, the optical proximity effect is reduced, the device density in the integrated circuit is increased and cross talk is reduced. In the preferred embodiment, the slant contact is combined with other techniques such as compound interconnection, butted local interconnection and slim spacers to reduce the layout area. In another embodiments, a six-transistor SRAM cell can be designed with a slant contact, compound interconnection and butted local interconnection to reduce the layout area.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
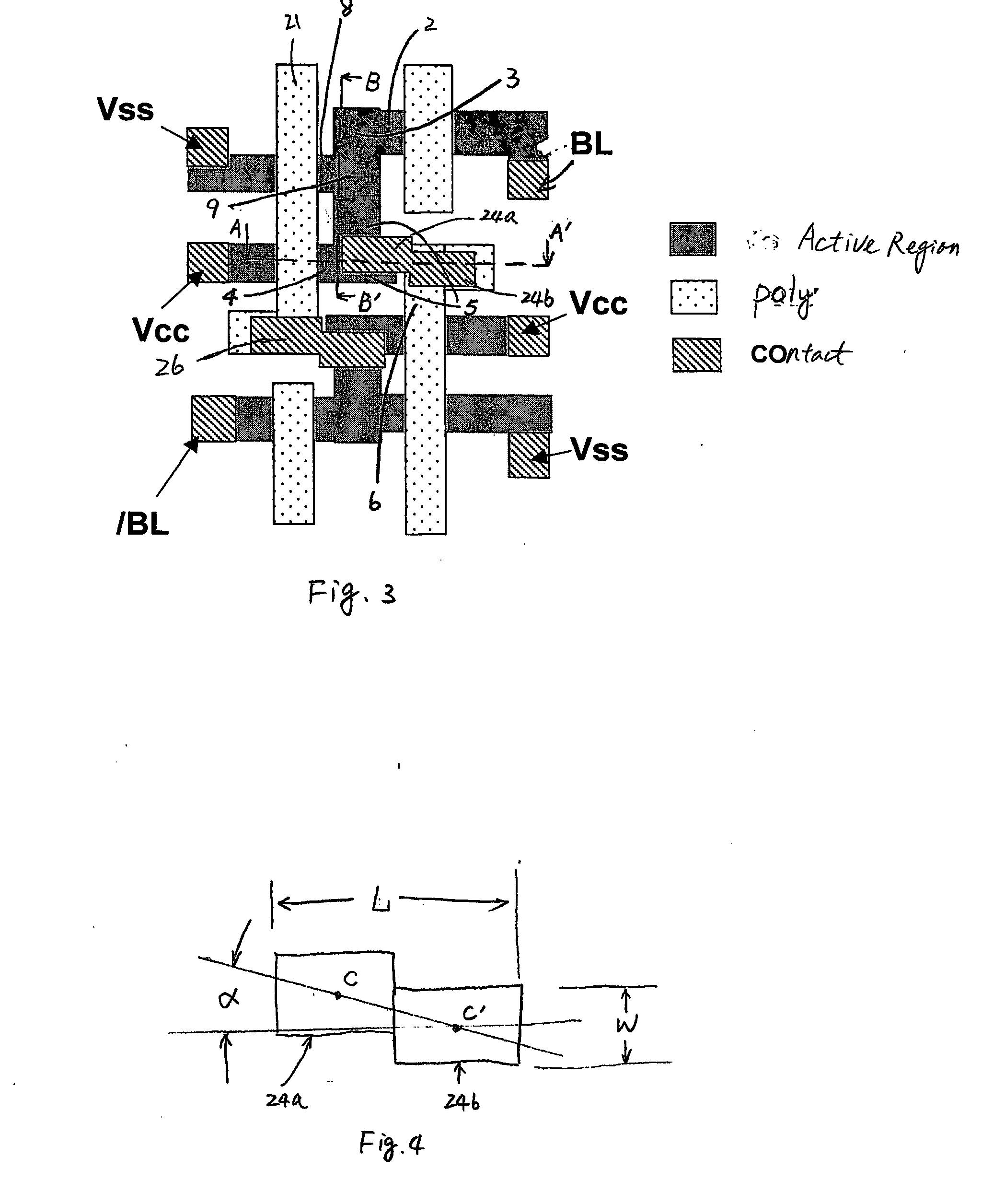
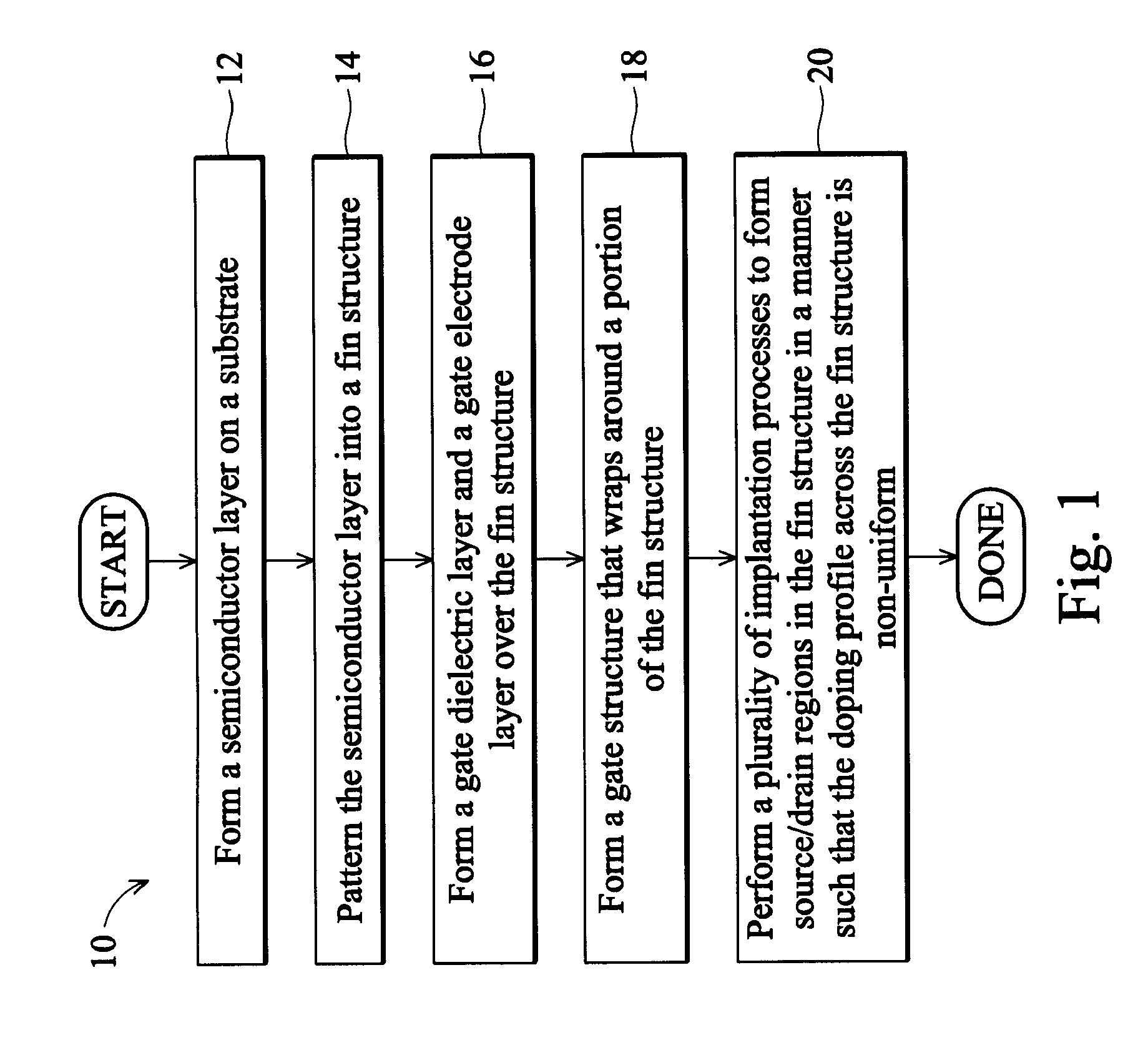
Non-uniform channel junction-less transistor
ActiveUS20120187486A1Easy to controlImprove device densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricDielectric layer
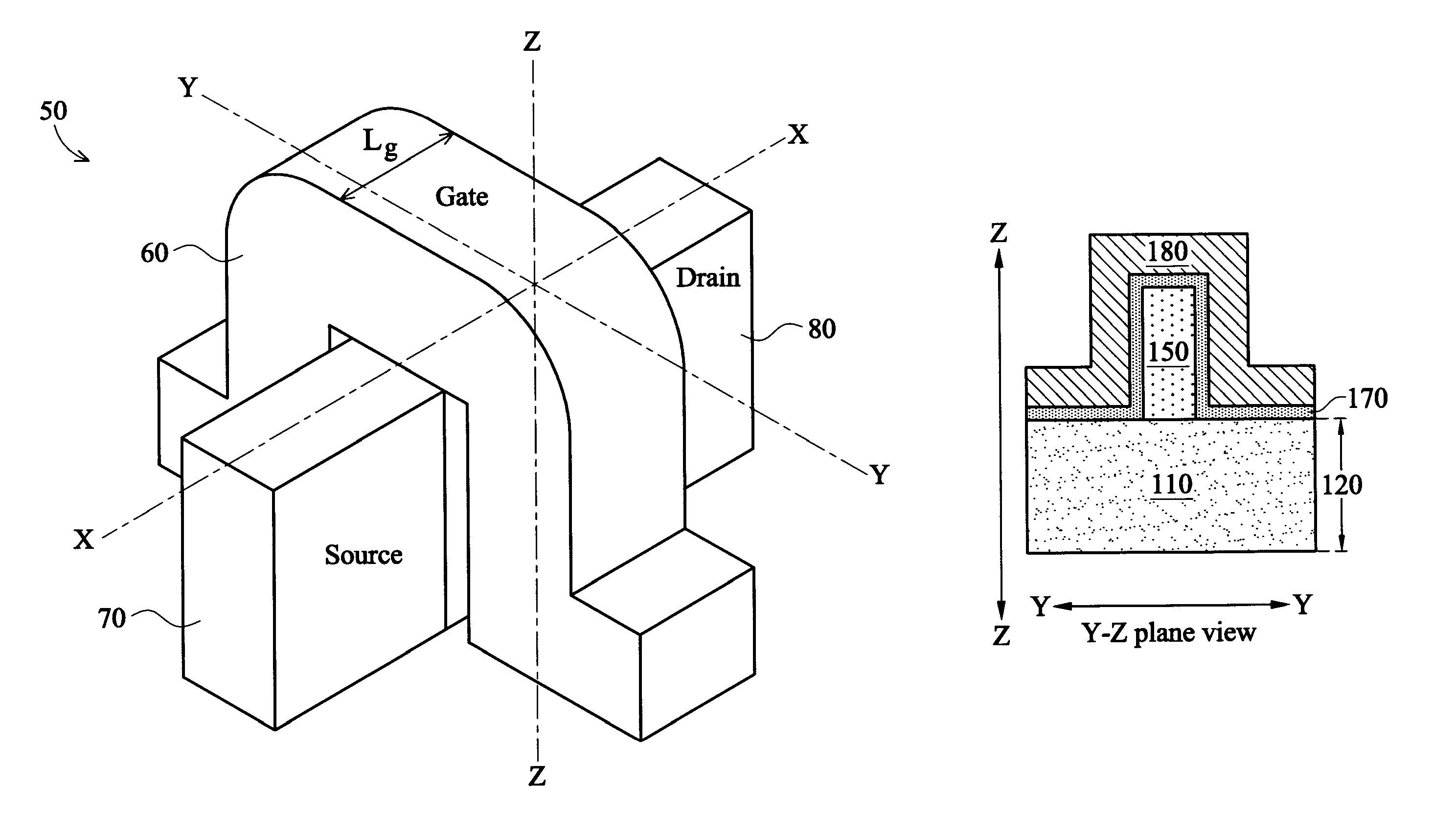
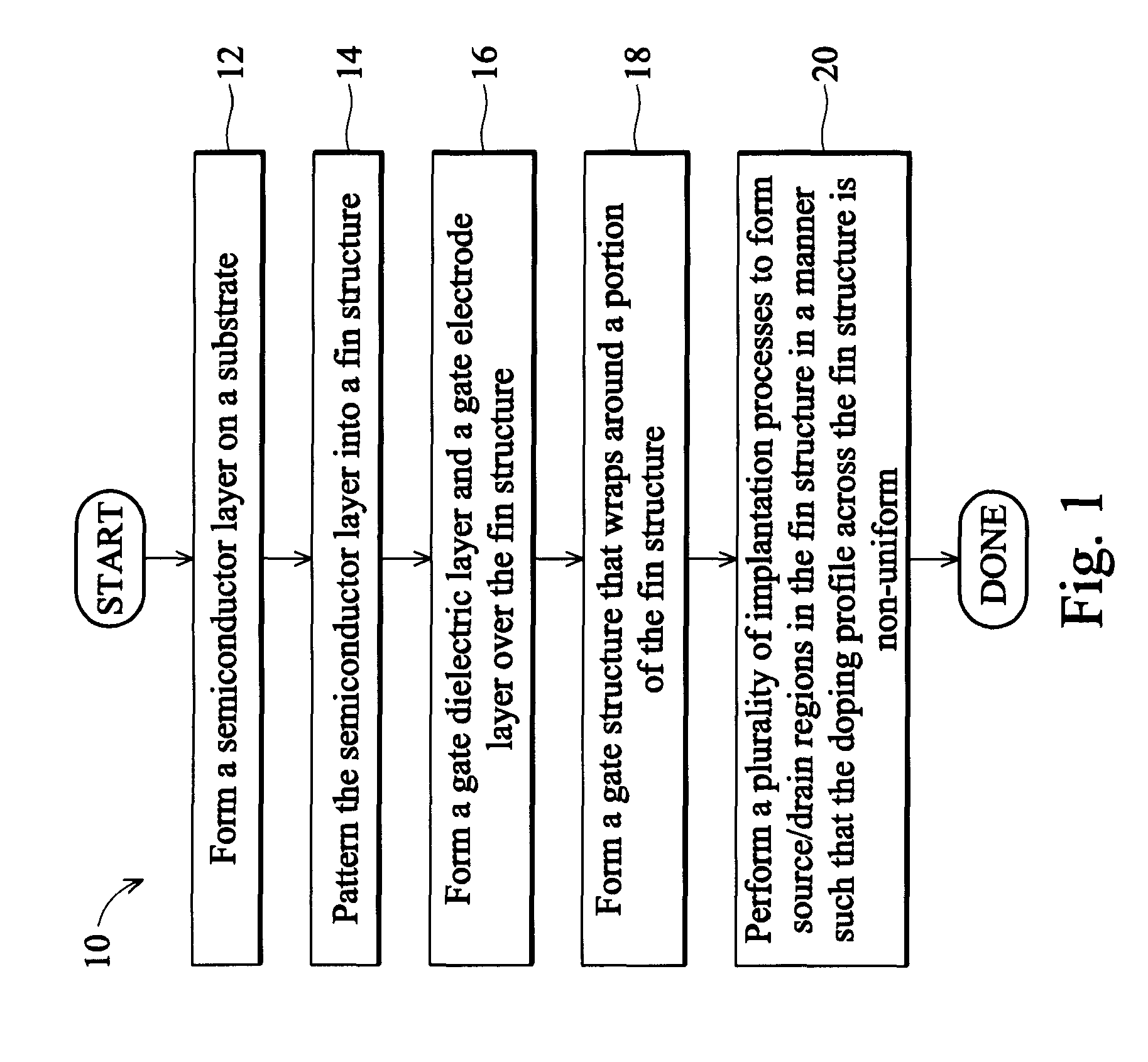
The present disclosure discloses a method of forming a semiconductor layer on a substrate. The method includes patterning the semiconductor layer into a fin structure. The method includes forming a gate dielectric layer and a gate electrode layer over the fin structure. The method includes patterning the gate dielectric layer and the gate electrode layer to form a gate structure in a manner so that the gate structure wraps around a portion of the fin structure. The method includes performing a plurality of implantation processes to form source / drain regions in the fin structure. The plurality of implantation processes are carried out in a manner so that a doping profile across the fin structure is non-uniform, and a first region of the portion of the fin structure that is wrapped around by the gate structure has a lower doping concentration level than other regions of the fin structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
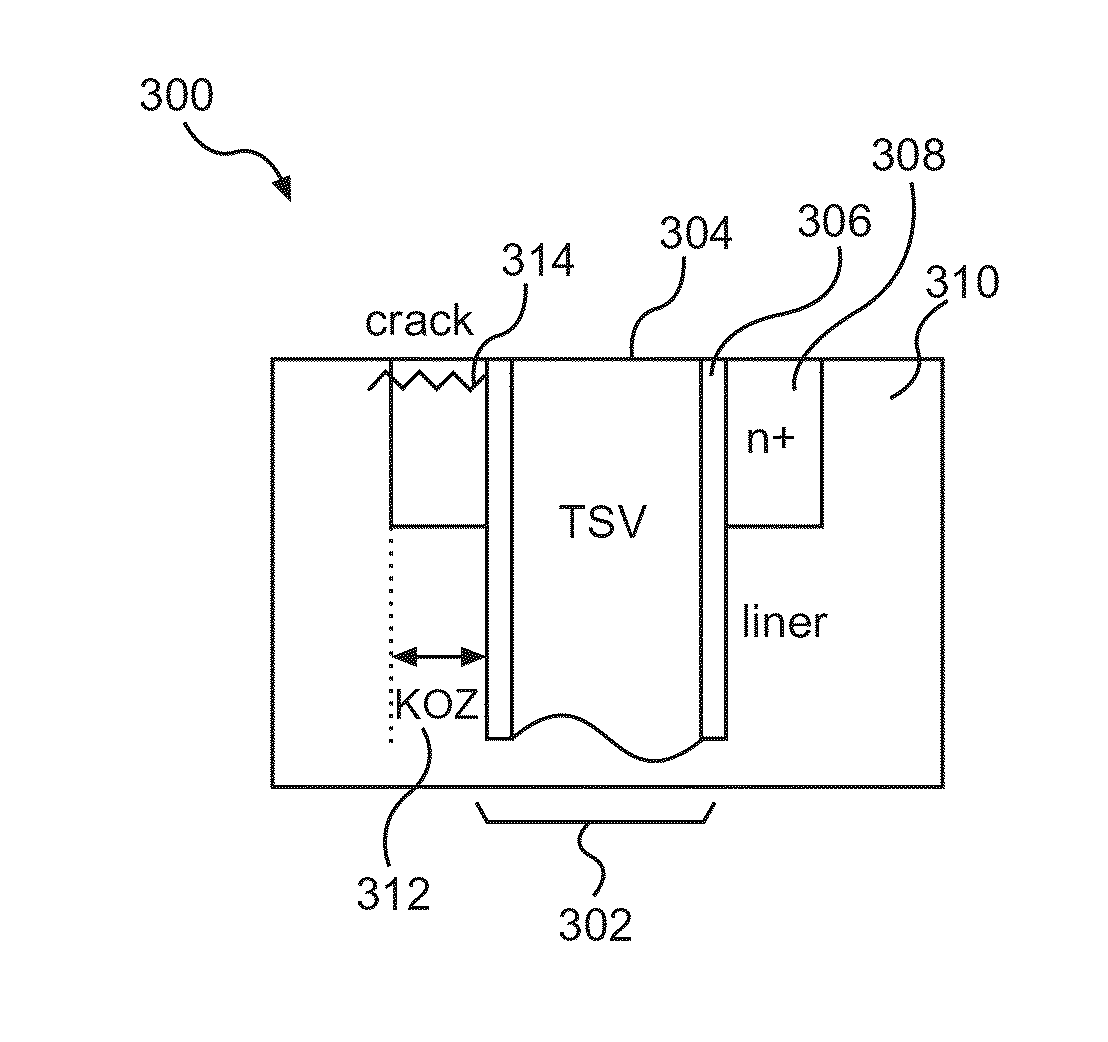
THROUGH-SILICON VIA (TSV) CRACK SENSORS FOR DETECTING TSV CRACKS IN THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) INTEGRATED CIRCUITS (ICs) (3DICs), AND RELATED METHODS AND SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20160258996A1Improve the immunityConvenient direct detectionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingEngineeringThrough-silicon via
Through-silicon via (TSV) crack sensors for detecting TSV cracks in three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuits (ICs) (3DICs), and related methods and systems are disclosed. In one aspect, a TSV crack sensor circuit is provided in which doped rings for a plurality of TSVs are interconnected in parallel such that all interconnected TSV doped rings may be tested at the same time by providing a single current into the contacts of the interconnected doped rings. In another aspect, a TSV crack sensor circuit is provided including one or more redundant TSVs. Each doped ring for a corresponding TSV is tested independently, and a defective TSV may be replaced with a spare TSV whose doped ring is not detected to be cracked. This circuit allows for correction of a compromised 3DIC by replacing possibly compromised TSVs with spare TSVs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Methods for using a silylation technique to reduce cell pitch in semiconductor devices
InactiveUS7253113B2Reduce cell pitchSimple and feasibleSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingSilylationPhotoresist
A method for forming a semiconductor device having a reduced pitch is provided. The method includes providing a substrate, forming a material layer over the substrate, forming a photoresist layer over the material layer, exposing a top surface of the photoresist layer to radiation, and forming a silylated layer over the photoresist layer. The method further includes removing a portion of the silylated layer to expose the photoresist layer, removing the photoresist layer, removing portions of the material layer using the silylated layer as a mask, and removing another portion of the silylated layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Multiple die paddle leadframe and semiconductor device package
ActiveUS8436460B1Small and less-expensive to produceIncrease component densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCouplingSemiconductor package
A leadframe and semiconductor device package with multiple semiconductor device die paddles for accepting multiple semiconductor devices is disclosed, wherein the leadframe increases semiconductor device density and reduces cost by integrating the multiple dies into a semiconductor device package with a relatively small footprint. The leadframe may include at least one full-metal die paddle and at least one reduced-metal die paddle, which may form a unified or hybrid die paddle. The leadframe may enable electrical coupling of multiple semiconductor devices to a common leadfinger and / or die paddle, where internal leadfingers coupled to the common leadfingers and / or die paddles may receive the electrical coupling means from the semiconductor device. Surfaces of one or more die paddles of the leadframe may be exposed to the outside of the semiconductor device package to enable electrical testing of and / or provide heat dissipation from one or more of the semiconductor devices attached to the leadframe.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Non-volatile memory and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20170040334A1Improve reliabilityLow working voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricInsulation layer
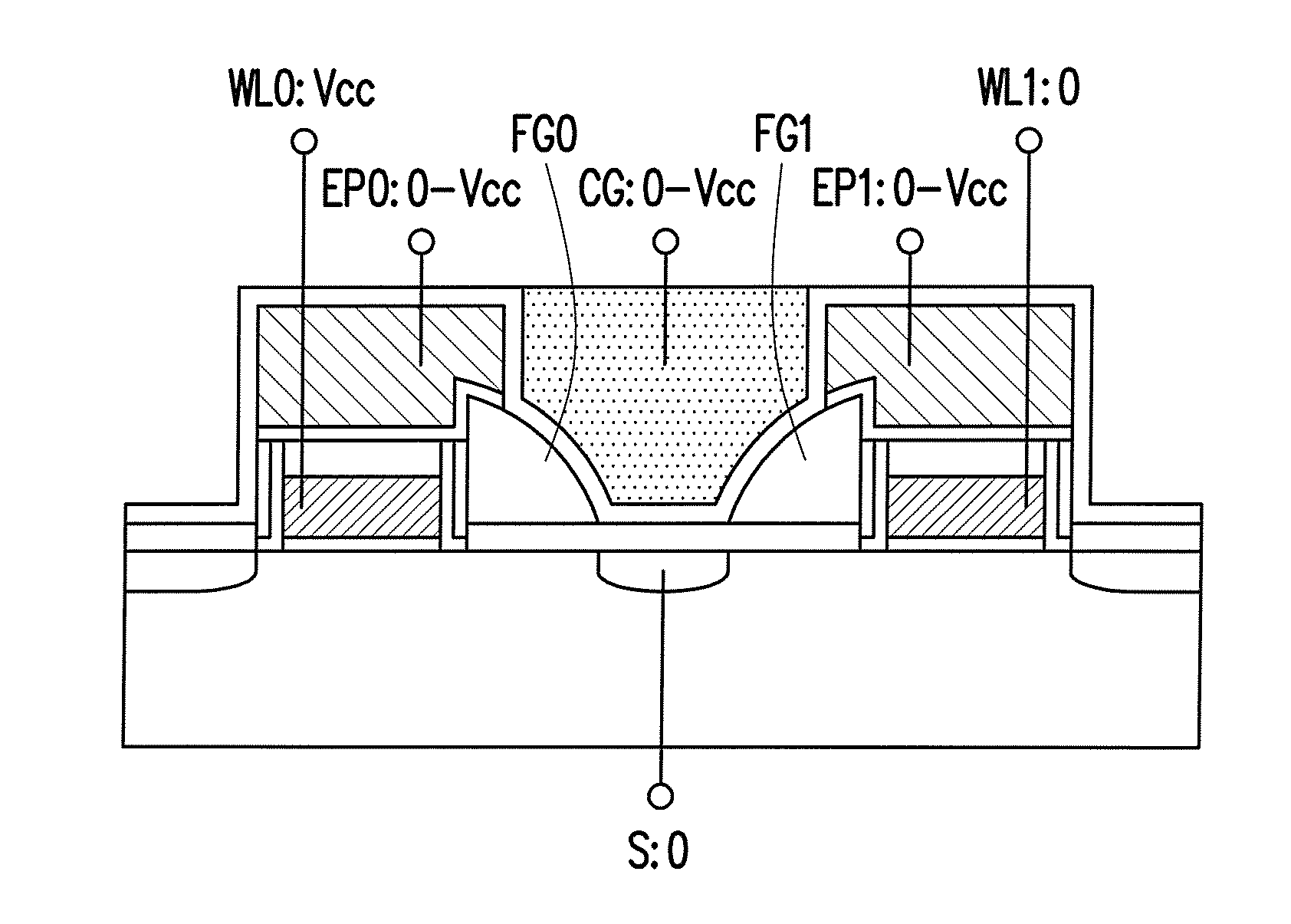
A non-volatile memory having memory cells is provided. A stacked gate structure has gate dielectric layer, assist gate, insulation layer, and erase gate disposed in order. The floating gate is disposed on a first sidewall of the stacked gate structure, the floating gate has a corner portion at the top portion, and erase gate covers the corner portion. The tunneling dielectric layer is disposed under the floating gate. The erase gate dielectric layer is disposed between the erase gate and the floating gate. The assist gate dielectric layer is disposed between the assist gate and the floating gate. The source region and the drain region are respectively disposed at two sides of the stacked structure and the floating gate. The control gate is disposed on the source region and the floating gate. The inter-gate dielectric layer is disposed between the control gate and the floating gate.
Owner:IOTMEMORY TECH +2
Memory array with surrounding gate access transistors and capacitors with global and staggered local bit lines
ActiveUS7510954B1Reduce resistanceIncreased fabrication footprintTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineAudio power amplifier
A memory array with staggered local data / bit lines extending generally in a first direction formed in an upper surface of a substrate and memory cell access transistors extending generally upward and aligned generally atop a corresponding local data / bit line. Selected columns of the memory cell access transistors are sacrificed to define local data / bit access transistors which are interconnected with overlying low resistance global data / bit lines. The global data / bit lines provide selectable low resistance paths between memory cells and sense amplifiers. The sacrificed memory cell access transistors and staggered local data / bit lines provide increased footprints for sense amplifiers to facilitate increased circuit integration.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Methods for using a silylation technique to reduce cell pitch in semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20050106870A1Reduce cell pitchSmall and fasterSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingDevice materialSilylation
A method for forming a semiconductor device having a reduced pitch is provided. The method includes providing a substrate, forming a material layer over the substrate, forming a photoresist layer over the material layer, exposing a top surface of the photoresist layer to radiation, and forming a silylated layer over the photoresist layer. The method further includes removing a portion of the silylated layer to expose the photoresist layer, removing the photoresist layer, removing portions of the material layer using the silylated layer as a mask, and removing another portion of the silylated layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
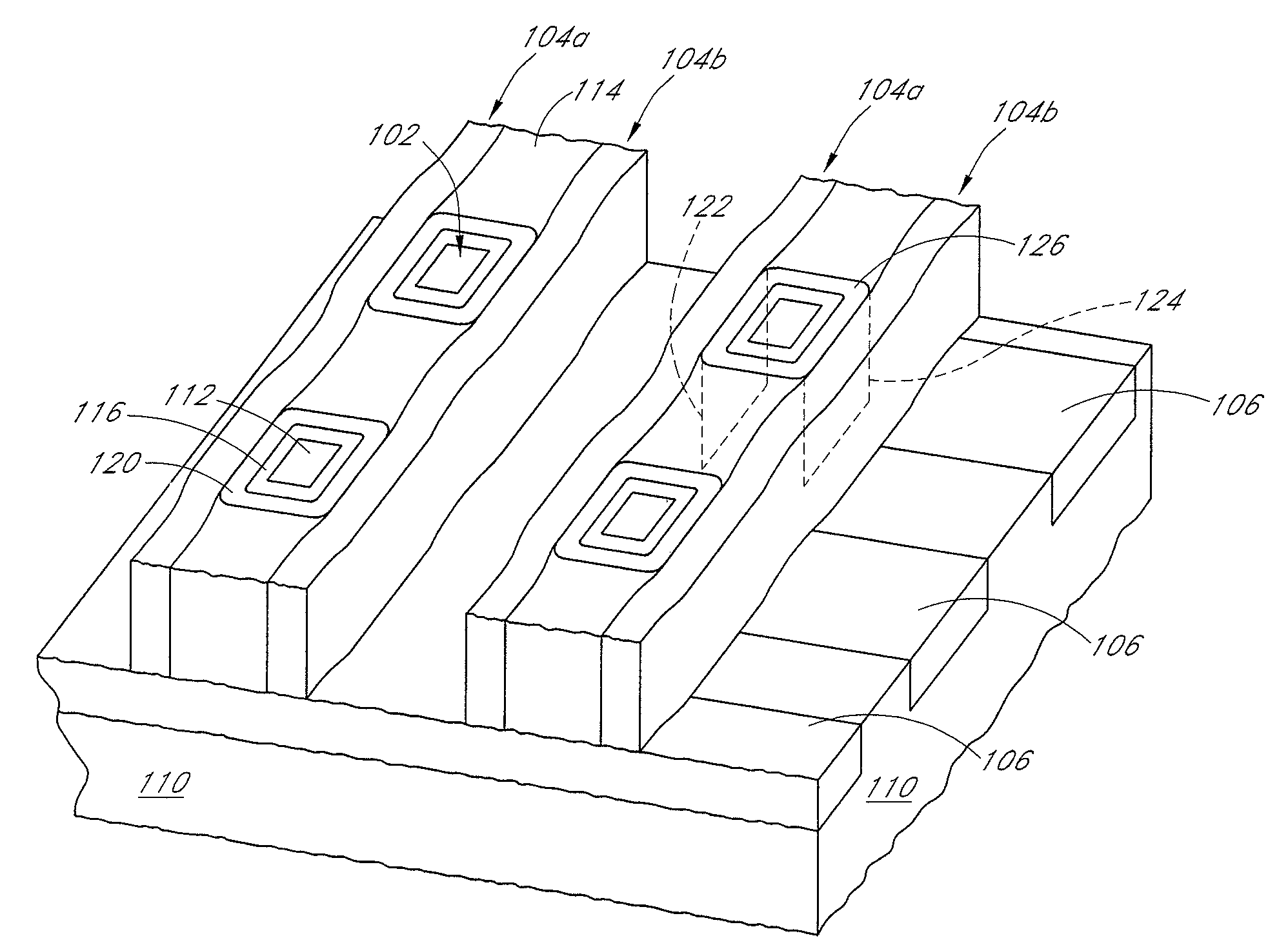
Method of Patterning Without Dummy Gates
ActiveUS20170040162A1Increase device densityImprove device densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Techniques herein provide precise cuts for fins and nanowires without needing dummy gate pairs to compensate for overlay misalignment. Techniques herein include using an etch mask to remove designated portions of gate structures to define a trench or open space having fin structures, nanowires, etc. The uncovered fin structures are etched away or otherwise removed from the trench segments. The etch mask and material defining the trench provide a combined etch mask for removing uncovered fin portions. Subsequently the trench segments are filled with dielectric material. Without needed dummy gate pairs a given substrate can fit significantly more electrical devices per unit area.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
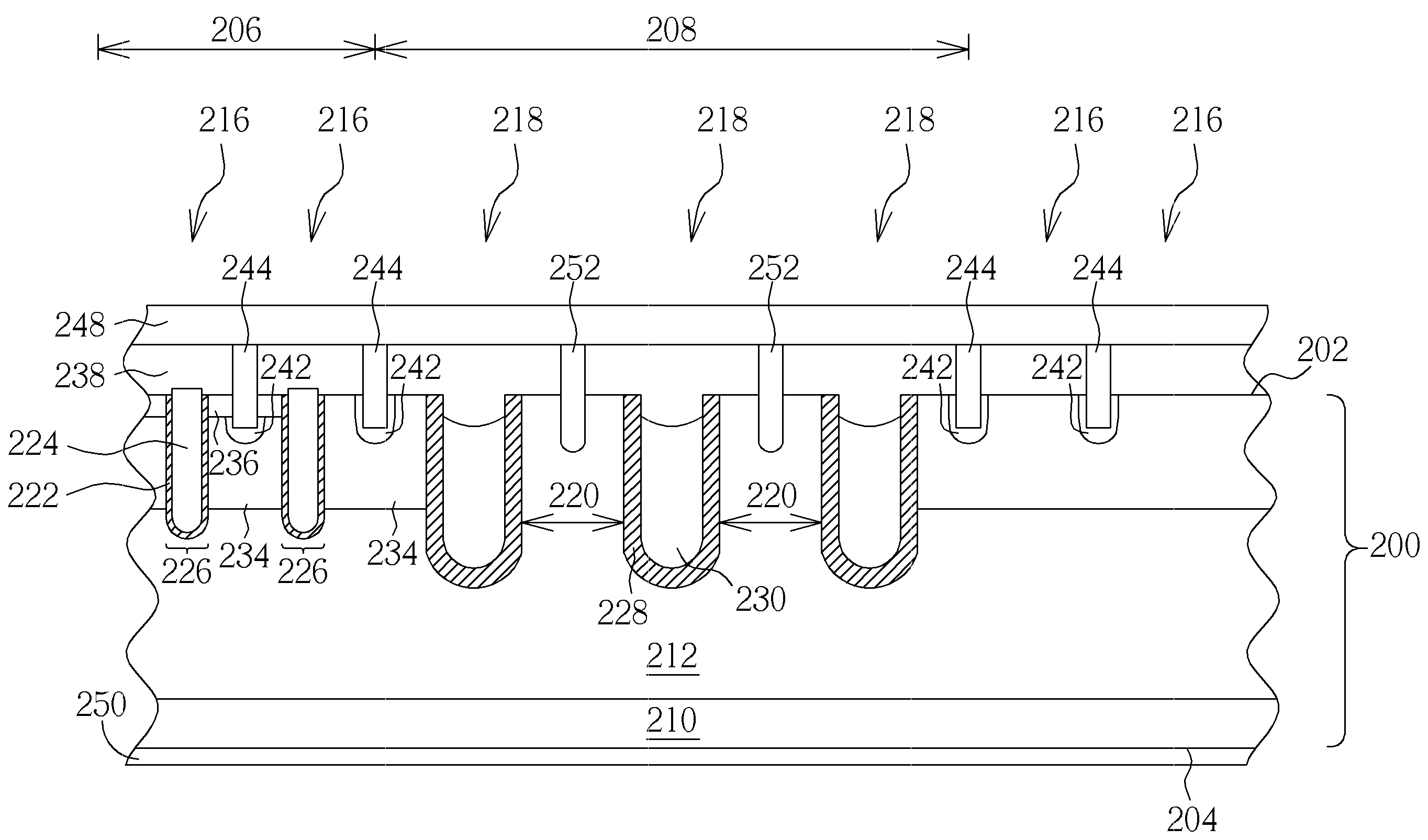
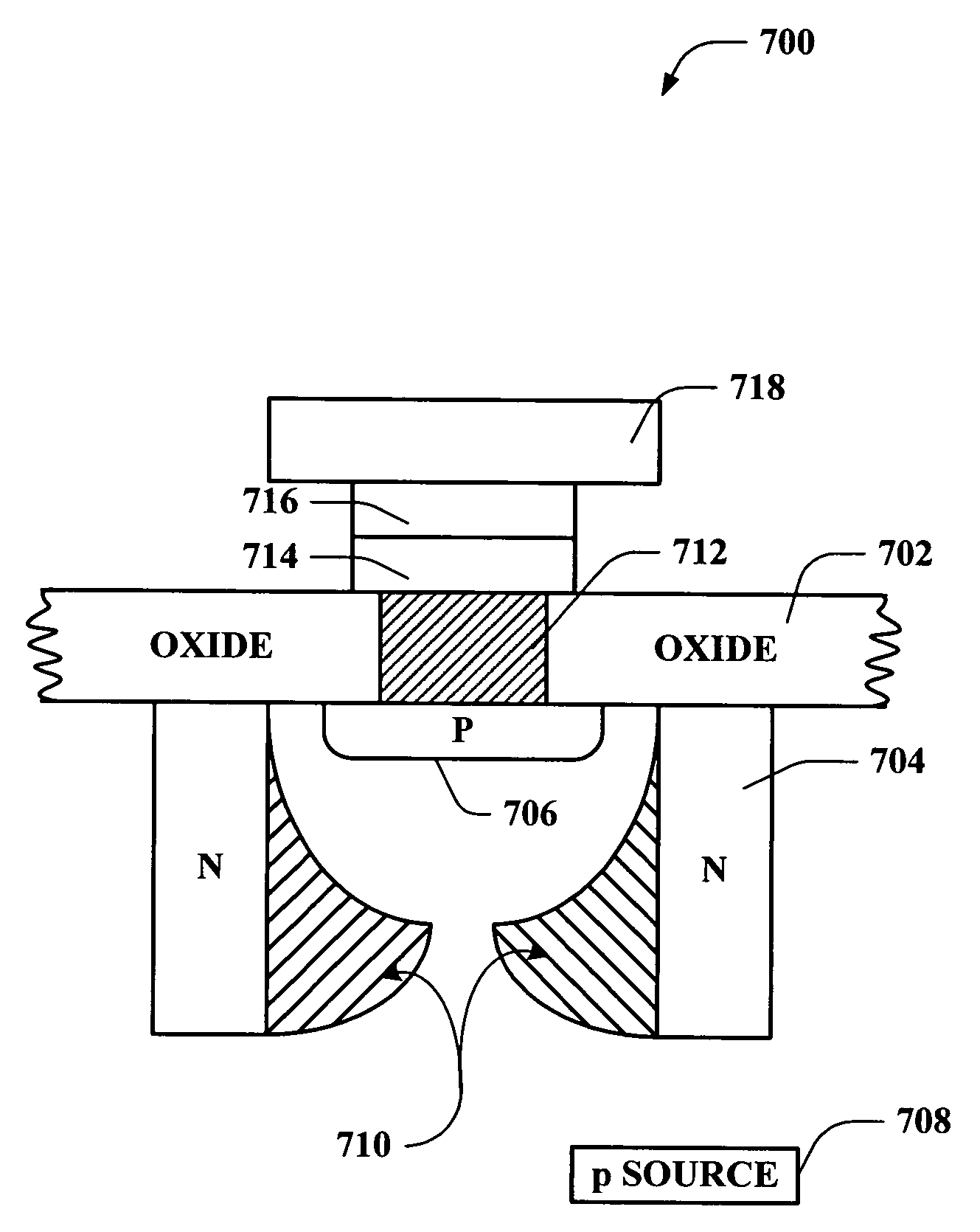
Vertical JFET as used for selective component in a memory array
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate providing a selective functionality to a polymer memory cell in a memory array while increasing device density in the memory cell array. A vertical JFET is described to which voltages can be selectively applied to control internal current flow there through, which in turn can be employed to manipulate the state of a polymer memory cell coupled to the vertical JFET. By mitigating gaps between gates, or wordlines, and drains of the vertical JFETs, feature size can be reduced to permit increased device density. Furthermore, vertical JFETs in the array can be coupled to gates on only two opposite sides, permitting the JFETs to be arranged without gate crossbars between them, further increasing device density. In this manner, the present invention provides switching characteristics to a memory cell and overcomes problematic bulkiness associated with conventional MOS devices.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Two-step MOSFET gate formation for high-density devices
InactiveUS20020042183A1Reduces device topographyReduces the demands on backend lithographySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETHigh density
A method of manufacturing a metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor MOSFET device gate includes patterning and etching the mesa of a gate material. A dielectric layer is formed on the mesa and is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing (CMP). The active gate dimension is patterned and etched to form source and drain wells that extend down to an active area on either side of the MOSFET gate. In one further embodiment, the wells are filled with metal and the metal is planarized. The MOSFET device, in one embodiment, includes source and drain wells equally spaced from the active gate.
Owner:INTELLEDGE CORP
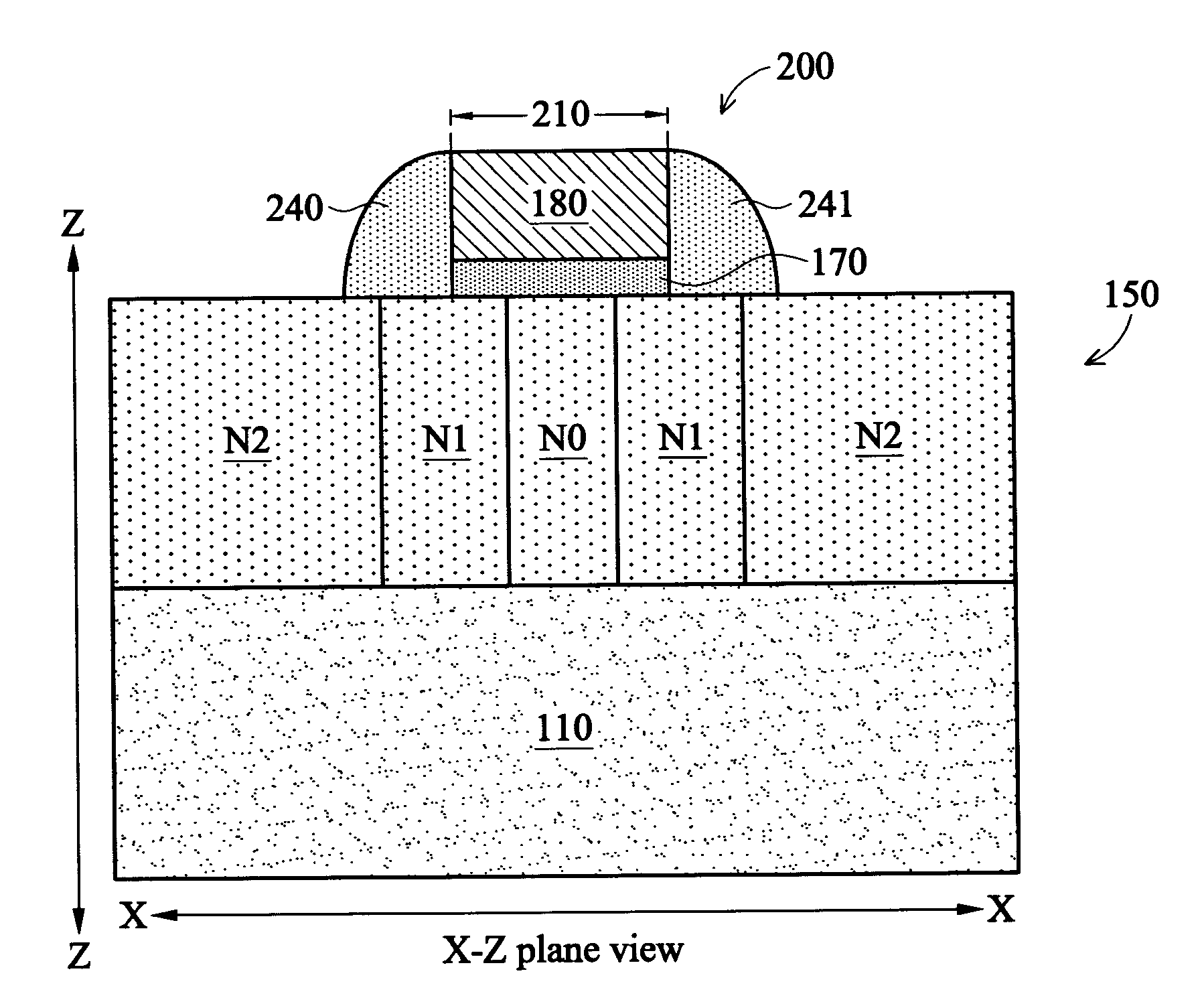
Integrated Circuit Device Fins
ActiveUS20190148520A1Reduce leakage currentIncrease powerSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringIntegrated circuit
Examples of an integrated circuit and a method for forming the integrated circuit are provided herein. In some examples, a method includes receiving a substrate that includes: a plurality of fins extending above a remainder of the substrate; a first region that includes a first fence region that contains a first subset of the plurality of fins; and a second region that includes a second fence region that contains a second subset of the plurality of fins. The first region has a first performance characteristic, and the second region has a second performance characteristic that is different from the first. Based on the first performance characteristic, the first subset of the plurality of fins is recessed to a first height, and based on the second performance characteristic, the second subset of the plurality of fins is recessed to a second height that is less than the first height.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
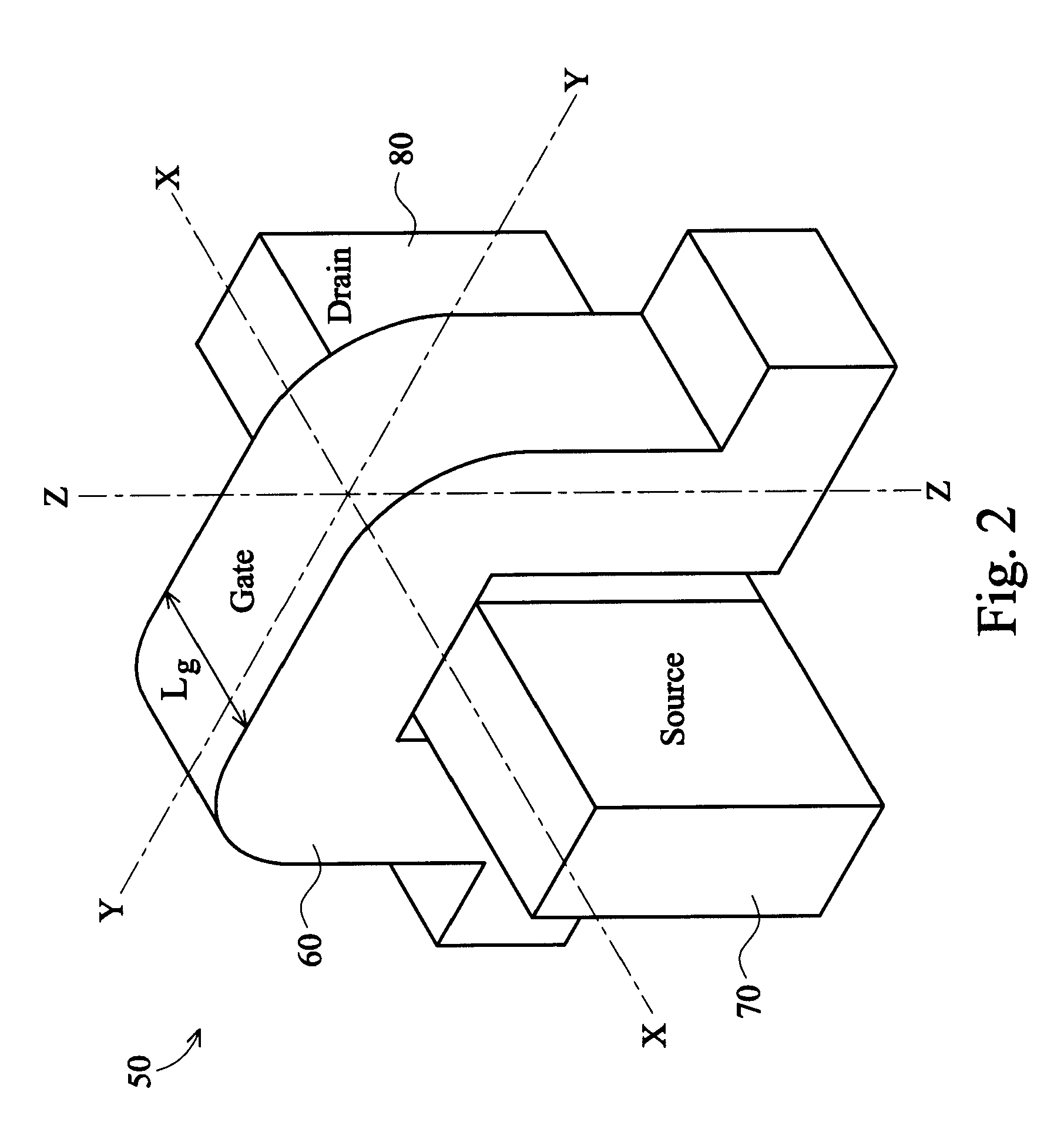
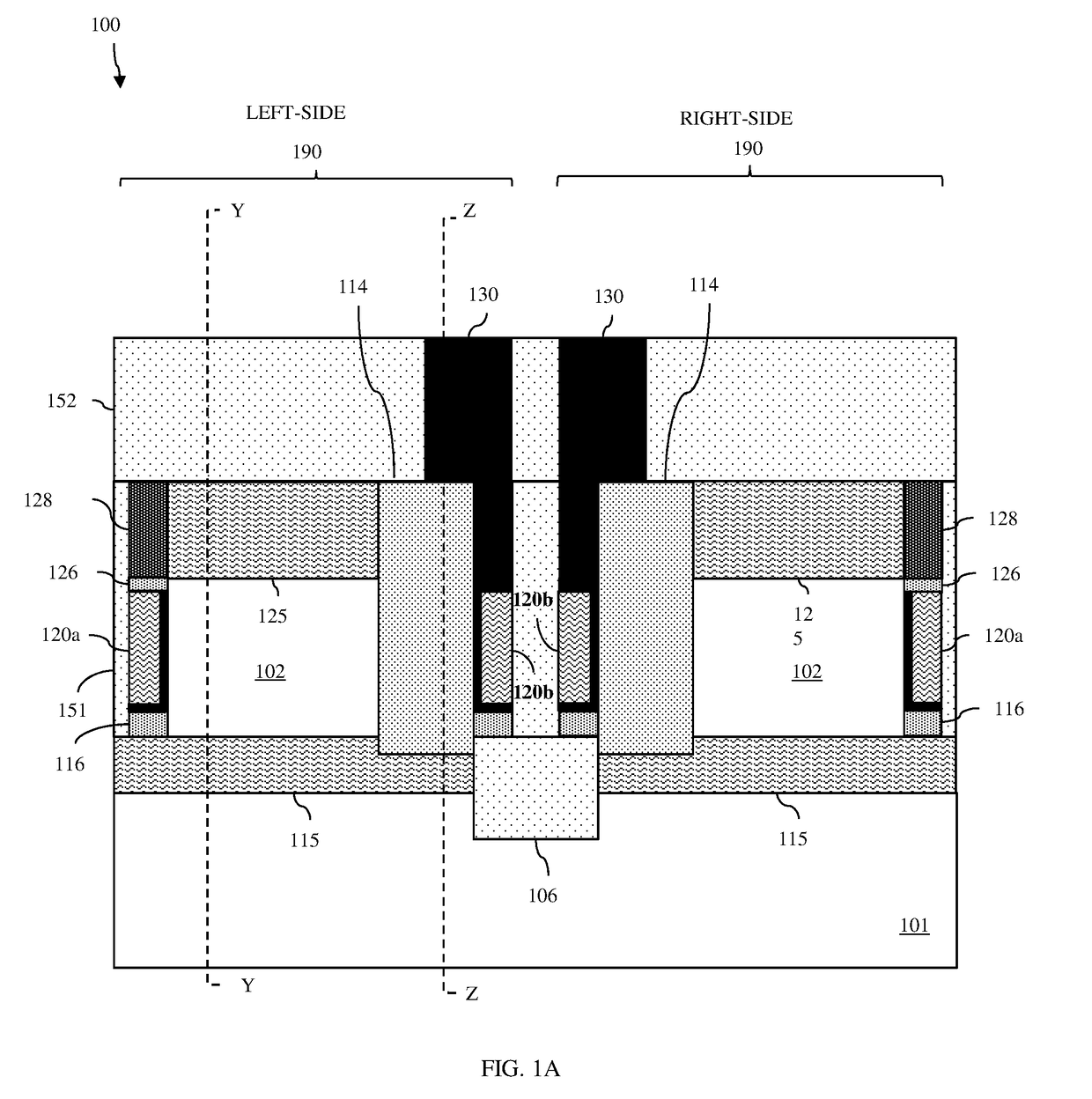
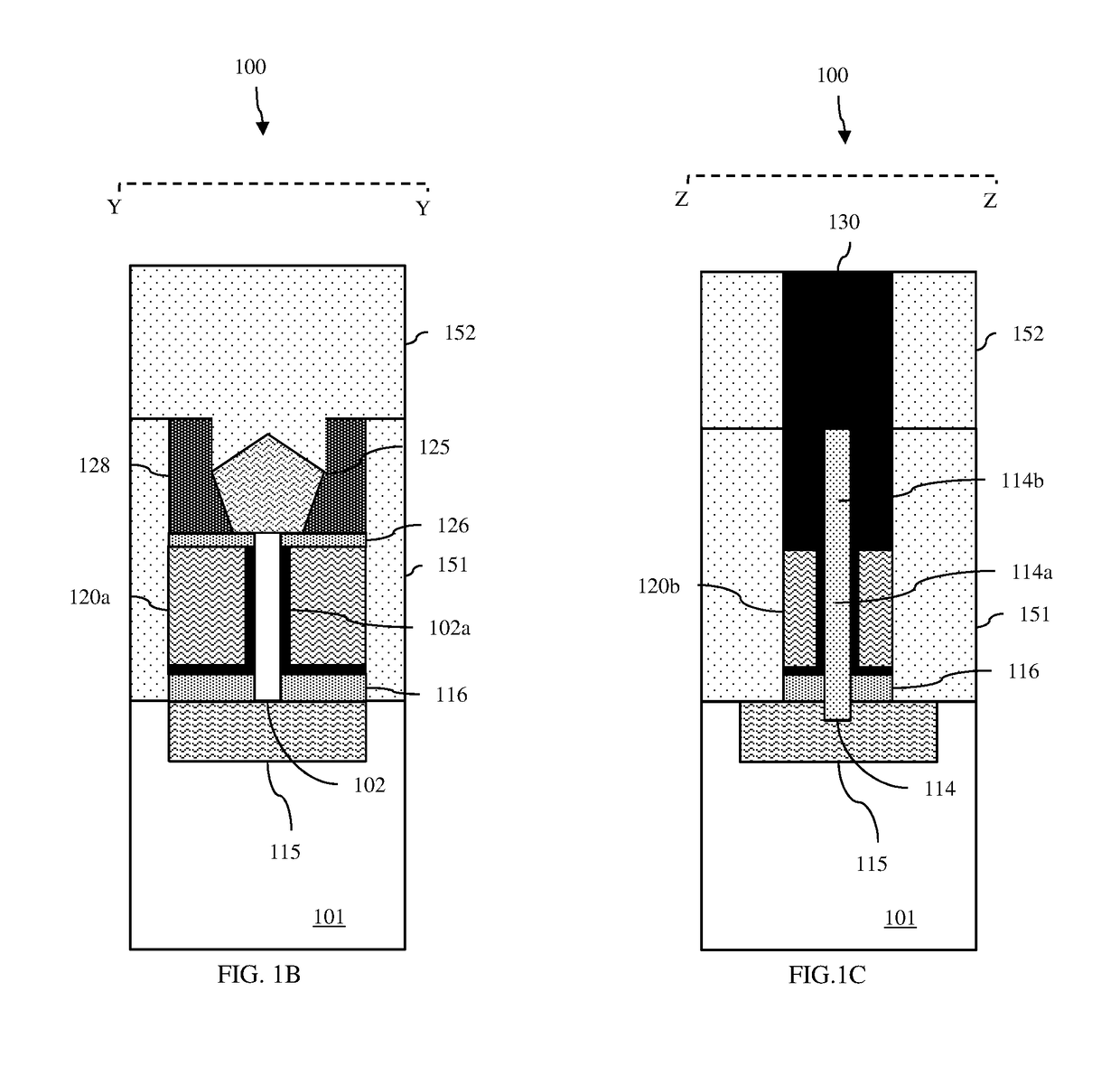
Vertical field effect transistor (VFET) having a self-aligned gate/gate extension structure and method
ActiveUS20190051733A1Gate pitch can be reducedImprove device densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureLower upper
Disclosed are embodiments of a semiconductor structure that includes a vertical field effect transistor (VFET). The VFET has a fin-shaped body that includes a semiconductor fin and an isolation fin. The semiconductor fin extends vertically between lower and upper source / drain regions. The isolation fin is adjacent to and in end-to-end alignment with the semiconductor fin. The VFET gate has a main section that wraps around an outer end and opposing sidewalls of the semiconductor fin and an extension section that extends from the main section along at least the opposing sidewalls of a lower portion the isolation fin and, optionally, around an outer end of that lower portion. A gate contact lands on the isolation fin and extends along the opposing sidewalls and, optionally, the outer end of the isolation fin down to the extension section. Also disclosed are method embodiments for forming these structures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Finfet and method of fabricating the same
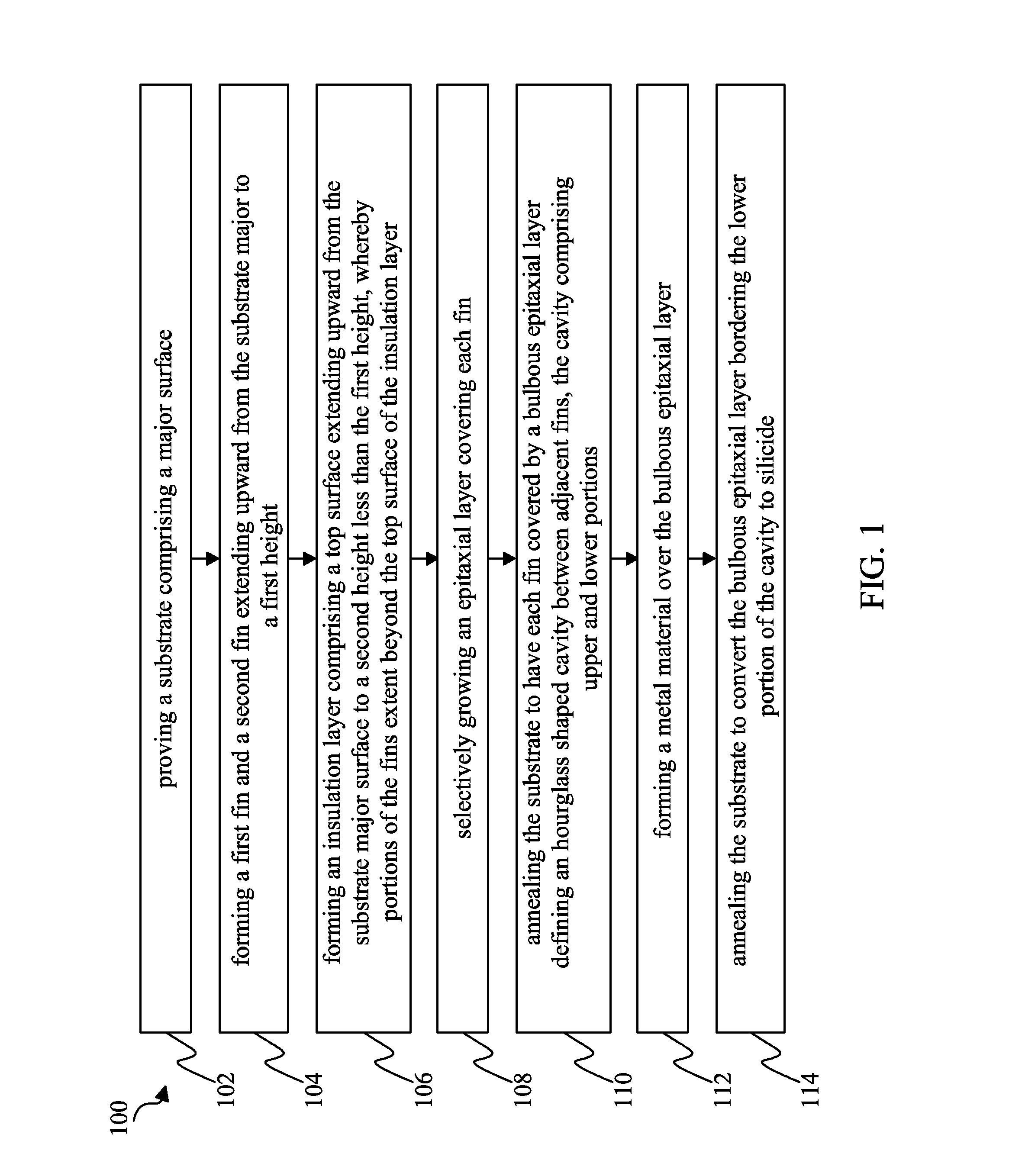
ActiveUS20140134831A1Improve device densityImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerMetallic materials
A method of fabricating a fin field effect transistor (FinFET) comprises providing a substrate comprising a major surface, forming a first and second fin extending upward from the substrate major surface to a first height, forming an insulation layer comprising a top surface extending upward from the substrate major surface to a second height less than the first height, wherein a portion of the first and second fin extend beyond the top surface of the insulation layer. The method also includes selectively growing an epitaxial layer covering each fin, annealing the substrate to have each fin covered by a bulbous epitaxial layer defining an hourglass shaped cavity between adjacent fins, wherein the cavity comprises an upper and lower portion. The method includes forming a metal material over the bulbous epitaxial layer and annealing the substrate to convert the bulbous epitaxial layer bordering the lower portion of the cavity to silicide.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Dynamic random access memory unit and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20150214231A1Improve device densityTransistorSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryEngineering
A dynamic random access memory unit includes a substrate having a trench disposed therein, a self-aligned trench isolation structure formed in the bottom portion of the trench, and a first trenched gate formed in the bottom portion of the trench and above the self-aligned trench isolation structure. The substrate includes at least one pillar-shaped active body having a drain region, a body region atop the drain region, and a source region atop the body region. The first trenched gate includes a first spacer formed on the side-wall in the bottom portion of the trench to selectively cover and surround the portion of the side-wall in the trench that comprises the drain region, such for defining the width of the self-aligned trench isolation structure.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com