Method for controlling non-metallic impurities in structural alloy steel
A technology of non-metallic inclusions and alloy structural steel, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of difficult gas diffusion, floating and overflow, weak adsorption capacity of inclusions, high gas content, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The following example further illustrates the present invention.
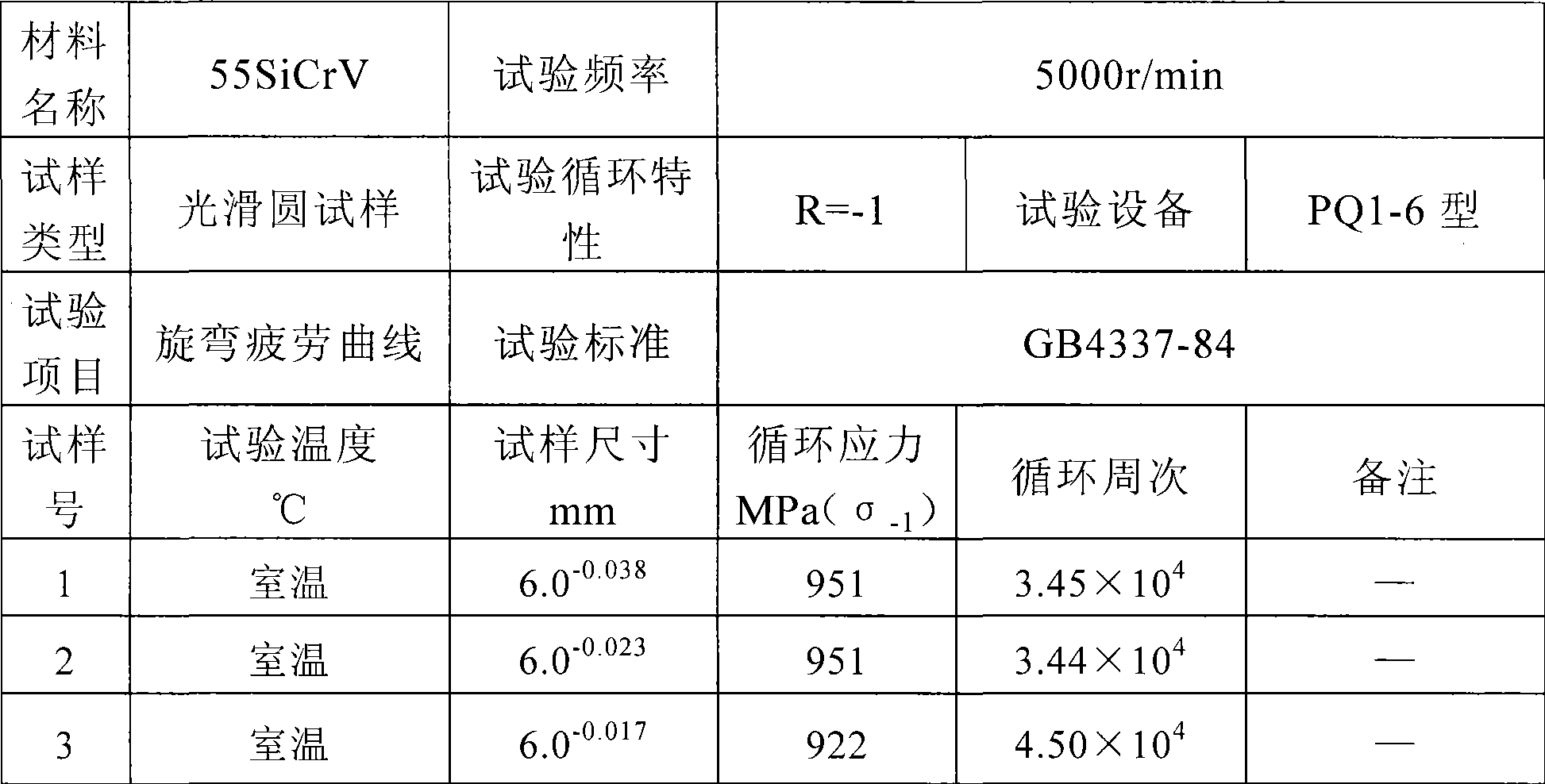
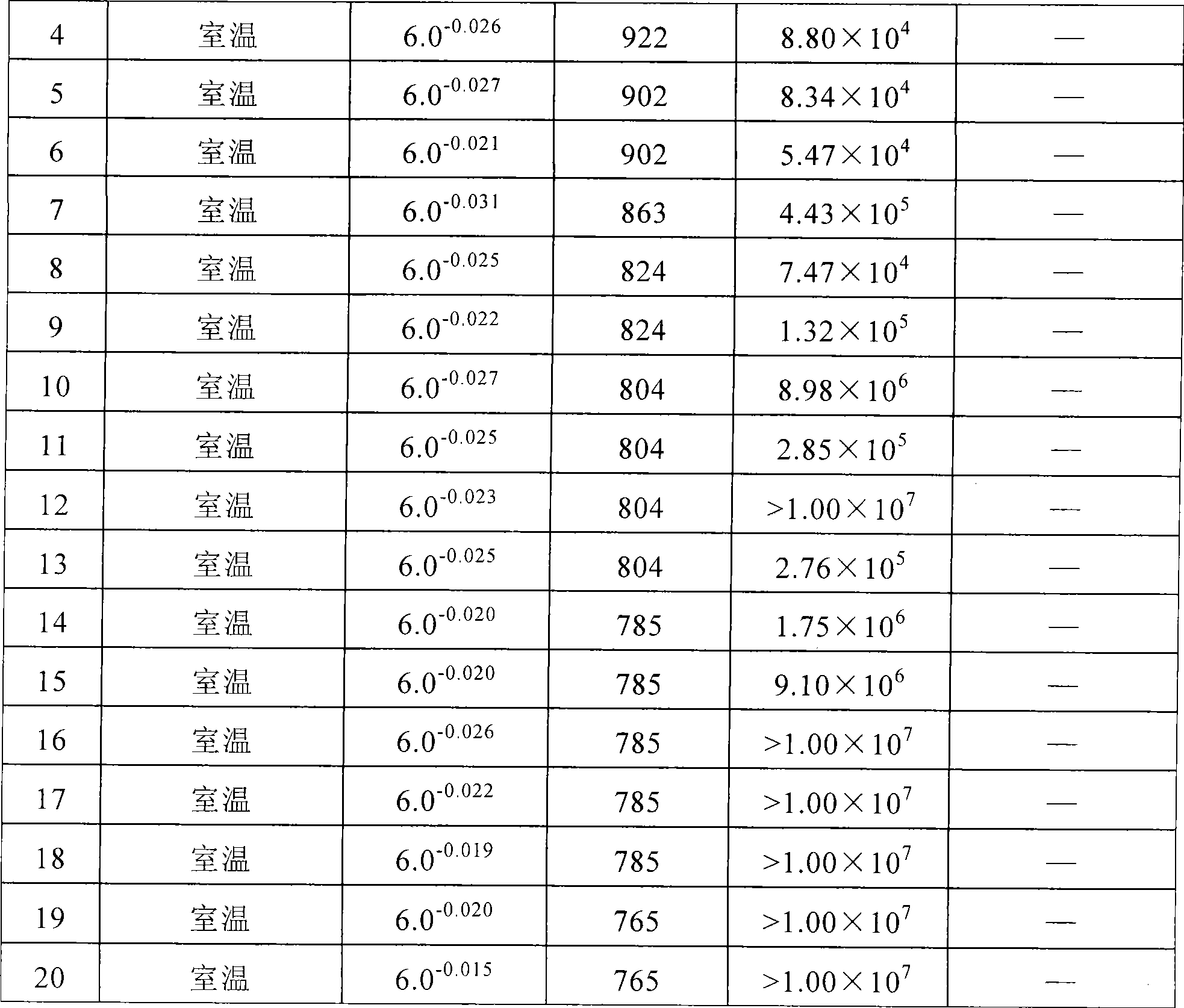
[0028] 1. Primary furnace
[0029] 1.1 Ingredients:
[0030] Ordinary steel scrap: accounting for 45% of the furnace charge; HBI (direct reduced iron), accounting for 30% of the furnace charge, scattered into the lower part of the hopper; low-sulfur pig iron, S≤0.030%, accounting for 25% of the furnace charge;
[0031] 1.2 Requirements for eccentric furnace
[0032] There is no cold steel with material in the tapping furnace of the previous furnace to prevent residual element pollution, and the remaining molten steel in the furnace should be poured out as much as possible; the EBT of the tapping port must be intact to ensure the smooth flow of the tapping steel;
[0033] 1.3 During the melting period, make slag in advance to prevent the molten steel from absorbing nitrogen from the atmosphere. 70% of the furnace charge is melted and added to HBI in batches by a vibrating feeder, 1000kg per batch; Argon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com