Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
540 results about "Calculation technique" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
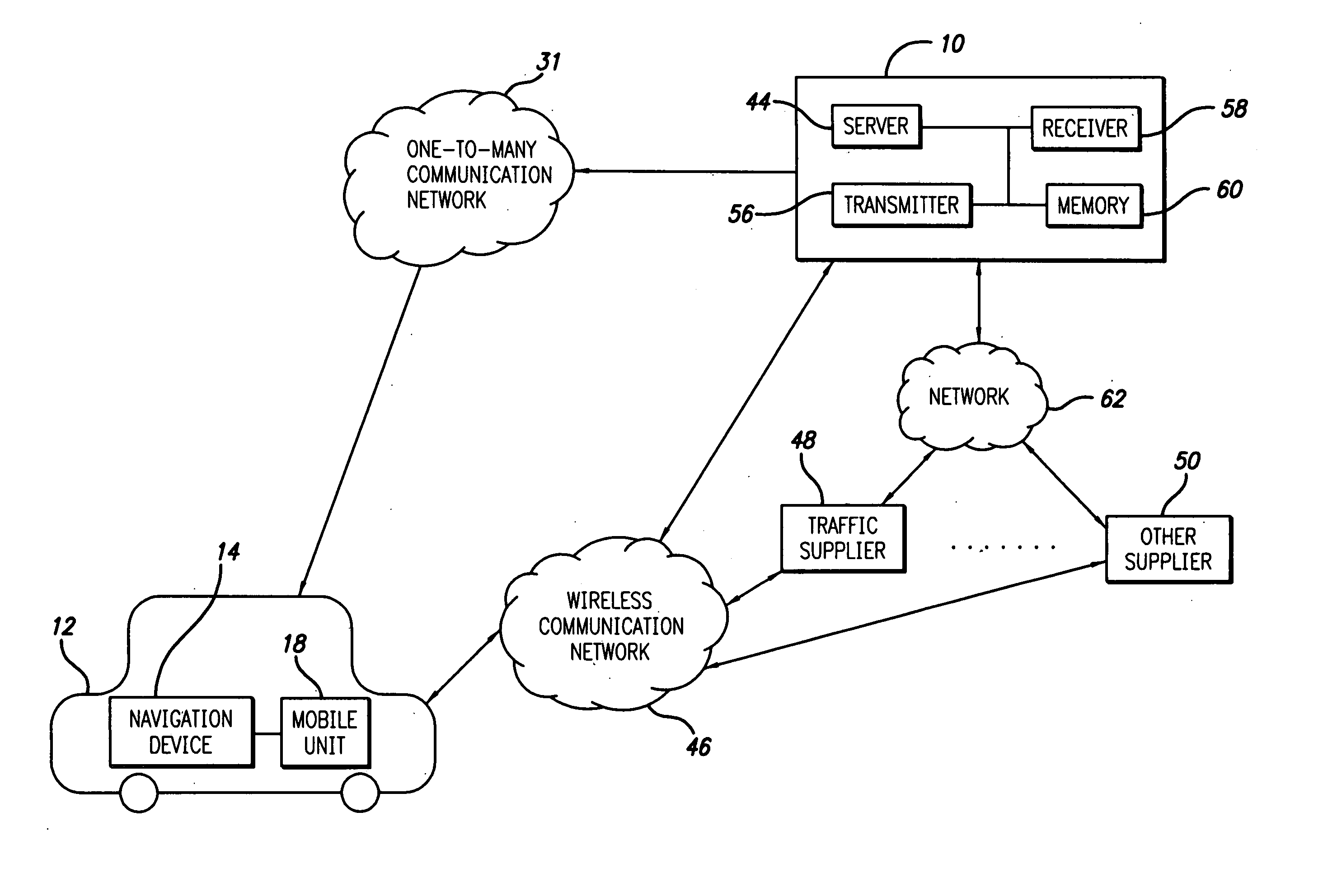
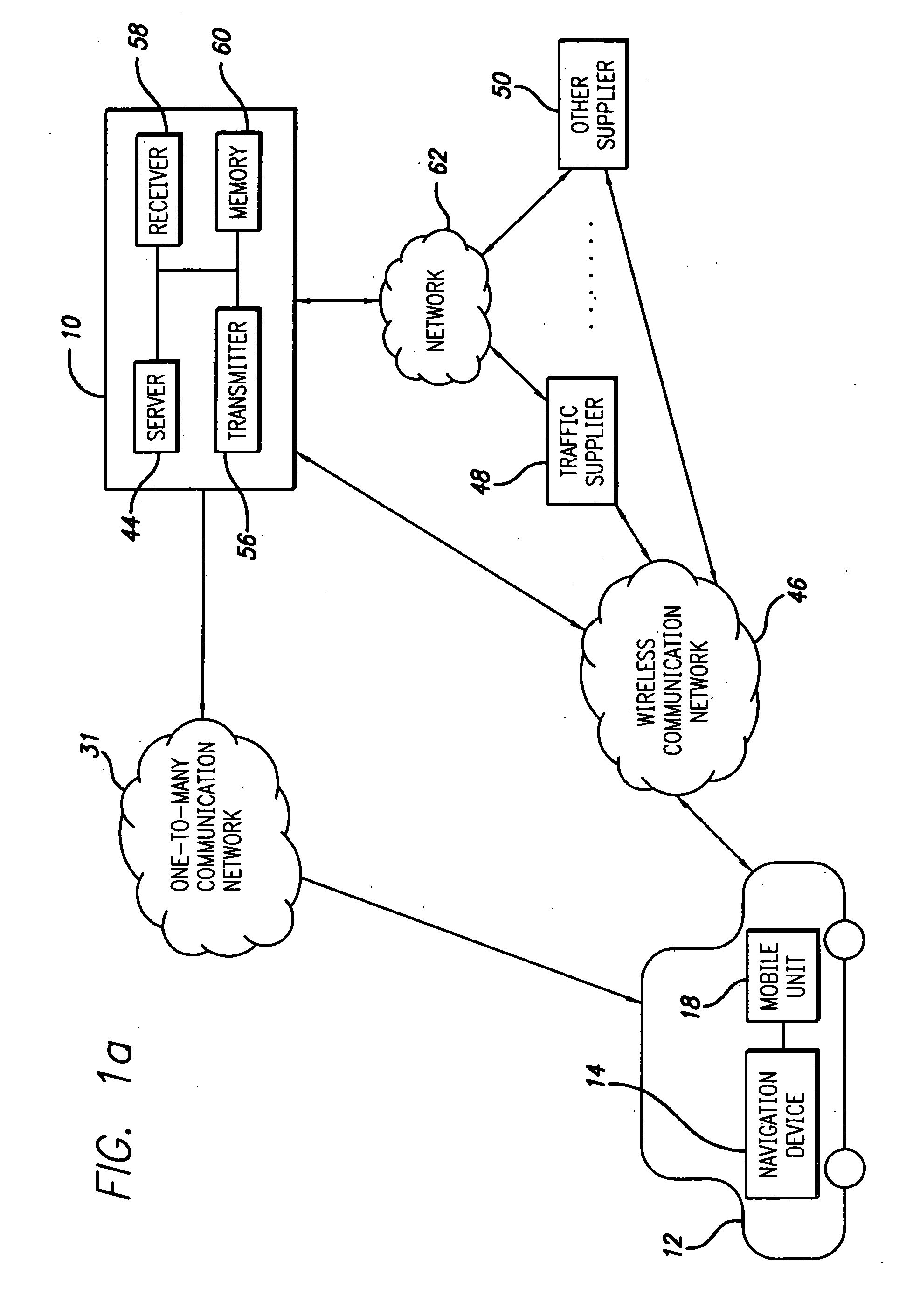
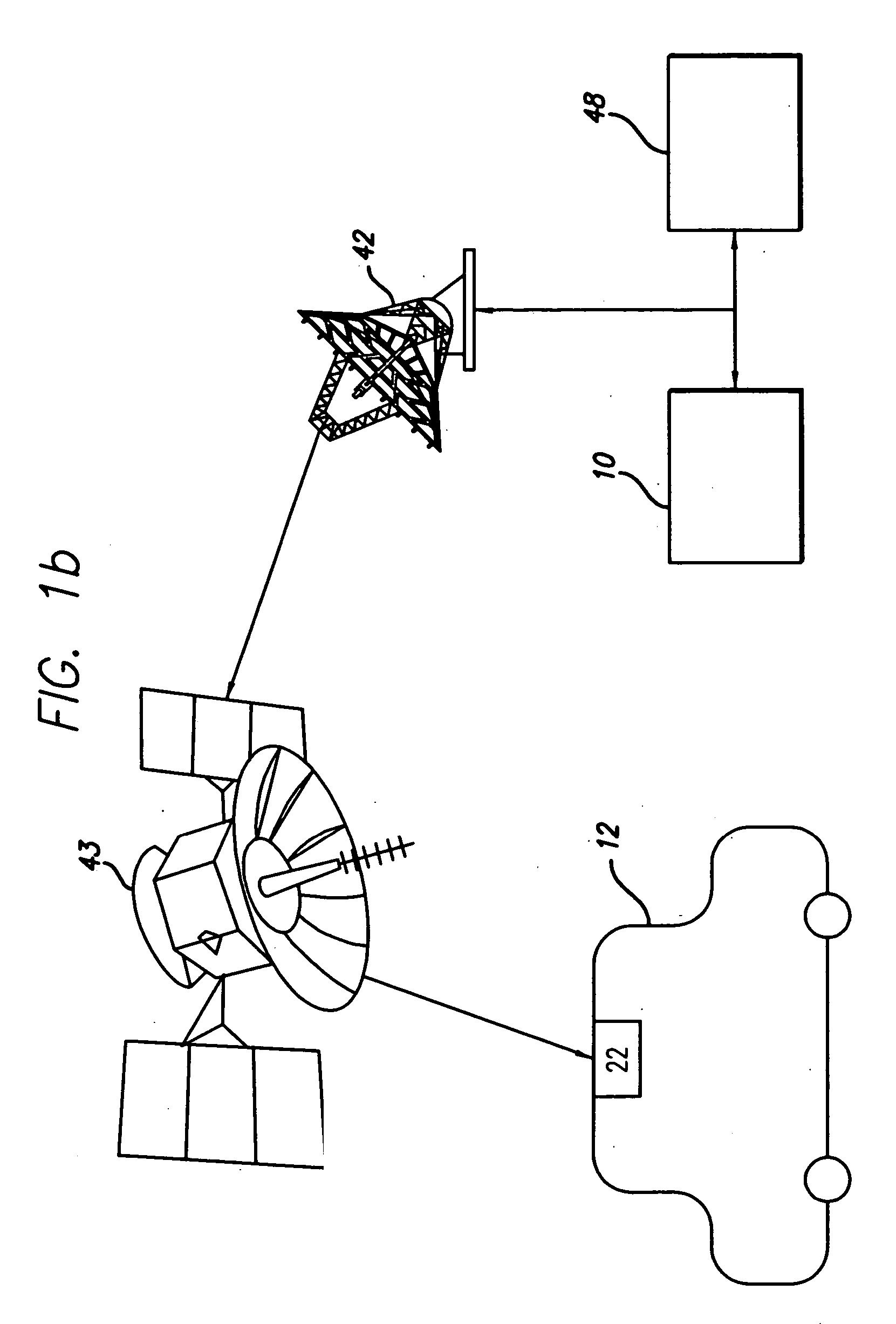
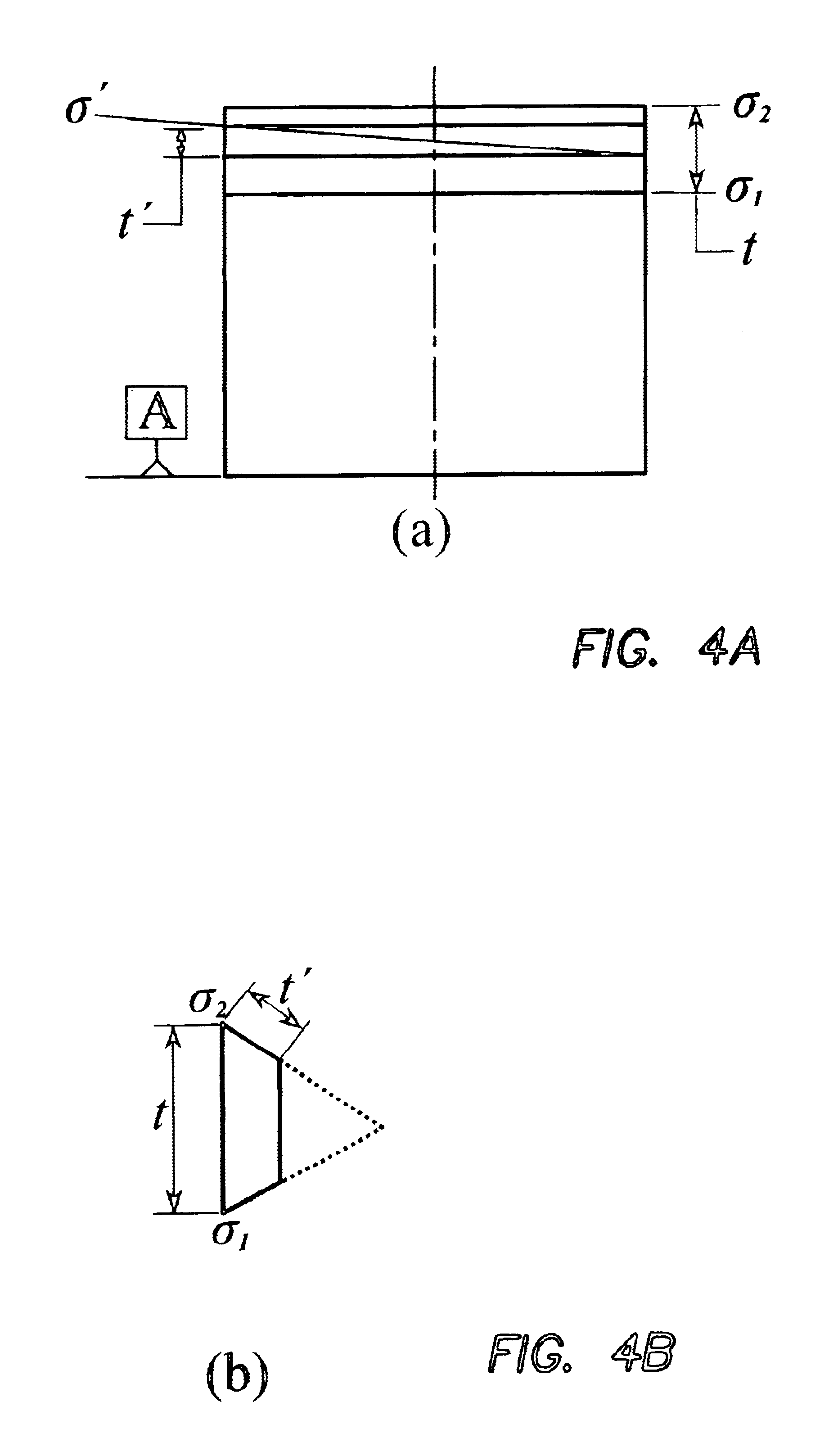
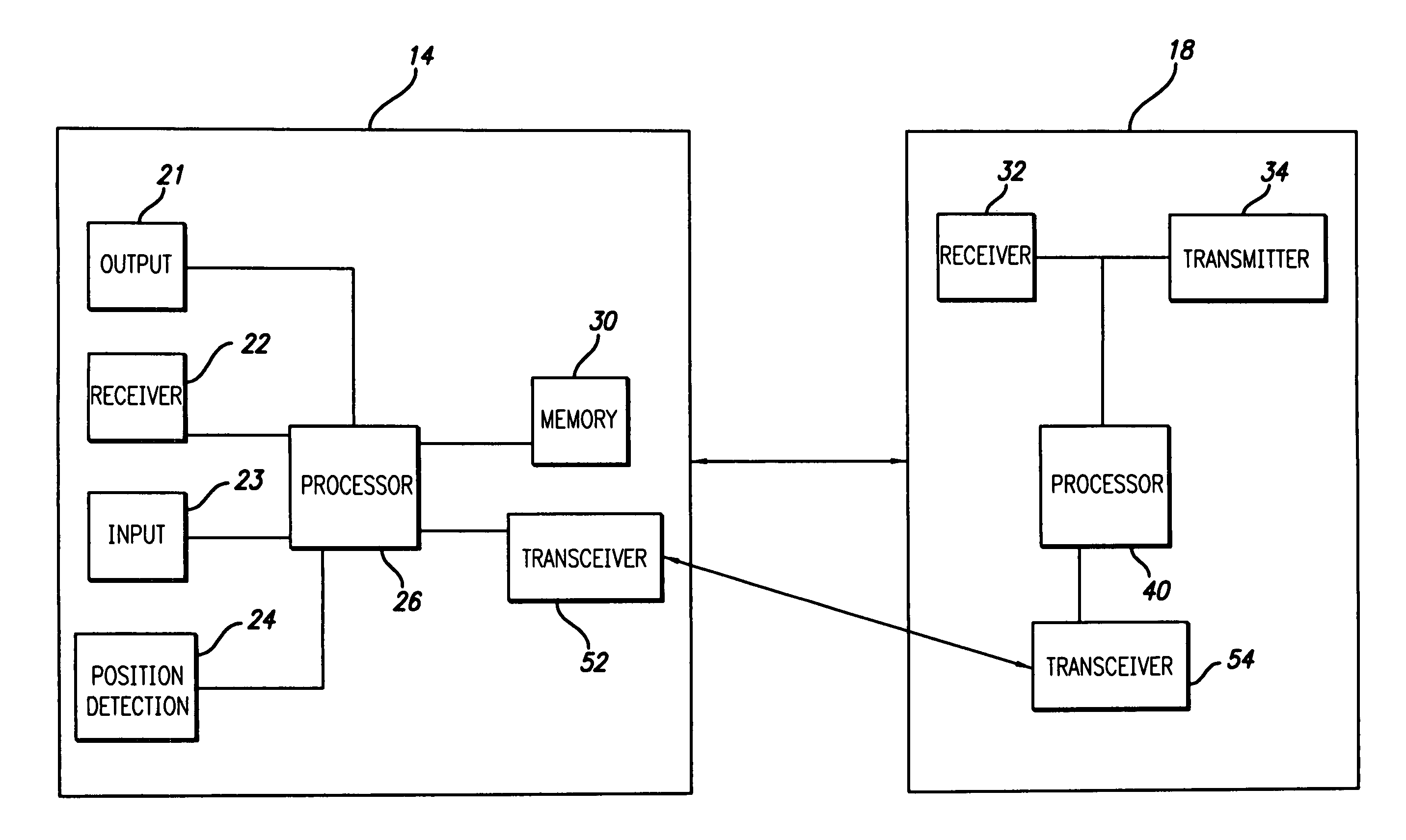
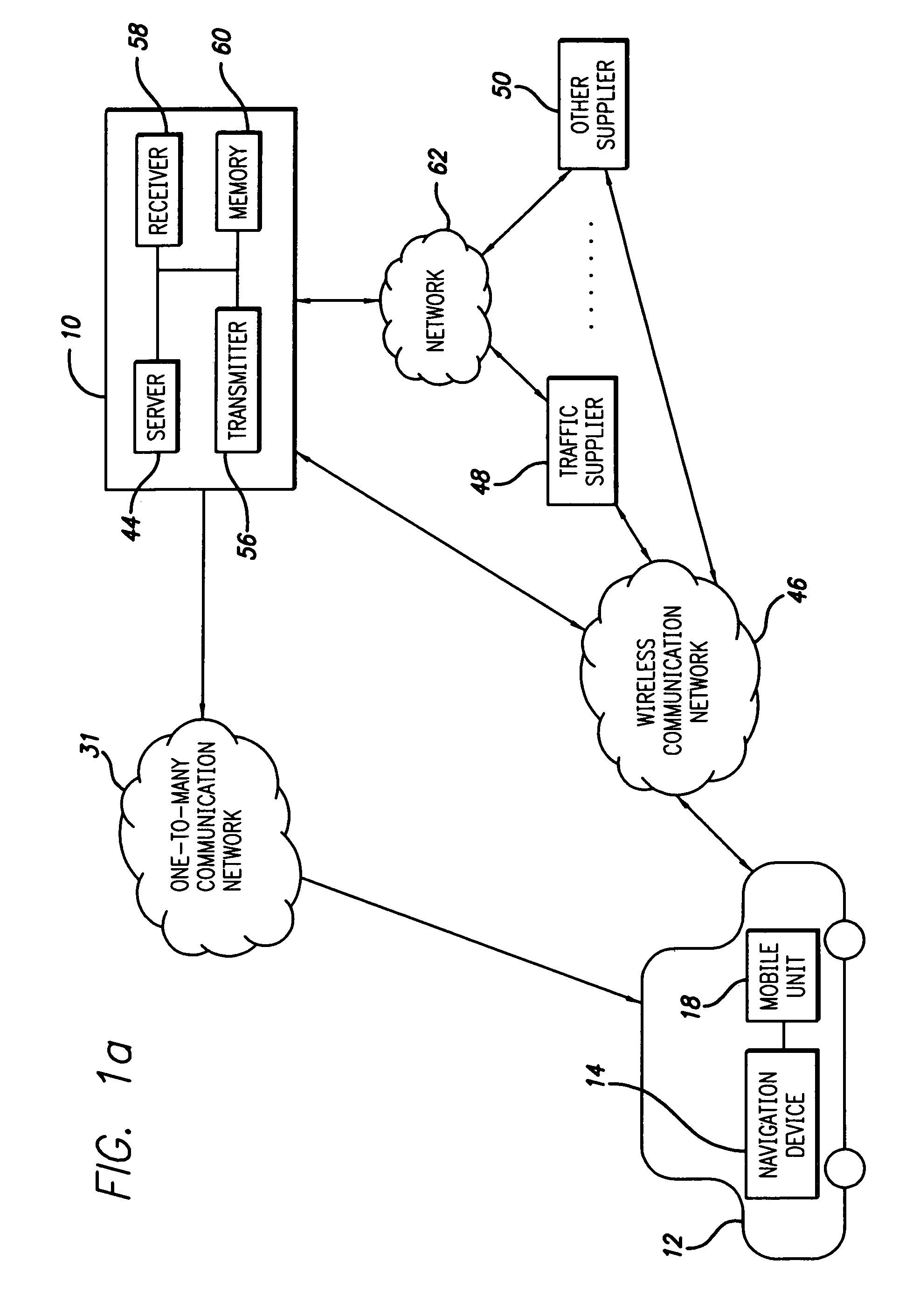
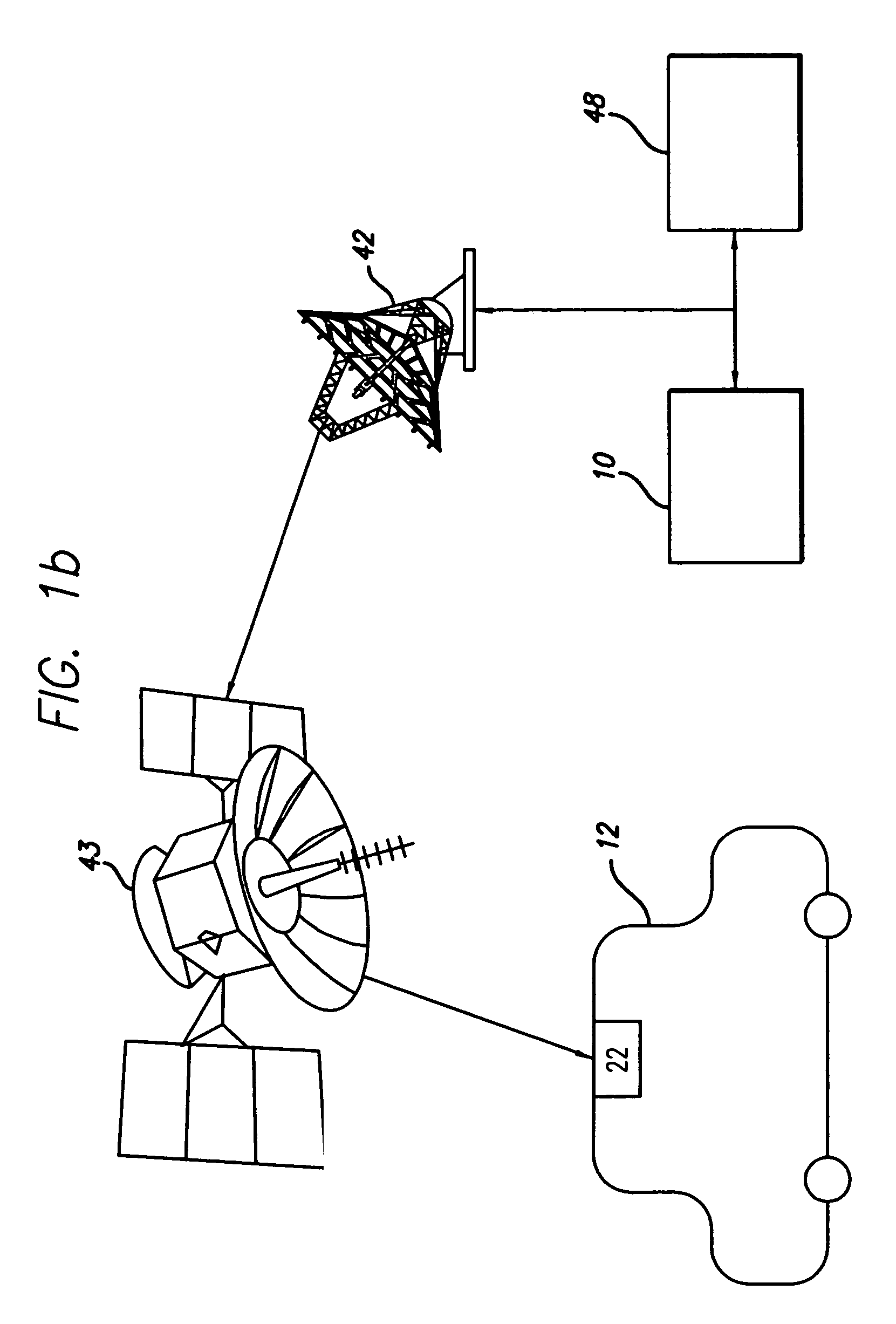
Route calculation method for a vehicle navigation system
ActiveUS20050222764A1Increase route calculationIncrease and decrease broadcastInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemReceipt
Traffic information, including flow information and incident information, obtained through a traffic management system for providing and facilitating the exchange of traffic information between a remote location and a vehicle may be used in route calculation by a navigation device. The navigation device may recalculate a route based on anticipated user error. Alternatively, the navigation device may recalculate a route using received traffic information triggered by the receipt of a traffic information update, or triggered by the passage of an amount of time. The broadcast rate of traffic information updates may vary temporally (providing more frequent updates during peak commute times) or geographically (providing more frequent updates to metropolitan areas with increased traffic information needs). If route calculation is triggered by an elapsed amount of time, the amount of time may vary to be shorter during peak commute times. Additional route calculation techniques allow the incorporation of historical traffic information or the use of the most recent traffic information if incomplete traffic information is available. Still further route calculation techniques may calculate a best route by avoiding zigzagging or evaluating an assigned cost of a potential route.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
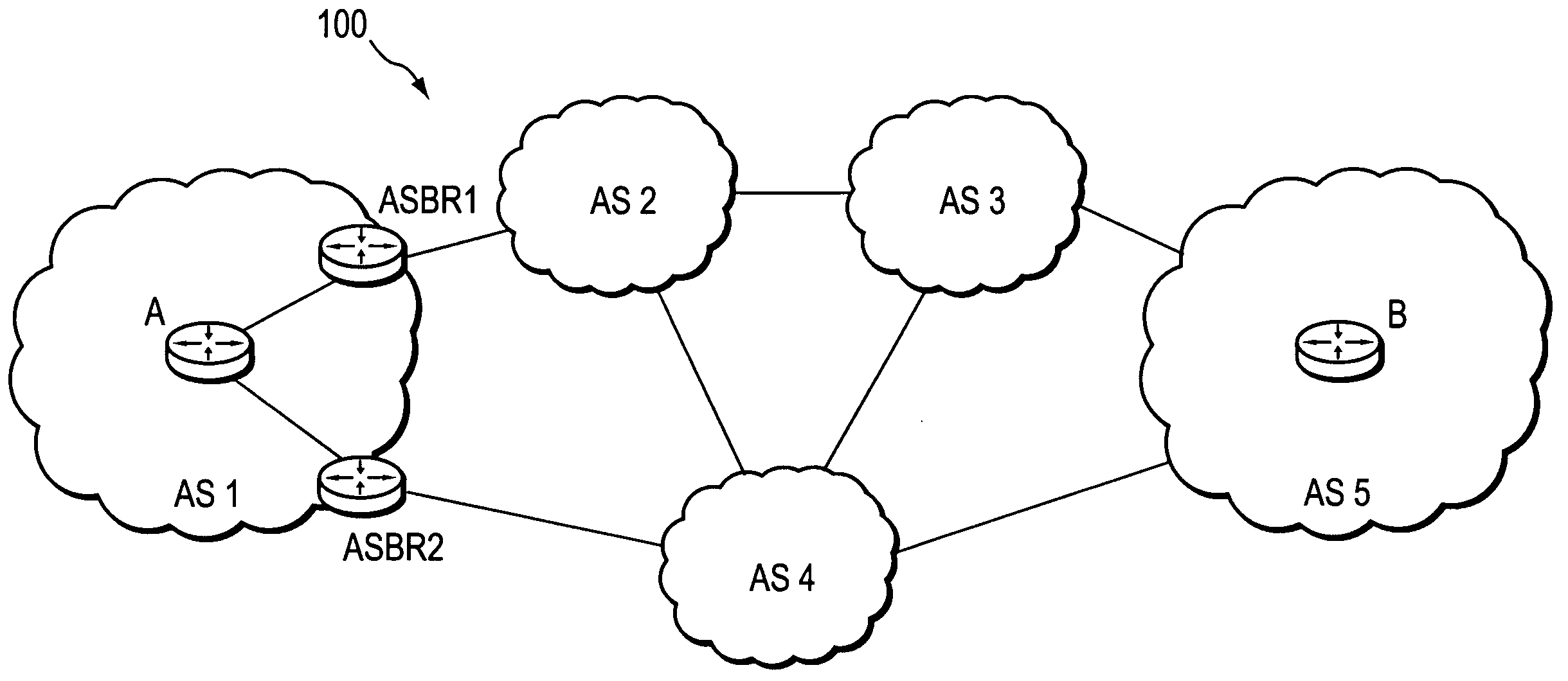
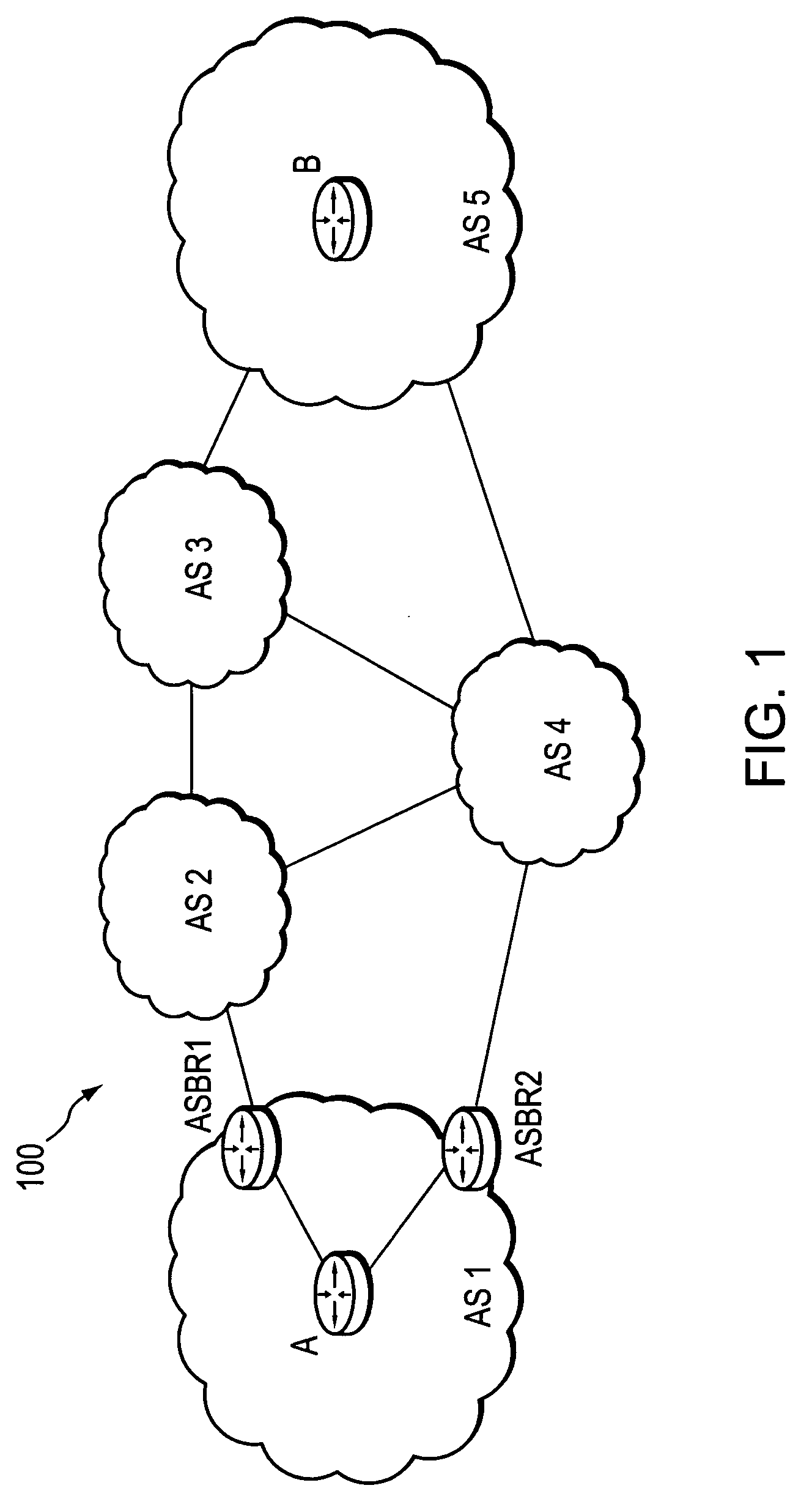
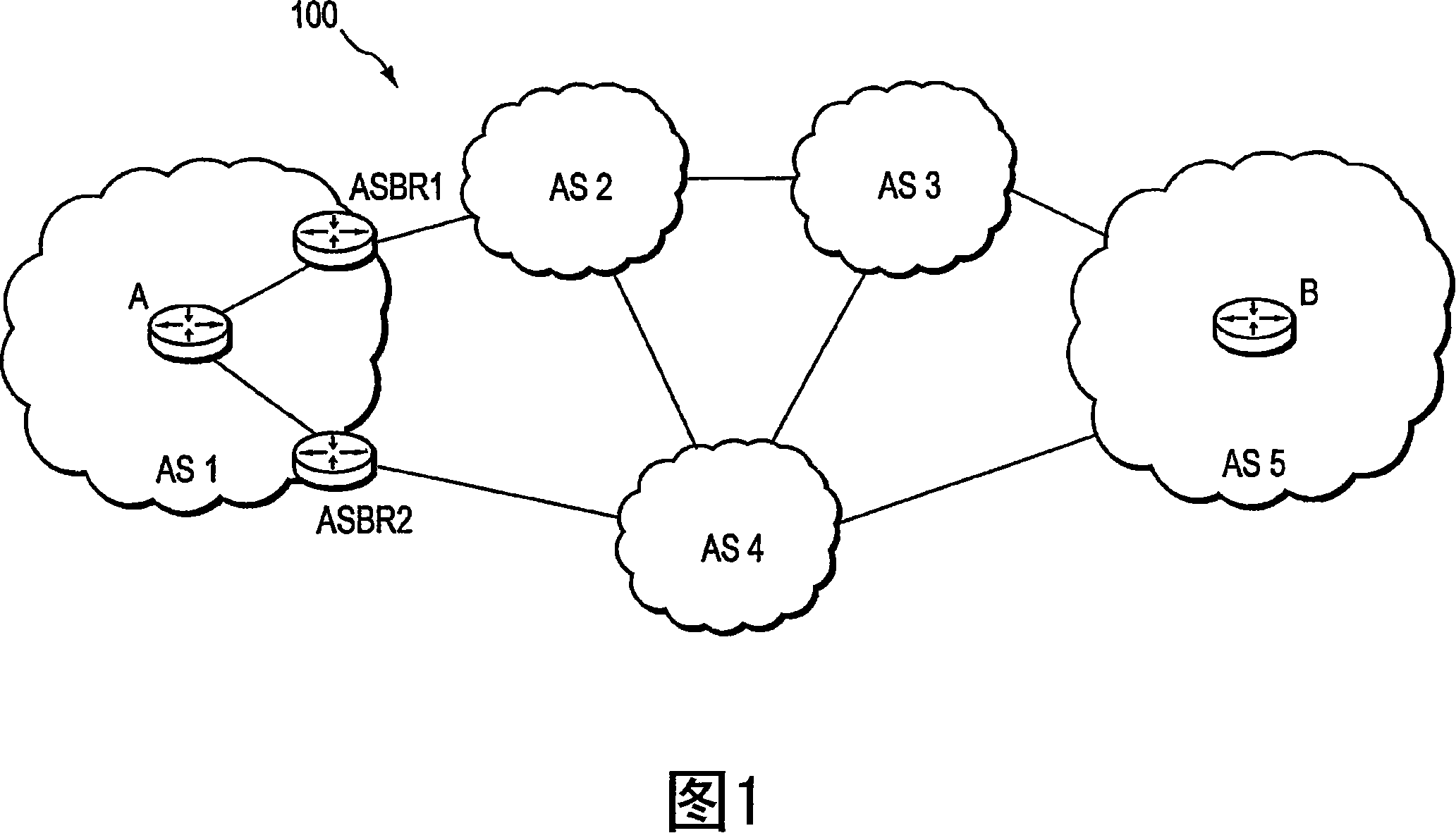
Computation of a shortest inter-domain TE-LSP across a set of autonomous systems
A technique calculates a shortest path for a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from a head-end node in a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain in a computer network. The novel path calculation technique determines a set of different remote domains through which the TE-LSP may traverse to reach the tail-end node (e.g., along “domain routes”). Once the set of possible routes is determined, the head-end node sends a path computation request to one or more path computation elements (PCEs) of its local domain requesting a computed path for each domain route. Upon receiving path responses for each possible domain route, the head-end node selects the optimal (shortest) path, and establishes the TE-LSP accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for geometric variations to integrate parametric computer aided design with tolerance analyses and optimization
InactiveUS6963824B1Convenient investigationReadily apparentPosition fixationComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsComputer Aided Design
The objective of the invention is a bi-level method for modeling geometric tolerances compatible with the ANSI / ASME tolerance standard. At the local level, the model represents each tolerance-zone for a plane or an axis (line) as a tolerance map, and it includes the computational techniques that relate interdependencies between these regions and subregions within them. The model includes formulations for variations in size, form, orientation, position, and runout, and combinations of these, because all of these variations can be modeled using points, lines, and planes. Since variations in simple profiles that are formed from lines and circular arcs also can be described by such combinations, they too are includable in the formulation. The primary method is to overlay the geometry of tolerance-zones onto some traditional modes for representing planes, lines, and points. At the global level, the model inter-relates all frames of reference on a part or an assembly.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Route calculation method for a vehicle navigation system
ActiveUS7680596B2Increase and decrease broadcastReduce twistInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemReceipt
Traffic information, including flow information and incident information, obtained through a traffic management system for providing and facilitating the exchange of traffic information between a remote location and a vehicle may be used in route calculation by a navigation device. The navigation device may recalculate a route based on anticipated user error. Alternatively, the navigation device may recalculate a route using received traffic information triggered by the receipt of a traffic information update, or triggered by the passage of an amount of time. The broadcast rate of traffic information updates may vary temporally (providing more frequent updates during peak commute times) or geographically (providing more frequent updates to metropolitan areas with increased traffic information needs). If route calculation is triggered by an elapsed amount of time, the amount of time may vary to be shorter during peak commute times. Additional route calculation techniques allow the incorporation of historical traffic information or the use of the most recent traffic information if incomplete traffic information is available. Still further route calculation techniques may calculate a best route by avoiding zigzagging or evaluating an assigned cost of a potential route.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Strategies for generating media consumption statistics
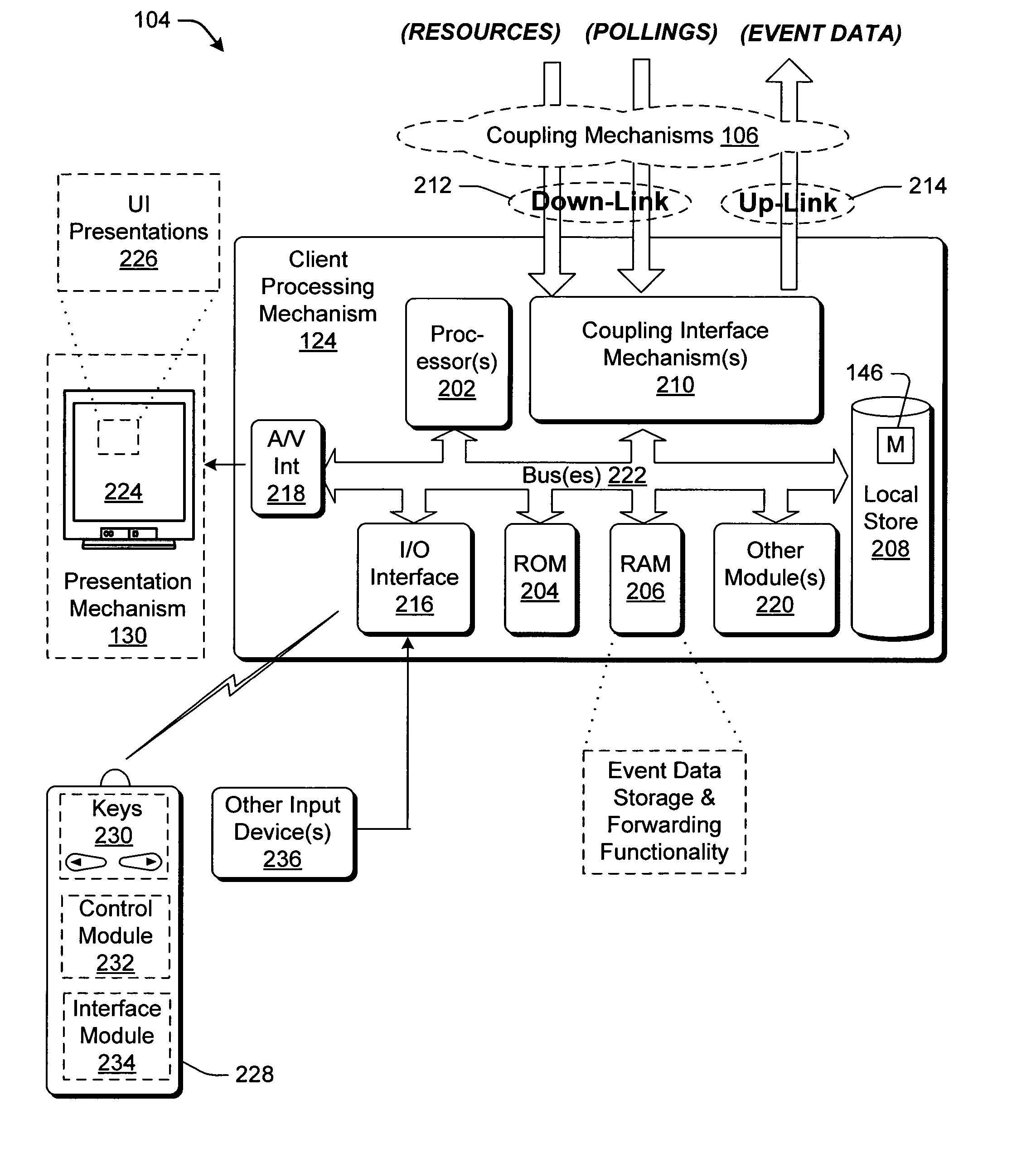
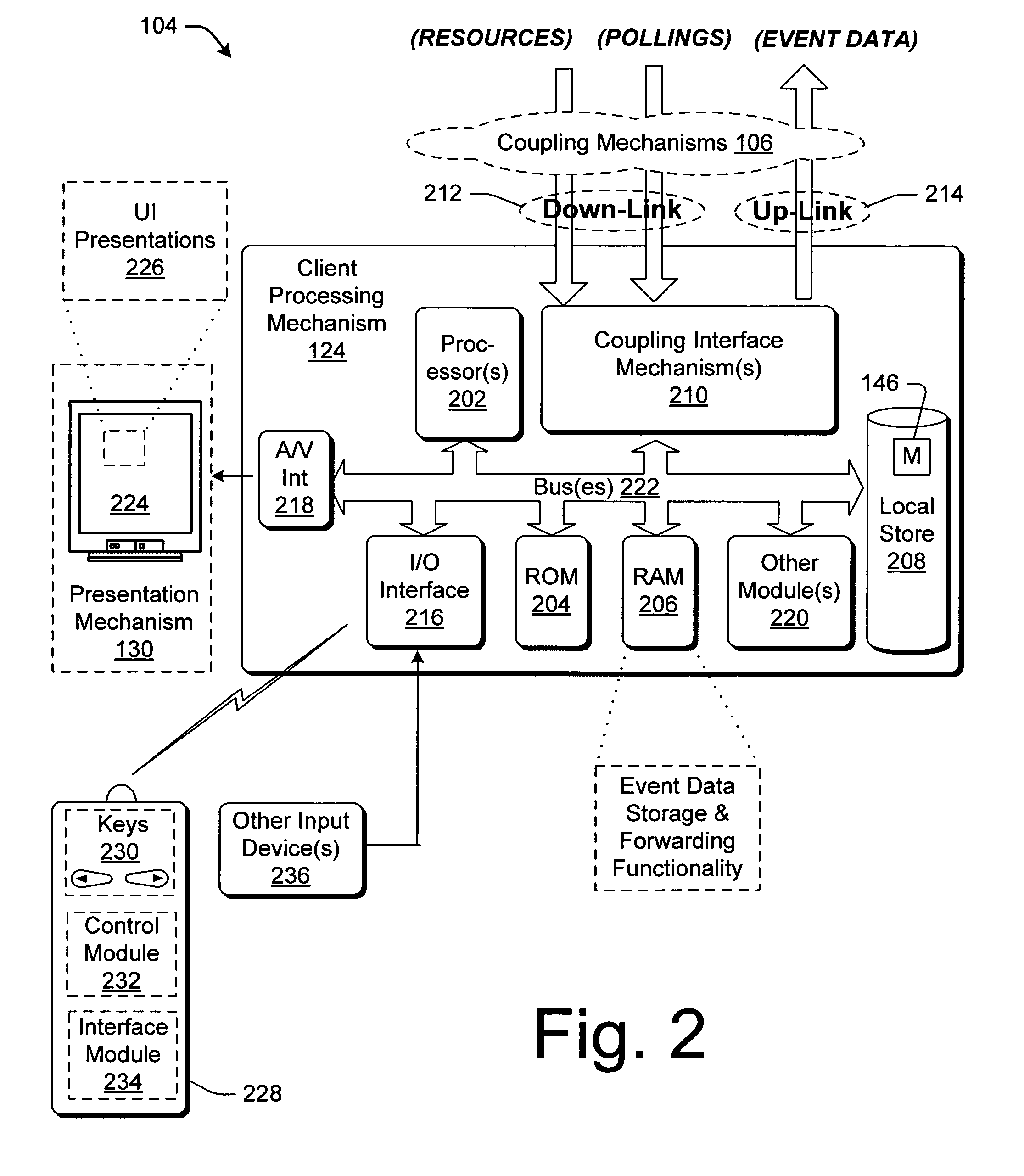
InactiveUS20060075420A1Eliminate consumptionAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringTime segmentEvent data
Techniques are described for generating statistics that reflect the consumption of media resources, such as television program resources. The techniques involve polling a group of devices identified in a random sample list or a custom sample list to collect event data describing the consumption of resources by the devices. Lower-bound and upper-bound thresholds are applied to remove or modify event data that may not accurately reflect the legitimate consumption of resources. Varying probability weights can also be assigned to events to reflect their likelihood of representing the legitimate consumption of resources. Based on such filtered event data, for a given device, a computation technique computes the percentage of time that the user has consumed a particular resource relative to a total amount of time in a time segment. Similar percentages are computed for other devices and other time segments to provide plural percentage values. Rating information and share information are computed based on these calculated percentage values. The tracking functionality compiles the calculated statistics into various web-enabled UI presentations and provides these reports to an operator over an intranet or like network.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Byte stream organization with improved random and keyed access to information structures
InactiveUS7216127B2Extension of timeMaximizes the invention's scope for producing highly efficient resultsData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAlgorithmByte
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
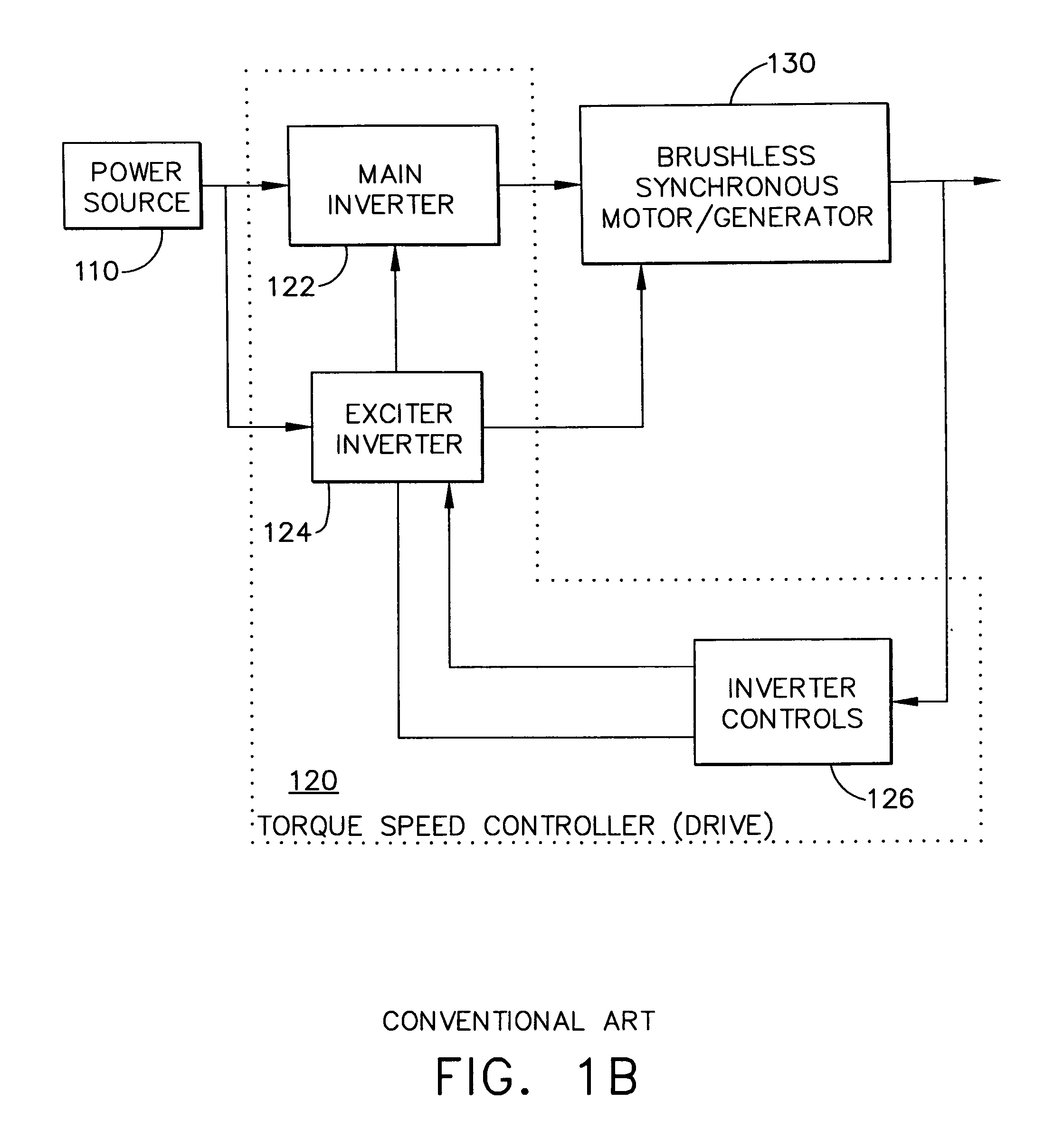
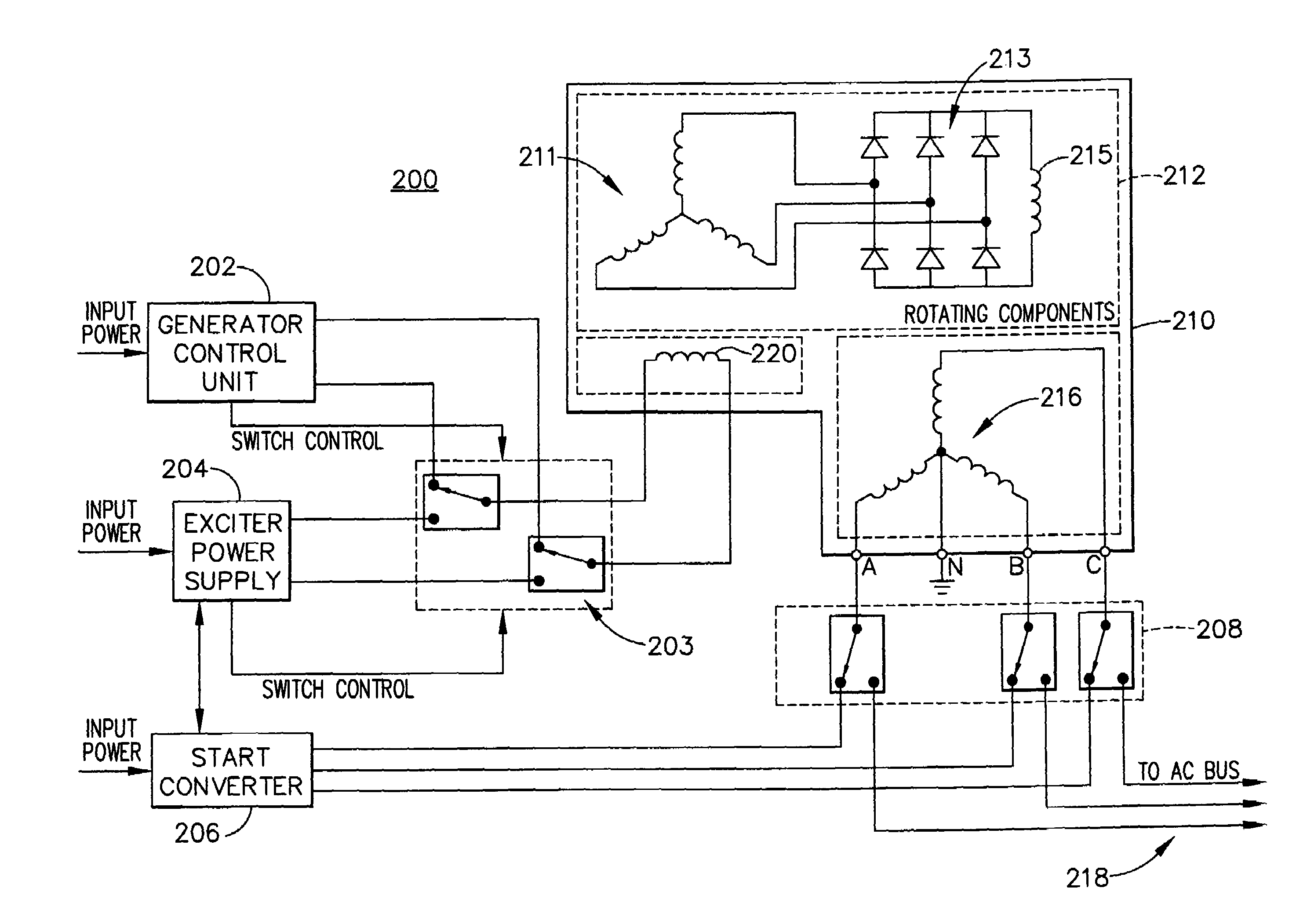
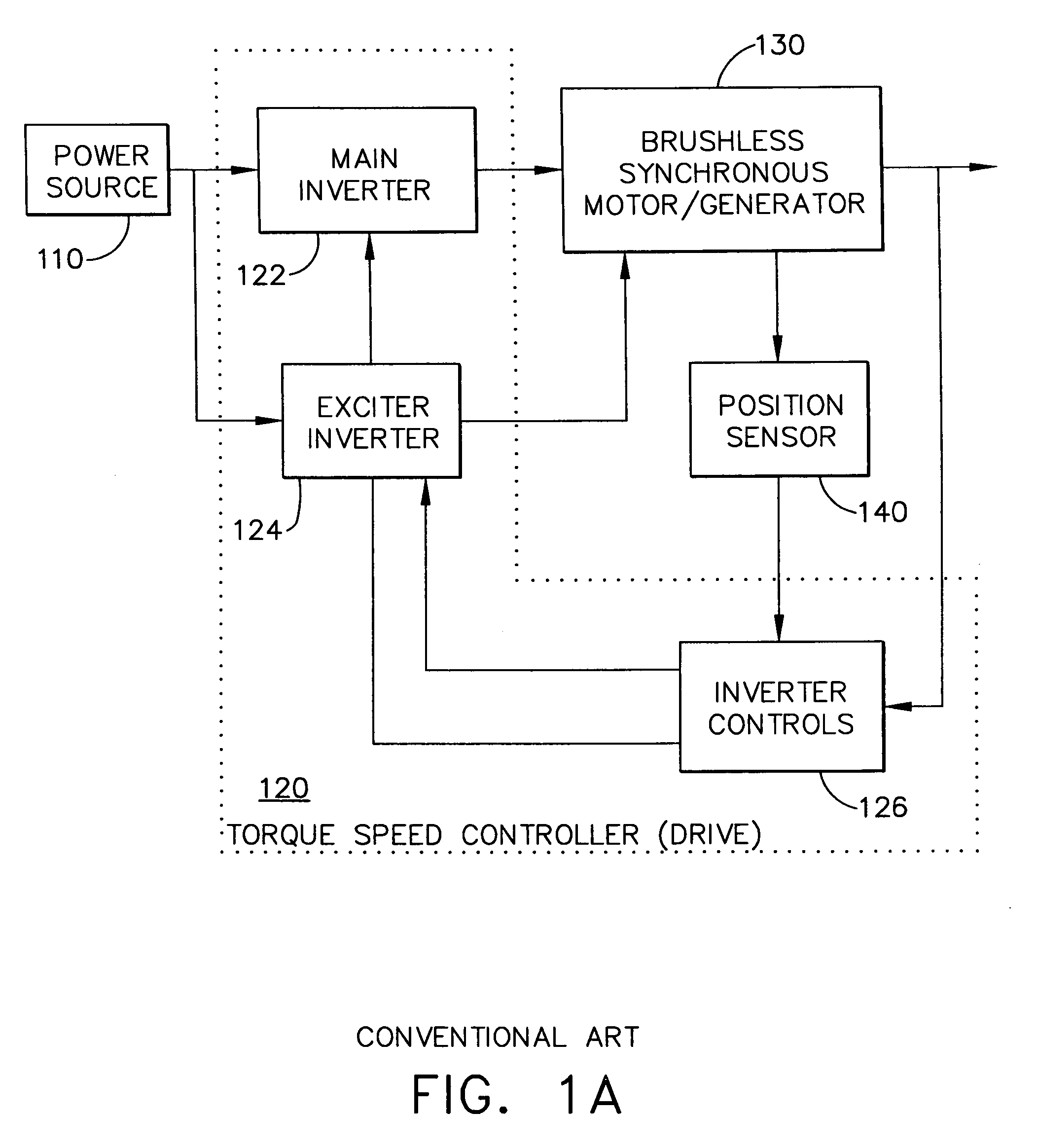
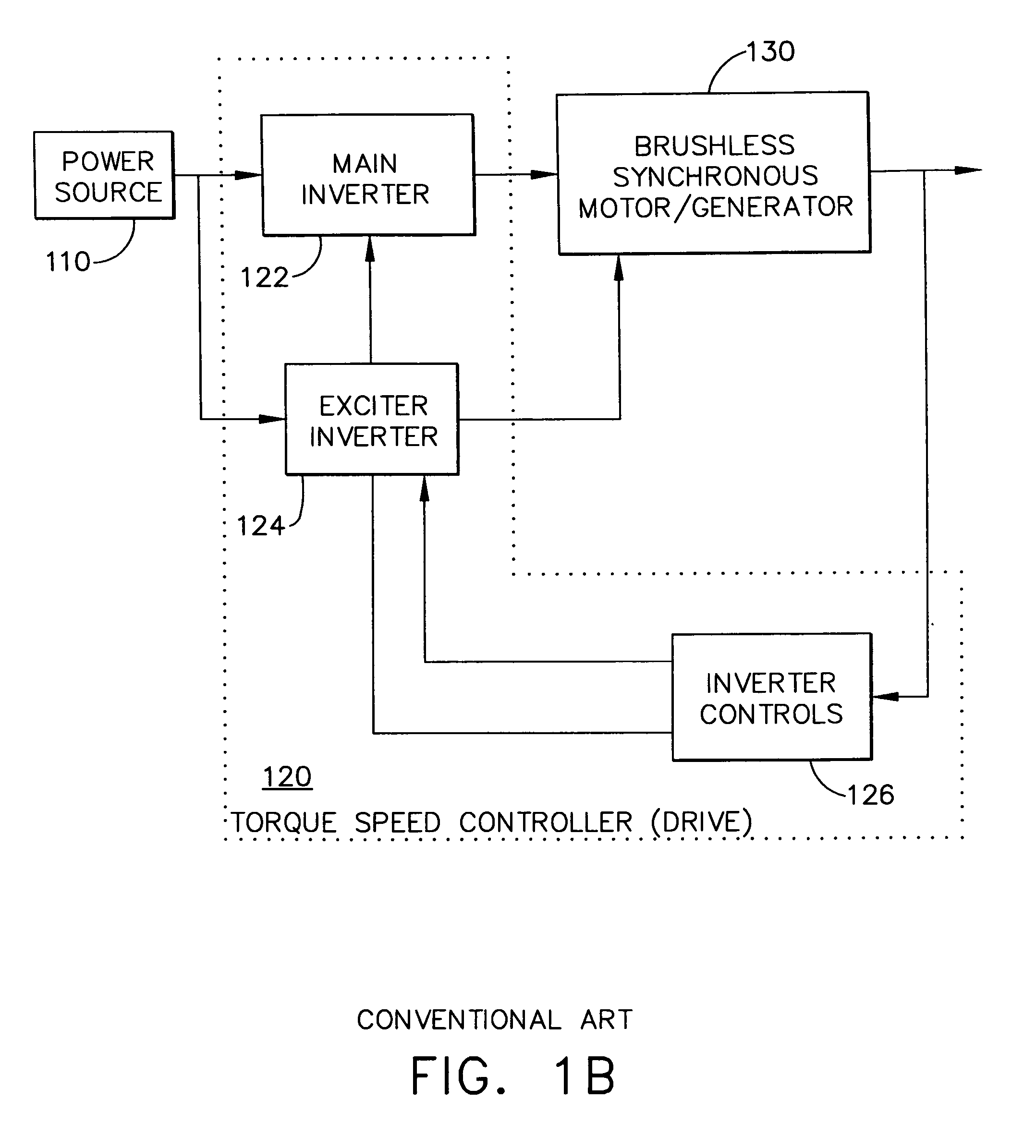
Adaptive position sensing method and apparatus for synchronous motor generator system
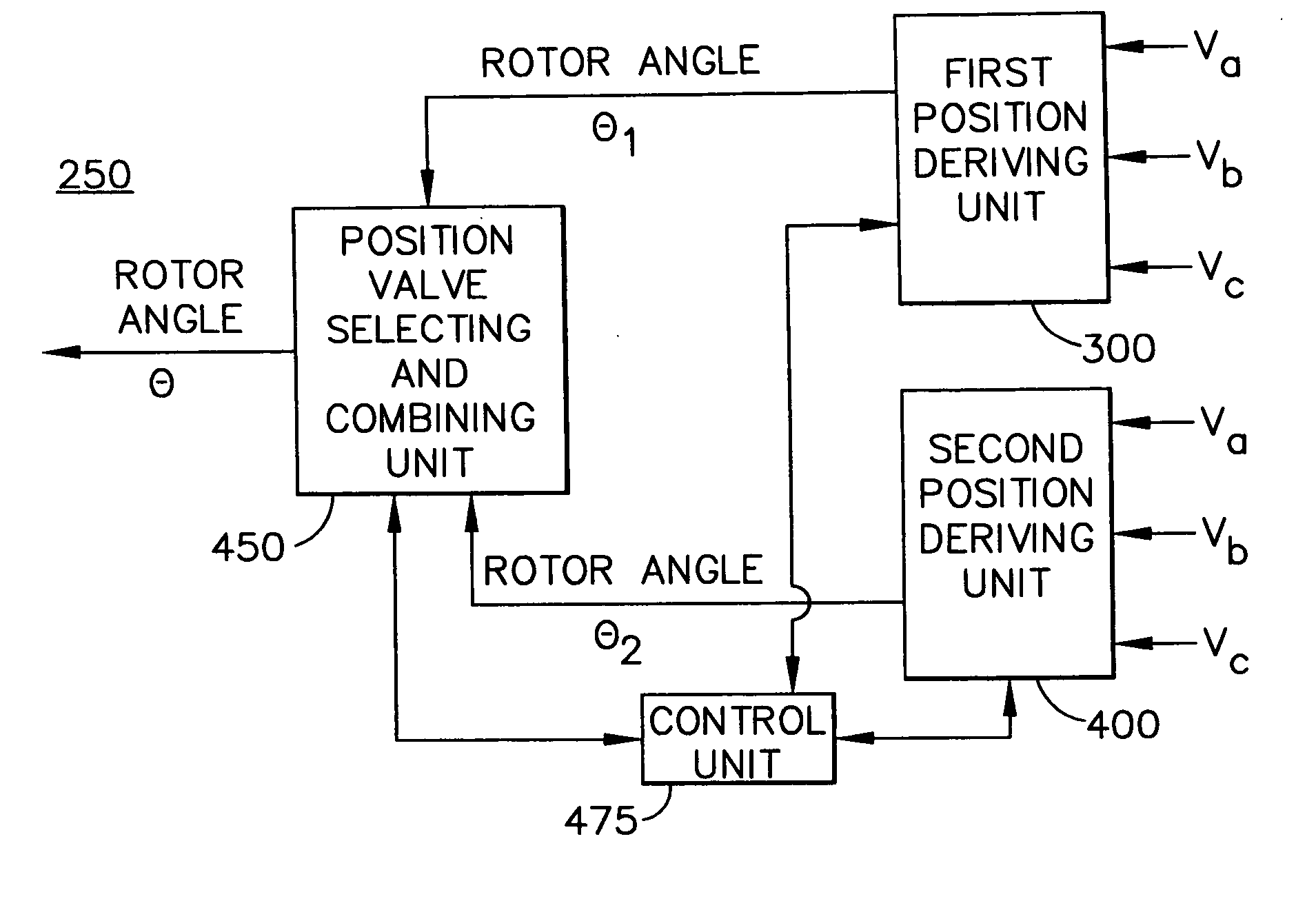
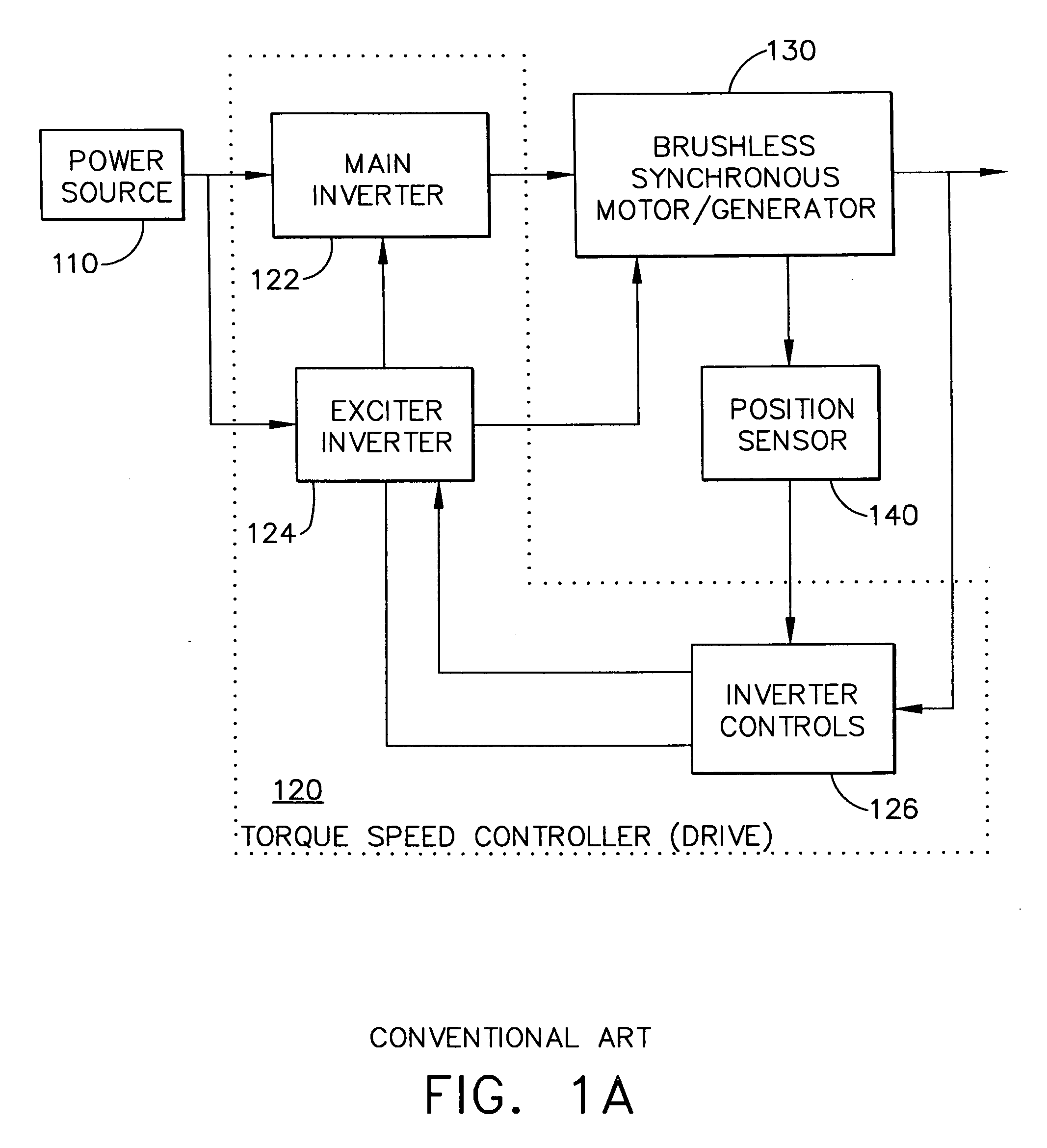
An adaptive, sensorless position sensing apparatus (250) derives rotor position of a synchronous machine (200). The apparatus (250) comprises a first rotor position deriving unit (300) for generating first rotor position values by applying a first sensorless rotor position calculation technique, which emulates a resolver; a second rotor position deriving unit (400) for generating second rotor position values by applying a second sensorless rotor position calculation technique; and a rotor position result output unit (450) for outputting rotor position results over a range of rotor speeds as a function of the first rotor position values, the second rotor position values, and rotor speed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
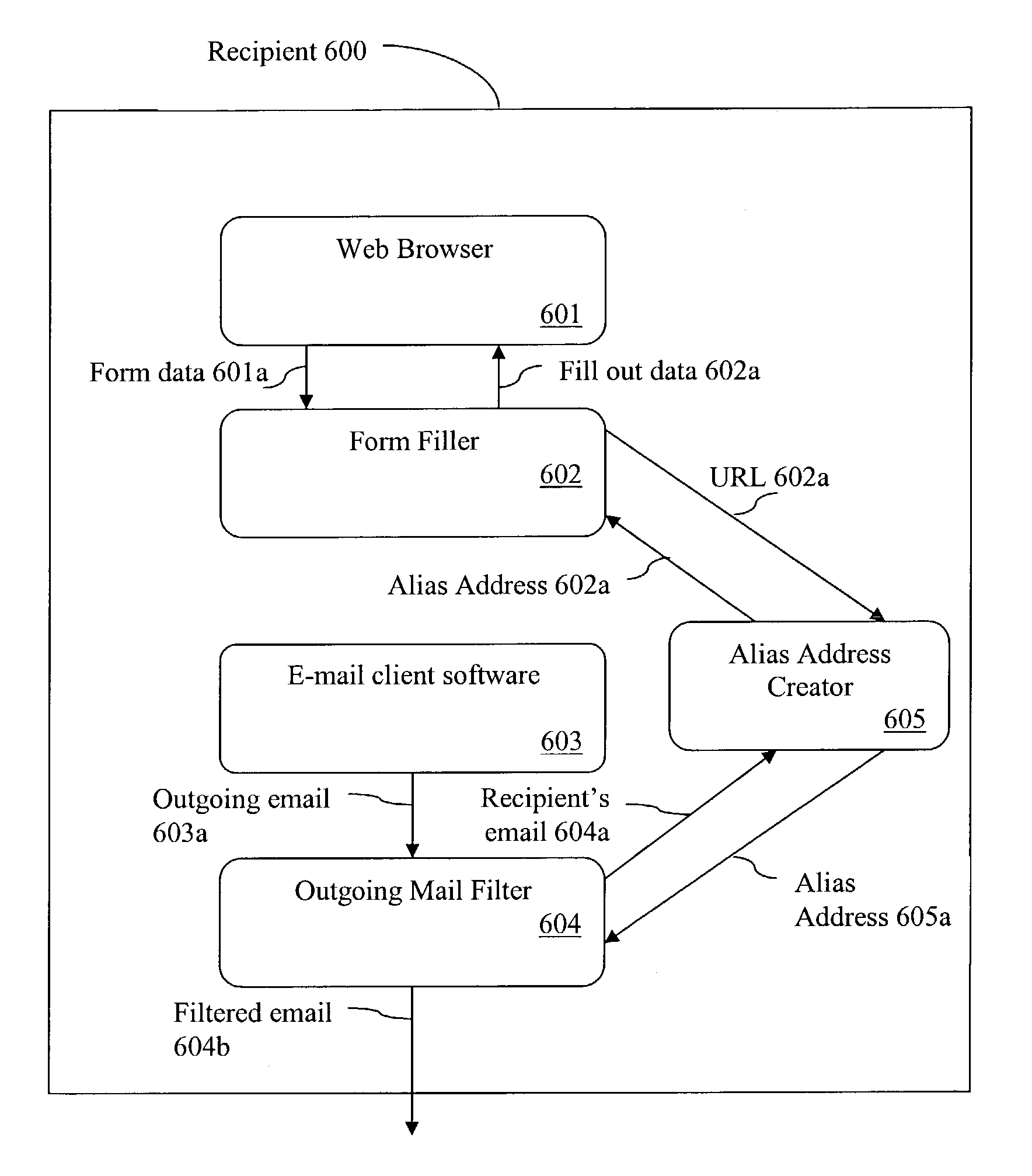
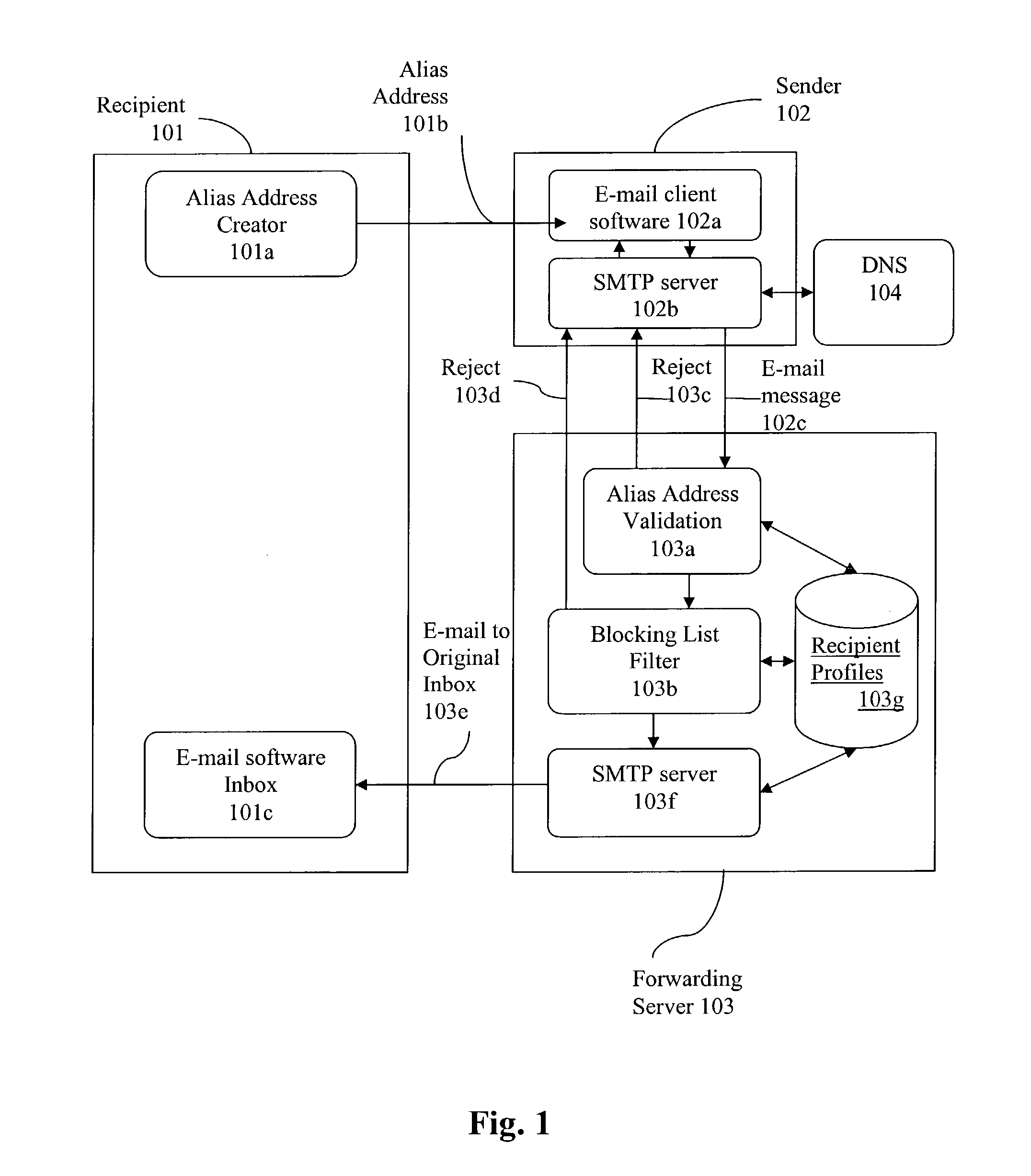
Method and system for controlling the use of addresses using address computation techniques
InactiveUS7216227B2Reduce decreaseMultiple digital computer combinationsSecret communicationMulticast addressCalculation technique
A system and method for controlling the use of addresses by using address computation techniques is described. A system comprising alias address creation software generates multiple alias addresses representing a single real address of a particular recipient. Each alias address is computed from data representing a prospective sender and a recipient. A sender is provided with an alias address by a recipient for communicating back to said recipient. Messages sent by a sender, employing alias addresses are analysed to a forwarding server which validates each alias address and checks it against a blocking list. Messages which pass these checks are directed to the recipient's real address registered with said forwarding server.
Owner:GRYNBERG AMIRAM
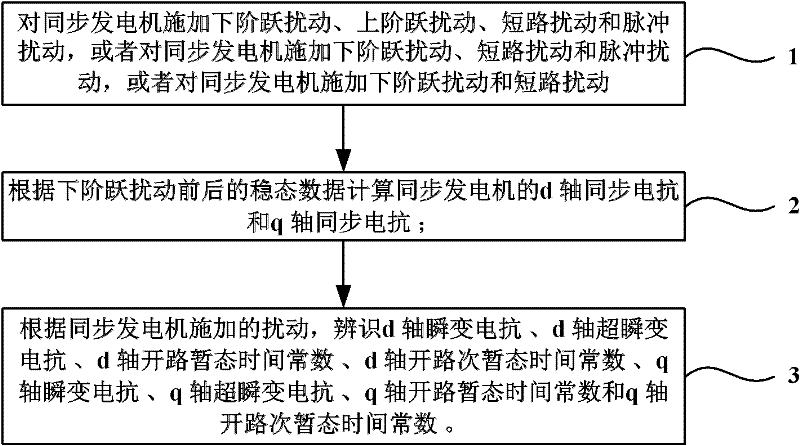
Synchronous generator model parameter multi-step identification method
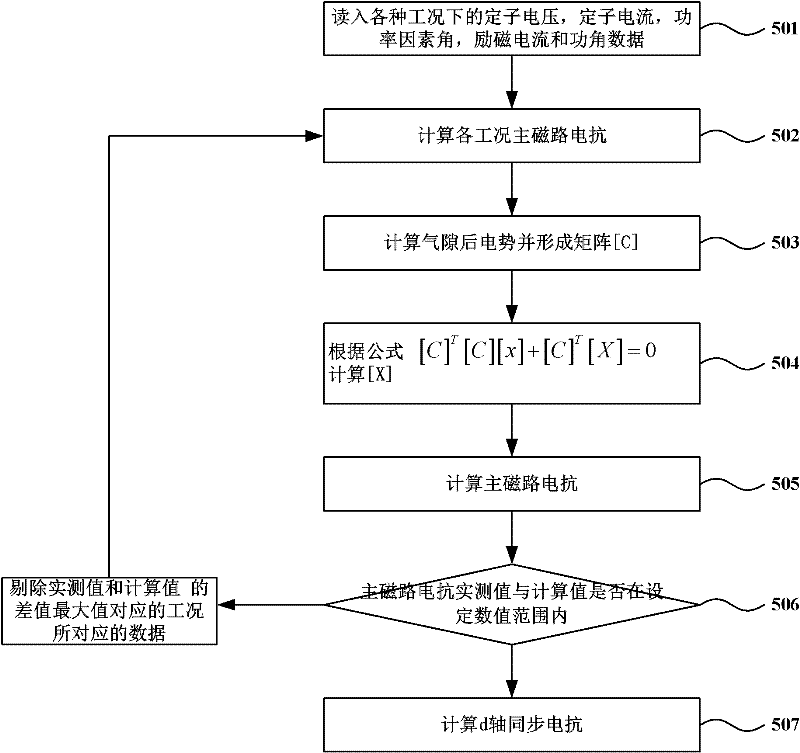
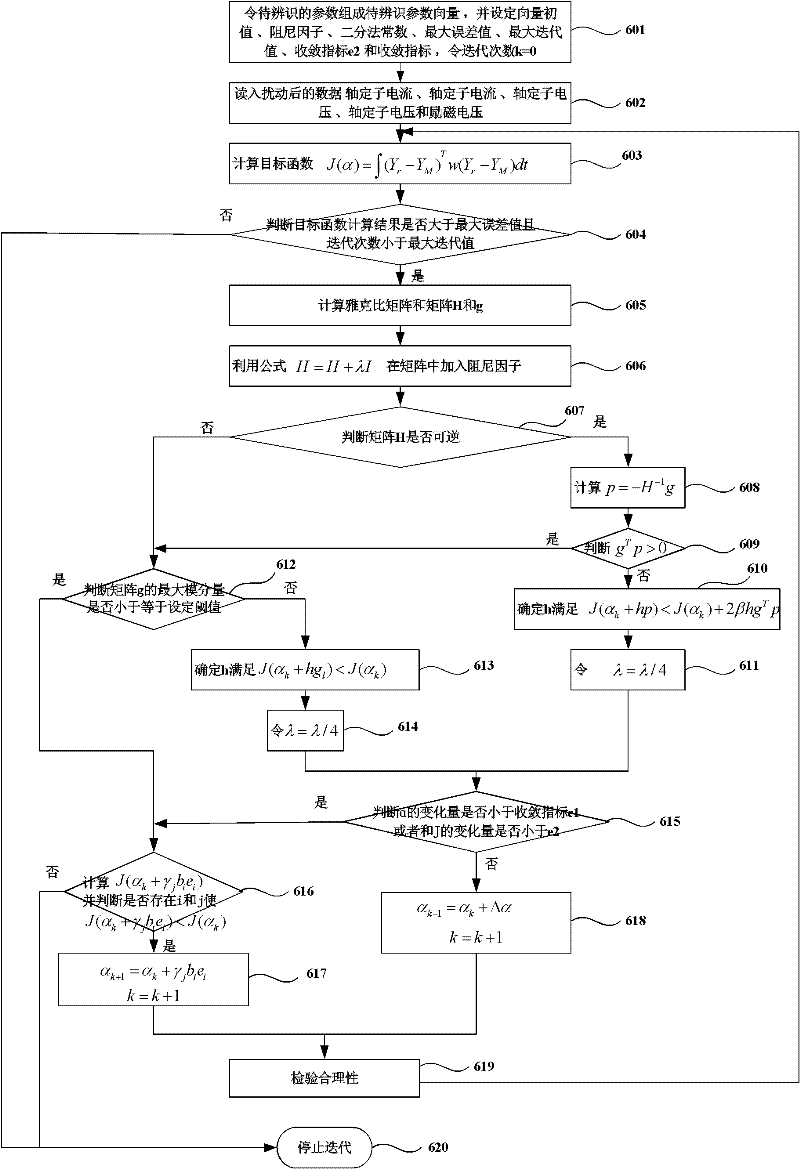
The invention discloses a synchronous generator model parameter multi-step identification method in the technical field of power grid analysis and calculation. The method comprises applying a down and an up step disturbance, a short circuit disturbance and a pulse disturbance to a synchronous generator, or applying a down step disturbance, a short circuit disturbance and a pulse disturbance to a synchronous generator, or applying a down step disturbance and a short circuit disturbance to a synchronous generator; calculating the d axis synchronous reactance xd and the q axis synchronous reactance xq of the synchronous generator according to the steady state data before and after down step disturbance; and identifying the d axis transient reactance x'd, the d axis sub-transient reactance x''d, the d axis open-circuit transient time constant T'd, the d axis open-circuit sub-transient time constant T''d, the q axis transient reactance x'q, the q axis sub-transient reactance x''q, the q axis open-circuit transient time constant T'q, and the q axis open-circuit sub-transient time constant T''q according to the disturbance applied to the synchronous generator. The invention improves parameter identification precision.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Method for obtaining road condition information in real time
InactiveCN102496280AMeet the needs of real-time traffic calculationDetection of traffic movementLocation information based serviceControl signalNetwork control
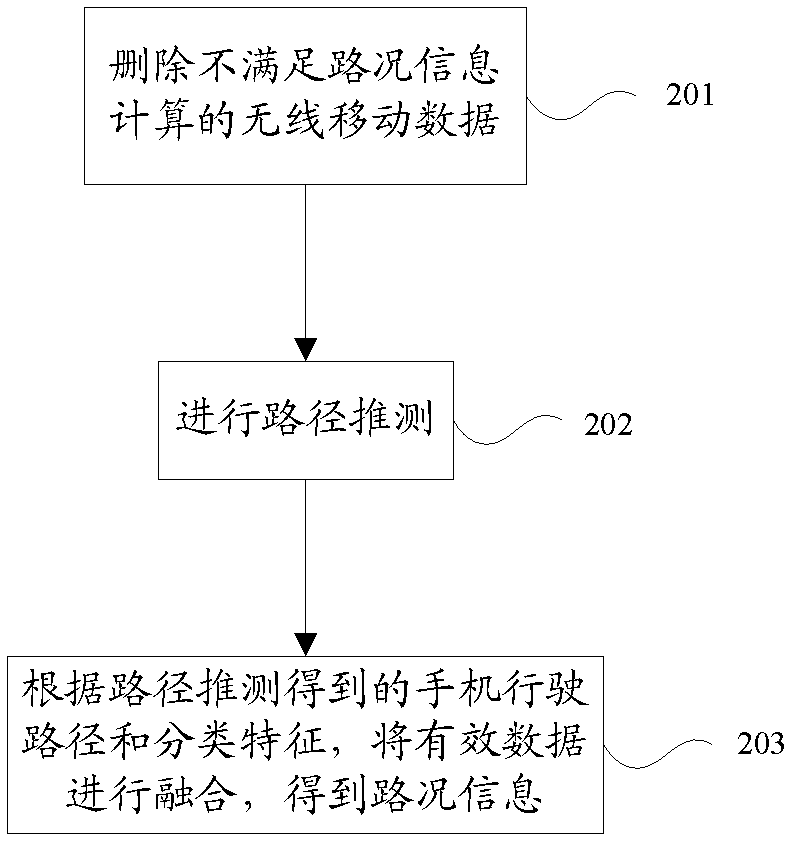
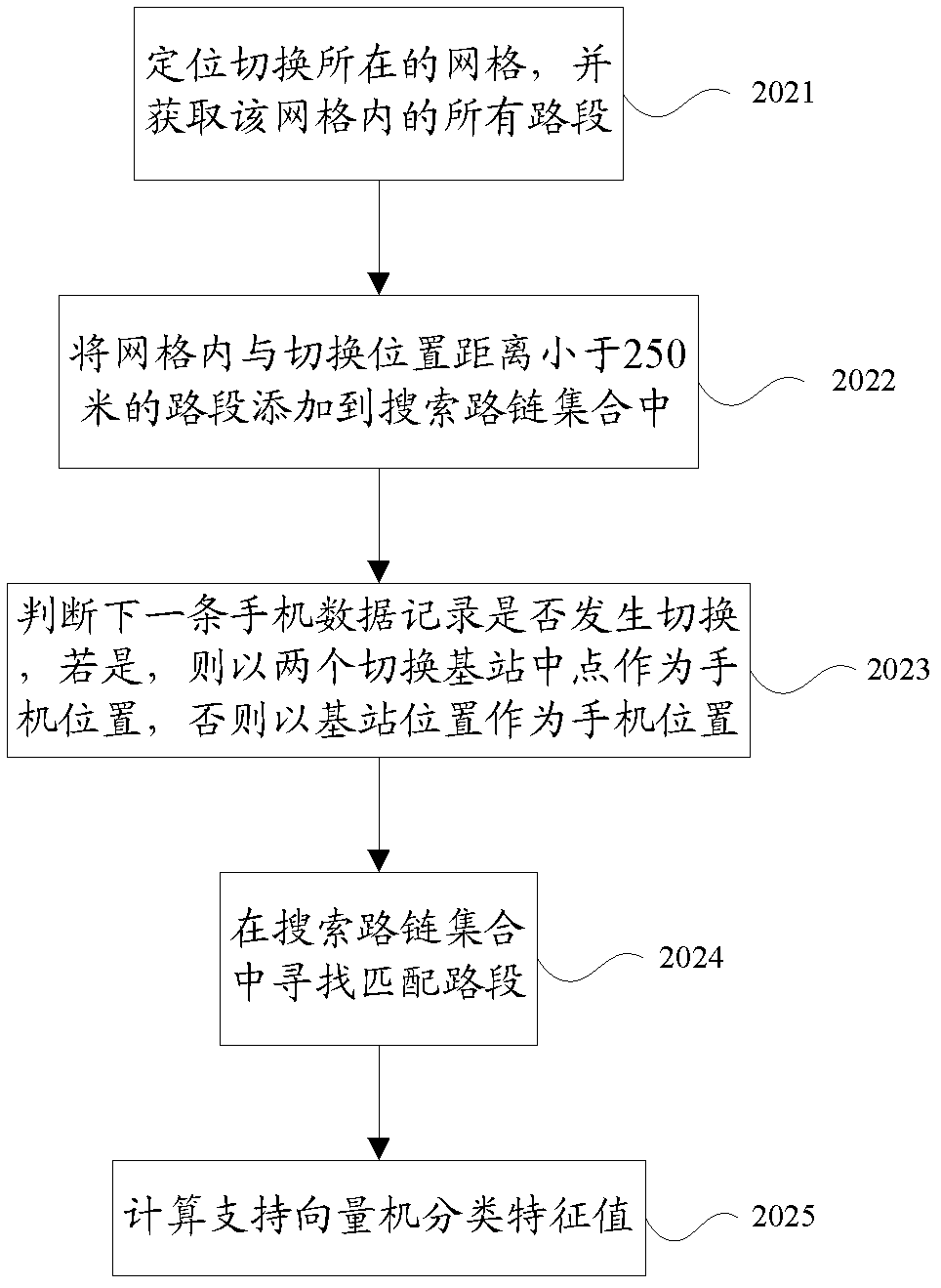
The invention discloses a method for obtaining road condition information in real time, which belongs to the field of intelligent transportation and includes deleting wireless mobile data not meeting the requirements of road condition information calculation, performing path speculation, judging validity of calculation on road chain travel time by the wireless mobile data according to travel paths and classified characteristic value obtained through path speculation, and integrating valid data to obtain road condition information. The method uses the existing wireless communication network control signals for demarcating travel tracks of vehicle-mounted cell phones so as to calculate road condition information. Due to the fact that the wireless positioning technology based on the network makes the best of the existing mobile communication facilities and network resources, all-weather road real-time transportation information collection covering all road nets can be achieved with small investment, and therefore the road condition information calculation technology based on wireless network control signals can meet the requirements of real-time road condition calculation in vast areas.
Owner:深圳市千方航实科技有限公司
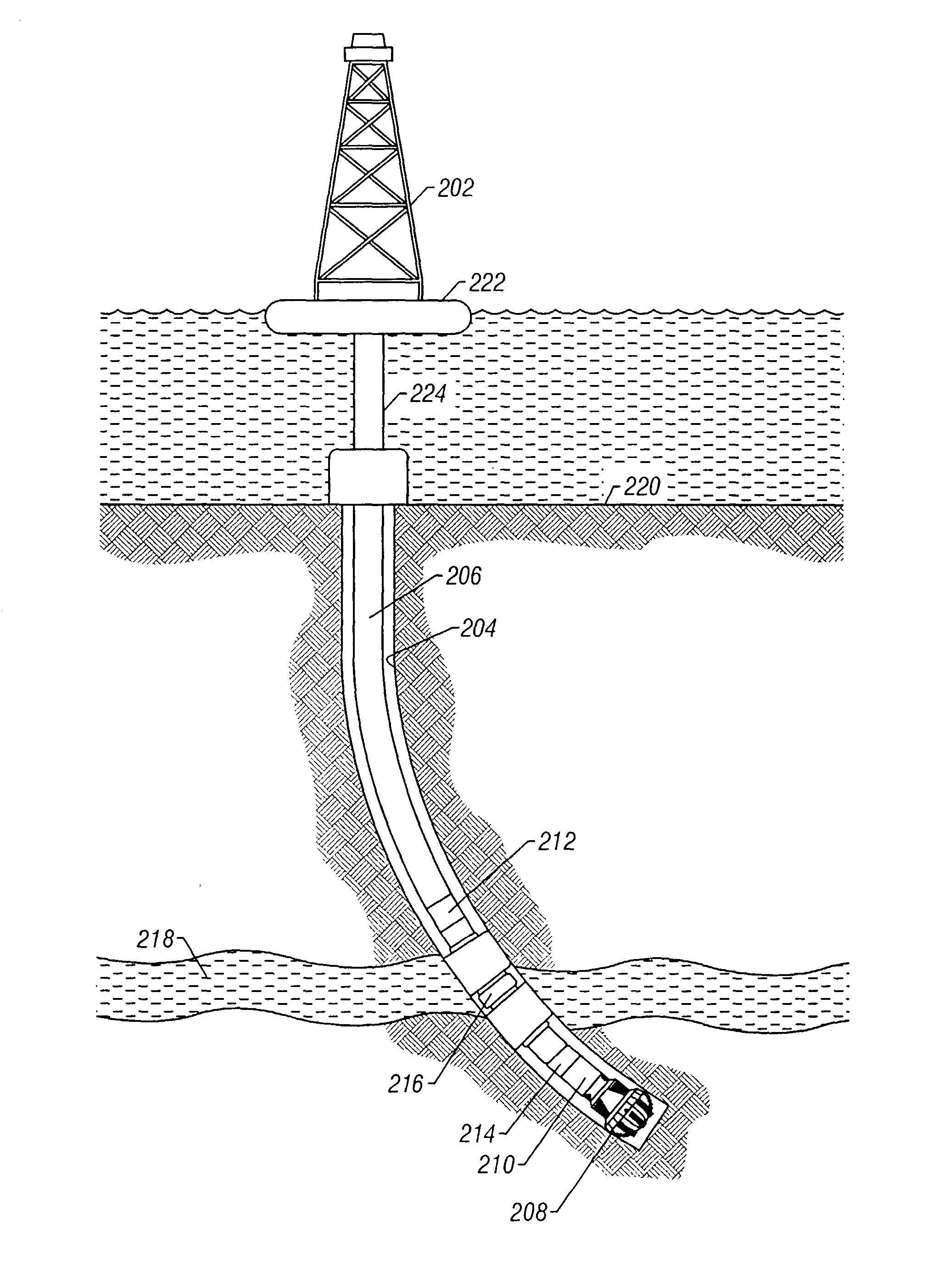
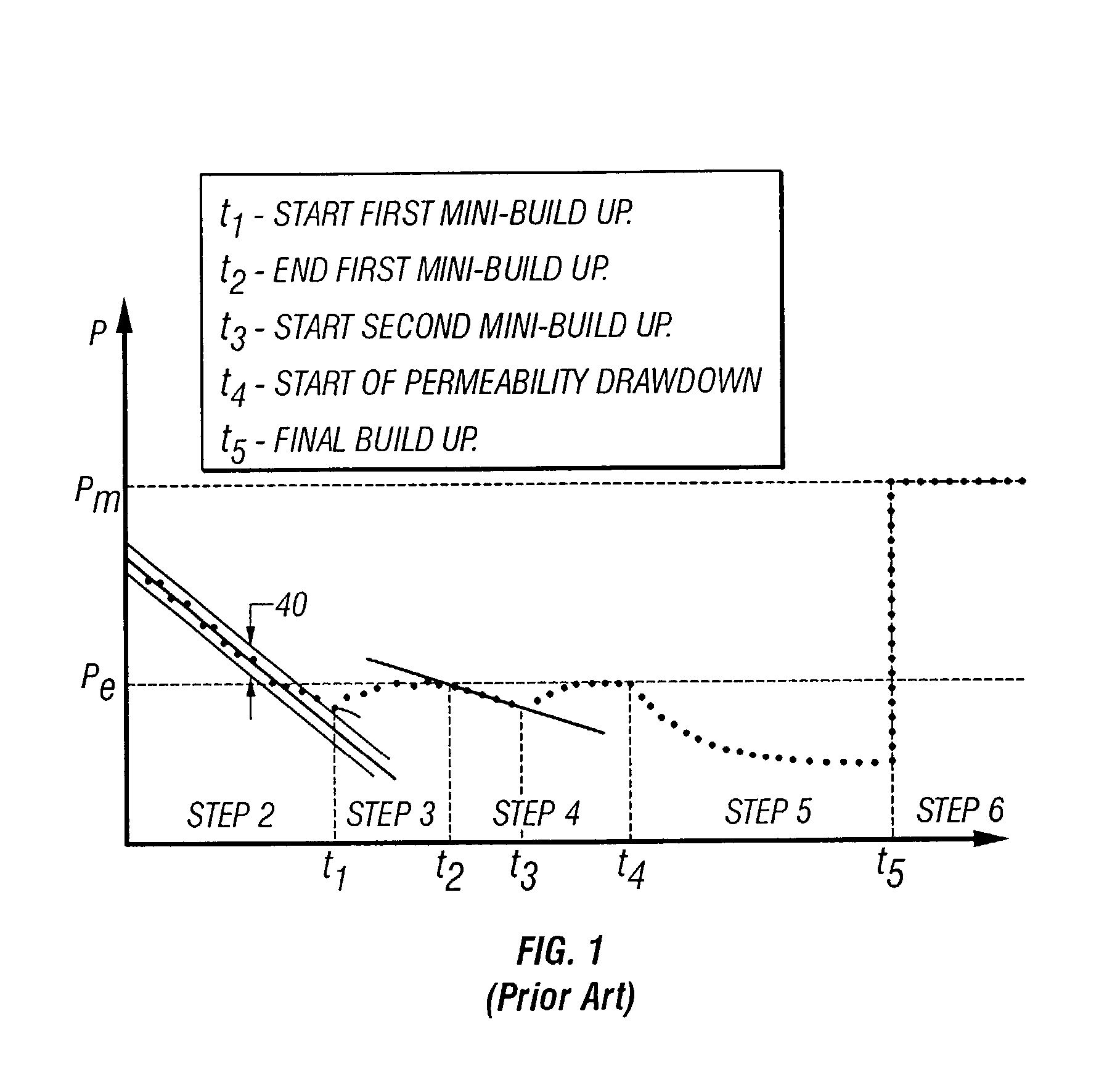
Methods to detect formation pressure
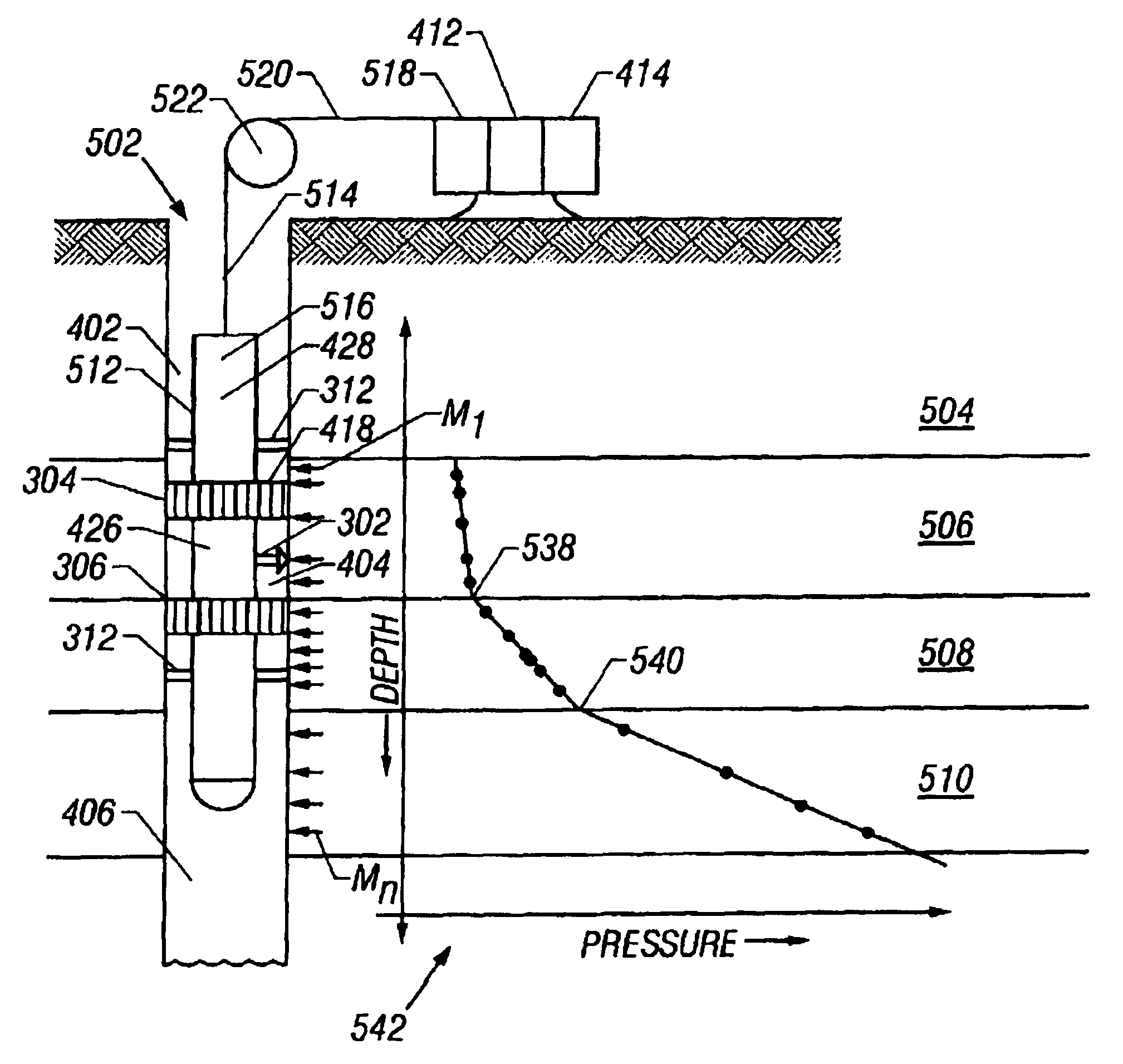
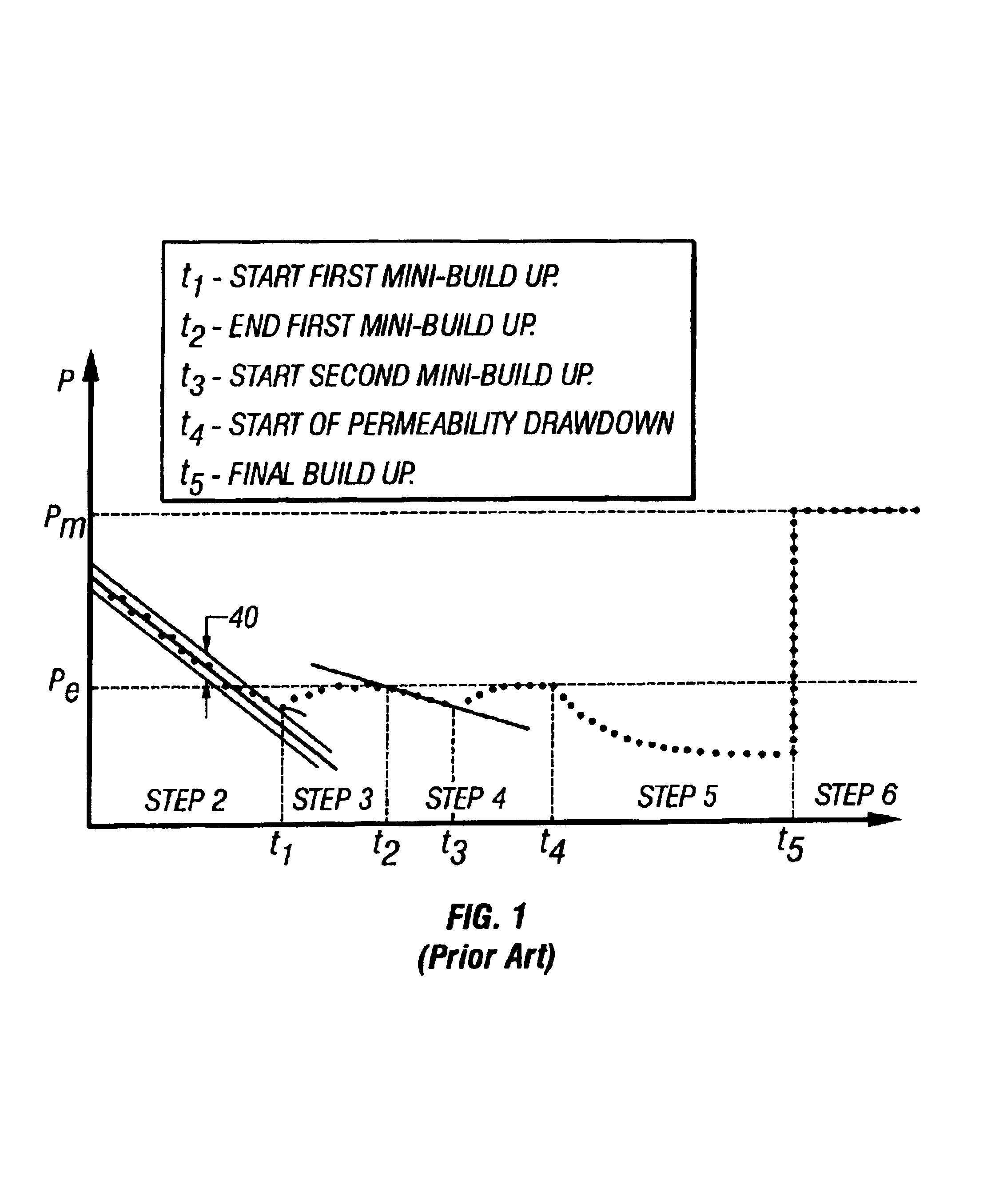
Methods for estimating formation pressure from data taken during the drawdown cycle are presented. In one aspect, a method of determining a formation pressure during drawdown of a formation comprises sampling fluid from a formation using a downhole tool having a sample volume and a fluid sampling device. At least one time dependent parameter of interest related to the fluid is determined during the drawdown. The at least one time dependent parameter is analyzed using a plurality of calculation techniques to determine the formation pressure. The techniques include (i) a first pressure derivative technique; (ii) a second pressure derivative technique; (iii) a formation rate analysis technique; (iv) a dp / dt-ratio technique; and (v) a stepwise drawdown technique.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
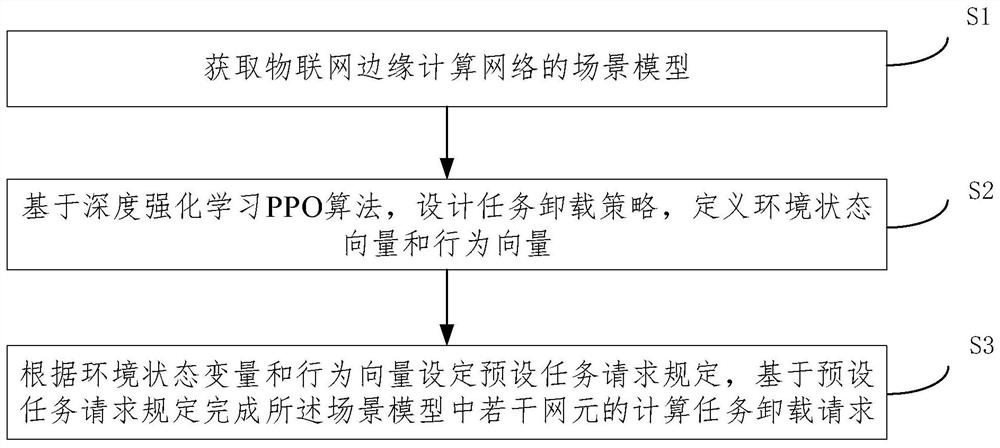
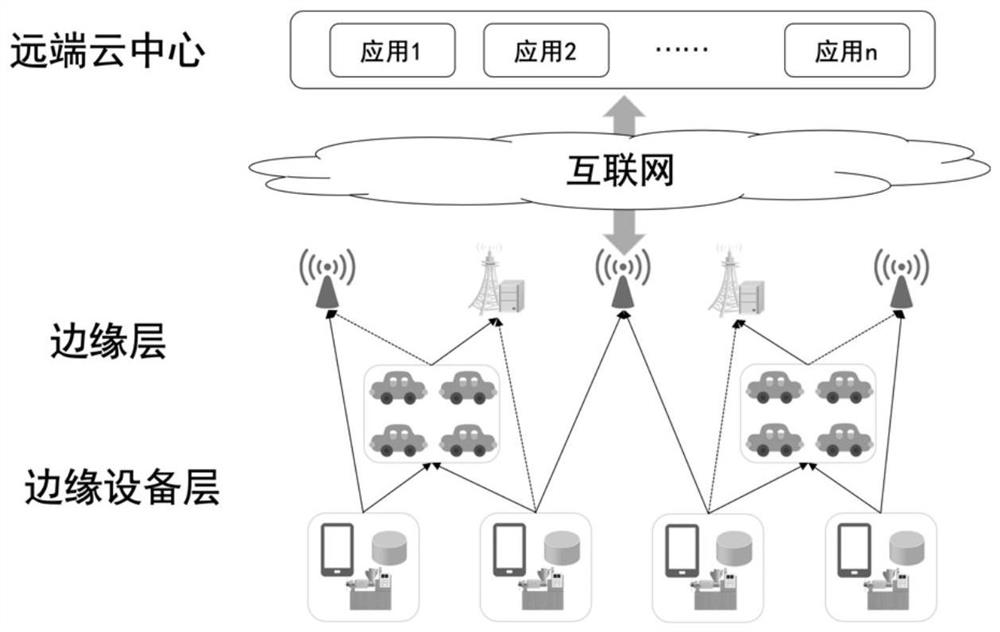
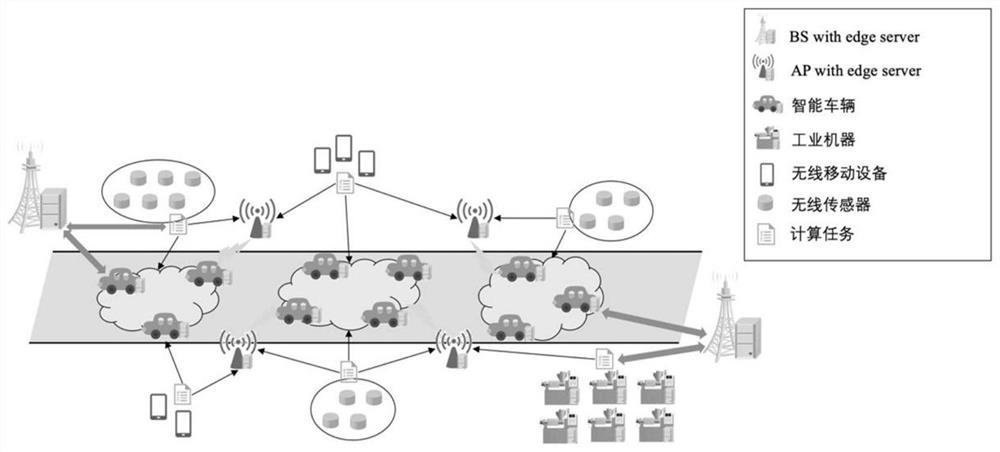
Internet of Things edge computing task unloading method and system
ActiveCN111835827AReduce latencyReduce complexityData switching networksEdge computingReinforcement learning algorithm
The embodiment of the invention provides an Internet of Things edge computing task unloading method and system. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a scene model of an Internet of Things edgecomputing network; designing a task unloading strategy based on a deep reinforcement learning PPO algorithm, and defining an environment state vector and a behavior vector; and setting a preset task request specification according to the environment state variable and the behavior vector, and completing calculation task unloading requests of a plurality of network elements in the scene model basedon the preset task request specification. According to the embodiment of the invention, the edge computing technology and the deep reinforcement learning technology are introduced under the scene ofthe Internet of Things, step-by-step learning is achieved by using the PPO algorithm in deep reinforcement learning and a neural network model is perfected, and a better edge computing task unloadingstrategy is applied, so that the network delay can be flexibly reduced under the condition of ensuring low complexity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +3
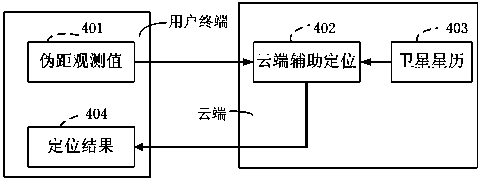
Positioning system based on cloud computing technology and positioning method
ActiveCN103852773AHigh precisionReduce power consumptionSatellite radio beaconingBaseline dataComputer terminal
The invention aims at providing a positioning method based on cloud computing. The method comprises steps: 1, a user terminal transmits reference data to the cloud end; 2, the cloud end carried out position computation according to the reference data; and 3, the cloud end returns position information. When the technical scheme of the invention is adopted, the problems that the computing ability of the user terminal is insufficient, the power consumption during the operation is large, the computing time is long, the real-time precision of a single machine is not high and the like in the current high-precision positioning structure and mode can be solved. The user only needs to pay for little network service fee and quick, high-precision and real-time positioning results can be acquired. The user terminal can be freed from heavy positioning computation, thereby reducing the power consumption of the user terminal and improving the continuous navigation ability. Once the cloud end is built successfully, the system can be used for a long time. Flexible use modes are provided. For the user terminal, especially the terminal user of Beidou, the cost and the power consumption can be greatly reduced, and industrialization development of Beidou is facilitated.
Owner:TECHTOTOP MICROELECTRONICS
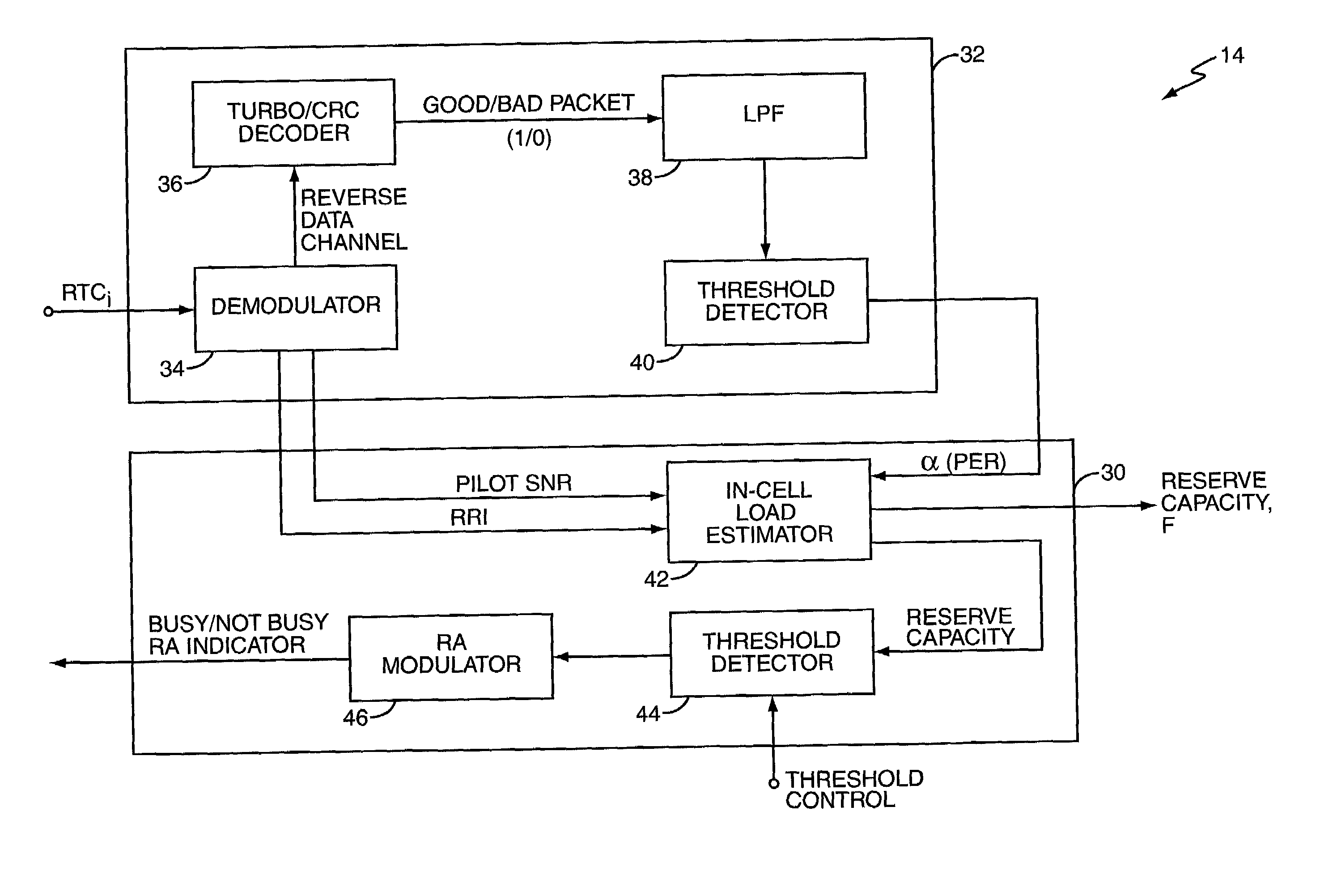
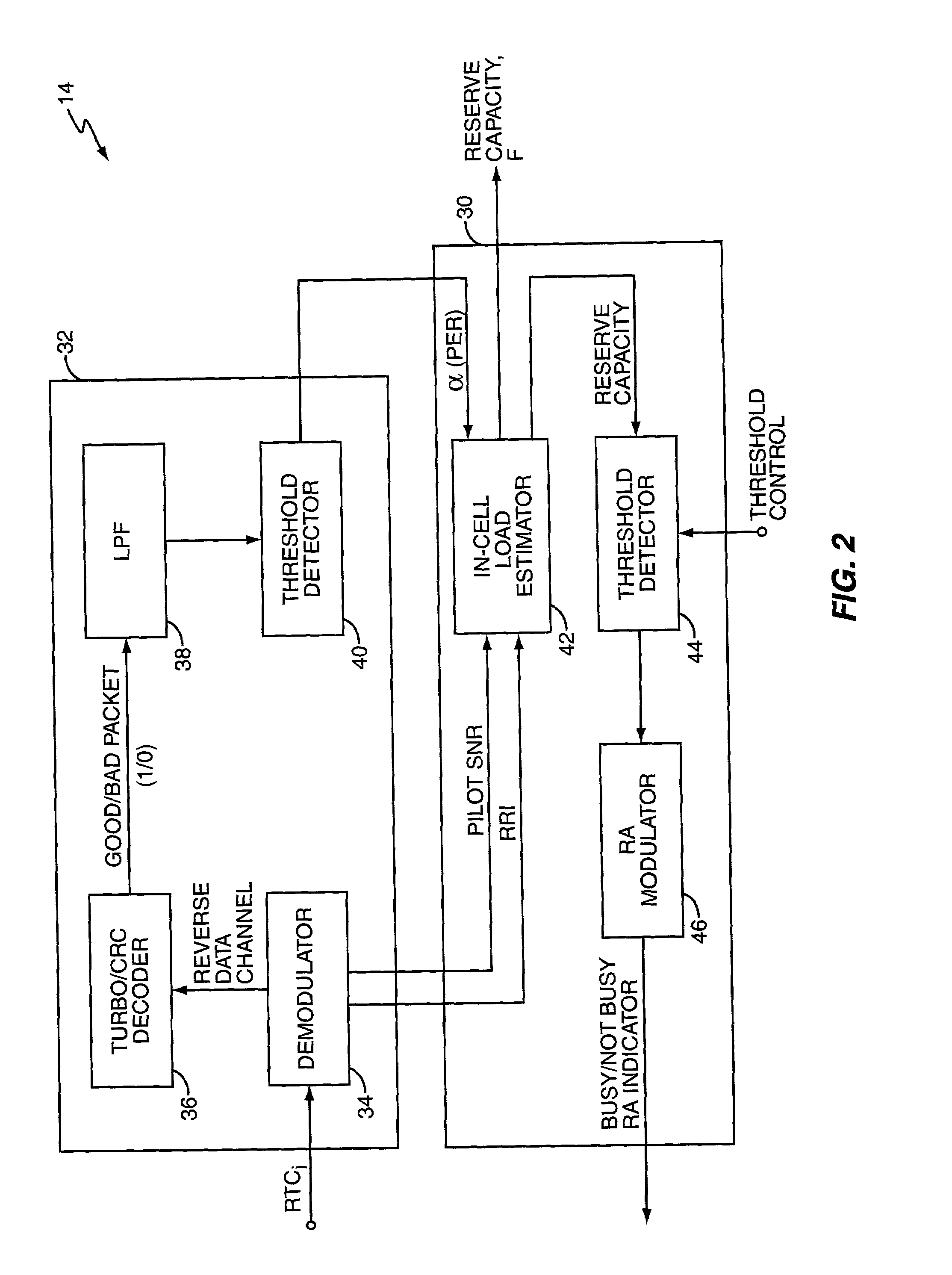
Fast flow control methods for communication networks
InactiveUS7221653B2Reduce distractionsMaximize capacityError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTraffic capacityLink data
Reverse link flow control in a high data rate network determines current reverse link data channel rates for access terminals served by a network sector to identify corresponding defined channel gains, which are used to rapidly and reliably estimate total sector interference on the reverse link. Total sector interference indicates reverse link capacity utilization, and when remaining capacity approaches a defined threshold, the sector sets an activity indicator to a busy state indicating reverse link congestion. This action causes at least some access terminals to reduce their reverse link data channel rate. Interference calculation techniques preferably involve baseband digital processing using defined channel gains, permitting rapid evaluation of reverse link capacity and quick, reliable activity indicator updating, which increases reverse link capacity utilization. These techniques may be applied to inter-sector control, wherein the reverse activity indicator status for one sector depends on interference in one or more other sectors.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
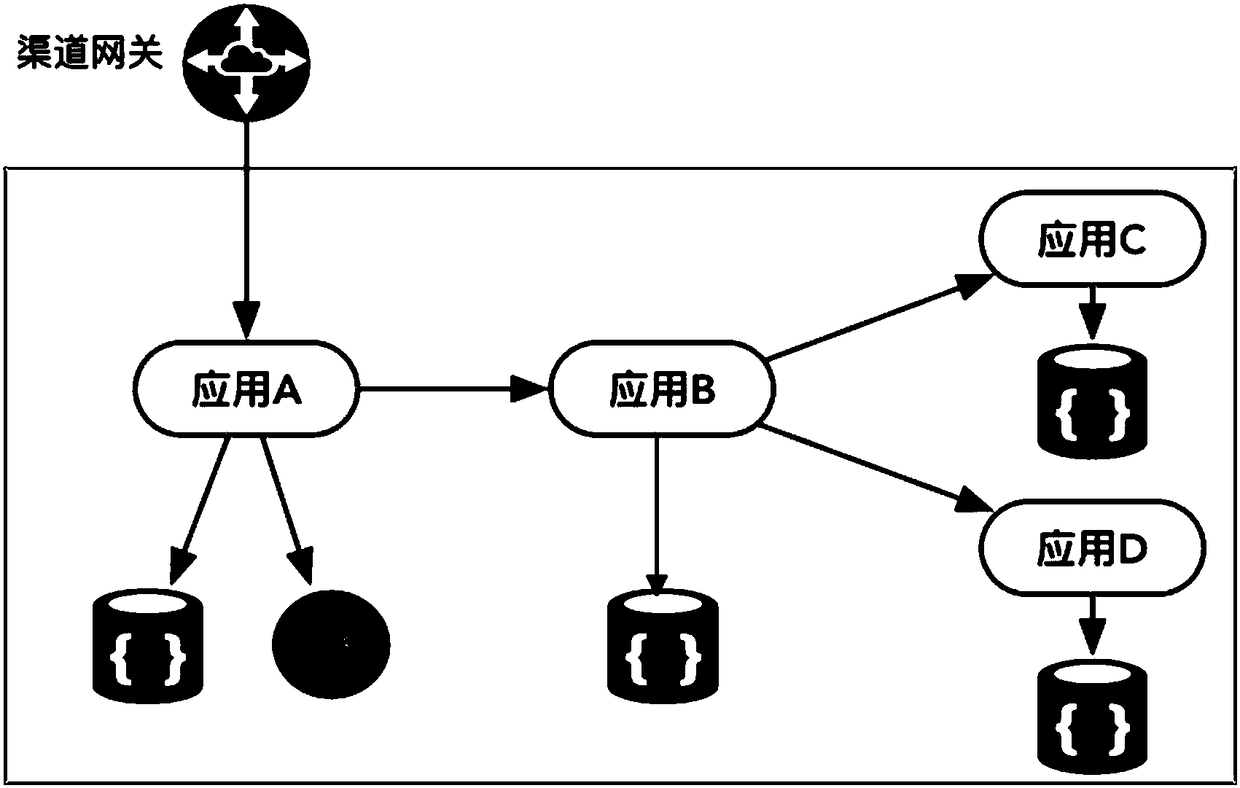
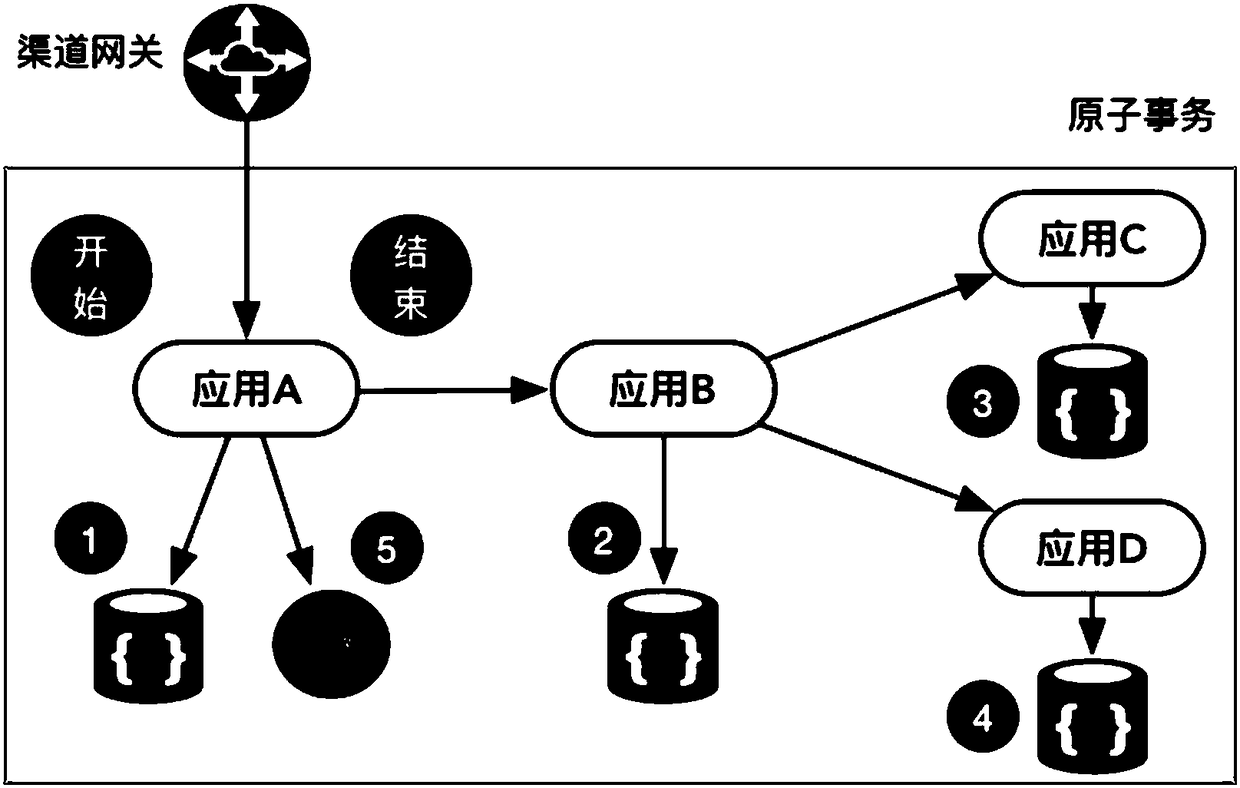
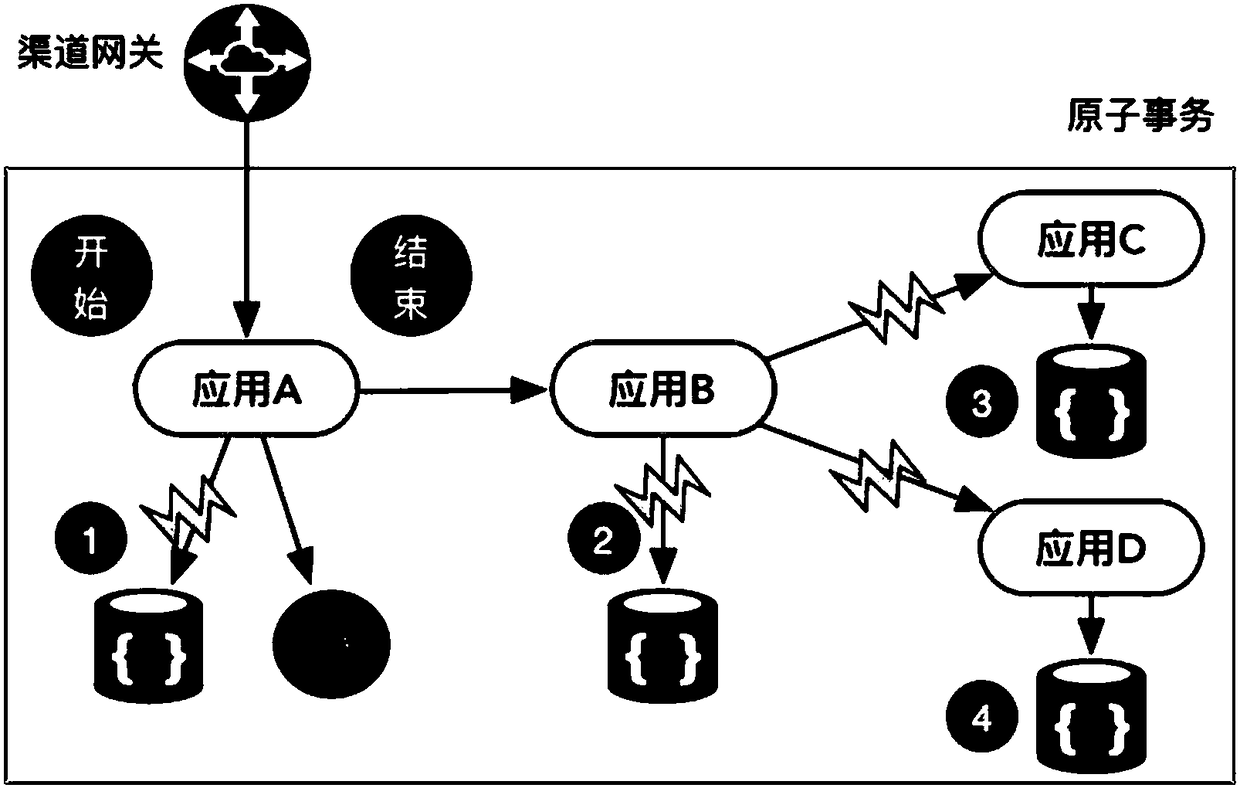
Distributed transaction processing method and device
ActiveCN108459919AGuaranteed atomicityImprove throughputInterprogram communicationDatabase distribution/replicationTransaction managementOperating system
The invention belongs to the technical field of distributed computation and discloses a distributed transaction processing method and a device thereof. The distributed transaction processing method includes the steps of application development, transaction management attribute definition, event definition, streaming calculation and transaction management. To be specific, the method includes the steps of acquiring and identifying event information in real time through the streaming calculation, acquiring transaction management attributes in real time, periodically verifying transaction status based on the event information and the transaction management attributes, initiating a verification request and / or a reversal request based on the transaction status, and sending transaction status verification instructions and / or reversal instructions through a transaction manager. With the above-mentioned scheme, the distributed transaction processing method and the device thereof have the advantages of allowing transaction control and the application development to be completely decoupled, not requiring development transaction control logic for the application development, greatly simplifying development difficulty, realizing fast rollback of transactions under abnormal scenarios, tolerating failure of any node and having no brain splitting problem.
Owner:CITIC AIBANK CORPORATION LIMITED
Adaptive position sensing method and apparatus for synchronous motor generator system
An adaptive, sensorless position sensing apparatus (250) derives rotor position of a synchronous machine (200). The apparatus (250) comprises a first rotor position deriving unit (300) for generating first rotor position values by applying a first sensorless rotor position calculation technique, which emulates a resolver; a second rotor position deriving unit (400) for generating second rotor position values by applying a second sensorless rotor position calculation technique; and a rotor position result output unit (450) for outputting rotor position results over a range of rotor speeds as a function of the first rotor position values, the second rotor position values, and rotor speed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
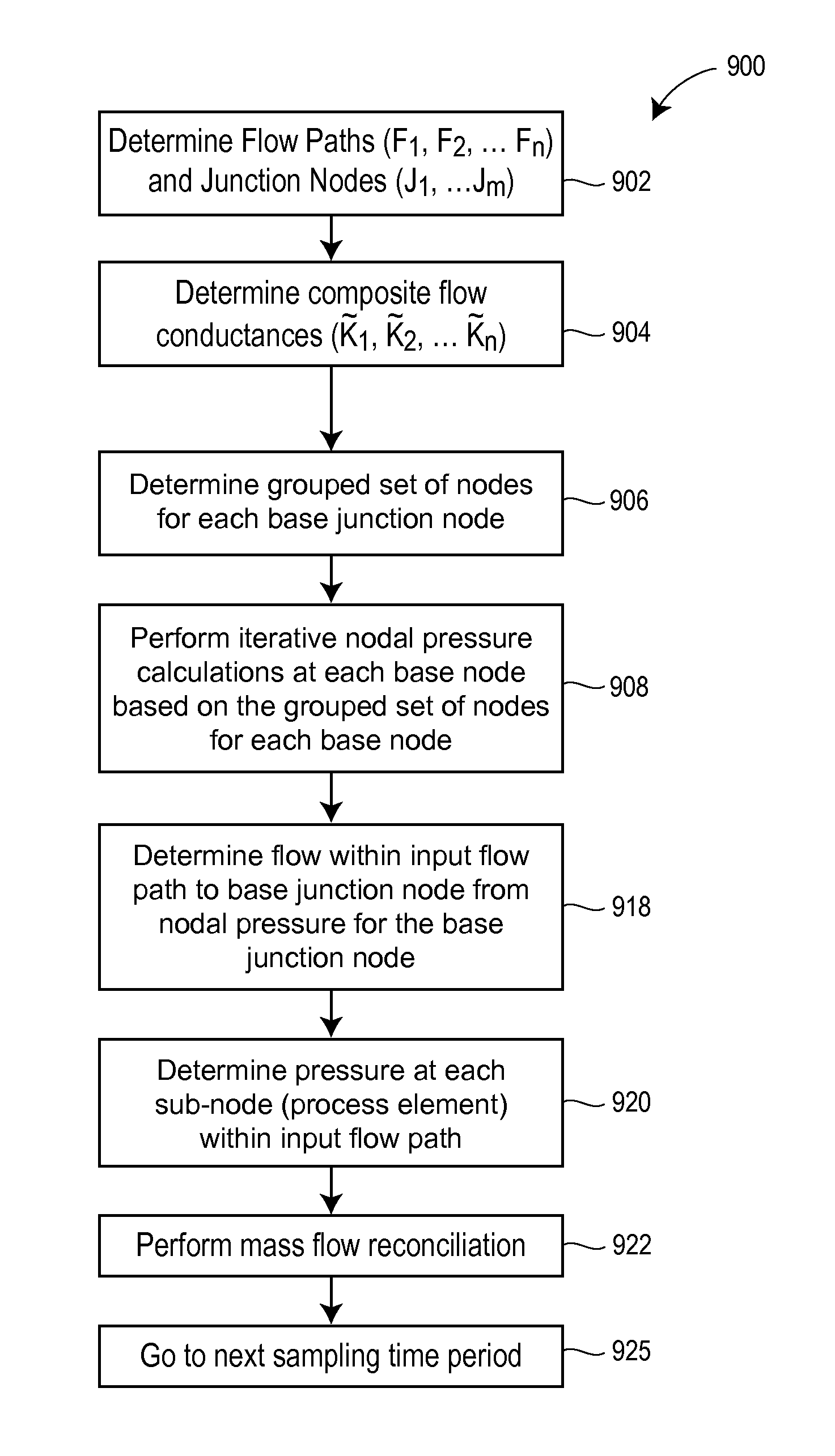
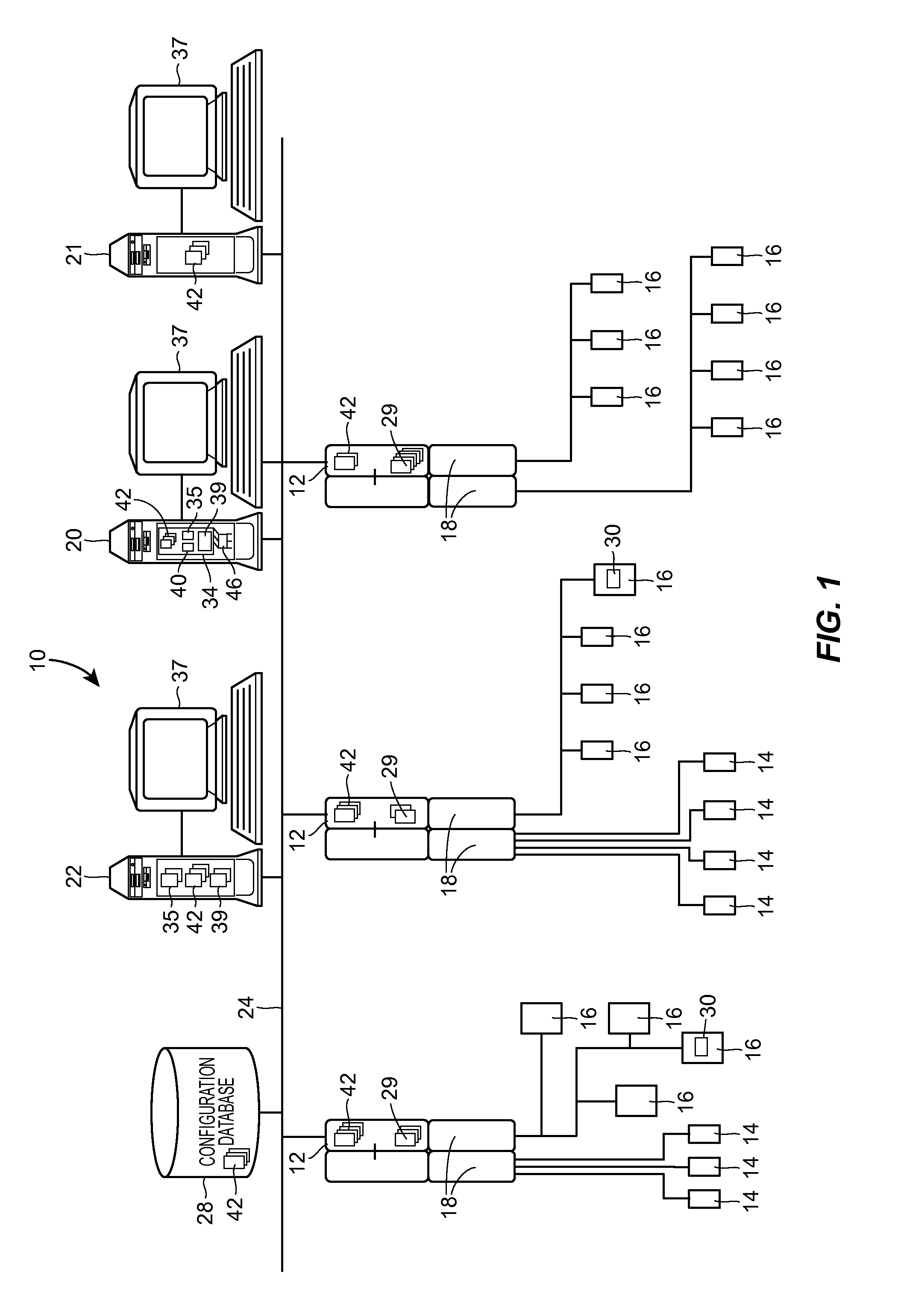
Enhanced sequential method for solving pressure/flow network parameters in a real-time distributed industrial process simulation system
ActiveUS20130204587A1Good and faster simulationImprove accuracyProgramme controlSimulator controlCalculation techniqueComputer engineering
A pressure and flow calculation technique can be used in a distributed process network simulation system that uses the sequential solving method to perform better or faster simulations of a process flow, especially with respect to process junction nodes at which flow either converges or diverges. The pressure and flow variable determination technique uses a grouped node identification technique that identifies a local set of nodes for each junction node of the process network to use when solving for the pressure at the junction node, a grouped node iteration technique that uses the grouped set of nodes at each junction node to perform iterative pressure calculations at the junction node, and a flow-based pressure calibration technique at each junction node to enable the system to perform highly accurate pressure and flow variable determination at each junction node in real-time.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
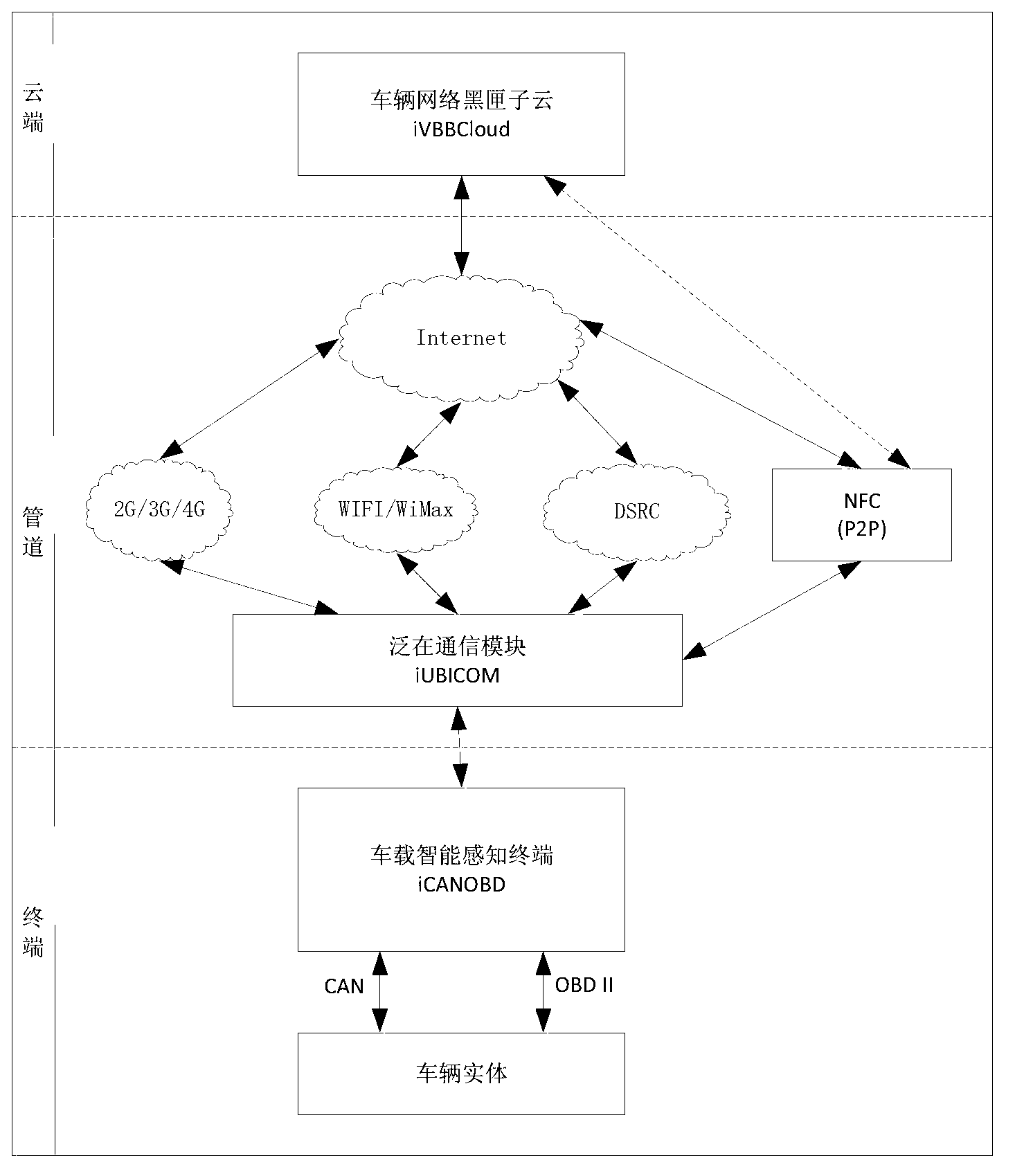
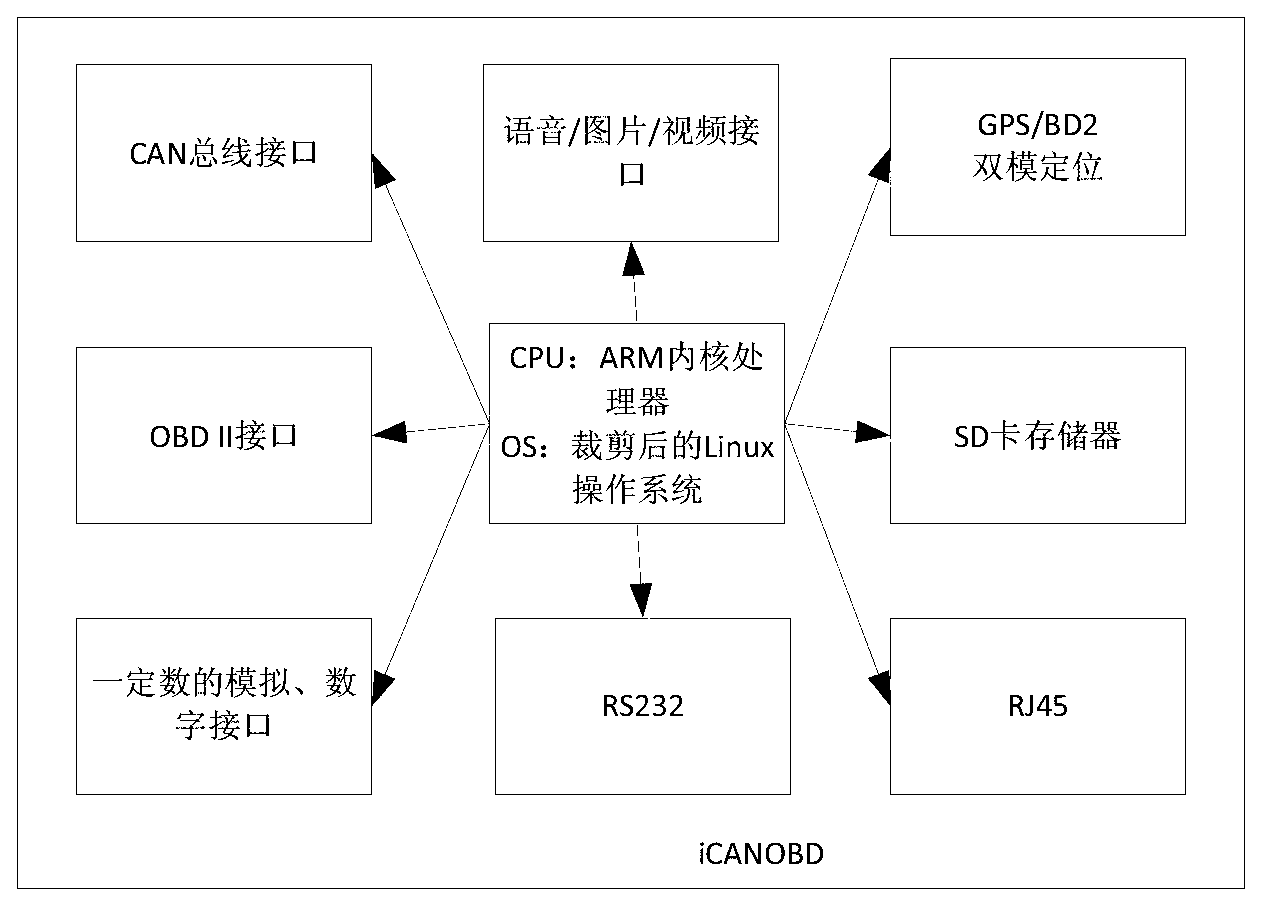
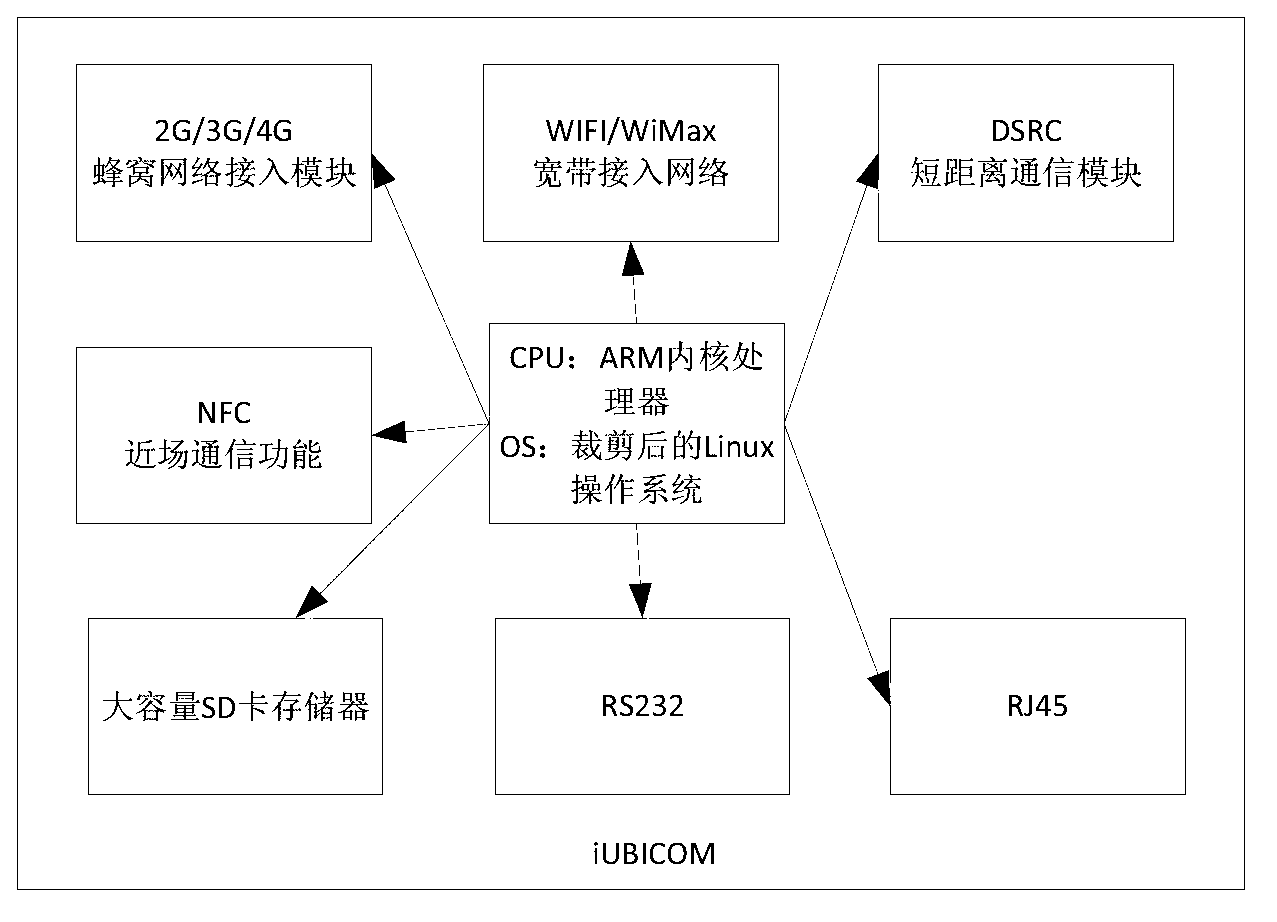
Automotive network black box system with cooperative terminal, pipeline and cloud end
The invention discloses an automotive network black box system with cooperative terminal, pipeline and cloud end. The system comprises a terminal, a pipeline and a cloud end. The invention relates to the relevant technical fields such as intelligent traffic systems, vehicle networks, cloud calculation, ubiquitous communications and mobile internet and the like; dynamic and static data of vehicles can be intelligently perceived through a CAN (controller area network) bus, an OBD II (on-board diagnostics) interface and intelligent analysis software running on a vehicle terminal; the data intelligently perceived from the black box of the vehicle are transmitted to the network cloud end in real time through a ubiquitous communication technique; black box cloud of the vehicle network is constructed through a cloud calculation technique, so that cloud storage, calculation and analysis are carried out on the converged mass black box data; and software service is provided for applications such as accident investigation, intelligent traffic and vehicle network and the like in an SaaS manner.
Owner:黑匣子(杭州)车联网科技有限公司
Byte stream organization with improved random and keyed access to information structures
InactiveUS20050131917A1Extension of timeMaximizes the invention's scope for producing highly efficient resultsData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAlgorithmByte
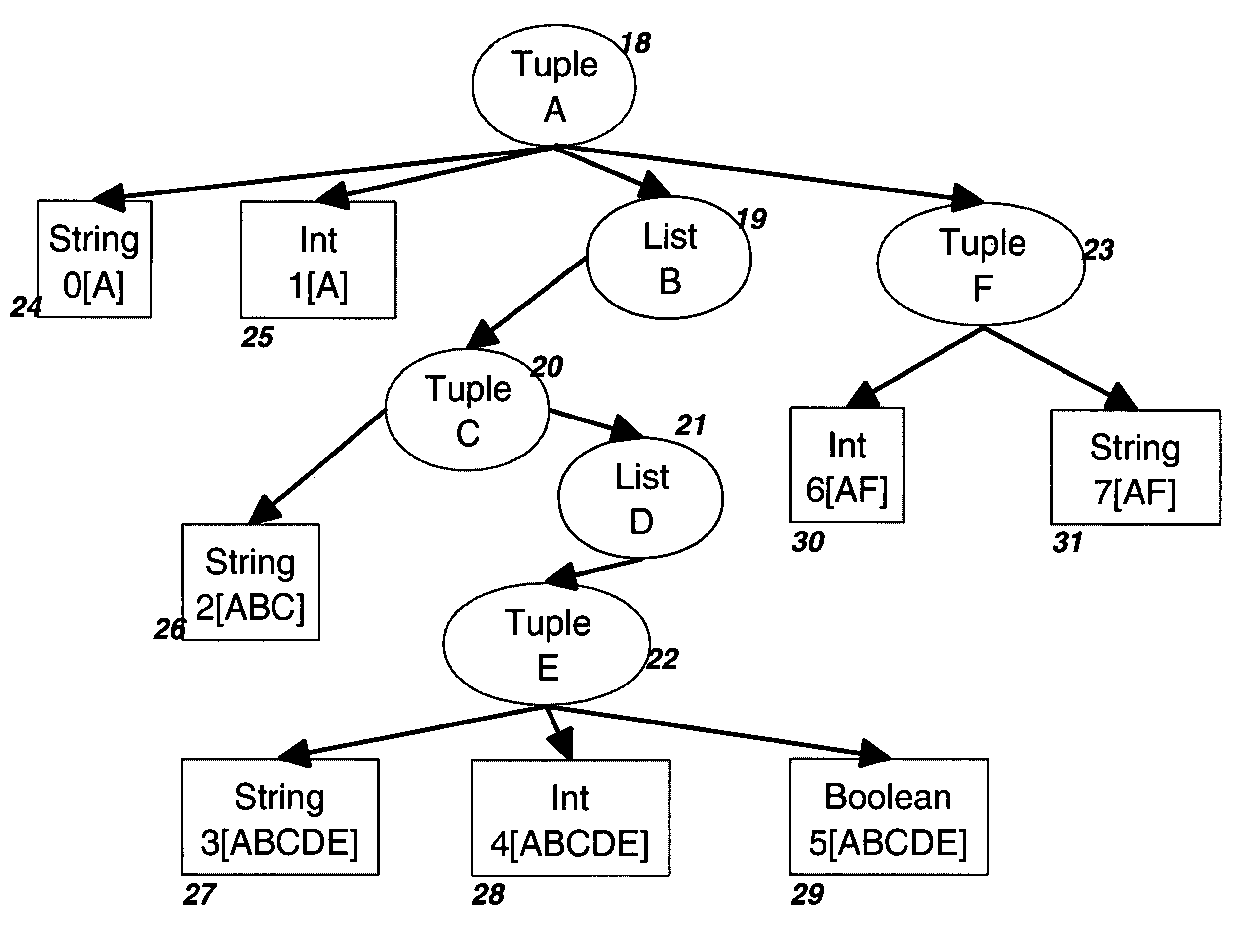
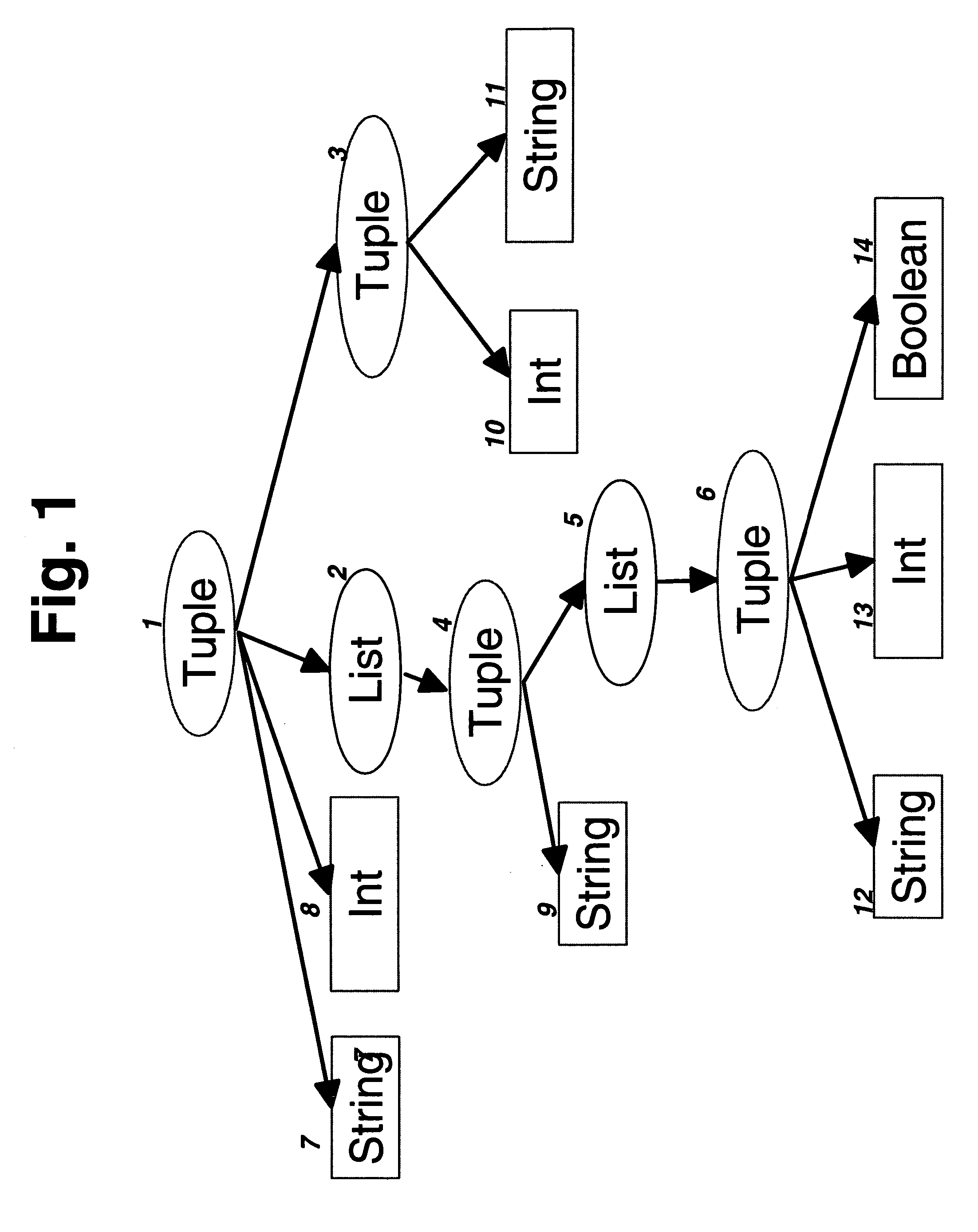
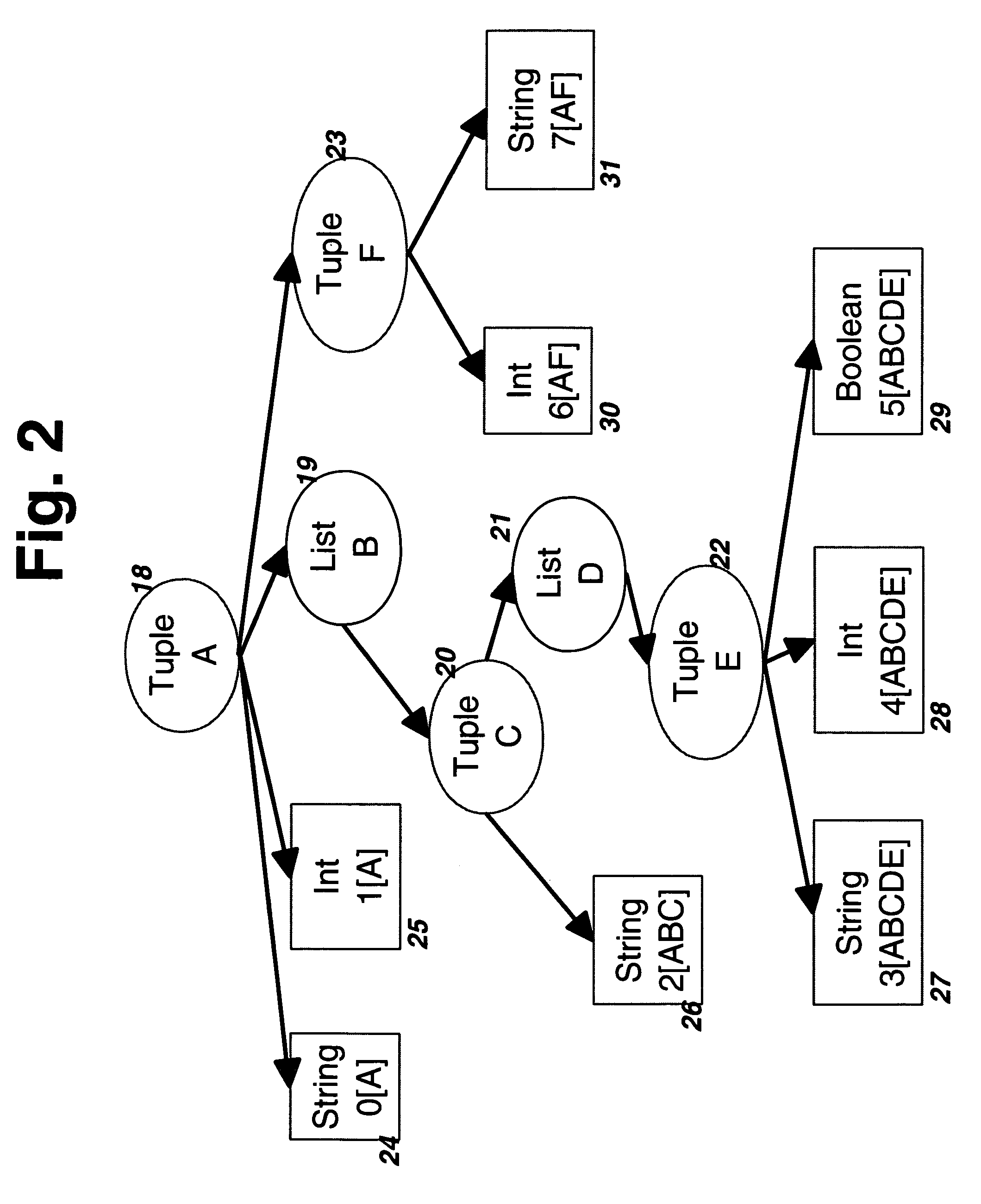
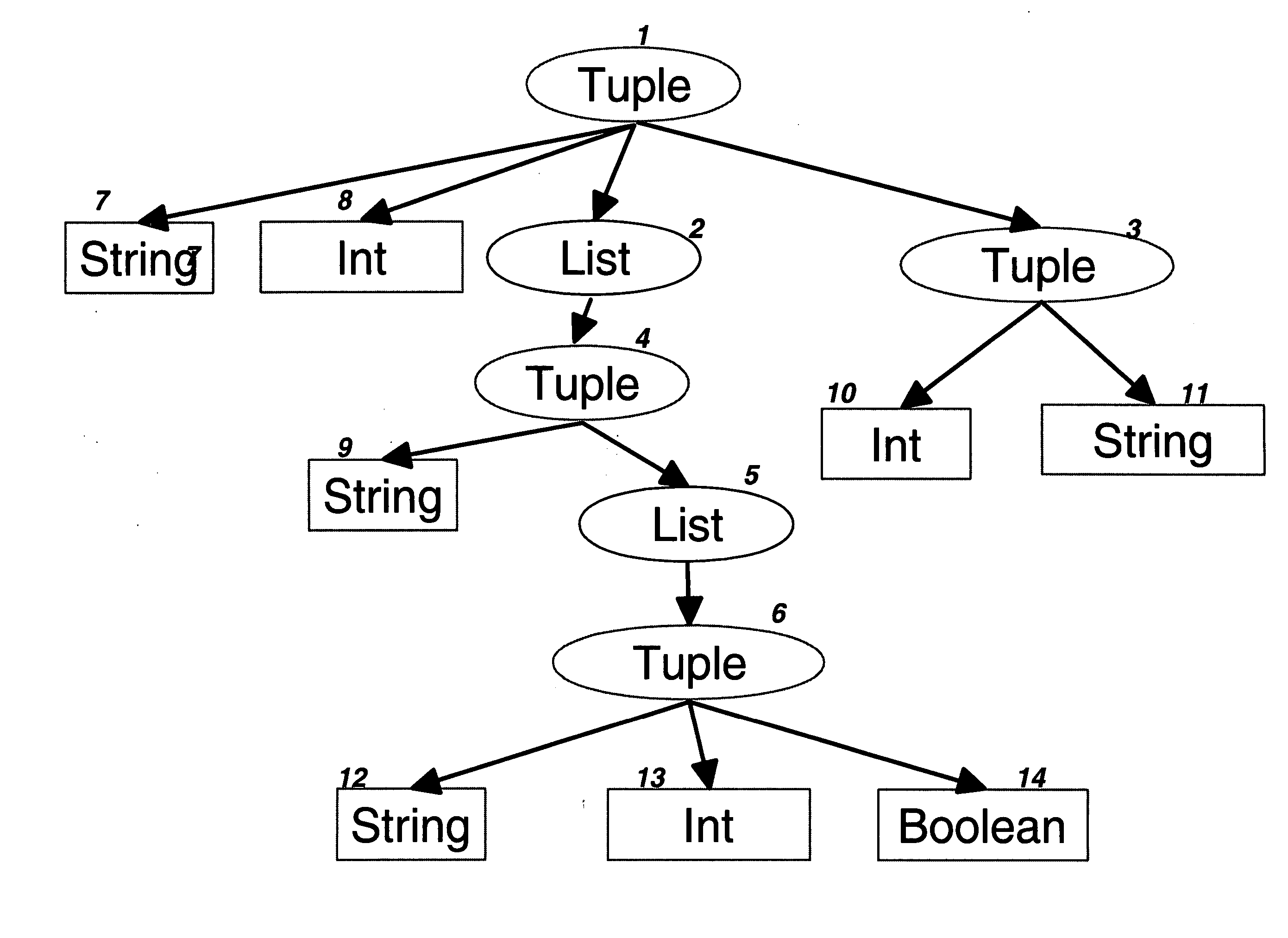
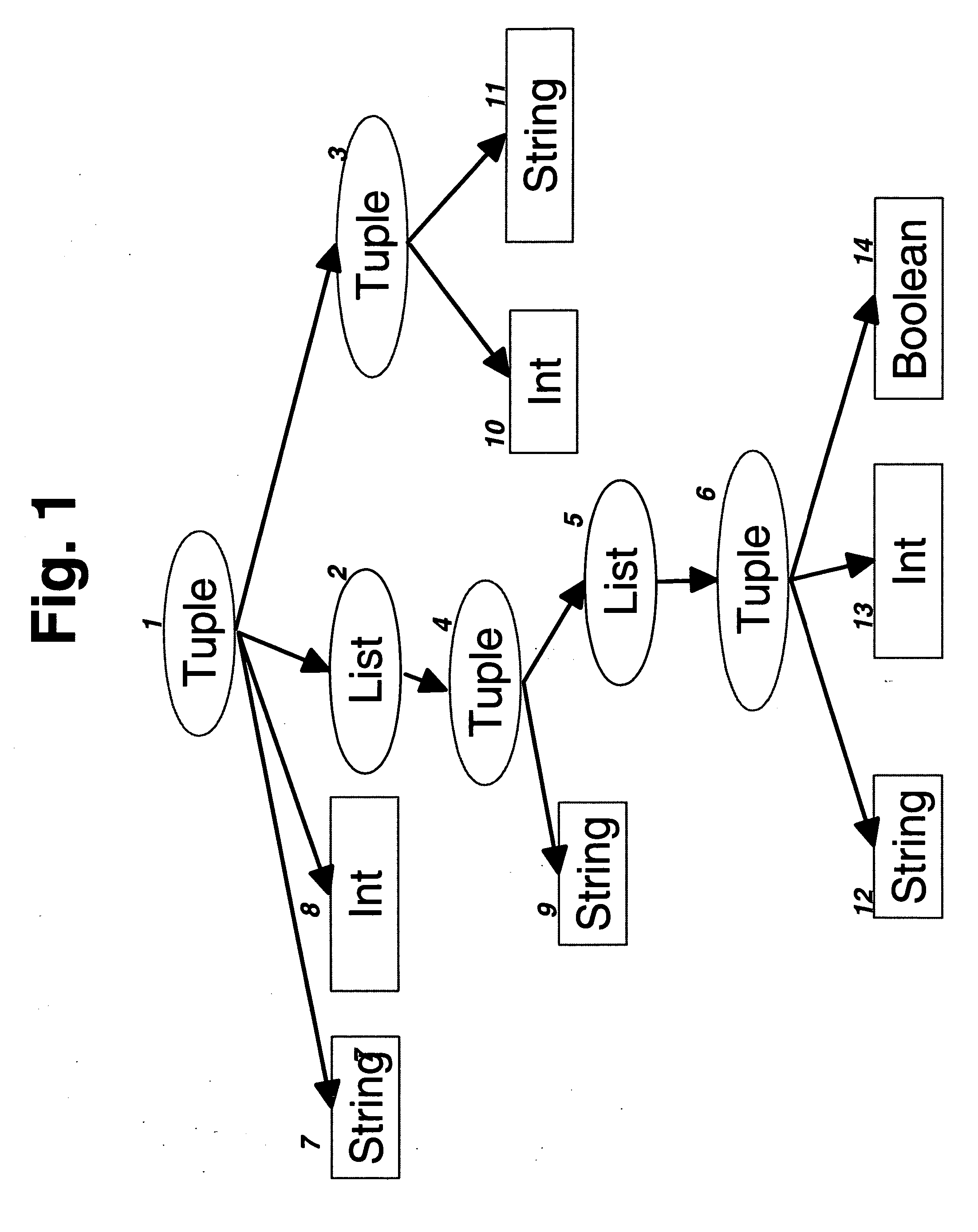
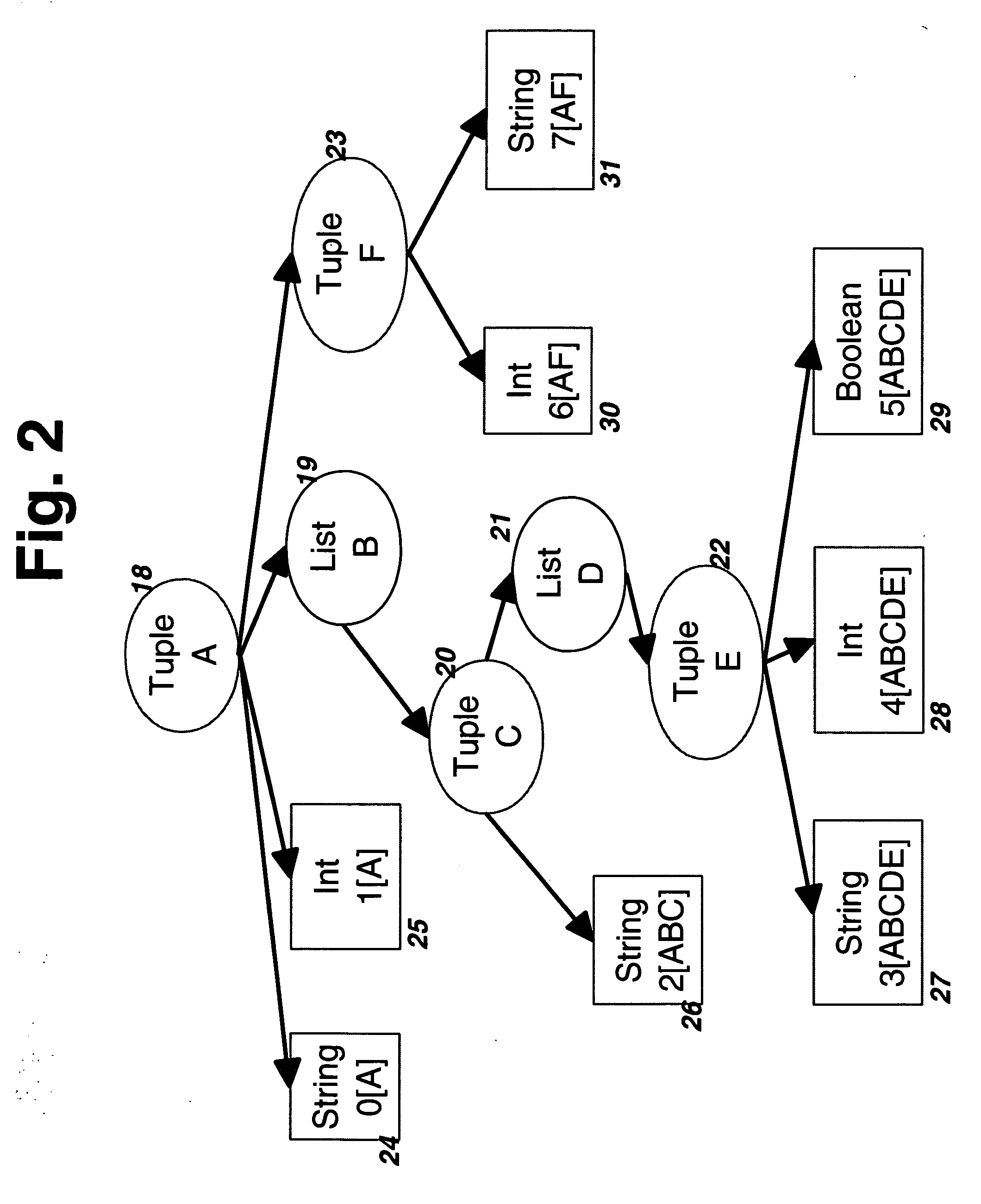
The invention improves processing time when accessing information in a byte stream and avoids the step of deserializing unneeded portions of the byte stream when the byte stream encodes an information structure corresponding to a schema with arbitrarily nested lists and tuples. It facilitates efficient keyed access when lists of tuples represent tables with key columns by storing tables in nested column order, which extends the well-known concept of column-order so as to apply to arbitrarily nested tables. Using well-known offset calculation techniques within the nested lists that result from nested column order, the invention achieves greater efficiency by grouping together all scalar information items that correspond to the same node in a tree representation of the schema.
Owner:IBM CORP
Engine crankshaft dynamic analysis method
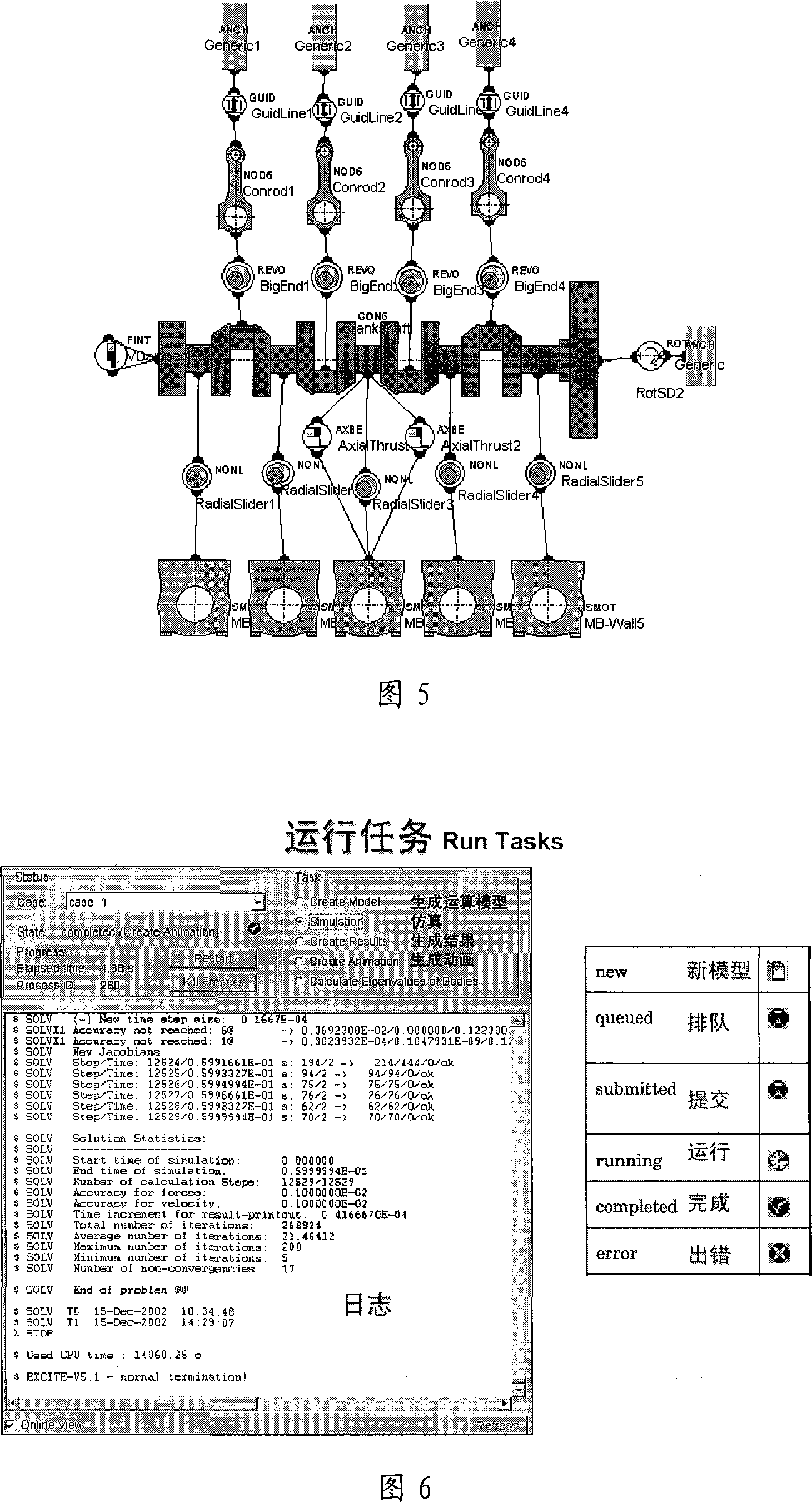
The invention discloses an analysis method of motor crank dynamics, which includes that: in Hypermesh software, a crank system is divided by finite element mesh generation into a crank, a flywheel, a belt pulley, a timing gear and a main bearing seat etc.; use Nastran software to execute the reduction solving of a finite element substructure; in EXCITE software, construct a model of the crank system dynamics, and exert the corresponding boundary condition on elements to implement simulation calculation; use the Nastran software to implement restoration solving of dynamic stress on the crank, perform post-processing and execute fatigue analysis on dangerous points; reasonably evaluate the crank system according to the results, and if the structure is not reasonable, the structure optimization is still needed. The method uses EXCITE calculation technique to execute dynamics analysis on the motor crank, obtains the strength and the fatigue parameters of the motor crank, and further evaluates the structure parameters of the crank and the related parts of the motor reasonably, therefore, making the improvement thereof.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
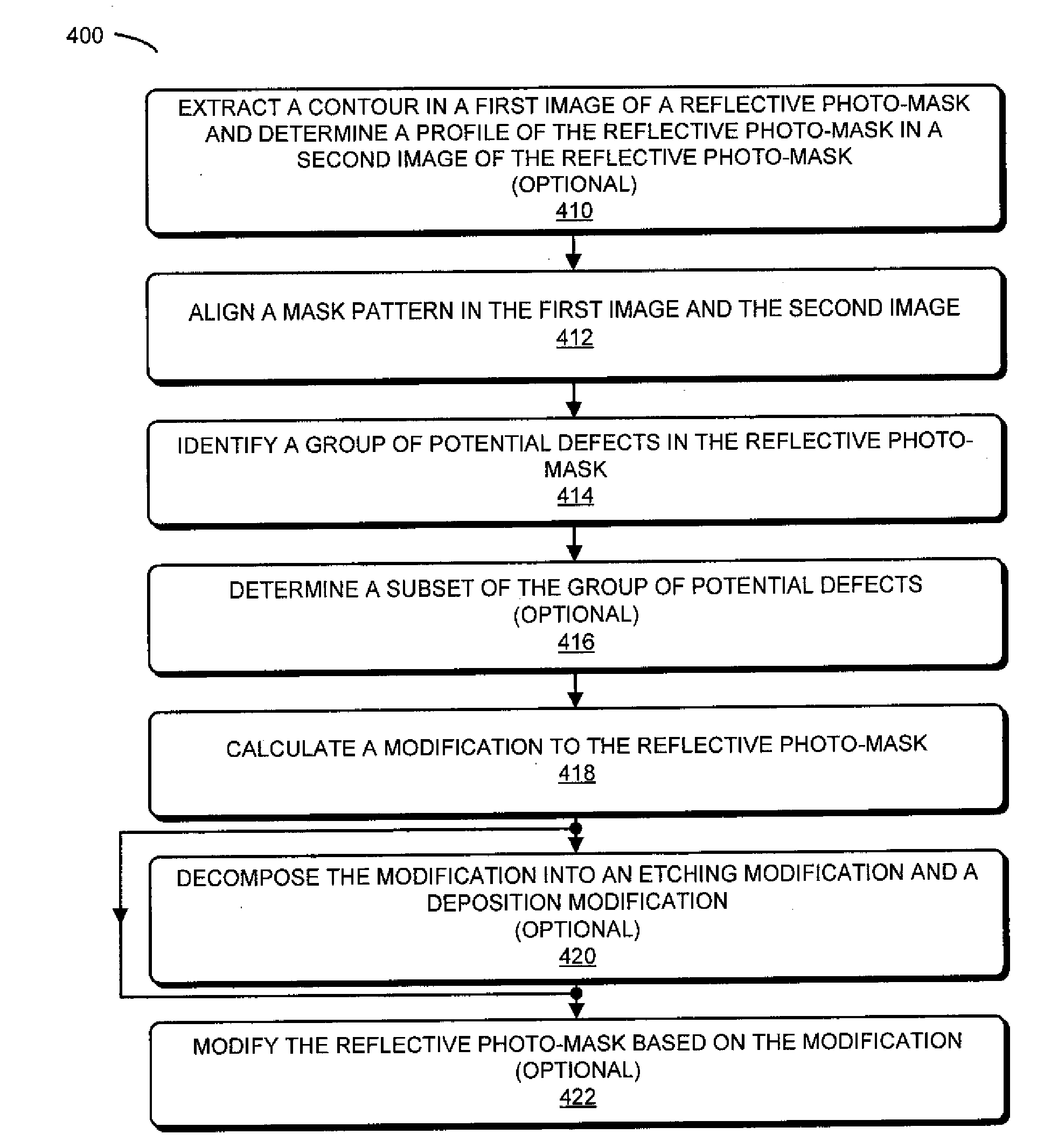
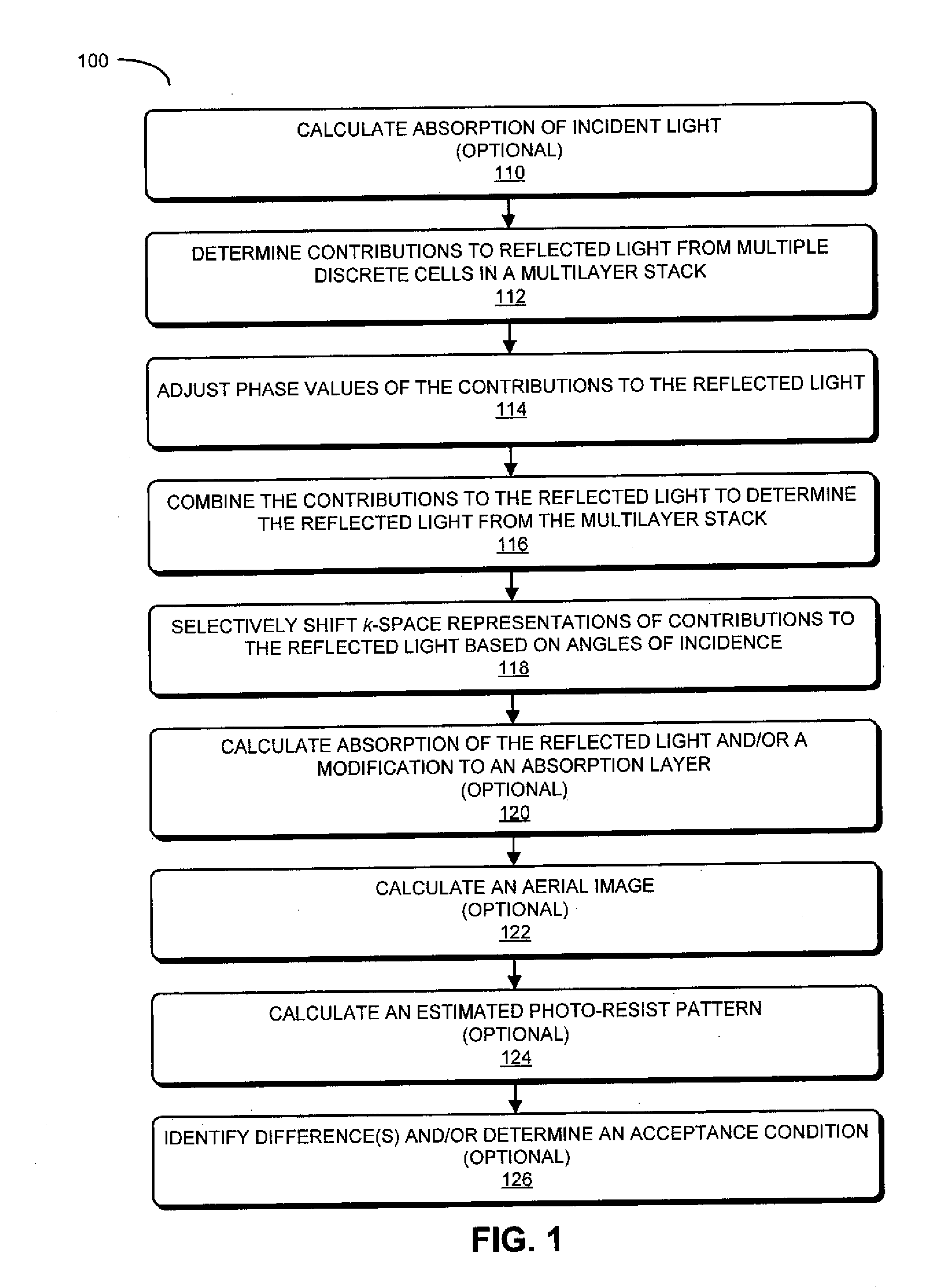
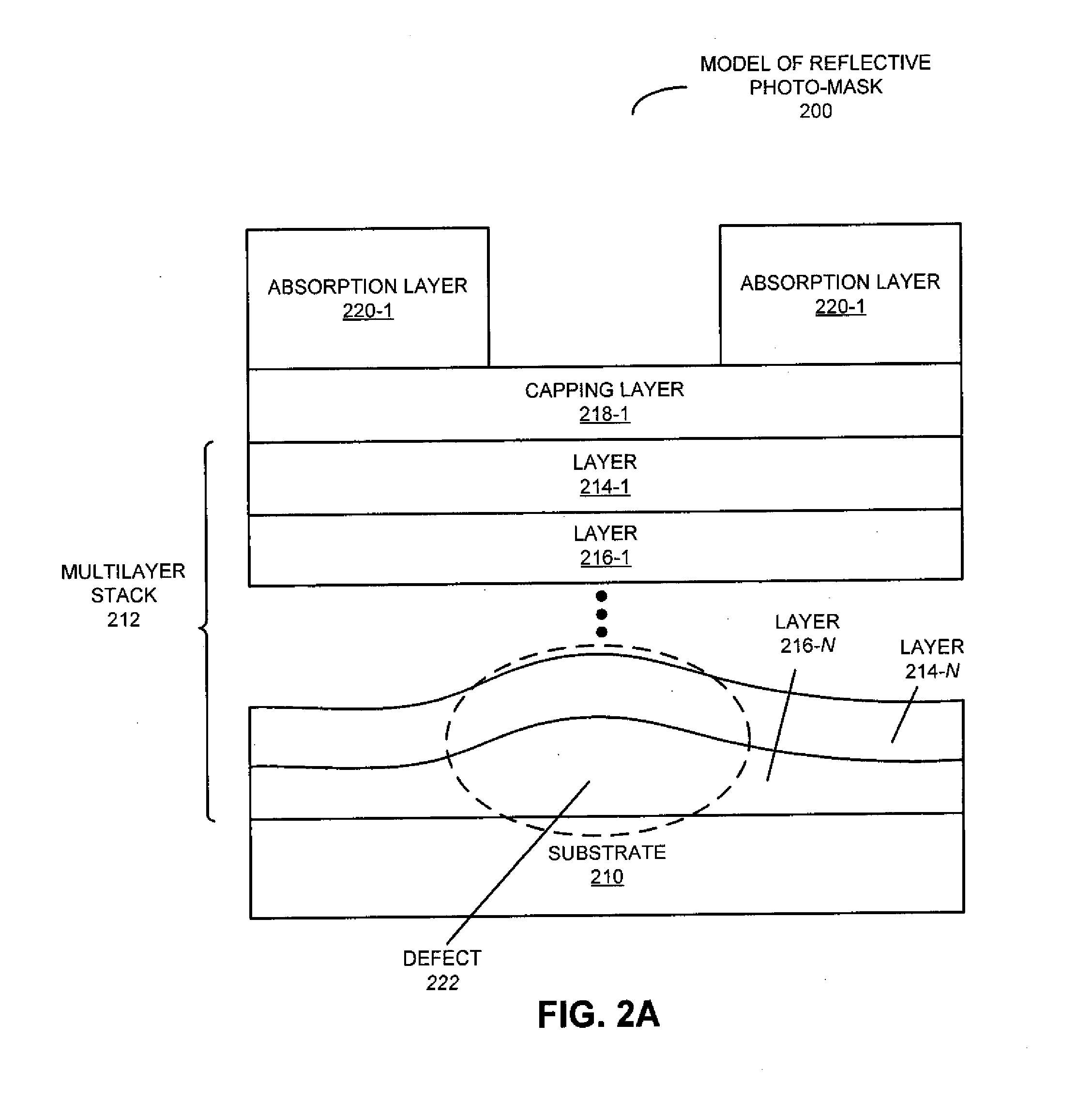
Technique for Repairing a Reflective Photo-Mask
ActiveUS20120066651A1Loose accuracyOriginals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceImage plane
During a calculation technique, a modification to a reflective photo-mask is calculated. In particular, using information associated with different types of analysis techniques a group of one or more potential defects in the reflective photo-mask is determined. Then, the modification to the reflective photo-mask is calculated based on at least a subset of the group of potential defects using an inverse optical calculation. In particular, during the inverse optical calculation, a cost function at an image plane in a model of the photolithographic process is used to determine the modification to the reflective photo-mask at an object plane in the model of the photolithographic process.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
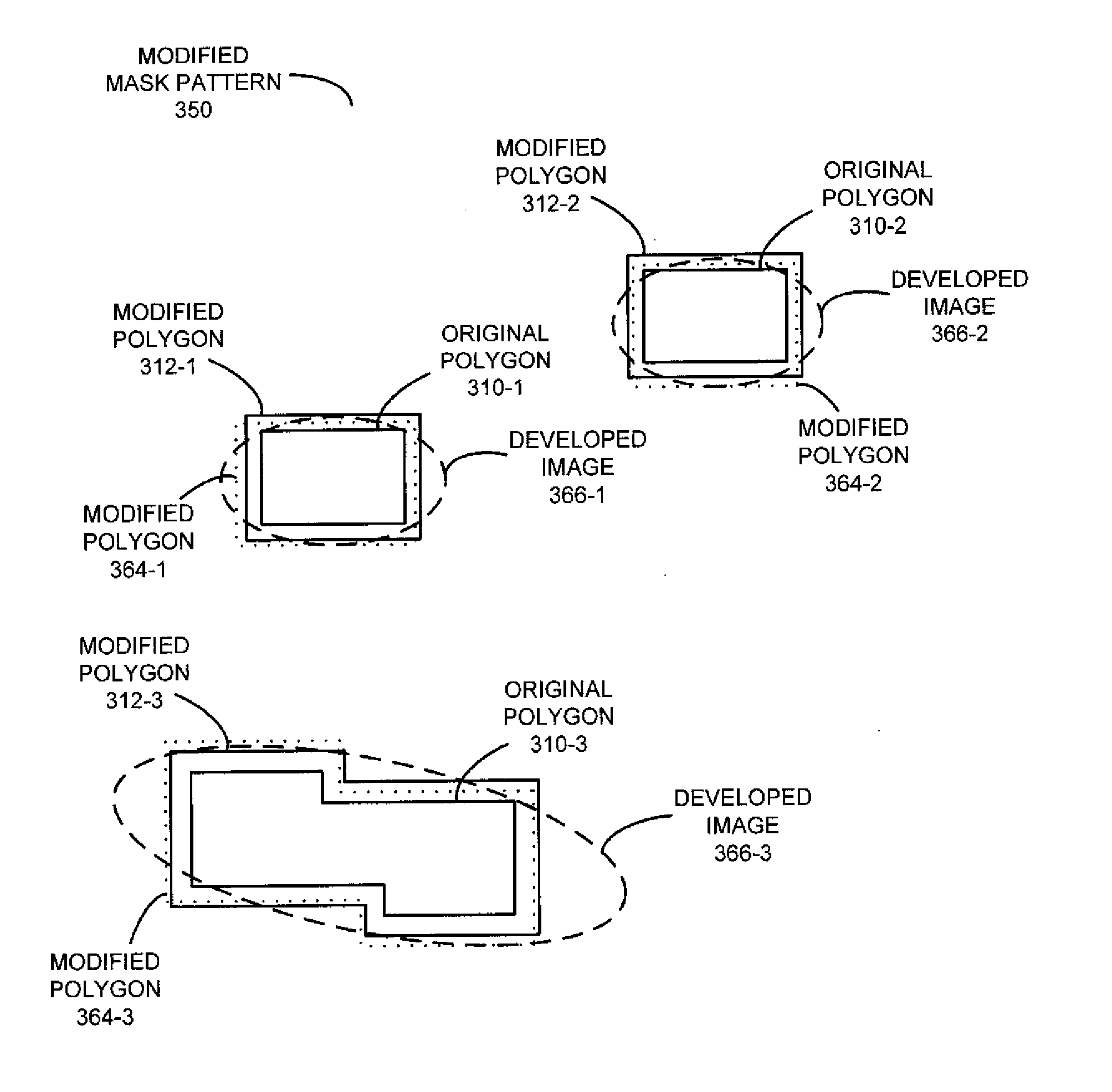
Lithographically enhanced edge determination
ActiveUS20130139116A1Originals for photomechanical treatmentSpecial data processing applicationsSemiconductor chipComputer science
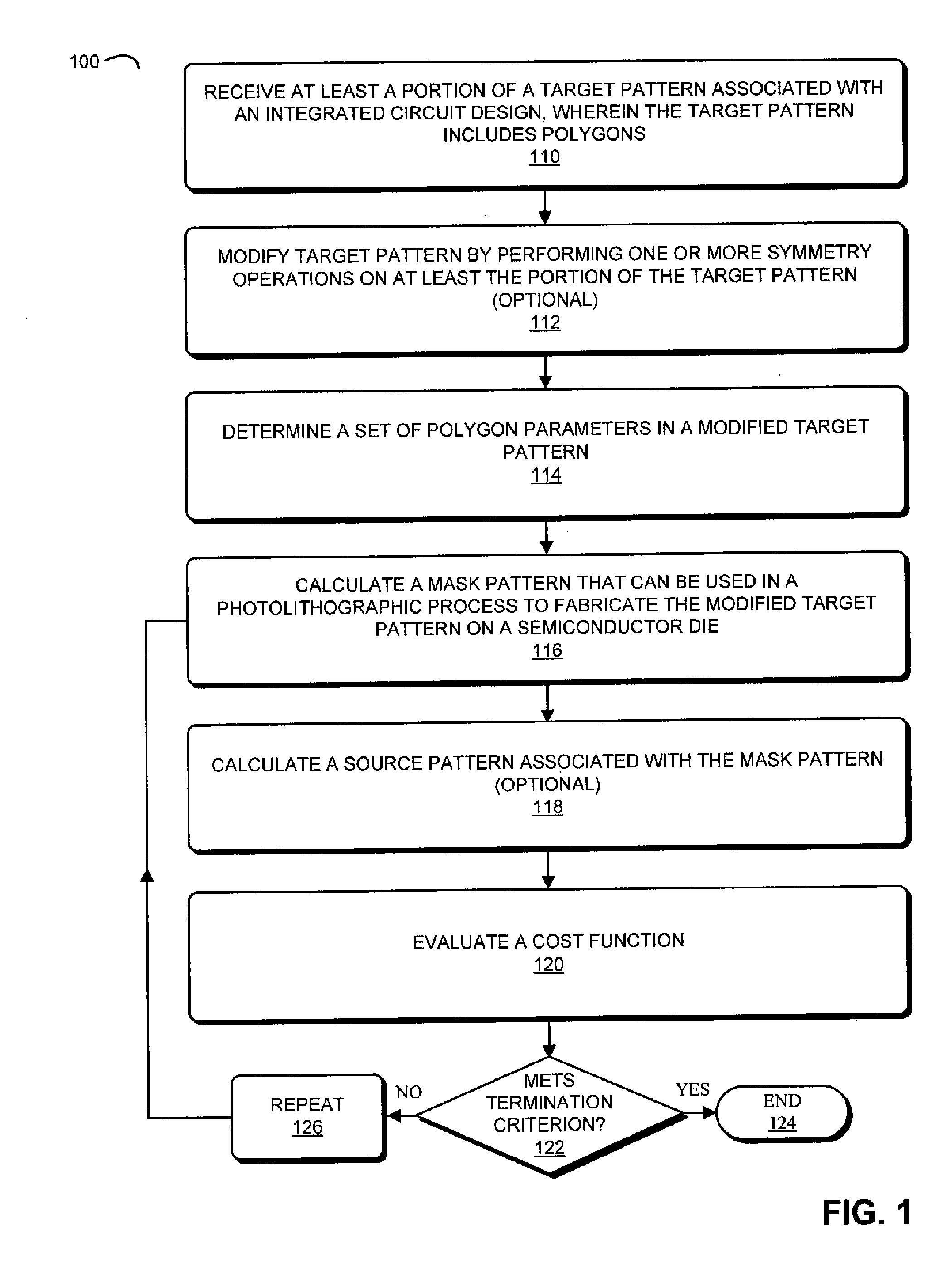
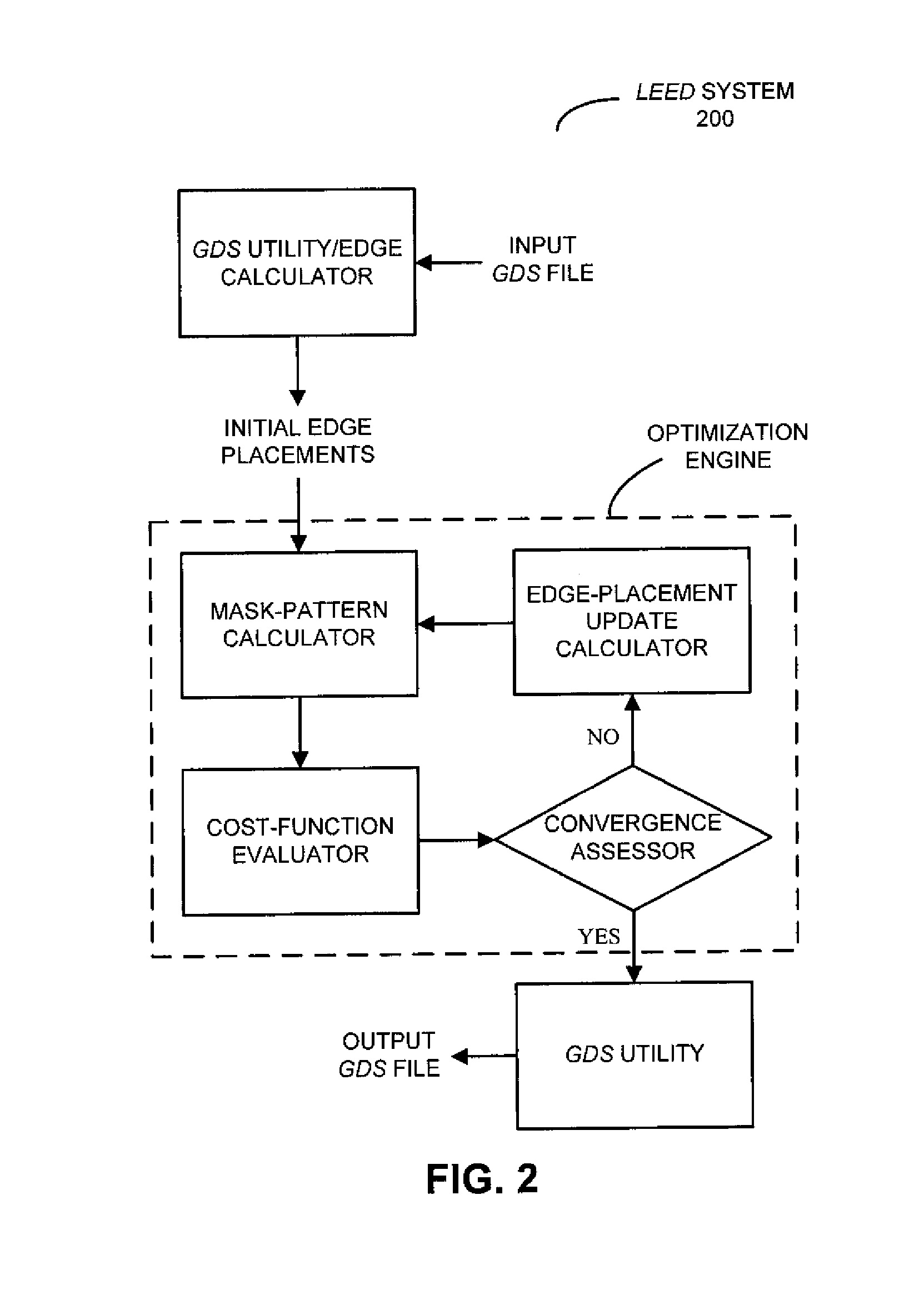
During a calculation technique, at least a portion of a target pattern associated with an integrated-circuit design is modified so that polygons in the target pattern, which represent features in the design, result in acceptable accuracy during a photolithographic process that fabricates the target pattern on a semiconductor die. In particular, a set of polygon parameters associated with the polygons are modified, as needed, so that a cost function that corresponds to a difference between a modified target pattern and an estimated target pattern produced during the photolithographic process meets a termination criterion. A mask pattern that can fabricate the modified target pattern on the semiconductor die is calculated using an inverse optical calculation in which the modified target pattern is at an image plane of an optical path associated with the photolithographic process and the mask pattern is at an object plane of the optical path.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Tunnel intelligent edge calculation management and control system
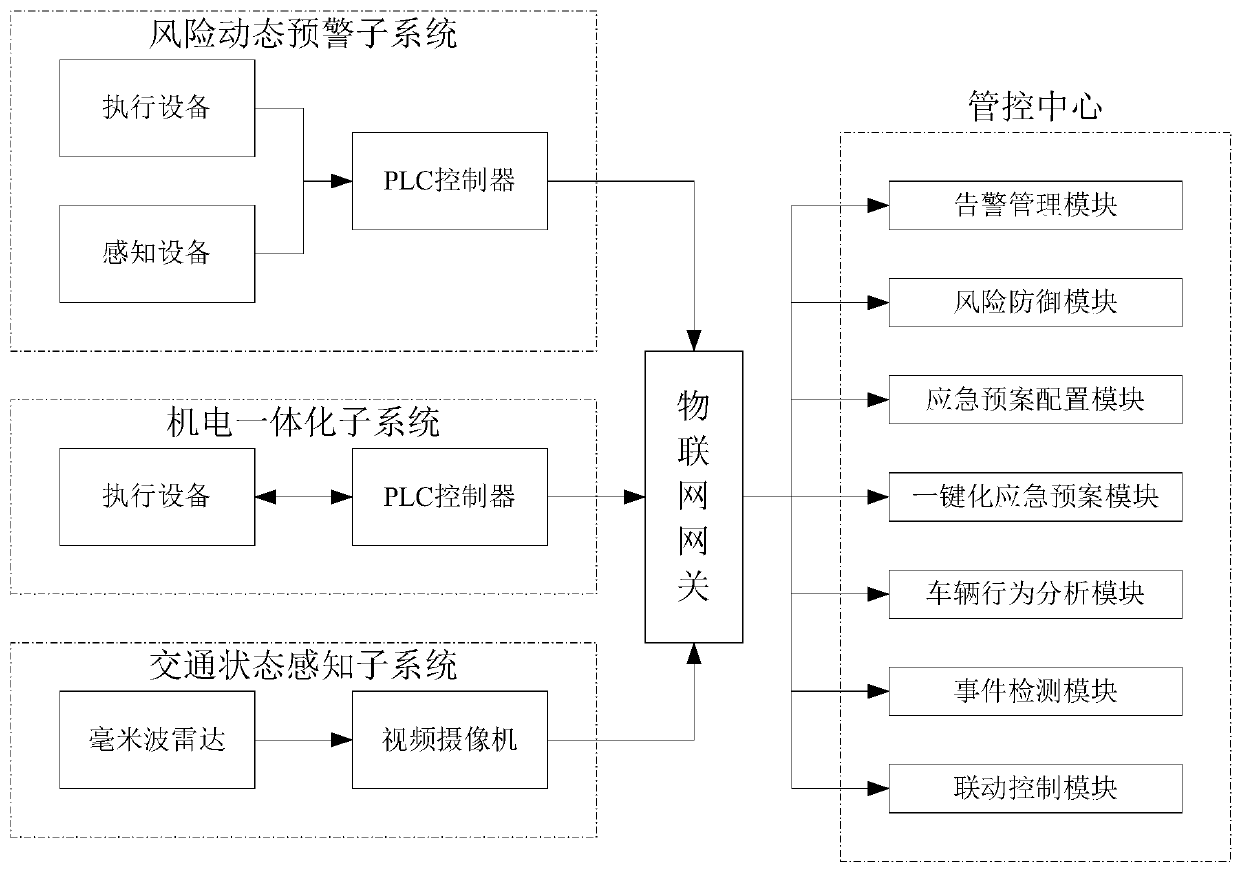
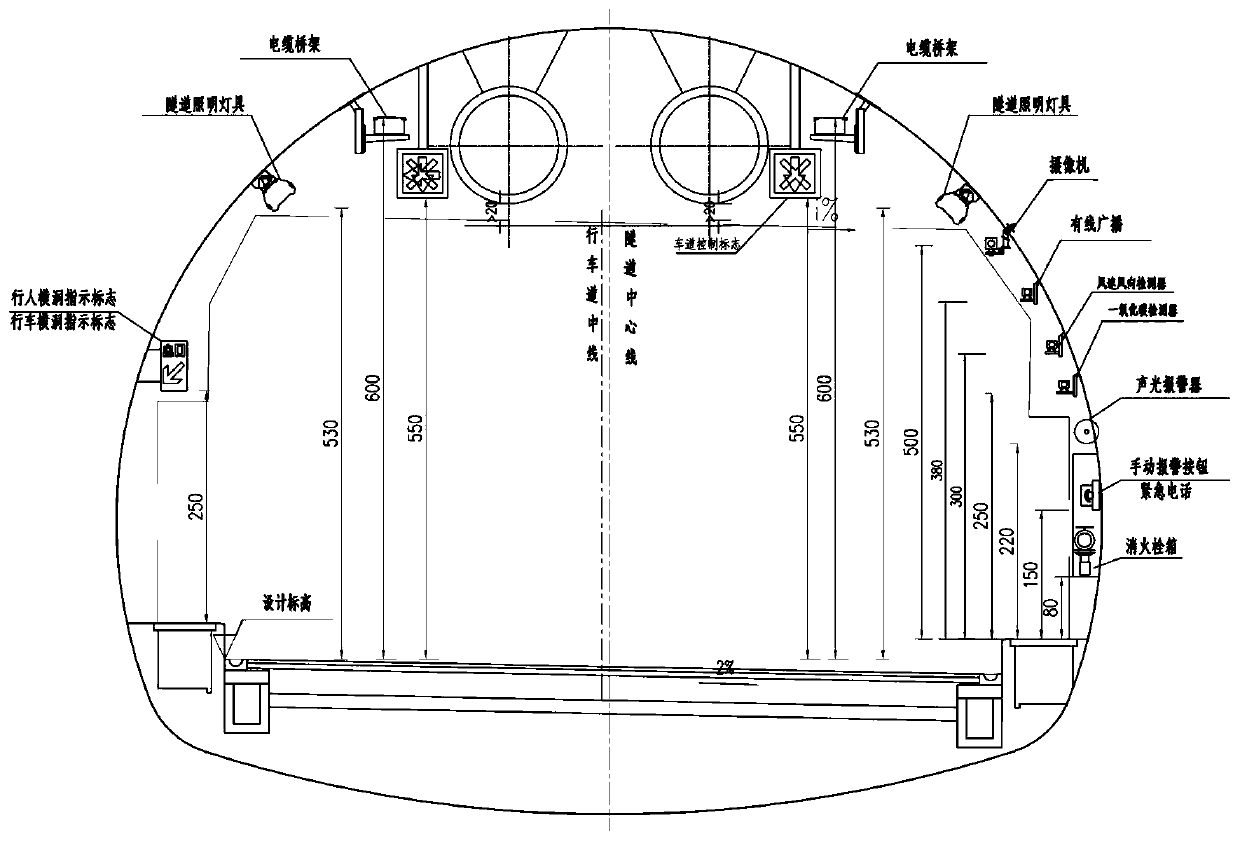
InactiveCN111325977AReduce stepsImprove reliabilityChecking time patrolsMining devicesInformatizationEmergency plan
The invention discloses a tunnel intelligent edge calculation management and control system, and belongs to the technical field of tunnel edge calculation. The system comprises a management and control center, and a risk dynamic early warning subsystem connected with the management and control center and used for monitoring the operation state of execution equipment in a tunnel and sensing the collected data of the equipment in real time, and carrying out abnormal warning and equipment inspection; a mechatronics subsystem, used for linking execution equipment in the tunnel and executing an emergency plan; a traffic state sensing subsystem used for visually sensing the traffic state of the tunnel through a radar and video fusion detection technology and detecting a traffic event; and a management and control center receiving the monitored operation states of the execution equipment and the sensing equipment, issuing a control command to the mechatronics subsystem, receiving the sensed traffic state, analyzing a traffic event and giving an alarm. The tunnel management and control system solves the problems that an existing tunnel management and control system is not integrated, low in association degree, lack of effective and standard informatization means and low in emergency disposal efficiency.
Owner:创捷运维智能科技有限责任公司
Computation of a shortest inter-domain te-lsp across a set of autonomous systems
A technique calculates a shortest path for a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from a head-end node in a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain in a computer network. The novel path calculation technique determines a set of differ- ent remote domains through which the TE-LSP may traverse to reach the tail-end node (e.g., along ''domain routes''). Once the set of possible routes is determined, the head-end node sends a path computation request to one or more path computation elements (PCEs) of its local domain requesting a computed path for each domain route. Upon receiving path responses for each possible domain route, the head-end node selects the optimal (shortest) path, and establishes the TE-LSP accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
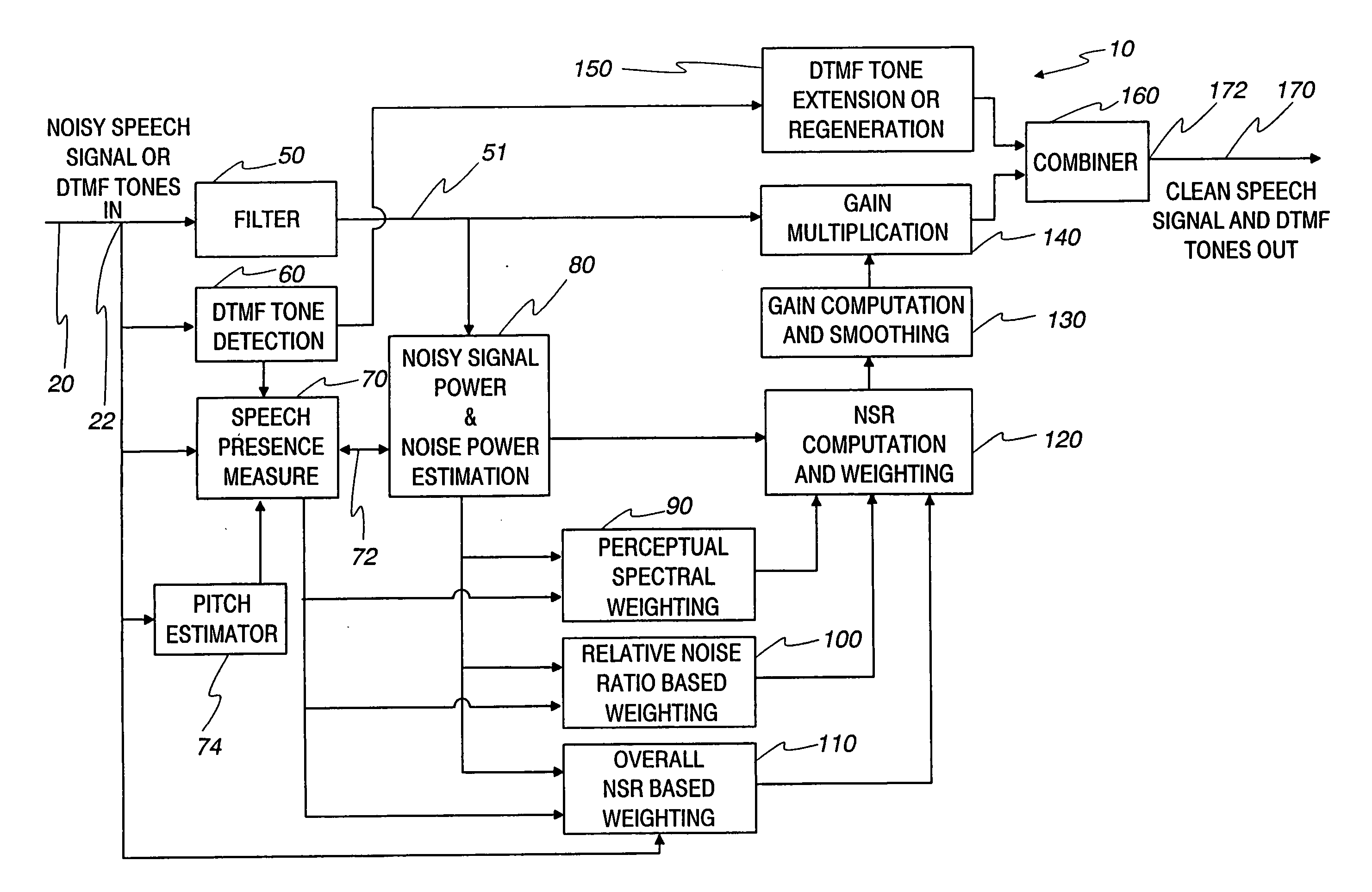
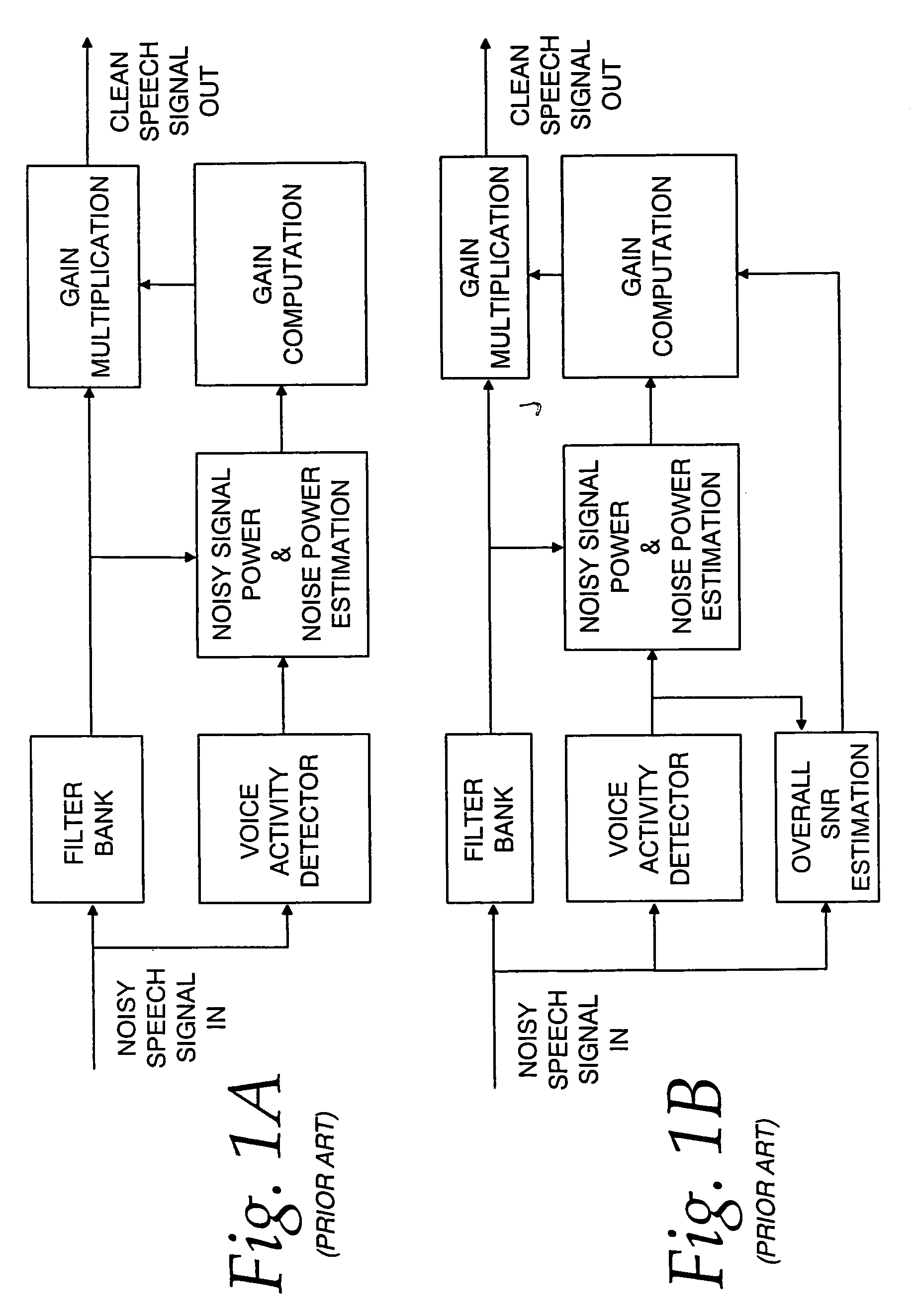
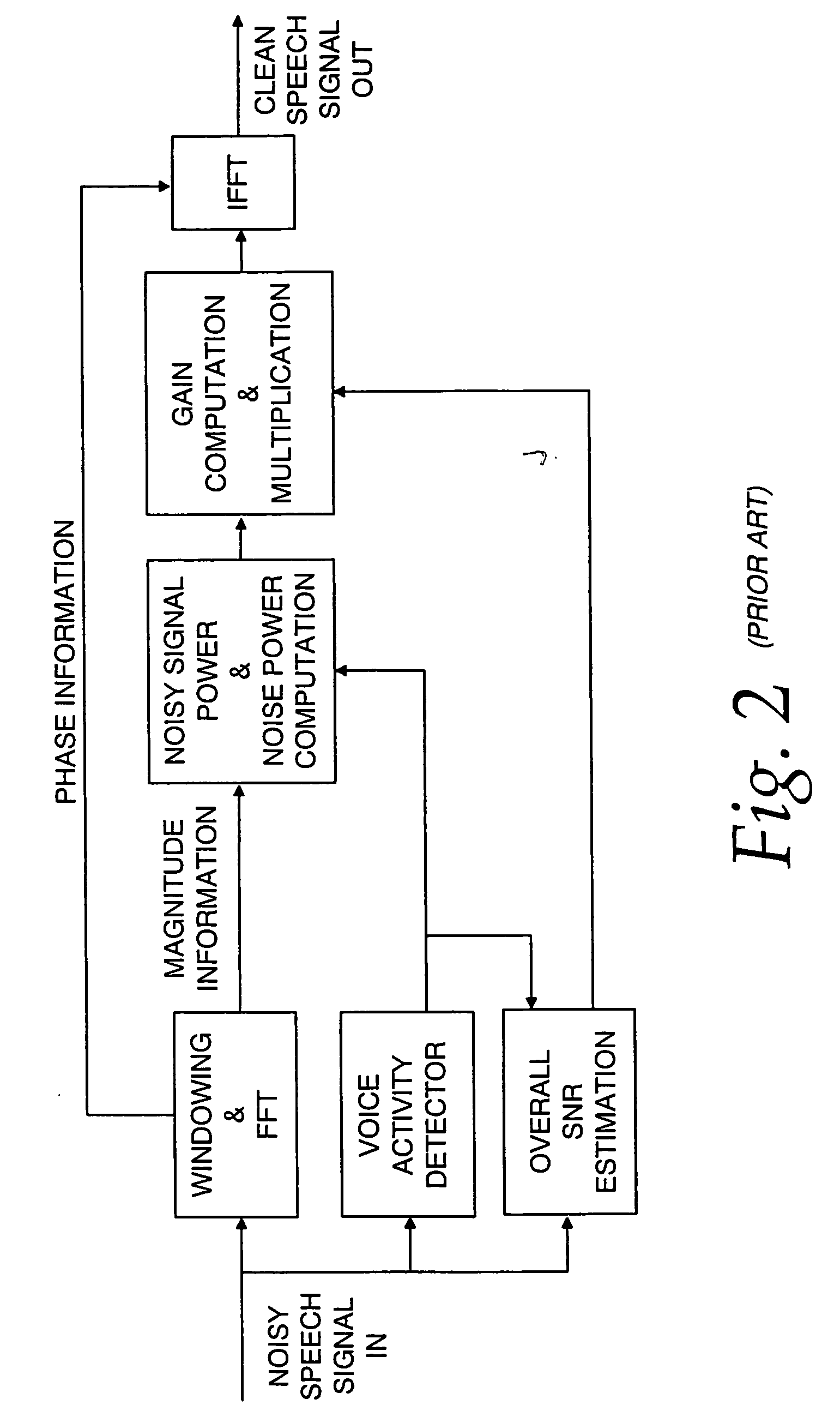
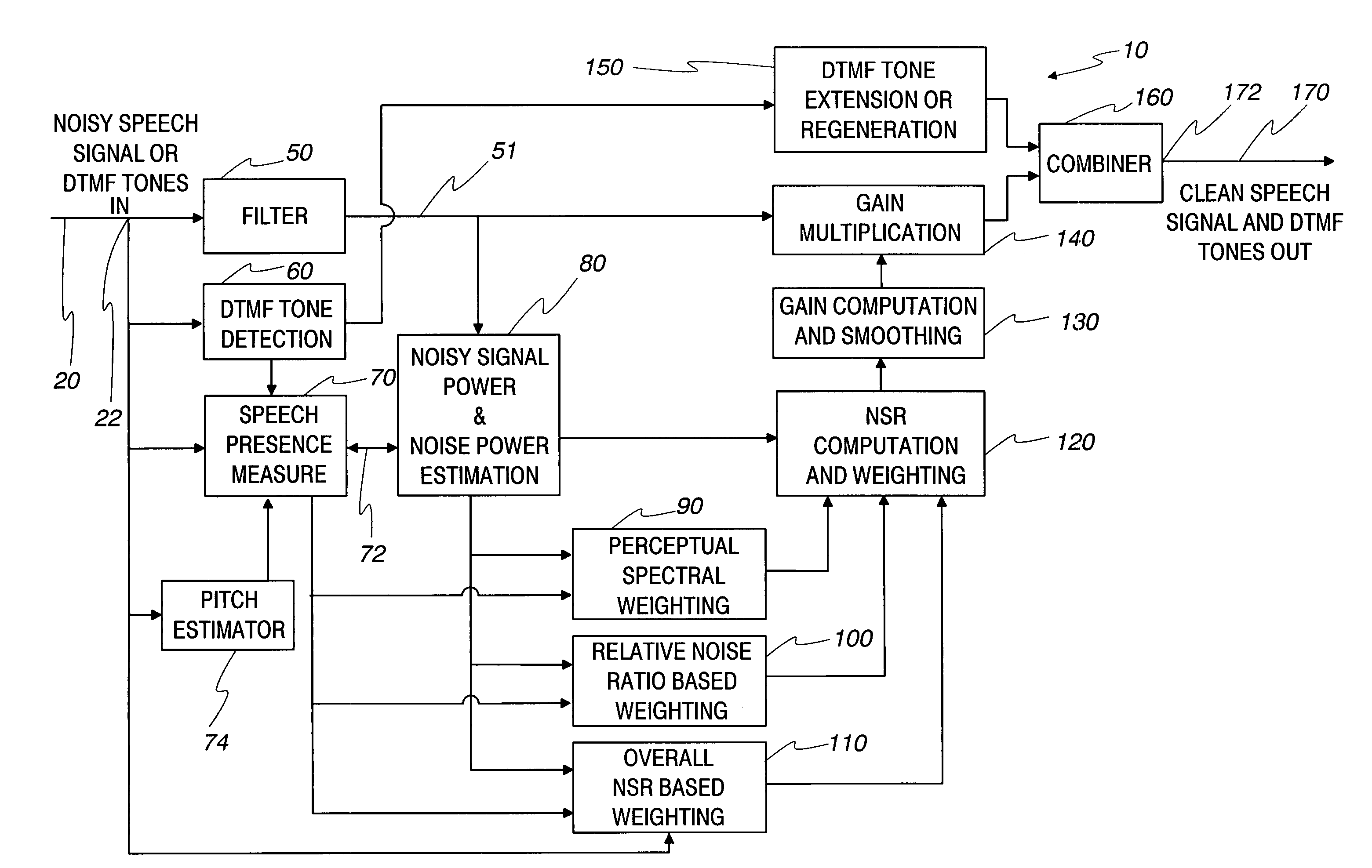
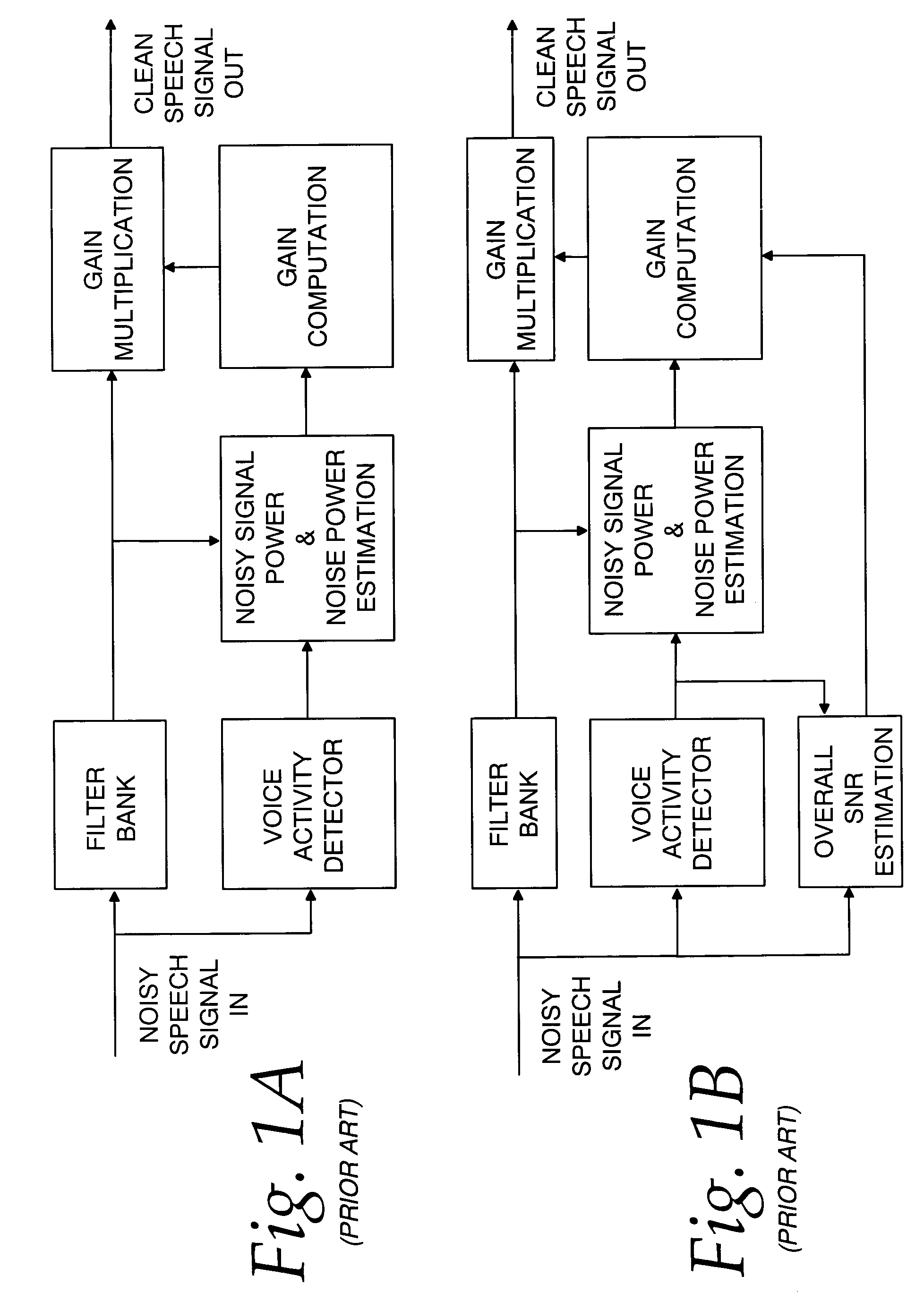
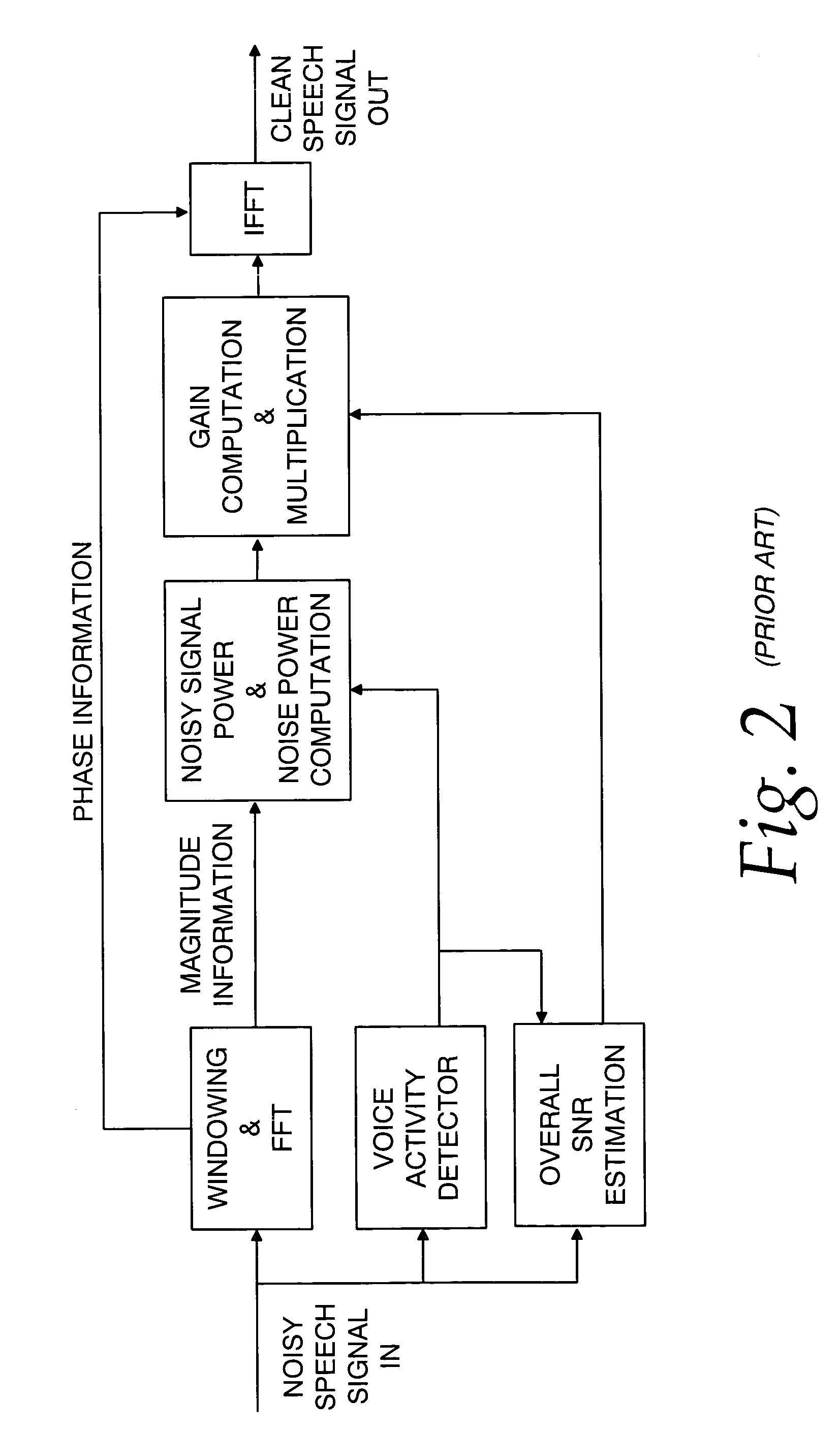
Communication system noise cancellation power signal calculation techniques
InactiveUS20060247923A1Improve communication signal qualitySpeech analysisCommunications systemCalculation technique
In order to enhance the quality of a communication signal derived from speech and noise, a filter divides the communication signal into a plurality of frequency band signals. A calculator generates a plurality of power band signals each having a power band value and corresponding to one of the frequency band signals. The power band values are based on estimating, over a time period, the power of one of the frequency band signals. The time period is different for different ones of the frequency band signals. The power band values are used to calculate weighting factors which are used to alter the frequency band signals that are combined to generate an improved communication signal.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
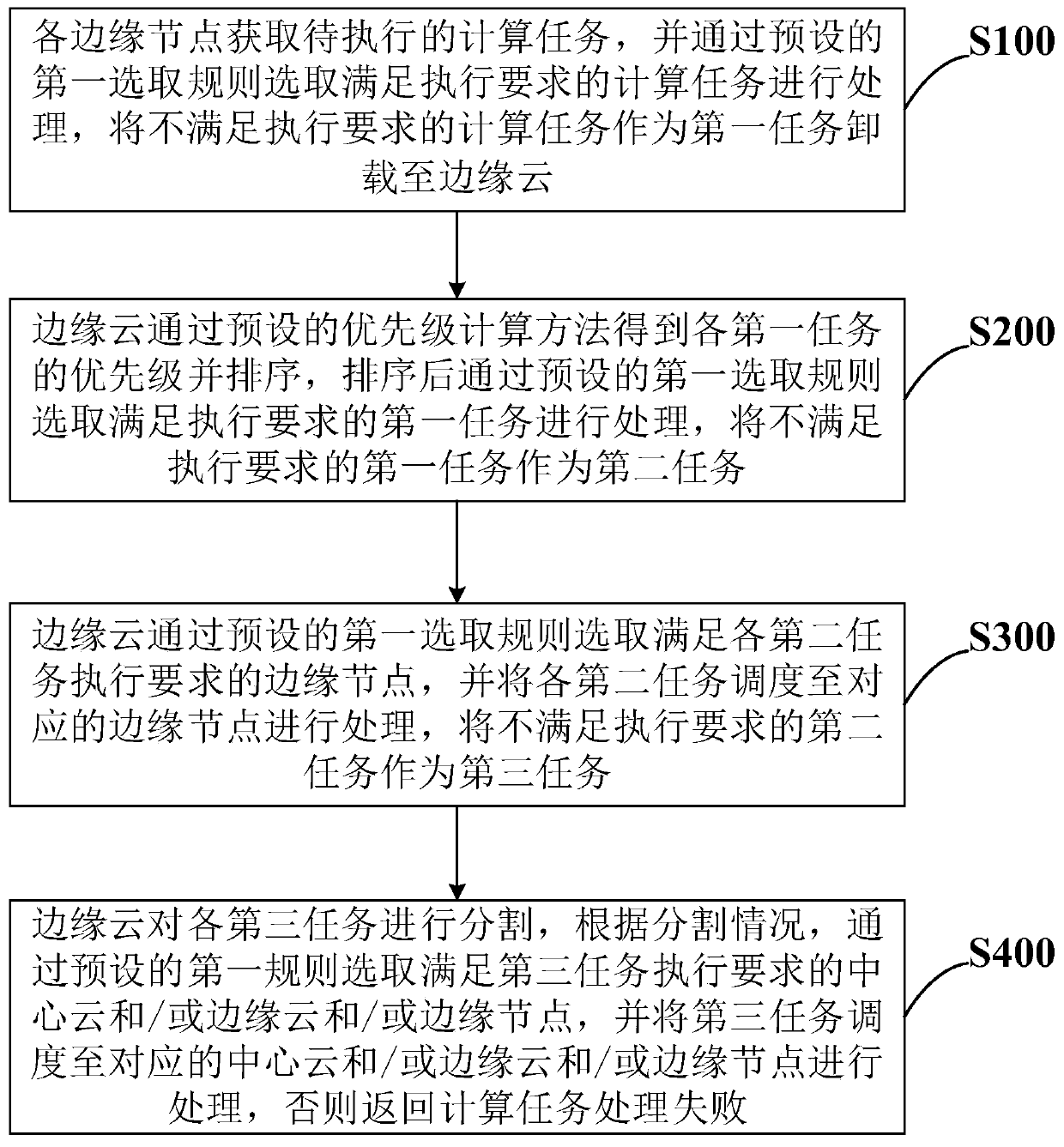
Calculation task scheduling method, system and device for edge calculation
PendingCN111427679AImprove real-time performanceEfficient schedulingProgram initiation/switchingEnergy efficient computingParallel computingEdge node
The invention belongs to the technical field of edge calculation, particularly relates to an edge calculation-oriented calculation task scheduling method, system and device, and aims to further improve the real-time performance of edge-side calculation task processing and maximally utilize edge-side resources. The method comprises the steps that each edge node obtains a to-be-executed calculationtask, selects a task meeting the execution requirement for processing, and does not meet the execution requirement to serve as a first task to be unloaded to an edge cloud; the edge cloud sorts the first tasks and selects and processes the first tasks meeting the execution requirements, and the first tasks which do not meet the execution requirements are used as second tasks; edge nodes meeting the execution requirements of the second tasks are selected and dispatched, If not, the edge nodes serve as third tasks; and segmenting the third task, selecting edge nodes and / or edge clouds and / or center clouds meeting execution requirements after segmentation, and performing scheduling processing, otherwise, performing processing unsuccessfully. According to the method, through cloud-edge-end cooperative processing, resources on the edge side are reasonably utilized, and the real-time performance of calculation task scheduling processing is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Communication system noise cancellation power signal calculation techniques
InactiveUS7096182B2Improve communication signal qualitySpeech analysisCommunications systemEngineering
In order to enhance the quality of a communication signal derived from speech and noise, a filter divides the communication signal into a plurality of frequency band signals. A calculator generates a plurality of power band signals each having a power band value and corresponding to one of the frequency band signals. The power band values are based on estimating, over a time period, the power of one of the frequency band signals. The time period is different for different ones of the frequency band signals. The power band values are used to calculate weighting factors which are used to alter the frequency band signals that are combined to generate an improved communication signal.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Tridimensional integral prestack depth migration method based on maximum energy travel calculation
InactiveCN101545986ASmall amount of calculationFlexible imagingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVibration amplitudeRectangular coordinates
The invention relates to the prestack depth migration technique during the data processing of petroleum seismic prospecting, including the following concrete steps: establishing depth rate pattern of prestack seismic data; well designing observation grids, and solving wave equation in sphere coordinate system to simulate the communication process of seismic waves; changing and converting the calculated seismic wave field of a frequency domain into a time domain, and fitting the Green function energy spectrum of the seismic wave field in the time domain to detect the arriving time and the vibration amplitude when the maximum energy arrives; transferring the travel time and the vibration amplitude field calculated in the sphere coordinate system to a rectangular coordinate system; accomplishing the maximum energy integral prestack depth migration according to the well calculated travel time and the vibration amplitude; analyzing the operation of speed to the imaging gather of the prestack depth migration to modify the depth rate pattern; and modifying the depth rate pattern by iteration, and outputting the ultimate result until the migration result meets the precision requirement. The invention provides the self-adapting variation difference grid calculation technique so as to achieve the purpose that the difference grids are automatically and gradually thinned along with radius increase, thereby guaranteeing the finite difference calculation precision.
Owner:匡斌
Methods to detect formation pressure
Methods for estimating formation pressure from data taken during the drawdown cycle are presented. In one aspect, a method of determining a formation pressure during drawdown of a formation comprises sampling fluid from a formation using a downhole tool having a sample volume and a fluid sampling device. At least one time dependent parameter of interest related to the fluid is determined during the drawdown. The at least one time dependent parameter is analyzed using a plurality of calculation techniques to determine the formation pressure. The techniques include (i) a first pressure derivative technique; (ii) a second pressure derivative technique; (iii) a formation rate analysis technique; (iv) a dp / dt-ratio technique; and (v) a stepwise drawdown technique.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
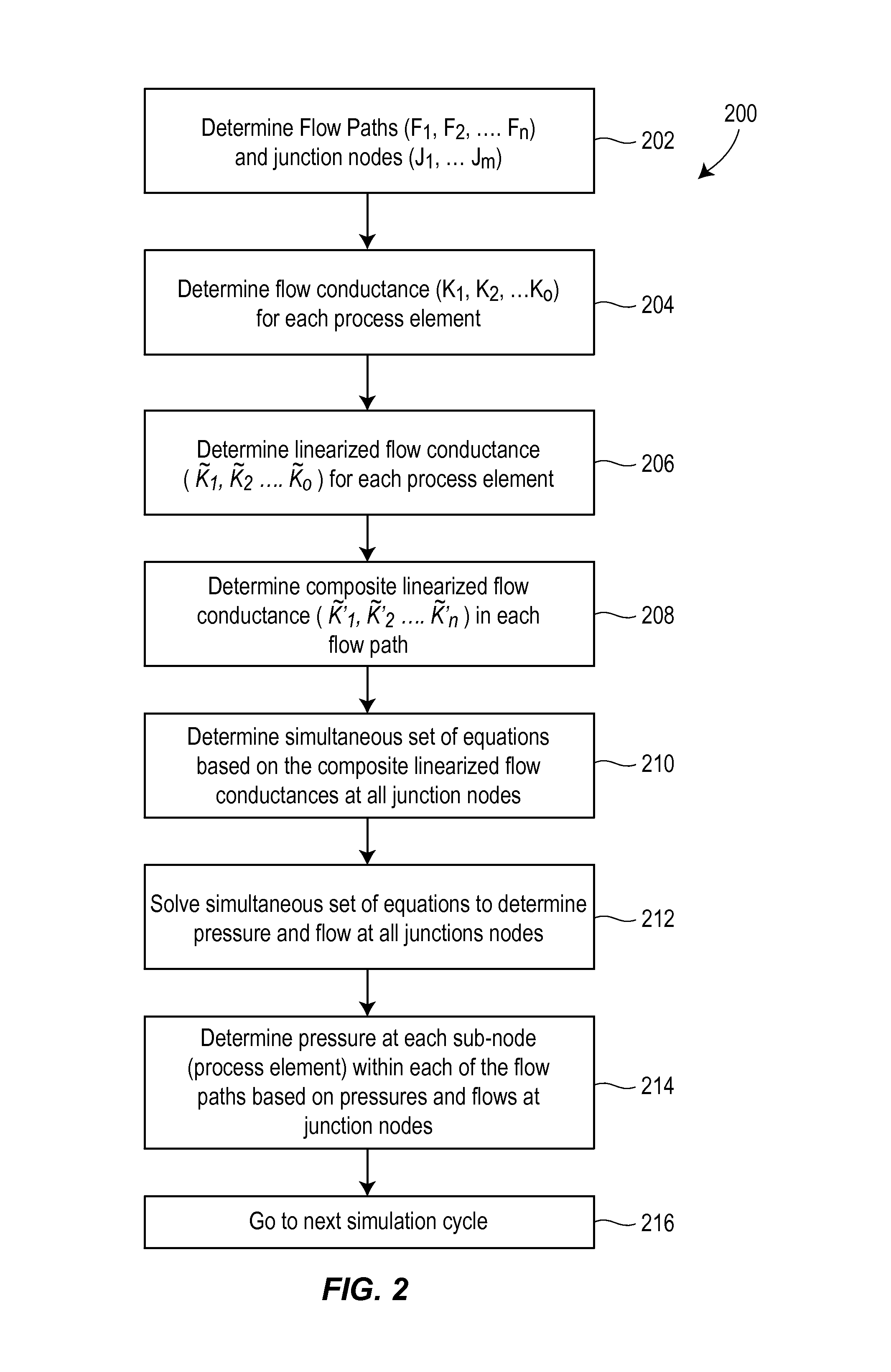
Hybrid sequential and simultaneous process simulation system
ActiveUS20130211601A1Fast executionStable numerical resultProgramme controlSimulator controlProcess simulationComputer science
A pressure and flow calculation technique that efficiently solves for pressures and flows within a process network uses both a simultaneous and a sequential solving method. The calculation technique first determines a flow conductance for each of the process network elements, linearizes pressure and flow relationships in each flow path by determining a linearized flow conductance for each process element and then determines a composite process network having a linearized, composite process component in each flow path to produce a simplified process network. A simultaneous solving method is then used to simultaneously solve for the pressures and flows at each of a set of junction nodes of the simplified process network and thereafter a sequential solving method is applied to determine the pressures and flows at the other nodes of the process network.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com