Computation of a shortest inter-domain te-lsp across a set of autonomous systems
一种标签交换路径、流量工程的技术,应用在流量工程标签交换路径计算最短路径领域,能够解决LSR或PCE没有知识等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
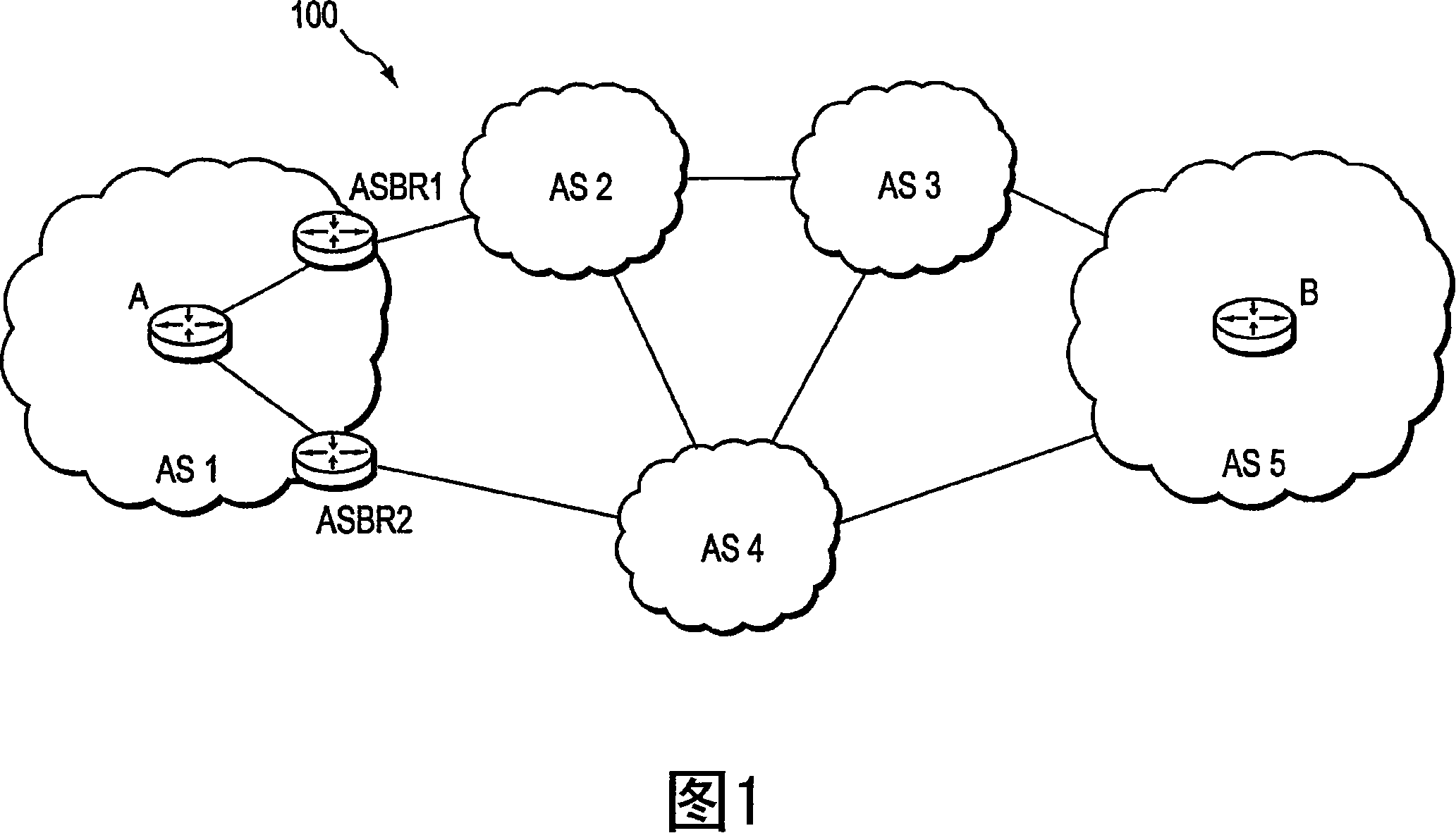
[0033] Figure 1 is a schematic block diagram of an exemplary computer network 100 including autonomous systems AS1 and AS5 interconnected by autonomous systems AS2, AS3 and AS4 as shown. An autonomous system (AS) is defined here as a group of intermediate nodes (eg, intra-domain routers) within a network that are subject to the same authority and implement one or more intra-domain routing protocols. Although each AS is shown as an autonomous system, those skilled in the art will appreciate that ASs may also be configured as routing domains or other networks or subnetworks. Autonomous system AS1 includes intra-domain routers, such as border routers ASBR1 and ASBR2, through which communications (eg, data packets) can enter and leave the AS to other AS border routers (not shown) in AS2 and AS4. Furthermore, within AS1 and AS5, there are exemplary intra-domain routers A and B, respectively. Those skilled in the art will understand that any number of routers may be used in the ASs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com