Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
229 results about "Flexural vibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
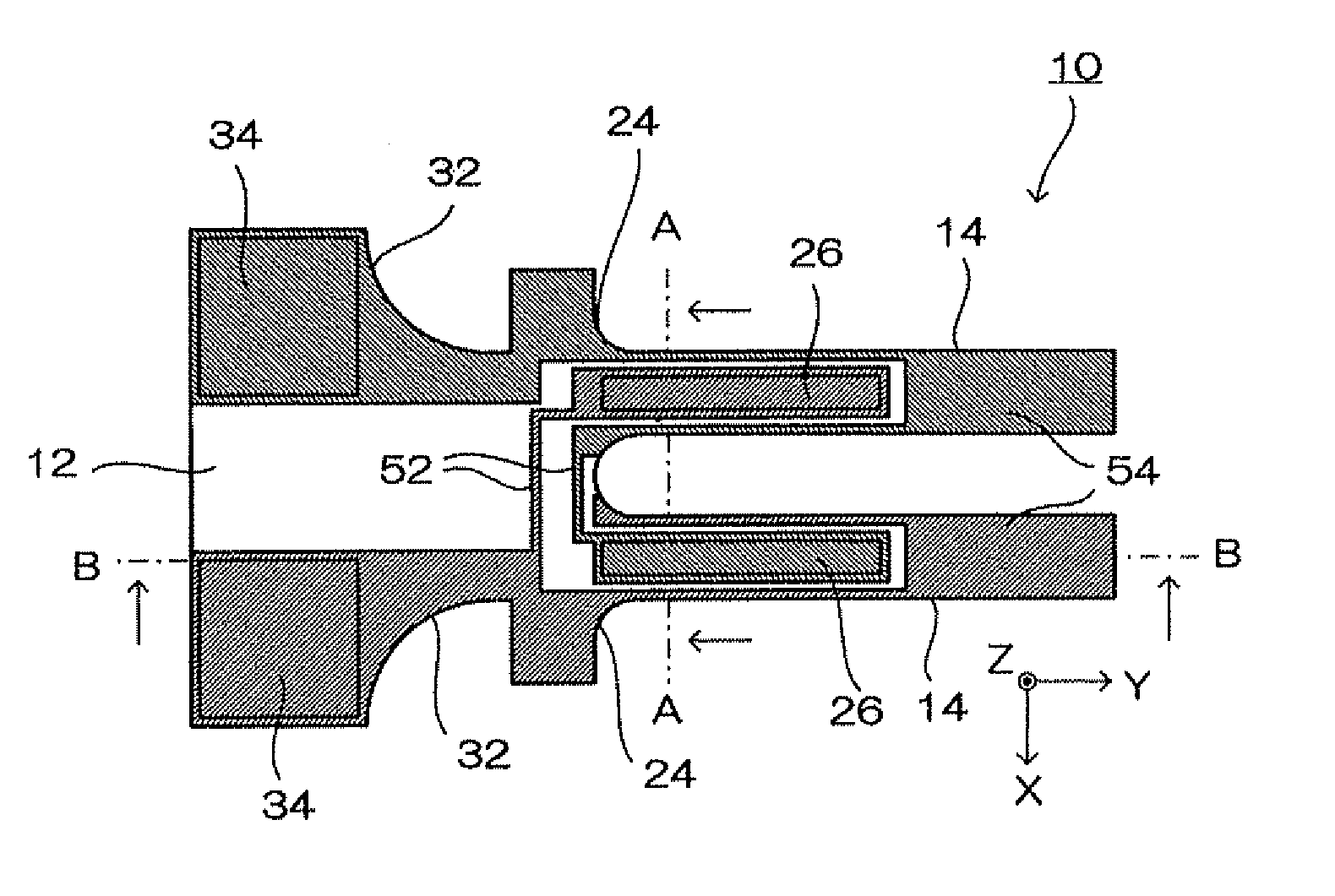
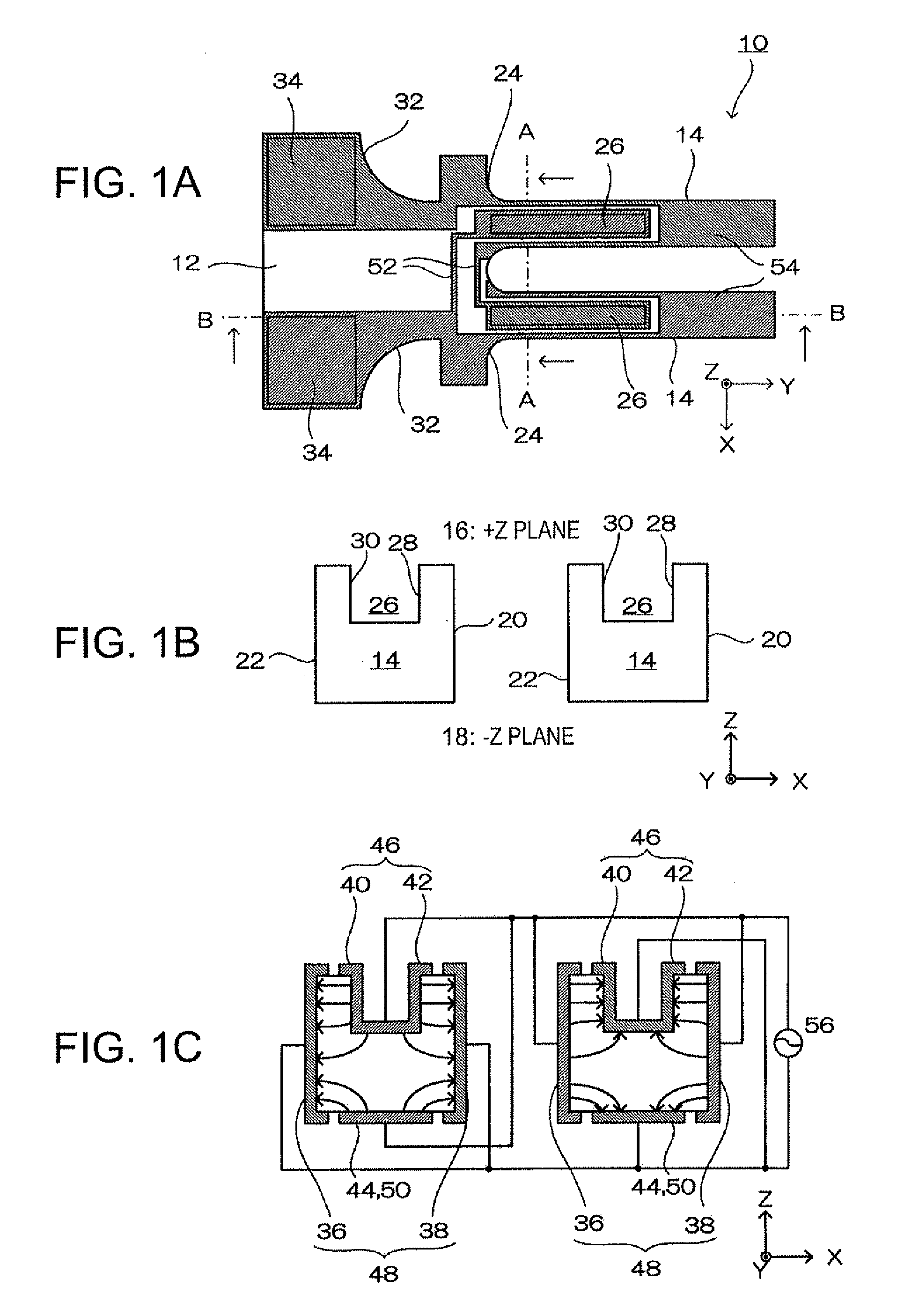
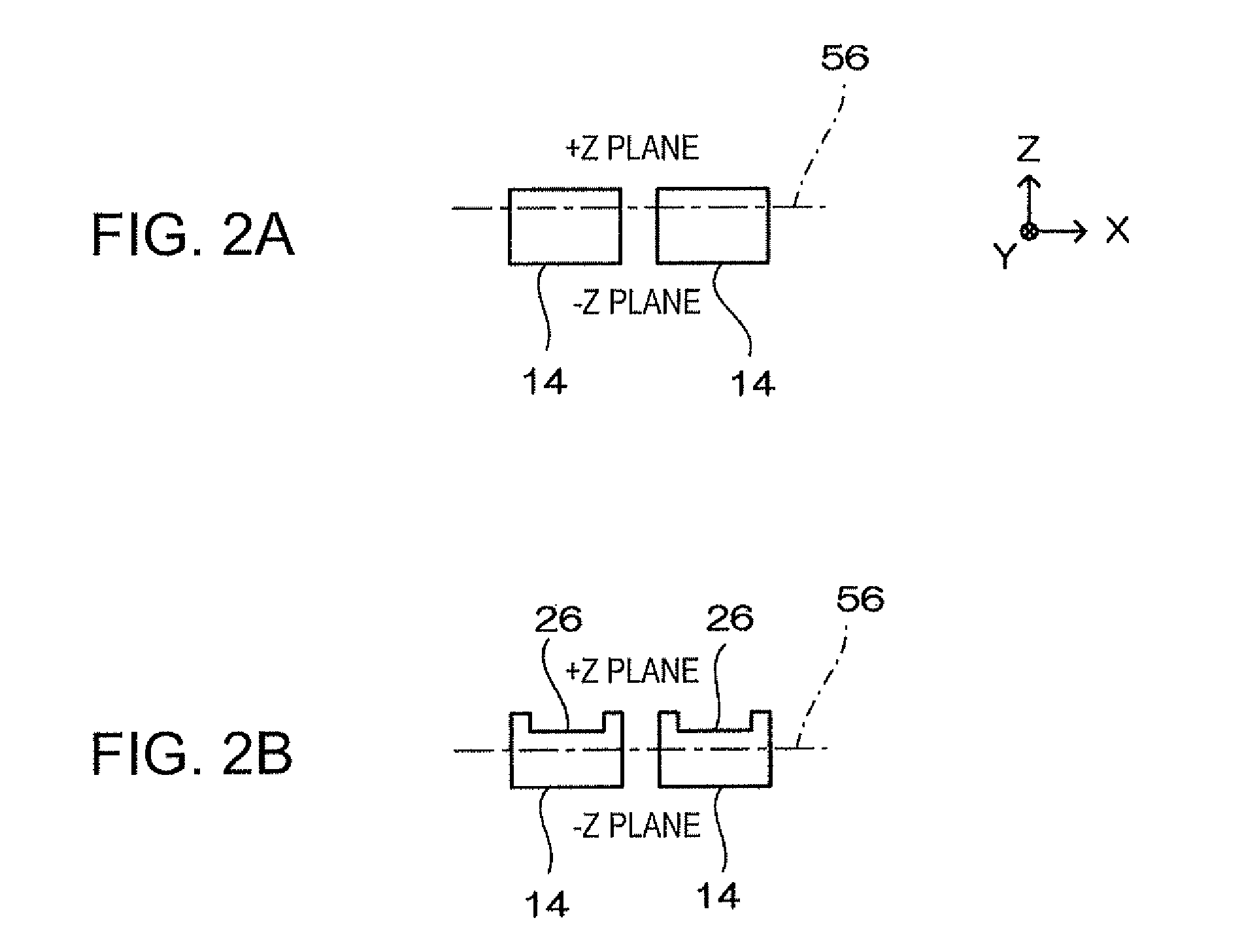
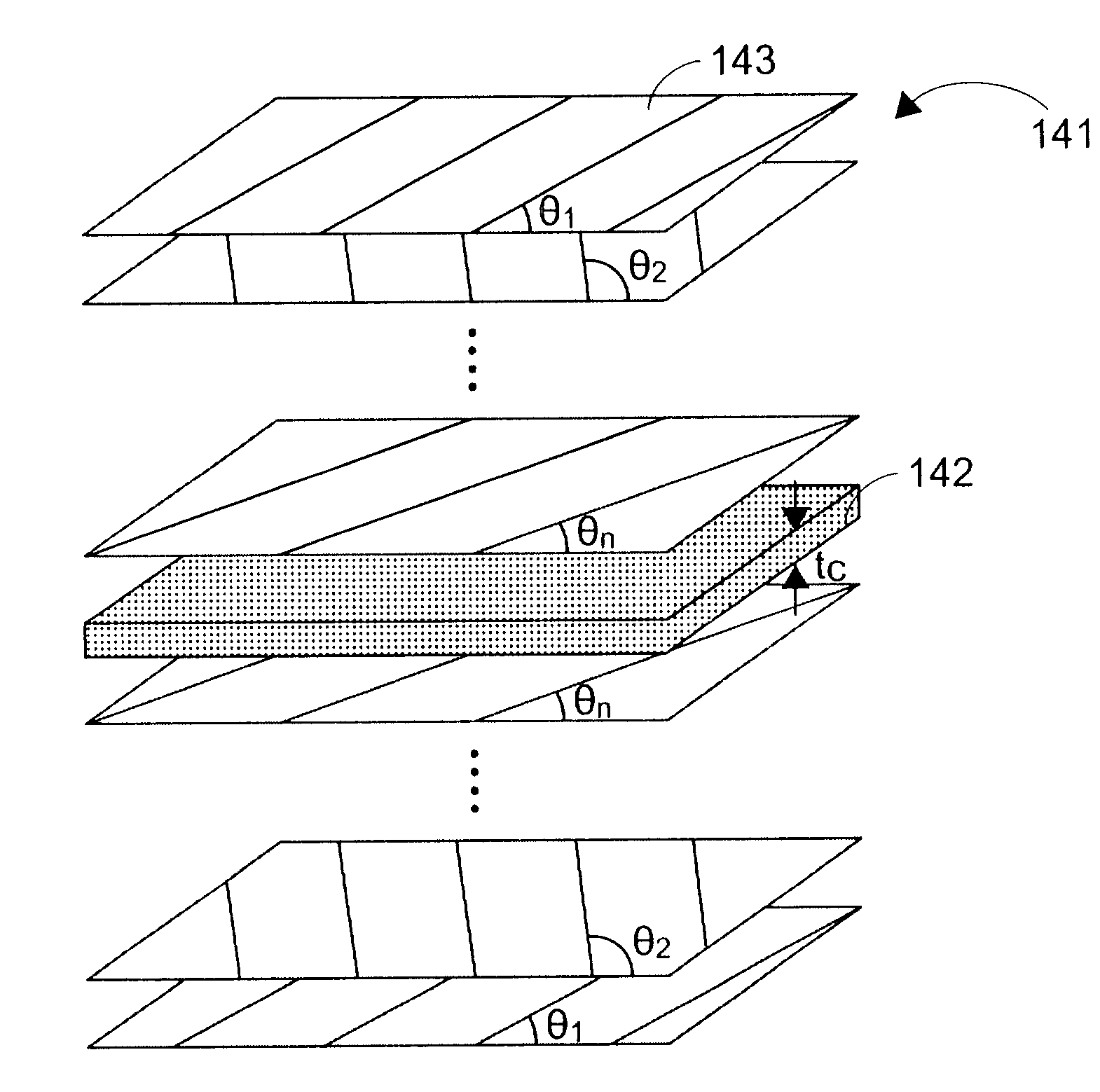
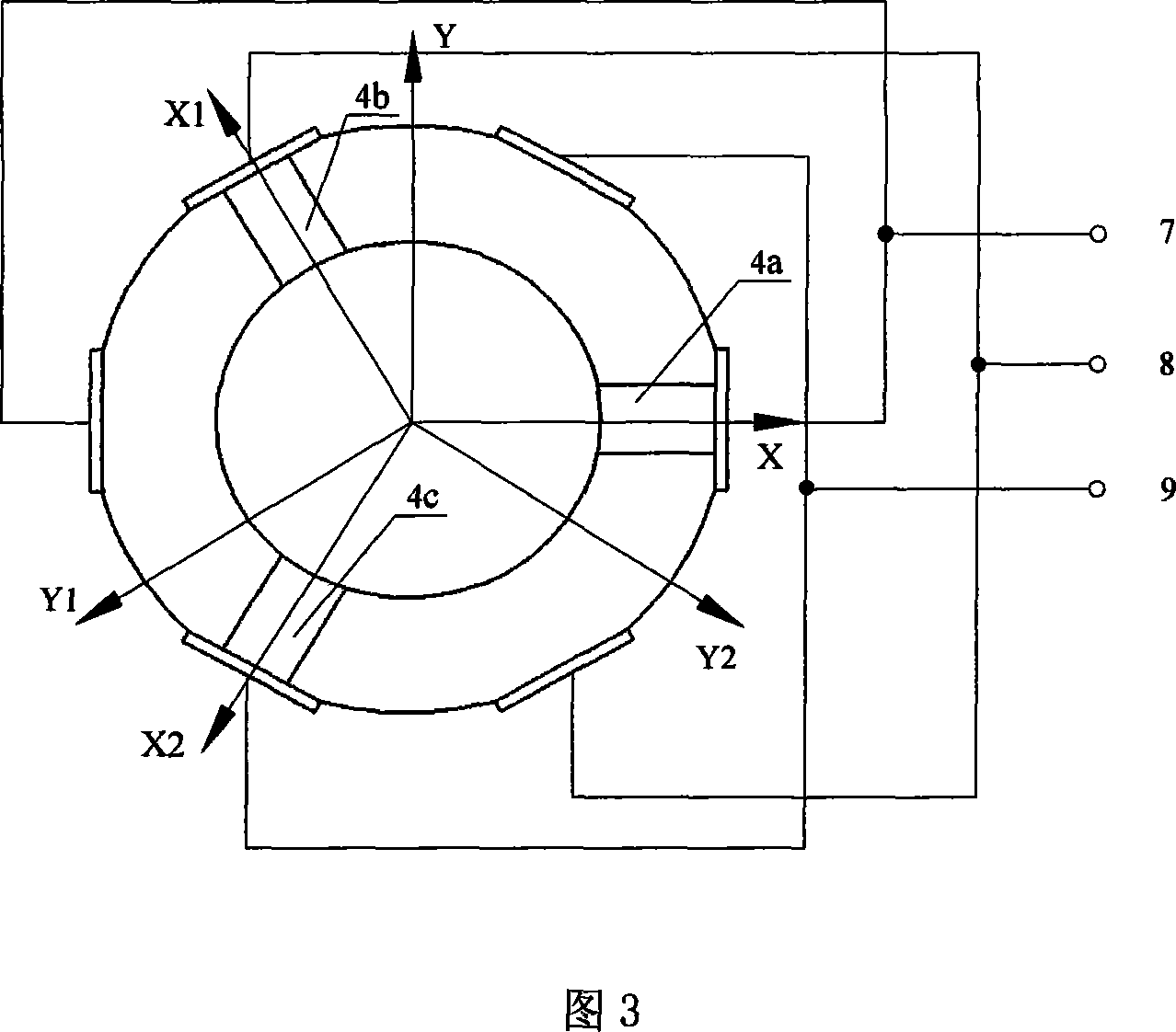
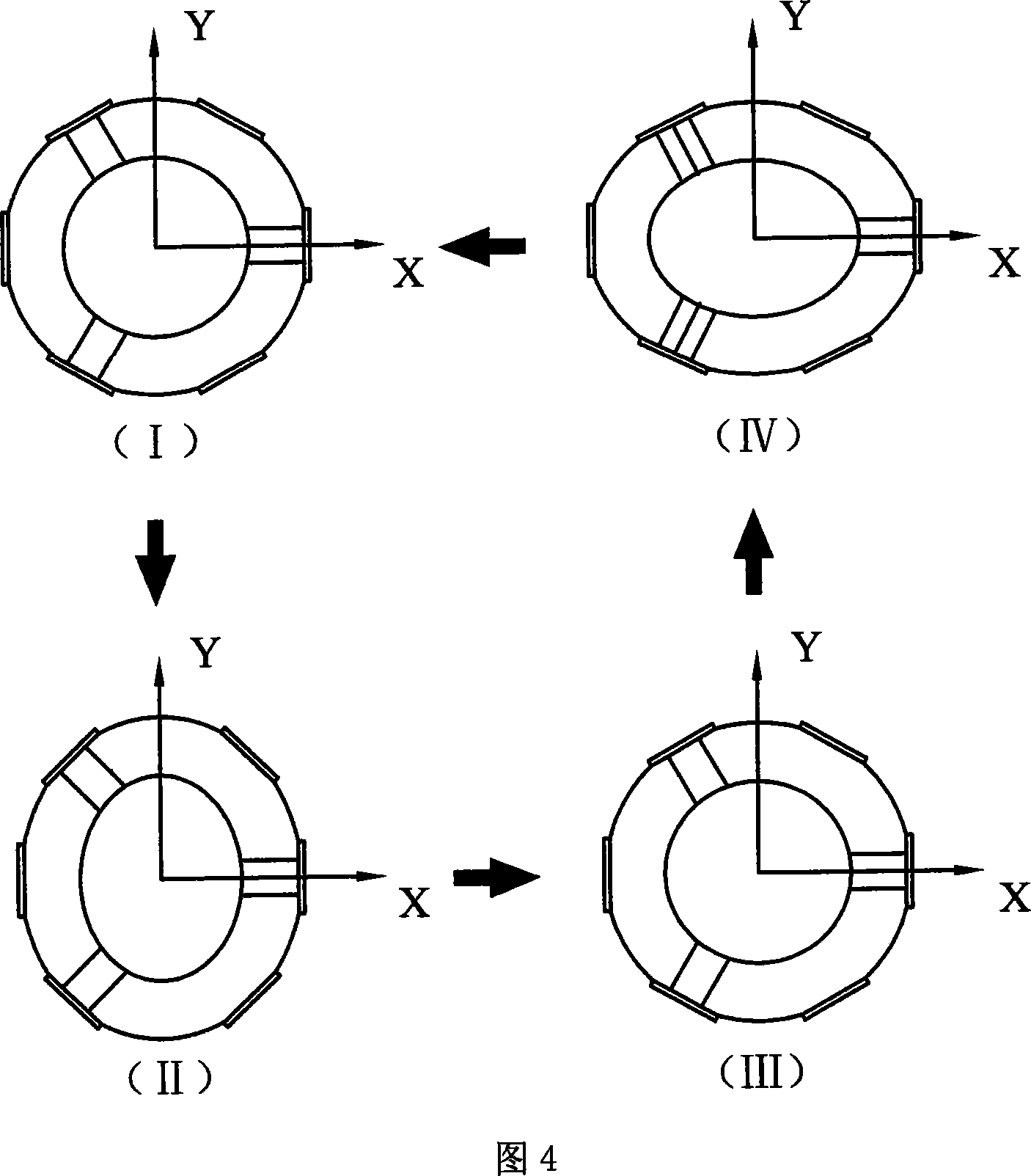
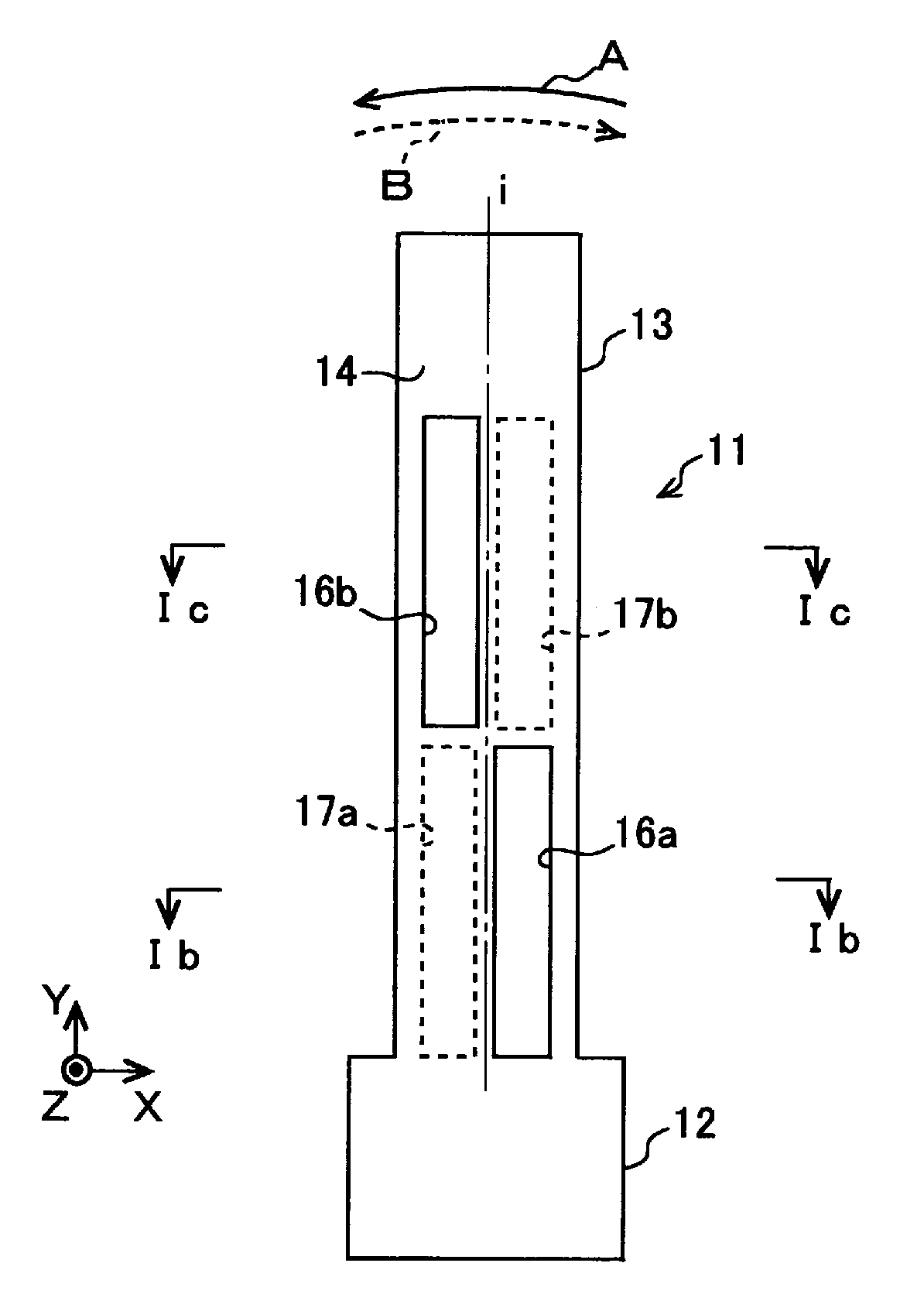
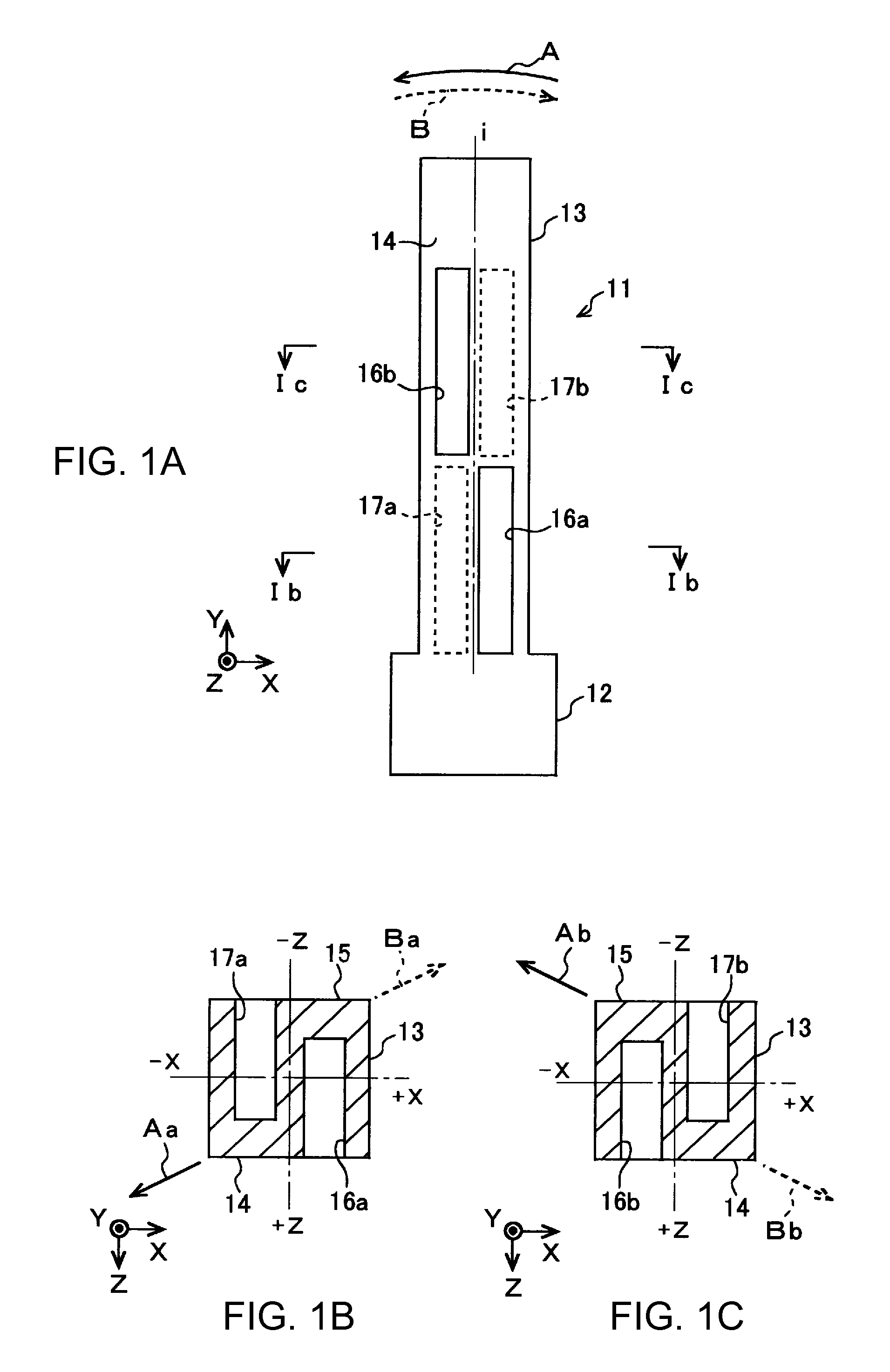
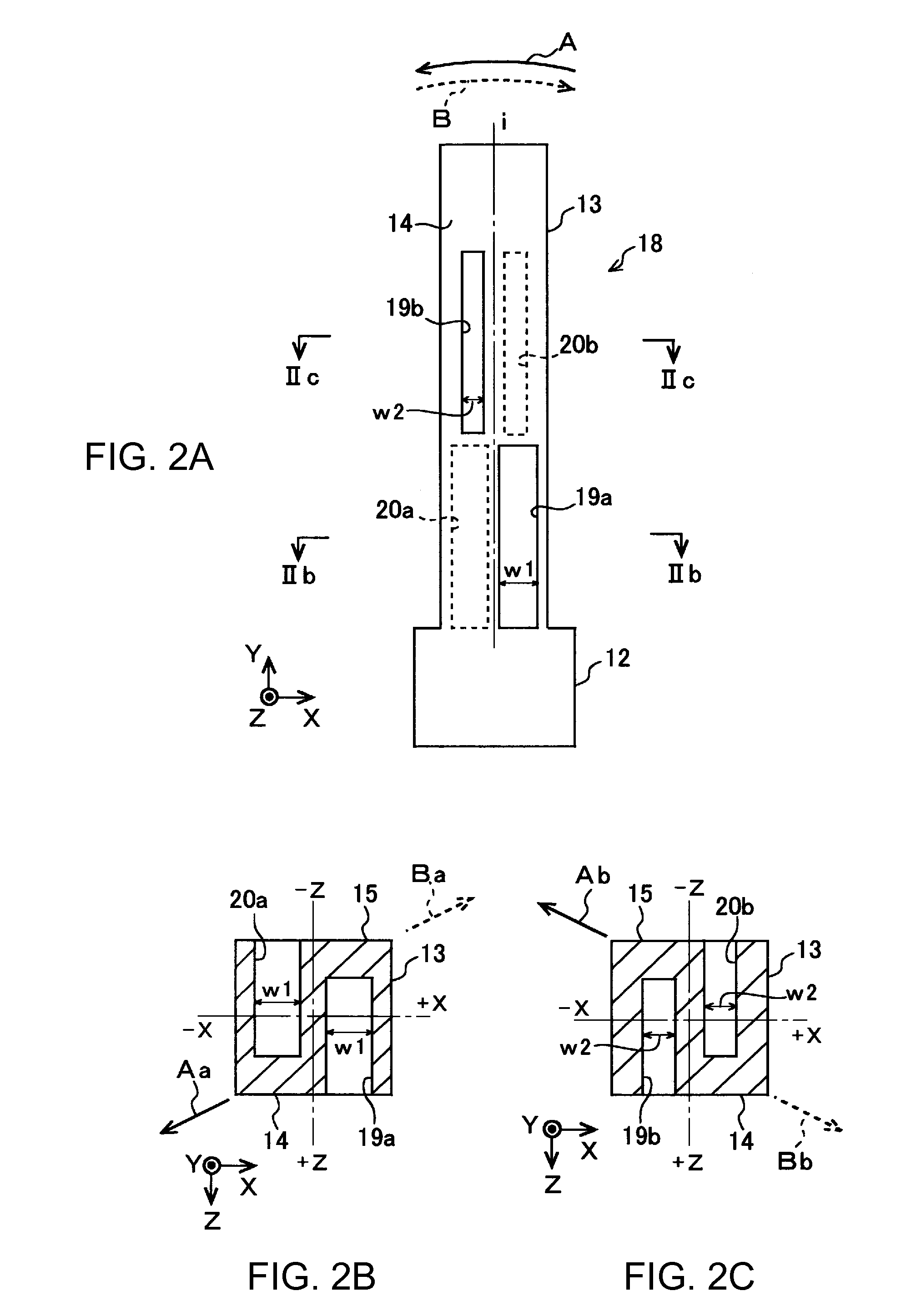
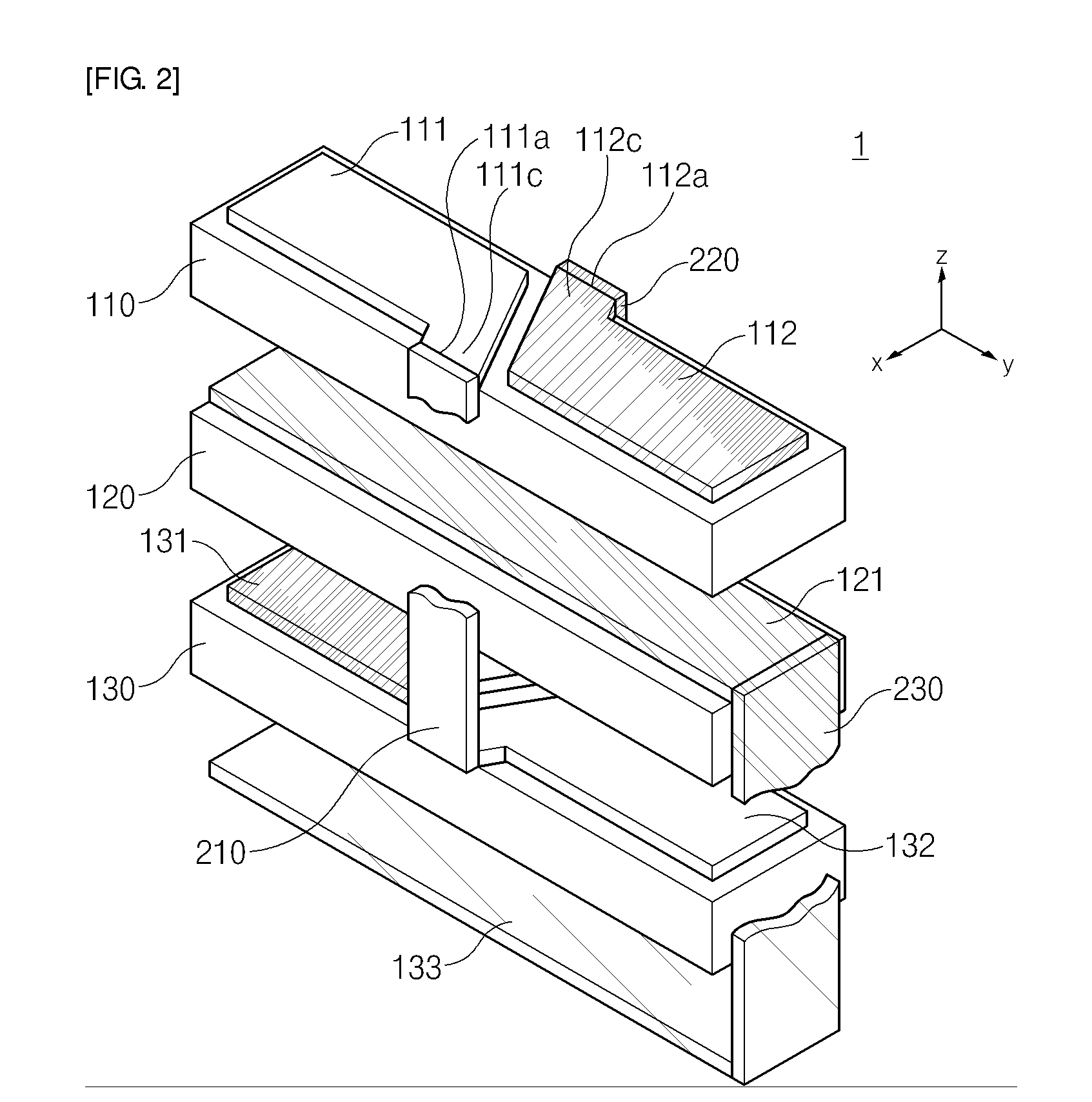
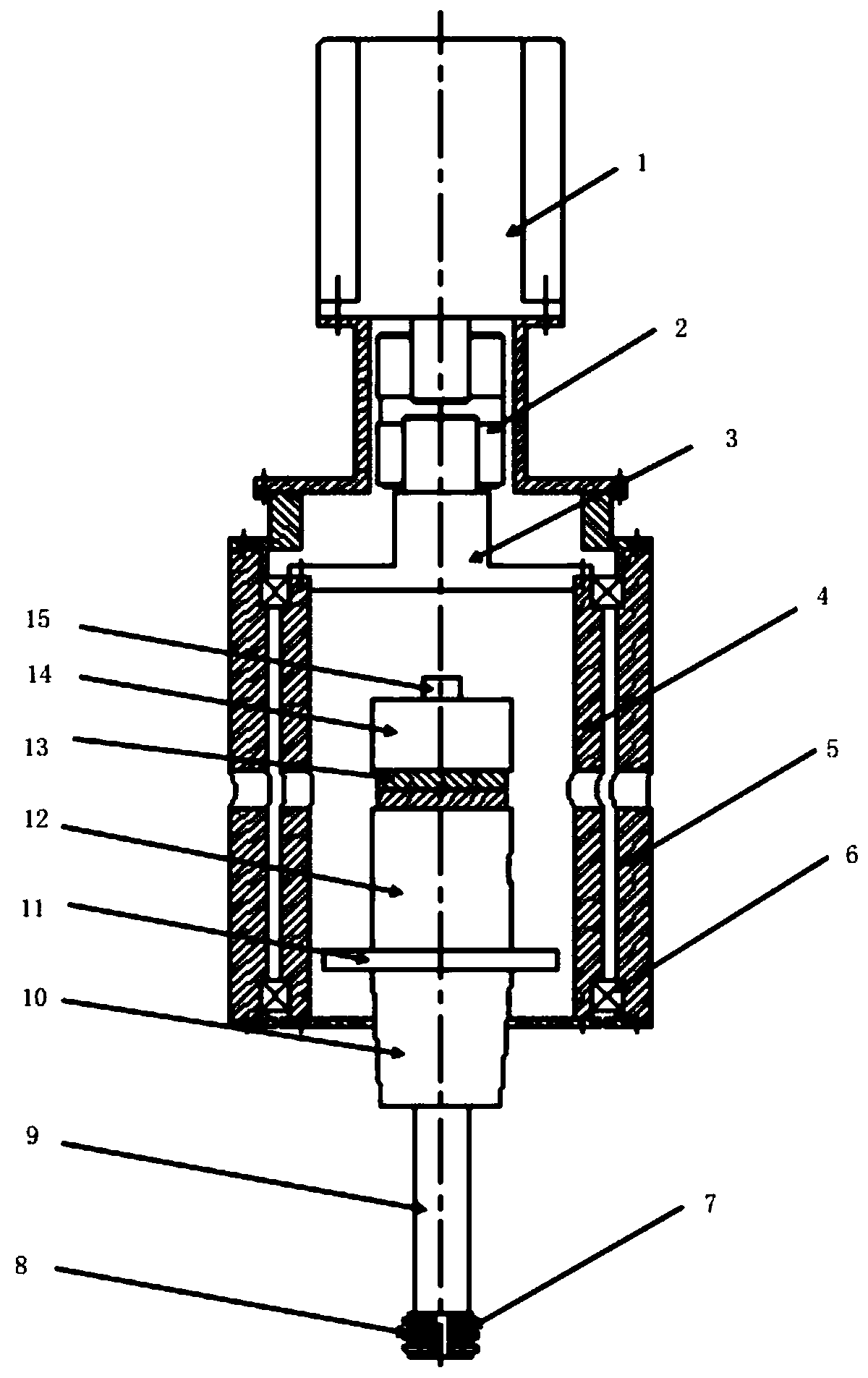
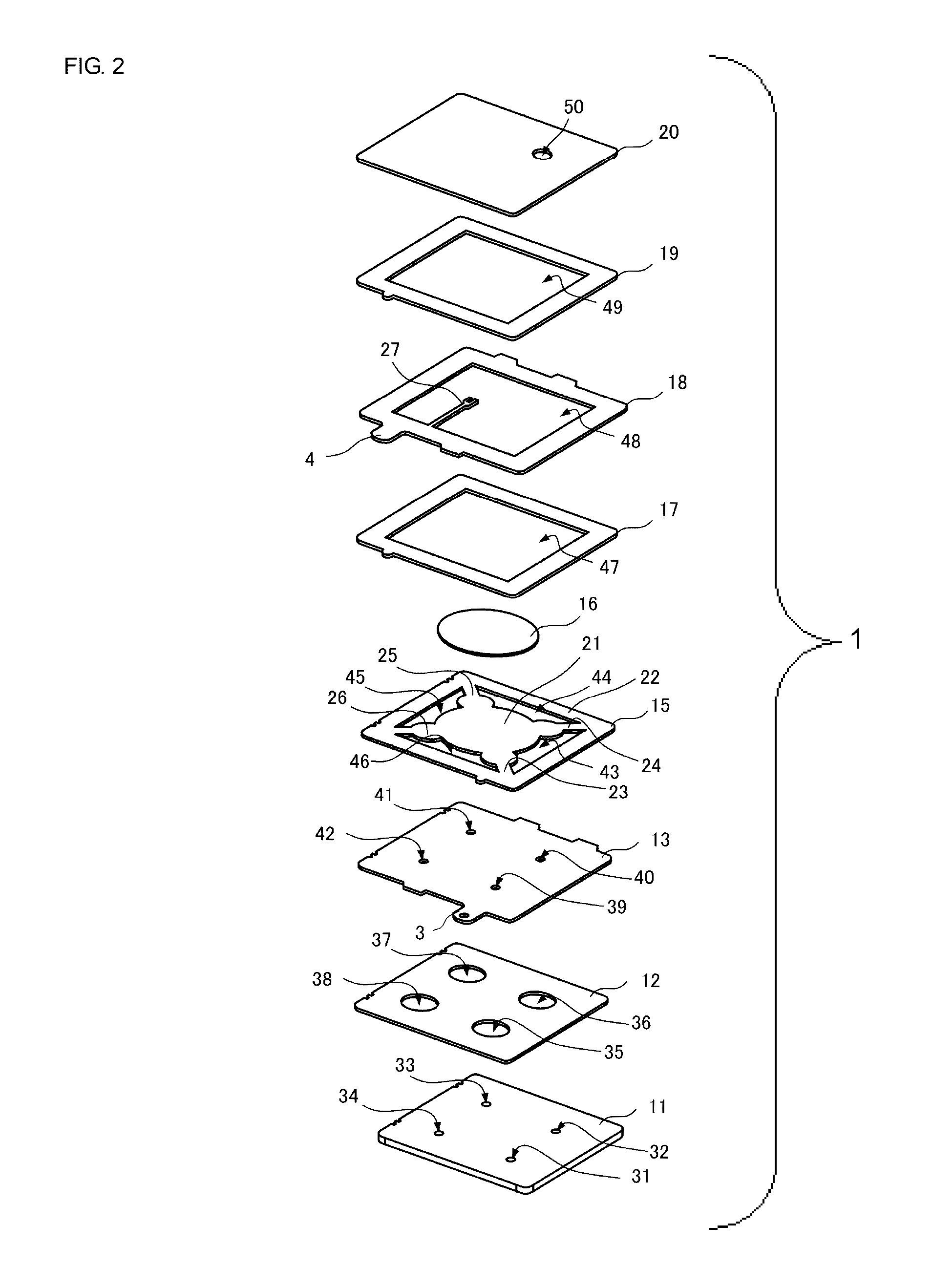
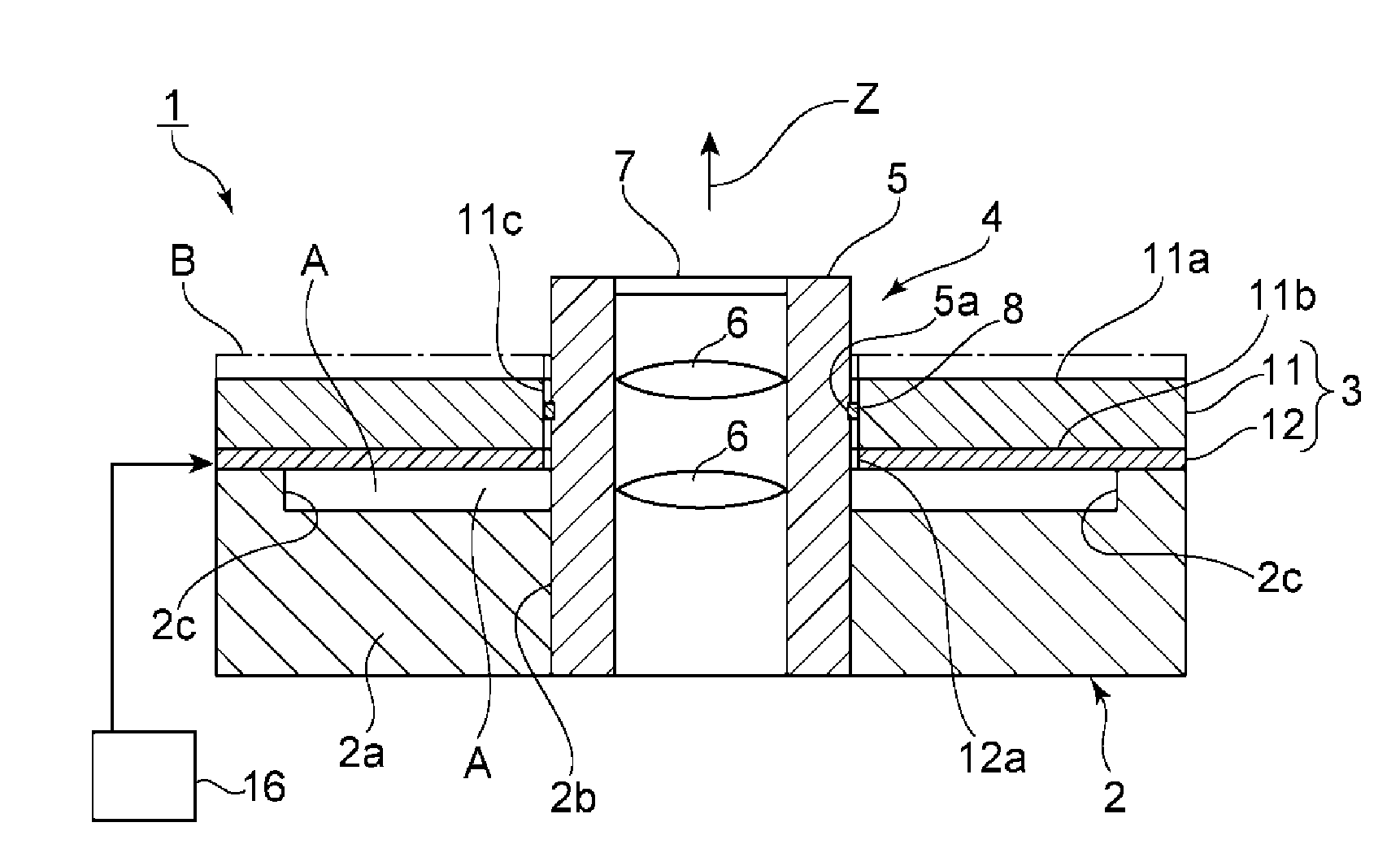
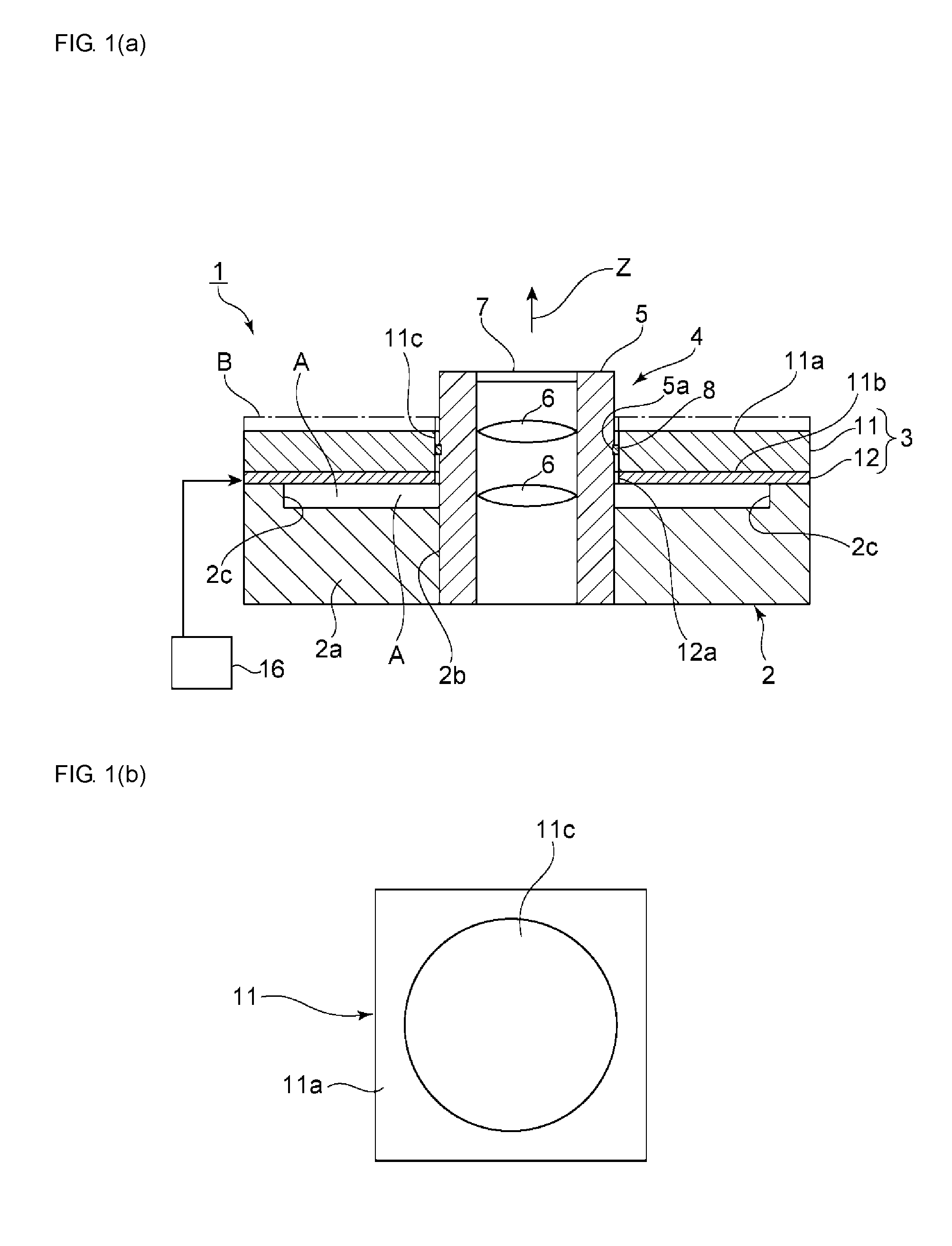
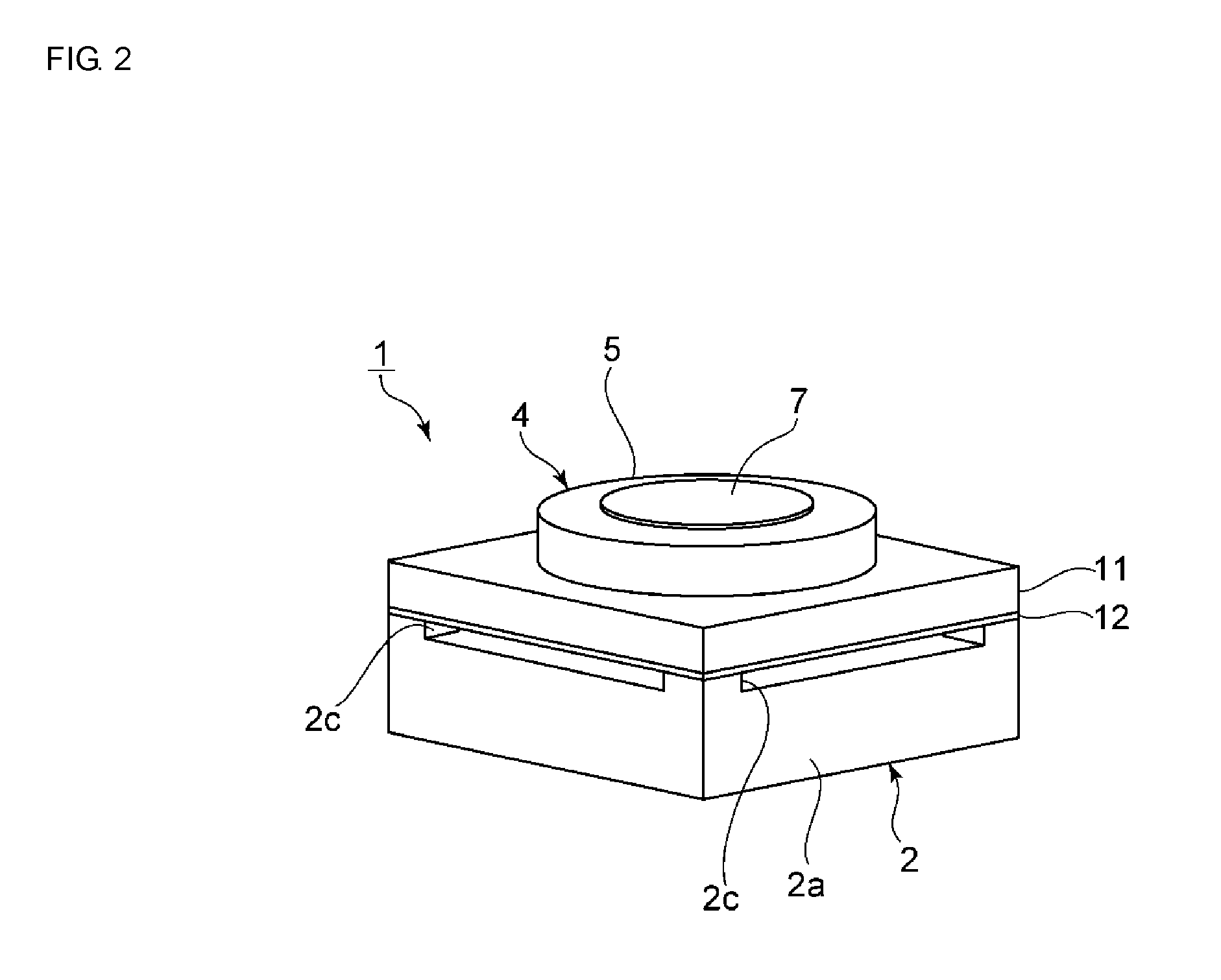
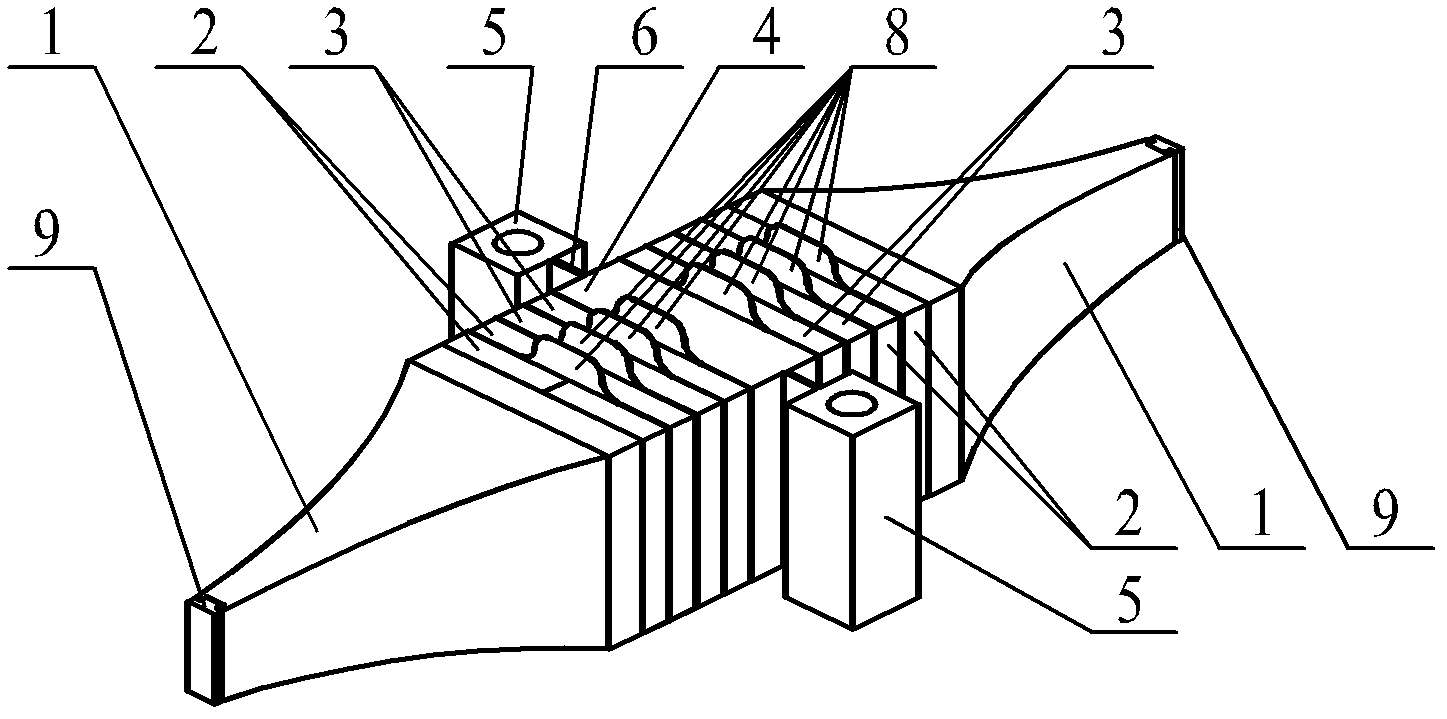
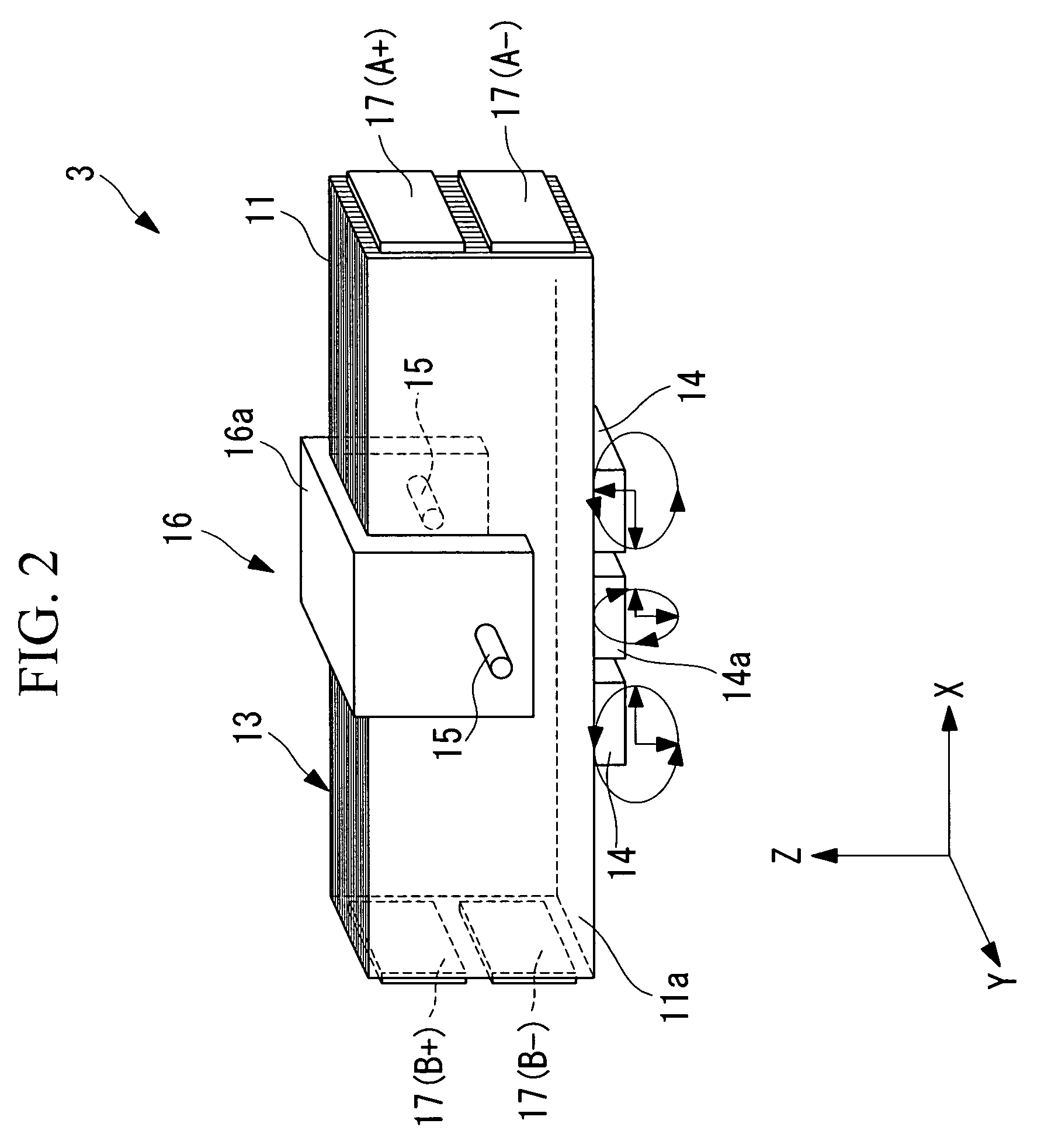
Vibratory transducer
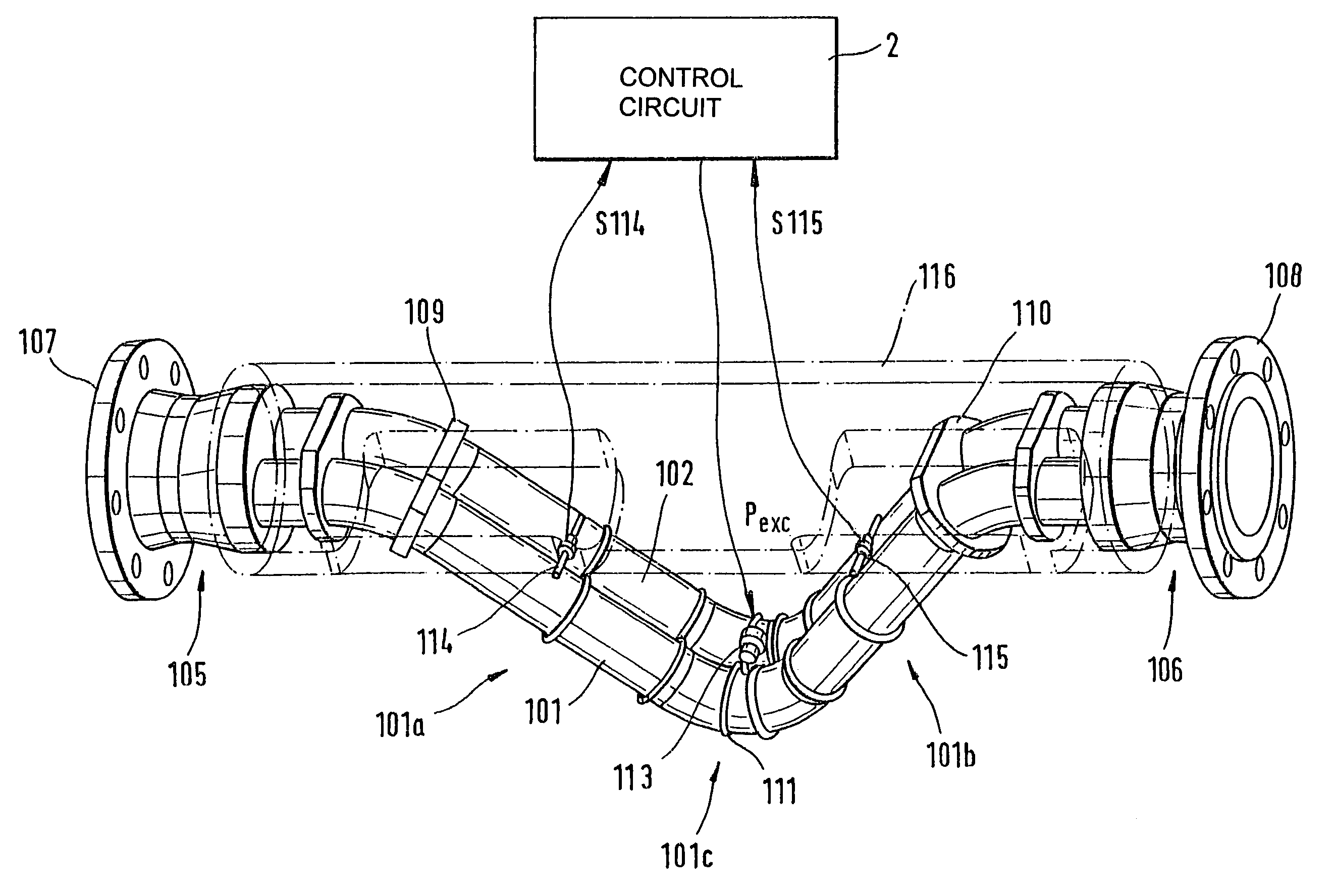
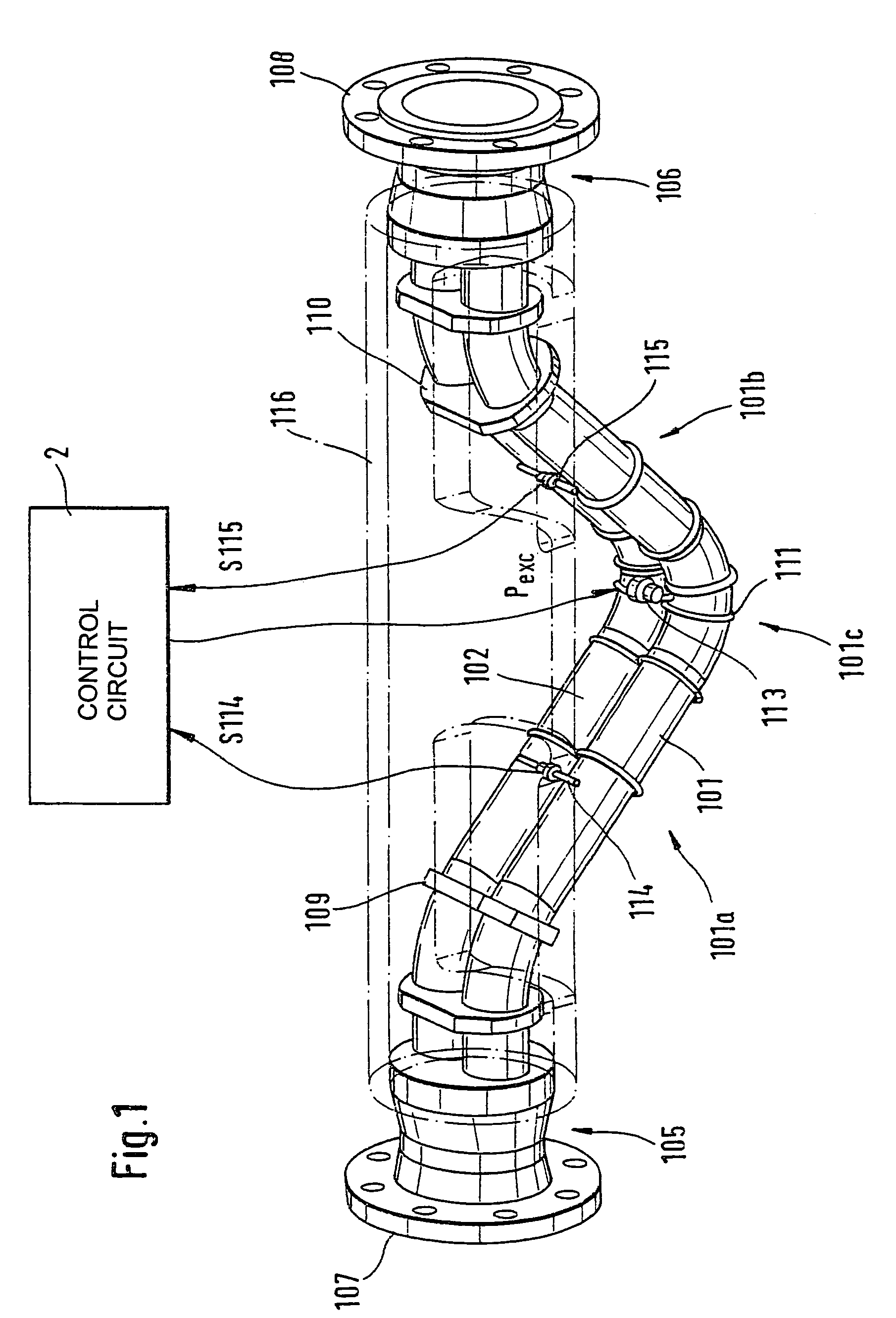
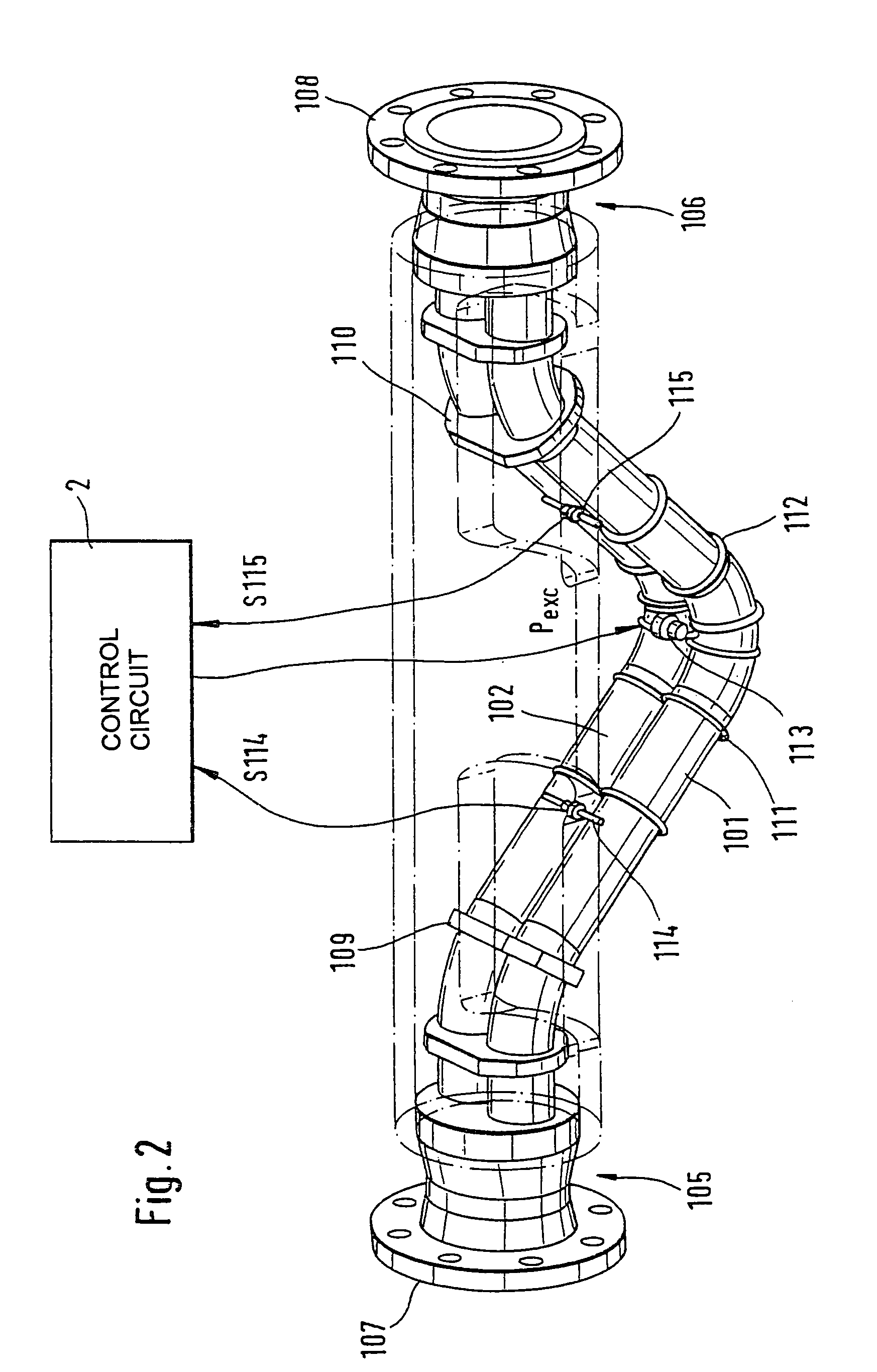
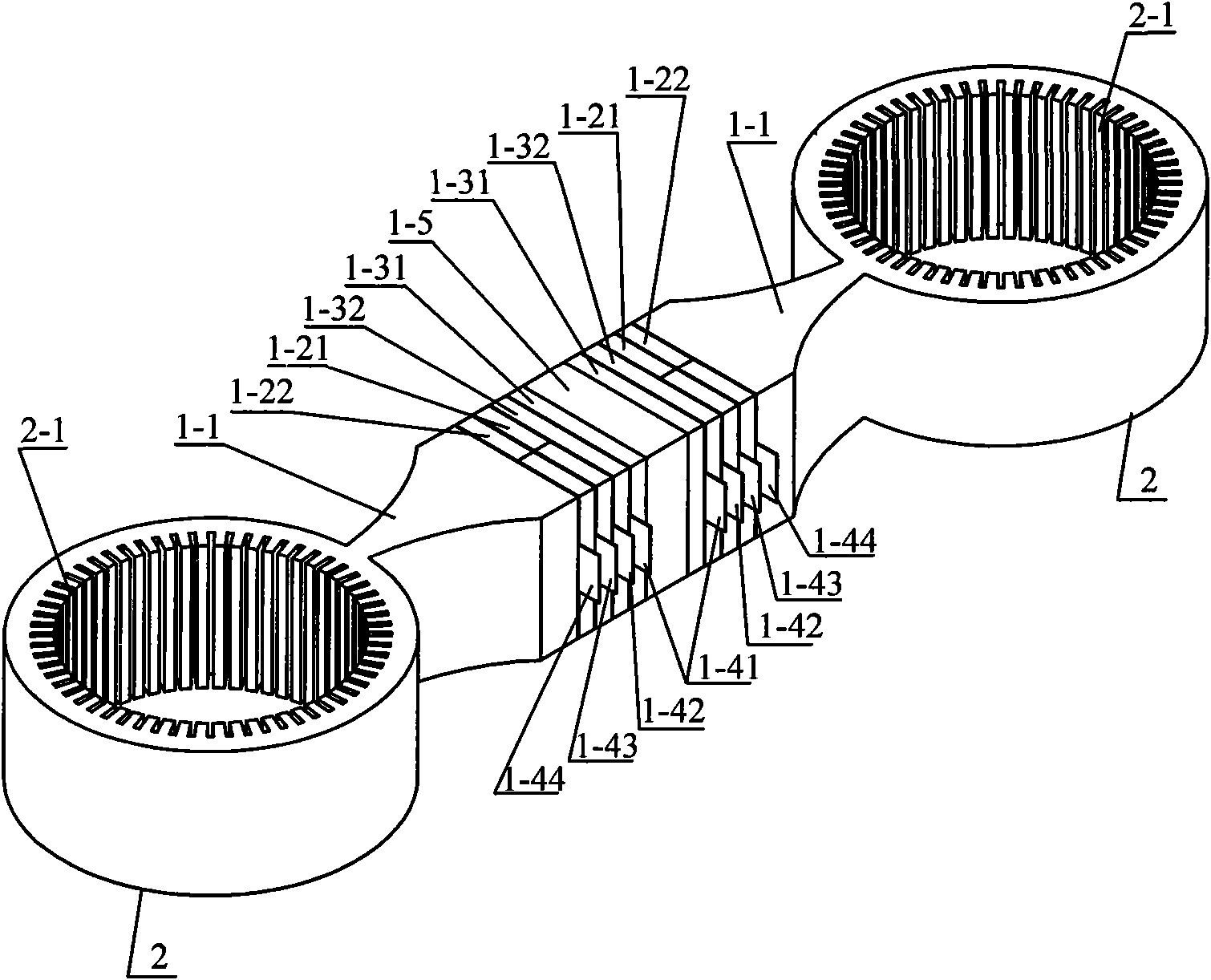
InactiveUS6920798B2Easy to manufactureEasy to bendMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
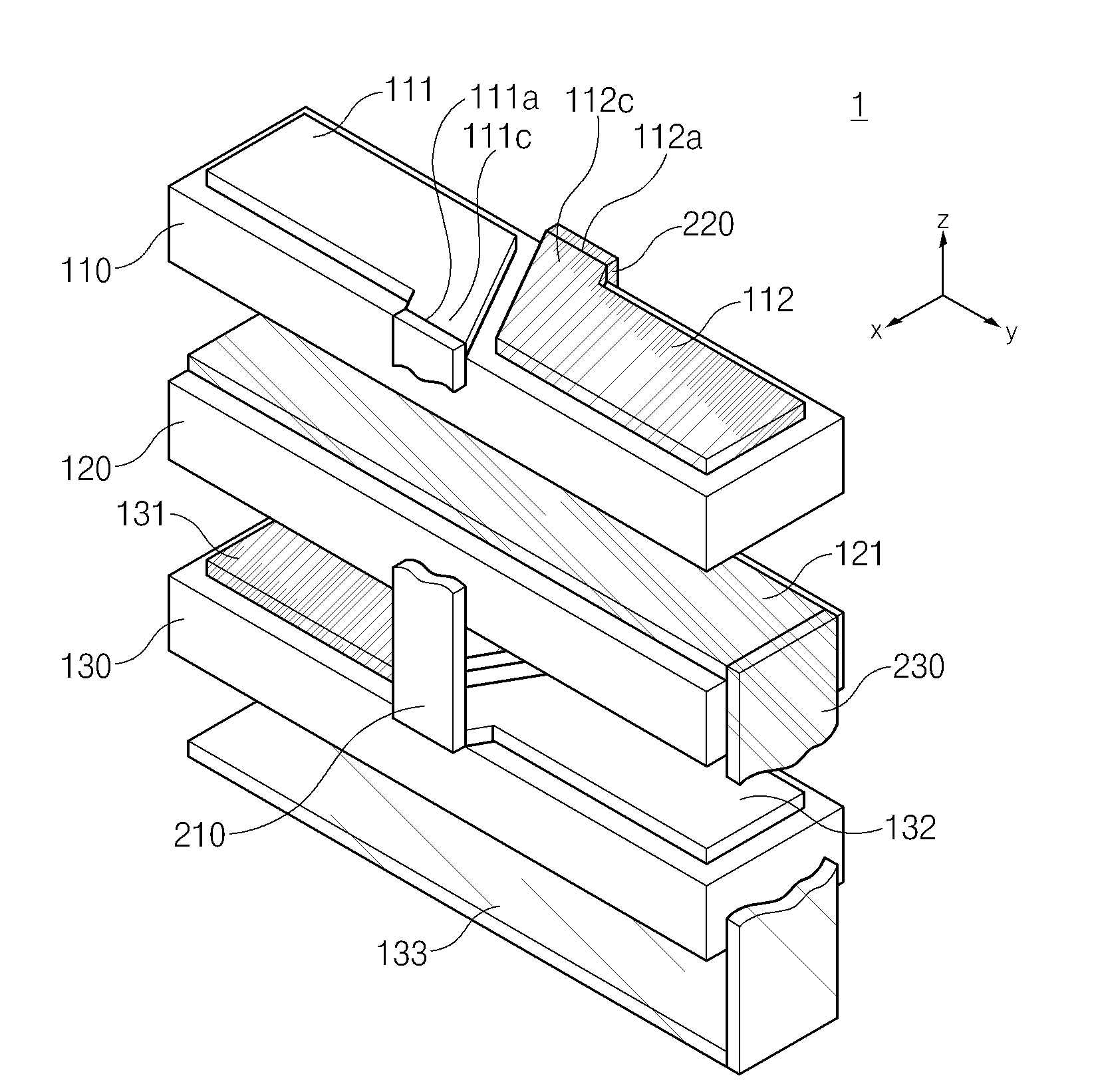
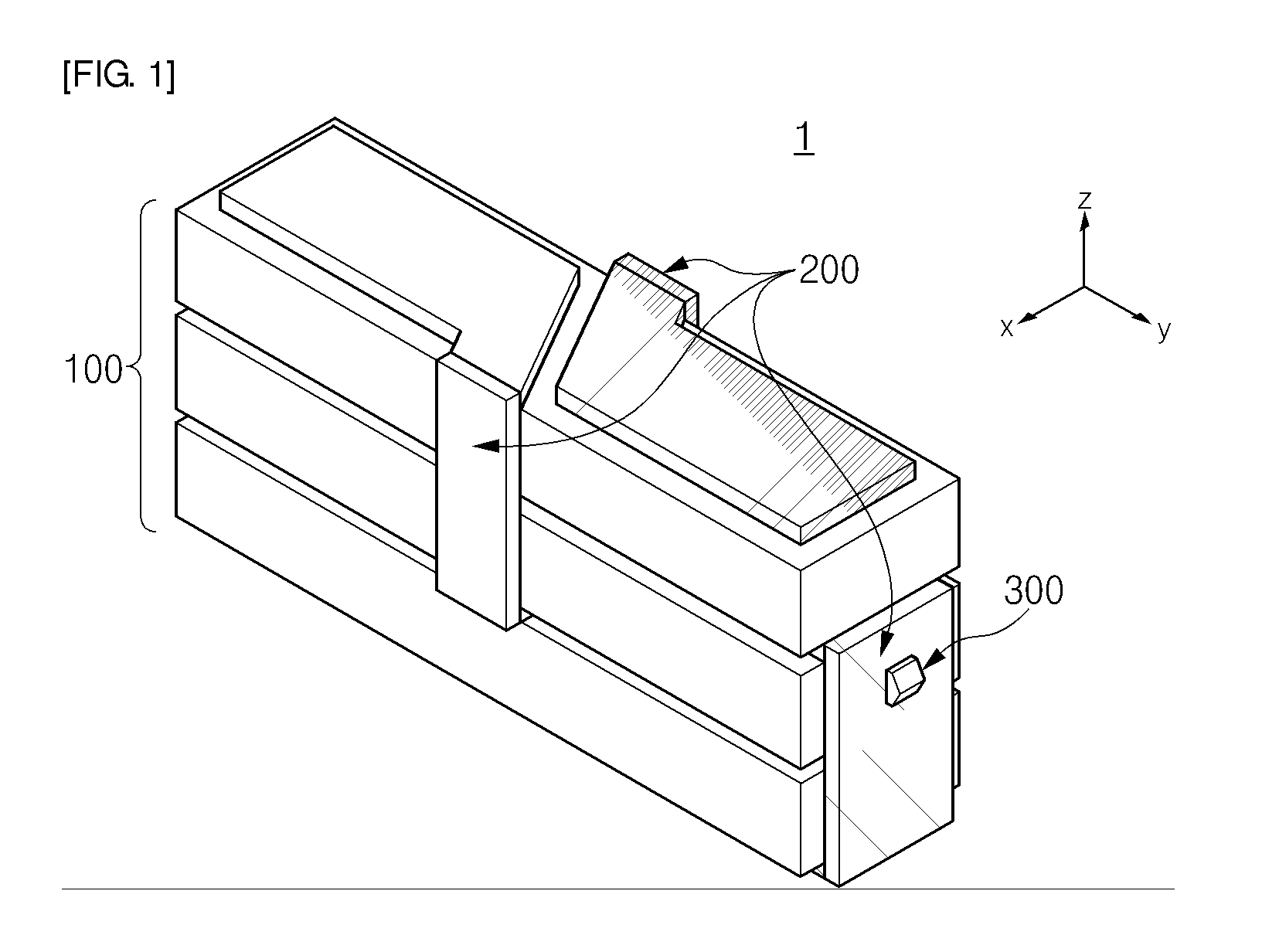
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Vibration-type driving device, control apparatus for controlling the driving of the vibration-type driving device, and electronic equipment having the vibration-type driving device and the control apparatus
ActiveUS7109639B2Reduce in quantityImprove assembly productivityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsMechanical energyEngineering
A vibration-type driving device comprises a vibration element including a driving member and an electro-mechanical energy conversion element having an electrode and arranged to displace the driving member with a driving signal supplied to the electrode, and a driven element that is kept in contact with the driving member of the vibration element. According to the driving signal supplied to the electrode of the electro-mechanical energy conversion element, the vibration element excites vibrations in two flexural vibration modes in which a direction of generation of a node in one mode is perpendicular to that in the other mode. With the use of the two flexural vibration modes, the natural vibration frequency of the vibration element can be prevented from increasing, and the position of a node occurring in one flexural vibration mode and the position of an antinode occurring in the other flexural vibration mode can be made to coincide with each other, so that the amount of displacement of the driving member can be made large.
Owner:CANON KK
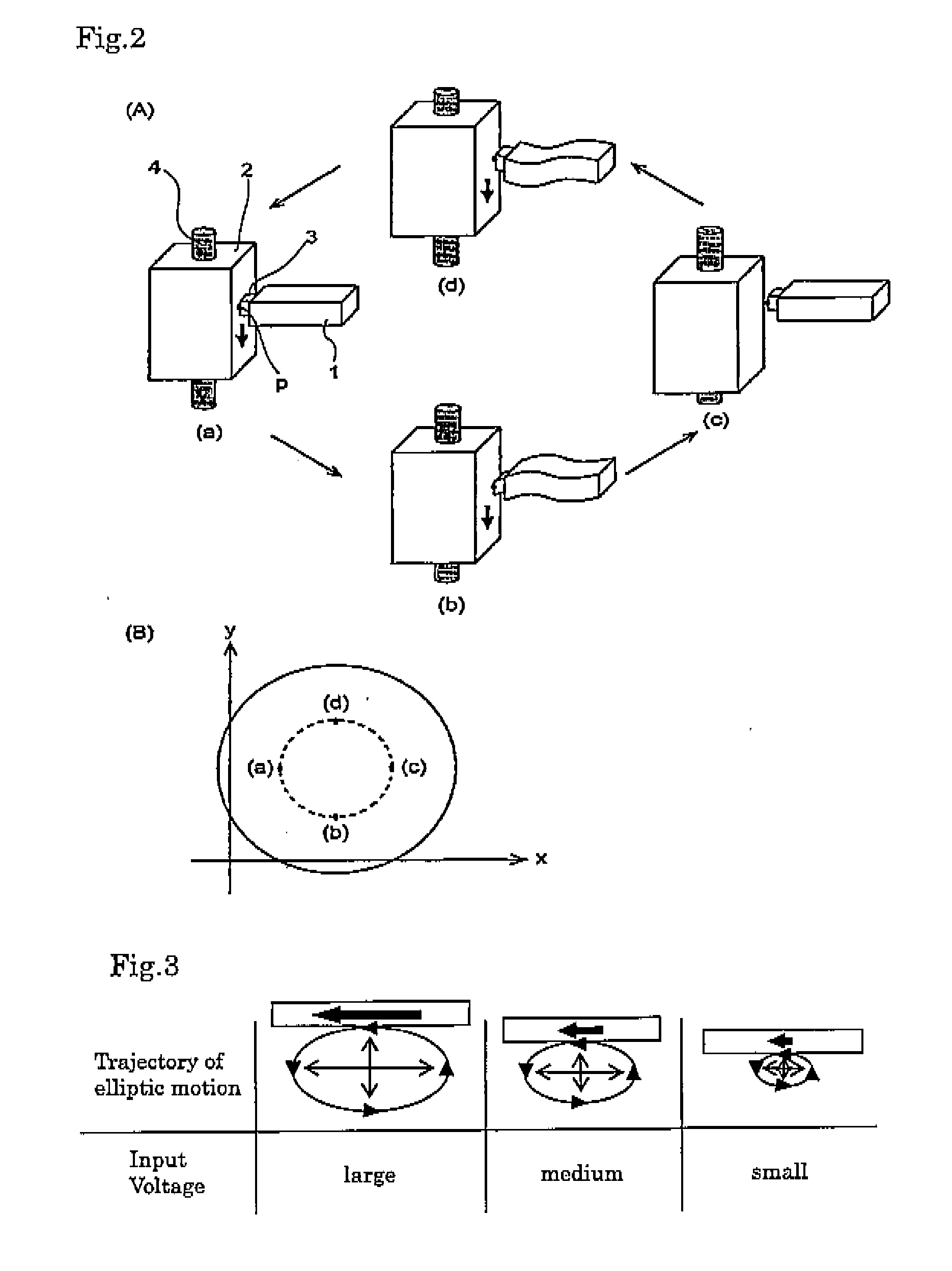
Elliptical ultrasonic vibration auxiliary cutting device with adjustable track
InactiveCN101804575AEasy to wearReduce wearMechanical vibrations separationFeeding apparatusTransformerEngineering
The invention relates to an elliptical ultrasonic vibration auxiliary cutting device with an adjustable track, which consists of a transducer, an amplitude transformer and a cutter, wherein the transducer adopts a basic structure of a longitudinal vibration sandwiched piezoelectric chip, has revolution asymmetric characteristic structures of an overlapping structure of semicircular ring-shaped piezoelectric ceramic chips and electrode chips separately, an off-axis type catenary variable-amplitude structure and the like, and initiates and strengthens flexural vibration when longitudinal vibration is output; the amplitude transformer is a cylindrical bar with uniform cross sections, and a relative angle between the amplitude transformer and a front cover plate is adjustable; and the cutter is installed in an offset way in the radial direction at the tail end of the amplitude transformer, and the offset degree can be adjusted. The working frequency of the invention is higher than 20kHz and can better achieve the ultrasonic machining effect; the elliptical cutting track is long, the minor axis proportion is reasonable, so that the advantages of elliptical cutting can be fully used; the elliptical track can be adjusted to better adapt to machining of different machining materials and different cutting consumption; and single-point diamond ultraprecise cutting can be hopefully expanded to machining of iron-based materials and optical crisp and hard materials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electronic apparatus
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
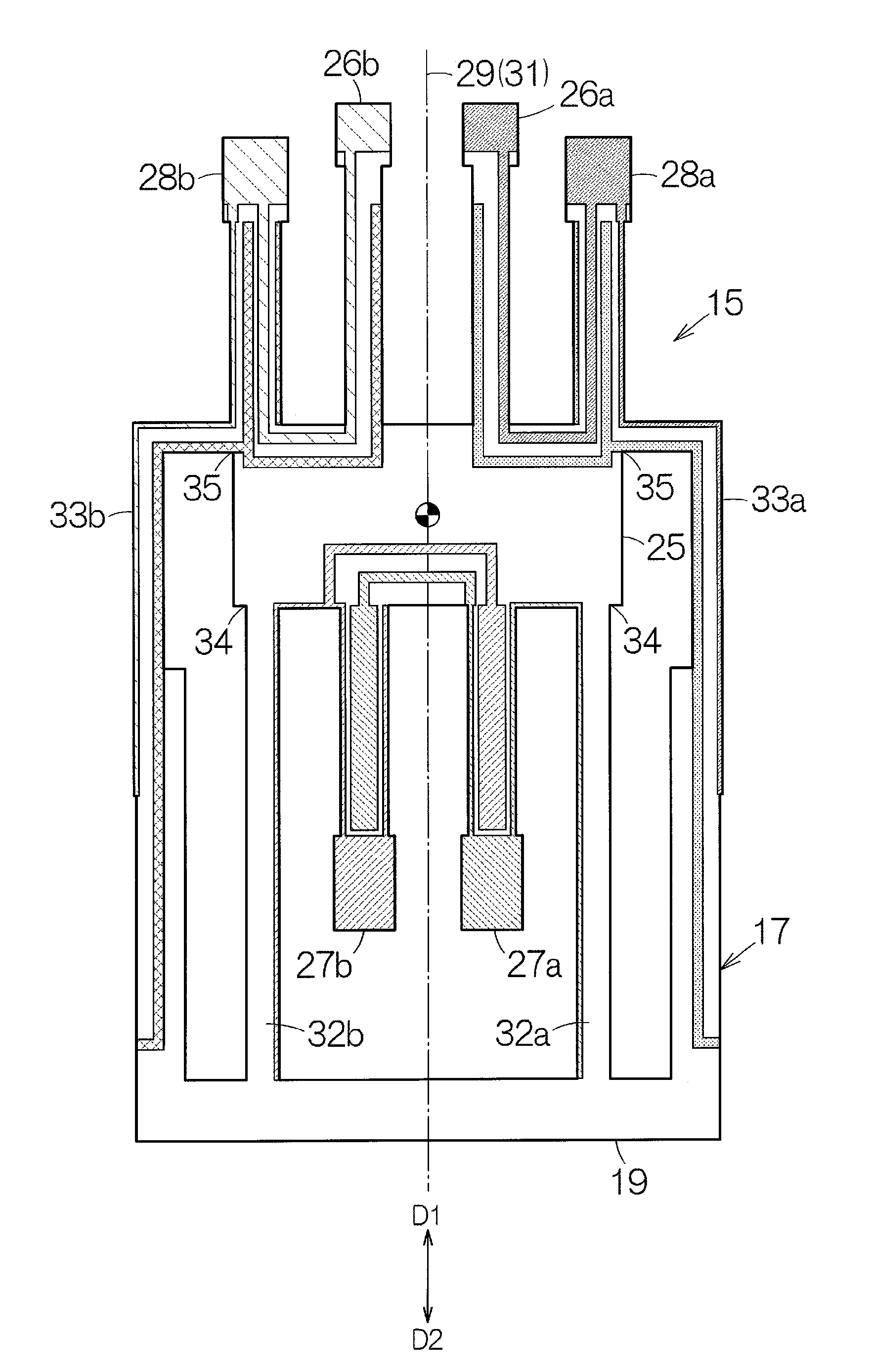
Piezoelectric resonator element, piezoelectric resonator, and acceleration sensor
InactiveUS20090115294A1Reduce sensitivityBalance rigidityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksClassical mechanicsCantilever
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
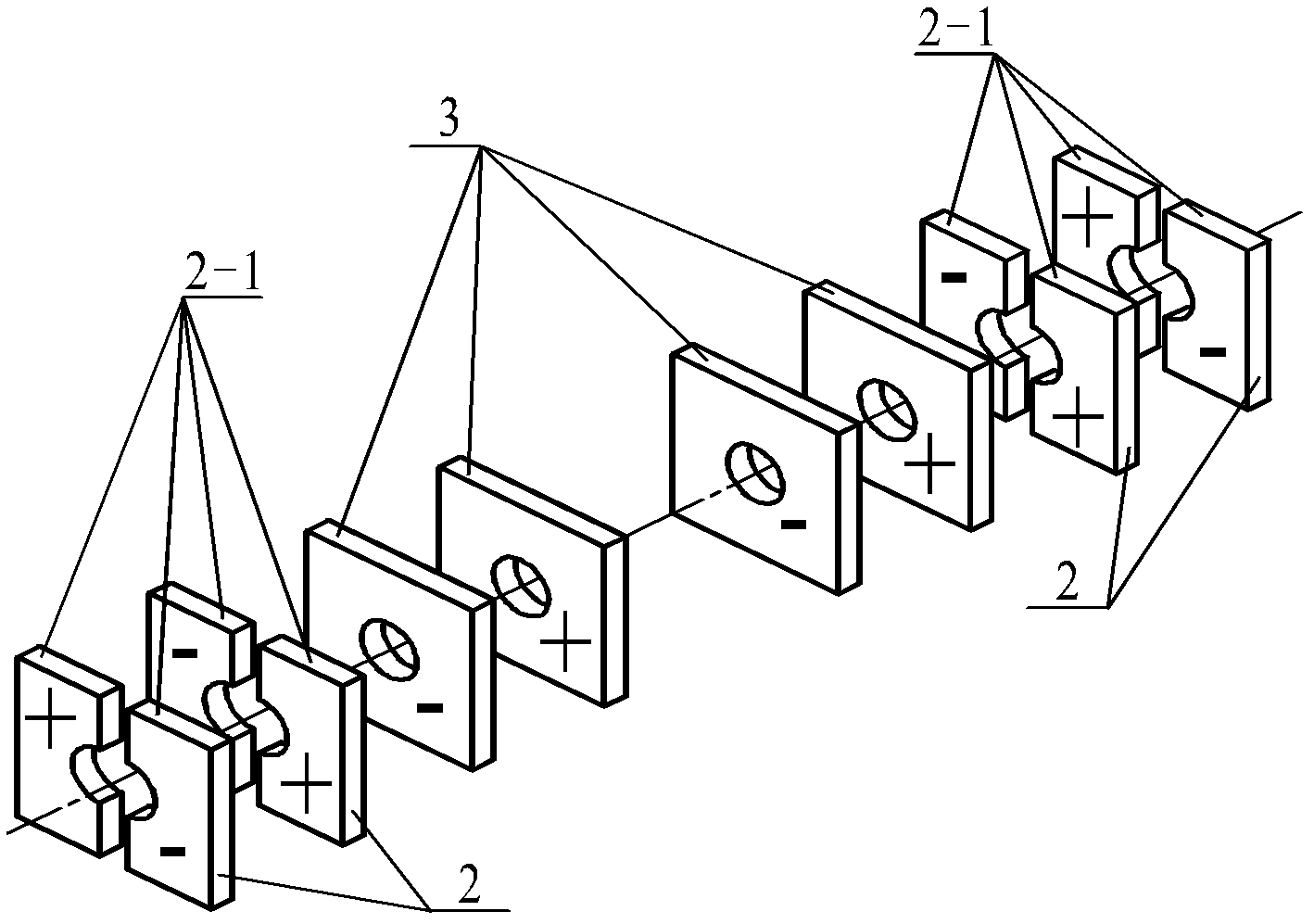
Sandwich transducer type longitudinal and bending linear ultrasound motor with frequency-modulating variable-amplitude rod
InactiveCN101022256AIncrease amplitudeIncrease vibration speedPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransducerLongitudinal vibration
A linear ultrasonic motor of sandwich transducer type with FM variable - amplitude rod is prepared as firm-connecting longitudinal-flexural vibration piezoelectric ceramic wafer and thin copper plate with big end of end cover through double-screw bolt and small end of end cover to big end of FM variable - amplitude rod through driving foot, arranging said driving foot and flexural vibration piezoelectric wafer separately at vibration wave loop of flexural vibration for setting polarization directions of flexural and longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic wafer and setting length of variable-amplitude rod to be 1 / 2 of longitudinal vibration wavelength.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rectangular panel-form loudspeaker and its radiating panel
InactiveUS7010143B2Uniform sound pressure sensitivity spectrumImprove sound radiation efficiencyPlane diaphragmsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsTransducerSoft materials
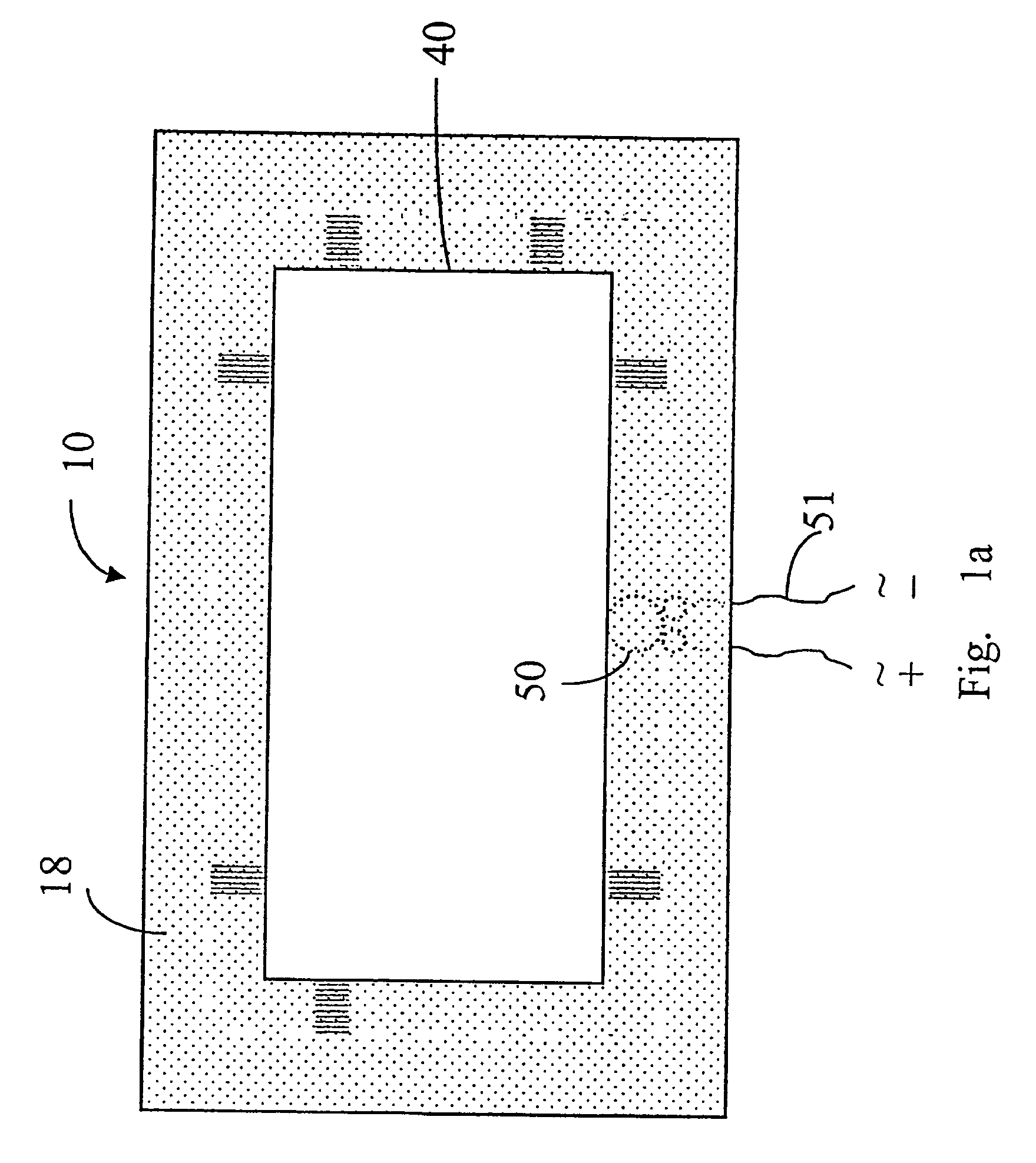
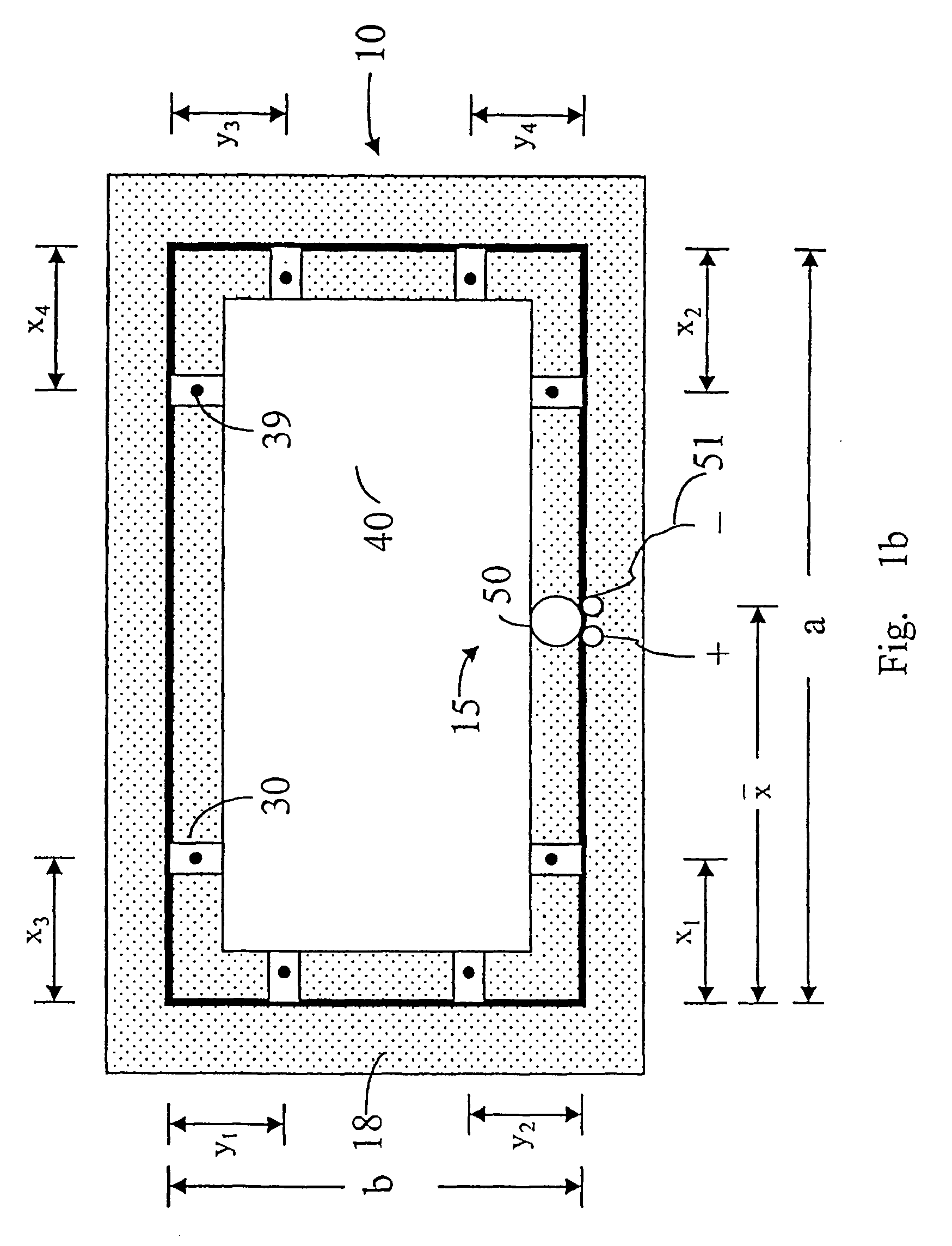
A structure of a rectangular panel-form loudspeaker is provided. The structure includes a radiating panel, a transducer, a frame and a suspending unit. The radiating panel includes a rectangular laminated composite plate with length b and width a, and the laminated composite plate includes an intermediate core layer sandwiched between two fiber-reinforced polymeric layers. The transducer is used for exciting the radiating panel to produce flexural vibration. The transducer includes a voice coil assembly and a magnet assembly, wherein the voice coil assembly is coupled to a first side of the laminated composite plate at a first specified location. The frame is used for positioning the laminated composite plate and the magnet assembly. The suspending unit is made of a soft material and disposed between peripheral edges of the laminated composite plate and the frame.
Owner:NEOSONICA TECH
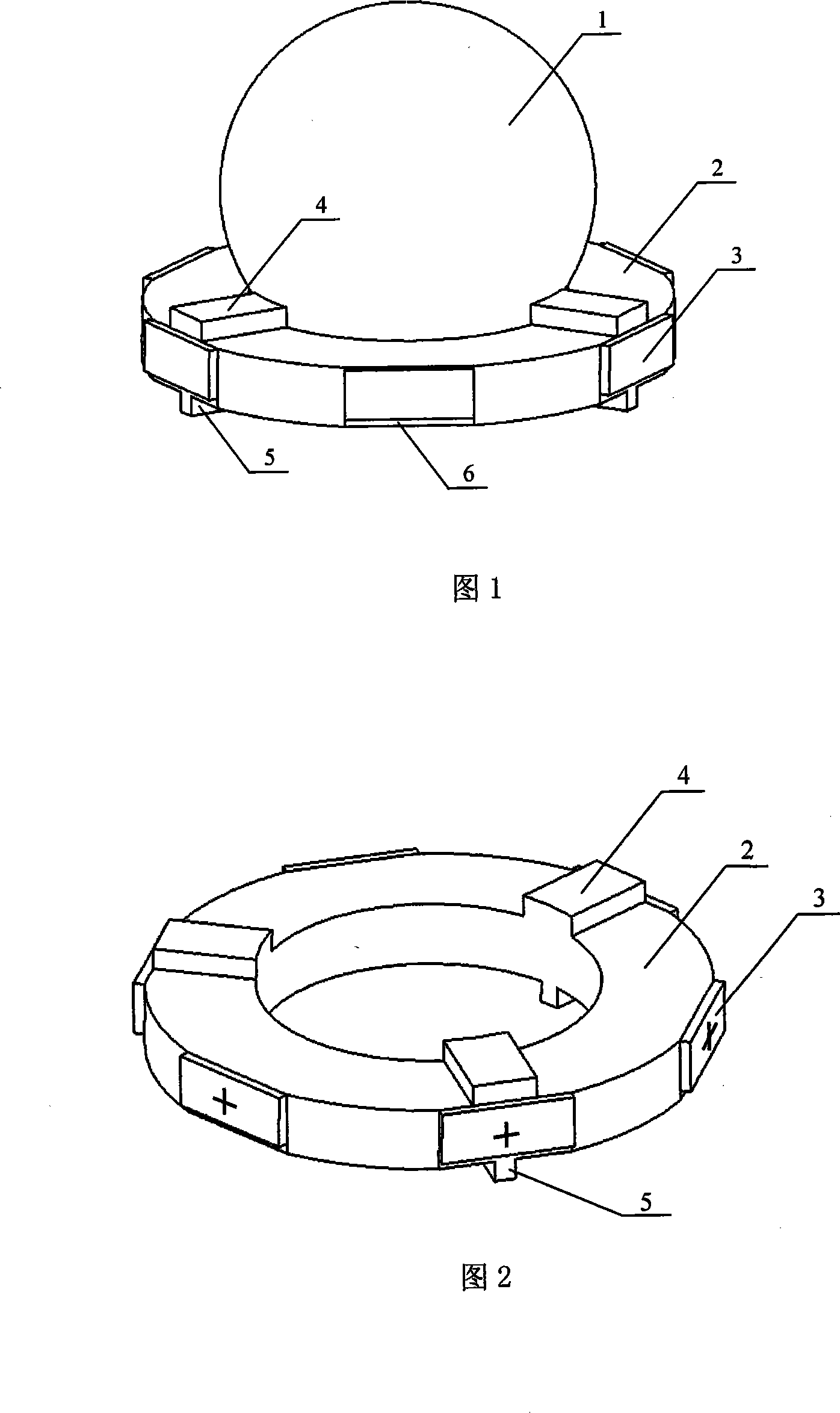
Round annular multiple freedom degrees ultrasound electric machine and electric excitation method thereof
InactiveCN101162877ASimple structureSimple driving circuitPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric machineMiniaturization
The invention relates to a ring-type multi-degree-of-freedom ultrasonic motor and an electric excitation method, pertaining to the field of ultrasonic motors. The ultrasonic motor comprises a rotor and a stator. The invention is characterized in that the rotor is a spherical rotor (1); the stator is a metal ring (2), and six piezo-electric ceramic pieces (3) are affixed on the flank of the ring stator; three upper bosses (4) are evenly distributed on the periphery of the upper end-face of the ring stator and arranged at the same position of the platform (6) affixed with ceramic pieces to support and drive the spherical stator; the rotor provides the prepress force required by the stator and the rotor; three small bosses (4) corresponding to the positions of the upper bosses (4) are also arranged on the lower end-face of the ring stator to support the whole motor. When the driving signal provides power supply to any two piezo-electric ceramic pieces (3) opposite to each other, the two flexural vibration modes in the face of the stator can be excited out to produce standing waves and drive the spherical rotor to round the spherical center of the rotor and rotate around the axial line parallel with the two piezo-electric ceramic pieces. The ultrasonic motor can realize the rotation of a plurality of rotating shafts; the invention has the advantages of a simple structure, a small size, high efficiency, reliable operation, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Flexural vibration piece and oscillator using the same
InactiveUS20100244989A1Reduction in Q value can be suppressedEfficient executionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksThermal conductivityPhysics
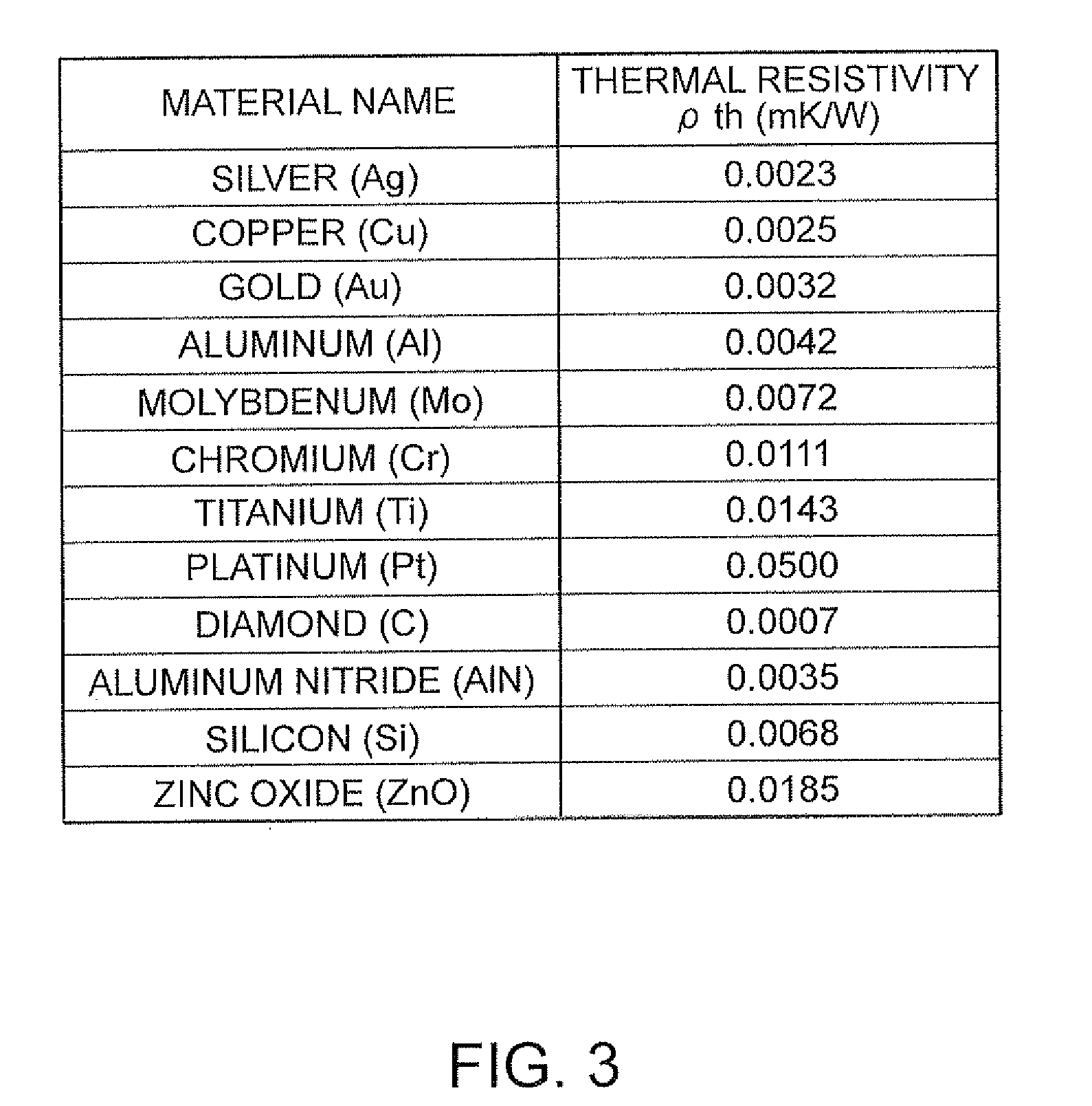
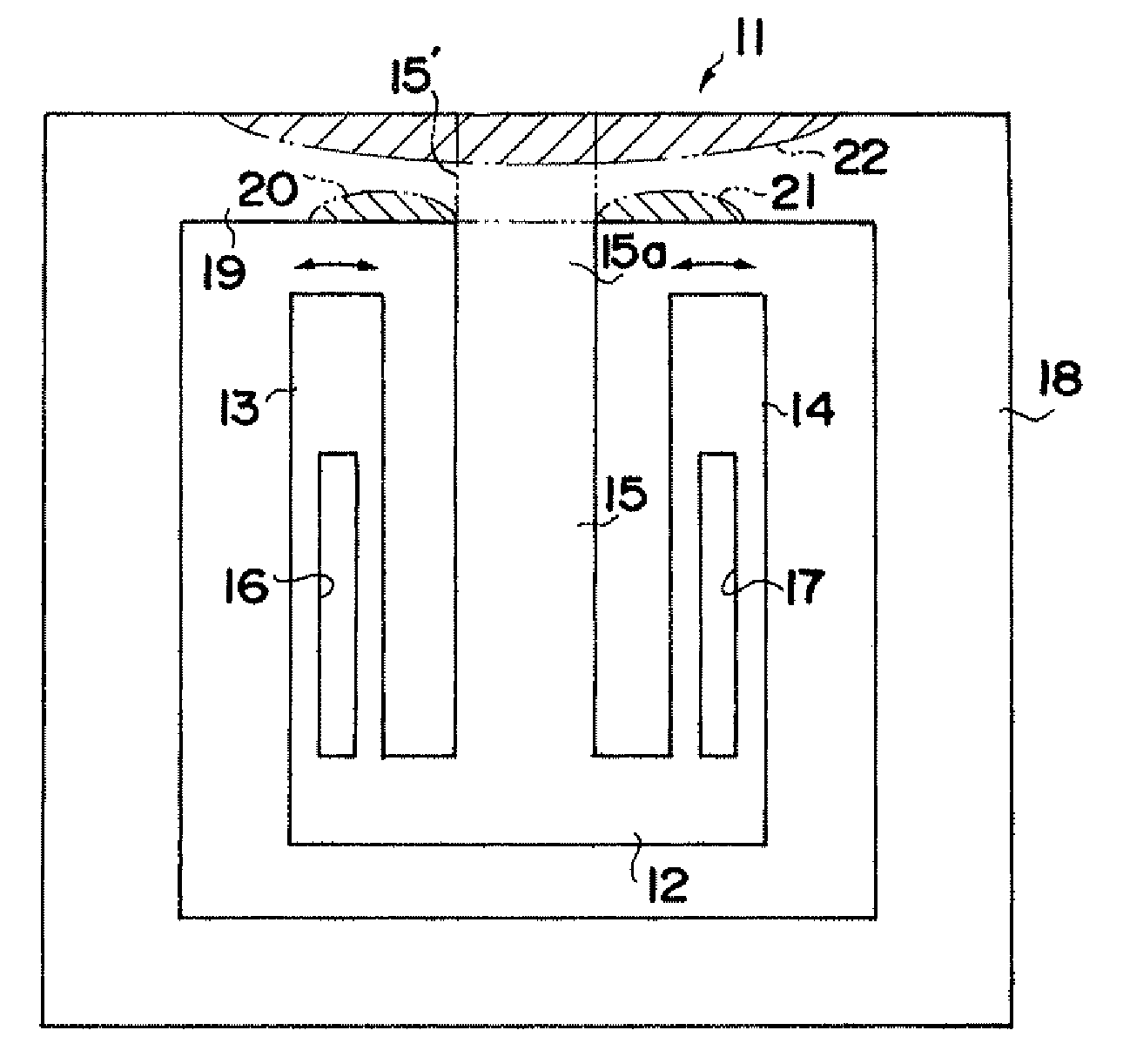
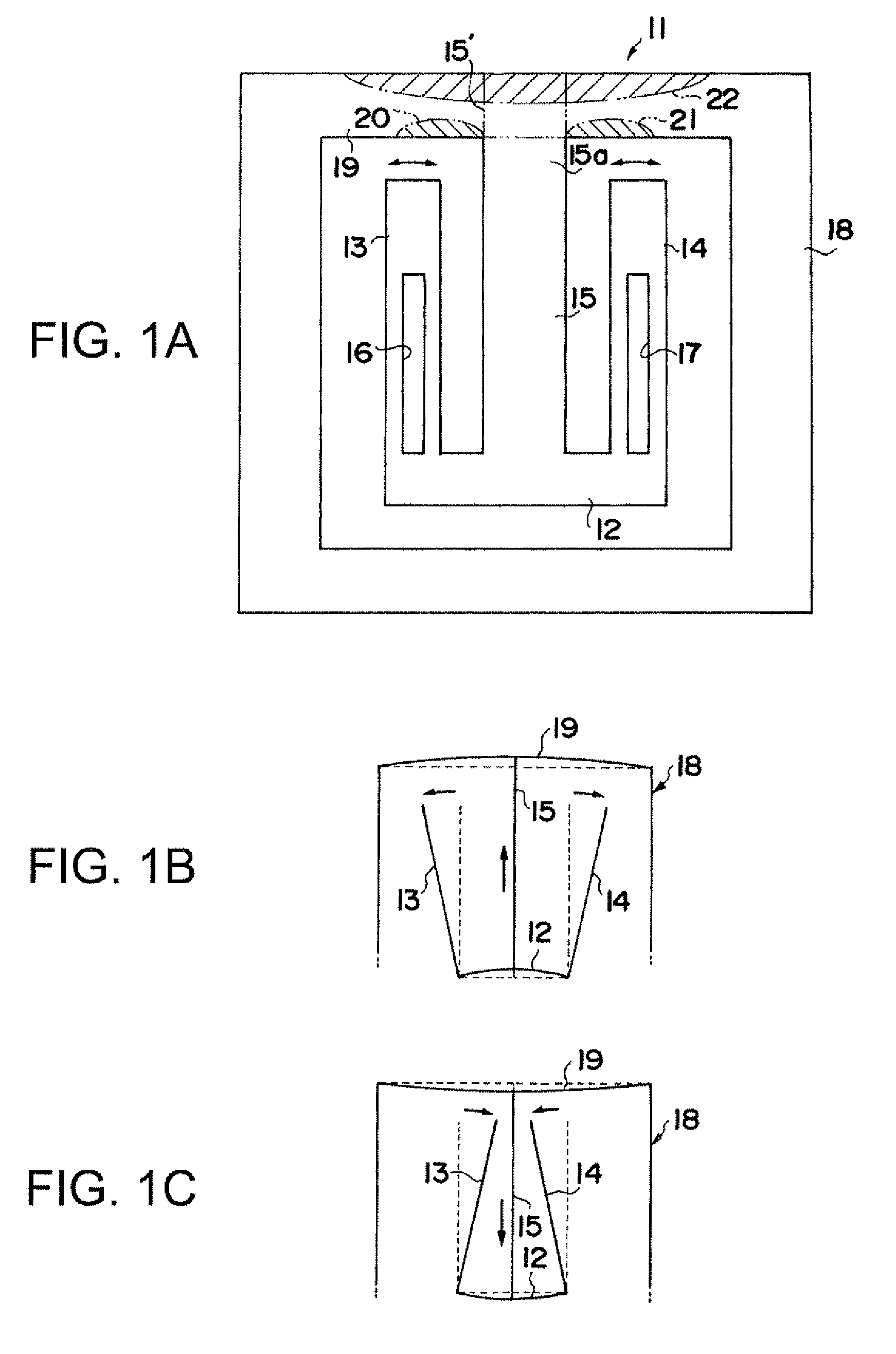
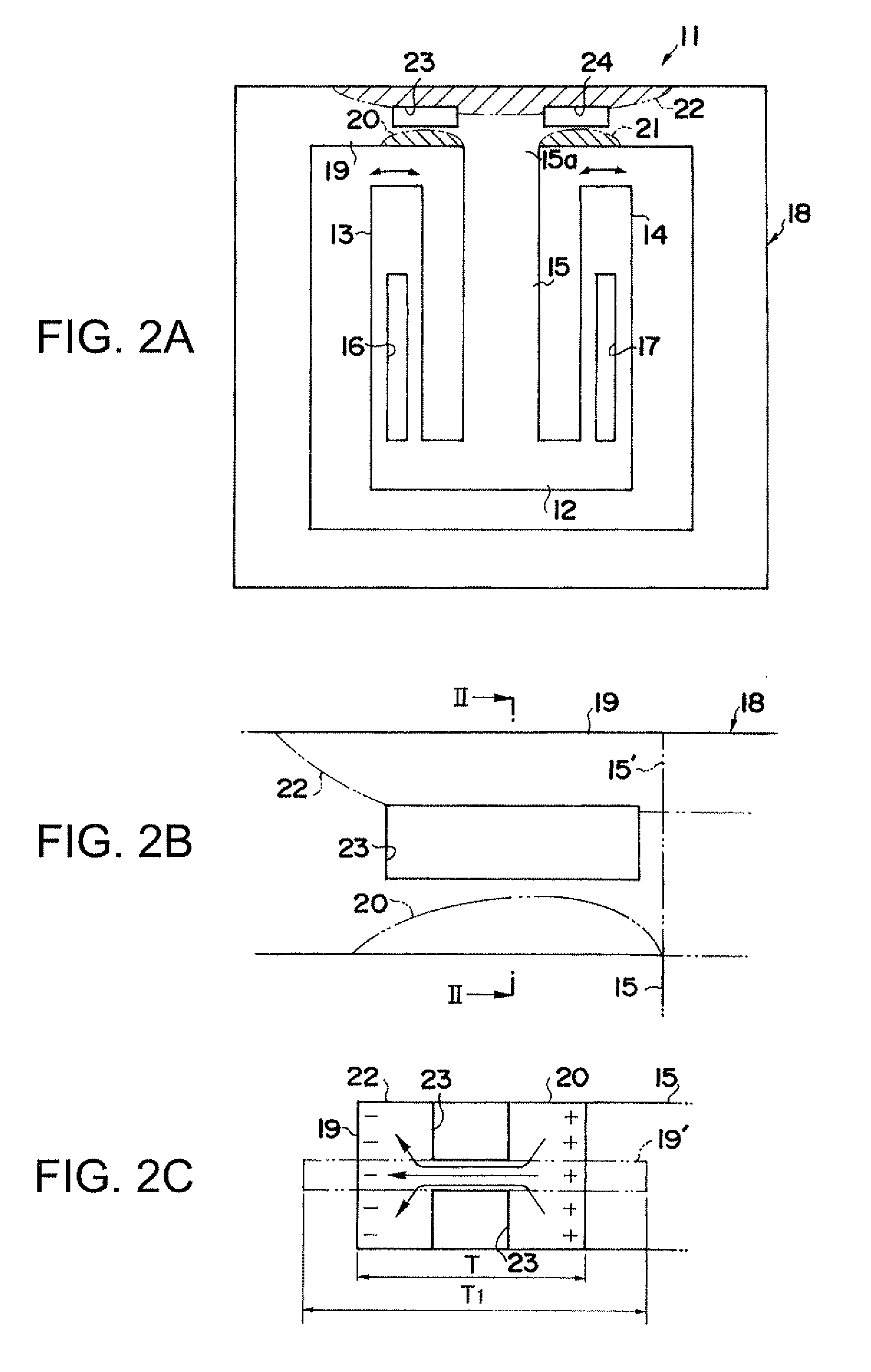
A flexural vibration piece includes: a flexural vibrator that has a first region on which a compressive stress or a tensile stress acts due to vibration and a second region having a relationship in which a tensile stress acts thereon when a compressive stress acts on the first region and a compressive stress acts thereon when a tensile stress acts on the first region, and performs flexural vibration in a first plane; and a heat conduction path, between the first region and the second region, that is formed of a material having a thermal conductivity higher than that of the flexural vibrator and thermally connects between the first region and the second region, wherein when m is the number of heat conduction paths, ρth is the thermal resistivity of the heat conduction path, ρv is the thermal resistivity of the flexural vibrator, tv is the thickness of the flexural vibrator in, a direction orthogonal to the first plane, and tth is the thickness of the heat conduction path, a relationship of tth≧(1 / m)×tv×(ρth / ρv) is satisfied.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Flexural vibration element and electronic component
InactiveUS20100171397A1Improve performanceSuppresses vibration leakagePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksEngineeringElectronic component
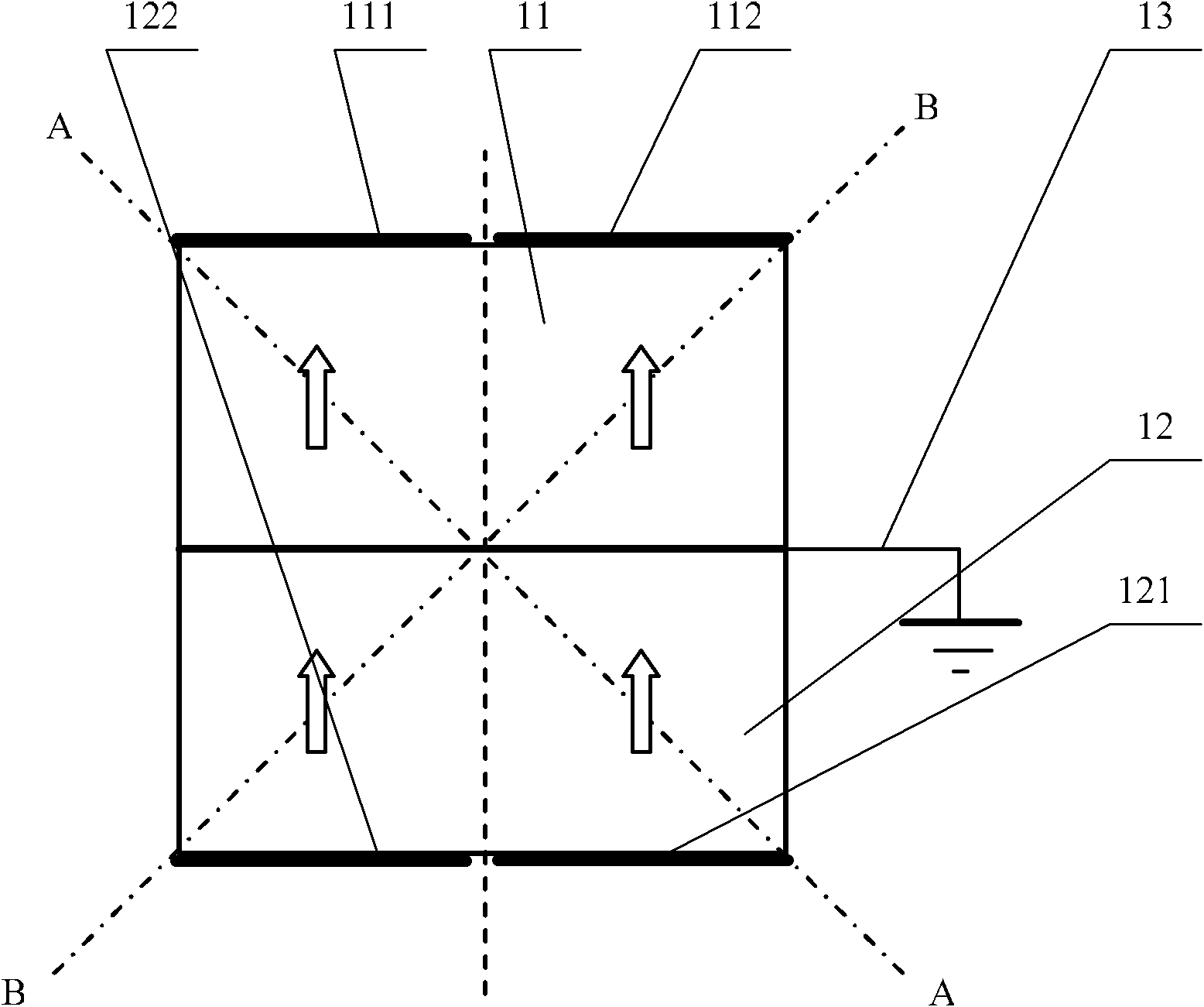
A flexural vibration element includes: a vibration element body composed of a plurality of vibrating arms provided in parallel, a connecting part connecting the vibrating arms, and one central supporting arm extending between the vibrating arms from the connecting part in parallel with the vibrating arms at equal distance from the arms; and a frame body disposed outside the vibration element body. In the flexural vibration element, the vibration element body is supported by the frame body at an end part, which is opposite to the connecting part, of the central supporting arm.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
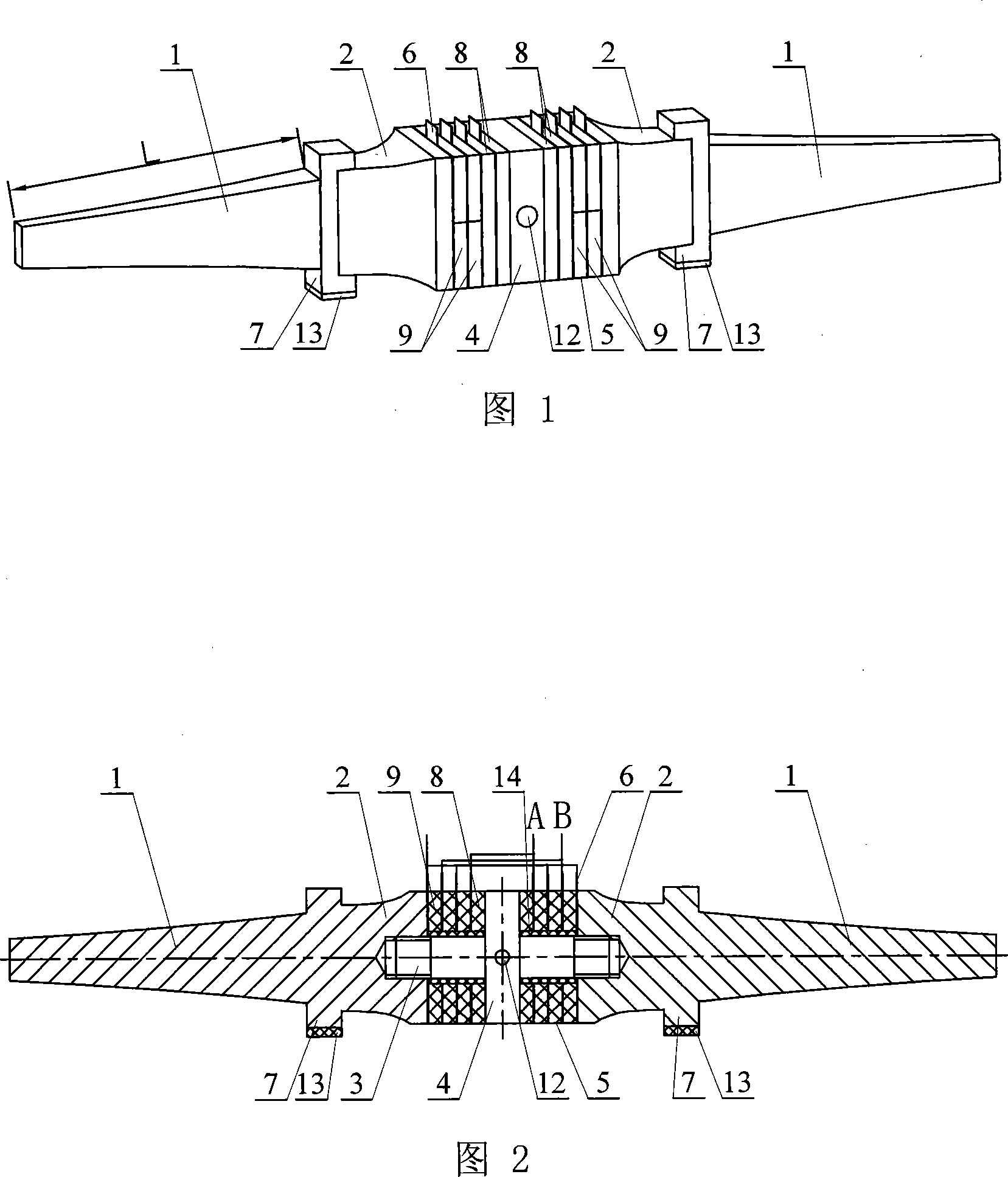
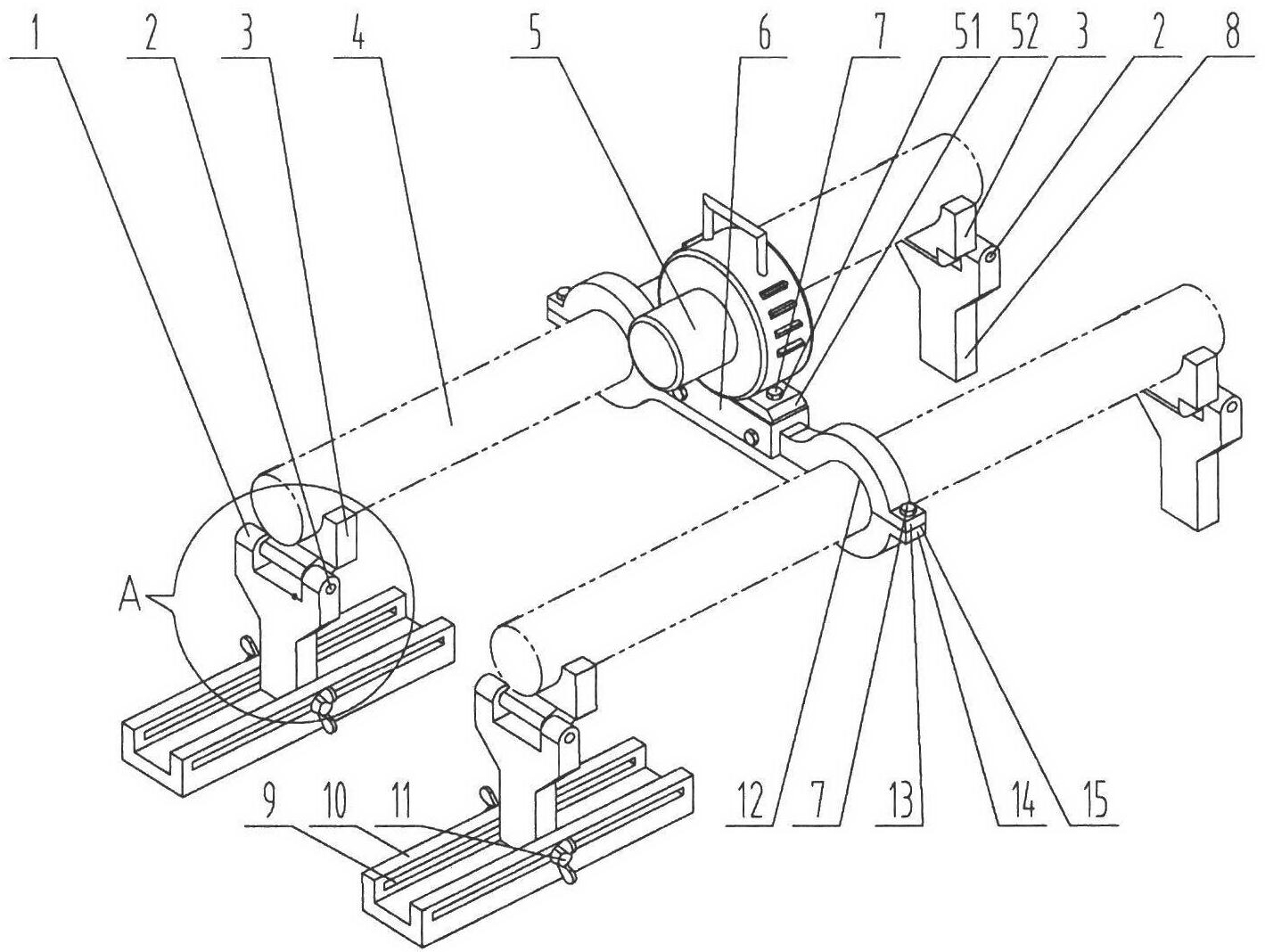
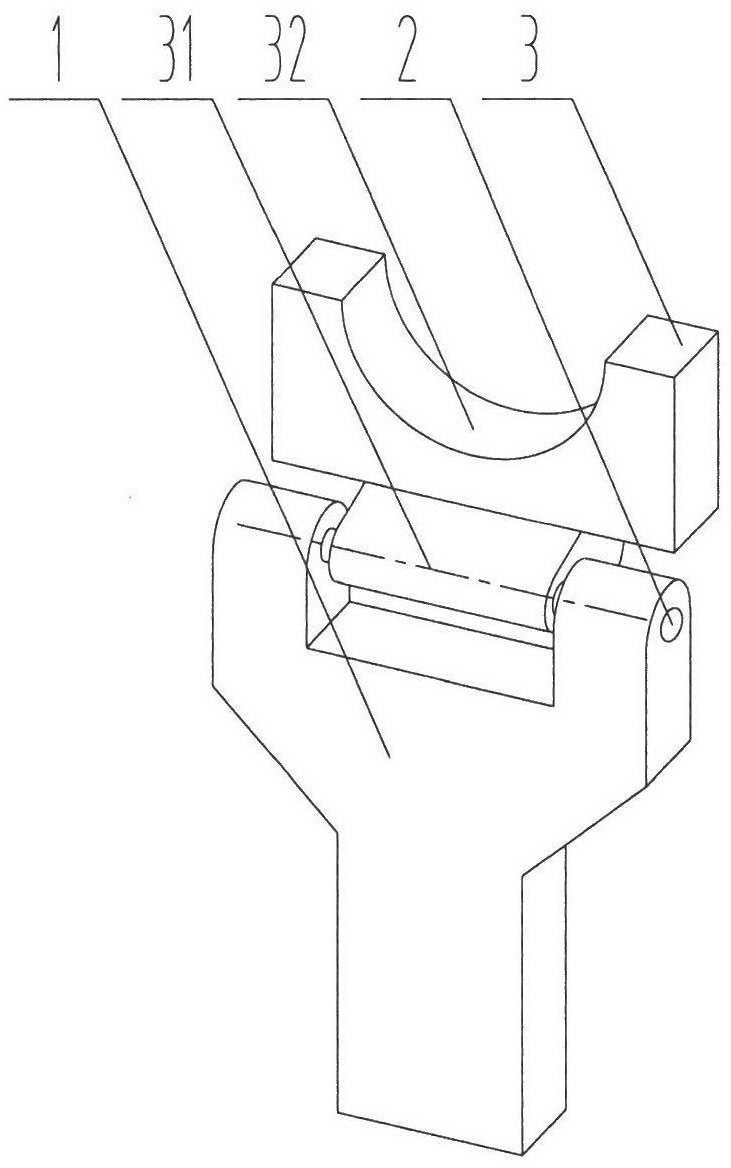
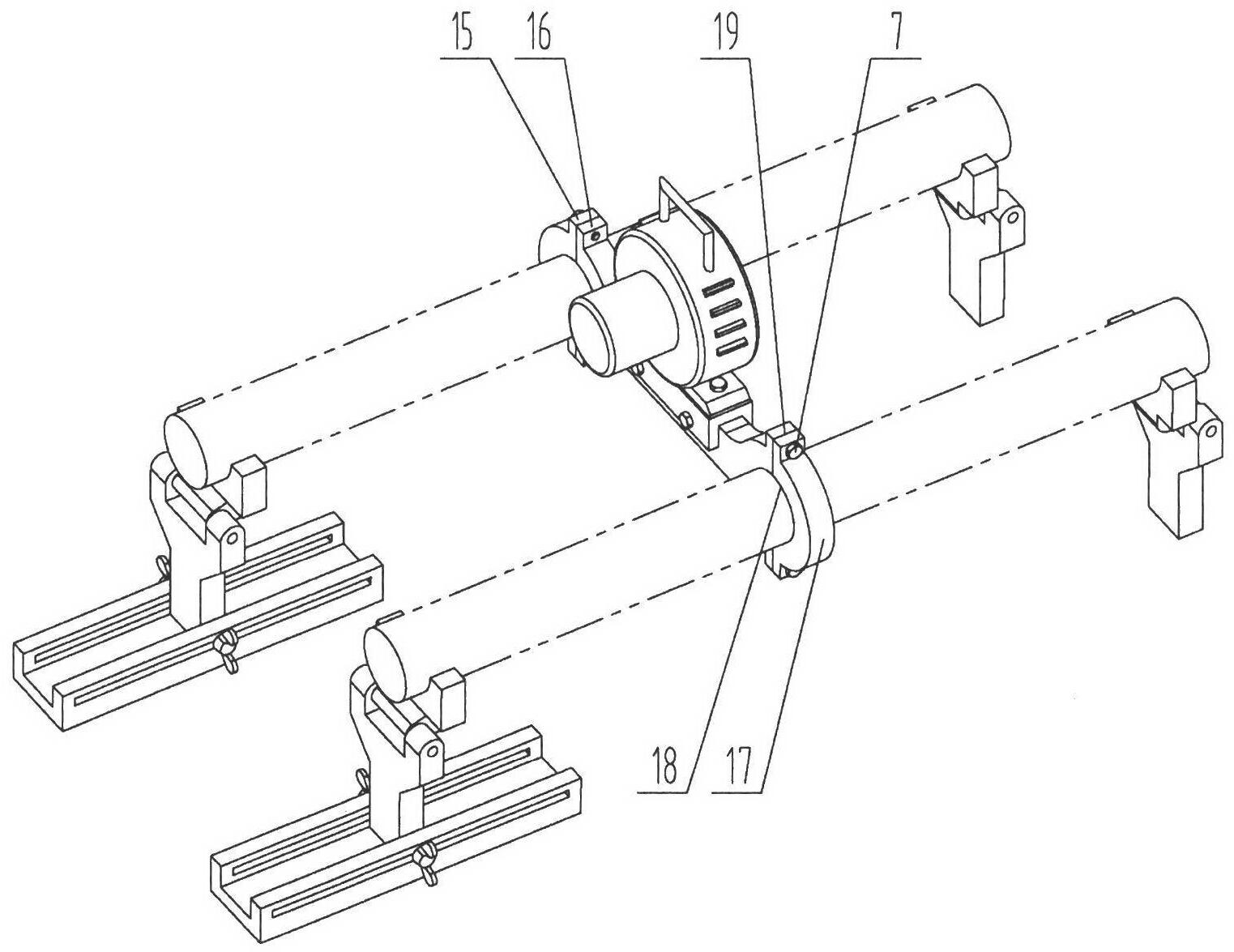
Vibratory stress relief apparatus for medium frequency and low frequency shaft type parts, and use method thereof
InactiveCN102321793AAddress effectivenessAddress stressFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMedium frequencyEngineering
The invention relates to a vibratory stress relief apparatus for medium frequency and low frequency shaft type parts, and a use method thereof. The apparatus comprises a vibration exciter, a support block for clamping and supporting a workpiece, and a support mechanism connected with the support block. The support mechanism comprises a pair of support frames comprising a left support frame and a right support frame, and a support seat for installing the left support frame and the right support frame, wherein the left support frame and the right support frame right are arranged relatively. Thesupport block respectively forms rotatable connections with the left support frame of the support mechanism and the right support frame of the support mechanism. The apparatus further comprises a vibration exciter base for installing the vibration exciter, wherein the vibration exciter base is arranged on the middle portion of the workpiece, the vibration exciter, the vibration exciter base and the workpiece synchronously vibrate during vibratory stress relief. According to the present invention, a simply supported beam form is adopted, the flexural vibration type primary resonance is generated by the shaft type parts under the excitation of the vibration exciter at the natural frequency adopted for shaft flexural vibration; in the prior art, the dynamic stress generated by the apparatus does not reach the requirement of residual stress decreasing, with the apparatus provided by the present invention, the problem in the prior art is solved; the deformation amounts on both ends of the shaft are substantially improved; the dynamic stress distribution of the shaft is uniform so as to effectively reduce the residual stress of the shaft part.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
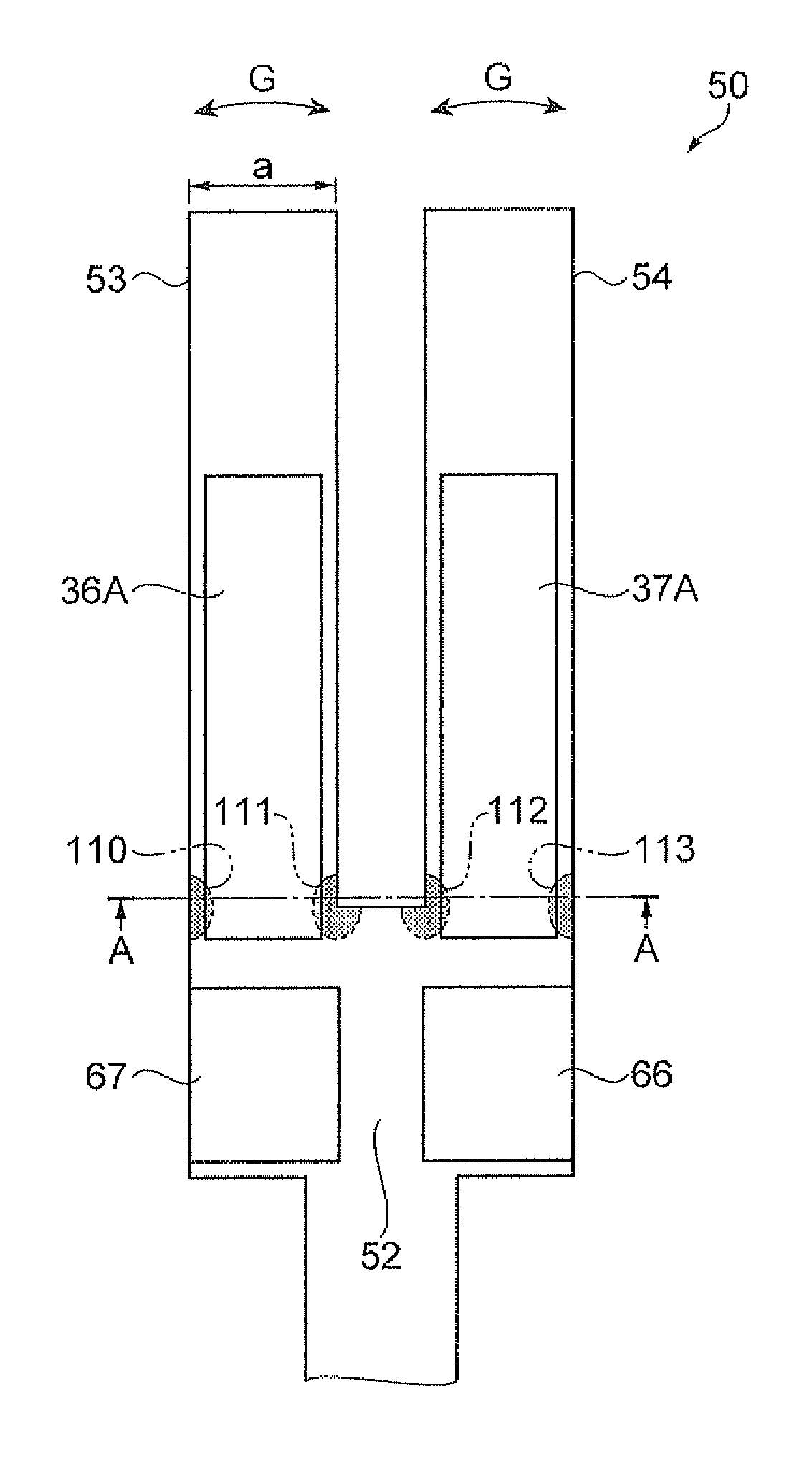
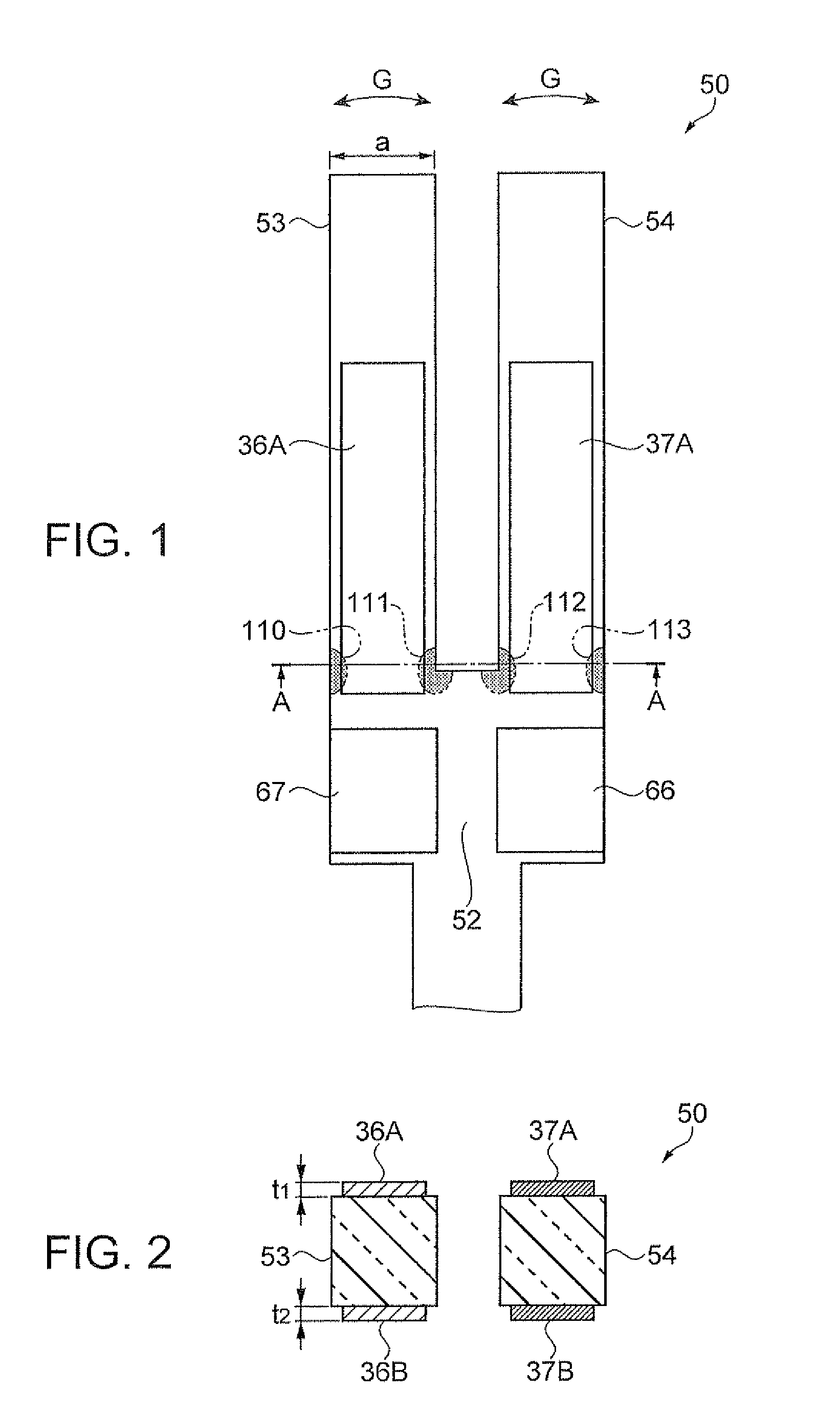
Fluid control device and pump
ActiveUS10480502B2Improve driving efficiencyIncrease in sizeFlexible member pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesFluid controlFlexural vibration
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
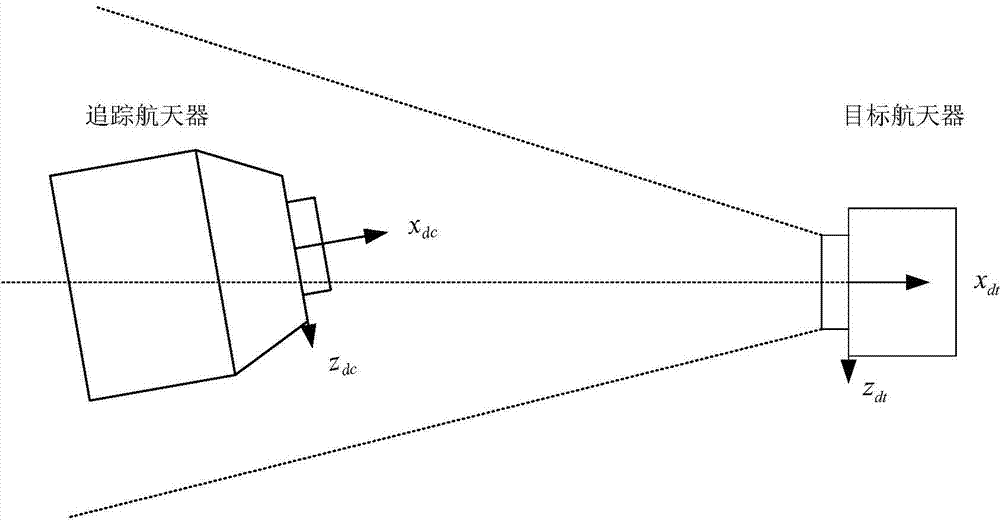
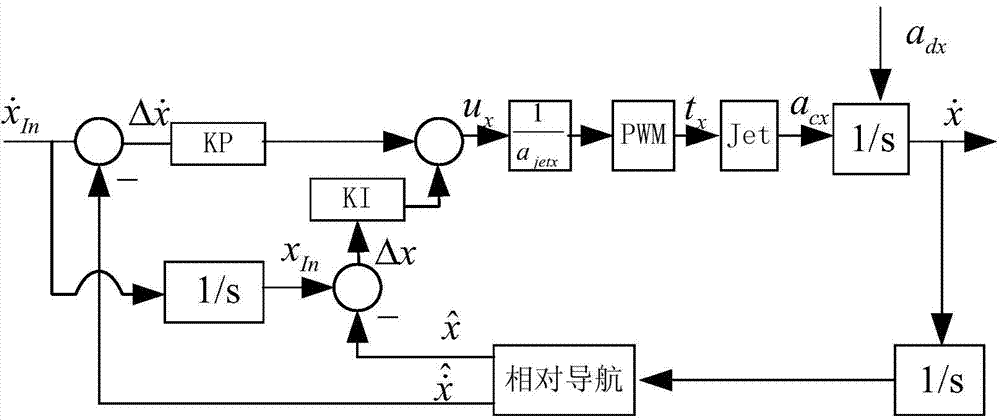
Rendezvous and docking six-degree-of-freedom relative control method
ActiveCN103576689AImprove performanceControllers with particular characteristicsAttitude controlAttitude controlDegrees of freedom
The invention relates to a rendezvous and docking six-degree-of-freedom relative control method. Firstly, dynamics modeling is performed on relative horizontal moving and relative rotation moving and then, the PI control law is adopted for designing an approaching direction (X direction) relative speed keeping controller and the PD control law is adopted for designing a horizontal position (Y / Z direction) keeping controller; the PID control law is adopted for designing a relative posture controller; a novel pulse width modulation method is provided for modulating an obtained continuous control amount to obtain an executing impulse width of a thruster; finally, a relative state controller design strategy set based on the PID control law is formed and a complete controller parameter selection design scheme is provided. According to the rendezvous and docking six-degree-of-freedom relative control method, the defect that when a phase plane control algorithm is adopted in the prior art, influences on the design of the controllers by disturbance factors such as flexural vibration are hard to analyze is overcome. Meanwhile, the defect that accurate relative speed tracking control is hard to perform in phase plane control is overcome and the high-precision rendezvous and docking relative state control is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Flexural vibration piece
InactiveUS20100277041A1Reducing and eliminating leakageIncrease valueImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeEngineering
A flexural vibration piece includes: a base portion; and a vibration arm extending from the base portion, wherein the vibration arm has first and second main faces which are arranged to be opposite each other, the first and second main faces respectively have first and second grooves which are formed in the longitudinal direction of the vibration arm, the first groove has a plurality of first groove portions which are divided in the longitudinal direction of the vibration arm and arranged to be alternately shifted on both sides with respect to the longitudinal center line of the vibration arm in the longitudinal direction, the second groove has a plurality of second groove portions which are divided in the longitudinal direction of the vibration arm, and arranged to be alternately shifted on both sides with respect to the longitudinal center line of the vibration arm in the longitudinal direction and on an opposite side to the first groove portions with respect to the longitudinal center line, and a predetermined voltage is applied to first excitation electrodes provided at the first groove and the second groove and second excitation electrodes provided on both side faces of the vibration arm, such that the vibration arm flexural-vibrates in the in-plane direction of the first or second main face.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transparent panel-form loudspeaker
A transparent panel-form loudspeaker consists of a transparent sound radiation panel that can radiate sound with desired pressure level over a specific frequency range when subjected to the flexural vibration induced by a preselected number of transducers located at specific positions on the peripheral edge of the transparent sound radiation panel and a rigid frame carrying a flexible suspension device which supports the periphery of the transparent sound radiation panel. The transparent sound radiation panel is made of a kind of transparent materials with the ratio of elastic modulus to density in the range from 3 to 180 GPa / (g / cm3) and the ratio of length to thickness of the transparent sound radiation panel in the range from 80 to 600. The flexible suspension device supporting the periphery of the transparent sound radiation panel is used to modify the vibrational characteristics of the transparent sound radiation panel for an effective generation of the vibrational normal modes which are beneficial for sound radiation. The transducers are situated at predetermined locations on the peripheral edge of the transparent sound radiation panel so that relatively high radiation efficiency and more uniform spread of sound pressure level spectrum can be produced by the transparent sound radiation panel over a desired operative acoustic frequency range.
Owner:NEOSONICA TECH
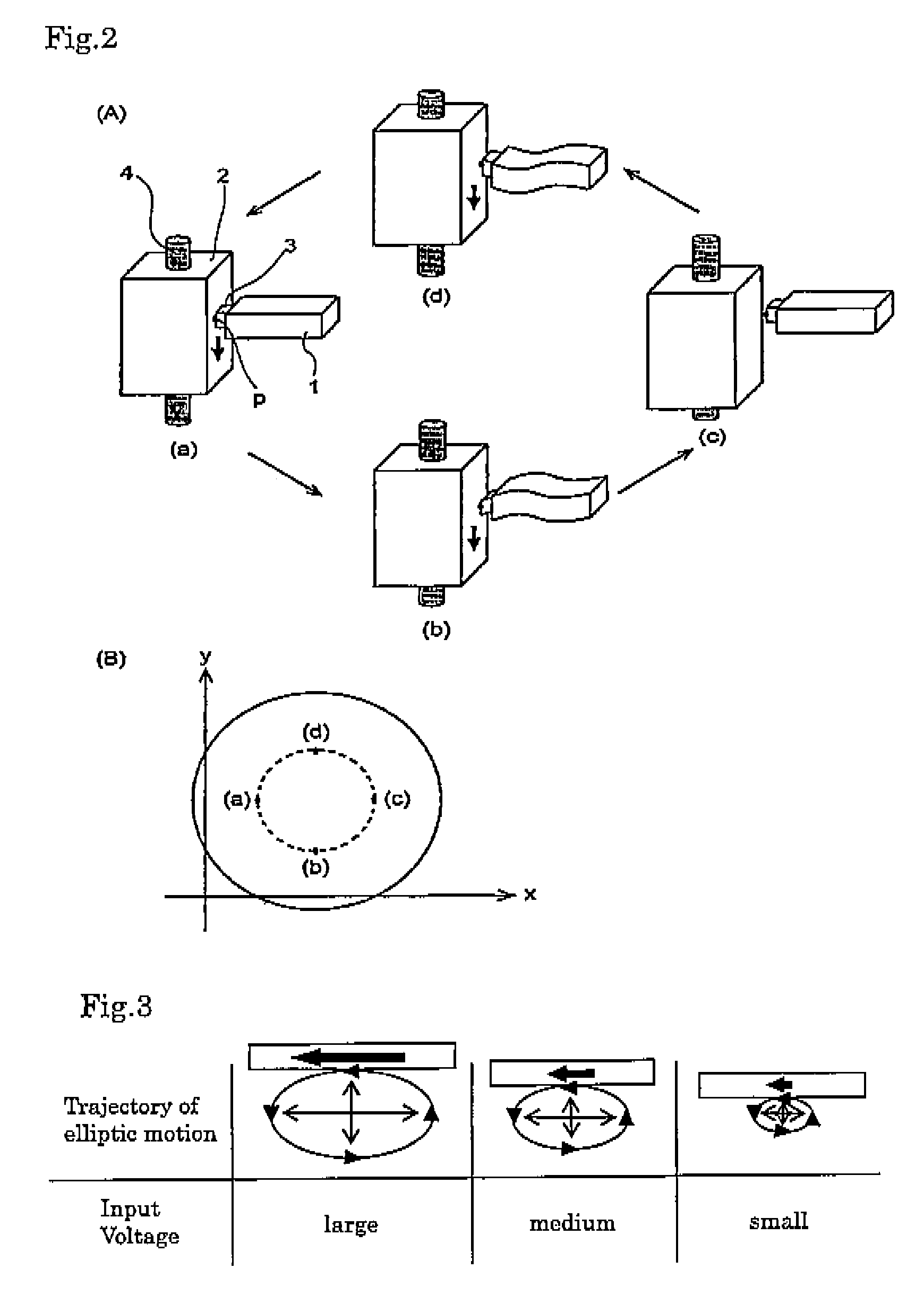
Piezoelectric vibrator
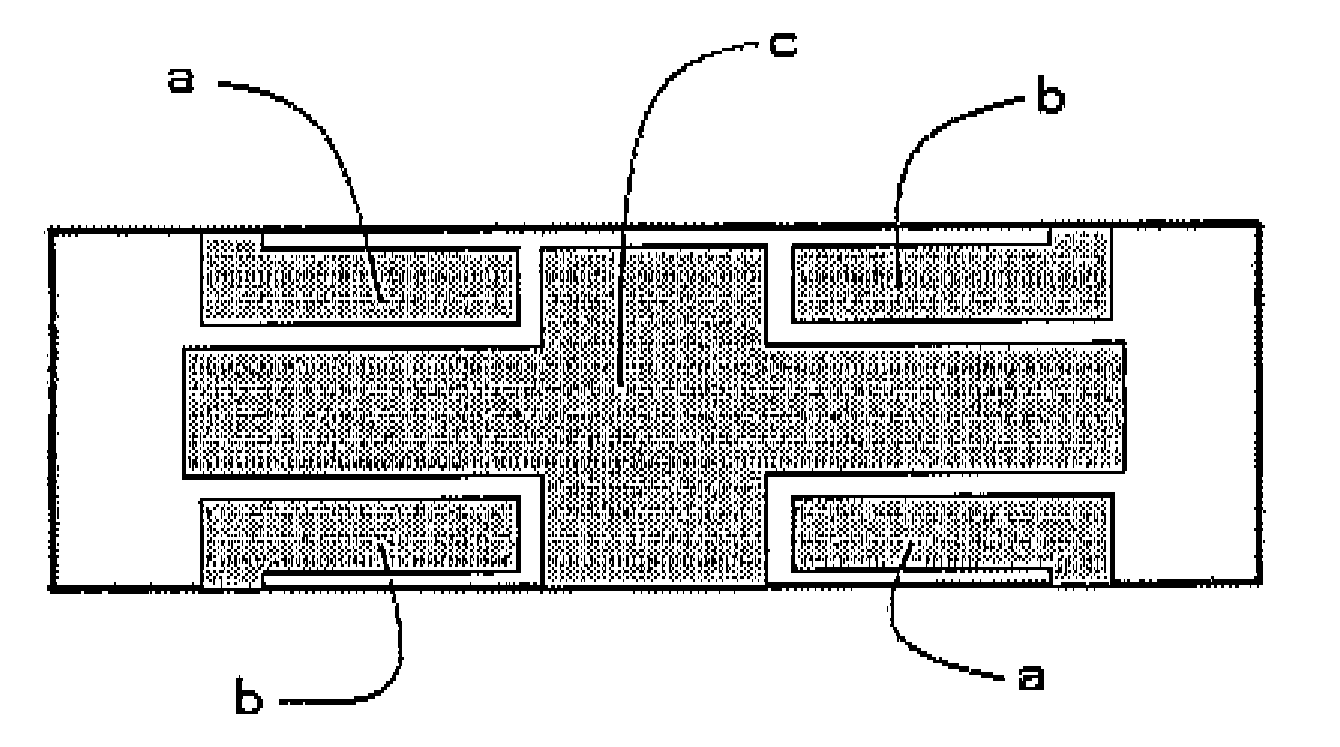
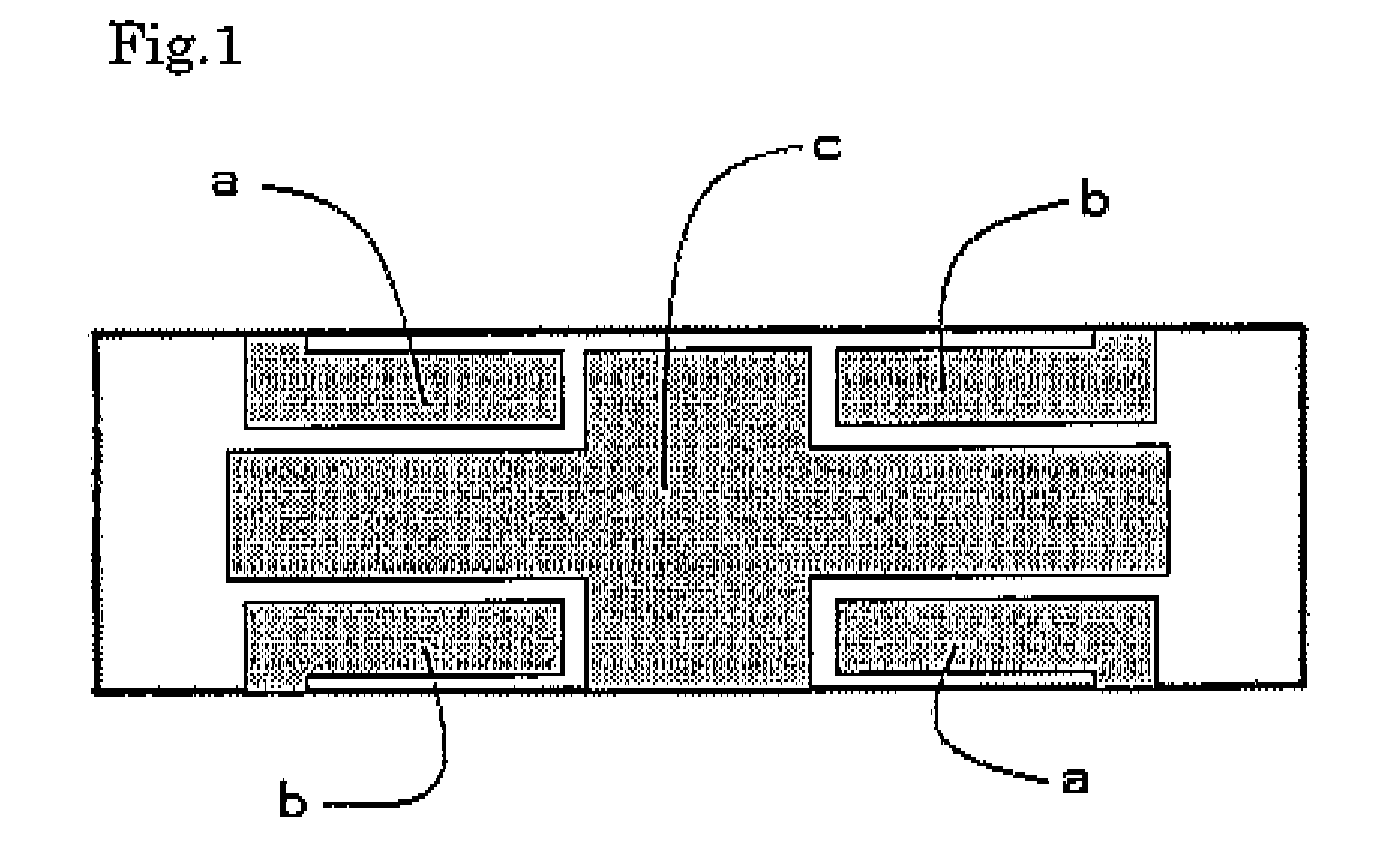
ActiveUS20070236106A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical vibrations separationPiezoelectric actuatorsEngineering
Provided is a piezoelectric vibrator that can finely drive a device by generating an elliptical motion using a combination of a longitudinal vibration and a flexural vibration. The piezoelectric vibrator can also provide high efficiency and be manufactured at low cost by using a simpler structure. The piezoelectric vibrator includes a piezoelectric element, first to third side electrodes, and a power transmission member. The piezoelectric element includes: a first piezoelectric element layer having a bisected top electrode formed thereon; a second piezoelectric element provided under the first piezoelectric element layer and having an internal ground electrode formed thereon; and a third piezoelectric element provided under the second piezoelectric element layer, the third piezoelectric element having an internal electrode symmetrical with the top electrode with respect to a stack plane, and a bottom electrode formed in a plane opposite to the plane where the internal electrode is formed. The first and second side electrodes electrically connect electrode patterns formed in a diagonal direction among the electrode patterns formed in the first and third piezoelectric element layers of the piezoelectric element, and the third side electrode electrically connects the internal ground electrode of the second piezoelectric element layer to the bottom electrode of the third piezoelectric element layer. The power transmission member is formed in one side of the piezoelectric element to transmit vibration generated from the piezoelectric element to the outside.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
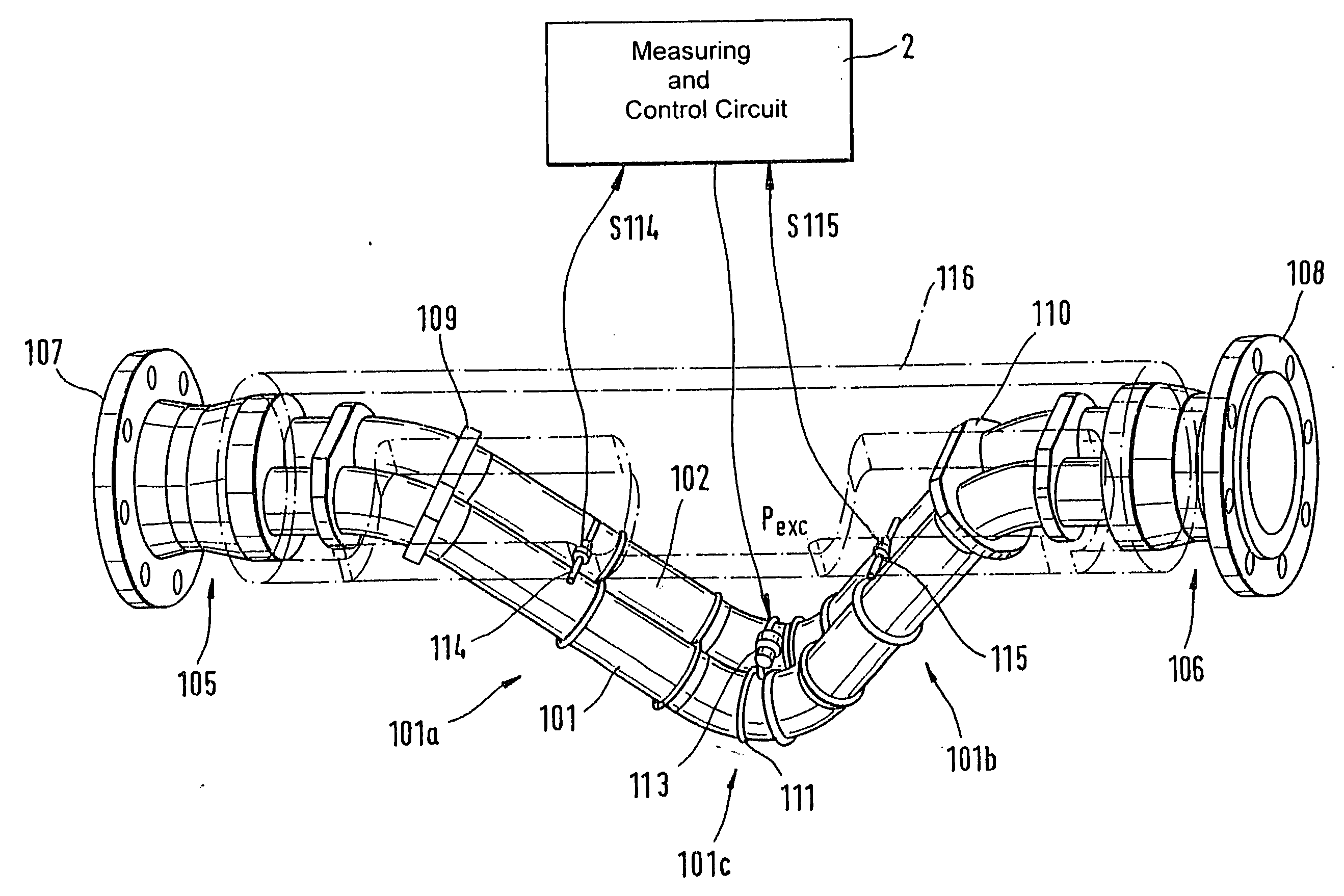
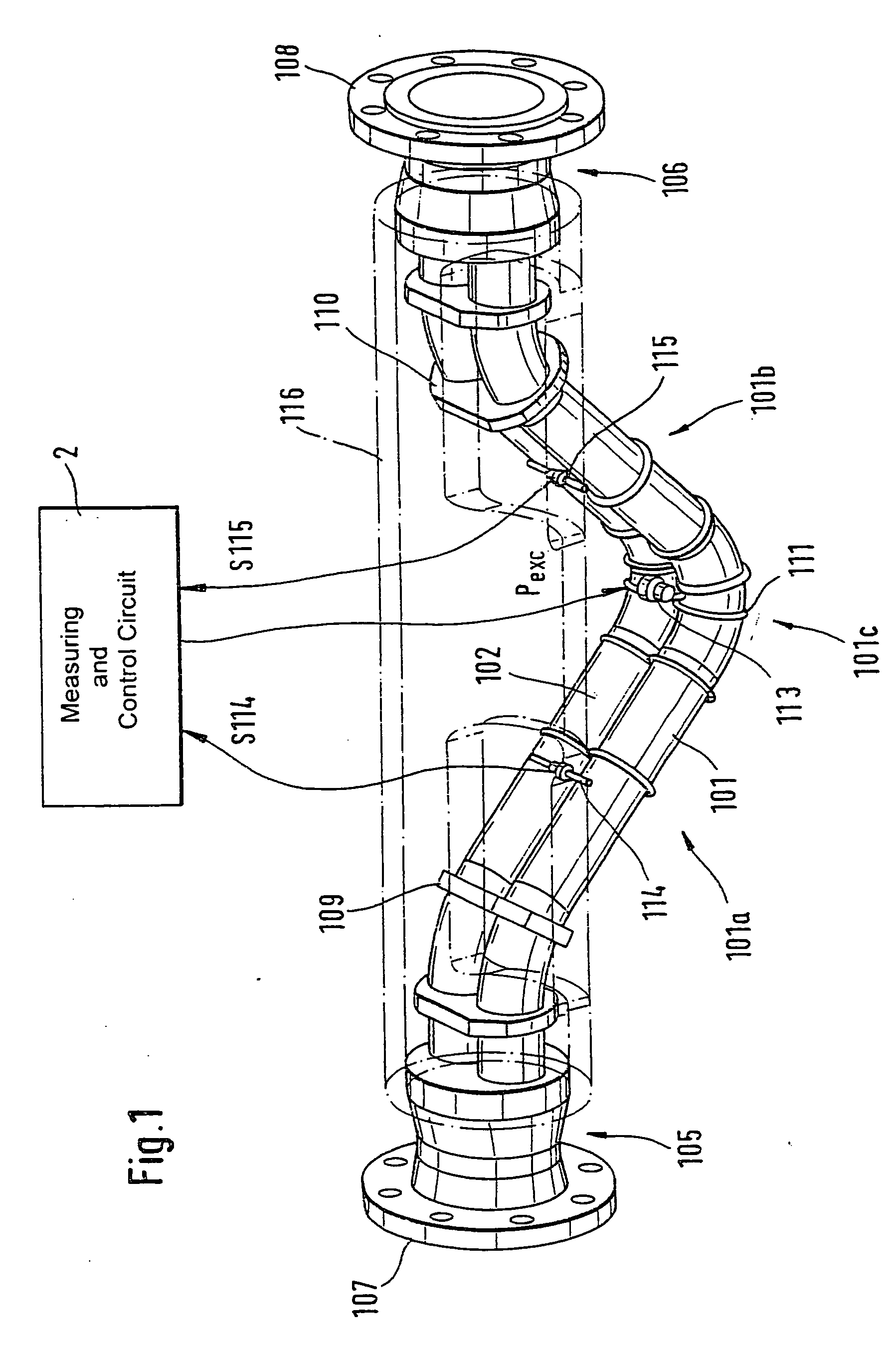
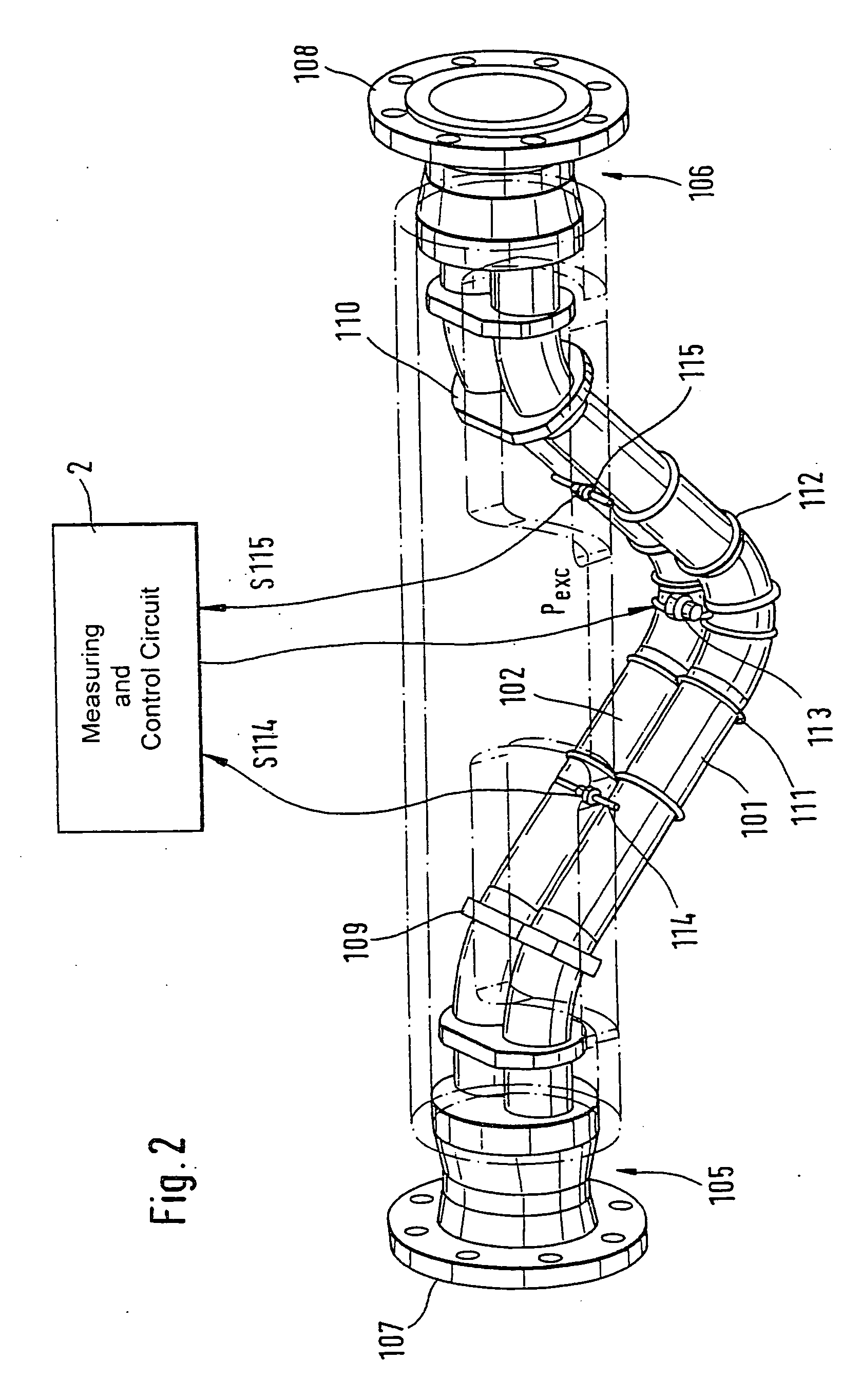
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS20050072238A1Reduce quality problemsHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
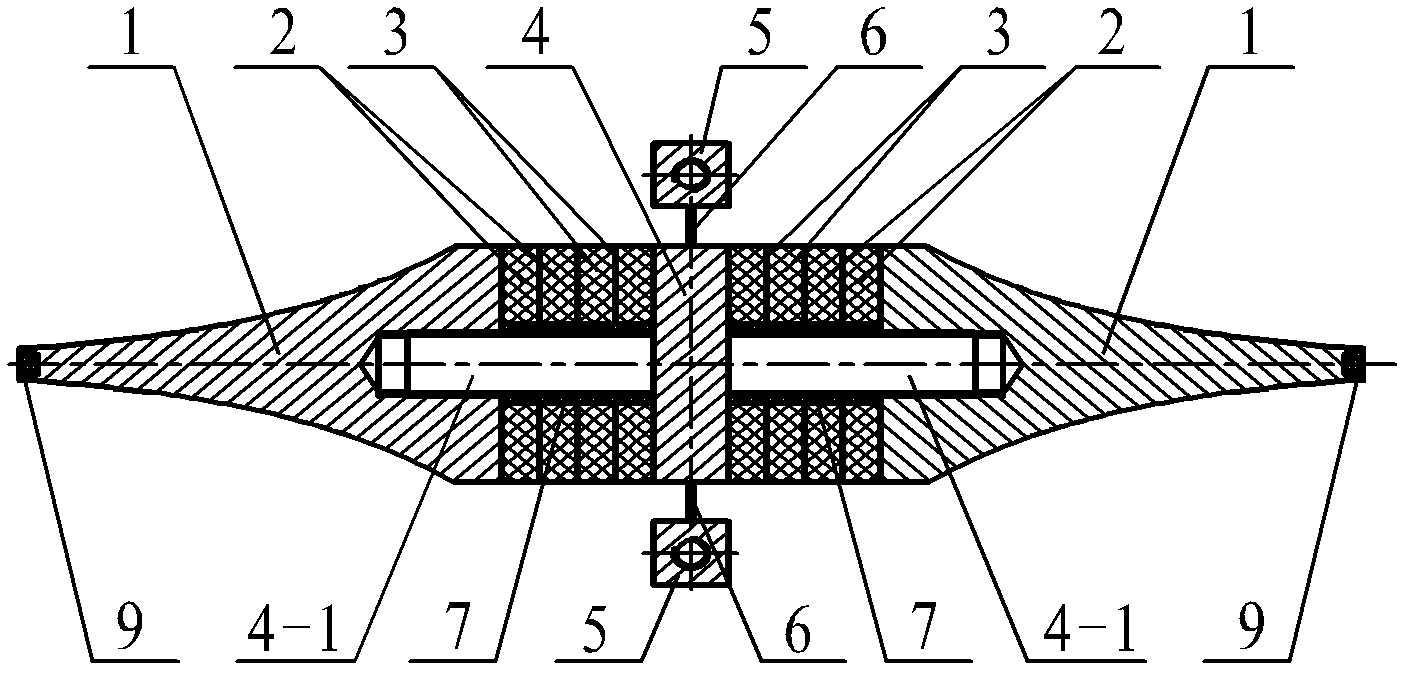
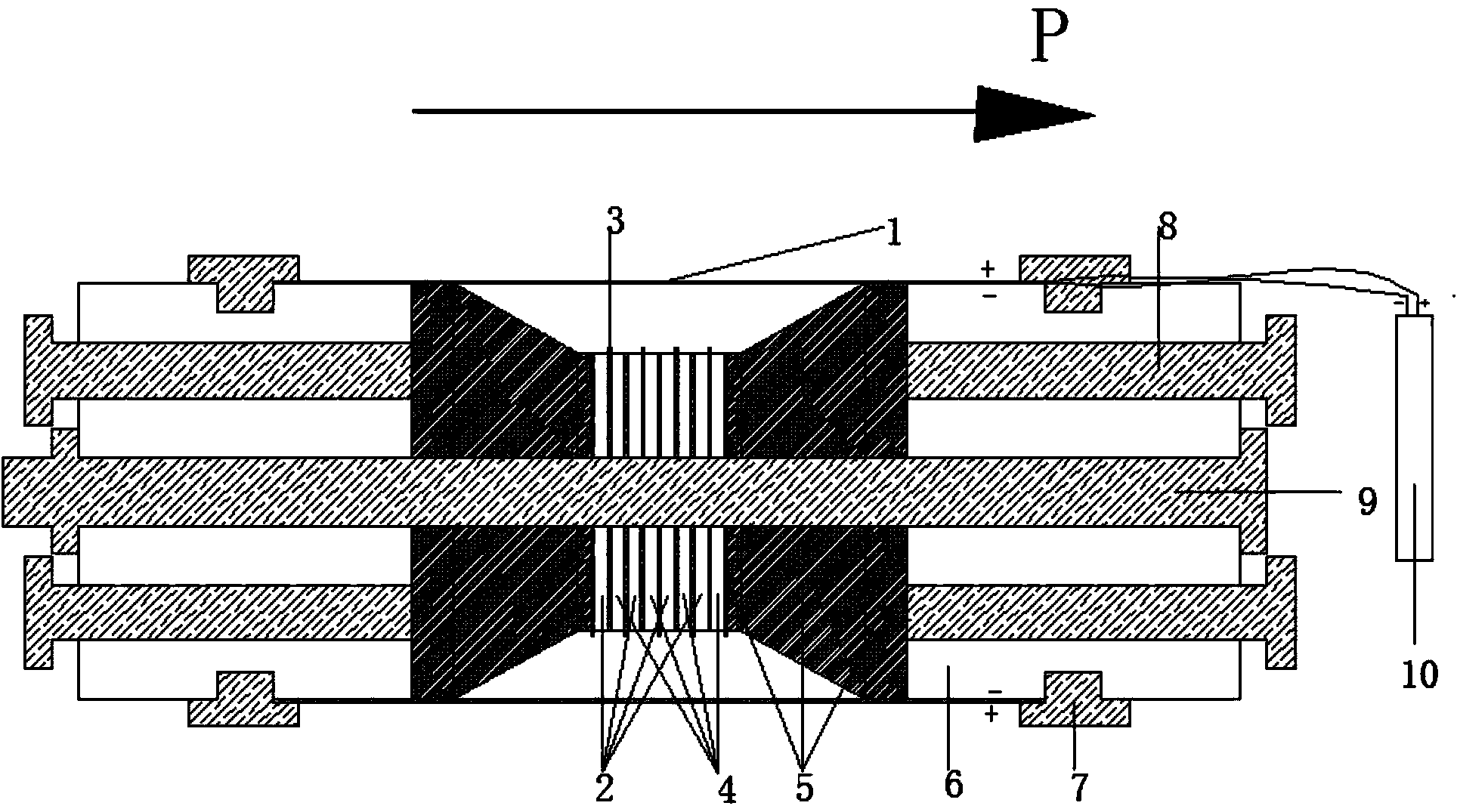
Deep hole ultrasonic vibration impact strengthening device and method
The invention discloses a deep hole inner surface ultrasonic vibration impact strengthening device and method, and relates to the technical field of deep hole inner surface strengthening treatment devices. The deep hole inner surface ultrasonic vibration impact strengthening device is characterized in that a high-frequency signal generated by an ultrasonic power source is converted by an ultrasonic flexural vibration transducer into flexural mechanical vibration, and an amplitude-change pole after amplifying the vibration amplitude of the high-frequency mechanical vibration at an outlet end ofthe transducer transmits the high-frequency mechanical vibration to an ultrasonic impact head so as to impact inner hole surface of parts. A rotation assist system provides radial rotation for the flexural vibration transducer to achieve higher coverage with a single treatment. The deep hole inner surface ultrasonic vibration impact strengthening device is suitable for strengthening the parts with deep holes and has the advantages of low energy consumption, small size, no pollution in the working field environment and good strengthening effect on the workpiece surface; and the strengthening direction does not need to be limited in the vertical direction, and impact at multiple angles and positions can be achieved; and filling and shot blasting do not need to be repeated during working, and certain practicability is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Vibrator element and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140290362A1High detection sensitivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesEngineeringCoriolis force
A vibrator element has a first vibration mode in which first and second detection portions perform flexural vibration in opposite directions in the opposite phase to first and second driving portions which vibrate in opposite directions according to a Coriolis force, and a second vibration mode in which the first and second detection portions perform flexural vibration in opposite directions in the same phase as the first and second driving portions which vibrate in opposite directions according to a Coriolis force. A ratio r=R2 / R1 of equivalent series resistance R2 at the time of the second vibration mode to equivalent series resistance R1 at the time of the first vibration mode is set between 0.15 and 6.0.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Resonator element, resonator, oscillator, electronic device, and frequency adjsutment method
InactiveUS20110156827A1Sufficient vibration propertyEfficient executionImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesClassical mechanicsVolumetric Mass Density
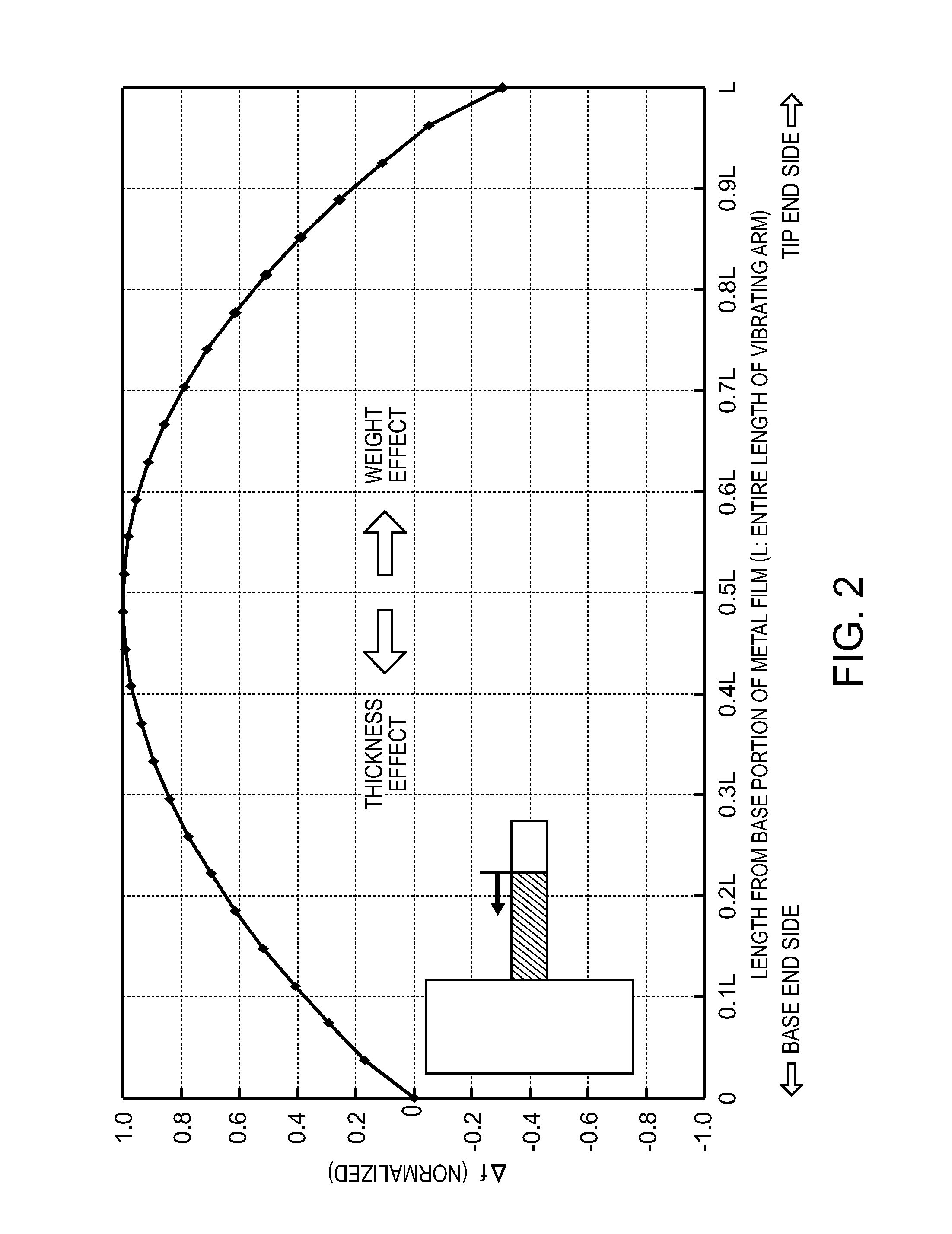
A resonator element includes: a base portion provided on a plane including a first axis and a second axis orthogonal to the first axis; a vibrating arm extending from the base portion in the first axis direction; an excitation electrode provided on the vibrating arm so as to excite the vibrating arm; and a first mass portion provided on the vibrating arm so as to adjust the frequency of the vibrating arm, wherein the vibrating arm performs flexural vibration in a direction perpendicular to the plane and wherein the first mass portion is provided in a region exceeding ½ of the entire length in the first axis direction of the vibrating arm from the end of the vibrating arm close to the base portion and is formed from a material whose density D (in units of 103 kg / m3) is in the range of 2.20≦D≦8.92.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Piezoelectric actuator and linear piezoelectric motor
ActiveCN102185096ASimple structureReduce the driving voltagePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
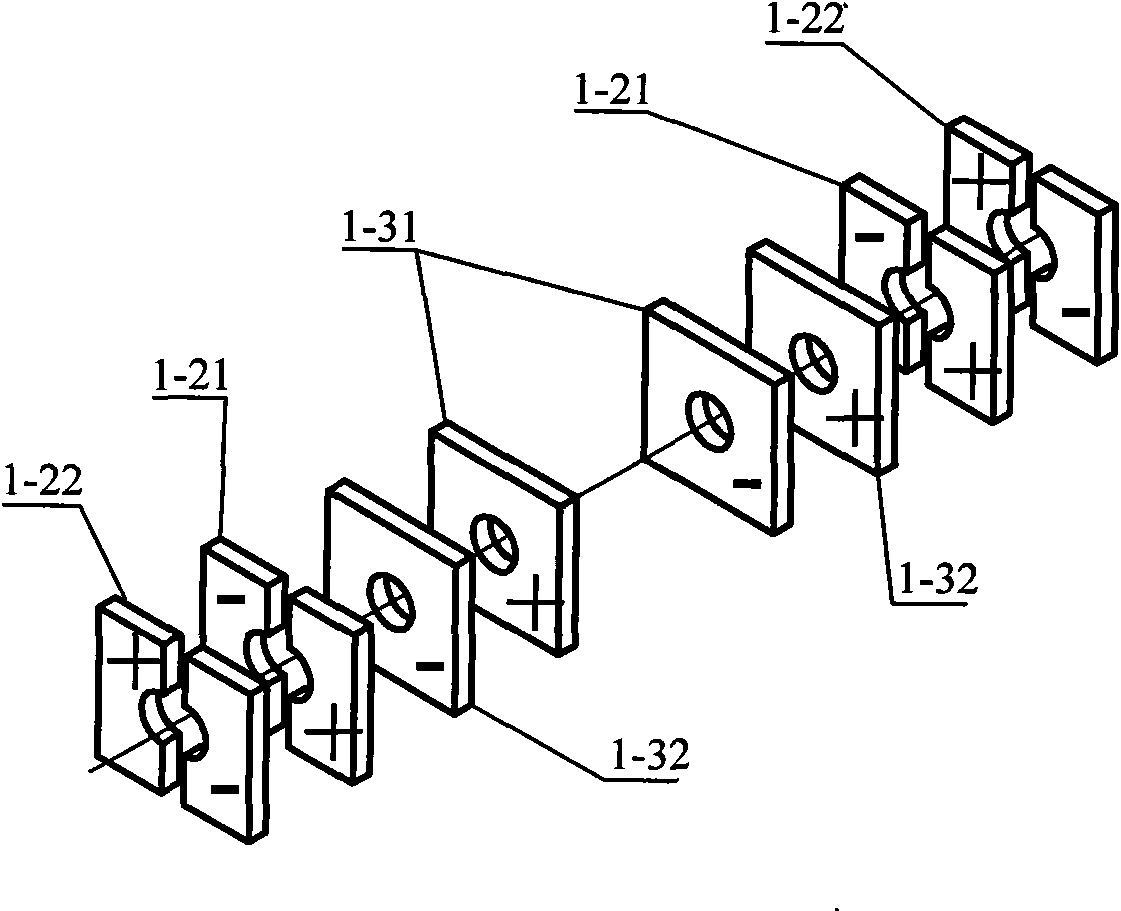
The invention discloses a piezoelectric actuator and a liner piezoelectric motor. The piezoelectric actuator comprises at least two piezoelectric chip which are overlapped, wherein each piezoelectric chip has a preset polarization distribution direction, and the surface of each piezoelectric chip is provided with a first driving electrode assembly and a second driving electrode assembly which are matched with the polarization distribution direction of the piezoelectric chip; under the action of driving voltage with a preset characteristic frequency applying to the first driving electrode assemblies and the second driving electrode assemblies, both piezoelectric chip can generate vibration deformation with the same frequency, thus, based on the composite vibration deformation of the two piezoelectric chips, the piezoelectric actuator can integrally generate standing wave harmonic oscillation or traveling wave motion in a first order flexural vibration mode. The piezoelectric actuator provided by the invention has simple structure, is practical and convenient, and can effectively reduce the driving voltage of the piezoelectric actuator and improve the driving force.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
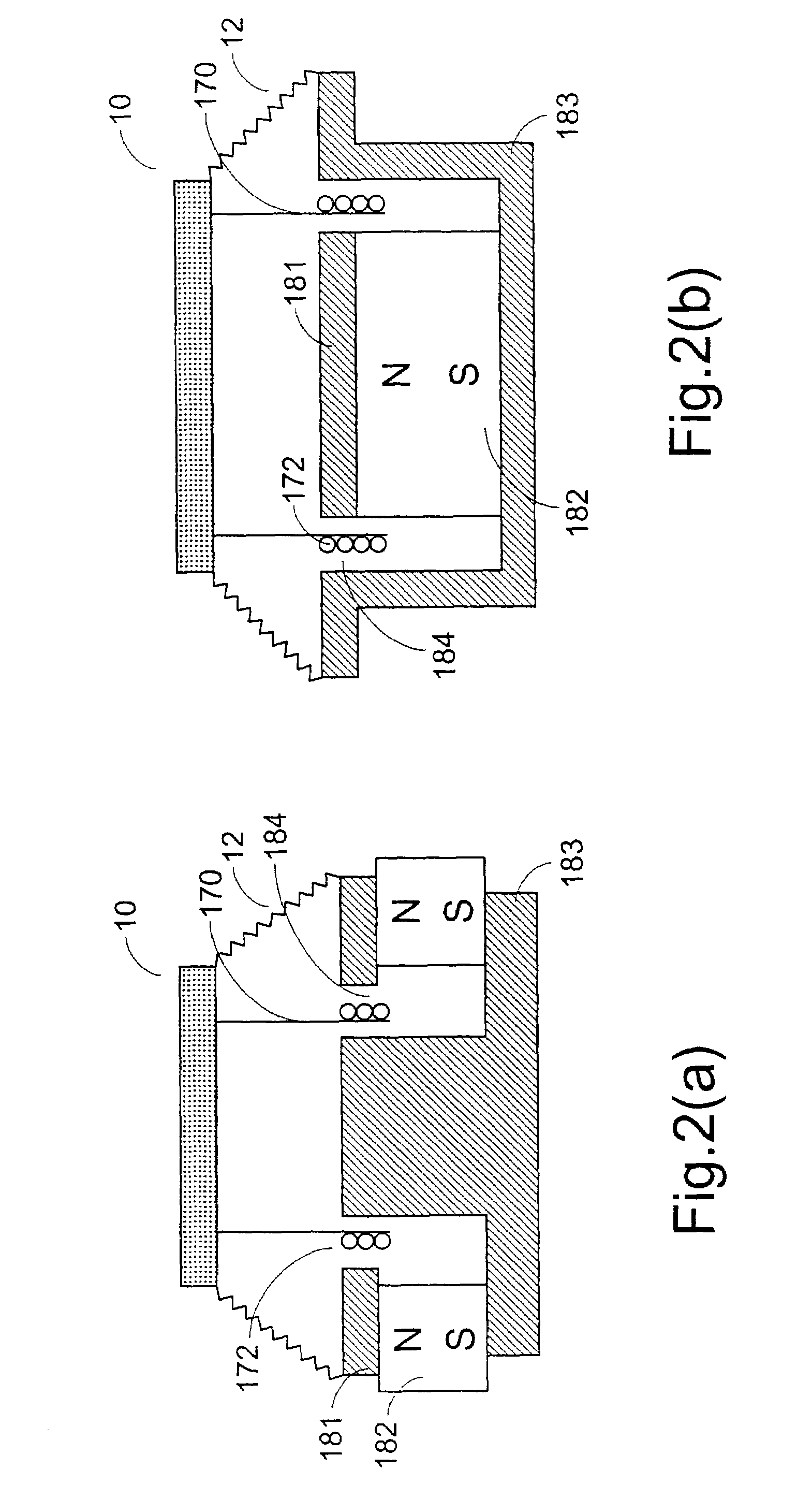
Vibrator for ultrasonic motor
InactiveUS20100072858A1Improve controllabilityImprove vibration efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesControllabilityAcoustics
In the invention, each piezoelectric element for a vibrator for an ultrasonic motor has electrode regions for exciting stretching vibration and flexural vibration separately. Thus, the invention provides a vibrator for an ultrasonic motor, in which electrodes are provided for applying voltage to each of the polarized region, and further provides a stack-type piezoelectric vibrator for an ultrasonic motor, consisting of a stack of the said vibrators and having an extraction electrode pattern provided for short circuit with an external electrode. The vibrator of the invention has high controllability, especially in a fine movement region and is useful as a driving source in a positioning device, in which enhanced vibration efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:ISHIKAWA PREFECTURAL GOVERNMENT +1
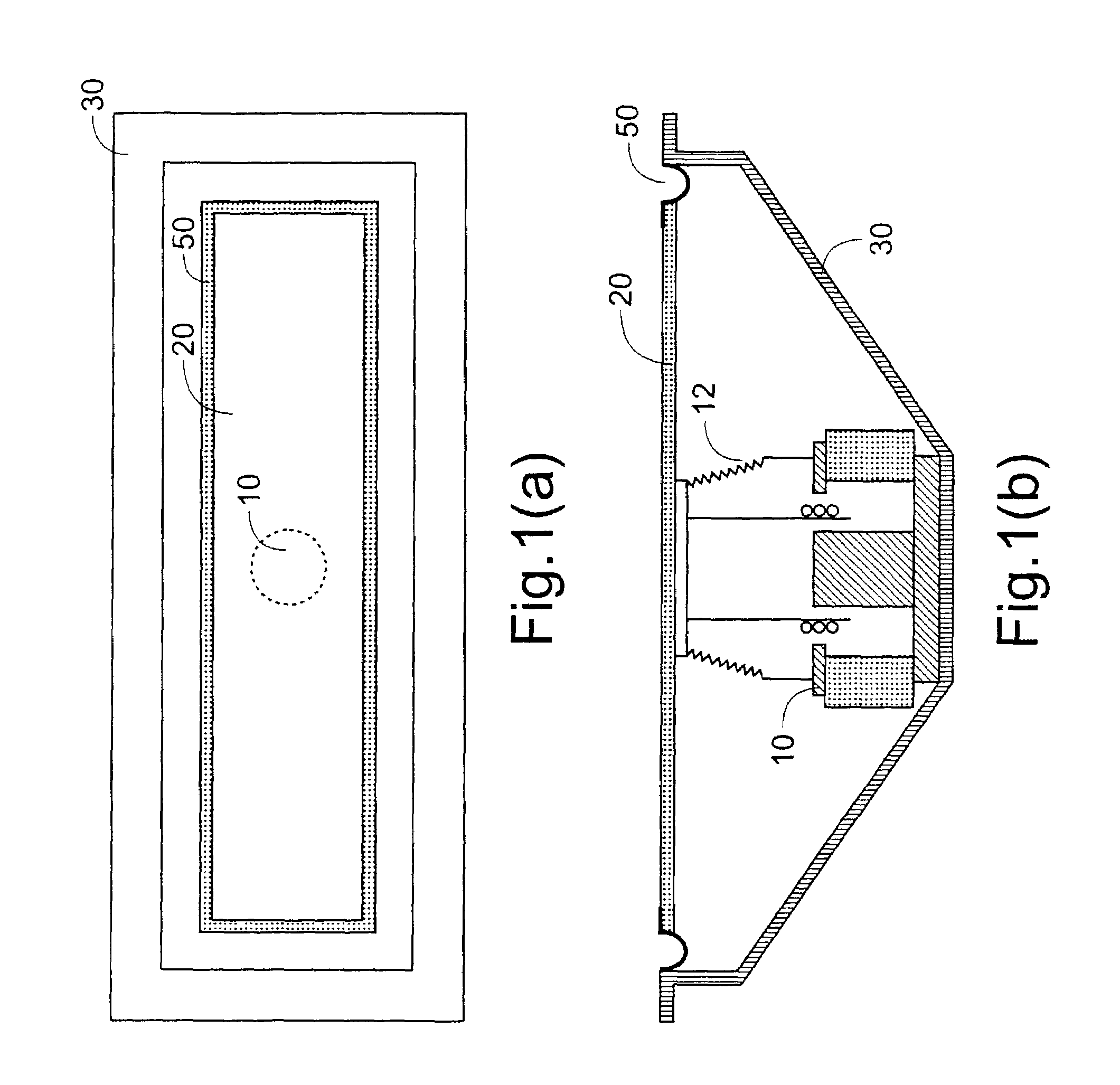
Electronic apparatus
InactiveCN1821935ASmooth vibrationBig vibrationInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsFixed frameEngineering
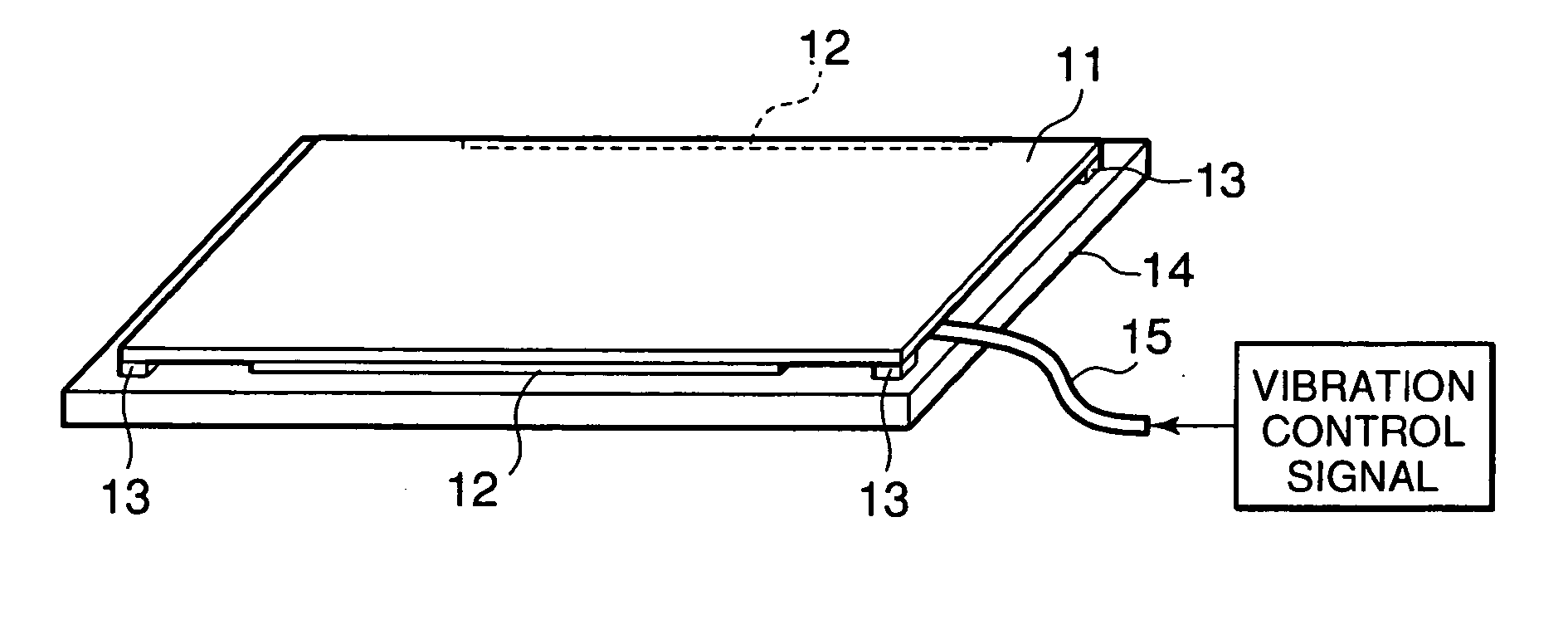
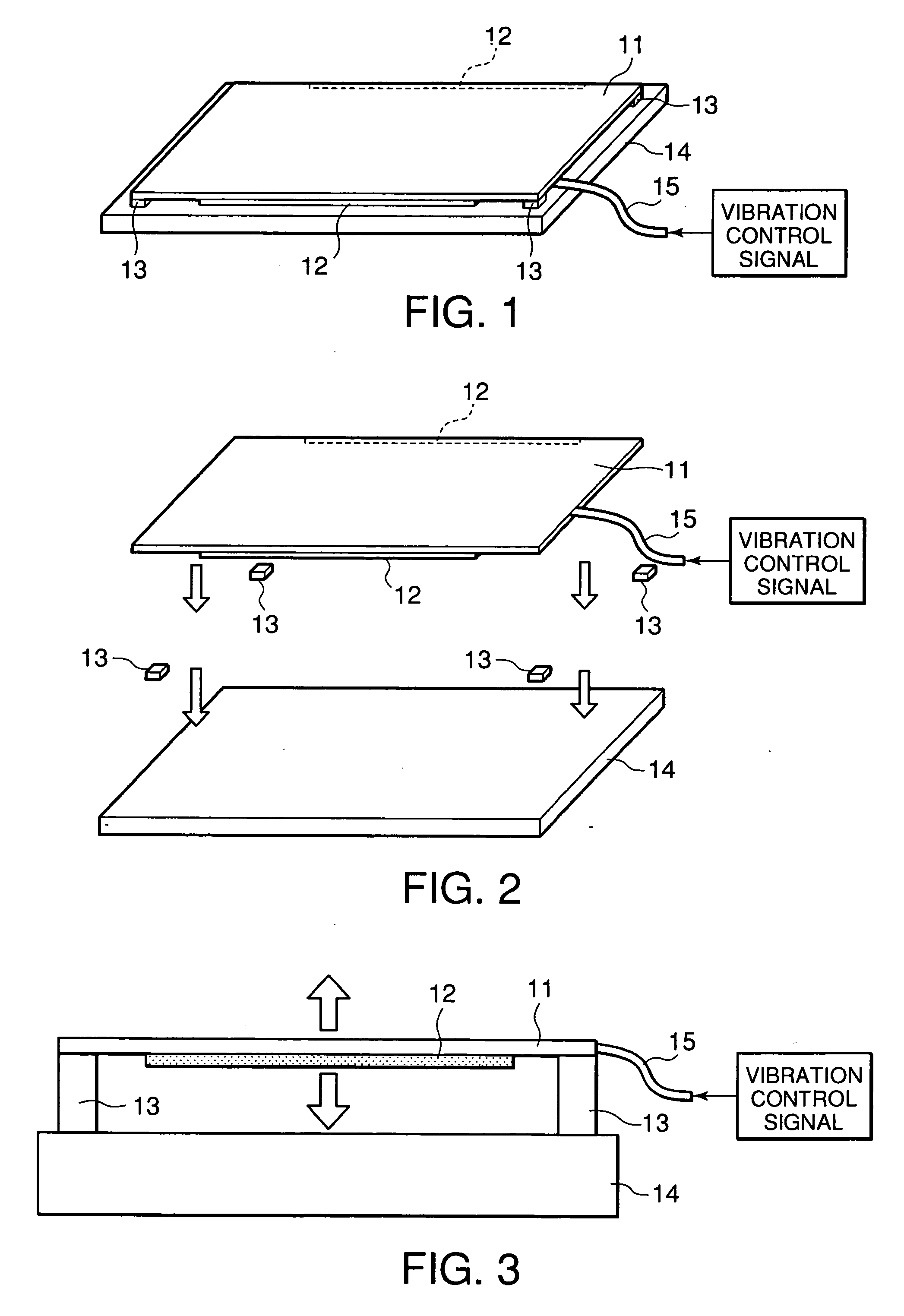
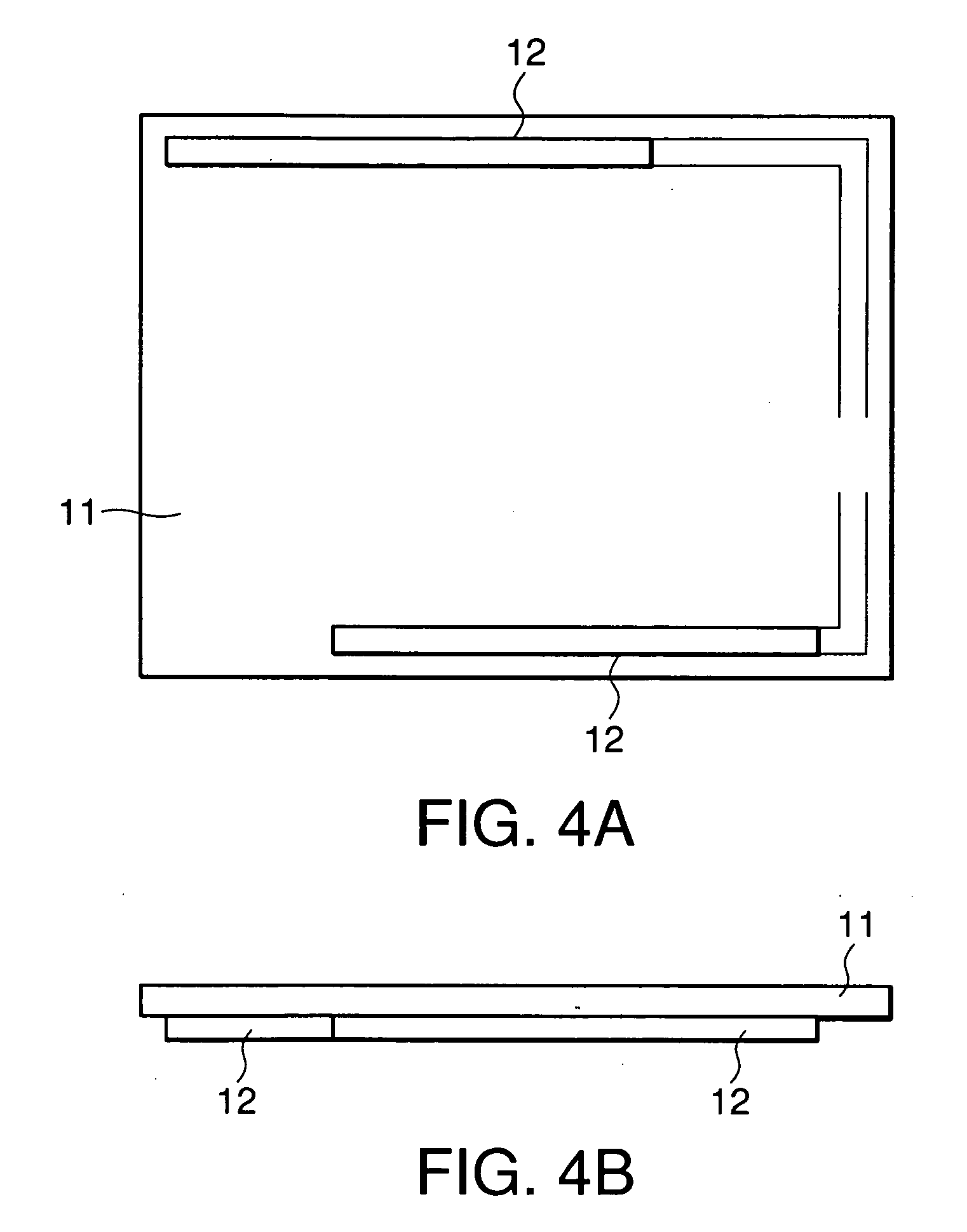
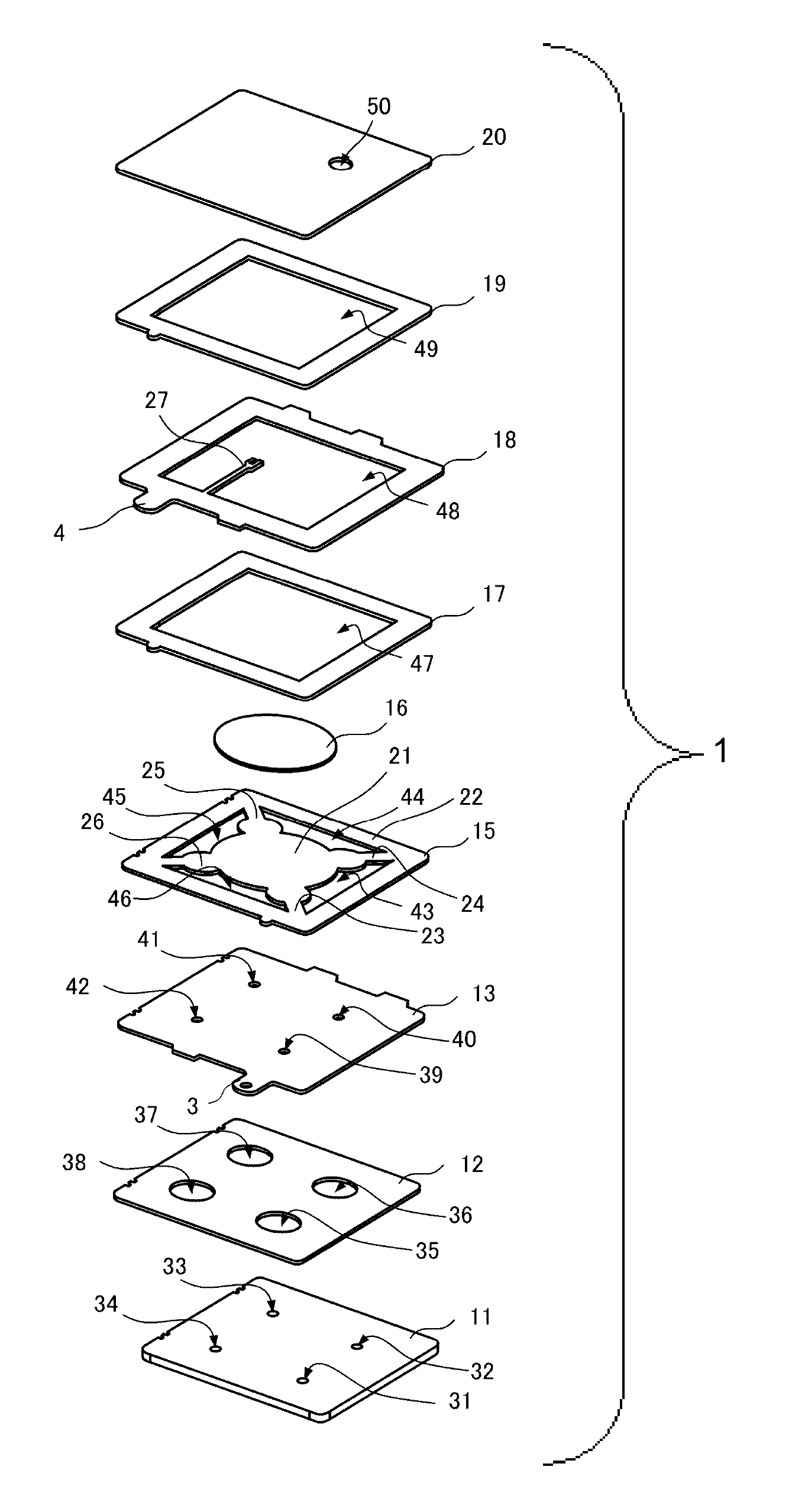
In an electronic apparatus having a touch panel, four fixing cushions are fixed at four corners of a rear surface of the touch panel. The fixing cushions are further fixed to a fixing frame to support the touch panel against to the fixing frame. Pair of vibrating elements are fixed to the rear surface of the touch panel along edges, which are parallel to each other, of the touch panel. The vibrating elements elastically bend the touch panel to cause flexural vibration to the touch panel. The fixing cushions have softness to allow the touch panel to vibrate and hardness to serve as fulcrums of the flexural vibration of the touch panel.
Owner:NEC INFRONTIA CORP
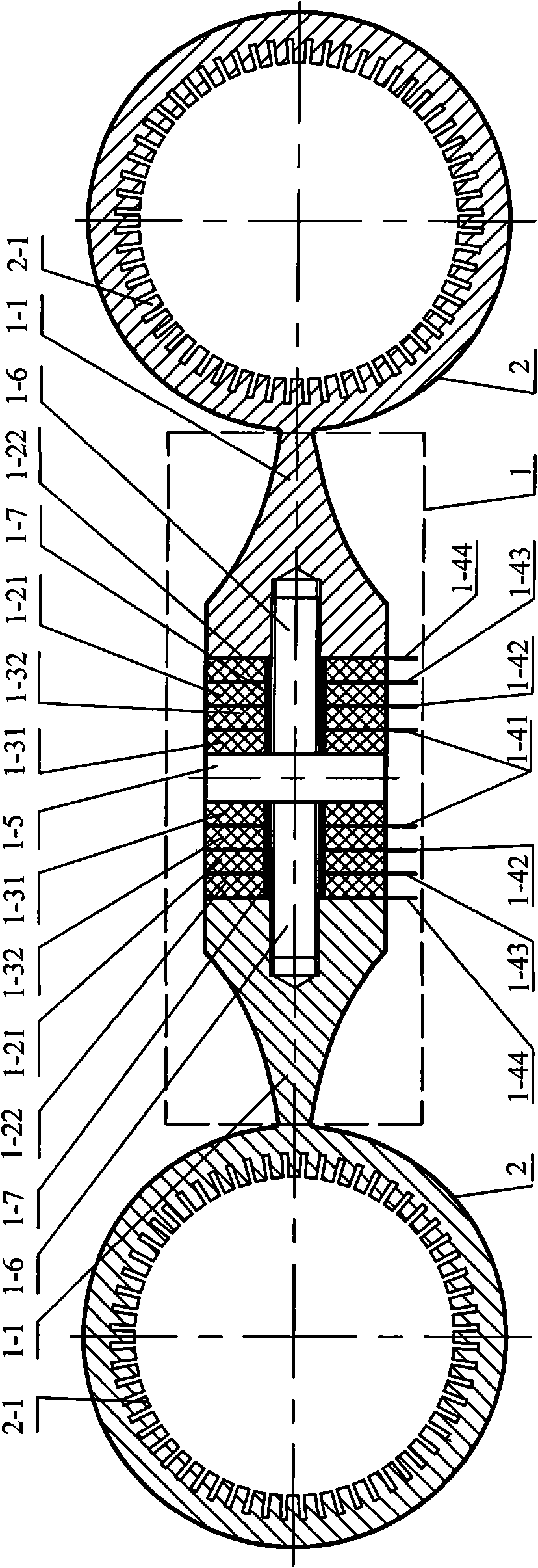
Longitudinal and flexural composite transducer type double cylinder-shaped traveling wave ultrasonic motor vibrator
InactiveCN101626206AImprove performanceAvoid Vibration Inconsistency IssuesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElastomerTransducer
A longitudinal and flexural composite transducer type double cylinder-shaped traveling wave ultrasonic motor vibration generator belongs to the technical field of a piezoelectric ultrasonic motor. The invention aims at solving the problems that the mechanical output capacity of an ultrasonic motor is restricted when the method that metal elastic body pastes a piezoelectric ceramic sheet is adopted for excitation by the existing ultrasonic motor vibration generator, vibration path distortion of vibration generator surface particle caused by the condition that multi-transducer can not be guaranteed to be completely consistent when the multi-transducer are adopted to drive simultaneously and the mechanical output capacity and maneuverability of the ultrasonic motor are reduced. The invention comprises a longitudinal and flexural composite sandwich transducer and two cylinders, the small end face of a front end cover of the longitudinal and flexural composite sandwich transducer is made into a whole with a cylinder, the big end face of the front end cover thereof is respectively connected with one end of a screw stud, a longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic plate and a flexural vibration piezoelectric ceramic plate respectively are sheathed on the screw stud with electrode plates in an interval manner, and the other end of the screw stud is connected with a flange. The traveling wave ultrasonic motor vibrator is applicable to the manufacturing field of the ultrasonic motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fluid control device and pump
ActiveUS20170058882A1Increase volumeImprove driving efficiencyFlexible member pumpsPositive-displacement liquid enginesFluid controlEngineering
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Piezoelectric vibrator for ultrasonic motor
InactiveUS7932661B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesElectricityControllability
In the invention, each piezoelectric element for a vibrator for an ultrasonic motor has electrode regions for exciting stretching vibration and flexural vibration separately. Thus, the invention provides a vibrator for an ultrasonic motor, in which electrodes are provided for applying voltage to each of the polarized region, and further provides a stack-type piezoelectric vibrator for an ultrasonic motor, consisting of a stack of the said vibrators and having an extraction electrode pattern provided for short circuit with an external electrode. The vibrator of the invention has high controllability, especially in a fine movement region and is useful as a driving source in a positioning device, in which enhanced vibration efficiency can be obtained.
Owner:ISHIKAWA PREFECTURAL GOVERNMENT +1
Driving device
ActiveUS20160268928A1Movement speed is stablePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsElastomerEngineering
A driving device that causes a movable body to move stably with minimal backward movement. The driving device includes a plate-shaped driving unit with an elastic body and a piezoelectric element joined to a main surface of the elastic body. Moreover, the movable body is disposed into a cavity of the elastic body and is moved by being pitch fed when the driving unit is driven. The driving unit vibrates with flexural vibration and one more other vibration modes or with vibration of a coupled mode in which the flexural vibration and the other vibration mode are coupled with each other.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Buckling composite modal sandwich type double-foot rotating ultrasonic motor vibrator with elastic supports
InactiveCN102361414AImprove performanceSolve efficiency problemsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityLongitudinal vibration
The invention discloses a buckling composite modal sandwich type double-foot rotating ultrasonic motor vibrator with elastic supports, and relates to the technical field of piezoelectric ultrasonic motors. The vibrator solves the problem that the vibration energy is utilized insufficiently and the mechanical output capacity is restricted in the conventional ultrasonic motor vibrator. The ultrasonic motor vibrator comprises two amplitude transformation rods, two pairs of flexural vibration piezoelectric ceramic chips, two pairs of longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic chips, a neutral plate, two mounting seats, two thin-wall beams, two insulating bushes, eight electrode plates and two friction plates; the amplitude transformation rods are blocks, the sections of which are rectangular and gradually thinned; the small end faces of the amplitude transformation rods are provided with driving feet; the friction plates are fixed in through slots of the small end faces of the amplitude transformation rods; two ends of the neutral plate are provided with studs; and the amplitude transformation rods are respectively screwed to the ends of the studs through thread holes of the big end faces, so that the flexural vibration piezoelectric ceramic chips and the longitudinal vibration piezoelectric ceramic chips are compacted between the amplitude transformation rods and the neutral plate. The vibrator is suitable for the conventional rotating ultrasonic motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Ultrasonic motor
InactiveUS20060202589A1Stably and finelyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPhase differenceEngineering
It is an object to provide an ultrasonic motor that can stably and finely (that is, minutely) move a driven body. The invention provides an ultrasonic motor comprising an ultrasonic vibrator which includes an electromechanical transducer and which is configured to simultaneously generate two different vibration modes to produce substantially elliptical vibrations at output terminals by supplying two sets of alternating-current voltages with a predetermined phase difference and a predetermined driving frequency to the electromechanical transducer; and a pressing unit for pressing the output terminals of the ultrasonic vibrator against a driven body. The output terminals include first friction-contact members disposed at positions substantially corresponding to antinodes of a flexural vibration and a second friction-contact member disposed substantially at the center in the longitudinal direction of the ultrasonic vibrator.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
A flextensional transducer using a PVDF piezoelectric film
ActiveCN103646643AImprove energy conversion efficiencyImprove receiver sensitivitySound producing devicesBroadband transmissionTransducer
The invention relates to a flextensional transducer using a PVDF piezoelectric film. The flextensional transducer comprises a piezoelectric ceramic wafer stack and a PVDF film. The PVDF film surrounds the piezoelectric ceramic wafer stack. A connecting piece is arranged between the PVDF film and the piezoelectric ceramic wafer stack. The flextensional transducer further comprises a device for enabling the PVDF film to generate prestress. The metallic housing of a conventional flextensional transducer is replaced by the PVDF film. The PVDF film and the piezoelectric ceramic wafer stack are used as sensitive elements. The PVDF film uses a film flexural vibration mode under a simple boundary condition. The piezoelectric ceramic wafer stack uses a longitudinal vibration mode. A wide bandwidth can be acquired by mode coupling so as to achieve broadband transmission sound waves. The flextensional transducer has characteristics of low frequency, a wide band, high receiving sensitivity, large acoustic radiation power, and horizontal omnidirectional directivity.
Owner:武汉国科舰航传感科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com