Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5294 results about "Straight tube" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
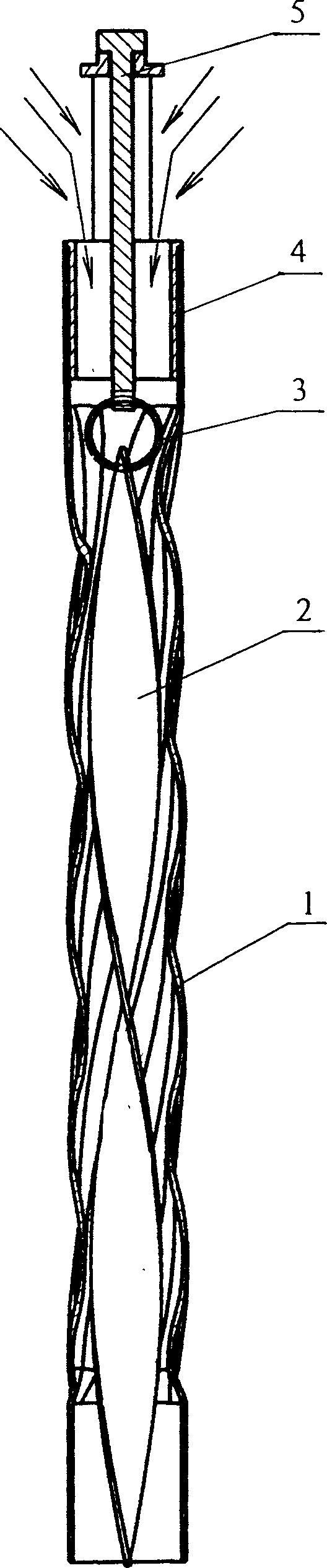
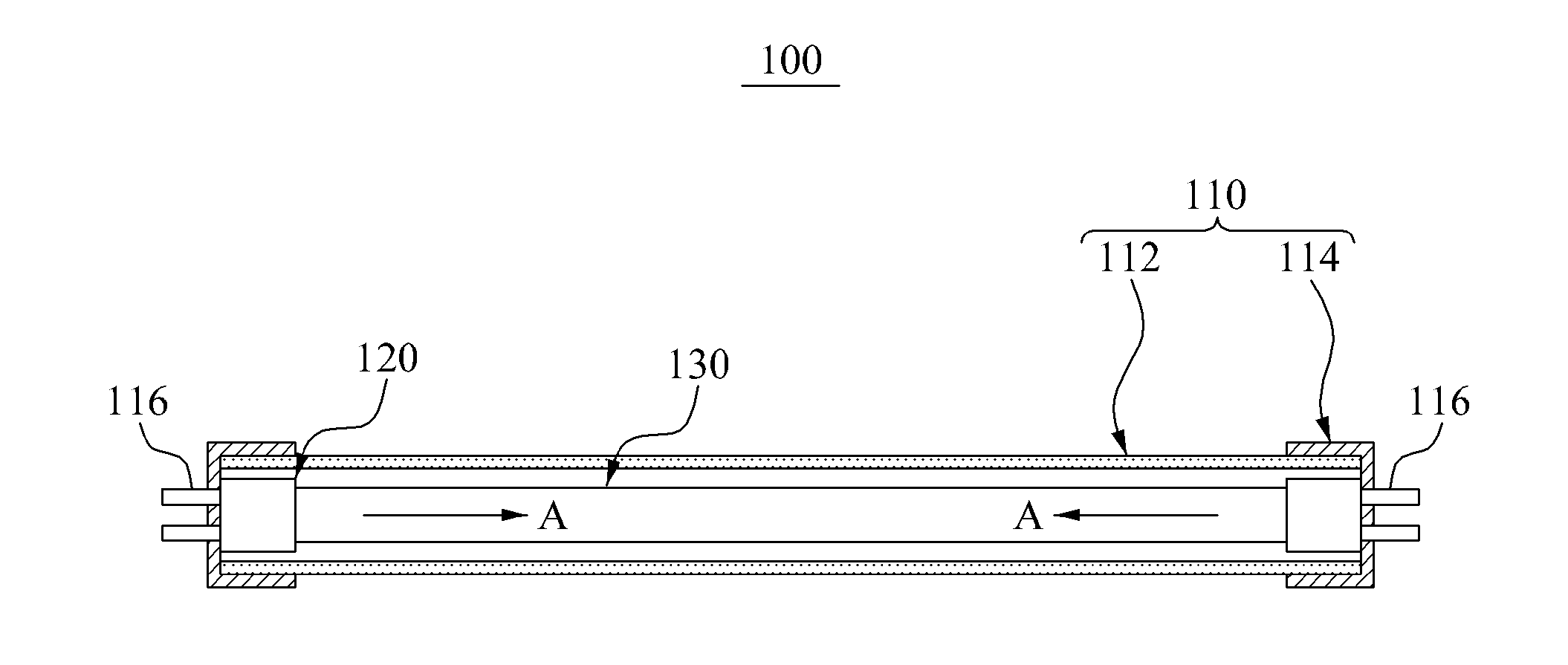
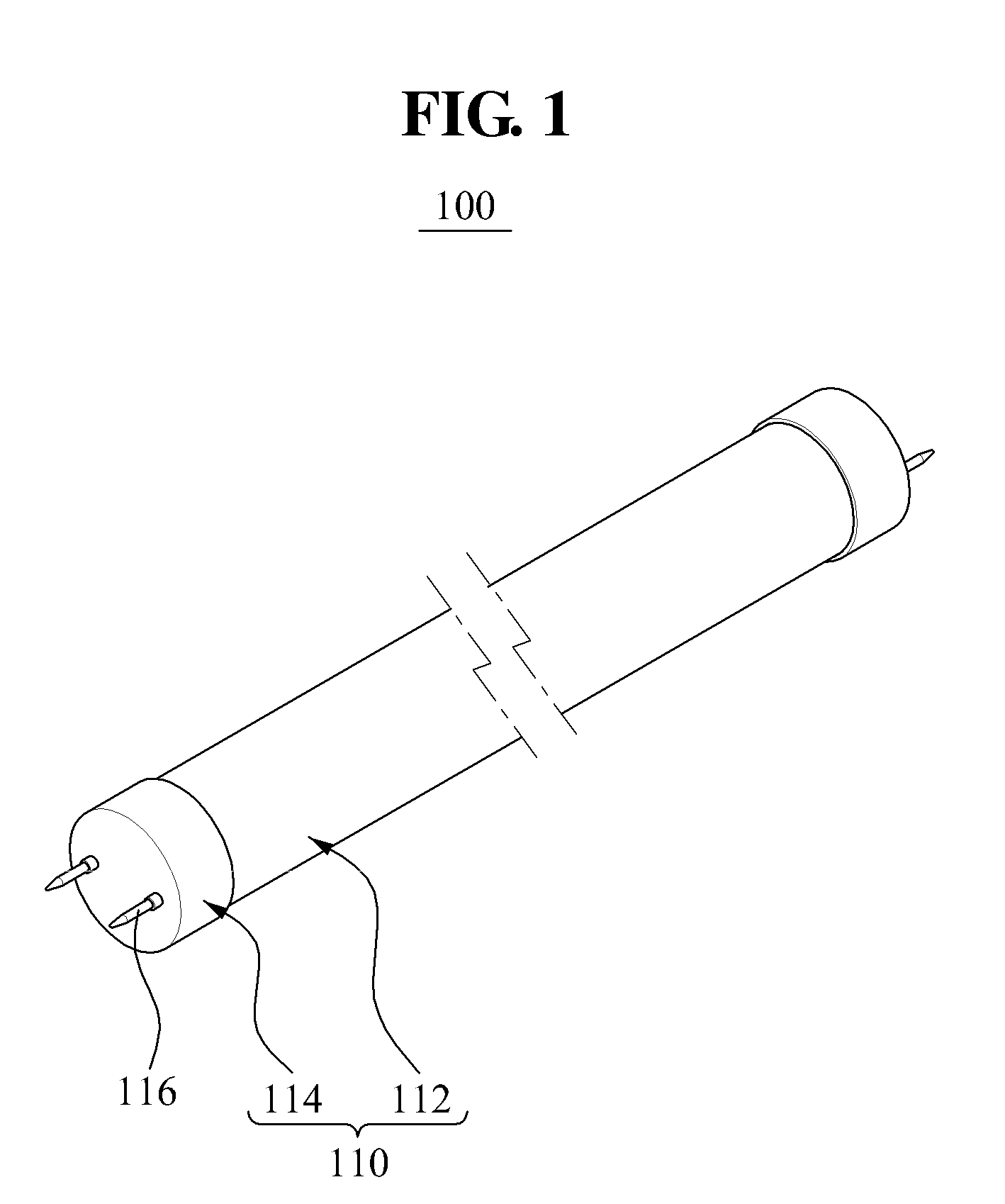
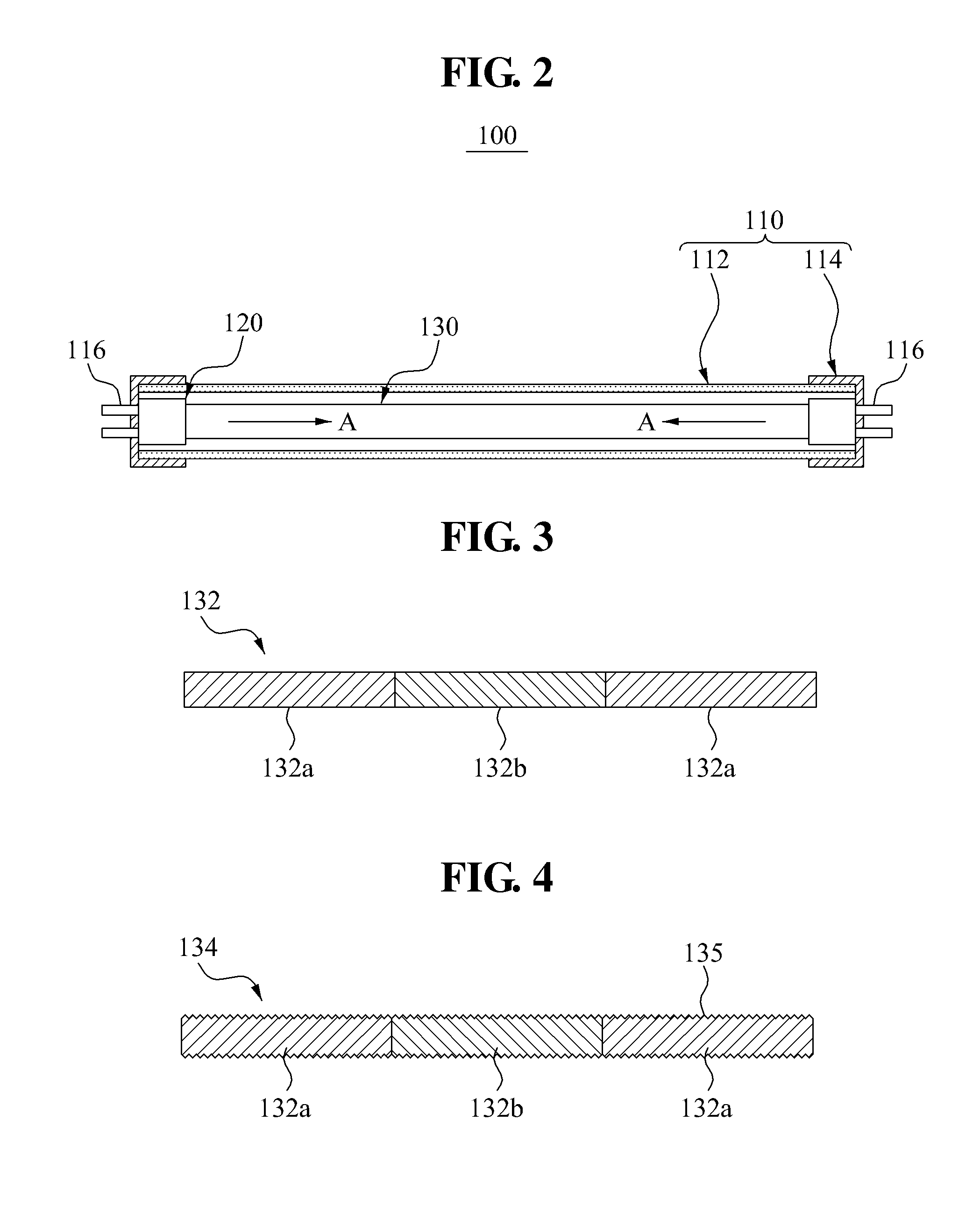
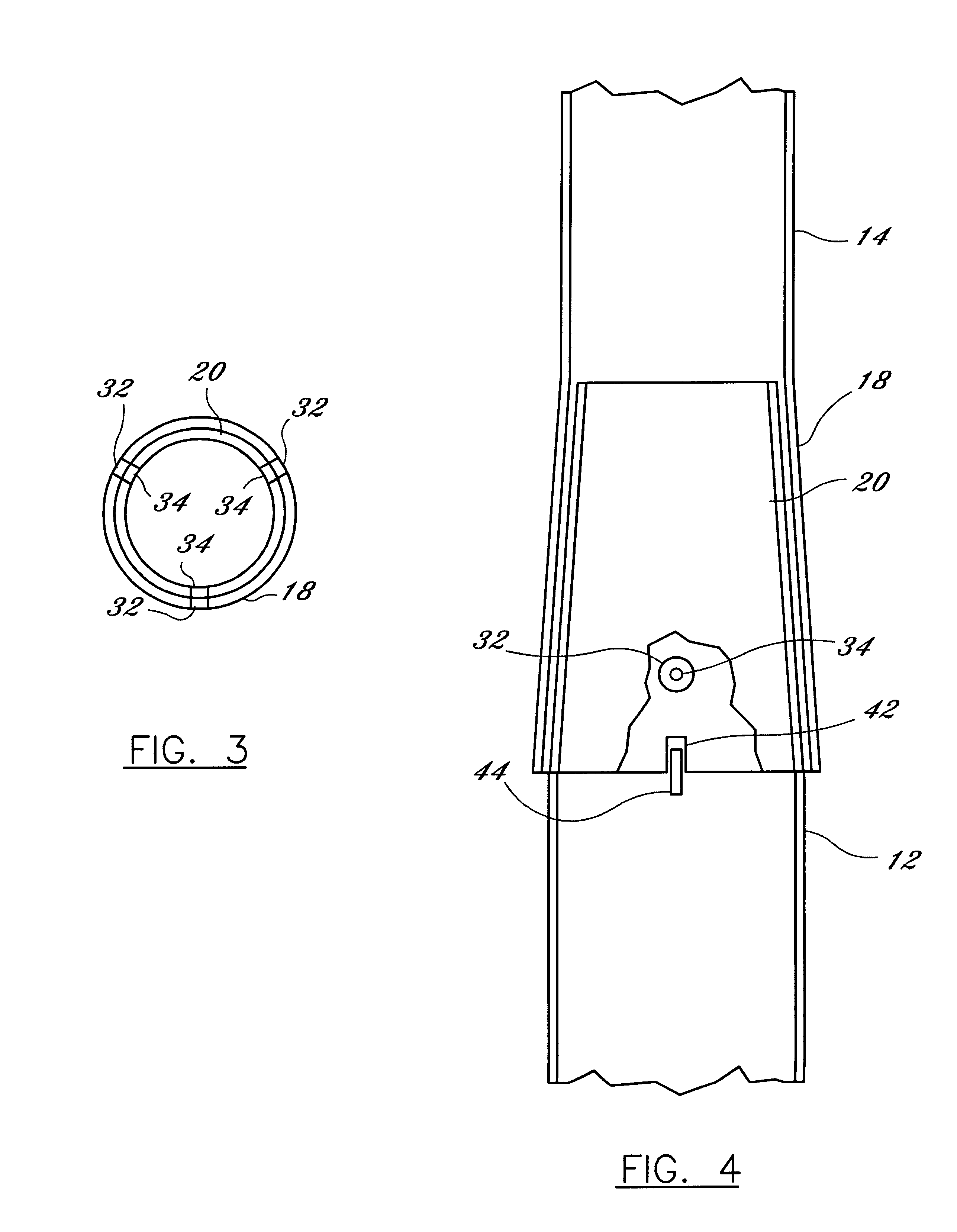
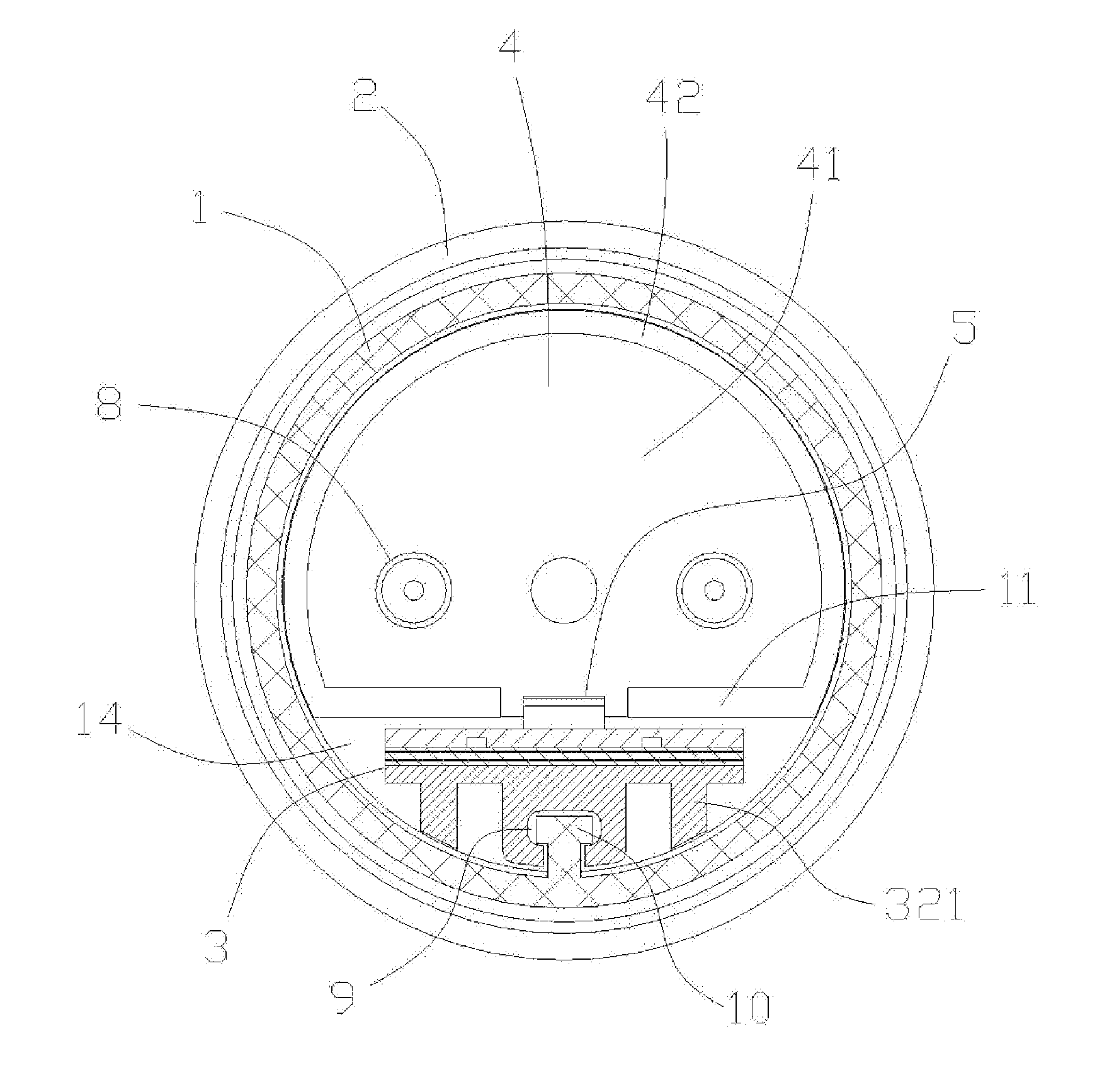
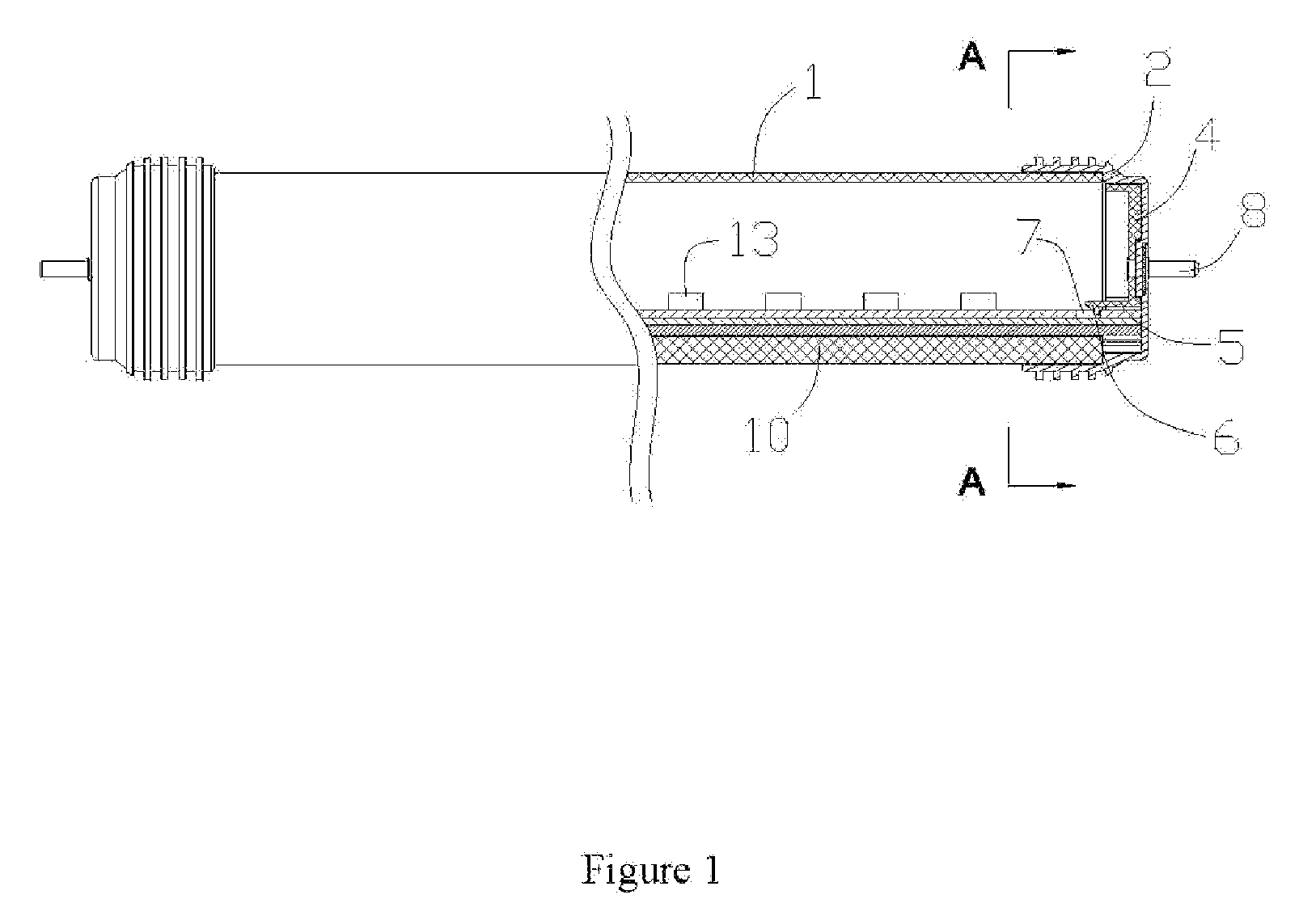
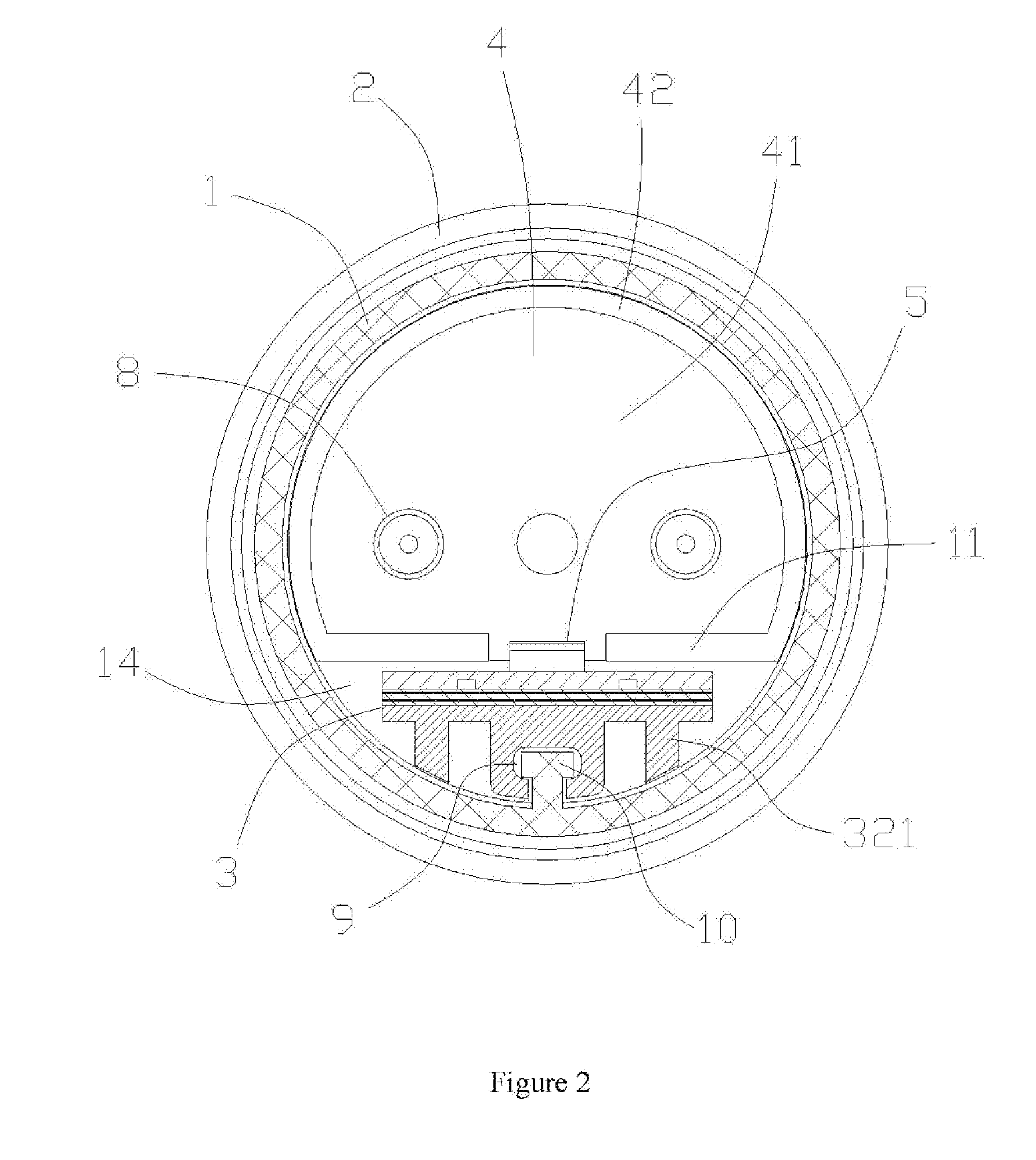
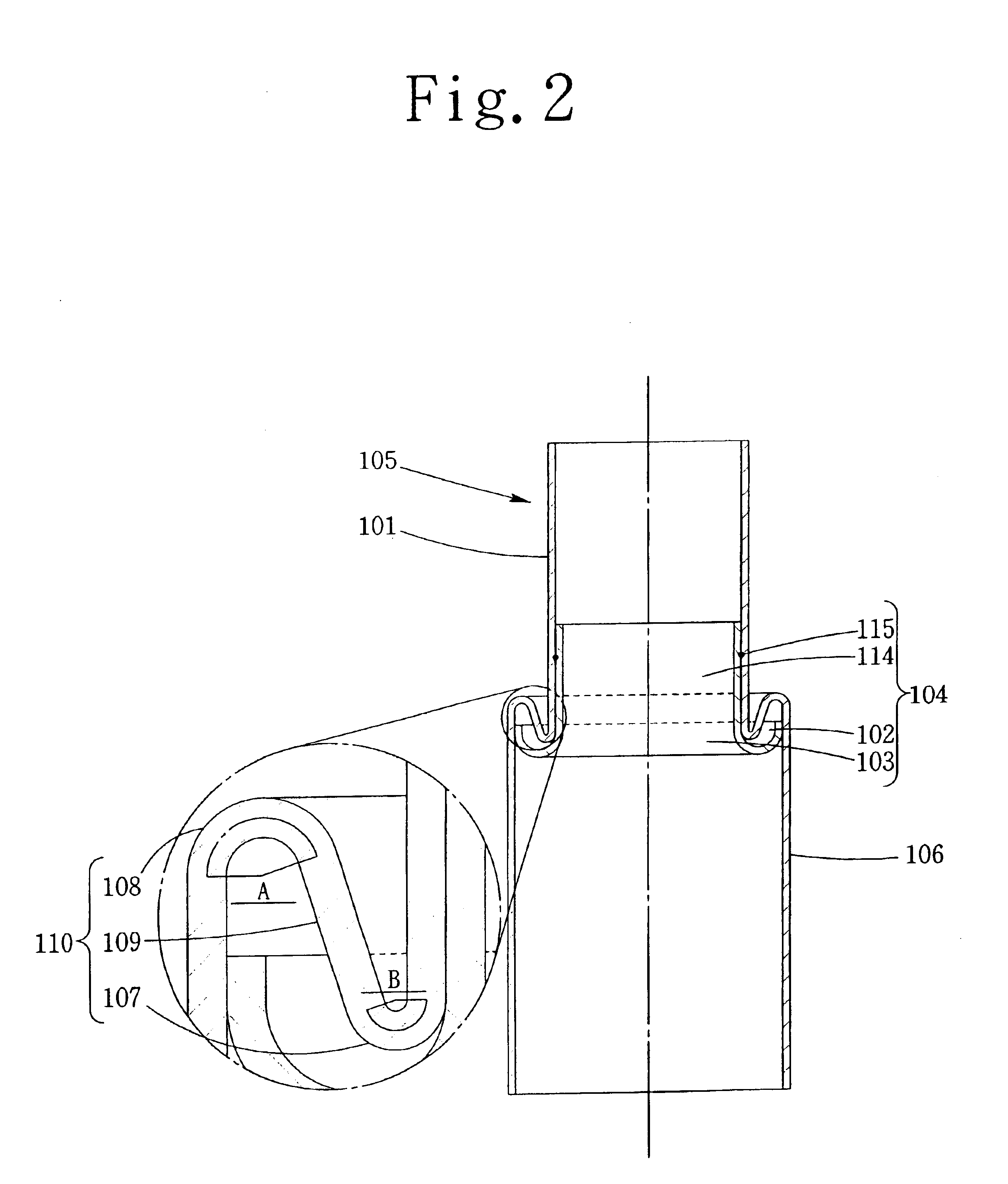
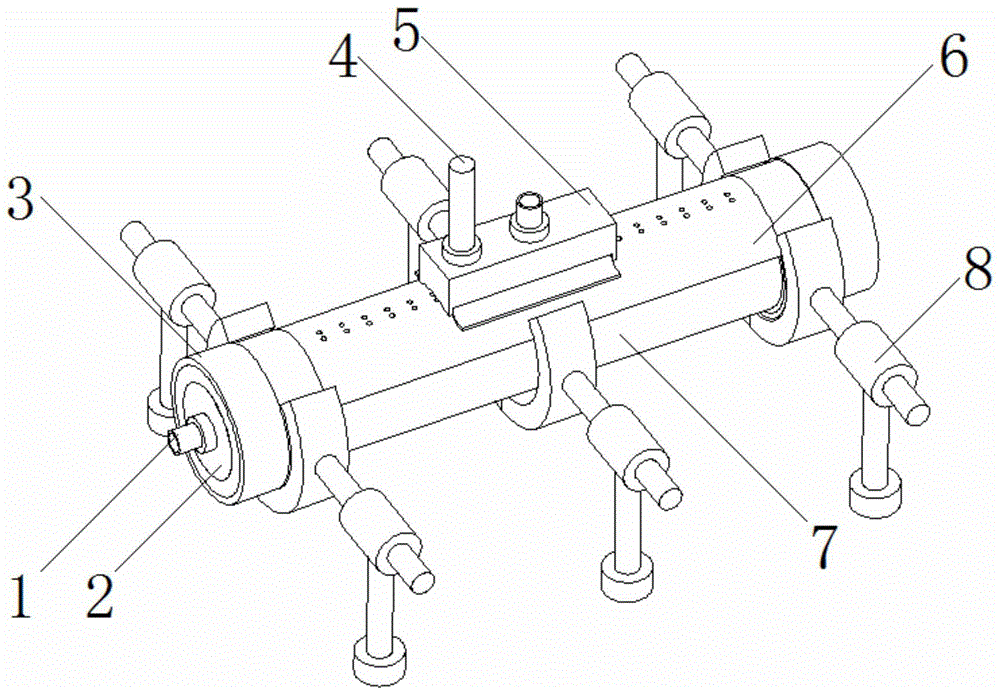
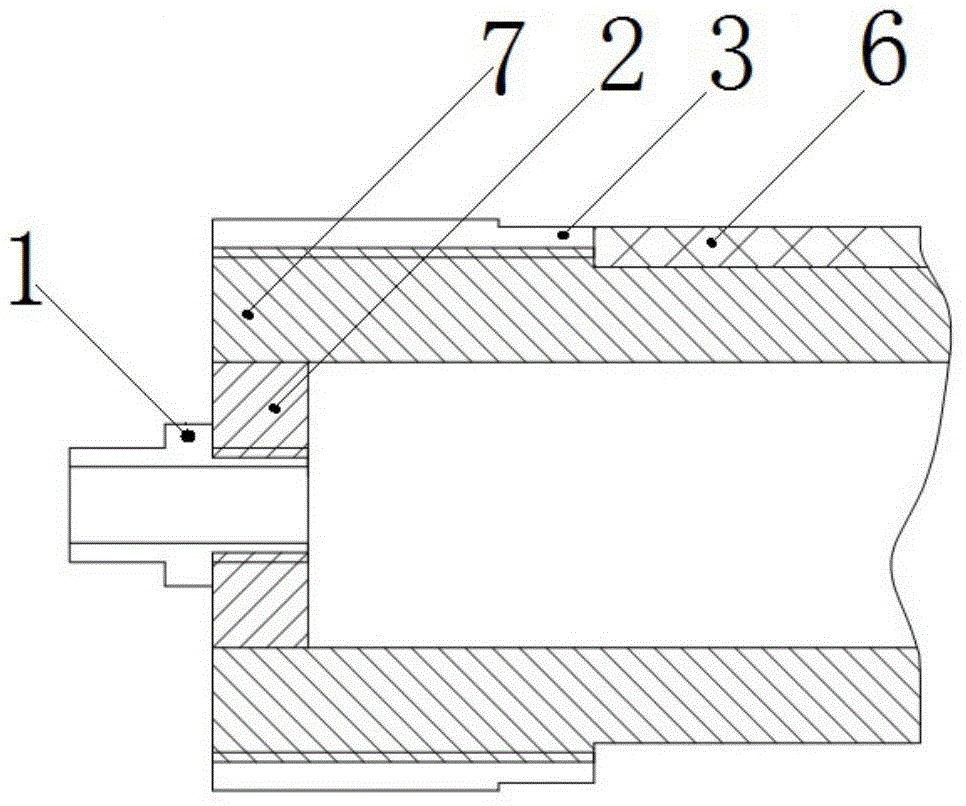
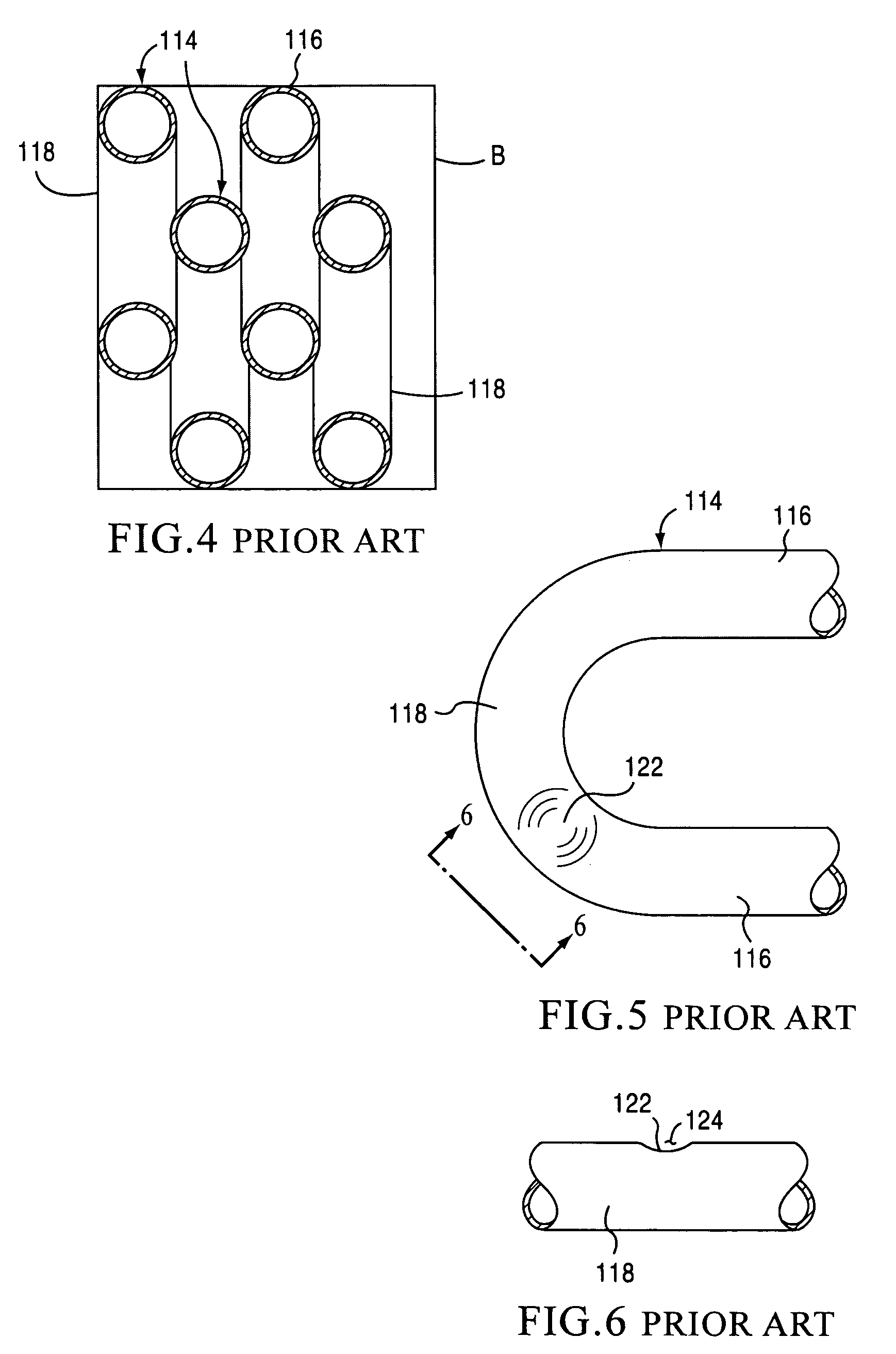
Vibratory transducer
InactiveUS6920798B2Easy to manufactureEasy to bendMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCross sensitivityStraight tube
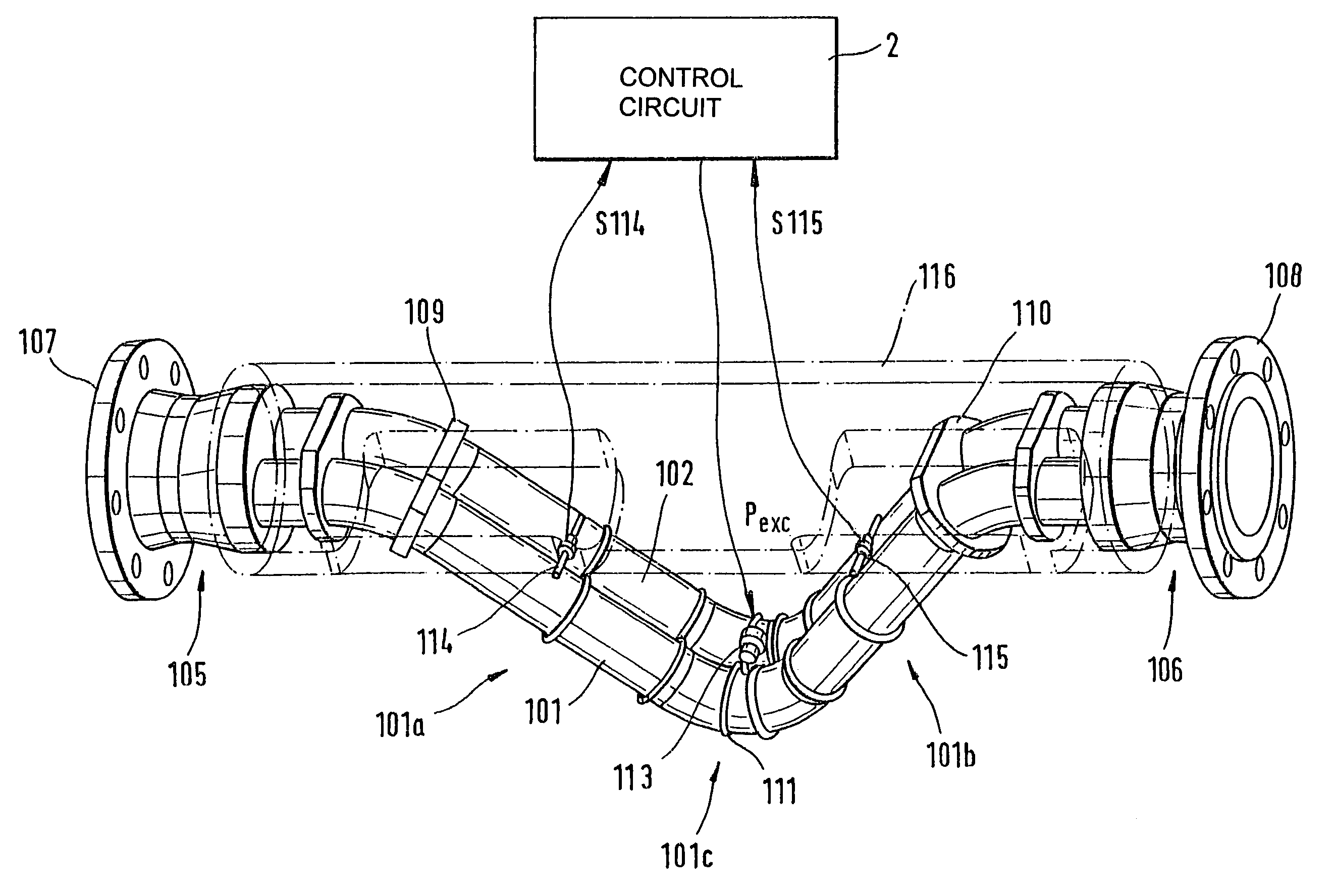
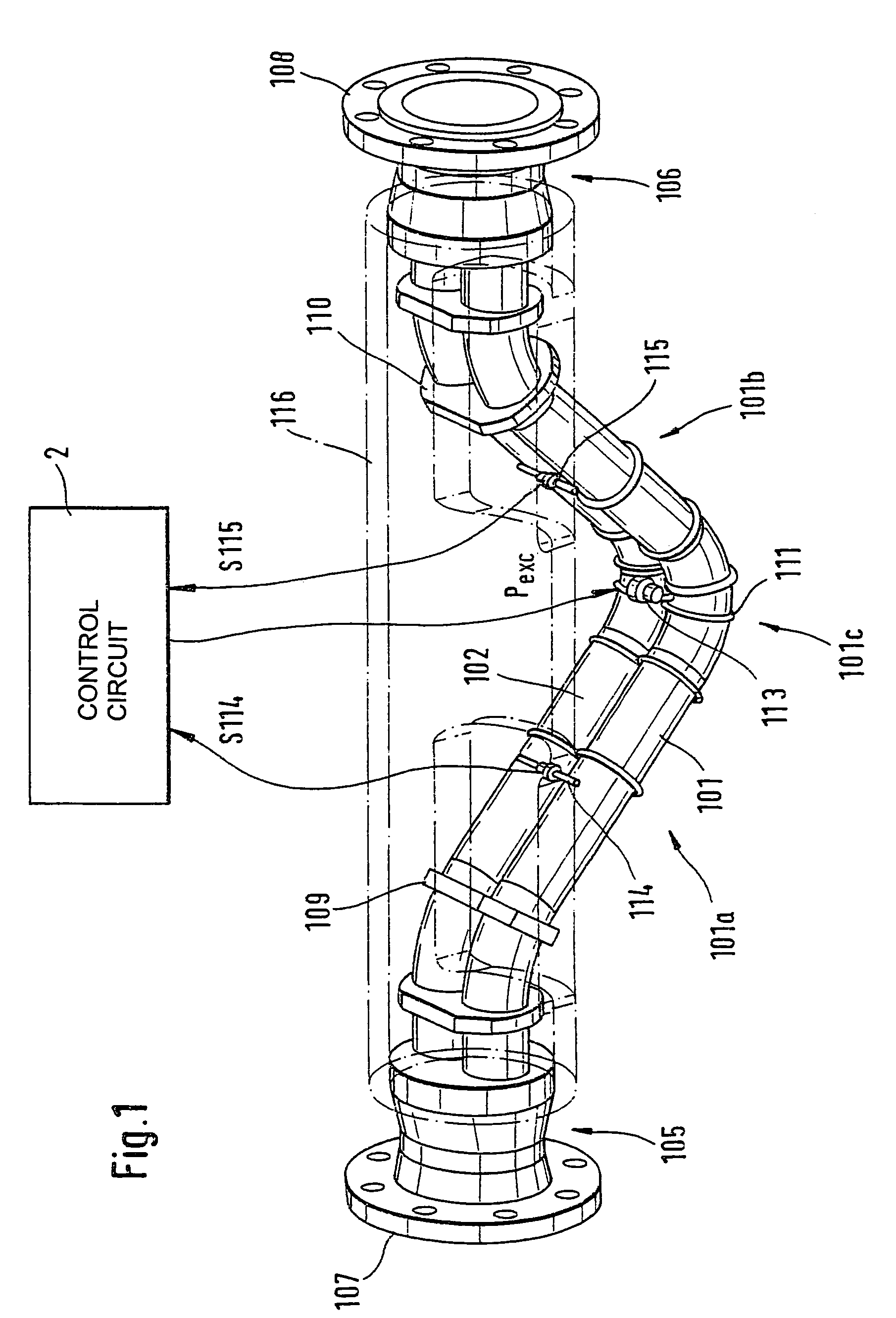
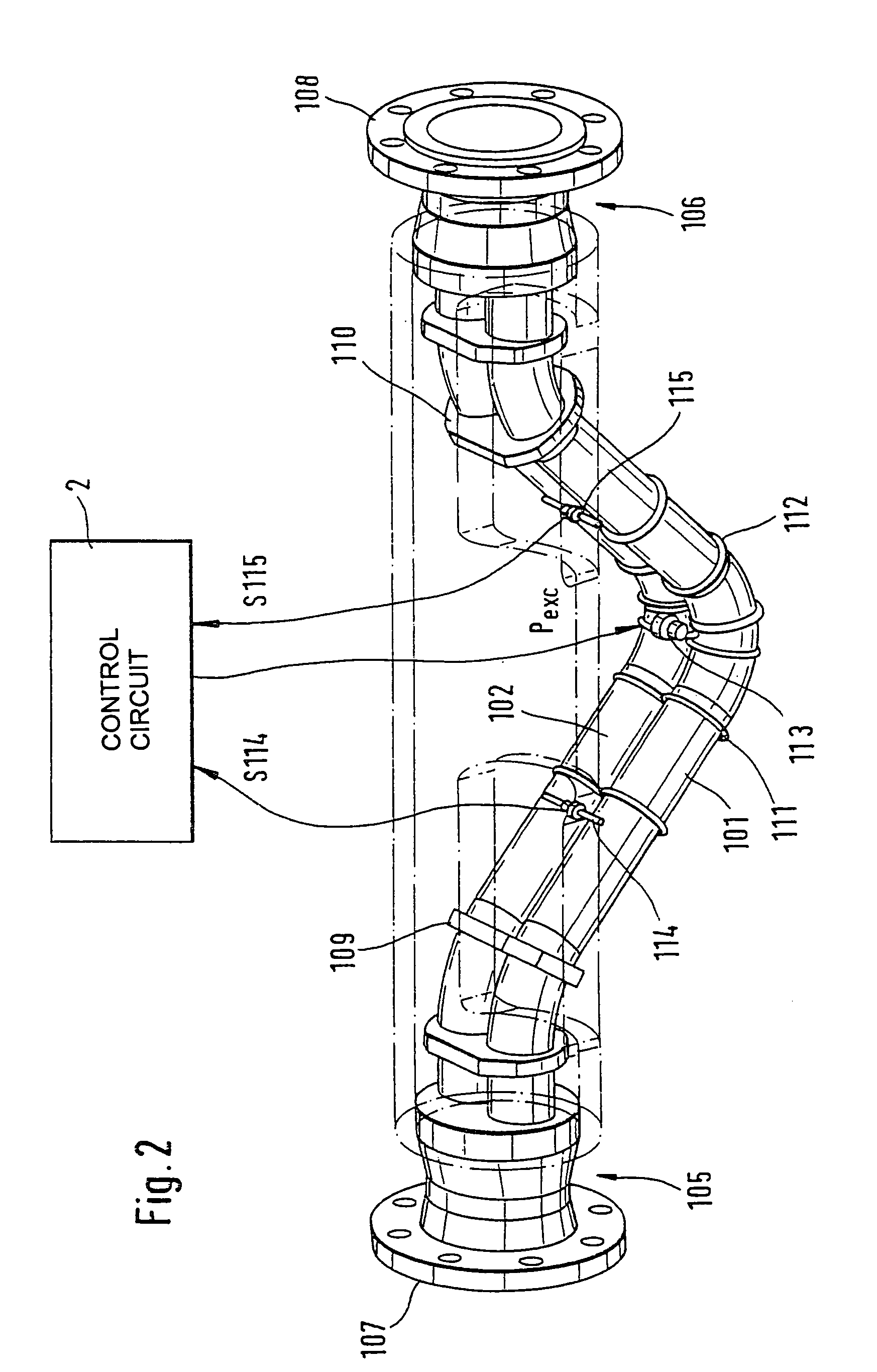
The transducer (1) has at least one at least temporarily vibrating flow tube (101) of predeterminable lumen for conducting a fluid. The flow tube (101) communicates with a connected pipe via an inlet tube section (103), ending in an inlet end, and an outlet tube section (104), ending in an outlet end, and in operation performs flexural vibrations about an axis of vibration joining the inlet and outlet ends. The flow tube (101) has at least one arcuate tube section (101c) of predeterminable three-dimensional shape which adjoins a straight tube segment (101a) on the inlet side and a straight tube segment (101b) on the outlet side. At least one stiffening element (111, 112) is fixed directly on or in close proximity to the arcuate tube segment (101c) to stabilize the three-dimensional shape. By means of the at least one stiffening element (111, 112), the cross sensitivity of the transducer (1) is greatly reduced, so that cross talks from pressure to mass flow signals are minimized and the accuracy of the transducer is improved.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
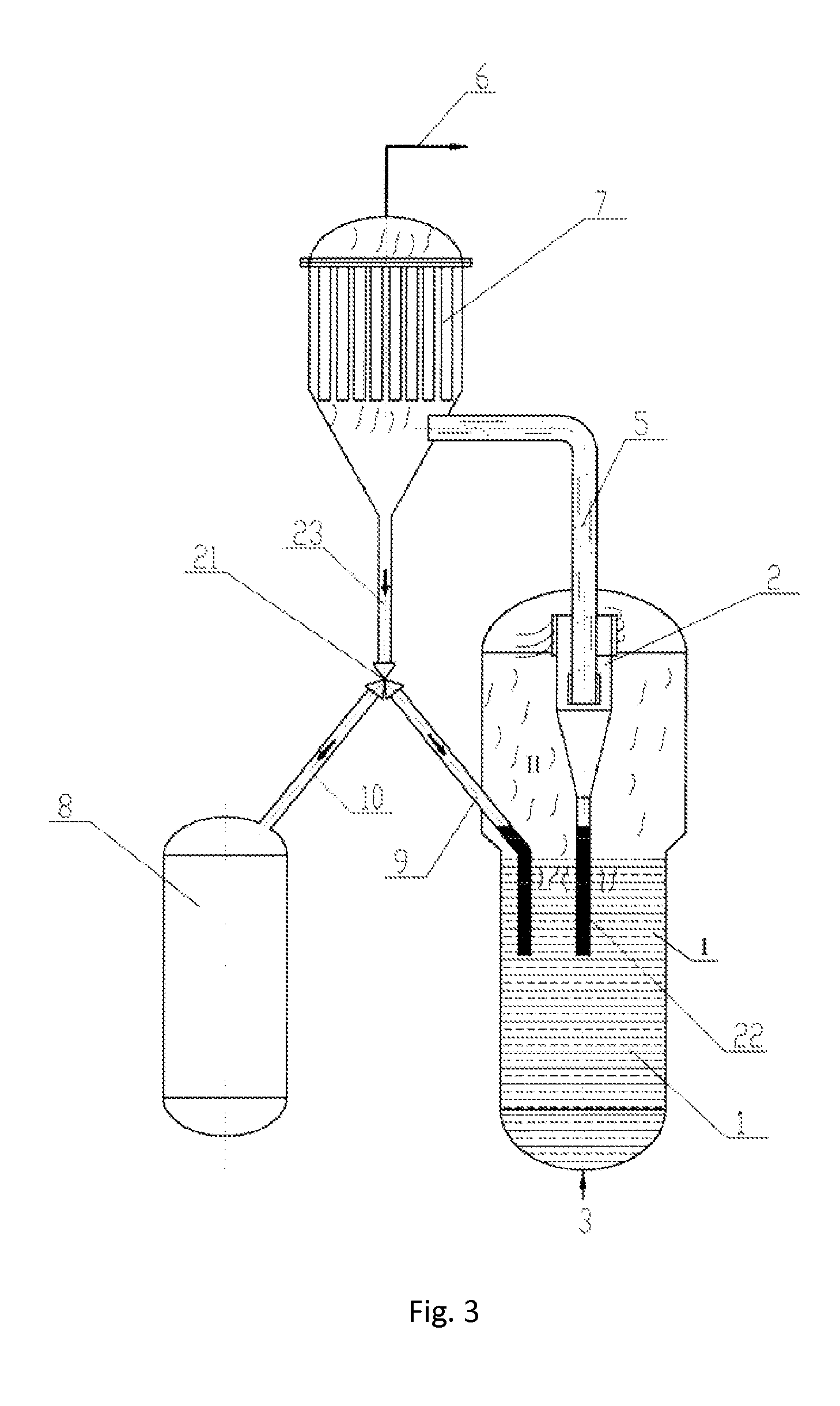
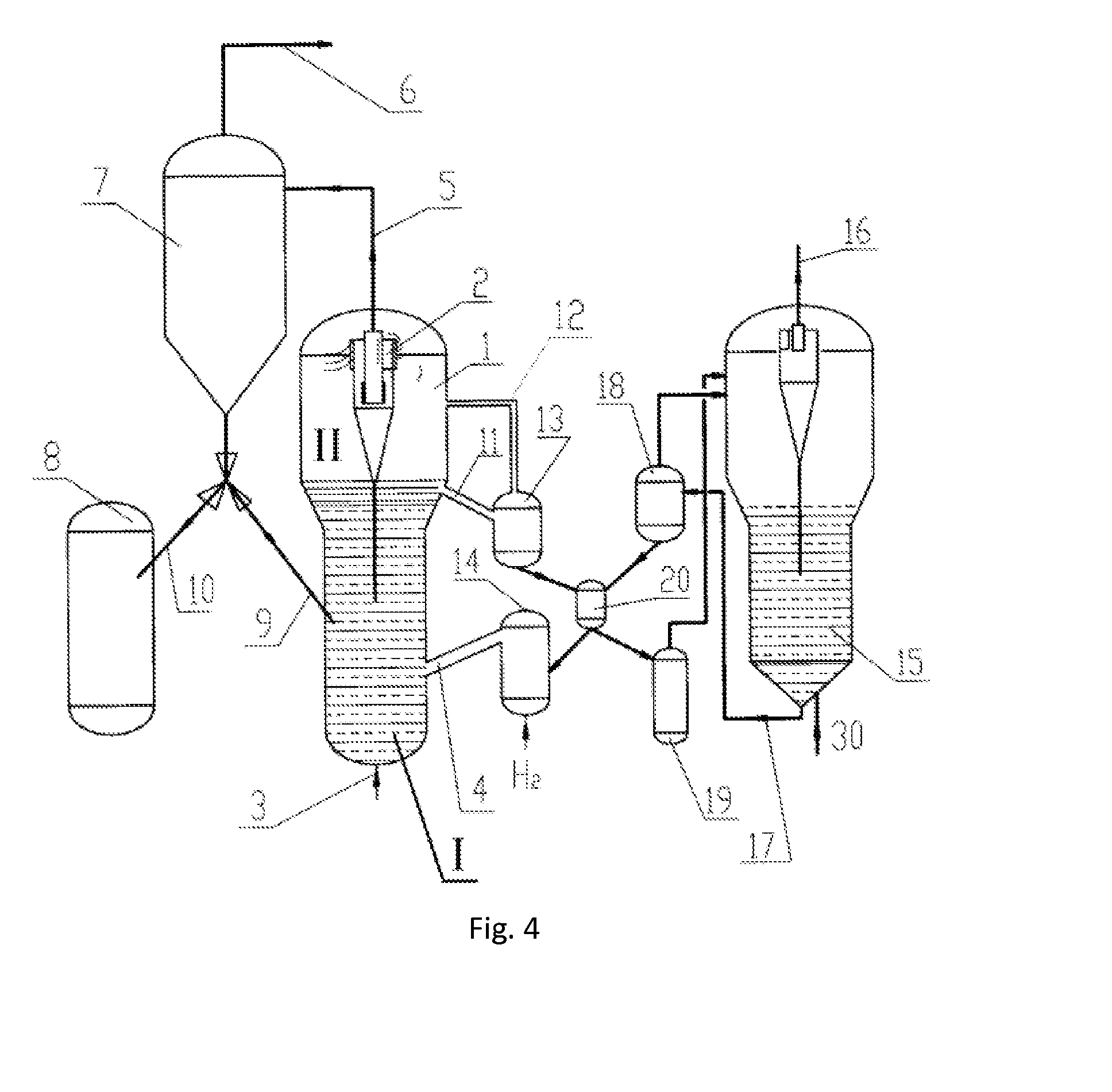
Adsorption Desulfurization Process for Hydrocarbons and a Reaction Apparatus Therefor
ActiveUS20140121438A1Efficient removalReduce flow rateReversed direction vortexHydrocarbonsFluidized bedStraight tube
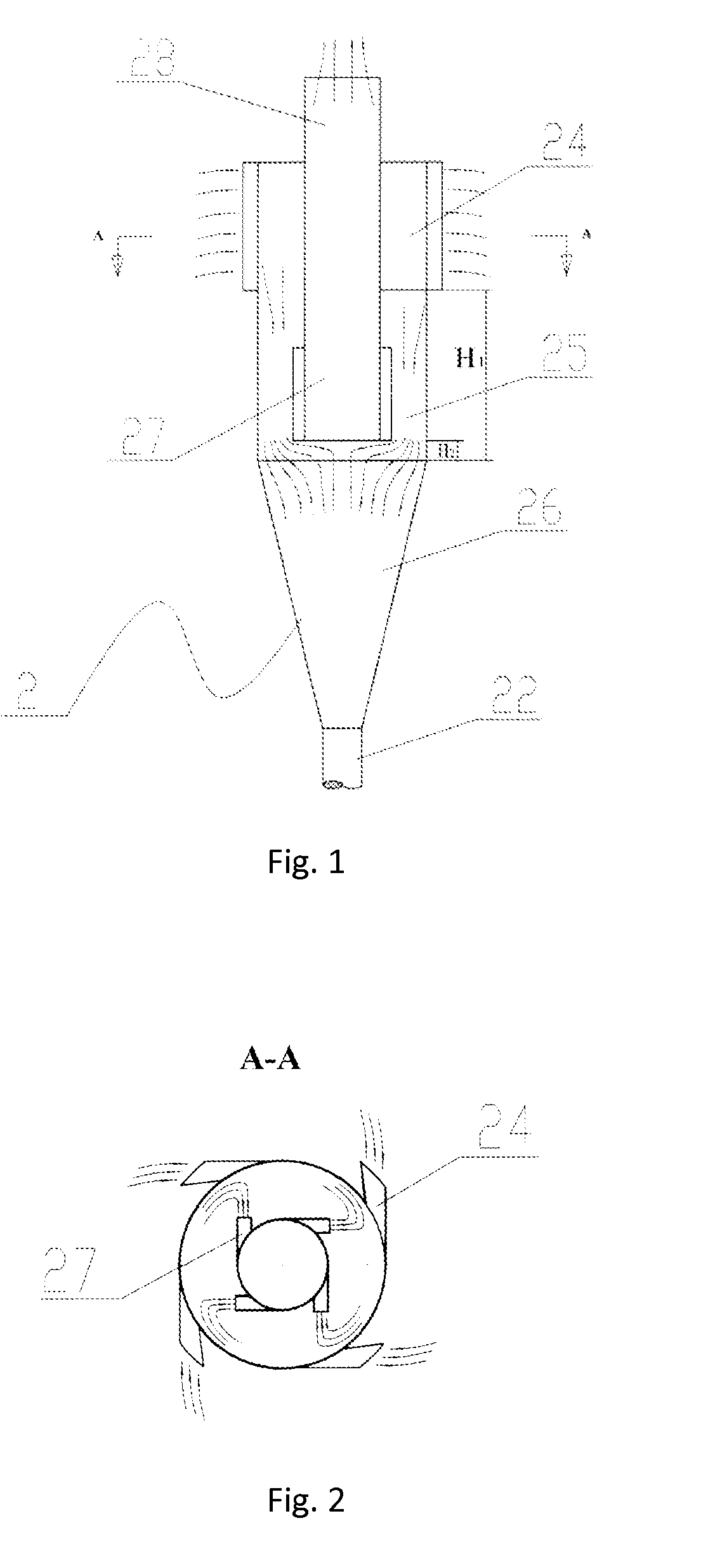
The present invention relates to an airflow particle sorter, comprising: a top-sealed sorter main body, a discharge port, an outtake tube and at least one directing-intake port; the inner space of the sorter main body, from the above to the bottom, includes, a straight tube zone and a cone zone, the conical bottom of the cone zone is connected to the straight tube zone; the discharge port is located at the bottom of the cone zone; the directing-intake port is installed in the upper part of the straight tube zone in a tangential direction of the straight tube zone, and is communicated with the inner space of the sorter main body; the outtake tube is hermetically inserted into the top of the sorter main body, and extends downwardly to the lower part of the straight tube zone, and the outtake tube has a sealed bottom end; the lower part of the outtake tube is installed with at least one directing-outtake port, which communicates the outtake tube with the inner space of the sorter main body, the directing-outtake port is installed in a tangential direction of the outtake tube. The present invention further relates to a fluidized bed reactor and an adsorption desulfurization reaction apparatus as well as an adsorption desulfurization process.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Stent delivery catheter
InactiveUS20040267280A1Large outer diameterIncreasing the thicknessStentsBalloon catheterInsertion stentBalloon catheter
The present invention provides a stent delivery catheter that can place a stent in a tortuous narrowed area with good maneuverability while preventing falling or displacement of the stent. The present invention provides a stent delivery catheter for delivering a stent for treating stenosis in a body to a narrowed area. A distal end of the catheter includes a collapsible balloon in a collapsed state and the stent in an undeployed state, the stent being mounted on the outer surface of the collapsed balloon, the balloon having frustoconical tapered segments and a cylindrical straight tubular segment. An inner tube for defining a guidewire lumen extends into the interior of the balloon, and displacement prevention mechanisms for preventing the stent from moving in the longitudinal direction of the stent delivery catheter are affixed to the inner surface of the balloon only. Another aspect of the present invention provides a stent delivery catheter that can prevent the stent from moving in the axis direction of the catheter without requiring additional components or additional steps that complicate the manufacturing process. In this catheter, the thickness T1 of a near-center portion of the distal-end tapered segment and the thickness T2 of a near-center portion of the straight tubular segment satisfy a predetermined relationship, and the thickness T3 of a near-center portion of the proximal-end tapered segment and the thickness T2 of the near-center portion of the straight tubular segment satisfy a predetermined relationship. In this manner, the distal-end and proximal-end tapered segments in the collapsed state prevent the movement of the stent. The present invention also provides a preferable RX balloon catheter, i.e., a stent delivery catheter, having improved maneuverability and enhanced responsiveness for expansion and contraction of the balloon without complicating the manufacturing process or increasing the cost.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Lighting source and lighting apparatus
ActiveUS20150077001A1Changing brightnessChanging consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight equipmentConstant power
A straight tube LED lamp according to one aspect of the present invention includes: a first LED array including first LED elements connected in series; a second LED array that includes second LED elements connected in series, and emits light having a different emission color from an emission color of the first LED array; a FET switch provided in a path through which current flows to the second LED array; and a constant power output circuit that outputs power without changing a total value of the power, wherein the number of the first LED elements connected in series is greater than the number of the second LED elements connected in series, a total forward voltage of the first LED array is greater than a total forward voltage of the second LED array, and the first LED elements are in alignment with the second LED elements.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Crawler for inspecting pipes
InactiveUS20090120215A1Extend cycle timeStructural/machines measurementPipeline systemsRoboticsStraight tube
Robotic external pipeline crawler system employs the use of logic control to provide a system capable of constantly and accurately maintaining a position at the vertex of the pipe. This apex positioning can be maintained as it traverses the length of the pipe being inspected. This system is adaptable to both straight and curved pipe, multiple pipe diameters, and will substantially reduce set up time and vertical pipeline support crossing time. The crawler system also employs an advanced bracketry system which allows quick disconnecting and auxiliary powered movement allowing for decreased cycle time across pipe supports. The unique tire interface allows for additional surface area contact making extreme environmental conditions possible.
Owner:FABTEC SOLUTIONS
Dual turbulent spiral forced heat exchanging and automatic descaling device
InactiveCN1424554AImprove heat exchange efficiencyLong-term stable jobHeat exchanger casingsFlush cleaningFixed frameStraight tube
A device of intensified heat exchange and automatic descaling in dual turbulation screw type includes screw tube, screw tie, connection rod, fixing frame and rotary rod as small end of the rotary rod sheathed into hole at exle liquid input end of fixing frame to form rotation cooperation, end point of small end of the rotary rod to be connected by connecting piece in hinge joint with end point of one end of the screw tie, the screw tube with external circle and intermediate internal hole being all the straight tube of screw shape and two end parts being round tube shape to be set on external cylindrical surface of cylinder shape end of the fixing frame. The present invention uses technique of combining the screw tube with the screw tie to bring the screw tie to rotate by flowing of fluid in the screw tube to make no fouling within the tube and heat conduction face can carry on desaling automatically under the dual turbulation of the screw tube and tie to enhance more the efficiency of heat exchange.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
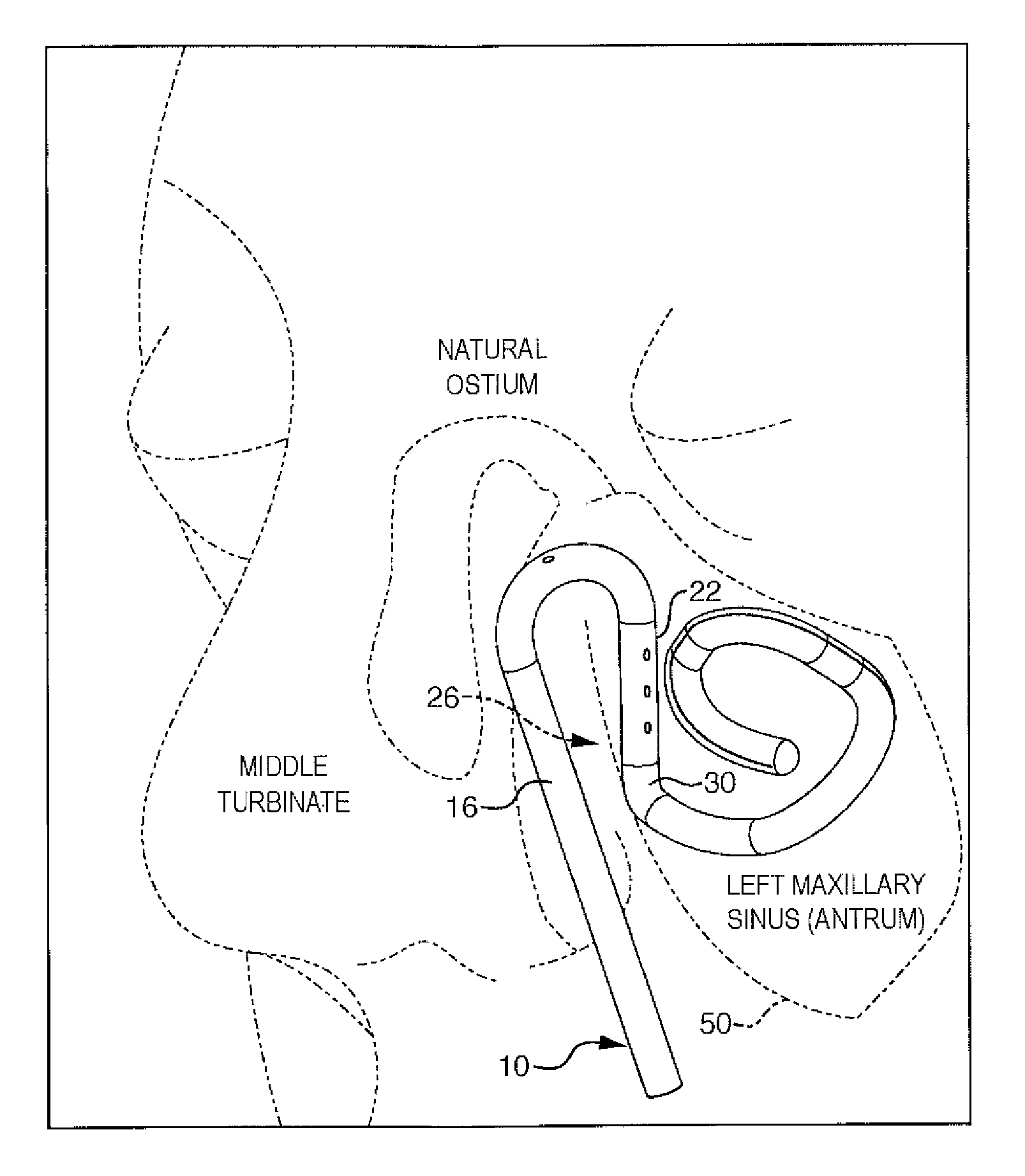
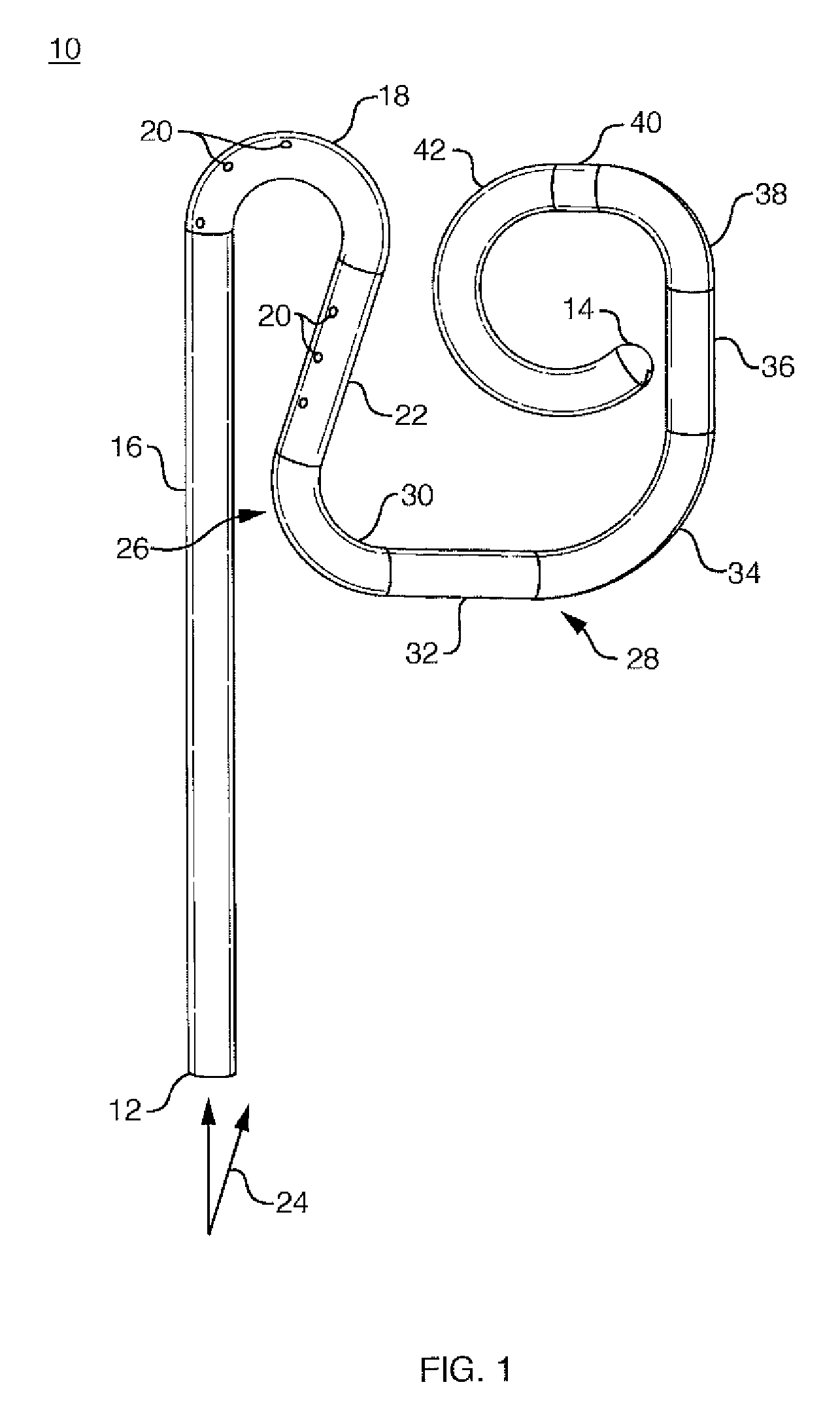
Stent for irrigation and delivery of medication
A stent comprises a flexible tube having a proximal end, a distal end, and a passageway extending from said proximal end toward said distal end. A first generally straight tube segment extends from the proximal end while a first generally curved segment extends from an end region of the first generally straight tube segment disposed away from the proximal end of the stent. A second generally straight tube segment extends from an end region of the first curved segment away from the first generally straight tube segment and is arranged at an acute angle relative to the first generally straight tube segment. A second generally curved tube segment extends from one end of the second generally straight tube segment and includes a channel on an exterior surface of the second generally curved tube segment. The first generally curved tube segment and the second generally straight tube segment further include at least one cavity irrigation hole extending from the tube passageway, for providing irrigation fluids into the cavity into which the stent is inserted. At least one segments includes a channel on an exterior surface. The channel is sized to serve as a reservoir to contain a predetermined amount of at least one form of medication for delivery, over a period of time, of the medication to a cavity region proximate which the stent has been inserted.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
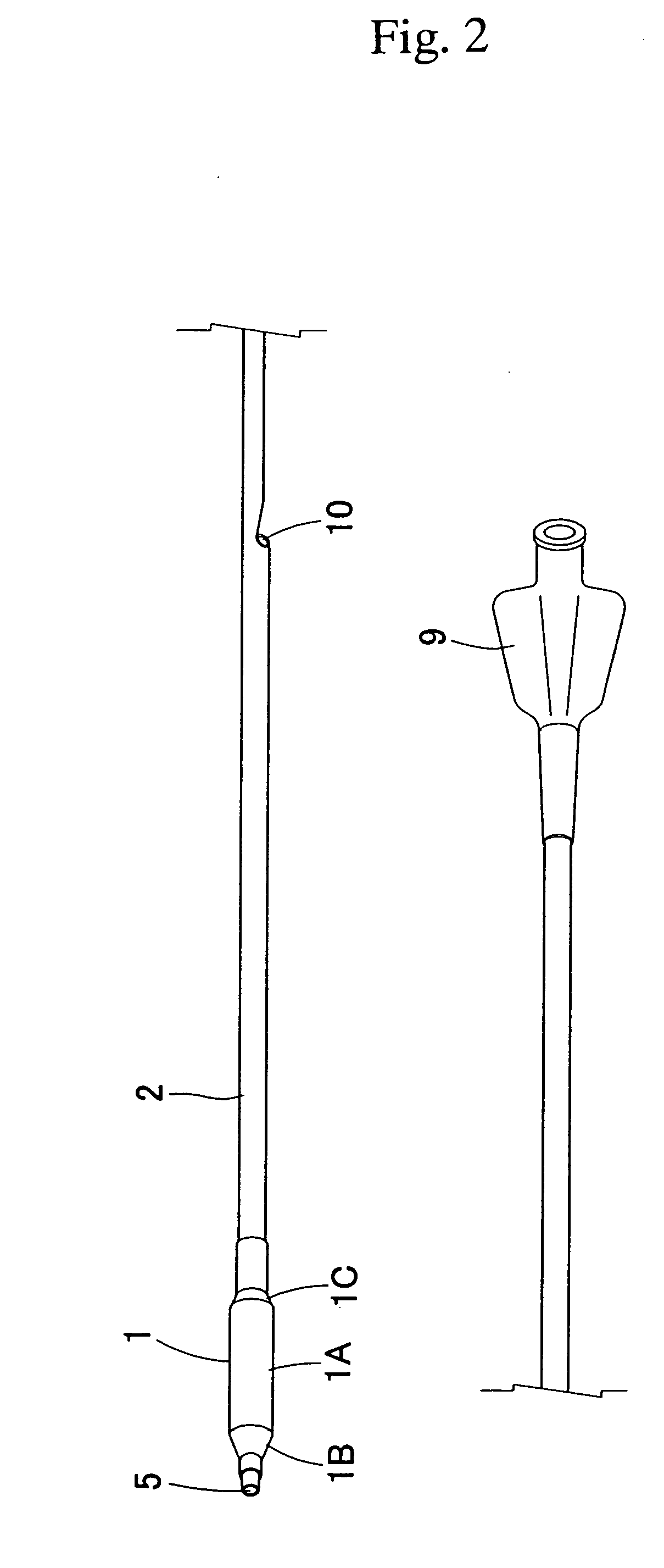
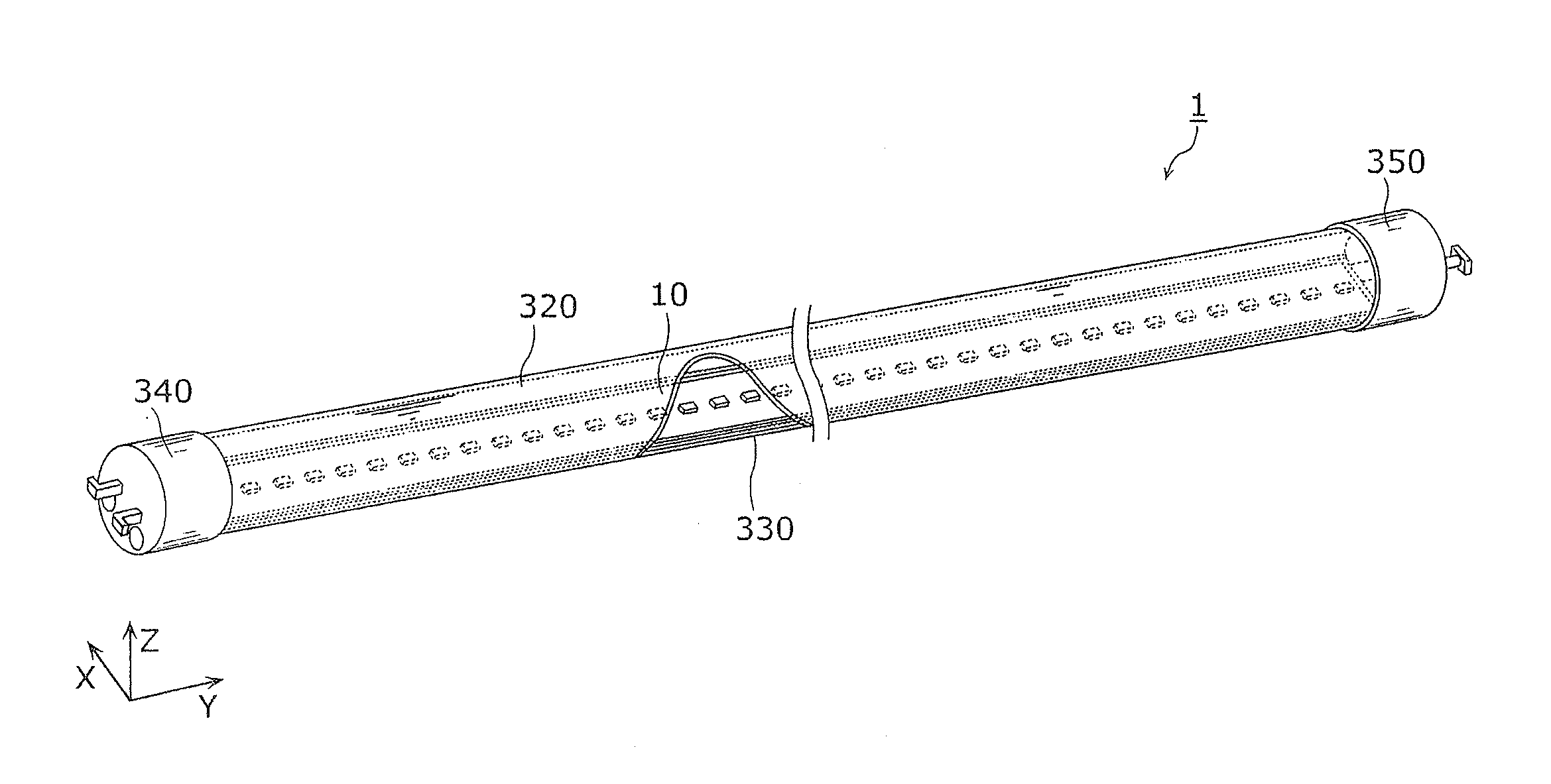
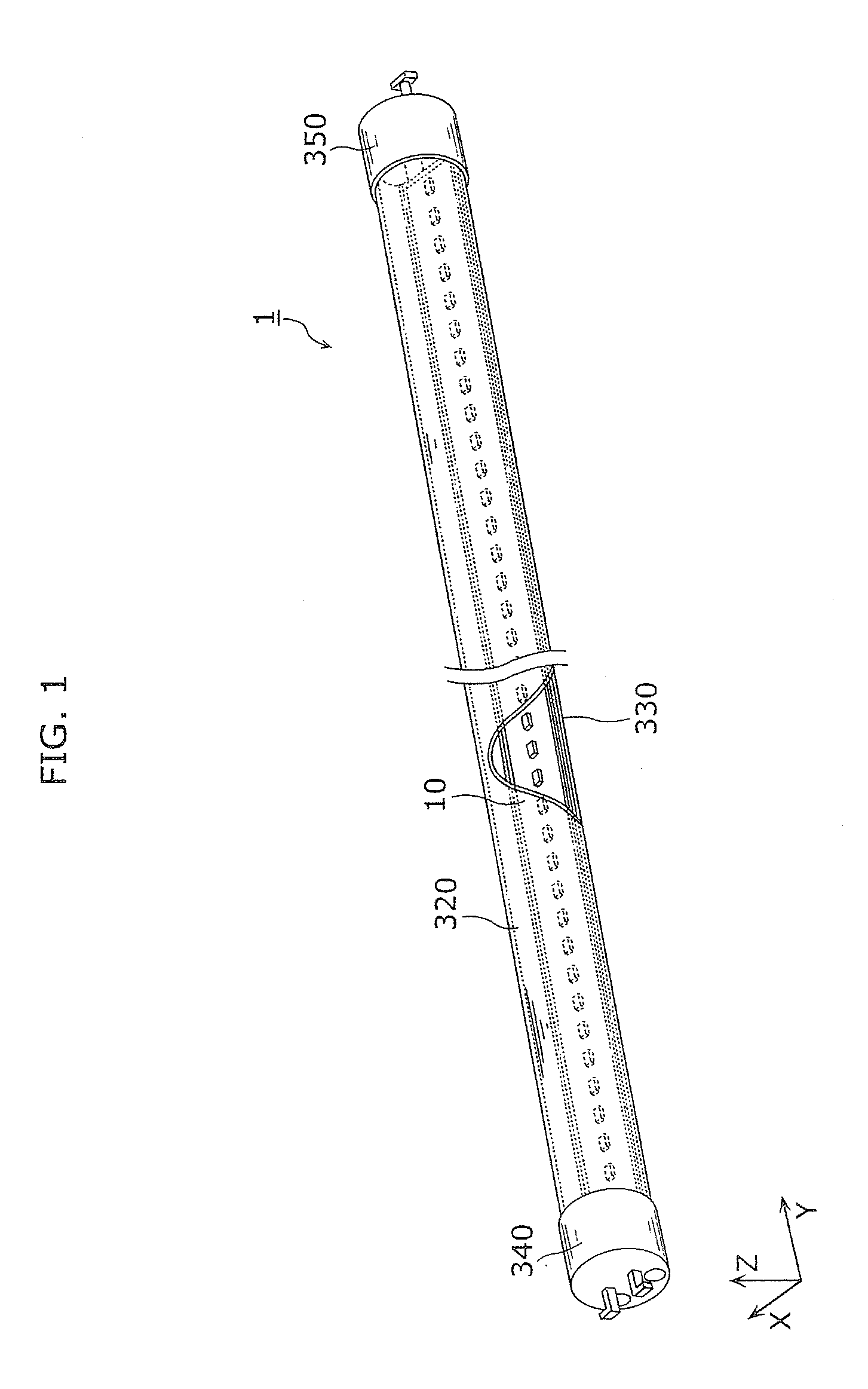
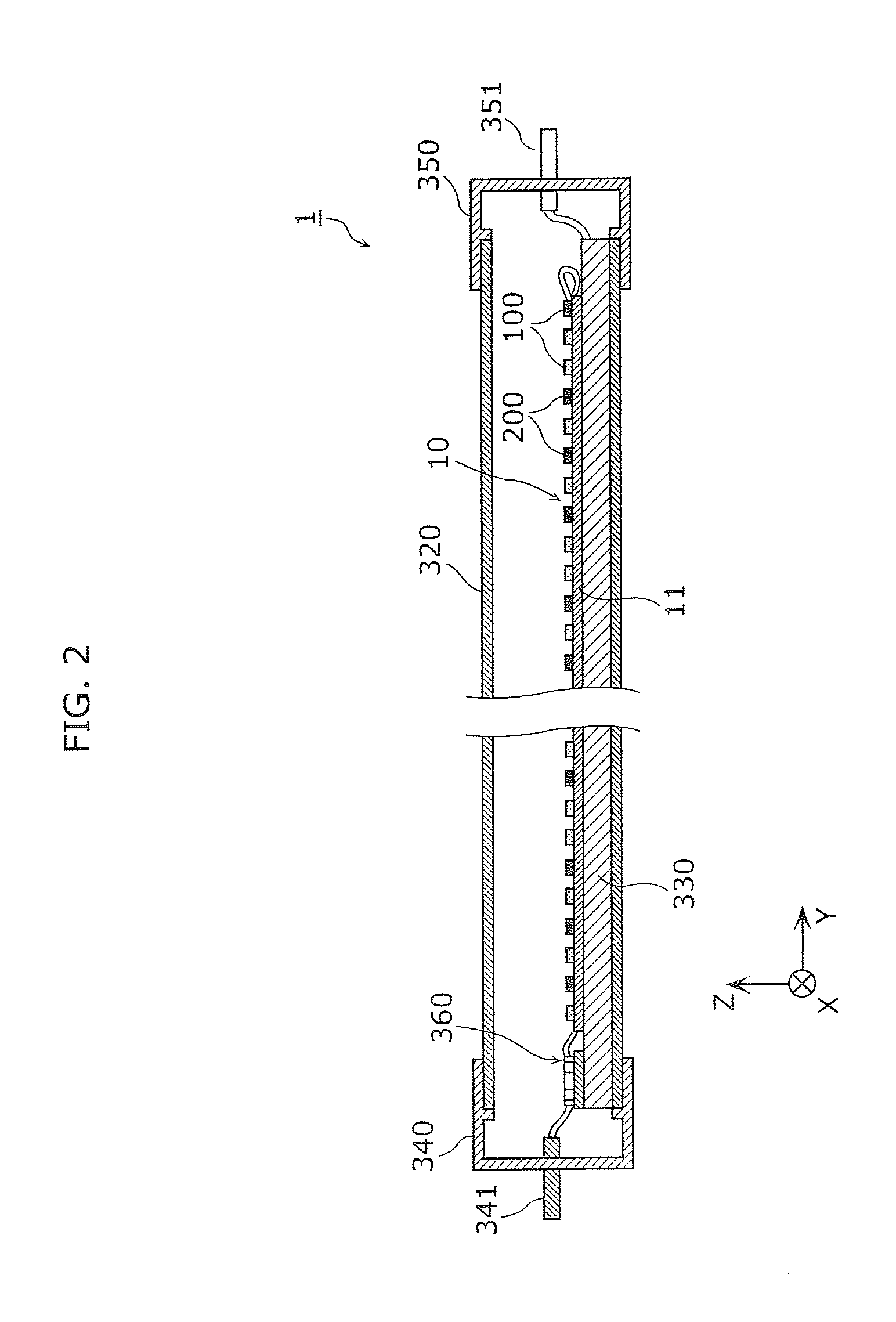
Straight tube LED lamp, lamp socket set, and lighting fixture
ActiveUS20130119896A1Reduce riskPoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesStraight tubeElectrical connection
A straight tube LED lamp includes: a straight tube in which a plurality of light emitting diodes is housed; a first cap for forming a power feeding connection to the plurality of light emitting diodes, provided on one axial direction end side of the straight tube; and a second cap for grounding, provided on another axial direction end side of the straight tube. A first terminal for forming an electrical connection to a power feeding terminal of a first lamp socket is provided in the first cap. A second terminal for forming an electrical connection to a grounding terminal of a second lamp socket is provided in the second cap.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +1
Therapeutic light source and method
InactiveUS6626932B2Increase intensityIncrease the areaOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhotodynamic therapyStraight tube
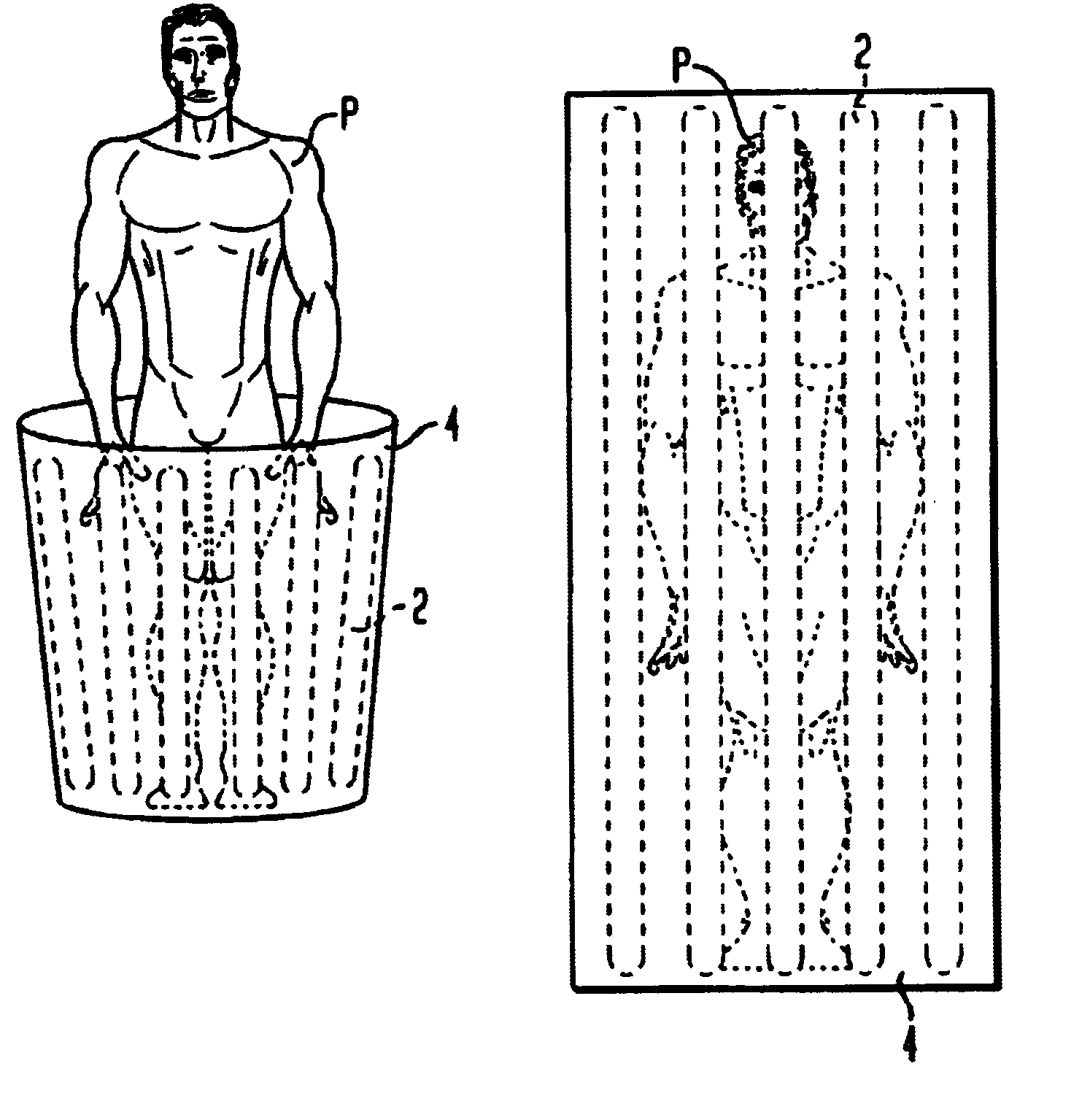
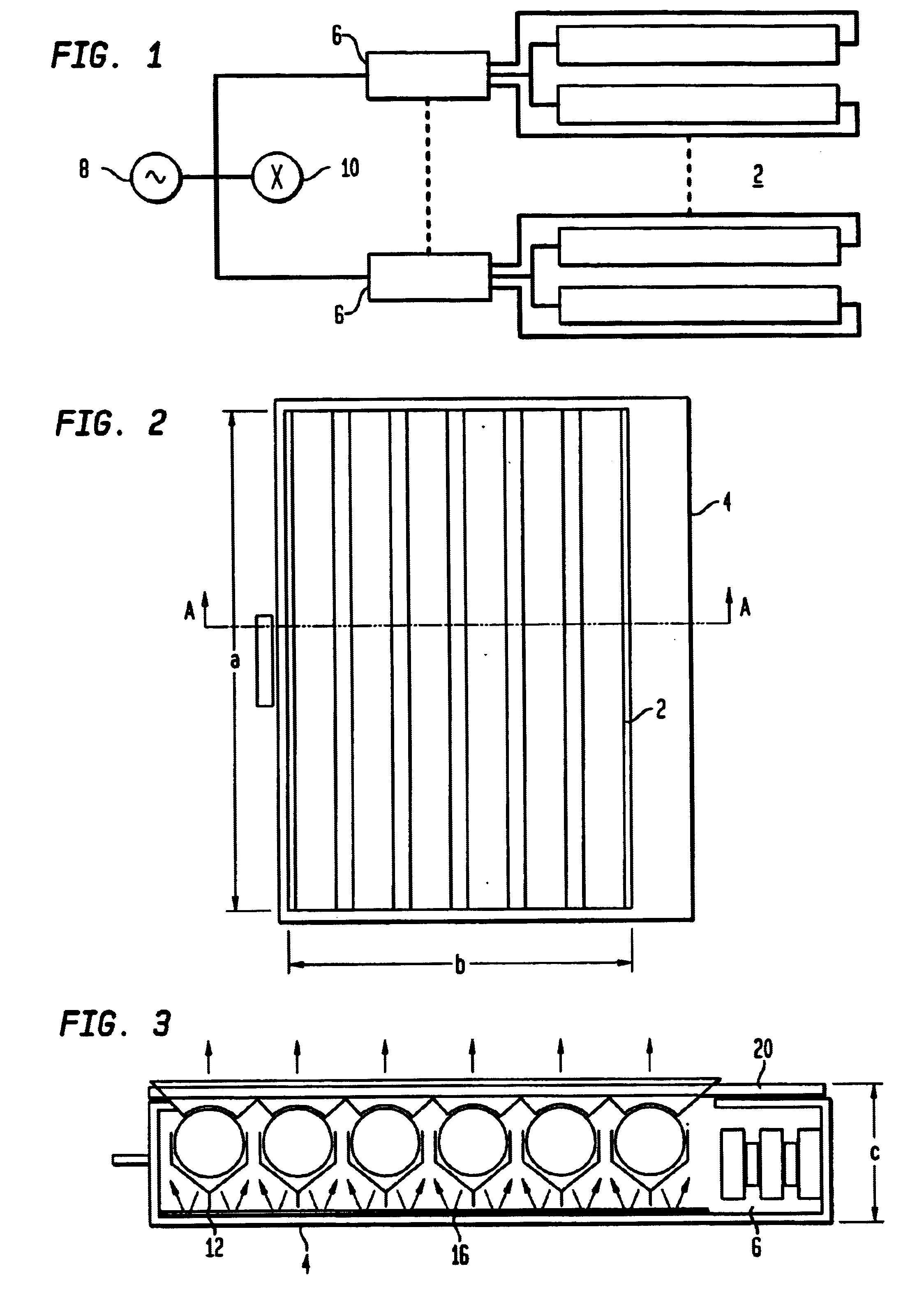
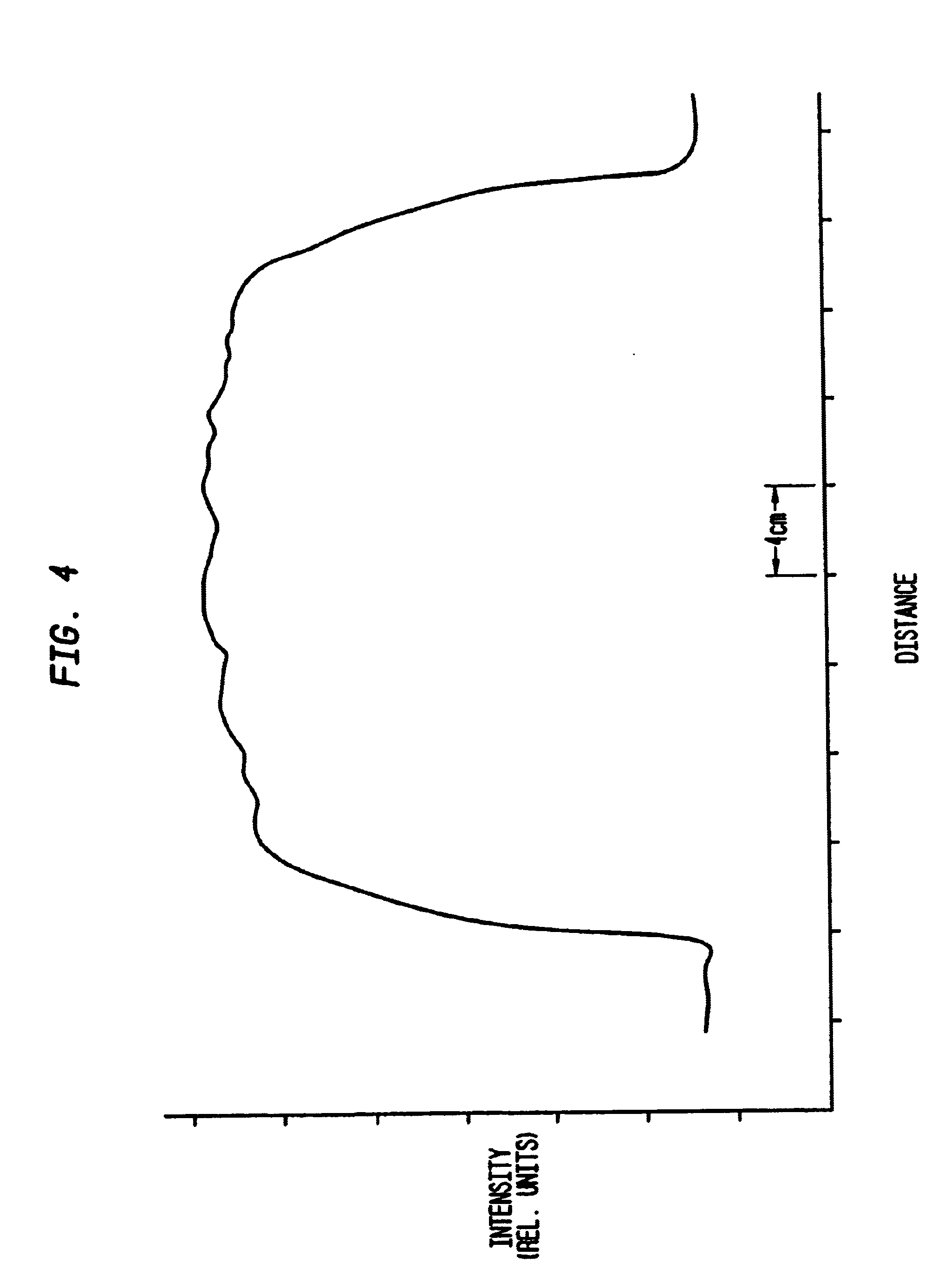
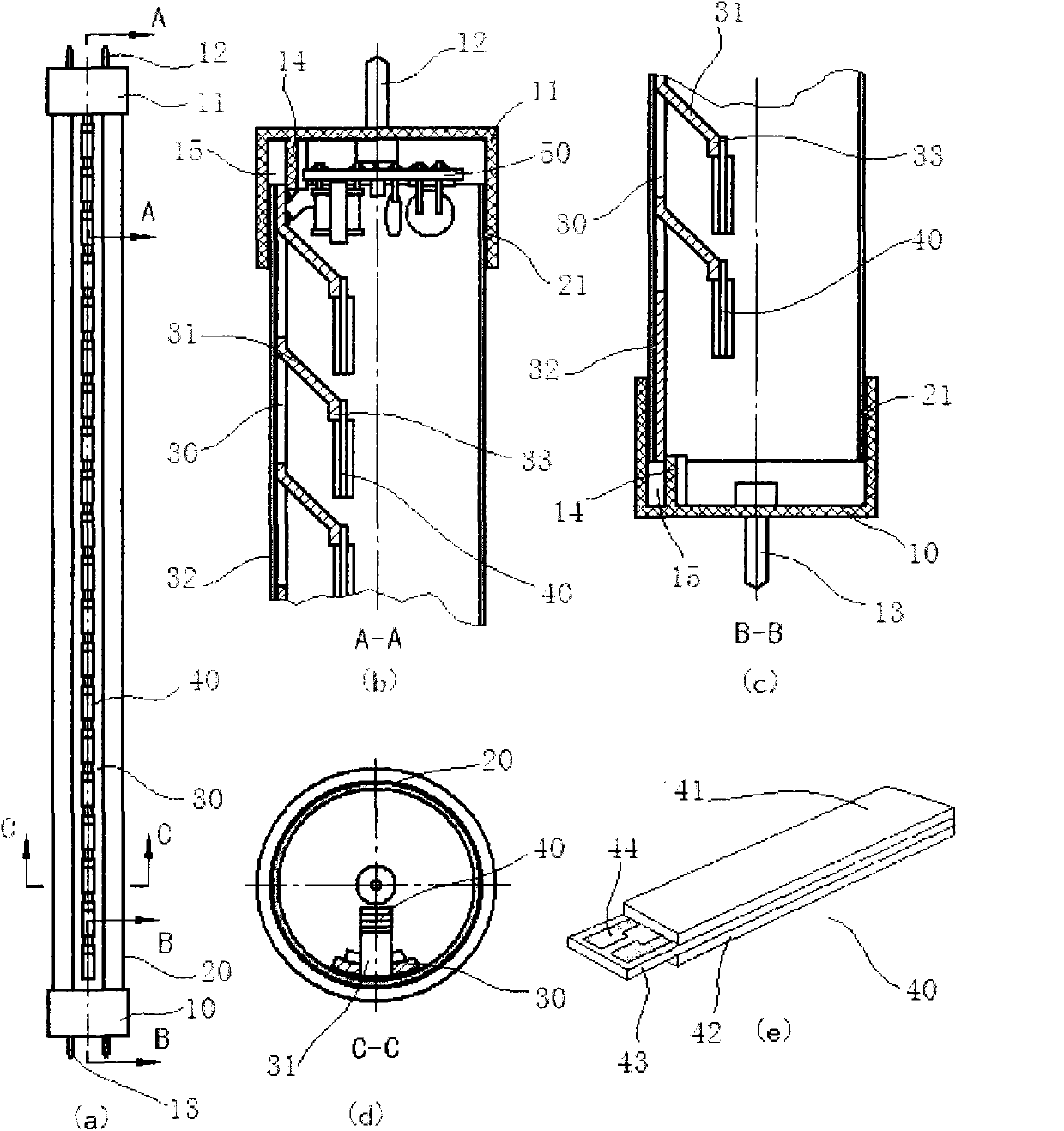
A light source for therapy, such as photodynamic therapy, comprises one or more low pressure or medium / high pressure discharge tubes. In one aspect, the light source comprises a non-planar array of substantially straight tubes. In another aspect, the light source comprises one or more such tubes mounted in a housing having an aperture allowing part of the patient to be located within the housing.
Owner:THE LOTUS GLOBAL GRP INC DBA GLOBALMED TECH CO
LED straight lamp made of transparent glass tube
InactiveCN103742875AReduce cooling requirementsFit tightlyPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesBeam angleStraight tube
The invention discloses an LED straight lamp made of a transparent glass tube. The LED straight lamp comprises a transparent glass tube body (20) and two lamp holders (10 and 11). Both the transparent glass tube body (20) and the lamp holders (10 and 11) meet the specifications of an ordinary straight tube fluorescent lamp, and the lamp holders (10 and 11) are respectively adhered to two ends of the transparent glass tube body (20). The LED straight lamp made of the transparent glass tube can also be made by the glass burn sealing technology of the ordinary straight tube fluorescent lamp. LED lamp filaments are directly welded to welding platforms (33) of LED supports (31) in the middle of an aluminum substrate (30). The outside of the bottom cross section of the aluminum substrate (30) is circular arc shaped with the curvature matching with that of the inner side of the cross section of the transparent glass tube body (20). Enough height is to be reserved between the welding platforms (33) and the aluminum substrate (30) so that light emitted from the LED lamp filaments is orthogonal to the inner wall of the transparent glass tube body (20), light consumption brought by multiple reflections is reduced, and the beam angle of the LED straight lamp made of the transparent glass tube can reach more than 300 degrees.
Owner:匡正芳
Rotatable and shape-changeable christmas tree
A rotatable and shape-changeable Christmas tree, wherein the trunk of the tree is pivotally installed on a base, and the trunk includes a plurality of straight pipes and a plurality of bent pipes being assembled to one another, on each of the straight pipes is arranged a bearing on which being mounted an annular support device, and between neighboring annular support devices are arranged a plurality of decorative leaves. During rotation of the trunk relative to the base, the annular support devices will be driven to rotate, and the decorative leaves will rotate along with the annular support devices and will appear to change in shape during the rotation of the annular support devices.
Owner:CHUN CHANG LIN
LED straight-tube lamp
PendingCN105465640AAvoid Electric Shock AccidentsAvoid breakingElongate light sourcesElectric circuit arrangementsFlexible circuitsStraight tube
The invention discloses an LED straight-tube lamp comprising a lamp tube, a lamp cap, a power source and a lamp panel, wherein the lamp cap is arranged at one end of the lamp tube; the power source is arranged in the lamp cap; the lamp panel is arranged in the lamp tube and is provided with a light source; the light source is electrically communicated with the power source through the lamp panel; and the lamp panel is a flexible circuit board of which the end part is provided with a light source pad, and holes are formed in the light source pad. The flexible circuit board is directly welded at the power output end of the lamp cap, so that the quality problem caused by conducting wire migration breakage generated by a wire bonding way in the production, transportation and use processes can be avoided.
Owner:JIAXING SUPER LIGHTING ELECTRIC APPLIANCE
Lighting device
InactiveUS20130170245A1Well representedImprove light uniformityMechanical apparatusFibre light guidesLight guideStraight tube
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
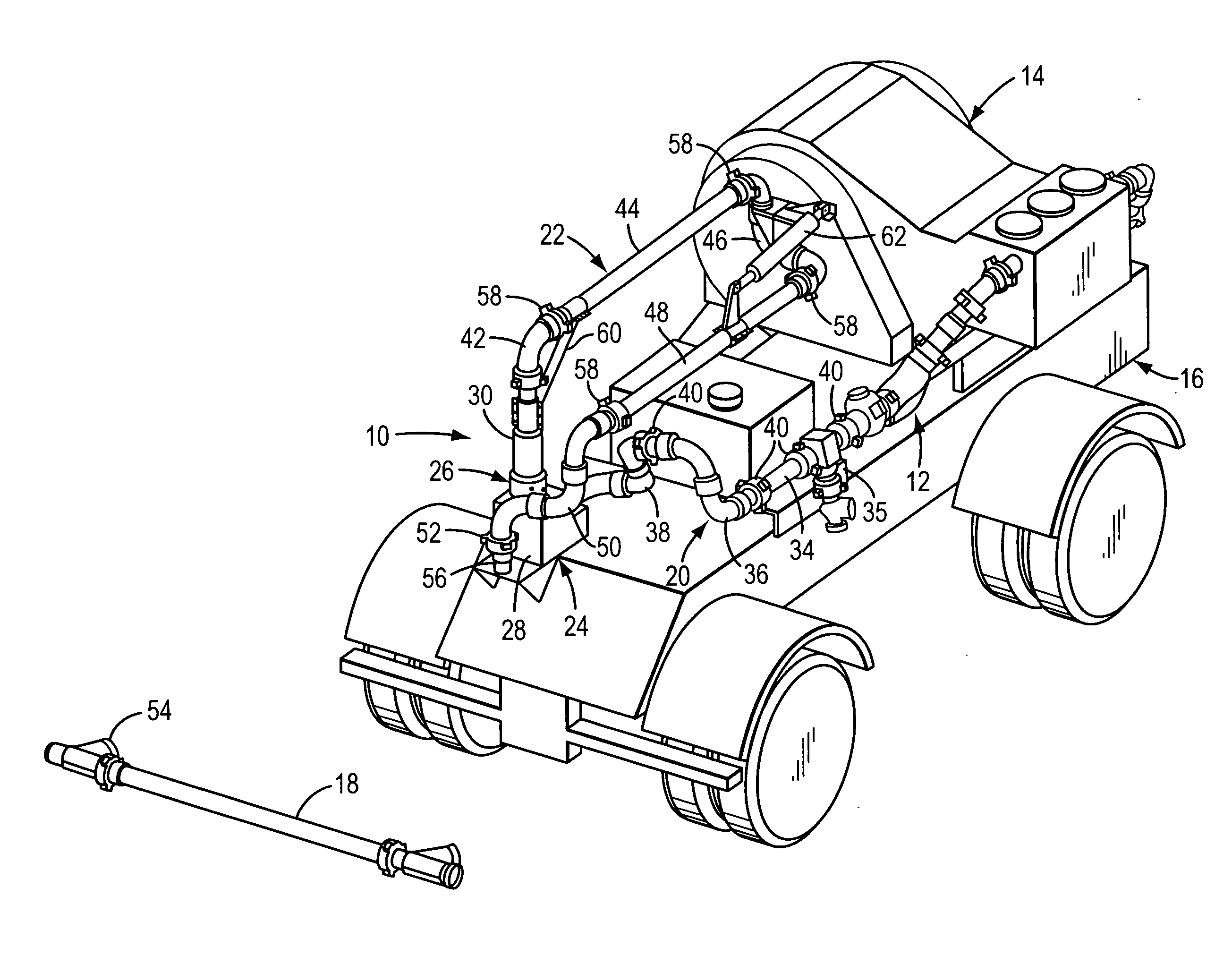
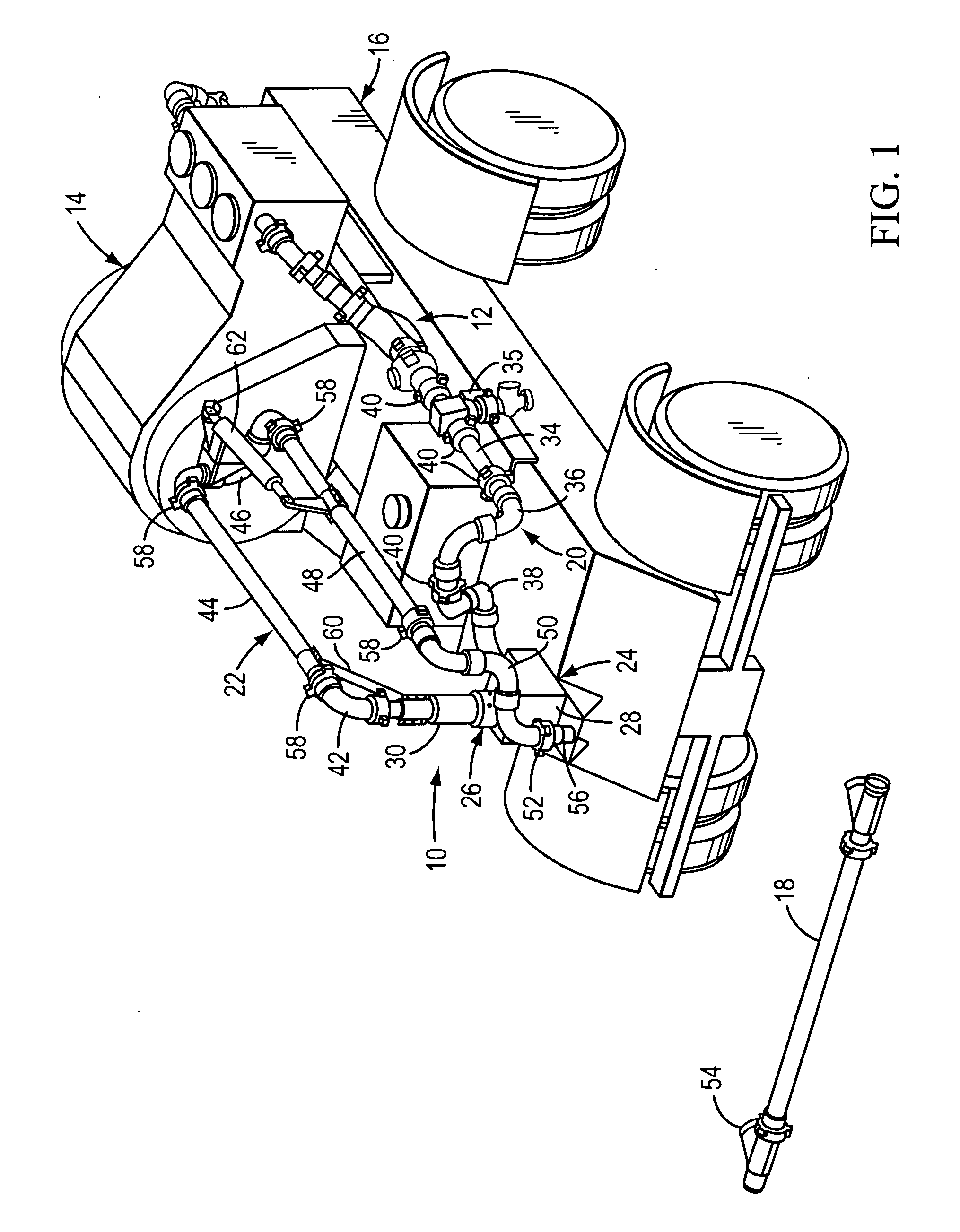
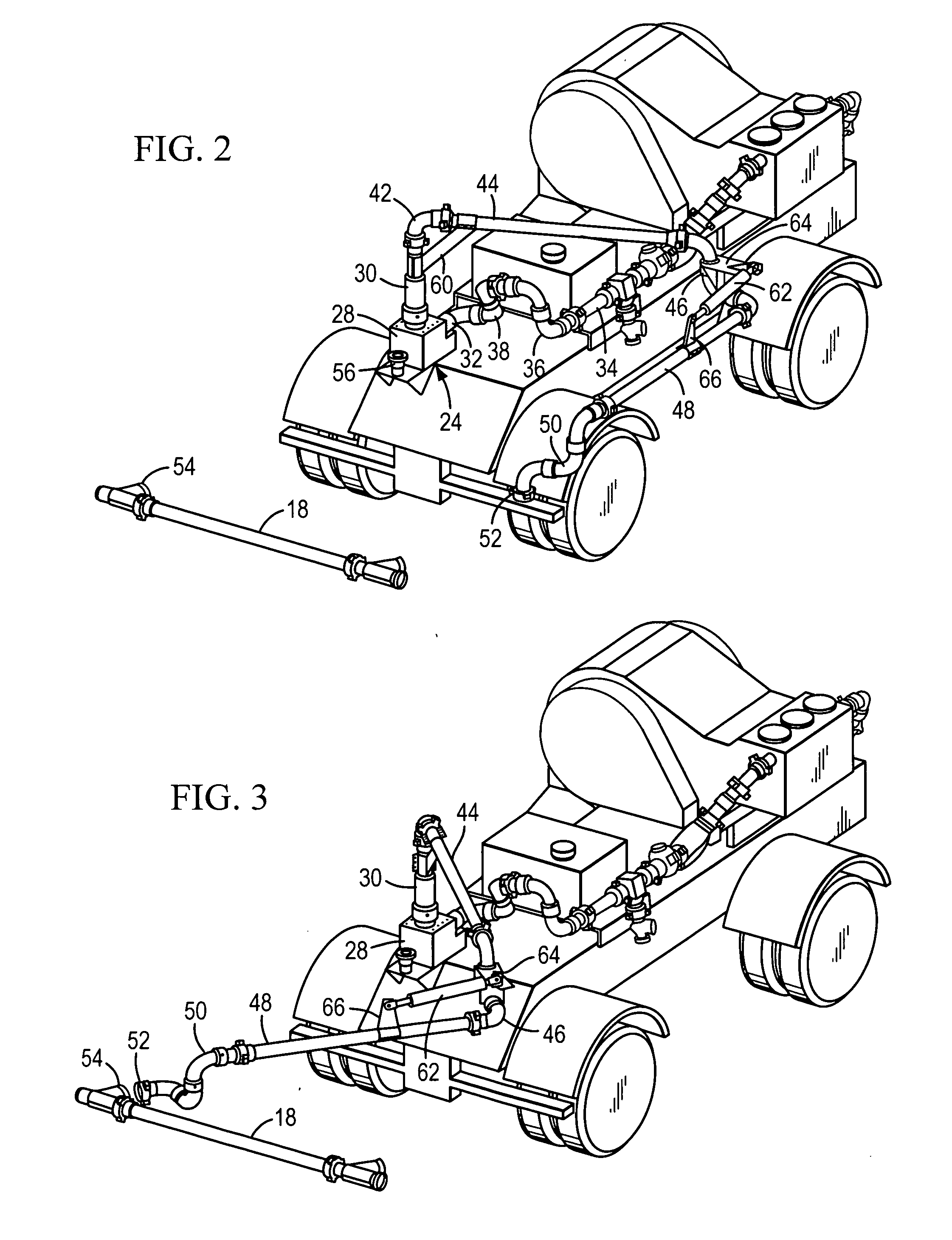
Discharge arm assembly for pumping units
ActiveUS20100193057A1Reduce confusionEliminates undue wearServomotor componentsSealing/packingStraight tubeTruck
A discharge arm assembly for a truck or trailer-mounted pumping unit comprises a jumper line which is connected to the outlet of the pumping unit, a base unit which is connected to the outlet of the jumper line, and an articulated arm which is connected to the outlet of the base unit. The base unit includes a base conduit which is rigidly secured to the truck or trailer and a swivel arm which is rotatable about a generally vertical axis. The articulated arm comprises a first generally straight pipe which is connected to the swivel arm by a generally 90° elbow. A brace member comprises a first end which is connected to the swivel arm and a second end which is connected to the first pipe to thereby support the first pipe for movement in a generally horizontal plane.
Owner:FMC TECH INC
Multi-sectional utility pole having slip-joint conical connections
InactiveUS6191355B1Reducing circumferenceImprove the circumferenceLoad-supporting elementsTowersStraight tubeSlip joint
A multi-sectional utility pole includes at least two sections of straight pipe, which are joined and connected by a slip joint connection. The slip joint preferably consists of two mating conical sections, with one attached to each section of the pole. The slip joint is compressed with the aid of rings, which are attached to the pipe, and a key and slot. The two conical sections are fastened together with bolts that pass through the female conical section and thread into the male conical section of the slip joint. The pole is easily assembled on the ground and the pole sections are fungible with other sections of the same diameter. The sections are also inexpensively manufactured. The conical sections can be swaged from the ends of the pipe, or can be fabricated separately and welded on to the ends of the pipe.
Owner:EDELSTEIN HANS P
Electric shock resistant electric water heater
InactiveCN1358971ASatisfy the requirement of safe lengthSimple processFluid heatersStraight tubeWater flow
The electroshock-proofing electric water heater includes shell, internal container, water intake tube, water discharging tube, water discharging lining tube and water intake lining tube. It is characterized by that the described water intake lining tube is an insulating tube, its tube body is placed in the internal container cavity, and adopts the structural forms of inverted U shaped, M-shape or water intake straight tube and casting tube cover assembly, so that it increases zigzag length of water flow line and makes the length L from water inlet of water intake lining tube to water outlet attain the the safe length requirement of that L is greater than 53 sq.r.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
Straight tube LED lamp having buckle connecting device for securing all parts together as one body
InactiveUS8319407B2Reasonable designEasy to assemblePoint-like light sourceElectric discharge tubesStraight tubeHeat conducting
A LED lamp with straight tube comprises a tube body, a lamp cover sheathed at two ends of the tube body and a lamp strip which is in inserted connection in the tube body and comprises a circuit board and a heat diffuser; the lamp cover is internally, fixedly provided with a connecting device connected with the lamp strip; the connecting device comprises a connecting piece on which a connecting arm extending along the length direction of the lamp strip is arranged; the connecting arm is provided with a buckle body; the corresponding position on the surface of the lamp strip is provided with a buckle seat matched with the buckle body; and the circuit board is overlapped and adhered with the radiator to be into a whole through an insulating heat conducting layer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SETEC LIGHTING
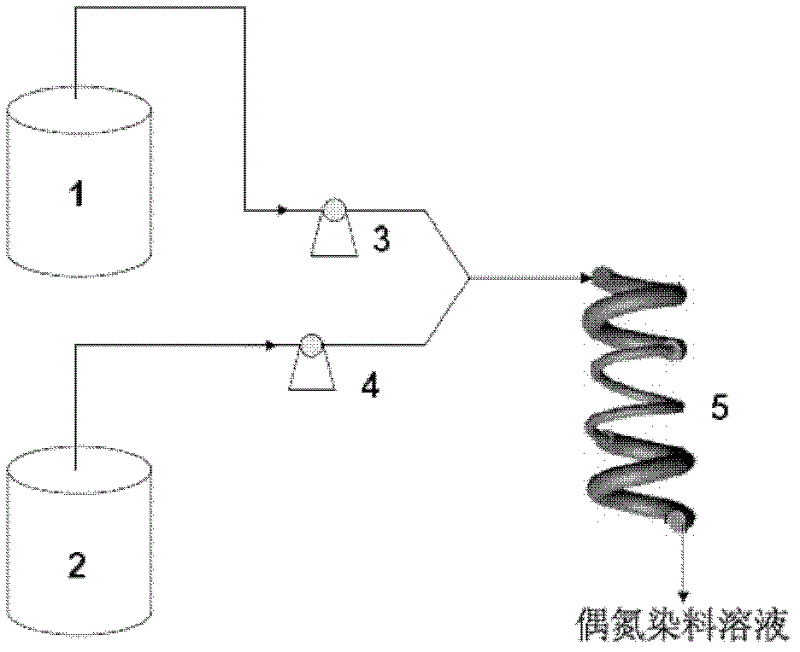
Method for preparing water-soluble azo dye continuously by chaos mixing of spiral tube
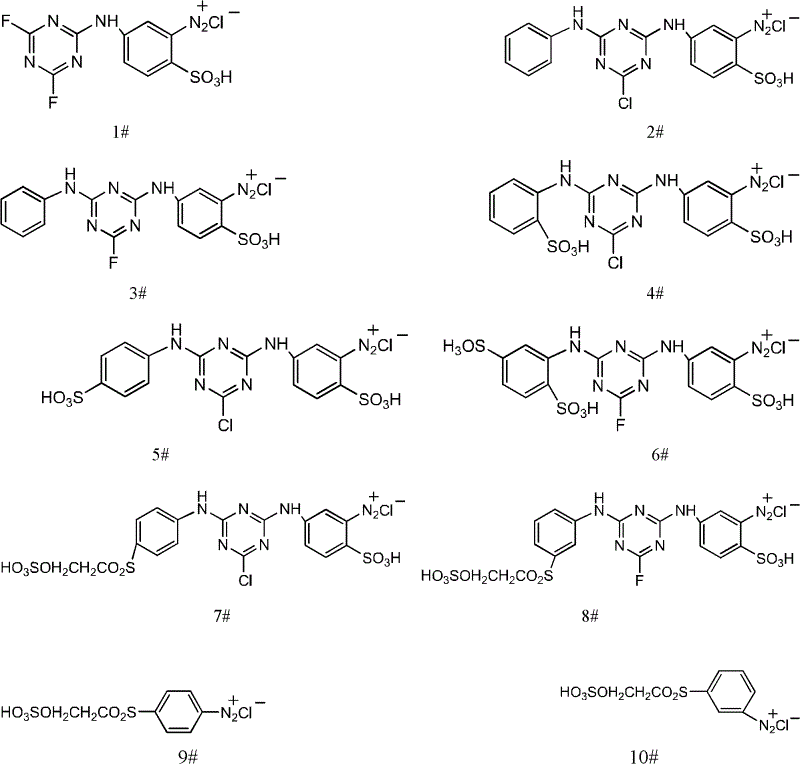
ActiveCN102618063ARapid serial productionFully contactedMonoazo dyesDisazo dyesMicroreactorDiffusion
The invention provides a method for preparing a water-soluble azo dye continuously by the chaos mixing of a spiral tube. The core is that a spiral tube sudden-expansion and sudden-contraction structure is adopted; compared with pure straight tube sudden-expansion and sudden-contraction mixed reaction, the method has the advantages that a mixed effect of a transverse secondary flow generated by fluid in a curved pipeline is far stronger than that of pure diffusion of a straight tube part; compared with the conventional spiral tube, the sudden-expansion and sudden-contraction part has the advantages that the motion trail of the fluid can be changed, the superficial area of a mixed interface can be increased and a chaos mixing effect can be enhanced; and the mixer has the advantages of quick and uniform mixing, stirring prevention, short retention time, high quality stability of the product, high speed of removing reaction heat by a tube wall and the like of a microreactor, and also overcomes the defects of small internal diameter and high possibility of blockage of the microreactor, so that the dye can be produced quickly and continuously, and the method is wide in industrial prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on Faraday cup
InactiveCN104730066AGuaranteed OrthogonalityGuaranteed collimationAnalysis by thermal excitationMass spectrometryDrift tube
The invention discloses a near-field plume mass-spectroscopic diagnostic E*B probe based on the Faraday cup and belongs to the technical field of plasma mass-spectroscopic diagnosis. The probe mainly applied to measuring near-field plumes of an ion thruster and of a Hall thruster comprises a central frame, ferrite permanent magnets, a flat electrode plate, an electrode plate holder, a collimator tube, a drift tube, a Faraday cup, six carbon steel shells and an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. According to the connectional relation, the central frame is used as a core part, the ferrite permanent magnets are distributed on upper and lower surfaces of the central frame, the electrode plate is fixed in the central frame, and an orthogonal electromagnetic field area is formed. The six carbon steel shells are used for packaging, and the front ends of the shells are coated with an anti-sputtering heat-insulating layer. The collimator tube of stainless steel and the drift tube are fitly fixed to the centers of two ends of the central frame through shaft holes. Ions different in valence are screened by adjusting voltage among the electrode plates, univalent and bivalent ion currents are acquired with the Faraday cup of aluminum, and the ratio of near-field plum bivalent ions is acquired by analytical computing.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
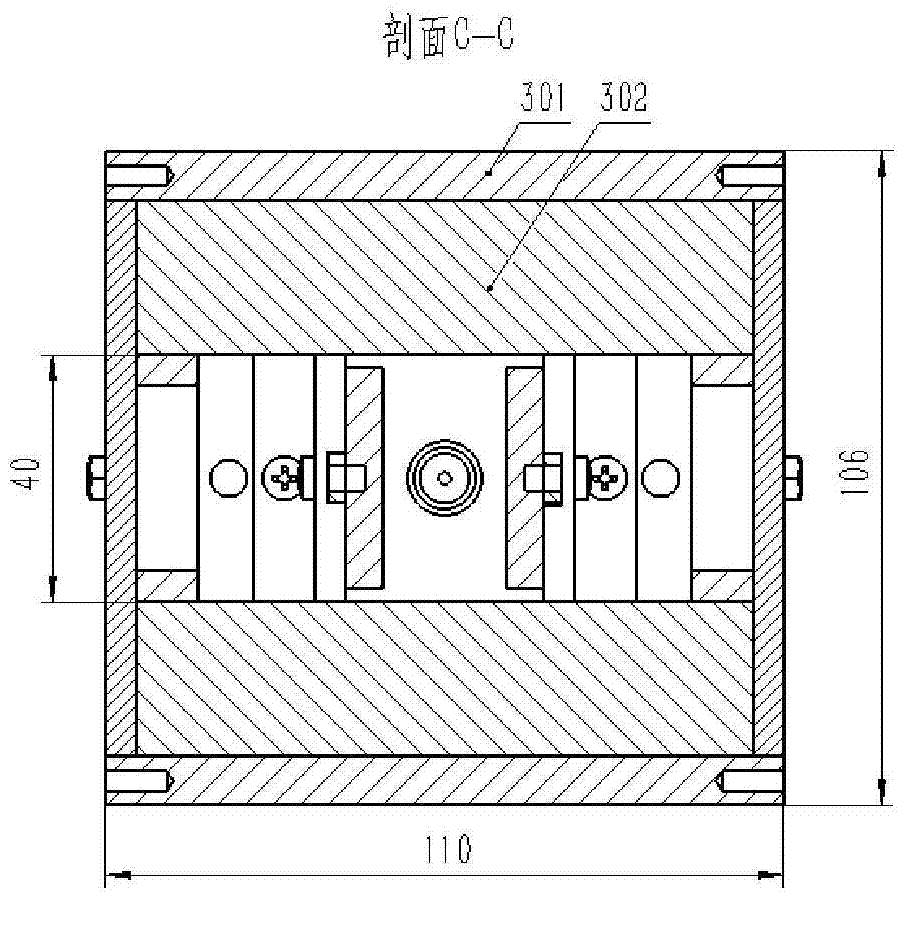
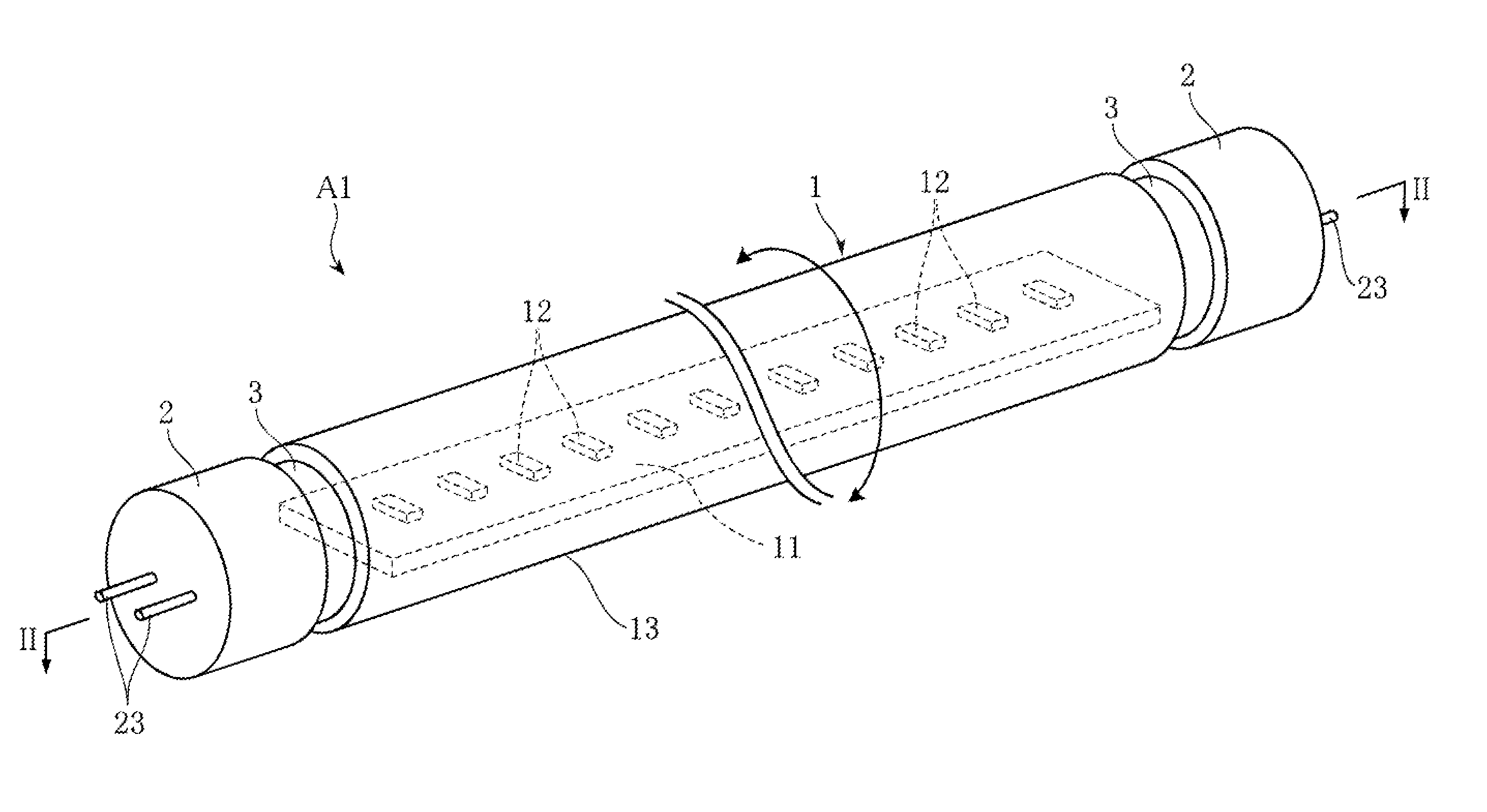
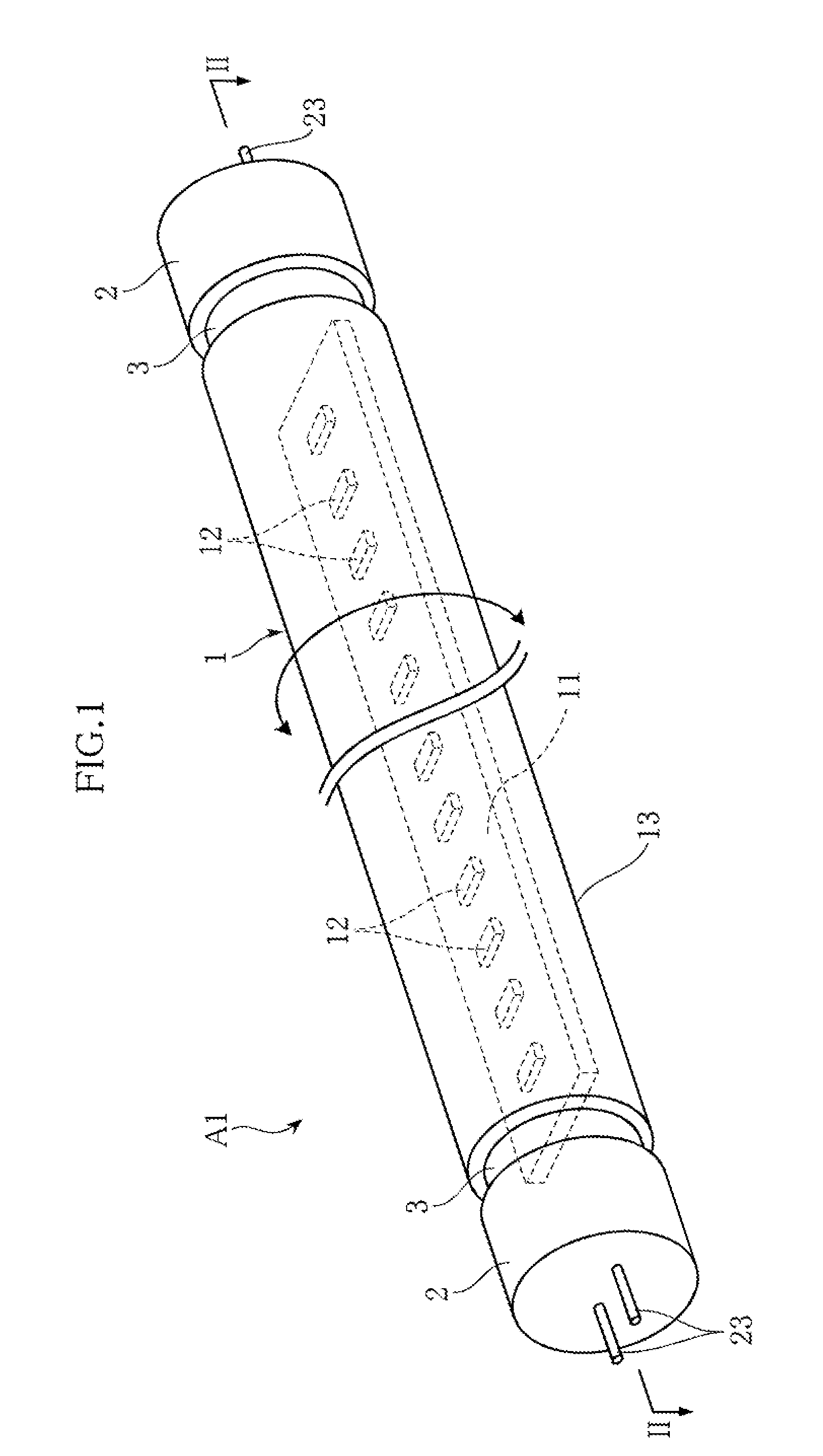
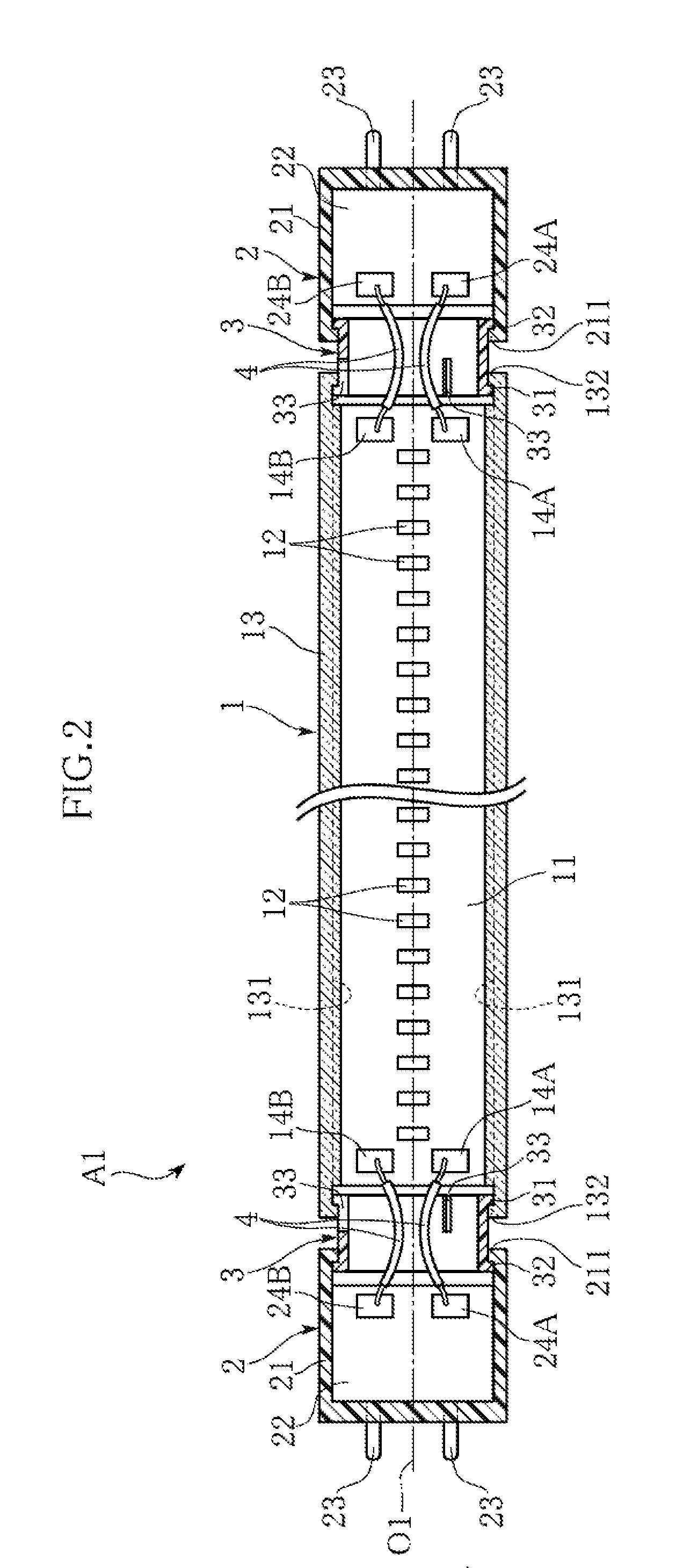
LED lamp
An LED lamp A1 includes an LED unit 1 in the shape of a straight tube with a plurality of LED modules 12 fixed therein, and also includes a pair of bases 2 that receive electric power from outside and are attached to the ends of the LED unit 1 spaced in the longitudinal direction of the LED unit. The LED unit 1 and the bases 2 are rotatable relative to each other about an axis extending in the longitudinal direction. With this arrangement, the direction of light emission can be changed, with the LED lamp attached to a general-use fluorescent lighting fixture.
Owner:IRIS OHYAMA
Shock absorber
A shock absorber as being of a bumper supporting member and a shock absorber as being of a side member, which retain the sinking motion of a smaller-diameter tube portion into a larger-diameter tube portion even if an impact is applied at a larger angle obliquely of an axial direction, thereby to achieve the absorption of the impact energy by a plastic deformation. A plastically deformable straight tube is partially reduced or partially enlarged to form a smaller-diameter tube portion and a larger-diameter tube portion, which join to each other through a step portion. The step portion is formed by joining a folded-back portion of the smaller-diameter tube portion and a folded-back portion of the larger-diameter tube portion, which have circular arc-shaped sections having arcuate angles more than 90 degrees.
Owner:ASTEER
Joint welding clamp of titanium alloy straight pipe and joint welding method
InactiveCN103978290AAvoid partial collapseEliminate influence of welding qualityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesCopperTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a joint welding clamp of a titanium alloy straight pipe and a joint welding method. The joint welding quality and precision of the titanium alloy straight pipe can be guaranteed by adopting auxiliary supporting and clamping inside the titanium alloy straight pipe and protecting a welding influenced region by inert gas. The method comprises the steps of sealing places where copper sleeves are matched with the titanium alloy straight pipe by sealing tapes at the two ends of a gas feeding pipe, feeding protective gas to a weld joint by two exhaust holes in the feeding pipe, and forming an integral part for supporting a welding region in an auxiliary way by fixedly connecting an arc-shaped copper block, with two exhaust holes, on the gas feeding pipe through super glue; taking out the gas feeding pipe and the arc-shaped copper block from the titanium alloy straight pipe after the completion of welding due to the fact that the radian of the arc-shaped copper block is smaller than a semicircle, performing gas protection on the welding joint outside the titanium alloy straight pipe by a protective cover, fixing a welding gun on the protective cover by a clamp ring, and driving the welding gun to move by moving the protective cover; clamping the titanium alloy straight pipe by adopting an arc-shaped clamp, in order to guarantee the welding continuity..
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
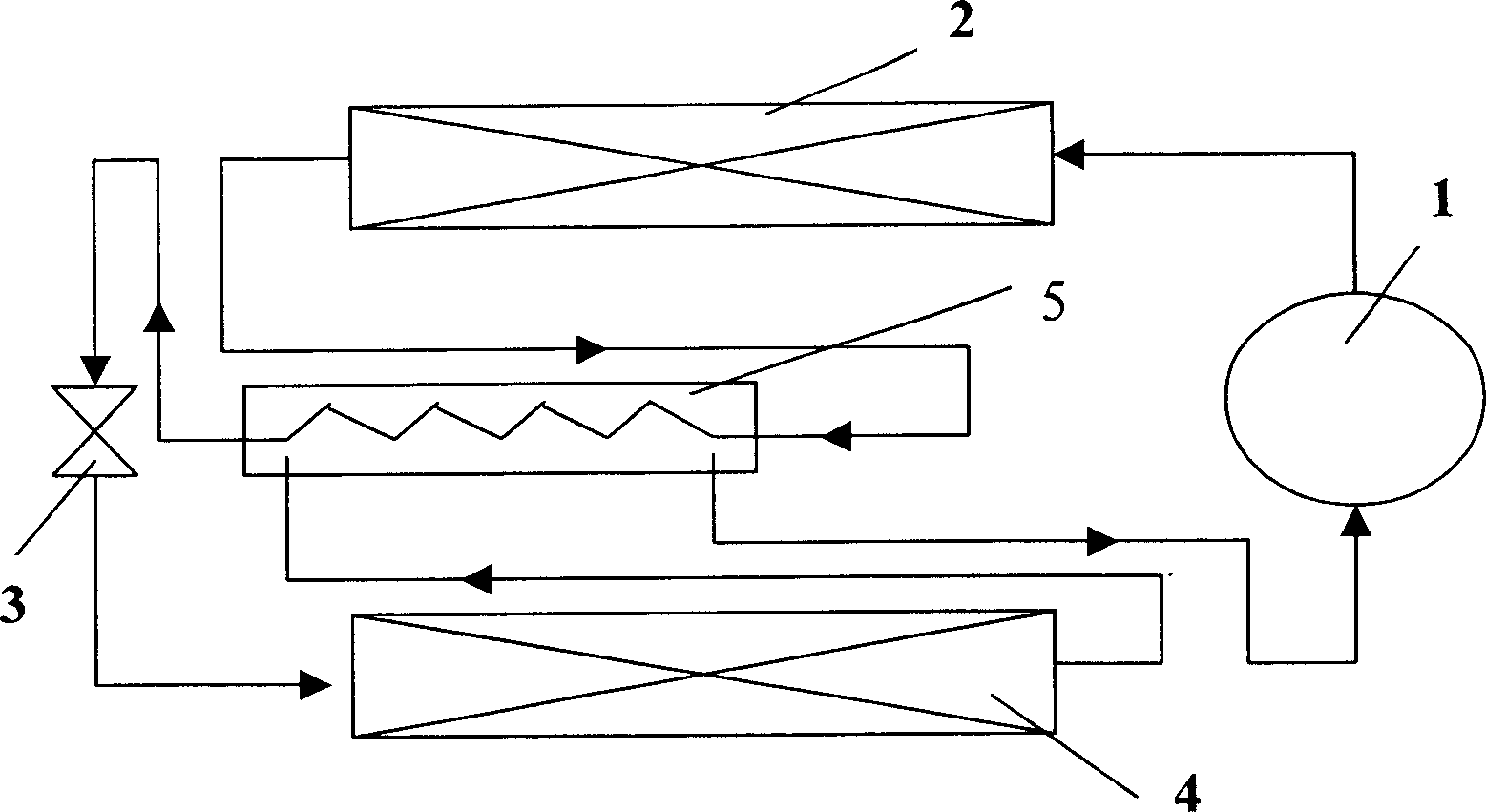
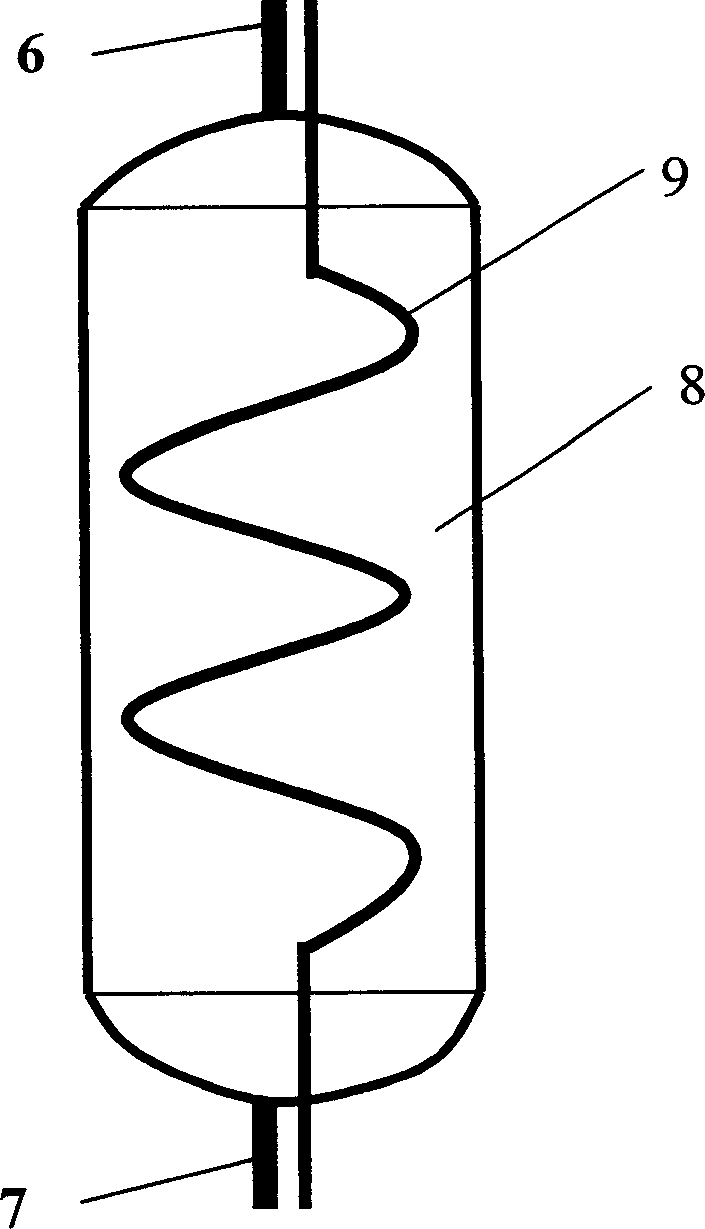
Air conditioner for regenerative cooling circulation system
InactiveCN1862151AReduce volumeReduce the impactCompression machines with non-reversible cycleSuperheatersStraight tubeEngineering
The present invention discloses a regenerative refrigeration cycle system air conditioner. It includes compressor, condenser, throttle device, evaporator and recuperative heat exchanger. The described recuperative heat exchanger includes a cylindrical tank body whose top portion and bottom portion are respectively equipped with low-pressure refrigerant outlet and inlet connected with compressor suction pipe and evaporator outlet, a straight tube which is placed in the interior of tank body along vertical direction and whose upper and lower ends are respectively connected with condenser outlet and throttle device and a heat-exchanging coiled tube, said coiled tube and straight tube are integrally formed into one body.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (TIANJIN) APPLIANCES CO LTD
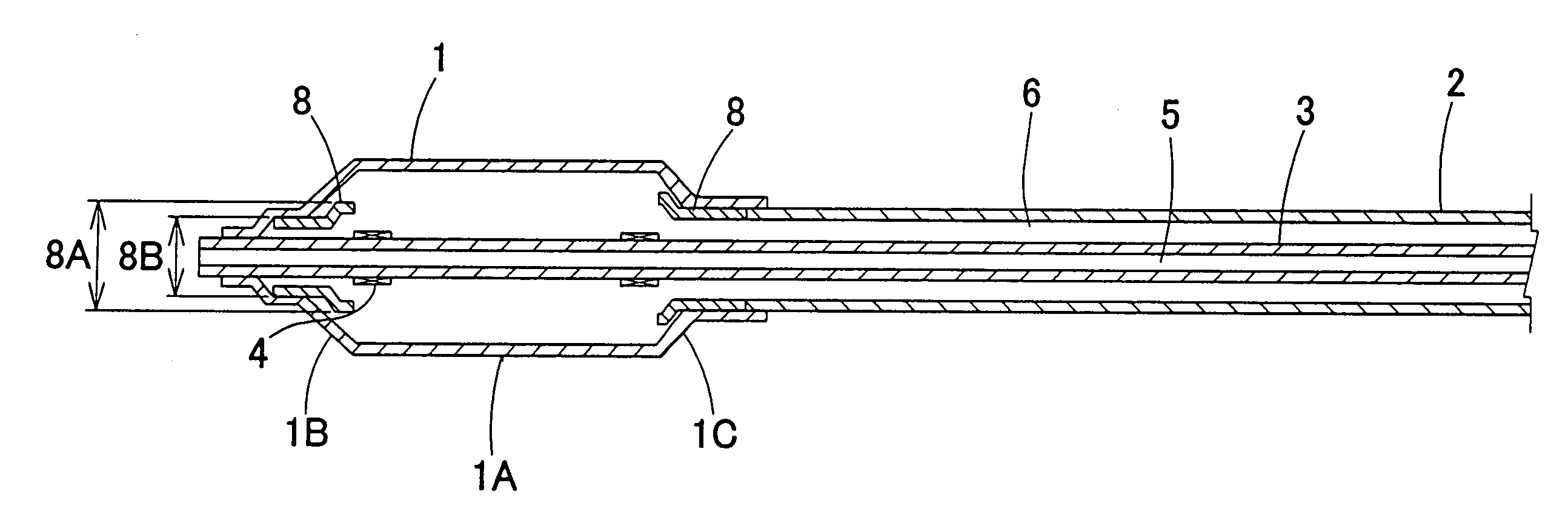
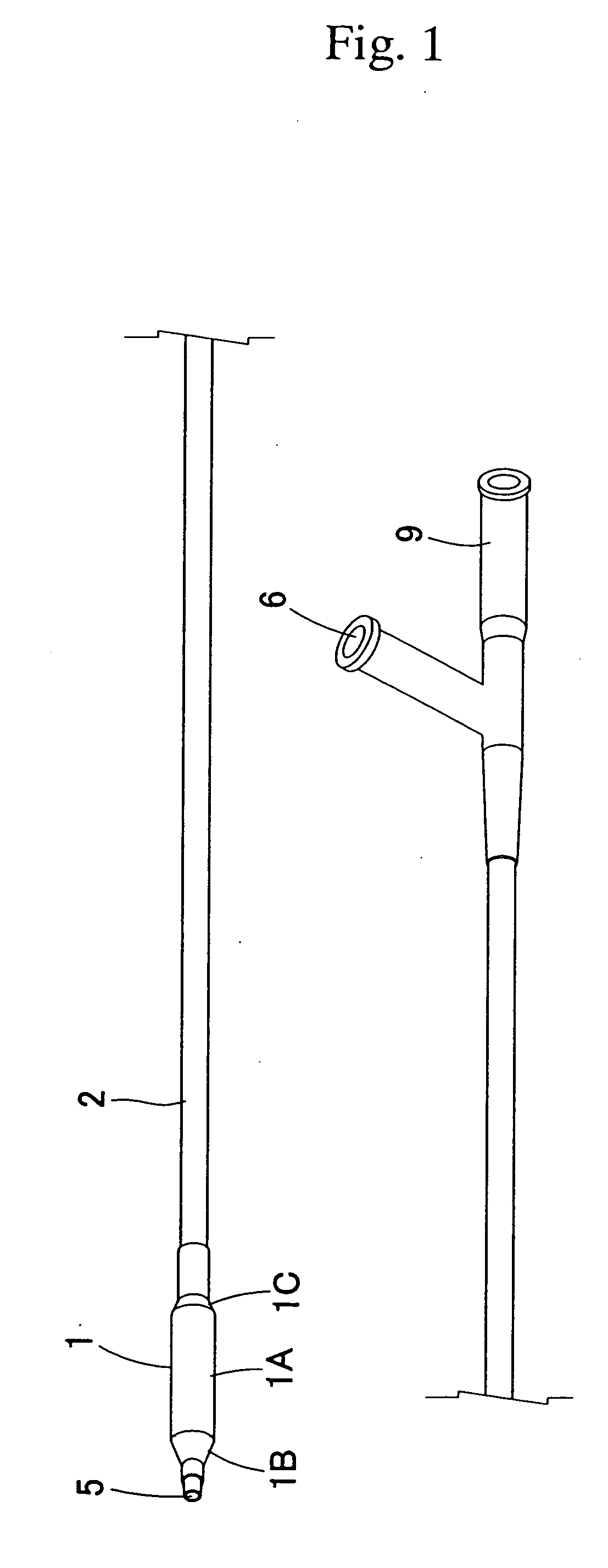
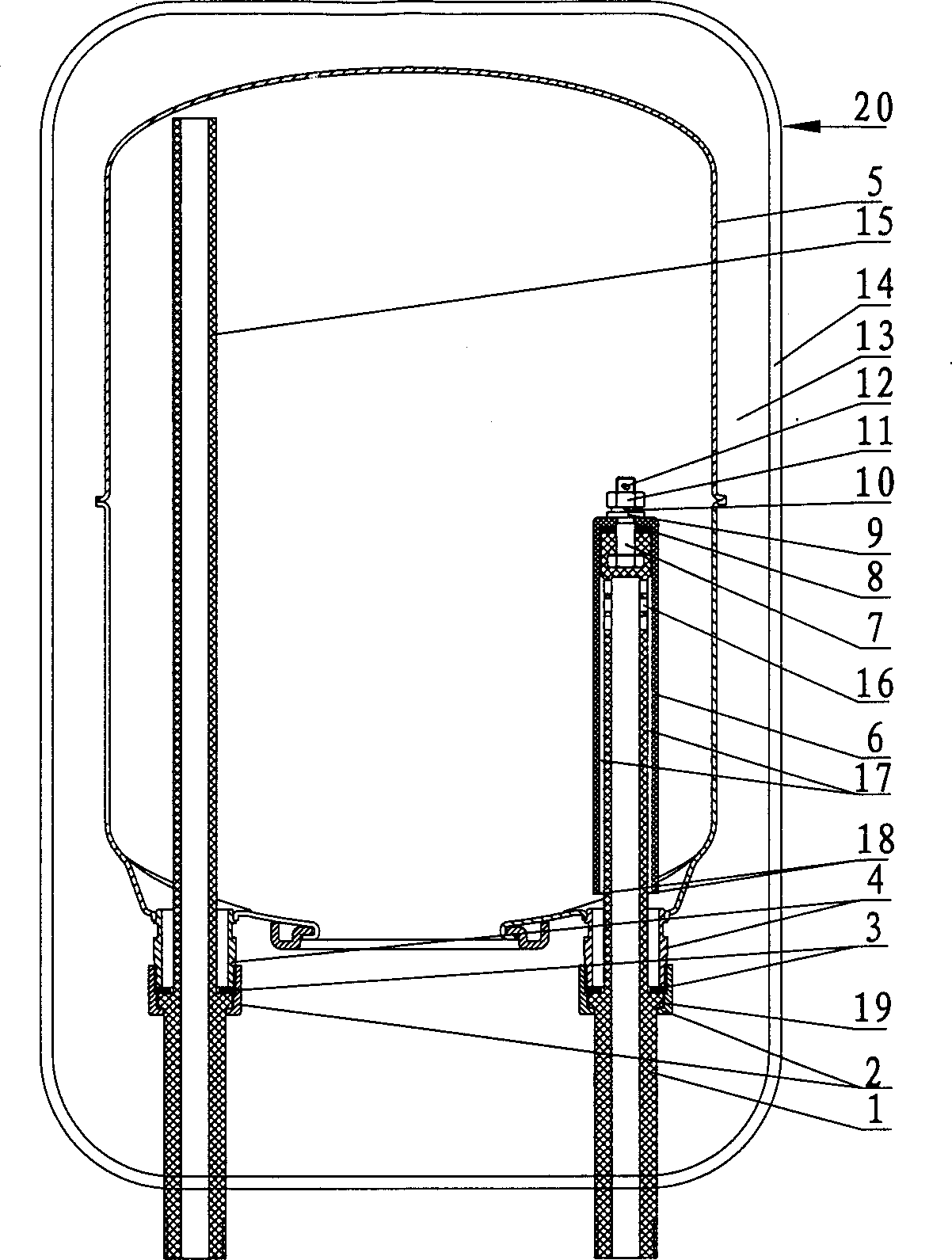
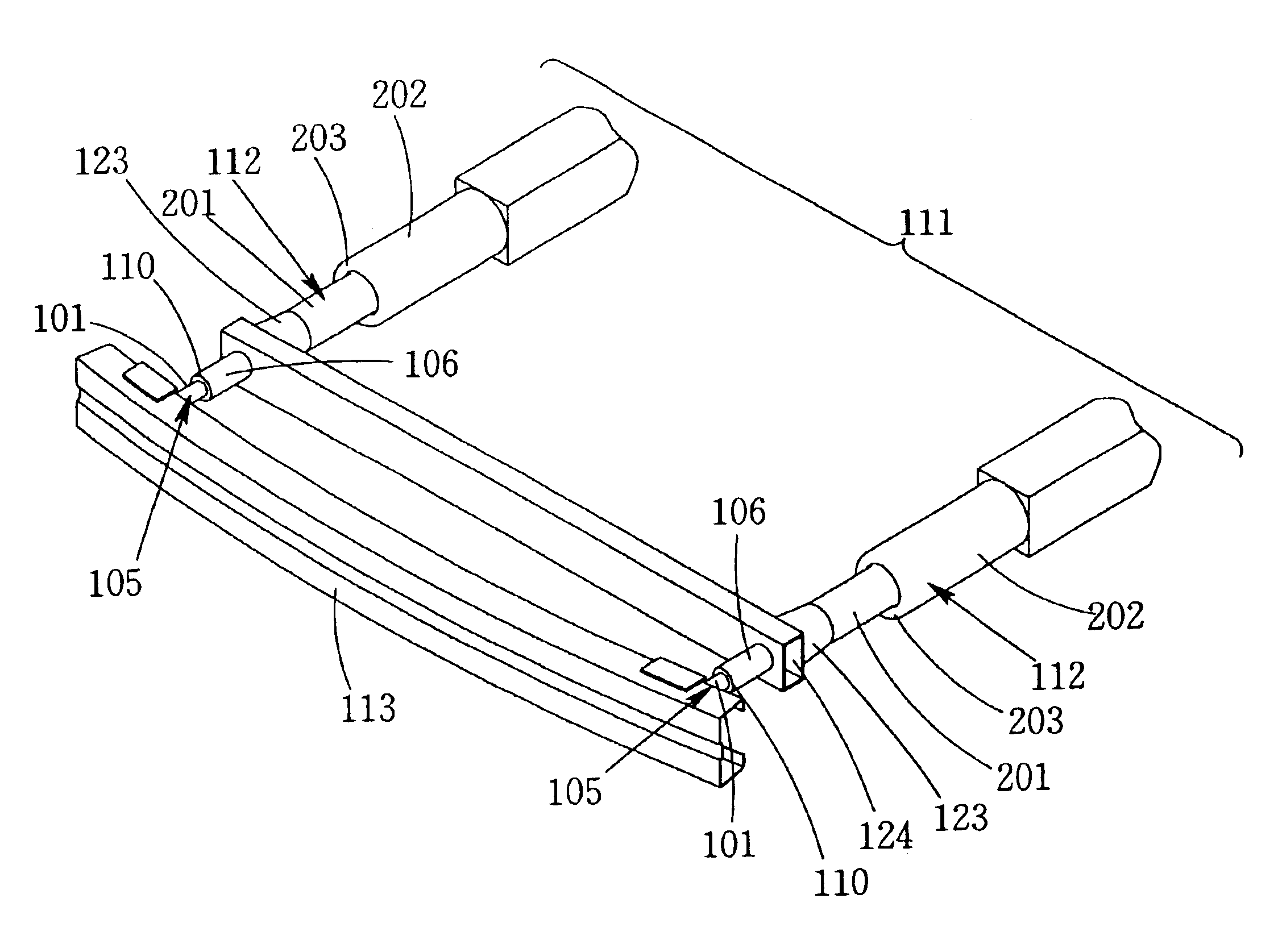
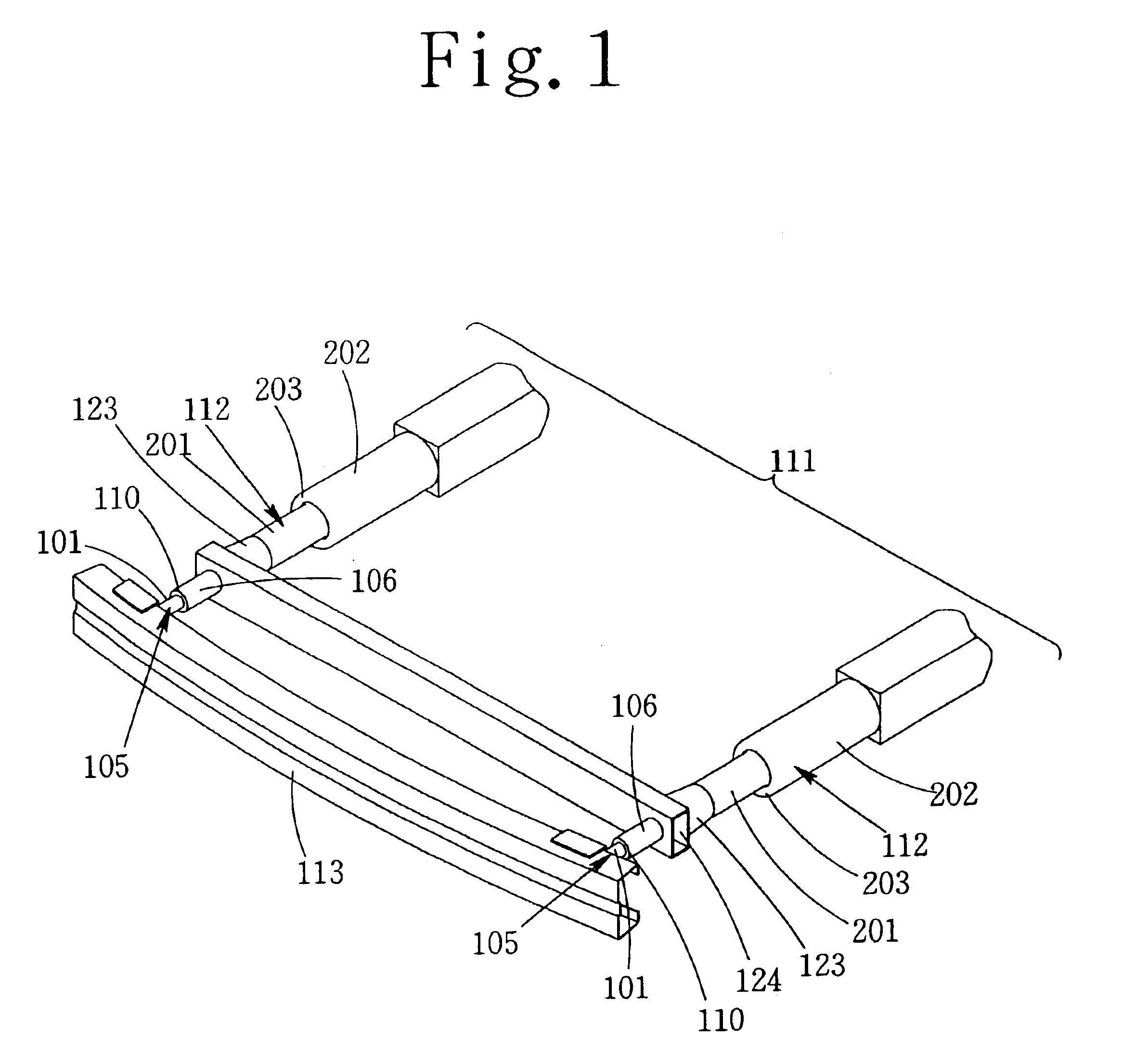
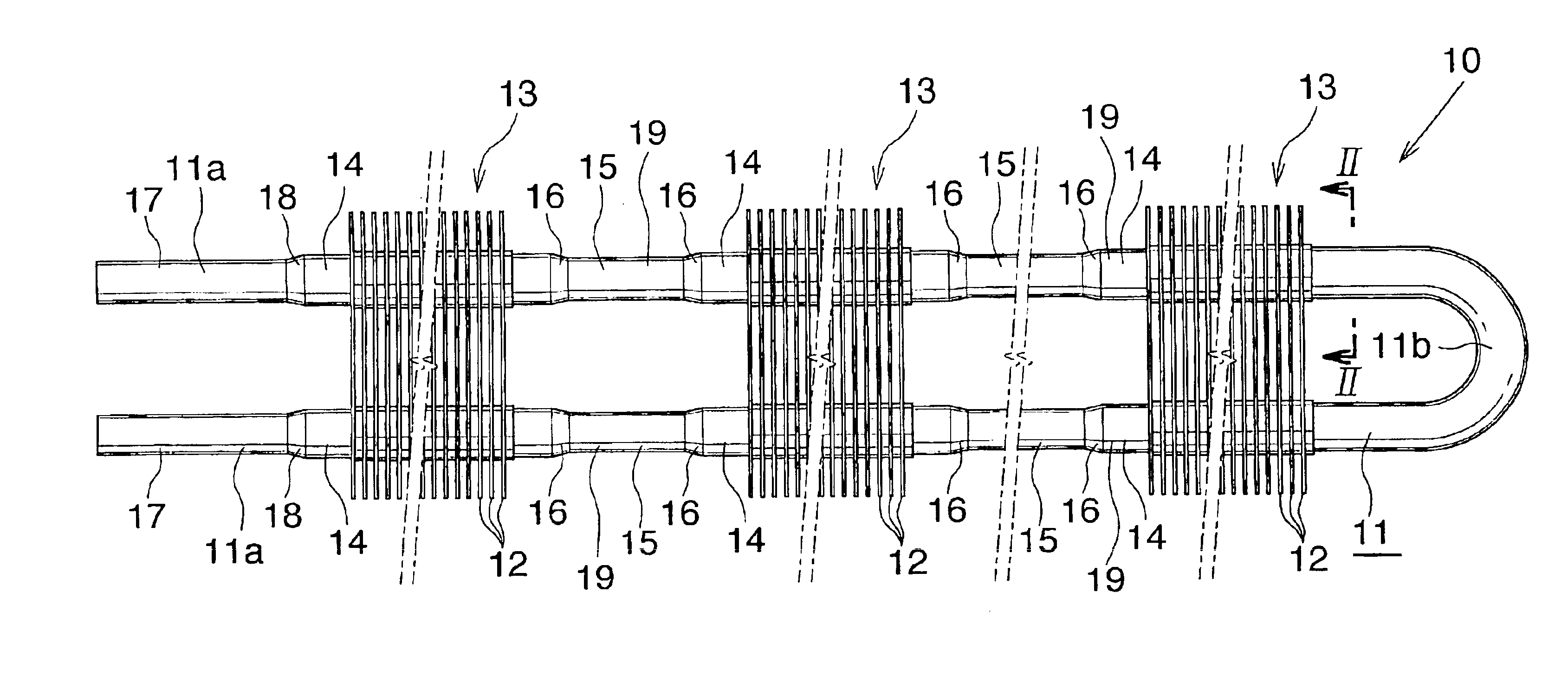
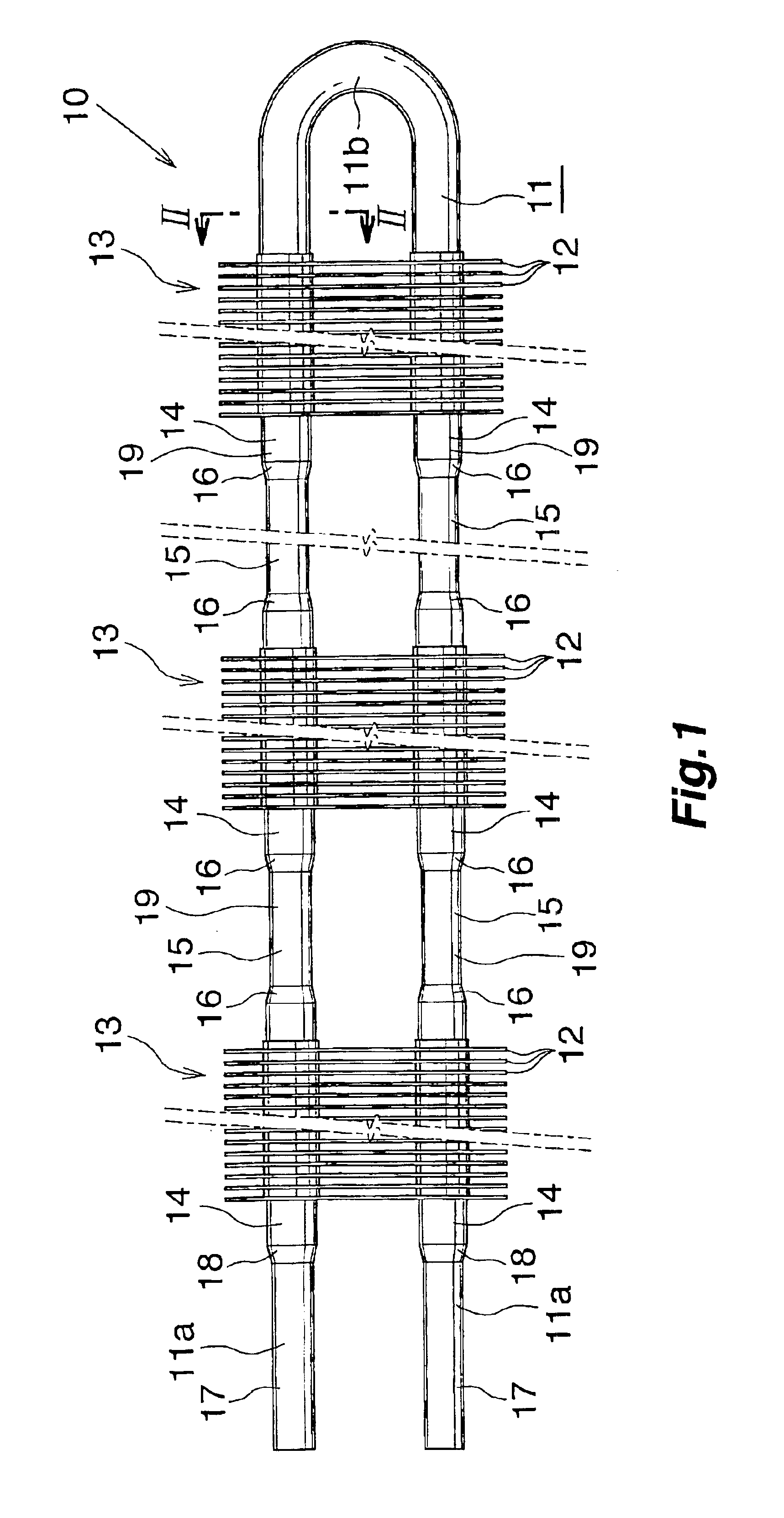
Coriolis mass flow rate/density/viscoy sensor with two bent measuring tubes
InactiveUS6860158B2Measurement accuracySimple and connectionVolume/mass flow by dynamic fluid flow effectDirect mass flowmetersTuning forkStraight tube
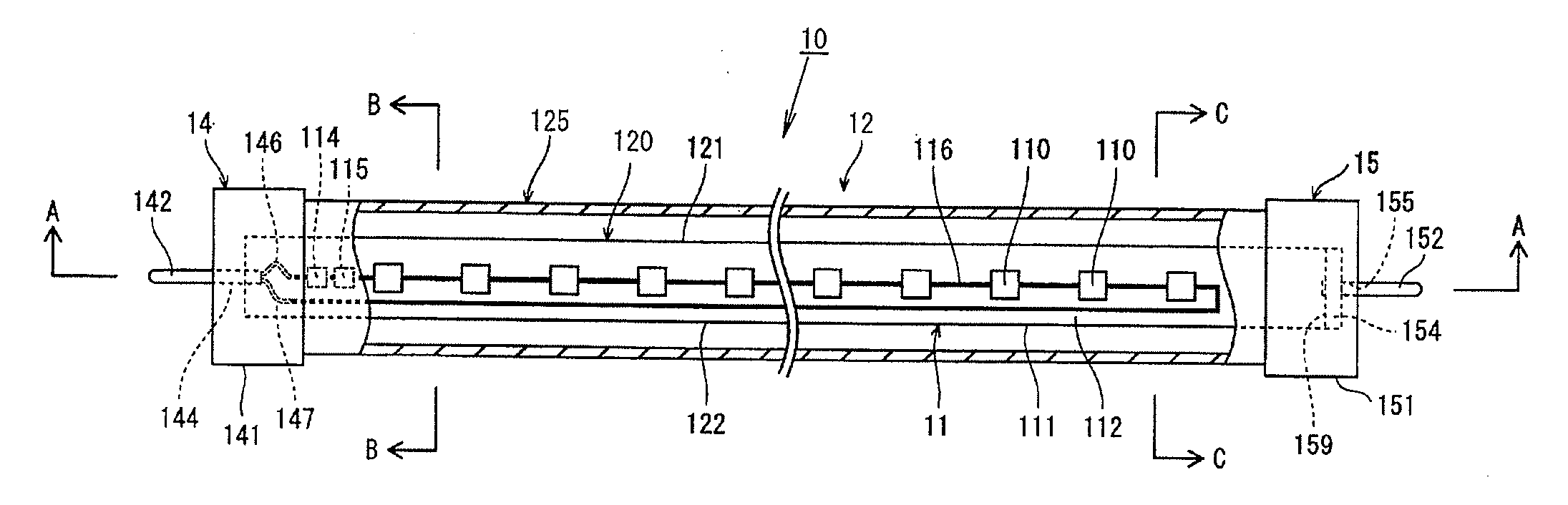
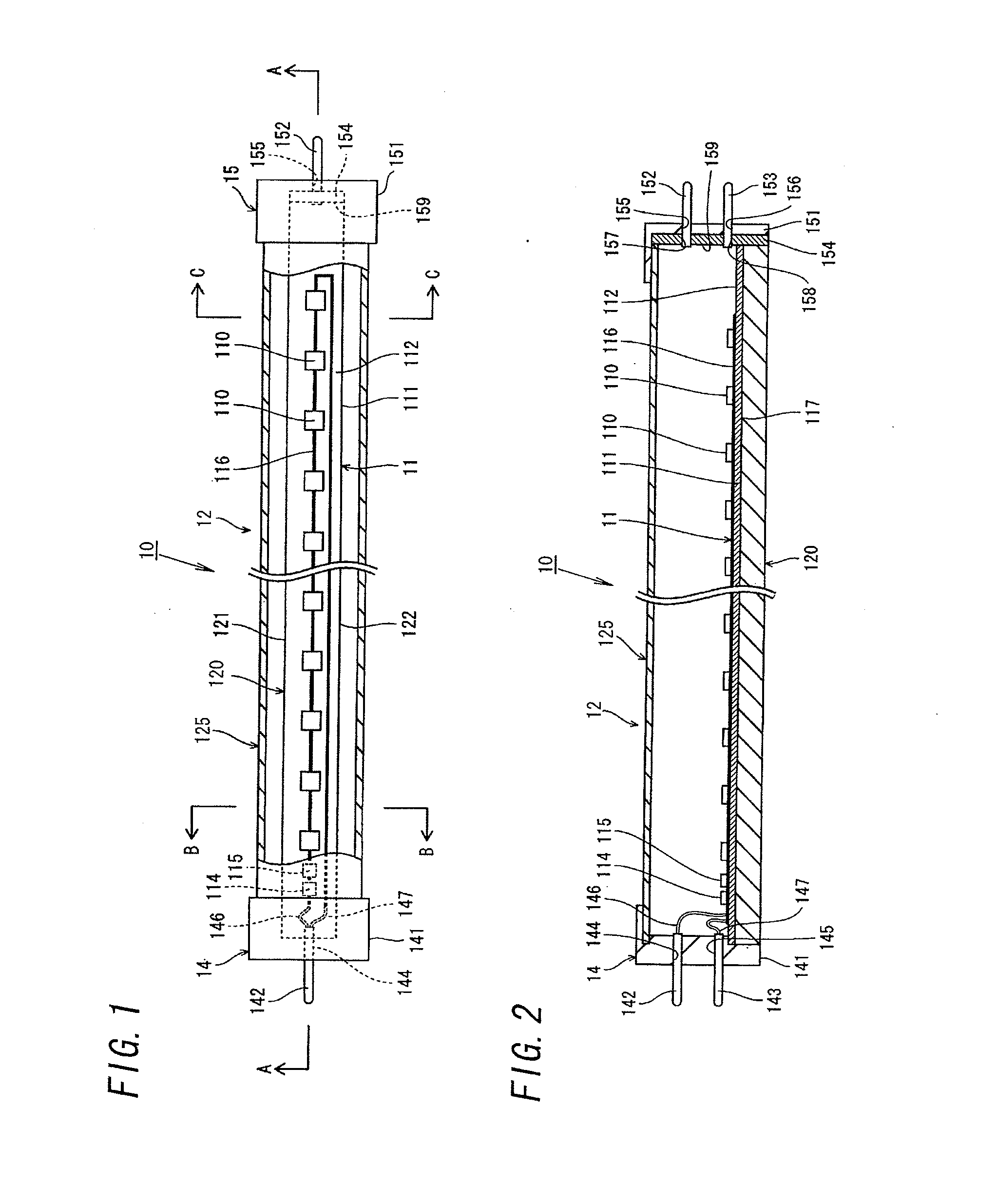
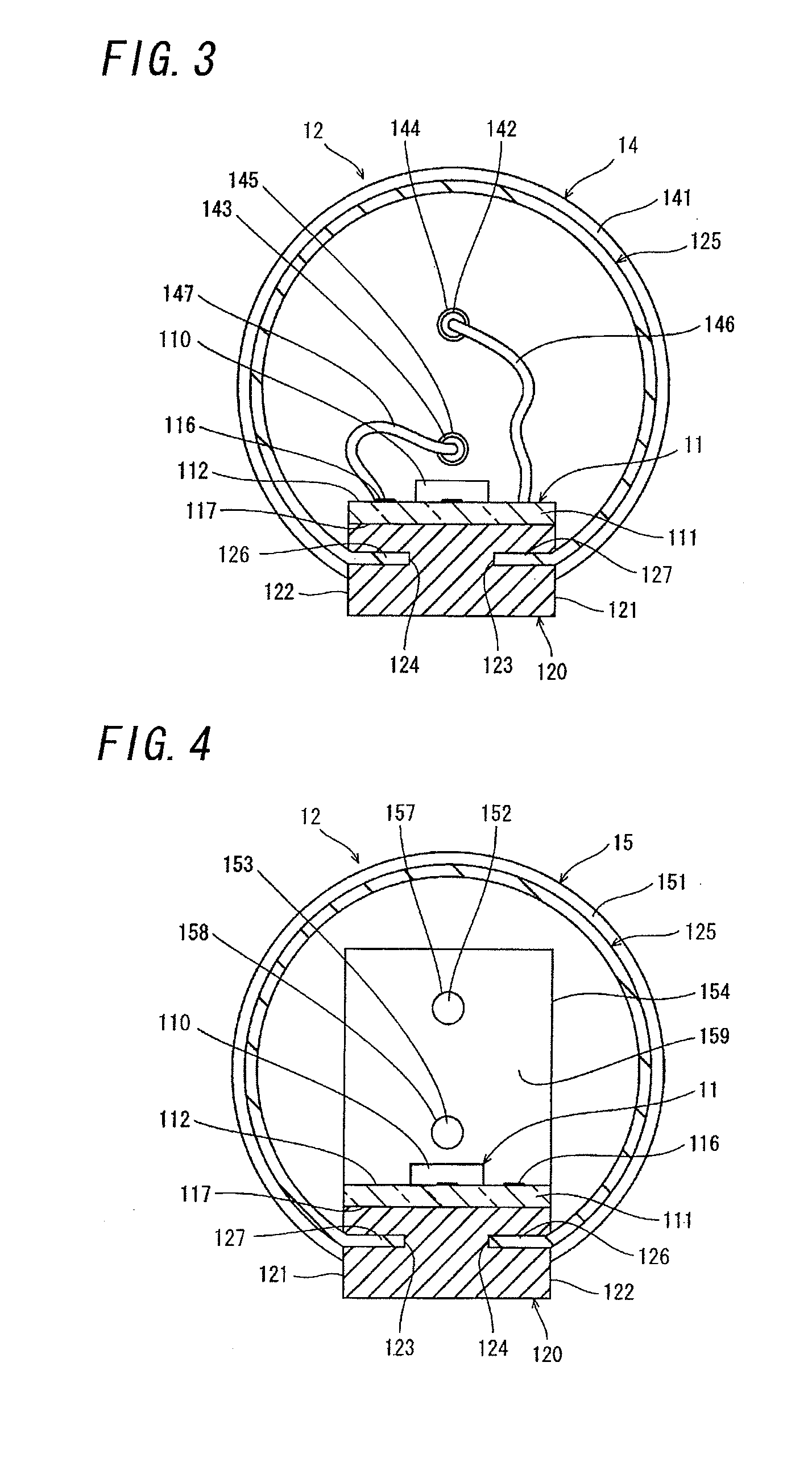
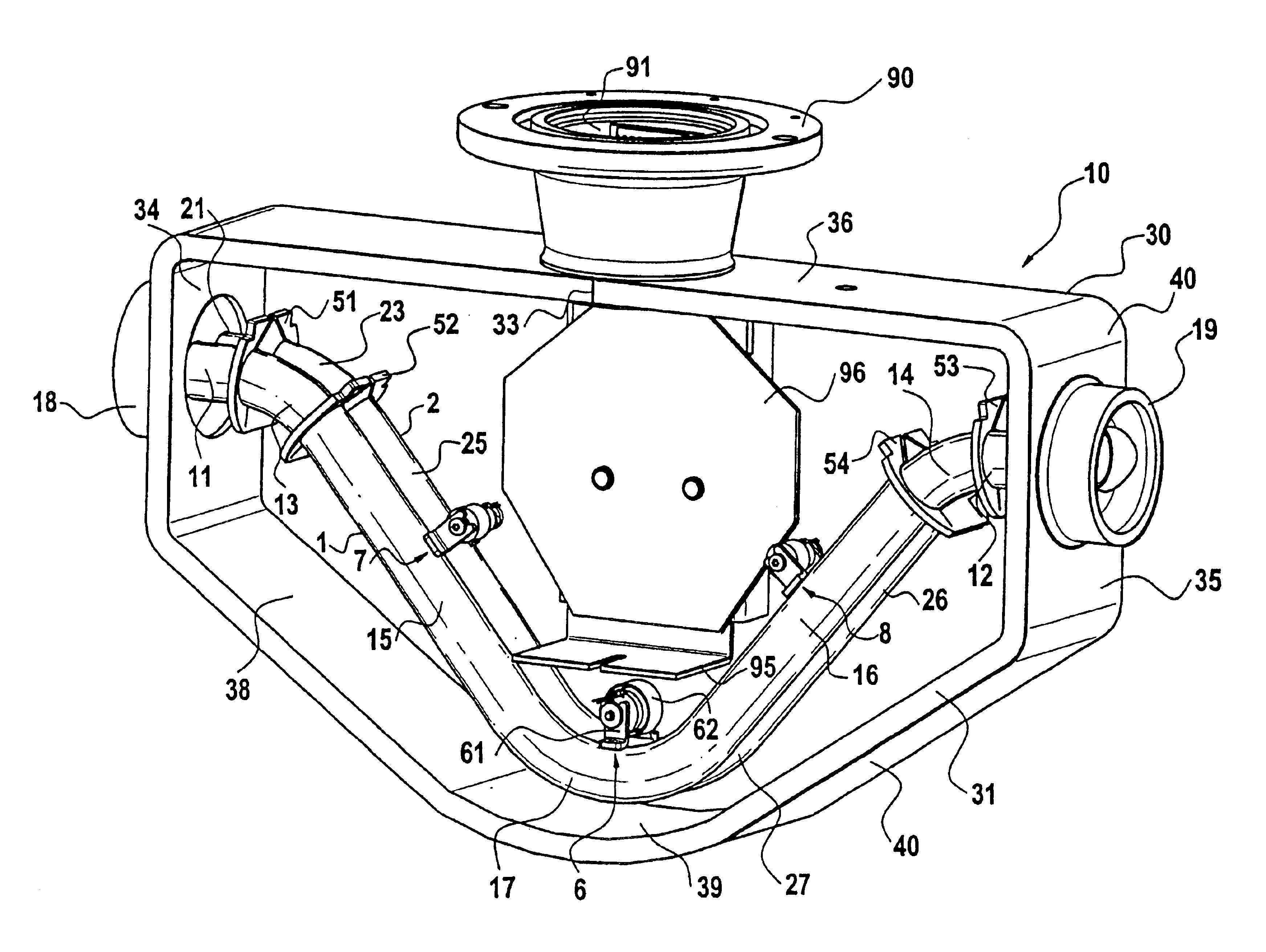
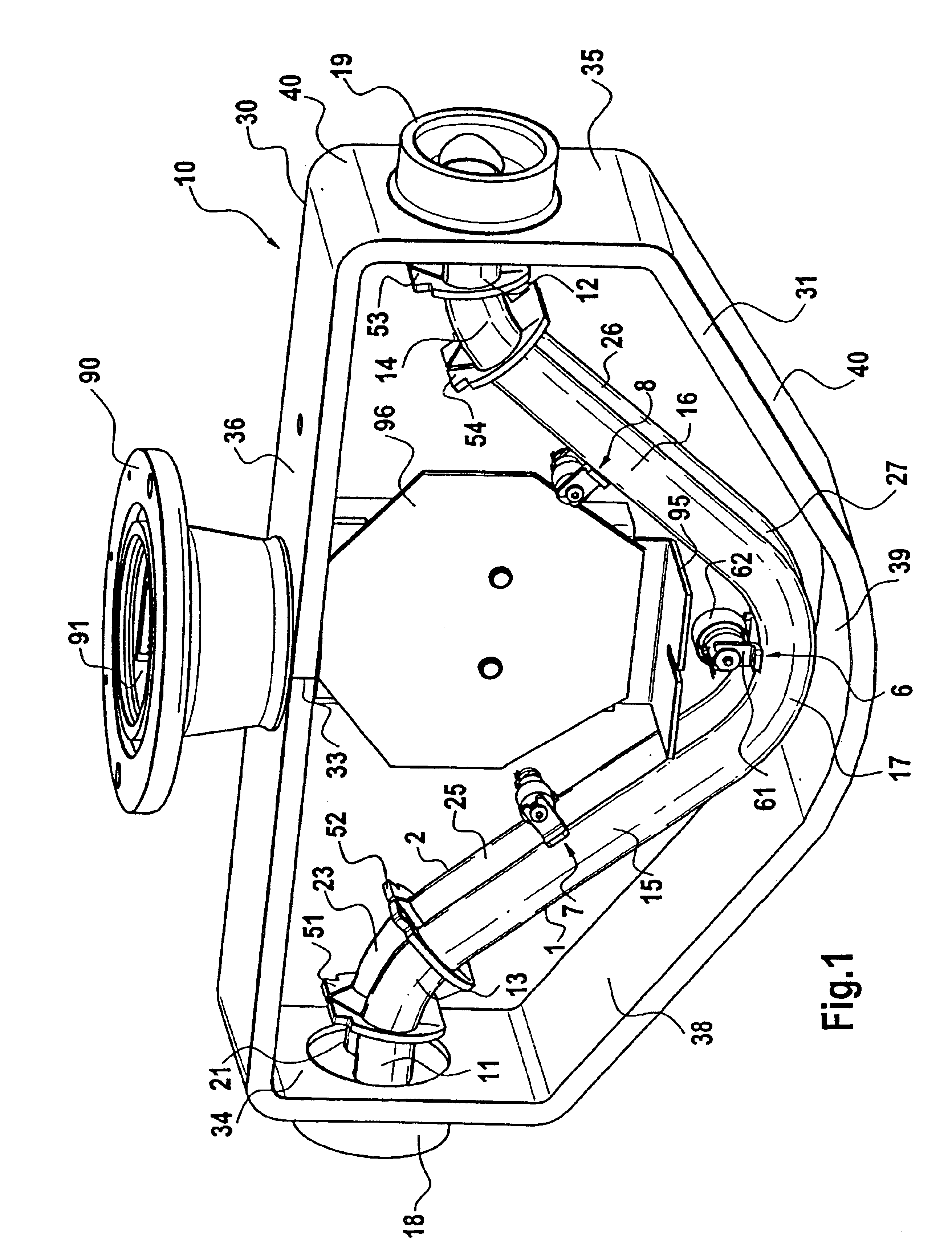
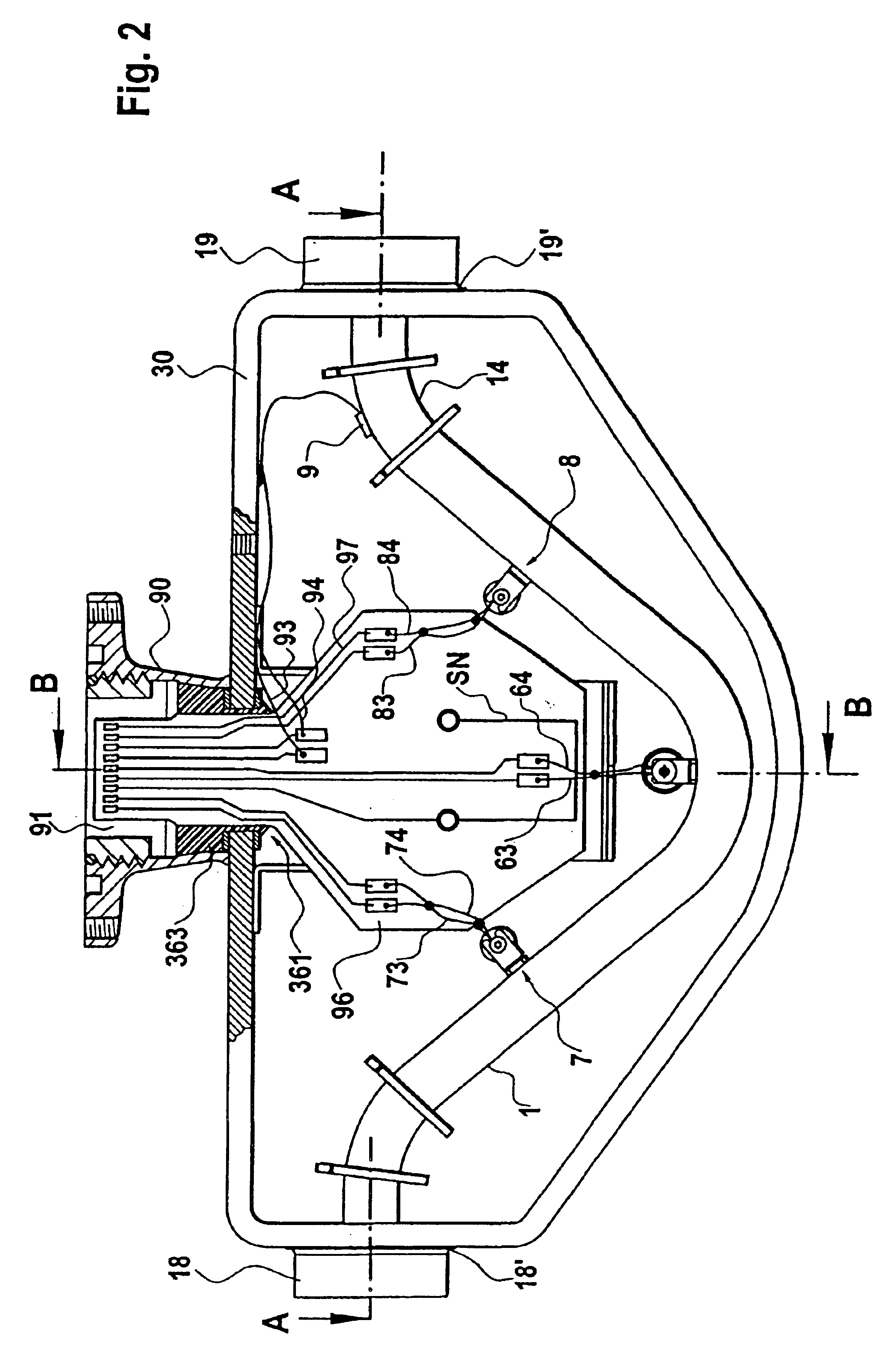
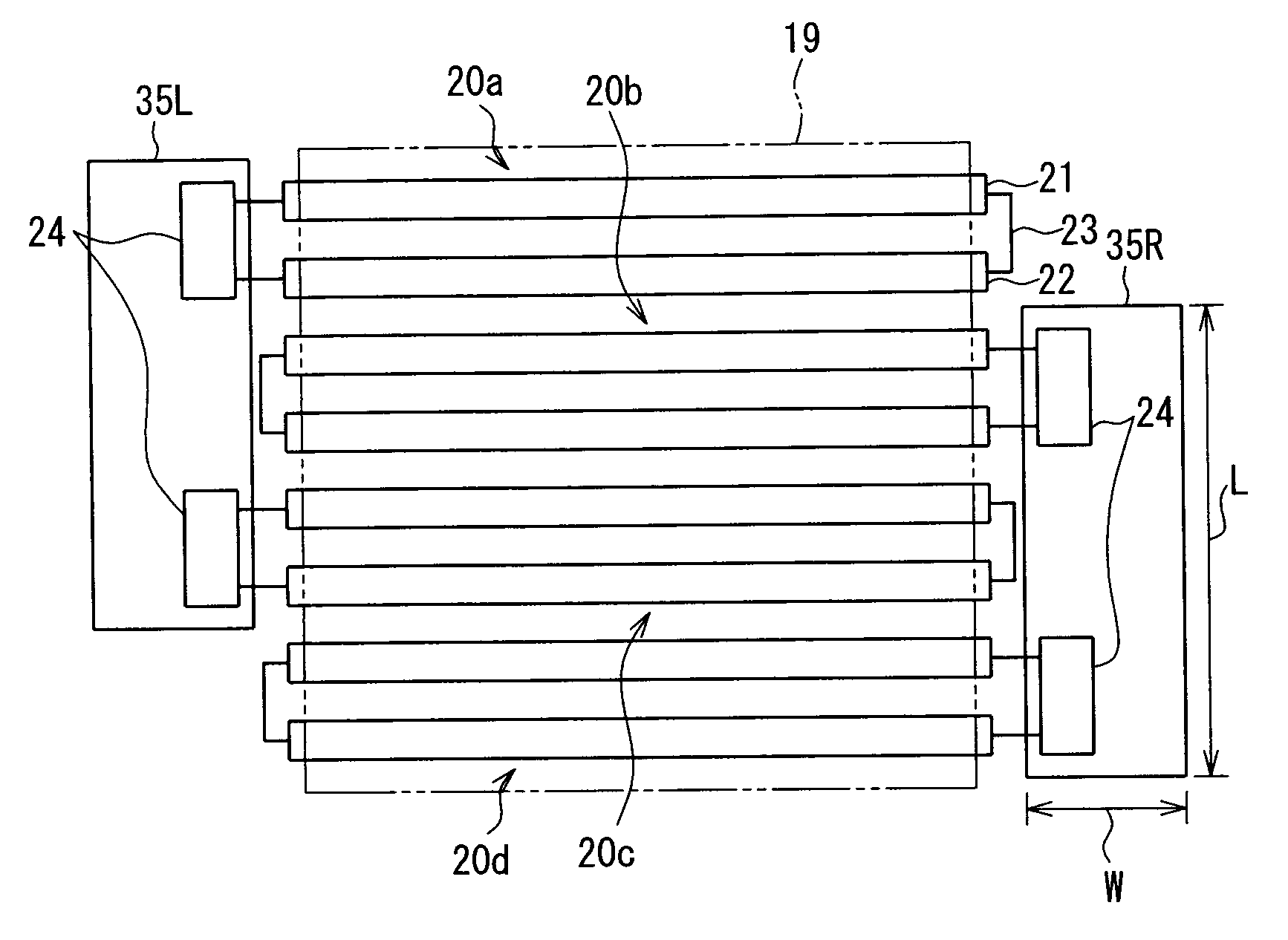
This sensor (10) generates accurate measuring results, for example with an error in the order of 0.5% of the measuring value, hat has mimimized production costs as well as a shorter overall length compared to that of conventional sensors. The sensor has two parallel V shaped measuring tubes (1, 2) each being of one-piece construction. Each tube has a straight inlet portion (11, 21), a straight outlet portion (12, 22), an inlet bend (13, 23) connected with the inlet portion, an outlet bend (14, 24) connected with the outlet portion, a straight tube portion (15, 25) connected with the inlet bend, a straight tube portion (16, 26) connected with the outlet bend, and a vertex bend (17, 27) connected with the first and second straight tube portions. The inlet portions (11, 21) are fixed in an inlet manifold (18) and the outlet portions in an outlet manifold (19); the manifolds (18, 19) are mounted in a support frame (30) which forms part of a housing (3). An excitation arrangement (6) causes the measuring tubes (1, 2) to vibrate as a tuning fork. Interspaced sensor elements (7, 8) are fixed to the measuring tubes. Mounted in the support frame (30) is a feedthrough (37) for a printed-circuit board (96) having conducting tracks (97) to which leads (63, 64, 73, 74, 83, 84) of the excitation system (6) and of the sensor elements (7, 8) are connected.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Backlight device and display device
InactiveUS20090103281A1Uniform brightnessElectric lightingIlluminated signsStraight tubeCold cathode
In a backlight device, lamp units including cold cathode-ray tubes (straight-tube lamp portions) and inverter circuits (driving circuits) for driving to switch on the cold cathode-ray tubes are arranged along a direction that is substantial perpendicular to a longitudinal direction of the cold cathode-ray tubes. Further, the inverter circuits of the lamp units are disposed separately on one end portion side and other end portion side in the longitudinal direction of the cold cathode-ray tubes. Thereby, even when using the longitudinal cold cathode-ray tubes, brightness on a light emitting surface can be made uniform.
Owner:SHARP KK
Heat exchanger apparatus incorporating elliptically-shaped serpentine tube bodies
A heat exchanger apparatus includes an inlet header, an inlet connection connected to the inlet header, an outlet header, an outlet connection connected to the outlet header and a plurality of serpentine tube bodies. The plurality of serpentine tube bodies interconnect and are in communication with the inlet header and outlet header. Each serpentine tube body has a plurality of straight tube sections and a plurality of U-shaped return bend sections. Each one of the straight tube sections and each one of the return bend sections have an elliptically-shaped cross-sectional configuration. The plurality of serpentine tube bodies are arranged in a juxtaposed manner with consecutive ones of the serpentine tube bodies contacting each other at a point defining a series of stacked common planes disposed parallel with one another.
Owner:EVAPCO
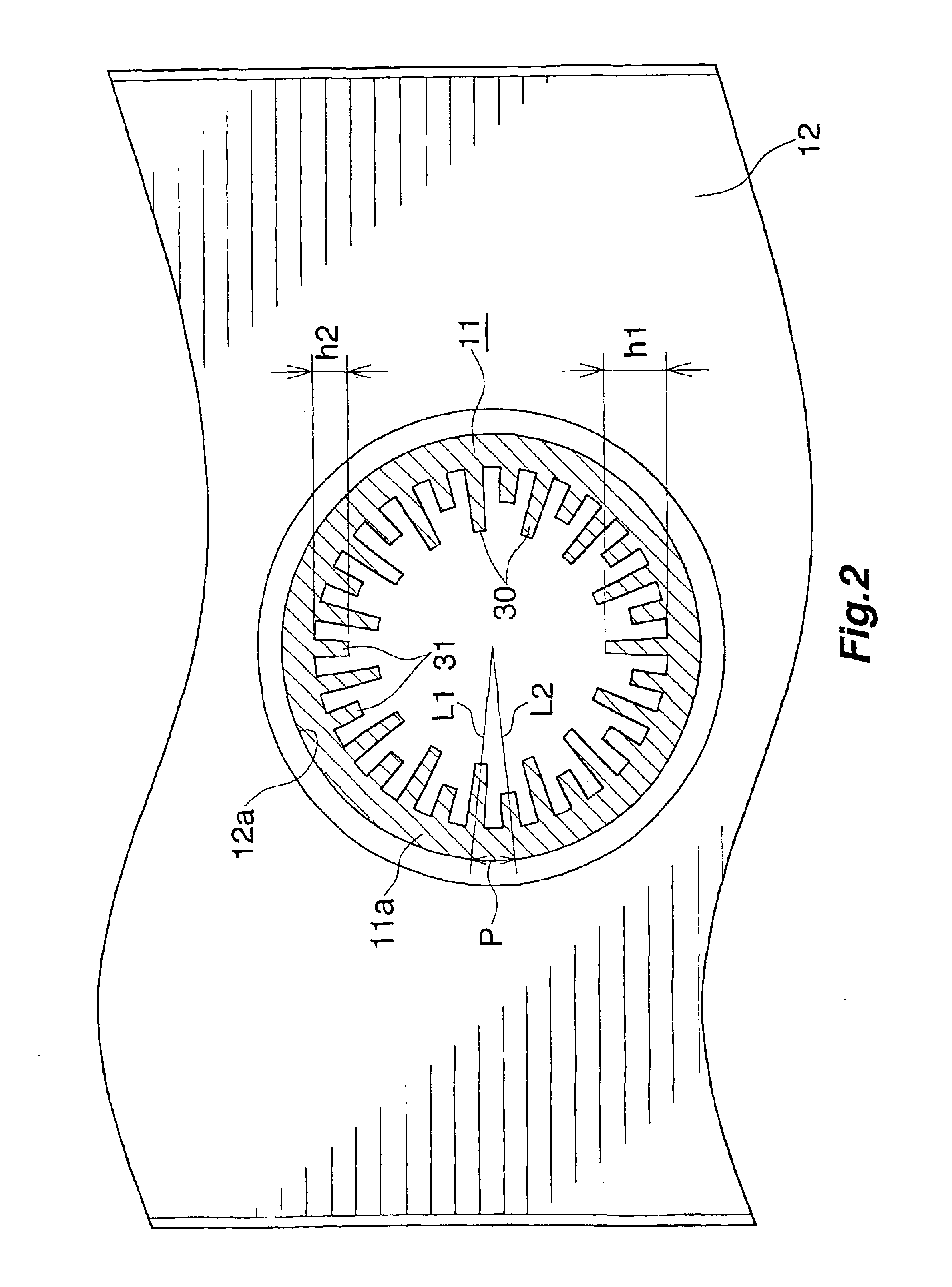
Finned tube for heat exchangers, heat exchanger, process for producing heat exchanger finned tube, and process for fabricating heat exchanger
InactiveUS6928833B2Easy to produceAvoid breakingShow cabinetsEvaporators/condensersStraight tubeEngineering
A heat exchanger finned tube 10 for use in fabricating a heat exchanger 1 useful as the evaporator for refrigerators or the like wherein a hydrocarbon refrigerant is used. Two tube insertion holes spaced apart from each other are formed in each of plate fins 12, and two straight tube portions 11a of a hairpin tube 11 are inserted through the respective holes of each plate fin to arrange the plate fins 12 in parallel into a plurality of fin groups 13 spaced apart on the straight tube portions 11a longitudinally thereof. The hairpin tube 11 is enlarged with use of a fluid to fixedly fit the plate fins 12 of each tin group 13 around an enlarged tube portion 14 of the hairpin tube 11 and provide a finless part 19 between each pair of adjacent fin groups 13 on each of the straight tube portions 11a. A restrained small-diameter portion 15 is provided in each of the finless parts 19 of each straight tube portion 11a. The heat exchanger 1 fabricated using the finned tube 10 exhibits the desired refrigeration performance with the leakage of refrigerant diminished.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Secondary separation cyclone
ActiveCN102847618AImprove efficiencyGood degreasing effectReversed direction vortexCycloneStraight tube
The invention provides a secondary separation cyclone which is mainly used for solving the problem that the existing cyclone separator has a poor effect on separating small oil drops. The secondary separation cyclone is characterized in that: the lower end of a first-grade cyclone pipe is sequentially connected with a second-grade cone section and a second-grade underflow pipe; a cyclone separator is fixed in the cyclone pipe and is formed by connecting a second-grade overflow pipe, a second-grade overflow cone section, a spiral sheet fixing pipe and a second-grade liquid collecting port; a diversion spiral sheet is fixed outside the spiral sheet fixing pipe, and the contour of the diversion spiral sheet is in contact with the inner wall of the first-grade cyclone pipe; a first-grade overflow pipe is connected outside the second-grade overflow pipe, and an annular gap is formed between the two pipes so that a medium in a first-grade cyclone cavity overflows along the annular gap; and the straight pipe length of the first-grade overflow pipe is less than the straight pipe length of the second-grade overflow pipe, both the first-grade overflow pipe and the second-grade overflow pipepenetrate through an upper end cover, and the outer wall of the first-grade overflow pipe is in closed connection with a corresponding hole of the upper end cover. The separation cyclone can increasethe separation efficiency of small oil drops and can realize secondary separation.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Stent-type blood vessel for intracavity treatment of complex abdominal aortic aneurysm
ActiveCN102379757AImprove installation convenienceImprove accuracyStentsSurgeryInsertion stentStraight tube
The invention discloses a stent-type blood vessel for the intracavity treatment of a complex abdominal aortic aneurysm, which comprises a main body stent and branch stents. The main body stent is funnel-shaped. Two front wall windows are arranged on the front wall of the upper part of the main body stent and two side wall windows are arranged on the side wall of the middle part of the main body stent. Straight tube stent-type blood vessel passages are respectively and upwards arranged on the side wall windows. Each branch stent is circular-tube-shaped and the thickness of the branch stent is adaptive to the diameter of a renal artery.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
High-pressure fuel injection pipe
ActiveUS6843275B2Reduce concentrationReduce stress concentrationSleeve/socket jointsJoints with sealing surfacesStraight tubeThick wall
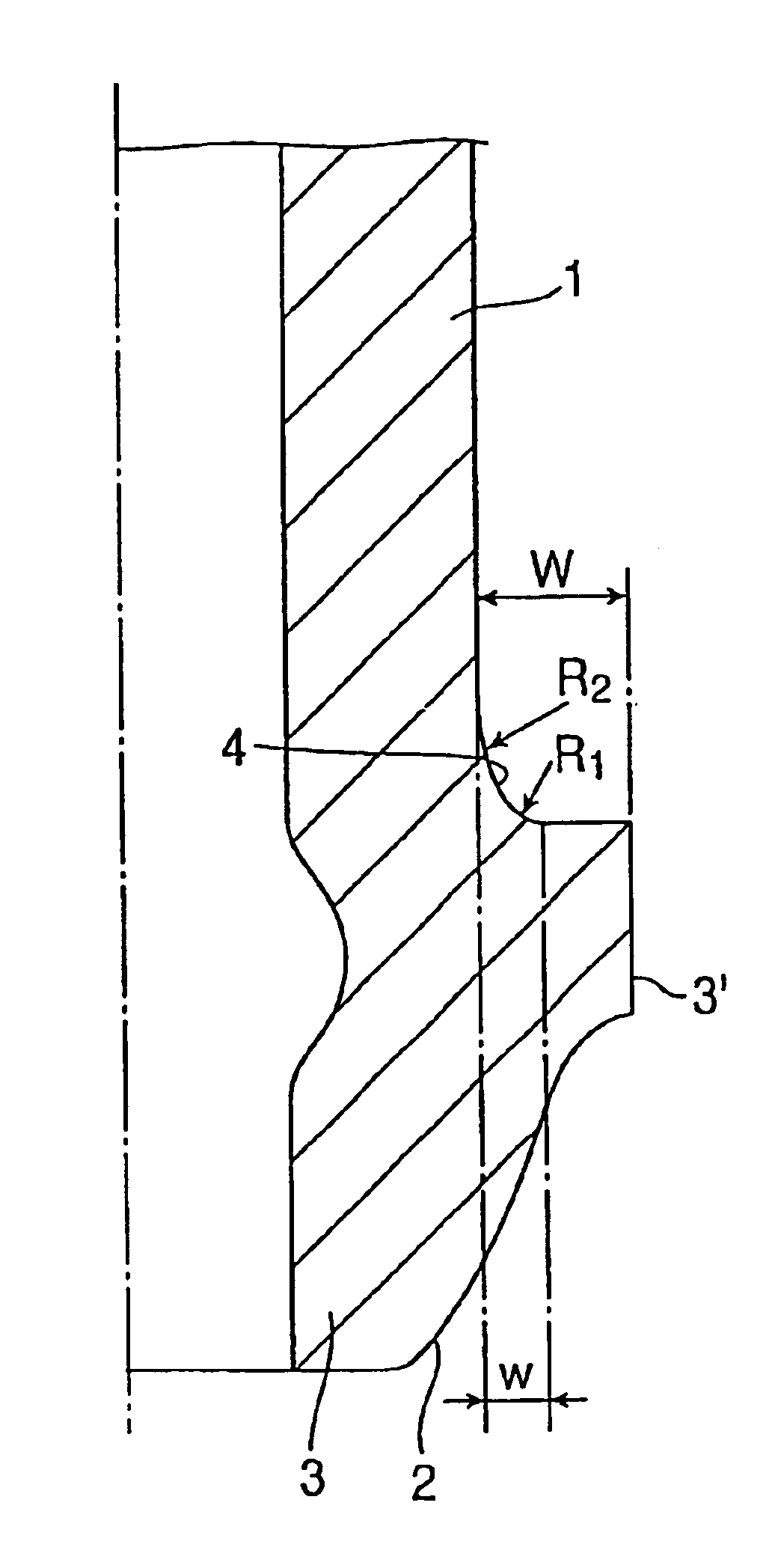
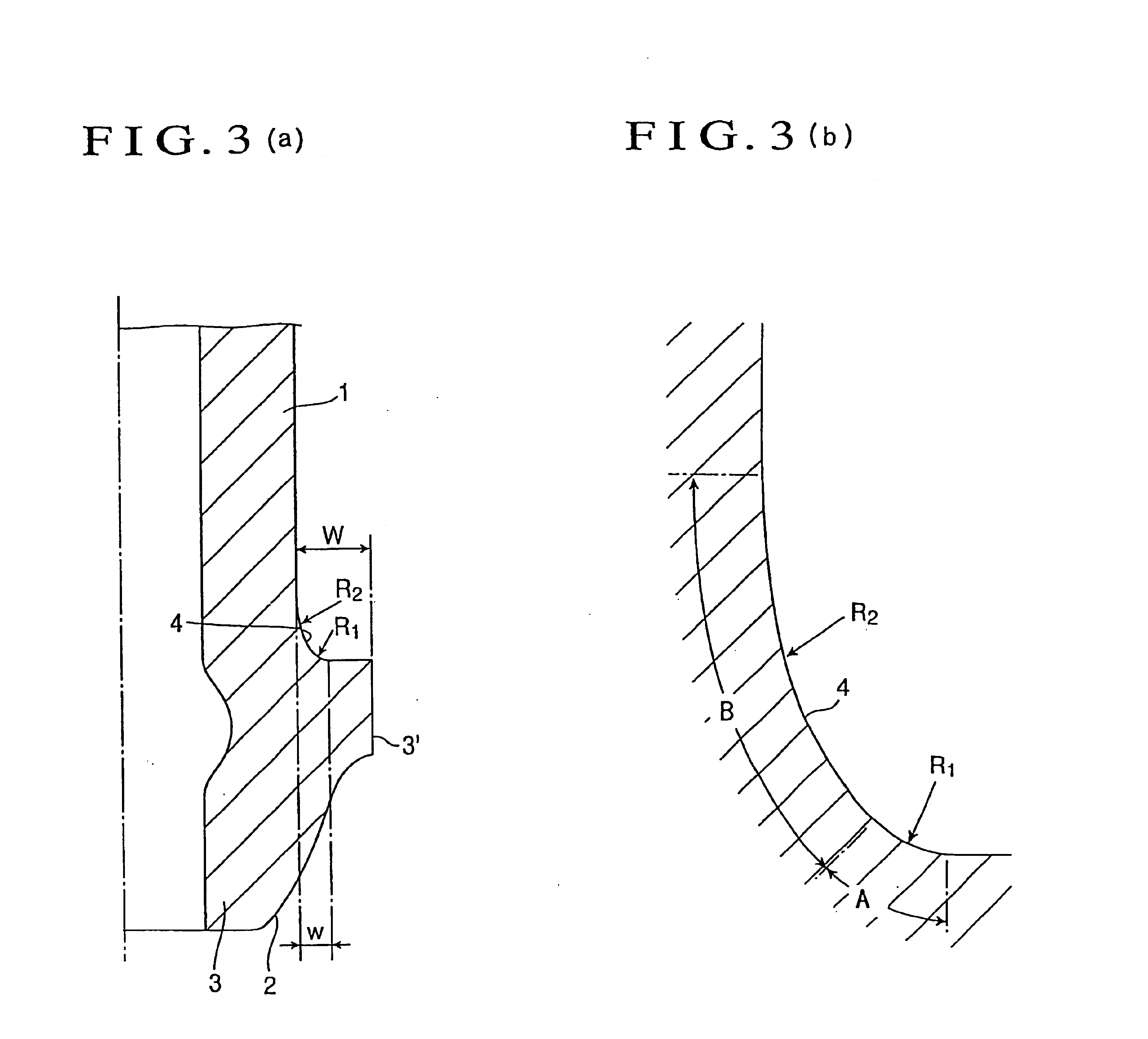
A high-pressure fuel injection pipe has a connecting head portion increased in diameter by buckling molding at the end of a thick and small-diameter metallic pipe. An under-head portion of the connecting head is formed with a thick wall portion that satisfies conditions of: a radius of curvature R1 of a portion A of the thick wall portion continuing to the connecting head is 0.03 to 0.15 times the outer diameter of the pipe; a radius of curvature R2 of a portion B continuing from the portion A of the thick wall portion to a straight pipe portion is 0.3 to 1.5 times the outer diameter of the pipe; and a maximum diametrical size w of the thick wall portion is 0.25 to 0.4 times a maximum diametrical projecting length W of the connecting head.
Owner:USUI KOKUSAI SANGYO KAISHA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com