Sandwich transducer type longitudinal and bending linear ultrasound motor with frequency-modulating variable-amplitude rod
A linear ultrasonic motor, horn technology, applied in piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, generators/motors, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of inability to form product serialization, low motor efficiency, problems such as high noise, to achieve the effects of low noise, reduced loss, and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
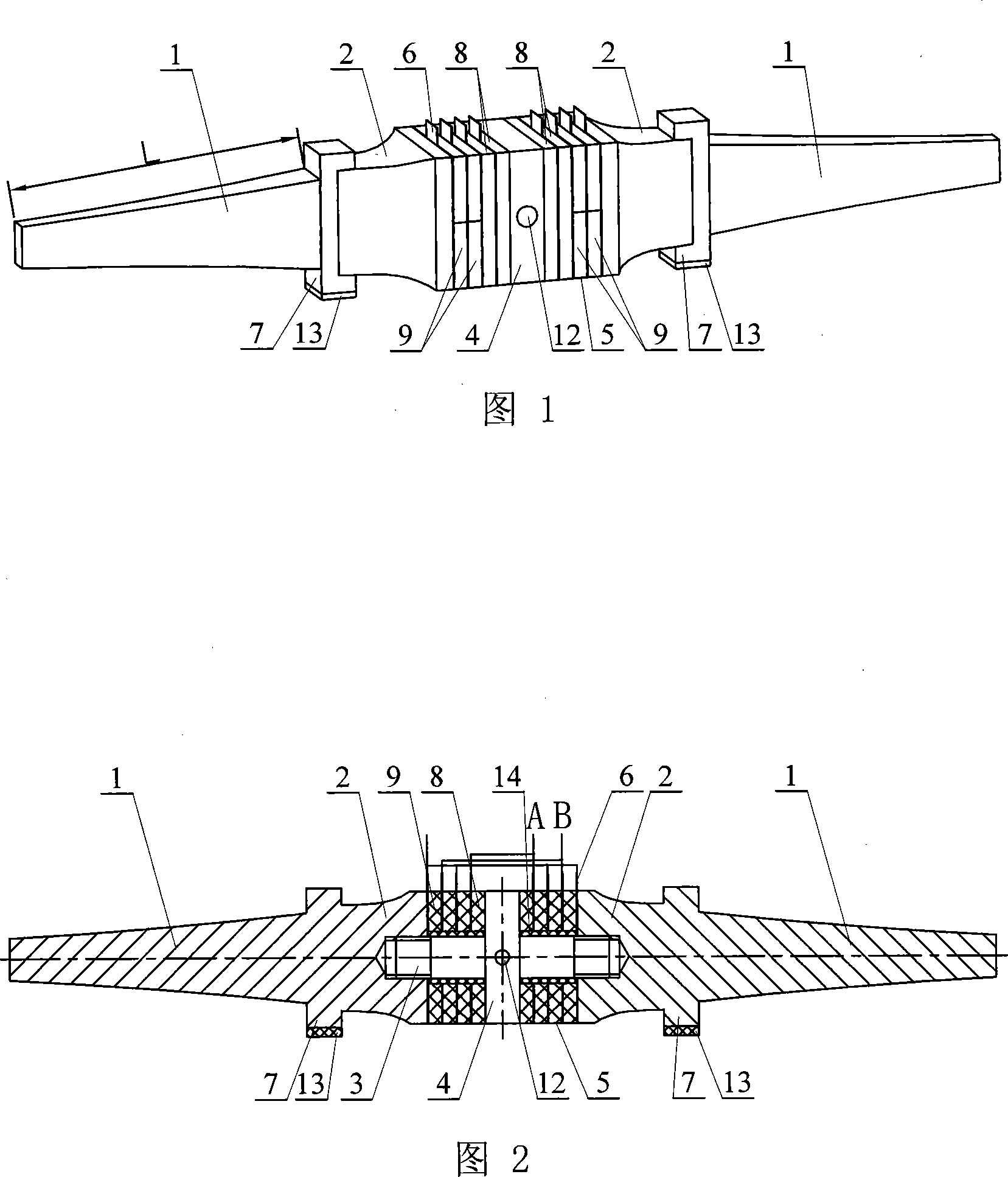
[0006] Specific embodiment 1: This embodiment is described in conjunction with Fig. 1 to Fig. 3. This embodiment is composed of a sandwich transducer and a driving foot 7; , flange 4, piezoelectric ceramic sheet group 5, and thin copper sheet 6; the middle position on the stud 3 is provided with a flange 4, the stud 3 on the left side of the flange 4 and the right side of the flange 4 The studs 3 are equipped with piezoelectric ceramic sheet groups 5 respectively, and thin copper sheets as electrodes are respectively installed between the piezoelectric ceramic sheets of the piezoelectric ceramic sheet group 5 and between the piezoelectric ceramic sheet group 5 and the end cover 2. 6. The piezoelectric ceramic sheet group 5 and the thin copper sheet 6 are fastened together with the large end of the end cover 2 through the stud 3, and the small end of the end cover 2 is affixed to the large end of the FM horn 1 through the driving foot 7 , the driving foot 7 is located at the an...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0008] Specific Embodiment 2: This embodiment is described with reference to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 . In this embodiment, a small conical hole 12 is drilled on the front side and the rear side of the flange 4 at the overlapping nodes of the longitudinal bending vibration. As the clamping point of the pre-tightening force mechanism of the linear ultrasonic motor, it is used to apply the pre-tightening force to generate driving friction. Choosing to drill two small conical holes 12 at this position can prevent resonance frequency drift and vibration distortion, and reduce energy loss. Other components and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0009] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is described in conjunction with Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: this embodiment also adds a hard ceramic friction plate 13; the hard ceramic friction plate 13 Bond with the lower end surface of the driving foot 7. Such setting can prevent the driving foot 7 from wearing out and prolong the service life of the driving foot 7 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com