Method for preparing and using vascular stent
A vascular stent and heat-sensitive technology, applied in the field of preparation of vascular stents, can solve problems such as blocked capillaries in the brain, necrosis, and damage to limb functions, and achieve the effects of simple preparation methods, simple use methods, and convenient storage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] 2.0g PEO (polyethylene oxide, molecular weight: 500-10,000 Daltons) and 0.32mL THDI (trimethylhexamethylene diisocyanate), in the presence of 30μL dibutyl tin dilaurate catalyst and nitrogen protection, React in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (20 mL) for one hour. The reaction temperature is maintained at 60-70°C. 4.7 mg (2% molar ratio) of cross-linked cinnamamide was dissolved in 1 mL of DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) and added to the reaction system. Continue stirring and keep the reaction temperature at 60-70°C for two hours. Finally, 22.7mg of MTX, namely methotrexate, with the chemical formula (2S)-2-[(4-{[(2,4-diaminopyridin-6-yl)methyl](methylamino}benzyl Acyl)amino]valeric acid, dissolve it in 2mL DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) and add it to the reaction system. Stir the mixture at 60-70°C for four hours, then stop heating. Let the reactants continue to stay at room temperature Stir overnight, react for 12 hours, and finally add 1 mL of methanol to terminate the polymerizat...
Embodiment 2
[0057] 2.0g PCL (polycaprolactone, molecular weight: 500-10,000 Daltons) and 0.32mL THDI (trimethylhexamethylene diisocyanate), in the presence of 30μL dibutyl tin dilaurate catalyst and under the protection of nitrogen, React in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (20 mL) for one hour. The reaction temperature is maintained at 60-70°C. 4.7 mg (2% molar ratio) of the cross-linking agent cinnamamide was dissolved in 1 mL of DMSO and then added to the reaction system. Continue stirring and keep the reaction temperature at 60-70°C for three hours. Finally, 22.7mg of MTX, namely methotrexate, with the chemical formula (2S)-2-[(4-{[(2,4-diaminopyridin-6-yl)methyl](methylamino}benzyl Acyl)amino]valeric acid, dissolve it in 2mL DMSO and add it to the reaction system. Stir the mixture at 60-70°C for five hours, then stop heating. Let the reactants continue to stir overnight at room temperature for 16 hours. Finally, 1 mL of methanol was added to terminate the polymerization reaction. The obta...
Embodiment 3
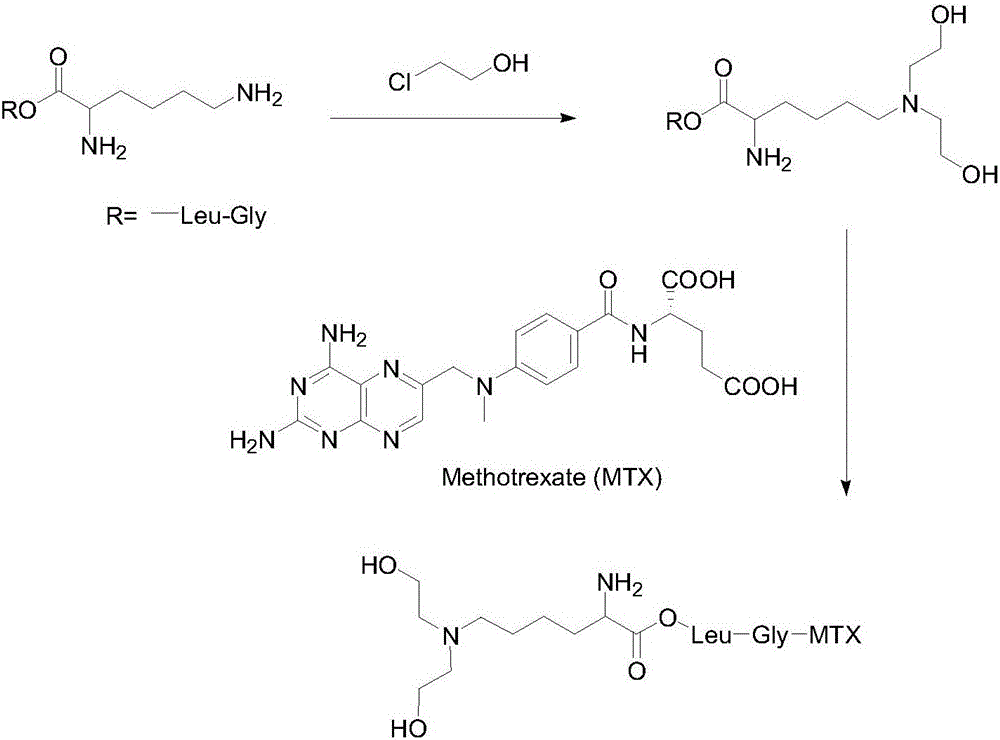
[0063] Dissolve 316 mg of glycine-leucine-lysine in 10 mL of THF (tetrahydrofuran), and add 2.5 molar equivalents of 2-chloroethanol. The mixture was heated to 50-60°C and continuously stirred for 6 hours, and then cooled to room temperature. The reaction mixture was washed with 5 mL of 1 M NaOH aqueous solution, and then extracted with dichloromethane. After removing the solvent, the diol derivative of the tripeptide was obtained with a yield of 60%.
[0064] The diol derivative of the obtained tripeptide and MTX (methotrexate, the chemical formula is (2S)-2-[(4-{[(2,4-diaminopyridin-6-yl)methyl]( Methylamino}benzoyl)amino]valeric acid) was dissolved in chloroform at a molar ratio of 1:1. 0.15 molar equivalent of dicyclohexylcarbimide (DCC) was added and stirred at room temperature for reaction for two hours. After the solvent is filtered and purified, the active drug, namely the tripeptide diol derivative of methotrexate, is obtained. The yield is> 90%.
[0065] Dissolve 1.9g ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com