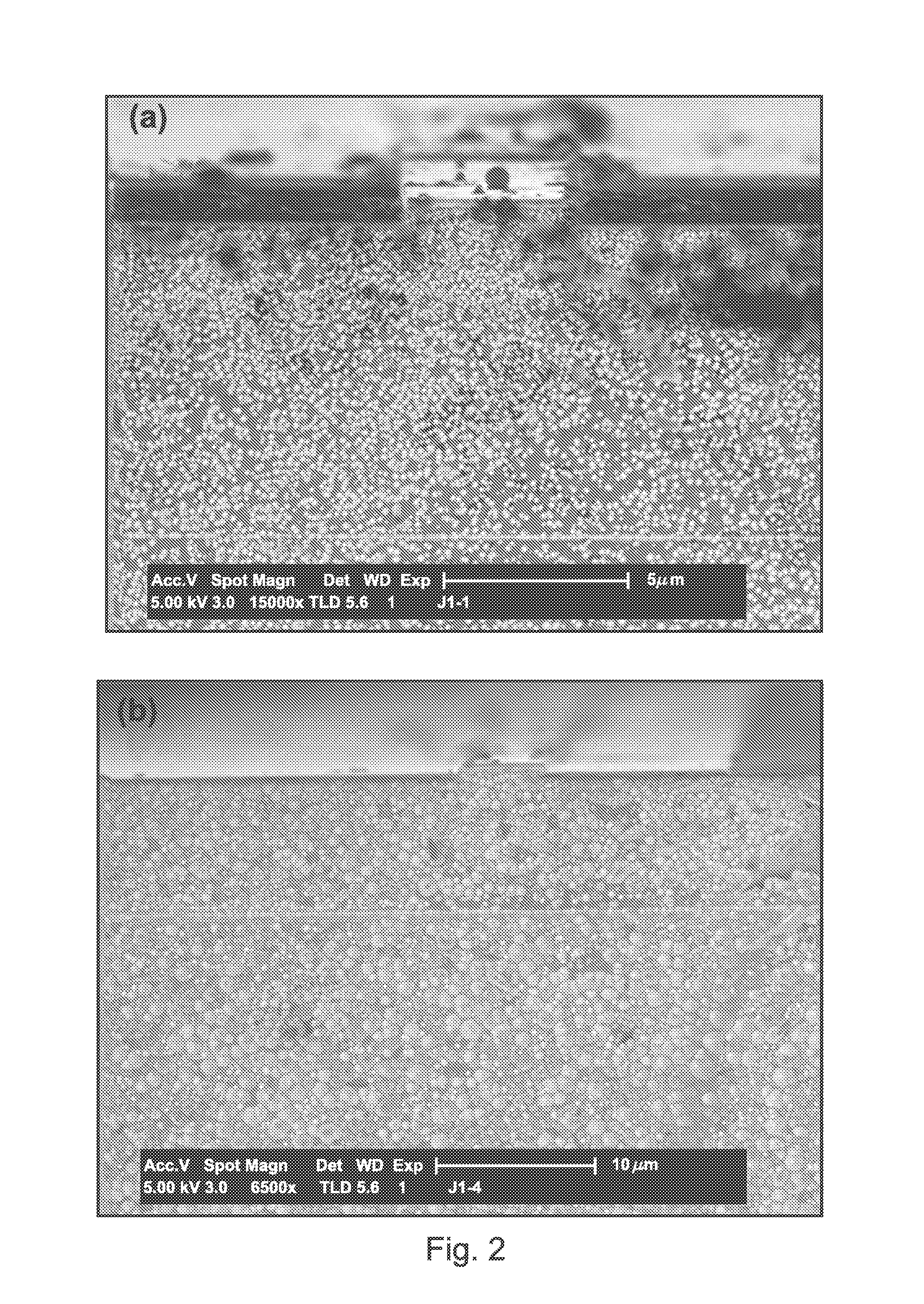
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
246 results about "Faceting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In geometry, faceting (also spelled facetting) is the process of removing parts of a polygon, polyhedron or polytope, without creating any new vertices. New edges of a faceted polyhedron may be created along face diagonals or internal space diagonals. A faceted polyhedron will have two faces on each edge and creates new polyhedra or compounds of polyhedra.
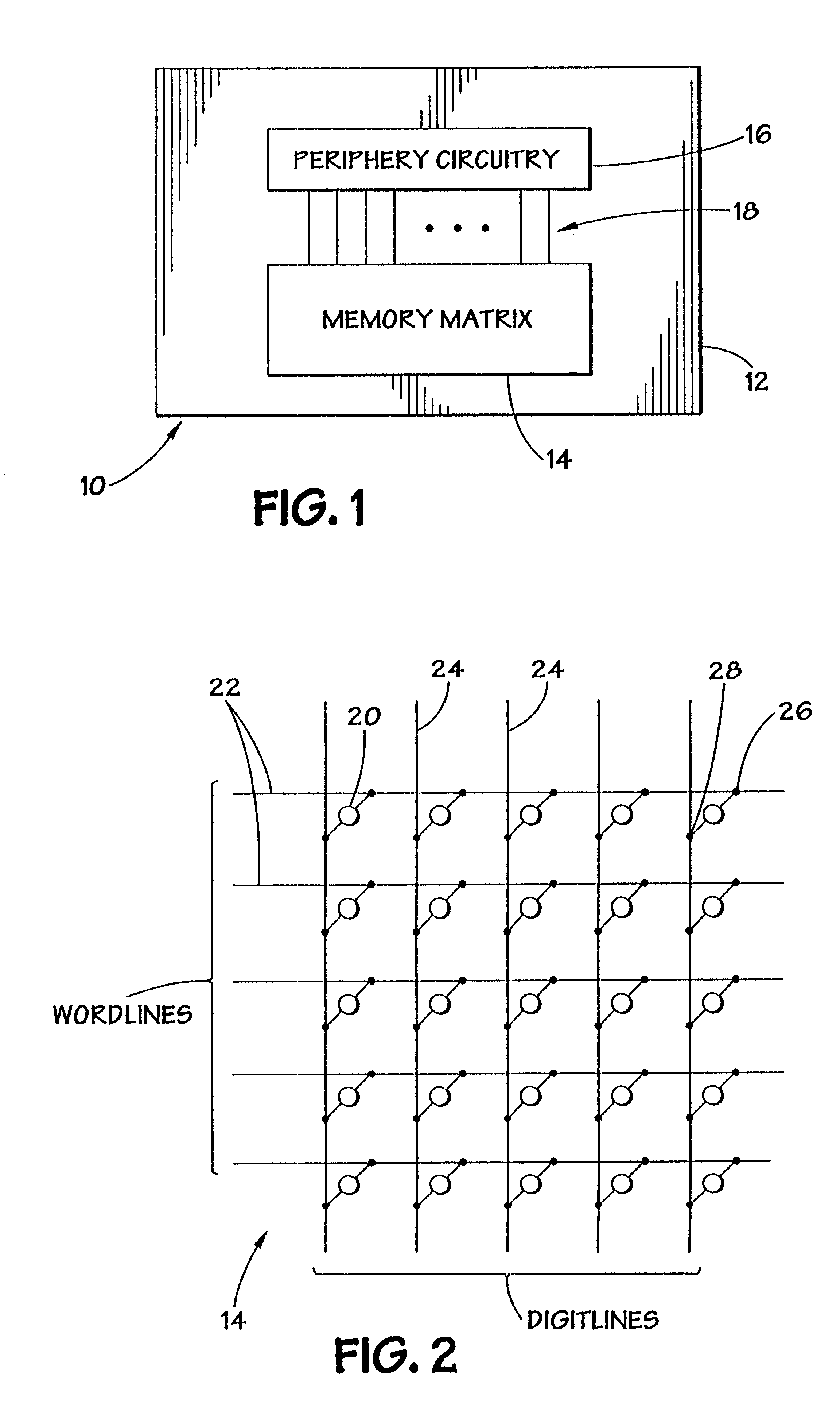
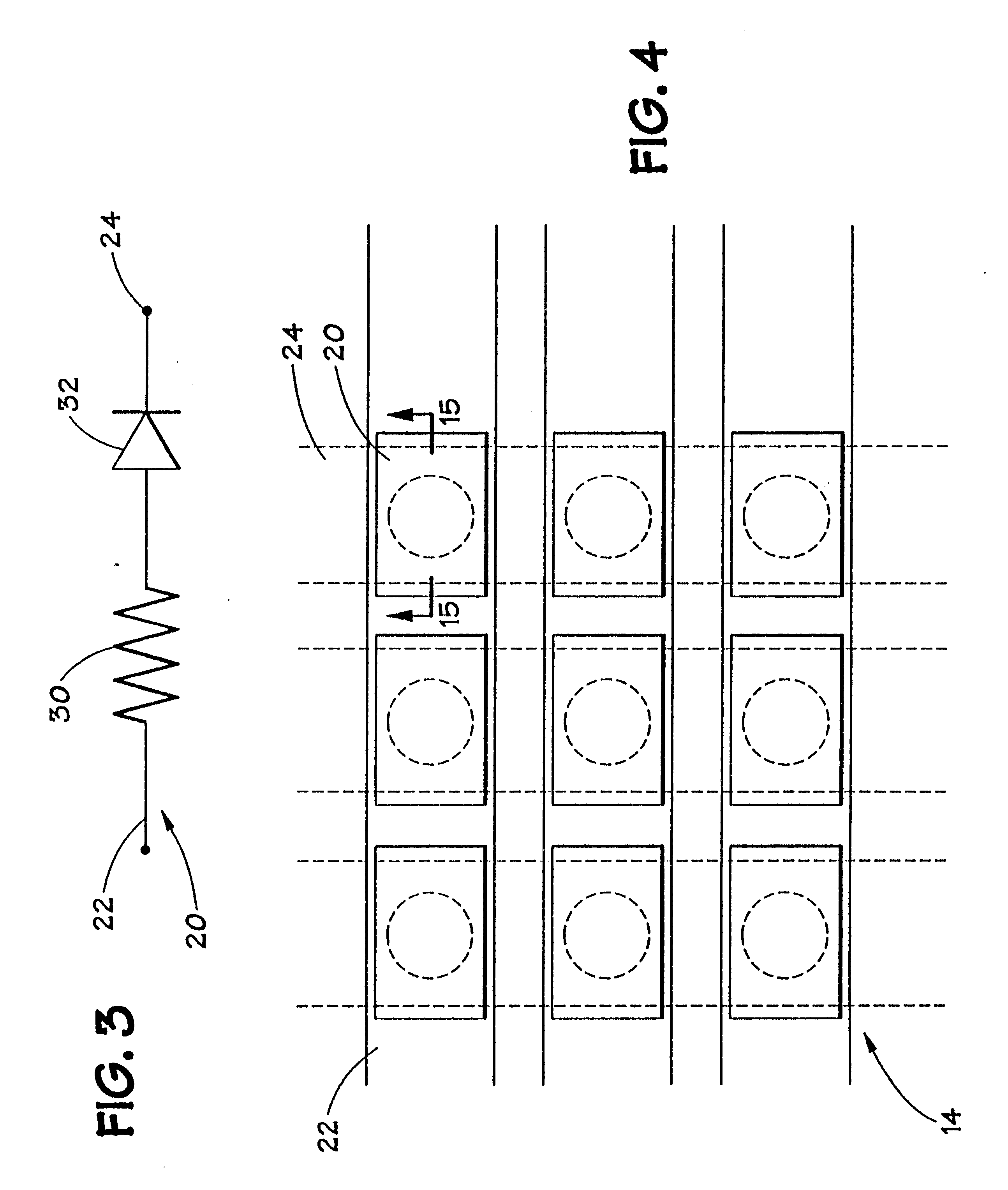
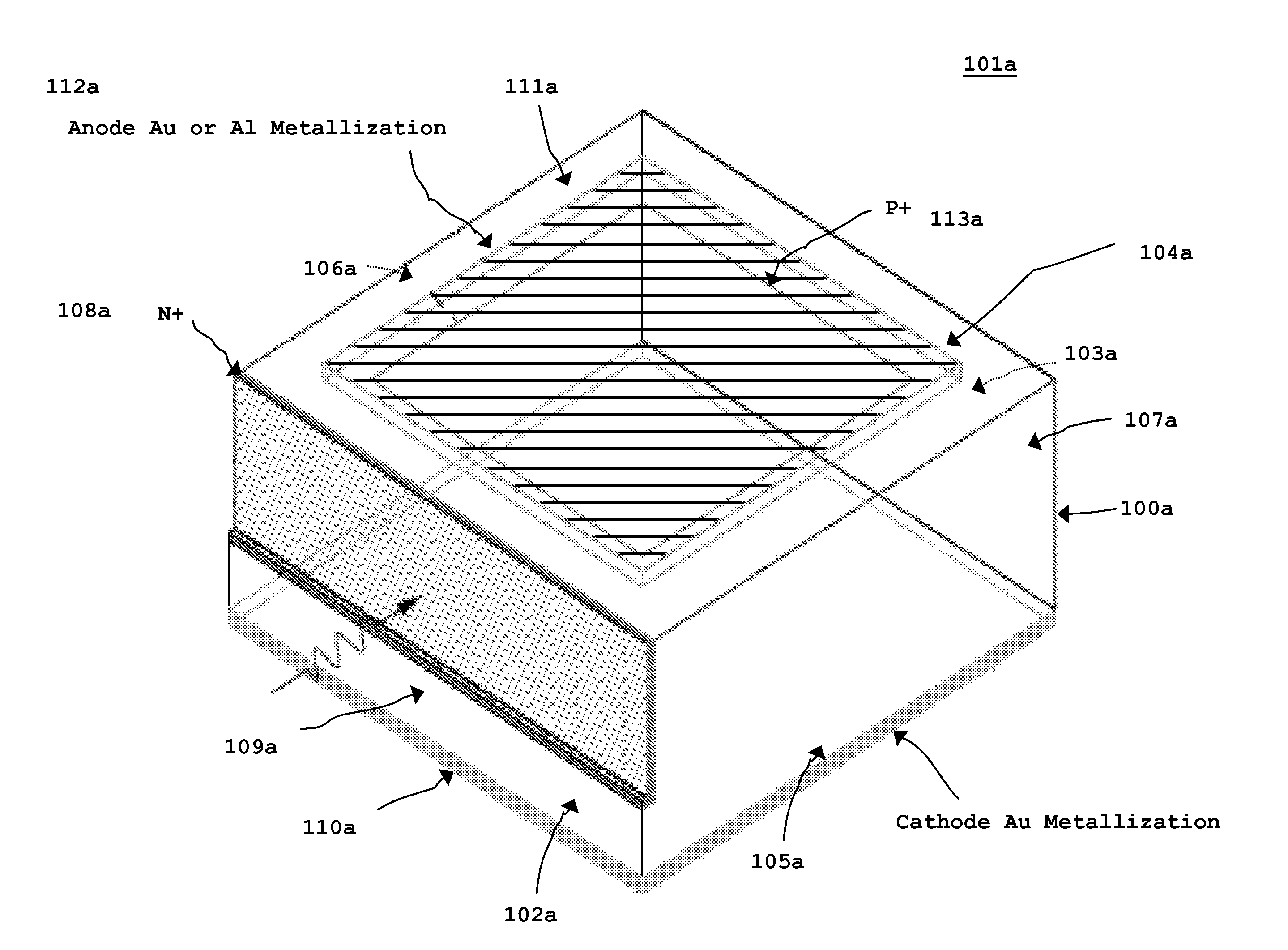
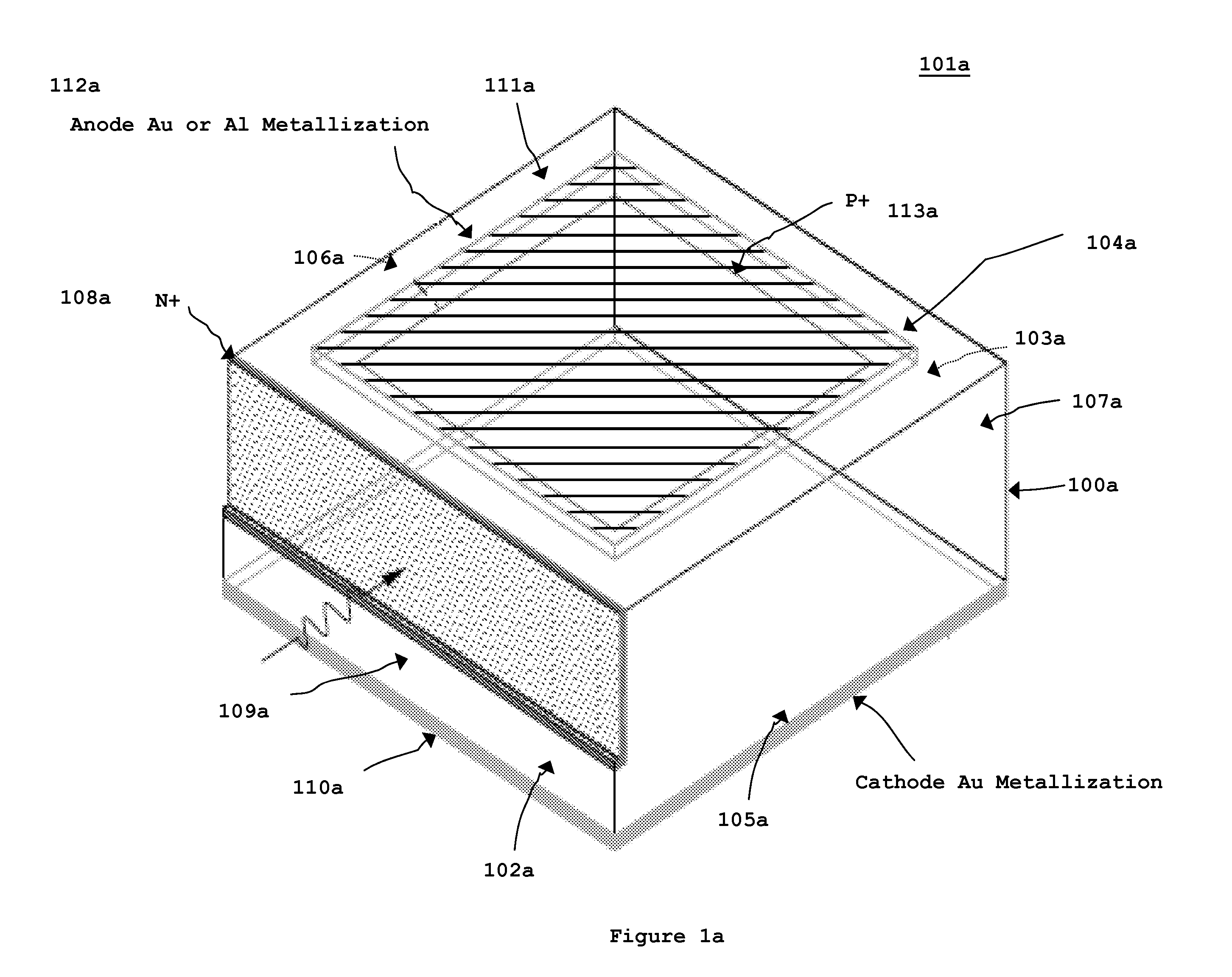
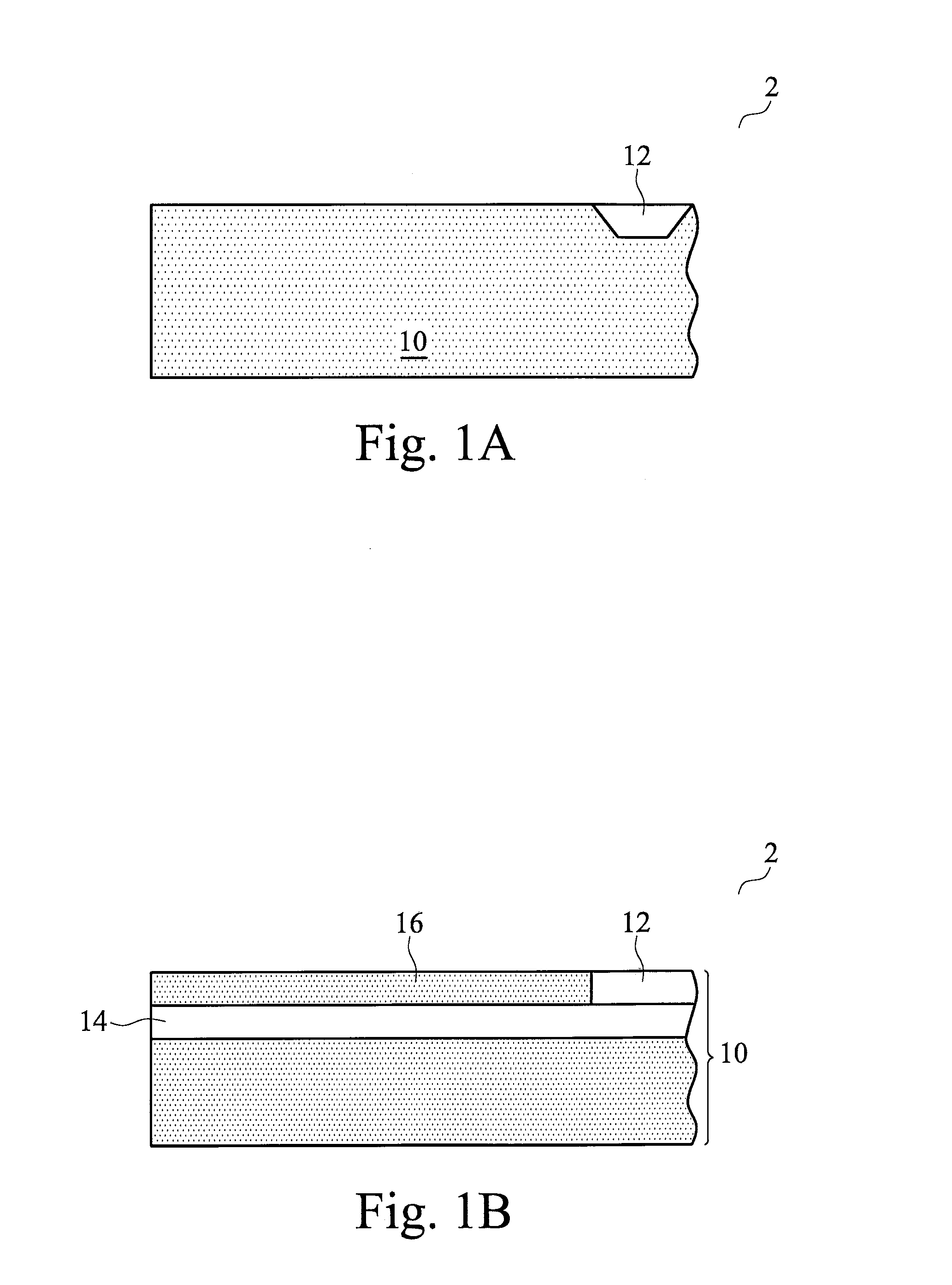
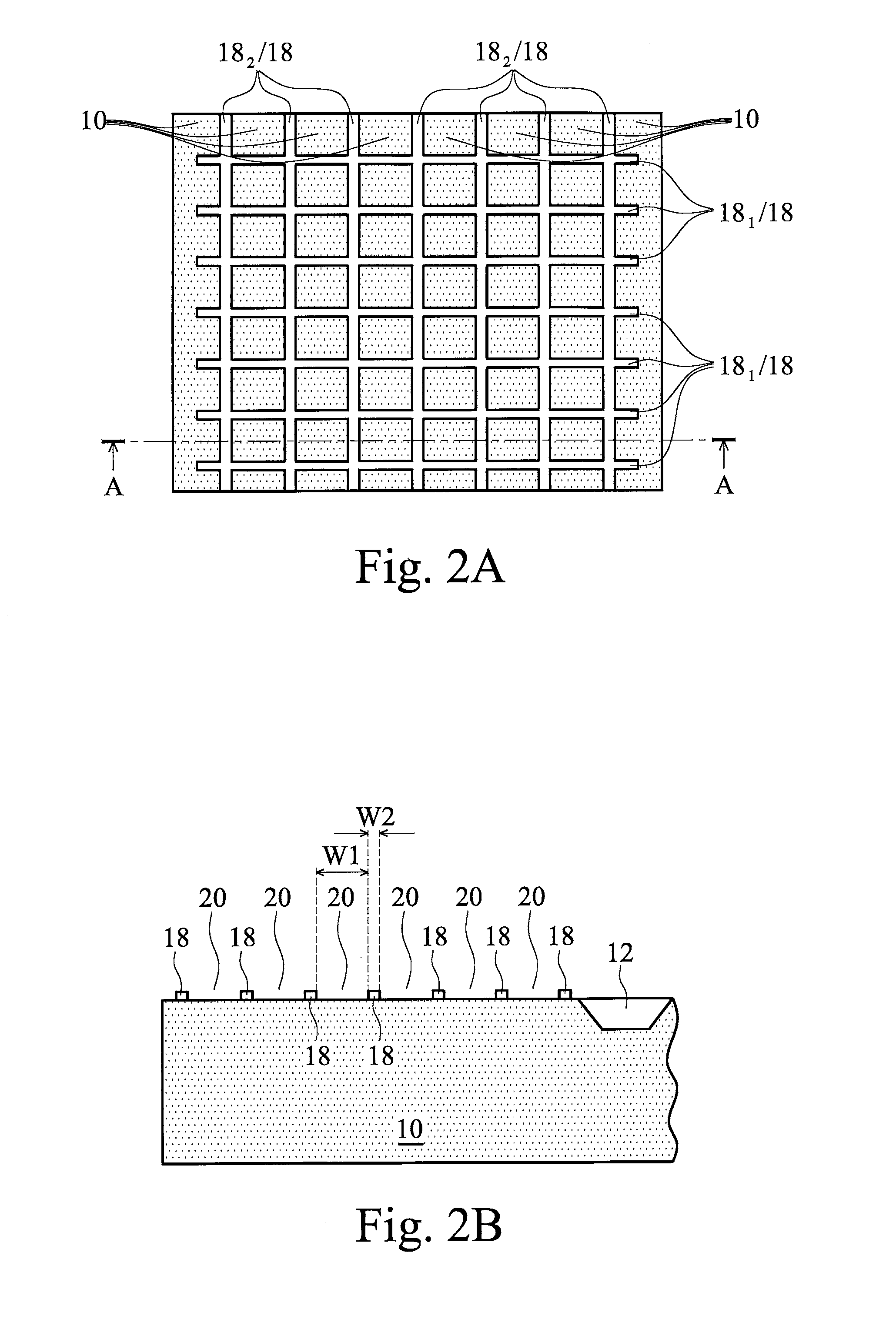
Memory elements and methods for making same
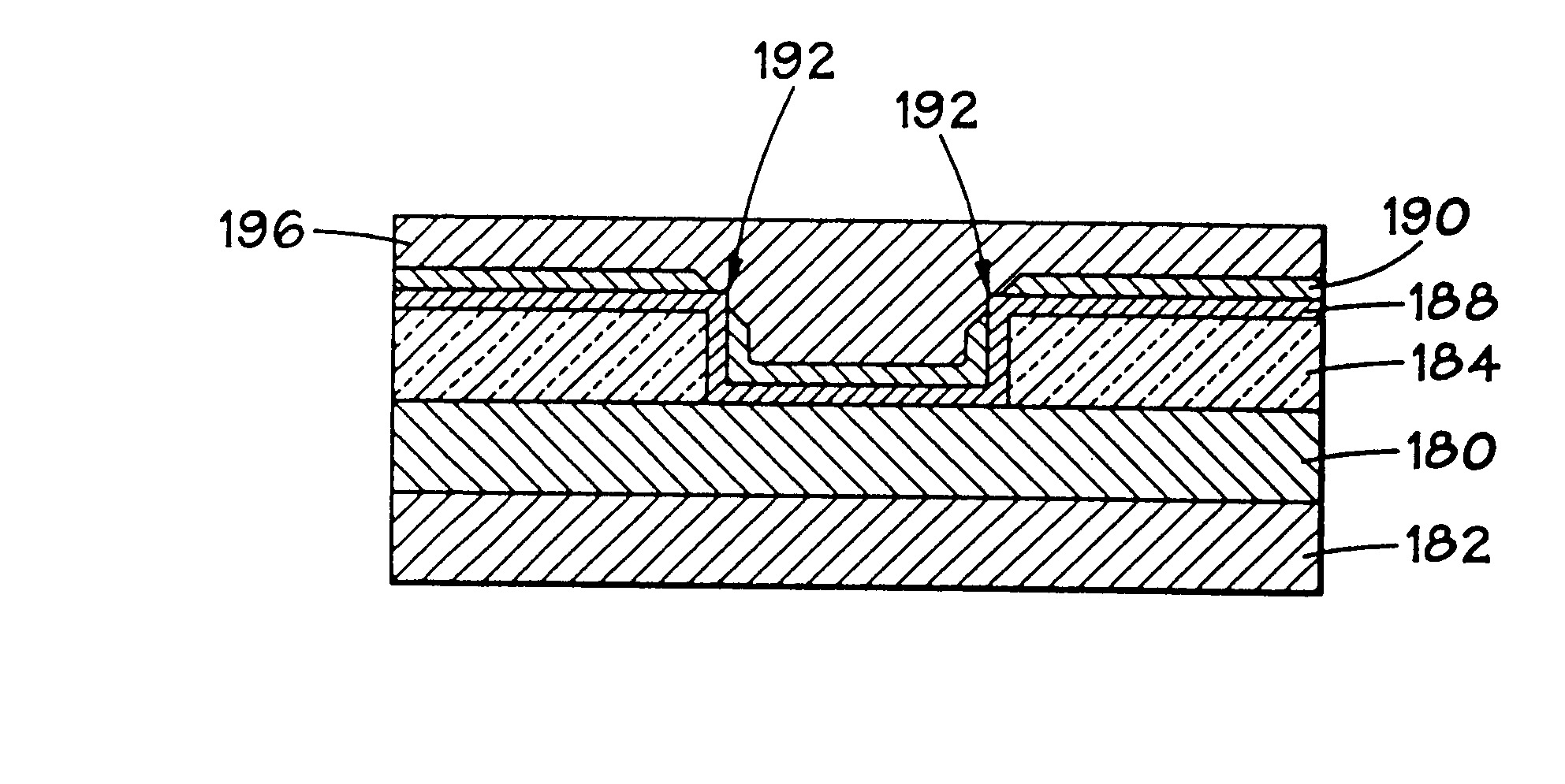
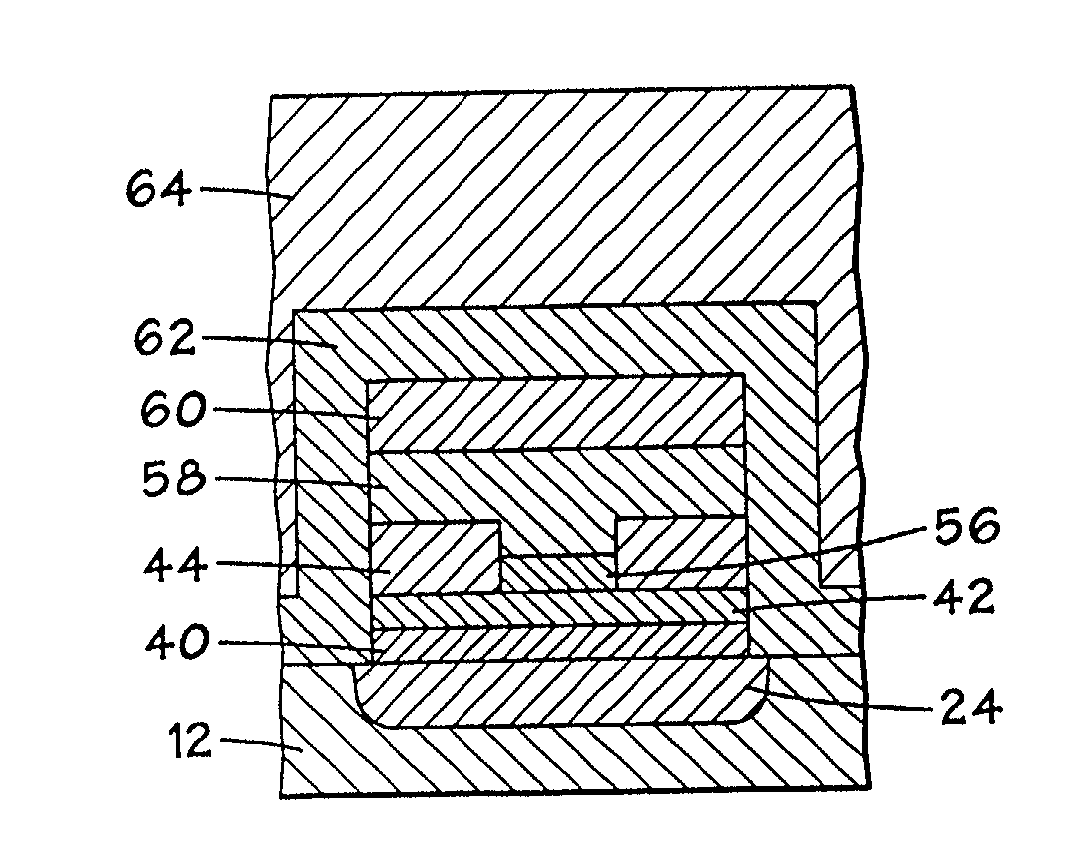
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method of forming a contact structure in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6440837B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess deviationsEtching
Annular and linear contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
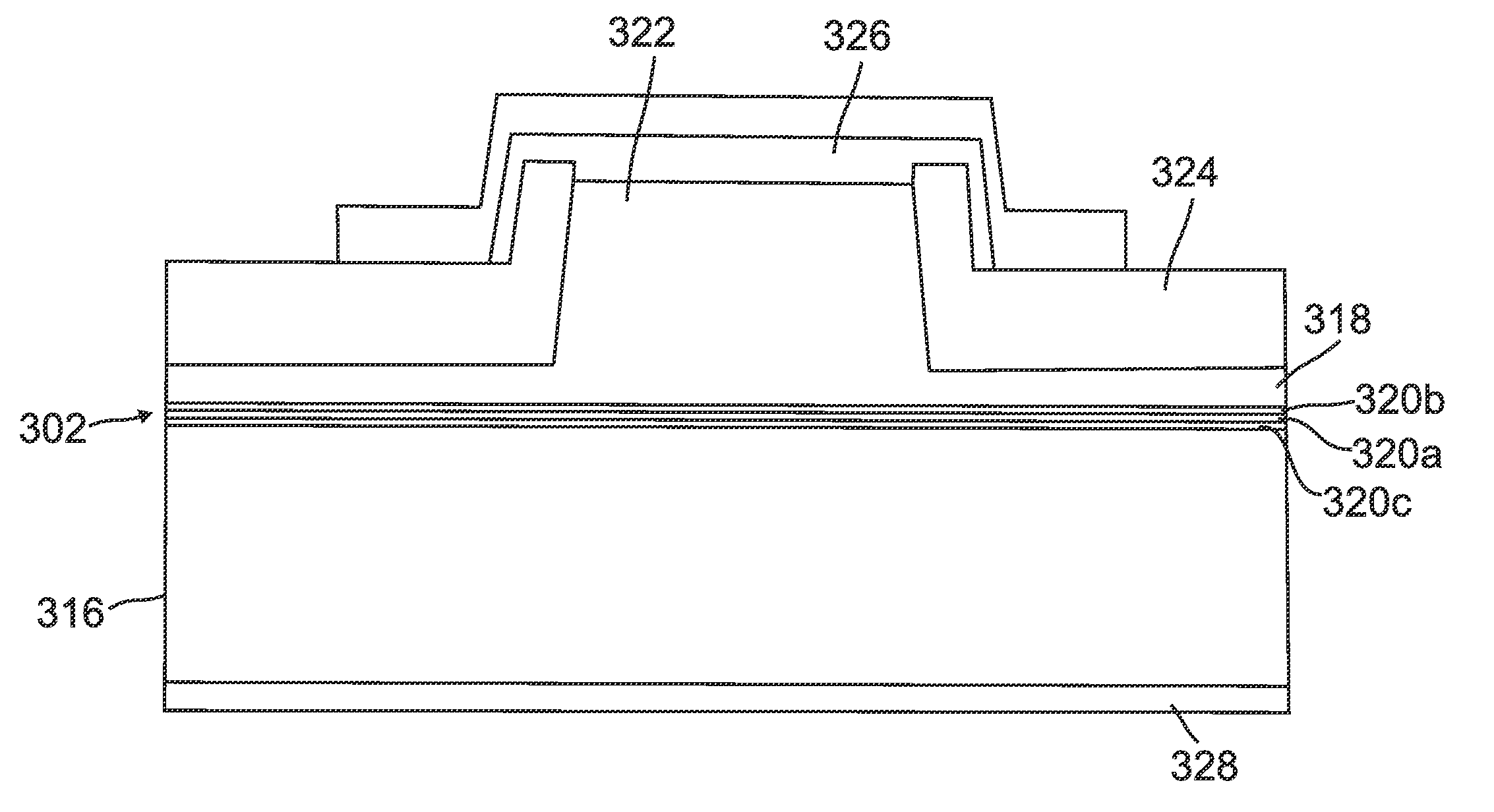
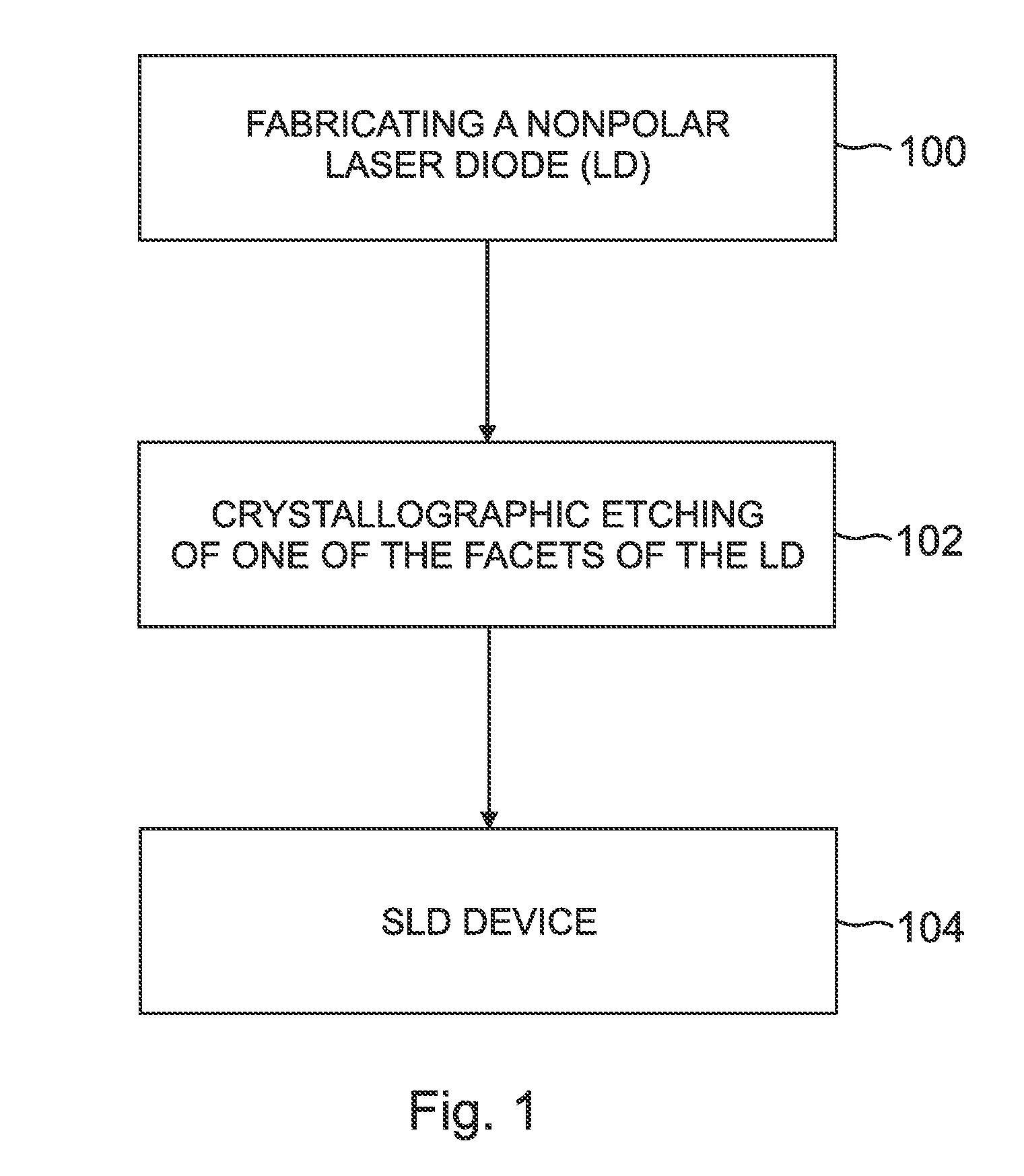
Superluminescent diodes by crystallographic etching
InactiveUS20110103418A1Reduce internal lossSignificant contributionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSuperluminescent diodeEtching
An optoelectronic device, comprising an active region and a waveguide structure to provide optical confinement of light emitted from the active region; a pair of facets on opposite ends of the device, having opposite surface polarity; and one of the facets which has been roughened by a crystallographic chemical etching process, wherein the device is a nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,In,Al,B)N based device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Faceted structure, article, sensor device, and method
A faceted structure is provided that includes a crystalline composition comprising a metal nitride. The metal comprises one or more of aluminum, boron, indium, or gallium. The crystalline composition has at least one exposed surface that is a grain boundary, an etched surface, or a naturally formed facet, and the surface has the same crystallographic orientation of a substrate on which the crystalline composition is grown. A sensor device is provided that includes a faceted structure. Associated methods of making and using the faceted structure in a sensor device are provided.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Memory elements and methods for making same
InactiveUS20020160551A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess deviationsEtching
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Implants and delivery system for treating defects in articulating surfaces
InactiveUS20060178748A1Precise positioningPrevent rotationDiagnosticsBone implantArticular surfacesTissue defect
The invention provides implant plugs having a complex clinically acceptable proximal surface. The invention also provides multi-phase implant plugs which have a nonplanar proximal surface. Suitable implant proximal surface shapes include, but are not limited to, concave surfaces, convex surfaces, faceted domes and angled surfaces formed by the convergence of two facets. The implants of the invention are suitable for repair of tissue defects in articulating surfaces. The invention also provides delivery devices and methods for delivering the implants of the invention. The invention also provides methods for creating defects suitable for use with the implants of the invention.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
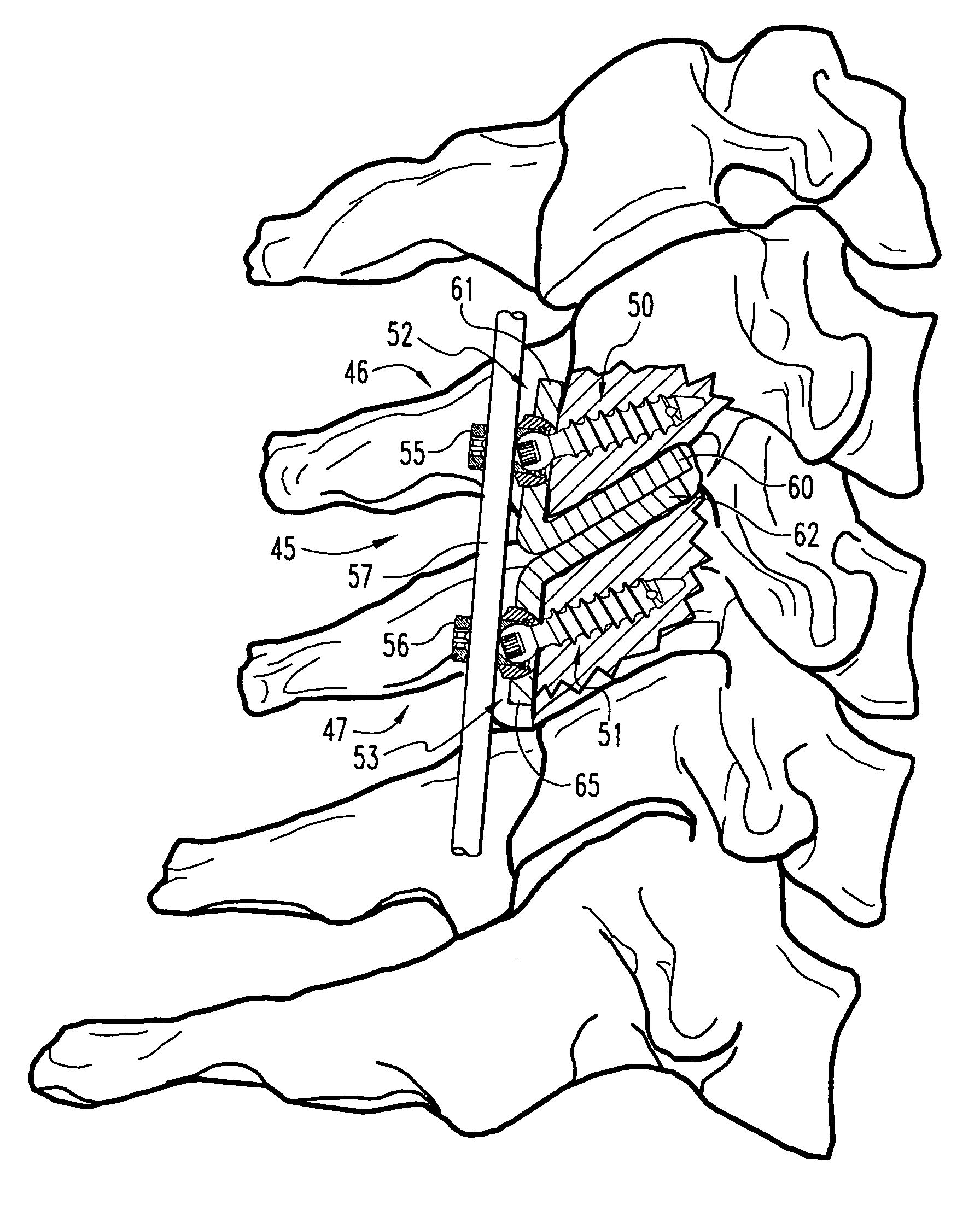
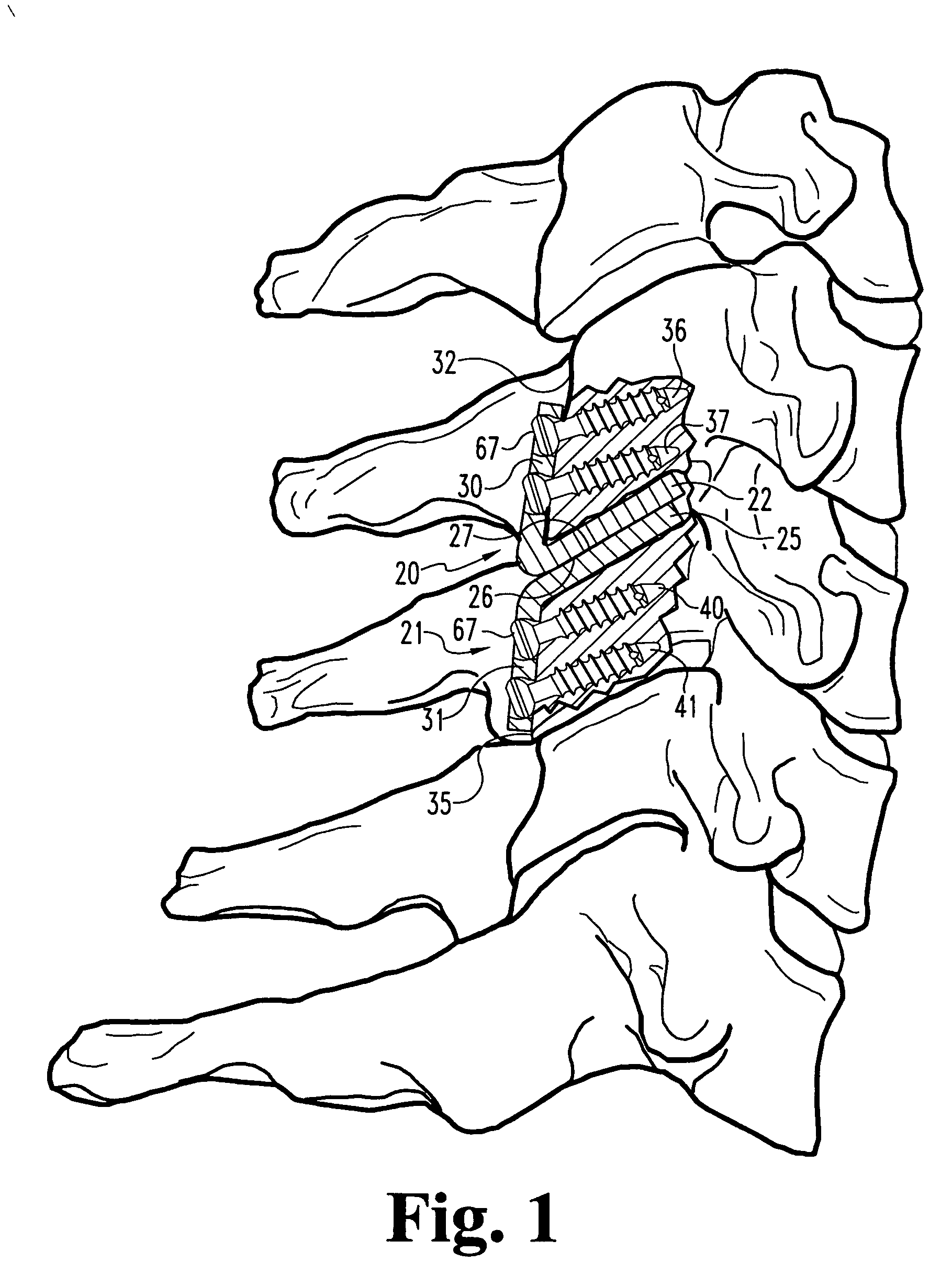
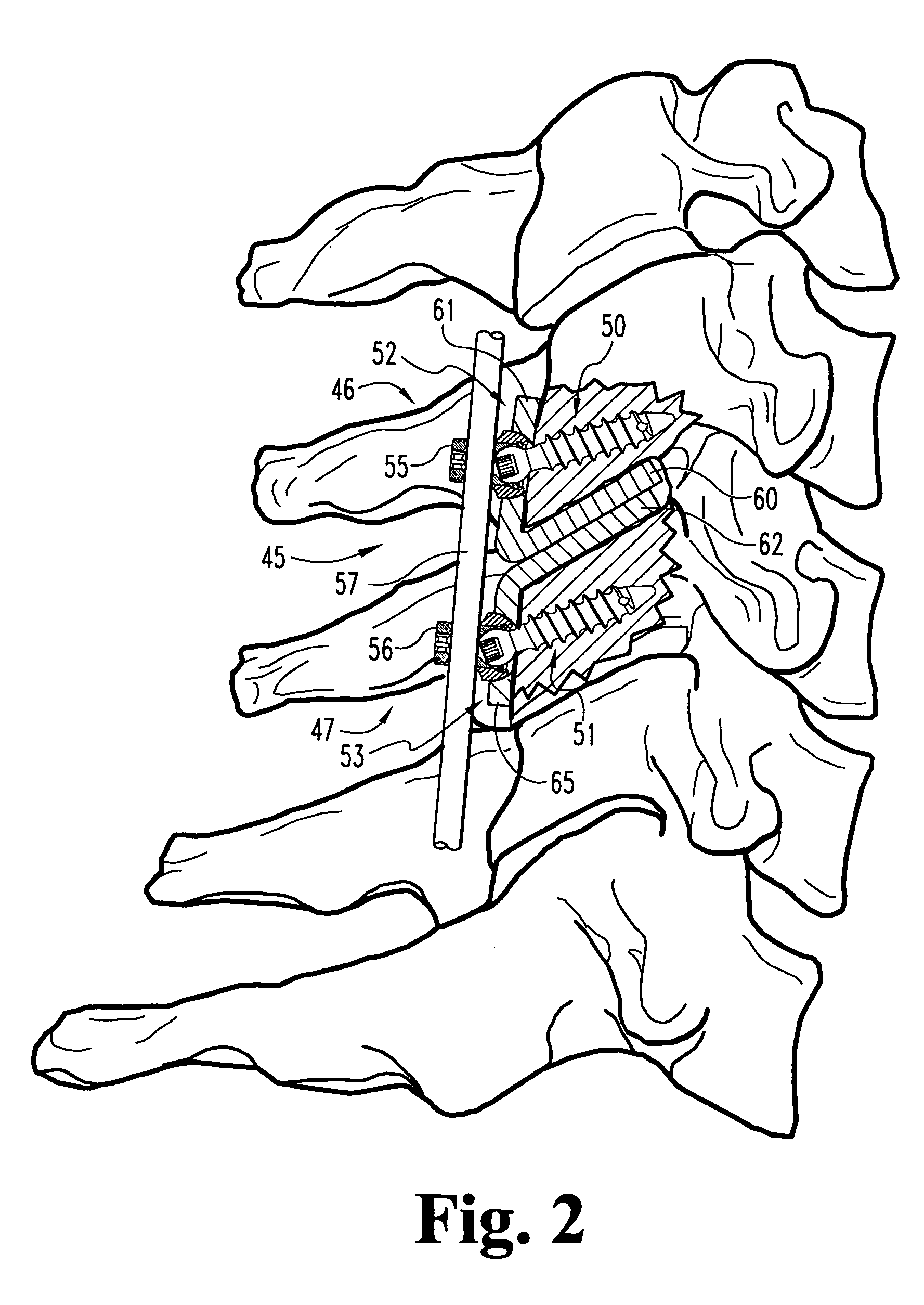
Replacement facet joint and method
Prostheses and methods for repair of a cervical fact joint. The articulating surfaces of the natural facets of the facet joint are removed only a sufficient amount to allow the insertion of flat or slightly curvilinear portions of protheses therebetween in an overlapping relationship. The portions are so inserted and the prostheses mounted by attachment to adjacent vertebrae. Also, a single natural facet may be similarly repaired with a single prosthesis.
Owner:SASSO RICARDO C +1
STRUCTURE AND METHOD FOR IMPROVED STRESS AND YIELD IN pFETS WITH EMBEDDED SiGe SOURCE/DRAIN REGIONS
ActiveUS20070018205A1High uniaxial stressAvoid problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceCMOS
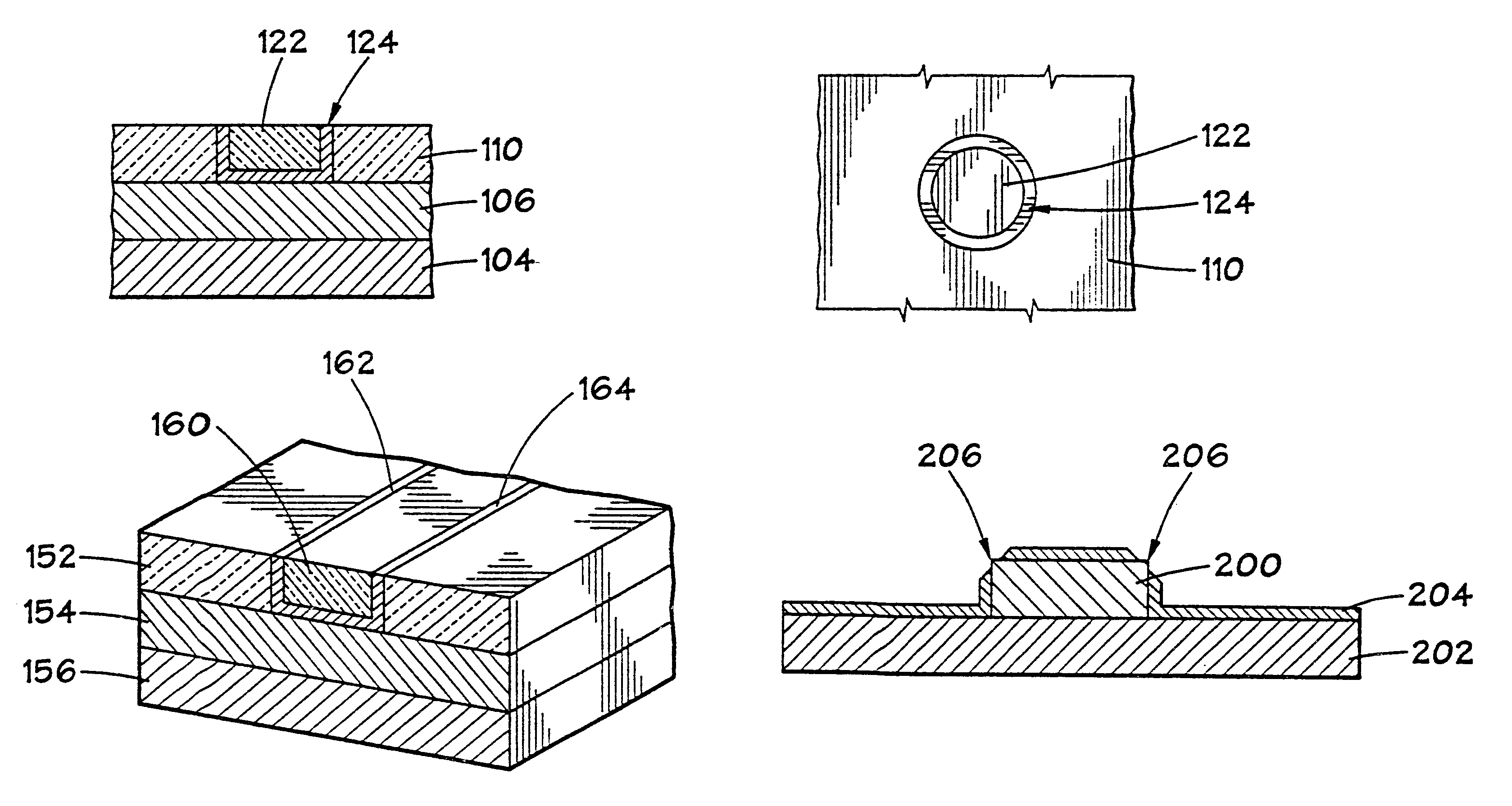
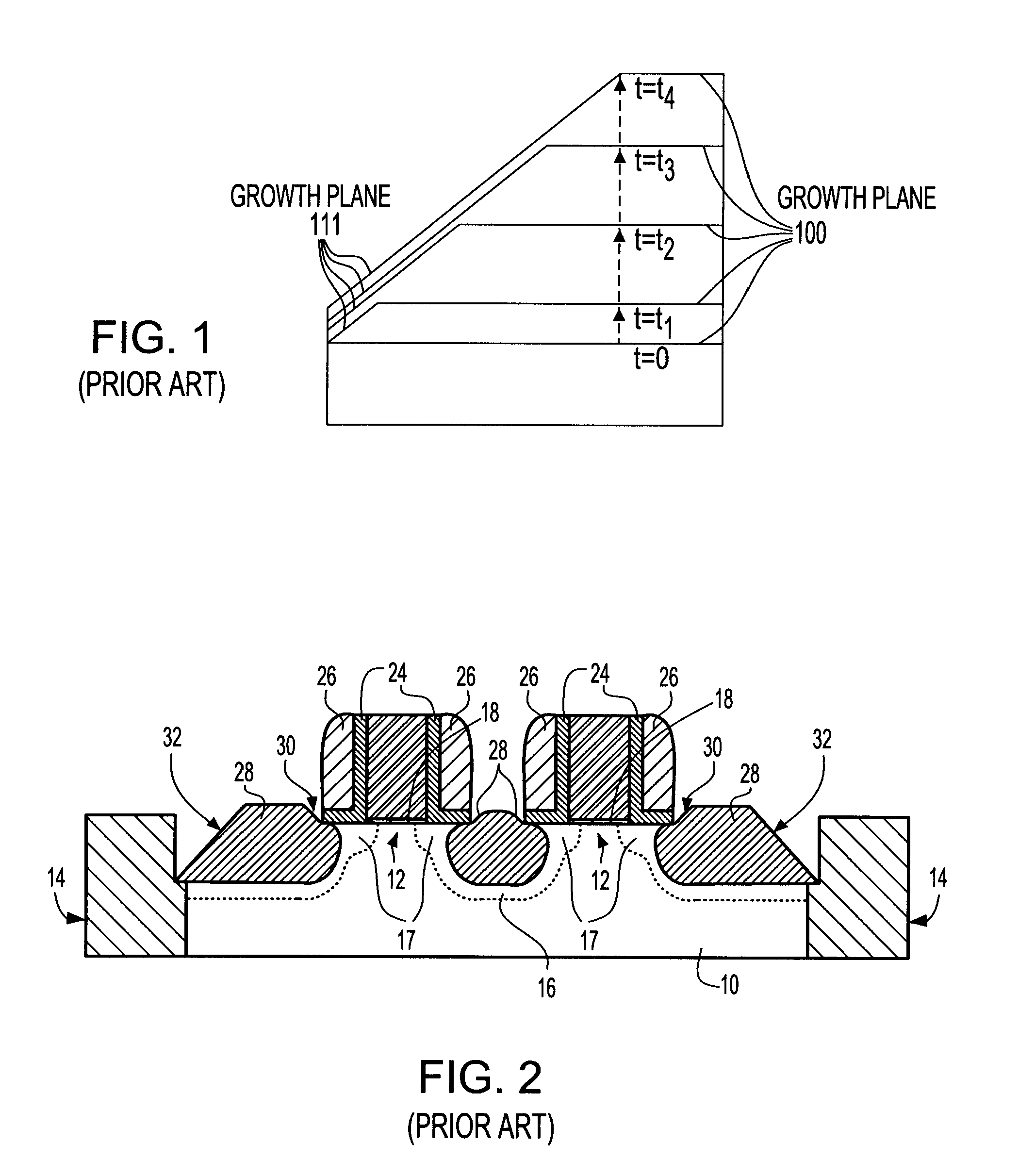
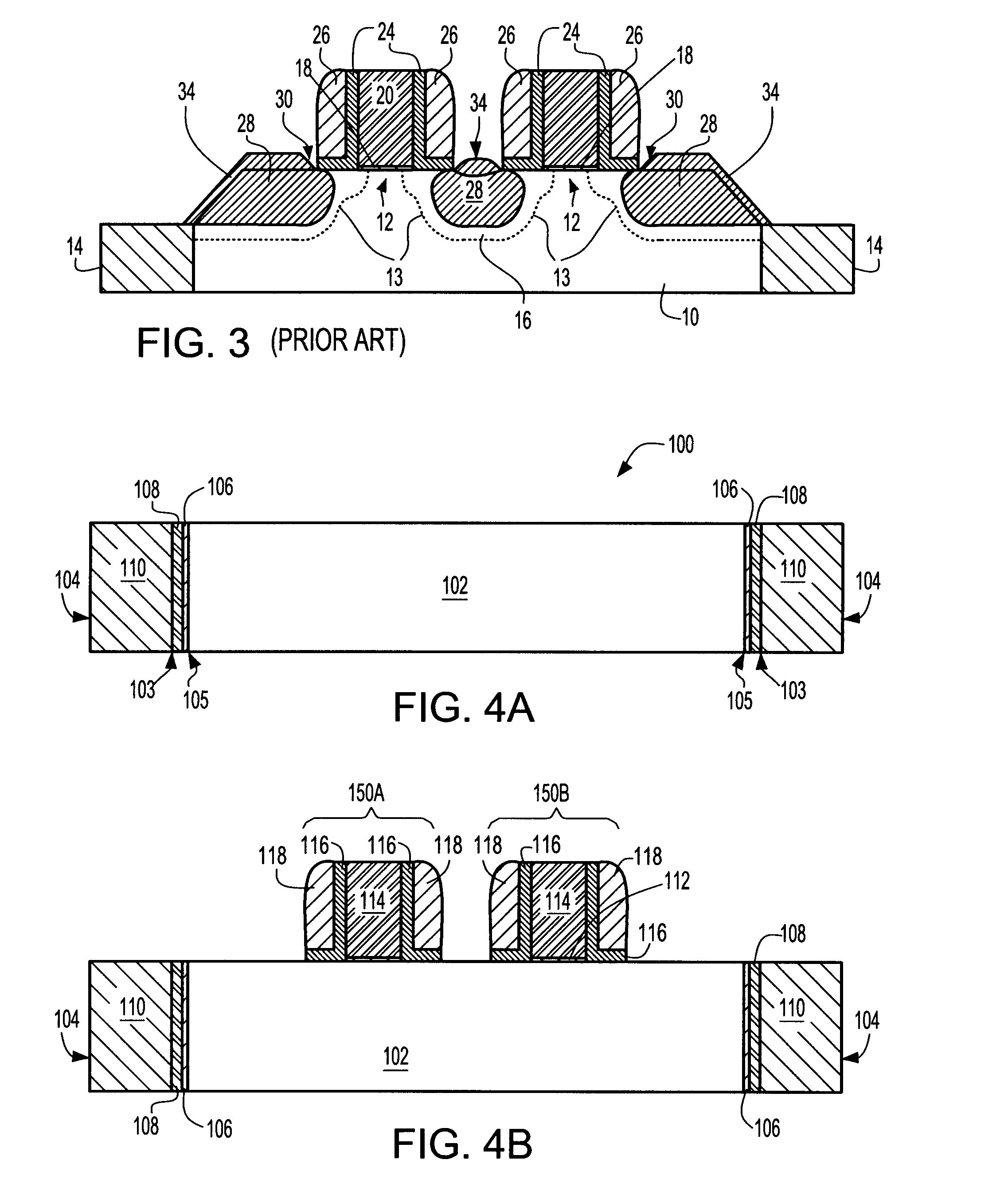
The present invention provides a technique for forming a CMOS structure including at least one pFET that has a stressed channel which avoids the problems mentioned in the prior art. Specifically, the present invention provides a method for avoiding formation of deep canyons at the interface between the active area and the trench isolation region, without requiring a trench isolation pulldown, thereby eliminating the problems of silicide to source / drain shorts and contact issues. At the same time, the method of the present invention provides a structure that allows for a facet to form at the spacer edge, retaining the Miller capacitance benefit that such a structure provides. The inventive structure also results in higher uniaxial stress in the MOSFET channel compared to one which allows for a facet to grow at the trench isolation edge.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
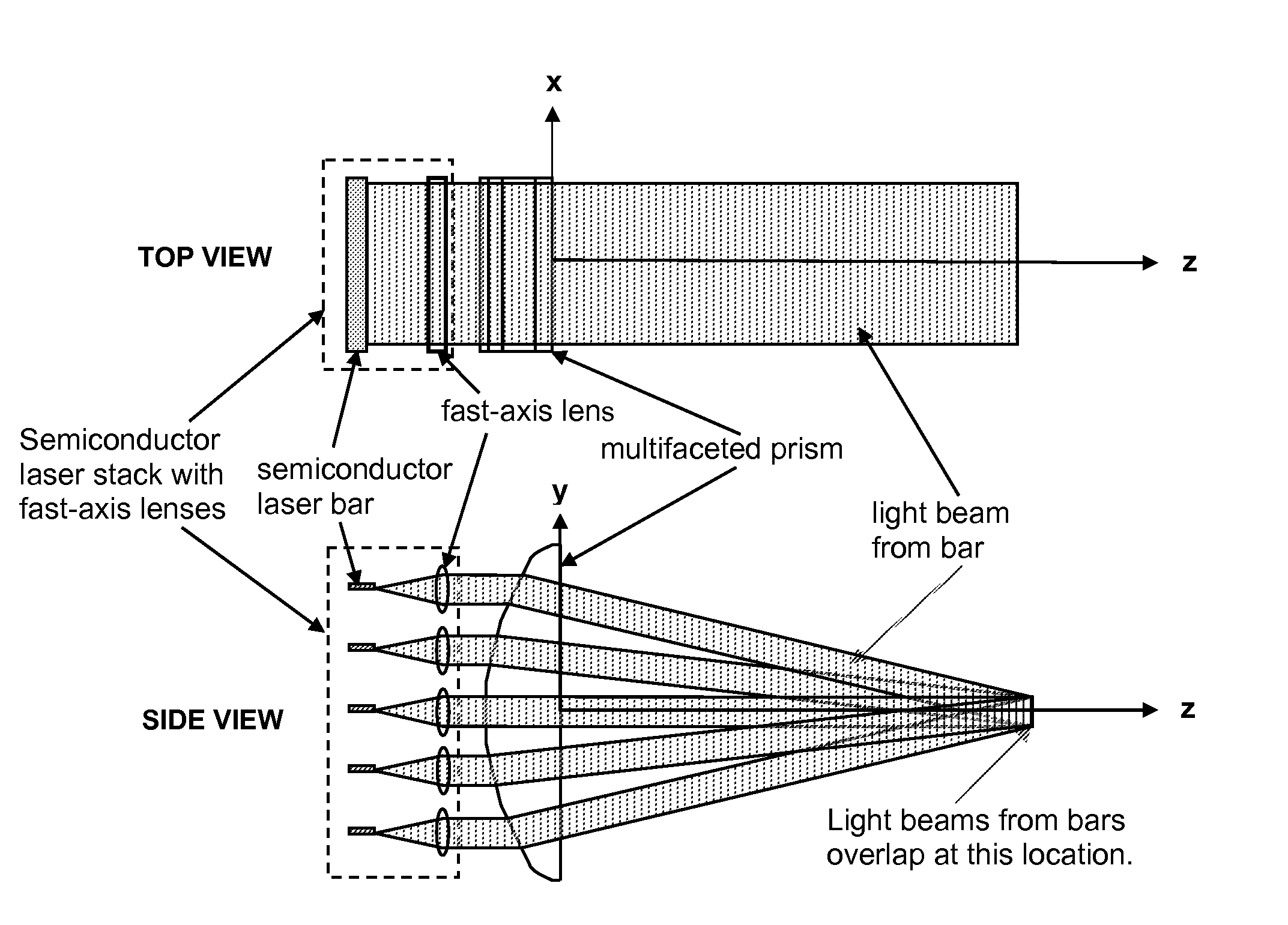
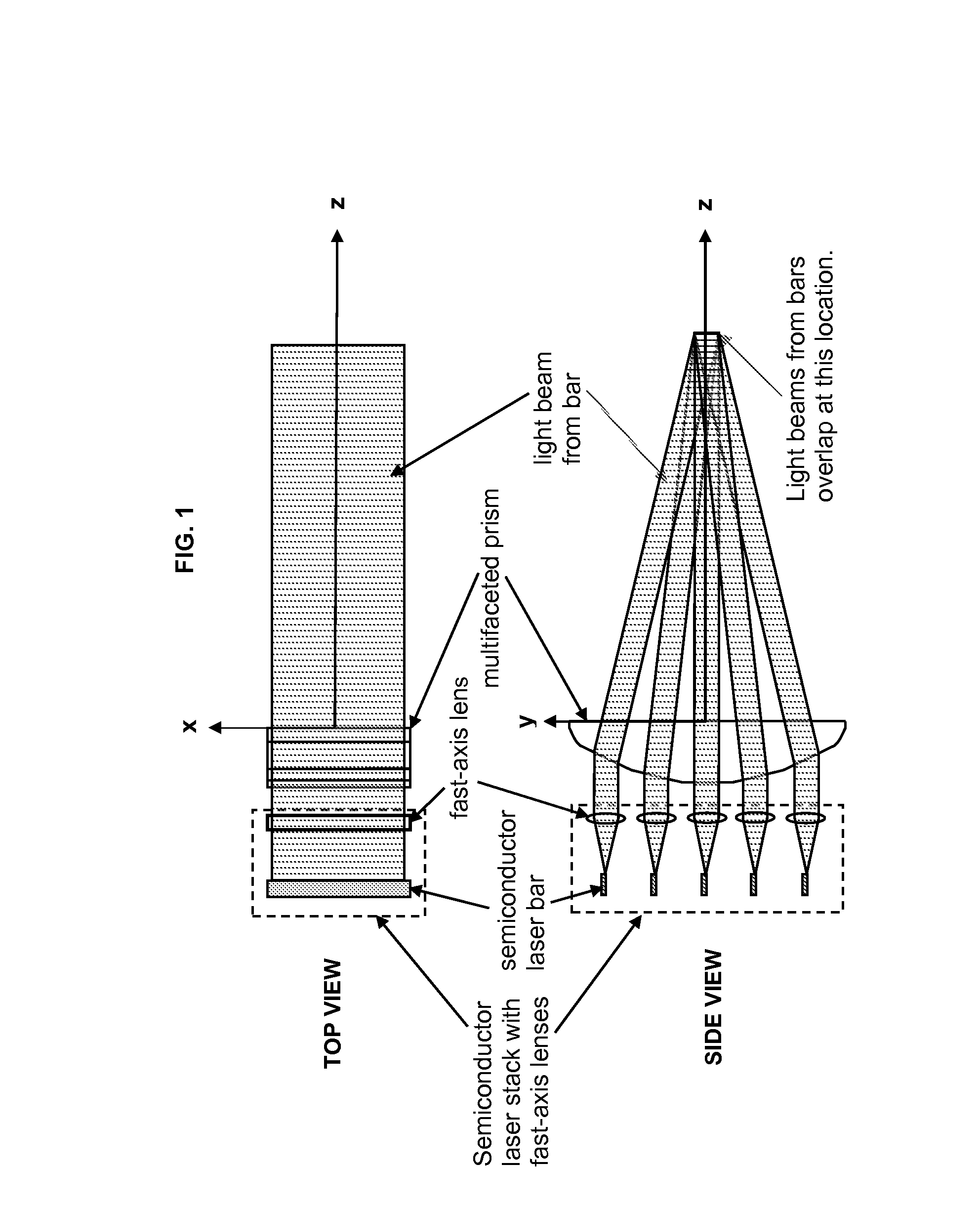
Multifaceted prism to cause the overlap of beams from a stack of diode laser bars
An optical element for homogenizing and, possibly, concentrating the output from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays, which has the basic shape of a convex-flat cylindrical lens with a facet cut into the convex surface for each individual semiconductor laser bar.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPSESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE +1
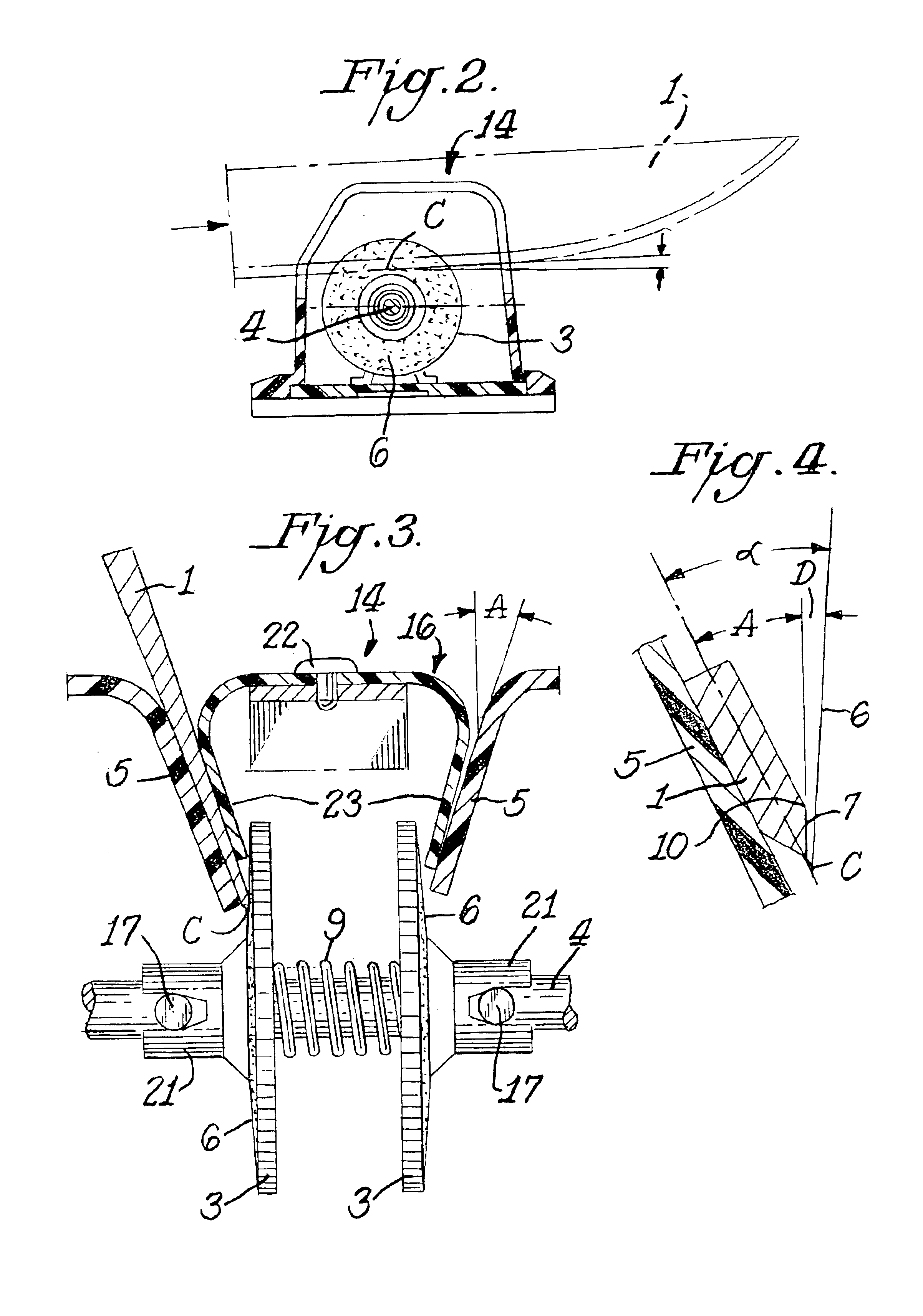
Apparatus for precision edge refinement of metallic cutting blades
InactiveUS6863600B2Delay premature failureEasy alignmentEdge grinding machinesOther manufacturing equipments/toolsEngineeringFaceting
A finishing apparatus modifies the physical structure along the edge of a metal knife blade wherein the edge is formed at the junction of two edge facets presharpened with abrasives. The finishing apparatus consists of at least one precision angular knife guide that positions the edge of the blade into contact with the rigid surface of a driven moving member and positions the plane of the adjacent edge facet at a precise predetermined angle relative to the plane of the rigid surface that is harder than the metal of the knife and is without tendency to abrade.
Owner:EDGECRAFT
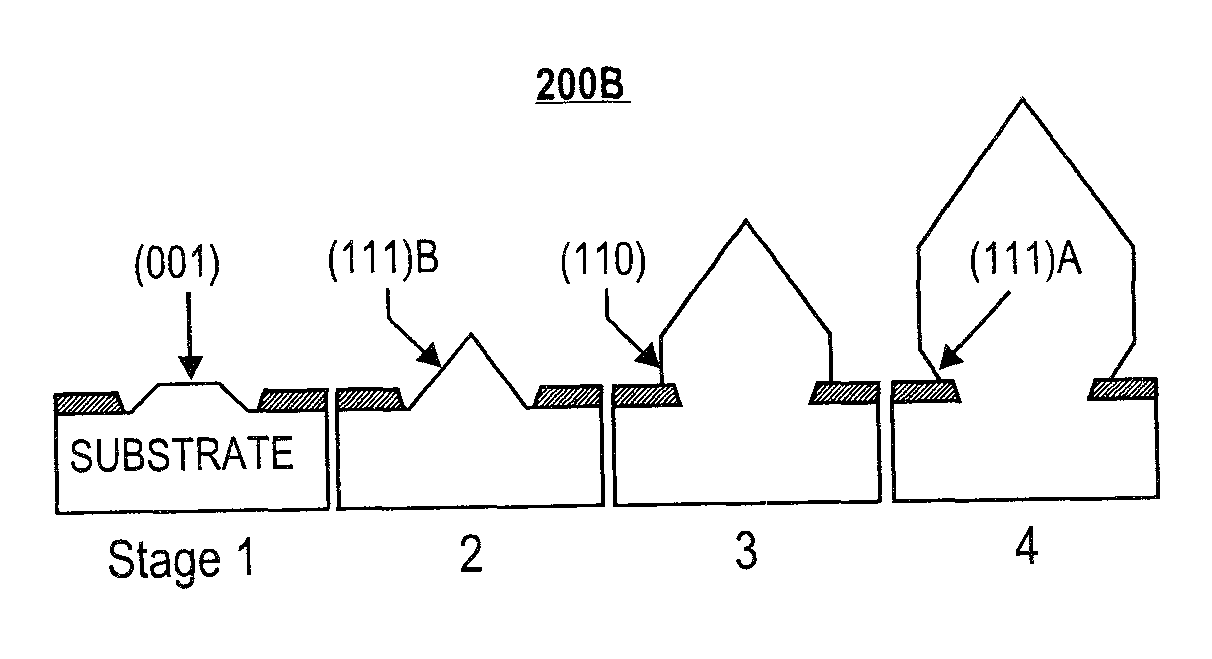
Nitride semiconductor substrate and method of producing same
ActiveUS20090155989A1Reduce dislocation densityEasily realizedPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseClosed loop
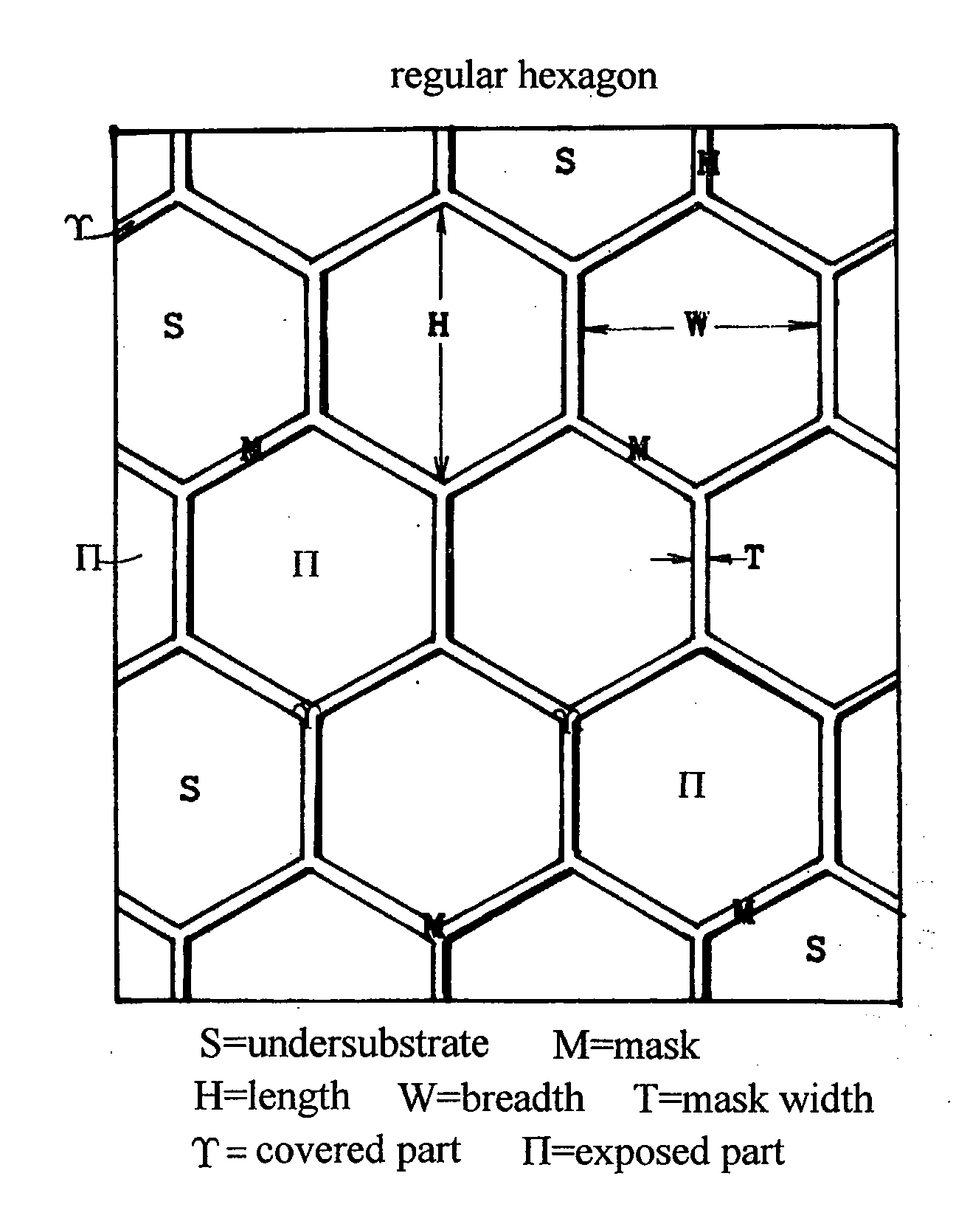
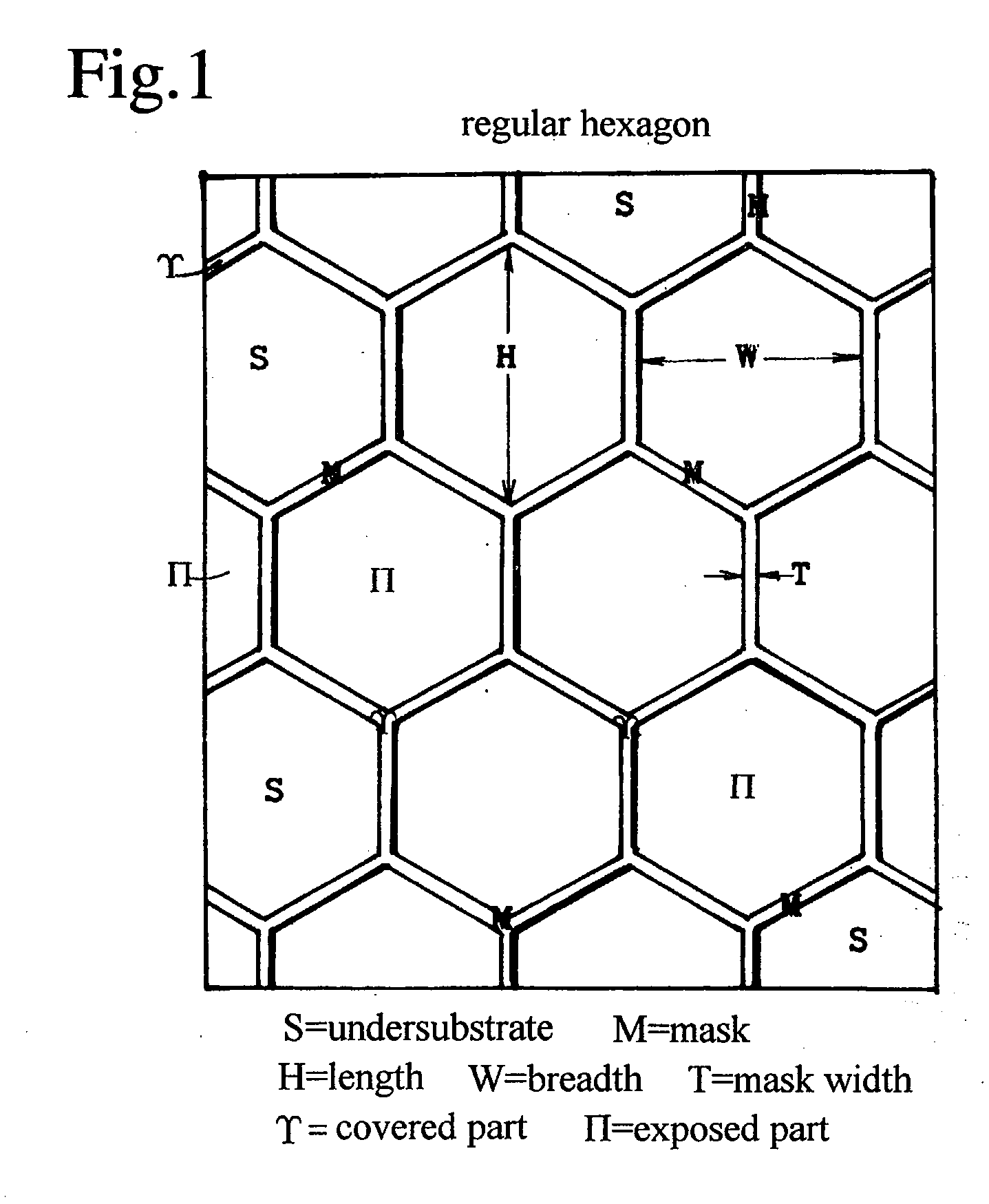
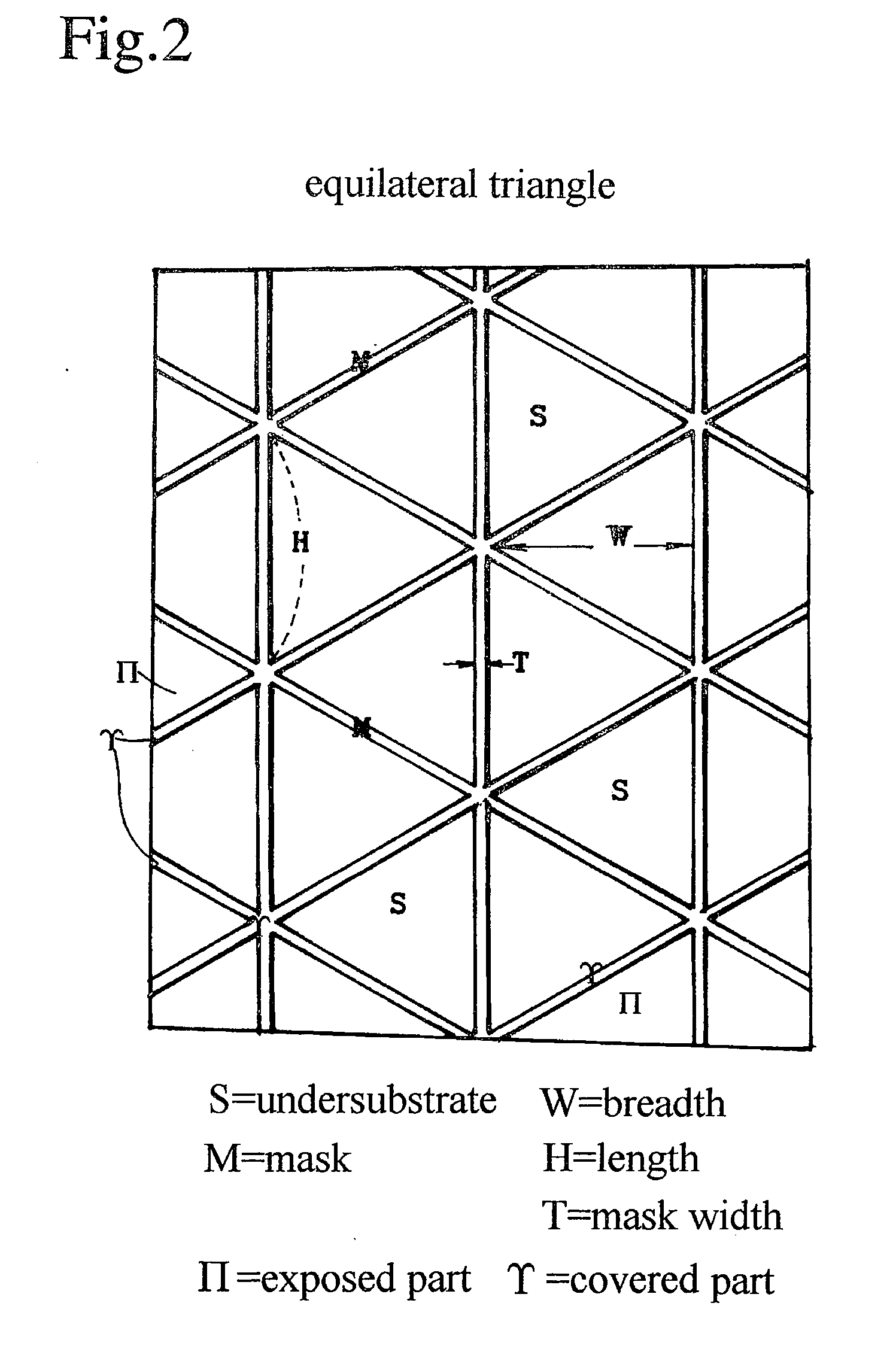
A nitride semiconductor crystal substrate is produced by forming a network mask repeating a closed loop unit shape upon an undersubstrate, growing a nitride semiconductor crystal in vapor phase, producing convex facet hills covered with facets on exposed parts Π, forming outlining concavities on mask-covered parts not burying the facets, maintaining the convex facet hills on Π and the network concavities on excluding dislocations in the facet hills down to the outlining concavities on forming a defect accumulating region H on decreasing dislocations in the facet hills and improving the facet hills to low defect density single crystal regions Z, producing a rugged nitride crystal, and slicing and polishing the nitride crystal into mirror nitride crystal wafers. After the fabrication of devices on the nitride wafer, dry-etching or wet etching of hot KOH or NaOH divides the device-carrying wafer into chips by corroding the network defect accumulating region H.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method and apparatus for creating optical images
ActiveUS20090086498A1Improve efficiencyLow costMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOptical axisWorking temperature
A device for creating a predetermined light output distribution having a substantially rectangular shape in angle space is provided having a lens with a revolved inner surface and a complex outer surface. The inner surface has a combination of reflective and refractive surface facets swept about an axis of revolution perpendicular to the optical axis of the device. The outer surface has a non-planar, non-circular, non-spherical shape. This outer surface generates an appropriate intensity distribution in a direction generally parallel to the major axis of the output rectangle and may also distribute energy generally parallelly to the minor axis of the output rectangle as well. The optical efficiency improvement in the design of this improved preferably LED-based product has several direct benefits including; increased reliability, lower operating temperature, reduced electrical requirements, greater product life and significantly reduced cost as compared to existing LED products. The resulting cost savings attendant with the implementation of the present invention makes high performance LED lamps more accessible to the general public and improves vehicle safety.
Owner:TECNIQ
Edge illuminated photodiodes
InactiveUS7279731B1Improve operationImproved structural characteristicPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyEdge surface
This invention comprises plurality of edge illuminated photodiodes. More specifically, the photodiodes of the present invention comprise novel structures designed to minimize reductions in responsivity due to edge surface recombination and improve quantum efficiency. The novel structures include, but are not limited to, angled facets, textured surface regions, and appropriately doped edge regions.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
Method of manufacturing an integral rotor blade disk and corresponding disk
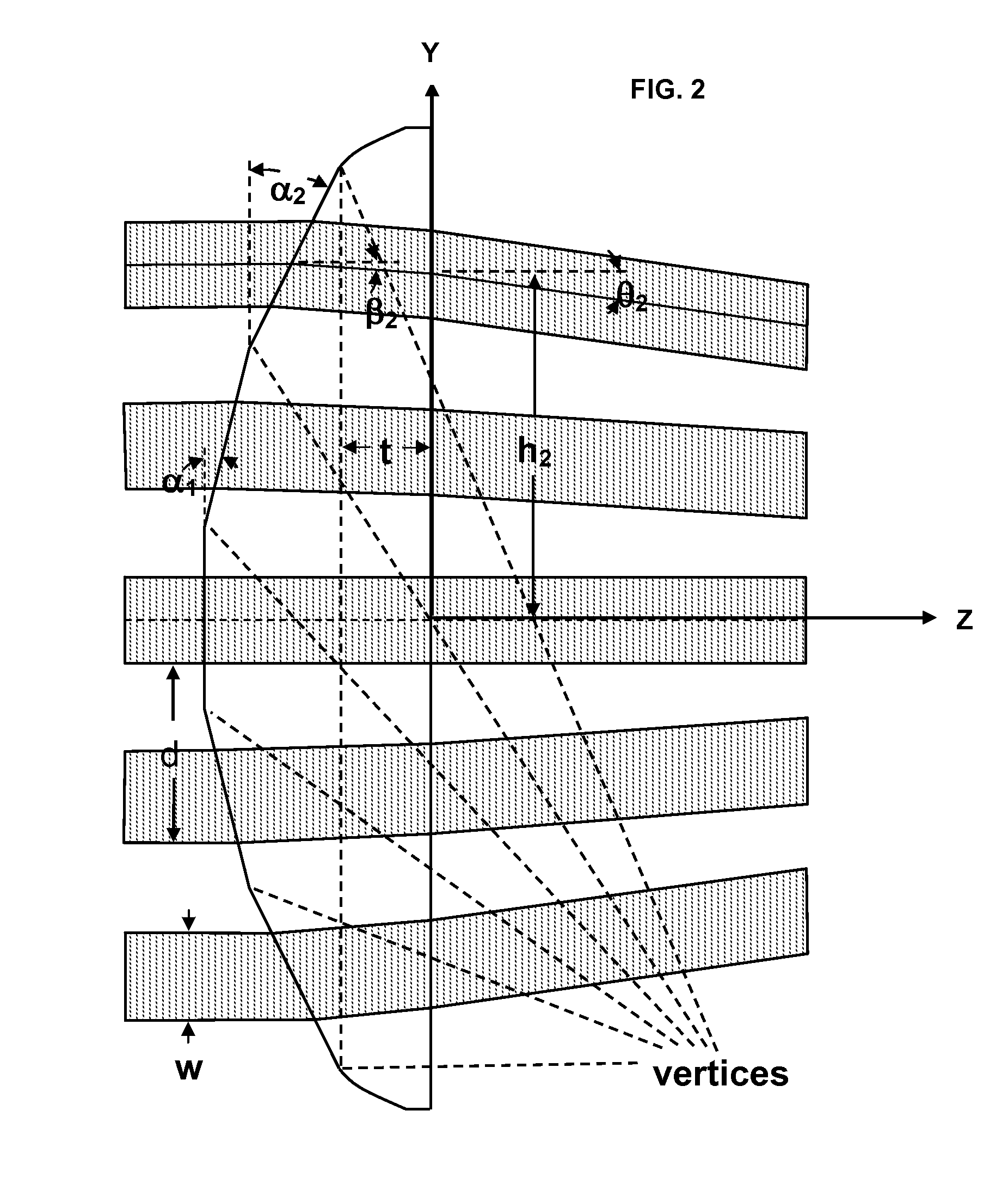
A method of manufacturing a blisk comprises the steps of cutting a disk to a rough shape comprising a hub with a plurality of blade blanks projecting radially therefrom, machining each blade blank by tangential milling using a tool with a rotation spindle perpendicular to the radial direction to make repeated radial passes, the tool being turned through a facet angle with respect to the disk between each pass. Each blade blank is thus milled to a blade having faceted surfaces. Preferably, the width of each facet is smaller that 5 mm, and adjacent facets subtend angles smaller than 5°, or even more preferably smaller than 3°.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
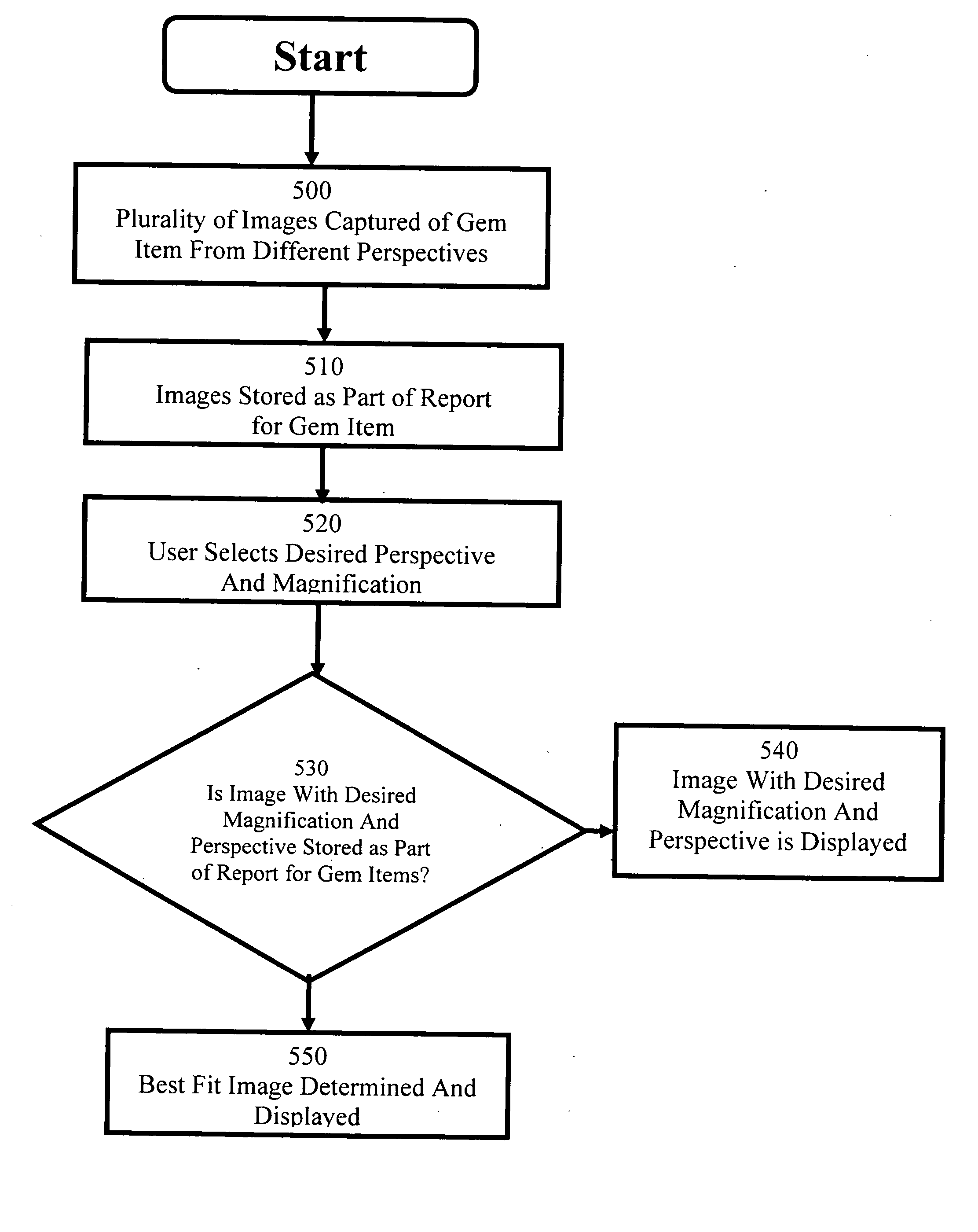
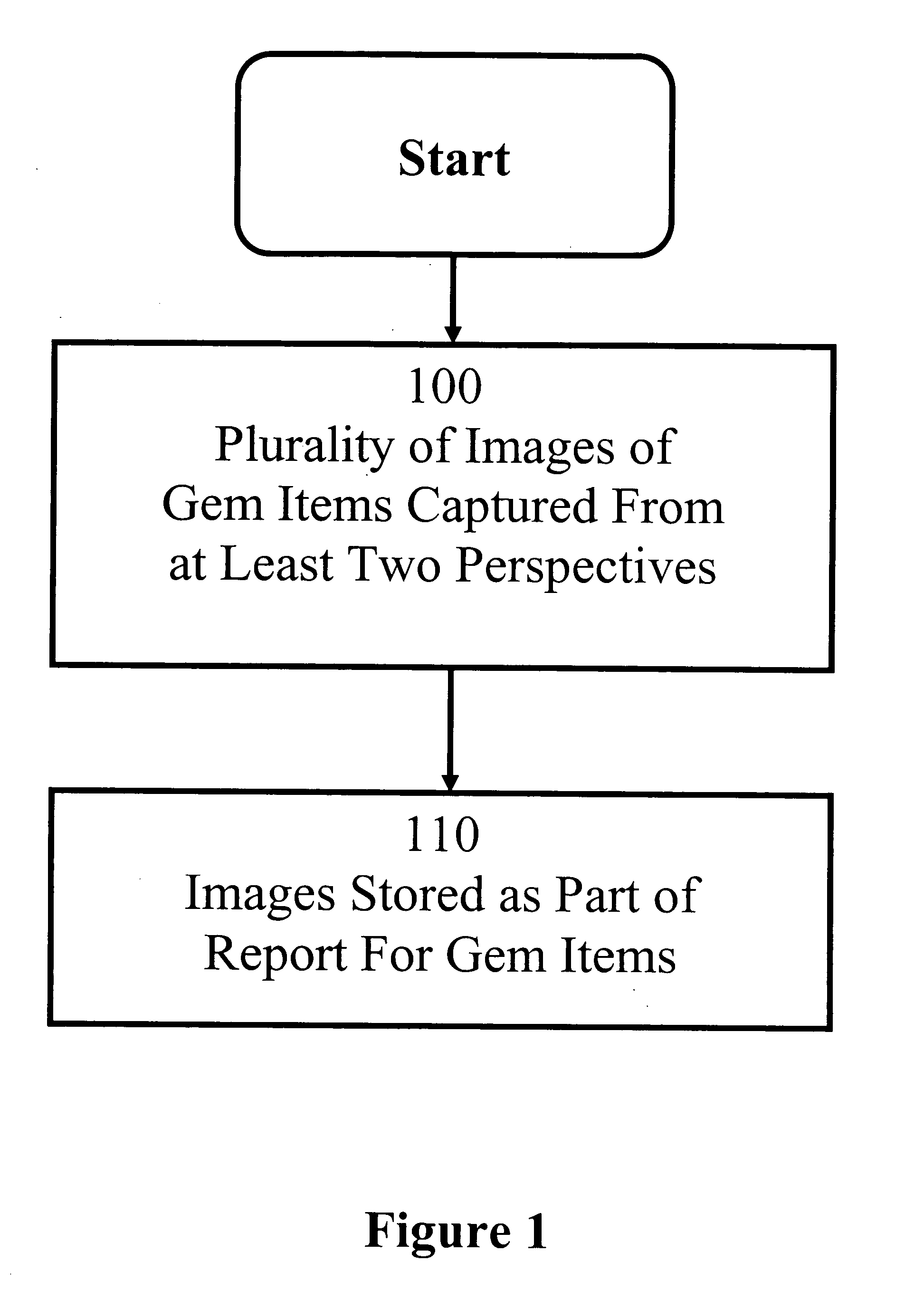
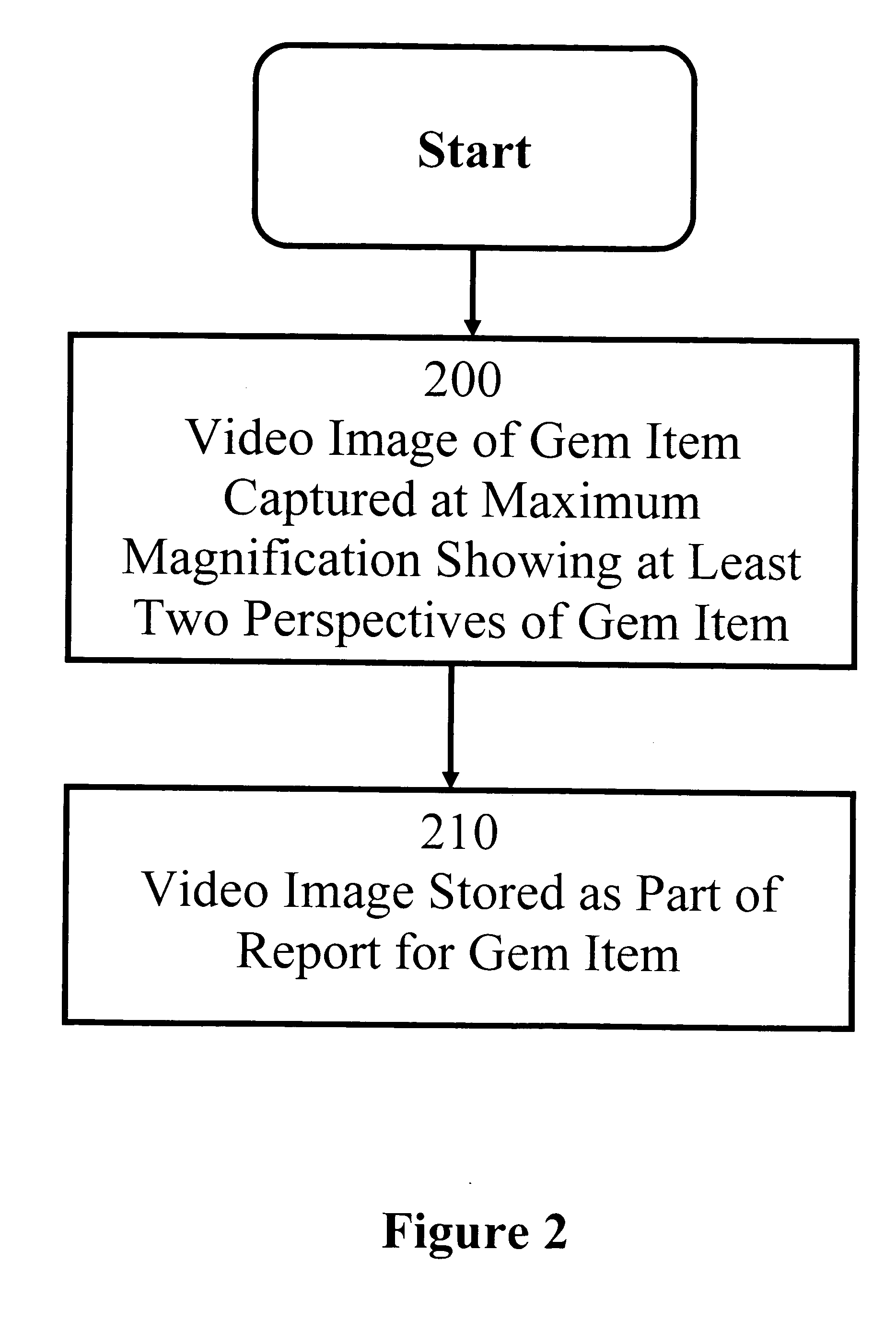
Gem item report method and system
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a method and system for a gem item report. In one embodiment of the present invention, a plurality of images of a gem item are stored as part of a report for the gem item. In one embodiment, a video of a gem item is stored as part of a report of the gem item. In another embodiment, the images display various characteristics of the gem item, including but not limited to the faceting arrangement, the inclusions, and any markings. In one embodiment, the images are of the gem item under magnification. In one embodiment, the images, taken together, provide a two dimensional or 360-degree three dimensional view of a gem item. In one embodiment, an interface is provided for viewing a stored image of a gem item from a desired perspective and at a desired magnification.
Owner:GEM CERTIFICATION & ASSURANCE LAB
Group-III Nitride Epitaxial Layer on Silicon Substrate
ActiveUS20090261363A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRepeat patternFaceting
A semiconductor device includes a silicon substrate; silicon faceted structures formed on a top surface of the silicon substrate; and a group-III nitride layer over the silicon faceted structures. The silicon faceted structures are separated from each other, and have a repeated pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
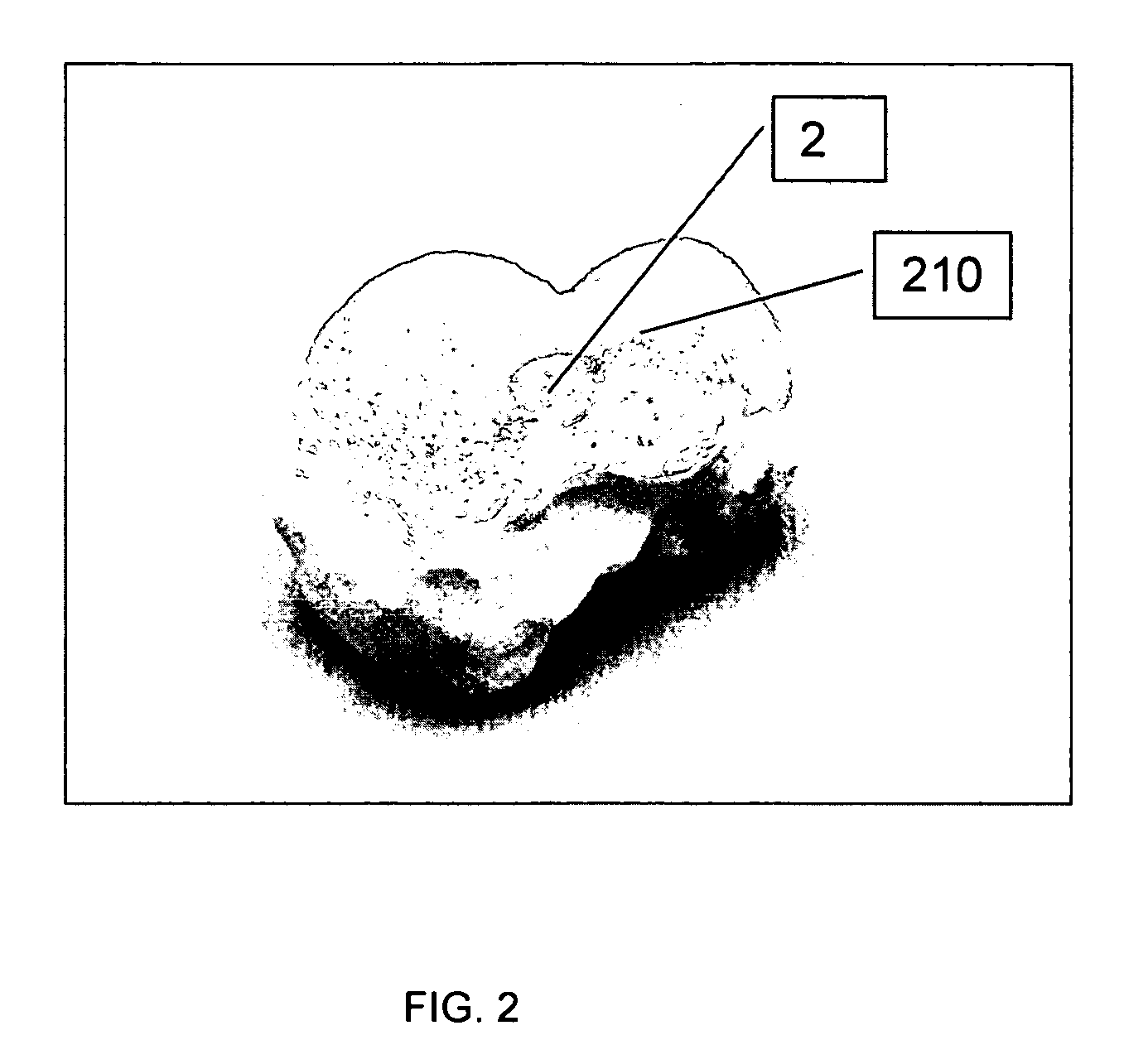
Polycrystalline diamond compact surfaces on facet arthroplasty devices
InactiveUS20060247769A1Improve wear resistanceReduce coefficient of frictionBone implantSpinal implantsPolycrystalline diamondChemical vapor deposition
At least a portion of an articulating surface of a facet arthroplasty device may comprise a polycrystalline diamond compact. The polycrystalline diamond compact may be useful to increase the wearability and decrease the coefficient of friction of the at least one articulating surface of the facet arthroplasty device. The polycrystalline diamond compact may be utilized with any facet arthroplasty device and may be formed by any appropriate method including, but not limited to, diamond sintering, chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, and energy beam ablation / deposition.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Epitaxial growth of in-plane nanowires and nanowire devices
Exemplary embodiments provide semiconductor nanowires and nanowire devices / applications and methods for their formation. In embodiments, in-plane nanowires can be epitaxially grown on a patterned substrate, which are more favorable than vertical ones for device processing and three-dimensional (3D) integrated circuits. In embodiments, the in-plane nanowire can be formed by selective epitaxy utilizing lateral overgrowth and faceting of an epilayer initially grown in a one-dimensional (1D) nanoscale opening. In embodiments, optical, electrical, and thermal connections can be established and controlled between the nanowire, the substrate, and additional electrical or optical components for better device and system performance.
Owner:STC UNM
Edge Illuminated Photodiodes
InactiveUS20070296005A1Photovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyEdge surface
This invention comprises plurality of edge illuminated photodiodes. More specifically, the photodiodes of the present invention comprise novel structures designed to minimize reductions in responsivity due to edge surface recombination and improve quantum efficiency. The novel structures include, but are not limited to, angled facets, textured surface regions, and appropriately doped edge regions.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
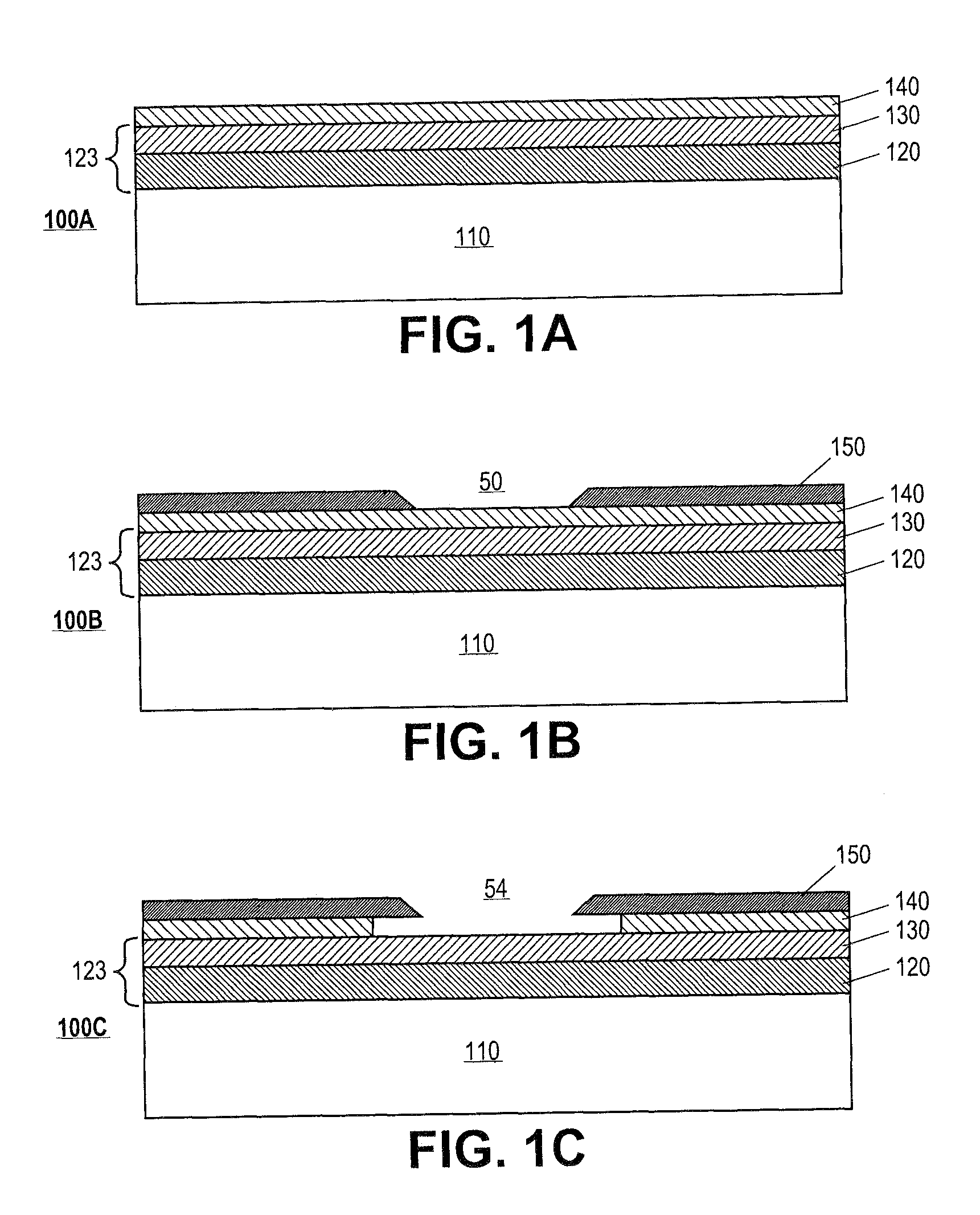
Methods of Forming Semiconductor Devices Having Faceted Semiconductor Patterns
ActiveUS20110230027A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialImpurity ions
Provided are methods of forming semiconductor devices. A method may include preparing a semiconductor substrate including a first region and a second region adjacent the first region. The method may also include forming sacrificial pattern covering the second region and exposing the first region. The method may further include forming a capping layer including a faceted sidewall on the first region using selective epitaxial growth (SEG). The faceted sidewall may be separate from the sacrificial pattern. The sacrificial pattern may be removed. Impurity ions may be implanted into the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
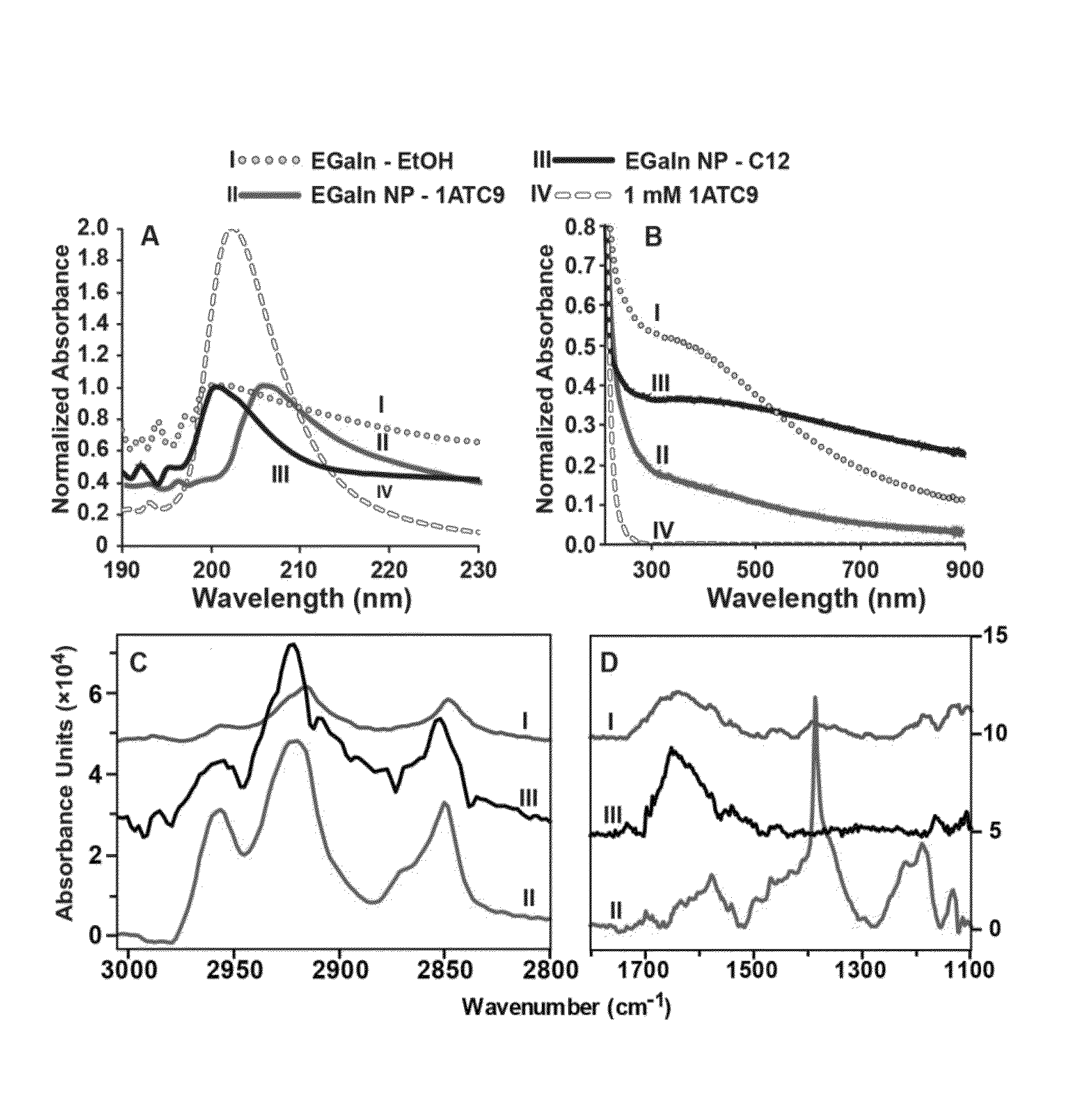
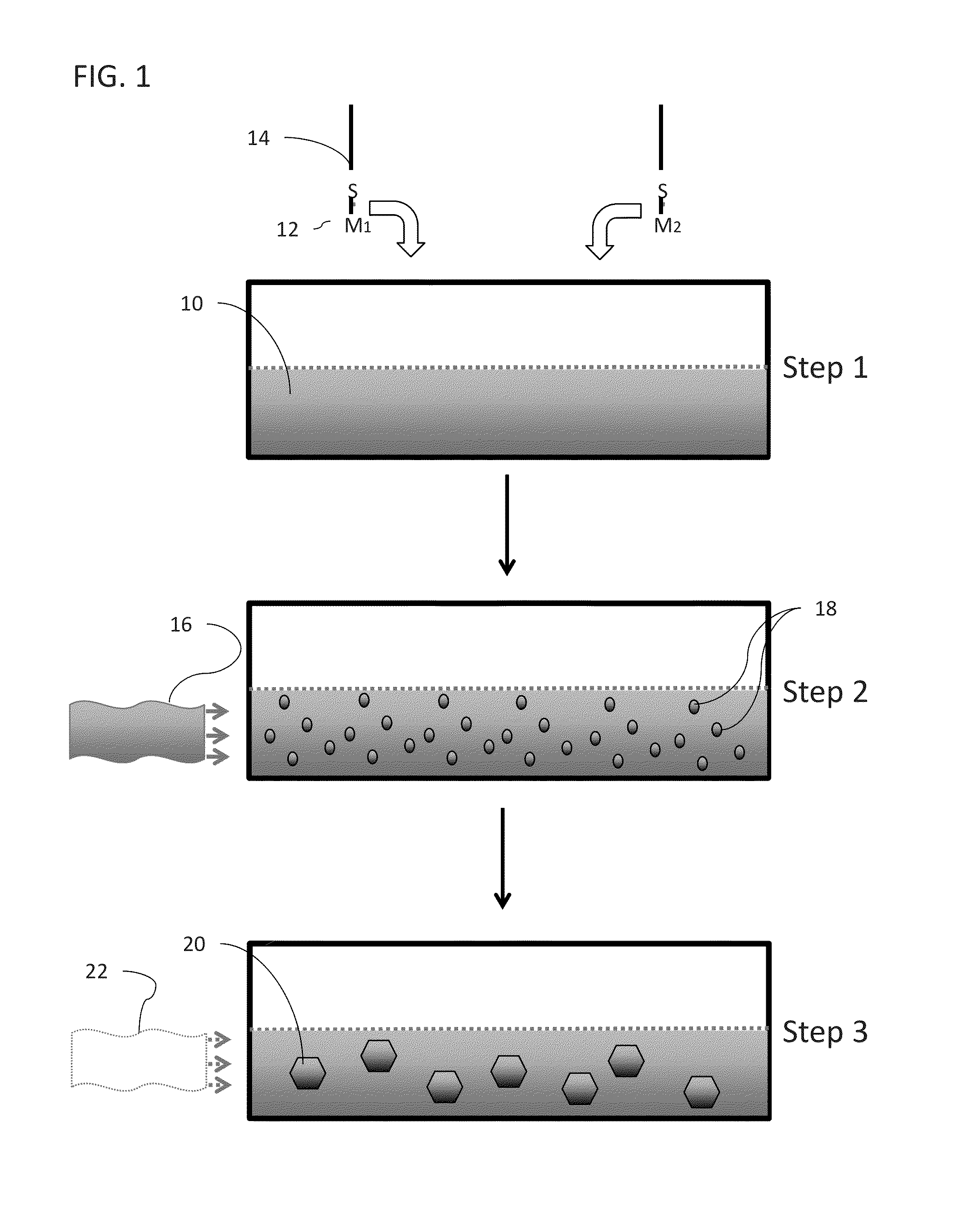
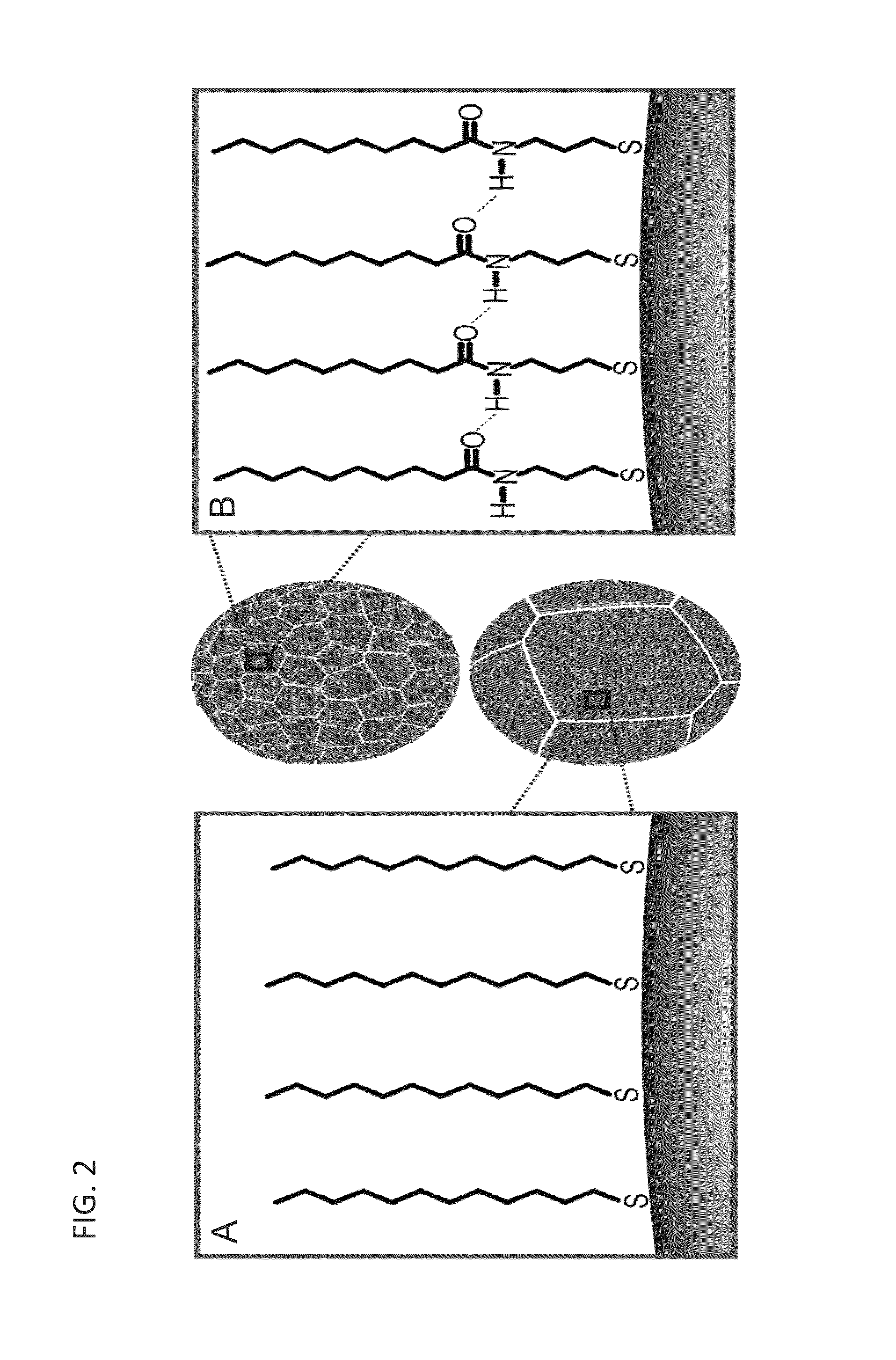
Metal alloy nanoparticle synthesis via self-assembled monolayer formation and ultrasound
ActiveUS20130244037A1Small sizeMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsIndiumSelf-assembled monolayer
Methods and assemblies for the construction of liquid-phase alloy nanoparticles are presented. Particle formation is directed by molecular self-assembly and assisted by sonication. In some embodiments, eutectic gallium-indium (EGaIn) nanoparticles are formed. In these embodiments, the bulk liquid alloy is ultrasonically dispersed, fast thiolate self-assembly at the EGaIn interface protects the material against oxidation. The assembly shell has been designed to include intermolecular hydrogen bonds, which induce surface strain, assisting in cleavage of the alloy particles to the nanoscale. X-ray diffraction and TEM analyses reveal that the nanoscale particles are in an amorphous or liquid phase, with no observed faceting.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
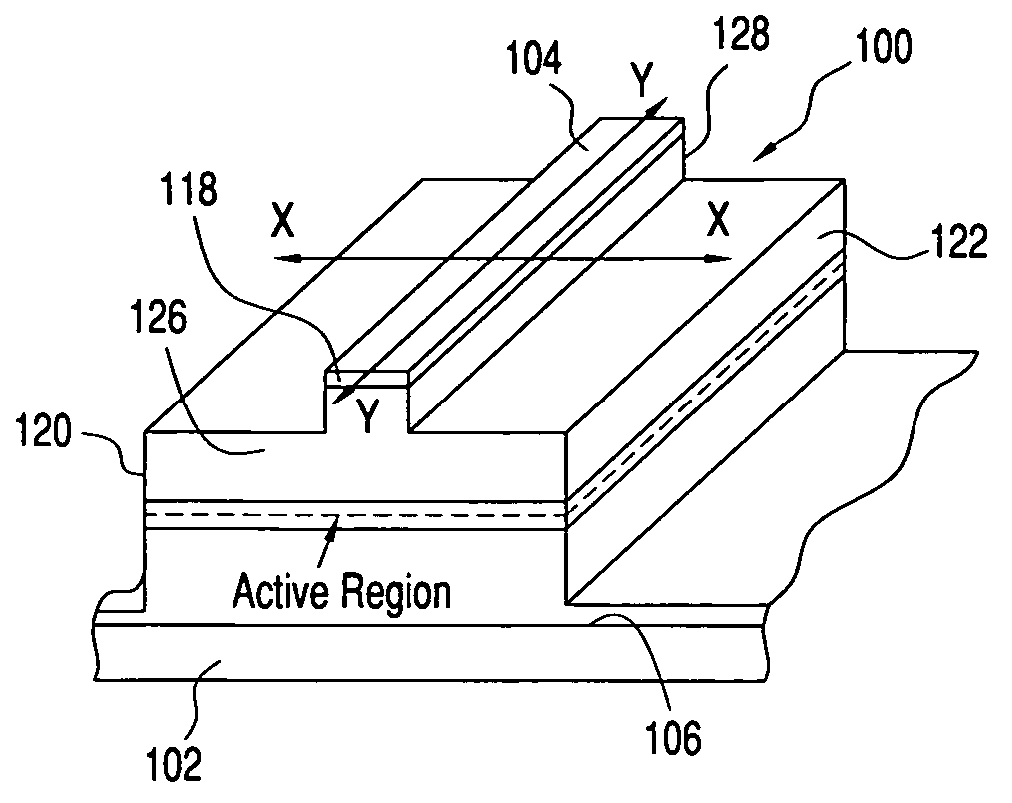
High reliability etched-facet photonic devices
ActiveUS20060187985A1Improve reliabilityGuaranteed uptimeOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonicsFaceting
Semiconductor photonic device surfaces are covered with a dielectric or a metal protective layer. The protective layer covers the entire device, including regions near facets at active regions, to prevent bare or unprotected semiconductor regions, thereby to form a very high reliability etched facet photonic device.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Frictional trans-epithelial tissue disruption collection apparatus and method of inducing an immune response
ActiveUS20110172557A1Minimal painSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue biopsyFaceting
In an embodiment of the invention, a frictional tissue sampling device with a head designed to be rotated without rotating off the designated site can be used to obtain tissue biopsy samples. A frictional tissue sampling device with a head designed to be rotated without rotating off the designated site can be used to obtain an epithelial tissue biopsy sample from lesions. The device can be otherwise used to sample specific locations. In various embodiments, the head of the device is narrow and pointed with a hybrid pear shaped diamond facet. Abrasive material can be adhered to the facet.
Owner:HISTOLOGICS
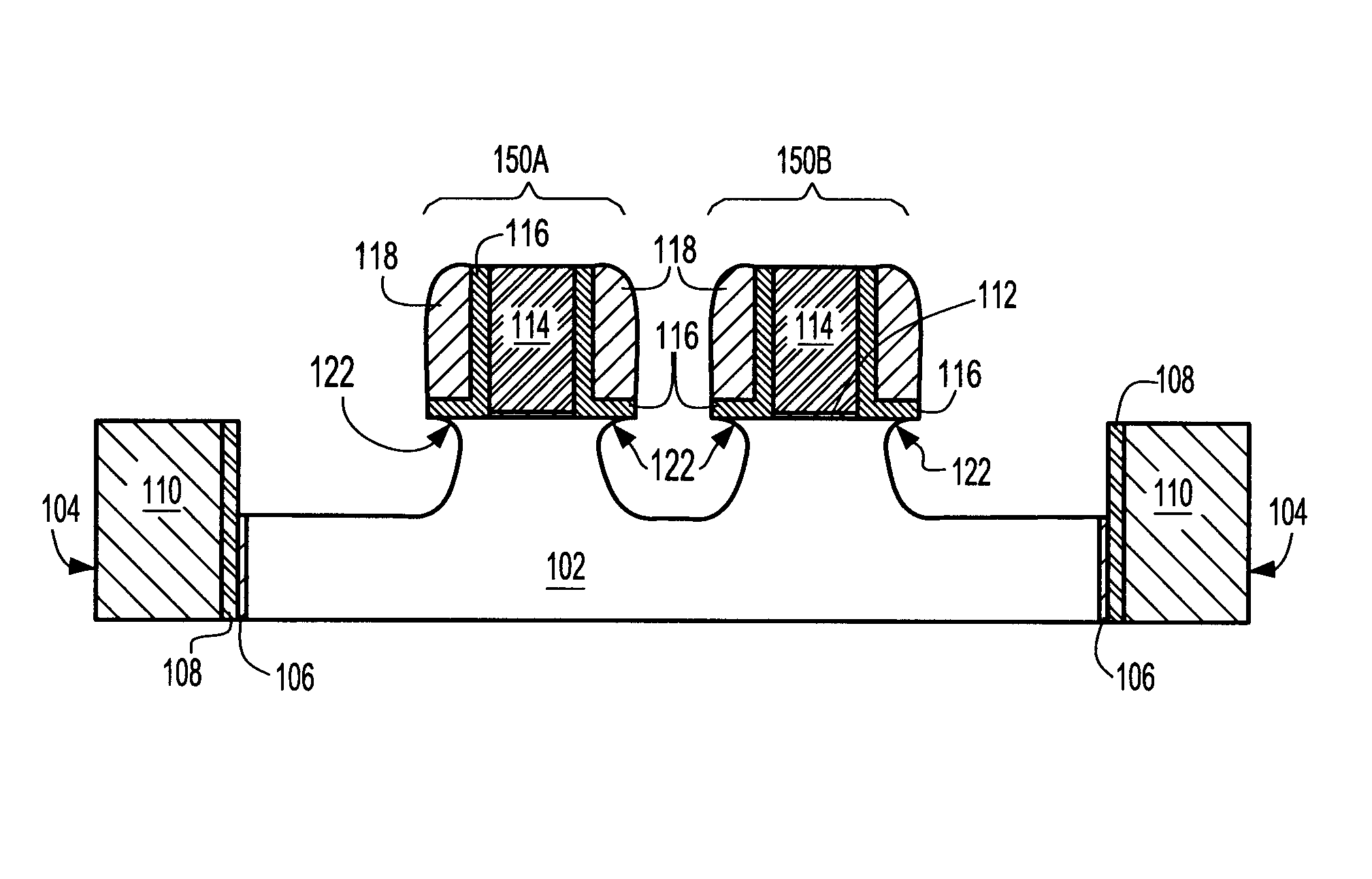
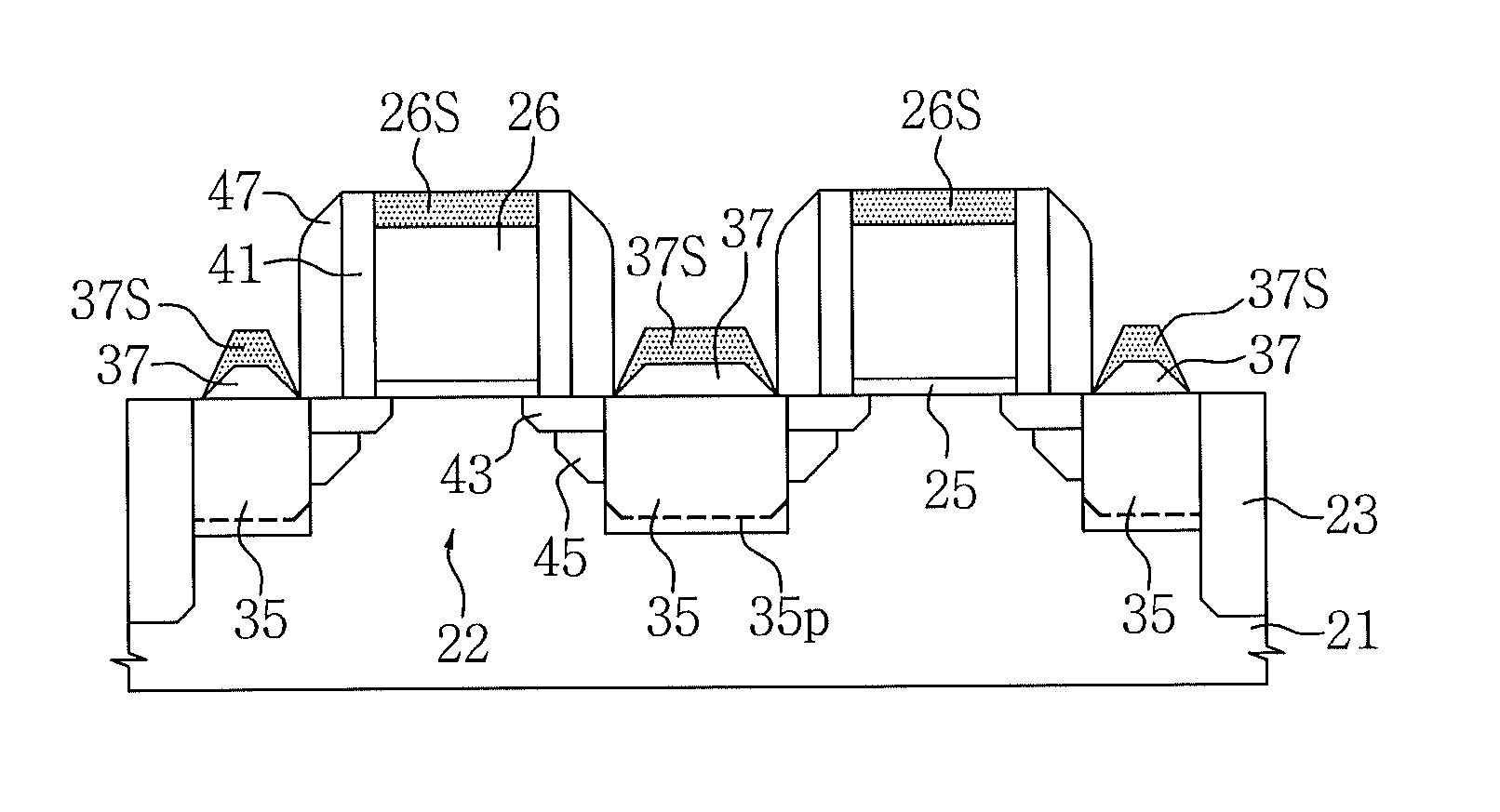
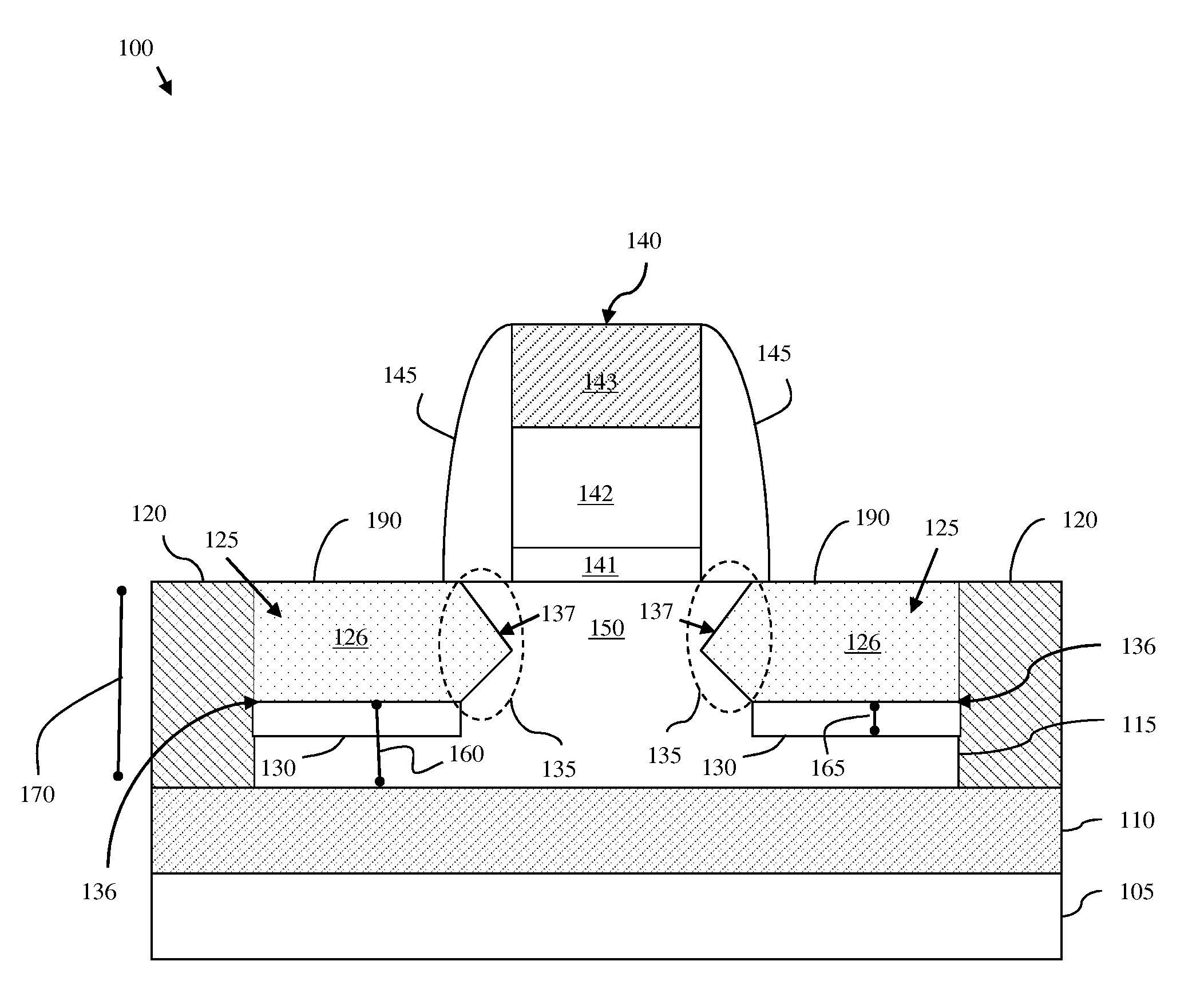
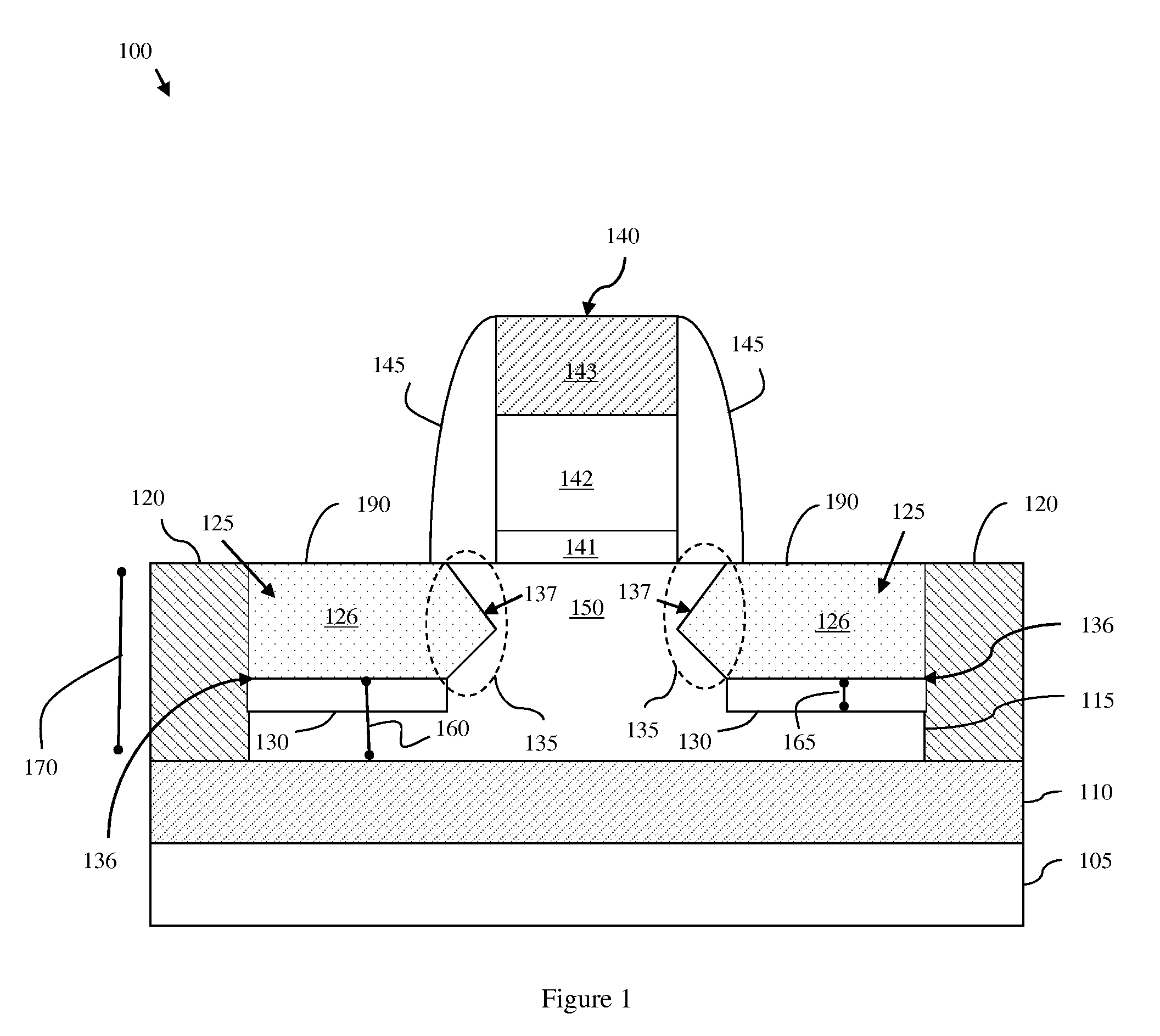
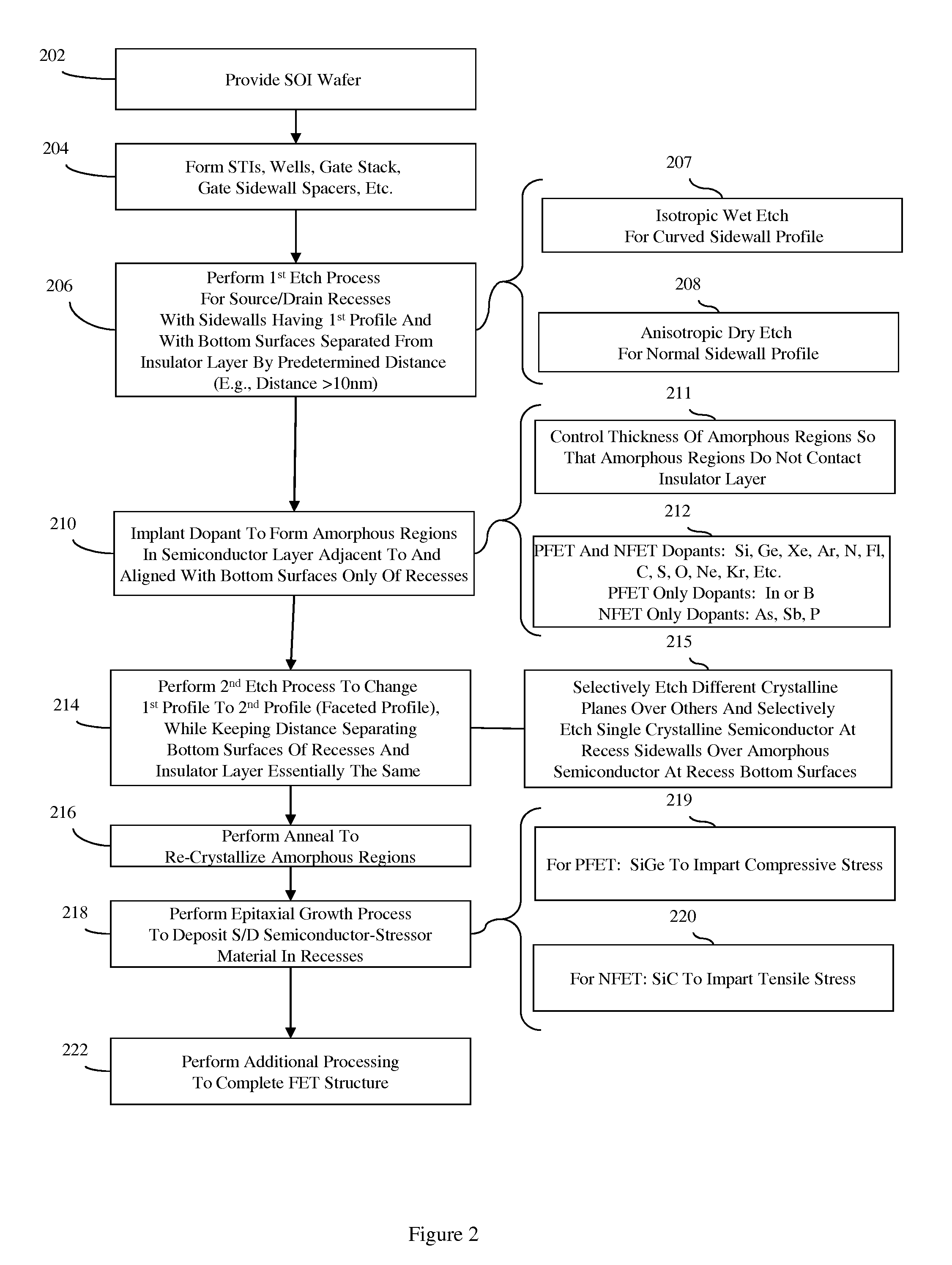
Method of forming a planar field effect transistor with embedded and faceted source/drain stressors on a silicon-on-insulator (S0I) wafer, a planar field effect transistor structure and a design structure for the planar field effect transistor
ActiveUS7951657B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic field-effect transistorSingle crystal
Disclosed are embodiments of a method of forming, on an SOI wafer, a planar FET with embedded and faceted source / drain stressors. The method incorporates a directional ion implant process to create amorphous regions at the bottom surfaces of source / drain recesses in a single crystalline semiconductor layer of an SOI wafer. Then, an etch process selective to different crystalline planes over others and further selective to single crystalline semiconductor material over amorphous semiconductor material can be performed in order to selectively adjust the shape (i.e., the profile) of the recess sidewalls without increasing the depth of the recesses. Subsequently, an anneal process can be performed to re-crystallize the amorphous regions and an epitaxial deposition process can be used to fill the recesses with source / drain stressor material. Also disclosed are embodiments of a planar FET structure and a design structure for the planar FET.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Apparatus for reshaping an optical beam bundle
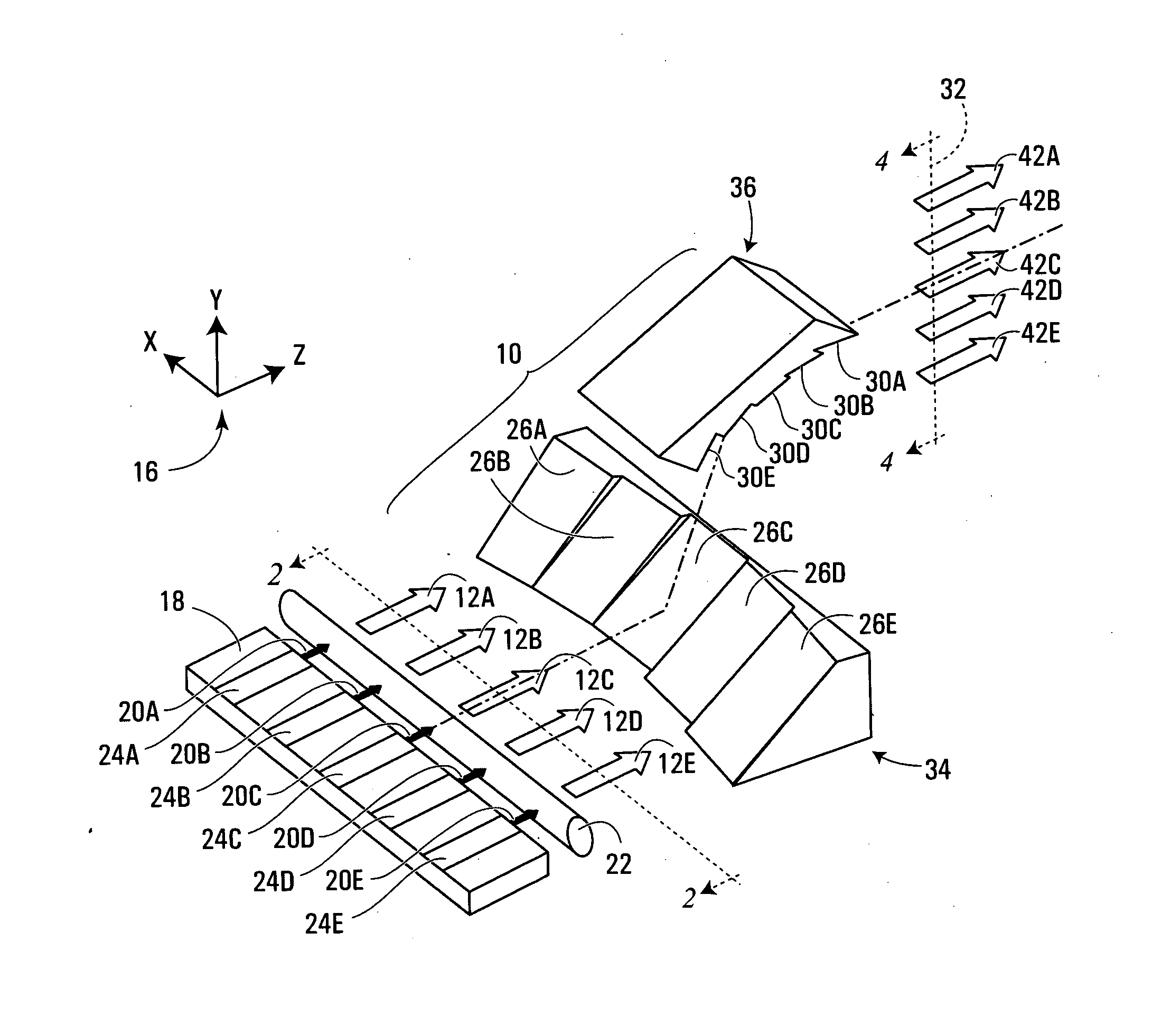
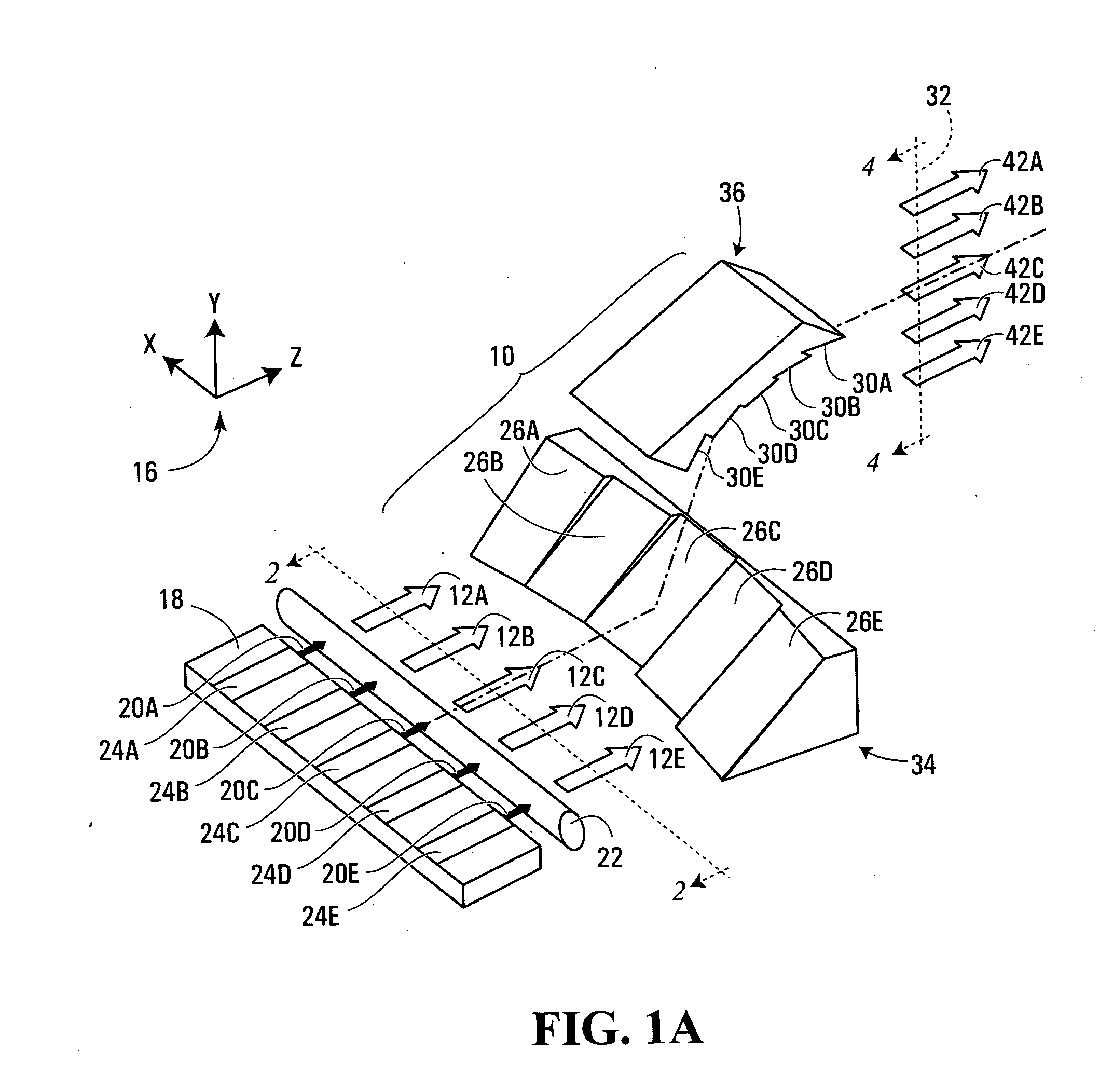
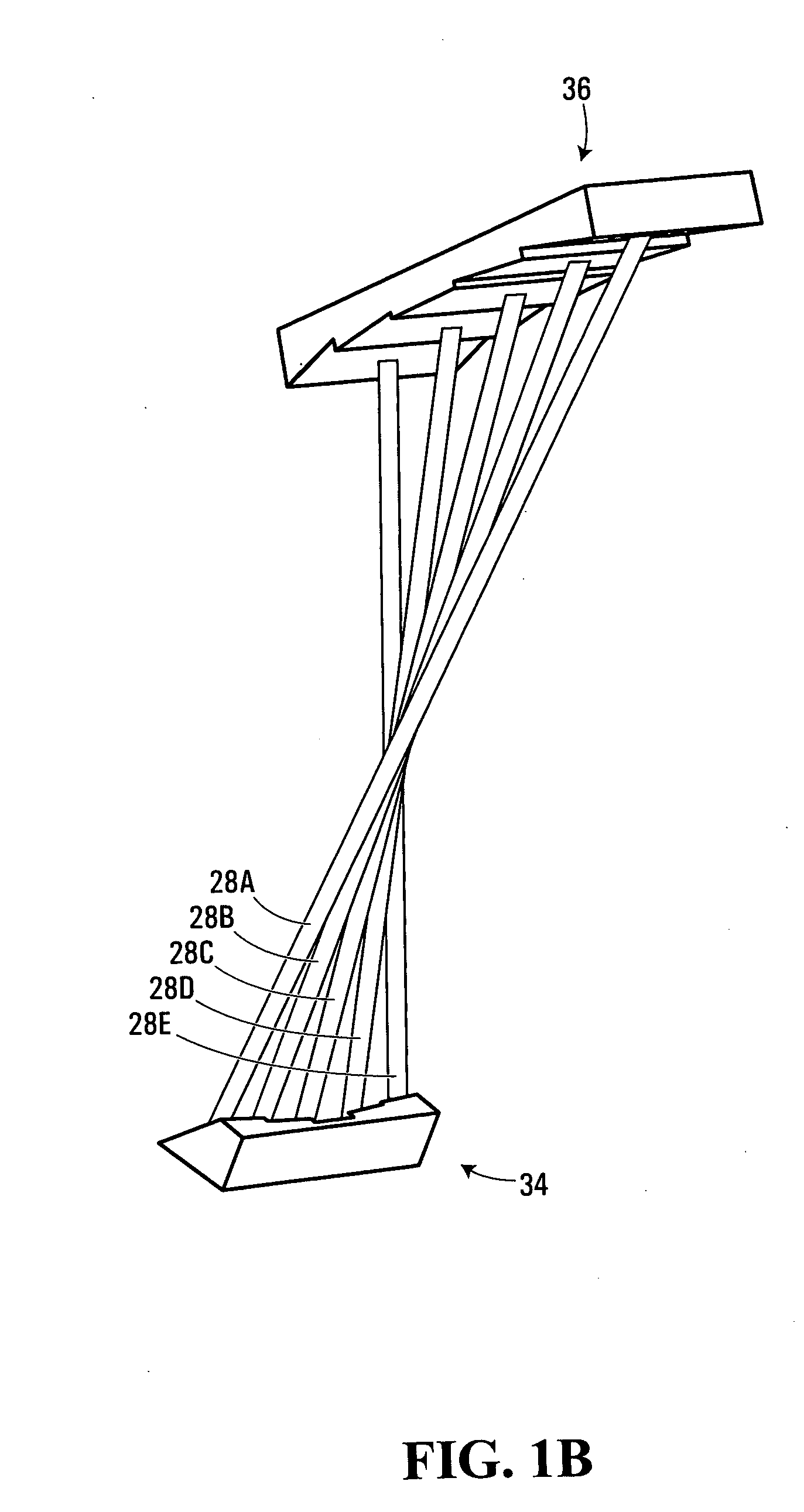
Apparatus for shaping an optical beam bundle carrying a plurality of substantially parallel optical beams disposed in a common plane of travel. First reflective facets and second reflective facets are provided, the first reflective facets being oriented so as to deflect the optical beams of the bundle into a plurality of intermediate, substantially non-parallel optical beams. Each of the second reflective facets is spatially disposed so as to receive a respective one of the intermediate optical beams at a different respective distance from the plane of travel of the optical beam bundle. Also, the second reflective facets are oriented so as to deflect the intermediate optical beams into a bundle of substantially parallel output optical beams. In this way, the output beam can be more adapted for a particular application. In certain cases, this also achieves increased brightness of a laser beam through reduced output beam divergence and / or total cross-sectional area.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
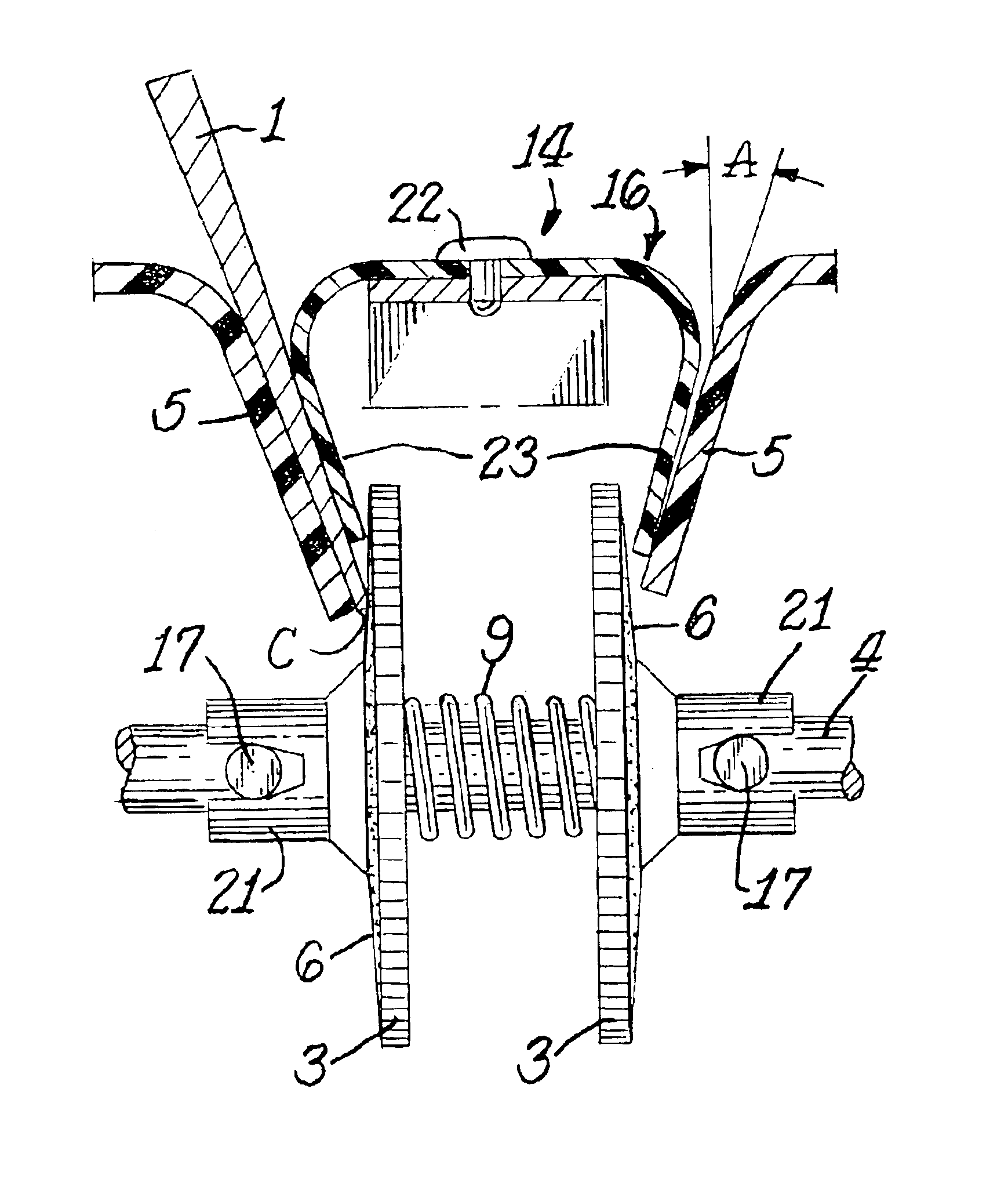
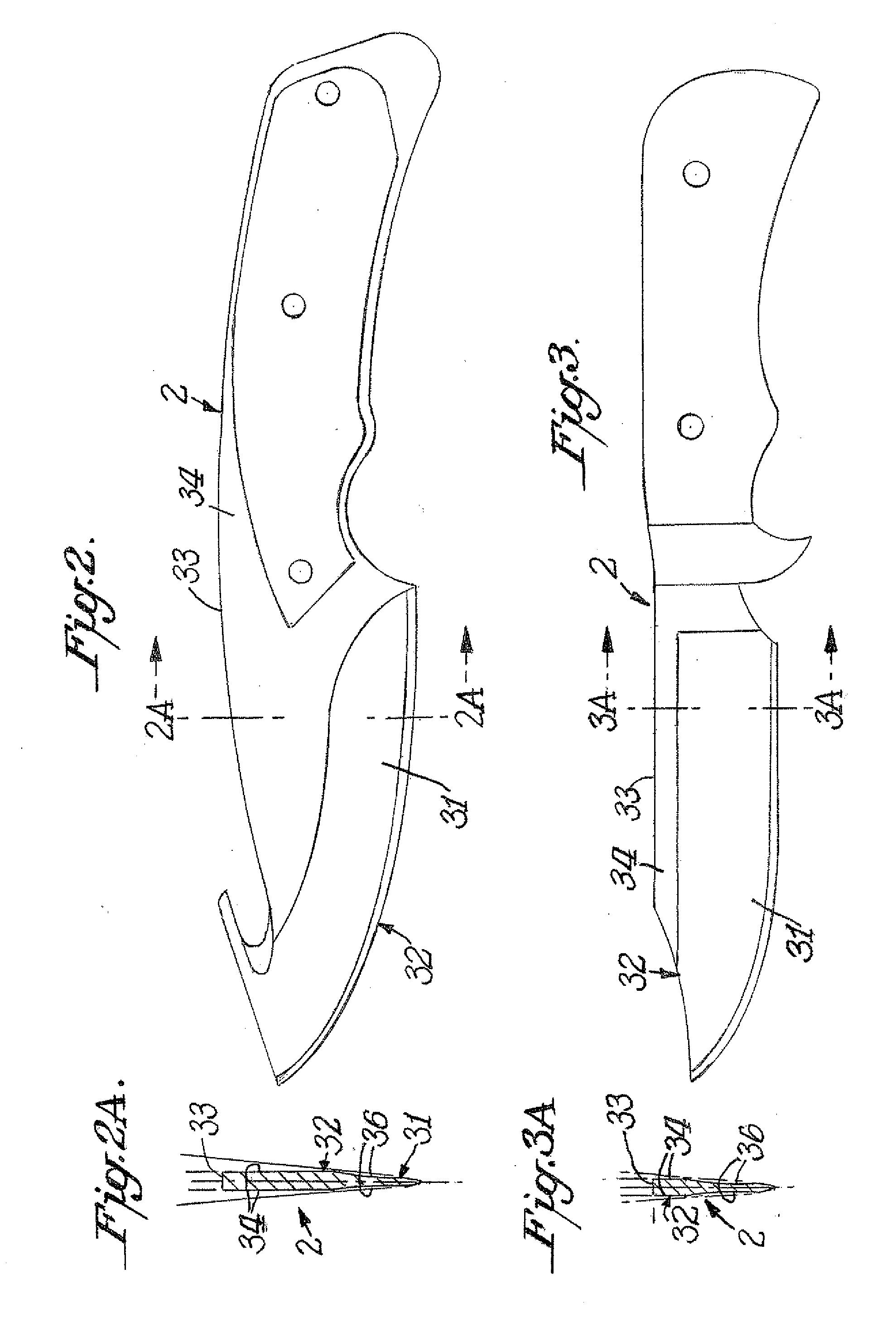
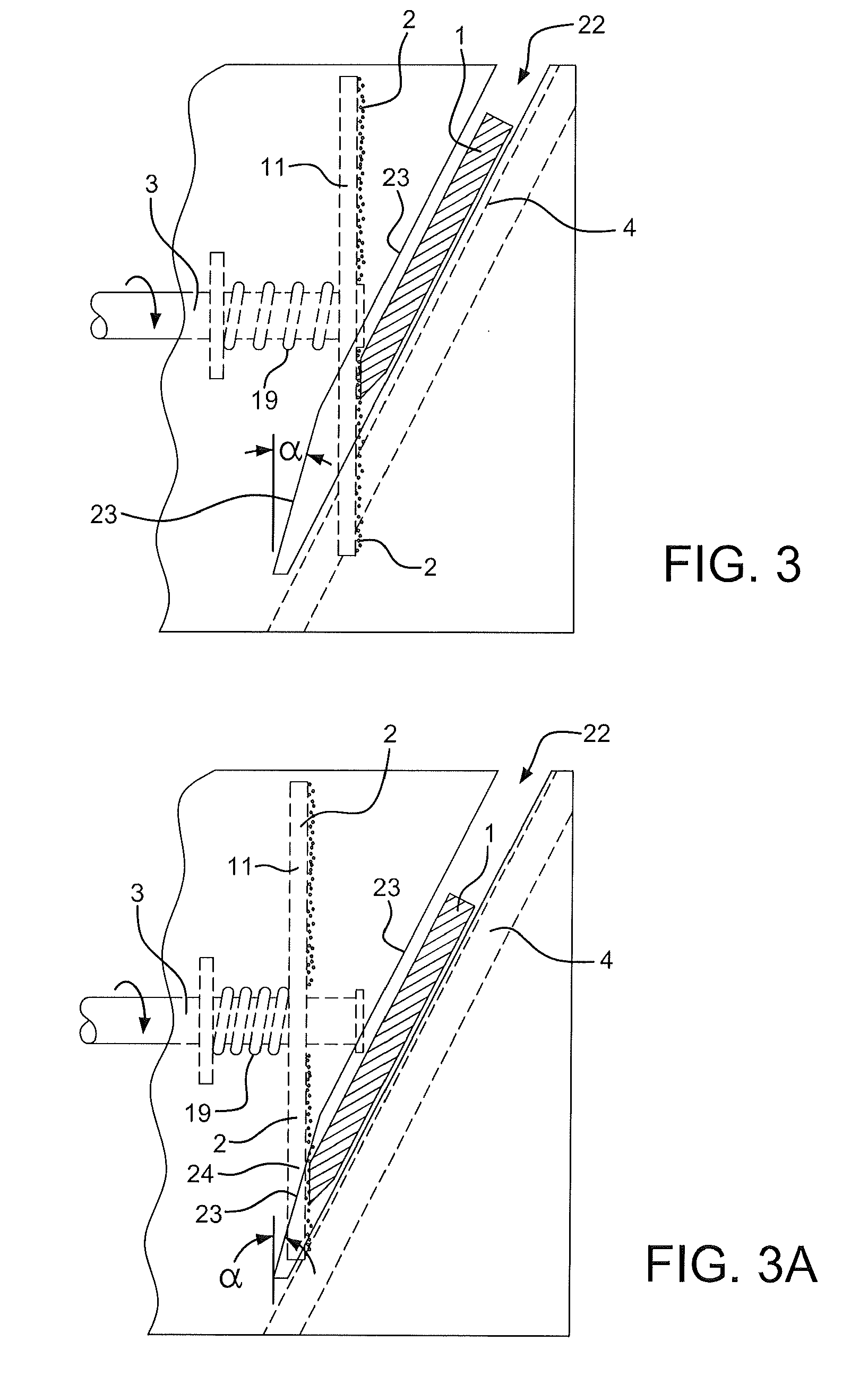
Precision sharpener for hunting and asian knives
ActiveUS20080261494A1Eliminate the problemPrecise alignmentEdge grinding machinesCutting toolsCoated surfaceKnife sharpener
A knife sharpener is provided which is capable of precision sharpening of hunting and similar knives that have a first and second blade face, each of which terminates at a facet that meets the corresponding facet to create the knife edge. At least the first of the blade faces has a lower distinct planar or concave section adjacent the edge facet with the lower planar or concave section of the face being set at an angle to the center line of the blade thickness that is different from the angle of the adjoining upper section of the same blade face located adjacent to the back of the blade. The sharpener includes a sharpening member such as one having an abrasive coated surface. The sharpener also includes a planar angle knife guide surface of a knife guide which is designed for intimate sliding and sustaining contact with the second face of the blade in order to position an edge facet on the first of the faces into precise angular relation with the sharpening surface. The sharpener also includes a knife holding spring that applies force against the first face of the blade predominantly at one or more locations on the lower planar or concave section of the first face that is adjacent to the edge facet being sharpened in order that the lower section adjacent the edge on the second face of the blade is pressured to align with and remain in intimate sliding alignment with the guide surface as the blade edge facet on the first face is being sharpened.
Owner:EDGECRAFT
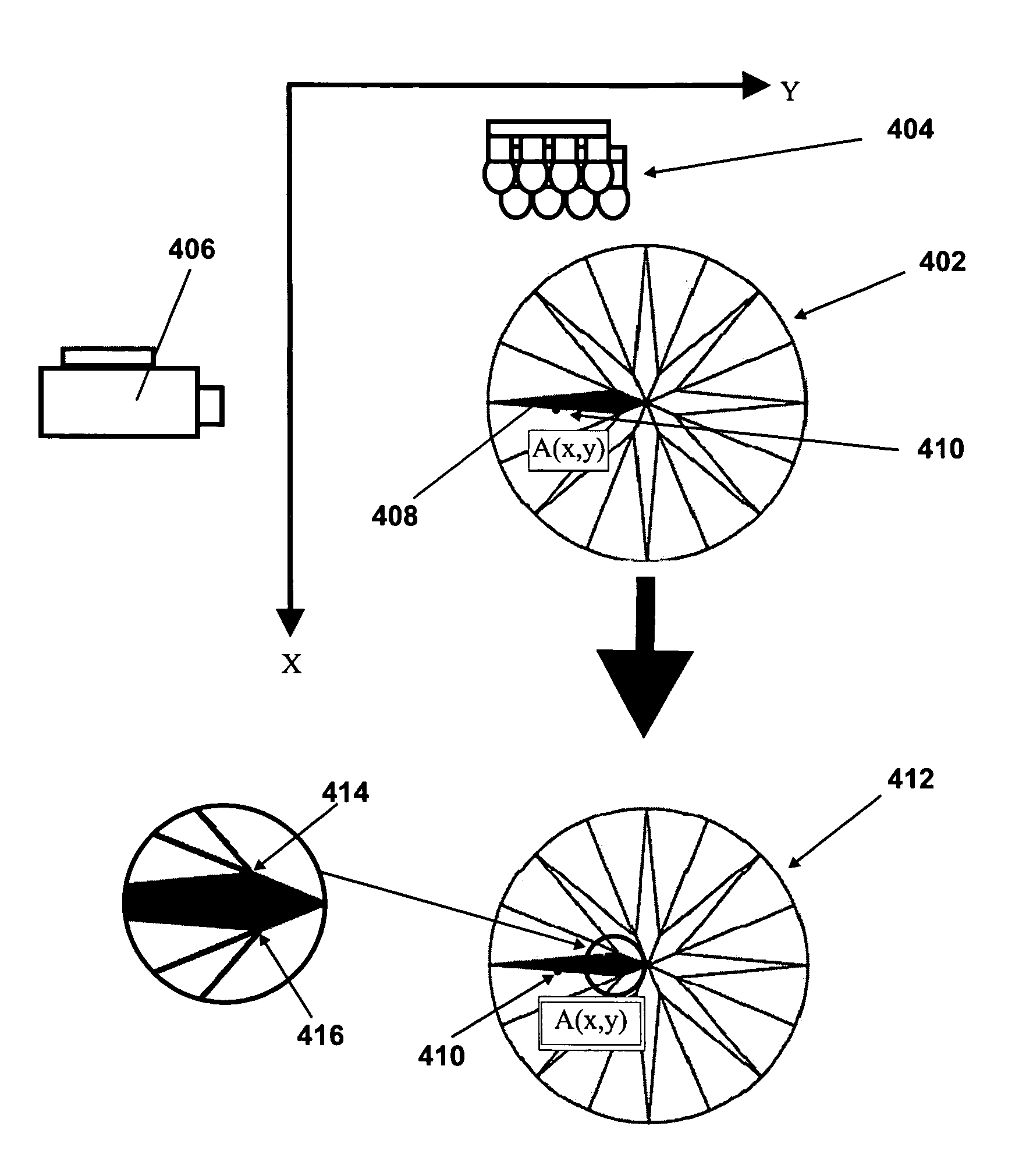
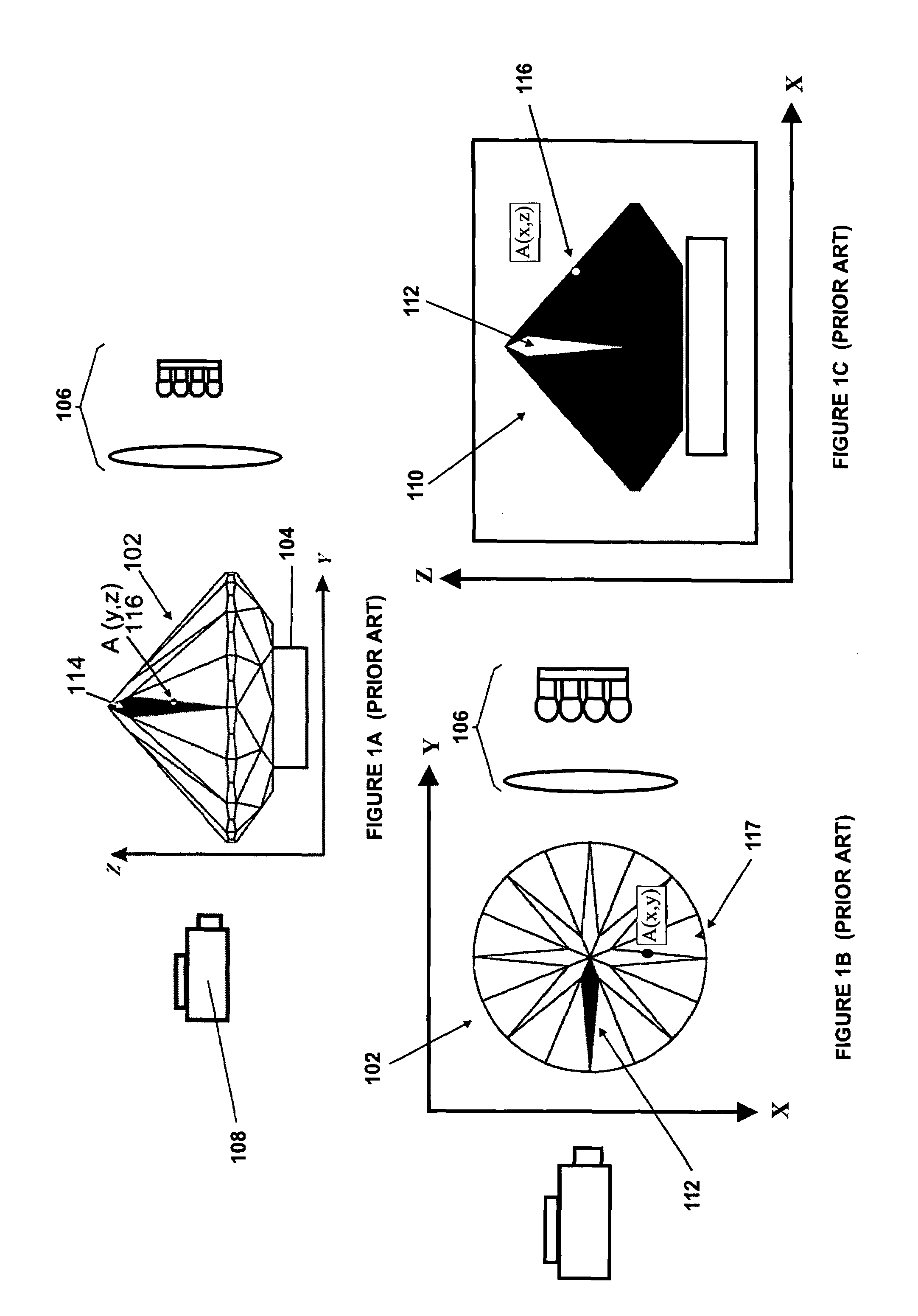
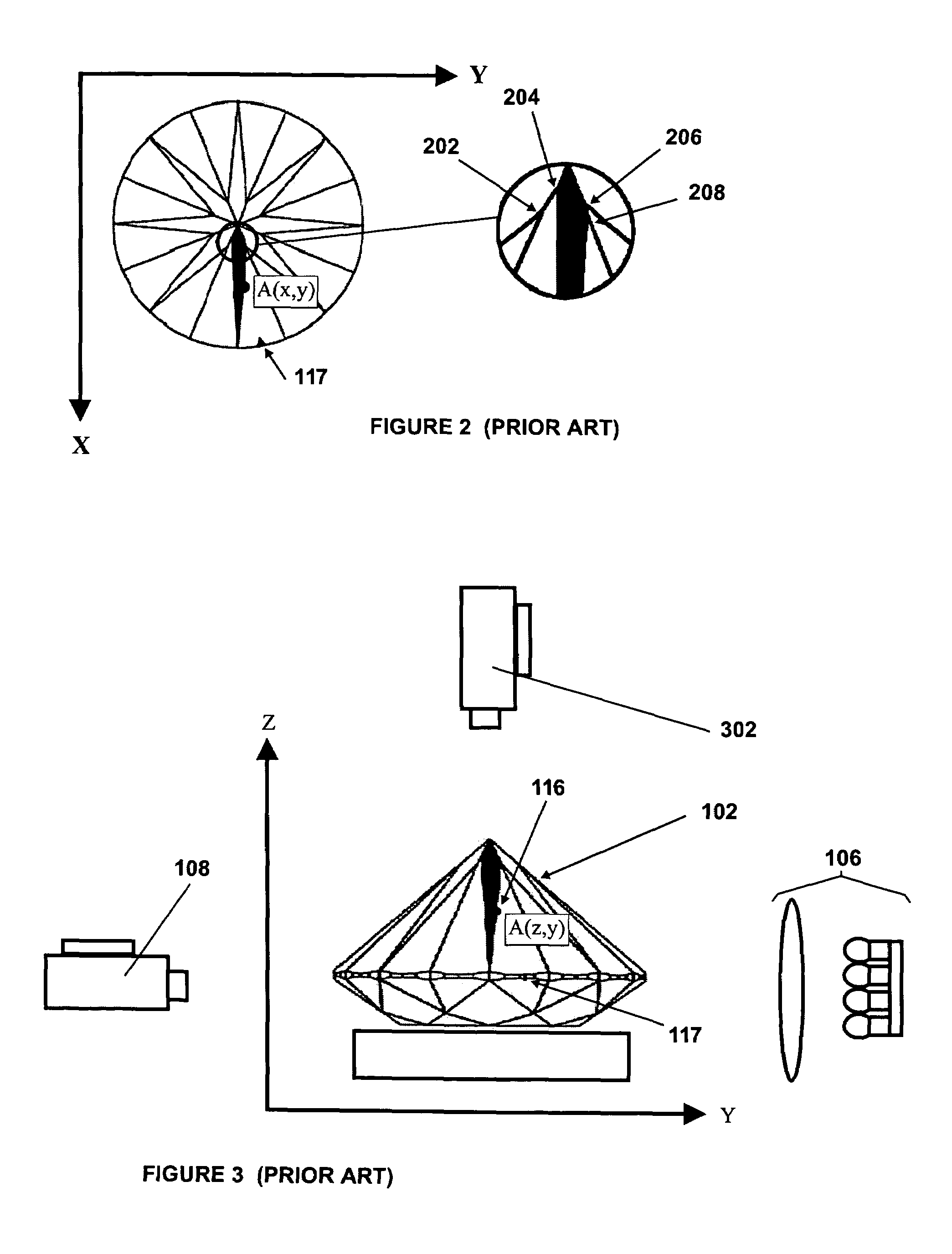
Method and apparatus for examining a diamond
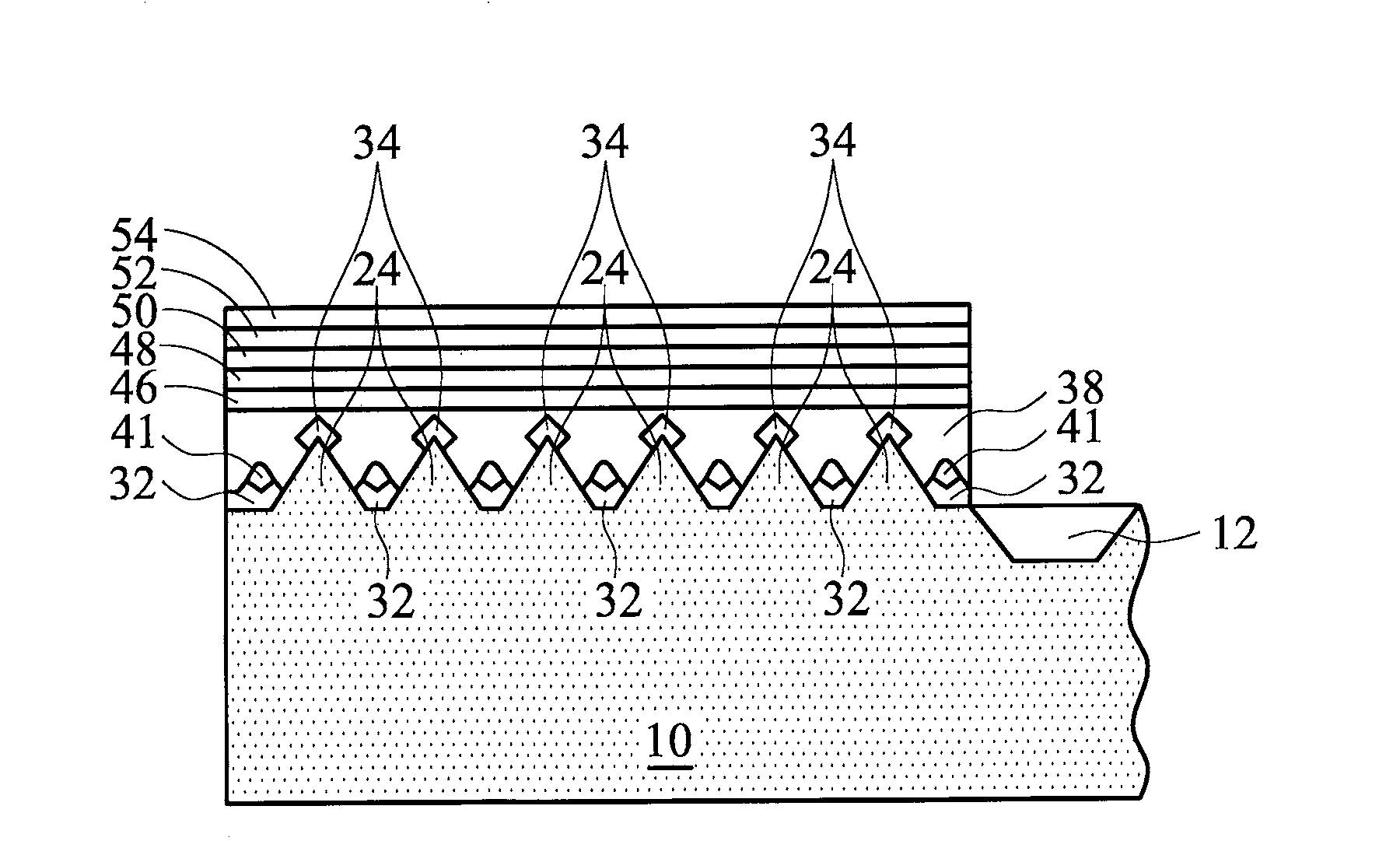
ActiveUS7259839B2Accurate judgmentAvoid the needInvestigating jewelsPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsMicrometerFaceting
Prior methods of measuring diamond proportions in order to construct a complete model, such as a three dimensional virtual wire-frame model, of a diamond have been found to be inadequate. In particular, there has been no commercially available, automated and objective method for measuring the dimensions of a diamond with similar or greater accuracy as compared with the accuracy that can be achieved with manual gauges or micrometers. The present invention provides a method of measuring a physical characteristic of a facet of a diamond, such as the location of one or more points on an edge of a facet. The method comprises illuminating the diamond to visually distinguish a facet from adjacent facets when viewed from a predetermined location, and then capturing an image of the diamond as viewed from this predetermined location. The image is then analyzed to determine the location of at least one point located on an edge of a facet by identifying a discontinuity in the properties of light transmitted from the diamond to the viewing location.
Owner:HOLLOWAY GARRY IAN +1
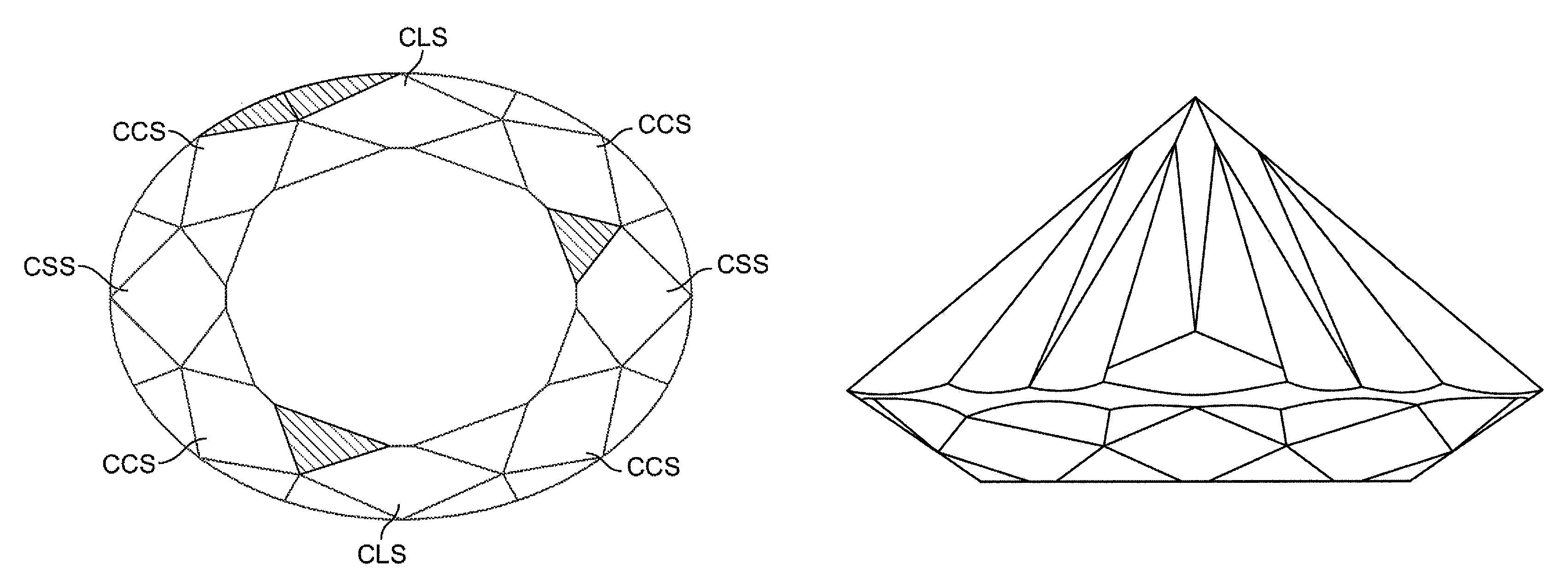
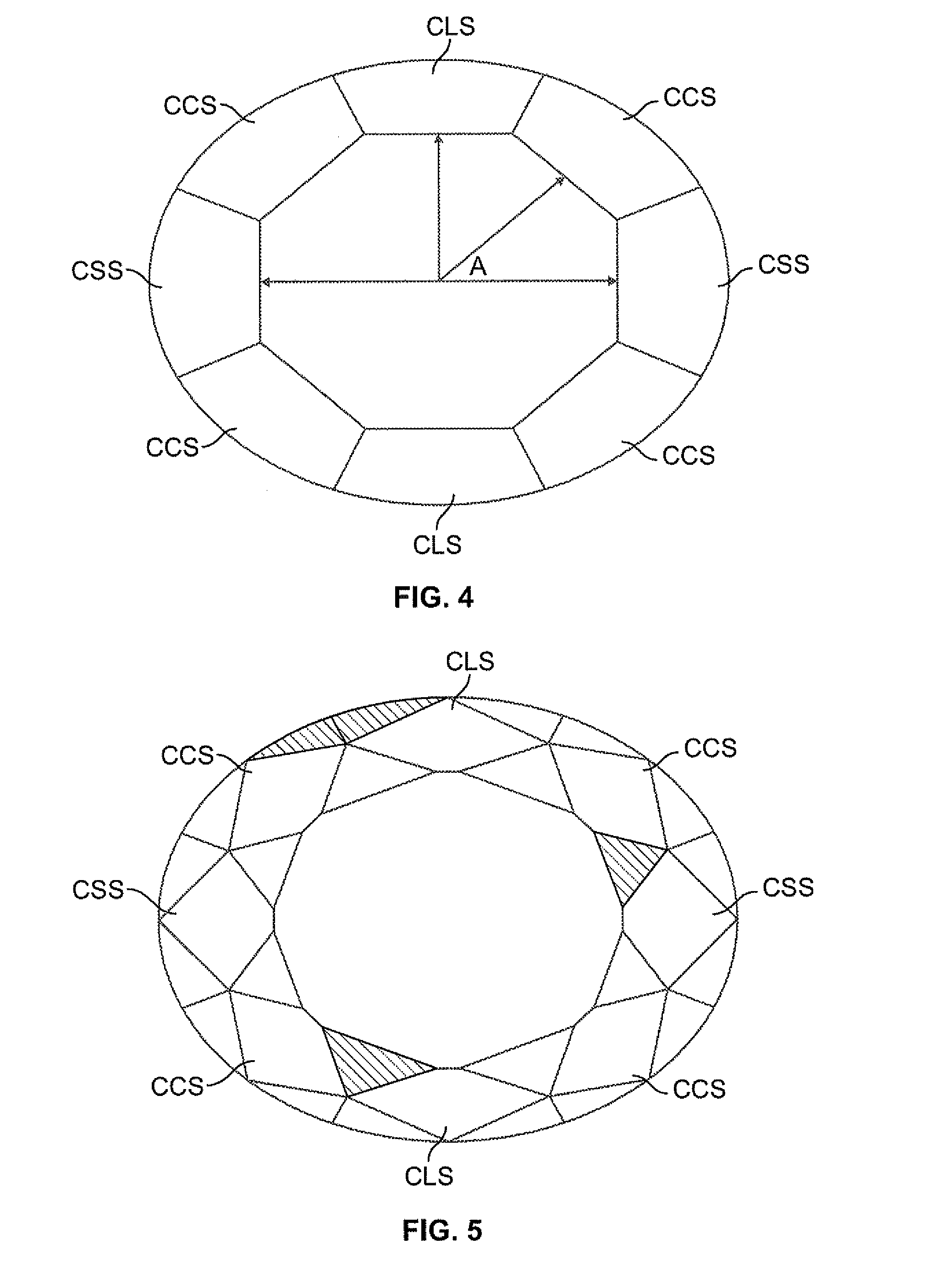
Oval shaped diamond cut having hearts and arrows pattern
An oval shaped diamond, adapted to display a hearts and arrows pattern when exposed to light characteristic of the hearts and arrows pattern in a round diamond, comprising: an oval shape having two long sides symmetrical to each other, two short sides symmetrical to each other and four corner sides symmetrically located between the long sides and the short sides respectively, eight main crown facets of unequal size and eight main pavilion facets of unequal size, sixteen pavilion half facets; a girdle of non-uniform thickness separating the crown and pavilion facets and two subsidiary pavilion facets in alignment with each other on the long sides of the diamond adjacent a main pavilion facet.
Owner:WORLDWIDE DIAMOND TRADEMARKS
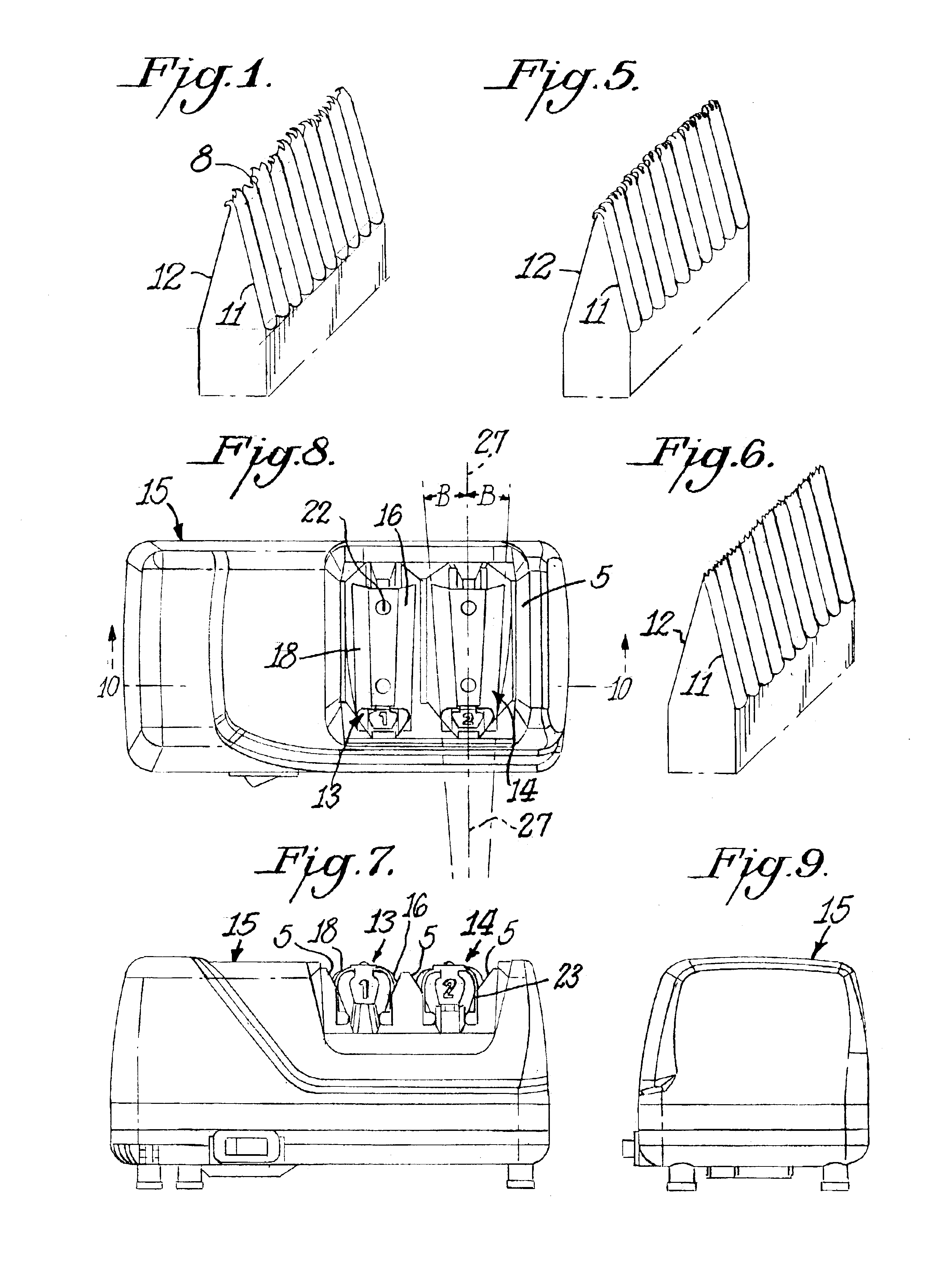
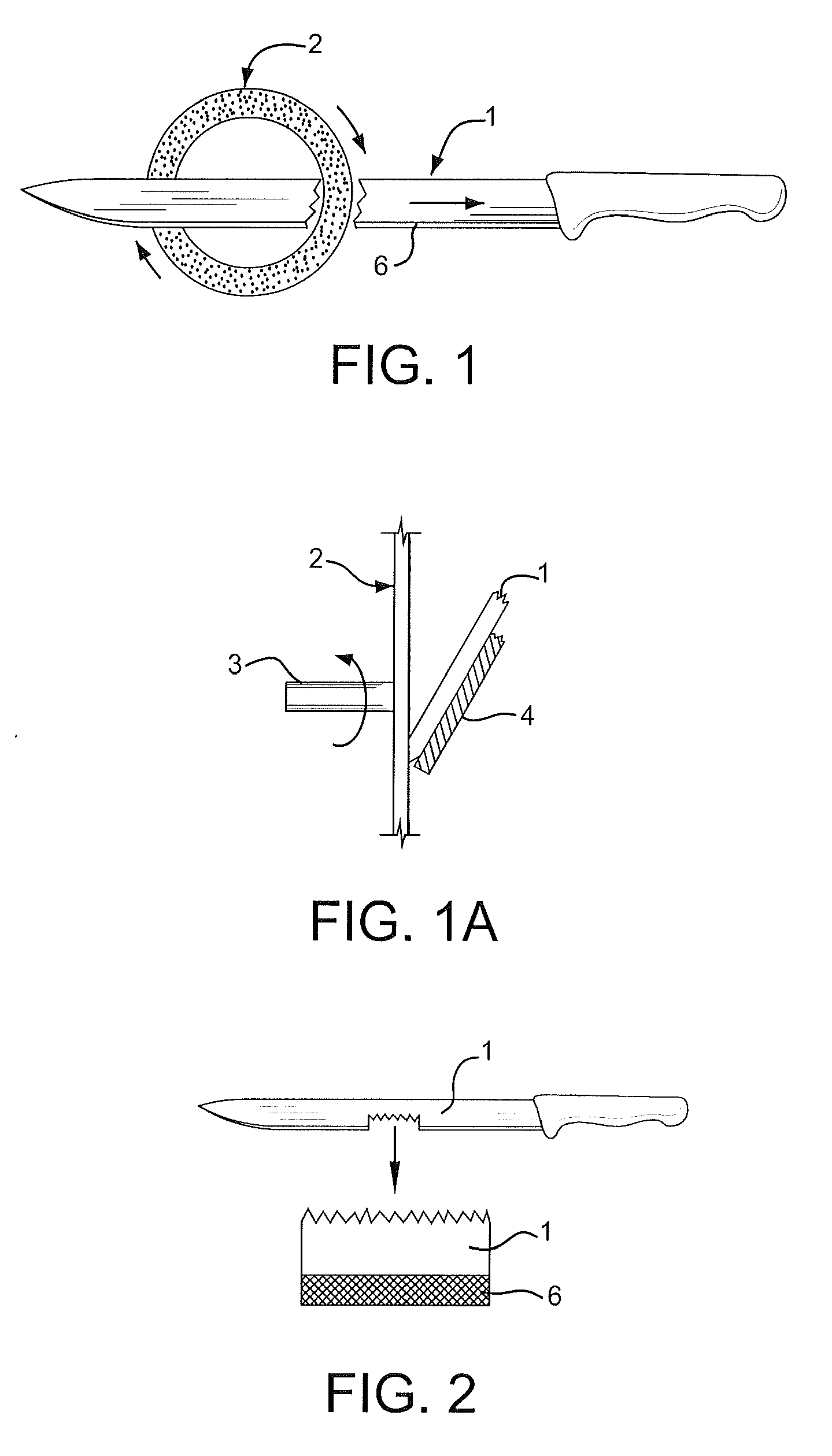
Novel sharpeners to create cross-grind knife edges
ActiveUS20110034111A1Highly effectiveSmall sizeEdge grinding machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesCircular discEngineering
A sharpener for creating cross-grind knife edges includes a nominally flat annular abrasive sharpening member which could be a ring or a disk and is rotated about its center and held against a moving knife edge facet to simultaneously and sequentially abrade the knife edge at multiple locations on the abrasive member. The disk may be slidably mounted on a shaft in opposition to a spring restraining force. The disk is nominally disposed in a vertical orientation. The sharpener may include multiple stages including a manual stage having a pair of off axis conical shaped rotatable abrasive coated disks which have abrading lines on opposing facets which are not parallel but cross and intersect in a crossing pattern at the blade edge.
Owner:EDGECRAFT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com