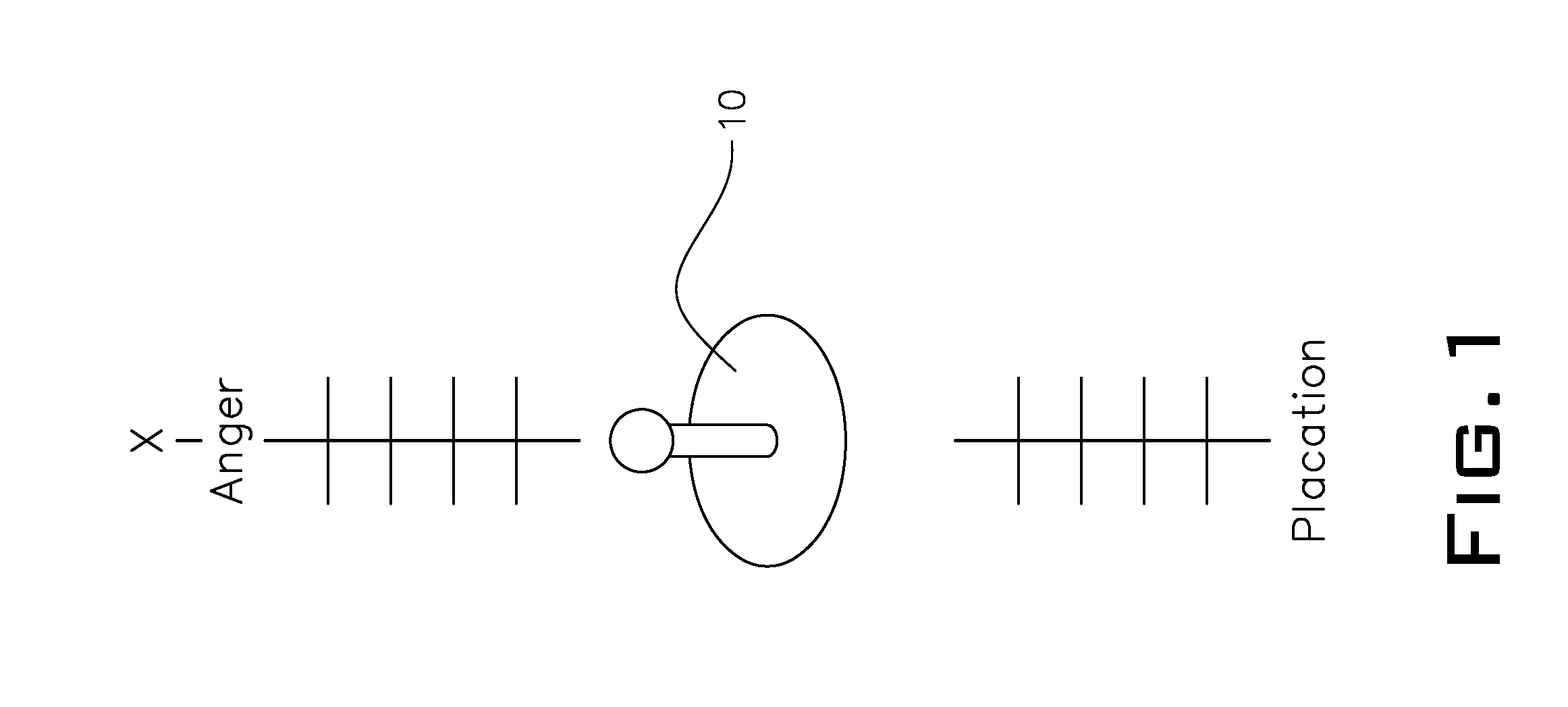Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
250results about How to "Quickly reach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
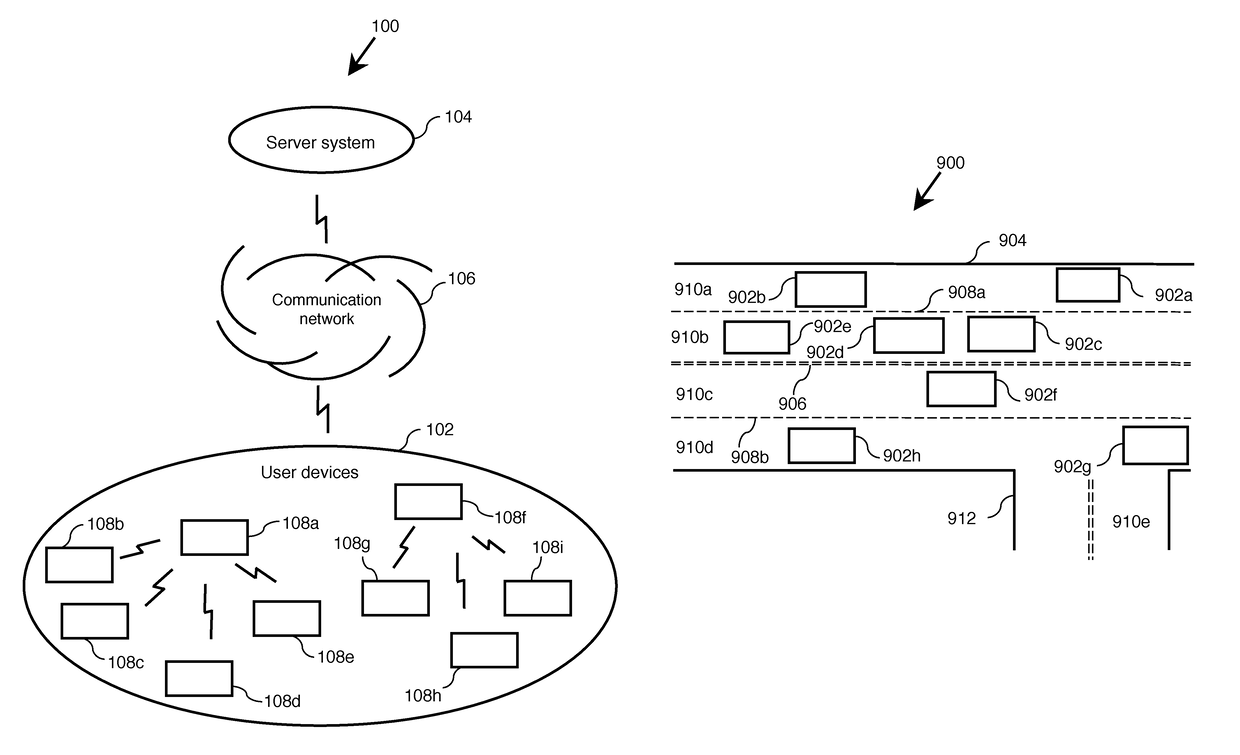
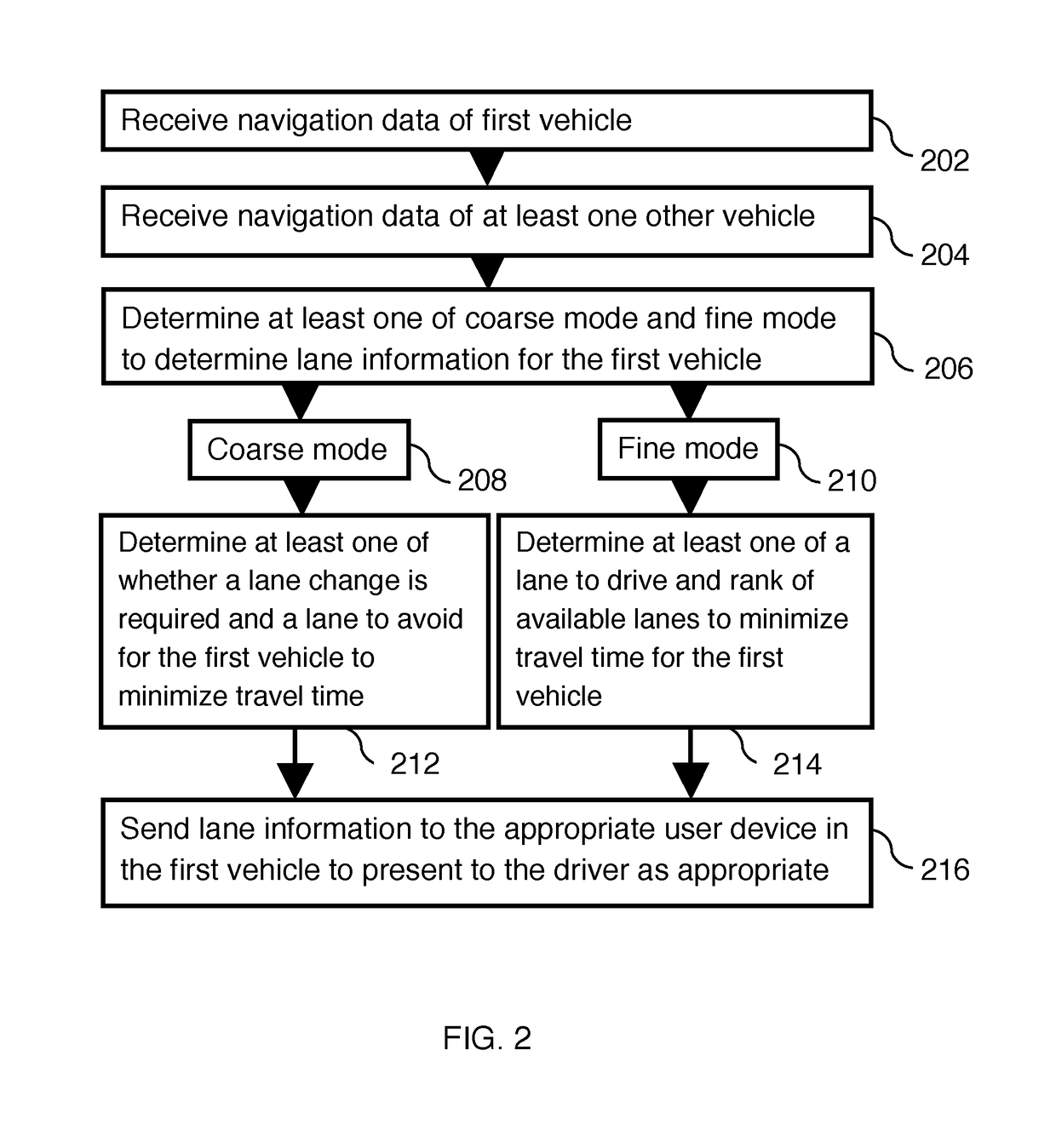
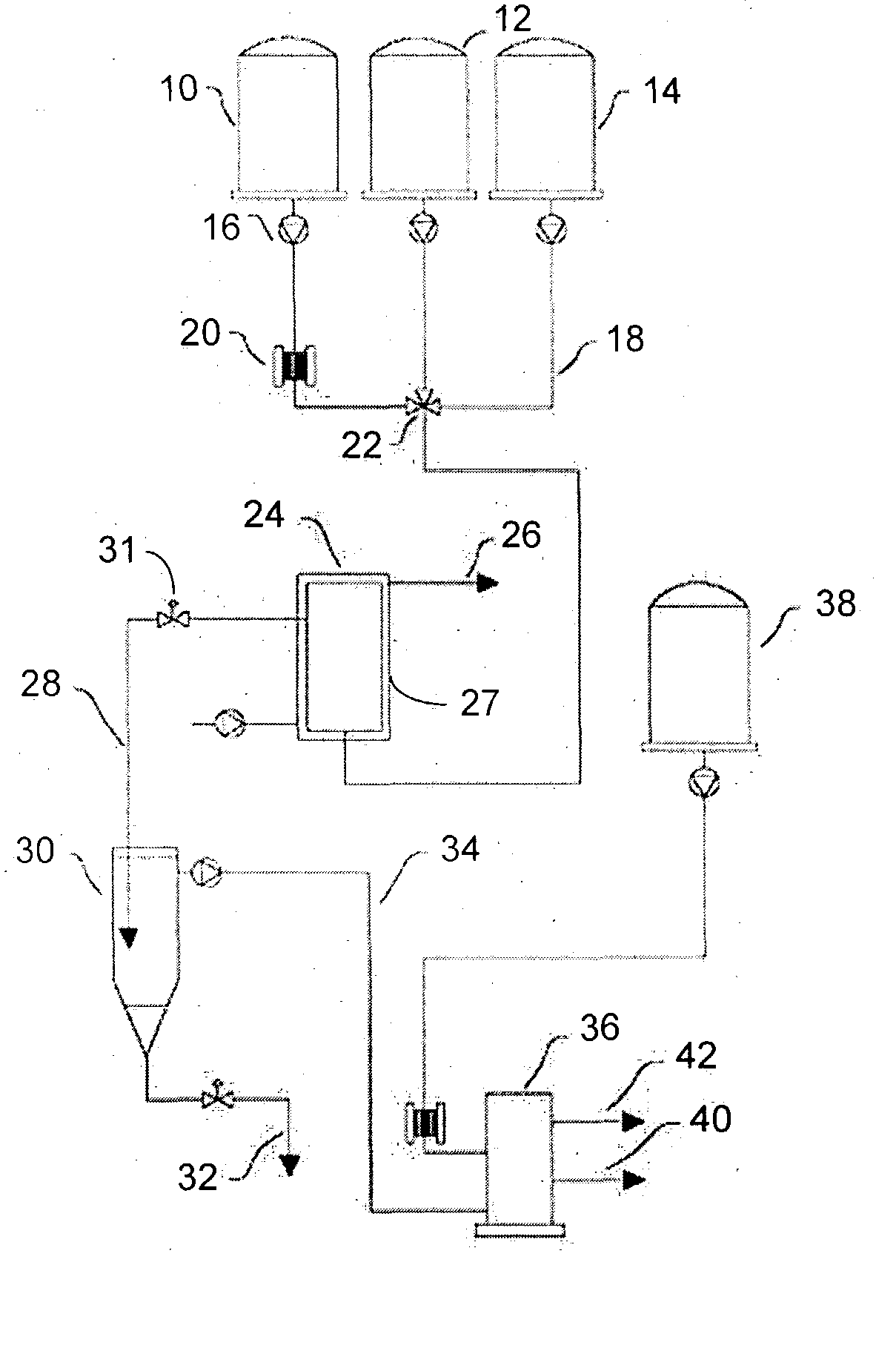
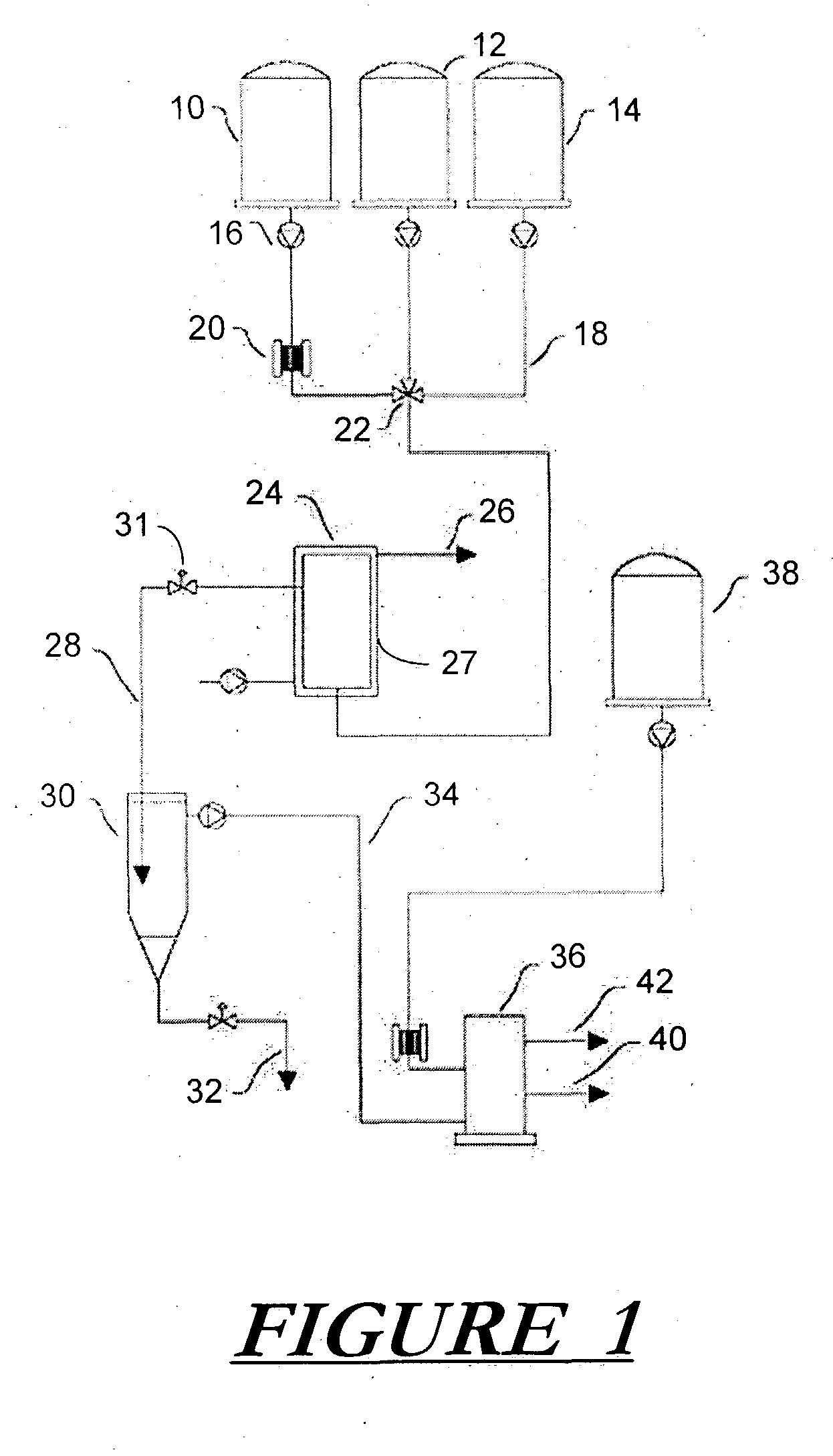
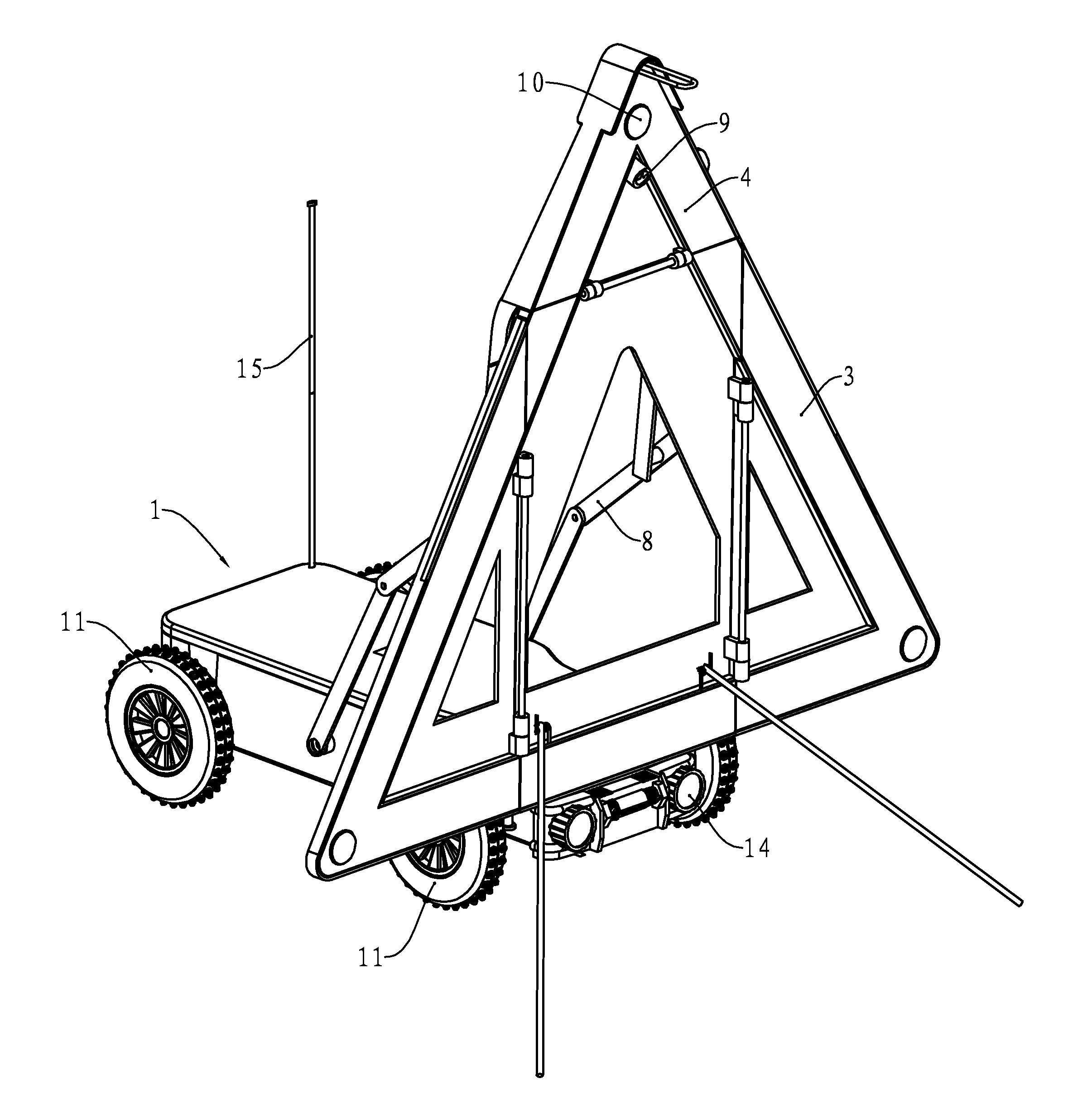
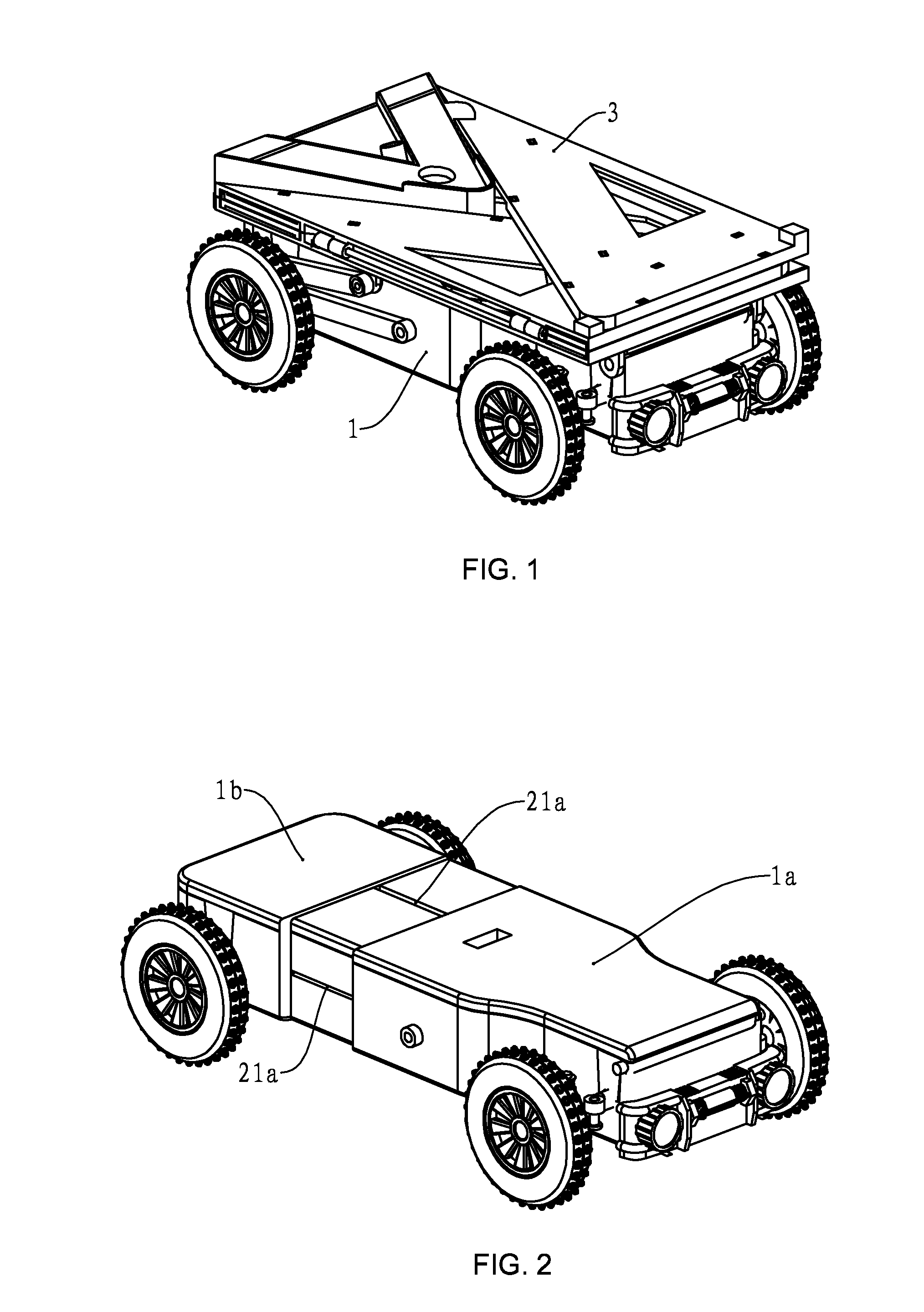
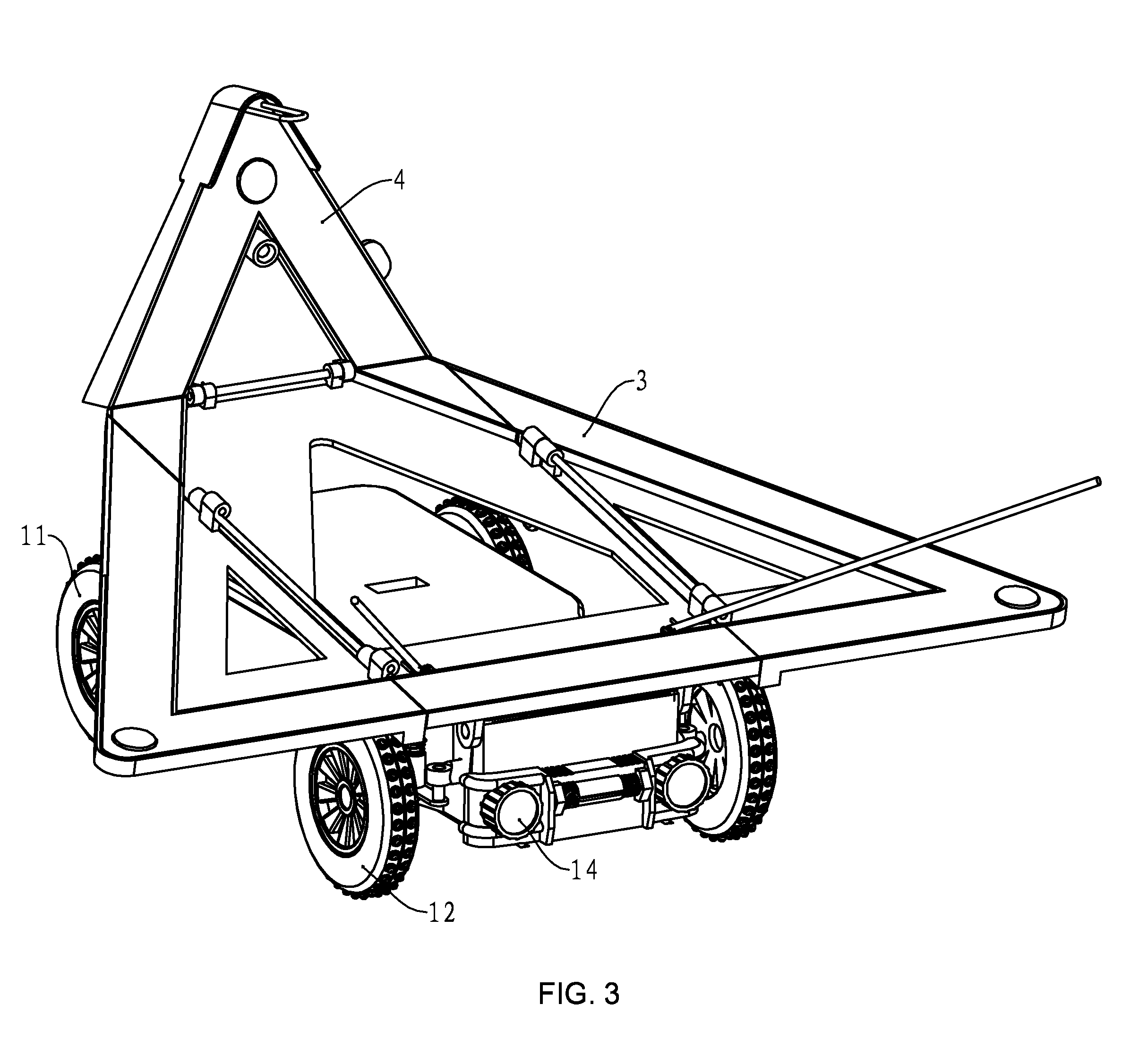
Traffic aware lane determination for human driver and autonomous vehicle driving system
ActiveUS9672734B1Minimize disruptionQuickly reachAnalogue computers for vehiclesParticular environment based servicesDriver/operatorUser device
A system, method, and computer program product for determining lane information in a road segment to drive a first vehicle to minimize travel time. According to an embodiment, navigation data of the first vehicle and at least one other vehicle in a road segment is sent to a computer server system via their respective clique leaders through a communication network. The lane information may include whether a change of lane is required, a lane to avoid, an optimum lane, and rank order of drivable lanes according to increasing order of travel time for the first vehicle to minimize travel time. The determined lane information is sent to the appropriate user device through its clique leader. The user device presents the lane information to a human driver and / or autonomous vehicle driving system of the first vehicle appropriately.
Owner:RATNASINGAM SIVALOGESWARAN
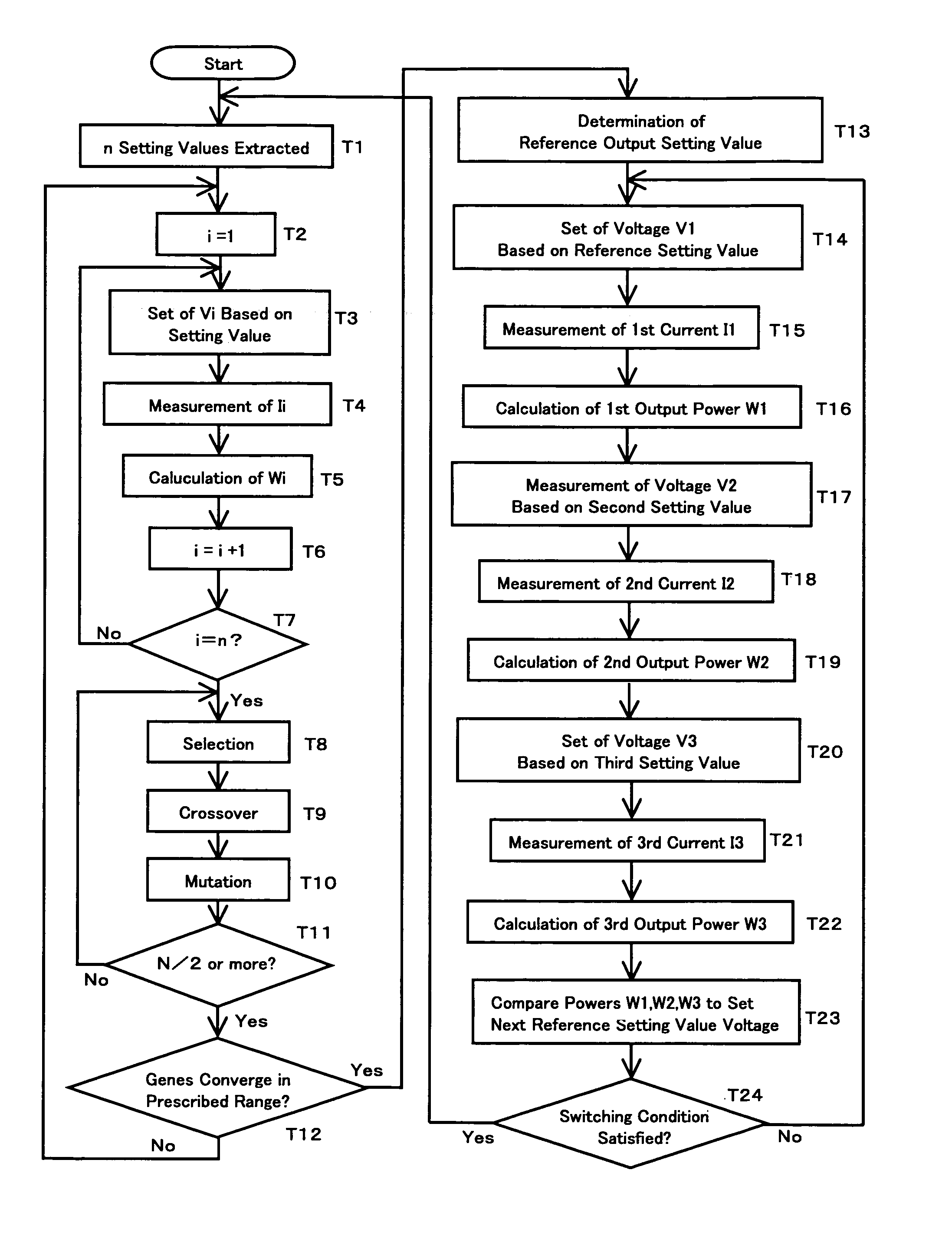
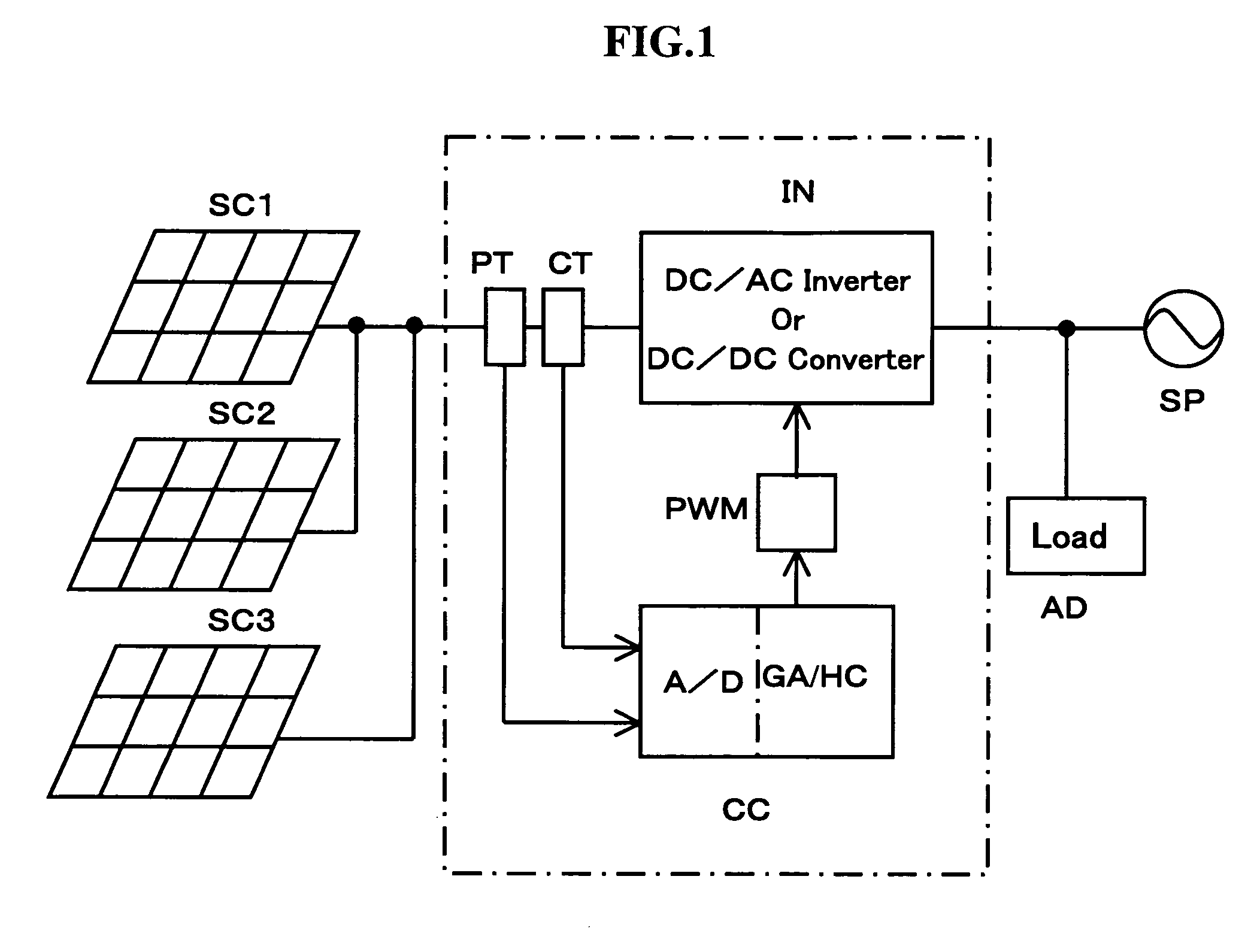
Method of controlling photovoltaic power generation system
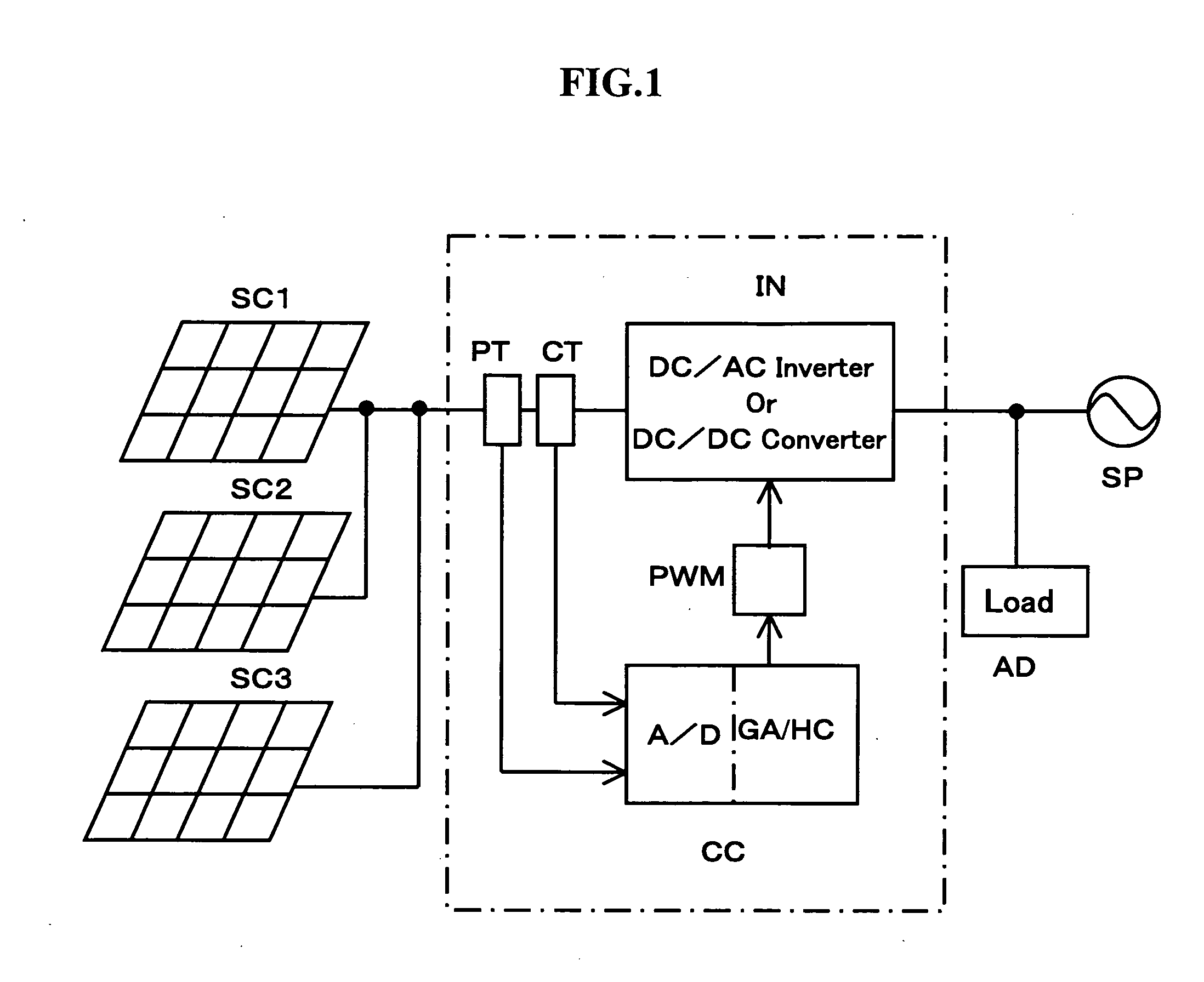
ActiveUS7042195B2Quickly reachGuaranteed to workBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringEngineeringSolar cell
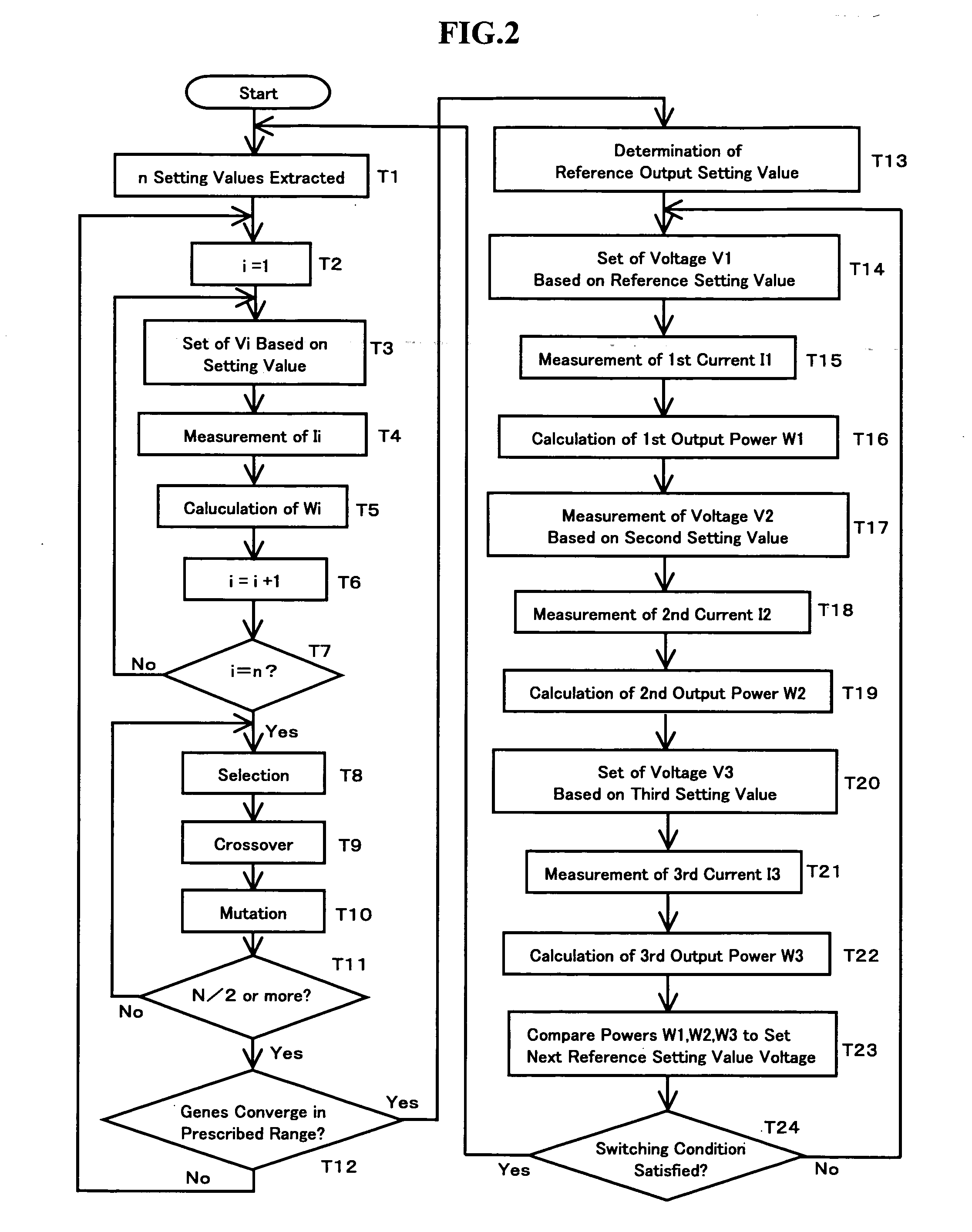
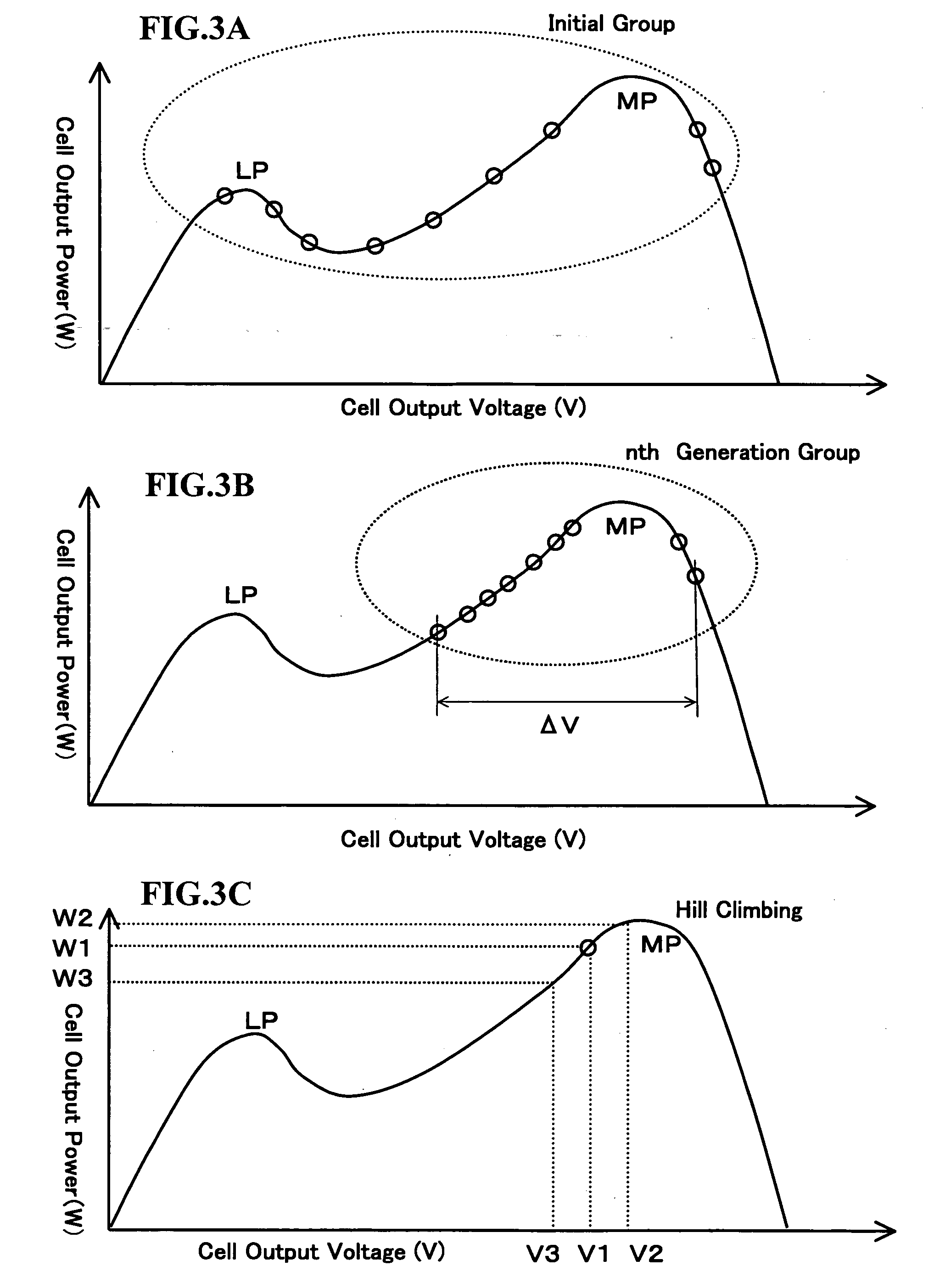
A conventional hill climbing method is not capable of tracking a maximum power when a shadow covers a part of a solar cell panel and a plurality of maximal values is thereby developed. The invention provides a photovoltaic power generation system control method that controls a photovoltaic output setting value to be an appropriate value by following up a variation in the solar irradiation, including a genetic algorithm process of employing the photovoltaic output setting value as a gene and the output power as an evaluation value thereof; randomly extracting a plurality of genes and repeating storage, selection and crossover / mutation of the output powers which are the evaluation values of the genes, so as to converge a difference between a maximum and minimum values of the output voltages into a predetermined range; and a hill climbing process of setting the photovoltaic output setting value corresponding to the greatest value of the converged output voltages, and a greater and a lower value than the photovoltaic output setting value by a predetermined amount, so as to select the greatest output power among these values; and repeating such steps to track the maximum output power.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
Method for transmitting multimedia messages and a multimedia message communication system
InactiveUS7289792B1Reduce loadMany timesMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationCommunications systemMobile communication network
The invention relates to a method for transmitting multimedia messages to a wireless terminal (MS1) in a data transmission system which comprises at least one mobile communication network (HPLMN) and at least one multimedia message server (MMSV). In the method, each wireless terminal (MS1) connected to the mobile communication network (HPLMN), is allocated an address specifying said wireless terminal (MS1), and at least one data transmission connection is activated for said wireless terminal (MS1). Information on the activation of the data transmission connection for said terminal (MS1) is transmitted to the multimedia message server (MMSV).
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
Probe tip thermal isolation and fast prediction algorithm
InactiveUS6839651B2Increase temperatureQuickly reachThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryThermal isolationPrediction algorithms
A prediction type electronic thermometer having an actively controlled heater element thermally isolating the probe tip from the probe shaft. Rapid and accurate temperature measurements are made using predictive algorithms. Control circuitry reads input from the temperature sensing element to compute best heater control signals so that the temperature of the probe shaft rapidly follows changes in the temperature of the probe tip. Thermal isolation between probe shaft and tip impedes heat flow from the heater element to the tip providing more accurate measurements. Rapid and accurate management of shaft temperature allows heat from the patient being measured to be most efficiently transmitted to the temperature sensor element resulting in very fast temperature measurements.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH IRELAND UNLTD
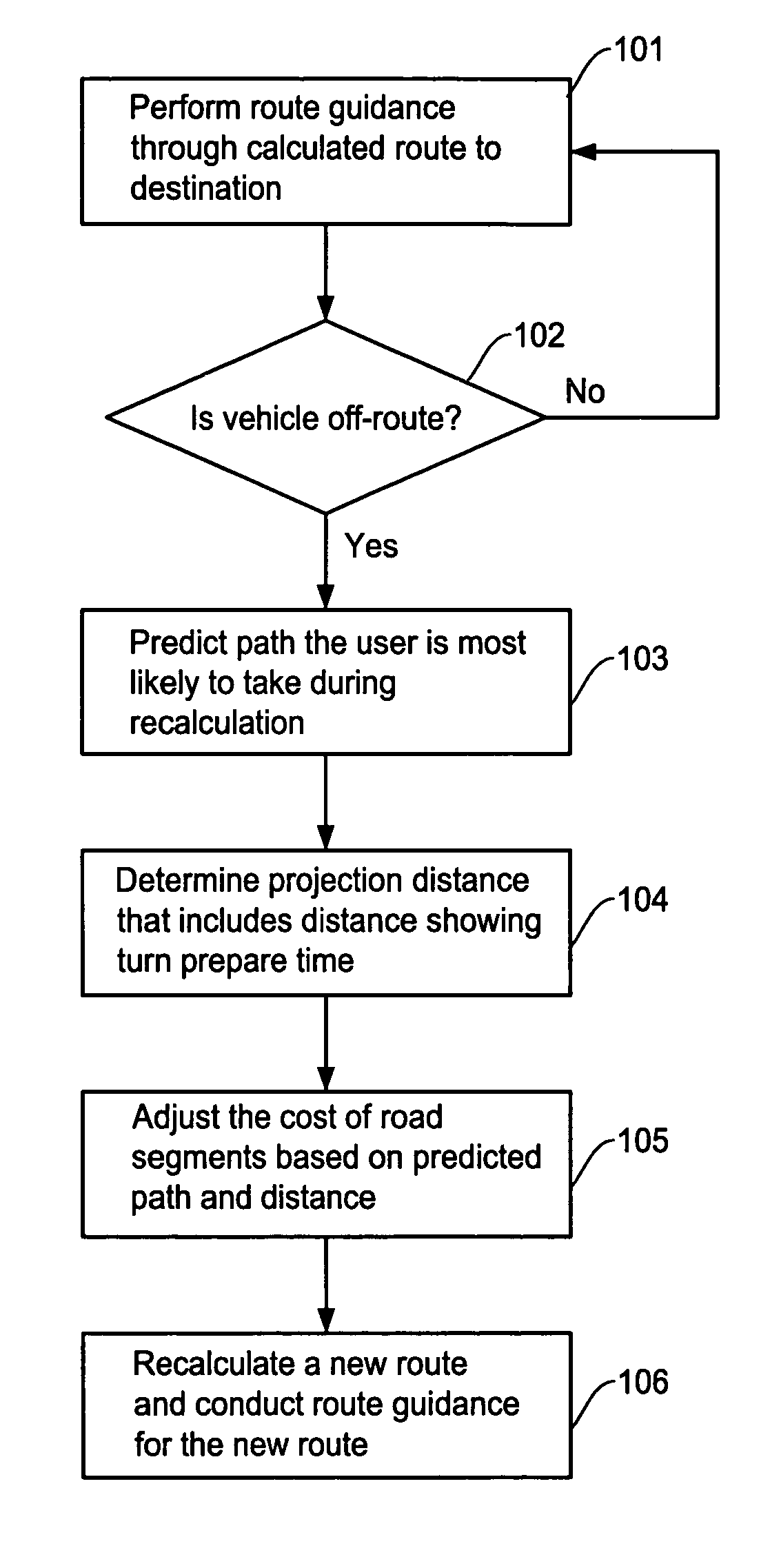
Off-route recalculation method and apparatus for navigation system
ActiveUS20070156334A1Safe and efficient drivingRecalculated efficientlyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation systemComputer science
An off-route recalculation method and apparatus for a navigation system calculates a new route when a vehicle is deviated from an originally calculated route to a destination. The method is comprised of the steps of: detecting whether a user vehicle has deviated from an originally calculated route; predicting a path that a user is likely to take until a new route to the destination is calculated; calculating a predicted distance that the user vehicle advances through the predicted path during a time the new route to the destination is calculated and during a turn prepare time, thereby determining a start position of the new route; calculating the new route to the destination incorporating the start position.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Driver assistance program
InactiveUS20110032119A1Good ideaQuality improvementArrangements for variable traffic instructionsSteering partsProgram planningEngineering
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
Emergency alert system
ActiveUS7679505B1Reach virtually all appropriate persons very quicklyEasy to operateElectric signalling detailsComputer scienceEmergency alert system
An emergency alert system is disclosed. The invention employs an emergency alert message, which directs end users to take some particular action like evacuating an identified geographic area. The invention further employs a geographic area message, which is based on a particular geographic area within which all persons should receive the emergency alert message. The invention utilizes an emergency alert enabled device that receives both the emergency alert message and the geographic area message. The emergency alert enabled device then determines whether it is located within the geographic area of concern, and if so, presents the emergency alert message to the end user.
Owner:ADVANCED COMP & COMM
Method and system for determining the altitude of a mobile wireless device
ActiveUS6999780B1Improve abilitiesAccurate measurementEmergency connection handlingDirection finders using radio wavesCellular telephoneMobile wireless
A method and system for determining the three-dimensional location of a mobile wireless device. In one implementation, the device is a cellular telephone making a 911 call from one floor of a multi-story building. An embodiment of the method of the invention includes establishing a database that associates transmission metrics with altitudes of x-y coordinate locations having more than one altitude at which the mobile wireless device could be located, receiving a communication from the mobile wireless device, determining an x-y coordinate location of the mobile wireless device, measuring a transmission metric of the mobile wireless device, and consulting the database to determine the altitude from the x-y coordinate location and the measured transmission metric. The transmission metric could be, for example, the transmission time or angle of arrival of a wireless signal received from the mobile wireless device.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Apparatus and method for the production of fatty acid alkyl ester
InactiveUS20050027137A1Eliminate operationShort possible reaction timeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAlcoholVegetable oil
An apparatus and method for producing fatty acid alkyl esters from fatty acids derived from vegetable oils and animal fats with an alkaline solution dissolved in stoichiometric or near stoichiometric levels of a monoalkyl alcohol to form a mixture. The method further comprises emulsifying the mixture as a means to reach a completed chemical reaction state in a reactor section, wherein the oils or fats are transesterified into fatty acid alkyl esters. The transesterification occurs when the natural boundary surfaces of the immiscible mixture are enlarged by ultrasonic cavitation in the reaction section and the transesterification is performed at, or near atmospheric pressure. The method finally includes, after reaching the chemical reaction state, separating residues from the fatty acid alkyl ester in a gravitational phase separation section.
Owner:HOOKER JEFFREY D
Computing device with improved user interface for menus
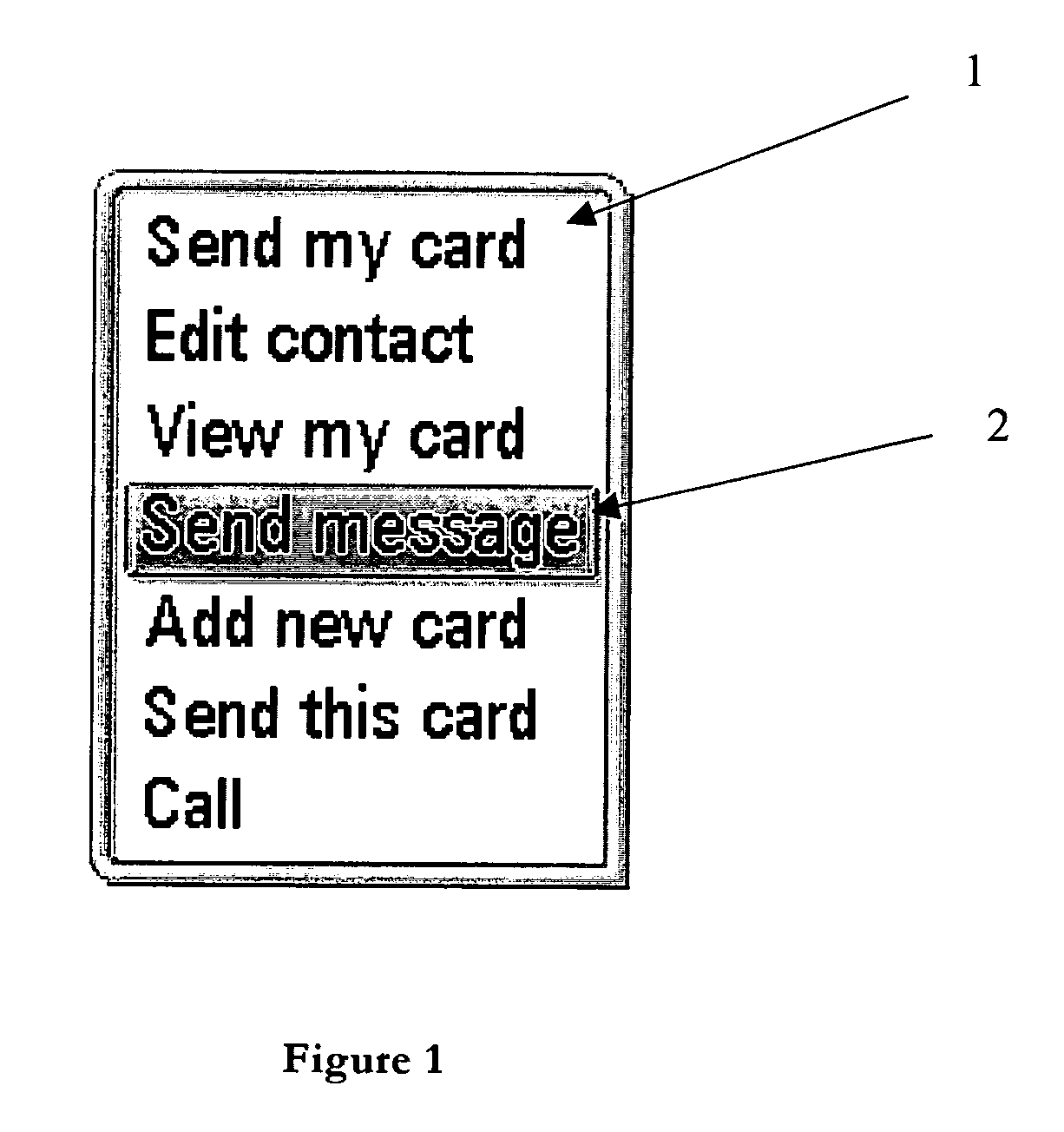
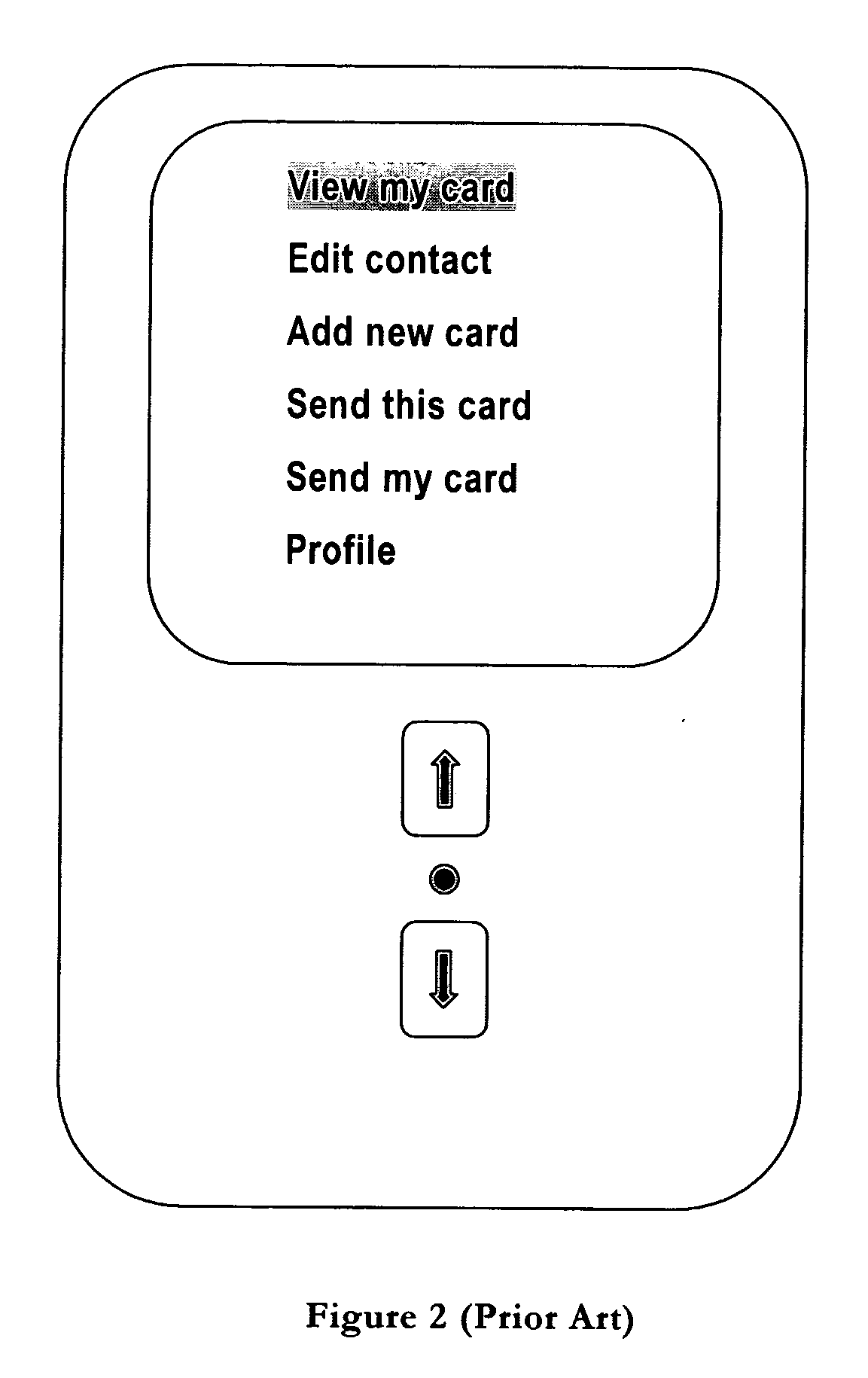
InactiveUS20040053605A1Quickly reachMinimal effortAutomatic exchangesTelephone set constructionsHuman–computer interactionMobile phone
A computing device such as a mobile telephone in which the most common menu item is placed, not at the top of the list, but instead in the middle. This makes it faster to reach with many conventional navigation tools.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Method and device for controlling player character dialog in a video game located on a computer-readable storage medium
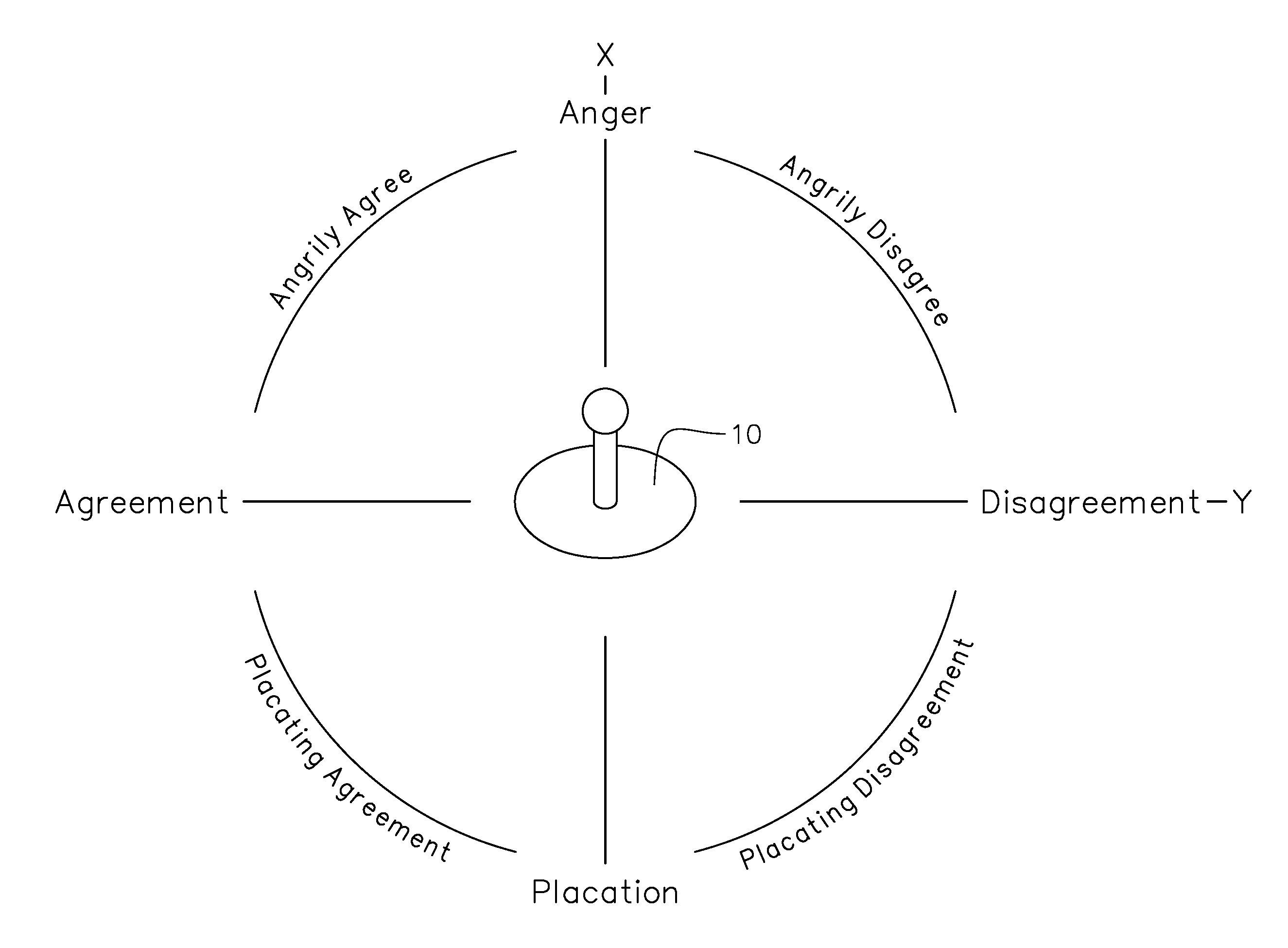
ActiveUS20100267450A1Easy to makeExcessive activityVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsGame playerDisplay device
In a computing machine having a processing unit, memory and a display device for playing a video game, the video game comprising at least one or more game characters, the at least one or more game character being controlled by a special purpose computing input device connected to said computer and operable by a game player, the video game further comprising character dialog between or among the at least one or more game characters, the character dialog comprising vignettes of dialog wherein movement from one vignette to another is determined by the game player introducing emotion into the dialog by means of the special purpose computing input device. The special purpose computing input device introduces emotion into the video game during a character dialog or character encounter along an axis of a joystick or other game controller element.
Owner:MCMAIN MICHAEL PARKER
Physiologic stimulation for stroke treatment
InactiveUS20100004709A1Restore blood flowIncrease arterial blood flowElectrotherapyDiagnosticsStroke treatmentMedicine
Owner:MISCHE HANS ALOIS
Hydraulic detent for a variable camshaft timing device
InactiveUS6666181B2Quickly reachImprove vibrationValve arrangementsOscillating piston enginesDetentEngineering
A phaser which includes a housing and a rotor disposed to rotate relative to each other is provided. The housing has at least one cavity disposed to be divided by a vane rigidly attached to the rotor. The vane divides the cavity into a first chamber and a second chamber. The phaser further includes passages connecting the first and the second chamber, thereby facilitating the oscillation of the vane within the cavity. The phaser includes: a) a valve disposed to form at least two openings for fluid flowing between the first chamber and the second chamber and being disposed to keep at least one opening closed; and b) at least one by-pass disposed to stop or slow down the rotation between the housing and the rotor, thereby allowing a locking mechanism to lock the housing and the rotor together independent of fluid flow.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Process for regulating the exposure time of a light sensor
InactiveUS7053954B1Avoid adjustmentOptimal exposure timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAlgorithmEngineering
This invention relates to a process for regulating the exposure time of a light sensor, characterized in that it comprises the following steps:a) setting the exposure time of the sensor to a value selected in a first range of M prefixed values defined between a minimum and a maximum value;b) acquiring an image of an object on the sensor, such image comprising a plurality of luminous pixels;c) analyzing the acquired image in order to detect its level of luminosity;d) comparing the detected level of luminosity with a prefixed higher (lower) global threshold level representative of a condition of overexposure (under-exposure) of the image;e) varying the exposure time of the sensor and iteratively repeating the previous steps until an optimum exposure time equal to the highest (lowest) exposure time is found, amongst the ones set, for which the image presents a level of luminosity which is smaller (greater) than the prefixed higher (lower) global threshold level.
Owner:DATALOGIC
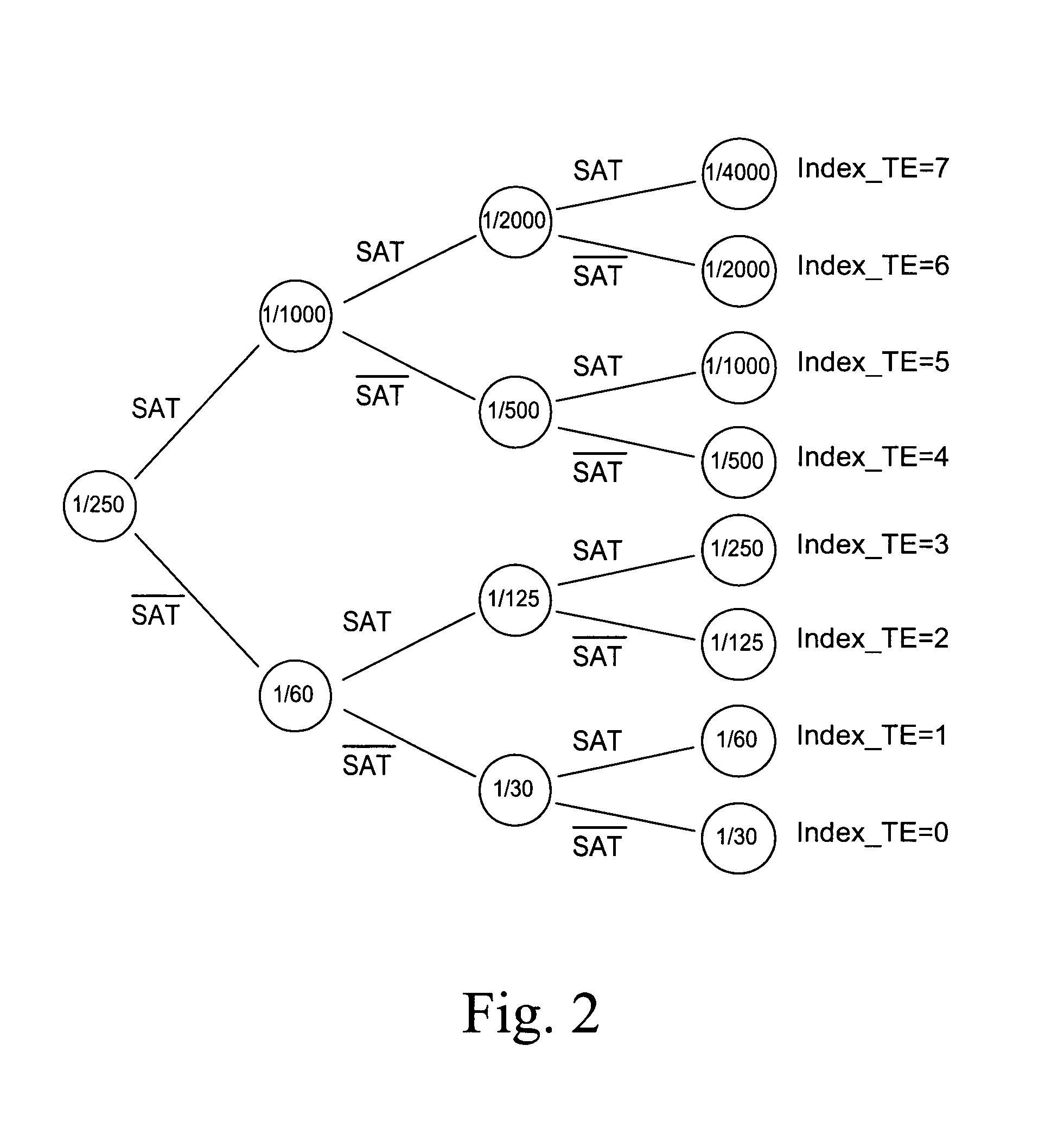
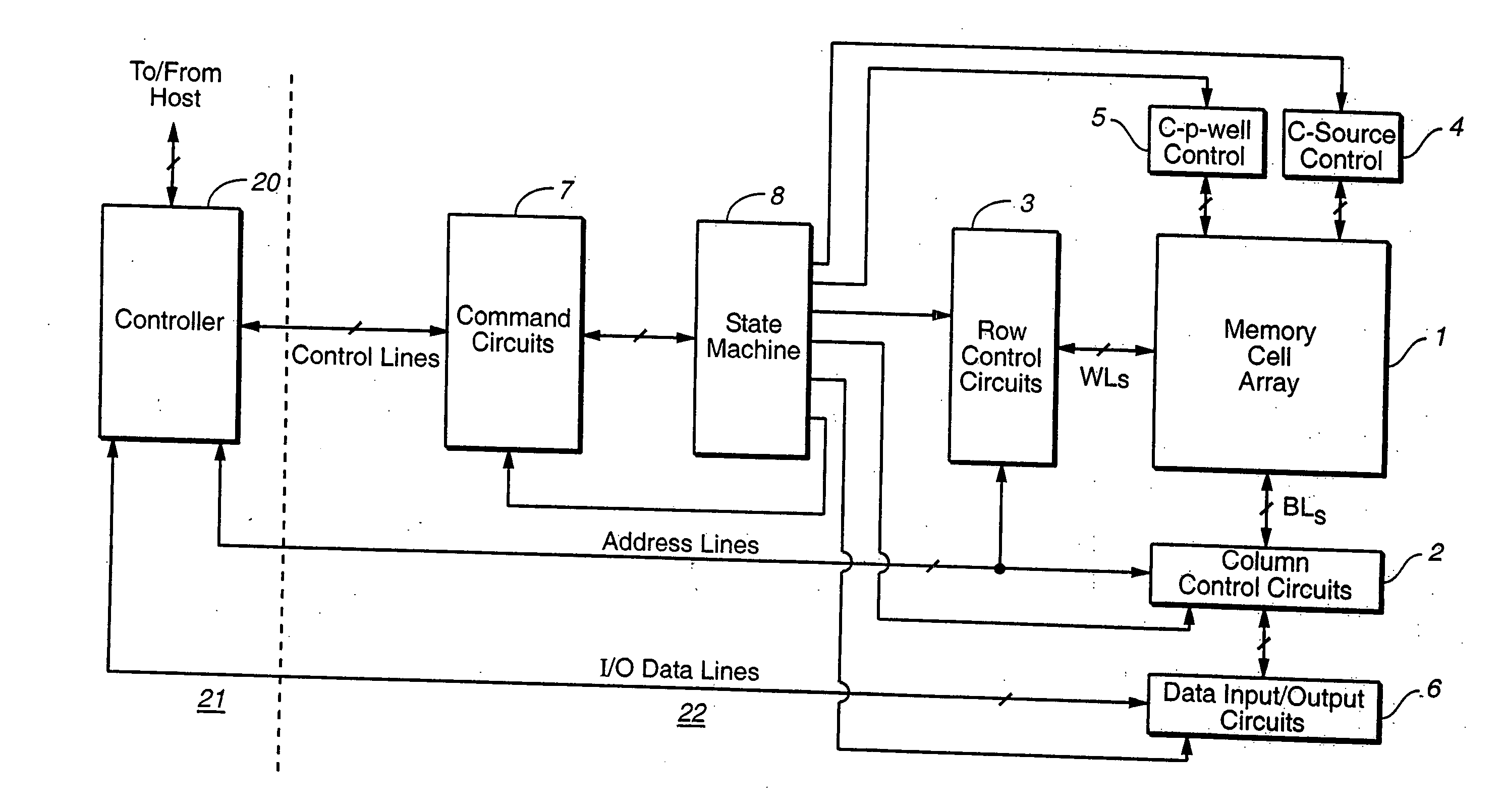
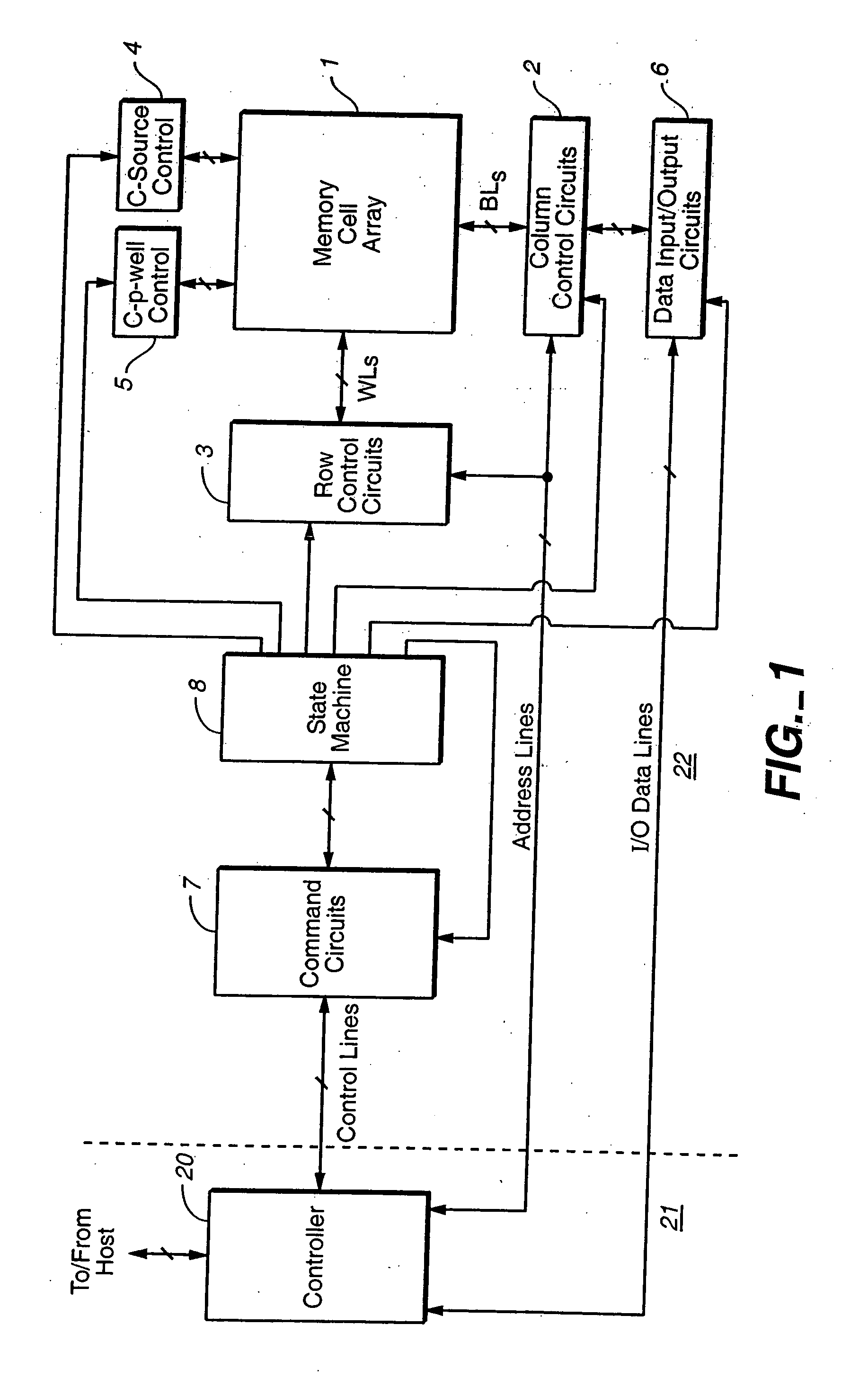
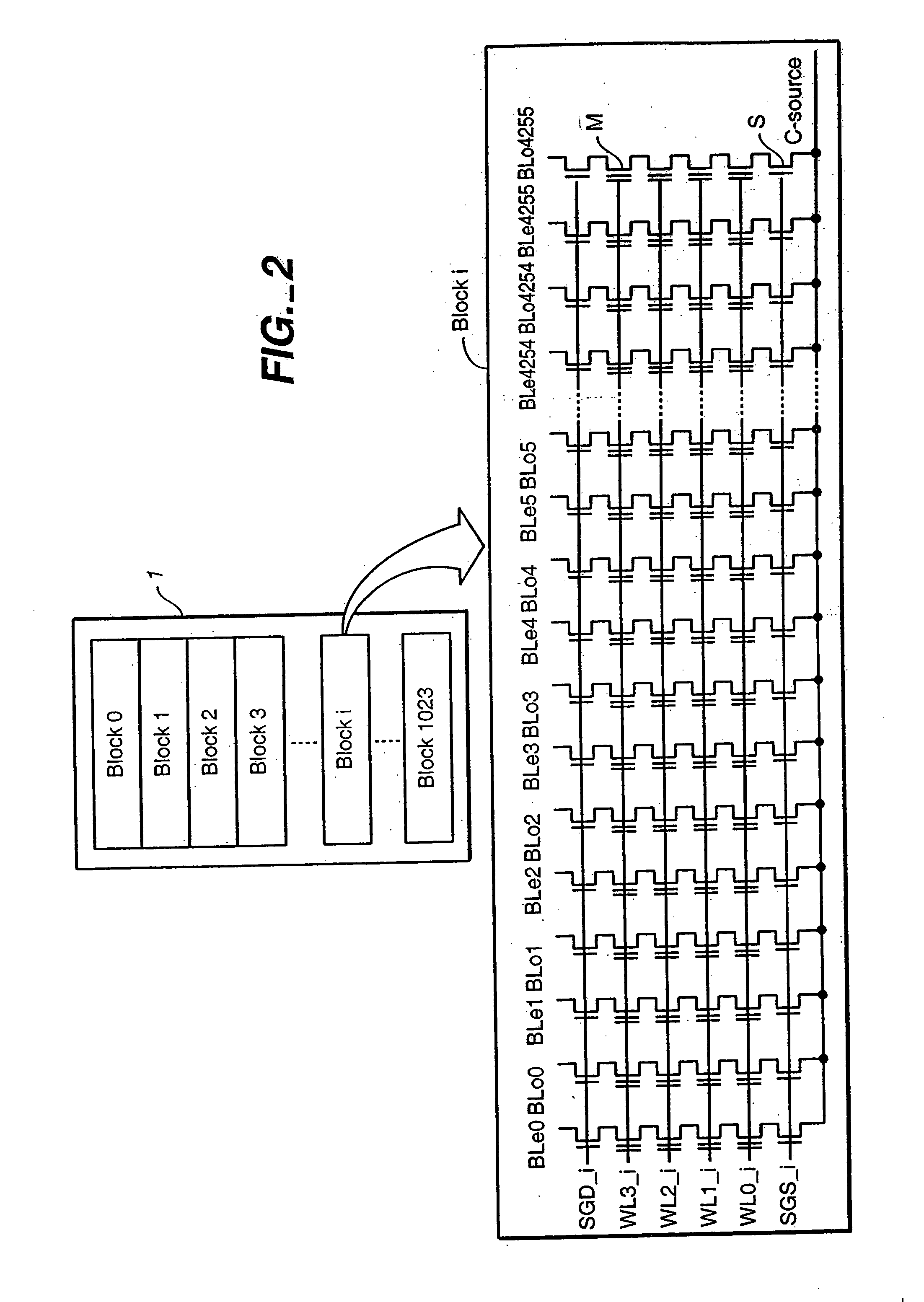
Operating techniques for reducing effects of coupling between storage elements of a non-volatile memory operated in multiple data states
InactiveUS20050276101A1Compensation effectAccurate readingTransistorSolid-state devicesProgrammable read-only memoryComputer science
Owner:TOSHIBA MEMORY CORP +1
Remote-controlled mobile warning sign
InactiveUS20150073623A1Expand effective visible distanceSufficient distancePortable emergency signal deviceDigital data processing detailsControl signalControl engineering
A remote-controlled mobile triangle sign includes a triangle sign having at least one surface with a reflective area; a remote controller configured to transmit control signals; and a remote-controlled car. The remote-controlled car includes a power supply module; a drive motor powered by the power supply module; and a remote control receiving and execution module for receiving the control signals. The triangle sign is mounted on top of the remote-controlled car, and the remote control receiving and execution module is electrically connected to the drive motor and provides output signals.
Owner:ZHUHAI REANDA INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
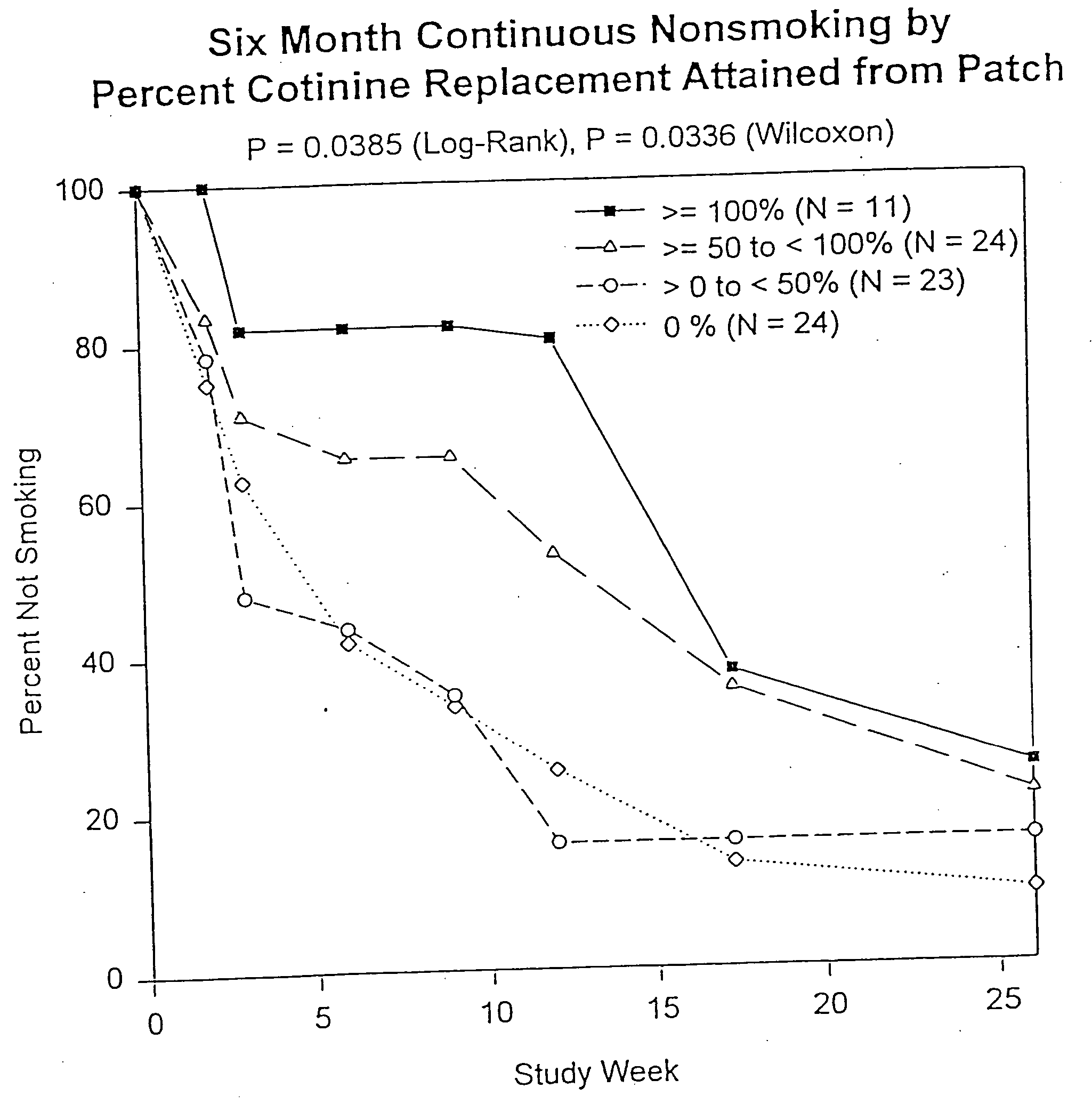
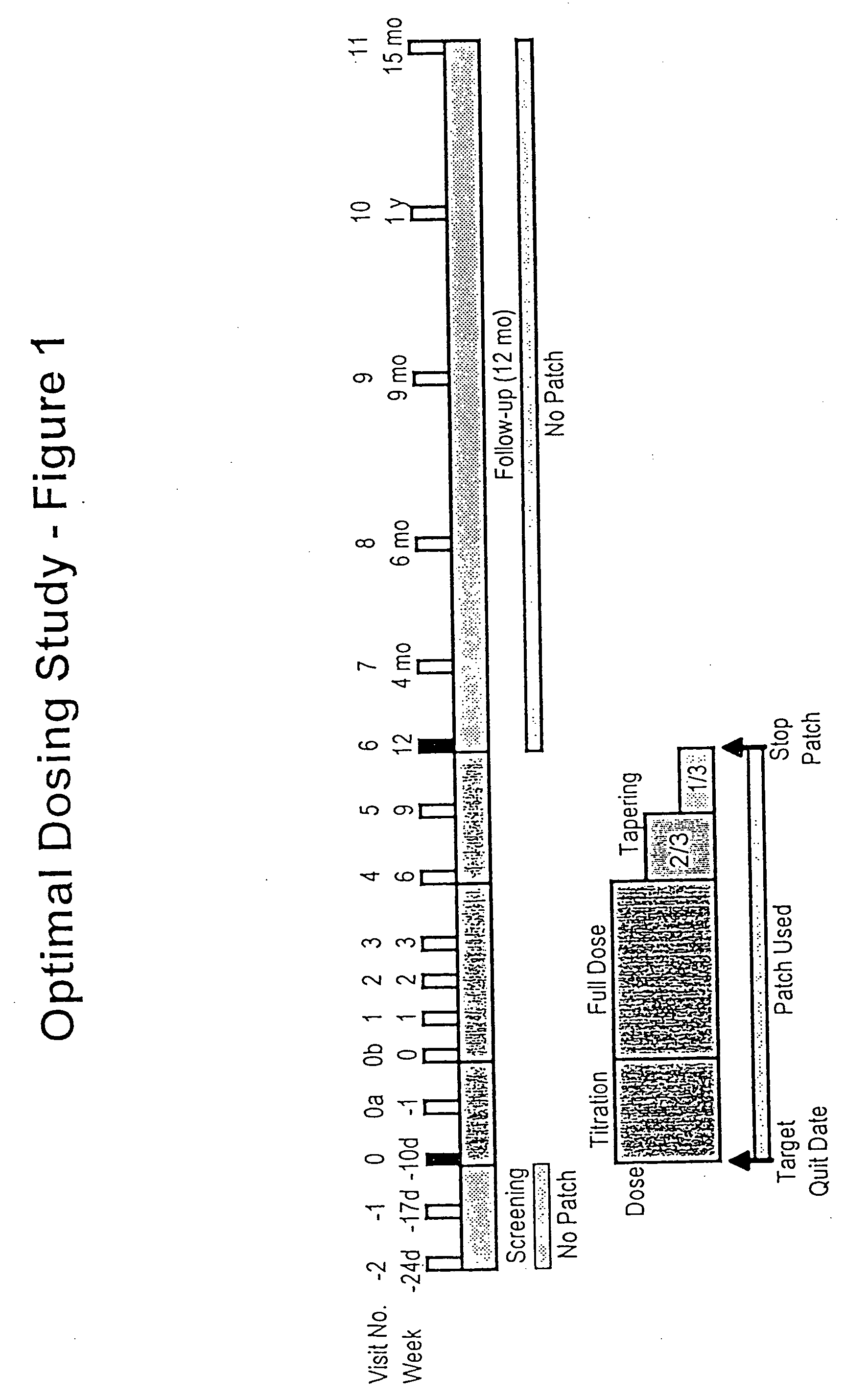
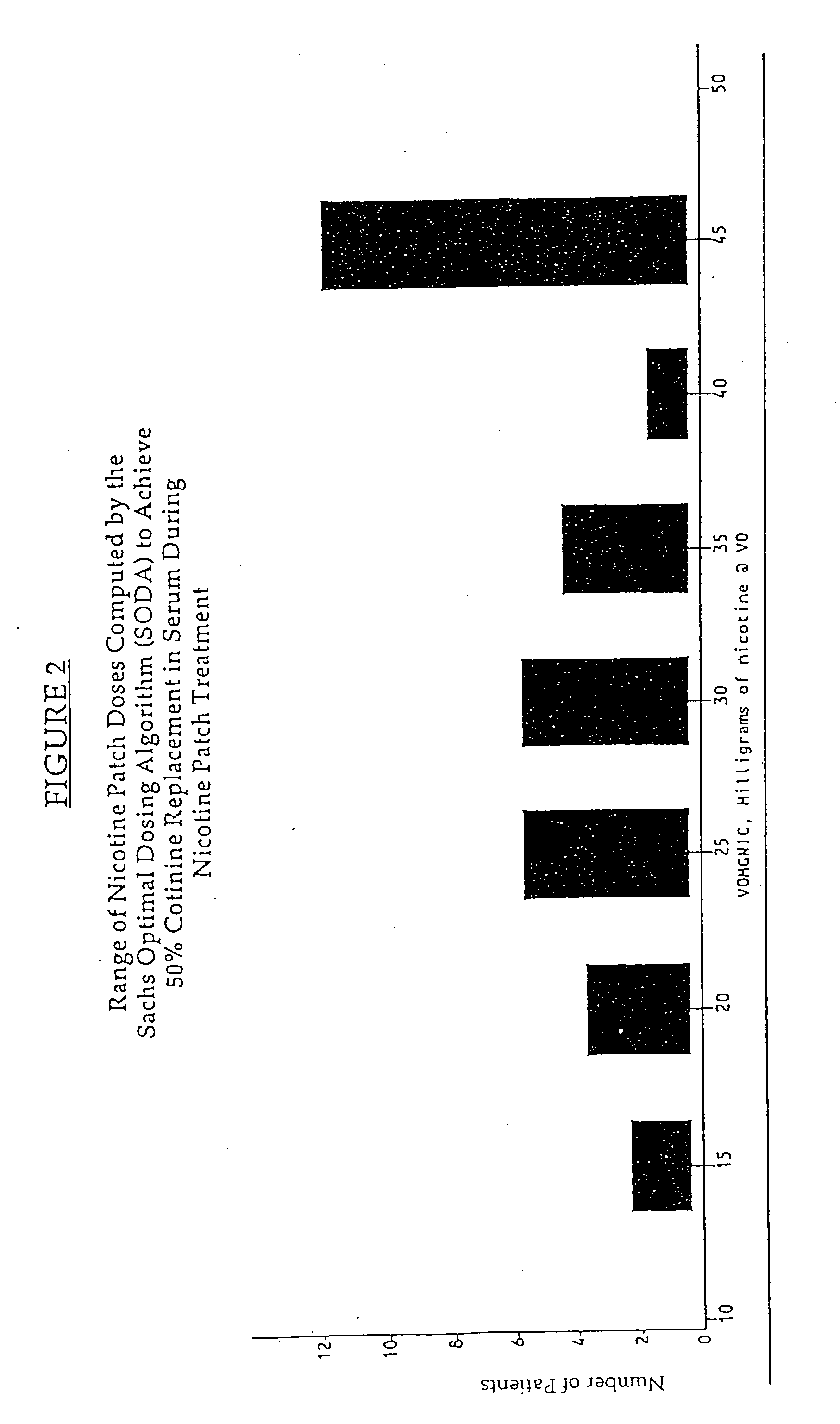
Methods for nicotine replacement dosage determination
InactiveUS20040006113A1Increased riskQuickly reachCompounds screening/testingBiocideNicotine replacementsSerum concentration
Owner:SACHS DAVID P L
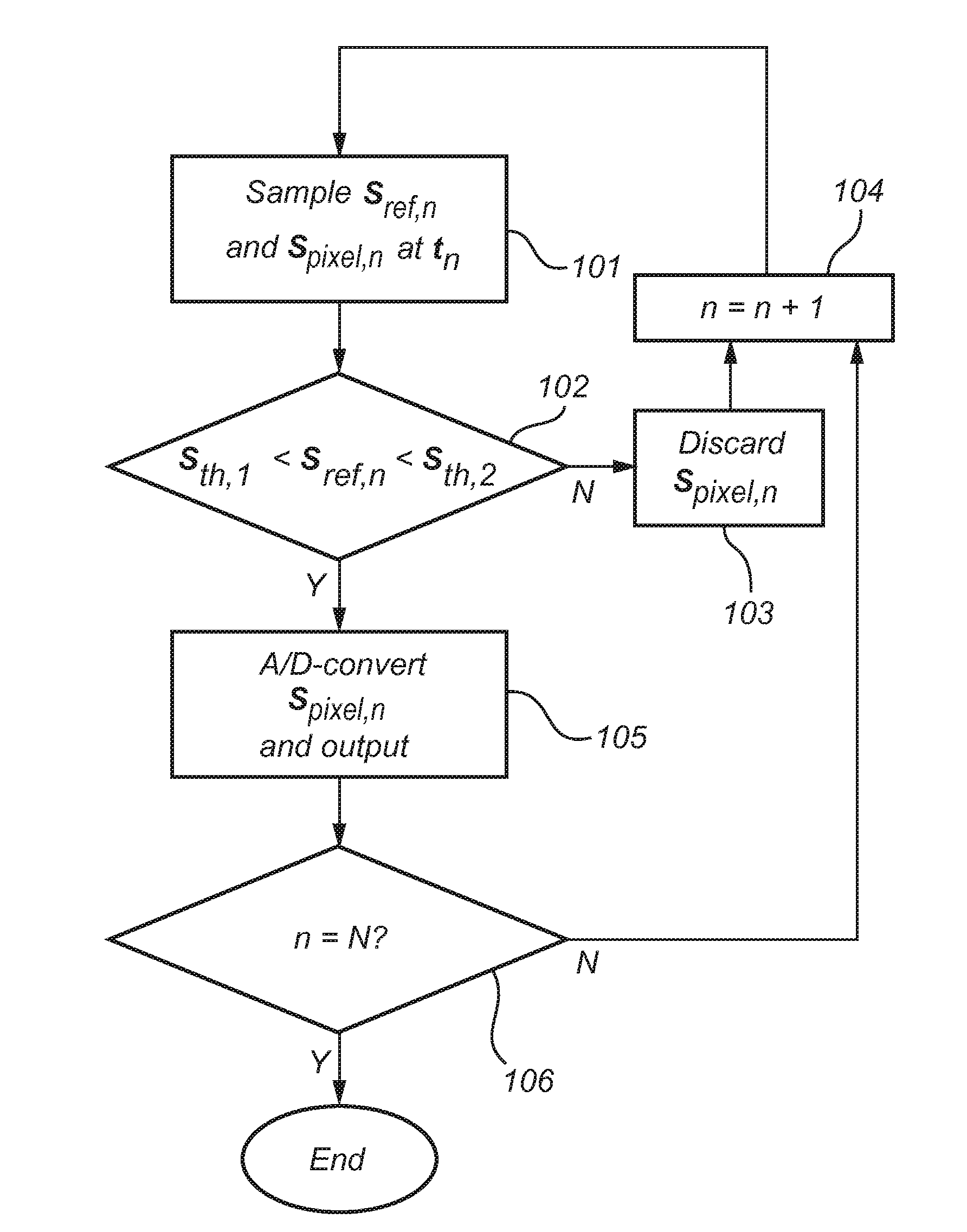
Fingerprint sensing system and method
ActiveUS20150169932A1Improved sensing of fingerprintsImprove overall senseColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsCapacitanceSignal quality
The present invention relates to a method of determining a representation of a fingerprint pattern. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a reference signal indicative of an electric coupling between a hand surface having friction ridges and a reference sensing structure extending across a plurality of the friction ridges; and determining the representation of the fingerprint pattern based on the reference signal and a capacitive coupling between the finger and each of a plurality of sensing elements. The acquired reference signal can, for example, be used for controlling the sensing elements so that the sensing performed by the sensing elements is carried out using favorable timing, when the signal quality is good. Alternatively, or in combination, the acquired reference signal may be used for post-processing, whereby the signals / signal values obtained by the sensing elements are modified depending on the corresponding values of the reference signal.
Owner:FINGERPRINT CARDS ANACATUM IP AB
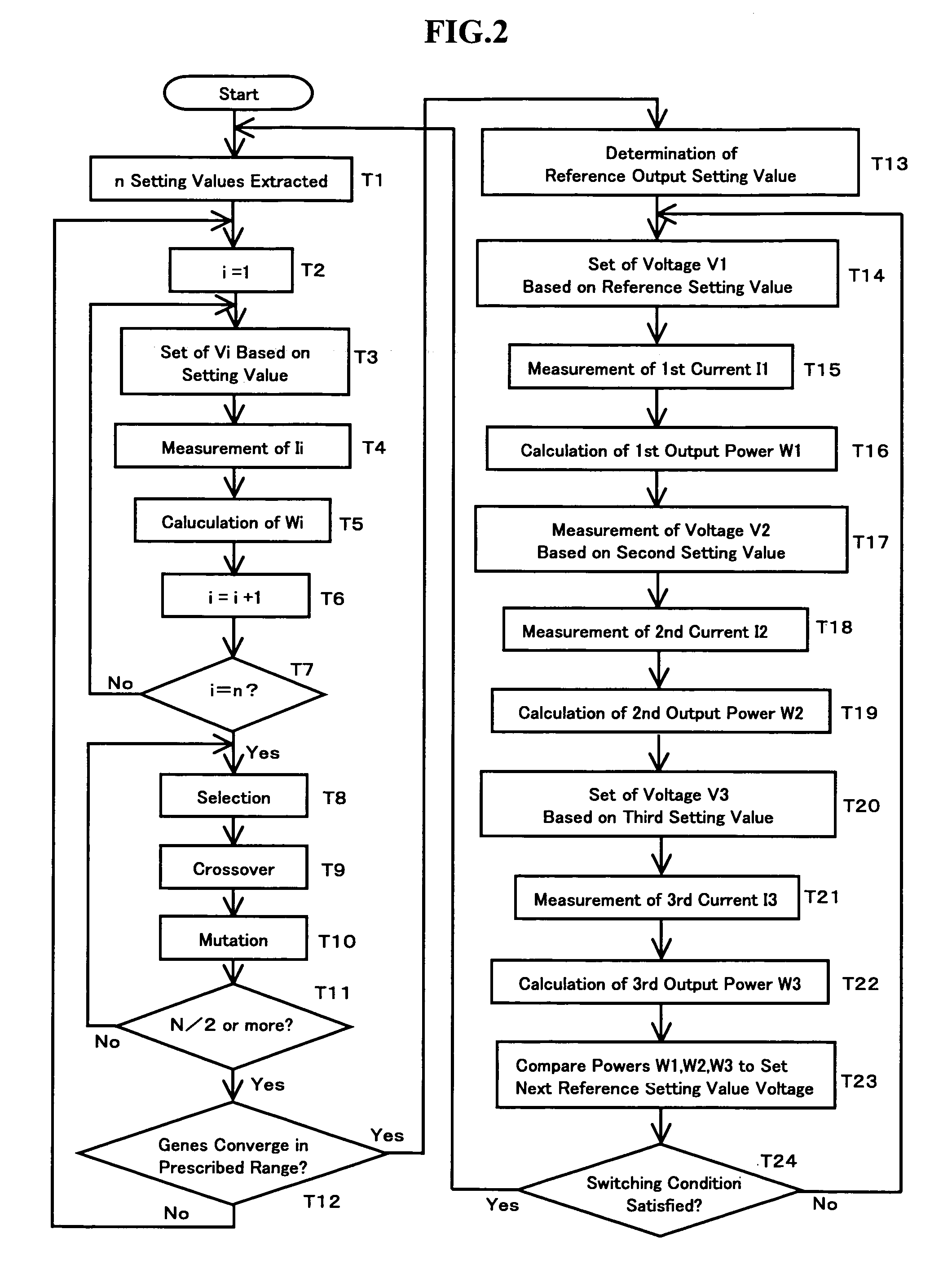
Method of controlling photovoltaic power generation system
ActiveUS20060055366A1Work efficiency be increaseImprove convergence speedBatteries circuit arrangementsPhotovoltaic monitoringEngineeringVoltage
A conventional hill climbing method is not capable of tracking a maximum power when a shadow covers a part of a solar cell panel and a plurality of maximal values is thereby developed. The invention provides a photovoltaic power generation system control method that controls a photovoltaic output setting value to be an appropriate value by following up a variation in the solar irradiation, including a genetic algorithm process of employing the photovoltaic output setting value as a gene and the output power as an evaluation value thereof; randomly extracting a plurality of genes and repeating storage, selection and crossover / mutation of the output powers which are the evaluation values of the genes, so as to converge a difference between a maximum and minimum values of the output voltages into a predetermined range; and a hill climbing process of setting the photovoltaic output setting value corresponding to the greatest value of the converged output voltages, and a greater and a lower value than the photovoltaic output setting value by a predetermined amount, so as to select the greatest output power among these values; and repeating such steps to track the maximum output power.
Owner:DAIHEN CORP
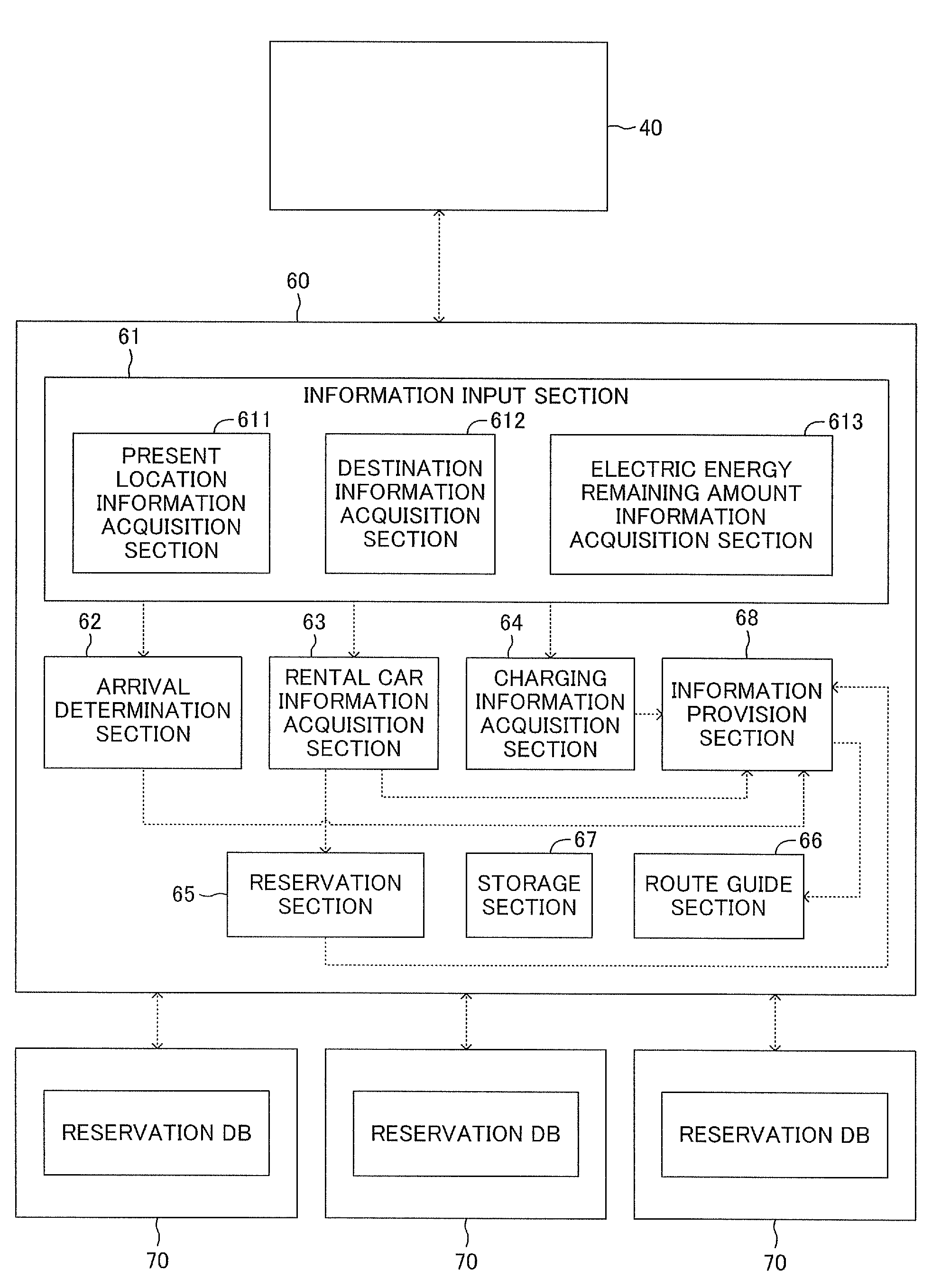
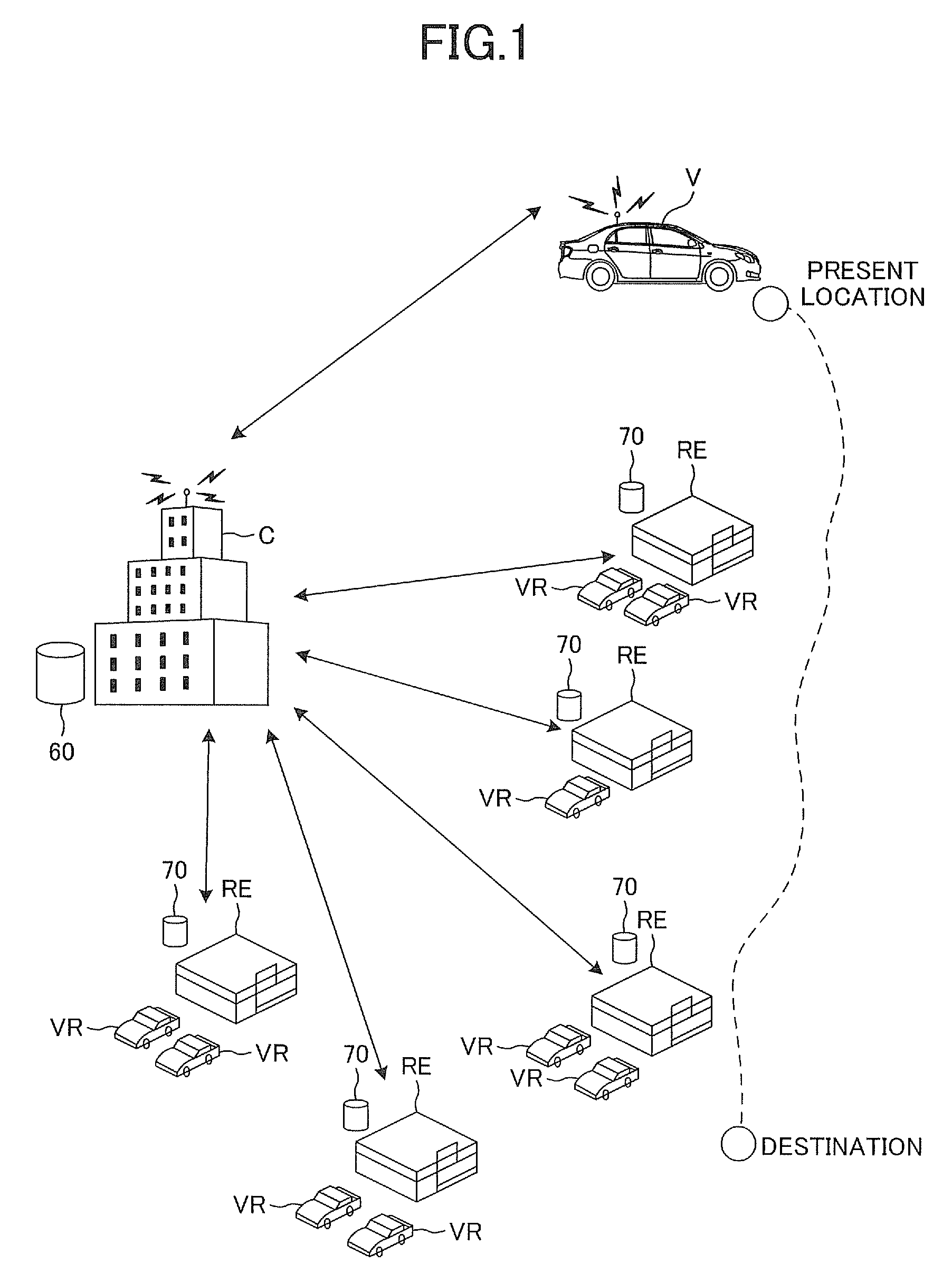
Information provision apparatus
ActiveUS20120271547A1Quickly reachInformation can be usedInstruments for road network navigationCharging stationsElectricityDriver/operator
A main computer includes an arrival determination section which determines, on the basis of present location information of a vehicle, destination information, and electric energy remaining amount information, whether the vehicle can reach the destination from the present location without charging an electricity storage unit of the vehicle, a rental car information acquisition section which acquires information regarding a rental car which the driver can change from the vehicle directly, and an information provision section which provides the rental car information to the driver of the vehicle, when the arrival determination section determines that the vehicle cannot reach the destination from the present location. On the basis of the rental car information, the driver of the vehicle can go to a rental car shop and rent a car. By changing from the vehicle to the rental car, the driver can quickly reach the destination by use of the rental car.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
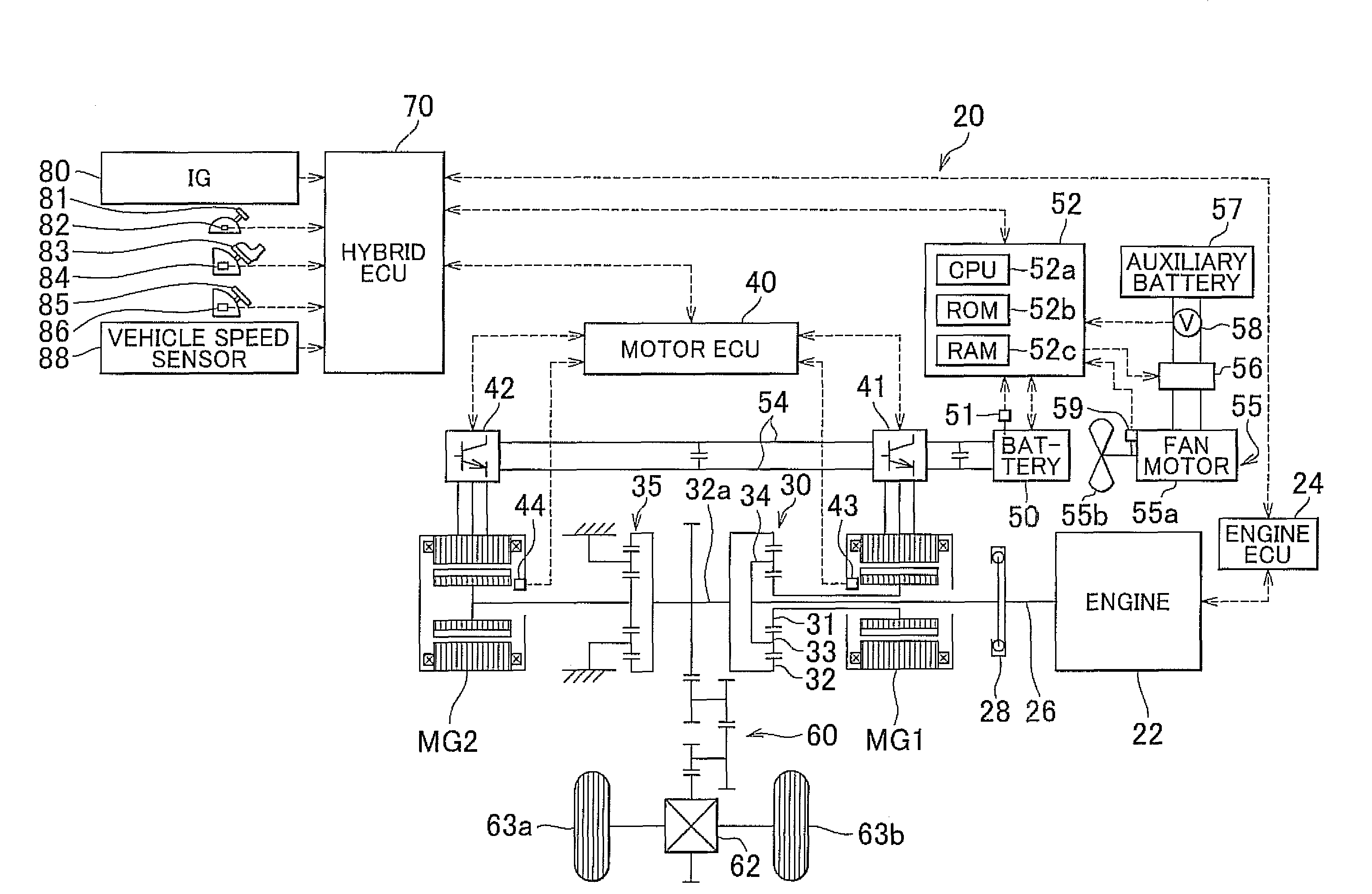
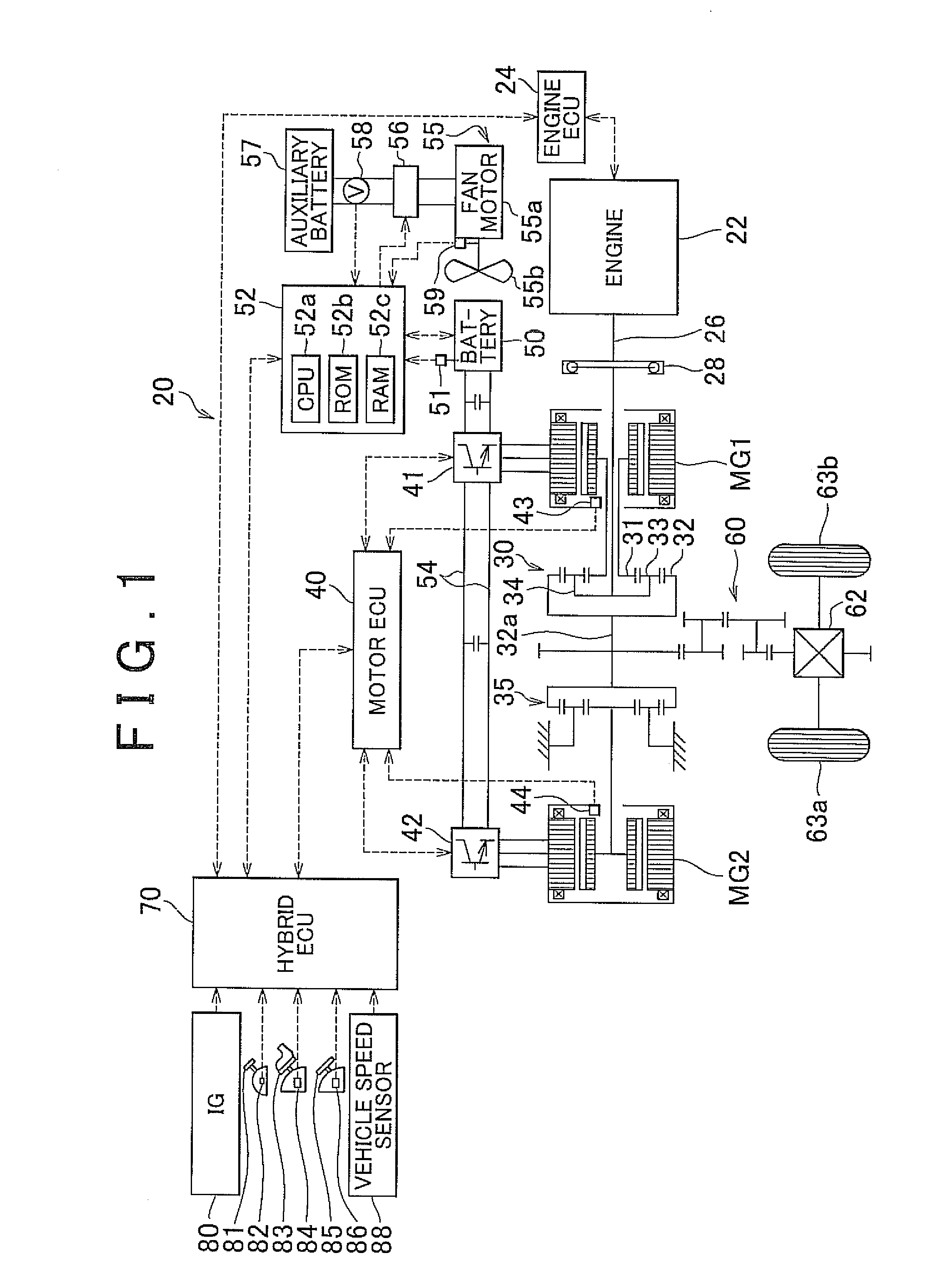
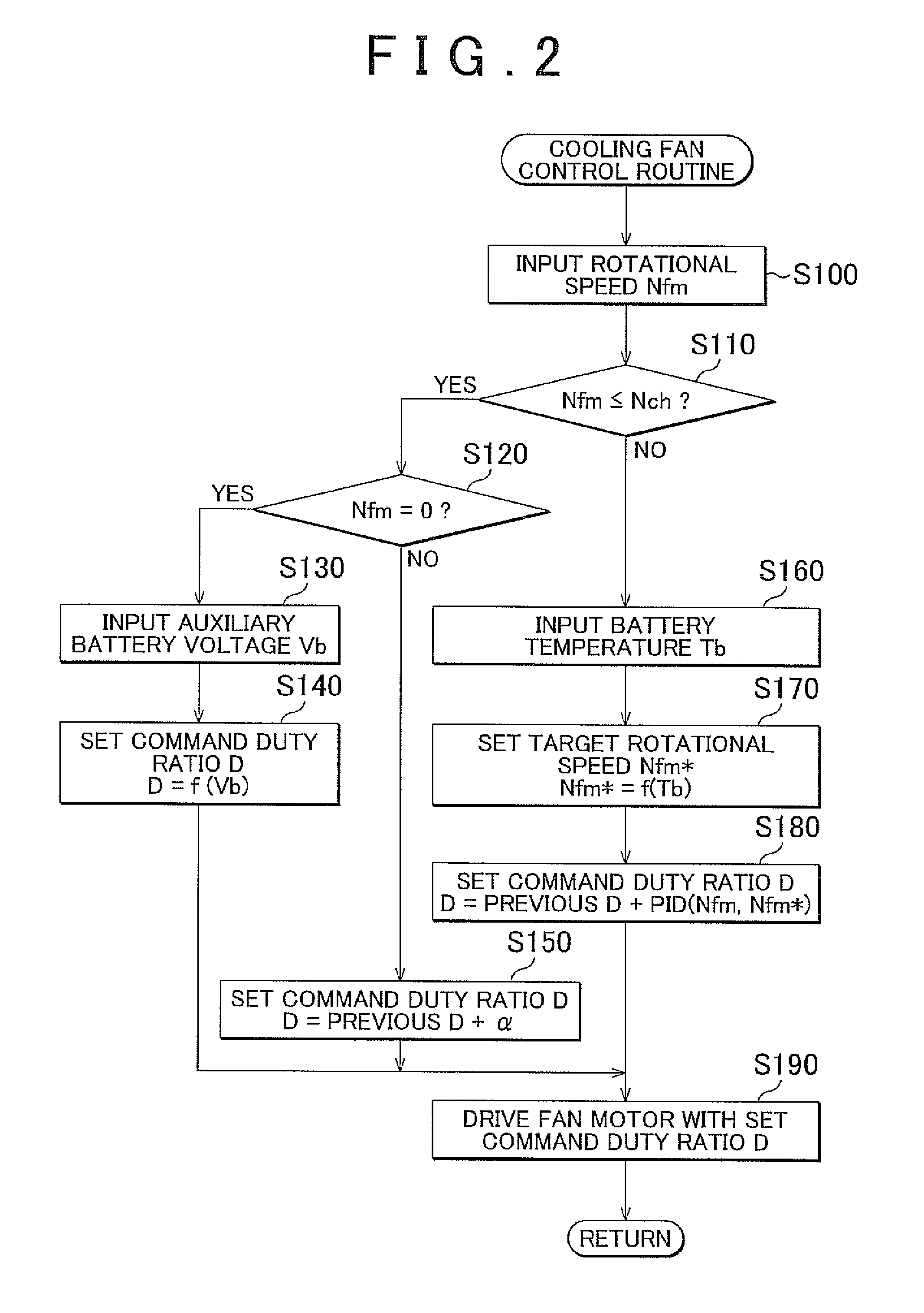
Cooling system, vehicle equipped with the cooling system, and method for controlling the cooling system
ActiveUS20100155162A1Reliably activatedAvoids excessive operating noiseHybrid vehiclesAC motor controlEngineeringControl switch
A fan motor is controlled via a switching circuit from the moment when a cooling fan control routine is started until the moment when the rotational speed of the fan motor reaches a control-switching speed so that the higher the detected auxiliary battery voltage is when the cooling fan control is started, the lower the command duty ratio that is set. Accordingly, it is possible to activate the fan motor more reliably and to avoid generating excessive operating noise by the cooling fan when the fan motor is activated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
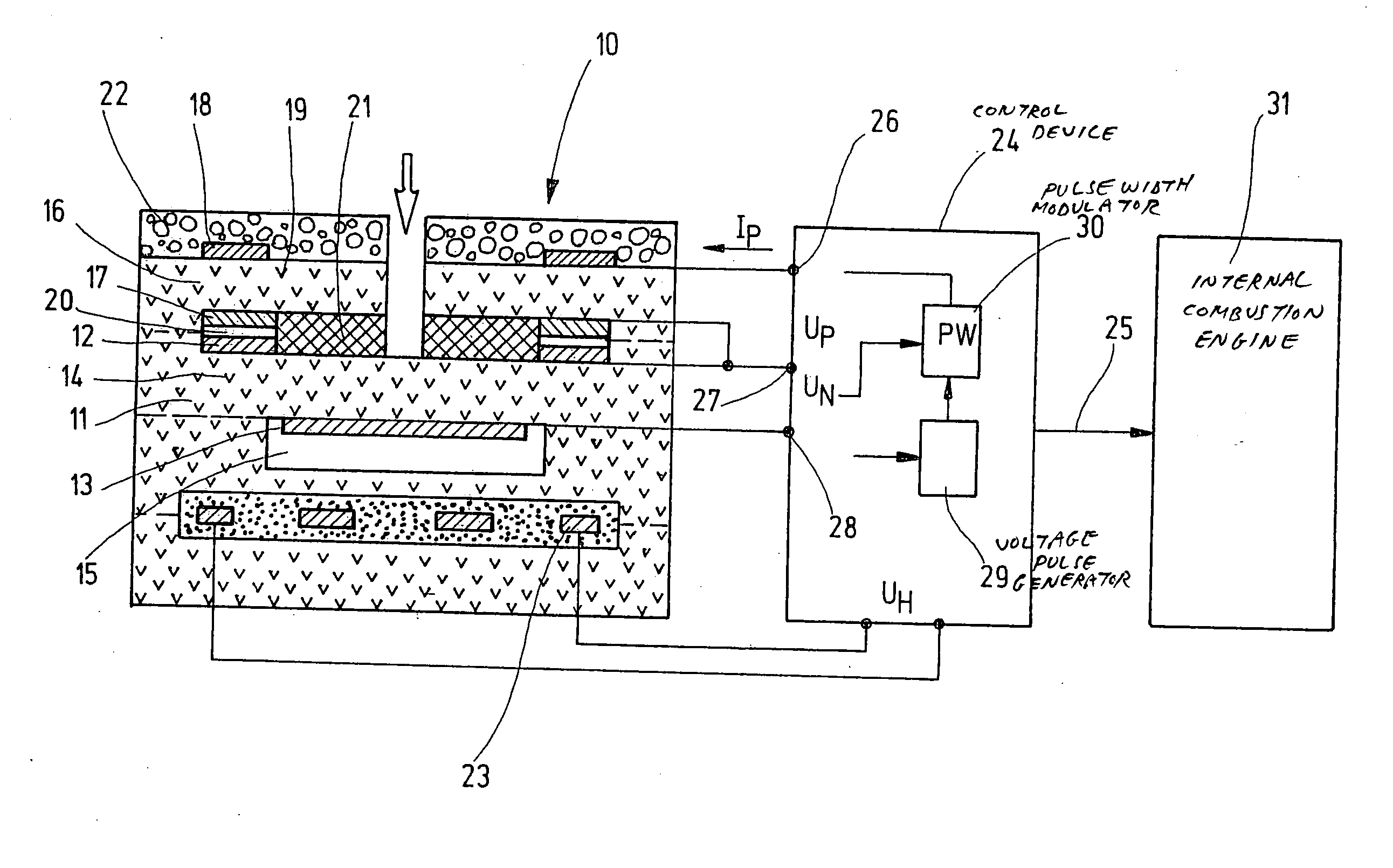
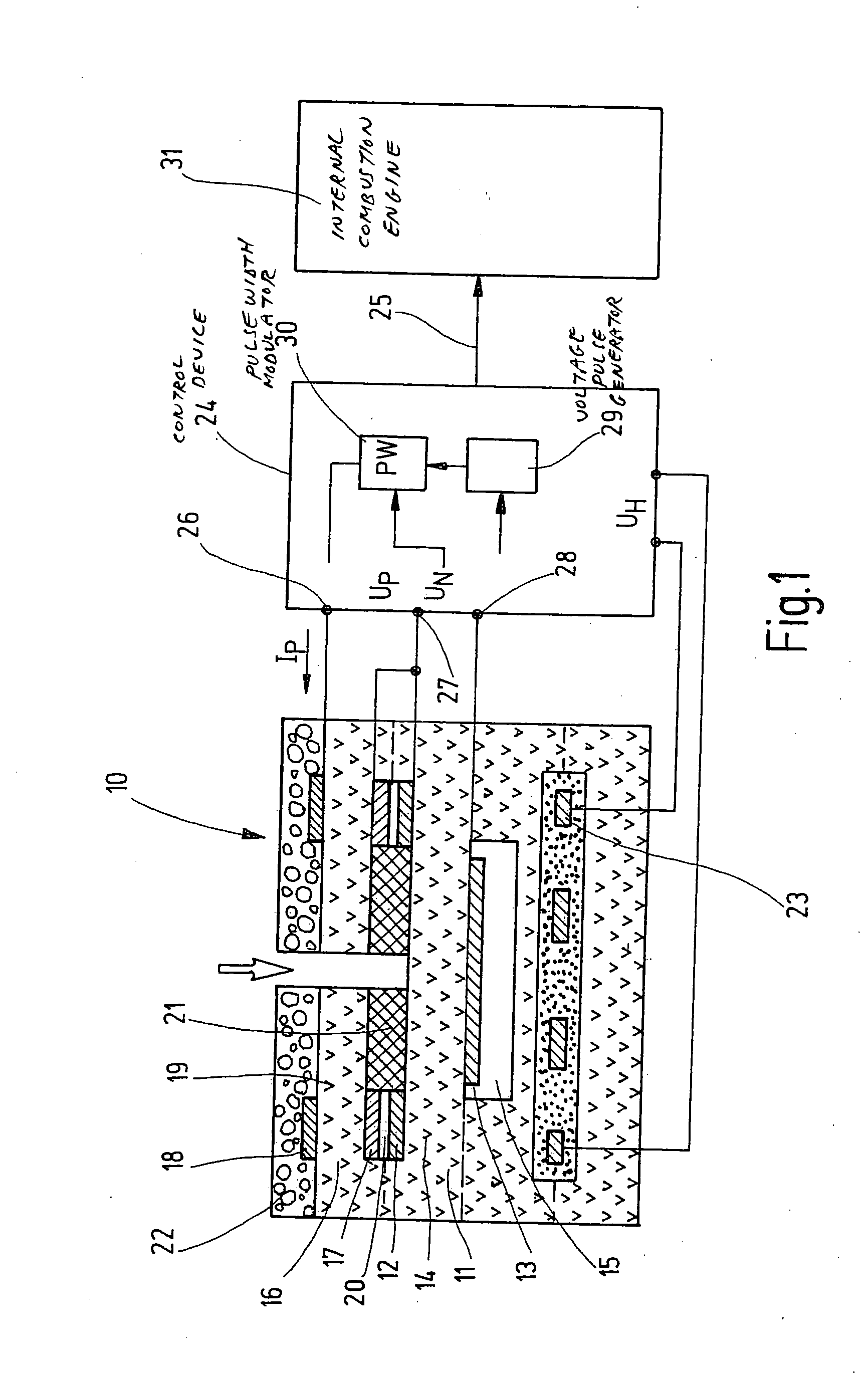
Method for operating a broadband lambda probe
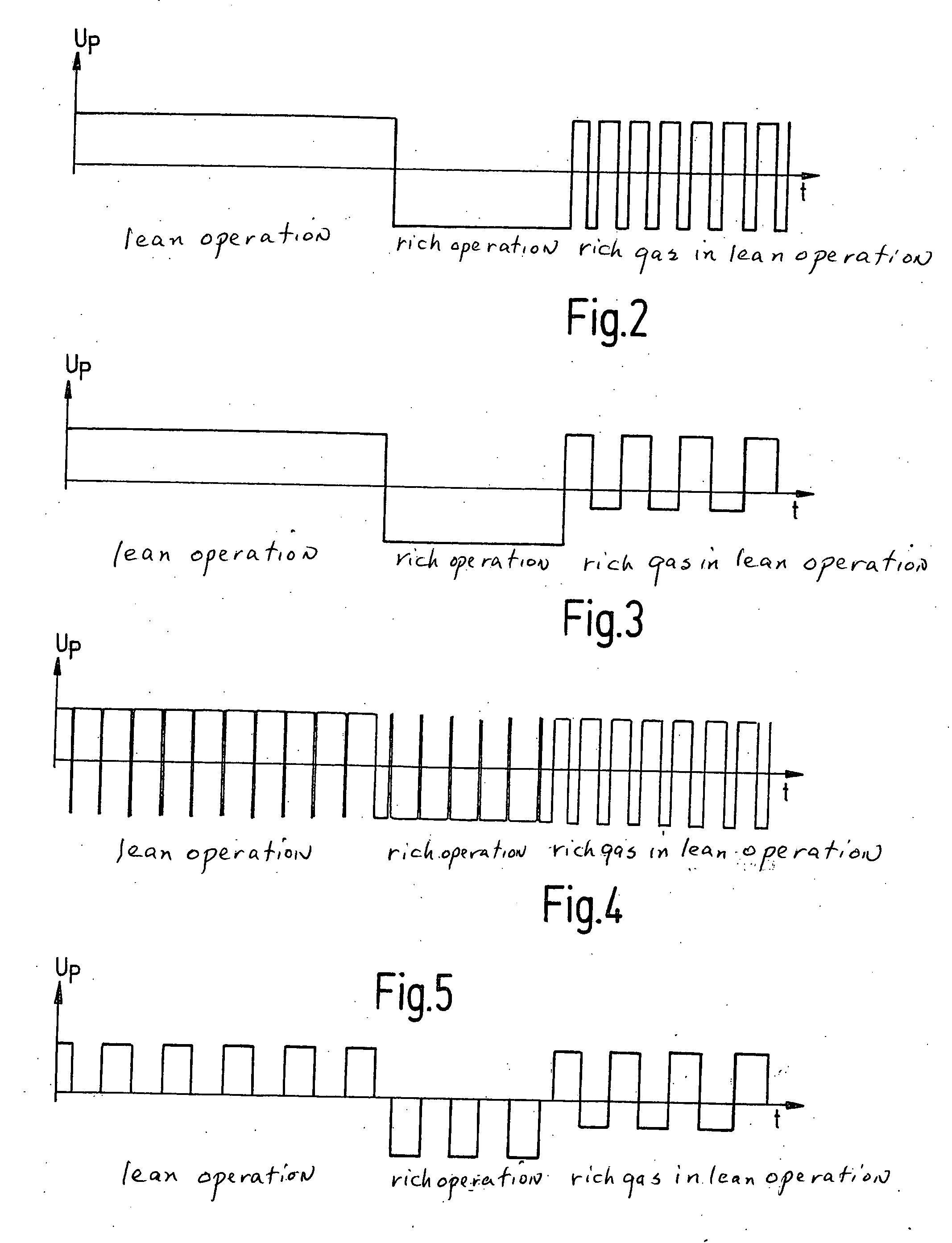
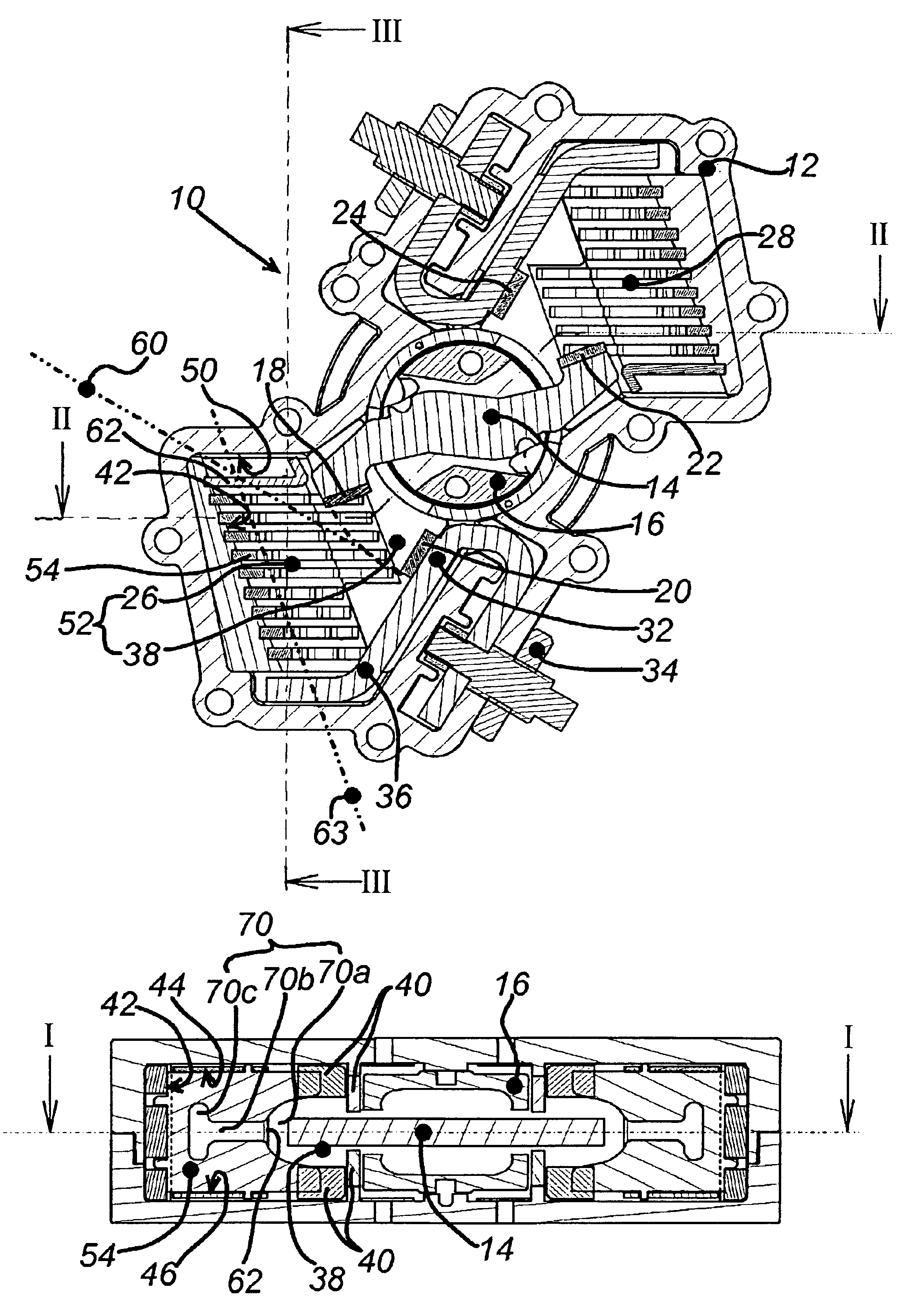
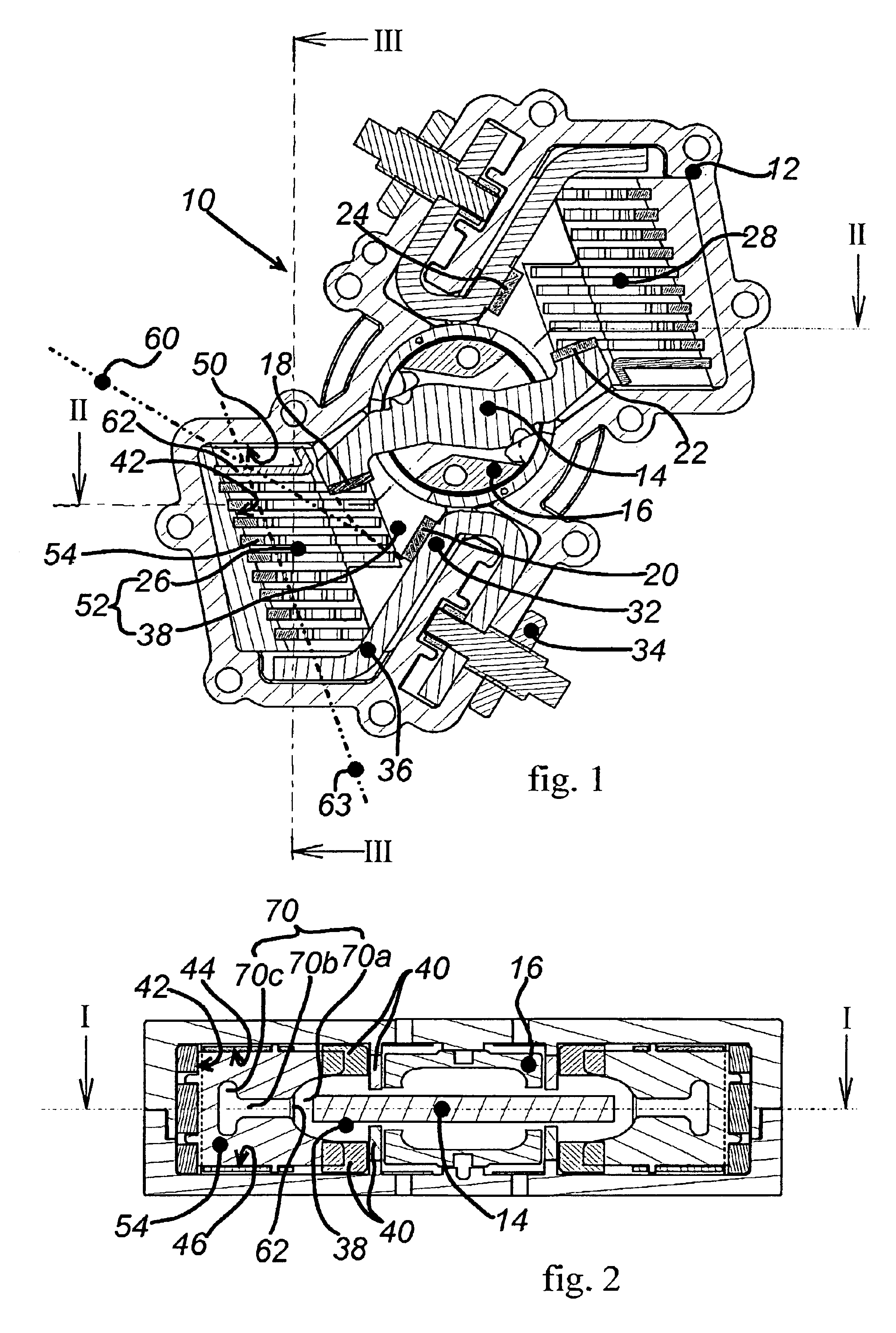
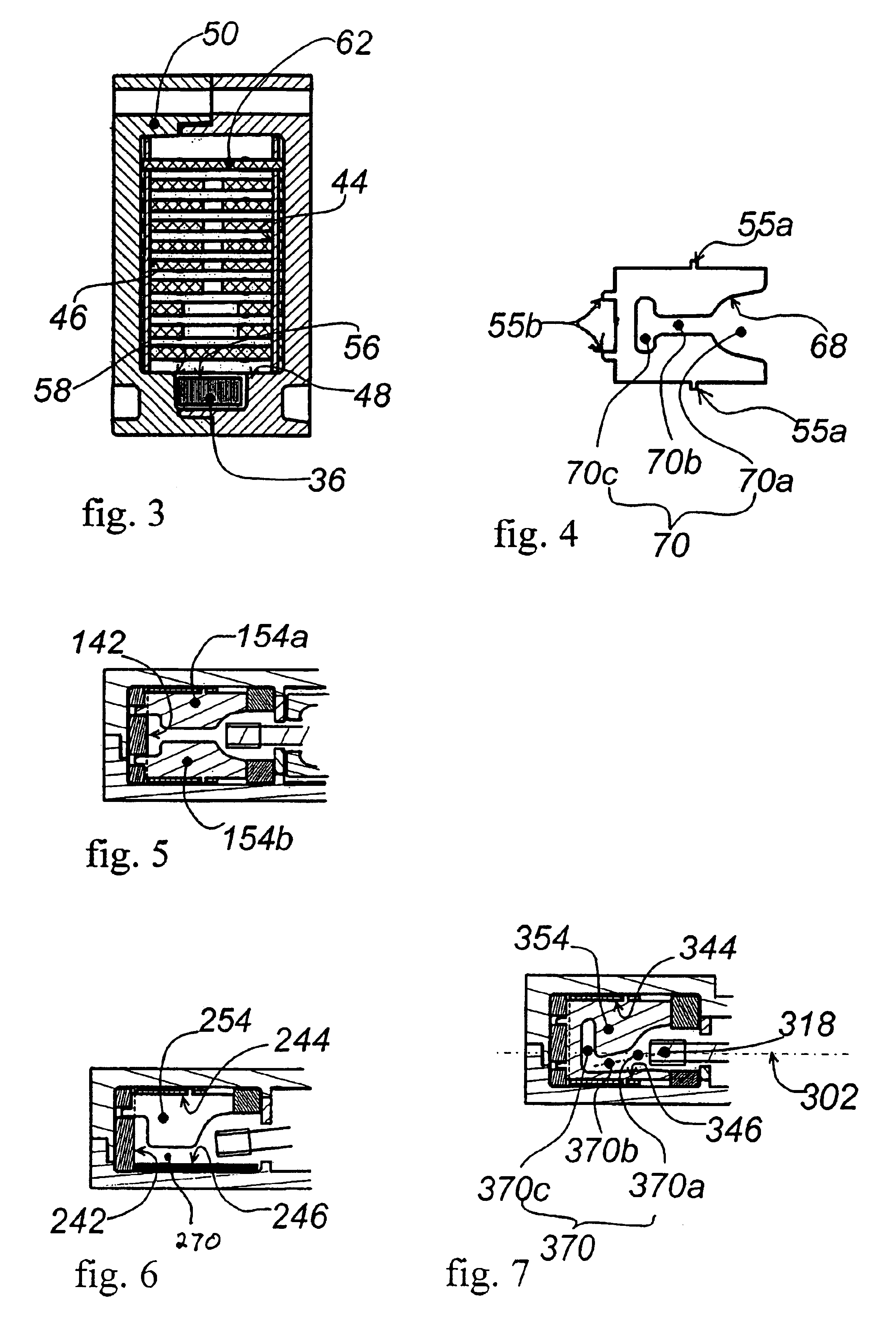
InactiveUS20050252771A1Simplify hardware designSimplify software designMaterial electrochemical variablesHydrocotyle bowlesioidesOxygen ions
A method for operating a broadband lambda sensor for determining the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust gas of an internal combustion engine operated with a fuel-air mixture is provided. In this method, a pump voltage (UP) is applied to the pump cell of the sensor, this voltage-being set dependent on a Nernst voltage (UN) tapped at the Nernst cell, and, dependent on the oxygen content of the exhaust gas, driving a cathodic or anodic pump current IP via the pump cell. In order to maintain the measurement sensitivity of the sensor even during secondary fuel injection in lean operation and / or in “fast light off” operation, the polarity of the pump voltage (UP) is repeatedly reversed during the duration of a secondary fuel injection and / or of the “fast light off” operation, so that an anodic pump current briefly arises that pumps oxygen ions into the measurement chamber, occupied by the measurement electrode of the Nernst cell and the inner electrode of the pump cell, in which chamber the oxygen ions oxidize the hydrocarbons.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Electrical switchgear apparatus comprising an arc extinguishing chamber equipped with deionizing fins
InactiveUS6794595B2Good energyStable and fastCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsProtective switchesFree edgeSwitchgear
A circuit breaker comprises a pair of separable contacts arranged in an opening volume. A plurality of flat de-ionization fins are arranged inside an arc extinguishing chamber opening out onto the opening volume. The chamber is bounded by two opposite side walls, a rear wall located away from the opening volume, a bottom wall and a top wall. Each fin has a free attack edge exposed to the arc. The free edges of the fins laterally bound a longitudinal gulley extending in a heightwise direction from the bottom electrode to the top wall, and longitudinally from a first longitudinal end opening out onto the opening volume at a second longitudinal end tapering to form a stack near to the rear wall, passing via a narrow intermediate portion. A bottom longitudinal electrode partially covers the bottom wall and extends longitudinally facing the gulley at least from the second contact up to the stack.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IND SAS
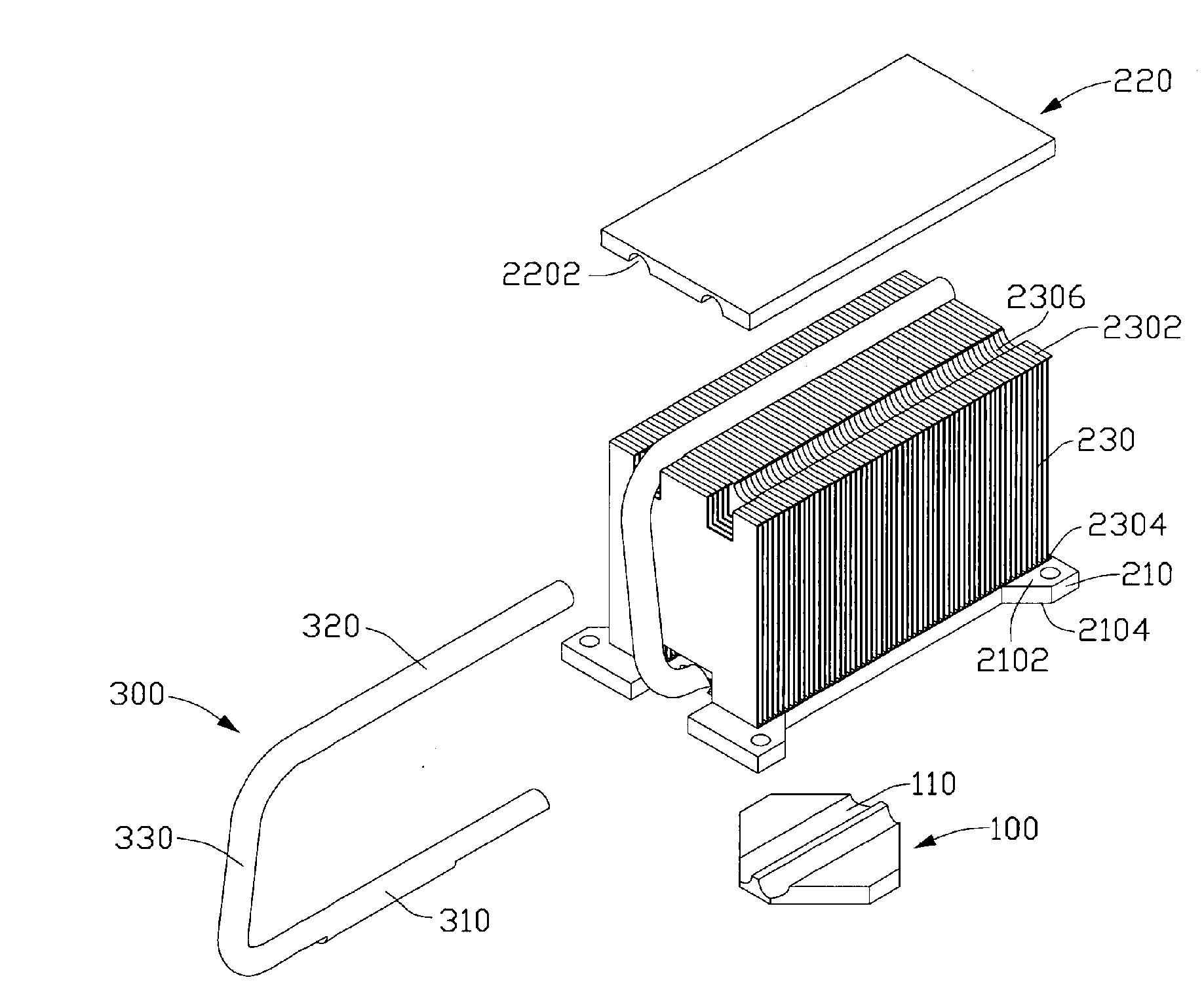
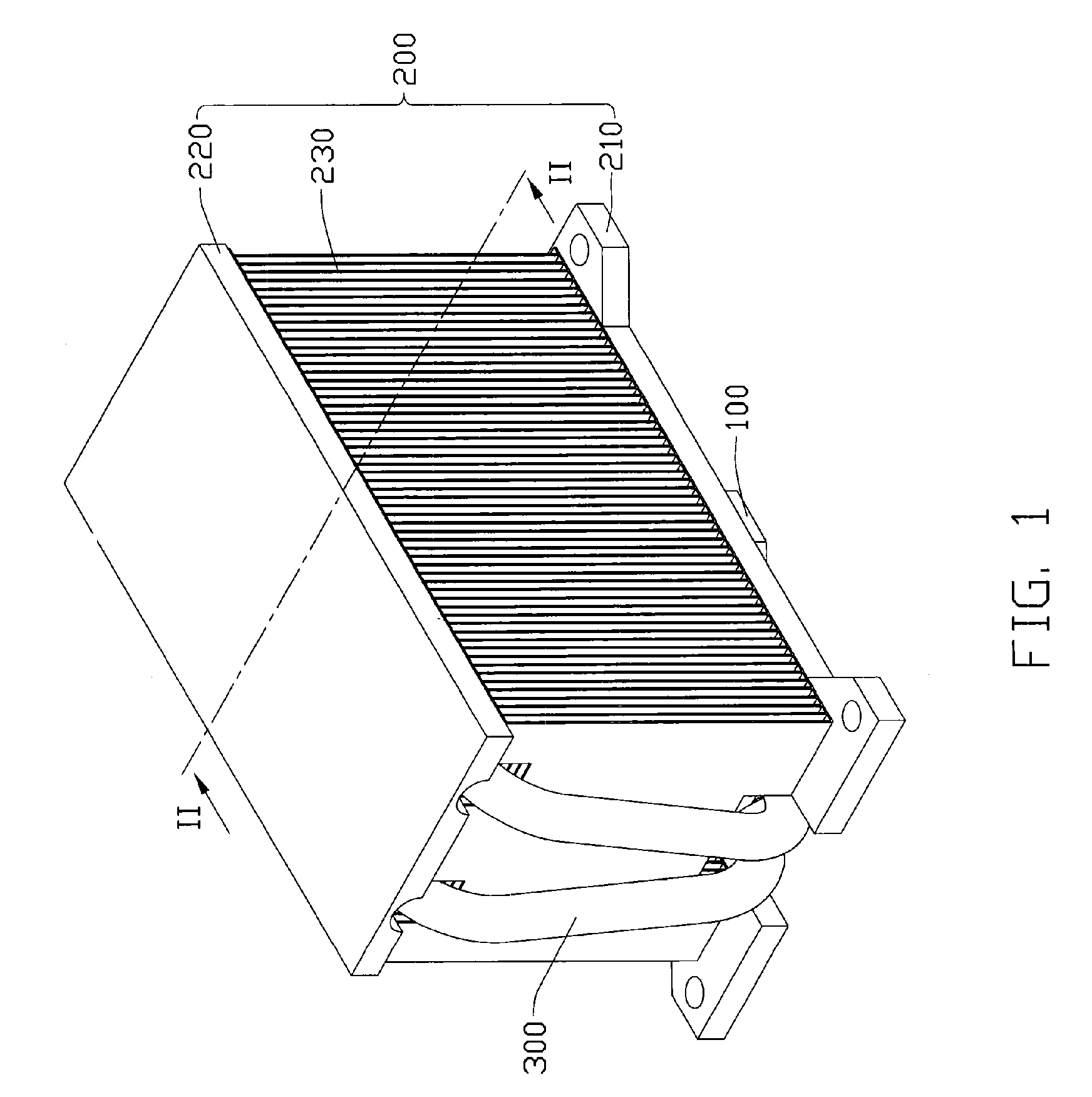
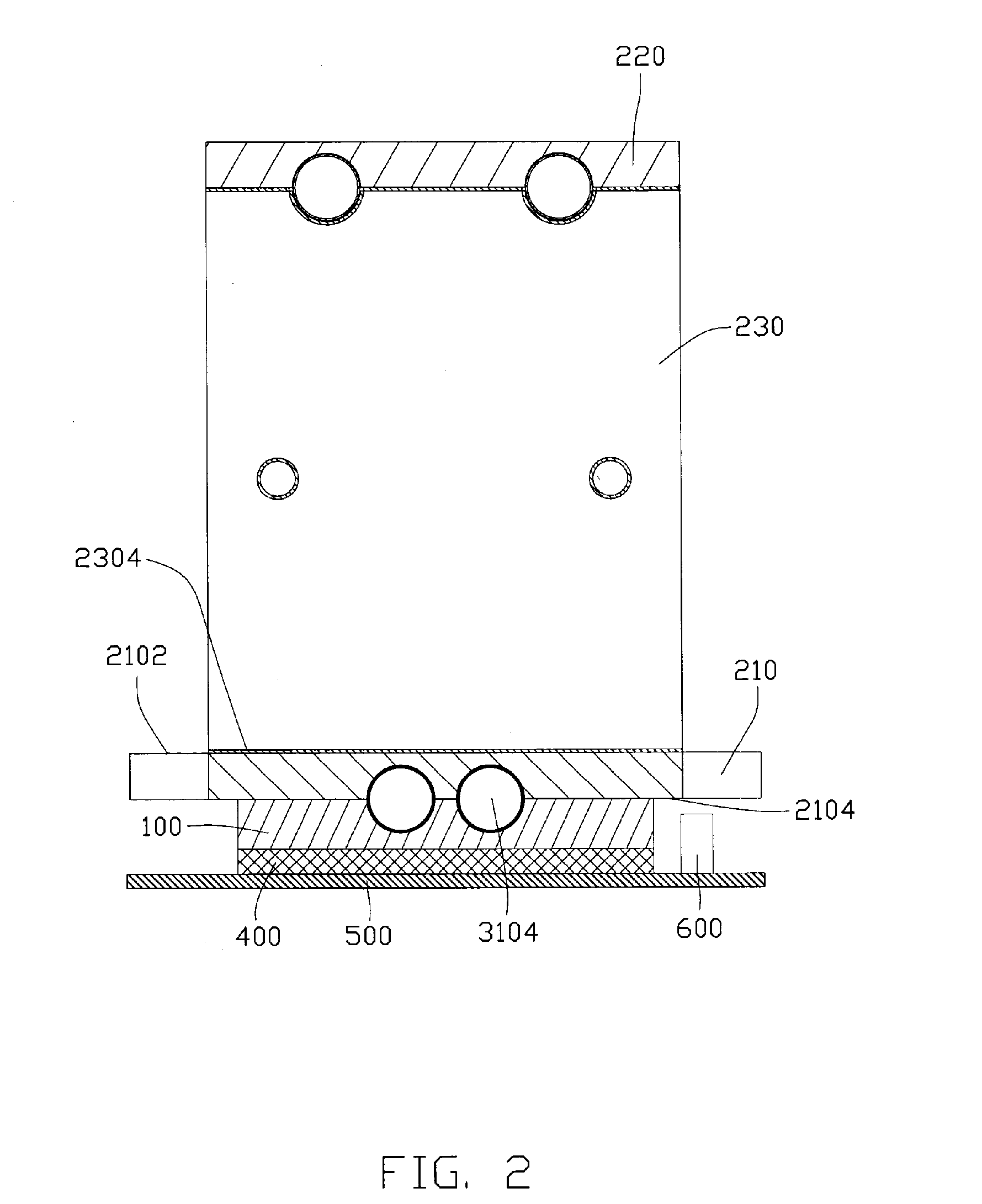
Heat dissipation device
InactiveUS20070217153A1Improve cooling effectReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHeat conductingEngineering
A heat dissipation device includes a heat conducting plate (100) for contacting with an electronic component (400), a heat sink (200) mounted on the heat conducting plate and a heat pipe (300). The heat conducting plate comprises a groove (110) defined in. The heat pipe comprises an evaporating portion (310) sandwiched between the heat conducting plate and the heat sink, and a condensing portion (320) thermally connecting with the heat sink. The evaporating portion comprises a middle portion (3104) having a circular cross section and accommodated in the groove of the heat conducting plate, and a pair of end portions (3102) formed on opposite sides of the middle portion. The end portions have flat bottom surfaces.
Owner:FU ZHUN PRECISION IND SHENZHEN +1
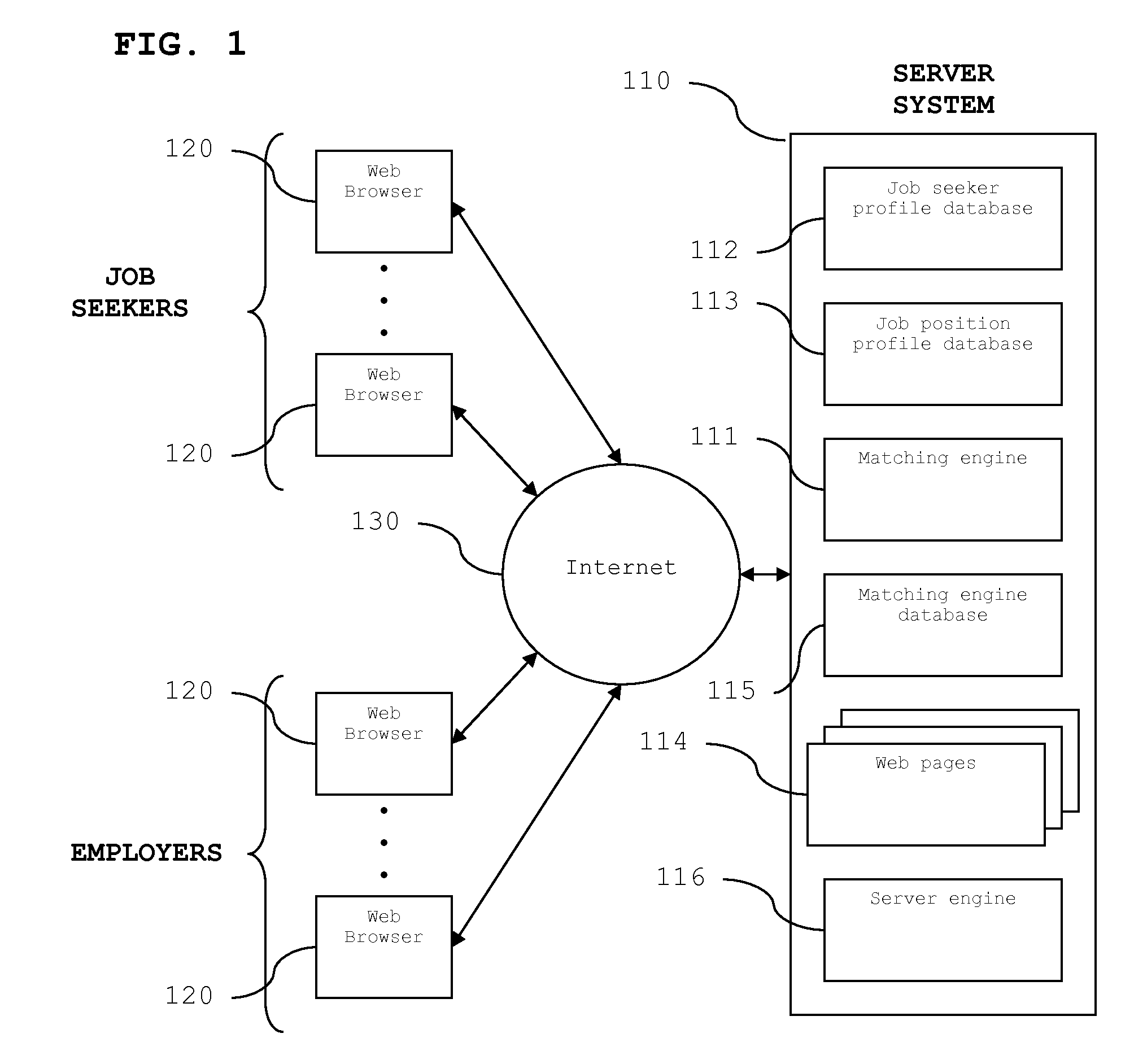
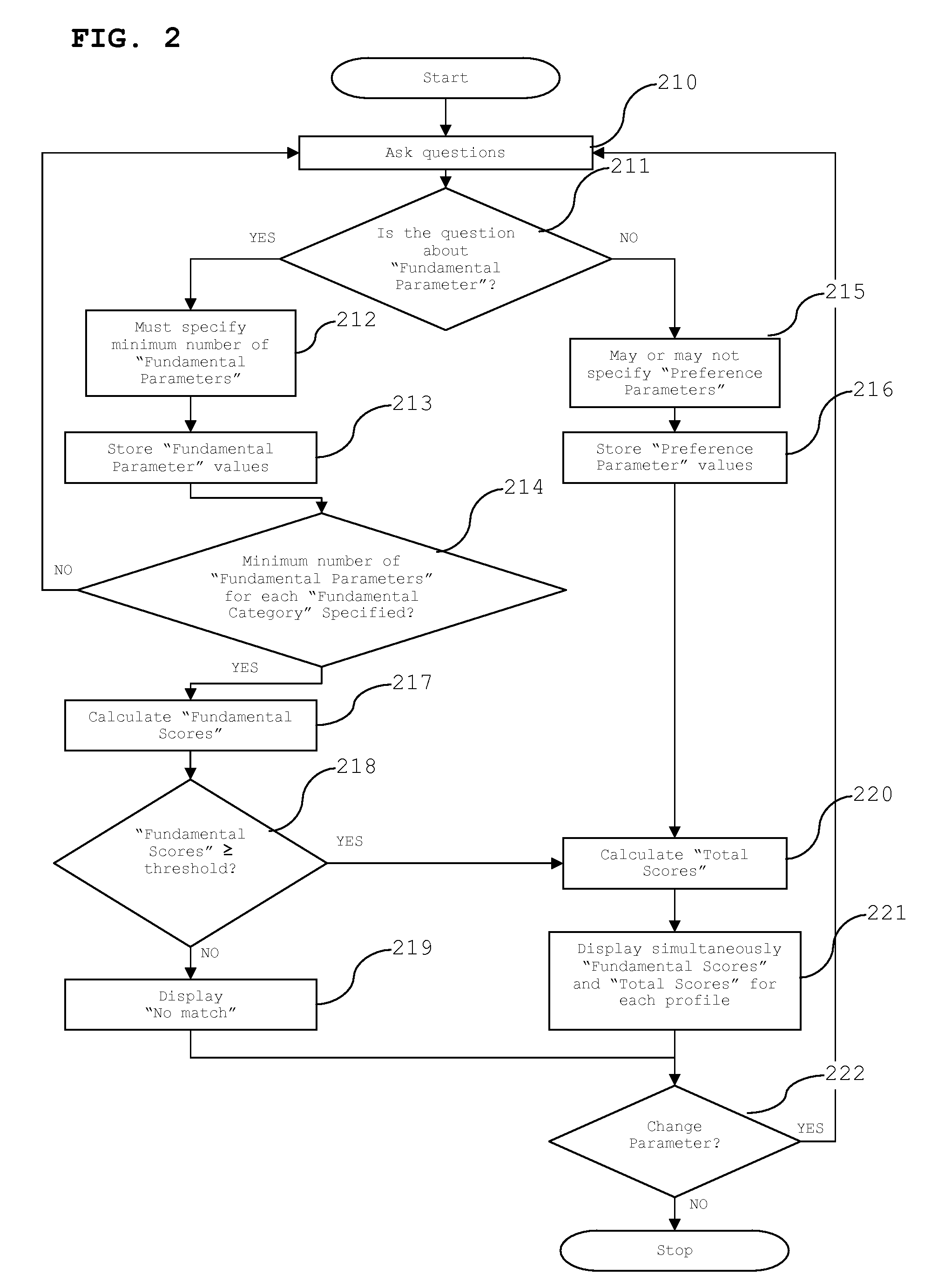
Approach to matching profiles and accessing contact information
InactiveUS20080016054A1Desirable efficiencyQuickly reachOffice automationResourcesData scienceSequential computation
A system and method for an on-line matching of job seekers with job openings and for score-based access to contact information is disclosed. Both the job seekers and the job openings are identified by their profiles and each profile has multiple parameters. The profile parameters are divided into two distinct categories, fundamental capabilities to perform a job and personal preferences regarding a job, to ensure that both the objective and subjective pictures of the job market are preserved. Correspondingly, two matching scores are calculated sequentially and the results presented simultaneously to job seekers and employers. A user's contact information is released only if the matching score meets the user's specified limit. The two score approach as well as the method for score-based access to contact information can work either together or separately in a variety of profile matching models.
Owner:VITRUVA
Security system and method
InactiveUS20060038678A1Rapid responseQuickly reachAircraft componentsRailway tracksEngineeringSafety zone
A patrol system comprising a carriage moving along guiding means. The carriage includes propulsion means, sensors for acquiring data from outside the carriage and control means. An automatic safety method comprising A. storing a digital map of safety zones in a computer; B. keeping track in real time of the carriage location and the area pointed at by the weapon; C. when a weapon activation command is issued, checking whether the intended attack will be pointed towards one of the safety zones; D. if the answer in step C is negative, then activating the weapon; if the answer is positive, then shooting will not be allowed.
Owner:AVNERI SHAHAR
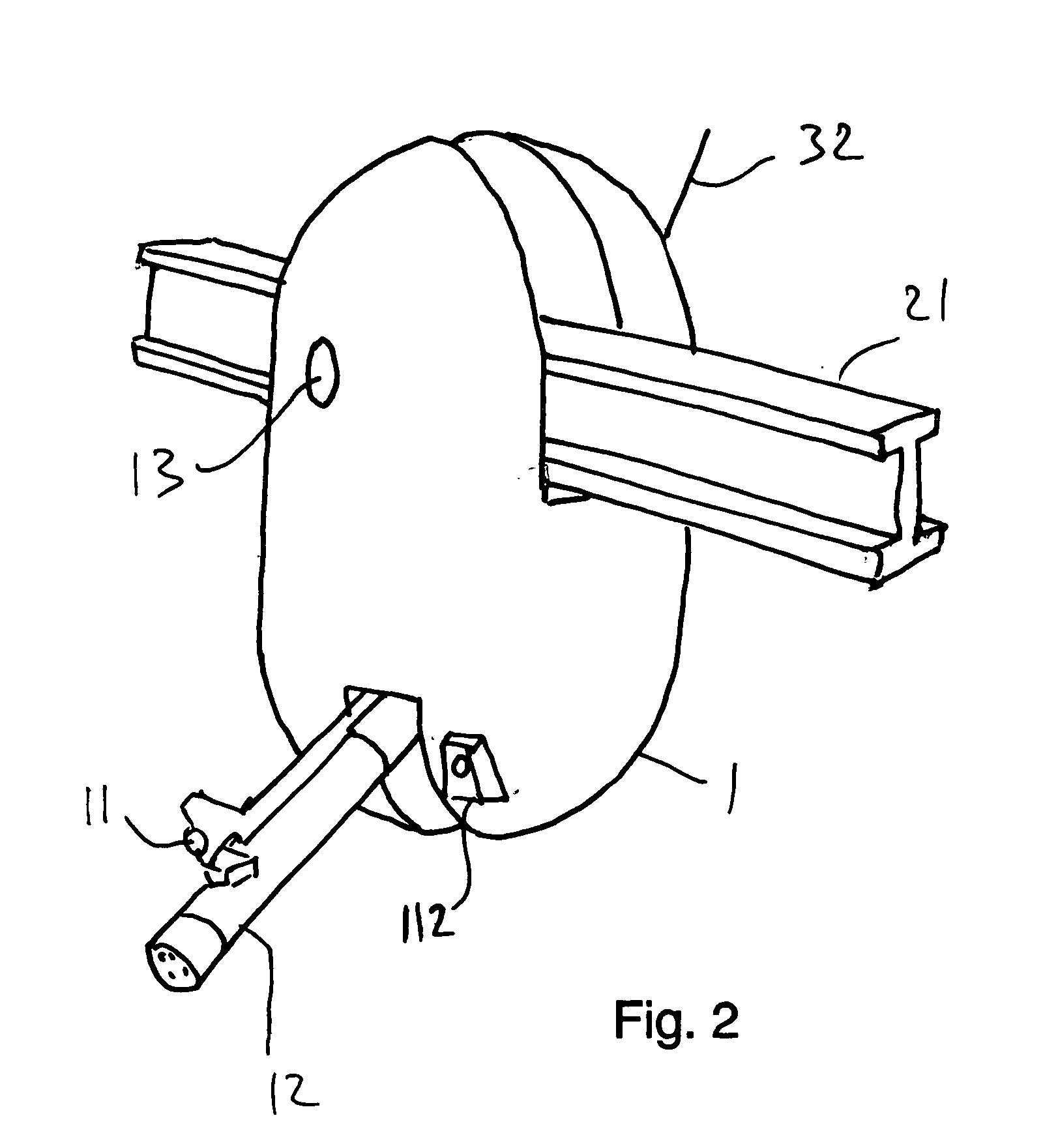
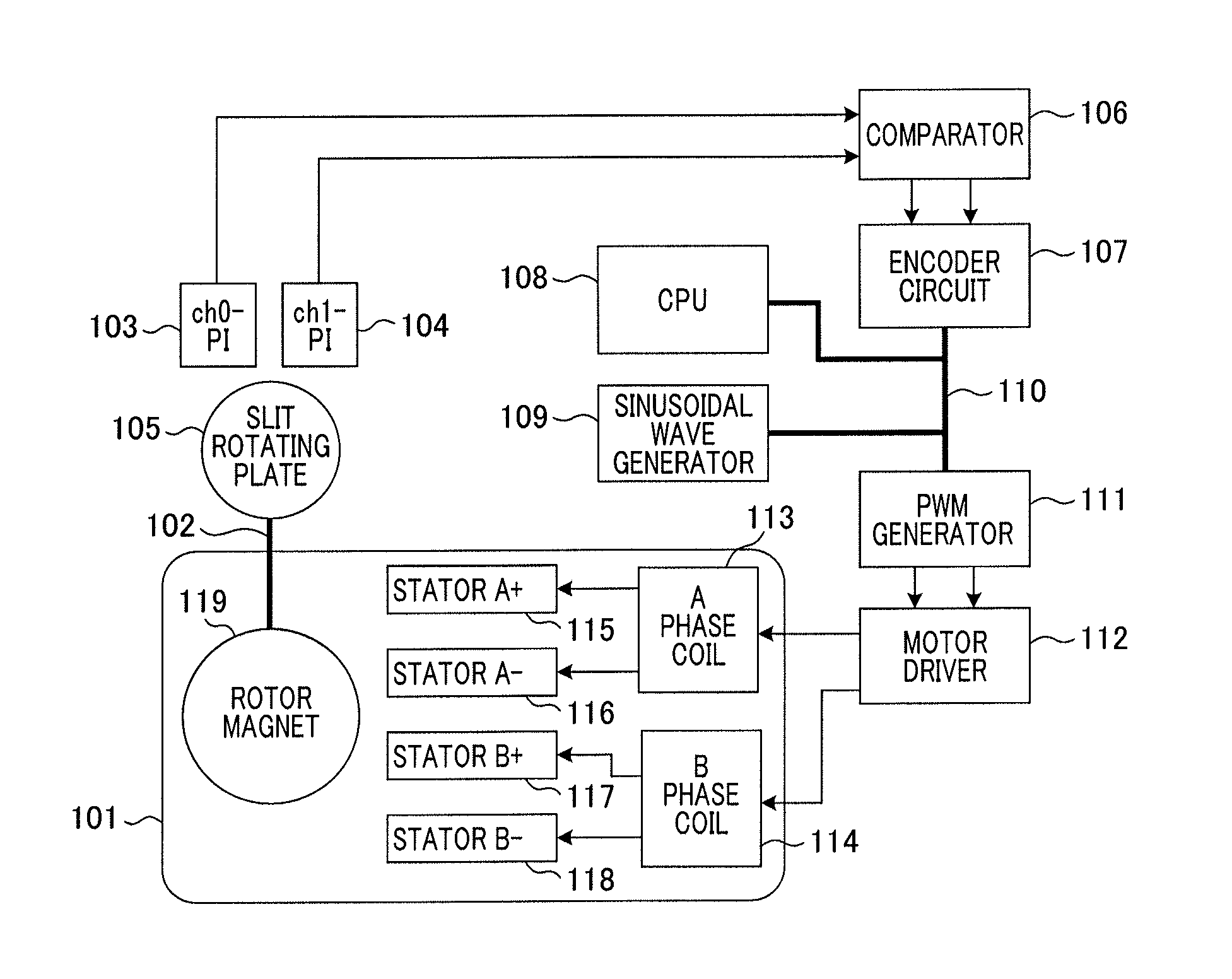
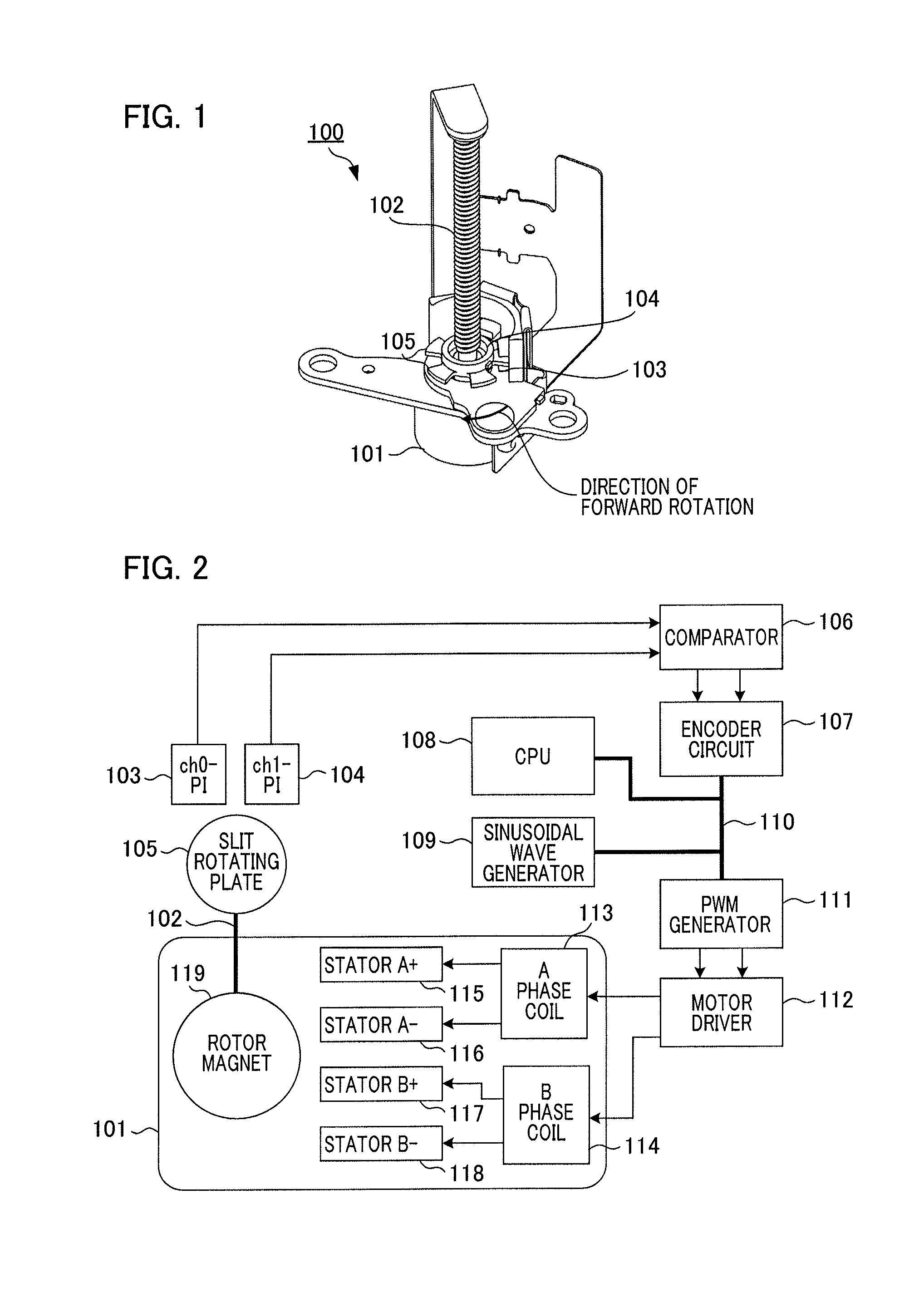
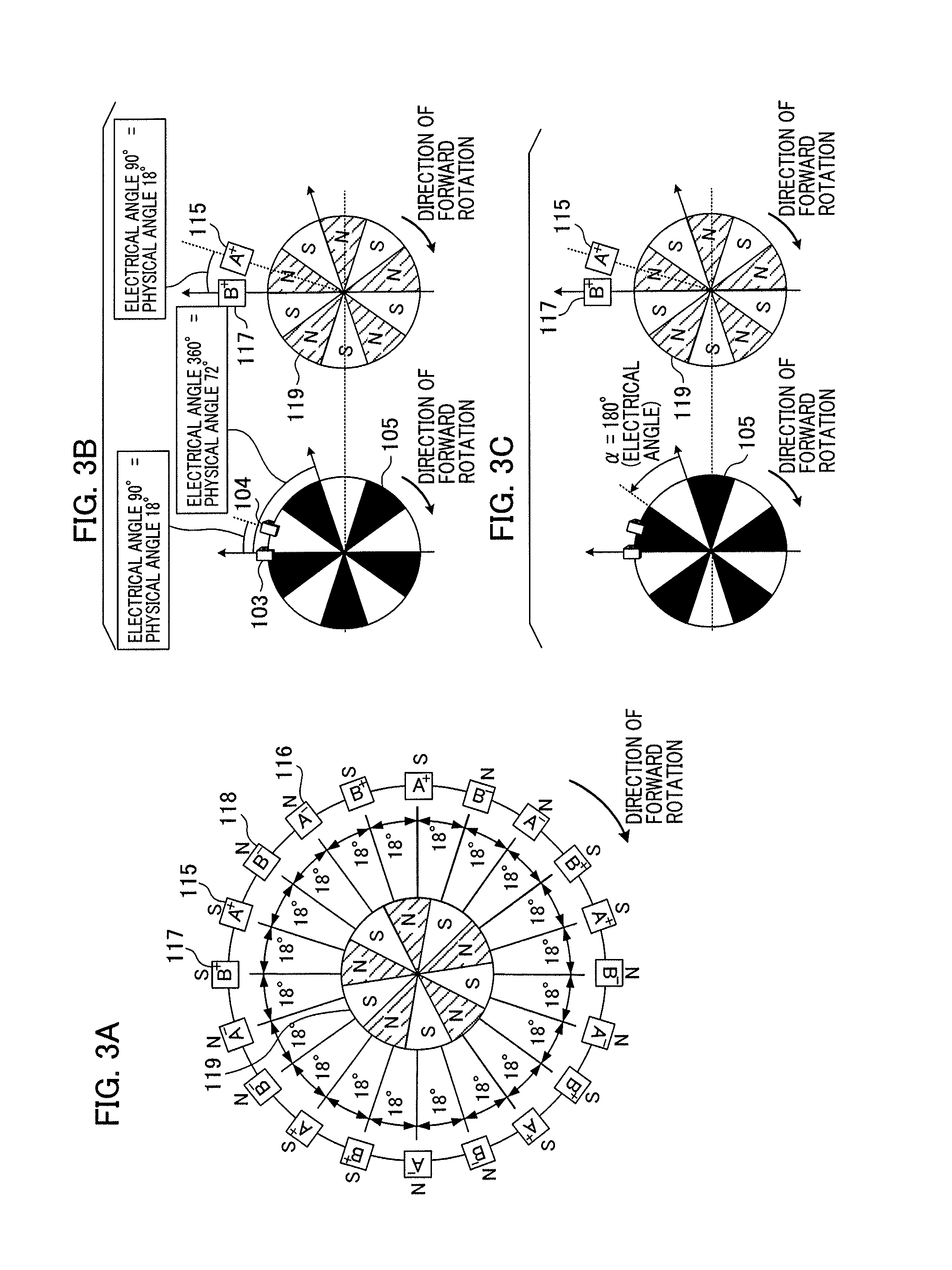
Motor control apparatus and motor control method
ActiveUS20140035496A1Simply and quickly adjustsQuickly reachMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlDriving currentElectric machine
A motor control apparatus applying a sinusoidal drive waveform to a motor and including a position detection unit outputting a signal according to a motor shaft's position; and a control unit: acquiring a phase value of the motor's drive waveform when a signal is output by the position detection unit, changing a cycle of the drive waveform by measuring time from a previously output signal to a presently output signal, comparing the phases of the drive waveform and the motor shaft, and controlling to change to a cycle at which a phase value of the drive waveform matches a target phase value when a travel time corresponding to a phase value for adjustment has elapsed from a present time when a phase value of the drive waveform presently acquired differs from a target phase value acquired when the motor's drive current and drive voltage are in a designated phase relationship.
Owner:CANON KK
Electronic clinical reference and education system and method of use
ActiveUS7593967B2Easy accessFacilitate data exchangeComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionMedical imagesClinical manifestationDiagnostic information
A clinical reference and education system and method of use, wherein medical condition diagnosis information is gathered, stored, and distributed. More specifically, information regarding clinical / pathological differential analyses, key facts, clinical presentations, pathology features, imaging findings, anatomy information, medical references with abstracts, expert imaging center information, continuing medical education information, and related data is made available in electronic and printed forms via a general infrastructure of the present system.
Owner:RELX INTPROP SA
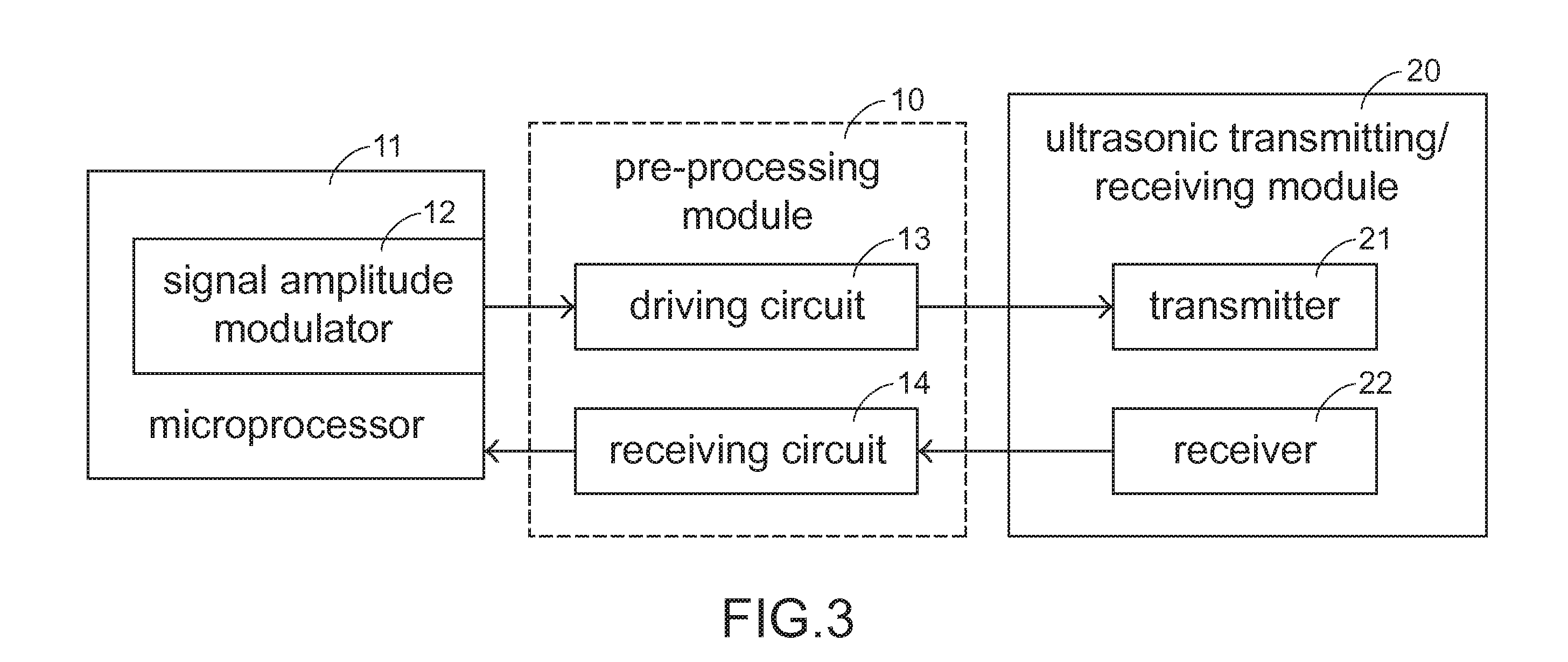
Ultrasonic transducer and signal decay time adjusting method applied thereto
InactiveUS20110026365A1Shorten the timeQuickly reachWave based measurement systemsTransmissionUltrasonic sensorEngineering
A signal decay time adjusting method is used in an ultrasonic transducer. Firstly, a first driving signal is generated by a pre-processing module. When the first driving signal is received, an ultrasonic transmitting / receiving module generates vibration and transmits a sensing wave according to the first driving signal. Then, the pre-processing module stops generating the first driving signal so that the vibration generated within the ultrasonic transmitting / receiving module is decayed as a decay signal. Then, a second driving signal is generated by the pre-processing module according to the first driving signal, and the second driving signal is transmitted to the ultrasonic transmitting / receiving module. When the second driving signal is received, the decay signal is offset according to the second driving signal, so that a decay time of the decay signal is shortened. When the sensing wave is reflected by an object, a reflective wave is received by the ultrasonic transmitting / receiving module.
Owner:LITE ON IT
Stabilized and solubilized drug formulation for topical application and transdermal efficacy for cosmetic improvement and methods of formulation
InactiveUS20150157728A1Increase absorption coefficientImprove drug deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePharmaceutical formulationDrug formulations
The invention relates to a novel stabilized and solubilized topical formulation for cosmetic improvements and methods of making the same comprising multiplexed molecular penetration enhancers and essential and semi-essential amino acid protein binders for the topical application and transdermal delivery of one or more active ingredients and / or pharmaceutical agents. The invention further relates to the use of the topical formulation in connection with the providing of cosmetic improvements in individuals.
Owner:TRANSDERMAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com