Memory device and method for exchanging data with memory device
A storage device and memory array technology, applied in the field of storage device access
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
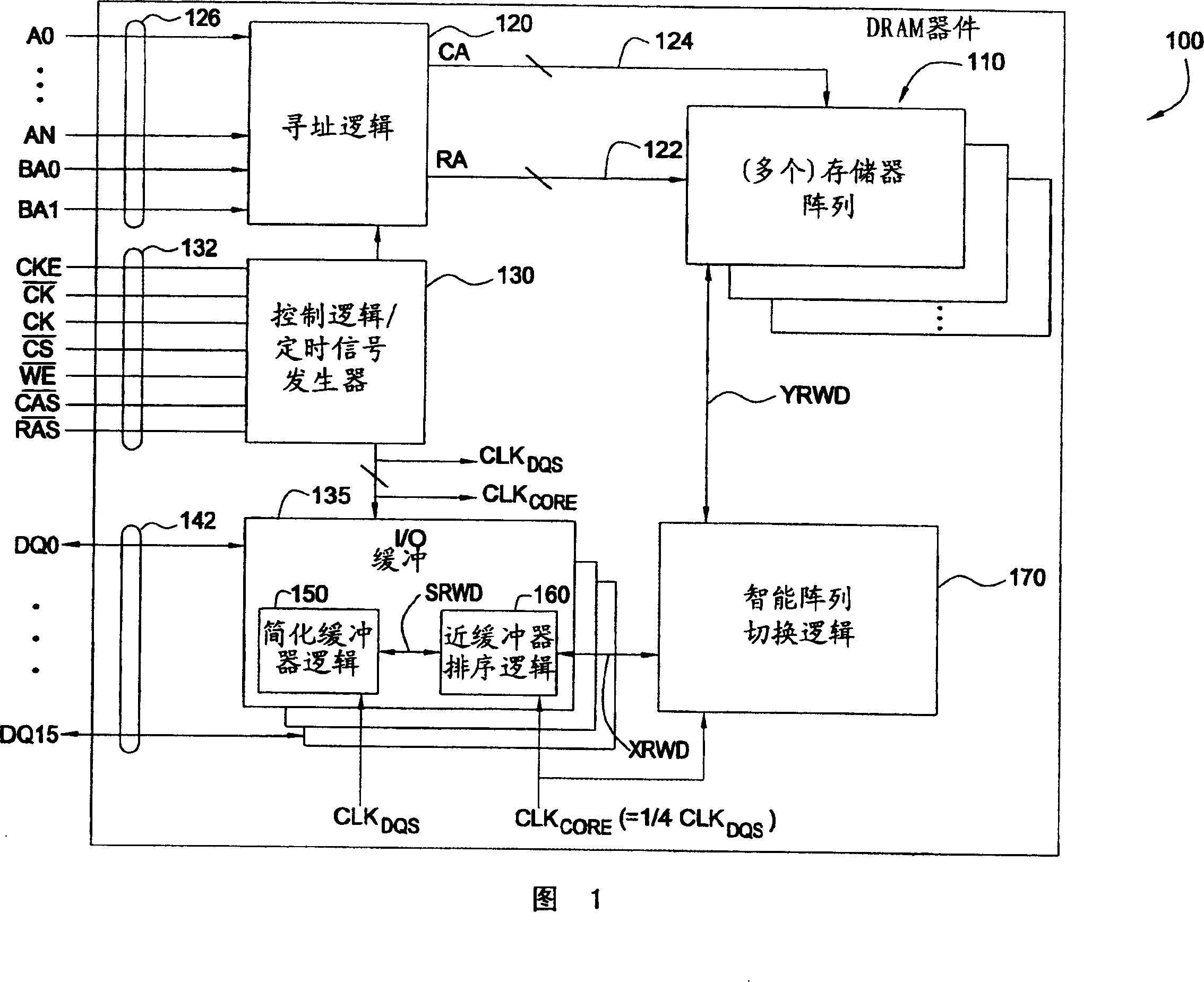
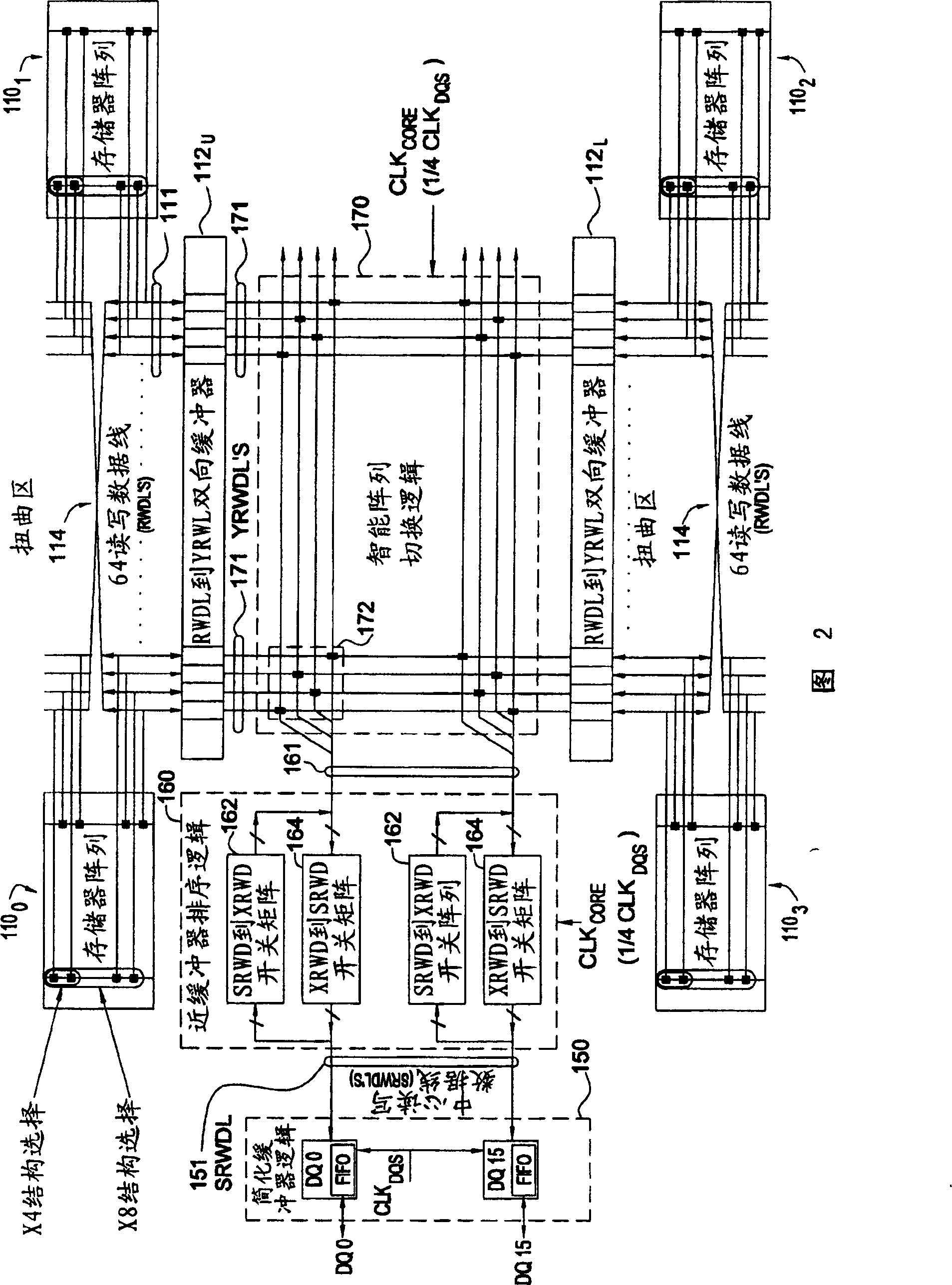
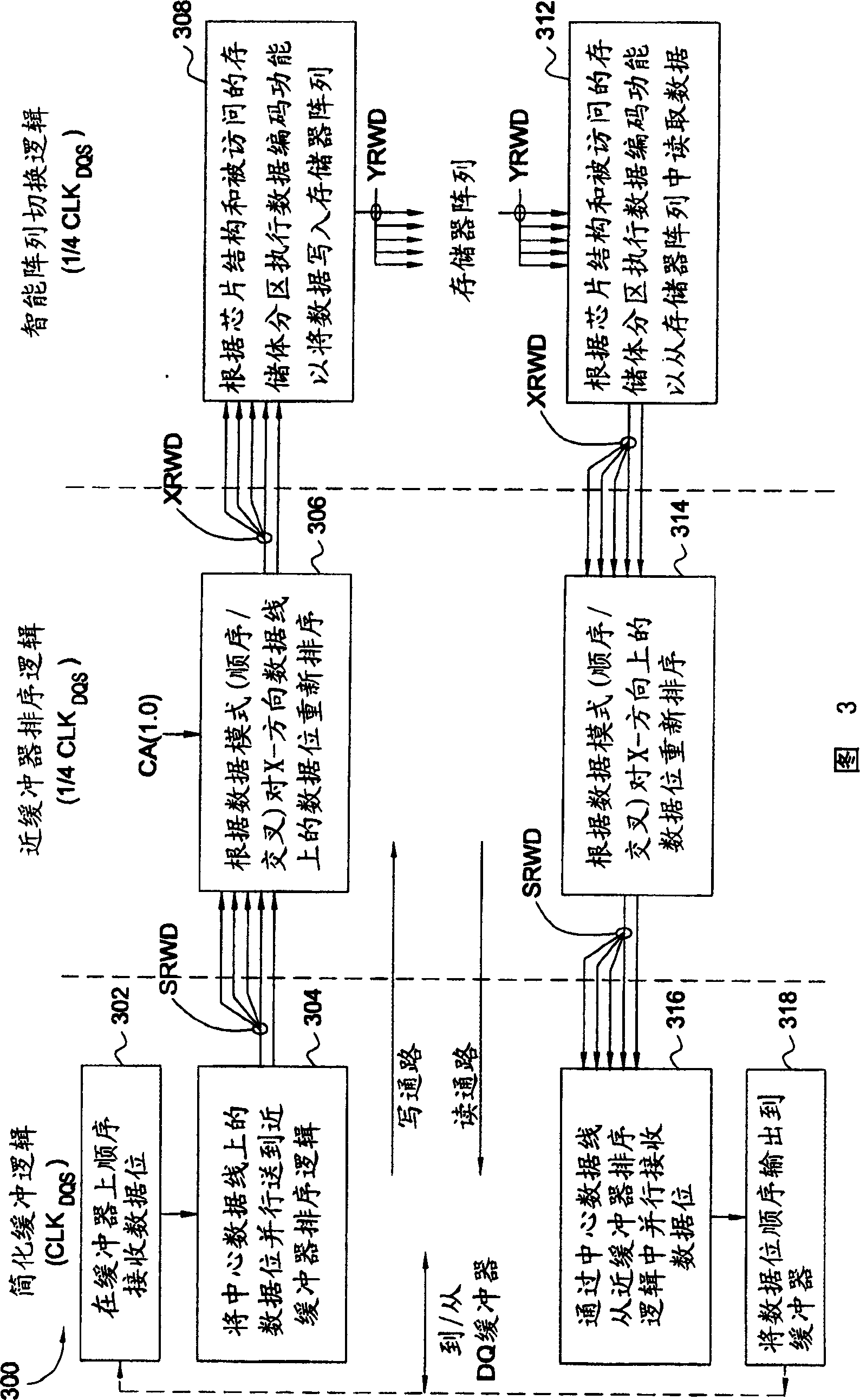
[0030]Embodiments of the present invention primarily provide techniques and circuits to support the switching operations required to transfer data between a memory array / bank and an external data buffer. On the write path, these switching operations include latching and assembling multiple bits received consecutively through a single data buffer, pairing them based on a particular type of access (e.g., interleaved or sequential, odd / even). The bits are reordered and coded based on the bank location accessed by the chip structure (eg ×4, ×8 or ×16). On the read path, similar operations can be performed (in reverse order) to prepare and assemble the data to be read from the device.
[0031] In the data path, by distributing these switching operations between different logic blocks, only some operations (such as latching data) can be performed at the data clock frequency, while the remaining operations (such as sorting and encoding) are performed at lower frequencies (such as 1 / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com