Semiconductor device
a semiconductor device and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, electrical devices, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of adverse influence, adverse influence of device properties, adverse influence of device residual stress, etc., and achieve uniform and high stability of semiconductor devices and improve yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
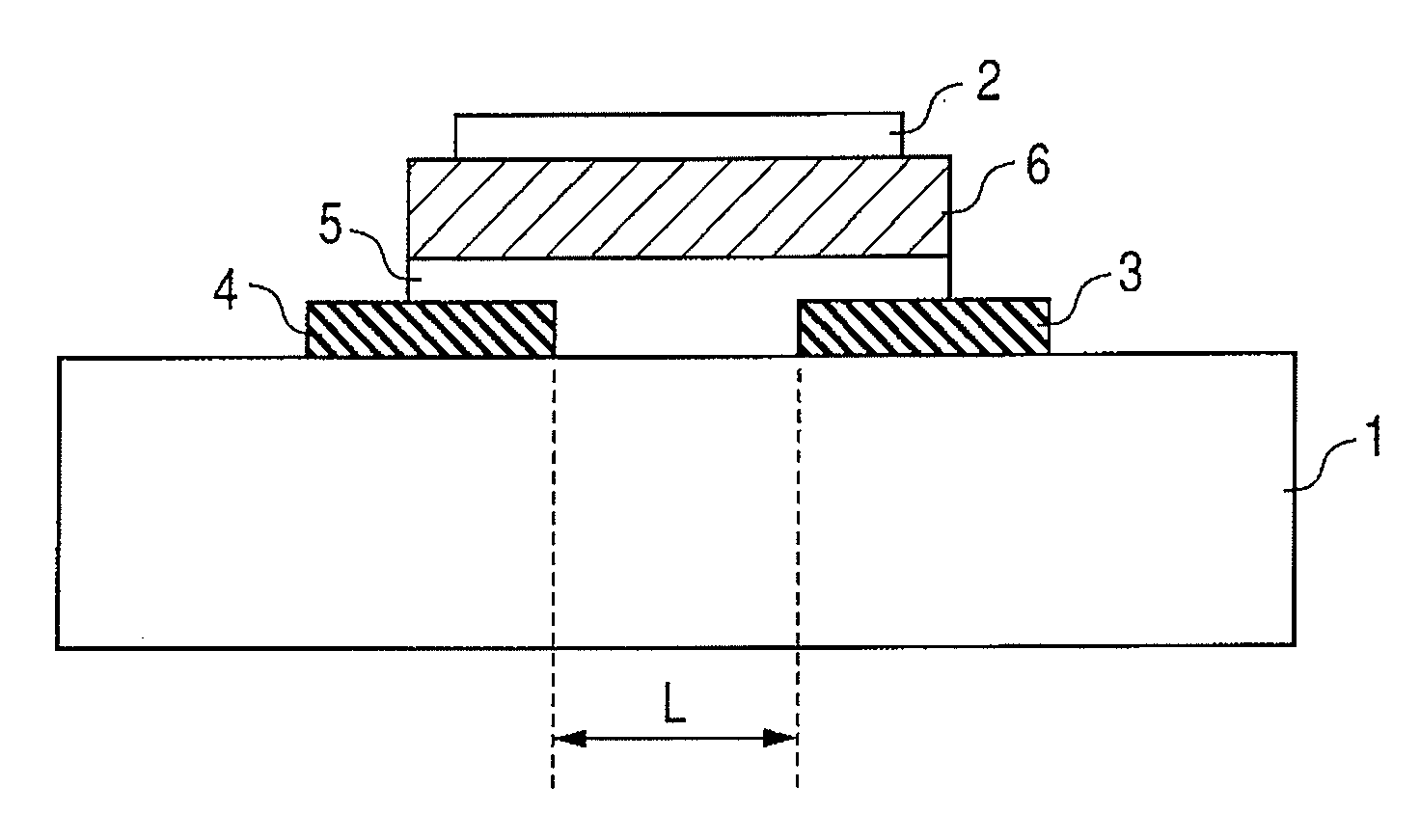
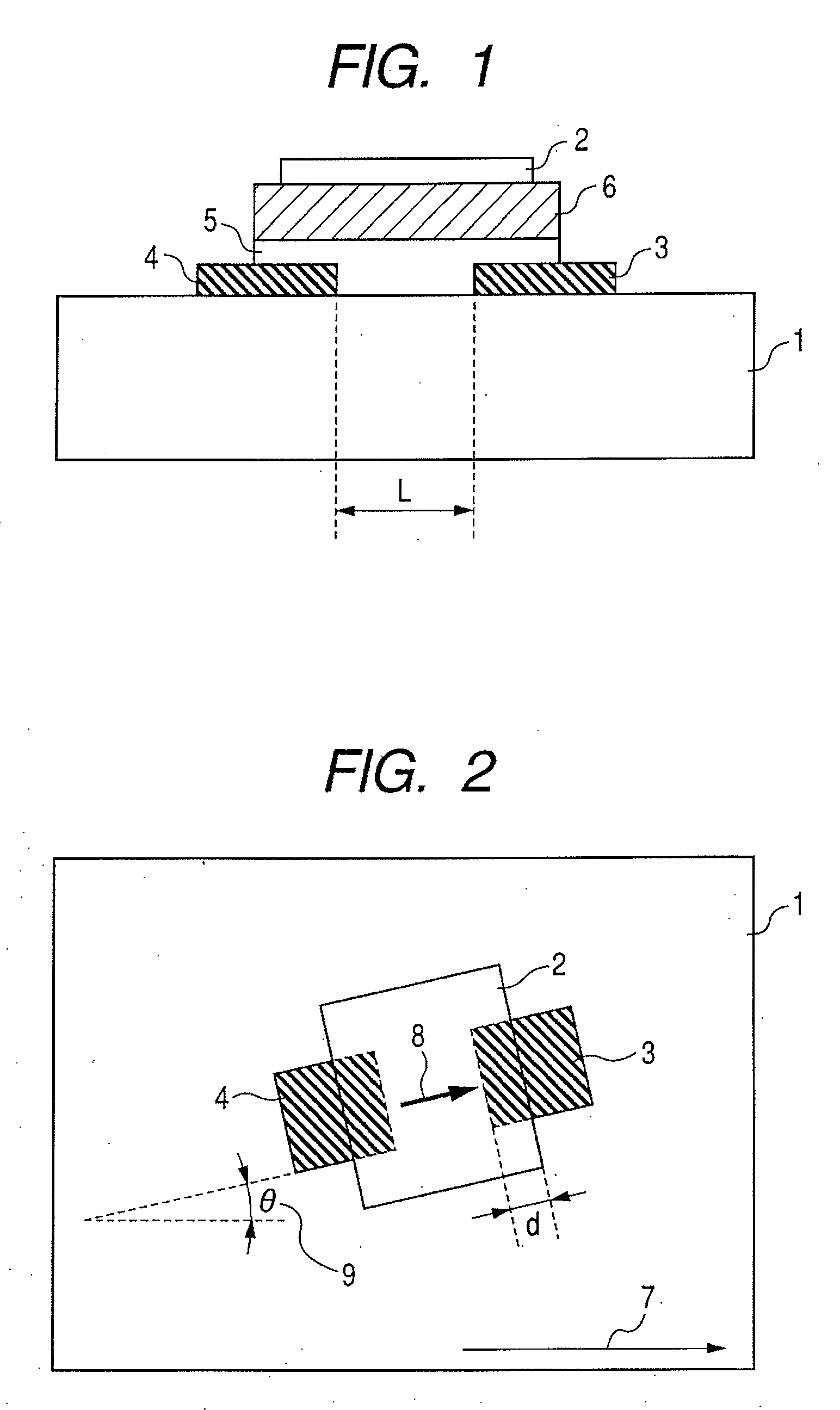
[0060]An example of fabrication of a TFT using an amorphous In—Ga—Zn—O thin film for a channel is shown in which the channel is formed on a biaxially stretched plastic film substrate such that the direction of a current flowing in the channel of the TFT is nonparallel to the direction in which thermal shrinkage rate of the plastic film substrate is largest. The TFT manufactured on the plastic film substrate is a top gate TFT device and has the same structure as that which is described earlier and shown in FIGS. 1 and 2.
[0061]The plastic film substrate to be used is a sheet-like plastic film (biaxially stretched polyethylene terephthalate film produced by TORAY Industries, Inc., whose product name is Lumira, product number is T56, thickness is 125 microns, size is 5 cm square, longitudinal (film longitudinal) thermal shrinkage rate is 1.2, andtransverse thermal shrinkage rate is 0.5).
[0062]As shown in FIG. 2, a drain electrode and a source electrode is patterned on a film surface by ...
example 2
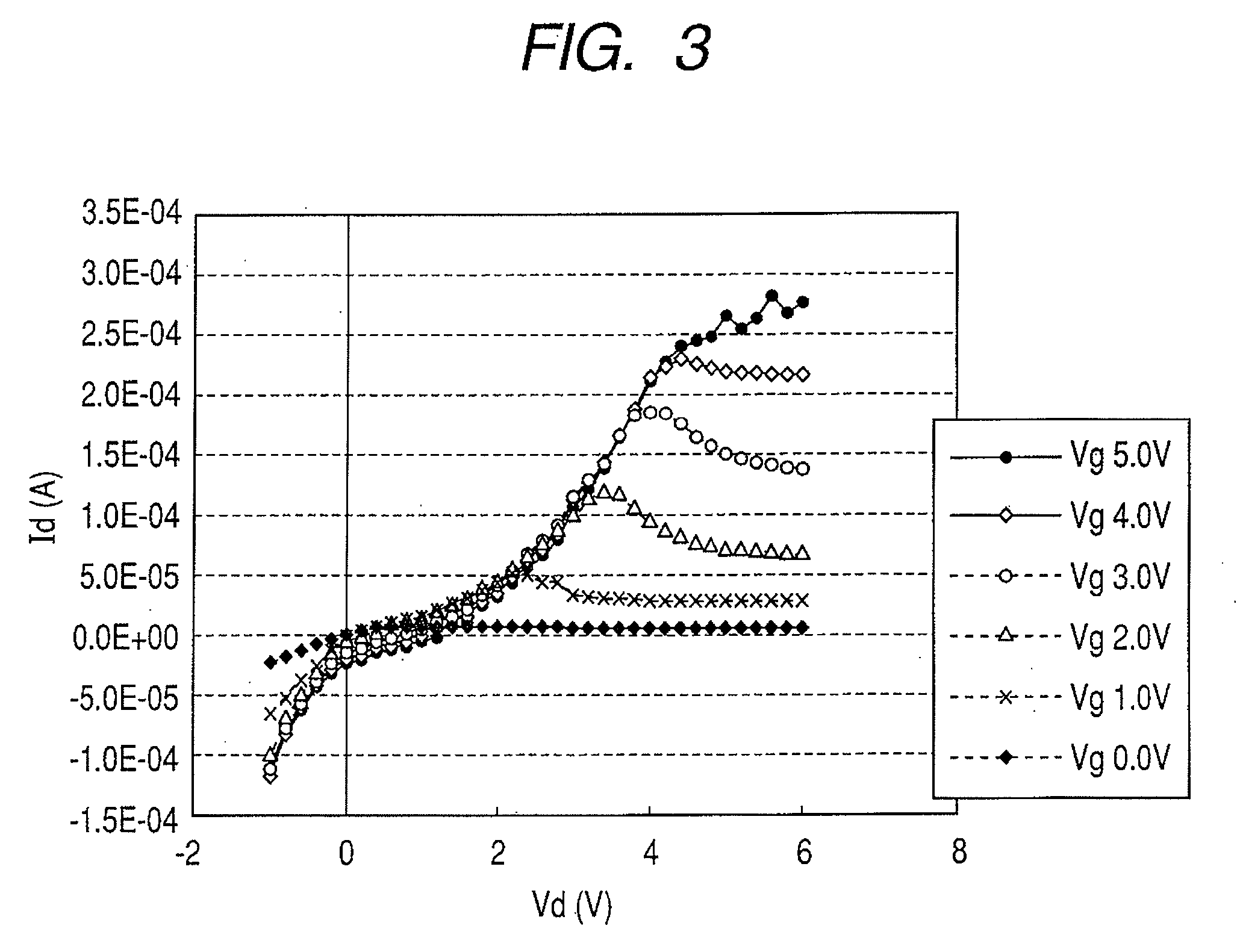
[0067]A TFT device having the same size as that in Example 1 is manufactured and the angle θ is set to 45°. FIG. 5 shows a current (IDS) to voltage (VDS) characteristic of the TFT device (whose channel length is 3 micron, channel width is 30 micron, and angle θ is 45°) which was measured at room temperature. FIG. 6 shows a current (IDS) to voltage (VGS) characteristic of the TFT device which was measured at the room temperature. The threshold value of the gate voltage VGS at VDS=6 V was approximately 0.64 V. At VGS=6 V, the current IDS=1.83×10−4 A flowed. The S-value of the sub-threshold slope characteristics was approximately 0.14 V / dec. The field-effect mobility was calculated from the output characteristics. As a result, the field-effect mobility was found to be approximately 17.1 cm2 (V·sec.)−1 in the saturation region.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com