Electrospun electroactive polymers
a technology of electroactive polymers and electroactive polymers, which is applied in the direction of filament/thread forming, transportation and packaging, yarn, etc., can solve the problems of labor-intensive and time-consuming current process, large equipment that is complex to maintain, and process that leads to -phase formation labor-intensive and time-consuming, etc., and achieves fast and easy operation and simple setup.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
(PVDF / DMF)
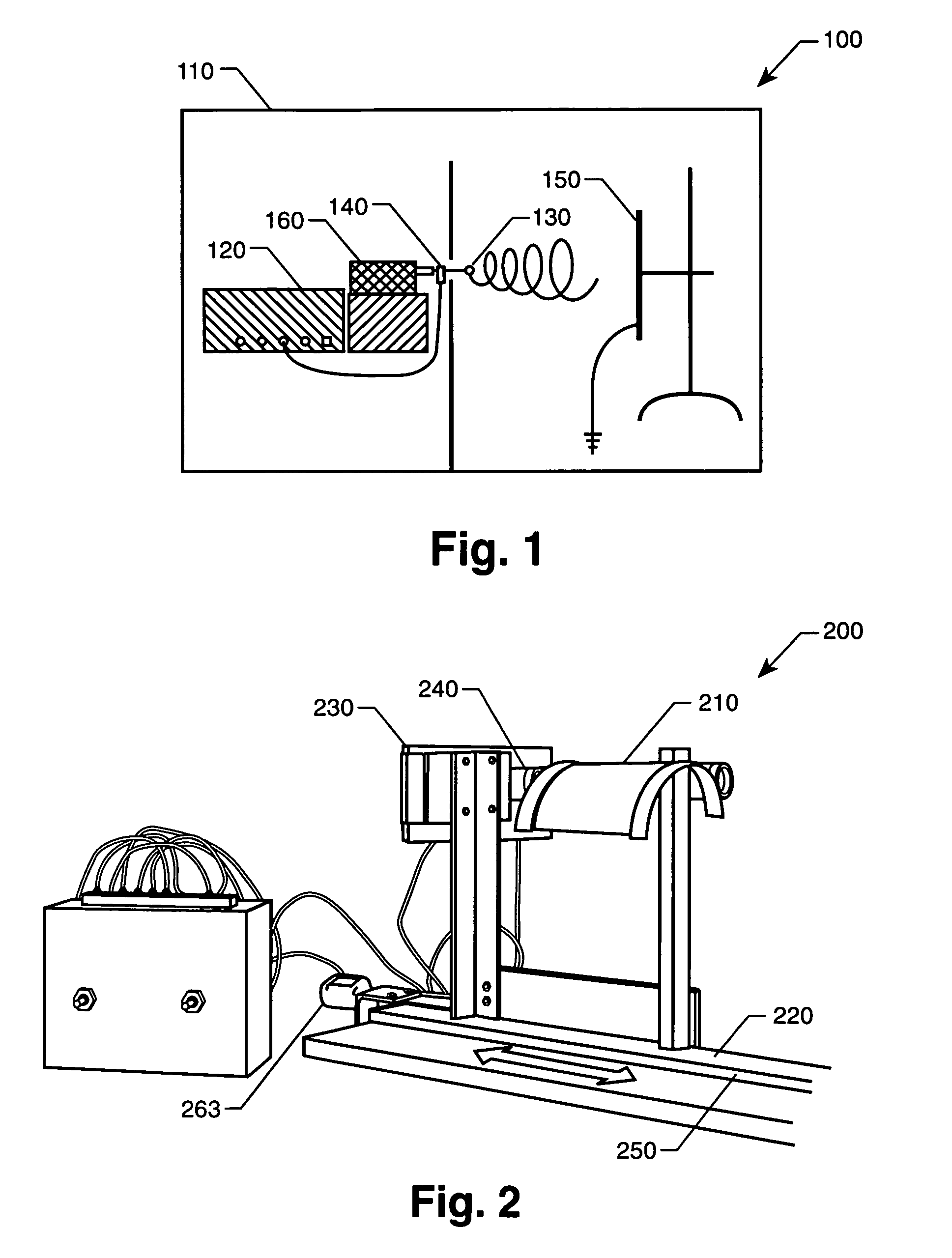
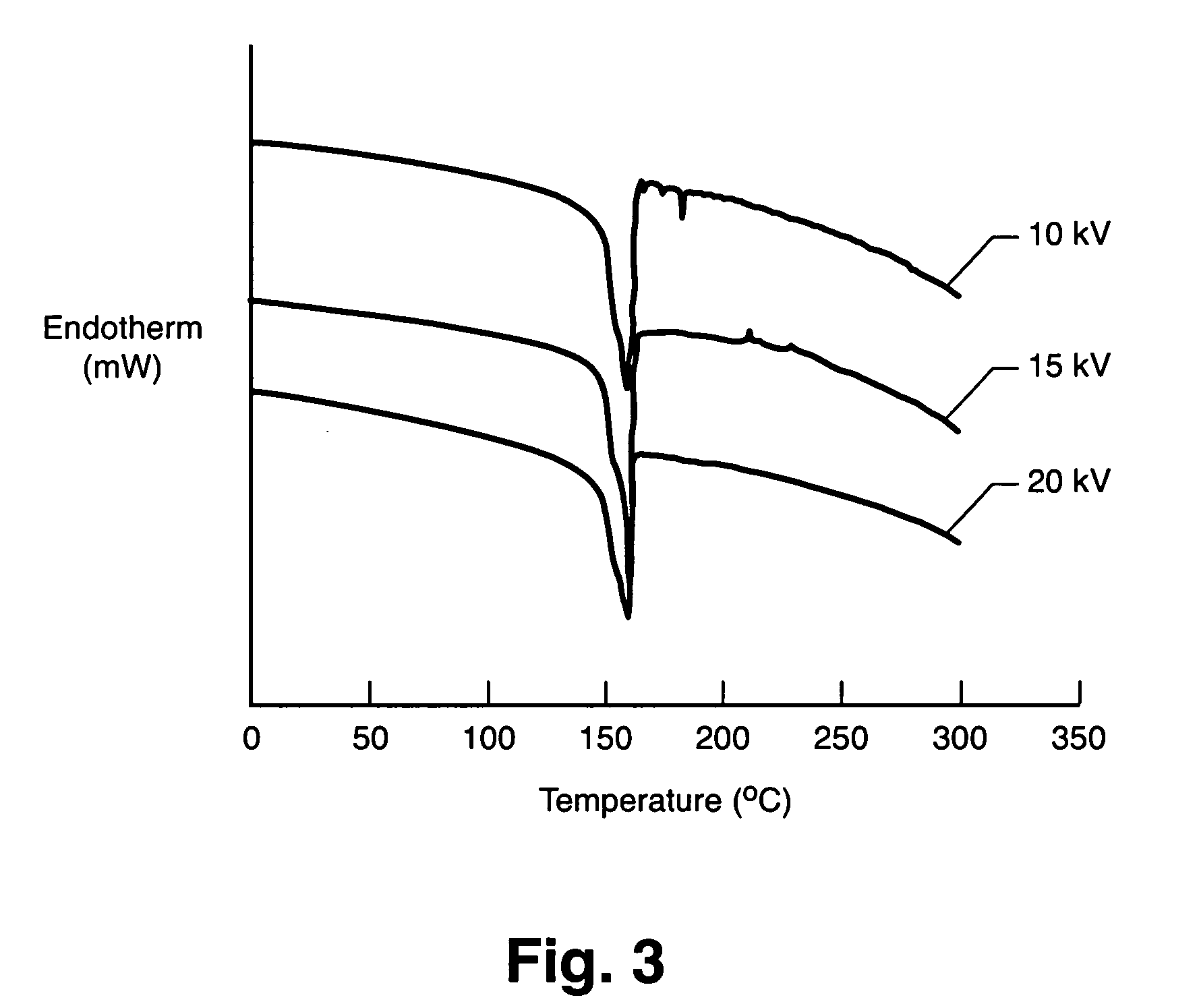
[0032] PVDF pellets (MW 530,000, Aldrich Chemical Company, Inc.) were dissolved into solvent DMF at a concentration of 30 weight percent (wt %) PVDF. The solutions were electrospun into fibers using the apparatus illustrated in FIG. 2. The polymer resins were delivered to the system using a plastic syringe (Becton Dickinson) equipped with an 18-gauge blunt needle tip. Metered infusion of the solution into the system was accomplished with a digitally-controlled syringe pump (KD Scientific, model 100). Voltage was applied to this supply system via an alligator clip connected to the needle and to a high voltage power supply unit (Spellman High Voltage Electronics Corporation, model CZE 1000R). The grounded target was a rotating drum, which imparted some degree of fiber orientation to the collected mat. For these experiments, the infusion pump was set to deliver polymer resin at a rate of 6.0 milliliters per hour (mL / hr). Distance between the needle tip and the grounded targe...
example 2
[0045] PVDF solutions in the solvent DMF with and without single wall nanotubes (SWNTs) were electrospun at various concentrations, as outlined in Table 2. PVDF pellets (MW 530,000, Aldrich Chemical Company, Inc.) were dissolved into DMF at a concentration of 30 weight percent (wt %) PVDF. A SWNT stock solution (1% w / w) in DMF was prepared to mix with PVDF / DMF solution to prepare various compositions of SWNT / PVDF / DMF solutions. The solutions were electrospun into fibers using the apparatus illustrated in FIG. 2. The polymer resins were delivered to the system using a plastic syringe (Becton Dickinson) equipped with an 18-gauge blunt needle tip. Metered infusion of the solution into the system was accomplished with a digitally-controlled syringe pump (KD Scientific, model 100). Voltage was applied to this supply system via an alligator clip connected to the needle and to a high voltage power supply unit (Spellman High Voltage Electronics Corporation, model CZE 1000R). The grounded ta...
example 3
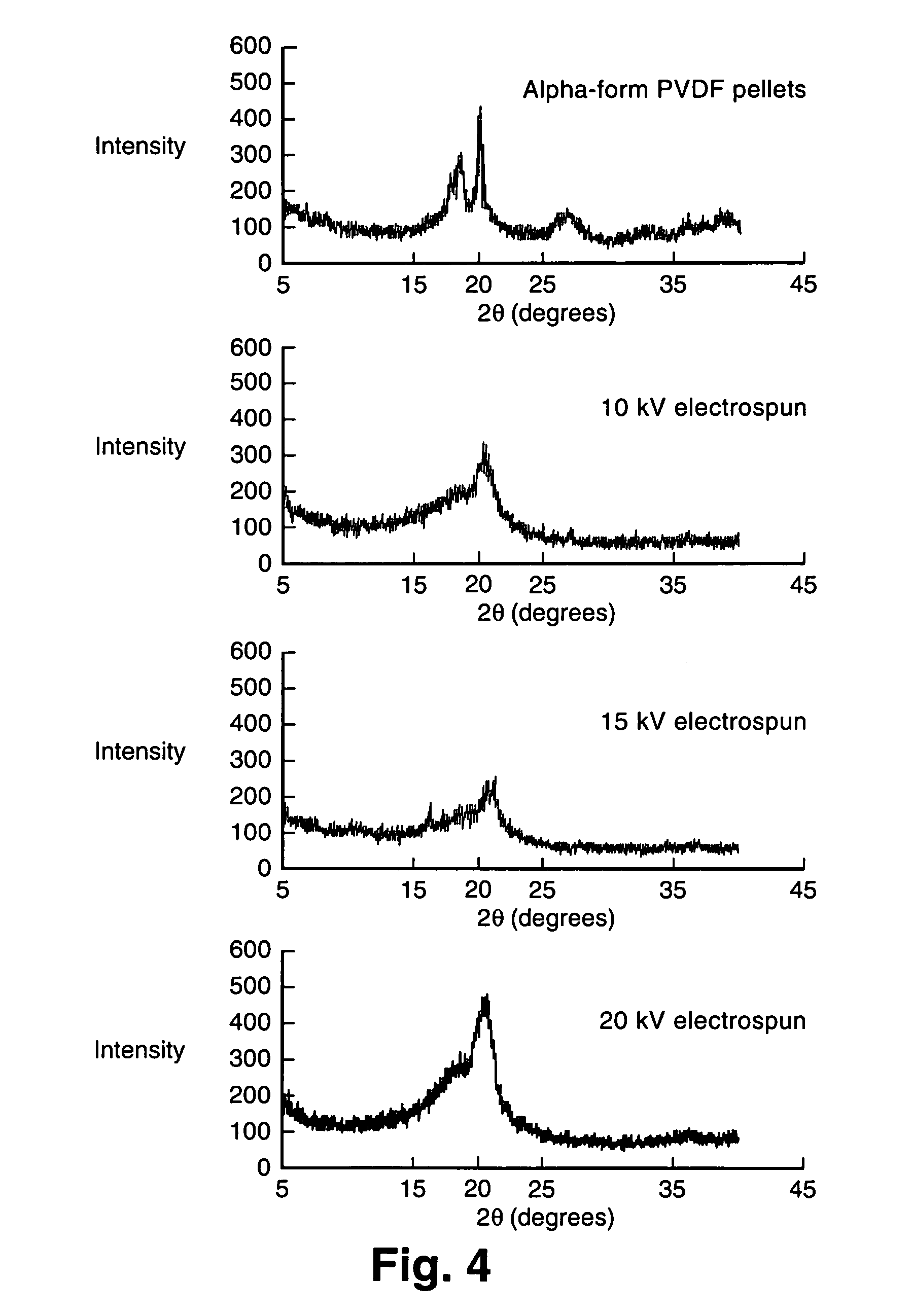
[0055] PVDF combined with carbon nanotubes was tested beginning with 0.1% SWNT in 15 wt % PVDF and 1.0% SWNT in 15 wt % PVDF. Small and few fibers formed. When the 1.0% SWNT was electrospun, black drops fell out of the solution as a result of the excessive concentration of SWNTs. A 0.1 % SMNT in 25 wt % PVDF spun well and was able to be spun onto a rotating roller, producing a nonwoven mat which was vacuum-dried at 60° C. A nonwoven mat was also produced from 0.2% SWNT in 25 wt % PVDF. Optimal conditions for the PVDF solutions with carbon nanotubes were slightly different depending on amount of carbon nanotubes and concentration of PVDF.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com