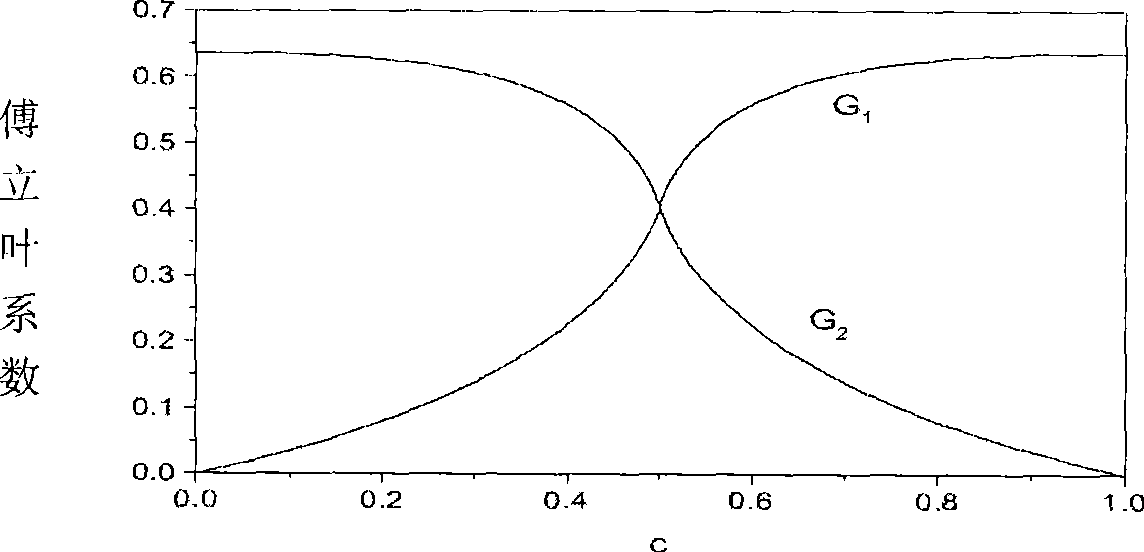Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Reciprocal lattice" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, the reciprocal lattice represents the Fourier transform of another lattice (usually a Bravais lattice). In normal usage, the initial lattice (whose transform is represented by the reciprocal lattice) is usually a periodic spatial function in real-space and is also known as the direct lattice. While the direct lattice exists in real-space and is what one would commonly understand as a physical lattice, the reciprocal lattice exists in reciprocal space (also known as momentum space or less commonly as K-space, due to the relationship between the Pontryagin duals momentum and position). The reciprocal of a reciprocal lattice is the original direct lattice, since the two are Fourier transforms of each other.
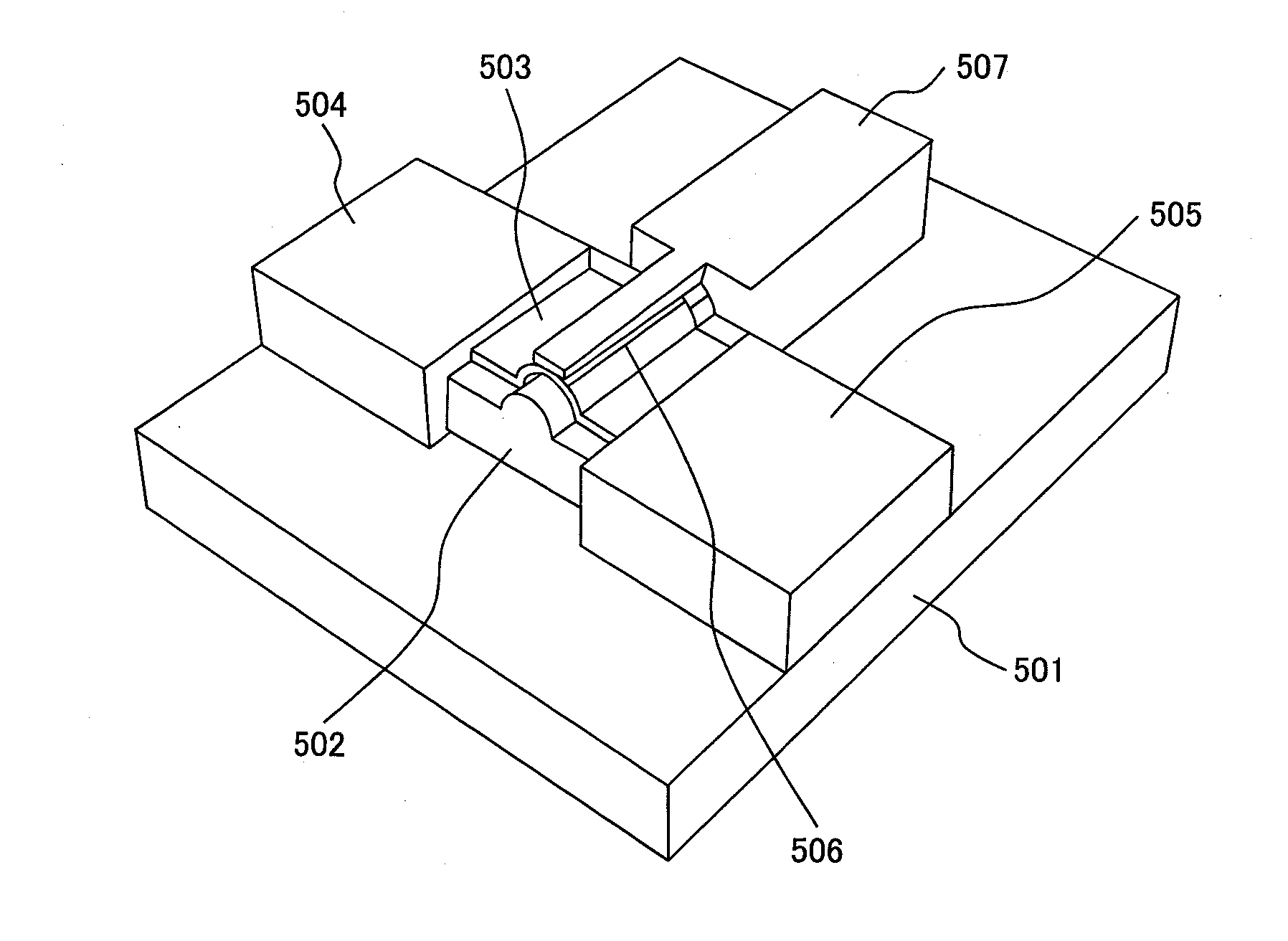
Electronic device, light-receiving and light-emitting device, electronic integrated circuit and optical integrated circuit using the devices
InactiveUS20110108805A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConvex structureReciprocal lattice
Provided are an electronic device and a light-receiving and light-emitting device which can control the electron configuration of a graphene sheet and the band gap thereof, and an electronic integrated circuit and an optical integrated circuit which use the devices. By shaping the graphene sheet into a curve, the electron configuration thereof is controlled. The graphene sheet can be shaped into a curve by forming the sheet on a base film having a convex structure or a concave structure. The local electron states in the curved part can be formed by bending the graphene sheet. Thus, the same electron states as the cylinder or cap part of a nanotube can be realized, and the band gaps at the K points in the reciprocal lattice space can be formed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
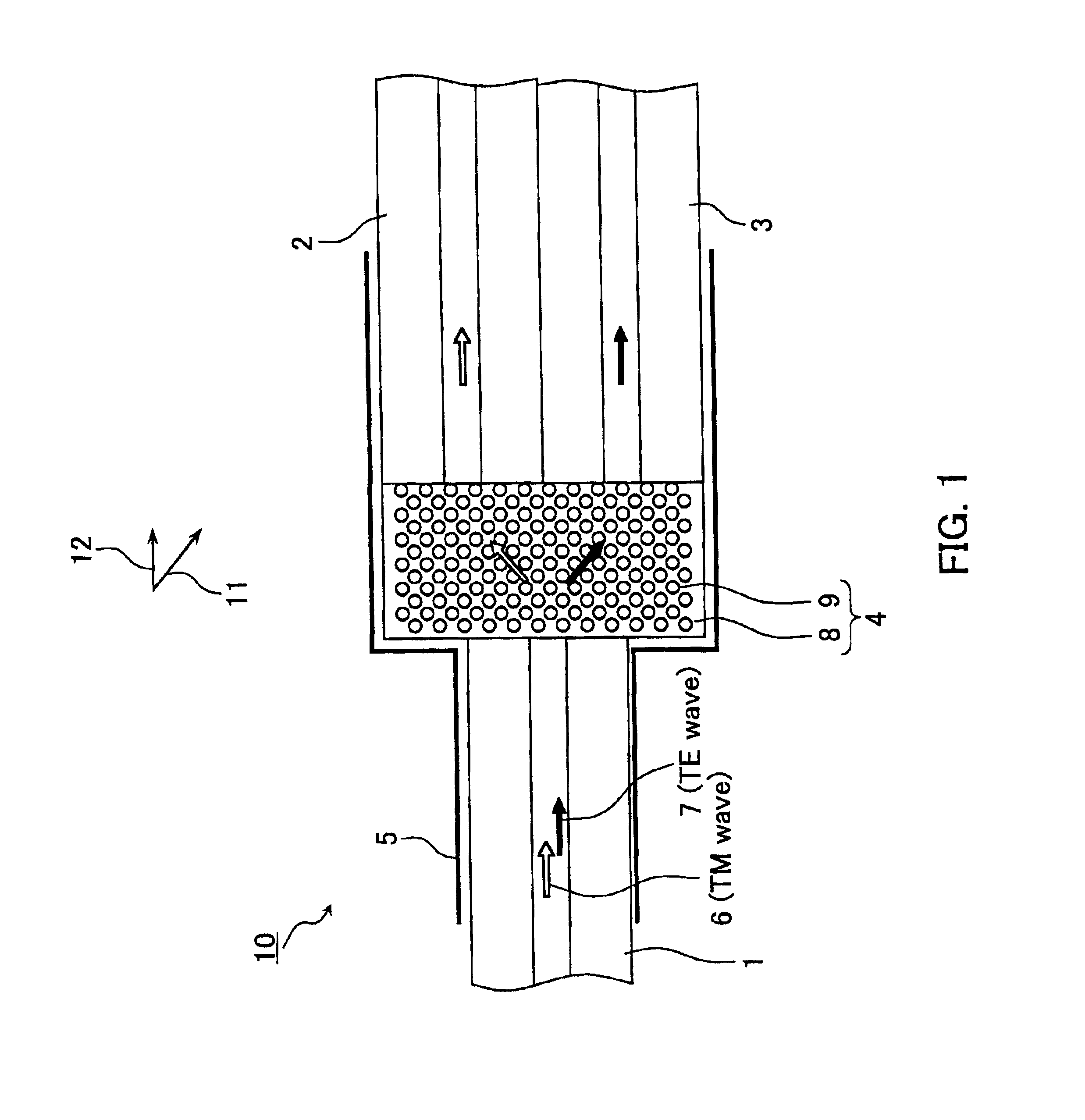
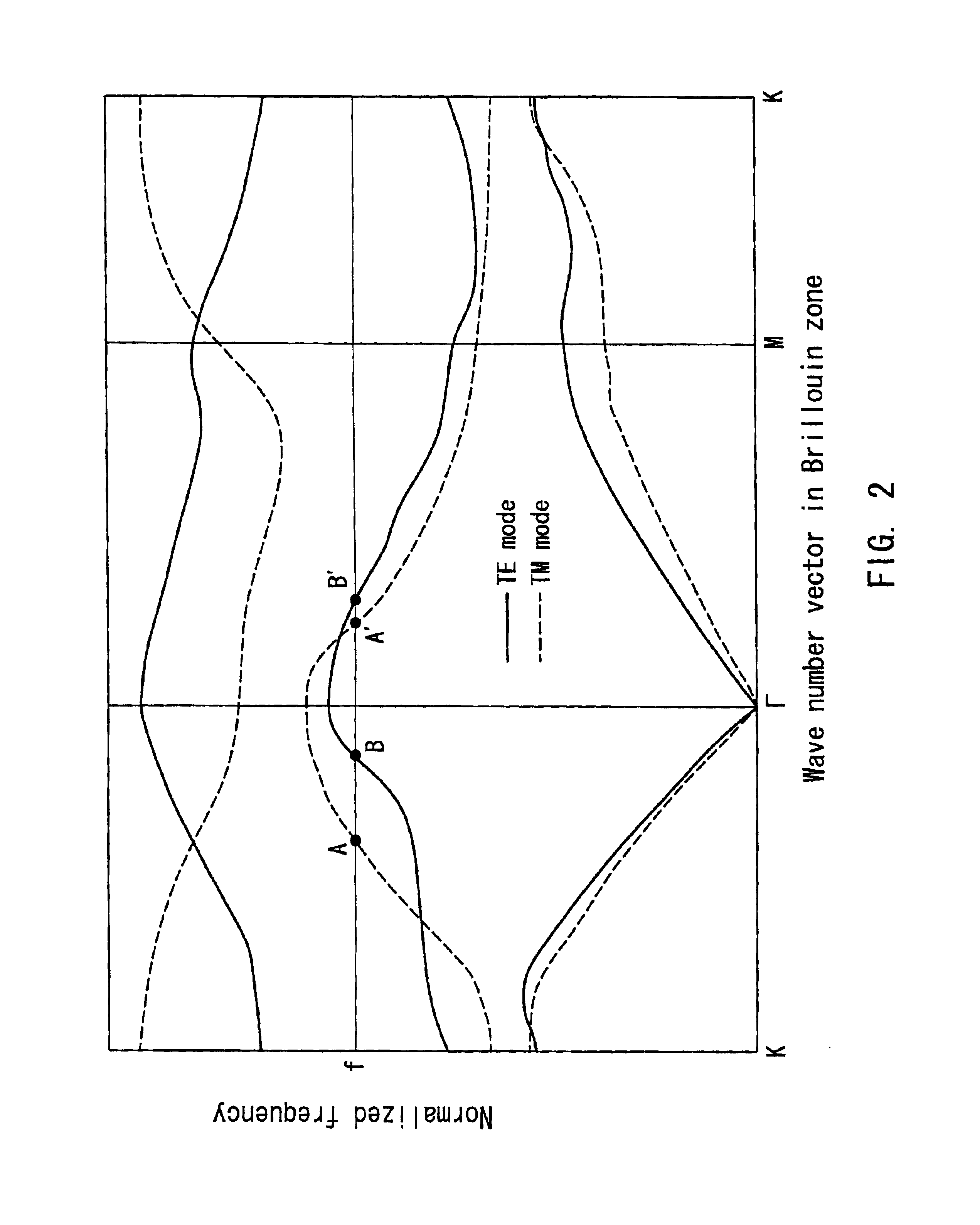
Optical device
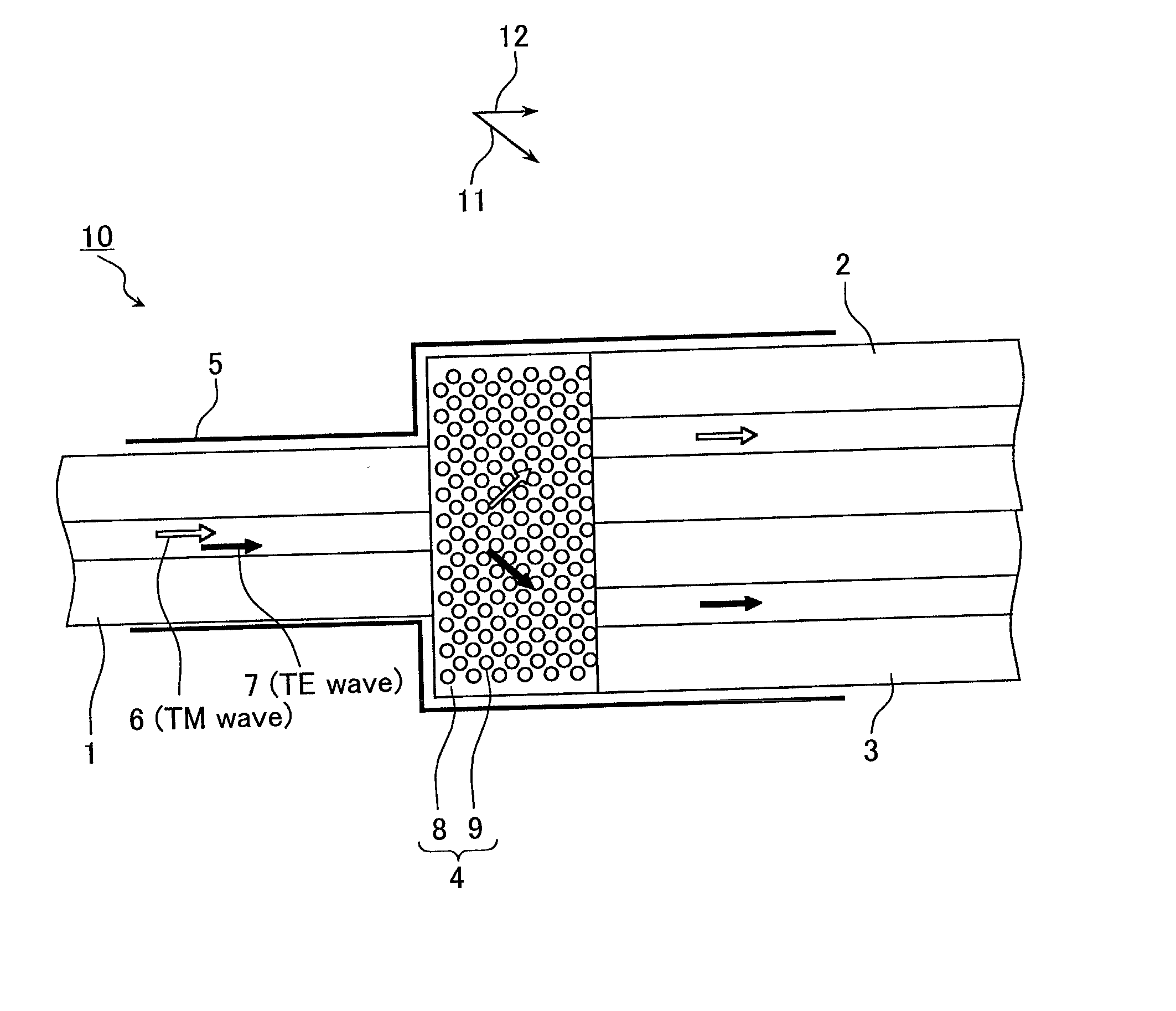
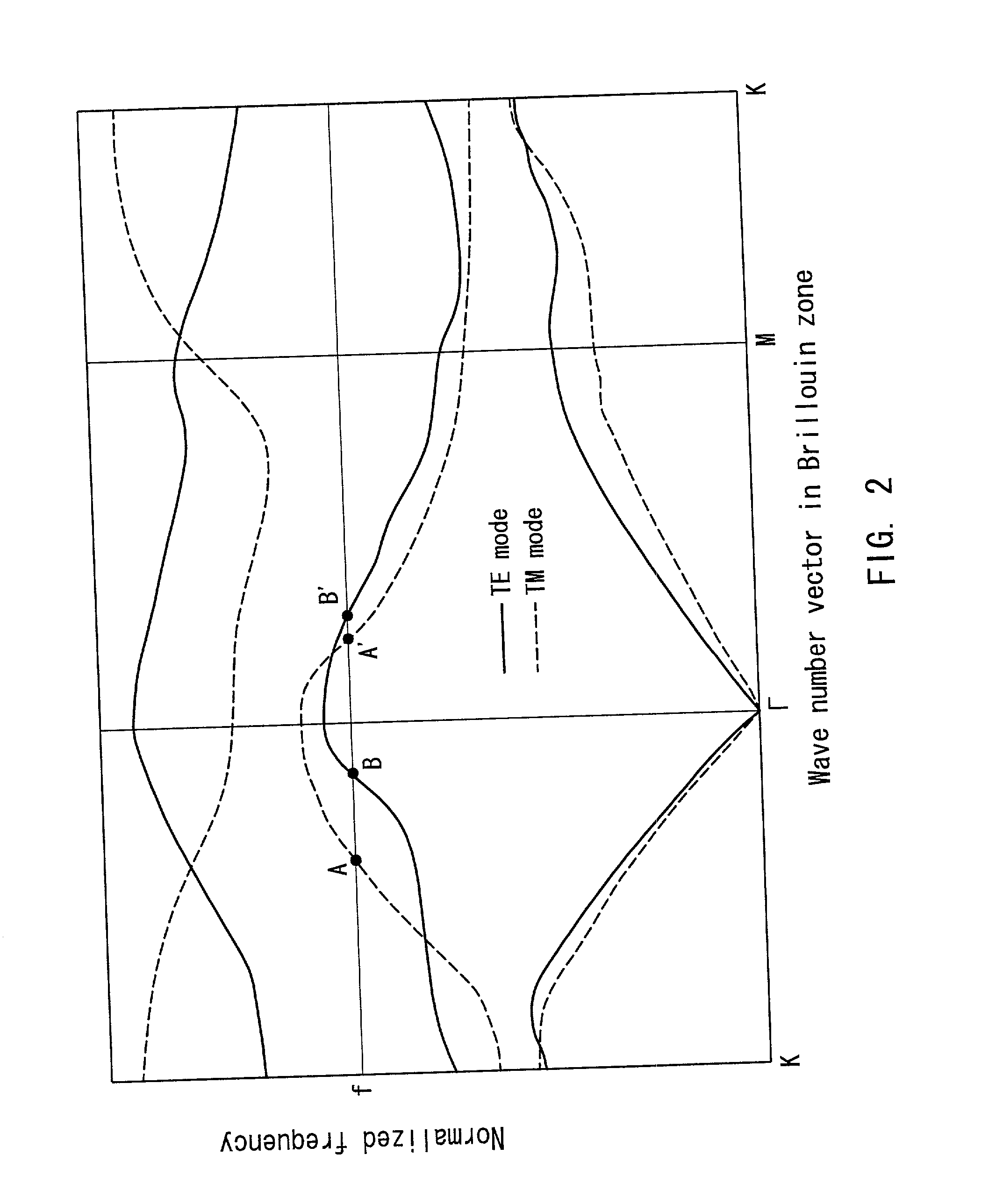
InactiveUS6813399B2Reduce in quantityLarge separationNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexWavelength
The invention provides a small optical device with which incident light can be demultiplexed. The optical device includes a demultiplexing portion 4 (first optical member) separating TE waves and TM waves of incident light of a wavelength lambda and an optical fiber 1 (optical input portion) inputting incident light into the demultiplexing portion 4. The demultiplexing portion 4 has a periodically changing refractive index. The angle defined by the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 and the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2 of the demultiplexing portion 4 at the wavelength lambda is not greater than 90°. In the direction of the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 the wave number of the TE wave is larger than the wave number of the TM wave. In the direction of the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2 the wave number of the TE wave is smaller than the wave number of the TM wave. The optical fiber 1 inputs the incident light in a direction that is parallel to a plane including the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 and the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical device
InactiveUS20020110306A1Reduce in quantityLarge separationNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexWavelength
The invention provides a small optical device with which incident light can be demultiplexed. The optical device includes a demultiplexing portion 4 (first optical member) separating TE waves and TM waves of incident light of a wavelength lambd and an optical fiber 1 (optical input portion) inputting incident light into the demultiplexing portion 4. The demultiplexing portion 4 has a periodically changing refractive index. The angle defined by the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 and the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2 of the demultiplexing portion 4 at the wavelength lambd is not greater than 90°. In the direction of the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 the wave number of the TE wave is larger than the wave number of the TM wave. In the direction of the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2 the wave number of the TE wave is smaller than the wave number of the TM wave. The optical fiber 1 inputs the incident light in a direction that is parallel to a plane including the first reciprocal lattice vector alpha1 and the second reciprocal lattice vector alpha2.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
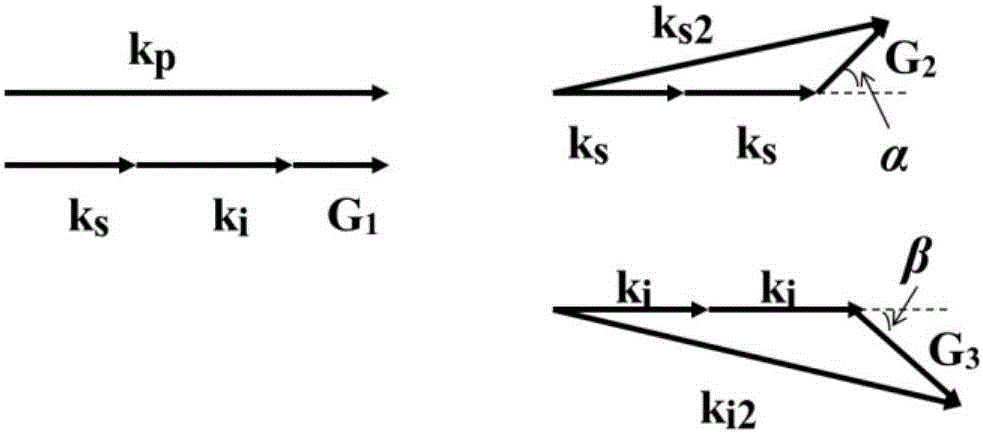
Infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of an infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice. By utilizing the optic superlattice of the structure, the structure of the optic superlattice provides two reciprocal lattice vectors simultaneously, wherein one reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in an OPO (optical parametric oscillation) process from near infrared to intermediate infrared, and the other reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in a signal light pump OPA (optical parametric amplification) from the OPO process, in the process, the intermediate infrared laser which is generated in the OPO process can be amplified further, thus more efficient intermediate infrared laser output of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained; and a commensurability ratio double periodic structure is adopted for the optic superlattice, thus the more efficient intermediate infrared laser of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
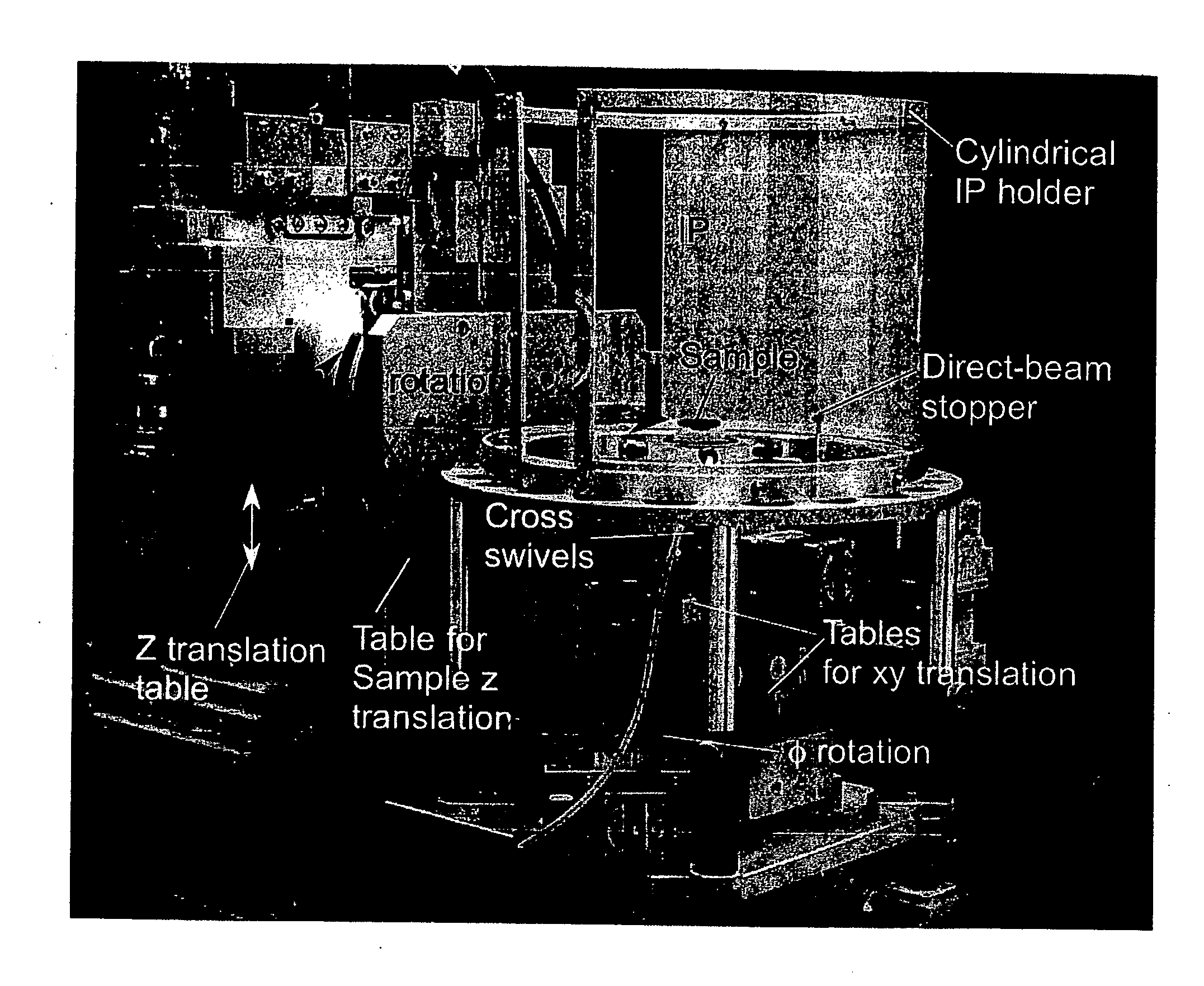
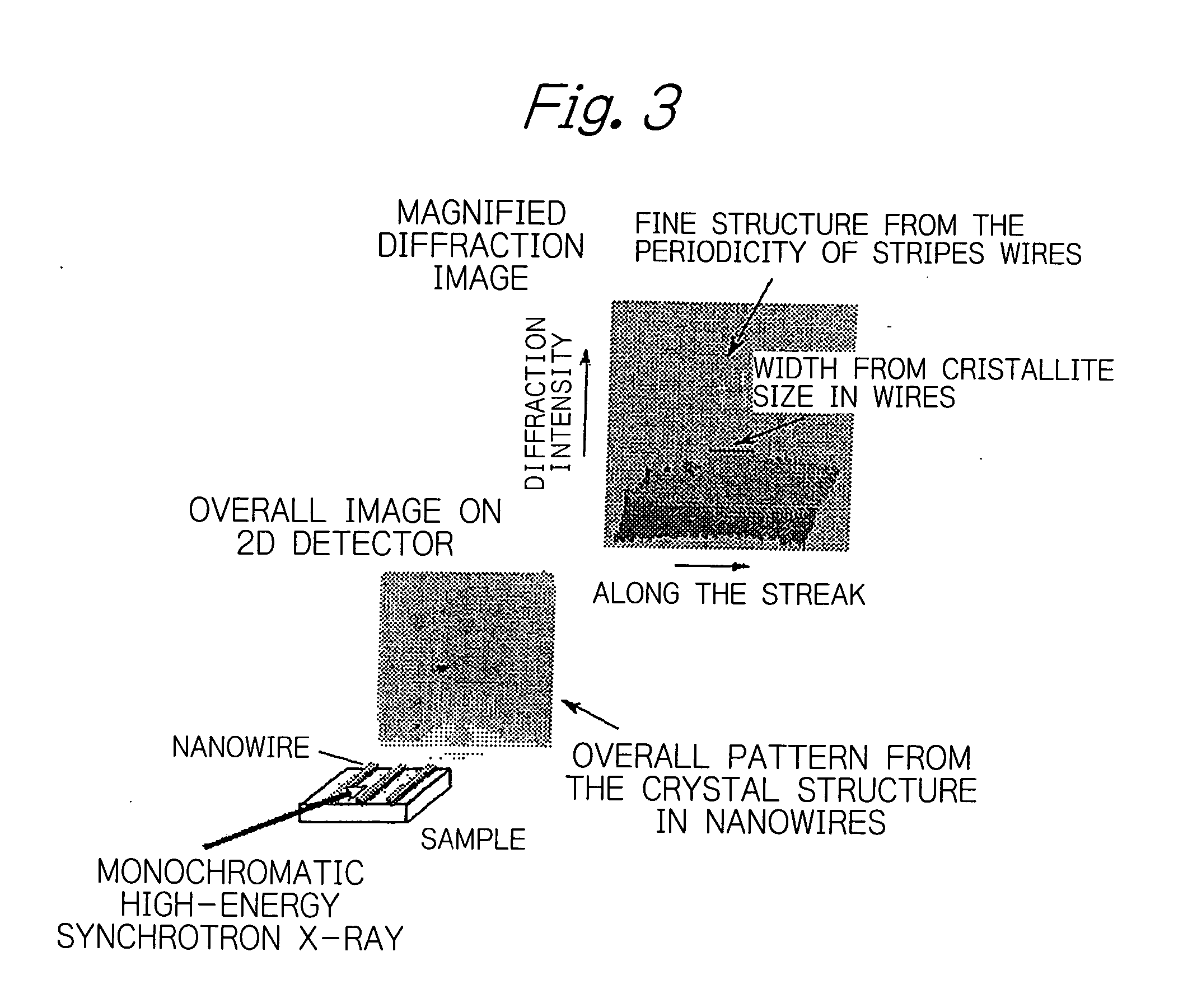
Rapid X-ray diffraction method for structural analysis of a nano material on a surface or at an interface and for structural analysis of a solid/liquid interface, and apparatus used for the method
InactiveUS20060032433A1Quick analysisLow costPolycrystalline material growthMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanowireX-ray
To characterize or evaluate ultra-fine structures such as ultra-fine nanowires grown on a substrate's crystal surface, buried ultra-fine nanolines or nanowires as sandwiched between a substrate's surface and an overlying cap layer, and thin-film crystals, or to solid-liquid interfacial structures comprising a solution and a solid, 0.1 nm or shorter-wavelength x-rays are incident on their surfaces at an angle of a few degrees or less and the diffracted x-rays are recorded with a two-dimensional x-ray detector in one action within a very short period of time, whereby the intensities of the diffracted x-rays from the ultra-fine structures or solid-liquid interfacial structures are visualized in the reciprocal lattice space and their structures are rapidly analyzed.
Owner:JAPAN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION RES INST
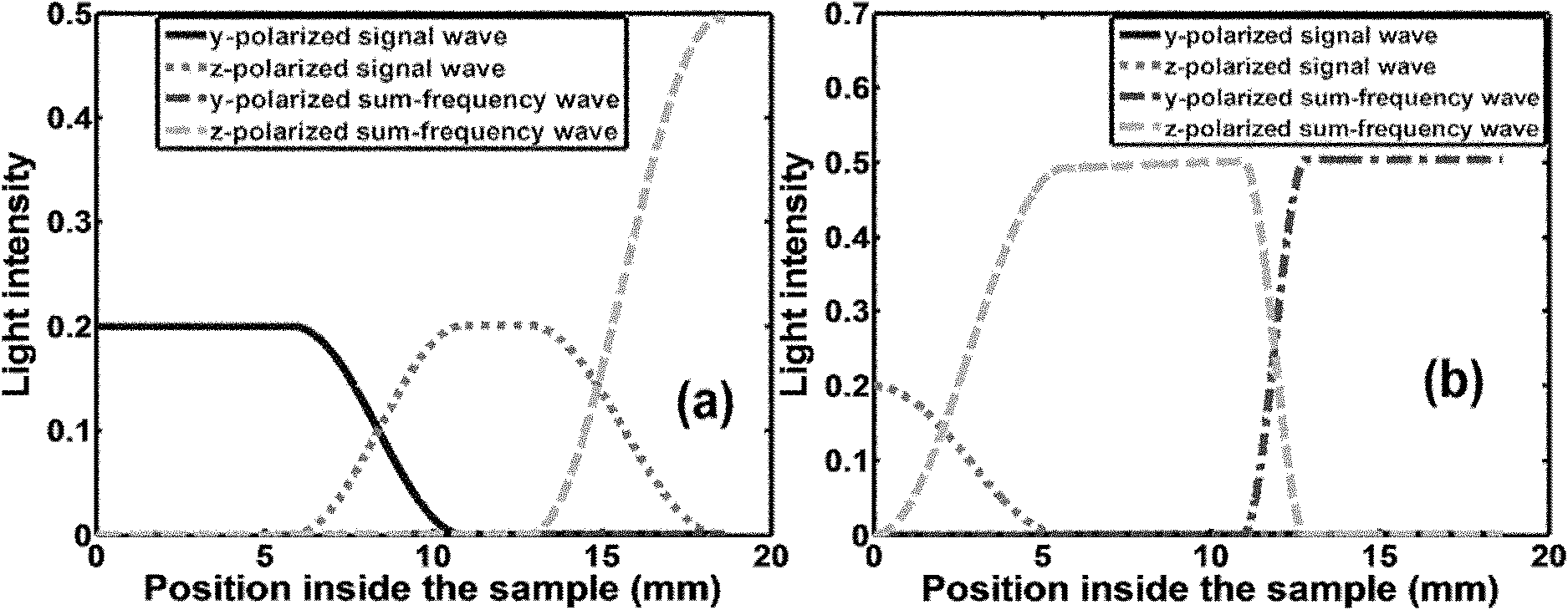
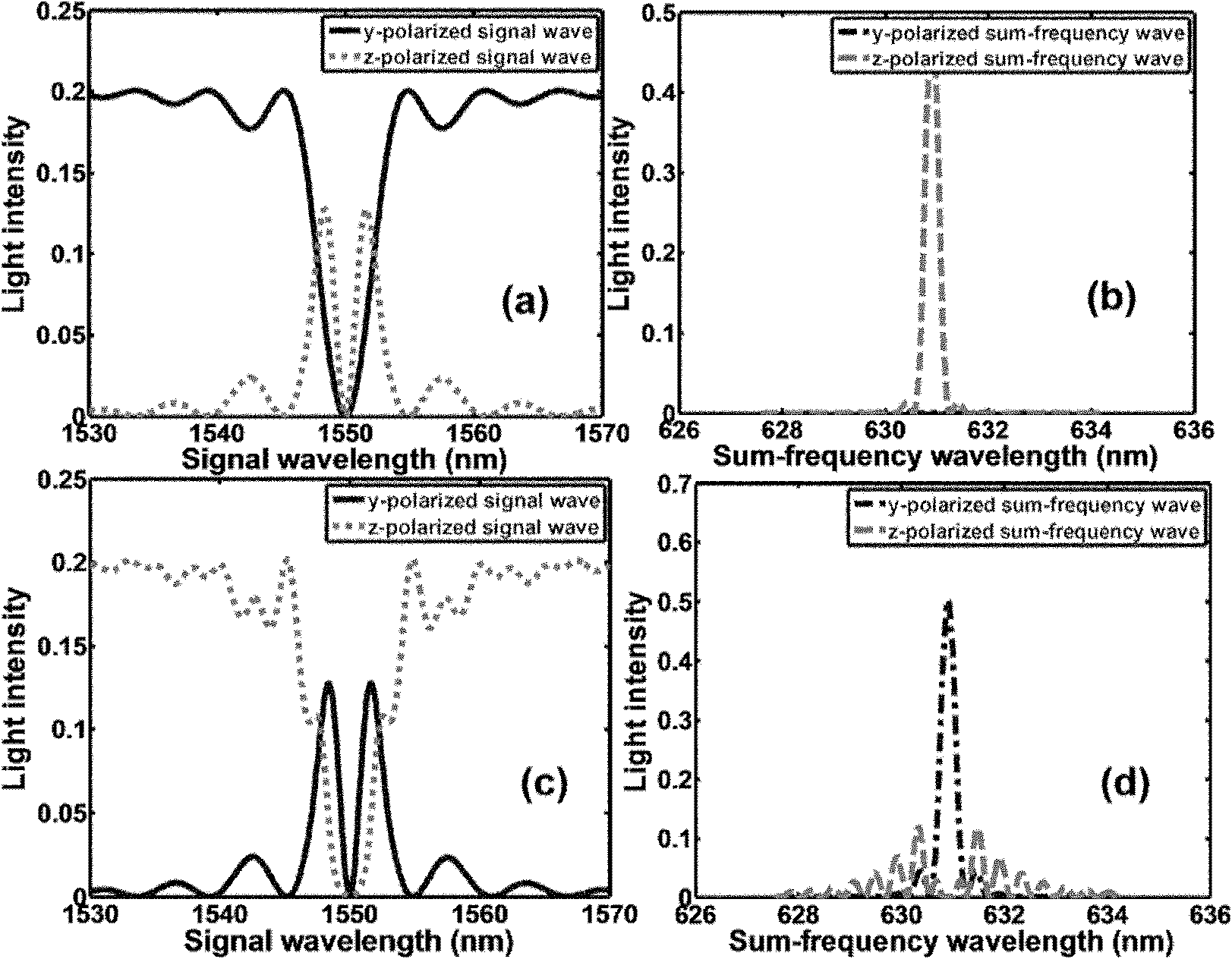
Single photon detector based on polarization unrelated frequency up-conversion
InactiveCN102147293AEasy to set upAchieving complete polarization independenceNon-linear opticsSemiconductor devicesSignal lightOptical coefficient
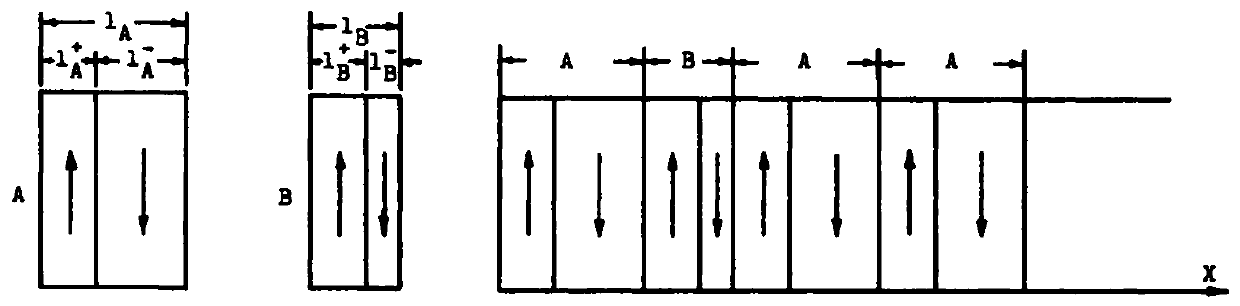
The invention relates to a signal photon detector based on polarization unrelated frequency up-conversion; the signal photon detector comprises a lithium niobate crystal which is formed by periodically superposing four parts and is periodically polarized, wherein for a first part and a fourth part, the periodic structures are same, the period length is lA and meets the quasi-phase matching condition of frequency up-conversion, and the period number is NA so that all signal lights can be converted into sum frequency lights; a second part is in a periodic structure used by reciprocal lattice vectors for compensating mismatching of wave vectors coupled and polarized by signal lights, and the period length is lB and meets the phase matching condition of signal light polarization rotation; and a third part is in a periodic structure used by reciprocal lattice vectors for compensating mismatching of wave vectors coupled and polarized by sum frequency lights, the period length is lC and meets the phase matching condition of signal light polarization rotation. An external direct-current power supply is applied to y-surfaces of the second part and the third part of a sample so as to realize the periodic modulation of optical coefficients, thereby leading the polarization direction of corresponding light waves to rotate. The signal photon detector is practicable in preparation and has wide application prospect in fields of quantum communication and photo-communication.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
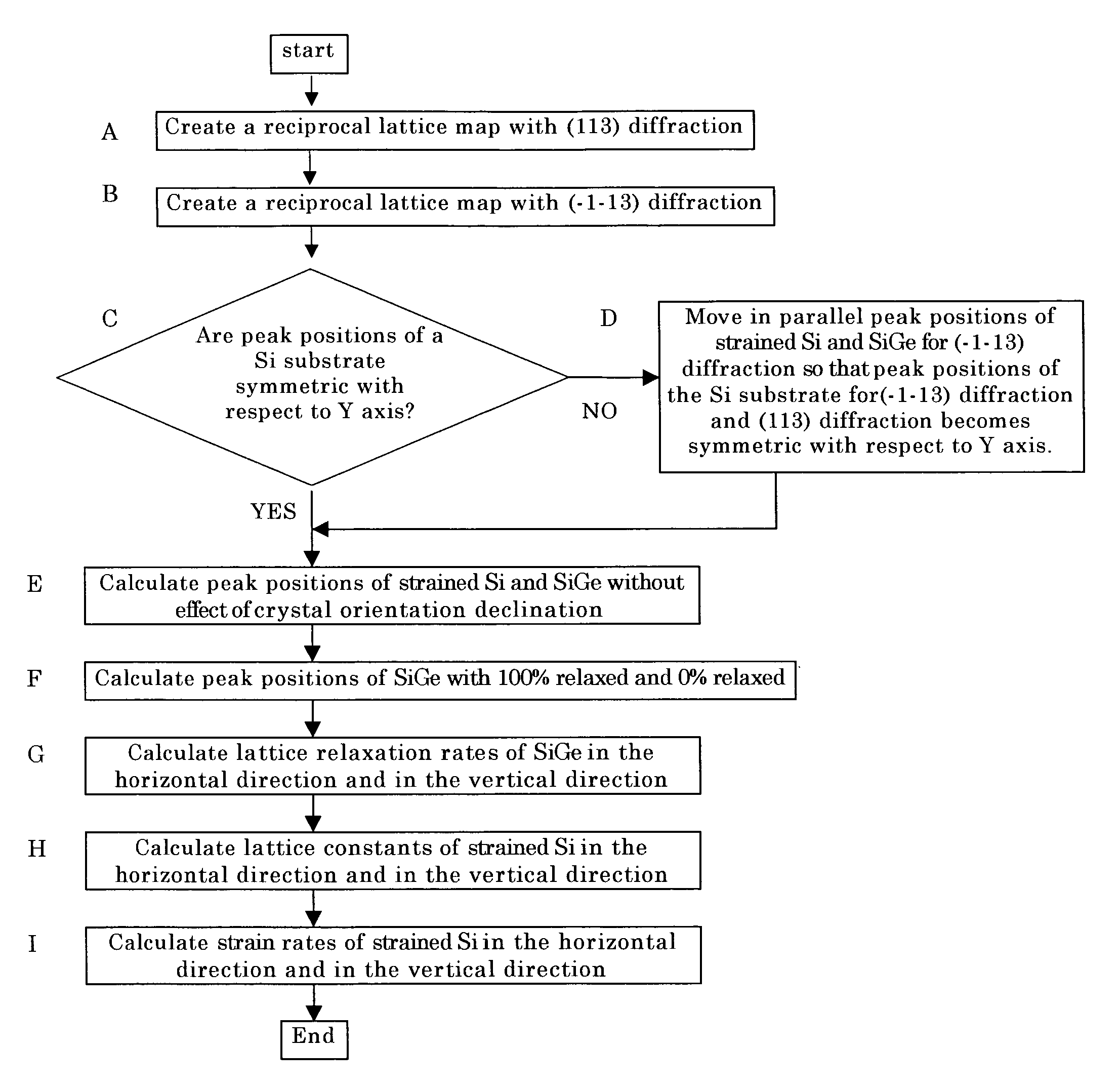
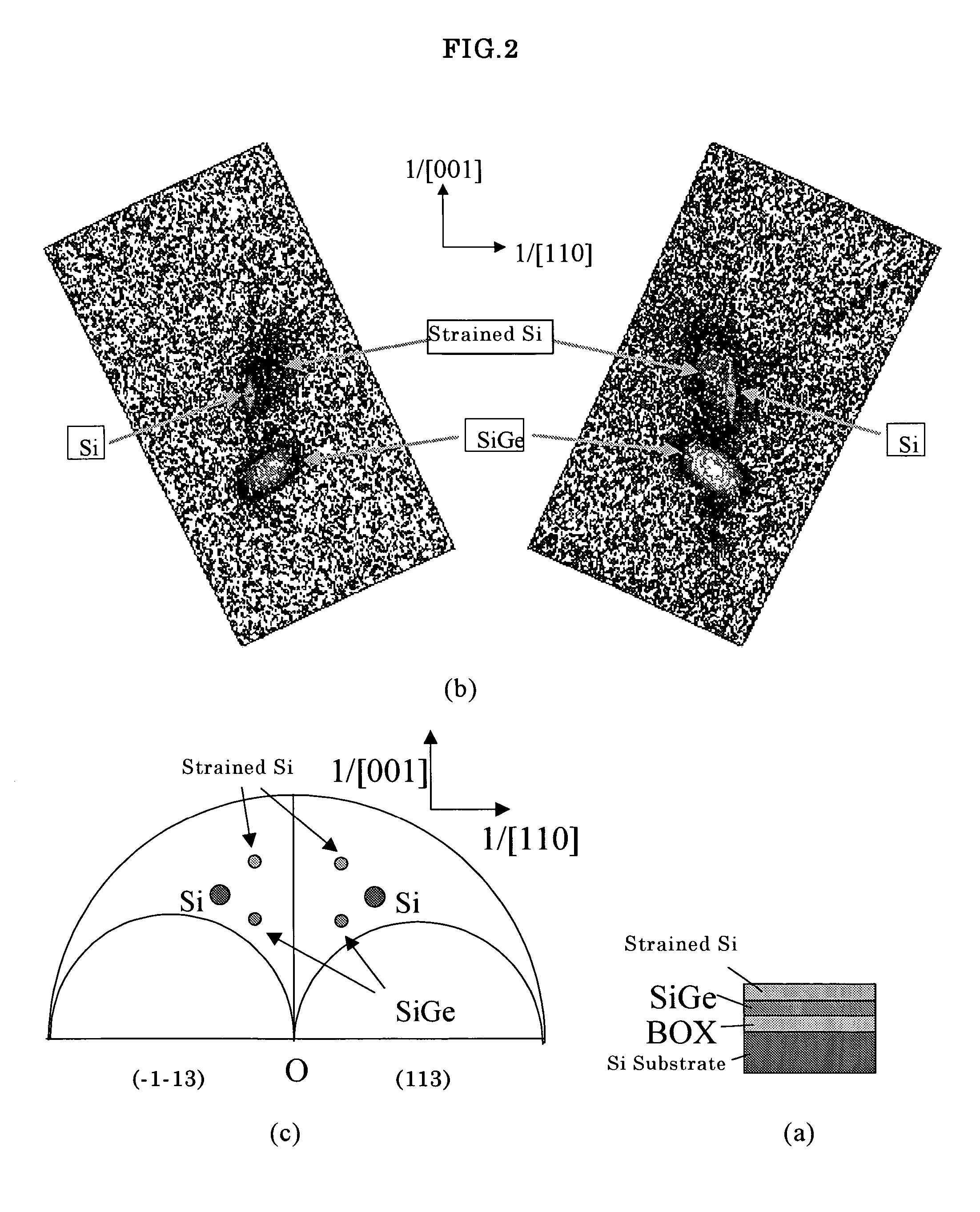
Method for measuring an amount of strain of a bonded strained wafer
ActiveUS20070166845A1Short timePrecise processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementNon symmetricX-ray
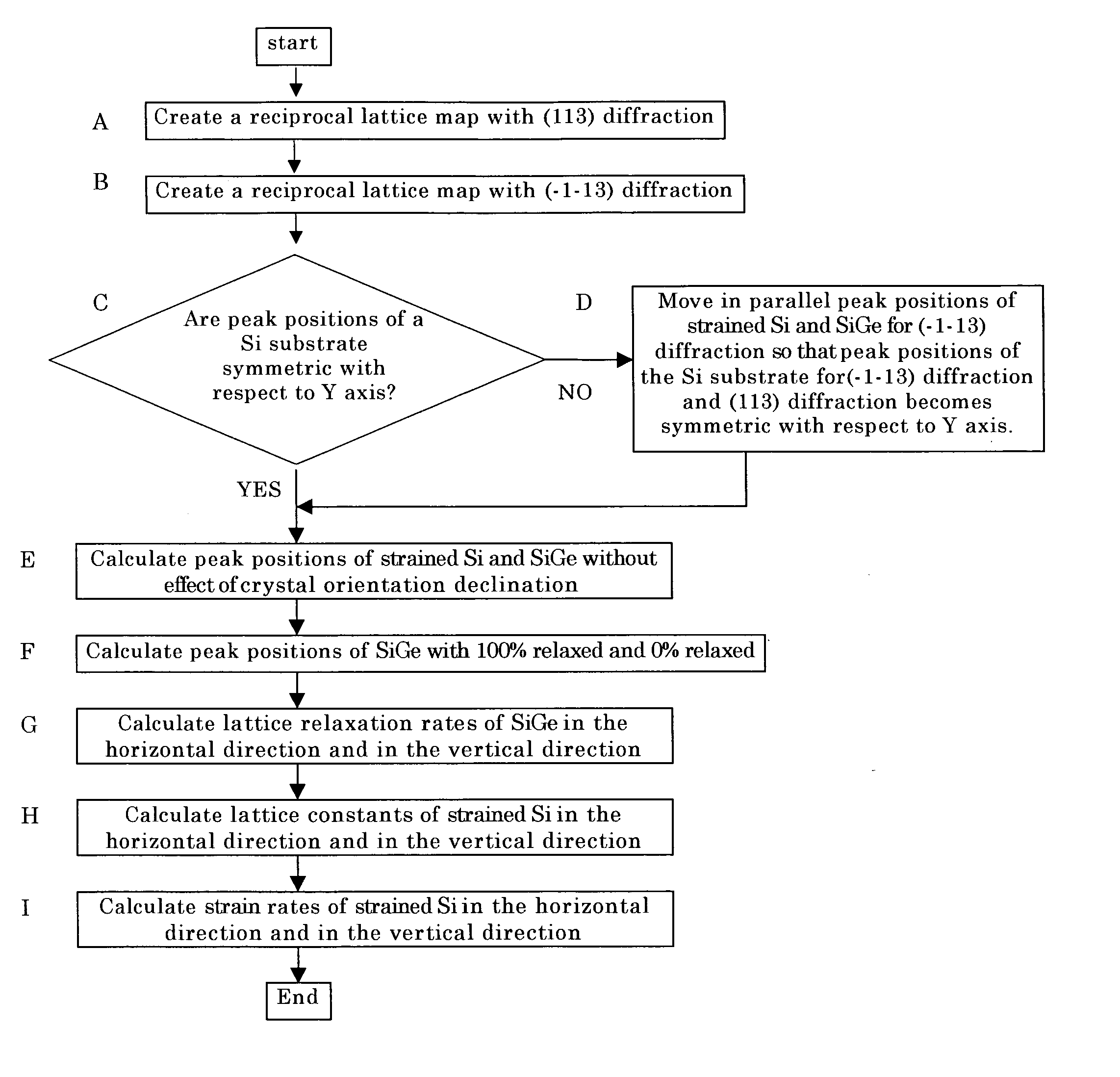
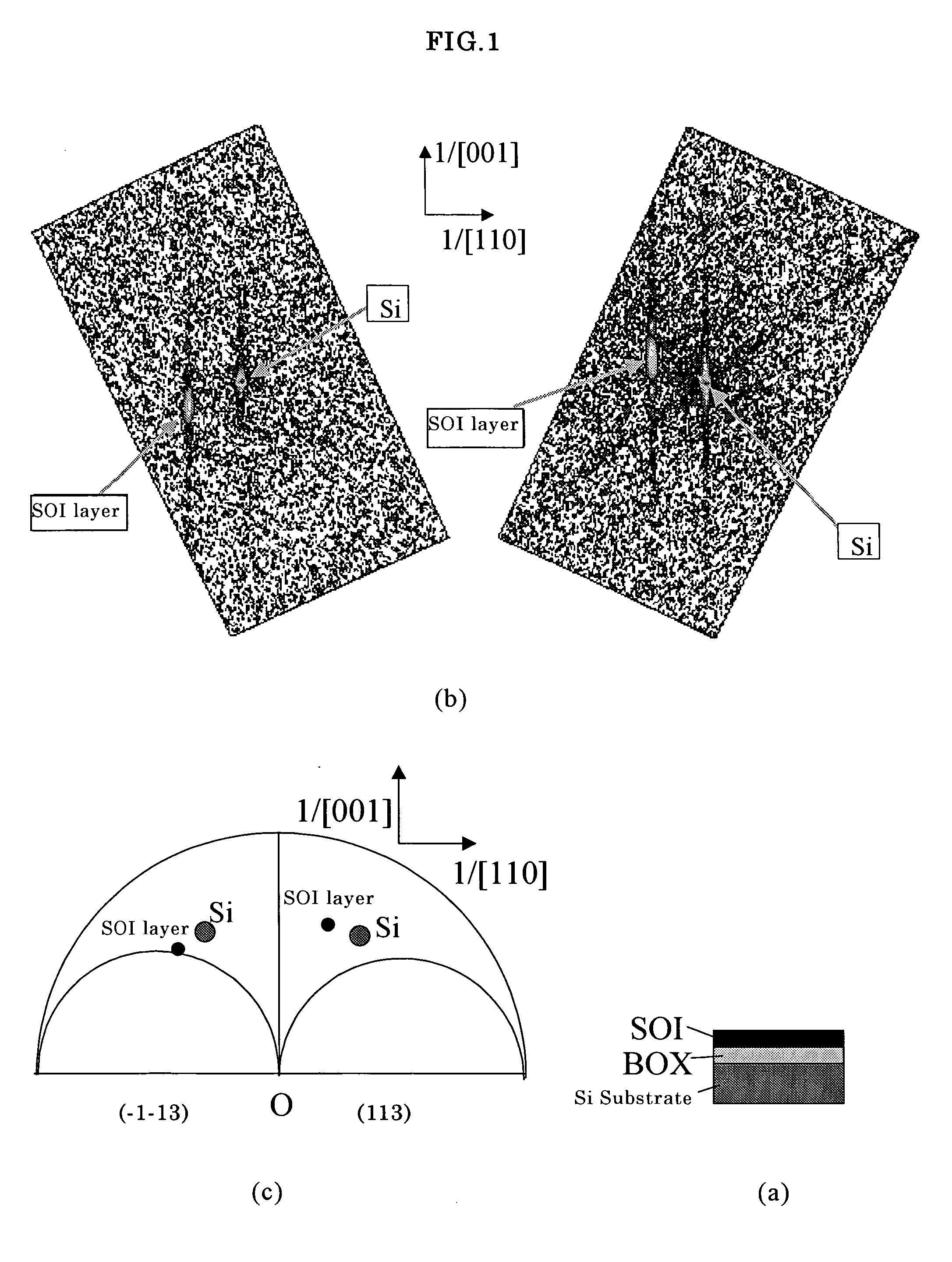
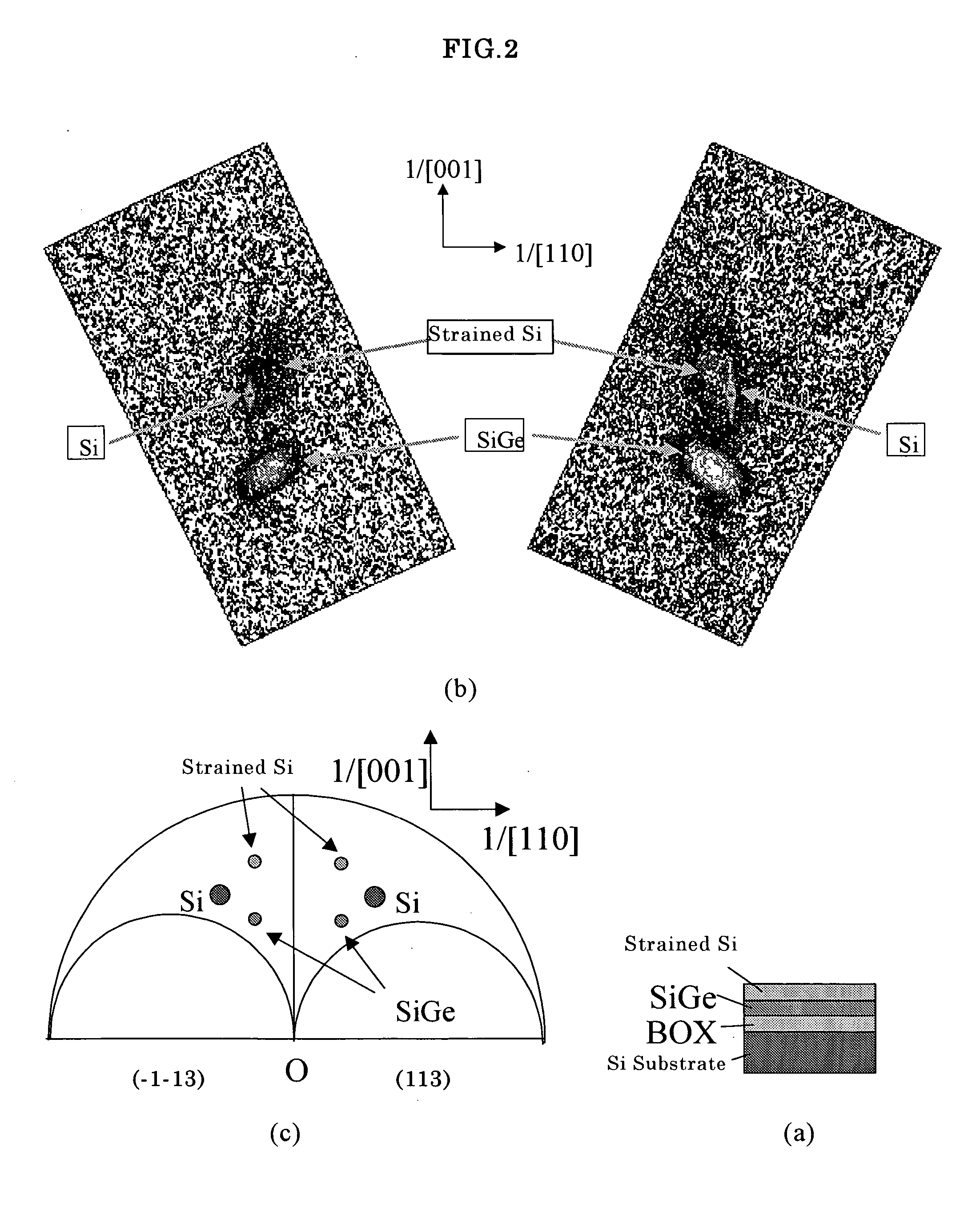
The present invention is a method for measuring an amount of strain of a bonded strained wafer in which at least one strained layer is formed on a single crystal substrate by a bonding method, wherein at least, the bonded strained wafer is measured with respect to two asymmetric diffraction planes with diffraction plane indices (XYZ) and (−X−YZ) by an X-ray diffraction method, a reciprocal lattice space map is created from the measured data, and the amount of strain of the strained layer is calculated from the peak positions for the respective diffraction planes of the single crystal substrate and the strained layer appearing on the reciprocal lattice space map. Thereby, there can be provided a method for measuring an amount of strain by which amounts of strain in the horizontal direction and in the vertical direction of the strained layer by an X-ray diffraction method in a bonded strained wafer can be measured in a shorter time and more simply.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Optical superlattice optimization structure setting method aiming at coupling nonlinear optical course
The invention relates to a method for setting an optical superlattice structure aiming at a coupling nonlinear optical process. Fourier transformation of a window is adopted to replace common whole fourier transformation; a local effective nonlinear coefficient and a spatial weighting function of a reciprocal lattice vector of an optical superlattice are introduced; the competitive relation between the fourier coefficients of each reciprocal lattice vector is considered; the spatial weighting function of the reciprocal lattice vector is subjected to optimized matching; for a triple-frequency coupling process, the spatial weighting function of the reciprocal lattice vector leans to the reciprocal lattice vector of the frequency doubling process in the initial stage and leans to the reciprocal lattice vector of the sum frequency process in the late stage; and through the optimization of the spatial distribution of the local fourier coefficients of two reciprocal lattice vectors, the method realizes the optimization of nonlinear conversion efficiency in the coupling process and carries out the setting of the optical superlattice structure on the basis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Periodic table group 13 metal nitride crystals and method for manufacturing periodic table group 13 metal nitride crystals
ActiveUS20150093318A1Easy to produceHigh luminous intensityPolycrystalline material growthNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsStacking faultX-ray
A periodic table Group 13 metal nitride crystals grown with a non-polar or semi-polar principal surface have numerous stacking faults. The purpose of the present invention is to provide a period table Group 13 metal nitride crystal wherein the occurrence of stacking faults of this kind are suppressed. The present invention achieves the foregoing by a periodic table Group 13 metal nitride crystal being characterized in that, in a Qx direction intensity profile that includes a maximum intensity and is derived from an isointensity contour plot obtained by x-ray reciprocal lattice mapping of (100) plane of the periodic table Group 13 metal nitride crystal, a Qx width at 1 / 300th of peak intensity is 6×10−4 rlu or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
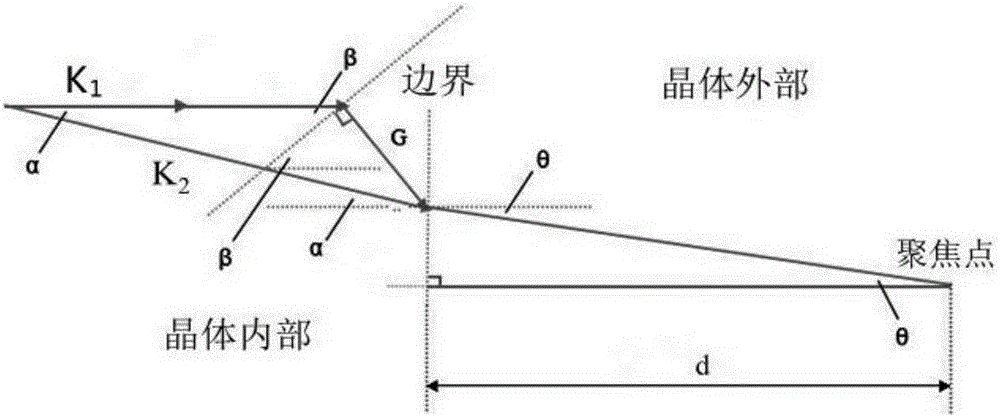
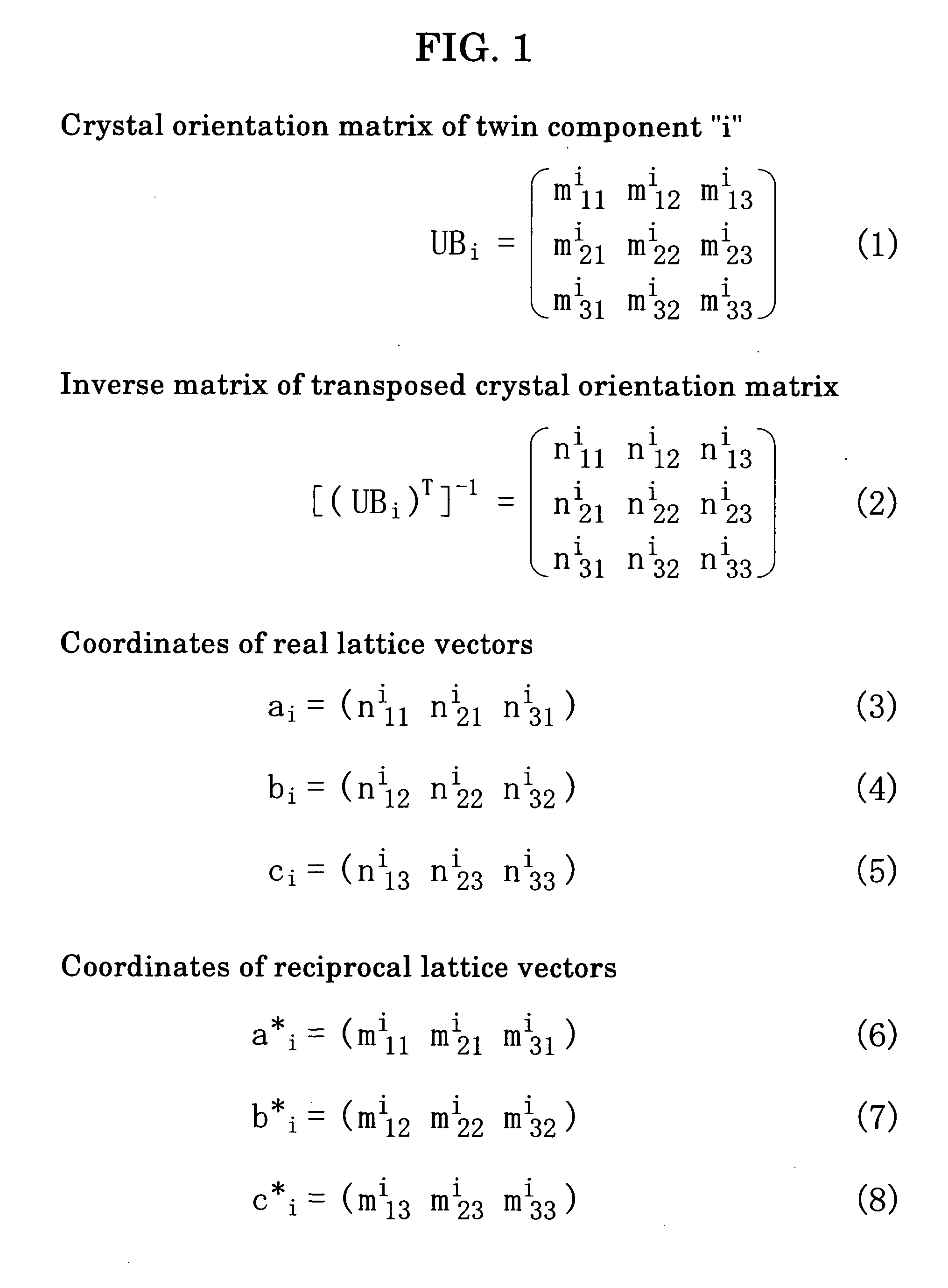
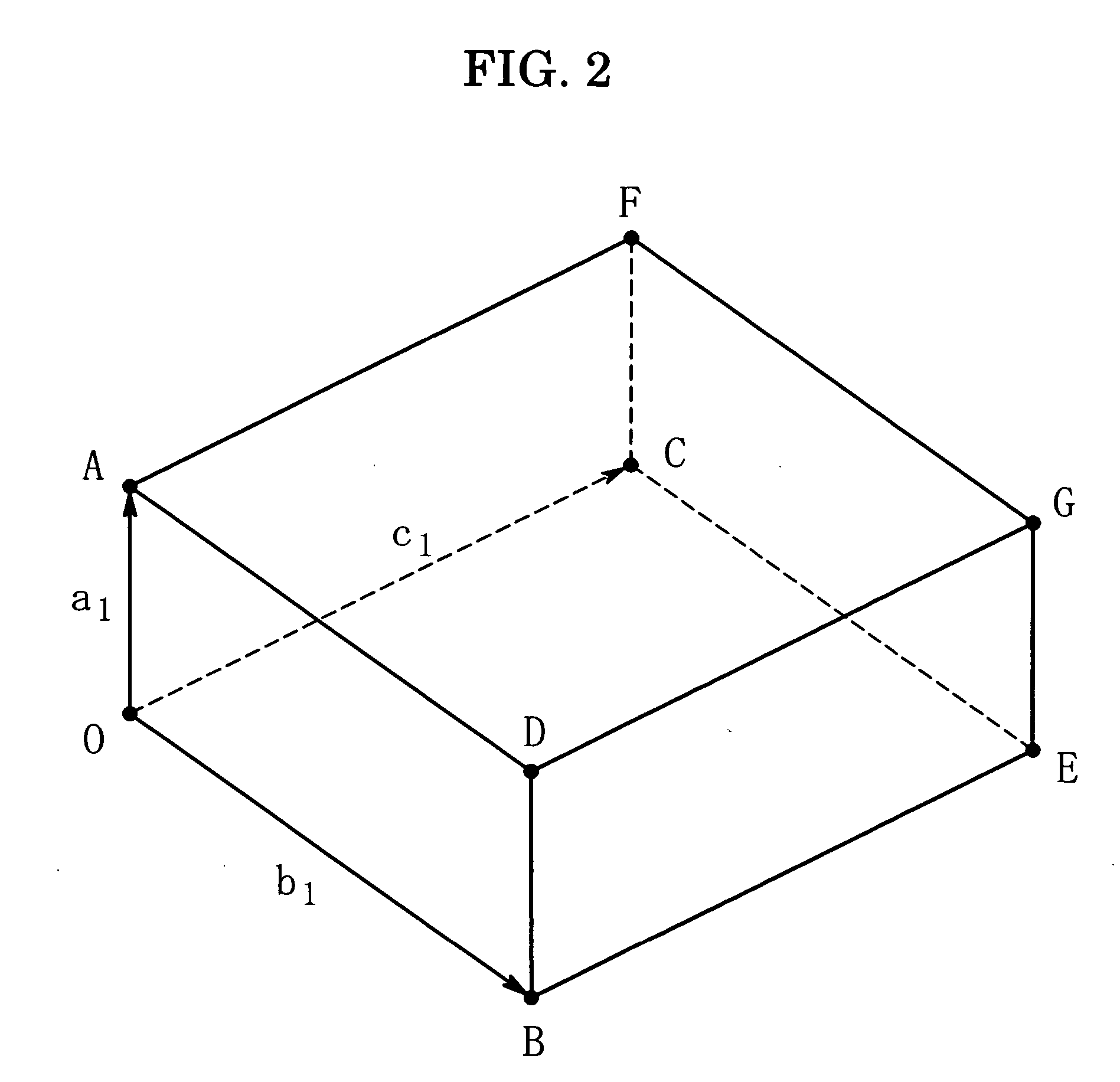
Method and apparatus for analyzing twinned crystal
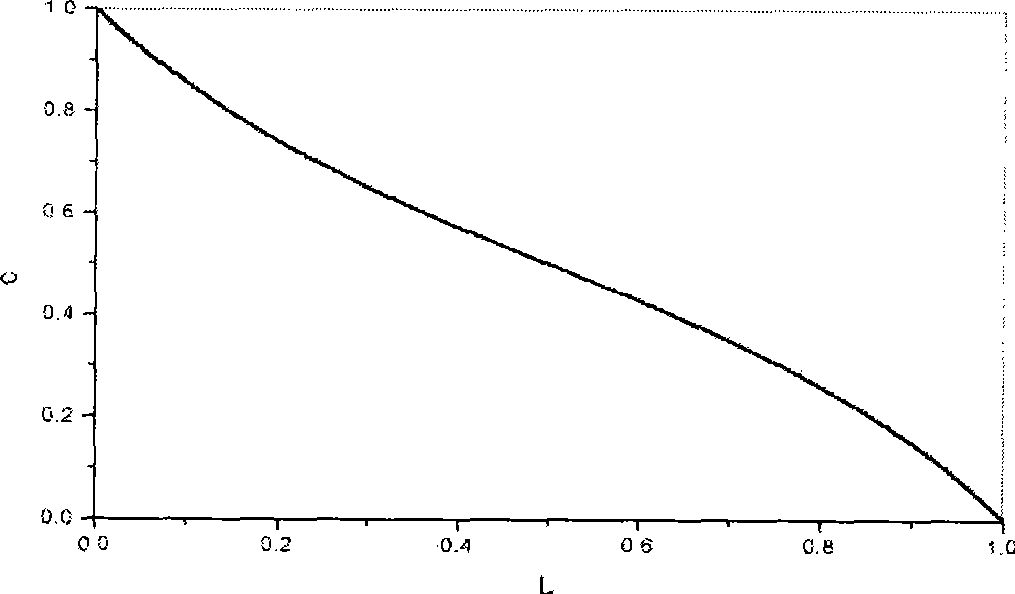
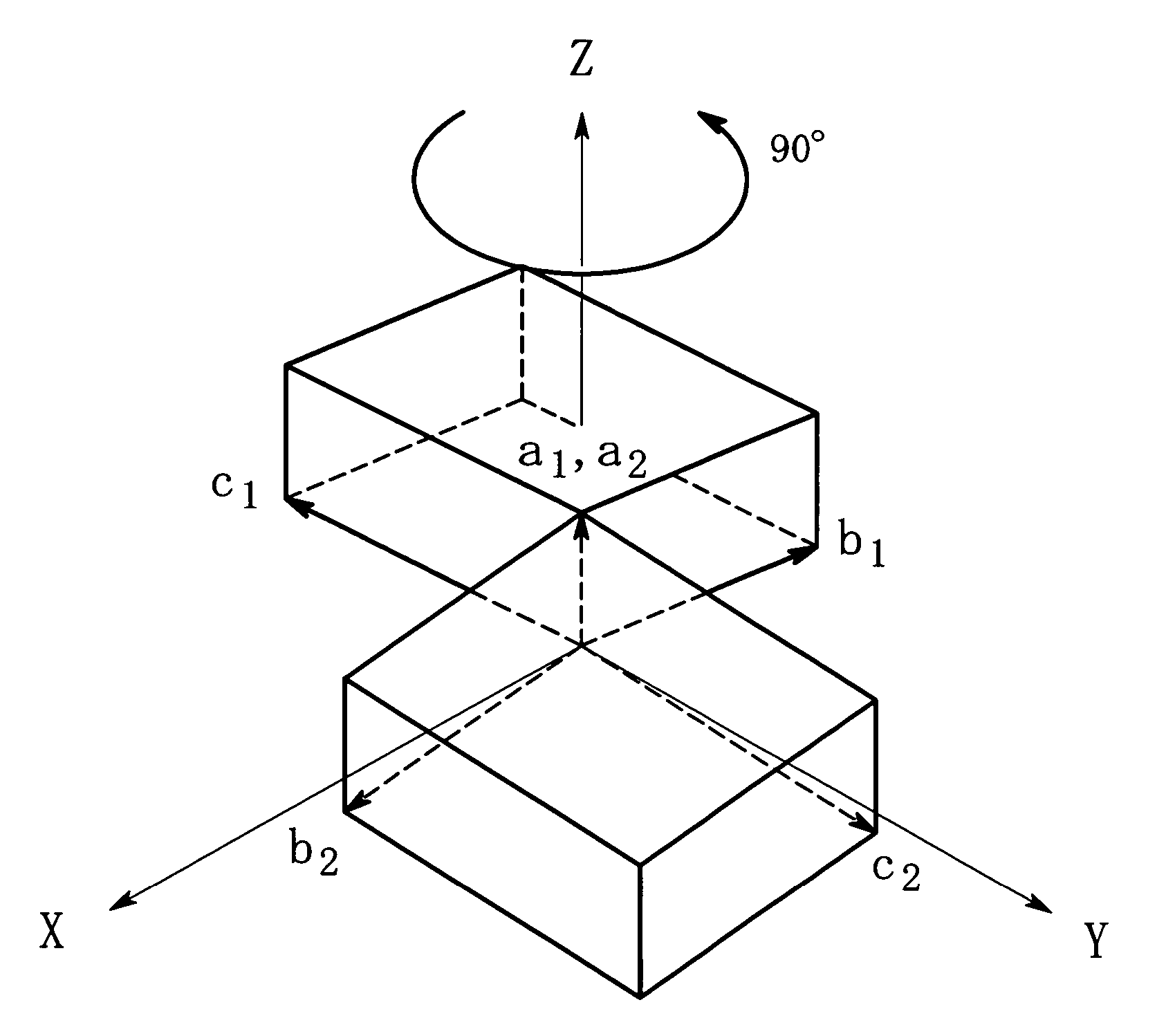
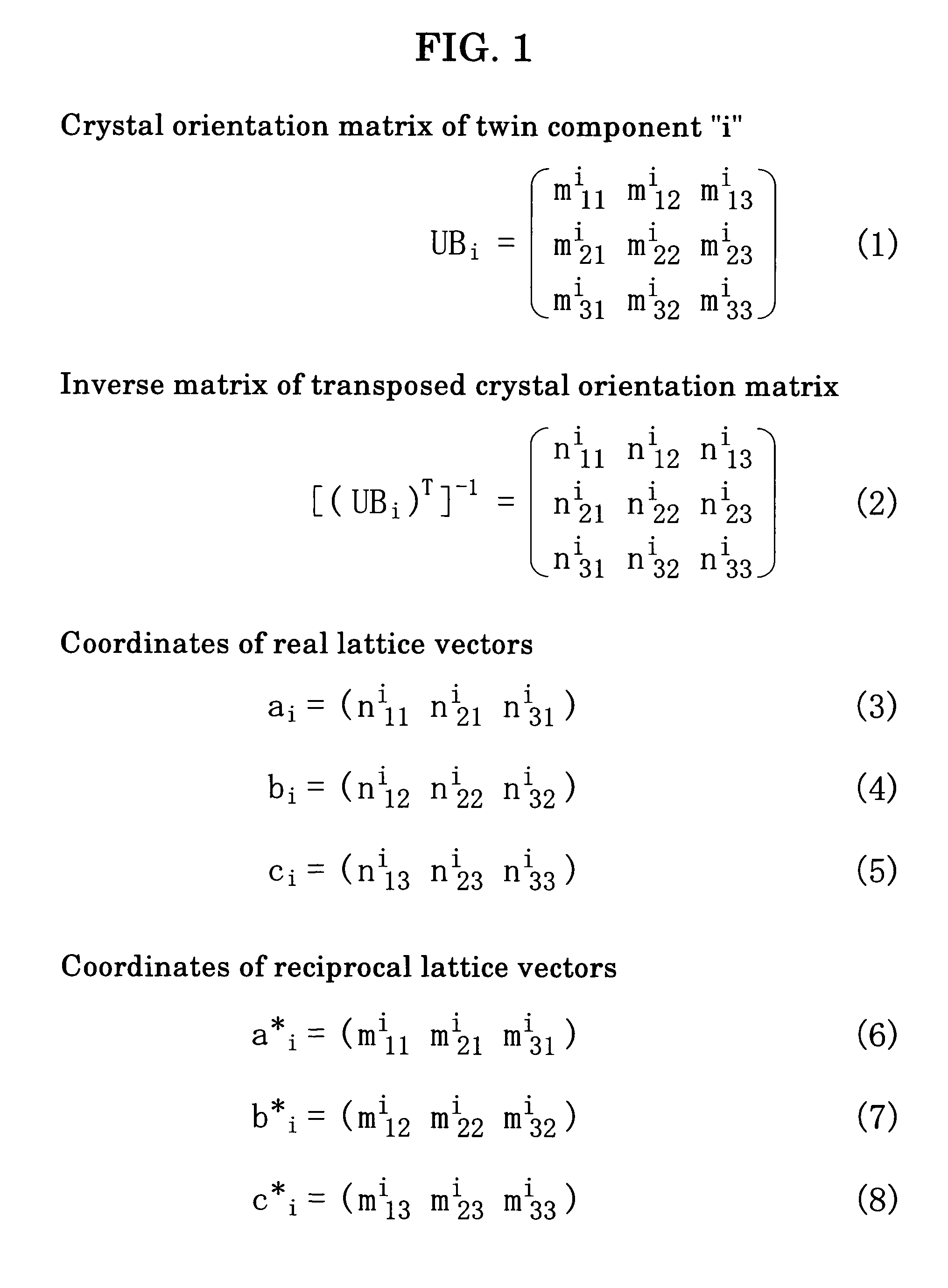
InactiveUS7696991B2Easy to understandFailure can not be analyzedSpecial data processing applicationsChemical methods analysisCrystal twinningStructure analysis
A method and an apparatus for analyzing a twinned crystal can display three-dimensionally the real space unit lattice, the reciprocal space primitive lattices and the reciprocal lattice points of each component of the twinned crystal. Respective crystal orientation matrices of the plural components of the twinned crystal are obtained with the use of X-ray single crystal structure analytical equipment. The first computing means finds the real-space unit lattices of the plural components based on the crystal orientation matrices and creates display data for displaying them three-dimensionally with possible their rotation, scaling up and down and translation. The second computing means finds the reciprocal-space primitive lattices and creates display data for displaying them three-dimensionally. The third computing means creates display data for displaying three-dimensionally reciprocal lattice points causing X-ray diffraction with a distinction between the components of the twinned crystal.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Method for measuring an amount of strain of a bonded strained wafer
ActiveUS7521265B2Short timePrecise processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementX-raySingle crystal substrate
In a method for measuring an amount of strain of a bonded strained wafer, at least one strained layer is formed on a single crystal substrate. The bonded strained wafer is measured with respect to two asymmetric diffraction planes with diffraction plane indices (XYZ) and (−X−YZ) by an X-ray diffraction method, a reciprocal lattice space map is created from the measured data, and the amount of strain of the strained layer is calculated from the peak positions for the respective diffraction planes of the single crystal substrate and the strained layer appearing on the reciprocal lattice space map. Thereby, amounts of strain in the horizontal direction and in the vertical direction of the strained layer can be measured in a shorter time and more simply.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
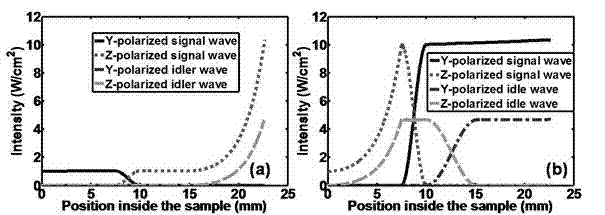
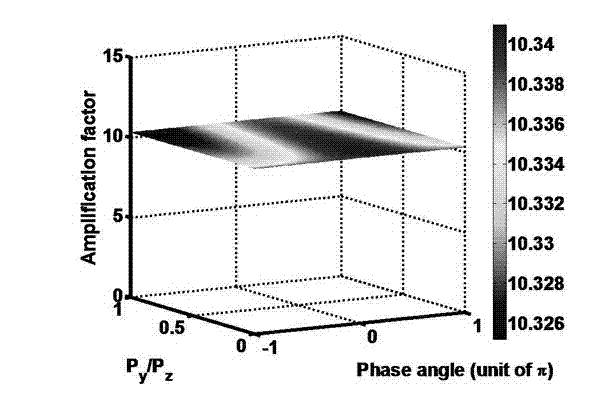
Vector beam amplifying and generating apparatus having polarization independent optical parametric amplification characteristics
ActiveCN102768451ASame magnificationAchieving Polarization Independent PropertiesNon-linear opticsPolar structureSignal light
The invention discloses a vector beam amplifying and generating apparatus having polarization independent optical parametric amplification characteristics, which comprises lithium niobate crystal (PPLN) or potassium niobate which is polarized according to different periods and divided into four parts, wherein optical parametric amplification of the first part and the fourth part cabn be realized, idle frequency light can be generated, and phase mismatch among a pump light, a signal light and an idle frequency light is compensated by means of a reciprocal lattice vector provided by a periodic polar structure; in the second part, the wave vector mismatch in which the signal light is polarized and coupled by means of the reciprocal lattice vector of the periodic polar structure can be compensated; the reciprocal lattice vector in the third part is designed to satisfy an electro-optic deflection reference matching process of the idle frequency light, the wave vector mismatch in which the idle frequency light is polarized and coupled can be compensated, the second part and the third part in the middle of the niobate crystal (PPLN) or the potassium niobate having different periodic polarity realize the periodic modulation of the electro-optical coefficients with an external DC (Direct Current) power supply on a y-surface perpendicular to a light propagation direction. The invention has wide application prospect in the all-optical switching and optical communication field.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Magnesium Oxide Single Crystal Having Controlled Crystallinity and Method for Producing the Same, and Substrate Using the Single Crystal
ActiveUS20080081767A1Controlled crystalline propertyImprove performancePolycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSingle crystalCrystallinity
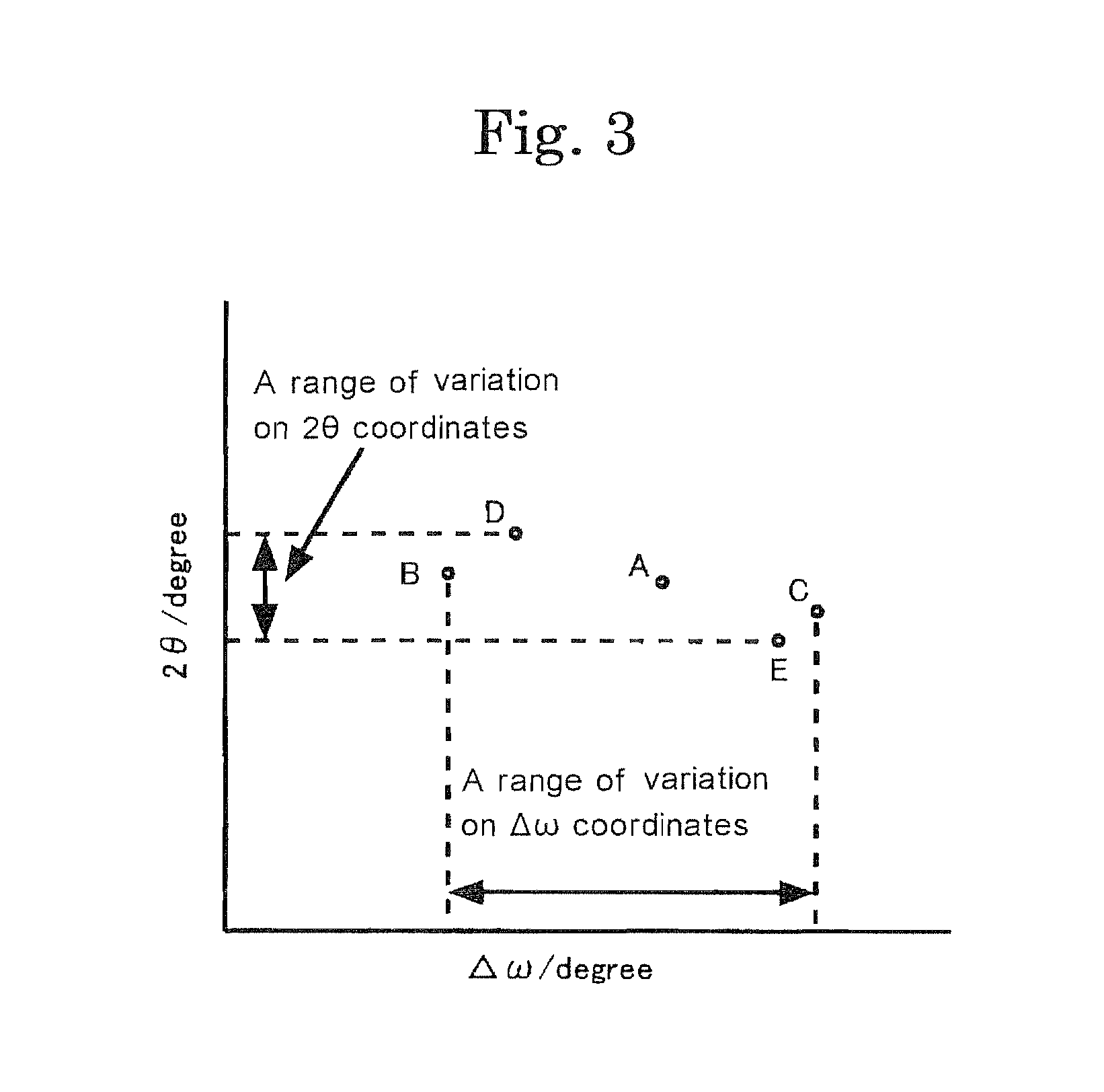
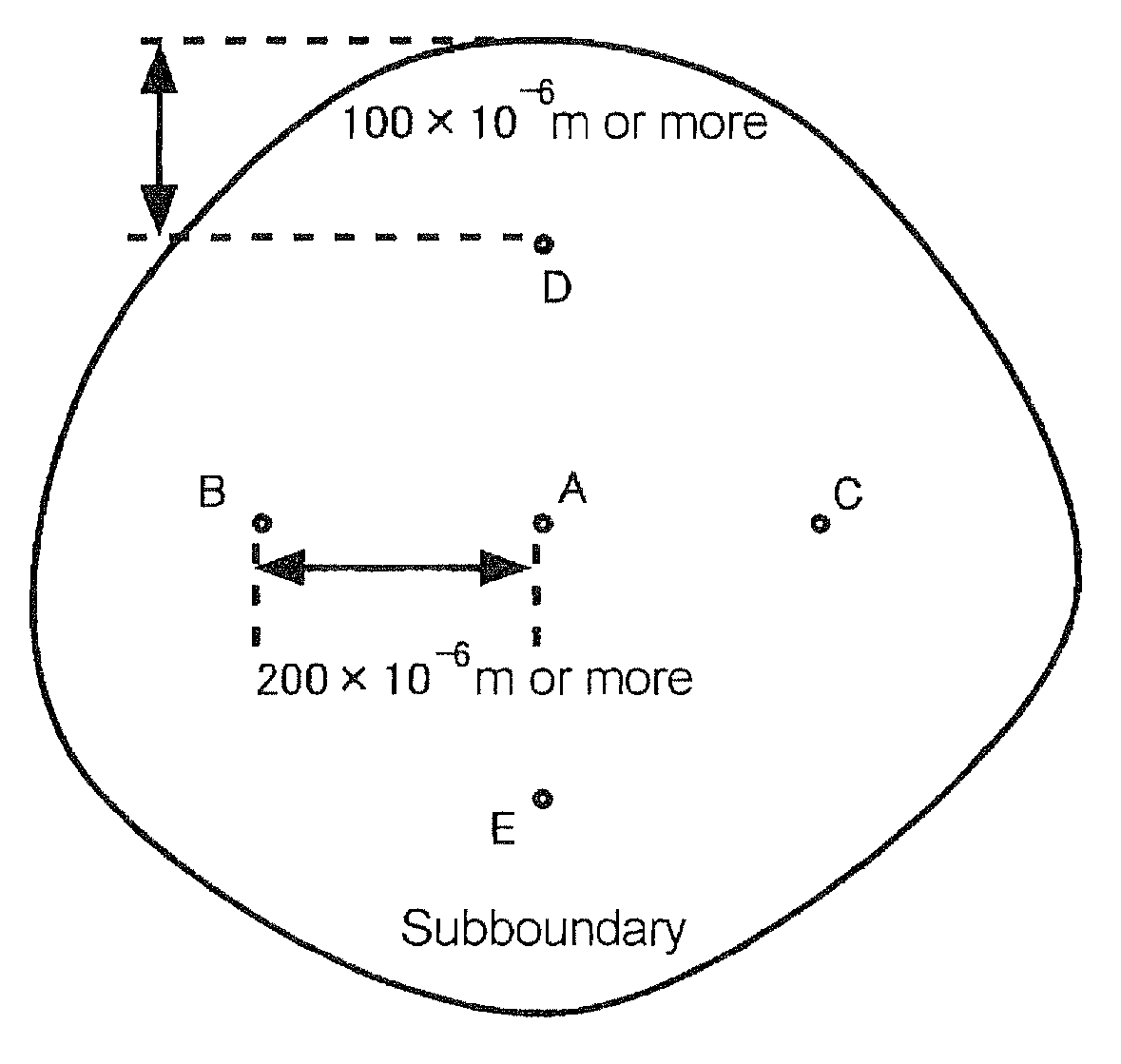
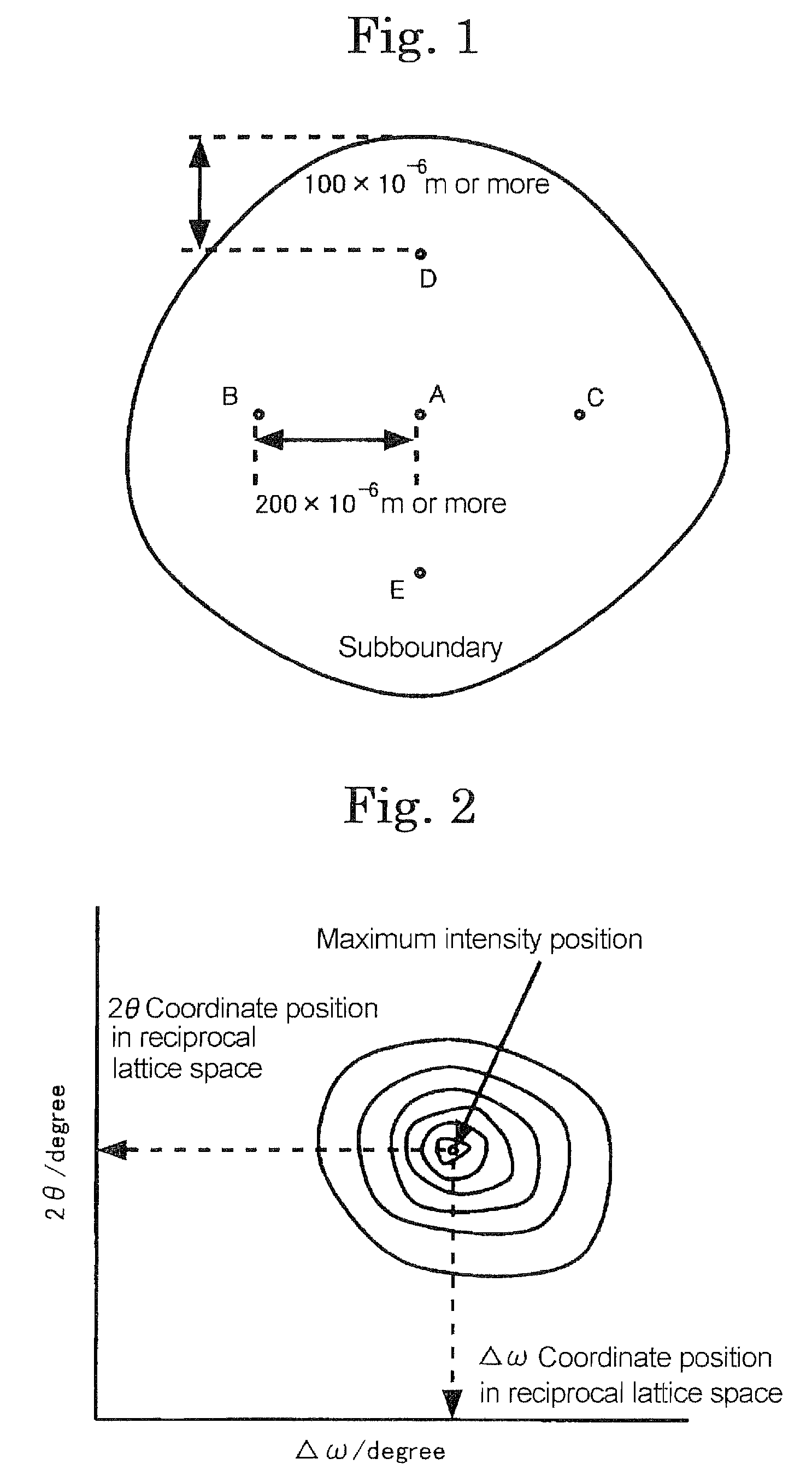
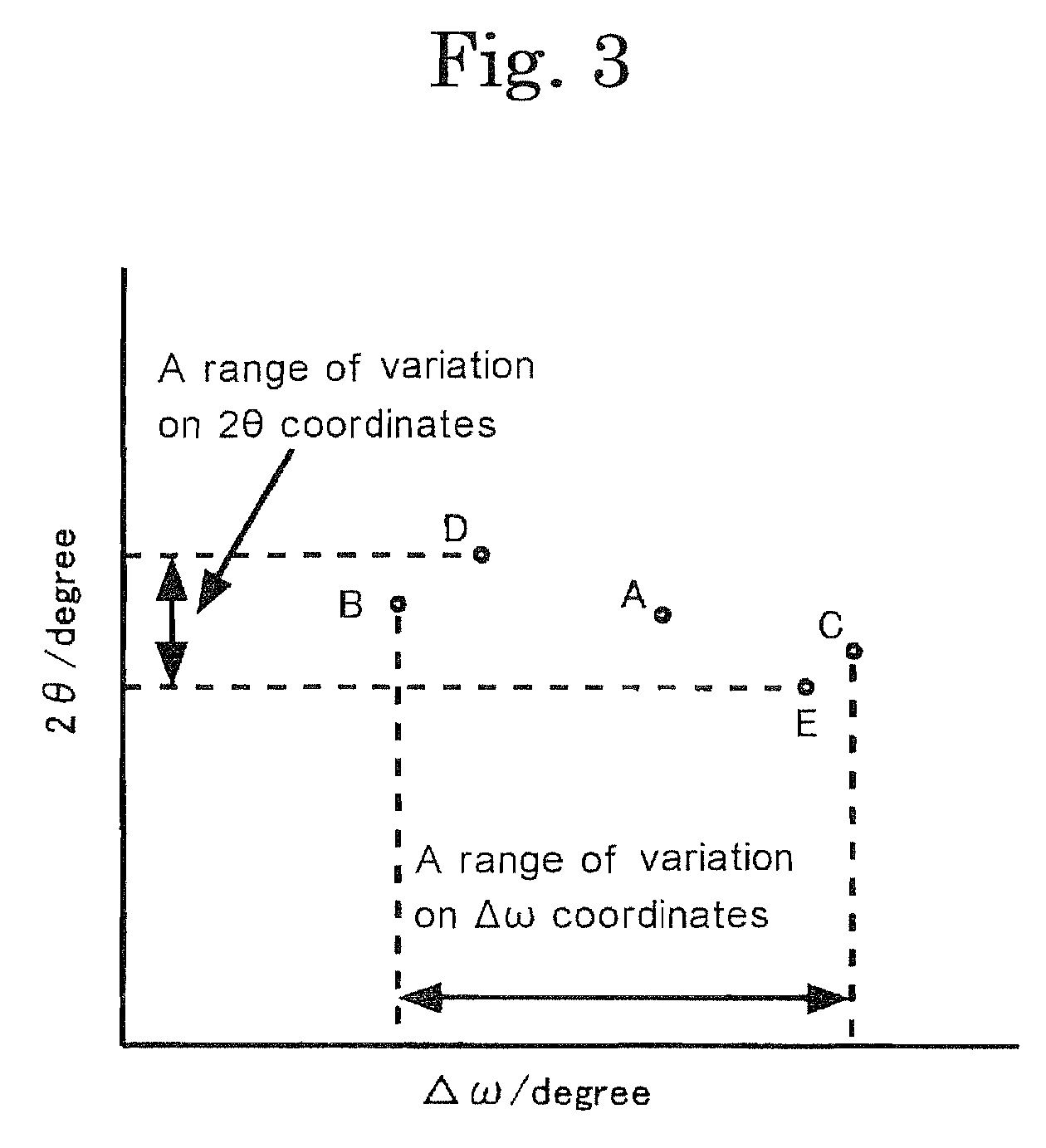
A magnesium oxide single crystal having controlled crystallinity comprising a subboundary, and ranges of variation of diffraction line positions, as measured for reciprocal lattice maps with respect to a region surrounded by the same subboundary, with the range of the variation of 1×10−3 to 2×10−2 degree of on Δω coordinates, and with the range of the variation of 4×10−4 to 5×10−3 degree on 2θ coordinates.
Owner:TATEHO CHEM IND CO
Preparation method of aperiodic wideband response electro-optic modulator
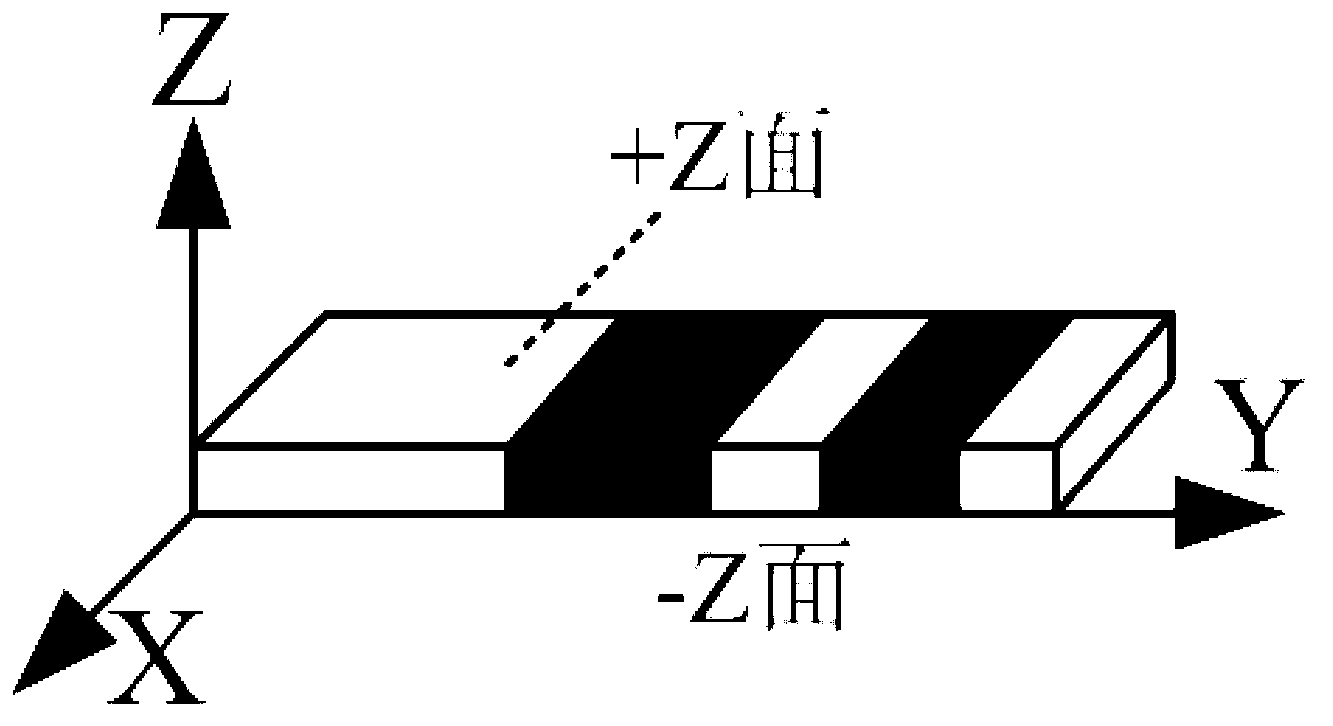
InactiveCN103309057AThe phase modulation effect is consistentExpandable and controllableNon-linear opticsEvaporationPolarizer
A preparation method of an aperiodic wideband response electro-optic modulator comprises the following steps: selecting a ferroelectric single domain crystal; selecting the widths d of the electric domains of a single acting sample in a to-be-prepared crystal and the number N of total electric domains, and obtaining the polarization direction of each electric domain by computing to acquire the arrangement sequences of the positive electric domains and the negative electric domains so as to form an aperiodic optical superlattice; performing room-temperature electric-field polarization to the structure of the aperiodic optical superlattice; preparing a running-wave electrode on the +Z surface of the aperiodic optical superlattice in an evaporation manner, connecting a high-frequency resistor to the tail part of the running-wave electrode in series, and arranging a polarizer before the crystal of the aperiodic optical superlattice to form the electrooptical modulator. The preparation method provides abundant reciprocal lattice vectors by virtue of the aperiodicity of the optical superlattice to compensate the phase velocity difference between a microwave and an optical wave with different frequencies so as to force the electro-optic modulator to acquire a modulating action with a consistent effect under the drive of different-frequency microwaves applicable to a bandwidth.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Electronic device, light-receiving and light-emitting device, electronic integrated circuit and optical integrated circuit using the devices
InactiveUS8507893B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConvex structureReciprocal lattice
Provided are an electronic device and a light-receiving and light-emitting device which can control the electron configuration of a graphene sheet and the band gap thereof, and an electronic integrated circuit and an optical integrated circuit which use the devices. By shaping the graphene sheet into a curve, the electron configuration thereof is controlled. The graphene sheet can be shaped into a curve by forming the sheet on a base film having a convex structure or a concave structure. The local electron states in the curved part can be formed by bending the graphene sheet. Thus, the same electron states as the cylinder or cap part of a nanotube can be realized, and the band gaps at the K points in the reciprocal lattice space can be formed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
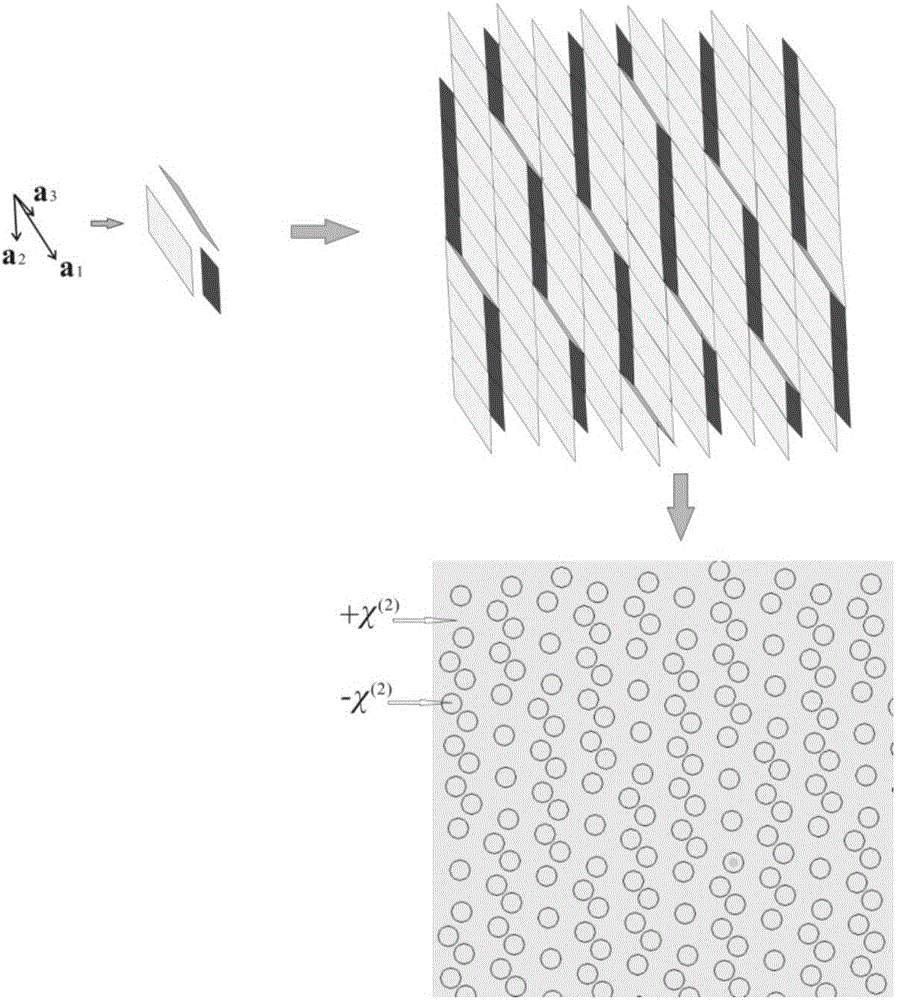
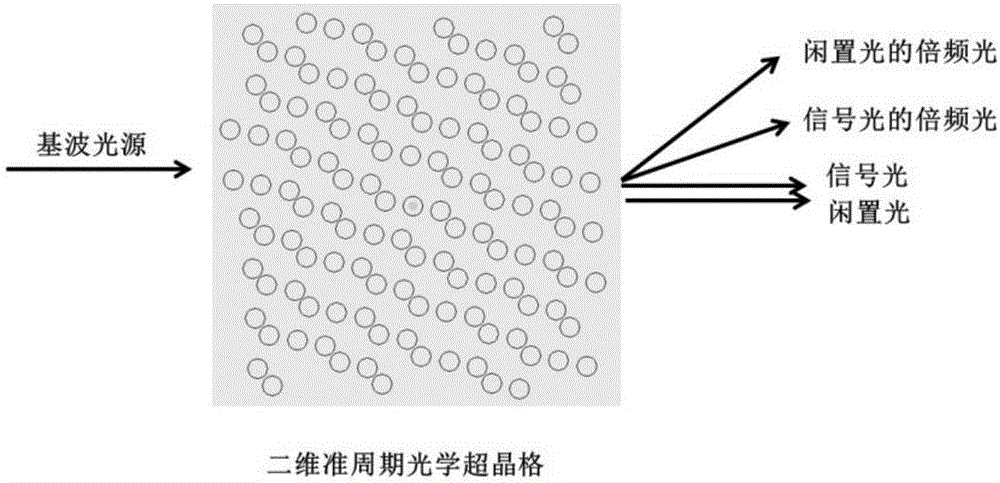
Design method of two-dimensional quasiperiodic optical super lattice structure
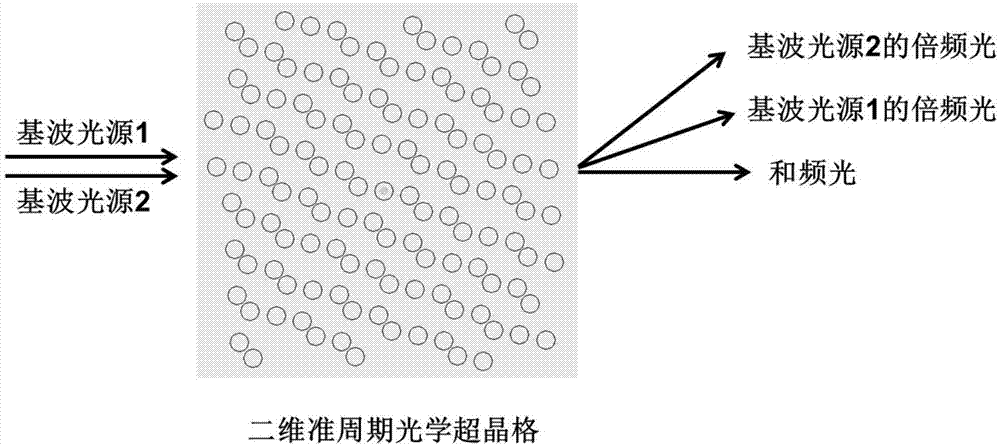
InactiveCN106842379AQuantum Optics ConvenienceFlexible approachNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDistribution VolumeReciprocal lattice
The invention discloses a design method of a two-dimensional quasiperiodic optical super lattice structure. The method comprises the steps that 1, the three non-linear processes are two frequency doubling processes of frequency down conversions and cascade connections; 2, the wave vector lost distribution volumes in the three non collinear processes in step 1 are used as three reciprocal lattice vectors in an inverted space of a two-dimensional quasi periodicity optical super lattice, the sizes of the three reciprocal lattice vectors are decided by a nonlinear process, the directions are optimized using the best Fourier coefficient of the structure; 3, three basis vectors in a two-dimensional positive space are obtained according to the orthogonality relation of the reciprocal lattice vectors obtained in step 2, the three basis vectors constitute three parallelograms, the three parallelograms are strewn throughout the positive space with quasiperiodic sequences, the vertex of the parallelogram is used as the center of a round domain of the two-dimensional quasiperiodic optical super lattice, and the two-dimensional quasiperiodic optical super lattice is obtained. Non-collinear multi-wavelength laser is achieved, complicated spectral device is not required, which provides more convenience for fields such as quantum optics.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method, device, and program for simulating NANO substance in electric field
InactiveUS20090299706A1Improve accuracyLow costNanoinformaticsComputation using non-denominational number representationReciprocal latticeCondensed matter physics
The present invention provides with a method for enabling a highly accurate simulation by calculating dynamical response of electrons in the electric field without using a “fitting parameter”. According to the present invention, the method for simulating a field distribution of a nano substance in an electric field comprises the step of a Fourier transform process by virtually applying a model on which a three-dimensional periodic boundary condition is imposed to the a field distribution of a nano substance in an electric field.Further, the method for simulating a field distribution of a nano substance in an electric field comprises the steps of arranging a virtual charge distribution on a space mesh, and evaluating a field distribution of a nano substance by calculating a potential distribution by way of Fourier-transforming a charge distribution into a reciprocal lattice space.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnesium oxide single crystal having controlled crystallinity and method for producing the same
ActiveUS7544345B2Improve performancePolycrystalline material growthSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSingle crystalCrystallinity
A magnesium oxide single crystal having controlled crystallinity has a subboundary, and ranges of variation of diffraction line positions, as measured for reciprocal lattice maps with respect to a region surrounded by the same subboundary, with the range of the variation of 1×10−3 to 2×10−2 degree of on Δω coordinates, and with the range of the variation of 4×10−4 to 5×10−3 degree on 2θ coordinates.
Owner:TATEHO CHEM IND CO
Method for simultaneously achieving laser frequency doubling and line aggregation in optical superlattice
InactiveCN105116664AAchieve multiplierAchieving line focusLaser detailsNon-linear opticsAxiconUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously achieving laser frequency doubling and line aggregation in an optical superlattice. The method comprises the following steps that 1, an upper inclined domain structure and a lower inclined domain structure with the same period are designed in the superlattice, and are distributed symmetric about the crystal light passing direction; 2, when fundamental waves are vertically shot into the superlattice in an incident mode, the upper half portion of the superlattice can generate laser frequency doubling waves bent downwards, the lower half portion of the superlattice can generate laser frequency doubling waves bent upwards, the laser frequency doubling waves generated by the upper half portion and the laser frequency doubling waves generated by the lower half portion are the same in bending angle and strength, and accordingly, a line focusing interference pattern similar to an axicon can be generated on the overlapped area of the upper half portion and the lower half portion; 3, after lasers enter the superlattice, reciprocal lattice vectors provided by the domain structures of the superlattice can compensate for wave vector mismatching between fundamental waves and the laser frequency doubling waves, and a triangle with matched wave vectors is formed. Frequency doubling of lasers and line aggregation are achieved simultaneously through the periodically-symmetric and inclined domain structures in the optical superlattice.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for analyzing twinned crystal
InactiveUS20070005268A1Failure can not be analyzedEasy to understandSpecial data processing applicationsChemical methods analysisCrystal orientationEngineering
A method and an apparatus for analyzing a twinned crystal can display three-dimensionally the real space unit lattice, the reciprocal space primitive lattices and the reciprocal lattice points of each component of the twinned crystal. Respective crystal orientation matrices of the plural components of the twinned crystal are obtained with the use of X-ray single crystal structure analytical equipment. The first computing means finds the real-space unit lattices of the plural components based on the crystal orientation matrices and creates display data for displaying them three-dimensionally with possible their rotation, scaling up and down and translation. The second computing means finds the reciprocal-space primitive lattices and creates display data for displaying them three-dimensionally. The third computing means creates display data for displaying three-dimensionally reciprocal lattice points causing X-ray diffraction with a distinction between the components of the twinned crystal.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice and construction method thereof
The construction method of mid-infrared laser based on the ultra-quantum conversion limit of optical superlattice uses the following structure of optical superlattice. The structure of optical superlattice provides two inverse lattice vectors at the same time, one of which is used to compensate The phase mismatch of the OPO process of optical parametric oscillation from near-infrared to mid-infrared is used. Another inverse lattice vector is used to compensate the phase mismatch of the OPA process of pumping optical parametric amplification by the signal light of the OPO process. This process can reduce the phase mismatch of the OPO process. The generated mid-infrared laser is further amplified, thereby obtaining a more efficient mid-infrared laser output that exceeds the quantum conversion limit; the optical superlattice adopts a common ratio double period structure. More efficient mid-infrared lasers beyond the quantum conversion limit.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
Two-dimensional periodic cushion vibration reduction ballast bed vibration isolation frequency band regulation and control design method
PendingCN112632673ARealize active regulationThe basic theory is simpleGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsWave equationClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a two-dimensional periodic cushion vibration reduction ballast bed vibration isolation frequency band regulation and control design method. The method is characterized in that under the basic assumption that a two-dimensional periodic cushion vibration reduction ballastbed is infinitely and repeatedly arranged along two periodic directions and infinitely extends along a line walking direction, with a plane strain condition being met, and starting from a wave equation of a two-dimensional periodic structure, a material coefficient and an amplitude modulation function of a Bloch wave are expanded into Fourier series, the elastic wave equation is expanded as a plane wave in reciprocal space to obtain an eigenvalue equation, and a reciprocal lattice vector is made to sweep a plane lattice irreducible Brillouin area to solve the energy band structure of the two-dimensional periodic cushion vibration reduction ballast bed. A vibration isolation frequency band is determined according to the forbidden band distribution range, the change rule of the forbidden band and the vibration isolation frequency band along with geometry and material parameters is obtained through influence factor analysis, and active regulation and control of the forbidden band and the vibration isolation frequency band are achieved. The method is simple in basic theory, wide in applicability and convenient to use, and the calculation result can completely meet the engineering design requirements.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY DESIGN GRP CO LTD
Methods for aligning a spectrometer
ActiveCN108603788ARadiation pyrometryHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionOptical spectrometerEngineering
An example method for aligning a spectrometer is described herein. The spectrometer includes a radiation source, a crystal analyzer, and a detector that are all positioned on an instrument plane. Themethod includes rotating the crystal analyzer about an axis that is within the instrument plane and perpendicular to a rotation plane such that (i) a reciprocal lattice vector of the crystal analyzeris within the instrument plane or (ii) a component of the reciprocal lattice vector within the rotation plane is perpendicular to the instrument plane. An origin of the reciprocal lattice vector is located on the axis. The method further includes tilting the crystal analyzer or translating the detector such that the reciprocal lattice vector bisects a line segment that is bounded by the detector and the radiation source. Example spectrometers related to the example method are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method for generating high-frequency ultrasonic waves based on dielectric body superlattice
ActiveCN101521007BRealize multi-frequency, multi-directional and multi-mode ultrasonic excitationSimple structureMechanical vibrations separationSound producing devicesElectricitySonification
The invention discloses a method for generating high-frequency ultrasonic waves based on a dielectric body superlattice and belongs to the field of electroacoustic energy transduction. The superlatticThe invention discloses a method for generating high-frequency ultrasonic waves based on a dielectric body superlattice and belongs to the field of electroacoustic energy transduction. The superlattice takes a piezoelectric crystal as a medium. An arranged two-dimension modulating structure provides a plurality of reciprocal lattice vectors at the same time and can realize multidirectional multi-fe takes a piezoelectric crystal as a medium. An arranged two-dimension modulating structure provides a plurality of reciprocal lattice vectors at the same time and can realize multidirectional multi-frequency and multimode ultrasound output at high frequency in an alternative electric field, wherein the ultrasonic waves at different frequency have different propagation directions and can be used irequency and multimode ultrasound output at high frequency in an alternative electric field, wherein the ultrasonic waves at different frequency have different propagation directions and can be used independently. The frequency, propagation direction and sound wave mode of high-frequency ultrasonic waves generated by the method can be designed and modulated by the two-dimension structure periodicandependently. The frequency, propagation direction and sound wave mode of high-frequency ultrasonic waves generated by the method can be designed and modulated by the two-dimension structure periodically and symmetrically. The method has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency and integration.lly and symmetrically. The method has the advantages of simplicity, high efficiency and integration.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Optical superlattice optimization structure setting method aiming at coupling nonlinear optical course
The invention relates to a method for setting an optical superlattice structure aiming at a coupling nonlinear optical process. Fourier transformation of a window is adopted to replace common whole fourier transformation; a local effective nonlinear coefficient and a spatial weighting function of a reciprocal lattice vector of an optical superlattice are introduced; the competitive relation between the fourier coefficients of each reciprocal lattice vector is considered; the spatial weighting function of the reciprocal lattice vector is subjected to optimized matching; for a triple-frequency coupling process, the spatial weighting function of the reciprocal lattice vector leans to the reciprocal lattice vector of the frequency doubling process in the initial stage and leans to the reciprocal lattice vector of the sum frequency process in the late stage; and through the optimization of the spatial distribution of the local fourier coefficients of two reciprocal lattice vectors, the method realizes the optimization of nonlinear conversion efficiency in the coupling process and carries out the setting of the optical superlattice structure on the basis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Light irradiation apparatus, light irradiation method, crystallization apparatus, crystallization method, and semiconductor device
InactiveCN101038862ABy zone-melting liquidsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingReciprocal latticeLight modulation
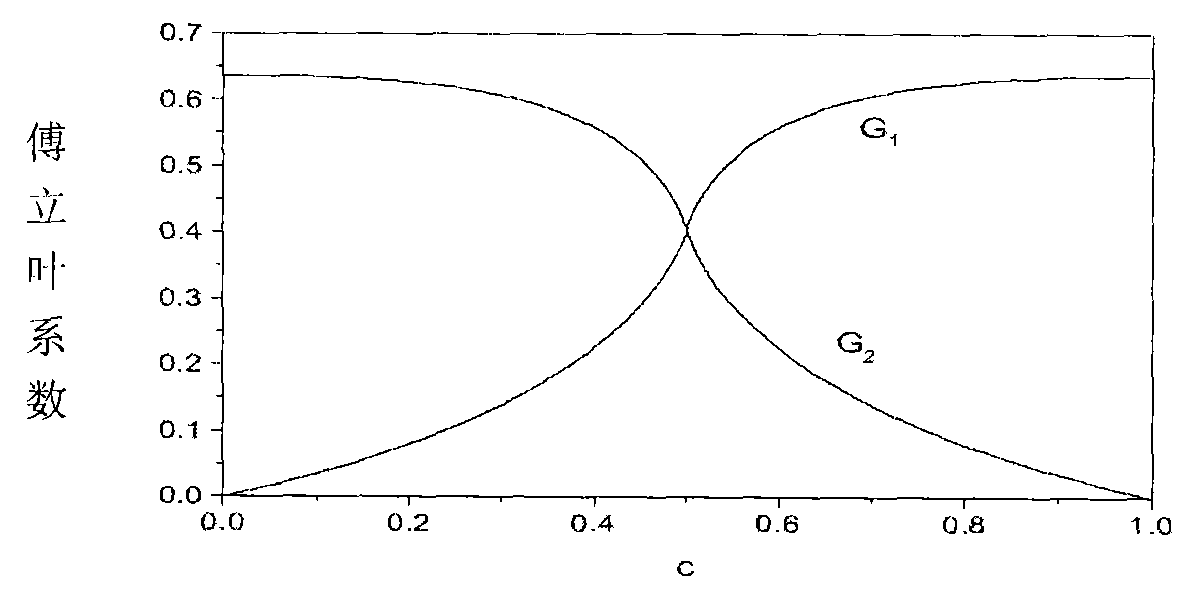
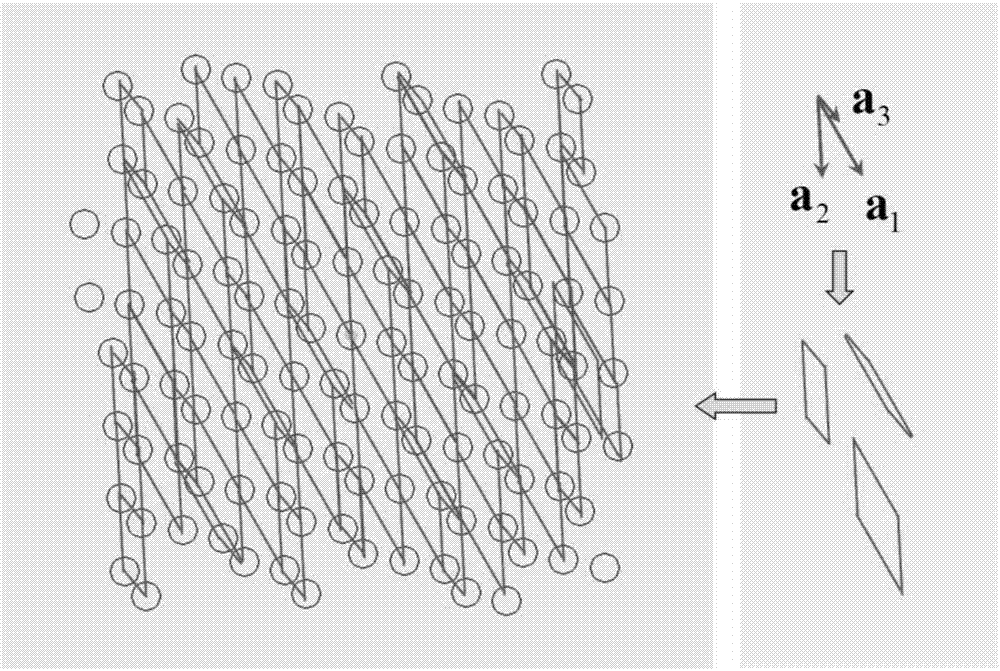
A light irradiation apparatus irradiates a target plane with light having a predetermined light intensity distribution. The apparatus includes a light modulation element having a light modulation pattern of a periodic structure represented by a primitive translation vector (a 1,a 2 ), an illumination system for illuminating the modulation element with the light, and an image forming optical system for forming the predetermined light intensity distribution obtained by the modulation pattern on the target plane. A shape of an exit pupil of the illumination system is similar to the Wigner-Seitz cell of a primitive reciprocal lattice vector (b 1,b 2 ) obtained from the primitive translation vector (a 1, a 2 ) by the following equations: b1=2pi(a2xa3) / (a1.(a2xa3)) and b2=2pi(a3xa1) / (a1.(a2xa3)) in which a 3 is a vector having an arbitrary size in a normal direction of a flat surface of the modulation pattern of the modulation element,''.'' is an inner product of the vector, and ''x'' is an outer product of the vector.
Owner:ADVANCED LCD TECH DEVMENT CENT
Design method of two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice structure for generating non-colinear three-wavelength laser
InactiveCN107015294AQuantum Optics ConvenienceFlexible approachNon-linear opticsOptical elementsReciprocal latticePhysics
The invention discloses a design method of a two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice structure for generating a non-colinear three-wavelength laser. The design method includes the following steps 1) determining two base wave sources, taking the three wave vector mismatch quantities in the non-linear process generated by the two base wave sources in the non-collinear three-wavelength laser process as the three reciprocal lattice vectors of the two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice in the reciprocal space, and optimizing the size and direction of the three reciprocal lattice vectors according to the Fourier expansion coefficients of the reciprocal lattice vectors; and 2) performing orthogonality relation on the reciprocal lattice vectors obtained in the step 1) to obtain the three base vectors of a positive space, forming three parallelograms by the three base vectors, filling the whole positive space with the three parallelograms according to the quasi-periodic sequence, taking the vertexes of the parallelograms as the center of the two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice circular domain to obtain the two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice. The non-colinear three-wavelength laser can be realized by the two-dimensional quasi-periodic optical superlattice structure, and more conveniences can be provided for the quantum optics filed.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Chirp quasi-periodic structure superlattice material and design method thereof
PendingCN111046588AIncreased Frequency Conversion BandwidthReduce harsh environmental requirementsPolycrystalline material growthDesign optimisation/simulationFrequency conversionEngineering
The invention discloses a chirp quasi-periodic structure superlattice material and a design method thereof. A common quasi-periodic structure has a plurality of reciprocal lattice vectors in a Fourierinversion space, and each reciprocal lattice vector is in a peak shape with a very narrow width. The phase matching of the peak-shaped reciprocal lattice vector requires that the ambient temperatureand the input laser wavelength are both narrow-band, otherwise, the power stability and efficiency of the frequency conversion of the peak-shaped reciprocal lattice vector fluctuate drastically, and the superlattice material with the periodic structure has higher condition requirements in actual use. According to the embodiment of the invention, the chirp structure is introduced into the design ofthe quasi-periodic structure, and one or more reciprocal lattice vectors are broadened and flattened through a chirp quasi-periodic structure, so that the bandwidths and the strengths of the reciprocal lattice vectors can be controlled at the same time, the frequency conversion bandwidths of quasi-periodic superlattices are improved, the stability of the conversion efficiency is improved, and theharsh environmental requirements of quasi-periodic materials in practical application are reduced.
Owner:NANJING NANZHI INST OF ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONIC INTEGRATION NANJING
Methods used to align the spectrometer
ActiveCN108603788BRadiation pyrometryHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionOptical spectrometerMechanical engineering
Exemplary methods for aligning spectrometers are described herein. The spectrometer includes a radiation source, a crystal analyzer, and a detector, all located in the instrument plane. The method includes rotating the crystal analyzer about an axis in the instrument plane and perpendicular to the plane of rotation such that (i) the reciprocal lattice vector of the crystal analyzer is in the instrument plane, or ( ii) The component of the reciprocal lattice vector in the plane of rotation is perpendicular to the instrument plane. The origin of the reciprocal lattice vectors lies on the axis. The method also includes tilting the crystal analyzer or translating the detector such that the reciprocal lattice vector bisects a line segment bounded by the detector and the radiation source. Exemplary spectrometers associated with the exemplary methods are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Double-layer C6v lattice metamaterial sensor based on three-dimensional metal printing technology
PendingCN114083882AHigh signal fidelityImprove signal-to-noise ratioAdditive manufacturing apparatusSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementNoiseWaveguide
The invention discloses a double-layer C6v lattice metamaterial sensor based on a three-dimensional metal printing technology, which comprises a first periodic lattice structure, a first substrate, a second periodic lattice structure, a second substrate and a third periodic lattice structure which are integrally formed by three-dimensional metal printing. The second periodic lattice structure is arranged between the lower surface of the first substrate and the upper surface of the second substrate; the first periodic lattice structure is arranged on the upper surface of the first substrate, and the third periodic lattice structure is arranged on the lower surface of the second substrate. In the design process, rich physical effects in condensed physics are ingeniously combined with the traditional acoustic waveguide structure design. In condensed state physics, due to structural periodicity and Bragg scattering, energy is in strip distribution in a reciprocal lattice vector space, so that propagation of the energy can be effectively regulated and controlled, and the signal fidelity and the signal-to-noise ratio of a traditional acoustic device are improved.
Owner:NANJING IND INST FOR ADVANCED INTELLIGENT EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com